Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
133 results about "Microarchitecture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
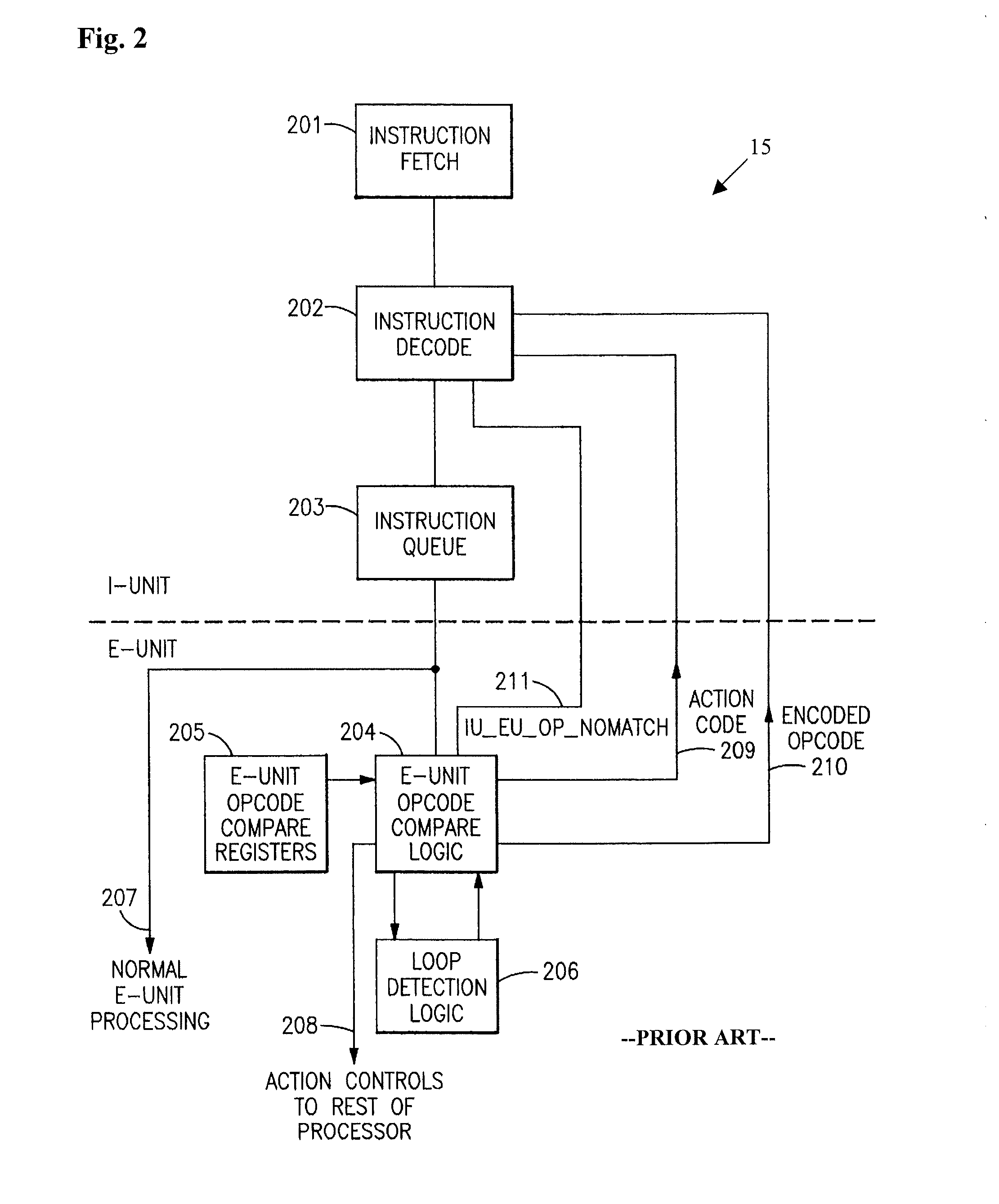
In computer engineering, microarchitecture, also called computer organization and sometimes abbreviated as µarch or uarch, is the way a given instruction set architecture (ISA) is implemented in a particular processor. A given ISA may be implemented with different microarchitectures; implementations may vary due to different goals of a given design or due to shifts in technology.
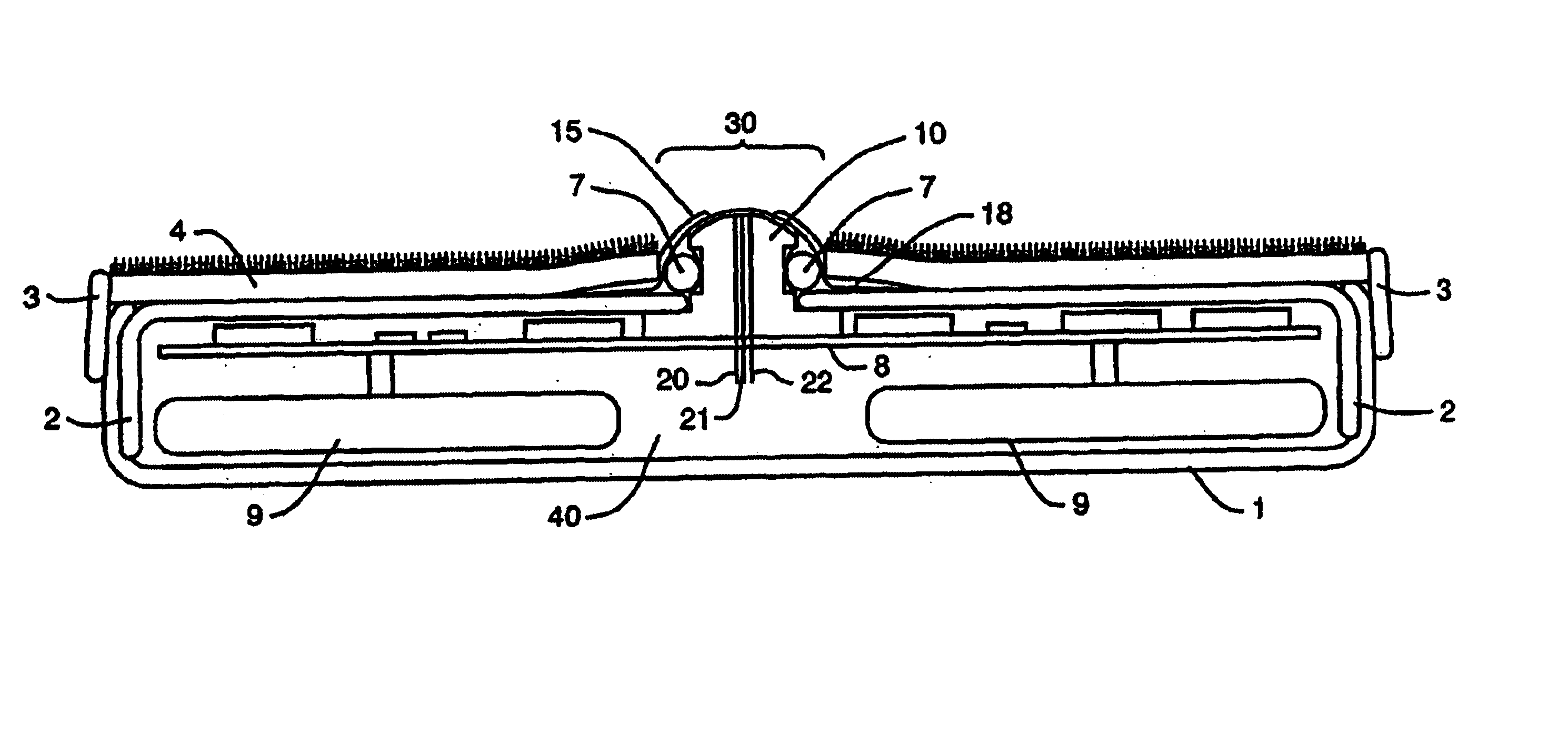
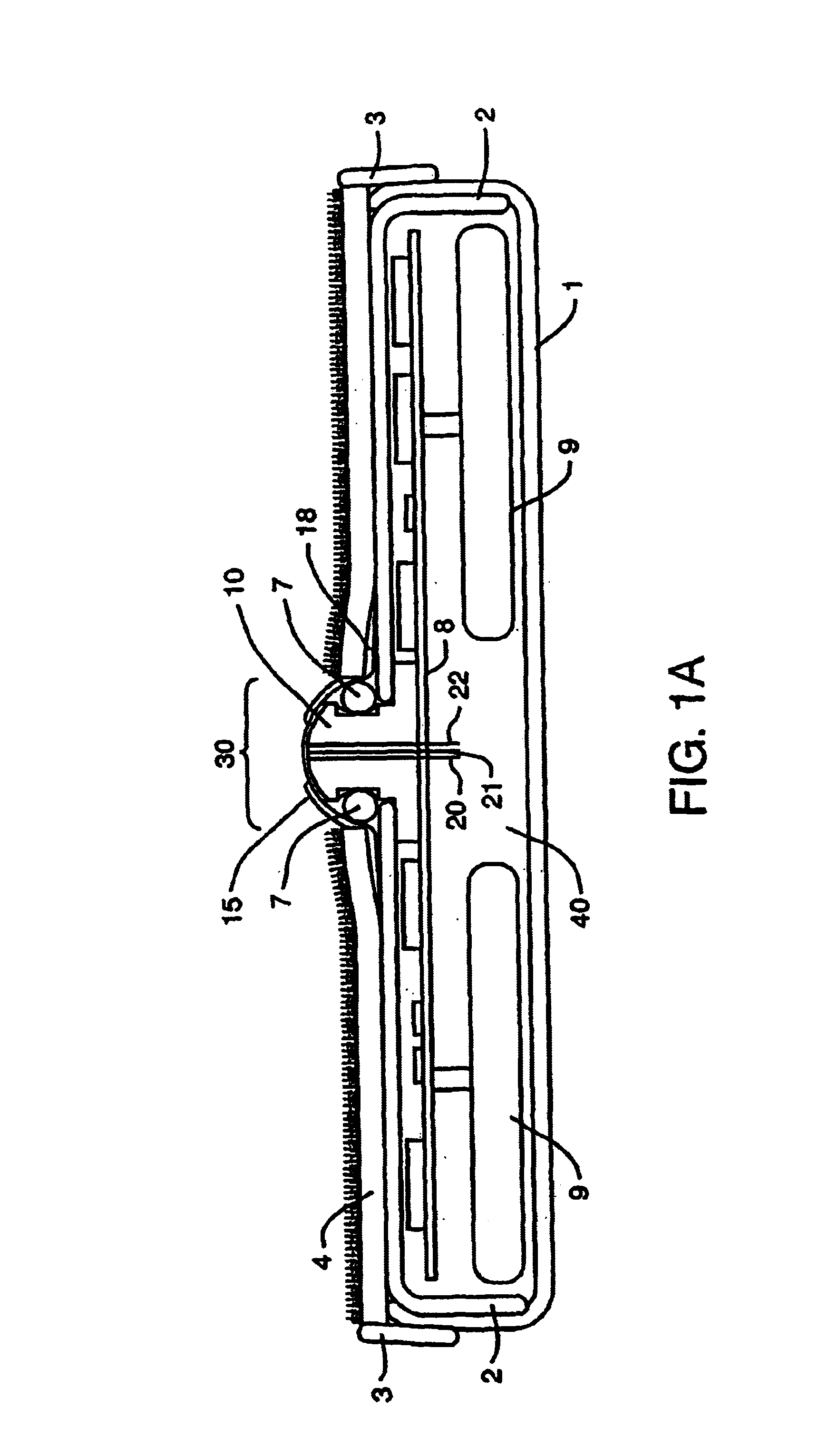
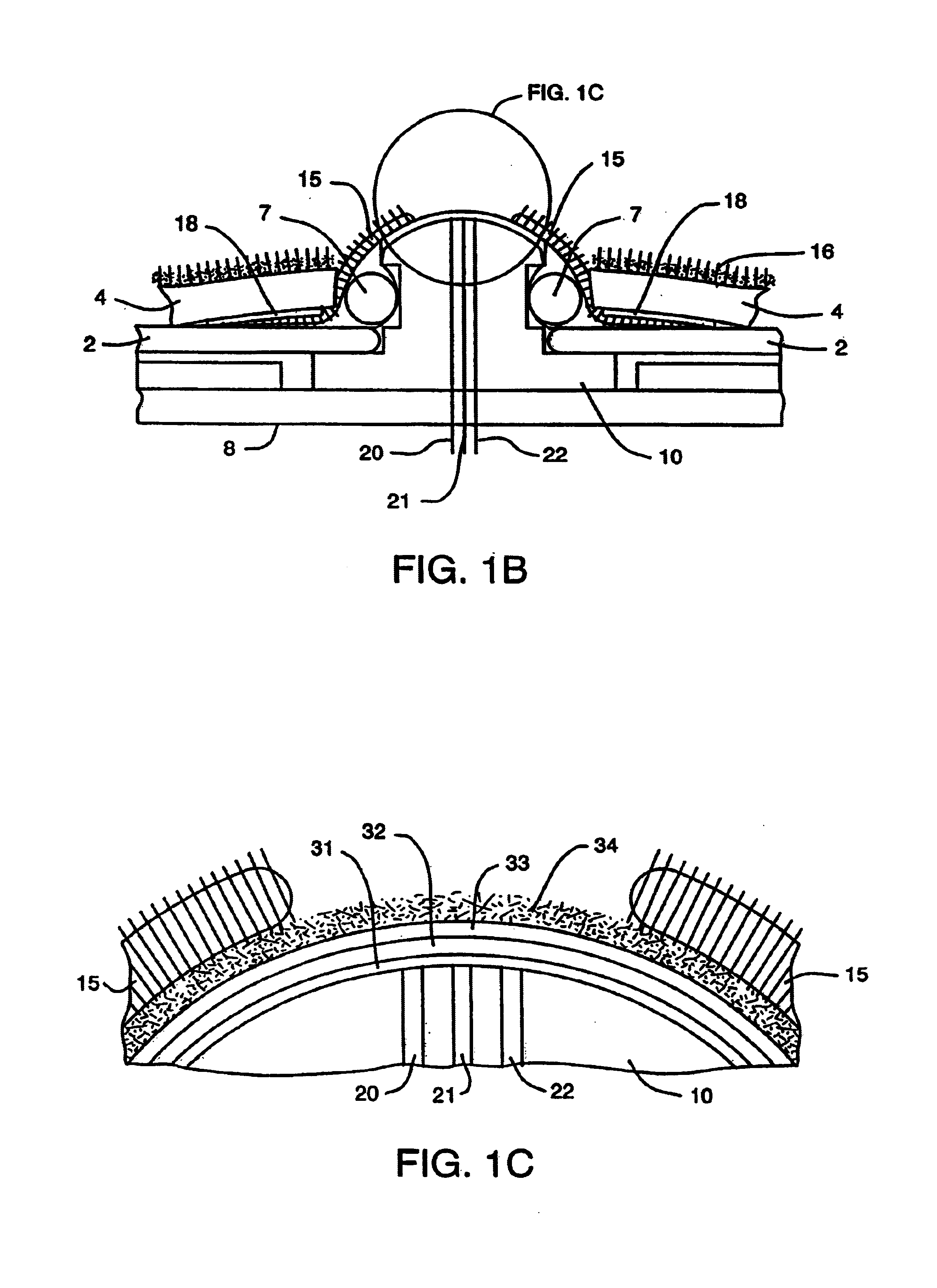
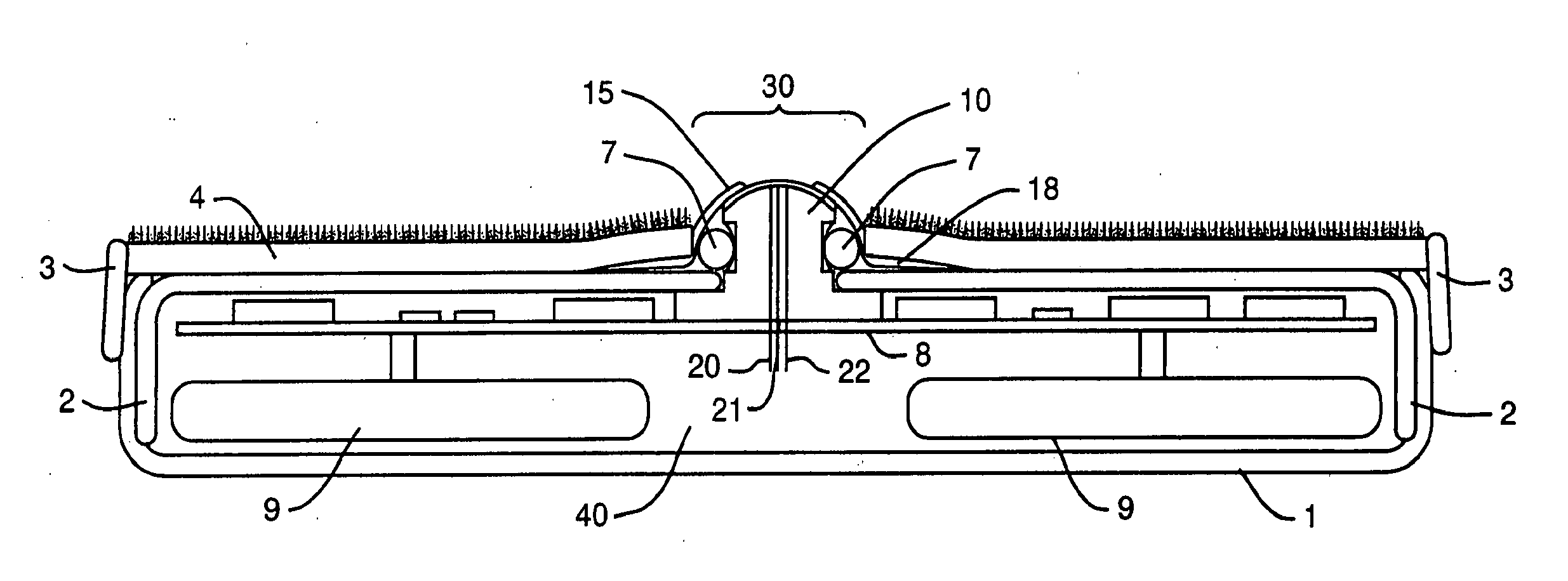
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS7110803B2Reducing and eliminating phenomenonEliminate and significantly delay environmental stress crackingMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesAnalyteImplanted device
Owner:DEXCOM
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS20100099971A1Reducing and eliminating phenomenonEliminate and significantly delay environmental stress crackingMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterAnalyteImplanted device
Devices and methods for determining analyte levels are described. The devices and methods allow for the implantation of analyte-monitoring devices, such as glucose monitoring devices, that result in the delivery of a dependable flow of blood to deliver sample to the implanted device. The devices comprise a unique microarchitectural arrangement in the sensor region that allows accurate data to be obtained over long periods of time.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS20100099970A1Reducing and eliminating phenomenonEliminate and significantly delay environmental stress crackingMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterAnalyteImplanted device
Devices and methods for determining analyte levels are described. The devices and methods allow for the implantation of analyte-monitoring devices, such as glucose monitoring devices, that result in the delivery of a dependable flow of blood to deliver sample to the implanted device. The devices comprise a unique microarchitectural arrangement in the sensor region that allows accurate data to be obtained over long periods of time.
Owner:DEXCOM
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS20050177036A1Reducing and eliminating phenomenonEliminate and significantly delay environmental stress crackingMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterAnalyteImplanted device
Devices and methods for determining analyte levels are described. The devices and methods allow for the implantation of analyte-monitoring devices, such as glucose monitoring devices, that result in the delivery of a dependable flow of blood to deliver sample to the implanted device. The devices comprise a unique microarchitectural arrangement in the sensor region that allows accurate data to be obtained over long periods of time.
Owner:DEXCOM
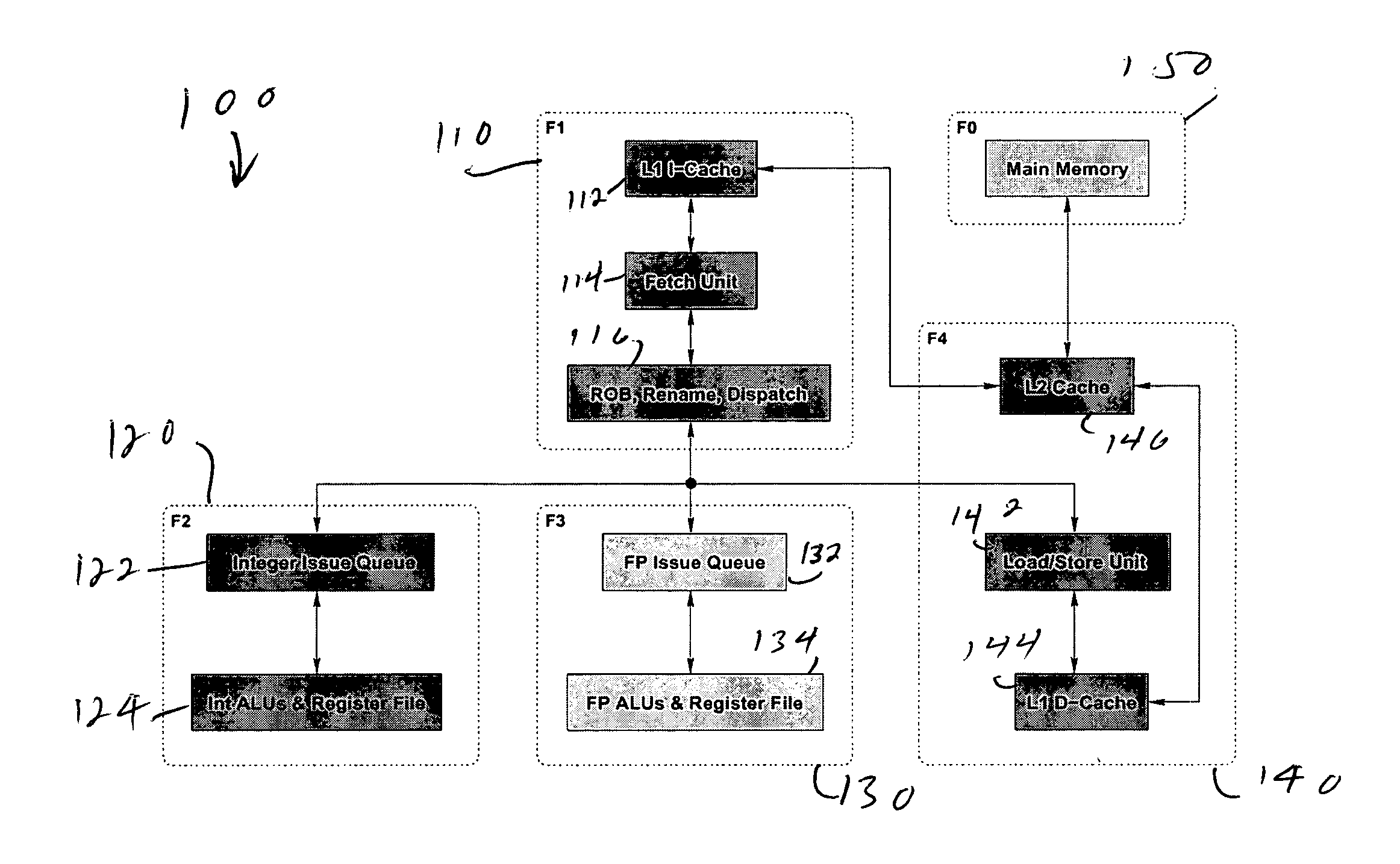
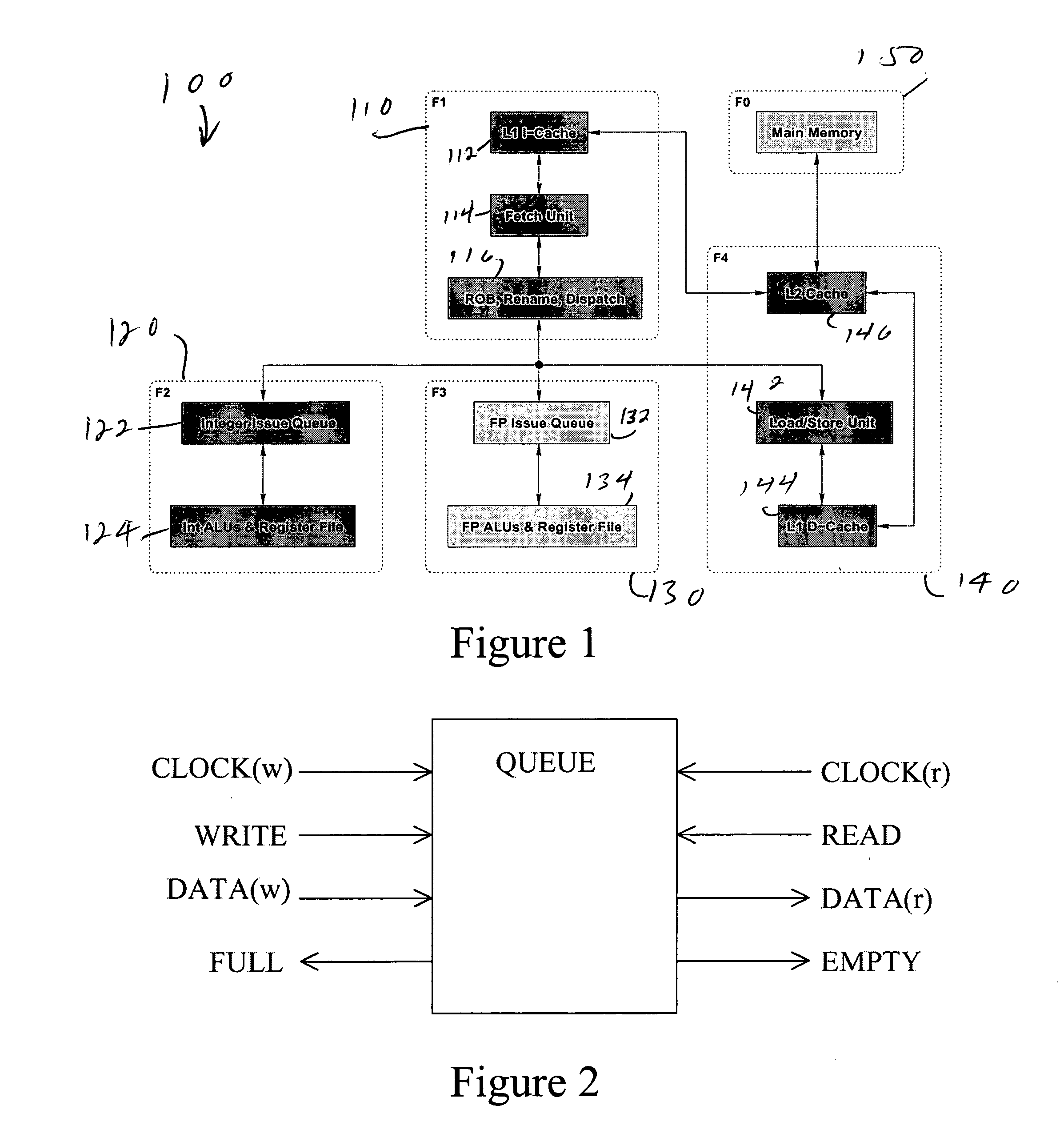
Multiple clock domain microprocessor
ActiveUS20070016817A1High frequencyImprove good performanceEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingComputer scienceInter-domain
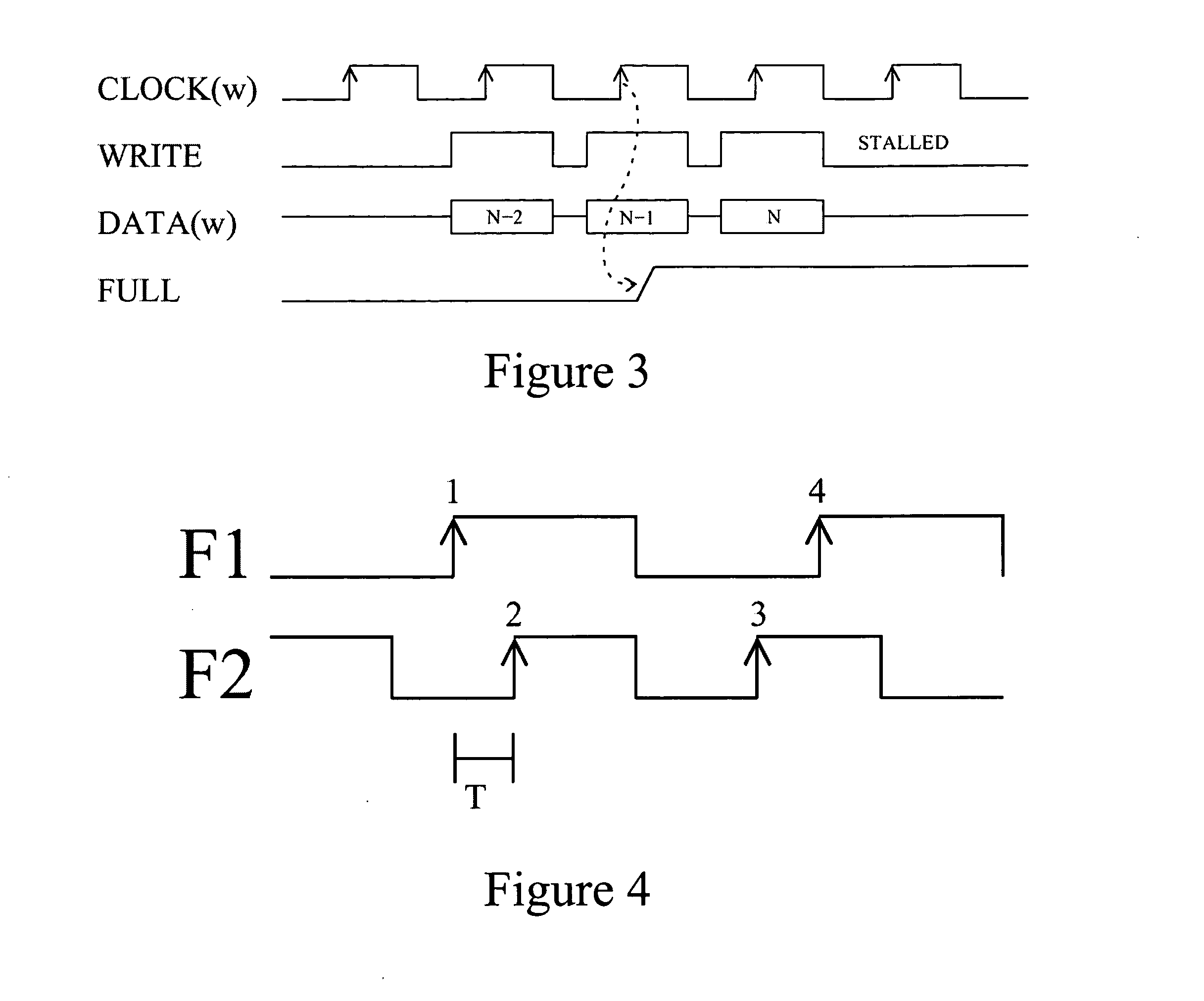
A multiple clock domain (MCD) microarchitecture uses a globally-asynchronous, locally-synchronous (GALS) clocking style. In an MCD microprocessor each functional block operates with a separately generated clock, and synchronizing circuits ensure reliable inter-domain communication. Thus, fully synchronous design practices are used in the design of each domain.
Owner:ALBONESI DAVID +5
Cycle segmented prefix circuits
InactiveUS6609189B1Improve performanceAvoid performanceComputation using non-contact making devicesGeneral purpose stored program computerExtensibilityScalar processor
The poor scalability of existing superscalar processors has been of great concern to the computer engineering community. In particular, the critical-path delays of many components in existing implementations grow quadratically with the issue width and the window size. This patent presents a novel way to reimplement these components and reduce their critical-path delay growth. It then describes an entire processor microarchitecture, called the Ultrascalar processor, that has better critical-path delay growth than existing superscalars. Most of our scalable designs are based on a single circuit, a cyclic segmented parallel prefix (cspp). We observe that processor components typically operate on a wrap-around sequence of instructions, computing some associative property of that sequence. For example, to assign an ALU to the oldest requesting instruction, each instruction in the instruction sequence must be told whether any preceding instructions are requesting an ALU. Similarly, to read an argument register, an instruction must somehow communicate with the most recent preceding instruction that wrote that register. A cspp circuit can implement such functions by computing for each instruction within a wrap-around instruction sequence the accumulative result of applying some associative operator to all the preceding instructions. A cspp circuit has a critical path gate delay logarithmic in the length of the instruction sequence. Depending on its associative operation and its layout, a cspp circuit can have a critical path wire delay sublinear in the length of the instruction sequence.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Parallel object detection method for heterogeneous multithreaded microarchitectures
ActiveUS20130243329A1Improve performanceTime-consuming to improveCharacter and pattern recognitionObject detectionMicroarchitecture
A parallel object detection method for heterogeneous microarchitectures. The method is designed for increasing the throughput of object detection in a computer system that is equipped with an array of cores including a shared memory, a constant memory, and functional units. Latency reduction is achieved through a multilevel parallelization method that exploits fine-grain data-level parallelism using multithreaded SIMD computations, and coarse-grain parallelism by relying on concurrent kernel execution.
Owner:HERTA SECURITY
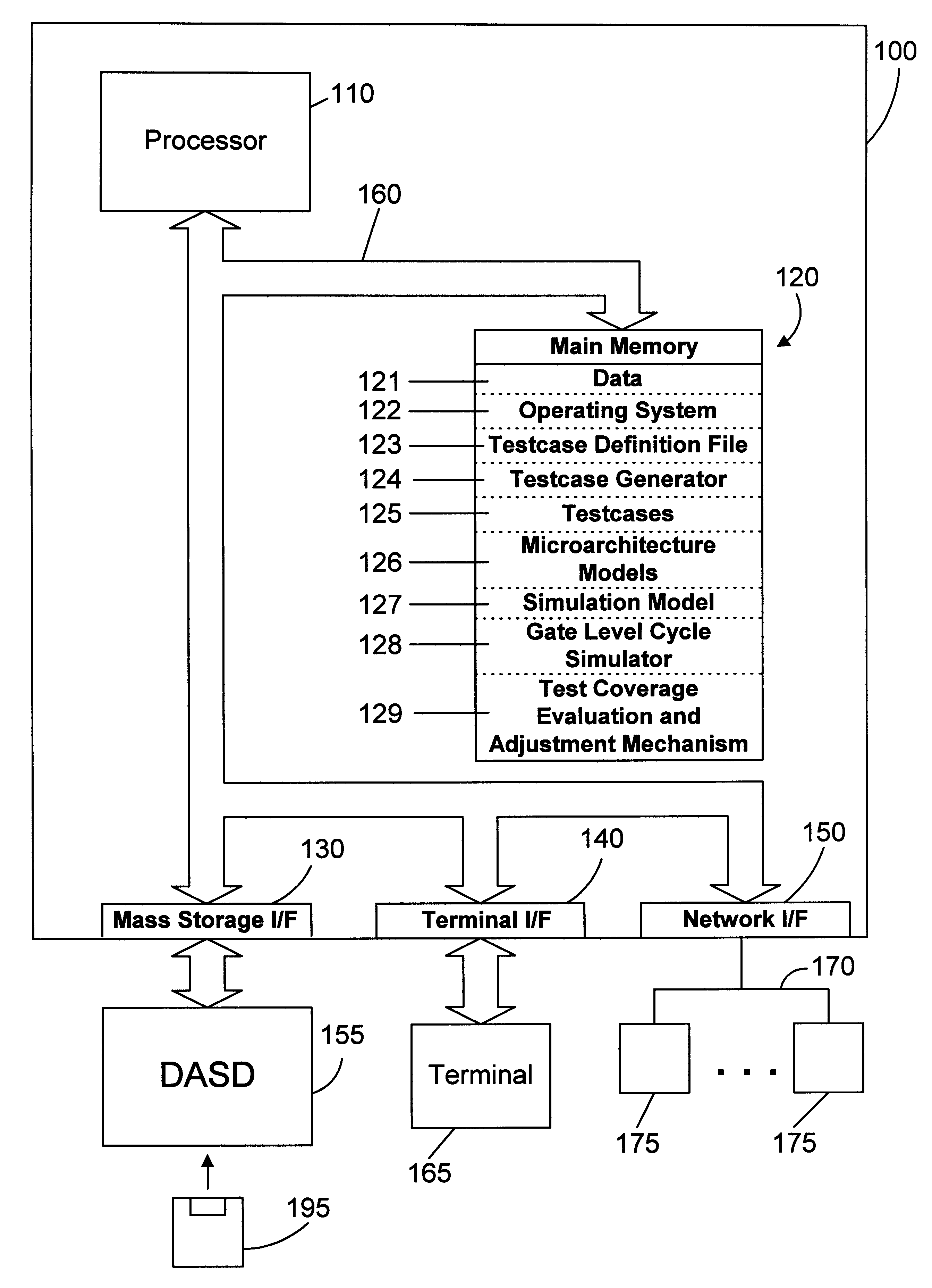
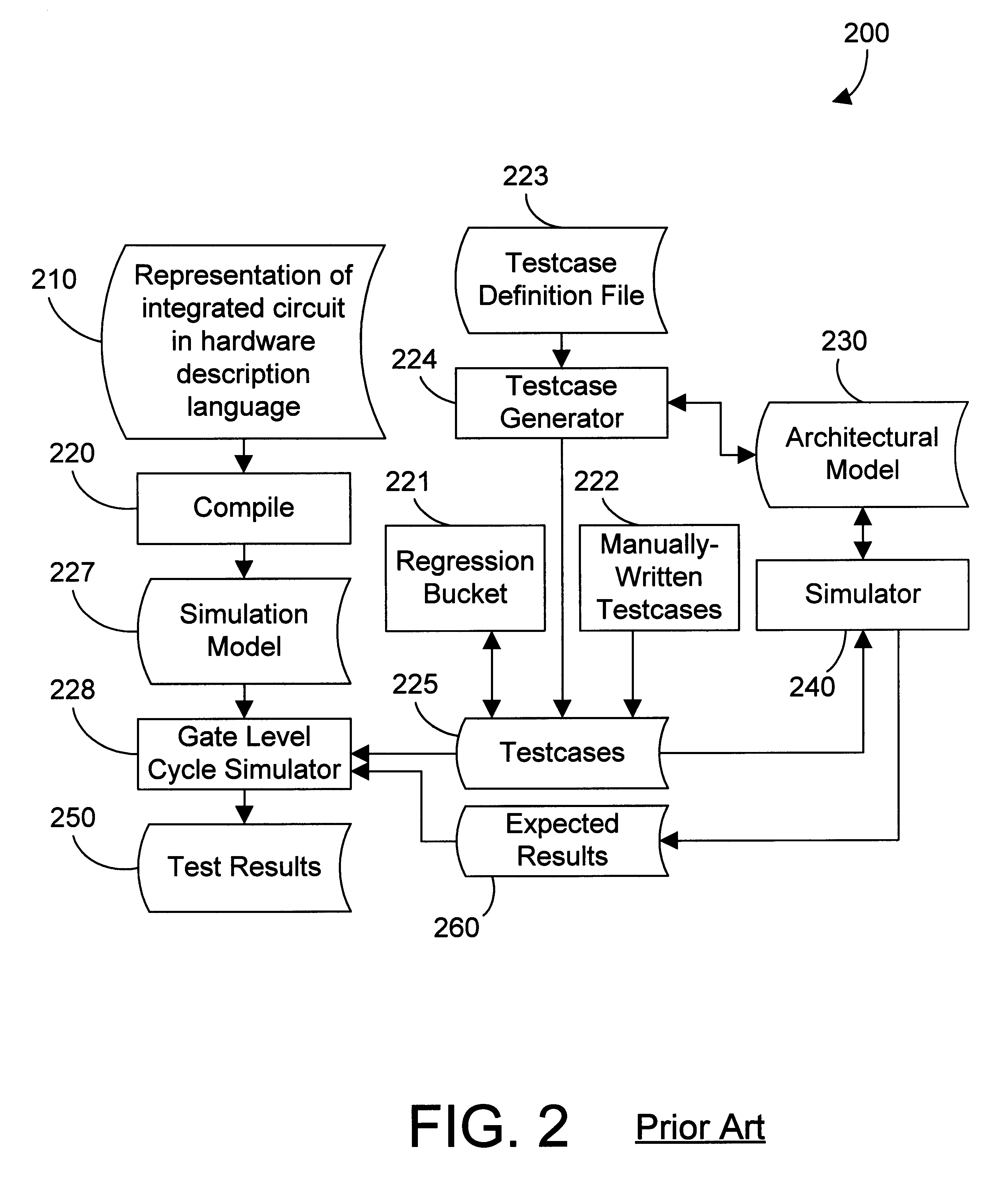
Integrated circuit test coverage evaluation and adjustment mechanism and method
InactiveUS6212667B1Reduce decreaseElectronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareDesign testingMicroarchitecture
Testcases are run to test the design of an integrated circuit. The coverage of the testcases is evaluated and compared against one or more microarchitecture models that define the behavior of a portion of the integrated circuit. If the coverage of the testcases is not adequate, new testcases are generated to test the previously untested behavior specified in the microarchitecture models.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Statically speculative memory accessing
ActiveUS6970985B2Reduce energy consumptionReduce complexityEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingRunning timeMicroarchitecture
A processor framework includes a compiler which compiles a computer program, the compiler extracting speculative static information about memory accesses during compilation, and a microarchitecture which performs a memory access using the speculative static information extracted during compiling. An instruction set architecture encodes information about accessing the memory at run time and selects access mechanisms to perform an individual memory access.
Owner:CSABA ANDRAS MORITZ PHD +1
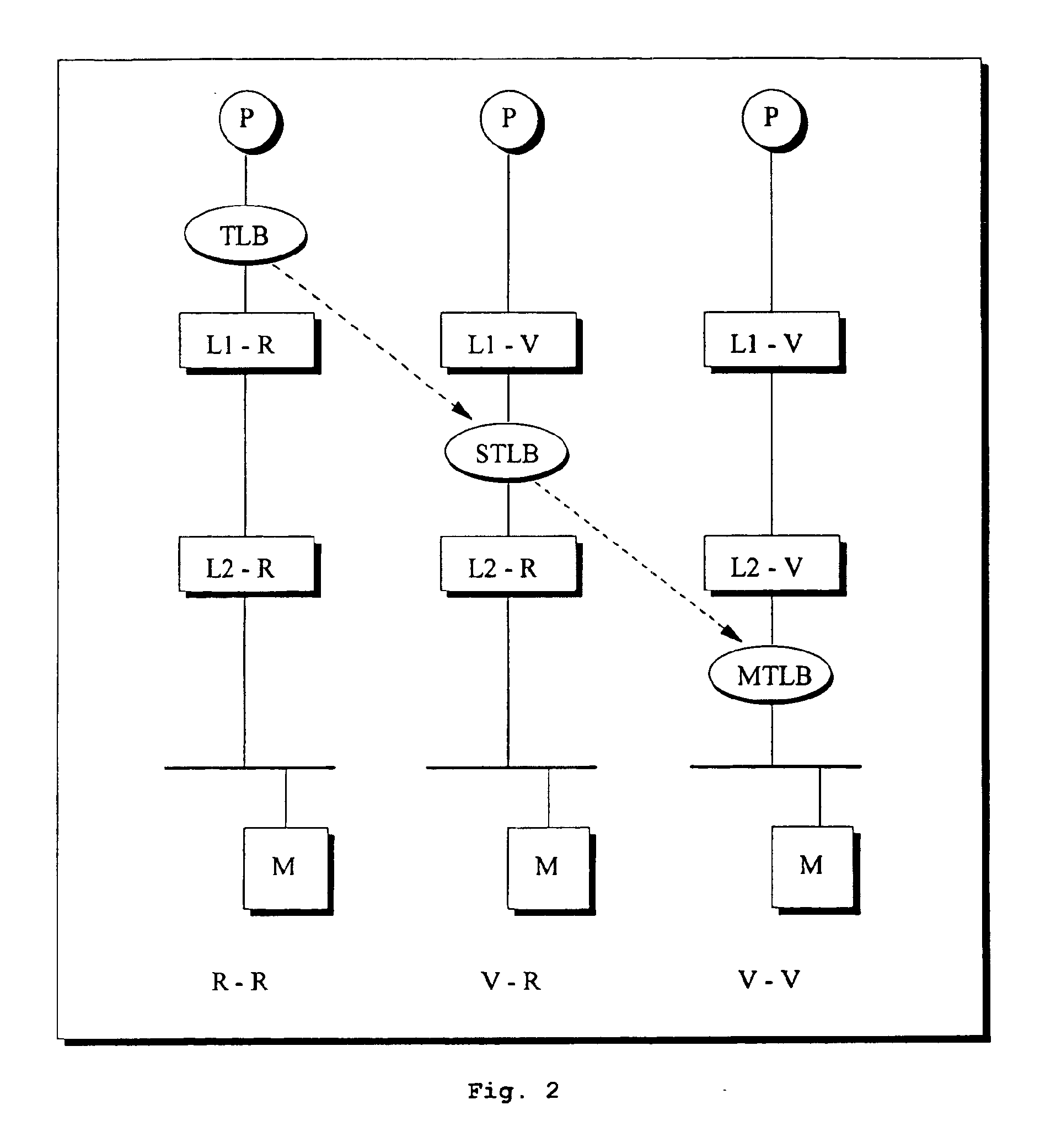
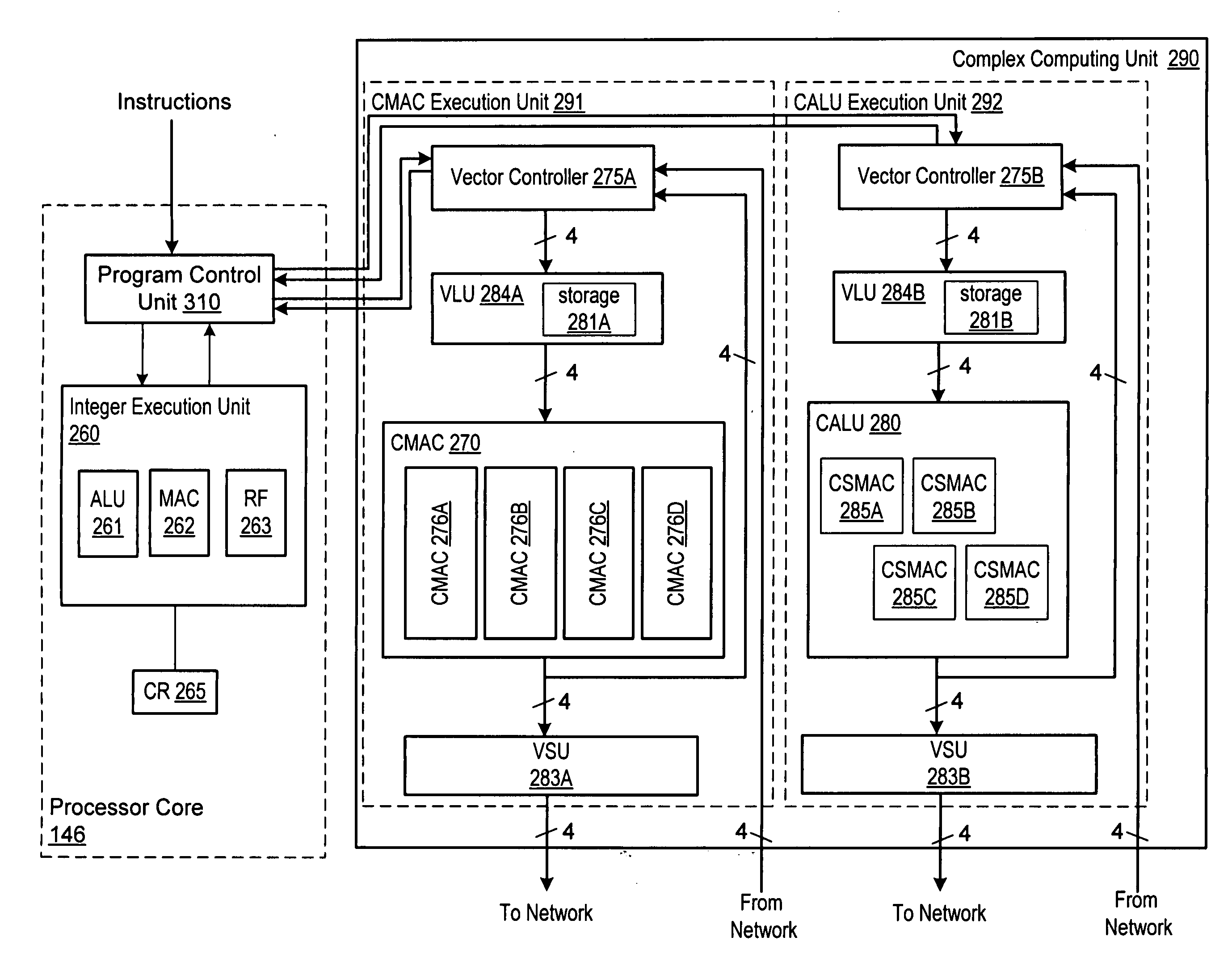
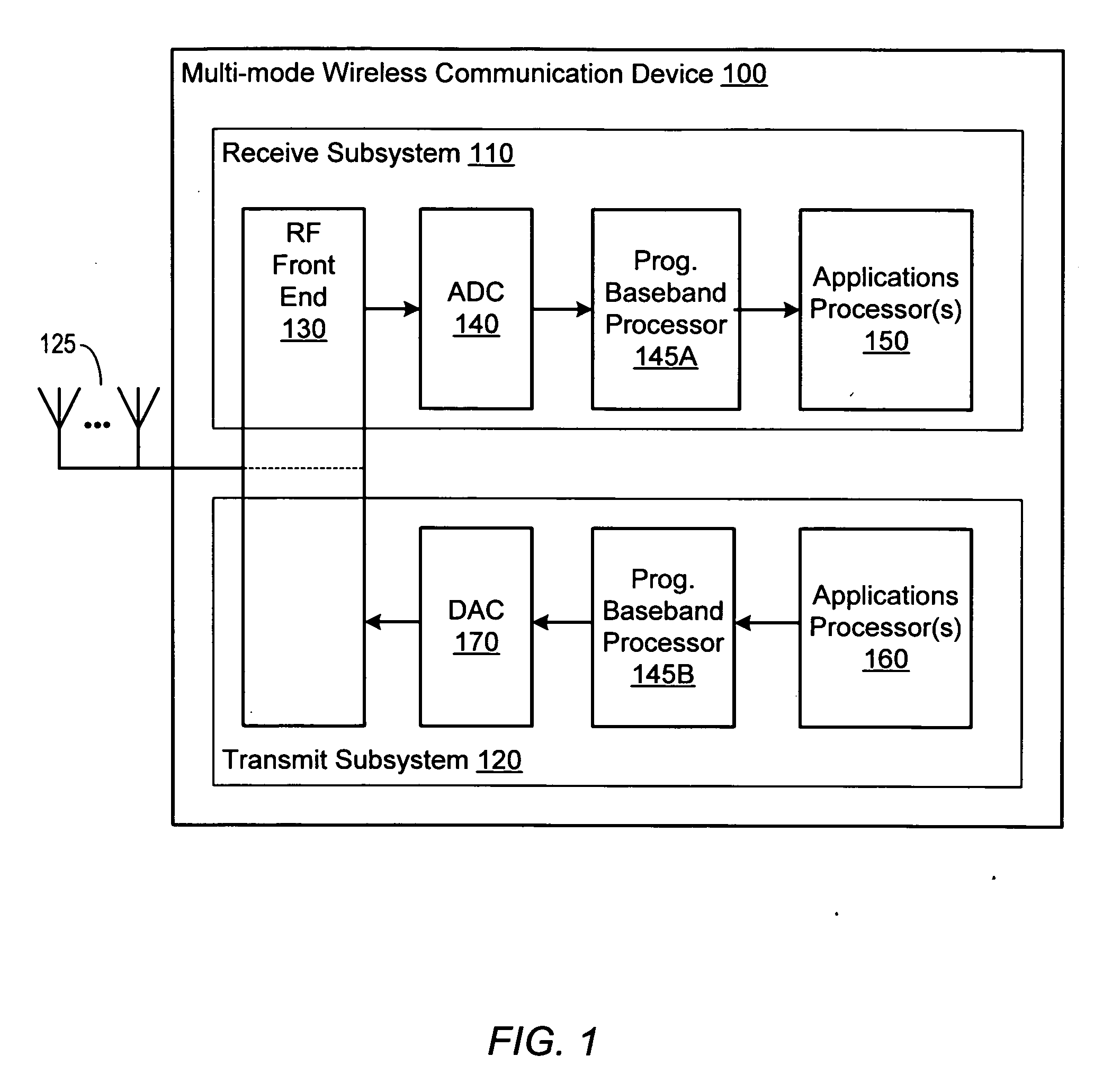
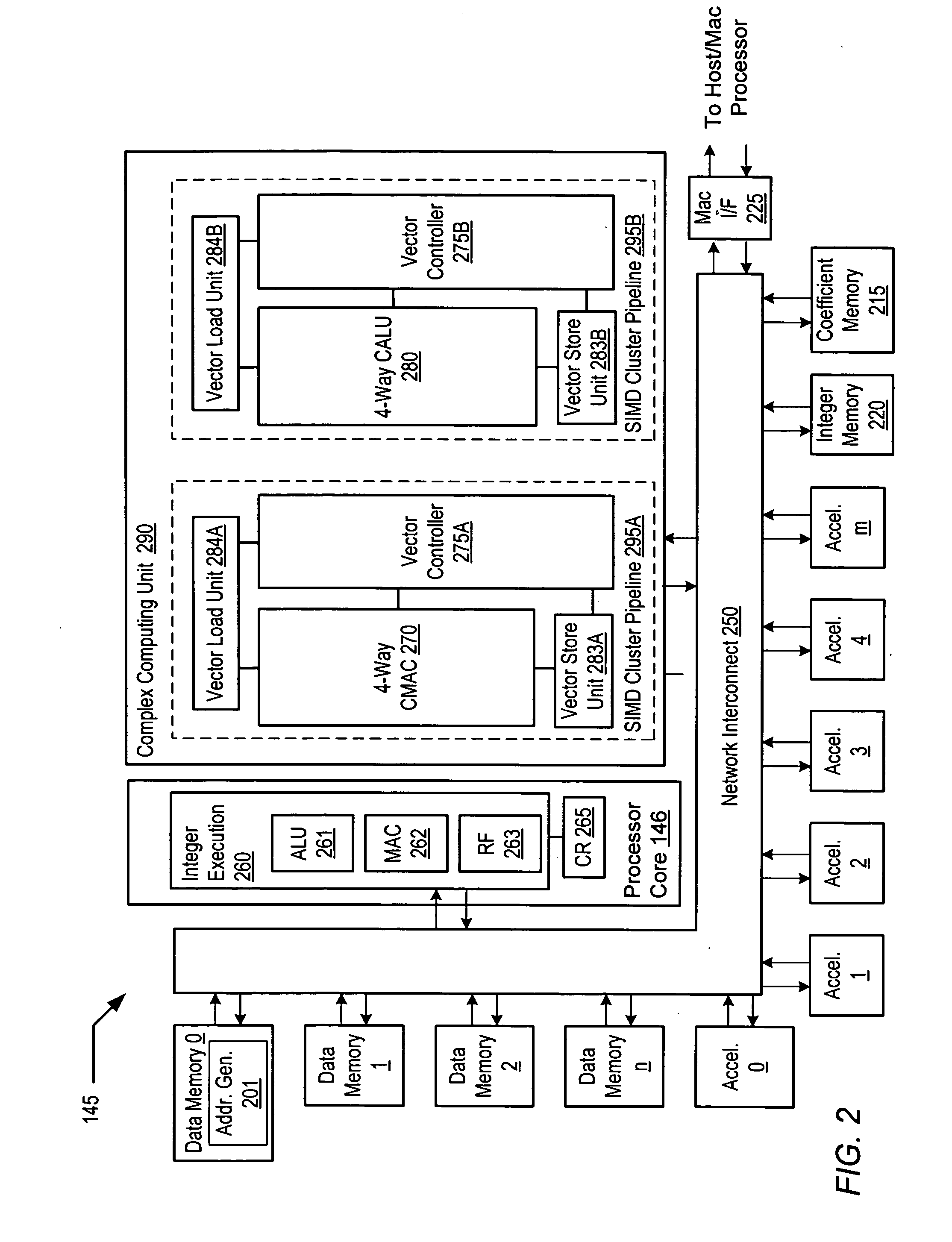
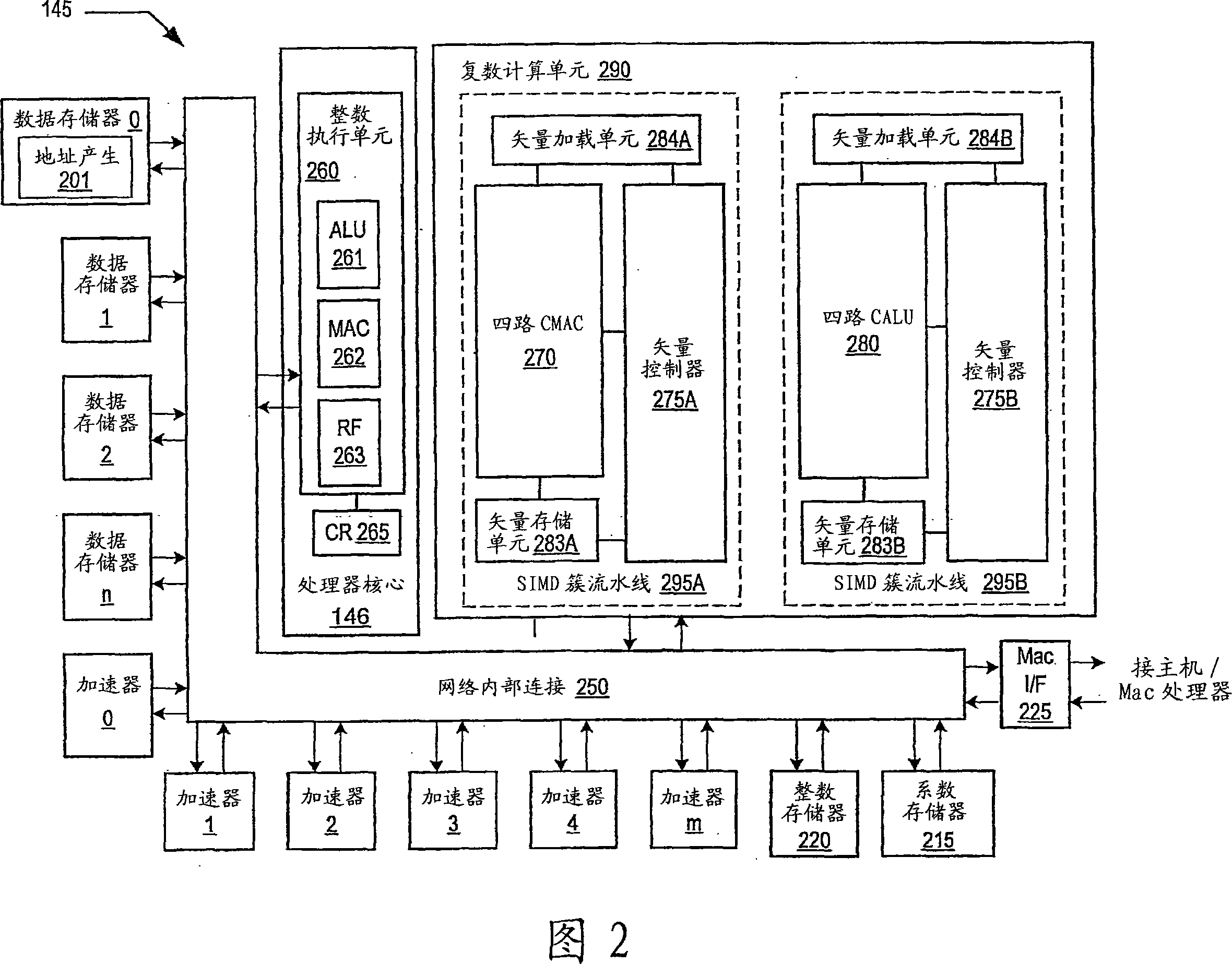
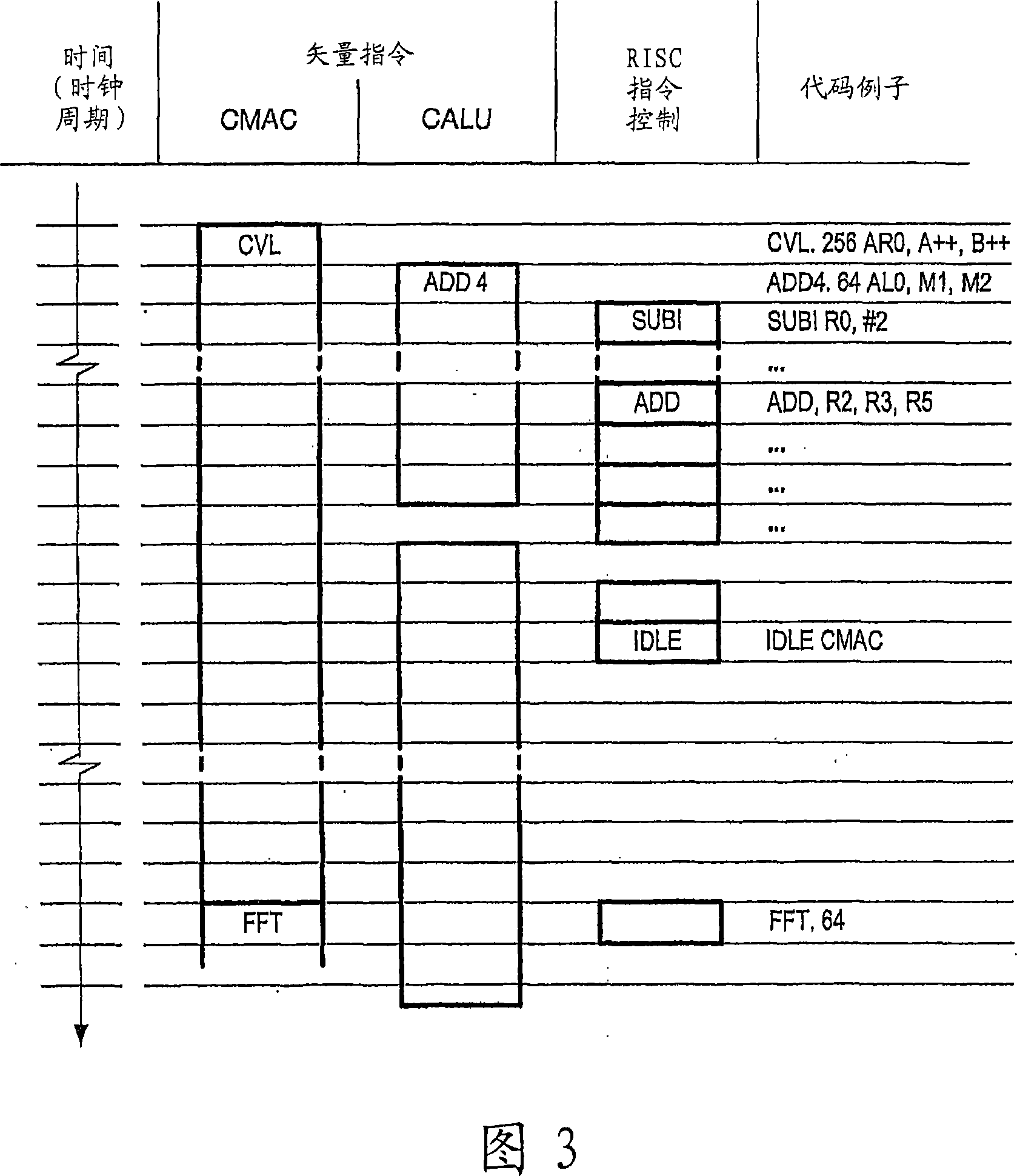
Programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture configured to execute complex vector instructions
ActiveUS20060271764A1General purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsArithmetic logic unitLine tubing
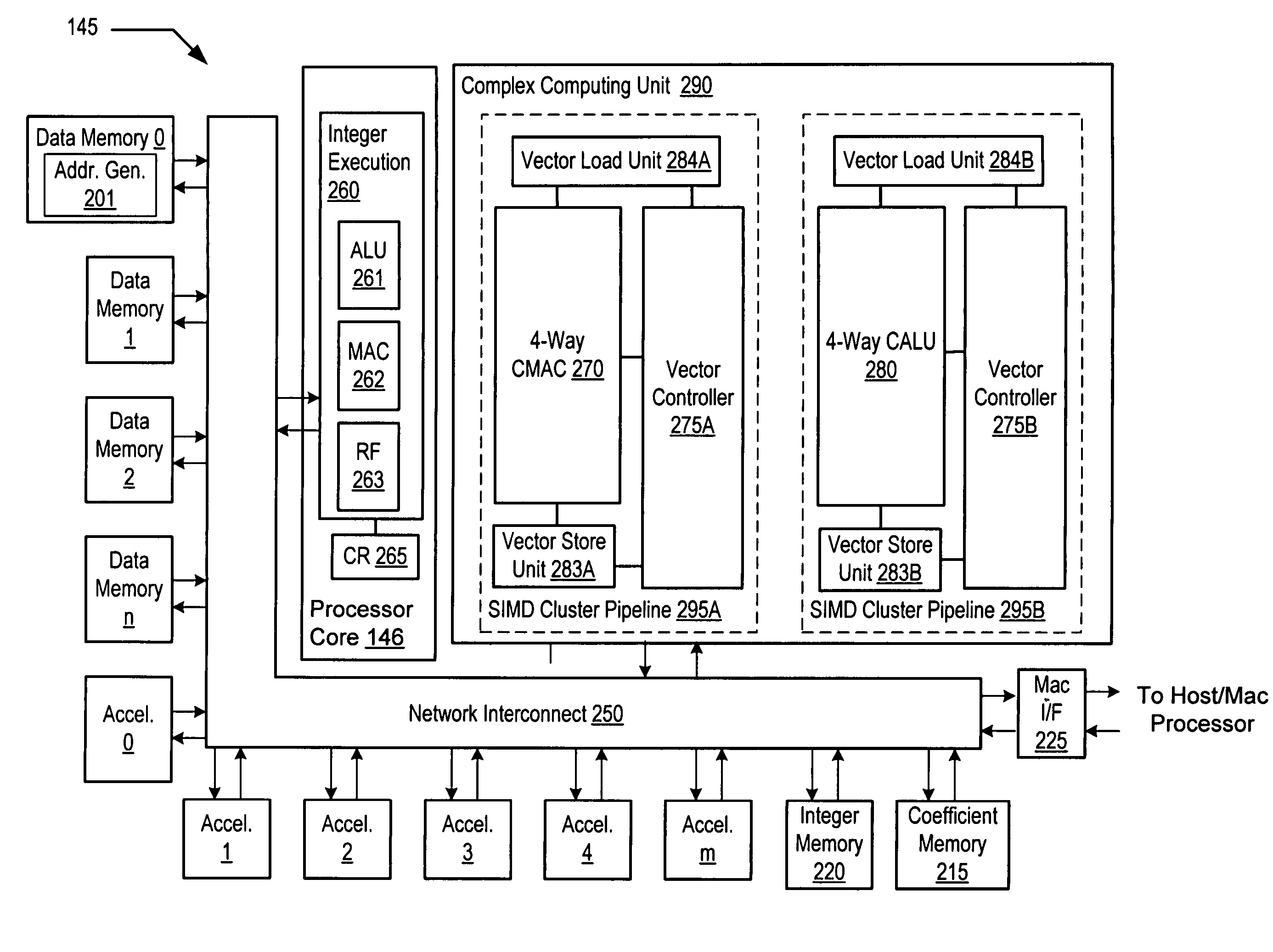
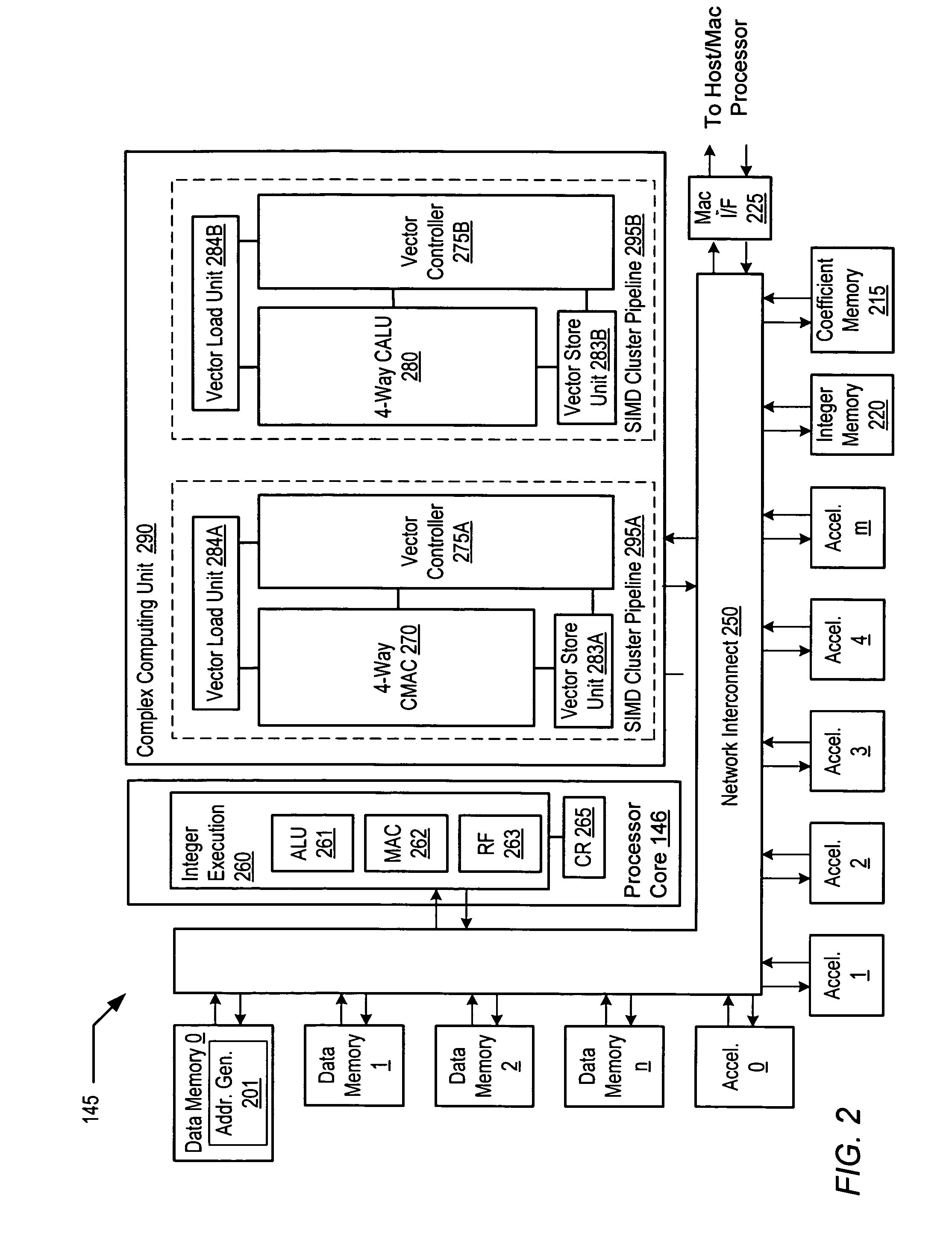
A programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture includes a plurality of accelerator units, a processor core and a complex computing unit. Each of the accelerator units may be configured to perform one or more dedicated functions. The processor core includes an integer execution unit that may be configured to execute integer instructions. The complex computing unit may be configured to execute complex vector instructions. The complex computing unit may include a first and a second clustered execution pipeline. The first clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex arithmetic logic unit datapaths configured to execute first complex vector instructions. The second clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex multiplier accumulator datapaths configured to execute second complex vector instructions.
Owner:CORESONIC AB
Vaginal matrices: nanofibers for contraception and prevention of HIV infection
Described are drug delivery systems incorporating electrospun fibers that comprise and deliver physicochemically diverse drug compounds. Such fibers provide significant advantages in drug agent release, such as adaptability for solid dosage delivery to mucosal tissues. This is in addition to allowing for controlled drug release. Systems and methods for large-scale electrospinning productivity are described, including novel microarchitectures allowing for variable pharmacokinetics in drug release.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
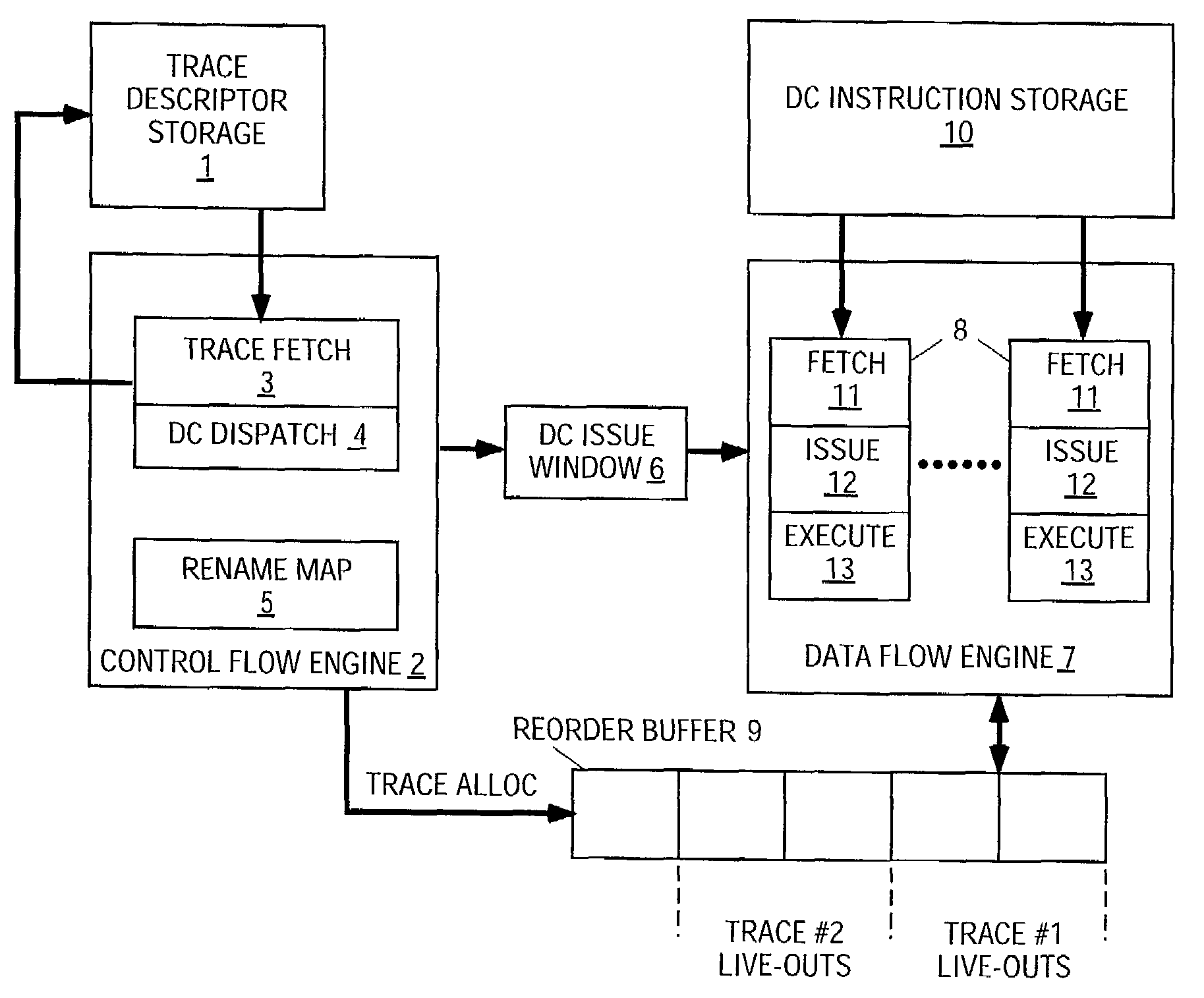
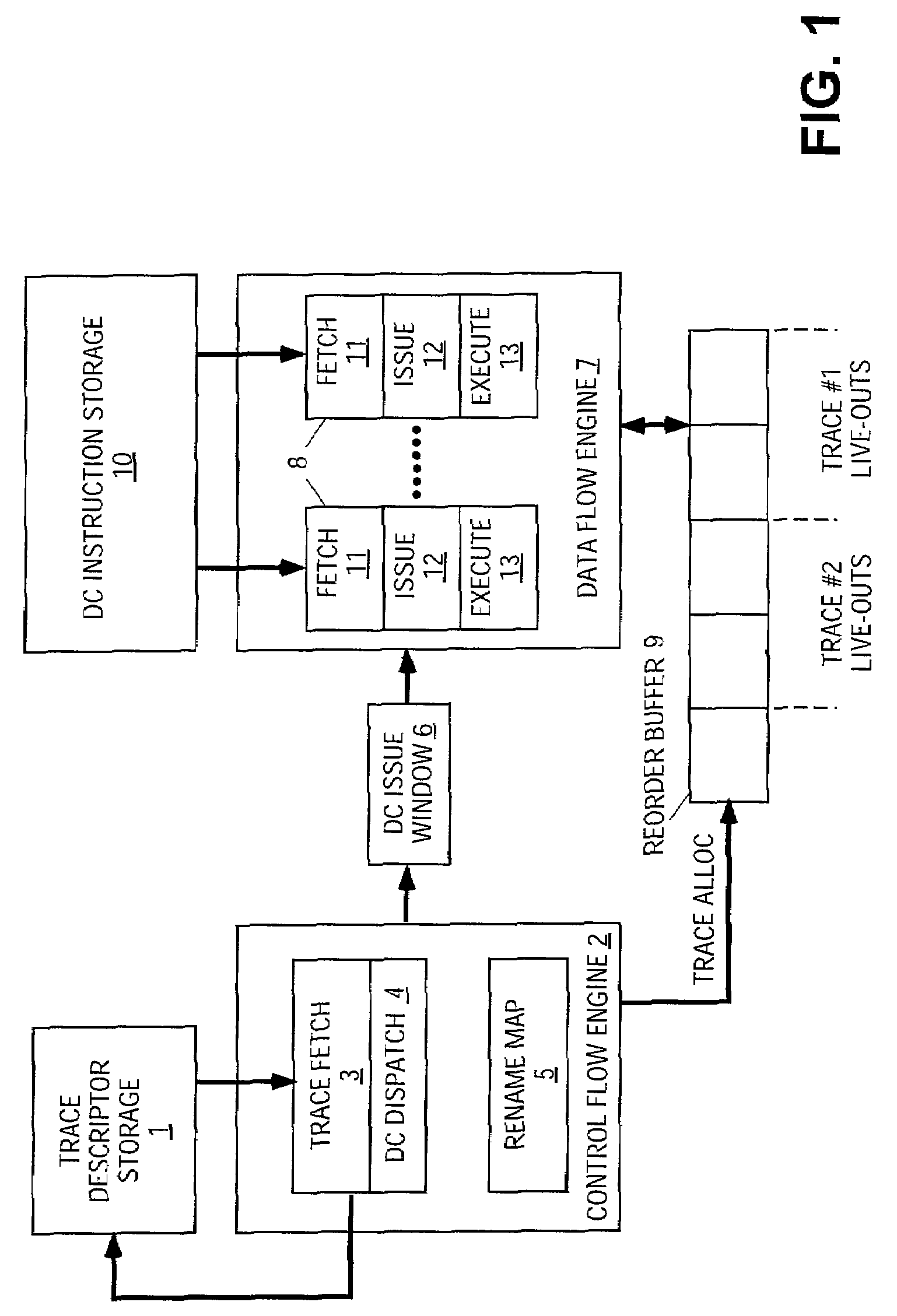
Dependence-chain processing using trace descriptors having dependency descriptors
InactiveUS7363467B2Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionProgram segmentData stream
An apparatus and method for a processor microarchitecture that quickly and efficiently takes large steps through program segments without fetching all intervening instructions. The microarchitecture processes descriptors of trace sequences in program order so as to locate and dispatch descriptors of dependence chains that are used to fetch and execute the instructions of the dependence chain in data flow order.
Owner:INTEL CORP
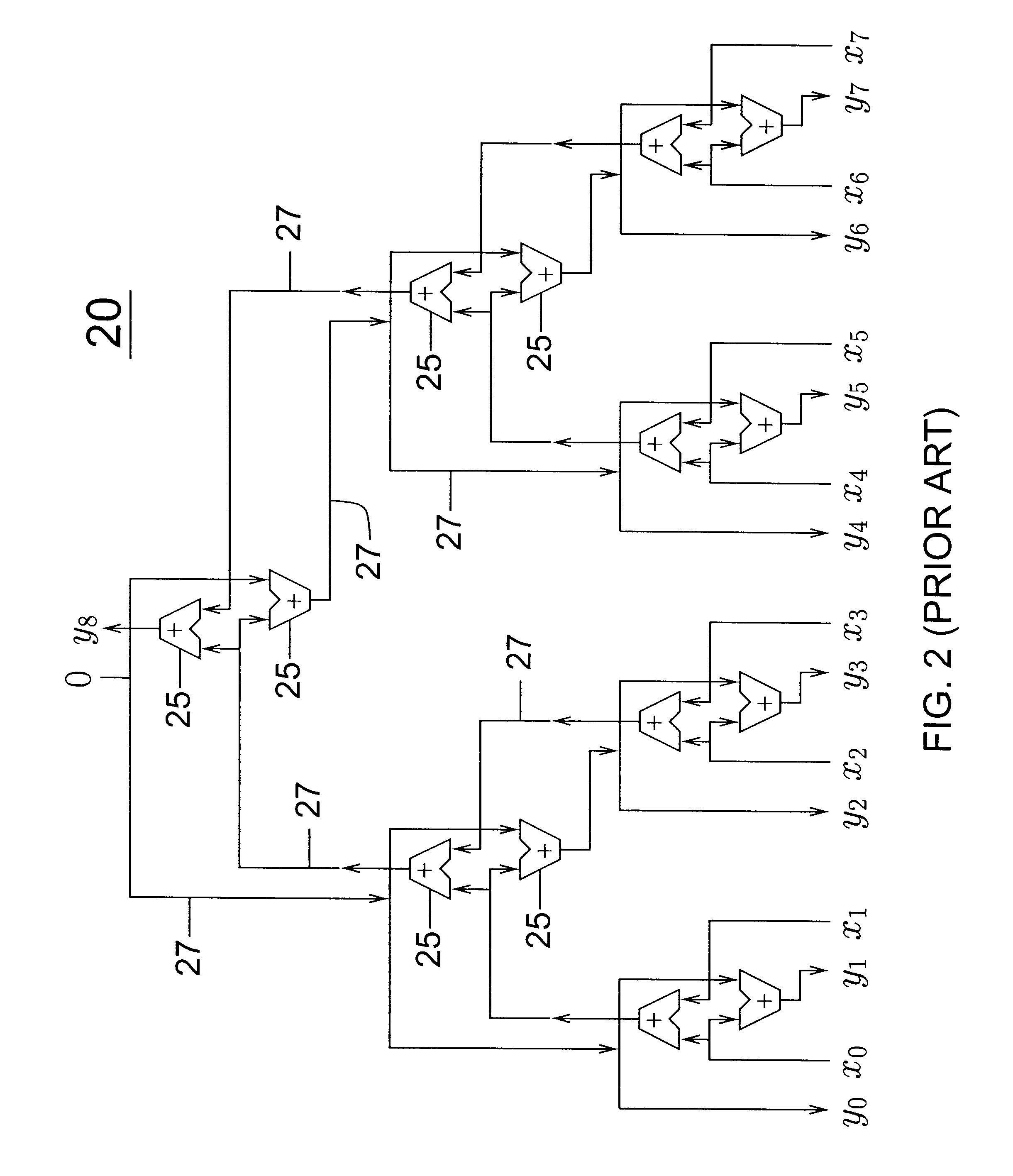
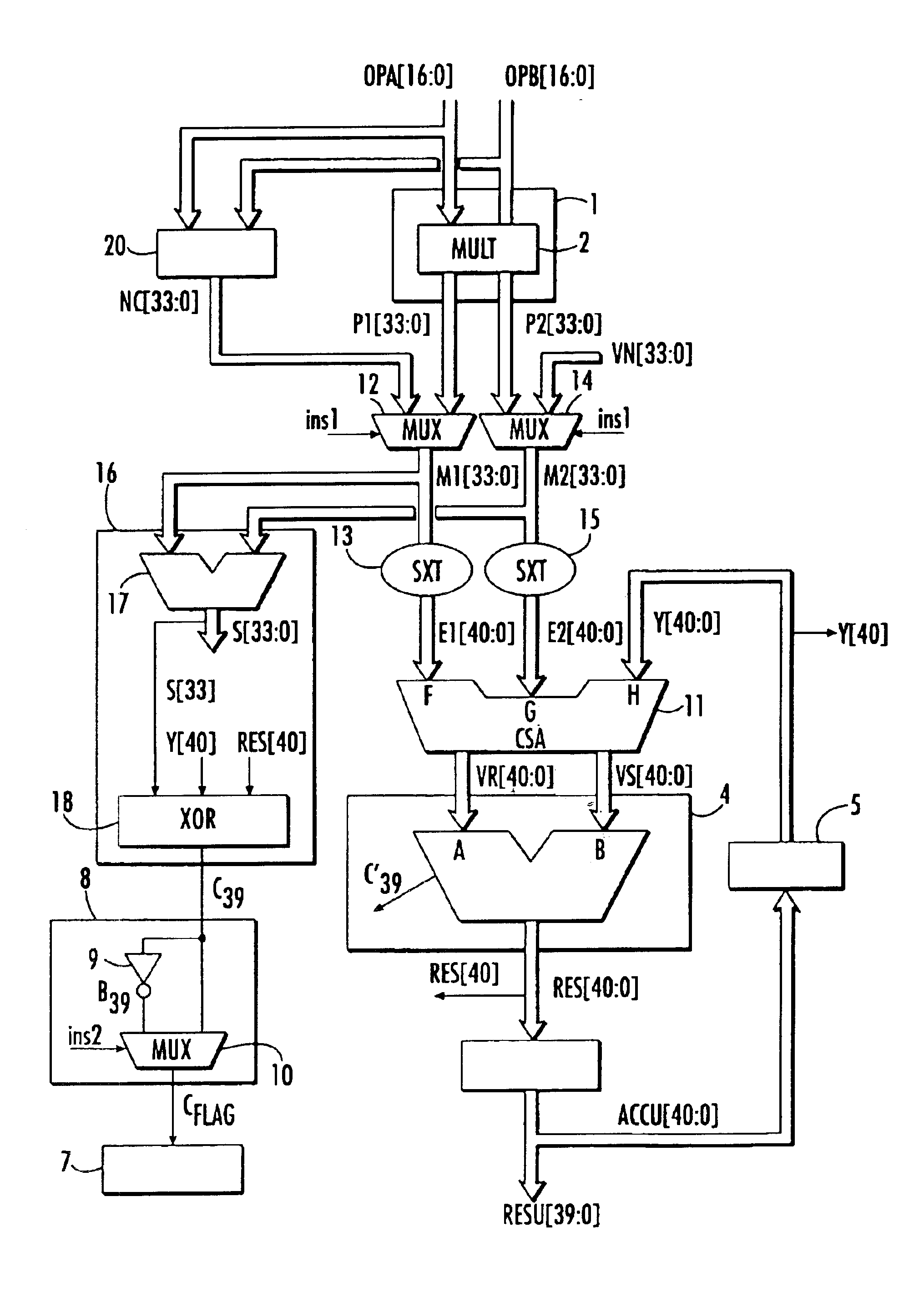
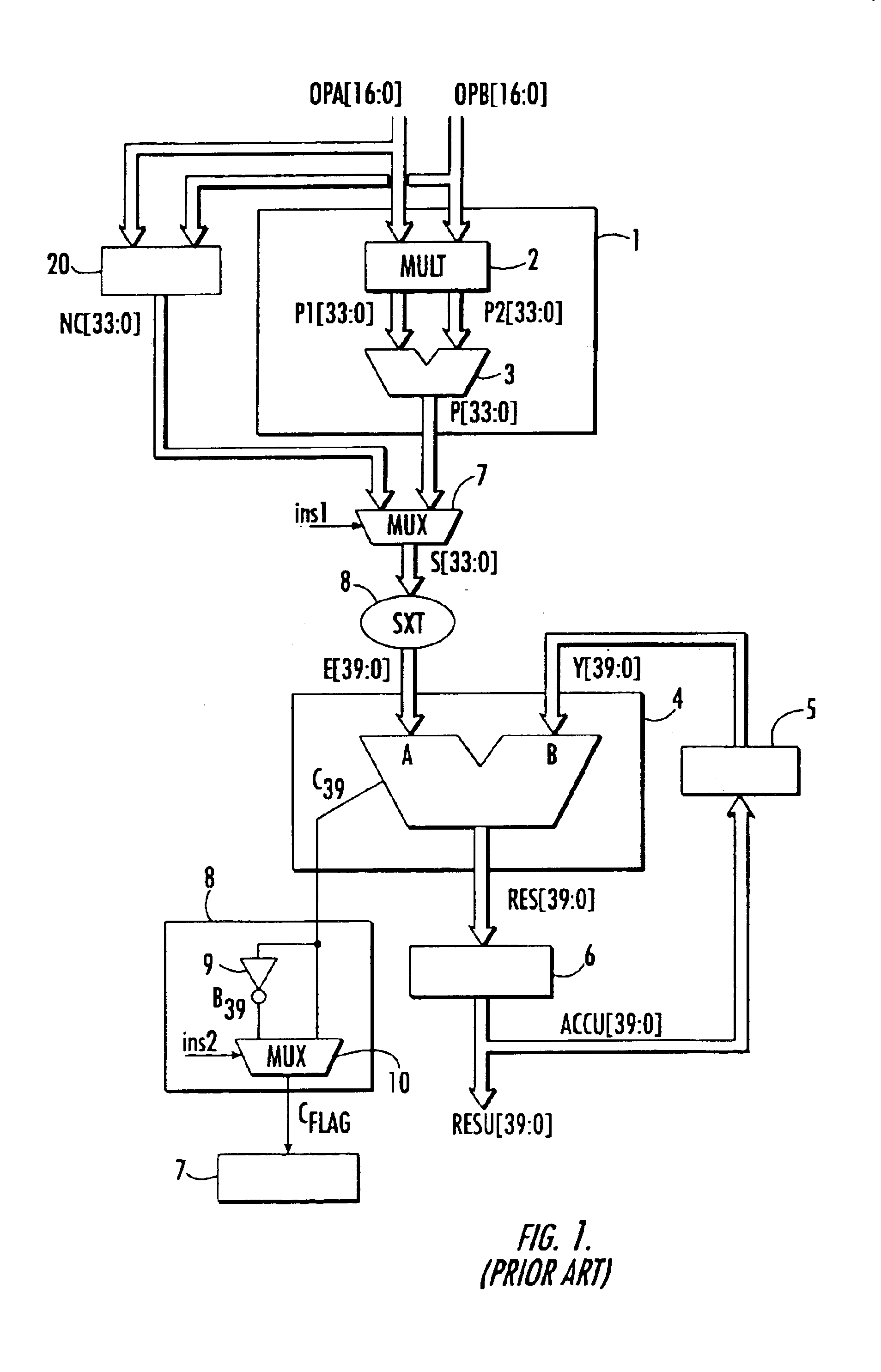
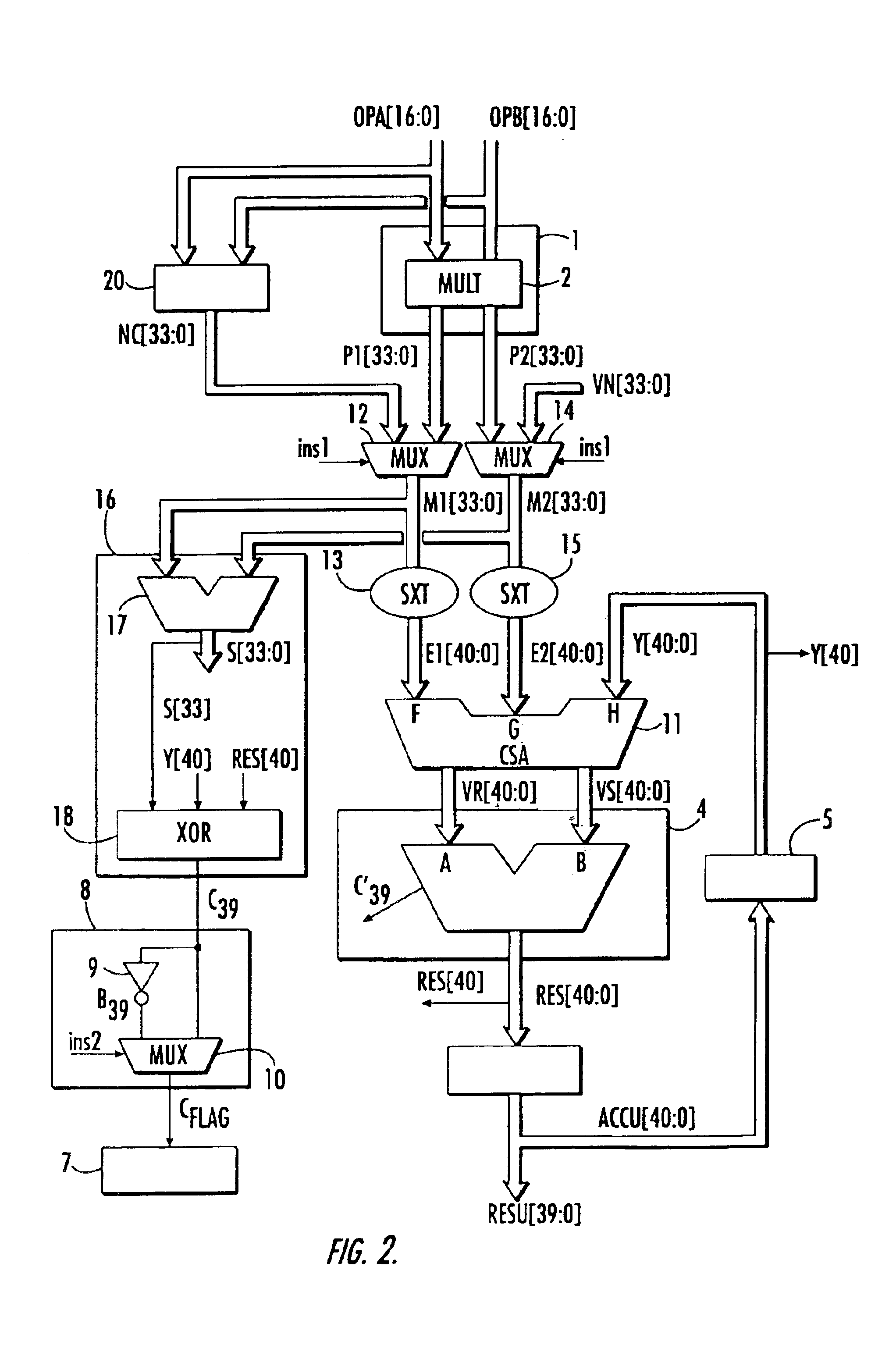
Microarchitecture of an arithmetic unit
The microarchitecture of the arithmetic unit includes two cascaded N bit adders to provide an N bits result in an accumulator. The arithmetic unit also includes a carry save adder, followed by an adder, which, along with the accumulator, are extended to N+1 bits. A circuit for determining the output carry value associated with the result is also provided.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Complex vector executing clustered SIMD micro-architecture DSP with accelerator coupled complex ALU paths each further including short multiplier/accumulator using two's complement
ActiveUS7299342B2General purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsArithmetic logic unitExecution unit
A programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture includes a plurality of accelerator units, a processor core and a complex computing unit. Each of the accelerator units may be configured to perform one or more dedicated functions. The processor core includes an integer execution unit that may be configured to execute integer instructions. The complex computing unit may be configured to execute complex vector instructions. The complex computing unit may include a first and a second clustered execution pipeline. The first clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex arithmetic logic unit datapaths configured to execute first complex vector instructions. The second clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex multiplier accumulator datapaths configured to execute second complex vector instructions.
Owner:CORESONIC AB
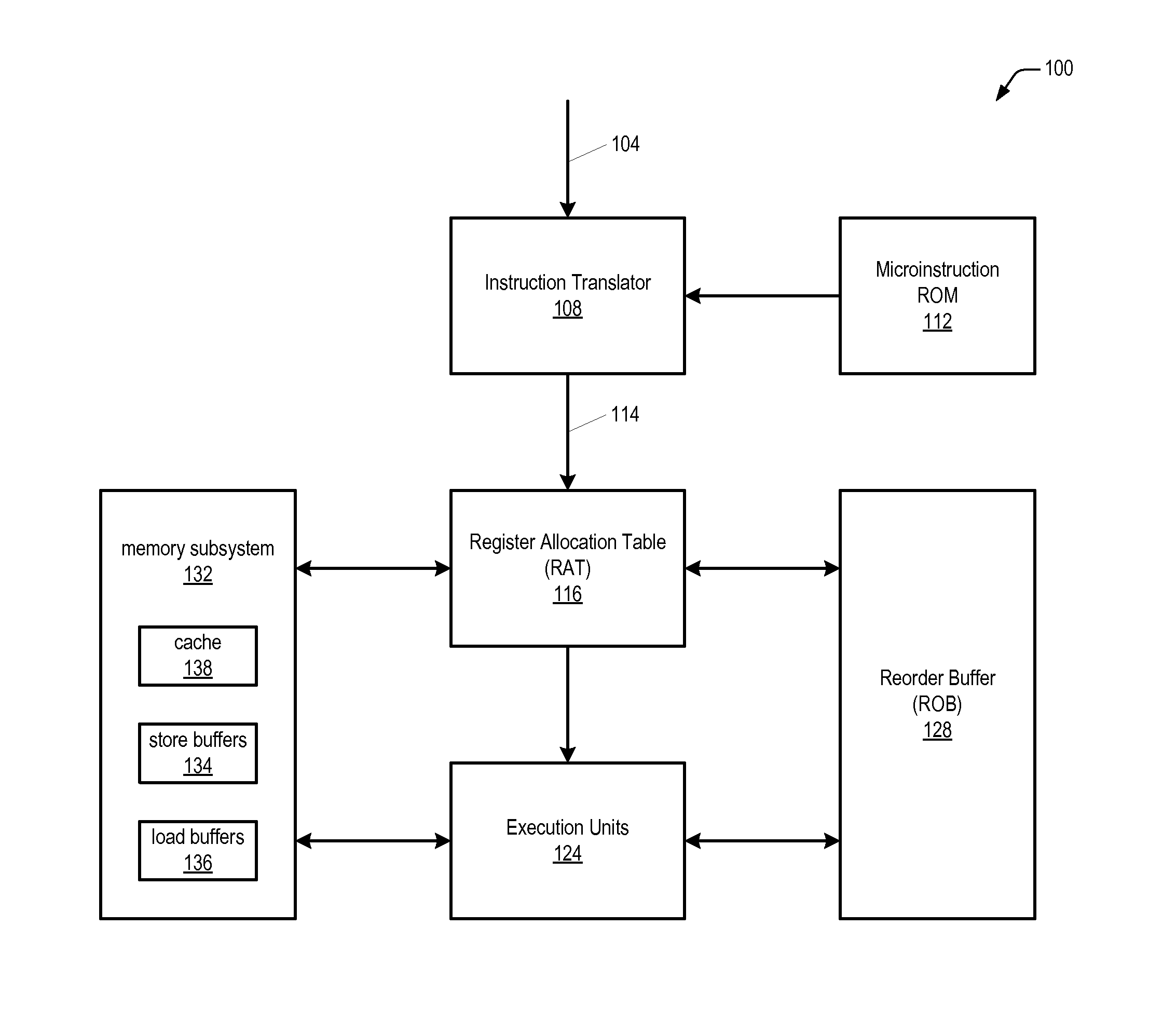
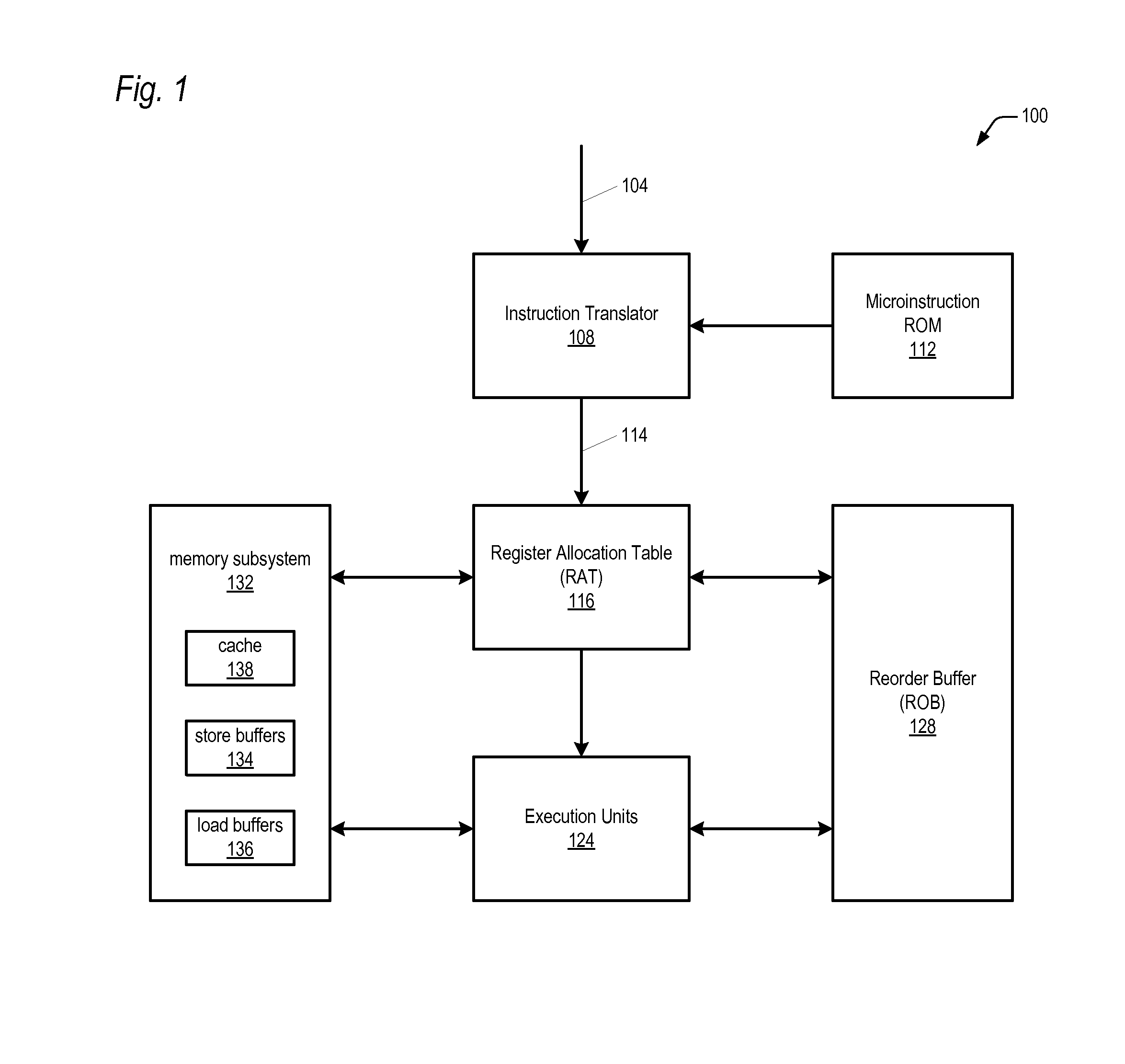
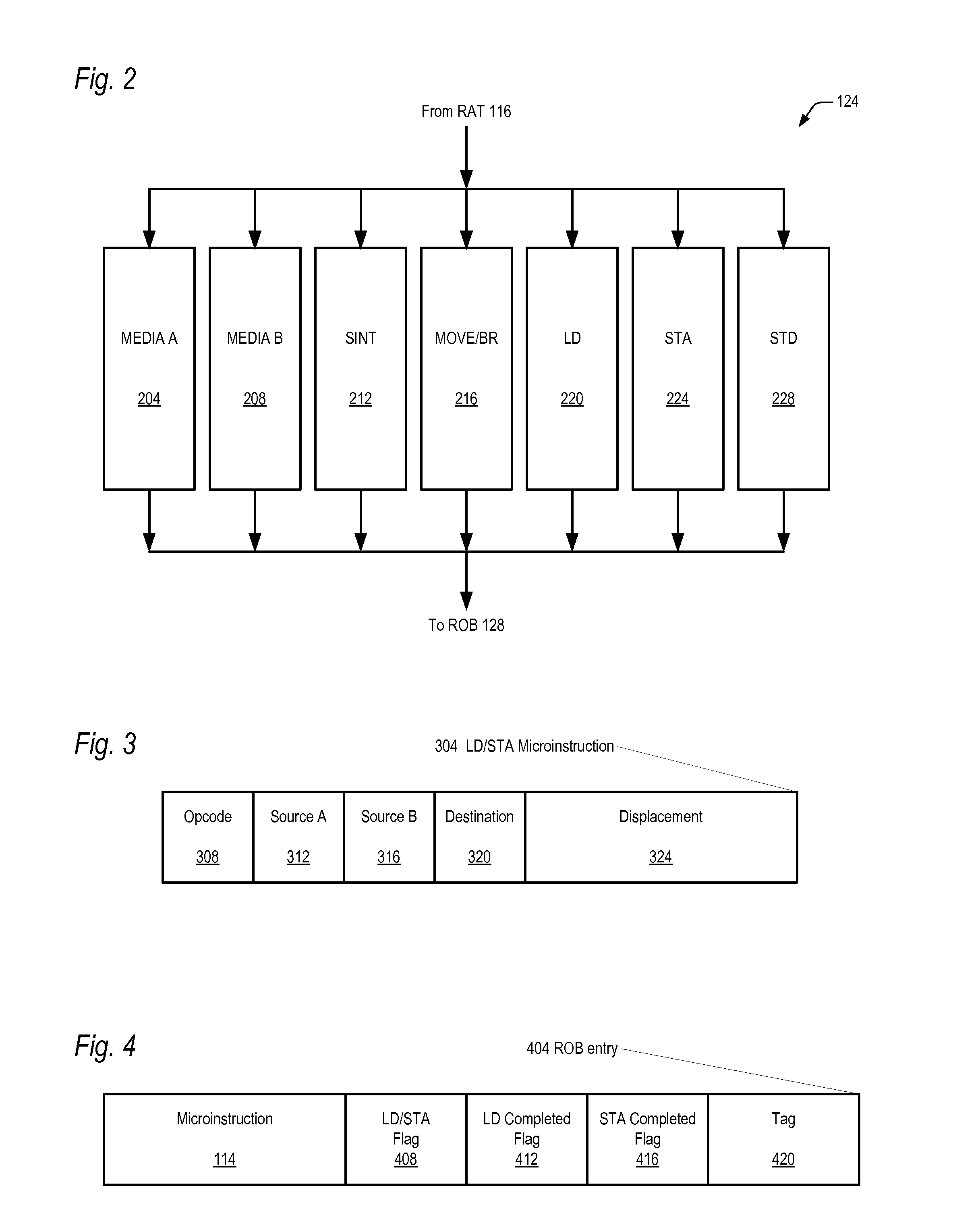
Microprocessor with microarchitecture for efficiently executing read/modify/write memory operand instructions
ActiveUS20090204800A1Reduce power consumptionImprove bindingRuntime instruction translationDigital computer detailsLogical operationsOperand
The microprocessor includes an instruction translator that translates a macroinstruction of a macroinstruction set in its macroarchitecture into exactly three microinstructions to perform a read / modify / write operation on a memory operand. The first microinstruction instructs the microprocessor to load the memory operand into the microprocessor from a memory location and to calculate a destination address of the memory location. The second microinstruction instructs the microprocessor to perform an arithmetic or logical operation on the loaded memory operand to generate a result. The third microinstruction instructs the microprocessor to write the result to the memory location whose destination address is calculated by the first microinstruction. A first execution unit receives the first microinstruction and responsively loads the memory operand into the microprocessor from the memory location, and a second distinct execution unit also receives the first microinstruction and responsively calculates the destination address of the memory location.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Three-dimensional fabrication of biocompatible structures in anatomical shapes and dimensions for tissue engineering and organ replacement
InactiveUS7718351B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorosityHosting environment
Methods and apparatuses involving biocompatible structures for tissue engineering and organ replacement and, more specifically, biocompatible structures formed by three-dimensional fabrication, are described. In some embodiments, the biocompatible structures are scaffolds for cells that can be used as tissue engineering templates and / or as artificial organs. The structures may be three-dimensional and can mimic the shapes and dimensions of tissues and / or organs, including the microarchitecture and porosities of the tissues and organs. Pores in the structure may allow delivery of molecules across the structure, and may facilitate cell migration and / or generation of connective tissue between the structure and its host environment. Structures of the invention can be implanted into a mammal and / or may be used ex vivo as bioartificial assist devices.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
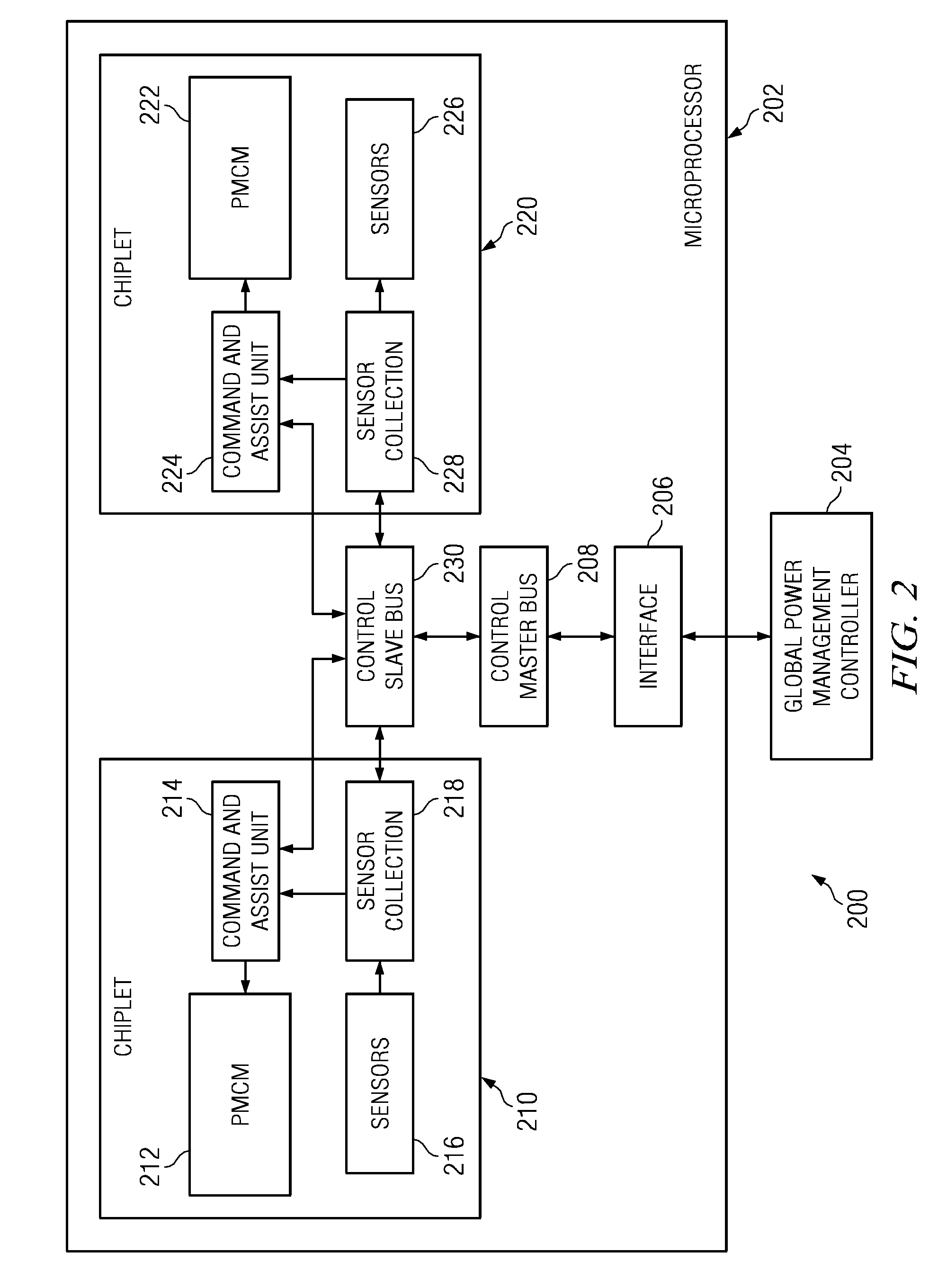
Method and system of multi-core microprocessor power management and control via per-chiplet, programmable power modes
A computer-implemented method and a system for managing power in a multi-core microprocessor are provided. A power management control microarchitecture in a chiplet translates a first command comprising a power setting. A chiplet comprises a processor core and associated memory cache. The power management control microarchitecture comprises power mode registers, power mode adjusters, translators, and microarchitectural power management techniques. The power management control microarchitecture sets microarchitectural power management techniques according to the power setting. The global power management controller issues the first command. The global power management controller may reside either on or off of the microprocessor. The global power management controller issues commands either directly for a specific chiplet out of the plurality of chiplets or to the plurality of chiplets and the control slave bus translates the command into sub-commands dedicated to specific chiplets within the plurality of chiplets. Each chiplet may be set to separate power levels.
Owner:IBM CORP
Programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture configured to execute complex vector instructions
InactiveCN101238455AProgram controlArchitecture with single central processing unitArithmetic logic unitLogic cell
Owner:CORESONIC AB
Multiple clock domain microprocessor
ActiveUS7089443B2Increase the number ofHigh frequencyEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingComputer hardwareHemt circuits
A multiple clock domain (MCD) microarchitecture uses a globally-asynchronous, locally-synchronous (GALS) clocking style. In an MCD microprocessor each functional block operates with a separately generated clock, and synchronizing circuits ensure reliable inter-domain communication. Thus, fully synchronous design practices are used in the design of each domain.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Multiple clock domain microprocessor
ActiveUS20050060597A1High frequencyMaintain designEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingComputer scienceInter-domain
A multiple clock domain (MCD) microarchitecture uses a globally-asynchronous, locally-synchronous (GALS) clocking style. In an MCD microprocessor each functional block operates with a separately generated clock, and synchronizing circuits ensure reliable inter-domain communication. Thus, fully synchronous design practices are used in the design of each domain.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
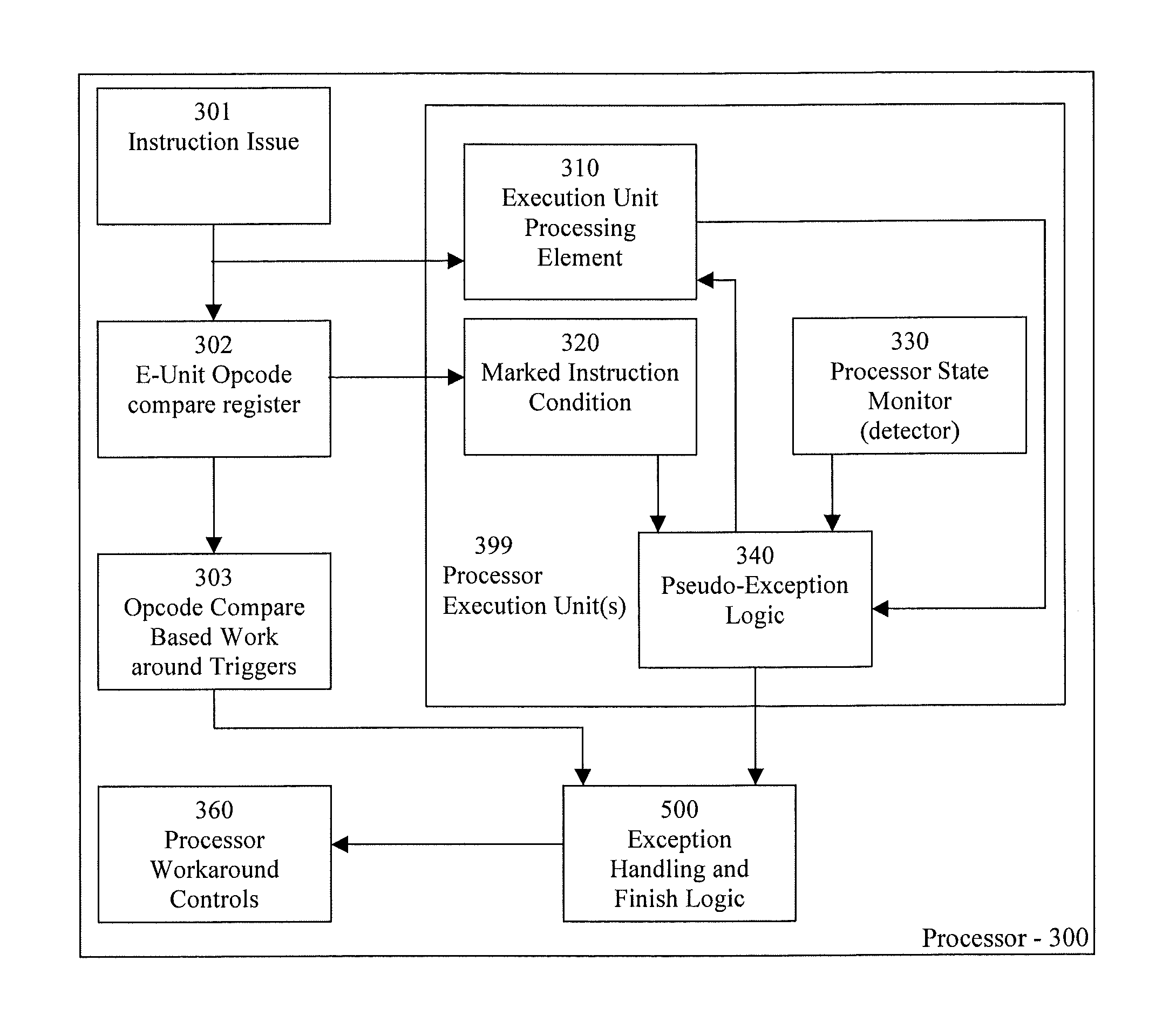
Processor and method for workaround trigger activated exceptions
InactiveUS20090210659A1Avoid processing defectsRuntime instruction translationDigital computer detailsWorkaroundMicroarchitecture
A processor includes a microarchitecture for working around a processing flaw, the microarchitecture including: at least one detector adapted for detecting a predetermined state associated with the processing flaw; and at least one mechanism to modify default processor processing behavior; and upon modification of processing behavior, the processing of an instruction involving the processing flaw can be completed by avoiding the processing flaw.
Owner:IBM CORP
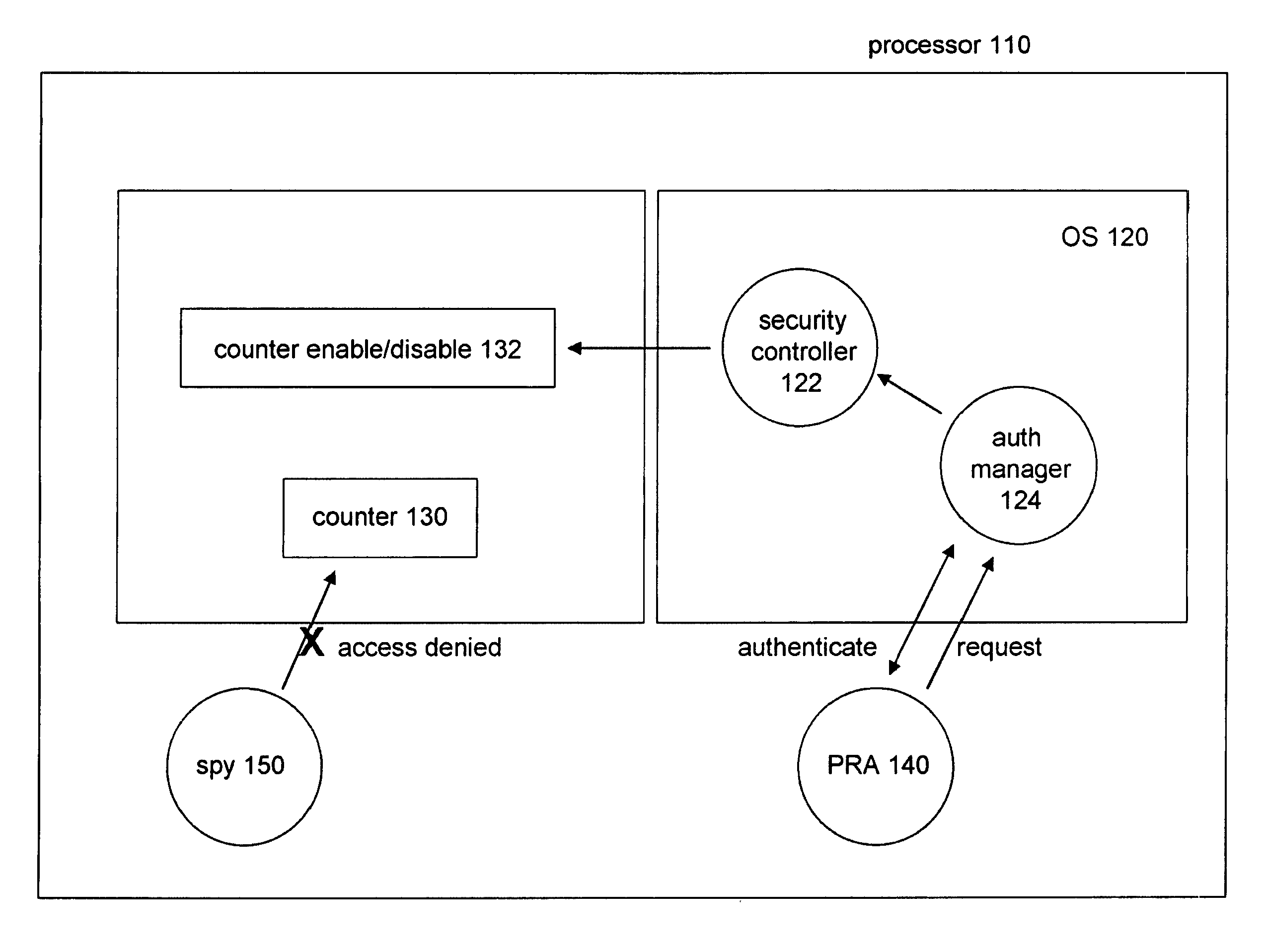
Mitigating Branch Prediction and Other Timing Based Side Channel Attacks
InactiveUS20080155679A1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionTimestampOperational system
To provide hardware protection against timing based side channel attacks, a processor's microarchitecture enables an OS to determine which applications have the privilege to read timestamp and performance counters. Using a white list of applications, and an authentication mechanism to authenticate applications, a legitimate Protection Required Application (PRA) may temporarily prevent other applications from reading timestamp and performance counters while it executes (or excutes sensitive operations).
Owner:INTEL CORP
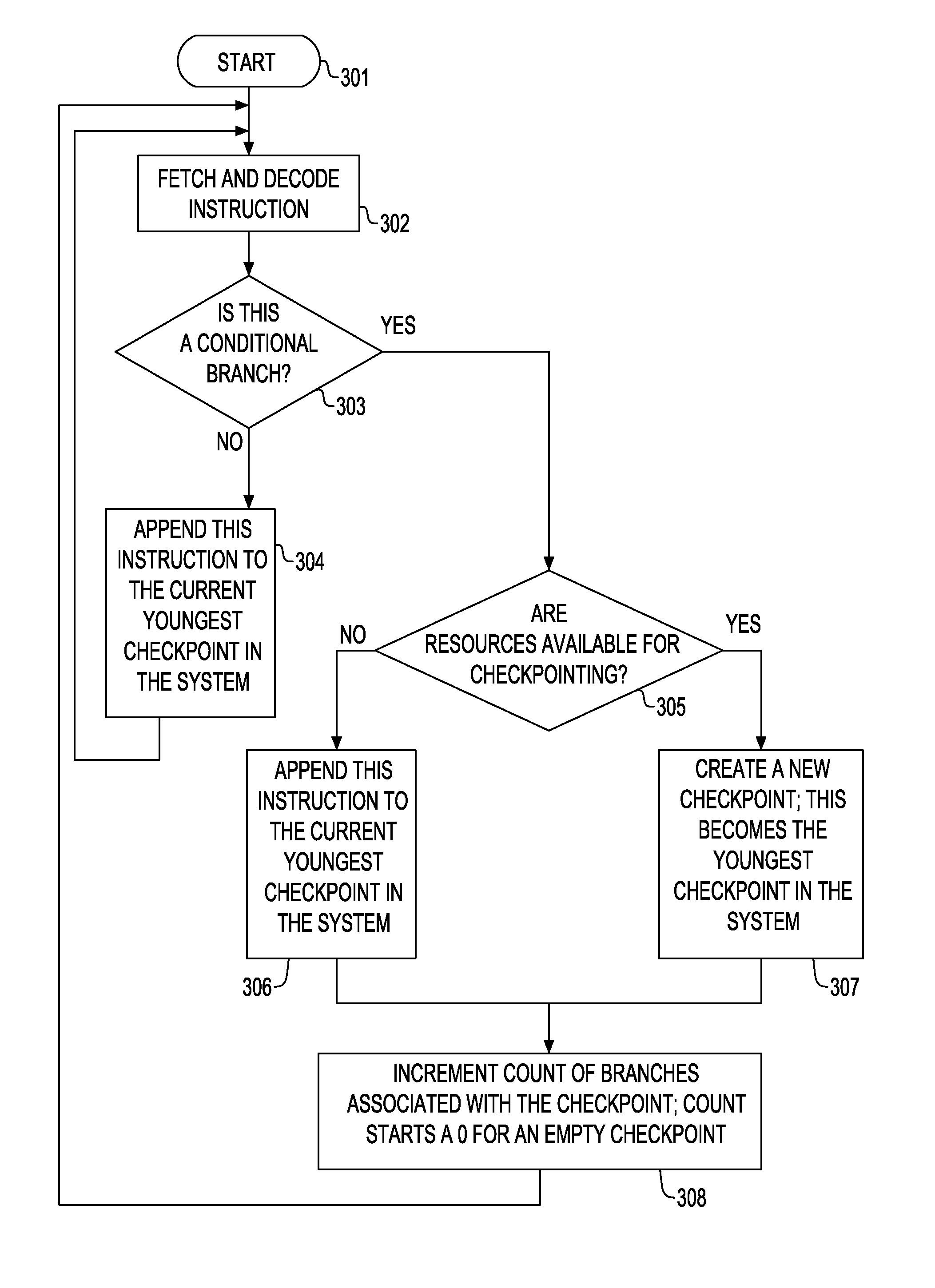
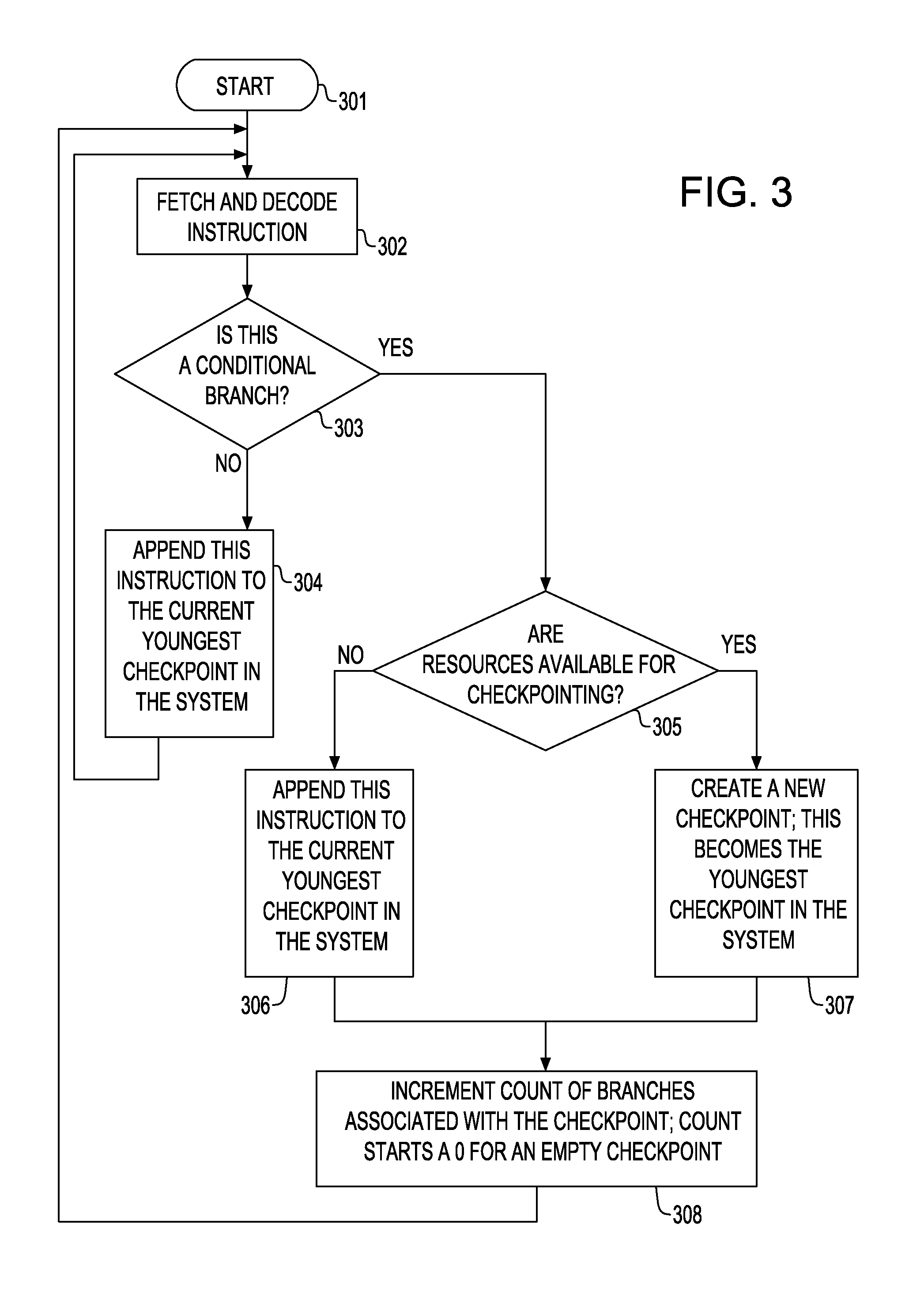
Out-of-Order Checkpoint Reclamation in a Checkpoint Processing and Recovery Core Microarchitecture
ActiveUS20140032884A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsOperating systemMicroarchitecture
Reclaiming checkpoints in a system in an order that differs from the order when the checkpoints are created. Reclaiming the checkpoints includes: creating one or more checkpoints, each of which having an initial state using system resources and holding the checkpoints state; identifying the completion of all the instructions associated with the checkpoint; reassigning all the instructions associated with the identified checkpoint to an immediately preceding checkpoint; and freeing the resources associated with the identified checkpoint. The checkpoint is created when the instruction that is checked is a conditional branch having a direction that cannot be predicted with a predetermined confidence level.
Owner:IBM CORP
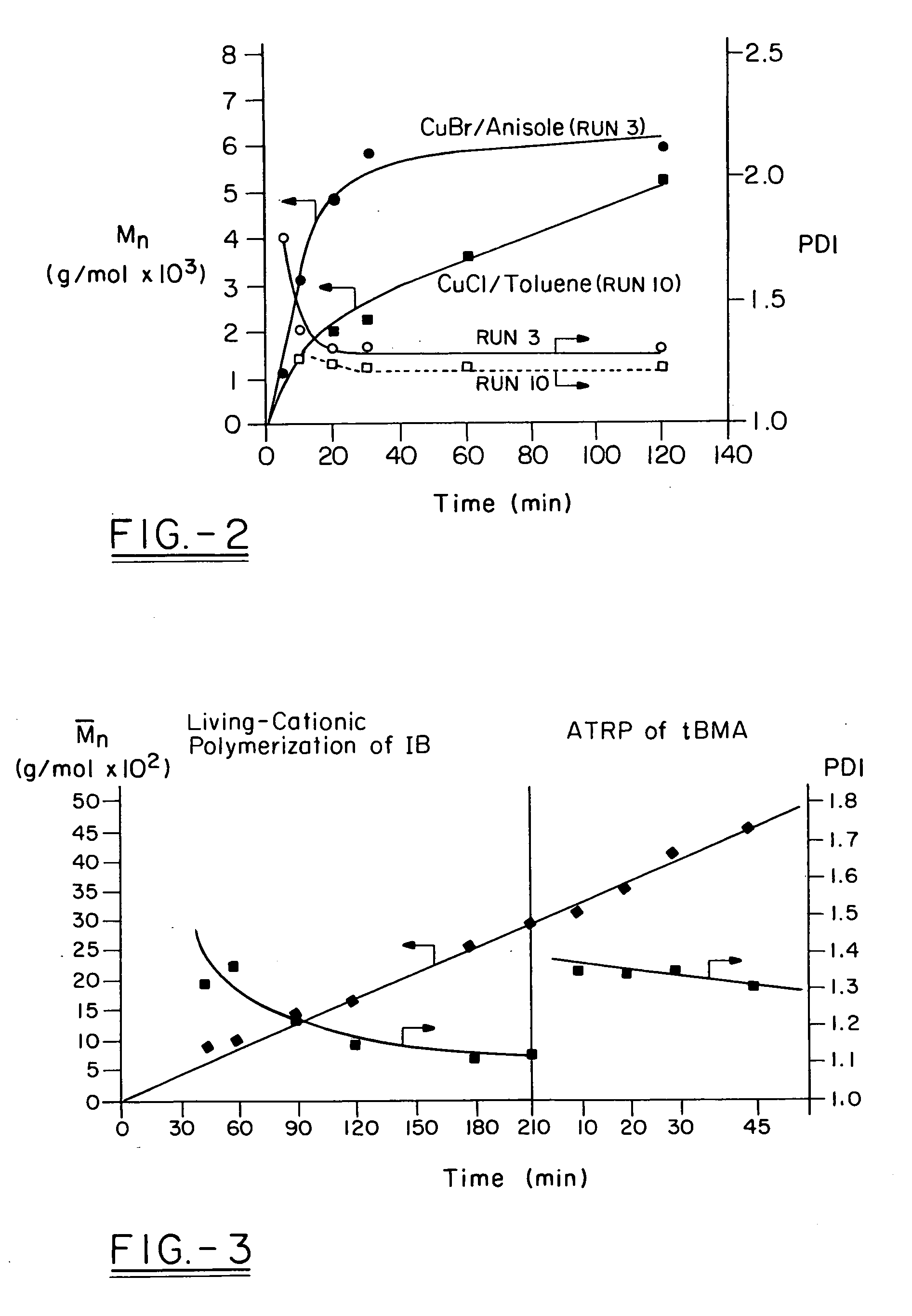
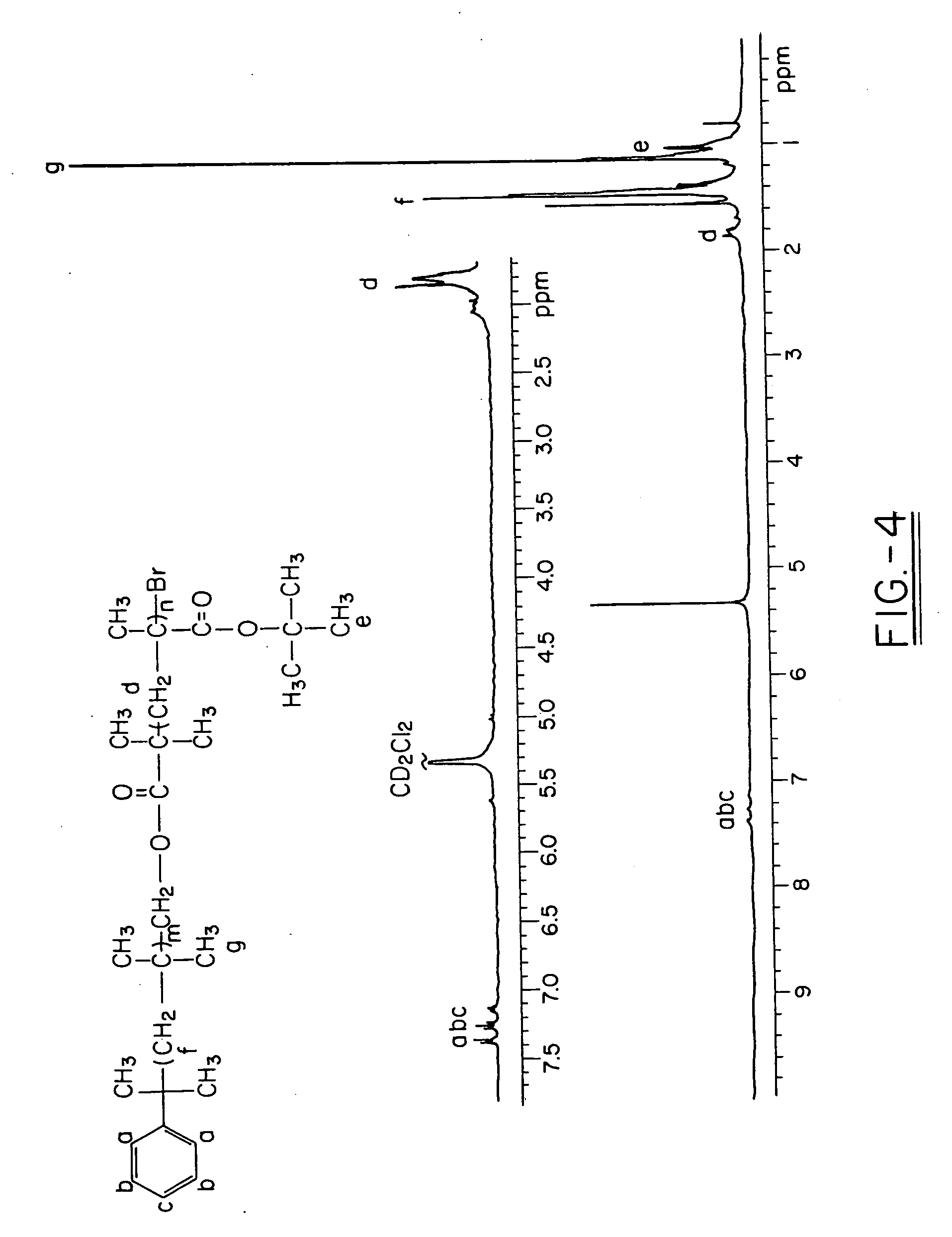
Polyisobutylene-based block anionomers and cationomers and synthesis thereof
Various novel block cationomers comprising polyisobutylene (PIB) and poly(2-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) segments have been synthesized and characterized. The specific targets were various molecular weight diblocks (PDMAEMA+) and triblocks (PDMAEMA+-b-PIB-b-PDMAEMA+) with the PIB blocks in the DPn=50-200 (Mn=3,000-9,000 g / mol) range connected to blocks of PDMAEMA+ cations in the DPn=5-20 range. The overall synthetic strategy for the preparation of these block cationomers comprised four steps: 1) Synthesis by living cationic polymerization of mono- and di-allyltelechelic polyisobutylenes, 2) End group transformation to obtain PIBs fitted with termini capable of mediating the atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of DMAEMA, 3) ATRP of DMAEMA and 4) Quaternization of PDMAEMA to PDMAEMA+I− by CH3I. Kinetic and model experiments provided guidance to develop convenient synthesis methods. The microarchitecture of PIB-PDMAEMA di-and triblock and the corresponding block cationomers were confirmed by 1H NMR and FTIR spectroscopy and solubility studies.
Owner:AKRON UNIV OF
Building a wavecache
InactiveUS7490218B2Improves code schedulingGranularity is very broadSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsProgram synchronisationControl flowApplication software
A microarchitecture and instruction set that supports multiple, simultaneously executing threads. The approach is disclosed in regard to its applicability in connection with a recently developed microarchitecture called “WaveScalar.” WaveScalar is a compiler that breaks a control flow graph for a program into pieces called waves having instructions that are partially ordered (i.e., a wave contains no back-edges), and for which control enters at a single point. Certain aspects of the present approach are also generally applicable to executing multiple threads on a more conventional microarchitecture. In one aspect of this approach, instructions are provided that enable and disable wave-ordered memory. Additional memory access instructions bypass wave-ordered memory, exposing additional parallelism. Also, a lightweight, interthread synchronization is employed that models hardware queue locks. Finally, a simple fence instruction is used to allow applications to handle relaxed memory consistency.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
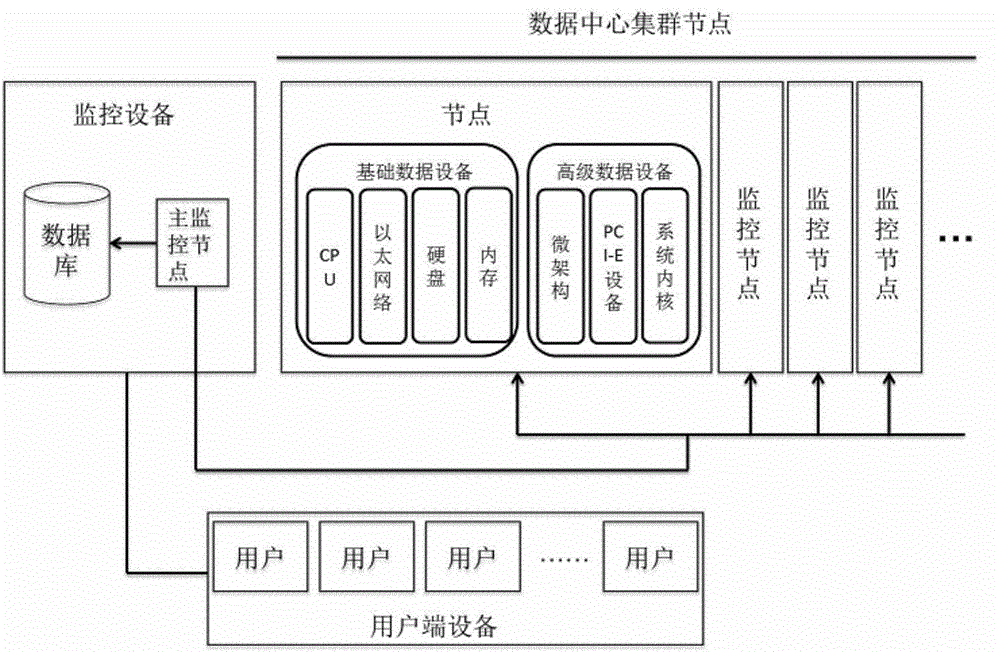
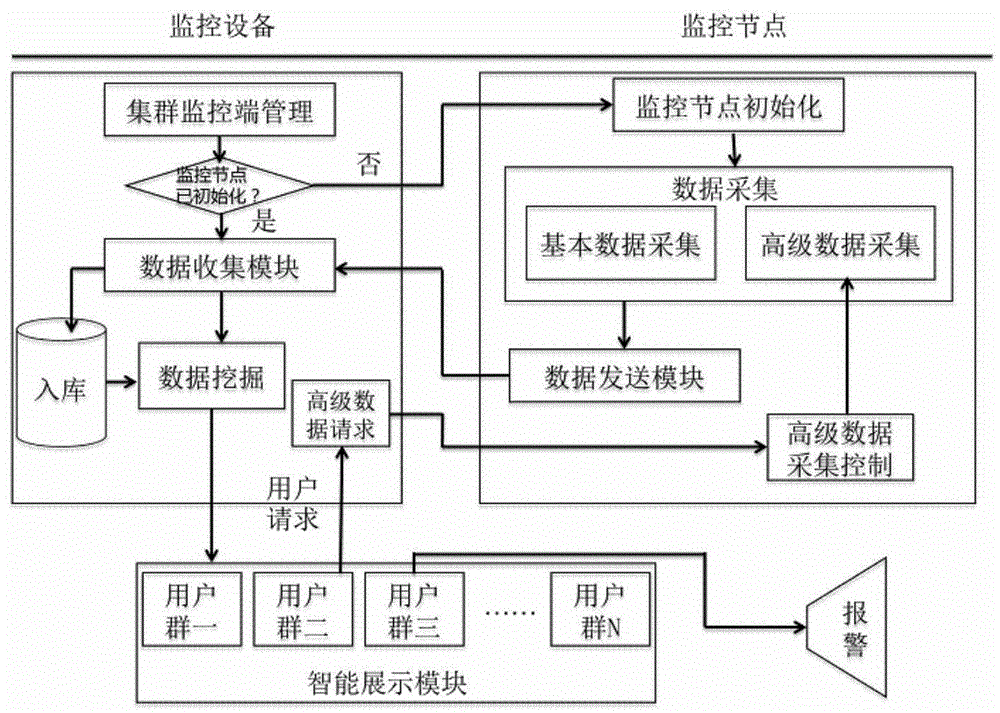
System and method for intelligently monitoring large-scale data center cluster computing nodes
The invention provides a system and a method for intelligently monitoring large-scale data center cluster computing nodes. Hardware microarchitecture data indexes of the computing nodes and data indexes related to processes of running applications are acquired through monitoring nodes in the system, the data indexes are transmitted to monitoring equipment in the system, big data analysis is executed via the monitoring equipment, and results are sent to customer premise equipment to be displayed to a user. By the system and the method, the microarchitecture data indexes of the computing nodes and the data indexes of the processes of the running applications are acquired, so that intelligent big data analysis is realized, the faulted computing nodes are positioned automatically, and fault causes are provided.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
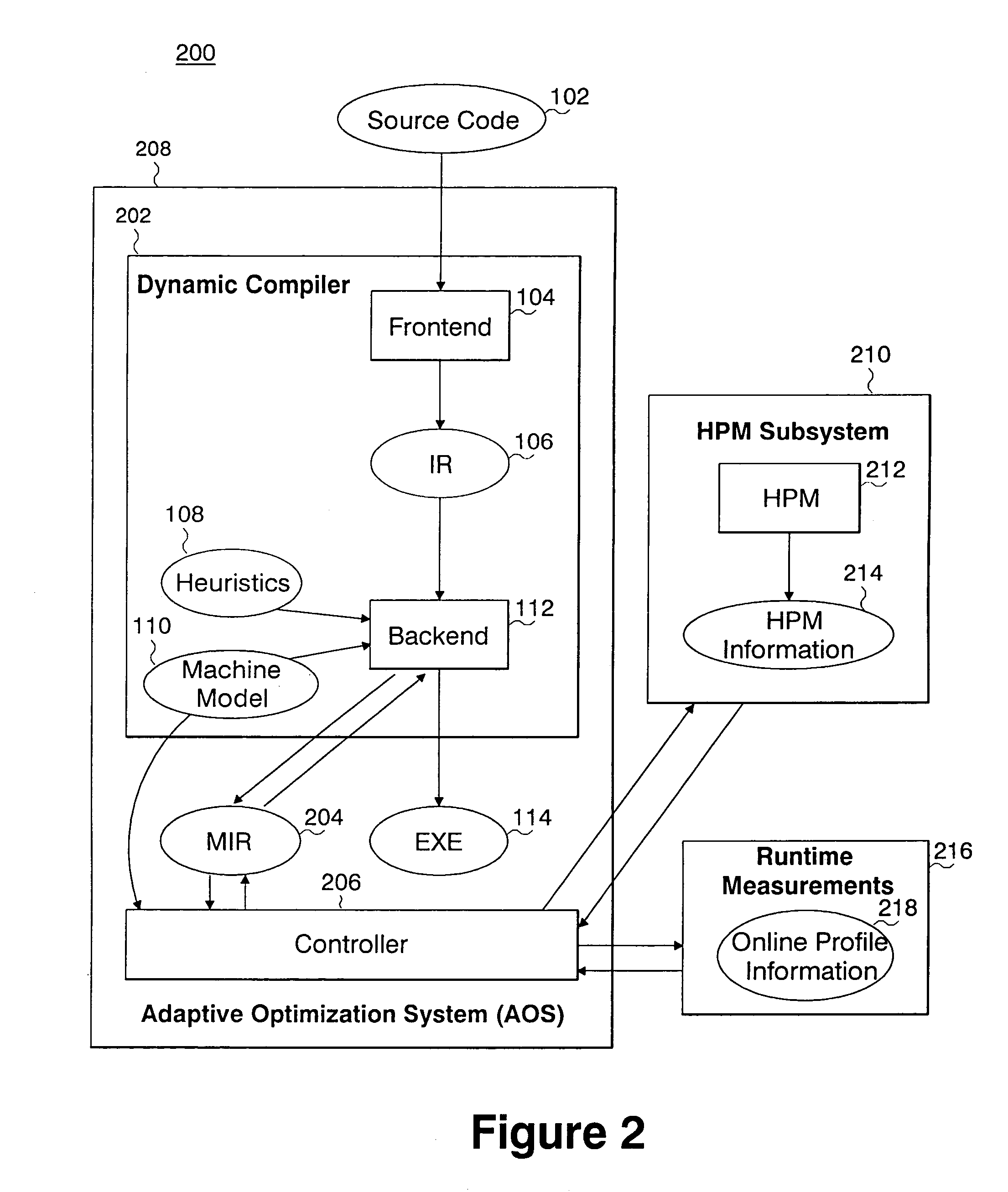
System and method for using hardware performance monitors to evaluate and modify the behavior of an application during execution of the application
InactiveUS7089403B2Improve performanceImprove application performanceError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsParallel computingApplication software
There is provided a method, system and program storage device for utilizing a hardware performance monitors for improving performance of an application comprising a plurality of instructions while the application is executing on a micro-architecture, comprising: creating a machine internal representation (MIR) for the plurality of instructions or a subset thereof for the hardware and generating an executable (EXE) from the MIR for execution on the hardware; determining hardware performance monitor (HPM) information for an event associated with a resource of the hardware during execution of the EXE to identify one or more instructions of the application that affect the execution of the application on the hardware; re-computing the MIR according to the HPM information; and re-generating the EXE from the re-computed MIR for execution on the hardware if the MIR and the re-computed MIR are different, thereby improving utilization of the resource by the application. Also provided is a hardware performance monitor (HPM) subsystem for improving performance of an application comprising a plurality of instructions while the application is executing on a hardware.
Owner:IBM CORP
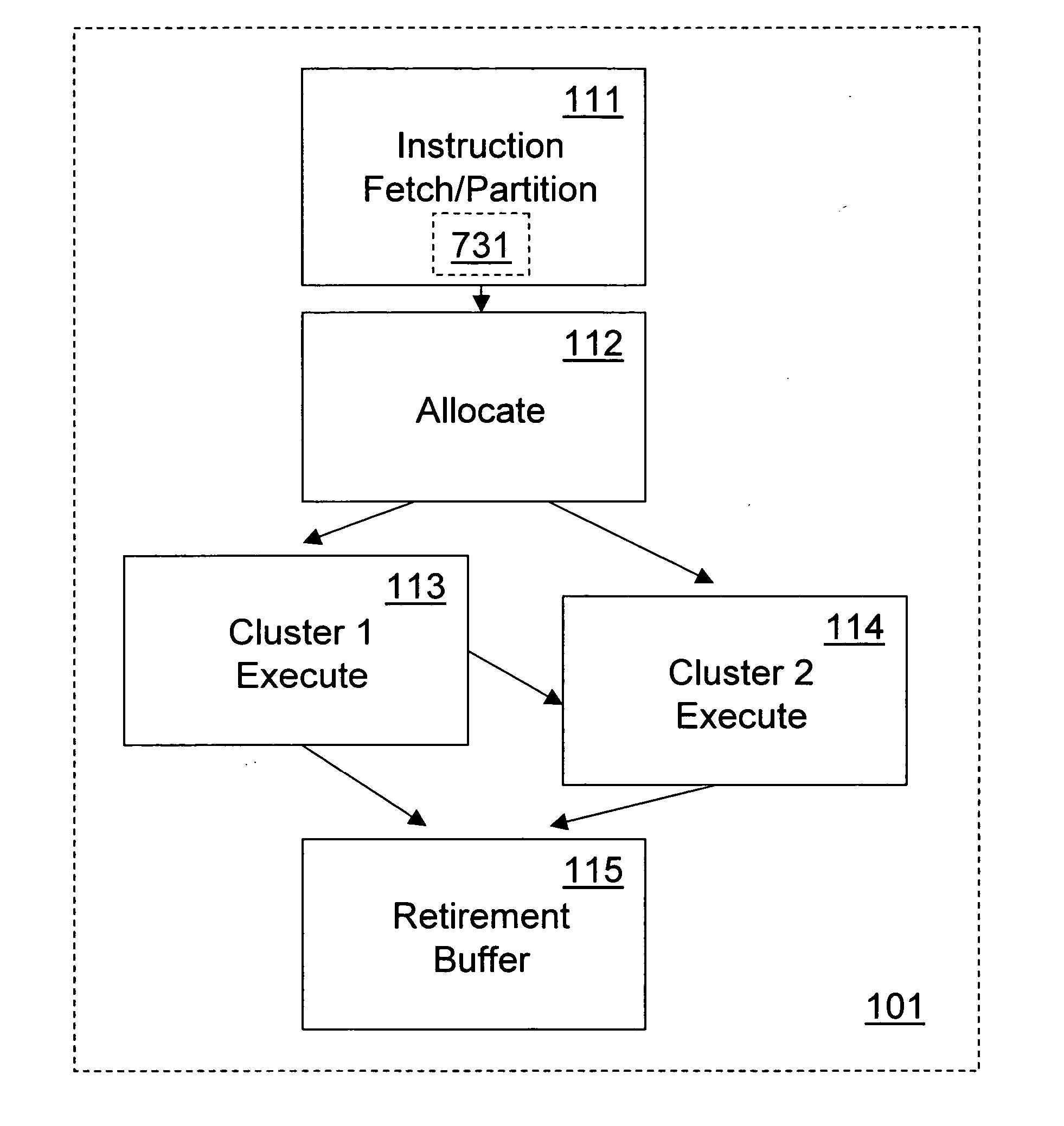
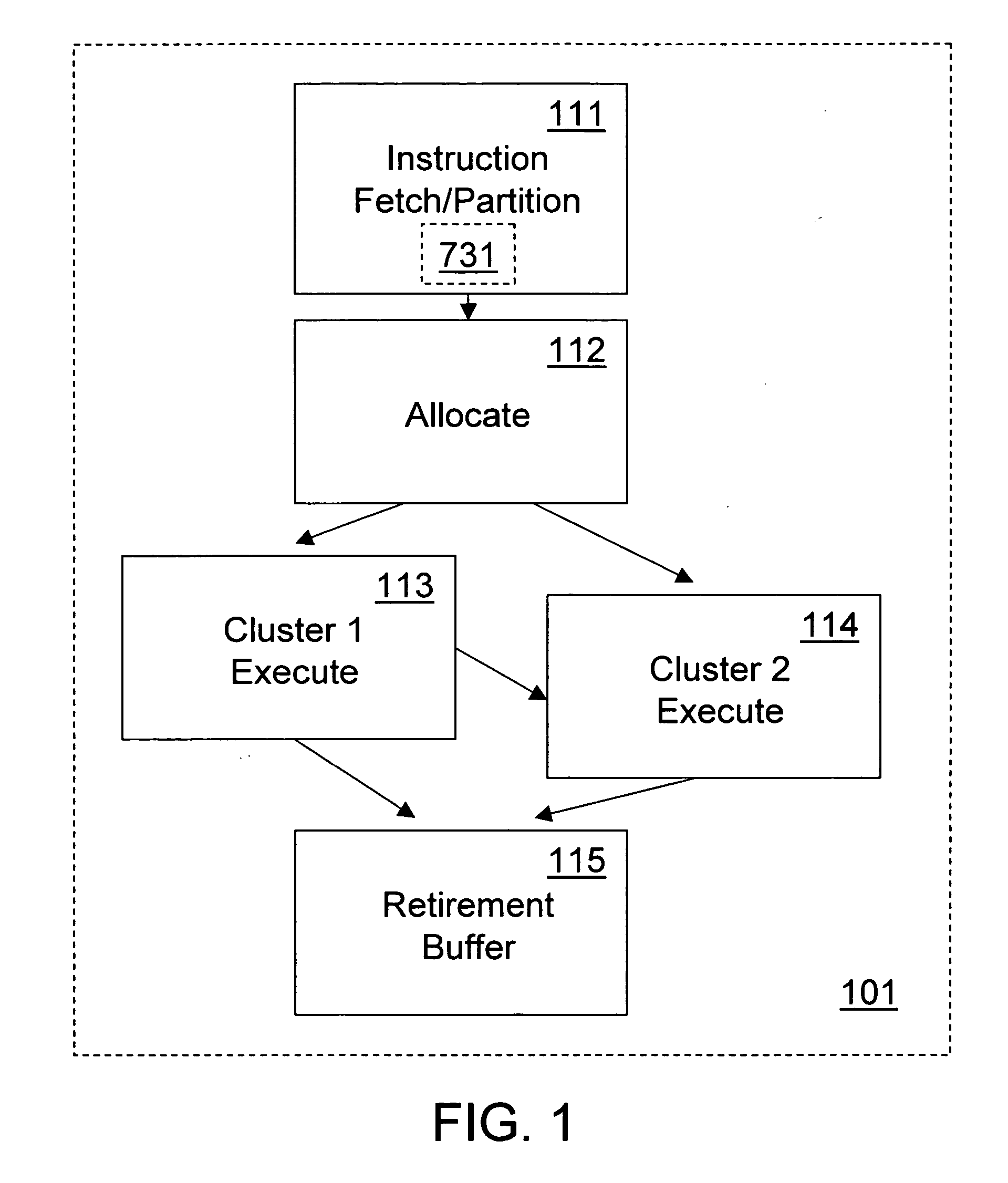
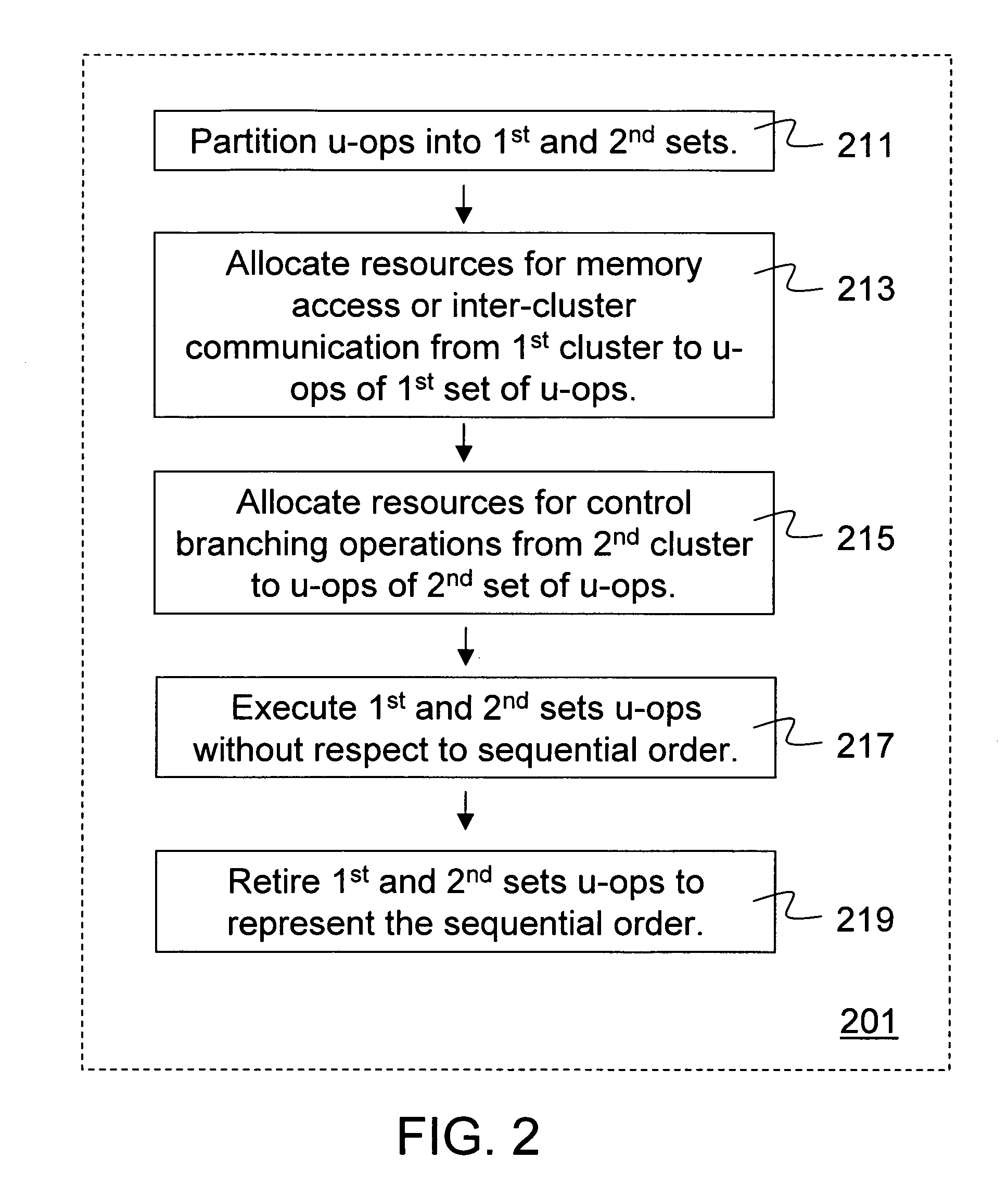
Method and apparatus for microarchitecture partitioning of execution clusters
ActiveUS20070157006A1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsMicro-operationResource allocation
Microarchitecture policies and structures partition execution resource clusters. In disclosed microarchitecture embodiments, micro-operations representing a sequential instruction ordering are partitioned into a two sets. To one set of micro-operations execution resources are allocated from a cluster of execution resources that can perform memory access operations but not branching operations. To the other set of micro-operations execution resources are allocated from a cluster of execution resources that can perform branching operations but not memory access operations. The first and second sets of micro-operations may be executed out of sequential order but are retired to represent their sequential instruction ordering.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Efficient methods for assessing and validating ecandidate protein-based therapeutic molecules encoded by nucleic acid sequences of interest
InactiveUS20030124565A1Microbiological testing/measurementIn-vivo testing preparationsIn vivoNucleic acid sequence
A method of determining at least one quantitative or qualitative pharmacological, physiological and / or therapeutic, parameter or effect of a recombinant gene product in vivo, the method comprises (a) obtaining at least one micro-organ explant from a donor subject, the micro-organ explant comprising a population of cells, the micro-organ explant maintaining a microarchitecture of an organ from which it is derived and at the same time having dimensions selected so as to allow diffusion of adequate nutrients and gases to cells in the micro-organ explant and diffusion of cellular waste out of the micro-organ explant so as to minimize cellular toxicity and concomitant death due to insufficient nutrition and accumulation of the waste in the micro-organ explant, at least some cells of the population of cells of the micro-organ explant expressing and secreting at least one recombinant gene product; (b) implanting the at least one micro-organ explant in a recipient subject; and (c) determining the at least one quantitative or qualitative pharmacological, physiological and / or therapeutic, parameter or effect of the recombinant gene product in the recipient subject.
Owner:MEDGENICS INC +1
Programmable digital signal processor having a clustered SIMD microarchitecture including a complex short multiplier and an independent vector load unit
A programmable digital signal processor with a clustered SIMD microarchitecture includes a plurality of accelerator units, a processor core, and a complex computing unit. Each of the accelerator units may perform one or more dedicated functions. The processor core includes an integer execution unit that may execute integer instructions. The complex computing unit may include a complex arithmetic logic unit execution pipeline that may include one or more datapaths configured to execute complex vector instructions, and a vector load unit. In addition, each datapath may include a complex short multiplier accumulator unit that may be configured to multiply a complex data value by values in the set of numbers including {0, + / -1}+ {0, + / -i}. The vector load unit may cause the complex data items to be fetched each clock cycle for use by any datapath in the complex arithmetic logic unit execution pipeline.
Owner:扩你科公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com