Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
133results about How to "High degree of enrichment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
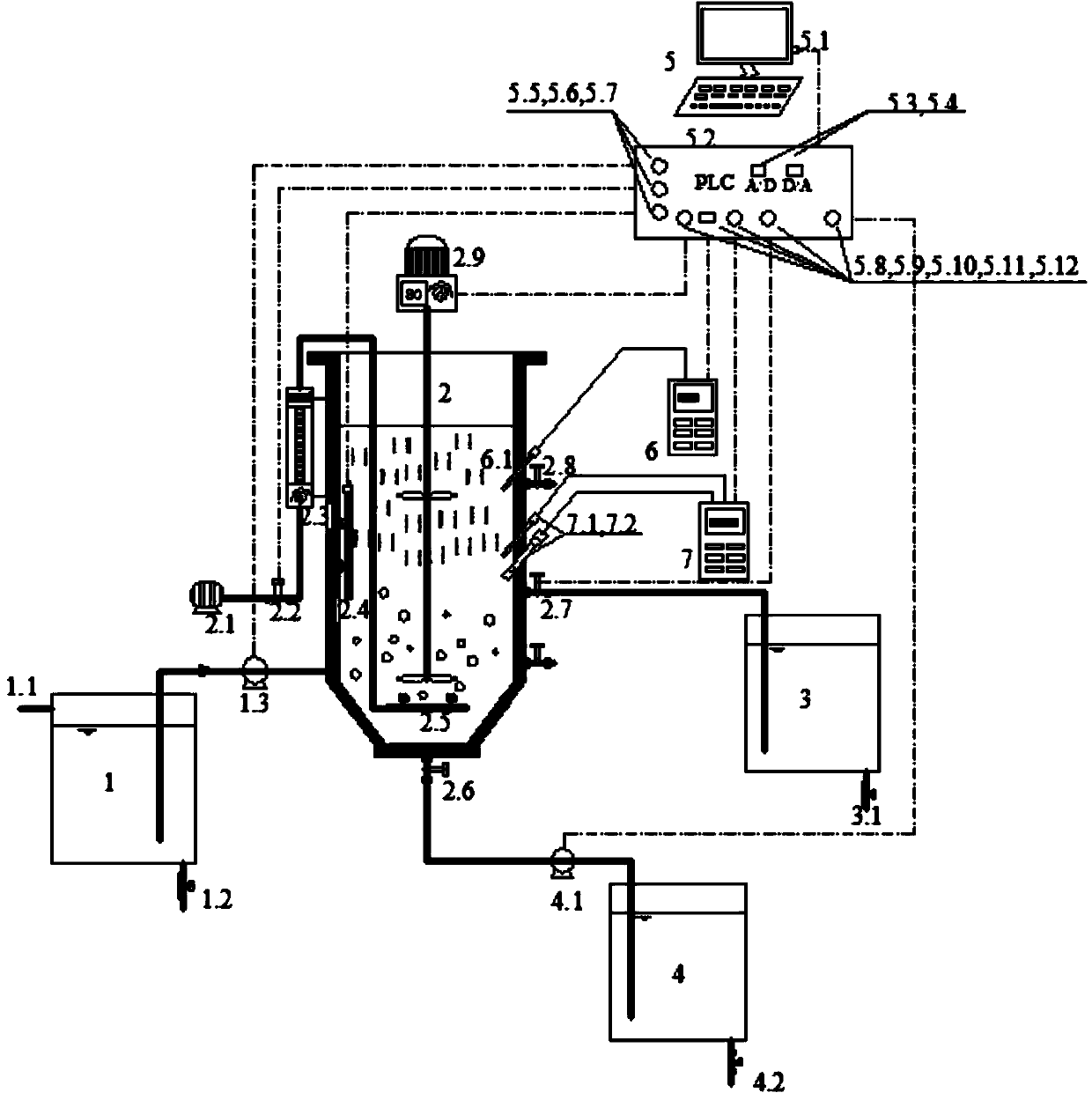
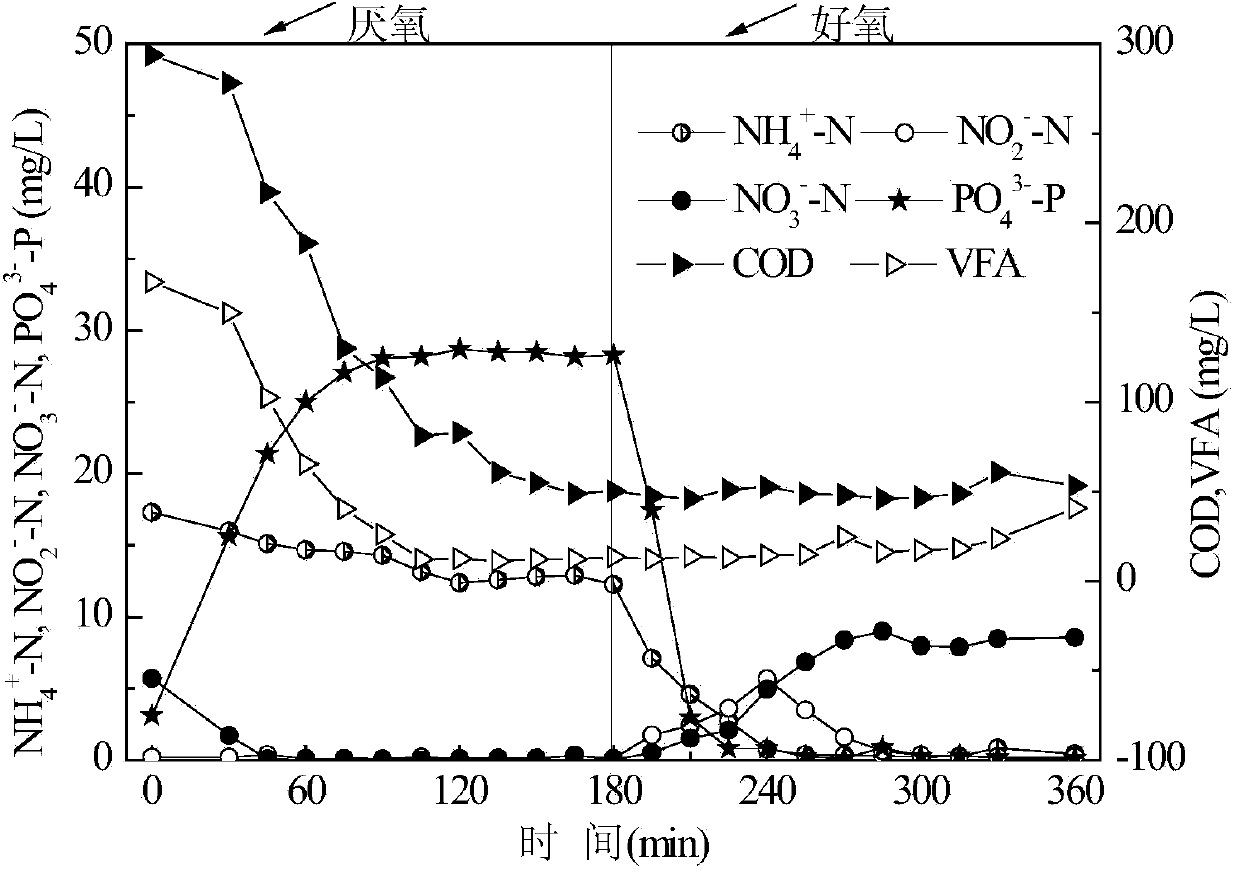
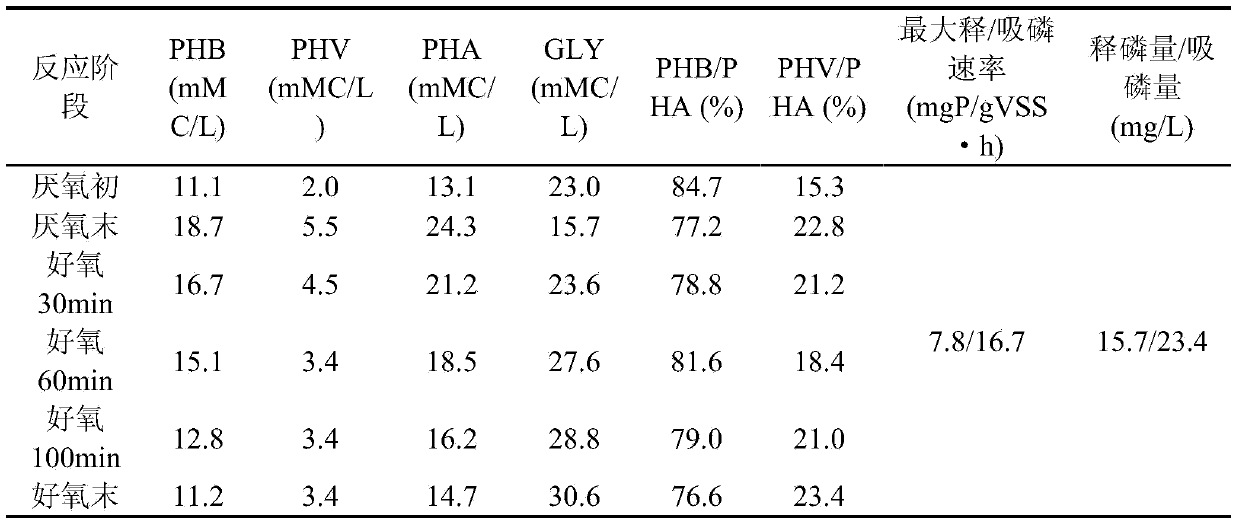
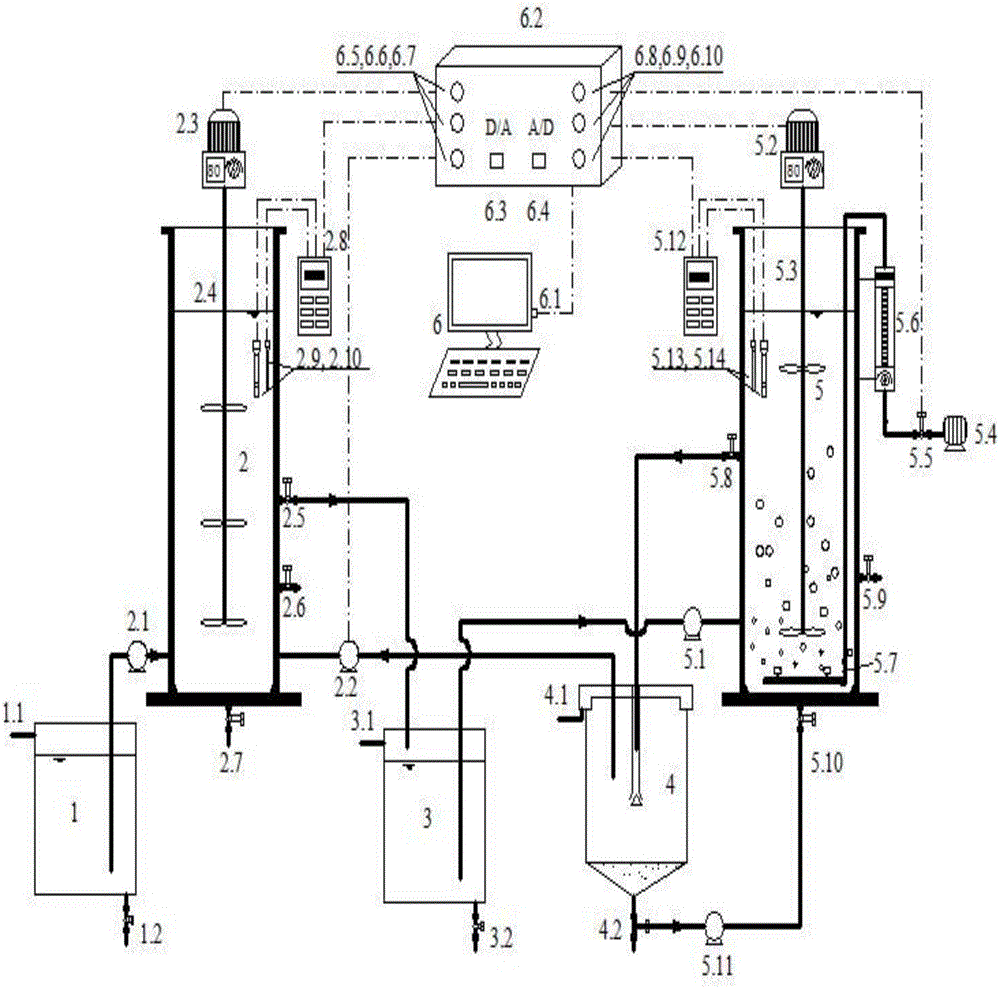
Process for treating domestic sewage with low CN (Carbon-Nitrogen) ratio by use of anaerobic/aerobic SNDPR (Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrification Phosphorus Removal) system capable of enriching phosphorus-accumulating bacteria
ActiveCN104193003AShorten the denitrification processCarbon savingTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesChemistryCarbon source
The invention provides a process for treating domestic sewage with low CN (Carbon-Nitrogen) ratio by use of an anaerobic / aerobic SNDPR (Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrification Phosphorus Removal) system capable of enriching phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and belongs to the field of biological sewage treatment. After the domestic sewage enters into an SNDPR SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor), delayed anoxic / anaerobic stirring is carried out firstly, nitrogen removal by denitrification is performed on NO3<-1>-N and NO2<-1>-N left in last cycle by use of denitrifying bacteria and by utilizing organic carbon sources in the sewage, the anaerobic phosphorus release is realized by use of the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and by utilizing the organic carbon sources in the sewage, and stored substances are synthesized in the cells of the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria. Due to delayed anaerobic treatment, after PAOs phosphorus release is finished, the denitrifying flora in the system is still capable of taking full advantage of organic matters in the sewage and storing the organic matters as an internal carbon source. Hereafter, aerobic aeration stirring is performed; as the concentration of dissolved oxygen is controlled, endogenous SNDPR of the denitrifying flora can be realized while phosphorus absorption of the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria is guaranteed. The method process for treating the domestic sewage with low CN ratio by use of the anaerobic / aerobic SNDPR system capable of enriching phosphorus-accumulating bacteria has the advantages that deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal of the sewage with low CN ratio is realized in one reactor, the process is simple, no external carbon source needs to be added, and the oxygen consumption and the energy consumption are reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Molecular engram polymer of pyrethroid-like pesticide and application thereof
InactiveCN101265310AGood choiceHigh degree of enrichmentComponent separationFunctional monomerIn situ polymerization
A molecular imprinting polymer of a pyrethroid insecticide is characterized in that the polymer is prepared by the following steps: a. a pyrethroid template molecule, a functional monomer for polymerization, a cross-linker and a pore-forming agent are mixed; b. the substances are arranged in a closed container after being uniformly mixed, the pure nitrogen aeration is used for removing the oxygen, the in-situ polymerization is carried out by adopting the thermal-initiation or the photo-initiation mode after the closing, thus generating the molecular imprinting polymer; c. the molecular imprinting polymer is ground, mixed liquid of organic solvent and acid is utilized for removing the template molecule; d. and the molecular imprinting polymer which is obtained in step c is dried in the vacuum condition. The invention further discloses an application of the polymer, compared with the prior art, the molecular imprinting polymer has the advantages that: the preparation process is simple, the operatability is strong and the preparation cost is low; the prepared polymer has good selectivity and high enrichment degree, which can be widely applied in the pre-treatment process of the pyrethroid insecticide residues of the environmental, biological and food samples, etc.
Owner:杨挺
Zinc leaching slag treatment method
ActiveCN103421955AShort processShorten the smelting processProcess efficiency improvementLead smeltingMolten bath
A zinc leaching slag treatment method comprises the following steps: 1) The dried zinc leaching slag is evenly mixed with coke powder, and then the mixture is added to a volatilization kiln through a feeding scraper-trough conveyer at the tail of the kiln; 2) under the high-temperature condition of the volatilization kiln, the mixture generates kiln slag and smoke, valuable metals in the zinc leaching slag are deoxidize, as a result, lead and zinc steam is generated and gathered in the smoke, and gold, silver and copper enters to the kiln slag; 3) the kiln slag is delivered to a smelting furnace, furnace burden is added from the top of the smelting furnace, oxygen-enriched air is blown through an oxygen lance, the furnace hearth is stirred, the smelting temperature of the smelting furnace and the ratio of oxygen quantity to kiln slag dry measure are controlled, and slagging smelting is completed; 4) after the slagging smelting carried out in step 3), the valuable metals gold, silver and copper in the kiln slag are gathered in matte, the generated lead steam is gathered in smoke, and the kiln slag is cooled gradually. According to the zinc leaching slag treatment method, the technological process is short, the energy consumption is low, the cost is low, and the valuable metal recovery rate is high.
Owner:HUNAN SHUI KOU SHAN NONFERROUS METALS GRP
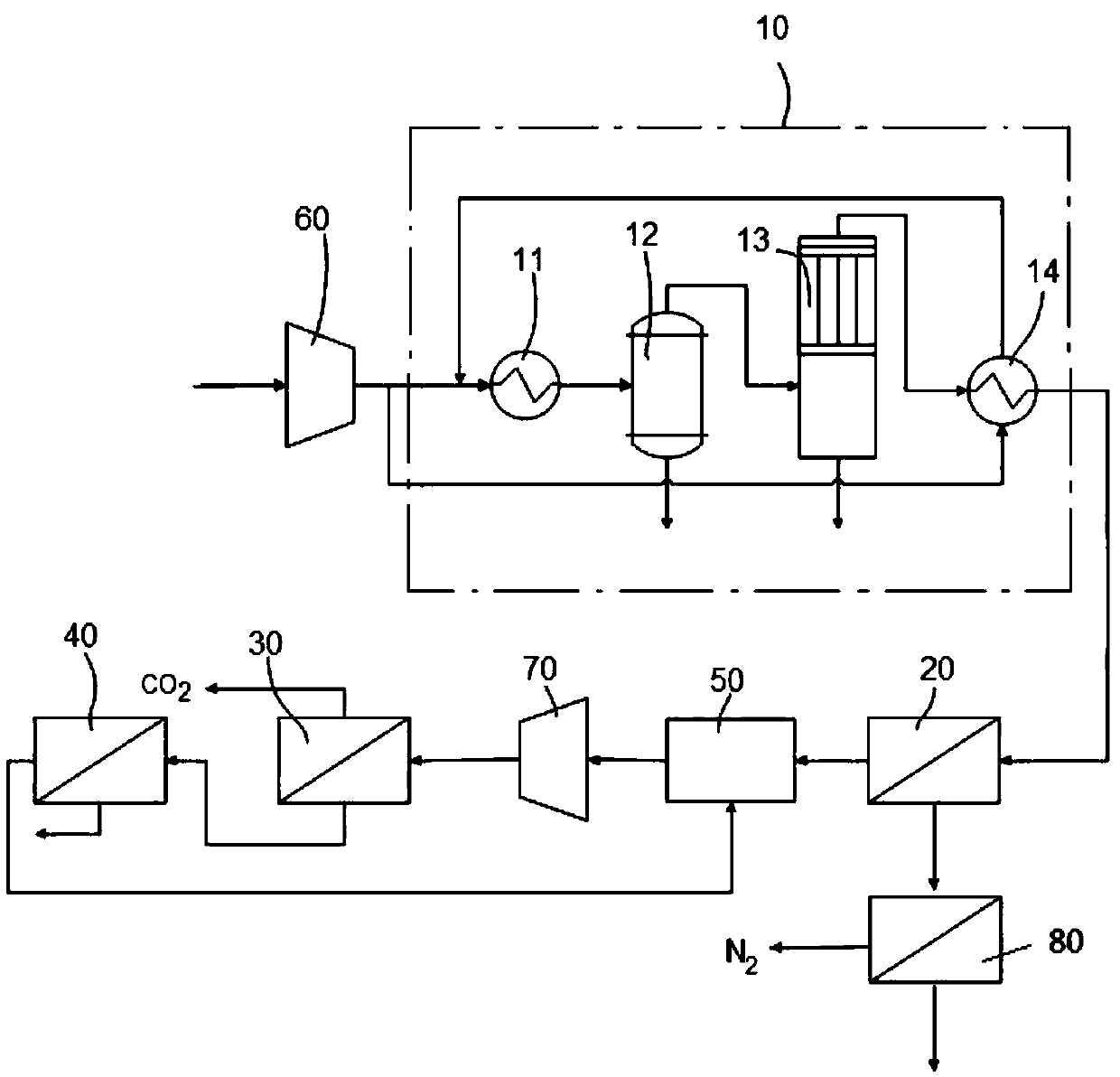
Device and method for jointly capturing and recovering carbon dioxide and nitrogen in flue gas
PendingCN107899376AAffect separation efficiencyAffect the degree of enrichmentNitrogen purification/separationCombination devicesChemistryCarbon dioxide
The invention provides a device and method for jointly capturing and recovering carbon dioxide and nitrogen in flue gas. The device comprises a flue gas treatment system, a first CO2 membrane separation unit, a second CO2 membrane separation unit and an N2 membrane separation unit, wherein the flue gas treatment system is provided with a treatment inlet and a treatment outlet, and is used for treating the flue gas; the first CO2 membrane separation unit is provided with a first gas inlet, a first carbon dioxide enriched gas outlet and a first high-pressure impermeable gas outlet, and the firstgas inlet is connected with the treatment outlet; the second CO2 membrane separation unit is provided with a second gas inlet, a carbon dioxide product gas outlet and a second high-pressure impermeable gas outlet, and the second gas inlet is connected with the first carbon dioxide enriched gas outlet; the N2 membrane separation unit is provided with a nitrogen enriched gas outlet, and a gas inletof the N2 membrane separation unit is connected with the first high-pressure impermeable gas outlet. The device has a high enrichment degree of carbon dioxide and can recover nitrogen, thereby avoiding resource waste.
Owner:北京集封环能科技有限责任公司
Device and method for treating low-carbon urban sewage through synchronization of anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling denitrifying phosphorus removal and endogenous denitrification
ActiveCN105906044AStable nitrogen and phosphorus removalHigh degree of enrichmentTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAeration rateDecomposition
The invention discloses a device and method for treating low-carbon urban sewage through synchronization of anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling denitrifying phosphorus removal and endogenous denitrification, and belongs to the field of biological sewage treatment. Urban sewage enters an endogenous denitrification coupling dephosphorization SBR reactor for anaerobic stirring, energy is provided for glycogen inside denitrification glycogen-accumulating organisms decomposition cells, volatile fatty acid VFA in sewage is absorbed for synthesizing an internal carbon source PHA to be stored into the body, meanwhile, the denitrification phosphate-accumulating organisms are subjected to anaerobic phosphorus release, and VFA in the sewage is absorbed for synthesizing PHA to be stored into the body; after anaerobic stirring is finished, precipitation and drainage are performed, outlet water is drained into a middle water tank; then, water containing ammonia nitrogen and phosphate in the middle water tank is made to enter an integrated partial nitrification anaerobic ammonia oxidation SBR reactor, intermittent hypoxia aeration stirring is performed, and water is drained and drained into a water outlet tank; the outlet water of the integrated partial nitrification anaerobic ammonia oxidation SBR reactor is made to enter the endogenous denitrification coupling dephosphorization SBR reactor for hypoxia aeration stirring. According to the method, organic carbon sources in raw water are efficiently utilized, and the aeration rate is saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for wet separation and recovery of valuable metal from Kaldo furnace smelting slag
ActiveCN106086440AHigh degree of enrichmentImprove compatibilitySelenium/tellurium compundsProcess efficiency improvementSlagBismuth
The invention discloses a method for wet separation and recovery of valuable metal from Kaldo furnace smelting slag. Kaldo furnace smelting slag is ground and dipped in water to remove soluble salt; copper, selenium and tellurium in the slag are leached out by using pressurization, oxidation and acid leaching for treatment to obtain copper sulfate solution, silver-selenium slag and copper telluride slag; tellurium, silver and selenium can be respectively recovered from the silver-selenium slag and the copper telluride slag; pressurized copper removing filter residue is mixed with hydrochloric acid for leaching out antimony and bismuth to finally obtain lead-silver slag capable of returning to a Kaldo furnace for smelting; and antimony and bismuth are further recovered from antimony-bismuth solution. According to the method, a mode of stepped removal and recovery of such metal as copper, antimony, bismuth, selenium, tellurium, silver and lead enriched in the Kaldo furnace smelting slag is adopted, compatibility of the method with a wet-fire combined flow for recovering rare and noble metal from Kaldo furnace treatment copper anode mud is excellent, the smelting slag is enabled to return to the Kaldo furnace for smelting so as to prevent adverse effects on the copper smelting by returning to a copper smelting system, and the lead-silver slag with higher enriching degree of such valuable metal as lead and silver is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
T7 peptide-modified active brain targeting nanometer drug delivery system and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107789632AAvoid interferenceHigh targeting and treatment efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliverySolventPeg plga
The invention relates to a T7 peptide-modified active brain targeting nanometer drug delivery system and a preparation method thereof. A T7 peptide (with a sequence of CHAIYPRH) is used as a specificbrain targeting ligand, a PEG-PLGA diblock copolymer is used as a carrier of a nanometer drug delivery system, an insoluble drug molecule is entrapped through an emulsification solvent volatilizationmethod, and the insoluble drug molecule is connected to the T7 peptide through a difunctional NHS-PEG-MAL covalent bond so that the active brain targeting nanometer drug delivery system is constructed. The preparation method has simple processes and mild reaction conditions, utilizes a less amount of an organic solvent, effectively reduces the cytotoxicity of the nanometer carrier material, prolongs the circulation time in the body and improves biocompatibility. The T7 peptide-modified active brain targeting nanometer drug delivery system has strong active targeting ability, greatly improves the efficiency of the nanometer carrier drug passing through the blood-brain barrier, enriches the drug in the lesion tissue, improves the bioavailability of the drug, effectively controls the drug release and has a good application prospect in treatment and diagnosis of ischemic stroke and brain tumors.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
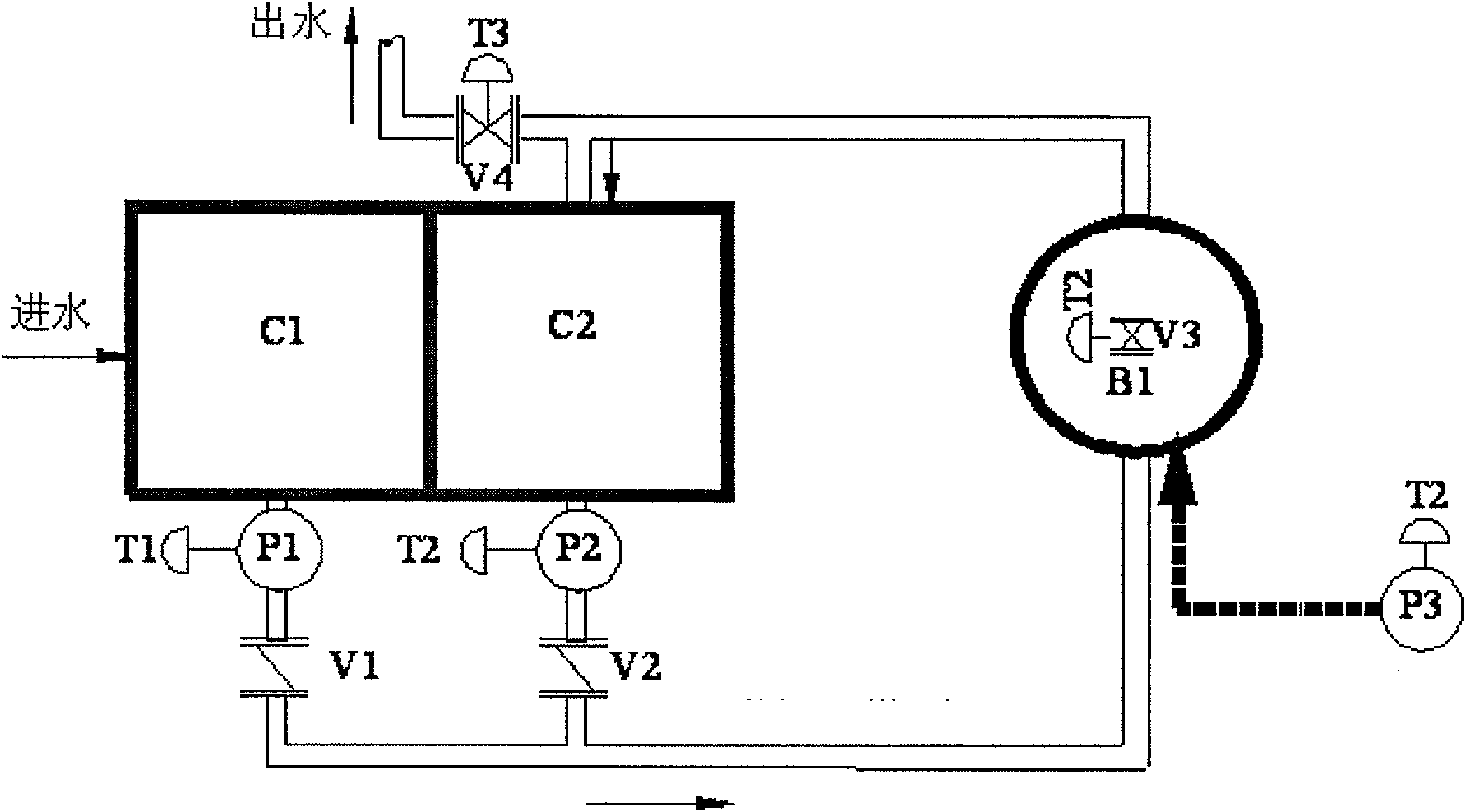
Device and method for continuously operation and reinforcement of biomembrane phosphate removing
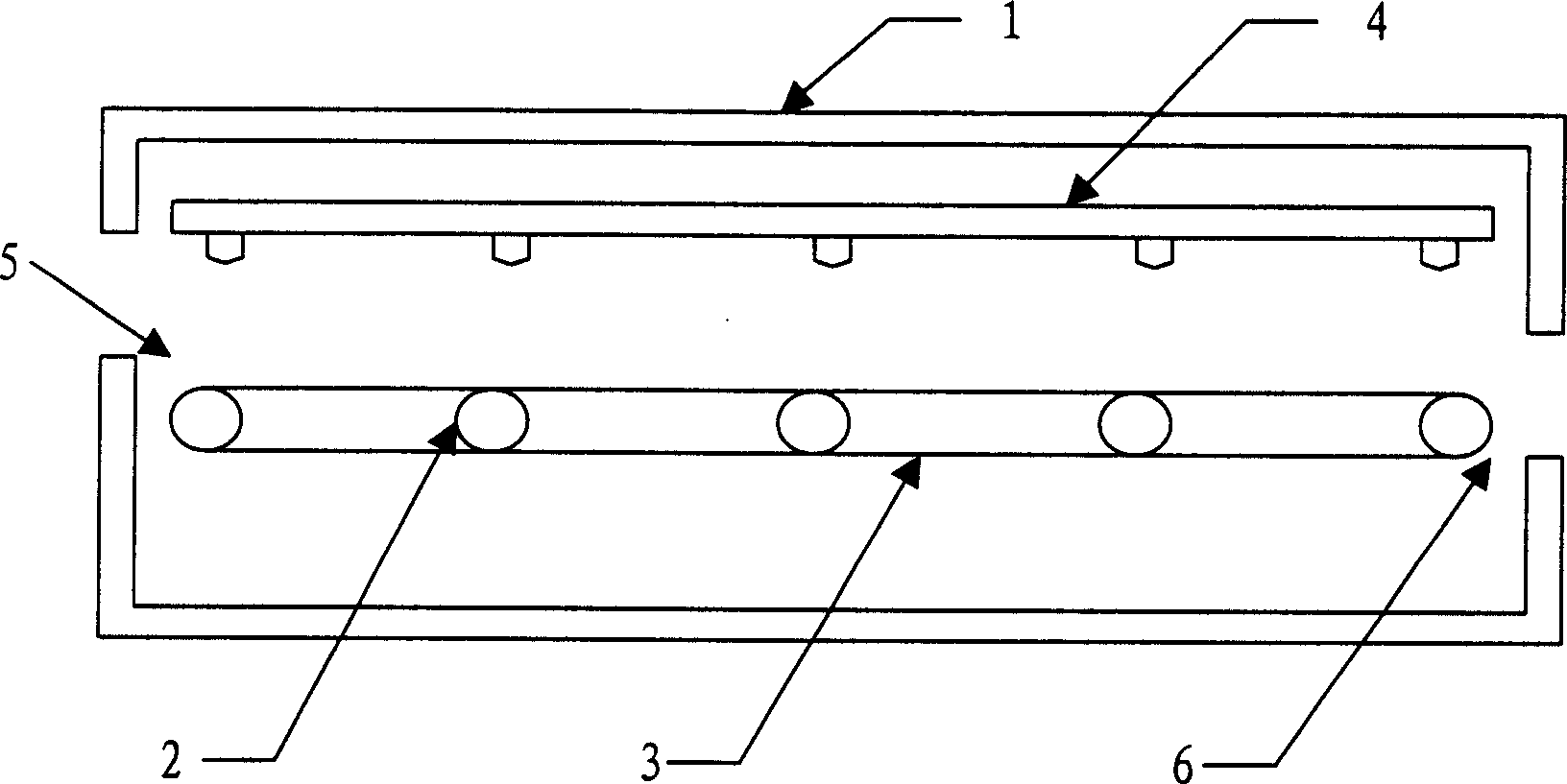
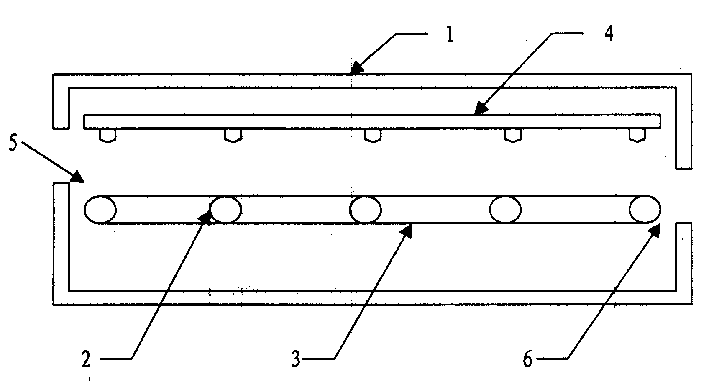
InactiveCN101654312AReduce complexityReduce labor intensityTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentPhosphateAtmospheric air
The invention relates to a device and a method for continuously operation and reinforcement of biomembrane phosphate removing. The device is composes of a water inlet tank, a middle water tank and a biological filter tank, which can realize the continuous biological phosphate removing. The biological filter tank adopts the anaerobic / aerobic alternative adhesion growth system, uses the quartz sandas a biological carrier, is formed with a mixed biomembrane flora composed of phosphate accumulating bacteria, common heterotrophic bacteria, nitrobacteria and denitrifying bacterium, applies an adjustable time program to control the water inlet and outlet direction of the reactor and the connection of the reactor and the atmosphere so as to expose the biomembrane alternatively in the anaerobic / aerobic environments and applies the phosphate accumulating bacteria to remove the phosphate in the waste water in the anaerobic phosphate releasing-aerobic phosphate accumulating circulation. The system can simultaneously denitrides and remove the organic matters in the waste water.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Assay for transposase accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) method applied to zebrafish embryos
InactiveCN105463089AHigh degree of enrichmentSimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationWater bathsFluorescence
The invention relates to an assay for transposase accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) method applied to zebrafish embryos. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing zebrafish embryo sample pretreatment; adding lysis buffer into the embryos; cracking the embryos in a water bath by using a wild-neck spearhead; performing a transposition reaction immediately and purifying DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid); determining a cycle number for library establishment by using a real-time fluorescence quantification method; directly performing library establishment and sequencing by using a further PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method. A regulatory sequence on genome chromatin can be located and decoded by the ATAC-seq method and a DNase-seq (DNase I hypersensitive sites sequencing) method, but the steps in ATAC-seq are simpler, a required cell quantity is smaller, the ATAC-seq is more helpful under the situation that a large quantity of cells cannot be obtained, and the data enriching degree of the ATAC-seq is higher according to an assay result. The ATAC-seq method is further applied to zebrafish embryo cells. Thus, an effective and simple method is provided for the researches of changes of chromatin structures in early developing processes of living organisms and corresponding gene expression regulation and control researches.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
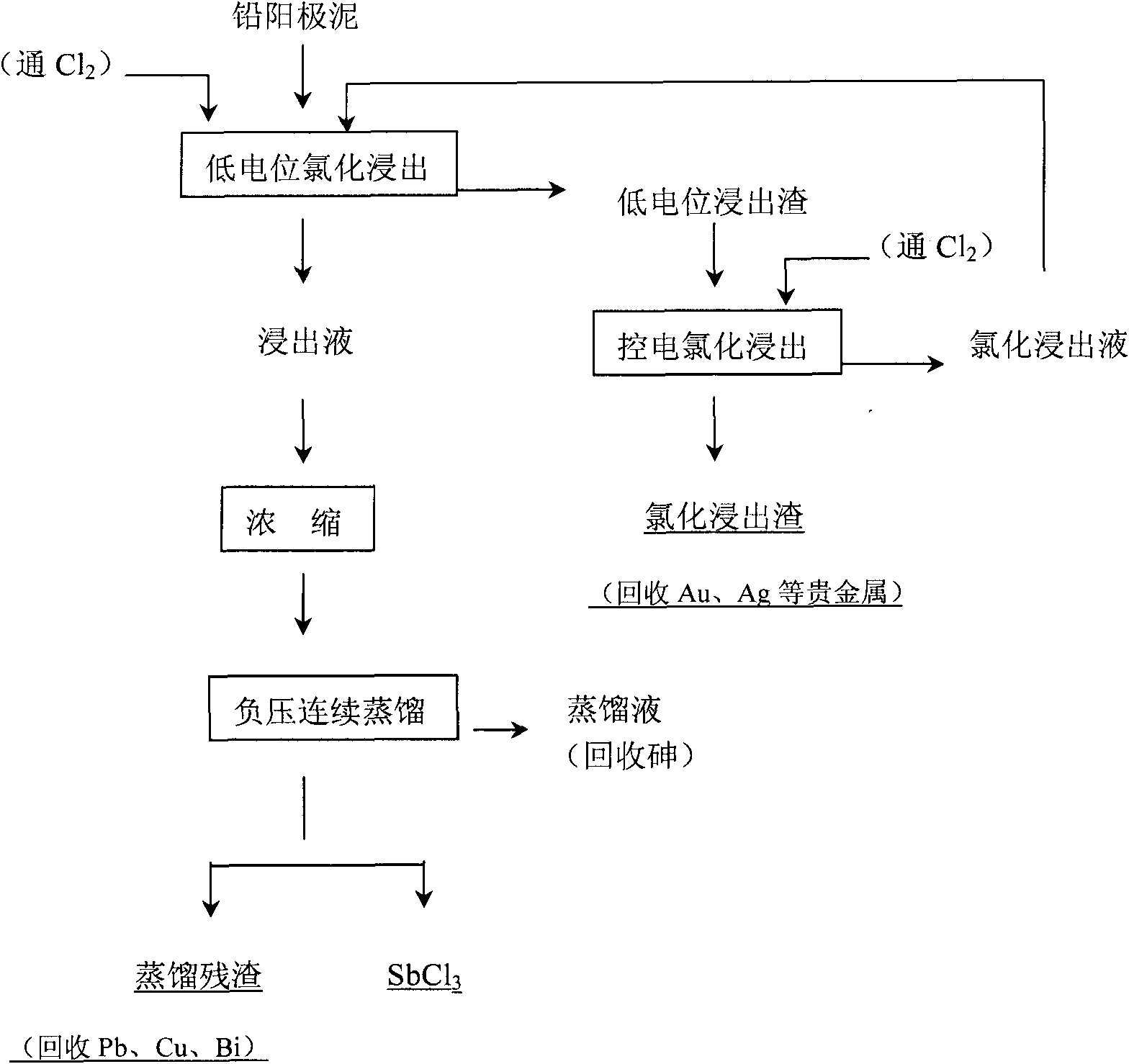
Method for wet processing of high antimony-lead anode mud
InactiveCN101787440AIncrease concentrationImprove leaching rateAntimony compoundsProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisDistillation
The invention discloses a method for wet processing of high antimony-lead anode mud, which comprises the following steps: putting high antimony-lead anode mud of which the content of antimony generated during the lead electrolysis is between 40% and 75% in hydrochloric aid medium, adopting two-section electric potential control of chlorination leaching, wherein oxidation-reduction potential of the end point of the first section chlorination leaching is controlled to be between 200-300mv, while oxidation-reduction potential of the end point of the second chlorination leaching is controlled to be 400-450mv, and 99.5% of golden and 99% of silver are enriched in the slag of the second chlorination leaching and can be subjected to further process. The silicofluoric acid in the first section chloridizing leachate is evaporated by concentration and distillation, the high-purity antimony butter is prepared from distilled and concentrated mother liquor by a continuous distillation method, and the yield of antimony metal is 95%.
Owner:广西华锡集团股份有限公司 +1
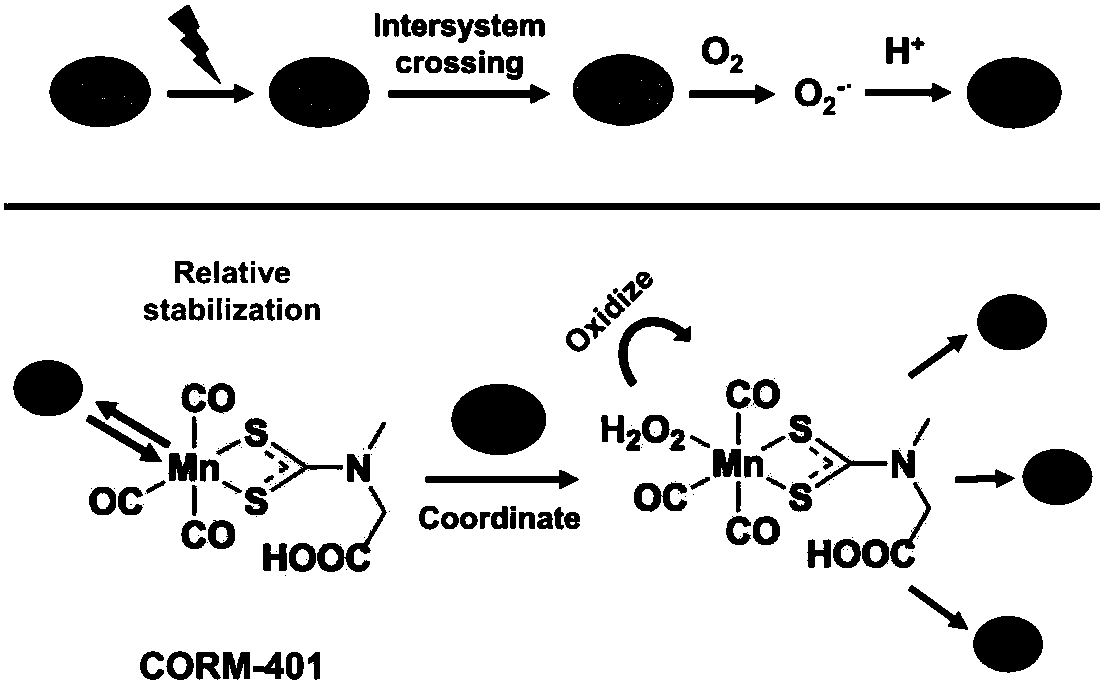
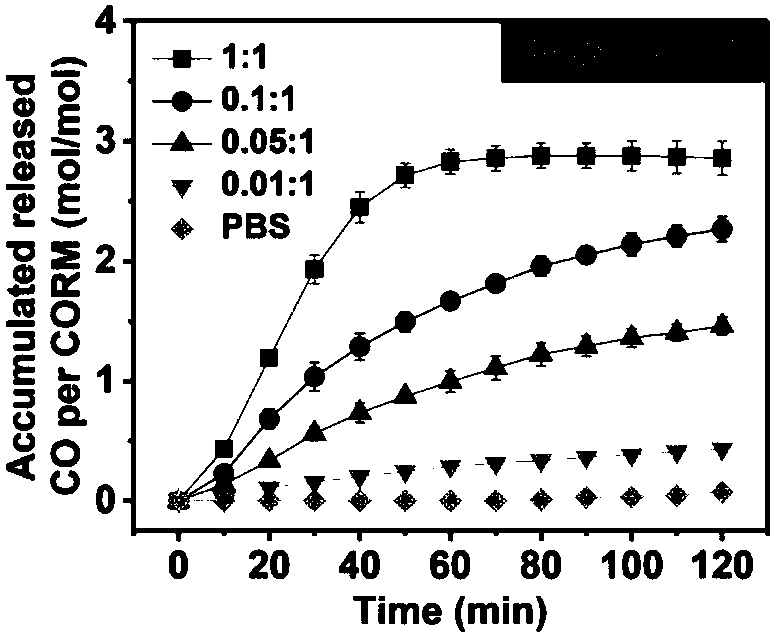
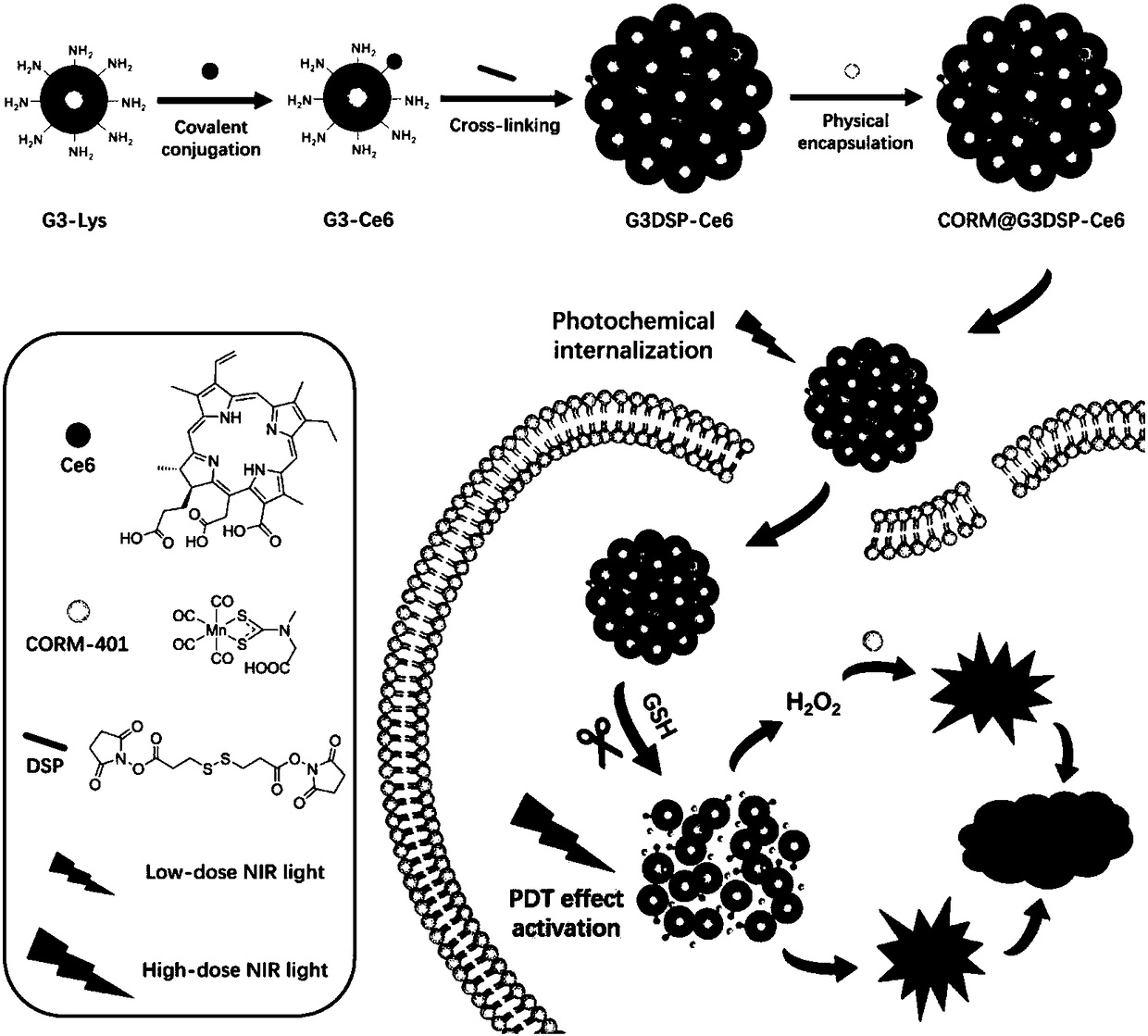
Photodynamic induced CO releasing method, CO controlled delivery system and building method thereof
ActiveCN108567980ATime controlled releaseControllable release of spaceEnergy modified materialsInorganic active ingredientsSinglet oxygenEngineering
The invention discloses a photodynamic induced CO releasing method, a CO controlled delivery system and a building method thereof. The CO releasing method is characterized by carrying out controlled release of CO under irradiation of near-infrared light by mixing a photosensitizer responding to the near-infrared light and applied to photodynamic therapy with carbon monoxide releasing molecules CORM-401. The CO controlled delivery system built on the basis of the photodynamic induced CO releasing method comprises a photosensitizer responding to near-infrared light and applied to photodynamic therapy, carbon monoxide releasing molecules CORM-401 and a carrier loaded or integrated with the photosensitizer and the carbon monoxide releasing molecules CORM-401. According to the CO controlled delivery system, the photochemical effect generated by the photosensitizer under induction of the near-infrared light is capable of accelerating the CO controlled delivery system to enter cells for decomposing the nanogel under the action of glutathione in the cells and releasing CORM-401; the near-infrared light activates and simultaneously generates singlet oxygen and CO; the singlet oxygen and COare respectively applied to photodynamic therapy and CO gas therapy; the combined therapy is achieved; the anti-tumor effect is obviously improved.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
A comprehensive utilization method for low-grade bauxite
InactiveCN104340998AEfficient separationAchieve cycleElectrolysis componentsAluminium hydroxide preparationFerric hydroxideAluminium hydroxide
The invention relates to a comprehensive utilization method for bauxite and particularly relates to a comprehensive utilization method for low-grade bauxite. The method includes following steps of: (1) mixing the low-grade bauxite with hydrochloric acid after ore grinding; (2) performing solid liquid separation and washing after the reaction is cooled; (3) adding the solution obtained in the step (2) into a sodium hydroxide solution to obtain an aluminium hydroxide precipitate, an iron hydroxide precipitate and a sodium chloride solution, performing solid liquid separation, and washing; (4) preparing the aluminium hydroxide and iron hydroxide solid obtained in the step (3) into metallurgy-level aluminum oxide and high-iron slag through a simple Bayer process; (5) subjecting the sodium chloride solution obtained in the step (3) to electrolysis by an ionic exchange membrane electrolytic cell to obtain hydrogen, chlorine and a sodium hydroxide solution; and (6) returning the sodium hydroxide solution that is discharged from an ionic membrane cathode zone in the step (5) into the step (3) and recycling. The method is obvious in environment protection effects, and effectively separates aluminum, iron and silicon in the low-grade bauxite to achieve comprehensive utilization.
Owner:SHENYANG ALUMINIUM MAGNESIUM INSTITUTE
Process for producing shikimic acid
InactiveCN101024609AReduce labor intensityReduce usageCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPlant ingredientsAcetic acidOrganic solvent
The invention supplies a shikimic acid producing method that includes the following steps: adding water into raw material chinese anise, taking recycling for 6-8 hours at 50-80 degree centigrade, concentrating to skikimic acid extractive raw material; mixing and whisking raw material and silica gel according to 1:1, leaching by ethyl acetate, testing and collecting eluate, concentrating and filtering to gain shikimic primary crystallization, taking recrystallization by using the same method. The invention sharply simplifies distilling process, improves working efficiency, decreases producing cost, and could shikimic acid of 90-95% purity.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
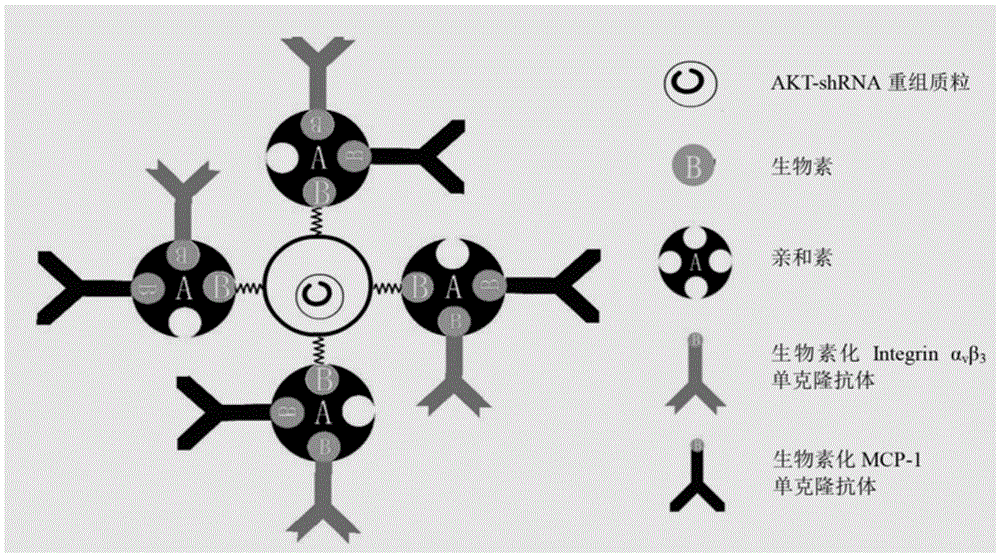
Dual-targeting ultrasonic contrast agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105617410AImprove targeting efficiencyReal-time observationEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsNon-active genetic ingredientsUltrasound contrast mediaTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a dual-targeting ultrasonic contrast agent and a preparation method thereof. The contrast agent is an Integrin alpha v beta 3 / MCP-1 dual-targeting micro-vesicle, the dual-targeting micro-vesicle comprises a lipid shell and a gas inner core, and the external surface of the lipid shell is connected with an Integrin alpha v beta 3 monoclonal antibody and an MCP-1 monoclonal antibody. Through the combined application of different target spots, the targeting efficiency of the contrast agent can be effectively increased, and the degree of enrichment of the carrying genes in the target tissue can be greatly increased. In addition, the contrast agent disclosed by the invention is an ultrasonic contrast agent with double functions of development and treatment, and tumor images can be accurately observed in real time through an ultrasonic imaging system; and after gene transfection is realized through high-strength ultrasonic irradiation, the tumor gene treatment effect can be achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Deuterated nucleoside derivative
ActiveCN105254694AHigh degree of Sp enrichmentHigh degree of enrichmentOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesStereochemistry
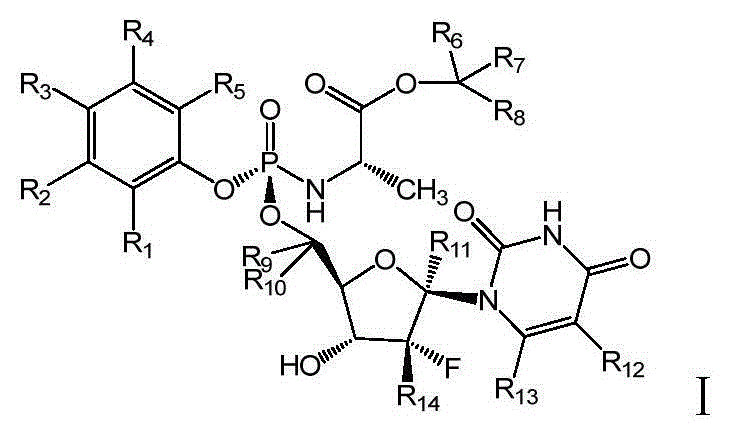
The present invention relates to deuterated nucleoside derivative, particularly to a compound having a structure represented by a formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. According to the present invention, the compound represented by the formula I has excellent pharmacokinetic properties and is expected to reduce the clinical dose so as to reduce the treatment and benefit more patients. The formula I is defined in the specification.
Owner:CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Tumor microenvironment responsive diagnosis and treatment integrated nano probe and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110193087AGood treatment effectEvenly dispersedEnergy modified materialsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsCross-linkBovine serum albumin
The invention relates to the technical field of a biomedical nano material, and more particularly to a tumor microenvironment responsive diagnosis and treatment integrated nano probe and a preparationmethod thereof. The nano probe uses bovine serum albumin as a template and a sulfur source to construct nanoparticles having uniform dispersion and uniform particle size with Bi2S3 and MnO2 by a biomineralization mode, and an activated carboxyl group of bovine serum albumin is cross-linked with an amino group of a peptide chain to link a matrix metalloproteinase-responsive peptide chain to provide the nano probe with multimodal imaging and treatment. The material is subjected to matrix metalloproteinases in the tumor microenvironment, and the peptide chain is sheared to promote the hydrophobic chain exposure, which results increase in the hydrophobic properties of the nanoparticles, the degree of enrichment of the material in the tumor site is enhanced, which can effectively improve the imaging and therapeutic performance of the nano probe.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Method for extracting and purifying artemisinin
InactiveCN103242335AHigh degree of enrichmentLow content of related substancesOrganic chemistrySilica gelSolvent
The invention discloses a method for extracting and purifying artemisinin. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) crushing artemisia apiacea and preparing artemisinin extractum; (2) melting the extractum: mixing the extractum and silica gel and drying to obtain material mixed silica gel; (3) performing wet column packing to obtain a silica gel column; (4) flatly paving the material mixed silica gel obtained in the step (2) on the silica gel column obtained in the step (3), standing, flushing the column and eluting; (5) collecting the eluent, concentrating, placing for 24 hours, crystallizing and centrifuging to obtain an artemisinin coarse product; and (6) refining the artemisinin coarse product obtained in the step (5). By adopting the method, the extraction efficiency is high, the artemisinin content is high, the using amount of solvents is small, and the method is favorable for industrial application.
Owner:SICHUAN YUTONG BIOTECH
Water sample and pretreatment method of nitrosoamine compound in suspended matter of water sample
InactiveCN104568562AEasy extractionComprehensive determination of concentration levelsComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationPretreatment methodN nitrosamines
The invention belongs to the field water treatment, and particularly relates to a water body and a pretreatment method of nitrosoamine compound in suspended matter of the water body. The pretreatment method comprises the following concrete steps: 1), obtaining the water sample and a suspended matter sample thereof; 2), performing extraction on nitrosoamine compound in the water sample; 3), extracting nitrosoamine compound in the suspension of the water sample. The pretreatment method of nitrosoamine compound in suspended matter of the water sample covers pretreatment process and extraction on nitrosoamine compound in the water sample and suspended matter of the water sample, so that a support is provided for more accurate and comprehensive measurement on concentration level of nitrosoamine compound in the water body; moreover, the pretreatment method further has the advantages of high extract content, and treated sample has a high enrichment degree on nitrosoamine compound, thereby being beneficial for subsequent detection.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Method for recovering rhodium from rhodium-containing waste liquid
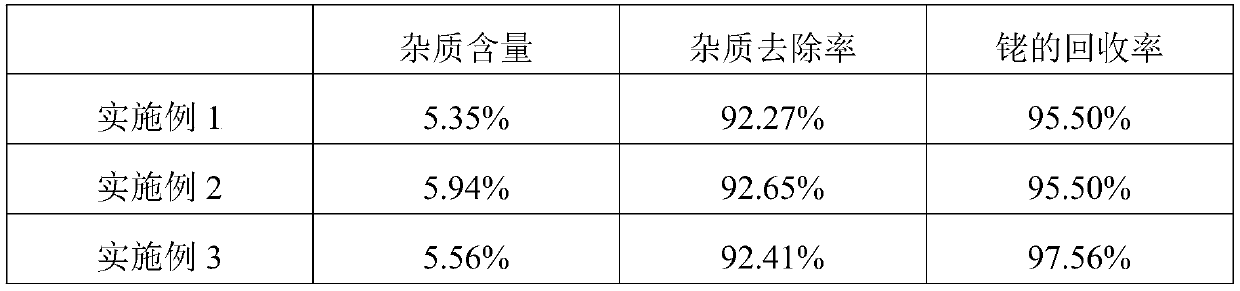
ActiveCN111020200AAvoid direct dischargeAvoid direct discharge of pollutionProcess efficiency improvementFlue gasEnvironmental engineering
The invention belongs to the field of rhodium recovery, and particularly discloses a method for recovering rhodium from rhodium-containing waste liquid. The method comprises the following steps of concentrating the rhodium-containing waste liquid to evaporate light components, mixing wood chips, carrying out primary incineration on the rhodium-containing waste liquid concentrated solution to obtain rhodium-containing carbon residues, and carrying out acid pickling and water washing; carrying out secondary incineration on the rhodium-containing carbon residues to obtain rhodium-containing ash residues, and carrying out acid pickling, water washing, alkali washing and water washing to completely remove acid-soluble and alkali-soluble impurities; in the primary incineration and secondary incineration processes, enabling flue gas to pass through a wet dust collector and a cyclone dust collector, collecting dust in the flue gas, avoiding direct emission of the flue gas to pollute the environment, and reducing rhodium loss in the incineration process; and combining the dust with incineration residues, reacting with alkali metal acid sulfate to generate soluble rhodium salt, and reactingthe soluble rhodium salt with active metal to obtain rhodium. According to the process, the rhodium loss in the incineration process can be reduced, the rhodium yield can be improved, impurities in the rhodium-containing ash residues can be removed, the rhodium enrichment degree is higher, and the recovery process is simplified.
Owner:山东博苑医药化学股份有限公司
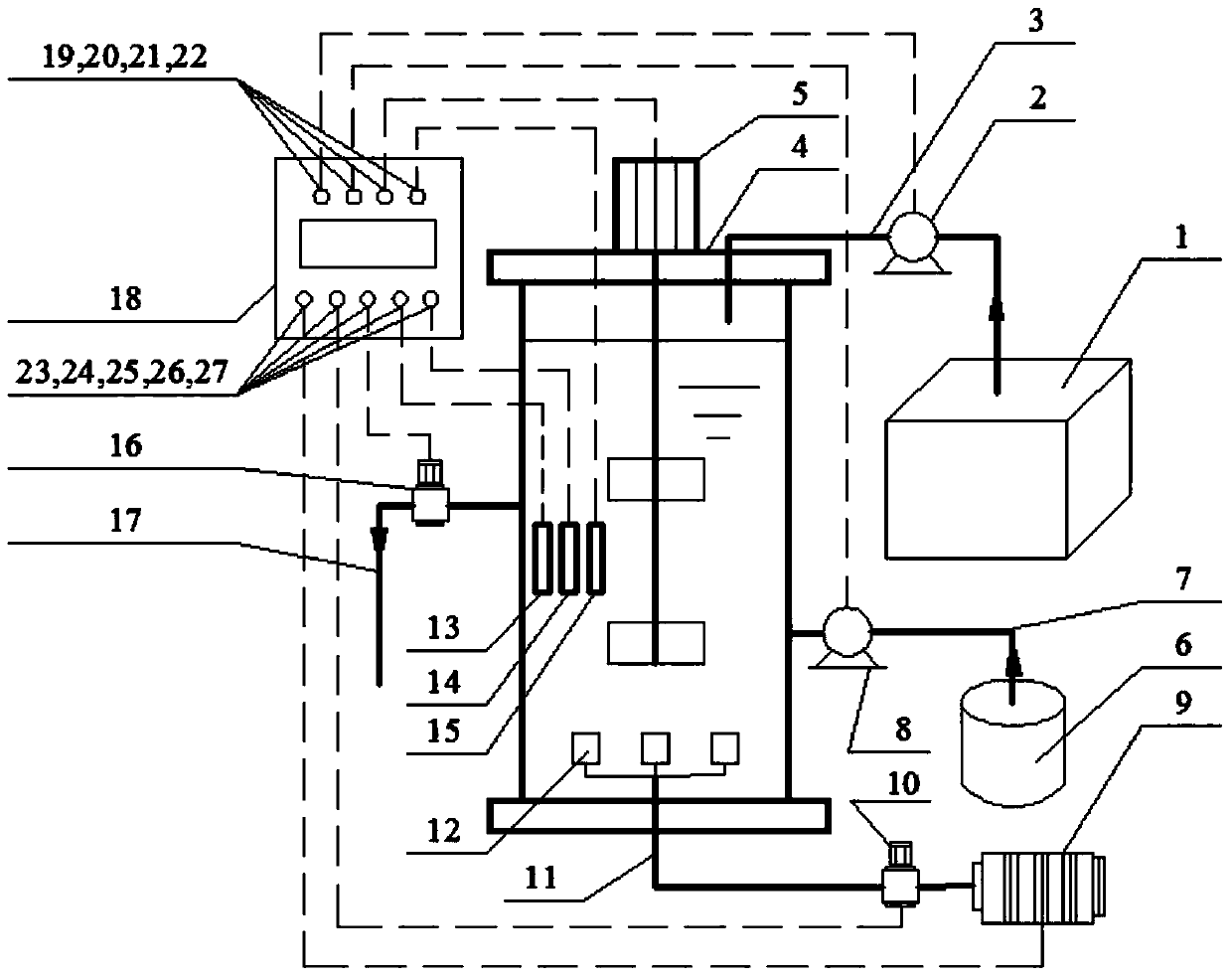
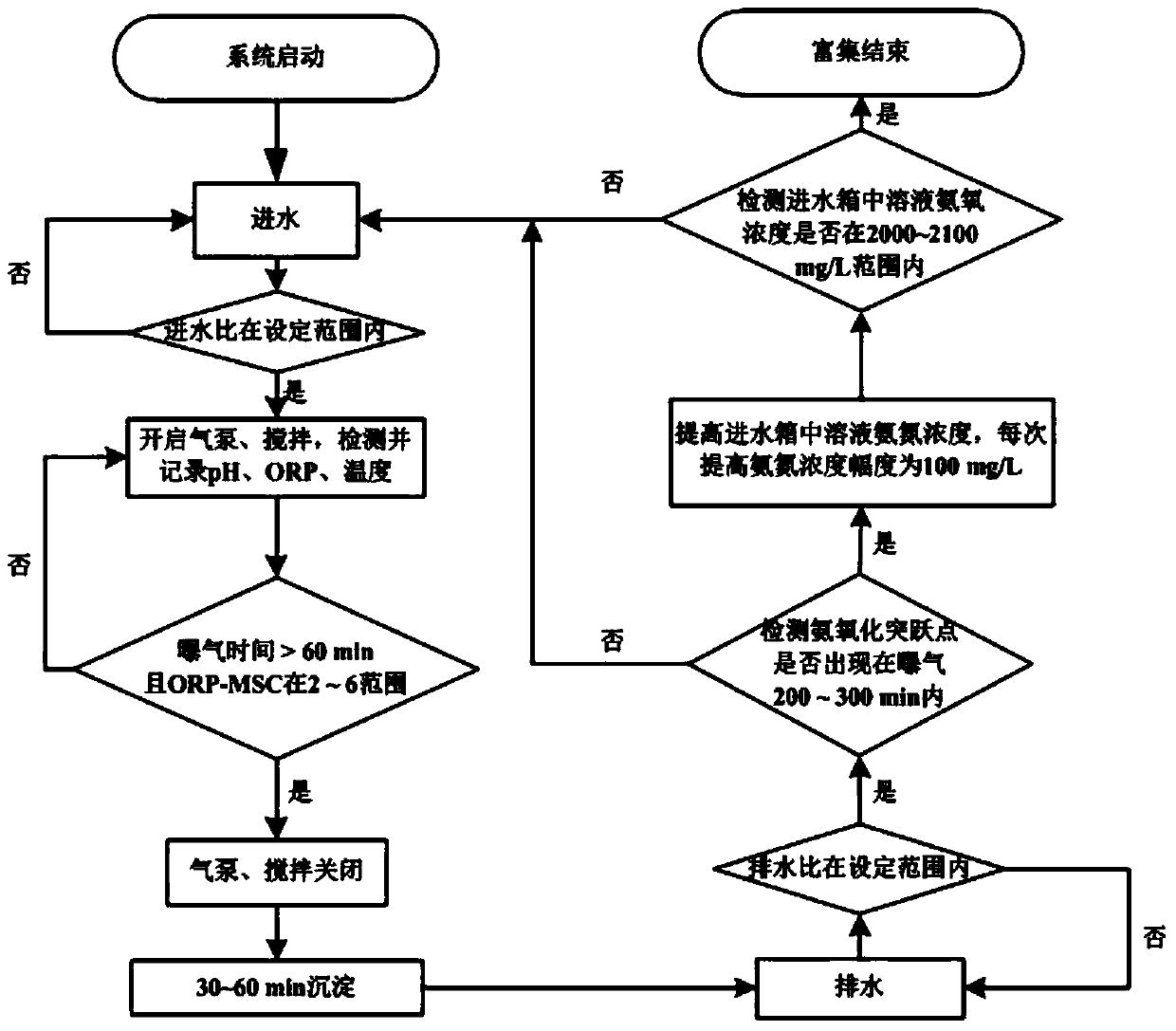
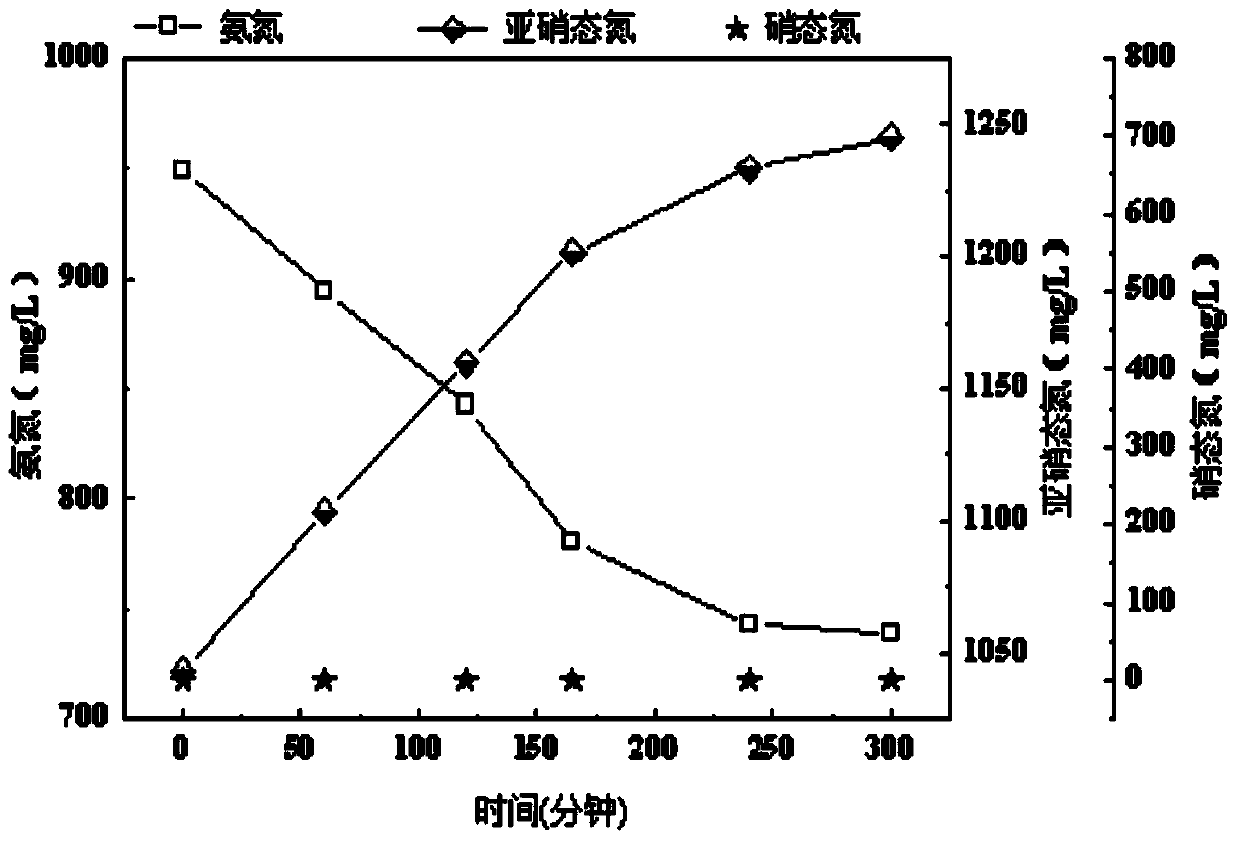
Method for quickly improving enrichment rate and degree of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in sequencing batch reactor (SBR)
ActiveCN103435166AIncrease speedImprove completenessBiological water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeSequencing batch reactor
The invention discloses a method for quickly improving the enrichment rate and degree of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR). The method is characterized by adopting an activated sludge process to treat ammonia-nitrogen wastewater in the SBR, using the mobile slope (MSC) of the oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) as an indication parameter of the ammoxidation process and increasing the enrichment rate of the AOB, improving the enrichment degree of the AOB by firstly improving the ammonia-nitrogen concentrations of feedwater gradually to culture the activities of nitrifying bacteria and then utilizing high free ammonia (50-65mg NH3 / L), high free nitrite acid (2-8mgHNO2-N / L) and proper amount of discharged sludge to elutriate nitrite nitrogen oxidizing bacteria and heterotrophic bacteria out of the system. The enrichment rate and degree of the AOB in the SBR are quickly improved by adopting the method. An AOB enrichment reactor can increase the proportion of the AOB in the total bacteria to 11% from 3% in about 40 days and improve the proportion to 90% in about 100 days. The sludge load can reach 1.31kgNH4<+>-N / (gvss.d). The method has the advantages of short AOB enrichment time, high AOB enrichment degree, flexibility in control and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing photopolymerizable organosilicon polyurethane acrylate aqueous oligomer and composition thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing a photopolymerizable organosilicon polyurethane acrylate aqueous oligomer and a composition thereof. The method is based on the shortcomings of the current photopolymerizable organosilicon polyurethane acrylate aqueous oligomer, and the method comprises the following steps: synthesizing 2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl) butyl acrylate (HBA), and introducing thematerial into the oligomer molecule to make the polymer side chain is rich in unsaturated carbon-carbon double bonds; synthesizing one-terminated hydroxypolydimethylsiloxane (Si-OH), and introducing the substrate to the end of a main chain of the aqueous polyurethane acrylate oligomer so that the substrates facilitate enrichment on the surface of the material. Through the above molecular design, the problems of poor water resistance and low hardness of the aqueous photocurable material caused by the low double bond content and low crosslink density of the photocurable material are effectivelysolved, and the disadvantages that silicone chain is easily wrapped by the crosslinked network when is in the middle of the main chain so that the silicone is not enriched at the surface of the material, so that the surface hydrophobicity of the material can be effectively increased.
Owner:安庆北化大科技园有限公司
Multifunction tunnel type unpolished rice sprouting device
InactiveCN1589599AHigh degree of enrichmentStable and consistent physiological activation treatment process conditionsFood preparationGerminating apparatusSprayerRice grain
A tunnel-type multifunctional germinating apparatus for the long-grained nonglutinous rice is composed of a tunnel body, roller-type driving mechanism, delivering netted belt, and multifunctional tubular sprayer for atomizing, passivating, enzymolyzing and washing. Its working method features that the rice grains are spred on the delivering netted belt and then reciprocated in tunnel body while the liquid is prayed from said sprayer.
Owner:杨春华 +2
Functional pork high in PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acid), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (dehydroacetic acid) content and low in n-6 PUFA/n-3 PUFA proportion and production method thereof
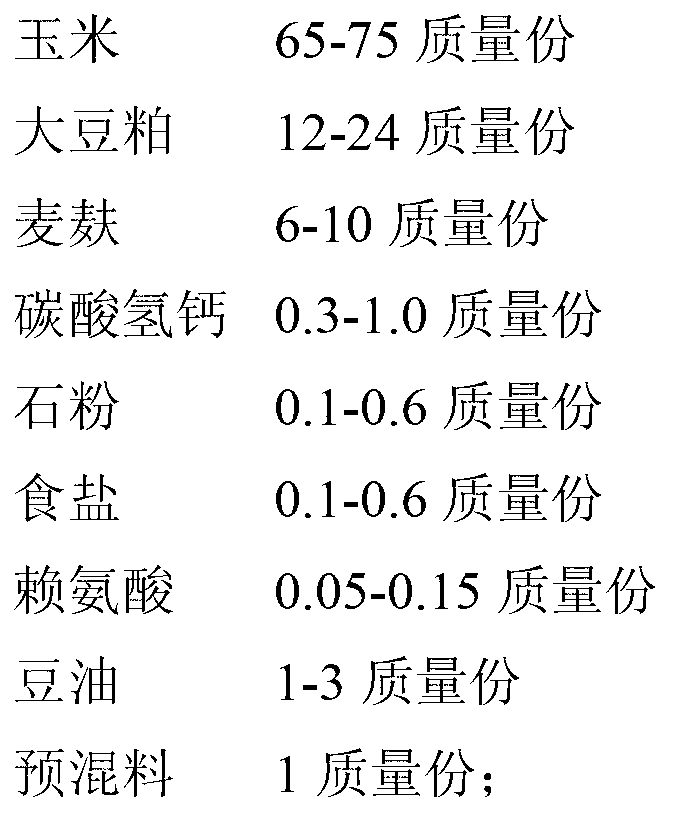
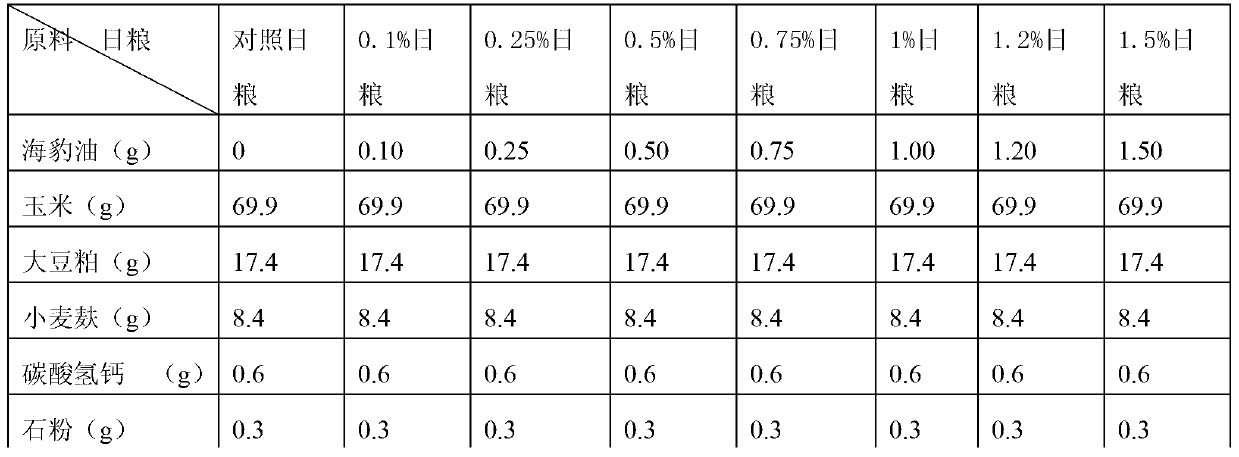
InactiveCN103125440ALow in PUFA fatty acidsLow in fatty acidsFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDehydroacetic acidEicosapentaenoic acid
The invention discloses functional pork high in PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acid), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (dehydroacetic acid) content and low in n-6 PUFA / n-3 PUFA proportion and a production method thereof. The production method of the functional pork includes steps of breeding pigs: breeding the pigs by seal-oil-containing ration in whole growing stage, wherein the seal-oil-containing ration is composed of common feed for pigs in growing stage and seal oil, the seal oil is 0.1%-1.5% of the common feed for pigs in growing stage by weight, and the seal oil contains no common feed for pigs in growing stage. According to low content and imbalance proportion of PUFA in pork and according to the principles and techniques in zoophysiology and animal nutrition, the seal oil is used as additive to improve fatty acid composition of the pig ration, so that richness of the PUFA in the pork is increased and the functional pork high in PUFA content, high in EPA content, high in DHA content and low in n-6 / n-3 PUFA proportion is produced.
Owner:SHENYANG AIDI BIOTECH
Device and method for capturing and recovering carbon dioxide in flue gas
PendingCN107899377AAffect separation efficiencyAffect the degree of enrichmentCombination devicesProductsFlue gasProduct gas
The invention provides a device and method for capturing and recovering carbon dioxide in flue gas. The device comprises a flue gas treatment system, a first membrane separation unit, a second membrane separation unit and a high-pressure energy recovery device, wherein the flue gas treatment system is provided with a treatment inlet and a treatment outlet and used for treating the flue gas; the first membrane separation unit is provided with a first gas inlet, a first carbon dioxide enriched gas outlet and a first high-pressure impermeable gas outlet, and the first gas inlet is connected withthe treatment outlet; the second membrane separation unit is provided with a second gas inlet, a carbon dioxide product gas outlet and a second high-pressure impermeable gas outlet, and the second gasinlet is connected with the first carbon dioxide enriched gas outlet; the high-pressure energy recovery device is connected with the first high-pressure impermeable gas outlet and used for recoveringpressure energy of the high-pressure gas produced by the first high-pressure impermeable gas outlet. The device provided by the invention can capture CO2 in recovered flue gas more effectively.
Owner:北京集封环能科技有限责任公司
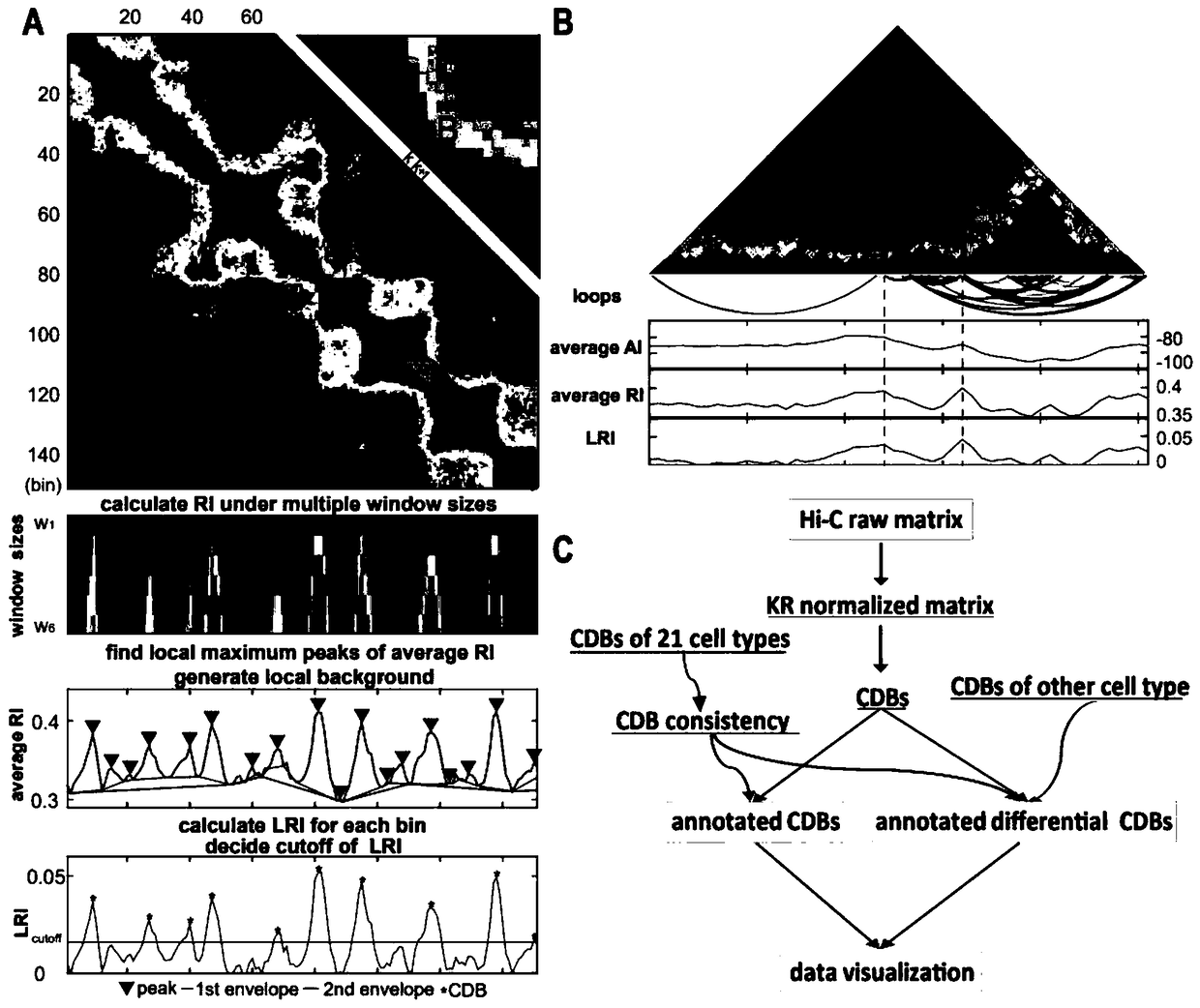
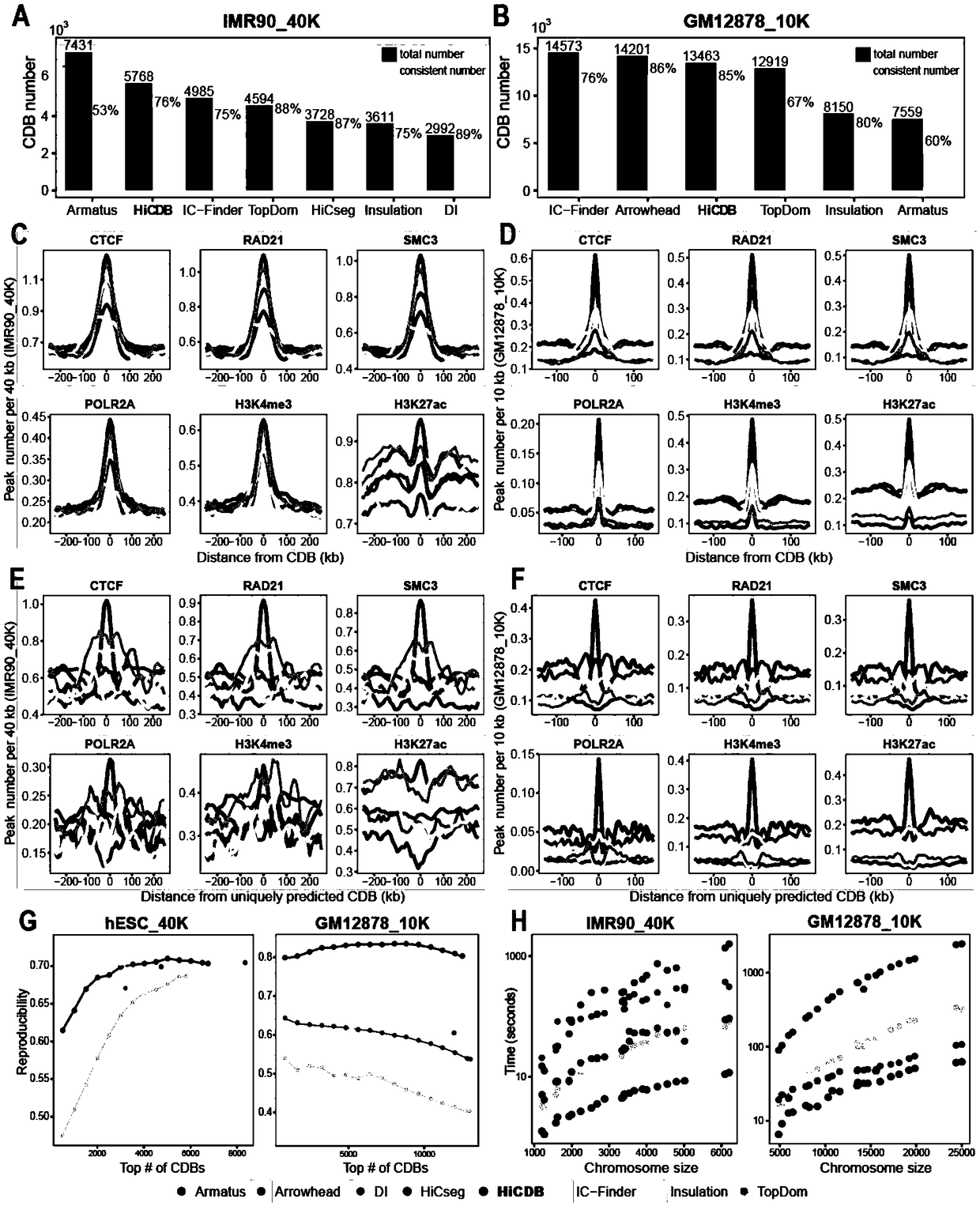
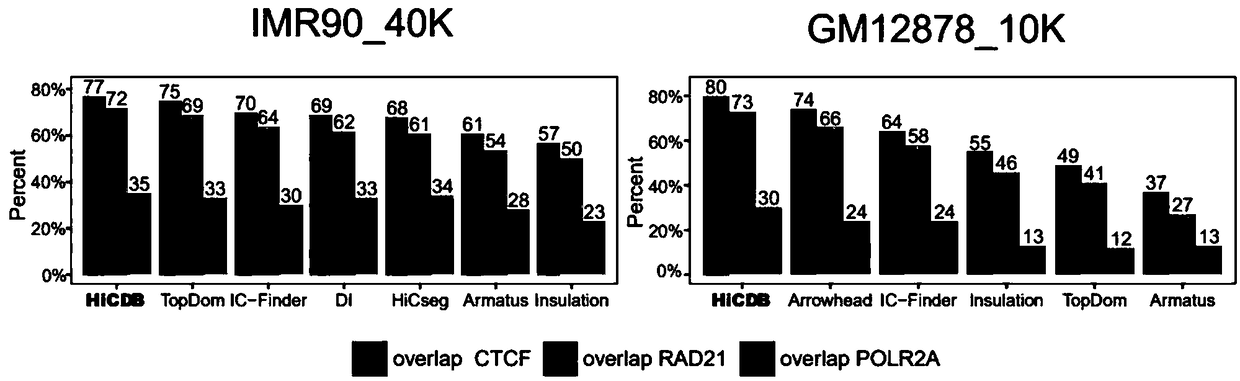
Analysis method for chromatin topological domain boundaries
ActiveCN109448783AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationAnalysis methodComputer science
The invention relates to an analysis method for chromatin structures, and specifically relates to an analysis method for chromatin topological domain boundaries.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
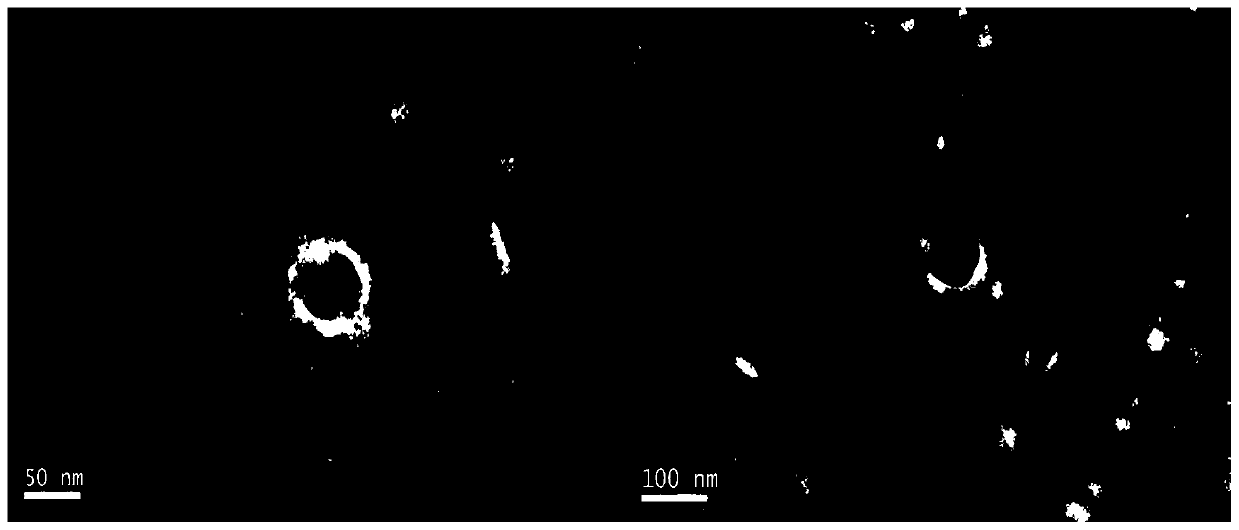
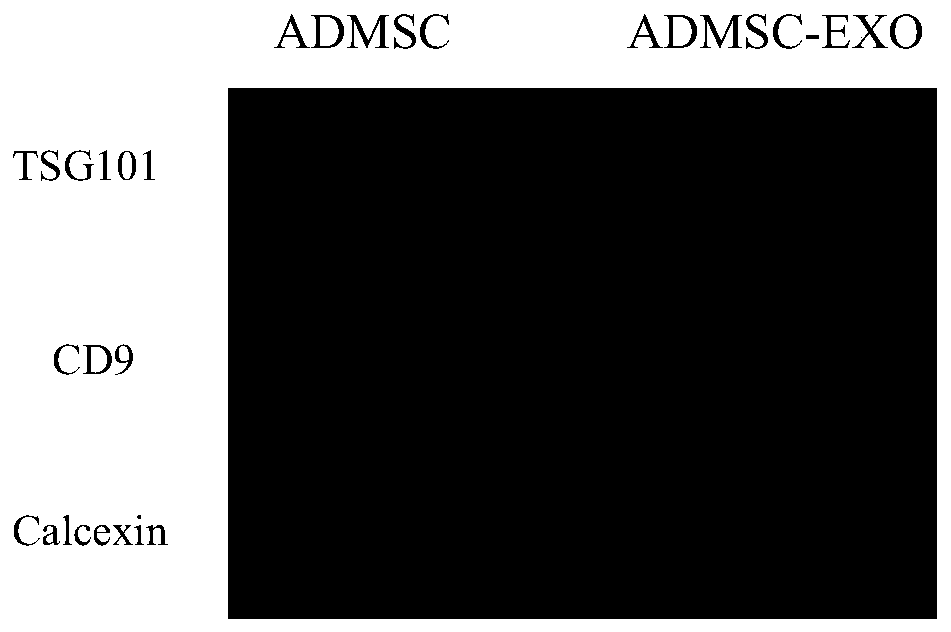
Intermittent hypoxia treated stem cell derived exosome and application in cardiac muscle tissue
ActiveCN110577931AEffective protectionRegulate the level of apoptosisCulture processUnknown materialsReperfusion injuryMesenchymal stem cell
The invention relates to an exosome derived from a mesenchymal stem cell. The exosome is prepared by intermittent hypoxic stimulation of the mesenchymal stem cell. The exosome prepared from the invention has stronger tissue and organ ischemia-reperfusion injury protective effect, and the biological effect of unit exosomes is improved, and treatment of diseases such as ischemic heart disease is more facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Sugar decreasing composition of fenugreek seed
InactiveCN1720982AEnhance body functionPromote pancreas functionMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsFenugreeksFenugreek seed
The invention relates to a antihypelipidemic composition of fenugreek seed, which comprises (by weight ratio) fenugreek seeds extract 30-90%, mulberry leaf extract 5-40%, astragalus root extract 3-30%, the fenugreek seeds extract contains total fiber 1-80%, the mulberry leaf extract contains total flavones 0.1-50%, and the astragalus root extract is the aqueous extract or organic solvent of astragalus root or the aqueous extract AND organic solvent of astragalus root.
Owner:陕西爱波卓科技有限责任公司
Chrysanthemum ester molecularly imprinted polymer preparing method
InactiveCN105017463AObvious porosity on the surfaceGood choiceOther chemical processesCross-linkPolymer science
The invention discloses a chrysanthemum ester molecularly imprinted polymer preparing method and relates to a molecularly imprinted polymer preparing method. The chrysanthemum ester molecularly imprinted polymer preparing method includes the following steps that firstly, chrysanthemum ester type template molecules, styrene, halomethane, a cross-linking agent, a stabilizing agent and an initiating agent are evenly mixed and are stirred at the temperature of 50-80 DEG C after nitrogen leading and aerating; secondly, after a reaction is over, standing and layering are conducted, supernatant is removed, a lower-layer solid is eluted through a carboxylic acid and alcohol mixing solution, and chrysanthemum ester molecularly imprinted polymer powder is obtained. The preparing chrysanthemum ester molecularly imprinted polymer is in a powder form, powder-form polymers are in a microsphere shape, surface hole forming is obvious, the powder-form polymers can be directly used for extracting chrysanthemum ester pesticide residues from food media without being ground, and the recovery rate can reach more than 90 percent. According to the chrysanthemum ester molecularly imprinted polymer preparing method, processing does not need to be conducted again, the preparing process is simple, the technology is stable, and the preparing cost is low.
Owner:福州市产品质量检验所
A method for wet separation and recovery of valuable metals in Kaldor furnace smelting slag
ActiveCN106086440BHigh degree of enrichmentImprove compatibilitySelenium/tellurium compundsProcess efficiency improvementSlagCopper sulfate
The invention discloses a method for wet separation and recovery of valuable metal from Kaldo furnace smelting slag. Kaldo furnace smelting slag is ground and dipped in water to remove soluble salt; copper, selenium and tellurium in the slag are leached out by using pressurization, oxidation and acid leaching for treatment to obtain copper sulfate solution, silver-selenium slag and copper telluride slag; tellurium, silver and selenium can be respectively recovered from the silver-selenium slag and the copper telluride slag; pressurized copper removing filter residue is mixed with hydrochloric acid for leaching out antimony and bismuth to finally obtain lead-silver slag capable of returning to a Kaldo furnace for smelting; and antimony and bismuth are further recovered from antimony-bismuth solution. According to the method, a mode of stepped removal and recovery of such metal as copper, antimony, bismuth, selenium, tellurium, silver and lead enriched in the Kaldo furnace smelting slag is adopted, compatibility of the method with a wet-fire combined flow for recovering rare and noble metal from Kaldo furnace treatment copper anode mud is excellent, the smelting slag is enabled to return to the Kaldo furnace for smelting so as to prevent adverse effects on the copper smelting by returning to a copper smelting system, and the lead-silver slag with higher enriching degree of such valuable metal as lead and silver is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
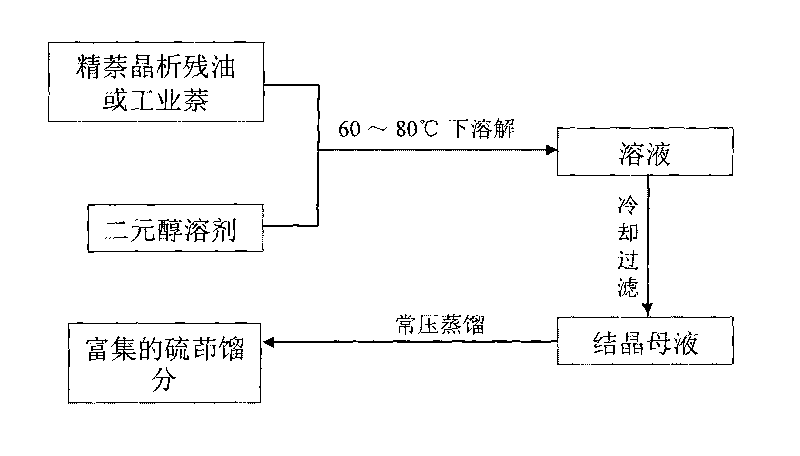
Method for enriching thianaphthene from mixtures containing thianaphthene and naphthalene
ActiveCN101747317AHigh degree of enrichmentReduces the chance of forming hydrogen bondsOrganic chemistrySolventMother liquor
The invention relates to a thianaphthene-enriching method, in particular to a method for enriching thianaphthene from mixtures containing thianaphthene and naphthalene, specifically a method for enriching thianaphthene from coal-tar downstream products. The method comprises the following: a) a step of dissolving, which is to dissolve a mixture containing thianaphthene and naphthalene in binary alcohol serving as solvent and form solution at 60 to 80 DEG C; b) a step of crystallizing, which is to cool the solution obtained in a step a) to room temperature and crystallize naphthalene and other impurities from the solution obtained in the step a); c) a step of filtering, which is to filter and separate the naphthalene and the other impure crystals and obtain crystallization mother liquor; and d) a step of distilling, which is to distill the crystallization mother liquor to remove the binary alcohol and obtain enriched thianaphthene fractions. Different from the prior naphthalene solvent crystallization adopting the monohydric alcohol as solvent in general, the method significantly raises the enrichment degree of thianaphthene by adopting the binary alcohol as the solvent.
Owner:BAOWU CHARCOAL MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com