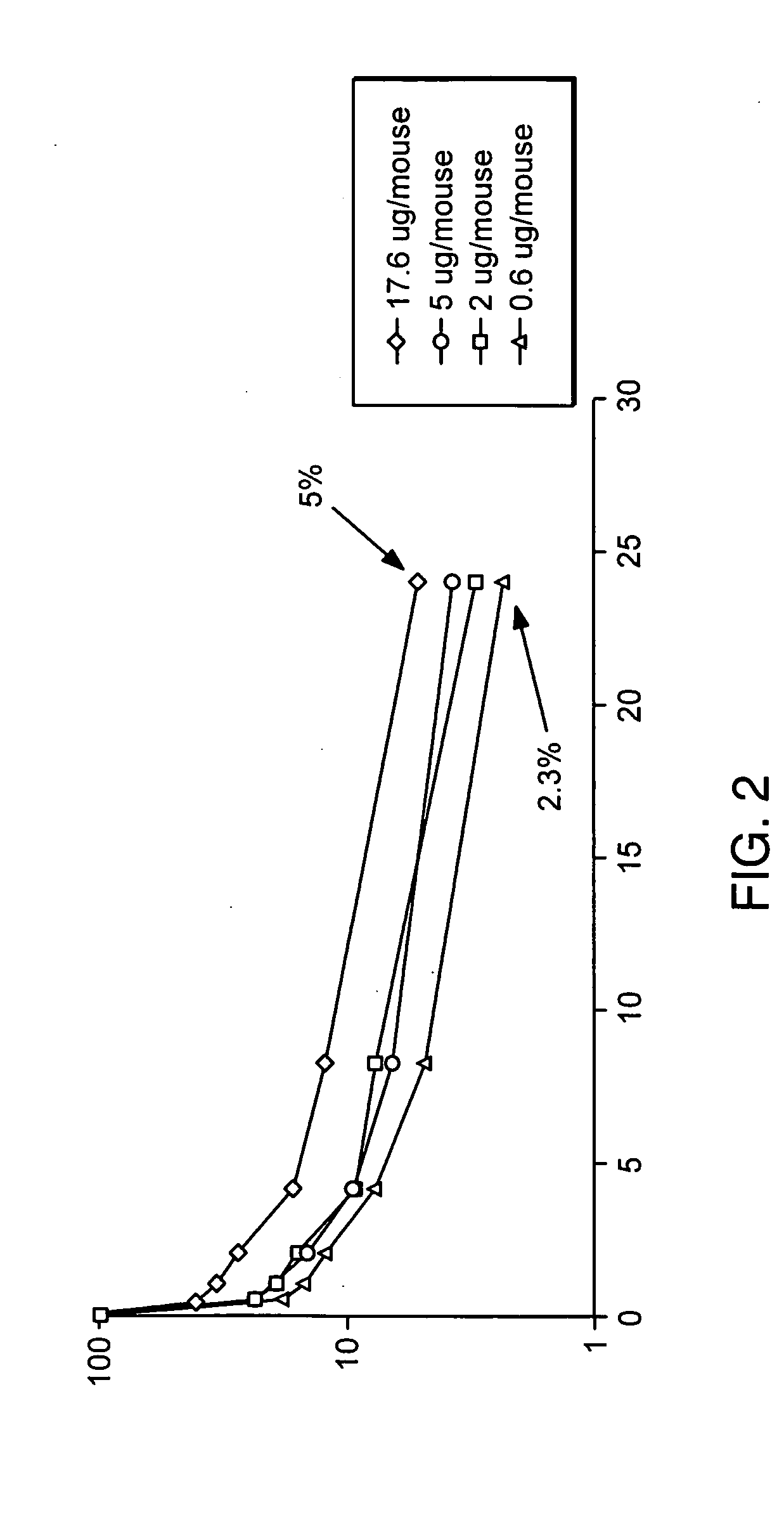
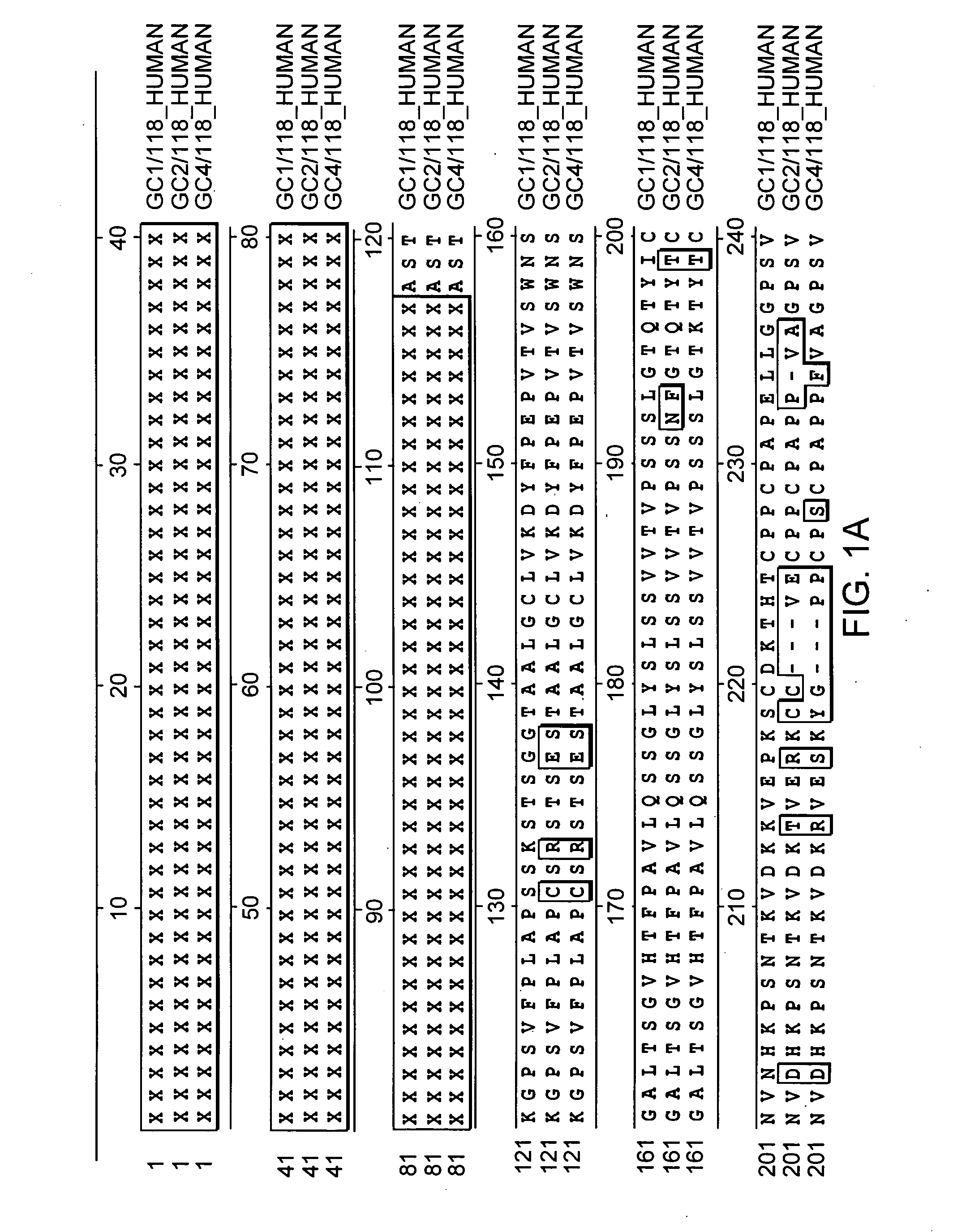
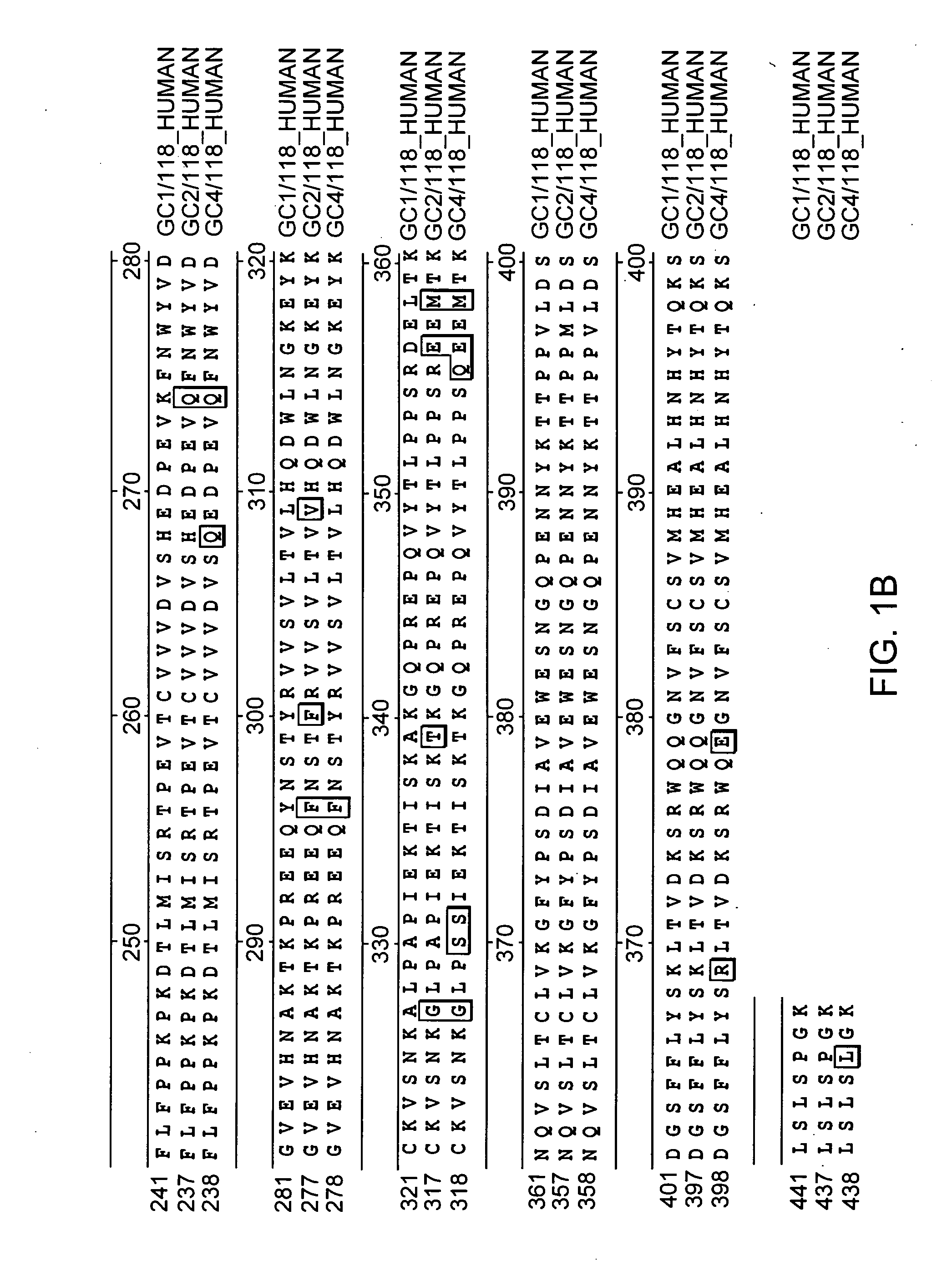
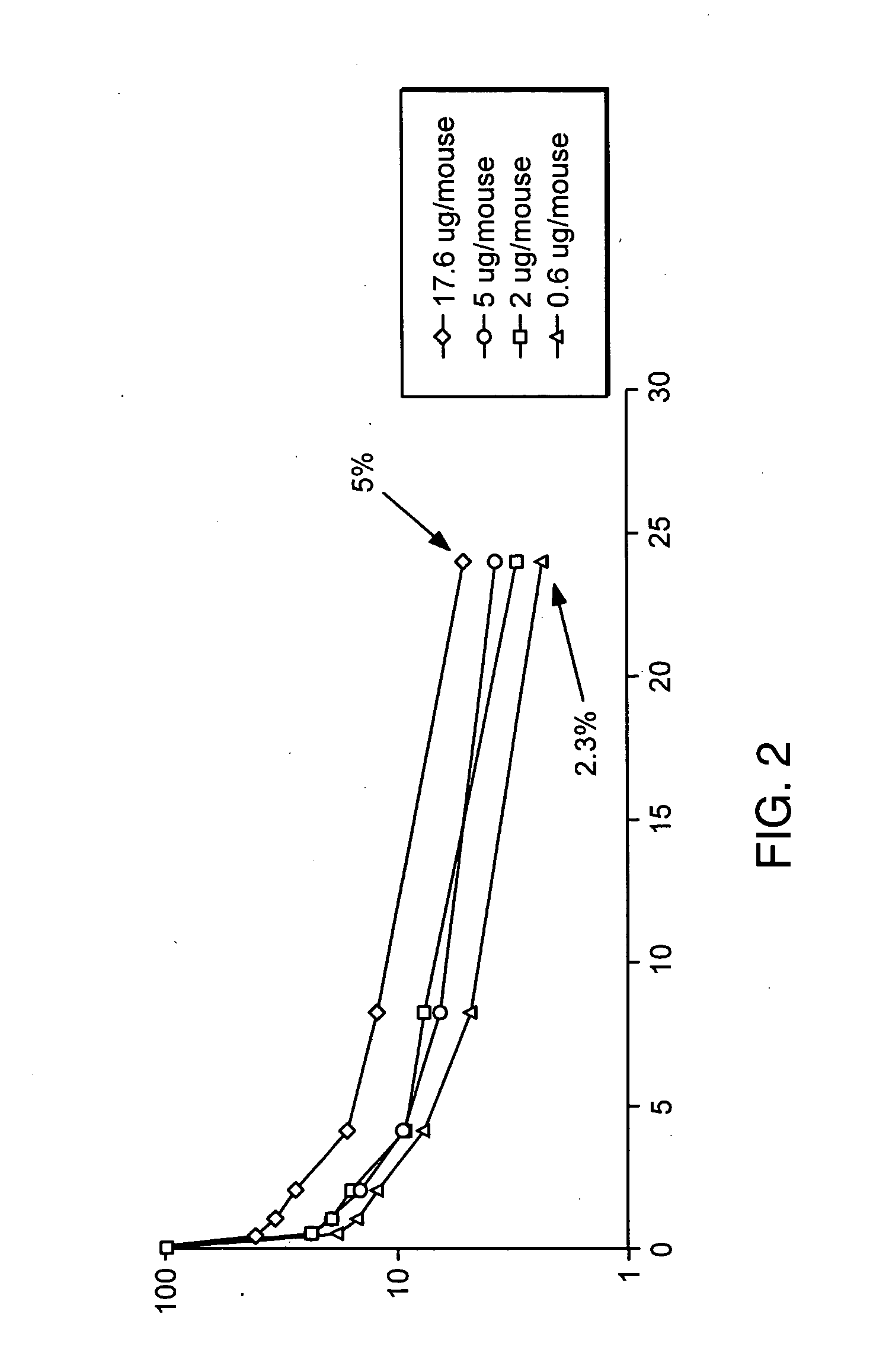
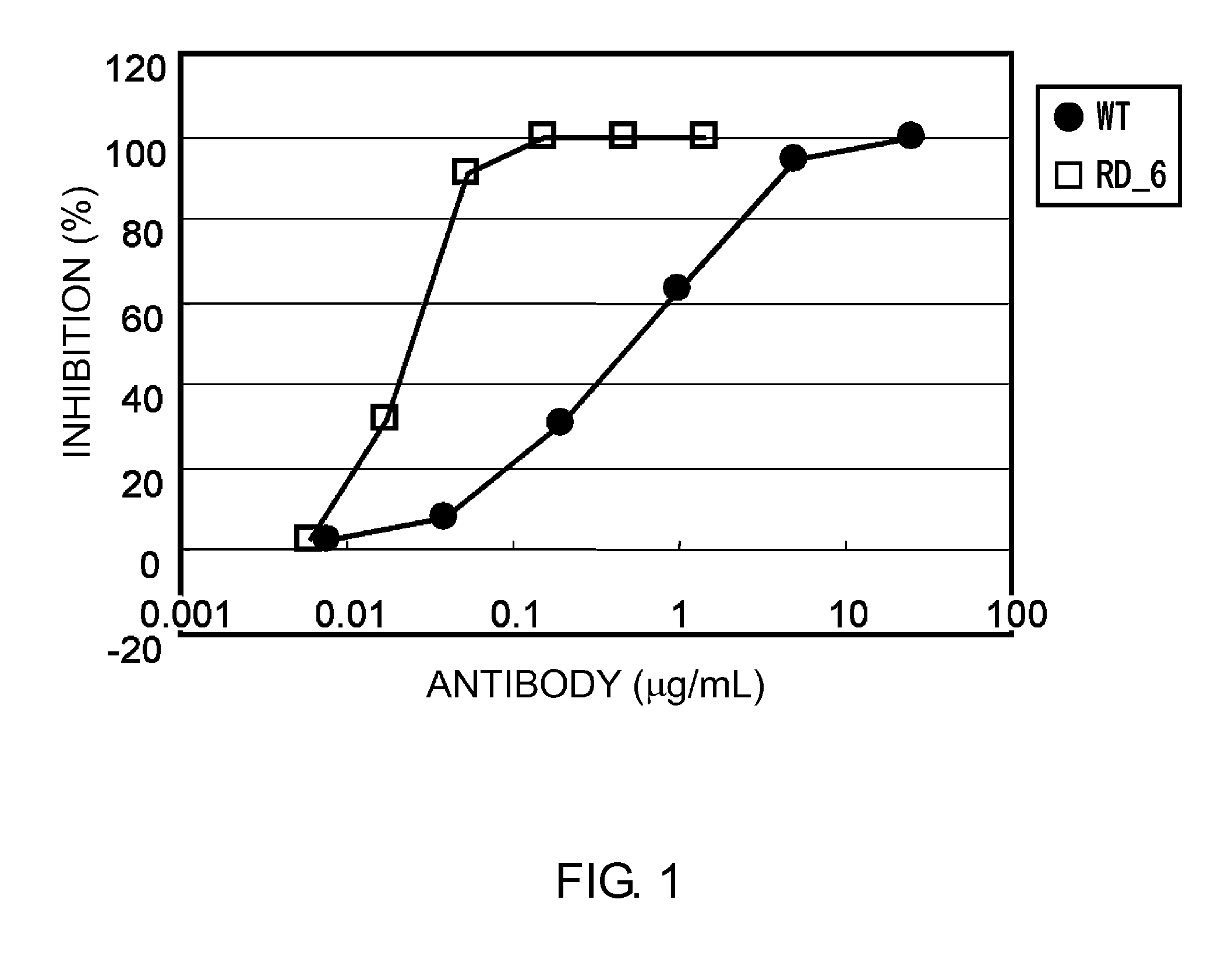
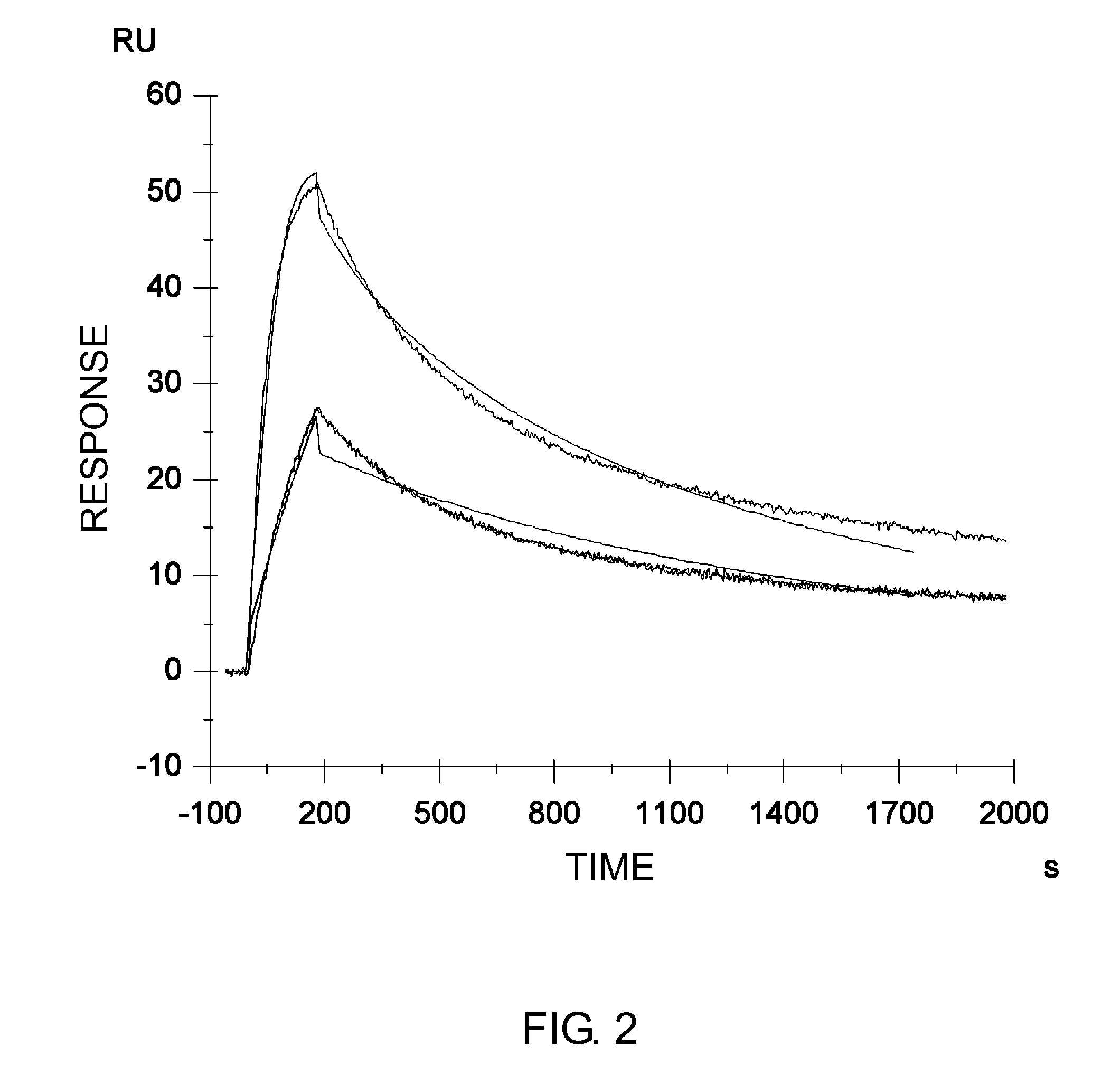
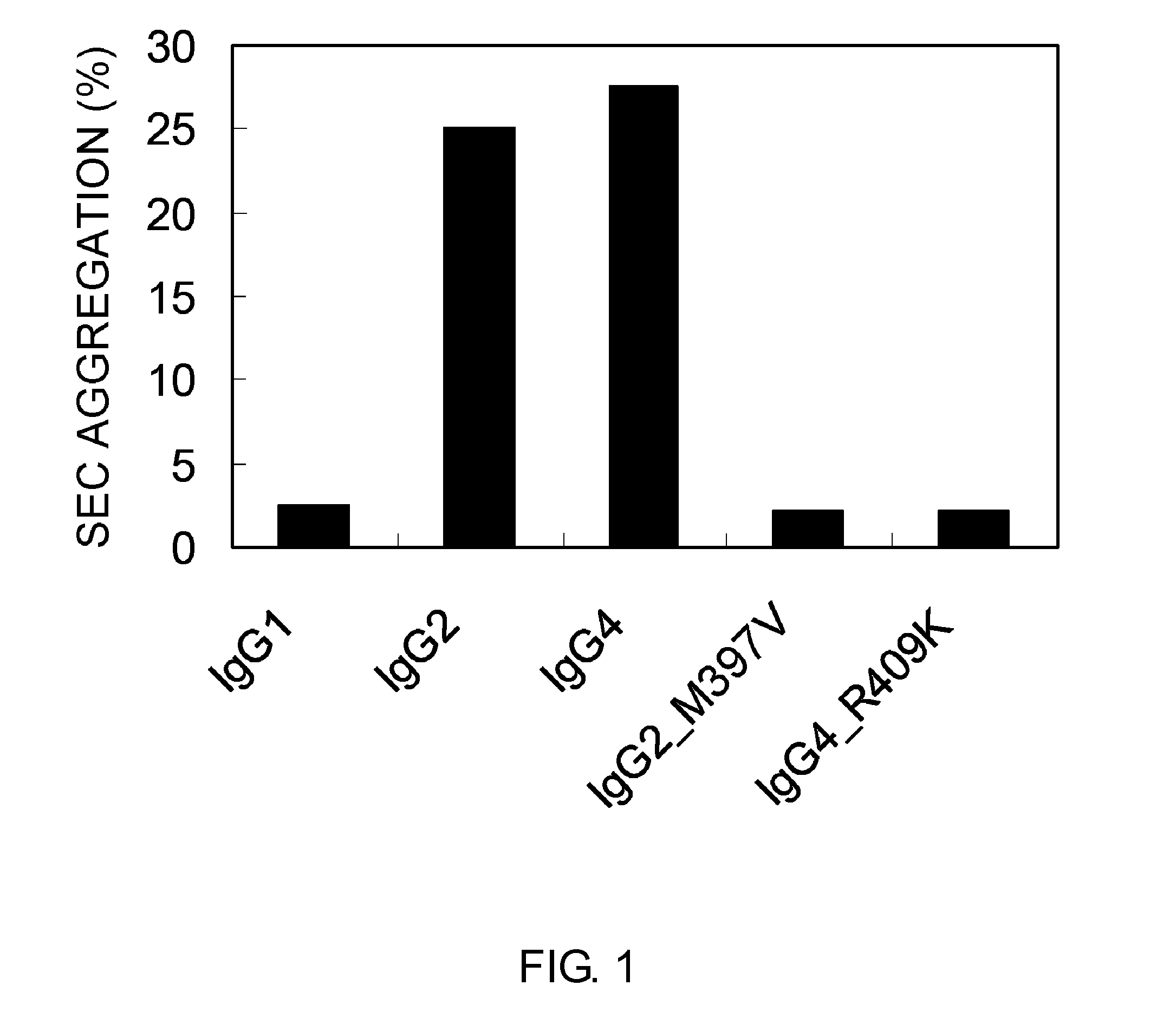
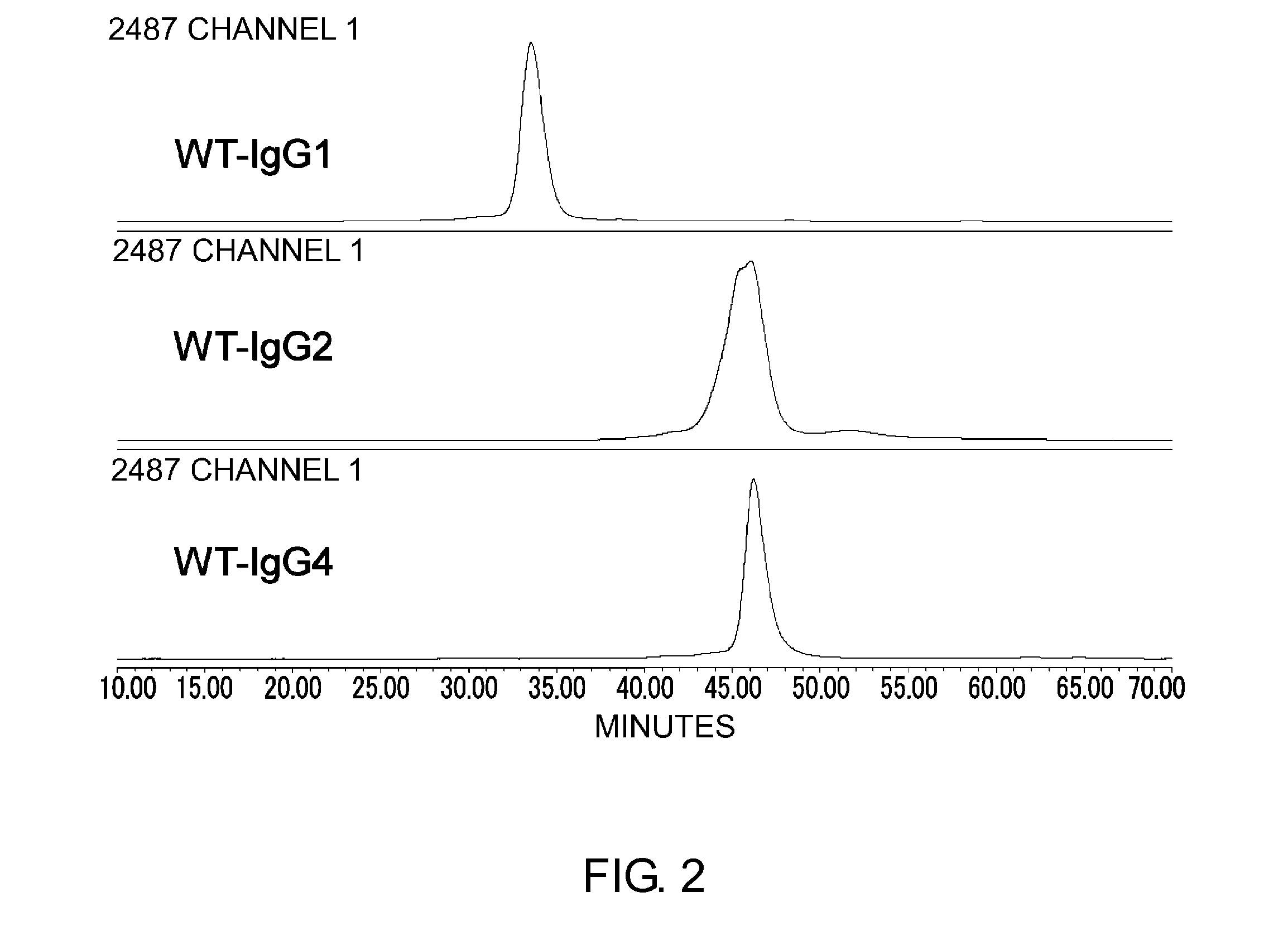
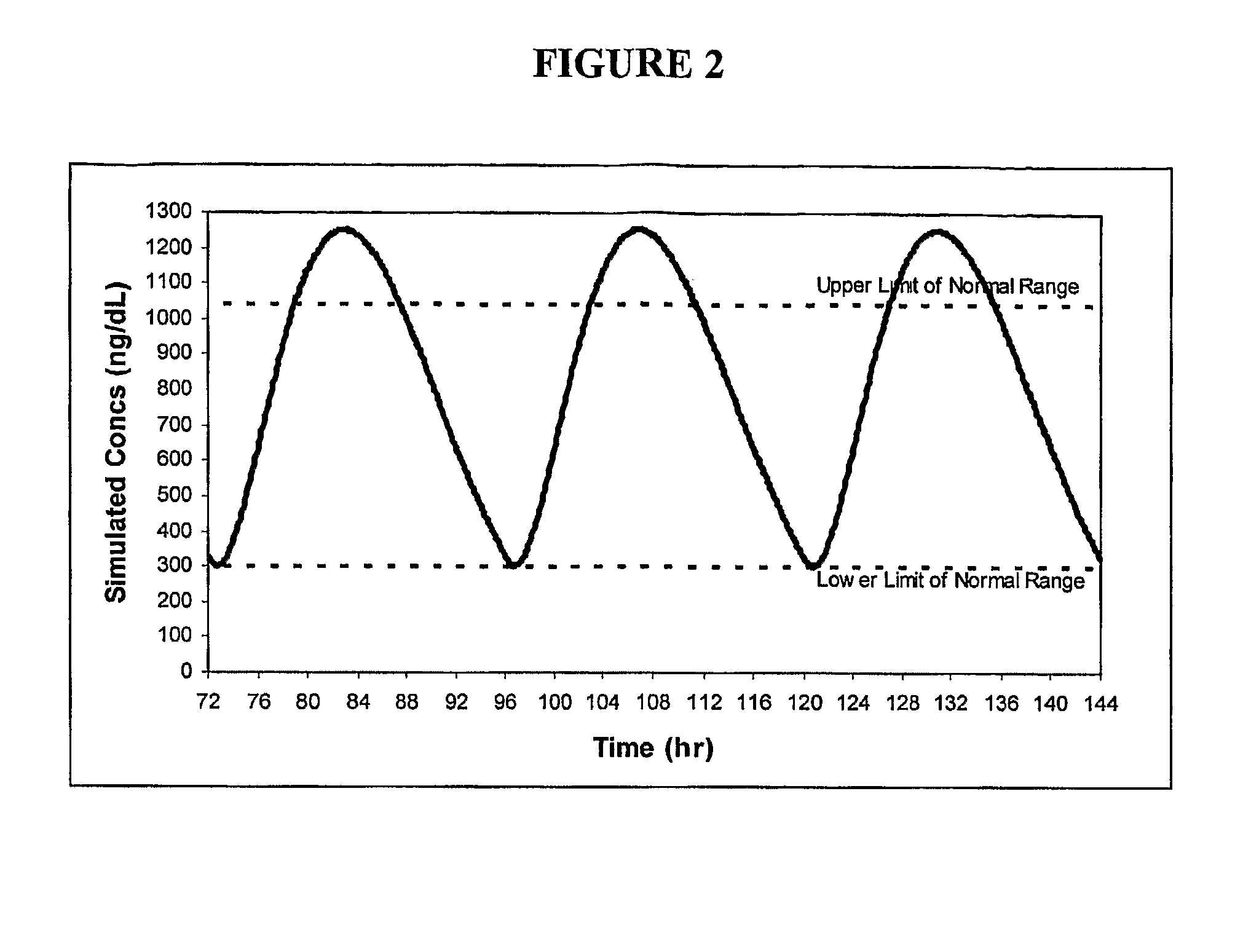
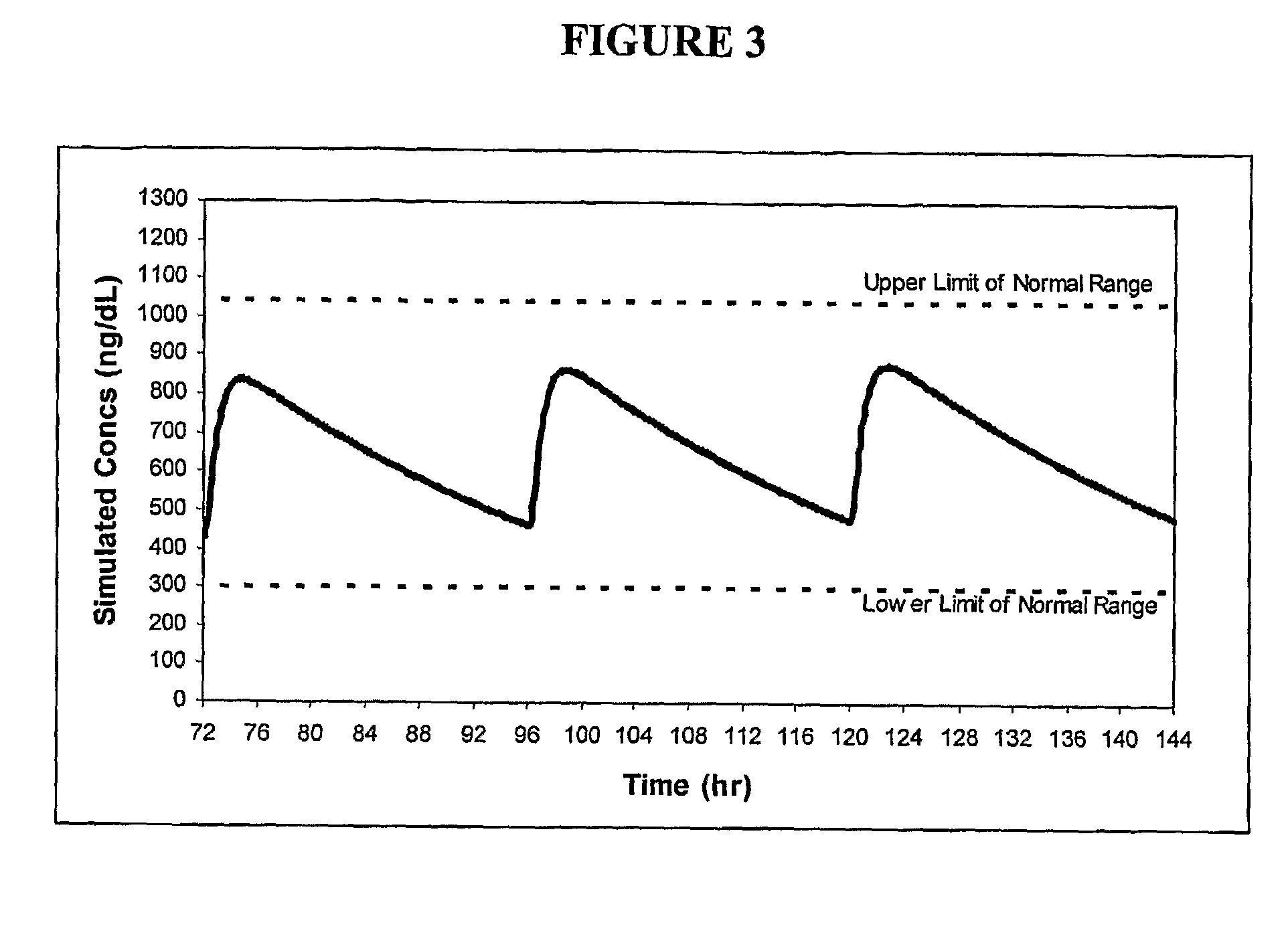
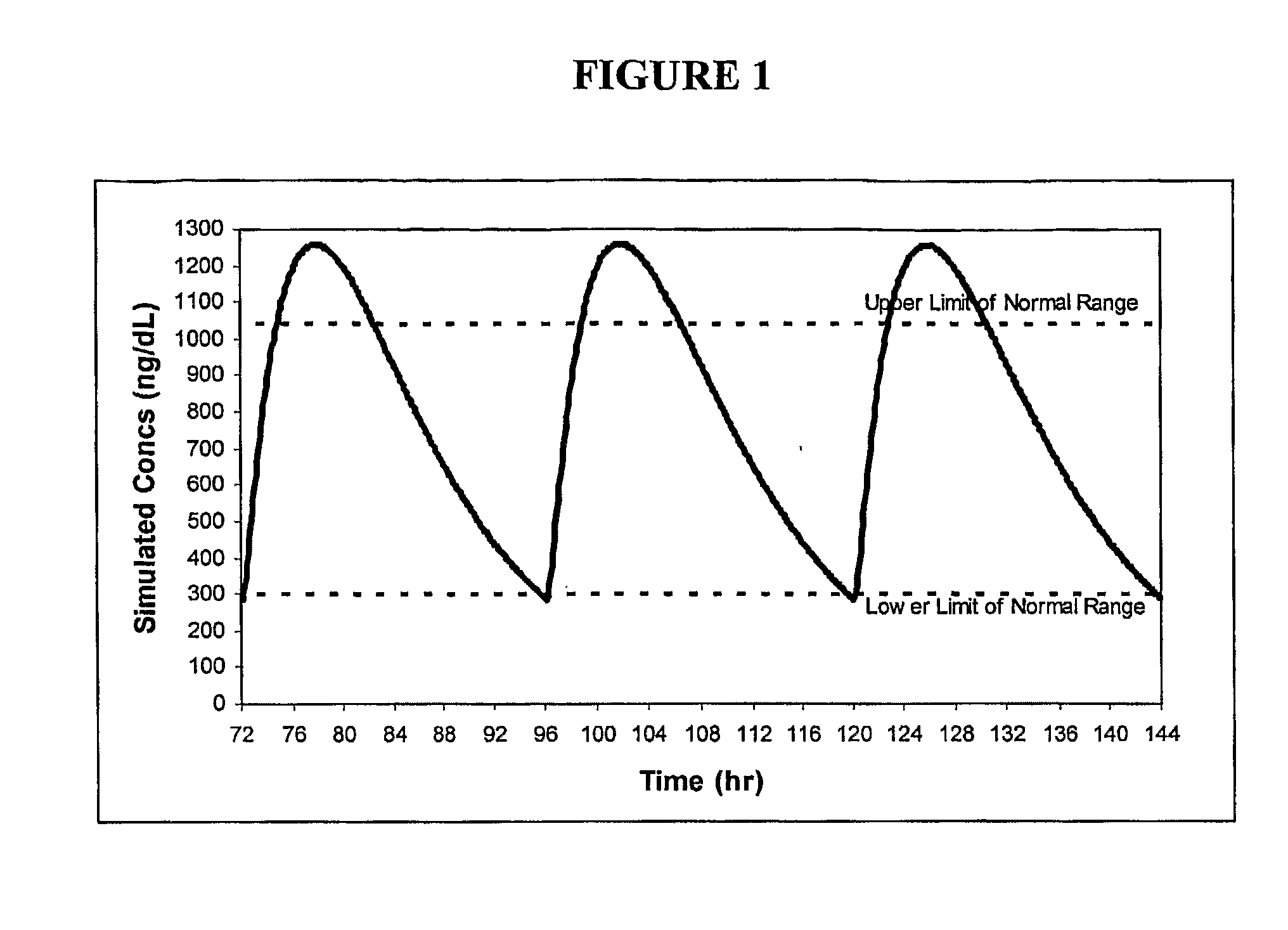
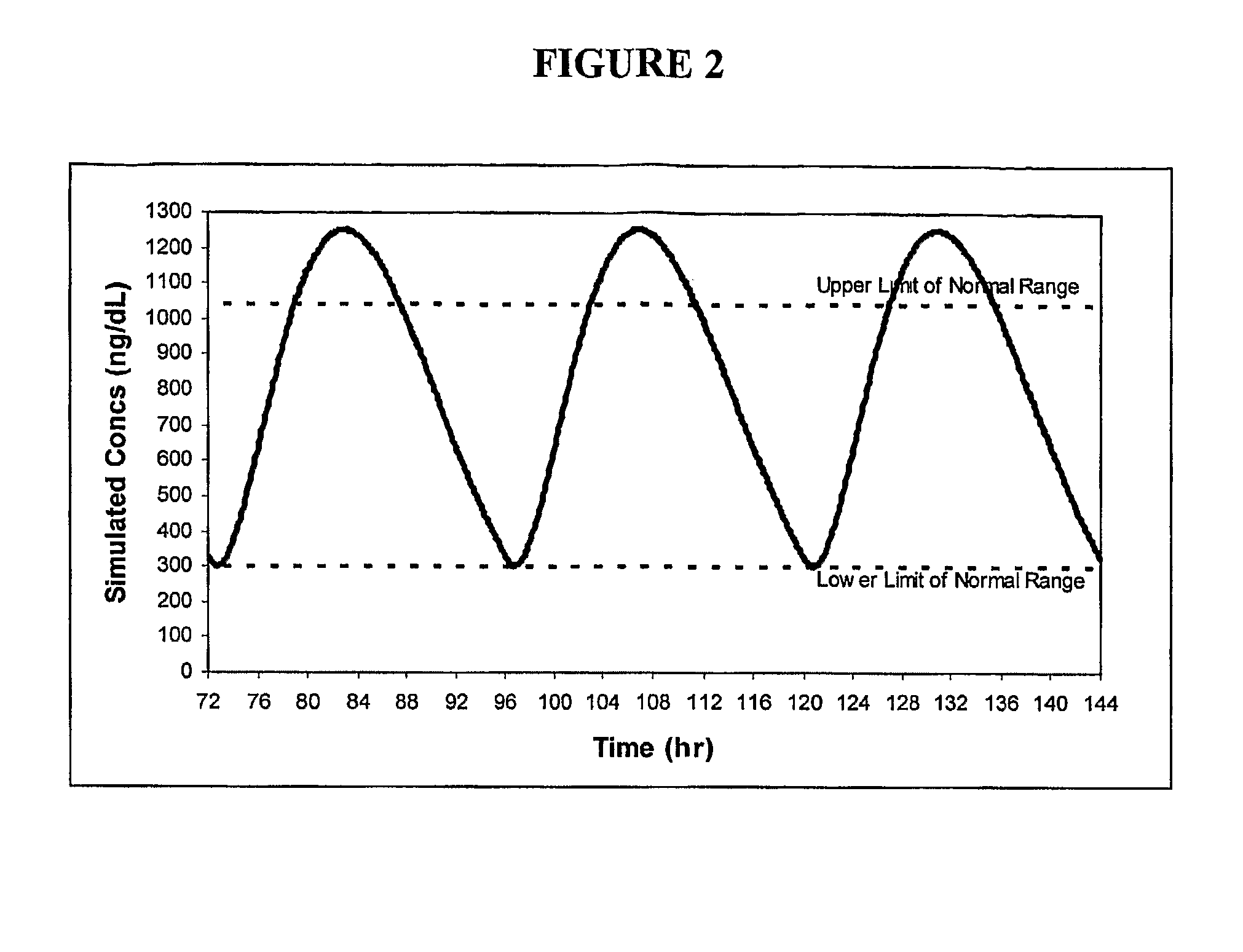
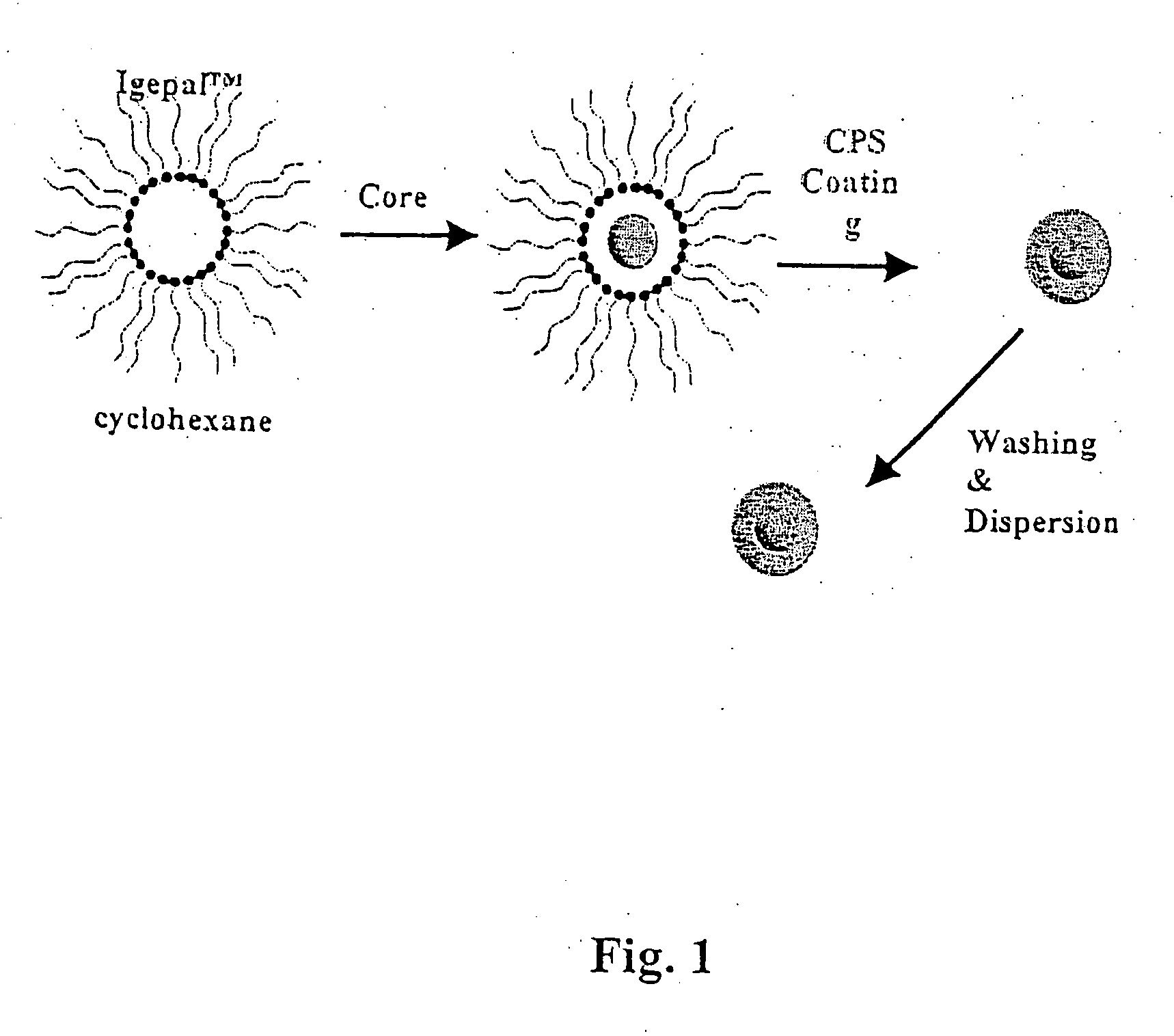
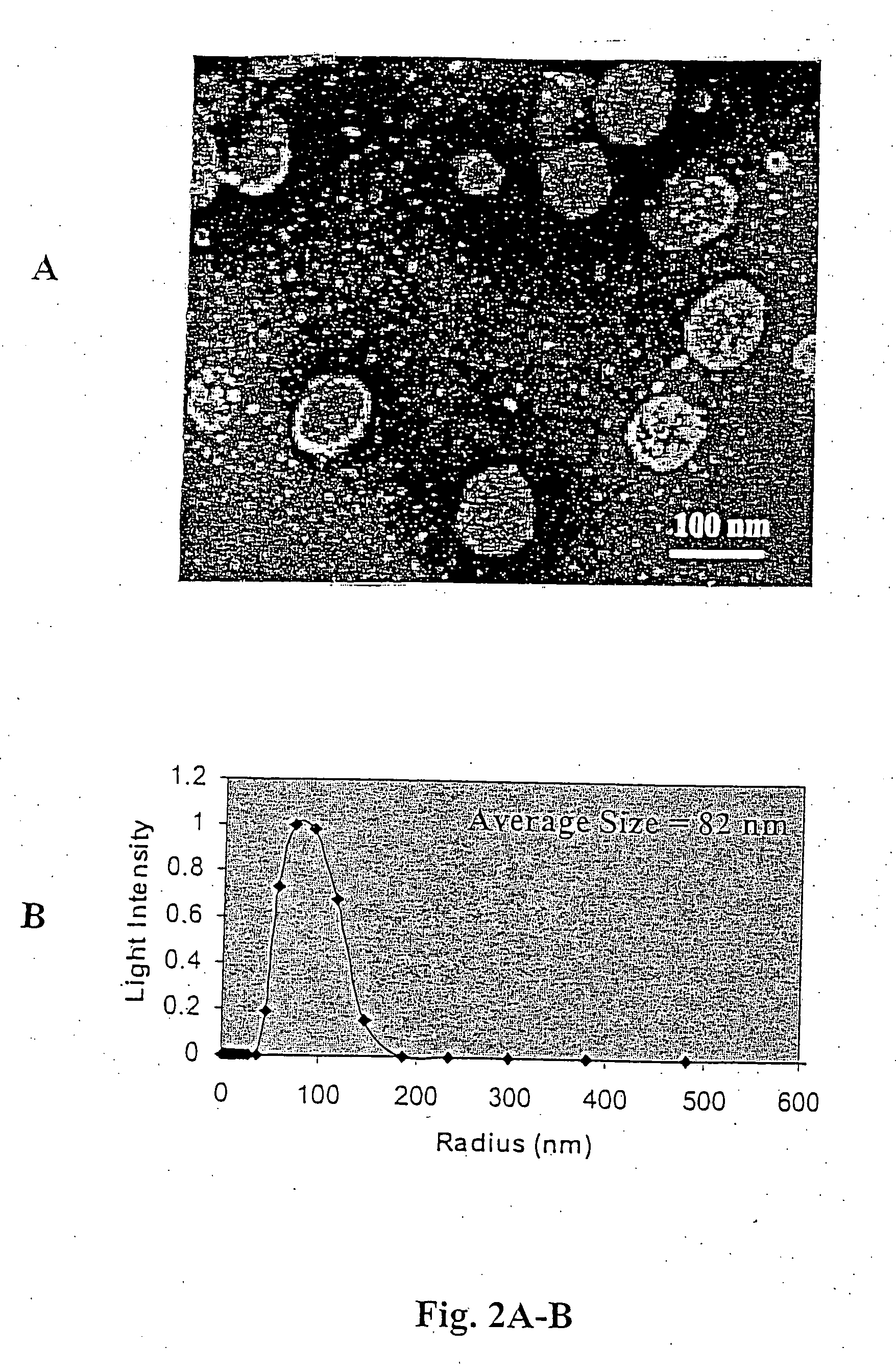
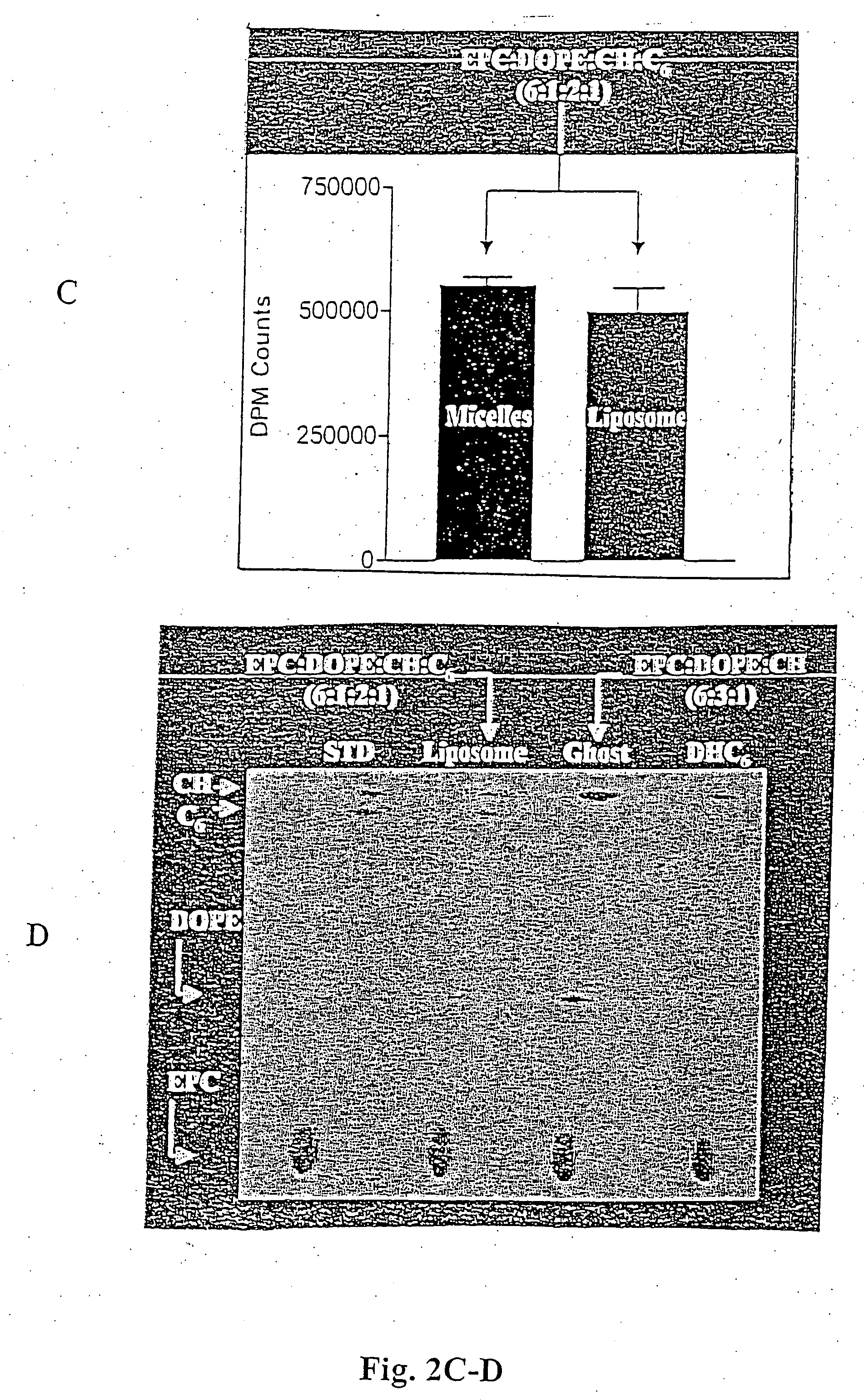
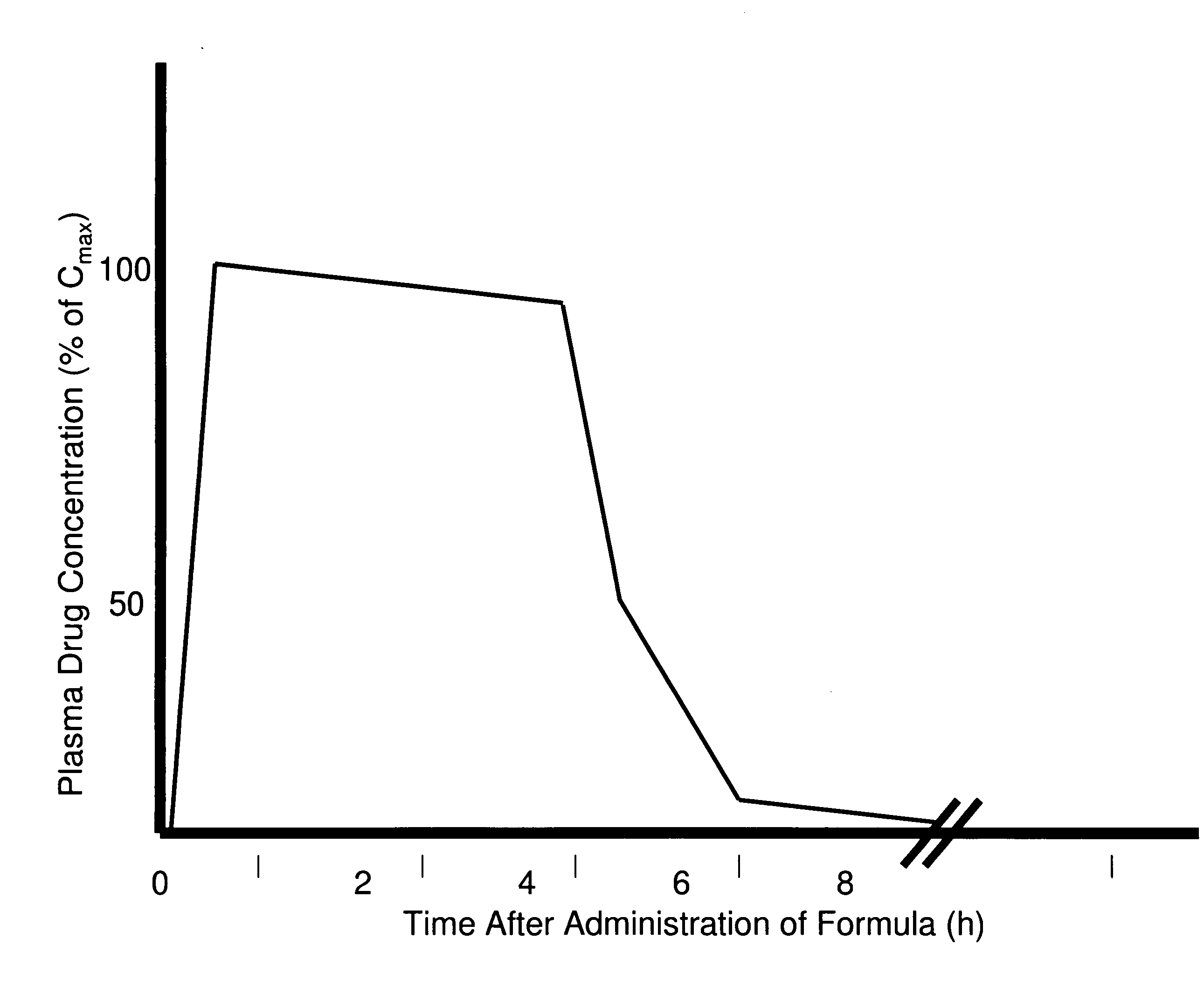
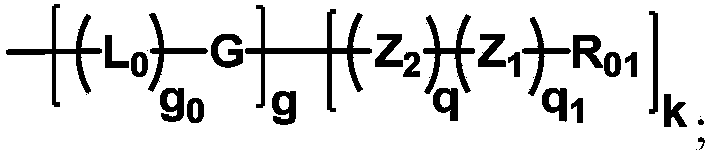Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1023 results about "Pharmacokinetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek pharmakon "drug" and kinetikos "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determine the fate of substances administered to a living organism. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as: pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects a drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects, as seen in PK/PD models.
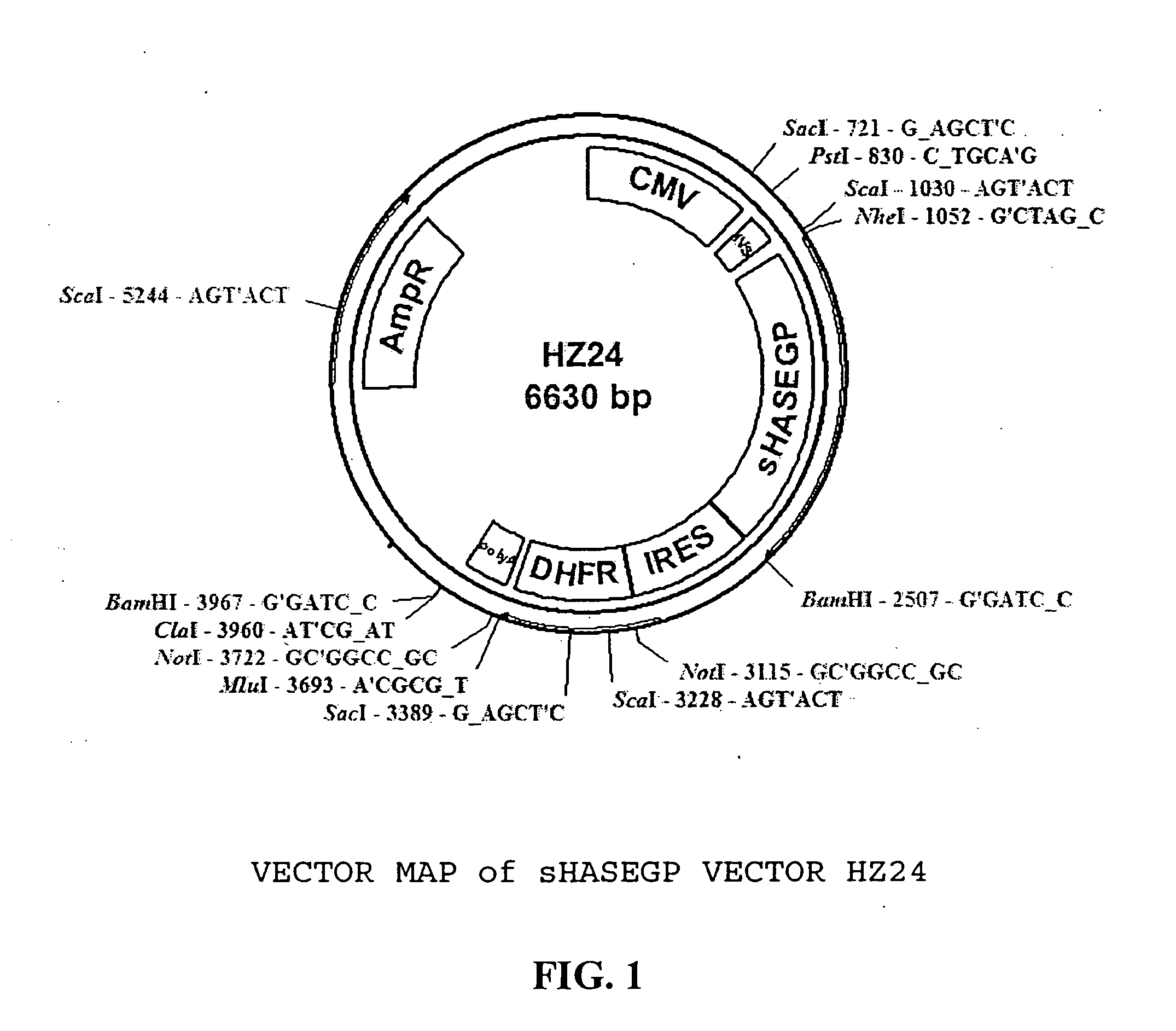
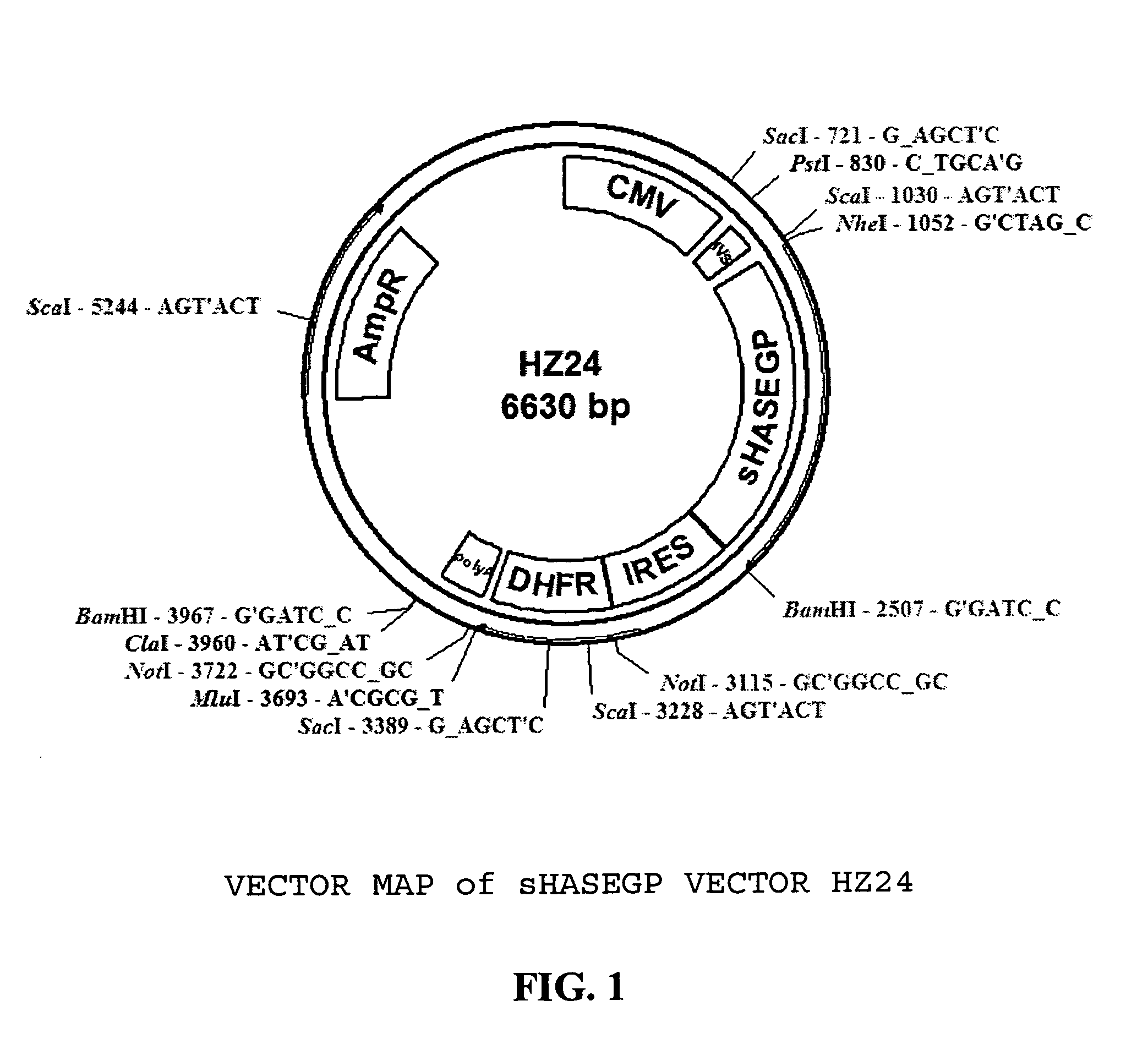
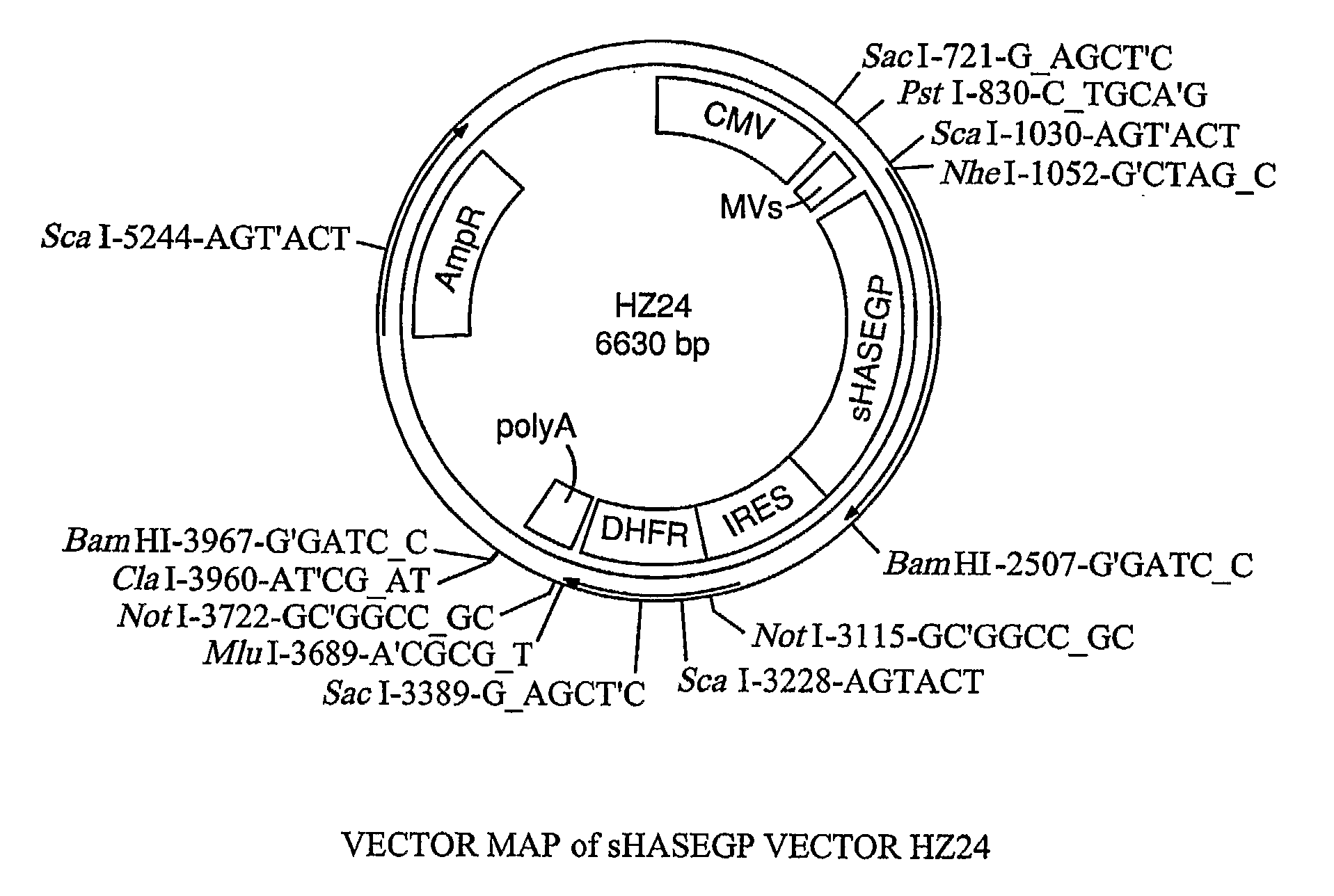
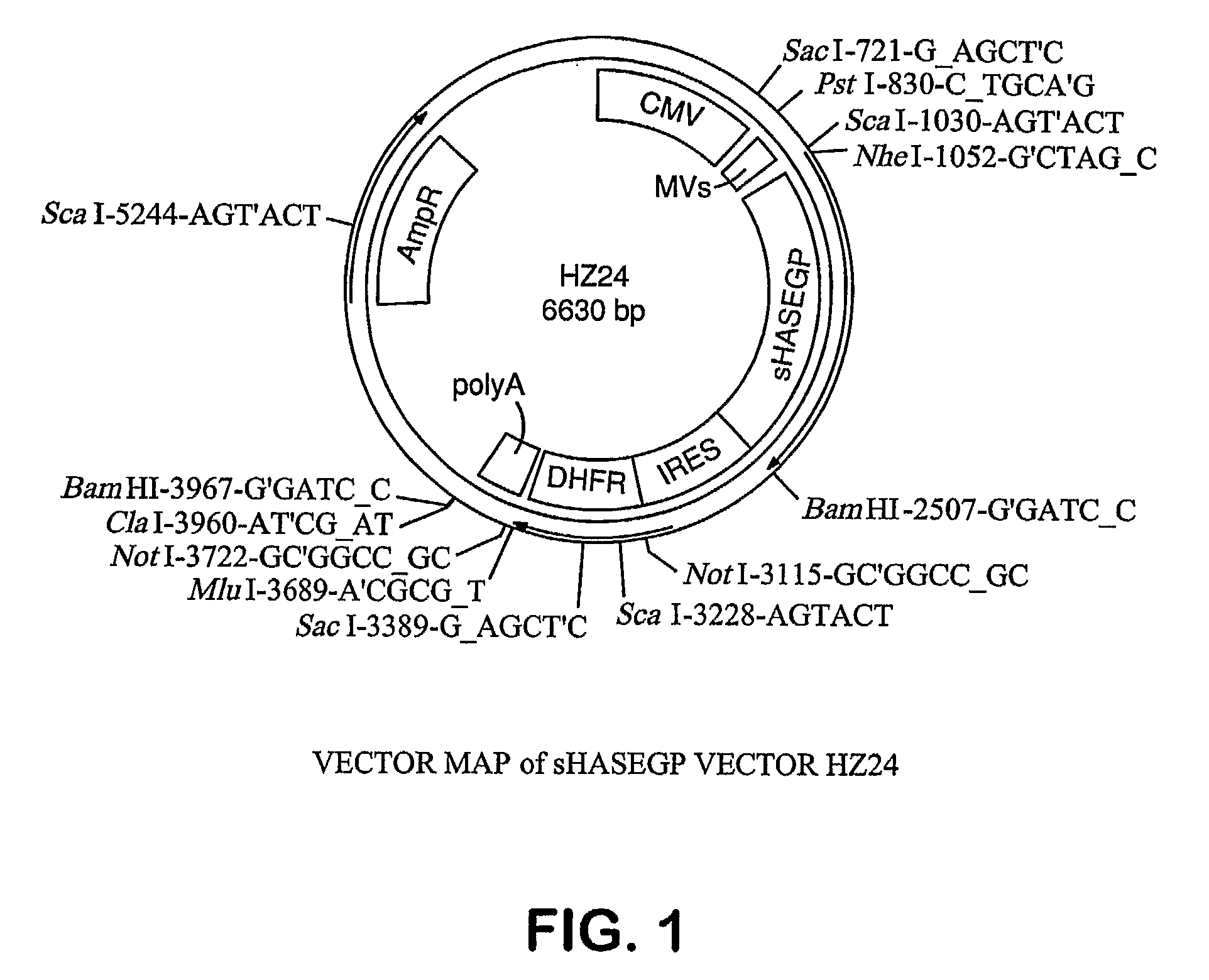
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminogly ycanases
PendingUS20060104968A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsSenses disorderNervous disorderHyaluronidaseRecombinant glycoprotein
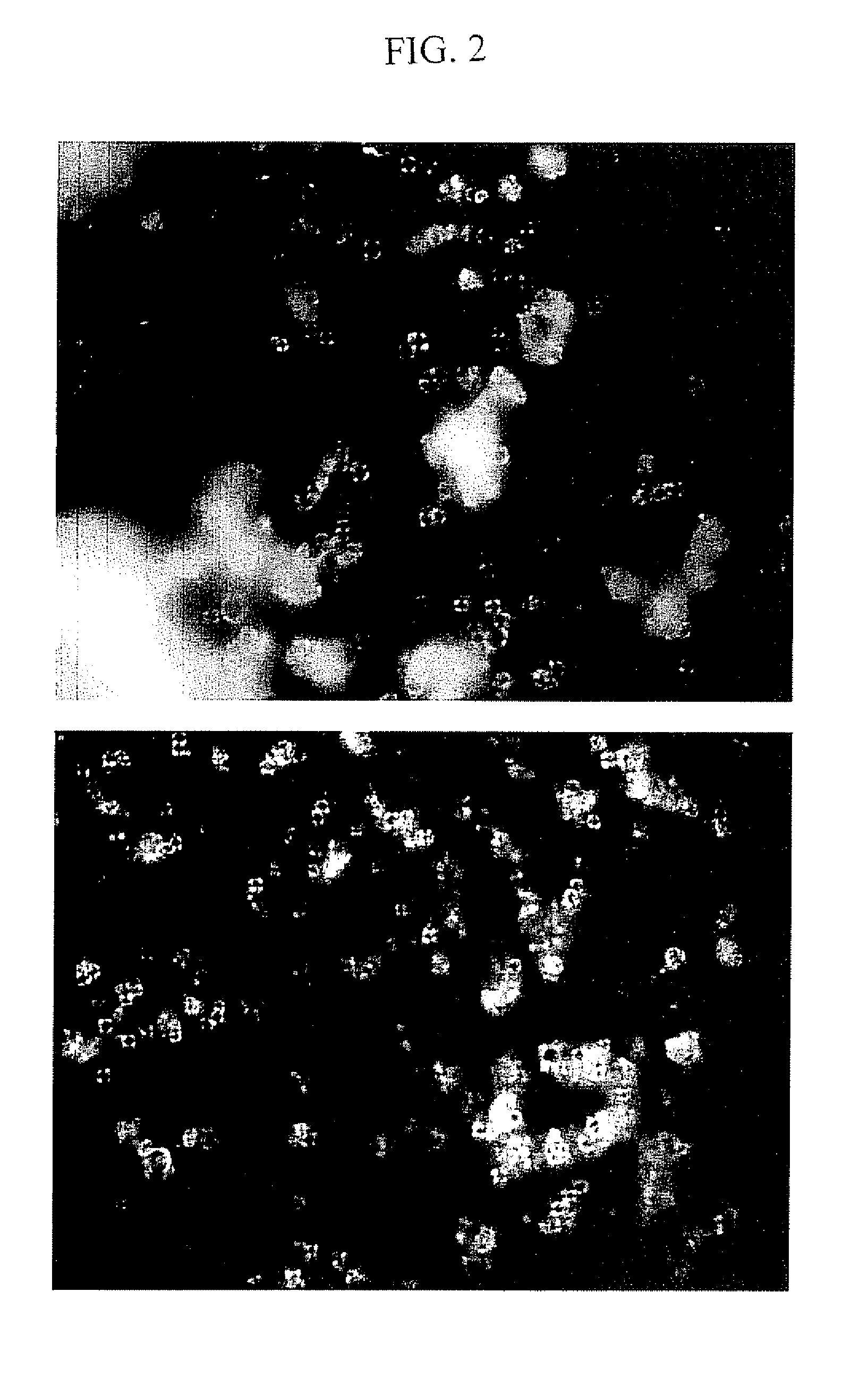
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Fc-erythropoietin fusion protein with improved pharmacokinetics
InactiveUS20050202538A1Improve pharmacokineticsSimplify erythropoietin therapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsErythropoietinNucleic acid
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Fc-erythropoietin fusion protein with improved pharmacokinetics
InactiveUS20050192211A1Improve pharmacokineticsSimplify erythropoietin therapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsErythropoietinNucleic acid
The present invention provides Fc-erythropoietin (“Fc-EPO”) fusion proteins with improved pharmacokinetics. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the production and practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Novel recombinant proteins with N-terminal free thiol
InactiveUS20050170457A1Extended half-lifeIncreases circulating serum half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureCysteine thiolateHalf-life
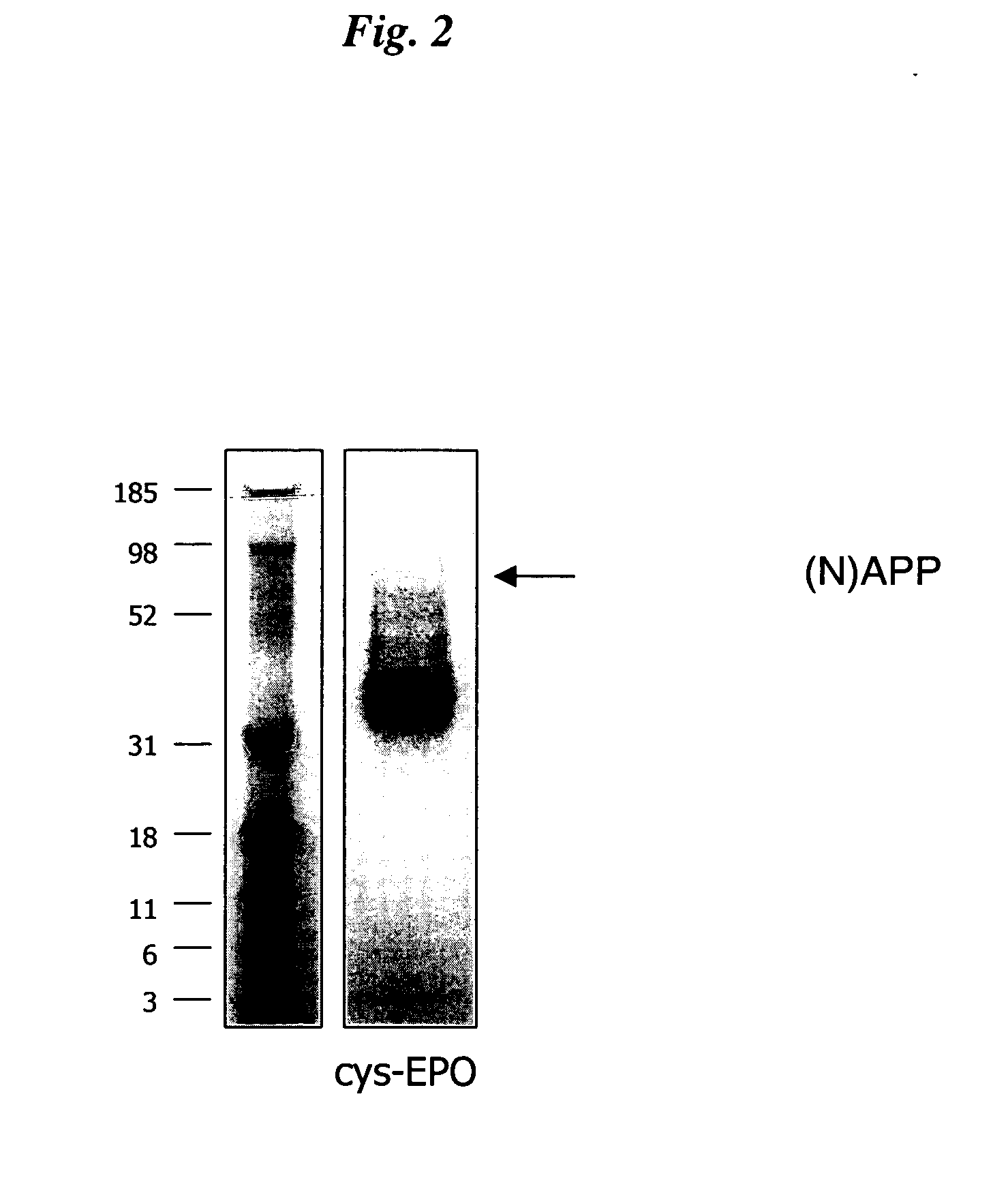
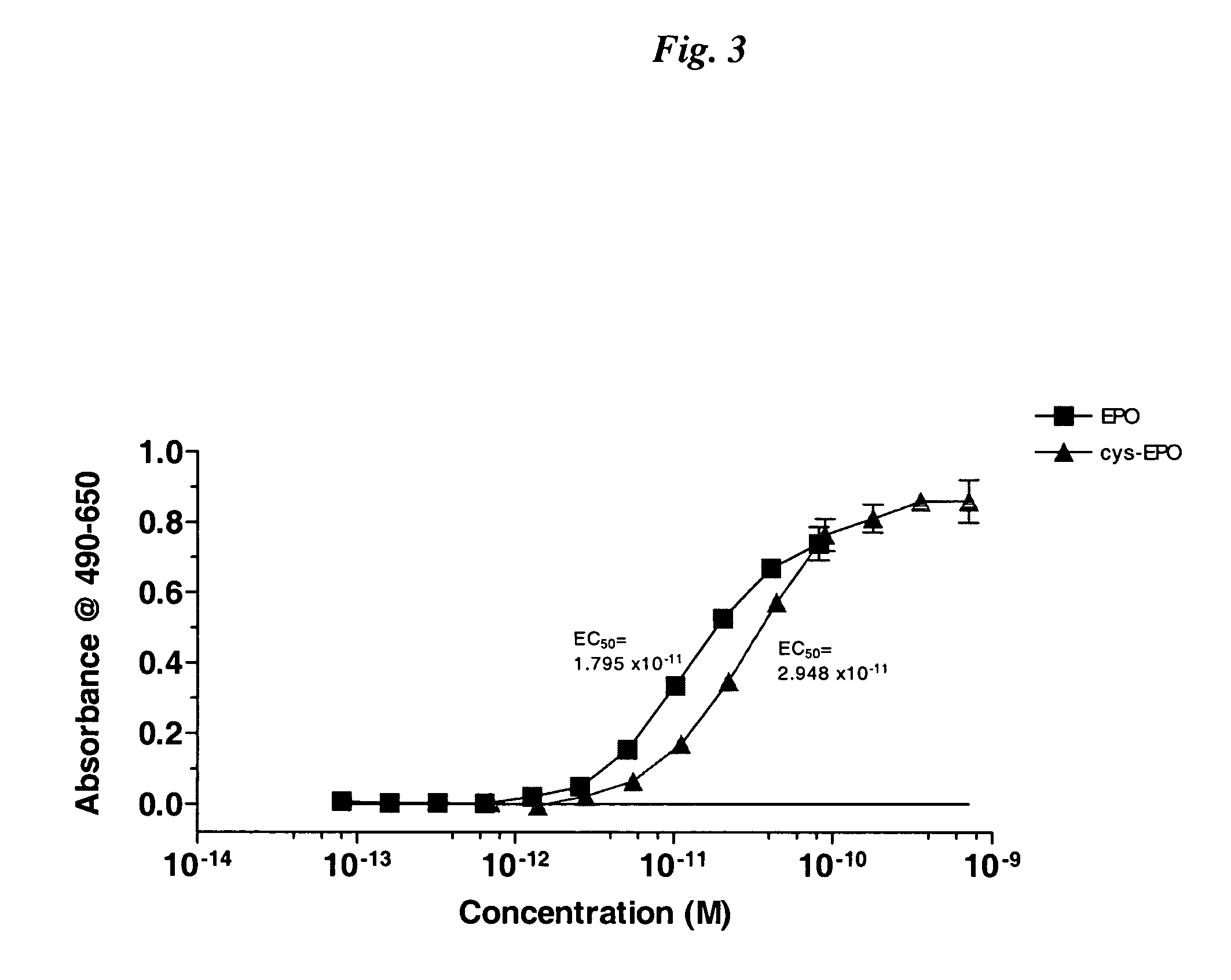
The present invention relates to novel modified proteins having N-terminal free thiols that can be produced by recombinant methods and are ready for further chemical derivatization. In particular, the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds having altered biochemical, physiochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. More particularly, one embodiment of the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds of the formula: (M)n-X-A-cys-EPO (I) where EPO is an erythropoeitin moiety selected from erythropoietin or an erythropoietin variant having at least one amino acid different from the wild-type human EPO, or any pharmaceutical acceptable derivatives thereof having biological properties of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of red blood cells; cys represents the amino acid cysteine and occurs at position −1 relative to the amino acid sequence of the erythropoietin moiety; A indicates the structure of the residual moiety used to chemically attach X to the thiol group of −1Cys; X is a water soluble polymer such as a polyalkylene glycol or other polymer; M is an organic molecule (including peptides and proteins) that increases the circulating half-life of the construct; and N is an integer from 0 to 15.
Owner:CENTOCOR
Serum albumin binding peptides for tumor targeting
InactiveUS20050287153A1Altered pharmacodynamicsFacilitated DiffusionImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAbnormal tissue growthPeptide ligand
Peptide ligands having affinity for serum albumin are useful for tumor targeting. Conjugate molecules comprising a serum albumin binding peptide fused to a biologically active molecule demonstrate modified pharmacokinetic properties as compared with the biologically active molecule alone, including tissue (e.g., tumor) uptake, infiltration, and diffusion.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Nanocell drug delivery system
InactiveUS20050266067A1Avoid flowIncreased toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationAntigen
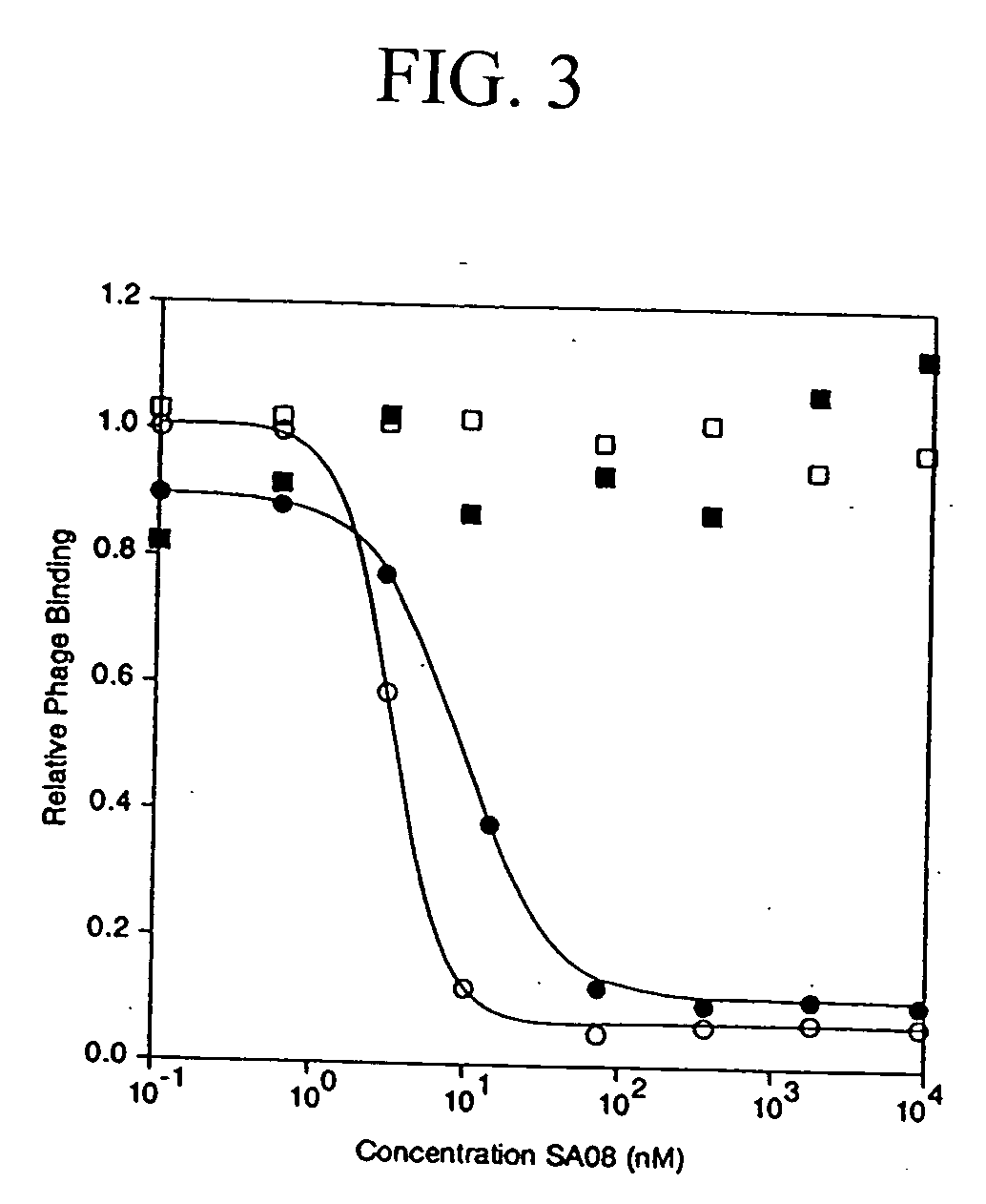
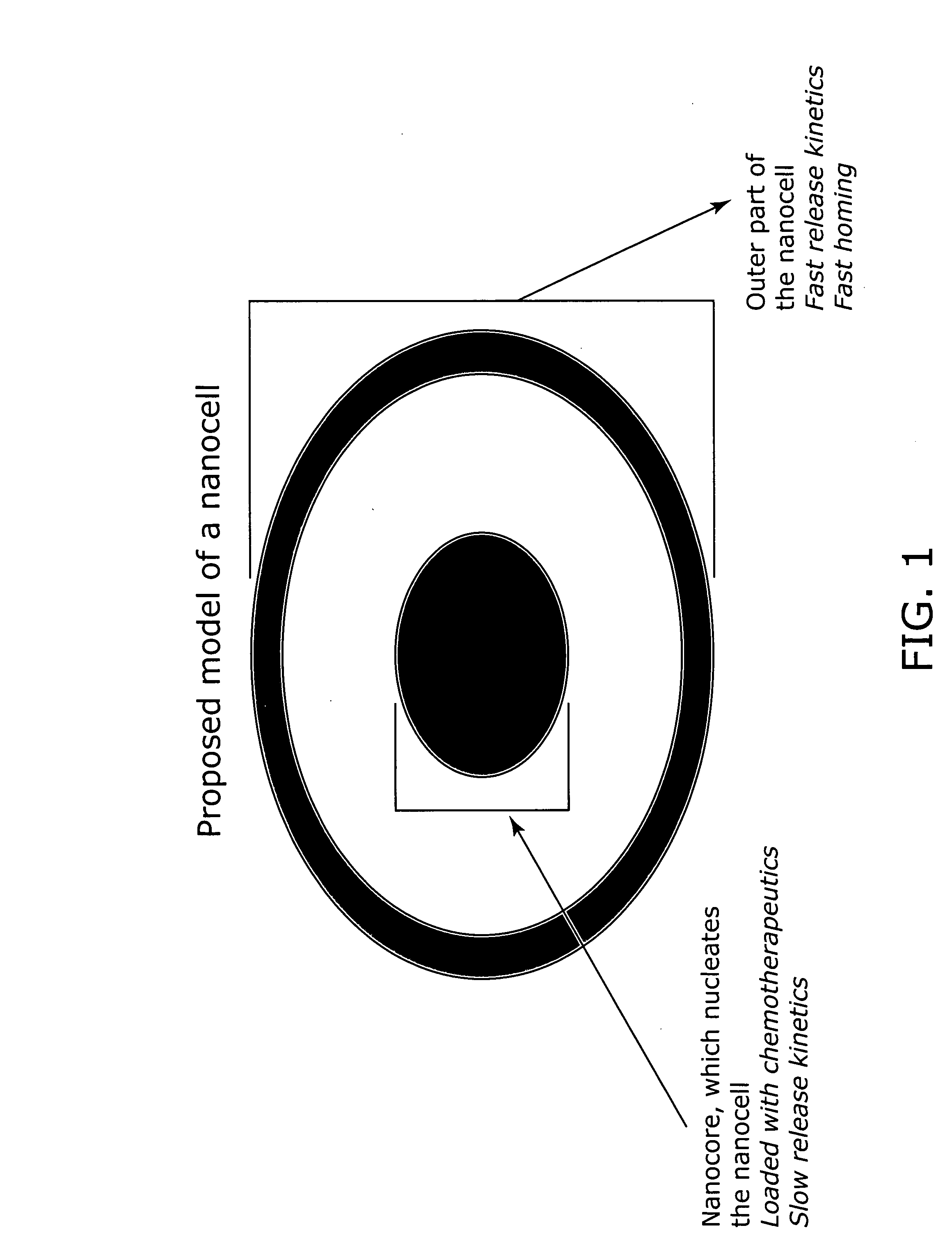
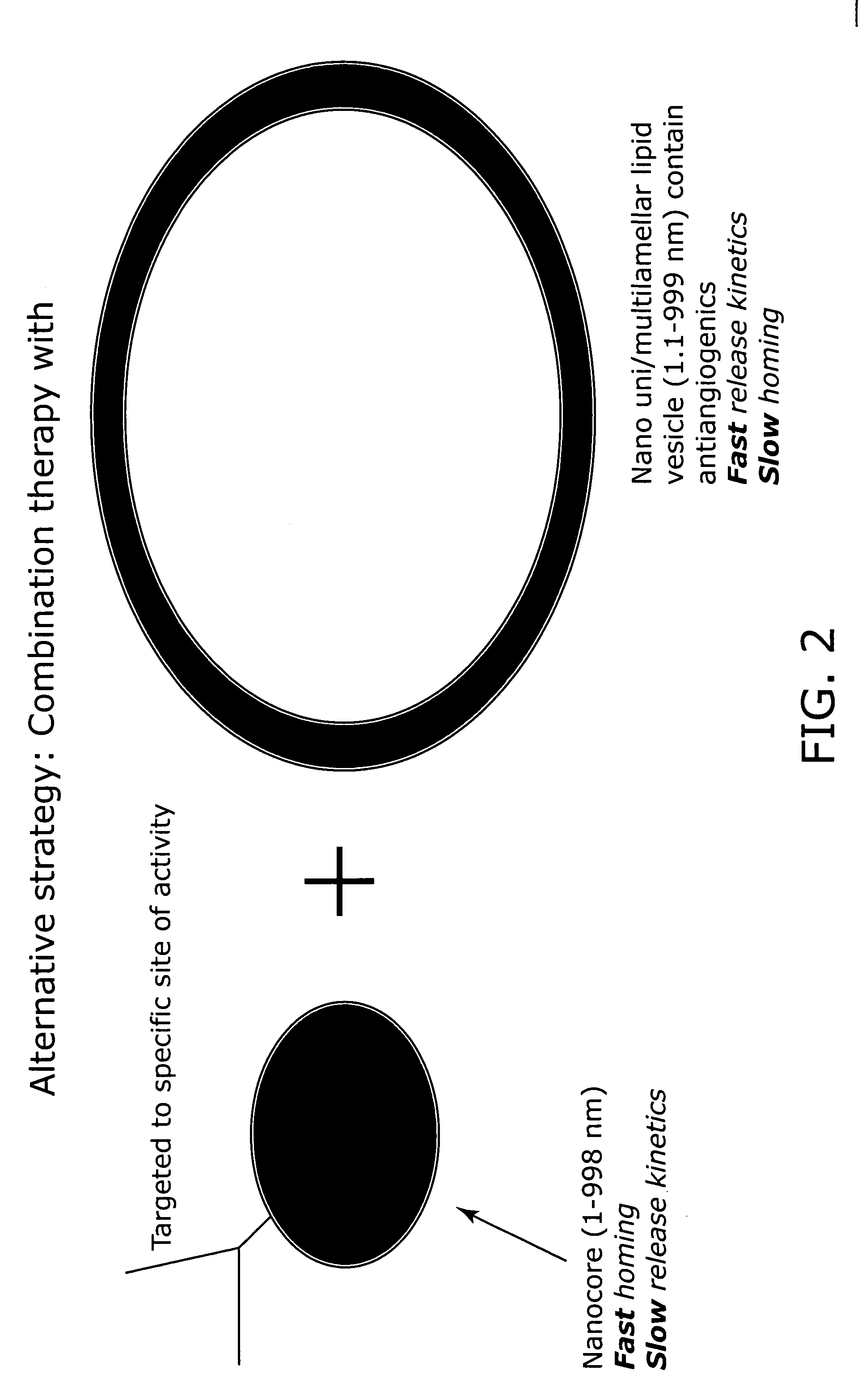
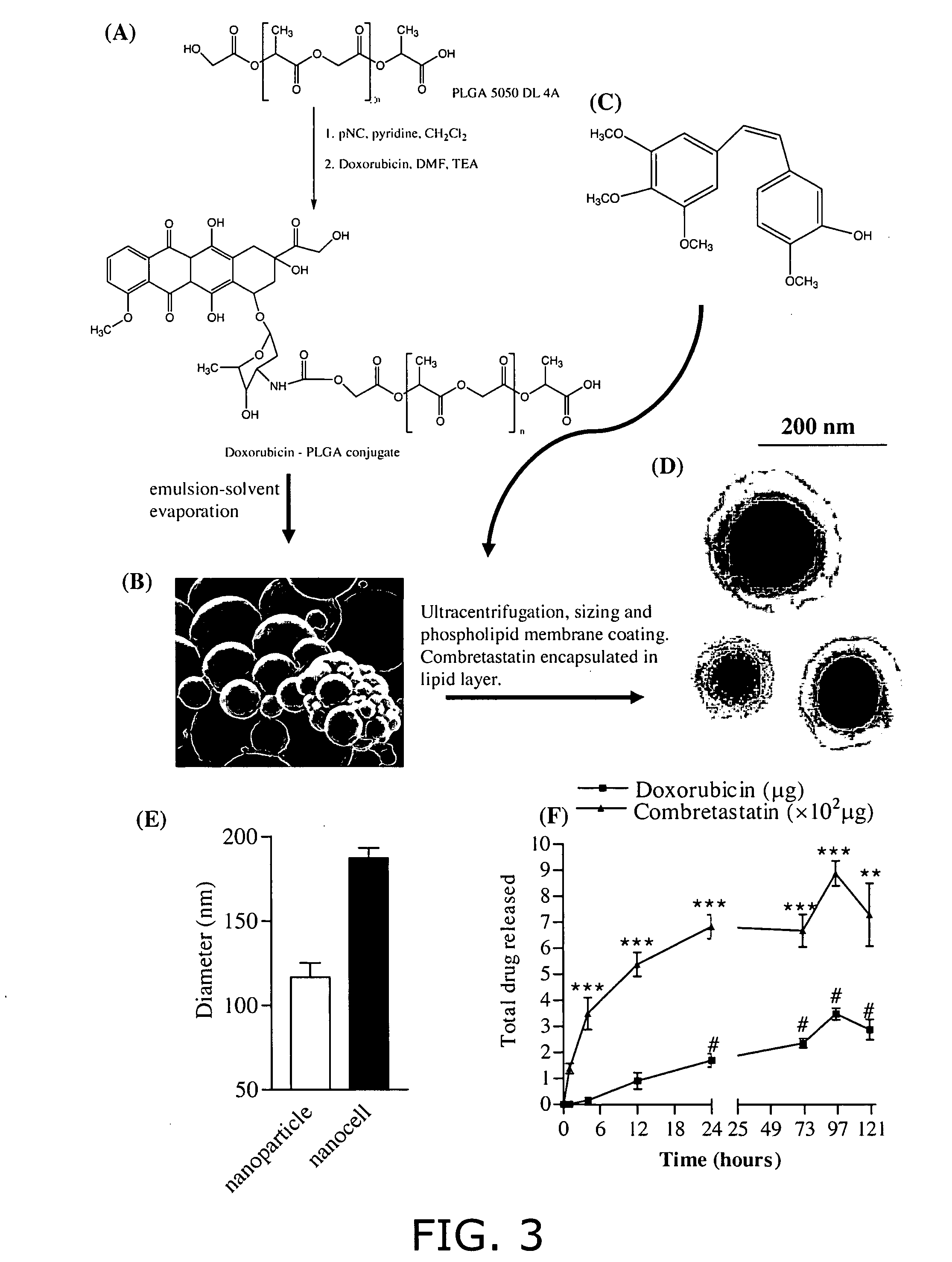
Nanocells allow the sequential delivery of two different therapeutic agents with different modes of action or different pharmacokinetics. A nanocell is formed by encapsulating a nanocore with a first agent inside a lipid vesicle containing a second agent. The agent in the outer lipid compartment is released first and may exert its effect before the agent in the nanocore is released. The nanocell delivery system may be formulated in pharmaceutical composition for delivery to patients suffering from diseases such as cancer, inflammatory diseases such as asthma, autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, infectious diseases, and neurological diseases such as epilepsy. In treating cancer, a traditional antineoplastic agent is contained in the outer lipid vesicle of the nanocell, and an antiangiogenic agent is loaded into the nanocore. This arrangement allows the antineoplastic agent to be released first and delivered to the tumor before the tumor's blood supply is cut off by the antianiogenic agent.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Single-stranded and double-stranded oligonucleotides comprising a 2-arylpropyl moiety
ActiveUS20060008822A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderNucleotidePhosphate
One aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one aralkyl ligand. In certain embodiments, an aralkyl ligand is bound to only one of the two oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, an aralkyl ligand is bound to both of the oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the aralkyl ligand is naproxen or ibuprofen. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one aralkyl ligand. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide comprises at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the aralkyl ligand is naproxen or ibuprofen. The aralkyl ligand improves the pharmacokinetic properties of the oligonucleotide.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Method of Modifying Isoelectric Point of Antibody Via Amino Acid Substitution in CDR
ActiveUS20110076275A1Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activityImprove retentionSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAmino acid substitution
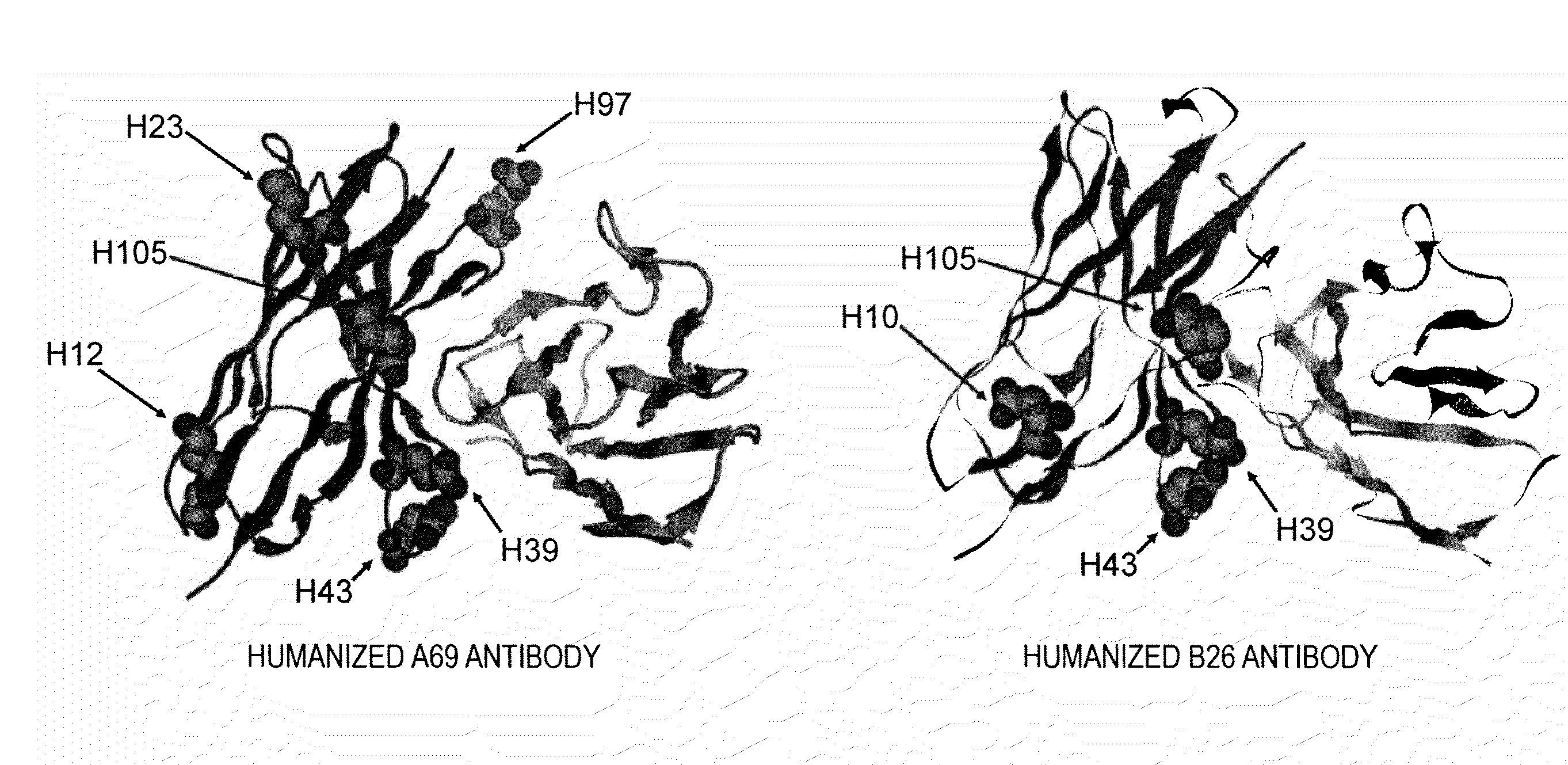
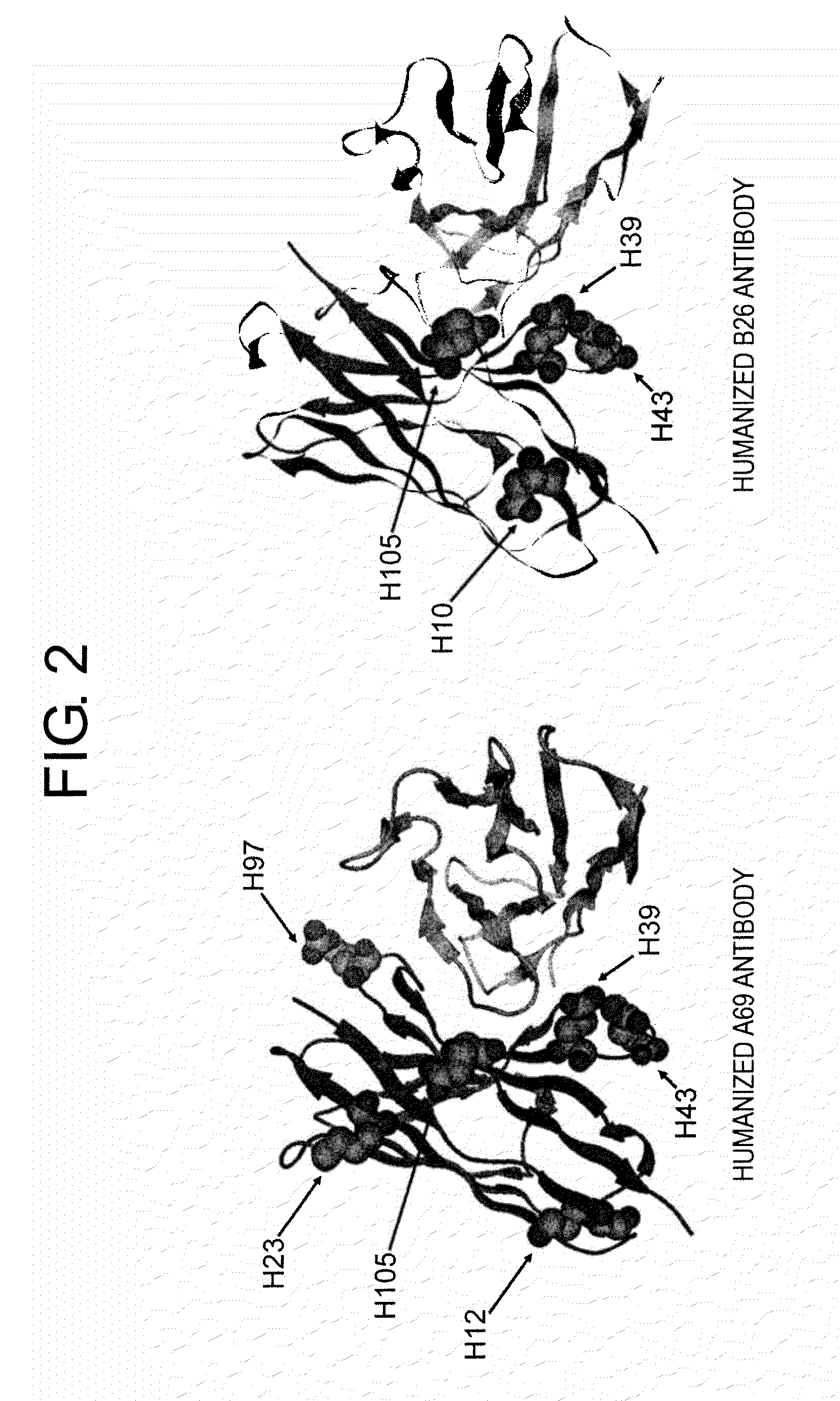
The present inventors provide methods for modifying the isoelectric point of an antibody while retaining its antigen-binding activity, comprising modifying the charge of at least one exposable amino acid residue on the surface of the complementarity determining region (CDR). The present invention also provides methods for purifying multispecific antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point, and methods for improving the plasma pharmacokinetics of antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point. The present invention further provides antibodies with a modified isoelectric point, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies as an active ingredient, and methods for producing the antibodies and compositions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Modified Antibody Constant Region
ActiveUS20100298542A1Improving immunogenicityImprove propertiesAntipyreticAnalgesicsHigh concentrationHinge region
The present inventors succeeded in improving the antibody constant region to have increased stability under acid conditions, reduced heterogeneity originated from disulfide bonds in the hinge region, reduced heterogeneity originated from the H chain C terminus, and increased stability at high concentrations as well as in discovering novel constant region sequences having reduced Fcγ receptor-binding, while minimizing the generation of novel T-cell epitope peptides. As a result, the present inventors successfully discovered antibody constant regions with improved physicochemical properties (stability and homogeneity), immunogenicity, safety, and pharmacokinetics.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Anti-IL-6 Receptor Antibody
InactiveUS20110245473A1Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activity and pharmacokineticsGood treatment effectCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHigh concentrationHinge region
The present inventors succeeded in discovering specific amino acid mutations in the variable region, framework region, and constant region of TOCILIZUMAB, and this enables to reduce immunogenicity risk and the heterogeneity originated from disulfide bonds in the hinge region, as well as to improve antigen binding activity, pharmacokinetics, stability under acidic conditions, and stability in high concentration preparations.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
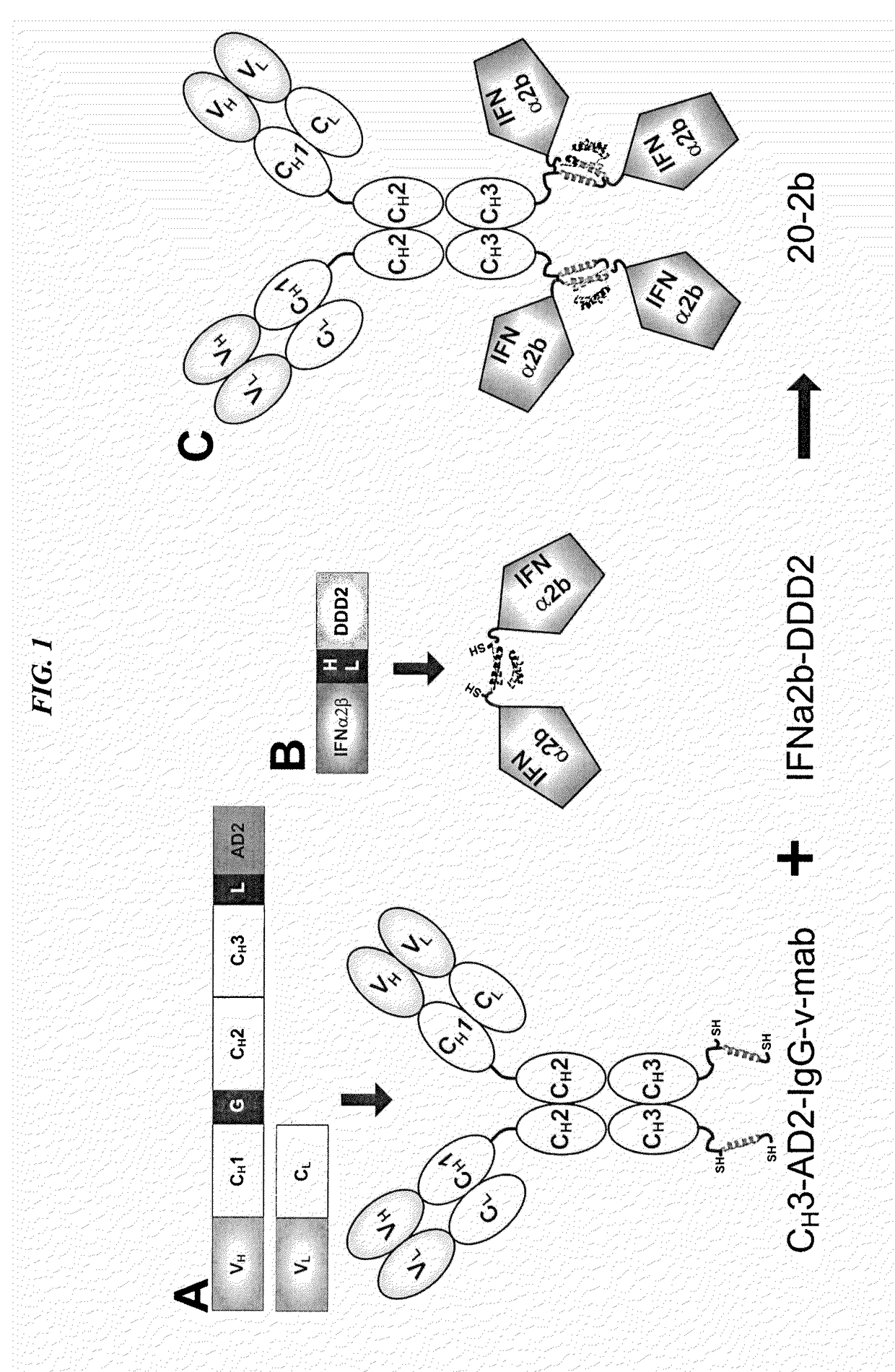
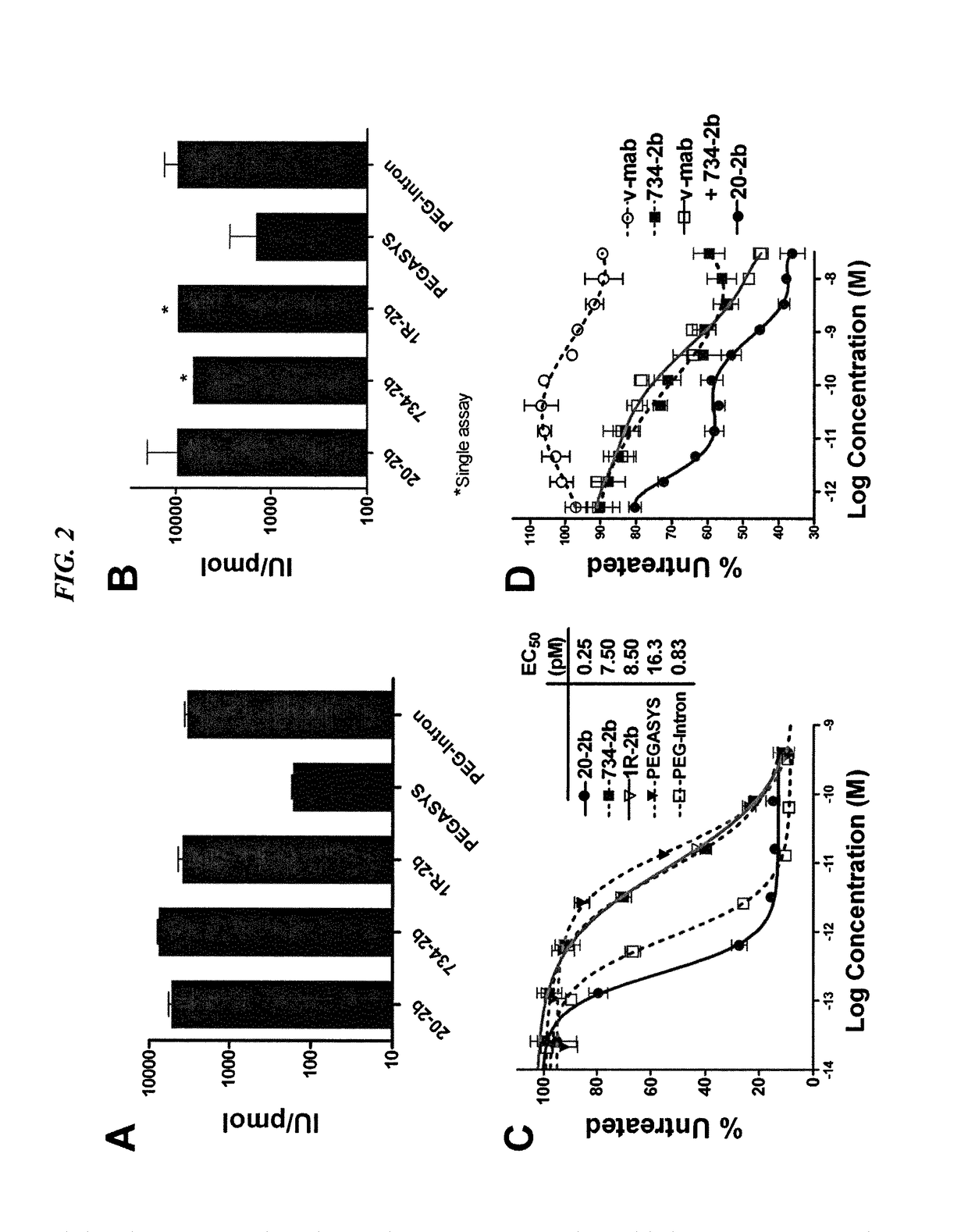
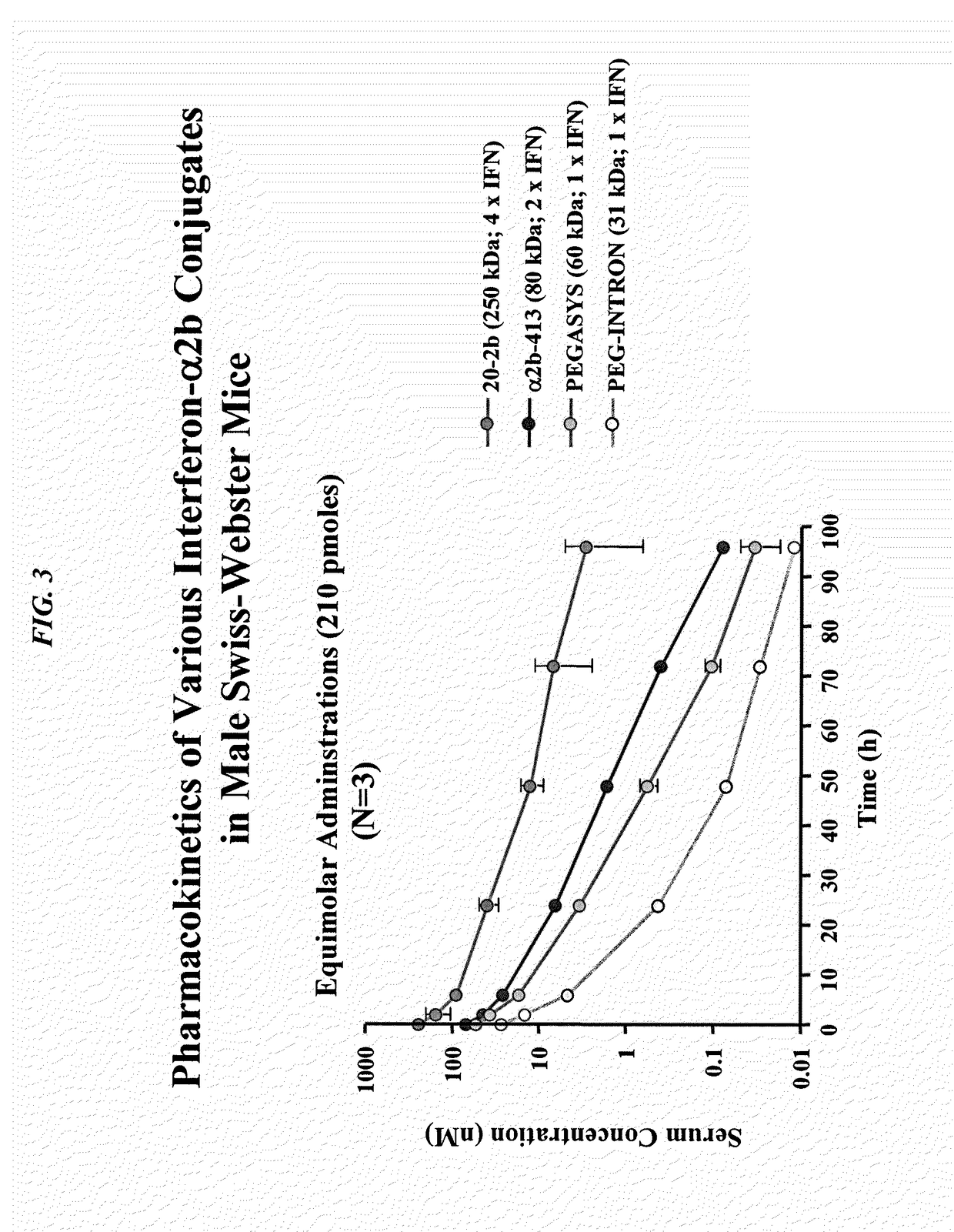
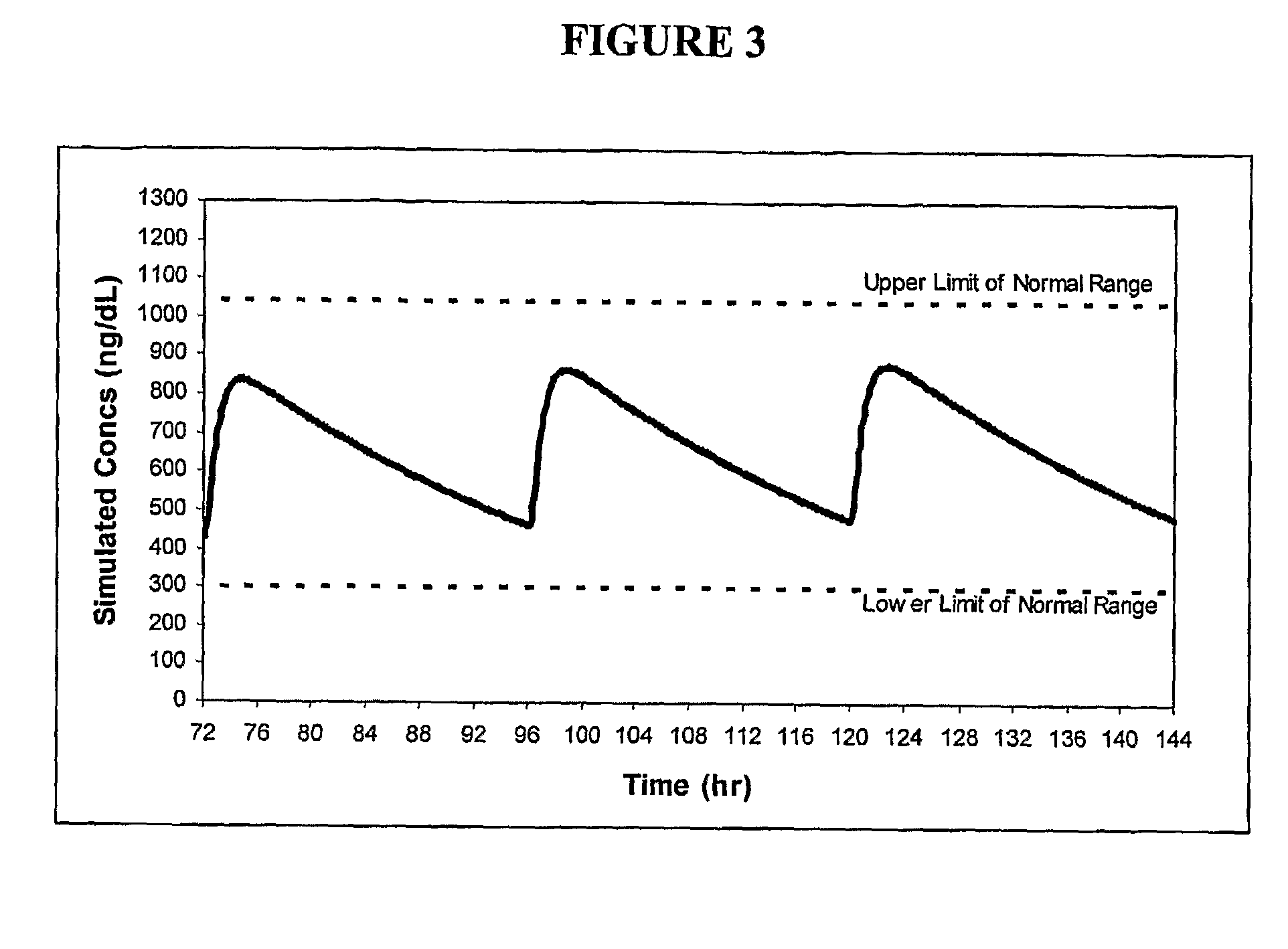
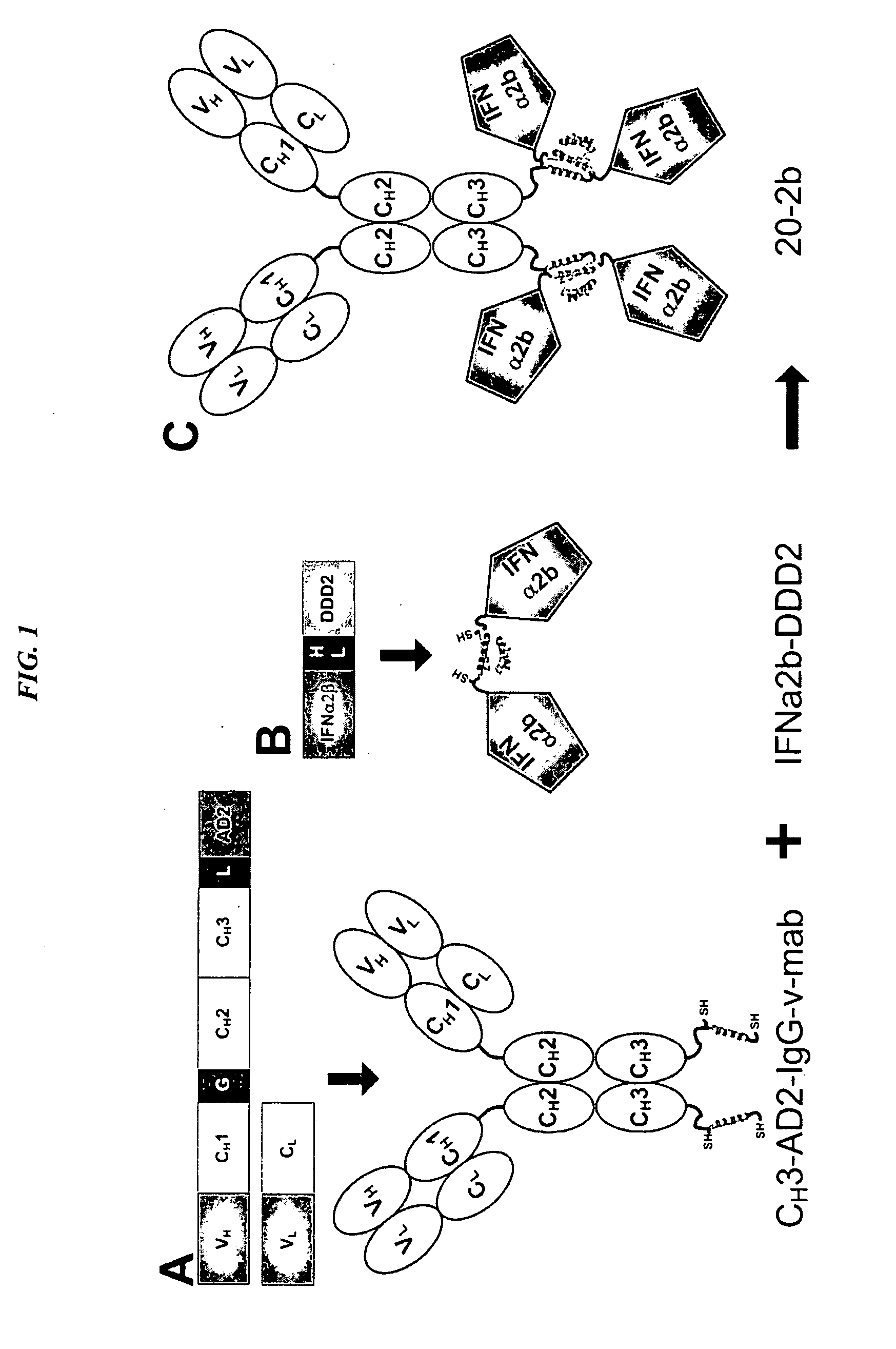
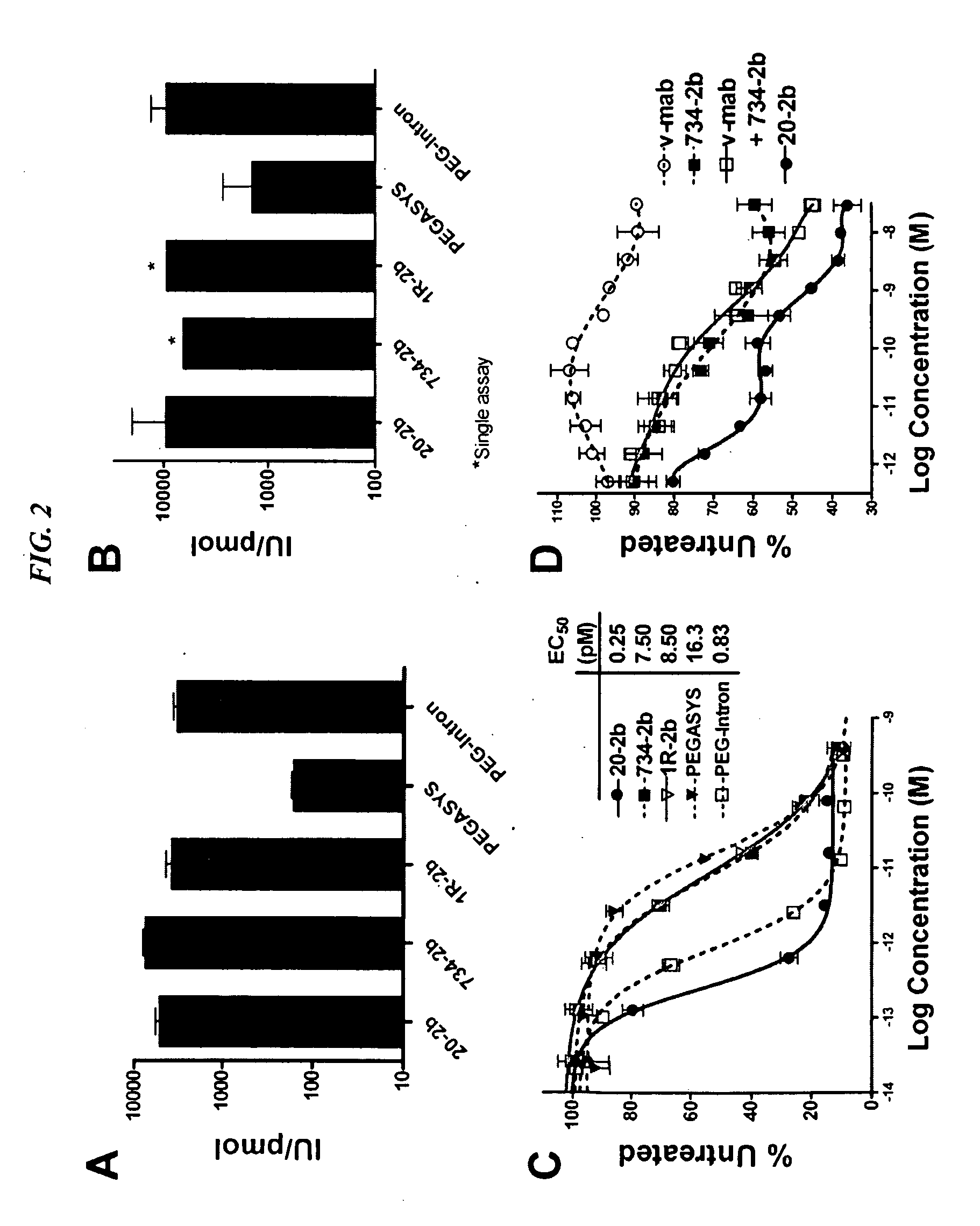
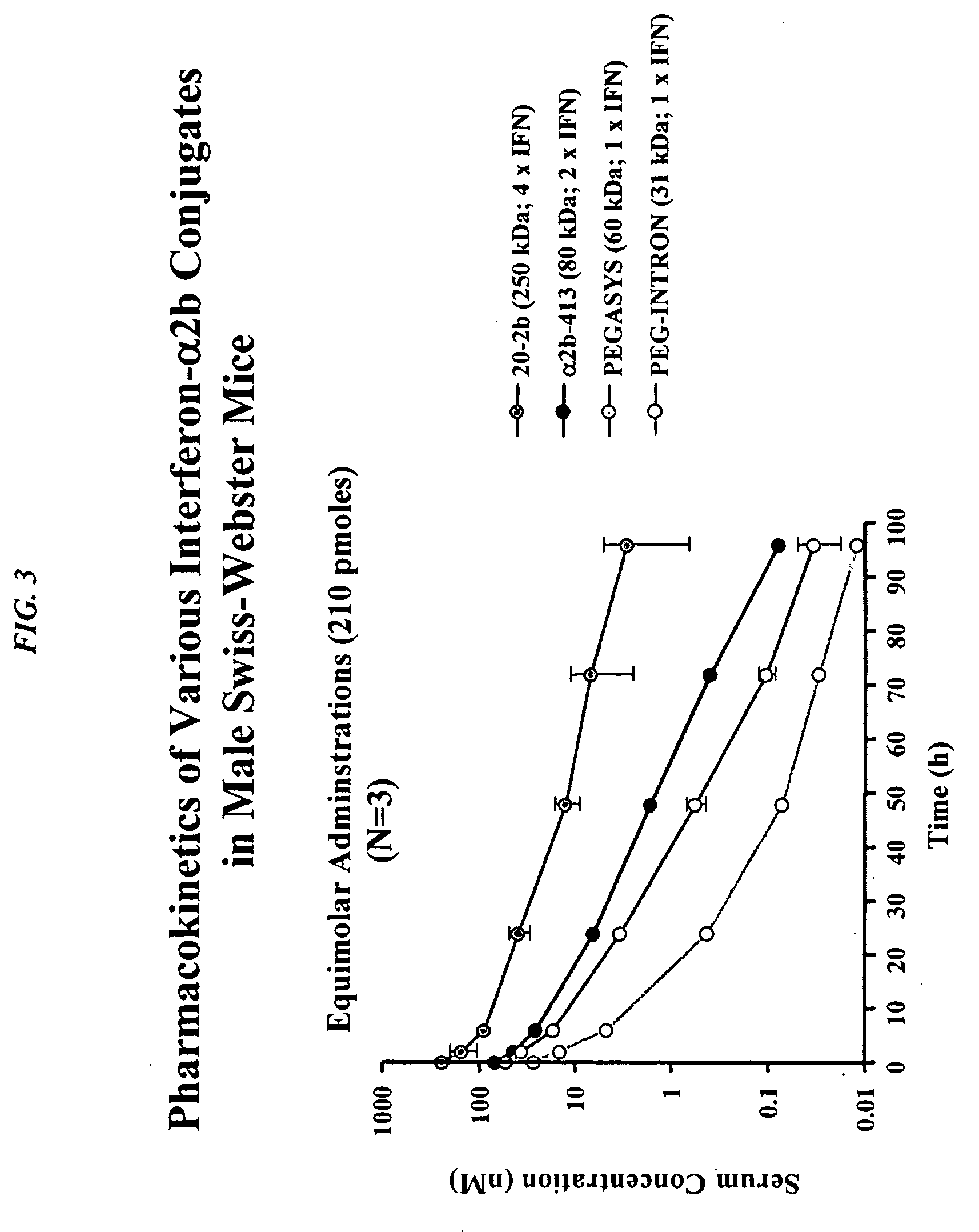
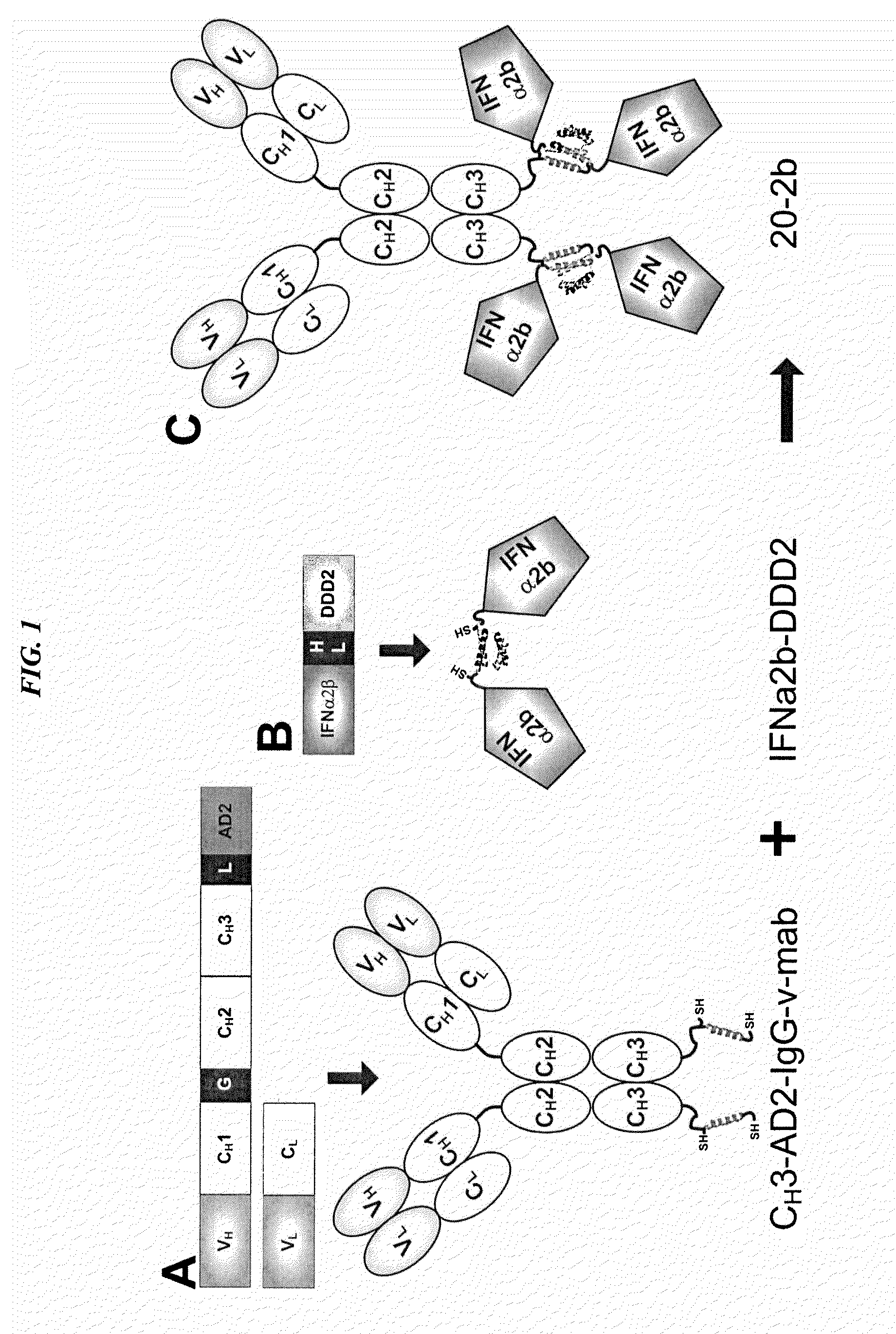
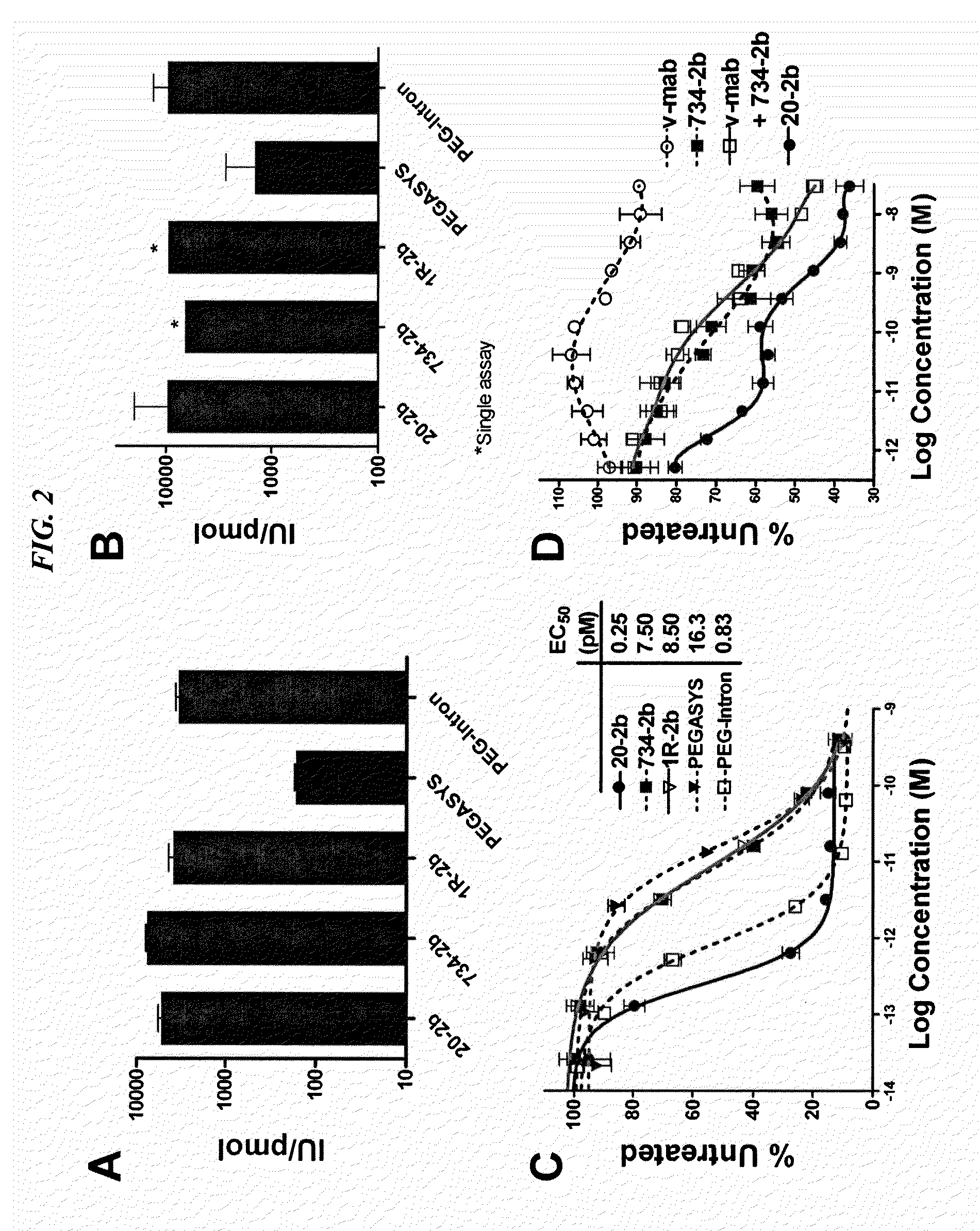
Modular method to prepare tetrameric cytokines with improved pharmacokinetics by the dock-and-lock (DNL) technology
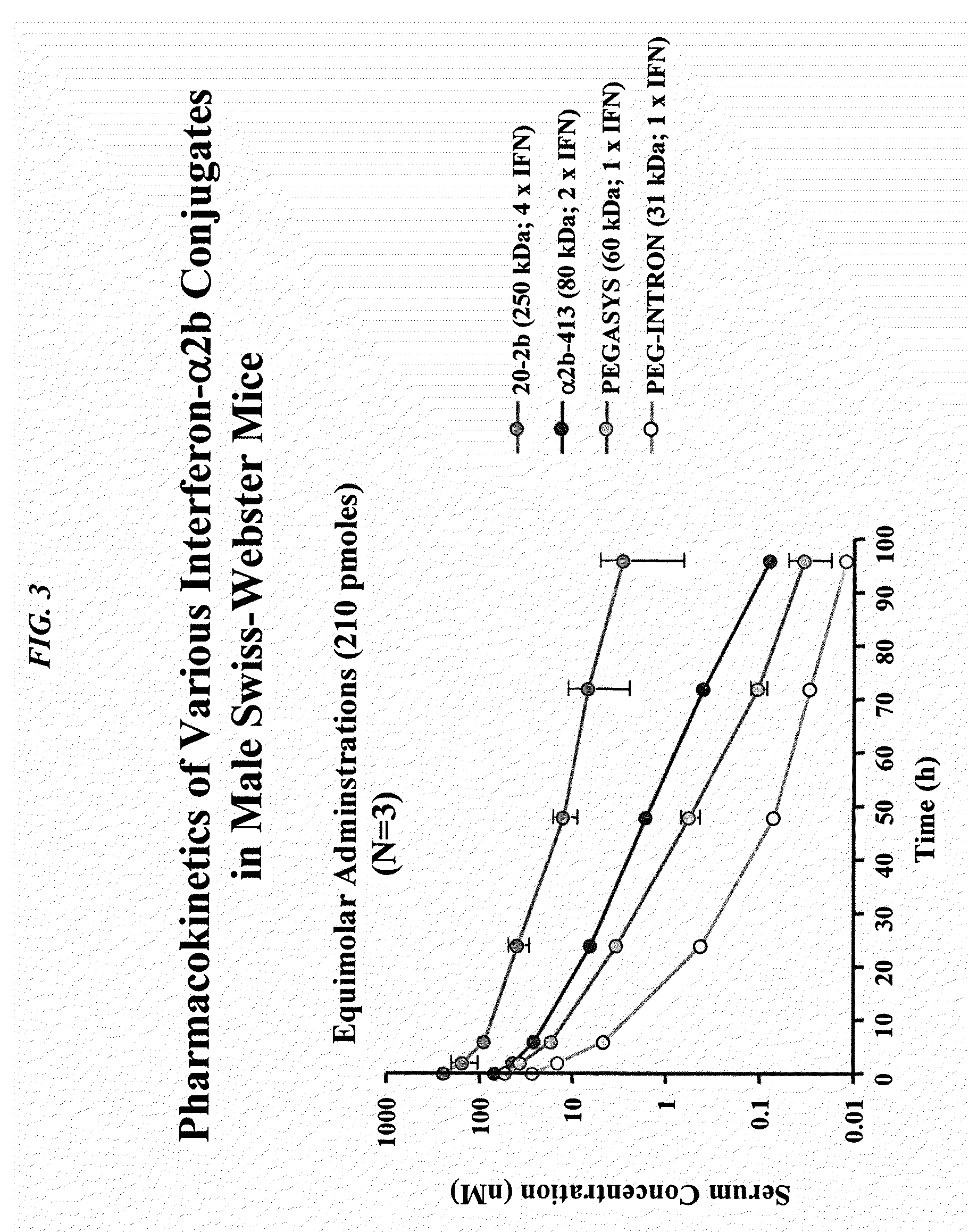
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming cytokine-antibody complexes using dock-and-lock technology. In preferred embodiments, the cytokine-MAb DNL complex comprises an IgG antibody attached to two AD (anchor domain) moieties and four cytokines, each attached to a DDD (docking and dimerization domain) moiety. The DDD moieties form dimers that bind to the AD moieties, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of DDD to AD. The cytokine-MAb complex exhibits improved pharmacokinetics, with a significantly longer serum half-life than either naked cytokine or PEGylated cytokine. The cytokine-MAb complex also exhibits significantly improved in vitro and in vivo efficacy compared to cytokine alone, antibody alone, unconjugated cytokine plus antibody or cytokine-MAb DNL complexes incorporating an irrelevant antibody. In a most preferred embodiment the complex comprises an anti-CD20 IgG antibody conjugated to four IFN-α2b moieties, although other antibodies and cytokines have been used to form effect DNL complexes.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Pharmaceutical delivery systems for hydrophobic drugs and compositions comprising same
ActiveUS8241664B2Preventing and alleviating symptomInhibition releaseBiocideOintment deliveryOral medicationMedicine
A drug delivery system for oral administration of hydrophobic drugs with enhanced and extended absorption and improved pharmacokinetics is provided. In one embodiment, formulations comprising testosterone and testosterone esters, e.g., testosterone palmitate, are disclosed. Methods of treating a hormone deficiency or effecting male contraception with the inventive formulations are also provided.
Owner:TOLMAR INC
Pharmaceutical Delivery Systems for Hydrophobic Drugs and Compositions Compositions Comprising Same
ActiveUS20080317844A1Preventing and alleviating symptomInhibition releaseBiocideOintment deliveryOral medicationDelivery system
A drug delivery system for oral administration of hydrophobic drugs with enhanced and extended absorption and improved pharmacokinetics is provided. In one embodiment, formulations comprising testosterone and testosterone esters, e.g., testosterone palmitate, are disclosed. Methods of treating a hormone deficiency or effecting male contraception with the inventive formulations are also provided.
Owner:TOLMAR INC
Modular Method to Prepare Tetrameric Cytokines with Improved Pharmacokinetics by the Dock-and-Lock (DNL) Technology
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming cytokine-antibody complexes using dock-and-lock technology. In preferred embodiments, the cytokine-MAb DNL complex comprises an IgG antibody attached to two AD (anchor domain) moieties and four cytokines, each attached to a DDD (docking and dimerization domain) moiety. The DDD moieties form dimers that bind to the AD moieties, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of DDD to AD. The cytokine-MAb complex exhibits improved pharmacokinetics, with a significantly longer serum half-life than either naked cytokine or PEGylated cytokine. The cytokine-MAb complex also exhibits significantly improved in vitro and in vivo efficacy compared to cytokine alone, antibody alone, unconjugated cytokine plus antibody or cytokine-MAb DNL complexes incorporating an irrelevant antibody. In a most preferred embodiment the complex comprises an anti-CD20 IgG antibody conjugated to four IFN-α2b moieties, although other antibodies and cytokines have been used to form effect DNL complexes.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
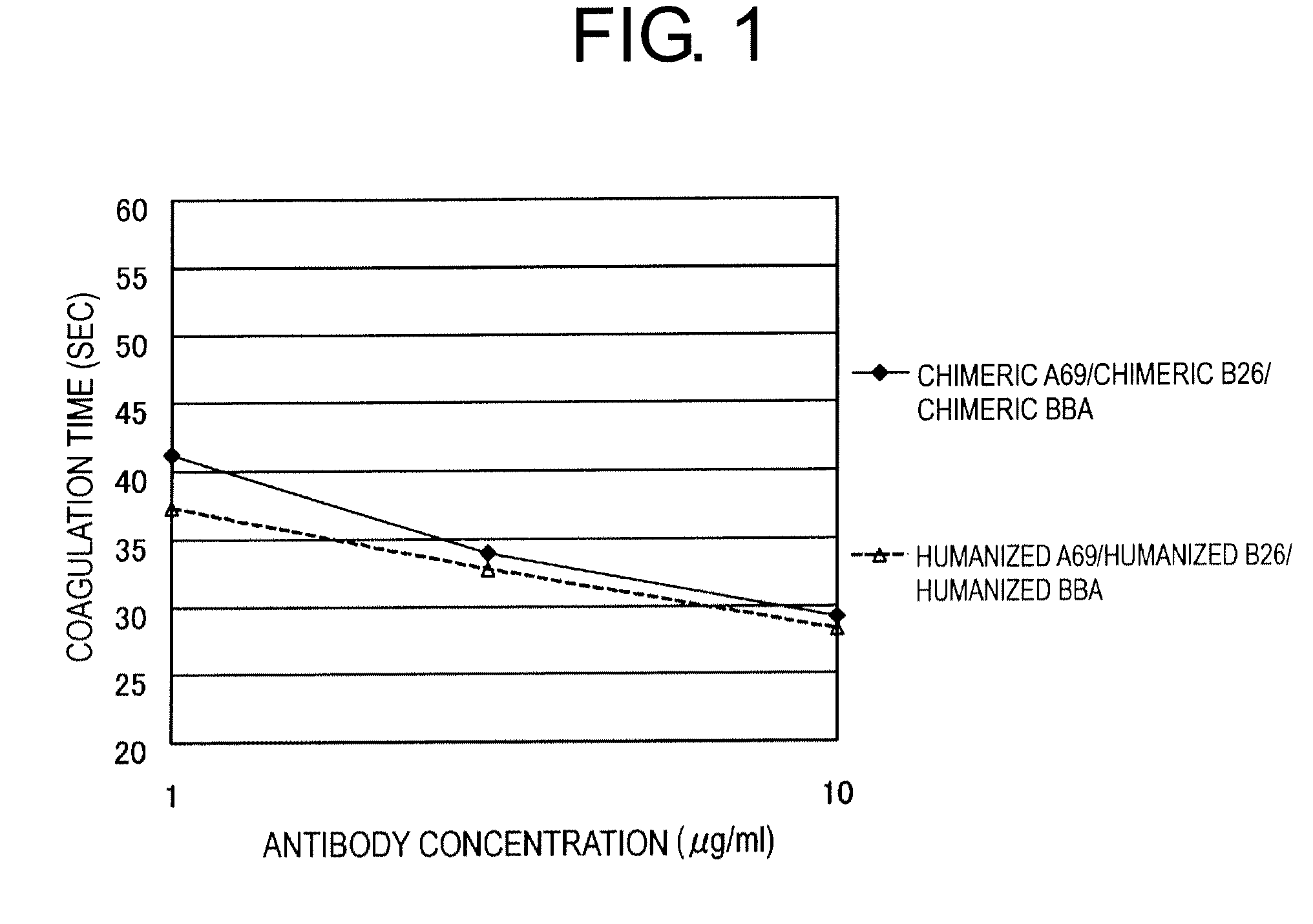
Methods for controlling blood pharmacokinetics of antibodies
The present inventors discovered that the half-life in blood of an IgG antibody which is a polypeptide comprising an FcRn-binding domain can be controlled by controlling the surface charge through modification of residues exposed on the surface among residues in the variable regions of the IgG antibody. Antibodies whose half-life in blood had been controlled by the methods of the present invention were confirmed to actually retain the original activity. The methods of the present invention are widely applicable to polypeptides comprising an FcRn-binding domain, such as IgG antibodies, which are recycled via the FcRn salvage pathway regardless of the type of target antigen.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
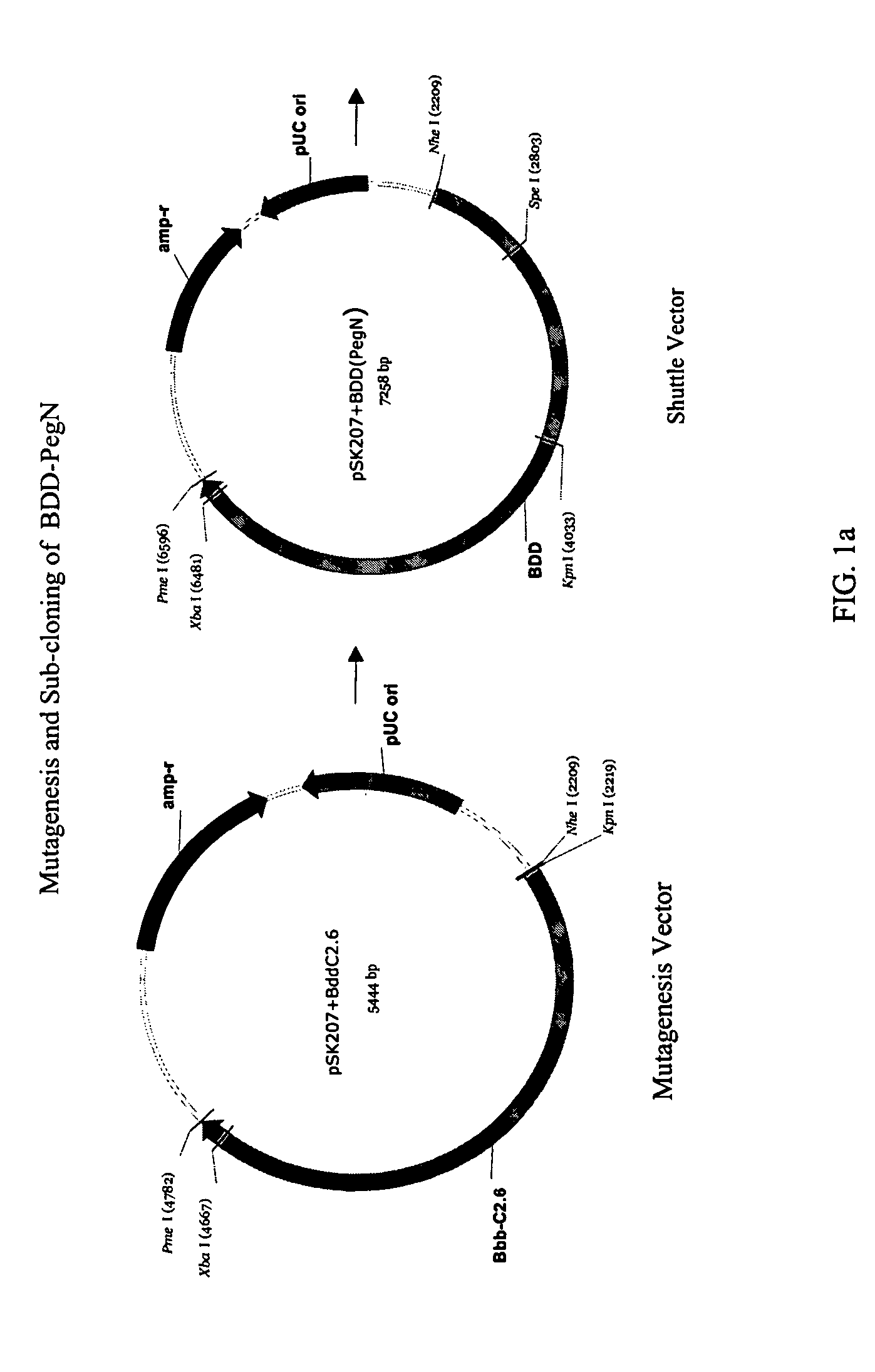
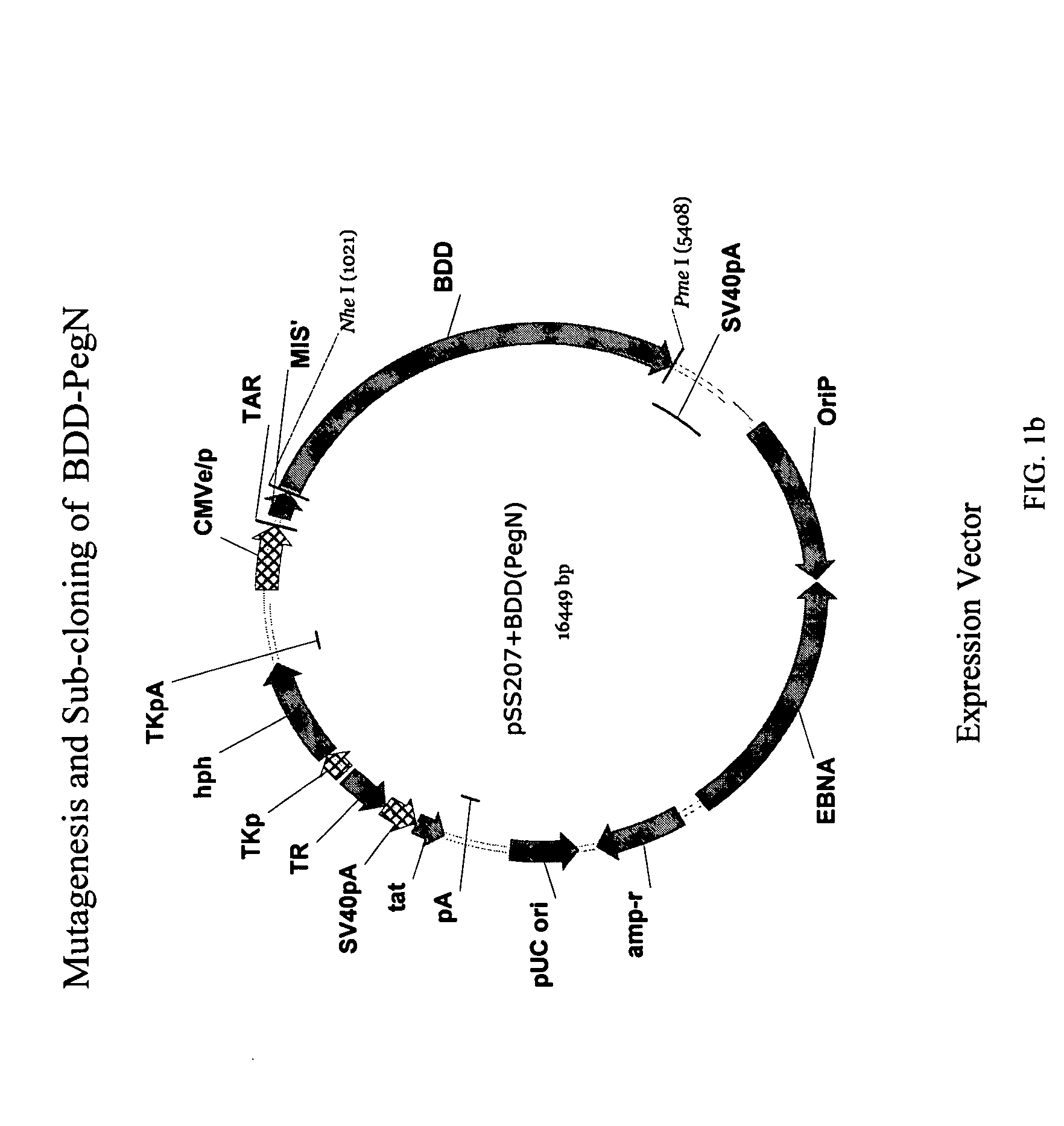
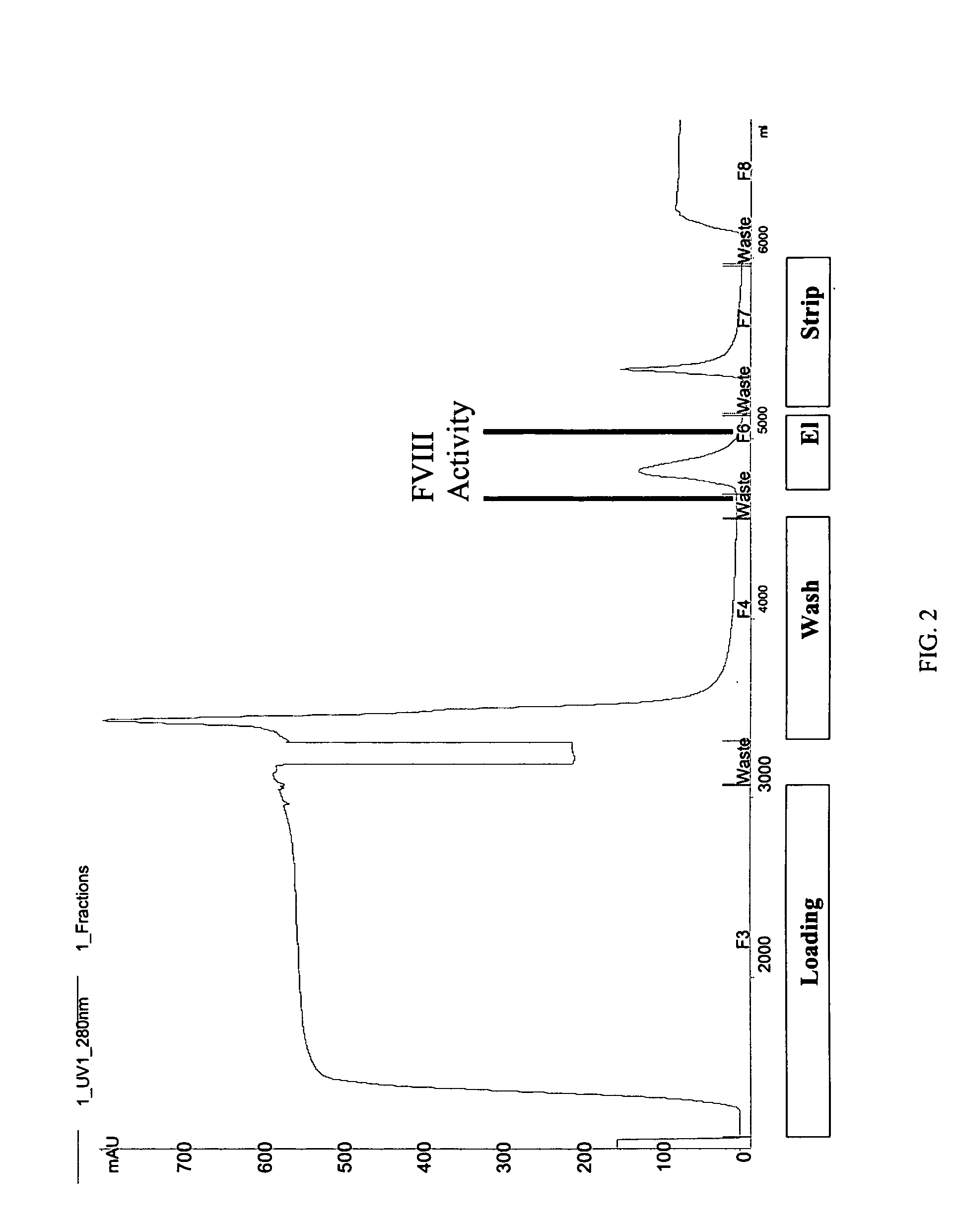
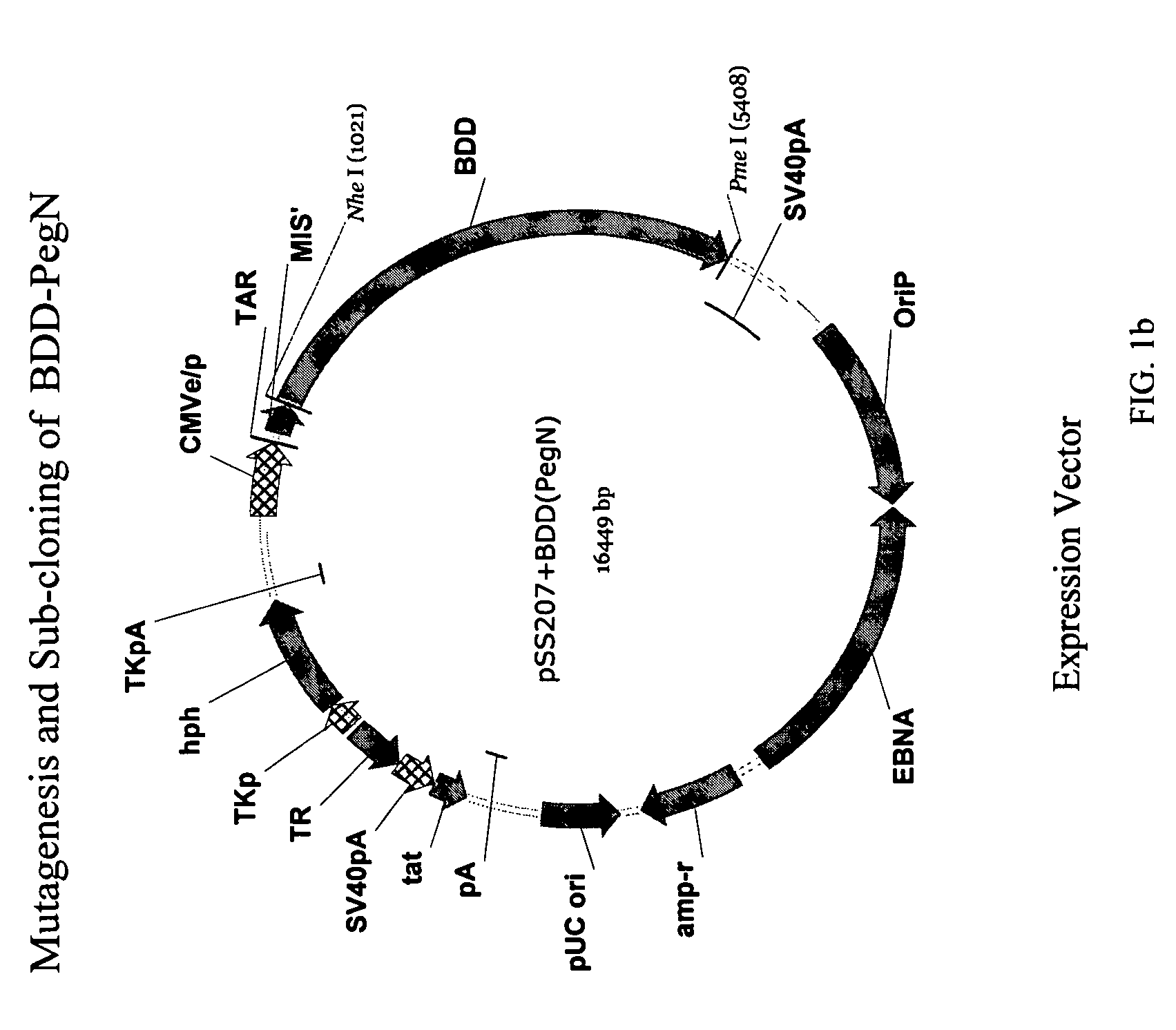
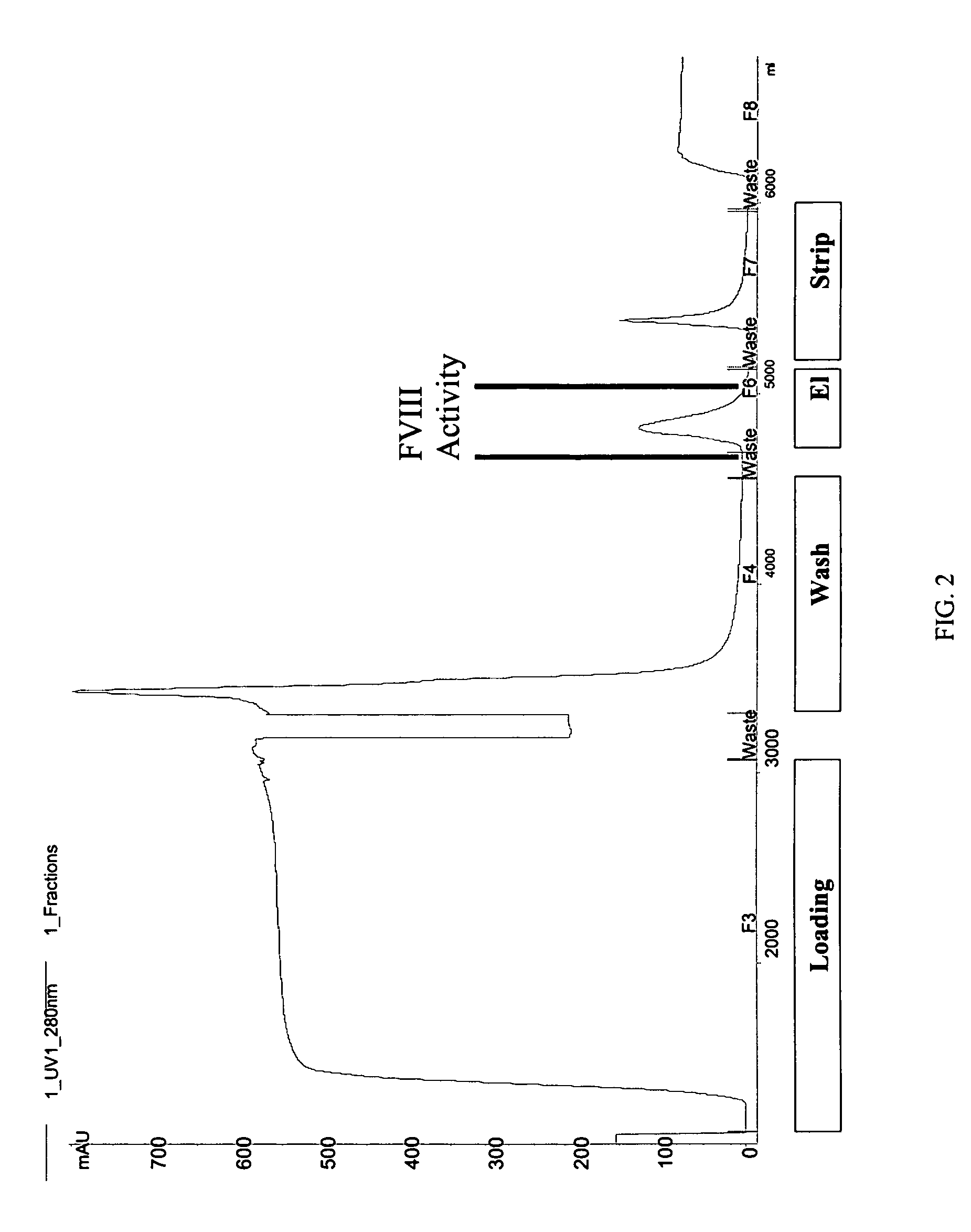
Site-directed modification of FVIII
ActiveUS20060115876A1Improve featuresImproved pharmacokinetic propertiesFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsPolyethylene glycolMutant protein
This invention relates to Factor VIII muteins that are covalently bound, at a predefined site that is not an N-terminal amine, to one or more biocompatible polymers such as polyethylene glycol. The mutein conjugates retain FVIII procoagulant activity and have improved pharmacokinetic properties.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases and Methods of Preparing and Using Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases
InactiveUS20090123367A1Facilitated DiffusionEnhance convective transportBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHyaluronidaseNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME +6
Conjugated oligomeric compounds and their use in gene modulation
The present invention provides modified oligomeric compounds that modulate gene expression via an RNA interference pathway. The oligomeric compounds of the invention include one or more conjugate moieties that can modify or enhance the pharmacokinetic and phamacodynamic properties of the attached oligomeric compound.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Site-directed modification of FVIII
ActiveUS7632921B2Improve featuresImproved pharmacokinetic propertiesFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIII deficiencyPolyethylene glycol
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Tetrameric cytokines with improved biological activity
ActiveUS8034352B2Keep for a long timeLow toxicityMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igeHalf-life
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming cytokine-antibody complexes using dock-and-lock technology. In preferred embodiments, the cytokine-MAb DNL complex comprises an IgG antibody attached to two AD (anchor domain) moieties and four cytokines, each attached to a DDD (docking and dimerization domain) moiety. The DDD moieties form dimers that bind to the AD moieties, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of DDD to AD. The cytokine-MAb complex exhibits improved pharmacokinetics, with a significantly longer serum half-life than either naked cytokine or PEGylated cytokine. The cytokine-MAb complex also exhibits significantly improved in vitro and in vivo efficacy compared to cytokine alone, antibody alone, unconjugated cytokine plus antibody or cytokine-MAb DNL complexes incorporating an irrelevant antibody. In more preferred embodiment the cytokine is G-CSF, erythropoietin or INF-α2b.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Parenteral formulations of dopamine agonists
InactiveUS20100035886A1Reducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorReducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorsBiocideMetabolism disorderParenteral nutritionParenteral Dosage Form
This invention relates to stable pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral administration comprising dopamine agonists and peripheral acting agents useful for treatment of metabolic disorders or key elements thereof. The parenteral dosage forms exhibit long stable shelf life and distinct pharmacokinetics.
Owner:VEROSCI
Protein Microspheres Retaining Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Properties
ActiveUS20070207210A1Reduce solubilityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsPowder deliveryHigh concentrationMicrosphere
The present disclosure relates to compositions of methods of making and compositions small compositions of particles of an active agent. In accordance with the method of production, the active agent is dissolved in an aqueous or aqueous-miscible solvent containing a dissolved phase-separation enhancing agent (PSEA) to form a solution in a single liquid phase. The solution is subjected to a liquid-solid phase separation to cause the active agent to form small spherical particles that are substantially amorphous or non-crystalline and are injectable through fine bore needles at high concentrations. The particles exhibit the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamnic properties of the active agent. The disclosure has special application for higher molecular weight proteins such as antibodies.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Antibodies with modified isoelectric points
ActiveUS20140249297A1Increased serum half-lifeMinimize the possibilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntiendomysial antibodiesBlood plasma
The invention relates generally to compositions and methods for altering the isoelectric point of an antibody, and in some cases, resulting in improved plasma pharmacokinetics, e.g. increased serum half-life in vivo.
Owner:XENCOR INC
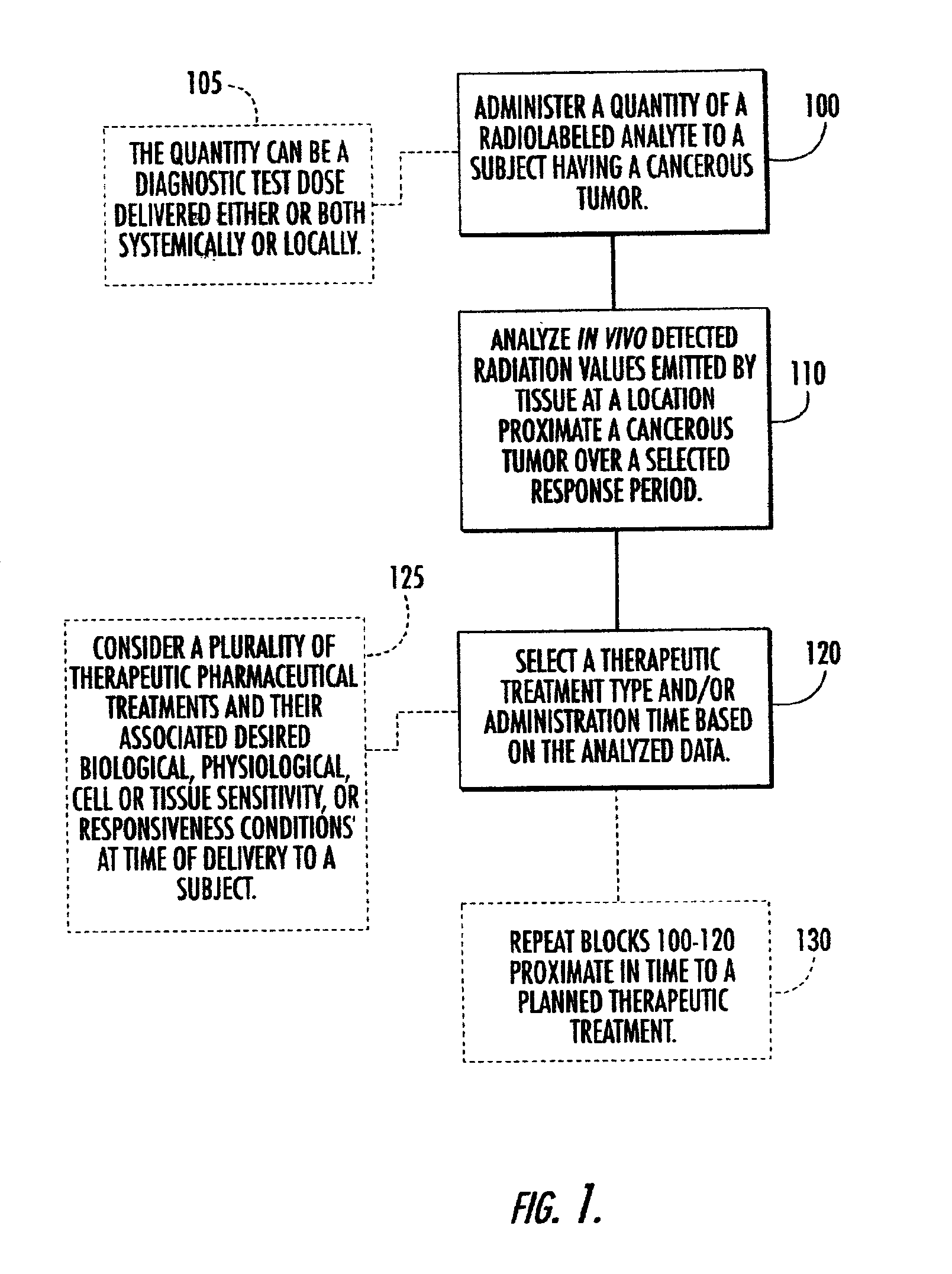
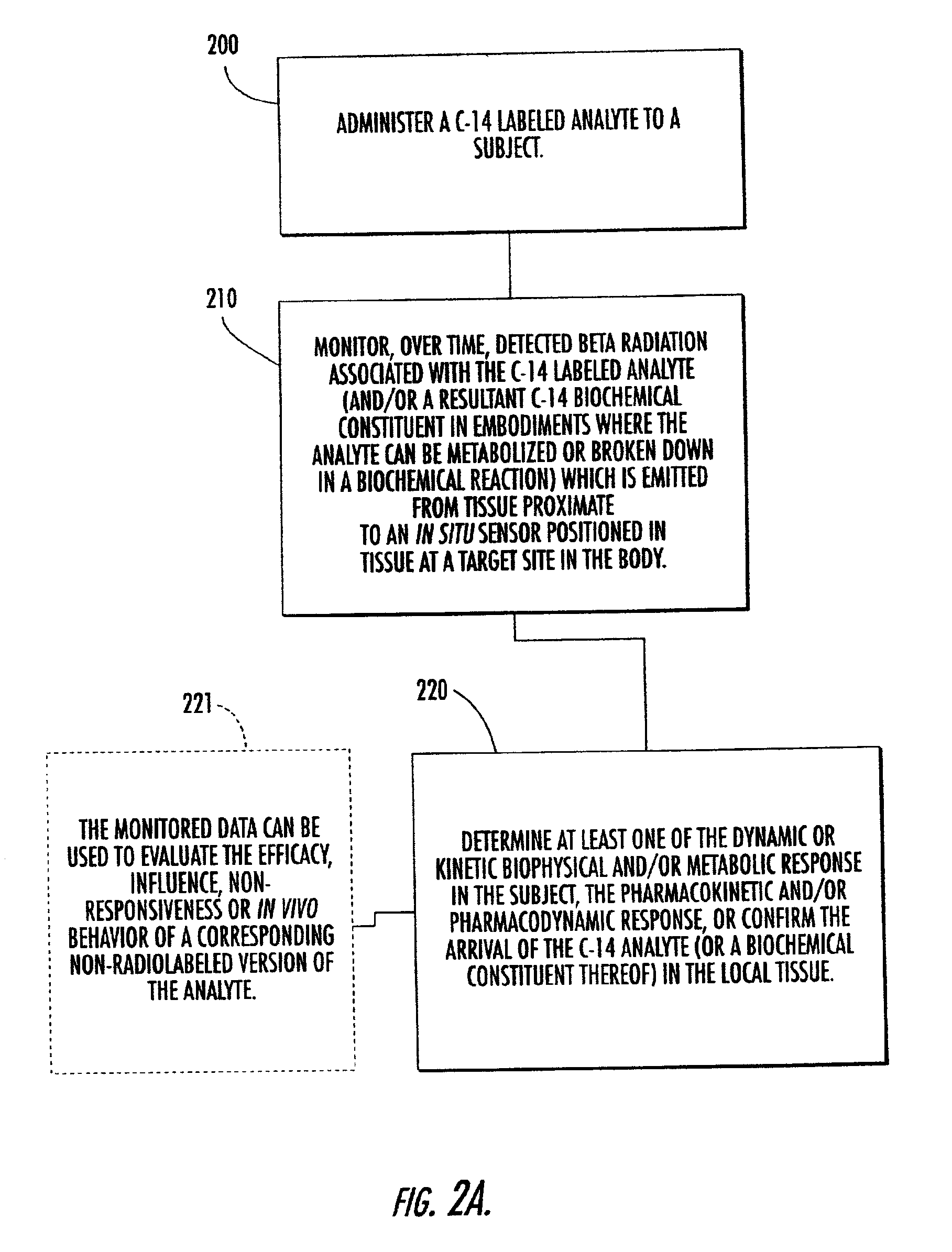
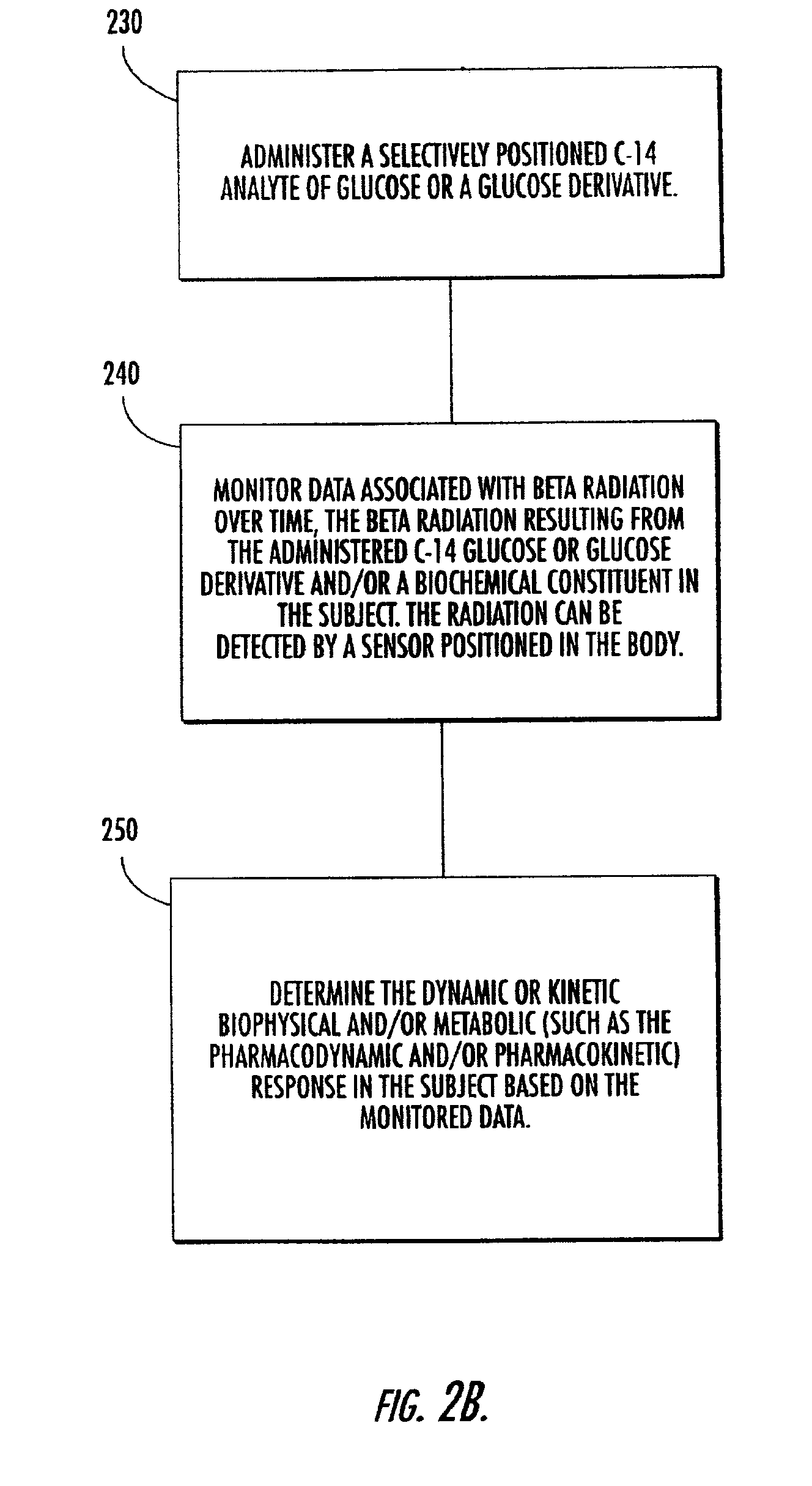
Systems, methods and devices for in vivo monitoring of a localized response via a radiolabeled analyte in a subject
InactiveUS7011814B2Cost-effective minimally invasiveImprove responseCompounds screening/testingRadioactive preparation carriersAbnormal tissue growthAnalyte
Methods, systems, devices and computer program products monitor in vivo detected radiation in a target localized site within a subject, over a selected time period, to do one or more of: (a) quantify a radiation dose received at a local site; (b) assess bioreceptiveness to a particular treatment time or type; (c) evaluate the pharmacokinetics of a radiolabeled analyte corresponding to a non-radiolabeled analyte; (d) monitor or evaluate metabolic activity; or (e) evaluate a tumor prior to or after a therapeutic treatment.
Owner:VTQ IP HLDG
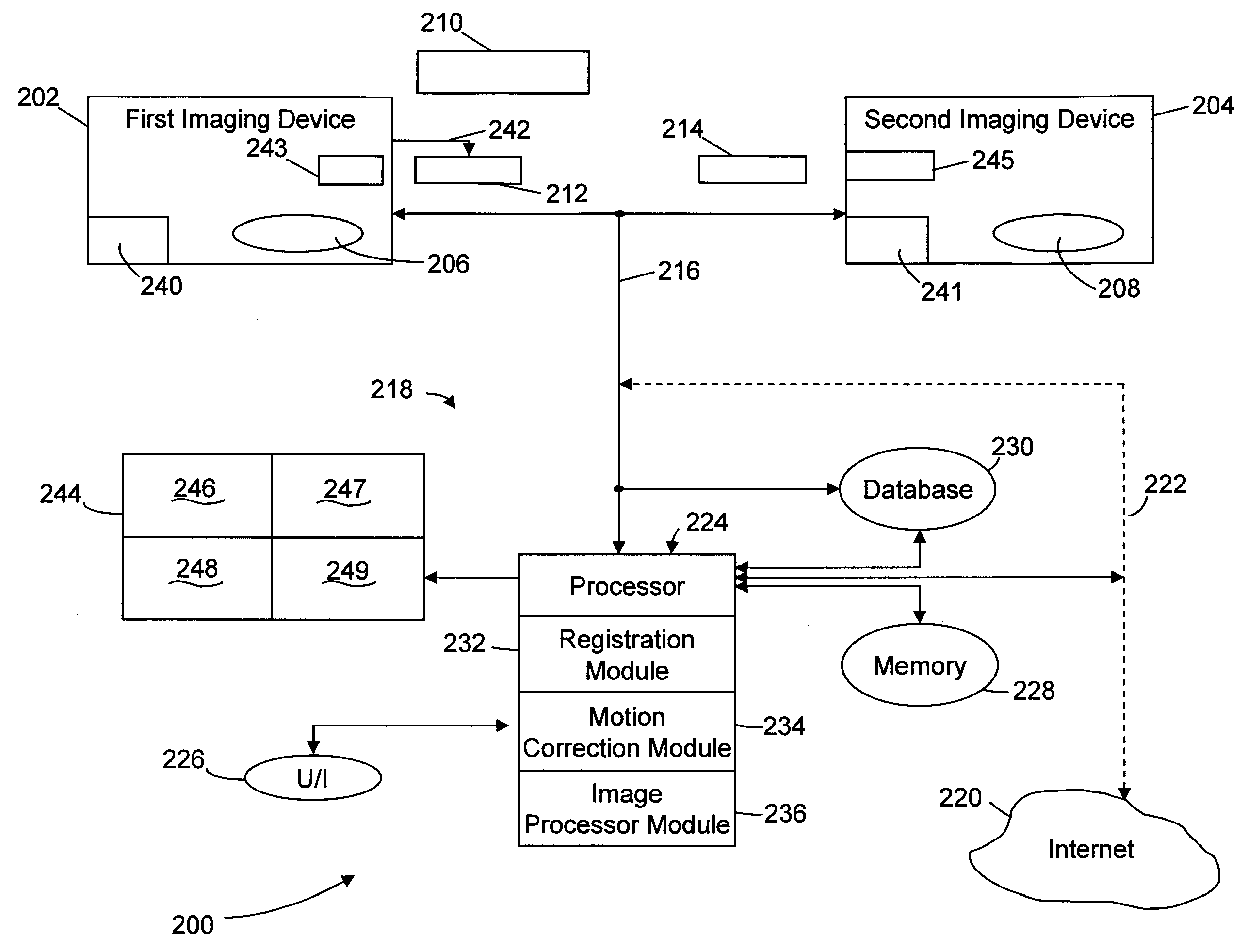
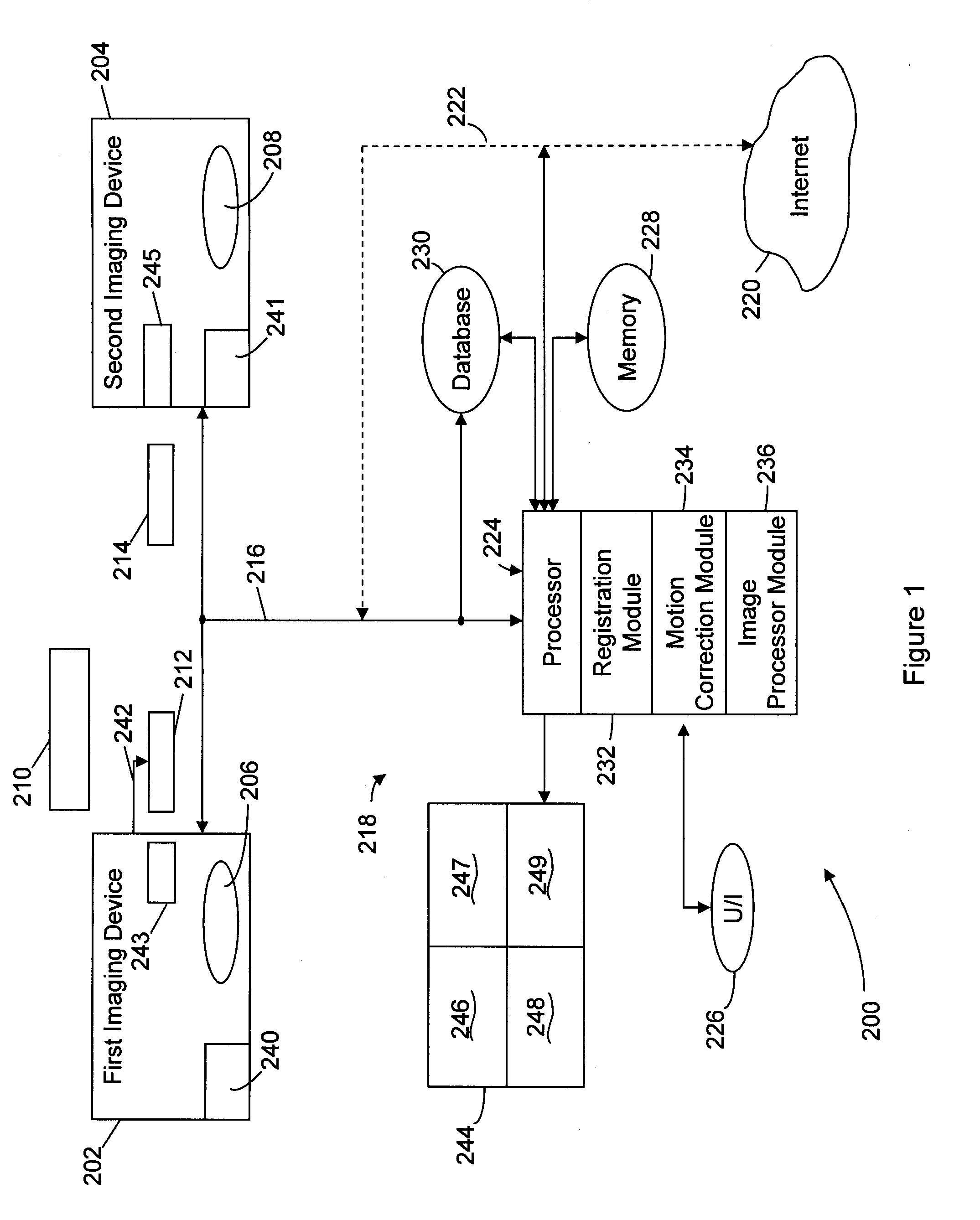
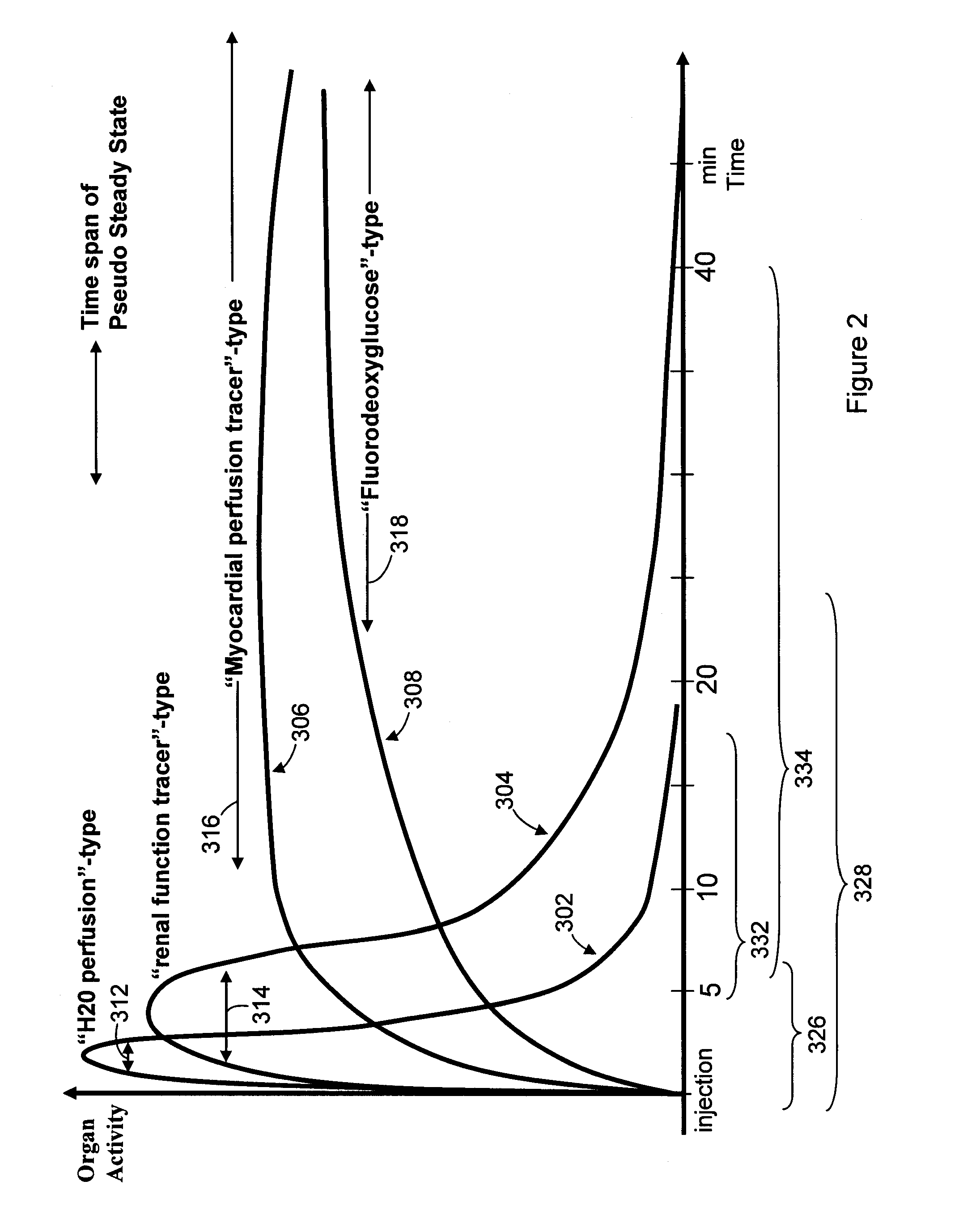
Method & system for multi-modality imaging of sequentially obtained pseudo-steady state data
Methods, protocols and systems are provided for multi-modality imaging based on pharmacokinetics of an imaging agent. An imaging agent is introduced into a subject, and is permitted to collect generally in a region of interest (ROI) in the subject until attaining a pseudo-steady state (PSS) distribution within the ROI. The imaging agent records a first functional state of the ROI at a given point in time. A first image data set is obtained with a first imaging modality during a first acquisition time interval that occurs prior or proximate in time with the PSS time interval. The subject is transferred from the first imaging modality to a second imaging modality during a transfer time interval that overlaps the PSS time interval. Once transfer is complete, a second image data set is obtained with the second imaging modality during a second acquisition time interval that also overlaps the PSS time interval in which the imaging agent maintains the PSS distribution in the ROI. In accordance with a protocol, the transfer time interval and second acquisition time interval substantially fall within the PSS time interval. The imaging agent collects in the ROI during an uptake time interval which may or may not precede the time interval during which first imaging modality obtains at least a portion of the first image data set. The second image data set is obtained while the imaging agent persists in the ROI at the PSS distribution reflective of the first functional state even after the ROI is no longer in the first functional state.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Biologically related substances modified by multifunctional H-type polyethylene glycol derivative
ActiveCN104530413ALow immunogenicityImprove distributionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFluorescencePolyethylene glycol
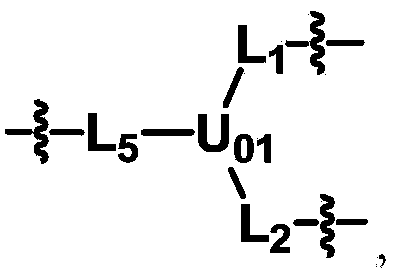
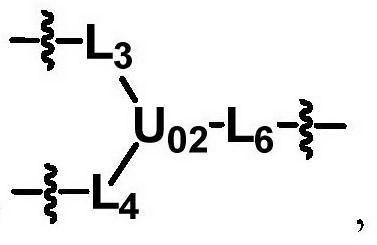
The invention discloses biologically related substances modified by a multifunctional H-type polyethylene glycol derivative. The derivative comprises a linear main axis LPEG and four PEG branched chains, and n1, n2, n3 and n4 are polymerization degrees of the branched chains, respectively; U1 and U2 are trivalent branching groups connecting the main axis LPEG with two PEG branched chains; F1 and F2 contain functional groups or their protected forms R01, and the number of R01 is one or more than one. Any linking group in the molecule or linking groups formed with adjacent heteroatom groups are stable or degradable; any PEG chain segment in the molecule independently shows polydispersity or monodispersity. One H-type molecule can modify multiple types of or multiple biologically related substances; the modified product has a flexible branching structure, a high drug loading capacity, optimized pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution, and can also carry two biologically related substances with different functions, so as to generate fluorescence property or targeting function.
Owner:XIAMEN SINOPEG BIOTECH
Method and system for systemic delivery of growth arresting, lipid-derived bioactive compounds
ActiveUS20050025820A1Maximizing systemic deliveryCorrection for dispersionOrganic active ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedDendrimerGene Therapy Agent
A system and method for optimizing the systemic delivery of growth-arresting lipid-derived bioactive drugs or gene therapy agents to an animal or human in need of such agents utilizing nanoscale assembly systems, such as liposomes, resorbable and non-aggregating nanoparticle dispersions, metal or semiconductor nanoparticles, or polymeric materials such as dendrimers or hydrogels, each of which exhibit improved lipid solubility, cell permeability, an increased circulation half life and pharmacokinetic profile with improved tumor or vascular targeting.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Parenteral Formulations of Dopamine Agonists
ActiveUS20090143390A1Reducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorReducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorsBiocideAntipyreticEnteral administrationParenteral Dosage Form
This invention relates to stable pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral administration comprising dopamine agonists and peripheral acting agents_useful for treatment of metabolic disorders or key elements thereof. The parenteral dosage forms exhibit long stable shelf life and distinct pharmacokinetics.
Owner:VEROSCI
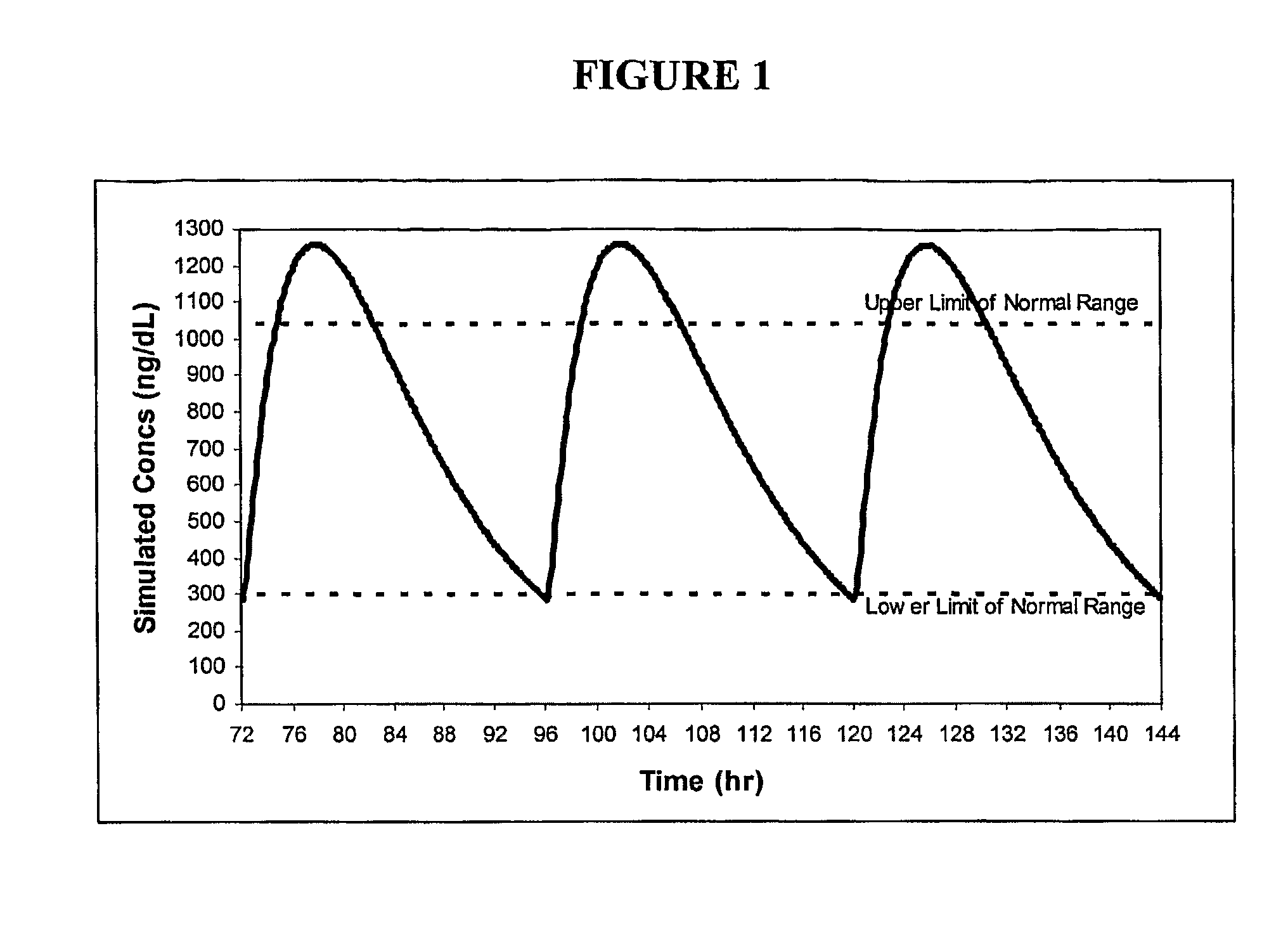
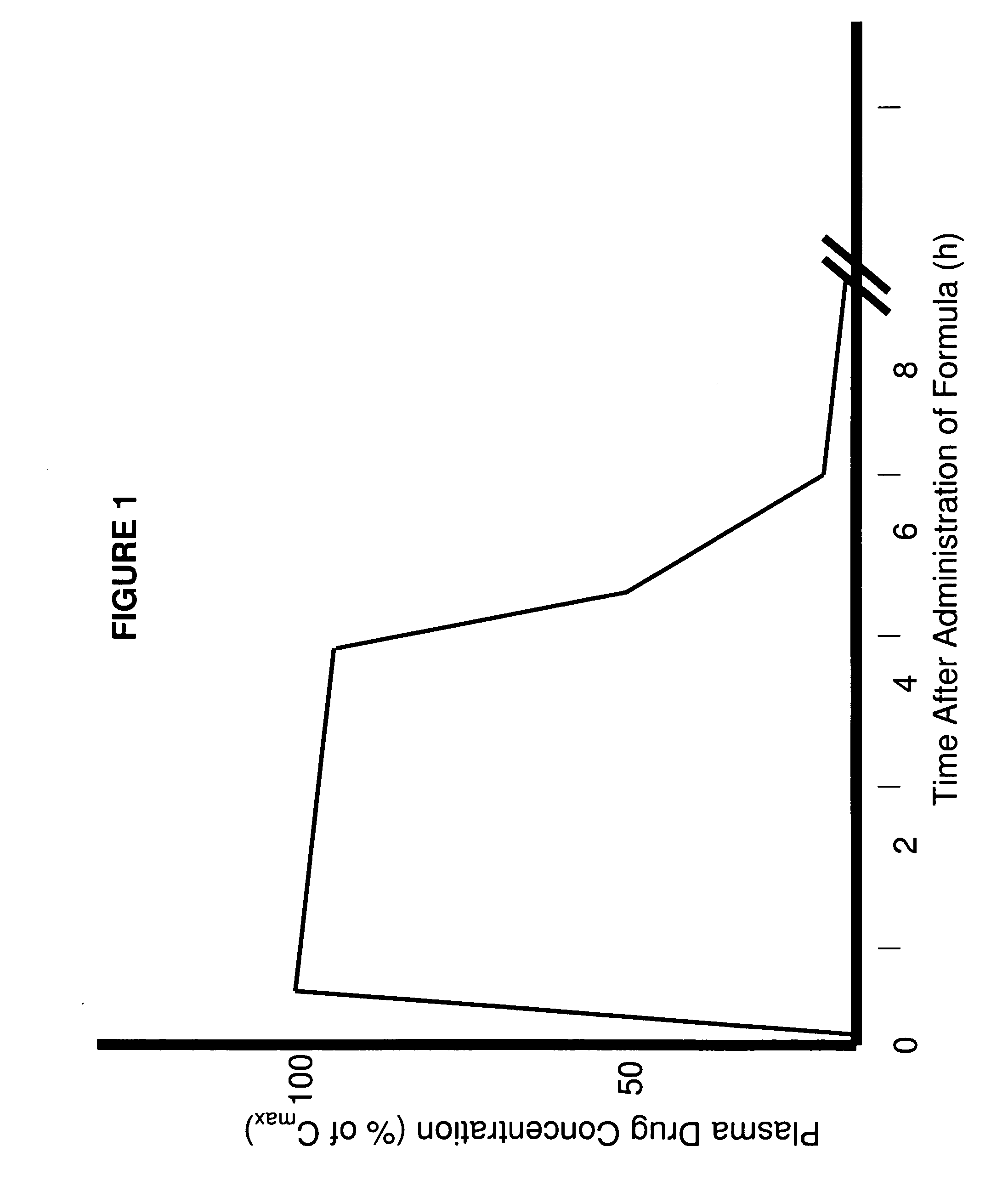
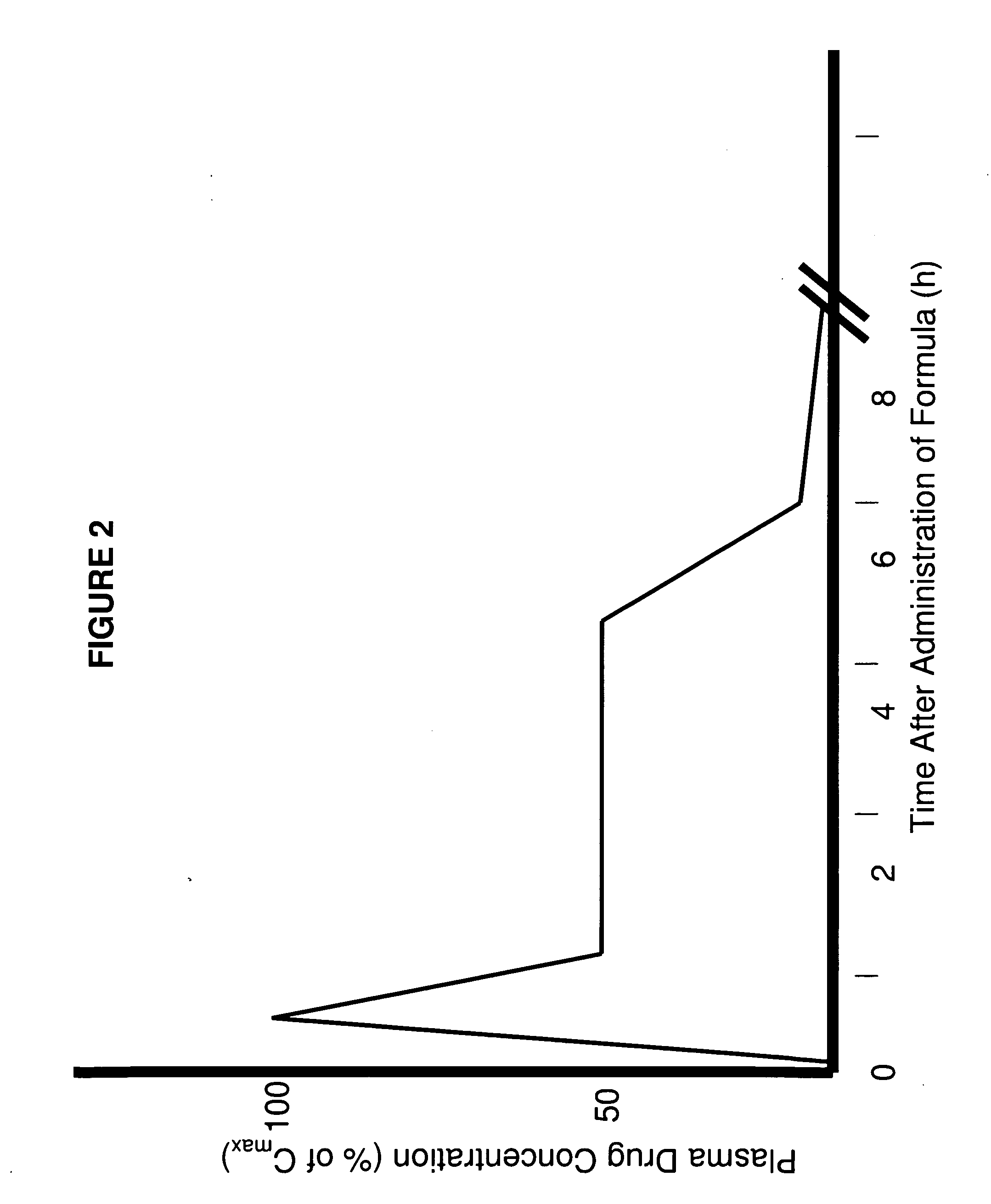
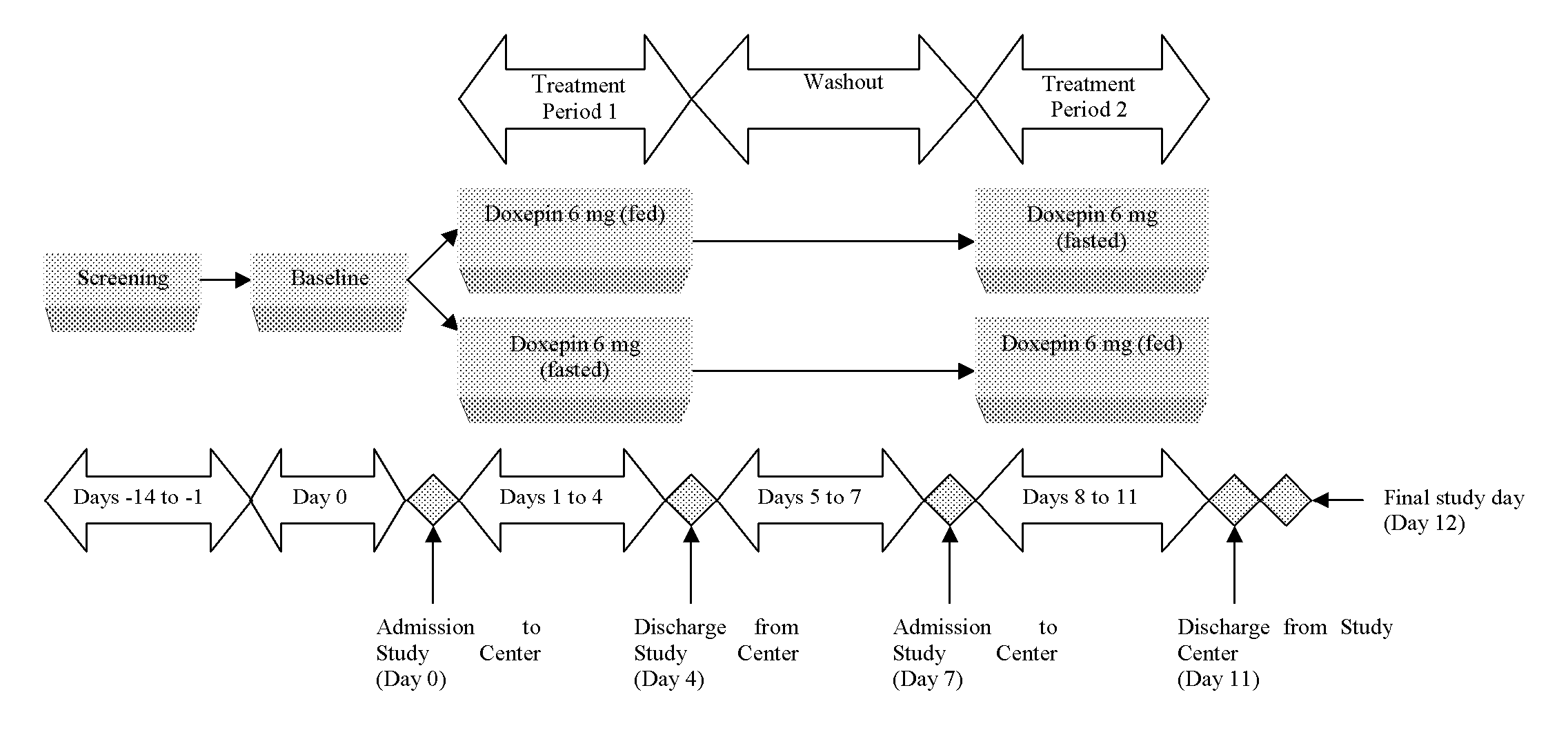
Methods of improving the pharmacokinetics of doxepin
Owner:CURRAX PHARMA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com