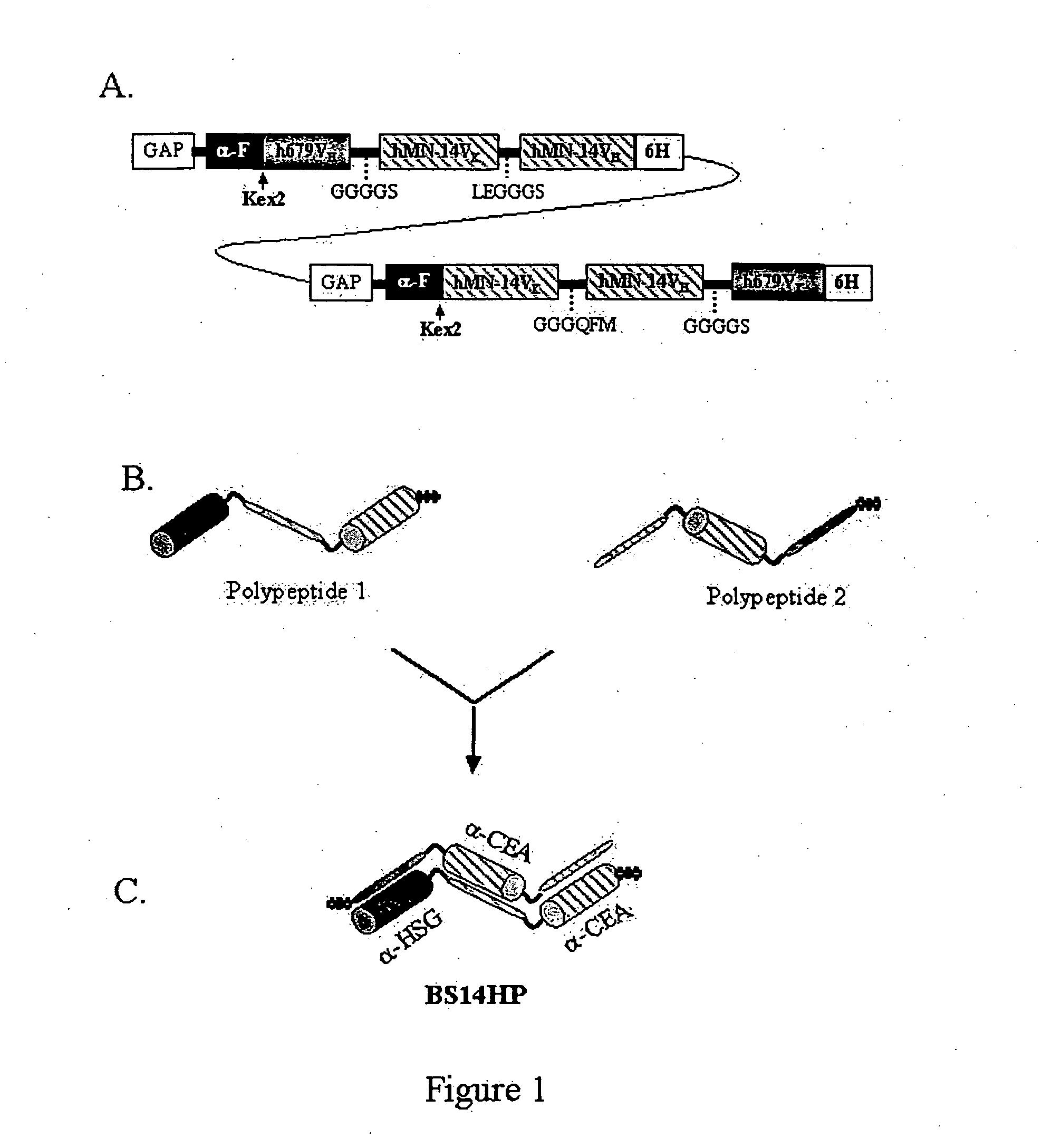
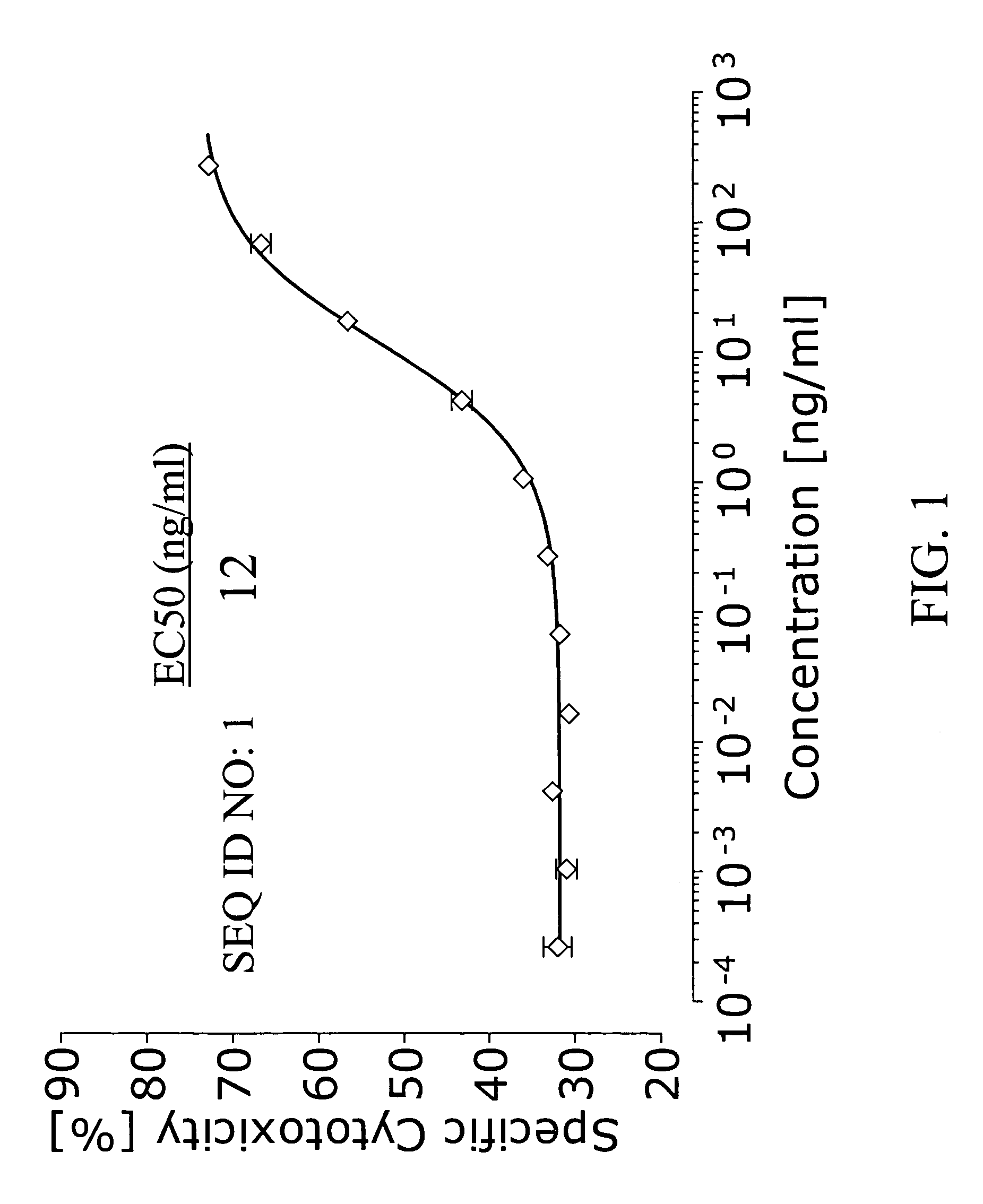
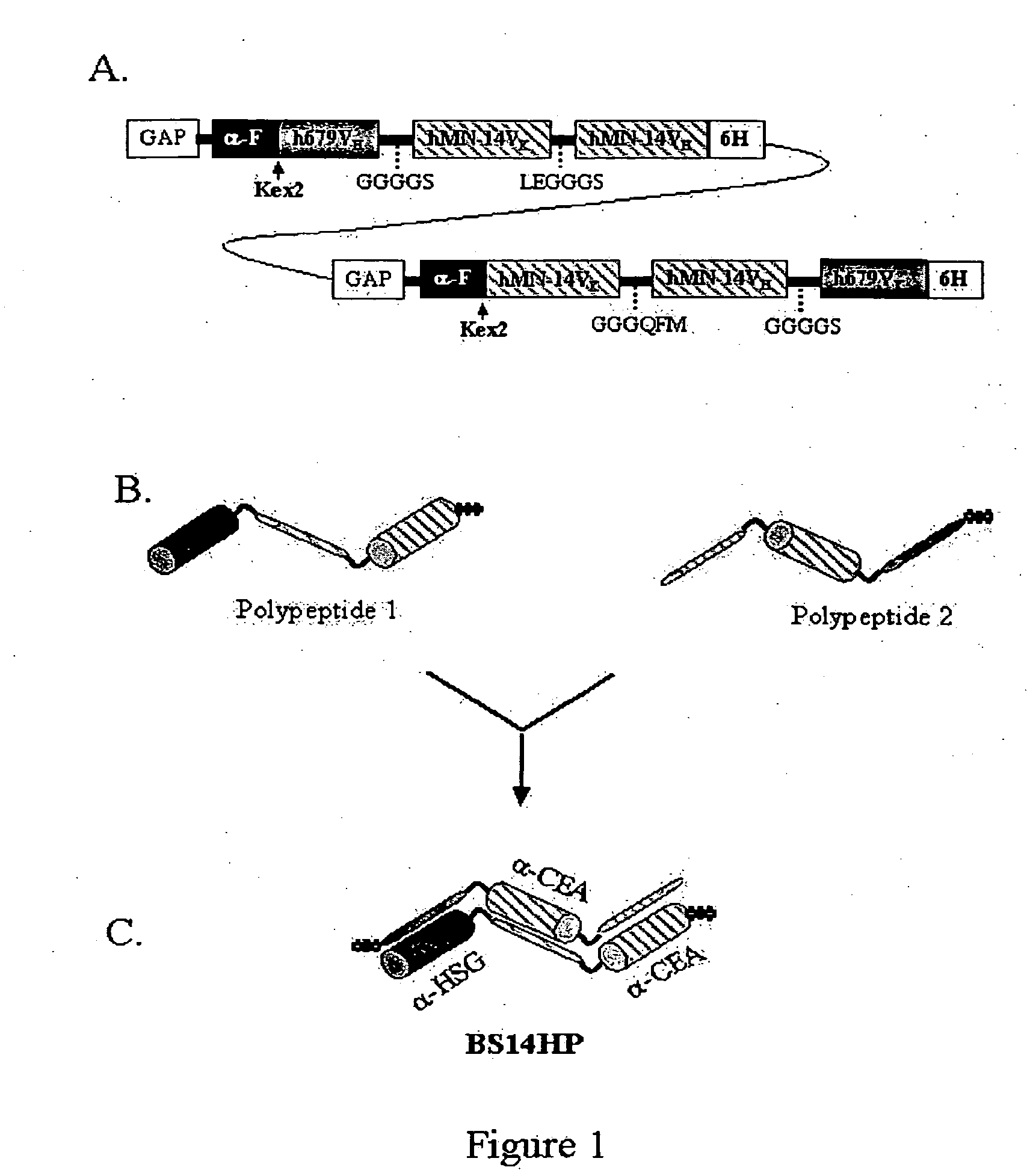
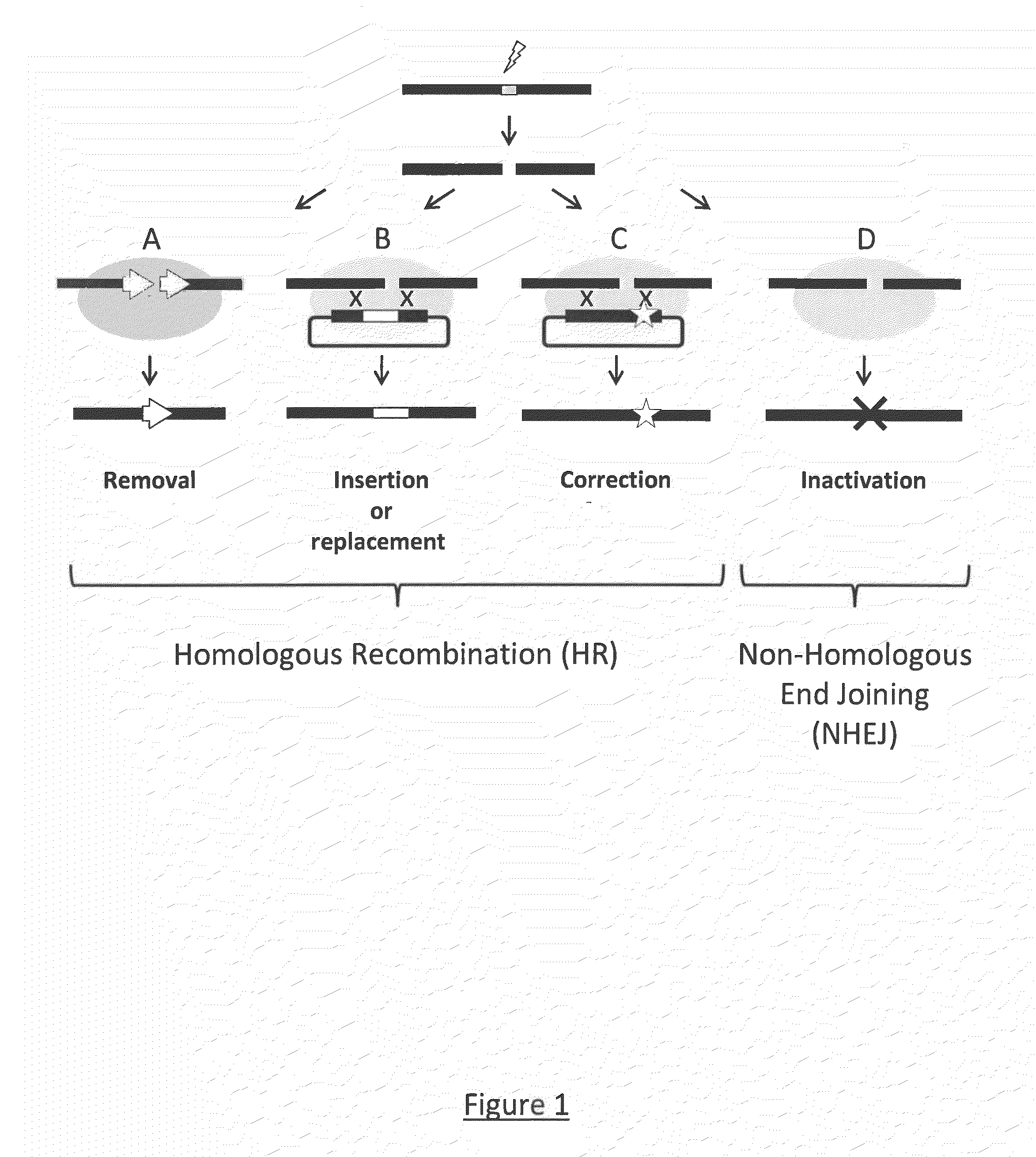
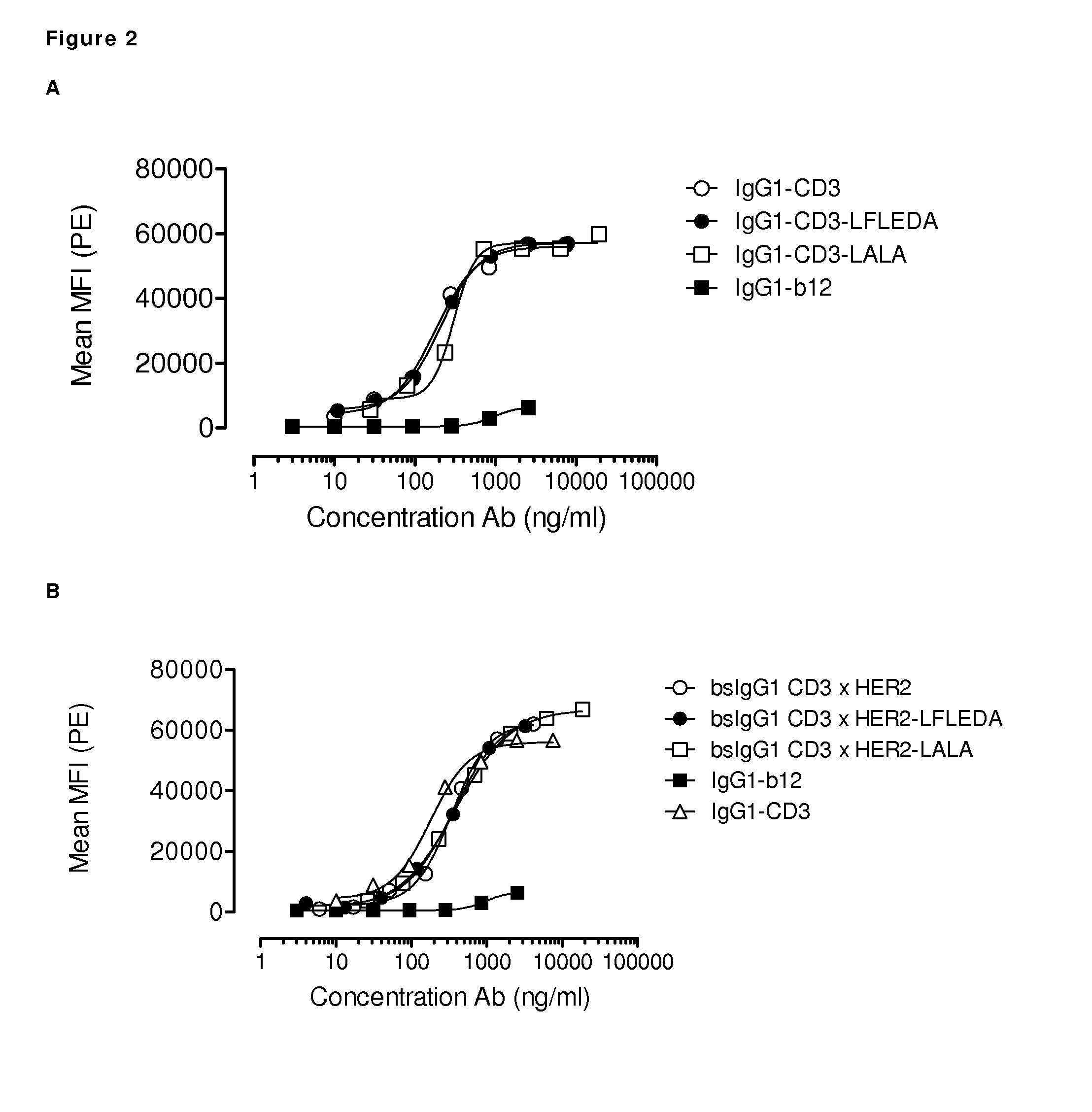
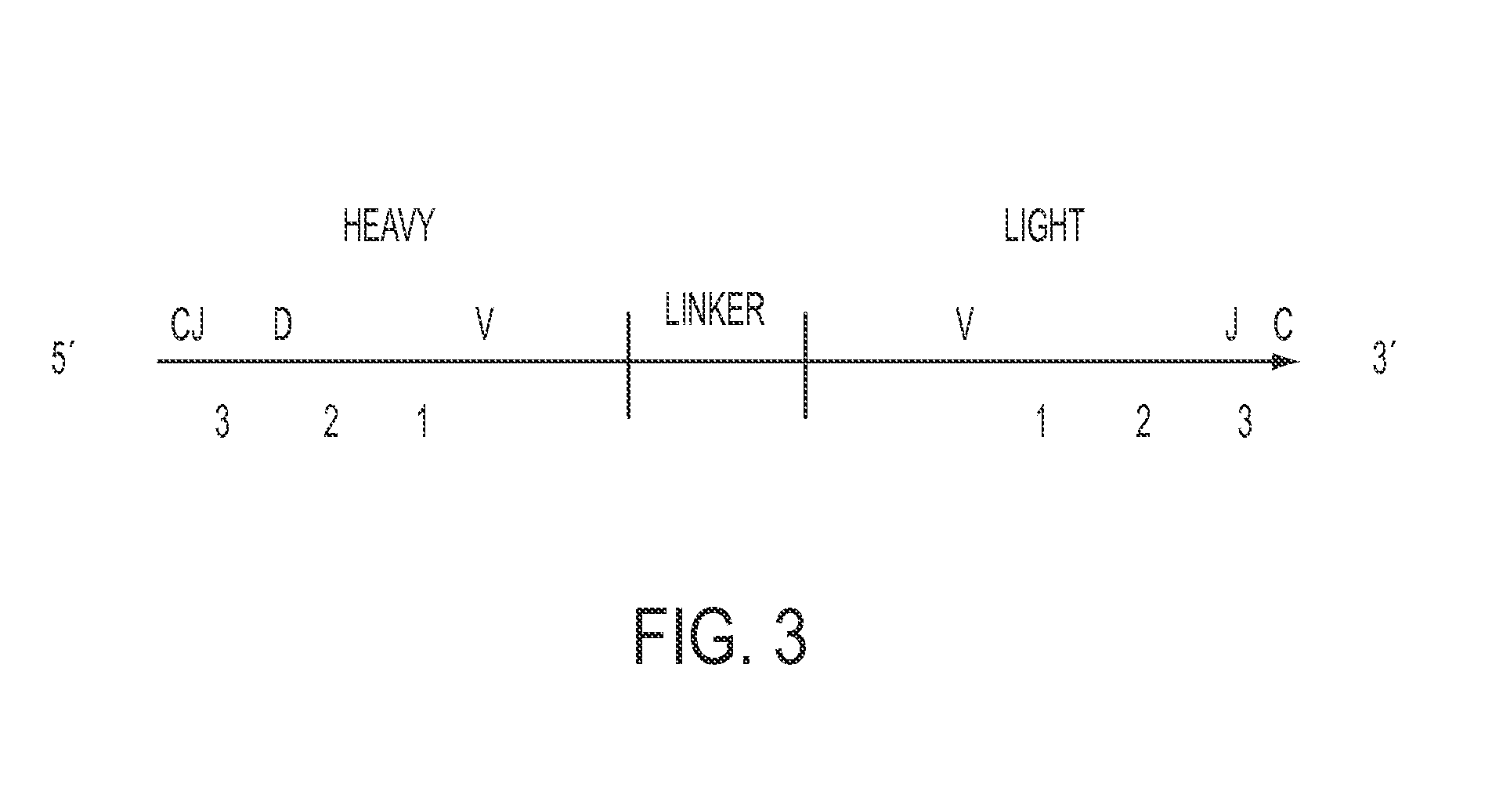
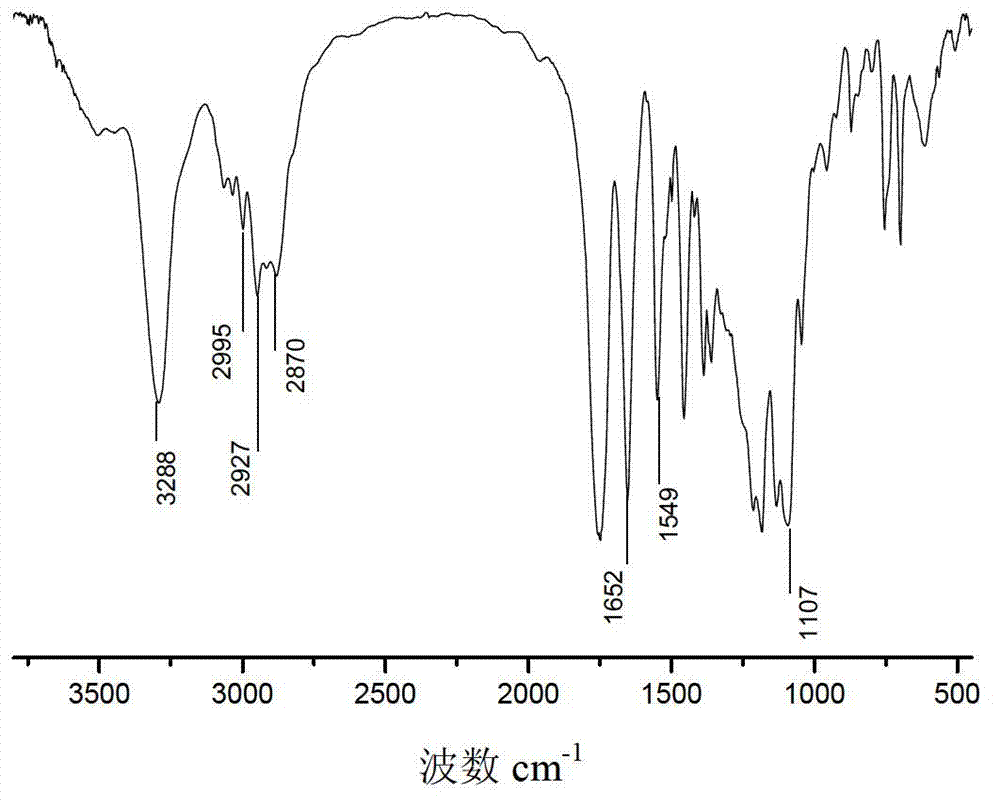
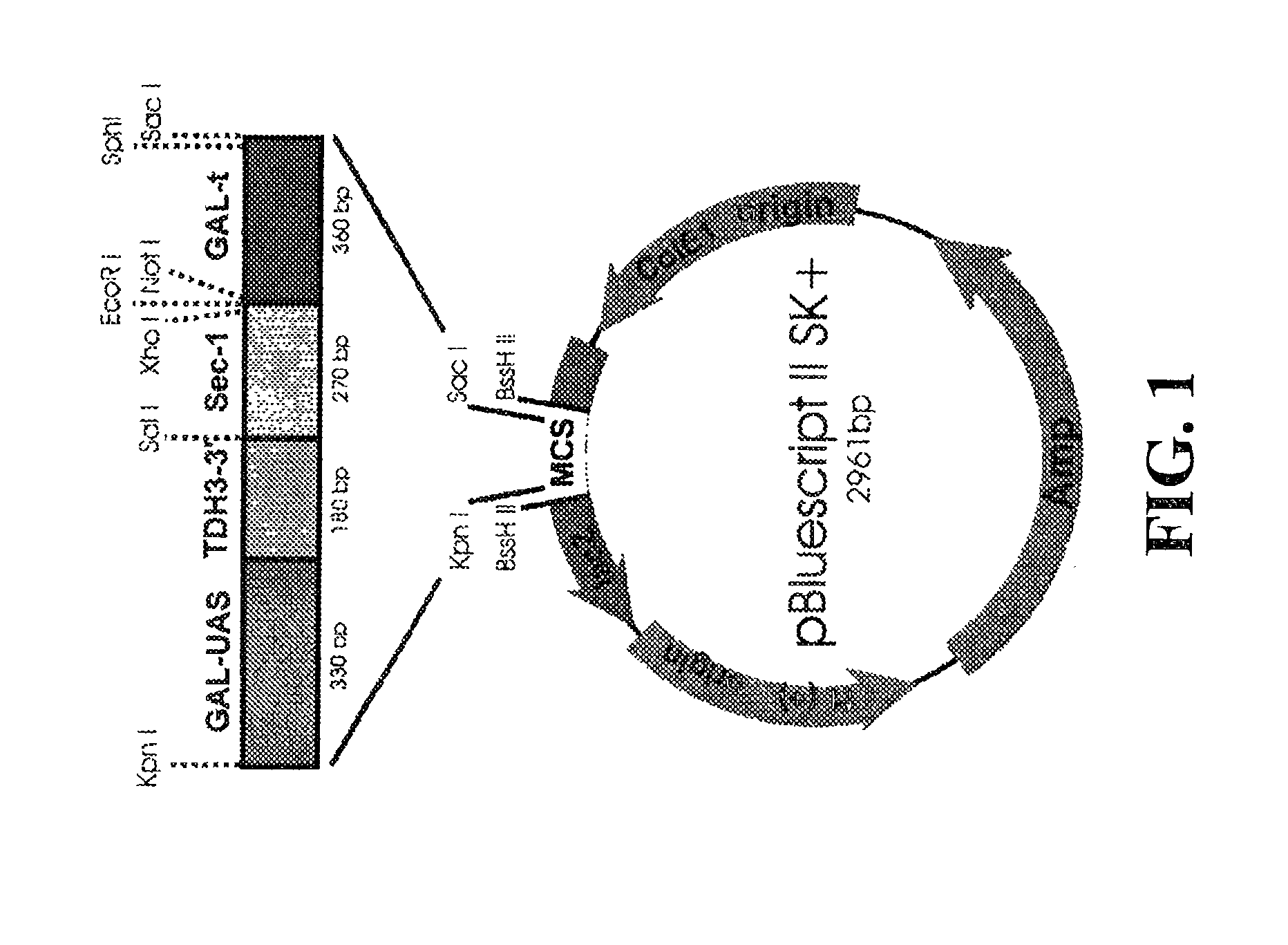
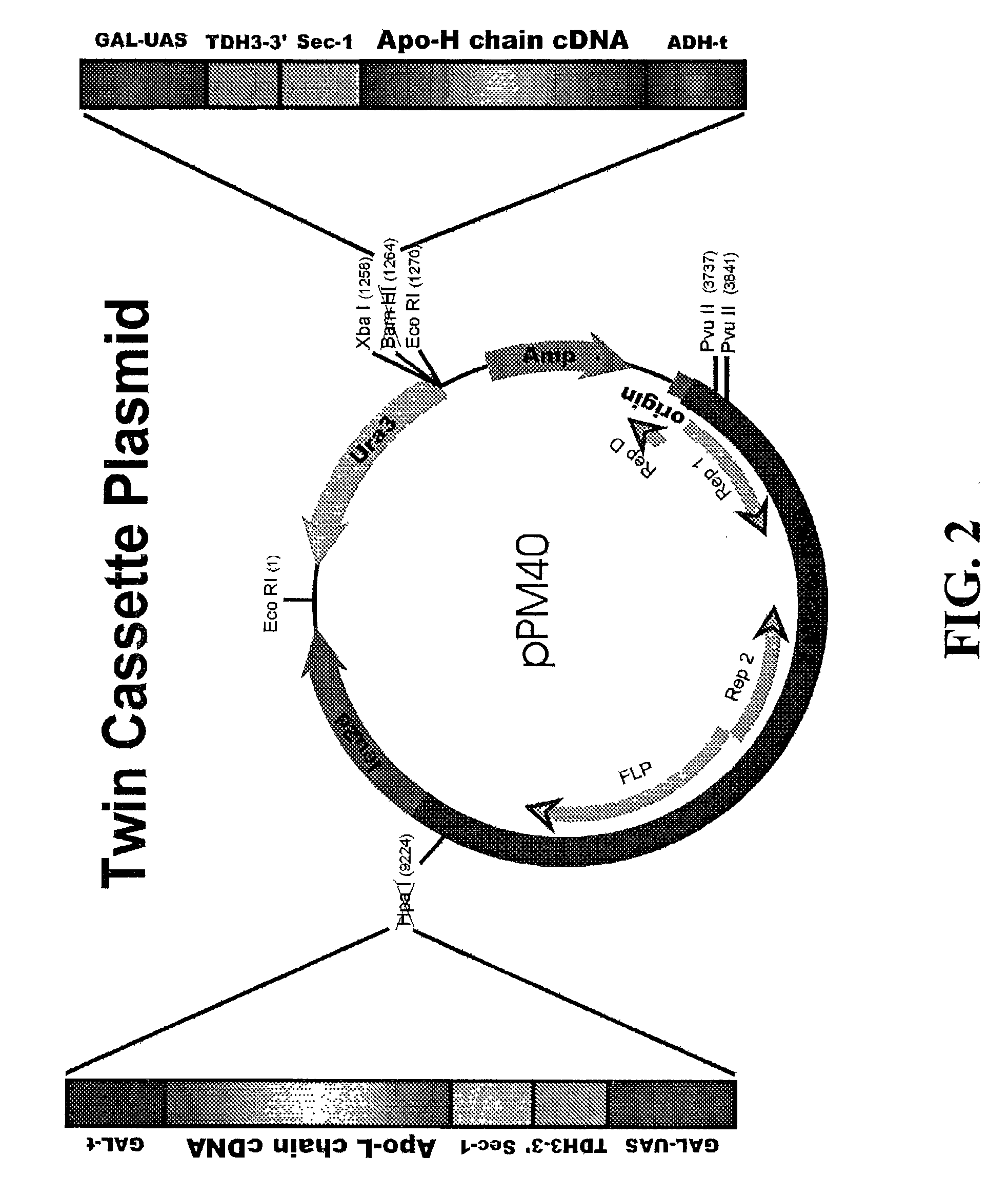
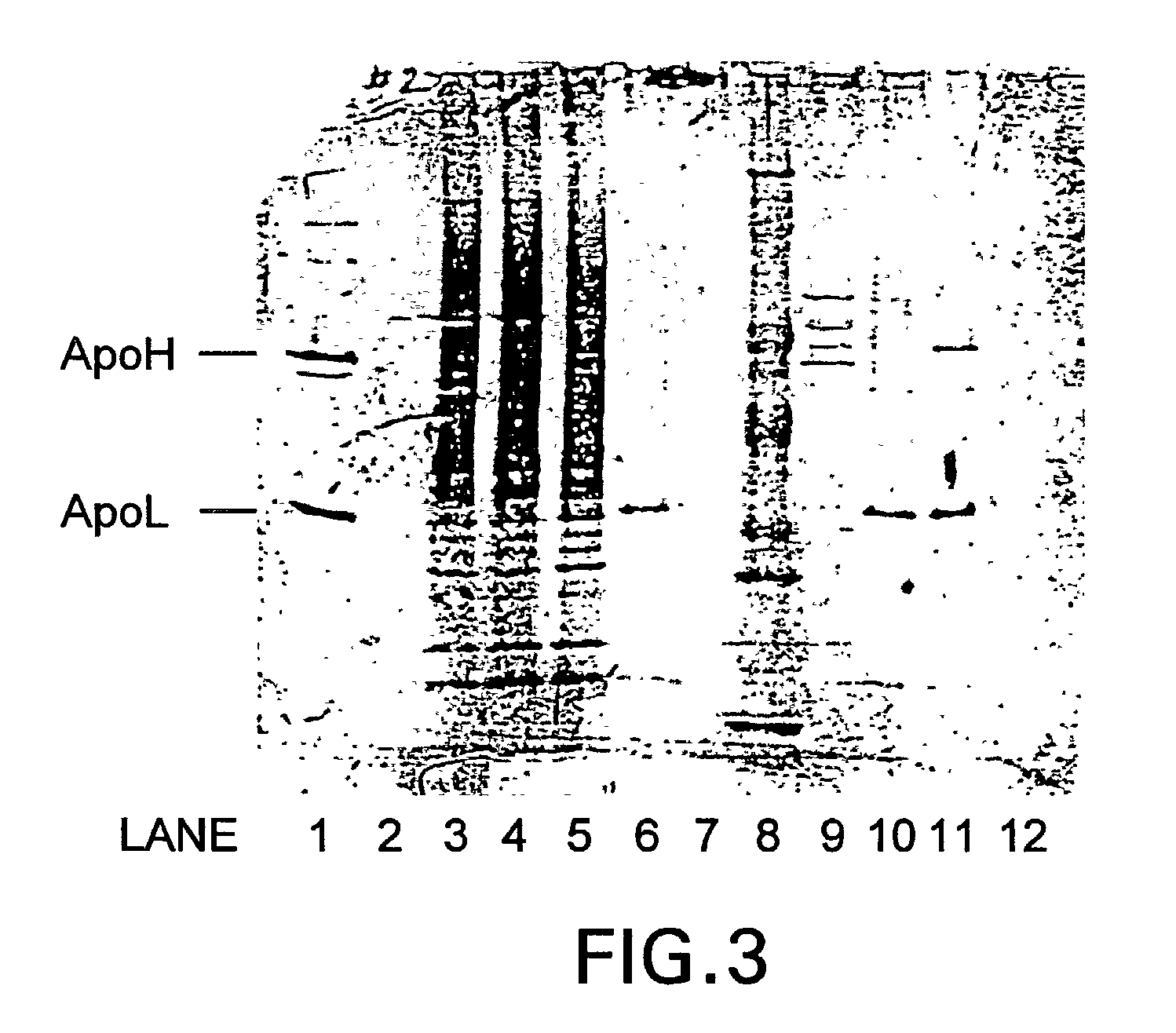
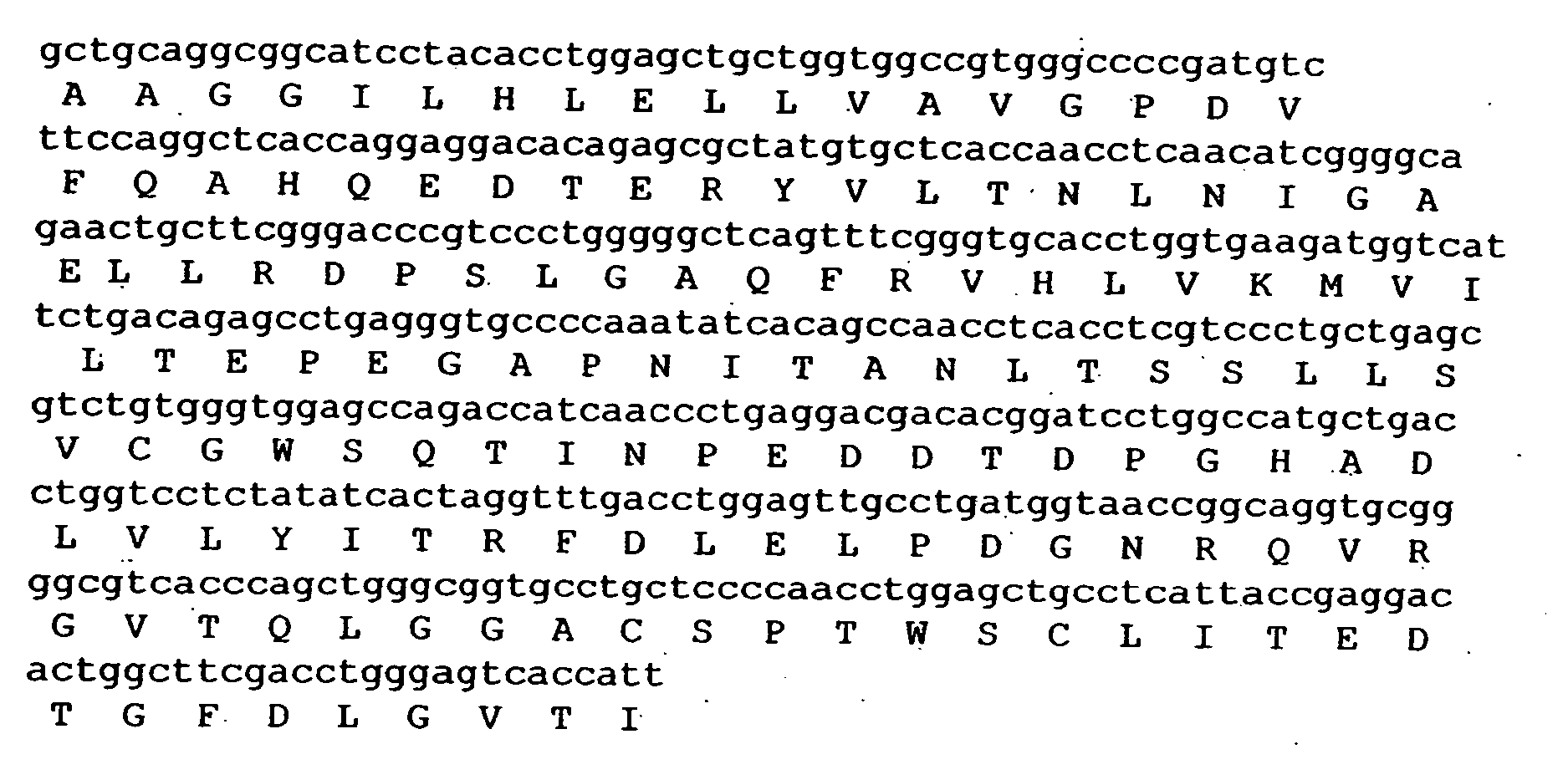Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
431 results about "Polypeptide chain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Each polypeptide chain consists of smaller sub-units or amino acids that are linked together. Amino acids serve as the building blocks of polypeptides, and polypeptides serve as the building blocks of proteins.
Polyvalent protein complex
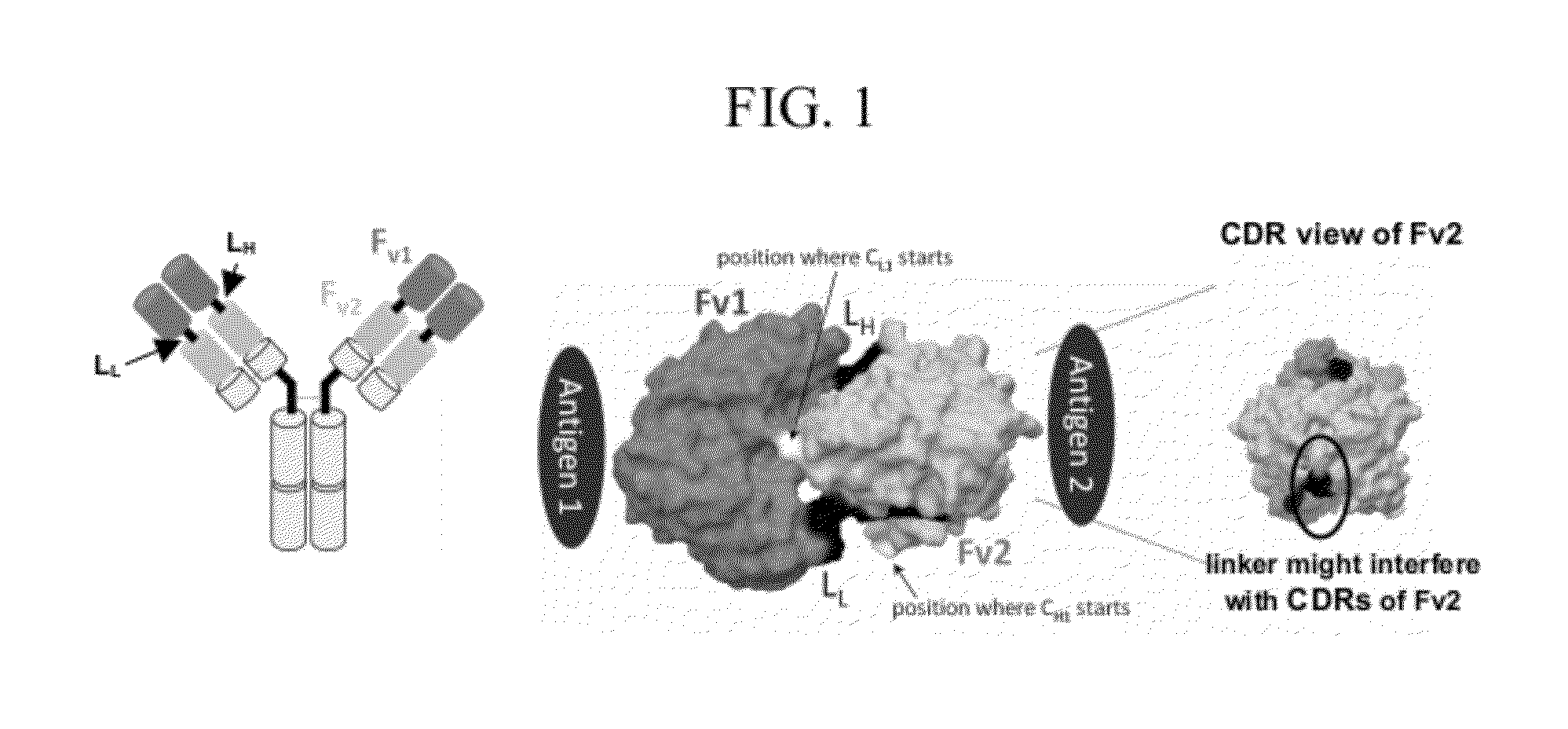
The invention provides for a polyvalent protein complex (PPC) comprising two polypeptide chains generally arranged laterally to one another. Each polypeptide chain typically comprises 3 or 4 “v-regions”, which comprise amino acid sequences capable of forming an antigen binding site when matched with a corresponding v-region on the opposite polypeptide chain. Up to about 6 “v-regions” can be used on each polypeptide chain. The v-regions of each polypeptide chain are connected linearly to one another and may be connected by interspersed linking regions. When arranged in the form of the PPC, the v-regions on each polypeptide chain form individual antigen binding sites.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS7235641B2Improve productivityImprove efficiencyAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBispecific antibodyImmune effector cell
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
Polyvalent protein complex
The invention provides for a polyvalent protein complex (PPC) comprising two polypeptide chains generally arranged laterally to one another. Each polypeptide chain typically comprises 3 or 4 “v-regions”, which comprise amino acid sequences capable of forming an antigen binding site when matched with a corresponding v-region on the opposite polypeptide chain. Up to about 6 “v-regions” can be used on each polypeptide chain. The v-regions of each polypeptide chain are connected linearly to one another and may be connected by interspersed linking regions. When arranged in the form of the PPC, the v-regions on each polypeptide chain form individual antigen binding sites.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Method for the generation of compact tale-nucleases and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130117869A1Simple processSimple and efficient vectorizationFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesDNA-binding domainNuclease
The present invention relates to a method for the generation of compact Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALENs) that can efficiently target and process double-stranded DNA. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for the creation of TALENs that consist of a single TALE DNA binding domain fused to at least one catalytic domain such that the active entity is composed of a single polypeptide chain for simple and efficient vectorization and does not require dimerization to target a specific single double-stranded DNA target sequence of interest and process DNA nearby said DNA target sequence. The present invention also relates to compact TALENs, vectors, compositions and kits used to implement the method.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Dual Variable Region Antibody-Like Binding Proteins Having Cross-Over Binding Region Orientation
The invention provides antibody-like binding proteins comprising four polypeptide chains that form four antigen binding sites, wherein each pair of polypeptides forming an antibody-like binding protein possesses dual variable domains having a cross-over orientation. The invention also provides methods for making such antigen-like binding proteins.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Expression of heterologous multi-domain proteins in yeast
InactiveUS6358733B1Increase productionCost effective productionSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsYeastSingle-Chain Antibodies
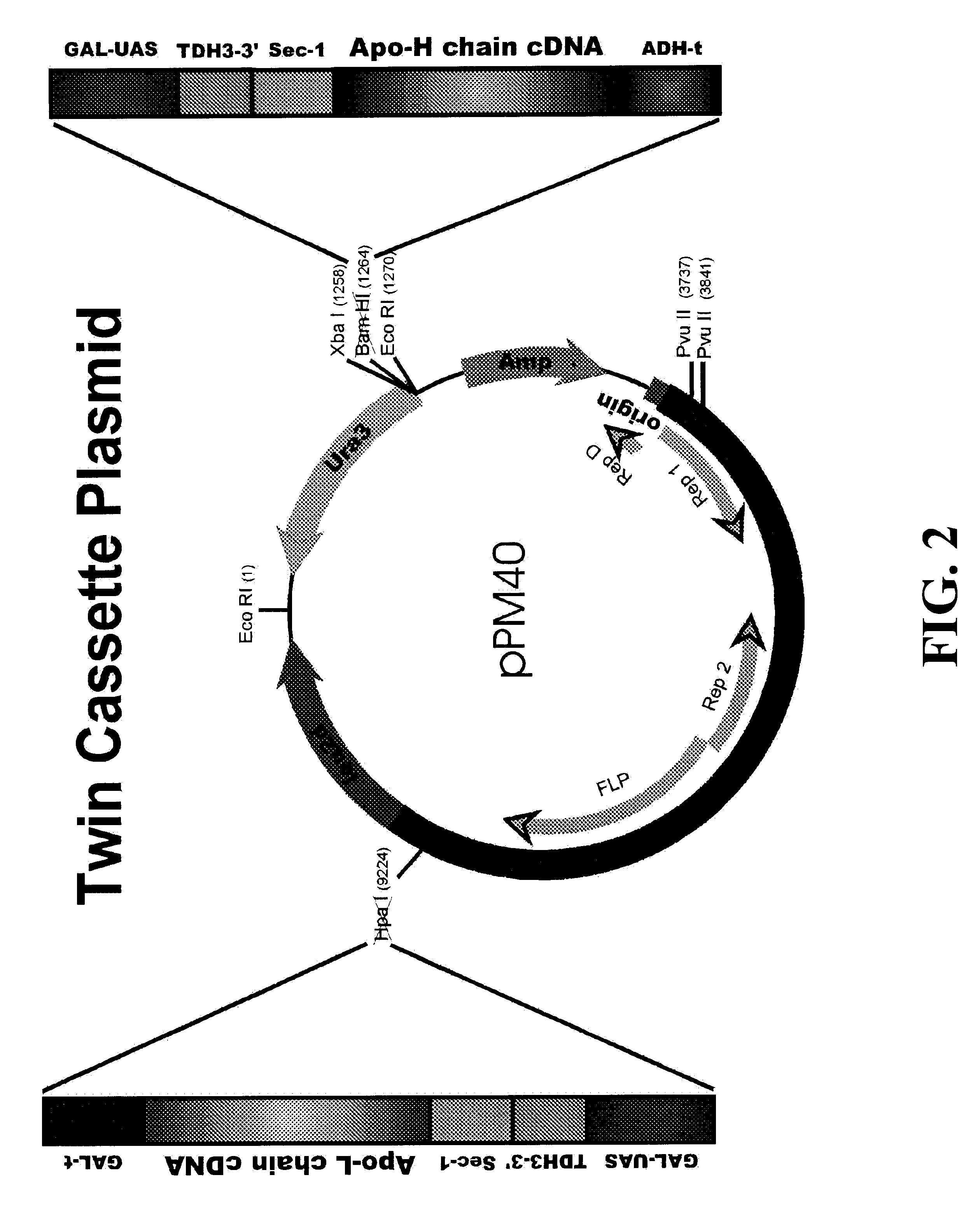
This invention demonstrates the utility of a yeast expression system for the expression of functional heterologous multi-domain proteins in yeast. The yeast expression system allows for the inclusion of a plurality of (up to three) modular expression cassettes which may encode multiple polypeptide chains of a heterologous multi-domain protein on a single plasmid (Twin Cassette). Because multiple polypeptide chains may be encoded for by the expression cassettes of the present invention in a single vector, the system can produce equivalent amounts of the multiple polypeptide chains, thereby enhancing the yield of a functional heterologous multi-domain protein. For example, functional monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) comprising a heavy chain and a light chain of an immunoglobulin (IgG), and functional immunotoxins comprising an antibody domain and an oxidase toxin may be produced using the Yeast expression system of the present invention. In addition, functional single chain antibodies, antibody fragments and chimeric antibodies may also be produced.
Owner:APOLIFE
Bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS20050136050A1Less complexReduce in quantityAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBispecific antibodyImmune effector cell
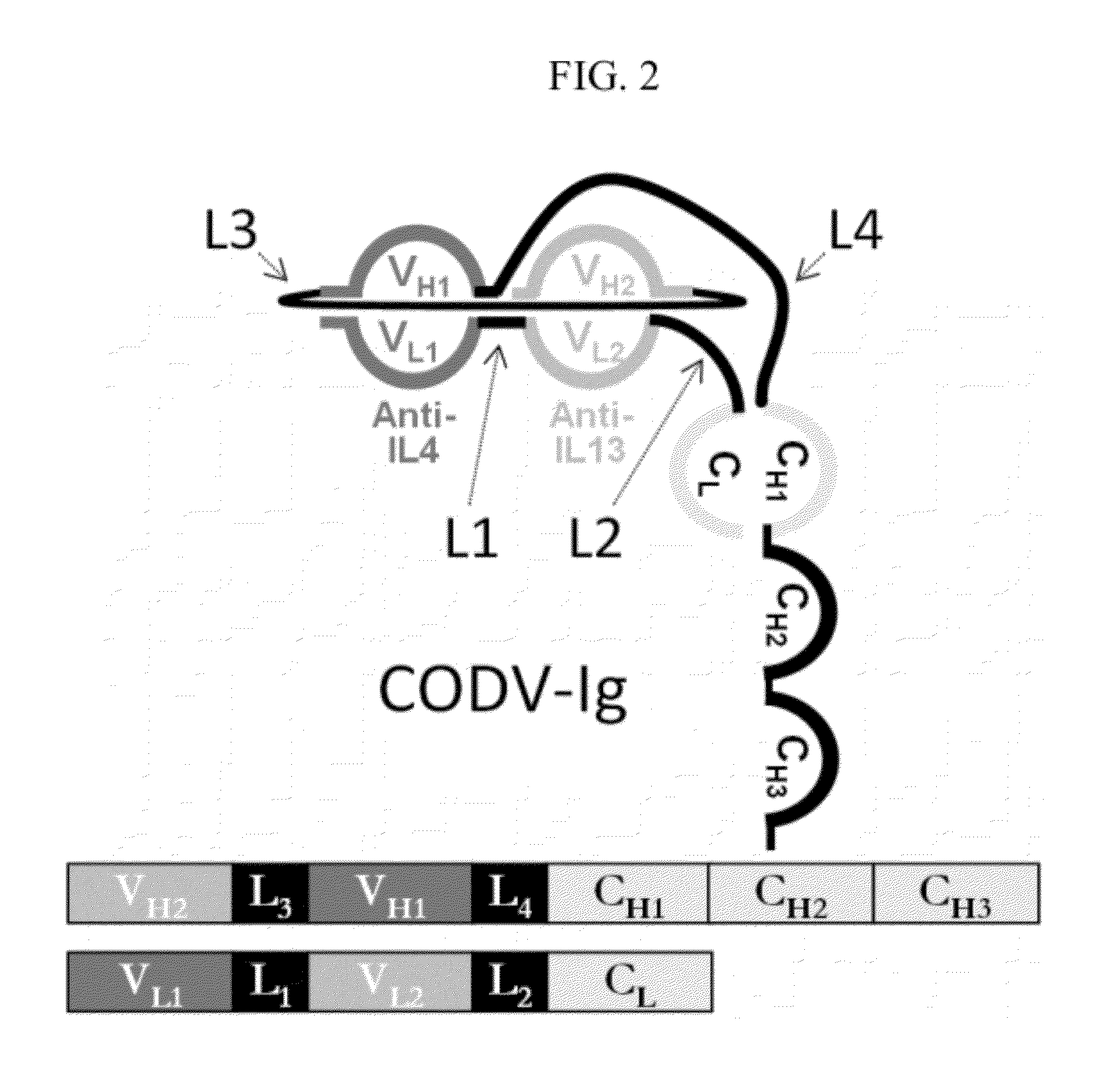
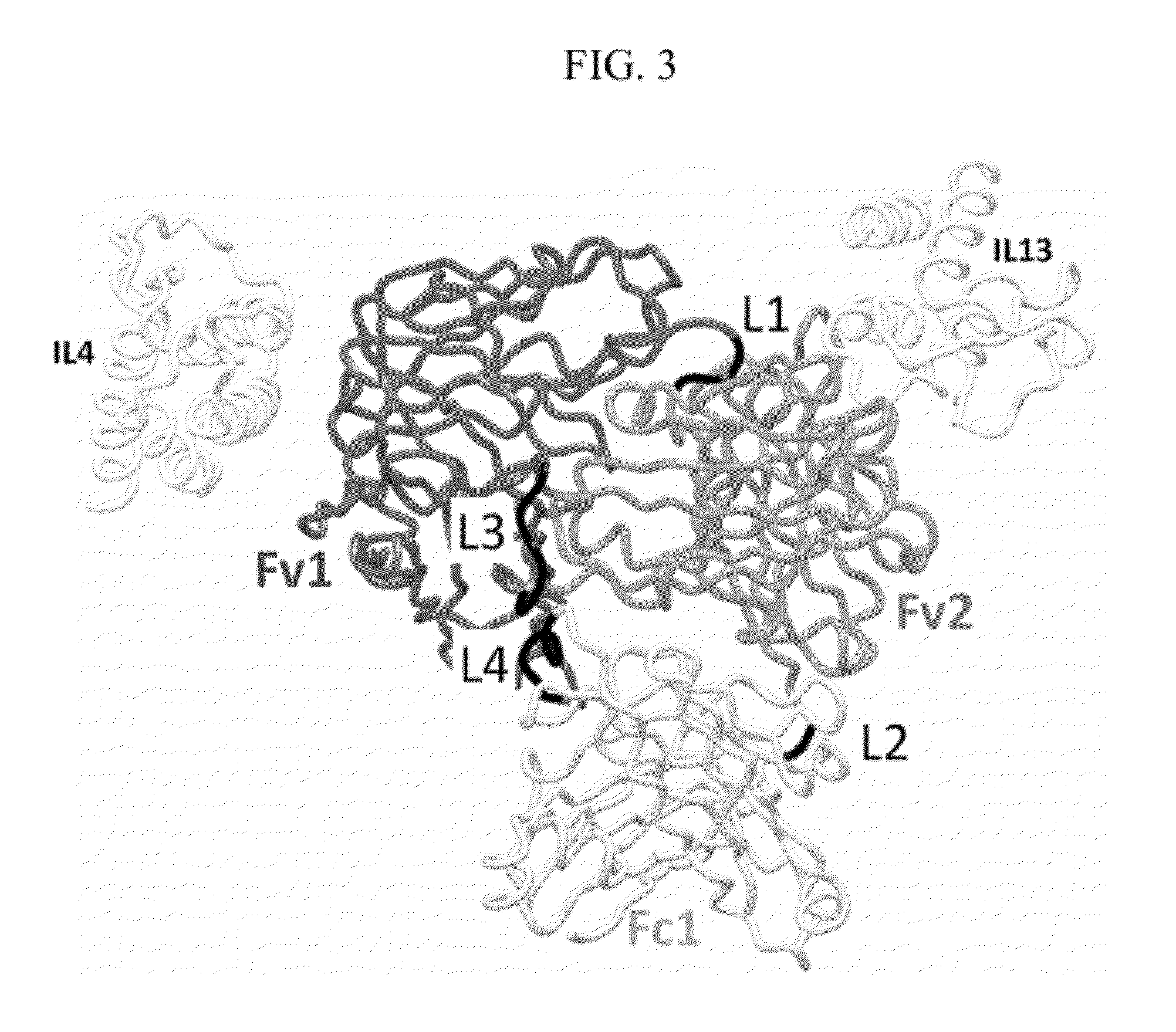
The present invention discloses bispecific antibodies comprising two antibody variable domains on a single polypeptide chain, wherein a first portion of the bispecific antibody is capable of recruiting the activity of a human immune effector cell by specifically binding to an effector antigen on the human immune effector cell, the first portion consisting of one antibody variable domain, and a second portion of the bispecific antibody specifically binding to a target antigen other than the effector antigen, the target antigen on a target cell other than the human immune effector cell, the second portion comprising one antibody variable domain.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
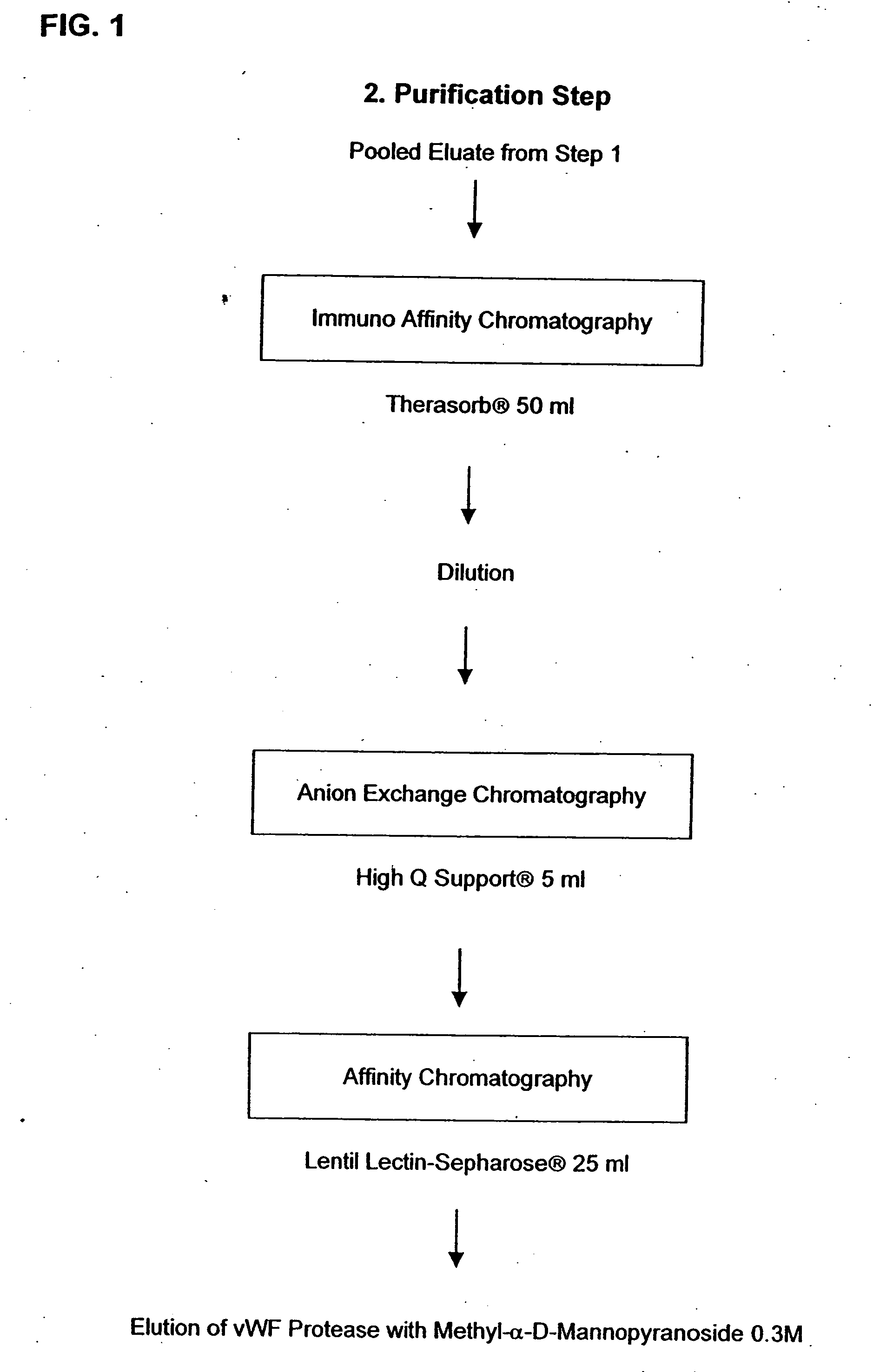
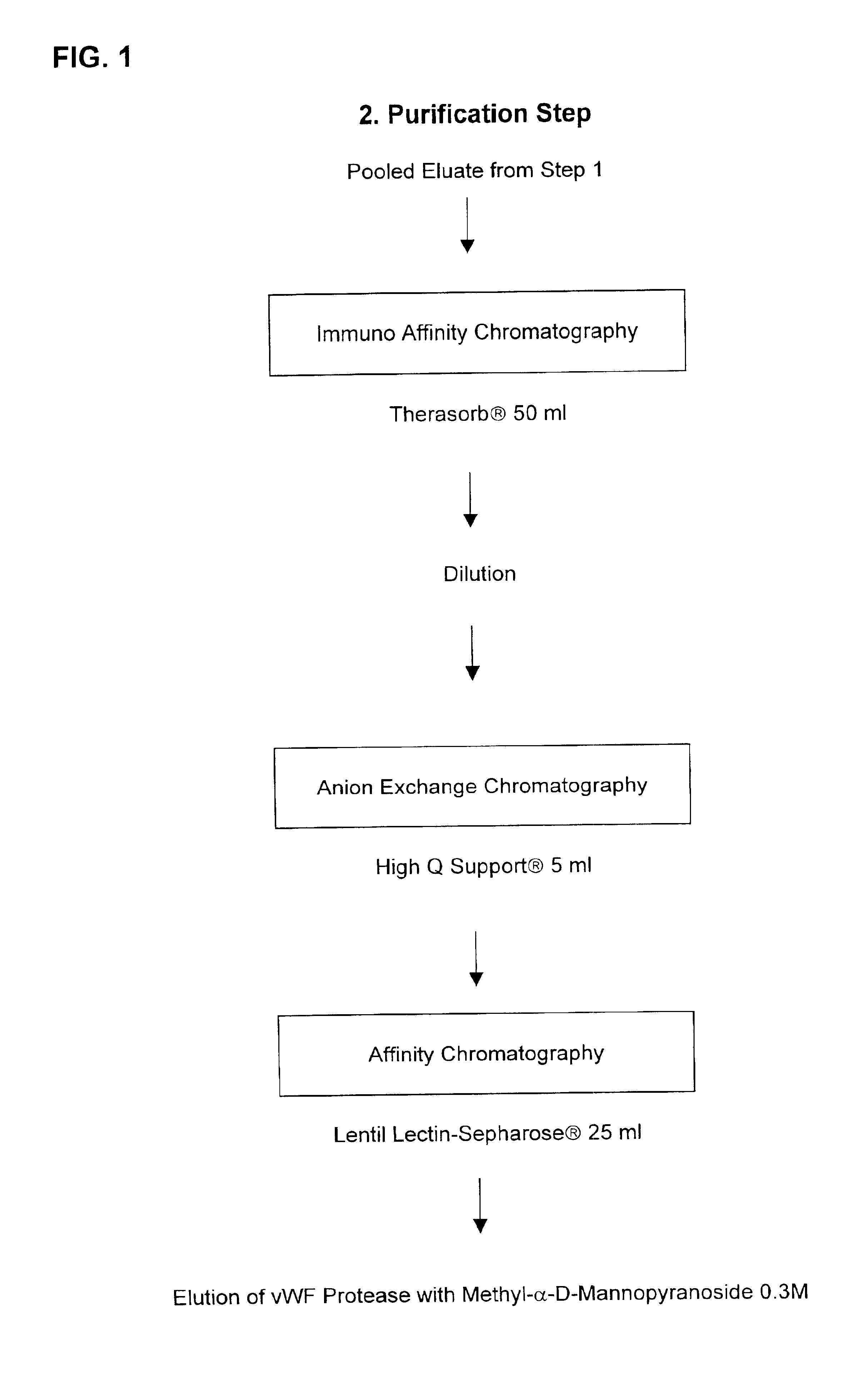
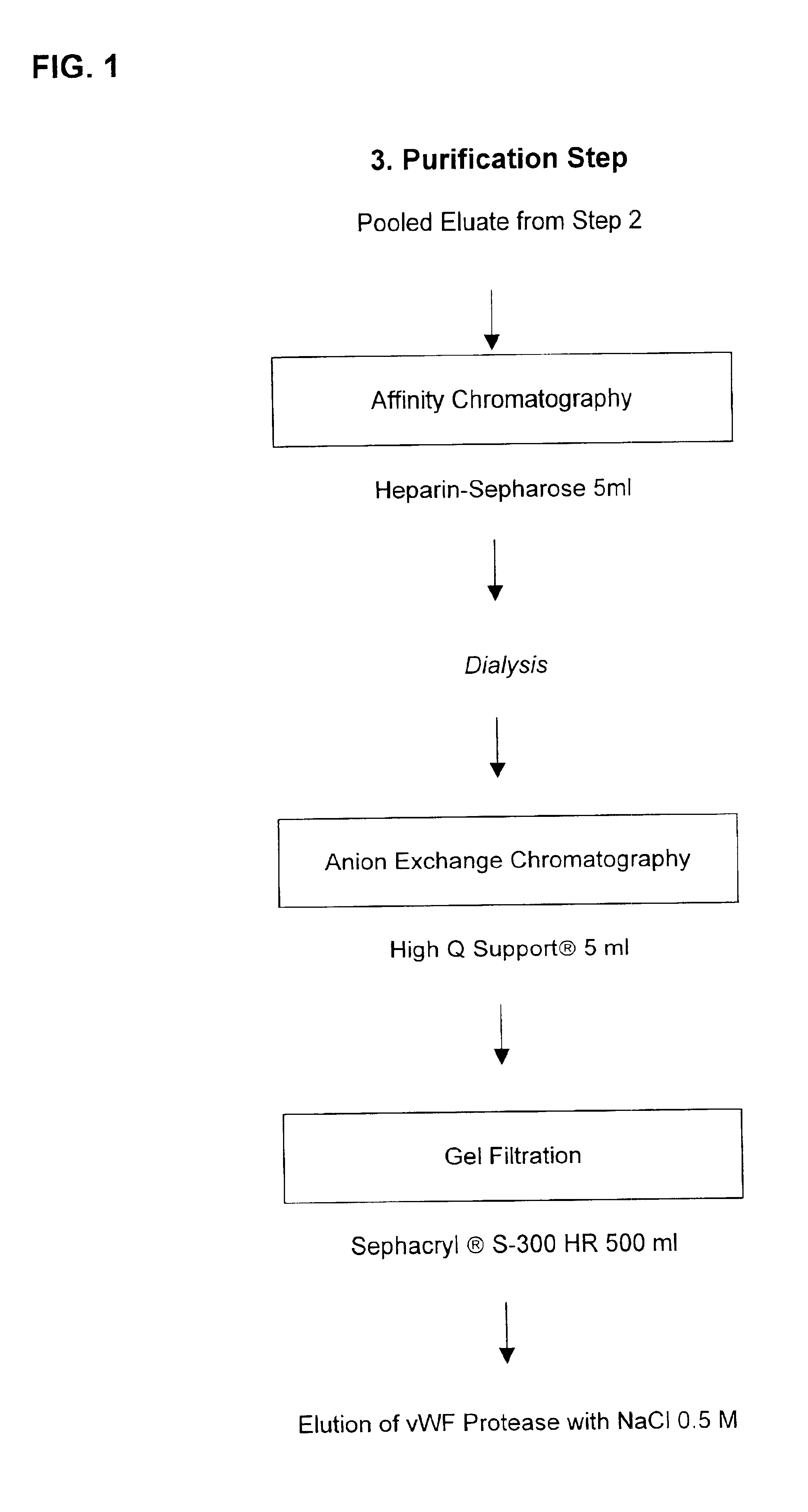
Composition exhibiting a von Willebrand factor (vWF) protease activity comprising a polypeptide chain with the amino acid sequence AAGGILHLELLV
InactiveUS20050266528A1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIFactor VIII vWFProteinase activity
Owner:BAXALTA INC
Multilayer films, coatings, and microcapsules comprising polypeptides
ActiveUS20070077276A1Great control over mechanical stability and diffusive propertyIncrease profitSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyPolyelectrolyte
Disclosed herein is a multilayer film comprising two or more layers of polyelectrolytes, wherein adjacent layers comprise oppositely charged polyelectrolytes. A first layer polyelectrolye comprises a composite polypeptide comprising one or more surface adsorption regions covalently linked to one or more functional regions forming a single polypeptide chain. The surface adsorption regions comprise one or more amino acid sequence motifs consisting of 5 to 15 amino acid residues. The one or more functional regions comprise 3 to about 250 amino acid residues.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH UNIV RES FOUND A DIV OF LOUISIANA TECH UNIV FOUND
Polyvinyl alcohol-polypeptide-polyethylene glycol graft copolymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102181060AEasy to manufacturePrecise control of relative contentDibutyl tin dilauratePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a polyvinyl alcohol-polypeptide-polyethylene glycol graft copolymer and a preparation method thereof. The molecular weight of polyvinyl alcohol is 20,000-80,000; the molecular weight of a polypeptide chain segment is 4,000-8,000; and the molecular weight of a polyethylene glycol chain segment is 350-750. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) synthesizing a polypeptide homopolymer which contains an end-NCO radical: adding the polypeptide homopolymer, diisocyanate, dibutyltin dilaurate serving as a catalyst and dimethyl sulfoxide serving as a solvent into a reactor for reacting to obtain a target product; (2) synthesizing a polyvinyl alcohol-polypeptide graft copolymer: adding the polypeptide homopolymer which contains the end-NCO radical, the solvent and the catalyst into the reactor, adding polyvinyl alcohol and reacting to obtain a target product; and (3) synthesizing a polyvinyl alcohol-polypeptide-polyethylene glycol graft copolymer: adding the polyvinyl alcohol-polypeptide graft copolymer, the solvent and the catalyst into a drying reactor, adding polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether and reacting to obtain a target product.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
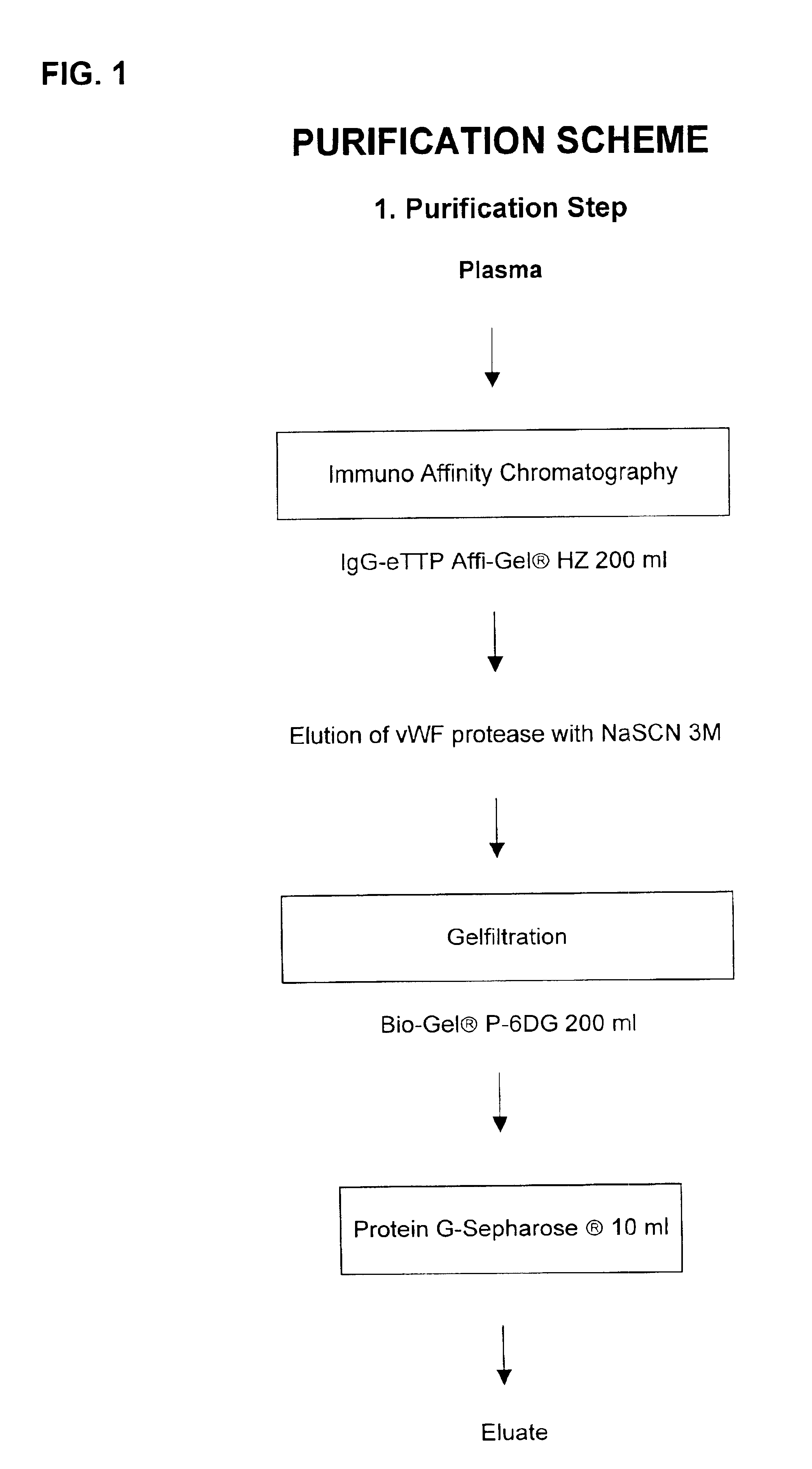
Composition exhibiting a von willebrand factor (vWF) protease activity comprising a polypeptide chain with the amino acid sequence AAGGILHLELLV
InactiveUS6926894B2Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIFactor VIII vWFProteinase activity
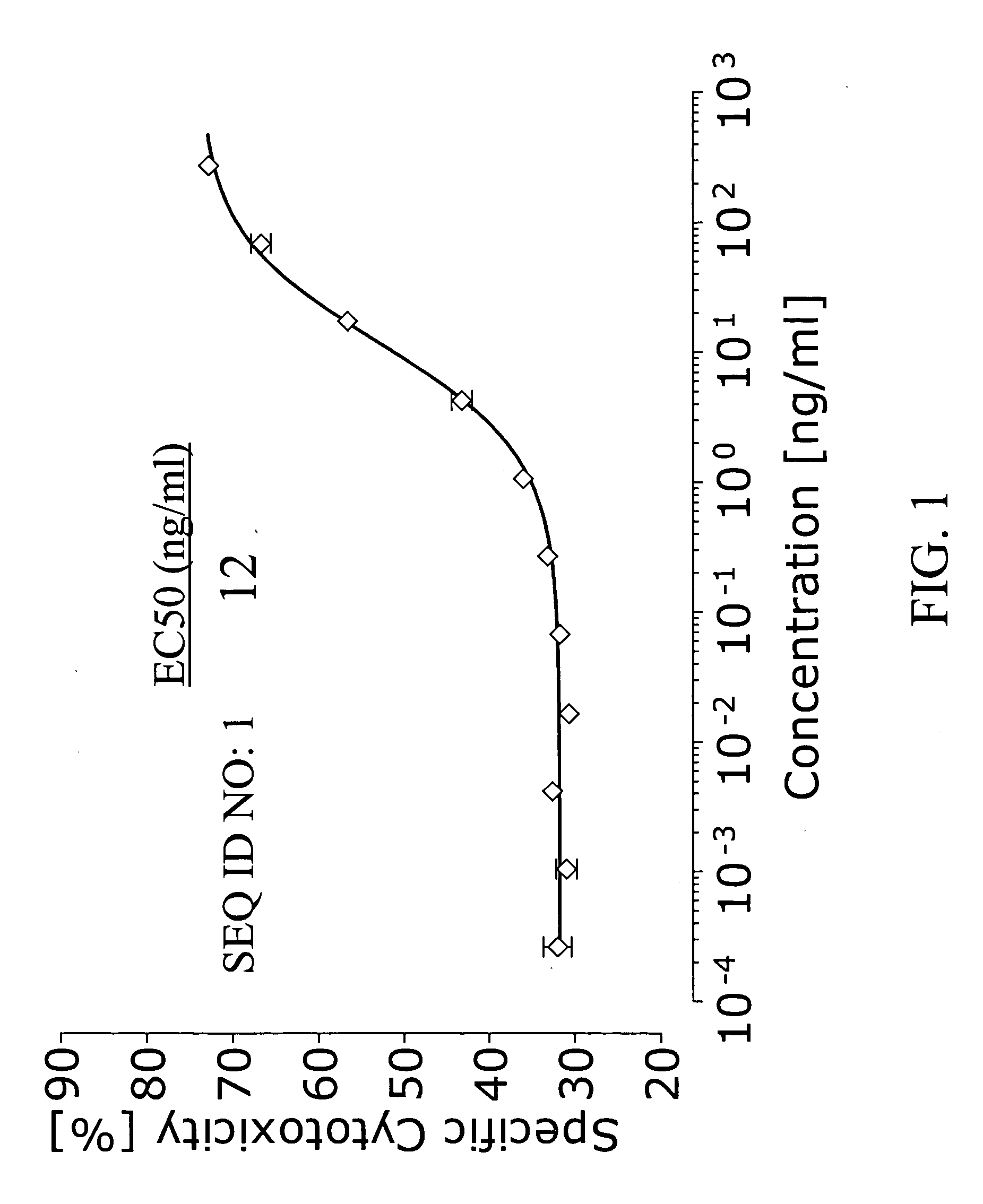
The invention relates to vWF cleaving entities having a molecular weight of 180 kD, 170 kD, 160 kD, 120 kD or 110 kD and an N-terminal amino acid sequence of AAGGILHLELLV (SEQ ID NO: 1), vWF cleaving complexes and methods for their production.
Owner:BAXALTA INC
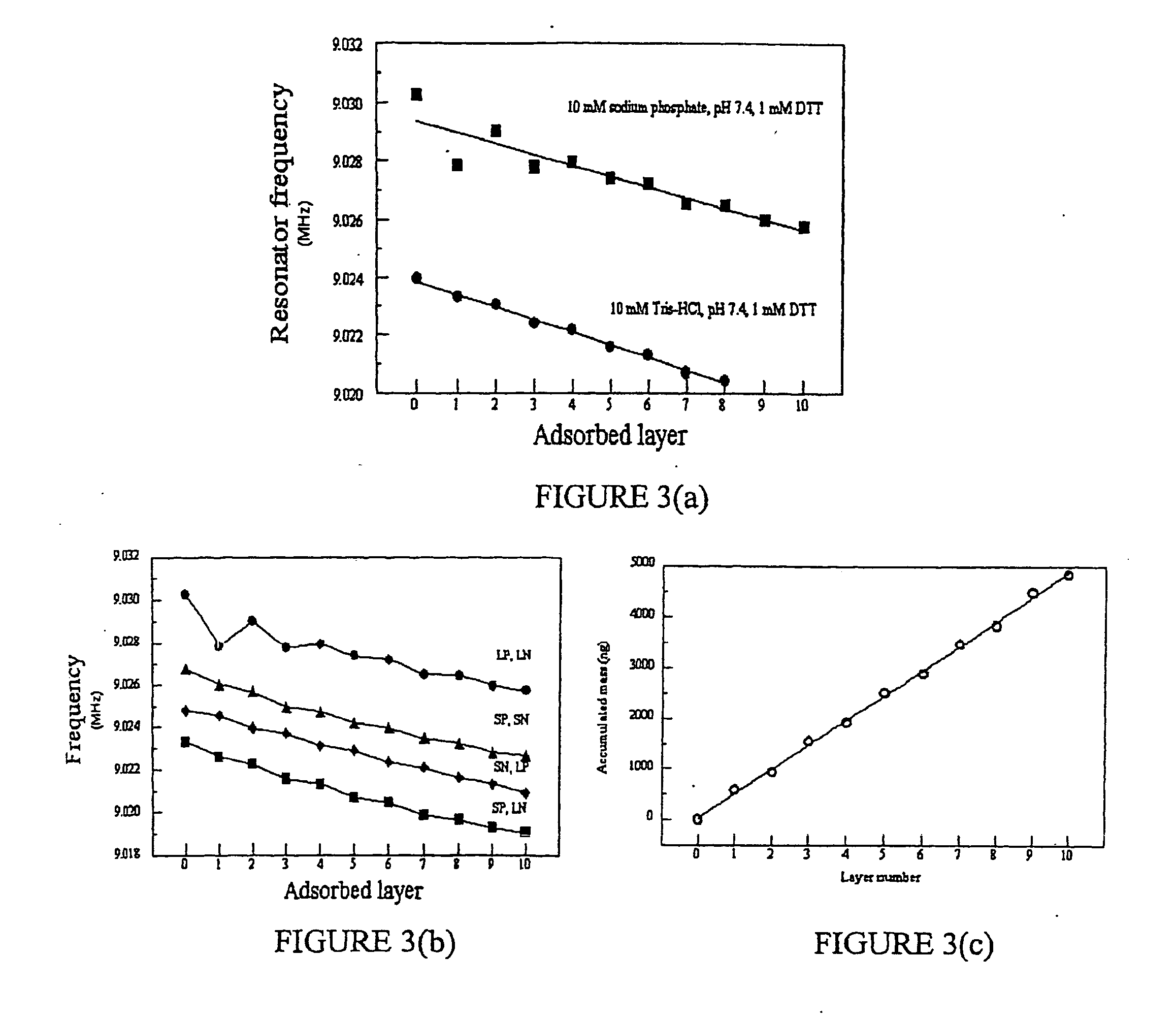
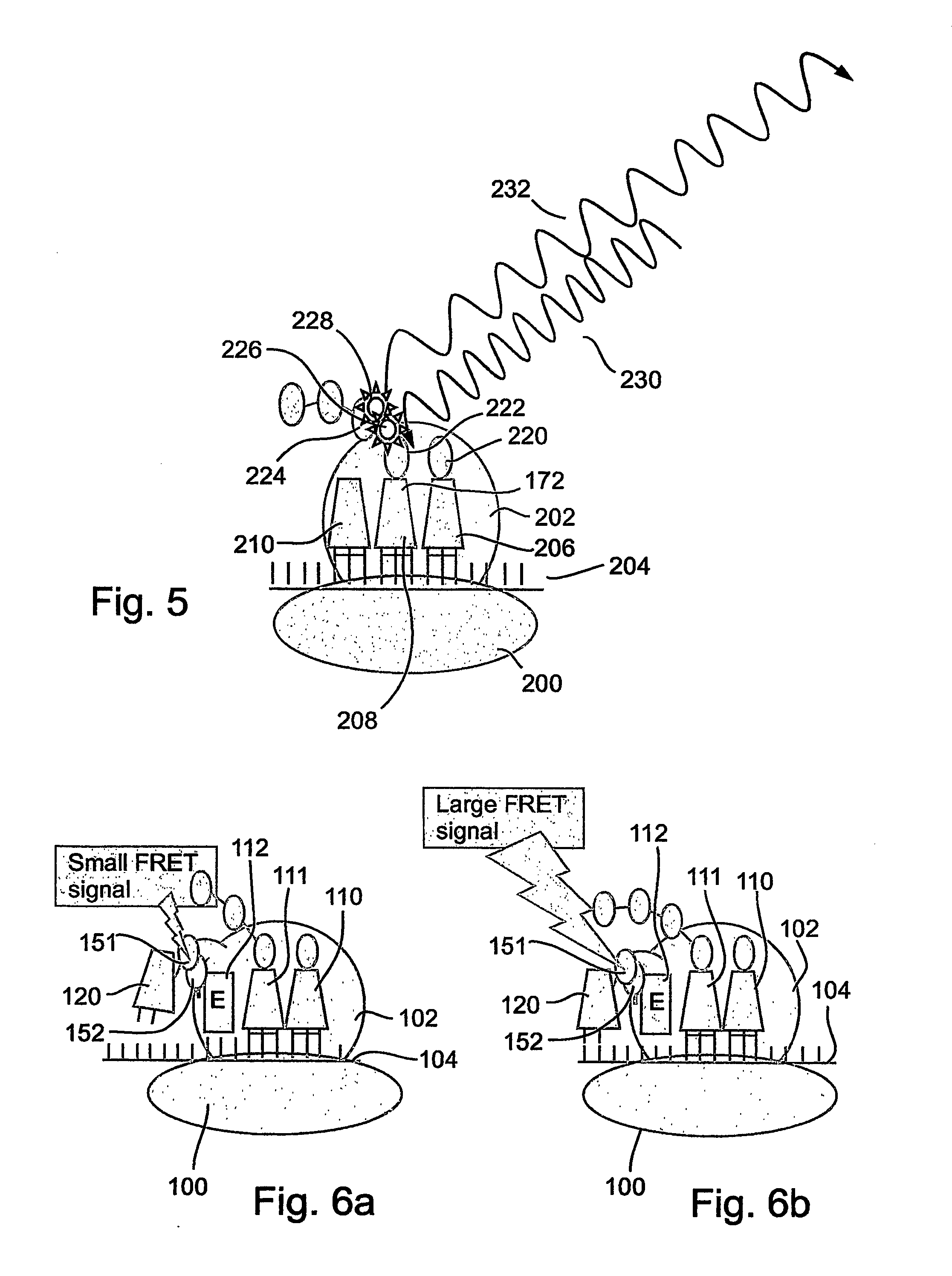
Protein synthesis monitoring (psm)
ActiveUS20060228708A1Unprecedented sensitivityHighly accurate quantitationPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorophoreIn vivo
A method and a device are disclosed for monitoring the synthesis of proteins by the ribosome in real time, in vivo as well as in in-vitro. The ribosome is engineered to carry a donor fluorophore, and tRNA and / or amino acids and / or some other part of the ribosome are either engineered to carry acceptor fluorophores or else their natural fluorescent properties are utilized as acceptors. As the ribosomes mechanism processed the mRNA and tRNA molecules and synthesizes a polypeptide chain, a light source illuminates the ribosome, exciting the donor fluorophores and thereby the acceptor fluorophores whenever these are in sufficient proximity to a donor. The resulting signals are detected and used as a key for real-time database searching and identification of the protein being synthesized. The resulting data can be tabulated and interpreted in different ways. FIG. (1) describes the properties of a FRET pair and the dependence of FRET on pair distance.
Owner:ANIMA CELL METROLOGY
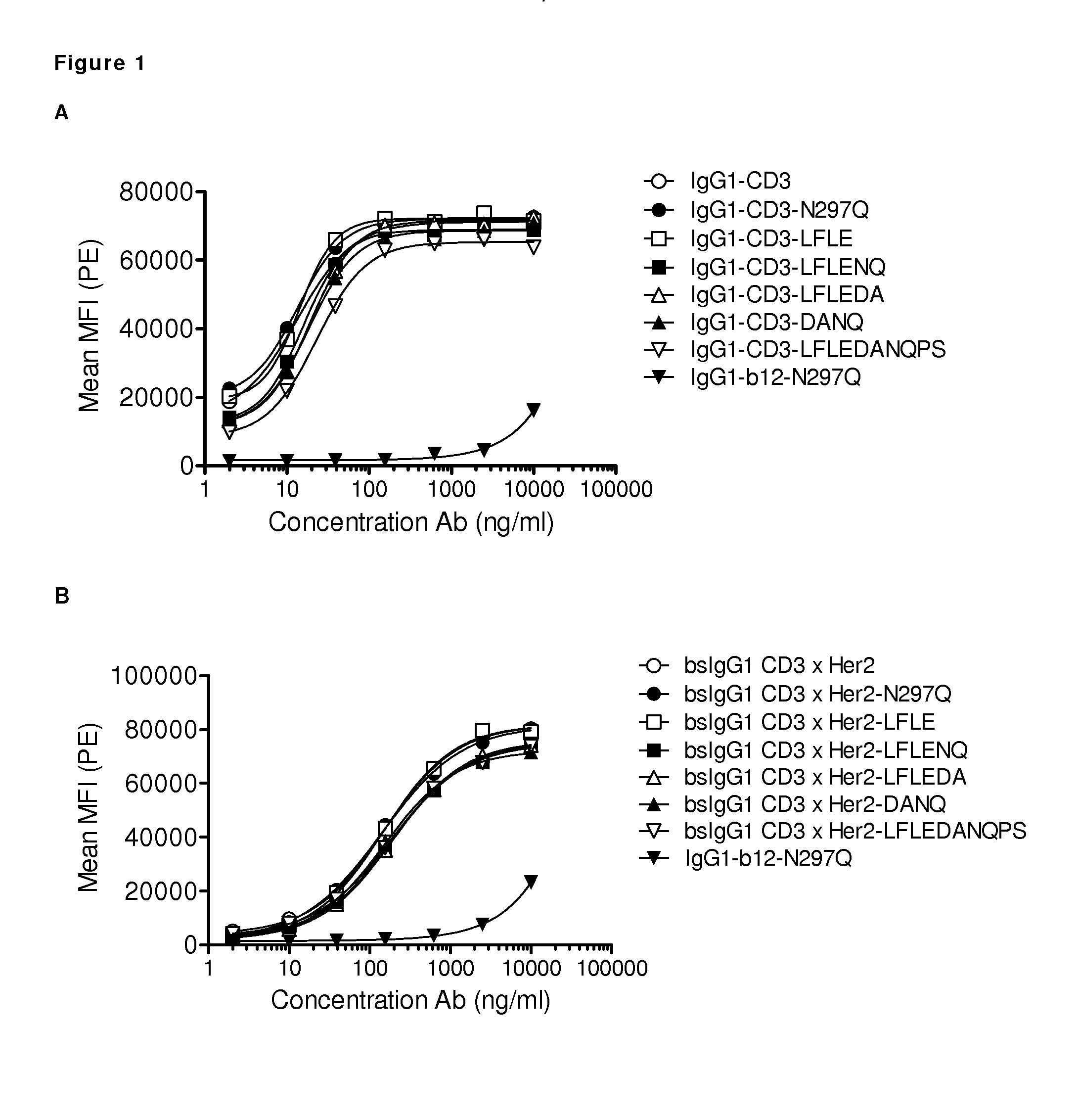
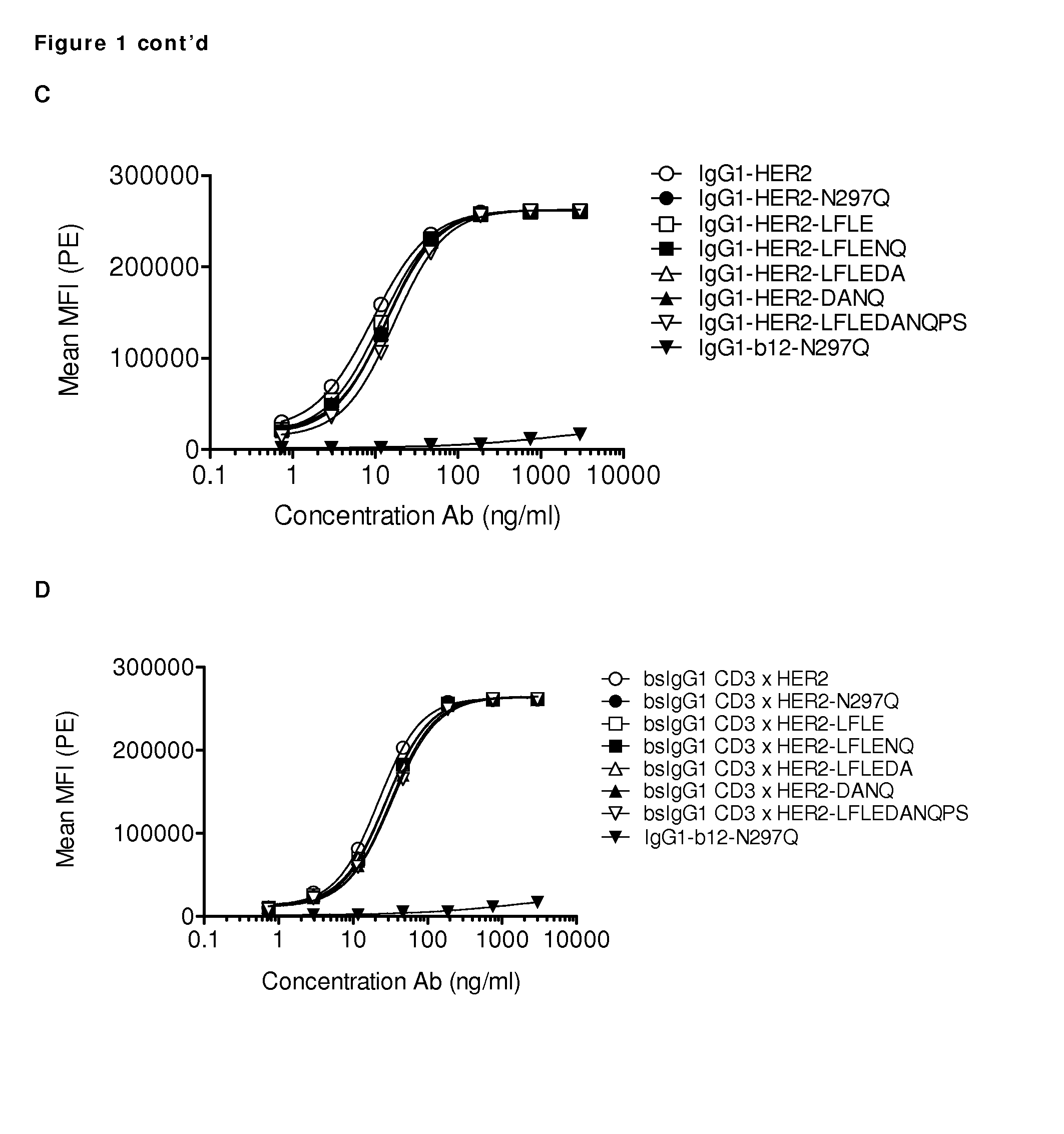
Inert format
ActiveUS20150337049A1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibacterial agentsAmino acid substitutionAmino acid
Described herein are, proteins comprising amino acid substitutions in at least one of a first and a second polypeptide chain. Furthermore, is described the uses and methods related to said proteins.
Owner:GENMAB AS
High throughput sequencing of multiple transcripts of a single cell
ActiveUS20150141261A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh throughput sequenceImmune receptor
The present disclosure generally relates to sequencing two or more genes expressed in a single cell in a high-throughput manner. More particularly, the present disclosure relates to a method for high-throughput sequencing of pairs of transcripts co expressed in single cells (e.g., antibody VH and VL coding sequence) to determine pairs of polypeptide chains that comprise immune receptors.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Polyurethane-polypeptide graft copolymer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a polyurethane-polypeptide graft copolymer and a preparation method thereof. The graft copolymer is a comb-shaped polymer, wherein the molecular weight of polyurethane is 10,000 to 100,000; and the molecular weight of the polypeptide chain segment is 500 to 5,000. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1) synthesis of polyurethane provided with lateral carboxyl on the molecular chain: adding diisocyanate, polypropylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, dibutyltin dilaurate catalyst and dimethyl formamide solvent into a dry reaction bottle, performing stirring reaction under inert atmosphere, adding dimethylolpropionic acid dissolved in dimethyl formamide to react, adding butanediol to react, finally adding butanol to react, and obtaining a target product; and 2) synthesis of the polyurethane-polypeptide graft copolymer: putting the polyurethane provided with lateral carboxyl on the molecular chain, a solvent and a condensation agent into a dry reactor, adding polypeptide homopolymer into the reactor, and performing stirring reaction under the inert atmosphere to obtain a target product with pH response.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Formative agent of protein complex
InactiveUS20020119946A1Keep for a long timePromote resultsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCartilage cellsCuticle
The present invention proposes formative agent of protein complex, in which a polyphenol is useful component, and the agent is useful as gene complex, cell adhesion inhibitor or immune tolerogen. The polyphenol of forming the agent is selected from catechin group consisting of epigallocatechin-gallate, tannic acids, or proanto-dianisidine, a protein of the protein complex is selected from proteins consisting of animal proteins composed of polypeptide chain of peptide-combined amino acids, vegetative proteins, nucleus proteins, glycogen proteins, lipo-proteins and metal proteins, the gene complex comprises by compositing genes by polyphenol catechins in order to introduce genes to cells of animals or human bodies, a cell composed of the cell adhesion inhibitor is selected from cells consisting of an animal cell including a stem cell, skin cell, mucosa cell, hepatocyte, islet cell, neural cell, cartilage cell, endothelial cell, epidermal cell, osteocyte or muscle cell isolated from human or animal organism, or sperm, ovum or fertilized egg of domestic animals or fishes and a tissue or an organ for transplantation of the immune tolerogen is selected from the tissue or the organ consisting of skin, blood vessel, cornea, kidney, heart, liver, umbilical cord, bowels, nerve, lung, placenta or pancreas.
Owner:BERTELSMANN MUSIC GROUP
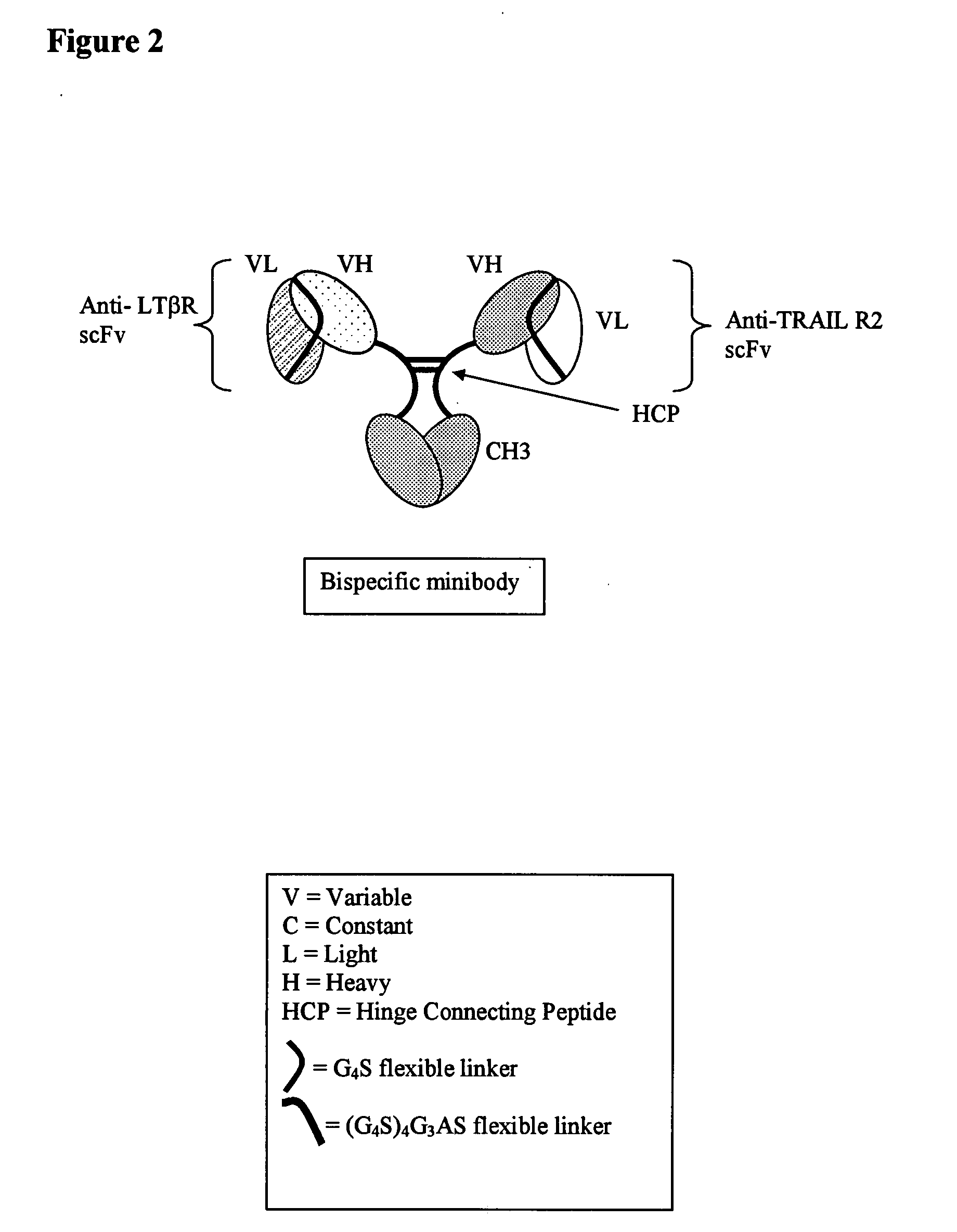
Multispecific binding molecules comprising connecting peptides
ActiveUS20090162380A1Enhance receptor signalingEnhanced signalSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsHeavy chainBinding site
The instant invention describes novel multispecific binding molecules comprising synthetic connecting peptides. The synthetic connecting peptides result in the preferential synthesis of multispecific binding molecules comprising polypeptide chains that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. In addition, the invention pertains to compositions in which a majority of the multispecific binding molecules comprising polypeptide chain that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or are not linked via at least one intrachain disulfide linkage. In a specific embodiment, the invention pertains to compositions comprising multispecific dimeric binding molecules said molecules comprising at least a first binding site specific for a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor or a ligand of a TNF receptor family member and at least a second binding site; and at least two polypeptide chains comprising at least one heavy chain portion and a synthetic connecting peptide; wherein greater than about 50% of the dimers comprise polypeptide chains that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage.
Owner:BIOGEN IDEC MA INC
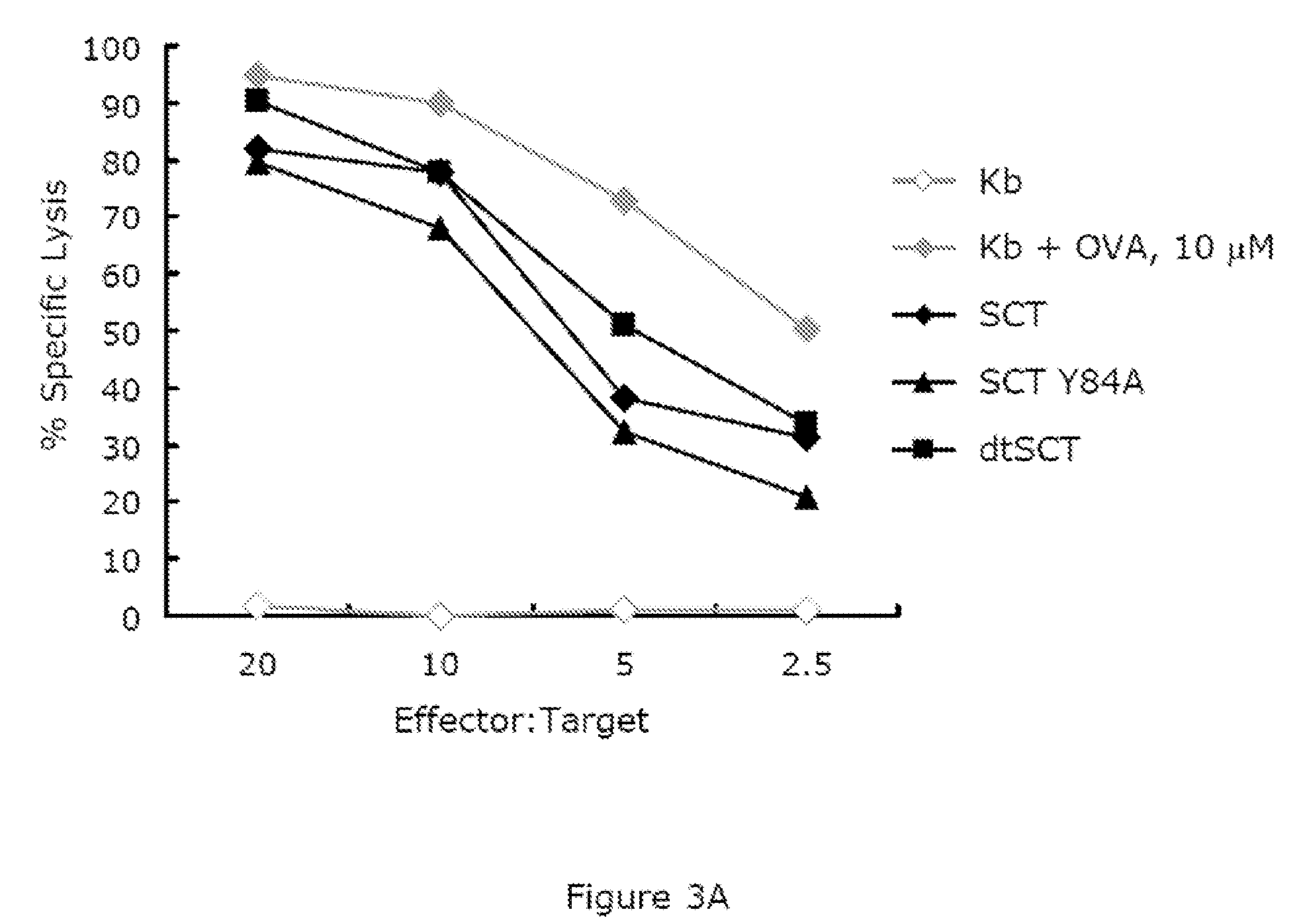
Disulfide trap MHC class I molecules and uses therefor
ActiveUS8992937B2Extended cell surface half-lifeLow efficiencyBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenMHC class I
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Stabilized proteins
InactiveUS7037894B2Prevent undesired cross-linkControl cross-link reactionHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsTyrosineProtein retention
Isolated polypeptides or polypeptide chains are modified by di-tyrosine cross-linking such that the retain at least one functional activity. In one embodiment, the isolated polypeptide or polypeptide chains comprise at least one di-tyrosine cross-link, wherein at least one tyrosine of the di-tyrosine cross-link originates from a point mutation to tyrosine, and wherein the di-tyrosine cross-linked protein retains at least one function displayed by the protein in the absence of di-tyrosine cross-linking. In another embodiment, the di-tyrosine cross-linked polypeptide or polypeptide chain has enhanced stability compared to the same polypeptide or polypeptide chain in the absence of di-tyrosine cross-linking. A method for stabilization of a polypeptide or polypeptide complex, by the introduction of intra-polypeptide and / or inter-polypeptide di-tyrosine bonds, which simultaneously maintains the structure and function of the polypeptide or polypeptide complex is also described.
Owner:CALDER BIOSCI INC
Mixture of binding proteins
ActiveUS8268756B2Simple processSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against virusesEpitopeNucleic acid sequencing
Described are methods for producing libraries of cells expressing at least two separate single polypeptide chain binding proteins, in which the binding proteins have different target epitopes. Such libraries are made by integration of the nucleic acid sequences encoding the polypeptide chains into the genome of the host cell, and selecting for cells that have successfully integrated these nucleic acids. The selected cells are preferably subjected to a cloning step. Mixtures of binding proteins are produced without having to individually produce each of the components of the mixture. A library of cells wherein essentially each cell encodes at least two single polypeptide chain binding proteins having different target epitopes is also herewith provided, as well as methods for producing a composition comprising at least two separate single polypeptide chain binding proteins having different target epitopes.
Owner:MERUS NV
Multilayer films, coatings, and microcapsules comprising polypeptides
InactiveUS7544770B2Great control over mechanical stability and diffusive propertyIncrease profitSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyPolyelectrolyte
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH UNIV RES FOUND A DIV OF LOUISIANA TECH UNIV FOUND
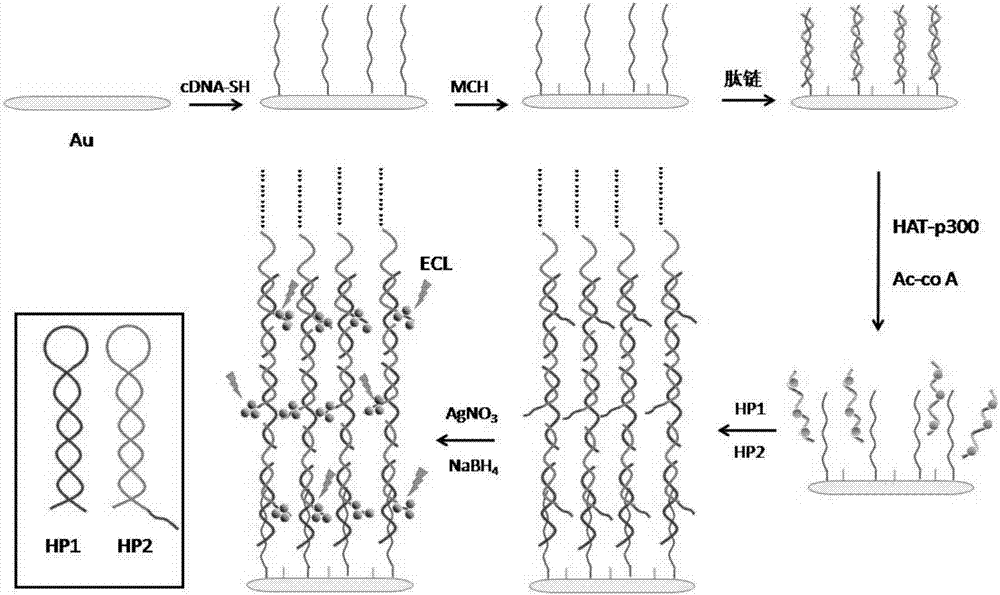
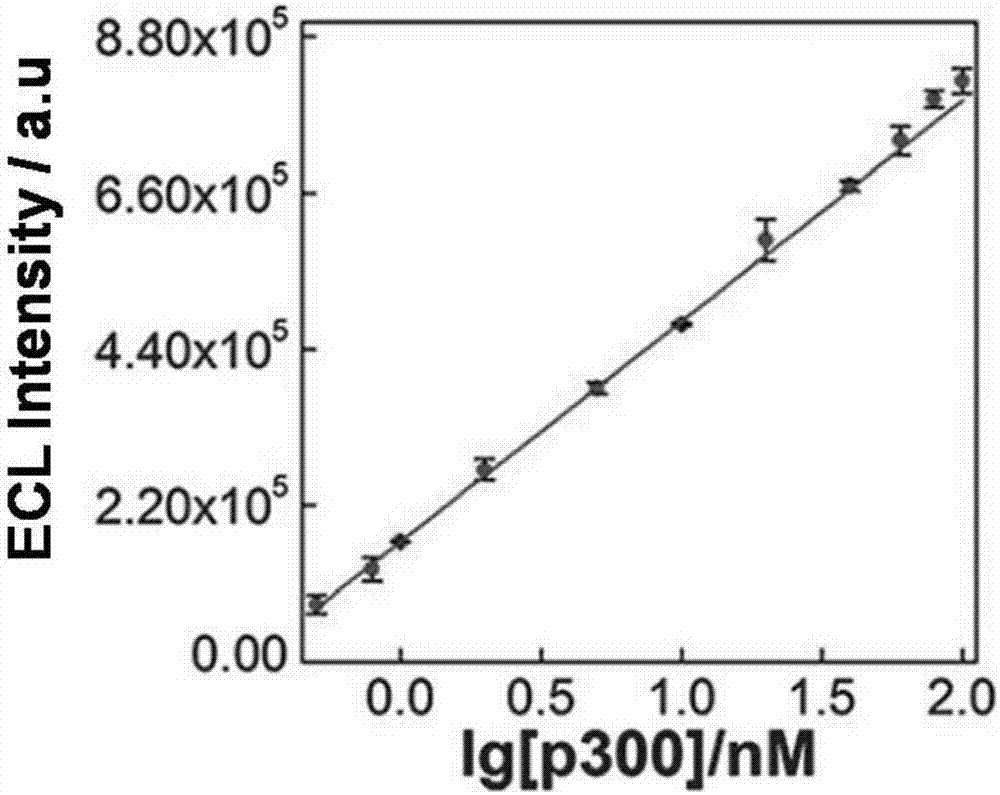
Construction of electrochemical luminescence sensor for detecting acetyltransferase activity
ActiveCN107101997AEasy to prepareEasy to operateChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhysical chemistryAcetyltransferase activity
The invention relates to a construction of an electrochemical luminescence sensor for detecting acetyltransferase activity. The construction comprises the following steps: firstly, polishing, cleaning and activating a gold electrode, assembling captured DNA on the surface of the electrode through action of gold-sulfur bond, and enclosing non-specific binding sites on the surface of the electrode with MCH; then adsorbing a polypeptide chains through electrostatic action, performing acetylation treatment on the polypeptide chains under the action of HATp300, so as to separate from the surface of the electrode; secondly, performing hybrid chain reaction on the electrode in a hybrid chain solution containing two hairpin DNA, and reducing a silver cluster; and finally, detecting electrochemical luminescence signal of the assembled electrochemical luminescence sensor in the solution. The ECL biosensor has remarkable advantages on the quantitative analysis of HAT p300 and the activity analysis on HAT p300 in complicated cell lysis buffering solution.
Owner:青岛卓越海特信息技术有限公司
Fusion proteins for prodrug activation
The invention relates to compounds which contain an antigen binding region which is bound to at least one enzyme which is able to metabolize a compound (prodrug) which has little or no cytotoxicity to a cytotoxic compound (drug), where the antigen binding region is composed of a single polypeptide chain. It is advantageous for covalently bonded carbohydrates to be present on the polypeptide chain.
Owner:BEHRINGWERKE AG
Method for producing target substance capturing protein and method for selecting component materials thereof
InactiveUS20060275811A1Convenient and practical selectionValid choicePeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingBinding domain
A combination of polypeptide chains used as a plurality of target substance-binding domains are selected by: (1) reacting a target substance with a first polypeptide chain with a known target substance-binding domain to obtain a first complex; (2) reacting the first complex with a second polypeptide chain library composed of polypeptide chains each having a site to be associated with the first polypeptide chain to obtain second complexes in which the second polypeptide chain is bonded with the target substance in the first complex; (3) washing the second complexes to obtain a third complex in which the first polypeptide chain and the second polypeptide chain are associated with each other and bonded with the target substance; and (4) obtaining a nucleic acid sequence of the second polypeptide chain from the third complex.
Owner:CANON KK
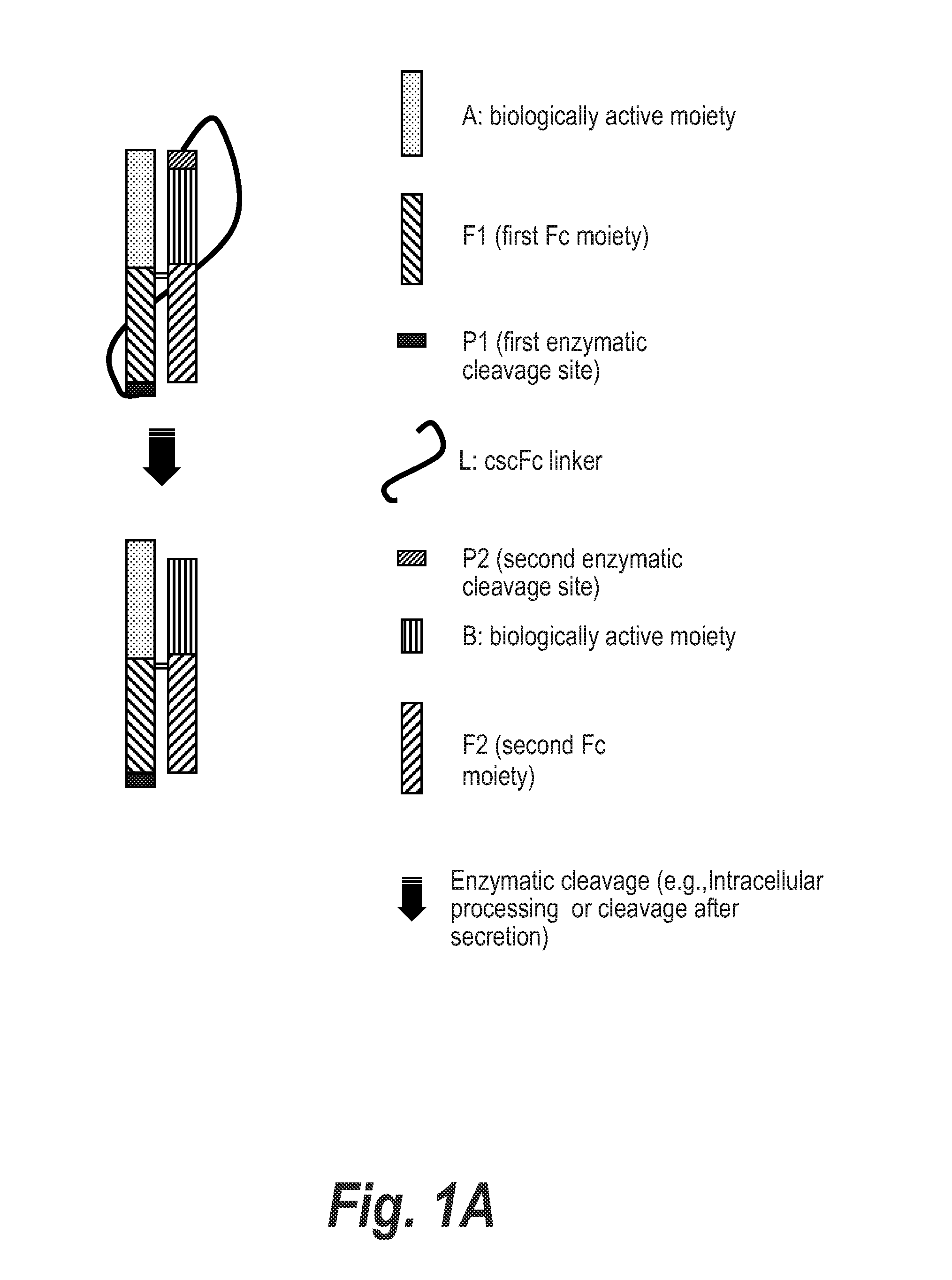
Processable Single Chain Molecules and Polypeptides Made Using Same
ActiveUS20130202596A1Improve manufacturabilityReduced immunogenicity riskHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzymeAmino acid
The present invention features inter alia nucleic acid molecules which encode polypeptides comprising a single chain Fc region and the polypeptides they encode. The Fc moieties of these constructs are linked by a cleavable scFc linker which is adjacent to at least one enzymatic cleavage site, e.g., an intracellular processing site. The resulting processed molecules comprise two polypeptide chains and substantially lack the extraneous amino acid sequence found in single chain Fc linker molecule. Methods of making and using these dimeric molecules are also described.
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for preparing polypeptide-polylactic acid-polyethyleneglycol dual-graft copolymer
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polypeptide-polylactic acid-polyethyleneglycol dual-graft copolymer. The method is characterized in that the molecular weight of a polypeptide chain segment in the copolymer is 20000-50000; the molecular weight of a polylactic acid chain segment is 1000-2000; and the molecular weight of a polyethylene glycol chain segment is 500-700. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1) synthesizing a polypeptide-polylactic acid graft copolymer, namely, adding a polypeptide homopolymer, polylactic acid lauryl ether, a solvent and a catalyst to a dry reactor, stirring and reacting for 3-4 days under an inert atmosphere at 55-58 DEG C, so as to prepare the target in manners of filtering, dialyzing and drying; and 2) synthesizing the polypeptide-polylactic acid-polyethyleneglycol dual-graft copolymer, namely adding the polypeptide-polylactic acid copolymer, the catalyst, the solvent and the methoxy polyethylene glycol to the dry reactor, stirring and reacting for 2-3 days under the inert atmosphere at 55-59 DEG C, so as to obtain the target in manners of filtering, dialyzing and drying. The method is simple in process; and the obtained target is a novel biodegradable material.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Expression of heterologous multi-domain proteins in yeast
InactiveUS20030100112A1Increase productionCost effective productionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsYeastSingle-Chain Antibodies
This invention demonstrates the utility of a yeast expression system for the expression of functional heterologous multi-domain proteins in yeast. The yeast expression system allows for the inclusion of a plurality of (up to three) modular expression cassettes which may encode multiple polypeptide chains of a heterologous multi-domain protein on a single plasmid (Twin Cassette). Because multiple polypeptide chains may be encoded for by the expression cassettes of the present invention in a single vector, the system can produce equivalent amounts of the multiple polypeptide chains, thereby enhancing the yield of a functional heterologous multi-domain protein. For example, functional monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) comprising a heavy chain and a light chain of an immunoglobulin (IgG), and functional immunotoxins comprising an antibody domain and an oxidase toxin may be produced using the Yeast expression system of the present invention. In addition, functional single chain antibodies, antibody fragments and chimeric antibodies may also be produced.
Owner:APOLIFE
Preparation method of bionic coating carrying bioactive factors
InactiveCN102327645AImprove long-term stabilityImprove stabilityImpression capsDentistry preparationsOsseointegrationArg-Gly-Asp
The invention provides a preparation method of bionic coating carrying bioactive factors, which is characterized in that: under a catalyzing system of carbodiimide and N-hydroxy-succinamide, Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) polypeptide chain containing a disulfide bond is grafted onto polyelectrolyte and then is prepared into RGD grafted polyanion electrolyte solution and RGD grafted bioactive-factor-loaded polycation electrolyte solution, the polyanion electrolyte solution is combined with the polycation electrolyte solution carrying the bioactive factors to establish an organic composite coating carrying the bioactive factors on the surface of planting body through a static self-assembling technology. The composite coating solves the bottleneck problem of bioactive factors used surrounding the planting body, can promote the early growth of osteogenesis surrounding the planting body so as to realize the early osseointegration, and facilitates the long-term stability of the planting body. The method is simple to operate, has moderate preparation conditions, is convenient to control and can realize the continuous production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Mixture of binding proteins
ActiveUS20070059766A1Simple processLibrary screeningImmunoglobulins against virusesEpitopeNucleic acid sequencing
Described are methods for producing libraries of cells expressing at least two separate single polypeptide chain binding proteins, in which the binding proteins have different target epitopes. Such libraries are made by integration of the nucleic acid sequences encoding the polypeptide chains into the genome of the host cell, and selecting for cells that have successfully integrated these nucleic acids. The selected cells are preferably subjected to a cloning step. Mixtures of binding proteins are produced without having to individually produce each of the components of the mixture. A library of cells wherein essentially each cell encodes at least two single polypeptide chain binding proteins having different target epitopes is also herewith provided, as well as methods for producing a composition comprising at least two separate single polypeptide chain binding proteins having different target epitopes.
Owner:MERUS NV
Preparation method of polypeptide
InactiveCN105504012AAvoid mismatched responsesEnhanced couplingPeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionSide chainNitrogen
The invention relates to the field of polypeptide, and especially relates to a preparation method of polypeptide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: coupling Arg with resin to prepare Arg-resin; individually coupling Arg-resin with Ala, Arg, Arg, Arg, Ala, and Cys (X) in sequence, carrying out amino acetylation on the nitrogen terminal to obtain a first peptide resin; removing the side chain protective group X in Cys (X) of the first peptide resin, then coupling the first peptide resin with Y-Cys to obtain a second peptide resin, and cracking the second peptide resin to obtain the polypeptide. The preparation method is carried out in pure solid state, the operation is simple and convenient, and the pseudo-dilution effect avoid the disulfide bond mispairing reactions between polypeptide chains in liquid phase reactions ( no reactions happens between peptide chains). The yield and purity of polypeptide Velcalcetide are both improved, and the side reactions are reduced.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com