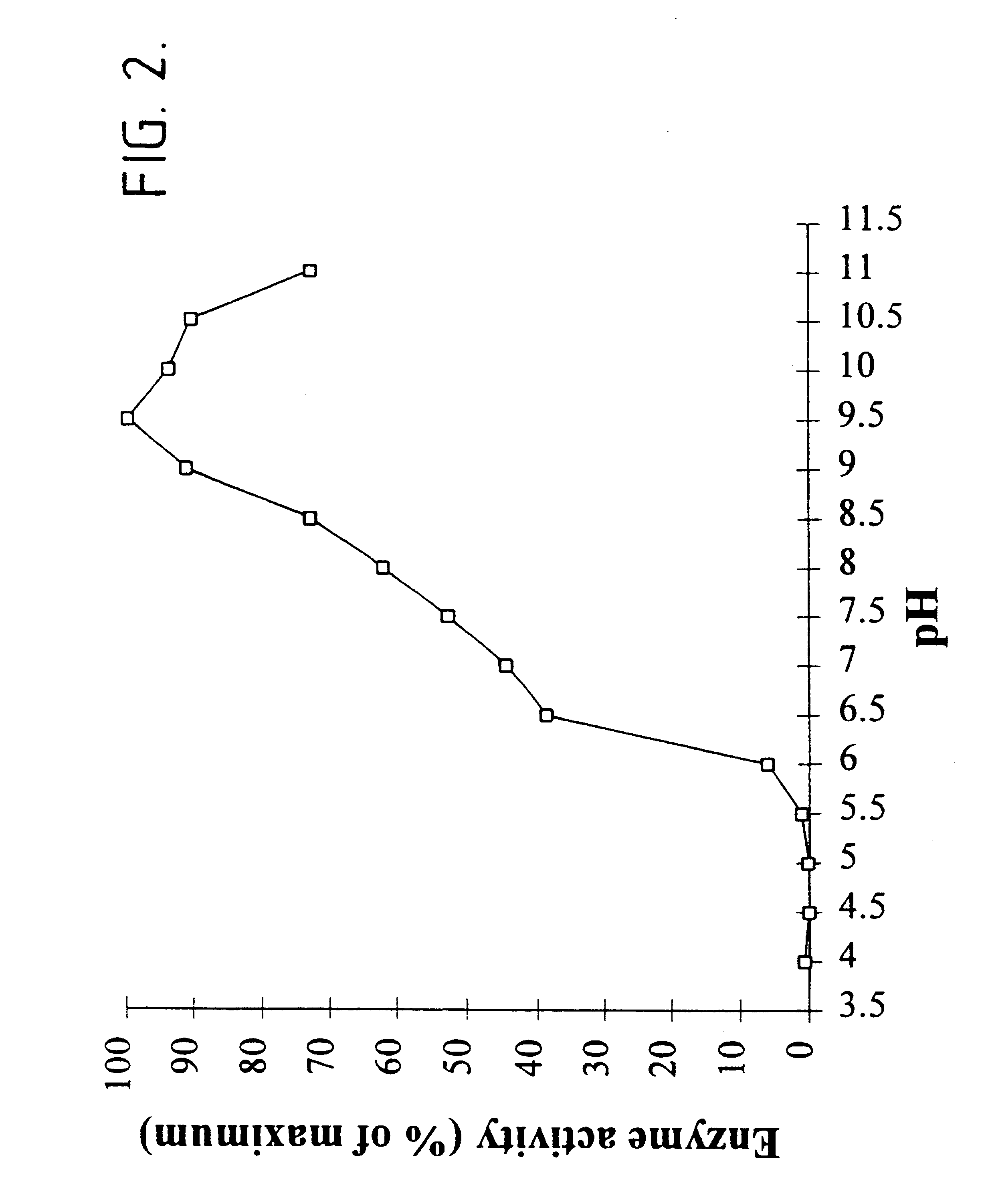
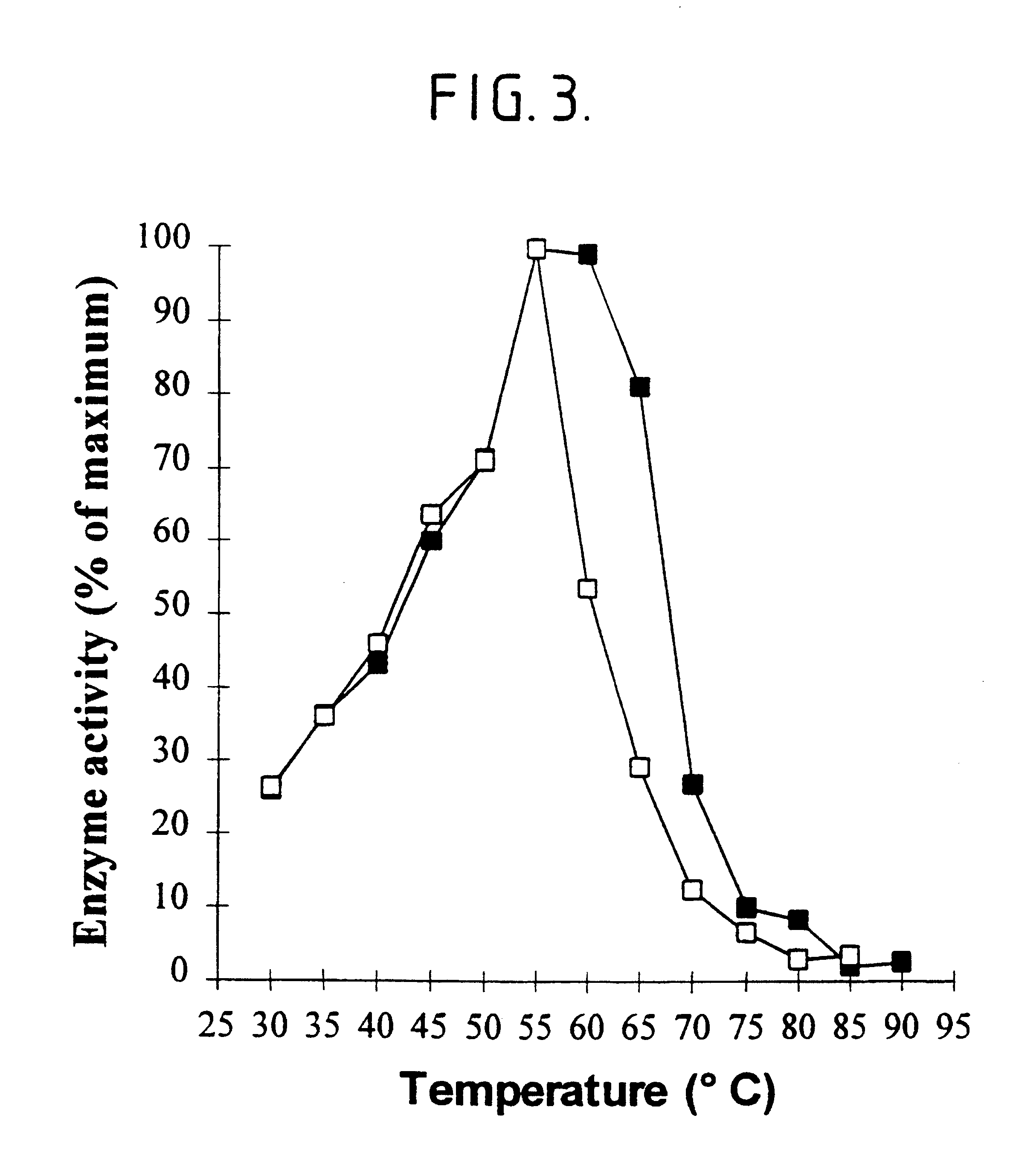
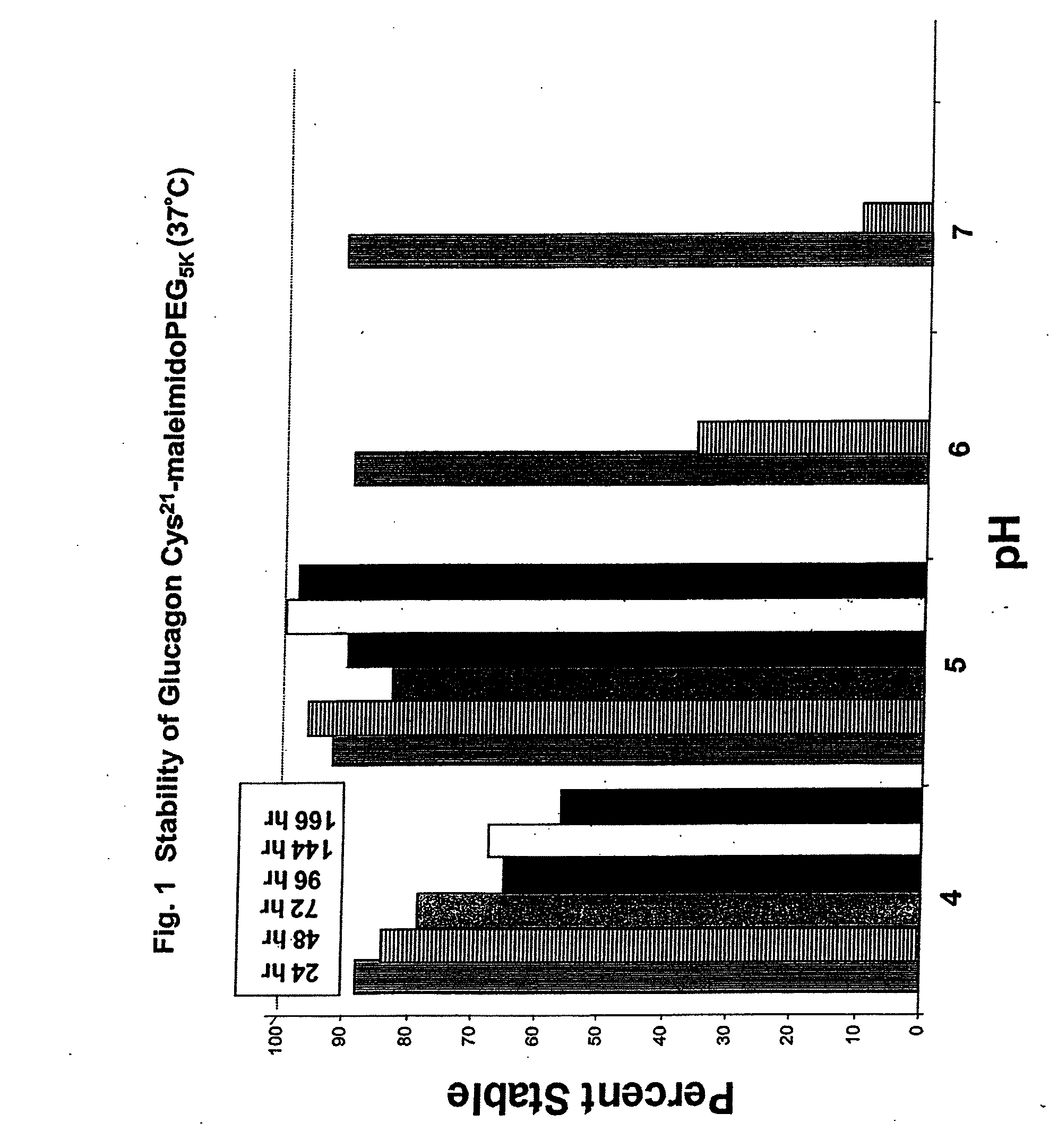
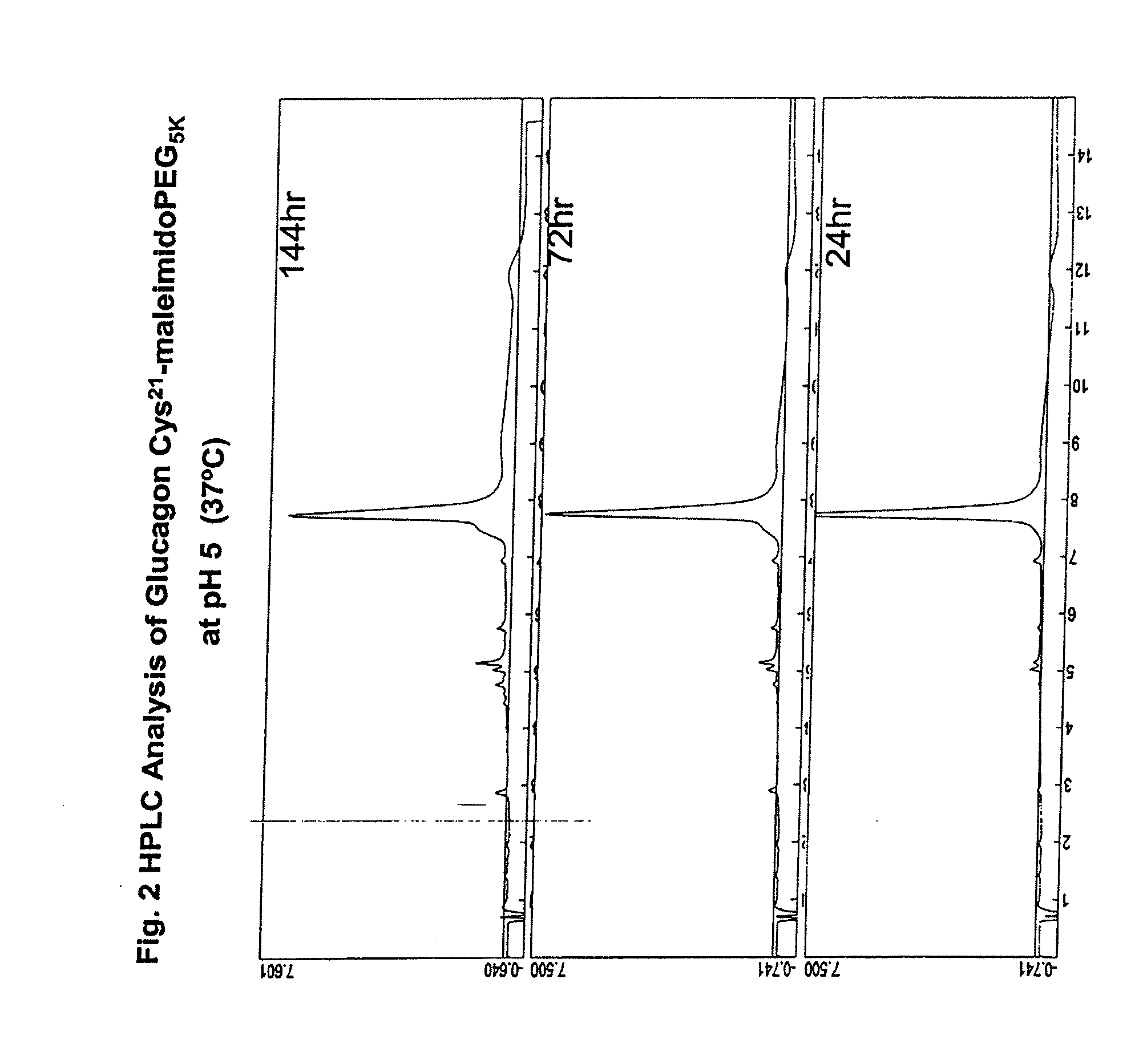
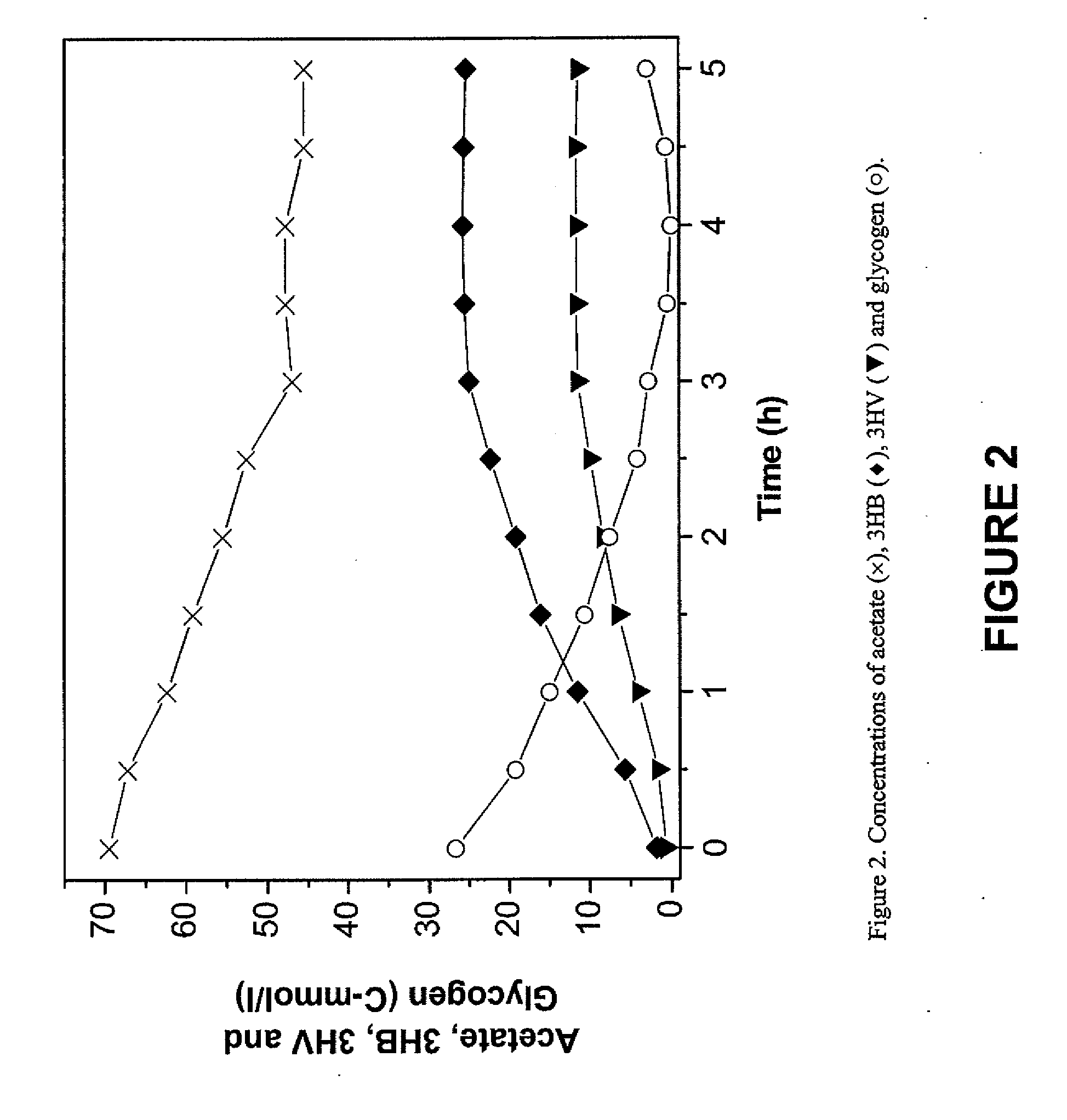
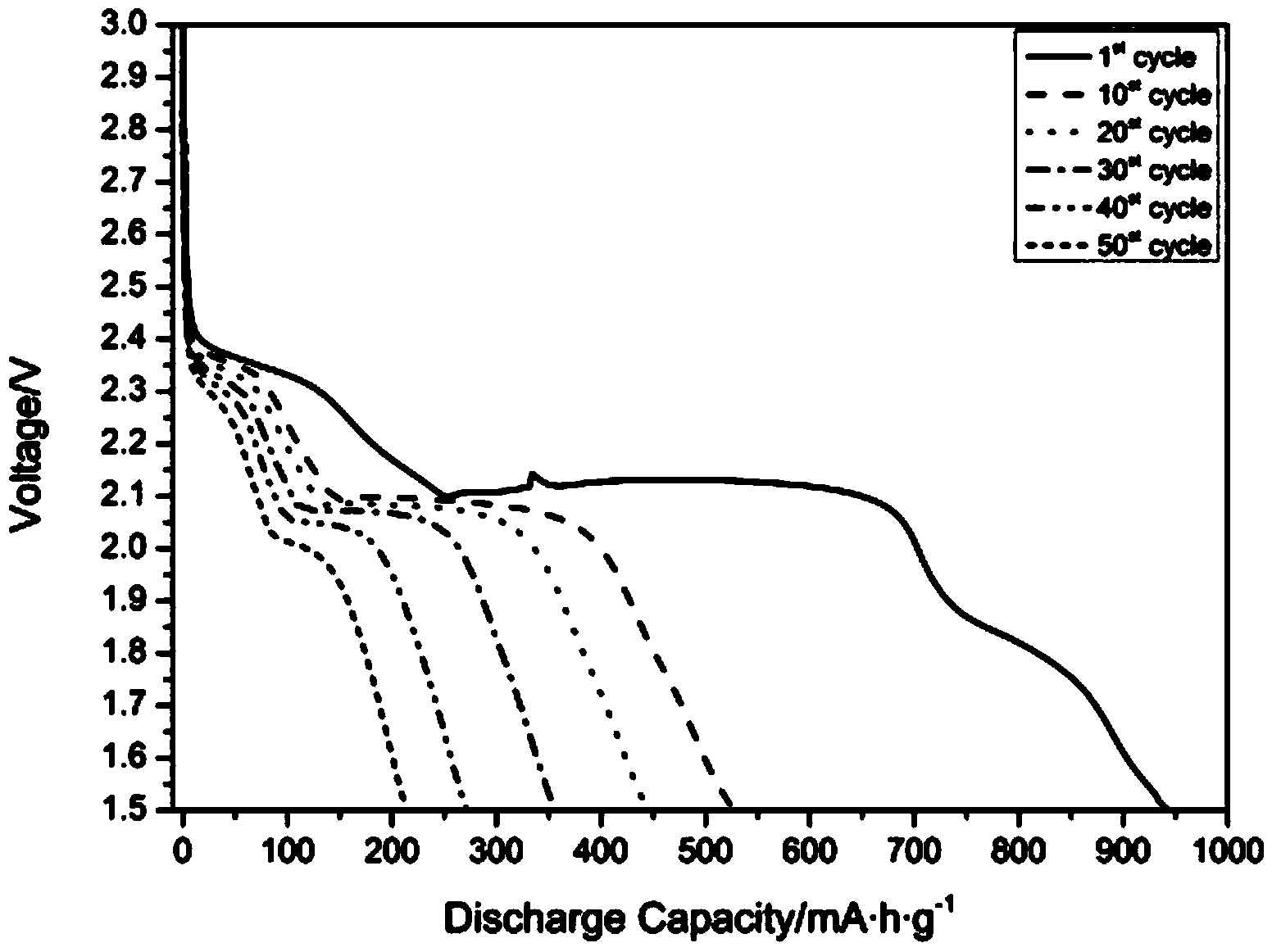
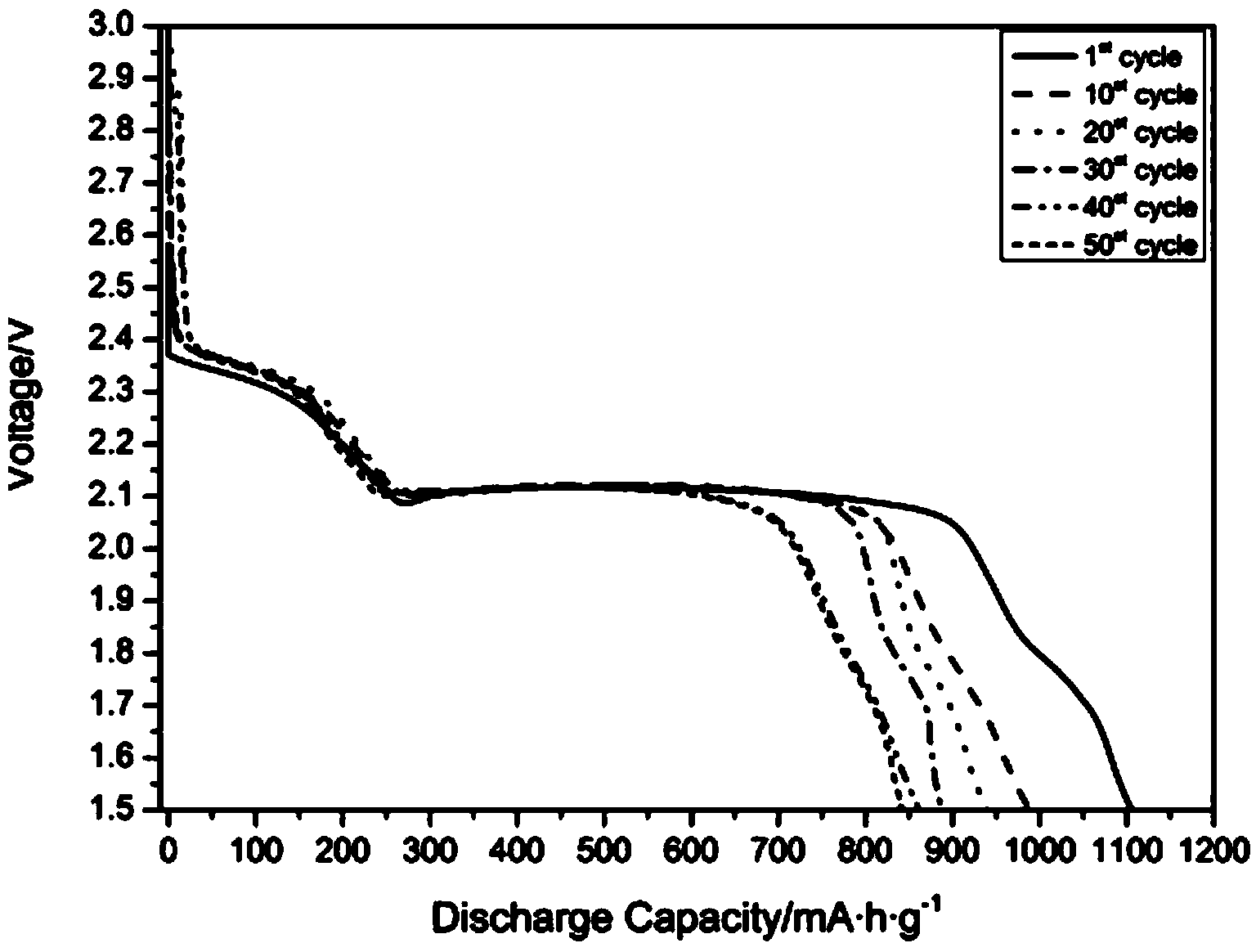
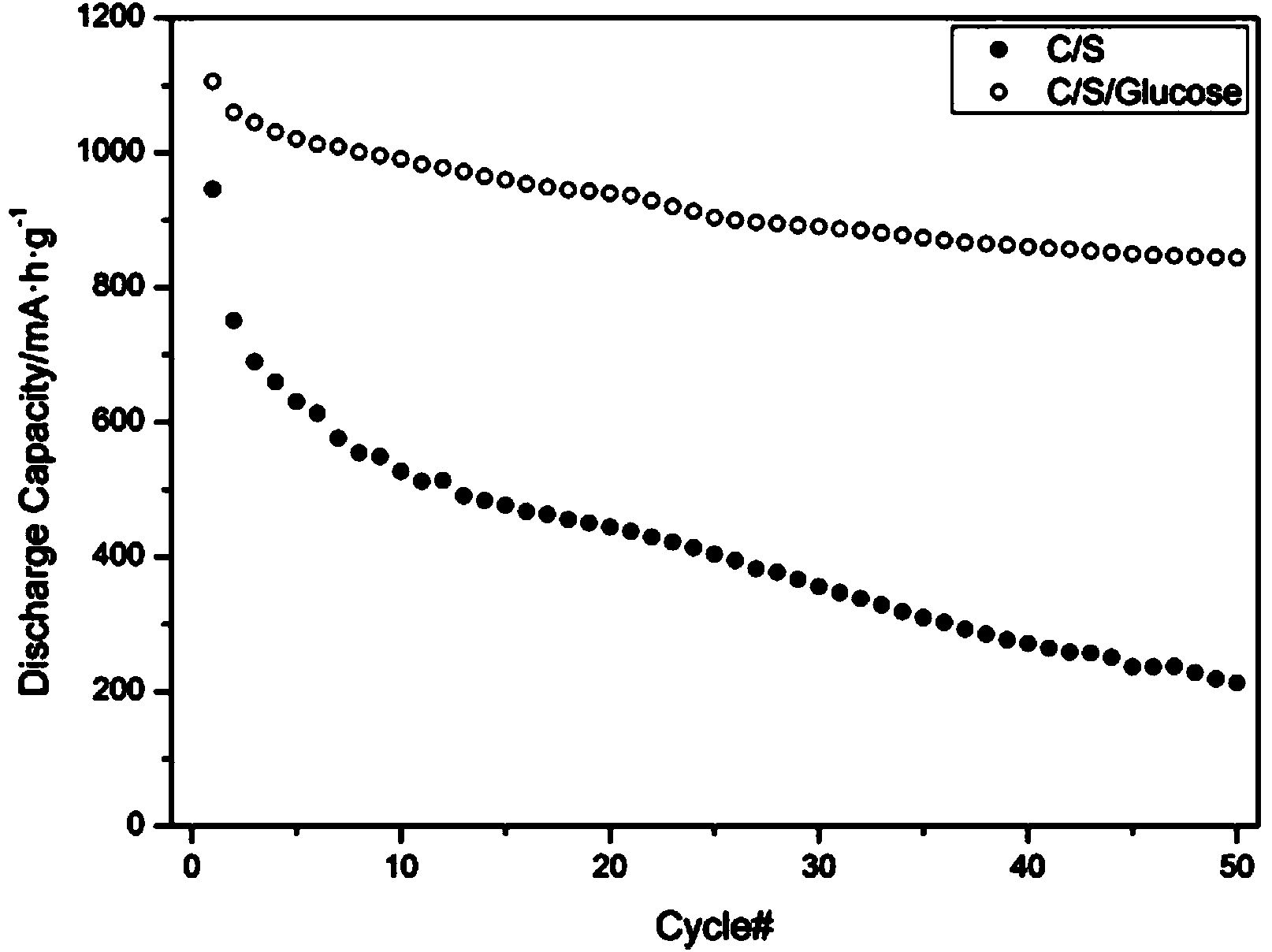
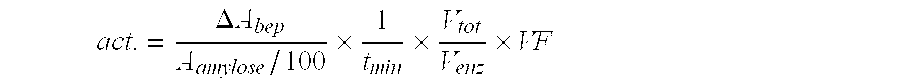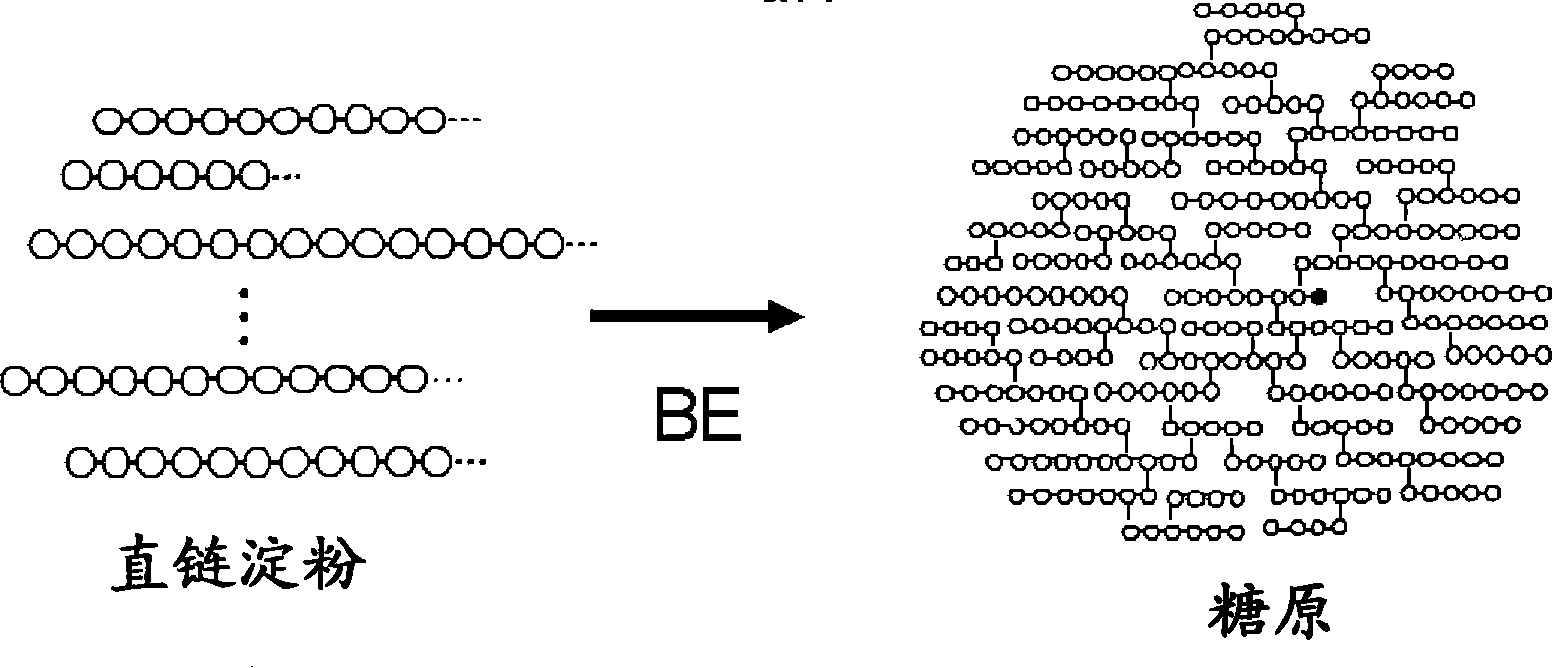Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
569 results about "Glycogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
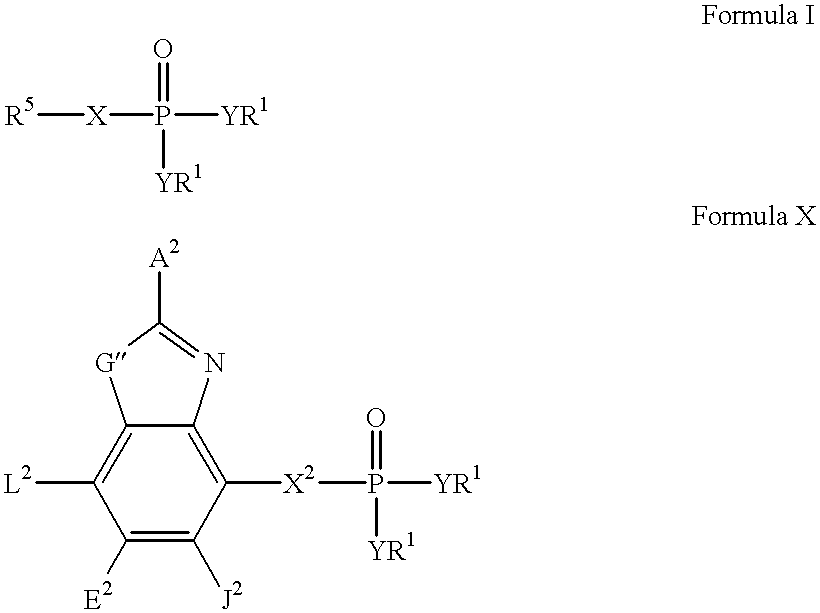
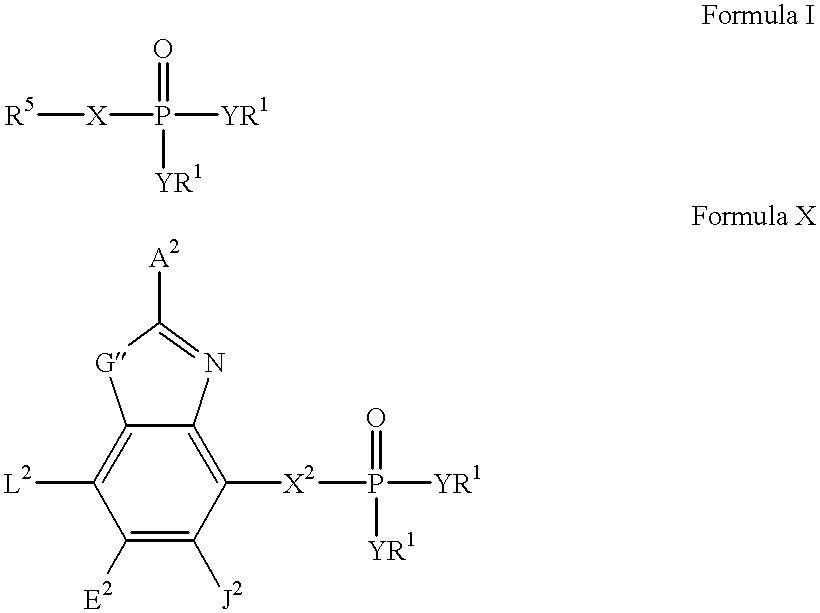
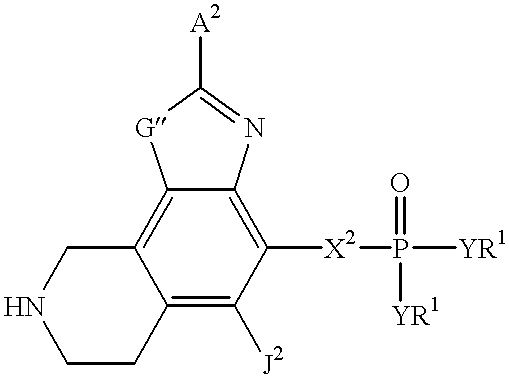
Heteroaromatic compounds containing a phosphonate group that are inhibitors of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
FBPase inhibitors of the formula I and Xare useful in the treatment of diabetes and other conditions associated with elevated blood glucose or excess glycogen storage.
Owner:METABASIS THERAPEUTICS INC
Non-maltogenic exoamylases and their use in retarding retrogradation of starch
InactiveUS6667065B1Highly effective in retarding or reducing detrimental retrogradationImprove propertiesDough treatmentHydrolasesAmylosucrase activitySide chain
The present invention relates to a process for making a bread product. The process includes the addition of a non-maltogenic exoamylase that hydrolyses starch to a starch medium, and the application of heat to the starch medium. The non-maltogenic exomylase cleaves one or more linear malto-oligosaccharides, predominantly consisting of from four to eight D-glucopyranosyl units, from non-reducing ends of amylopectin side chains. The non-maltogenic exoamylase has an endoamylase activity of less than 0.5 endoamylase units (EAU) per unit of exoamylase activity.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
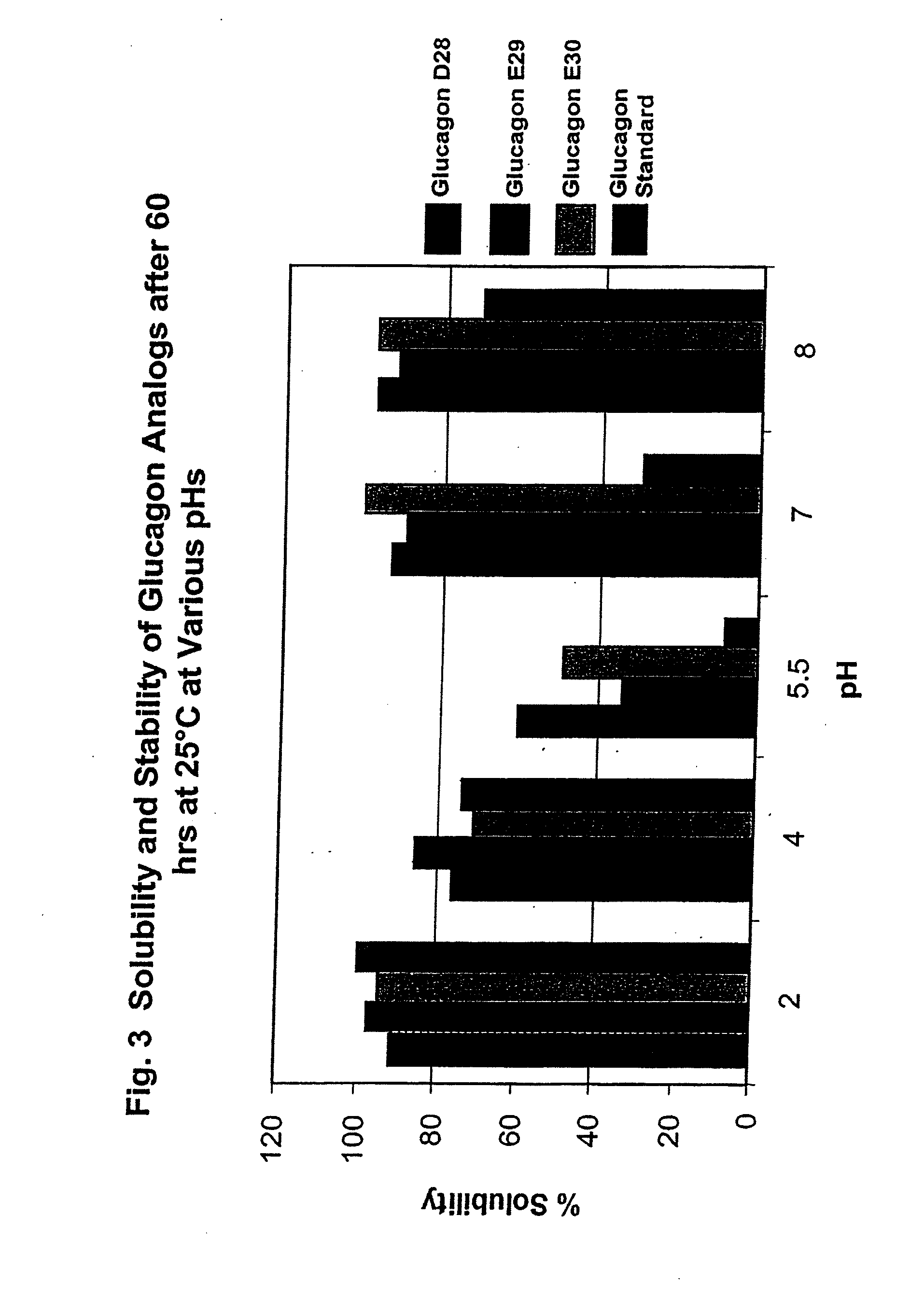
GLUCAGON ANALOGS EXHIBITING ENHANCED SOLUBILITY AND STABILITY IN PHYSIOLOGICAL pH BUFFERS
ActiveUS20110190200A1Rapidly increasing glucose levelNormalizing blood glucose levelAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionHalf-life
Modified glucagon peptides are disclosed having improved solubility and / or half-life while retaining glucagon agonist activity. The glycogen peptides have been modified by substitution of native amino acids with, and / or addition of, charged amino acids to the carboxy terminus of the peptide. The modified glucagon agonists can be further modified by pegylation, or the addition of a carboxy terminal peptide selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 20, SEQ ID NO: 21, SEQ ID NO: 23, or both to further enhance the solubility of the glucagon agonist analogs.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
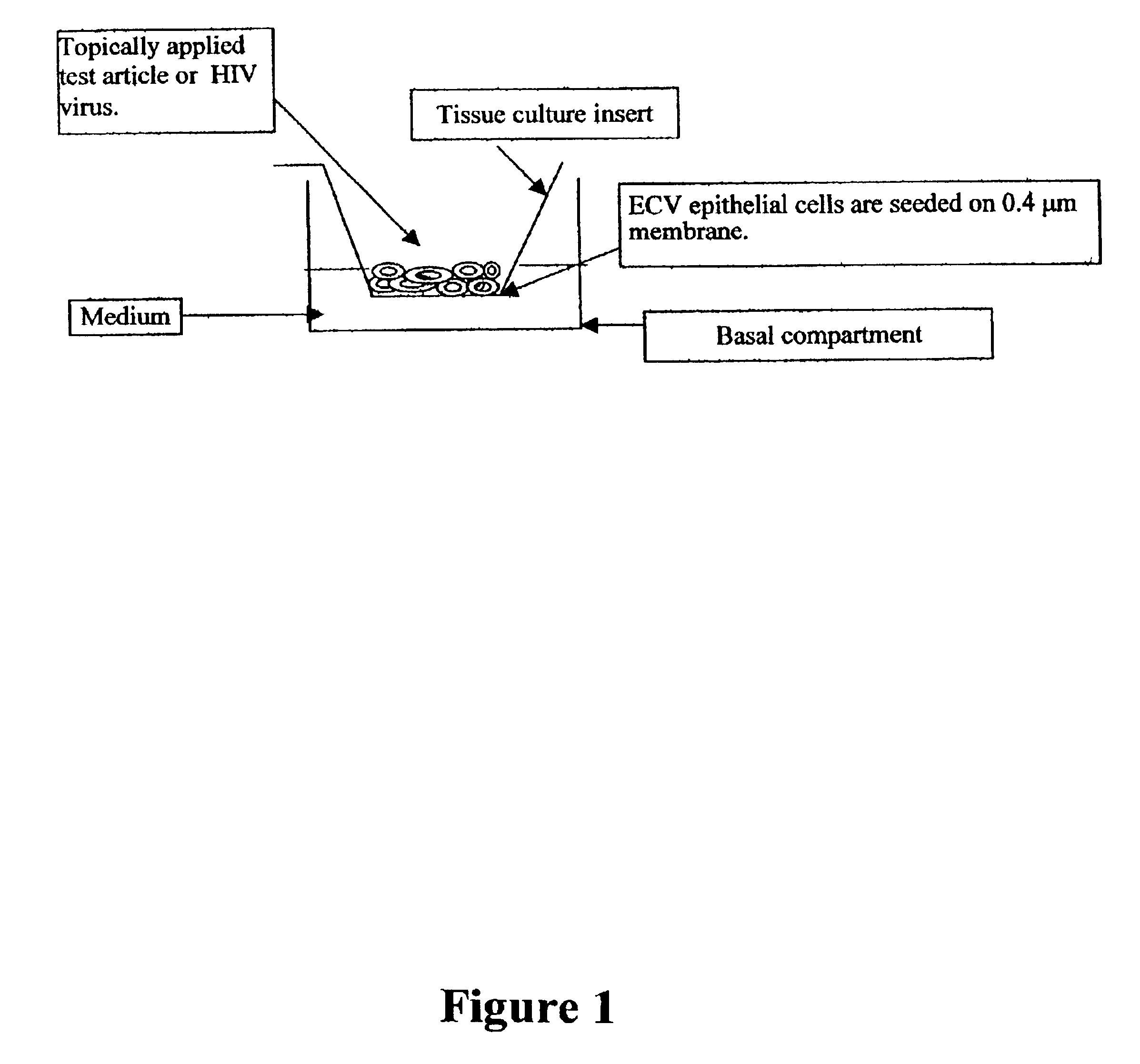
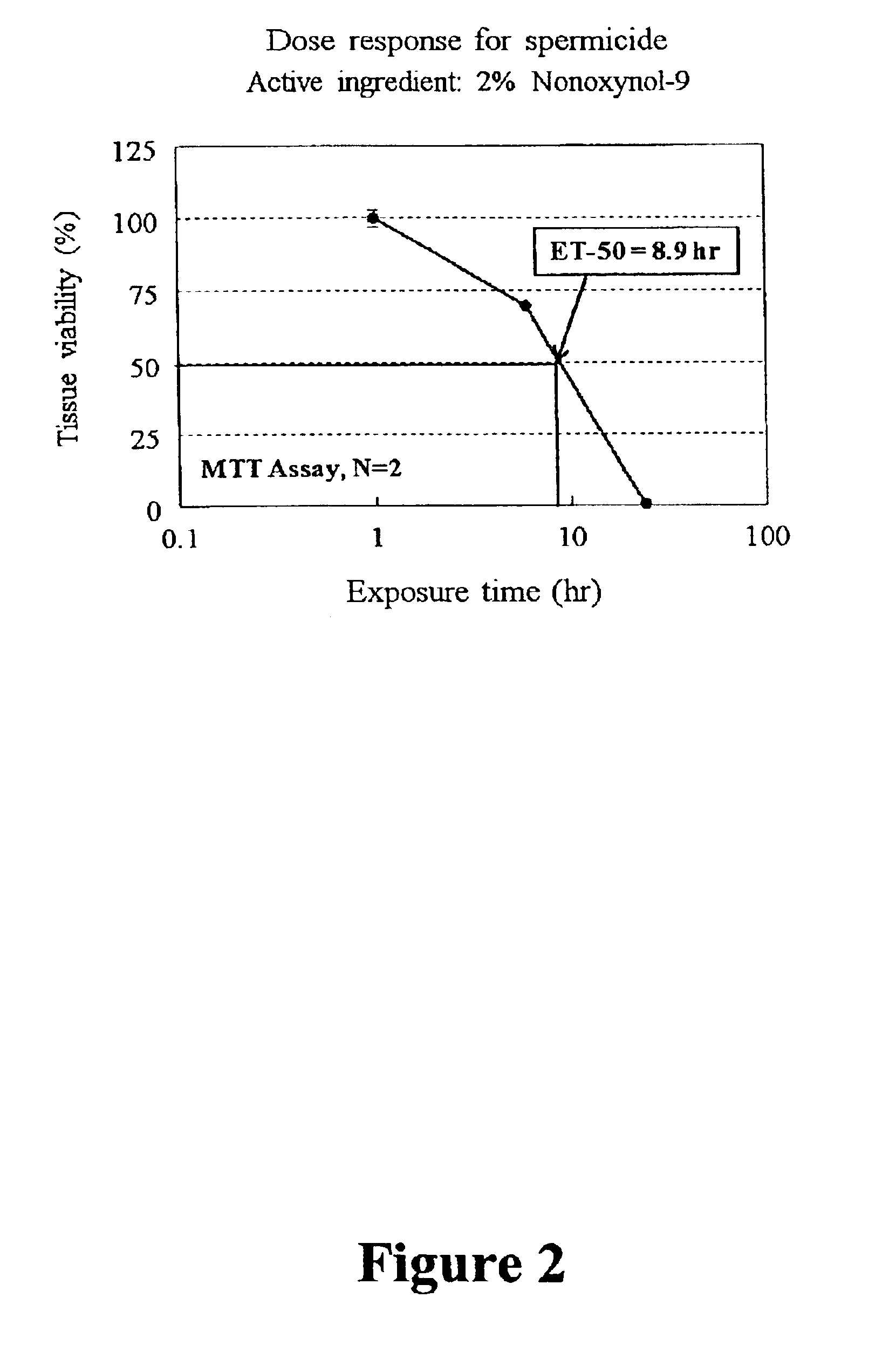
Three dimensional vaginal tissue model containing immune cells
InactiveUS6943021B2Improve survivabilityInduced proliferationBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsSerum free mediaAir liquid interface
Disclosed is a cervico-vaginal tissue equivalent comprised of vaginal epithelial cells and immune cells, cultured at the air-liquid interface. The tissue equivalent is capable of being infected with a sexually transmitted pathogen such as a virus (e.g., HIV), a bacteria, a helminthic parasite, or a fungus. The tissue equivalent is also capable of undergoing an allergic-type reaction or an irritant-type reaction. The tissue equivalent is characterized as having nucleated basal layer cells and nucleated suprabasal layer cells, and further as having cell layers external to the suprabasal layer progressively increasing in glycogen content and progressively decreasing in nuclei content. Immune cells of the tissue equivalent are primarily located in the basal and suprabasal layers. Also disclosed are methods for producing the tissue equivalent. The methods involve providing vaginal epithelial cells and immune cells, seeding the cells onto a porous support, and co culturing the seeded cells at the air-liquid interface under conditions appropriate for differentiation. One such method disclosed is for generation of the tissue equivalent in serum free medium. Specific cells from which the tissue equivalent is generated, and also specific preferred components of the medium in which the tissue equivalent is generated are provided. Also disclosed is a cervico-vaginal tissue equivalent produced by the methods disclosed herein.
Owner:MATTEK CORP
Compositions for Preventing and Reducing Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness
InactiveUS20080317886A1Inhibit inflammationSpeed up recoveryBiocideSugar food ingredientsSucroseL glutamate
The present invention relates to the compositions that enhance post-exercise recovery processes to increase both strength and muscle mass, replace glycogen stores, and prevent inflammation, resulting in the prevention and / or reduction of delayed onset muscle soreness. Additionally, it provides a feeling of muscle relaxation as well as a feeling of mental tranquility immediately following exercise. The composition consists of any or all high-glycemic sugars and / or polysaccharides (e.g., sucrose, glucose, maltodextrin), all essential amino acids and beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate and can include other amino acids sources (e.g. whey protein), performance enhancing agents (e.g., caffeine, L-glutamate), anti-inflammatory agents (e.g., ginger, boswellia, curcumen), antioxidants (vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, polyphenols,), insulin-mimicking agents (cinnamon, Banaba), analgesics (e.g. aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, acetaminophen), and to methods of treating humans and animals by administration of these novel compositions to humans and animals in need thereof.
Owner:SOUTHWEST IMMUNOLOGY
Biological preparation capable of preventing and treating cruciferae club root and use thereof
InactiveCN101416641AGood control effectSolve prevention and control problemsBiocideBacteriaSucroseRussulaceae
The invention relates to a biological agent against crucifer club root and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of bio-pesticide. The strain for production is Bacillus subtilis XF-1, whose preserving number is CGMCC NO.2357. The stain has the characteristics as follows: (1) the primary colony on the LB culture substrate is white and round having a wet surface; the later colony is light yellow having uneven edge with dry and crimple surface; observed from the microscope, the strain is short-bar shaped and movable with spore, peritricha and dimension of 0.7 - 0.8 * 2.0-2.4 mum; (2) the strain is Gram-positive and aerobic and makes use of glycogen, sugar, citrate, gelatin hydrolysate, starch and casein, but does not make use of cellulose, tyrosine and catalase positive; (3) the stain has the function of sterilization, disease prevention, and yield improvement. The embodiment of the invention is as follows: using the test tube of Bacillus subtilis XF-1 stain, shake cultivation, and culture solution for fermentation to prepare biological agent, then applying the biological agent to the rhizosphere soil of crucifer crops, thereby having good effect in preventing and treating, and simple production.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Formative agent of protein complex
InactiveUS20020119946A1Keep for a long timePromote resultsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCartilage cellsCuticle
The present invention proposes formative agent of protein complex, in which a polyphenol is useful component, and the agent is useful as gene complex, cell adhesion inhibitor or immune tolerogen. The polyphenol of forming the agent is selected from catechin group consisting of epigallocatechin-gallate, tannic acids, or proanto-dianisidine, a protein of the protein complex is selected from proteins consisting of animal proteins composed of polypeptide chain of peptide-combined amino acids, vegetative proteins, nucleus proteins, glycogen proteins, lipo-proteins and metal proteins, the gene complex comprises by compositing genes by polyphenol catechins in order to introduce genes to cells of animals or human bodies, a cell composed of the cell adhesion inhibitor is selected from cells consisting of an animal cell including a stem cell, skin cell, mucosa cell, hepatocyte, islet cell, neural cell, cartilage cell, endothelial cell, epidermal cell, osteocyte or muscle cell isolated from human or animal organism, or sperm, ovum or fertilized egg of domestic animals or fishes and a tissue or an organ for transplantation of the immune tolerogen is selected from the tissue or the organ consisting of skin, blood vessel, cornea, kidney, heart, liver, umbilical cord, bowels, nerve, lung, placenta or pancreas.
Owner:BERTELSMANN MUSIC GROUP
Palatable suspending vehicle for pharmaceutical ingredients
ActiveUS20060034873A1Improved Theological characteristic and stabilityEasy and quick resuspensionDispersion deliverySolution deliveryAdditive ingredientSuspending Agents
The invention relates to a liquid vehicle that can be used to create suspensions and / or solutions of liquid or powdered medications. The vehicle is thixotropic and has improved stability and rheologic characteristics. Vehicles of the invention include an aqueous medium and a suspending agent comprising a polysaccharide having at least 50% glucose repeating saccharide units and at least 90% beta linkages. The polysaccharide can be a starch, modified starch, or glycogen. The aqueous medium and individual components of the vehicle provide a palatable and easily ingested drug preparation. The invention also provides a vehicle containing an aqueous medium, suspending agent comprising a polysaccharide having at least 50% glucose repeating saccharide units and at least 90% beta linkages, buffer, and artificial sweetener, the combined suspending vehicle having a pH of about 3 to about 10 and an osmolality of 300 mOmsol or less.
Owner:GALLIPOT
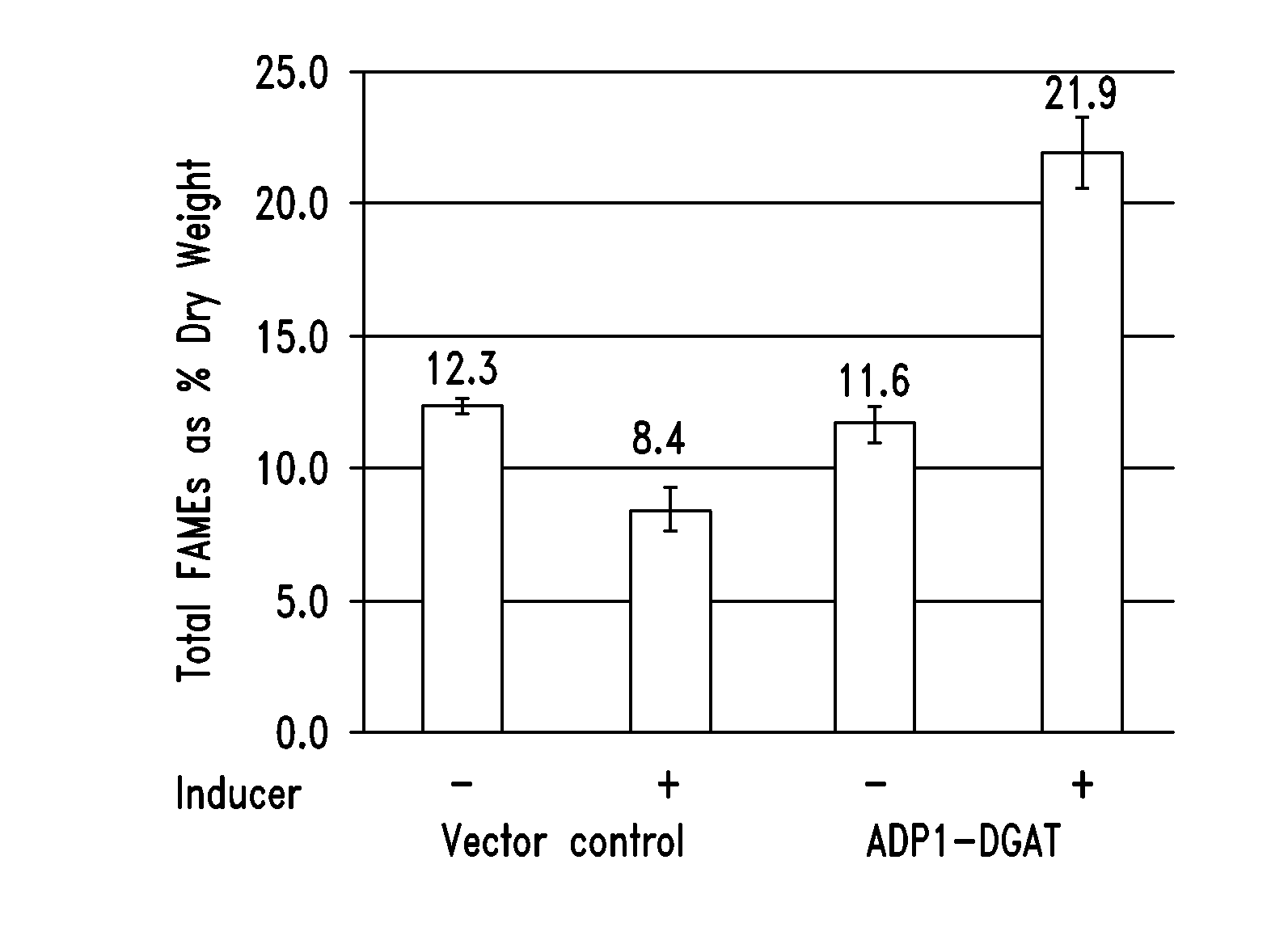
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing lipids
ActiveUS20110250659A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease volumeHydrolasesUnicellular algaePhylum CyanobacteriaLipid formation
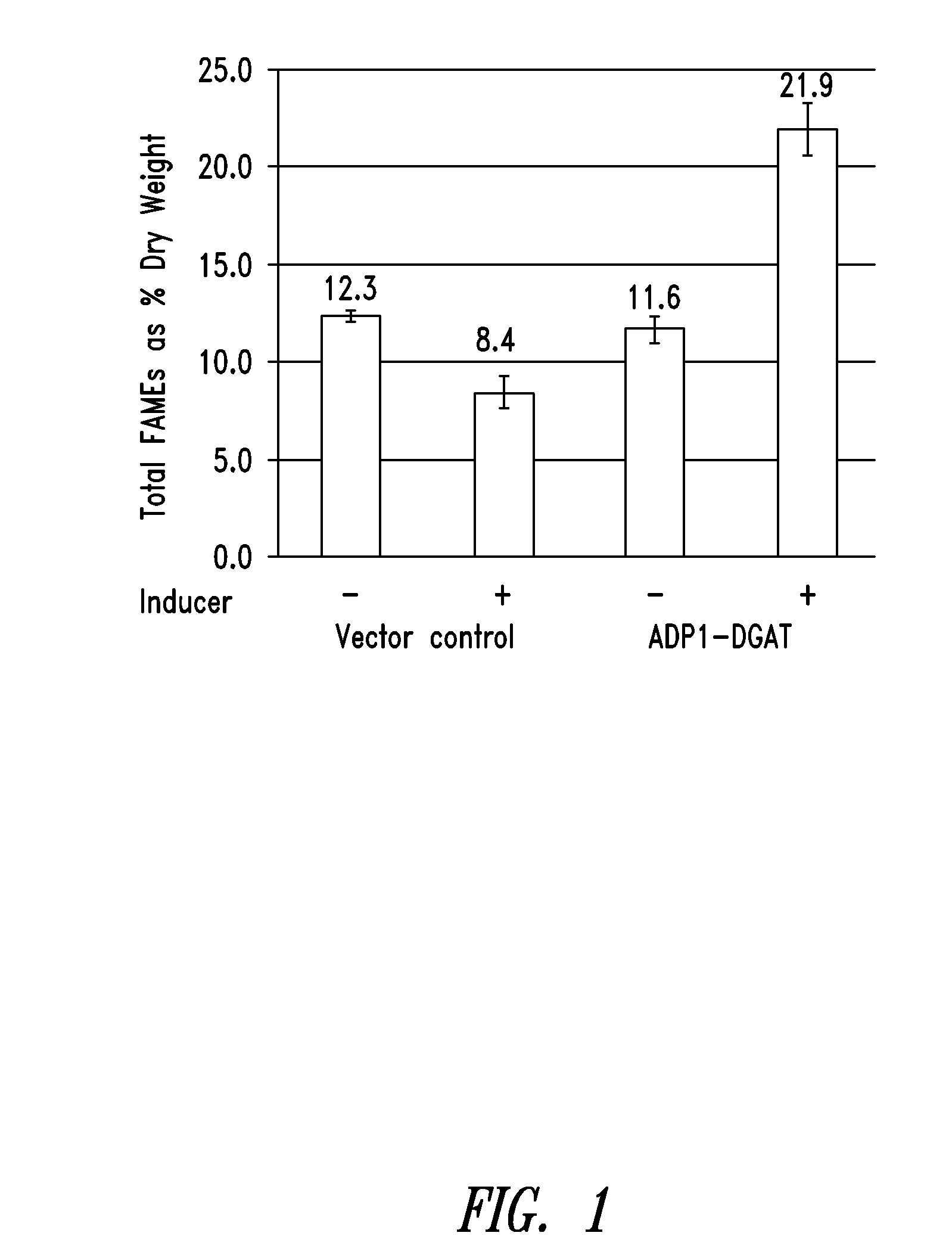
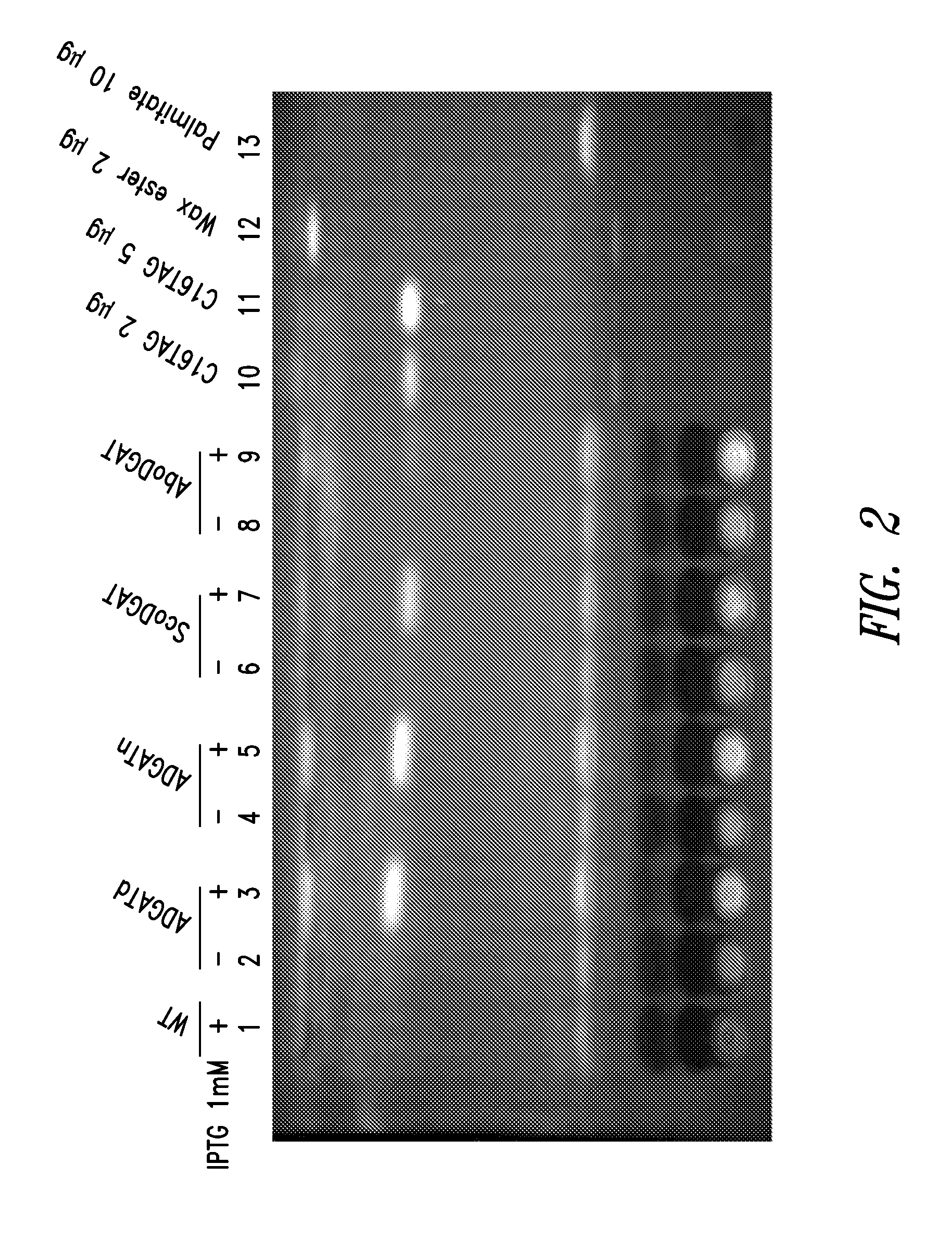
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, e.g., Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a phospholipase and / or thioesterase, which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. This disclosure also describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides, as well as photosynthetic microorganism comprising mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen under reduced nitrogen conditions as compared to a wild type photosynthetic microorganism.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Methods for determining the metabolism of sugars and fats in an individual
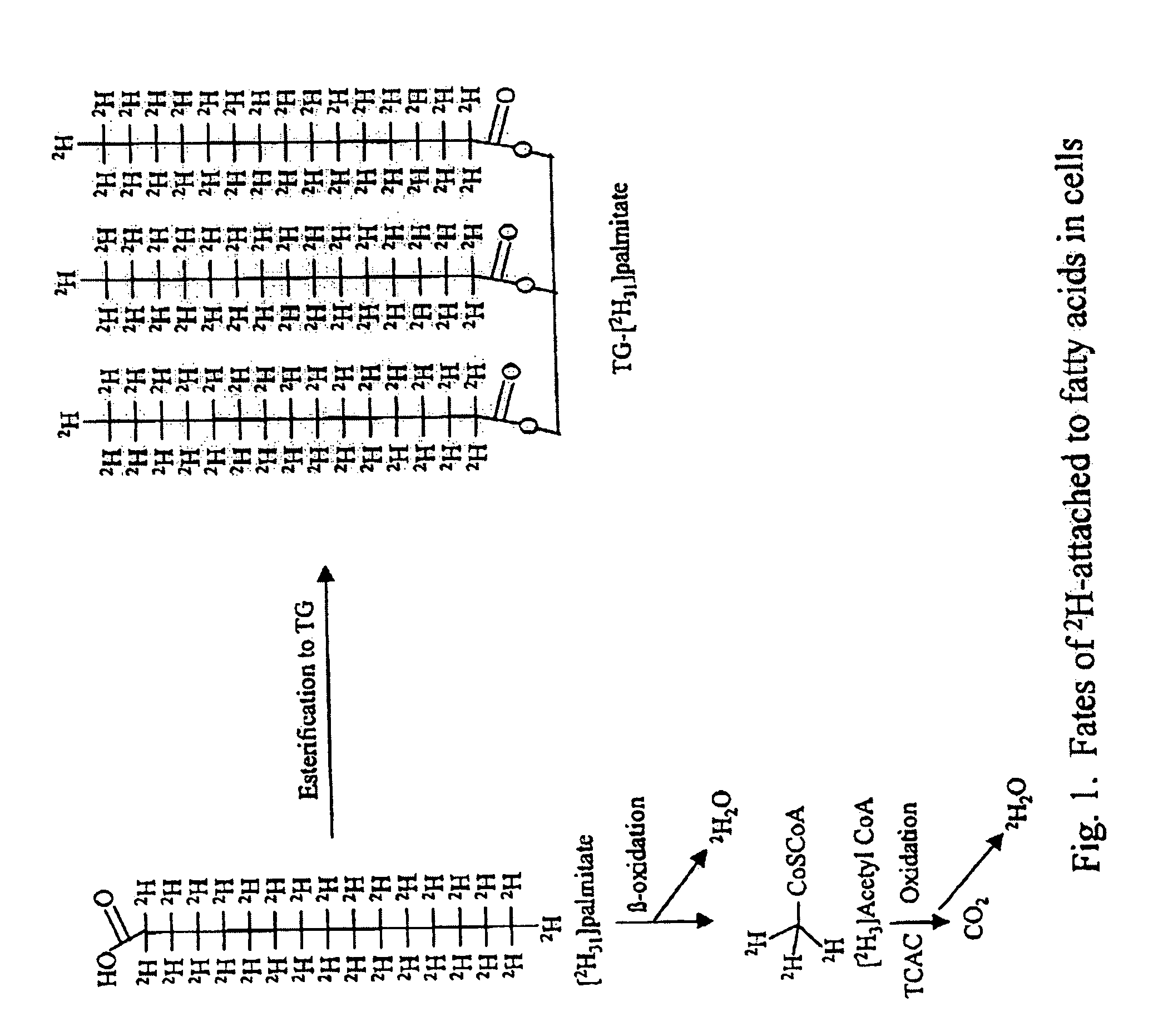
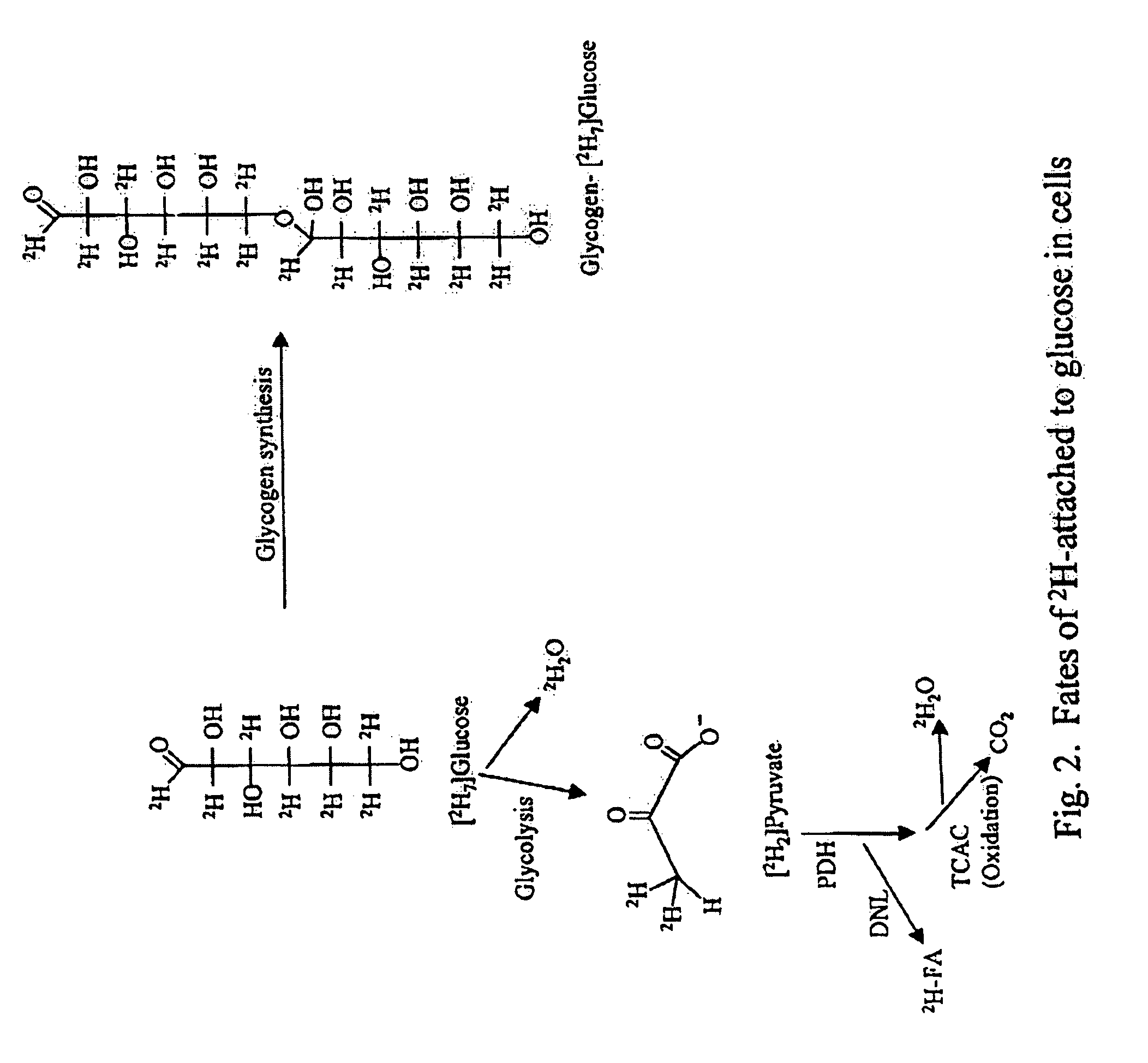
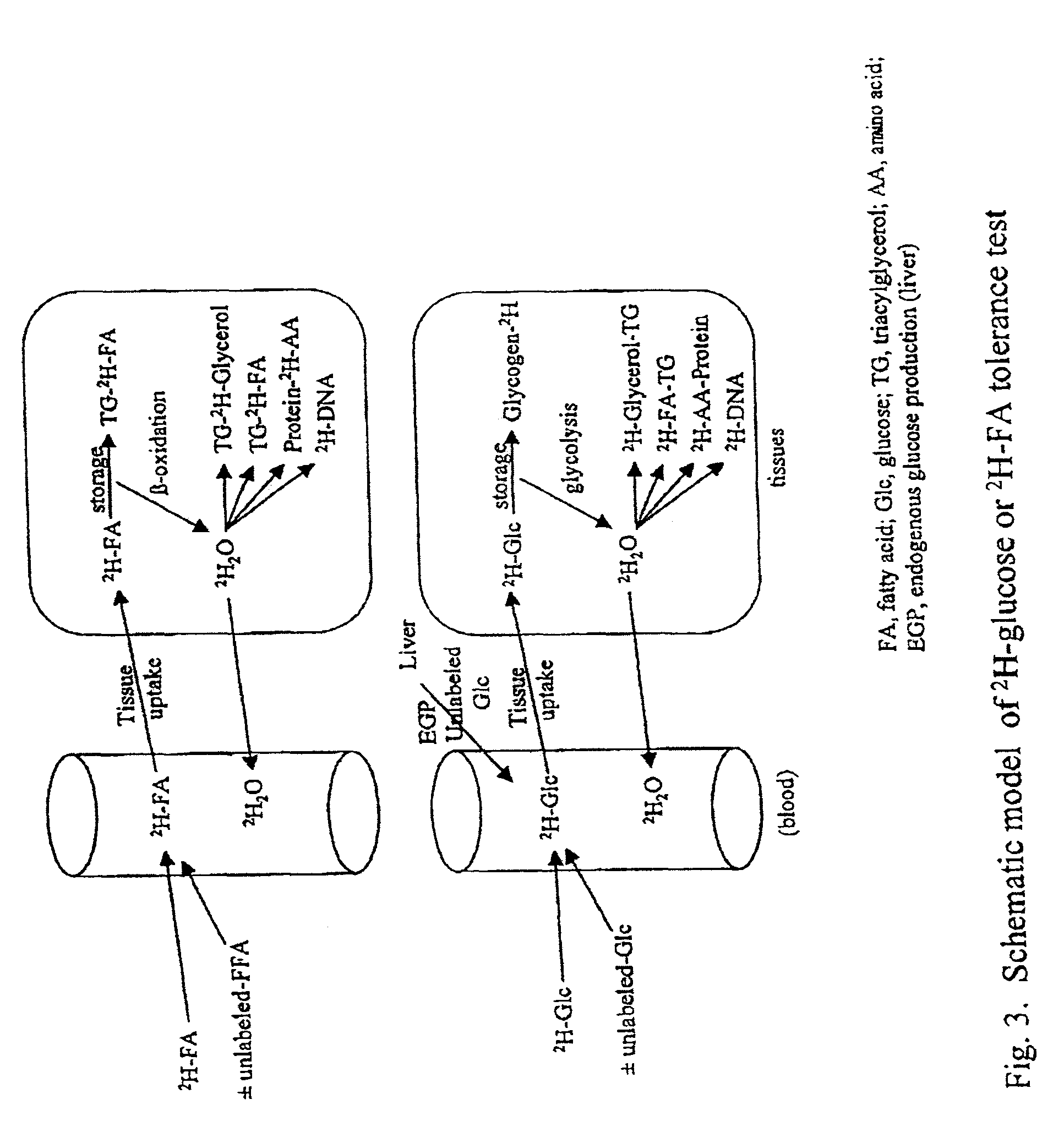
ActiveUS7504233B2Compounds screening/testingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsTrial drugPreclinical testing
Provided herein are methods for determining the metabolism of one or more sugars and / or fatty acids, and applications thereof. Such applications include determining the rate of glycogen synthesis and glycolysis, which are believed to be early markers for predicting elevated risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Other applications include methods for screening drugs that effect sugar and / or fatty acid metabolism. The methods are useful for at least partially characterizing drugs for desirable or undesirable (toxic) characteristics. Drugs that are at least partially characterized using the methods of the invention can then be further developed in pre-clinical testing and clinical trials. Such drugs may be found to be useful in treating obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other disorders of metabolism.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
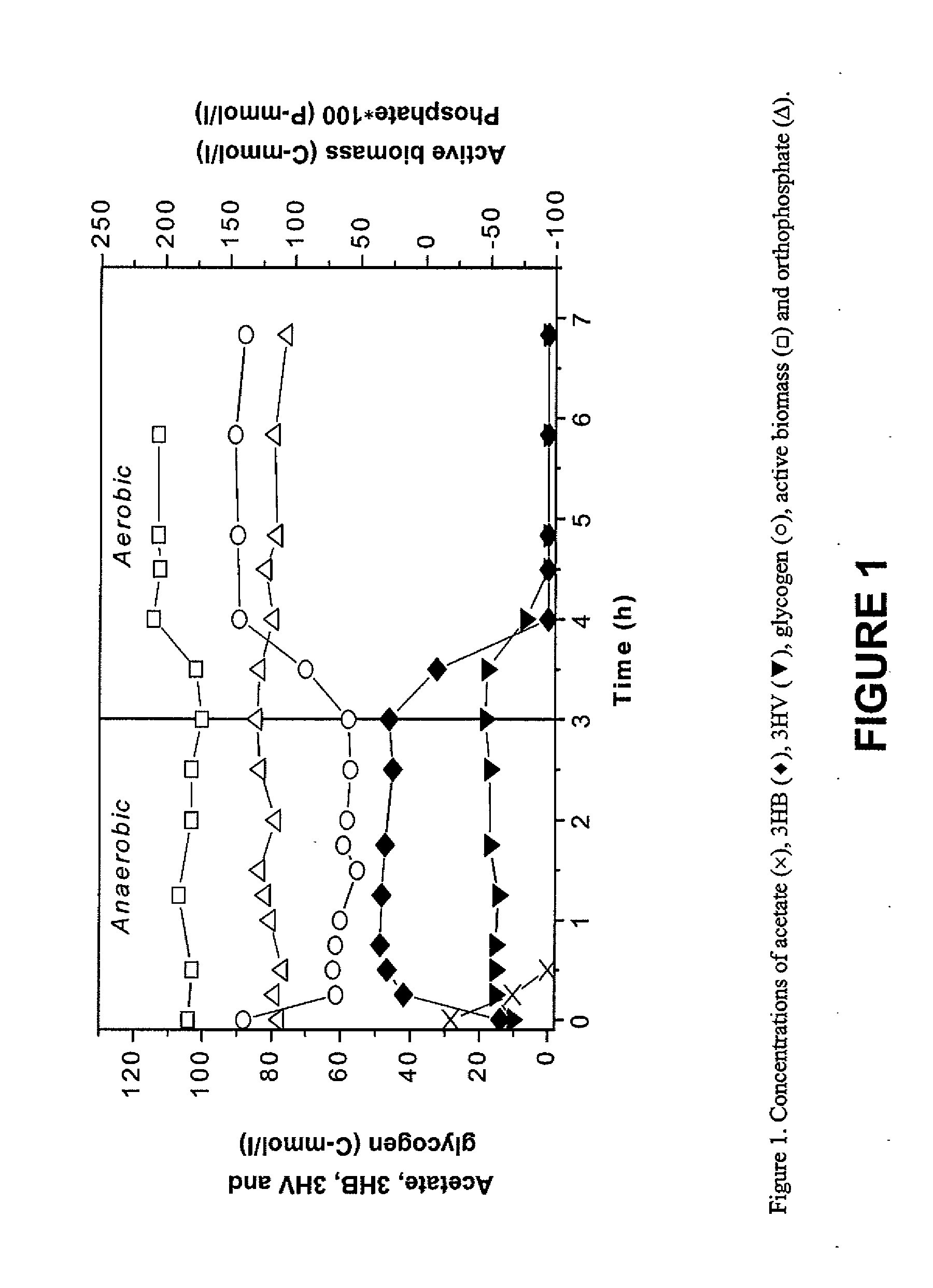
Process for Maximizing PHA Production in Glycogen Accumulating Organisms
InactiveUS20100200498A1High load rateHigh level of intracellularBacteriaSolid waste disposalBiological bodyAnaerobic aerobic
A process is provided for increasing the production of PHA in a mixed culture biomass. In a first stage of the process, organic material associated with a substrate is converted to volatile fatty acids. In the case of a wastewater treatment process, if the wastewater includes sufficient volatile fatty acids (VFAs) to support the process, then it is unnecessary to convert organic material to VFAs. In a second stage of the process, an anaerobic-aerobic selection process is utilized to select glycogen accumulating organisms that cause these organisms to proliferate and dominate the open mixed culture biomass. By providing relatively high organic loading in the form of VFAs in the anaerobic treatment phase of the selection process, glycogen accumulating organisms having a relatively high level of stored glycogen are produced. In a third stage, the PHA accumulation process is practiced where the glycogen rich organisms are fed VFAs under anaerobic or aerobic conditions or combinations thereof. Through the consumption of externally supplied VFAs and internally stored glycogen, relatively high levels of PHA in the biomass are produced. Thereafter PHA is separated from the residual biomass.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER SOLUTIONS & TECH SUPPORT
Additive for battery, cathode material containing same and preparation method for cathode material
InactiveCN103515614AInhibition of dissolutionImprove cycle performanceElectrolyte layer coatingDissolutionElectron
The invention provides an additive for a lithium sulphur battery, a cathode material containing the same and a preparation method for the cathode material. The additive is a product formed by carbonizing and compounding a carbon material and monosaccharide or polysaccharide polymerized by monosaccharide, wherein the monosaccharide and the polysaccharide contain intensive arc pair electron groups. The intensive arc pair electron group is -C=O or -OH. The monosaccharide is selected from glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, glycogen and ribodesose. The conductive carbon material in the cathode material has good adsorption capacity, large specific surface area, and high pore volume and adopts a porous structure, and the electrochemical active substance is sulphur. The additive is the substance containing the intensive arc pair electron group. Polysulfide lithium produced during the discharge process can perform interaction with the additive in a mode of coordination and the like, so that the dissolution of the polysulfide lithium in electrolyte is restrained, and the loss of the active substance and the lithium cathode corrosion, rapid capacity fading influence and the like can be effectively reduced.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
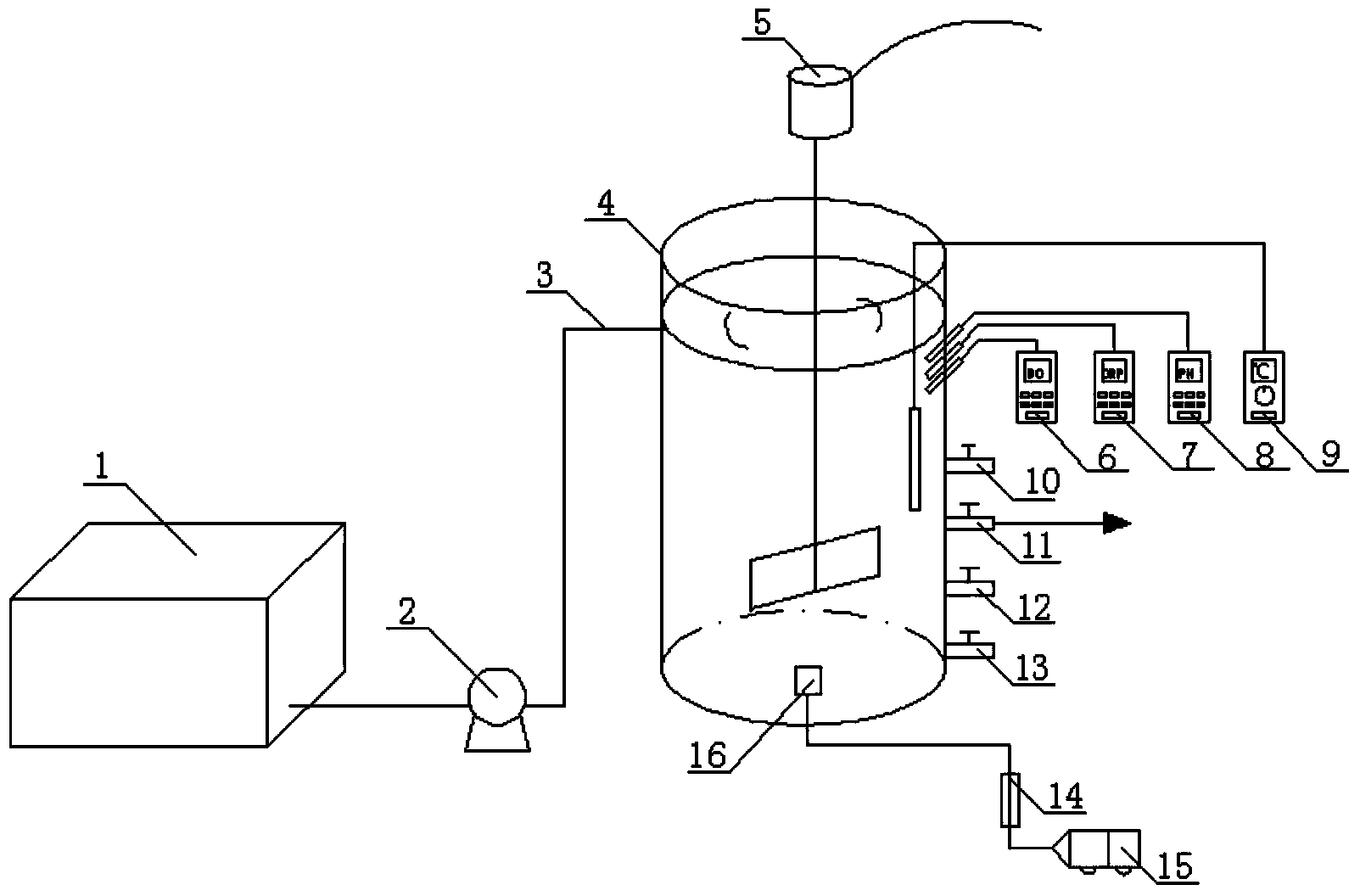
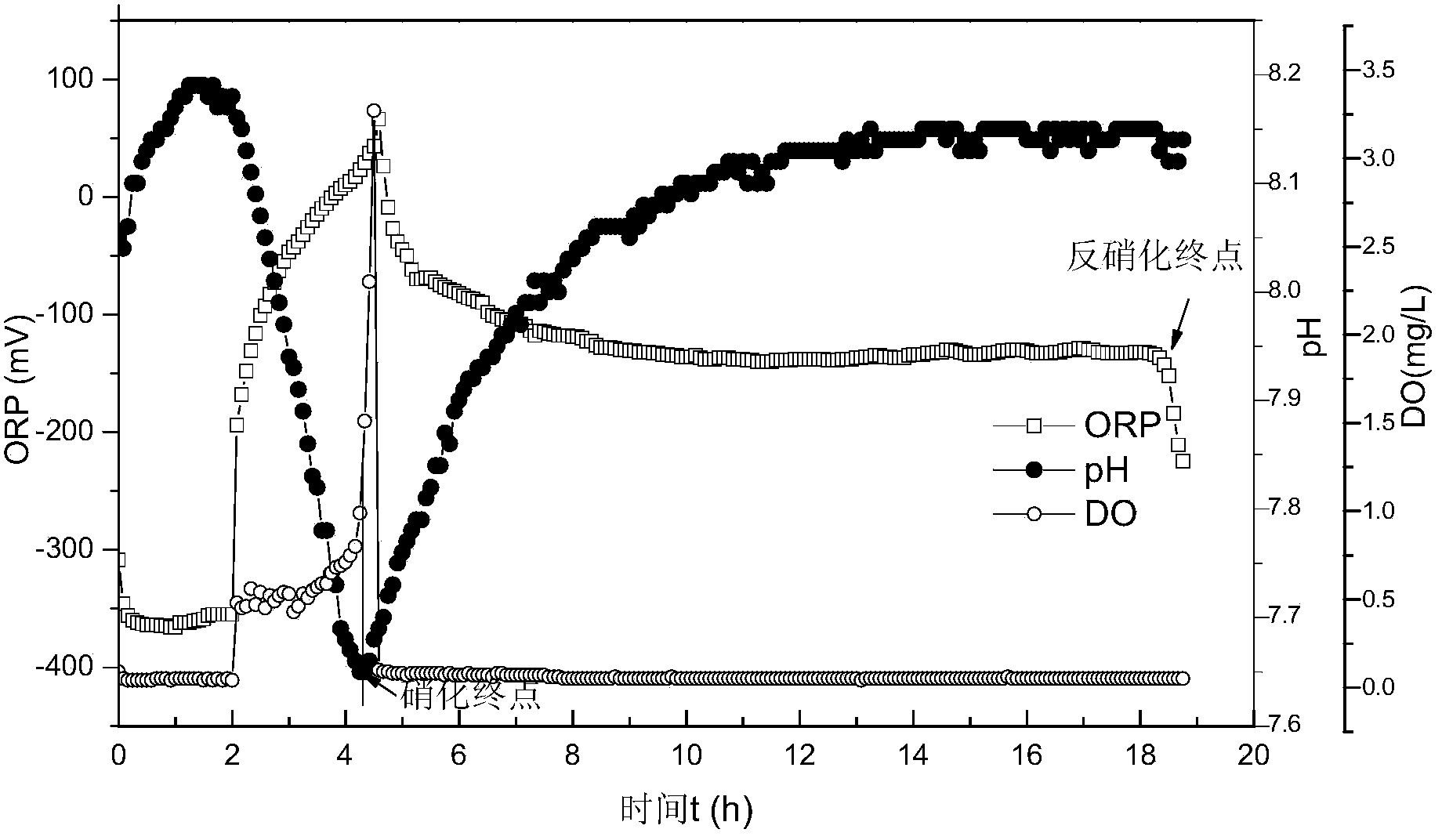
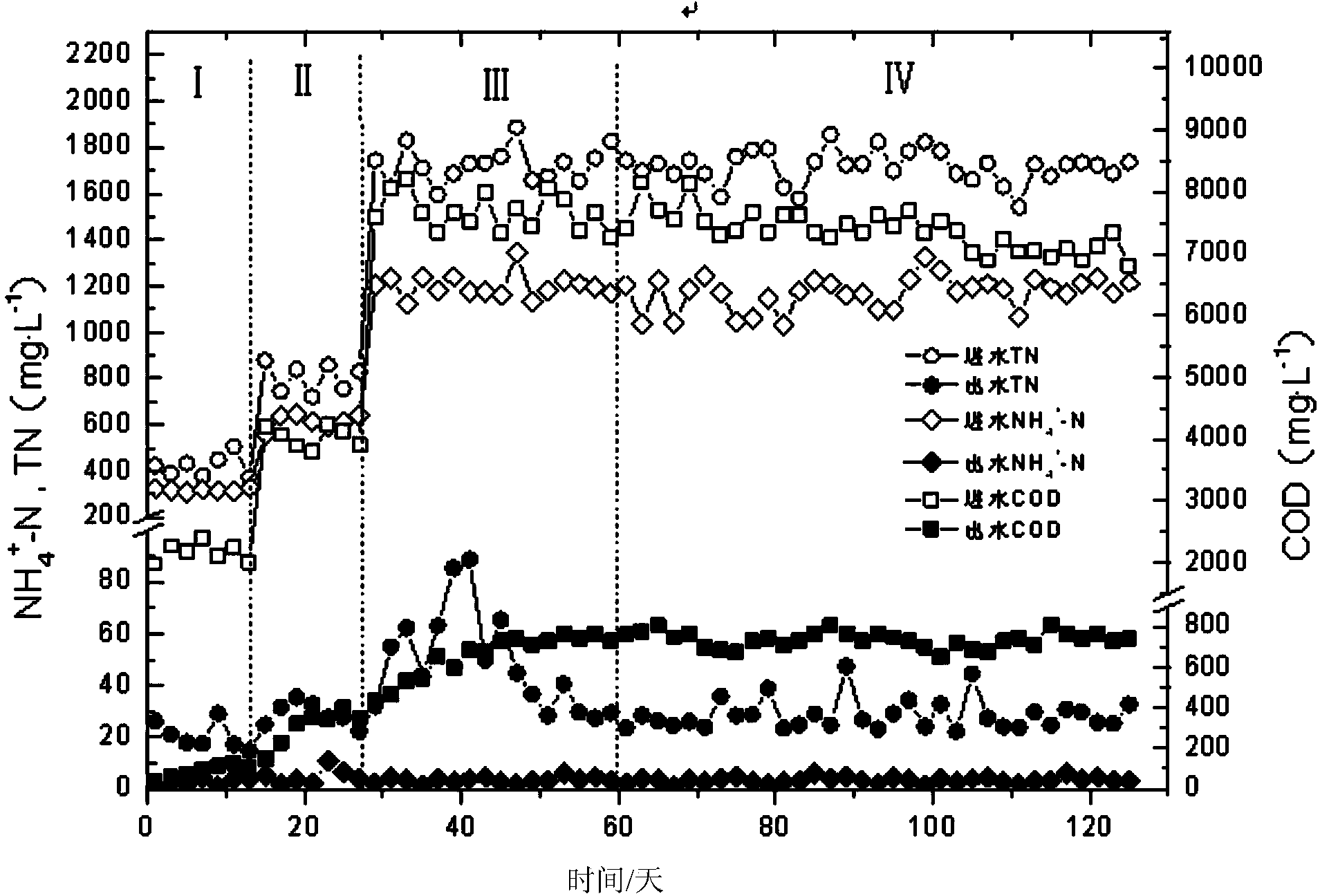
Quick starting method of SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) for synchronously denitrifying and removing phosphor
InactiveCN103588300AReduce startup timeEffective proliferationBacteriaTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorFungicide
The invention discloses a quick starting method of an SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) for synchronously denitrifying and removing phosphor, and belongs to the field of sewage treatment. The quick starting method using a batch-injection chronological sequencing batch reactor comprises the following steps: (1), operating the SBR system under an anaerobic / aerobiotic alternation condition, and domesticating and enriching phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, so that the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria intake phosphor under the aerobiotic condition and release phosphor under the anaerobic condition; removing phosphate in water by removing mud; (2), changing an operating way of the system, and enriching denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms; increasing an anoxic zone and shortening the aeration time, so that the denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms utilize an intracellular carbon source and use nitrate / nitrite as an electron acceptor to intake phosphor; (3), adding a compound fungicide into the reaction, so that biological enhancement is repeatedly coupled with anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic / aerobiotic starting method, DPB (Denitrifying Phosphorus-removal Bacteria) are effectively proliferated, glycogen accumulating organisms are restrained, the starting time of the reactor is shortened, and the water outlet effect is improved. The starting way disclosed by the invention operates about 50 days in total, can be used for saving about 30 days and saving the aeration time by about 30% in comparison with an anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic starting method.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
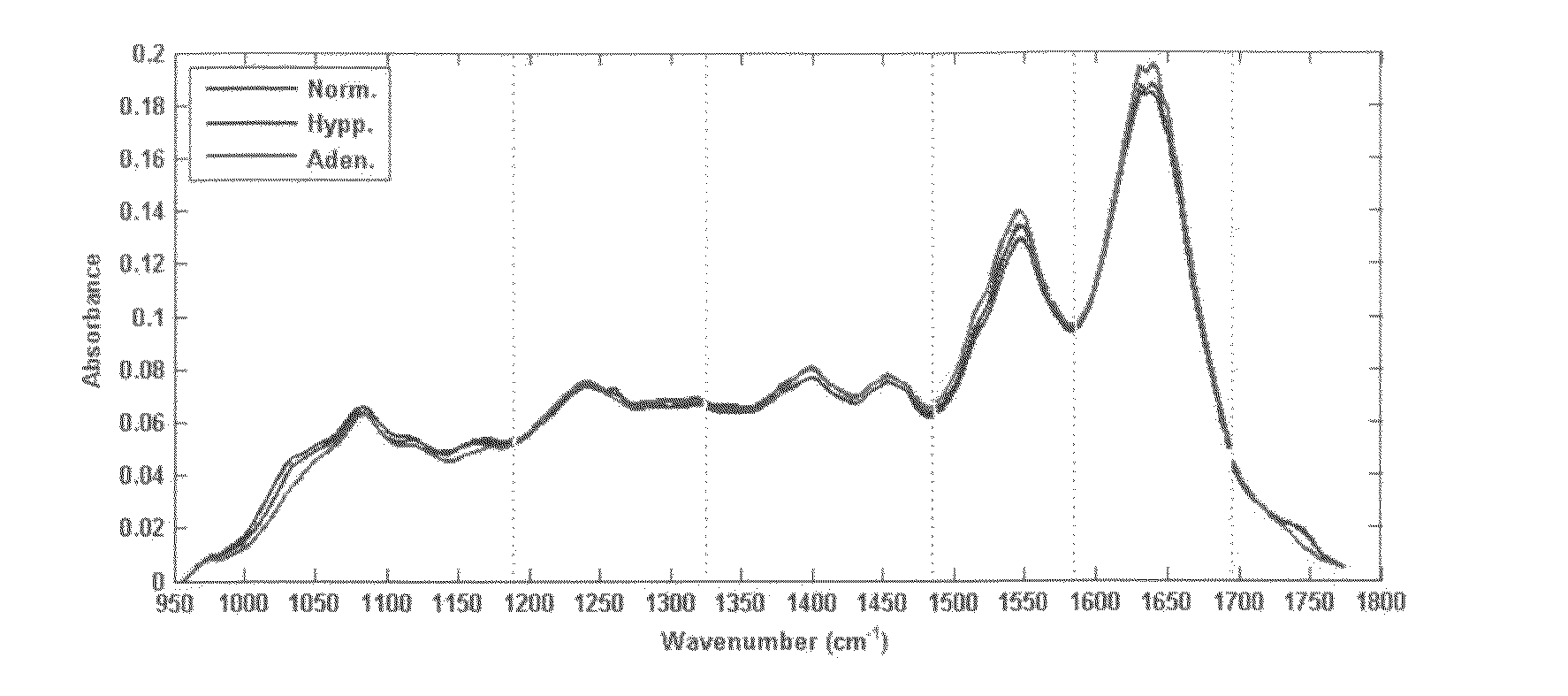
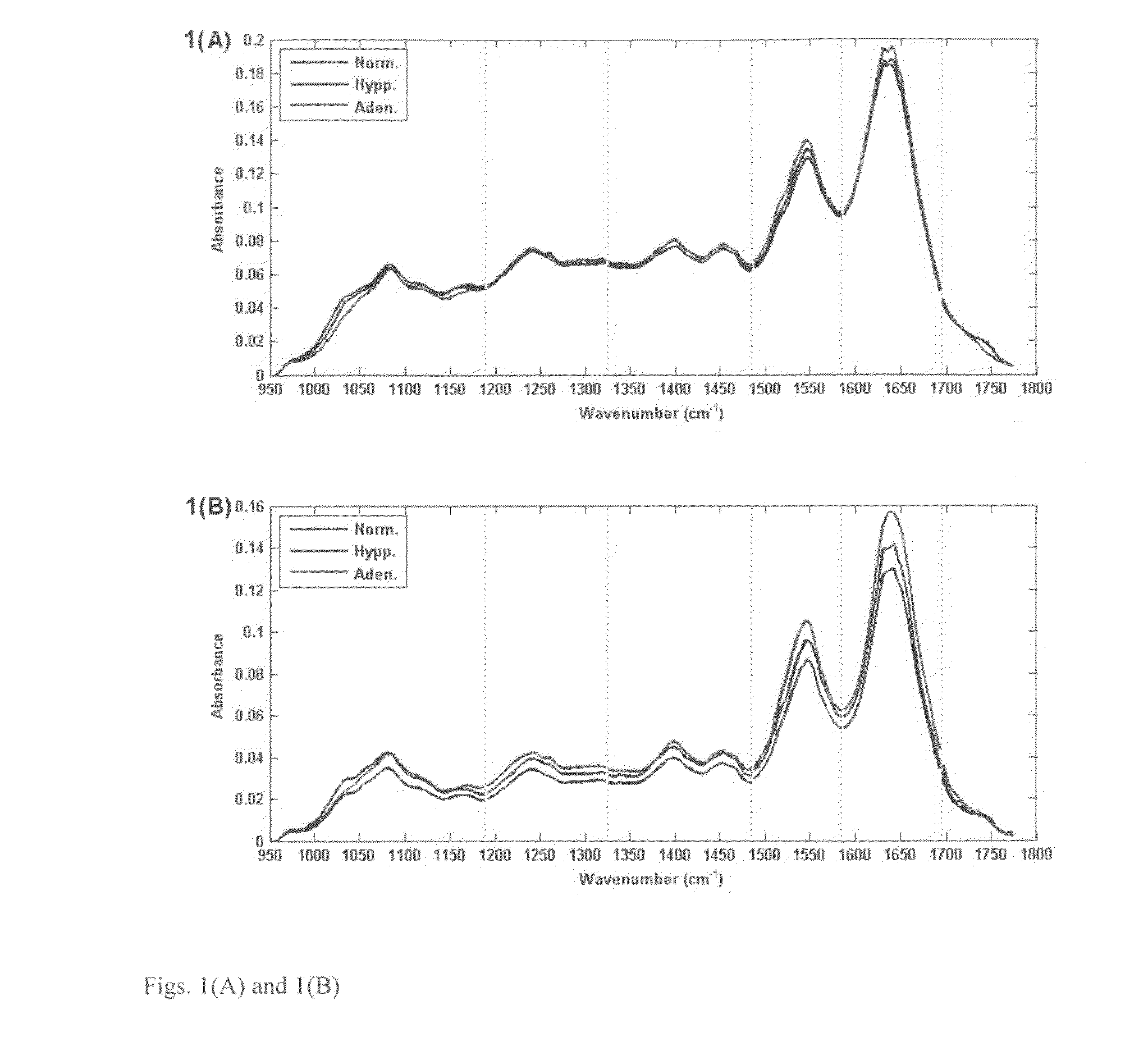
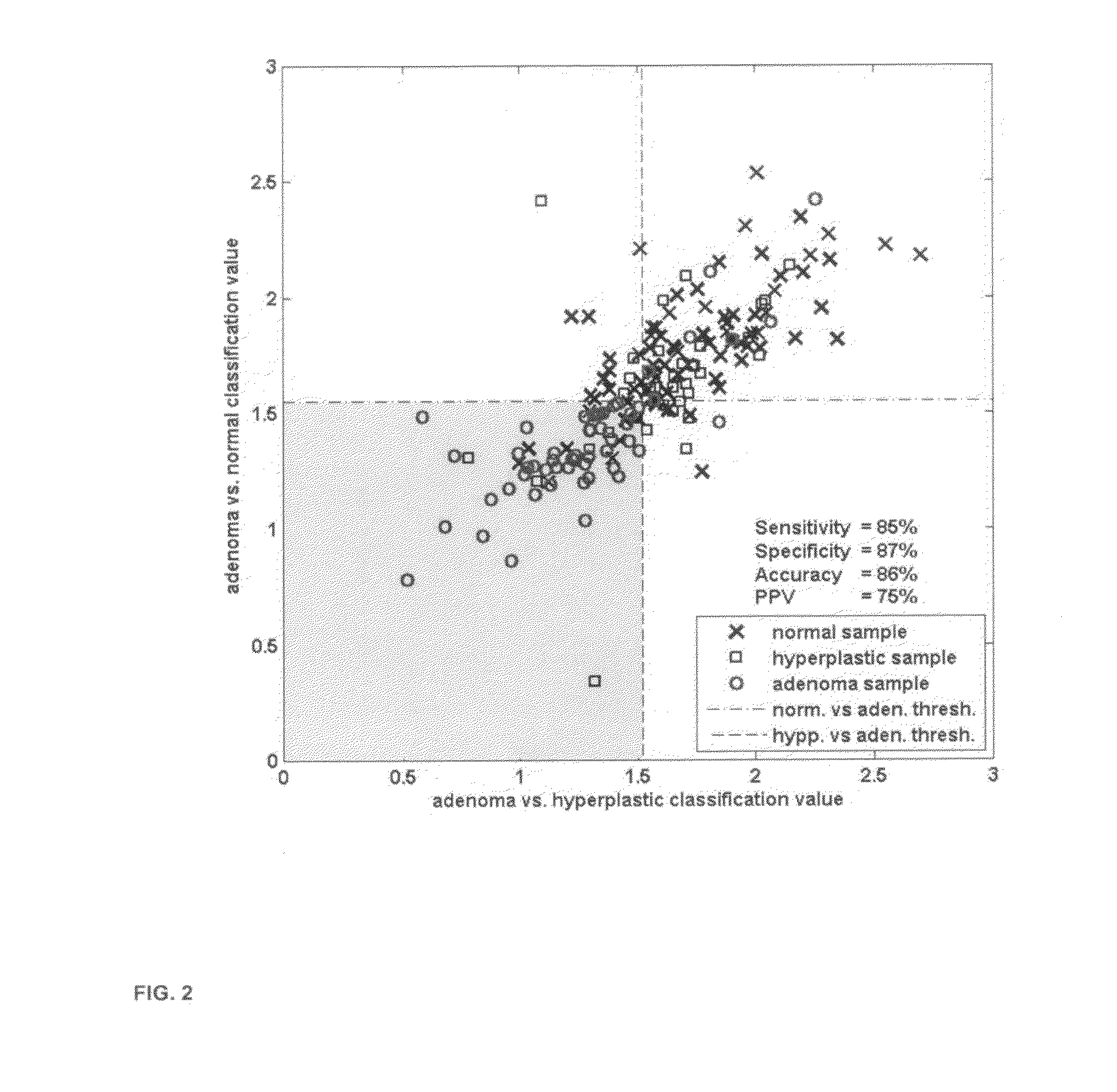
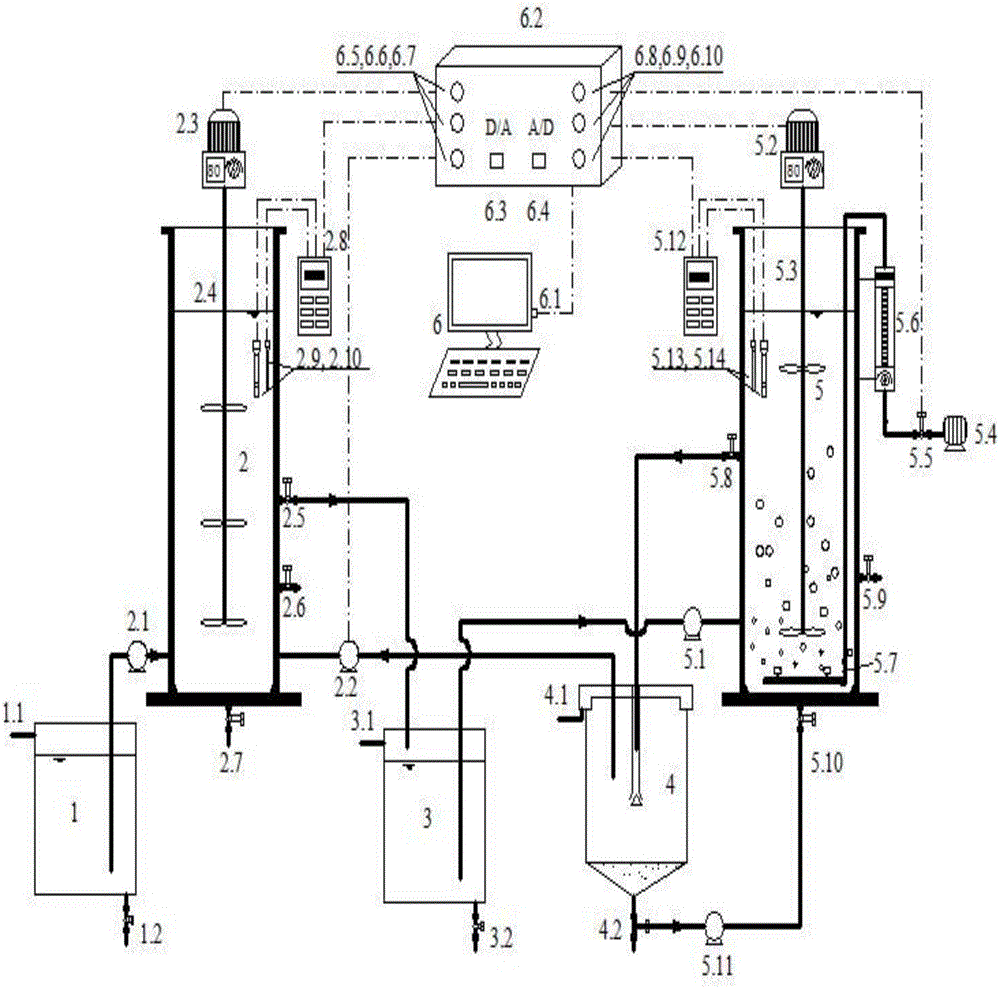
Process and device for detection of precancer tissues with infrared spectroscopy
InactiveUS20100130868A1Promote resultsBetter signal to noiseDiagnostics using spectroscopyMedical automated diagnosisLipid formationPhosphate
A process for determining whether tissue is precancer, in which tests discriminating between precancer and benign tissue and between precancer and normal tissue are combined, and tissue that is classified as precancer in both tests is determined to be precancer, in which neither of the tests to be combined is the most selective. Further, a process and device in which certain optimal wavelengths of glycogen, phosphate and lipid, but not protein, discriminate between normal and precancer tissues.
Owner:CADES SCHUTTE A LIMITED LIABILITY LAW PARTNERSHIP
Special diet for hyperglycemia patients
ActiveCN103404757AStable healthEffect on reducing the development of coronary heart disease-related conditionsFood preparationAcute hyperglycaemiaChinese traditional
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine-food homologous formula food and particularly relates to special diet for hyperglycemia patients. The reason inducing hyperglycemia is that hepatic glycogen output is increased, too much high-fat food is ingested, the pancreatic islet function can not excellently secrete insulin, and then, the blood sugar content is increased. The traditional Chinese medical science always stresses that dietotherapy is better than medication, so as to avoid injection and medication and even pain of surgery. According to the special diet, whole grains are perfectly combined with medicine-food homologous and new-resource-food traditional Chinese medicines, and diet and health preserving are organically combined so as to regulate, prevent and resist hyperglycemia; probiotics are creatively utilized as a pioneer based on the inheritance of Chinese traditional Chinese medicine treasure treatment methods, and the proliferation of the probiotics is promoted, so that the movement functions of the spleen and stomach are enhanced; and meanwhile, various natural and original ecological medicine-food homologous edible materials are added according to the physical characteristics of hyperglycemia patients, so that the special diet has the unique advantage of integrated dietotherapy, prevention and regulation effects.
Owner:杭州劲膳美健康管理有限公司
Preparation process of fruit can
InactiveCN102550650AEasy to synthesizeGood colorClimate change adaptationFruits/vegetable preservation using sugarsVitamin CCanned fruit
A preparation process of a fruit can is characterized in that the formula of the fruit can includes following materials by weight: 55%-60% of fruits, 8%-10% of sugar mixture, 0.3% of citric acid, 0.2% of neotame, 0.05% of vitamin C and the balance of water, the sugar mixture includes 60%-70% of xylitol and 30%-40% of fructose, and the xylitol is a novel sweetener and an intermediate of saccharometabolism in a human body and can penetrates through a cell membrane to be absorbed and utilized by tissues without the promotion of insulin under the condition that the saccharometabolism is influenced due to the shortage of insulin in a human body, so that the glycogen is promoted to be synthesized, the nutrition and energy are provided for cells, and the blood glucose value cannot be increased. The fruit can provided by the invention is a low-sugar fruit can which has beautiful pulp color and good mouthfeel and is suitable for the old and the young.
Owner:DALIAN YUMAN FOOD
Wastewater advanced denitrification apparatus and method employing single-stage SBBR (sequencing batch biofilm reactor) short-cut nitrification anammox coupled endogenous denitrification
ActiveCN106348439AAchieving synergistic couplingEfficient deep denitrification processWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsBiofilmNitrogen removal
A wastewater advanced denitrification apparatus and method employing single-stage SBBR (sequencing batch biofilm reactor) short-cut nitrification anammox coupling with endogenous denitrification belong to the field of wastewater bio-treatment. Wastewater enters a single-stage SBBR short-cut nitrification coupled endogenous denitrification reactor through a water pump; in anaerobic stirring phase, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and glycogen accumulating organisms make use of an inorganic carbon source in raw water to store internal carbon sources; in hypoxic aeration stirring phase, ammonia oxidizing bacteria convert partial NH4<+>-N in the raw water into NO2<->-H, part of NO2<->-H is subjected to autotrophic nitrogen removal with the rest NH4<+>-N in the raw water via anammox effect, and the other part of NO2<->-H and little NO3<->-H produced in anammox are utilized by the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and glycogen accumulating organisms in the subsequent anoxic stirring phase to provide endogenous denitrification. According to the method, by coupled application of short-cut nitrification, anammox and endogenous denitrification to wastewater bio-treatment, it is possible to provide wastewater advanced denitrification based on energy saving, and full utilization of carbon sources.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for treating low-carbon urban sewage through synchronization of anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling denitrifying phosphorus removal and endogenous denitrification
ActiveCN105906044AStable nitrogen and phosphorus removalHigh degree of enrichmentTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAeration rateDecomposition
The invention discloses a device and method for treating low-carbon urban sewage through synchronization of anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling denitrifying phosphorus removal and endogenous denitrification, and belongs to the field of biological sewage treatment. Urban sewage enters an endogenous denitrification coupling dephosphorization SBR reactor for anaerobic stirring, energy is provided for glycogen inside denitrification glycogen-accumulating organisms decomposition cells, volatile fatty acid VFA in sewage is absorbed for synthesizing an internal carbon source PHA to be stored into the body, meanwhile, the denitrification phosphate-accumulating organisms are subjected to anaerobic phosphorus release, and VFA in the sewage is absorbed for synthesizing PHA to be stored into the body; after anaerobic stirring is finished, precipitation and drainage are performed, outlet water is drained into a middle water tank; then, water containing ammonia nitrogen and phosphate in the middle water tank is made to enter an integrated partial nitrification anaerobic ammonia oxidation SBR reactor, intermittent hypoxia aeration stirring is performed, and water is drained and drained into a water outlet tank; the outlet water of the integrated partial nitrification anaerobic ammonia oxidation SBR reactor is made to enter the endogenous denitrification coupling dephosphorization SBR reactor for hypoxia aeration stirring. According to the method, organic carbon sources in raw water are efficiently utilized, and the aeration rate is saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for deep denitrification of metaphase landfill leachate through single-stage SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) post denitrification treatment
ActiveCN103755028AStart fastThe reaction device is simpleTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesVolatile fatty acidsEmission standard
The invention discloses a method for deep denitrification of metaphase landfill leachate through single-stage SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) post denitrification treatment, which belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment by using biochemical process. Aiming at the characteristics that the landfill leachate is high in organism concentration, high in ammonia concentration, high in C / P ratio (grater than 200), the invention discloses a real-time control method with the combination of 'anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic' operation modes, and SBR post denitrification is achieved. Under long-term domestication, glycan bacteria (GAO) can be enriched, volatile organic acids (VFA (Volatile Fatty Acid)) in water are converted into poly-beta-hydroxy-alkanoic acid ester (PHA) through glycogen glycolysis at an anaerobic stage by using GAO, in an aerobiotic stage (the dissolved oxygen is less than 0.8mg / L), when partial nitrification is carried out, most part of PHA is converted into glycogen, and in the anoxic stage, the residual PHA and the glycogen are utilized to perform carbon source denitrification, so that the effluent meets the latest national emission standard. The method has the advantages of simple devices, rapid starting, freedom of external carbon source, good denitrification effect, simplicity in operation, low cost and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Modified Photosynthetic Microorganisms With Reduced Glycogen and Their Use in Producing Carbon-Based Products
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen as compared to a wild type Cyanobacterium, and which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. In certain embodiments, the genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms also contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of lipids or fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Methods for identifying the effect of a drug agent on the metabolism of sugars and fats in an individual
InactiveUS7910323B2Compounds screening/testingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPharmacologyGlycolysis
Provided herein are methods for determining the metabolism of one or more sugars and / or fatty acids, and applications thereof. Such applications include determining the rate of glycogen synthesis and glycolysis, which are believed to be early markers for predicting elevated risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Other applications include methods for screening drugs that effect sugar and / or fatty acid metabolism. The methods are useful for at least partially characterizing drugs for desirable or undesirable (toxic) characteristics. Drugs that are at least partially characterized using the methods of the invention can then be further developed in pre-clinical testing and clinical trials. Such drugs may be found to be useful in treating obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other disorders of metabolism.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Municipal domestic sewage AOA mud-membrane mixed deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal system
InactiveCN113173642AImprove settlement performanceEasy to useWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeDenitrifying bacteria
The invention discloses a municipal domestic sewage AOA mud-membrane mixed deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal system, which comprises the following operation steps that municipal domestic sewage enters a biochemical system and is mixed with first reflux sludge in an anaerobic tank, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and glycogen-accumulating bacteria in the sludge utilize a carbon source in raw water to synthesize an internal carbon source in vivo, then the sludge enters an aerobic zone, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria in the aerobic zone perform aerobic excessive phosphorus absorption to completely absorb phosphorus in the domestic sewage while activated sludge in the aerobic zone and nitrifying bacteria on a filler perform nitrification under the aerobic condition, at the moment, the mixed liquid and the sludge reflux to enter the anoxic zone, and the activated sludge and endogenous denitrifying bacteria on the filler perform deep denitrification on nitrate nitrogen in the sewage by utilizing an internal carbon source accumulated in the anaerobic zone. According to the invention, the system consists of a pretreatment unit, an AOA mud-membrane mixed reactor, a secondary sedimentation tank and a disinfection system, and the effluent reaches the four-class standard.
Owner:JIANGSU YULONG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Extraction method of apostichopus japonicus body-wall total RNA
InactiveCN101864414AMeet Gene Expression AnalysisFulfil requirementsDNA preparationWater bathsTotal rna
The invention discloses a high-extraction-purity, good-integrity and high-yield extraction method of apostichopus japonicus body-wall total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid). The method comprises the following steps of: quickly freezing apostichopus japonicus body-wall tissue in liquid nitrogen; grinding and putting the frozen tissue in lysate to homogenate, centrifugate and take supernatant fluid; adding chloroform to the supernatant fluid and centrifugating to take the supernatant fluid to another centrifuge tube; then, adding a high-salt solution and isopropyl alcohol and filtering precipitation with ethanol; dissolving the precipitation with DEPC (diethypyrocarbonate) treated water to have constant volume; sequentially adding a DNA enzyme buffer solution without RNA enzymes, DNA enzymes without RNA enzymes and an RNA enzyme inhibitor to the dissolved solution to mix; carrying out a water bath at 37 DEG C to obtain DNA lysate; adding phenol and chloroform in a ratio of 5:1 to the DNA lysate to mix, centrifugate and take supernatant fluid; adding a glycogen solution, a potassium acetate solution and pre-cooling ethanol to the supernatant fluid; mixing and staying over night; centrifugating to discard the supernatant fluid; washing and dying the precipitation with ethanol; dissolving the solution with the DEPC treated water to have constant volume of 20 mu l; and storing at 80 DEG C below zero.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Functionalized polysaccharides for active agent delivery
Embodiments of the invention include functionalized polysaccharides and compositions and structures including the same. In an embodiment, the invention includes an active agent delivery composition including a polysaccharide functionalized with a coupling group, wherein the polysaccharide lacks charged groups at a pH of between 6 and 8; and a complex comprising a nucleic acid and a transfection agent. In an embodiment, the invention includes an active agent delivery structure including a matrix comprising a polysaccharide covalently cross-linked through the residue of a coupling group on the polysaccharide, the polysaccharide lacking charged groups at a pH of between 6 and 8; and a nucleic acid delivery complex disposed within the active agent delivery structure. In an embodiment, the invention includes a material for medical applications including glycogen functionalized with coupling groups at a degree of substitution of between about 0.01 and 0.5. Other embodiments are also included herein.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
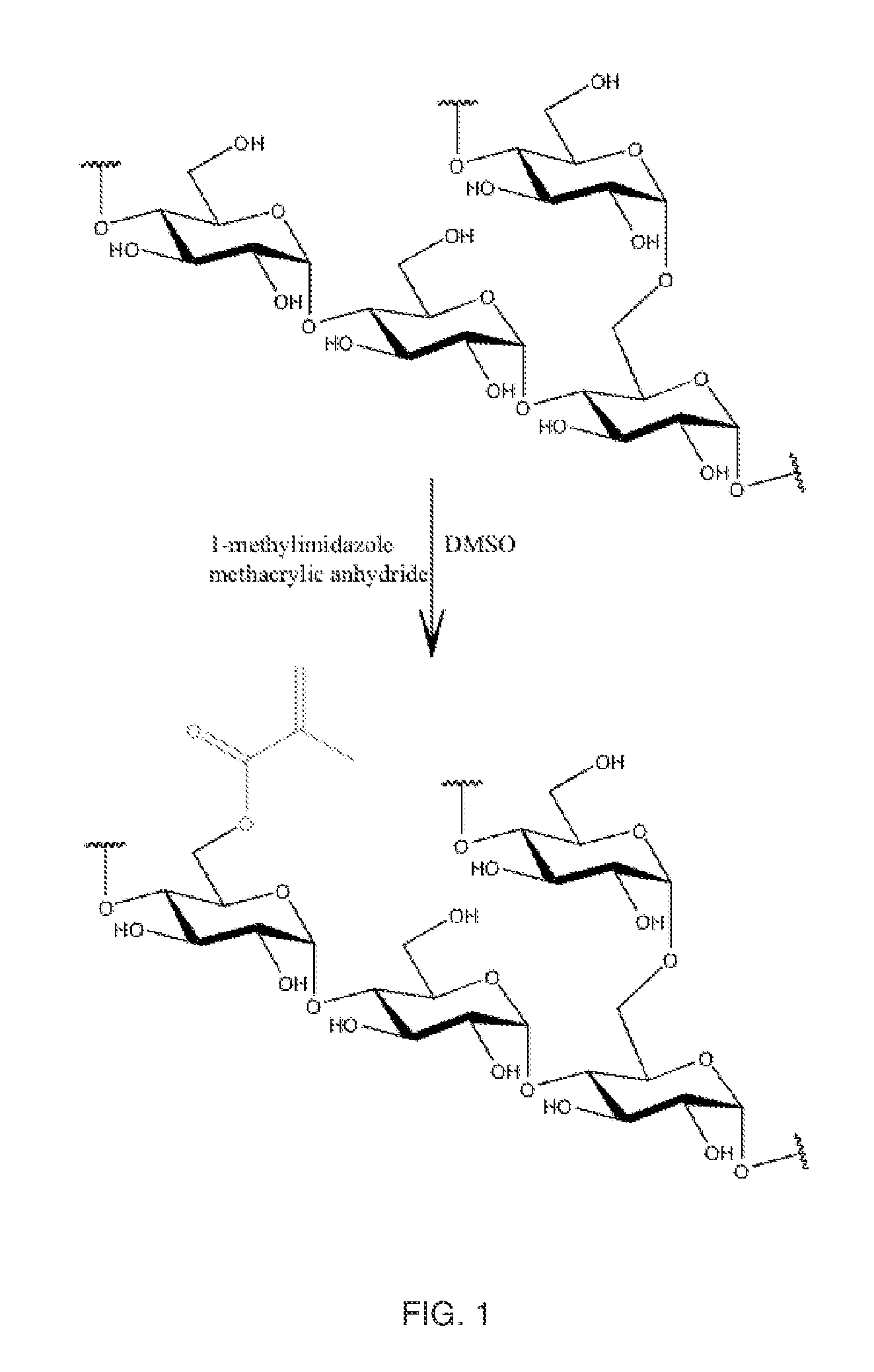
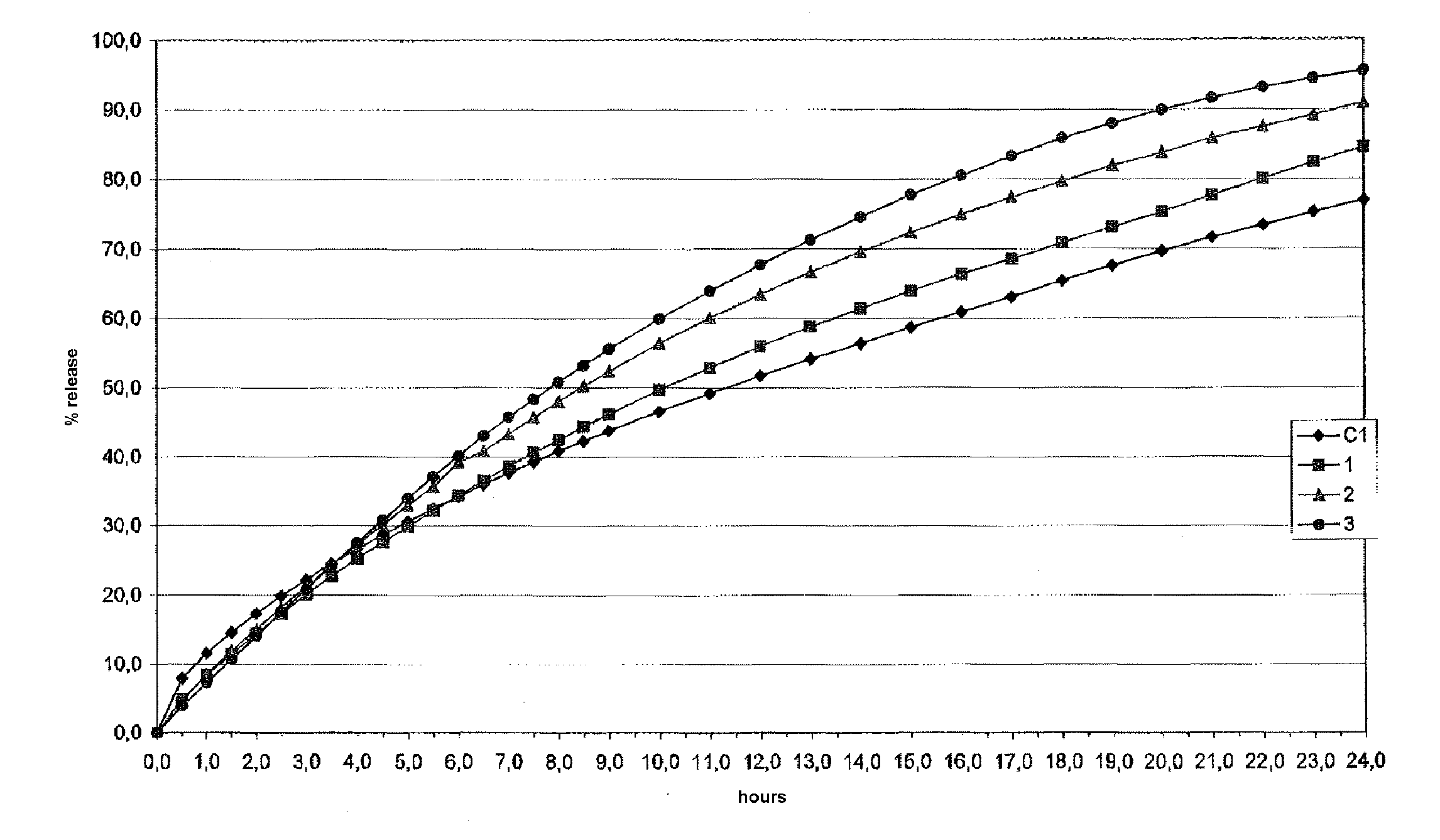
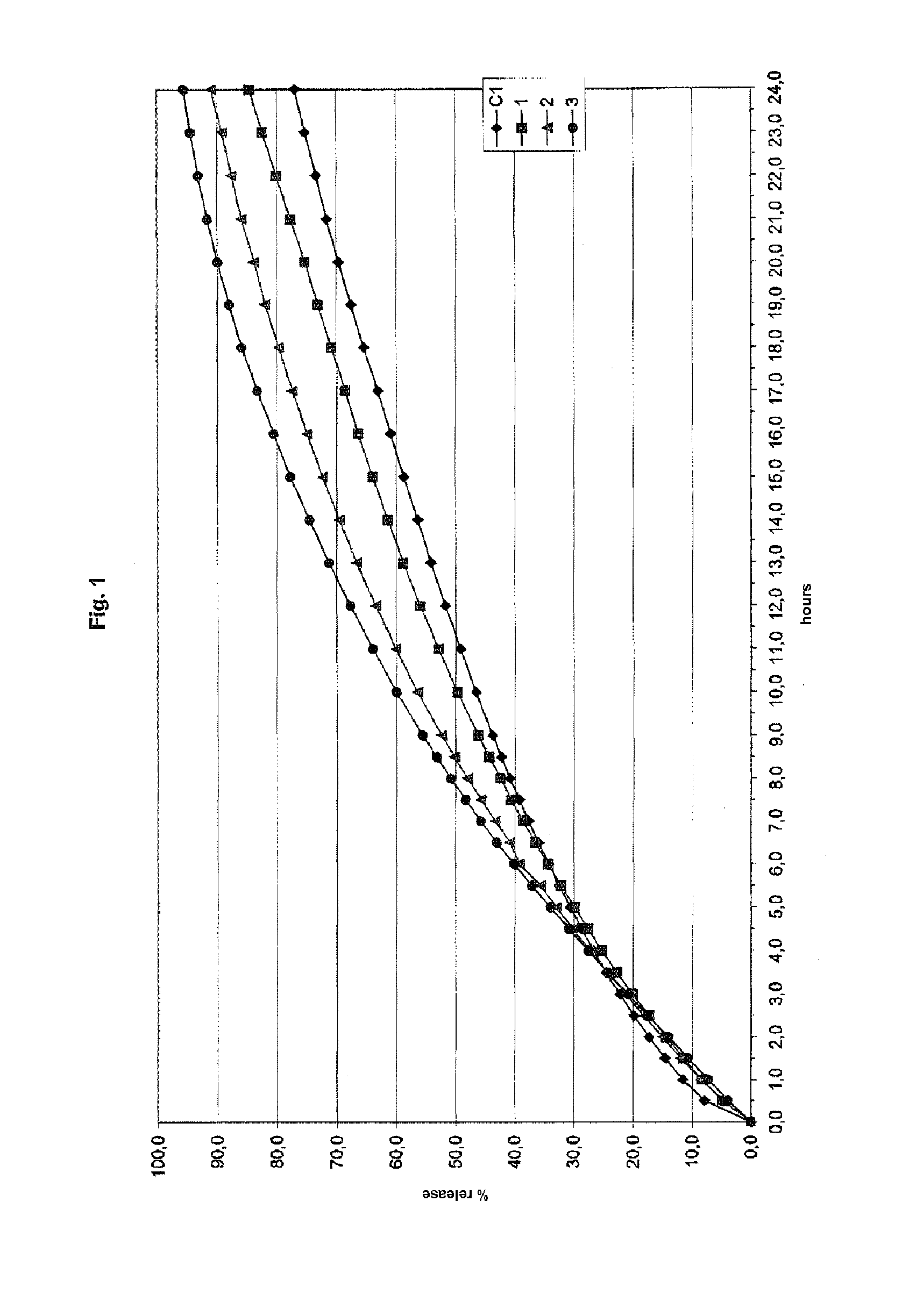
Controlled release pharmaceutical or food formulation and process for its preparation
ActiveUS20110318321A1Good reproducibilityImproved release profileHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideControlled releaseFood formulation
The present invention relates to a controlled release pharmaceutical or food formulation comprising at least one active pharmaceutical or food ingredient dispersed in a mixture of a glycogen with a polysaccharide, and the process for its preparation. The invention also relates to a slow release system represented by a mixture of a glycogen with a polysaccharide, and its use for the preparation of slow release pharmaceutical or food formulations.
Owner:AZIENDE CHIMHE RIUNITE ANGELINI FRANCESCO A C R A F
Novel slowly digestible storage carbohydrate
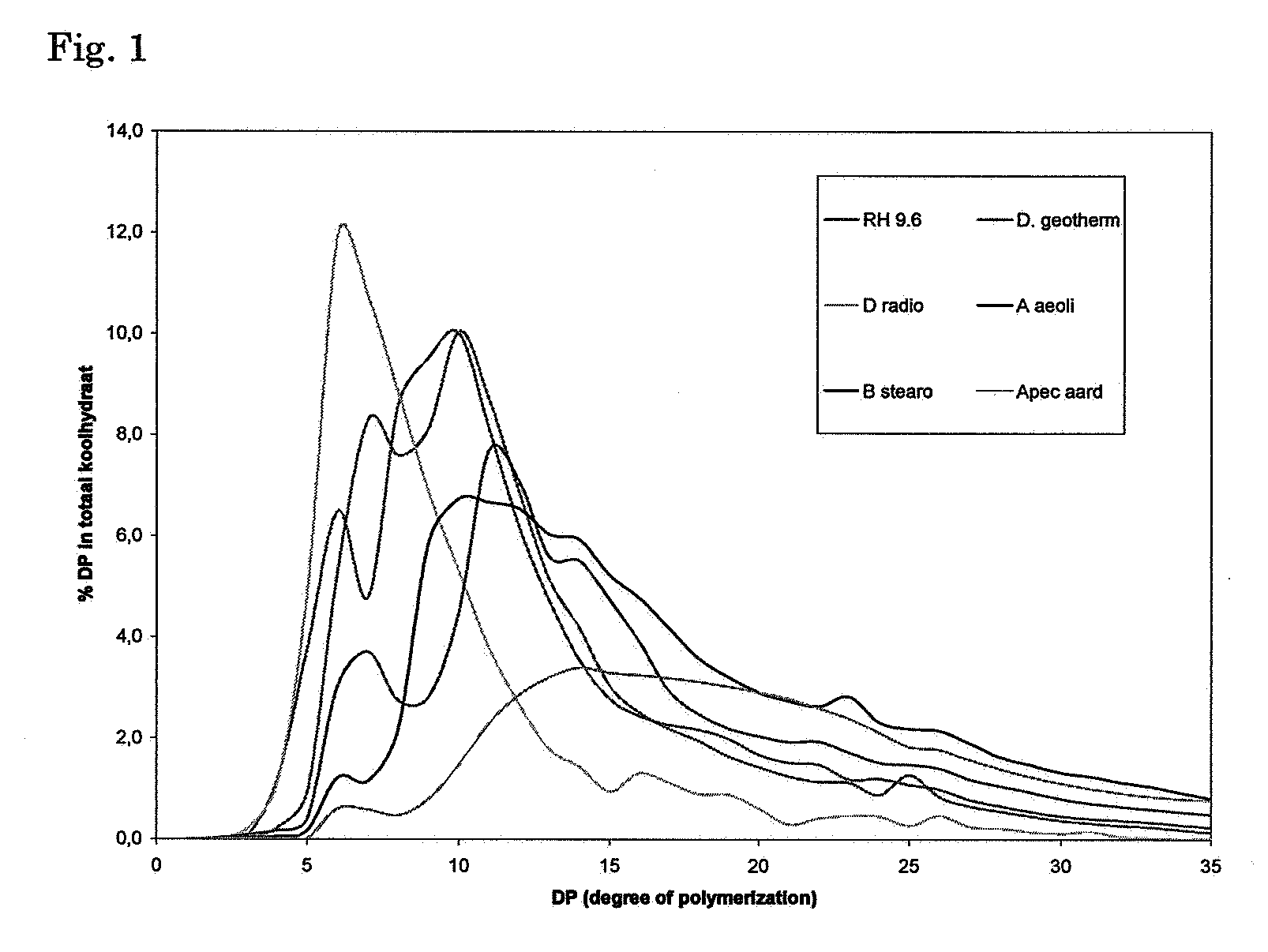
The present invention relates to slowly digestible storage carbohydrates (starch, glycogen) having a branching degree of at least 8.5% and a side chain composition comprising at least 10% of DP 5-7. Said slowly digestible carbohydrates can be produced by treating the substrate (glycogen, starch) from a native source with a glycogen branching enzyme derived from Rhodothermus obamensis, Rhodothermus marinus, Deinococcus radiodurans or Deinococcus geothermalis.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
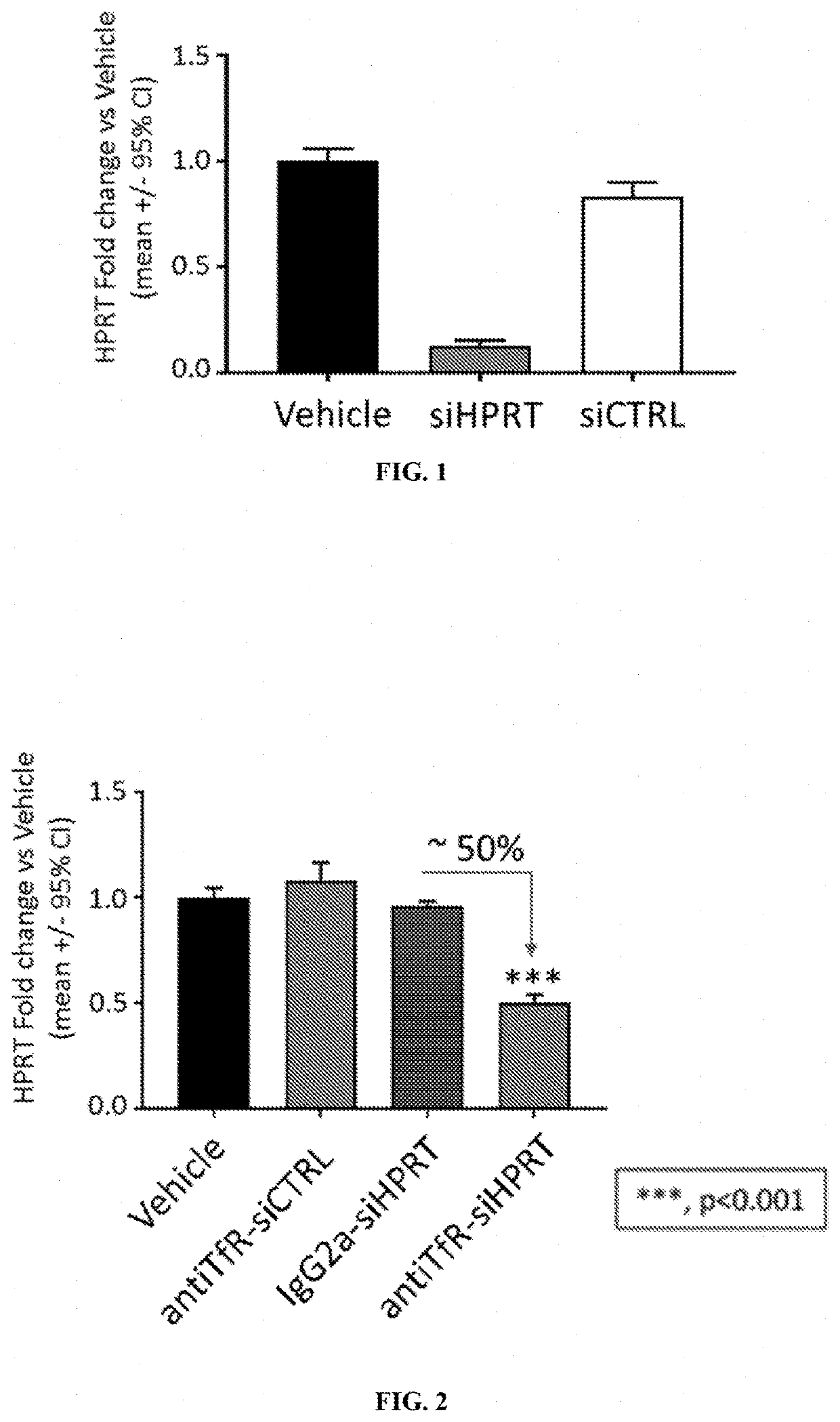
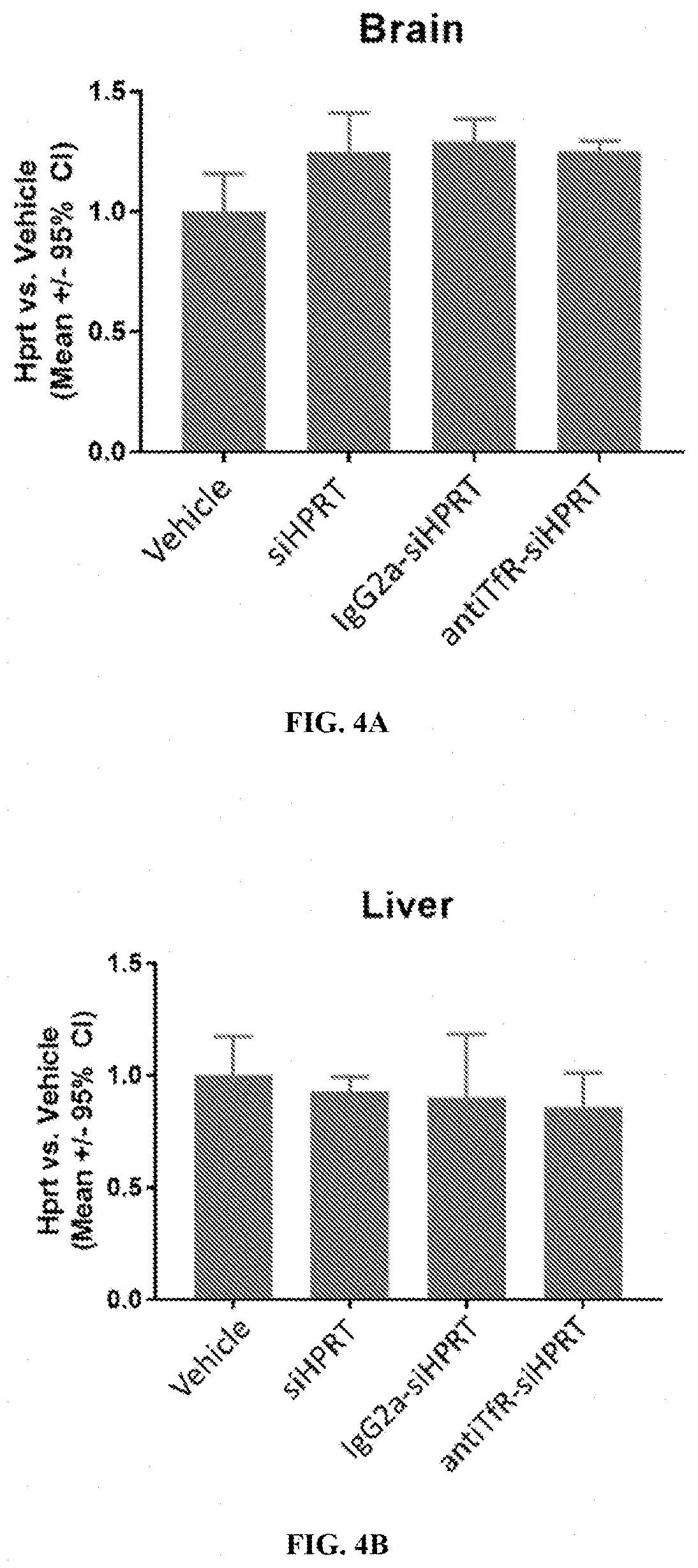
Muscle targeting complexes and uses thereof for treating pompe disease
PendingUS20210317226A1Reducing glycogen levelSpecial deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseInternalization
Aspects of the disclosure relate to complexes comprising a muscle-targeting agent covalently linked to a molecular payload. In some embodiments, the muscle-targeting agent specifically binds to an internalizing cell surface receptor on muscle cells. In some embodiments, the molecular payload reduces glycogen levels in a cell.
Owner:DYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for synthesizing poly(hydroxyalkanoate)
ActiveCN101323864ALow running costMicroorganism based processesFermentationSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
The invention belongs to the environmental protection technology field, more particularly relating to a method that utilizes activated sludge rich in glycogen-accumulating organisms (GAO for short) to synthesize Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA for short) under anaerobic condition. Namely, the GAO is enriched by cultivating and acclimating the excess sludge of a wastewater treatment plant, short chain fatty acid is used as a carbon source in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR for short), and microbes in the activated sludge rich in the GAO are stirred for a period of time under anaerobic condition to synthesize the PHA by controlling influent PH and the concentration of ammonia nitrogen. The method provides a new method for synthesizing the PHA, and reduces the production cost of the PHA.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
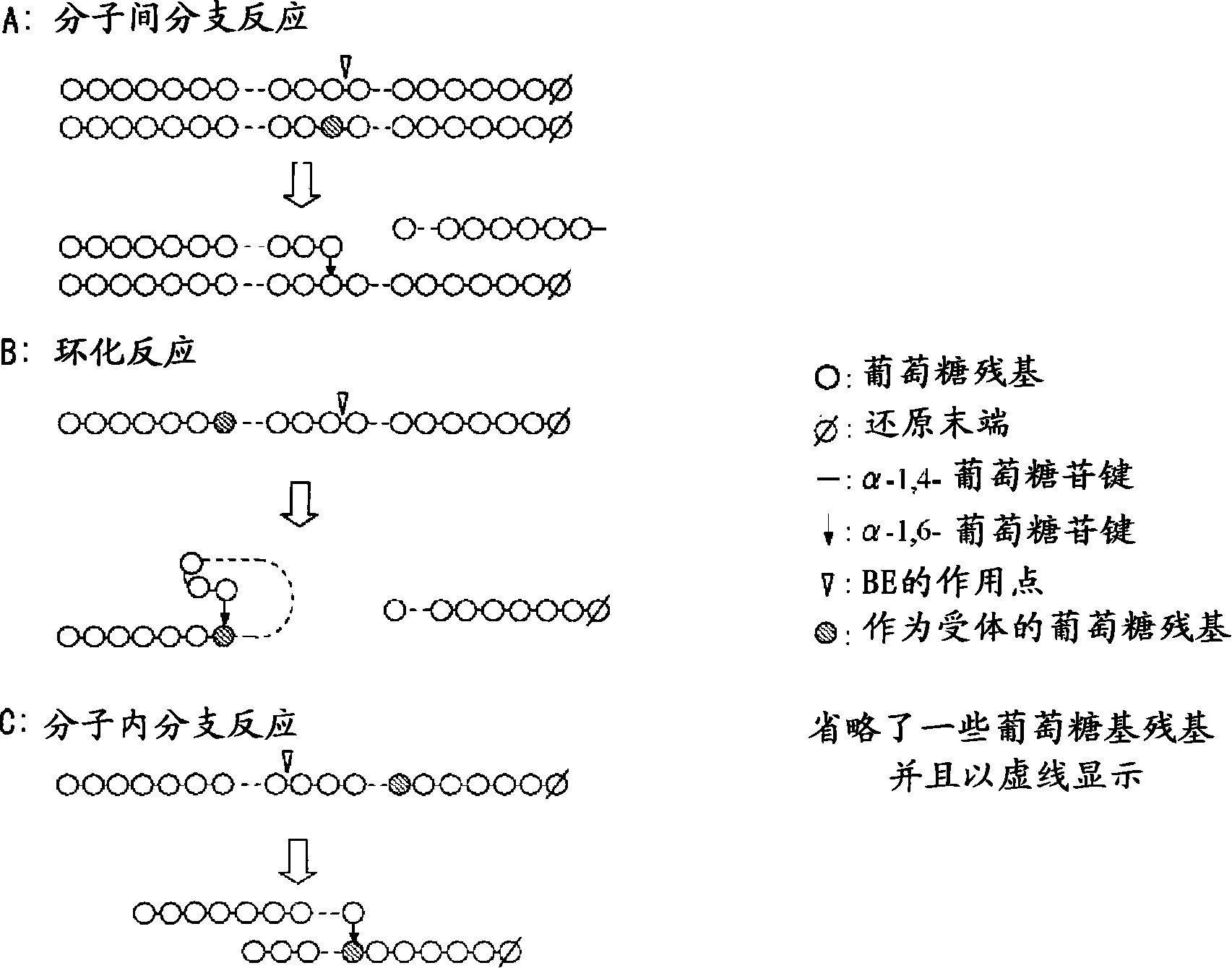
Method of producing glycogen
A method of producing glycogen comprising a step of: allowing a branching enzyme having the ability to synthesize glycogen to act on a substrate in a solution to produce a glycogen, wherein the substrate is an ±-glucan being linked mainly with ±-1,4-glucosidic bonds and having a degree of polymerization of 4 or more, and the number-average molecular weight of saccharides in the solution before initiation of the reaction is more than 180 but not more than 150,000. (The branching enzyme activity of the branching enzyme) / (the molecular-weight-decreasing activity of the branching enzyme) can be 500 or less. The branching enzyme can be a thermostable branching enzyme.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
Polishing composition and polishing method
ActiveUS20050215060A1Suitable for useDeterioration in polishing capabilityOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingColloidal silicaPullulan
A polishing composition contains a deterioration inhibitor for inhibiting deterioration of polishing capability of the polishing composition, an abrasive, and water. The deterioration inhibitor is at least one selected from polysaccharide and polyvinyl alcohol. The polysaccharide is starch, amylopectin, glycogen, cellulose, pectin, hemicellulose, pullulan, or elsinan. Among them, pullulan is preferable. The abrasive is at least one selected from aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, preferably at least one selected from fumed silica, fumed alumina, and colloidal silica. The polishing composition can be suitably used in polishing for forming wiring a semiconductor device.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com