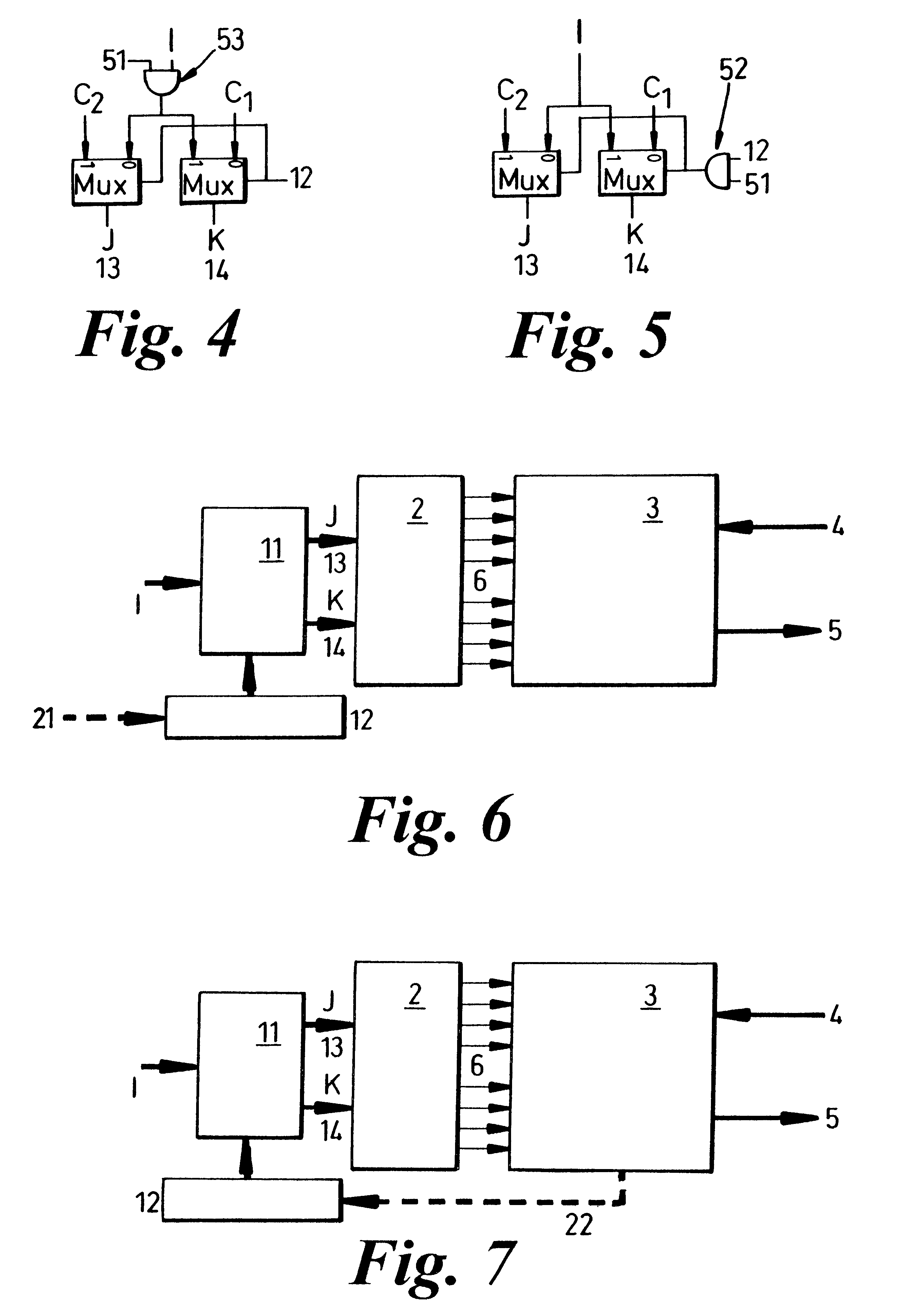
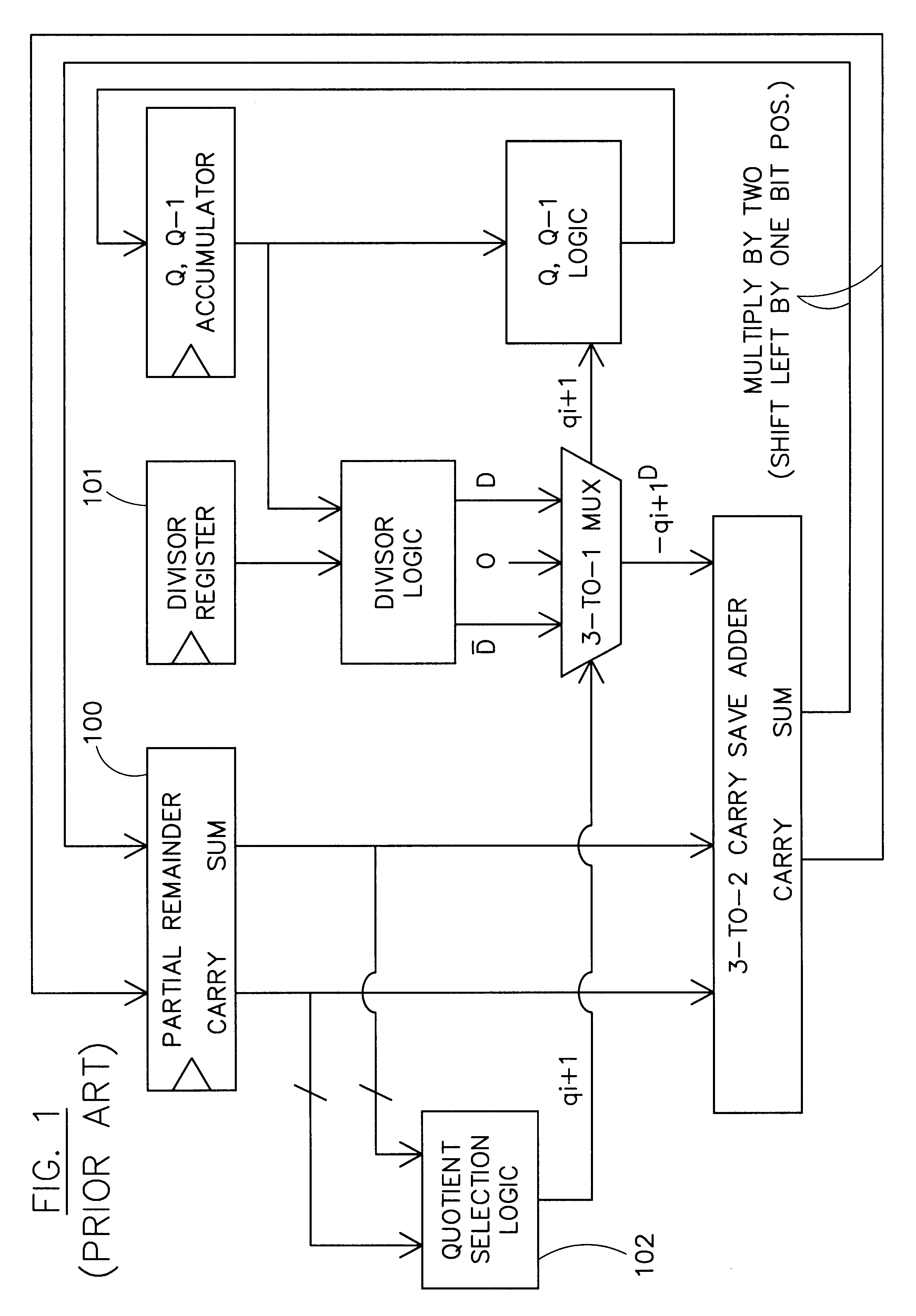
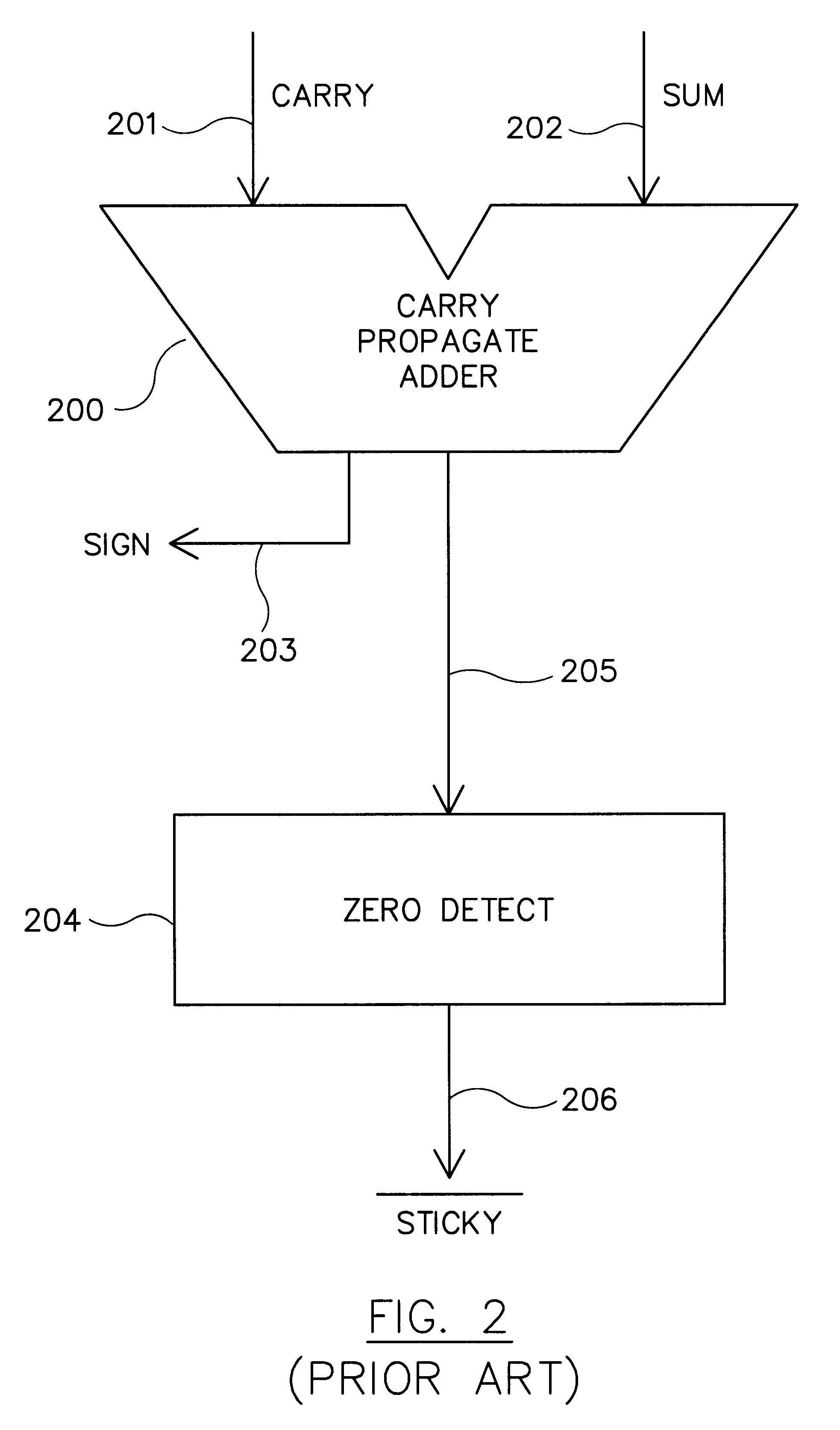
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2466results about "Computation using non-contact making devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
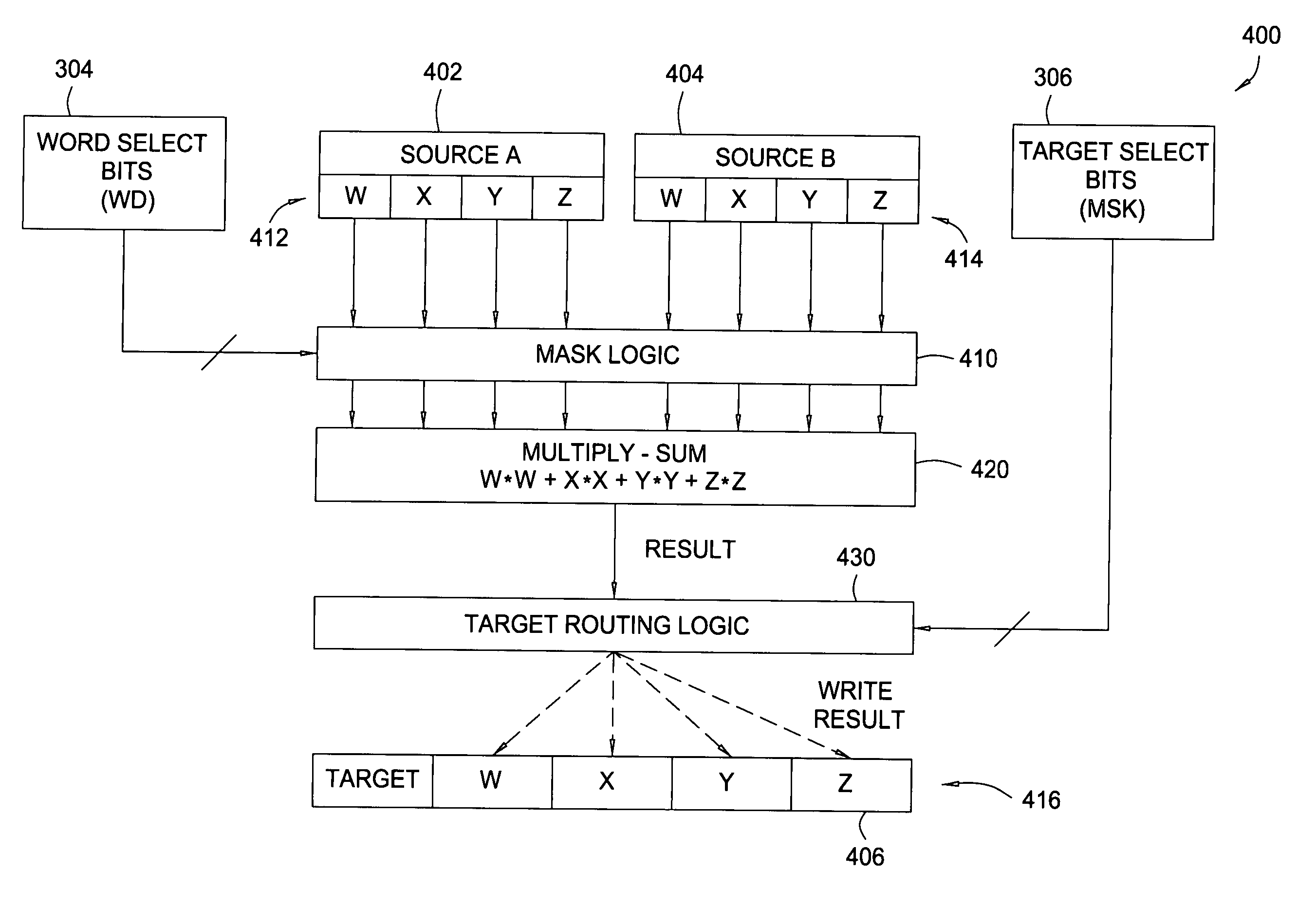
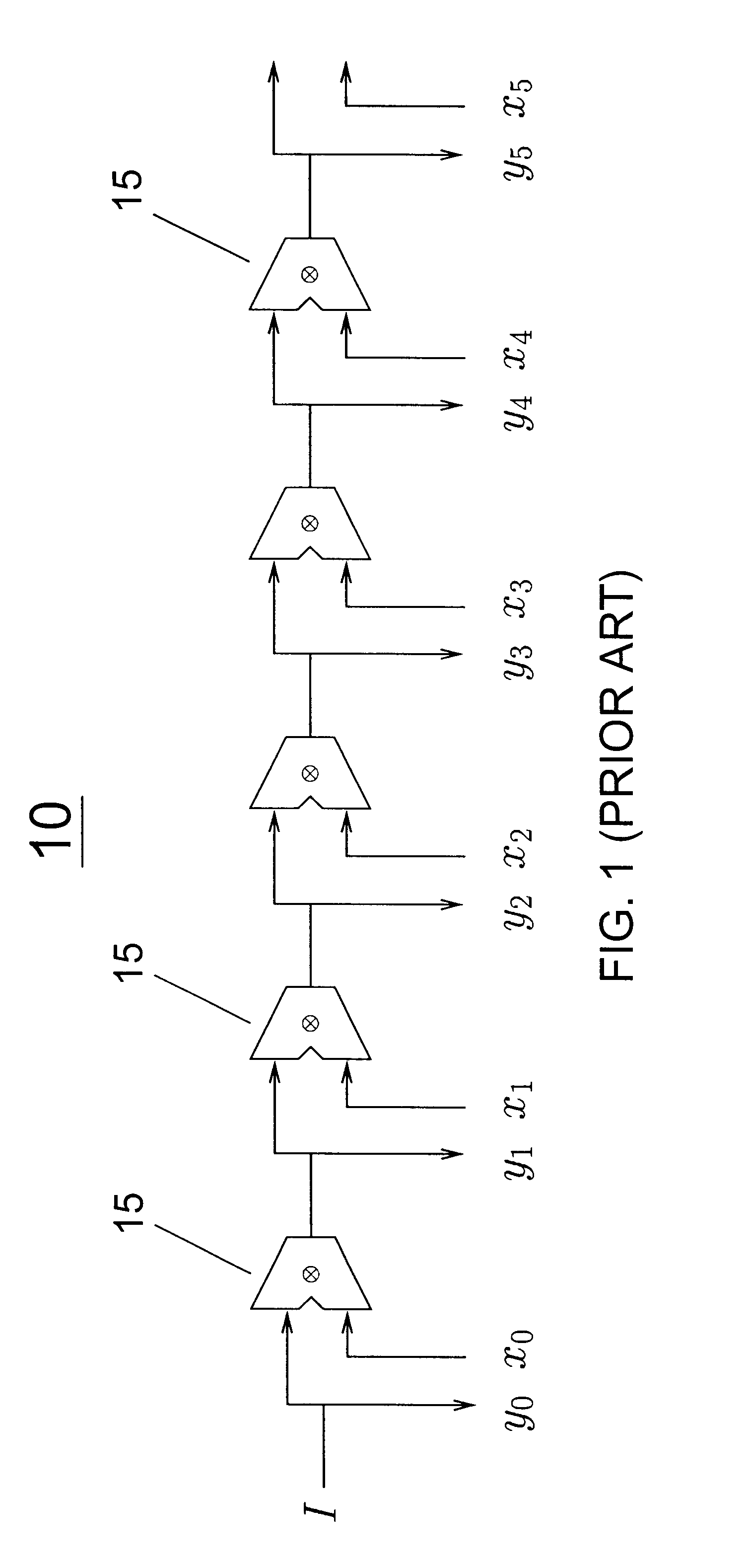
Multiply-sum dot product instruction with mask and splat
Owner:IBM CORP
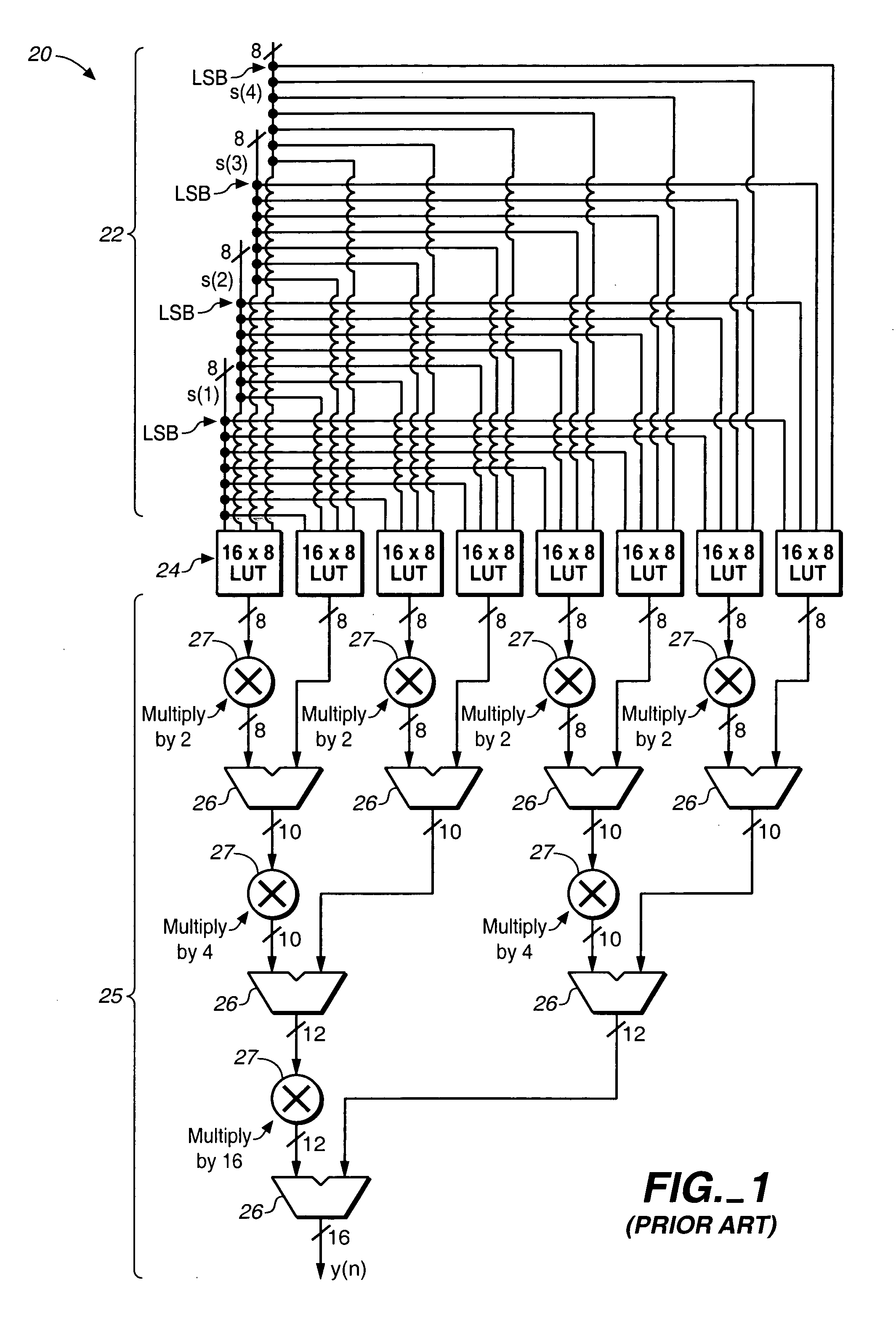
Variable fixed multipliers using memory blocks
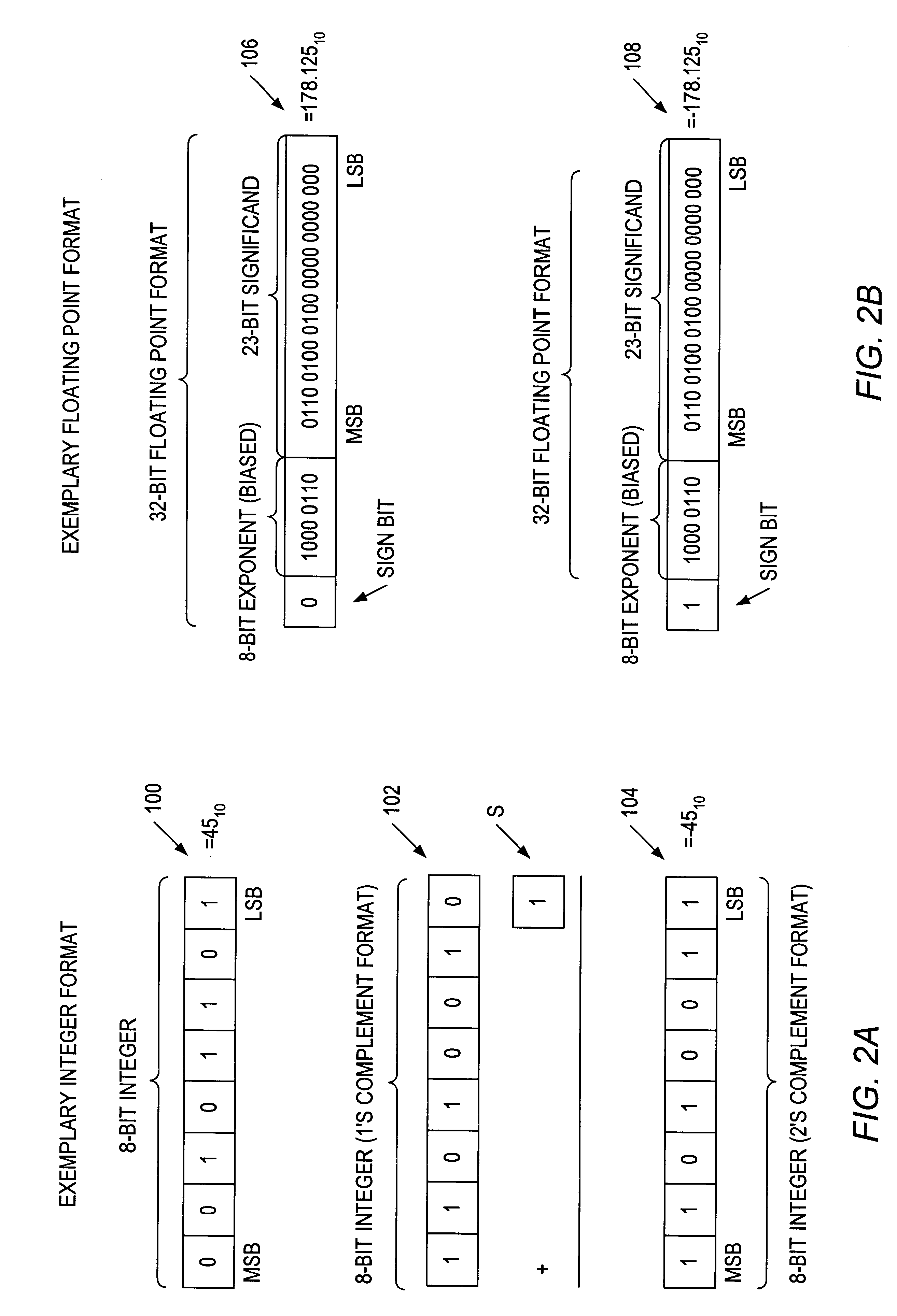
InactiveUS6943579B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesProgrammable logic deviceOperand
A programmable logic device includes at least one RAM block generating a first multi-bit calculation result which may, but does not necessarily, involve a multiplication of two operands. A shift operation is driven by a second multi-bit calculation result shifts the second multi-bit calculation result by at least one bit to generate a shifted second multi-bit calculation result. A multi-bit adder coupled to the at least one RAM block adds the shifted second multi-bit calculation result to the first multi-bit calculation result.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
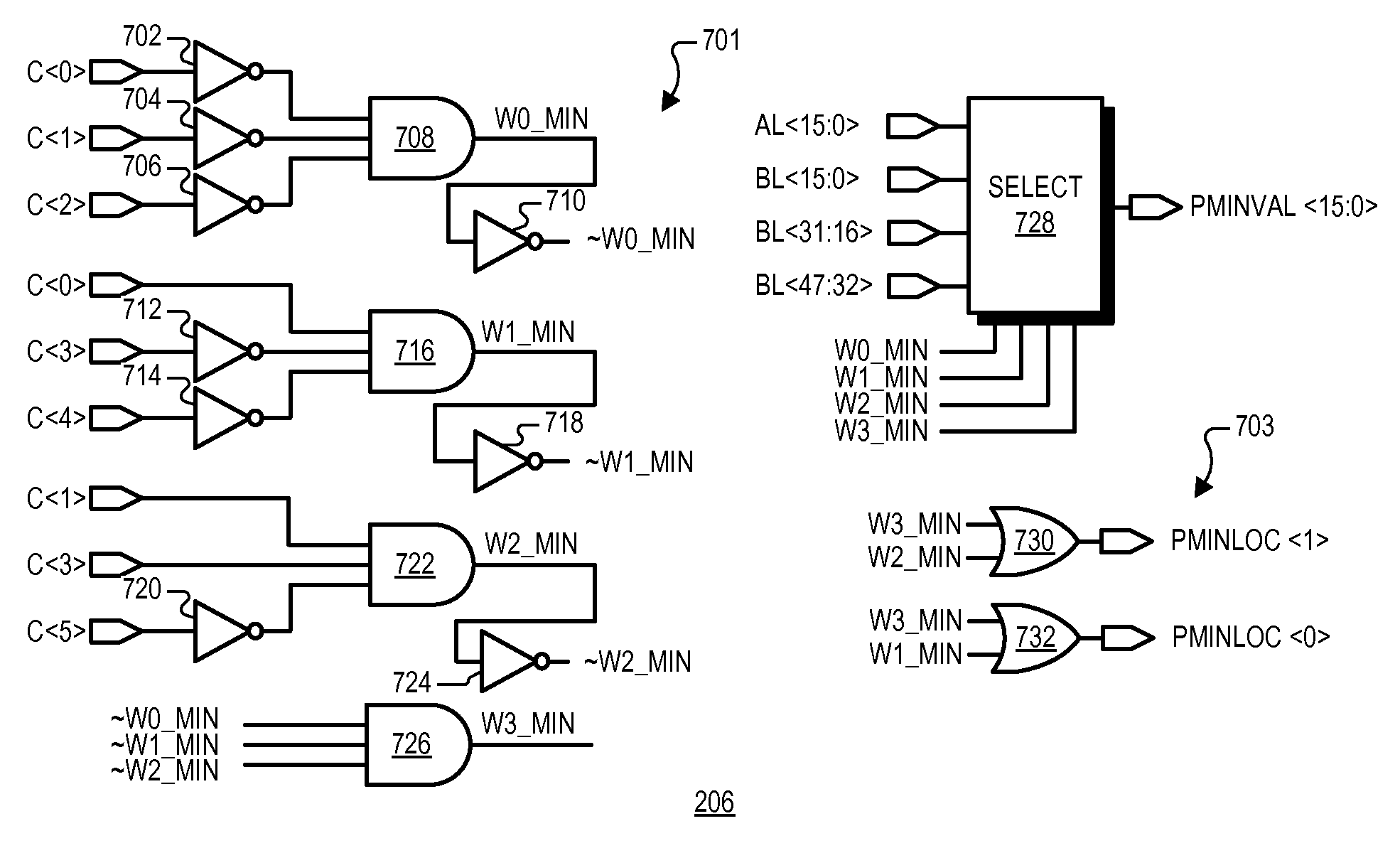
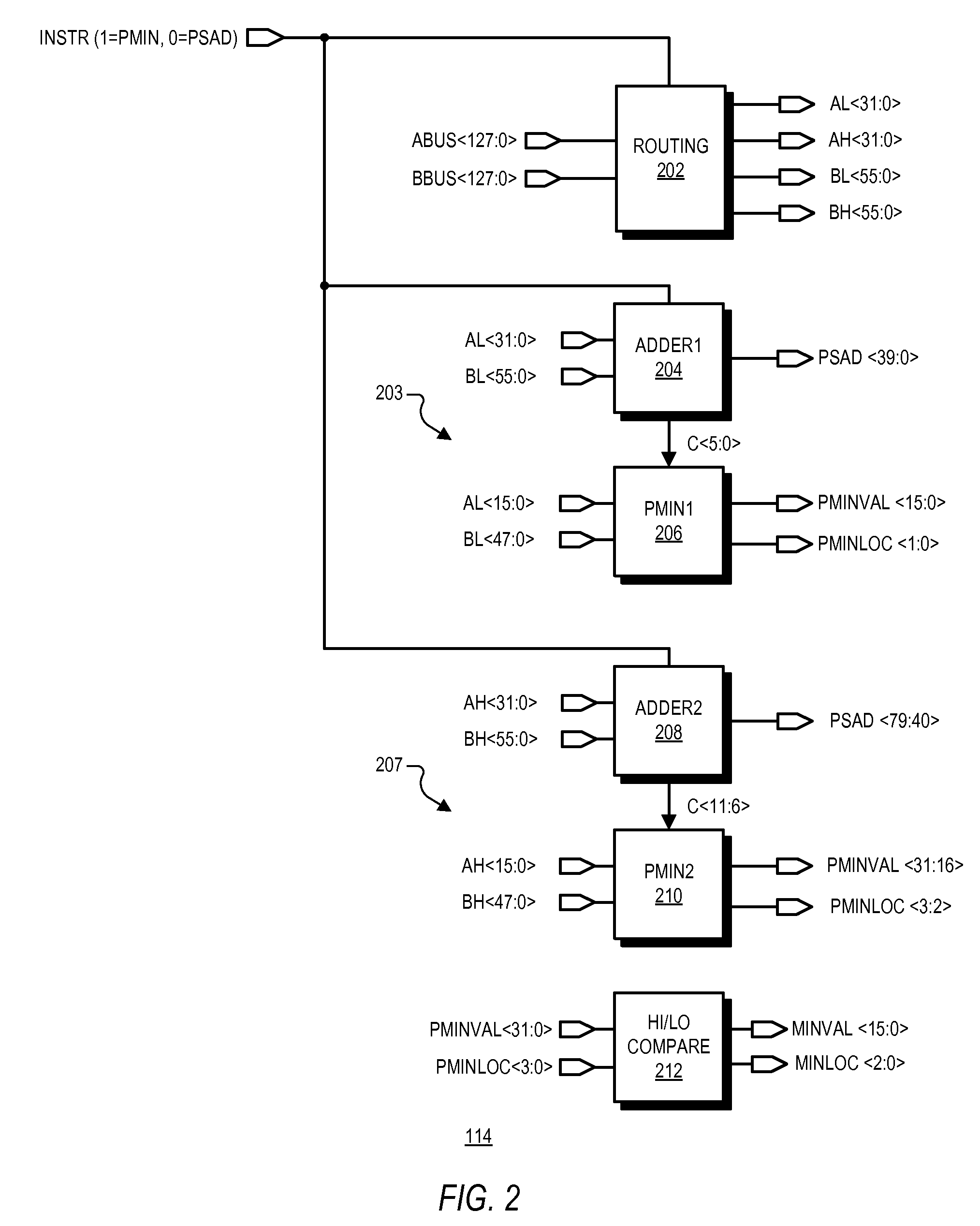
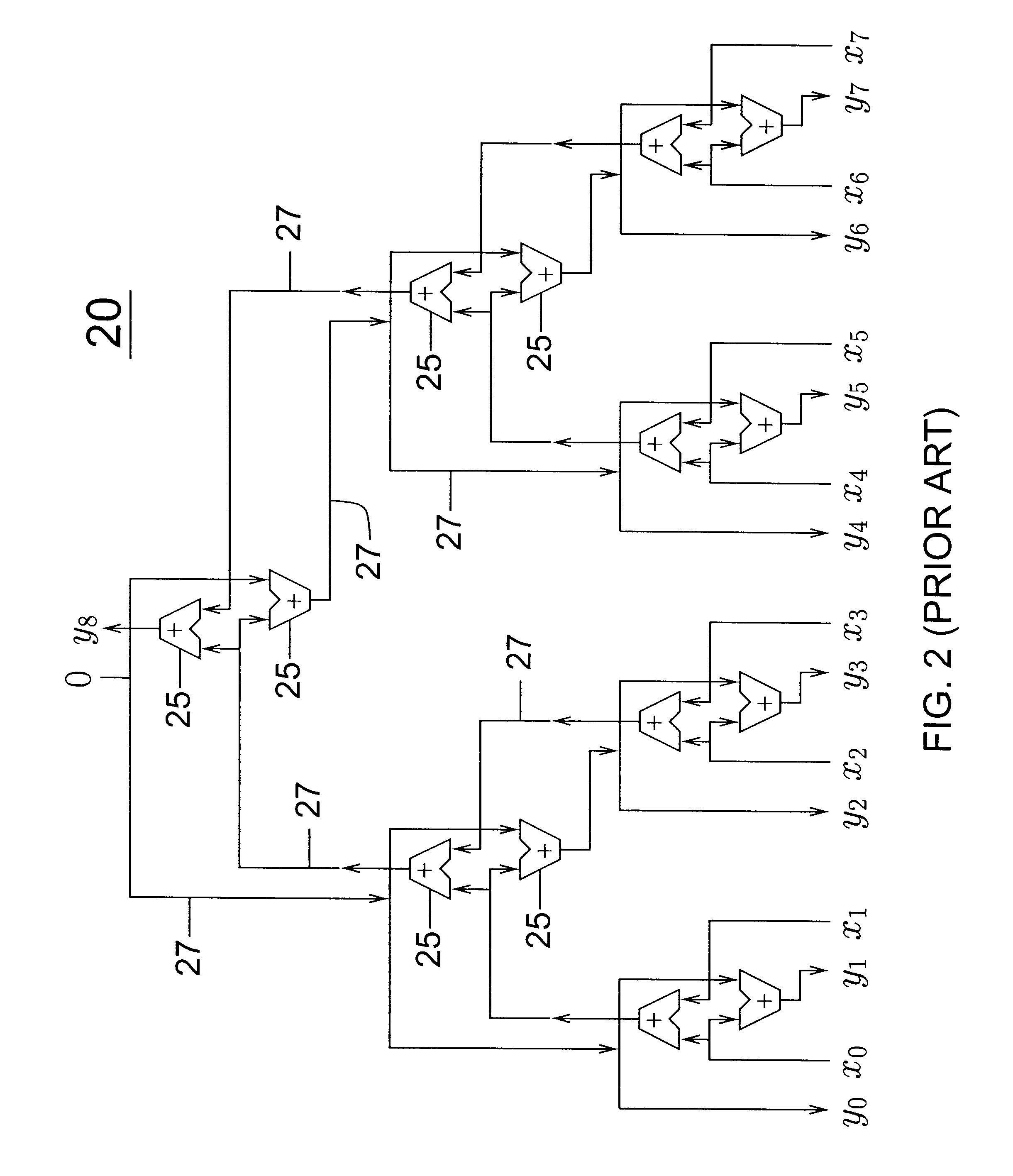
System and method for determination of a horizontal minimum of digital values
ActiveUS8650232B2Logic circuits characterised by logic functionComputation using non-contact making devicesComputer science
A system for fast determination of a horizontal minimum of multiple digital values including a difference circuit and a compare circuit. The difference circuit may include first and second adders in which the first adder compares upper bits of a first digital value with upper bits of a second digital value and provides a first carry output and a propagate output. The second adder compares lower bits of the first digital value with lower bits of the second digital value and provides a second carry output. The compare circuit determines whether the first digital value is greater than the second digital value based on the carry and propagate outputs. Multiple difference circuits may be used to compare each of multiple digital values with every other digital value to provide corresponding compare bits, which are then used to determine a minimum one of the digital values and its corresponding location.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
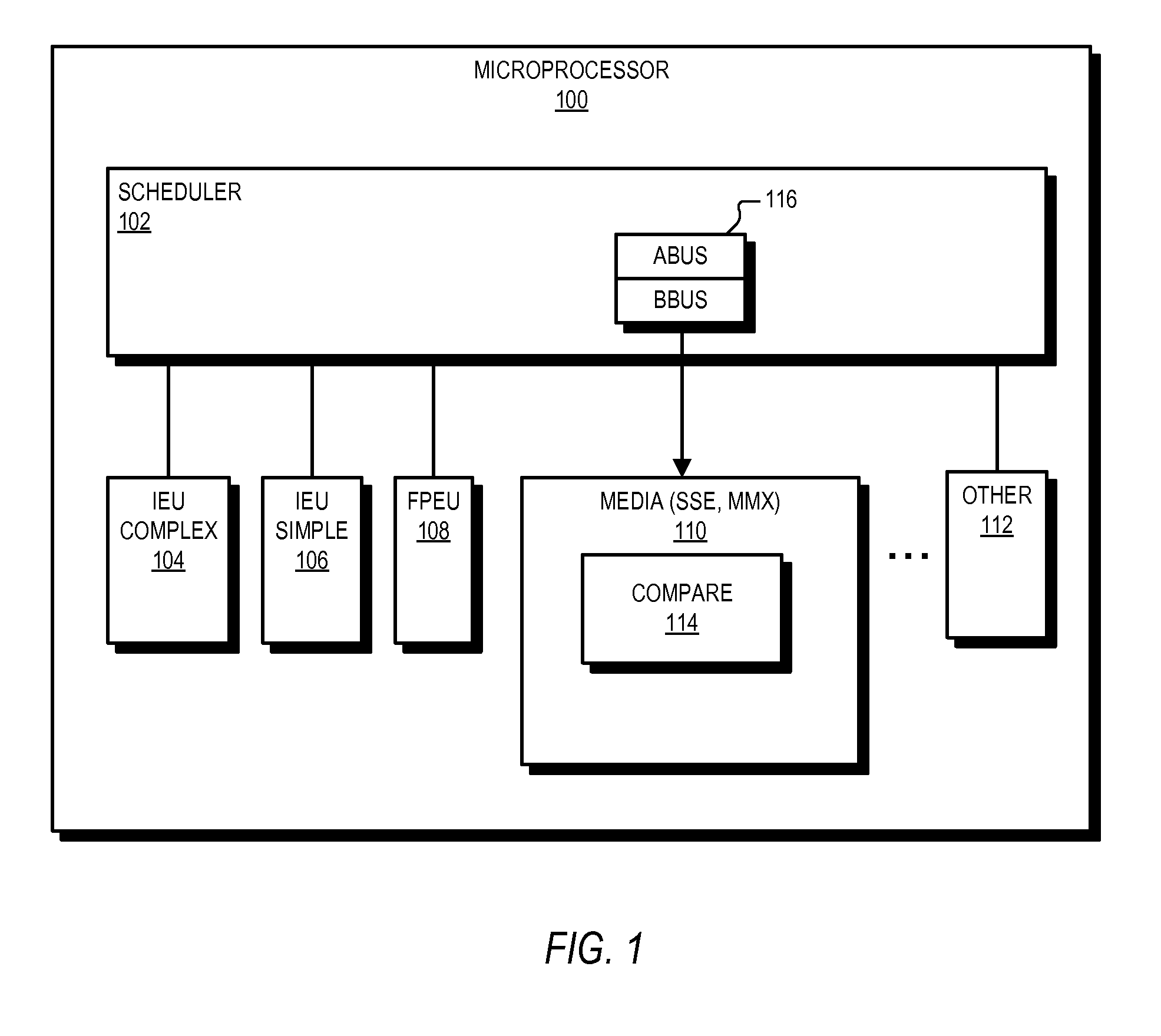
High performance microprocessor having variable speed system clock
InactiveUS6598148B1Improve performanceWithout sacrificing microprocessor speedRandom number generatorsInstruction analysisComputer architectureStatic random-access memory
A microprocessor integrated circuit including a processing unit disposed upon an integrated circuit substrate is disclosed herein. The processing unit is designed to operate in accordance with a predefined sequence of program instructions stored within an instruction register. A memory, capable of storing information provided by the processing unit and occupying a larger area of the integrated circuit substrate than the processing unit, is also provided within the microprocessor integrated circuit. The memory may be implemented using, for example dynamic or static random-access memory. A variable output frequency system clock, such as generated by a ring oscillator, is also disposed on the integrated circuit substrate.
Owner:MOORE CHARLES H TTE UTD 03 21 2006 THE EQUINOX TRUST
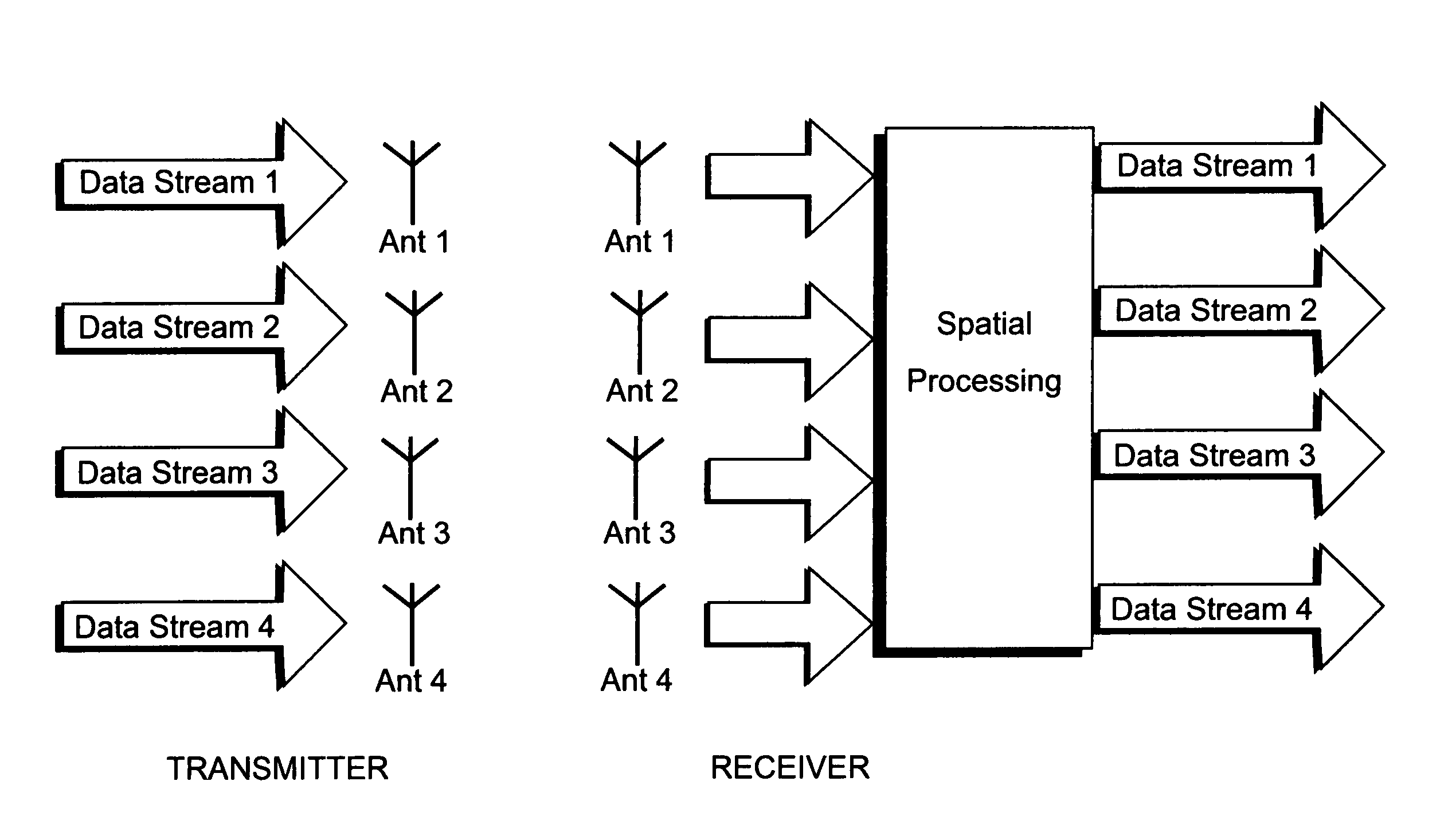
MIMO wireless precoding system robust to power imbalance
InactiveUS20080303699A1Sacrificing scheduling flexibilityAvoid power imbalanceComputation using non-contact making devicesCode conversionPrecodingUser equipment
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for preventing power imbalance in a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) wireless precoding system. According to one aspect of the present invention, a codebook is constructed with a first subset of codewords that are constant modulus matrices, and a second subset of codewords that are non-constant modulus matrices. A mapping scheme is established between the first subset of codewords and the second subset of codewords. When a unit of user equipment feeds back a first codeword that is a non-constant modulus matrix, the Node-B may replace the first codewords with a second codeword that is selected from the first subset of codewords and that corresponds to the first codeword in accordance with the mapping scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cycle segmented prefix circuits
InactiveUS6609189B1Improve performanceAvoid performanceComputation using non-contact making devicesGeneral purpose stored program computerExtensibilityScalar processor
The poor scalability of existing superscalar processors has been of great concern to the computer engineering community. In particular, the critical-path delays of many components in existing implementations grow quadratically with the issue width and the window size. This patent presents a novel way to reimplement these components and reduce their critical-path delay growth. It then describes an entire processor microarchitecture, called the Ultrascalar processor, that has better critical-path delay growth than existing superscalars. Most of our scalable designs are based on a single circuit, a cyclic segmented parallel prefix (cspp). We observe that processor components typically operate on a wrap-around sequence of instructions, computing some associative property of that sequence. For example, to assign an ALU to the oldest requesting instruction, each instruction in the instruction sequence must be told whether any preceding instructions are requesting an ALU. Similarly, to read an argument register, an instruction must somehow communicate with the most recent preceding instruction that wrote that register. A cspp circuit can implement such functions by computing for each instruction within a wrap-around instruction sequence the accumulative result of applying some associative operator to all the preceding instructions. A cspp circuit has a critical path gate delay logarithmic in the length of the instruction sequence. Depending on its associative operation and its layout, a cspp circuit can have a critical path wire delay sublinear in the length of the instruction sequence.
Owner:YALE UNIV
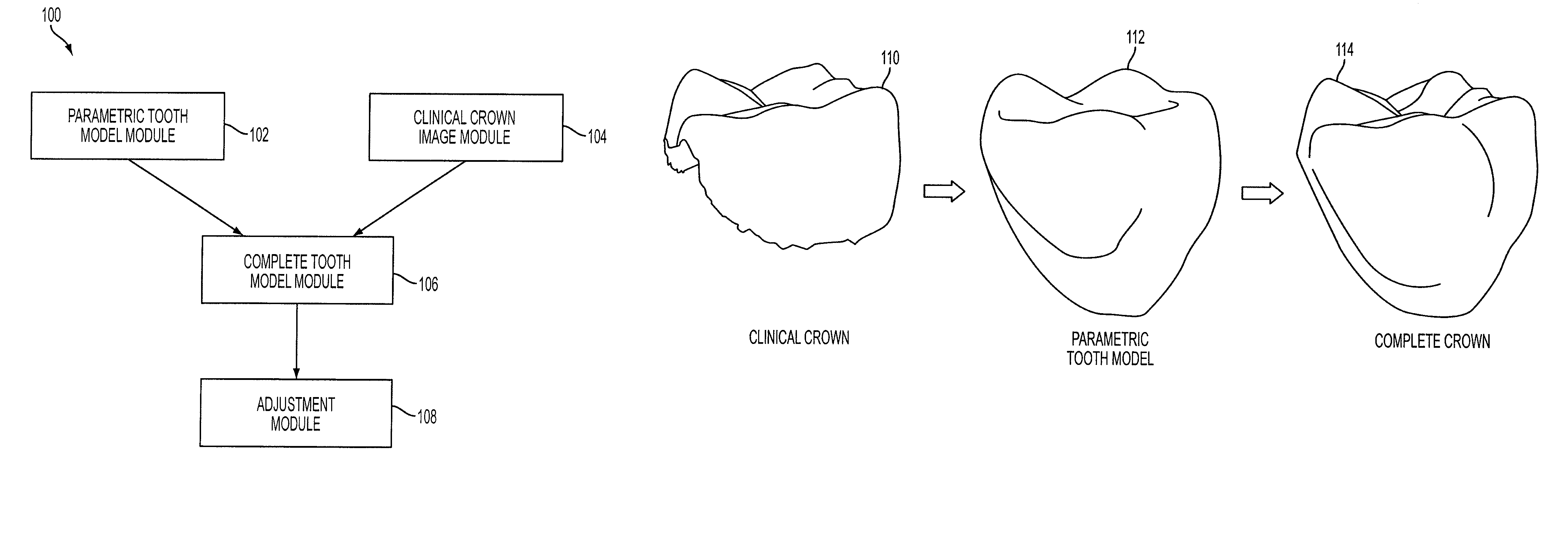
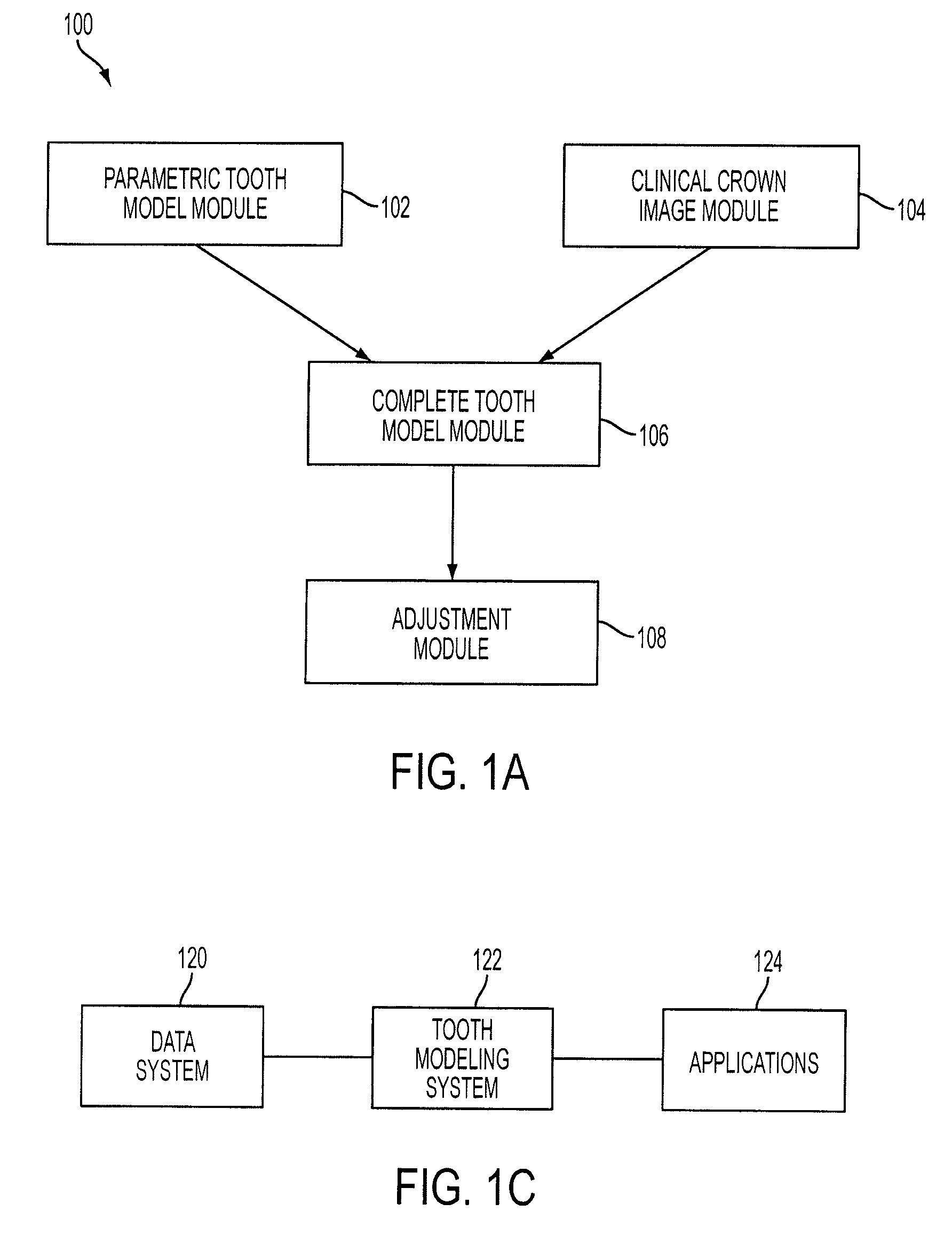
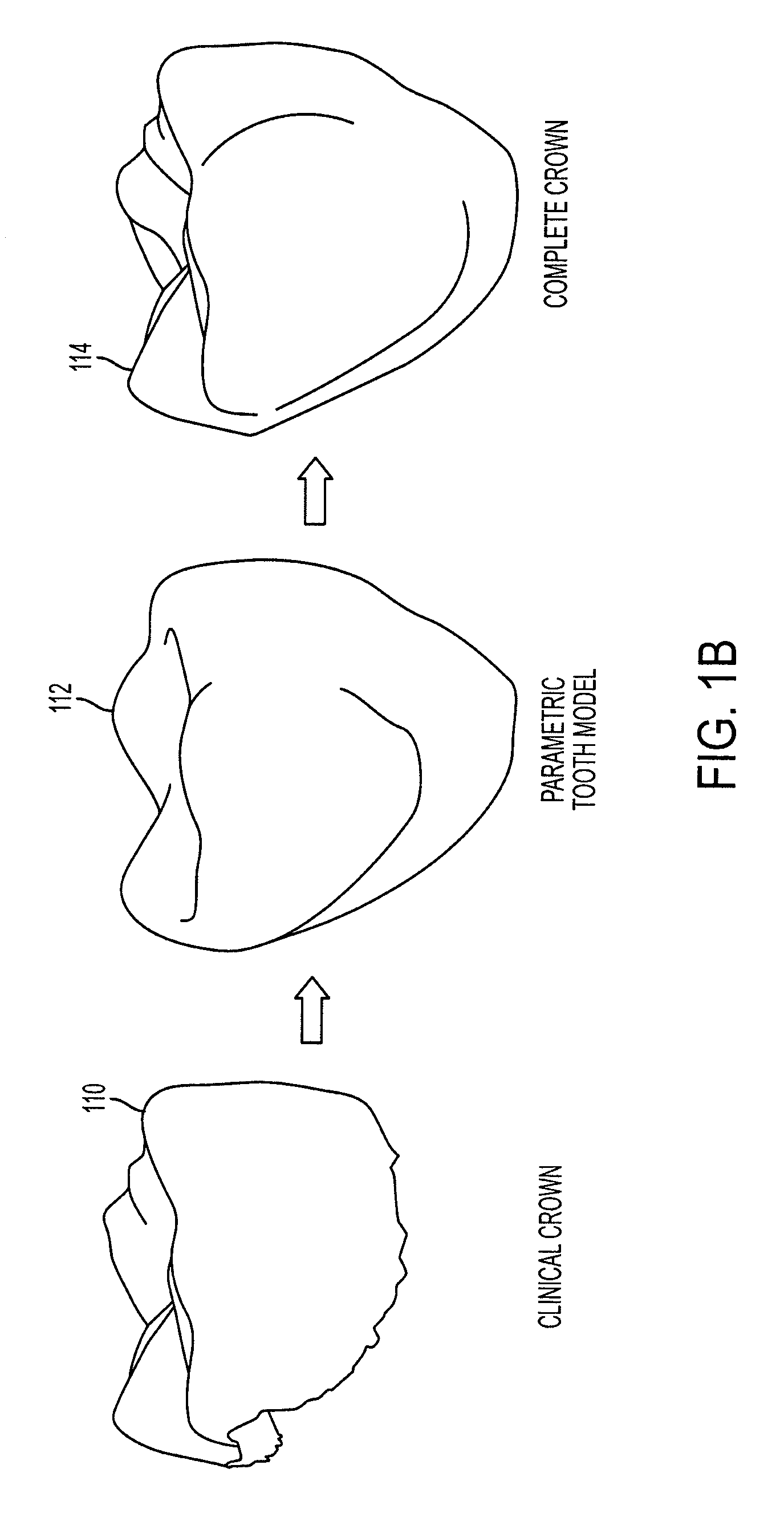
Reconstruction of non-visible part of tooth
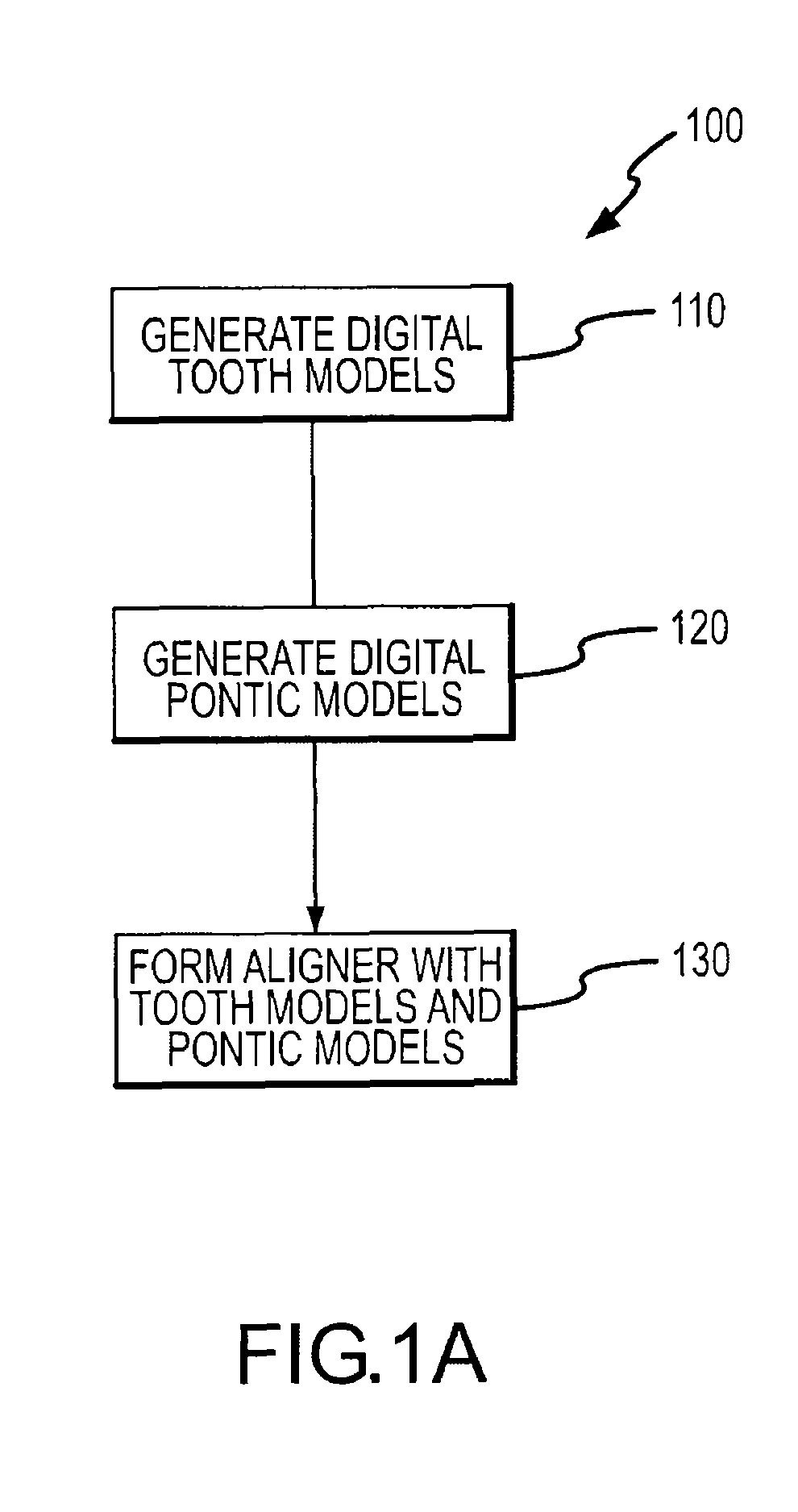
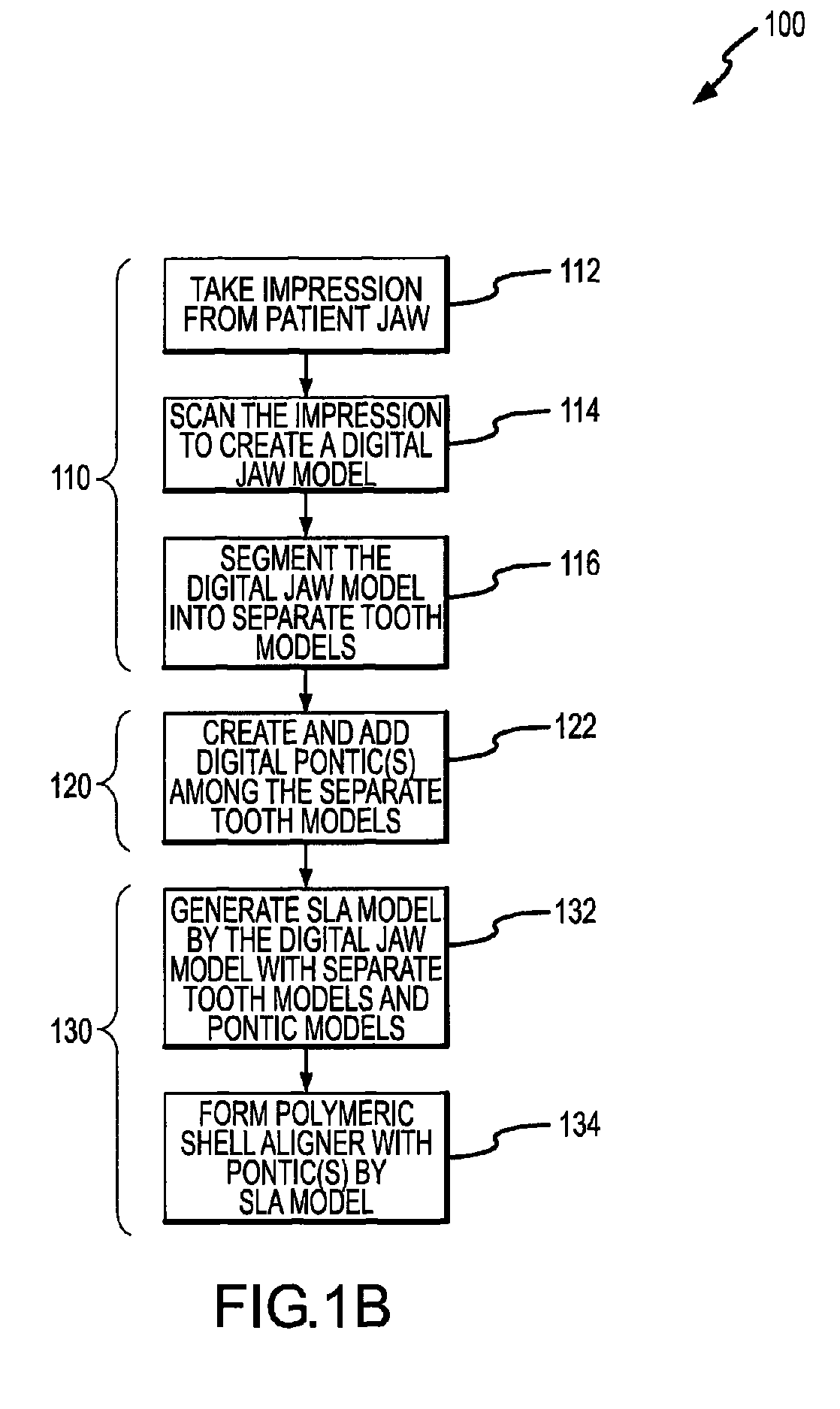
Modeling a complete tooth of a patient to facilitate dental and / or orthodontic treatment includes generating a first set of digital data representing a clinical crown; generating a second set of digital data representing a plurality of digital tooth models of a particular tooth type each having a first parameterization; processing the second set of digital data to obtain a third set of digital data representing an average tooth model of the particular tooth type having a second parameterization which is less than the first parameterization; fitting the third set of digital data to the first set of digital data to create a set of digital data representing an interim tooth model; and morphing the set of digital data representing the interim tooth model to substantially mimic the anatomical shape of the clinical crown of the first set of digital data.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Data processing circuits and interfaces
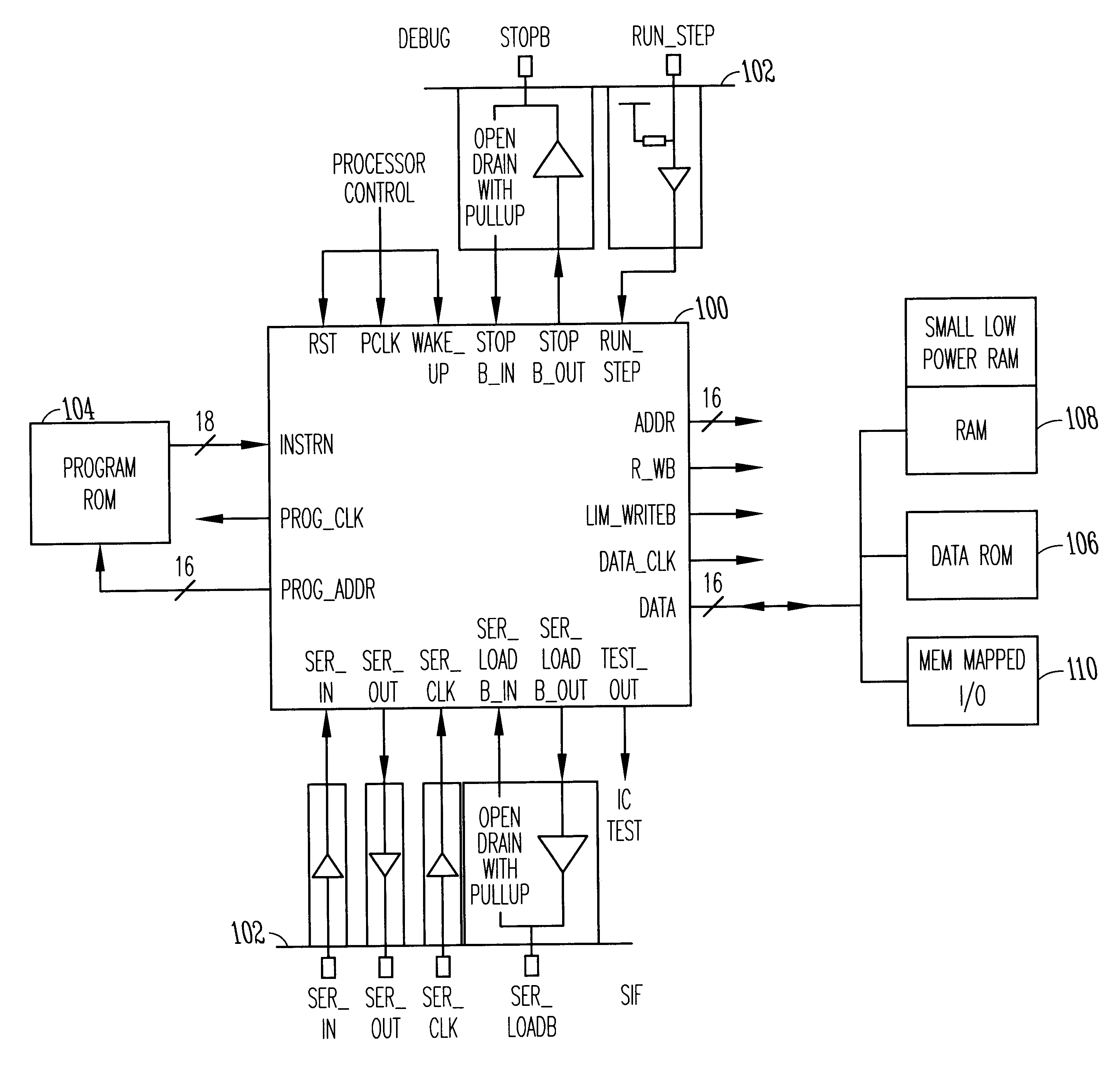
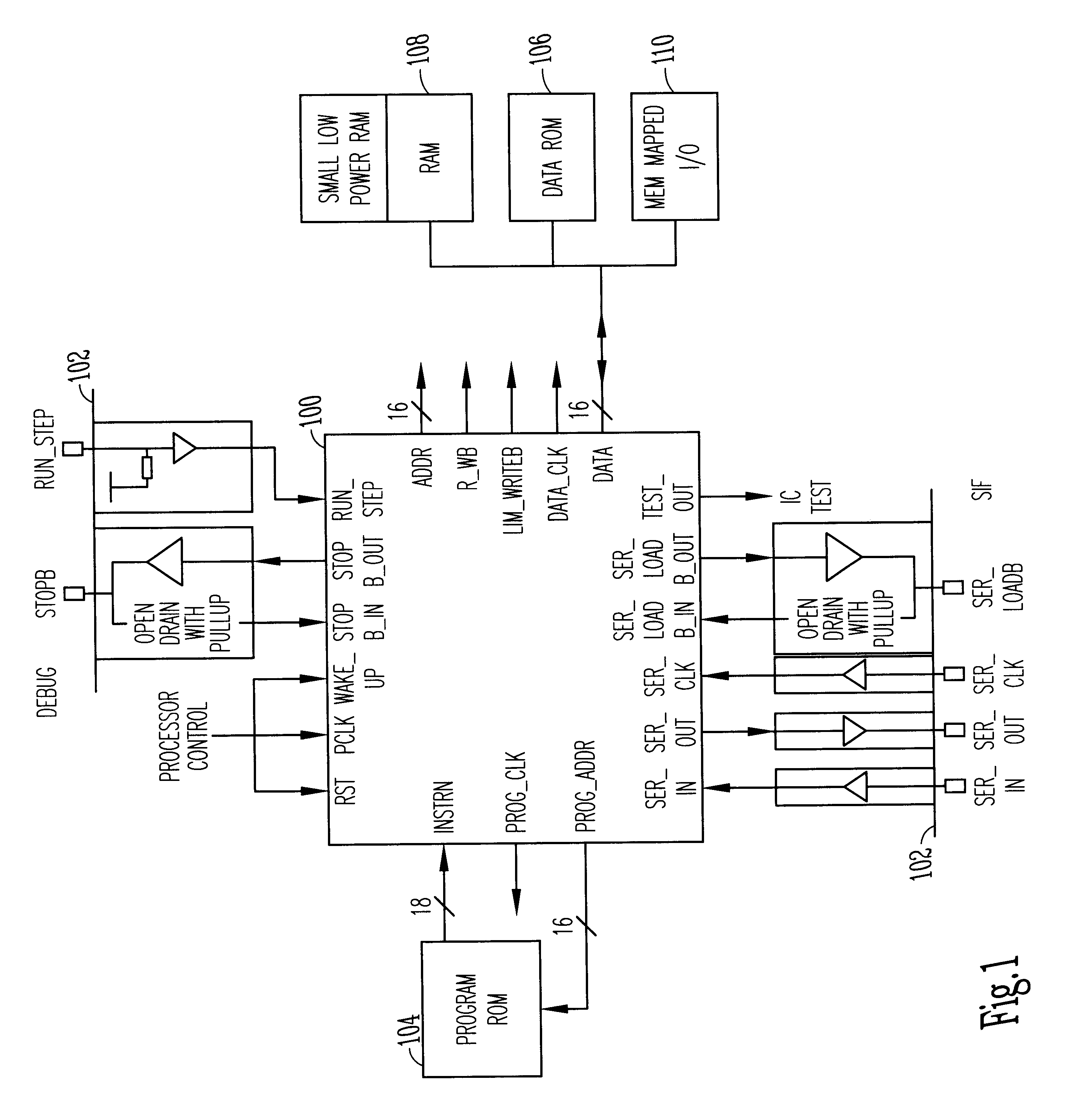
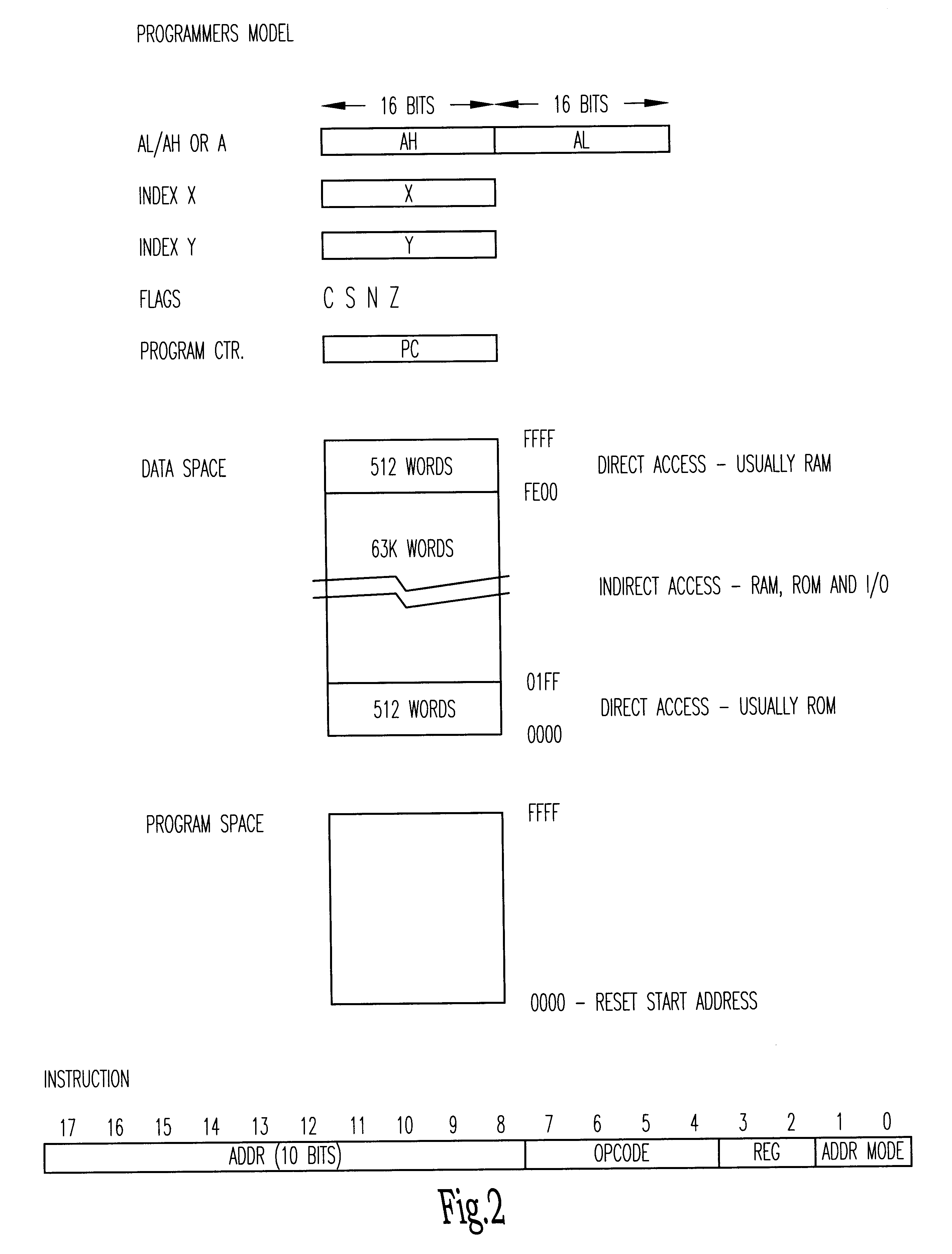
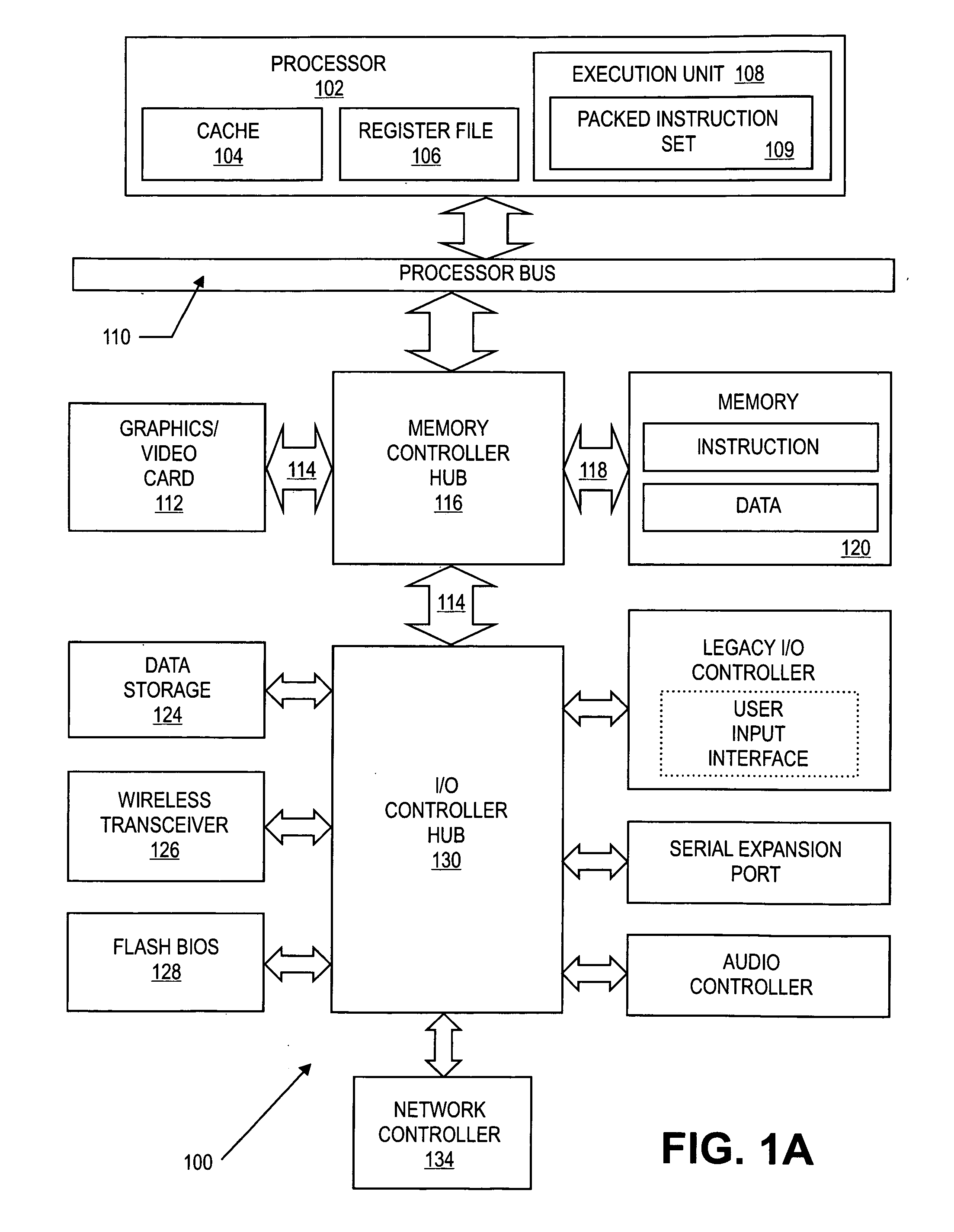
An integrated circuit contains a microprocessor core, program memory and separate data storage, together with analogue and digital signal processing circuitry. The ALU is 16 bits wide, but a 32-bit shift unit is provided, using a pair of 16-bit registers. The processor has a fixed length instruction format, with an instruction set including multiply and divide operations which use the shift unit over several cycles. No interrupts are provided. External pins of the integrated circuit allow for single stepping and other debug operations, and a serial interface (SIF) which allows external communication of test data or working data as necessary. The serial interface has four wires (SERIN, SEROUT, SER-CLK, SERLOADB), allowing handshaking with a master apparatus, and allowing direct access to the memory space of the processor core, without specific program control. Within each processor cycle, the processor circuitry is divided into plural stages, and latches are interposed between the stages to minimize power consumption.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE CONSULTANTS LTD
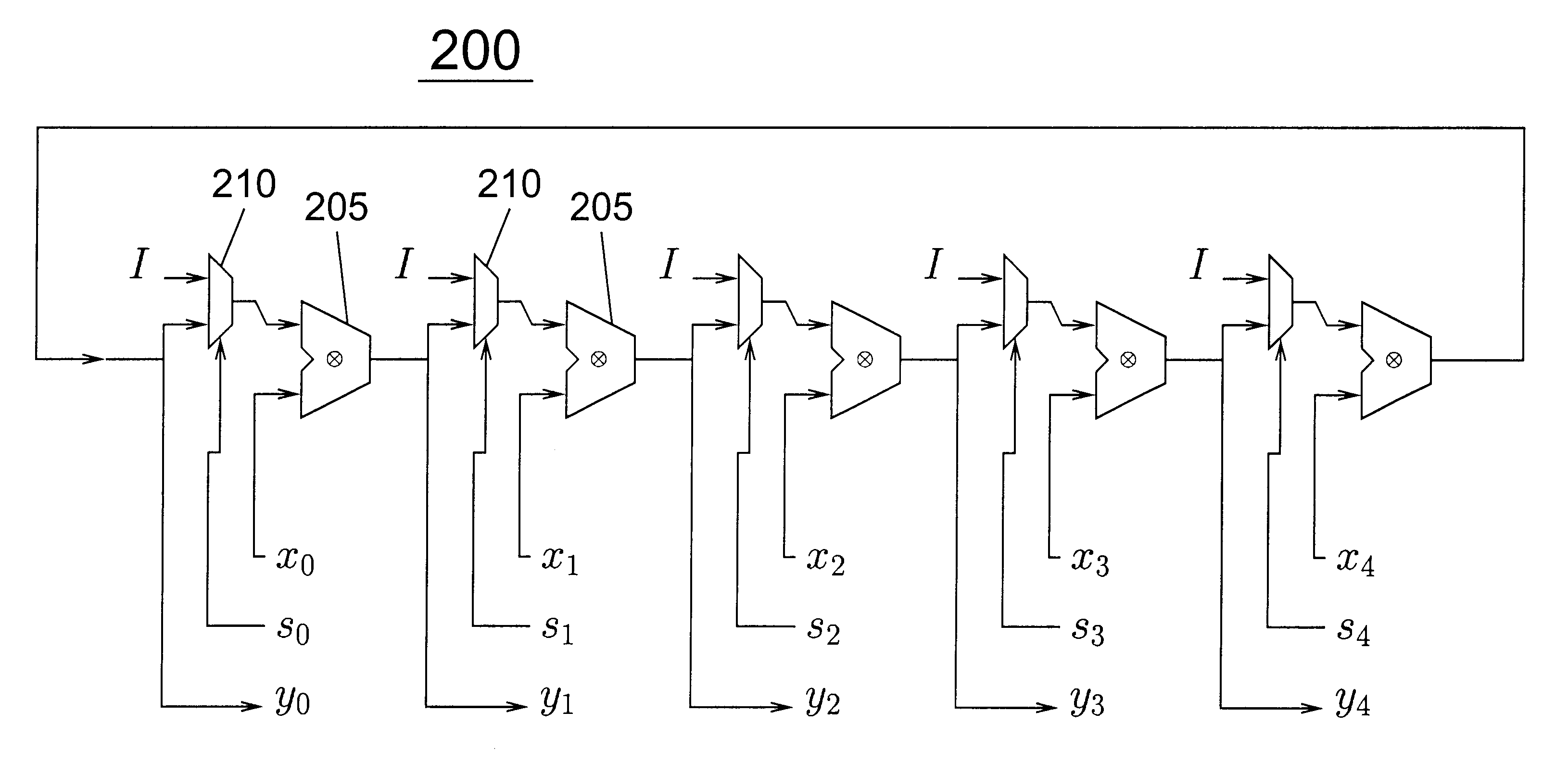
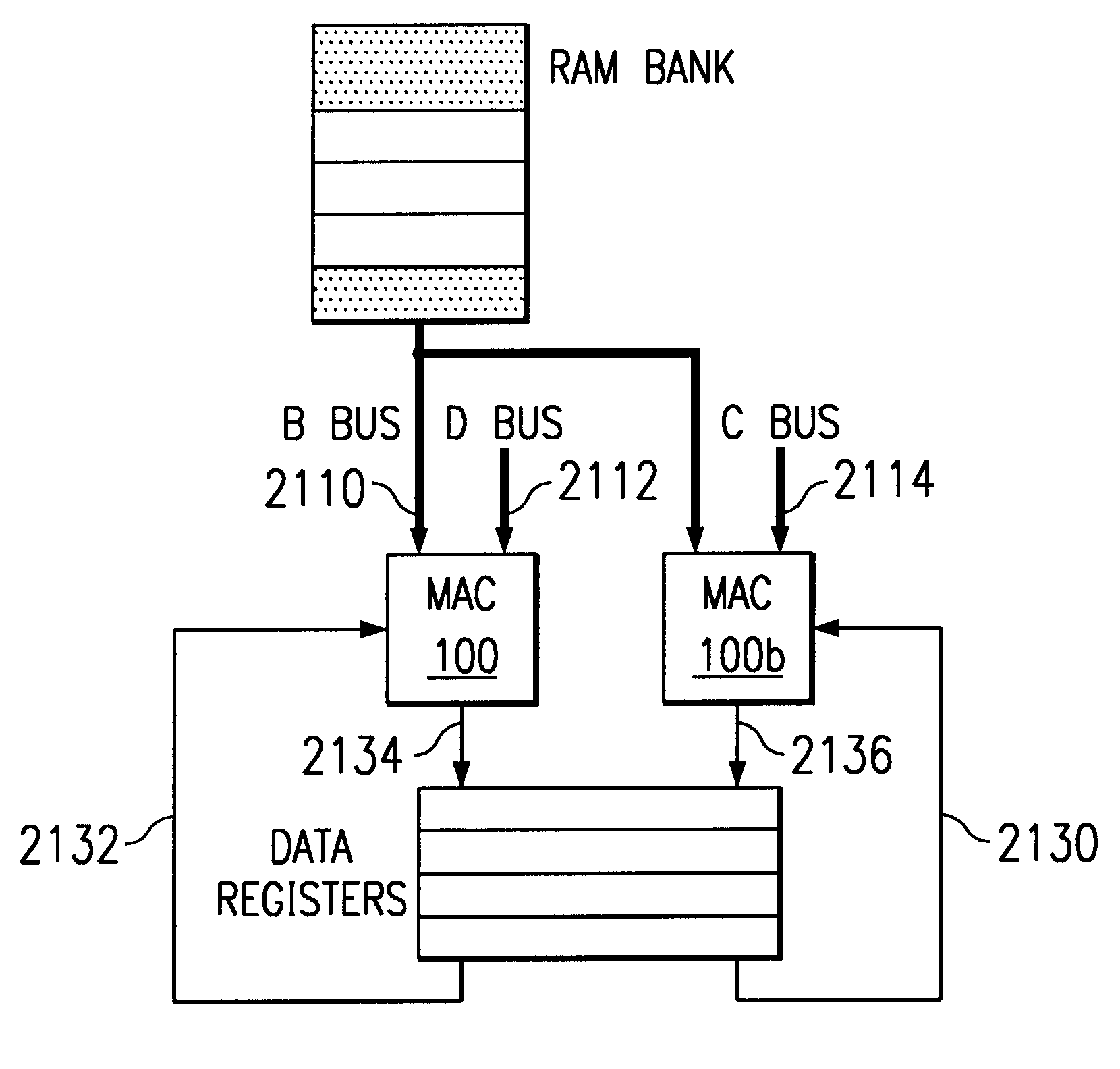
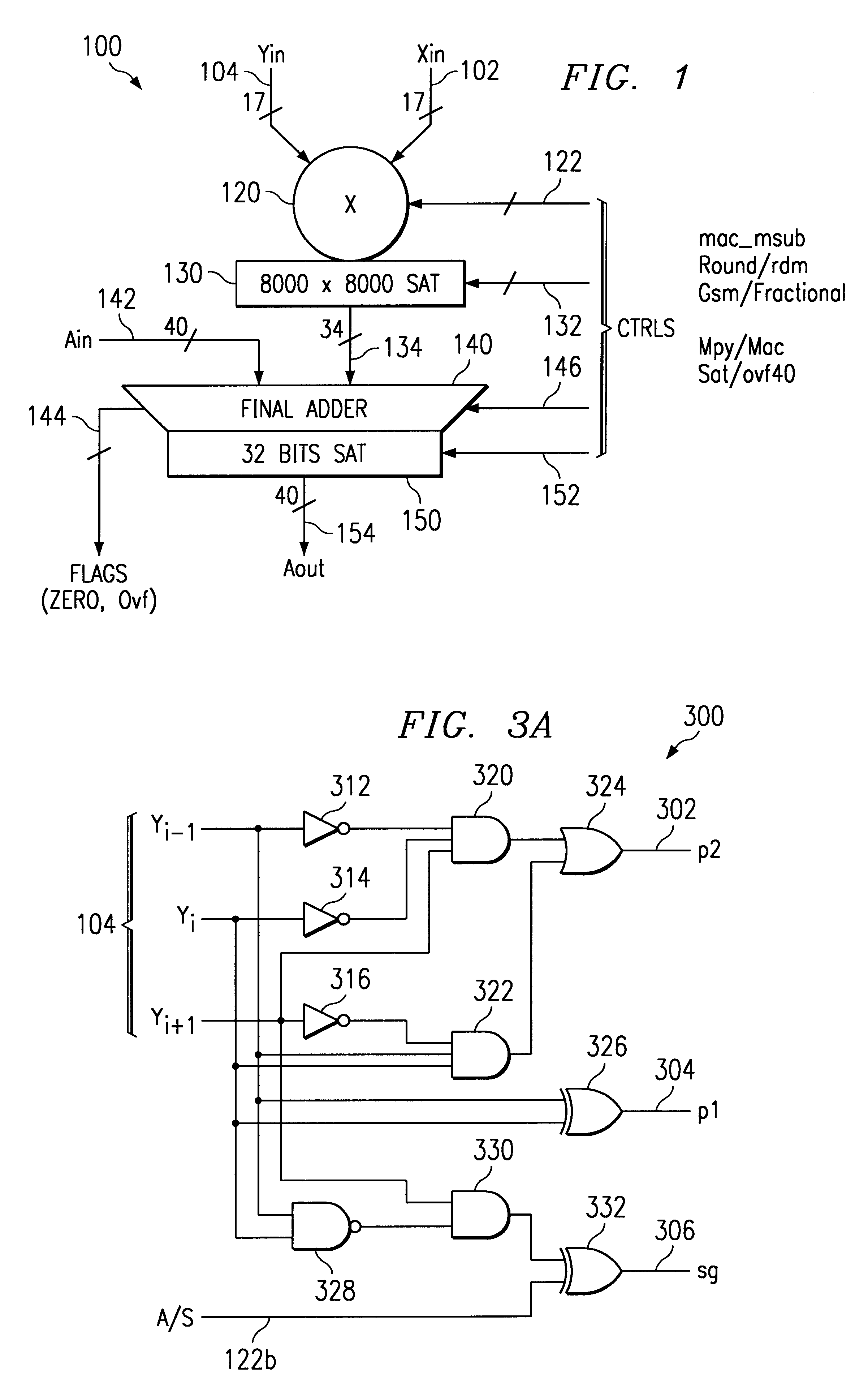
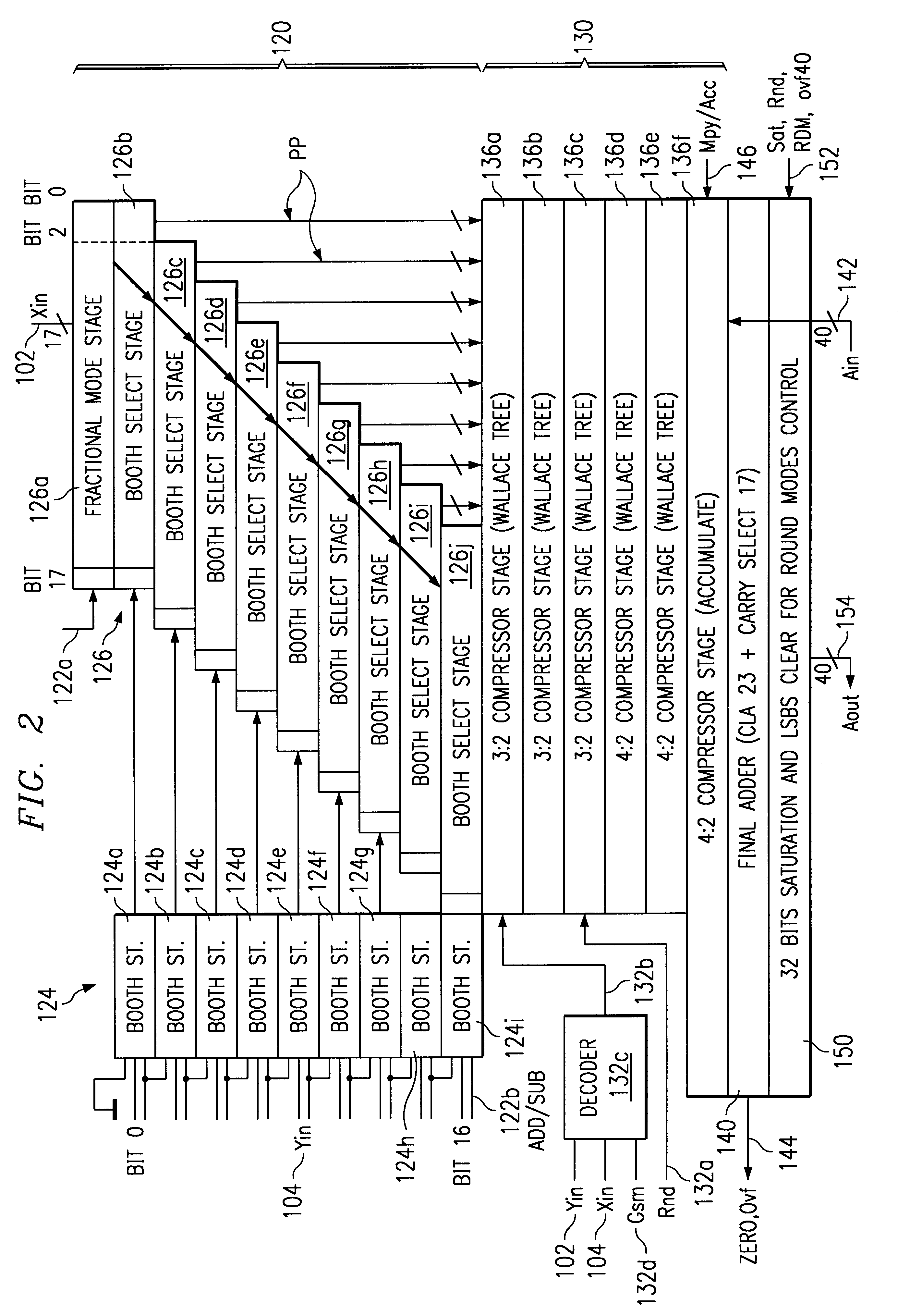
Multiplier accumulator circuits
A multiply-accumulate (MAC) unit, having a first binary operand X, a second binary operand Y, a third binary operand, Booth recode logic for generating a plurality of partial products from said first and second operands, a Wallace tree adder for reducing the partial products and for selectively arithmetically combining the reduced partial products with said third operand, a final adder for generating a final sum, and a saturation circuitry for selectively rounding or saturating said final sum is provided. A dual MAC unit is also provided.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
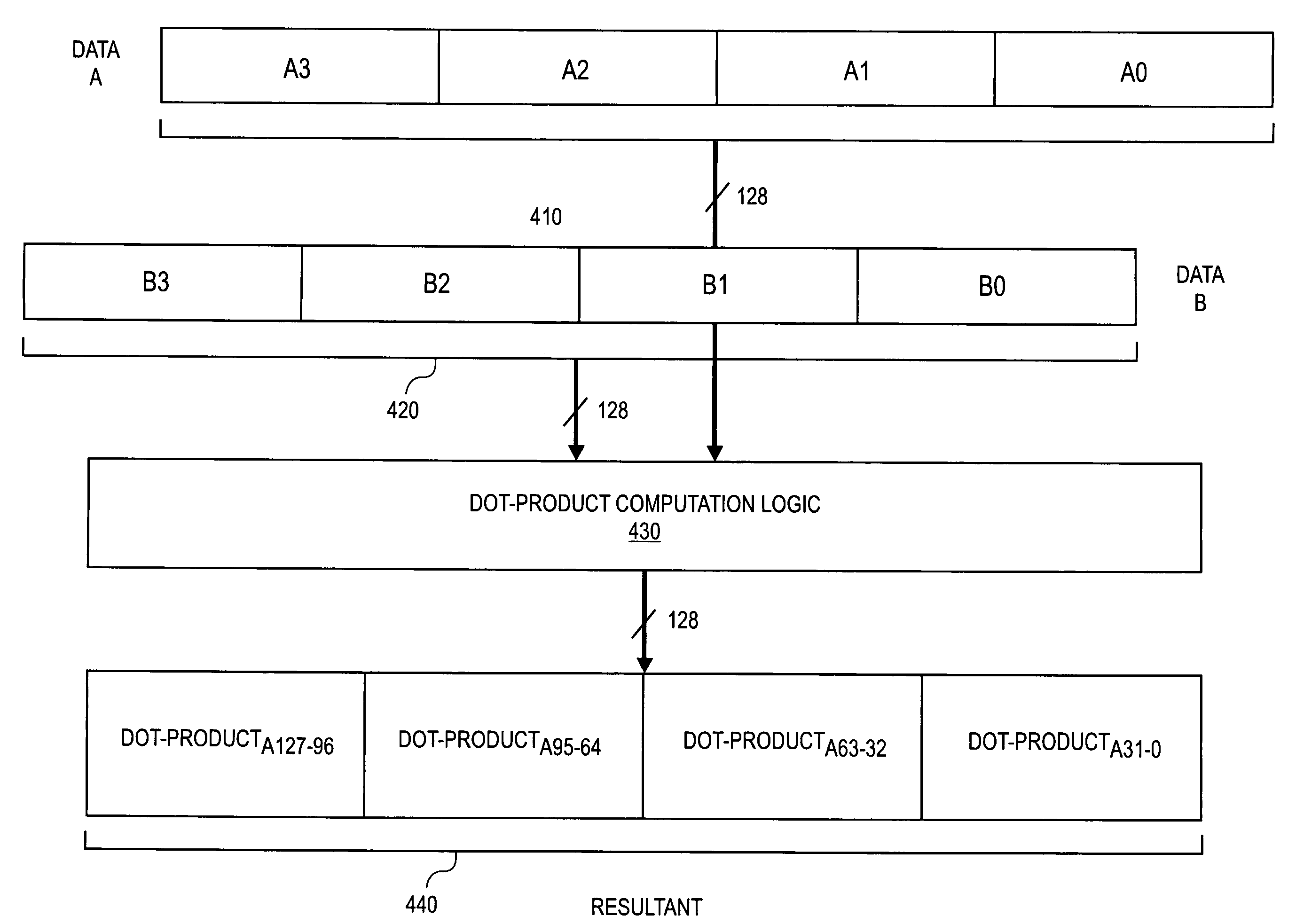
Instruction and logic for performing a dot-product operation
InactiveUS20080071851A1Program control using stored programsComputation using non-contact making devicesOperand
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for multi-function arithmetic
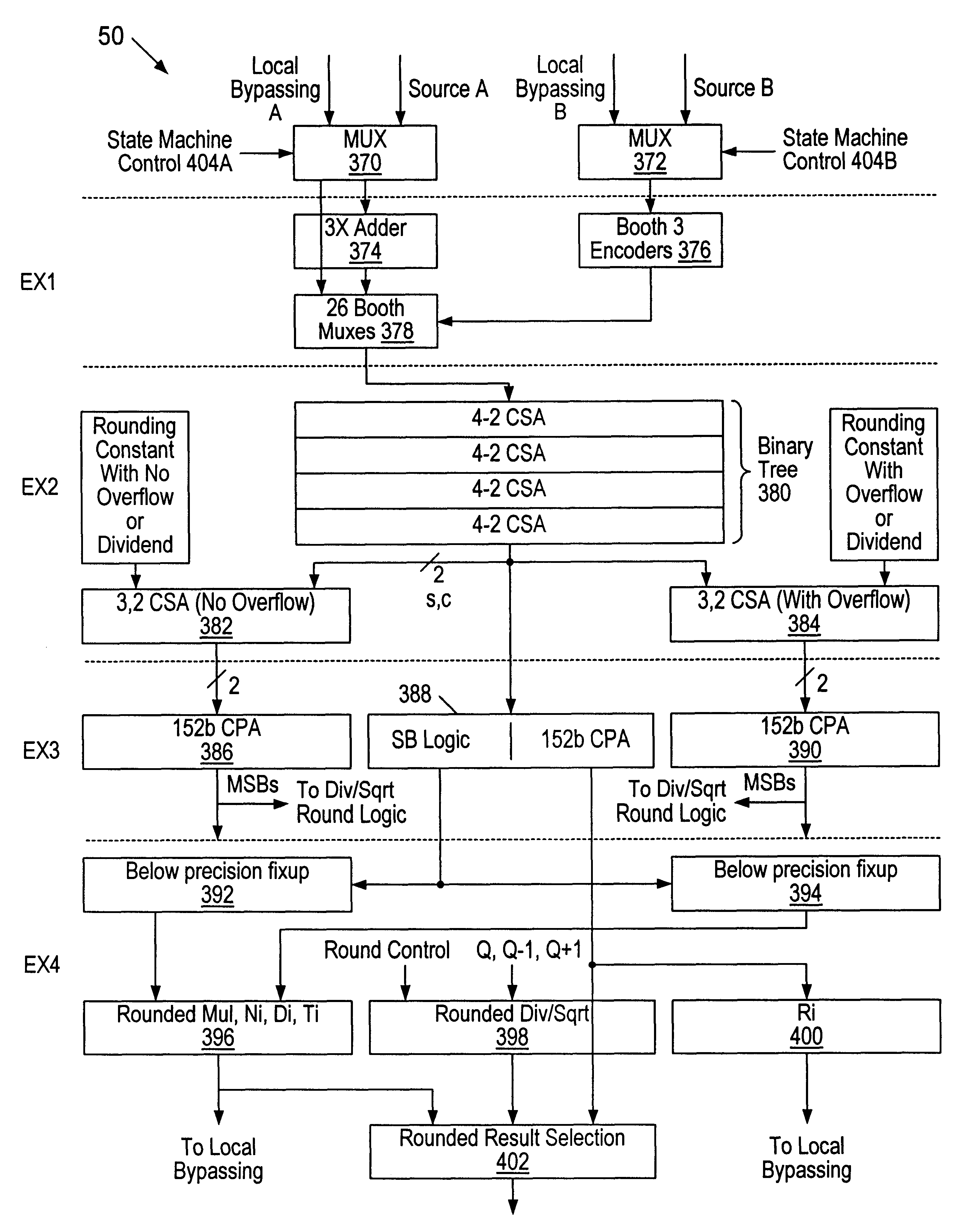
InactiveUS6223198B1Runtime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesConstant powerRounding
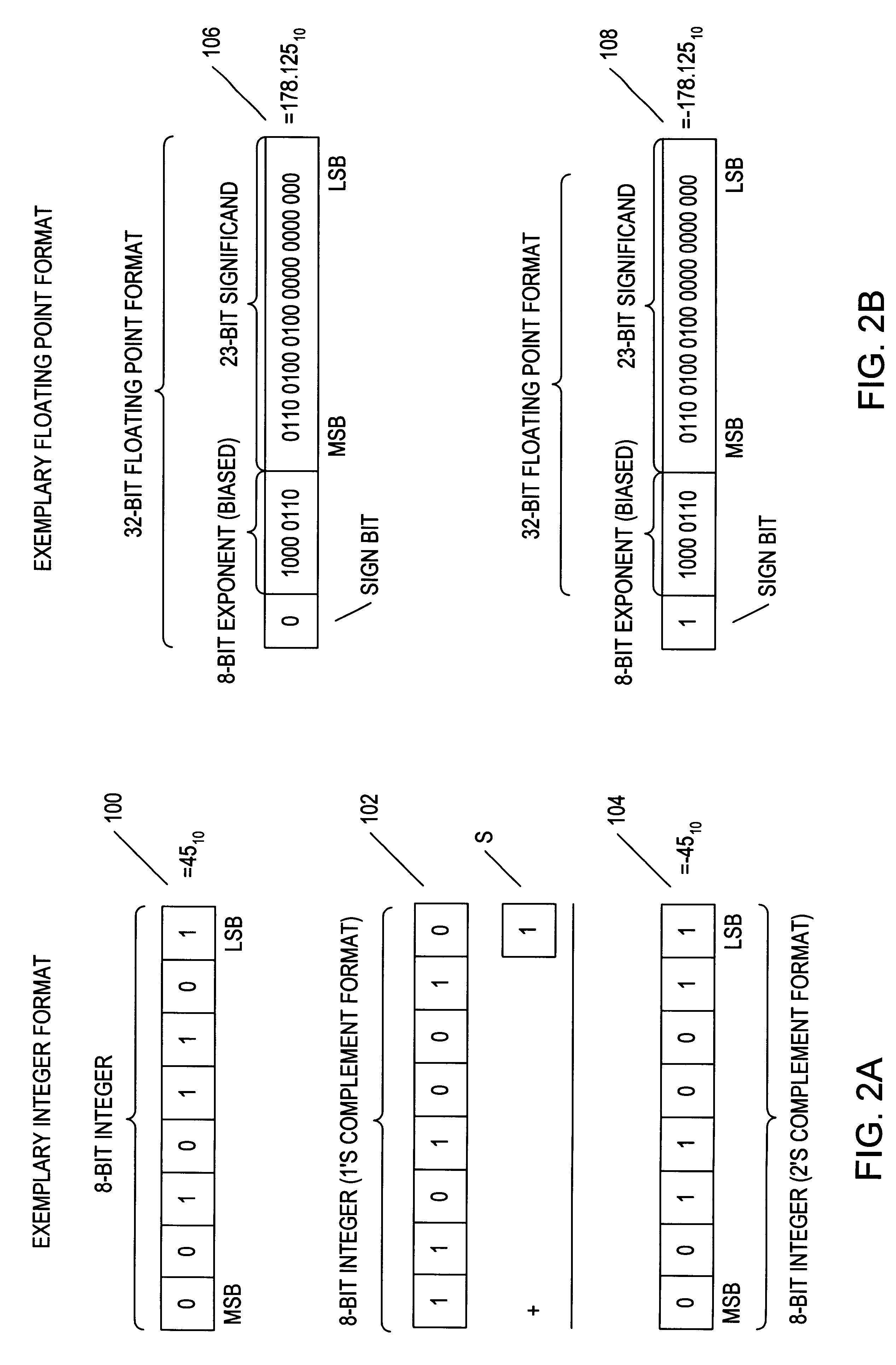
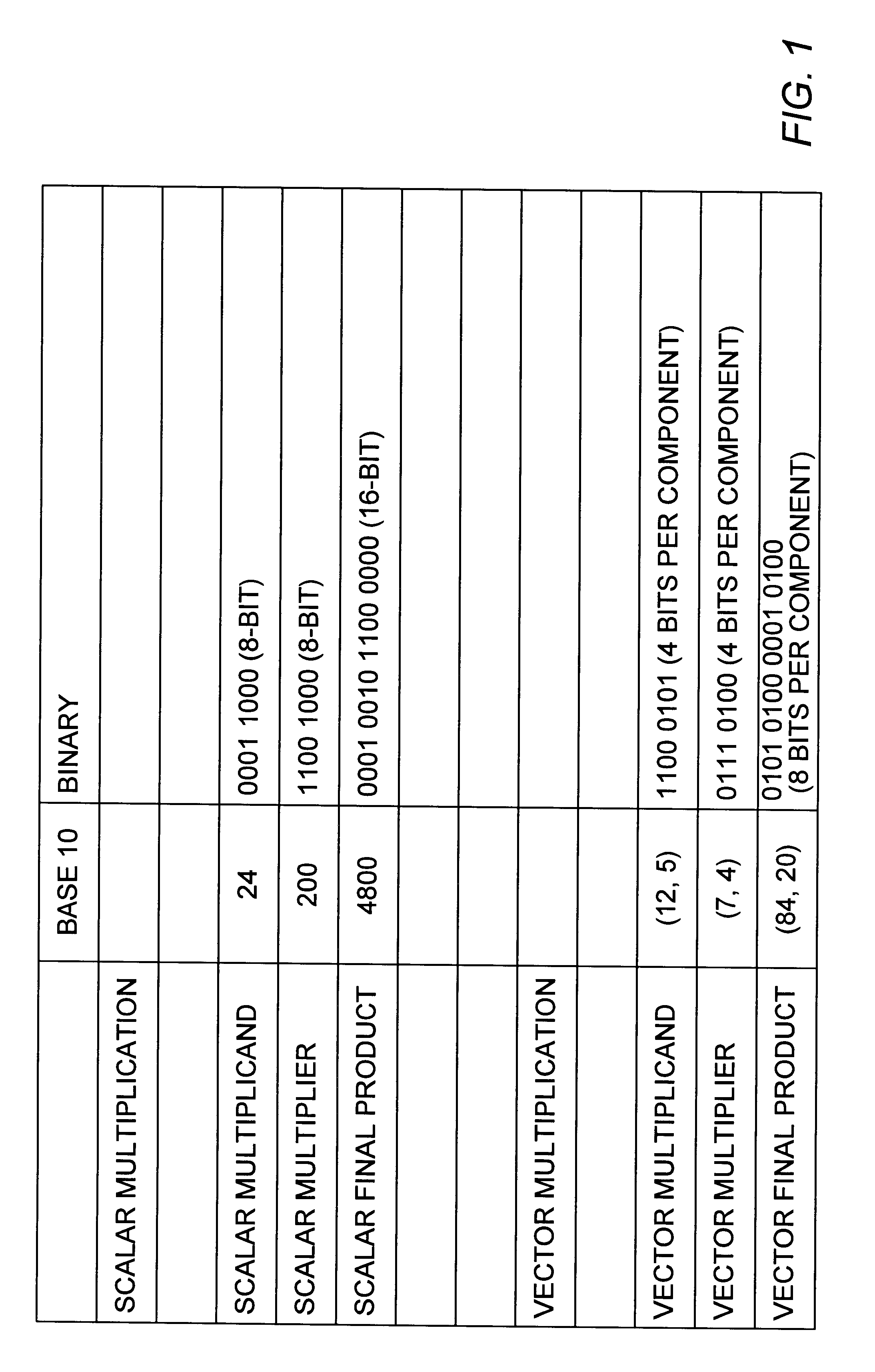
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated and used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur. The multiplier may also be configured to perform iterative calculations to evaluate constant powers of an operand. Intermediate products that are formed may be rounded and normalized in two paths and then compressed and stored for use in the next iteration. An adjustment constant may also be added to increase the frequency of exactly rounded results.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
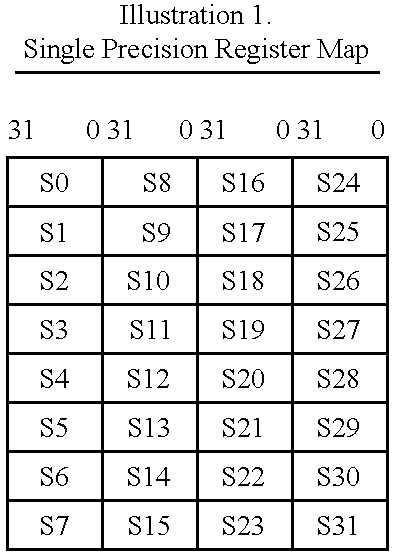
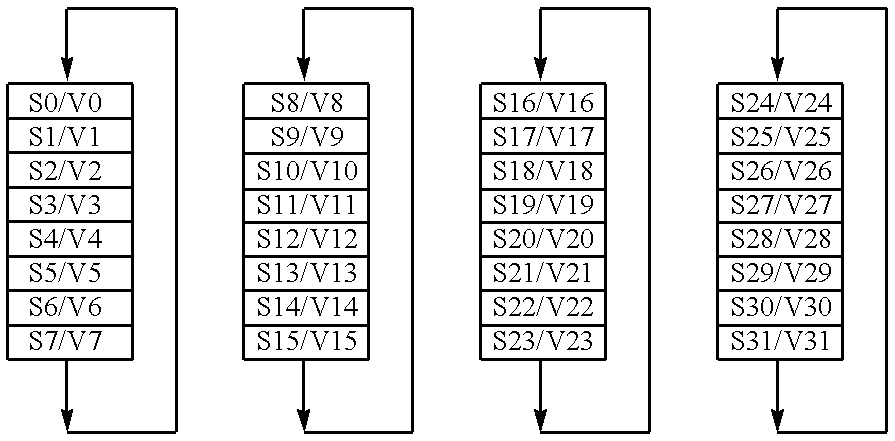
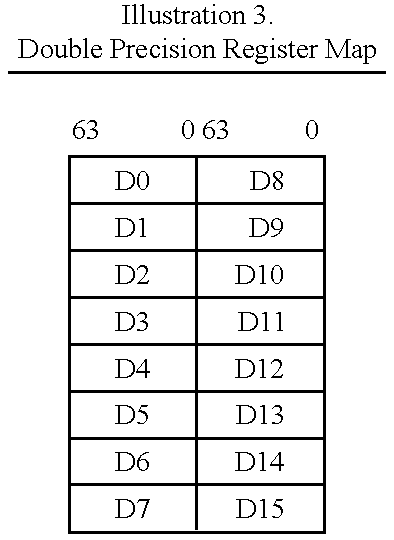
Vector register addressing
InactiveUS6332186B1Without complexityWithout costRegister arrangementsInstruction analysisMemory addressProcessing Instruction
A floating point unit 26 is provided with a register bank 38 comprising 32 registers that may be used as either vector registers V or scalar registers S. Data values are transferred between memory 30 and the registers within the register bank 38 using contiguous block memory access instructions. Vector processing instructions specify a sequence of processing operations to be performed upon data values within a sequence of registers. The register address is incremented between each operation by an amount controlled by a stride value. Accordingly, the register address can be incremented by values such as 0, 1, 2 or 4 between each iteration. This provides a mechanism for retaining block memory access instructions to contiguous memory addresses whilst supporting vector matrix and / or complex operations in which the data values needed for each iteration are not adjacent to one another in the memory 30.
Owner:ARM LTD
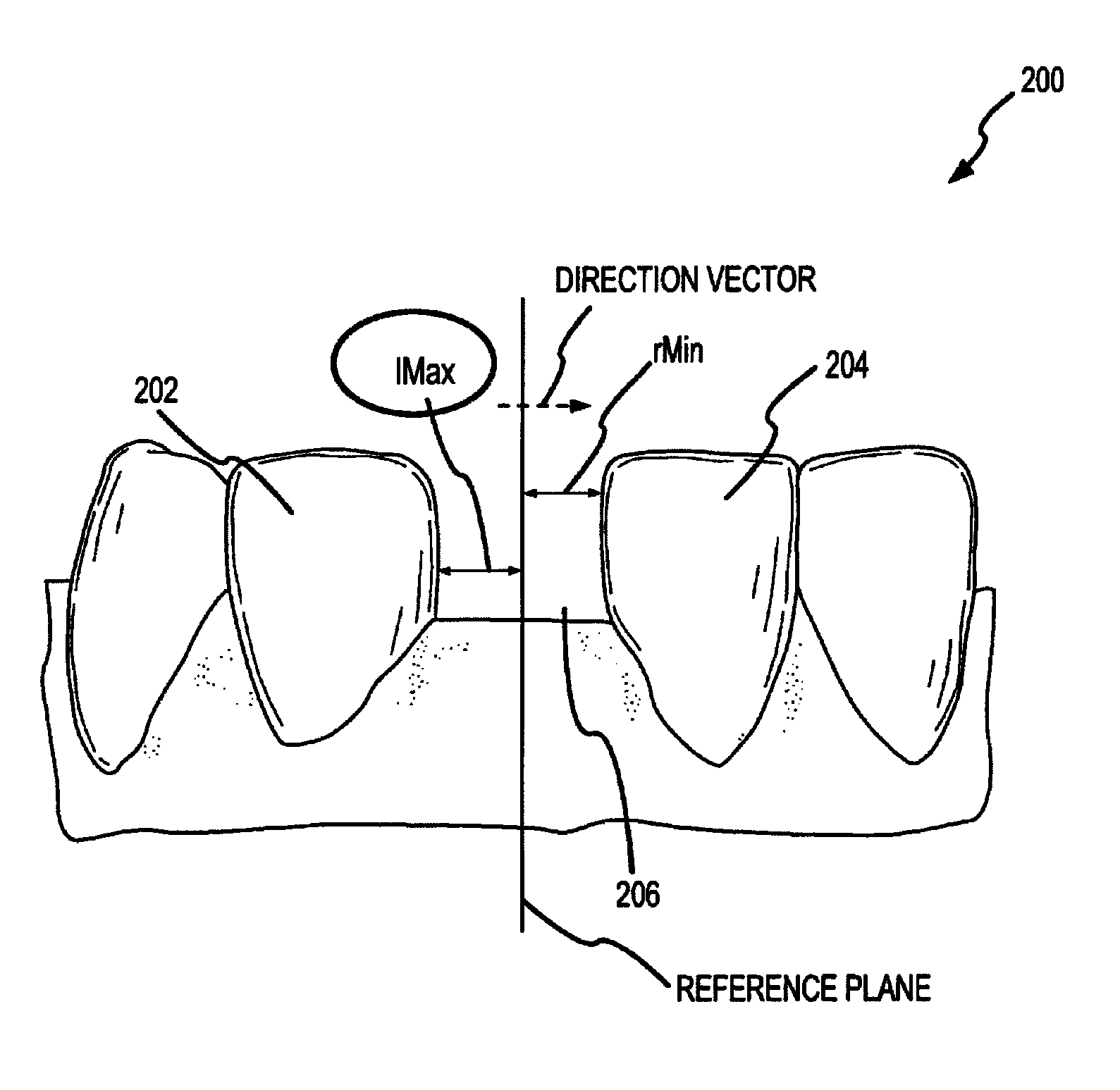
System and method for representation, modeling and application of three-dimensional digital pontics
Modeling pontics at successive treatment stages includes: (1) calculating space measurements between first and second teeth by getting first and second tooth transformations at a treatment stage i; (2) applying the first and second tooth transformations to get positions of the first and second teeth at the stage i; (3) calculating a direction vector of the space measurements at the stage i; (4) calculating a reference plane using the direction vector as a normal; (5) determining whether the space is available for a pontic by measuring the distance from the closest point on each of the first and second teeth to the reference plane; (6) generating an original pontic geometry for a first treatment stage; and (7) generating pontic geometries at each successive stage by calculating deformation parameters based on the original pontic geometry and size characteristics of the space and of the first and second teeth at each stage.
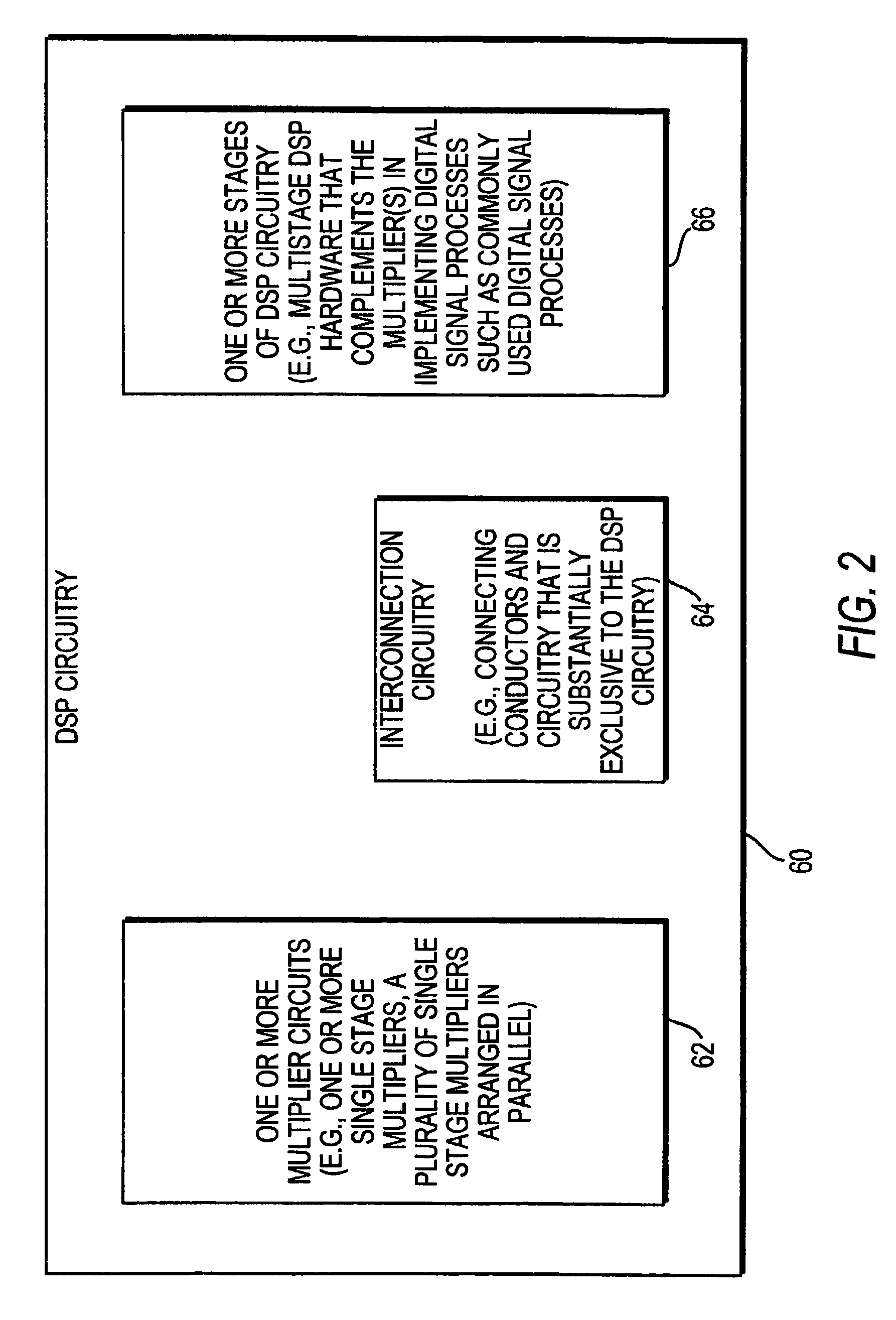
Owner:ALIGN TECH
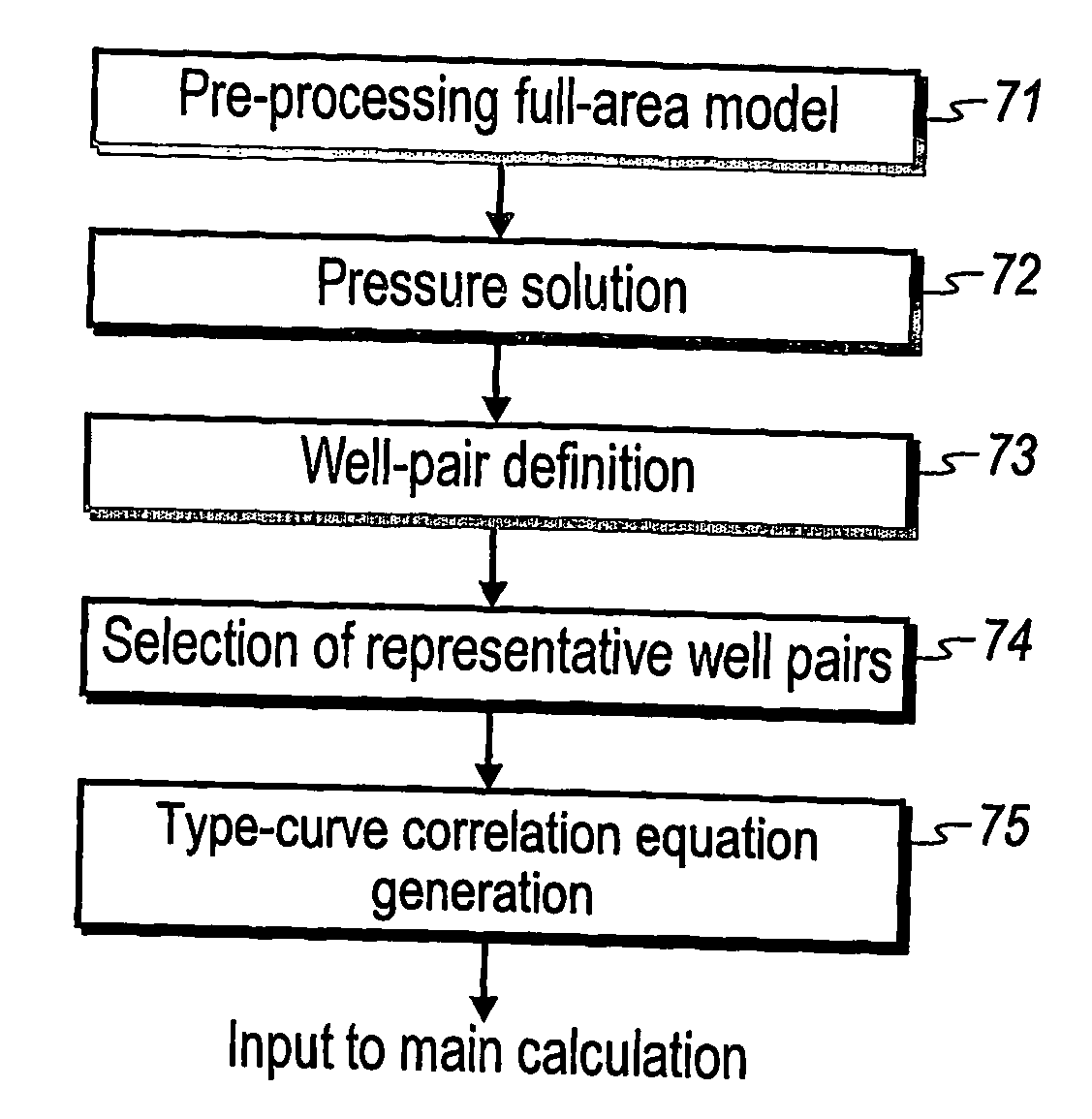
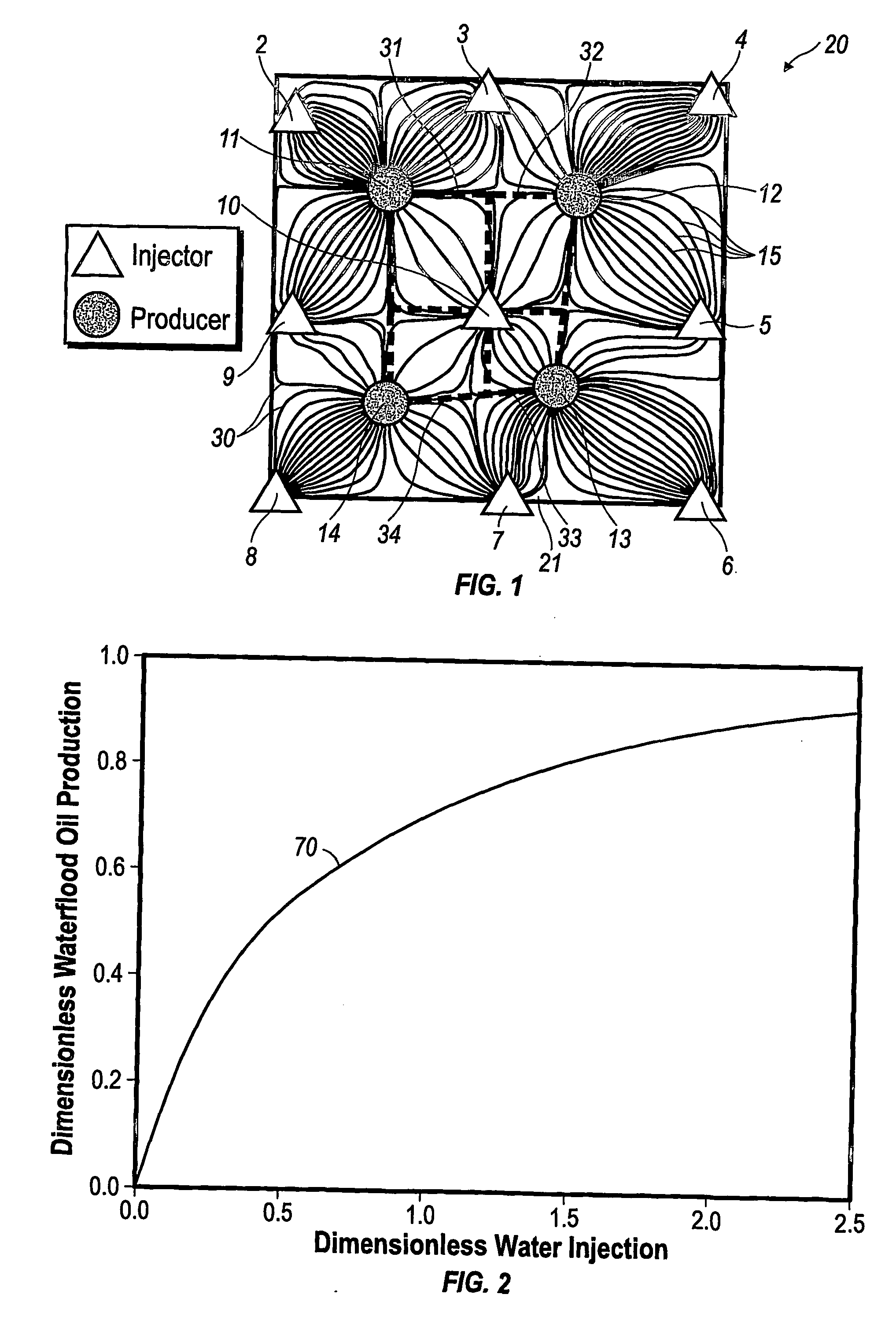
Performance prediction method for hydrocarbon recovery processes
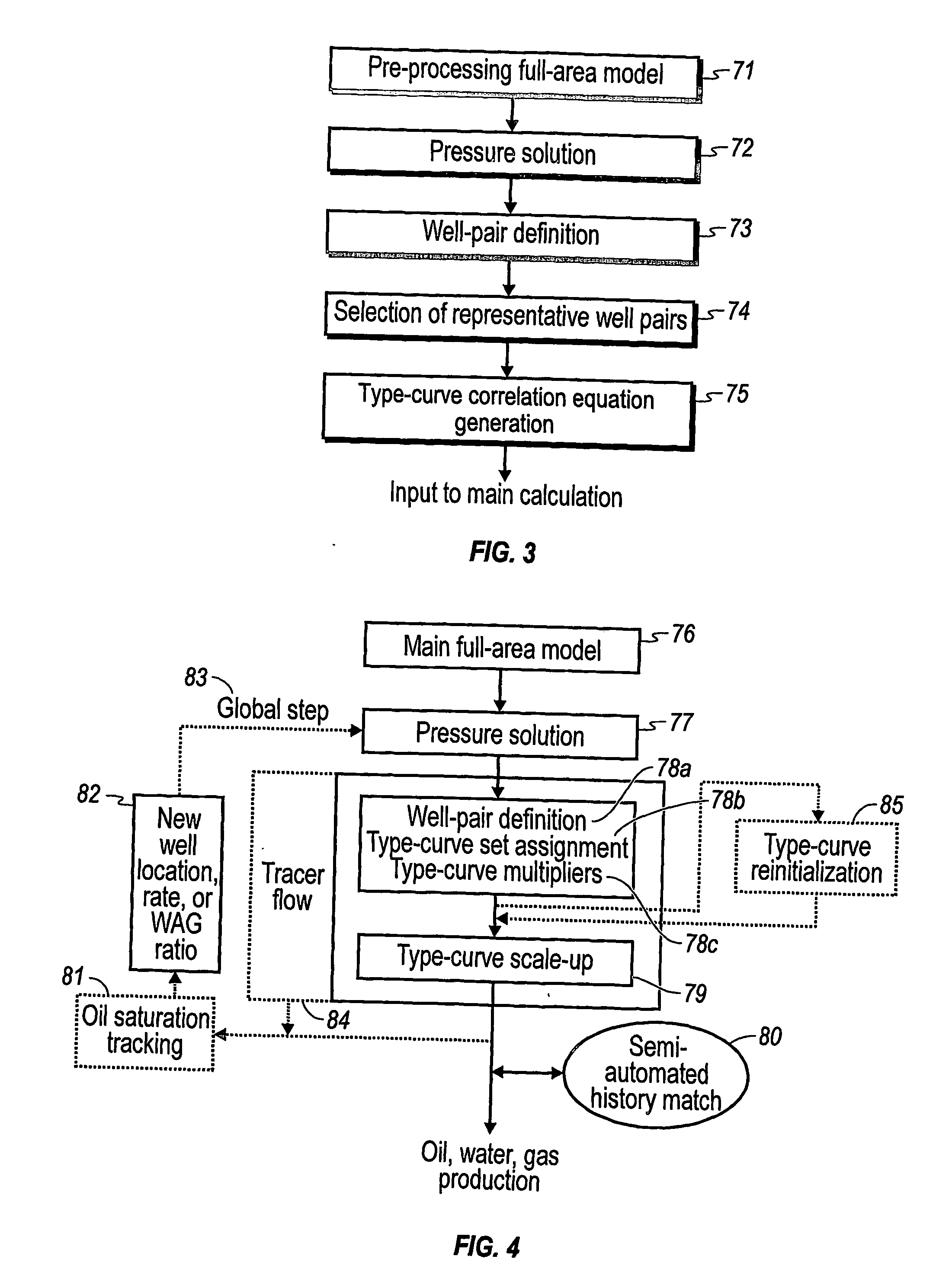
The invention relates to a method for predicting the performance of large-scale hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir floods. One embodiment of the invention includes a method for predicting performance of a patterned flooding process in a subterranean hydrocarbon-bearing formation, said formation being penetrated by a plurality of injector wells and producer wells, comprising the steps of: determining flow-based pairs of injector to producer wells [FIG. 4, item 78a] (first well pairs) using a geological model [item 76]; developing a connective pore volume distribution curve for each first well pair item [78b]; selecting at least two first well pairs (selected well pairs) that reflect narrow and wide connective pore volume distributions that correspond to high and lower oil recovery levels; developing a 3-D simulation model for each selected well pair, performing a reservoir simulation for each selected well pair for the corresponding flooding process; and generating prototype performance curves for each selected well pair. An alternate embodiment of the invention includes a method for predicting the performance of large-scale hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir floods where injection well location, production well location, a process parameter, or a well processing rate is modified.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
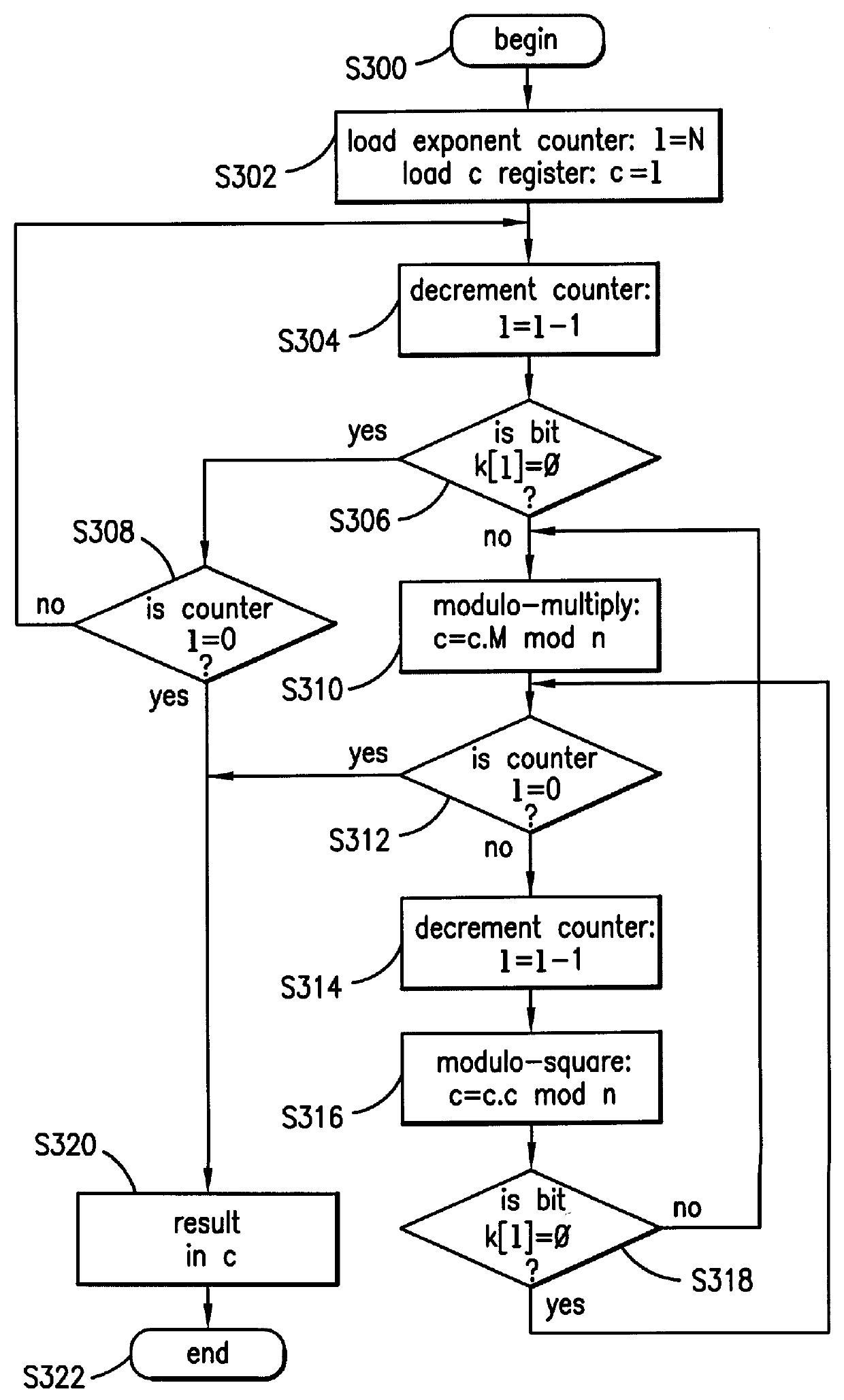
Method and apparatus for masking modulo exponentiation calculations in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6064740APublic key for secure communicationComputation using non-contact making devicesComputer hardwareIntegrated circuit
Circuitry which performs modular mathematics to solve the equation C=Mk mod n and n is performed in a manner to mask the exponent k's signature from timing or power monitoring attacks. The modular exponentation function is performed in a normalized manner such that binary ones and zeros in the exponent are calculated by being modulo-squared and modulo-multiplied.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
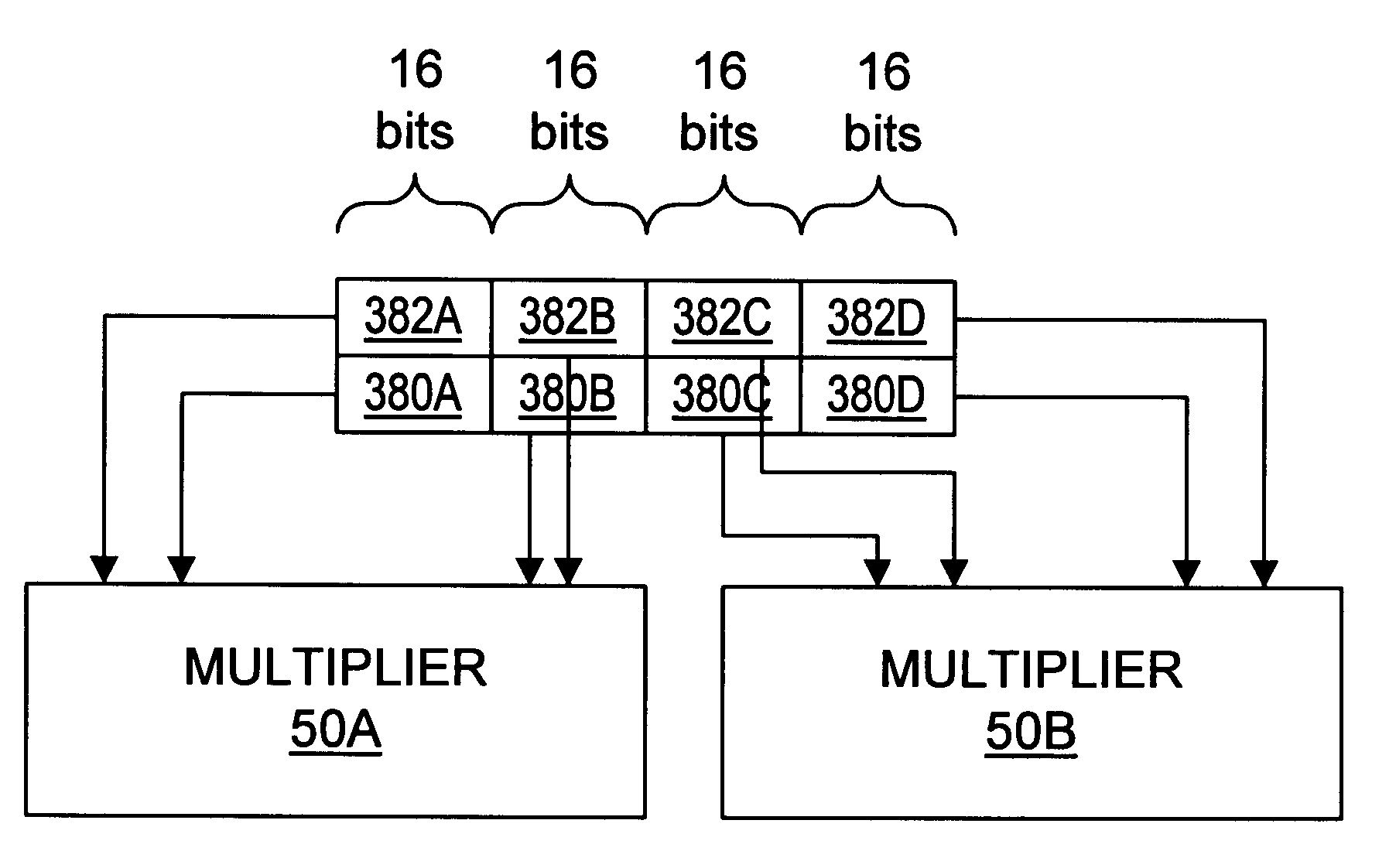
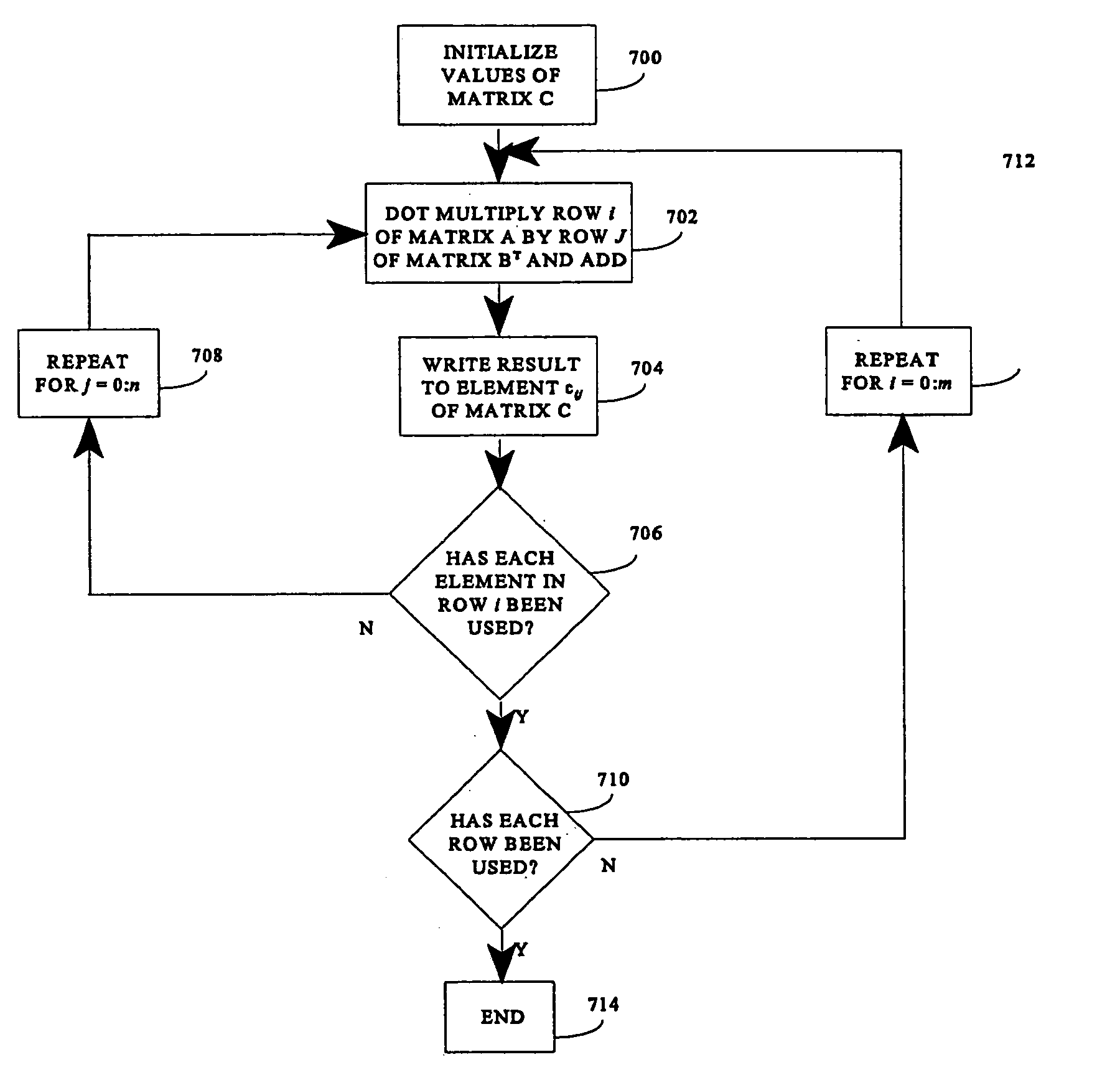
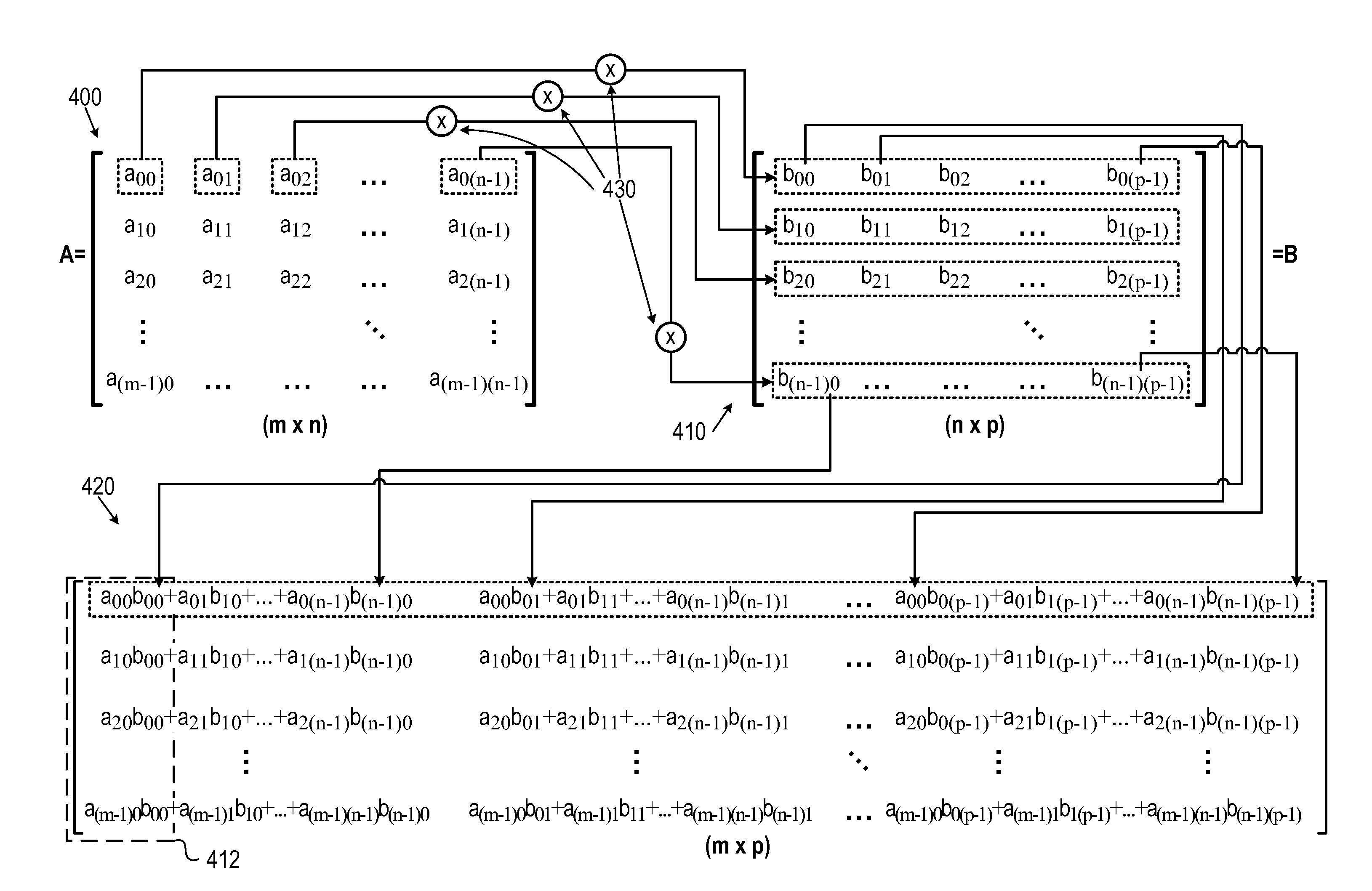
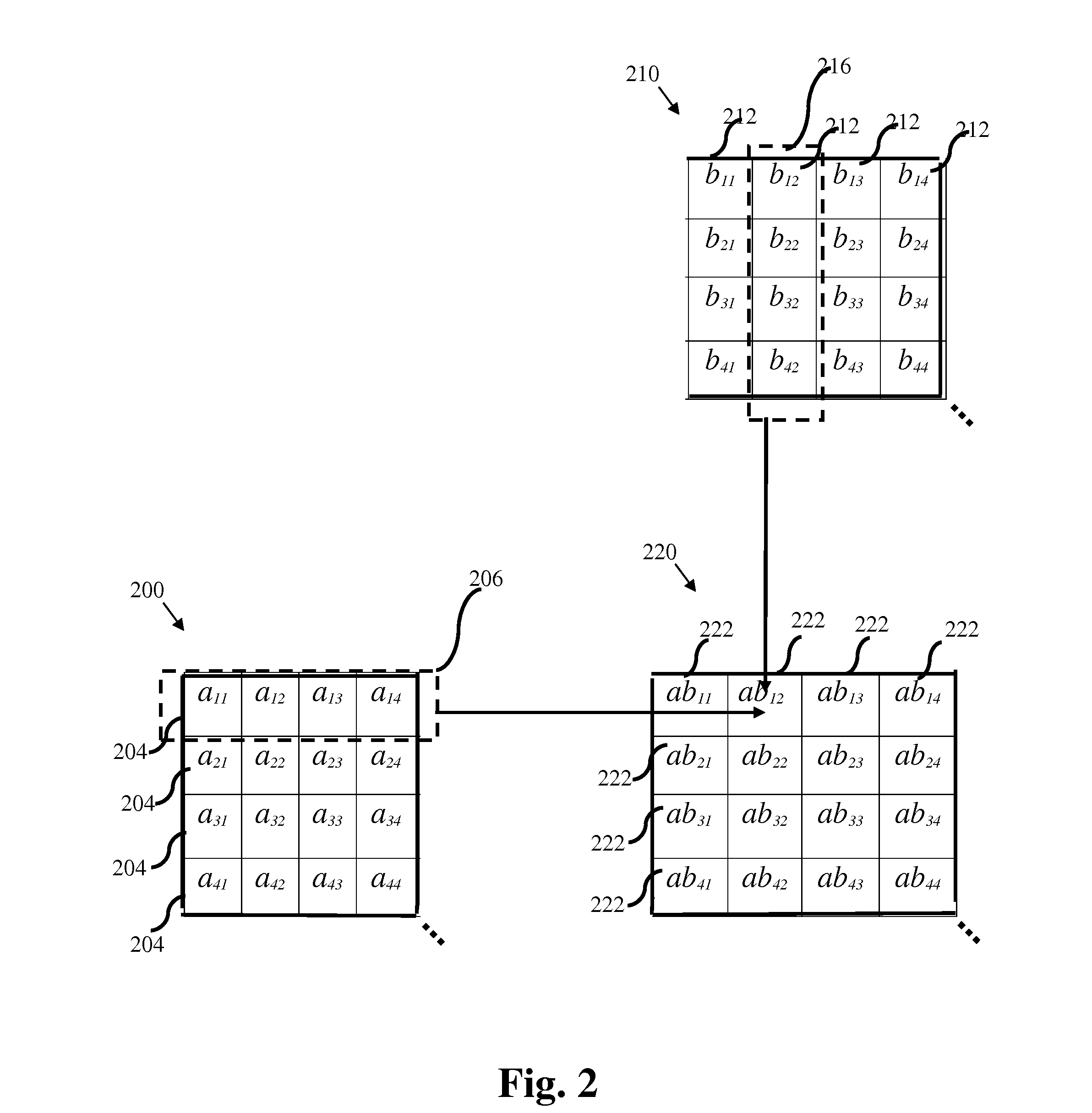
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS20050193050A1Efficient and rapid matrix multiplicationEfficient executionComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlAlgorithmProcessor register
To perform multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system, partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which form a product matrix. Each matrix can be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
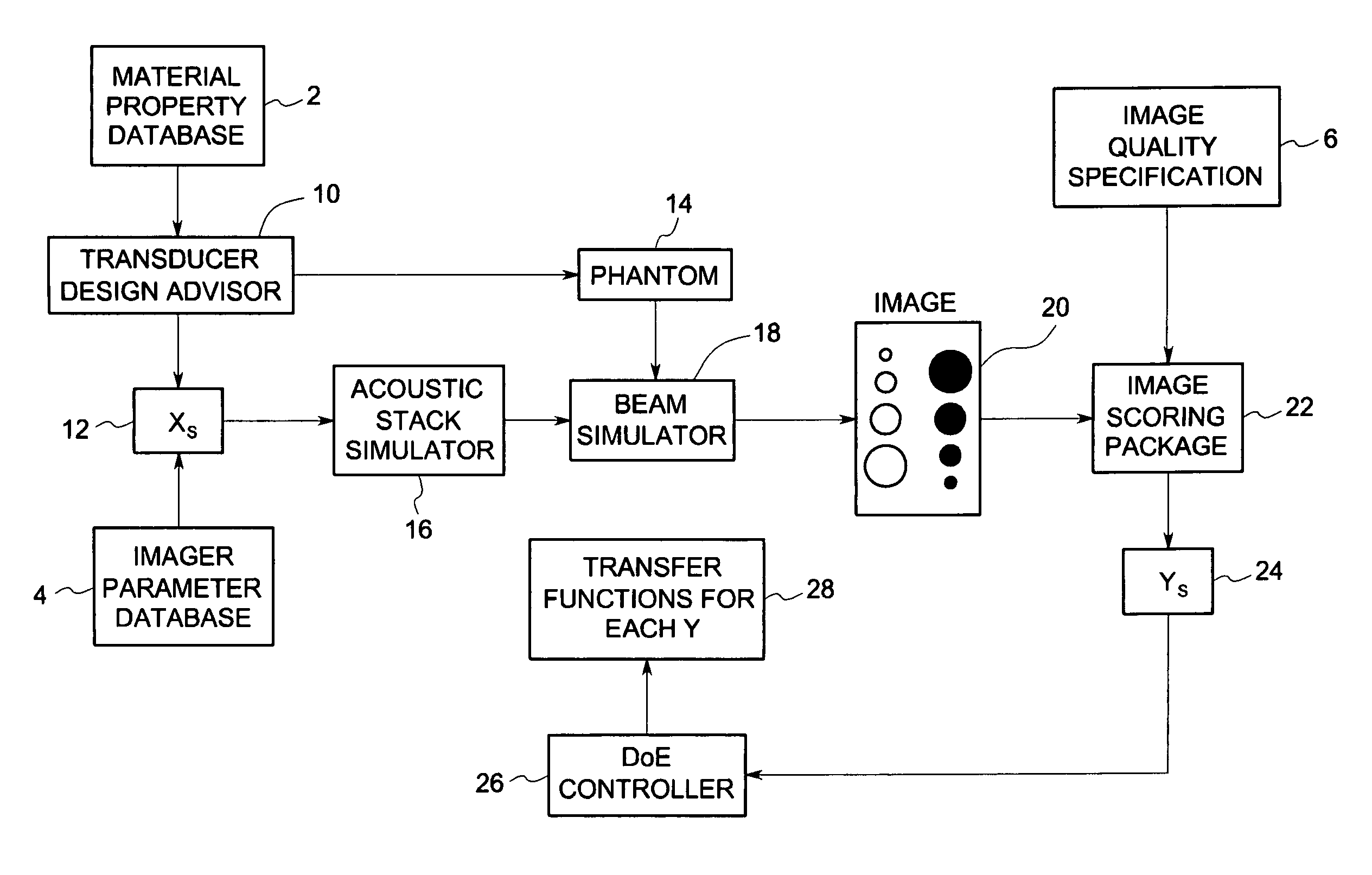
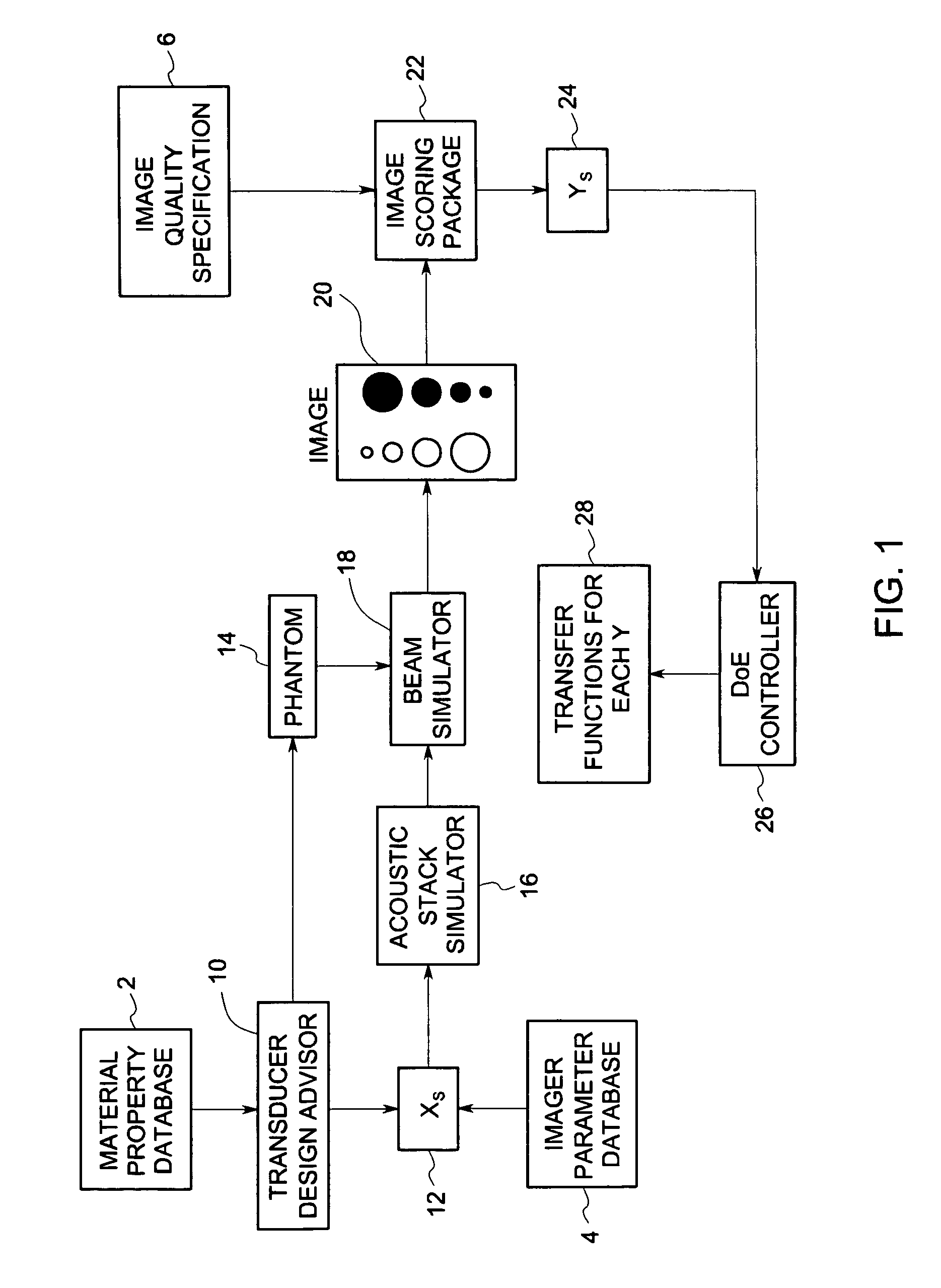
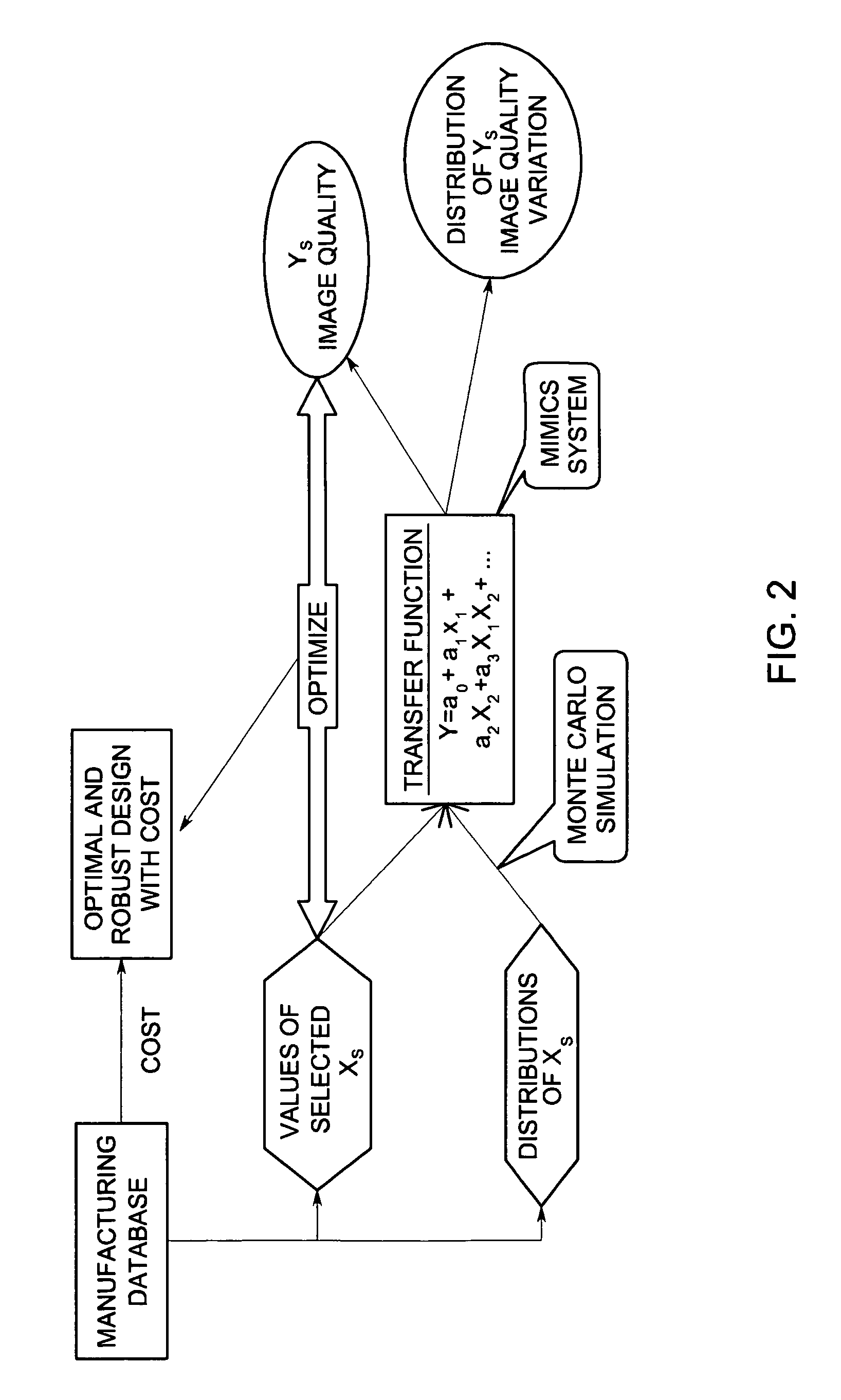
System and method for statistical design of ultrasound probe and imaging system
InactiveUS7006955B2Affect image qualityImprove image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCritical to qualitySonification
A system and method for statistical design of an ultrasound probe and imager system, and an associated graphical user interface for selecting input parameters to be used in an ultrasound simulation. The process and computer code allow the performance of a probe and imager combination to be specified and jointly optimized in image quality terms. The designs produced optimize both the image quality and other CTQ (critical to quality) parameters, such as the distribution of regulatory power indices and mechanical index. These CTQs indirectly affect image quality through their effect on patient dose. The Transducer Design Advisor incorporates a graphical user interface for facilitating selection of a parameter set to be used in the simulation. The user selects a desired parameter set by navigating across and interacting with a succession of windows. The user specifies various geometric characteristics of the transducer and how the user wants to simulate the imager system. Finally, the user specifies weights for the various CTQs at different depths. Based on these inputs, the Transducer Design Advisor creates the files needed by the ultrasound simulator.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Method and apparatus for performing multiple types of multiplication including signed and unsigned multiplication
InactiveUS6144980ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesControl signalOperand
A multiplier capable of performing both signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured for use in a microprocessor and may include a partial product generator, a selection logic unit, and an adder. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. The multiplier is also configured to receive a first control signal indicative of whether signed or unsigned multiplication is to be performed and a second control signal indicative of whether vector multiplication is to be performed. The multiplier is configured to calculate an effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands based upon each operand's most significant bit and the control signal. The effective signs may then be used by the partial product generation unit and the selection logic to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, the adder is configured to sum them and output the results, which may be signed or unsigned. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier is configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
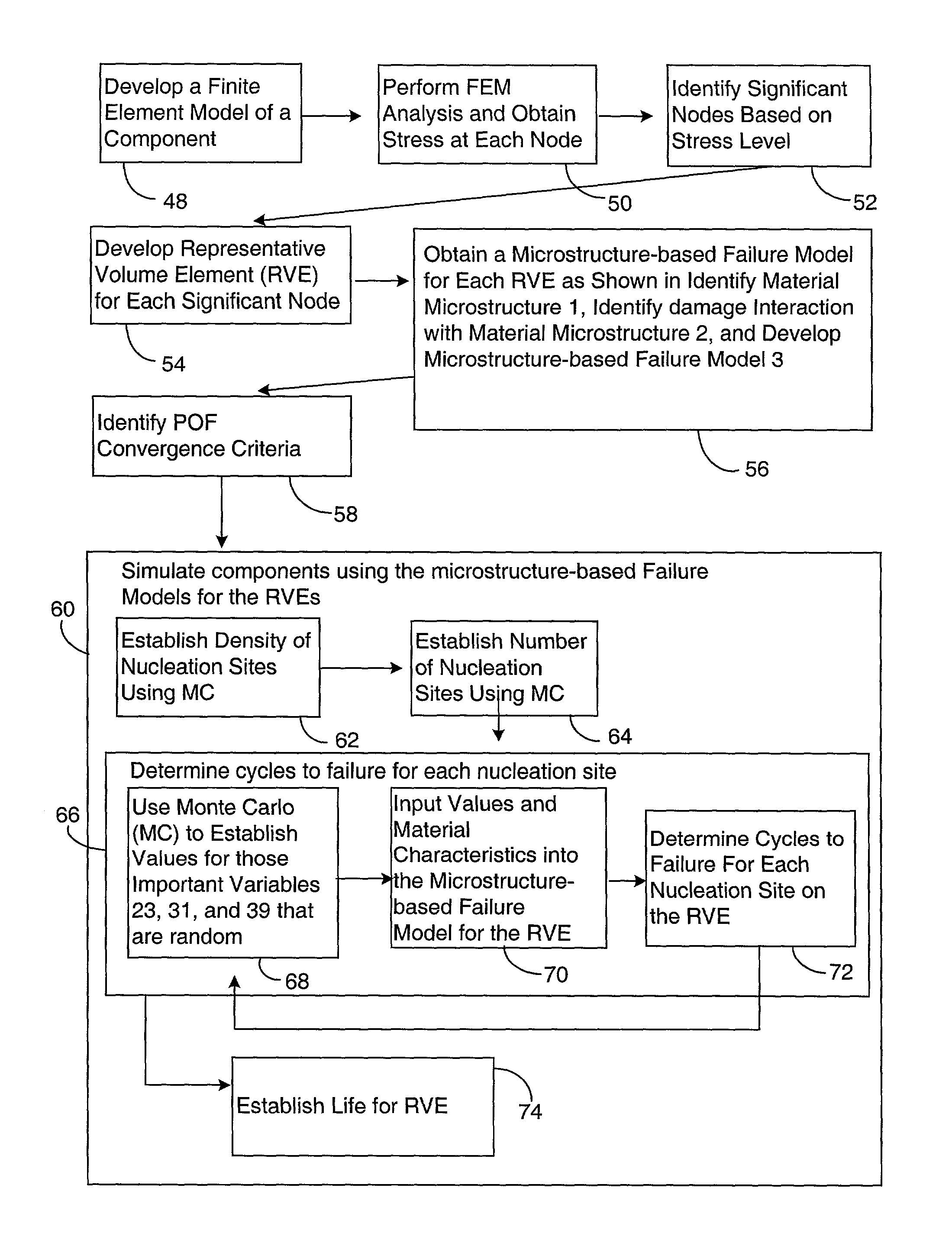
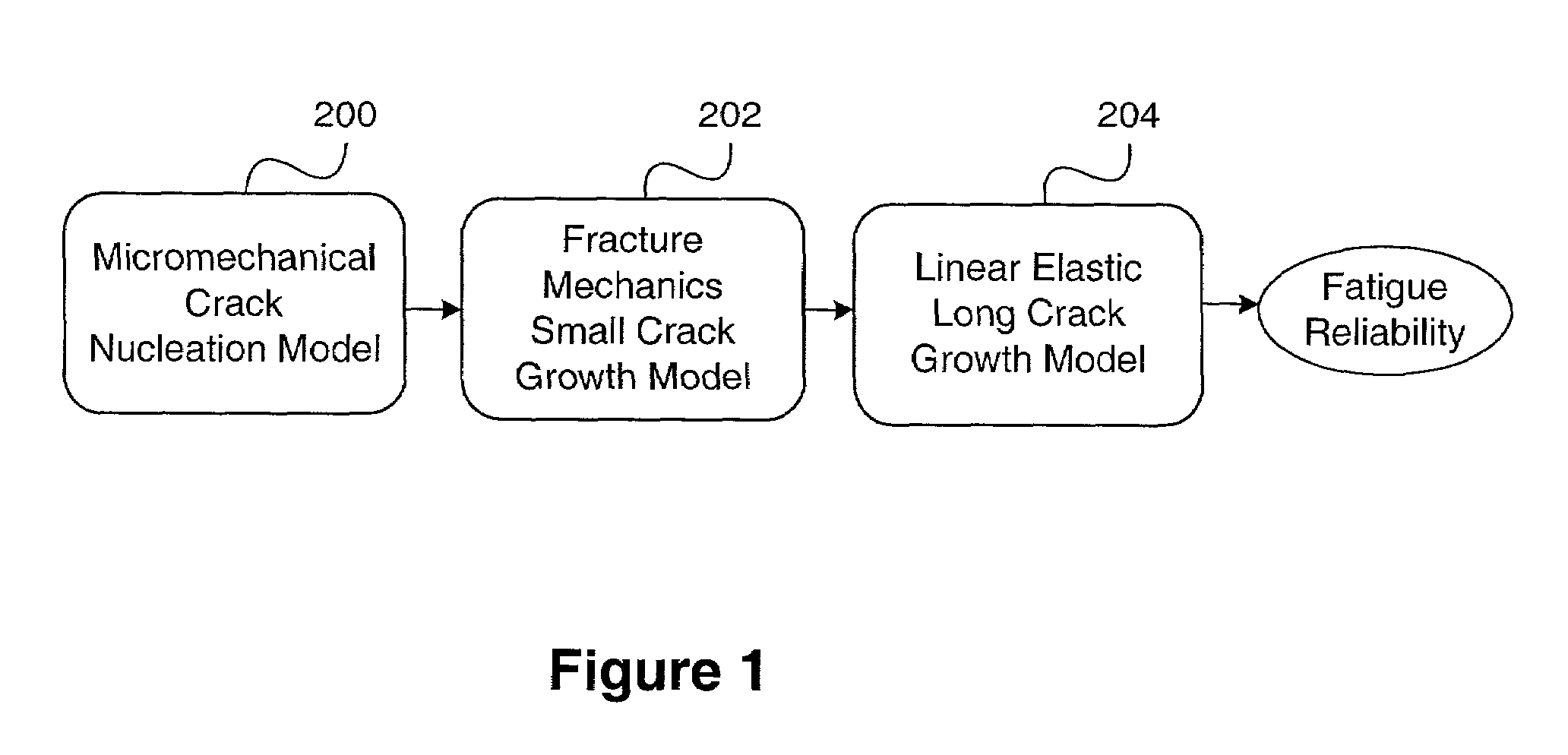
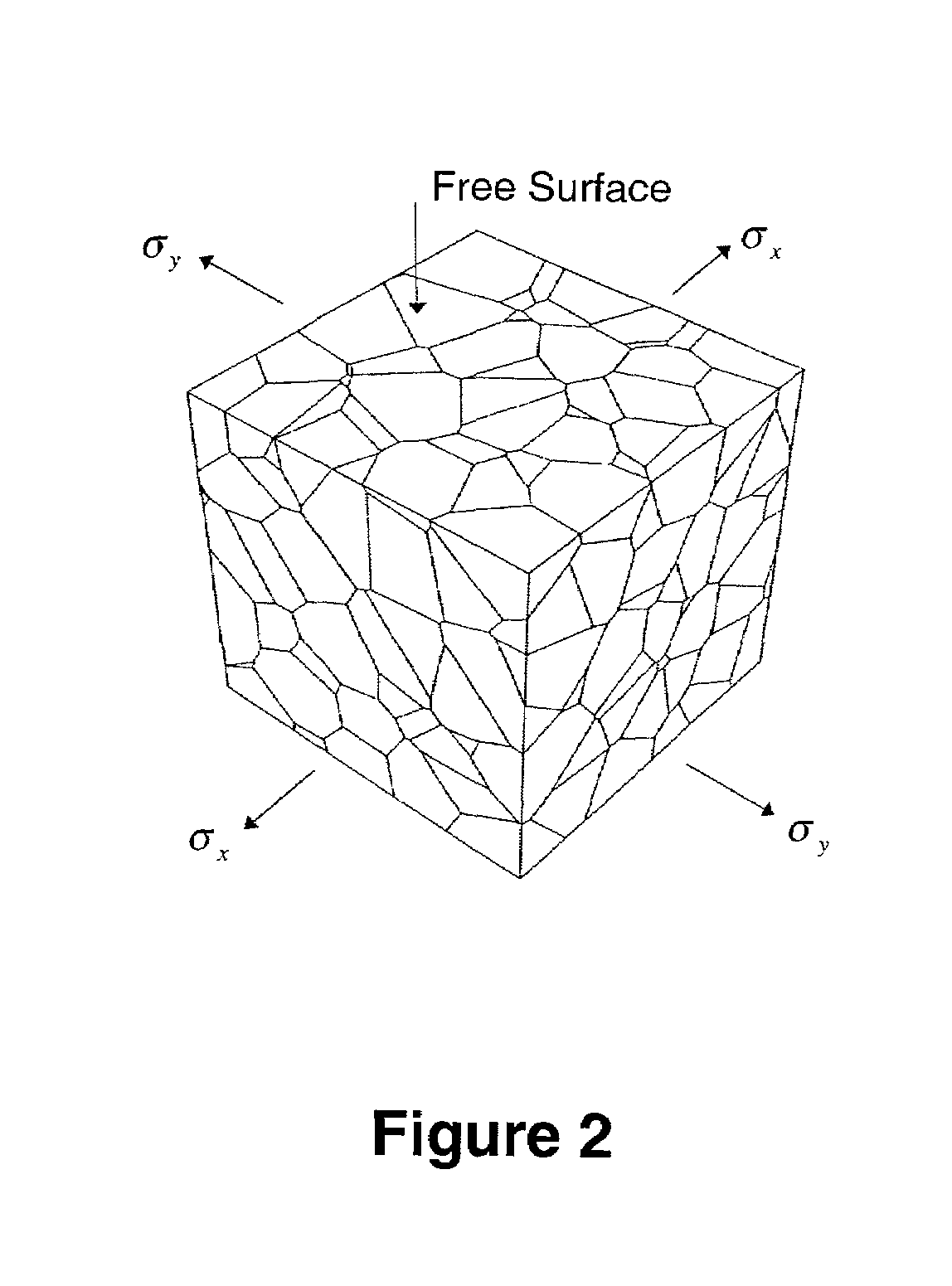
Method and apparatus for predicting the failure of a component
ActiveUS7016825B1Plug gaugesComputation using non-contact making devicesProbit modelComputer science
The invention provides a method and apparatus for predicting the failure of a component using a probabilistic model of a material's microstructural-based response to fatigue. The method predicts the component failure by a computer simulation of multiple incarnations of real material behavior, or virtual prototyping. The virtual prototyping simulates the effects of characteristics that include grain size, grain orientation, micro-applied stress and micro-yield strength that are difficult to simulate with real specimens. The invention provides an apparatus for predicting the response of a component to fatigue using the method.
Owner:VEXTEC CORP
Shared FP and SIMD 3D multiplier
InactiveUS6490607B1Computations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationComputerized systemTheoretical computer science
A multiplier configured to perform multiplication of both scalar floating point values (XxY) and packed floating point values (i.e., X1xY1 and X2xY2). In addition, the multiplier may be configured to calculate XxY-Z. The multiplier comprises selection logic for selecting source operands, a partial product generator, an adder tree, and two or more adders configured to sum the results from the adder tree to achieve a final result. The multiplier may also be configured to perform iterative multiplication operations to implement such arithmetical operations such as division and square root. The multiplier may be configured to generate two versions of the final result, one assuming there is an overflow, and another assuming there is not an overflow. A computer system and method for performing multiplication are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Method and apparatus for providing instruction streams to a processing device
InactiveUS6523107B1Efficient expansionIncrease profitComputation using non-contact making devicesConcurrent instruction executionInstruction stream
A circuit is provided to provide instruction streams to a processing device: embodiments of the circuit are appropriate for use with RISC CPUs, whereas other embodiments are useable with other processing devices, such as small processing devices used in a field programmable array. The circuit receives an external instruction stream which provides a first set of instruction values, and has a memory which contains a second set of instruction values. Two or more outputs provide instruction streams to the processing device. The circuit has a control input in the form of a mask which causes a selection means to allocate bits from the first and second sets of instruction values to different instruction streams to the processing device.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Quotient digit selection logic for floating point division/square root
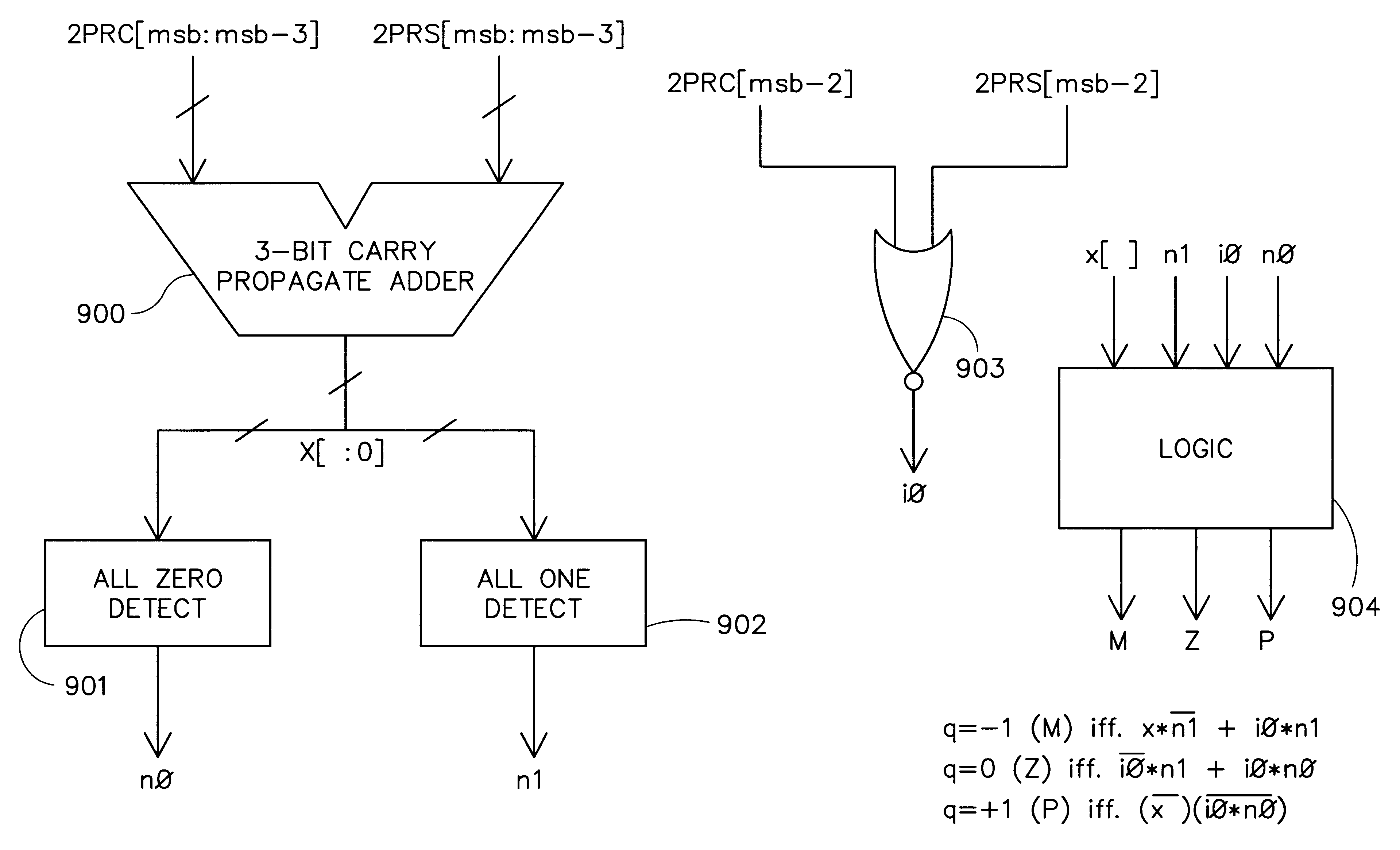
InactiveUS6594681B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesCarry propagationAlgorithm
Quotient digit selection logic using a three-bit carry propagate adder is presented. An enhanced quotient digit selection function prevents the working partial remainder from becoming negative if the result is exact. The enhanced quotient digit selection logic chooses a quotient digit of zero instead of a quotient digit of one when the actual partial remainder is zero. Using a four bit estimated partial remainder where the upper four bits are zero, a possible carry propagation into fourth most significant bit is detected. This can be accomplished by looking at the fourth most significant sum and carry bits of the redundant partial remainder. If they are both zero, then a carry propagation out of that bit position into the least significant position of the estimated partial remainder is not possible, and a quotient digit of zero is chosen. This provides a one cycle savings since negative partial remainders no longer need to be restored before calculating the sticky bit. Extra hardware is eliminated because it is no longer necessary to provide any extra mechanism for restoring the preliminary final partial remainder. Latency is improved because no additional cycle time is required to restore negative preliminary partial remainders. In an alternative embodiment, where the upper three bits of the estimated partial remainder are ones while the fourth most significant bit is zero, a quotient digit of negative one is chosen. This alternative embodiment allows correct exact results in all rounding modes including rounding toward plus or minus infinity.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
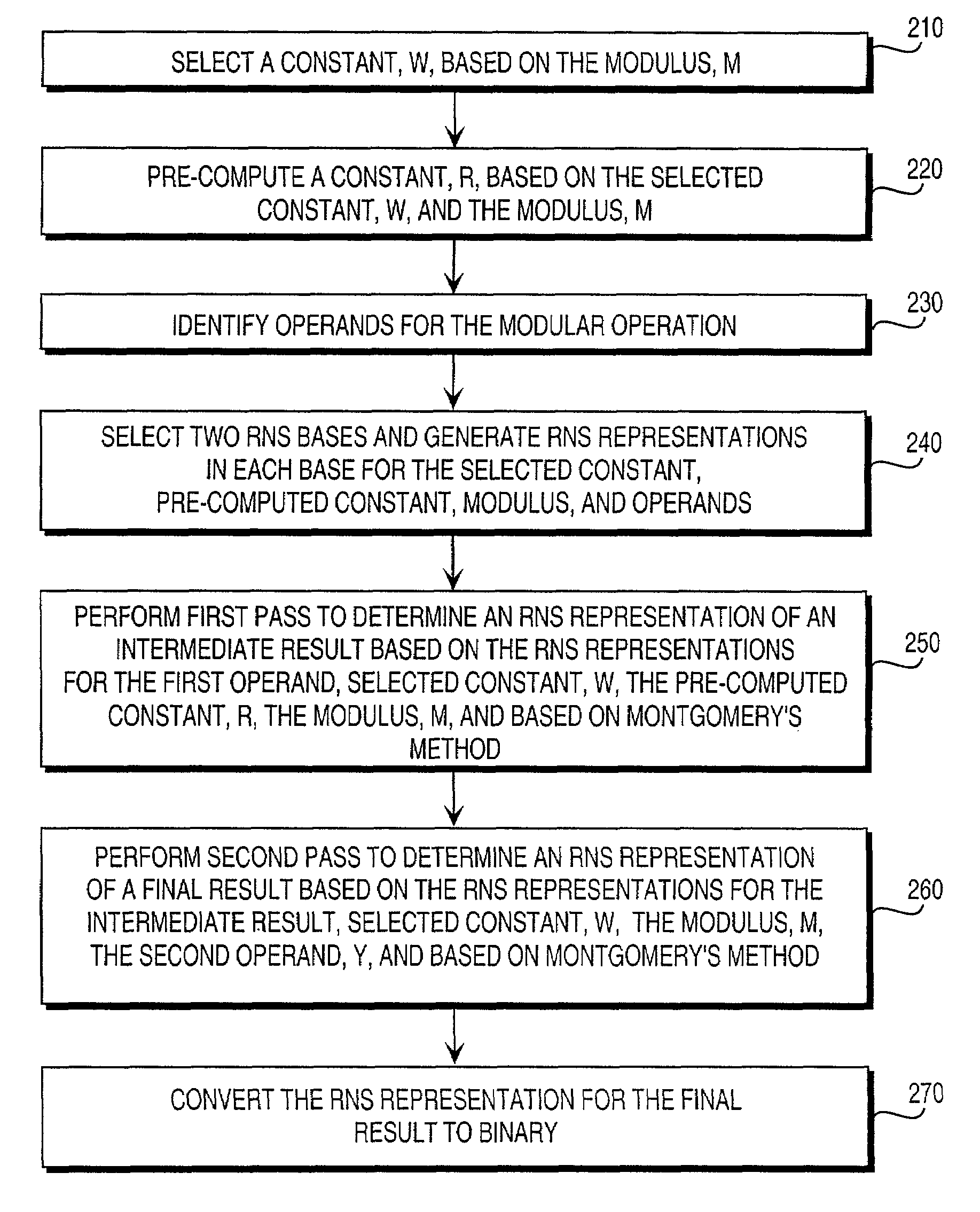
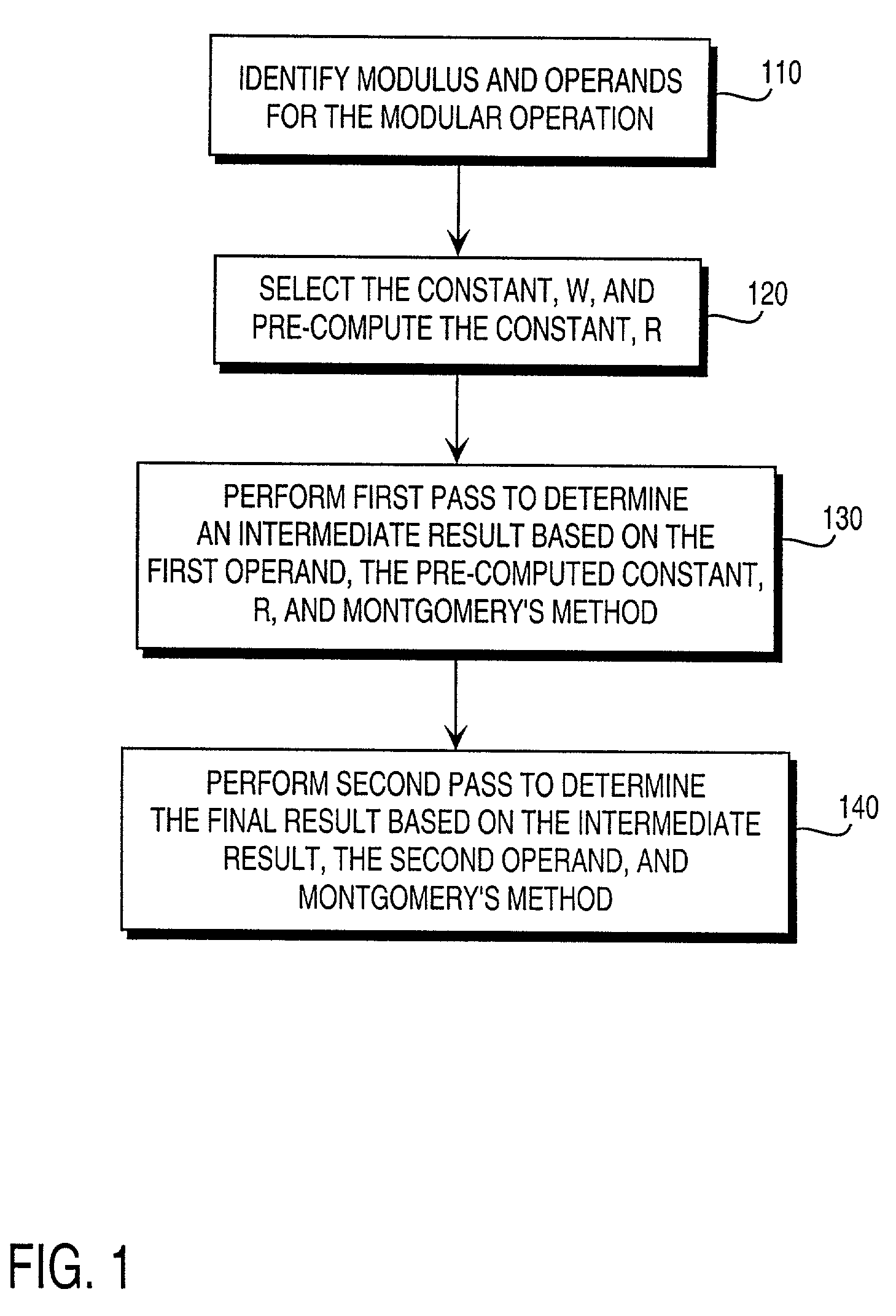
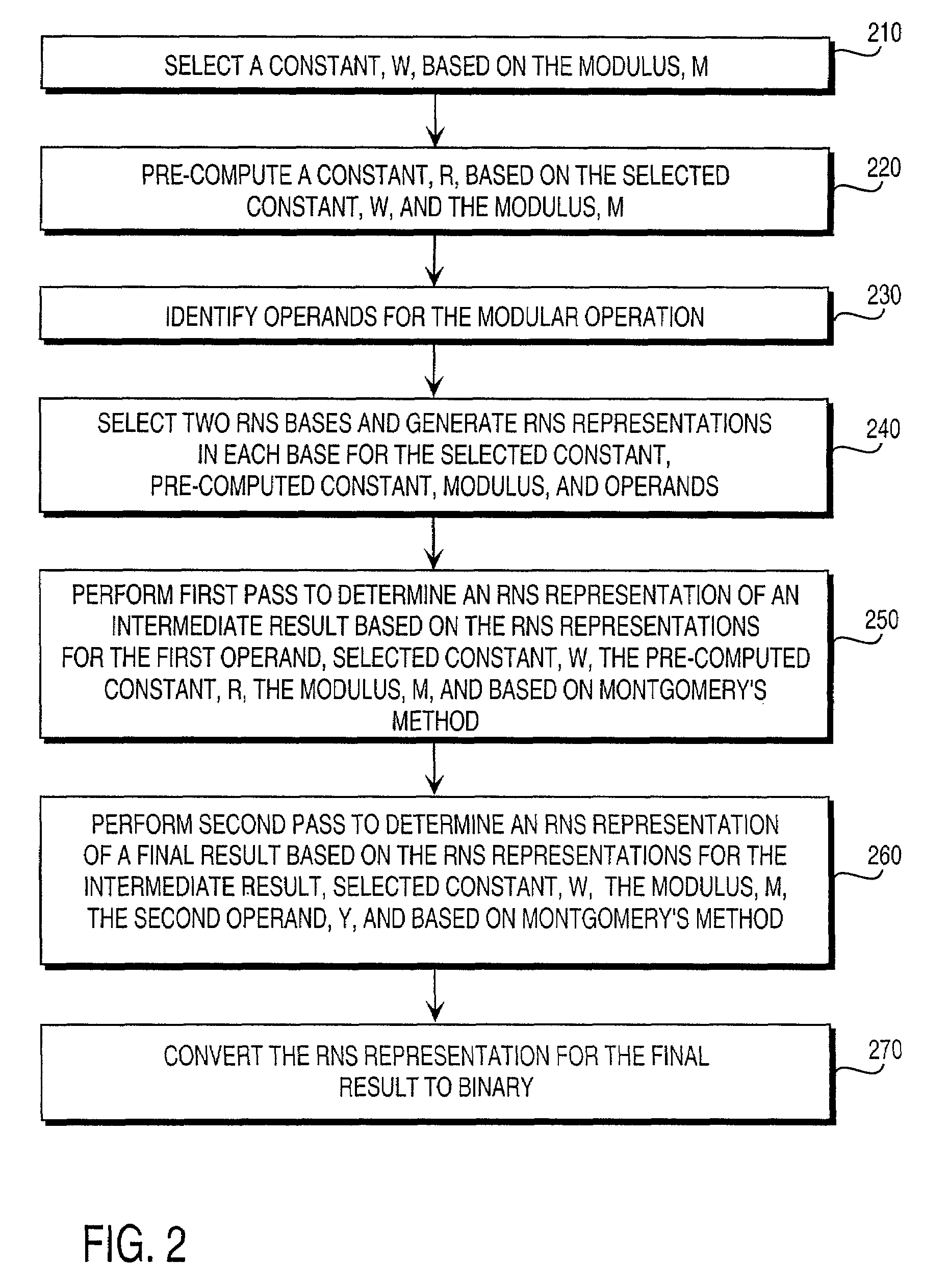
Residue number system based pre-computation and dual-pass arithmetic modular operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits
InactiveUS7027598B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerModularity
A pre-computation and dual-pass modular operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits is disclosed. An encrypted electronic message is received and another electronic message generated based on the encryption protocol. Two passes of Montgomery's method are used for a modular operation that is associated with the encryption protocol along with pre-computation of a constant based on a modulus. The modular operation may be a modular multiplication or a modular exponentiation. Modular arithmetic may be performed using the residue number system (RNS) and two RNS bases with conversions between the two RNS bases. A minimal number of register files are used for the computations along with an array of multiplier circuits and an array of modular reduction circuits. The approach described allows for high throughput for large encryption keys with a relatively small number of logical gates.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for rounding and normalizing results within a multiplier
InactiveUS6269384B1Computations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Devices and methods with programmable logic and digital signal processing regions
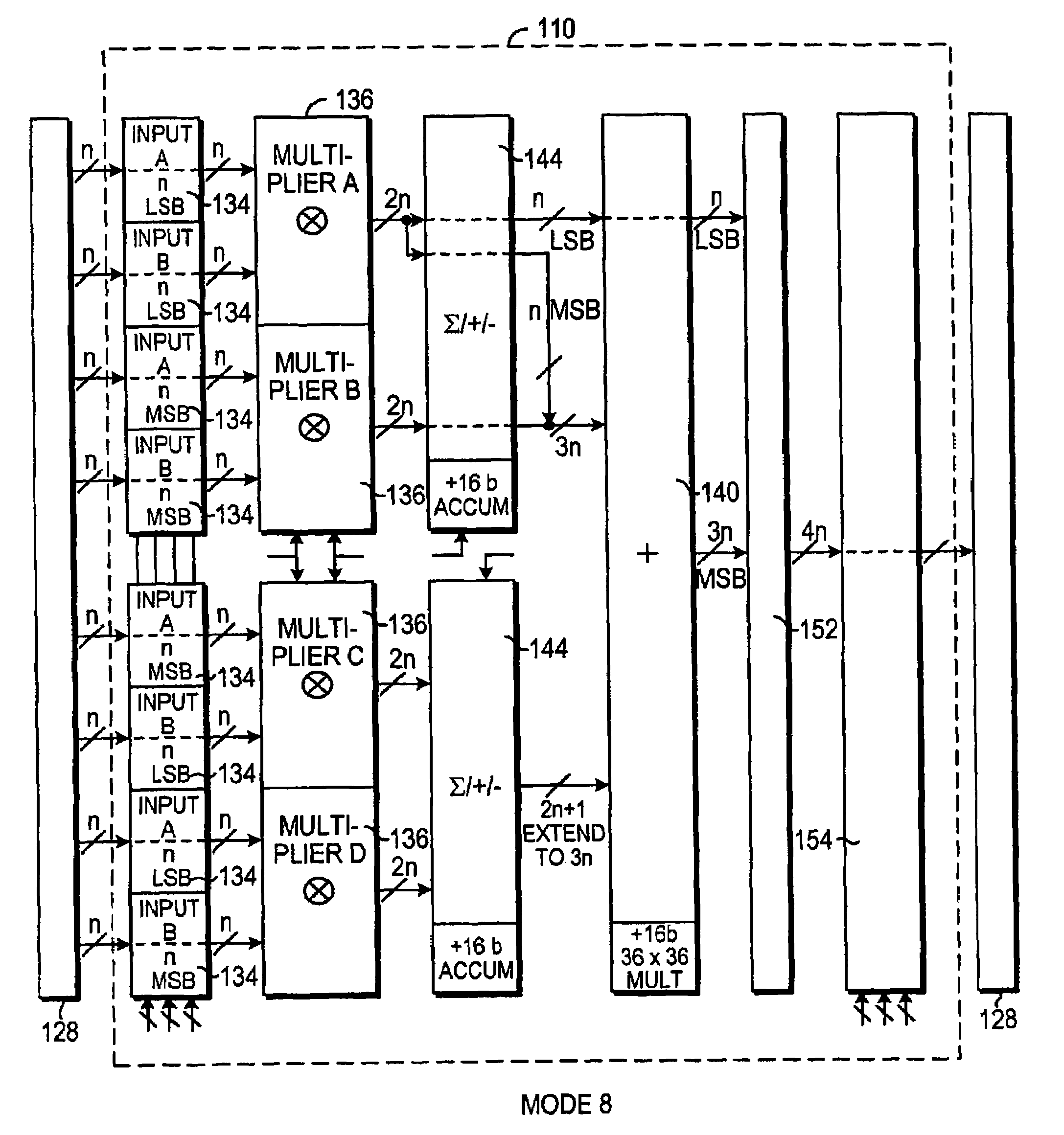
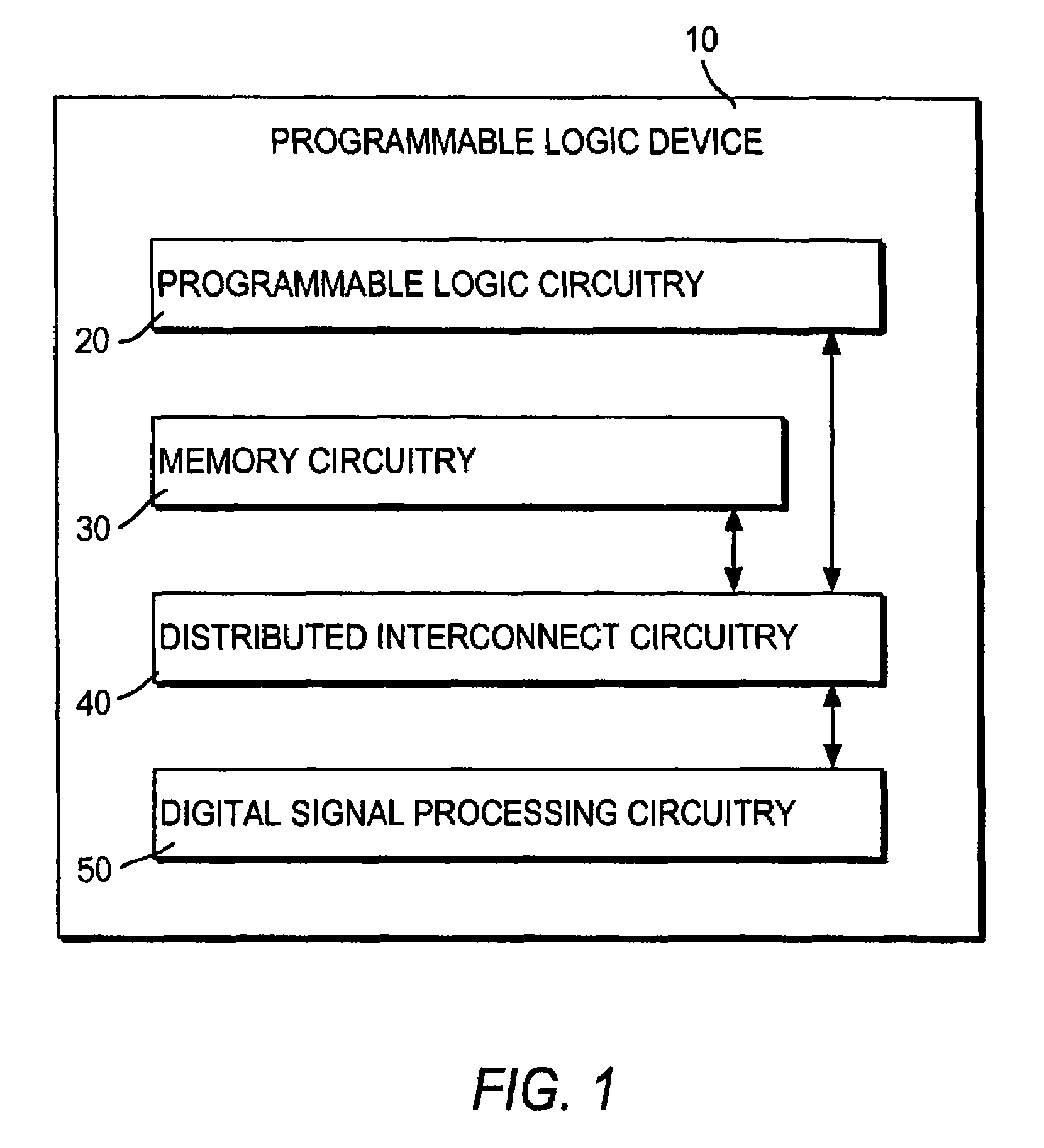
InactiveUS7346644B1High speedImprove latencyComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesGeneral purposeDigital signal processing
A programmable logic integrated circuit device (“PLD”) includes programmable logic and a dedicated (i.e., at least partly hard-wired) digital signal processing region for performing or at least helping to perform digital signal processing tasks that are unduly inefficient to implement in the more general-purpose programmable logic and / or that, if implemented in the programmable logic, would operate unacceptably or at least undesirably slowly. The digital signal processing region may include multiple digital signal processing stages. The digital signal processing region may include a multiplier stage and one or more stages that can operate in combination with the multiplier stage. The digital signal processing region has a plurality of modes such as for providing multiply-and-accumulate operation, multiply-and-add operation, etc.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
System, device, and method for multiplying multi-dimensional data arrays
InactiveUS20120113133A1Register arrangementsComputation using non-contact making devicesArray data structureSingle element
A system, processor, and method for multiplying multi-dimensional data, for example, matrices, stored in vector memories. Each data element in a vector memory representing a sequential single element in a row of a left operand data array may be multiplied with a respective vector in a vector memory representing a sequential row in the right operand data array. The memory element representing the left operand element may be multiplied with the memory vector representing the right operand row that is in the same sequential order. A plurality of vectors of product elements may be generated by the multiplying. A single product element from each of the plurality of vectors of product elements may be added to a sum of product elements to generate each respective element in the same sequential order in a row of a product data array to generate a vector of a complete row of elements of the product data array.
Owner:CEVA D S P LTD
Method and apparatus for simultaneously multiplying two or more independent pairs of operands and calculating a rounded products
InactiveUS6038583ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
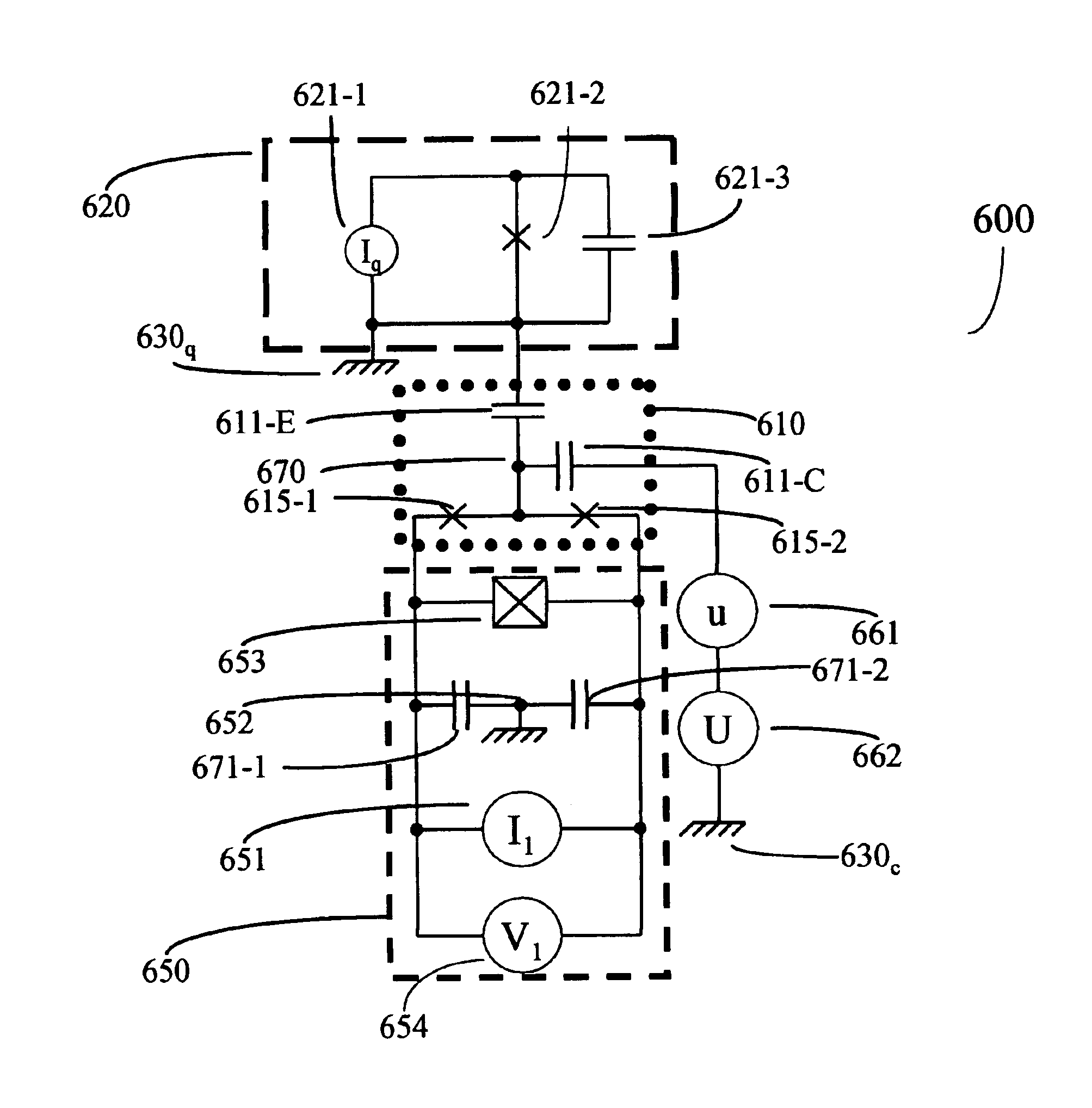
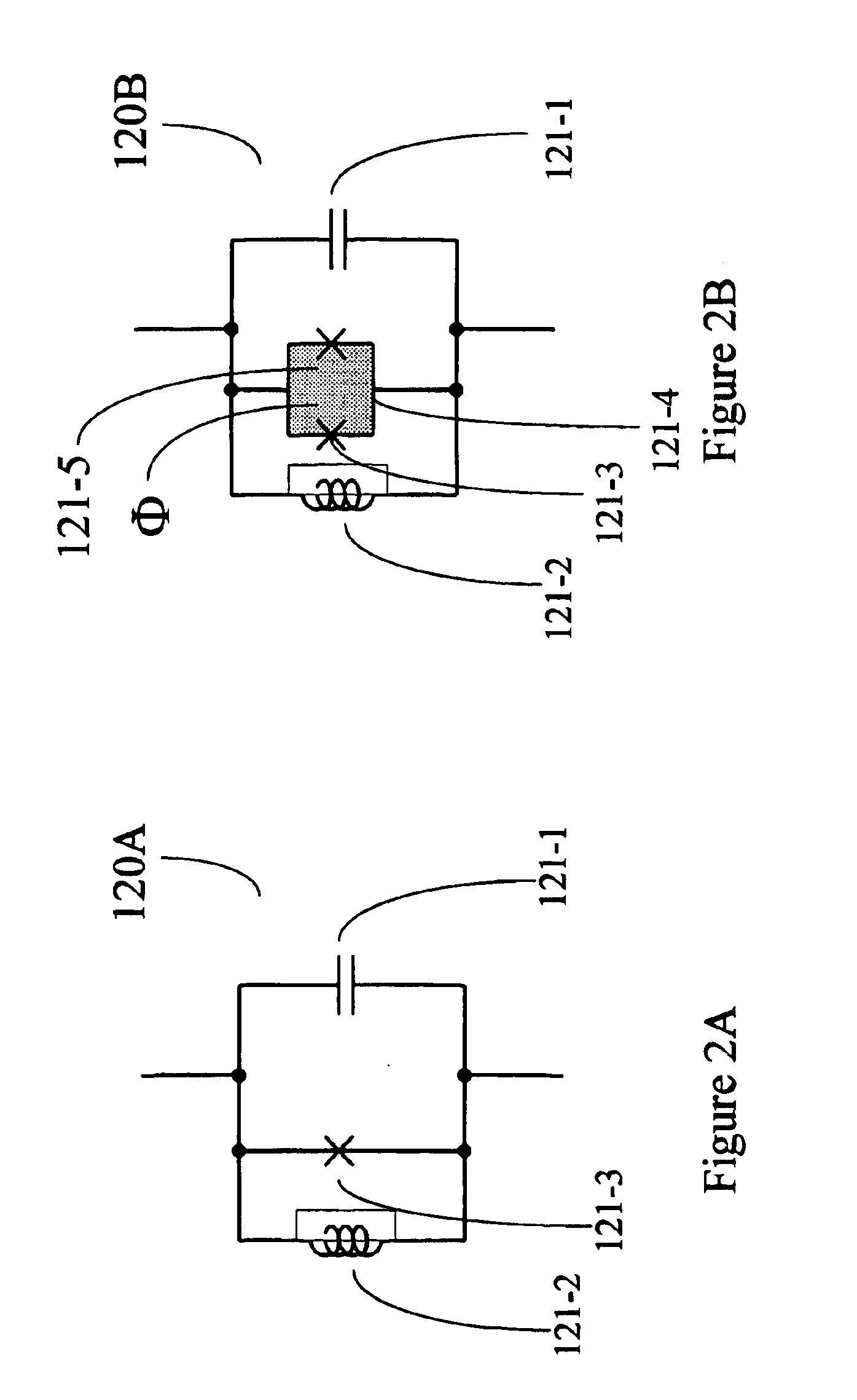
Resonant controlled qubit system
Methods for coupling a superconducting qubit to a resonant control circuit. An interaction term between the qubit and the circuit initially has a diagonal component. A recoupling operation is applied to the qubit. The circuit is tuned so that a frequency of the qubit and circuit match. A second recoupling operation transforms the term to have only off-diagonal components. A method for entangling a state of two qubits coupled to a bus with a control circuit. An interaction term between at least one of the qubits and the circuit has a diagonal component. A recoupling operation is applied to at least one of the qubits such that the term has only off-diagonal components. The frequency of the circuit is tuned to the frequency of the first qubit, and then tuned to the frequency of the second qubit. The recoupling operation is reapplied to at least one of the qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
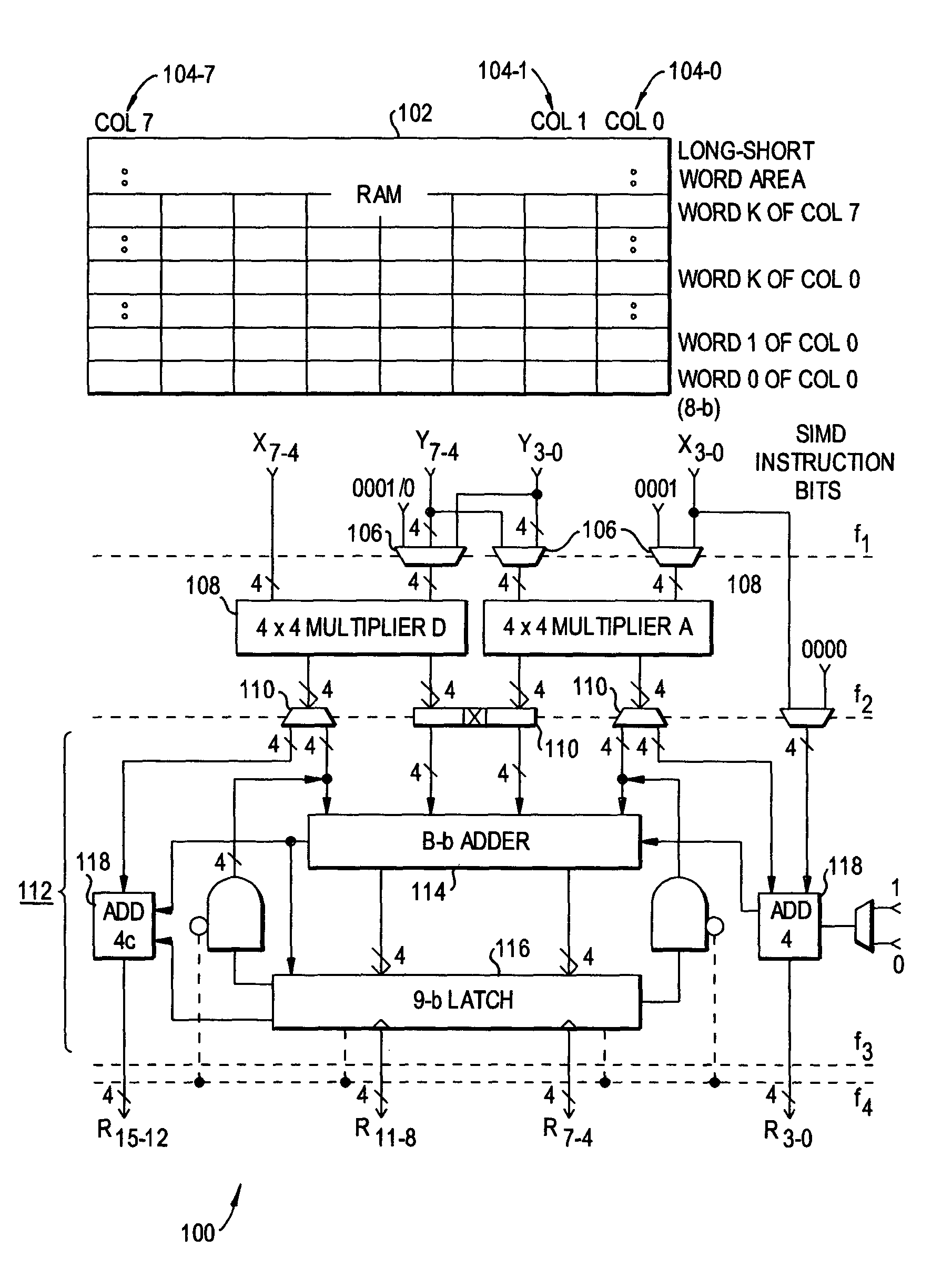
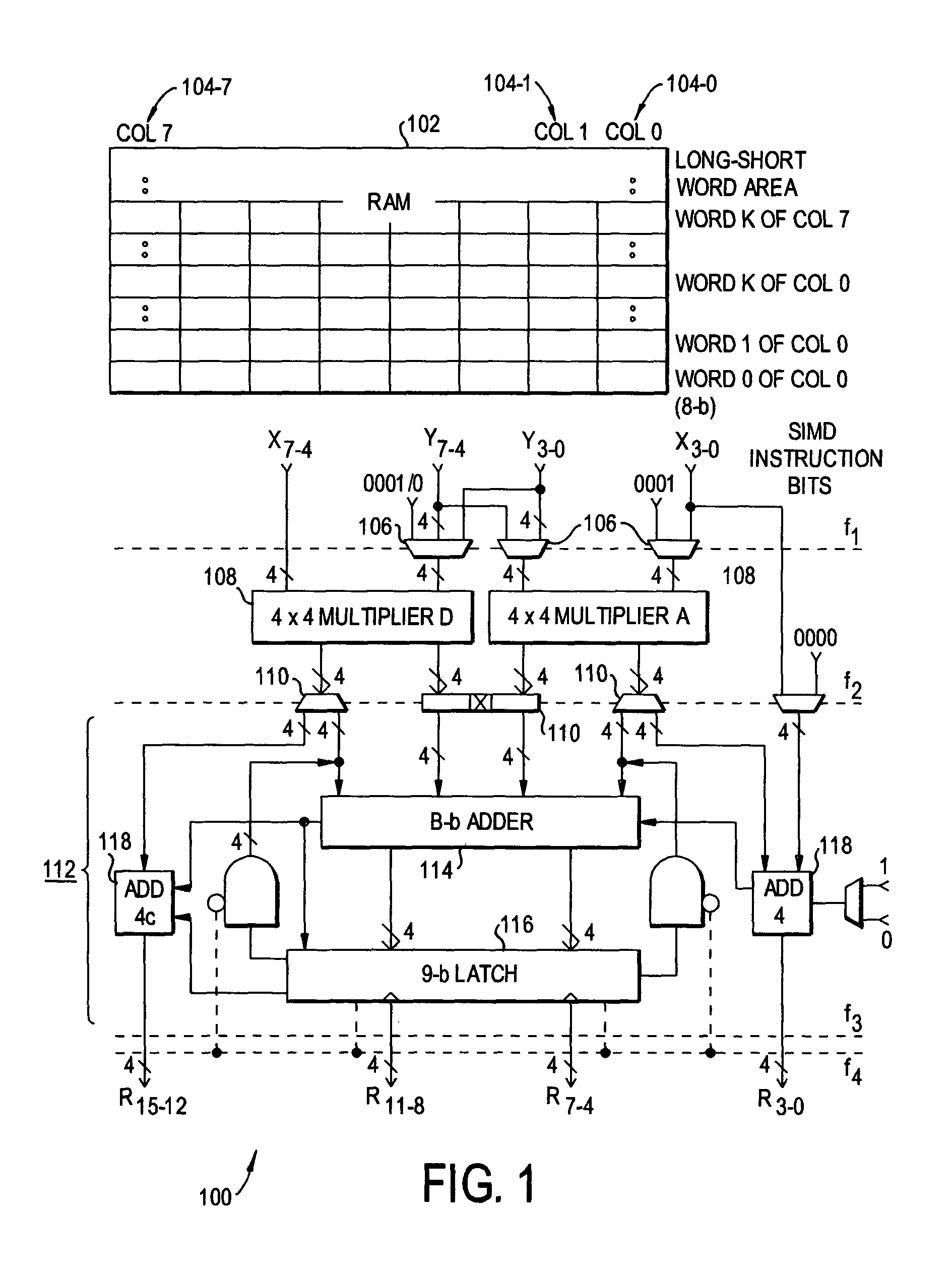
Multiplier-based processor-in-memory architectures for image and graphics processing
InactiveUS7167890B2Efficiently reconfiguredNegligible amountComputation using non-contact making devicesImage memory managementGraphicsComputational science
A Procesor-In-Memory (PIM) includes a digital accelerator for image and graphics processing. The digital accelerator is based on an ALU having multipliers for processing combinations of bits smaller than those in the input data (e.g., 4×4 adders if the input data are 8-bit numbers). The ALU implements various arithmetic algorithms for addition, multiplication, and other operations. A secondary processing logic includes adders in series and parallel to permit vector operations as well as operations on longer scalars. A self-repairing ALU is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +2
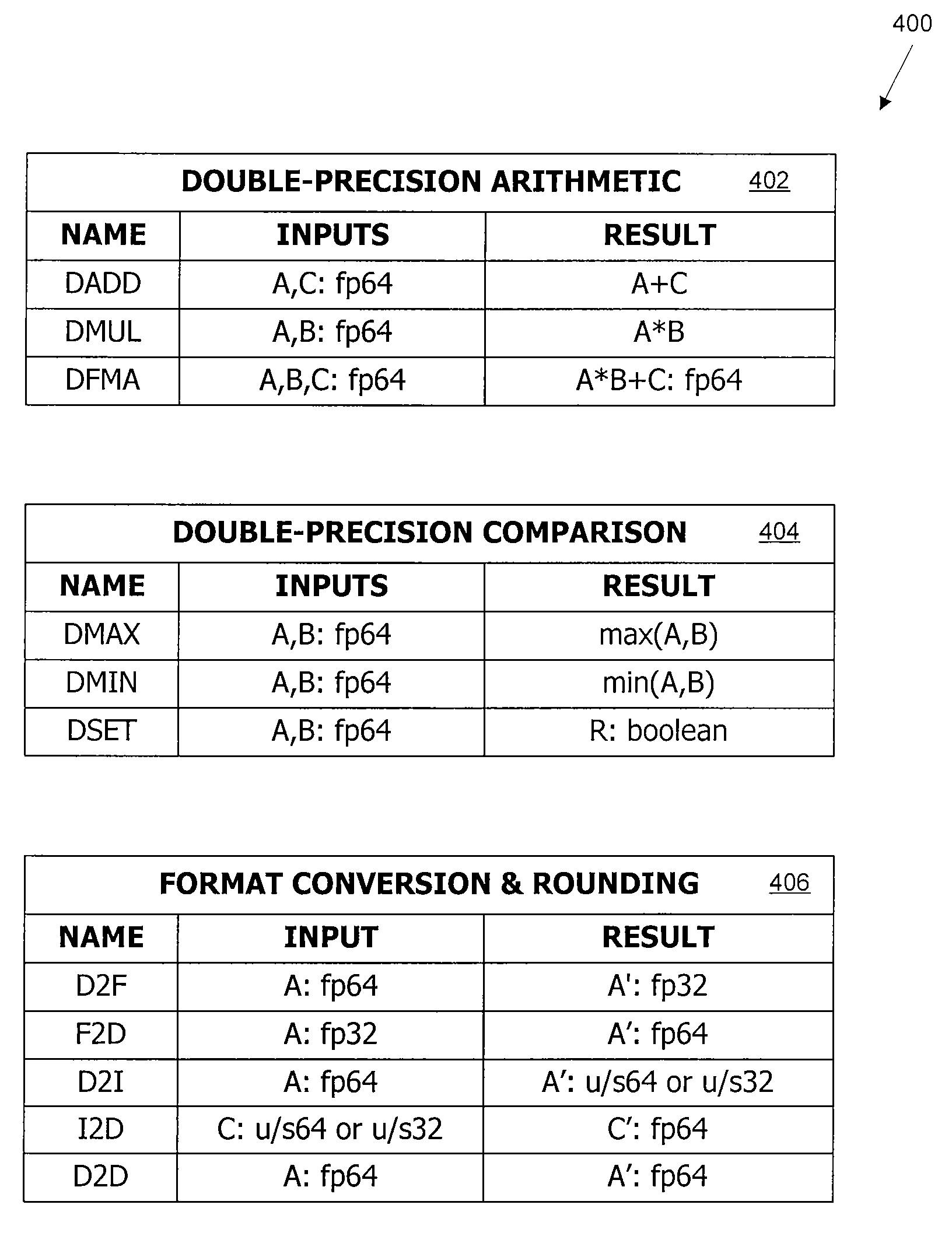
Fused multiply-add functional unit
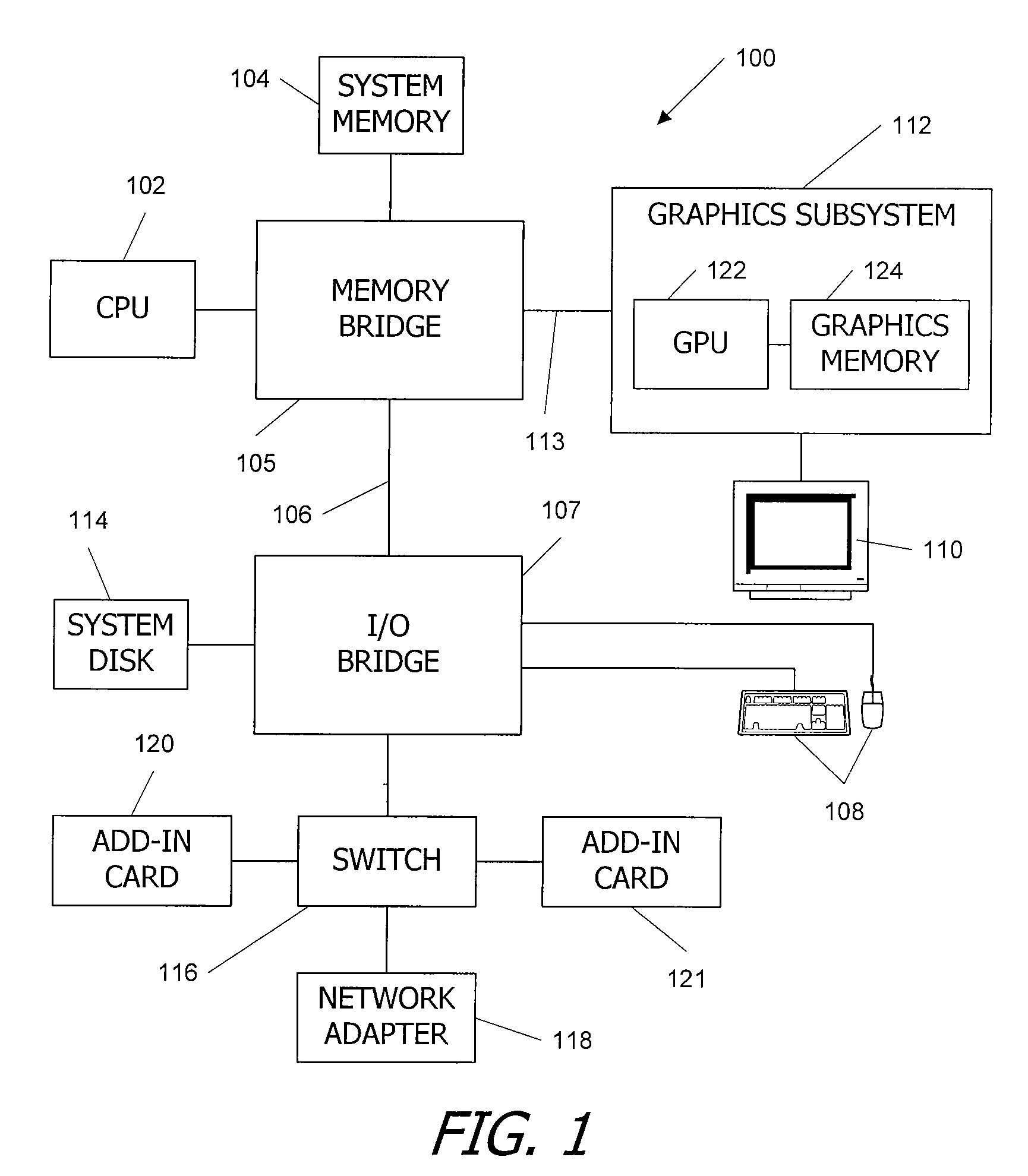
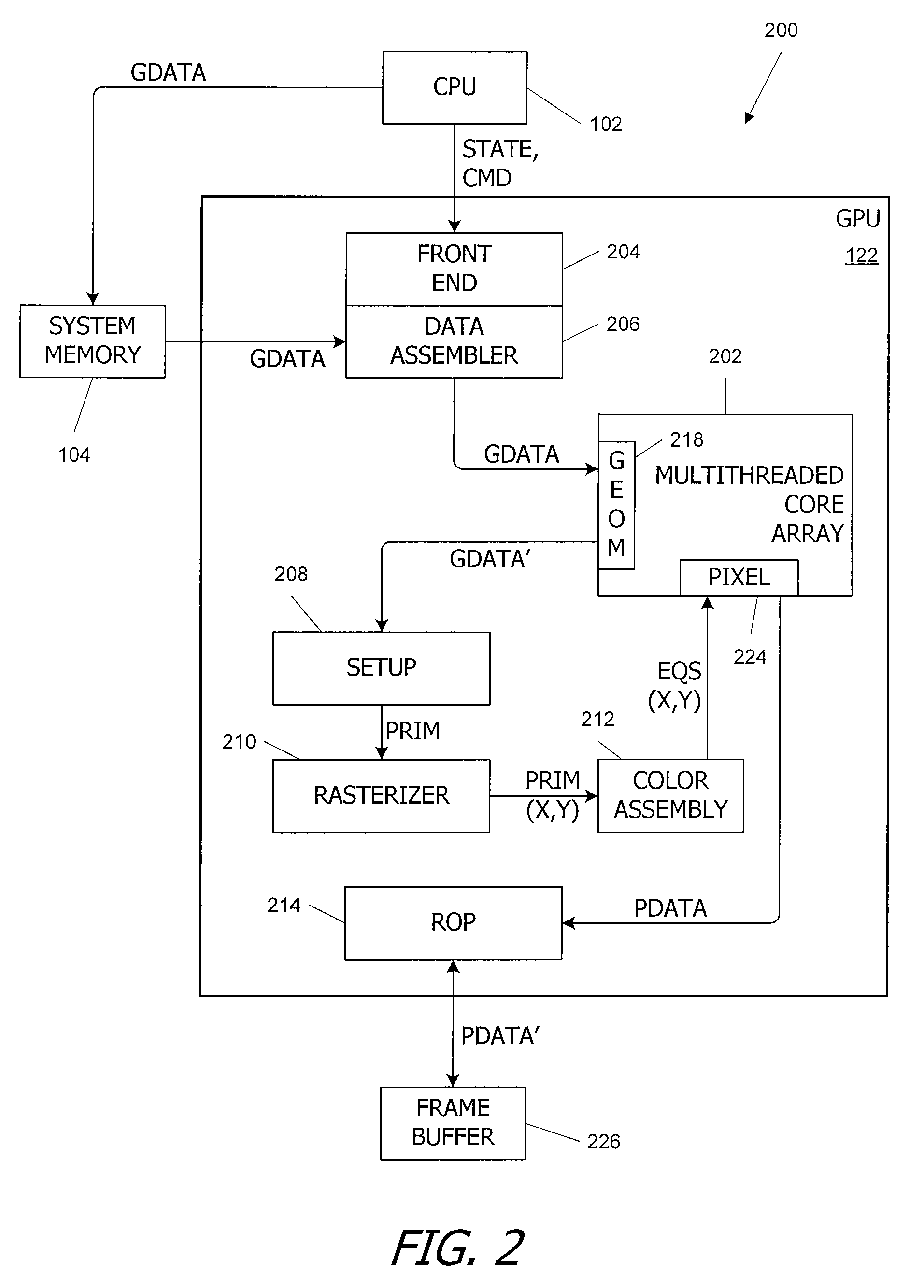
ActiveUS20090150654A1Reduce the impactReduce impactRegister arrangementsComputation using non-contact making devicesGraphicsDatapath
A functional unit is added to a graphics processor to provide direct support for double-precision arithmetic, in addition to the single-precision functional units used for rendering. The double-precision functional unit can execute a number of different operations, including fused multiply-add, on double-precision inputs using data paths and / or logic circuits that are at least double-precision width. The double-precision and single-precision functional units can be controlled by a shared instruction issue circuit, and the number of copies of the double-precision functional unit included in a core can be less than the number of copies of the single-precision functional units, thereby reducing the effect of adding support for double-precision on chip area.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Popular searches
Logic circuits using elementary logic circuit components Digital computer details Digital storage Comparison of digital values Microcontrol arrangements Memory adressing/allocation/relocation Handling data according to predetermined rules Next instruction address formation Architecture with single central processing unit Angle modulation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com