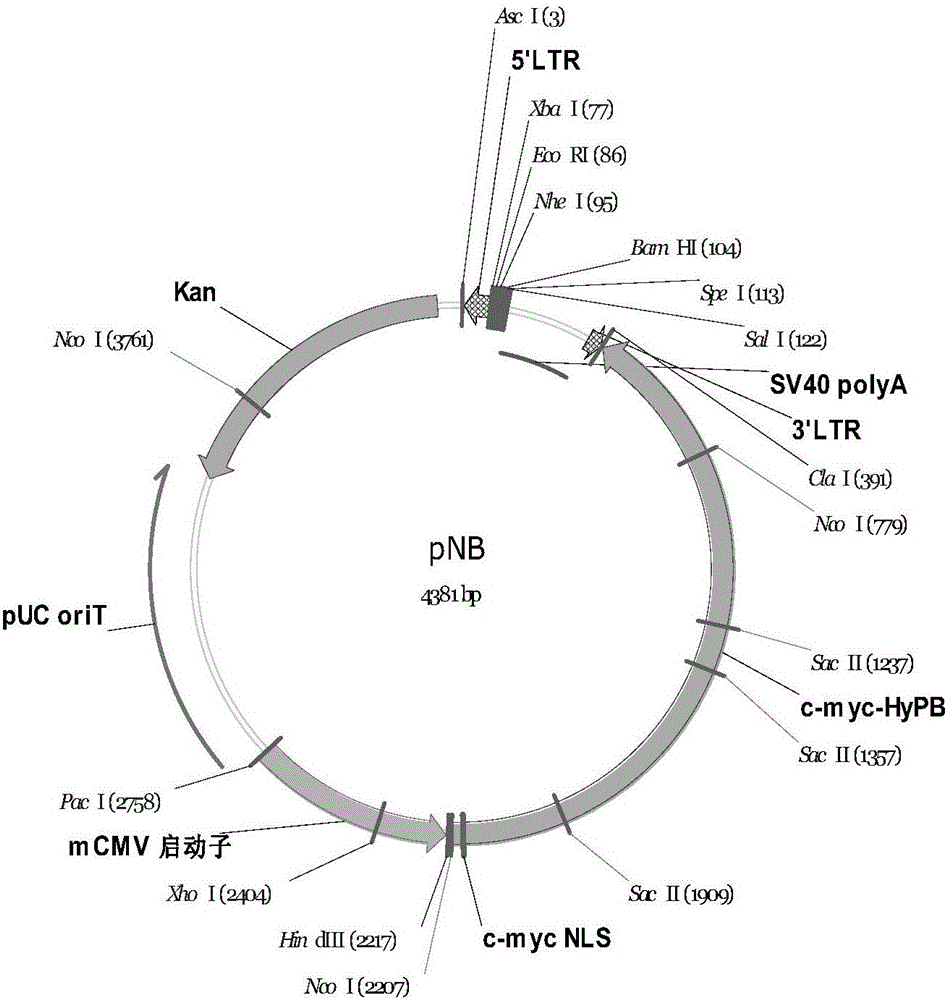
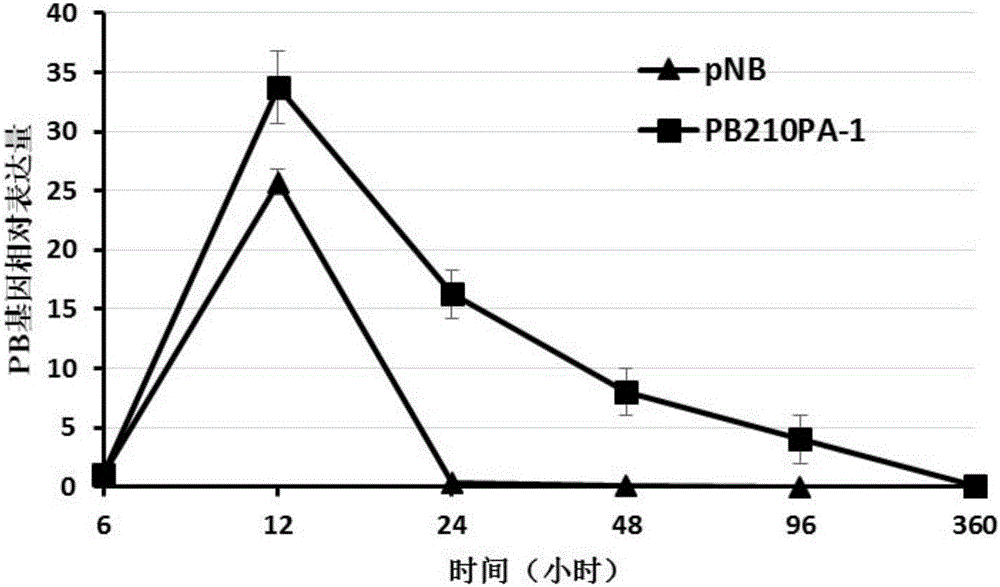
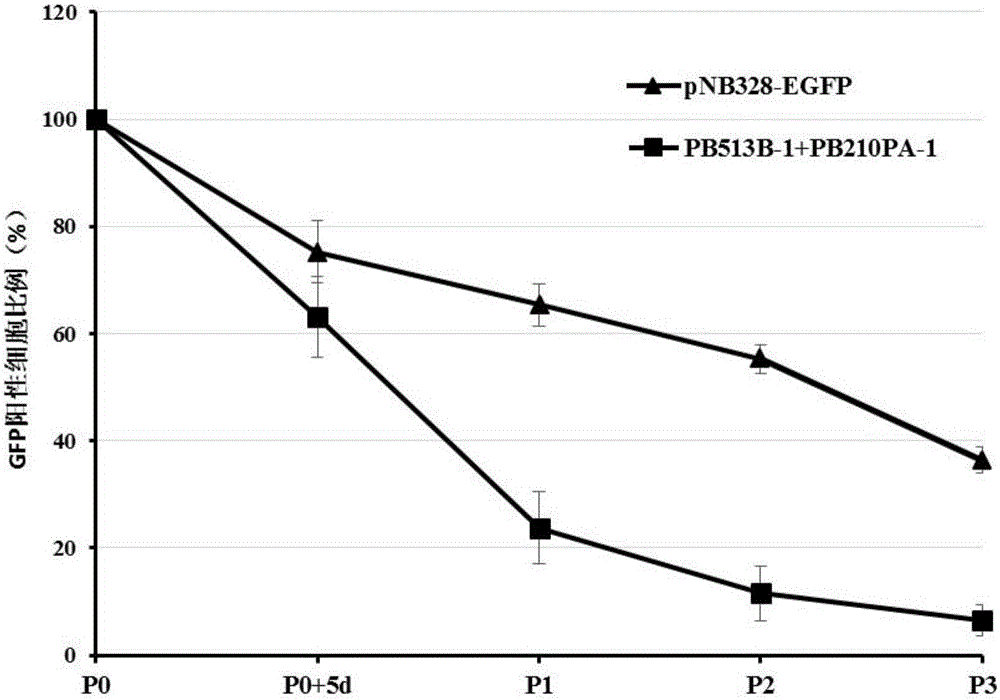
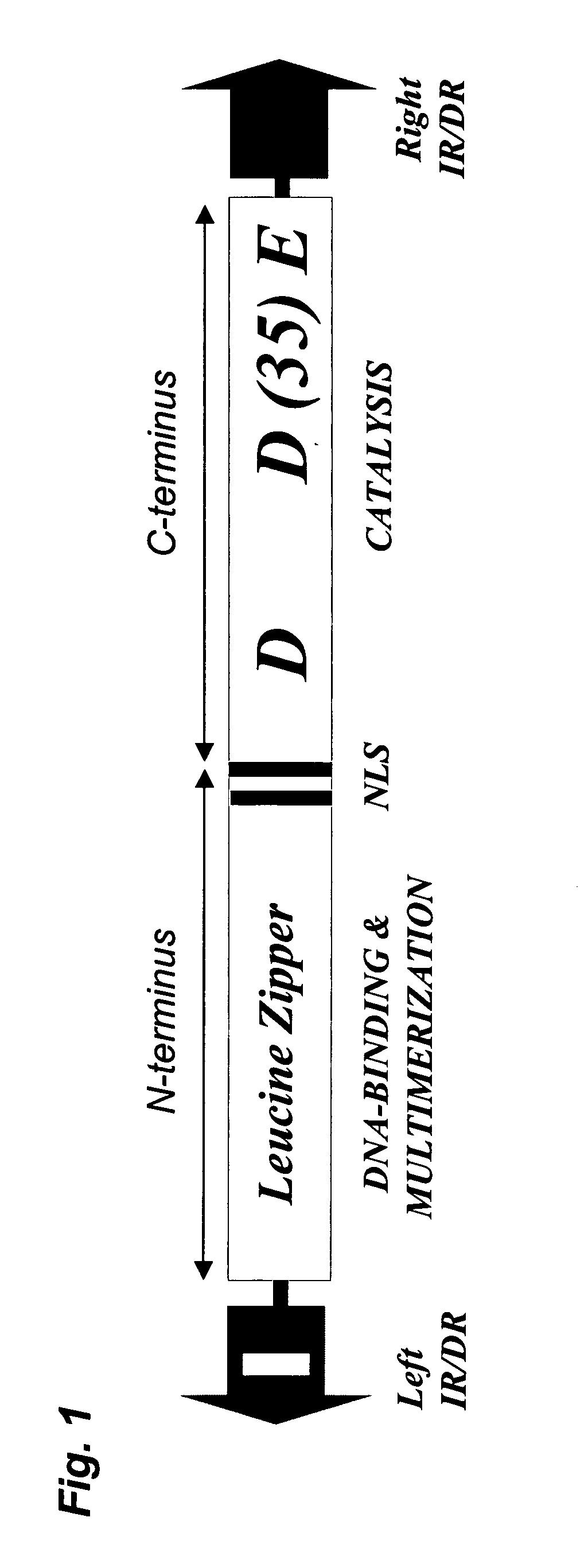
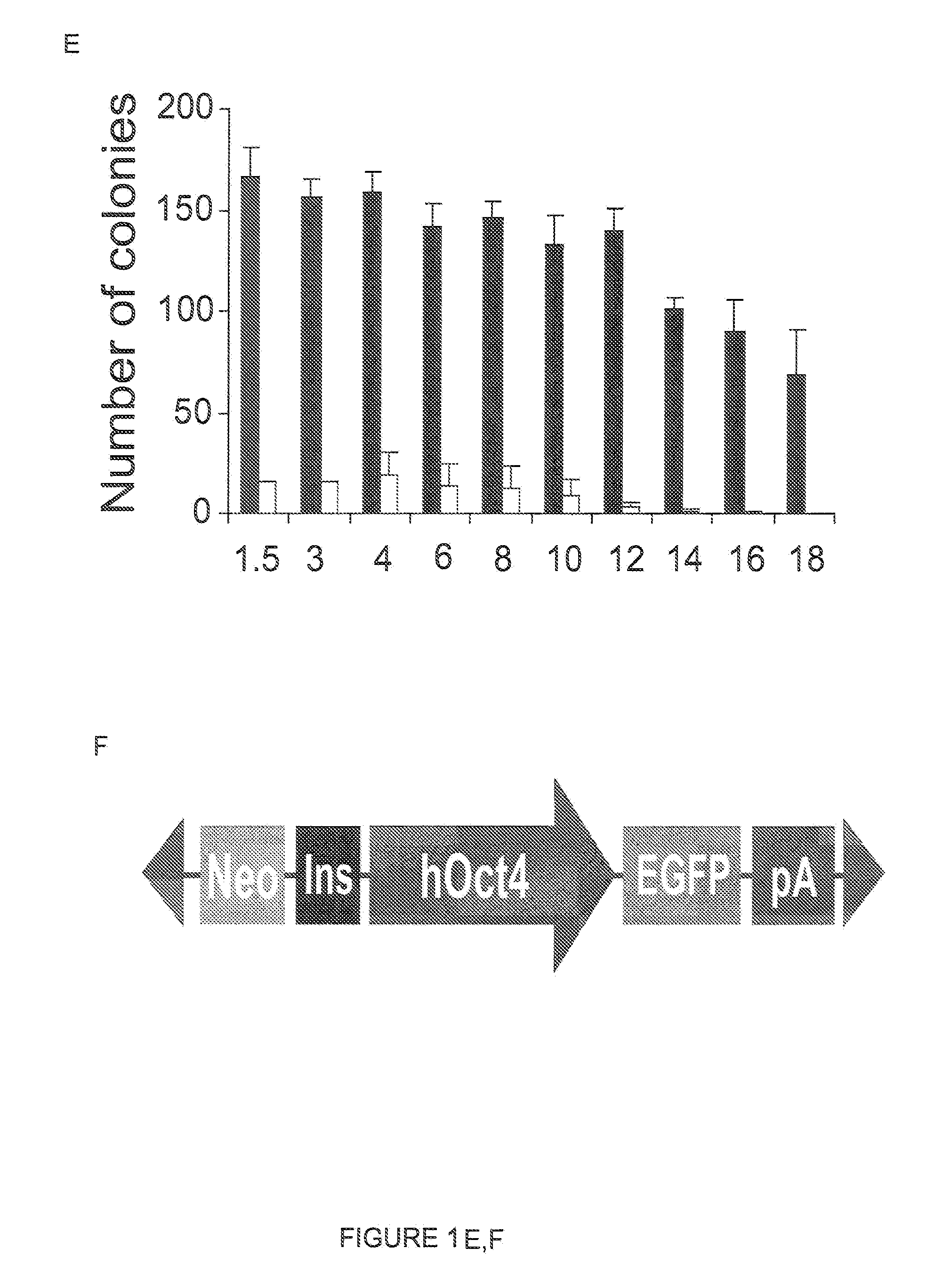
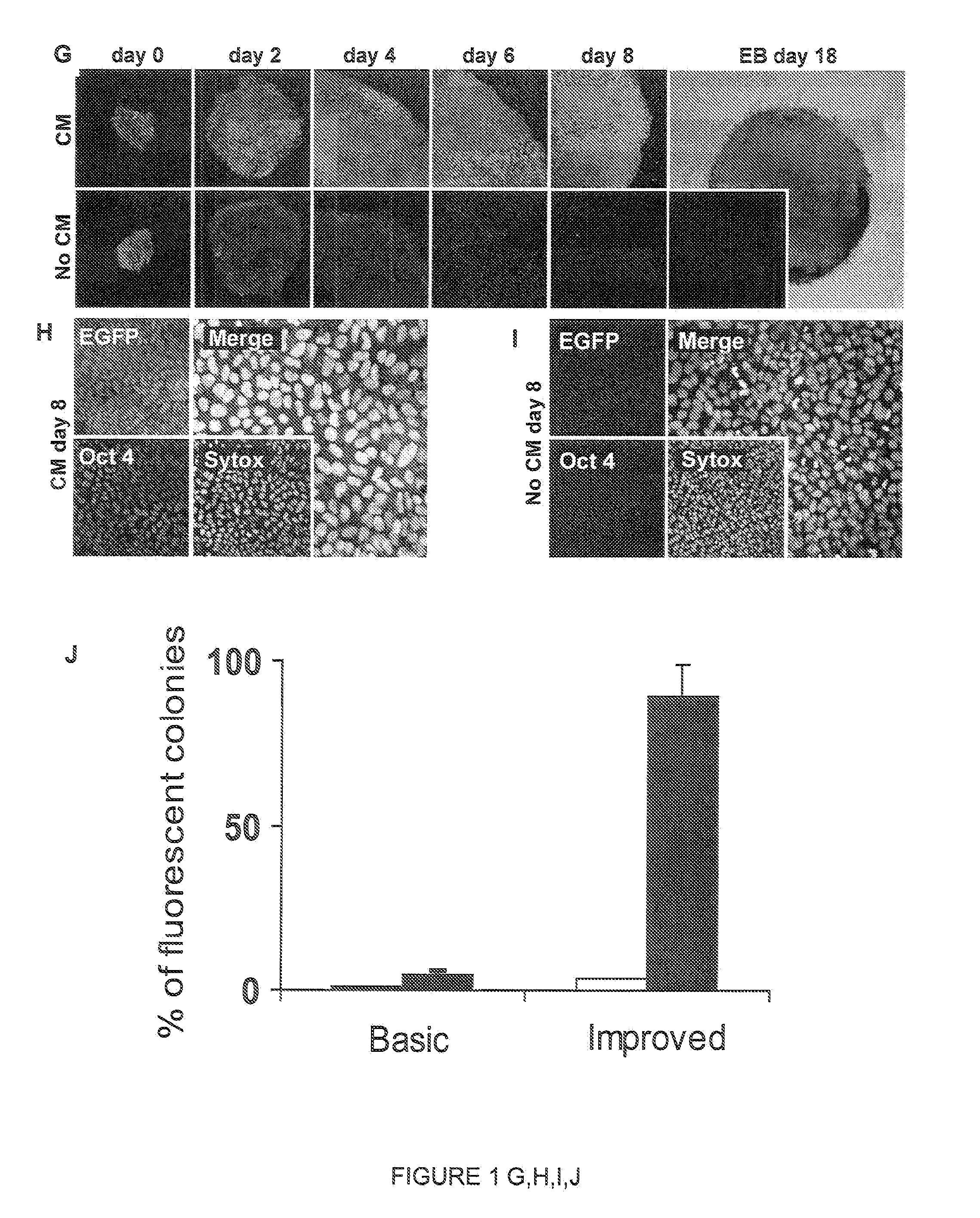
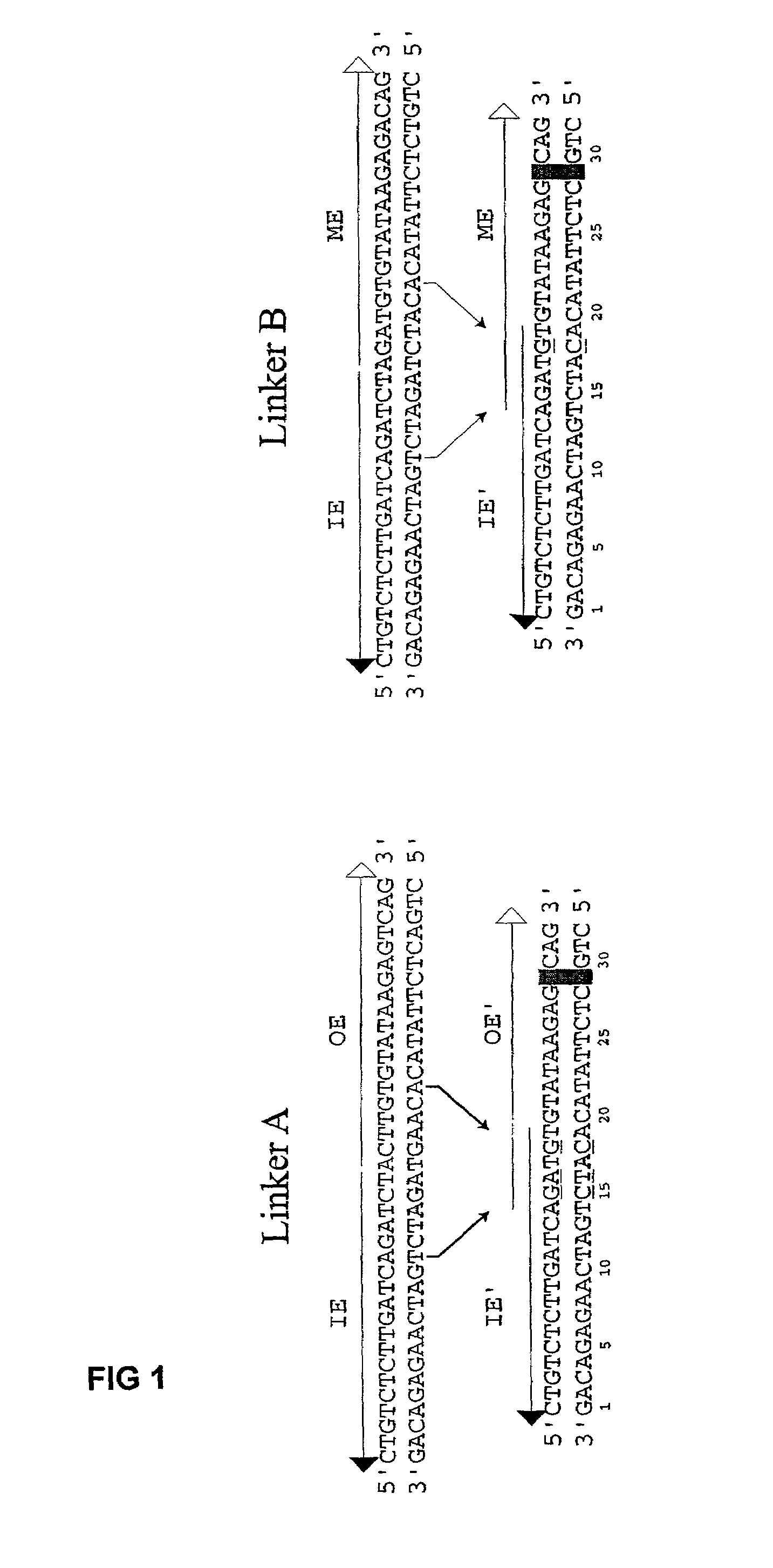
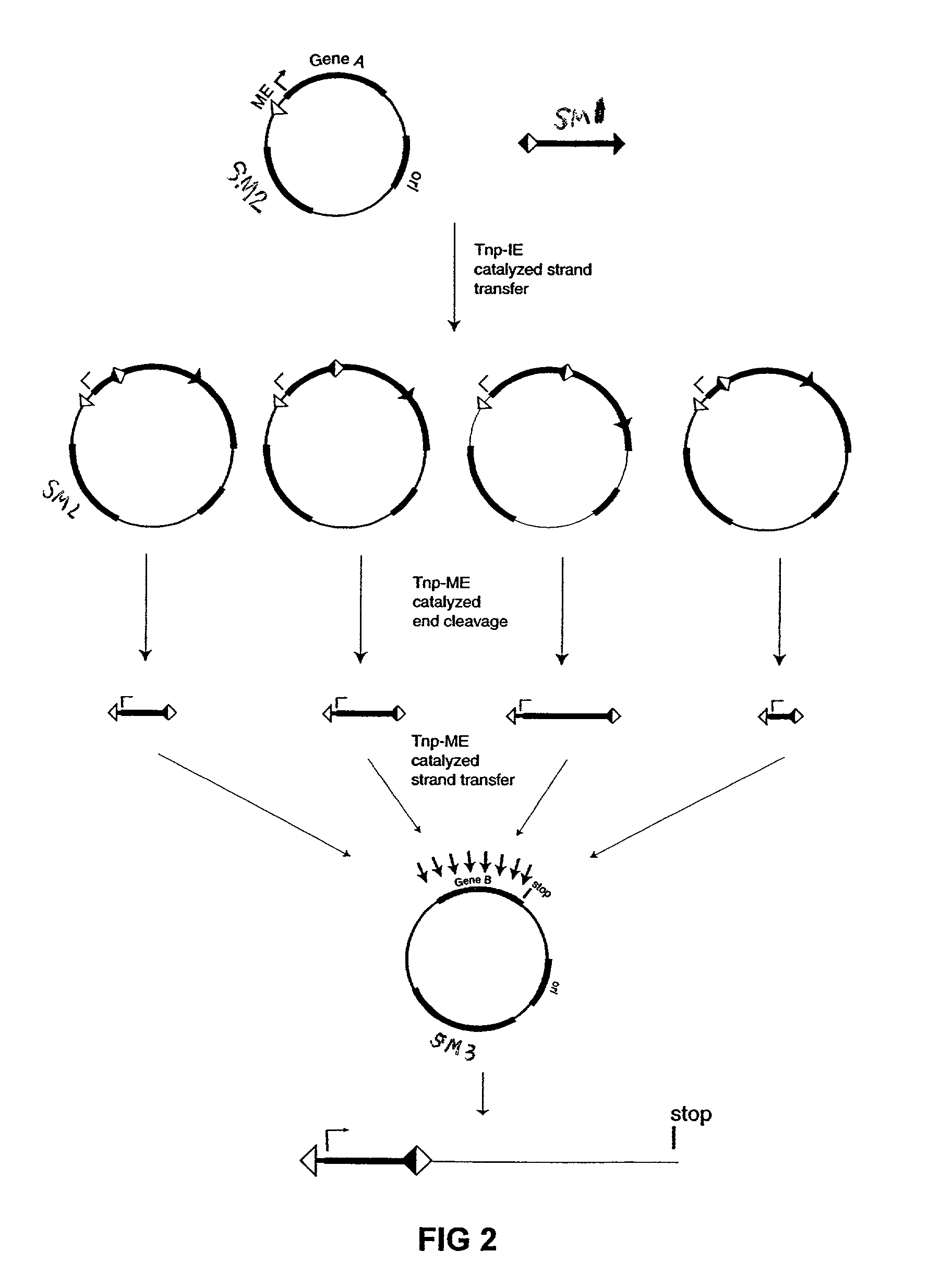
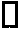Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
365 results about "Transposase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
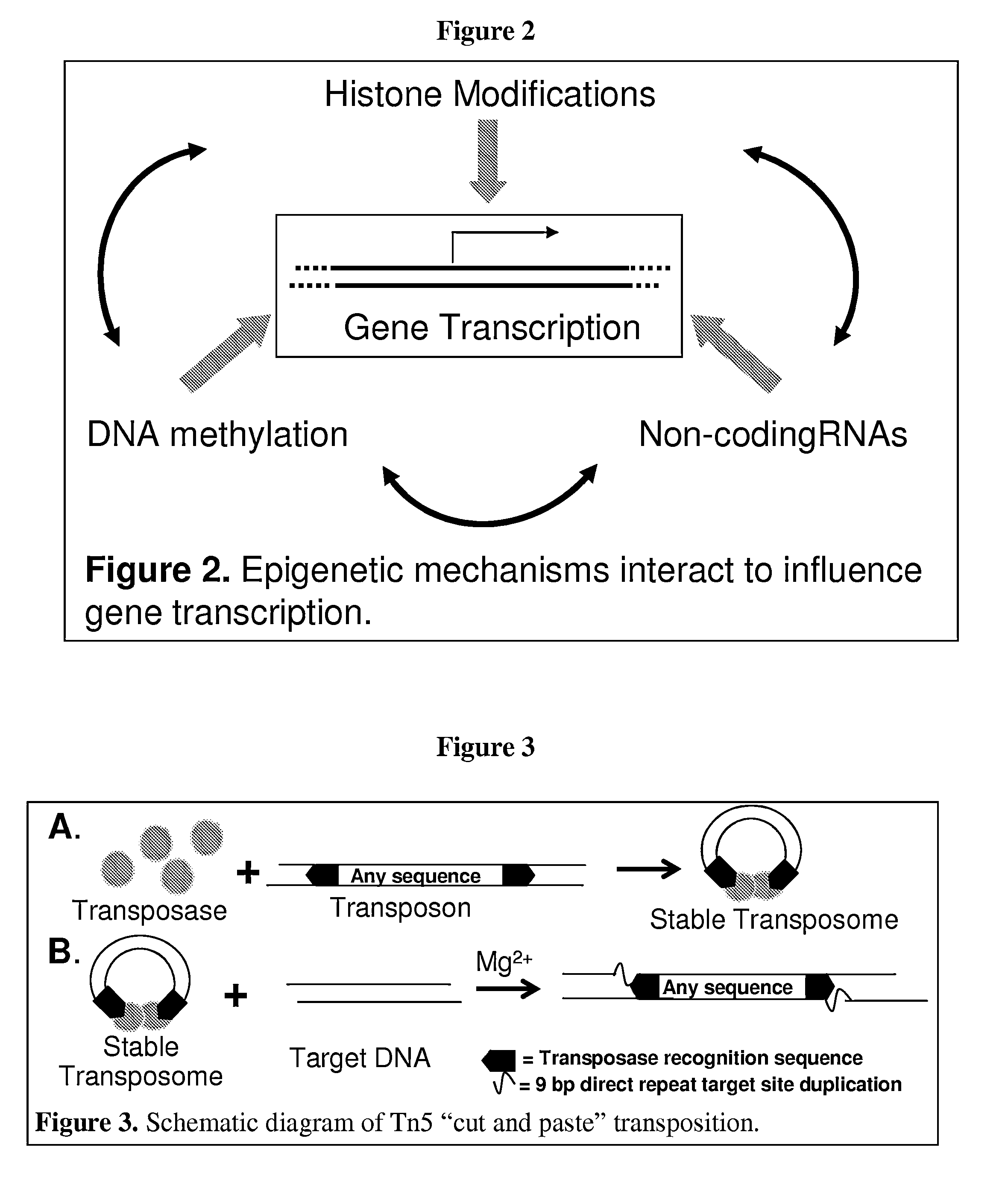
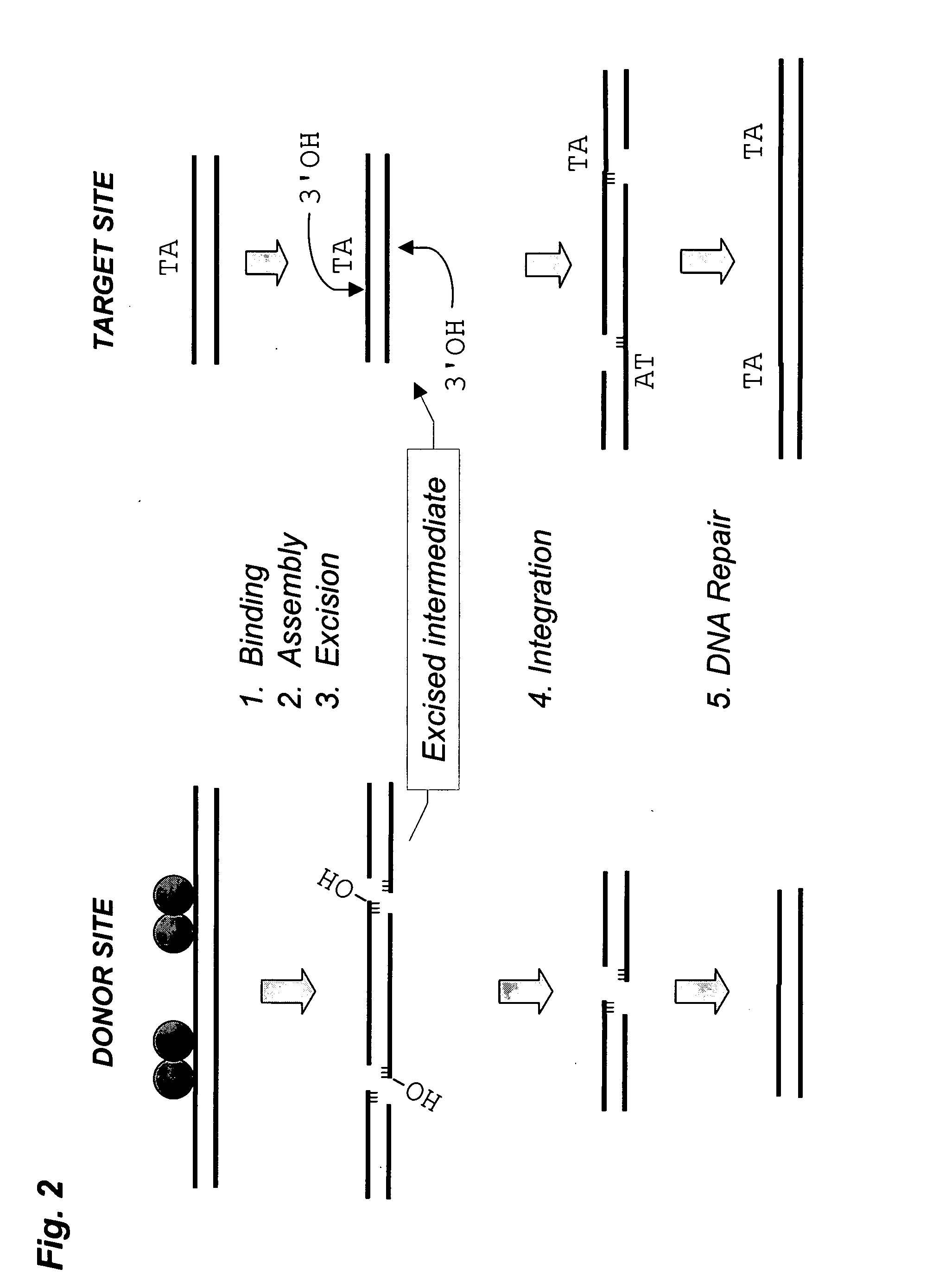
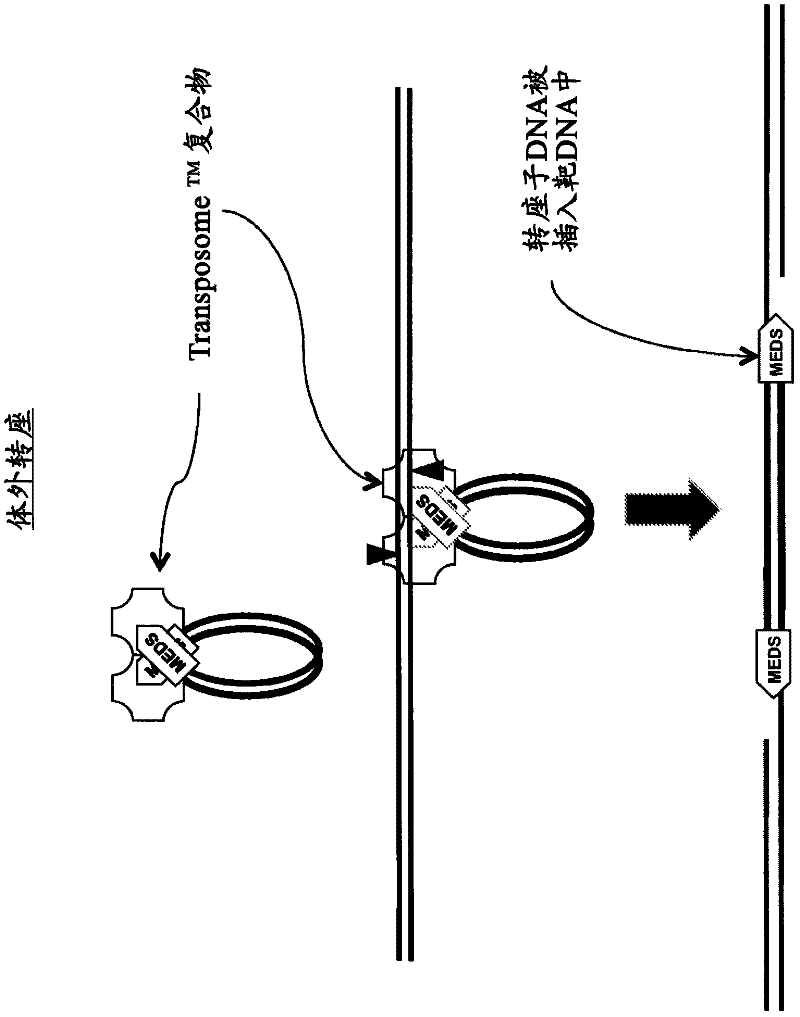
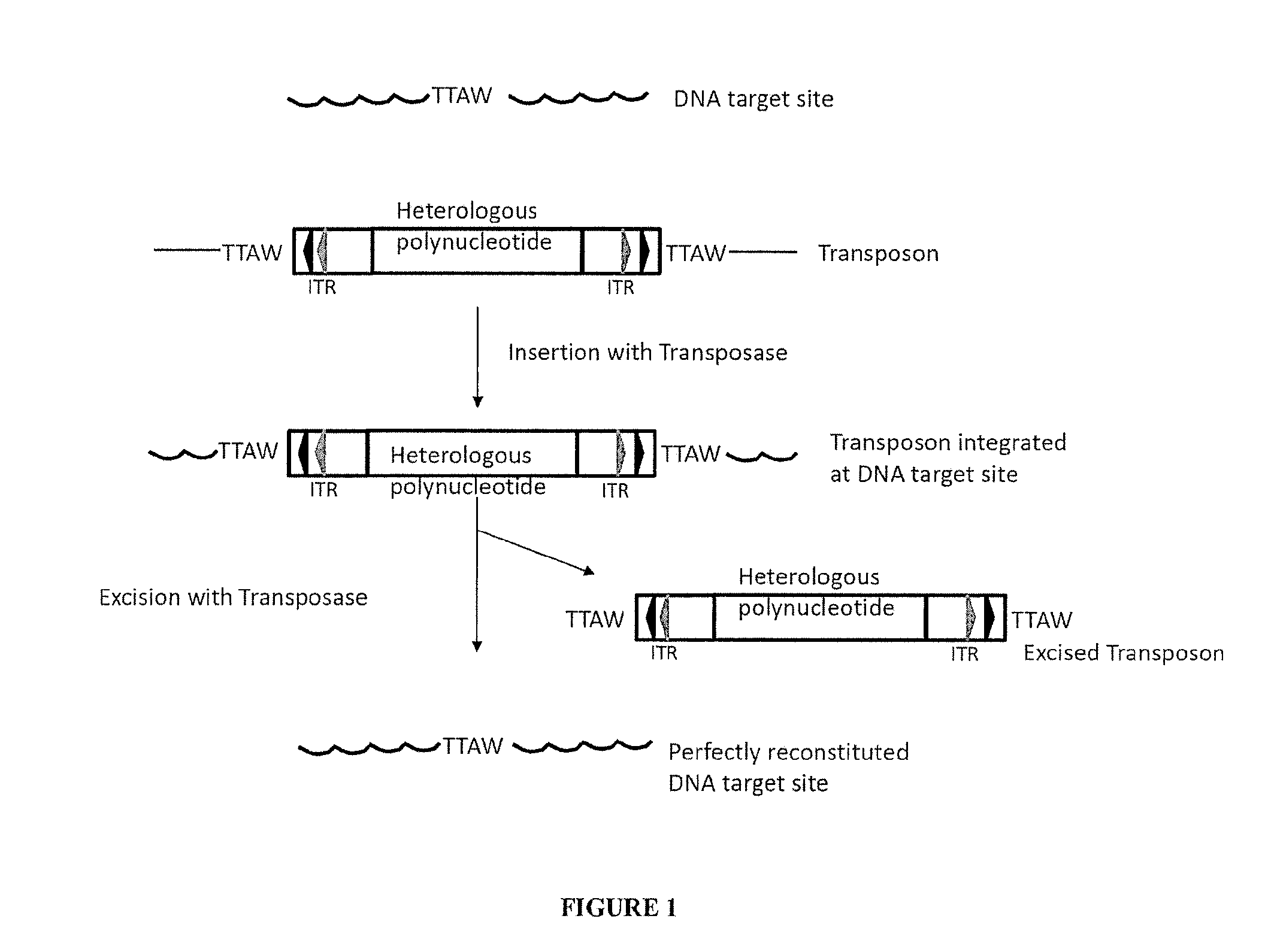
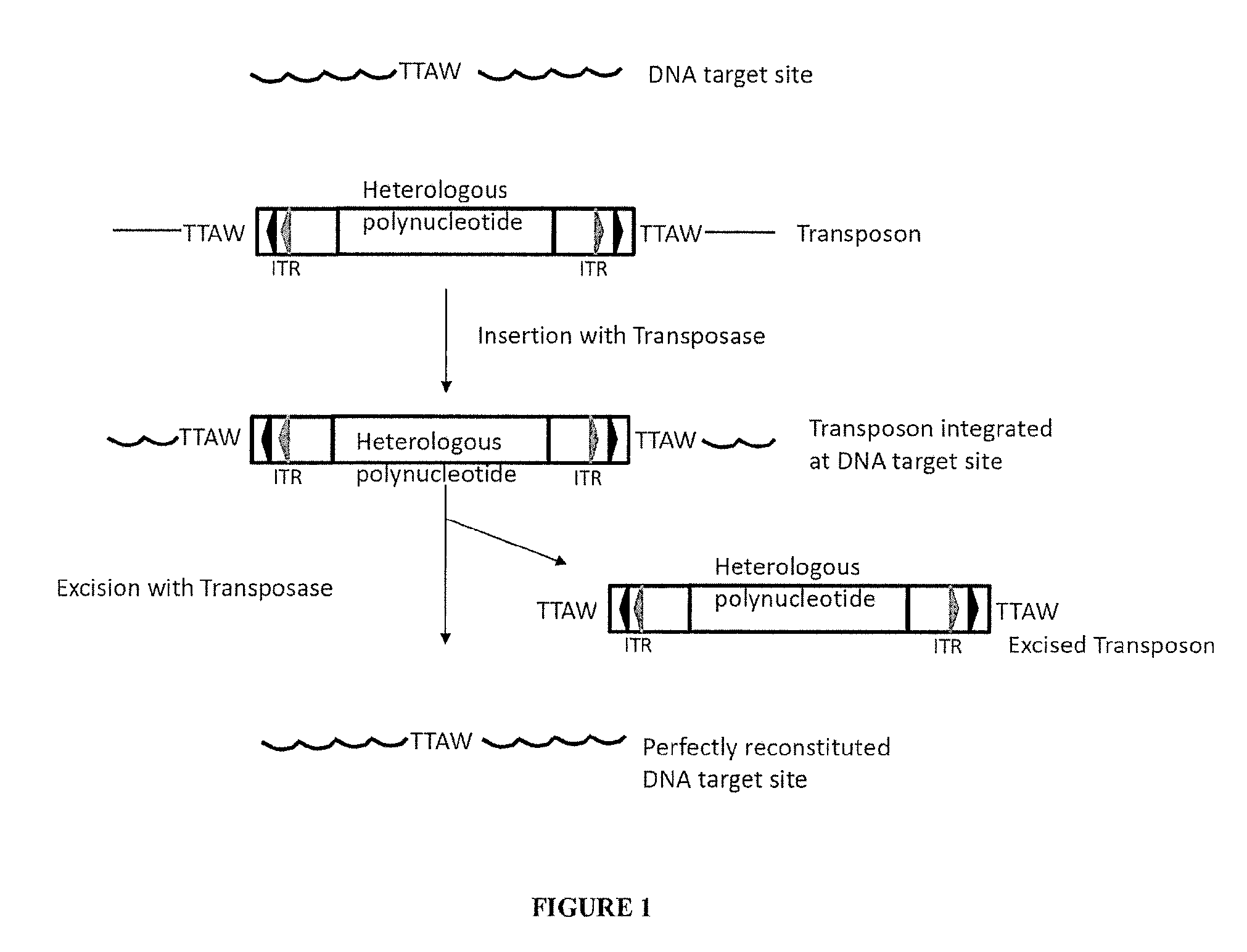
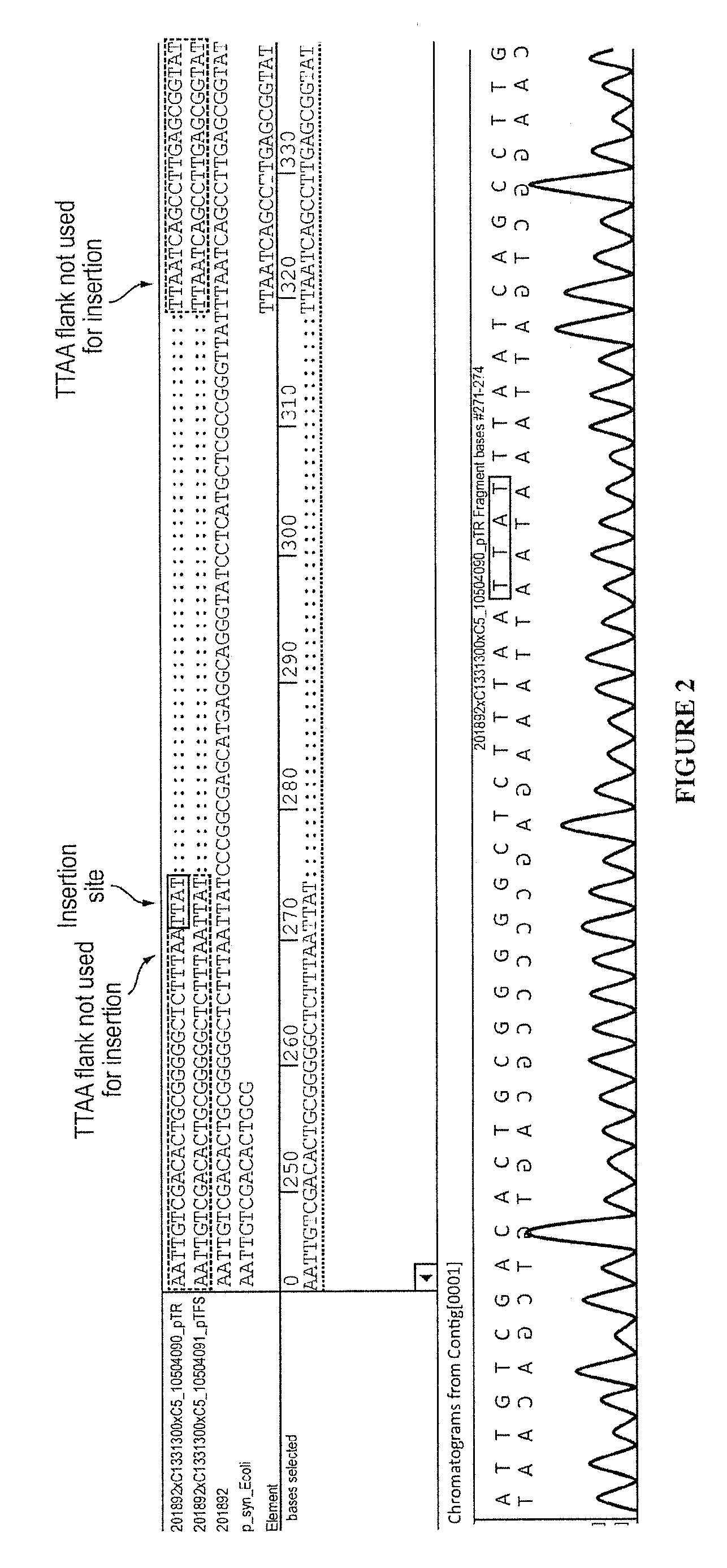
Transposase is an enzyme that binds to the end of a transposon and catalyzes its movement to another part of the genome by a cut and paste mechanism or a replicative transposition mechanism. The word "transposase" was first coined by the individuals who cloned the enzyme required for transposition of the Tn3 transposon. The existence of transposons was postulated in the late 1940s by Barbara McClintock, who was studying the inheritance of maize, but the actual molecular basis for transposition was described by later groups. McClintock discovered that pieces of the chromosomes changed their position, jumping from one chromosome to another. The repositioning of these transposons (which coded for color) allowed other genes for pigment to be expressed. Transposition in maize causes changes in color; however, in other organisms, such as bacteria, it can cause antibiotic resistance. Transposition is also important in creating genetic diversity within species and adaptability to changing living conditions. During the course of human evolution, as much as 40% of the human genome has moved around via methods such as transposition of transposons.
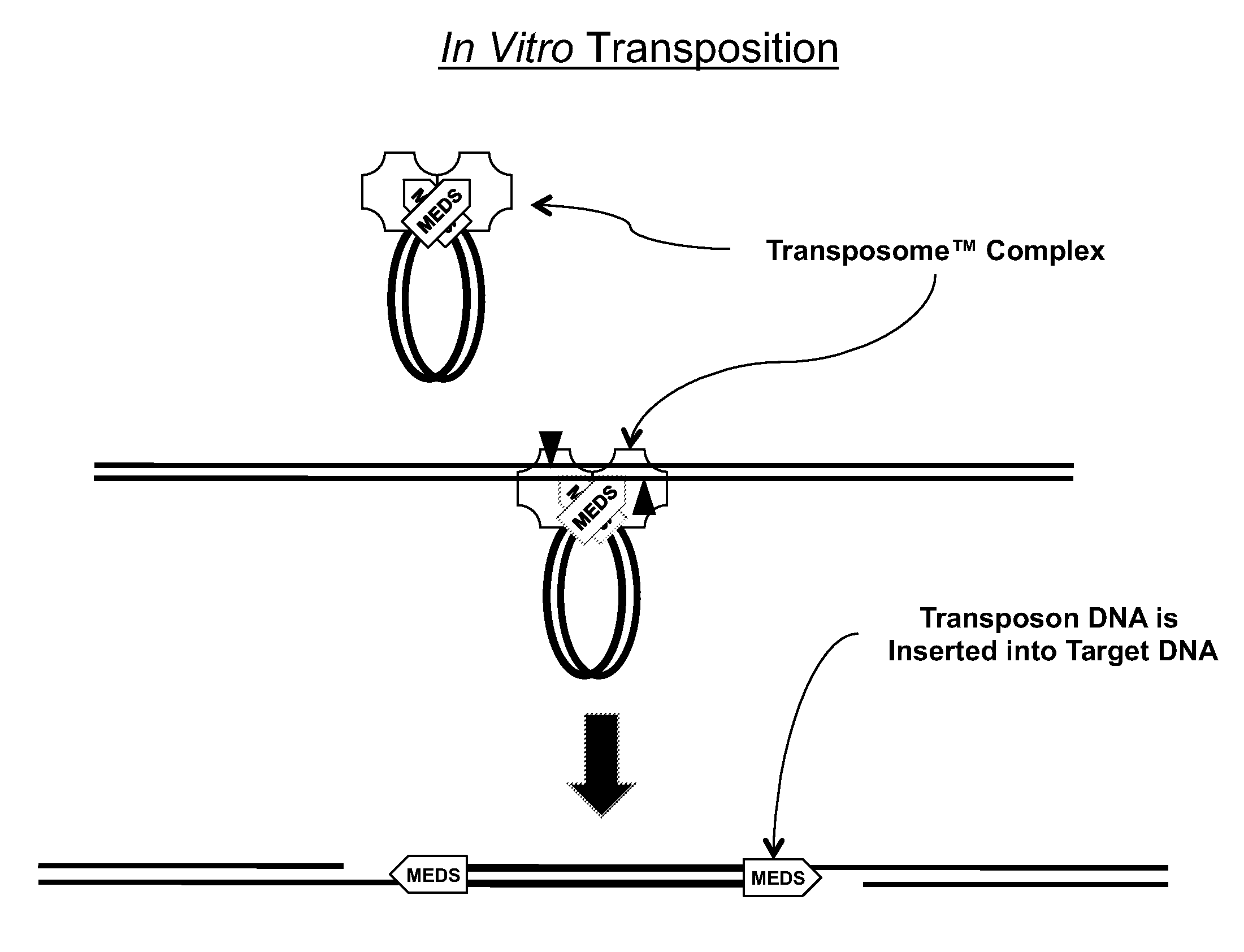
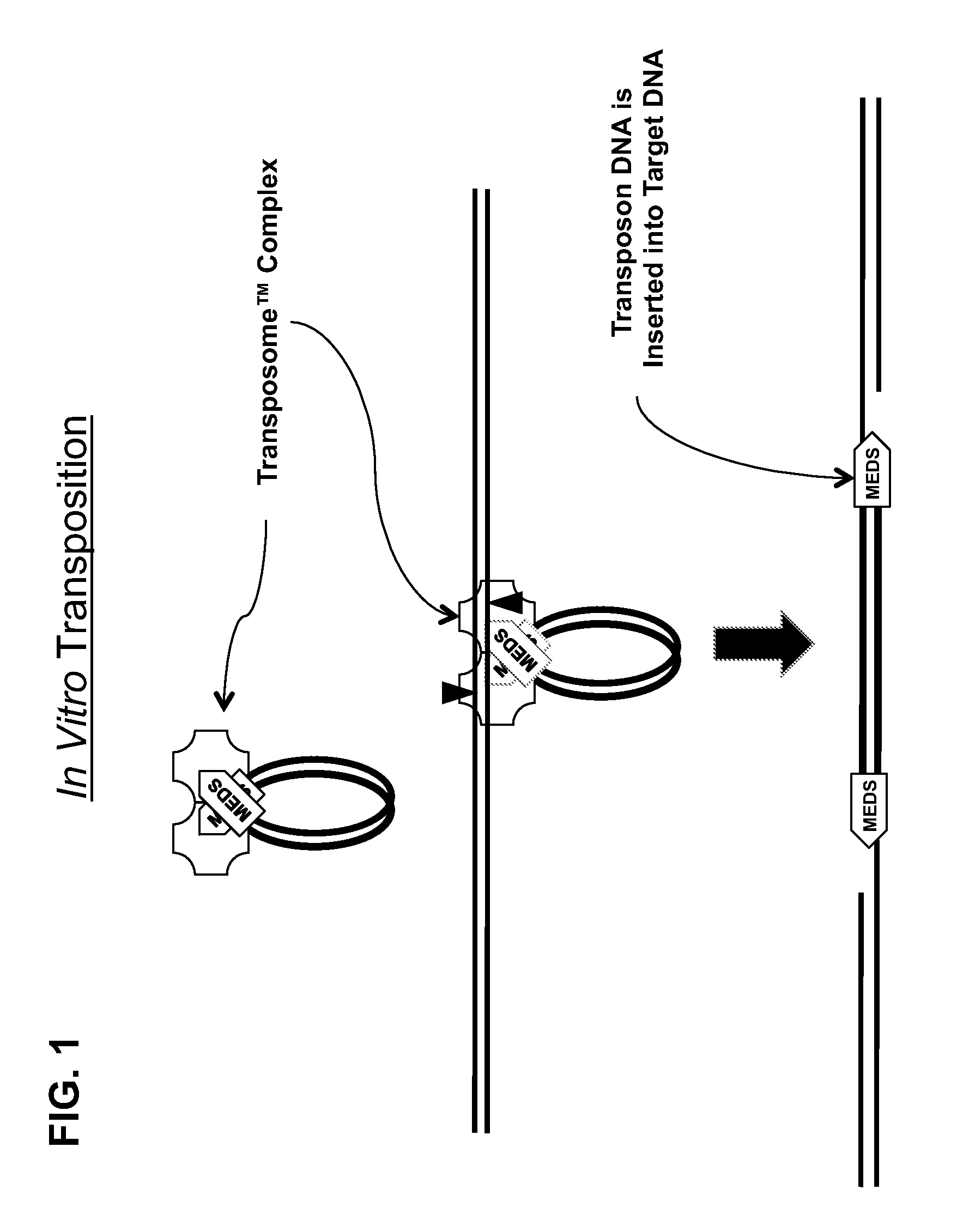
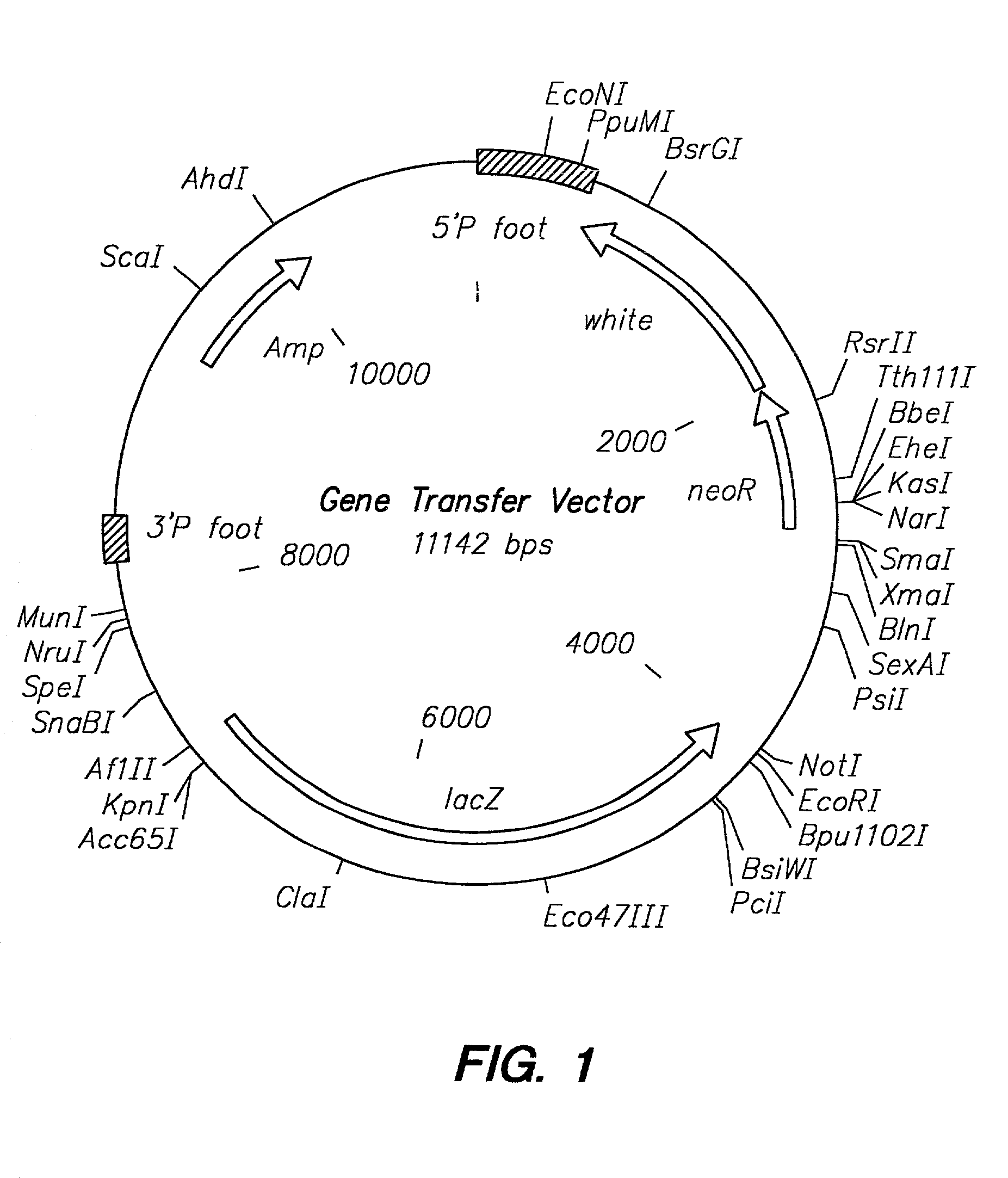
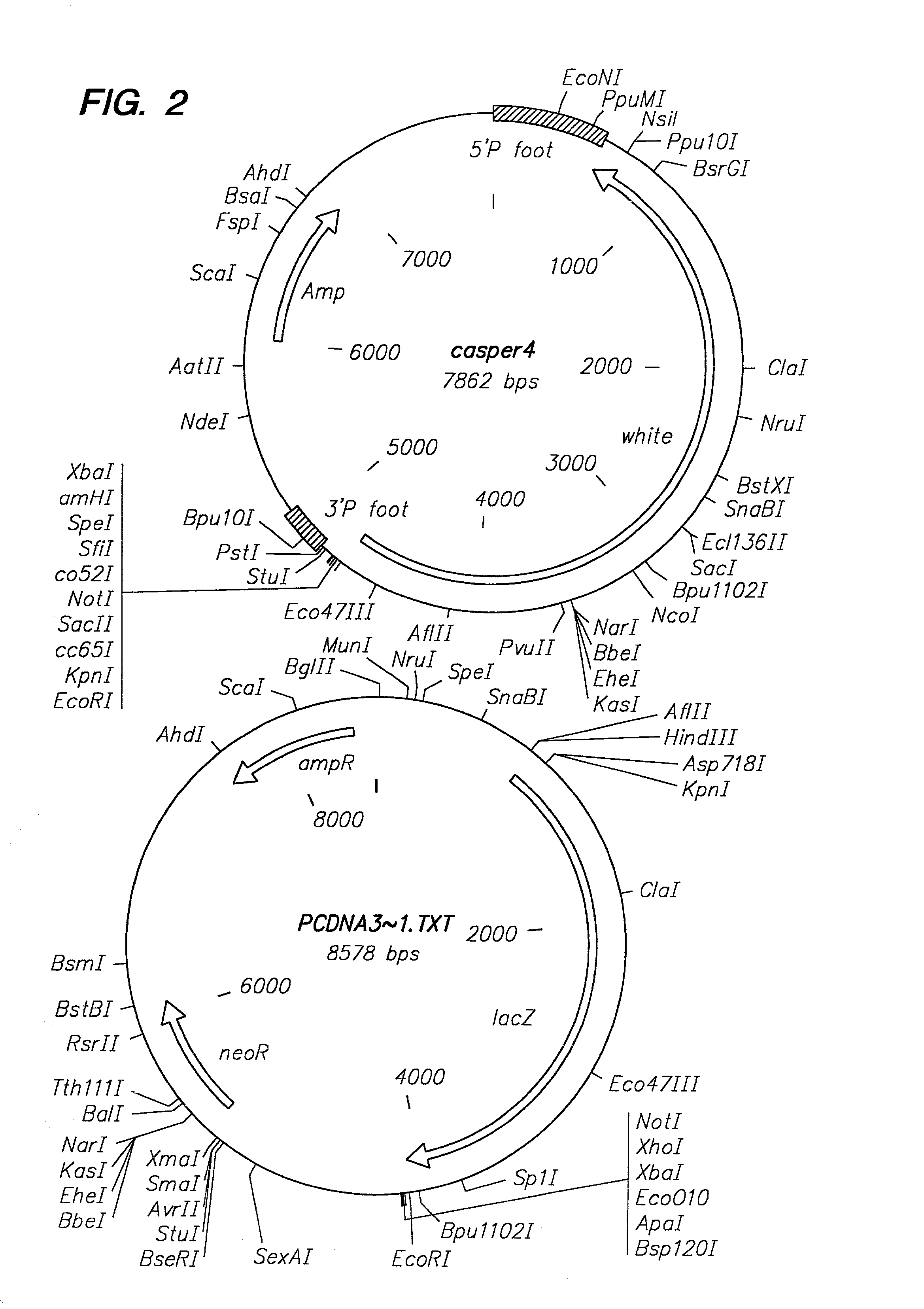
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100120098A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingPolymerase L
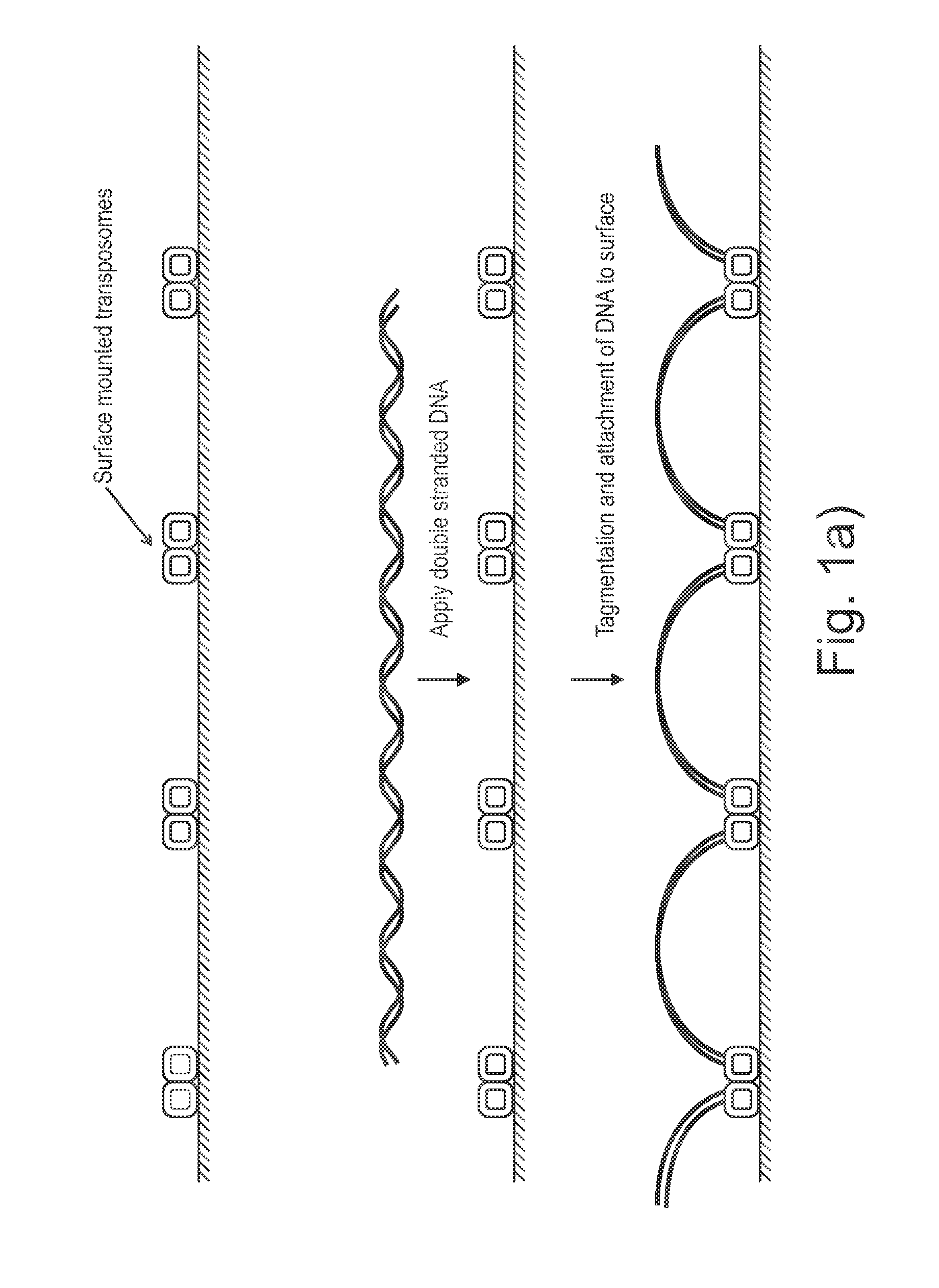
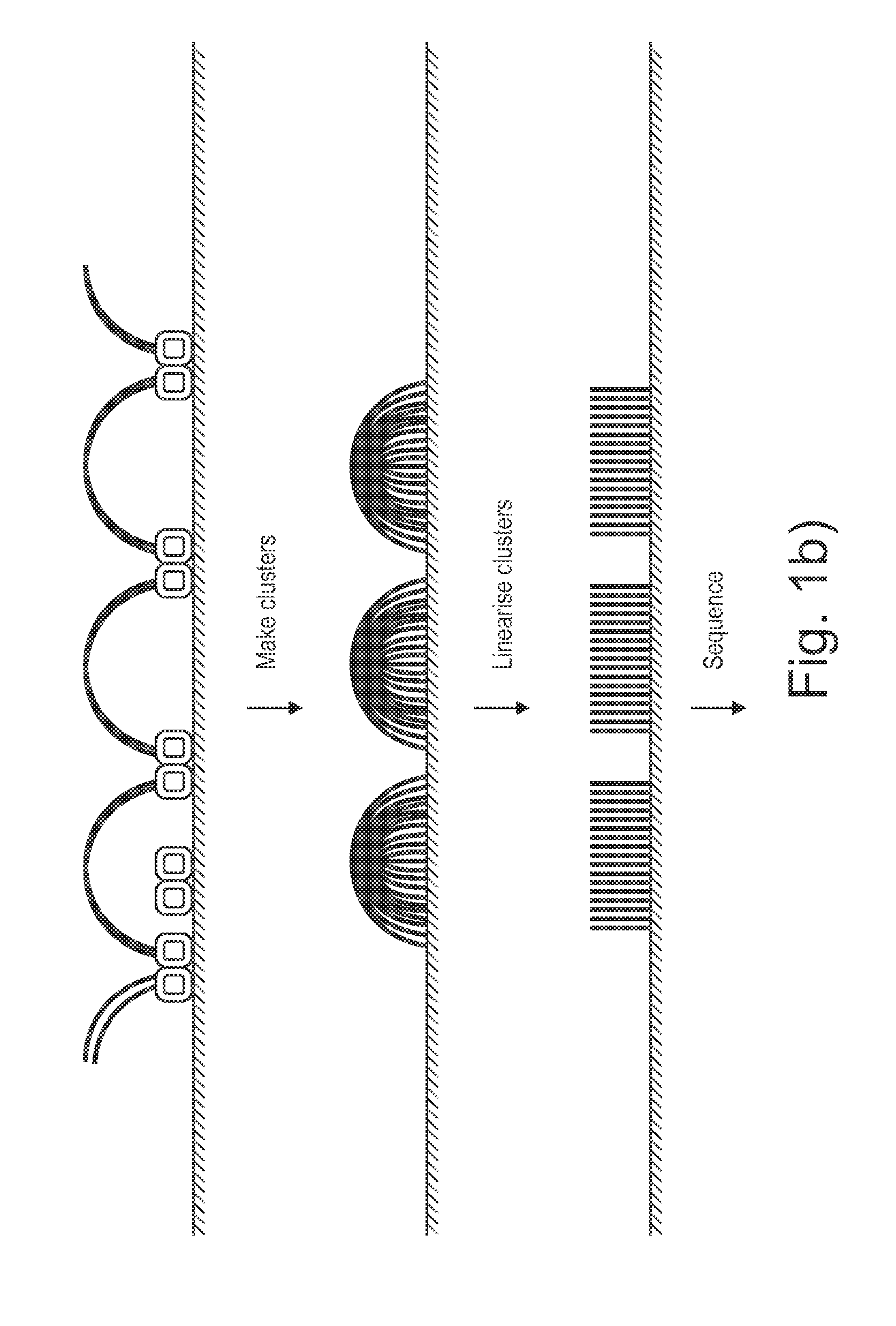
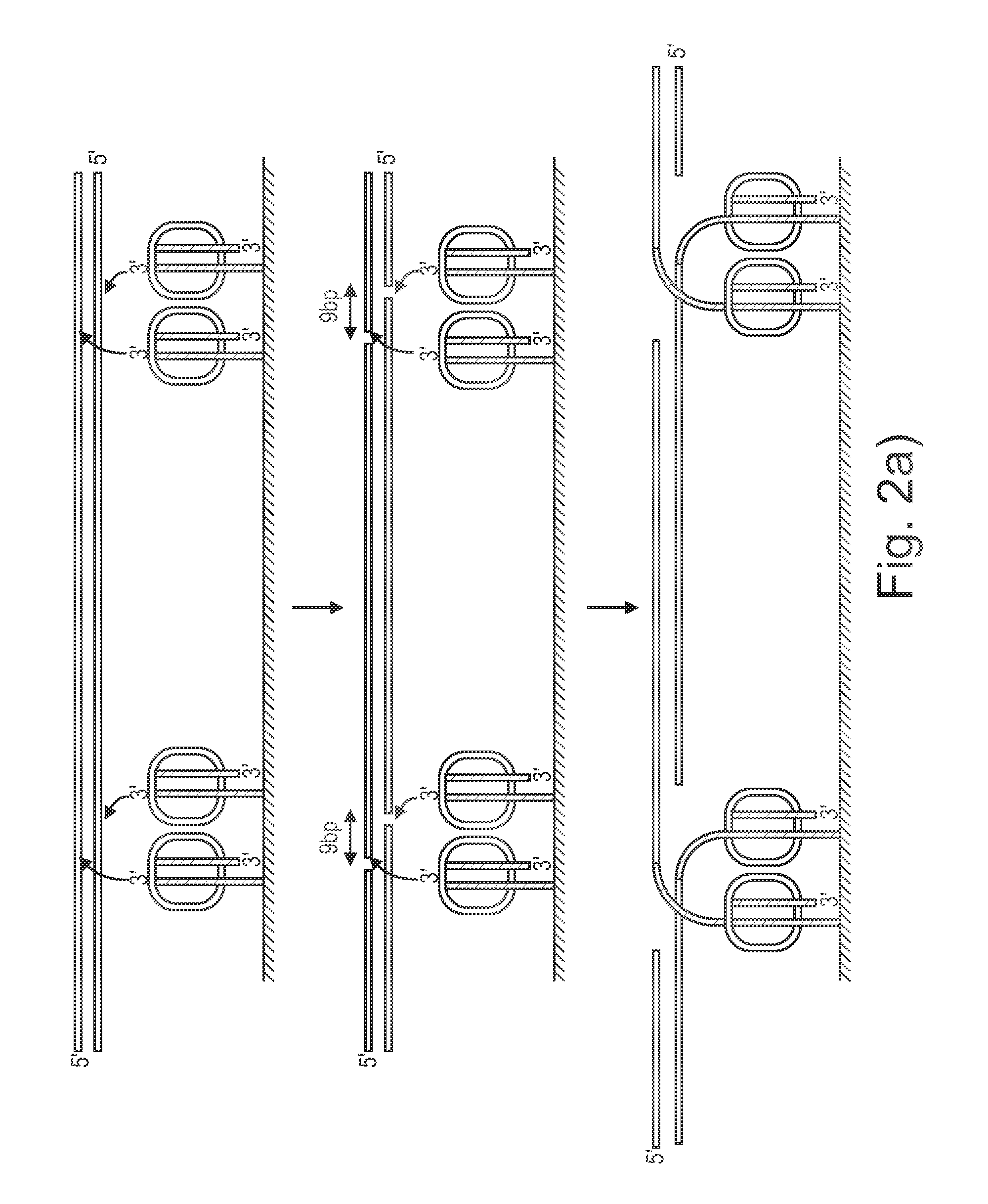
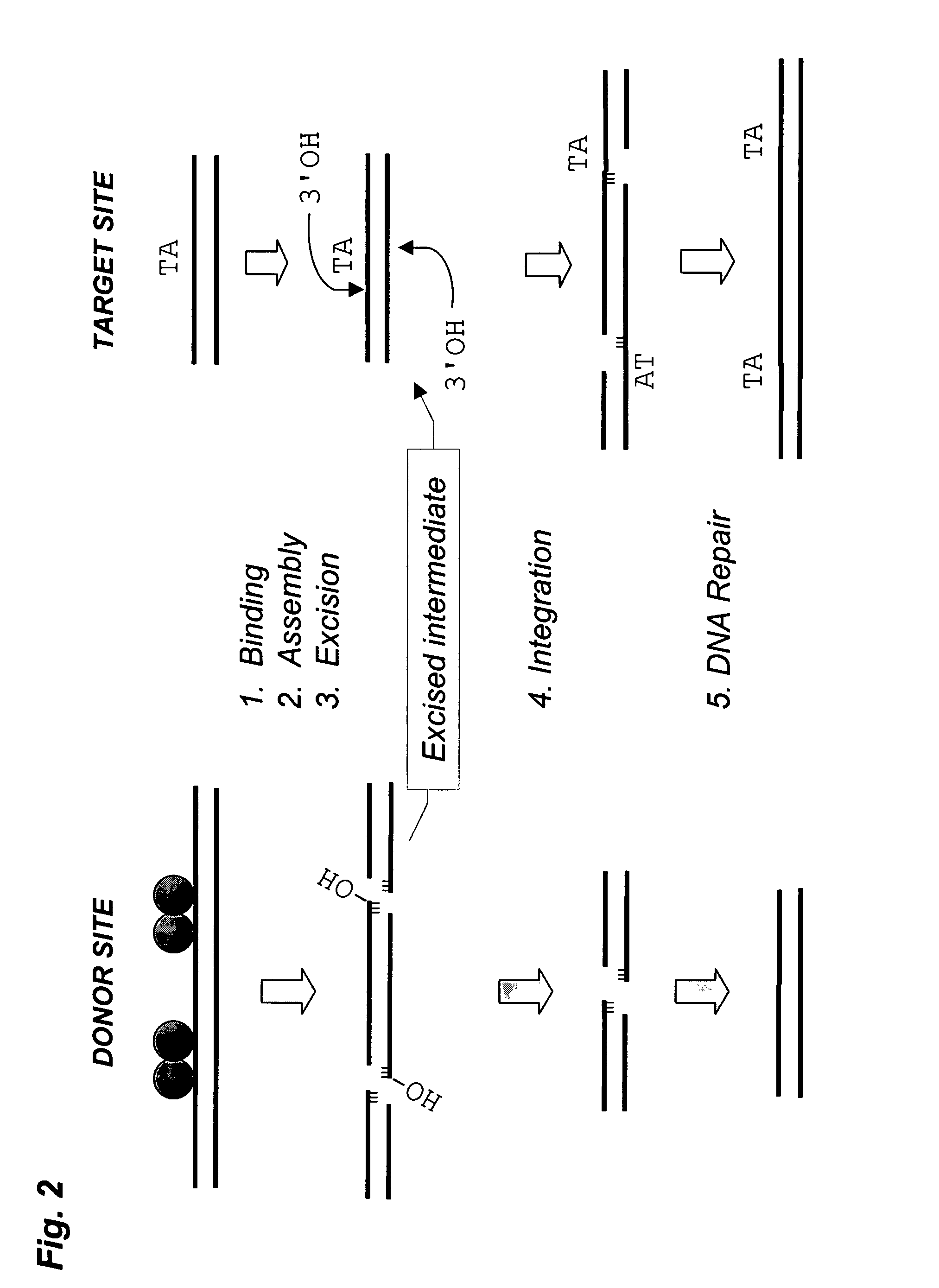
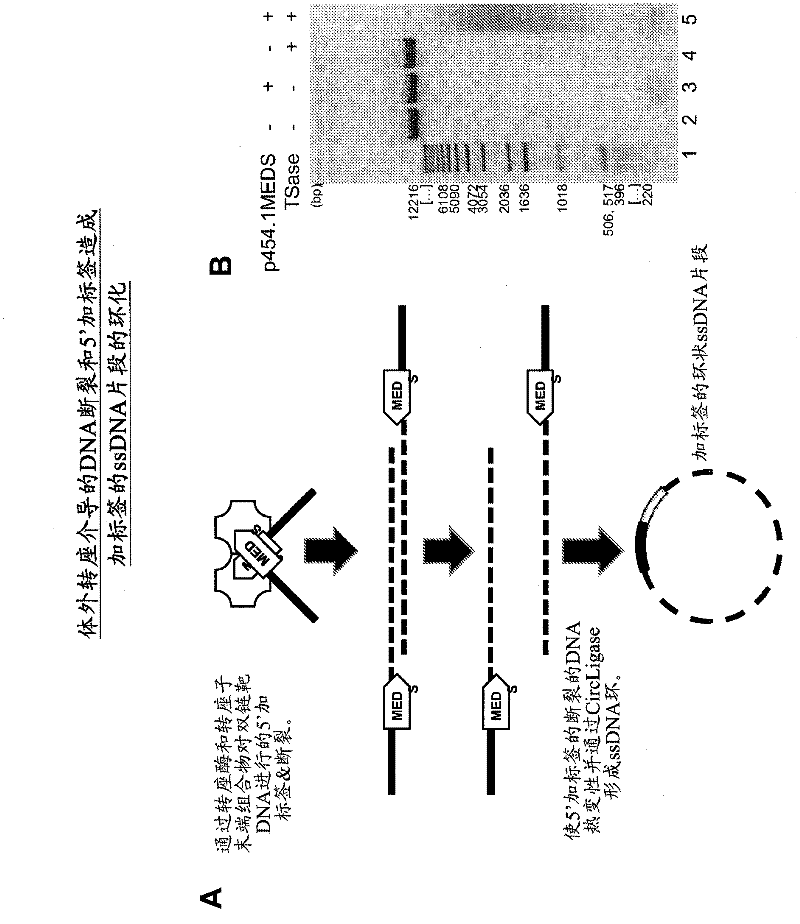
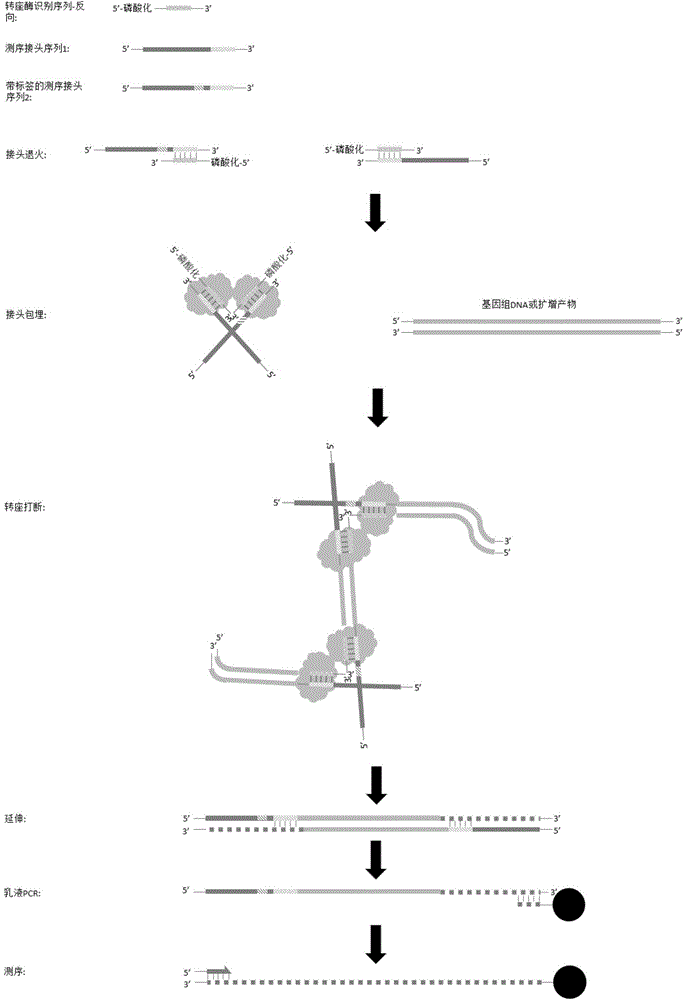
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for using a transposase and a transposon end for generating extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, then using a DNA polymerase for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged single-stranded DNA fragments without performing a PCR amplification reaction, wherein the first tag on the 5′-ends exhibits the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally, an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second tag on the 3′-ends exhibits a different sequence from the sequence exhibited by the first tag. The method is useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including processes for metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and comparative genomic sequencing (CGS), including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called “next-generation sequencing.)
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
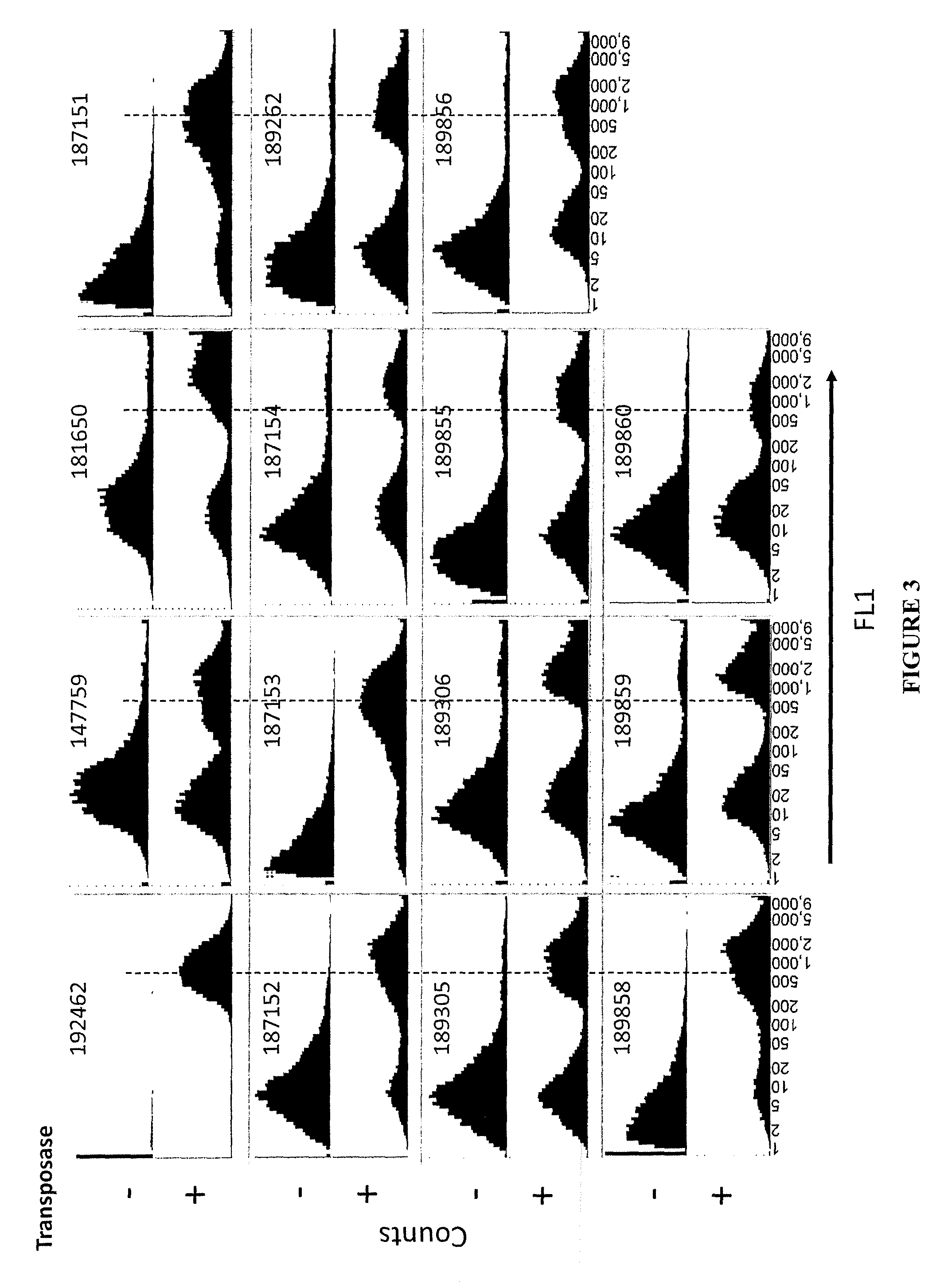
Mutated Tn5 transposase proteins and the use thereof
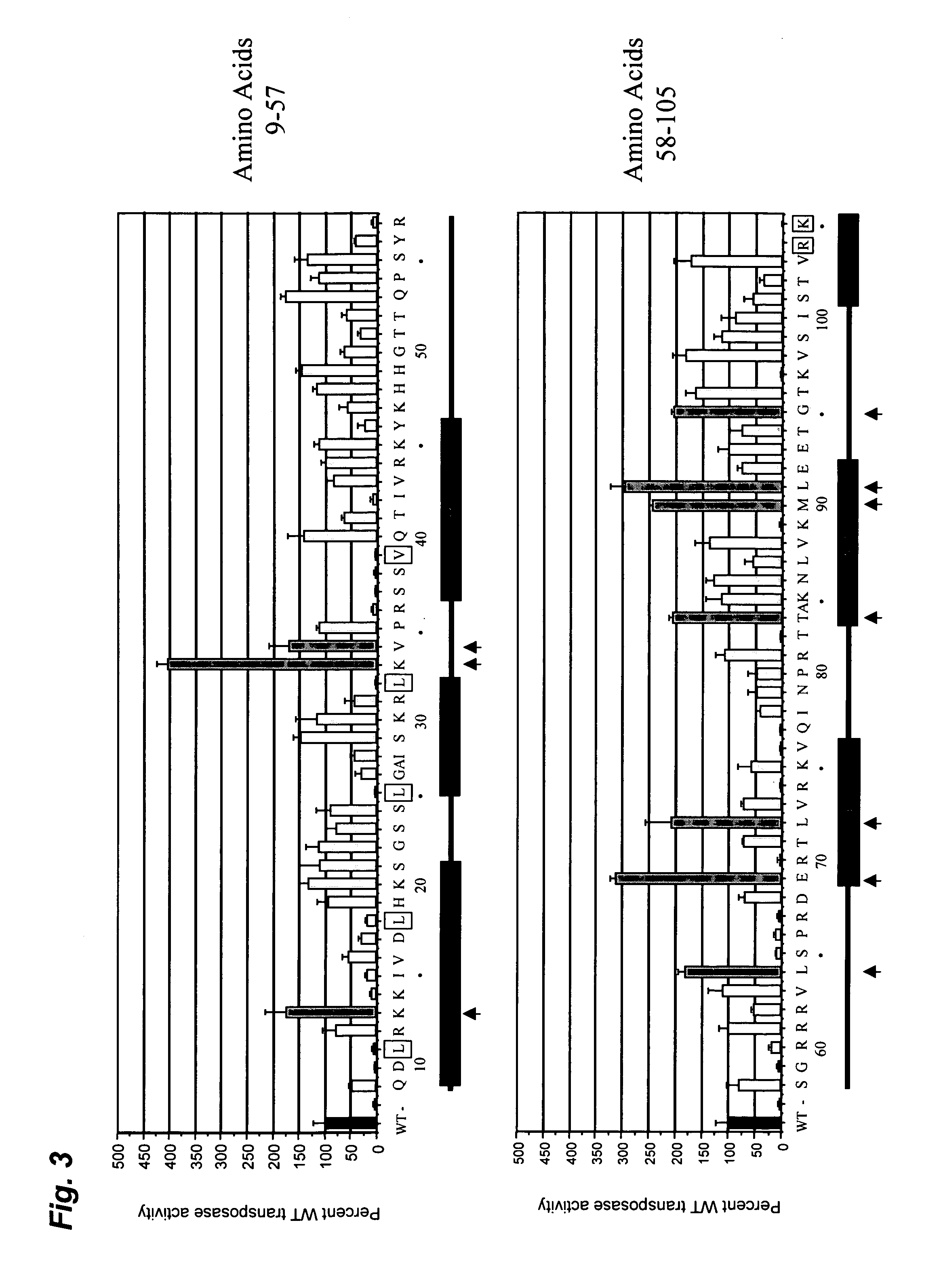
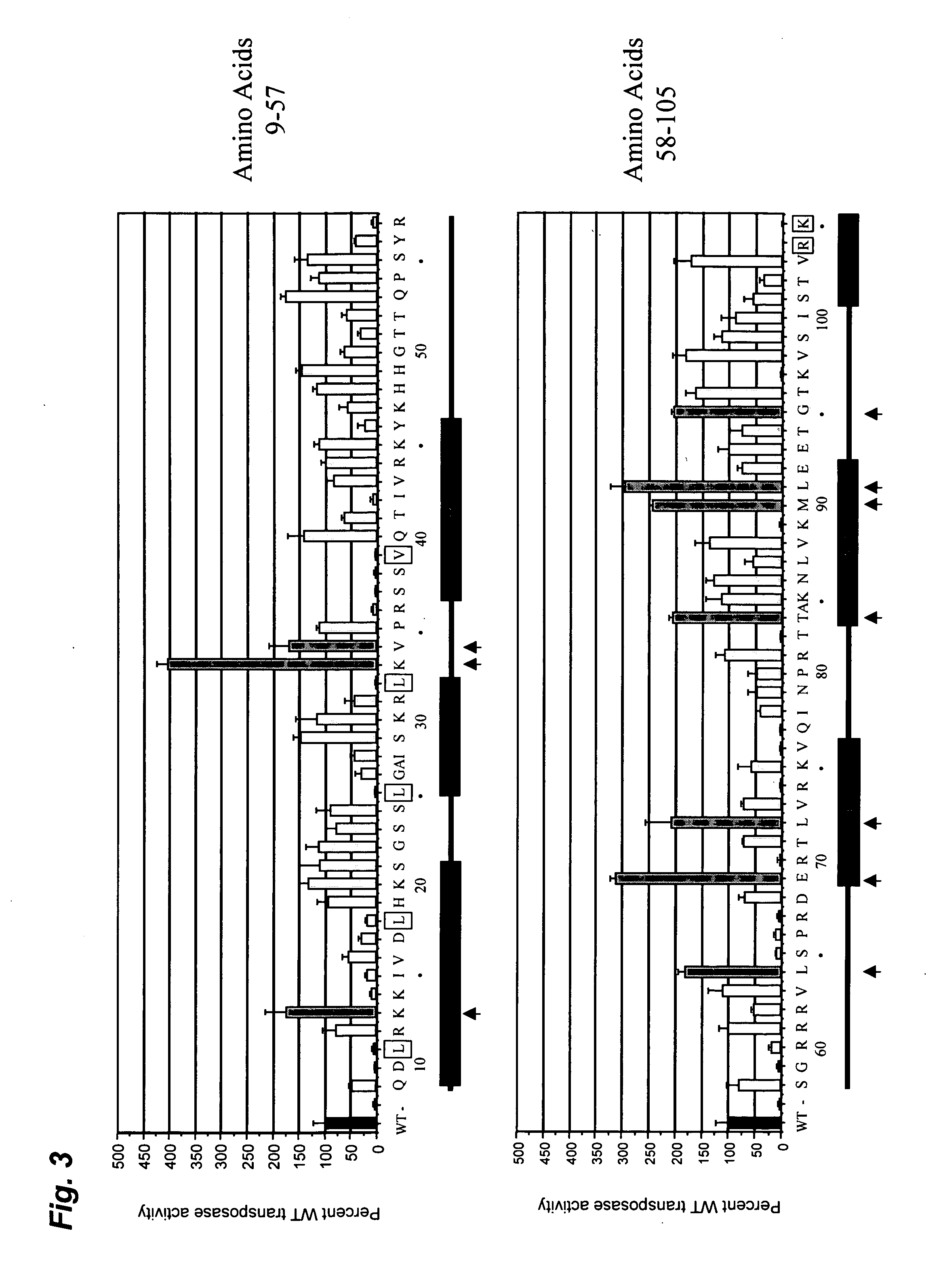
Transposase proteins that are modified relative to and have higher transposase activities than the wild-type Tn5 transposase are disclosed. A transposase protein of the present invention differs from the wild-type Tn5 transposase at amino acid position 41, 42, 450, or 454 and has greater avidity than the wild-type Tn5 transposase for at least one of a Tn5 outside end sequence as defined by SEQ ID NO:3, a Tn5 inside end sequence as defined by SEQ ID NO:4, and a modified Tn5 outside end sequence as defined by SEQ ID NO:5. Also disclosed are various systems and methods of using the transposase proteins of the present invention for in vitro or in vivo transposition.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
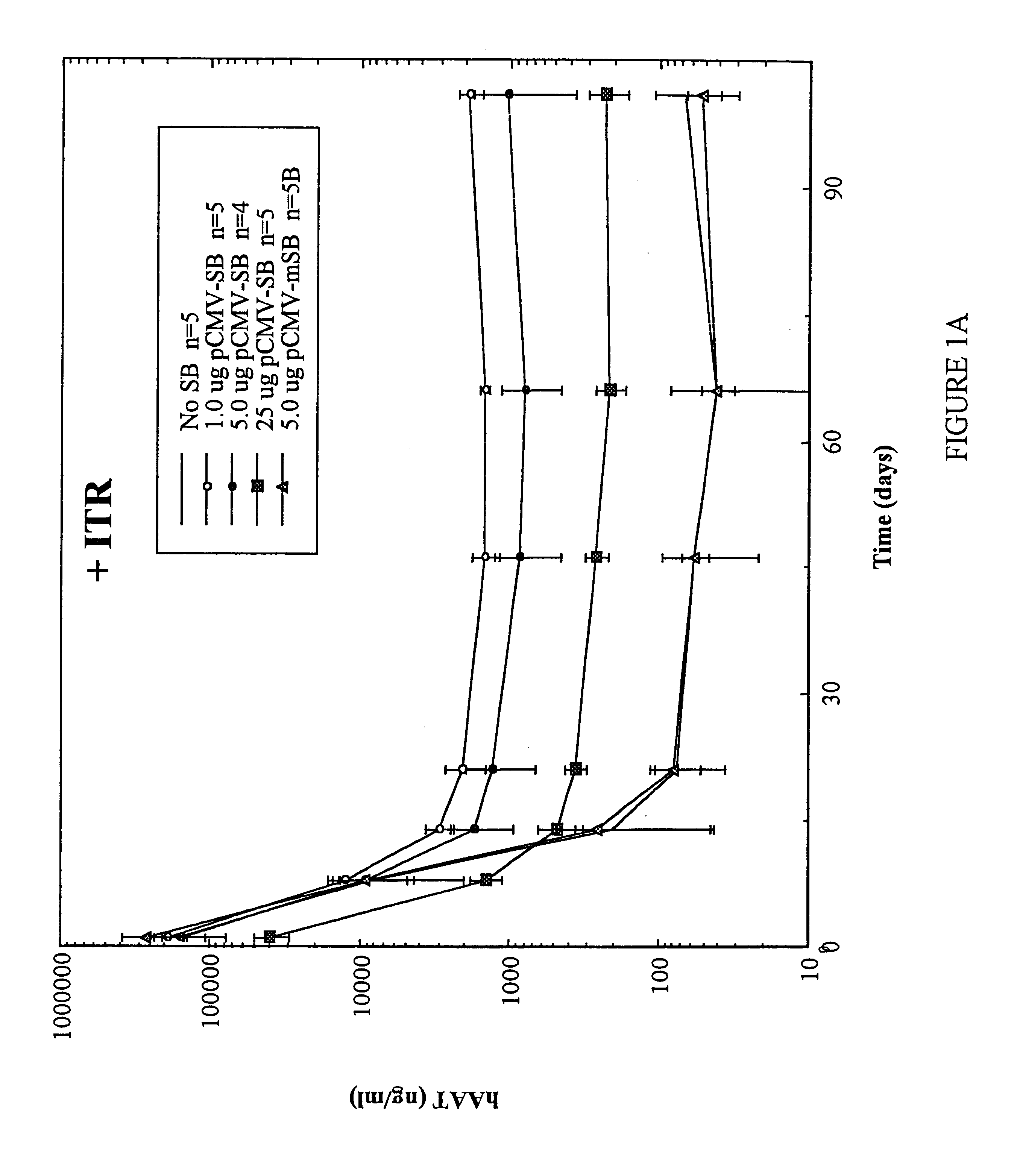
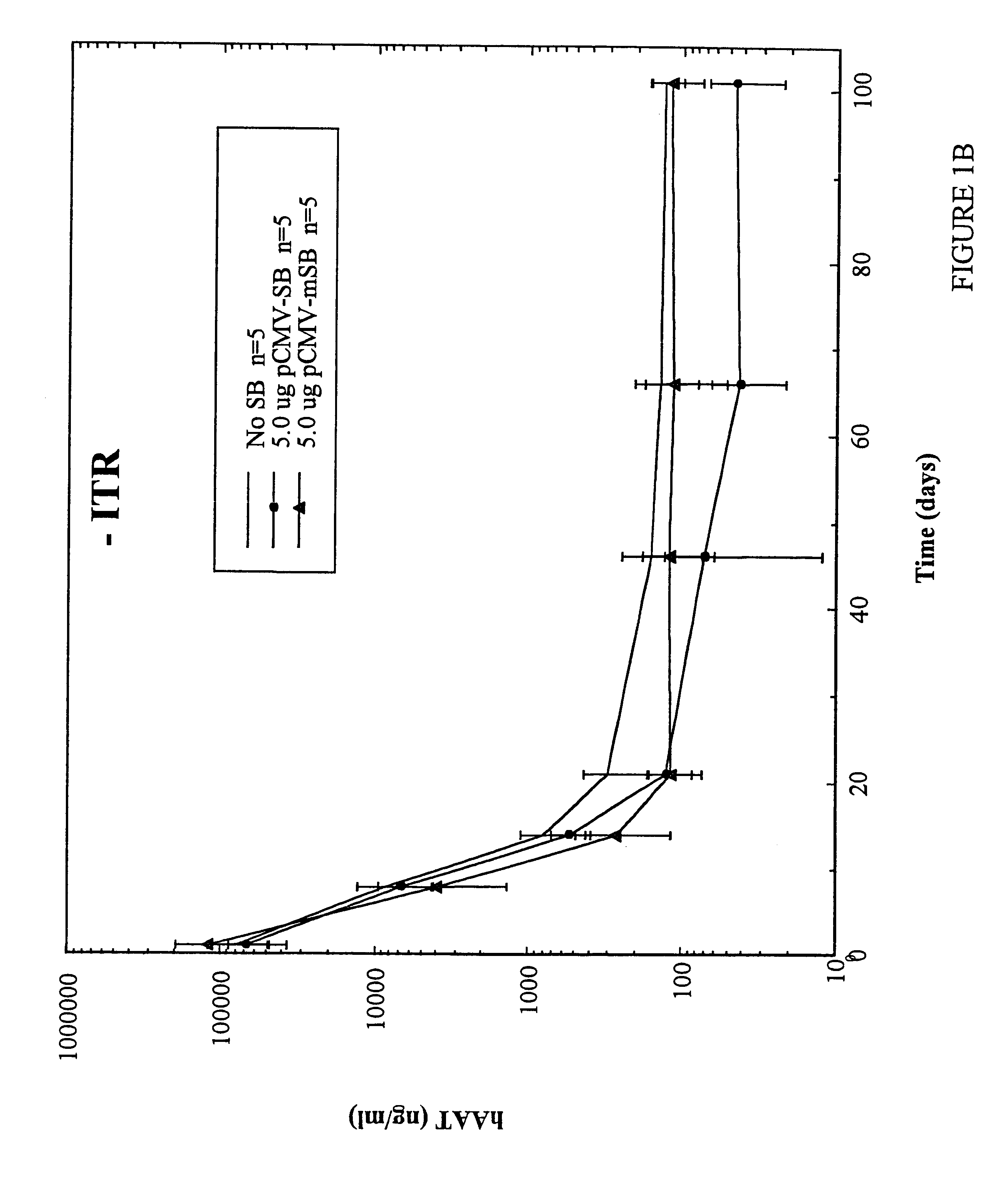
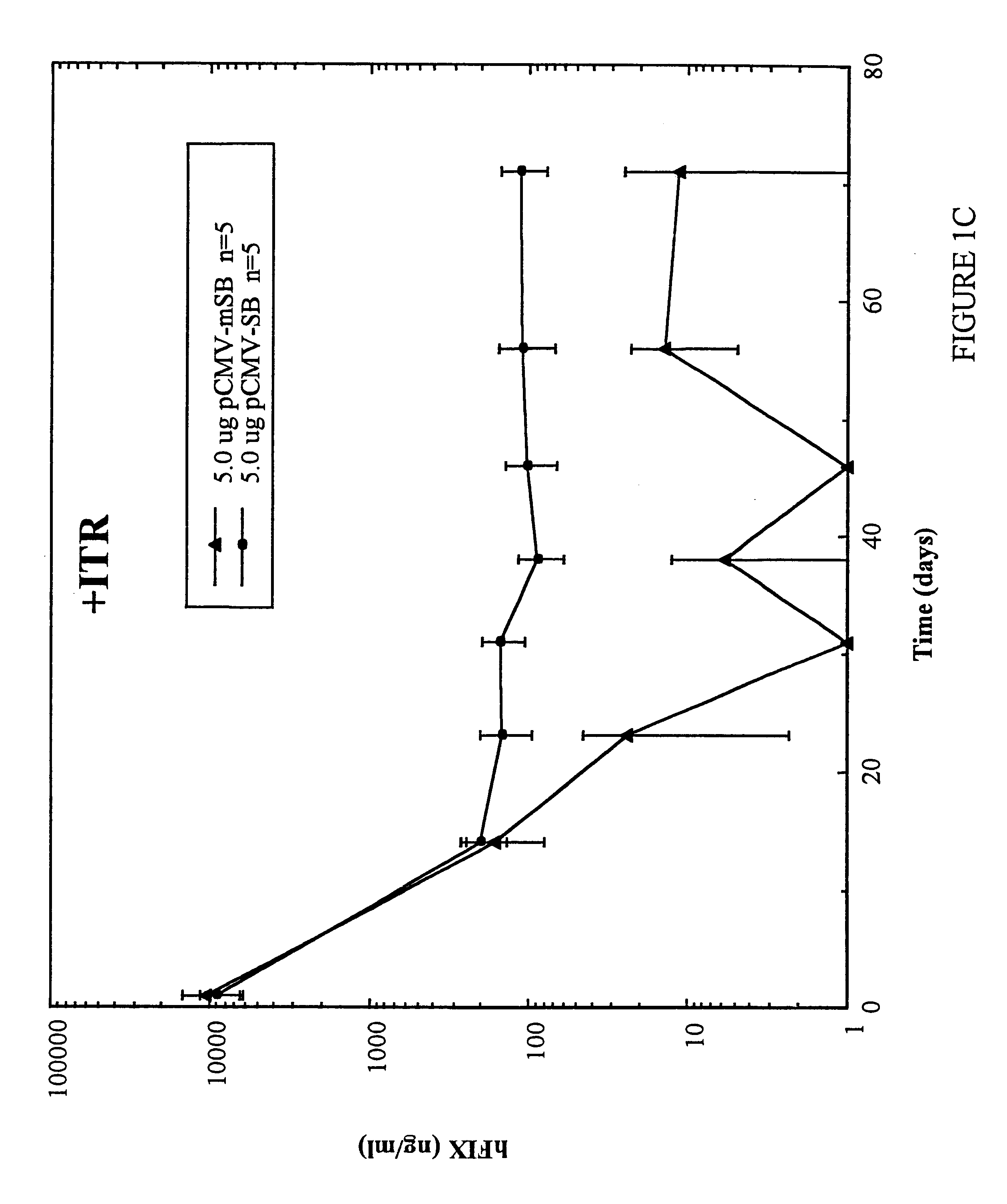
Methods of in vivo gene transfer using a sleeping beauty transposon system
InactiveUS6613752B2Observed effectPromote cloningBiocideHydrolasesSleeping Beauty transposon systemMulticellular organism
Methods and compositions for introducing a nucleic acid into the genome of at least one cell of a multicellular organism are provided. In the subject methods, a Sleeping Beauty transposon that includes the nucleic acid is administered to the multicellular organism along with a source of a Sleeping Beauty transposase activity. Administration of the transposon and transposase results in integration of the transposon, as well as the nucleic acid present therein, into the genome of at least one cell of the multicellular organism The subject methods find use in a variety of different applications, including the in vivo transfer of genes for use in, among other applications, gene therapy applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
P element derived vector and methods for its use
Novel P element derived vectors and methods for their use to insert an exogenous nucleic acid into the genome of a target cell are provided. The subject vectors have a pair of P element transposase recognized insertion sites, e.g. 31 base pair inverted repeats, flanking at least two transcriptionally active genes. In practicing the subject methods, a vector of the subject invention is introduced into the target cell under conditions sufficient for transposition to occur. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the insertion of an exogenous nucleic acid into the genome of a target cell is desired, e.g. include research, synthesis and therapeutic applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Nucleic acid transfer vector for the introduction of nucleic acid into the DNA of a cell
InactiveUS7148203B2Sugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid sequencingTransfer vector
This invention relates to a system for introducing nucleic acid into the DNA of a cell. The system includes the use of a member of the SB family of transposases (SB) or nucleic acid encoding the transposase and a nucleic acid fragment that includes a nucleic acid sequence with flanking inverted repeats. The transposase recognizes at least a portion of an inverted repeats and incorporates the nucleic acid sequence into the DNA. Methods for use of this system are discussed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Tn5 transposase mutants and the use thereof
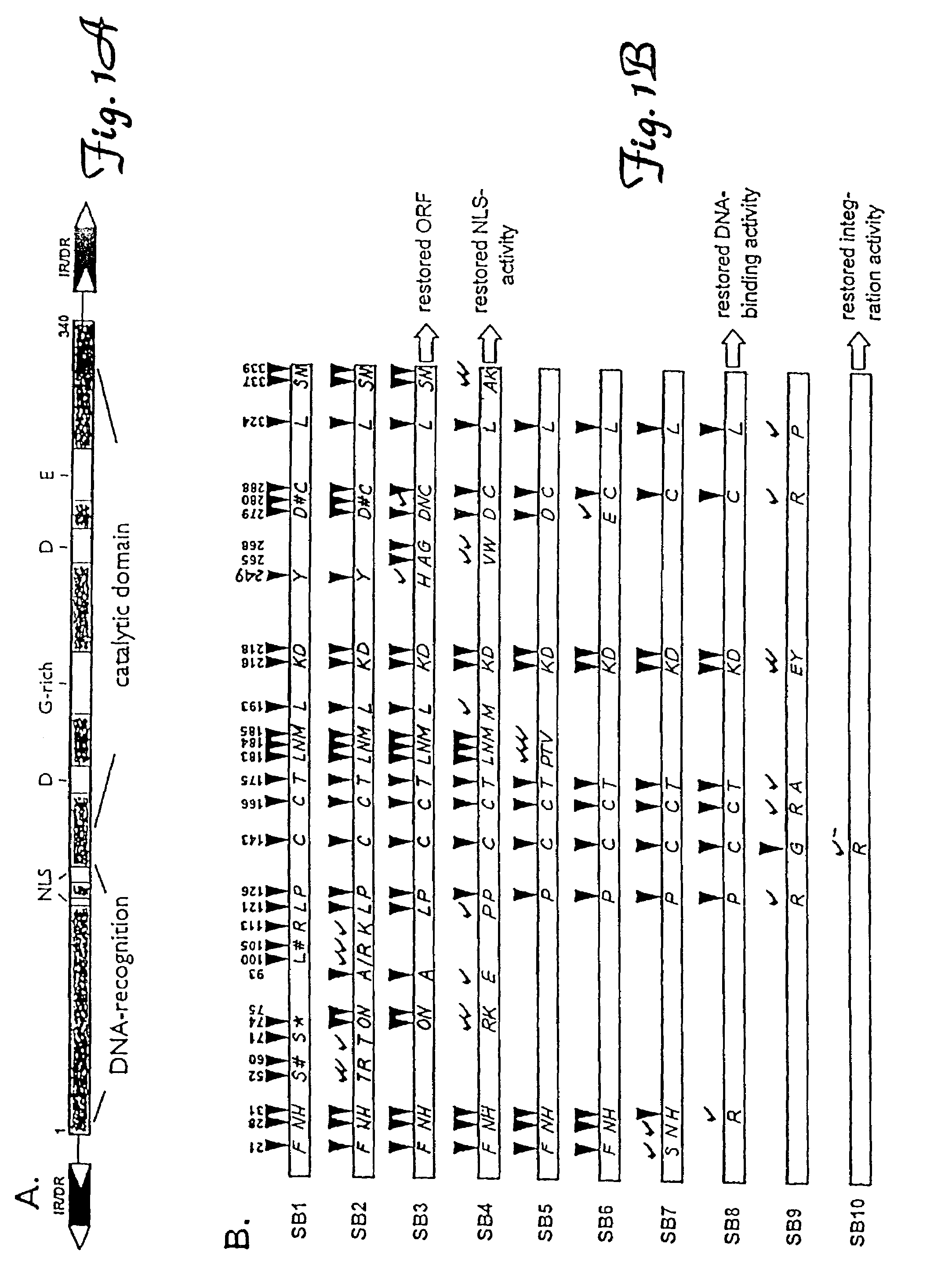
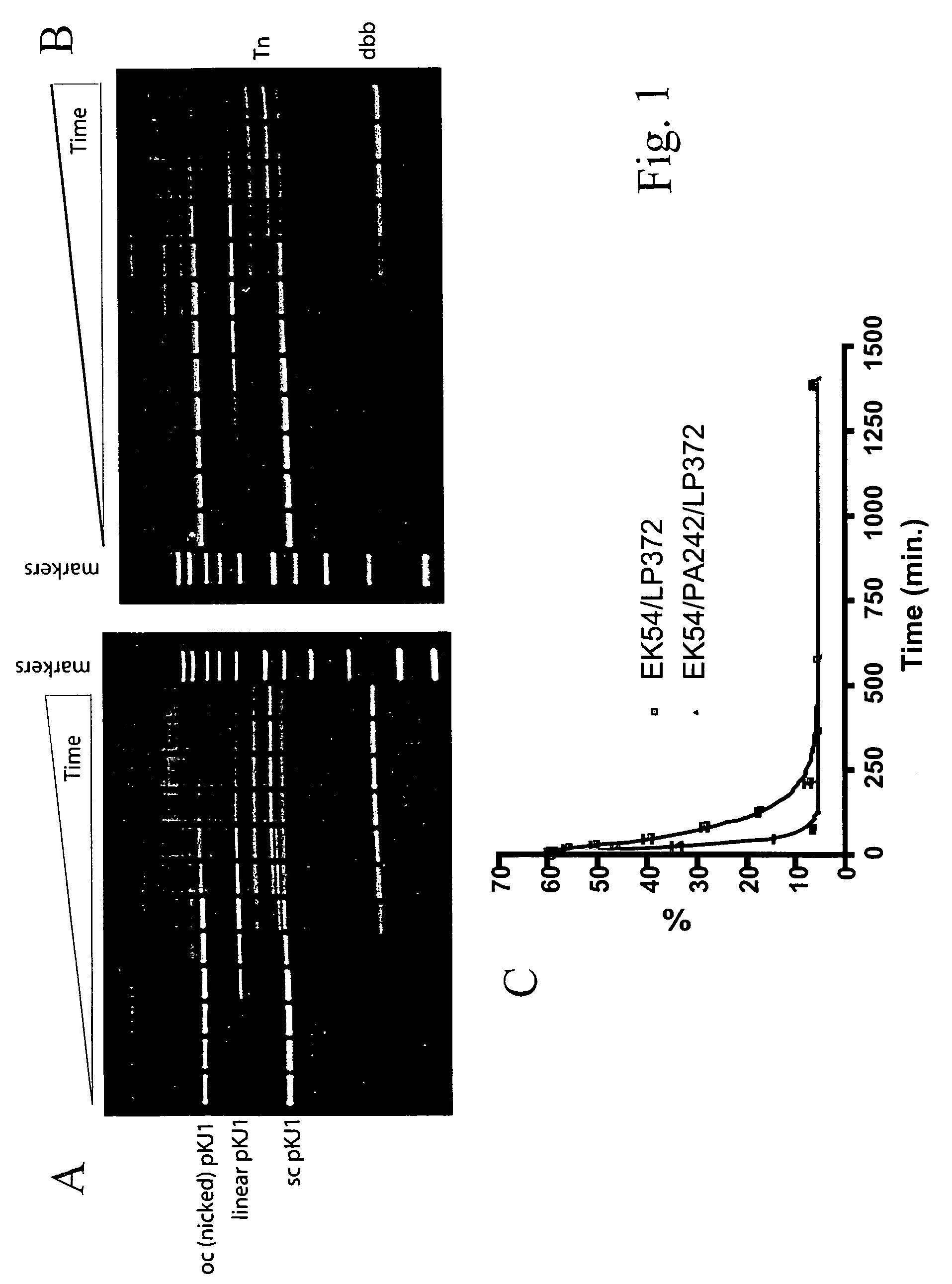
Tn5 transposase (Tnp) mutants that have higher transposase activities than the wild-type Tnp are disclosed. The Tn5 Tnp mutants differ from the wild-type Tnp at amino acid positions 54, 242, and 372 and have greater avidity than the wild-type Tnp for at least one of a wild-type Tn5 outside end sequence as defined by SEQ ID NO:3 and a modified Tn5 outside end sequence as defined by SEQ ID NO:5. Also disclosed are various systems and methods of using the Tnp mutants for in vitro or in vivo transposition.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
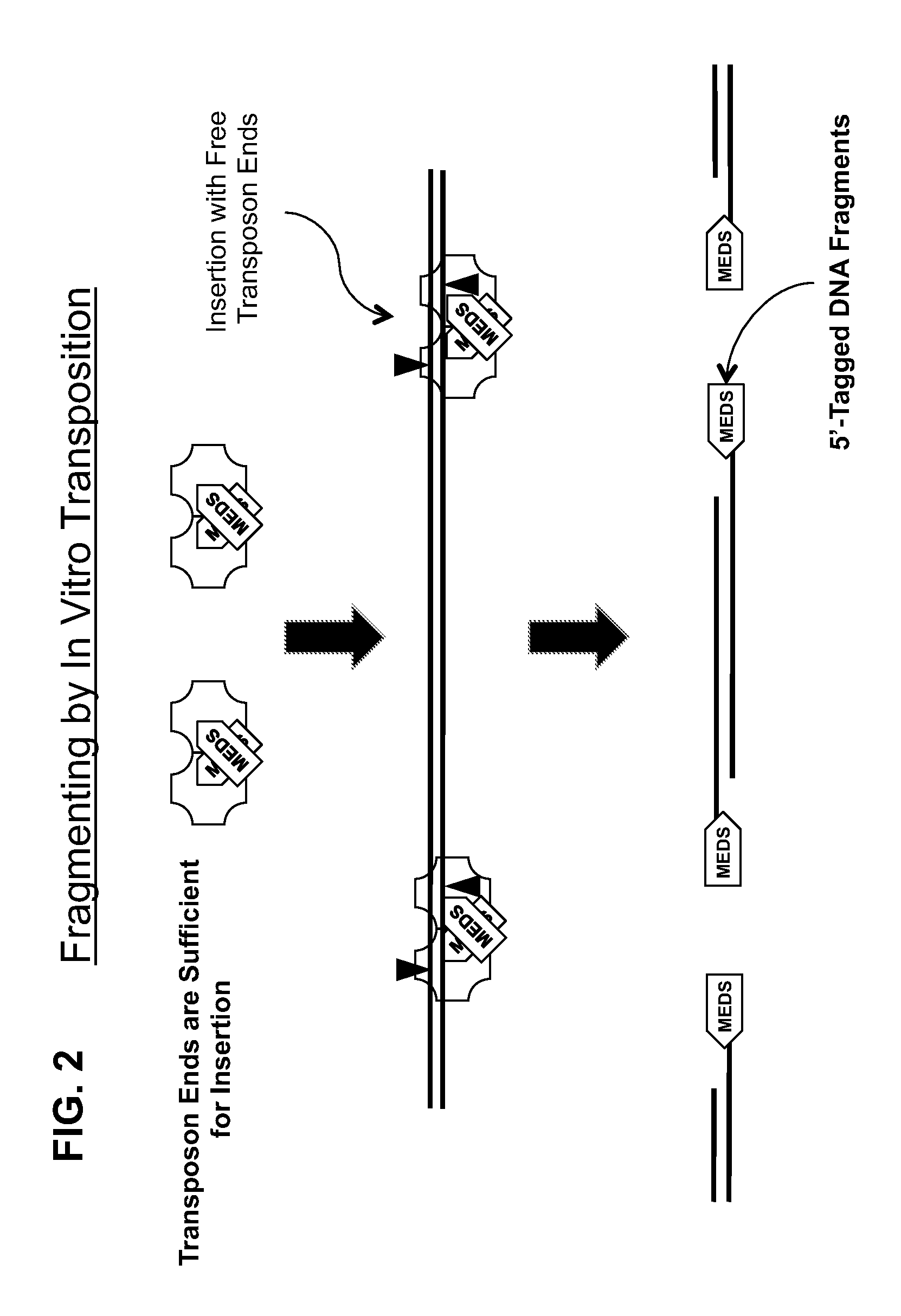
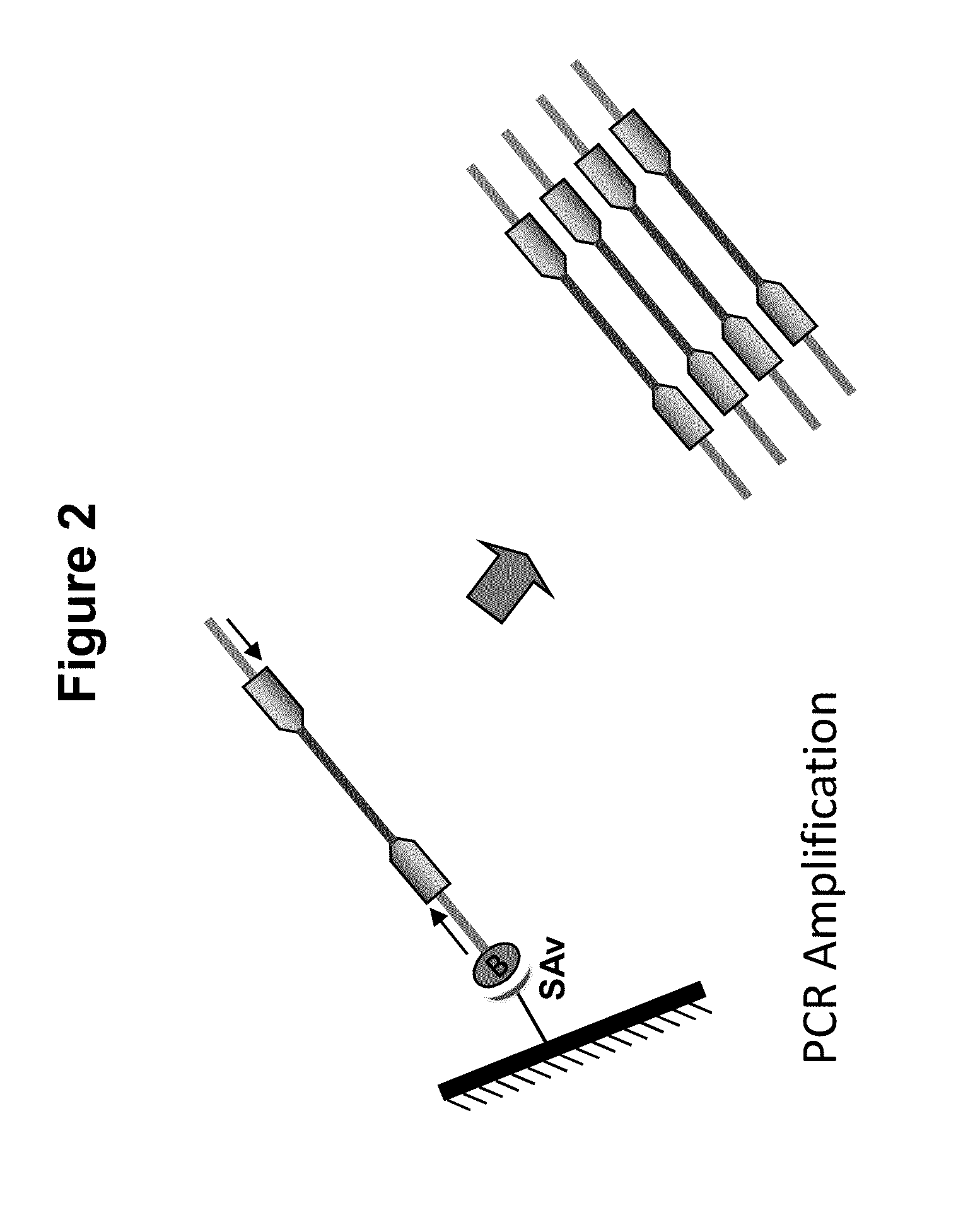
Methods and compositions for DNA fragmentation and tagging by transposases
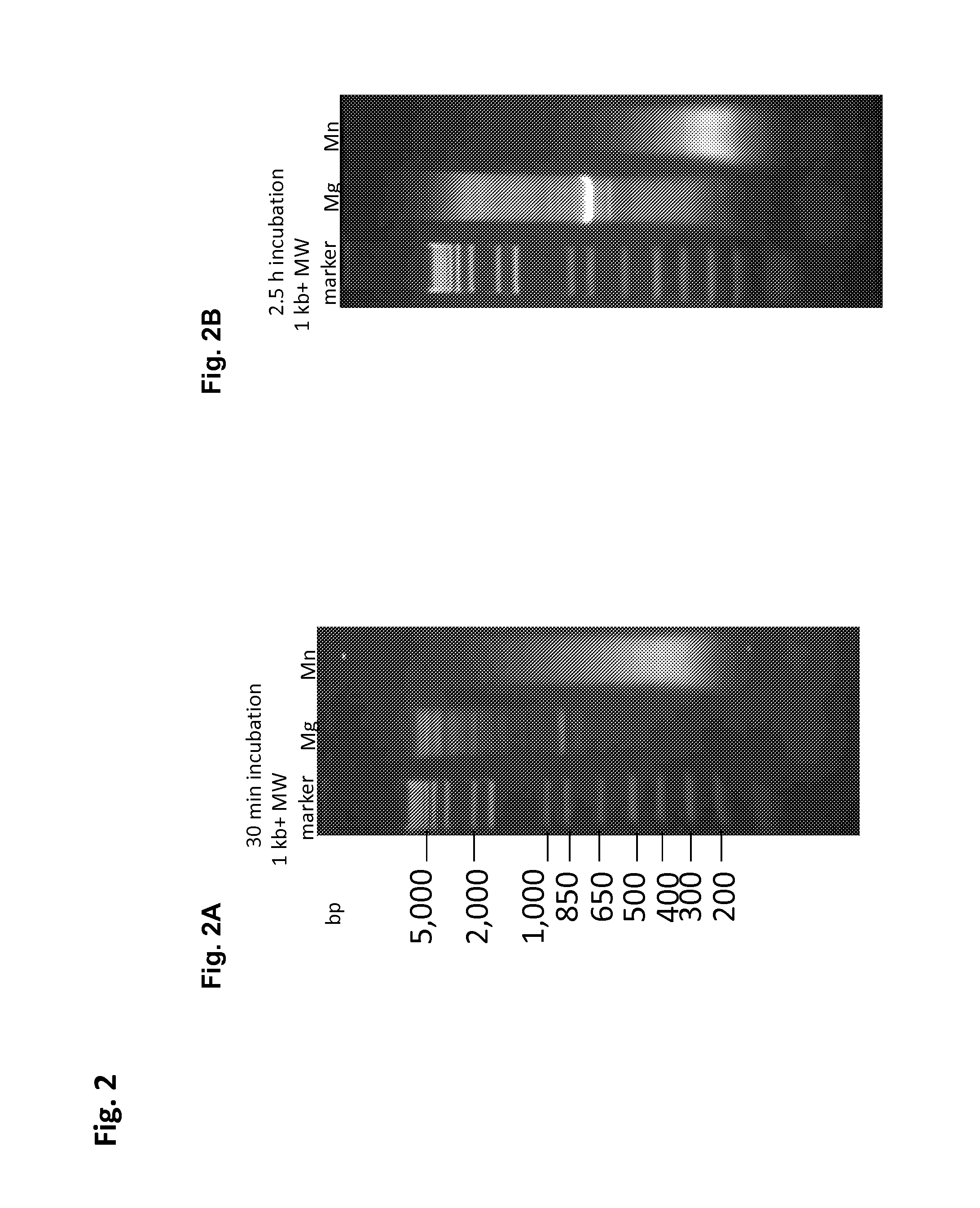
ActiveUS9005935B2Broadens transposase reaction conditionsReduce concentrationSugar derivativesTransferasesDNA fragmentationWild type
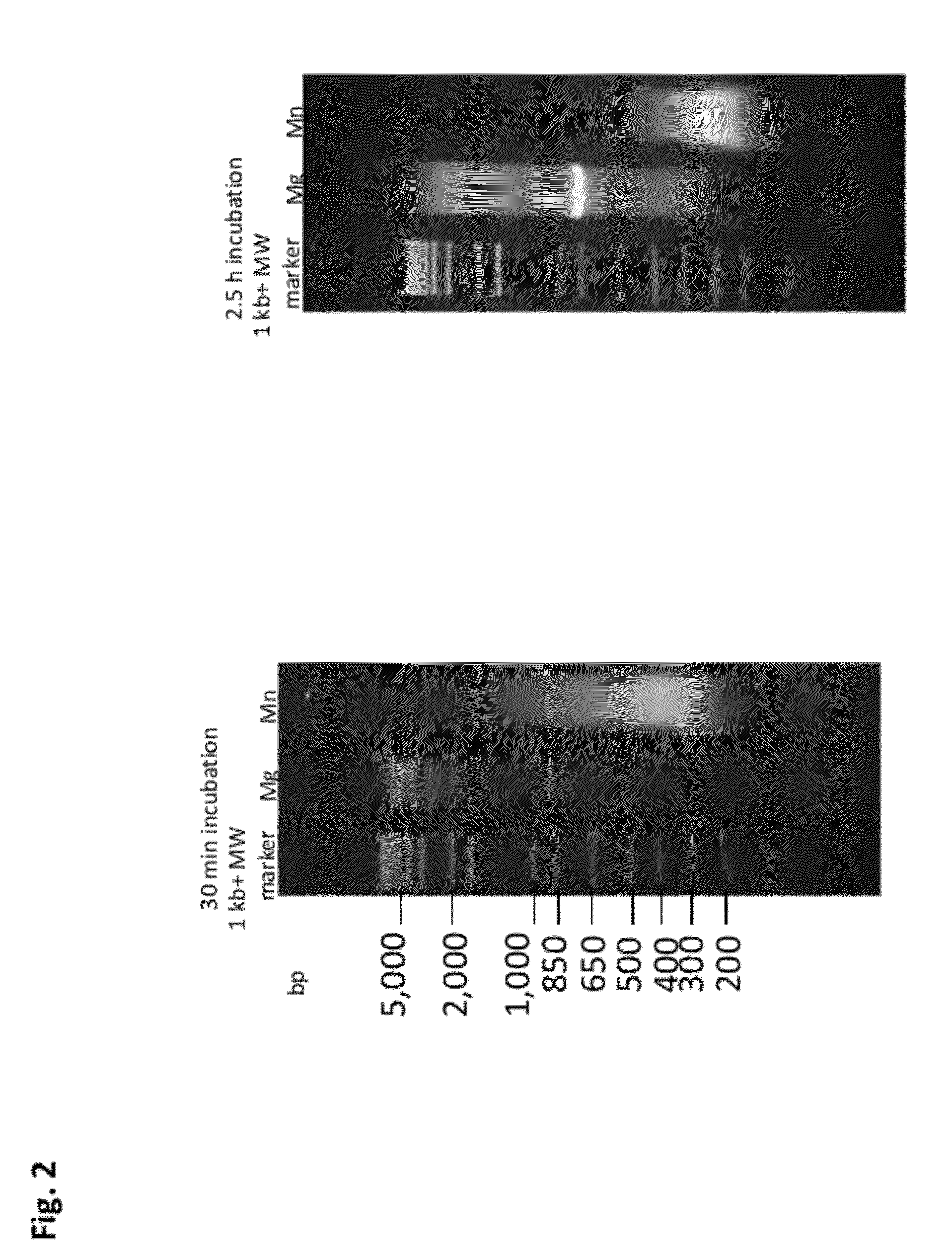
The present invention provides new compositions for transposase-mediated fragmenting and tagging DNA targets. The invention relates to the surprising discovery that use of manganese ions (Mn2+) in transposase reactions improves the transposase reaction. It also relates to the surprising discovery that Mg2+ ions can be used in a transposase reaction with wild-type and / or engineered transposases at levels much higher than previously thought. The invention provides for the use of naturally-occurring transposases in in vitro reactions, as well as improved schemes for cleaving, tagging, and amplifying target DNA.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Sample preparation on a solid support
ActiveUS20140194324A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid massDNA fragmentation
Presented are methods and compositions for using immobilized transposase and a transposon end for generating an immobilized library of 5′-tagged double-stranded target DNA on a surface. The methods are useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including massively parallel DNA sequencing.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
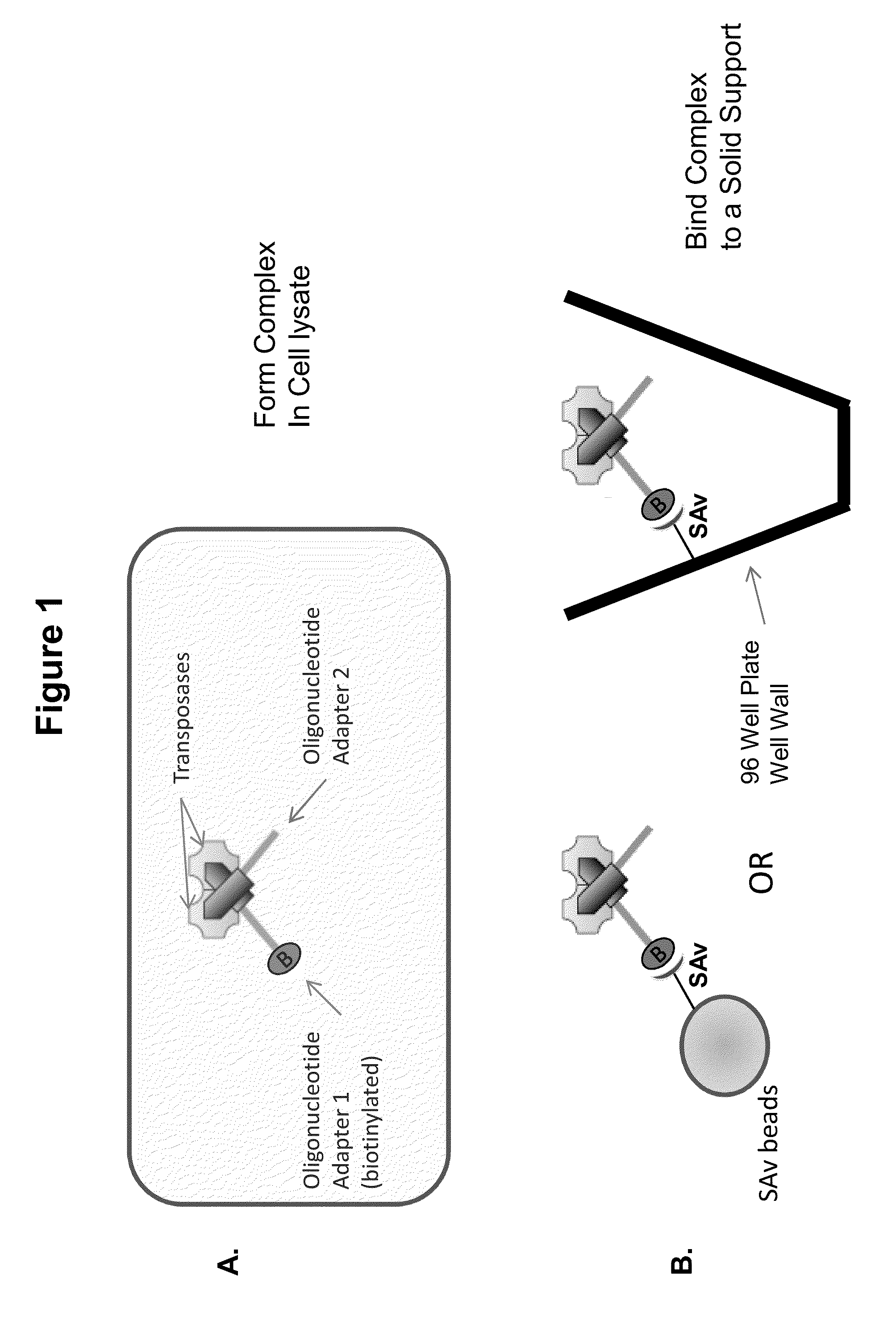
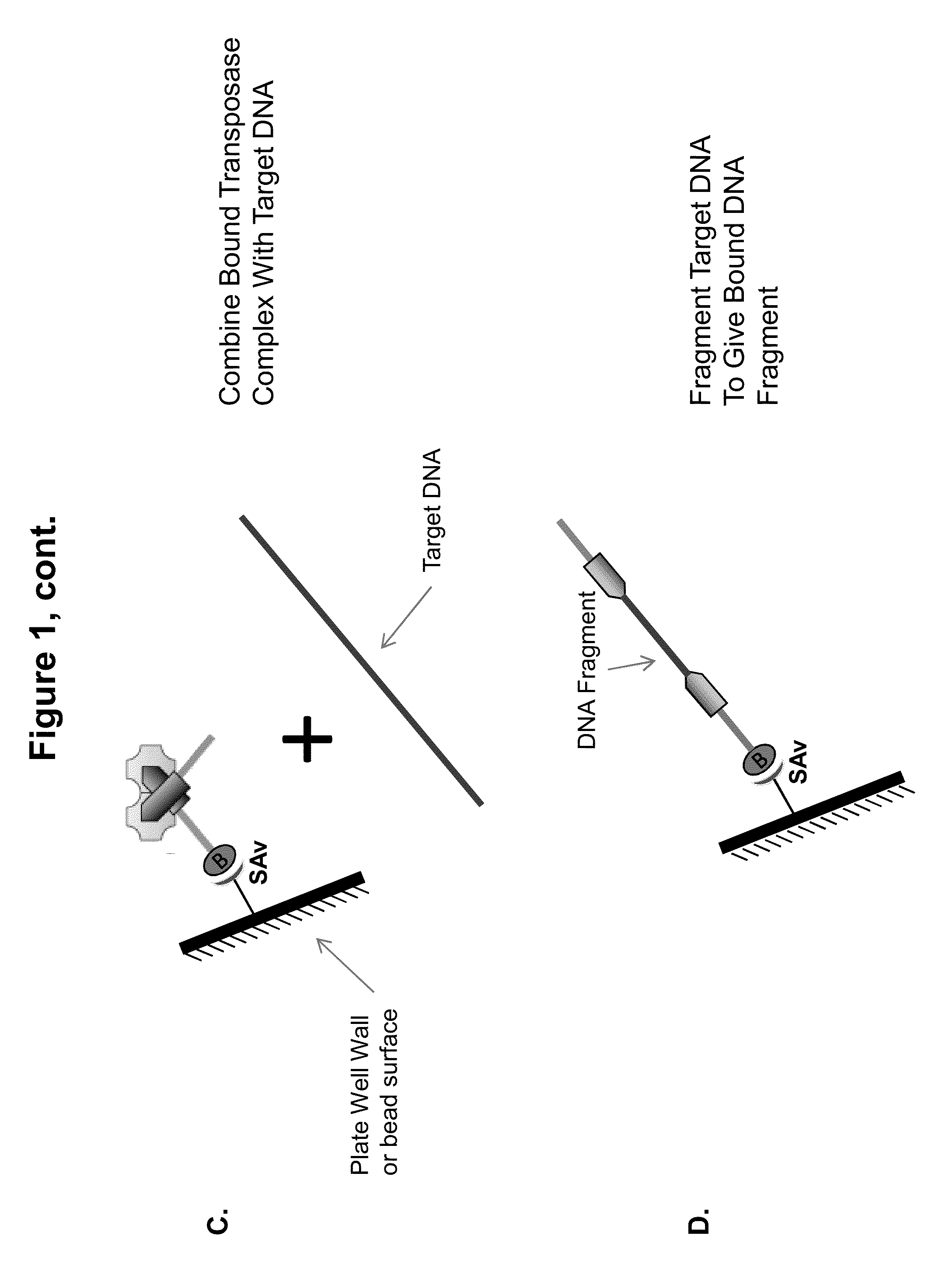
Immobilized transposase complexes for DNA fragmentation and tagging
ActiveUS20140093916A1Maintain good propertiesExcellent characteristicsHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationOligonucleotide Linker
The present invention provides a simple and rapid method for preparing purified transposase complexes that are highly suited for fragmenting DNA. The method includes forming transposase complexes with oligonucleotide adapters in cell lysate, then purifying the complexes from the other substance in the cell lysate. Purification is accomplished using a specific binding pair, in which one member of the pair is bound to an oligonucleotide adapter of the complex and the other member of the pair is bound to a solid substrate. The bound complexes can be immediately used in DNA fragmentation reactions to produce solid substrate-bound DNA fragments, which can be used for any number of purposes, including as templates for amplification and sequencing.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Enhanced sleeping beauty transposon system and methods for using the same
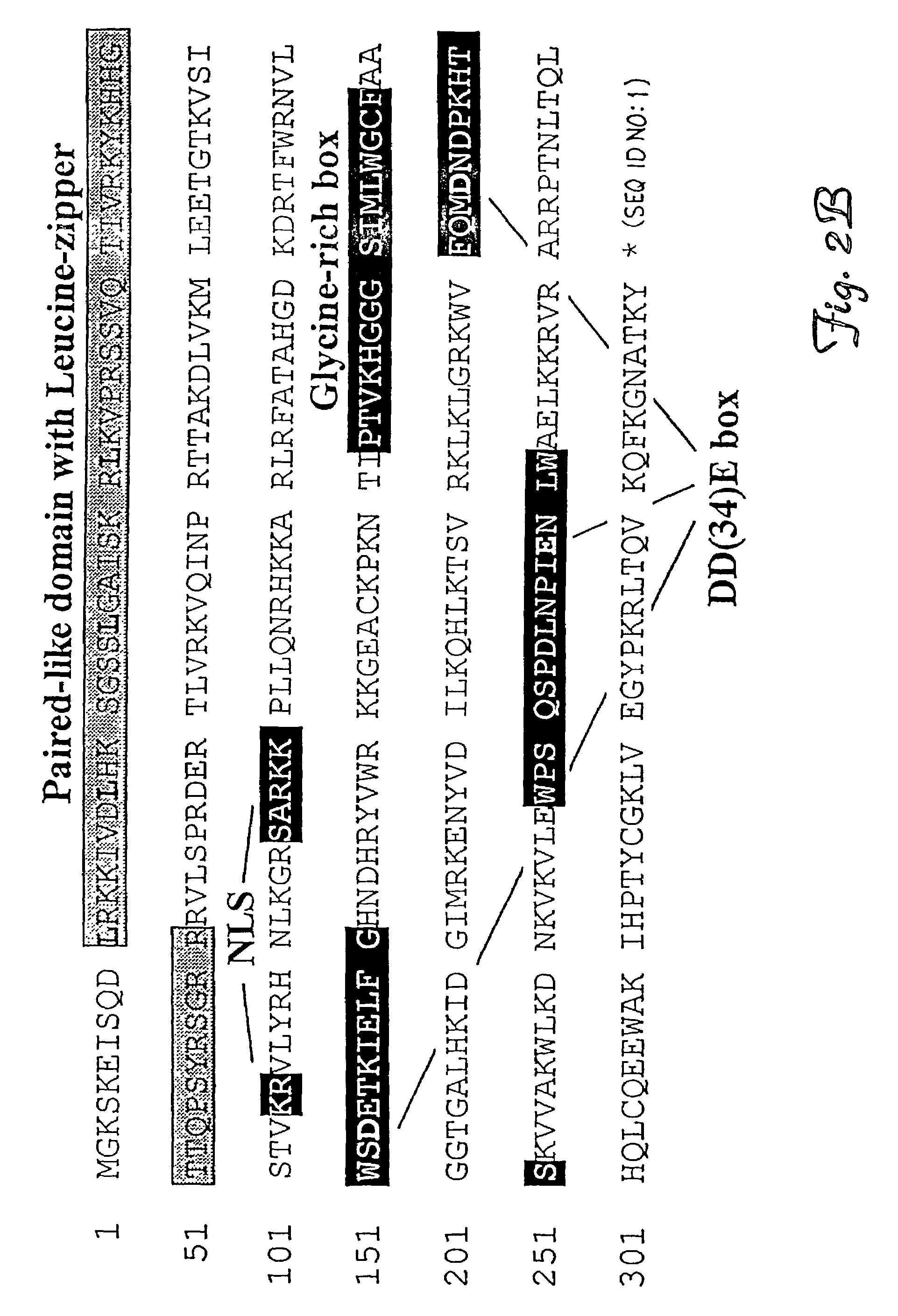
Methods and compositions for introducing a nucleic acid into the genome of a cell are provided. In the subject methods, a Sleeping Beauty transposon that includes the nucleic acid is introduced into the cell along with a source of a mutant Sleeping Beauty transposase that provides for enhanced integration as compared to the wild-type Sleeping Beauty transposase having an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:01. Introduction of the mutant Sleeping Beauty Transposase and transposon results in integration of the nucleic acid into the cell genome. Also provided are mutant transposases and transposons, as well as systems and kits thereof, that find use in practicing the subject methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Multiplex isolation of protein-associated nucleic acids
ActiveUS20150111788A1Microbiological testing/measurementEnzyme stabilisationGenomeChromatin immunoprecipitation
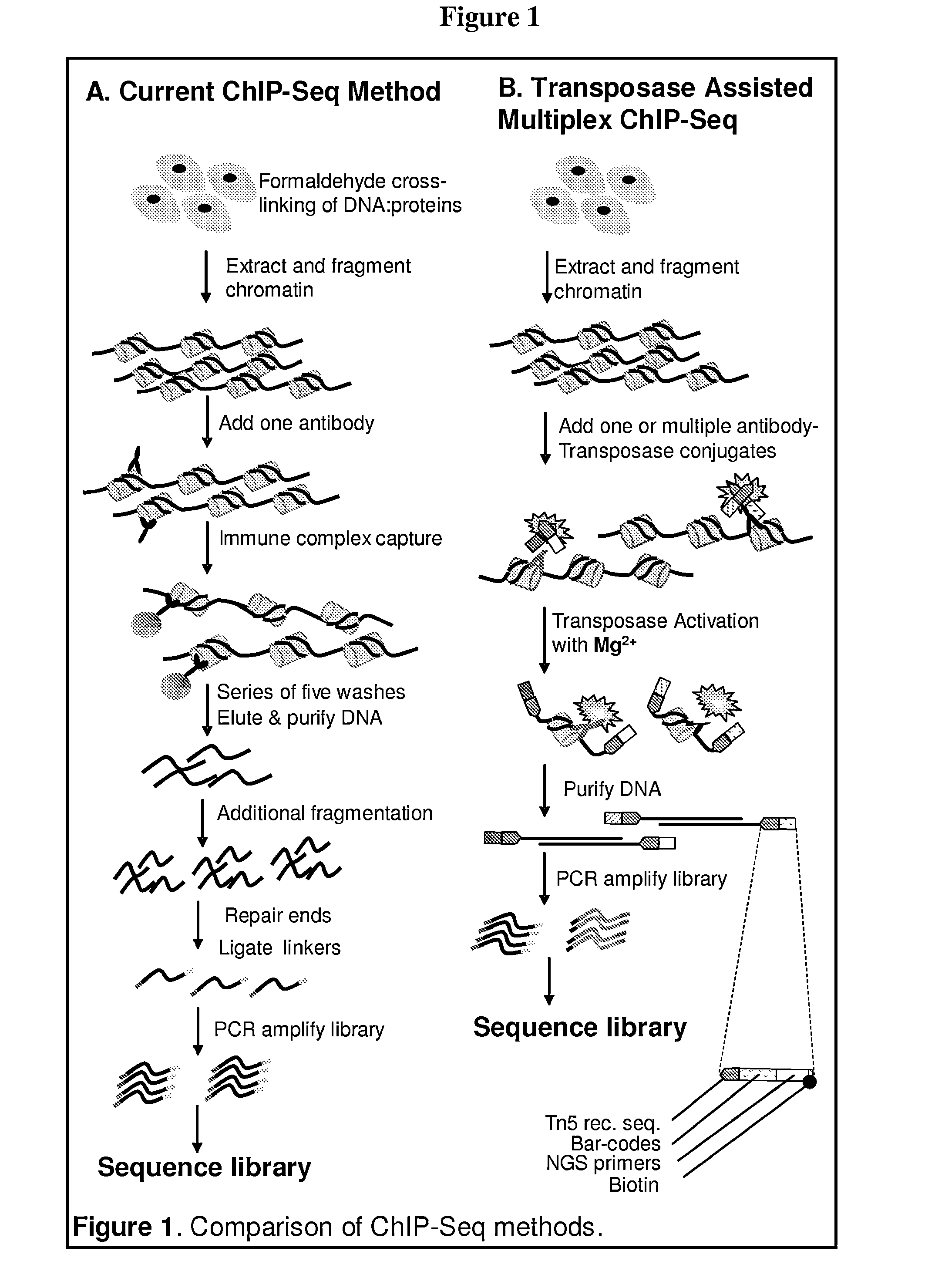
The invention provides novel methods and materials for genetic and genomic analysis using single or multiplex isolation of protein-associated nucleic acids, including transposase-assisted chromatin immunoprecipitation (TAM-ChIP) and antibody-oligonucleotide proximity ligation. These methods comprise tagging and isolating chromatin or other protein-associated nucleic acids and using antibody-oligonucleotide complexes that recognize the proteins associated with such nucleic acids.
Owner:ACTIVE MOTIF INC
Haploidome determination by digitized transposons
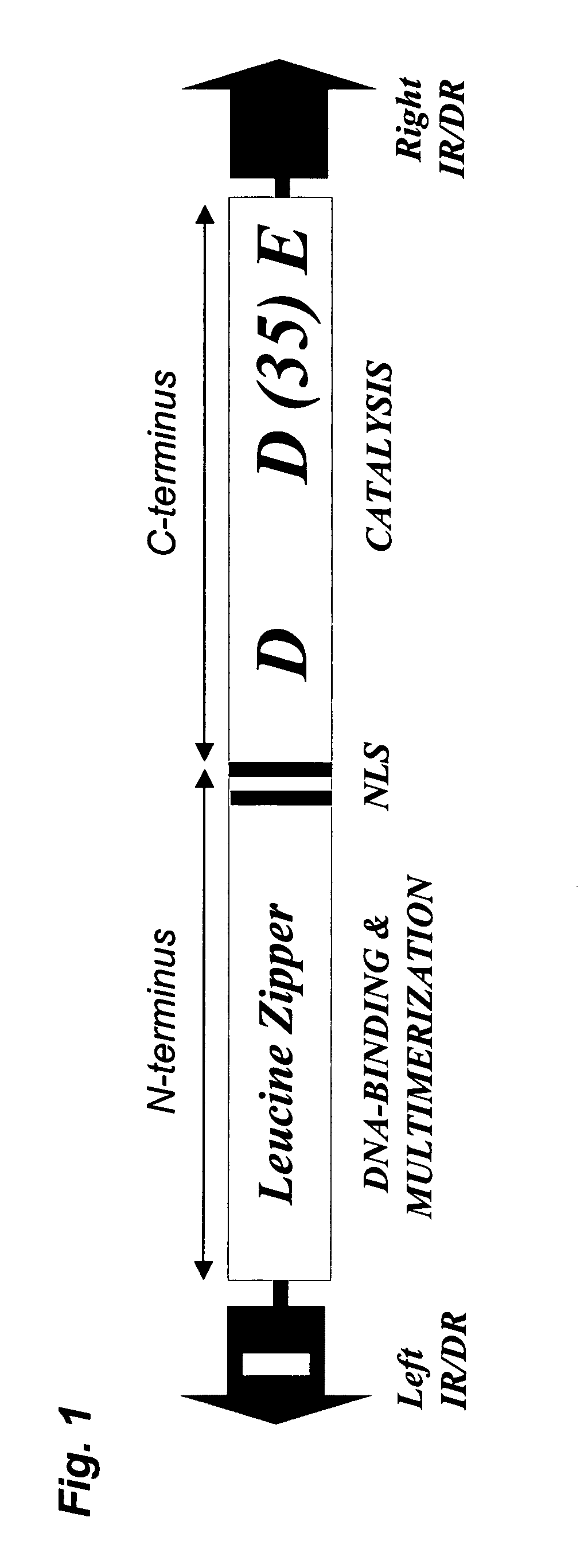
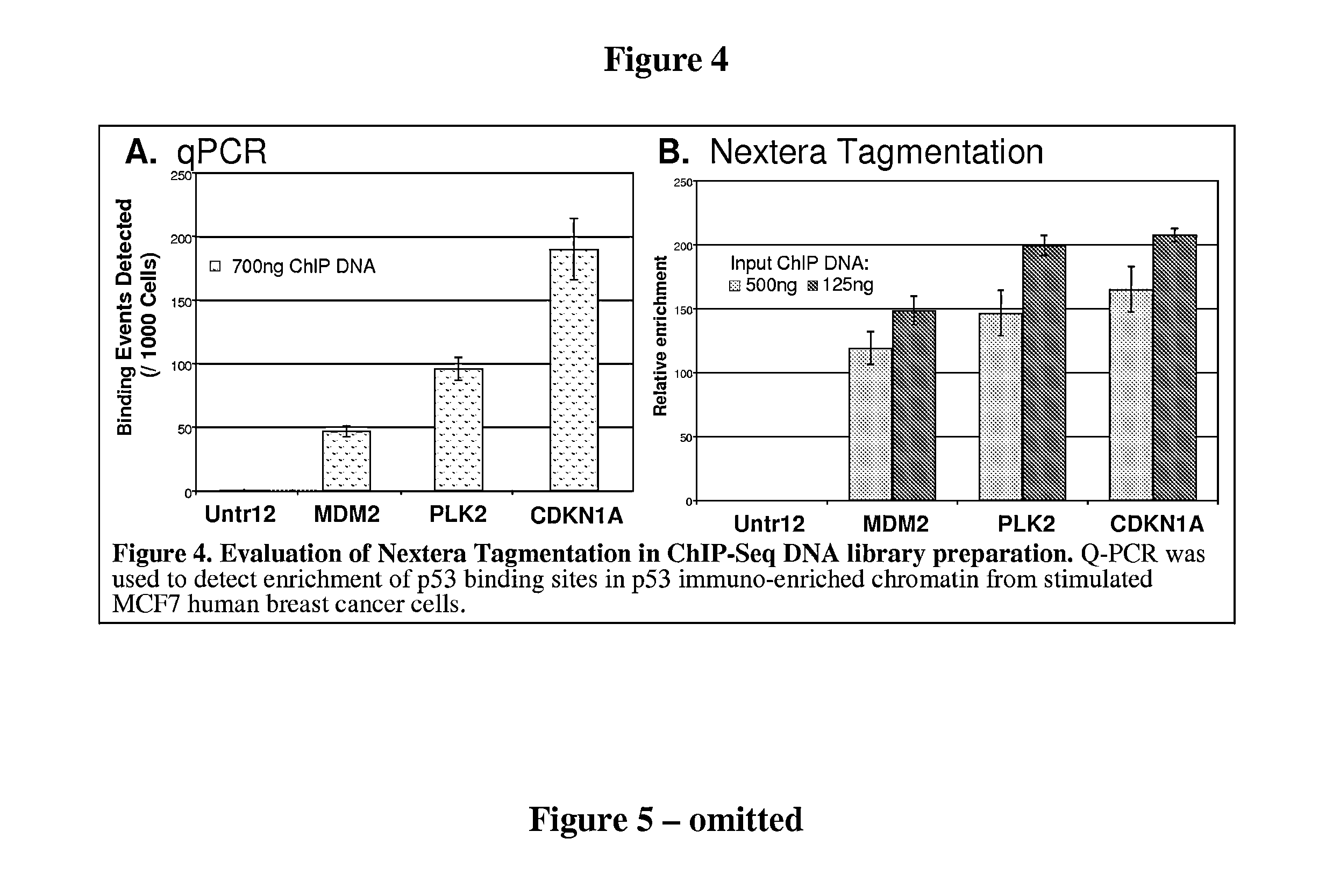
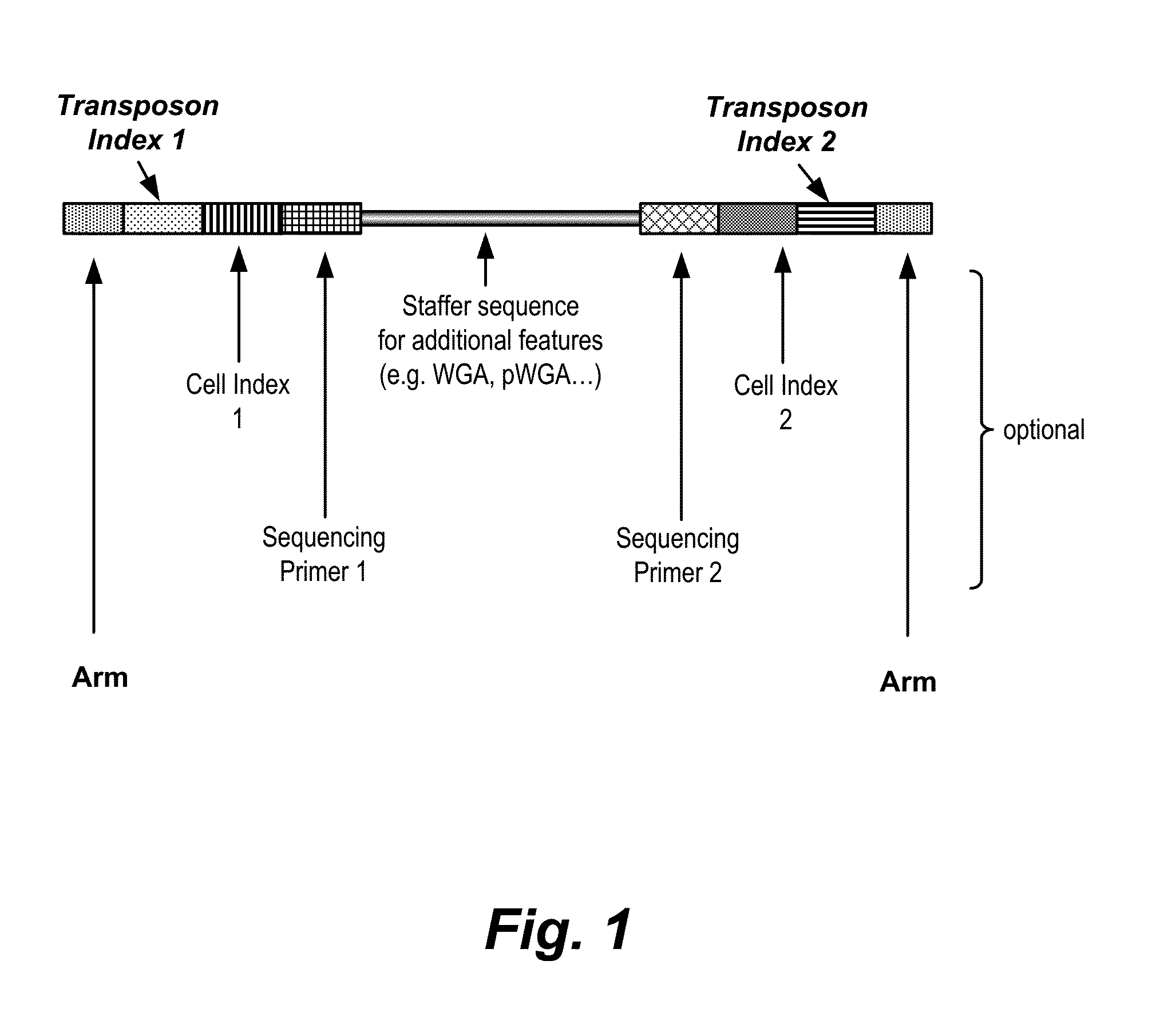
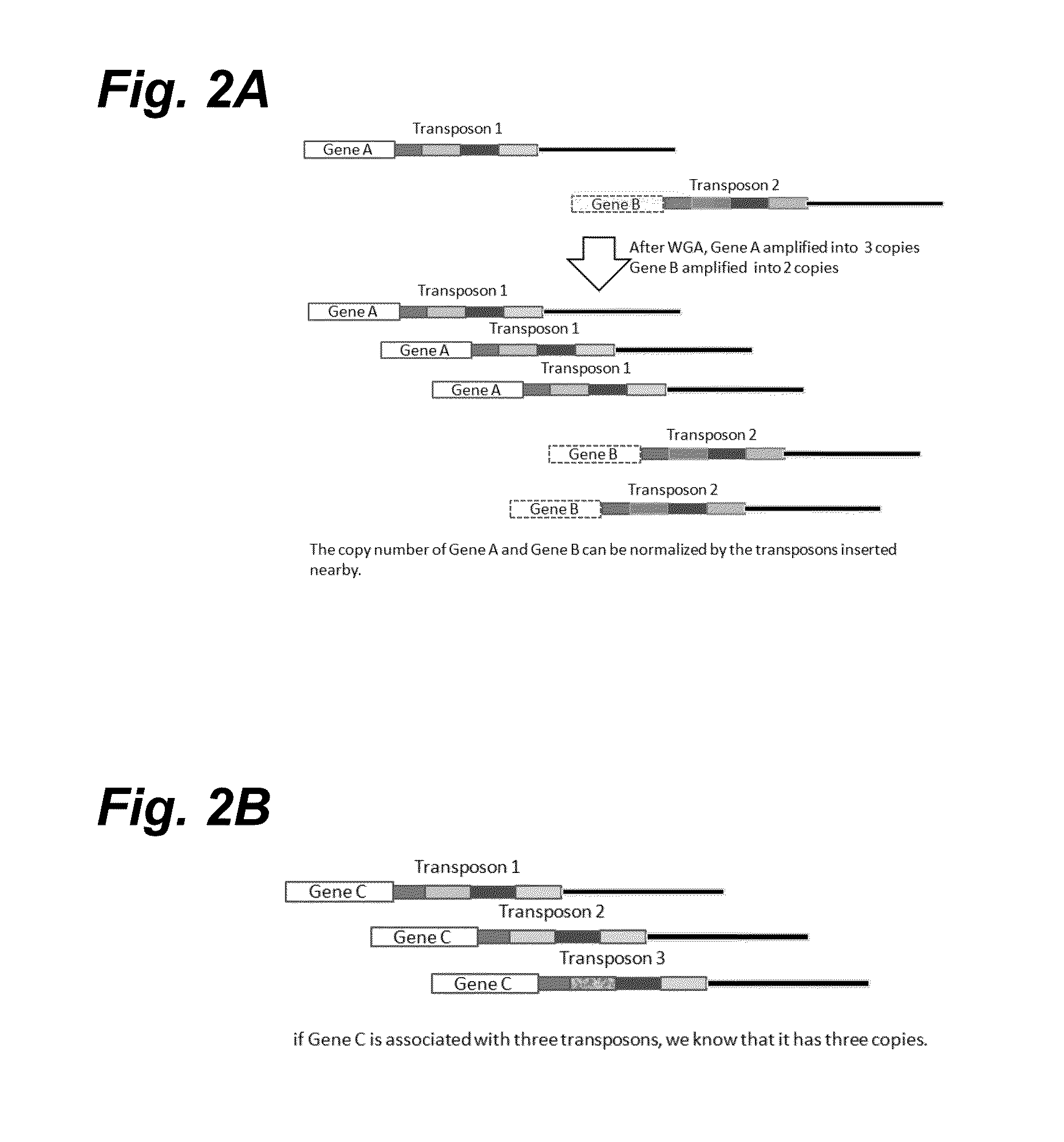
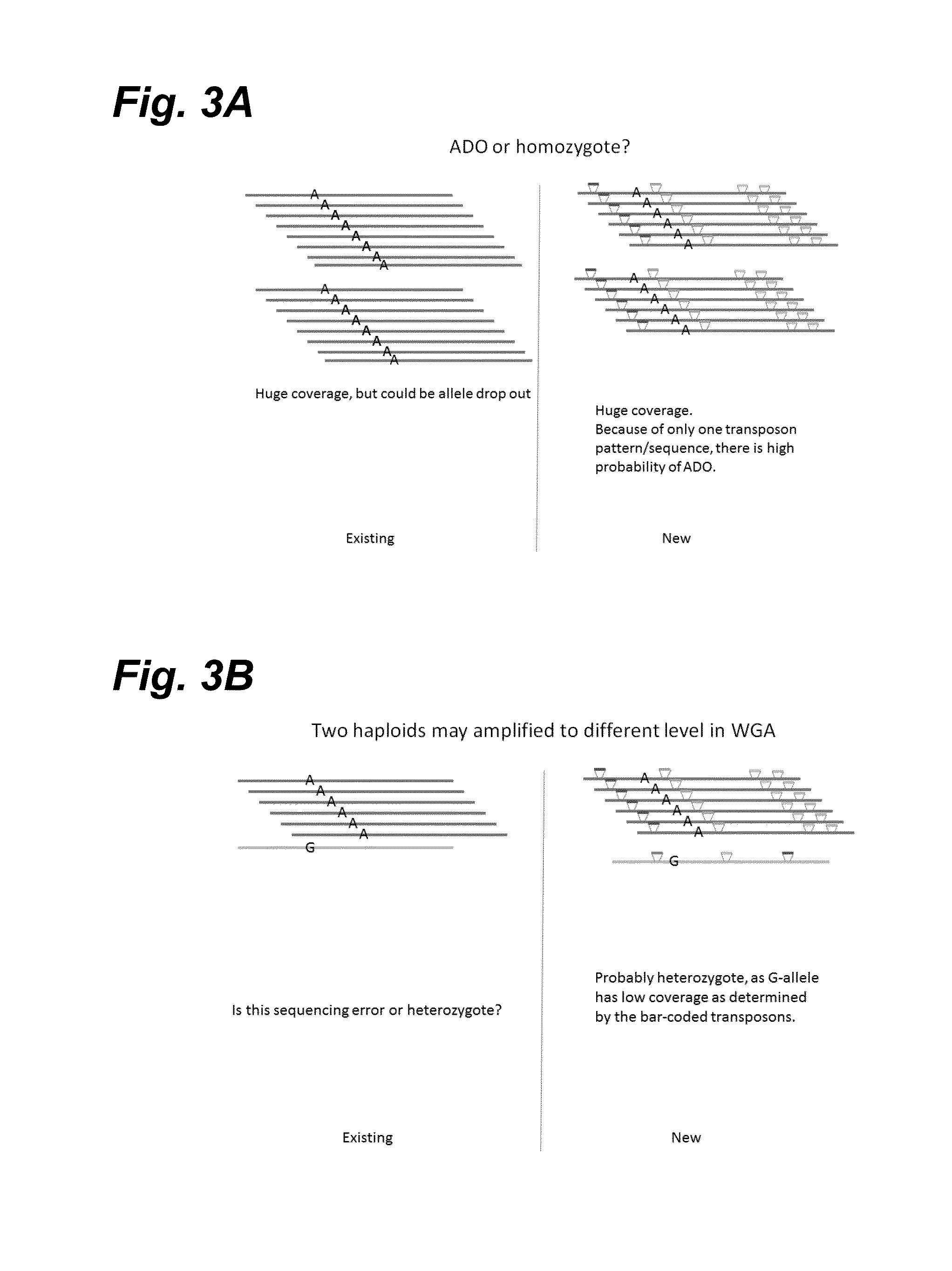
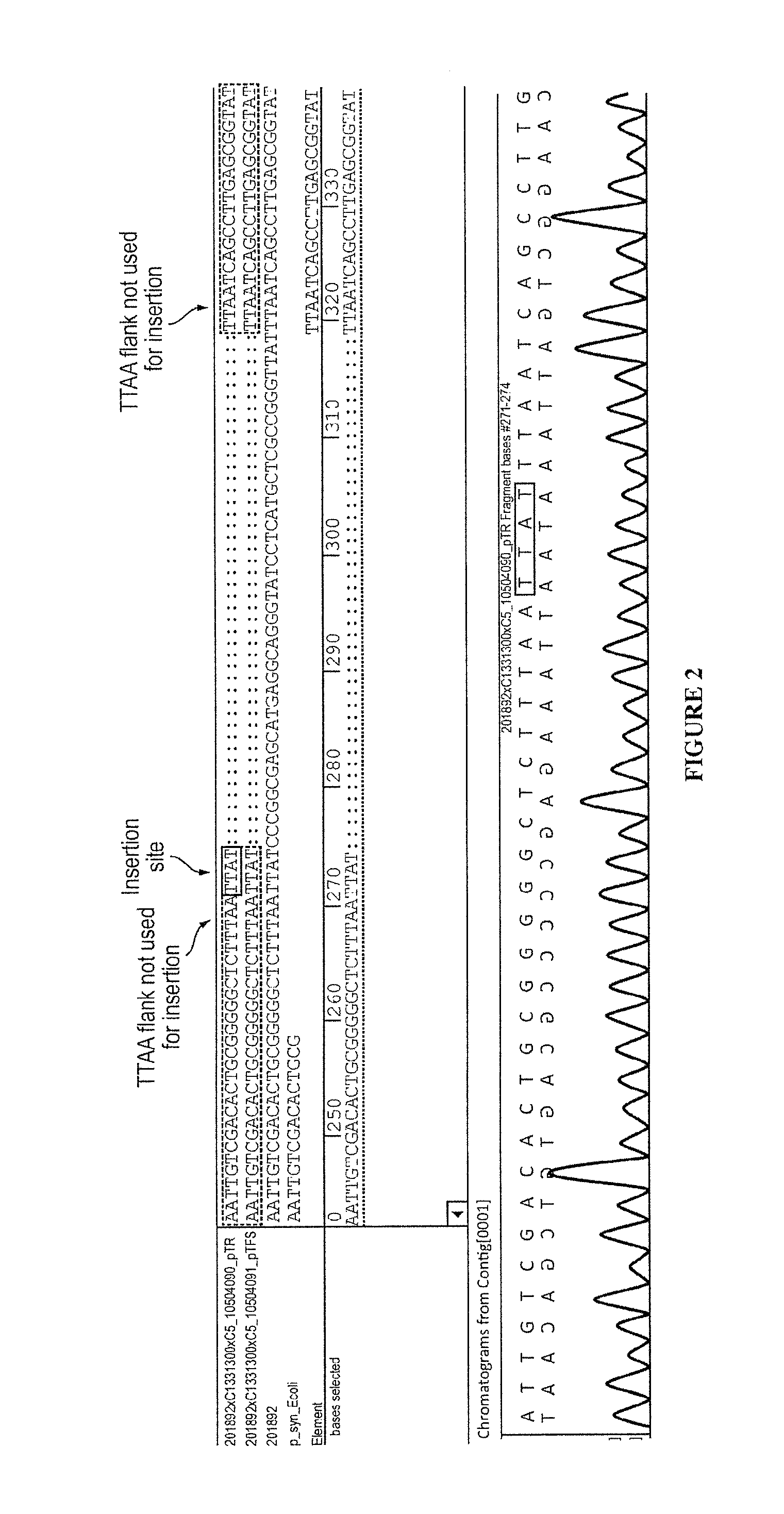
In certain embodiments, the present invention provides a way of “digitally” marking different the alleles of different chromosomes by using a transposase to insert differently barcoded transposons into genomic DNA before further analysis. According to this method, each allele becomes marked with a unique pattern of transposon barcodes. Because each unique pattern of transposon barcodes identifies a particular allele, the method facilitates determinations of ploidy and copy number variation, improves the ability to discriminate among homozygotes, heterozygotes, and patterns arising from sequencing errors, and allows loci separated by uninformative stretches of DNA to be identified as linked loci, thereby facilitating haplotype determinations. Also provided is a novel artificial transposon end that includes a barcode sequence in two or more positions that are not essential for transposition.
Owner:DIGENOMIX CORP
Efficient and safe transposable element integration system and application thereof
ActiveCN105154473AAvoid risks caused by random insertionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyTransposon integrationInsertion site
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, relates to an efficient and safe transposable element integration system and application thereof and further relates to a nucleic acid construction body and application thereof. The nucleic acid construction body concretely and sequentially comprises the following elements of a transposable element 5' terminal repetition sequence, a polyclone insertion site, a poly A tailing signal sequence, a transposable element 3' terminal repetition sequence, a transposase coding sequence and a promoter controlling the expression of transposase. The polyclone insertion site is used for inserting an exogenous gene coding sequence and a selective promoter for controlling the expression of exogenous genes in an operability mode. The poly A tailing signal sequence has a poly A tailing signal function in the forward and reverse directions, and the direction of an expression cassette of transposase is reverse to that of an exogenous gene expression cassette. The nucleic acid construction body can be used for efficiently and safely expressing mediated exogenous genes in host cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY RES INST +1
Enhanced sleeping beauty transposon system and methods for using the same
Methods and compositions for introducing a nucleic acid into the genome of a cell are provided. In the subject methods, a Sleeping Beauty transposon that includes the nucleic acid is introduced into the cell along with a source of a mutant Sleeping Beauty transposase that provides for enhanced integration as compared to the wild-type Sleeping Beauty transposase having an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:01. Introduction of the mutant Sleeping Beauty Transposase and transposon results in integration of the nucleic acid into the cell genome. Also provided are mutant transposases and transposons, as well as systems and kits thereof, that find use in practicing the subject methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and compositions for DNA fragmentation and tagging by transposases
ActiveUS20120301925A1Short reaction timeReduce concentrationFermentationDNA preparationDNA fragmentationWild type
The present invention provides new compositions for transposase-mediated fragmenting and tagging DNA targets. The invention relates to the surprising discovery that use of manganese ions (Mn2+) in transposase reactions improves the transposase reaction. It also relates to the surprising discovery that Mg2+ ions can be used in a transposase reaction with wild-type and / or engineered transposases at levels much higher than previously thought. The invention provides for the use of naturally-occurring transposases in in vitro reactions, as well as improved schemes for cleaving, tagging, and amplifying target DNA.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
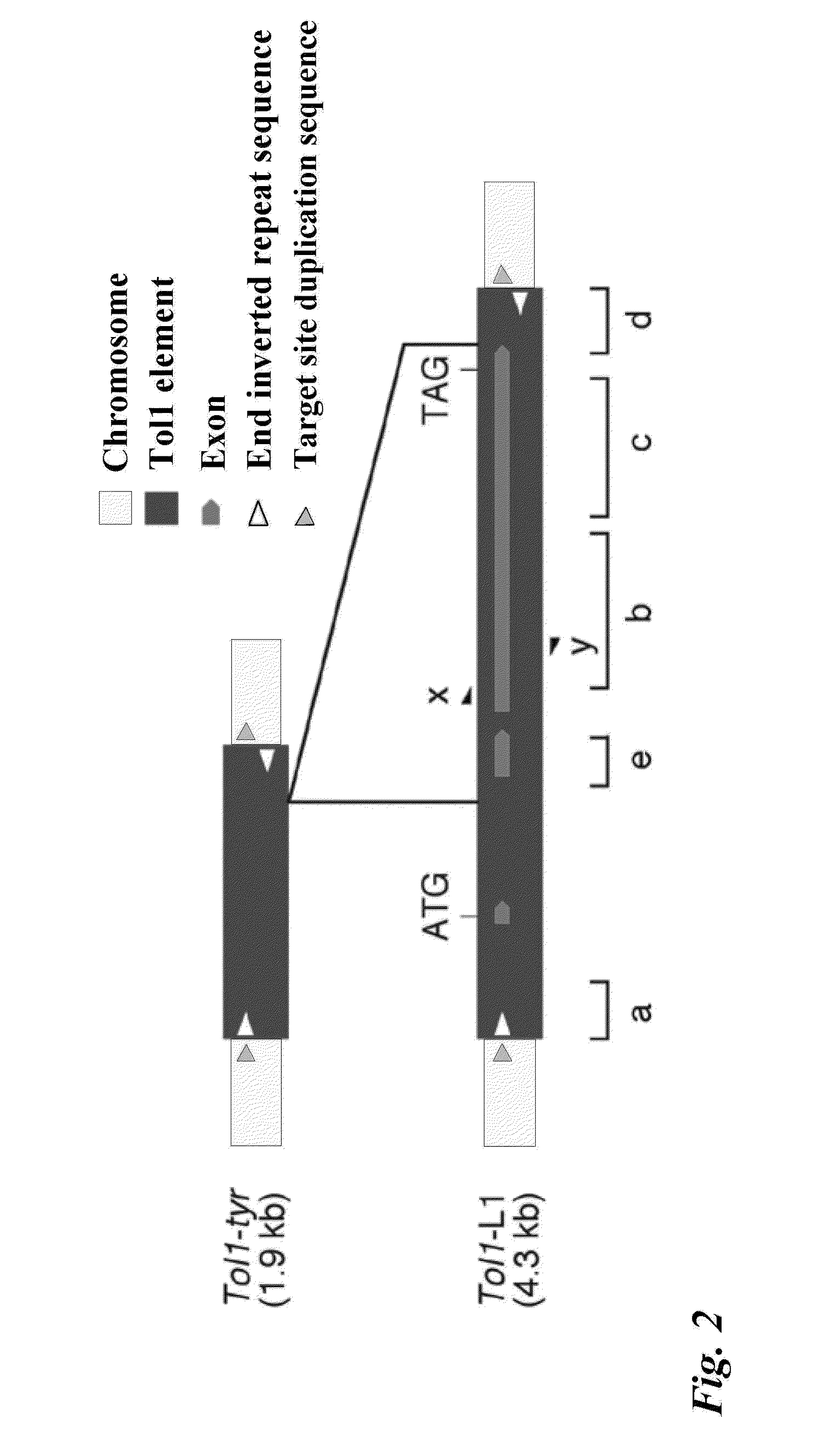
Tol1 factor transposase and DNA introduction system using the same
InactiveUS8598328B2High transposition frequencyEffectively actSugar derivativesHydrolasesGene defectNucleotide
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY +1
P element derived vector and methods for its use
Novel P element derived vectors and methods for their use to insert an exogenous nucleic acid into the genome of a target cell are provided. The subject vectors have a pair of P element transposase recognized insertion sites, e.g. 31 base pair inverted repeats, flanking at least two transcriptionally active genes. In practicing the subject methods, a vector of the subject invention is introduced into the target cell under conditions sufficient for transposition to occur. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the insertion of an exogenous nucleic acid into the genome of a target cell is desired, e.g. include research, synthesis and therapeutic applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
The present invention provides the use of transposases and transposon ends to generate extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, followed by the use of DNA polymerases to generate 5′- and 3′-tagged single DNA without PCR amplification reactions. Methods, compositions and kits for stranded DNA fragments, wherein the first label on the 5' end shows the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second label on the 3' end shows the same The first tab shows a sequence different from the sequence. The method can be used to generate 5' and 3' tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes including metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called "next generation sequencing") involves the process of comparative genome sequencing (CGS).
Owner:EPICENT TECH CORP
Tool for efficient site-specific transposition of genes and application of tool
ActiveCN105646719ARealize transposition functionRealize site-specific transgeneHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGene engineeringAnimal genome
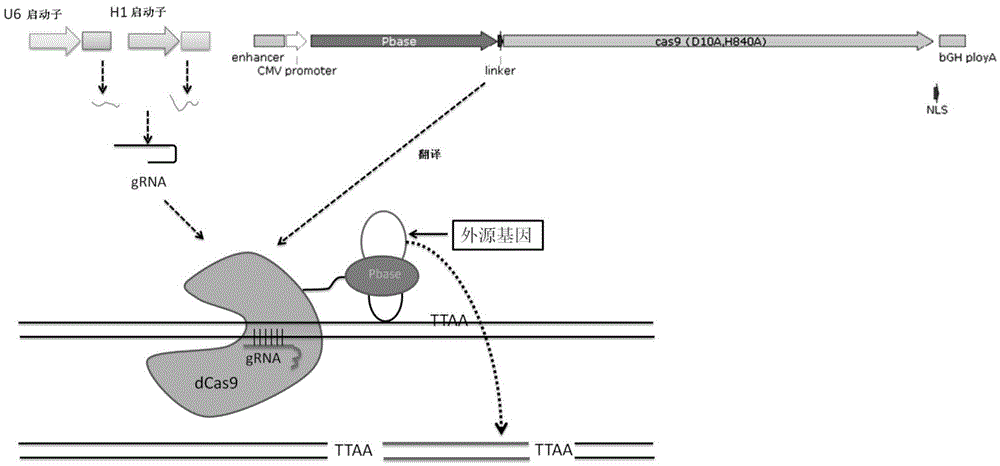
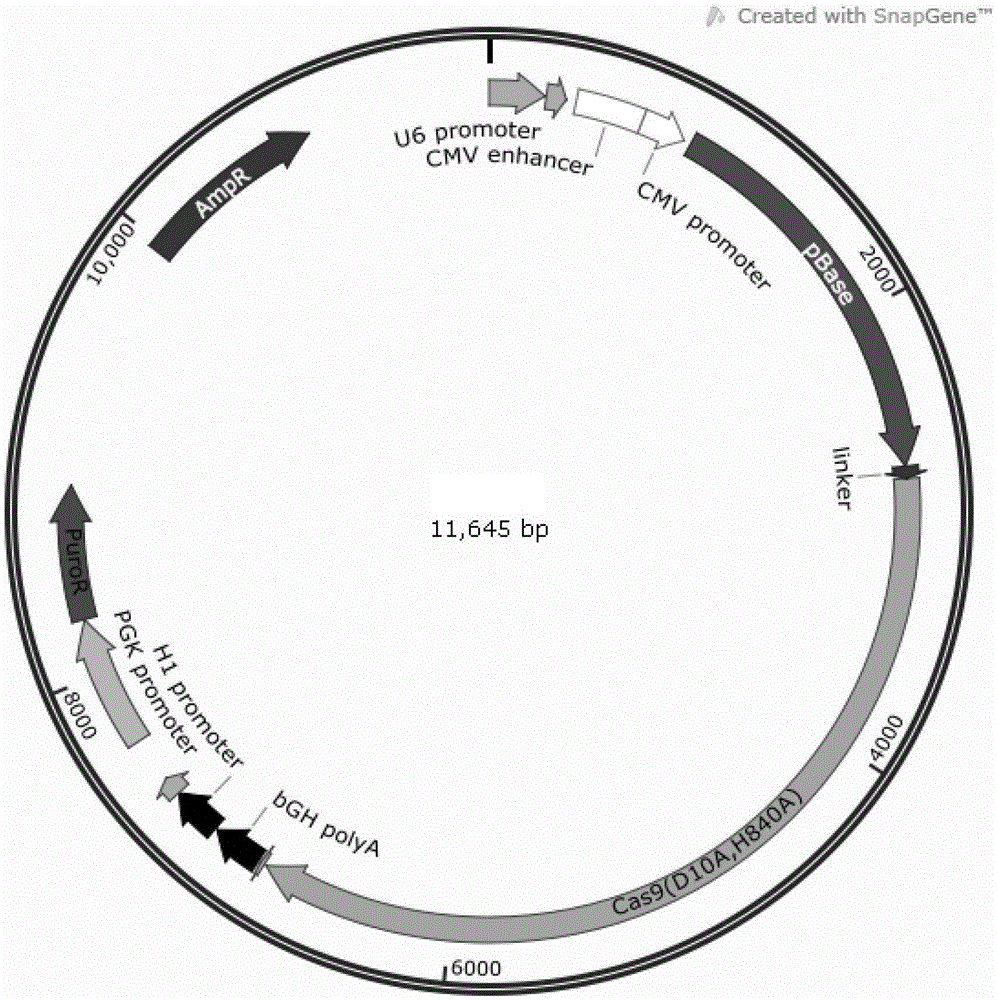
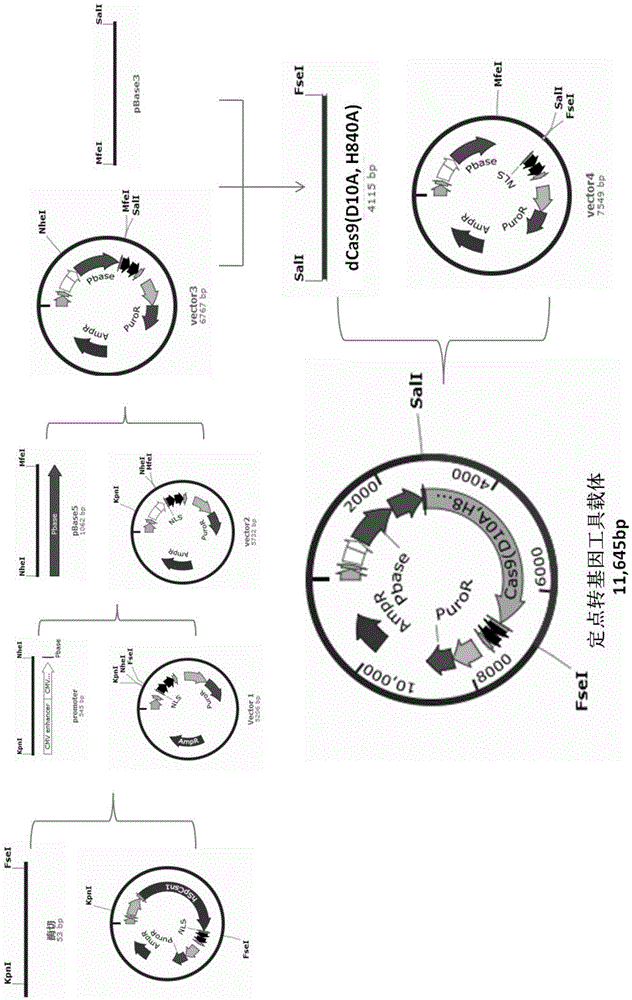
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering and particularly discloses a tool for efficient site-specific transposition of genes. The tool comprises or can produce a gRNA-Cas9 protein (without incision enzyme activity)-PB transposase compound, and gRNA targets the specific site of a genome; the Cas9 protein without incision enzyme activity is double-mutant Cas9 protein with 10th-site amino acid residue D mutating into A and 840th-site amino acid residue H mutating into A. Through design of gRNA (guide RNA) targeting the animal genome, under the coexpression condition of gRNA and site-specific transposase, PB transposase is targeted to a specific position of the genome along with a CRISPR / cas9 and gRNA compound, the PB transposase realizes a transposition function at the specific site, accordingly, donor plasmids (carriers containing exogenous target genes) are simultaneously co-transfected, the exogenous target carriers can be transposed to the specific site in the genome through transposition, and site-specific transposition of the genes is realized.
Owner:WUXI MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH HOSPITAL
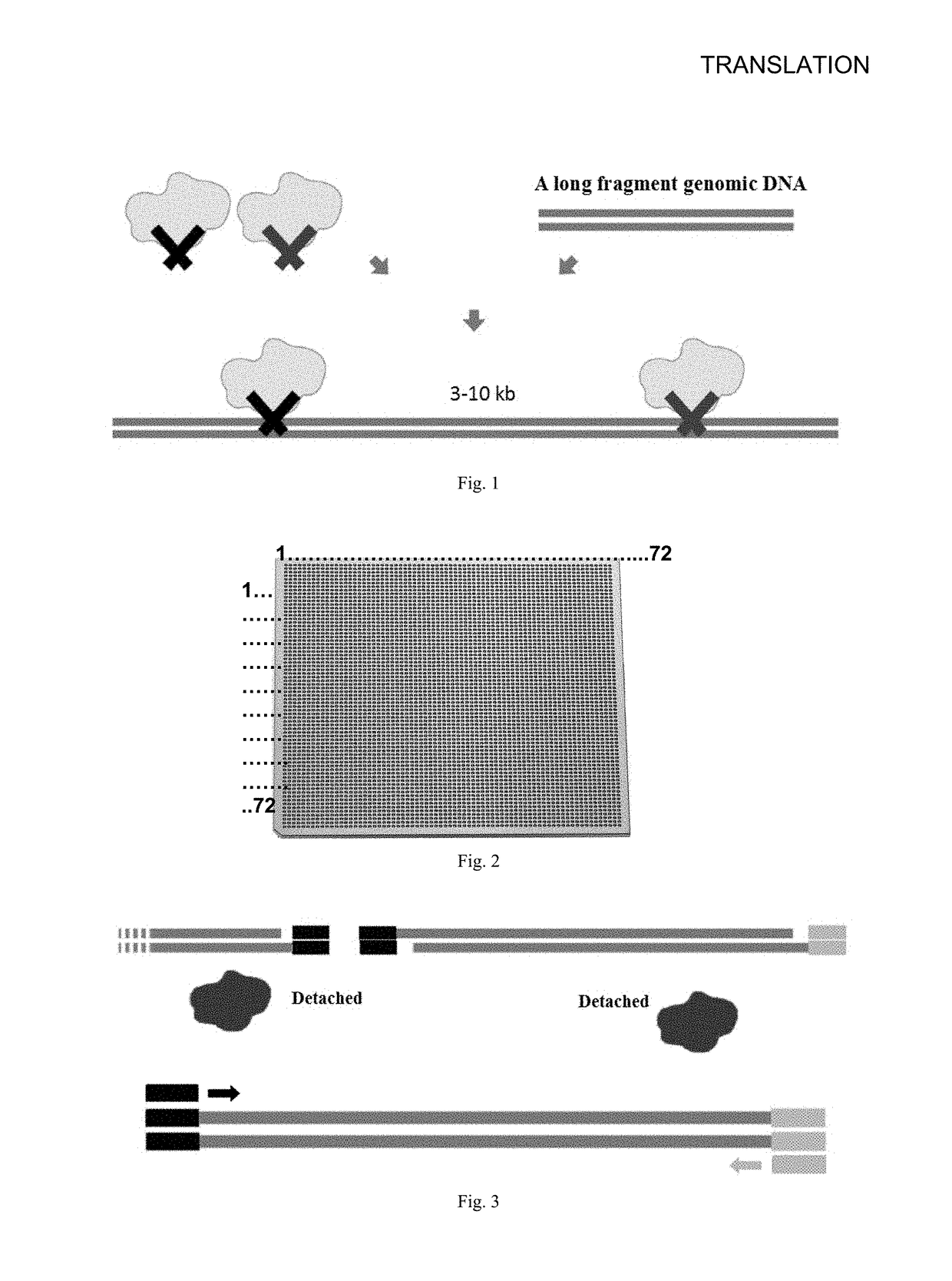
Method for constructing long fragment DNA library
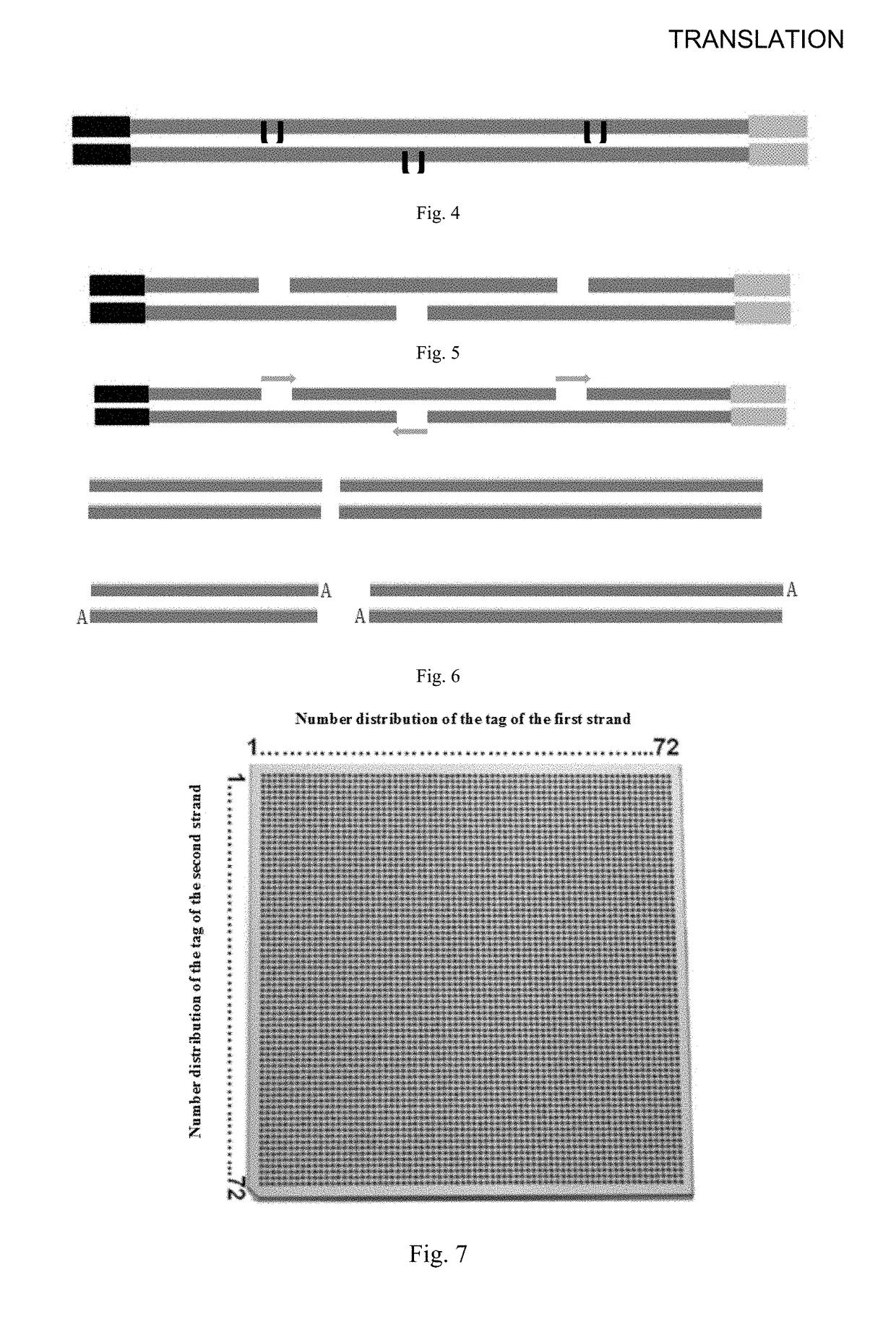
Disclosed is a method for constructing a long fragment DNA library, comprising the following steps: 1) breaking a long fragment DNA into target fragments of 3-10 kb by transposase, then amplifying the target fragments, and obtaining target fragment amplification products containing dUTP; 2) amplifying the dUTP in the products by removing the target fragments, fragmenting the target fragments secondarily into DNA short fragments of 300-1200 bp; 3) connecting both ends of the DNA short fragments with sequencing linker single chains A and sequencing linker single chains B respectively; and obtaining connecting sequencing linker products; and 4) PCR amplifying the connecting sequencing linker products, to obtain amplification products.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST +1
Development of a transposon system for site-specific DNA integration in mammalian cells
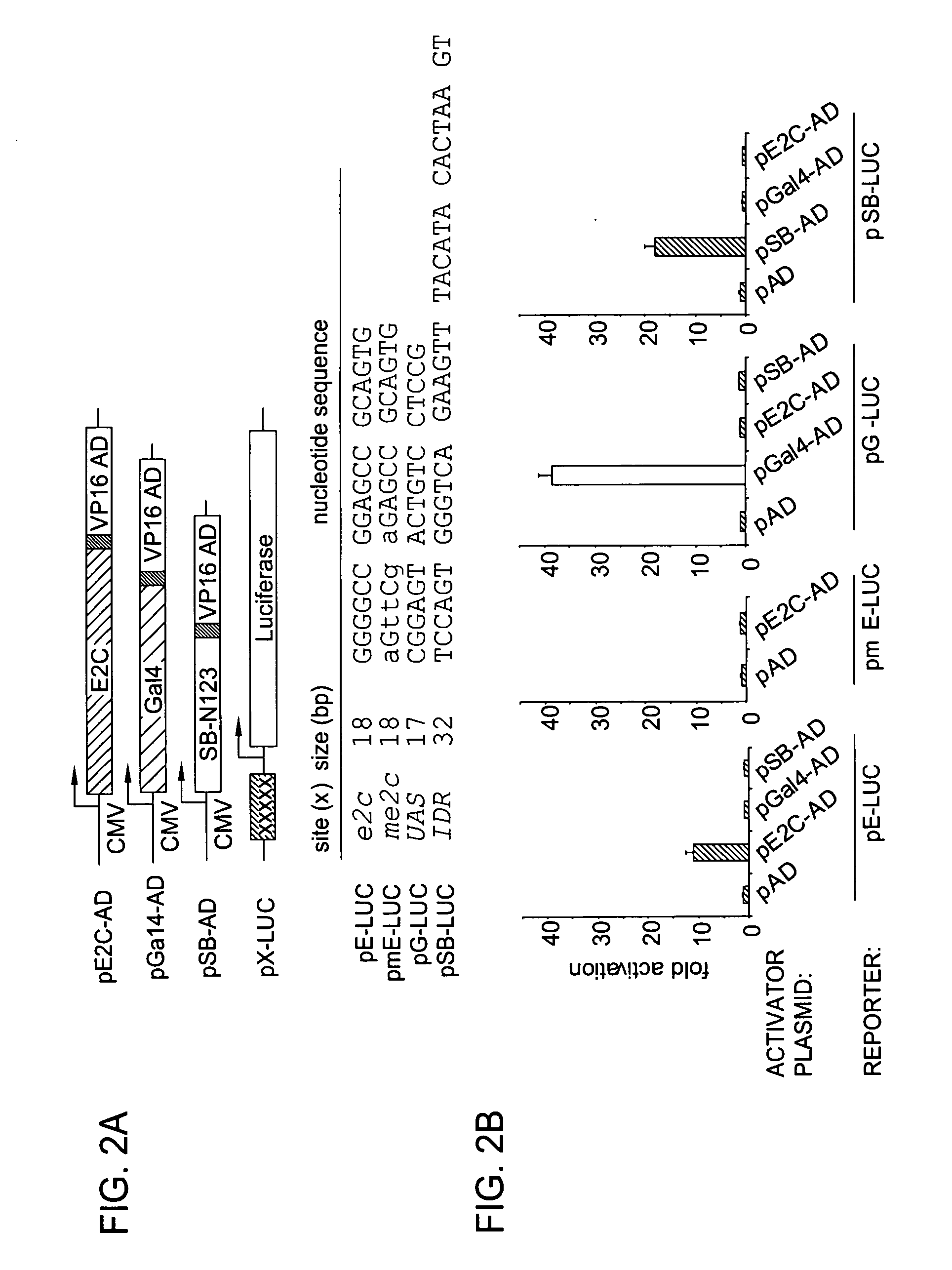
The present invention provides a method and compositions for integrating an exogenous nucleic acid into a targeted region of a nucleic acid of a mammalian cell. The compositions include transposase fusion proteins that are adapted to recognize a target site in a nucleic acid. Transposase fusion proteins that include a Sleeping Beauty transposase are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIVERRSITY
Systems for gene targeting and producing stable genomic transgene insertions
InactiveUS20090083870A1Improve stabilityStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorInstabilityTransgene
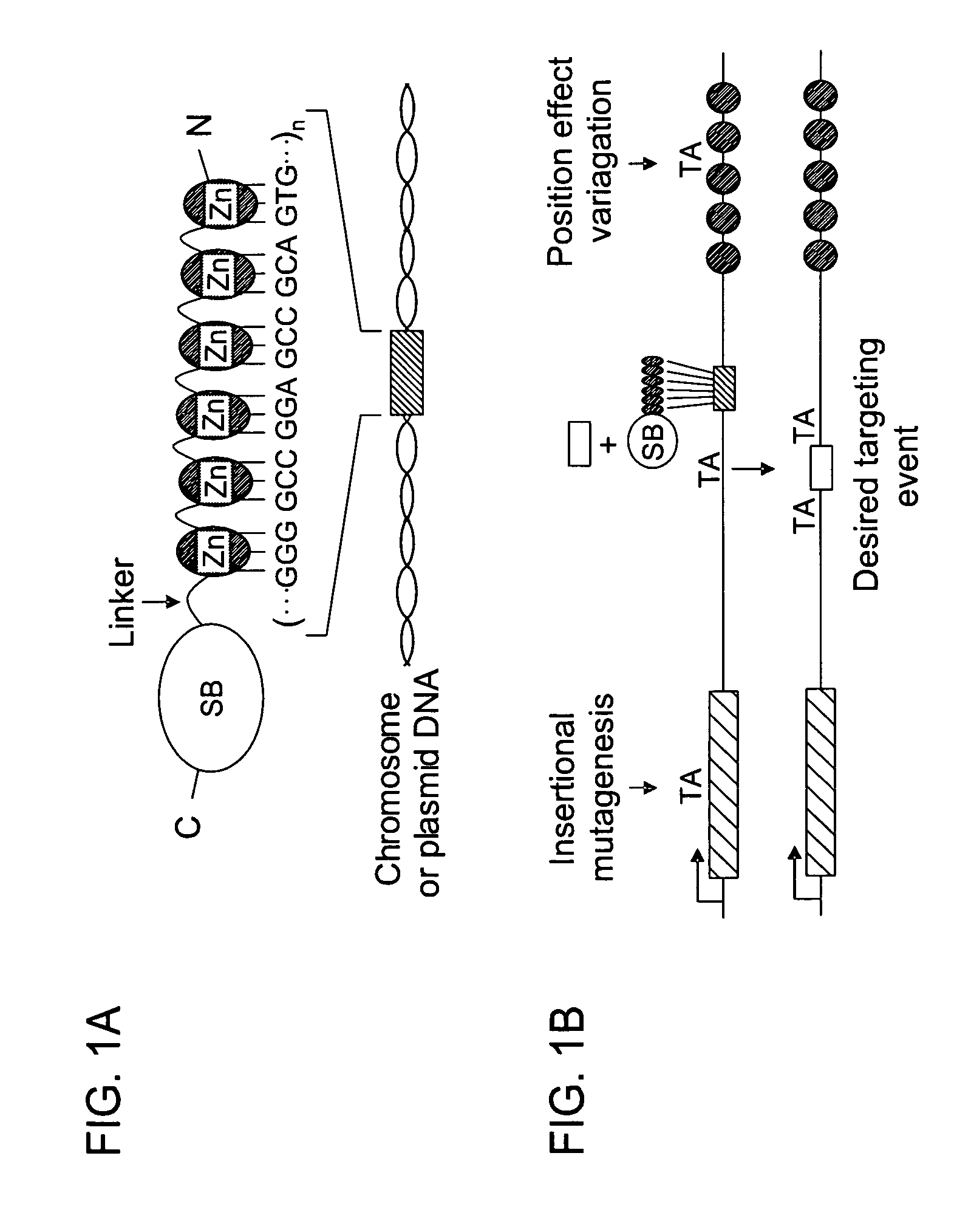
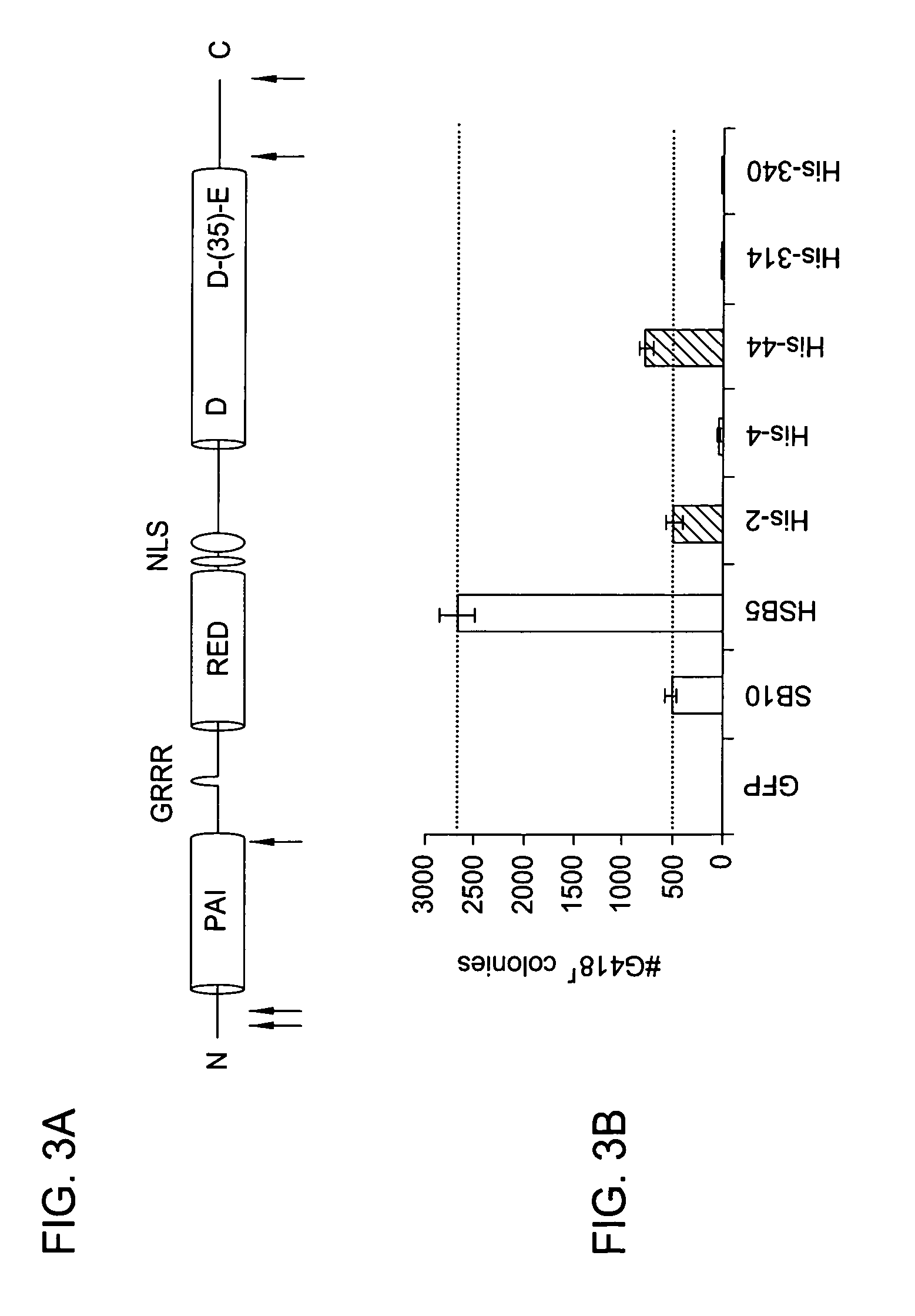
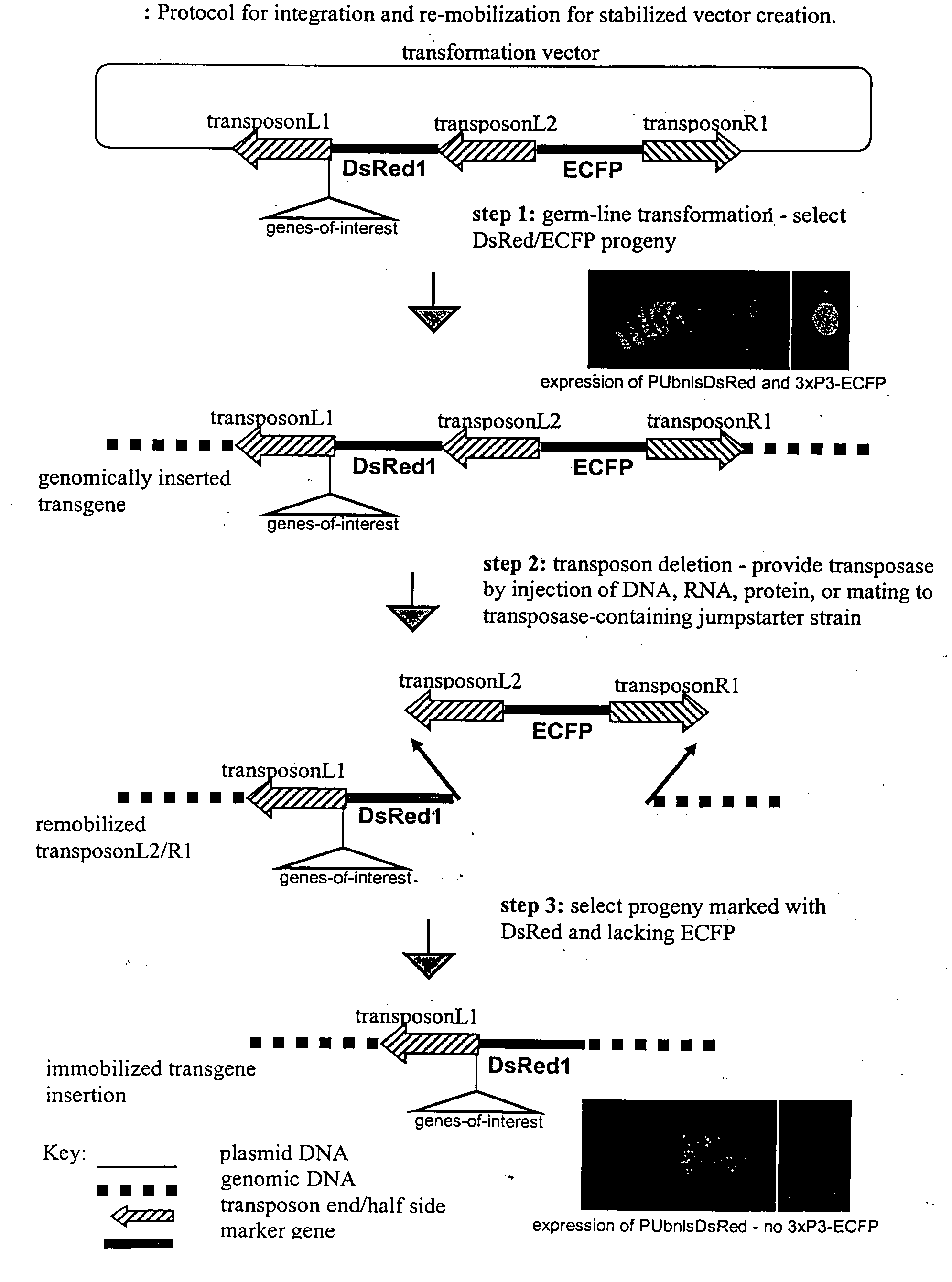
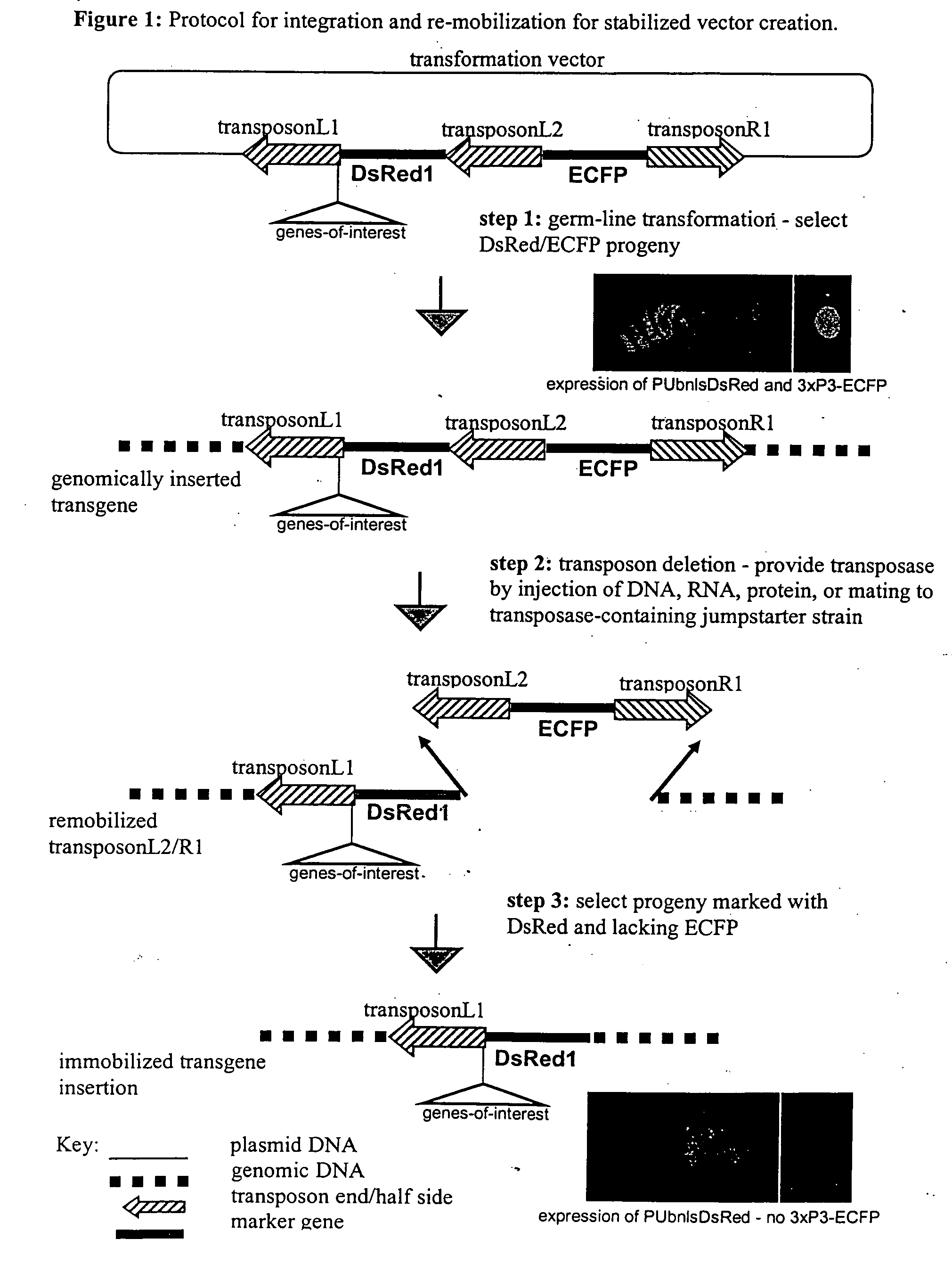
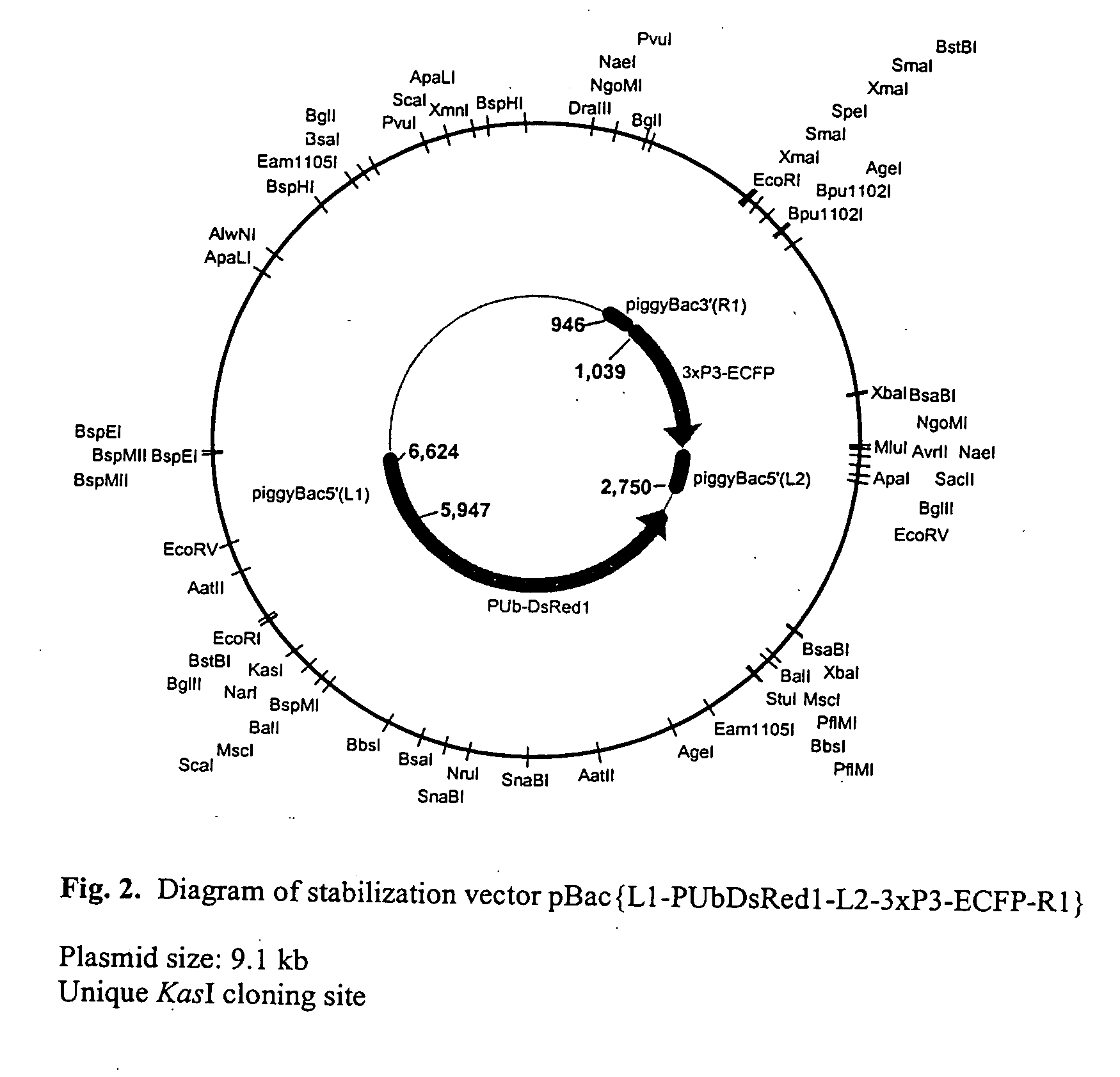
The novel germ-line transformation systems disclosed in this patent application allow the physical deletion of transposon DNA following the transformation process, and the targeting of transgene integrations into predefined target sites. In this way, transposase-mediated mobilization of genes-of-interest is excluded mechanistically and random genomic integrations eliminated. In contrast to conventional germ-line transformation technology, our systems provide enhanced stability to the transgene insertion. Furthermore, DNA sequences required for the transgene modification (e.g. transformation marker genes, transposase or recombinase target sites), are largely removed from the genome after the final transgene insertion, thereby eliminating the possibility for instability generated by these processes. The RMCE technology, which is disclosed in this patent application for invertebrate organisms (exemplified in Drosophila melanogaster) represents an extremely versatile tool with application potential far beyond the goal of transgene immobilization. RMCE makes possible the targeted integration of DNA cassettes into a specific genomic loci that are pre-defined by the integration of the RMCE acceptor plasmid. The loci can be characterized prior to a targeting experiment allowing optimal integration sites to be pre-selected for specific applications, and allowing selection of host strains with optimal fitness. In addition, multiple cassette exchange reactions can be performed in a repetitive way where an acceptor cassette can be repetitively exchanged by multiple donor cassettes. In this way several different transgenes can be placed precisely at the same genomic locus, allowing, for the first time, the ability to eliminate genomic positional effects and to comparatively study the biological effects of different transgenes.
Owner:HORN CARSTEN +1
Sequencing library construction method, and kit and application thereof
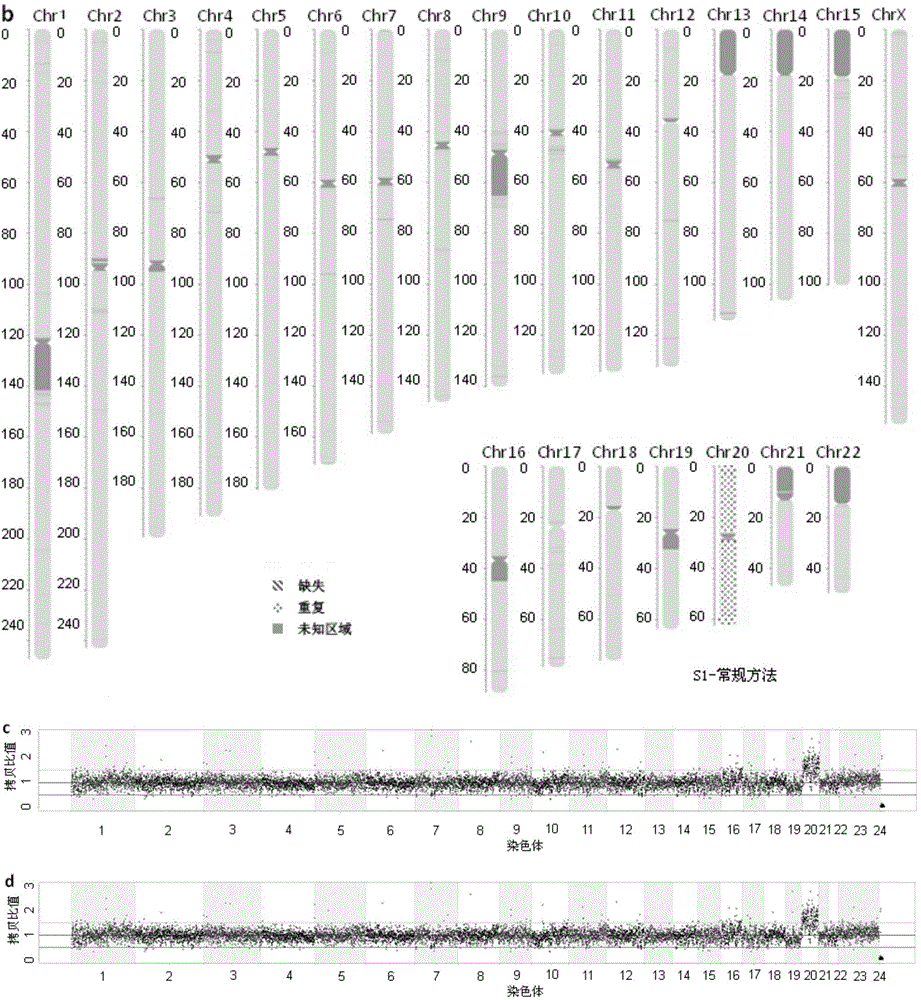
ActiveCN105525357ASave construction timeImplement number anomaly detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationA-DNARecognition sequence
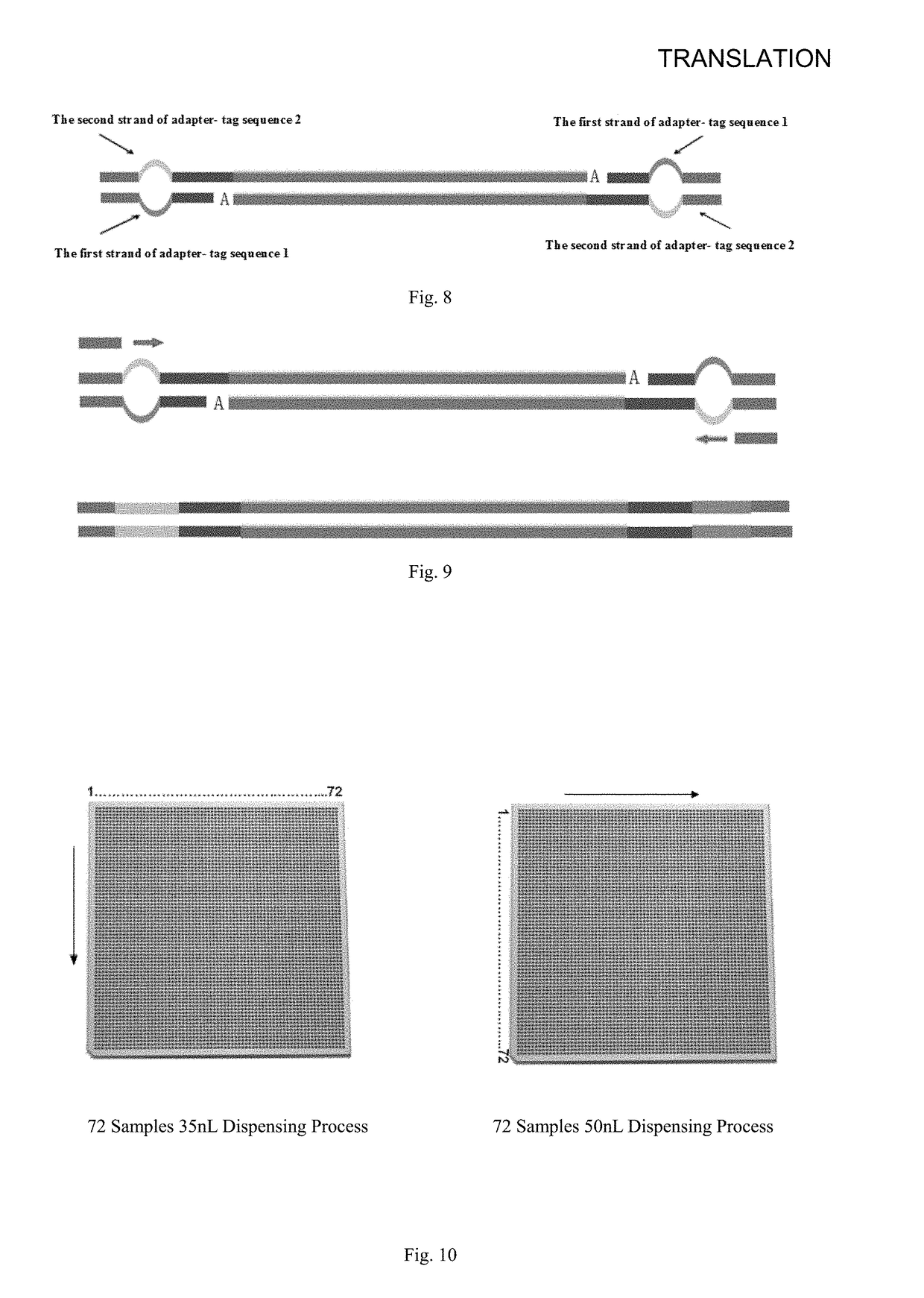
The invention discloses a sequencing library construction method, and a kit and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: target DNA and a transposase-embedding complex are incubated under transposition reaction conditions, such that a DNA library with double linkers on the two ends is produced, wherein the transposase-embedding complex comprises transposase, a transposase recognition sequence complementary sequence, a first sequencing linker sequence and a second sequencing linker sequence. The first sequencing linker sequence comprises a first sequencing tag sequence at the 5' end and a transposase recognition sequence at the 3' end. The second sequencing linker sequence comprises a second sequencing tag sequence at the 5' end, a sample tag sequence and a transposase recognition sequence at the 3' end. With the method provided by the invention, with transposase, DNA can be broken with a one-step method, and sequencing linkers can be respectively added to the 5' end and the 3' end. Compared with a conventional library construction method, the method is time-saving, and the operation is simple.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +1
Stable knockout single plasmid vector with coordination of transposon and CRISPR/Cas9 system and application of stable knockout single plasmid vector
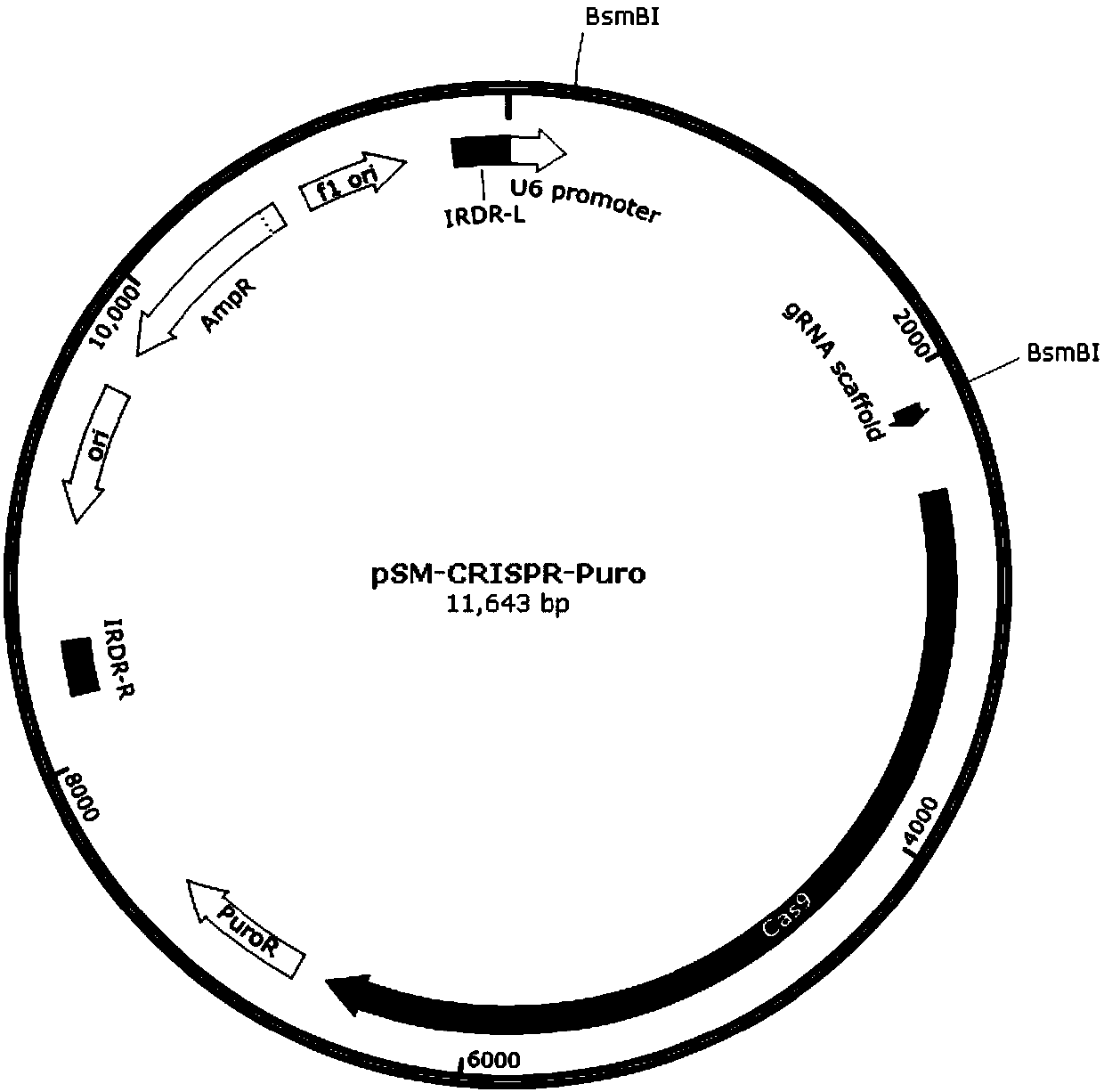
InactiveCN107686848ASimplify the build processThe process is simpleHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAStable cell lineBiology
The invention discloses a stable knockout single plasmid vector with coordination of transposon and a CRISPR / Cas9 system and application of stable knockout single plasmid vector and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The single plasmid vector is a double-stranded circular plasmid containing an IRDR-L-IRDR-R box, and the IRDR-L-IRDR-R box comprises an IRDR-L sequence, a promoter, a gRNA scaffold sequence, a Cas9 protein sequence, a resistance screening gene sequence and an IRDR-R sequence. The single plasmid vector provided by the invention can realize expression of sgRNA and a Cas9 protein only needing once construction and once transfection. A method is simple in process, is efficient and rapid, greatly simplifies a plasmid construction flow, shortens an experiment period and improves the working efficiency. The vector provided by the invention carries a transposase recognition sequence, does not use a virus, can conveniently, rapidly and safely establish a gene knockout stablecell line and is beneficial to screening stable cell lines by comprising the puromycin screening resistance.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for constructing a nucleic acid library, reagent and kit
InactiveCN102703426AImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationPacific biosciencesDNA fragmentation
The invention provides a method, reagent and a kit for establishing a nucleic acid library with a mark and uses an in vitro transposition method; the method comprises the following steps: firstly, breaking target DNA at random by transposase, and then, treating the target DNA by nuclease and DNA polymerase to generate a DNA library with a mark; according to the invention, any DNA segment which needs a mark is allowed to be connected, so that the generated DNA segment with the mark can be directly applied to different second generation of sequencing platforms which include but are not limited to those instruments manufactured by companies of Illumina, Life Technologies (ABI), Roche, HelicosBiotechnologies, Pacific Biosciences; similarly, the above-mentioned DNA segment can also be applied to sequencing instruments produced by other manufacturers.
Owner:WUJIANG HUIJIE BIOTECH
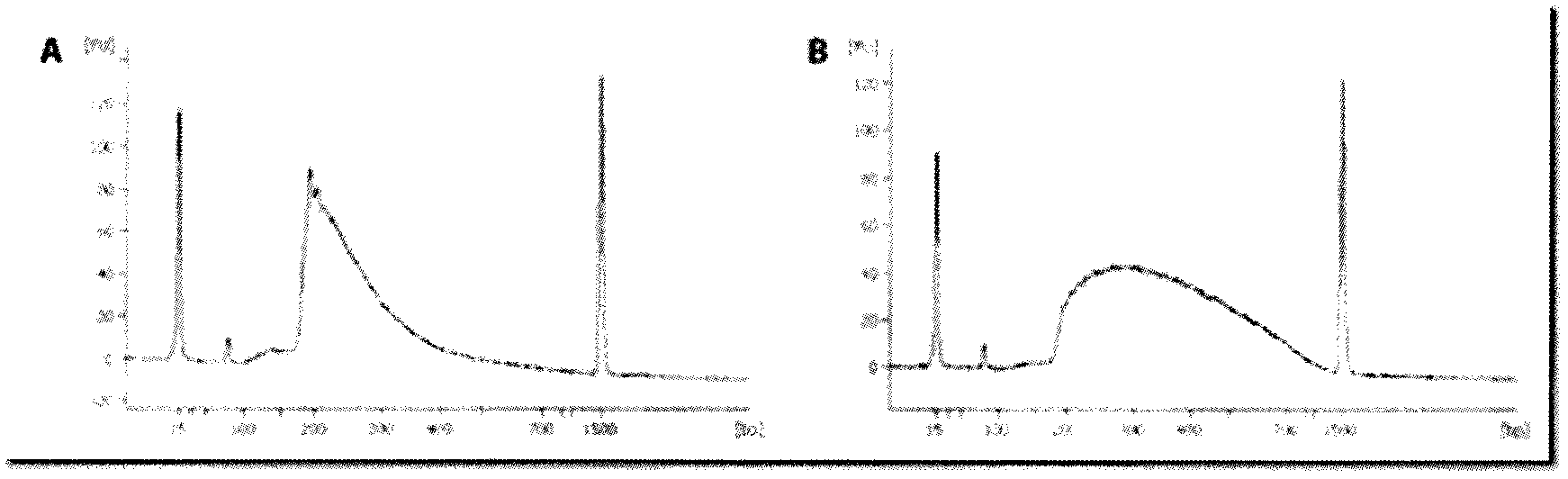
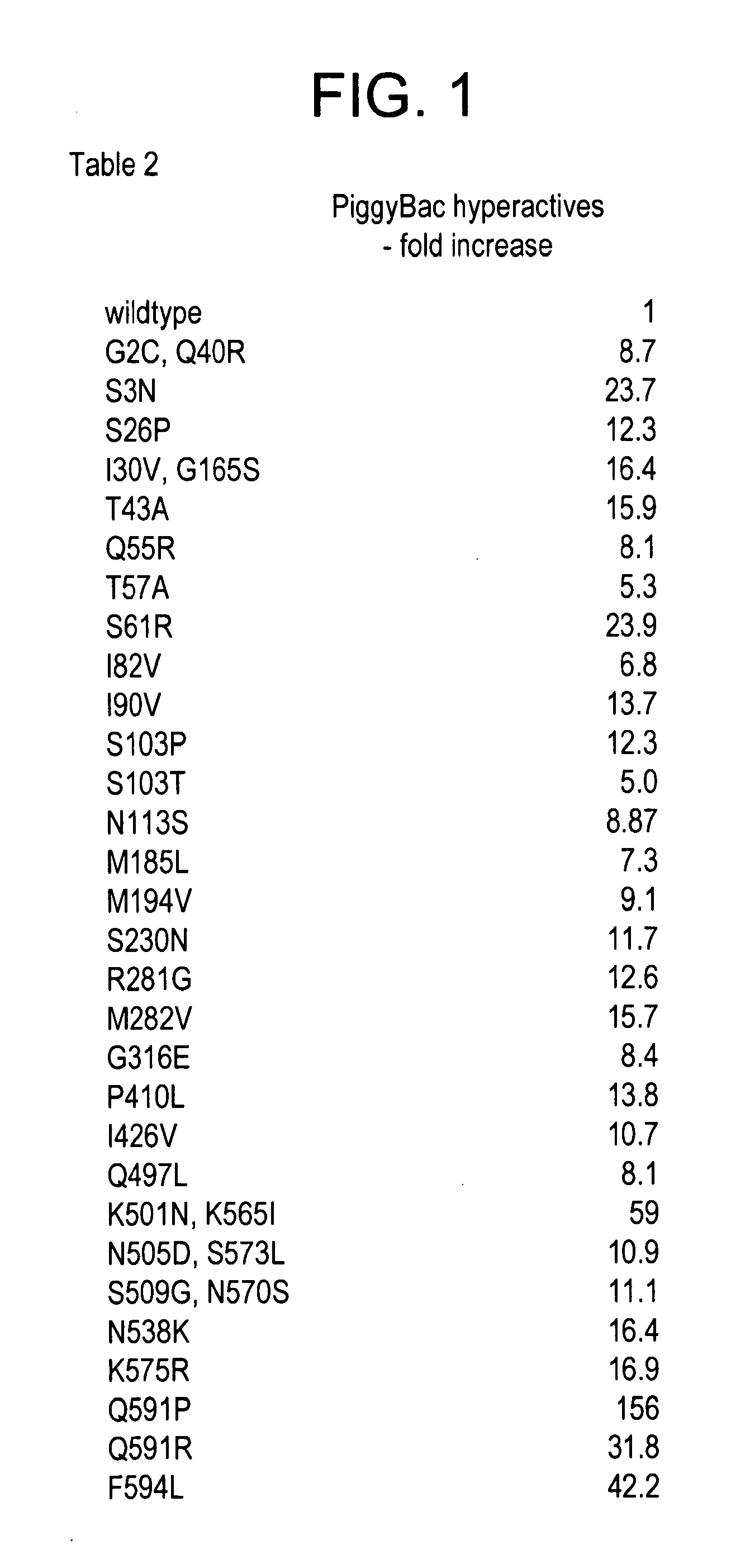
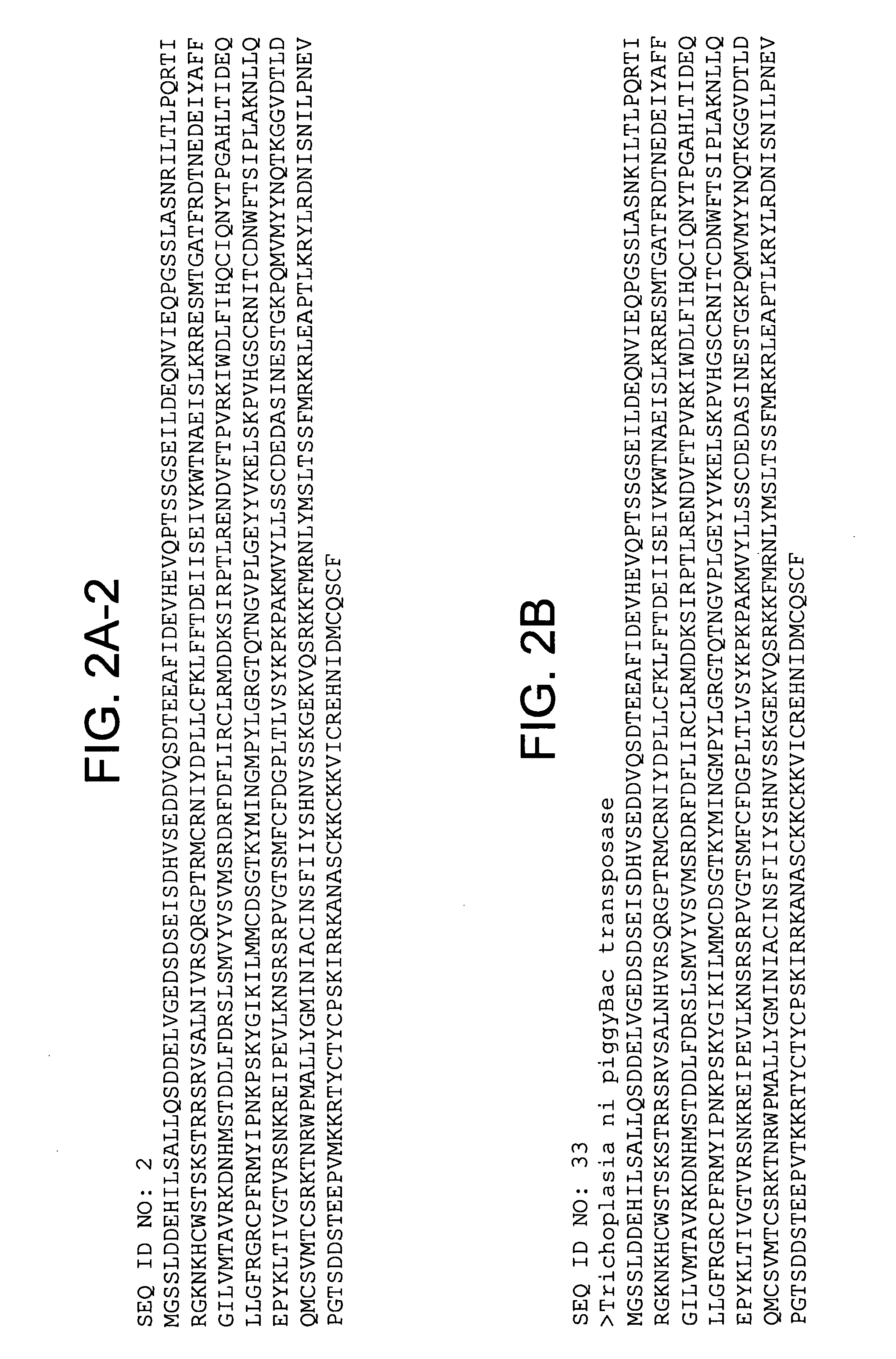
Piggybac transposon variants and methods of use
InactiveUS20110311506A1Low integration rateSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeCabbage looper
The present invention provides hyperactive piggyBac transposons, in particular hyperactive piggyBac transposons from Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper moth) that transpose at a higher frequency than wildtype. The invention also features integration defective piggyBac transposons. The piggyBac transposons and transposases can be used in gene transfer systems for stably introducing nucleic acids into the DNA of a cell. The gene transfer system can be used in methods, for example, but not limited to, gene therapy, insertional mutagenesis, or gene discovery.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Enhanced nucleic acid constructs for eukaryotic gene expression
ActiveUS9428767B2High expressionReduce interferencePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsHeterologousEukaryotic gene
The present invention provides polynucleotide vectors for high expression of heterologous genes, and methods for constructing such vectors. Some vectors further comprise novel transposons and transposases that further improve expression. Further disclosed are vectors that can be used in a gene transfer system for stably introducing nucleic acids into the DNA of a cell. The gene transfer systems can be used in methods, for example, but not limited to, gene expression, gene therapy, insertional mutagenesis, or gene discovery.
Owner:DNA2 0
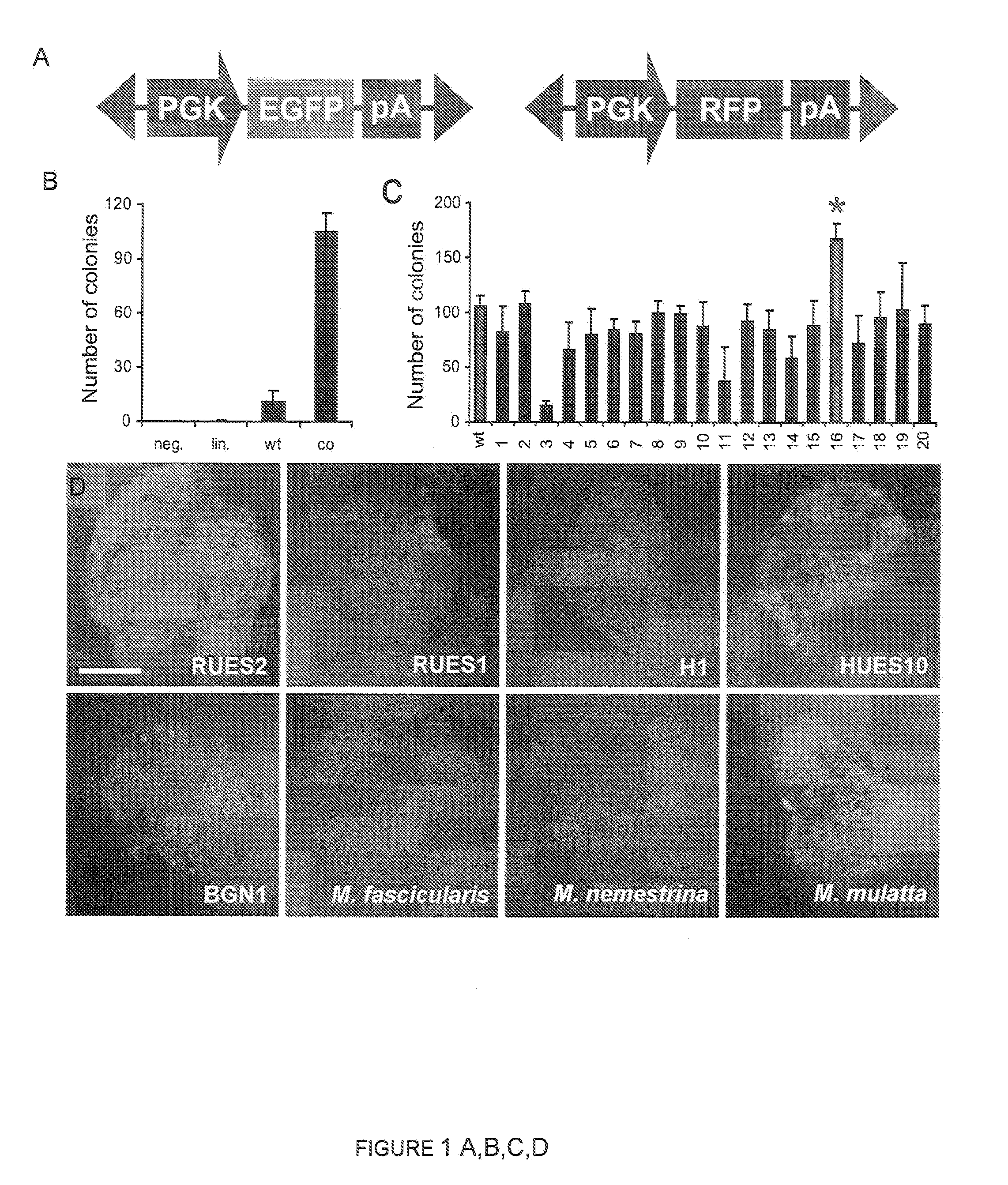
Compositions and Methods for Transposon Mutagenesis of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
InactiveUS20100240133A1Increase heightIncreased frequency of transpositionSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNATransposon mutagenesisExogenous DNA
PiggyBac transposons and transposases with enhanced transposition activity in cells are provided. Also provided are associated methods and kits for both introducing exogenous DNA inserts into the genomes of host cells as well as for the removal of the inserts from the host cell genomes. Cells obtained by use of the compositions, methods and kits are also provided.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
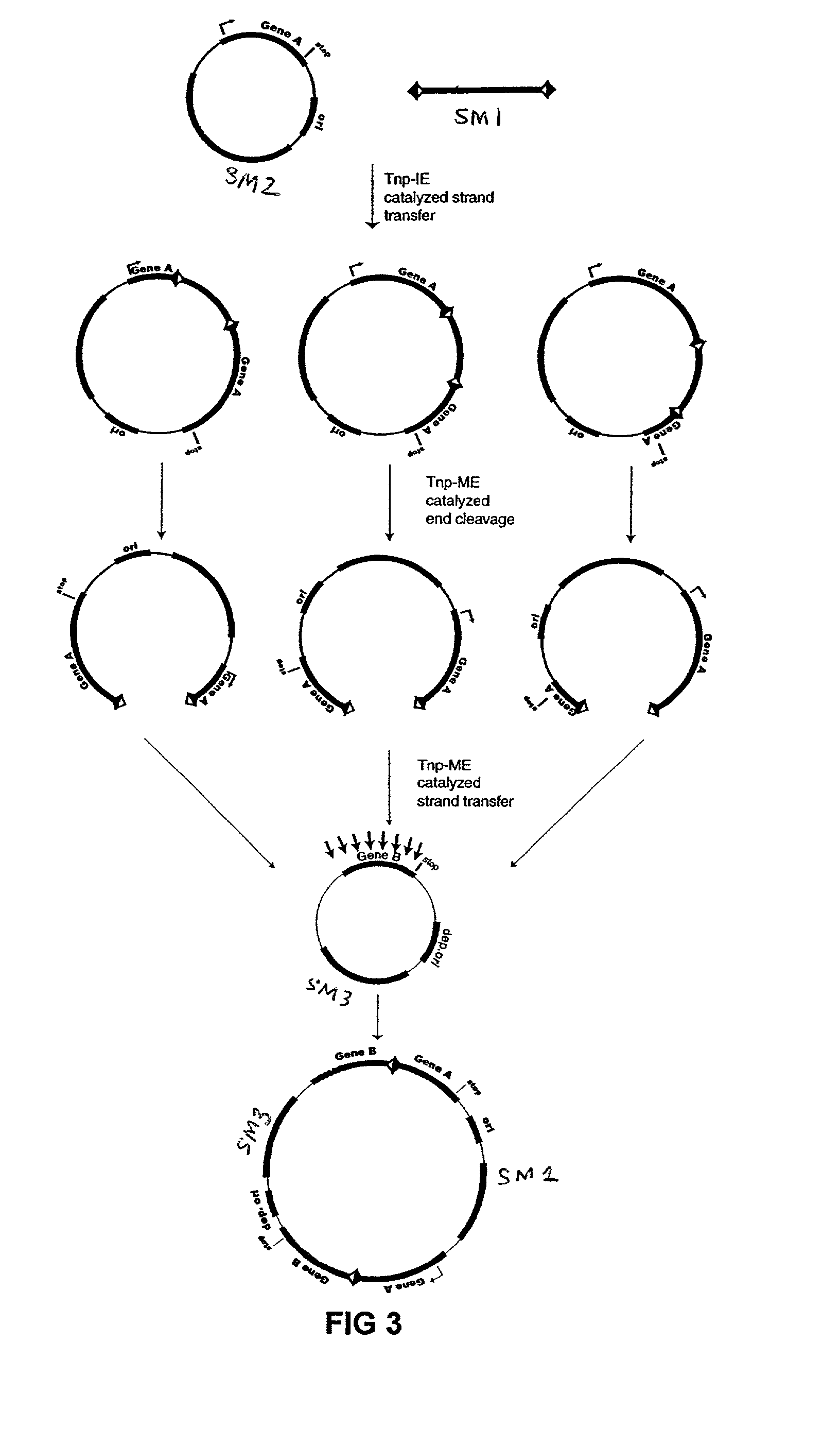
Double transposition methods for manipulating nucleic acids
InactiveUS7067644B2Increase variabilityLibrary to become largeBacteriaSugar derivativesNucleotidePolynucleotide
Methods are provided for manipulating nucleic acid to produce gene fusions, to delete or clone a portion of a chromosome, or to insert a sequence into a chromosome. The methods employ sequential transposition processes using two or more pairs of inverted repeat transposase-interacting sequences on a transposable polynucleotide wherein each pair of transposase-interacting sequences interacts with a distinct transposase enzyme.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Enhanced nucleic acid constructs for eukaryotic gene expression
InactiveUS20150291975A1High expressionReduce interferenceOrganic active ingredientsFusion with DNA-binding domainHeterologousEukaryotic gene
The present invention provides polynucleotide vectors for high expression of heterologous genes, and methods for constructing such vectors. Some vectors further comprise novel transposons and transposases that further improve expression. Further disclosed are vectors that can be used in a gene transfer system for stably introducing nucleic acids into the DNA of a cell. The gene transfer systems can be used in methods, for example, but not limited to, gene expression, gene therapy, insertional mutagenesis, or gene discovery.
Owner:DNA2 0
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com