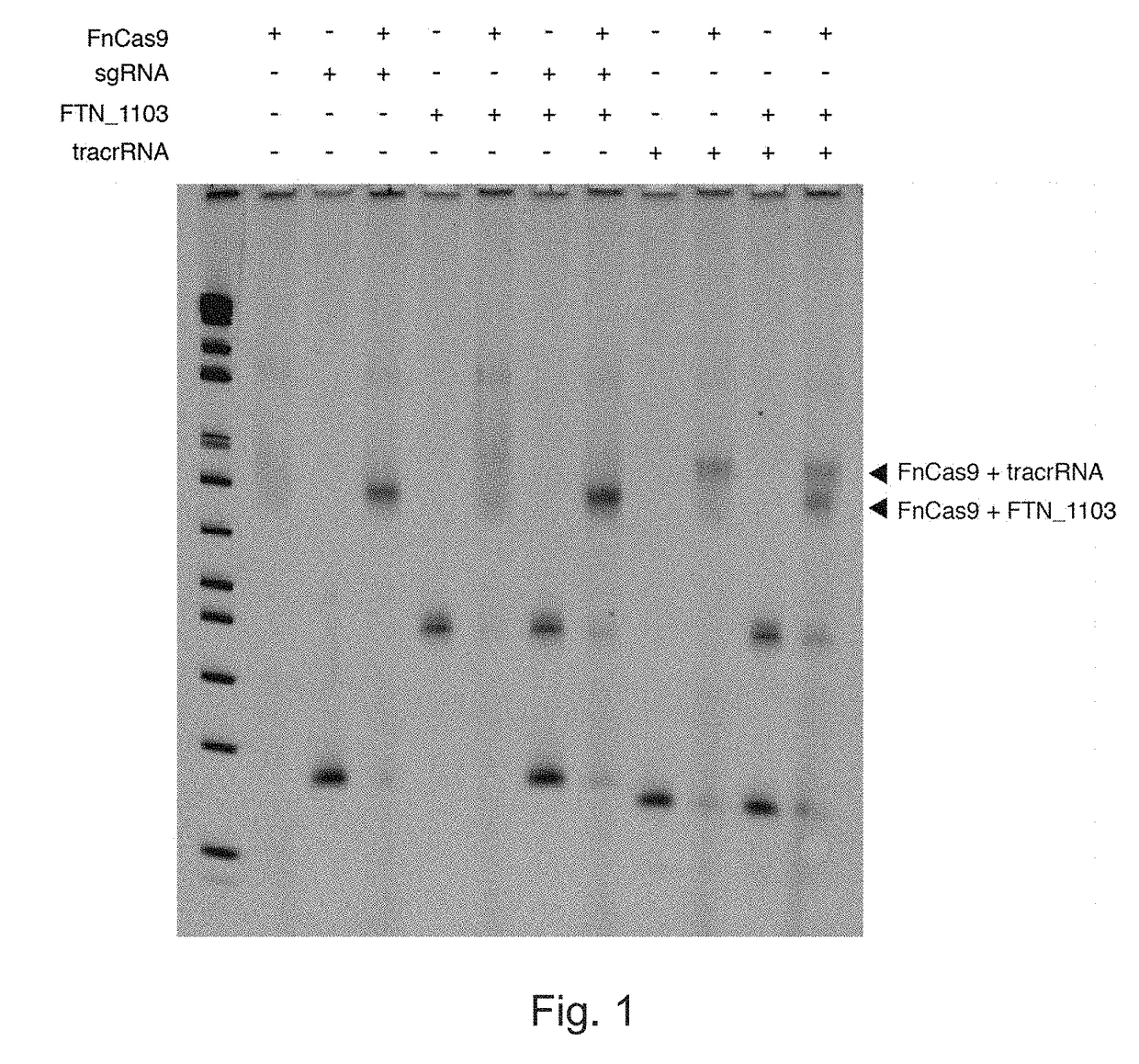
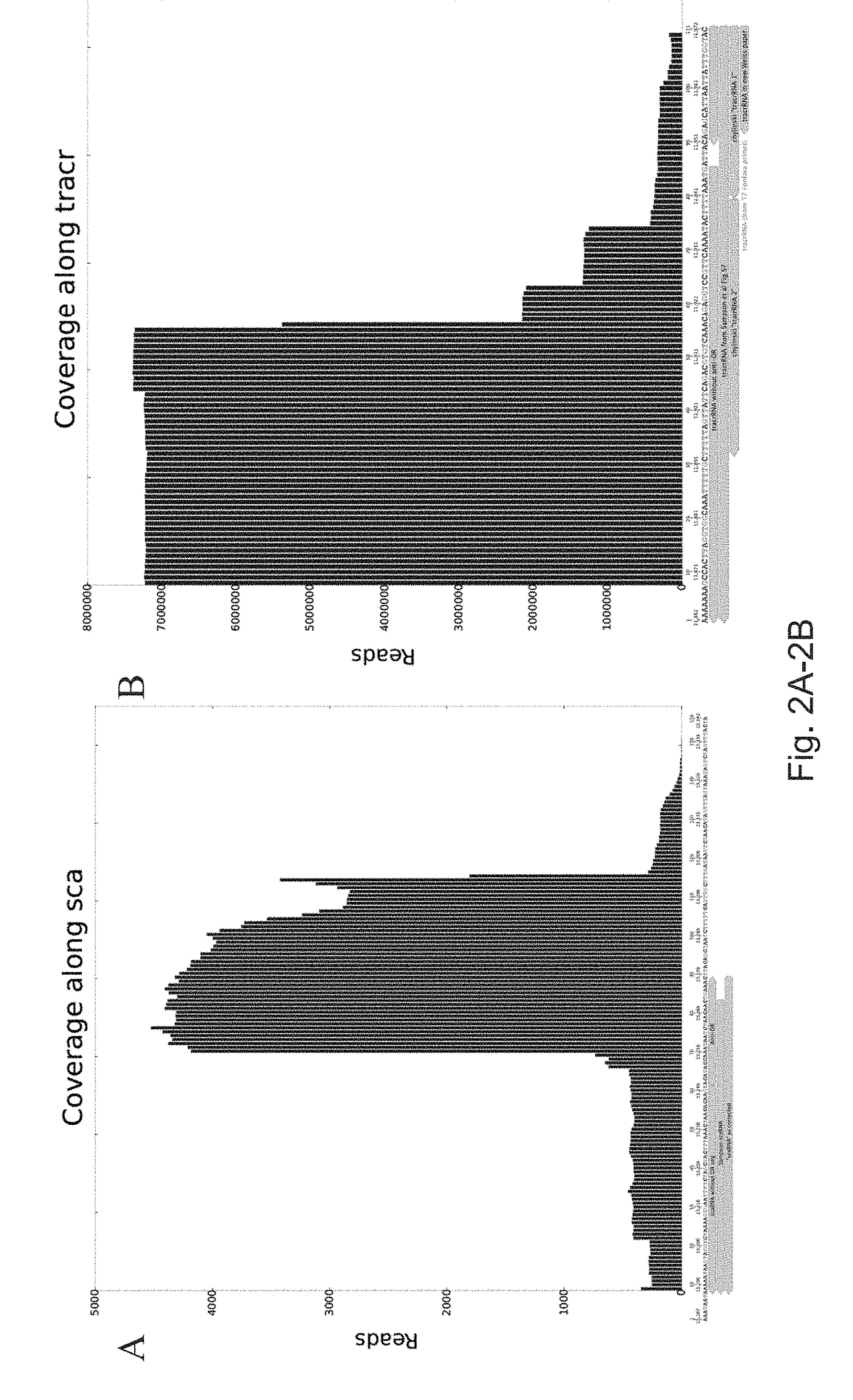
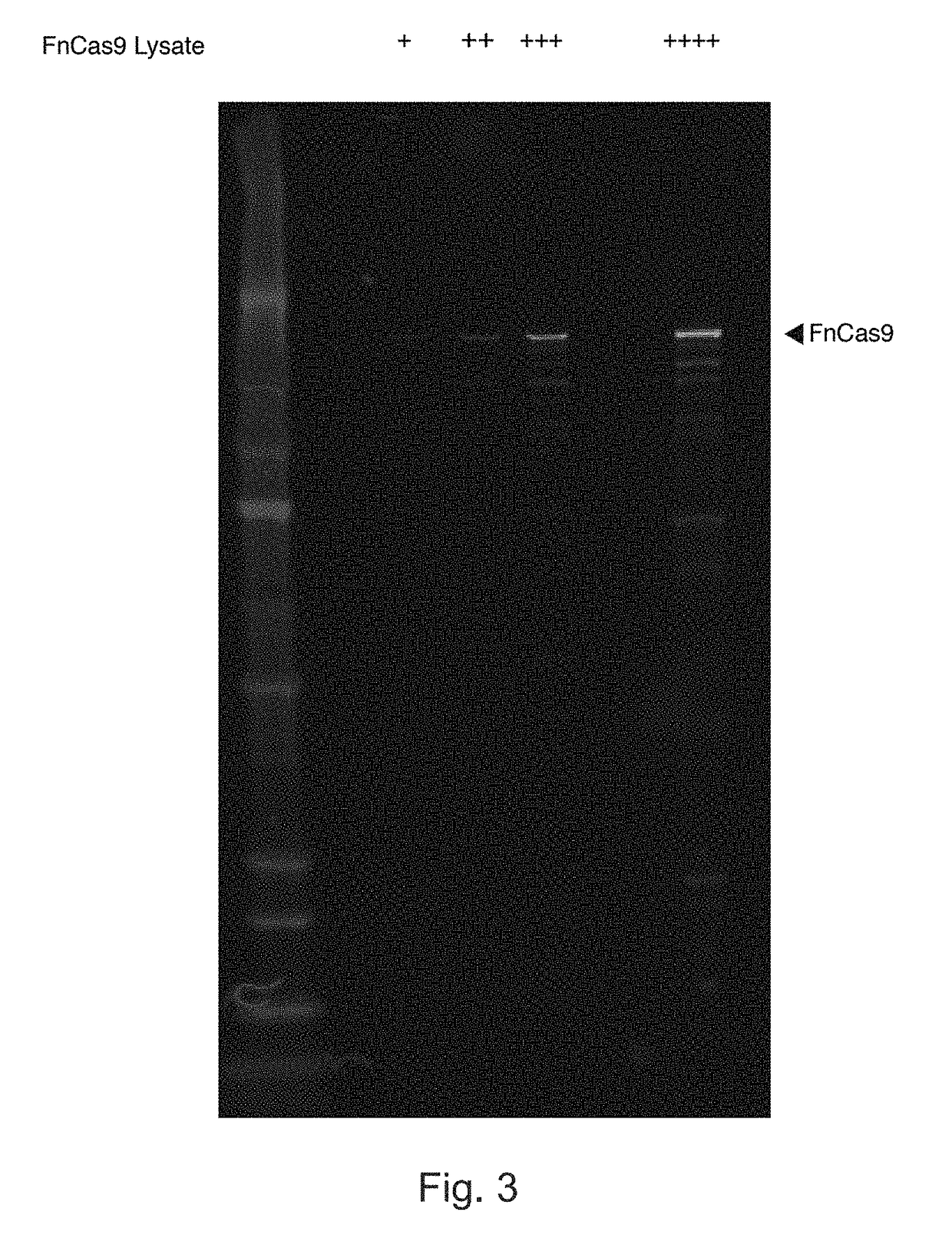
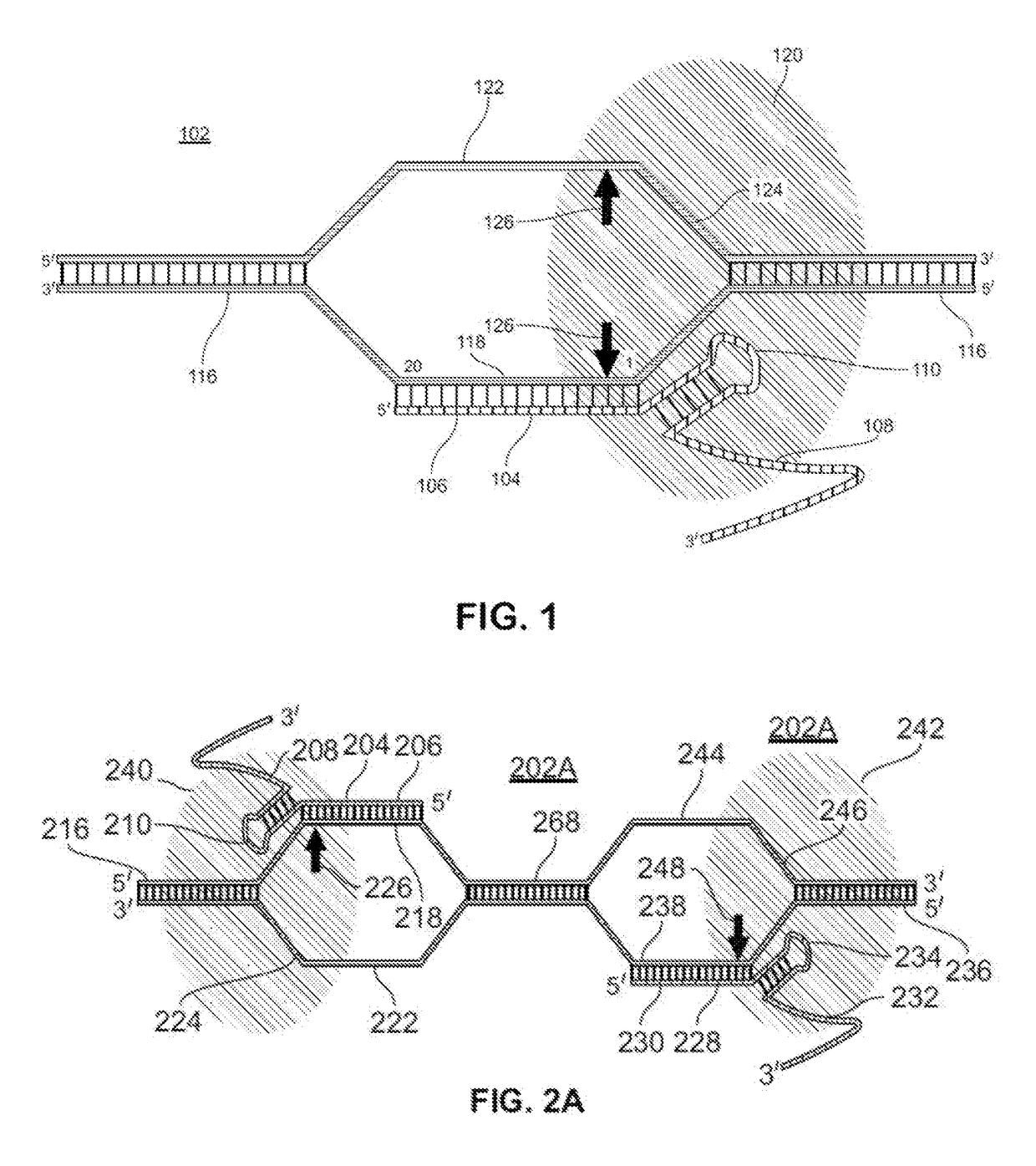
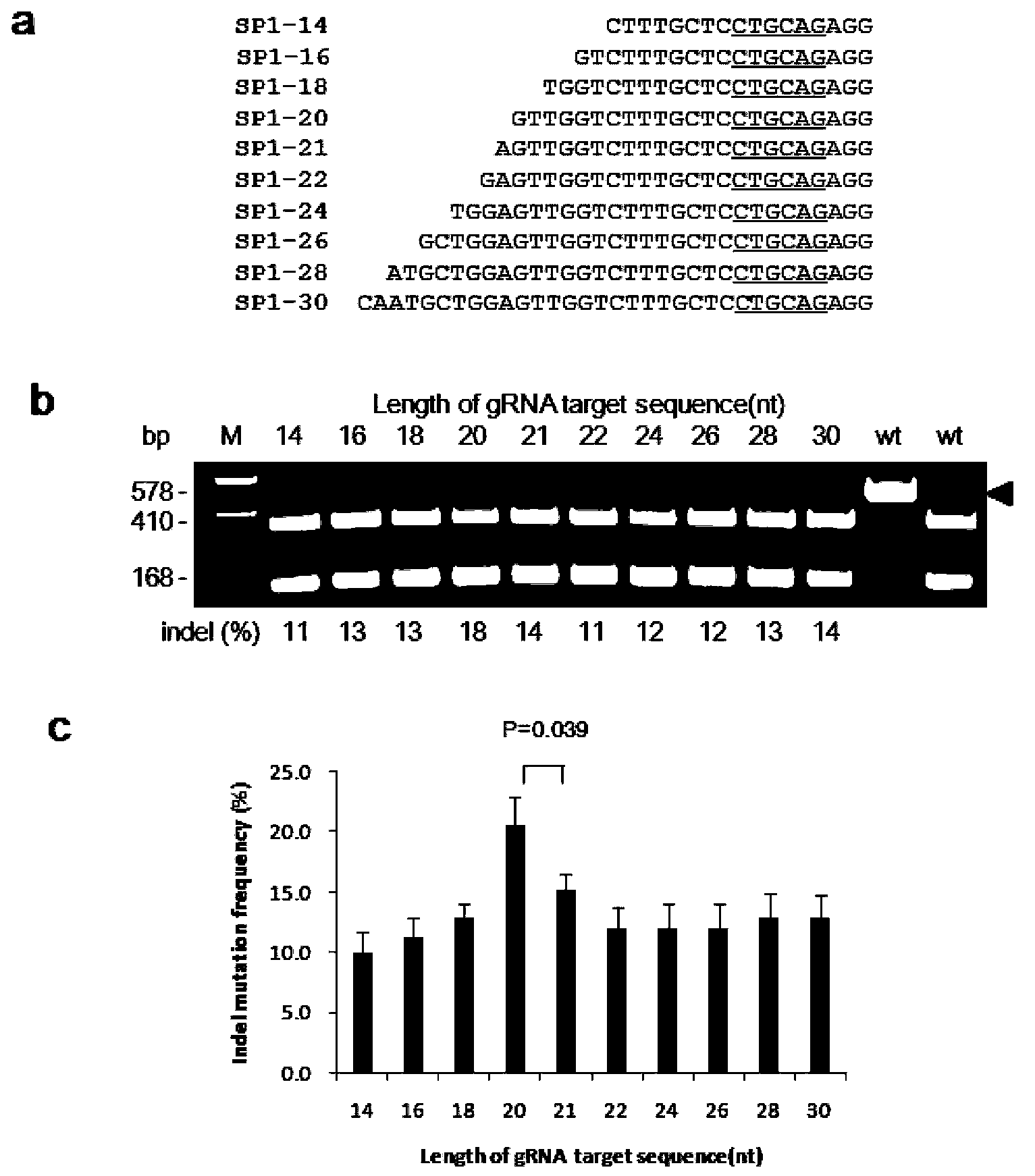
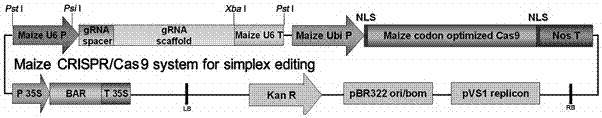
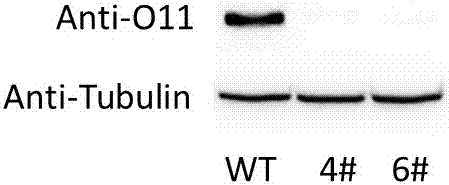
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
409 results about "Guide RNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
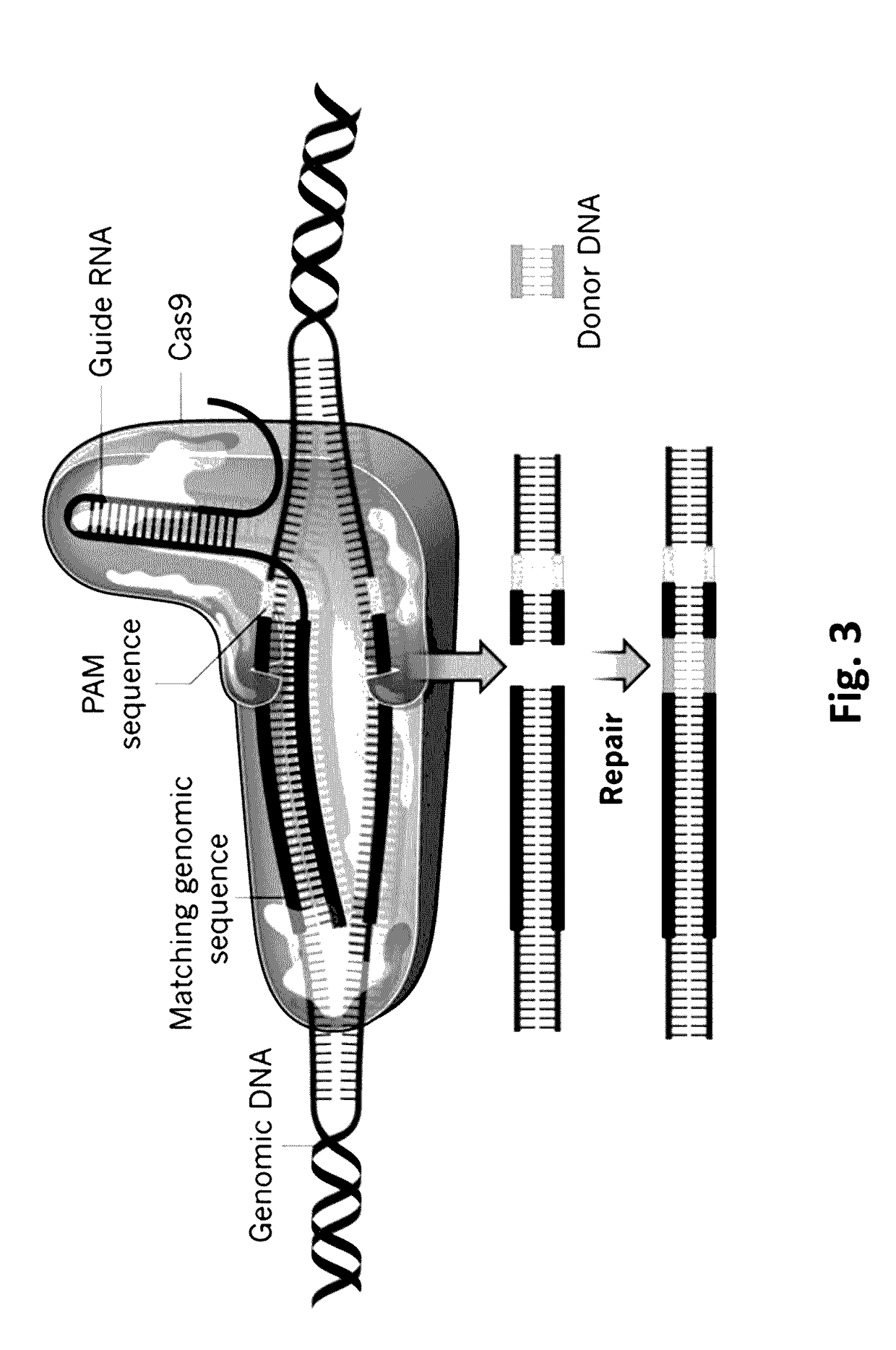
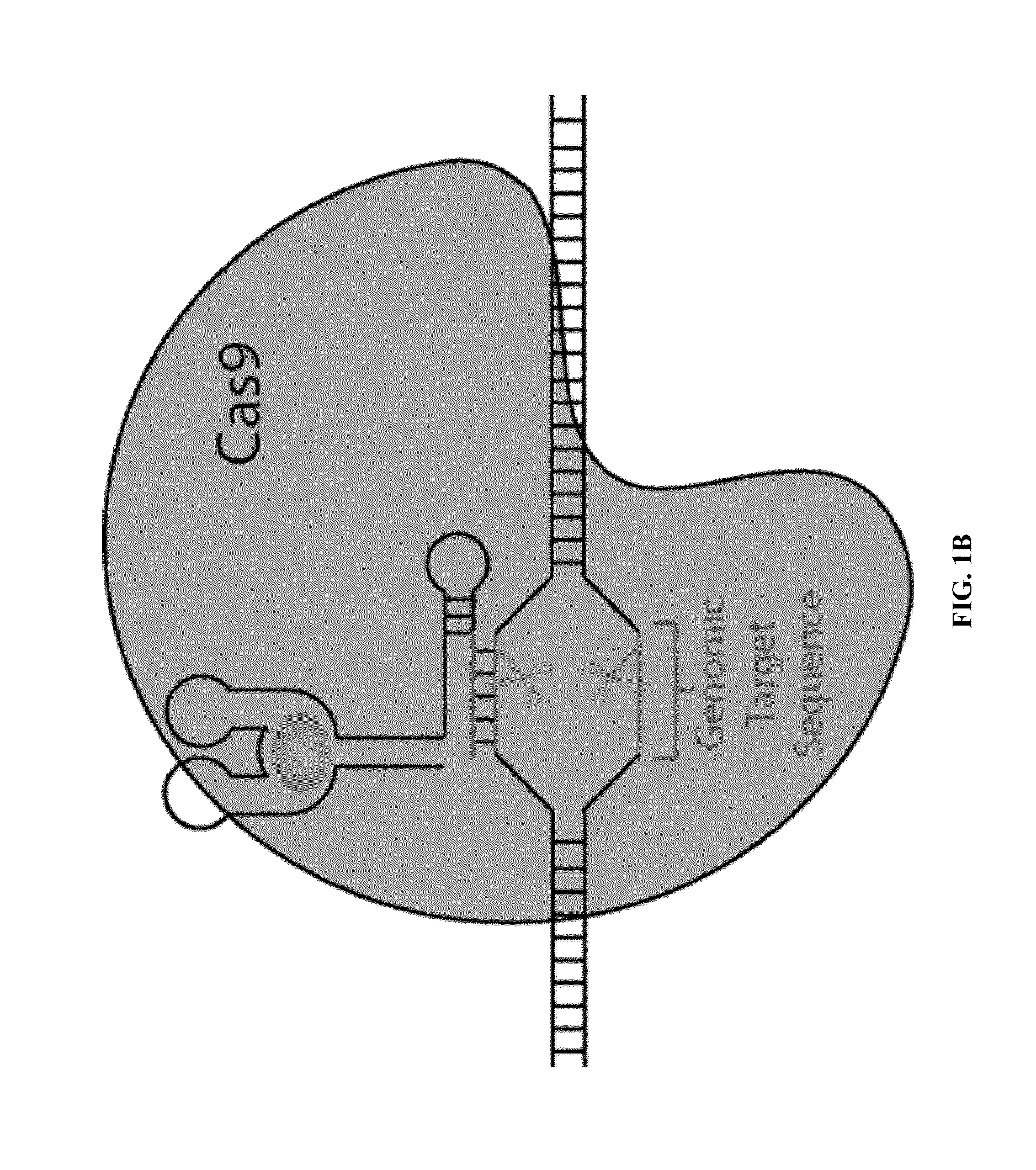
Guide RNAs (a.k.a. gRNA) are the RNAs that guide the insertion or deletion of uridine residues into mitochondrial mRNAs in kinetoplastid protists in a process known as RNA editing. The terms "guide RNA" and "gRNA" are also used in prokaryotic DNA editing involving CRISPR and Cas9.
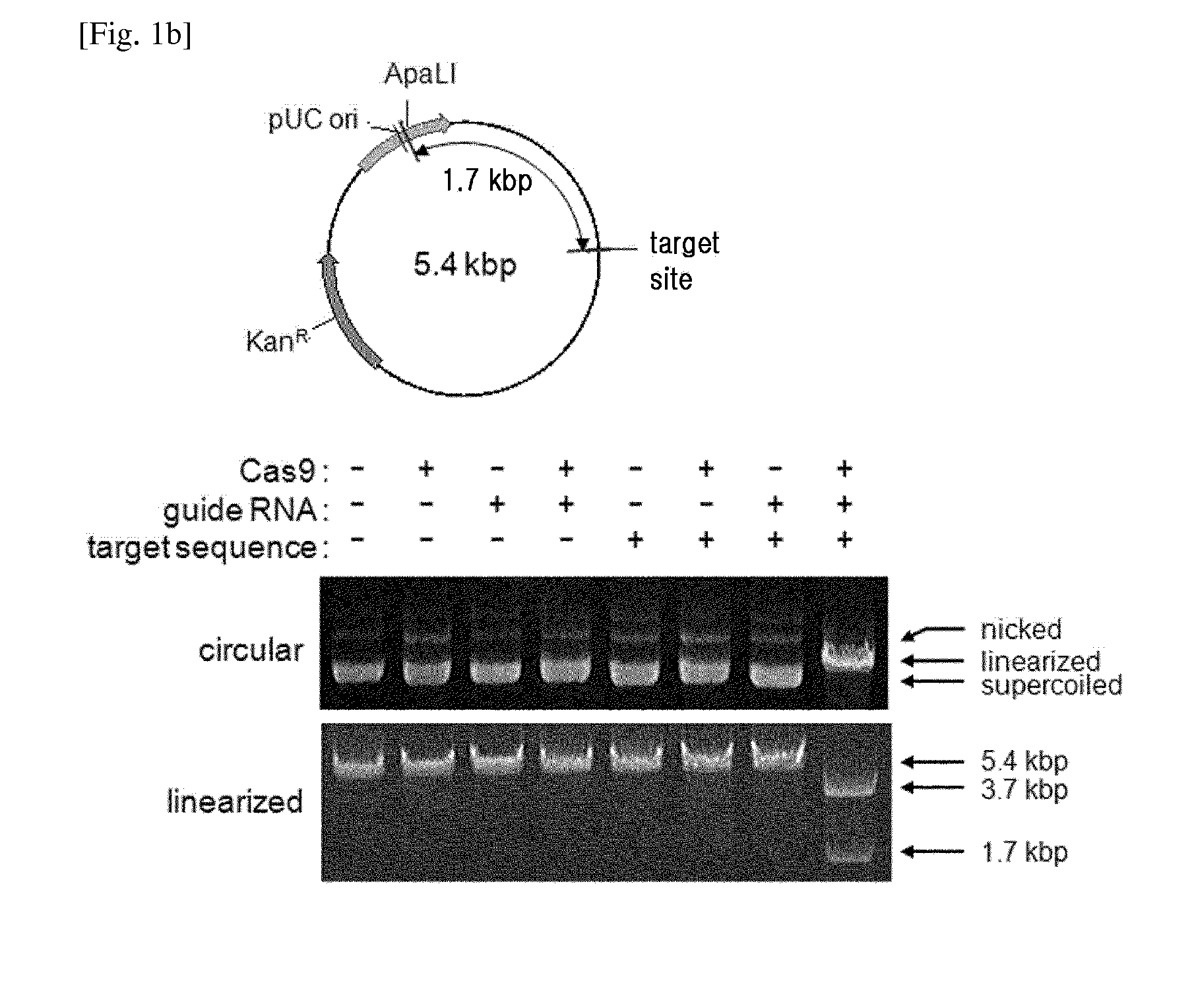
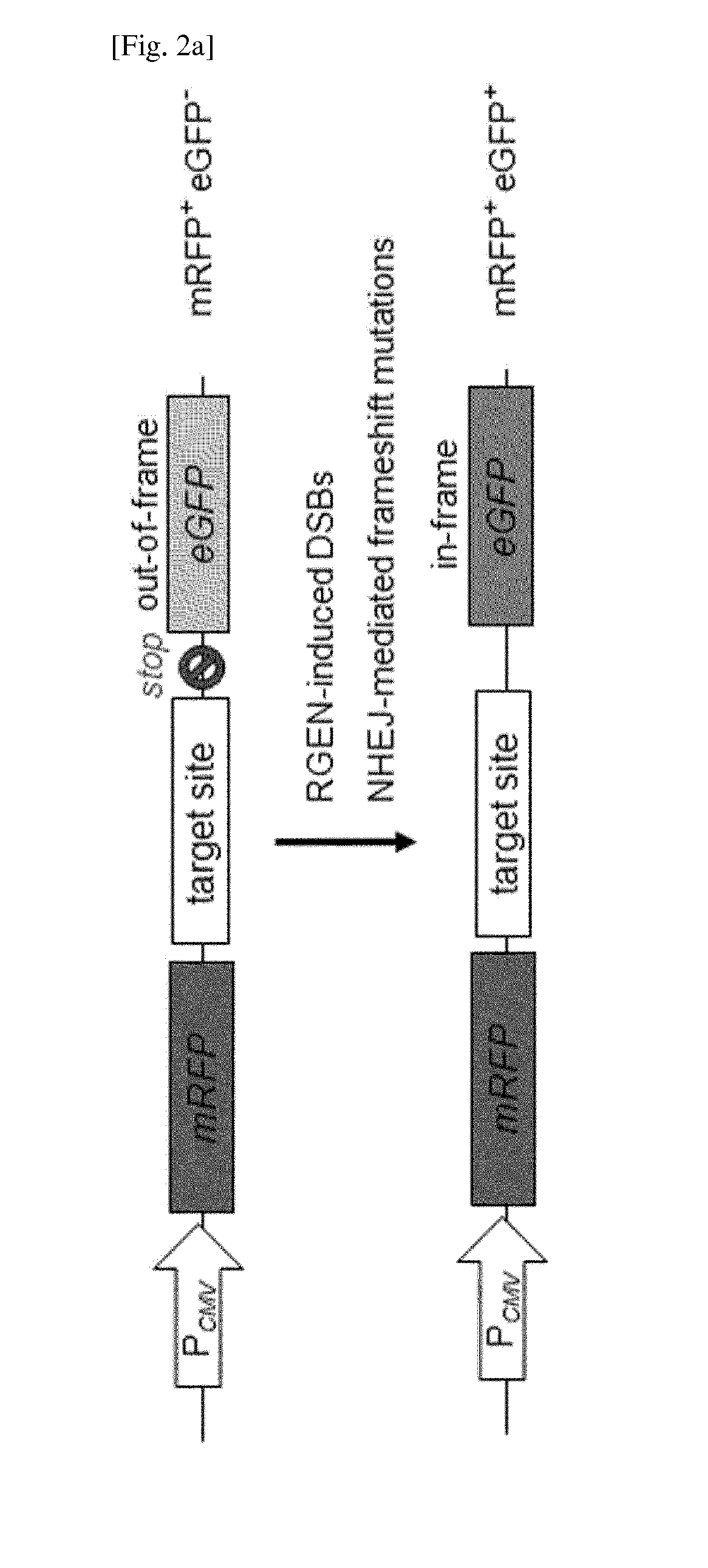
Composition for cleaving a target DNA comprising a guide RNA specific for the target DNA and cas protein-encoding nucleic acid or cas protein, and use thereof
The present invention relates to targeted genome editing in eukaryotic cells or organisms. More particularly, the present invention relates to a composition for cleaving a target DNA in eukaryotic cells or organisms comprising a guide RNA specific for the target DNA and Cas protein-encoding nucleic acid or Cas protein, and use thereof.
Owner:TOOLGEN INC
Composition for cleaving a target DNA comprising a guide RNA specific for the target DNA and cas protein-encoding nucleic acid or cas protein, and use thereof
The present invention relates to targeted genome editing in eukaryotic cells or organisms. More particularly, the present invention relates to a composition for cleaving a target DNA in eukaryotic cells or organisms comprising a guide RNA specific for the target DNA and Cas protein-encoding nucleic acid or Cas protein, and use thereof.
Owner:TOOLGEN INC
Method for human PD1 gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) and sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting PD1 gene
ActiveCN103820454APermanent effectEffective research and developmentVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic engineeringBioinformatics
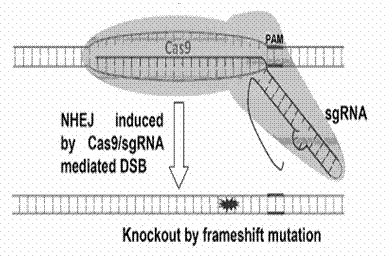
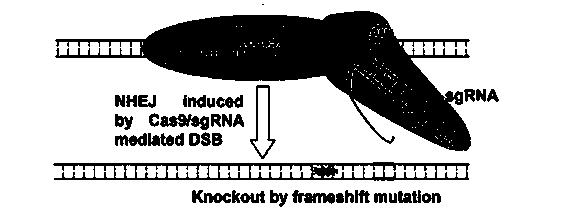
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, particularly relates to a method for human PD1 gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) and sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting a PD1 gene, and provides a method for human PD1 gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA(single guide RNA) for specially targeting a PD1 gene. The sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting a human PD1 gene, prepared through adopting the method provided by the invention, can be used for accurately targeting the human PD1 gene and realizes gene knockout; the preparing method has simple steps, the targeting performance of the sgRNA is good, and the knockout efficiency of a CRISPR-Cas9 system is high.
Owner:AOMIAO BIOTECH GUANGZHOU CO LTD
Methods and compositions for the production of guide RNA
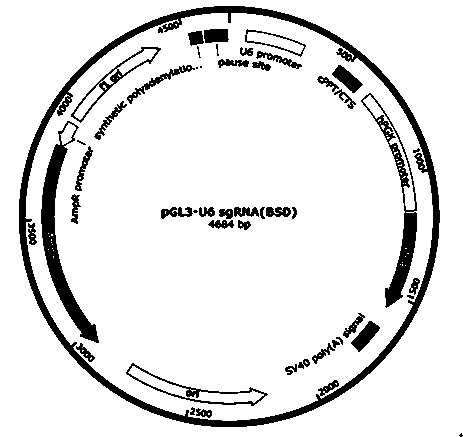
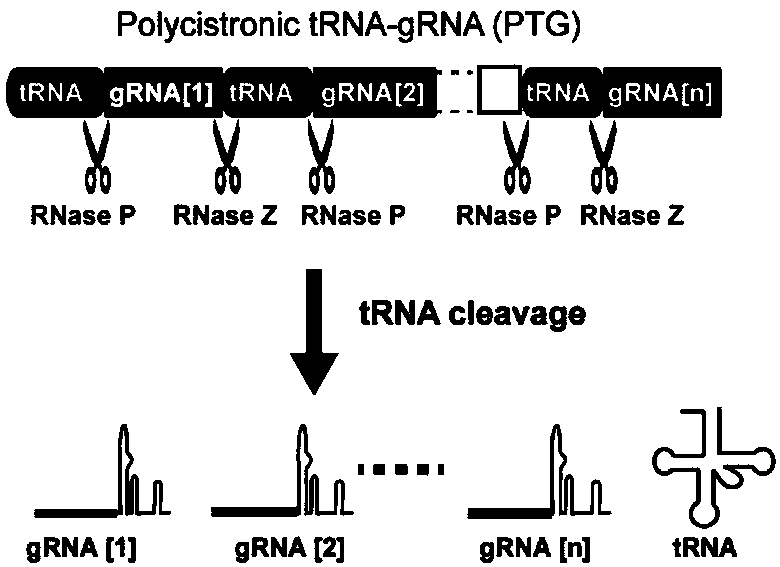
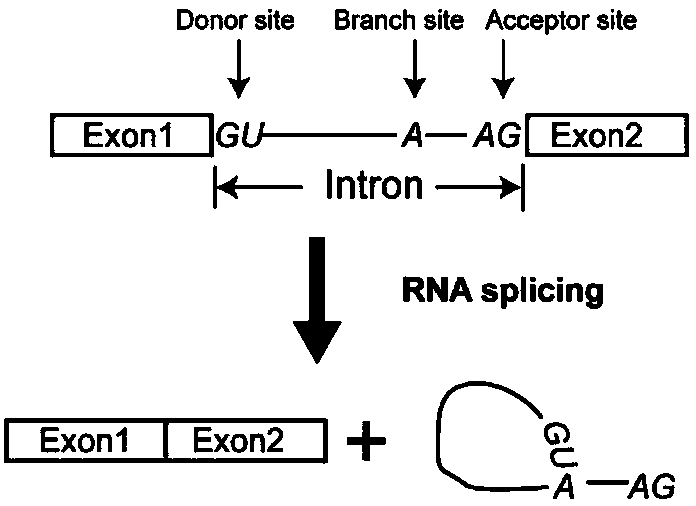
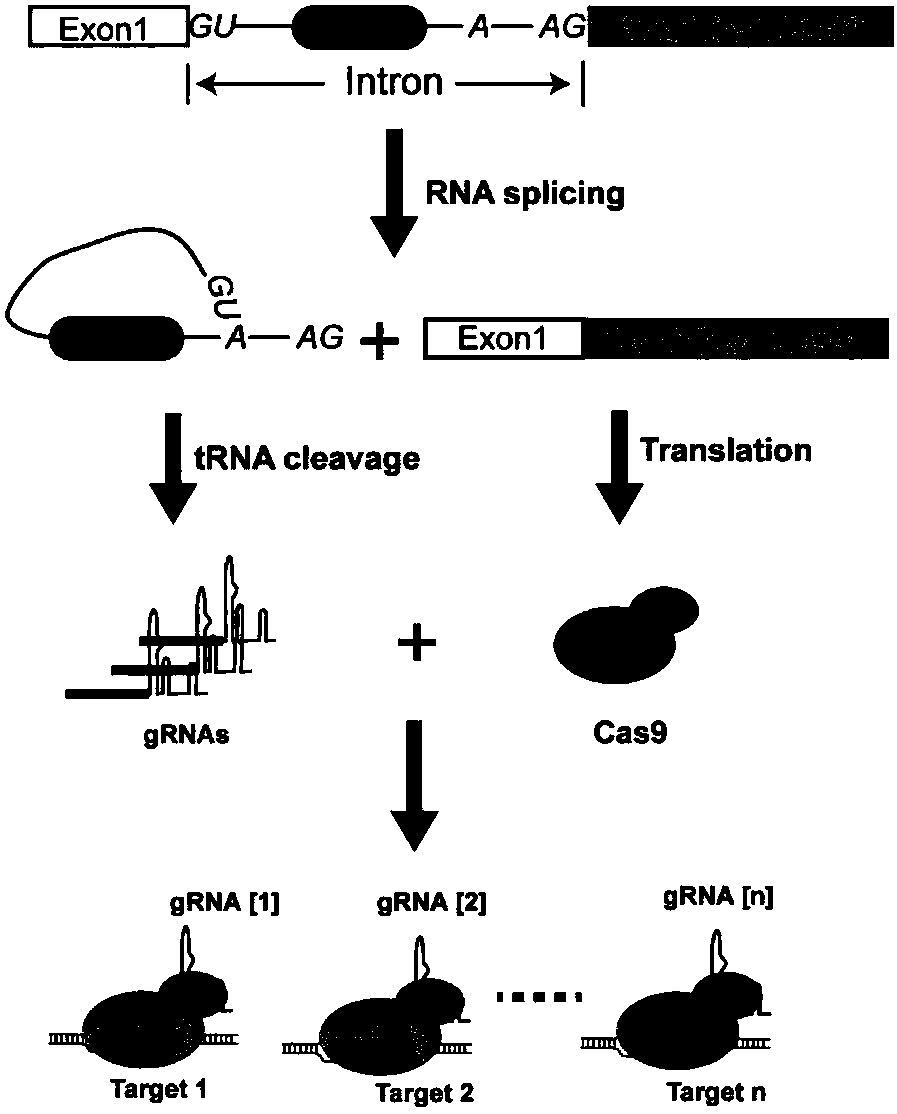
Various aspects and embodiments of the present disclosure relate to methods and compositions that combine multiple mammalian RNA regulatory strategies, including RNA triple helix structures, introns, microRNAs, and ribozymes with Cas-based CRISPR transcription factors and ribonuclease-based RNA processing in human cells. The methods and compositions of the present disclosure, in some embodiments, enable multiplexed production of proteins and multiple guide RNAs from a single compact RNA-polymerase-II-expressed transcript for efficient modulation of synthetic constructs and endogenous human promoters.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
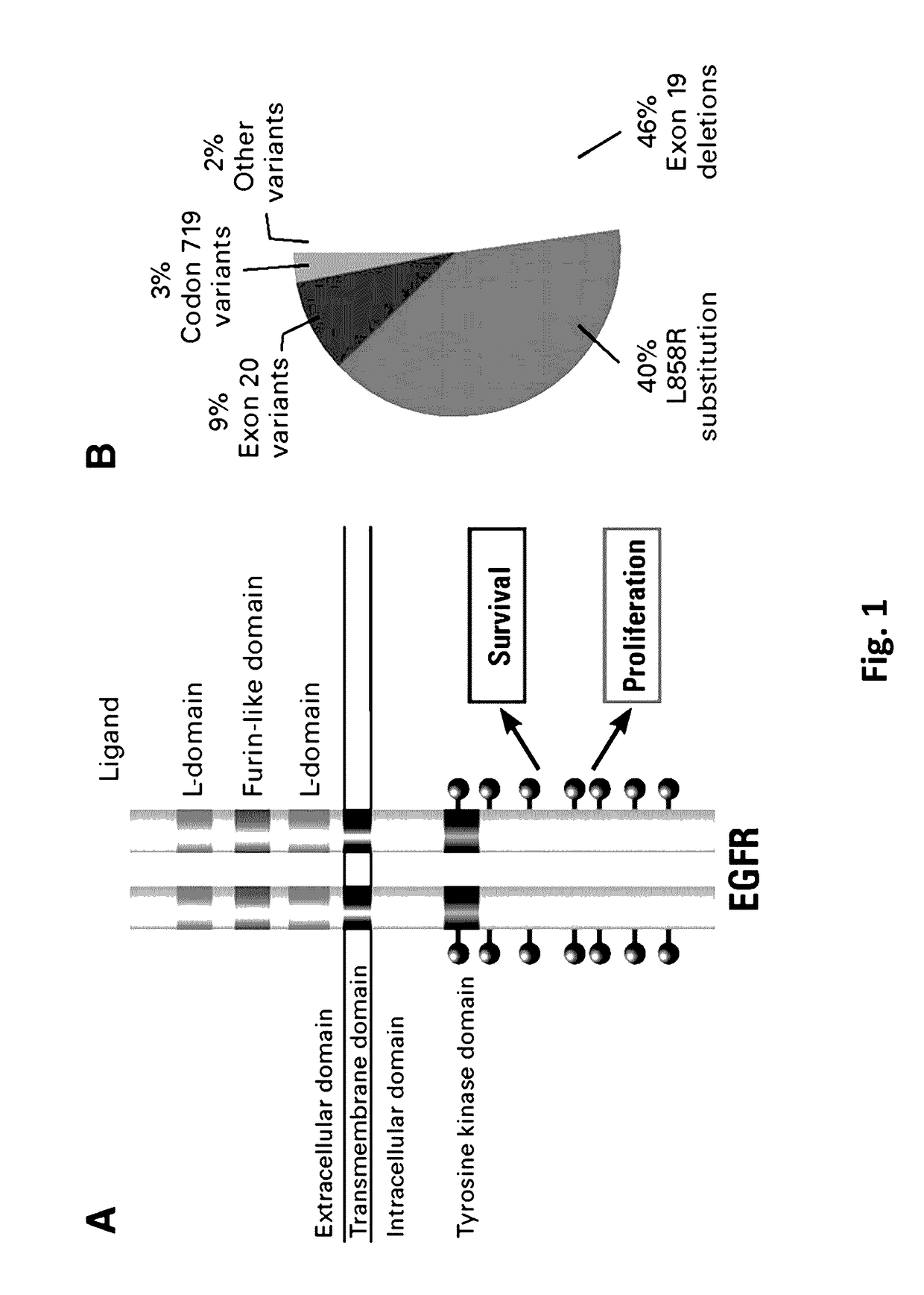
Crispr/cas-mediated genome editing to treat egfr-mutant lung cancer
The invention relates to a clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) / Cas guide RNA (gRNA) comprising a targeting domain that is complementary to human genomic Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) DNA, and a vector system including one or more packaged vector(s) including: (a) a first regulatory element operably linked to a gRNA, and (b) a second regulatory element operably linked to a nucleic acid encoding a Cas protein. Also disclosed are methods of altering a nucleic acid sequence encoding EGFR in a cell including contacting the cell with a vector system, methods of treating lung cancer, and methods of selectively inducing apoptosis in a cell including administering a gRNA to the cell.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
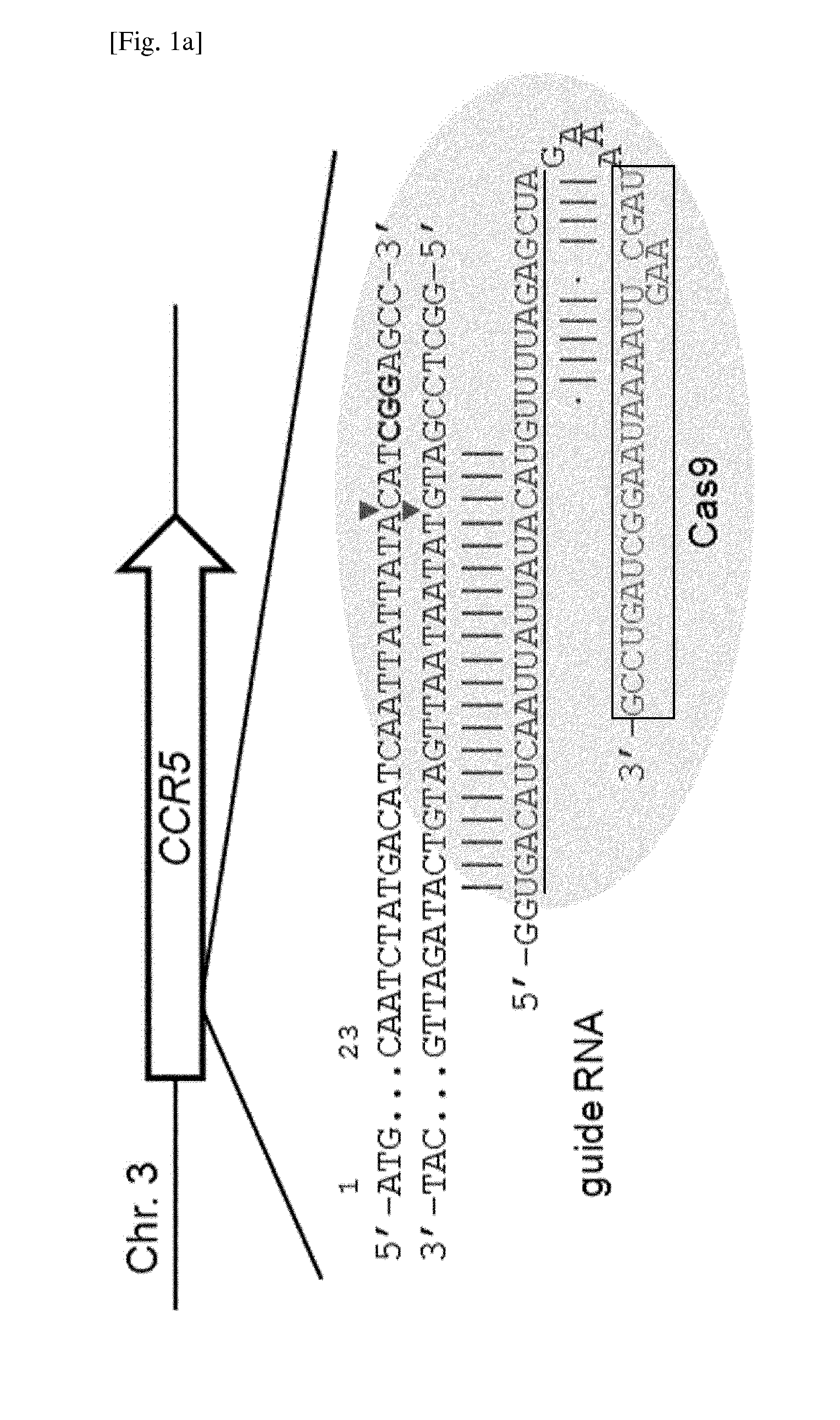
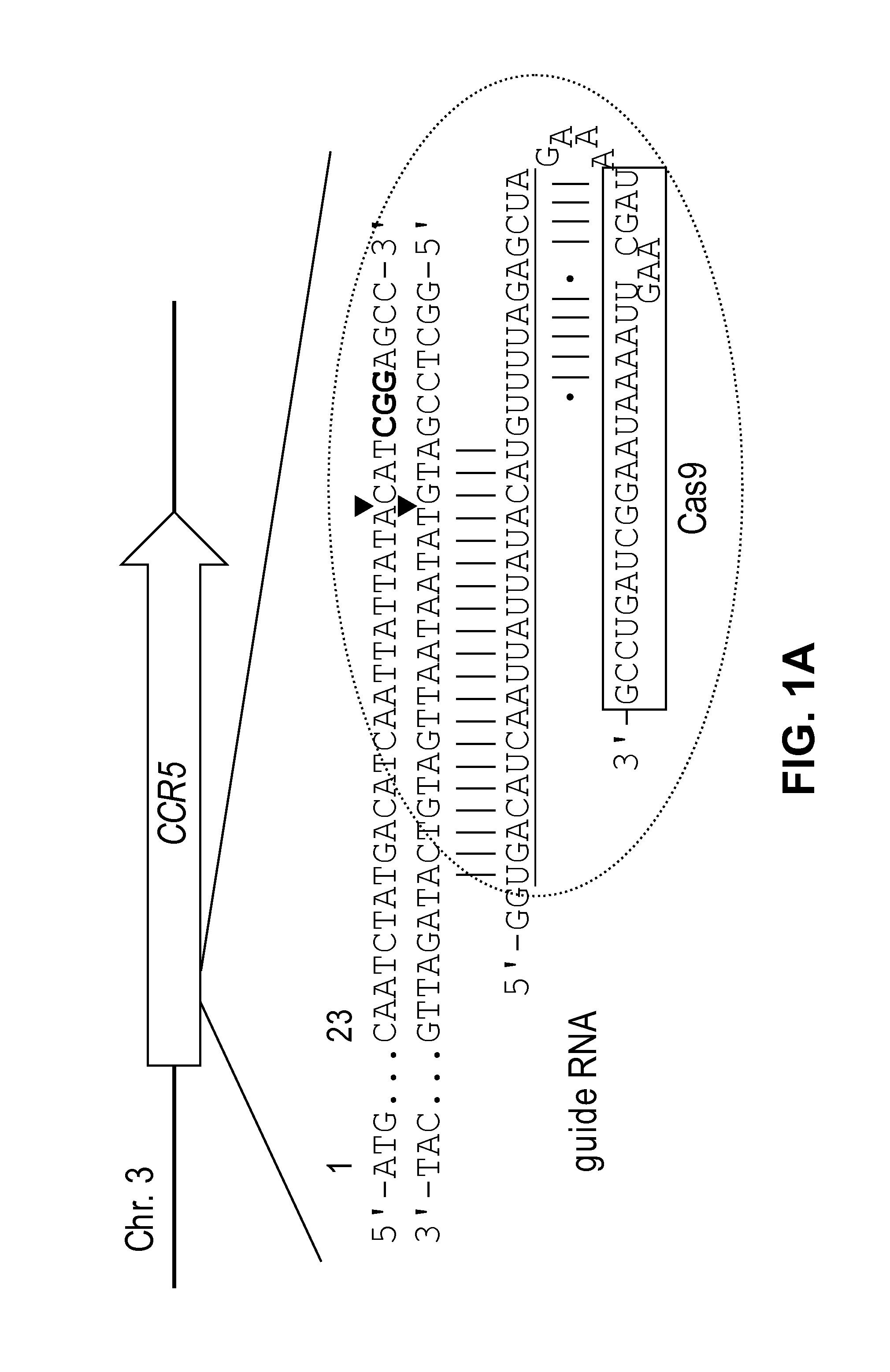
Method for specifically knocking out human CCR5 (Chemokine Receptor 5) gene by CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat-associated)-Cas 9 and SgRNA (single guide RNA) for specifically targeting CCR5 gene
ActiveCN103923911AKnockout efficiency is lowImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic engineeringGuide RNA
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and particularly relates to a method for specifically knocking out a human CCR5 (Chemokine Receptor 5) gene by CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat-associated)-Cas 9 and SgRNA (single guide RNA) for specifically targeting the CCR5 gene as well as an intermediate carrier and application thereof. The sgRNA for specifically targeting the human CCR5 gene, prepared by the method disclosed by the invention, can be used for accurately targeting the human CCR5 gene and realizing gene knockout. The preparation method is simple in steps and good in sgRNA targeting property; the knockout efficiency of a CRISPR-Cas 9 system is high.
Owner:AOMIAO BIOTECH GUANGZHOU CO LTD
Method for human CTLA4 gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) and sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting CTLA4 gene
ActiveCN103820441APermanent effectEffective research and developmentVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic engineeringCTLA4 Gene
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, particularly relates to a method for human CTLA4 gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) and sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting a CTLA4 gene, and provides a method for human CTLA4 gene specific knockout through CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting a CTLA4 gene. The sgRNA(single guide RNA)for specially targeting a human CTLA4 gene, prepared through adopting the method provided by the invention, can be used for accurately targeting the human CTLA4 gene and realizes gene knockout; the preparing method has simple steps, the targeting performance of the sgRNA is good, and the knockout efficiency of a CRISPR-Cas9 system is high.
Owner:AOMIAO BIOTECH GUANGZHOU CO LTD
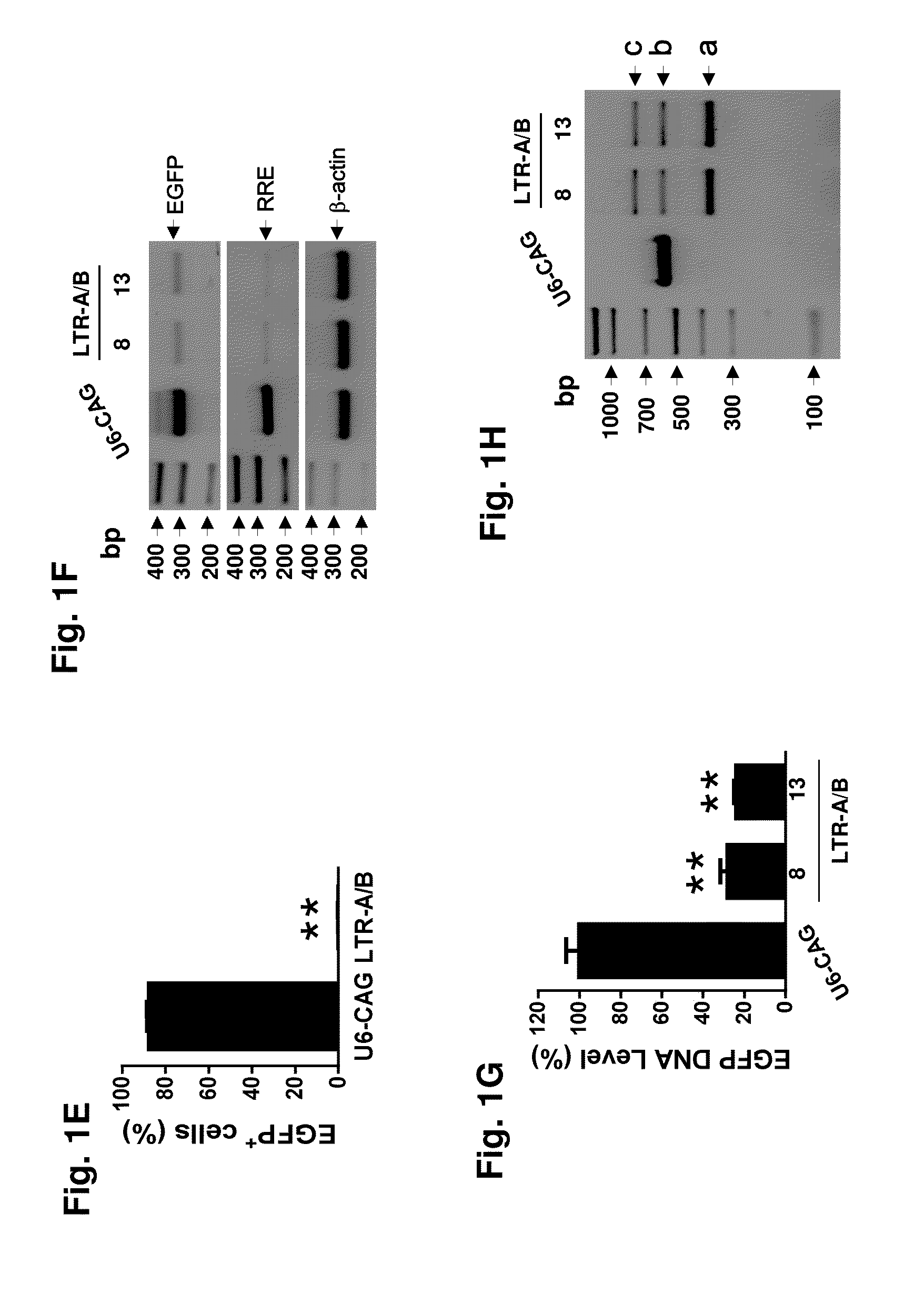
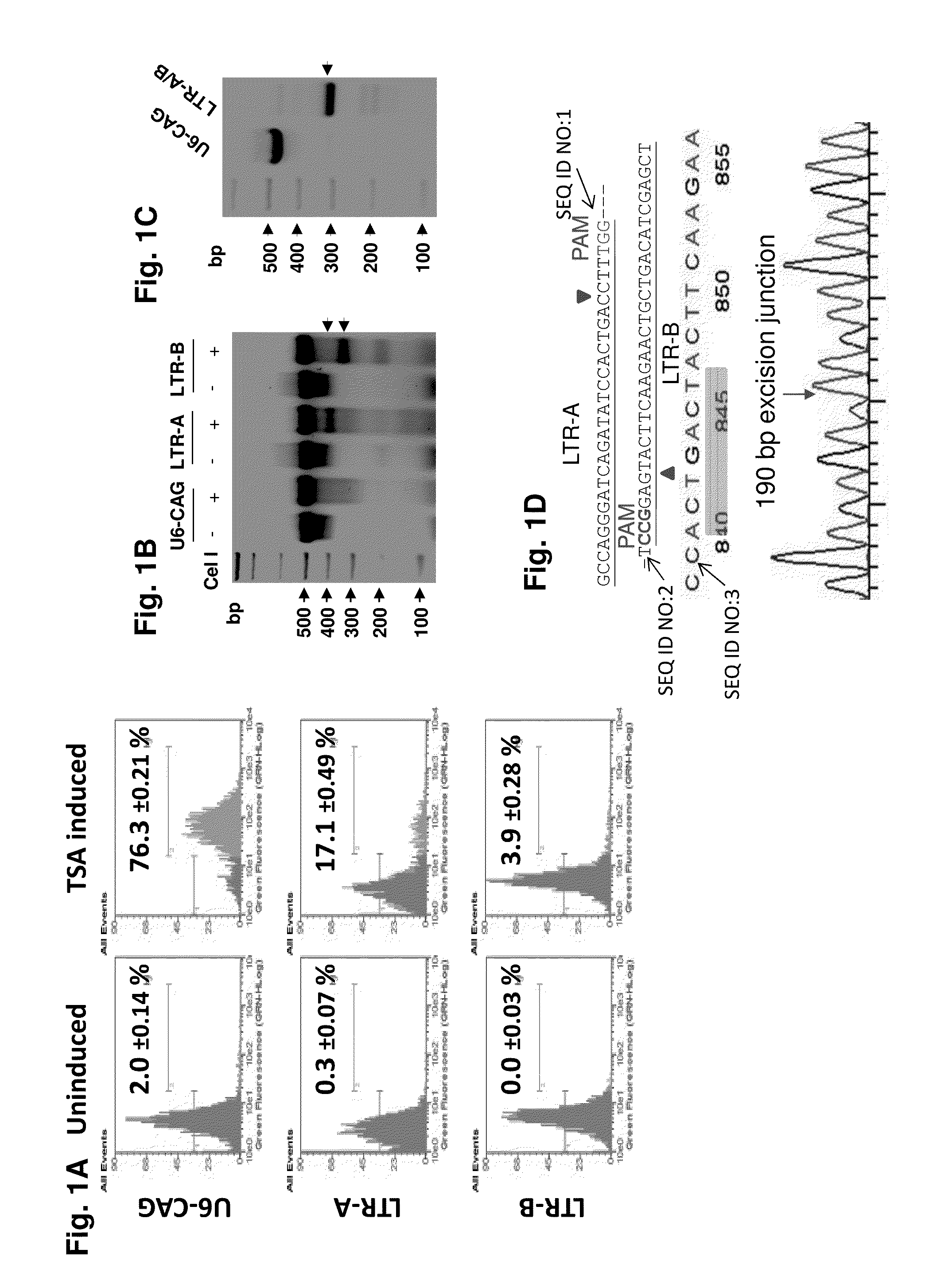
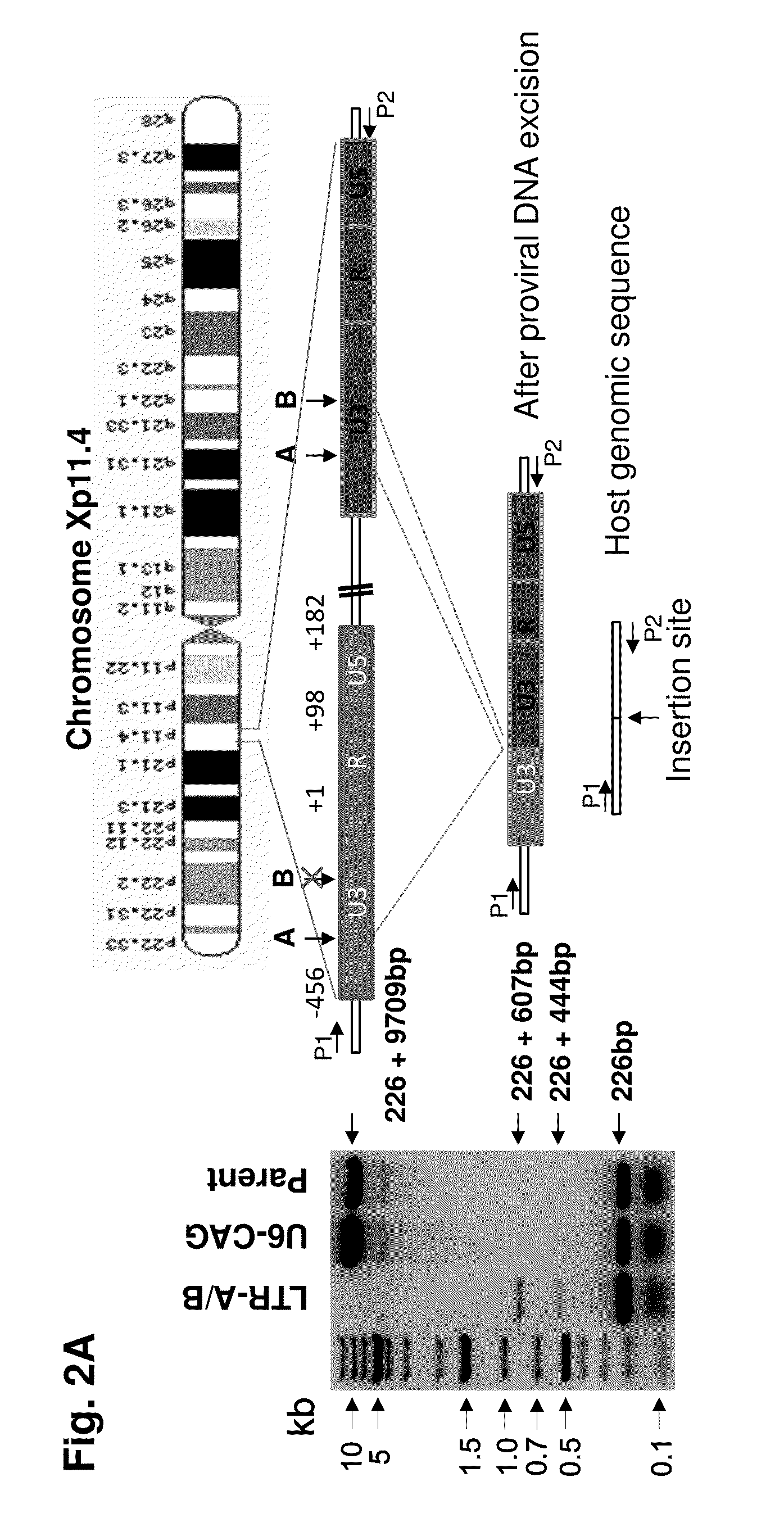
Methods and compositions for rna-guided treatment of HIV infection
A method of inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus by treating the host cell with a composition comprising a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)-associated endonuclease, and two or more different guide RNAs (gRNAs), wherein each of the at least two gRNAs is complementary to a different target nucleic acid sequence in a long terminal repeat (LTR) in the proviral DNA, and inactivating the proviral DNA. A composition for use in inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus including isolated nucleic acid sequences comprising a CRISPR-associated endonuclease and a guide RNA, wherein the guide RNA is complementary to a target sequence in a human immunodeficiency virus.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Compounds and methods for crispr/cas-based genome editing by homologous recombination
The present invention relates to guide RNAs comprising adaptor segments having one or more modifications, and their use in homologous recombination by CRISPR:Cas systems. The modified adaptor segments are resistant to degradation by RNaseH. The present invention also relates to a dual guide RNA strategy in which a first guide RNA directs a Cas enzyme to make a double-strand break at a first target sequence, and a second guide RNA comprises an adaptor segment attached to a donor polynucleotide, and binds a second target sequence that is offset from the first target sequence.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
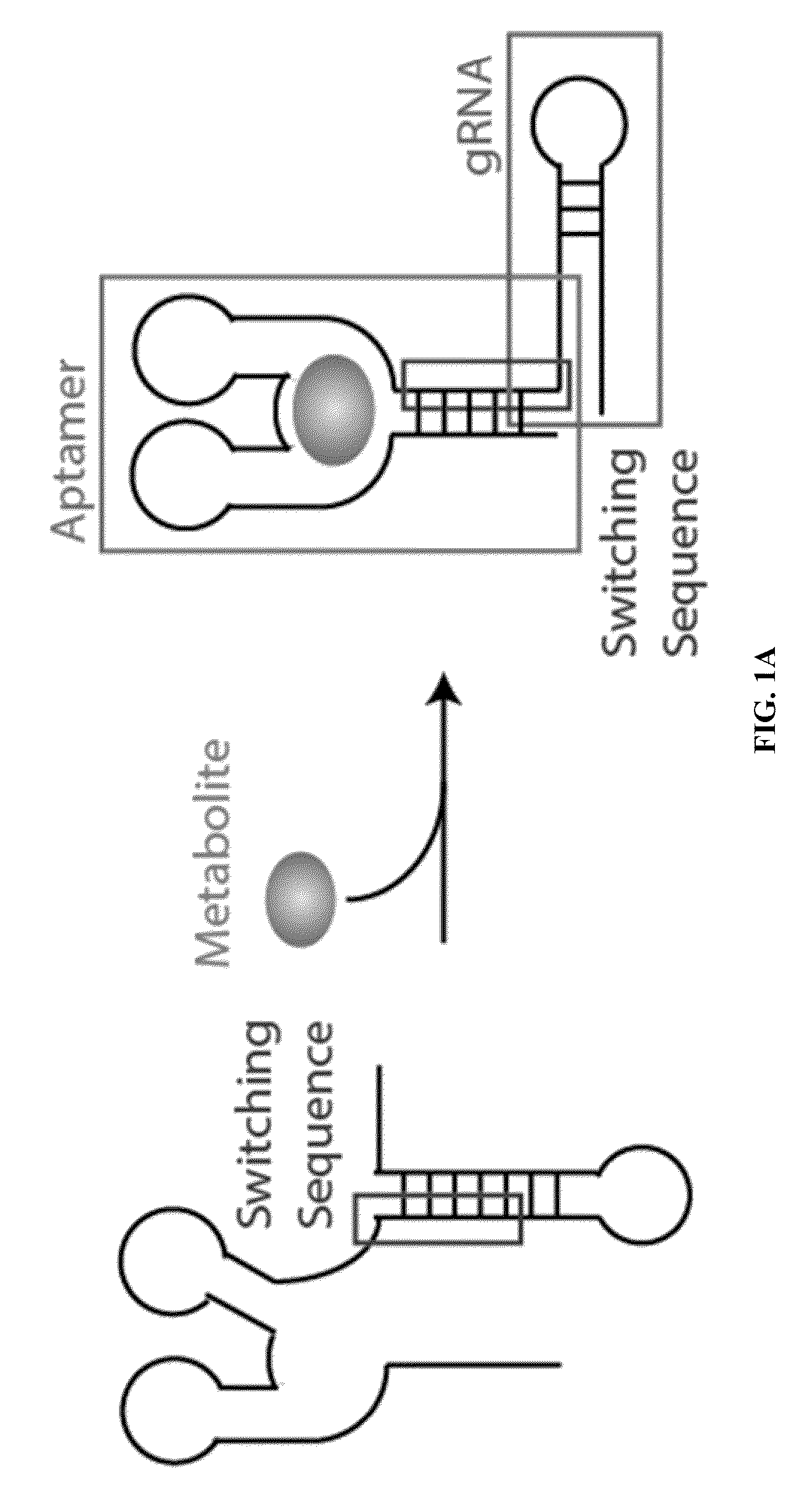
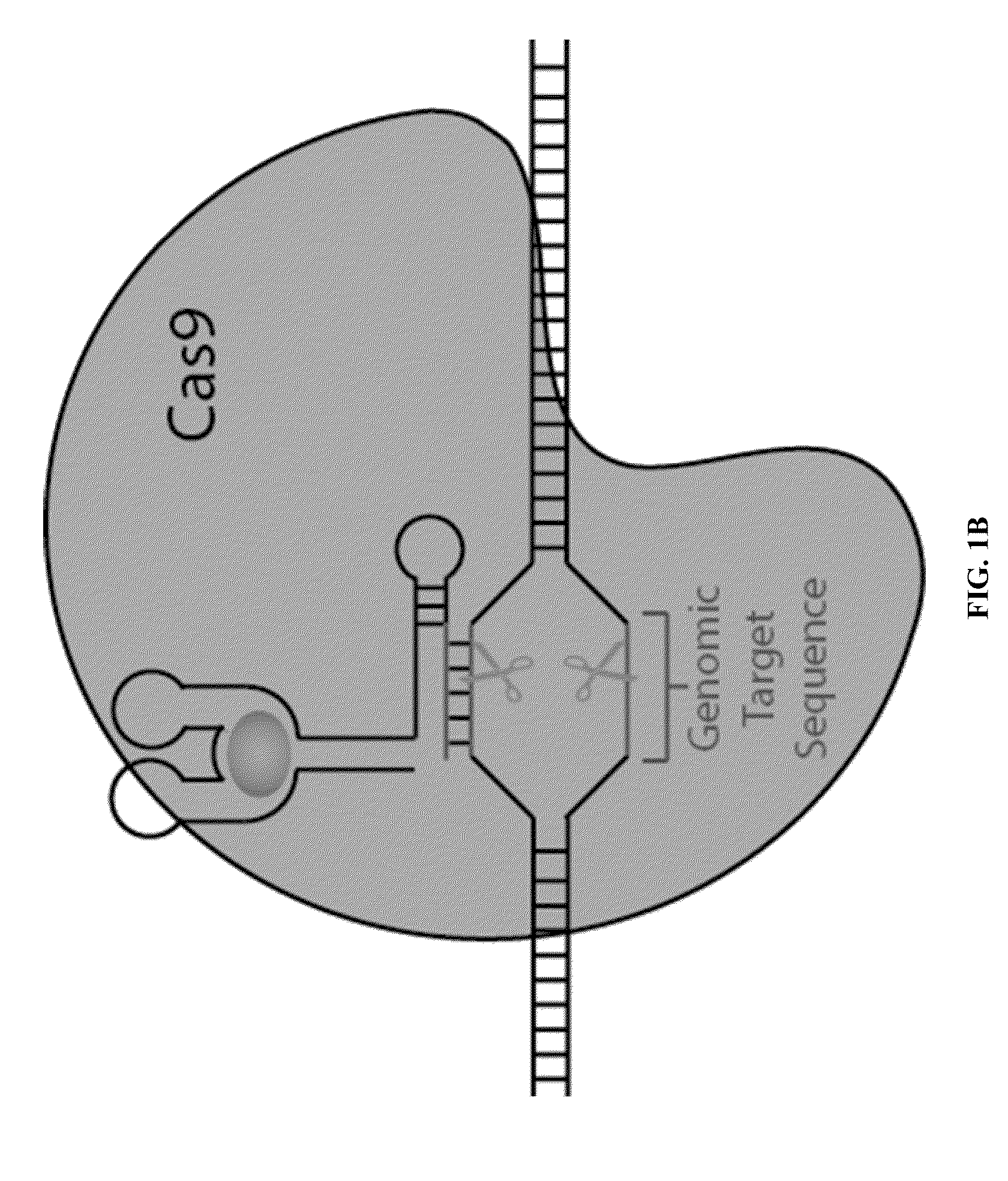
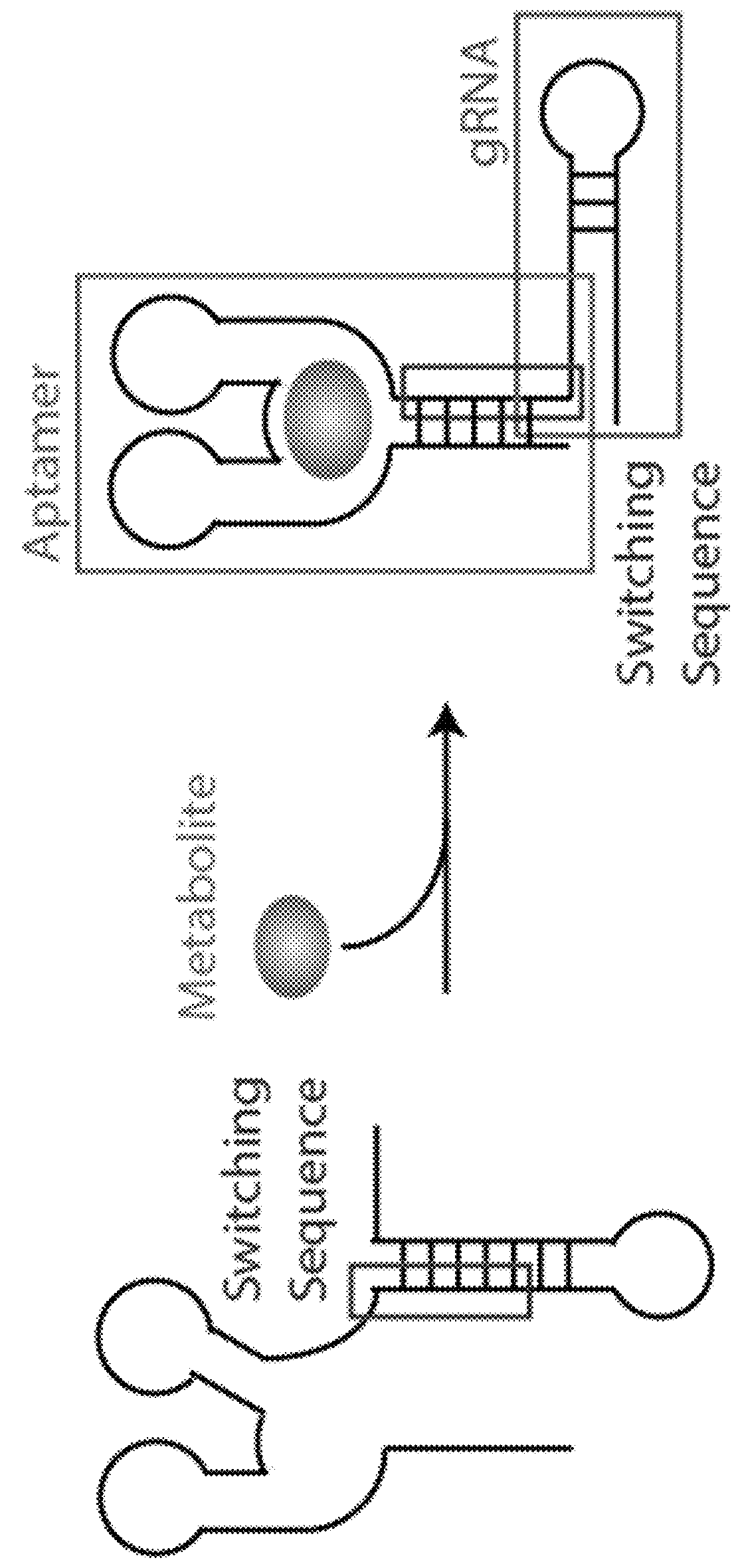
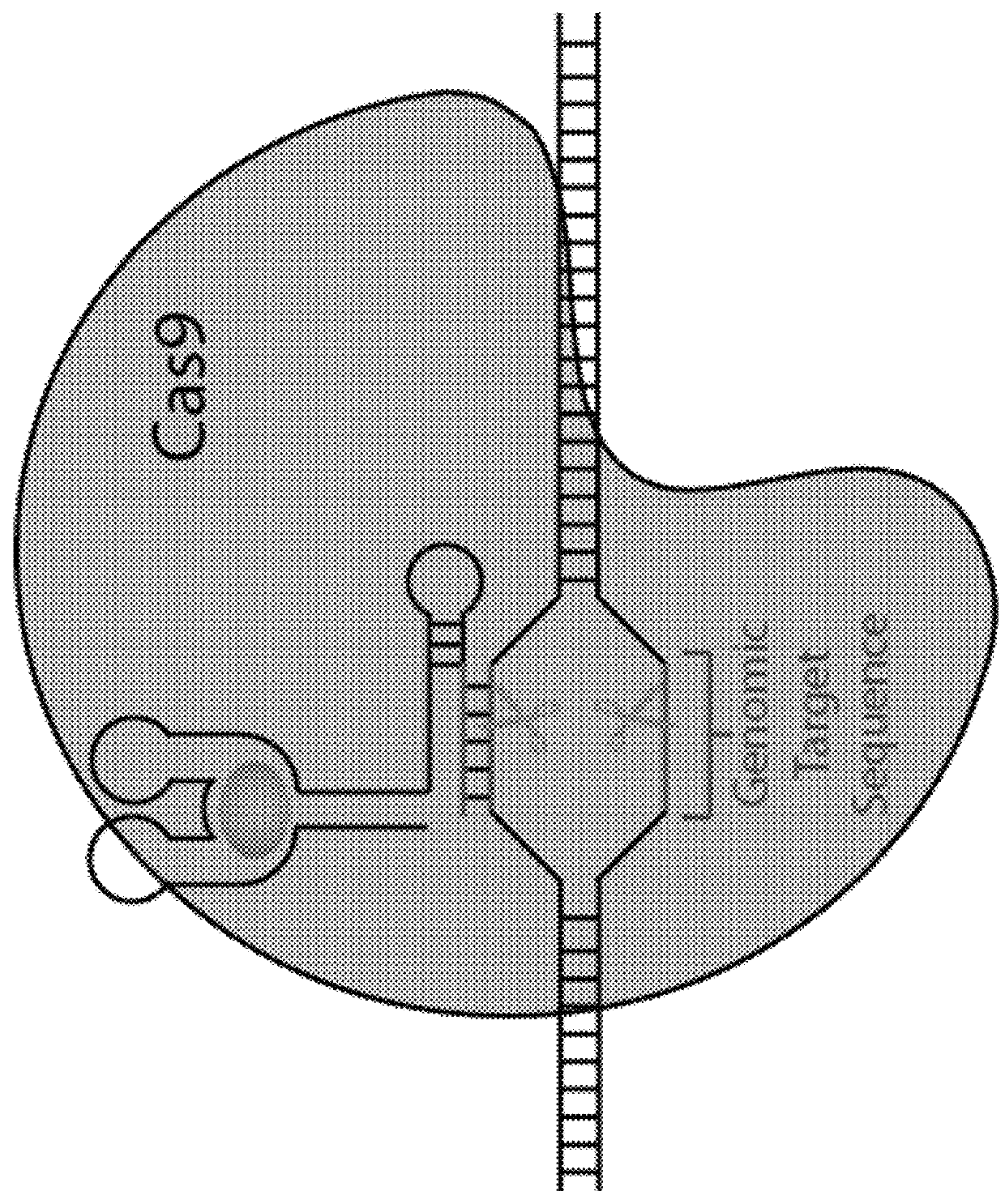
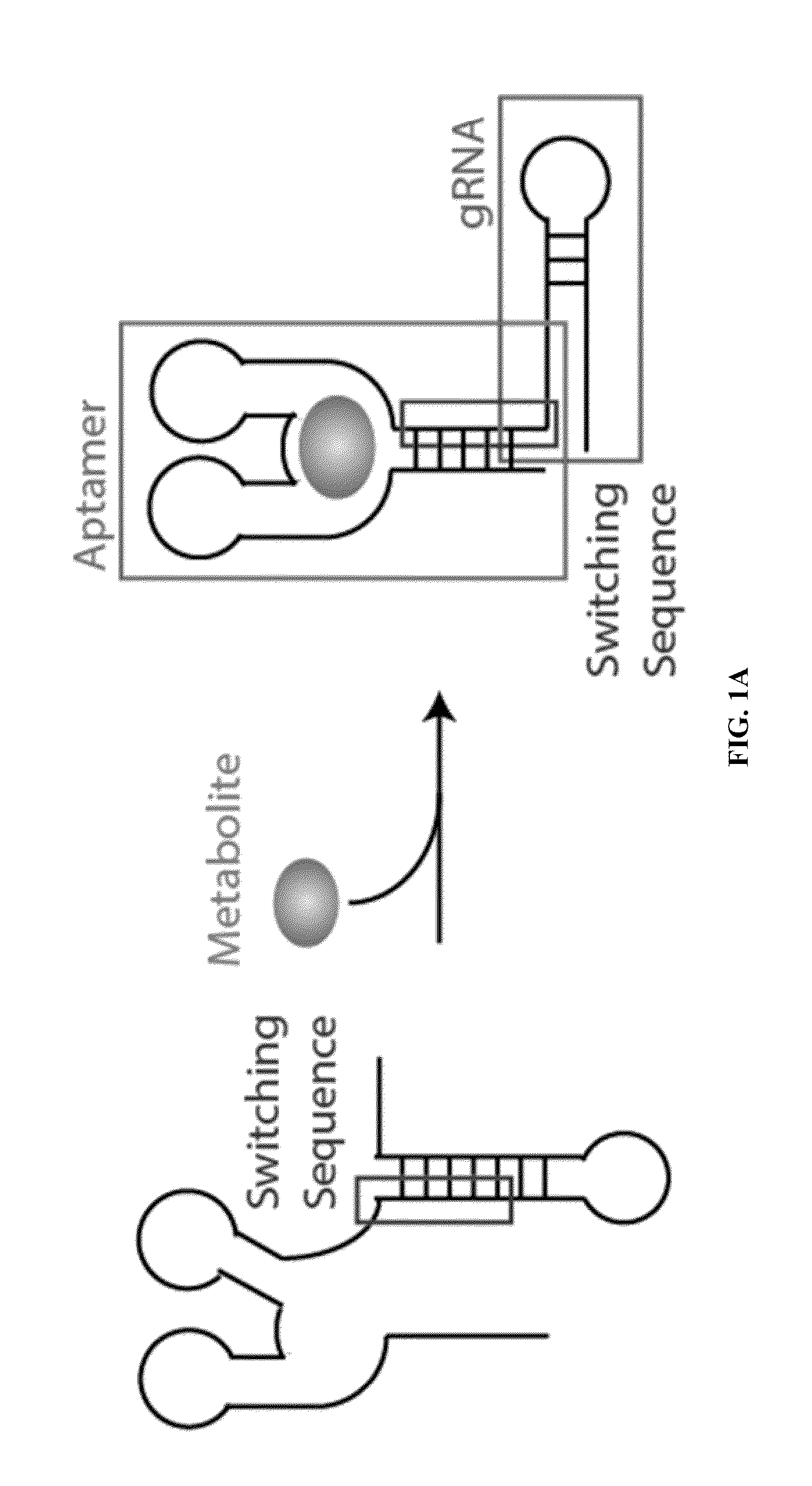
Switchable grnas comprising aptamers
ActiveUS20150071900A1Reduce the possibilityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologyDNA Endonuclease
Some aspects of this disclosure provide compositions, methods, systems, and kits for controlling the activity and / or improving the specificity of RNA-programmable endonucleases, such as Cas9. For example, provided are guide RNAs (gRNAs) that are engineered to exist in an “on” or “off” state, which control the binding and hence cleavage activity of RNA-programmable endonucleases.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Switchable gRNAs comprising aptamers
Some aspects of this disclosure provide compositions, methods, systems, and kits for controlling the activity and / or improving the specificity of RNA-programmable endonucleases, such as Cas9. For example, provided are guide RNAs (gRNAs) that are engineered to exist in an “on” or “off” state, which control the binding and hence cleavage activity of RNA-programmable endonucleases.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods and compositions for using argonaute to modify a single stranded target nucleic acid
The present disclosure provides compositions, kits, genetically modified cells, non-human transgenic organisms, and methods for binding and / or cleaving a single stranded target nucleic acid. A method of cleaving includes contacting a single stranded target nucleic acid with (e.g., introducing into a cell) a subject argonaute (Ago) polypeptide and a guide RNA (e.g., having a 5′-OH). In some embodiments, a subject Ago polypeptide includes an amino acid sequence having 70% or more sequence identity with amino acids 282-430 and / or 431-639 of the Marinitoga piezophila argonaute (MpAgo) protein set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1. The present disclosure provides variant Ago polypeptides; and methods of use of same.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Functional genomics using crispr-cas systems, compositions, methods, screens and applications thereof
ActiveUS20160251648A1Simplify methodologyImprove abilitiesStable introduction of DNAScreening processGenome scaleGenomics
The present invention generally relates to libraries, kits, methods, applications and screens used in functional genomics that focus on gene function in a cell and that may use vector systems and other aspects related to Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-Cas systems and components thereof. The present invention also relates to rules for making potent single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) for use in CRISPR-Cas systems. Provided are genomic libraries and genome wide libraries, kits, methods of knocking out in parallel every gene in the genome, methods of selecting individual cell knock outs that survive under a selective pressure, methods of identifying the genetic basis of one or more medical symptoms exhibited by a patient, and methods for designing a genome-scale sgRNA library.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Extended DNA-Sensing GRNAS
ActiveUS20150071902A1Reduce the possibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsActivity regulationBiologyGuide RNA
Some aspects of this disclosure provide compositions, methods, systems, and kits for controlling the activity and / or improving the specificity of RNA-programmable endonucleases, such as Cas9. For example, provided are guide RNAs (gRNAs) that are engineered to exist in an “on” or “off” state, which control the binding and hence cleavage activity of RNA-programmable endonucleases. Some aspects of this disclosure provide gRNAs that modulate the activity of an RNA-programmable endonuclease based on the presence or absence of an extended DNA (xDNA).
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
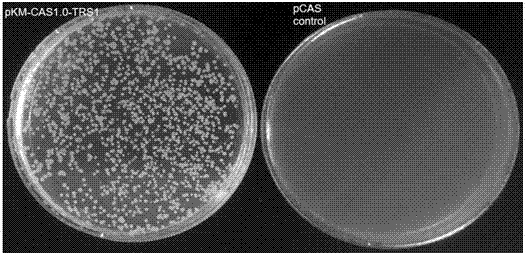
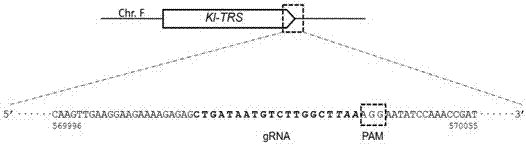
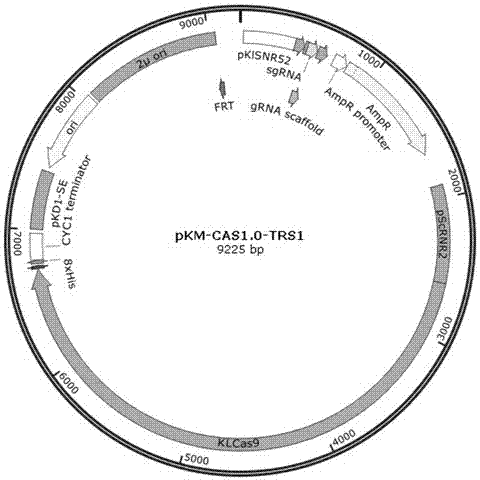
Efficient CRISPR/Cas (Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated) 9 gene editing system for Kluyveromyces optimization
ActiveCN107574179AStable gene editingEfficient gene editingFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTime transformation
The invention relates to a special safe and efficient CRISPR / Cas (Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats / CRISPR associated) 9 gene editing system for Kluyveromyces optimization, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. In the prior art, pCAS plasmids used in saccharomyces cerevisiae have Cas9 gene sequences and gRNA (guide RNA) elements at the same time, and efficient genomemodification in the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be realized through one-time transformation, but stable copying and expression cannot be realized in Kluyveromyces. According to the system, Cas9 / gRNAfusion plasmids are transformed in Kluyveromyces cells, the plasmids are targetedly delivered to endogenous DNA sequences of the Kluyveromyces cells, and double strand breaks are generated; and donorDNA sequences are transformed in the Kluyveromyces cells, the sequences generate homologous recombination at the double strand breaks and target sites, and Tag sequences are inserted in the target sites. Through the modification, the new safe and efficient CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system which is specially used for the Kluyveromyces and can perform stable copying and expression in the Kluyveromyces and perform gene modification is established.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
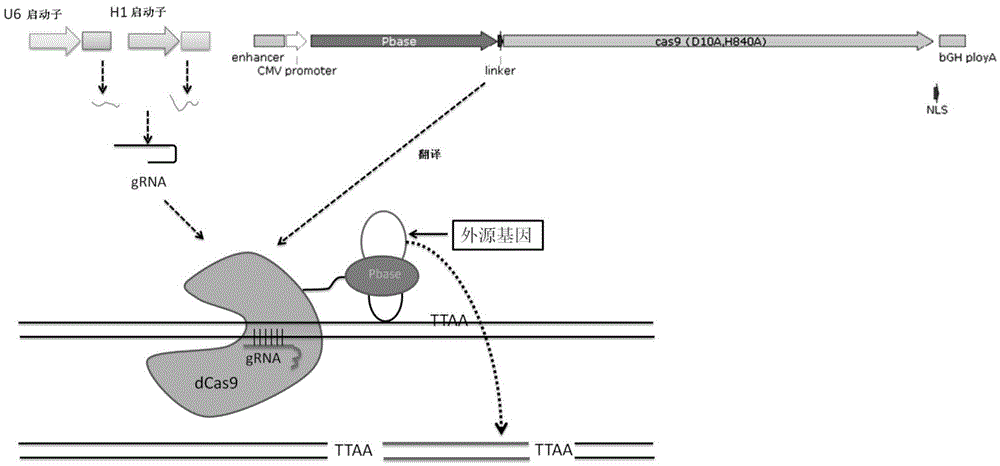
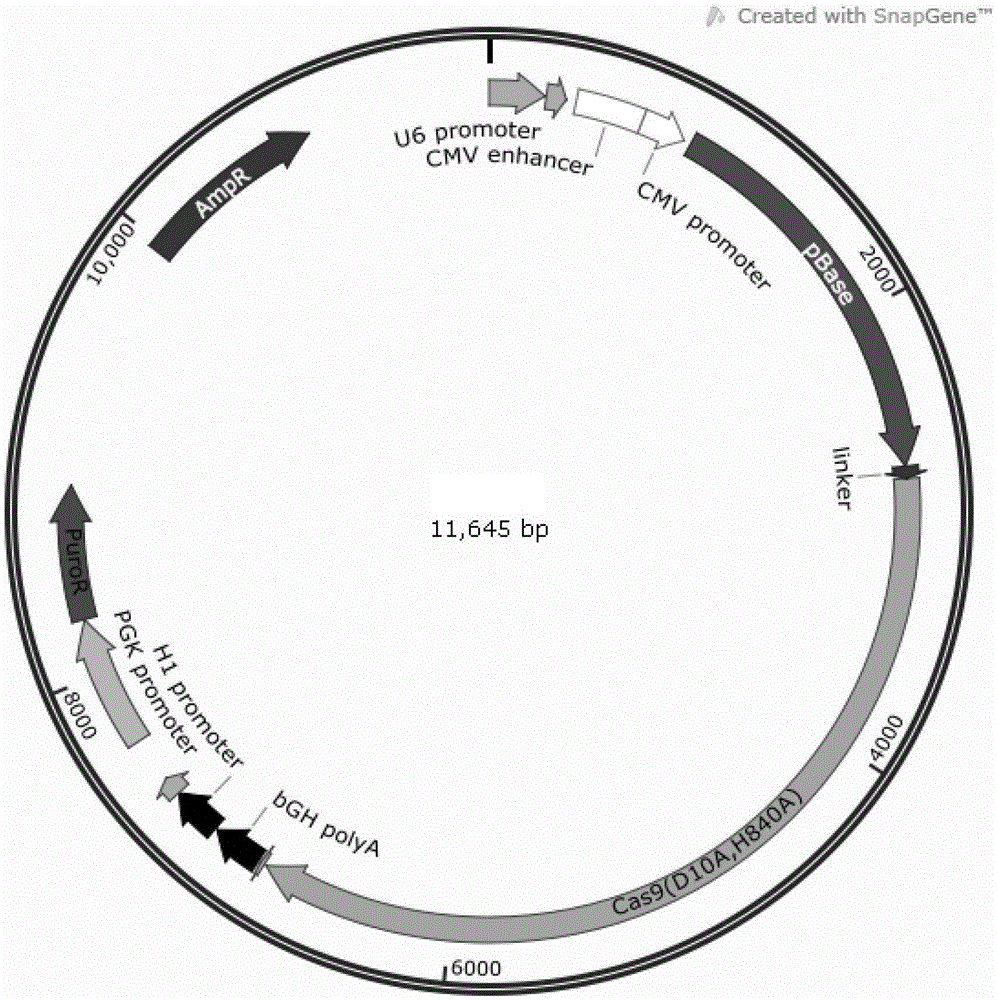
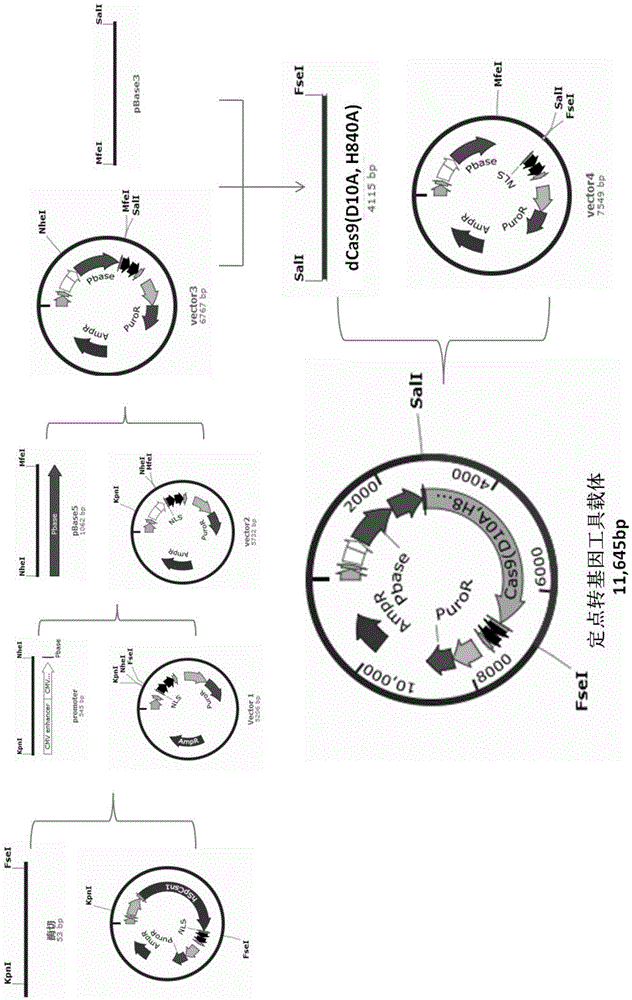
Tool for efficient site-specific transposition of genes and application of tool
ActiveCN105646719ARealize transposition functionRealize site-specific transgeneHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGene engineeringAnimal genome
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering and particularly discloses a tool for efficient site-specific transposition of genes. The tool comprises or can produce a gRNA-Cas9 protein (without incision enzyme activity)-PB transposase compound, and gRNA targets the specific site of a genome; the Cas9 protein without incision enzyme activity is double-mutant Cas9 protein with 10th-site amino acid residue D mutating into A and 840th-site amino acid residue H mutating into A. Through design of gRNA (guide RNA) targeting the animal genome, under the coexpression condition of gRNA and site-specific transposase, PB transposase is targeted to a specific position of the genome along with a CRISPR / cas9 and gRNA compound, the PB transposase realizes a transposition function at the specific site, accordingly, donor plasmids (carriers containing exogenous target genes) are simultaneously co-transfected, the exogenous target carriers can be transposed to the specific site in the genome through transposition, and site-specific transposition of the genes is realized.
Owner:WUXI MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH HOSPITAL
CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated protein 9) target knockout human Lin28A gene and specific gRNA (guide Ribonucleic Acid) of CRUSPR/Cas9 target knockout human Lin28A gene
InactiveCN106868008AVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsHuman melanomaWilms' tumor
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and biomedicine and in particular relates to application of a gRNA (guide Ribonucleic Acid) sequence based on a CRISPR / Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats / CRISPR associated protein 9) system on knockout of a human Lin28A gene and application to tumor treatment. According to a design principle of CRISPR / Cas9, 6 guide RNAs (gRNA) are designed and a sequence table is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.6; the guide RNAs are constructed on a PX458 carrier and two efficient target gRNAs are obtained through activity detection and screening. The CRISPR / Cas9 system guided by the two gRNAs is utilized in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (HepG2) and human melanoma cell lines (A375), and the human Lin28A gene can be effectively knocked out; the system is easy to operate and the human Lin28A gene knockout efficiency is high, so that the system is applicable to various tumor cell models. The gRNA provided by the invention is hopefully applied to a new drug for treating tumors.
Owner:重庆高圣生物医药有限责任公司
CRISPR-Cas9 system used for assembling DNA and DNA assembly method
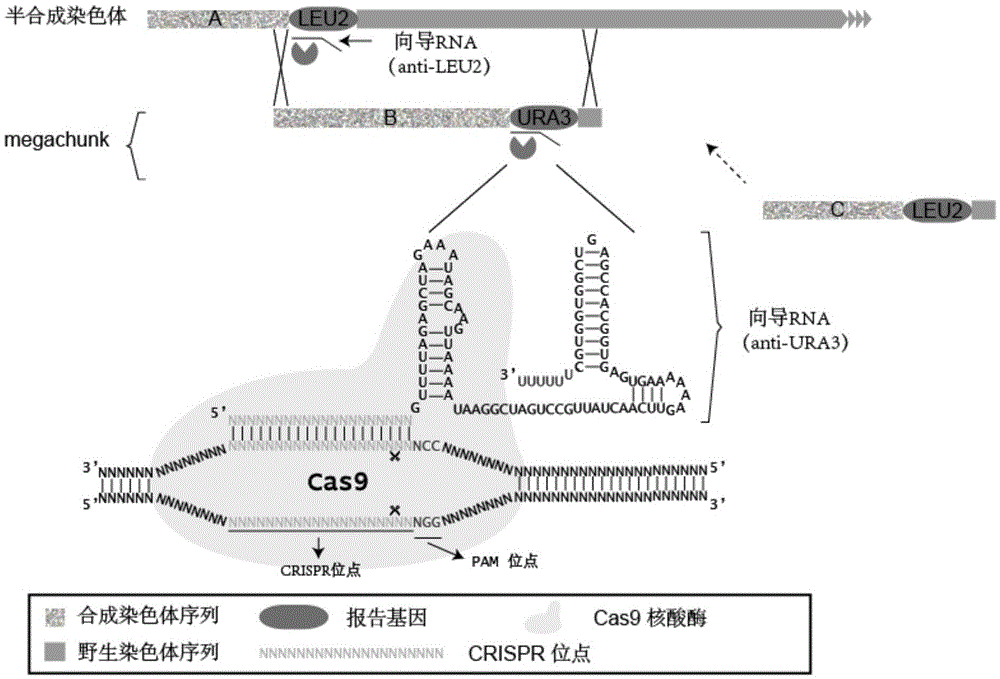
InactiveCN105821072ARepeatableSuccessfully synthesizedFungiMicroorganism based processesReporter geneGuide RNA
The invention discloses a CRISPR-Cas9 system used for assembling DNA and a DNA assembly method. The CRISPR-Cas9 system includes the following parts: a plasmid used for expressing Cas9 gene, a first guide RNA, and / or a plasmid used for expressing the first guide RNA, wherein the first guide RNA has a CRISPR site. The CRISPR site is combined with a first reporter gene carried by a semisynthetic chromosome used for assembling according to base complementation pairing rule. The CRISPR-Cas9 system has advantages of high replacement success rate of homologous recombination, less species of guide RNA which needs to design and use, less harmful effect subjected by the genomic sequence, and low off-target rate.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
Site-directed mutation method for genomes of saccharomyces cerevisiae
InactiveCN105624187AEfficient mutationRapid implementation of mutationsFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRepair site
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a site-directed mutation method for genomes of saccharomyces cerevisiae. To-be-repaired single-base mutation sites on the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be repaired by the aid of CRISPR / Cas9 technologies. Effects can be realized near the to-be-repaired sites by Cas9 proteins under the guidance actions of guide RNA (ribonucleic acid) if the mutation sites are positioned in PAM sequences (NGG) or front 11bp of the PAM sequences, and the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be subjected to double-strand break at cut positions, so that donor DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) can be efficiently recombined. Compared with existing results, the site-directed mutation method has the advantages that the sites of the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be efficiently and quickly mutated, and screening markers do not need to be integrated for the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
CRISPR/Cas9 targeted knockout human hepatitis B virus P gene and specific gRNA thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a guide RNA (gRNA) sequence based on a CRISPR / Cas9 system and combinations thereof, as well as gRNA for a specific targeted knockout hepatitis B virus cccDNA P gene. In the invention, 30 gRNAs are designed according to design principles of CRISPR / Cas9, have a sequence table as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-30, and are constructed on a PX458 vector, to screen out four more efficient gRNAs. The CRISPR / Cas9 system guided by the four gRNAs and combinations thereof is utilized in a human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HepG2.2.15) to effectively knock out the human hepatitis B virus cccDNA P gene. The gRNA of the specific targeted hepatitis B virus cccDNA prepared in the invention can accurately target the hepatitis B virus cccDNA and realize gene knockout. The preparation method is simple in operation; the gRNA has a good targeting property; the CRISPR / Cas9 system is high in knockout efficiency.
Owner:重庆高圣生物医药有限责任公司
Genome editing method based on CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat) system and application thereof
ActiveCN107937432AImprove editing efficiencyImprove editing abilityHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionInteinFusion gene
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
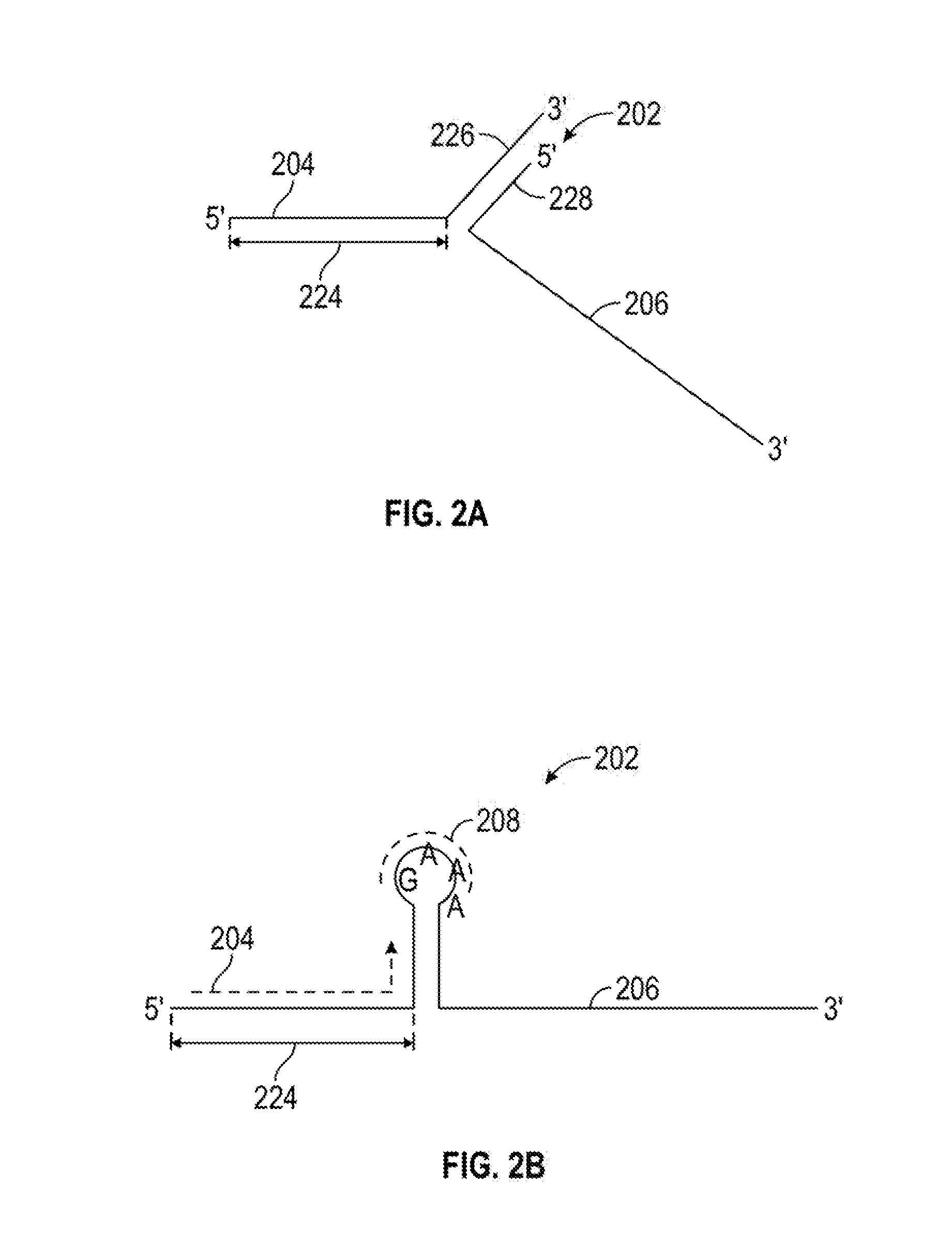
Rna-guided nucleic acid modifying enzymes and methods of use thereof
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
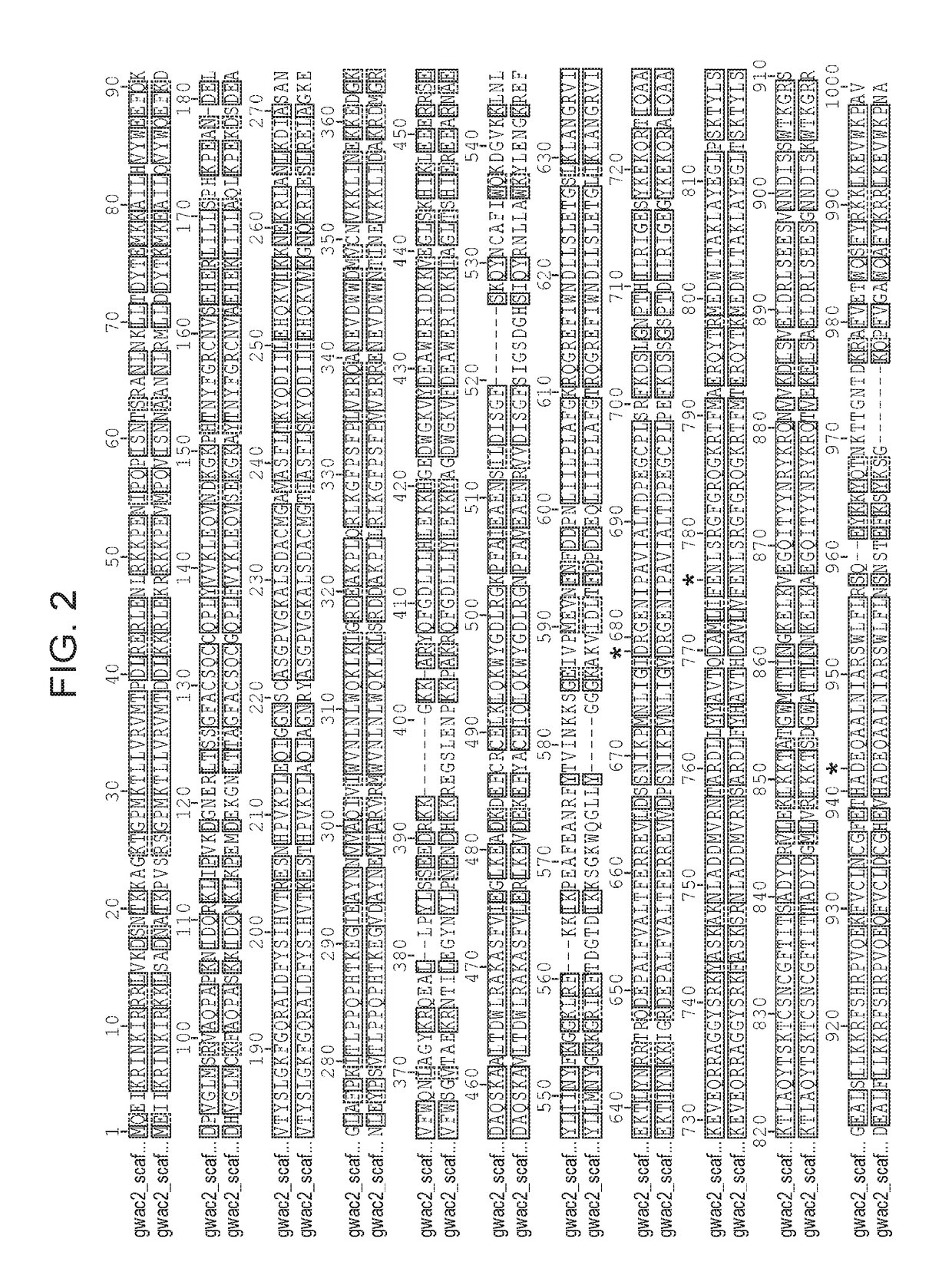
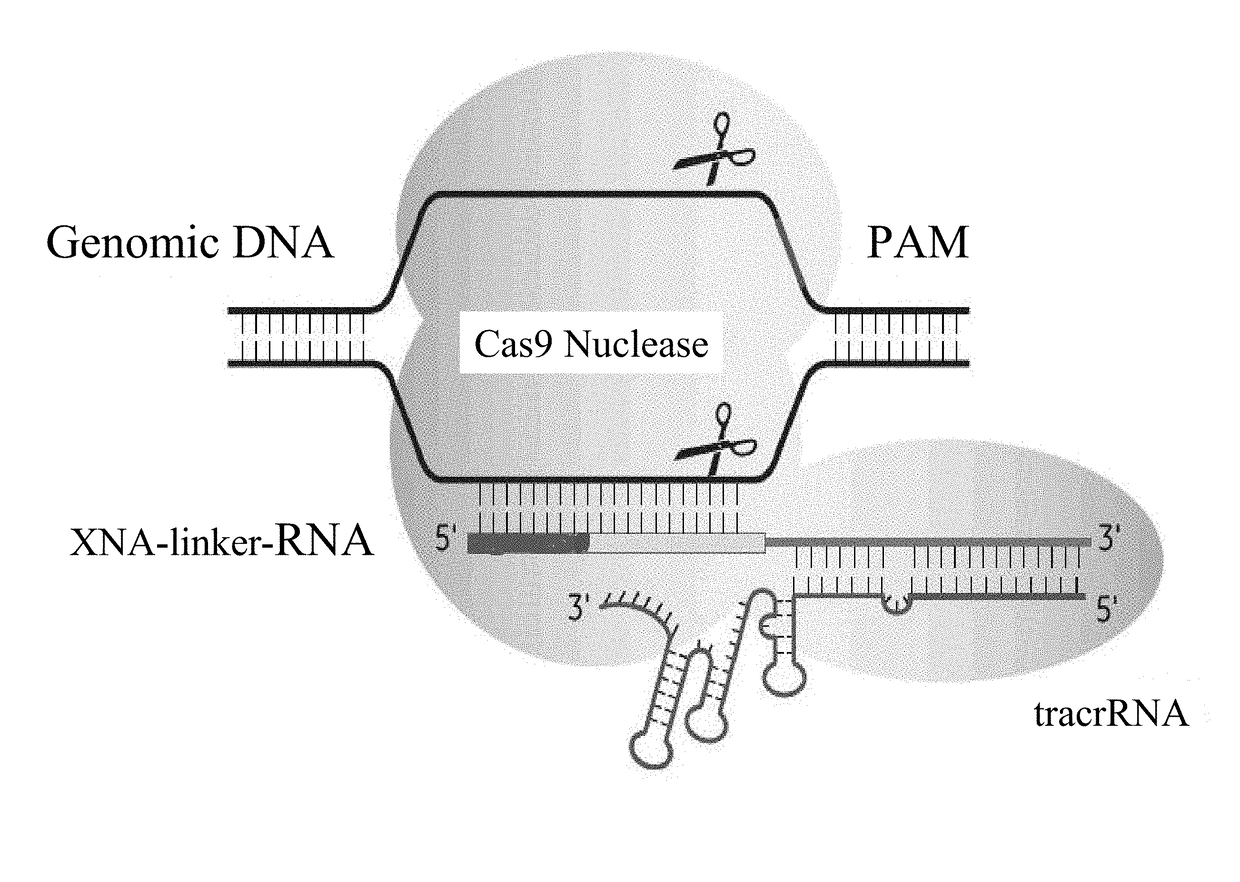
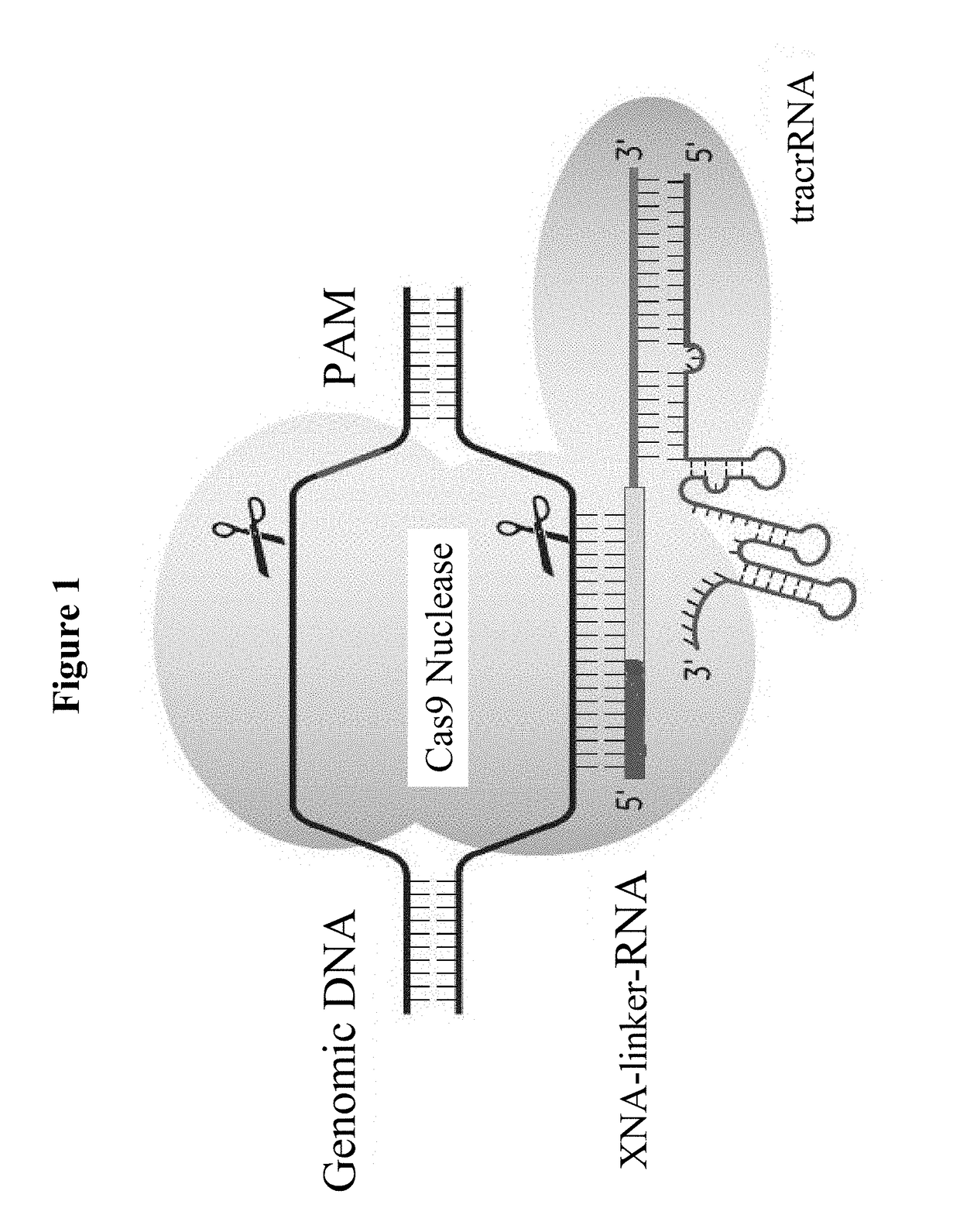
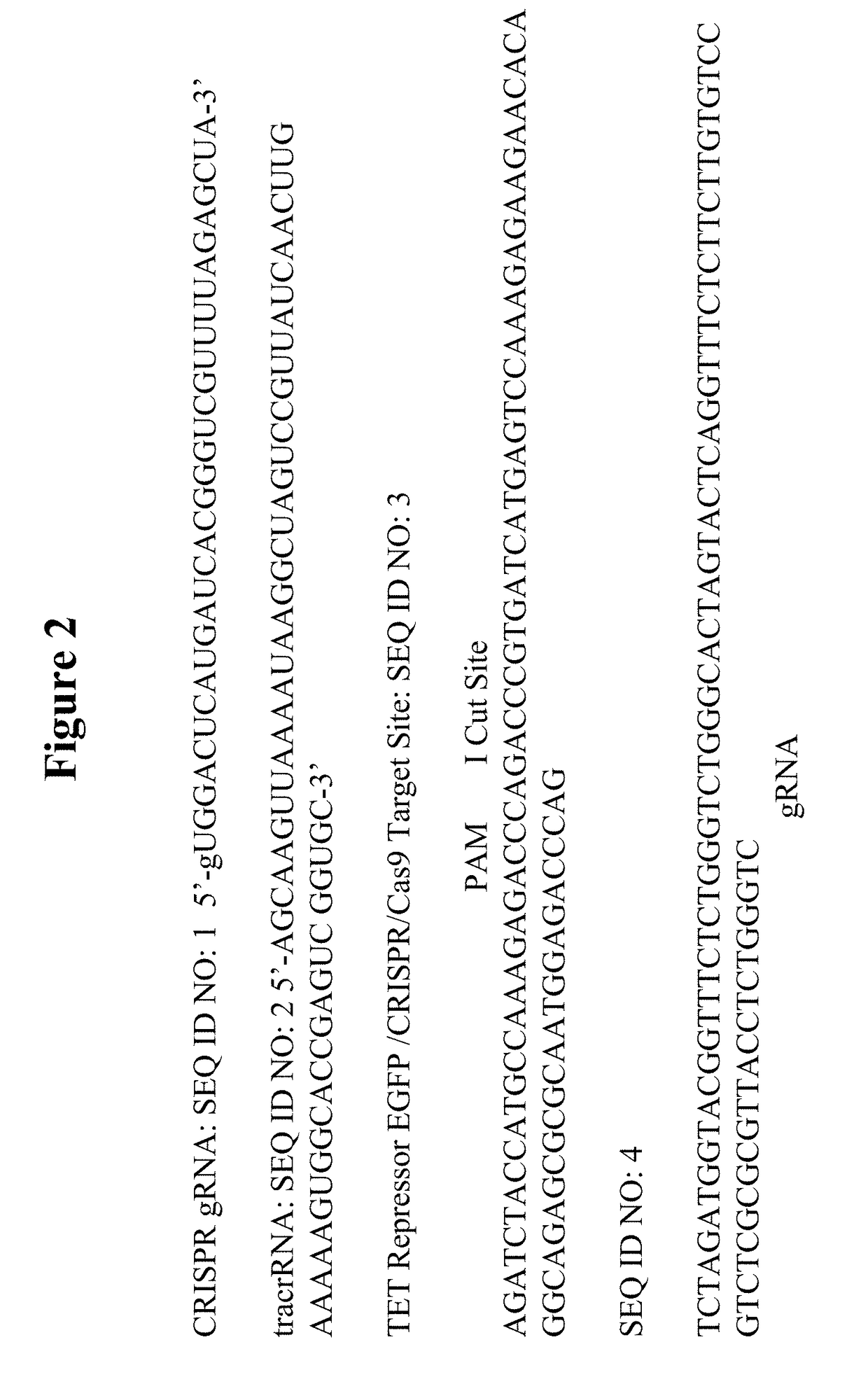
SPECIFIC SYNTHETIC CHIMERIC XENONUCLEIC ACID GUIDE RNA; s(XNA-gRNA) FOR ENHANCING CRISPR MEDIATED GENOME EDITING EFFICIENCY
ActiveUS20180066258A1Enhancing crispr mediated genome editing efficiencyImprove editing efficiencySugar derivativesStable introduction of DNADiseasePrimary cell
The invention provides specific synthetic chimeric xenonucleic acid guide RNA; s(XNA-gRNA) for enhancing crispr mediated genome editing efficiency. The invention also provides methods and compositions for inducing CRISPR / Cas-based gene editing / regulation (e.g., genome editing or gene expression) of a target nucleic acid (e.g., target DNA or target RNA) in a cell. The methods include using single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) that have been chemically modified with xeno nucleic acids which enhance gene regulation of the target nucleic acid in a primary cell for use in ex vivo therapy or in a cell in a subject for use in in vivo therapy. Additionally, provided herein are methods for preventing or treating a genetic disease in a subject by administering a sufficient amount of a sgRNA that has been chemically modified with xeno nucleic acids to correct a mutation in a target gene associated with the genetic disease.
Owner:DIACARTA LTD
Rna-targeting system
PendingUS20170306335A1Efficient use ofStrong specificityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesGuide RNARna hybridization
The invention provides for systems, methods, and compositions for targeting RNA. In particular, the invention provides a non-naturally occurring or engineered RNA-targeting system comprising an RNA-targeting Cas protein and at least one RNA-targeting guide RNA, wherein said RNA-targeting guide RNA is capable of hybridizing with a target RNA in a cell.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Methods and compositions for blocking off-target nucleic acids from cleavage by crispr proteins
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
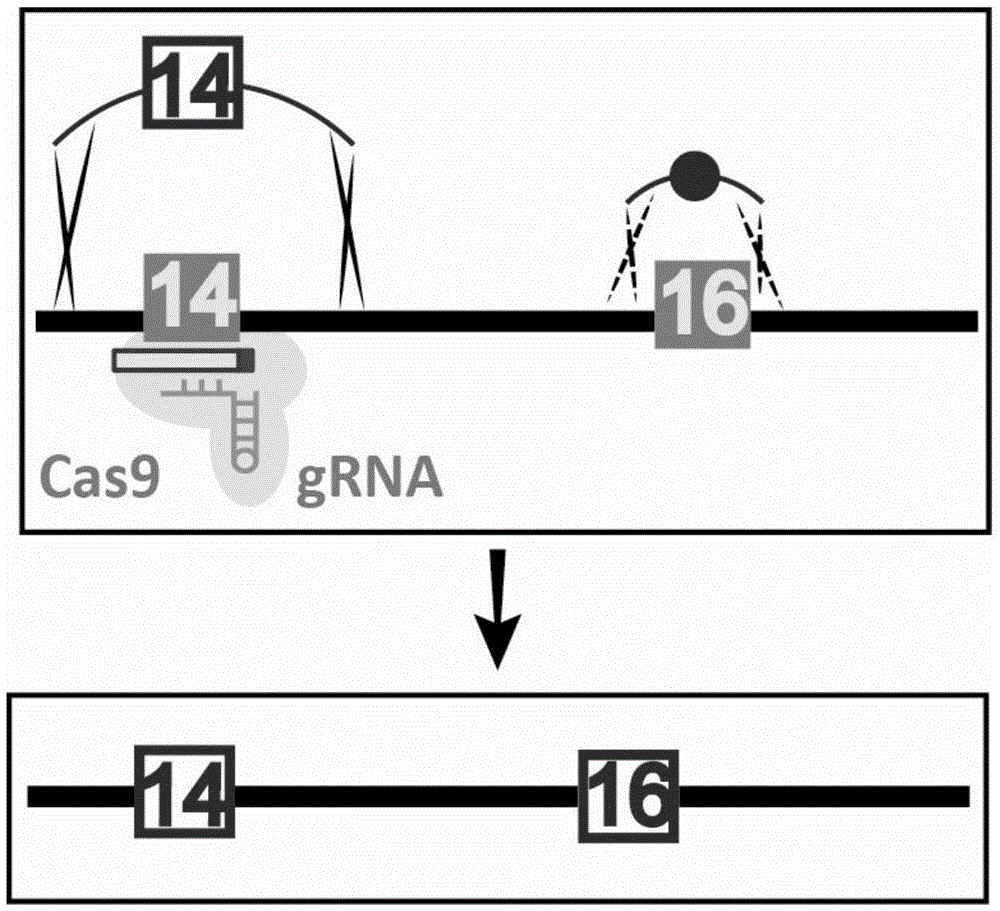
Method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome
ActiveCN107858346AKnockout simpleKnockout EfficientHydrolasesStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and specifically discloses a method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome. The method is characterized in that the complete yeast chromosome is cut according to the CRISPR / Cas9 base technology; a specificity target close to centromere is selected; a corresponding guide RNA is designed to guide Cas9 protein to generate an incision closeto the centromere, thus realizing the knocking down of the whole chromosome. Compared with the conventional method for losing the whole chromosome in manners such as inducing through a Ga1 promoter, and reductional division, the method has the advantages that the brewing yeast chromosome is simply, efficiently and quickly cut; the cross exchange of sister chromatids can be avoided; the chromosome-knocked-down homozygous brewing yeast diploid strain can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Chemically Ligated RNAs for CRISPR/Cas9-lgRNA Complexes as Antiviral Therapeutic Agents
InactiveUS20180230464A1Good effectSmall sizeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical ligationNucleotide
Owner:ZHONG MINGHONG
Site-directed modification method of rice genome
The invention discloses a gene modification method which is capable of realizing random insertion and / or random deletion on a target segment of a rice target gene. The gene modification method comprises following steps: a guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease are induced in rice tissues; the double-chain target segment of the target gene is sliced because of the combined effect of the guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease; and then the random insertion and / or random deletion on the target segment of the rice target gene are / is realized because of DNA self-repairing function of rice cells. The gene modification method is capable of inducing gene mutation of rice.
Owner:SUZHOU QI BIODESIGN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Corn transcription factor ZmbHLH167 and application thereof
The invention relates to a corn transcription factor ZmbHLH167 and an application of the corn transcription factor ZmbHLH167. A base sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO (sequence identifier number): 1. A corn immature embryo is transformed by taking a gene segment SEQ ID NO: 2 of the sequential coding protein ZmbHLH167 as guide RNA (ribonucleic acid) by use of a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas9 technology, and a plant of a gene deletion mutant is obtained. Compared with a wild seed, a corn seed of the genetically modified mutant is smaller significantly, but a germination rate is not influenced. Biochemical analysis shows that a starch content of the corn seed of the genetically modified mutant is decreased obviously, a content of protein and total oil and fat is significantly increased, and a genetic resource is provided for creating high quality corn.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
CRISPR-Cas9 system and application therefore in treating breast cancer diseases
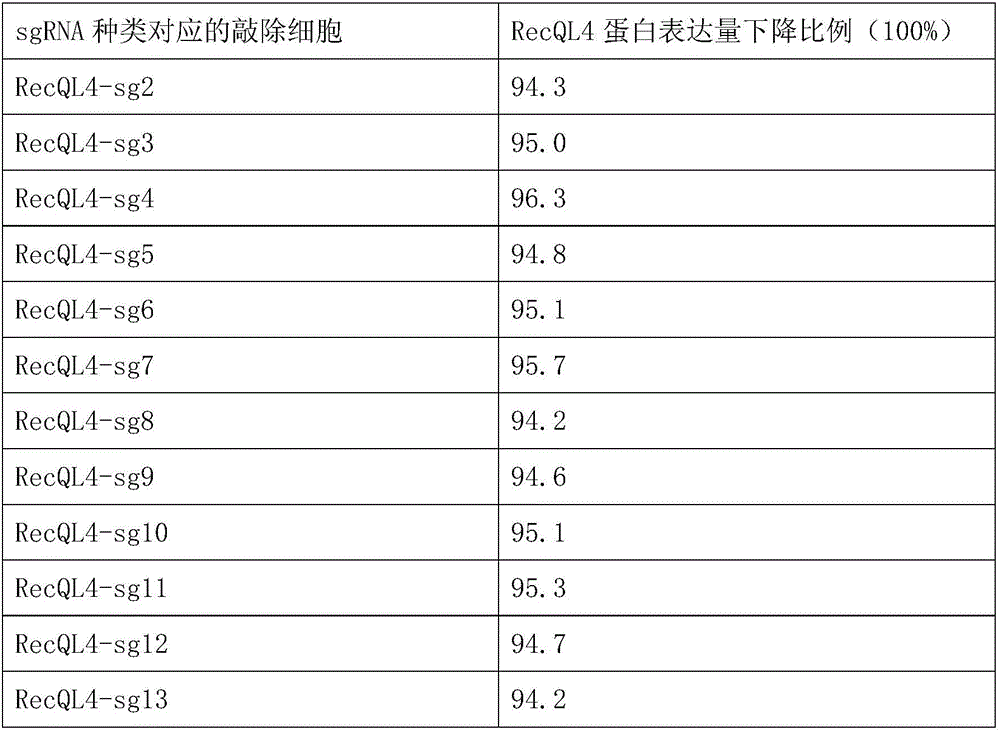
ActiveCN106191071AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to analyzeOrganic active ingredientsNucleic acid vectorDiseaseGene targets
The invention provides a CRISPR-Cas9 system and an application thereof in treating breast cancer diseases, wherein by providing a plurality of sgRNAs (single guide RNAs), the efficient knockout of an RecQL4 gene can be achieved. In comparison with ZFNs and TALENs complex expression structures, siRNA is low in using complexity and efficiency; a Cas9 expression structure in the CRISPR-Cas9 system is fixed; for different genes, system building can be completed by interpolating recognition sequences into the sgRNA expression structure, so that operations are simplified and cost is reduced; and the system is applicable to mammal gene targeting in a large scale.
Owner:广东龄值生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com