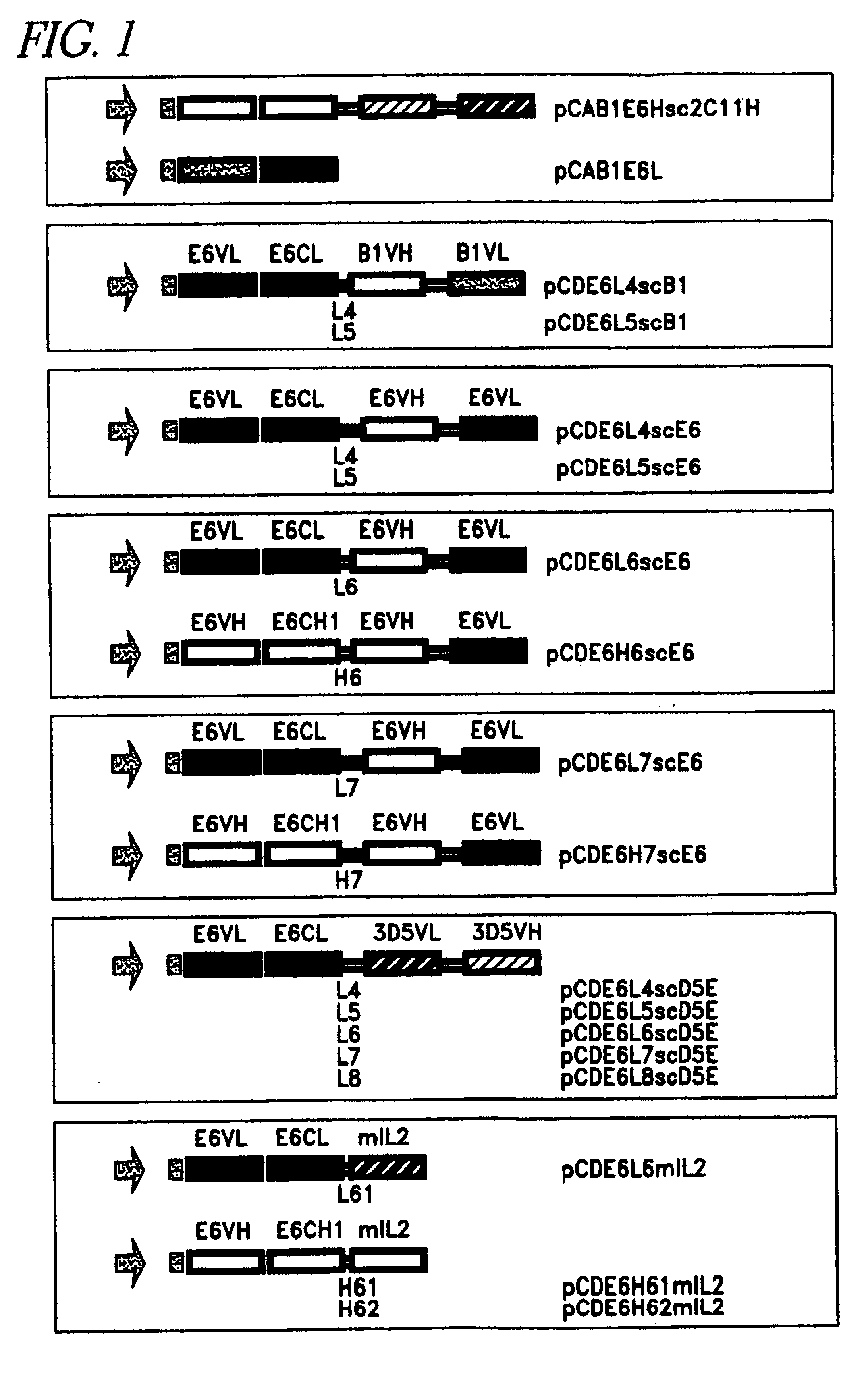
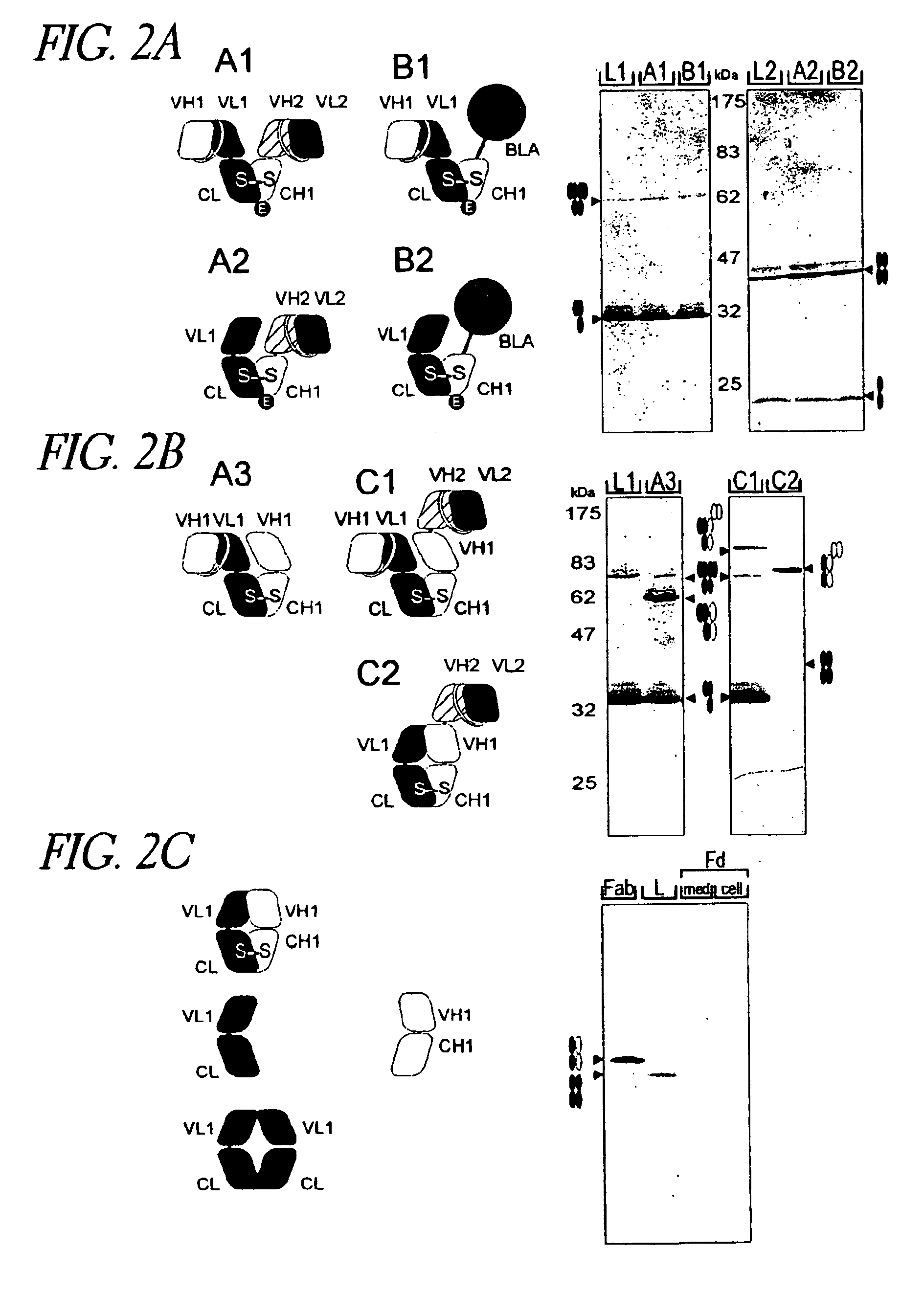
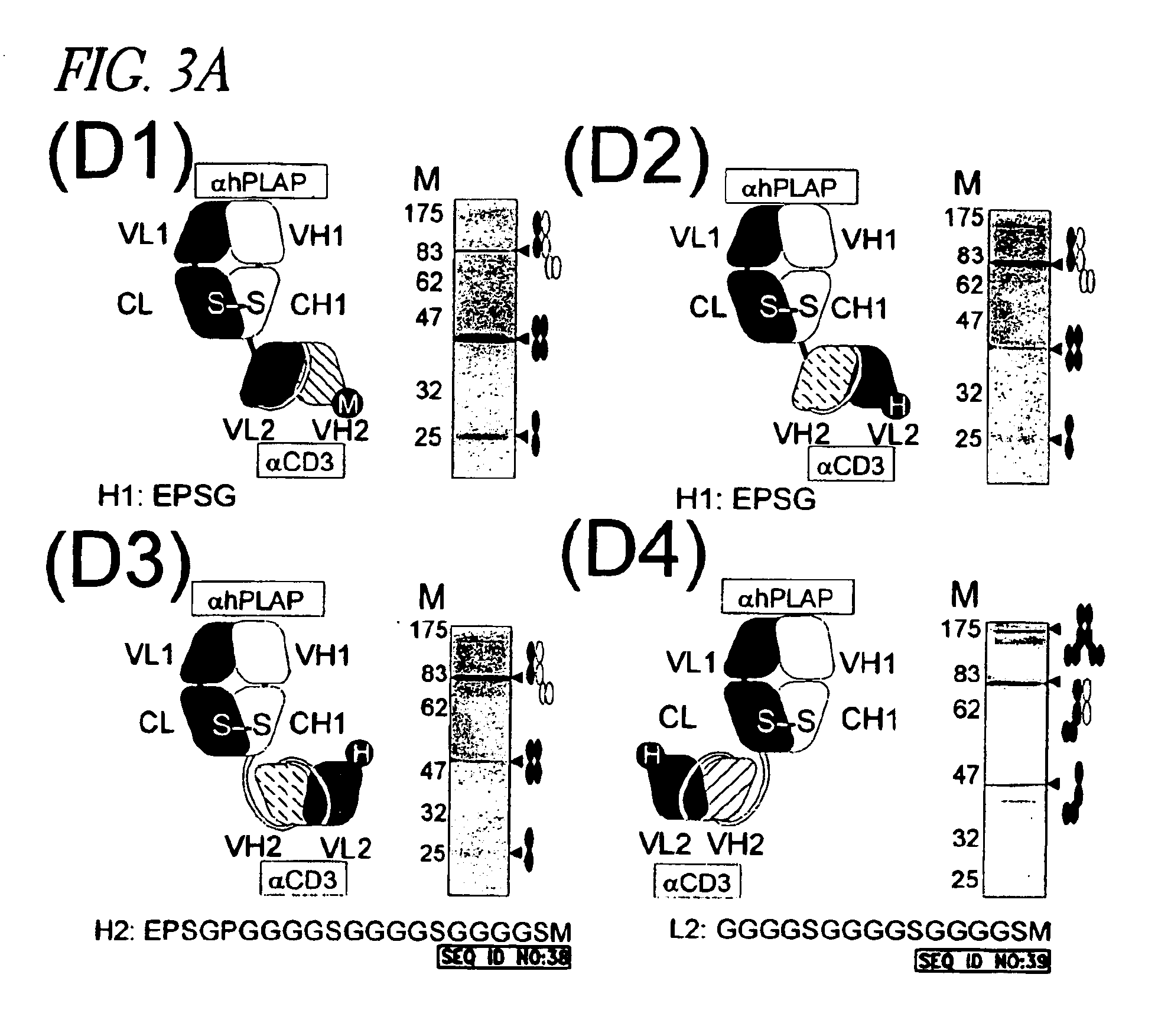
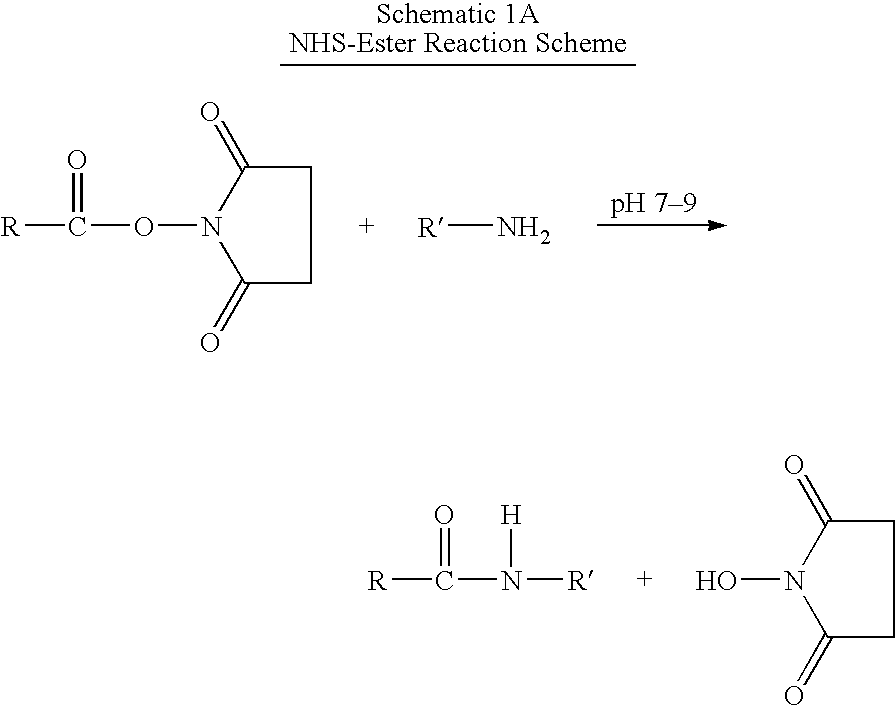
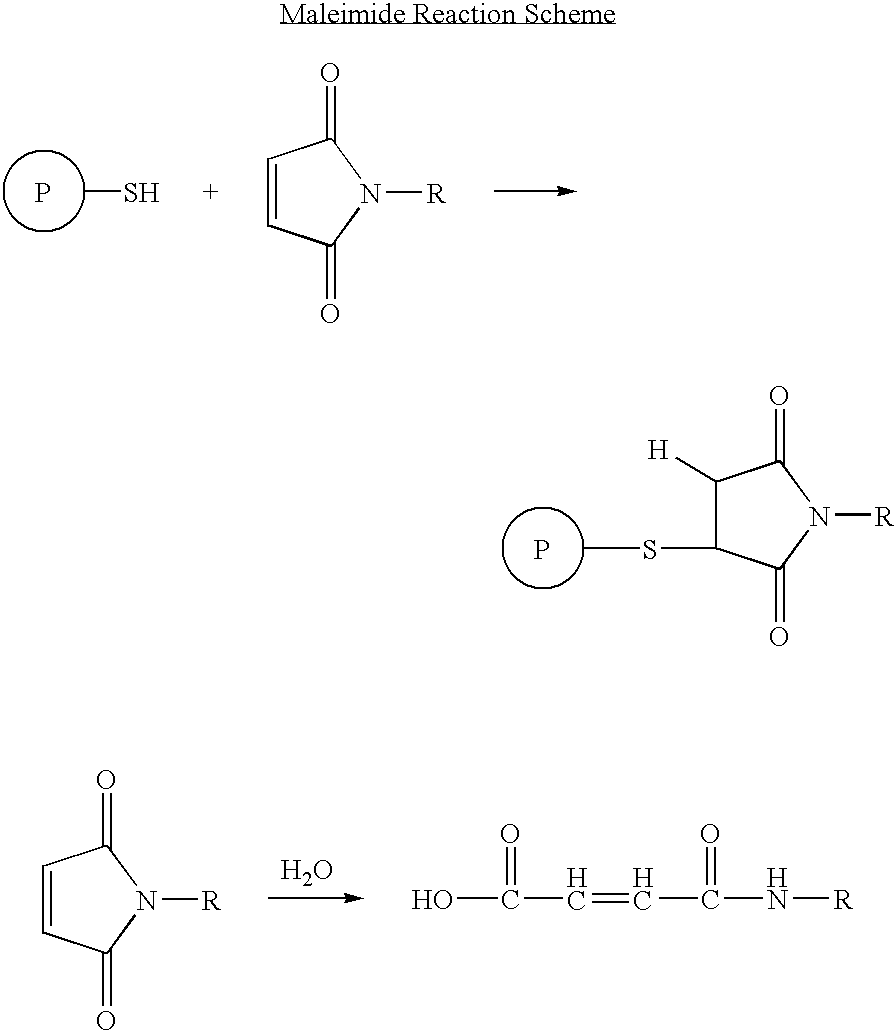
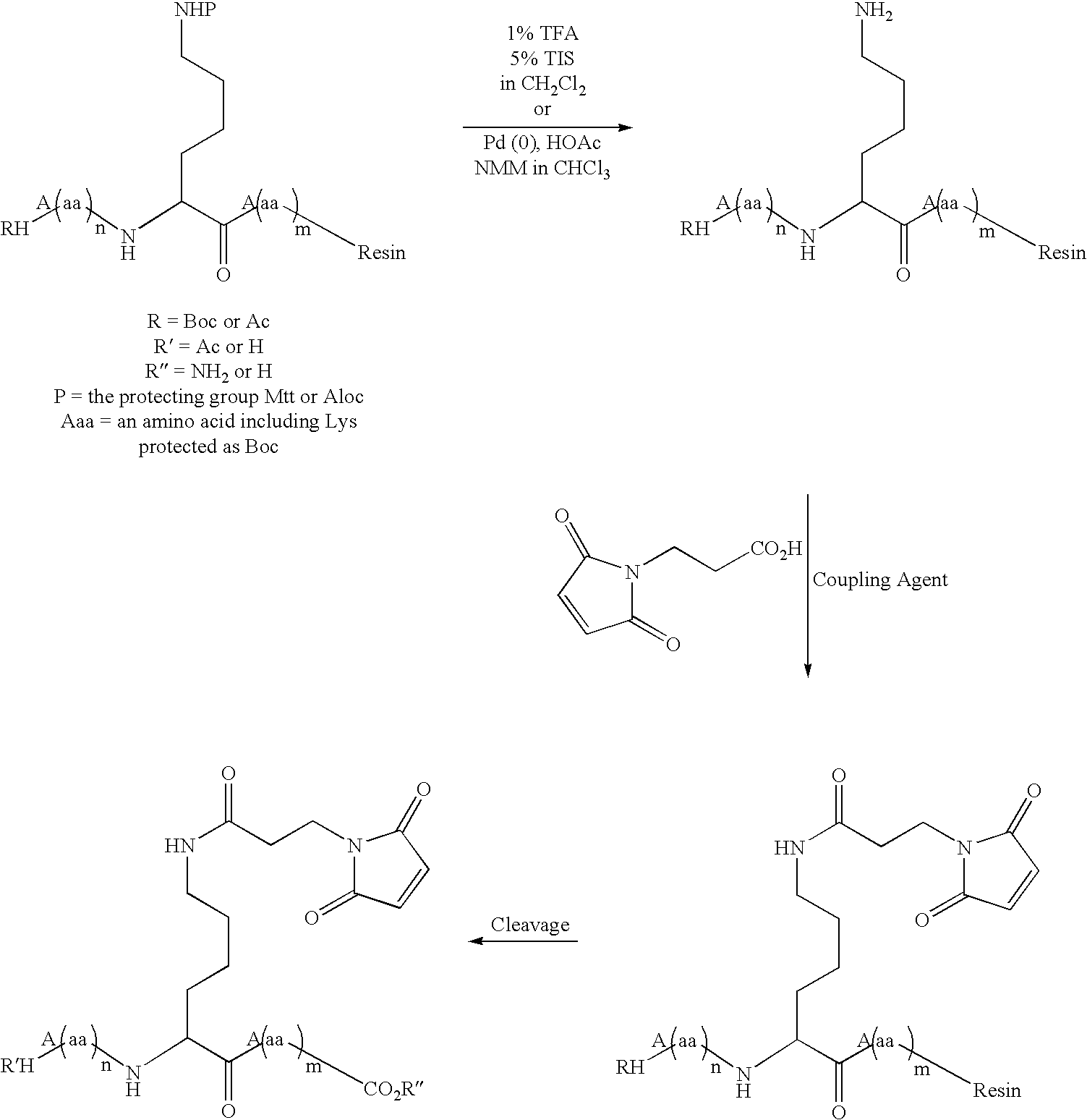
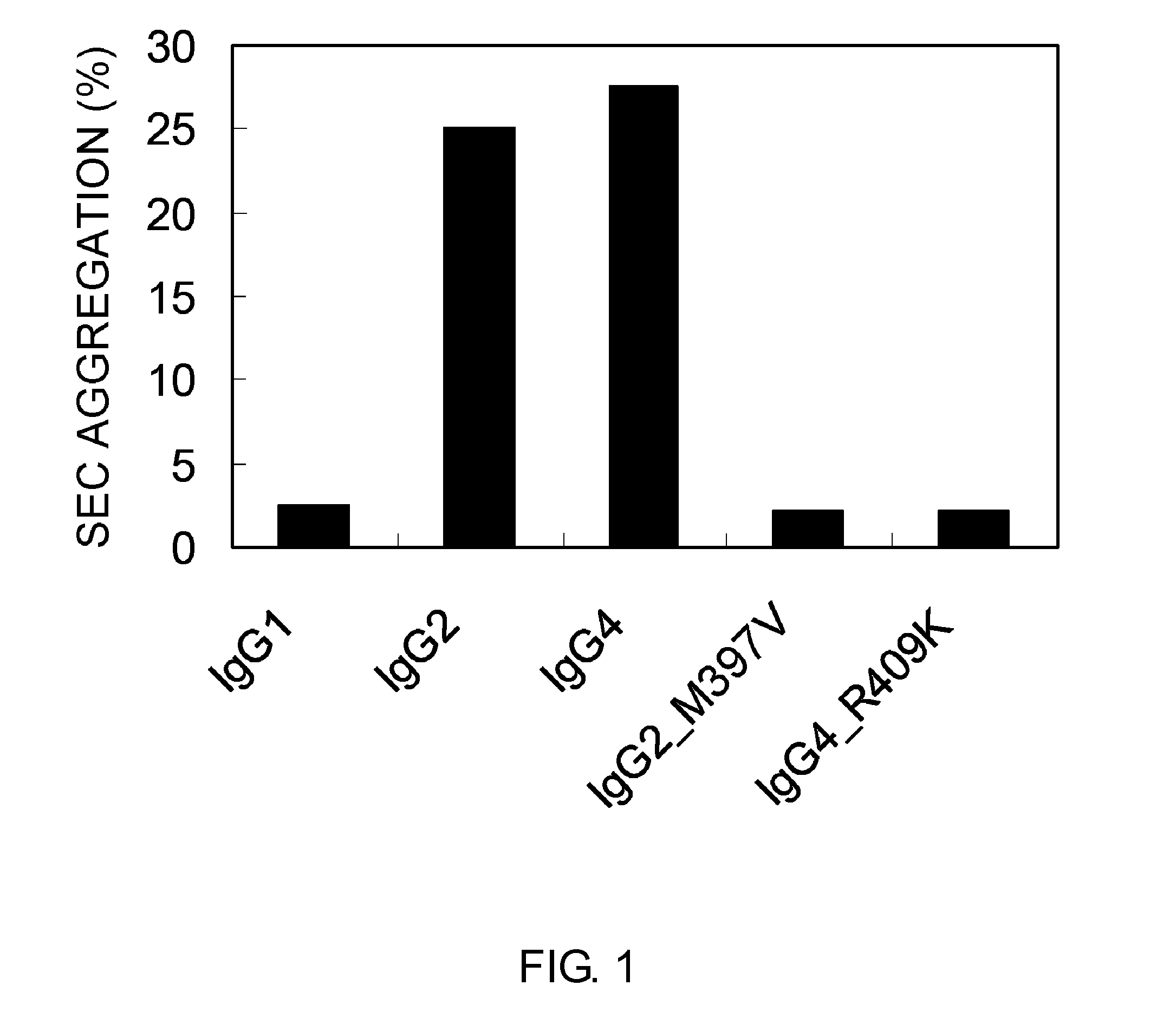
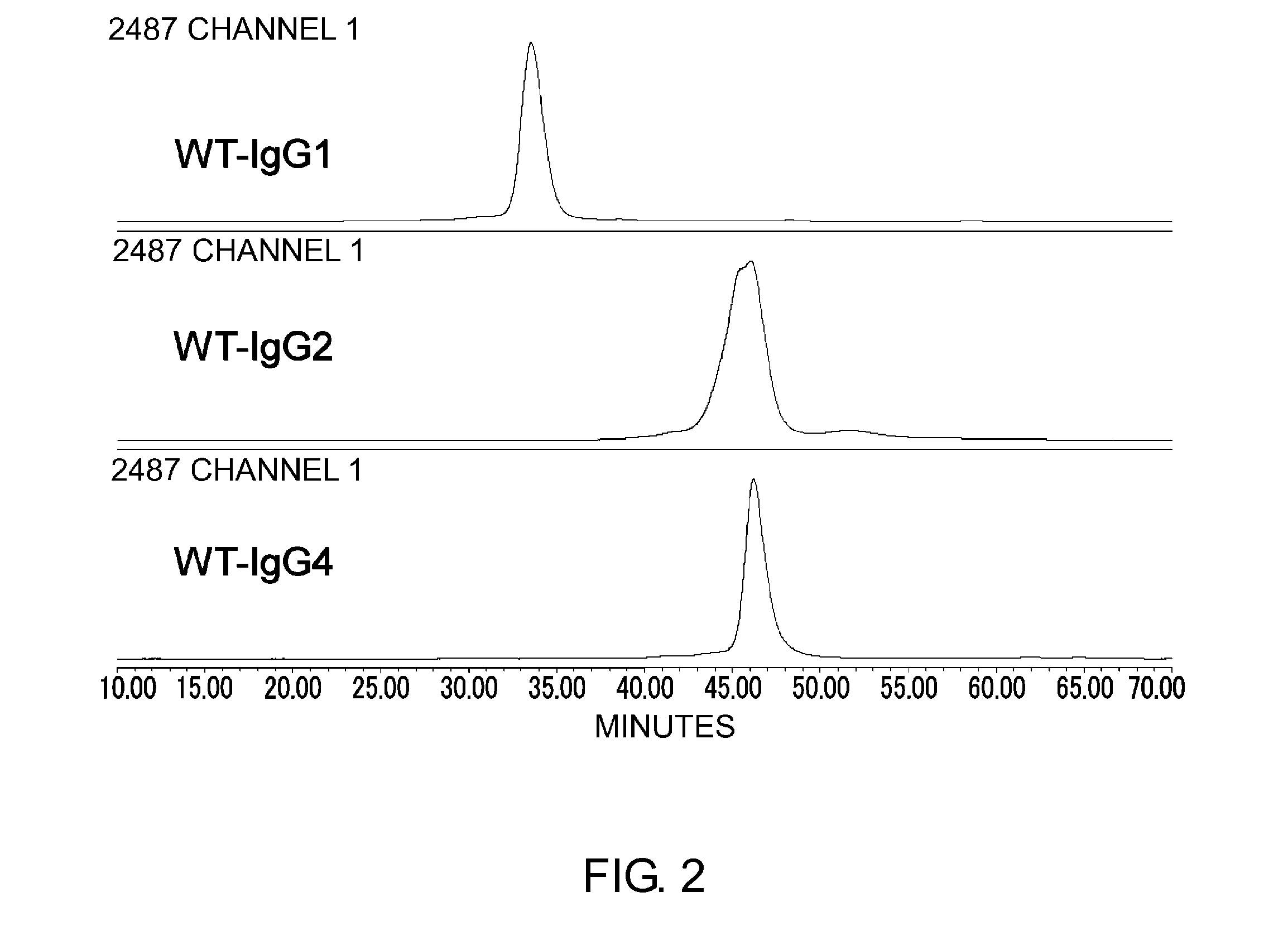
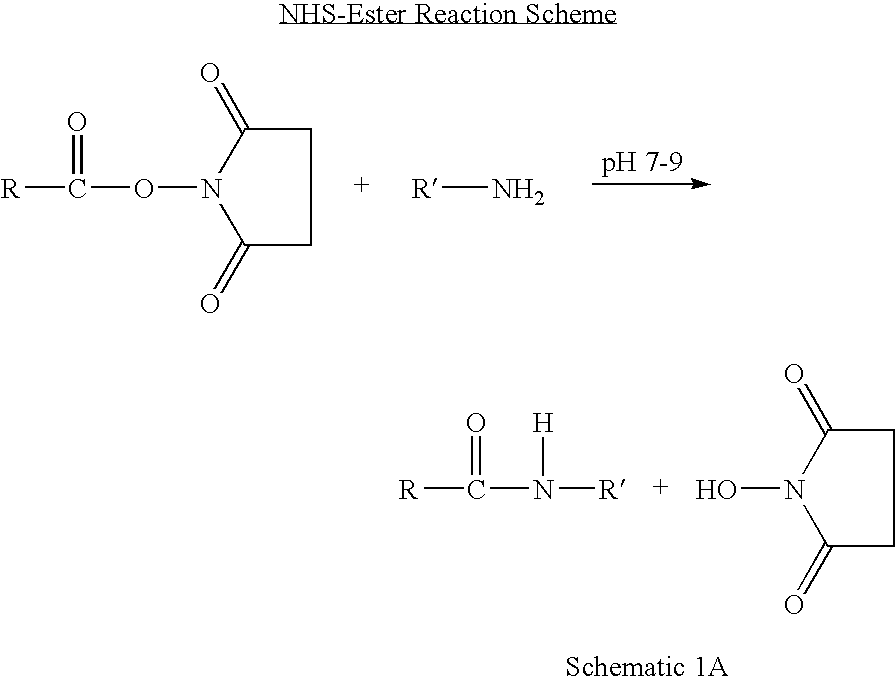
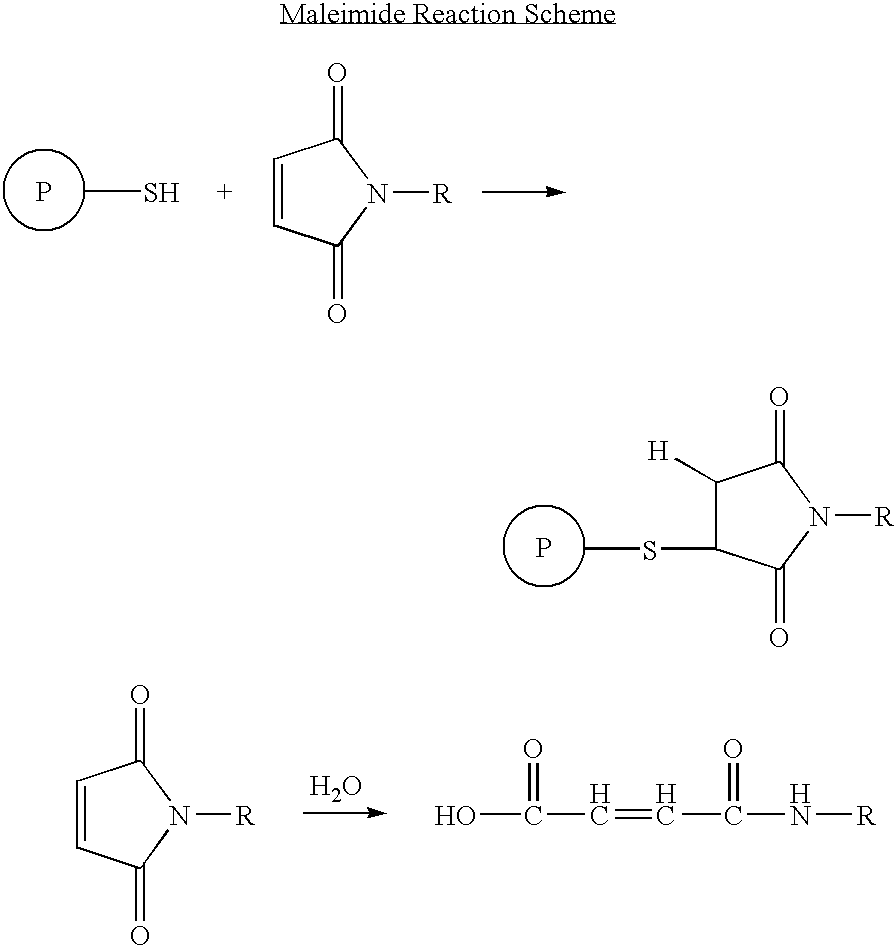
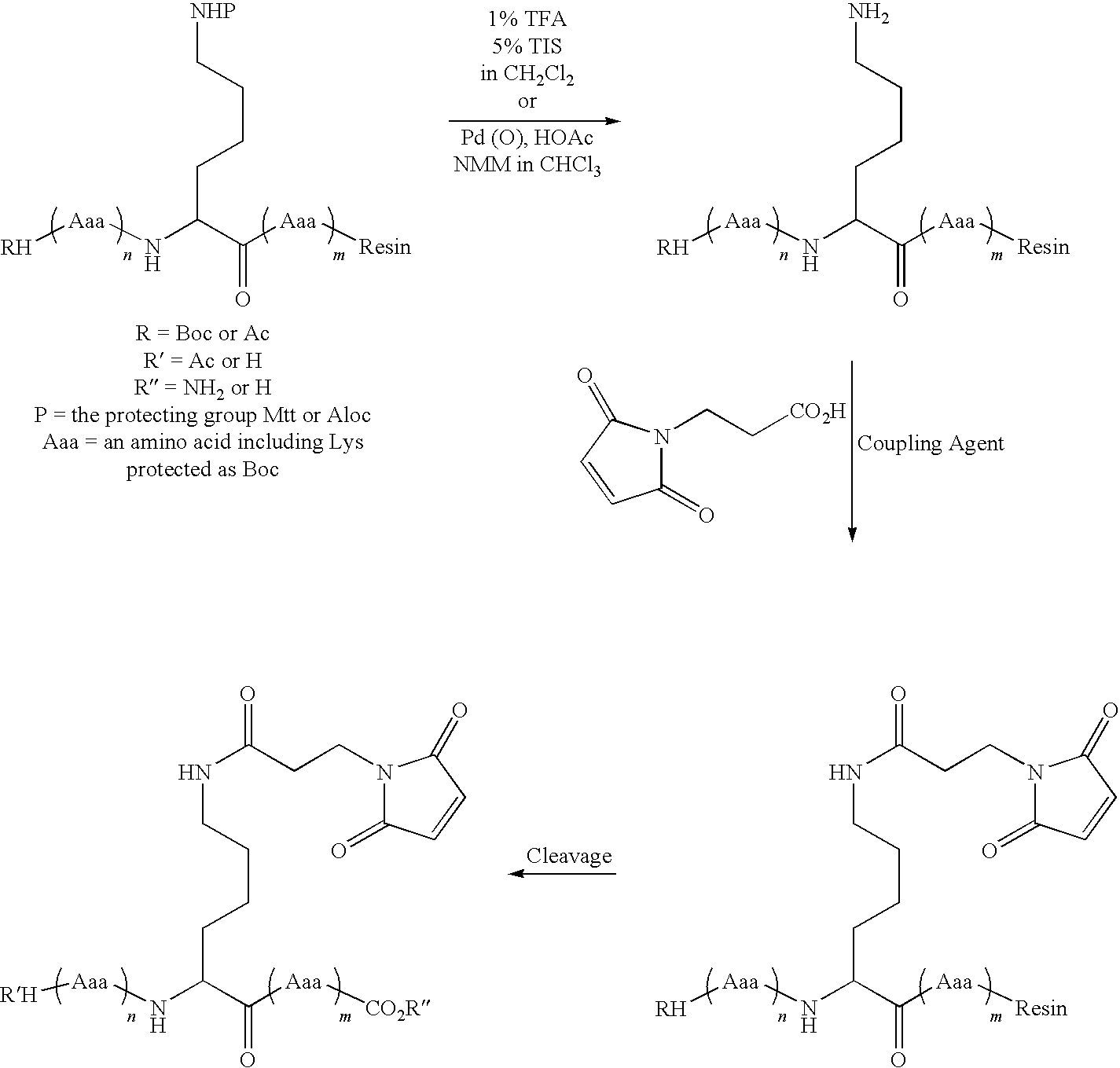
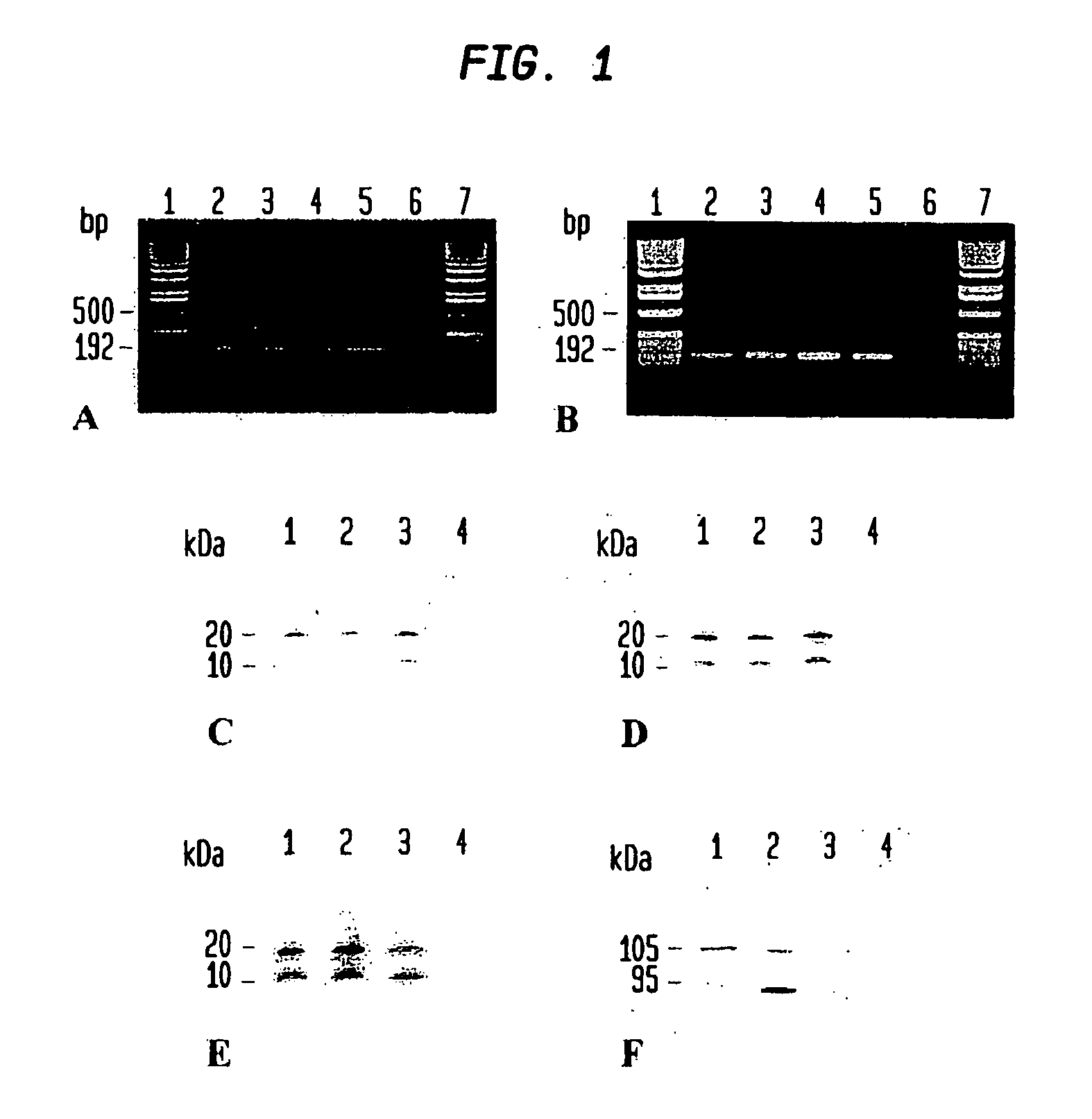
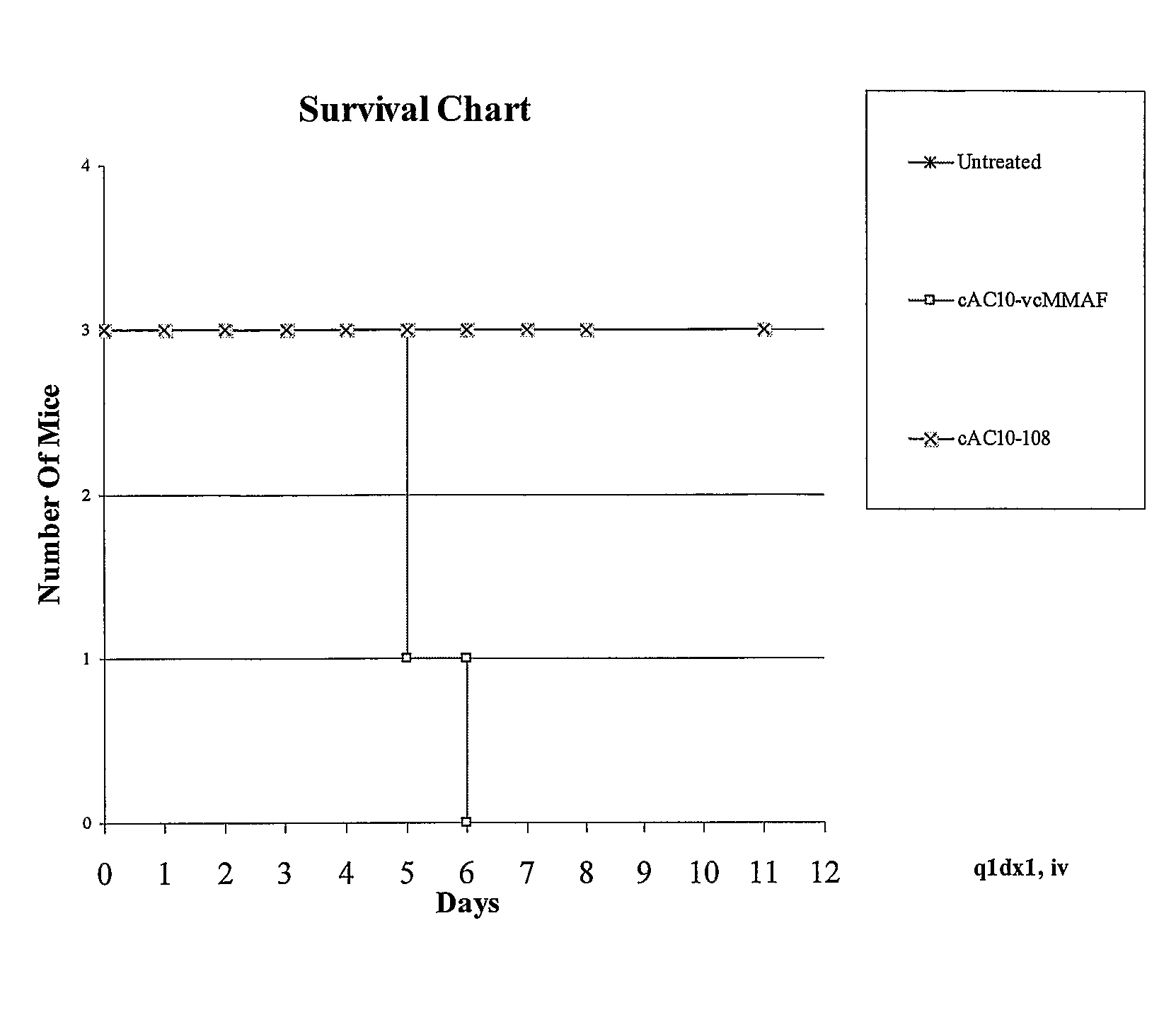
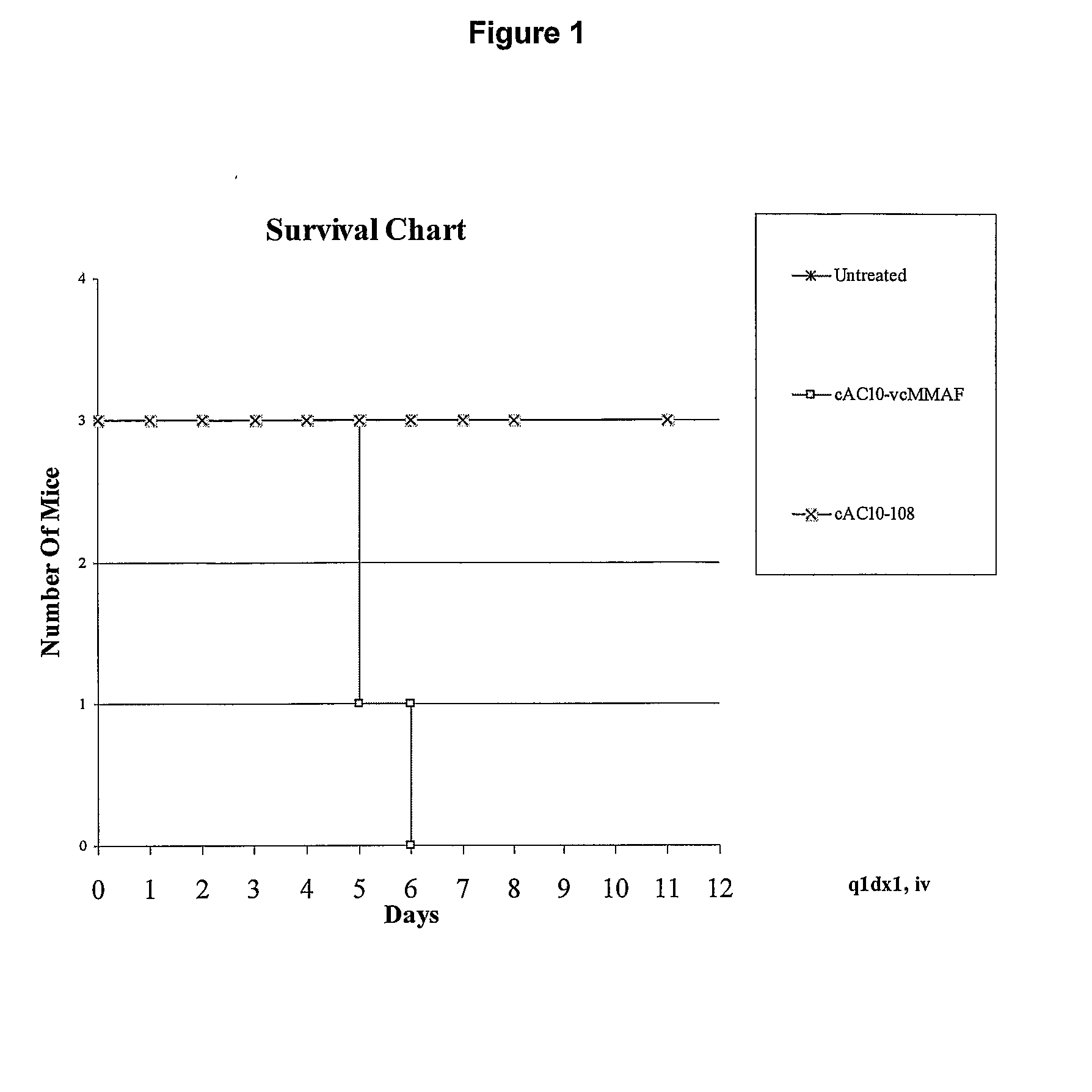
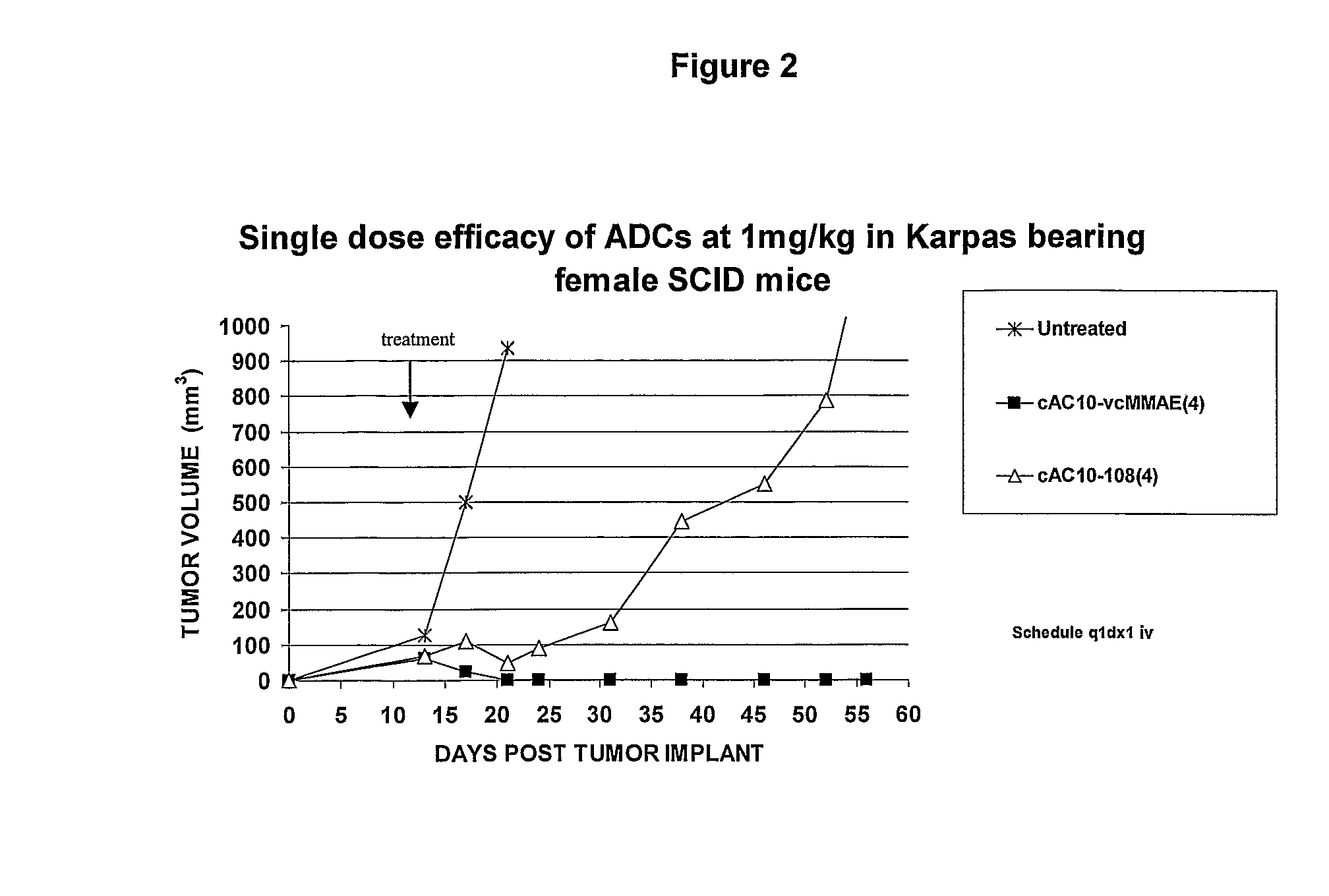
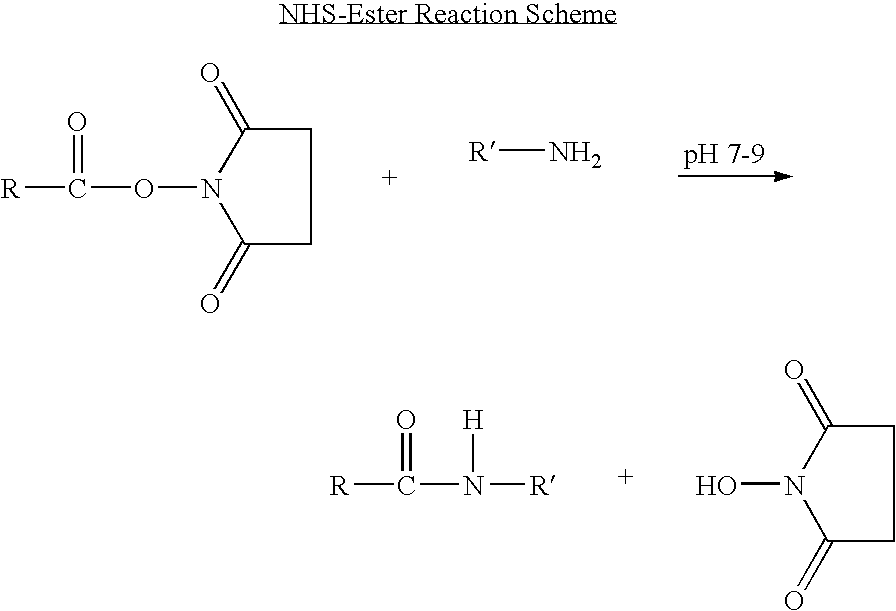
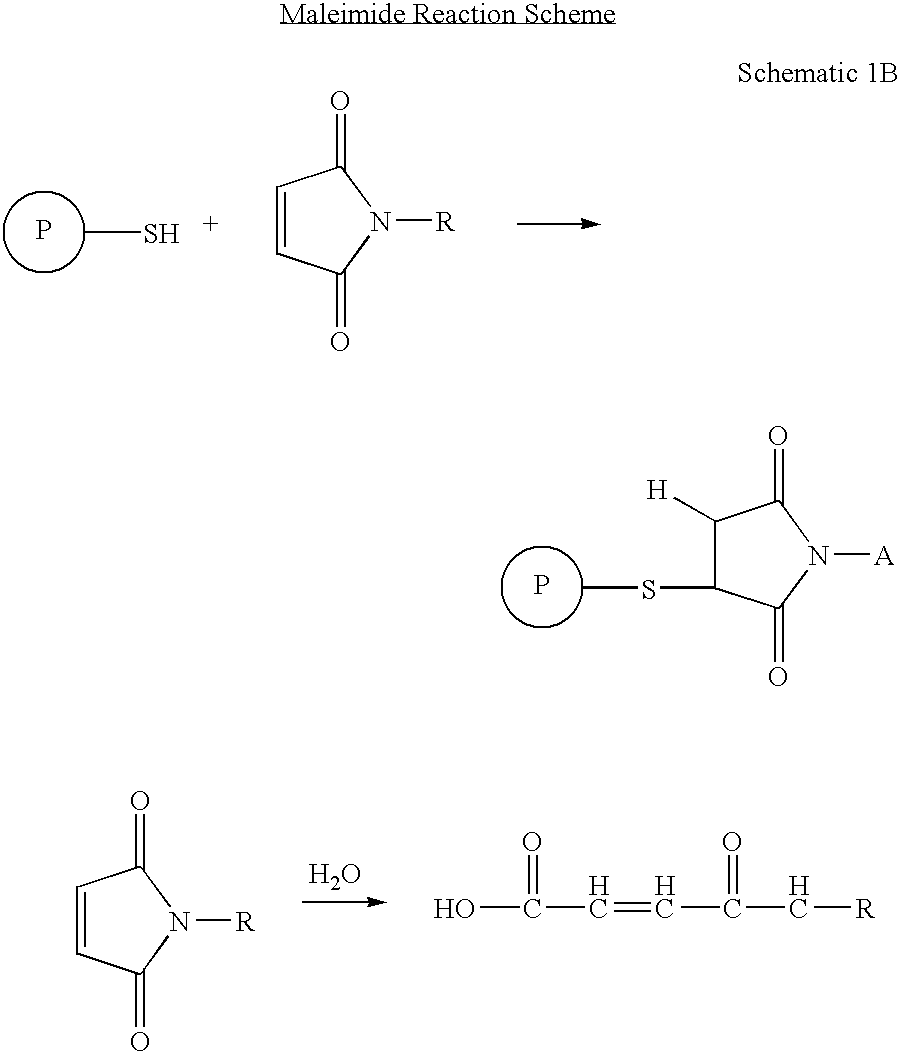
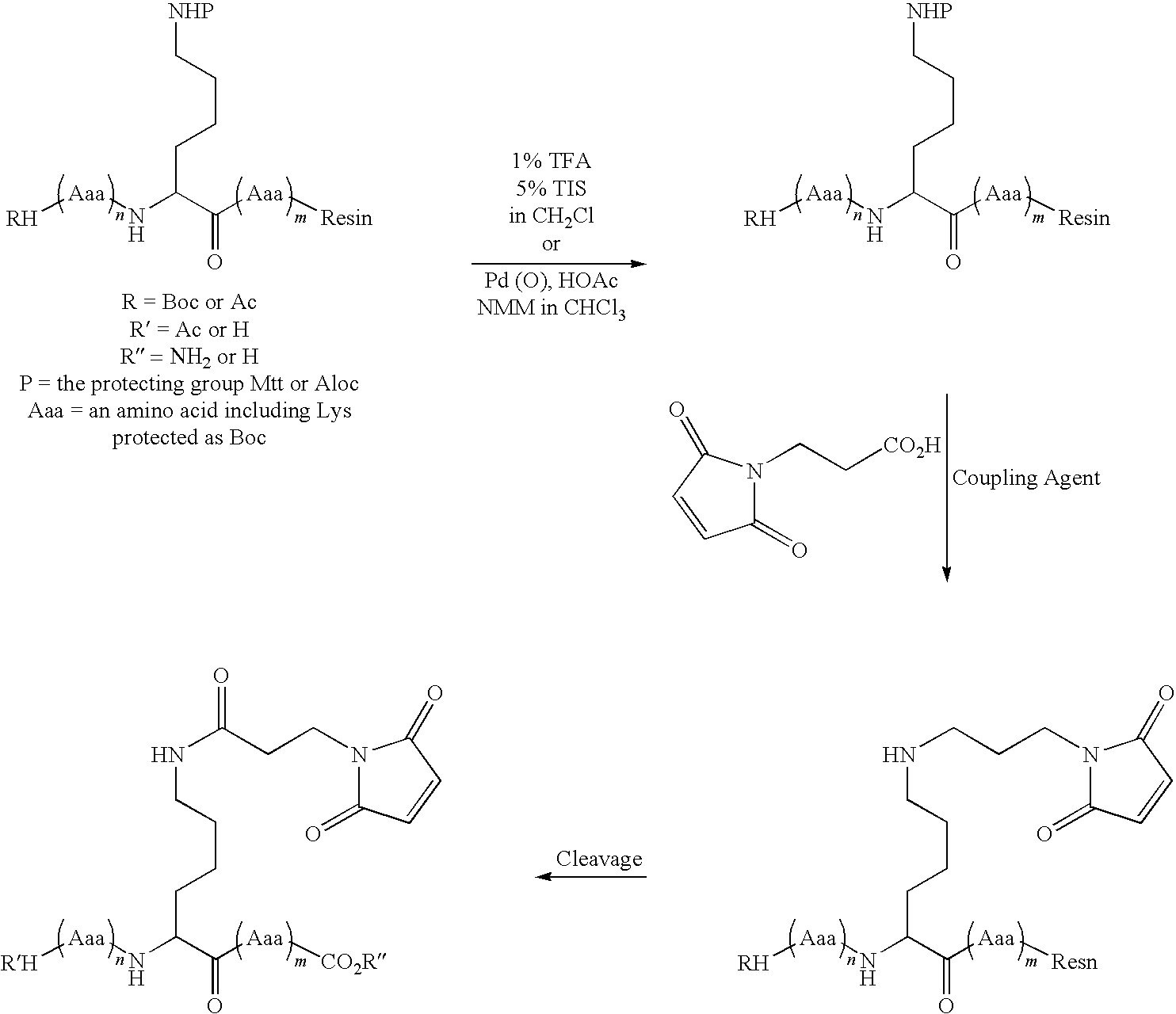
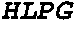Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
820 results about "C-terminus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus.
Multipurpose antibody derivatives
InactiveUS6809185B1Efficient preparationEfficient productionHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsSignalling moleculesHormones regulation
The present invention relates to a class of molecules specified as novel multipurpose antibody derivatives. This class of molecules is created by heterodimerization of two constituting components. Heterodimerization is obtained by the specific heterotypic interaction of a chosen VH-CH1 combination of immunoglobulin domains, with a chosen VL-CL combination of immunoglobulin domains. The appropriate VH and VL domains in the VHCH1 and VLCL context, a binding specificity can be constitituted by the heterodimerization scaffold itself. One or both of the comprising VHCH1 and VLCL chains can thus be extended at either the N- or the C-terminus or both with other molecules, such as a toxin polypeptide, an enzyme, a hormone, a cytokine, a signaling molecule, or a single chain linked Fv fragment with the same or a different specificity.
Owner:BIOTECNOL LTD +1
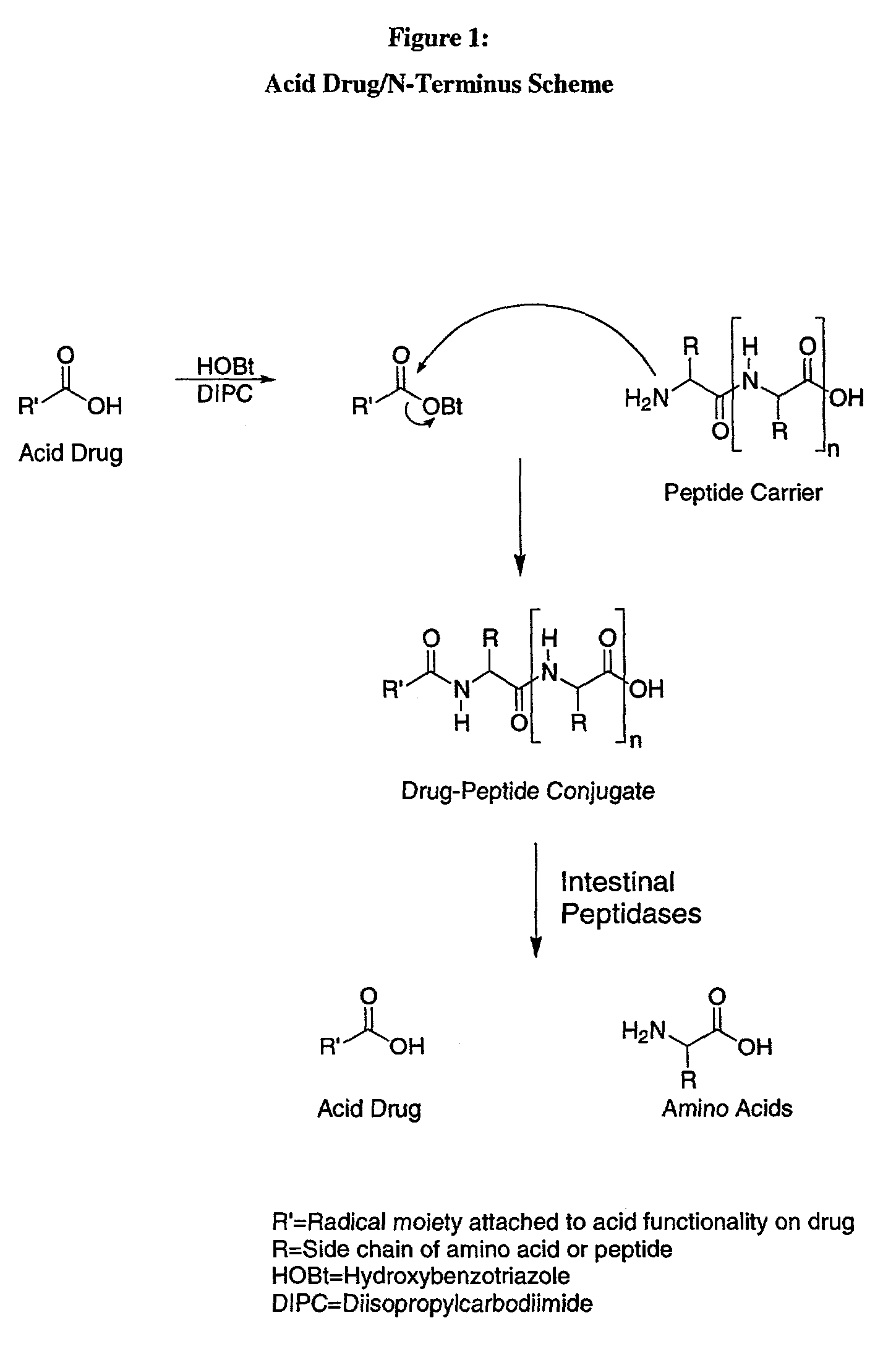
Protection of endogenous therapeutic peptides from peptidase activity through conjugation to blood components
InactiveUS6887470B1Easy to testPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBlood componentCombinatorial chemistry
A method for protecting a peptide from peptidase activity in vivo, the peptide being composed of between 2 and 50 amino acids and having a C-terminus and an N-terminus and a C-terminus amino acid and an N-terminus amino acid is described. In the first step of the method, the peptide is modified by attaching a reactive group to the C-terminus amino acid, to the N-terminus amino acid, or to an amino acid located between the N-terminus and the C-terminus, such that the modified peptide is capable of forming a covalent bond in vivo with a reactive functionality on a blood component. In the next step, a covalent bond is formed between the reactive group and a reactive functionality on a blood component to form a peptide-blood component conjugate, thereby protecting said peptide from peptidase activity. The final step of the method involves the analyzing of the stability of the peptide-blood component conjugate to assess the protection of the peptide from peptidase activity.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
Modified Antibody Constant Region
ActiveUS20100298542A1Improving immunogenicityImprove propertiesAntipyreticAnalgesicsHigh concentrationHinge region
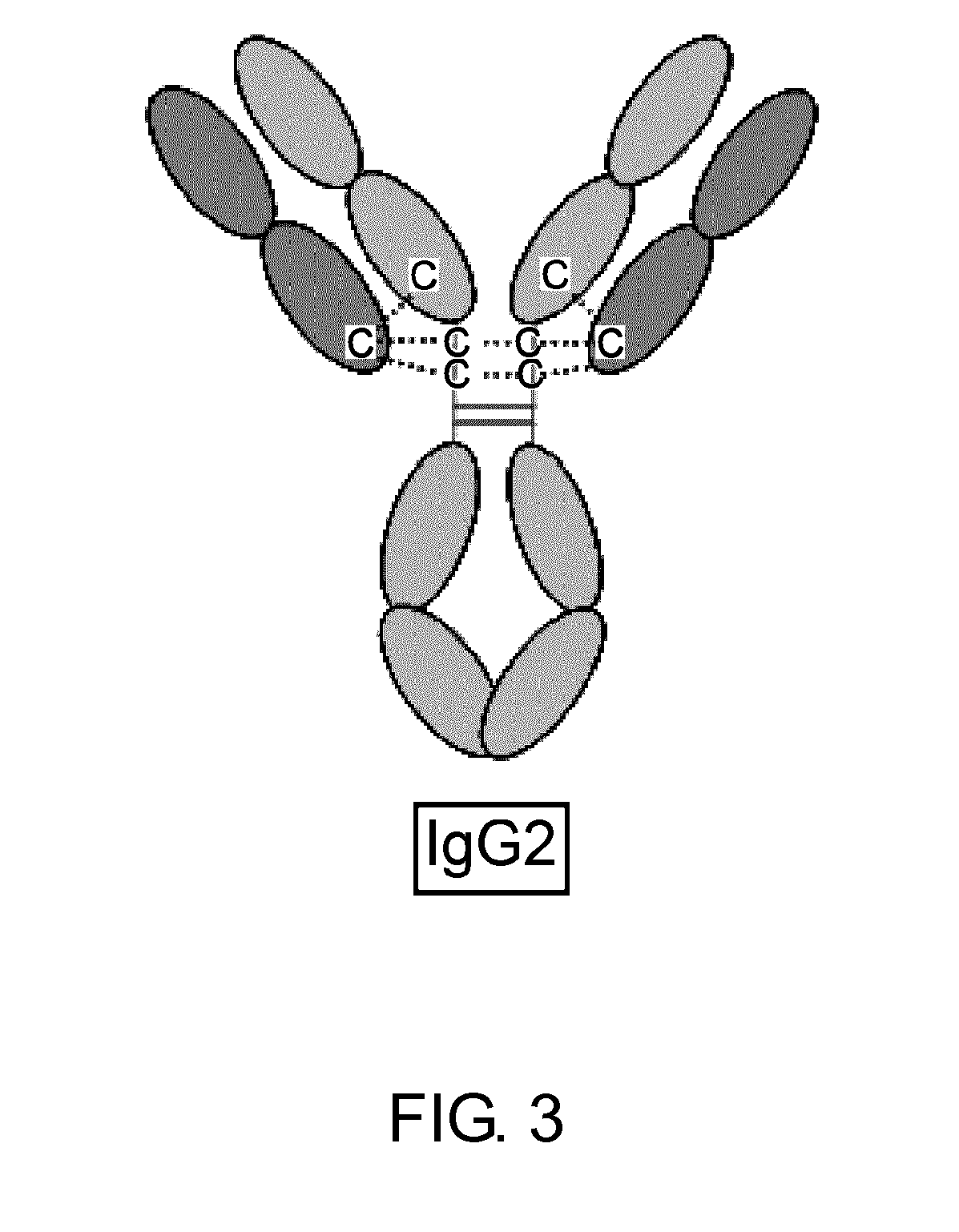
The present inventors succeeded in improving the antibody constant region to have increased stability under acid conditions, reduced heterogeneity originated from disulfide bonds in the hinge region, reduced heterogeneity originated from the H chain C terminus, and increased stability at high concentrations as well as in discovering novel constant region sequences having reduced Fcγ receptor-binding, while minimizing the generation of novel T-cell epitope peptides. As a result, the present inventors successfully discovered antibody constant regions with improved physicochemical properties (stability and homogeneity), immunogenicity, safety, and pharmacokinetics.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Intein-mediated protein ligation of expressed proteins
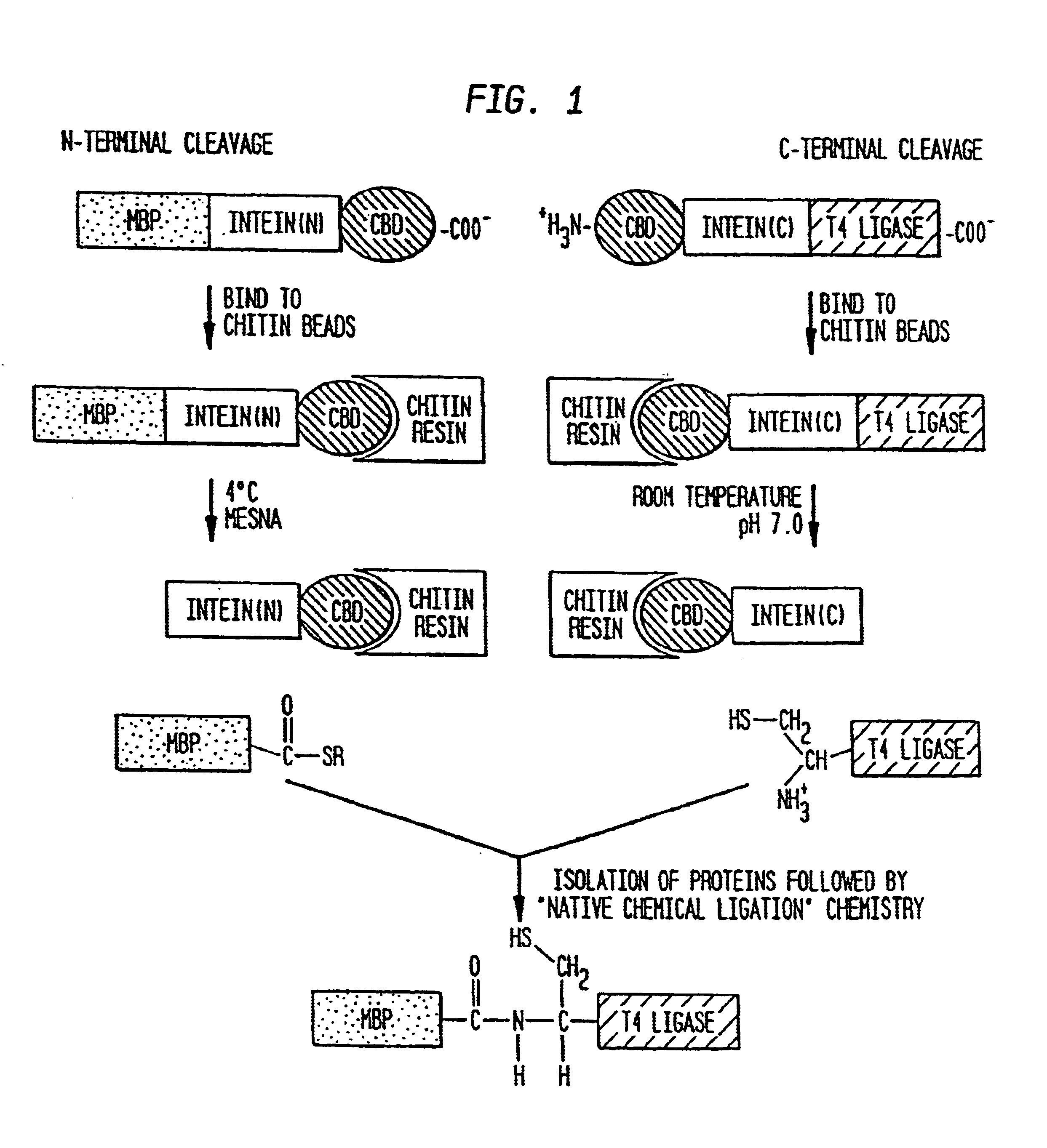
InactiveUS6849428B1Eliminate needBacteriaFusion with post-translational modification motifProtein targetIntein
A method for the ligation of expressed proteins which utilizes inteins, for example the RIR1 intein from Methanobacterium thermotrophicum, is provided. Constructs of the Mth RIR1 intein in which either the C-terminal asparagine or N-terminal cysteine of the intein are replaced with alanine enable the facile isolation of a protein with a specified N-terminal, for example, cysteine for use in the fusion of two or more expressed proteins. The method involves the steps of generating a C-terminal thioester-tagged target protein and a second target protein having a specified N-terminal via inteins, such as the modified Mth RIR1 intein, and ligating these proteins. A similar method for producing a cyclic or polymerized protein is provided. Modified inteins engineered to cleave at their C-terminus or N-terminus, respectively, and DNA and plasmids encoding these modified inteins are also provided.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Modified therapeutic peptides with extended half-lives in vivo
A method for protecting a peptide from peptidase activity in vivo, the peptide being composed of between 2 and 50 amino acids and having a C-terminus and an N-terminus and a C-terminus amino acid and an N-terminus amino acid is described. In the first step of the method, the peptide is modified by attaching a reactive group to the C-terminus amino acid, to the N-terminus amino acid, or to an amino acid located between the N-terminus and the C-terminus, such that the modified peptide is capable of forming a covalent bond in vivo with a reactive functionality on a blood component. In the next step, a covalent bond is formed between the reactive group and a reactive functionality on a blood component to form a peptide-blood component conjugate, thereby protecting said peptide from peptidase activity. The final step of the method involves the analyzing of the stability of the peptide-blood component conjugate to assess the protection of the peptide from peptidase activity.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
Single chain recombinant T cell receptors
InactiveUS7569664B2Improve stabilityUseful purposeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionExtracellularC-terminus
A single chain T cell receptor (scTCR) comprising an a segment constituted by a TCR α chain variable region sequence fused to the N terminus of a TCR α chain constant region extracellular sequence, a β segment constituted by a TCR β chain variable region fused to the N terminus of a TCR β chain constant region extracellular sequence, and a linker sequence linking the C terminus of the α segment to the N terminus of the β segment, or vice versa, the constant region extracellular sequences of the α and β segments being linked by a disulfide bond, the length of the linker sequence and the position of the disulfide bond being such that the variable region sequences of the α and β segments are mutually orientated substantially as in native αβ T cell receptors. Complexes of two or more such scTCRs, and use of the scTCRs in therapy and in various screening applications are also disclosed.
Owner:IMMUNOCORE LTD +1
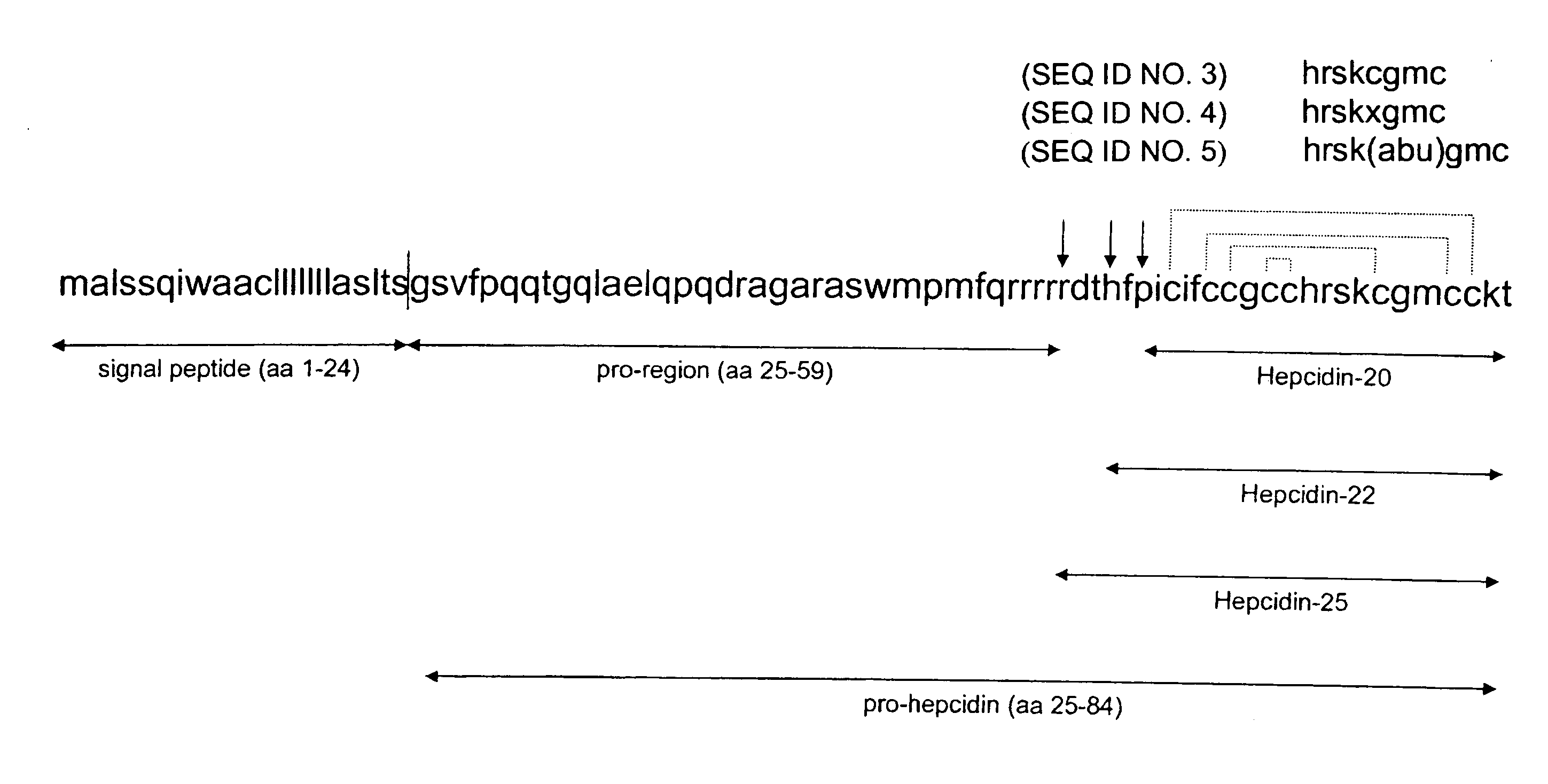
Diagnostic methods for diseases by screening for hepcidin in human or animal tissues, blood or body fluids; monoclonal antibodies specific to human hepcidin and associated uses therefor
ActiveUS20070224186A1Modulate bindingUseful in treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAssayMonoclonal antibody
The present invention concerns antibodies specific for the C-terminus of human hepcidin, and related methods and kits for diagnosing and / or treating a disease condition characterized by non-physiological levels of hepcidin protein, including prohepcidin and fragments thereof, comprising obtaining a tissue or fluid sample from a subject; contacting the sample with an antibody or fragment thereof that specifically binds to a polypeptide corresponding to the amino acid sequence between and including amino acids 60 and 84, or, in another embodiment, amino acids 74 and 81, as aligned with the human pre-pro-hepcidin precursor protein, and quantifying the pro-hepcidin and / or mature hepcidin level using an assay based on binding of the antibody and the polypeptide; wherein the non-physiological level of prohepcidin / mature hepcidin is indicative of the disease condition. The present invention also concerns diagnostic methods and kits for applications in genetic technological approaches, such as for overexpressing or downregulating hepcidin.
Owner:DRG INTERNATIONAL INC
Auristatins Having an Aminobenzoic Acid Unit at the N Terminus
Owner:SEAGEN INC
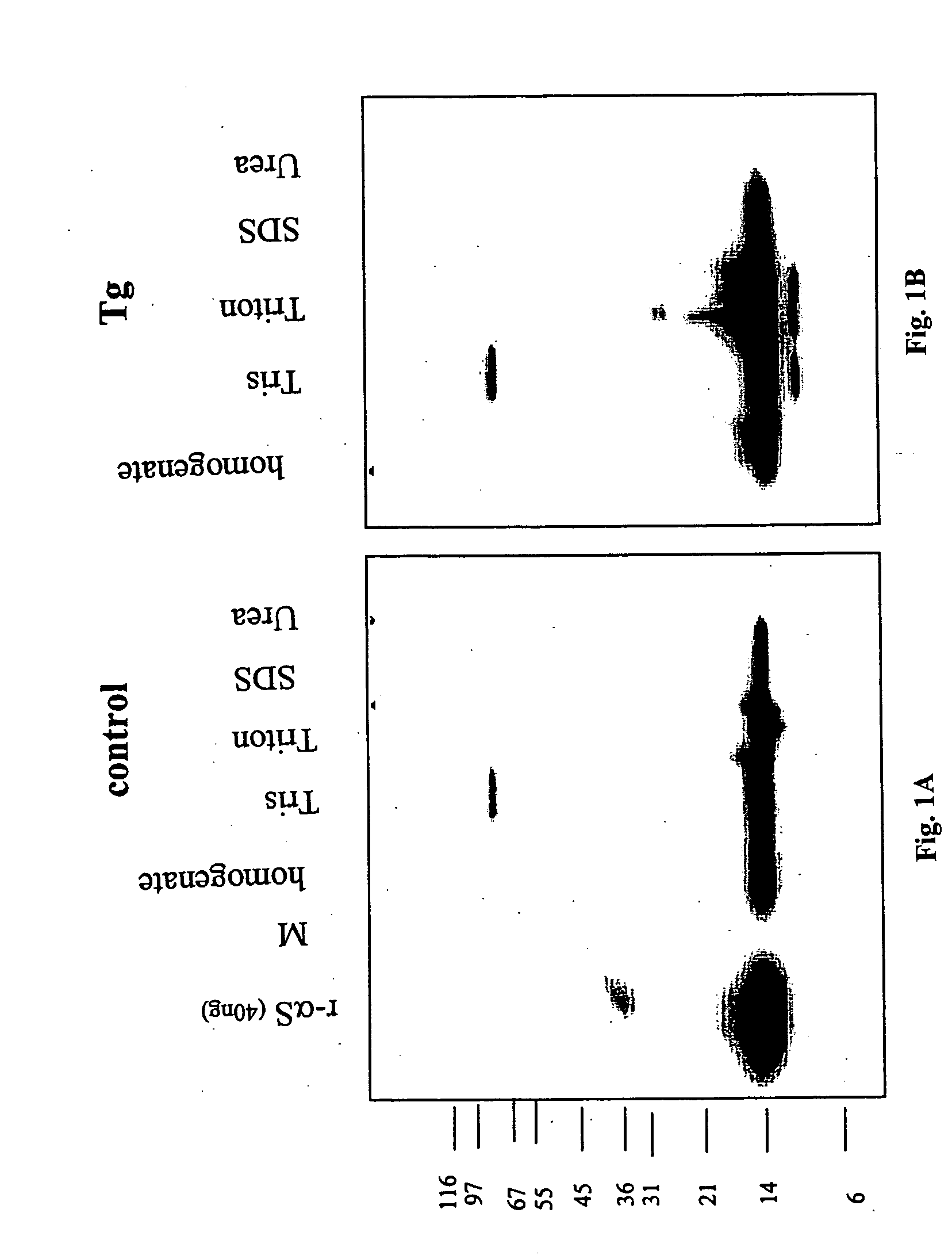
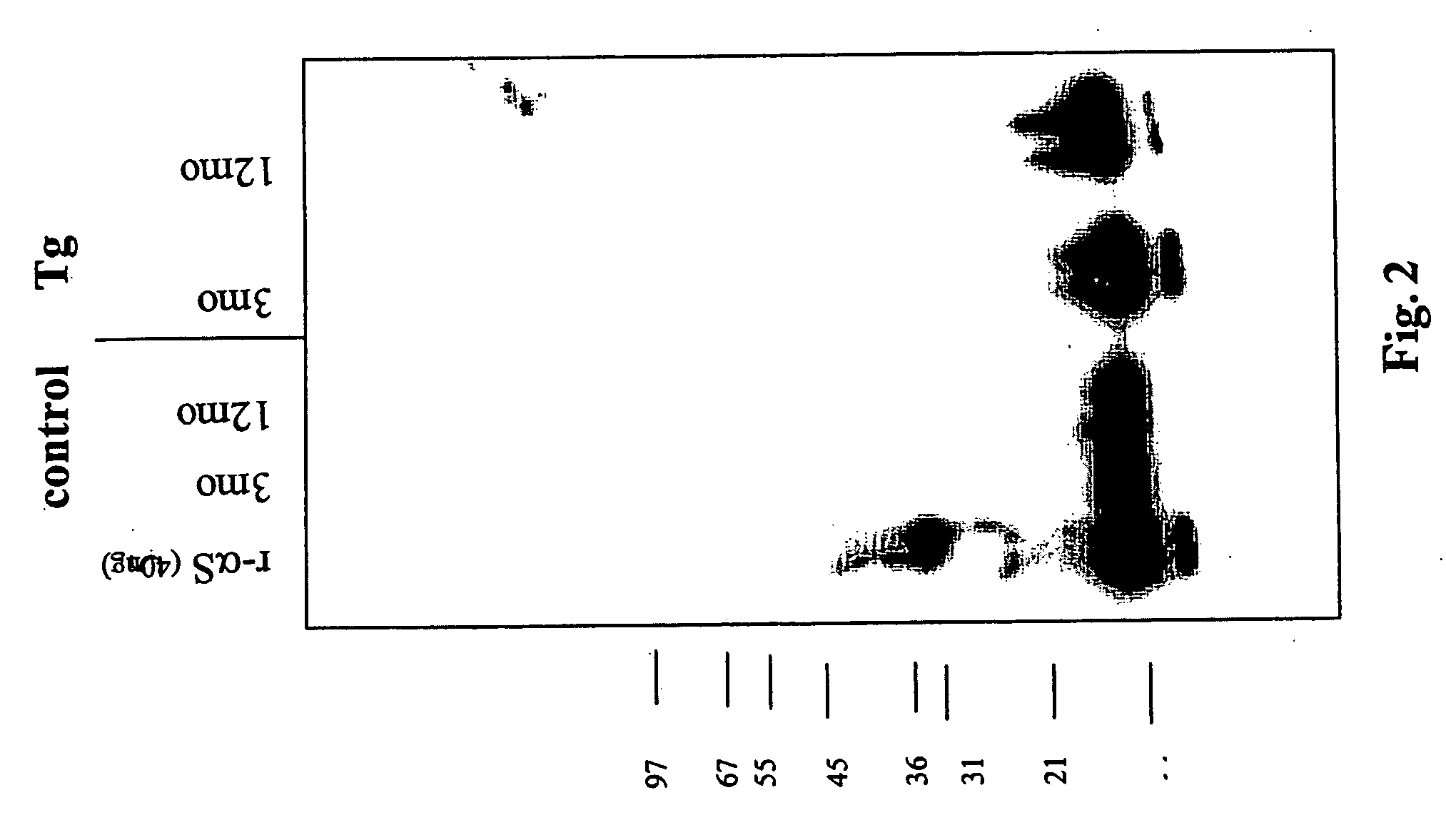
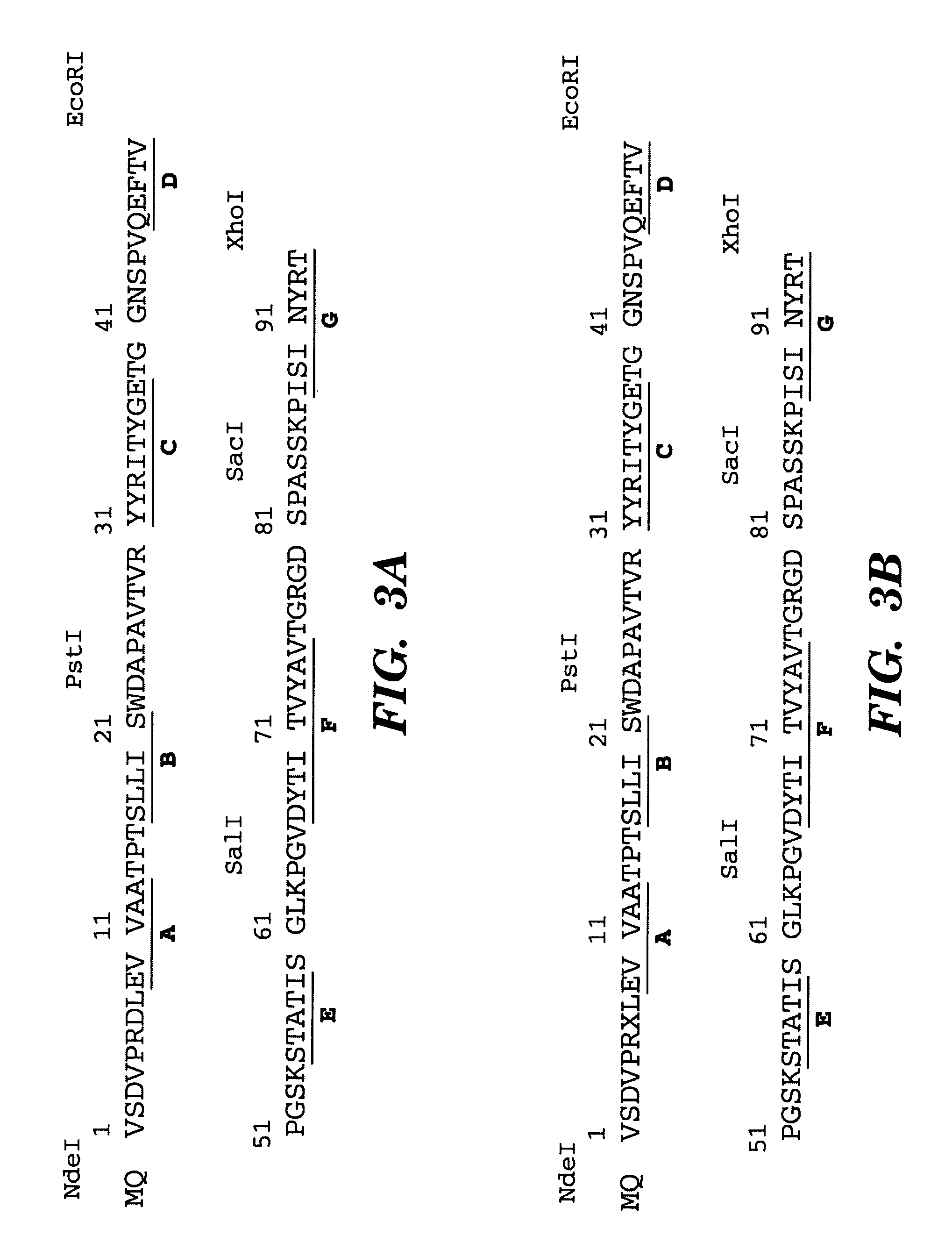
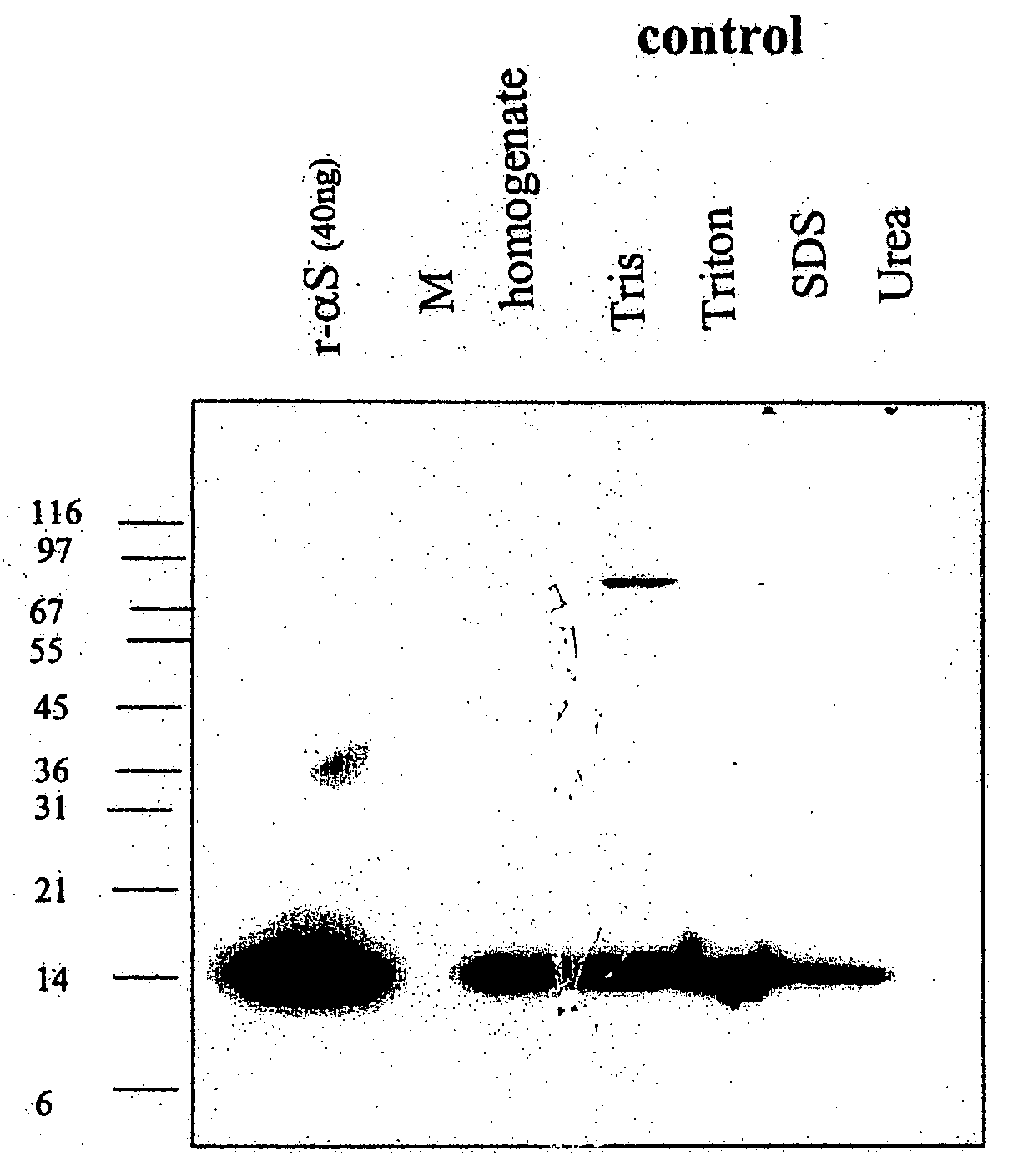
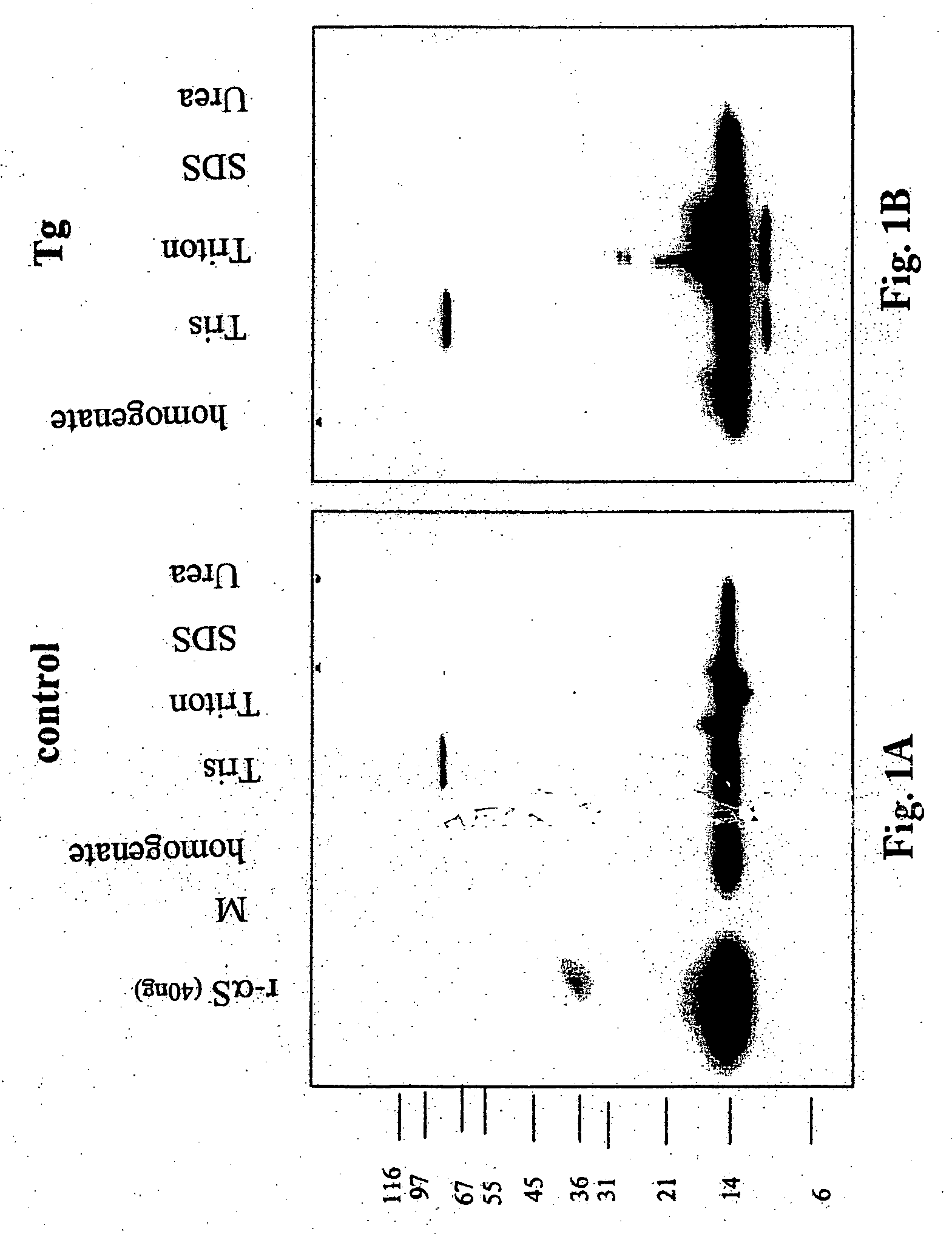
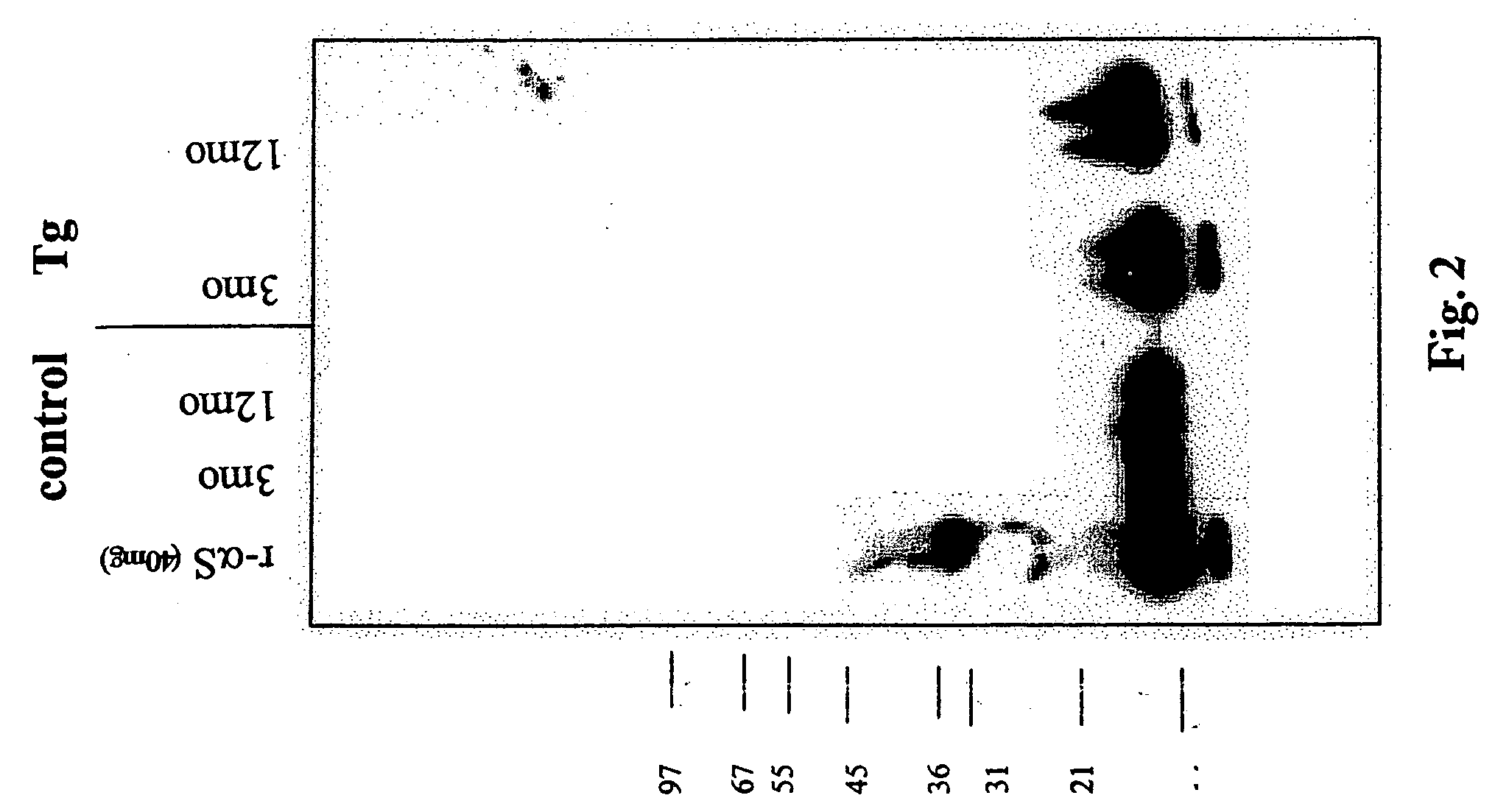
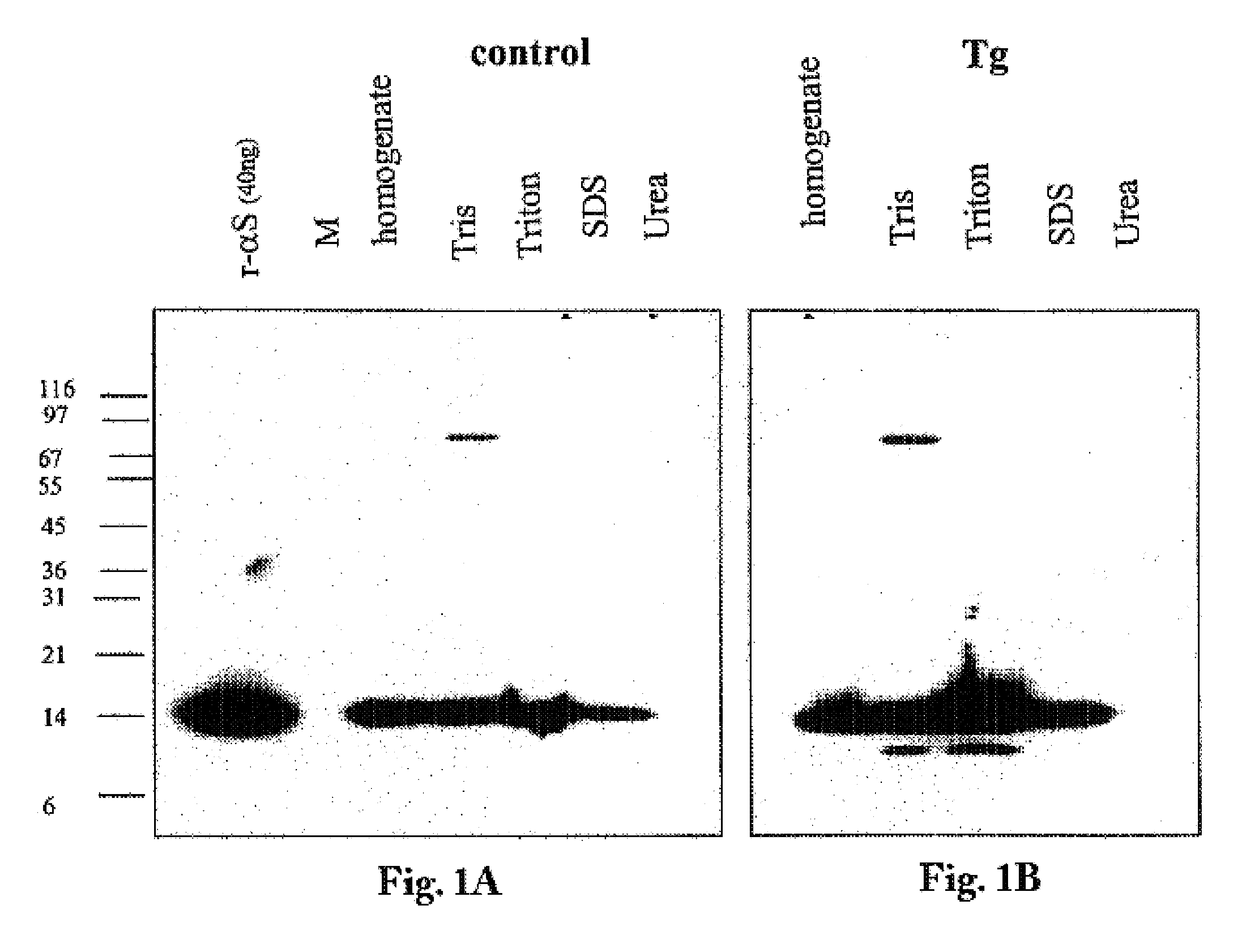
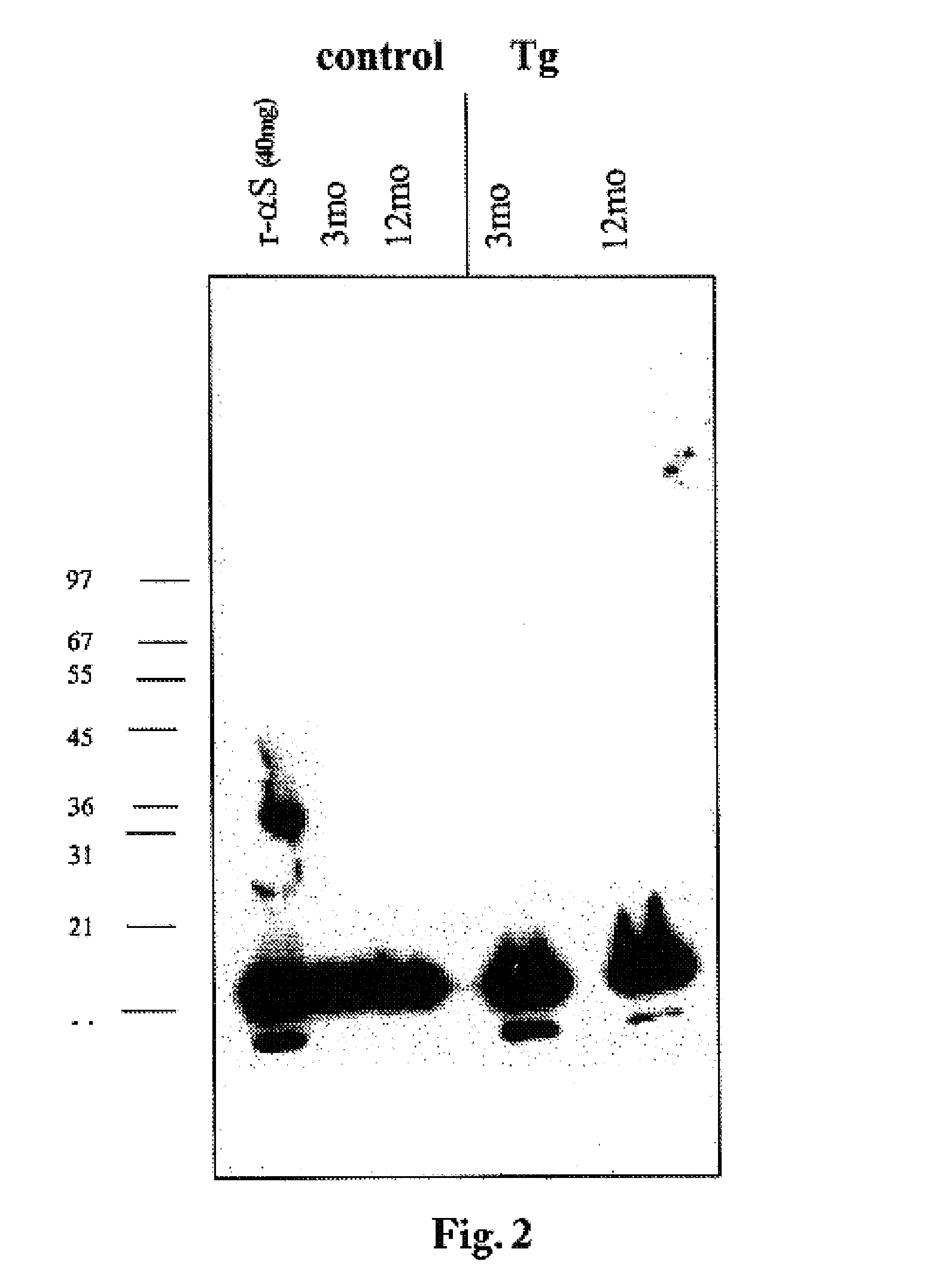
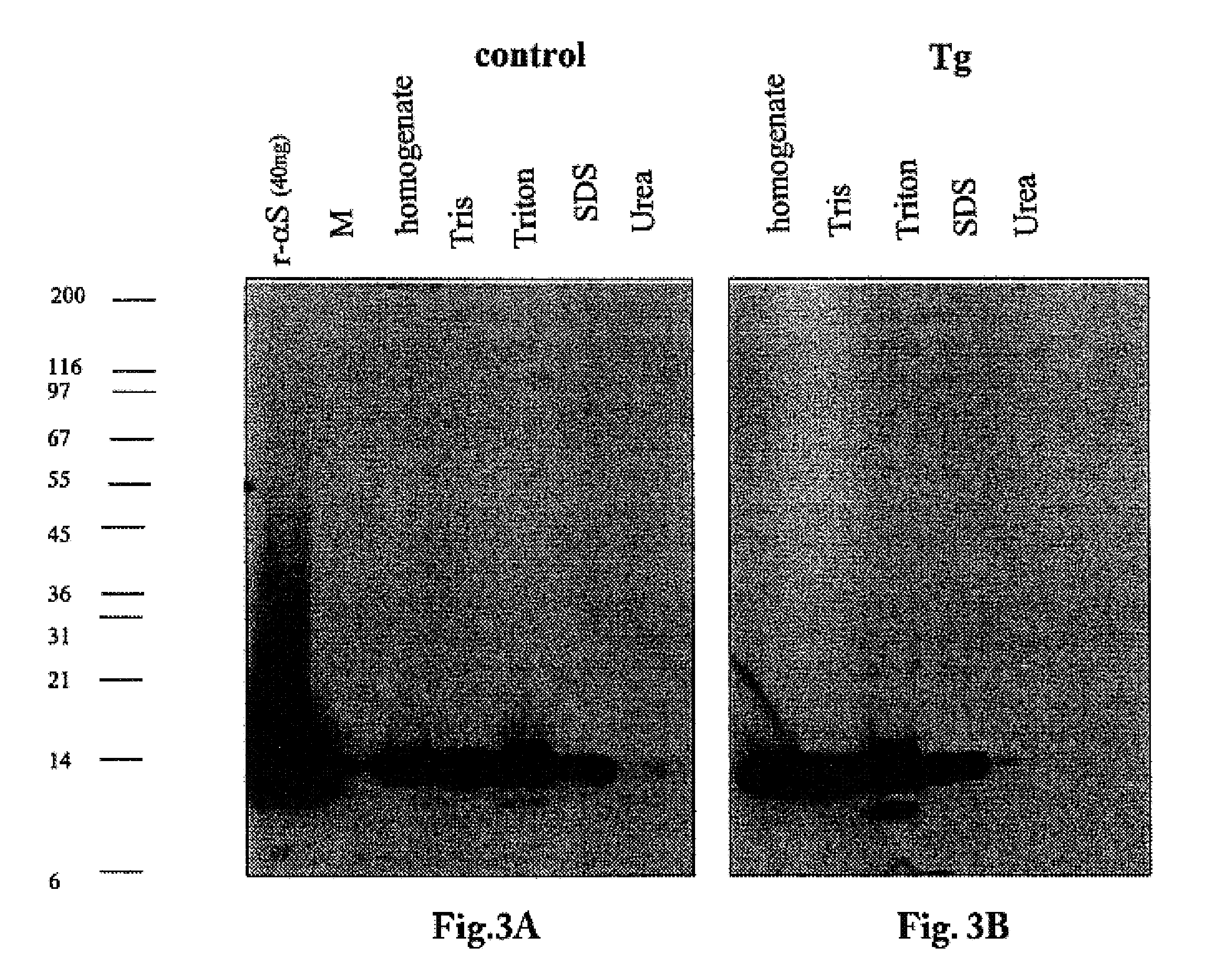
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease
ActiveUS20050198694A1Useful pharmacological activityBiocideNervous disorderGel electrophoresisC-terminus
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to fill-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF FLINDERS UNIV +2
Bcr-abl truncation mutations
ActiveUS20110072889A1Good effectReduced growth rateMicrobiological testing/measurementFlow propertiesGene productTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
Truncation variants of BCR-ABL mRNA that produces BCR-ABL proteins with a truncated C-terminus and its role in resistance to treatment with kinase inhibitors is described. Vectors for expressing the truncated gene products are described as well as recombinant cells that express the truncated gene products from cDNA constructs. Also provided are methods compositions and kits for detecting the BCR-ABL truncation variants. Also provided are methods for determining the prognosis of a patient diagnosed as having myeloproliferative disease, and methods for predicting the likelihood for resistance to a treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitor in a patient diagnosed as having myeloproliferative disease. Additionally, methods for screening BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase domain inhibitors which rely on the recombinant cells are also disclosed.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
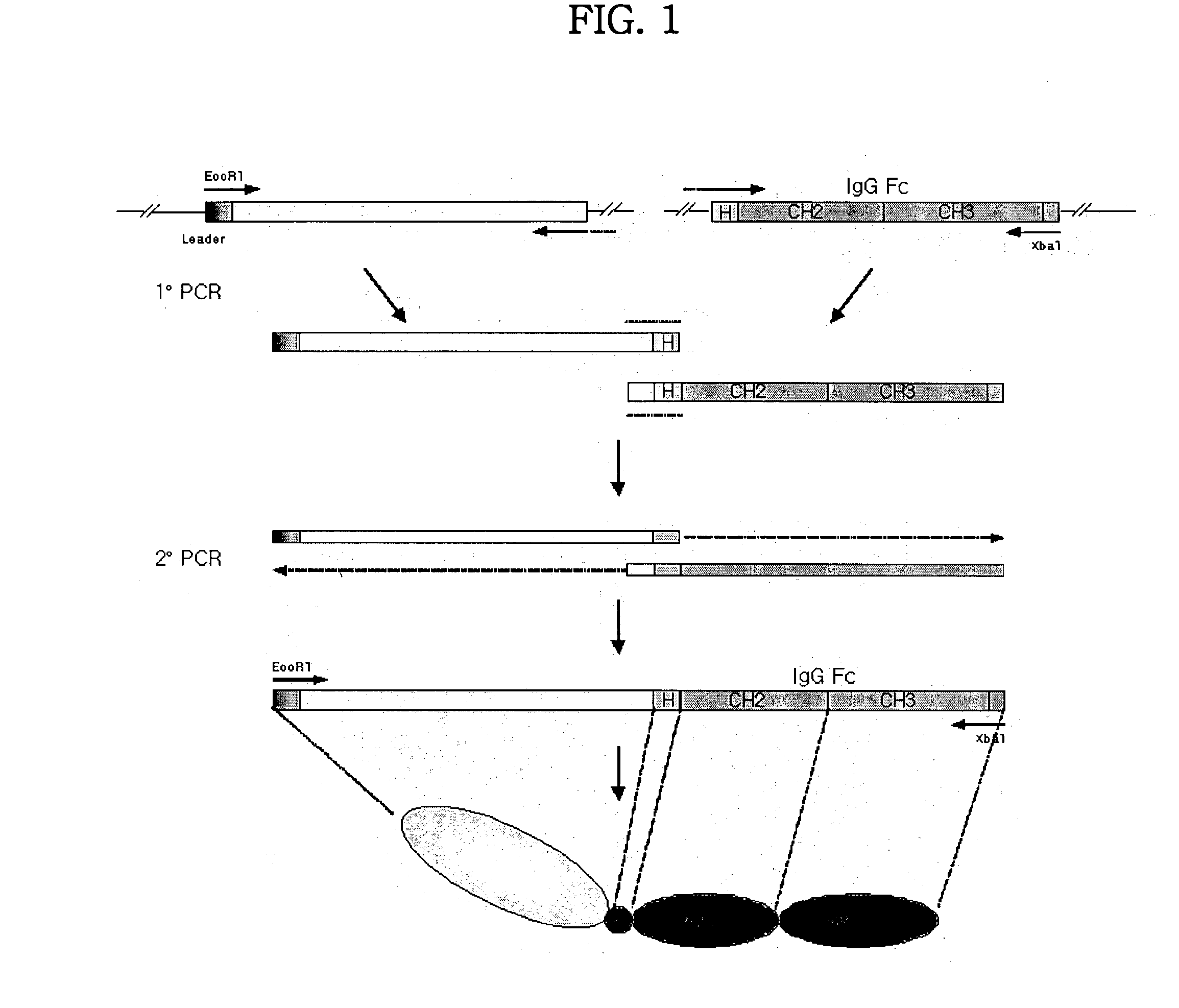
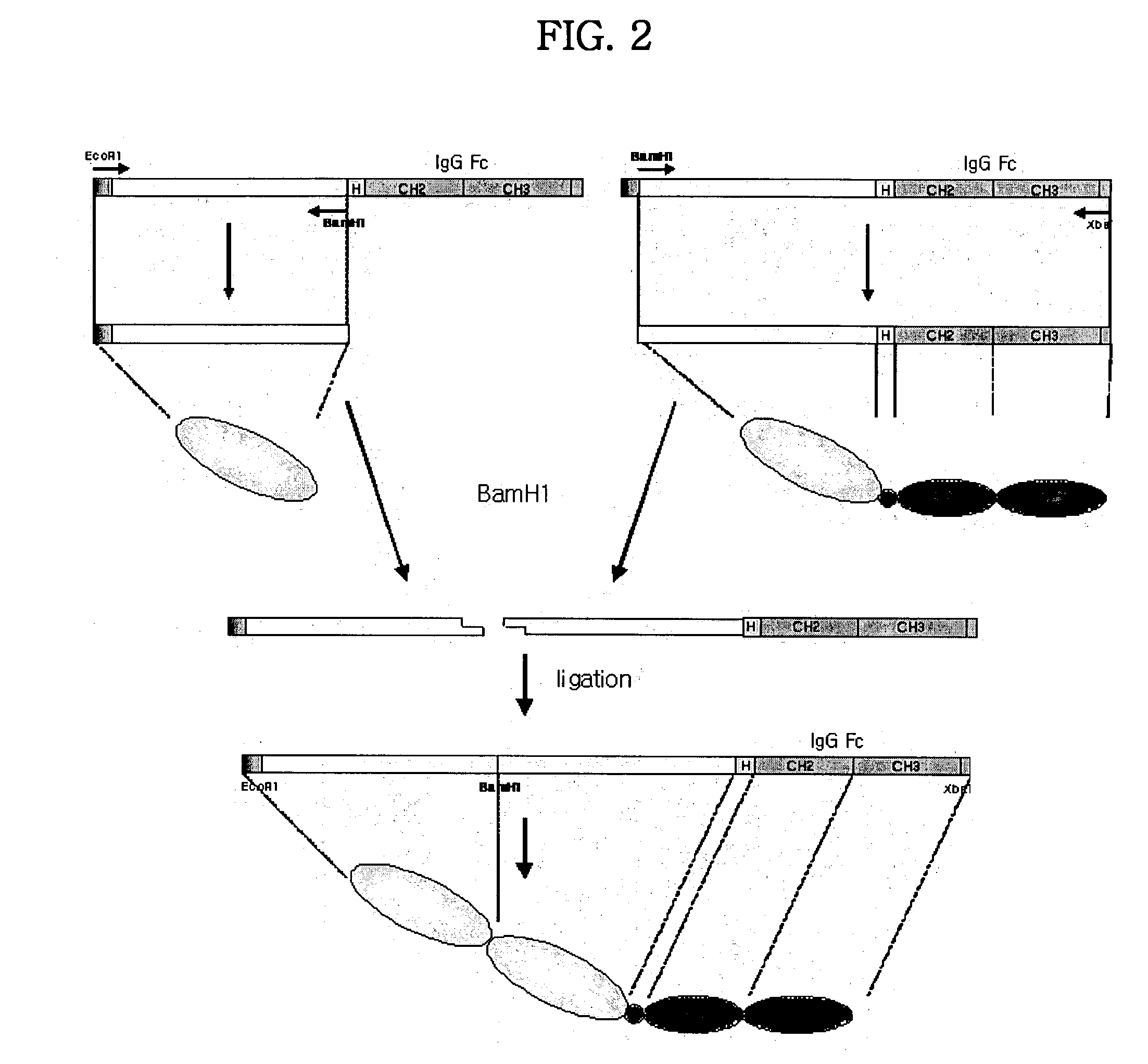
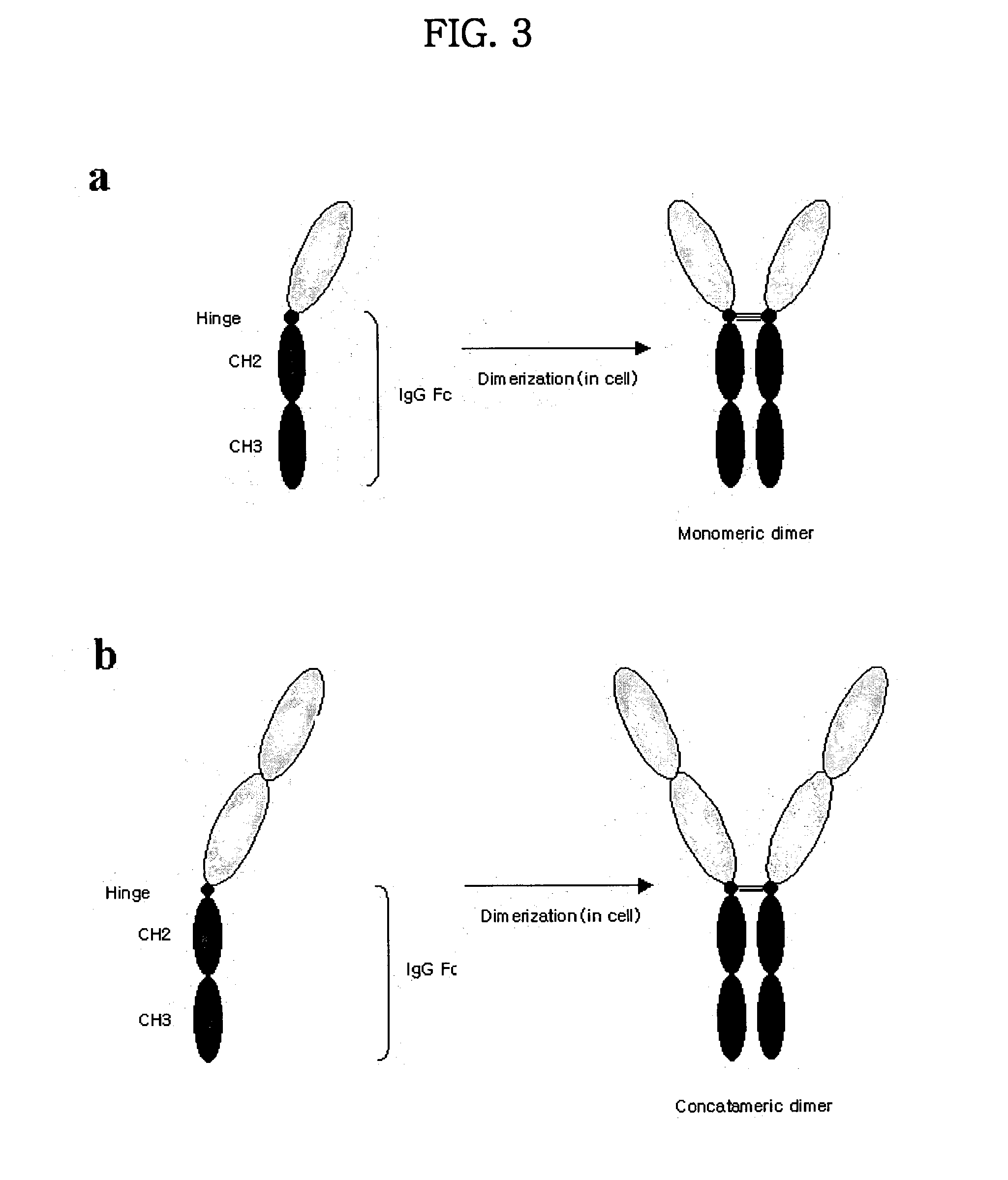
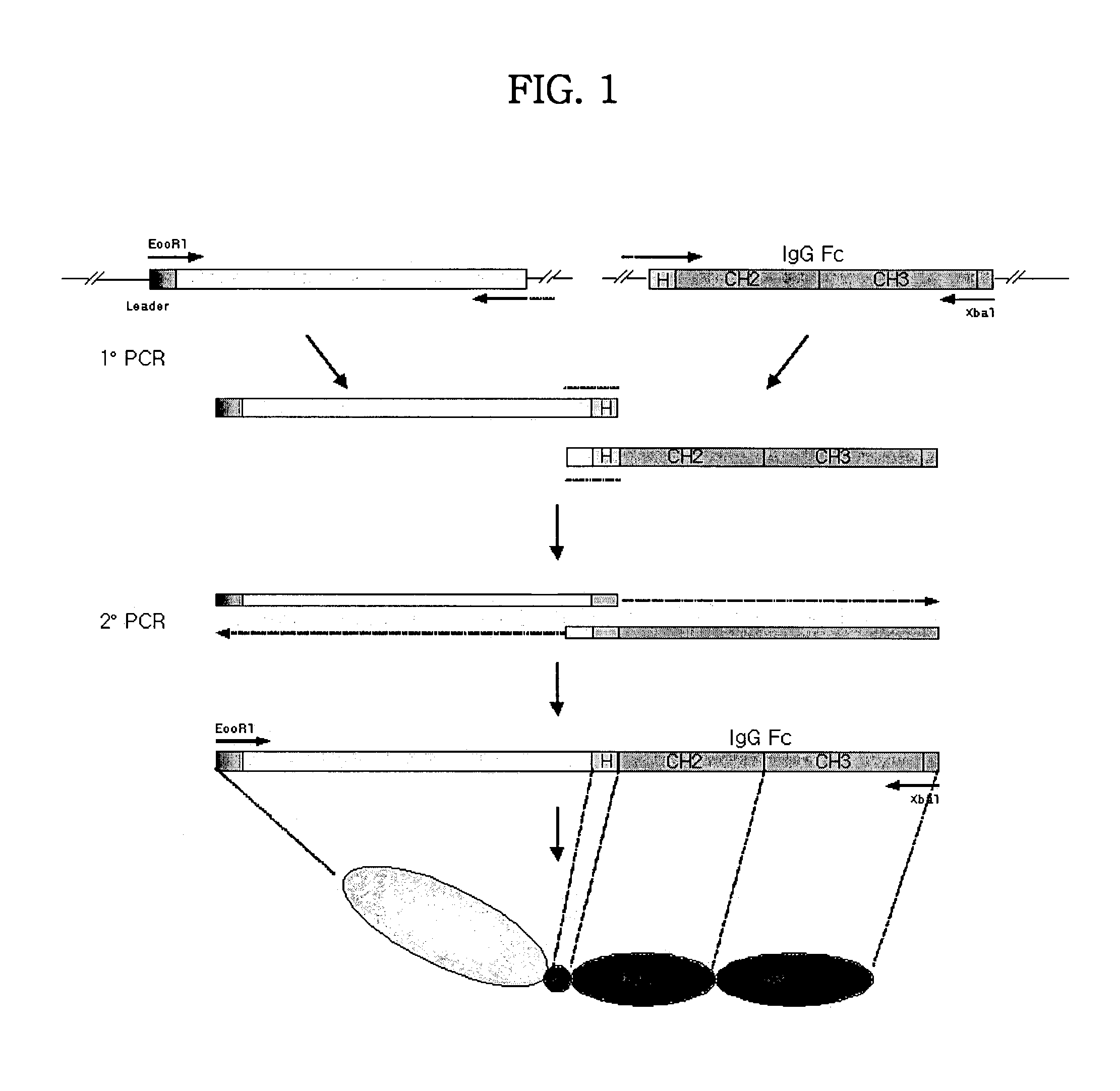
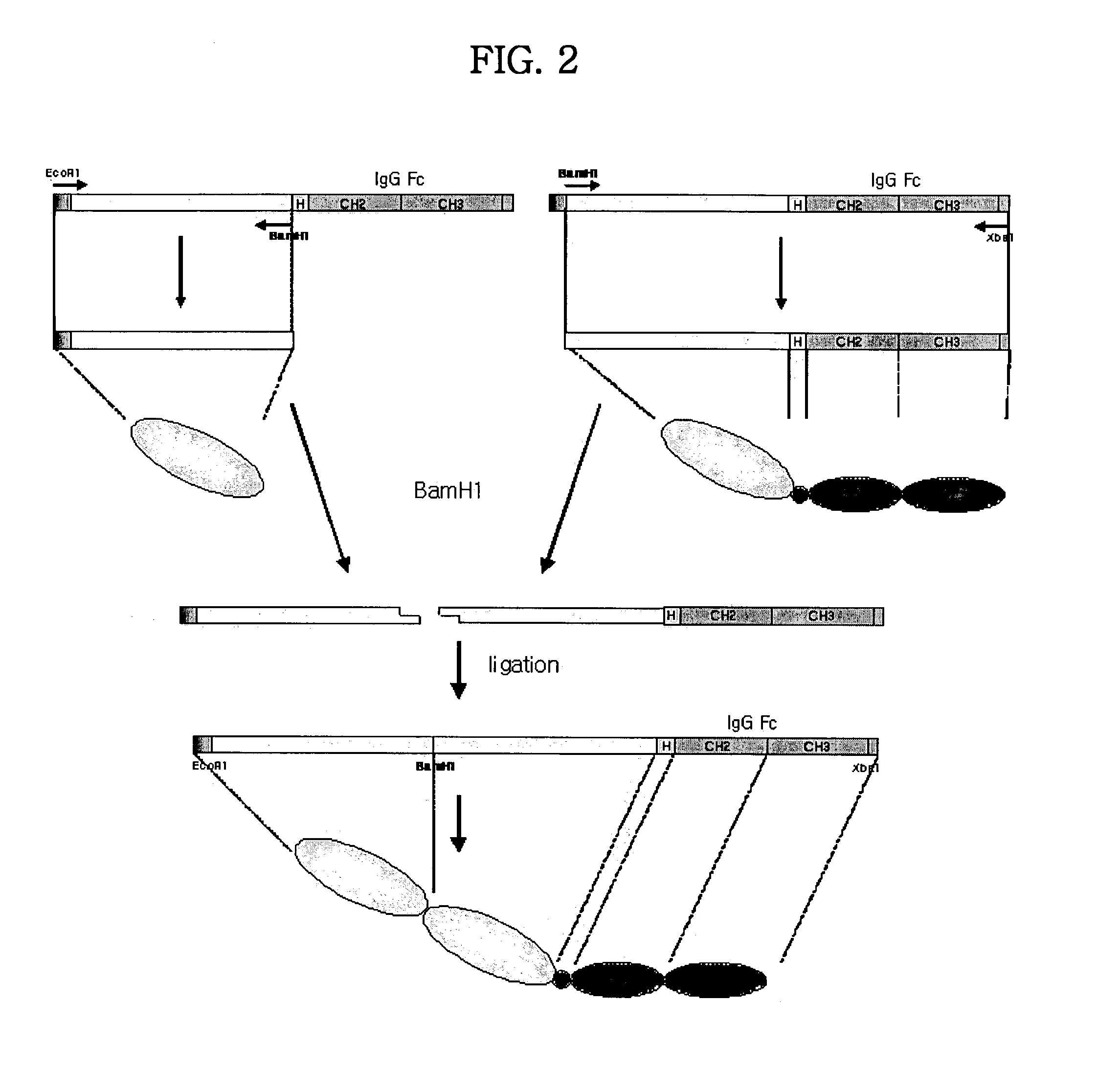
Concatameric immunoadhesion
ActiveUS20030195338A1Improve efficacyImprove stabilityAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA constructActive protein
Disclosed are concatameric proteins comprising two soluble domains, in which the C-terminus of a soluble domain of a biologically active protein is linked to the N-terminus of an identical soluble domain or a distinct soluble domain of a biologically active protein. Also, the present invention discloses dimeric proteins formed by formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds at the hinge region of two monomeric proteins formed by linkage of a concatamer of two identical soluble extracellular regions of proteins involving immune response to an Fc fragment of an immunoglobulin molecule, their glycosylated proteins, DNA constructs encoding the monomeric proteins, recombinant expression plasmids containing the DNA construct, host cells transformed or transfected with the recombinant expression plasmids, and a method of preparing the dimeric proteins by culturing the host cells. Further, the present invention discloses pharmaceutical or diagnostic compositions comprising the dimeric protein or its glycosylated form.
Owner:MEDEXGEN
Method of identifying polypeptide monobodies which bind to target proteins and use thereof
InactiveUS7598352B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainProtein target
A method of identifying a polypeptide monobody having target protein binding activity, said method comprising: providing a host cell comprising (i) a reporter gene under control of a 5′ regulatory region operable in the host cell, (ii) a first chimeric gene which encodes a first fusion polypeptide comprising a target protein, or fragment thereof, fused to a C-terminus of a DNA-binding domain which binds to the 5′ regulatory region of the reporter gene, and (iii) a second chimeric gene which encodes a second fusion polypeptide comprising a polypeptide monobody fused to a transcriptional activation domain; and detecting expression of the reporter gene, which indicates binding of the polypeptide monobody of the second fusion polypeptide to the target protein such that the transcriptional activation domain of the second fusion polypeptide is in sufficient proximity to the DNA-binding domain of the first fusion polypeptide to allow expression of the reporter gene.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy Body Disease
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to full-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:PROTHENA BIOSCI LTD
Chimeric fibroblast growth factor 23 proteins and methods of use
ActiveUS20140243260A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsChimera ProteinFibroblast growth factor 23
The present invention relates to an isolated chimeric protein. The isolated chimeric protein includes an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes an N-terminal portion from a fibroblast growth factor (“FGF”) 23 molecule and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion from an FGF19 molecule. The present invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition including an isolated chimeric protein and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The isolated chimeric protein includes an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes an N-terminal portion from a fibroblast growth factor (“FGF”) 23 molecule and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion from an FGF19 molecule, and a pharmaceutically-acceptable carrier. Yet another aspect of the present invention relates to a method for treating a subject suffering from a disorder. This method includes selecting a subject suffering from the disorder and administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a chimeric protein according to the present invention.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Tetravalent etanercept
ActiveUS7229962B2Improve efficacyImprove stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntipyreticDNA constructEtanercept
Disclosed are concatameric proteins comprising two soluble domains, in which the C-terminus of a soluble domain of a biologically active protein is linked to the N-terminus of an identical soluble domain or a distinct soluble domain of a biologically active protein. Also, the present invention discloses dimeric proteins formed by formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds at the hinge region of two monomeric proteins formed by linkage of a concatamer of two identical soluble extracellular regions of proteins involving immune response to an Fc fragment of an immunoglobulin molecule, their glycosylated proteins, DNA constructs encoding the monomeric proteins, recombinant expression plasmids containing the DNA construct, host cells transformed or transfected with the recombinant expression plasmids, and a method of preparing the dimeric proteins by culturing the host cells. Further, the present invention discloses pharmaceutical or diagnostic compositions comprising the dimeric protein or its glycosylated form.
Owner:MEDEXGEN
Cyclic peptide compositions and methods for treatment of sexual dysfunction
InactiveUS7176279B2Rapidly pharmaceutically activeGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsPeptide sourcesCyclic peptideNasal cavity
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
Single chain recombinant t cell receptors
InactiveUS20060166875A1Improve stabilityUseful purposeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDisulfide bondingExtracellular
A single chain T cell receptor (scTCR) comprising an a segment constituted by a TCR α chain variable region sequence fused to the N terminus of a TCR α chain constant region extracellular sequence, a β segment constituted by a TCR β chain variable region fused to the N terminus of a TCR β chain constant region extracellular sequence, and a linker sequence linking the C terminus of the a segment to the N terminus of the β segment, or vice versa, the constant region extracellular sequences of the α and β segments being linked by a disulfide bond, the length of the linker sequence and the position of the disulfide bond being such that the variable region sequences of the α and β segments are mutually orientated substantially as in native αβ T cell receptors. Complexes of two or more such scTCRs, and use of the scTCRs in therapy and in various screening applications are also disclosed.
Owner:IMMUNOCORE LTD +1
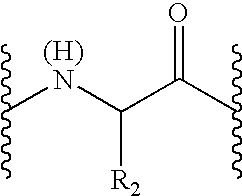
Cyclic peptide compositions for treatment of sexual dysfunction
InactiveUS20060111281A1Without deleterious side effectGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsPeptide sourcesCyclic peptideSexual impotence
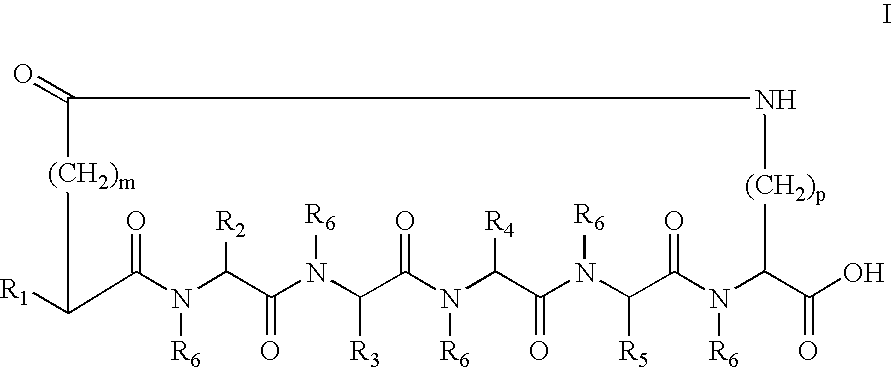
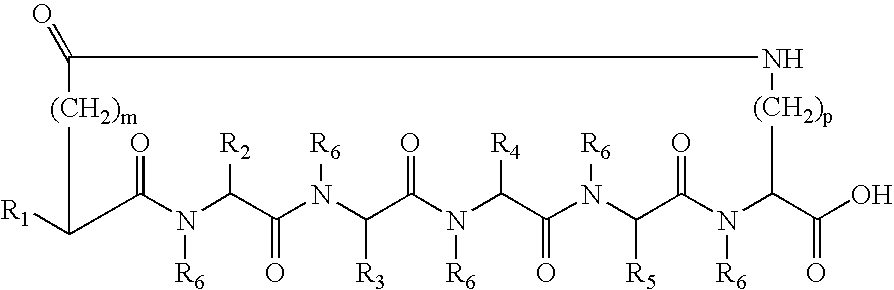
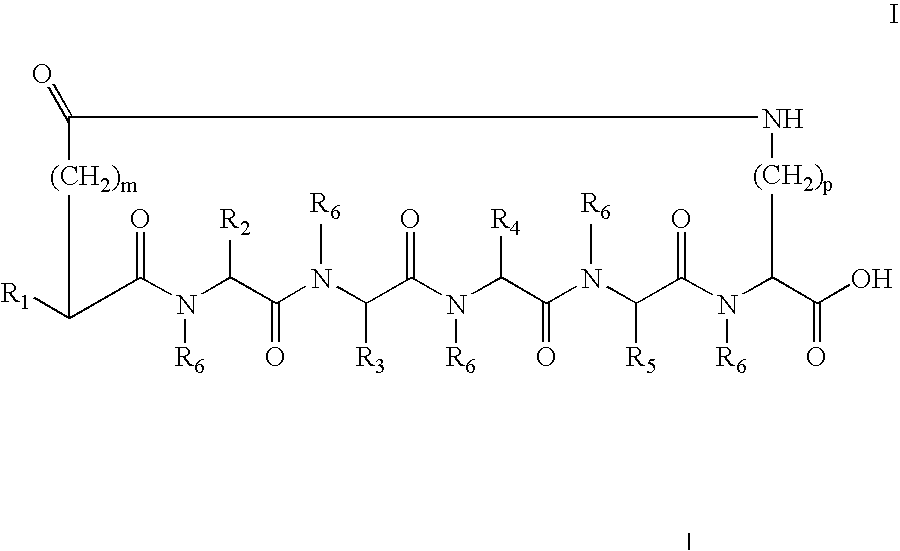
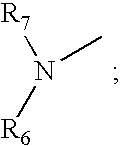
A cyclic peptide of the structural formula: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, m and p are as defined. Further provided are compositions for treatment of sexual dysfunction in mammals, including male sexual dysfunction, such as erectile dysfunction, and female sexual dysfunction, by administration of a cyclic peptide including a C-terminus —OH group. Routes of administration include injection, oral, urethral, vaginal, nasal and mucosal administration.
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to full-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:PROTHENA BIOSCI LTD
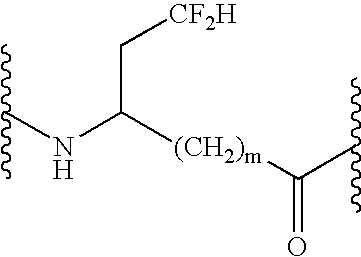
Peptide inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease
InactiveUS6867284B1Organic compound preparationTripeptide ingredientsProteinase activityHcv hepatitis
Fluorinated oligopeptides, especially those having 4,4-difluoro-2-amino butyric acid at the C terminus, may be effective inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease. Examples of hexapeptides of the invention, optimized for binding in the S1 specificity pocket of the enzyme, may display IC50s at the sub-micromolar level. Embodiments of tripeptides of the invention, having a keto-acid group at the C-terminus are, likewise, potent inhibitors of NS3 protease.
Owner:IST DI RICERCHE DI BIOLOGIA MOLECOLARE P ANGELETTI
Yeast cell surface display of proteins and uses thereof
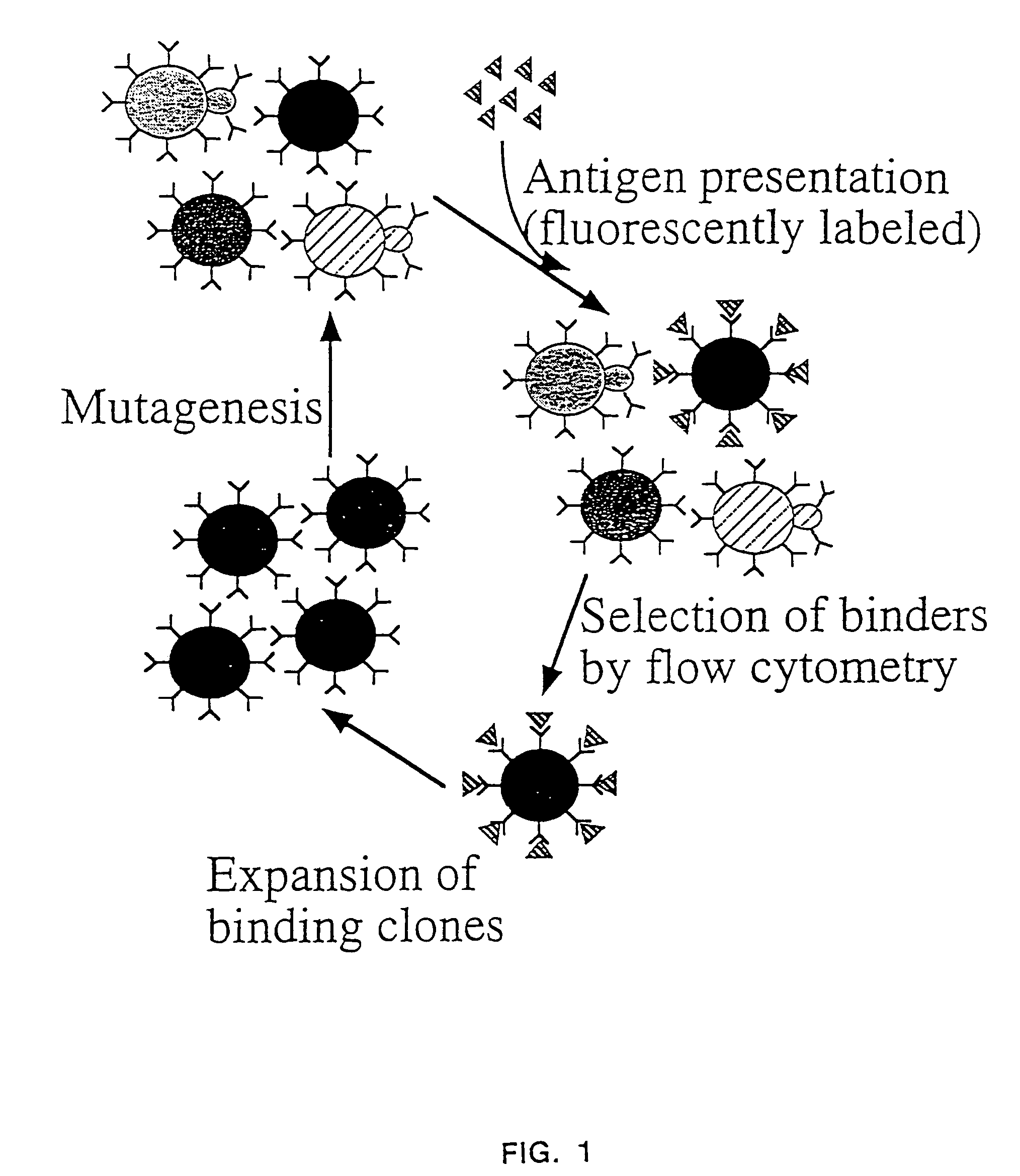
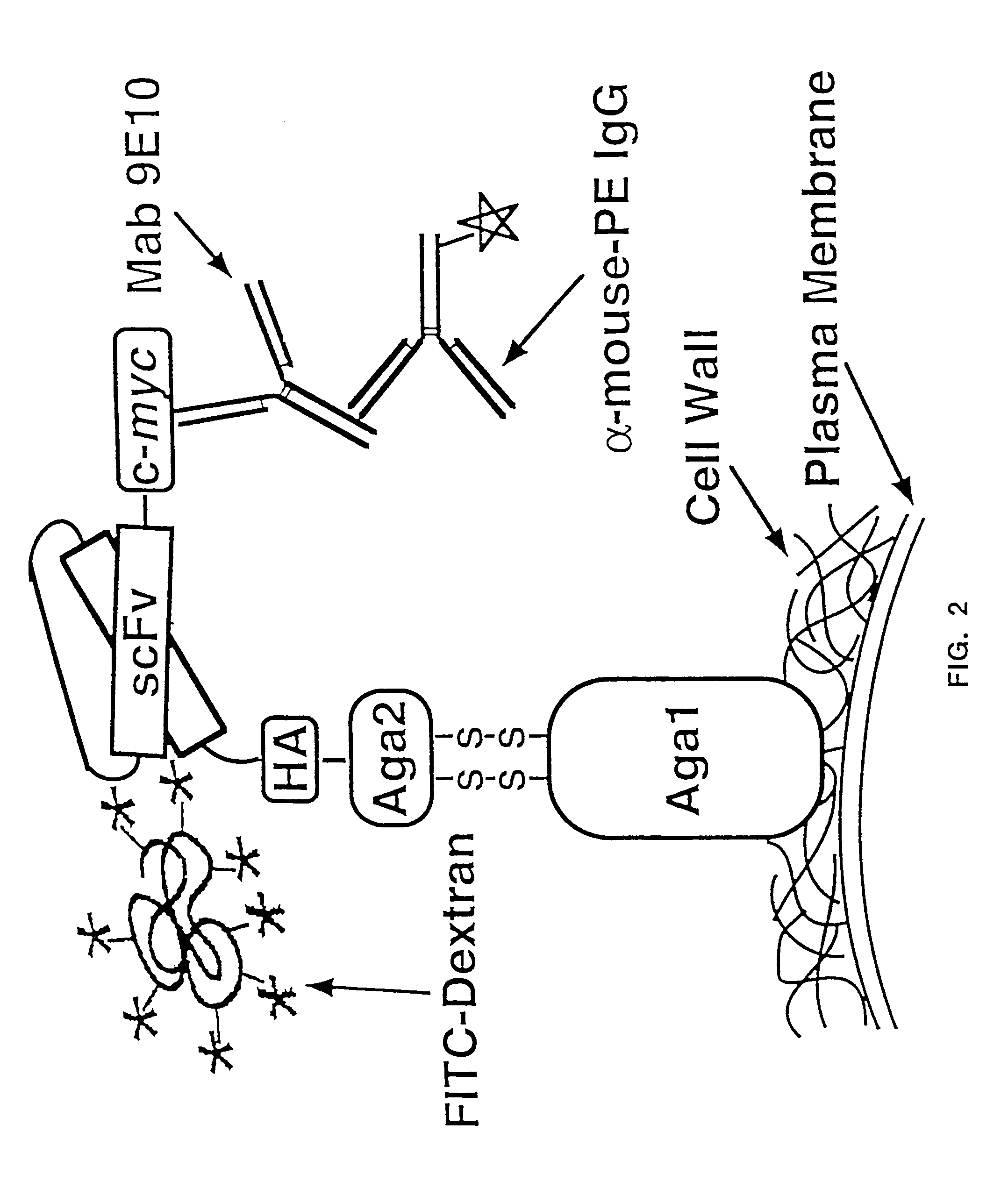
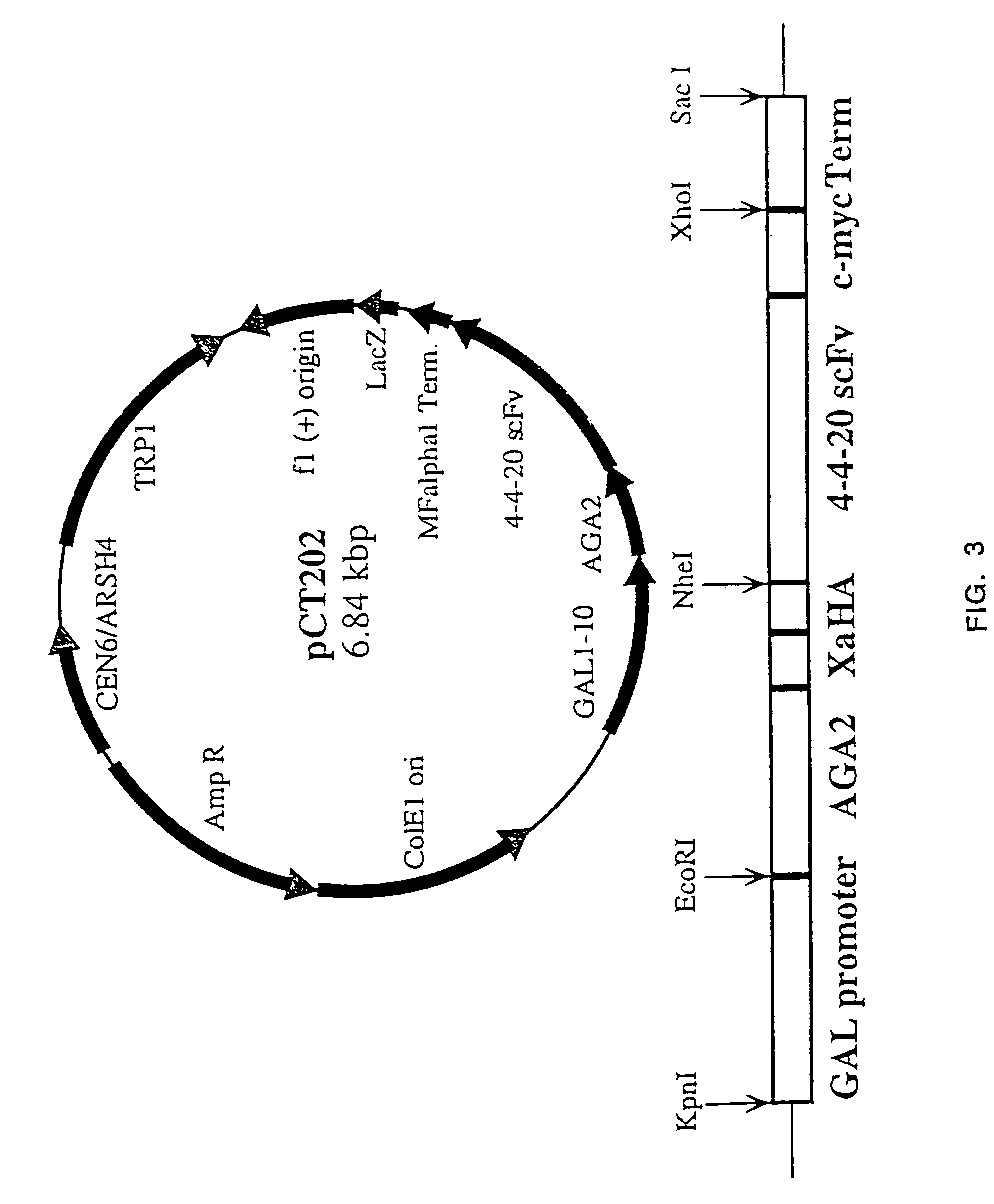
InactiveUS7465787B2Improve the level ofEnhance level of cell surface expression of cellFungiDirected macromolecular evolutionSurface displayAgglutinin-B
The present invention provides a genetic method for tethering polypeptides to the yeast cell wall in a form accessible for binding to macromolecules. Combining this method with fluorescence-activated cell sorting provides a means of selecting proteins with increased or decreased affinity for another molecule, altered specificity, or conditional binding. Also provided is a method for genetic fusion of the N terminus of a polypeptide of interest to the C-terminus of the yeast Aga2p cell wall protein. The outer wall of each yeast cell can display approximately 10 protein agglutinins. The native agglutinins serve as specific adhesion contacts to fuse yeast cells of opposite mating type during mating. In effect, yeast has evolved a platform for protein-protein binding without steric hindrance from cell wall components.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
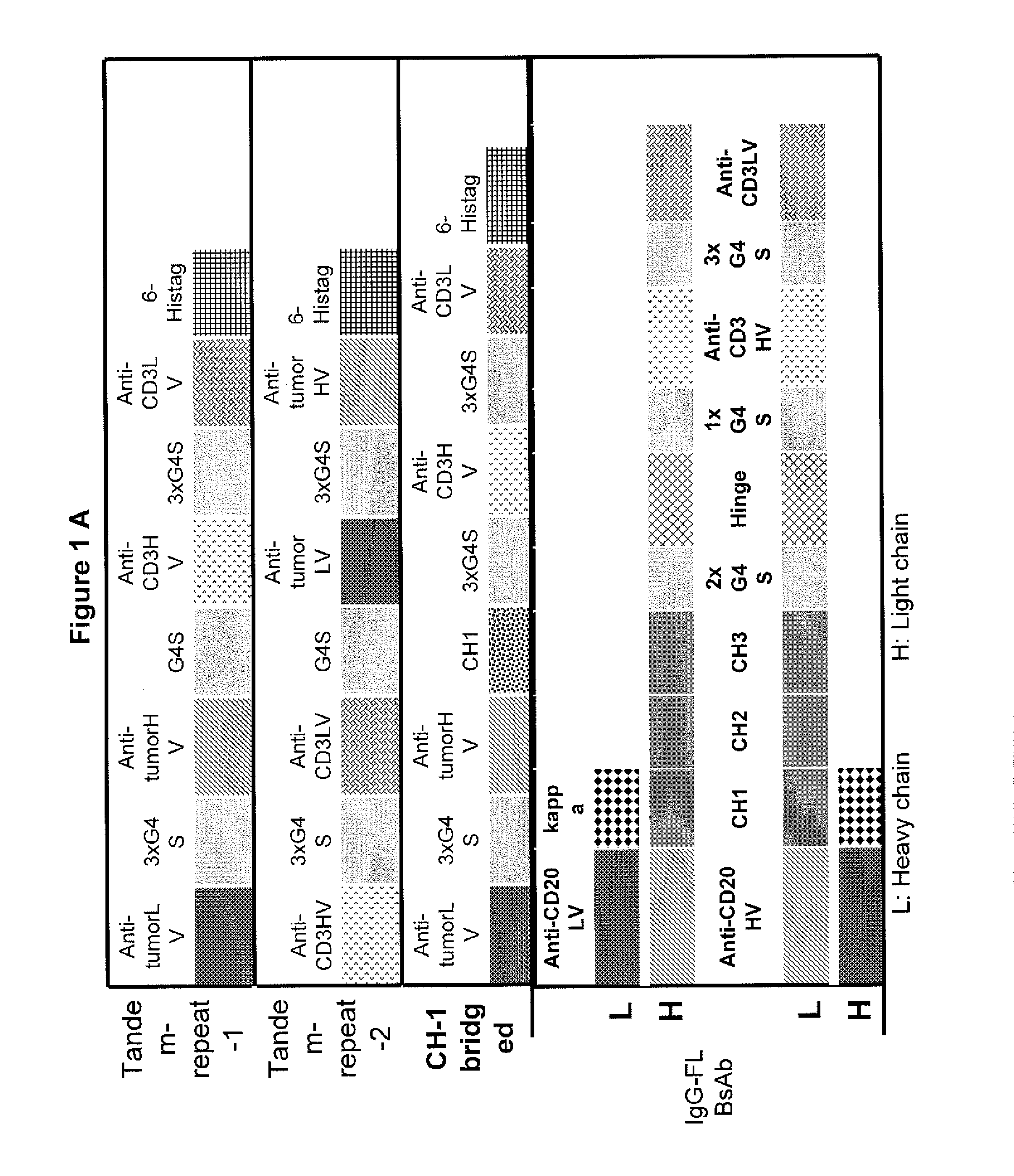
Light chain-bridged bispecific antibody
InactiveUS20130165638A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBispecific antibodyClinical therapy
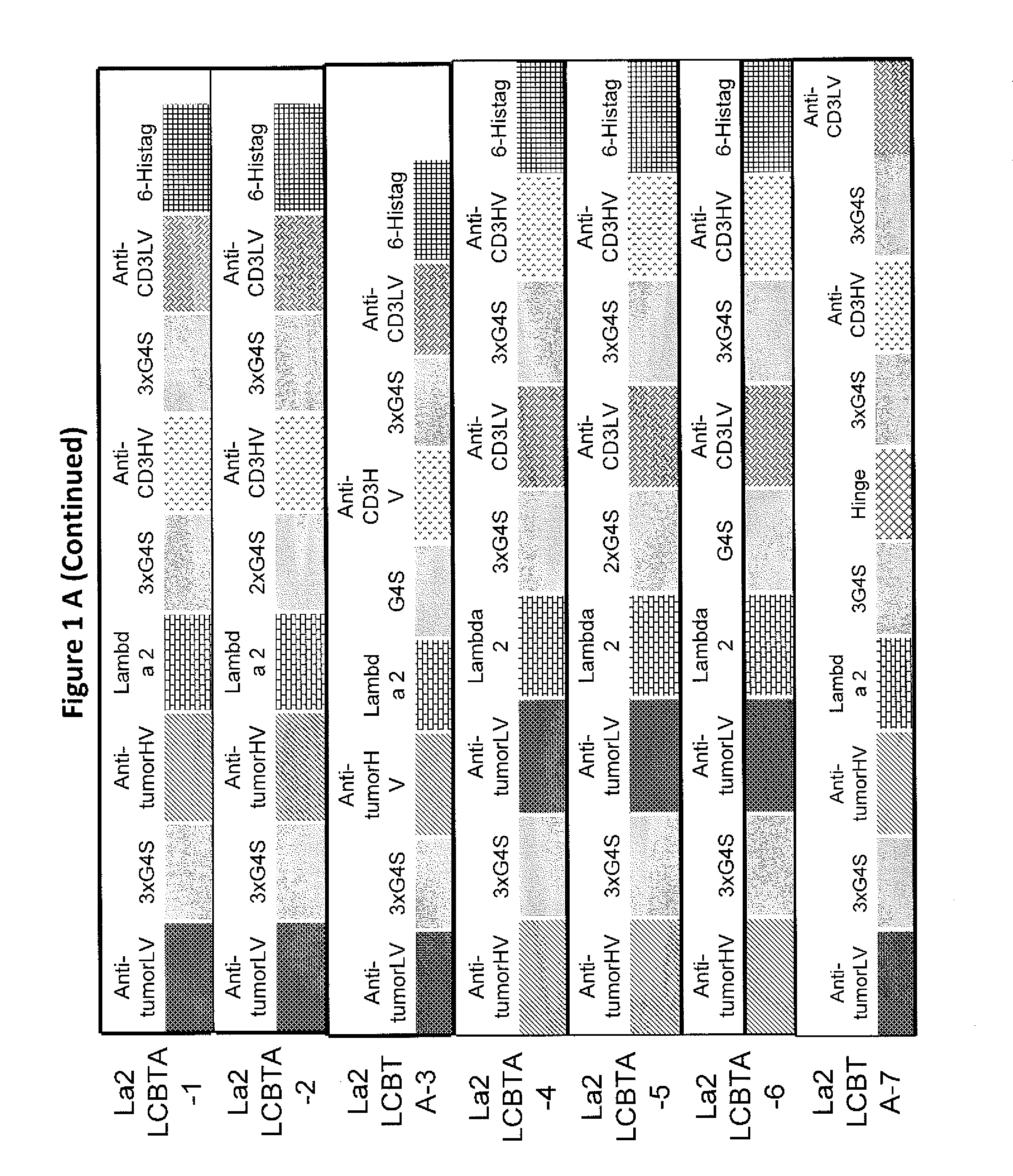
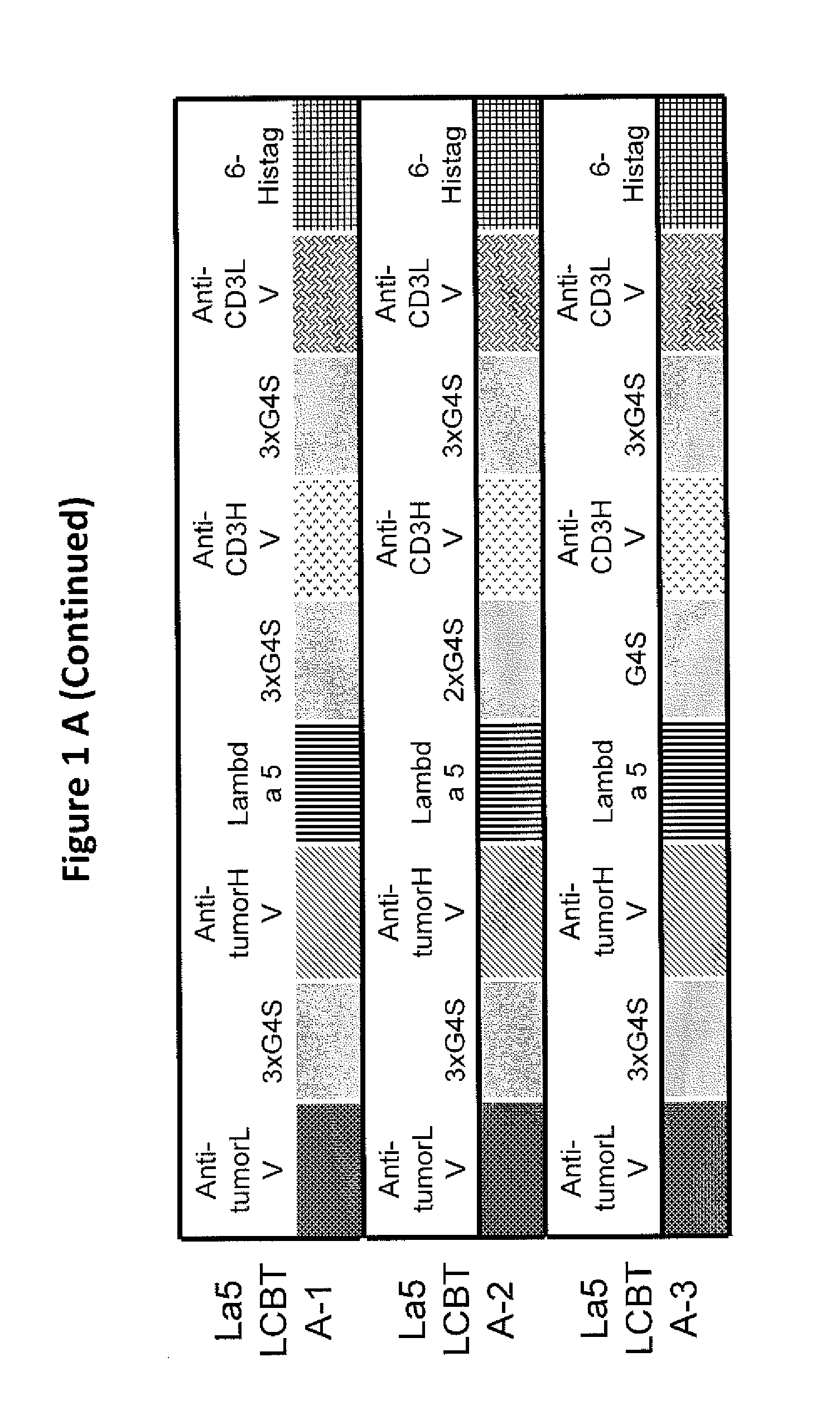
This invention describes a novel format of monomeric bispecific fusion protein with immune activating property for clinical therapies. A bispecific fusion protein includes a first targeting domain with a specificity for a first target of interest; a bridging domain derived from a constant region of a light chain or heavy chain of an immunoglobulin, which may be a human immunoglobulin; and a second targeting domain with a specificity for a second target of interest. The bispecific fusion protein may further include a linker fused to the N-terminus or the C-terminus of the bridging domain. The first targeting domain is fused to the bridging domain and the second targeting domain is fused to the bridging domain or the linker. The linker may include a GGGGS sequence. The first target of interest may be CD20, Her2 / neu, or EpCAM, and the second targeting domain is a T-lymphocyte activating domain.
Owner:DEV CENT FOR BIOTECHNOLOGY +1
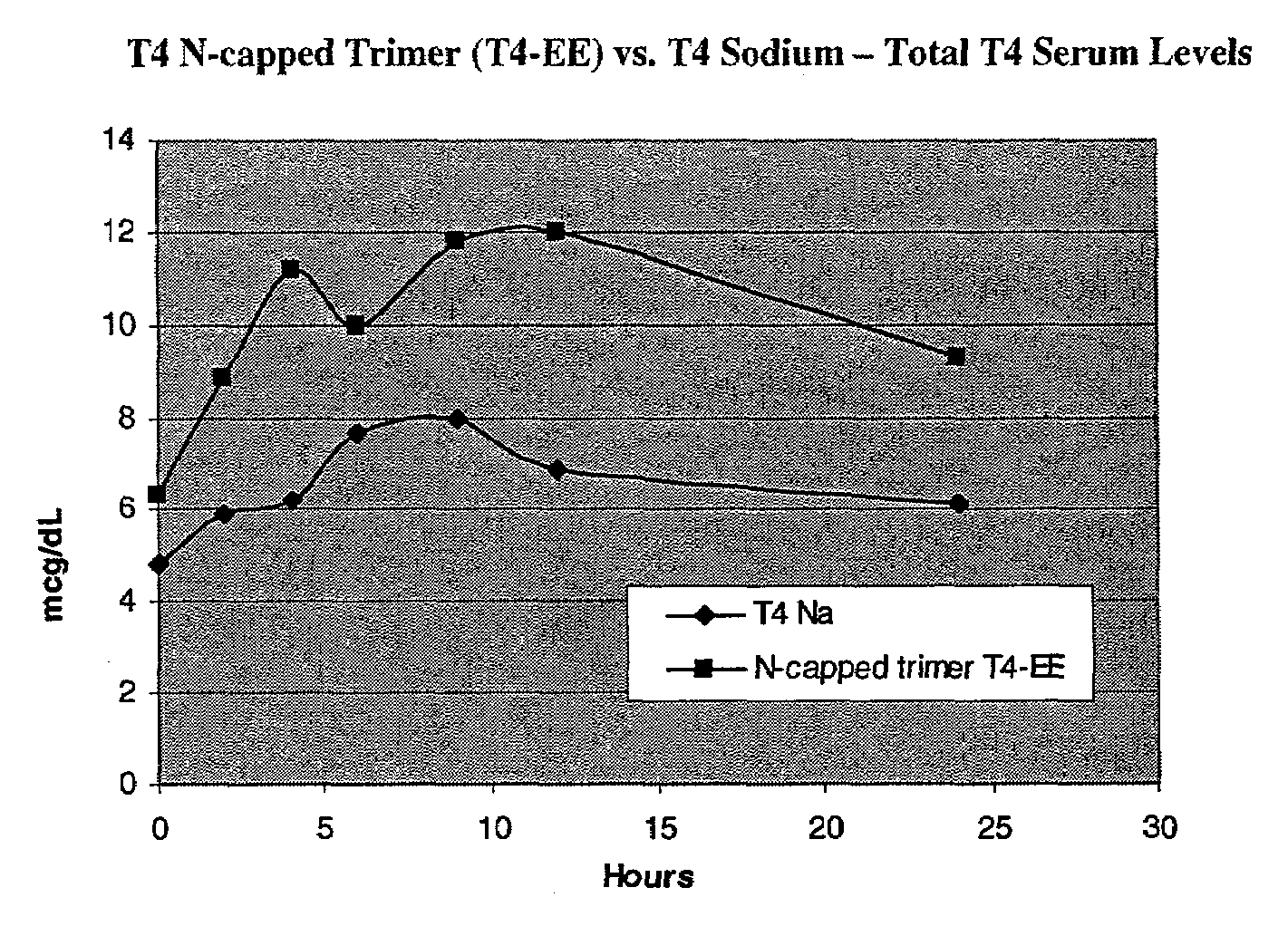
Iodothyronine compositions
InactiveUS7163918B2Improve stabilityEnhanced time-release propertyHormone peptidesDipeptide ingredientsThyroxine measurementSide chain
The present invention relates to compositions comprising thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). More specifically, the invention relates to thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) compositions that include a peptide carrier and thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) covalently attached to at least one of the N-terminus, the C-terminus, a side chain of the peptide carrier, and / or interspersed within the peptide chain; methods for protecting and administering thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3); and methods for treating thyroid disorders.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Stabilized bioactive peptides and methods of identification, synthesis, and use
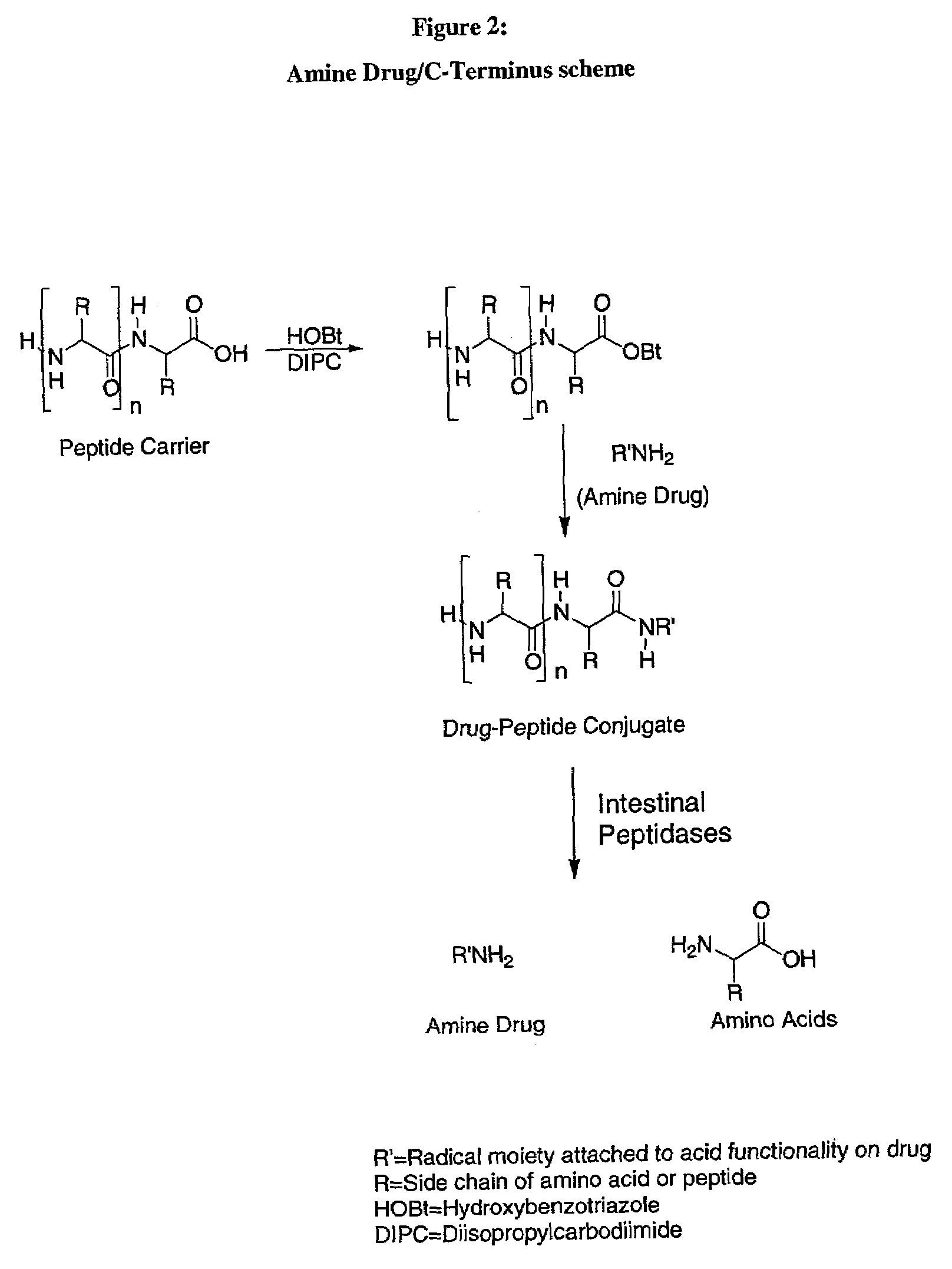
InactiveUS20060099571A1Slow down rate of intracellular degradationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsLac operonΑ helical
An intracellular selection system allows screening for peptide bioactivity and stability. Randomized recombinant peptides are screened for bioactivity in a tightly regulated expression system, preferably derived from the wild-type lac operon. Bioactive peptides thus identified are inherently protease- and peptidase-resistant. Also provided are bioactive peptides stabilized by a stabilizing group at the N-terminus, the C-terminus, or both. The stabilizing group can be a small stable protein, such as the Rop protein, glutathione sulfotransferase, thioredoxin, maltose binding protein, or glutathione reductase, an α-helical moiety, or one or more proline residues.
Owner:PEPTIDE BIOSCI
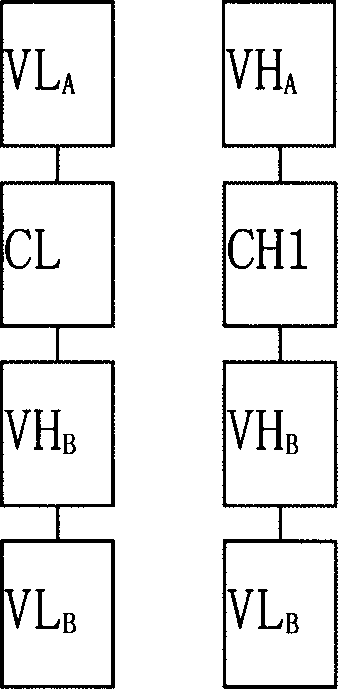
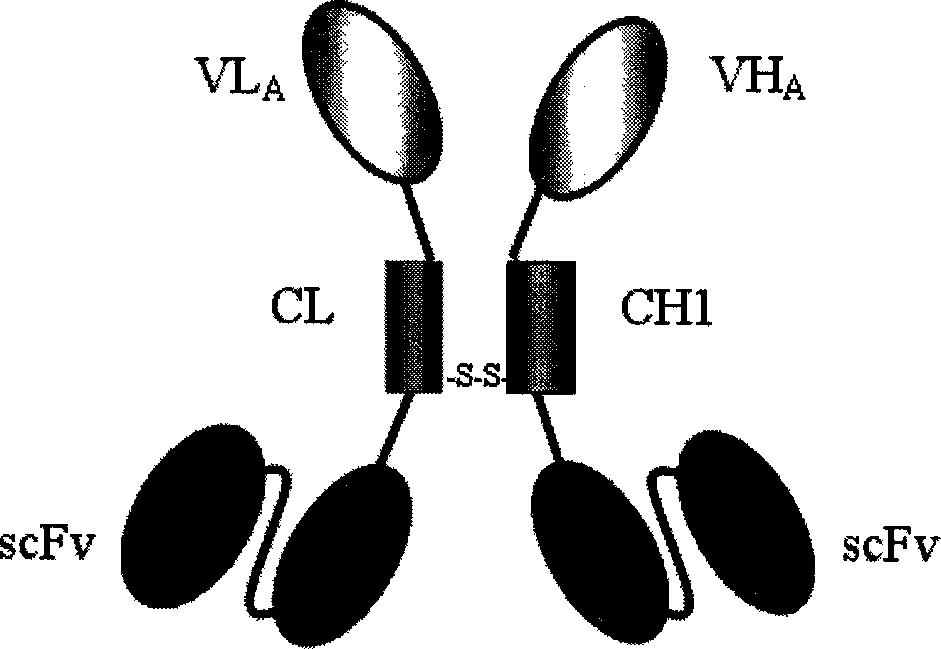
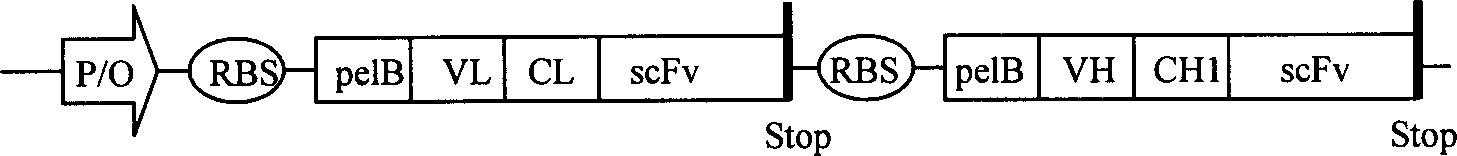
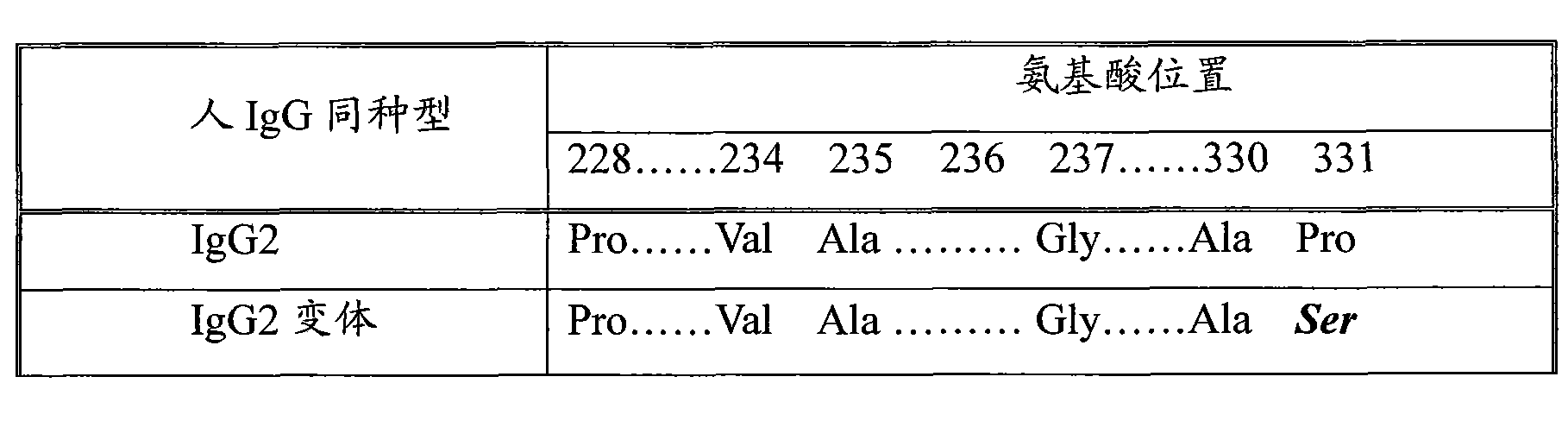
Trivalent bispecific antibody and its preparation process and use
InactiveCN1603345AReduce concentrationLow affinityAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsSide effectBispecific antibody
This invention discloses a preparation of tervalence double specificity antibody and its service application. The antibody includes person IgG1 heavy chain first constant region CH1, k chain constant region CL structure field, heavy chain heavy chain variable region VH and light chain variable region VL antibody A, and single chain variable region scFv of antibody B. VH is connected to N terminal of CH1, scFv connected to C terminal of CH1, VL connected to N terminal of CL, scFv to C terminal of CL. The preparation procedures include building of express carrier, express and detect of double specificity antibody, purification of double specificity antibody, combination analysis of double specificity antibody etc. there are little side effect, good guidance quality etc. advantages of the tervalence double specificity antibody of this invention, it can be used to prepare curing medicine of cancer.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Long-acting recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone-Fc fusion protein (hFSH-Fc)
ActiveCN103539860AImprove biological activitySmall toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRecombinant human follicle stimulating hormoneSide effect
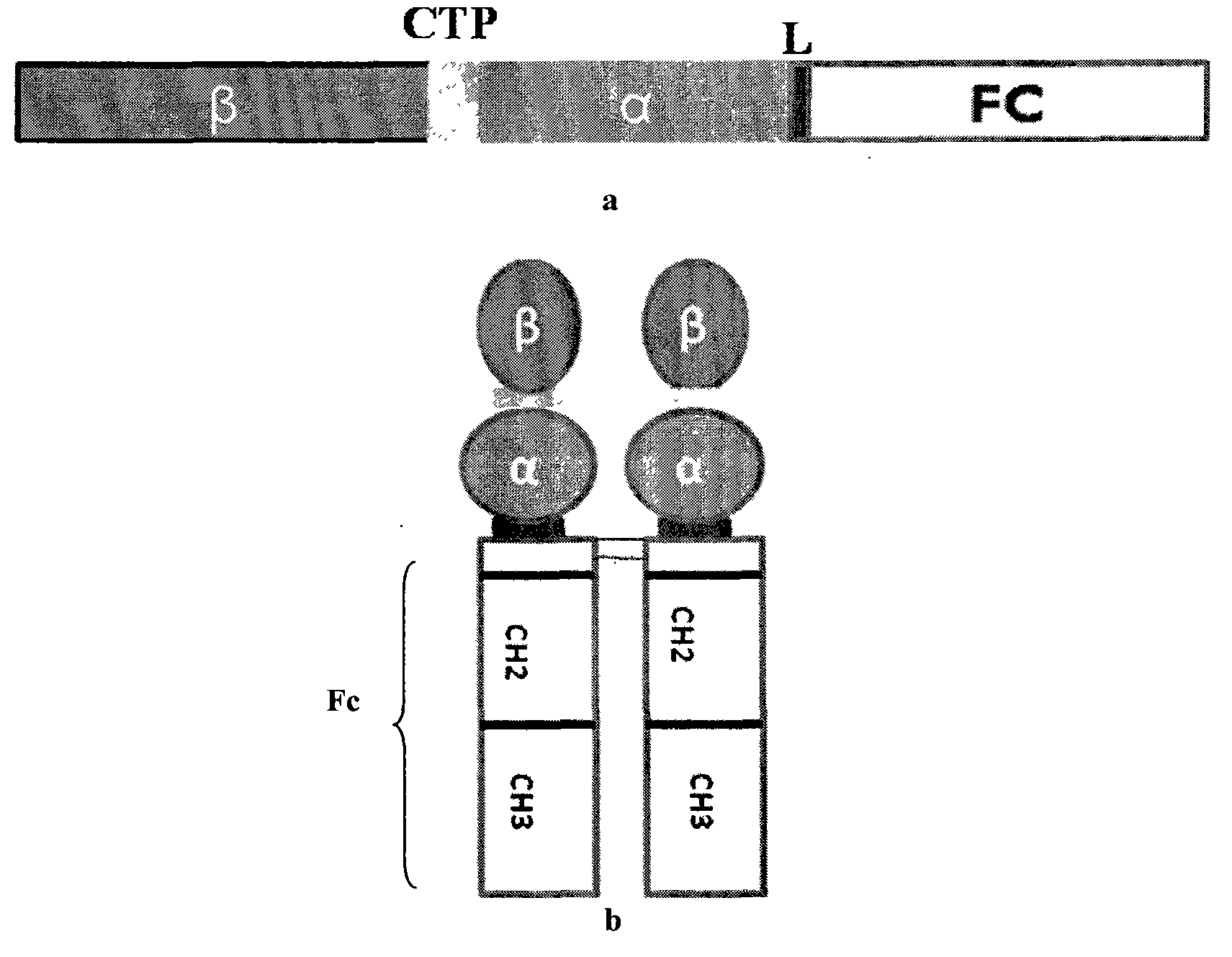
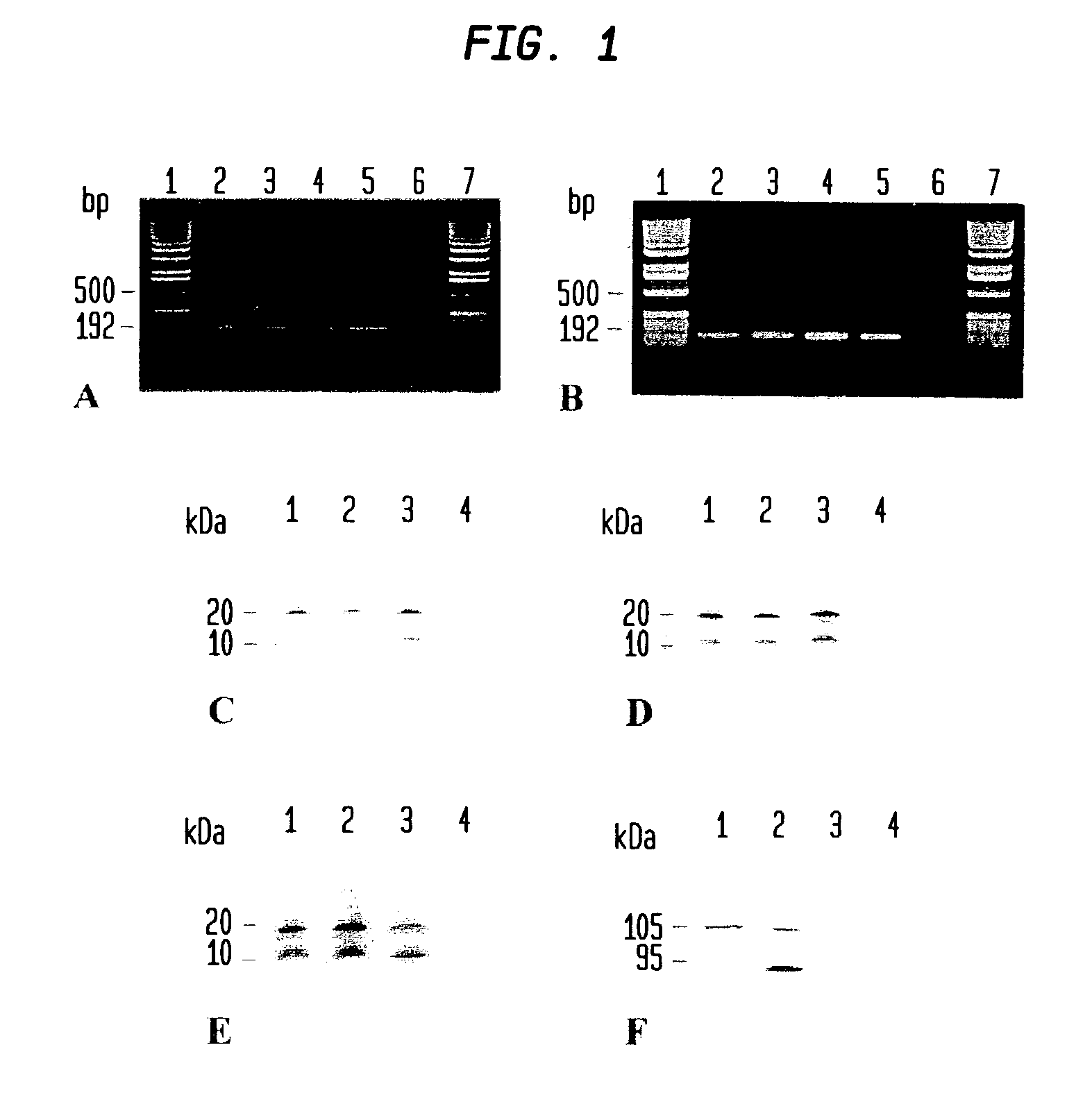
The invention discloses a long-acting recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone-Fc fusion protein (hFSH-Fc) and a preparation method thereof. The recombinant hFSH-Fc is a dimerization fusion protein. An amino acid sequence of the hFSH-Fc comprises an hFSHbeta subunit, CTP (carboxy-terminal peptide), an hFSHalpha subunit, a flexible peptide linker and a human IgG (immunoglobulin G)2 Fc variant from the N terminal to the C terminal in sequence. The hFSH-Fc has longer half-life in vivo and smaller side effects than existing hFSH. The invention also relates to an application of a recombinant hFSH-Fc composition to preparation of drugs for treating and / or preventing infertility.
Owner:UNICOHEALTH CO LTD
Diagnostic method for diseases by screening for hepcidin in human or animal tissues, blood or body fluids and therapeutic uses therefor
The present invention concerns methods and kits for diagnosing a disease condition characterized by non-physiological levels of hepcidin, comprising obtaining a tissue or fluid sample from a subject; contacting the sample with an antibody or fragment thereof that specifically binds to a polypeptide corresponding to the mid-portion or C terminus of a hepcidin protein, and quantifying the hepcidin level using an assay based on binding of the antibody and the polypeptide; wherein the non-physiological level of hepcidin is indicative of the disease condition. The present invention also concerns diagnostic methods and kits for applications in genetic technological approaches, such as for overexpressing or downregulating hepcidin. The present invention further concerns therapeutic treatment of certain diseases by treatment of subjects with hepcidin and agonists or antagonists of hepcidin.
Owner:DRG INTERNATIONAL INC
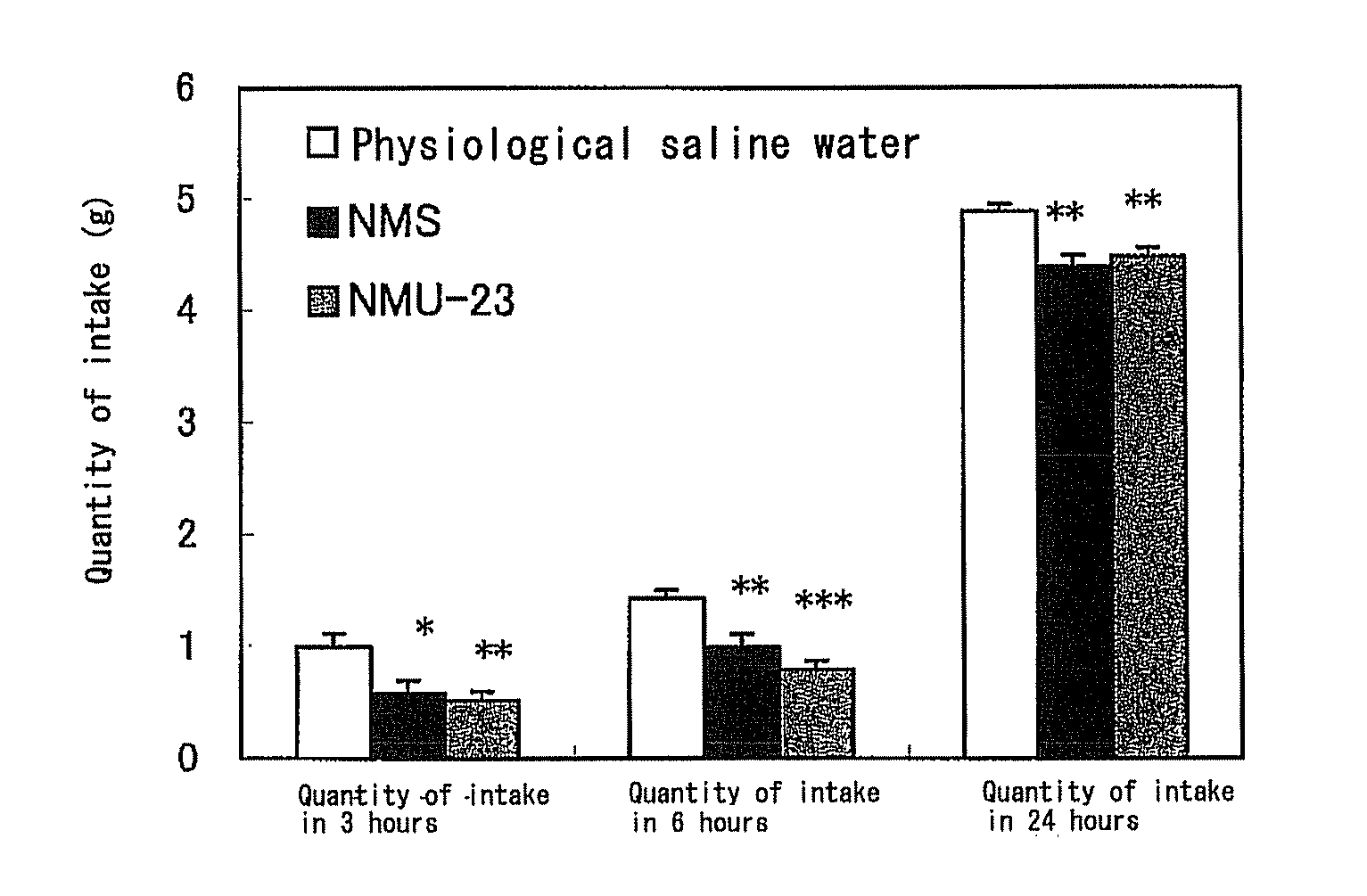
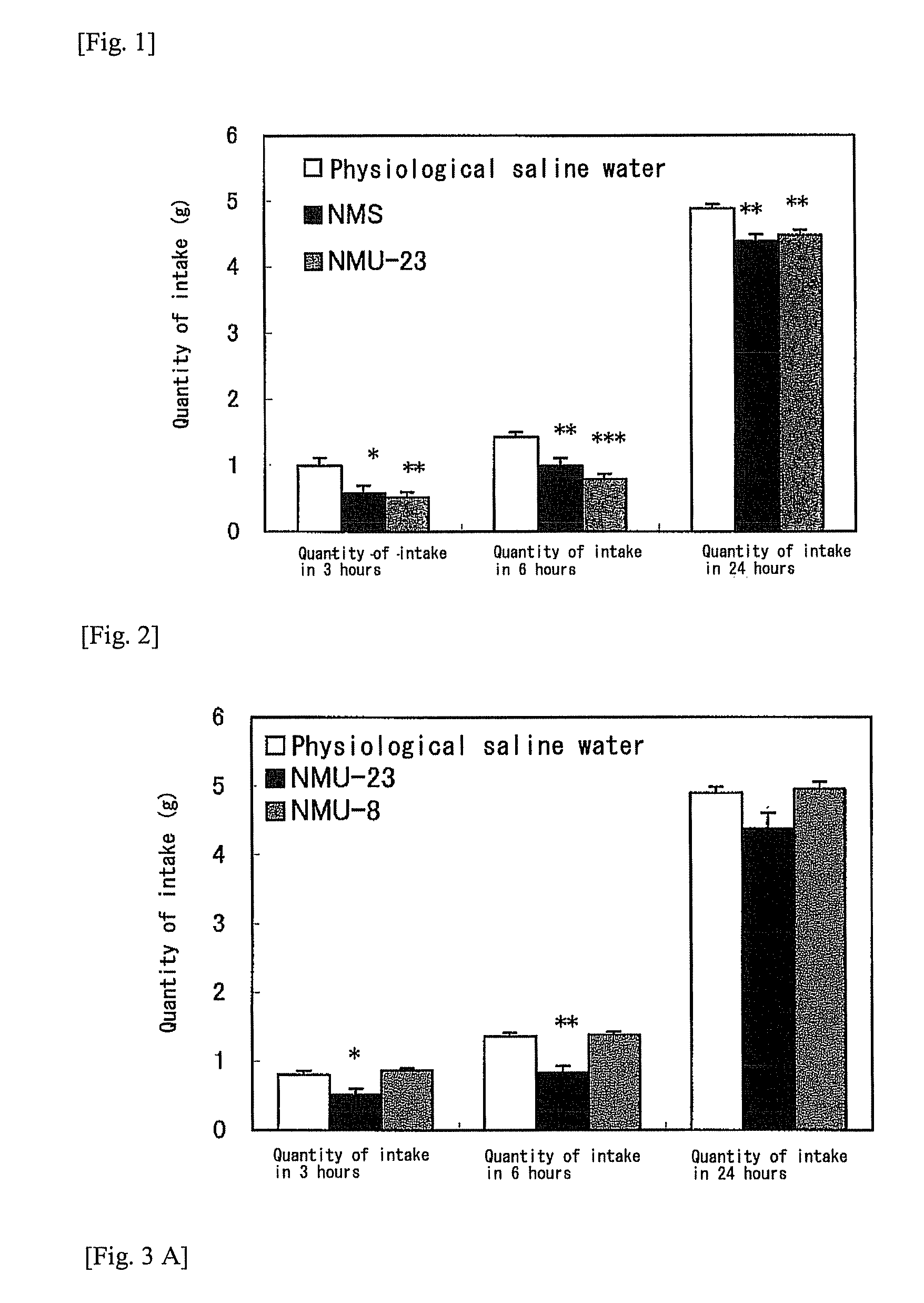
Neuromedin u derivative
InactiveUS20100286035A1Improve stabilityHigh activityHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsC-terminusOrganic chemistry
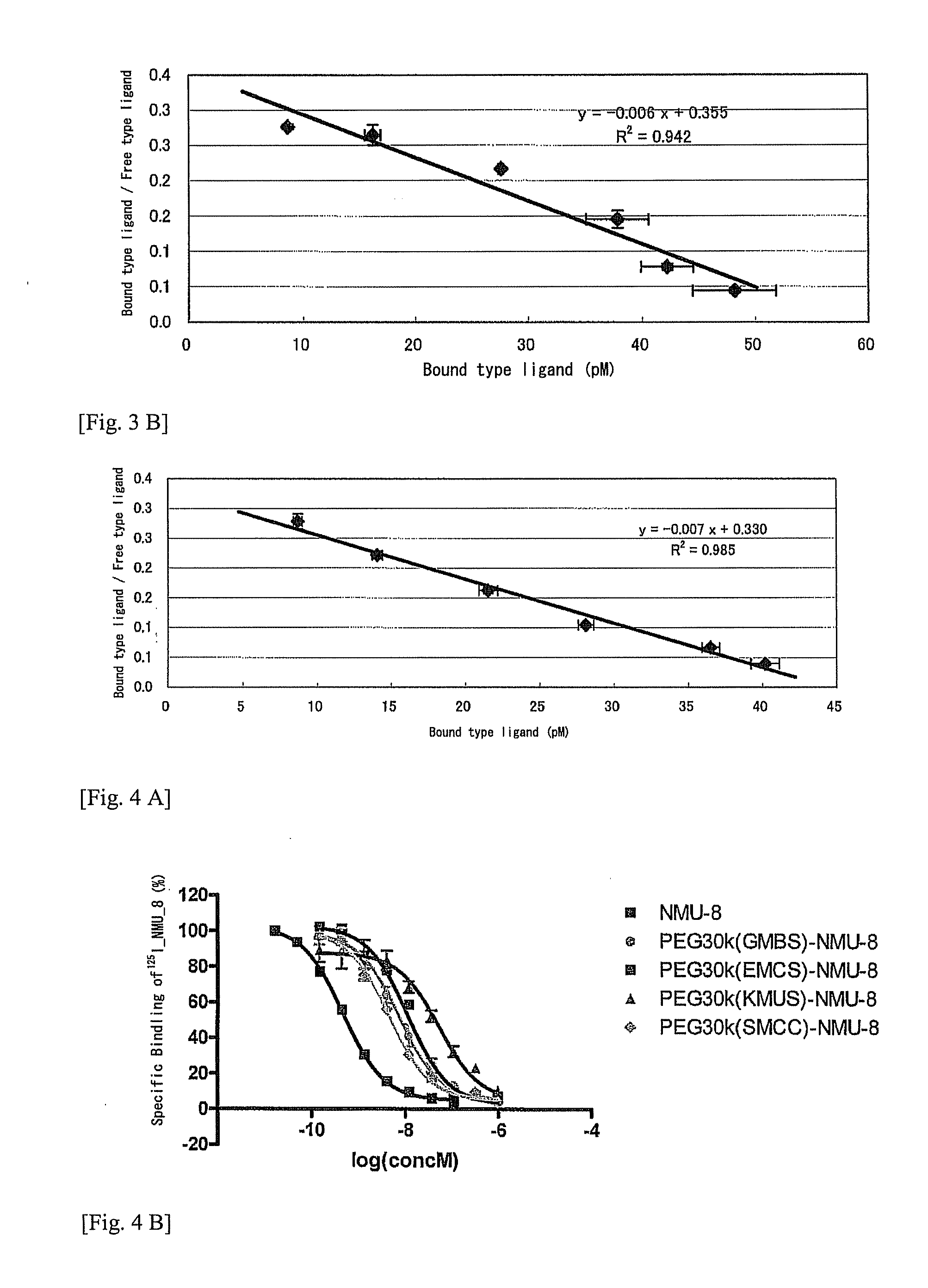
The objective of the present invention is to provide a new antifeedant. The other objective of the present invention is to provide a NMU derivative showing a high antifeedant activity even in common administration forms such as peripheral administration. A neuromedin U derivative wherein a methoxypolyethylene glycol is bound via a linker having a specific structure to a polypeptide which contains at least 8 amino acids of the C-terminus of an amino acid sequence of neuromedin U and which consists of the same or substantially the same amino acid sequence as the amino acid sequence of neuromedin U.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Novel chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof
ActiveCN106279438AImprove securityAdd control switchFermentationHybrid peptidesAntigenAntigen receptors
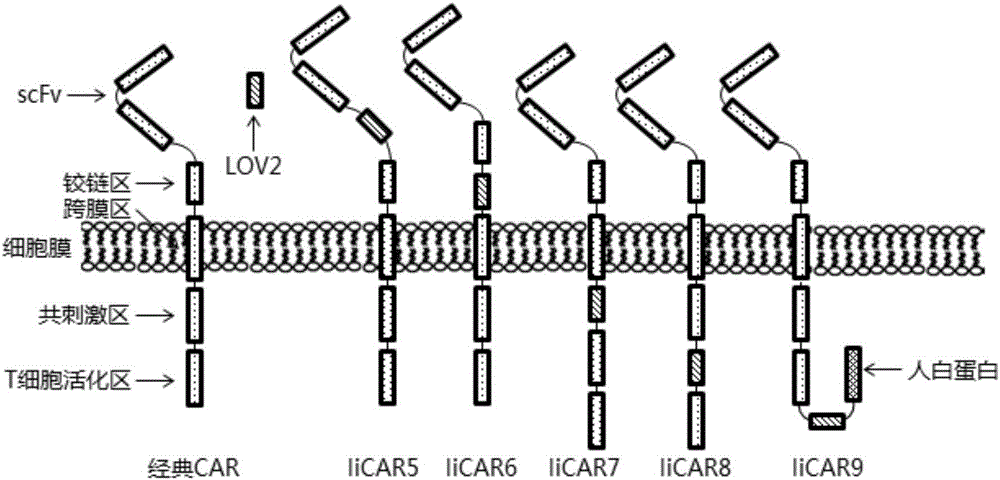
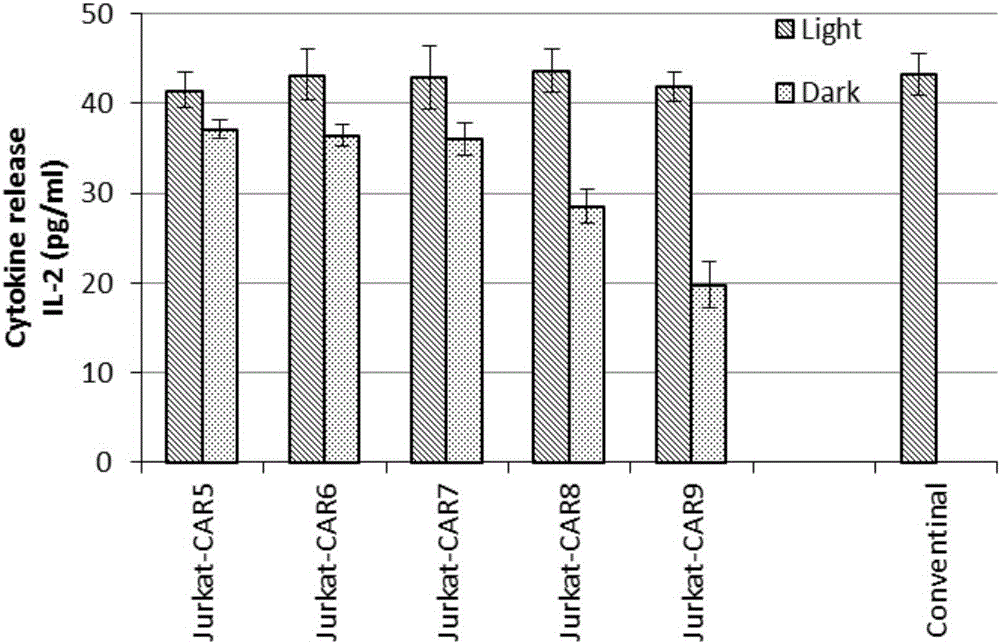
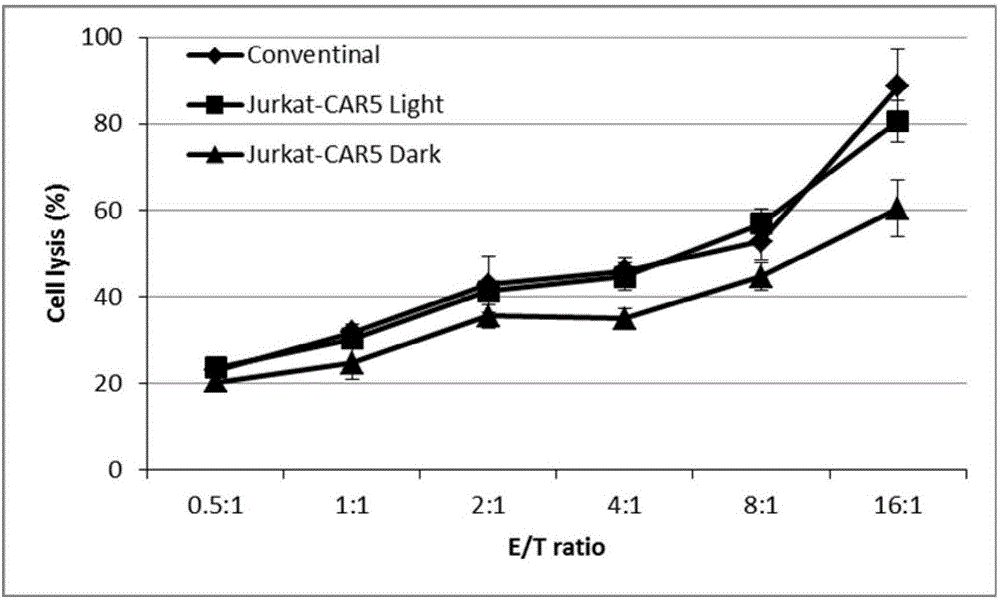
The invention discloses a recombined chimeric antigen receptor with a photoinduction element. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an antigen combining area, a transmembrane structure area, a co-stimulatory signal transduction area and T cell signal transduction area functional structure domains, wherein the photoinduction element is inserted at the N terminal or C terminal of the recombined chimeric antigen receptor or between the functional structure domains. According to the chimeric antigen receptor, photoinduction element LOV2 genes are cloned into plasmids Lenti-EF1alpha-CD19CAR with a molecular cloning method to establish a co-expression vector of the recombined chimeric antigen receptor with the photoinduction element, 293T cells are used for packaging to obtain a lentiviral vector with photoinduction CAR molecules. After the recombined chimeric antigen receptor is expressed in T cells through the lentiviral vector, the damage toxicity of T cells is reversely controlled by LOV2, and an importable approach is provided for improving the safety of CAR-T in treating cancer clinically.
Owner:北京领柯生物科技有限公司
Protection of exendin-4 peptides through conjugation
InactiveUS20090093408A1Easy to testPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum albuminBlood componentCombinatorial chemistry
A method for protecting a peptide from peptidase activity in vivo, the peptide being composed of between 2 and 50 amino acids and having a C-terminus and an N-terminus and a C-terminus amino acid and an N-terminus amino acid is described. In the first step of the method, the peptide is modified by attaching a react group to the C-terminus amino acid, to the N-terminus amino acid, or to an amino acid located between the N-terminus and the C-terminus, such that the modified peptide is capable of forming a covalent bond in vivo with a reactive functionality on a blood component. In the next step, a covalent bond is formed between the reactive group and a reactive functionality on a blood component to form a peptide-blood component conjugate, thereby protecting said peptide from peptidase activity. The final step of the method involves the analyzing of the stability of the peptide-blood component conjugate to assess the protection of the peptide from peptidase activity.
Owner:CONJUCHEM +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com