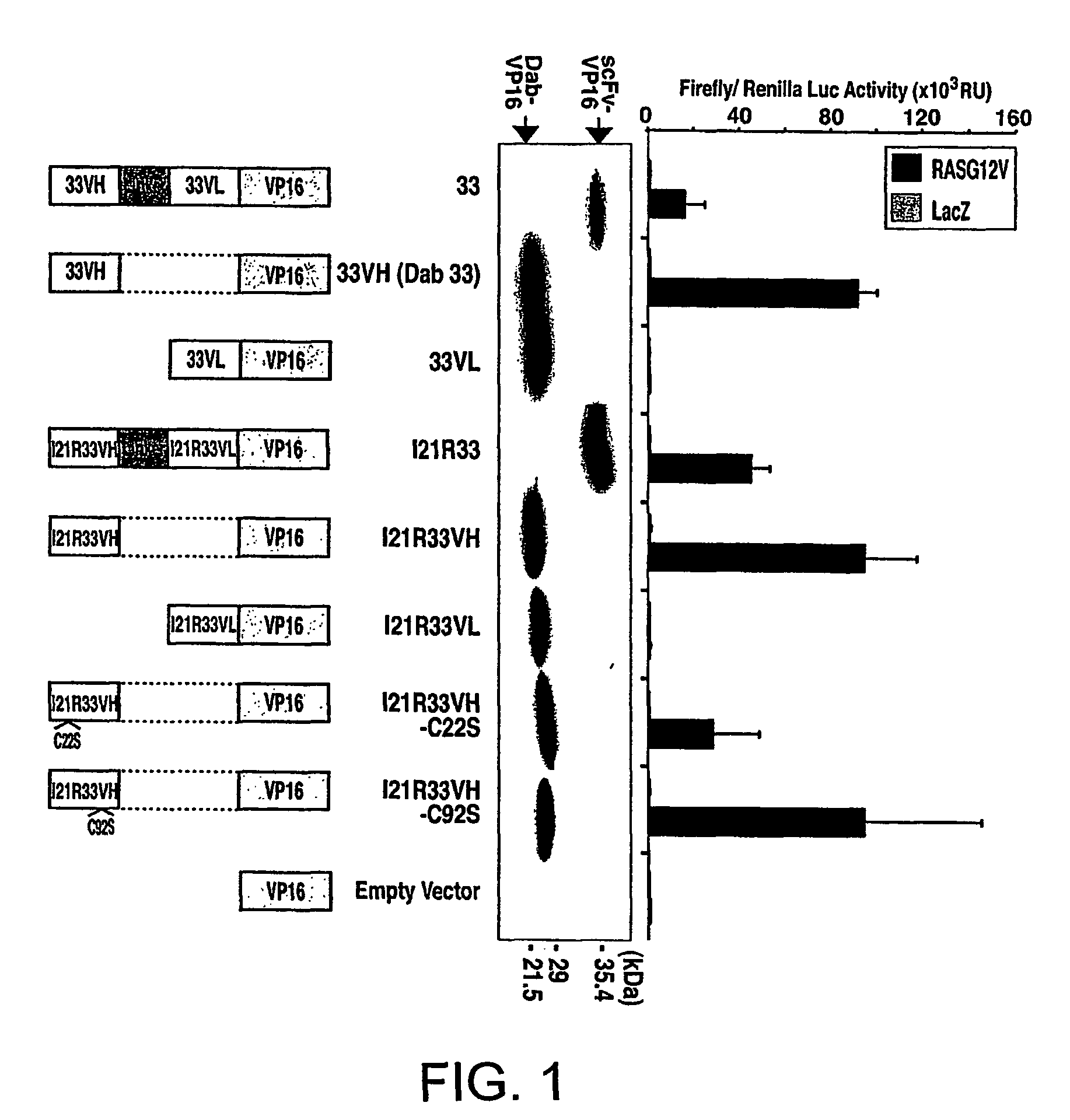
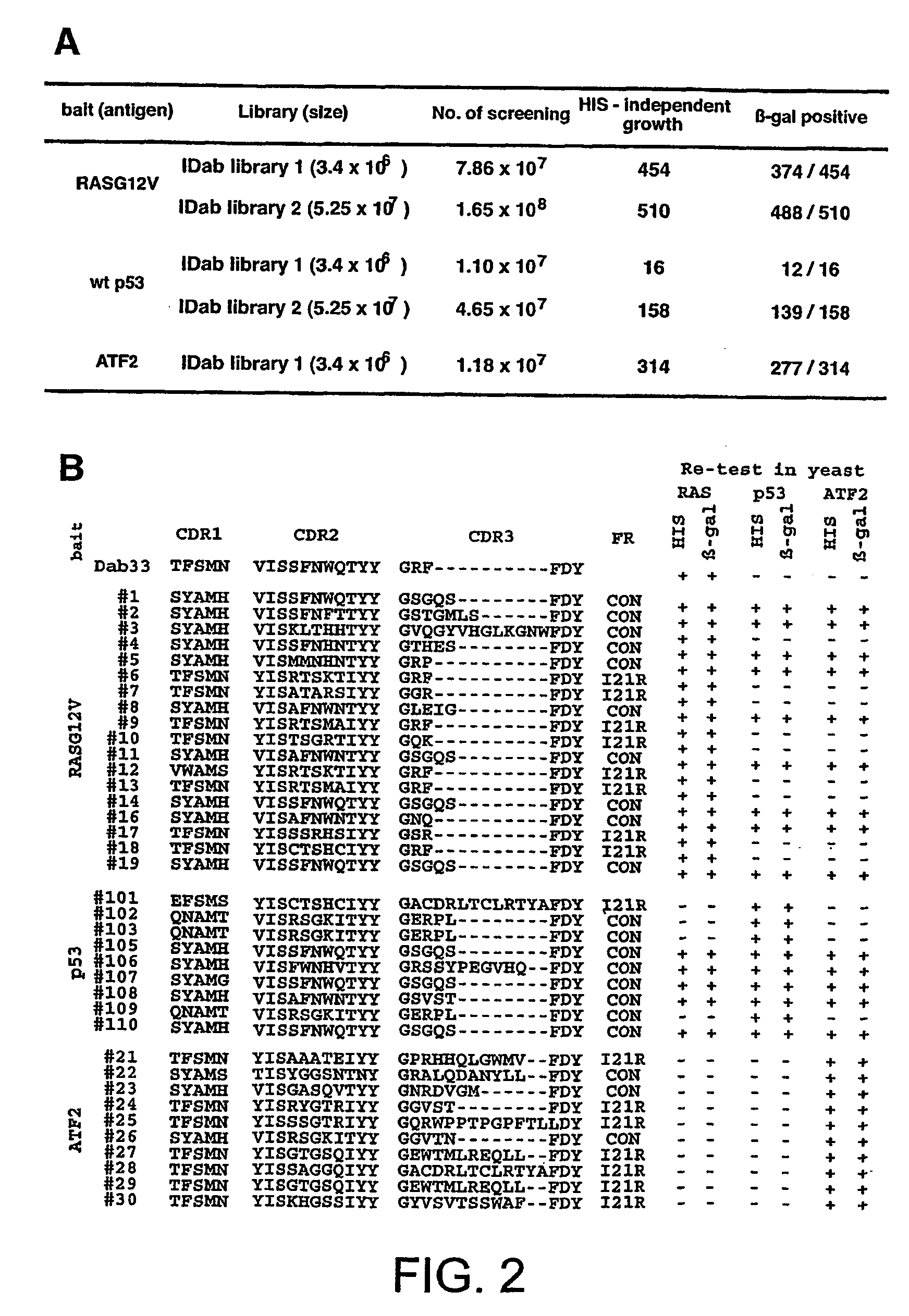
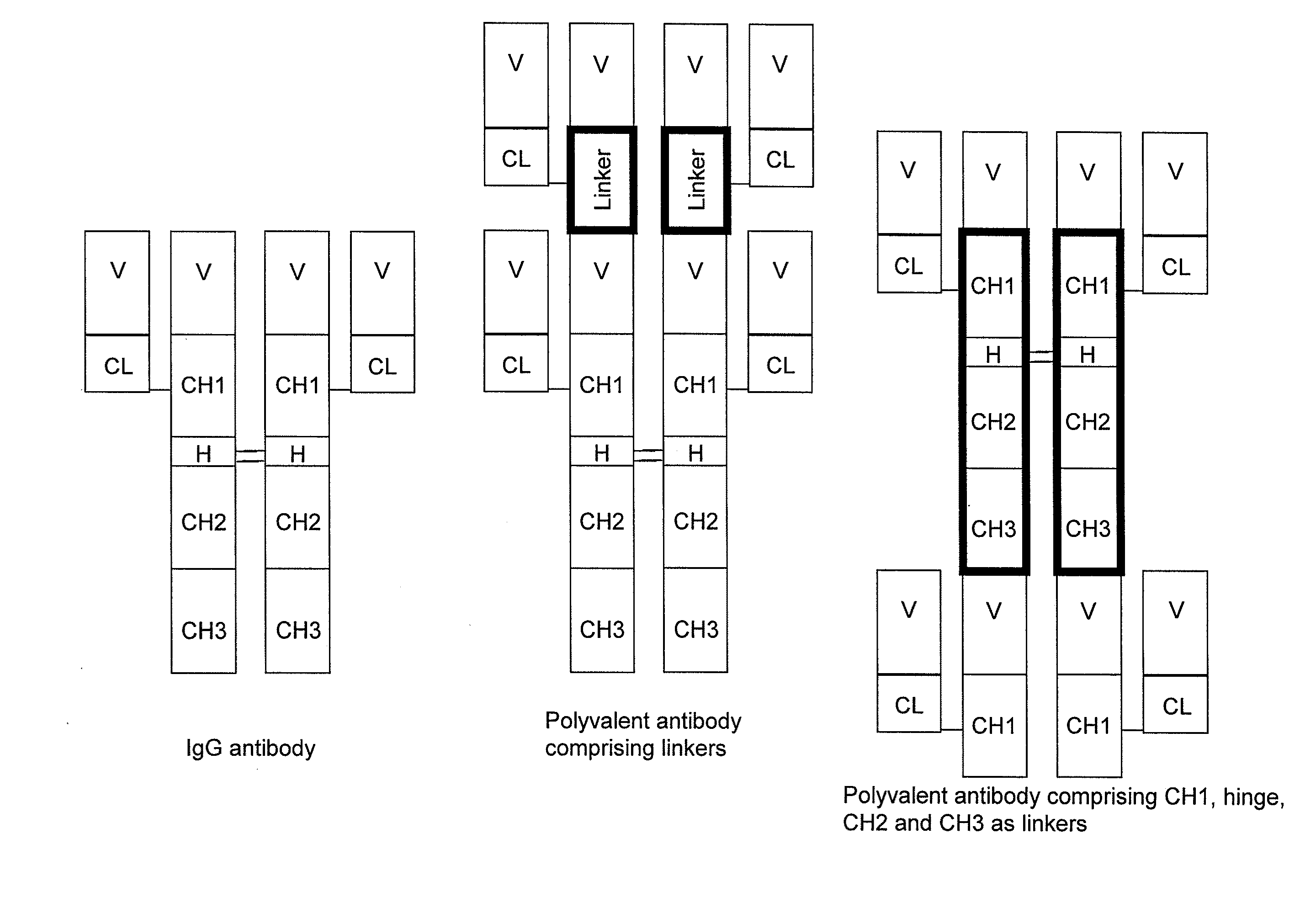
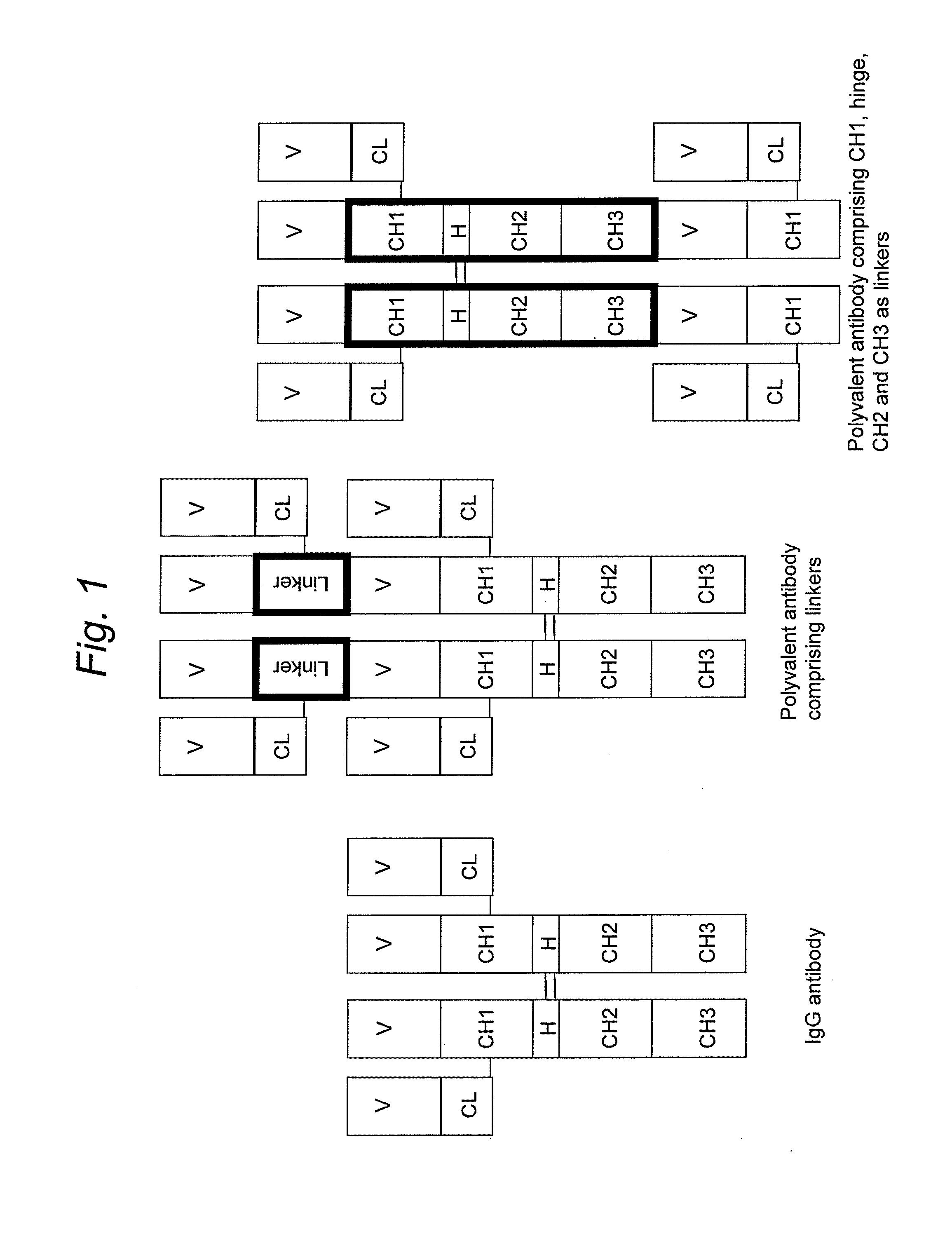
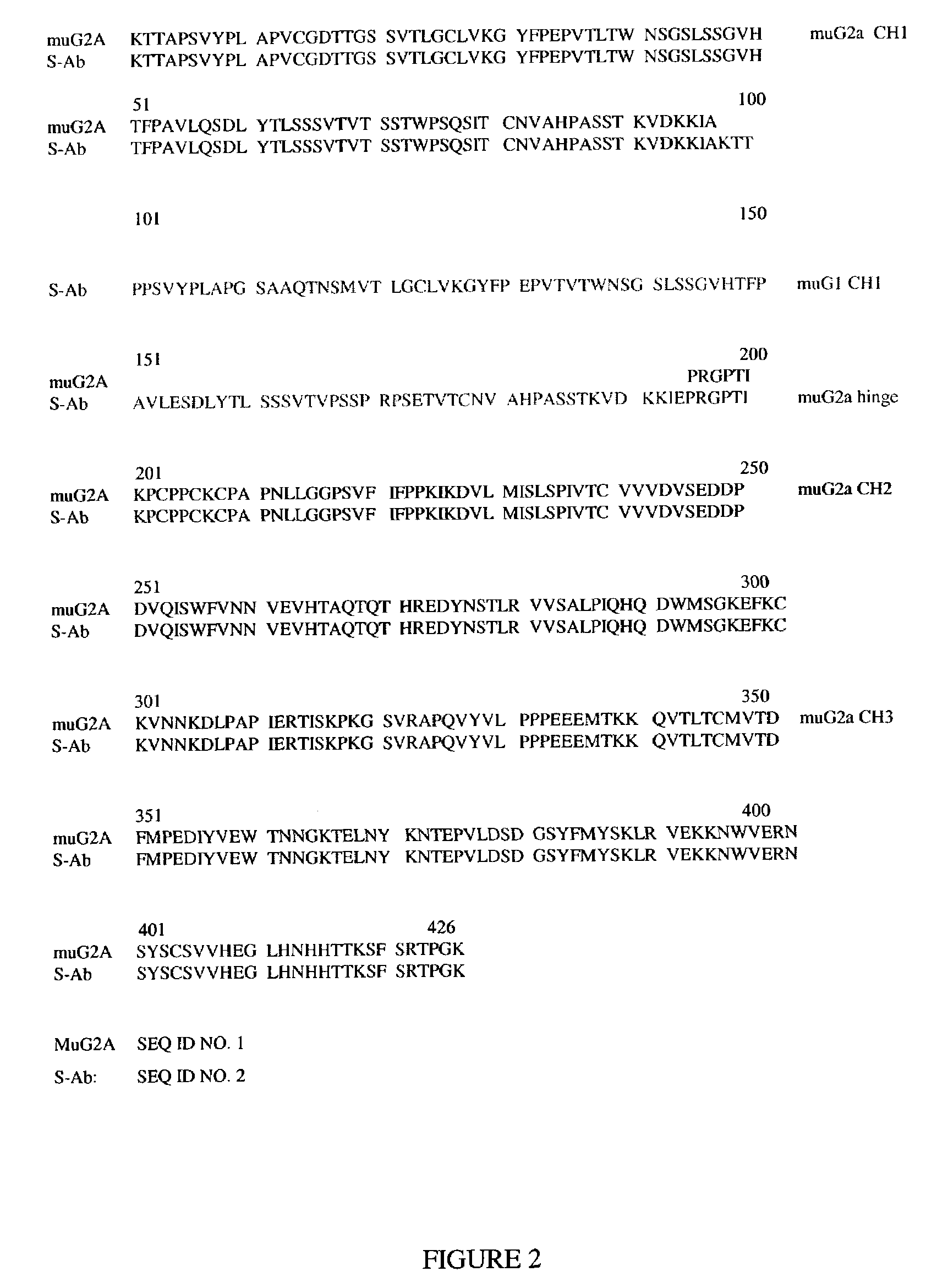
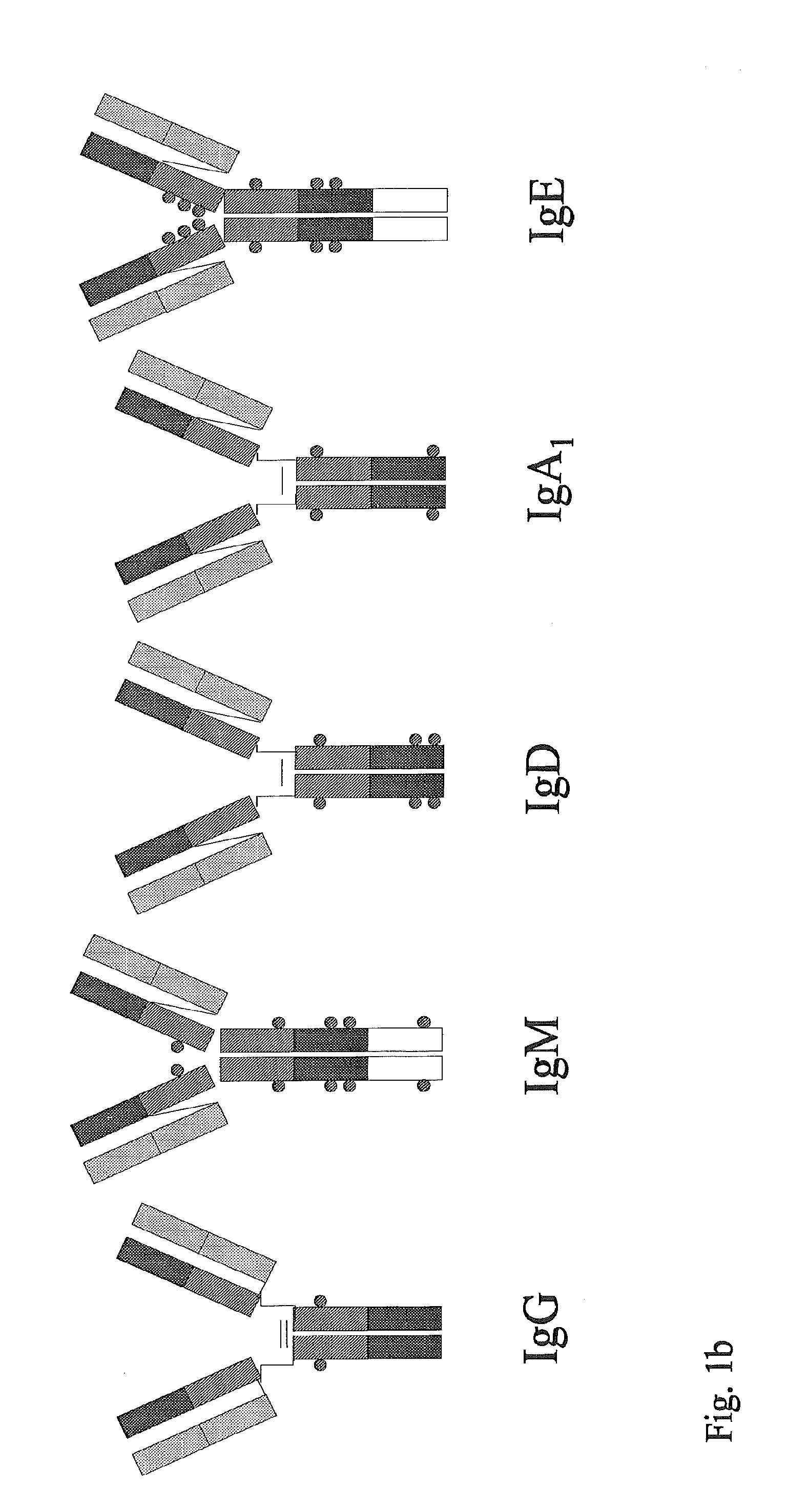
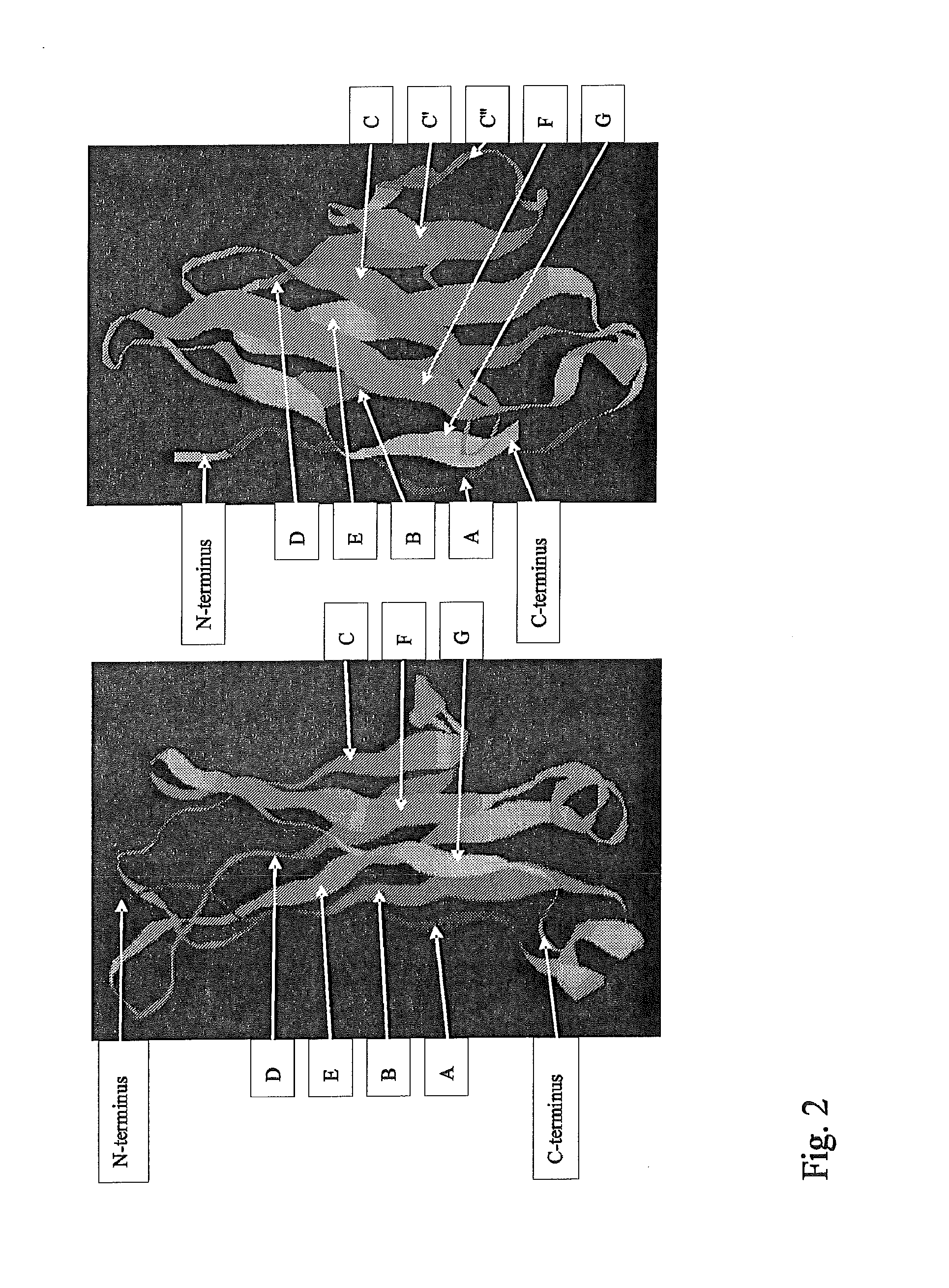
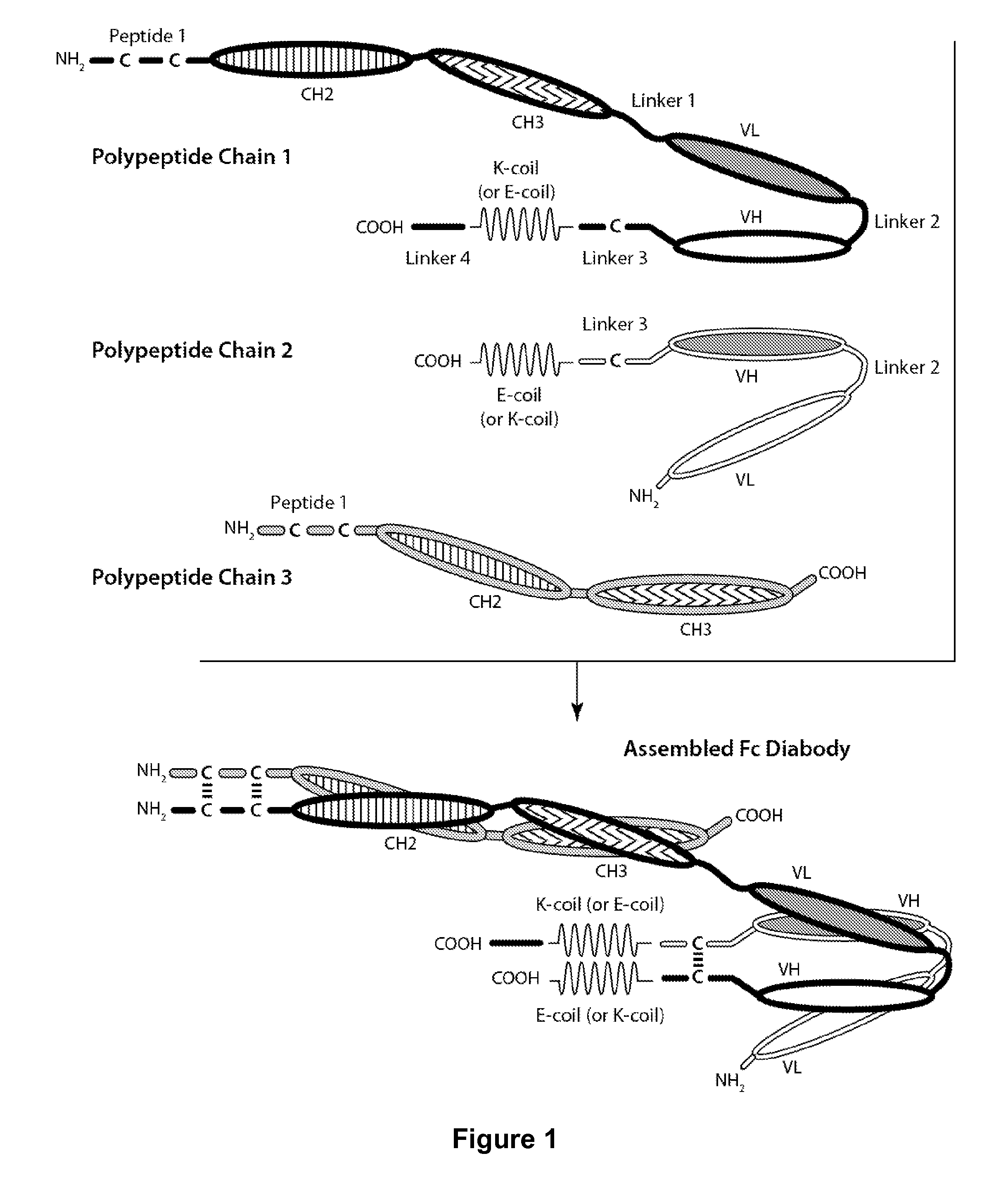
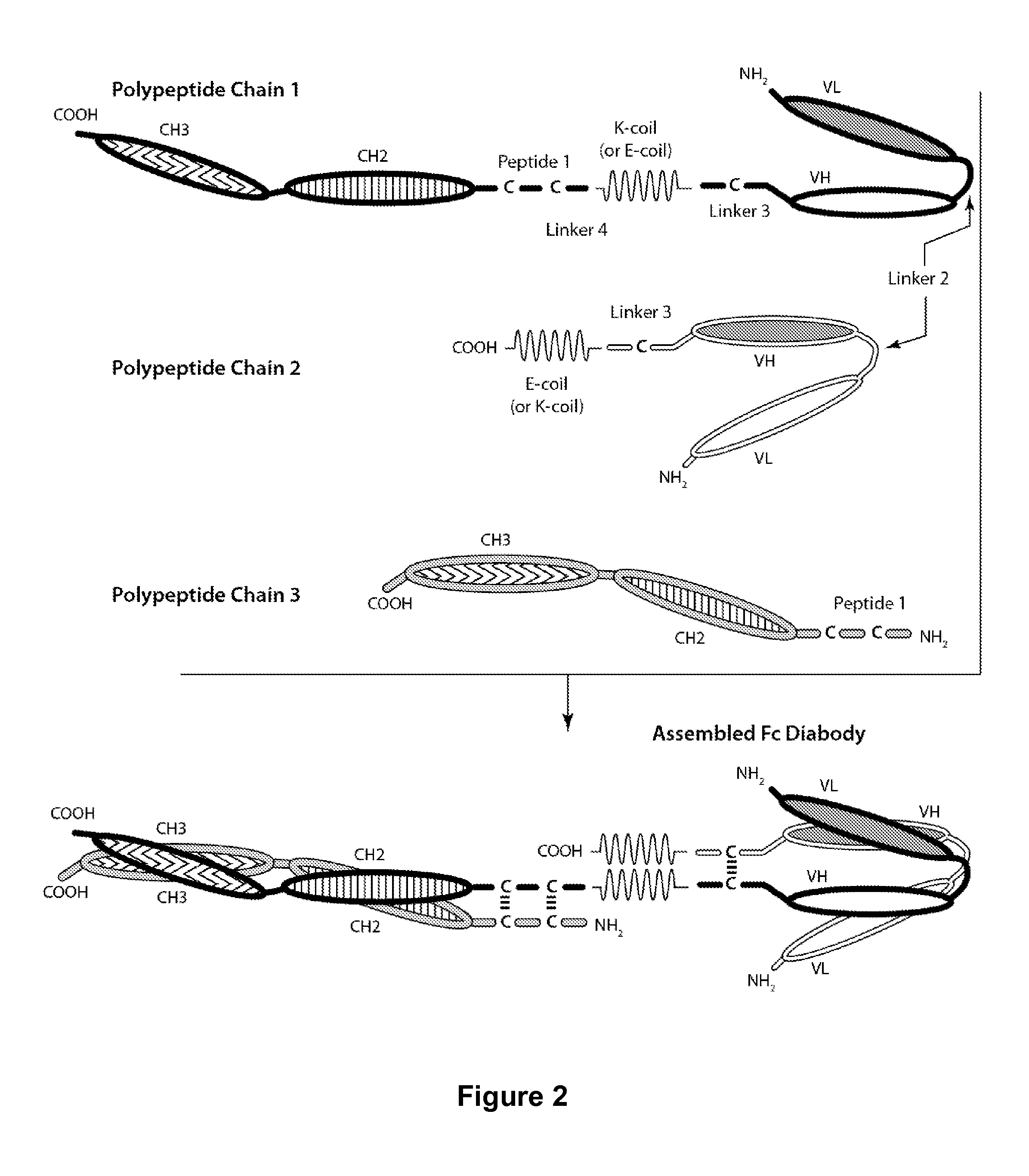
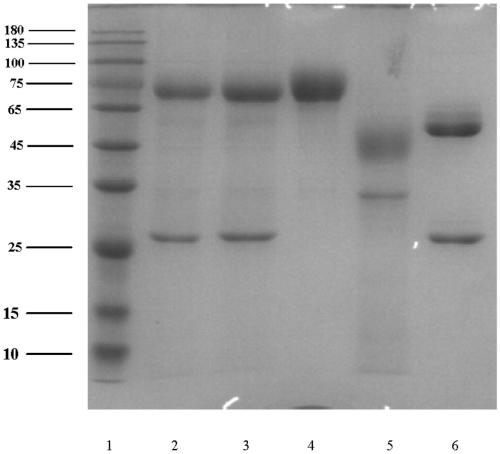
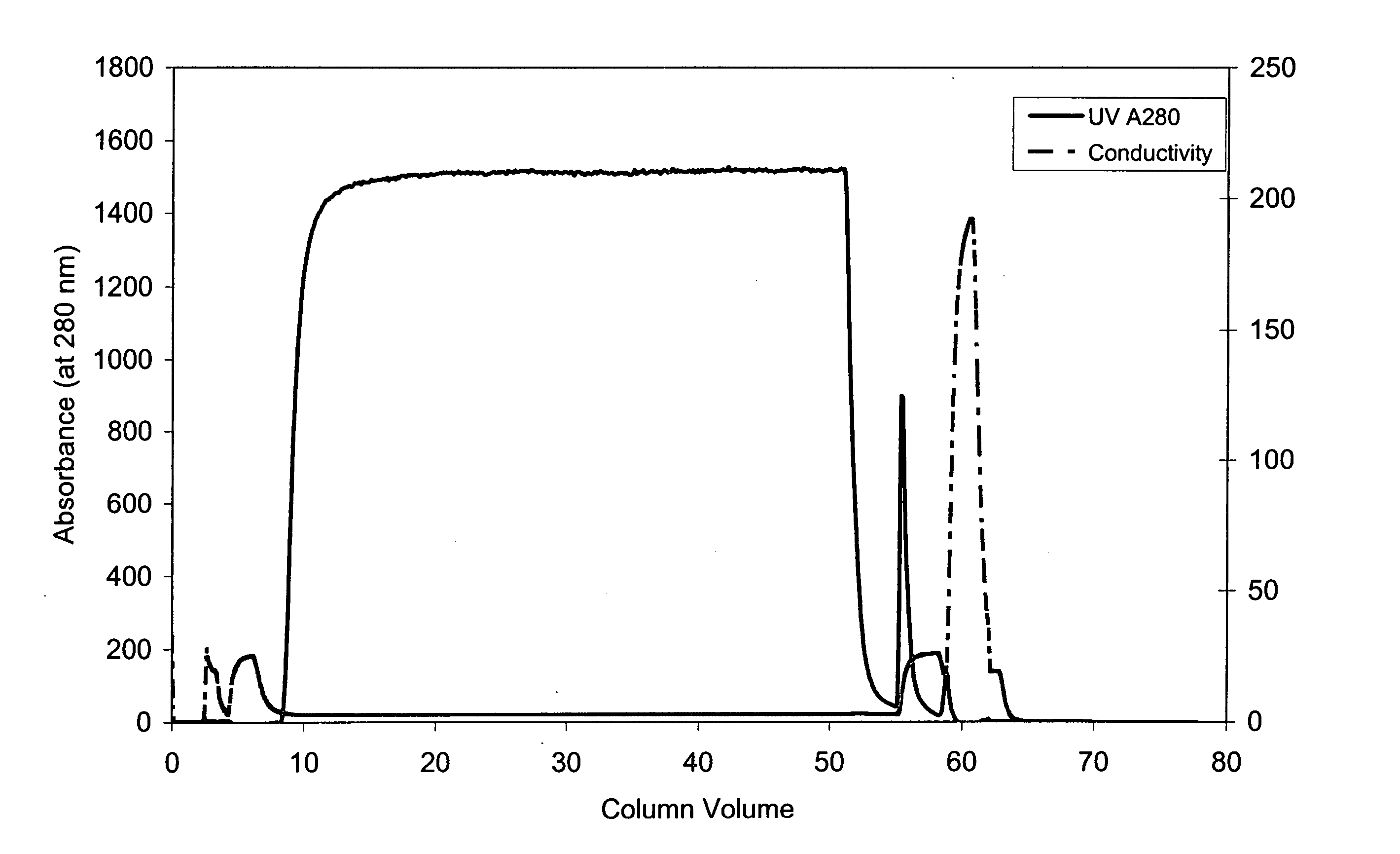
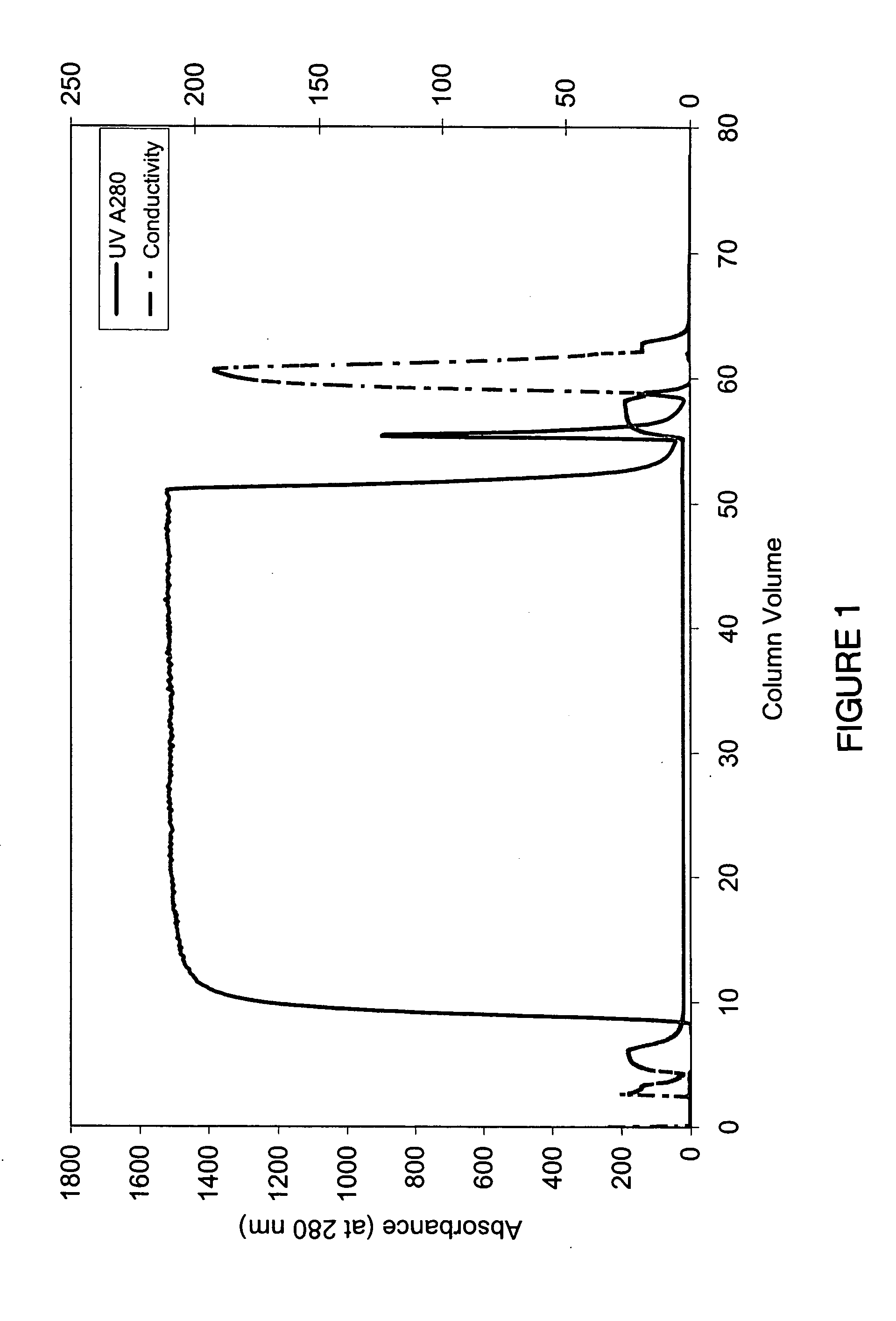
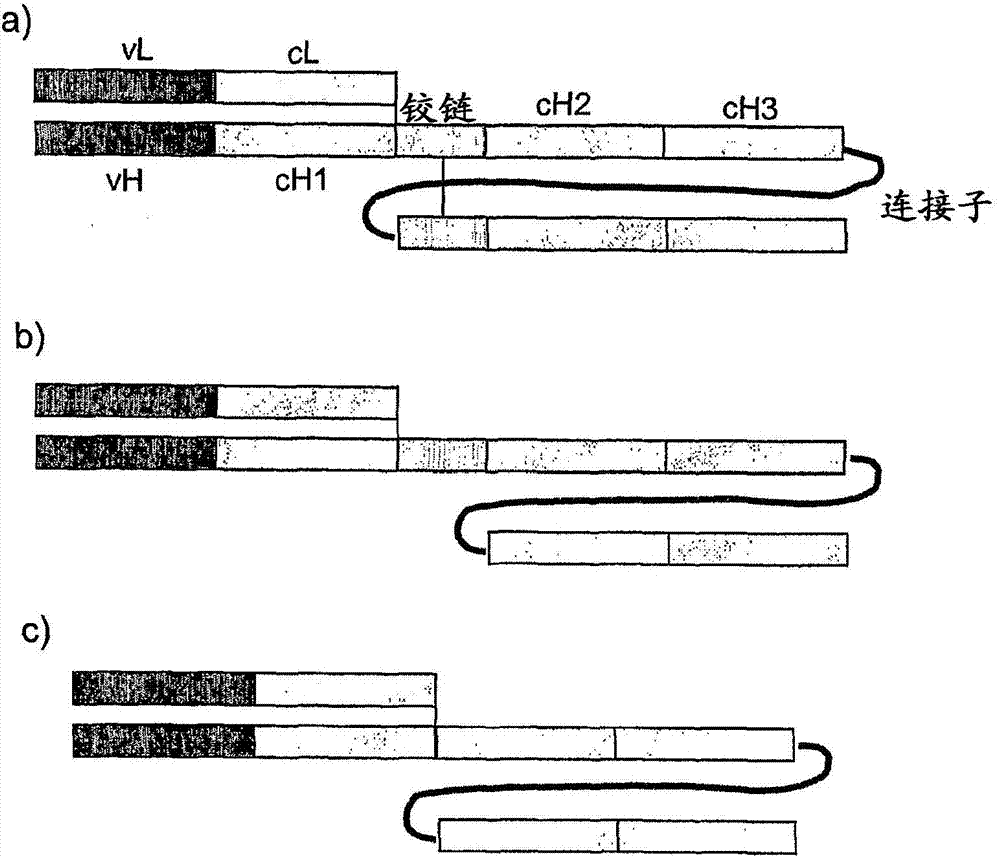
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63 results about "Immunoglobulin domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
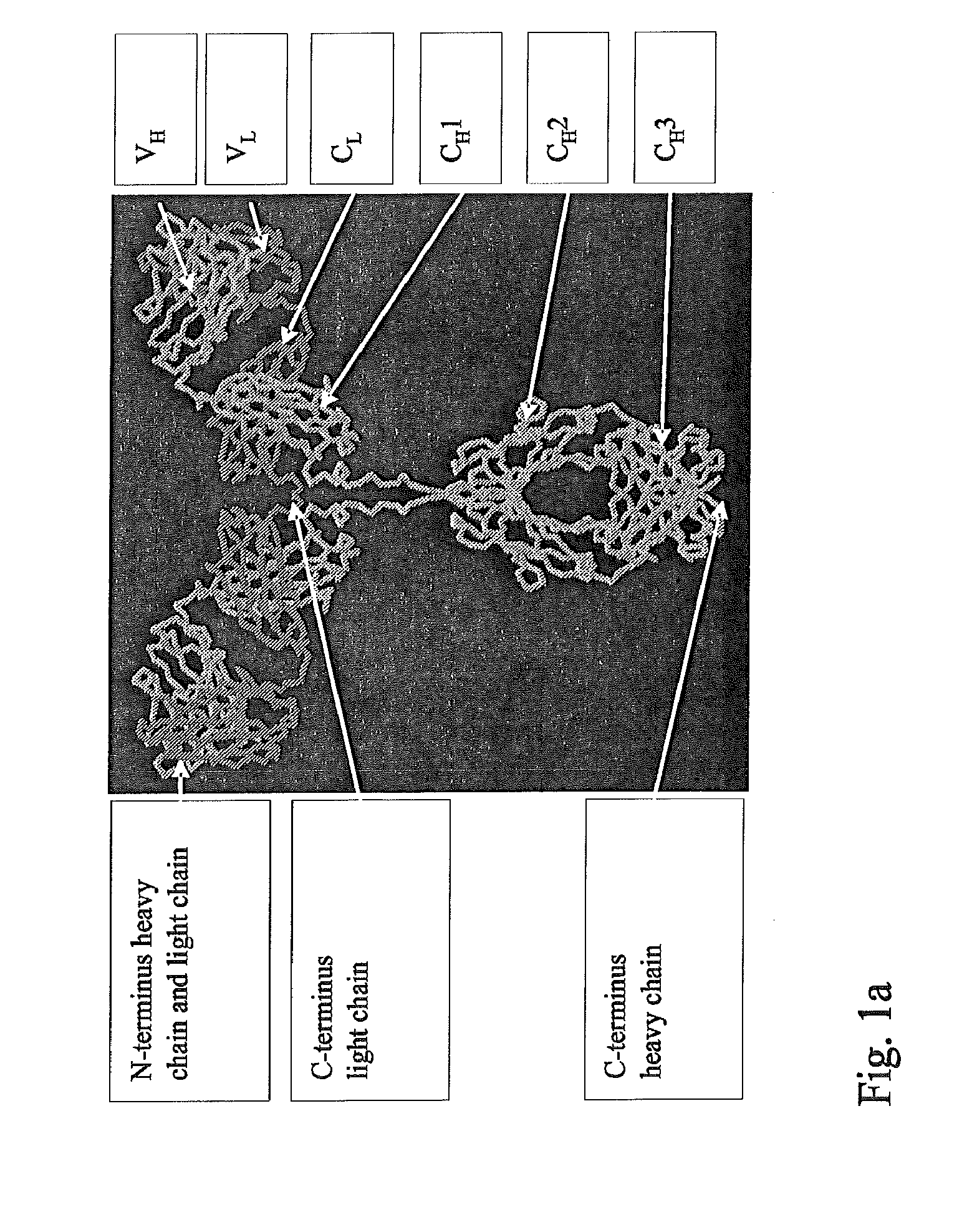
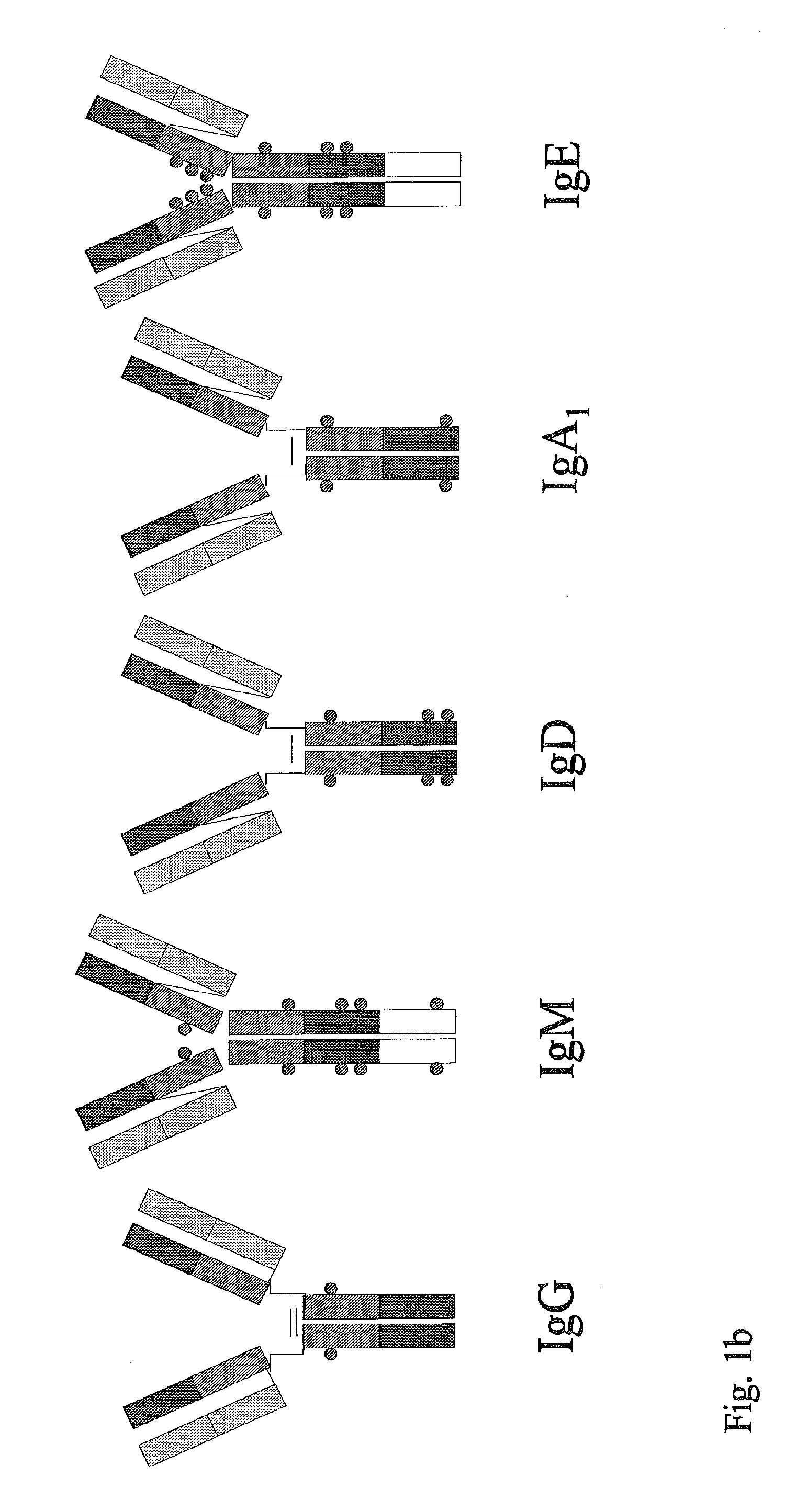
The immunoglobulin domain is a type of protein domain that consists of a 2-layer sandwich of 7-9 antiparallel β-strands arranged in two β-sheets with a Greek key topology, consisting of about 125 amino acids.
Multipurpose antibody derivatives
InactiveUS6809185B1Efficient preparationEfficient productionHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsSignalling moleculesHormones regulation
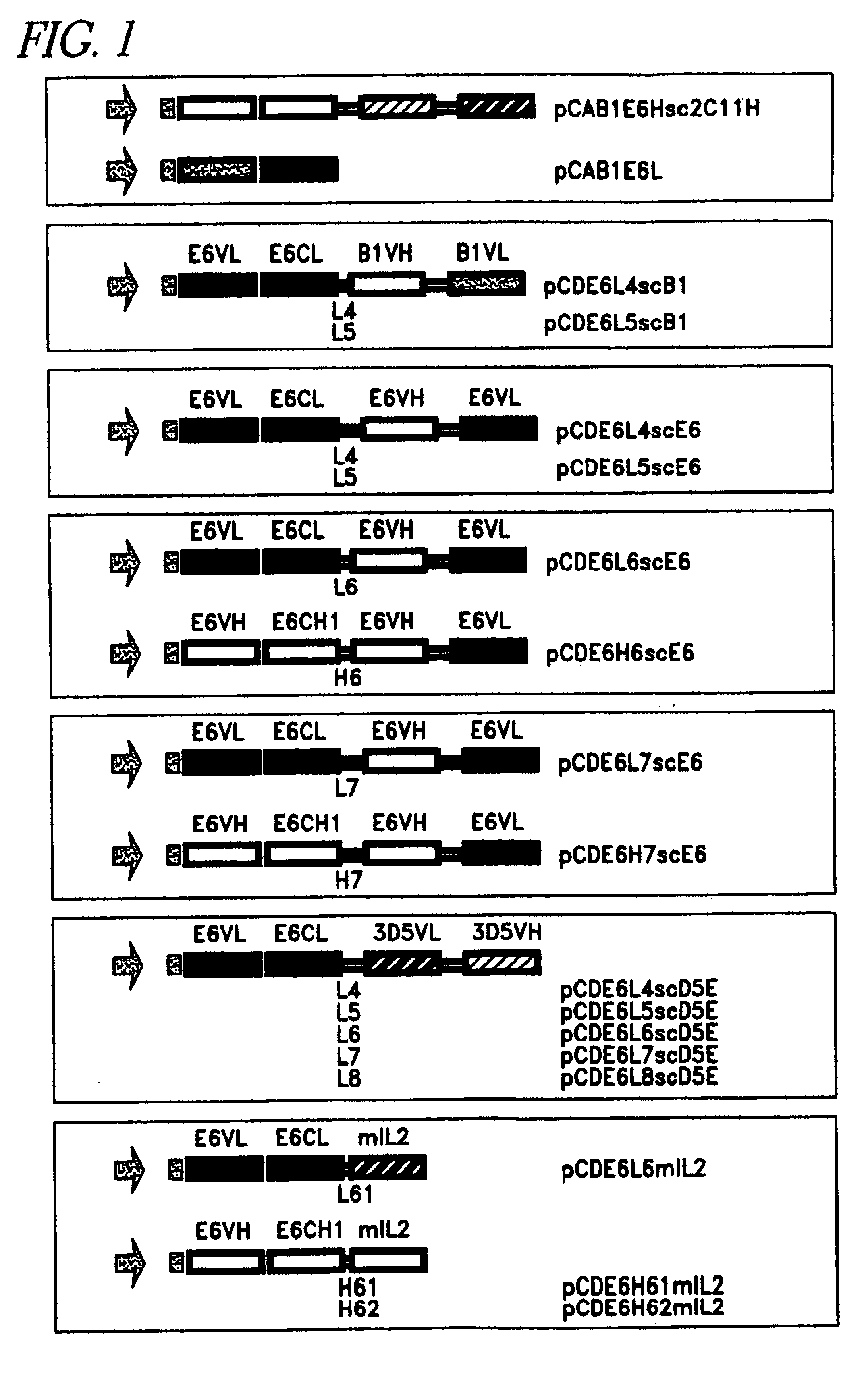
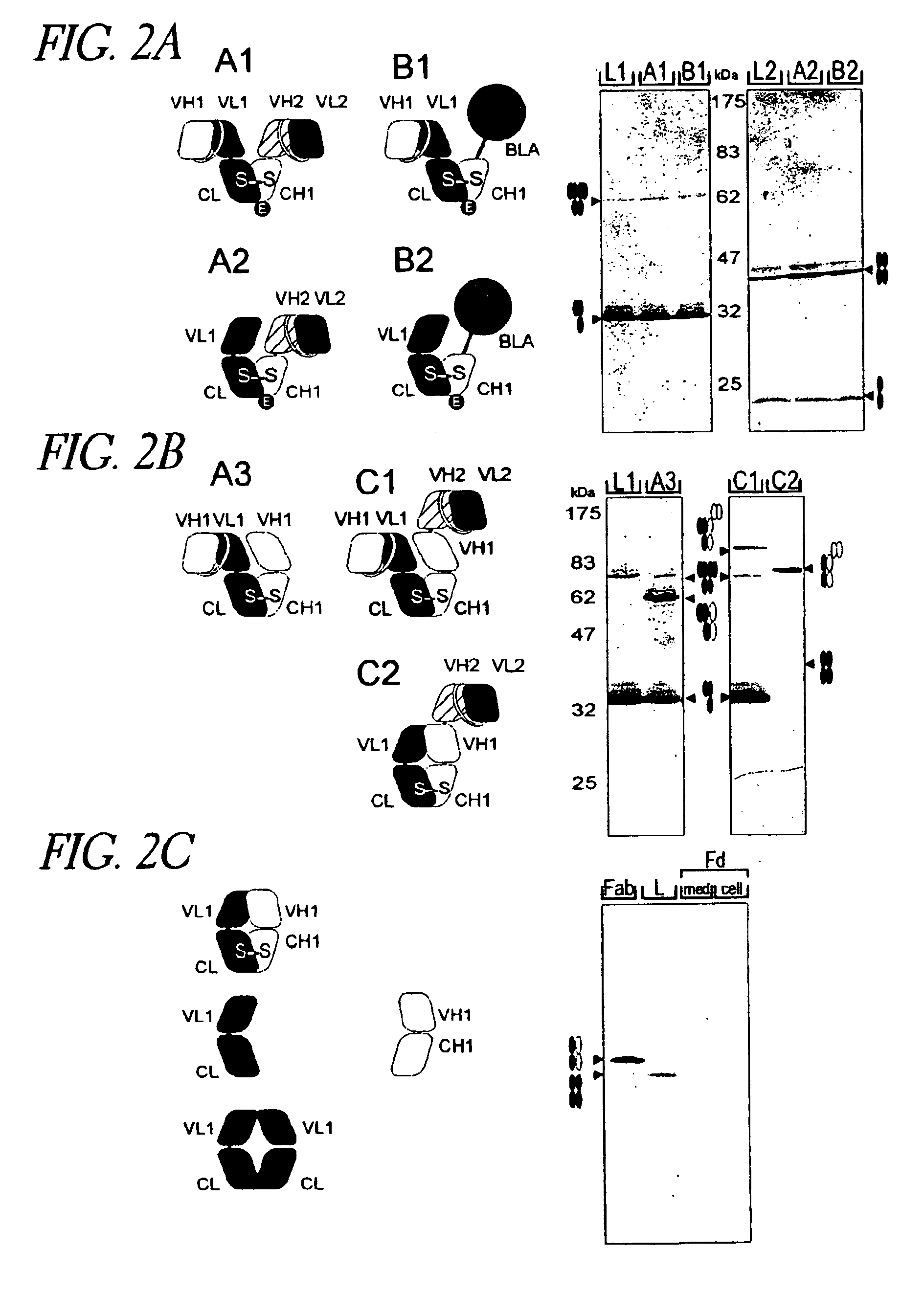
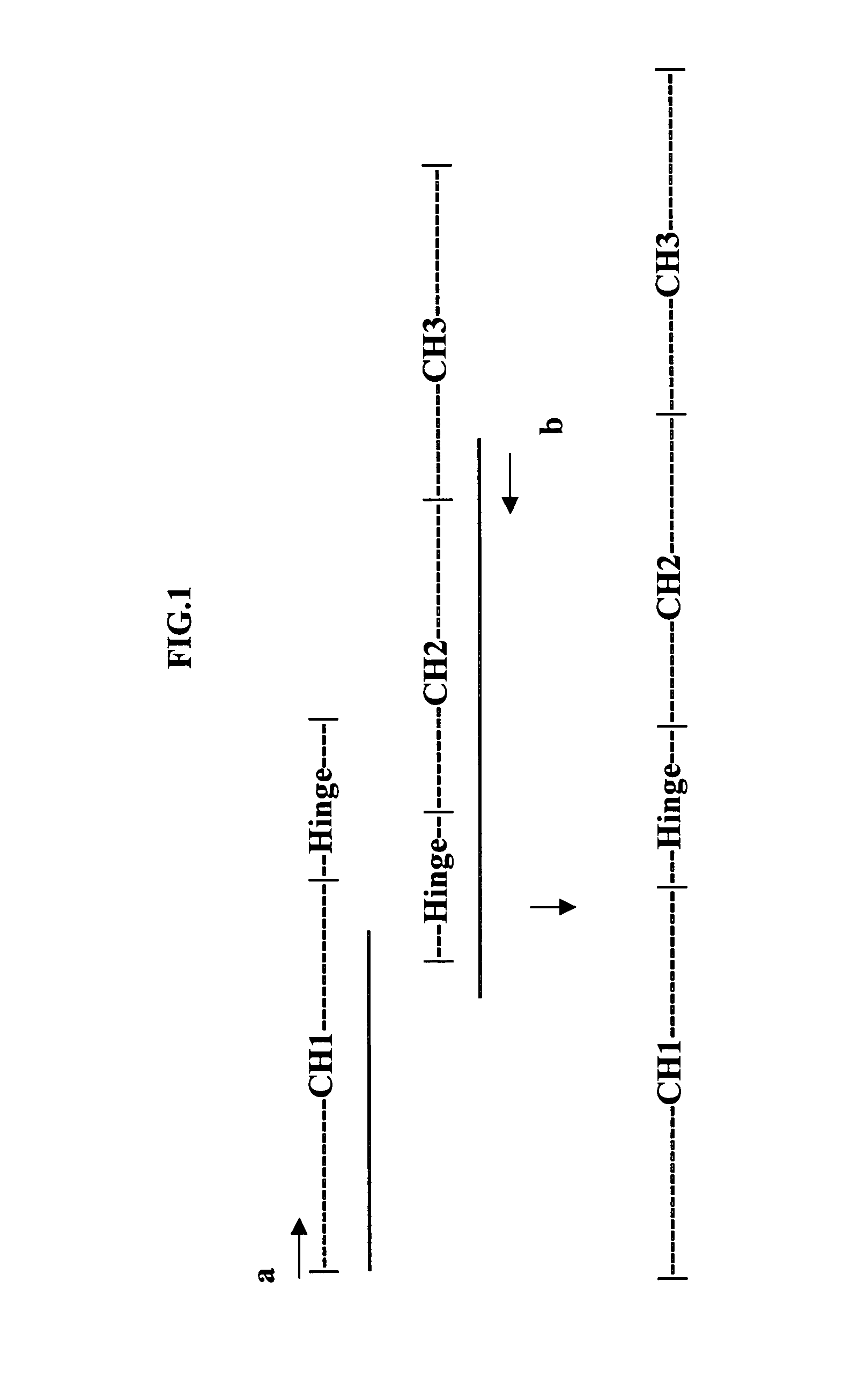
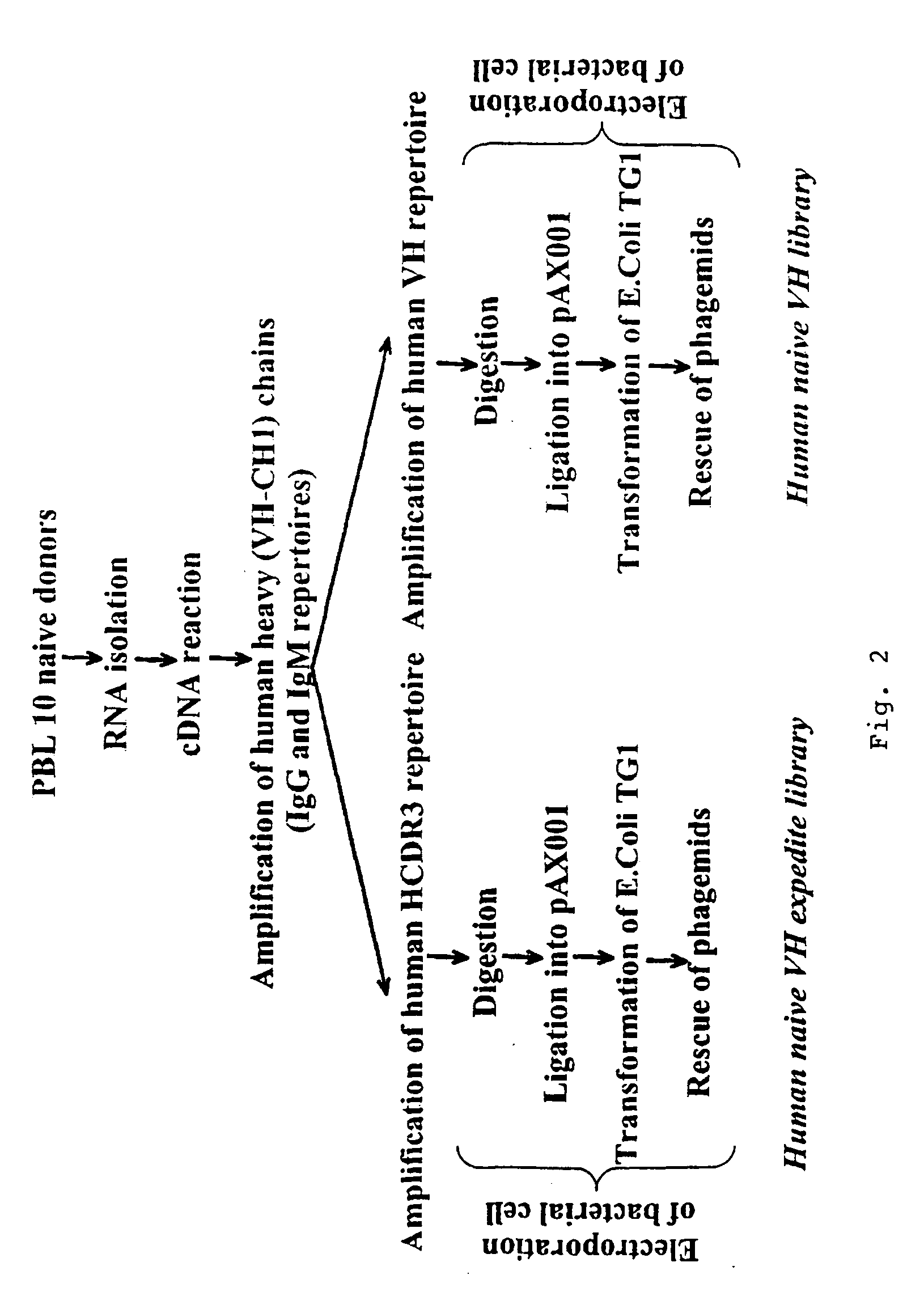
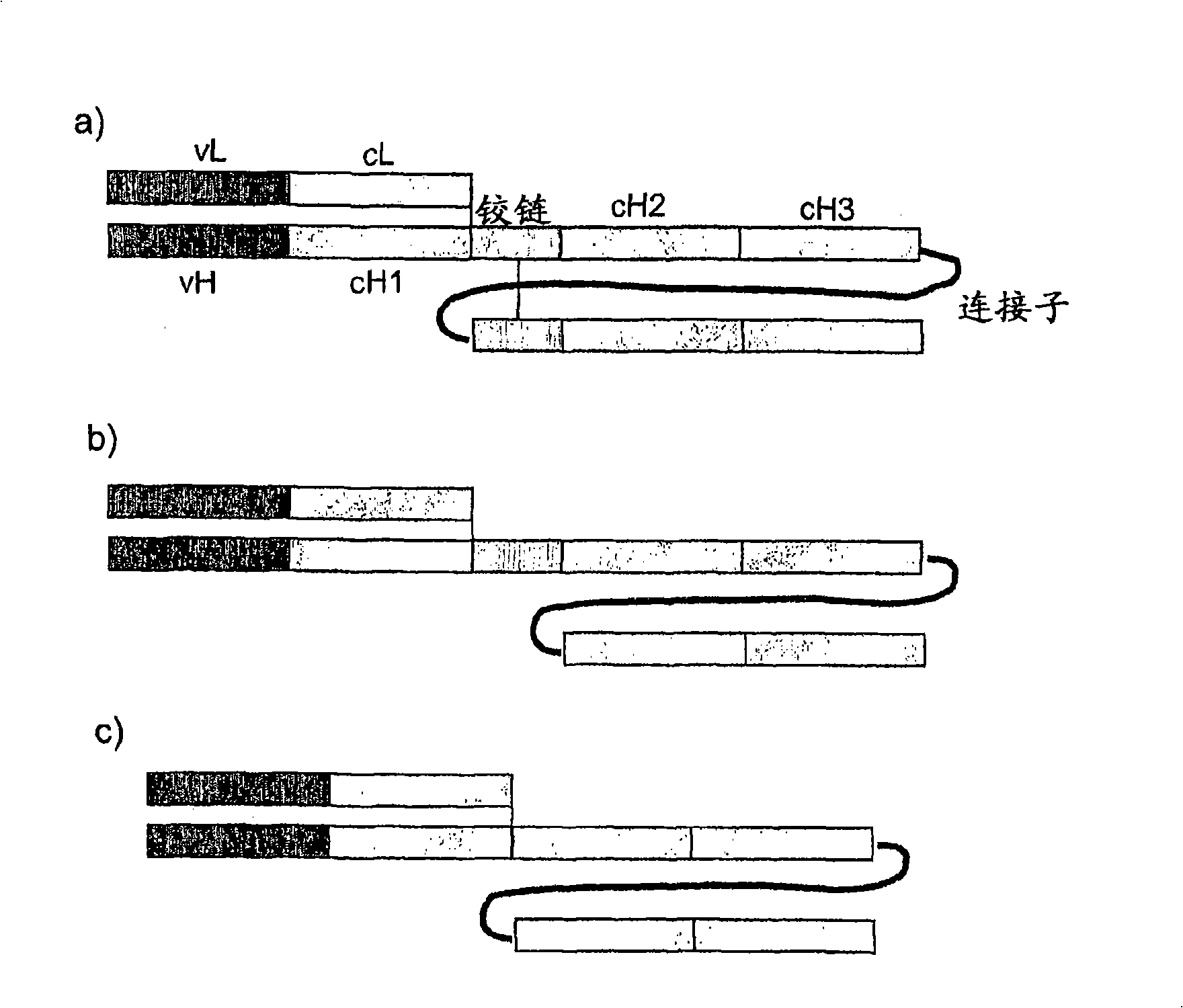
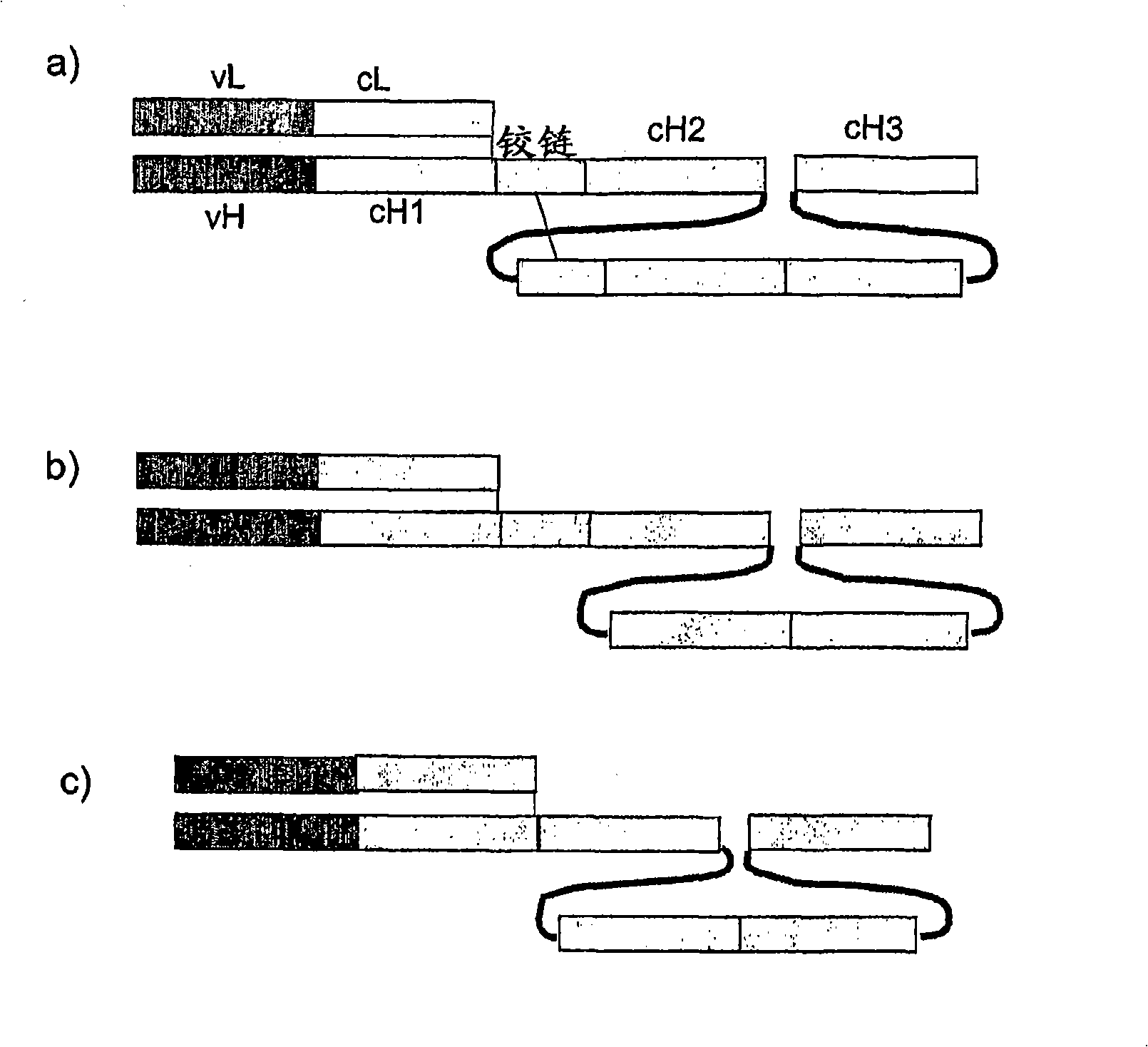
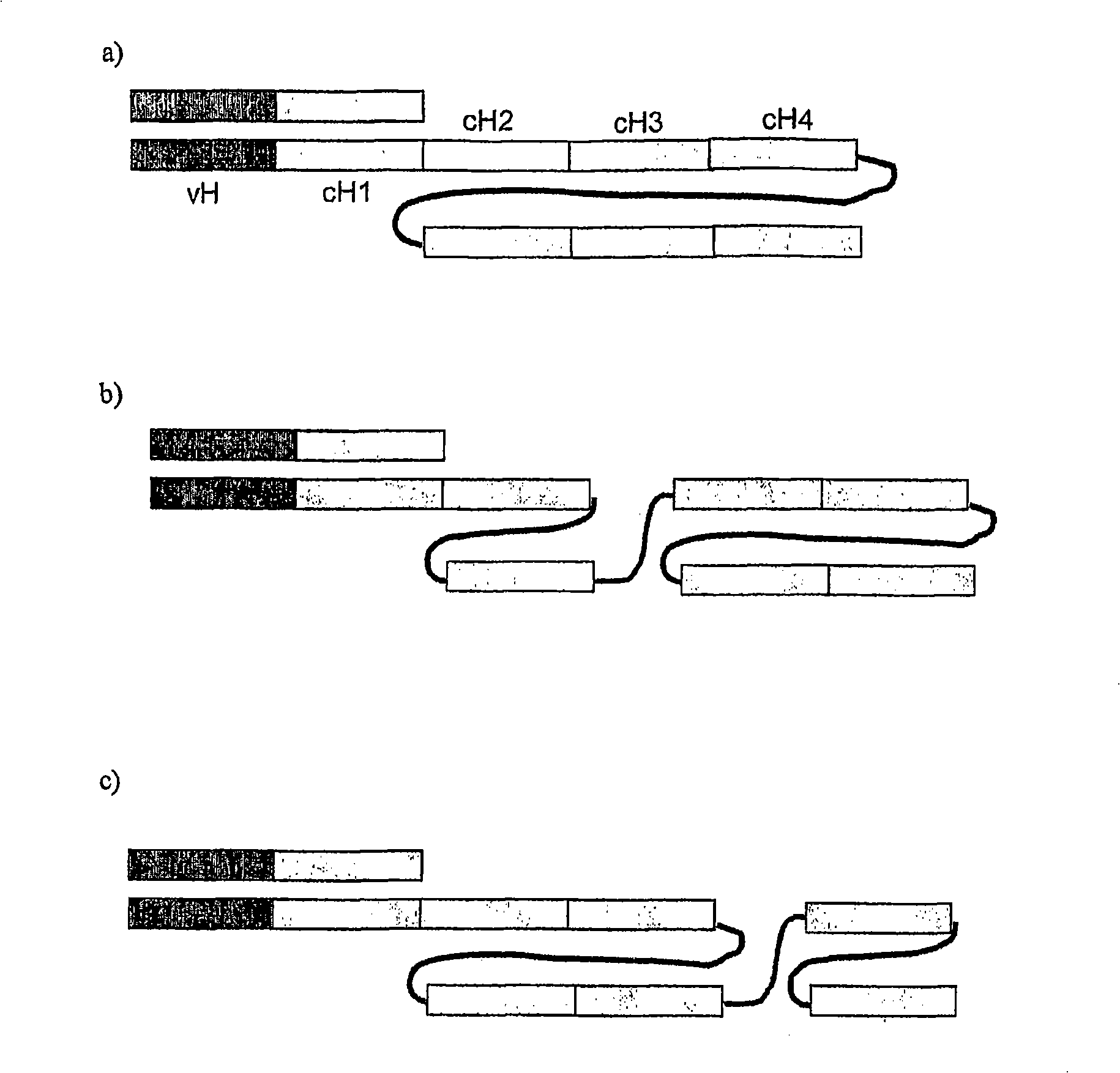
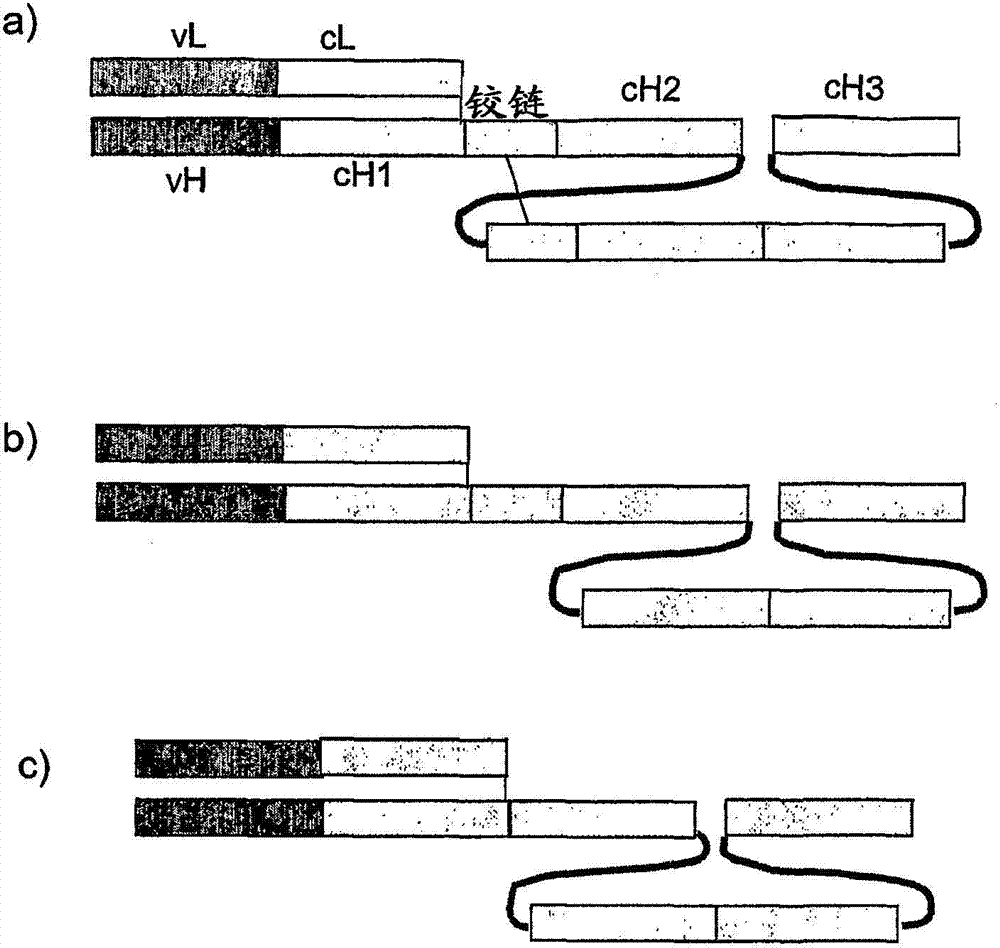
The present invention relates to a class of molecules specified as novel multipurpose antibody derivatives. This class of molecules is created by heterodimerization of two constituting components. Heterodimerization is obtained by the specific heterotypic interaction of a chosen VH-CH1 combination of immunoglobulin domains, with a chosen VL-CL combination of immunoglobulin domains. The appropriate VH and VL domains in the VHCH1 and VLCL context, a binding specificity can be constitituted by the heterodimerization scaffold itself. One or both of the comprising VHCH1 and VLCL chains can thus be extended at either the N- or the C-terminus or both with other molecules, such as a toxin polypeptide, an enzyme, a hormone, a cytokine, a signaling molecule, or a single chain linked Fv fragment with the same or a different specificity.
Owner:BIOTECNOL LTD +1
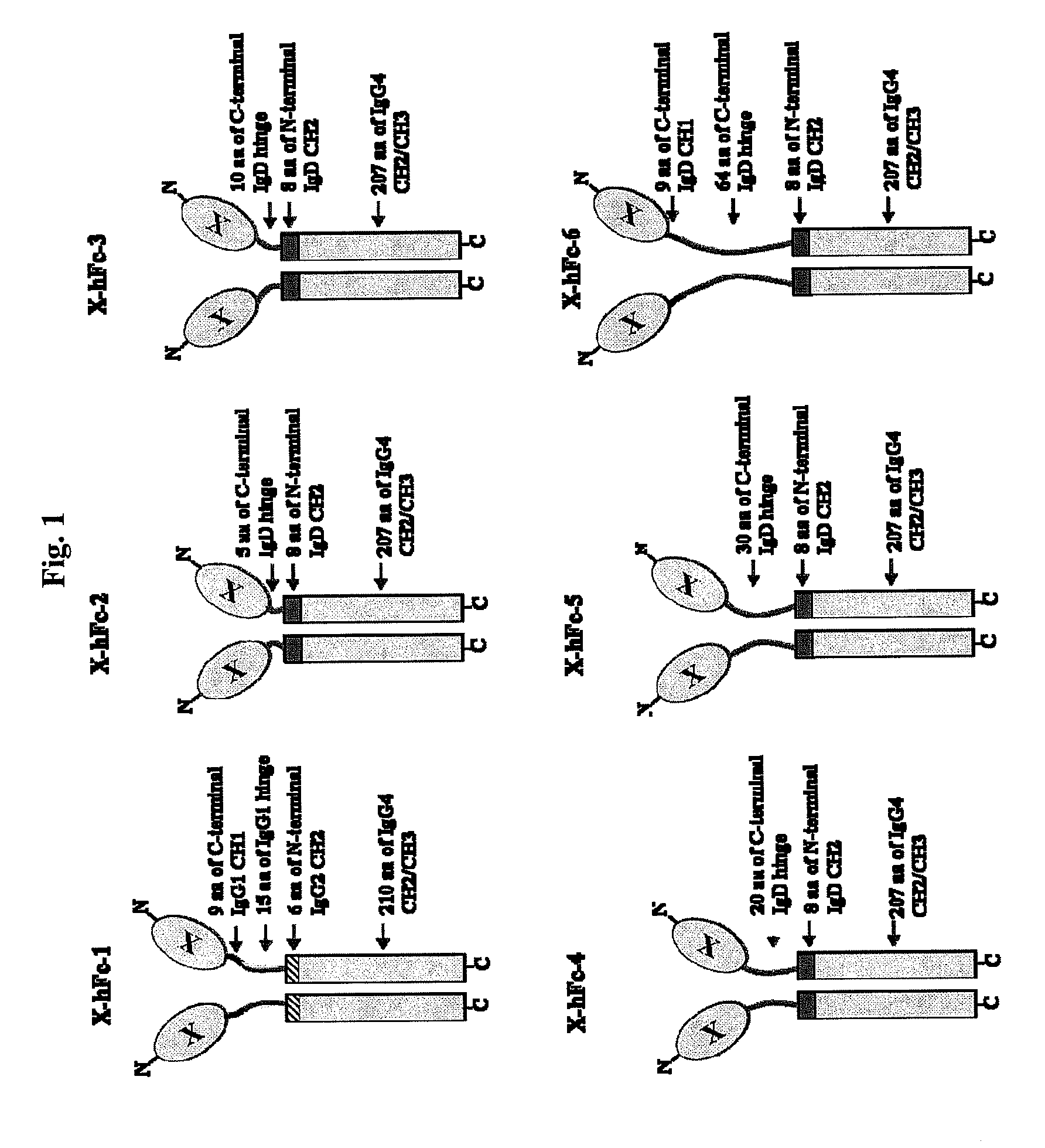
Immunoglobulin fusion proteins
ActiveUS7867491B2Extended half-lifeImprove expression levelPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticFc domainBioactive molecules
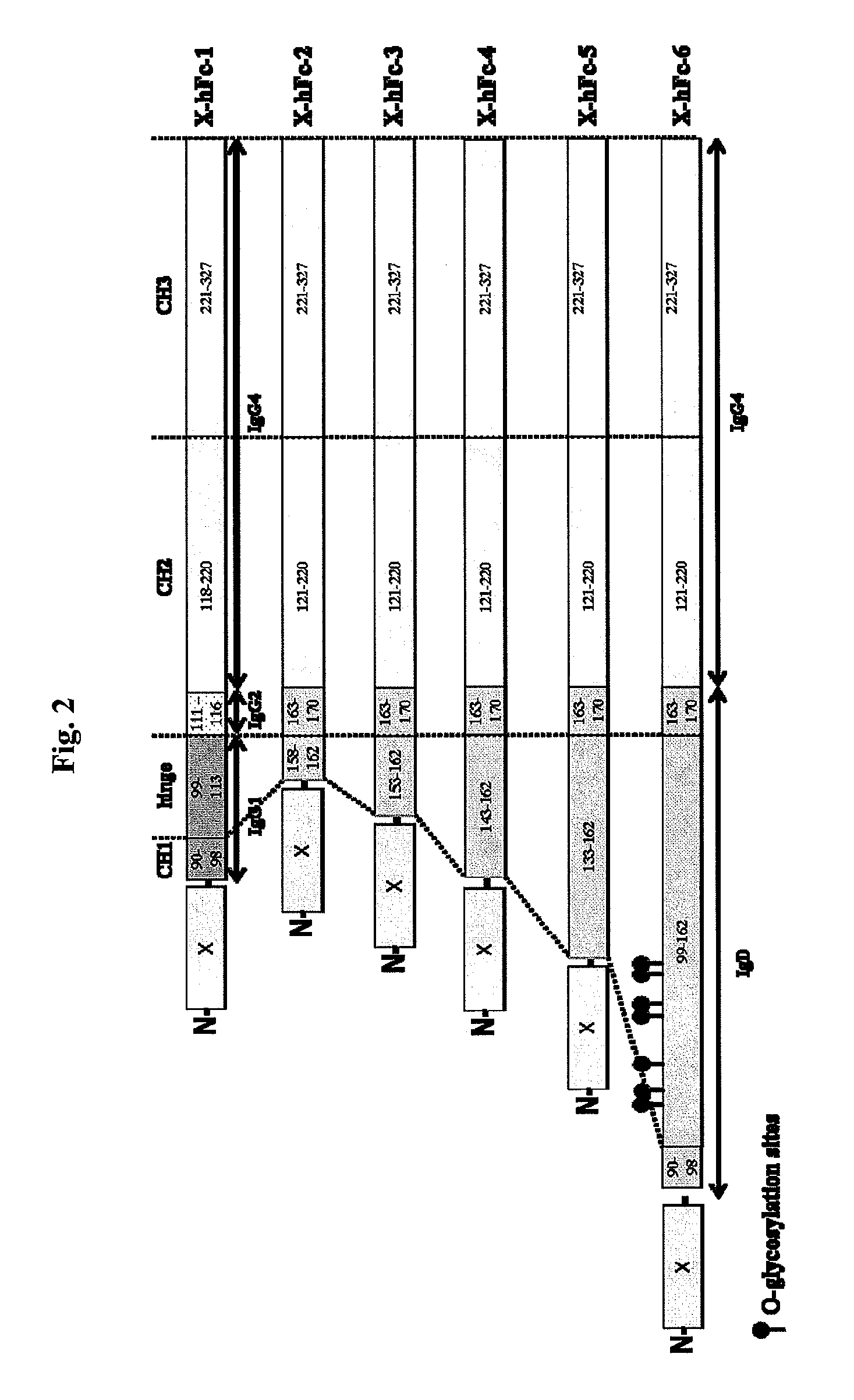
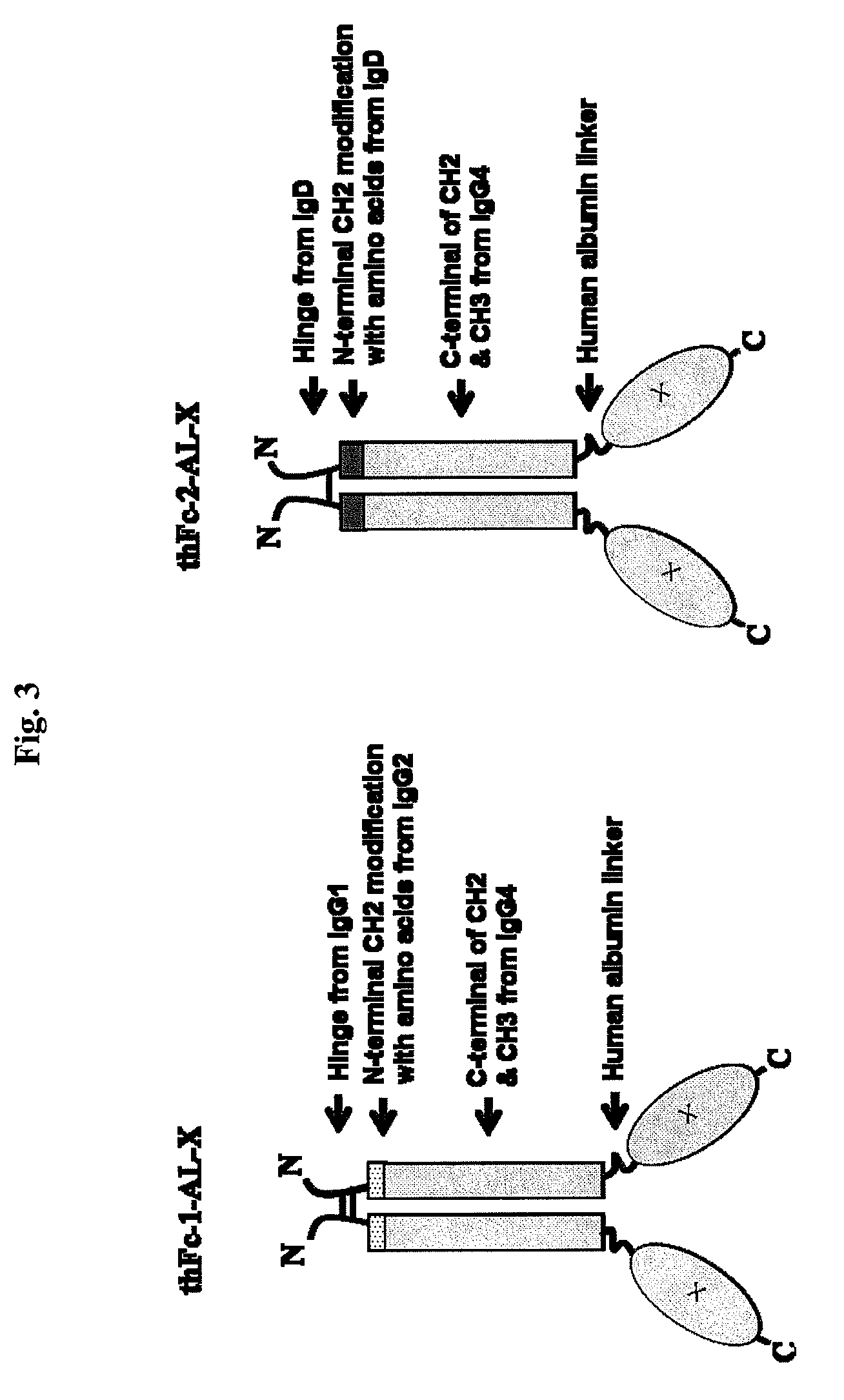
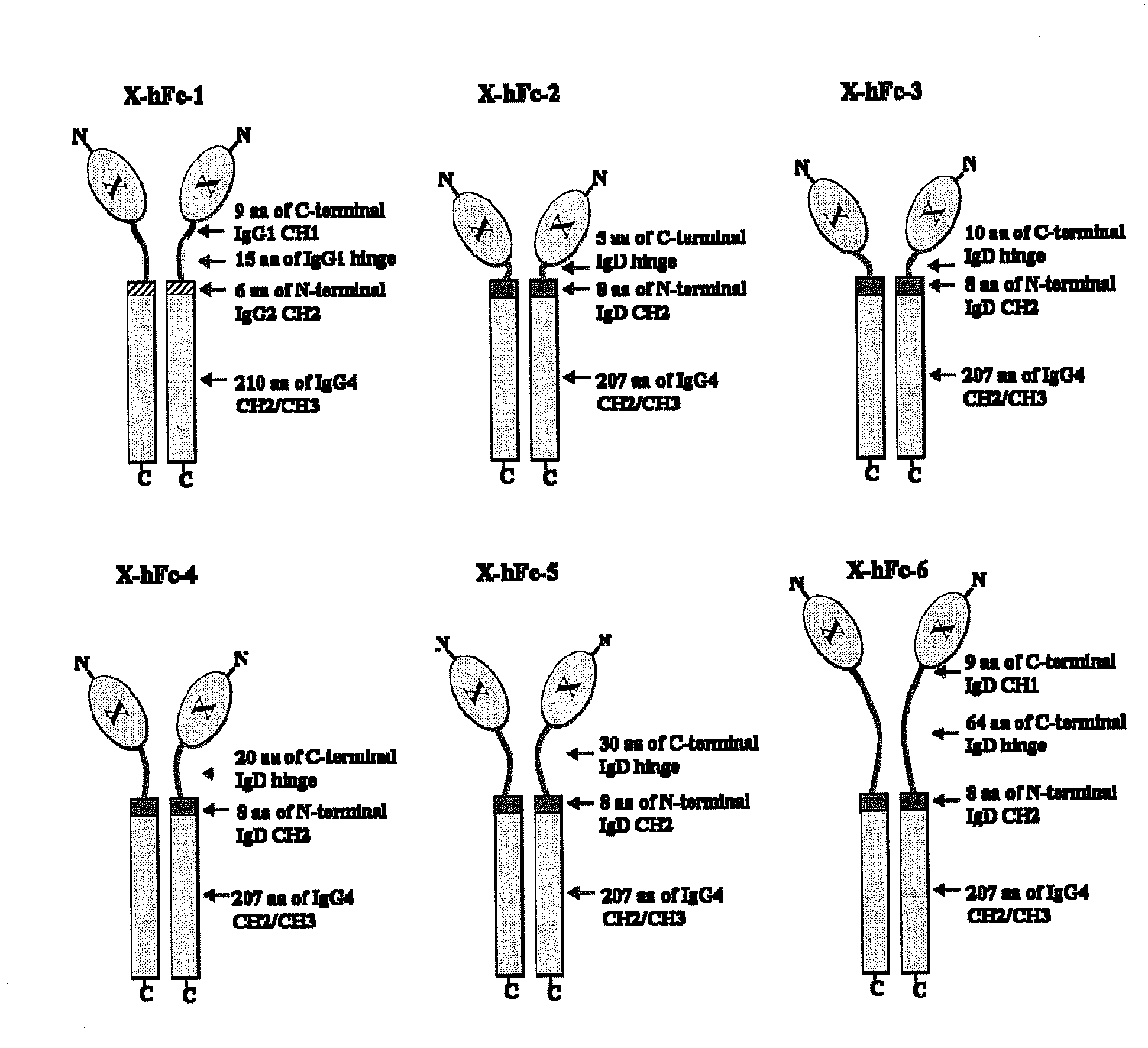
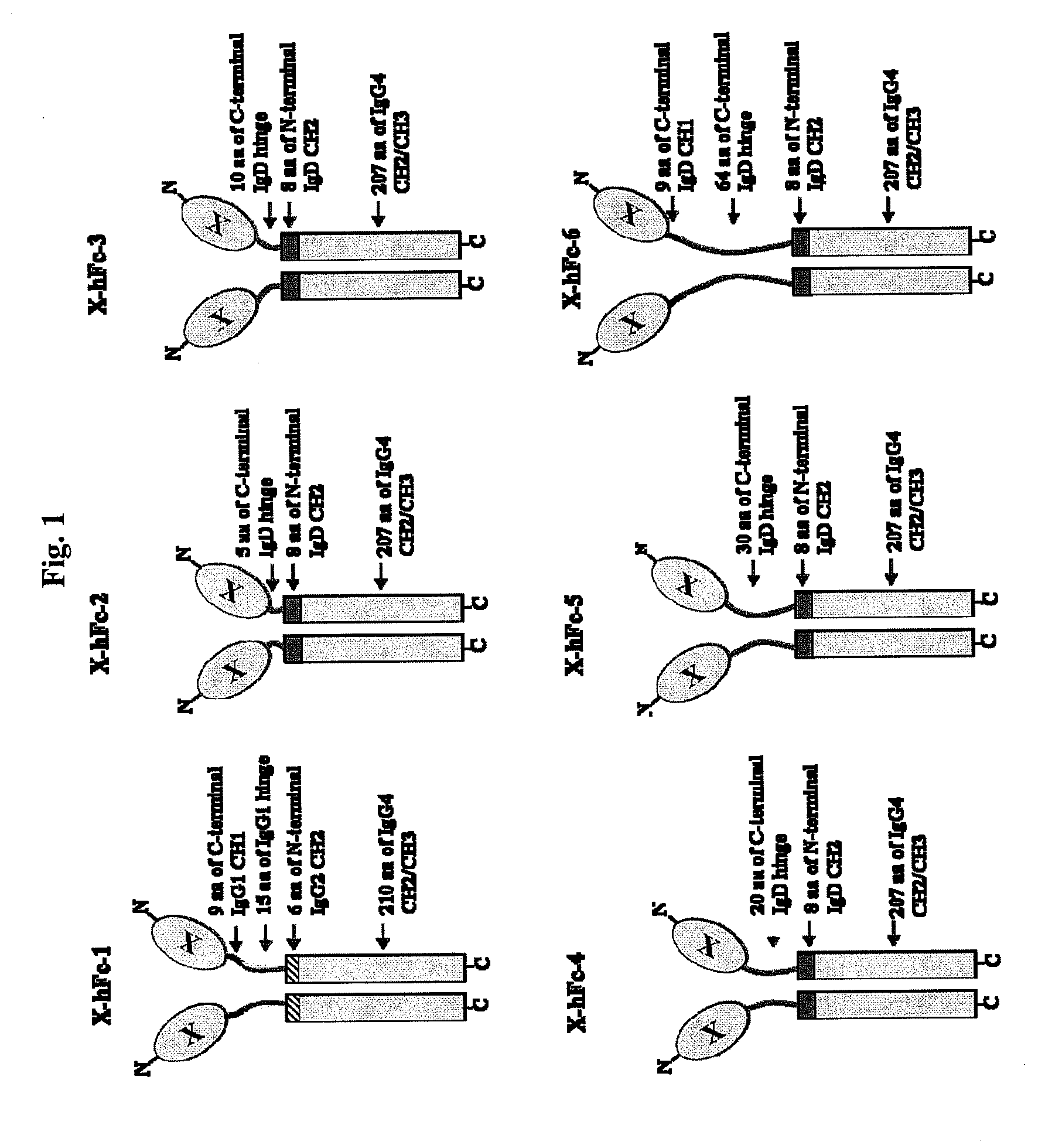
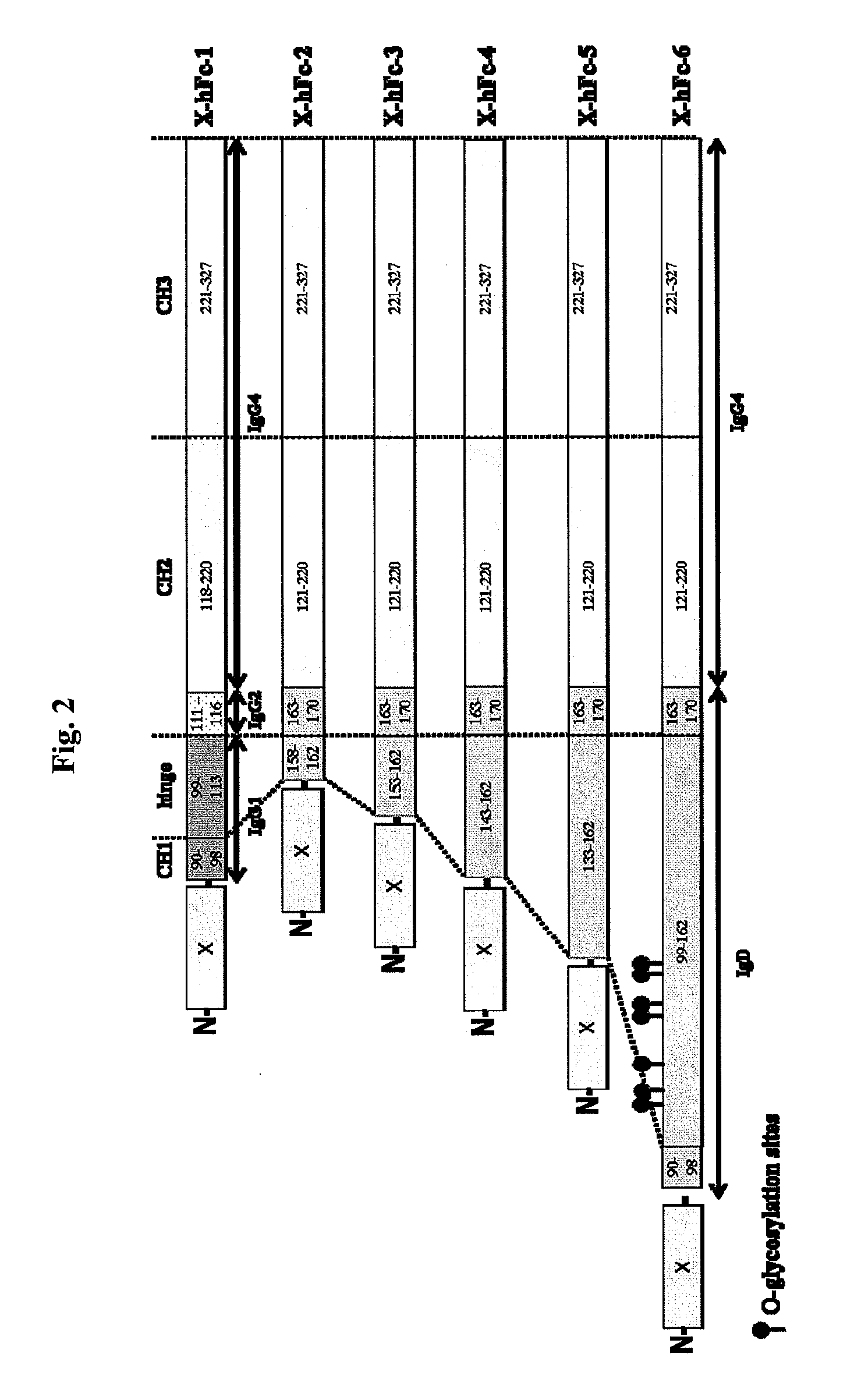
Disclosed are fusion proteins comprising a biologically active molecule and an immunoglobulin (Ig) Fc domain which is linked to the biologically active molecule. The Fc domain is a hybrid human Fc domain of (i) IgG1, IgG2 or IgG4 or (ii) IgG4 and IgD. The hybrid Fc is useful as a carrier of biologically active molecules.
Owner:POSTECH ACADEMY IND FOUND OF POHANG UNIV OF SCI & TECH POSTECH +1
Monomeric immunoglobulin Fc domains
InactiveUS20060074225A1Increase contentReduce disulfide bondImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMonomerImmunoglobulin Fc
Design and production of immunoglobulin Fc domains including variants to stabilize their monomeric forms are provided.
Owner:XENCOR
Methods for purifying protein
ActiveUS7122641B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyAntibody Affinity ChromatographyImmunoglobulin domain
A method is provided for separating a protein from one or more other proteins using hydroxyapatite chromatography in which the protein does not bind to hydroxyapatite but the other protein(s) does. In some embodiments, a second protein affixed to a solid support has been used previously to purify the protein by affinity chromatography, and small amounts of the second protein are introduced in the sample during this process. The protein being purified can comprise at least one constant antibody immunoglobulin domain. The second protein can bind to proteins comprising such a domain.
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
Immunoglobulin Fusion Proteins
ActiveUS20080300188A1Extended half-lifeImprove expression levelOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFc domainBioactive molecules
Disclosed are fusion proteins comprising a biologically active molecule and an immunoglobulin (Ig) Fc domain which is linked to the biologically active molecule. The Fc domain is a hybrid human Fc domain of (i) IgG1, IgG2 or IgG4 or (ii) IgG4 and IgD. The hybrid Fc is useful as a carrier of biologically active molecules.
Owner:POSTECH ACADEMY IND FOUND OF POHANG UNIV OF SCI & TECH POSTECH +1
Cytokine antagonist molecules
This invention relates to a novel protein (INSP052), herein identified as an immunoglobulin domain-containing cell surface recognition molecule and to the use of this proteins and nucleic acid sequences from the encoding gene in the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of disease. The invention also relates to the identification of the extracellular domain of INSP052.
Owner:ARES TRADING SA
Intracellular antibodies
InactiveUS20050272107A1Prevent oncogenic transformationDown-regulated expressionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsIntracellularImmunoglobulin domain
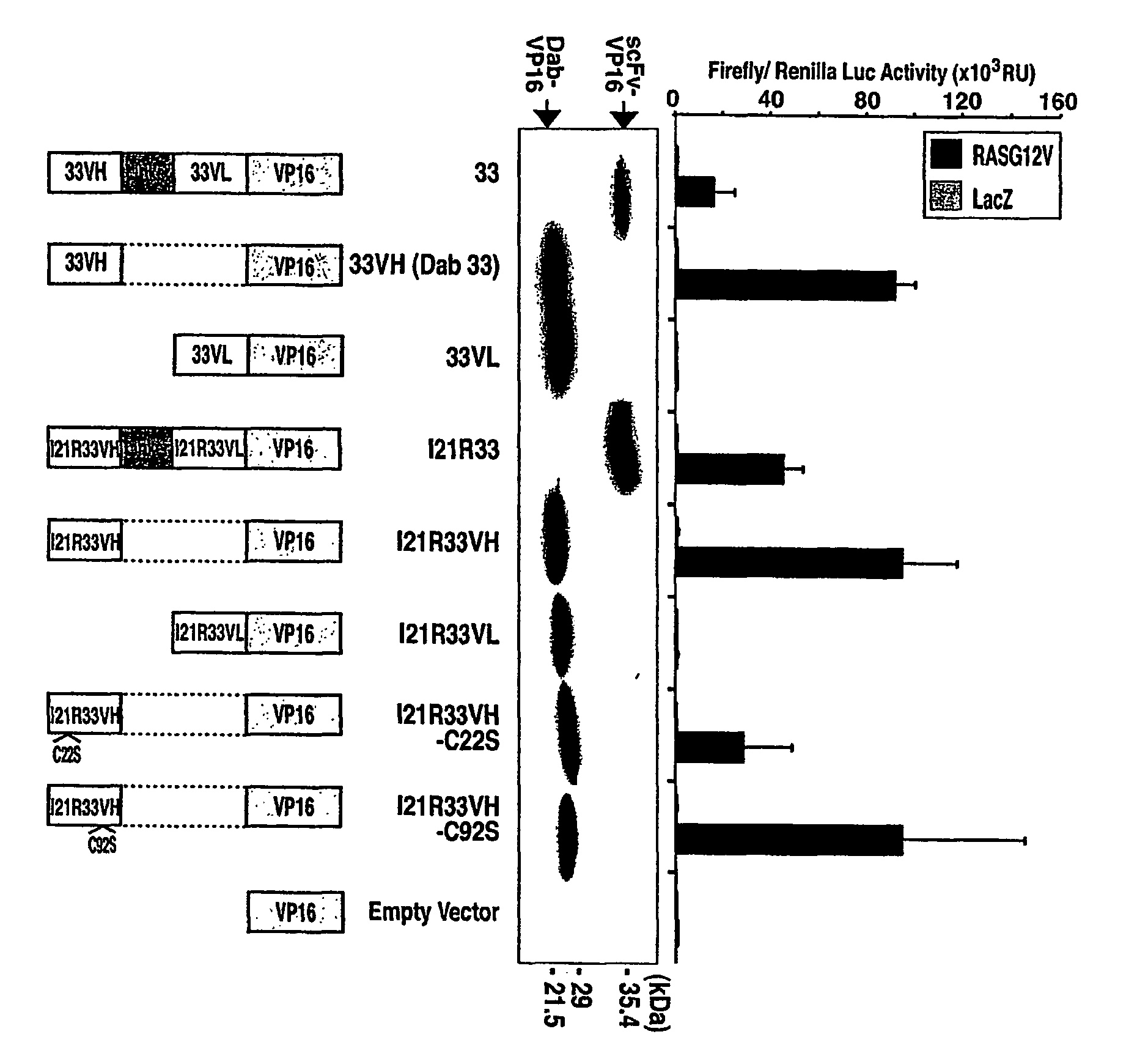
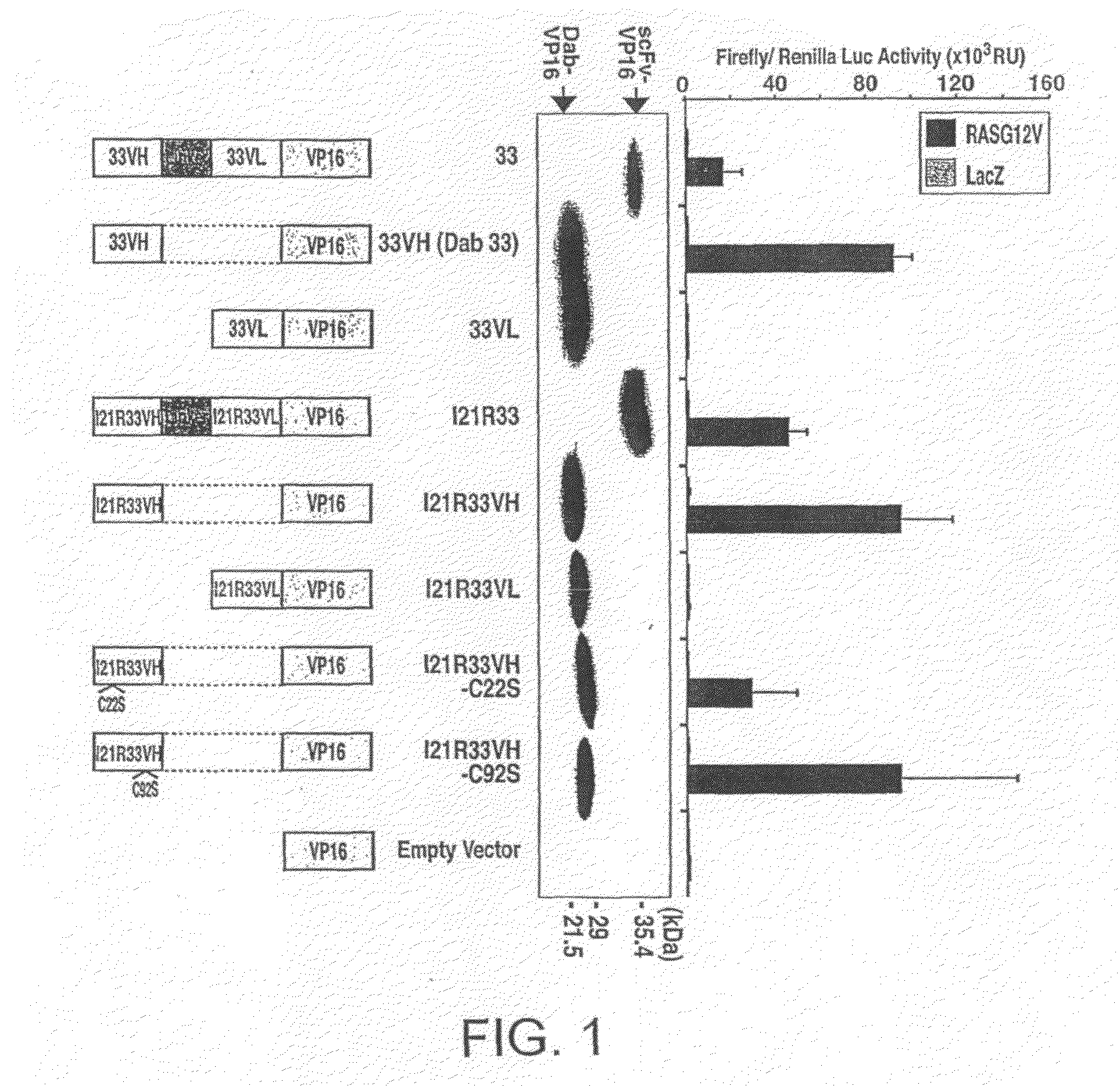
The invention related to intracellular single domain immunoglobulins, and to a method for determining the ability of an immunoglobulin single domain to bind to a target in an intracellular environment, comprising the steps of: a) providing a first molecule and a second molecule, wherein stable interaction of the first and second molecules leads to the generation of a signal; b) providing a single intracellular immunoglobulin domain which is associated with the first molecule, said single immunoglobulin domain being free of complementary immunoglobulin domains; c) providing an intracellular target which is associated with the second molecule, such that association of the immunoglobulin domain and the target leads to stable interaction of the first and second molecules and generation of the signal; and d) assessing the intracellular interaction between the immunoglobulin domain and the target by monitoring the signal.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Stable multivalent antibody
ActiveUS20110076722A1Increase production capacityImprove productivitySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeavy chainAmino acid
The present invention relates to a multivalent antibody comprising multiple heavy chain variable regions of antibody linked to each other via a linker comprising an amino acid sequence encoding an immunoglobulin domain or a fragment thereof.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Immunoglobulin fusion proteins
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Method for displaying loops from immunoglobulin domains in different contexts
InactiveUS20050214857A1Improve stabilityPeptide librariesCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenImmunoglobulin domain
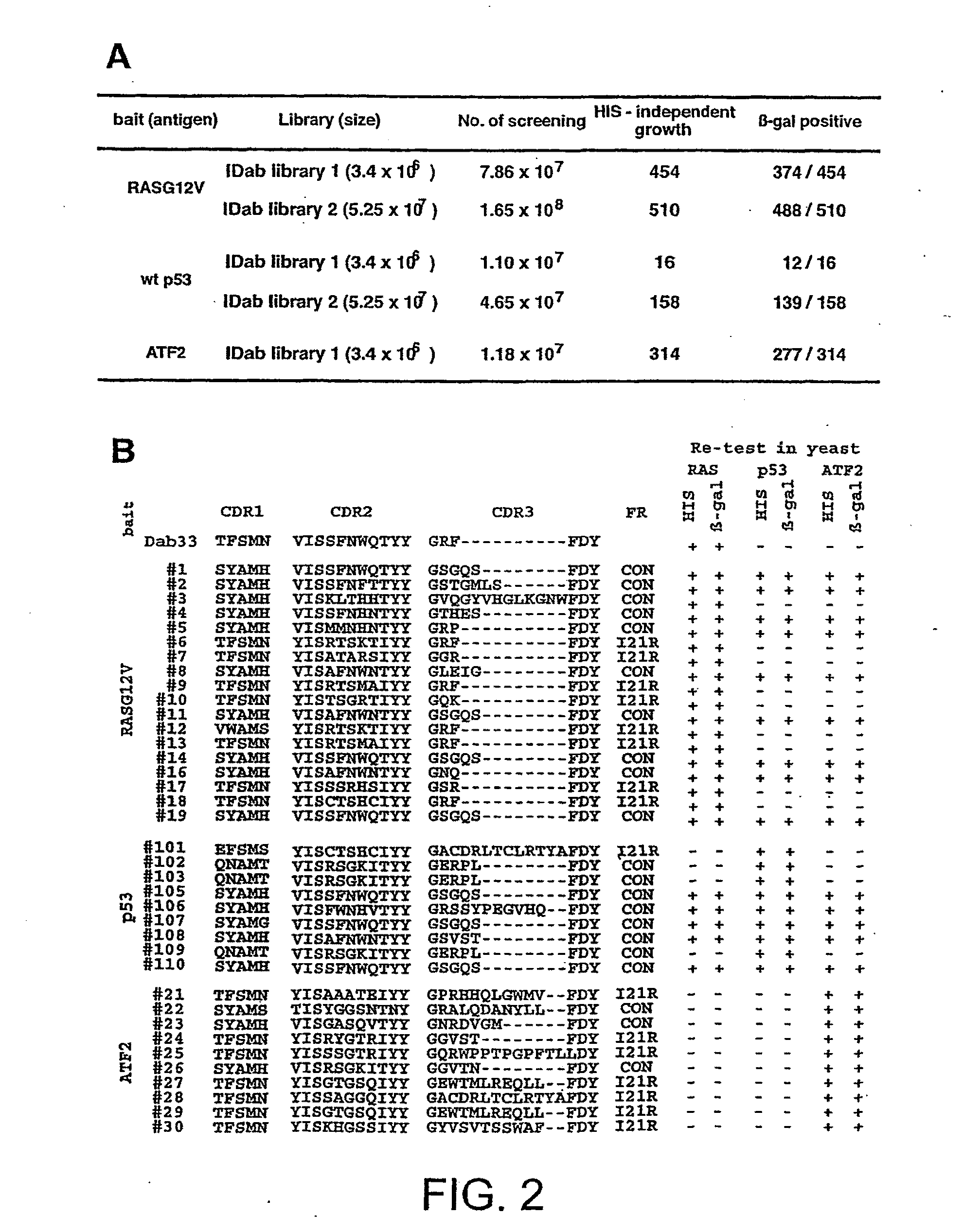
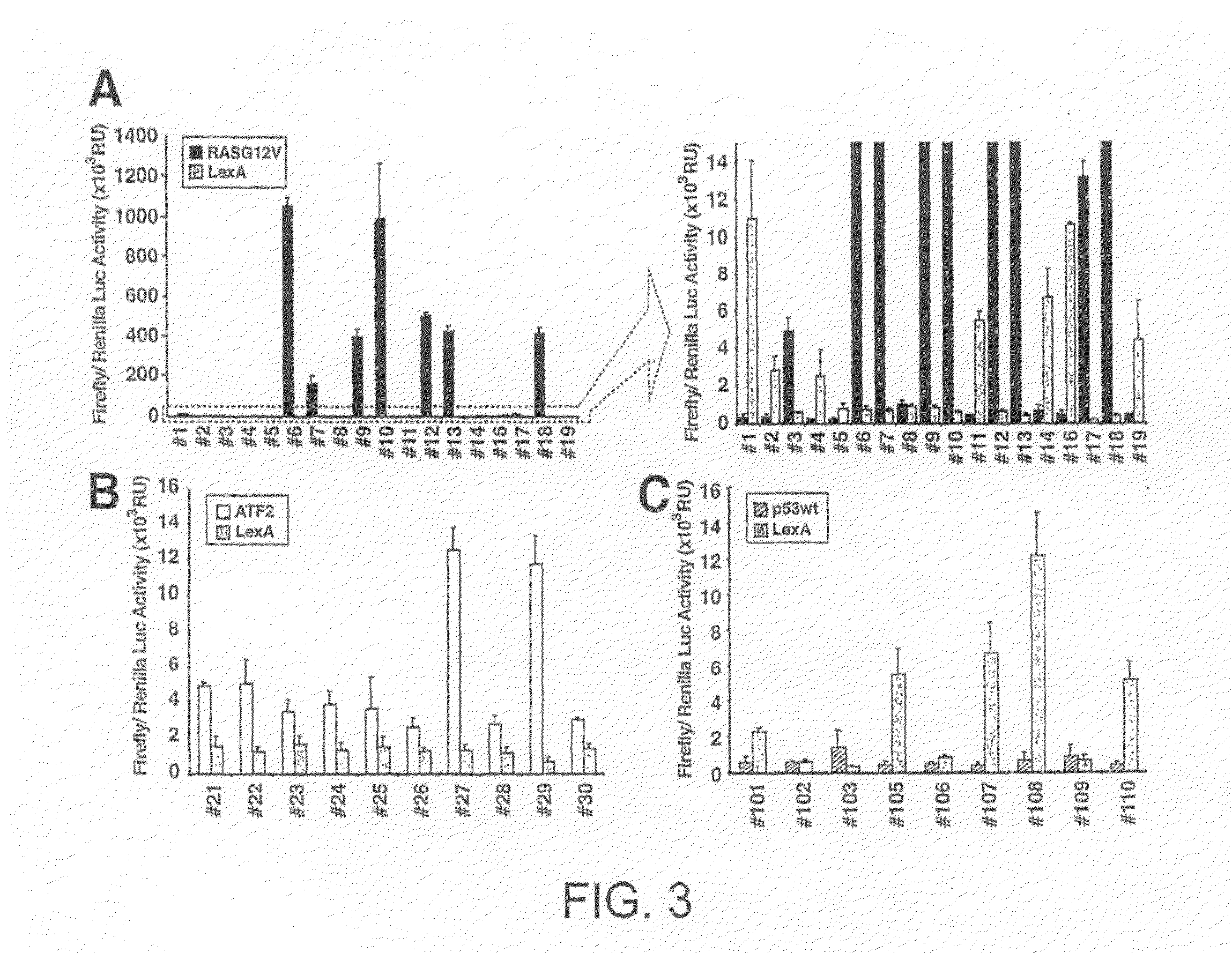
The present invention is related to an isolated polypeptide micro-scaffold displaying immunoglobulin CDR2 or CDR3 polypeptide sequences, comprising a CDR2 or CDR3 polypeptide sequence interconnecting fragments of the adjacent framework polypeptide sequences, which are arranged to form two anti-parallel β-strands. The present invention is further related to a method to search, select or screen for immunoglobulin CDR2 or CDR3 polypeptide sequences that bind to a given antigen or mixture of antigens, comprising the steps of: Creating a CDR library with the method of claim 13 from the genetic information of an individual or group of individuals; Select a CDR, which binds to said antigen or mixture of antigens.
Owner:ALGONOMICS +1
Intracellular antibodies
InactiveUS20100143939A1Prevent oncogenic transformationDown-regulated expressionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsIntracellularImmunoglobulin domain
The invention related to intracellular single domain immunoglobulins, and to a method for determining the ability of an immunoglobulin single domain to bind to a target in an intracellular environment, comprising the steps of: a) providing a first molecule and a second molecule, wherein stable interaction of the first and second molecules leads to the generation of a signal; b) providing a single intracellular immunoglobulin domain which is associated with the first molecule, said single immunoglobulin domain being free of complementary immunoglobulin domains; c) providing an intracellular target which is associated with the second molecule, such that association of the immunoglobulin domain and the target leads to stable interaction of the first and second molecules and generation of the signal; and d) assessing the intracellular interaction between the immunoglobulin domain and the target by monitoring the signal.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Isolating cells expressing secreted proteins
InactiveUS20140072979A1DifferentiateImprove the level ofAnimal cellsBacteriaMolecular bindingSecretory protein
A method of detecting and isolating cells that produce a secreted protein of interest (POI) that has an immunoglobulin CH3 domain and / or substituted CH3 domain, comprising: a) constructing a cell line transiently or stably expressing a cell surface capture molecule, which binds the POI, by transfecting the cell line with a nucleic acid that encodes such cell surface capture molecule; b) transfecting said cell simultaneously or subsequently with a second nucleic acid that encodes a POI wherein such POI is secreted; c) detecting the surface-displayed POI by contacting the cells with a detection molecule, which binds the POI; and d) isolating cells based on the detection molecule.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Immunoglobulin fusion proteins
The present invention relates to novel methods for making fusion proteins comprising a cytokine or growth factor fused to an immunoglobulin domain. The growth factor / cytokine can be fused directly to an immunoglobulin domain or through a peptide linker. The purified growth factor / cytokine-IgG fusion proteins produced by the novel methods are biologically active and can be used to treat diseases for which the non-fused growth factor / cytokine are useful.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
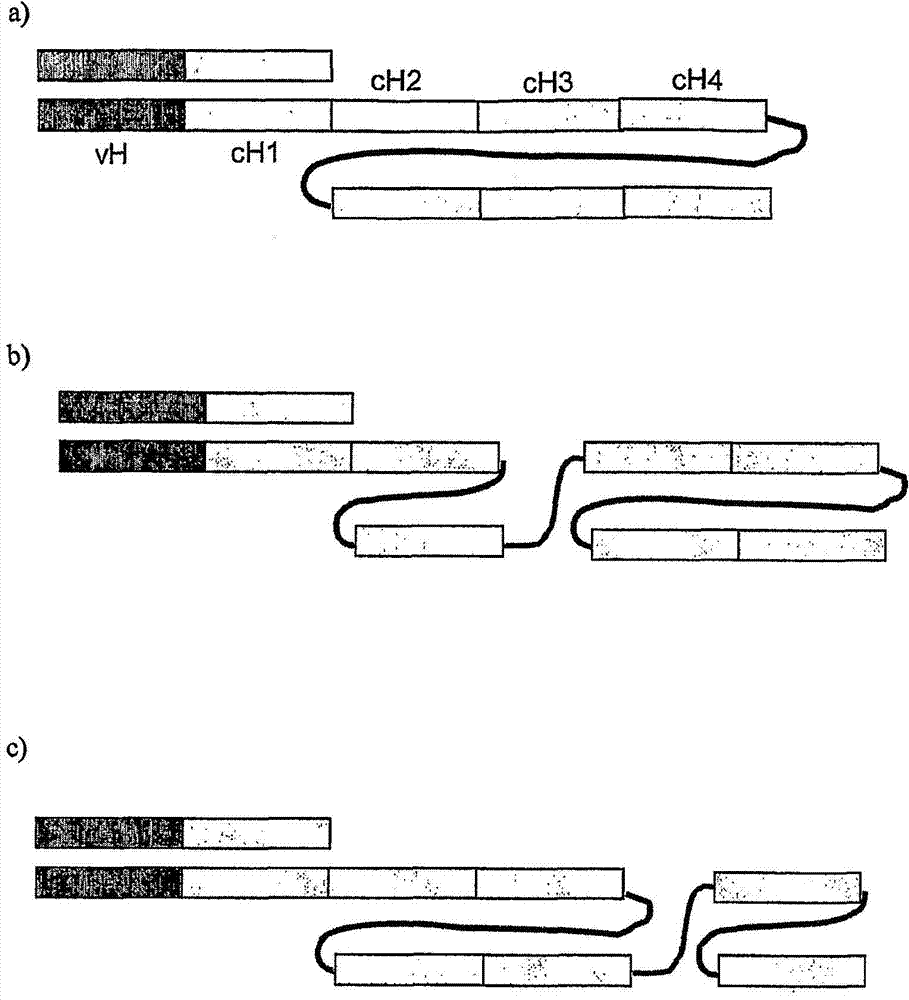
Single chain FC polypeptides
The present invention relates to single chain polypeptides comprising one or more immunoglobulin Fc domains. In particular the present invention relates to single-chain Fc polypeptides in which at least one functional Fc domain is formed within the polypeptide chain.
Owner:UCB SA
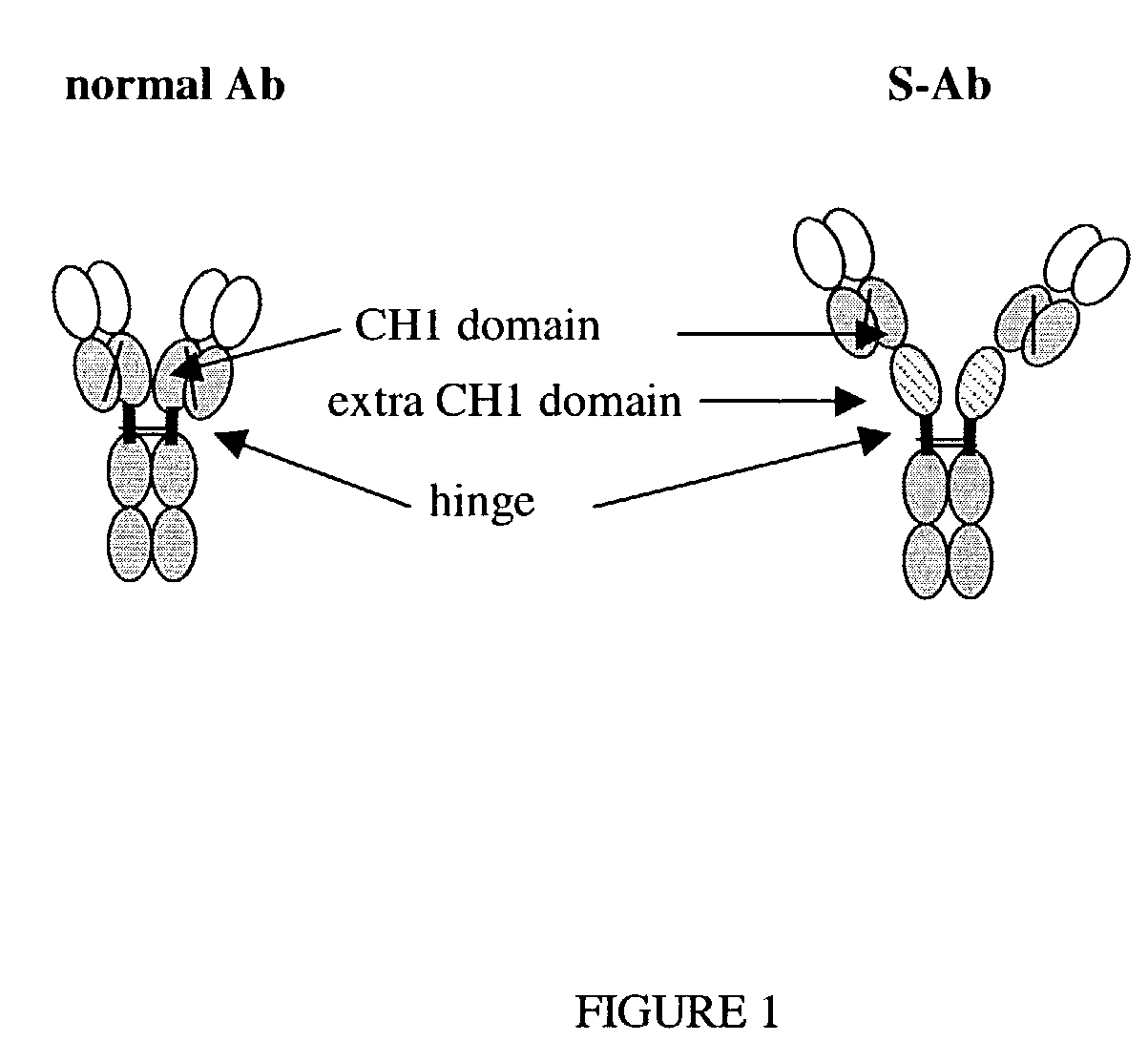
Modified "S" antibodies
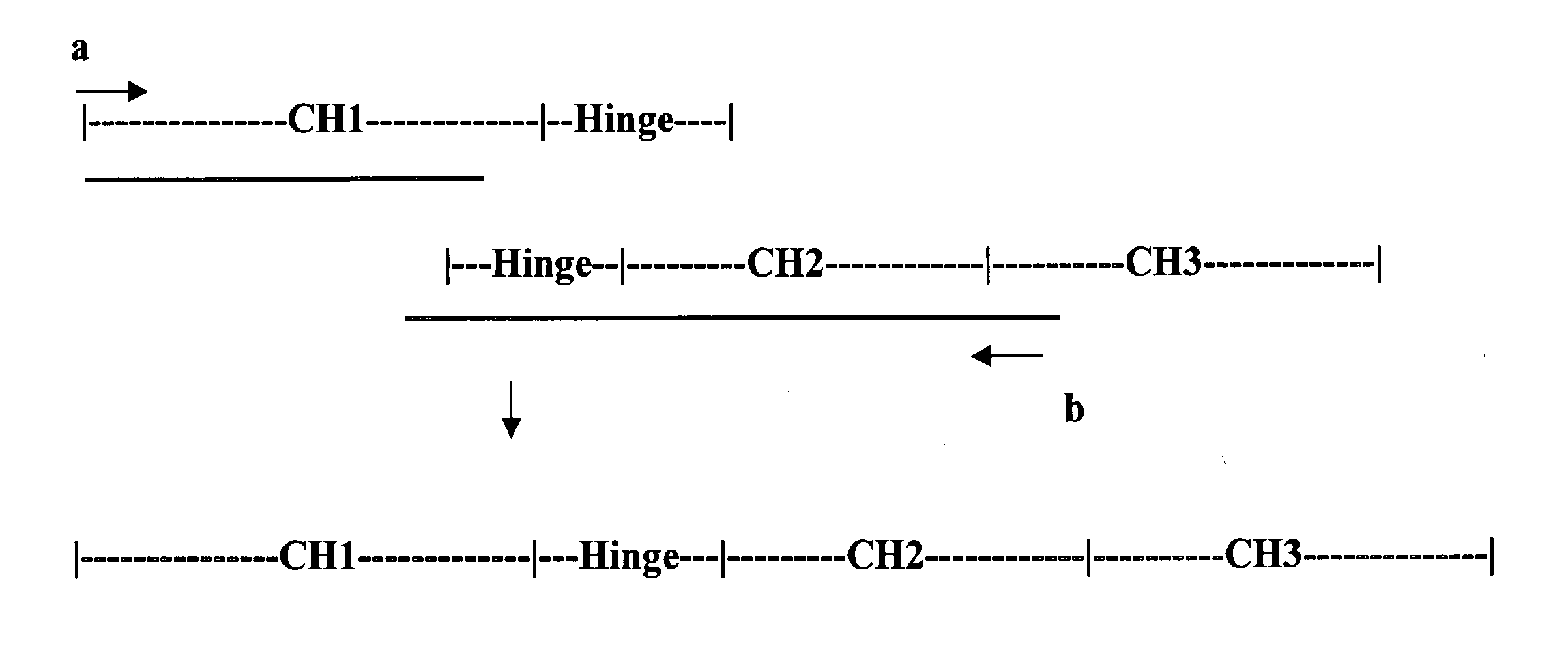
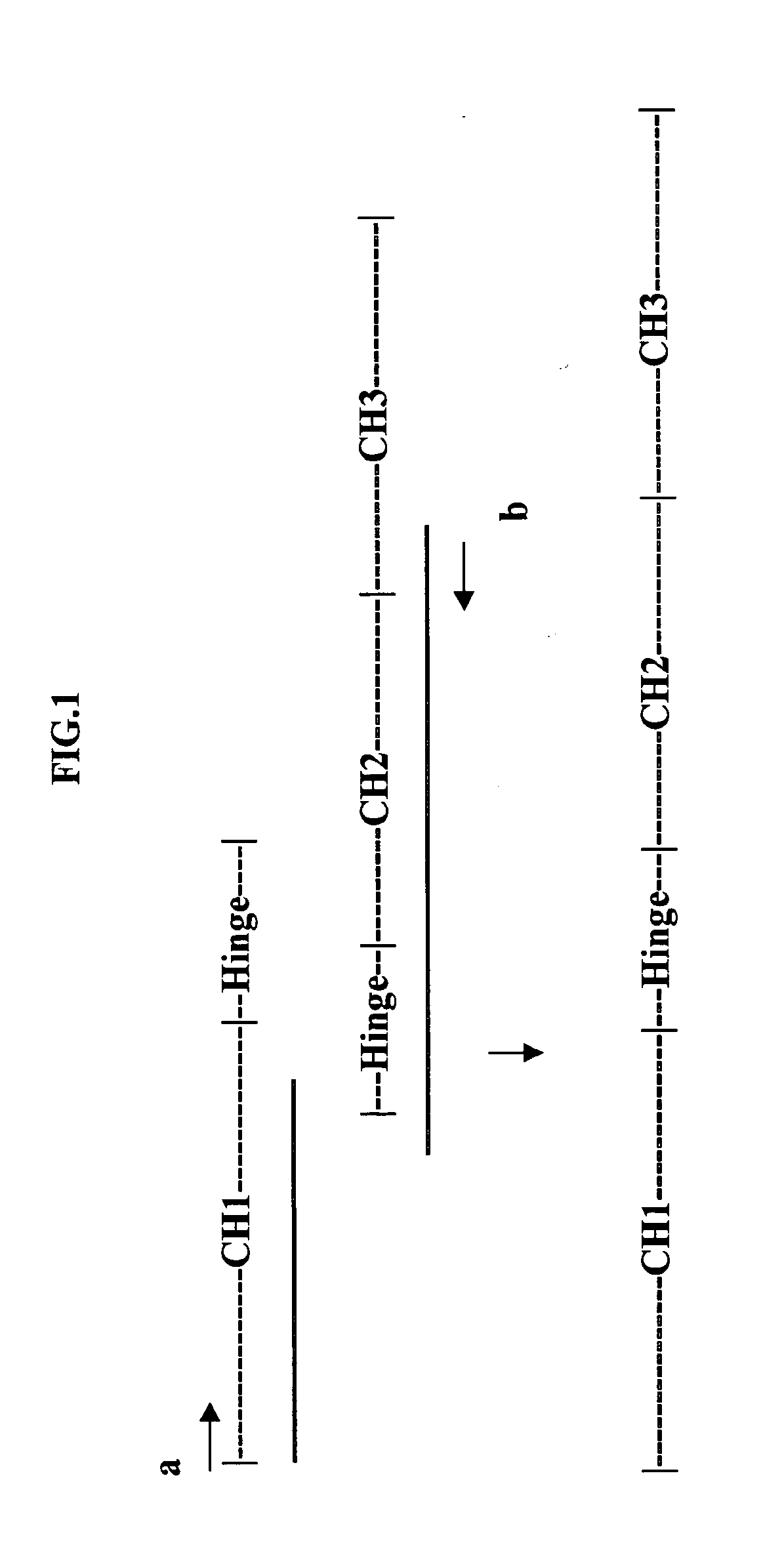
ActiveUS7427471B2Increase distanceIncrease flexibilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesConstant regionImmunoglobulin domain
The invention relates to the field of antibodies, and particularly to modified antibodies, methods of preparing modified antibodies and uses thereof. More particularly, the invention relates to the preparation of more active IgG antibodies by the addition of an extra immunoglobulin domain to the constant region.
Owner:CENTOCOR
Methods of delivery of molecules to cells using a ricin subunit and compositions relating to same
A method of preparing molecules of interest for delivery to eukaryotic cells is shown, wherein a ricin B chain subunit not having a ribosome inactivating subunit and retaining lectin activity is modified by modifying the first cysteine residue to be absent or substituted with an amino acid other than cysteine, or removing a protease sensitive site at the N-terminal of the subunit, or adding an endoplasmic reticulum retrieval signal, and operatively associating the subunit with a molecule of interest. Methods of operatively associating the subunit and molecule of interest include chemical conjugation at primary amines, conjugation with N-glycans of the subunit, a disulfide bond, and assembly of immunoglobulin domains. The invention provides for operatively associating multiple molecules of interest with a ricin B chain subunit, and delivery into targeted cells, cell components, and combination of cells.
Owner:ARKANSAS STATE UNIV
Synthetic immunoglobulin domains with binding properties engineered in regions of the molecule different from the complementarity determining regions
InactiveUS20110251375A1Peptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeComplementarity determining region
Immunoglobulins which each have one or more amino acid modifications in at least one structural loop region of such immunoglobulins, where the modified loop region specifically binds to an epitope of an antigen to which an unmodified immunoglobulin does not significantly bind, obtained from display libraries.
Owner:F STAR BIOTECHNOLOGISCHE FORSCHUNGS & ENTWICKLUNGS GMBH
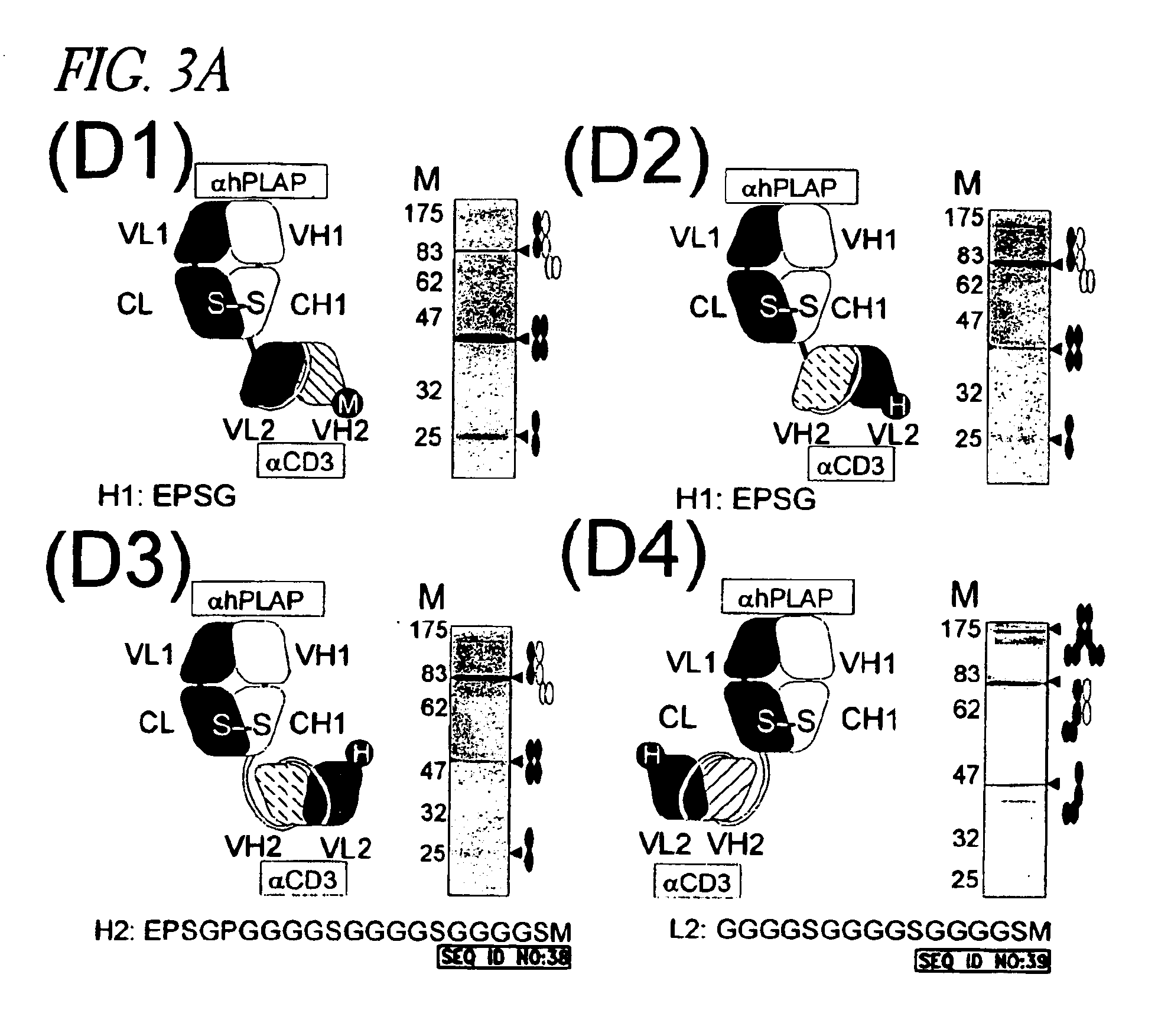
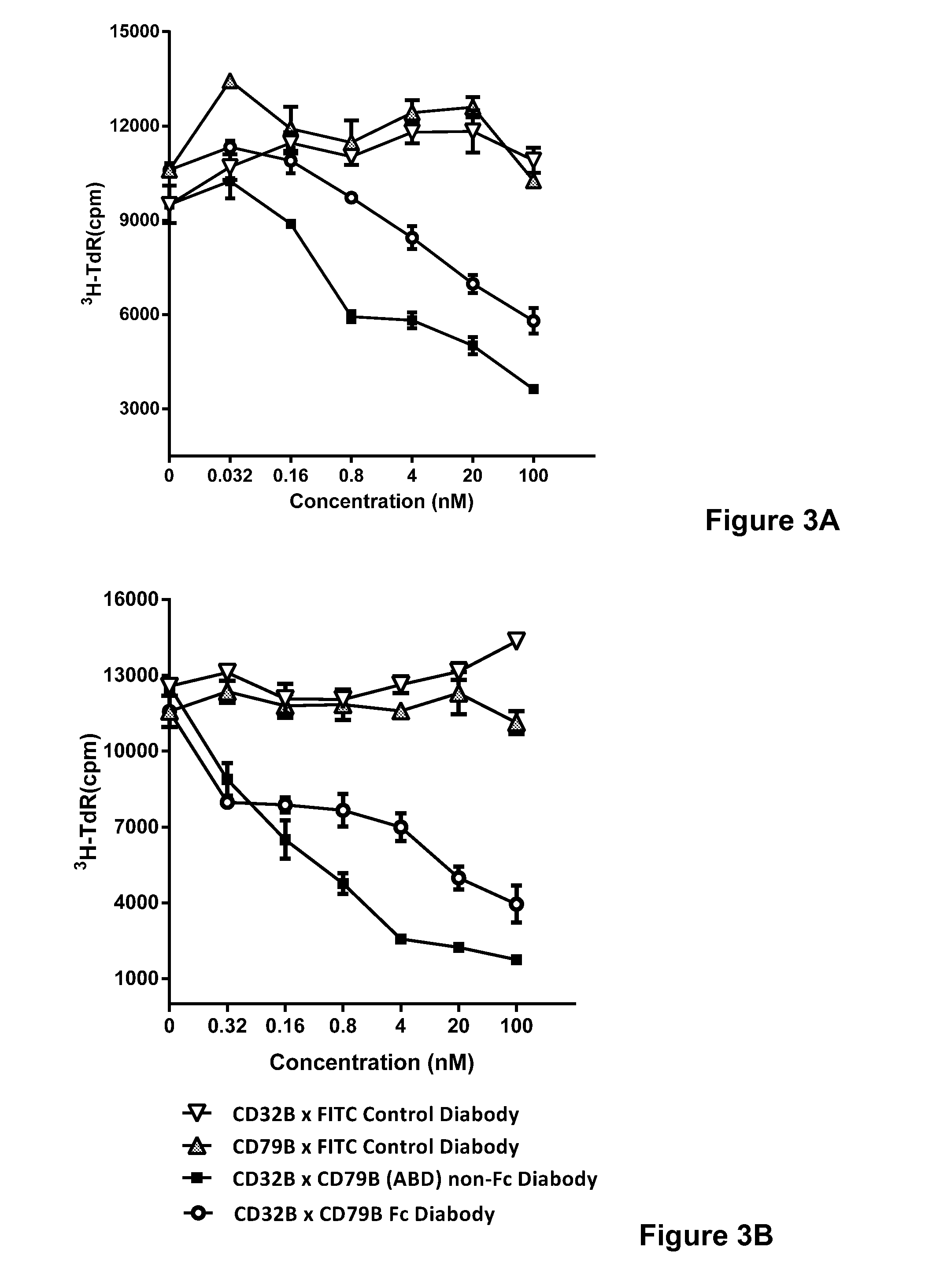
Bi-Specific Monovalent Fc Diabodies That Are Capable of Binding CD32B and CD79b and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20160194396A1Prevent proliferationHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeBinding site
The present invention is directed to bi-specific monovalent diabodies that comprise an immunoglobulin Fc Domain (“bi-specific monovalent Fc diabodies”) and are composed of three polypeptide chains and which possess at least one binding site specific for an epitope of CD32B and one binding site specific for an epitope of CD79b (i.e., a “CD32B×CD79b bi-specific monovalent Fc diabody”). The bi-specific monovalent Fc diabodies of the present invention are capable of simultaneous binding to CD32B and CD79b. The invention is directed to such compositions, to pharmaceutical compositions that contain such bi-specific monovalent Fc diabodies and to methods for their use in the treatment of inflammatory diseases or conditions, and in particular, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and graft vs. host disease.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
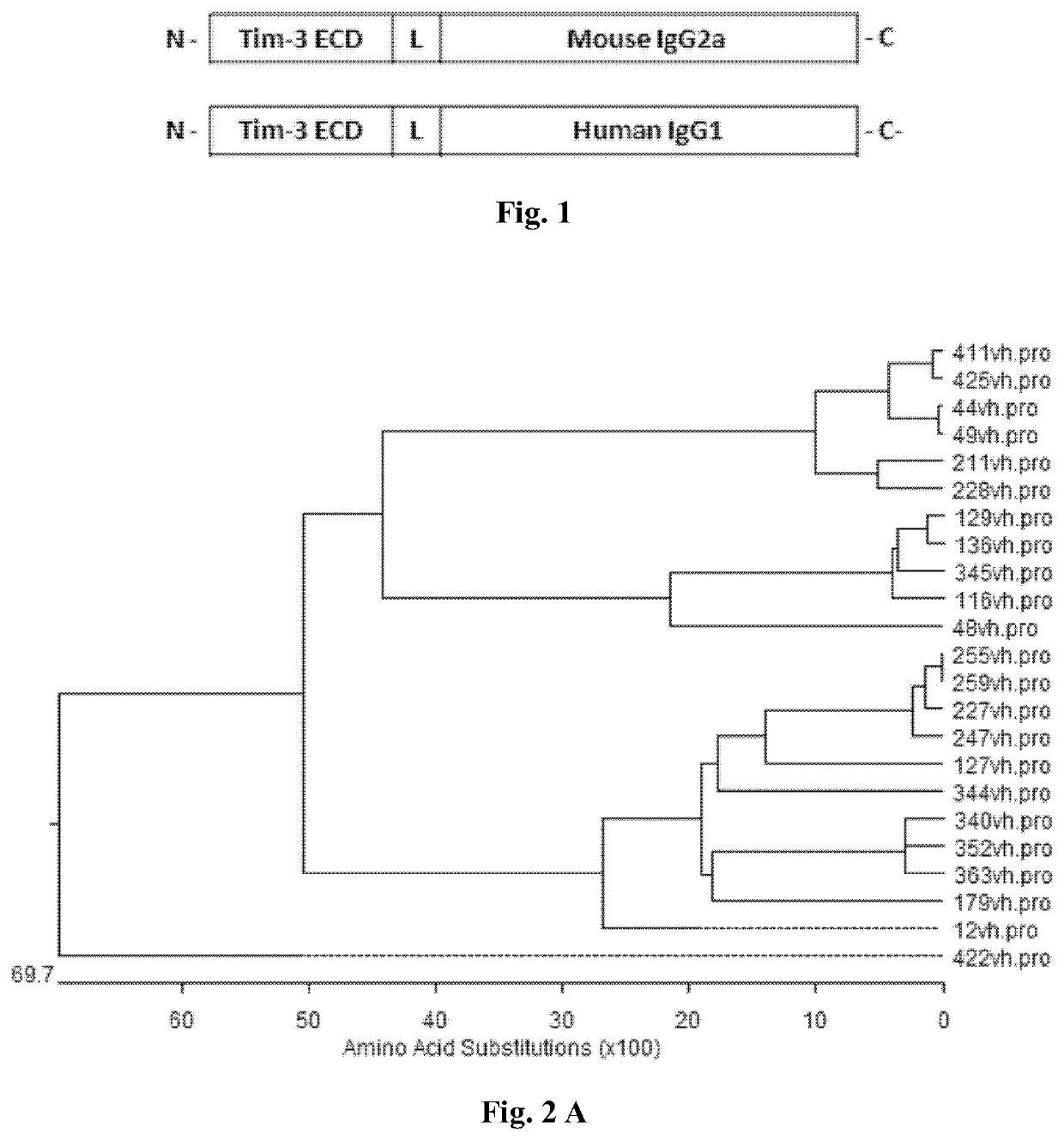
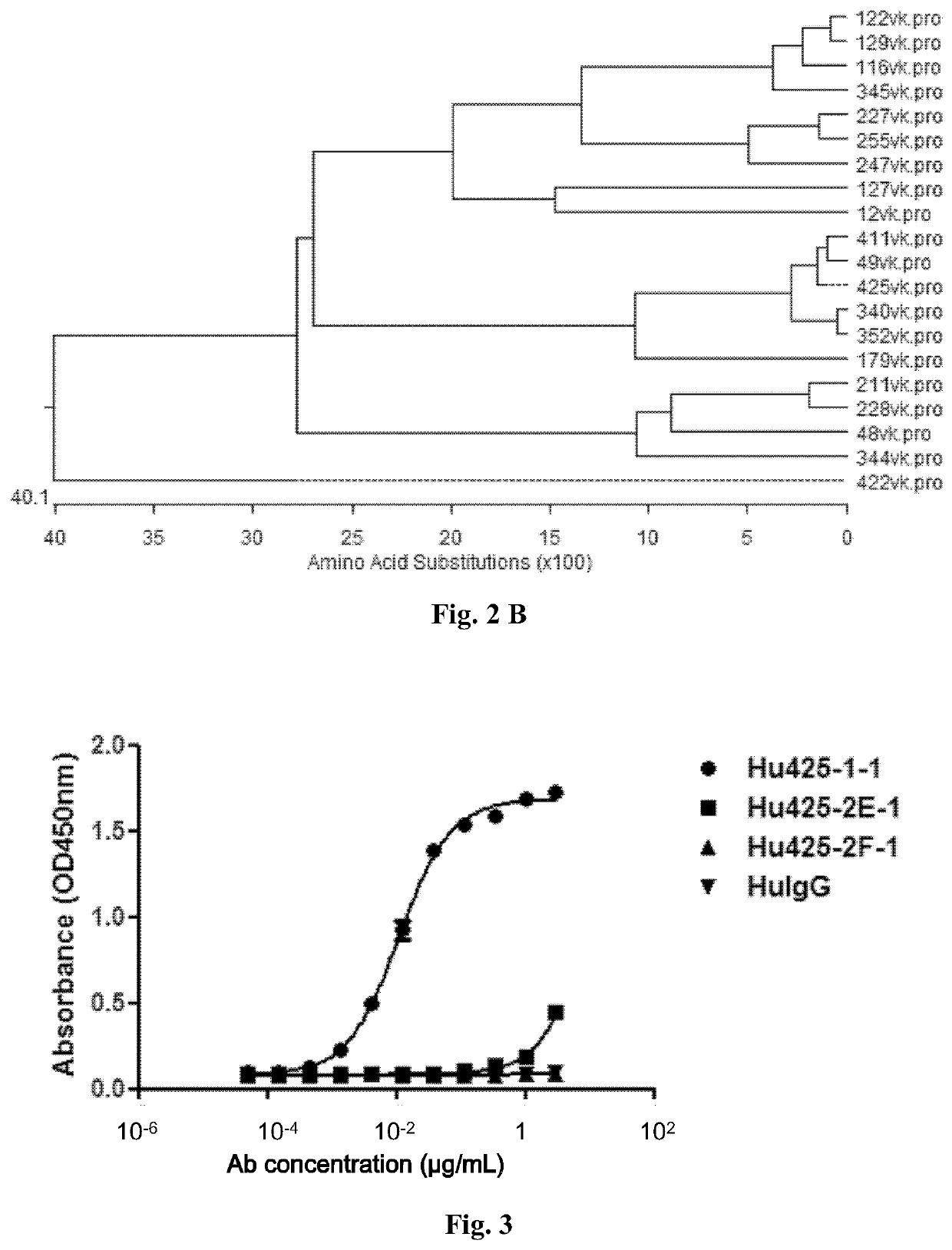
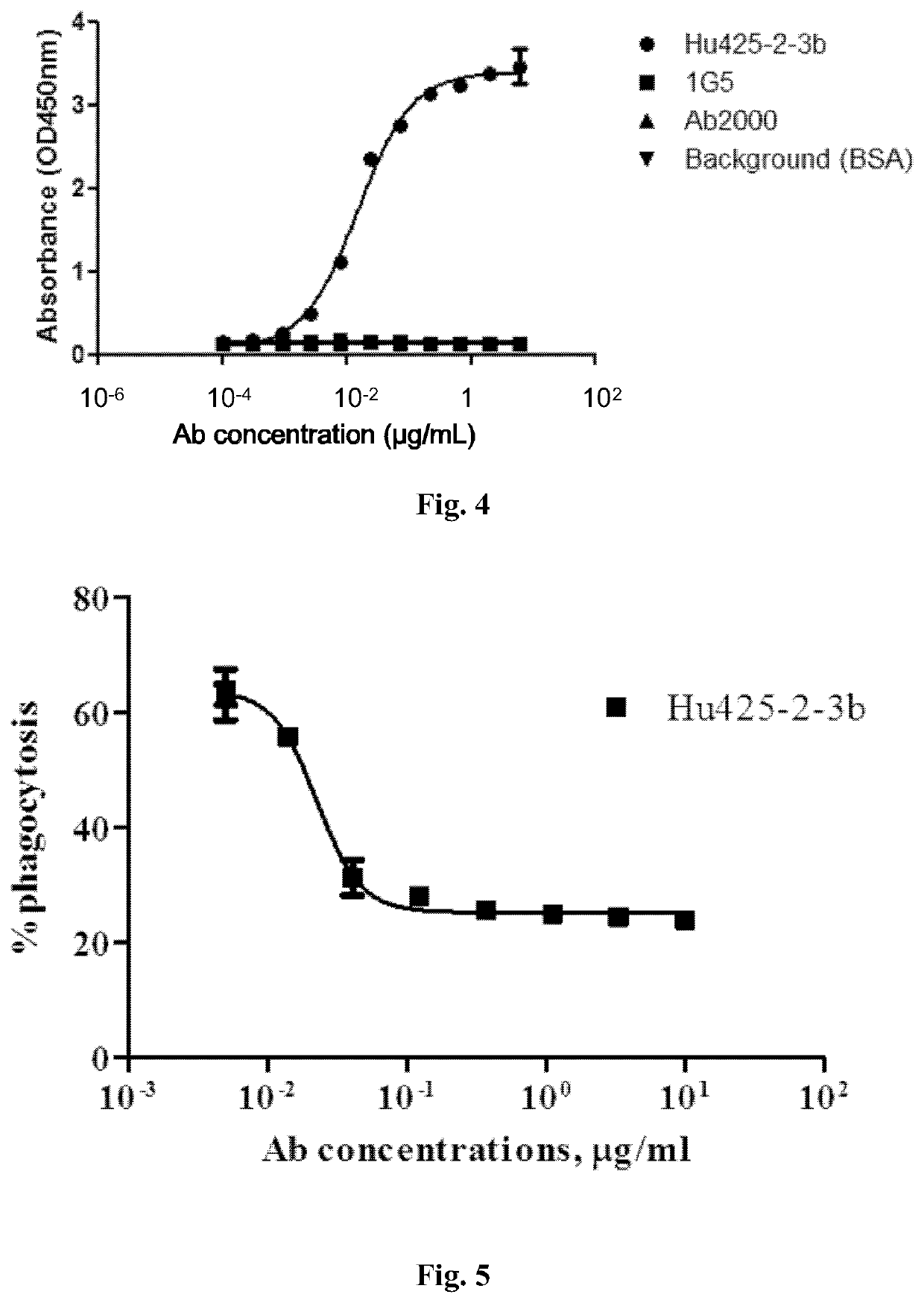
Anti-Tim-3 antibodies and use thereof
ActiveUS11203637B2Inhibit Tim-3-mediated cellular signalingHigh similarityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiviralsAntiendomysial antibodiesInfectious Disorder
Provided are antibodies that specifically bind to T-cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain 3 (Tim-3). The anti-Tim-3 antibodies can be used to treat, prevent or diagnose immune, cancerous, infectious diseases or other pathological disorders that may be modulated by Tim-3-mediated functions.
Owner:BEIGENE SWITZERLAND GMBH
Heterologous intron within an immunoglobulin domain
ActiveUS20140234893A1Driving strong and stable gene expressionHigh expressionAnimal cellsVectorsHeterologousCloned genes
The invention concerns the field of recombinant gene engineering. It concerns novel introns and compositions comprising such introns as well as a method to improve expression of polypeptides from nucleic acids such as cloned genes with heterologous introns, especially genes encoding antibodies and antibody derived fragments, and the production of various polypeptides in eukaryotic host cells using said novel intron sequences as heterologous introns.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Engineering of immunoglobulin domains
ActiveUS20130303406A1Improve stabilityIncreased protease resistancePeptide librariesBacteriaSingle-domain antibodyDisulfide bond
The present invention provides a single domain antibody (sdAb) scaffold comprising one or more than one non-canonical disulfide bond in the framework region (FR). The one or more than one non-canonical disulfide bond may be formed between cysteines introduced by mutations in FR2 and FR3. In the case where the sdAb scaffold is a VH, the Cys may be introduced at any one of positions (47-49) and any one of positions (67-71), based on Kabat numbering; in one example, the Cys may be introduced at positions (49) and (69), based on Kabat numbering. In the case where the sdAb scaffold is a VL, the Cys residues may be introduced at any one of positions 46-49 and any one of positions (62-66), based on Kabat numbering; in one example, the Cys residues may be introduced at positions (48 and 64), based on Kabat numbering.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Synthetic immunoglobulin domains with binding properties engineered in regions of the molecule different from the complementarity determining regions
ActiveUS20120028839A1Peptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeComplementarity determining region
Libraries of immunoglobulins which each have one or more amino acid modifications in at least one structural loop region of such immunoglobulins, where the modified loop region specifically binds to an epitope of an antigen to which an unmodified immunoglobulin does not significantly bind.
Owner:F STAR THERAPEUTICS LTD
Prostate gland specificity antigen diagnosis reagent kit
The invention belongs to the biotechnology field, discloses fusion protein of a prostate specific antigen (PSA) and G-type immunoglobulin domain (IgG Fc), and also discloses a PSA detection kit containing the fusion protein as the standard sample. The invention carries out the fusion expression of the IgG Fc and the PSA, therefore, not only a large amount of fusion protein can be obtained, but also the purification of the fusion protein is very simple, and the bioactivity of the fusion protein is closer to that of the natural PSA. The invention overcomes the technical defects of the difficult recombinant expression and the recombined PSA closer to the natural PSA in the prior art, and greatly reduces the manufacturing cost of the PSA detection kit.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Engineering of immunoglobulin domains
ActiveUS9371371B2Improve stabilityIncrease resistancePeptide librariesBacteriaDisulfide bondingSingle-domain antibody
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Mouse anti-human TIM3 (T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain protein 3) monoclonal antibody and immunohistochemical application thereof
InactiveCN108794630AImprove featuresImprove reliabilityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingDiseaseAntigen
The invention discloses a mouse anti-human TIM3 (T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain protein 3) monoclonal antibody. The mouse anti-human TIM3 monoclonal antibody is stable in performance, high in potency and capable of particularly recognizing expression of TIM3 on surfaces of immune cells and tumor cells. The invention further relates to application of the mouse anti-human TIM3 monoclonal antibody in preparation of an immunohistochemical TIM3 detecting tool. An immunohistochemical method is used to detect the TIM3 for the first time, and scientific references are provided for clinical diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, colon cancer, esophageal cancer and other tumors as well as septicopyemia, systemiclupus erythematosus or related infections and autoimmune diseases. The monoclonal antibody generated from different hybridomas is discovered for the first time can recognize different states of TIM3of a same antigen, by the aid of the discovery, the TIM3 monoclonal antibodies can be screened purposefully, and basic medical research value is realized.
Owner:镇江爱必梦生物科技有限公司
RAGE fusion proteins and methods of use
InactiveCN101410411AMetabolic stabilityInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderHigh affinity bindingChemistry
Disclosed are RAGE fusion proteins comprising RAGE polypeptide sequences linked to a second, non-RAGE polypeptide. The RAGE fusion protein may utilize a RAGE polypeptide domain comprising a RAGE ligand binding site and an interdomain linker directly linked to an immunoglobulin CH2 domain. Such fusion proteins may provide specific, high affinity binding to RAGE ligands. Also disclosed is the use of the RAGE fusion proteins as therapeutics for RAGE-mediated pathologies.
Owner:TRANSTECH PHARMA
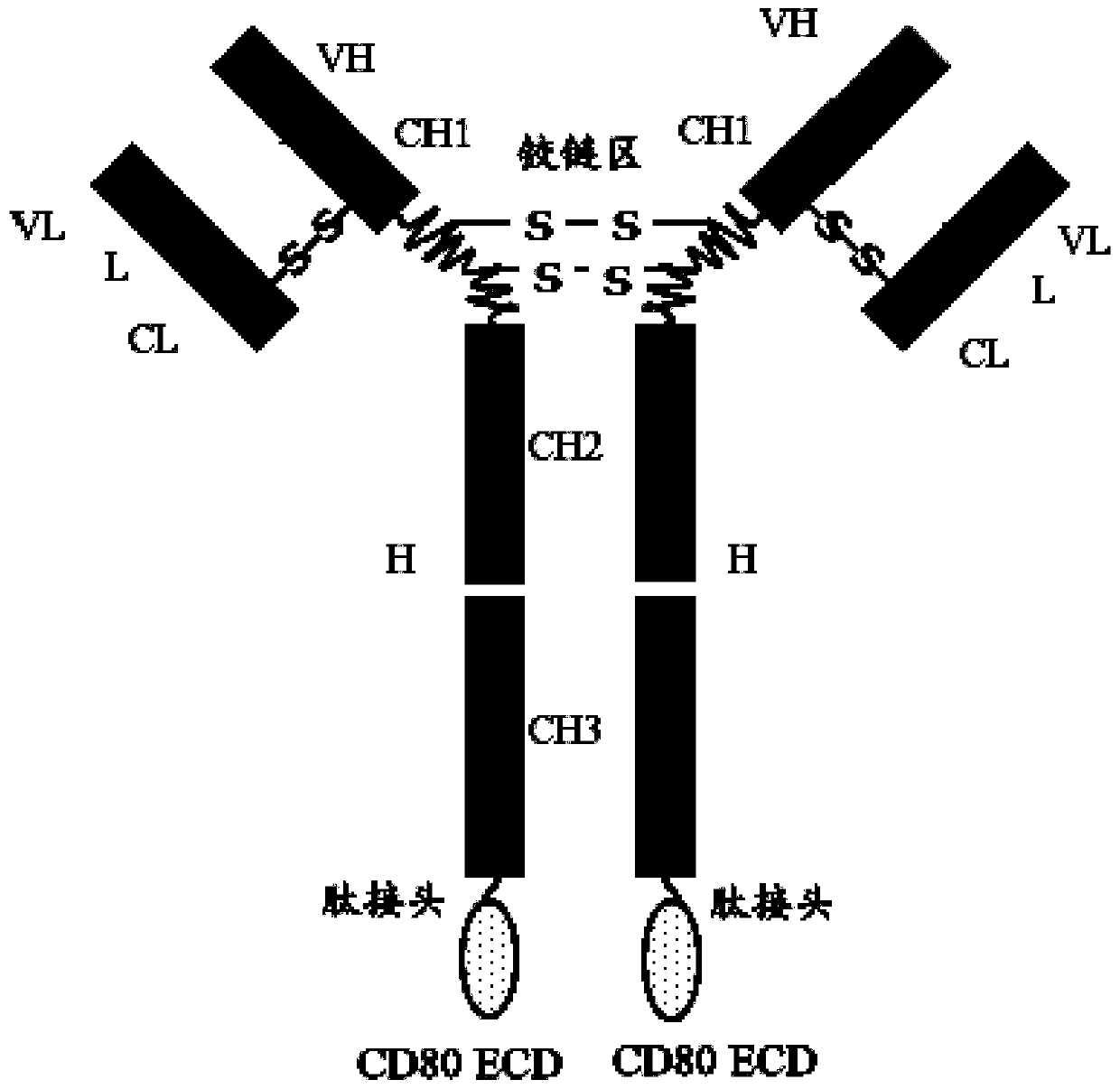
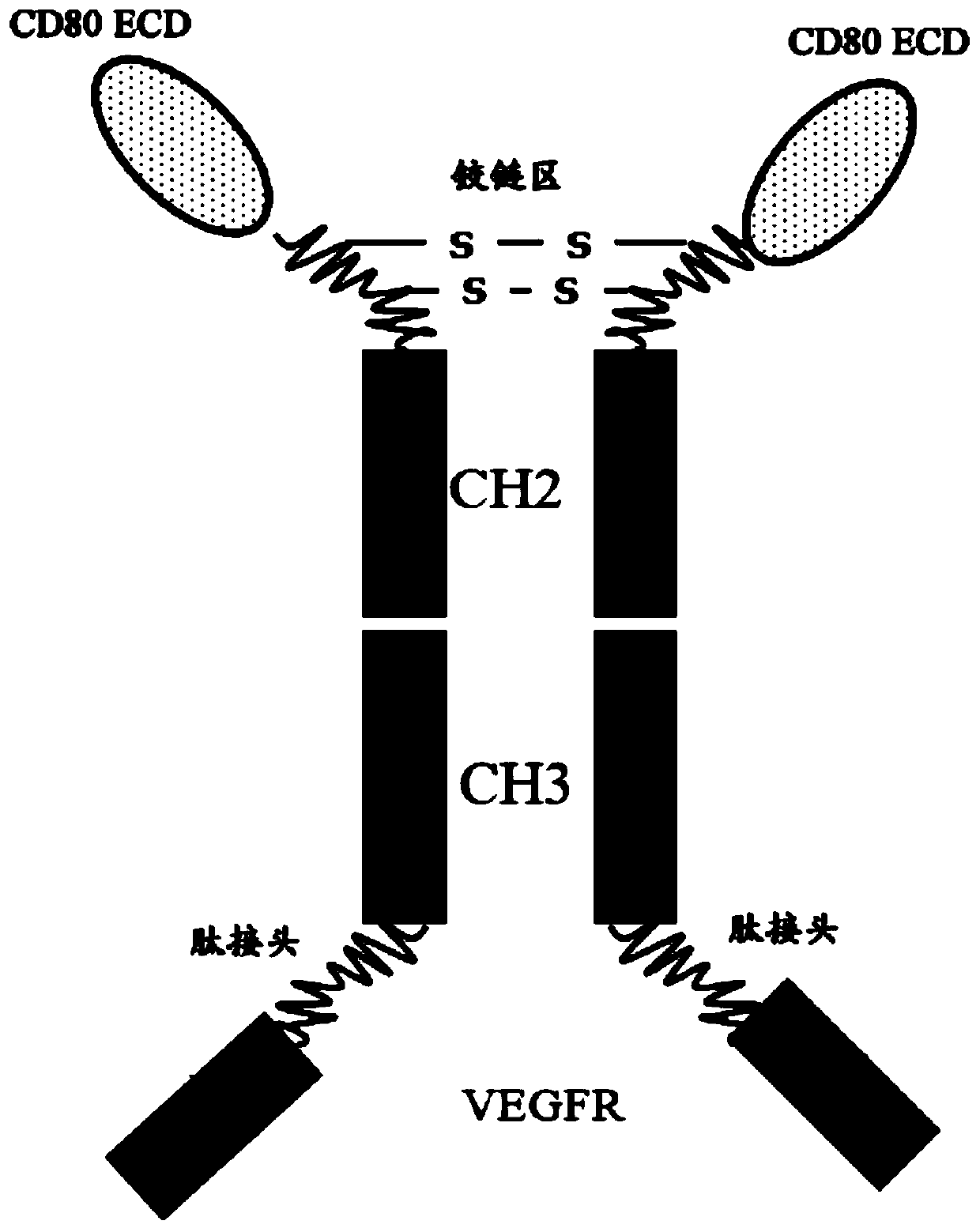
Multi-target fusion protein capable of blocking growth of vascular endothelial cells and activating T cells, and pharmaceutical composition comprising multi-target fusion protein
PendingCN111423512AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsDiseaseVascular endothelium
The present invention provides a multi-target fusion protein capable of blocking growth of vascular endothelial cells and activating T cells. The multi-targeted fusion protein comprises (i) a vascularendothelial growth inhibition structural domain; (ii) an immunoglobulin Fc structural domain; and (iii) a CD80 extracellular domain (ECD). The invention also provides a polynucleotide encoding the multi-target fusion protein, a vector comprising the polynucleotide, a host cell comprising the polynucleotide or vector, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the multi-target fusion protein andan anti-PD-1 antibody. The multi-target fusion protein and pharmaceutical composition provided by the invention can treat or prevent cancerous diseases in an individual.
Owner:BEIJING BIYANG BIOTECH
Methods for purifying protein
InactiveUS20070010661A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsA domainAntibody Affinity Chromatography
A method is provided for separating a protein from one or more other proteins using hydroxyapatite chromatography in which the protein does not bind to hydroxyapatite but the other protein(s) does. In some embodiments, a second protein affixed to a solid support has been used previously to purify the protein by affinity chromatography, and small amounts of the second protein are introduced in the sample during this process. The protein being purified can comprise at least one constant antibody immunoglobulin domain. The second protein can bind to proteins comprising such a domain.
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
Single chain fc polypeptides
The present invention relates to single chain polypeptides comprising one or more immunoglobulin Fc domains. In particular the present invention relates to single-chain Fc polypeptides in which at least one functional Fc domain is formed within the polypeptide chain.
Owner:UCB SA
A selective high-affinity immune stimulatory reagent and uses thereof
InactiveUS20150368316A1Immunoglobulin superfamilySugar derivativesActivation cellsProgrammed cell death 1
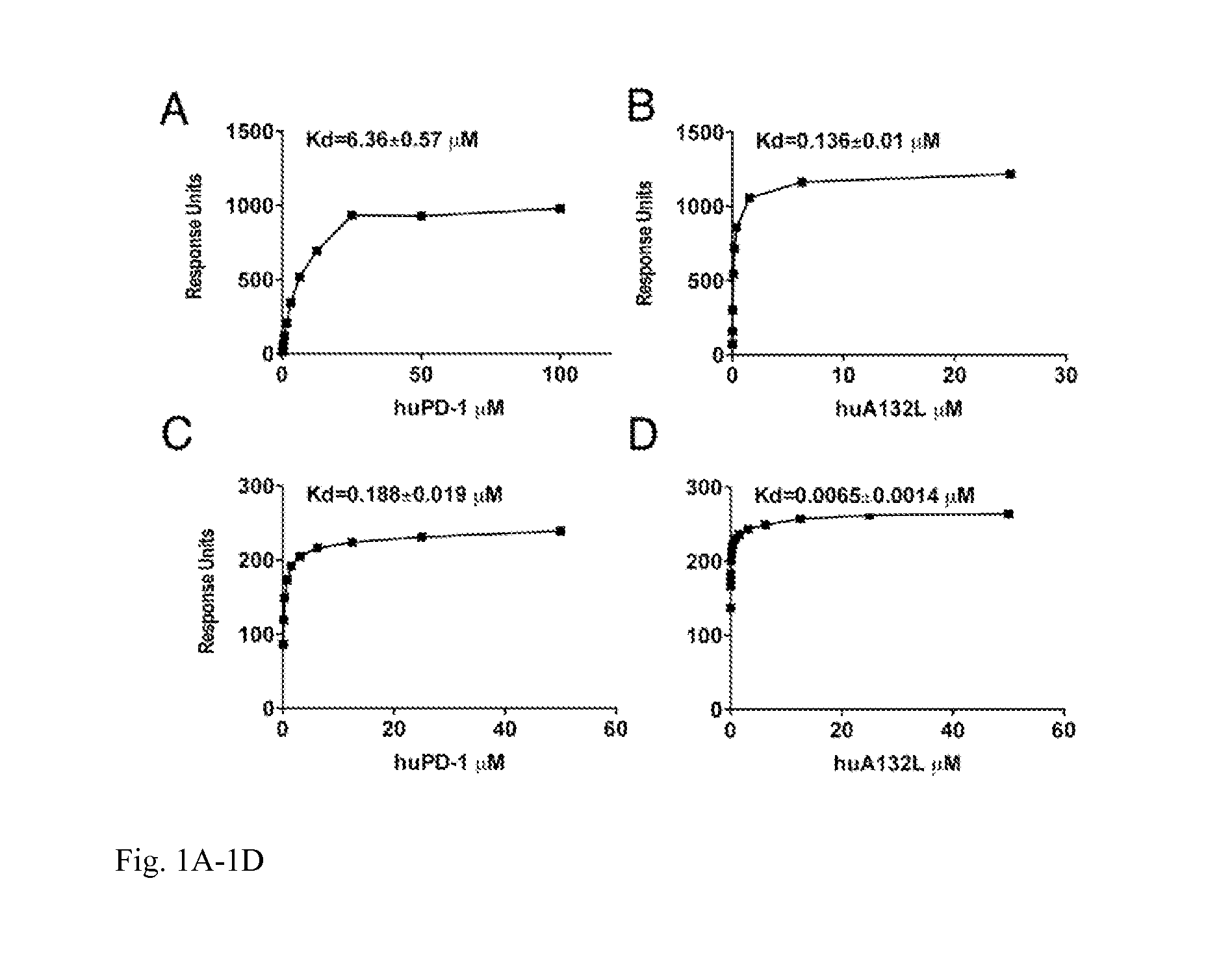
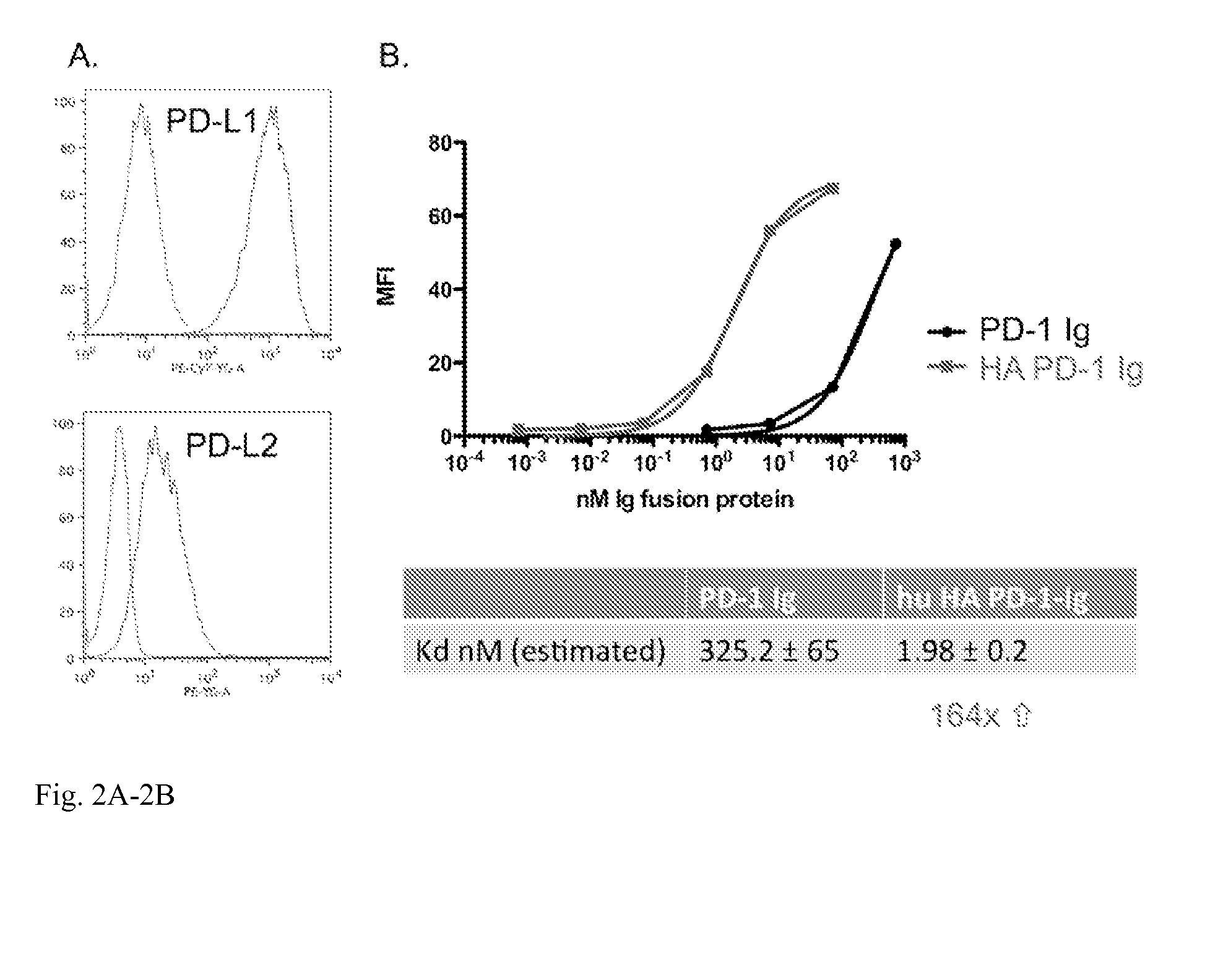
Isolated polypeptides comprising a mutant programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) polypeptide and fusion polypeptides comprising an isolated mutant PD-1 polypeptide fused to an immunoglobulin domain polypeptide are provided. Further provided are methods of using a composition comprising the fusion polypeptide for stimulating T cell activation for treating disorders including a tumor or an infection.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com