Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1578 results about "Electromagnetic pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An electromagnetic pulse (EMP), also sometimes called a transient electromagnetic disturbance, is a short burst of electromagnetic energy. Such a pulse's origin may be a natural occurrence or man-made and can occur as a radiated, electric, or magnetic field or a conducted electric current, depending on the source.
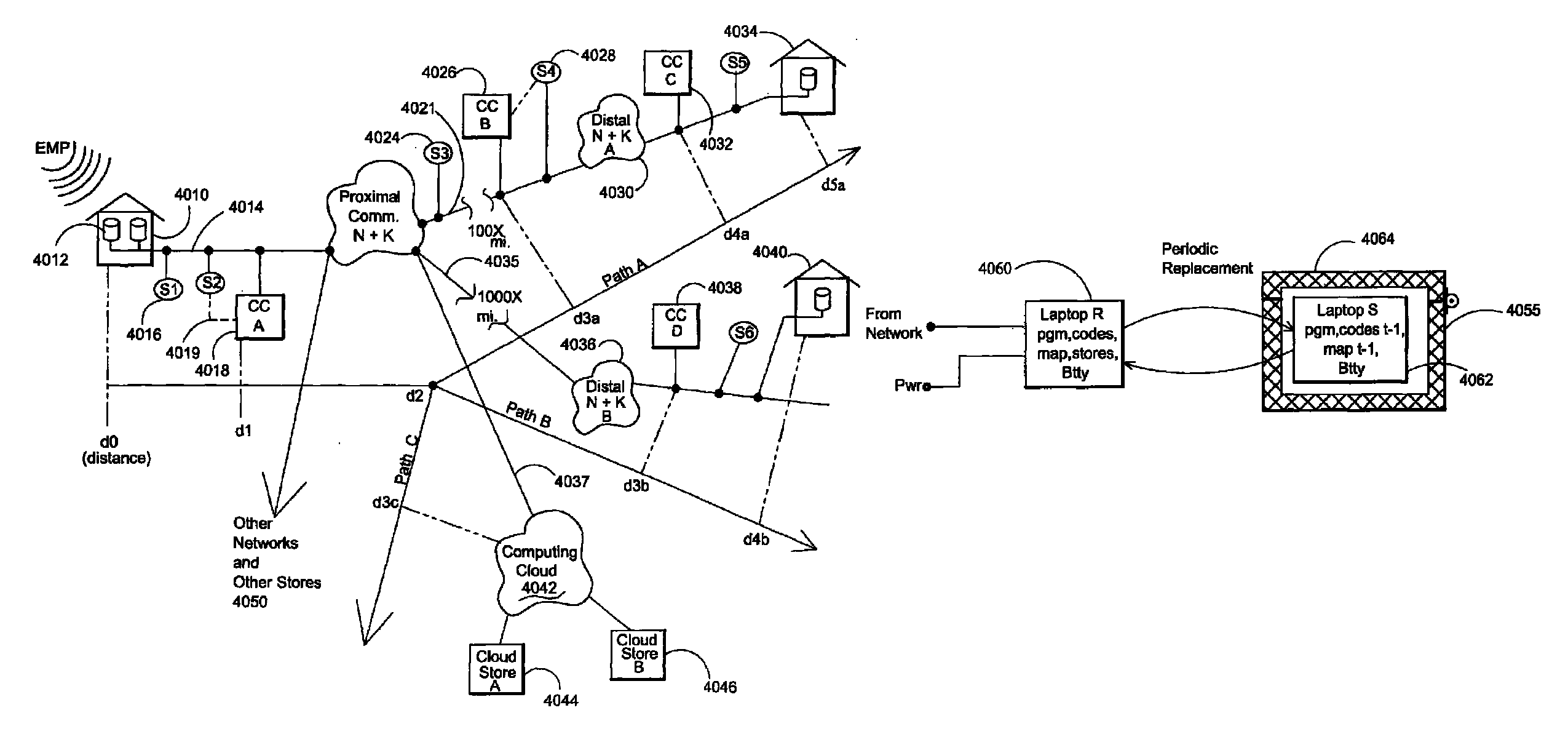
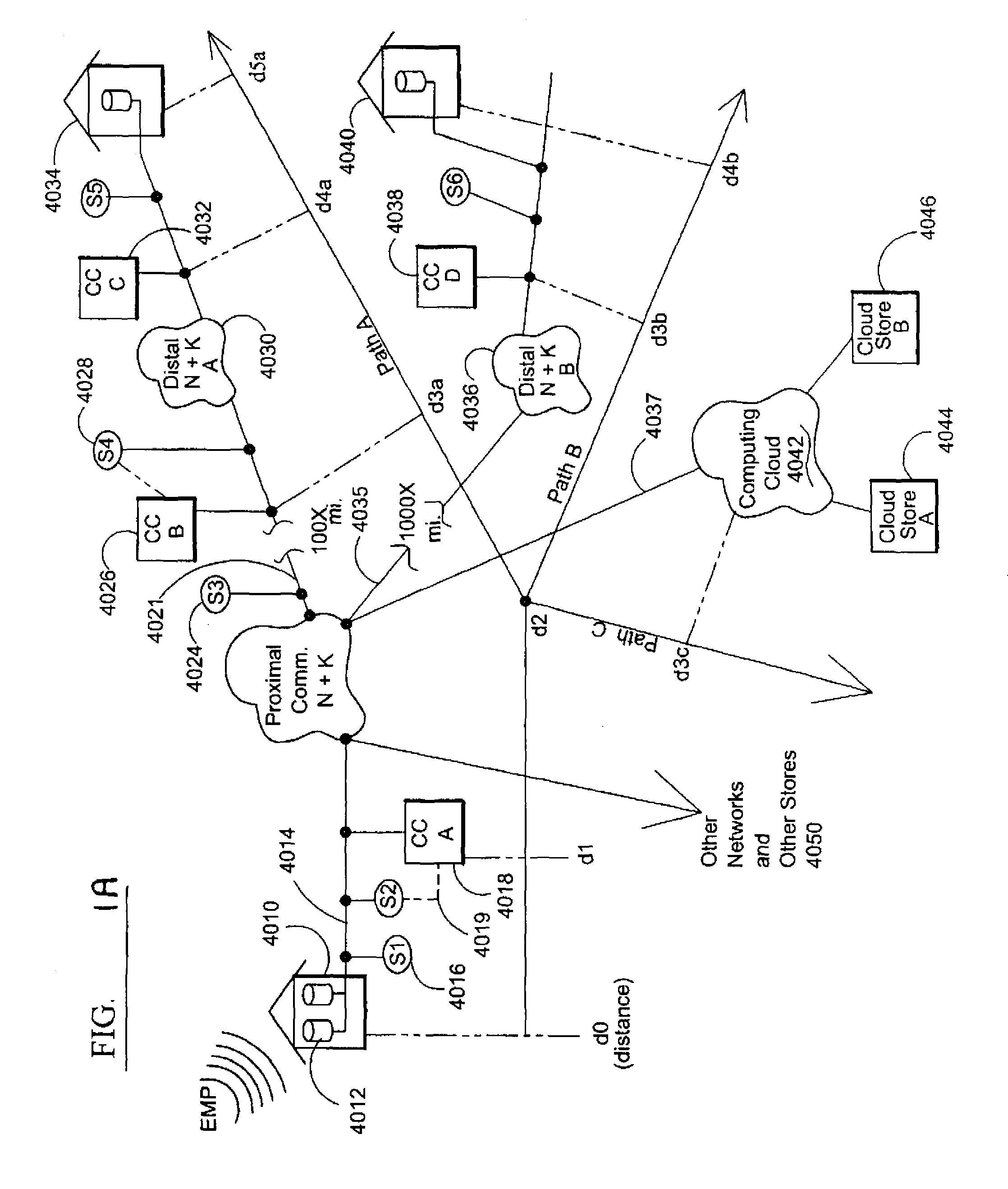
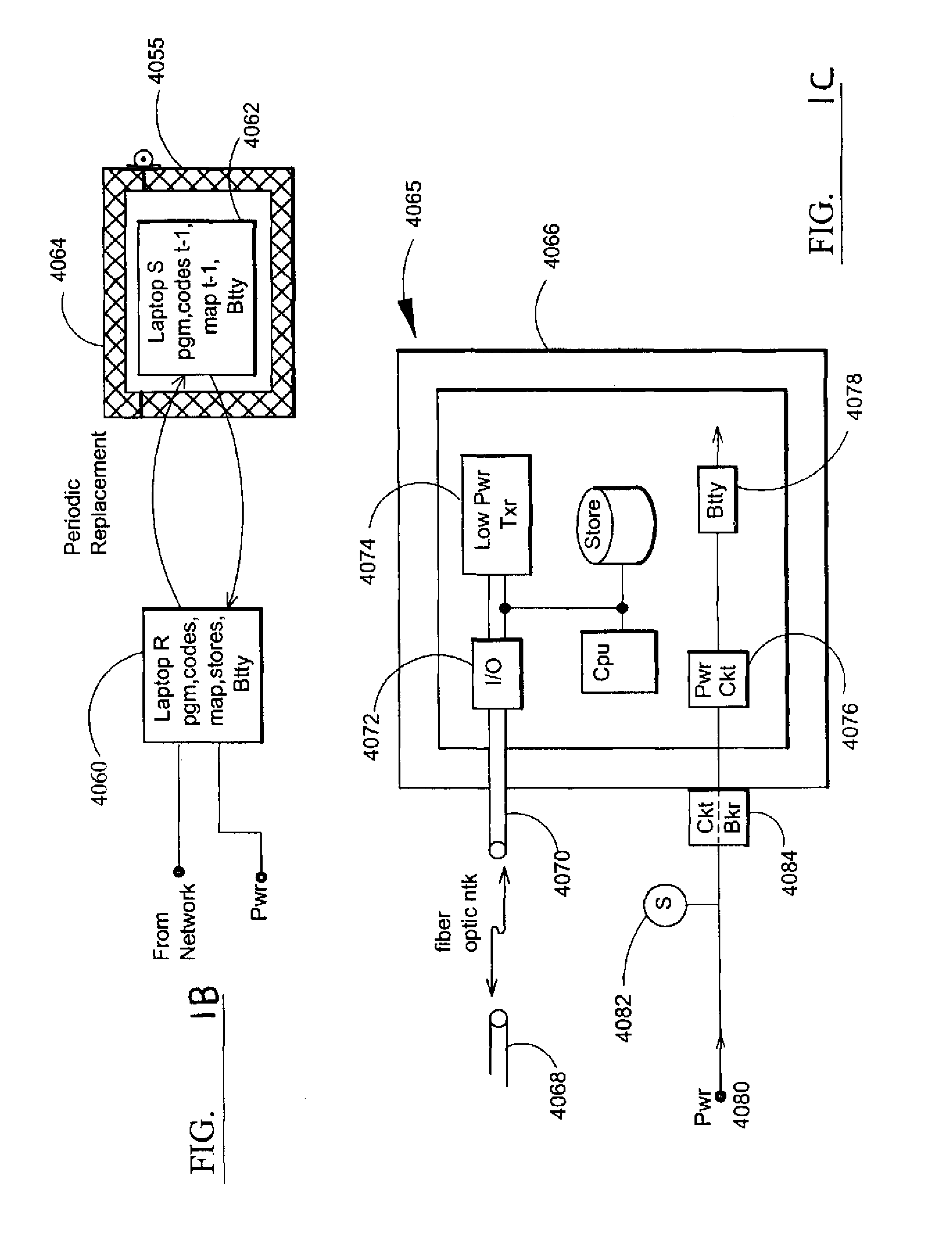
Electromagnetic pulse (EMP) hardened information infrastructure with extractor, cloud dispersal, secure storage, content analysis and classification and method therefor
ActiveUS8655939B2Improve the level ofImprove security levelDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionElectromagnetic pulseContent analytics
A method and system processes data in a distributed computing system to survive an electromagnetic pulse (EMP) attack. The computing system has proximal select content (SC) data stores and geographically distributed distal data stores, all with respective access controls. The data input or put through the computing system is processed to obtain the SC and other associated content. The process then extracts and stores such content in the proximal SC data stores and geographically distributed distal SC data stores. The system further processes data to geographically distribute the data with data processes including: copy, extract, archive, distribute, and a copy-extract-archive and distribute process with a sequential and supplemental data destruction process. In this manner, the data input is distributed or spread out over the geographically distributed distal SC data stores. The system and method permits reconstruction of the processed data only in the presence of a respective access control.
Owner:DIGITAL DOORS
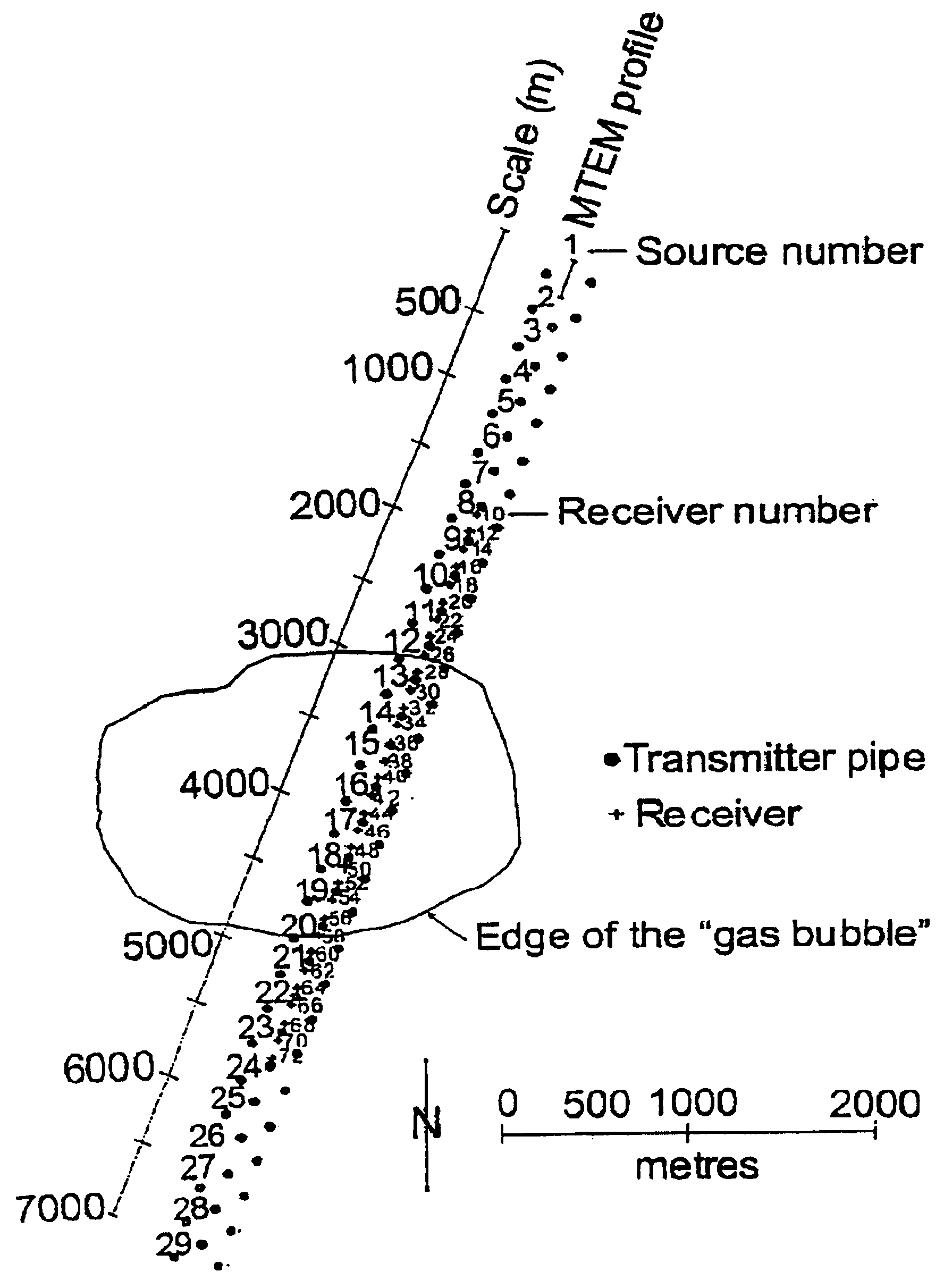
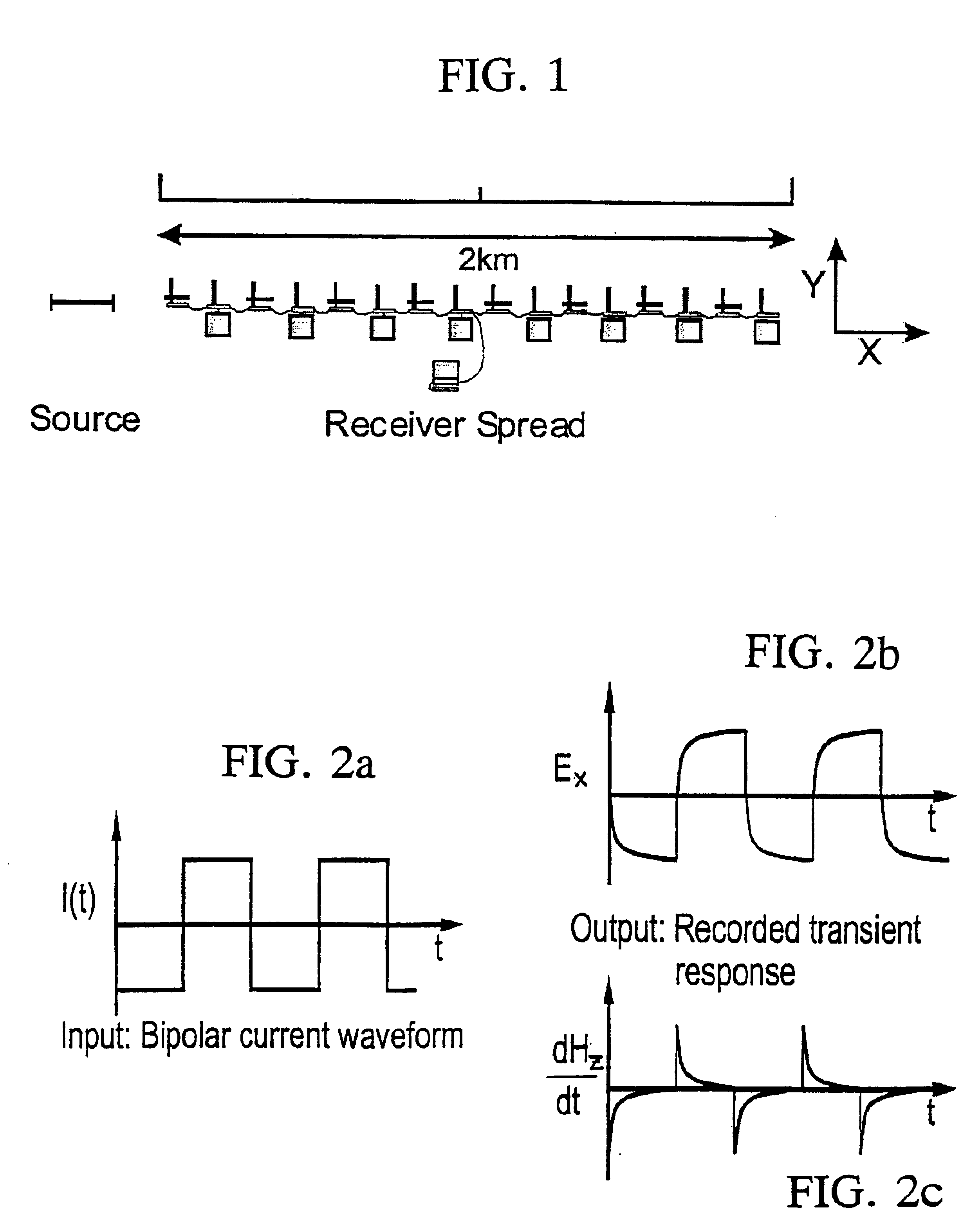
Detection of subsurface resistivity contrasts with application to location of fluids
InactiveUS6914433B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsElectromagnetic pulseImpulse response
The invention relates to a method of mapping subsurface resistivity contrasts by making multichannel transient electromagnetic (MTEM) measurements on or near the earth's surface using at least one source, receiving means for measuring the system response and at least one receiver for measuring the resultant earth response. All signals from the or each source-receiver pair are processed to recover the corresponding electromagnetic impulse response of the earth and such impulse responses, or any transformation of such impulse responses, are displayed to create a subsurface representation of resistivity contrasts. The invention enables subsurface fluid deposits to be located and identified and the movement of such fluids to be monitored.
Owner:PGS EM
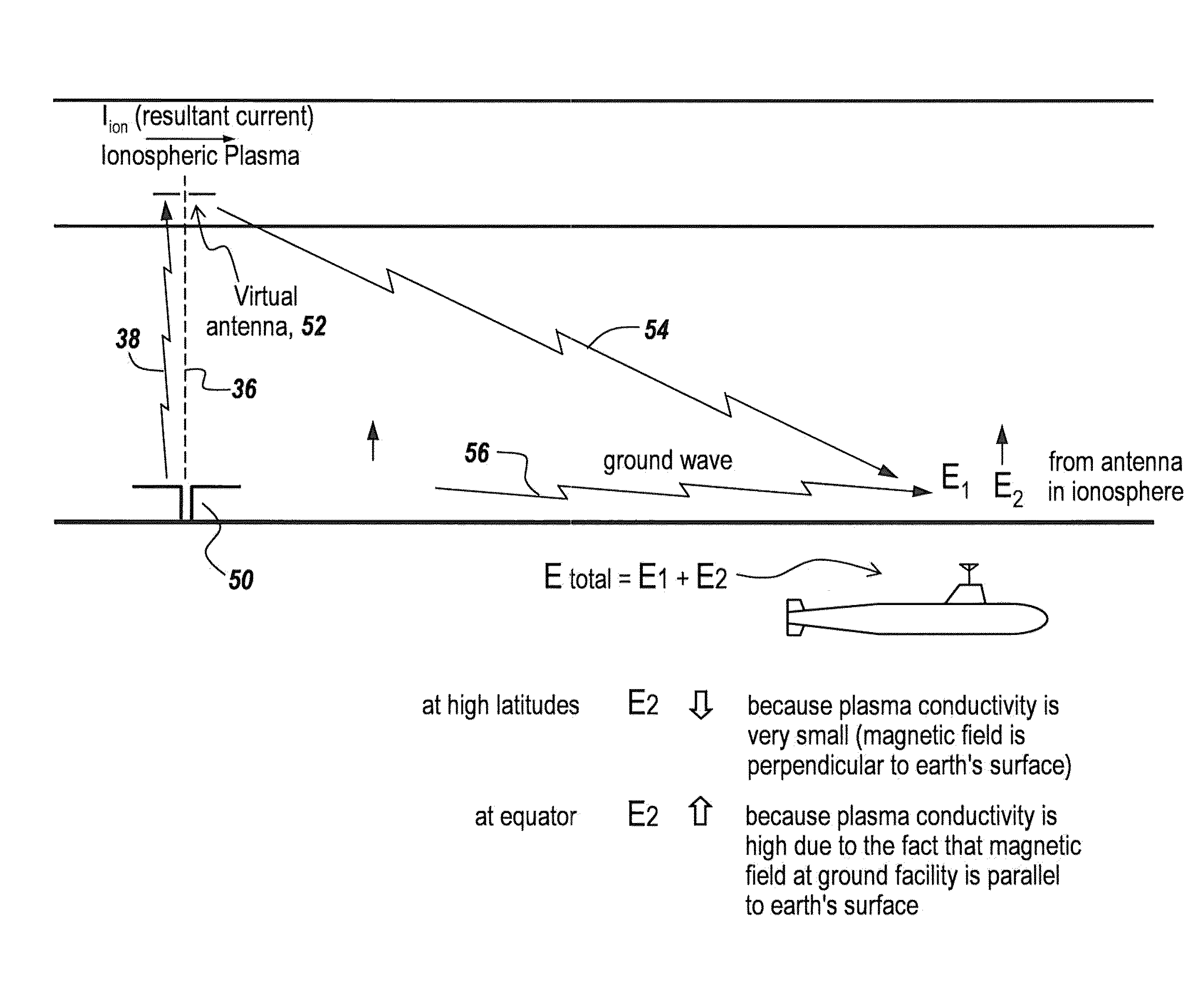
Method and apparatus for establishing low frequency/ultra low frequency and very low frequency communications
InactiveUS8299936B2Increase signal strengthShorten speedElectric signal transmission systemsDirection finders using radio wavesIonosphereElectromagnetic pulse
A method for generating electromagnetic waves in the ELF / ULF comprising the steps of using a ground-based Horizontal Electric Dipole (HED) antenna to send electromagnetic pulses upwardly in the E-region of the ionosphere to form an oscillatory or pulsed electric field; allowing said pulsed electric field to interact with magnetized plasma of the lower ionosphere to generate a pulsed horizontal and vertical current which have associated Horizontal and Vertical Electric Dipole moment; and allowing them to radiate.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
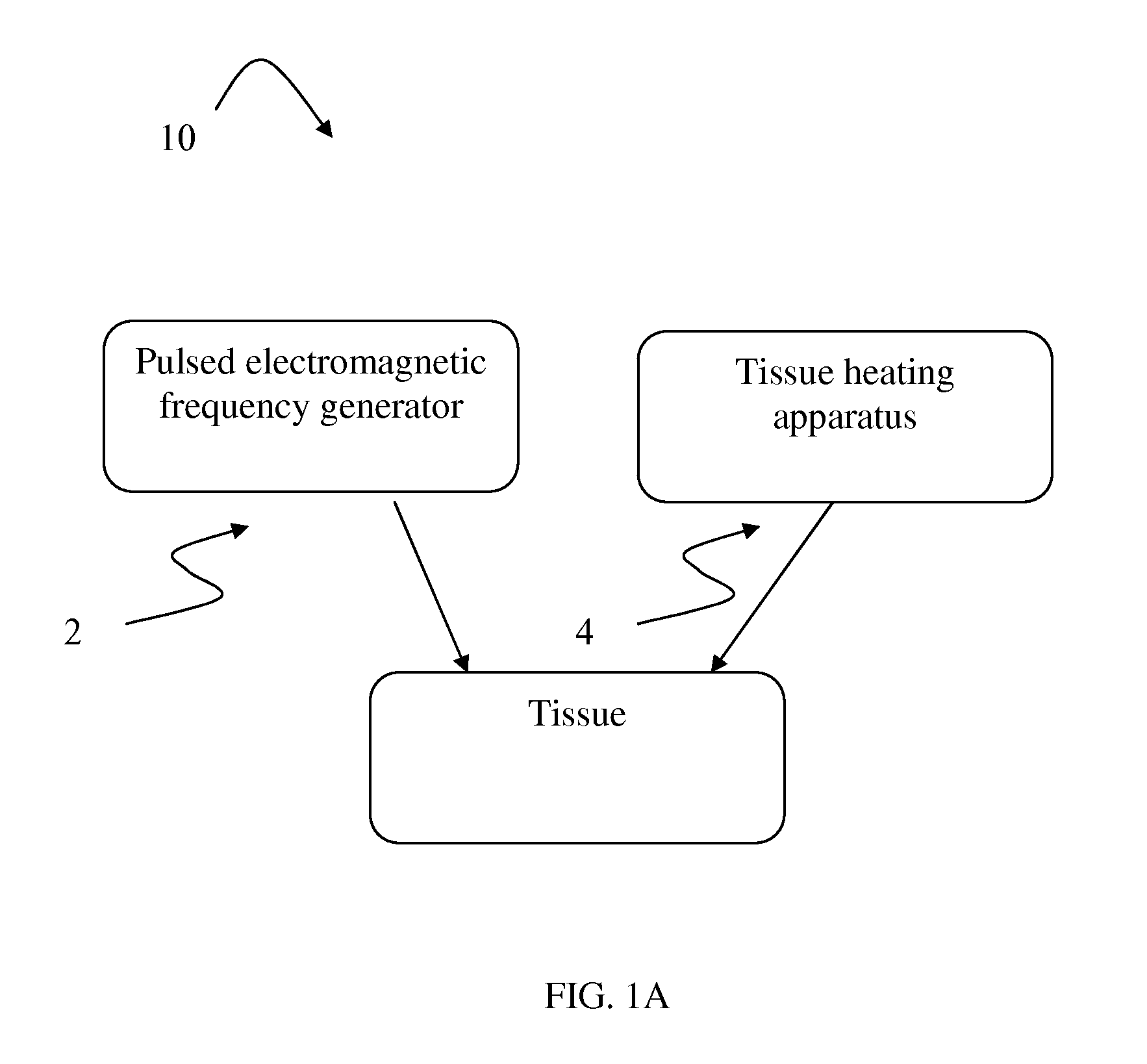
Esthetic apparatus useful for increasing skin rejuvenation and methods thereof
ActiveUS20110130618A1Increase skin rejuvenationReducing sideUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyDiathermy deviceElectromagnetic pulse
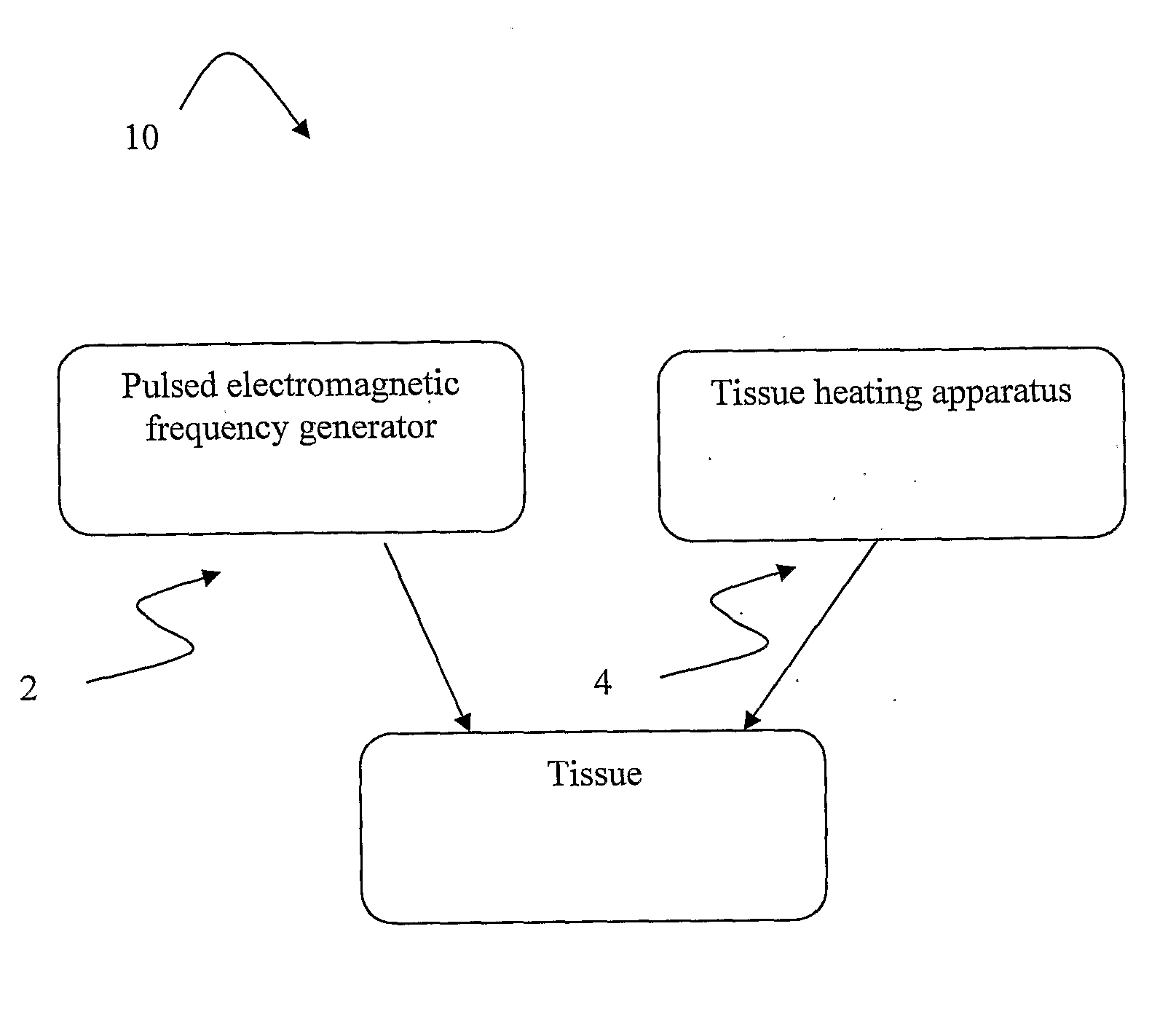
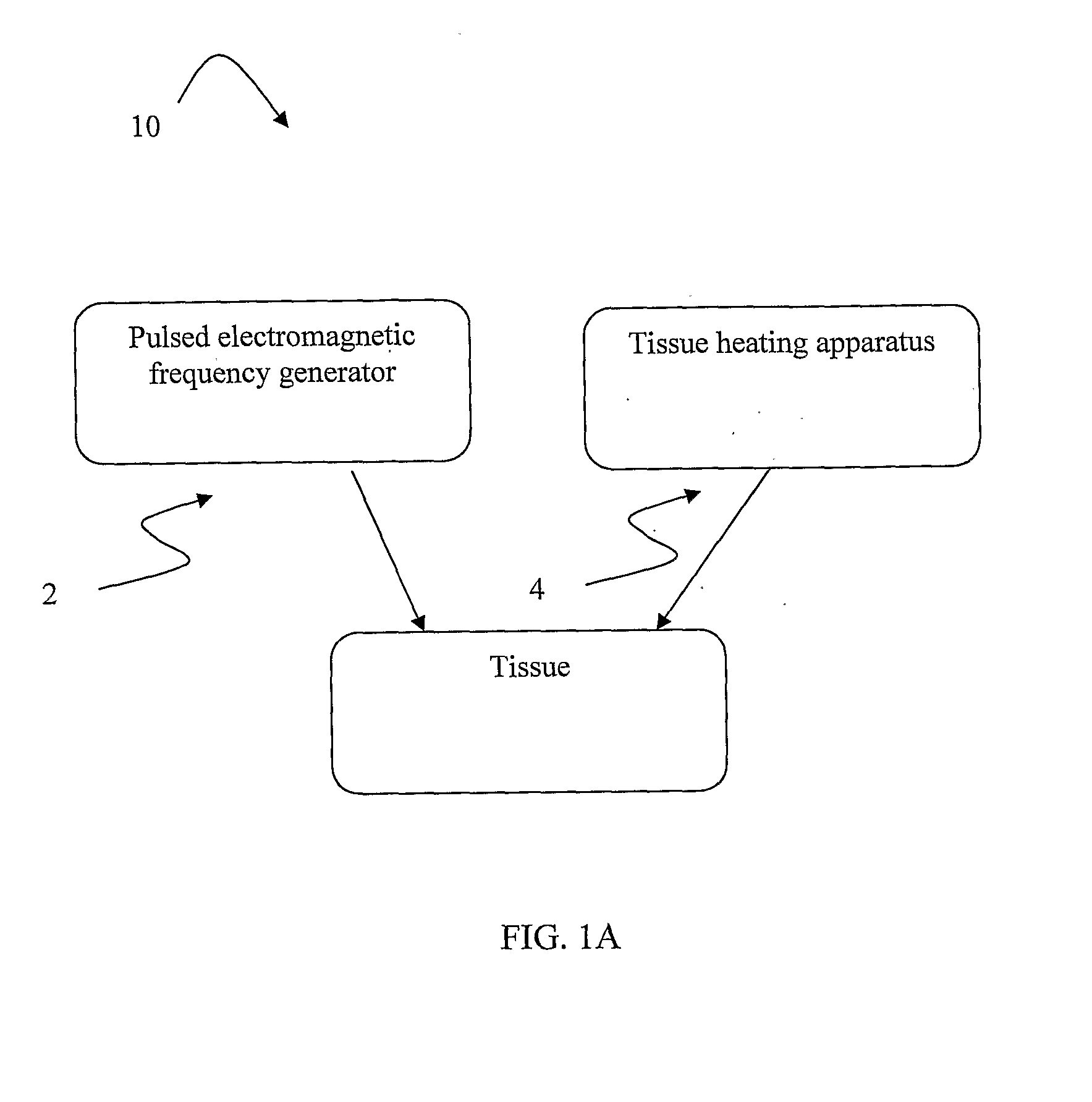
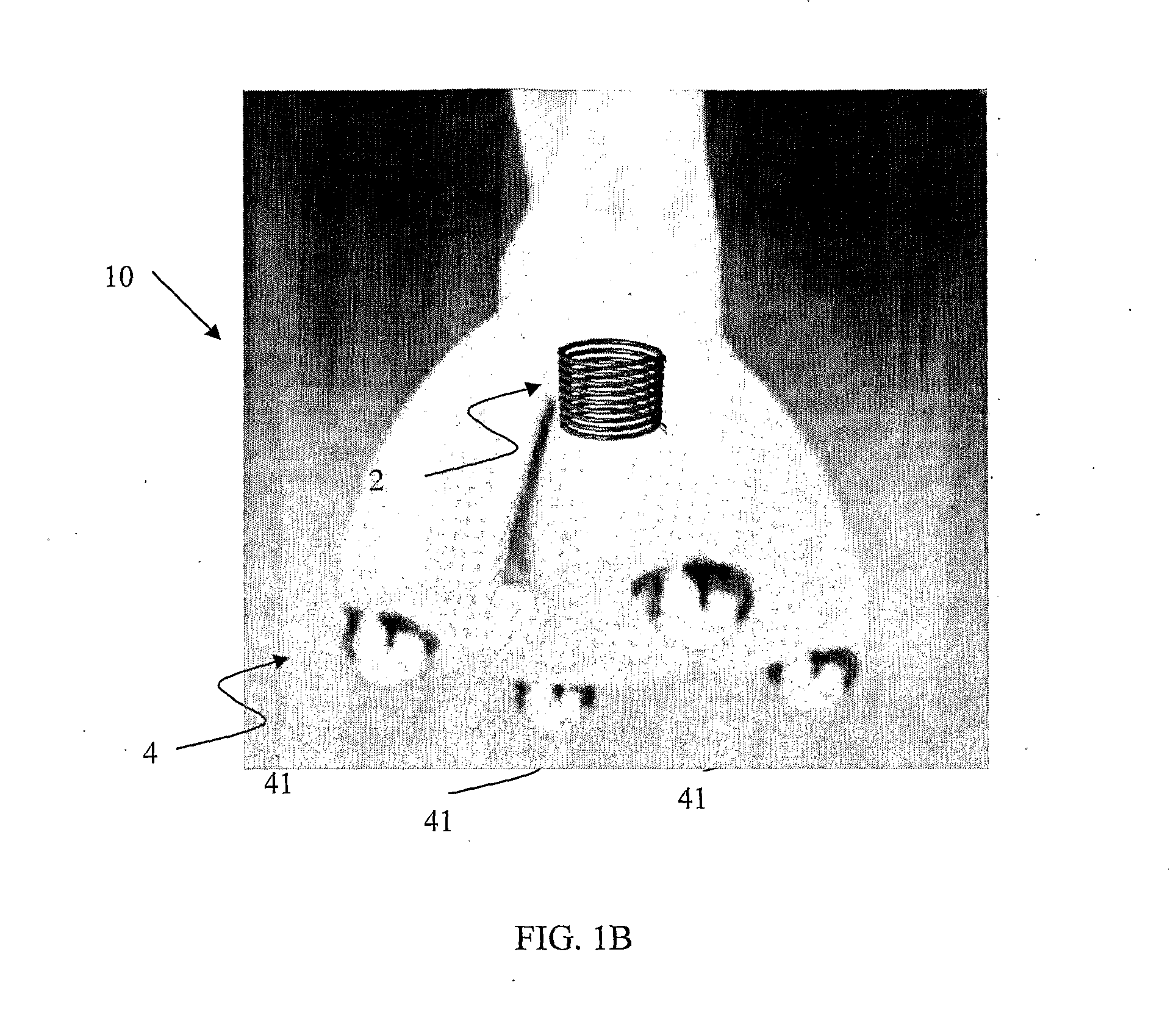
The present invention provides a system for increasing skin rejuvenation of a region of a patient's skin comprising a pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) frequency generator for constantly providing electromagnetic pulses to said region of a patient's skin and a deep tissue diathermy device for constantly applying heat to said region of a patient's skin up to temperature T. The system is adapted for simultaneously applying heat and PEMF to the region of a patient's skin,—wherein application of the system increases skin rejuvenation such that the skin rejuvenation increase (SRI) is greater than the sum of the SRI provided by electromagnetic pulses increase and the SRI provided by the deep tissue diathermy device increase.
Owner:VENUS CONCEPT
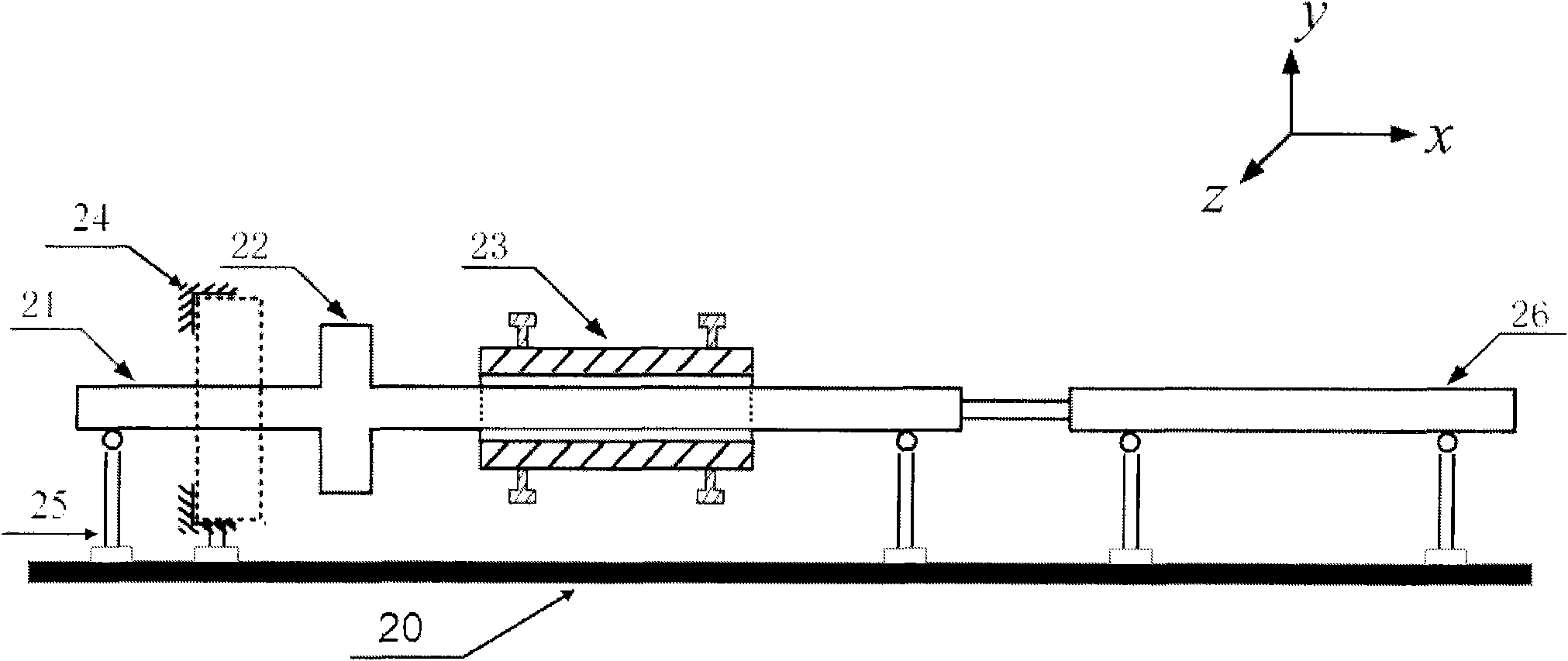
System and method for performing impact loading on micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property
InactiveCN102135480ASolve the study of dynamic mechanical properties at high strain ratesLaunch fastStrength propertiesFerroelectric thin filmsStress–strain curve
The invention relates to a system and a method for performing impact loading on a micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property. The method comprises the following steps of: instantly accelerating a bullet by using an electromagnetic pulse launch technology and launching the bullet at high speed; transmitting a stretching stress wave generated by collision of the bullet to the micro test piece by using a separated Hopkinson bar technology so as to generate the impact loading on the micro test piece; recording strain data of an input bar and an output bar, and acquiring an enlarged surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece; analyzing and obtaining a stress strain curve of the micro test piece subjected to the impact loading having different strain rates; and analyzing the surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece and obtaining a distribution of a bidimensional displacement field and a strain field during dynamic impact loading of the micro test piece. By the system and the method, the problem of research on the dynamic mechanical property of a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS), and membrane materials such as piezoelectric thin films, ferroelectric thin films and the like is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
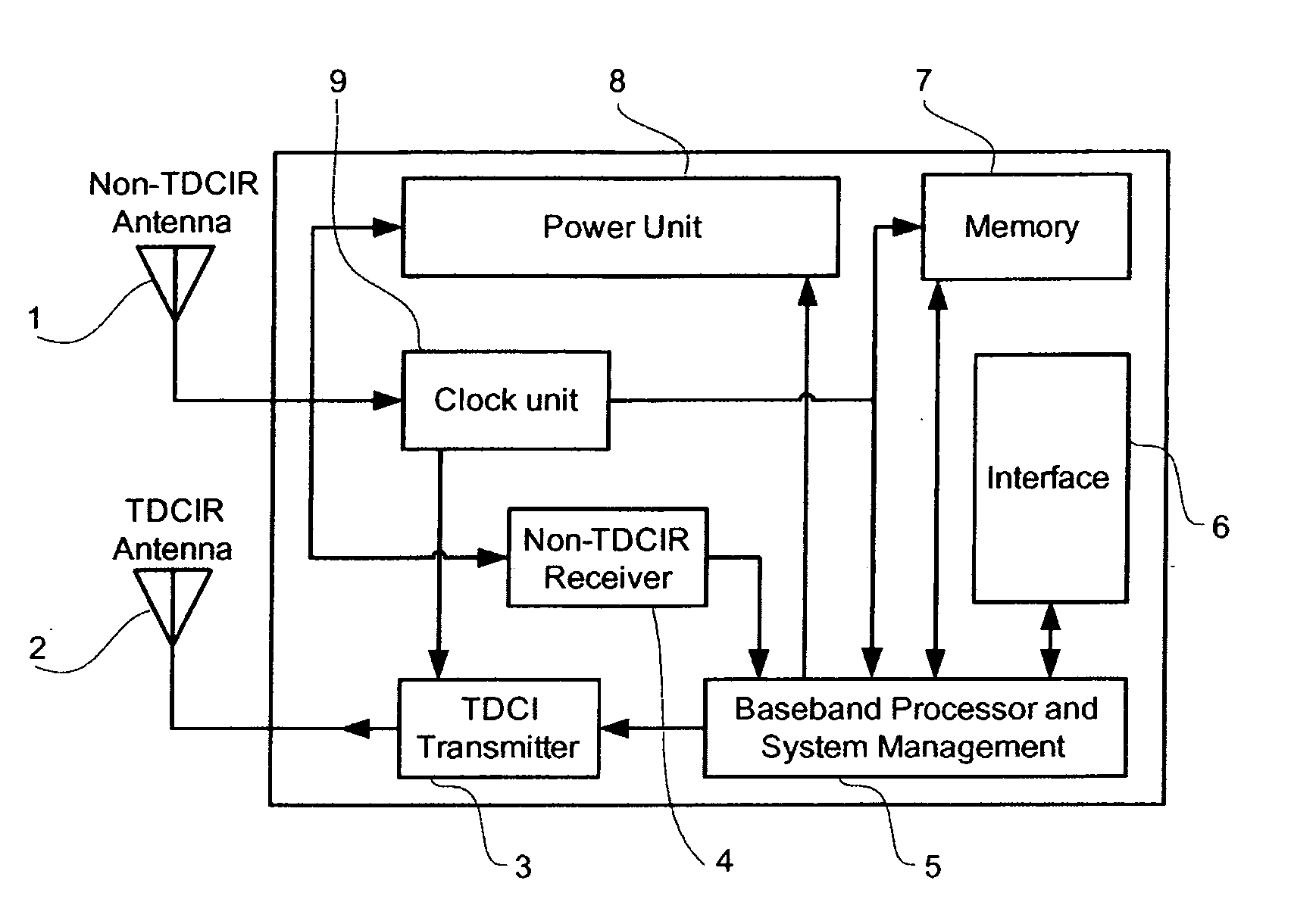
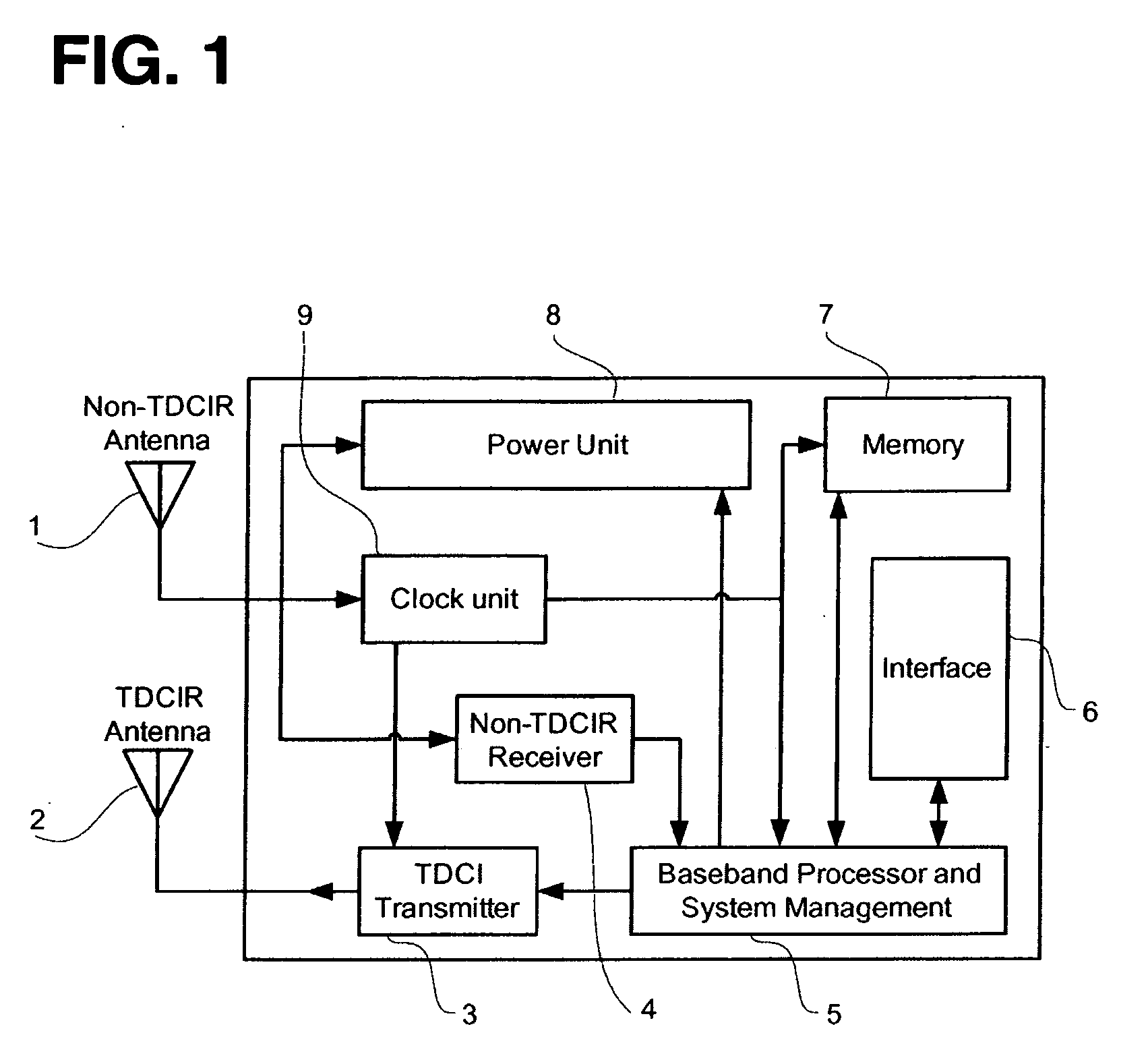
Radio frequency tag and reader with asymmetric communication bandwidth
InactiveUS20060103535A1Increase speedIncrease data rateMemory record carrier reading problemsTransmissionCarrier signalElectromagnetic pulse
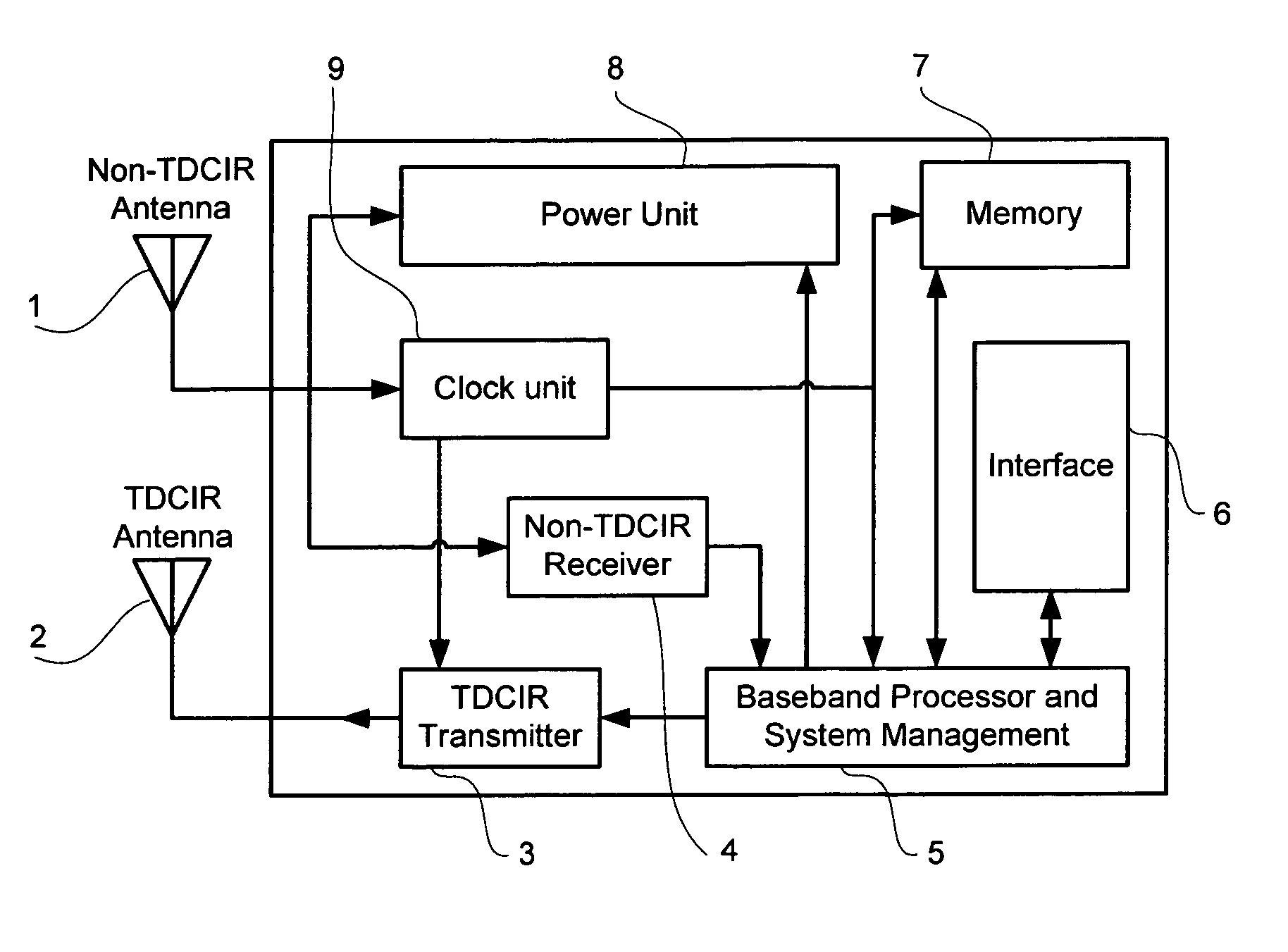
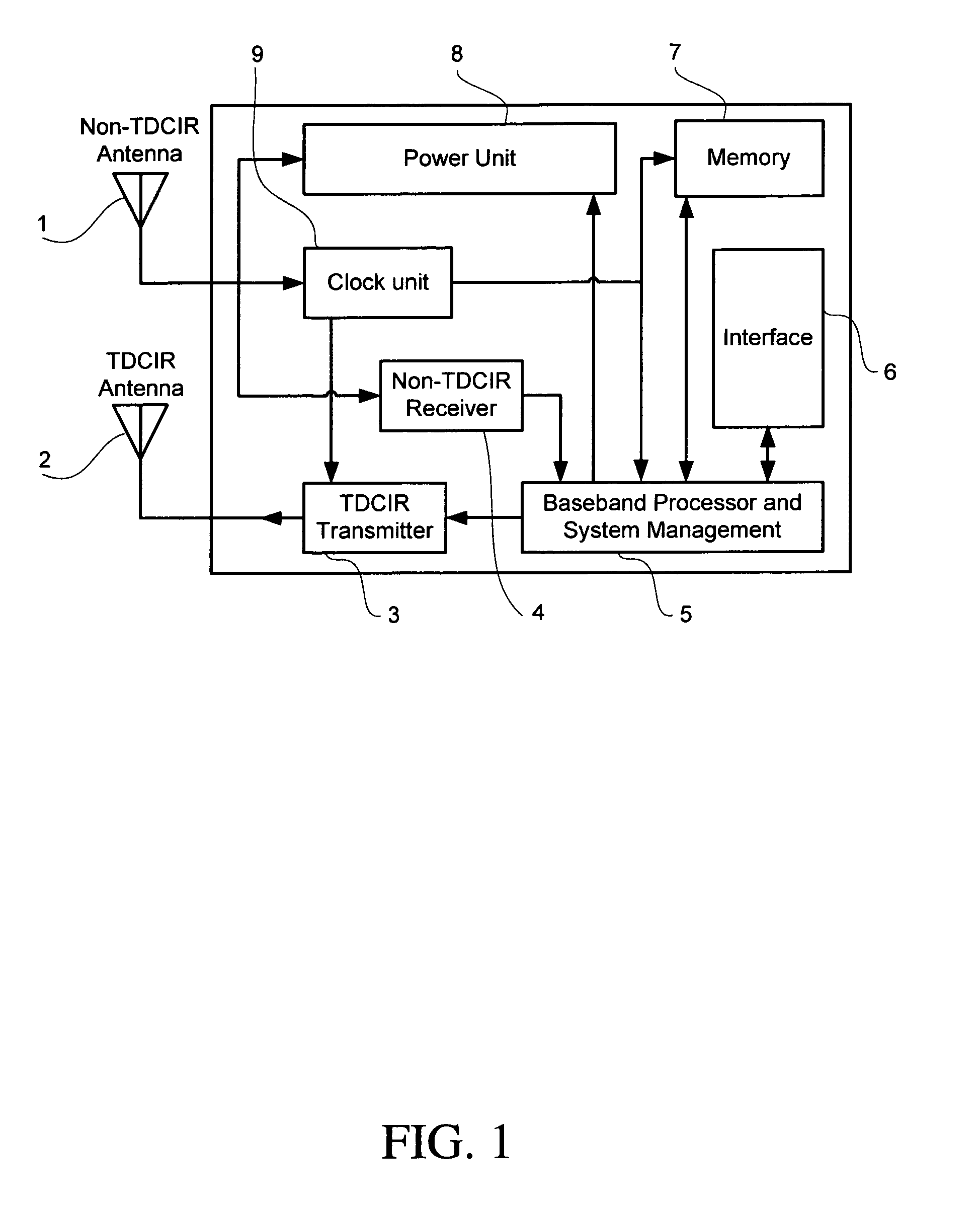
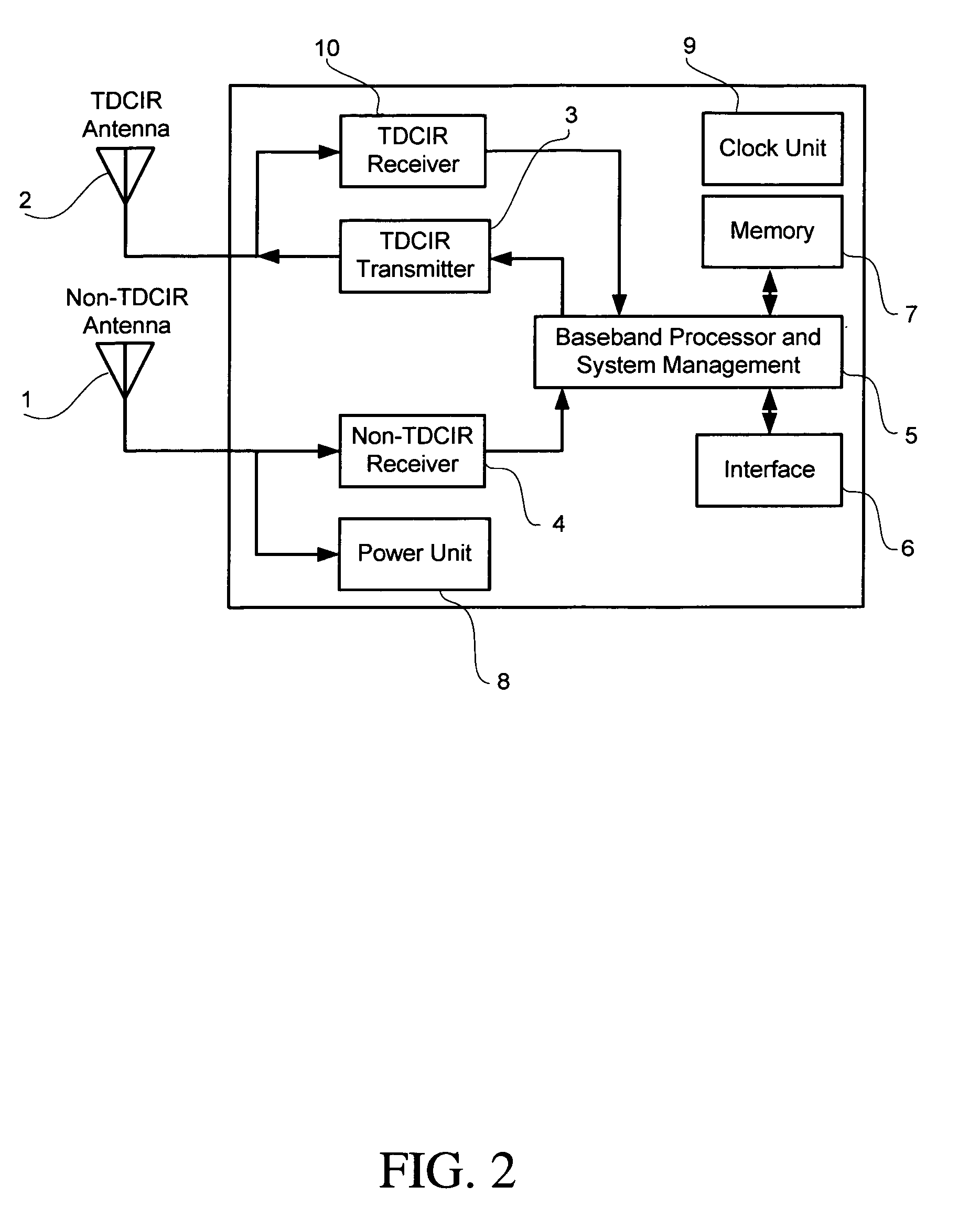
An asymmetric bandwidth communication system enables wireless communication between interrogators / readers and transponders / tags. A transponder transmits TDCIR (Time Domain Carrierless Impulse Radio) signals in the uplink direction and receives non-TDCIR signals, such as electromagnetic continuous waves, in the downlink direction. The transponder may receive partial or whole power from non-TDCIR signals. The TDCIR utilizes electromagnetic impulses with short duration and ultra wide bandwidth. It offers high data rate reliable communication at low power and design complexity. It also demonstrates resilience against path fading, selective absorption and reflection by physical matters and excellent location determination capabilities.
Owner:TAGARRAY
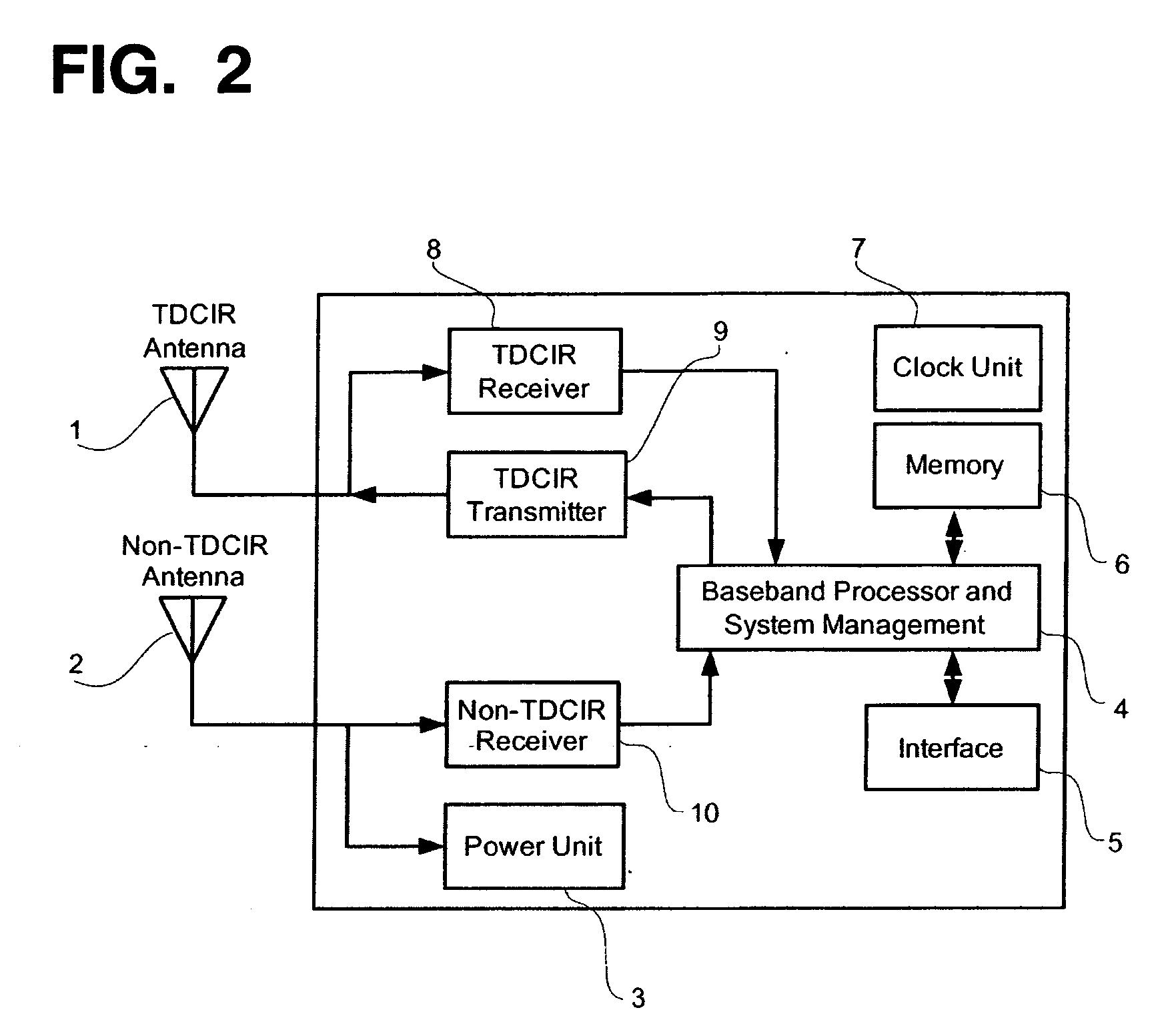
Radio frequency tag and reader with asymmetric communication bandwidth
InactiveUS7180421B2Continuous communicationEffects of continuousMemory record carrier reading problemsTransmissionCarrier signalElectromagnetic pulse
Owner:TAGARRAY
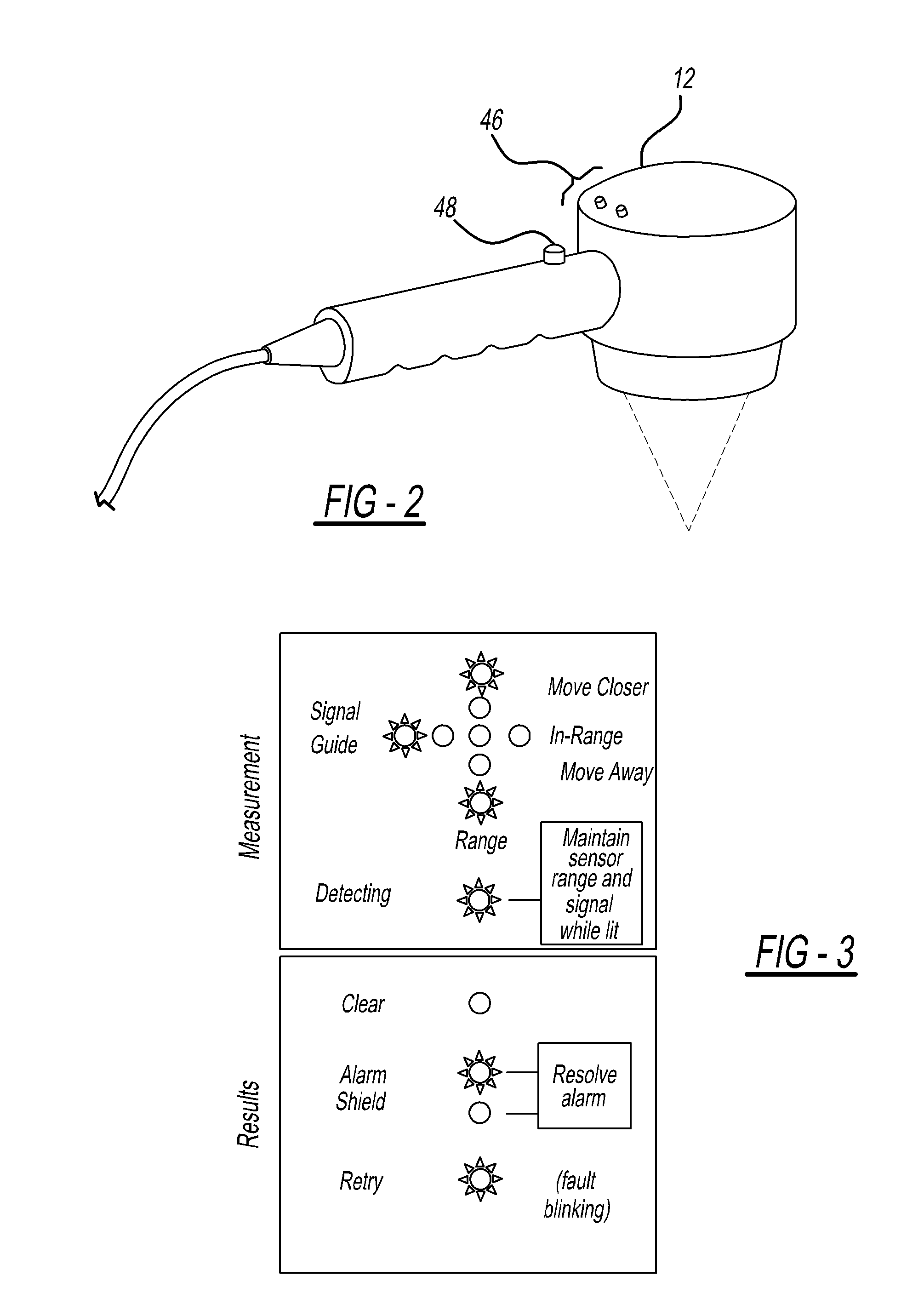
Method and apparatus for pulsed electromagnetic therapy
An apparatus and method for applying pulsed electromagnetic therapy to humans and animals. A straight wire element is employed to generate the magnetic field. A power and timer circuit supplies current pulses that approximate square pulses in form, so that the straight wire element generates magnetic pulses having rapid rise and fall times. Peak field strength is approximately 2 gauss at a 1 cm distance from the straight wire element, and the duration of peak field strength is approximately 200 nanoseconds. The pulses are repeated at a frequency of about 70 Hz. The straight wire element and circuit may be housed in a hand-held probe, with an LED illuminating the skin area to provide a visual indication of effective range, or a plurality of the straight wire elements and associated circuits may be embedded in a conformable pad that is placed over the affected area of the body.
Owner:GORDON GLEN A
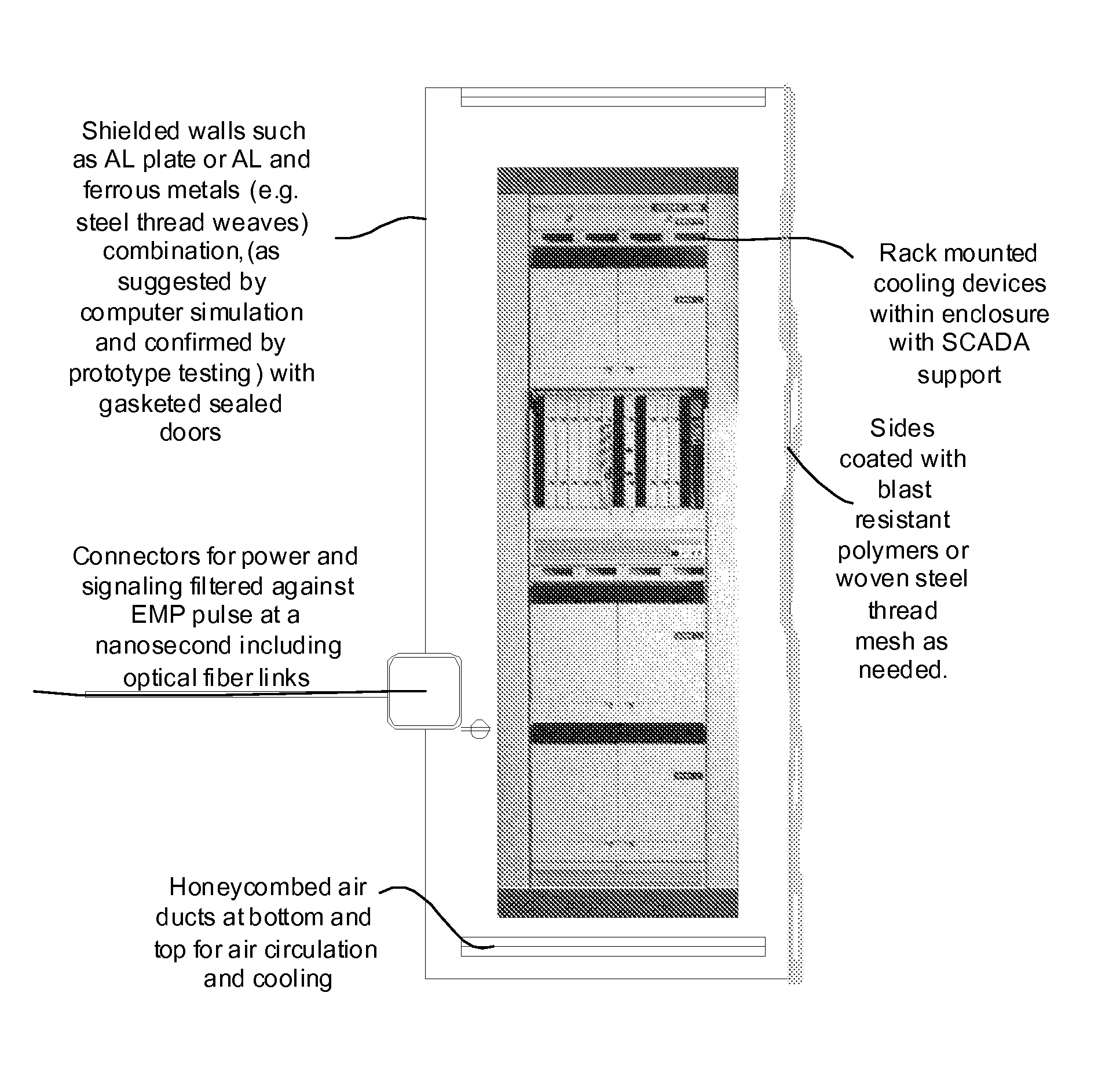
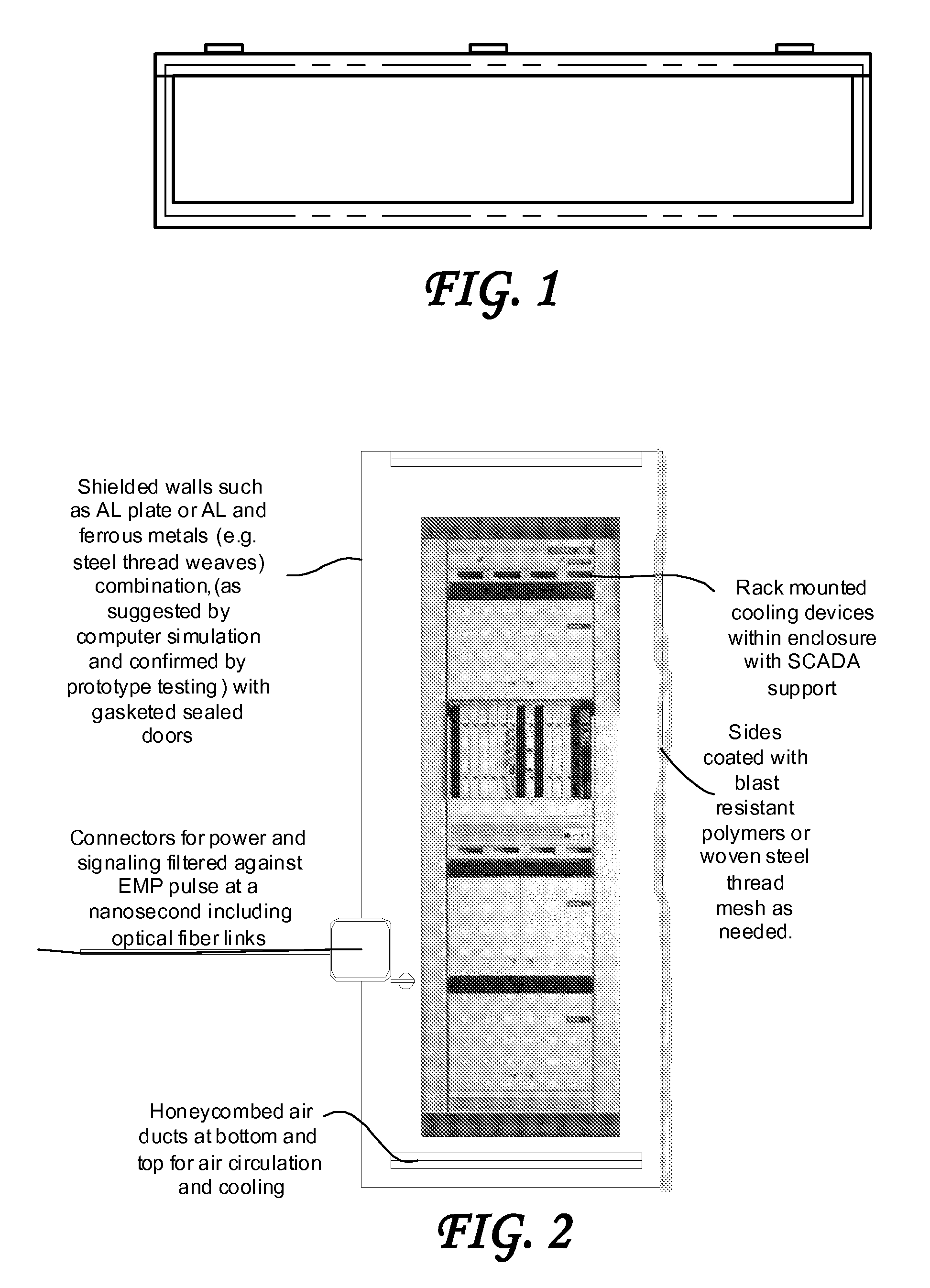
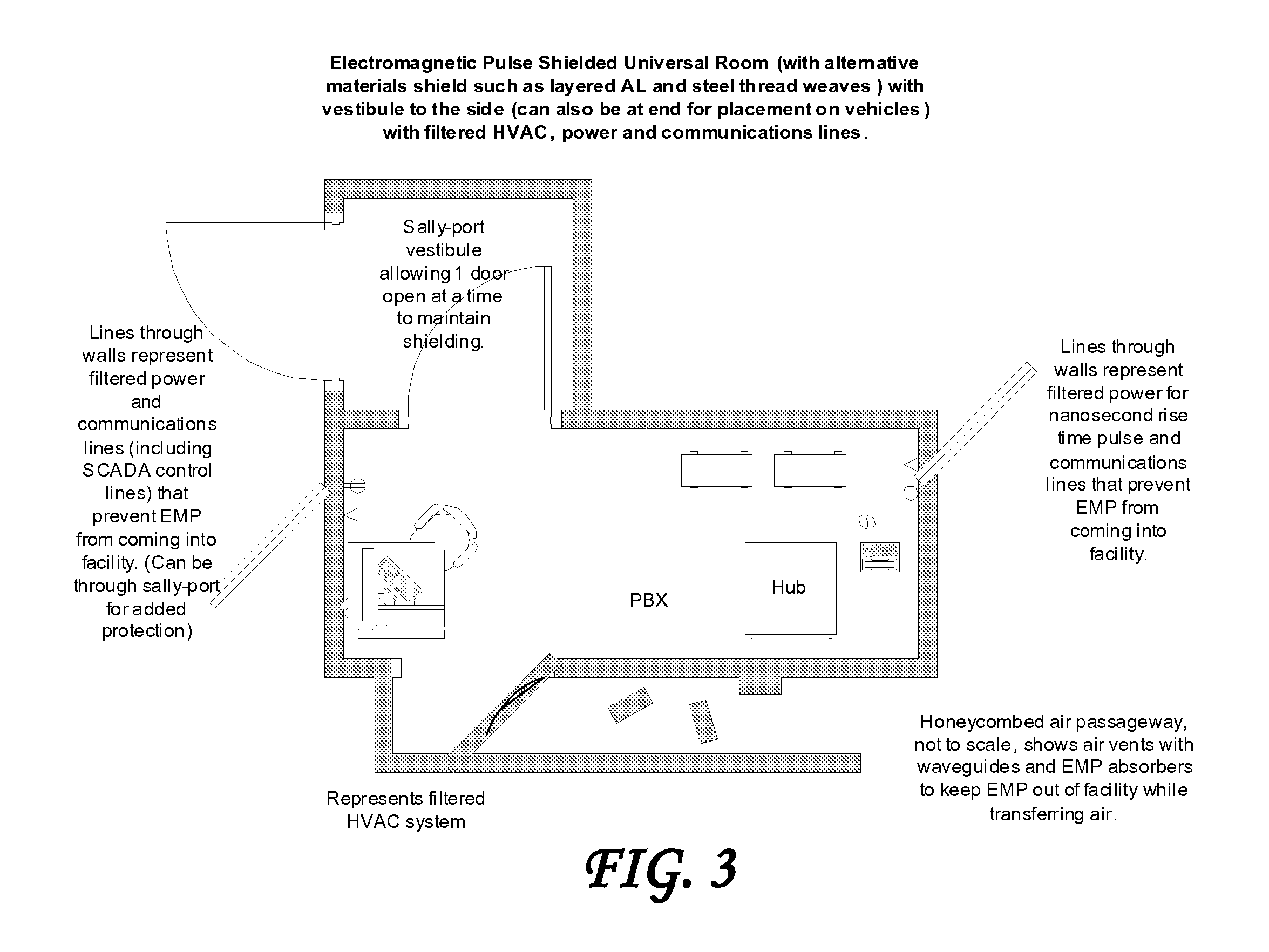
System and method for providing certifiable electromagnetic pulse and rfi protection through mass-produced shielded containers and rooms
InactiveUS20070105445A1Light weightControlled heatingScreening rooms/chambersShielding materialsElectricitySCADA
Disclosed are a system and method for providing certifiable shielded cabinets and rooms, or pods, to protect devices, equipment and people from electromagnetic interference such as electromagnetic pulse, and directed energy attack. The method simulates the separate electric and magnetic shield requirements and capabilities of each type of materials, simulating them separately and together to form a combined set of materials layered for an enhanced electromagnetic shield that is lighter weight and less expensive. Further disclosed is a system and method for SCADA, RFID, and OID monitoring and controls to enable initial and ongoing testing and control.
Owner:INSTANT ACCESS NETWORKS
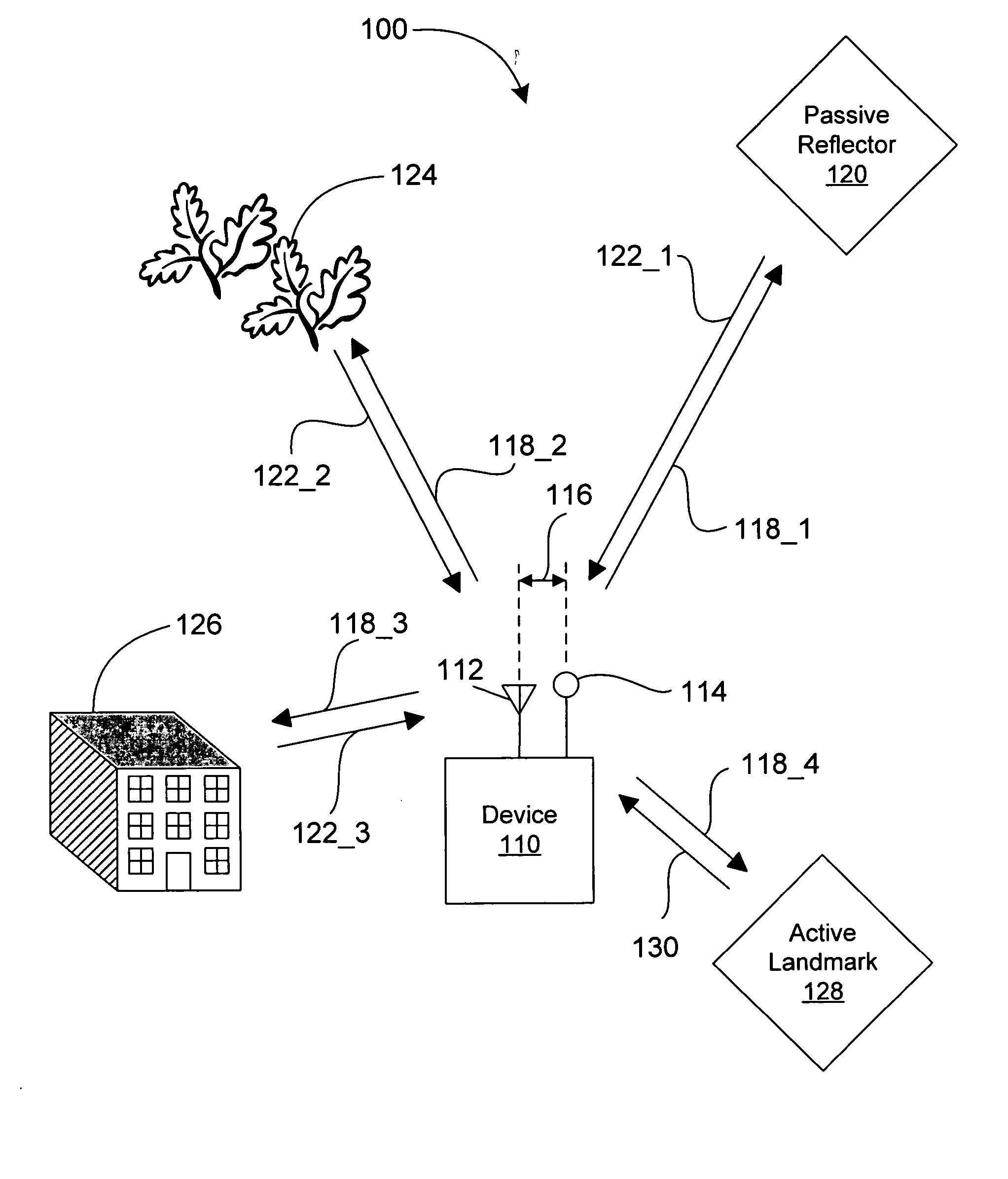
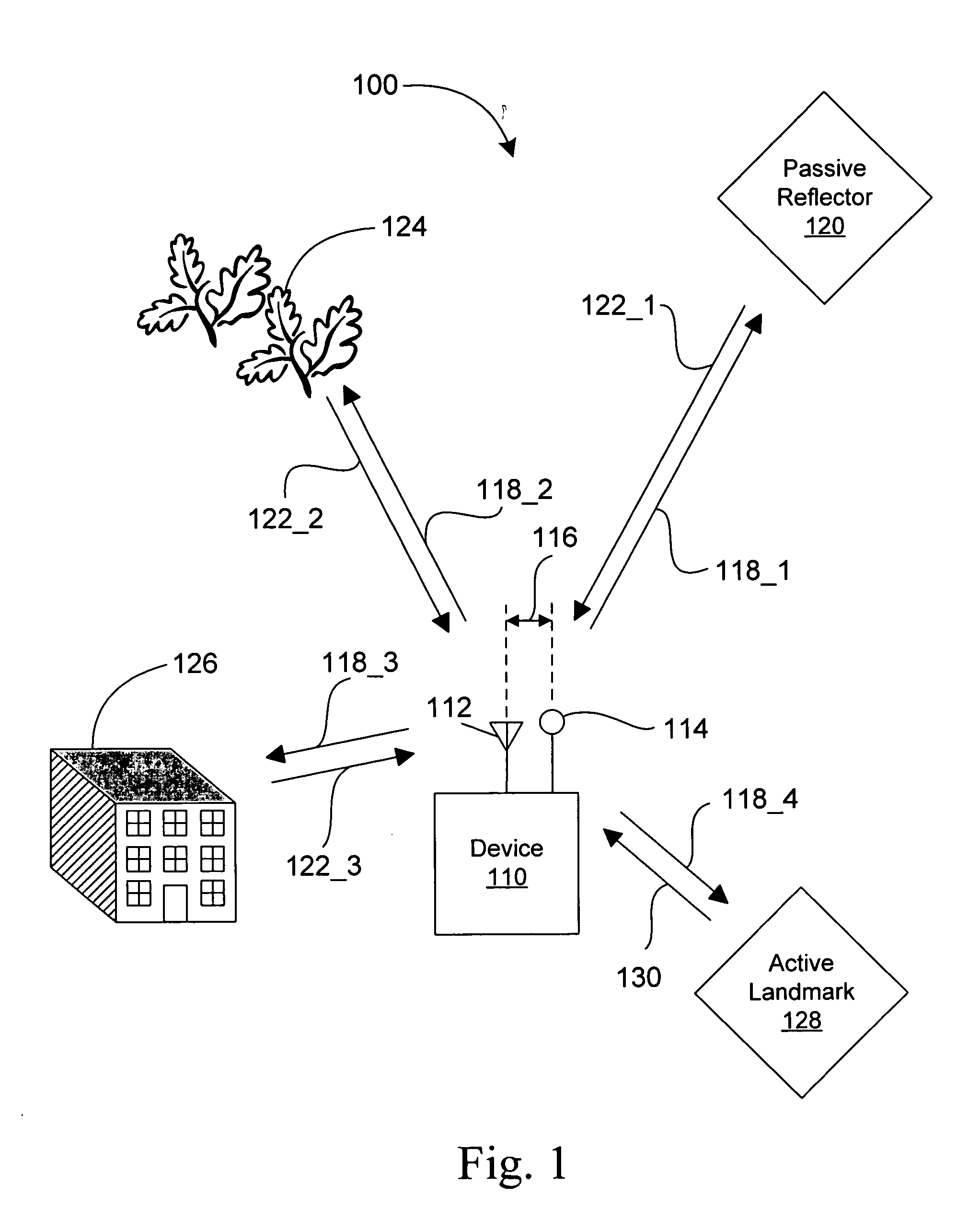
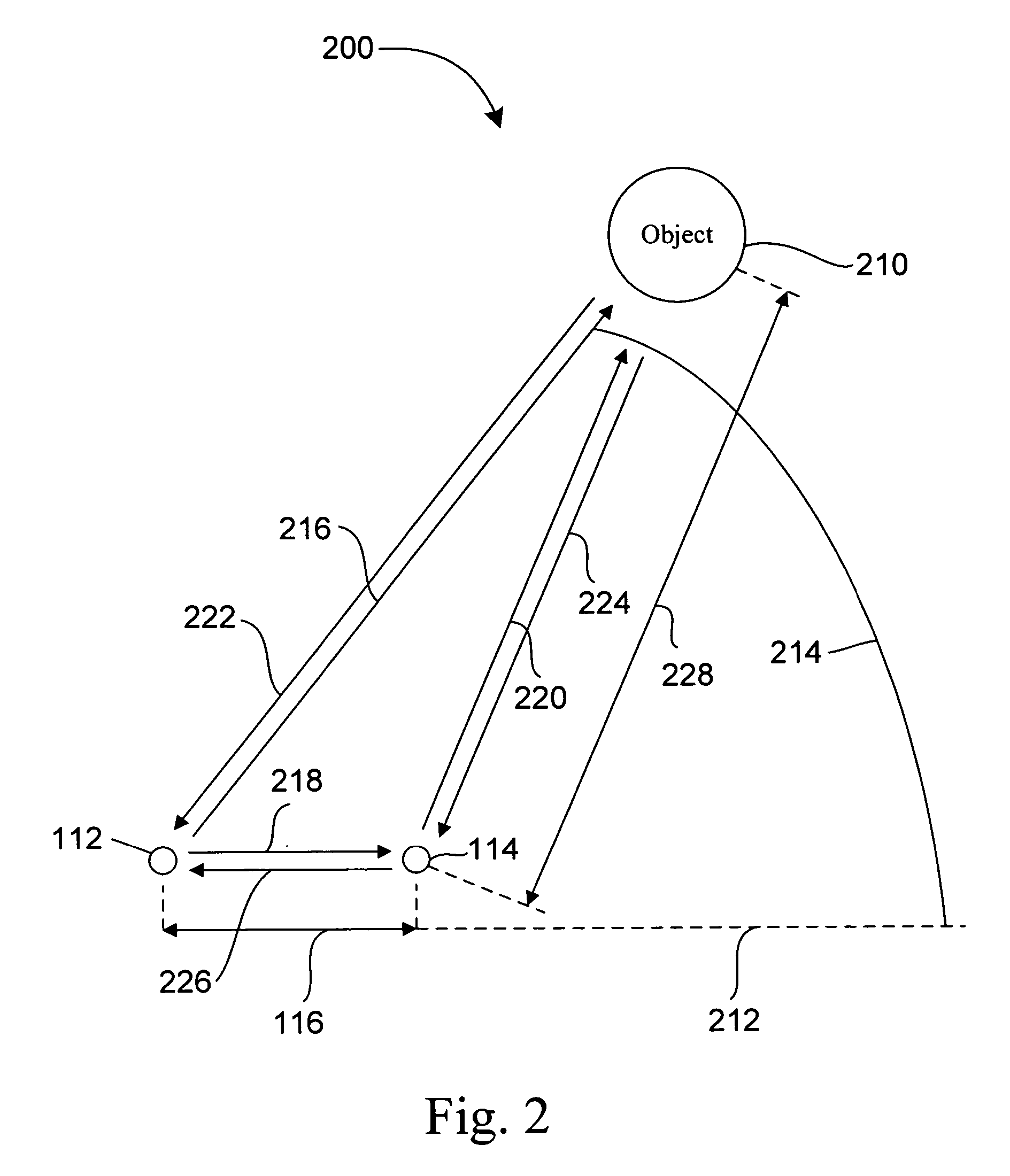
Positioning system with intentional multi-path signal
ActiveUS20050270227A1Improve accuracyDirection-finding diversity systems using radio wavesPosition fixationCarrier signalElectromagnetic pulse
A positioning system includes a device, having an antenna and a reflector with a known position proximate to the antenna, that transmits at least an electromagnetic pulse having a carrier signal frequency. The device receives a return signal over a period of time, wherein the return signal includes a return pulse from an object within a radar detection area of the device and at least one multi-path pulse. The device processes the return signal so as to isolate the return pulse and the at least one multi-path pulse from the return signal. The device determines a range from the device to the object and the position of the device relative to the object. The range is determined in accordance with a time of arrival of the return pulse and the position is determined in accordance with a time of arrival of the at least one multi-path pulse.
Owner:DEERE & CO
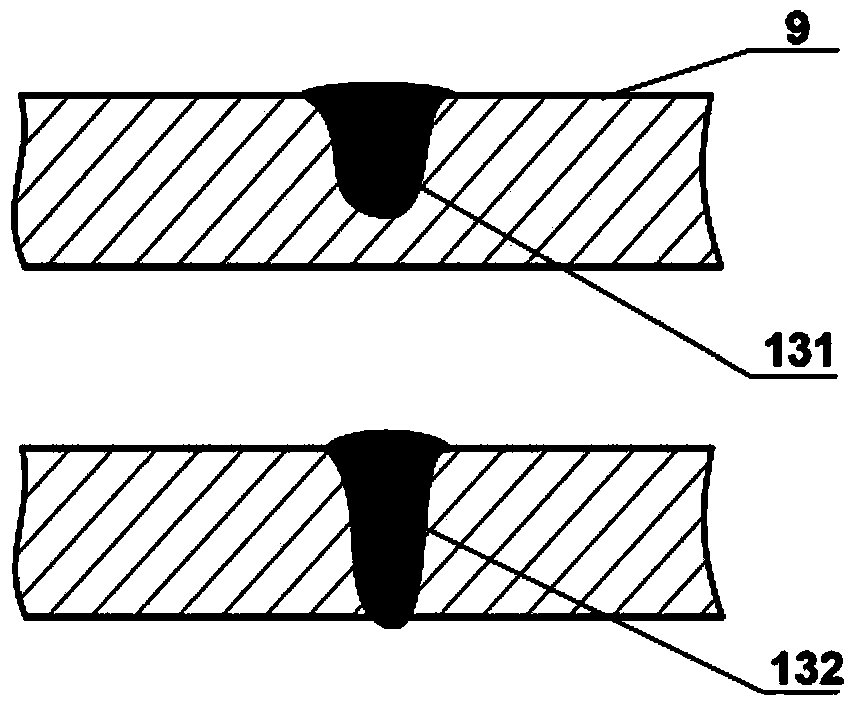
Magnetic pulse connecting method and joint structure for thin-wall metal pipelines
InactiveCN101905375AIncreased processing flexibilityHigh strengthNon-electric welding apparatusHeat-affected zoneEngineering
The invention discloses a magnetic pulse connecting method and a joint structure for thin-wall metal pipelines and provides a safe and high-efficiency magnetic pulse connecting method and a magnetic pulse connecting joint structure for similar and dissimilar thin-wall metal pipelines. A coil-magnetic concentrator composite inductor or a coil inductor is connected with electromagnetic pulse forming equipment so that the pipelines of various metal materials or various structure shapes can be connected in a magnetic pulse way. The transition area of the joint connecting interface is small, the brittle phase or intermetallic compound almost cannot be generated, and the joint almost has no heat affected area and torsion deformation and has high strength and corrosion-resistance property; the tension strength and torsion strength of the joint are respectively higher than those of weak base metal; the subsequent cleaning procedure and post-weld heat treatment are not needed; and the connected pipeline satisfies certain rigidity requirement, cannot be subjected to the plastic deformation in the magnetic pulse connecting process and has high process flexibility.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Environment-friendly plastic pipe fusion bonding method
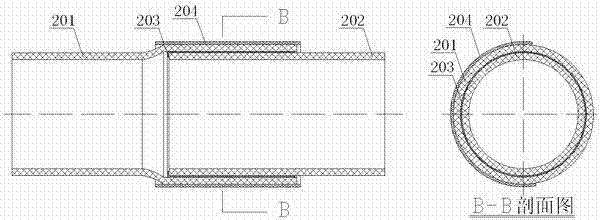
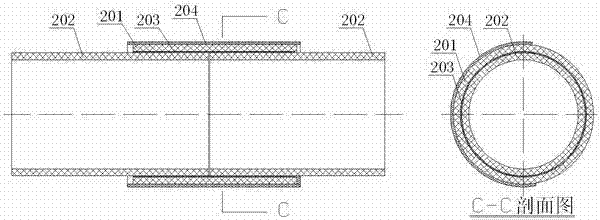
InactiveCN102889446AEasy constructionObvious cost advantagePipe connection arrangementsInduction heating apparatusElectromagnetic pulseEngineering
The invention discloses an environment-friendly plastic pipe fusion bonding method which comprises a magnetic conductivity material net (203) of a plastic pipe fusion bonding material and a portable type electromagnetic heating device. The magnetic conductivity material net (203) is placed in the middle of a flared pipe (201)and a straight cutting pipe (202) of a plastic pipe, and the portable type electromagnetic heating device is spliced on the exterior of the flared pipe (201) of the plastic pipe; the portable type electromagnetic heating device transfers high frequency electromagnetic pulse heating power to act on the magnetic conductivity material net (203) so as to generate vortex to heat, the heat can generate partial fusion with a contact surface of a contacting part, and the fusion splice of the plastic pipe is finished; the portable type electromagnetic heating device drives an electromagnetic heating belt (204), and the heating of the magnetic conductivity material net (203) is finished in step by step; and the fusion splice of the plastic pipe is repeatedly performed for many times, and the splice quality is guaranteed. The plastic pipe fusion bonding method provided by the invention is also suitable for plastic board materials.
Owner:李文忠
Lidar scanner
ActiveUS20140268098A1Low costOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationElectromagnetic pulseLidar
A LiDAR sensor can include a laser, a directional sensor, a window, an electromagnetic pulse receiving sensor, and a processor. The laser can be configured to emit a narrow electromagnetic pulse. Further, the directional sensor can be configured to measure the direction of the narrow electromagnetic pulse emitted by the laser. The narrow emitted electromagnetic pulse can pass through the window. The pulse can then be reflected by at least the window and an object external from the LiDAR sensor, creating at least two reflected pulses. The electromagnetic pulse receiving sensor can be configured to measure the two reflected pulses resulting from the narrow pulse emitted by the laser. The processor can be configured to receive information from the sensors, indicating a position of the object relative to the LiDAR sensor. Further, the processor can be configured to measure the intensity of the pulse being reflected by the window.
Owner:UATC LLC
System and method to detect anomalies
ActiveUS20150060673A1Minimal equipment footprintMinimal ease-of-useRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic launchElectromagnetic pulse
A system and method for detecting anomalies concealed upon a person may include a detection probe having an electromagnetic transmitter and an electromagnetic receiver. The electromagnetic transmitter is configured to emit electromagnetic pulses, while the electromagnetic receiver is configured to sample electromagnetic pulses from the electromagnetic receiver at specified times within a waveform window. The electromagnetic pulses may span the terahertz spectral region of 0.04 to 4 THz. The system may also have optical fibers connected to the electromagnetic transmitter and electromagnetic receiver, wherein femtosecond laser pulses are directed from a source to the electromagnetic transmitter and the electromagnetic receiver by the optical fibers.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
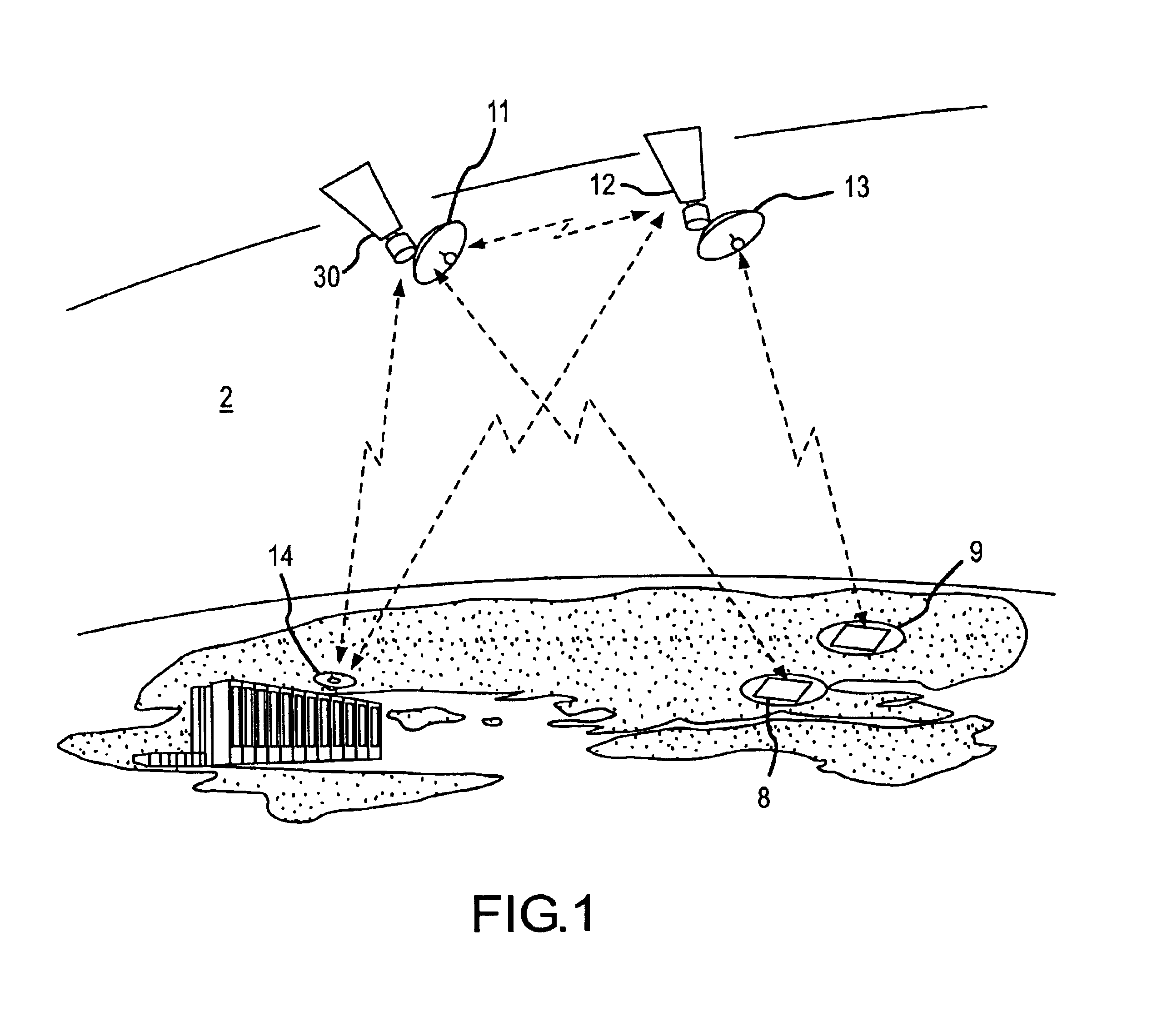
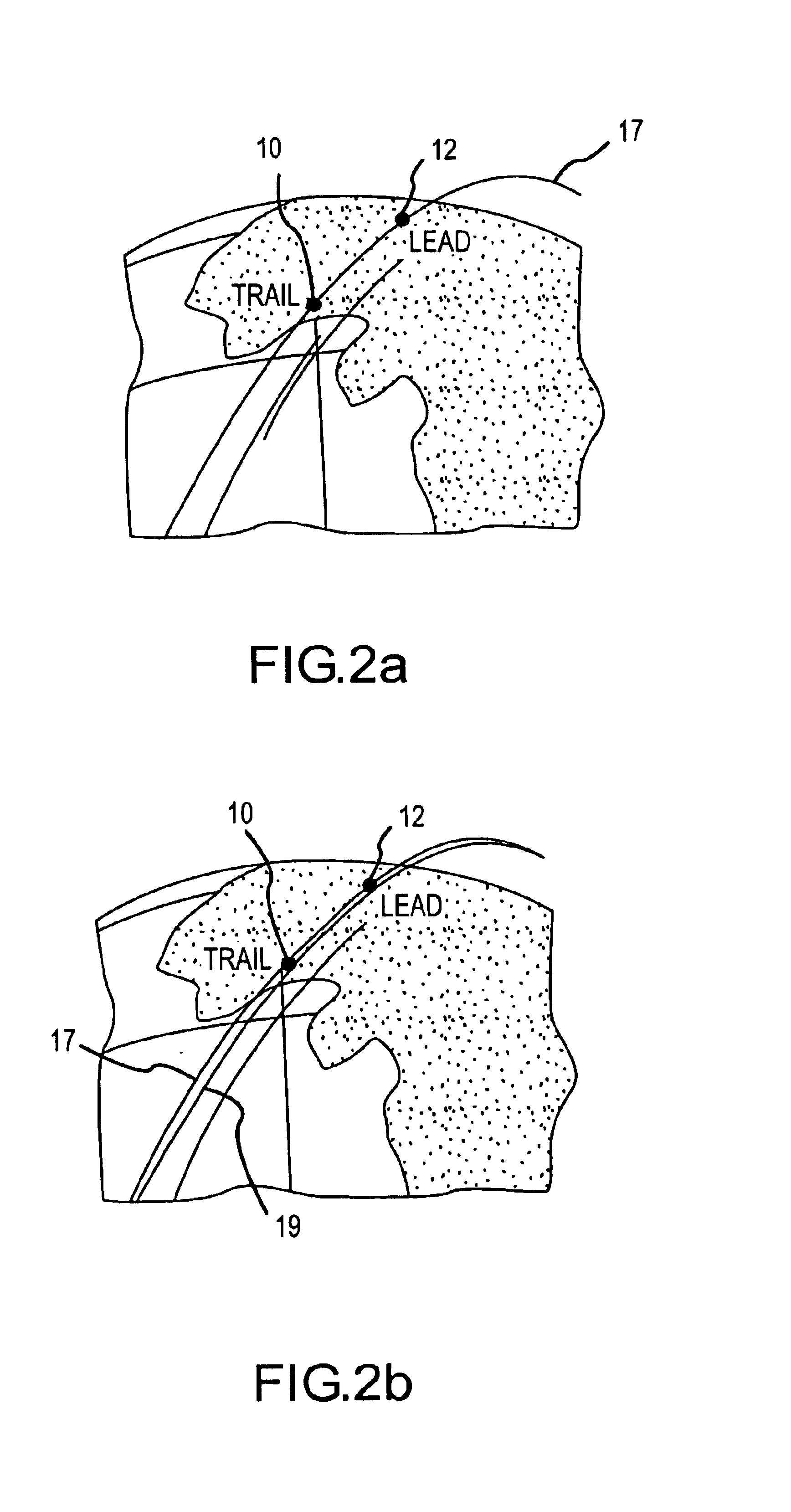
Method and apparatus for collection and processing of interferometric synthetic aperture radar data
InactiveUS6864828B1Minimize decorrelation effectAvoid interferenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarImaging processing
A system and method provide for the collection of interferometric synthetic aperture radar (IFSAR) data. In the system, a first space vehicle configured for emitting electro-magnetic energy and collecting the reflection from a region of interest (ROI), may be directed along a first orbital track. The collected image data may be stored and later provided to a ground station for image and interferometric processing. A second space vehicle may also be configured for emission and collection of electro-magnetic energy reflected from the plurality of ROI's. The second space vehicle is positioned in an aligned orbit with respect to the first space vehicle where the separation between the vehicles is known. In order to minimize decorrelation of the ROI during image processing, the lead and trail satellite are configured to substantially simultaneously emit electromagnetic pulses image data collection. In order to avoid interference in the collection of this image data, each system is configured to control the emission of pulses such that the receipt of direct and bistatic pulses by the other vehicles does not interfere with data collection.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Composite EMP shielding of bulk-solidifying amorphous alloys and method of making same
InactiveUS20070003782A1Improve corrosion resistanceHigh hardnessMagnetic/electric field screeningThin material handlingMicrowaveAlloy
An electromagnetic pulse (EMP) and high power microwave (HPM) shielding enclosure made of bulk-solidifying amorphous alloys and composites with high hardness, corrosion resistance, high strength-to-weight ratio and high conductivity, and a method of making such shielding enclosures is provided.
Owner:LIQUIDMETAL TECH
Detection of subsurface resistivity contrasts with application to location of fluids
InactiveUS20050237063A1Detection using electromagnetic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationClassical mechanicsElectromagnetic pulse
The invention relates to a method of mapping subsurface resistivity contrasts by making multichannel transient electromagnetic (MTEM) measurements on or near the earth's surface using at least one source, receiving means for measuring the system response and at least one receiver for measuring the resultant earth response. All signals from the or each source-receiver pair are processed to recover the corresponding electromagnetic impulse response of the earth and such impulse responses, or any transformation of such impulse responses, are displayed to create a subsurface representation of resistivity contrasts. The invention enables subsurface fluid deposits to be located and identified and the movement of such fluids to be monitored.
Owner:WRIGHT DAVID +2
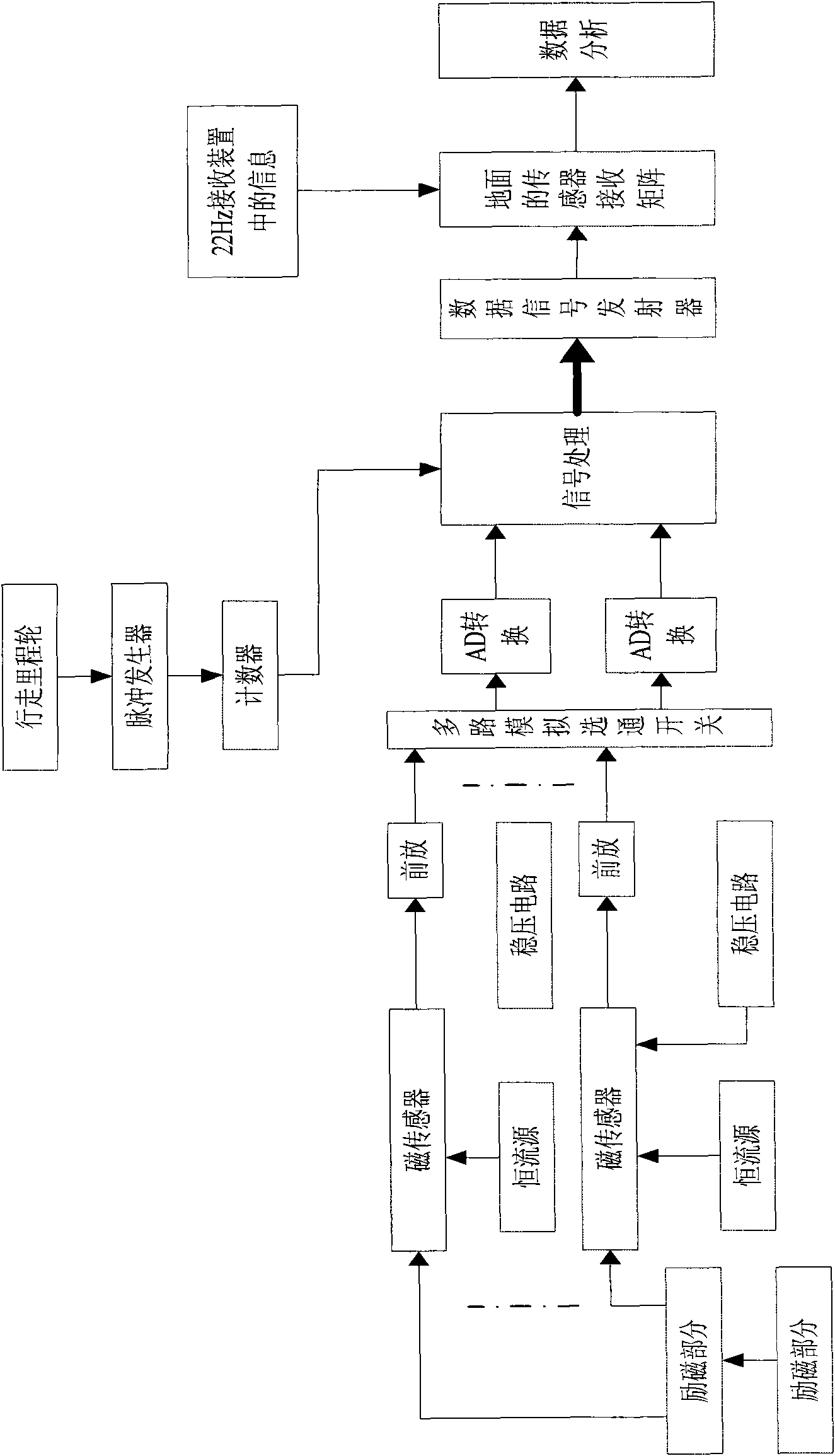
Petroleum pipeline detecting system
The invention provides a petroleum pipeline detecting system which comprises an excitation device, a detecting device, a mileage wheel, a data processing unit, a pipe internal and external data transmission device based on an ultra-low frequency electromagnetic pulse emitter, a low frequency signal emitter based on 22Hz, a low frequency signal receiver based on 22Hz, a driving device, a speed control device, a receiving sensor array, and a data analyzing unit. The system guarantees the stable running of a petroleum pipeline detector by installing a supporting wheel below the pipe internal andexternal data transmission device based on the ultra-low frequency electromagnetic pulse emitter, reduces the situation that detects of the pipeline are undetected by installing the speed control device, improves the locating precision of the pipeline defects by installing a pipe external defect locating device of the low frequency signal generator based on 22Hz, is beneficial to timely finding out defect positions in the pipe by installing the pipe internal and external data transmission device based on the ultra-low frequency electromagnetic pulse emitter.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Terahertz transceivers and methods for emission and detection of terahertz pulses using such transceivers
InactiveUS6844552B2Reduce noiseNoise-reducedRadiation pyrometryResistance/reactance/impedenceAudio power amplifierTransceiver
A system for emitting and detecting terahertz frequency electromagnetic pulses. The system comprises a single transceiver device, which may be an electro-optic crystal or photoconductive antenna, for both emitting and detecting the pulses. A related method comprises using a single transceiver device to both emit and detect electromagnetic terahertz frequency pulses. The transceiver device is excited by a pump pulse to emit a terahertz output pulse, which is modulated with a chopper. An object reflects the terahertz pulse and the reflected pulse is detected in the transceiver using a probe pulse. A lock-in amplifier set to the same frequency of the chopper is used to reduce noise in the signal detected by the transceiver. An image of the object may be created using the intensity or the timing of the peak amplitude of the terahertz pulses reflected from the object.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
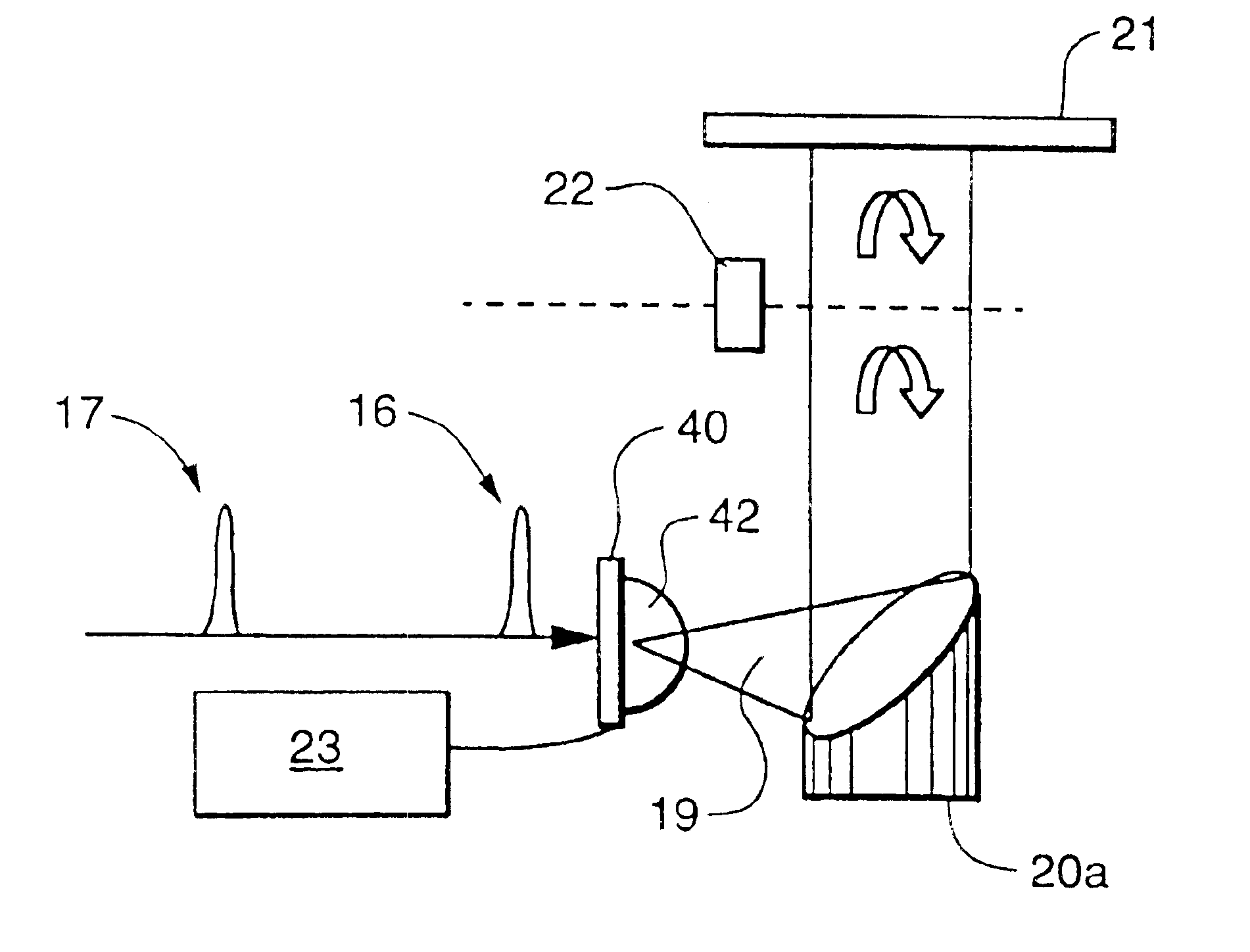
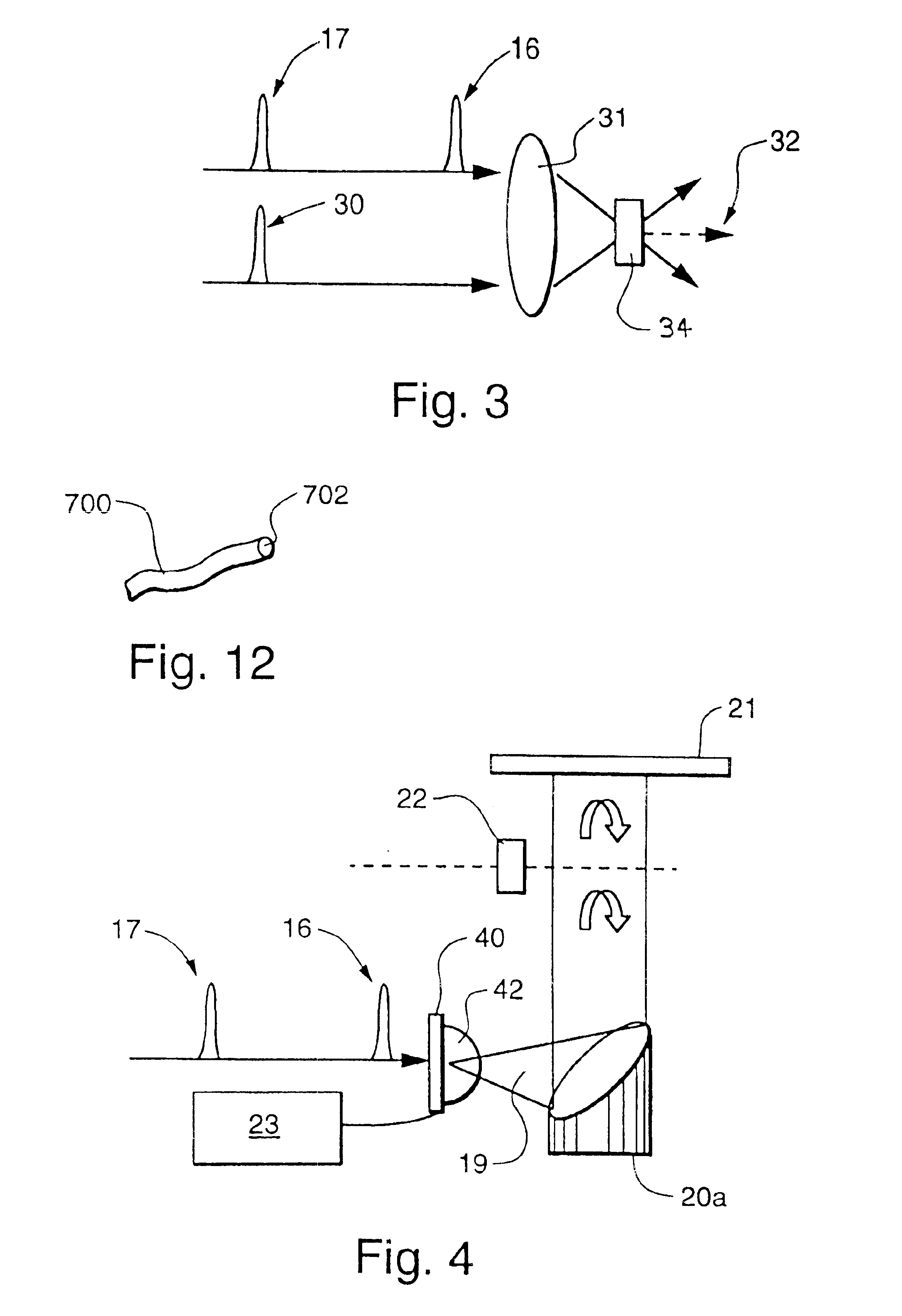
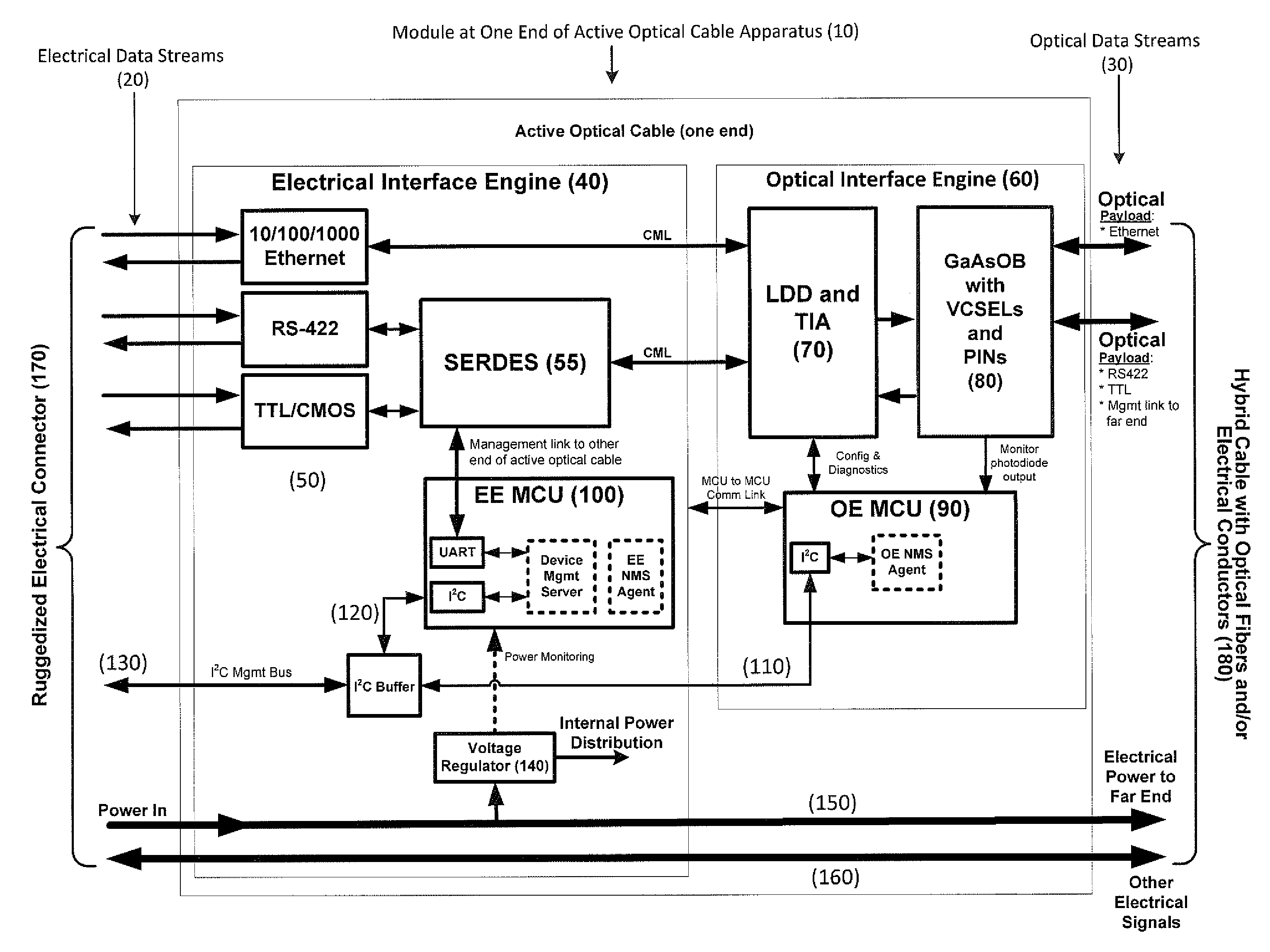
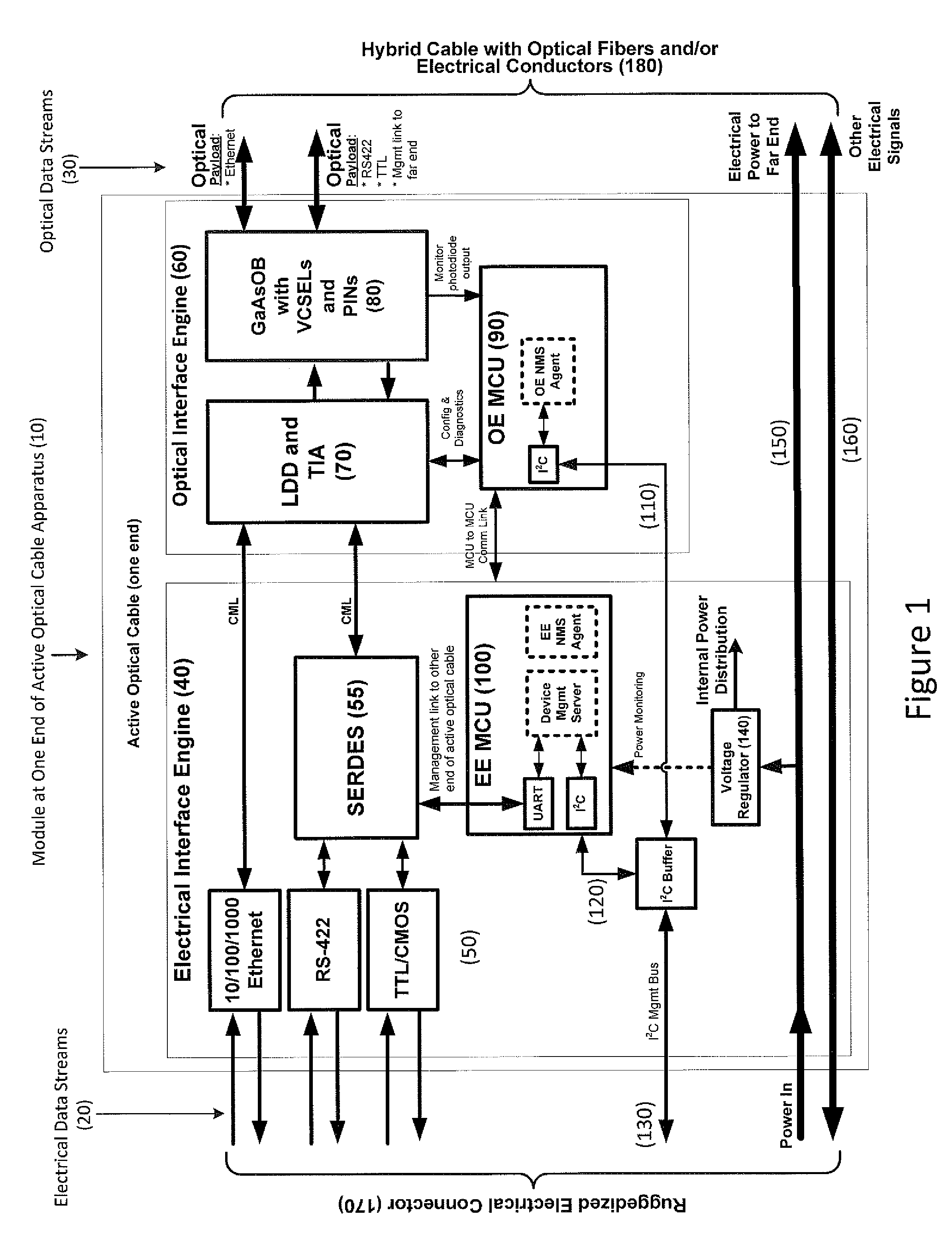
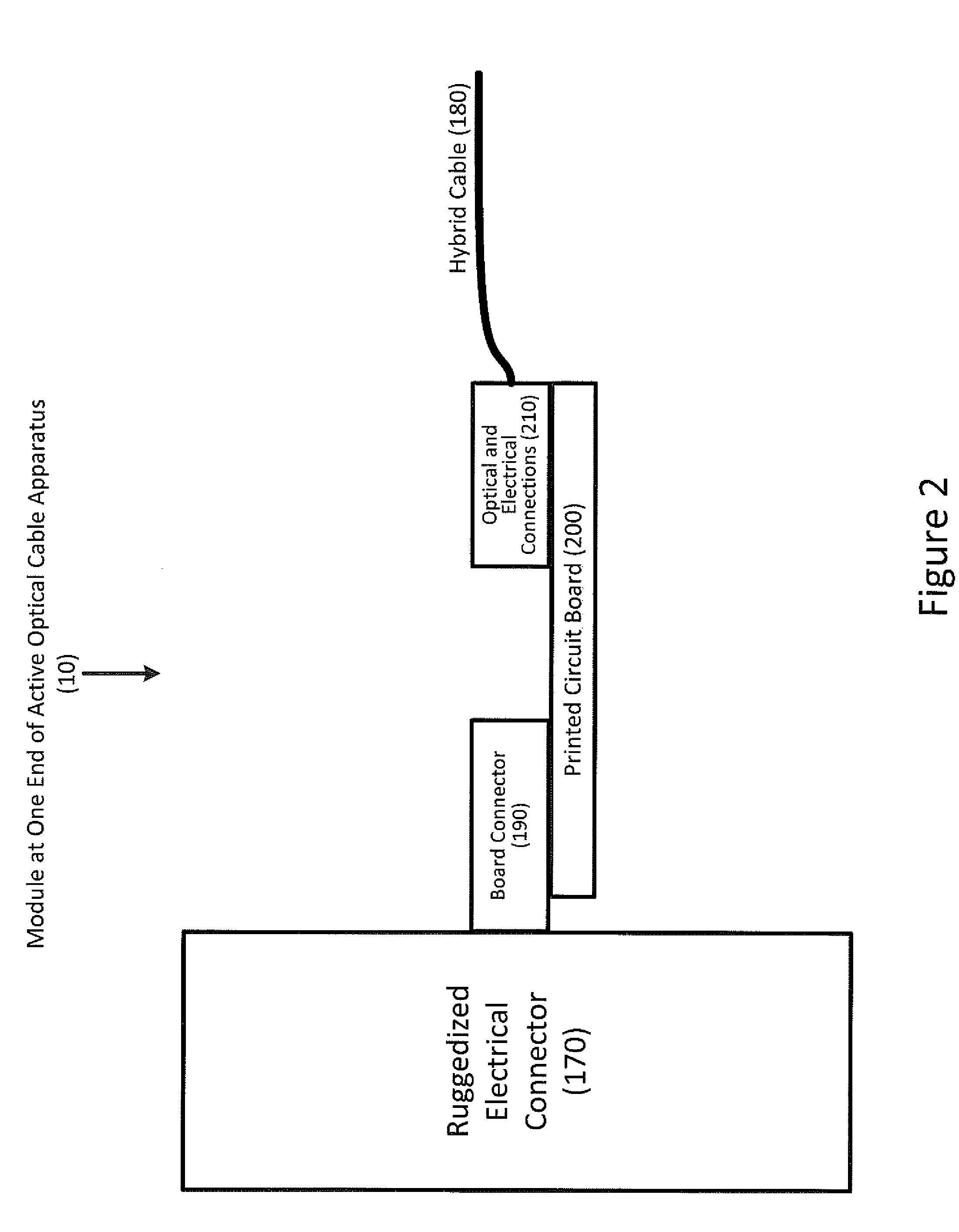
Apparatus for modular implementation of multi-function active optical cables
ActiveUS20140186023A1Protect connectionImprove linearityTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsLow noiseElectromagnetic pulse
Apparatus enabling modular implementation of active optical cable (AOC) with multiple integrated functions including: integration of different types of data on the AOC via media conversion; distribution of electrical power over the AOC; electrical multiplexing data channels for optical fibers; integration of voltage regulators enabling AOC operation at different supply voltages; integration of voltage regulators to provide stable, low noise power source; ruggedized, blind-mateable electrical connectors; integration of electronics and optoelectronics inside a connector backshell; implementation of health monitoring and test channel enabling monitoring, test, and control of both ends of the AOC and monitoring and control of upstream systems and components; and enabling a form, fit, function replacement of existing electrical cables to improve SWaP, electromagnetic interference resiliency, length-bandwidth product, electromagnetic pulse resistance, signal integrity, system reliability, testability and maintenance. AOCs are customized for different connectors, pin-outs, electrical data combinations, power distribution and power supplies with minimal redesign / requalification.
Owner:ZEPHYR PHOTONICS
Method and system for protecting data
InactiveUS20080112300A1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsRecord information storageComputer hardwareElectromagnetic pulse
A system for protecting data within a portable storage device. A self-destruct unit associated with the portable storage device is enabled. If the portable storage device is not within a pre-specified route tolerance or if the portable storage device is not at a pre-selected identification checkpoint, an alert message is sent. In response to receiving a particular response, a self-destruct signal is sent to the enabled self-destruct unit. Then the enabled self-destruct unit creates an electromagnetic pulse from a xenon flash tube to render confidential data within the portable storage device unusable.
Owner:IBM CORP
LiDAR scanner
A LiDAR sensor can include a laser, a directional sensor, a window, an electromagnetic pulse receiving sensor, and a processor. The laser can be configured to emit a narrow electromagnetic pulse. Further, the directional sensor can be configured to measure the direction of the narrow electromagnetic pulse emitted by the laser. The narrow emitted electromagnetic pulse can pass through the window. The pulse can then be reflected by at least the window and an object external from the LiDAR sensor, creating at least two reflected pulses. The electromagnetic pulse receiving sensor can be configured to measure the two reflected pulses resulting from the narrow pulse emitted by the laser. The processor can be configured to receive information from the sensors, indicating a position of the object relative to the LiDAR sensor. Further, the processor can be configured to measure the intensity of the pulse being reflected by the window.
Owner:UATC LLC
Portable wireless charging apparatus and system
InactiveUS20140308995A1Efficient chargingPower managementCircuit monitoring/indicationElectromagnetic pulseEngineering
A portable wireless charging apparatus may include a battery; a coil configured to detect whether a receiver of a first mobile device is nearby and to emit electrical magnetic pulses to realize the wireless charging; a wireless charging modulator configured to take direct current from the battery, transform the direct current into alternate current pulses and send the alternate current pulses to the coil; and a power control circuit to manage usage of the battery. In an exemplary embodiment, the power control circuit has a power managing unit and a detecting unit, said power managing unit configured to raise a battery level of the battery to a predetermined charging level, and said detecting unit continuously monitoring battery levels of the battery and a first battery in the first mobile device respectively to determine whether to terminate the wireless charging of the first mobile device.
Owner:WU CHE MIN
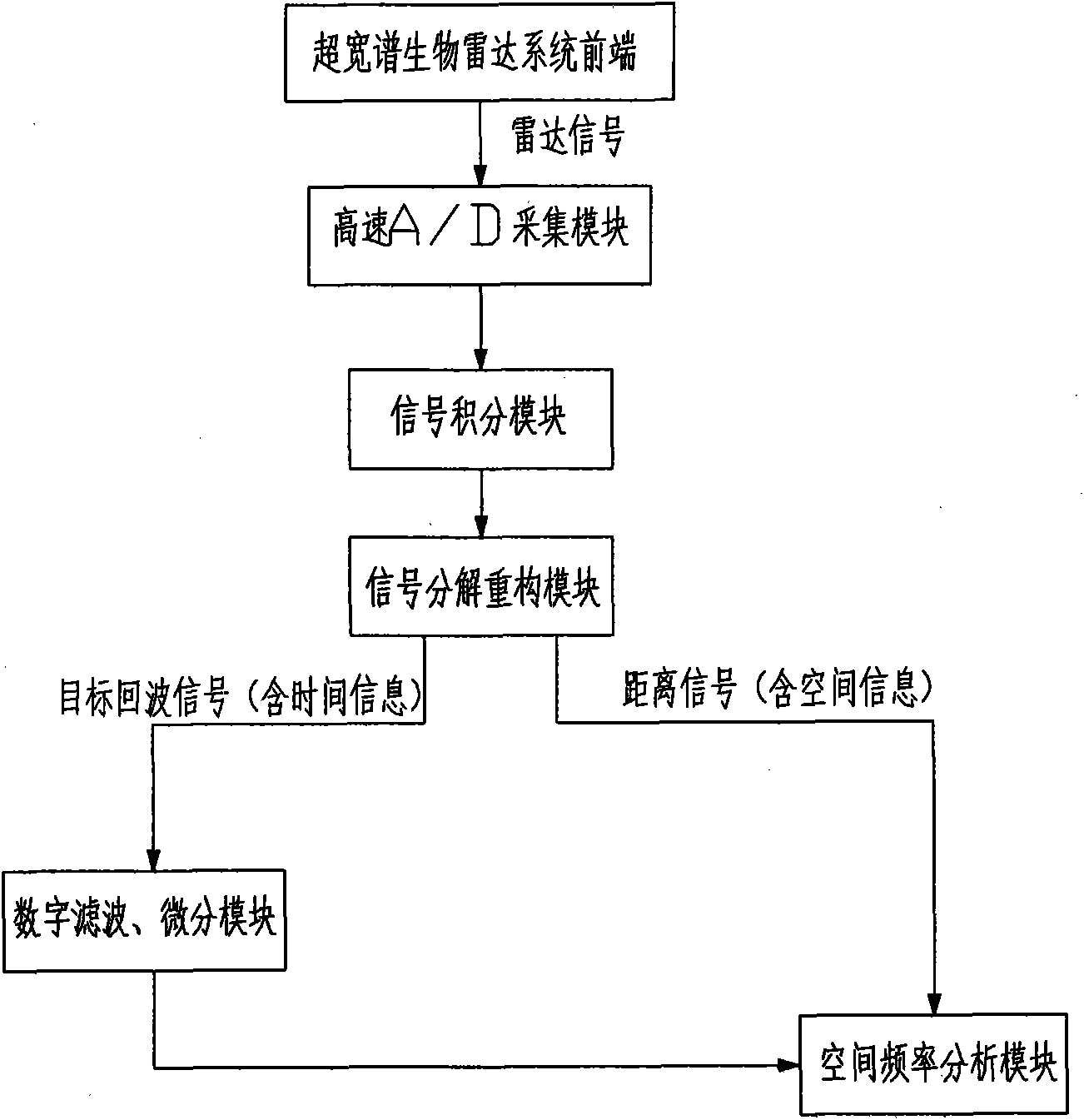
Single-channel UWB-based radar type life detection instrument for multi-target detection
InactiveCN102008291AThe target's weak vital signs are enhancedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsIntegratorAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a single-channel ultra-wide bandwidth (UWB)-based radar type life detection instrument for multi-target detection. The life detection instrument comprises a UWB biologic radar front end and a calculating unit, wherein the UWB biologic radar front end comprises a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna, a pulse oscillator, an electromagnetic pulse generator and a sampling integrator; the pulse oscillator generates a pulse signal; the signal triggers the electromagnetic pulse generator to generate a narrow pulse and radiates the narrow pulse out through the transmitting antenna; a reflected signal is transmitted to the sampling integrator through the receiving antenna; a pulse signal generated by the pulse oscillator simultaneously generates a distance gate through a delay circuit and a distance gate generator to select a received signal; the signal passes through a sampling integration circuit; a weak signal is detected after accumulation, amplified and filtered by an amplifier and a filter, sampled by a high-speed analogue / digital (A / D) acquisition card and transmitted to the calculating unit; and the acquired signal is analyzed by the calculating unit to extract life information and each target distance of multiple human targets.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method and device for laser pulse and electromagnetic pulse composite forming of metal sheet
InactiveCN102125951AMeet the forming requirementsLocality of changeManufacturing technologyEnergy absorption
The invention discloses a method and device for laser pulse and electromagnetic pulse composite forming of a metal sheet and relates to the technical field of processing and manufacturing fastening holes. The head part of an energy absorption rod (10) is a conical surface; a high-power pulse laser outputs an annular laser pulse (8) by means of a light spot regulator (15); the annular laser pulse (8) accommodates the tip part of the conical surface on the head part of the energy absorption rod (10) in a hollow part of a laser beam, and meanwhile, the annular laser pulse (8) is acted on the conical surface on the head part of the energy absorption rod (10) to induce plasma (17) to explode and generate impact waves acted on the internal walls of the fastening holes, so that the fastening holes are strengthened. The method and the device are suitable for strengthening the fastening holes with small diameter; the hollow part of the annular laser pulse (8) keeps away from the tip part of the conical surface of the energy absorption rod (10), so that the energy absorption rod (10) is difficult to damage, which is beneficial to continuously working and achieving a good strengthening effect.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Esthetic apparatus useful for increasing skin rejuvenation and methods thereof
ActiveUS20130317282A1Reducing sideUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyDiathermy deviceElectromagnetic pulse
Systems and methods for increasing skin rejuvenation of a region of a patient's skin. The system includes: a pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) frequency generator that emits electromagnetic pulses to the region of the patient's skin; and a deep tissue diathermy device that applies heat to the region of the patient's skin up to temperature T. The system simultaneously applies the heat and the PEMF to the region of a patient's skin.
Owner:VENUS CONCEPT
Medium frequency pseudo noise geological radar
System and methods are disclosed for transmitting and receiving electromagnetic pulses through a geological formation. A preferably programmable transmitter having an all-digital portion in a preferred embodiment may be operated at frequencies below 1 MHz without loss of target resolution by transmitting and over sampling received long PN codes. A gated and stored portion of the received signal may be correlated with the PN code to determine distances of interfaces within the geological formation, such as the distance of a water interfaces from a wellbore. The received signal is oversampled preferably at rates such as five to fifty times as high as a carrier frequency. In one method of the invention, an oil well with multiple production zones may be kept in production by detecting an approaching water front in one of the production zones and shutting down that particular production zone thereby permitting the remaining production zones to continue operating.
Owner:ADMINISTATOR OF AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE +1
Device and method for vehicular invisible road illumination and imaging
InactiveUS20020191388A1Improve visibilityIncrease volumeLaser detailsPosition fixationDriver/operatorEngineering
A device and method for vehicular invisible road illumination and imaging is provided. The device includes invisible for human eye and precisely synchronized for all vehicles pulsed laser or nonlaser sources of light to illuminate the road. The design and method of the invention involves providing a low probability of being blinded by oncoming vehicles and illumination of the road by light pulses which are shorter than the time which is necessary for the light pulse to travel the illuminated distance observed by the driver. Using a timing signal acquired from at least one satellite global positioning system, the period between the illuminating pulses is set the same for all vehicles with a high level of precision. The period between the illuminating pulses is divided into a predetermined number of time zones with a predetermined duration for each zone. Each predetermined time zone is assigned to a predetermined group of vehicles, for example, for military, government, law enforcement, ambulance, fire rescue, trucks, luxury vehicles, small, large vehicles etc. In order to further decrease the probability of being blinded by oncoming vehicles and also to reduce the necessary pulse energy of the illumination laser, the imaging system uses gated, spectrally selective imaging detectors with a luminosity-resolving power product at least 104 cm2 Sr. To increase the reliability for the whole system, especially for the most demanding types of vehicles such as police, ambulance and fire rescue, an additional improvement is included. For these purposes an additional generator of triggering pulse is included which illuminates an electromagnetic pulse of a different frequency from that which is used to illuminate the road. This additional triggering pulse is generated prior to the pulse which illuminates the road with a predetermined time difference, precisely set for all vehicles.
Owner:MATVEEV OLEG
Hybrid welding method and hybrid welding equipment for laser electromagnetic pulse
ActiveCN103737176AImprove adoption efficiencyReduce welding defectsLaser beam welding apparatusStructural deformationMetallic materials
The invention discloses a hybrid welding method and hybrid welding equipment for laser electromagnetic pulse. The method can be used for laser seam welding and laser spot welding technology, a pulsed high magnetic field is applied to a welding region during the process of laser welding on a workpiece with the effect of laser beams so as to mutually react with an induced plasma, a welding pool and a stress strain field through welding and complete welding task. The equipment comprises a laser device, an electromagnetic pulse generator, a numerical control system, an optical transmission system and a laser electromagnetic pulse combined machining head. The combined machining head is used for integrating the laser beams with the pulsed high magnetic field and adjusting the distance between an electromagnetic conversion device and the workpiece; the combined machining head is arranged on a machine tool. The structural deformation can be reduced, the welding quality and machining efficiency are improved, and insurmountable technical problems when a metallic material structure is manufactured through existing single welding technology are solved.
Owner:武汉飞能达激光技术有限公司
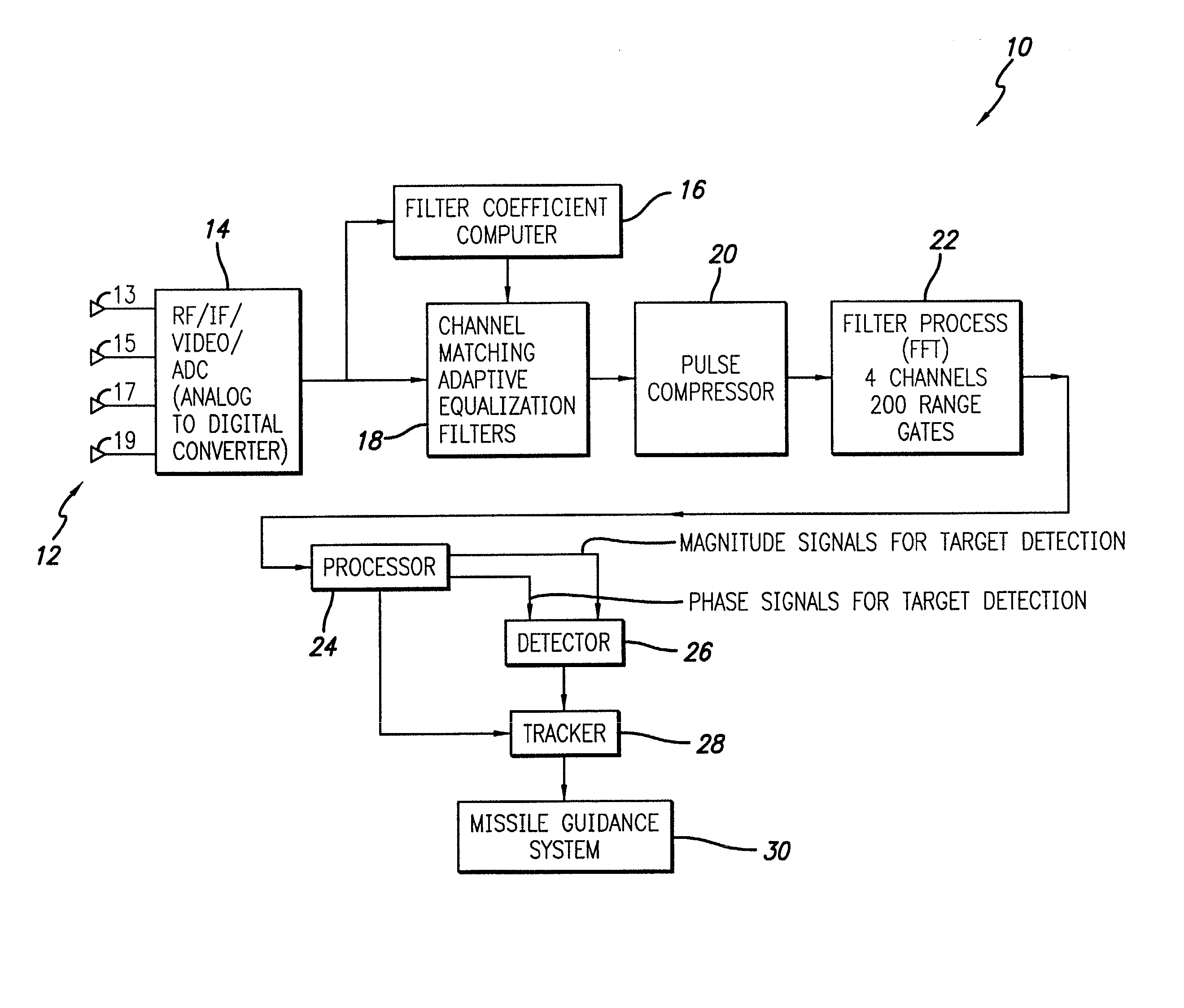
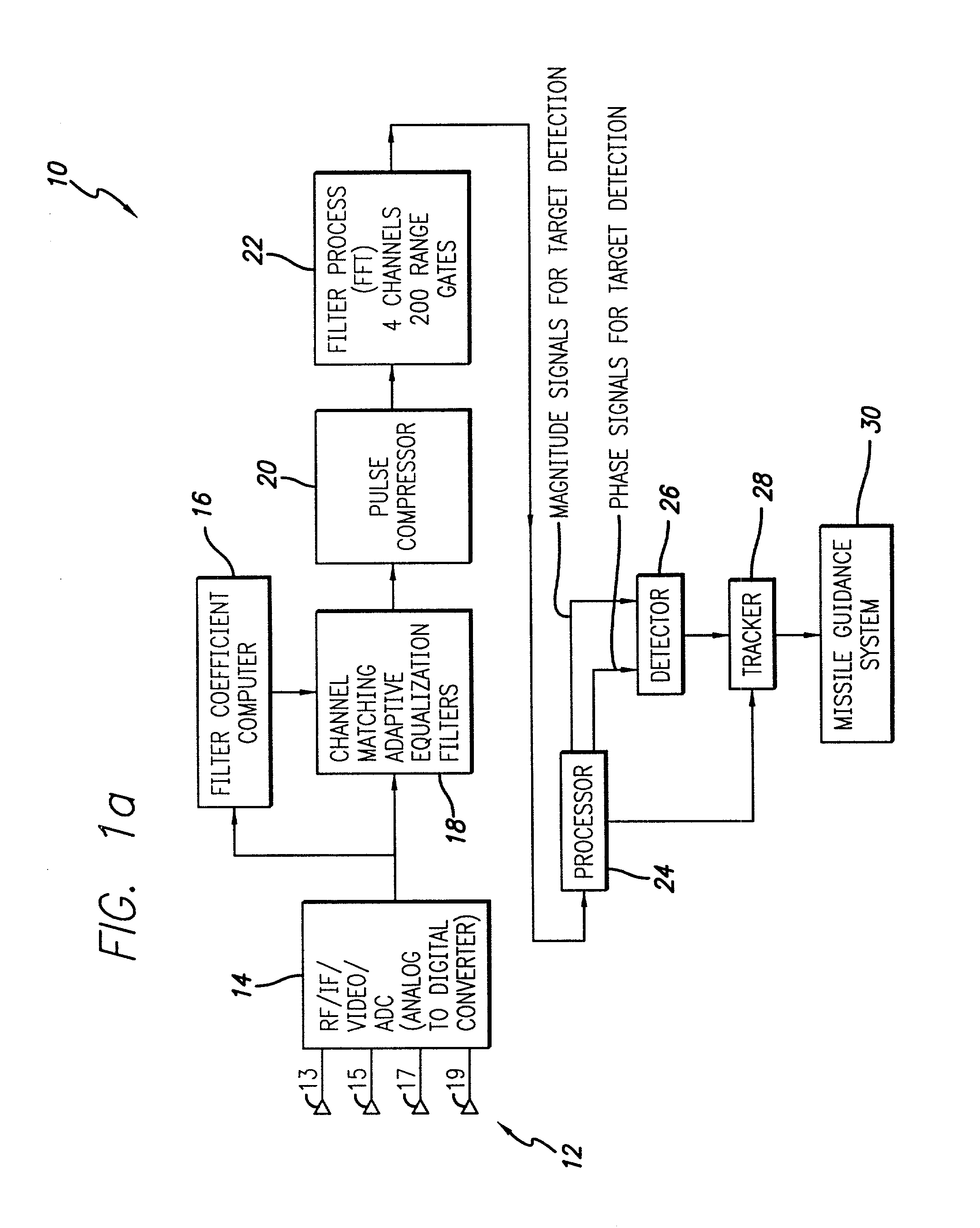
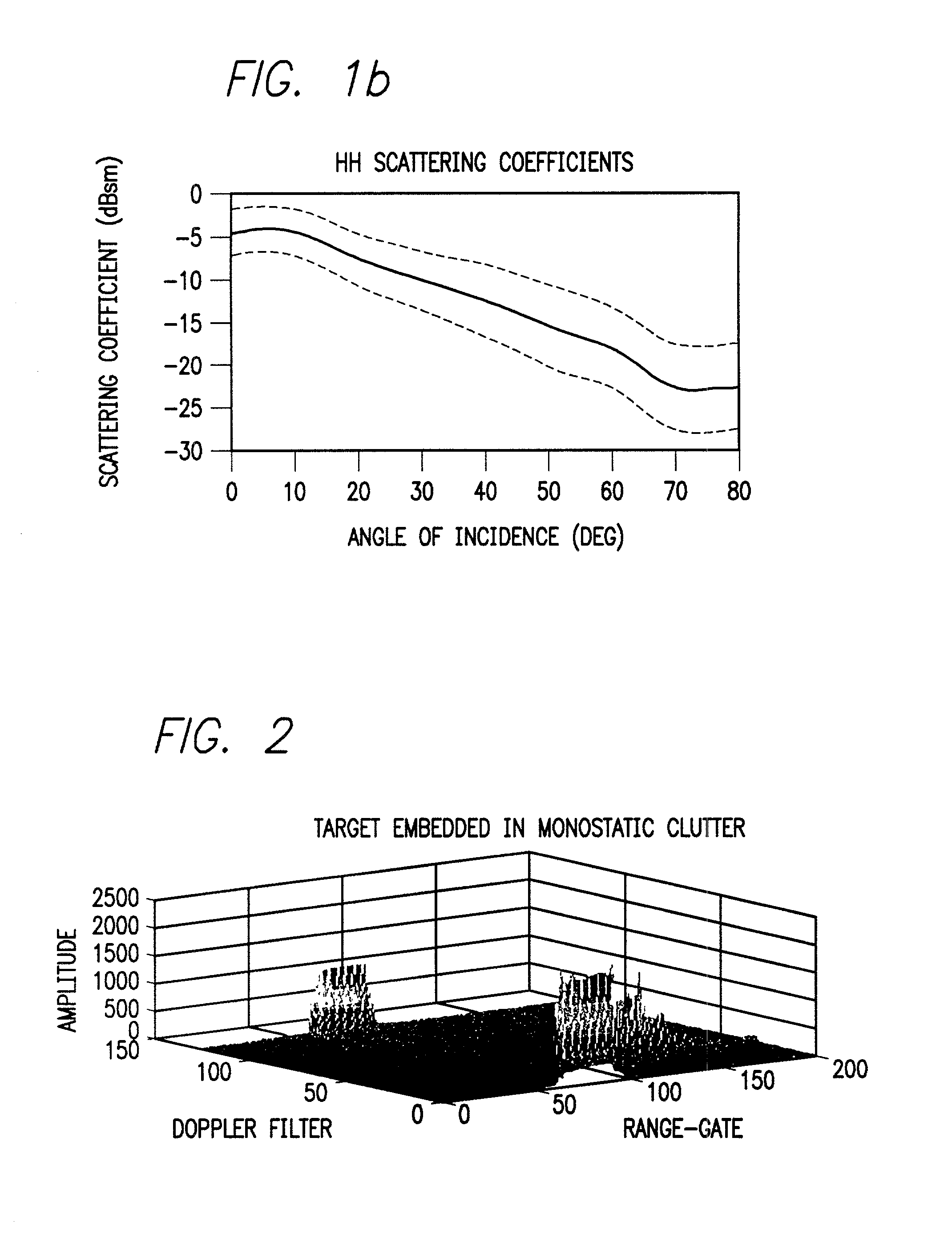
System and method for detecting and estimating the direction of near-stationary targets in monostatic clutter using phase information
InactiveUS20030189512A1Optical rangefindersHeight/levelling measurementElectromagnetic pulseComplex valued
A system and method for detecting a target. The inventive method includes the steps of receiving a complex return signal of an electromagnetic pulse having a real and an imaginary component; extracting from the imaginary component information representative of the phase component of the return signal; and utilizing the phase component to detect the target. Specifically, the phase components are those found from the complex range-Doppler map. More specific embodiments further include the steps of determining a power spectral density of the phase component of the return signal; performing a cross-correlation of power spectral density of the phase component of the return signal between different antenna-subarray (quadrant channels); and averaging the cross-correlated power spectral density of the low frequency components. In an alternative embodiment, the cross-correlation is performed on the phase component of the range-Doppler map directly. This signal can then be averaged to potentially provide improved detection of targets. The cross-correlations of the power spectral densities derived from the complex valued range-Doppler map are then used to detect the target in the presence of monostatic clutter. An additional teaching relates to a utilization of the phase component to ascertain a direction of the target and thereby effect target tracking as well as target detection.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com