Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1820 results about "Ultra high frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (one decimeter). Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, and numerous other applications.
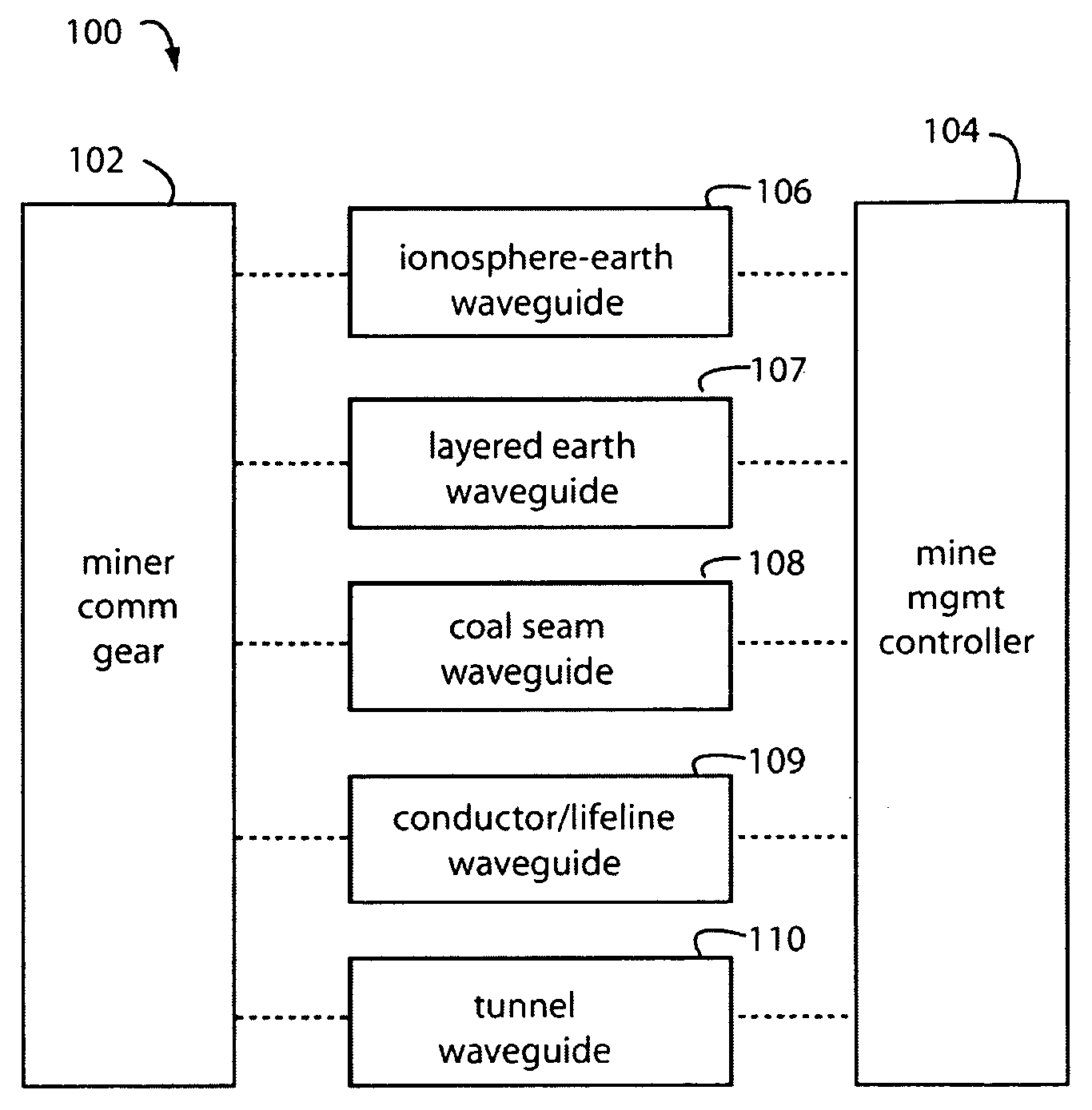
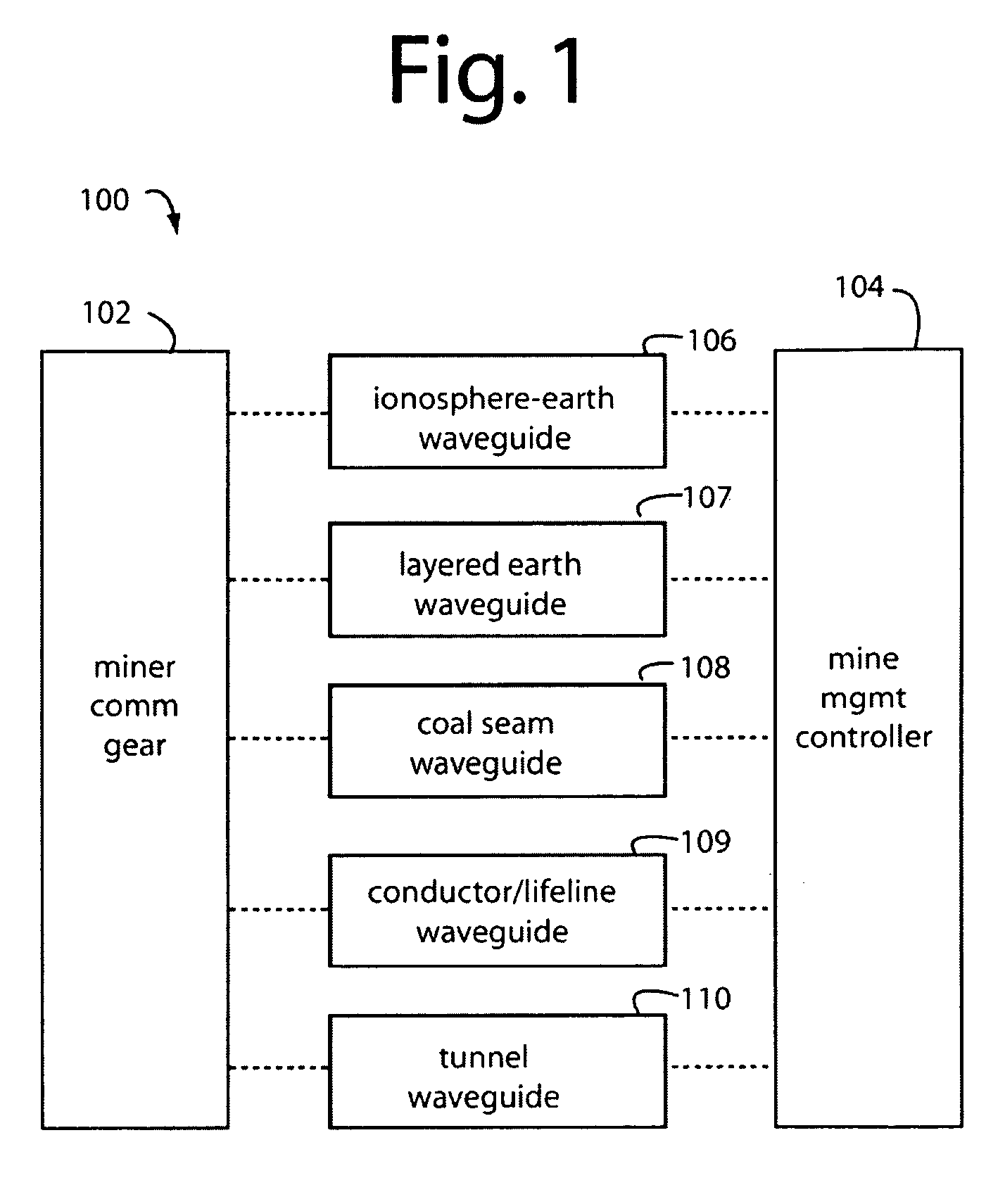
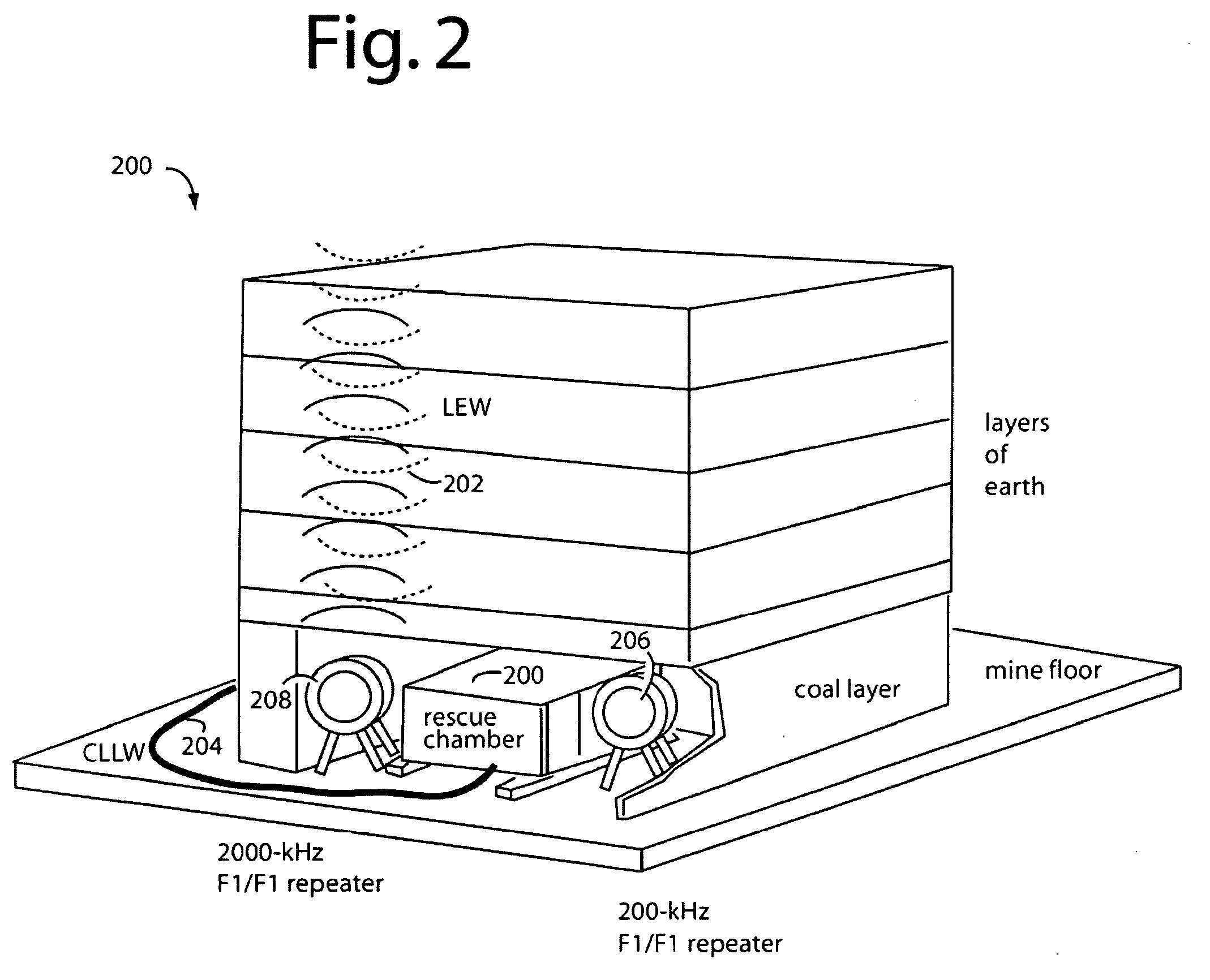
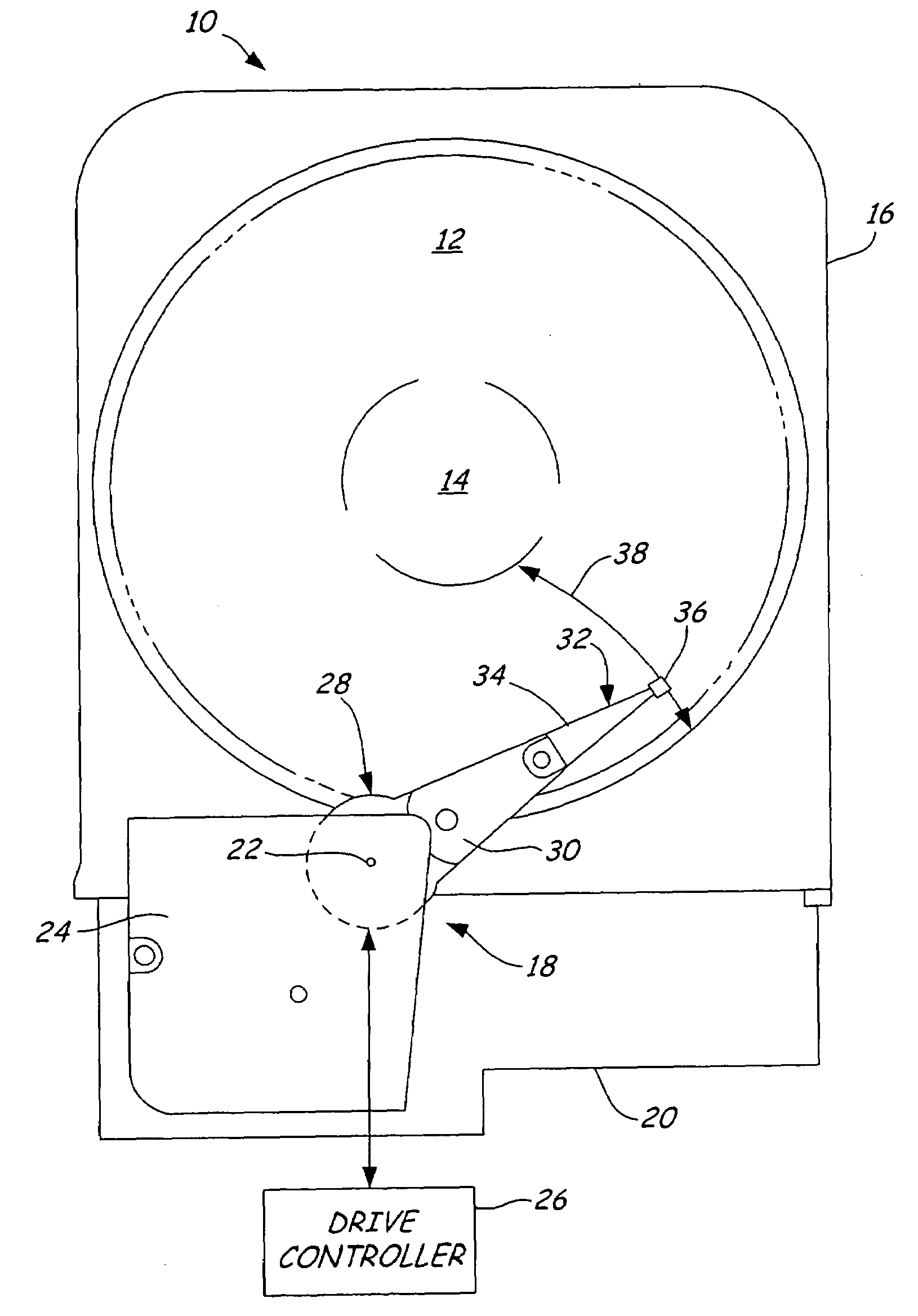
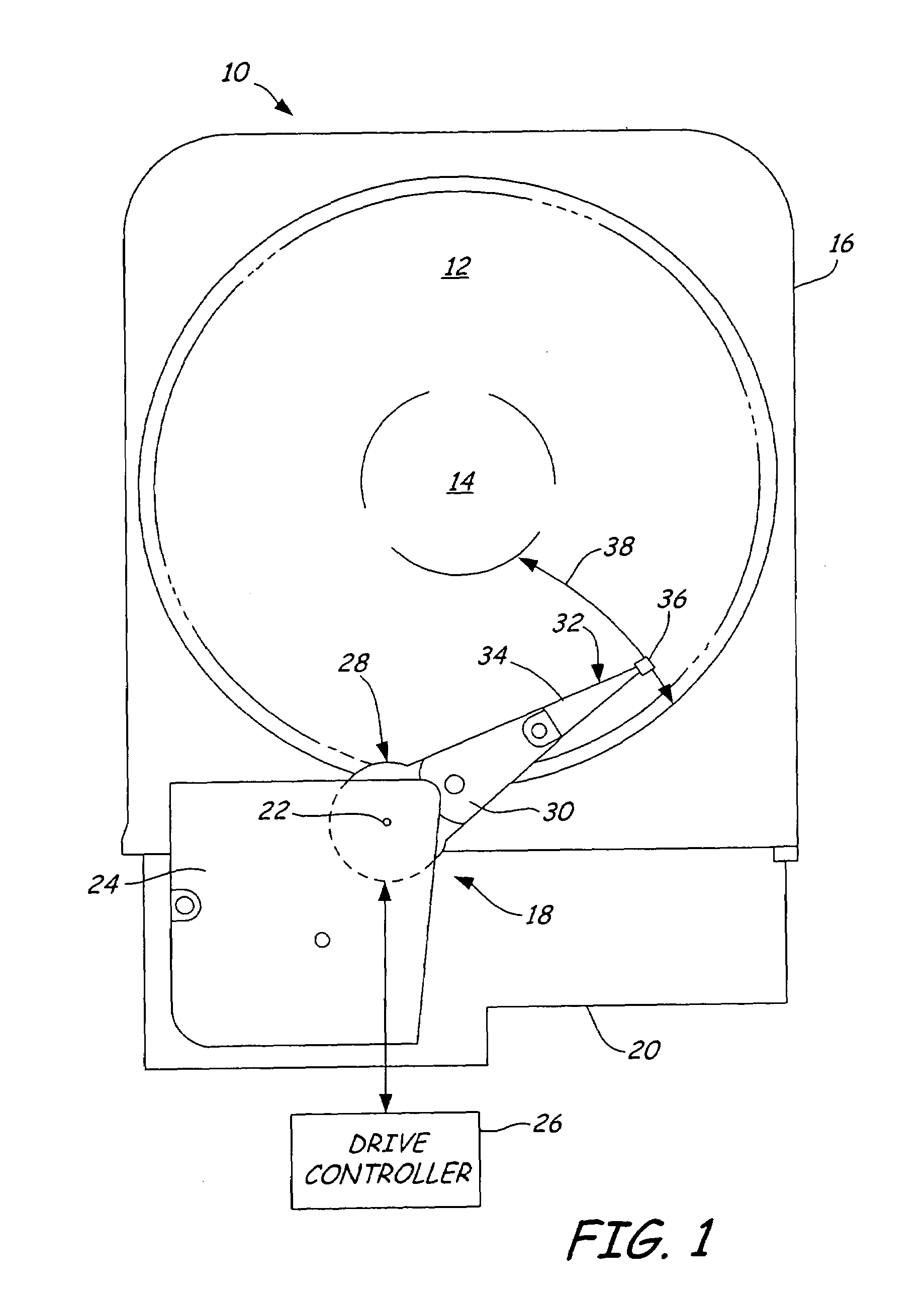
Underground radio communications and personnel tracking system
InactiveUS20090140852A1Function providedSubaqueous/subterranean adaptionElectric signalling detailsTransceiverElectrical conductor
An underground radio communications and personnel tracking system uses a portable communications device worn by a miner when underground in a mine. A cap-lamp transceiver provides voice and text communication on ultra-low frequency (ULF) to ultra-high frequency (UHF) carrier frequencies and modulation adapted by programming of a software defined radio to making selective and agile radio contacts via through-the-earth, conductor / lifeline, coal seam, tunnel, and ionosphere / earth-surface waveguides for transmission of electromagnetic waves. These waveguides comprise layered earth coal and mineral deposits, and manmade mining complex infrastructures which serendipitously form efficient waveguides. Ultra-Low Frequency F1 / F1 repeaters are placed underground in the mine, and providing for extended range of communication of the cap-lamp transceiver with radios and tracking devices above ground of the mine.
Owner:STOLAR
Low/high frequency shared leakage antenna, base station apparatus and close-range detection system using the antenna
InactiveUS8811278B2Improve reliabilitySecure power sourceSimultaneous aerial operationsError preventionElectrical conductorEngineering
The present invention provides a high / low frequency dual wireless location detection and information transmission system which is high in reliability and maintainability, and can be easily installed.A leakage coaxial inner conductor and a conductor line provided in parallel are short-circuited at an end, a single leakage coaxial operation and a loop operation of the inner conductor and the conductor line are performed at the same time, the ID of a tag is communicated using magnetic fields which locally exist near the conductor line by the loop, and wireless position detection and information communications which are less affected by the influence of ambient environments due to electromagnetic waves in a closed area are realized by open-type lines.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Compact broad-band admittance tunnel incorporating gaussian beam antennas
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Providing enhanced haptic feedback effects
InactiveUS7218310B2Enhanced tactile sensationStrong tactile effectInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTactile sensationEngineering
Method and apparatus for providing high strength, low frequency tactile sensations using an inertial actuator in a haptic feedback interface device, such as an actuator driving an oscillating inertial mass. A commanded low frequency is modulated or combined with a higher frequency at which the tactile sensations feel stronger, where the resulting signal is used to output a tactile sensation at the higher frequency and convey the commanded low frequency to the user. One embodiment provides higher frequency pulse bursts at the desired low frequency wherein the higher frequency pulse bursts are at or near a resonant frequency of the actuator; other embodiments modulate or otherwise vary the amplitude of the higher frequency signal according to the desired low frequency.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
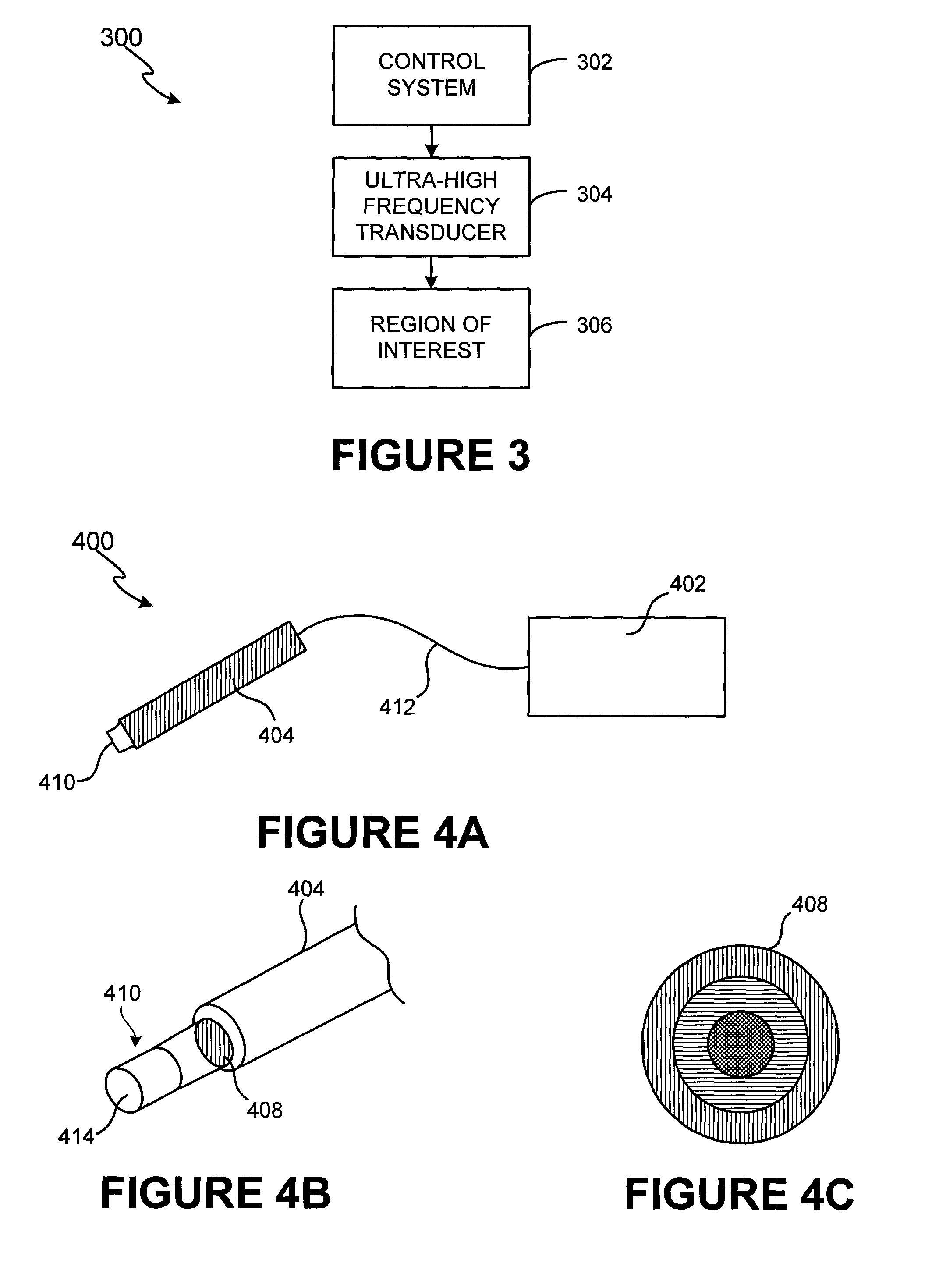
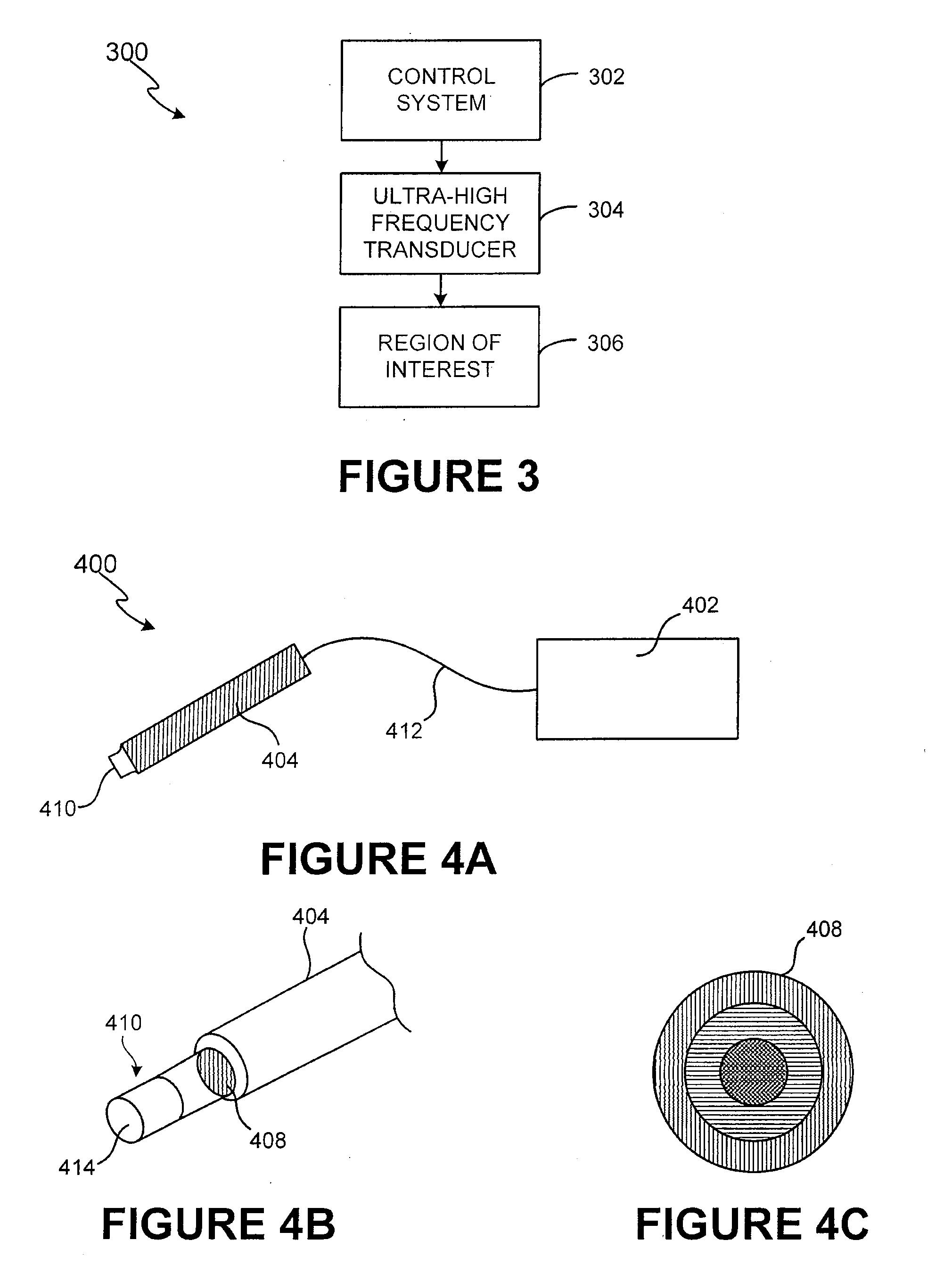
Method and system for ultra-high frequency ultrasound treatment
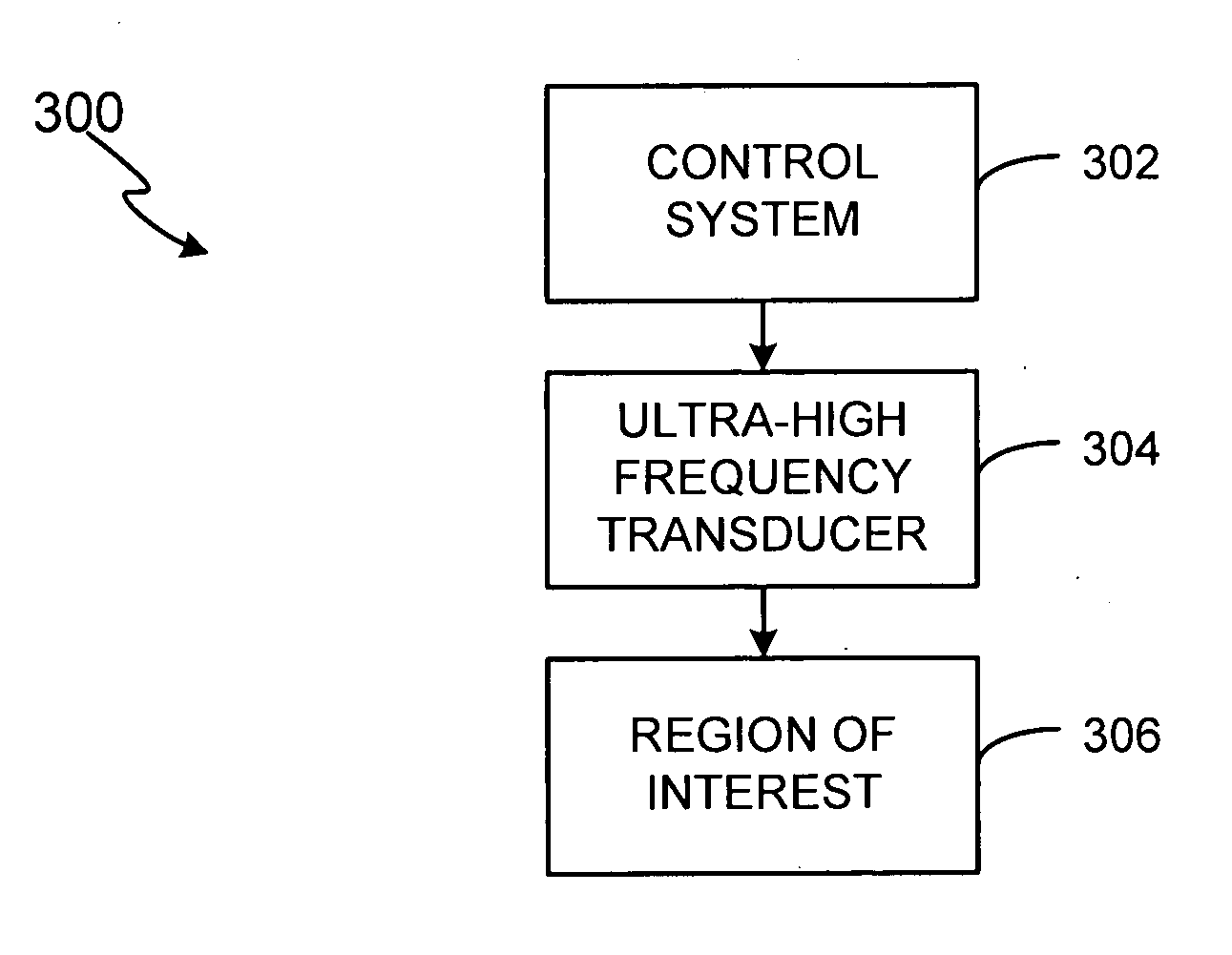
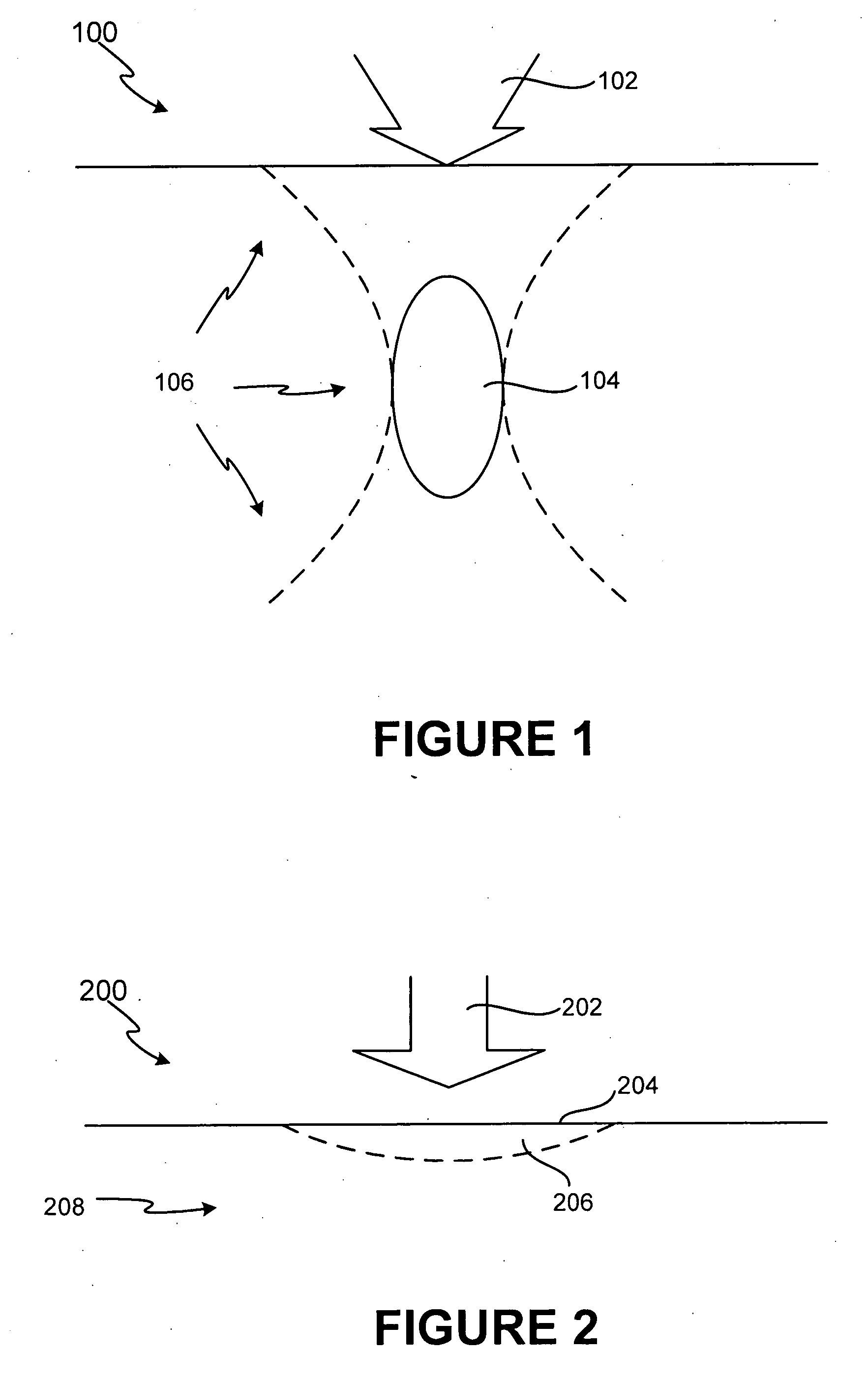
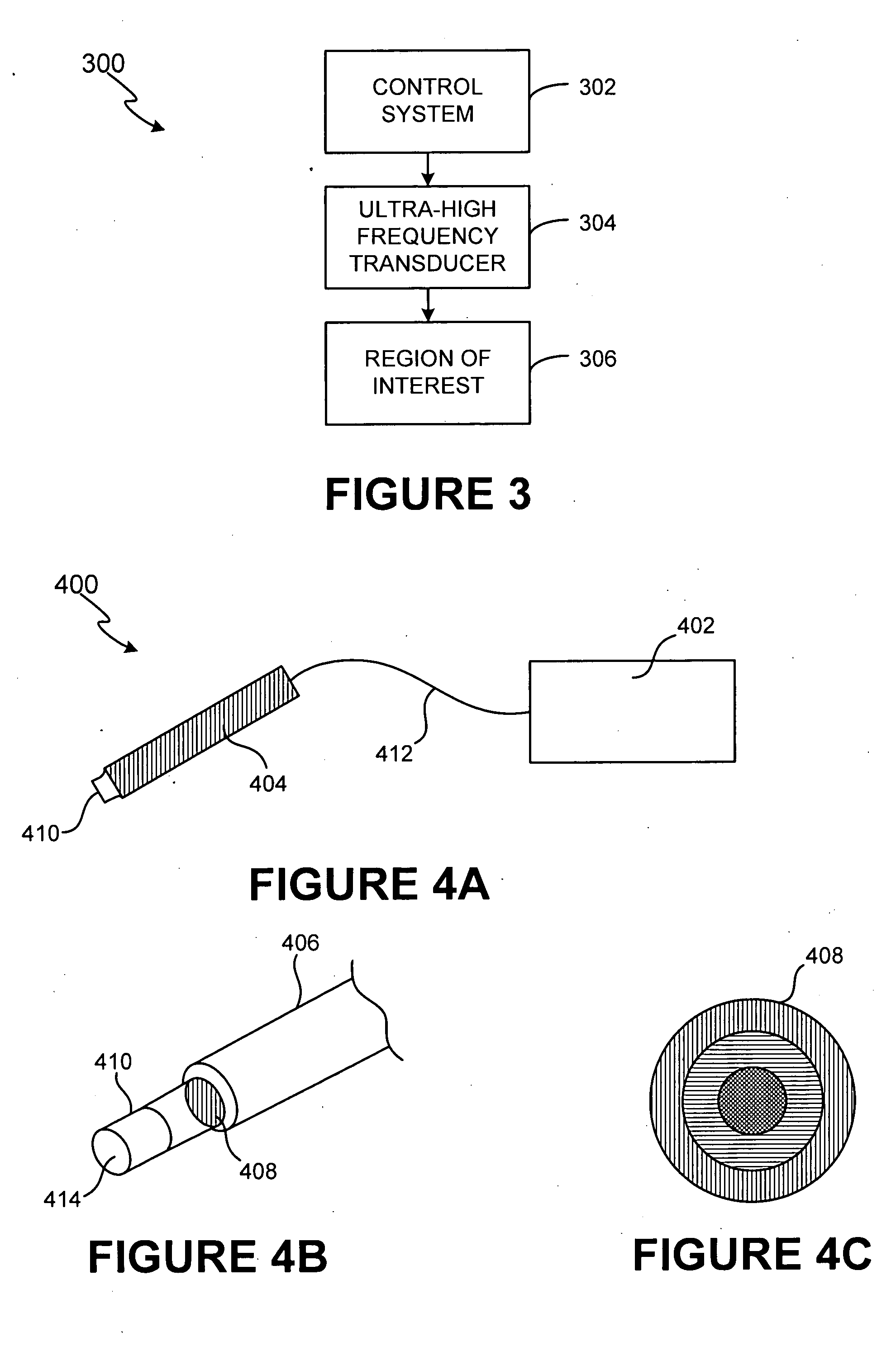
ActiveUS20060084891A1Facilitate acoustic outputFacilitate maximum efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorSonification
A non-invasive ultra-high frequency ultrasound treatment method and system are provided. An exemplary method and system comprise a high-frequency ultrasound transducer system configured for providing ultrasound treatment to a patient such that the superficial and / or subcutaneous regions of the patient can be treated. An exemplary high-frequency ultrasound transducer system comprises a control system and a transducer configured to provide treatment to the superficial and / or subcutaneous regions of interest. The high-frequency ultrasound transducer may be configured to operate at higher frequencies and controlled power levels to provide treatment to the superficial and / or subcutaneous regions of interest. For example, higher frequencies within the range from approximately 20 MHz to 500 MHz or more may be utilized.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
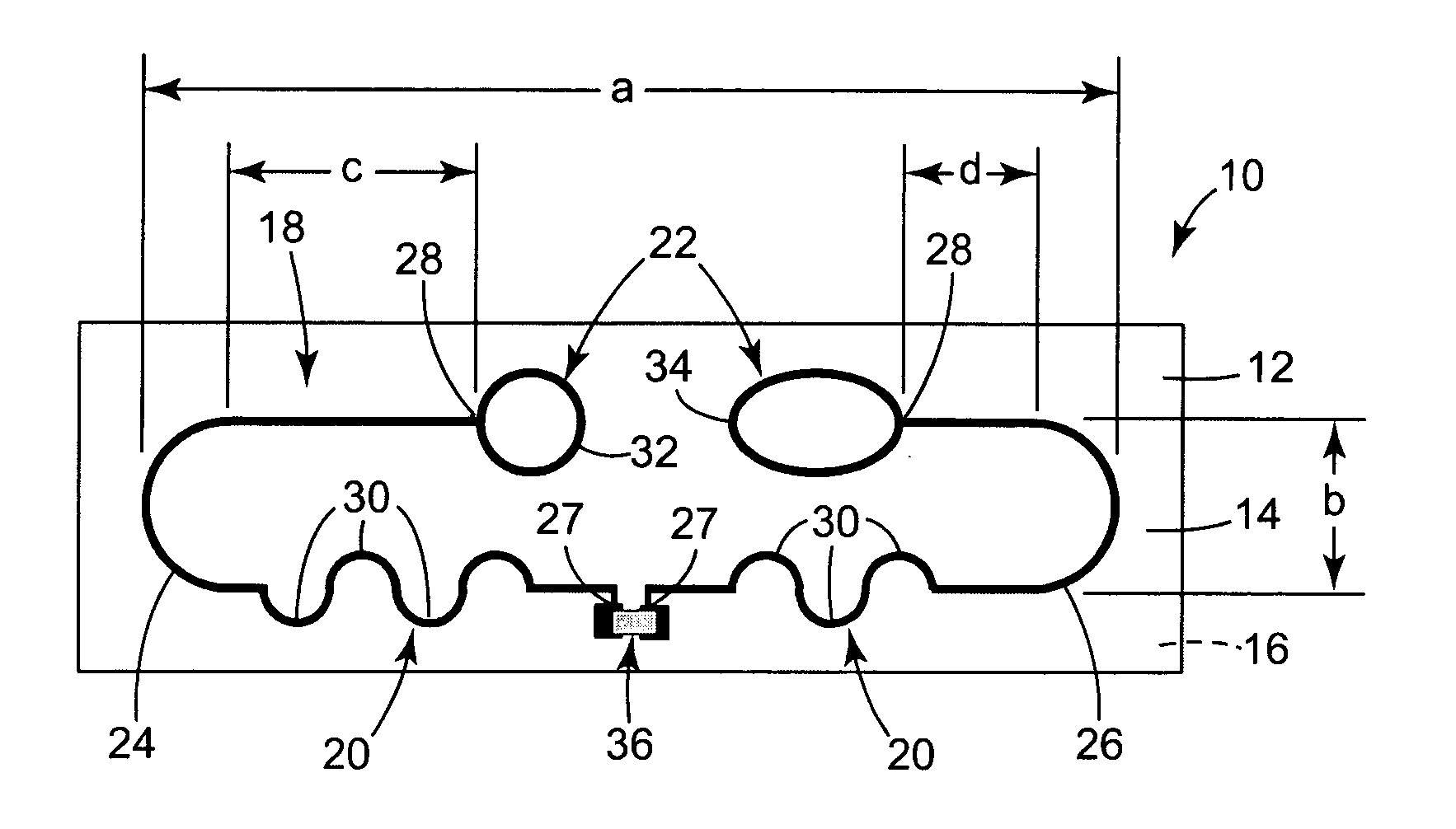
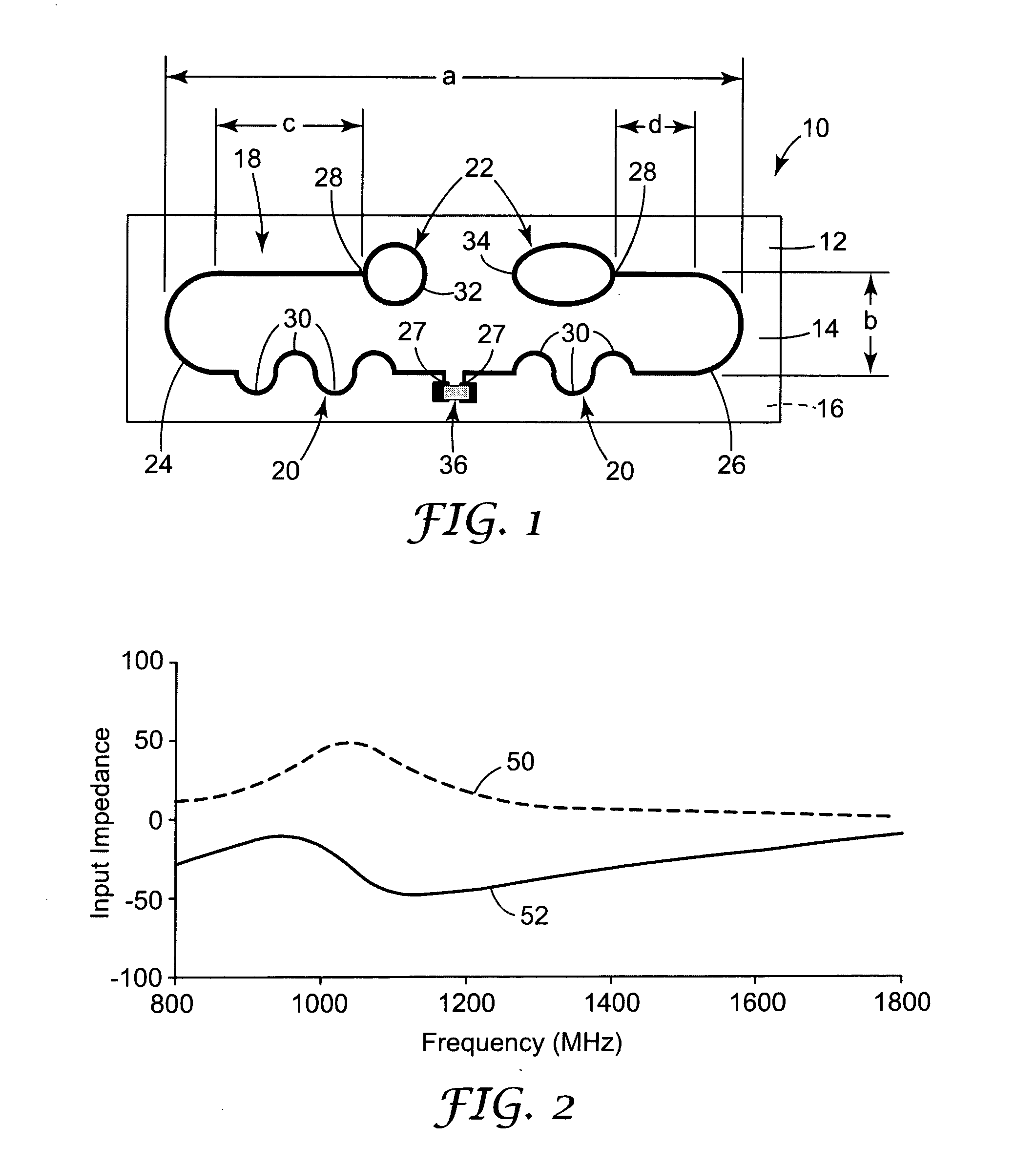
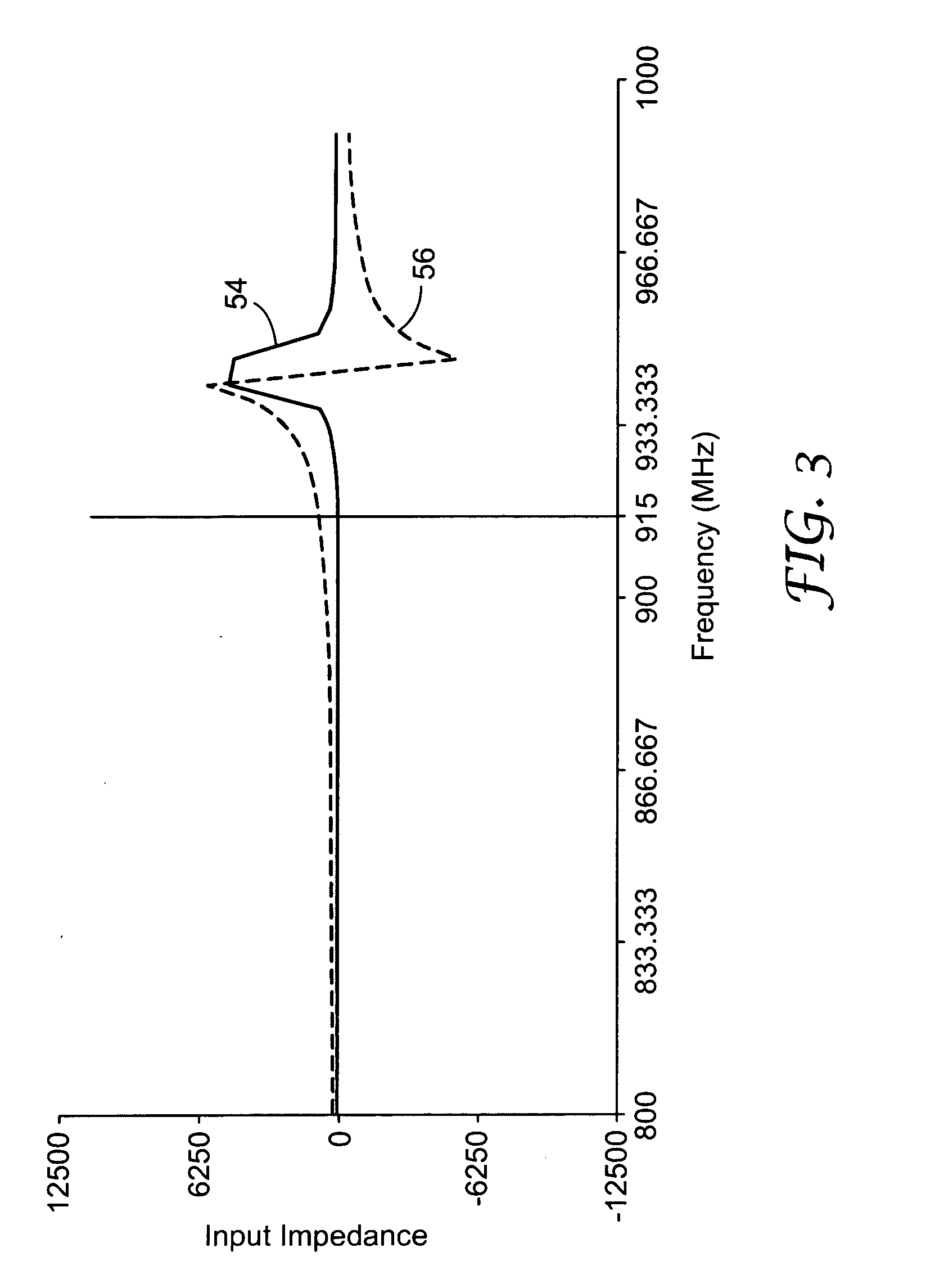
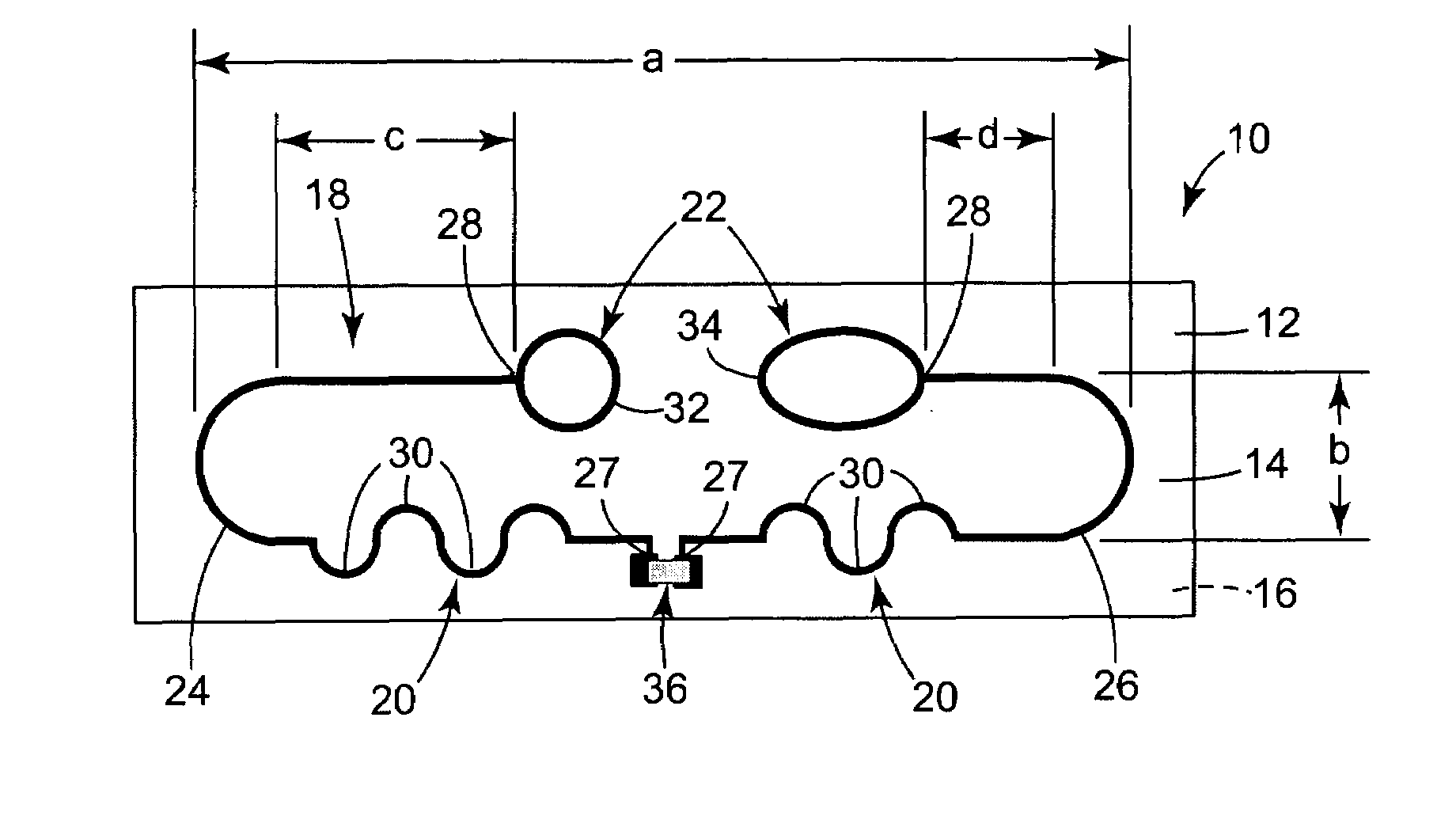
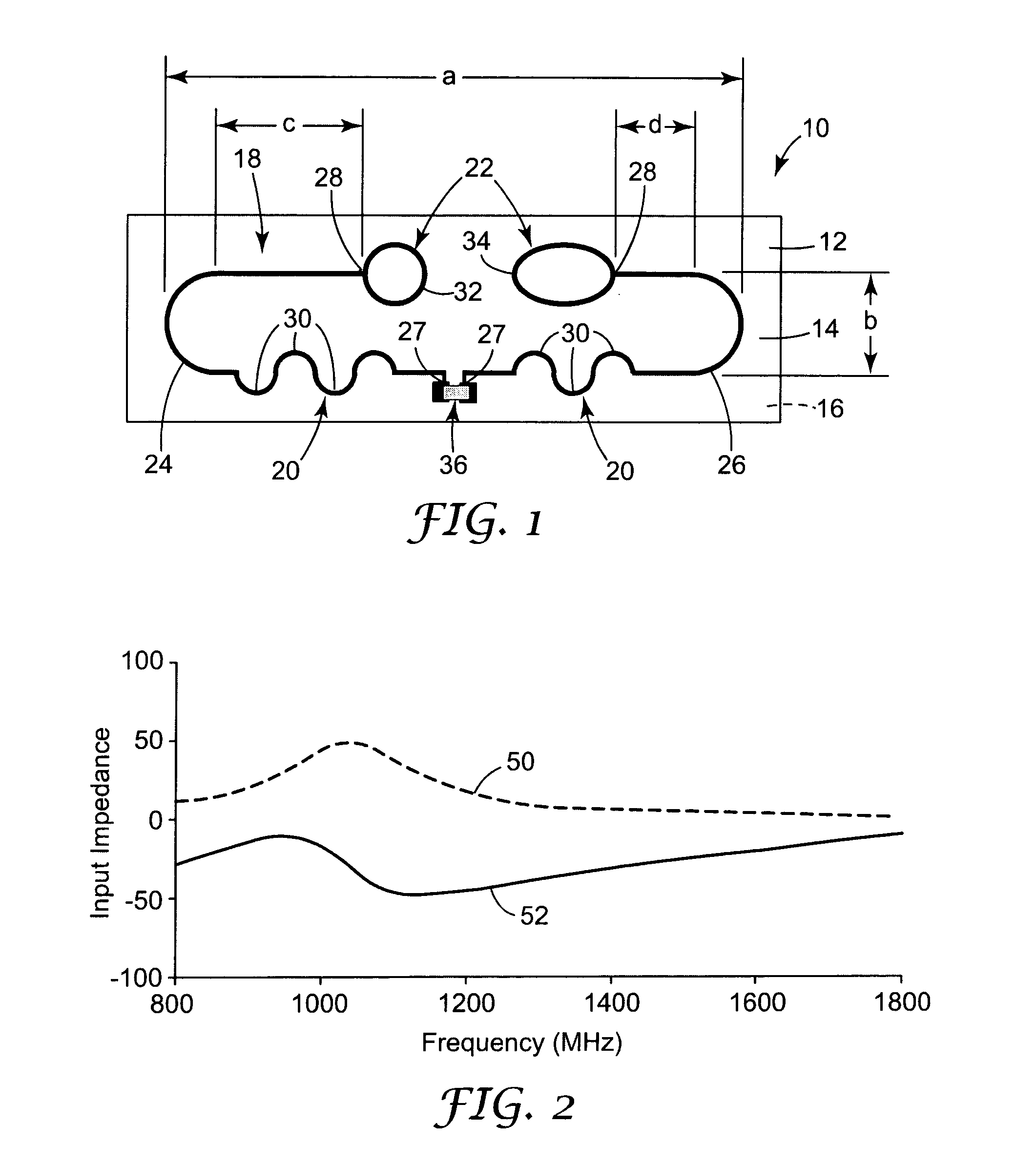
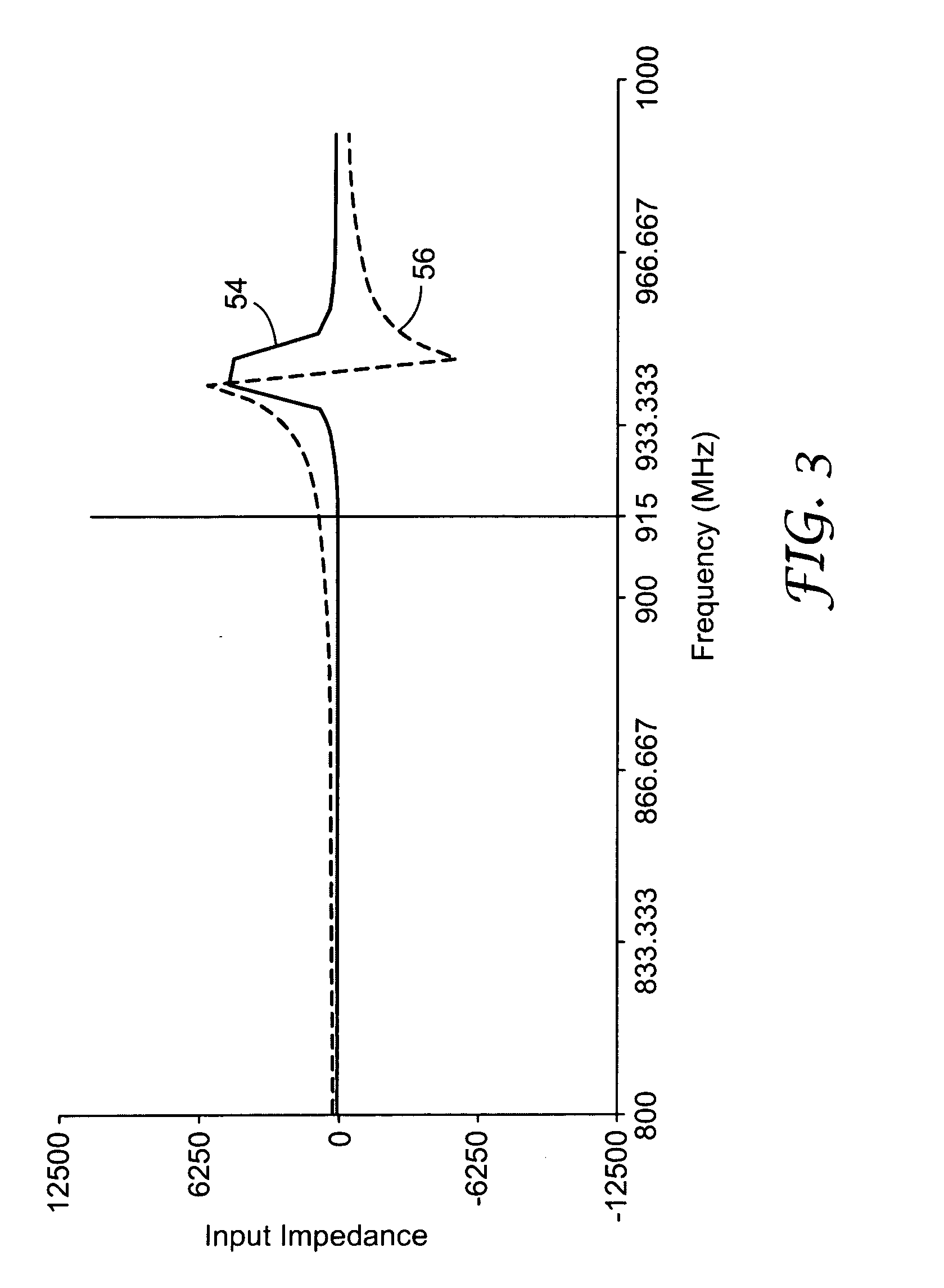
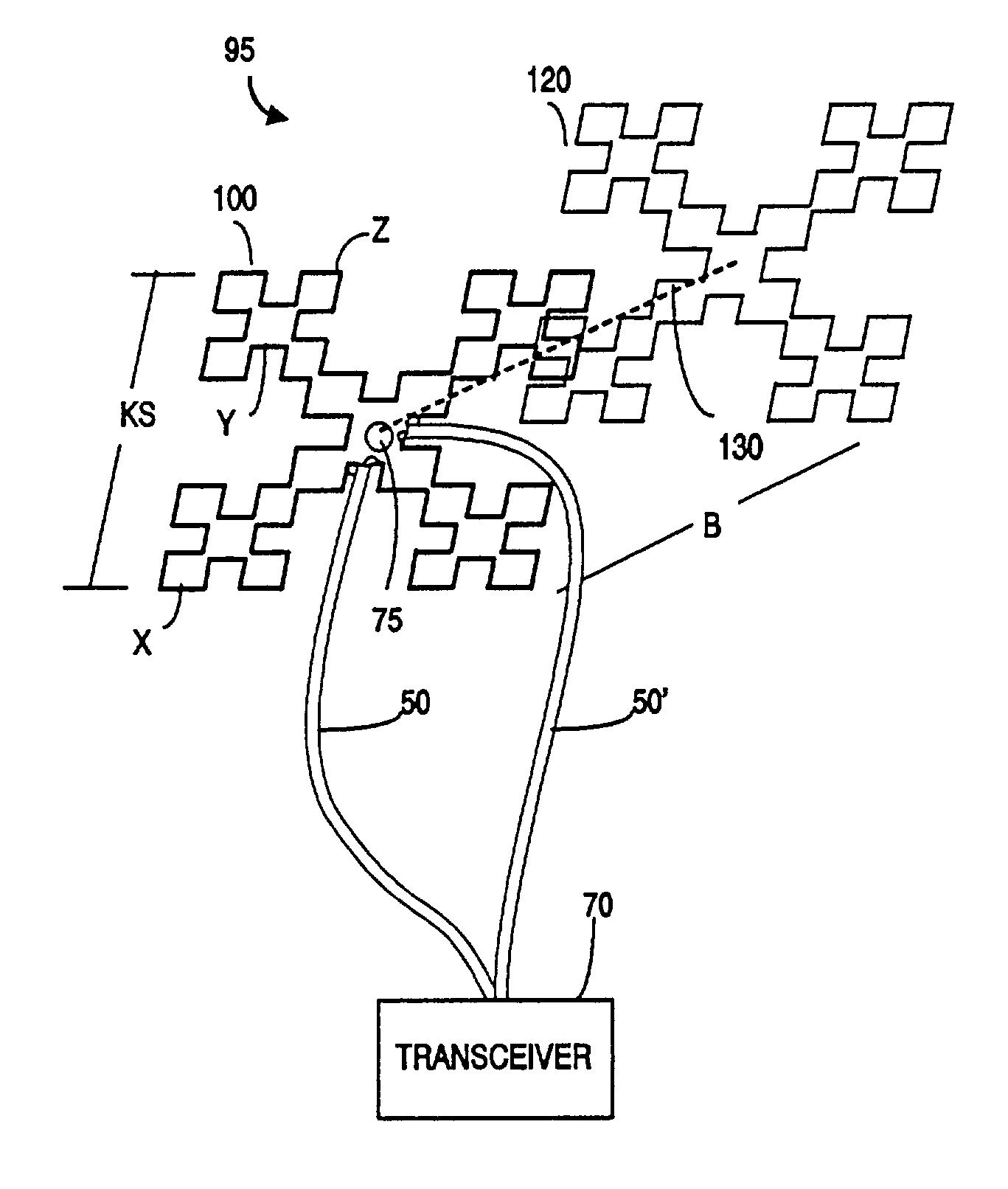
Ultra high frequency radio frequency identification tag
An antenna design for radio frequency identification (“RFID”) tags. More particularly, the present invention relates to design for RFID tags particularly operating in the ultra high frequency (“UHF”) operating band.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method and system for ultra-high frequency ultrasound treatment
ActiveUS7758524B2Enhanced couplingConvenient treatmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationControl power
A non-invasive ultra-high frequency ultrasound treatment method and system are provided. An exemplary method and system comprise a high-frequency ultrasound transducer system configured for providing ultrasound treatment to a patient such that the superficial and / or subcutaneous regions of the patient can be treated. An exemplary high-frequency ultrasound transducer system comprises a control system and a transducer configured to provide treatment to the superficial and / or subcutaneous regions of interest. The high-frequency ultrasound transducer may be configured to operate at higher frequencies and controlled power levels to provide treatment to the superficial and / or subcutaneous regions of interest. For example, higher frequencies within the range from approximately 20 MHz to 500 MHz or more may be utilized.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
Ultra high frequency radio frequency identification tag
InactiveUS6999028B2Antenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna designRadio-frequency identification
An antenna design for radio frequency identification (“RFID”) tags. More particularly, the present invention relates to design for RFID tags particularly operating in the ultra high frequency (“UHF”) operating band.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Component ultrasound transducer
InactiveUS20080200813A1Eliminate dangerUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyUltrasonic sensorTransducer
An ultrasound transducer having multiple focal zones is described. In one embodiment there is an ultrasound transducer manufactured as a single piece but having two or more focal zones. In a second embodiment there is a transducer assembly combining a high frequency and low frequency transducer. In a third embodiment there is an interchangeable assembly allowing for different ultrasound transducers to be used based on procedural needs. Variations of each embodiment are also disclosed.
Owner:LIPOSONIX
High frequency and low frequency audio signal encoding and decoding system
InactiveUS6772114B1Low computing performanceCode conversionTransmissionFrequency spectrumTransmitter
In an audio transmission system, an input signal is split up into two spectral portions in a transmitter. These spectral portions are coded by their own respective coder. The low-frequency signal portion is coded by a regular narrow-band coder and the high frequency portion is coded using a coder that outputs LPC codes and signal amplitude codes. In the receiver, the low frequency signal portion is reconstructed by a narrow-band decoder and the high frequency portion is reconstructed by applying a high pass filter to a white noise signal and applying an LPC filter that is controlled by the LPC codes to this filtered white noise signal and adjusting the signal amplitude with an amplifier that is controlled using the amplitude codes of the transmitter. The reconstructed low frequency signal and the reconstructed high frequency signal are then combined to yield a reconstructed output signal containing both frequency ranges.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
System and method for ultra-high frequency ultrasound treatment
ActiveUS20100241035A1Enhanced couplingConvenient treatmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationControl power
A non-invasive ultra-high frequency ultrasound treatment method and system are provided. An exemplary method and system comprise a high-frequency ultrasound transducer system configured for providing ultrasound treatment to a patient such that the superficial and / or subcutaneous regions of the patient can be treated. An exemplary high-frequency ultrasound transducer system comprises a control system and a transducer configured to provide treatment to the superficial and / or subcutaneous regions of interest. The high-frequency ultrasound transducer may be configured to operate at higher frequencies and controlled power levels to provide treatment to the superficial and / or subcutaneous regions of interest. For example, higher frequencies within the range from approximately 20 MHz to 500 MHz or more may be utilized.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
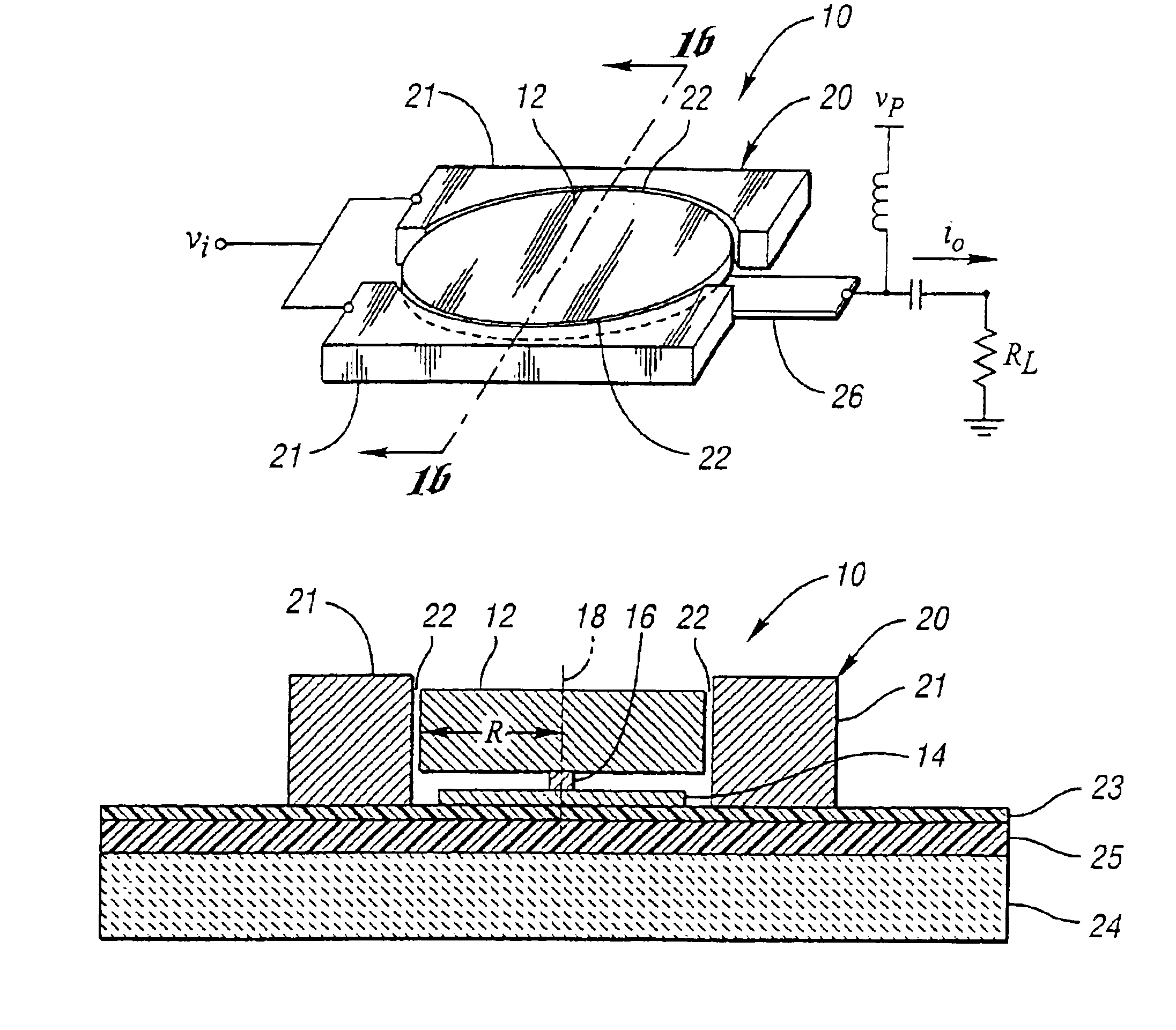
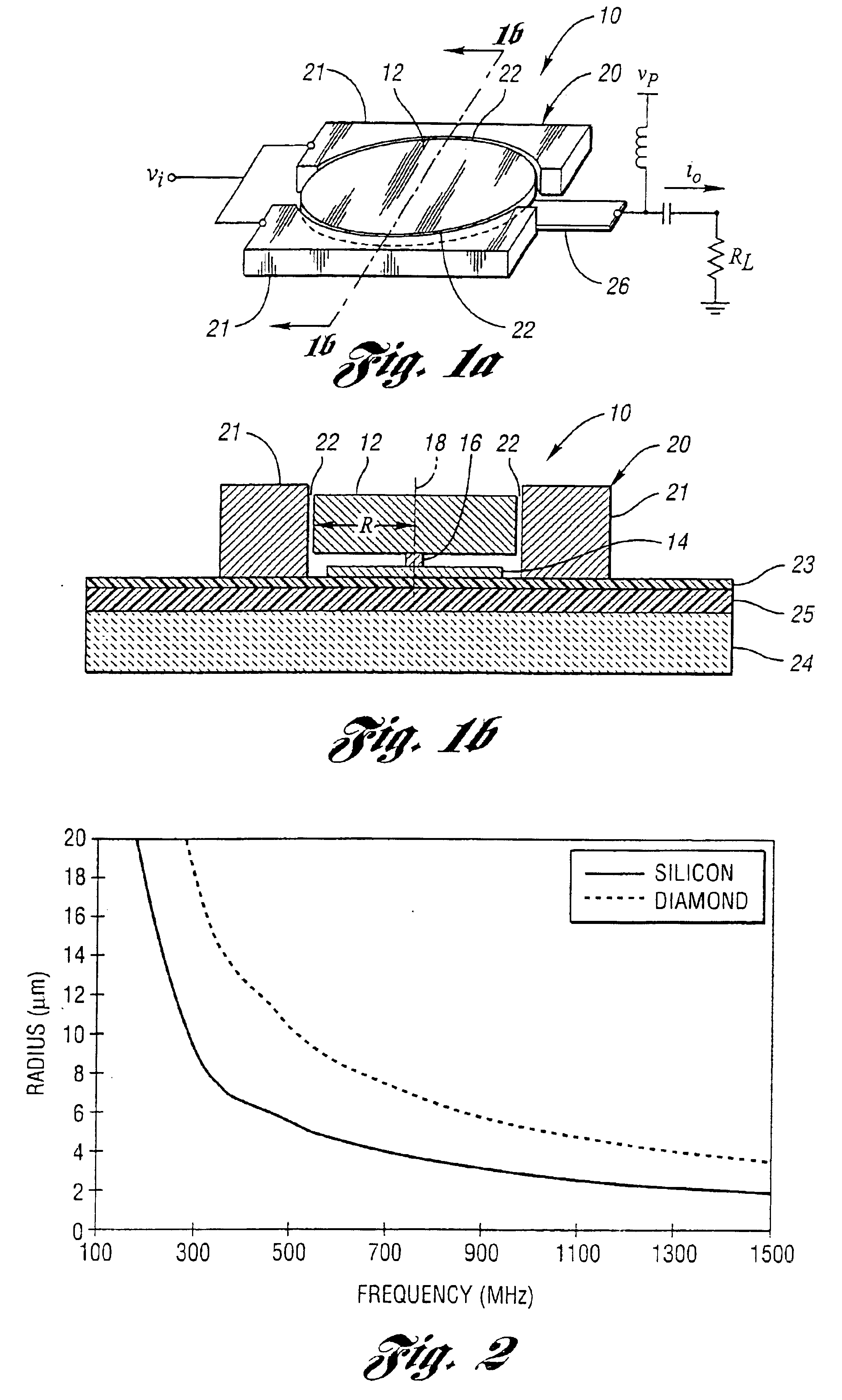
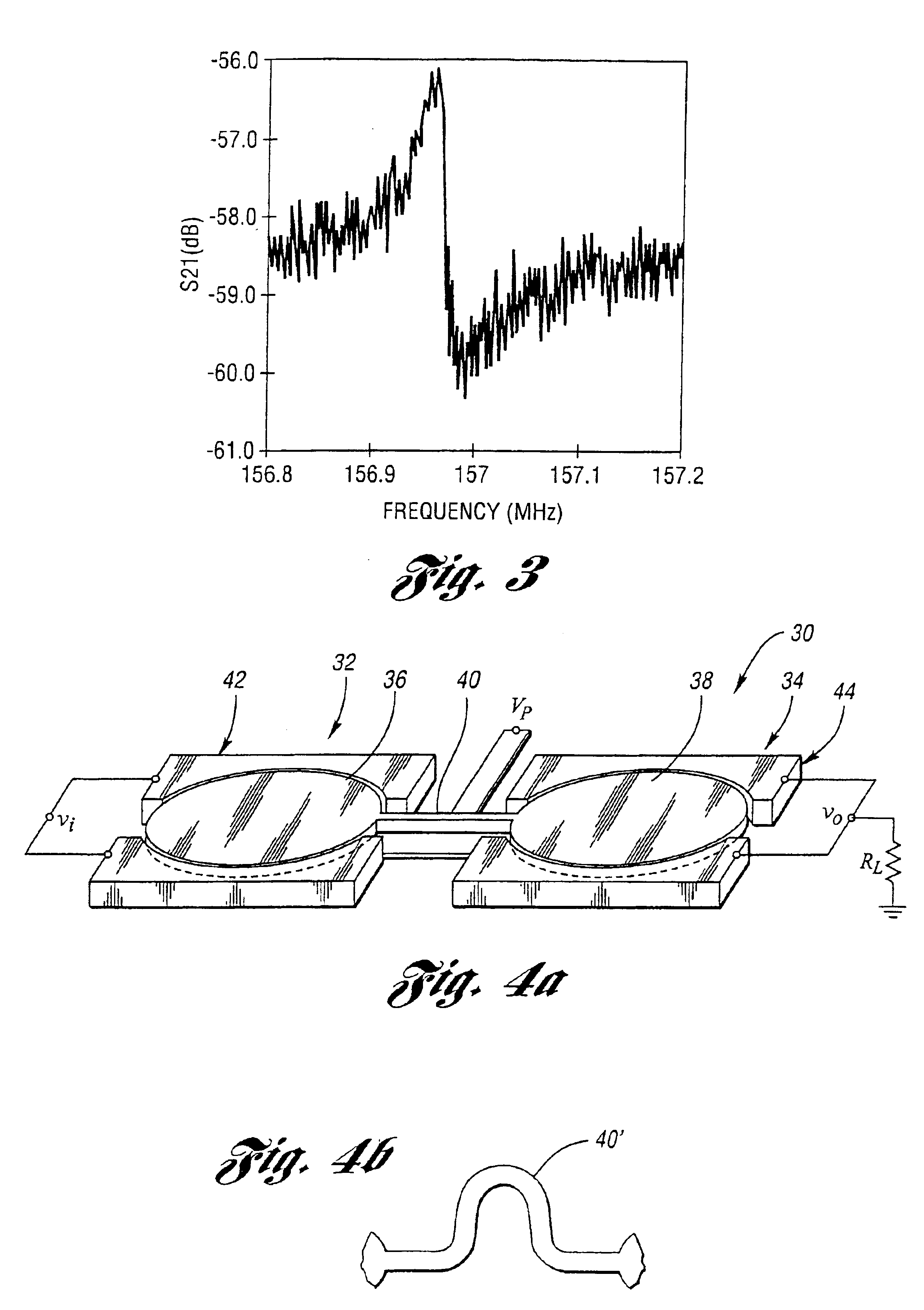
Micromechanical resonator device and micromechanical device utilizing same
InactiveUS6856217B1Improving QHigh Power Handling CapabilityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksWireless transceiverTransceiver
A micromechanical resonator device and a micromechanical device utilizing same are disclosed based upon a radially or laterally vibrating disk structure and capable of vibrating at frequencies well past the GHz range. The center of the disk is a nodal point, so when the disk resonator is supported at its center, anchor dissipation to the substrate is minimized, allowing this design to retain high-Q at high frequency. In addition, this design retains high stiffness at high frequencies and so maximizes dynamic range. Furthermore, the sidewall surface area of this disk resonator is often larger than that attainable in previous flexural-mode resonator designs, allowing this disk design to achieve a smaller series motional resistance than its counterparts when using capacitive (or electrostatic) transduction at a given frequency. Capacitive detection is not required in this design, and piezoelectric, magnetostrictive, etc. detection are also possible. The frequency and dynamic range attainable by this resonator makes it applicable to high-Q RF filtering and oscillator applications in a wide variety of communication systems. Its size also makes it particularly suited for portable, wireless applications, where, if used in large numbers, such a resonator can greatly lower the power consumption, increase robustness, and extend the range of application of high performance wireless transceivers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Fractal antennas and fractal resonators
InactiveUS7256751B2High bandwidthImprove efficiencyLogperiodic antennasAntenna supports/mountingsPhysical shapeImpedance matching
An antenna includes at least one element whose physical shape is at least partially defined as a second or higher iteration deterministic fractal. The resultant fractal antenna does not rely upon an opening angle for performance, and may be fabricated as a dipole, a vertical, or a quad, among other configurations. The number of resonant frequencies for the fractal antenna increases with iteration number N and more such frequencies are present than in a prior art Euclidean antenna. Further, the resonant frequencies can include non-harmonically related frequencies. At the high frequencies associated with wireless and cellular telephone communications, a second or third iteration, preferably Minkowski fractal antenna is implemented on a printed circuit board that is small enough to fit within the telephone housing. A fractal antenna according to the present invention is substantially smaller than its Euclidean counterpart, yet exhibits at least similar gain, efficiency, SWR, and provides a 50Ω termination impedance without requiring impedance matching.
Owner:FRACTAL ANTENNA SYST
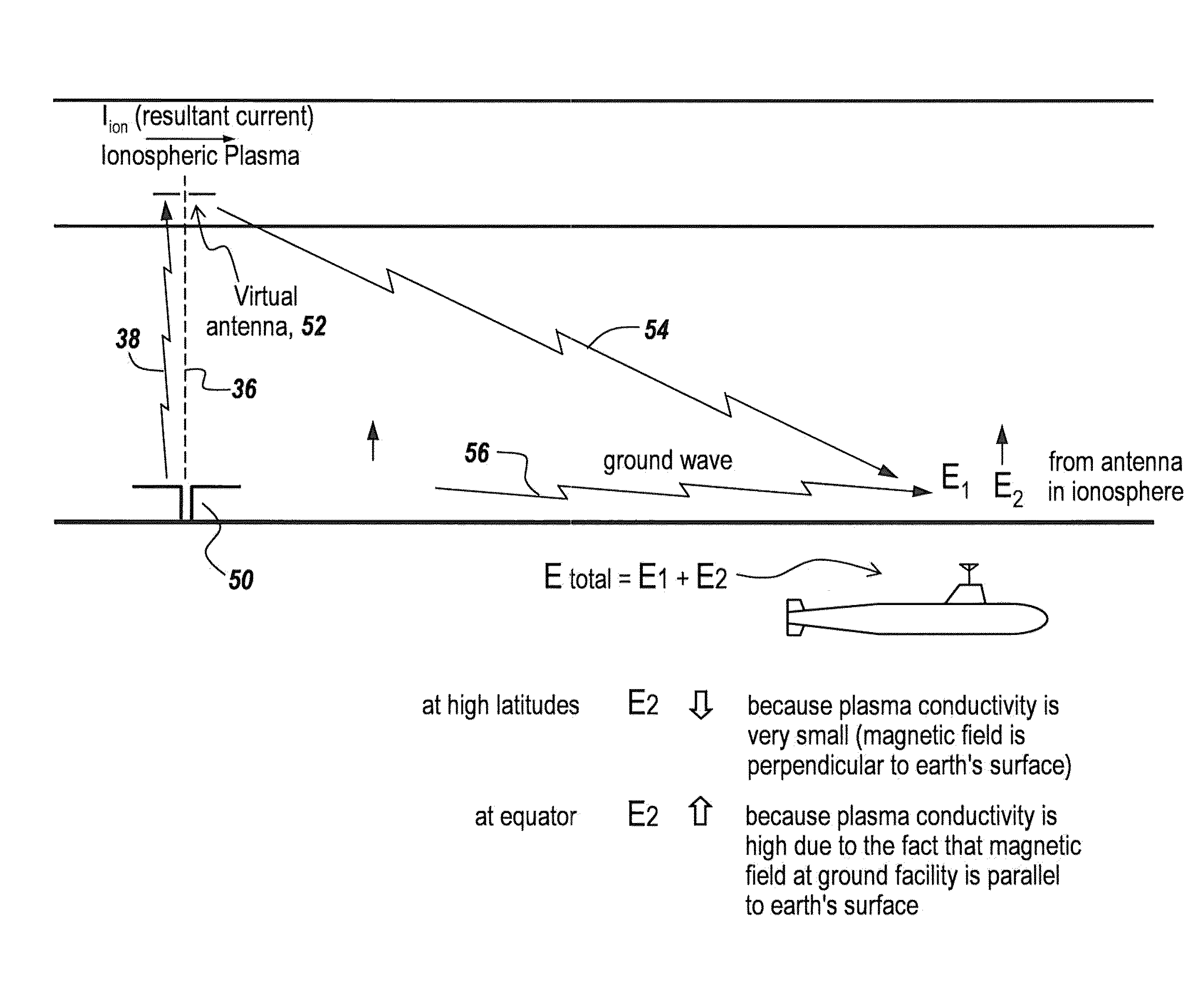
Method and apparatus for establishing low frequency/ultra low frequency and very low frequency communications
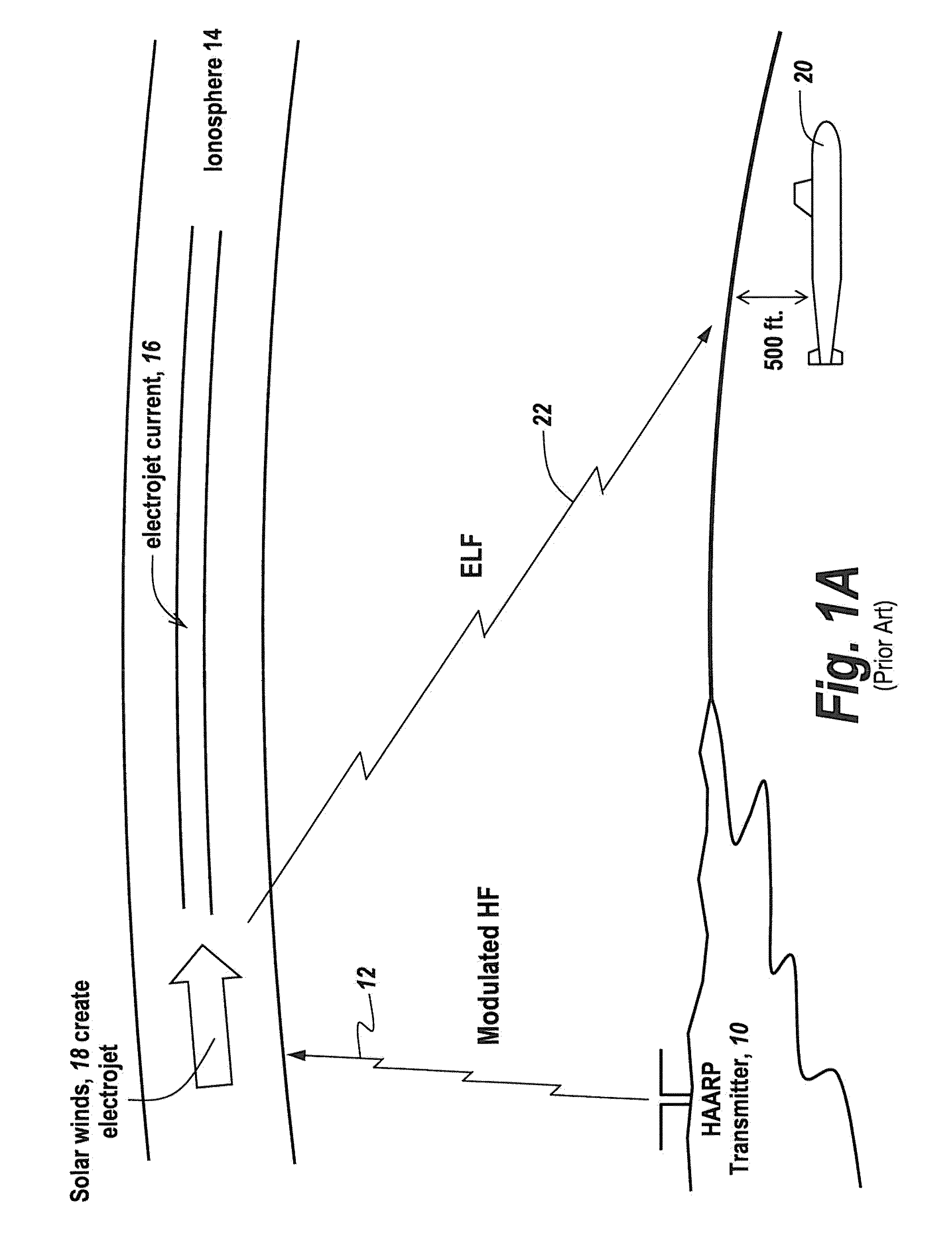
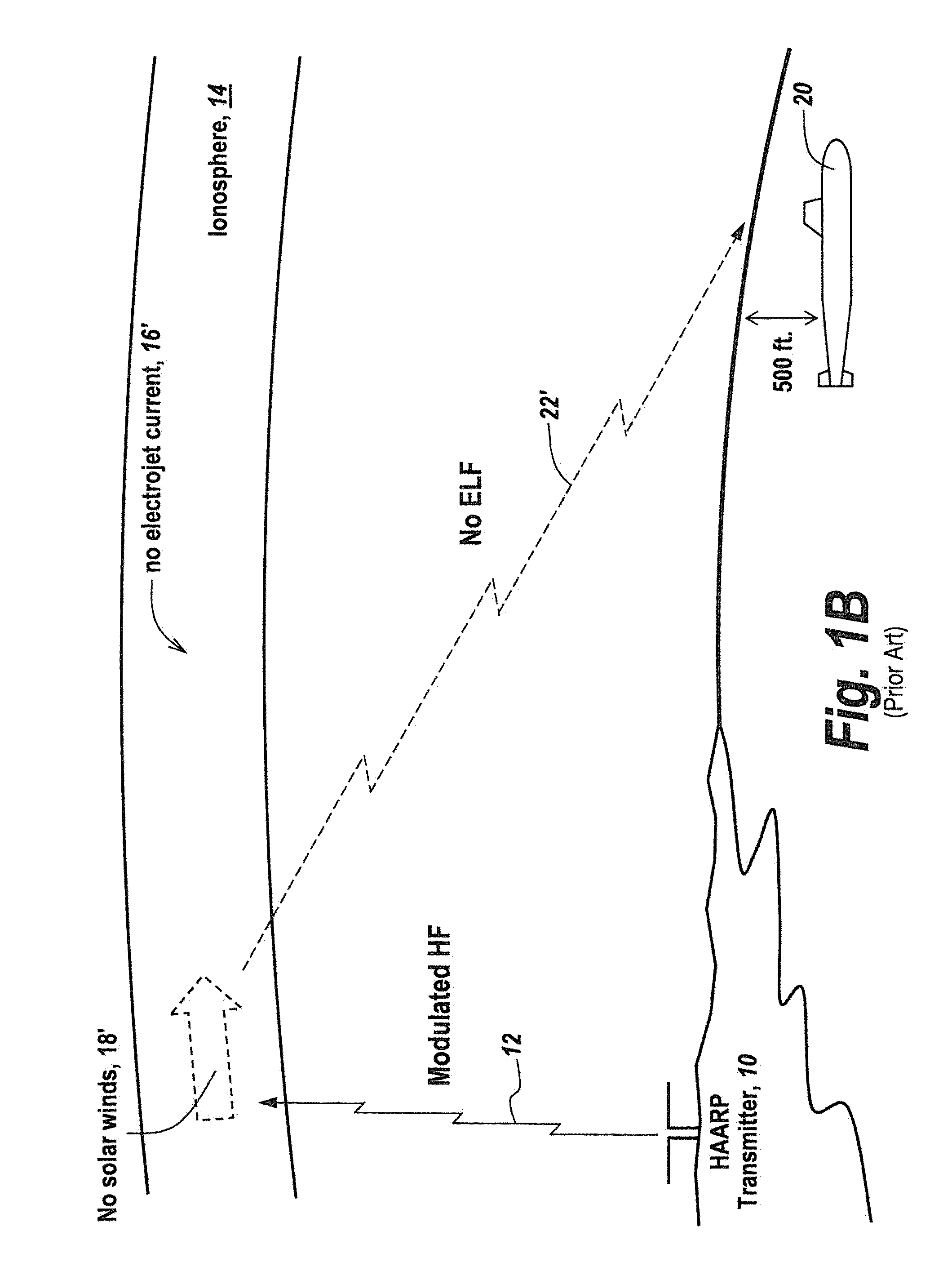
InactiveUS8299936B2Increase signal strengthShorten speedElectric signal transmission systemsDirection finders using radio wavesIonosphereElectromagnetic pulse
A method for generating electromagnetic waves in the ELF / ULF comprising the steps of using a ground-based Horizontal Electric Dipole (HED) antenna to send electromagnetic pulses upwardly in the E-region of the ionosphere to form an oscillatory or pulsed electric field; allowing said pulsed electric field to interact with magnetized plasma of the lower ionosphere to generate a pulsed horizontal and vertical current which have associated Horizontal and Vertical Electric Dipole moment; and allowing them to radiate.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Refrigeration method of low temperature environment air conditioner
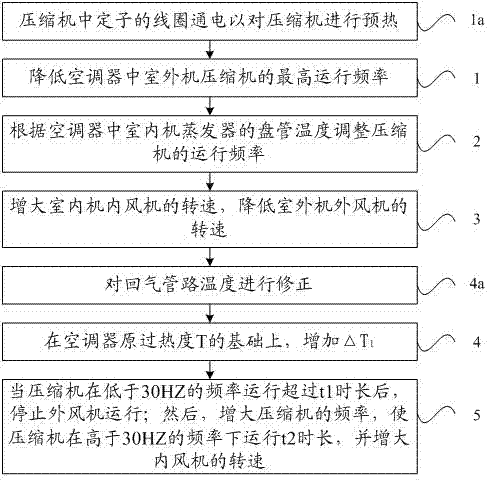
ActiveCN103115417AAchieve normal coolingAvoid frequent downtimeSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsEngineeringRefrigeration
The invention provides a refrigeration method of a low temperature environment air conditioner. When the air conditioner operates to refrigerate, the refrigeration method comprises the following steps of: step 1, reducing the topmost operating frequency of an outer door machine compressor in the air conditioner; step 2, adjusting the operating frequency of the compressor according to the temperature of a coil of an indoor machine evaporator in the air conditioner; and step 3, increasing the rotation speed of an inner fan of an indoor machine, and reducing the rotation speed of an outer door of an outdoor machine. The topmost operating frequency of the compressor is reduced, the compressor is frequently lifted frequency because of high frequency under the low temperature environment to be avoided, the frequency of the compressor is adjusted according to the temperature of the coil, and an evaporator is iced so that the compressor is stopped to be avoided; and the wind speed of the inner fan is increased, the evaporator and indoor heat transfer quantity is improved, the wind speed of the outer fan is reduced, the heat transfer quantity of a condenser is reduced, the air conditioner can normally refrigerate under the low temperature environment to be realized, and the refrigerating effect is optimized.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER JIAOZHOU AIR CONDITIONER
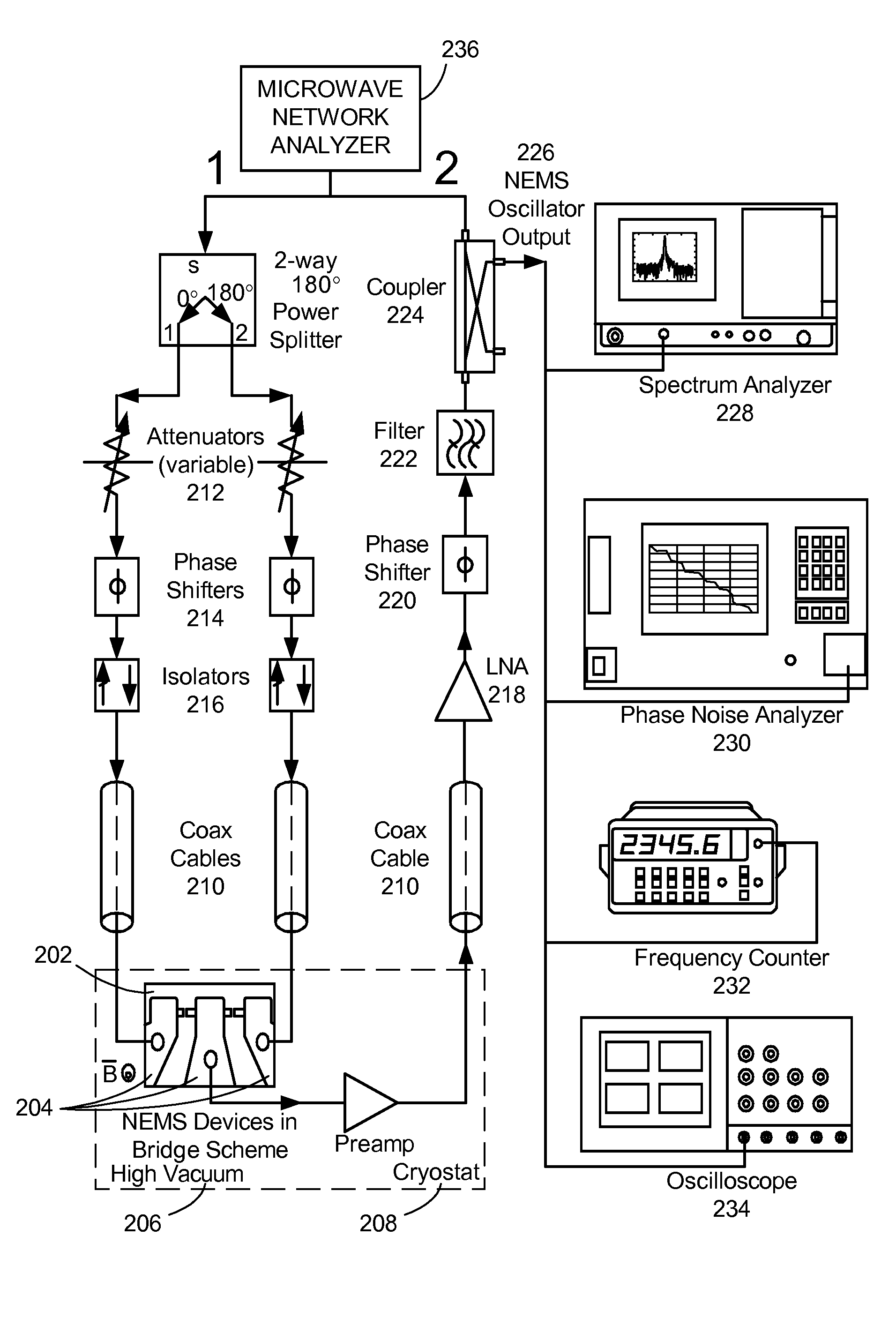
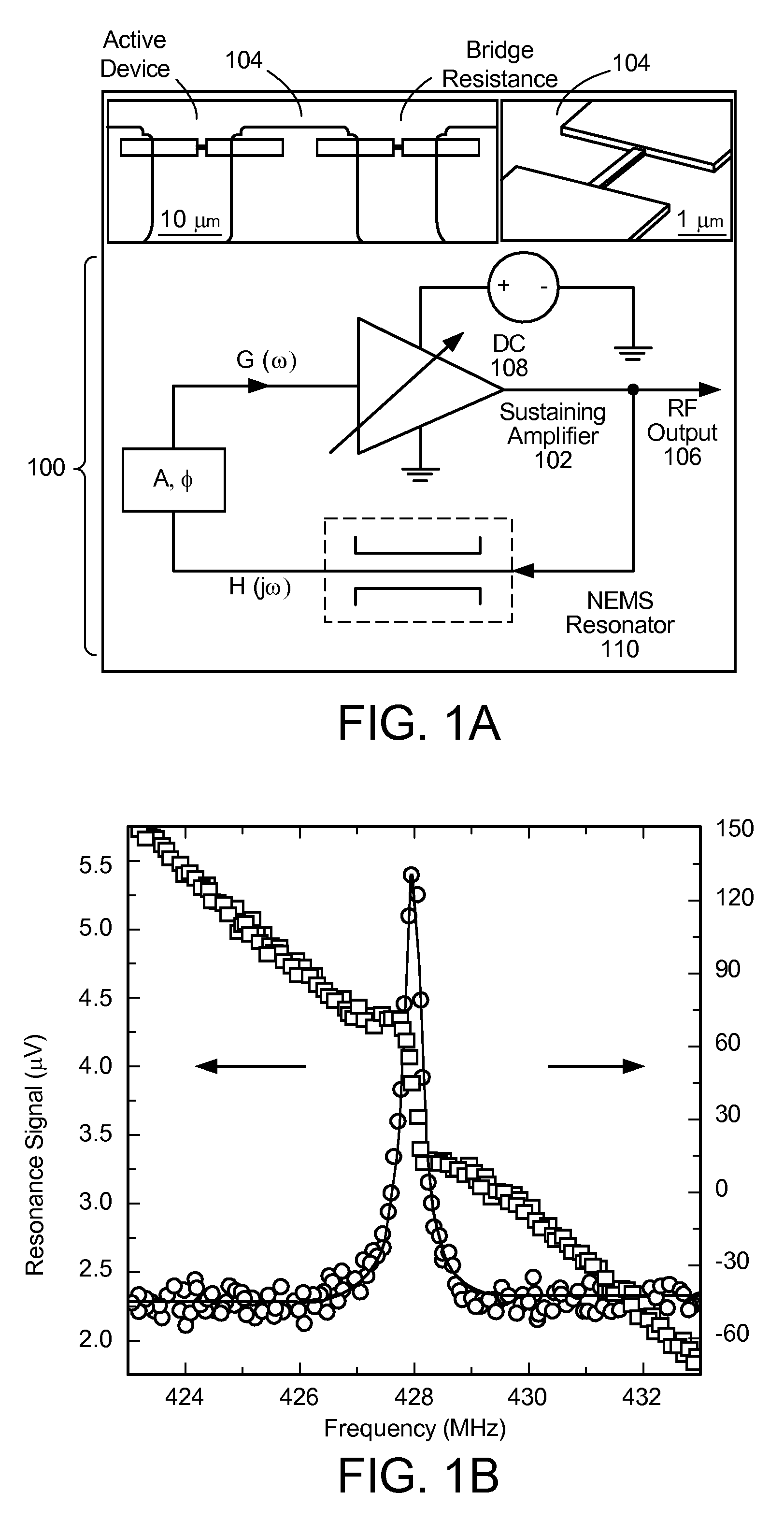
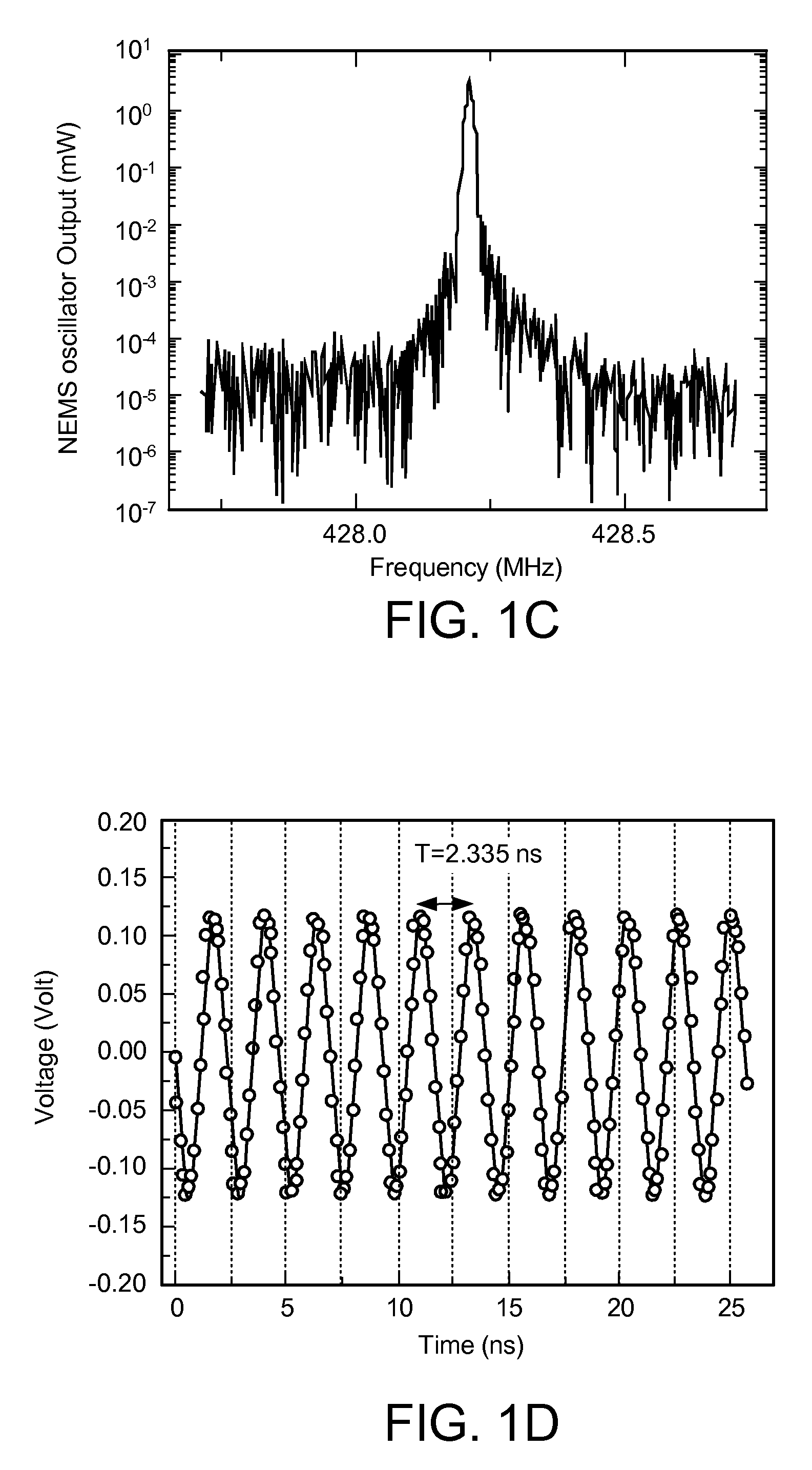
Ultra-high frequency self-sustaining oscillators, coupled oscillators, voltage-controlled oscillators, and oscillator arrays based on vibrating nanoelectromechanical resonators
ActiveUS7724103B2Noteworthy performanceNoteworthy stabilityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersBeam resonatorVIT signals
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
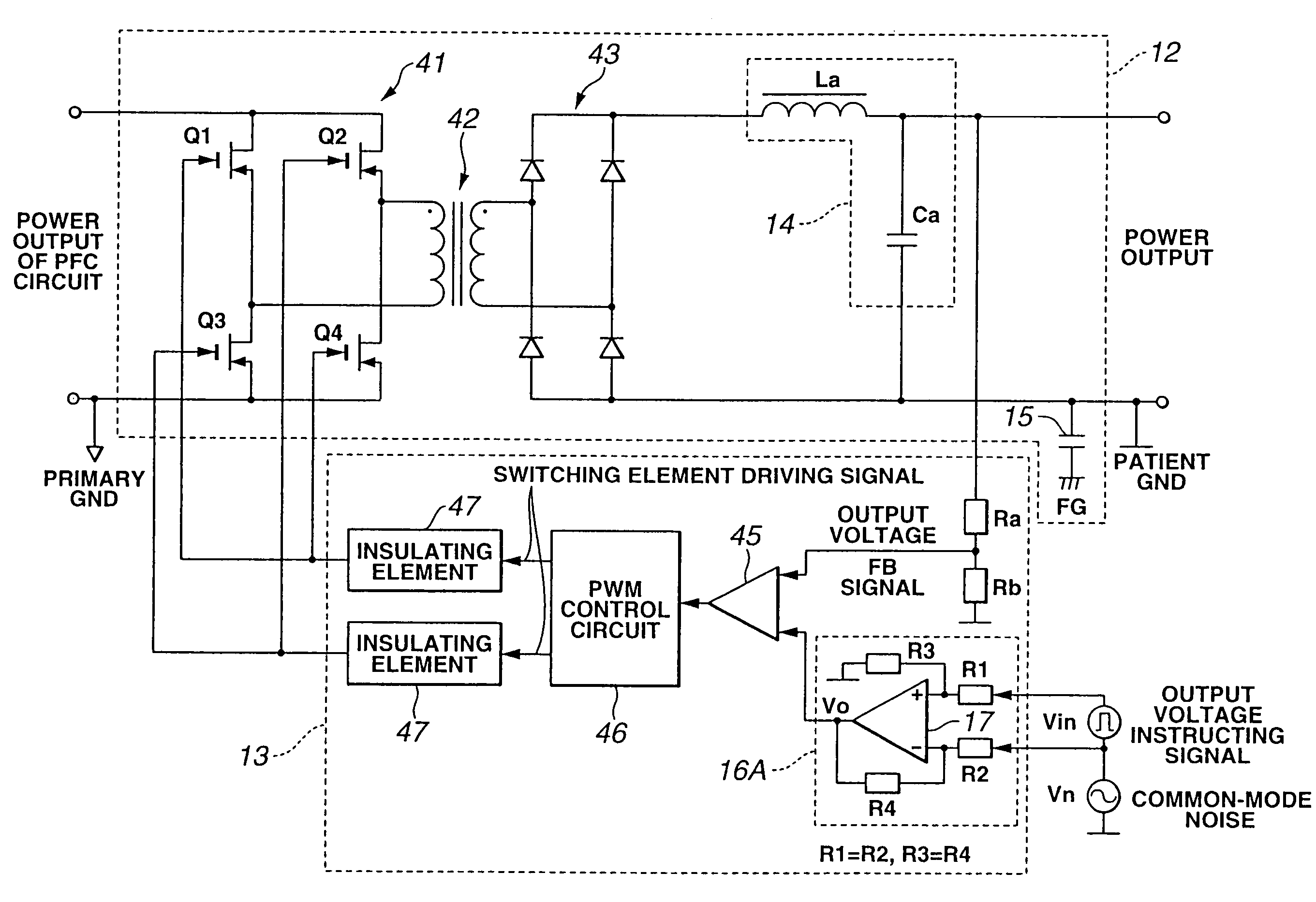
Power supply apparatus for electric operation
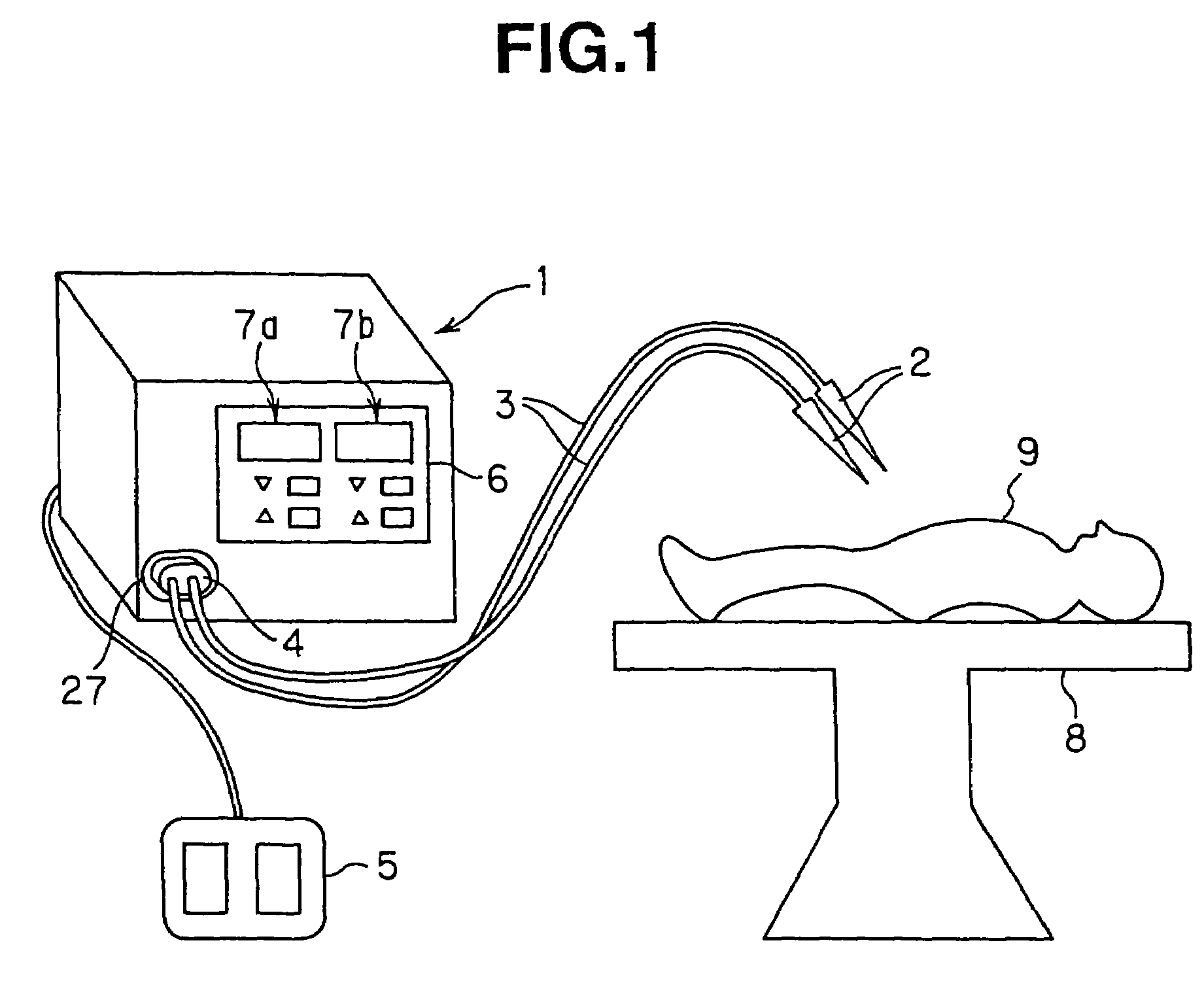
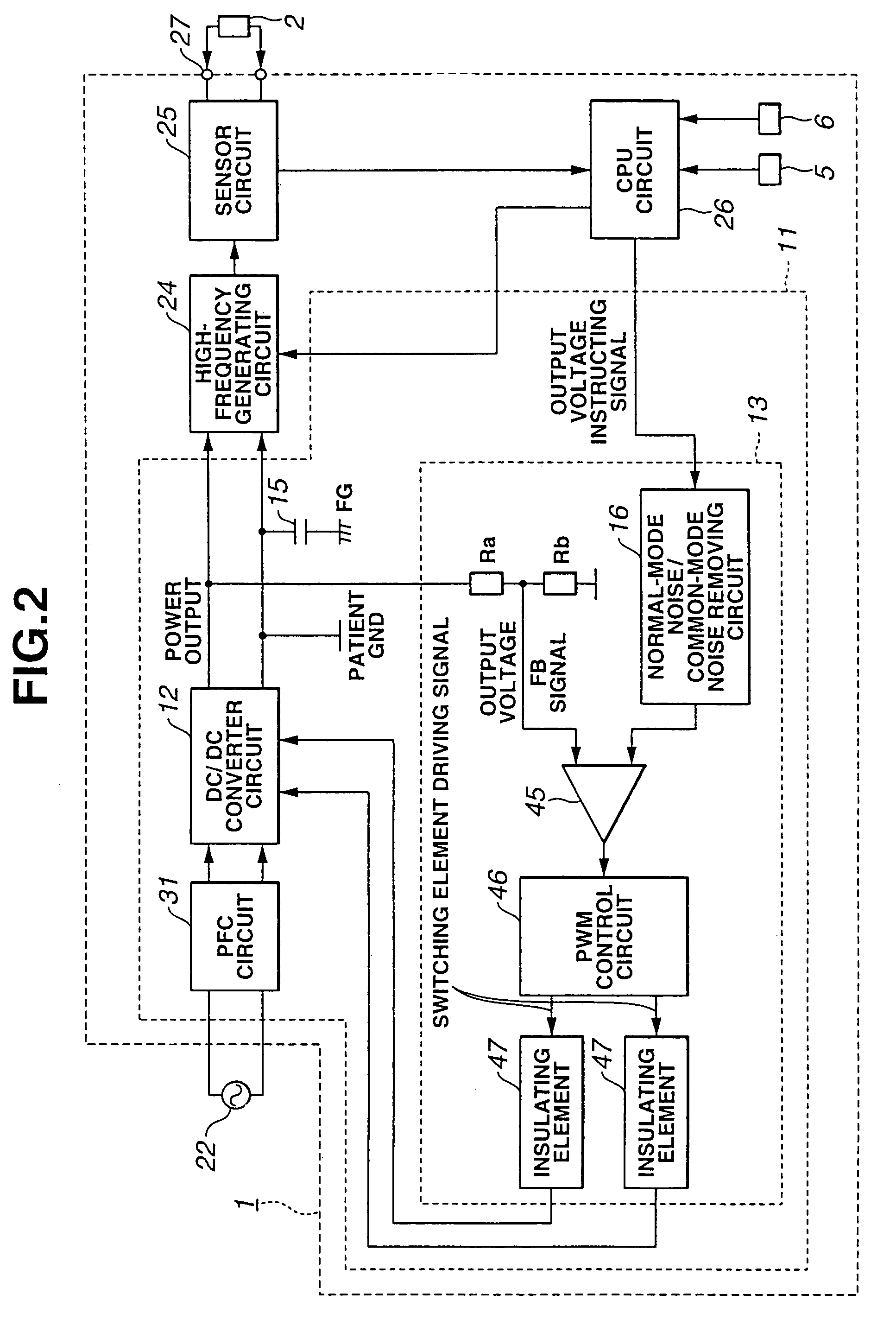
ActiveUS7324357B2High frequencyReduce common mode noiseDc-dc conversionSurgical instruments for heatingNormal modeEngineering
A power supply apparatus for electric operation is provided for an electric operation apparatus, and includes an instructing signal input portion which generates a DC output voltage to a high-frequency generating circuit that generates a high frequency and which receives an instructing signal for controlling the output voltage. The instructing signal input portion includes at least a noise reducing circuit which reduces a normal-mode noise.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
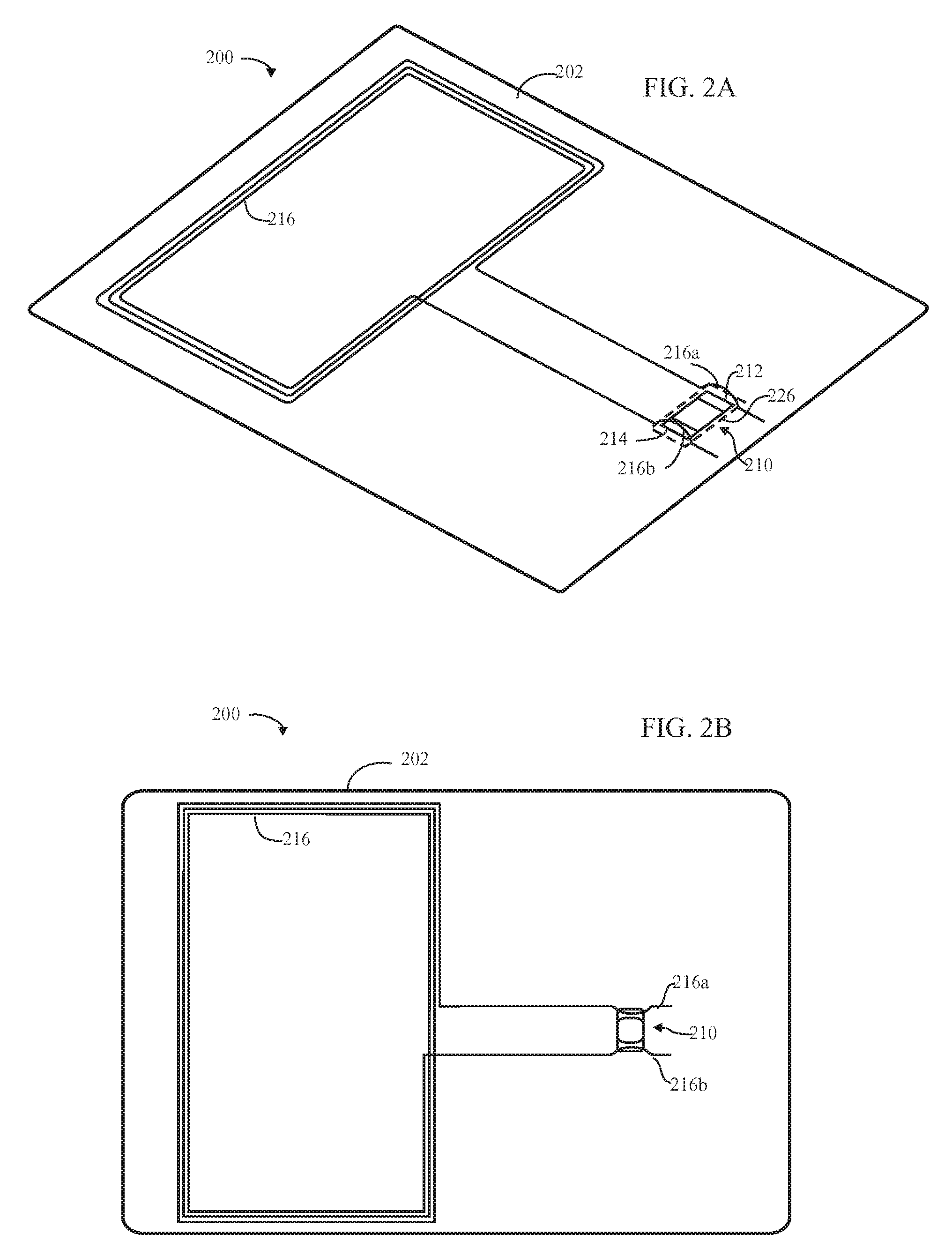
Secure high frequency / ultra high frequency inlay, and method and apparatus for making the inlay
InactiveUS20080072423A1Little strengthEasy to controlPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsEngineeringInterconnection
Forming an inlay comprising an antenna wire having two end portions and a site for a transponder chip, comprises: mounting the wire to a surface of substrate; and leaving the end portions of the antenna wire free-standing, as loops adjacent terminal areas of a site on the substrate for the transponder chip. With the transponder chip installed on the substrate, the free-standing loops are repositioned to be substantially directly over the terminals of the transponder chip, in preparation for interconnection of the loops to the terminals of the transponder chip, then are bonded to the terminals. An embedding tool for mounting the wire on the substrate may embed the wire in or adhesively place a self-bonding wire on a surface of the substrate. The substrate may have two transponder chips, and function as a secure inlay. An anti-skimming feature is included in the inlay.
Owner:HID GLOBAL GMBH
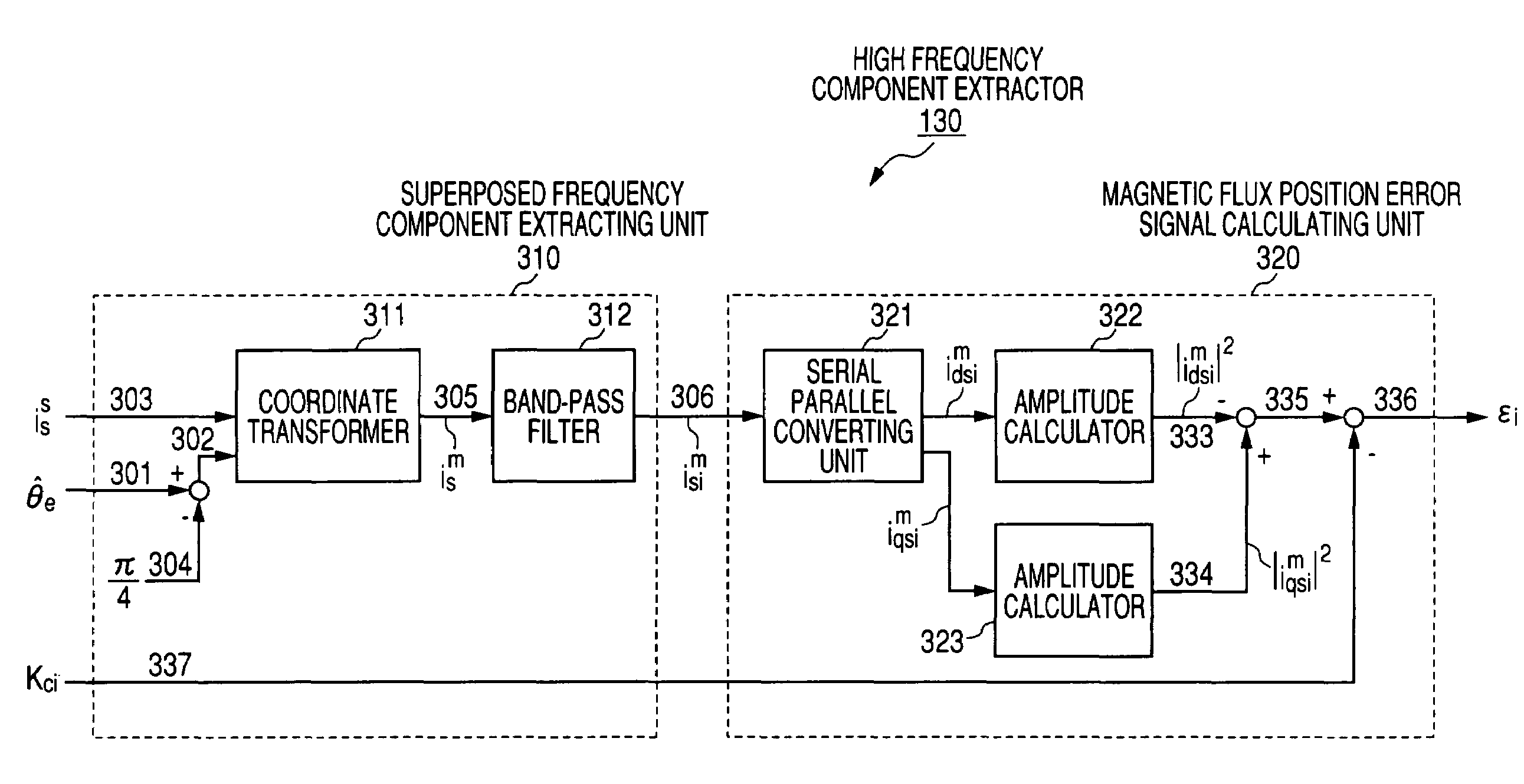
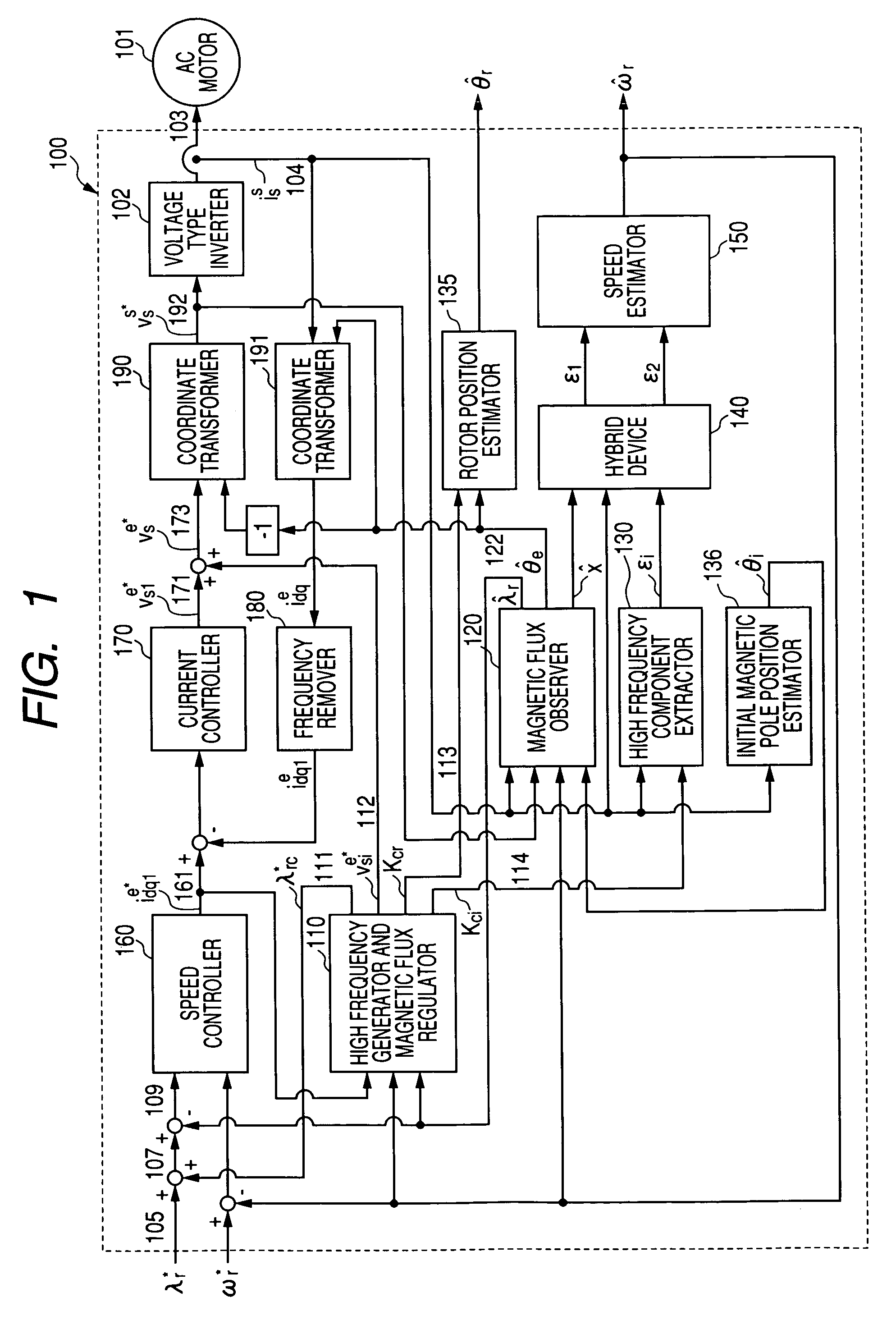
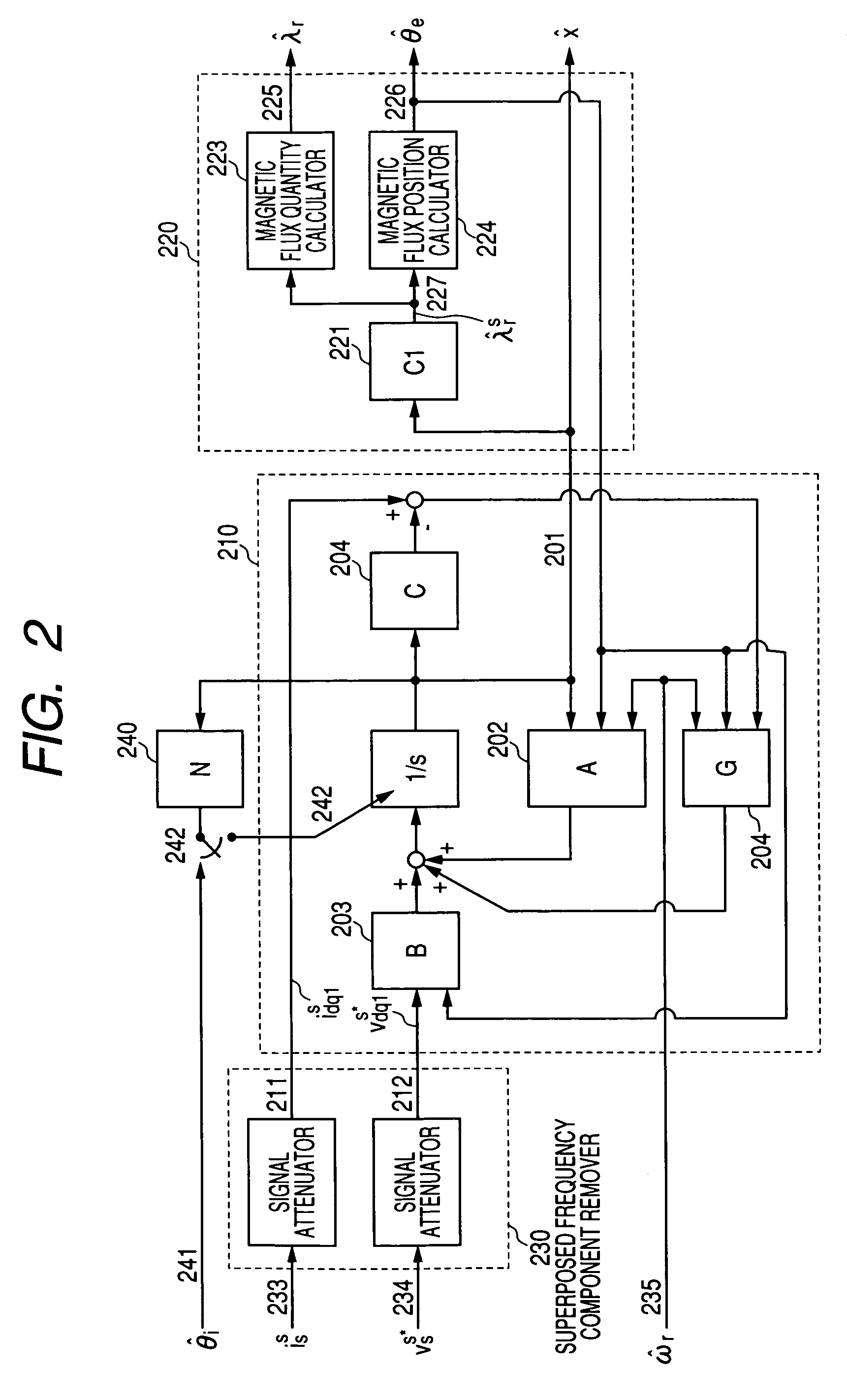
Sensorless controller of AC motor and control method
InactiveUS7045988B2Improve efficiencyMagnetic saliency at the high frequency is reducedVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlLow speedSignal on
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
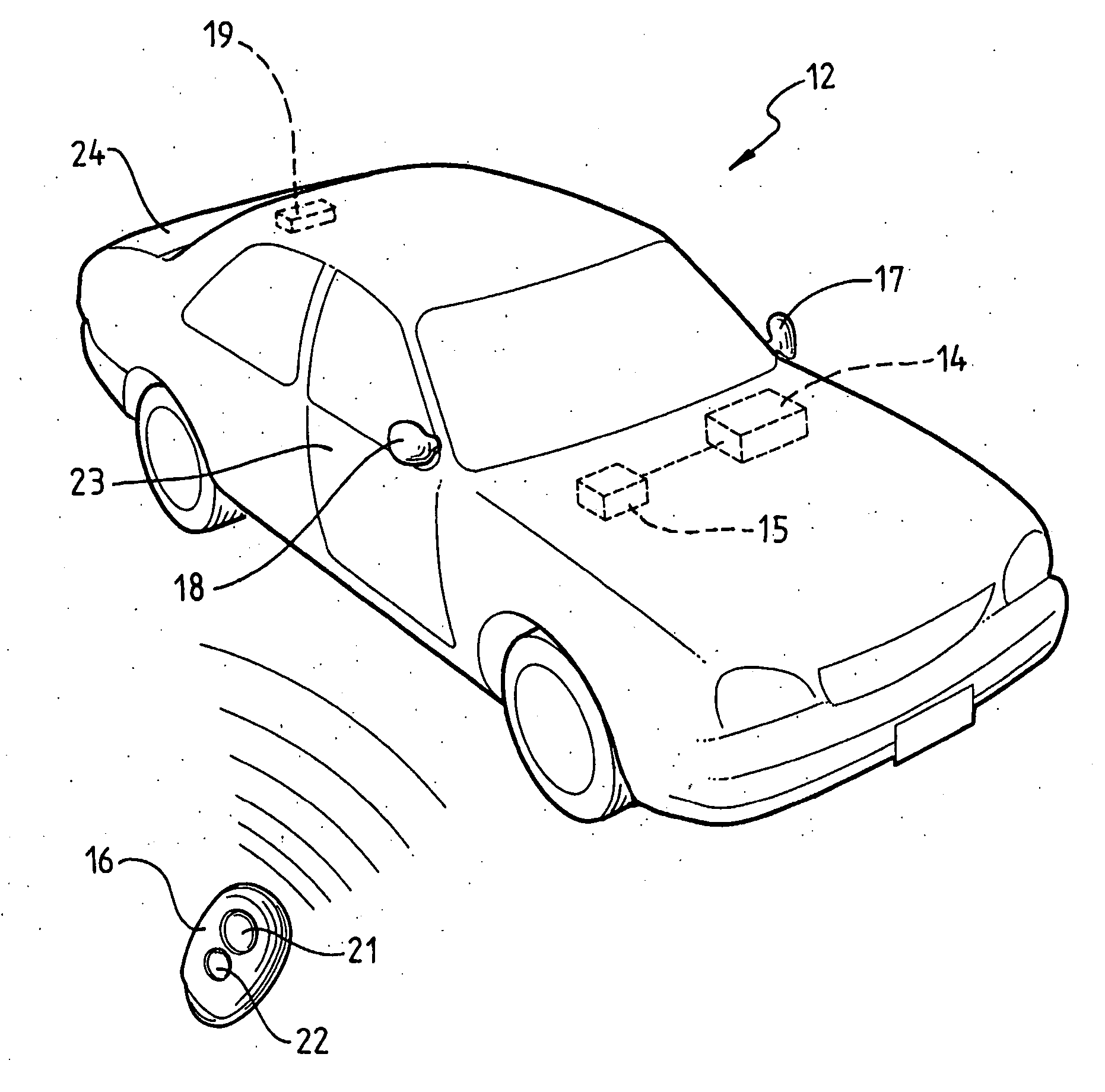
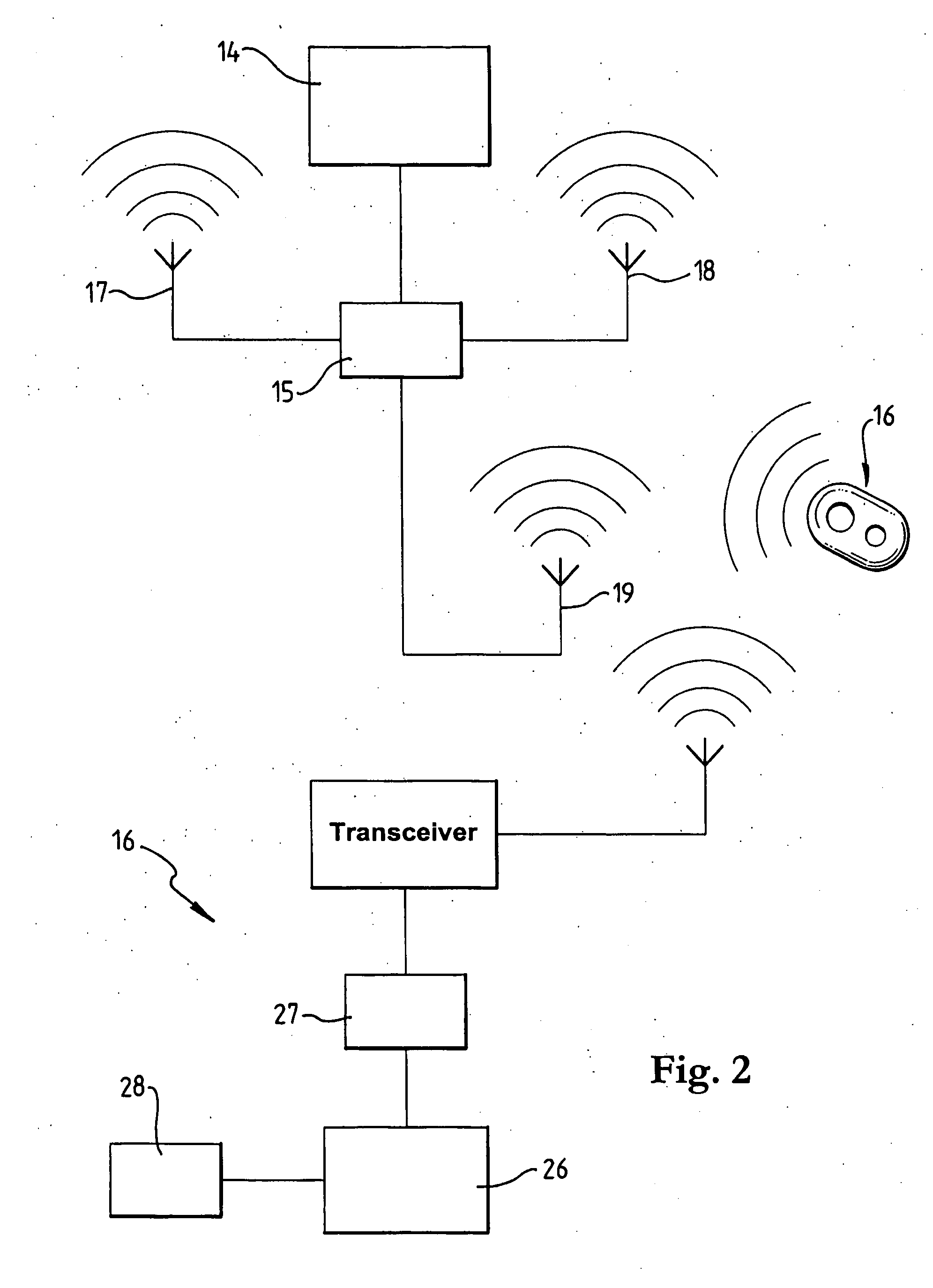
Bi-Directional Radio Monitoring System
InactiveUS20070268110A1Reduce unnecessary power consumptionReduce frequencyElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsTransceiverMonitoring system
A bi-directional radio monitoring system includes a base unit (14) having a base RF transceiver (15) with two or more fixed antennae (17, 18, 19) associated therewith. The base unit communicates with a portable transceiver (16) using ultra high frequency (UHF) radio signals whereby, by using the two or more antennae (17, 18, 19), the base unit (14) is able to determine a relative position of the portable transceiver (16), depending on the closeness of the movable transceiver (16) to each of the fixed transceiver antennae (17, 18, 19). The RF signal transmission by the base unit (14) may vary in terms of channel, power, packet length, data rate and packet contents transmitted from each antennae (17, 18, 19) to give rise to responses from the portable transceiver (16) that enable the base unit (14) to track the movement of the portable transceiver (16).
Owner:AUSTRALIAN ARROW
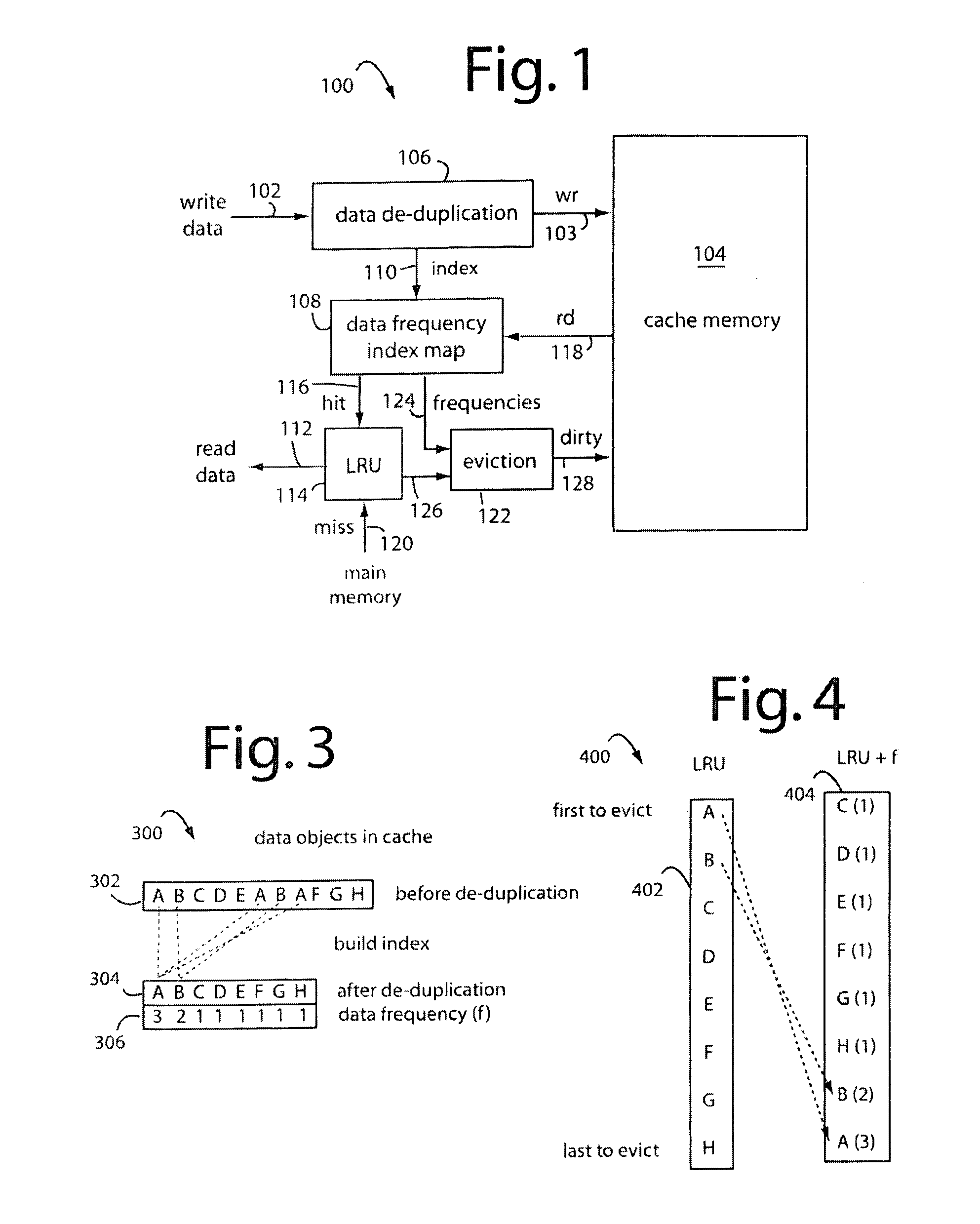
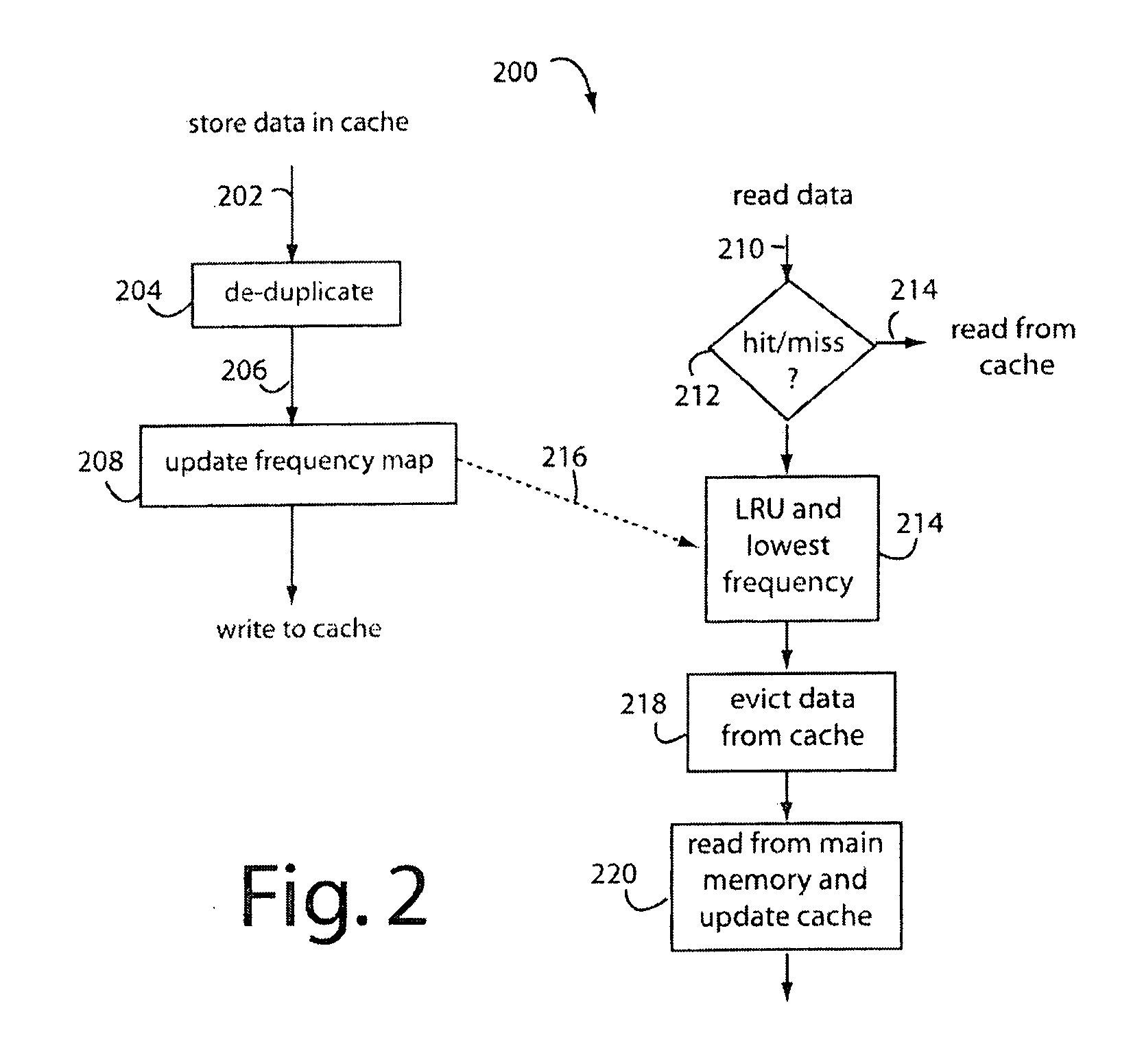
Data block frequency map dependent caching
InactiveUS20090204765A1Improve caching capacityImprove system performanceMemory systemsParallel computingCache algorithms
A method for increasing the performance and utilization of cache memory by combining the data block frequency map generated by data de-duplication mechanism and page prefetching and eviction algorithms like Least Recently Used (LRU) policy. The data block frequency map provides weight directly proportional to the frequency count of the block in the dataset. This weight is used to influence the caching algorithms like LRU. Data blocks that have lesser frequency count in the dataset are evicted before those with higher frequencies, even though they may not have been the topmost blocks for page eviction by caching algorithms. The method effectively combines the weight of the block in the frequency map and its eviction status by caching algorithms like LRU to get an improved performance and utilization of the cache memory.
Owner:IBM CORP
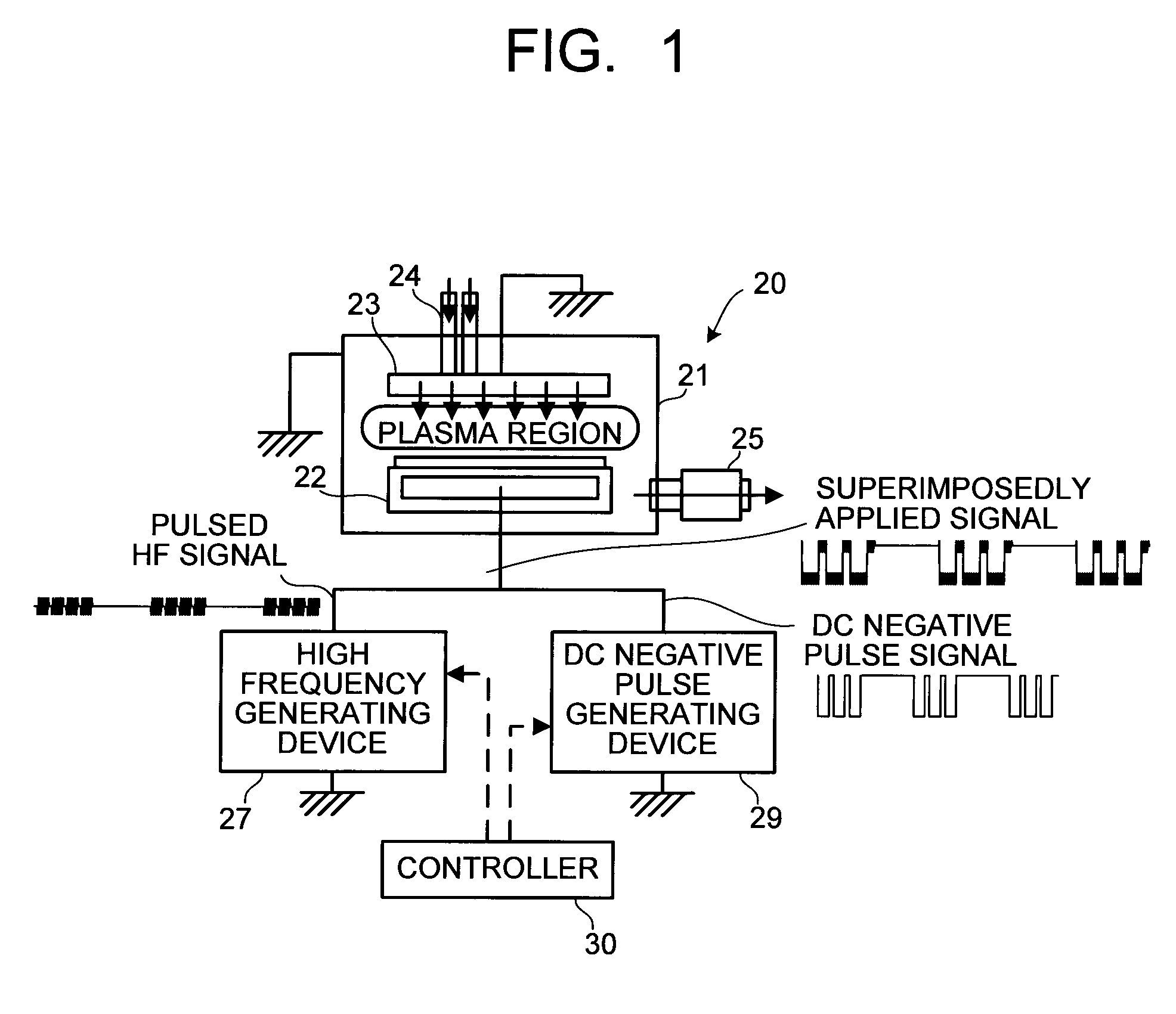
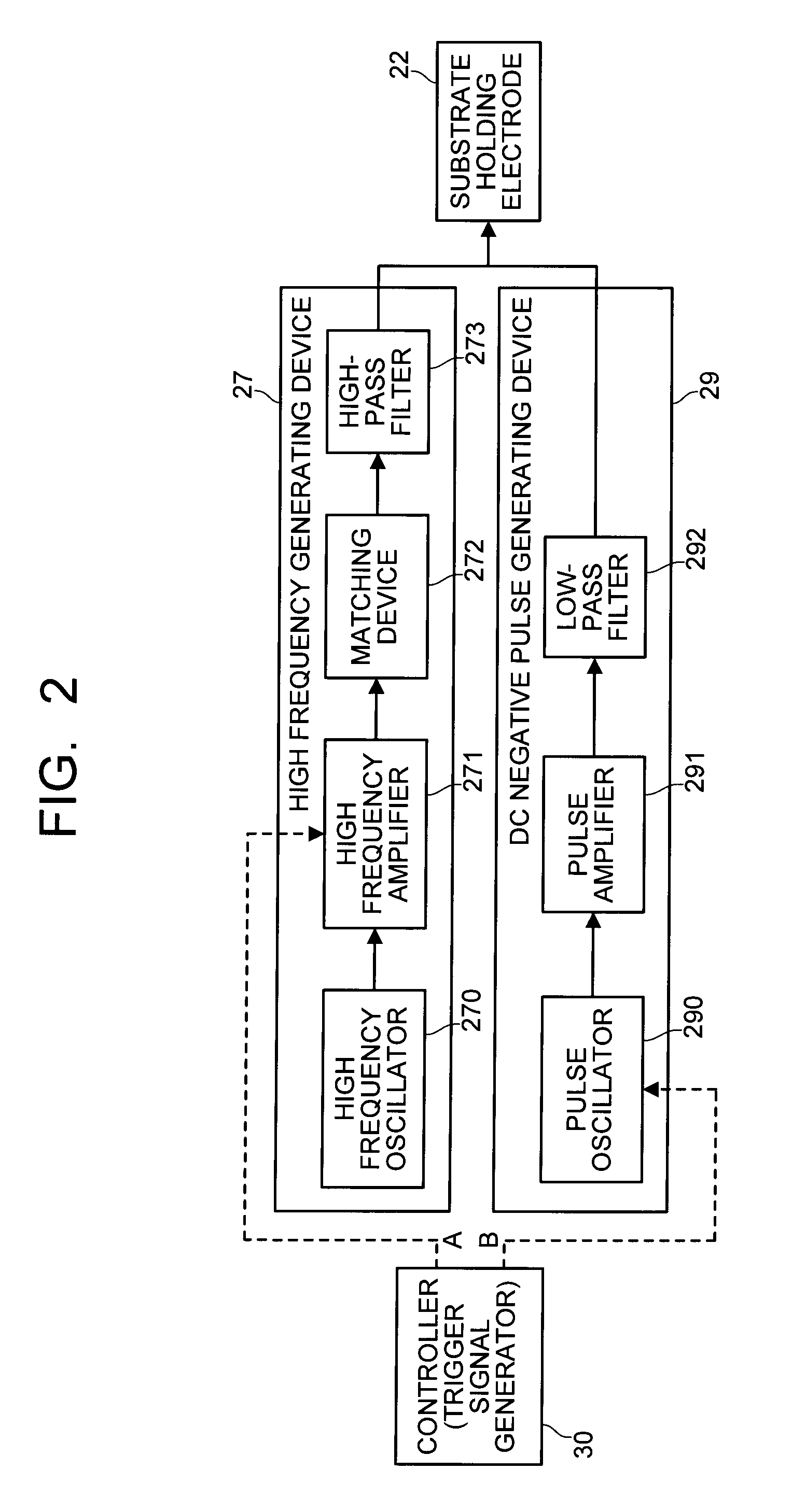
Substrate plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
ActiveUS20090194508A1Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsPulse voltagePlasma processing
A substrate plasma processing apparatus includes a substrate holding electrode and a counter electrode which are arranged in a chamber, a high frequency generating device which applies a high frequency of 50 MHZ or higher to the substrate holding electrode, a DC negative pulse generating device which applies a DC negative pulse voltage in a manner of superimposing on the high frequency, and a controller controlling to cause intermittent application of the high frequency and cause intermittent application of the DC negative pulse voltage according to the timing of on or off of the high frequency.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Method and apparatus for achieving higher frequencies of exactly rounded results
InactiveUS6134574ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesBinary multiplierOperand
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
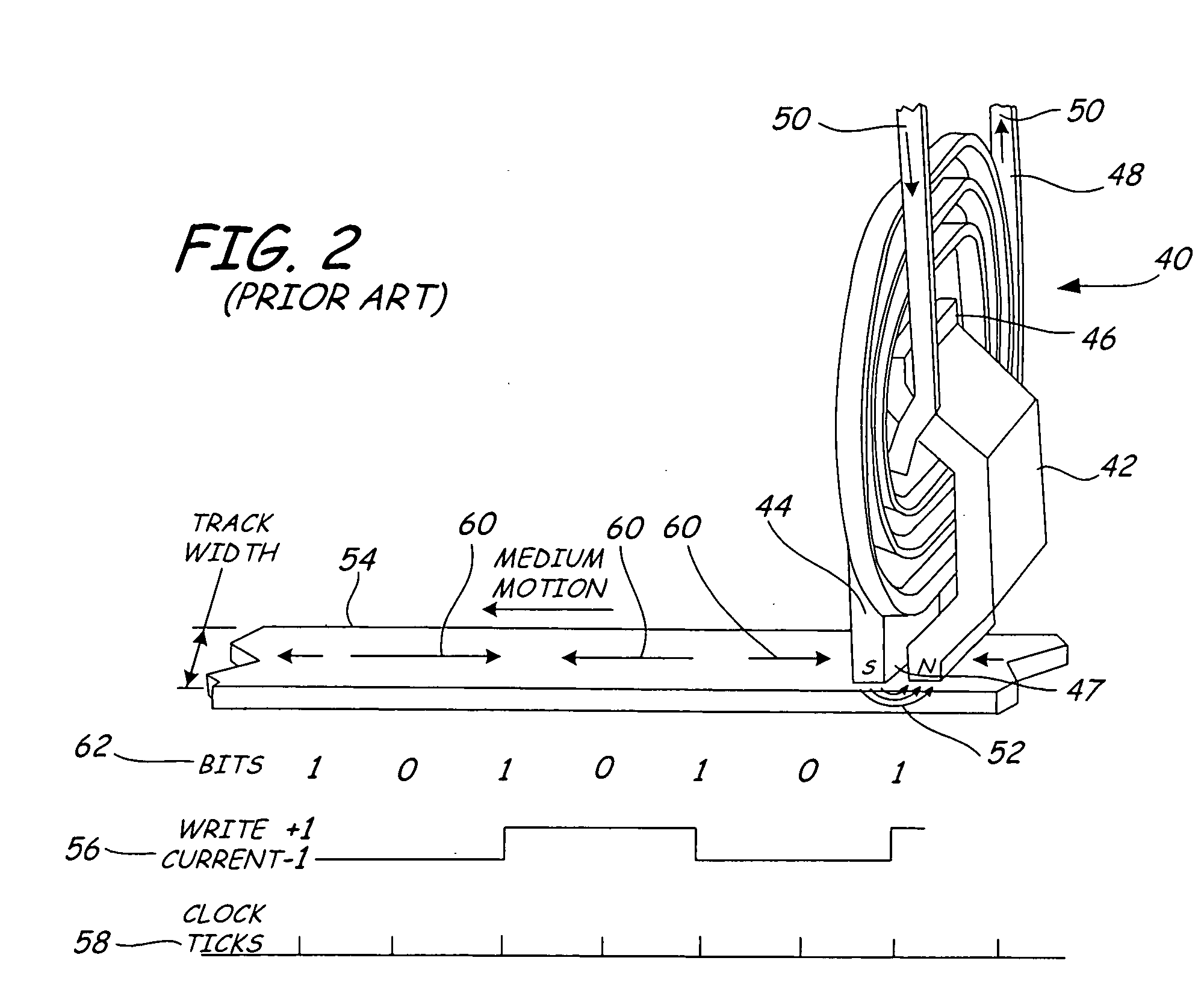
High frequency assisted writing
InactiveUS7256955B2Easy to switchHigh frequency magnetic fieldRecord information storageDigital recordingMagnetic mediaElectrical current
Data is written to a magnetic media, by applying a magnetic write field to the magnetic media with a write pole, in conjunction with a high frequency magnetic field, to the magnetic media to assist writing to the magnetic media. The high frequency magnetic field is generated by applying a specific write current waveform to the magnetic writer, resulting in the generation of a high frequency magnetic write field.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
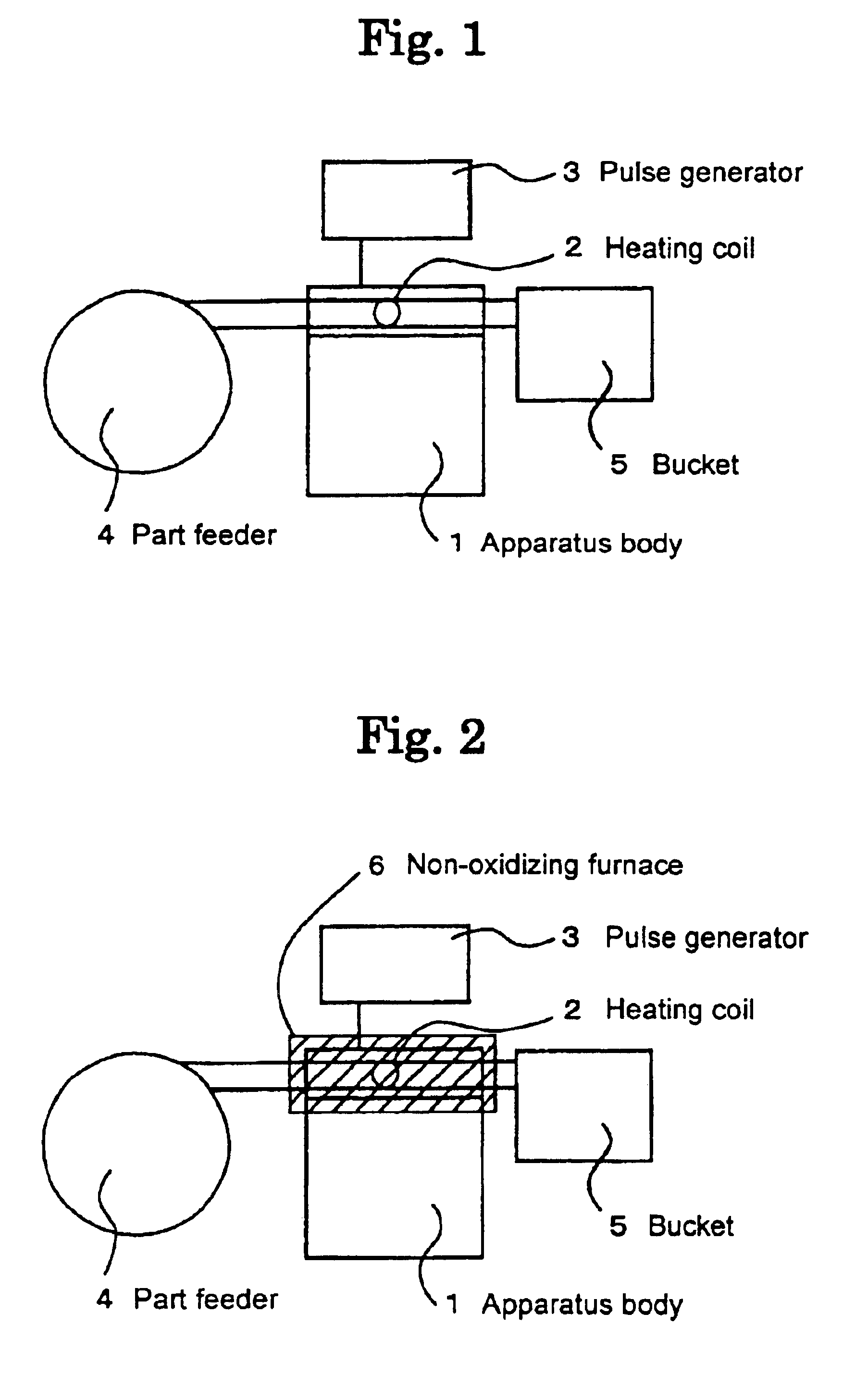
Method of baking treatment of steel product parts
InactiveUS6855217B2Shorten the timeImprove facilitiesIncreasing energy efficiencyFurnace typesSurface layerMetallurgy
The present invention relates to a method of baking treatment of steel product parts using a high frequency or ultra-high frequency for preventing delayed fracture from occurring due to diffusive hydrogen occluded in steel parts, for example, screws, bolts and the like, or for heating surface layers of the steel parts to generate a difference in temperature between the surface layers and interiors of the steel parts, thereby causing distortion in lattices, wherein the surface layers of the steel parts are rapidly heated to 100 to 300° C. with a high frequency or ultra-high frequency at 10 KHz or higher to remove the diffusive hydrogen which is involved in hydrogen embrittlement, or to transfer an existing state to non-diffusive hydrogen which is not involved in the hydrogen embrittlement.
Owner:AOYAMA SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
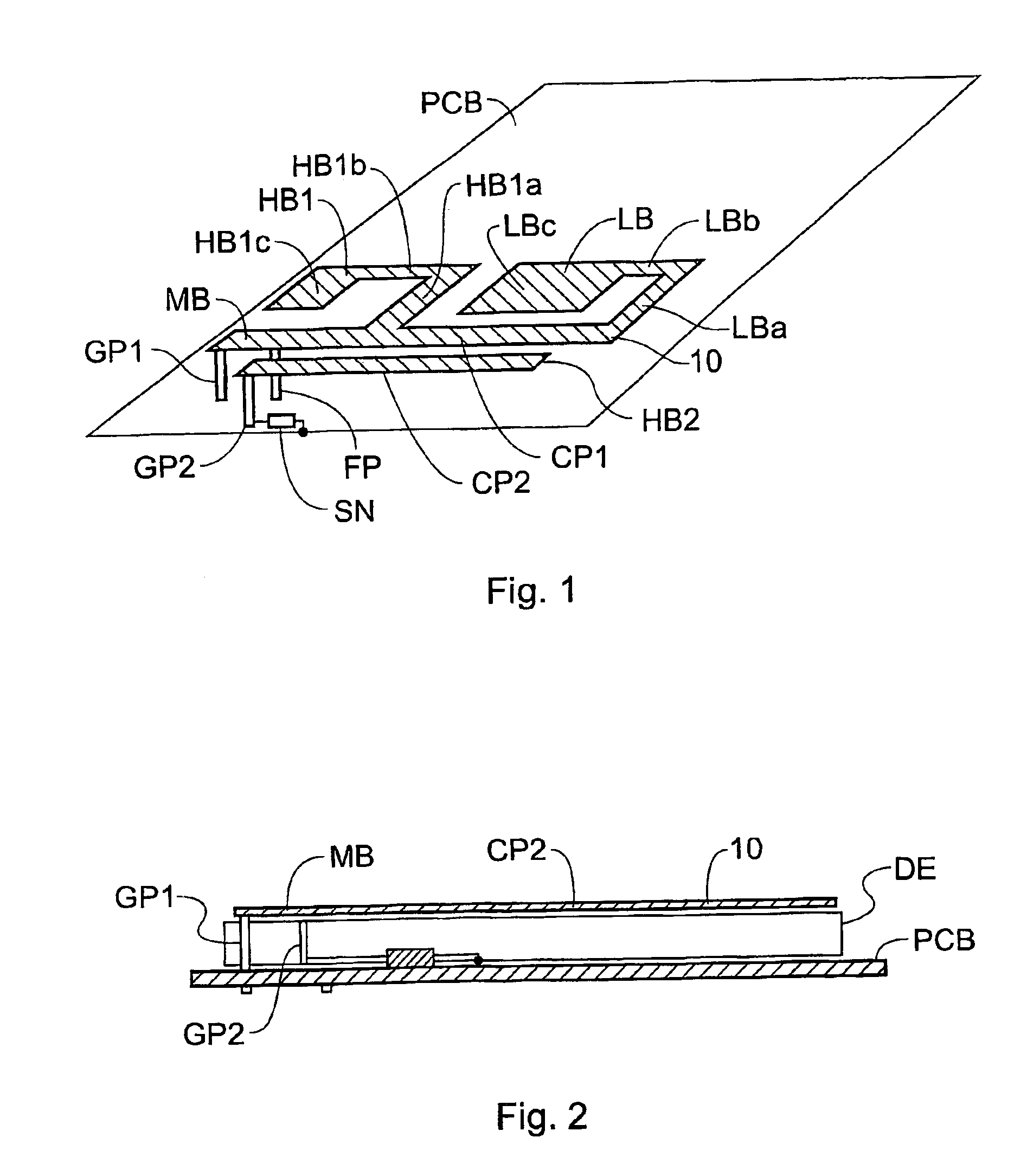
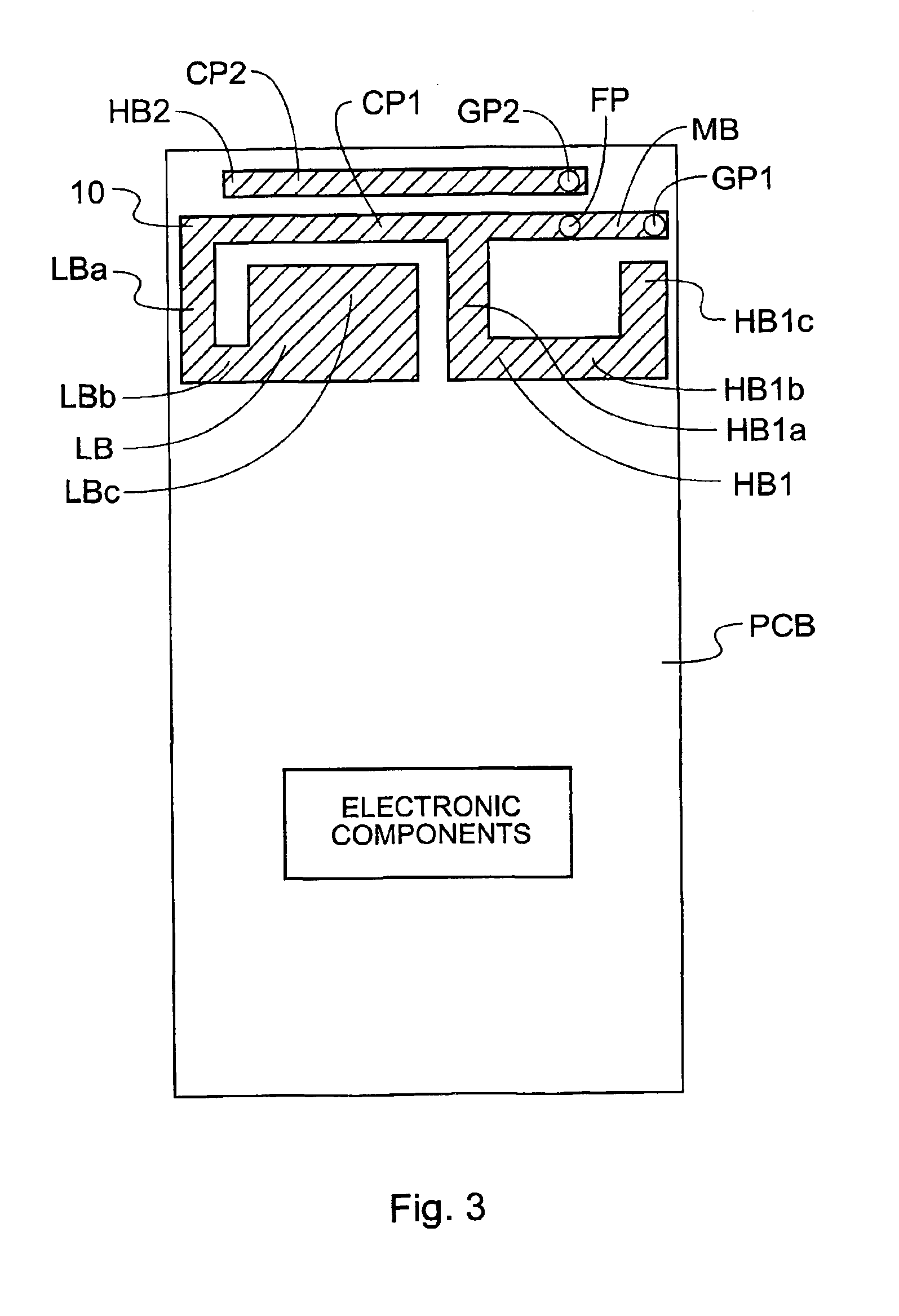
Mobile communication device
InactiveUS6950065B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorNetwork connection
A mobile communications device has a multifrequency band antenna with a low band portion (LB) tuned to a low frequency band, and a first high band portion (HB1) tuned to a first high frequency band at higher frequencies than the low frequency band. The low band portion (LB) and the first high band portion (HB1) have a common first grounding point (GP1), a common feeding point (FP) for feeding input signals to the antenna and for receiving signals from the antenna, and a first conductor portion (CP1), which forms part of the low band portion (LB) and of the first high band portion (HB1). The first conductor portion (CP1) is electrically connected to the first grounding point (GP1) and to the common feeding point (FP). A second high band portion (HB2) is coupled to the first conductor portion (CP1) and tuned to a second high frequency band at a higher frequency than the low frequency band and different from the first high frequency band. A switching network is connected between the second high band portion and ground, allowing the resonant frequency of the second high band portion to be varied, on the basis of a signal which depends on the operating mode of the device, thereby allowing four band operation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
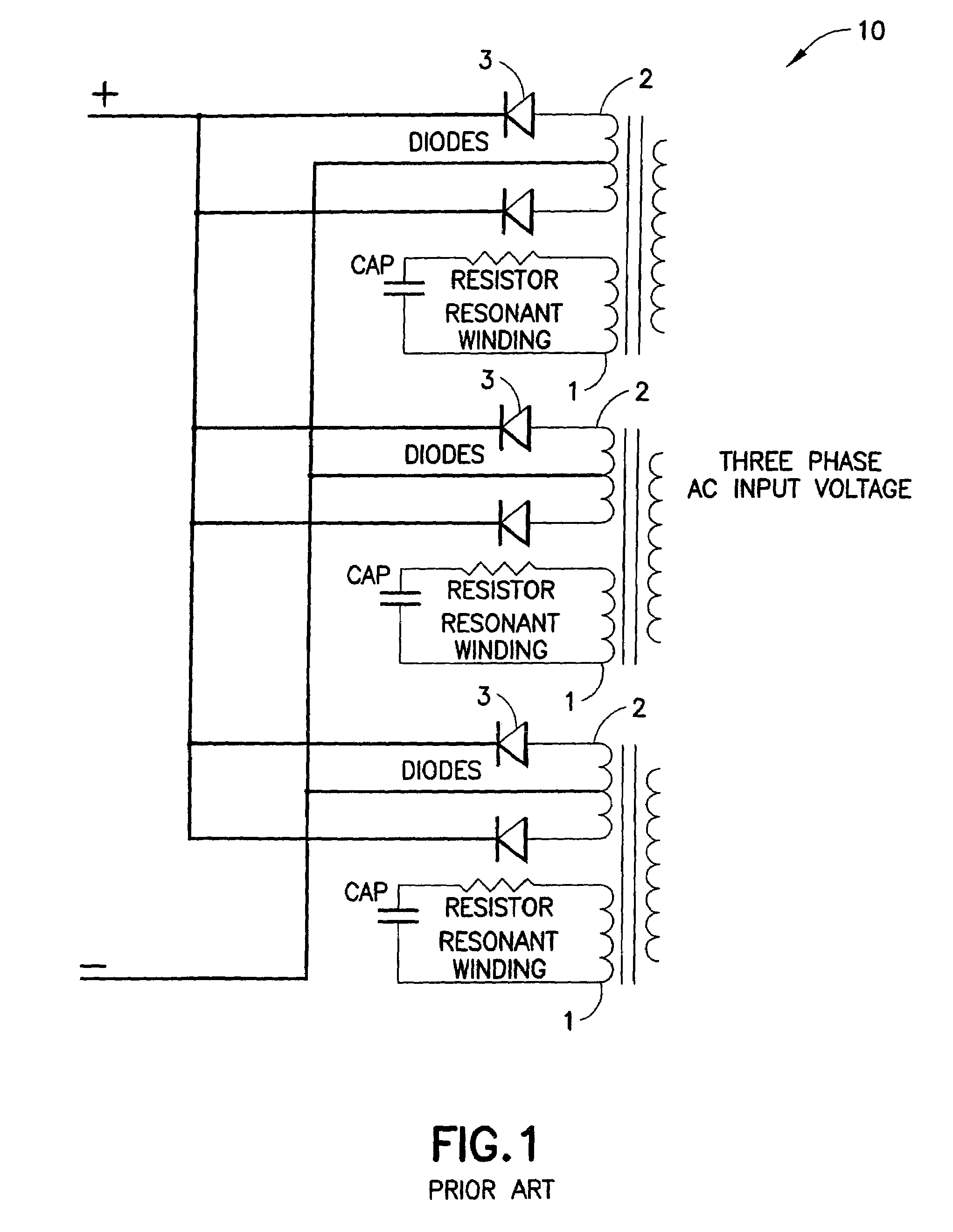
Fast charger for high capacity batteries
InactiveUS7301308B2Reduce heatMinimise currentCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingFast chargingEngineering
A highly efficient fast charger for high capacity batteries and methods for fast charging high capacity batteries. The fast charger preferably comprises a rectified AC input of single or preferably three phases, with an optional power factor corrected input, minimally filtered with high frequency, high ripple current capacitors, which is switched with a power switching circuit in the “buck” configuration into an inductor / capacitor output filter. Metallized film capacitors are employed, to minimize the rectified 360 Hertz AC component filtering while providing transient switch protection and ripple current requirements for the buck regulator, to provide a high current fast charger with substantially improved power factor. High power, high frequency switching with minimized output filter size provides a highly filtered DC output. The fast charger is adapted to be constructed in a modular design for simple maintenance.
Owner:AKER WADE POWER TECH
Transposed winding for random-wound electrical machines operating at high frequencies
InactiveUS20020096959A1Synchronous machinesAsynchronous induction motorsElectric machineInterconnection
A random-wound winding for an electrical machine including interconnected wire layers, wherein the interconnected wire layers include randomly wound wires and are configured upon placement in the electrical machine to have substantially the same impedance. Accordingly, the random wound windings can include a first coil having layers of wires randomly wound on the first coil with the layers configured in a first layering order, a second coil having layers of wires randomly wound on the second coil with the layers configured in a second layering order transposed relative to the first layering order, and at least one electrical interconnection configured to serially connect the layers of the first coil to the layers of the second coil such that an average axial position of all interconnected layers is substantially the same. The random wound windings can include a coil having layers of wires randomly wound on the coil with one side of the coil having the layers configured in a first layering order and an opposing side of the coil having the layers configured in a second layering order transposed relative to the first layering order, wherein an average axial position of the layers substantially the same.
Owner:CAPSTONE TURBINE
Multi-metal coplanar waveguide
InactiveUS20070241844A1Reduce decreaseImprove performanceMultiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSCoplanar waveguide
A coplanar waveguide CPW using multi-layer interconnection CMOS technology is provided. In the CPW including an interlayer insulator disposed on a substrate, metal multilayers disposed on the interlayer insulator, and a ground line-a signal line-a ground line formed of an uppermost metal layer, when a ground line of a lowermost layer is connected to the ground line of the uppermost layer, intermediate metal layers are designed to gradually increase or decrease in width, or to be uneven so as to maximize an area where an ultra-high frequency spreads, thereby minimizing CPW loss and maximizing a slow wave effect. As a result, it is possible to improve performance of an ultra-high frequency circuit and miniaturize the circuit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
High frequency and multi frequency band ultrasound transducers based on ceramic films
InactiveUS6761692B2Maximizing electromechanical couplingImprove stabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMulti bandTransceiver
A design and a manufacturing method of ultrasound transducers based on films of ferro-electric ceramic material is presented, the transducers being particularly useful for operating at frequencies above 10 MHz. The designs also involve acoustic load matching layers that provides particularly wide bandwidth of the transducers, and also multiple electric port transducers using multiple piezoelectric layers, for multi-band operation of the transducers over an even wider band of frequencies that covers ~4 harmonics of a fundamental band. A transceiver drive system for the multi-port transducers that provides simple selection of the frequency bands of transmitted pulses as well as transmission of multi-band pulses, and reception of scattered signals in multiple frequency bands, is presented. The basic designs can be used for elements in a transducer array, that provides all the features of the single element transducer for array steering of the focus and possibly also direction of a pulsed ultrasound beam at high frequencies and multi-band frequencies. The manufacturing technique can involve tape-casting of the ceramic films, deposition of the ceramic films onto a substrate with thick film printing, sol-gel, or other deposition techniques, where manufacturing methods for load matching layers and composite ceramic layers are described.
Owner:PREXION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com