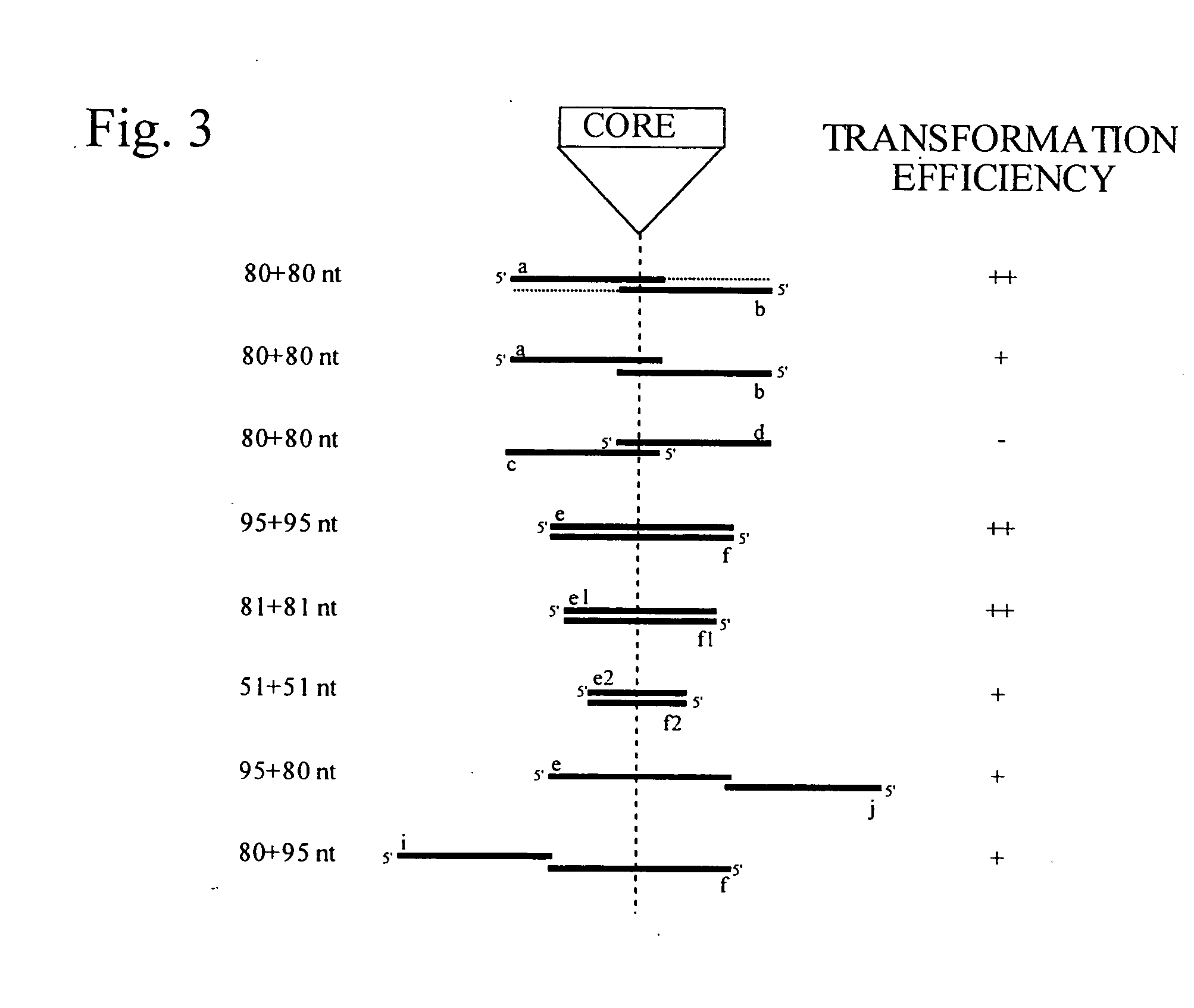
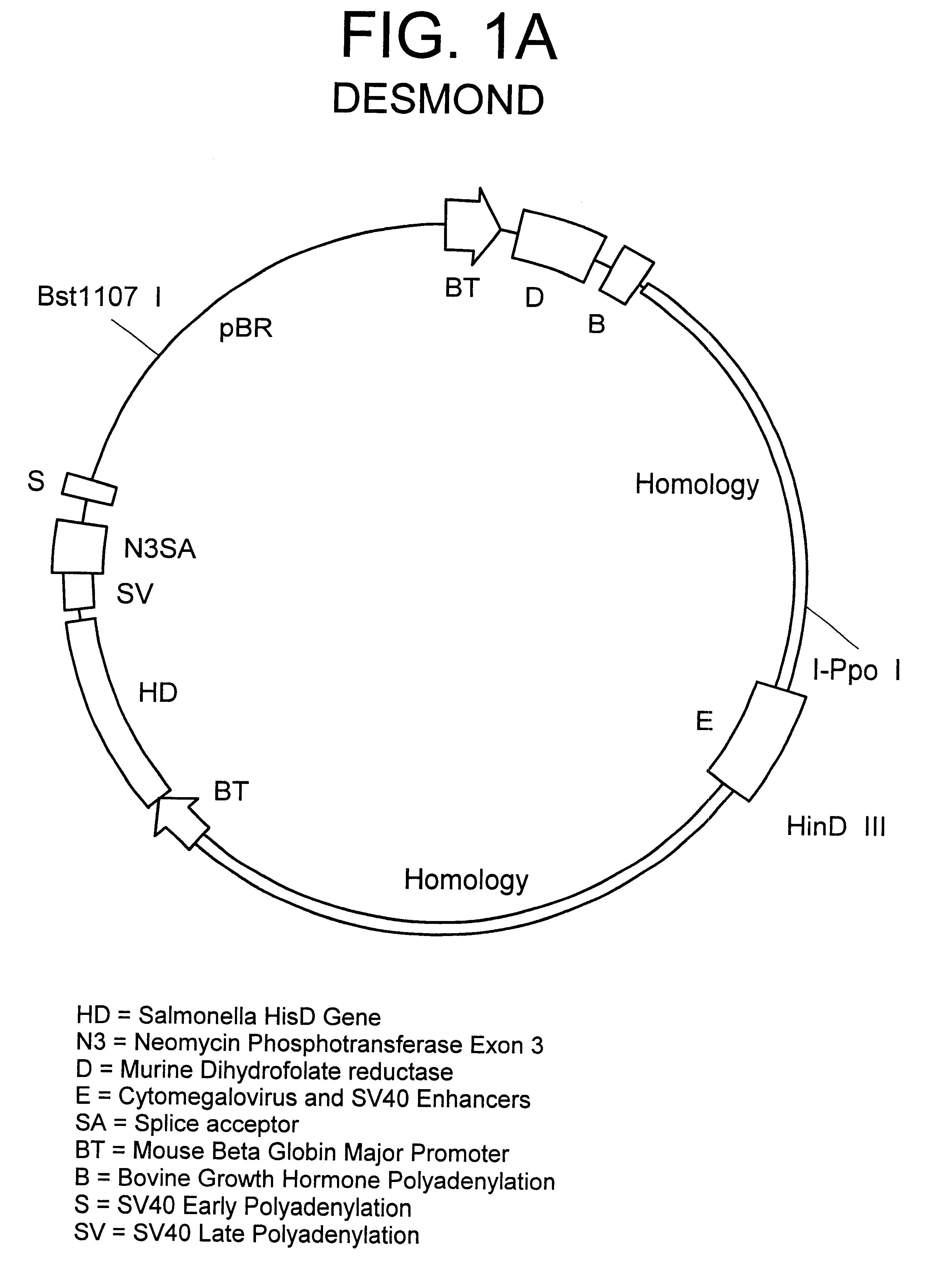
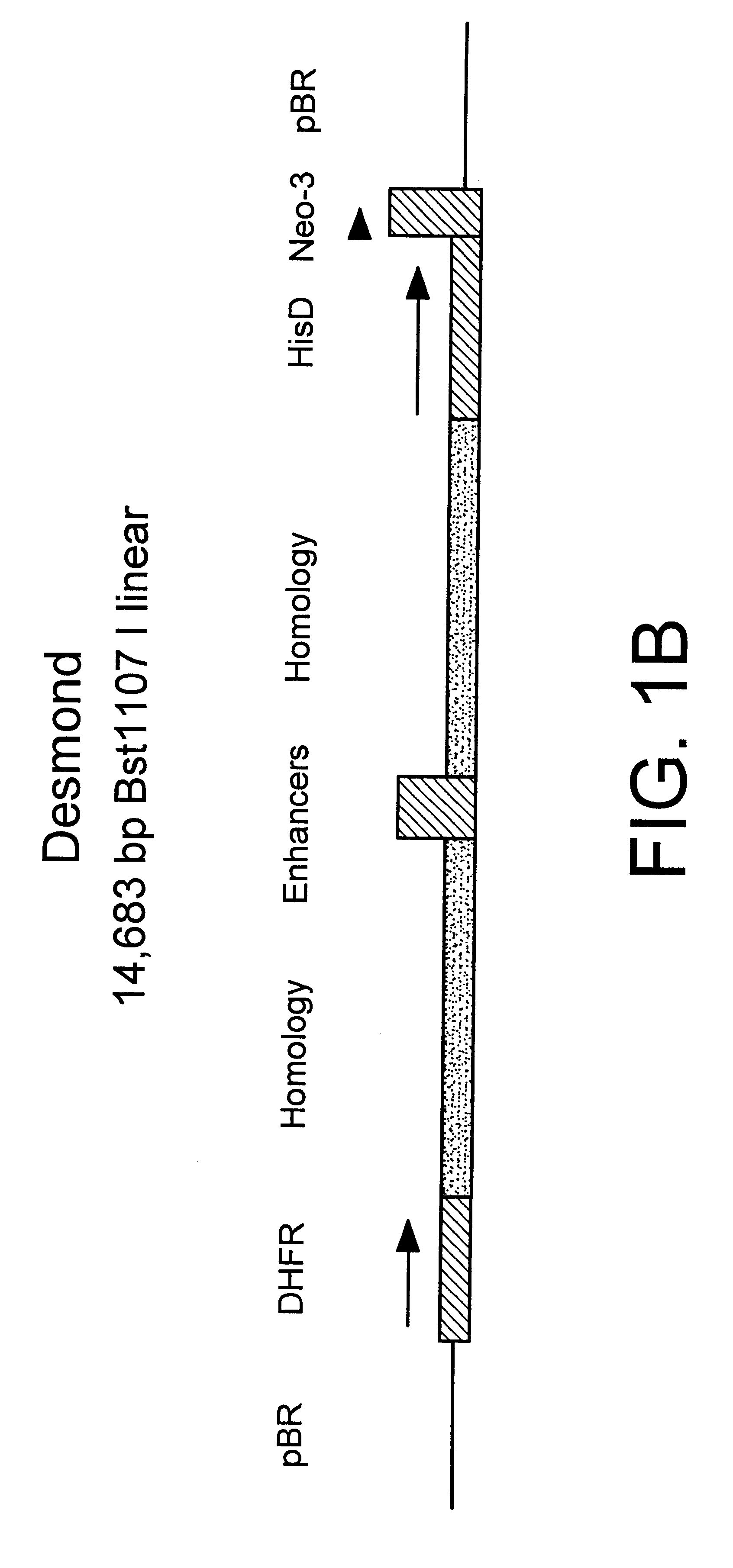
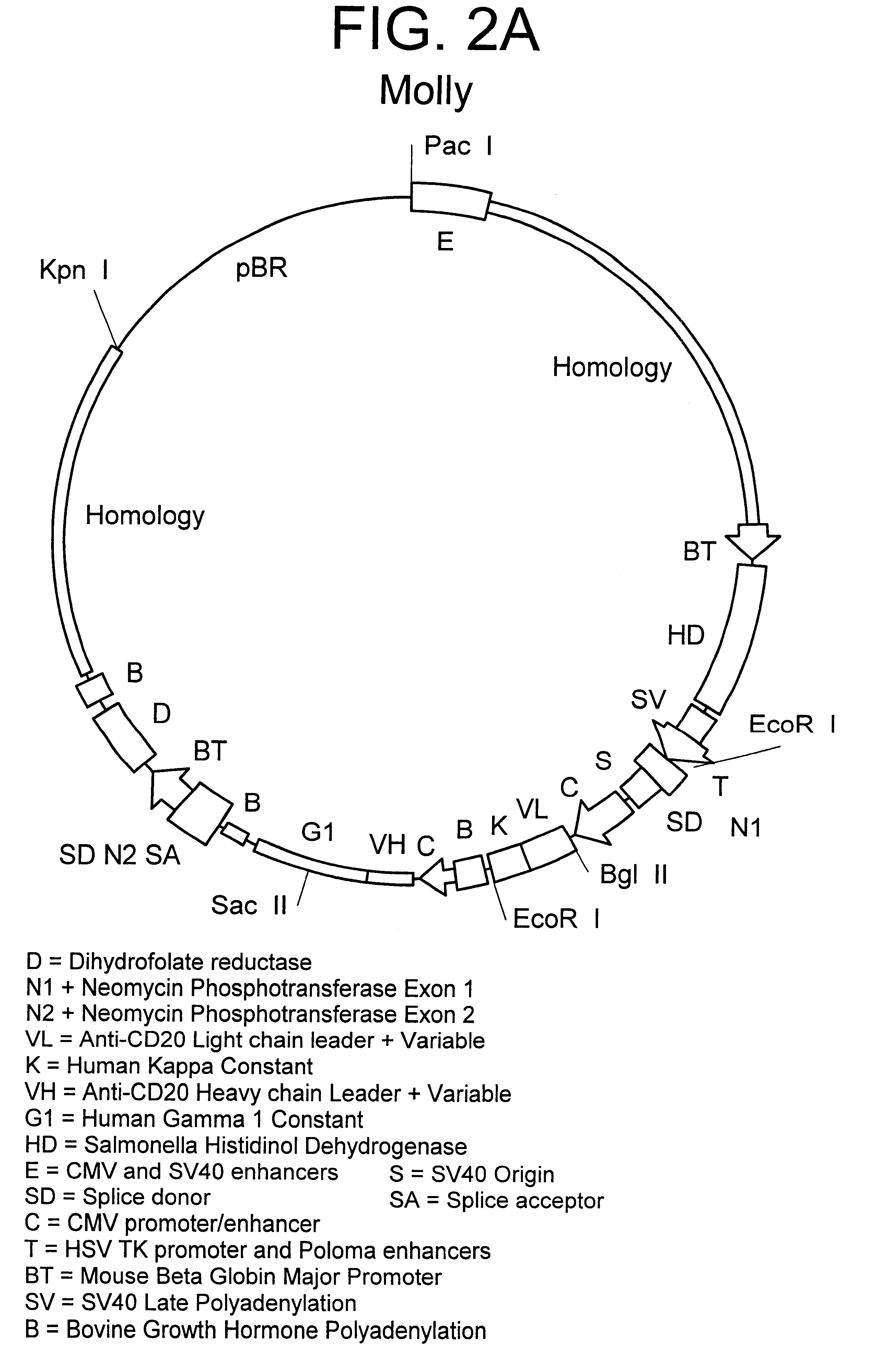
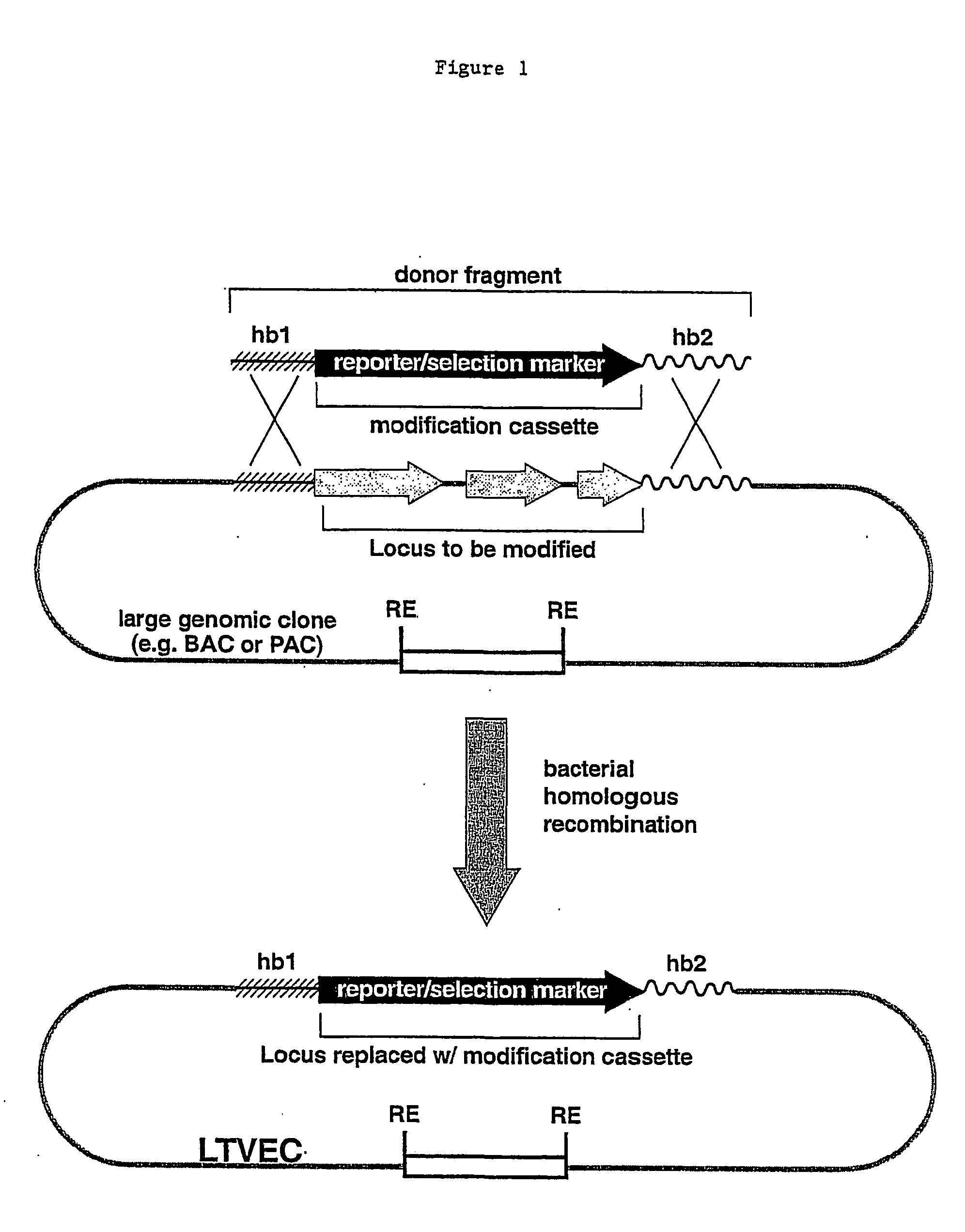
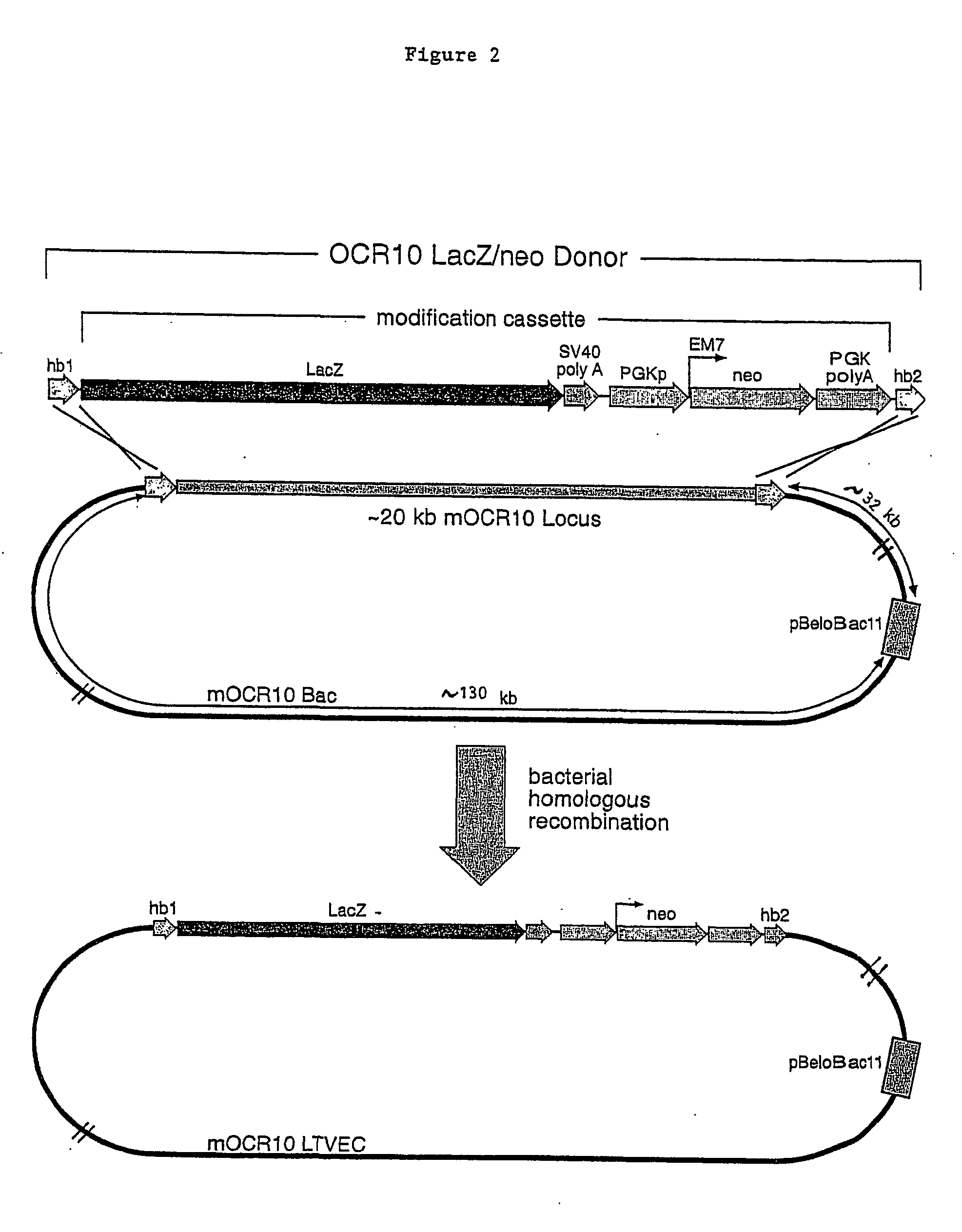
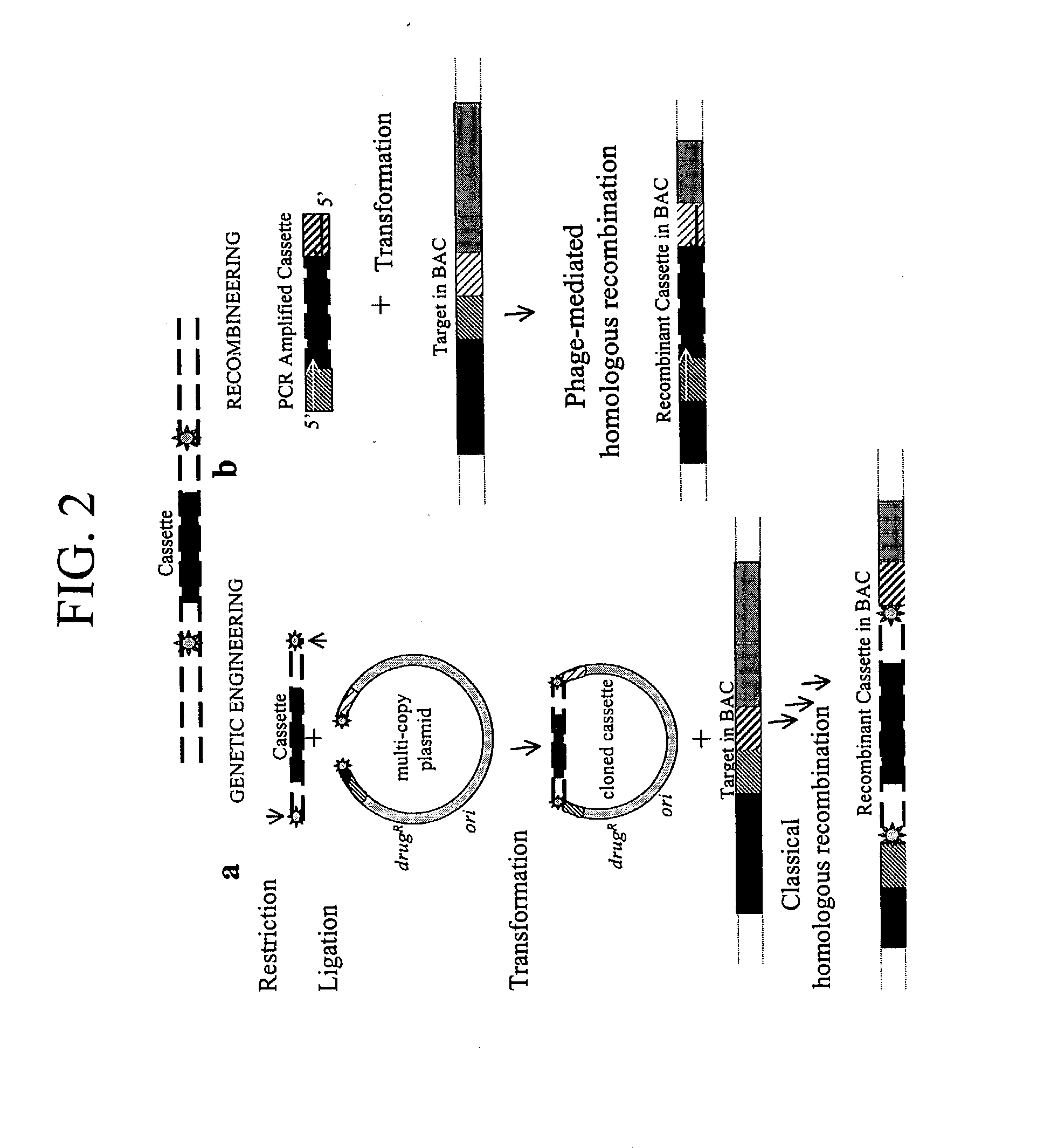
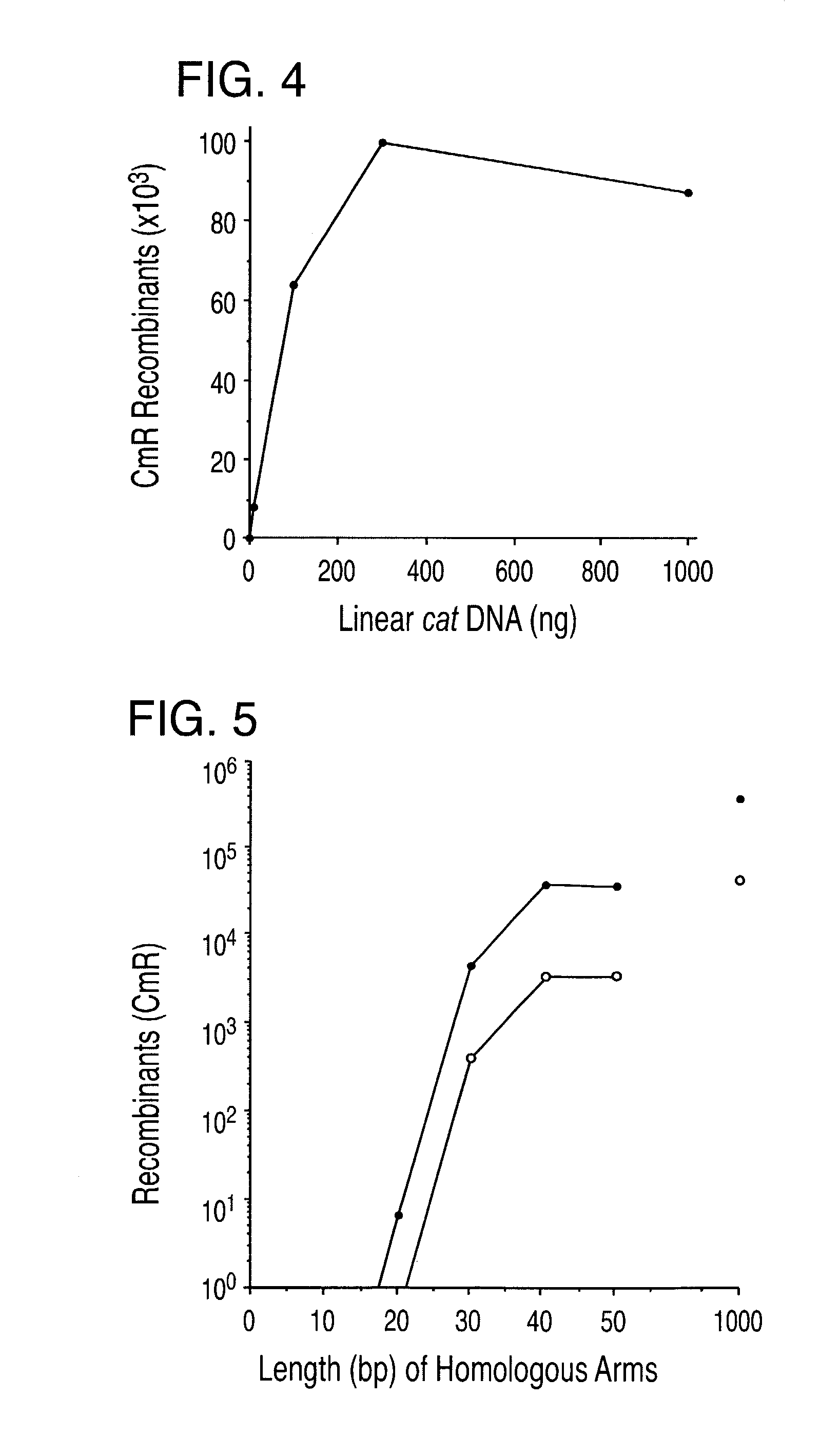
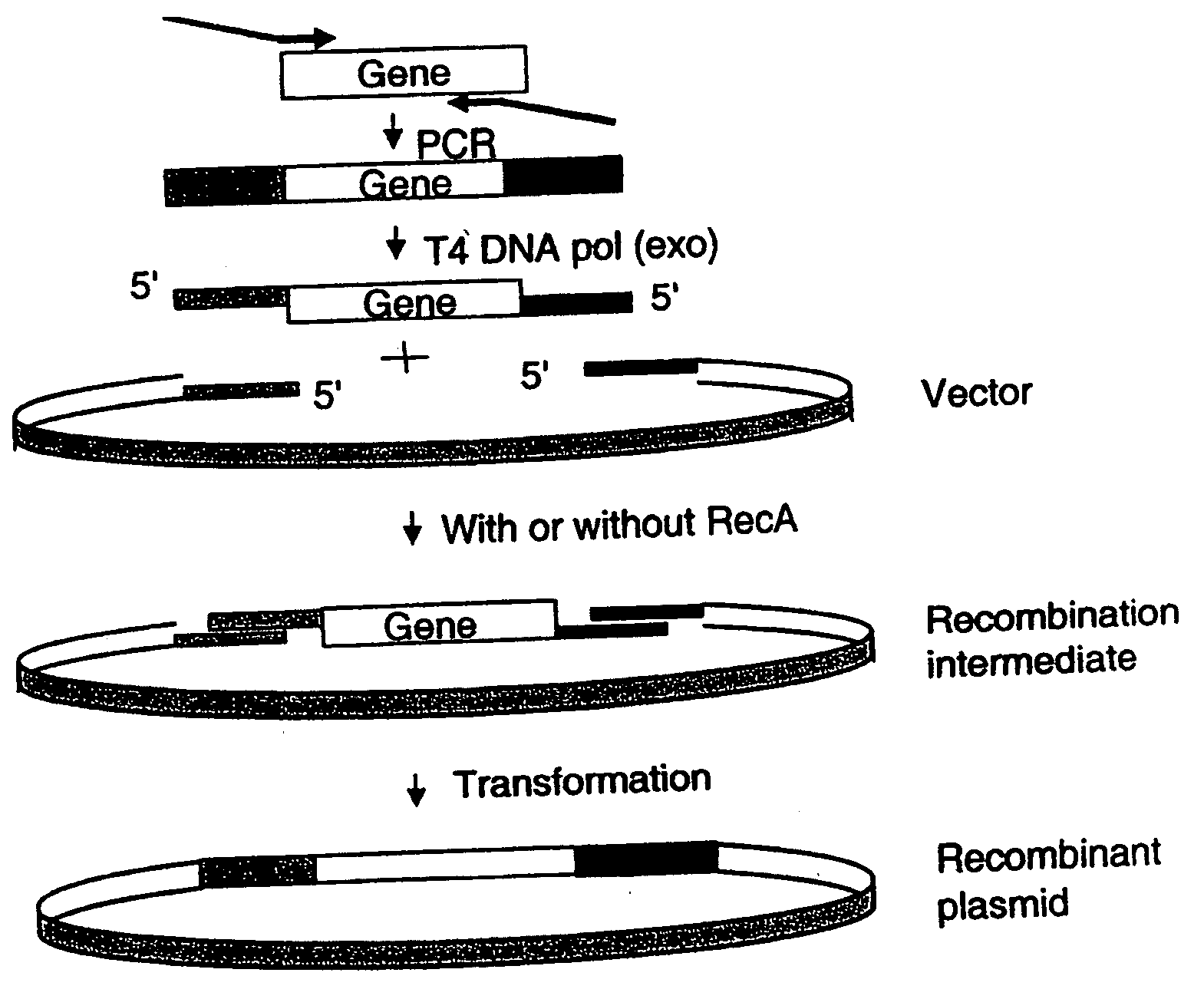
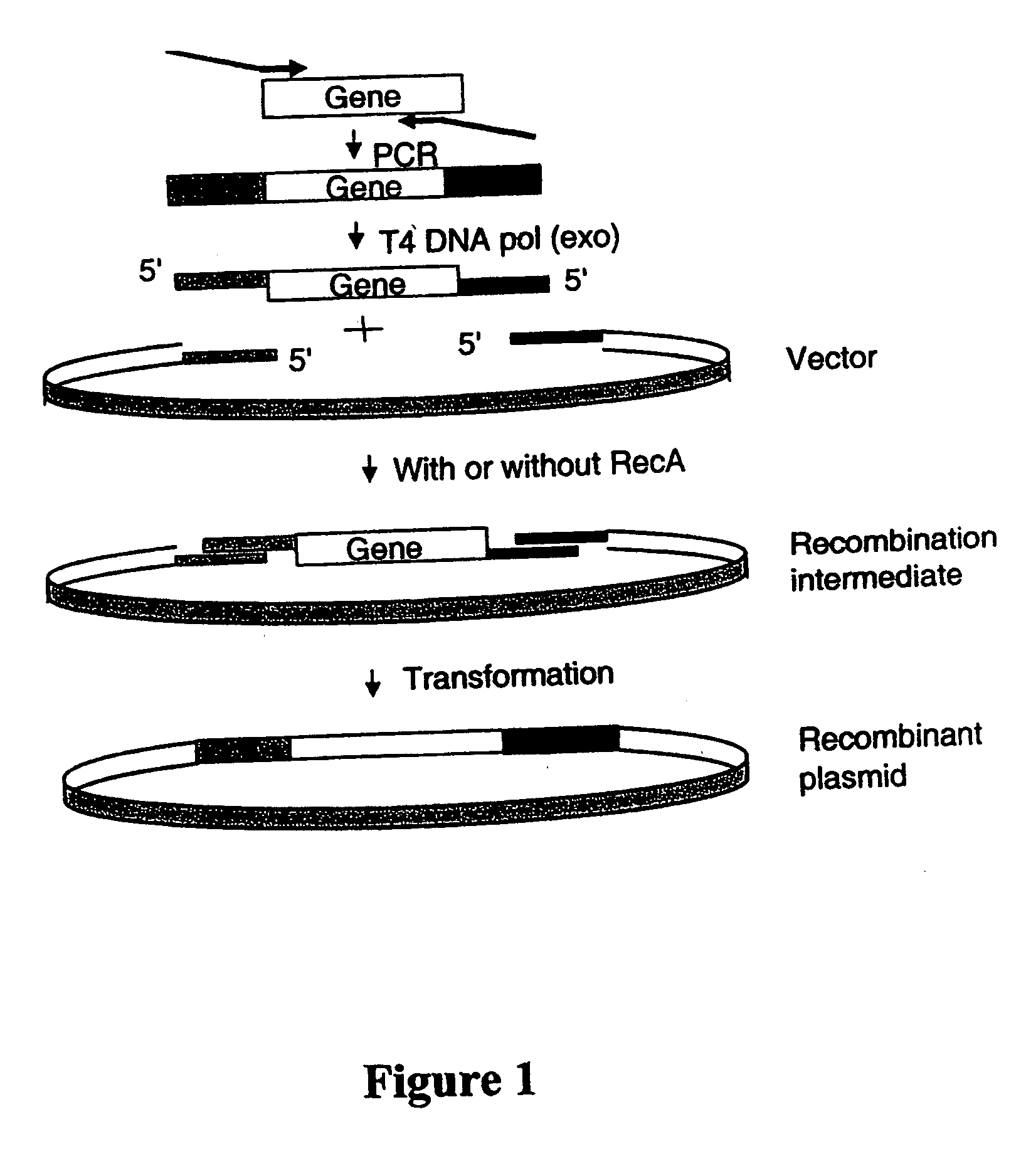
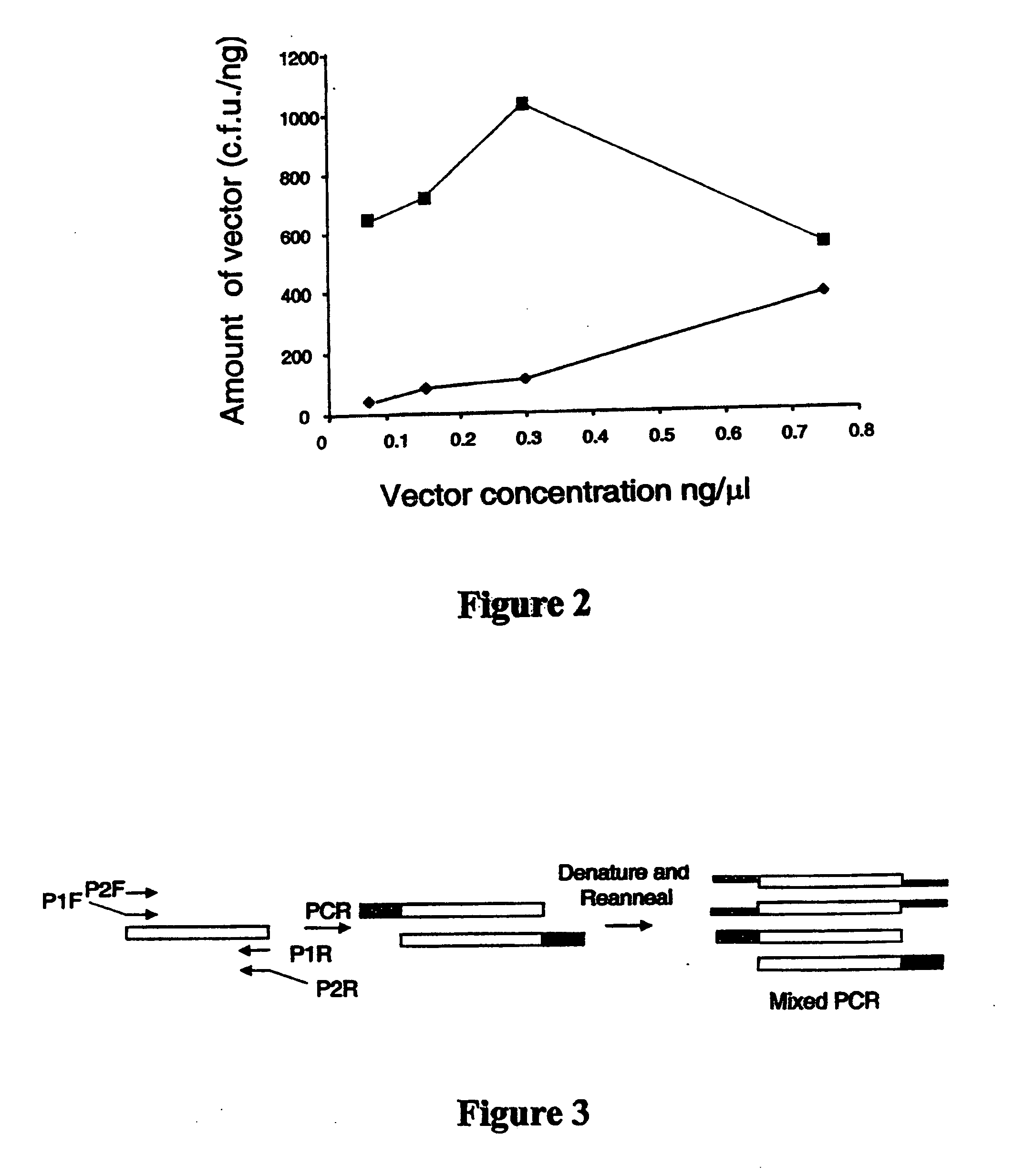
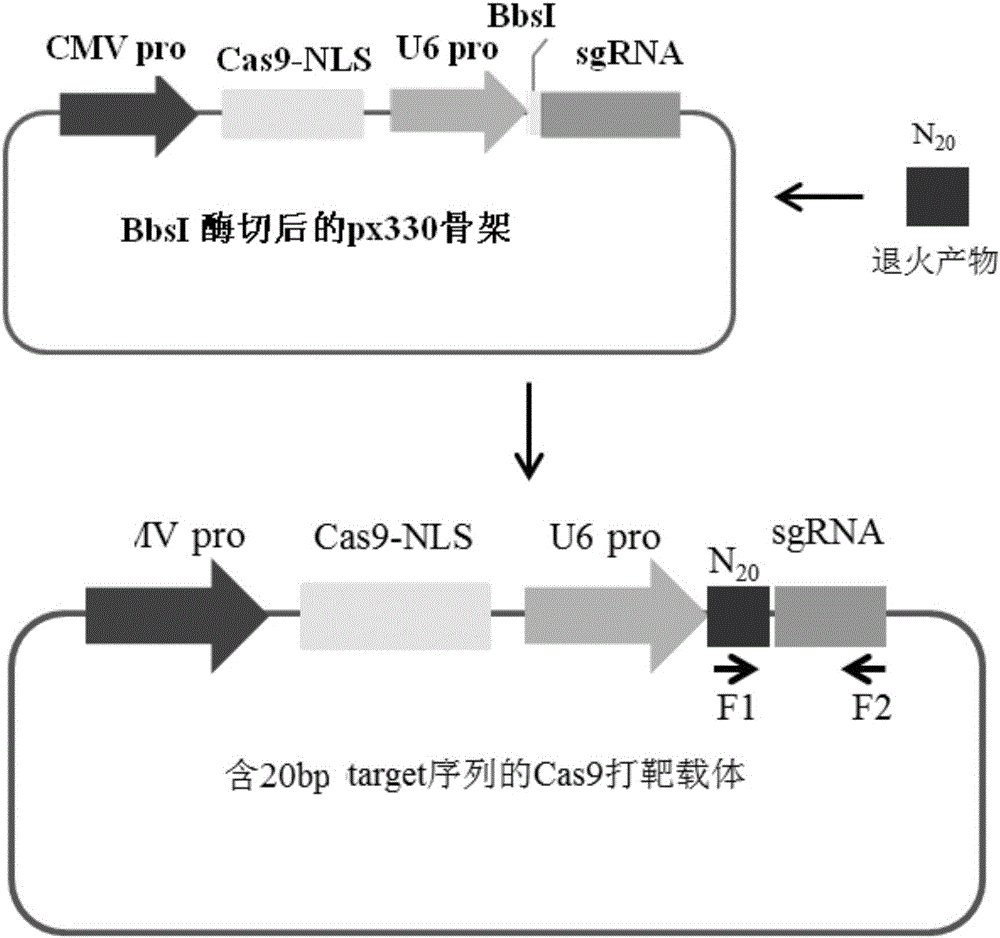
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1882 results about "Homologous recombination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks (DSB). Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses.
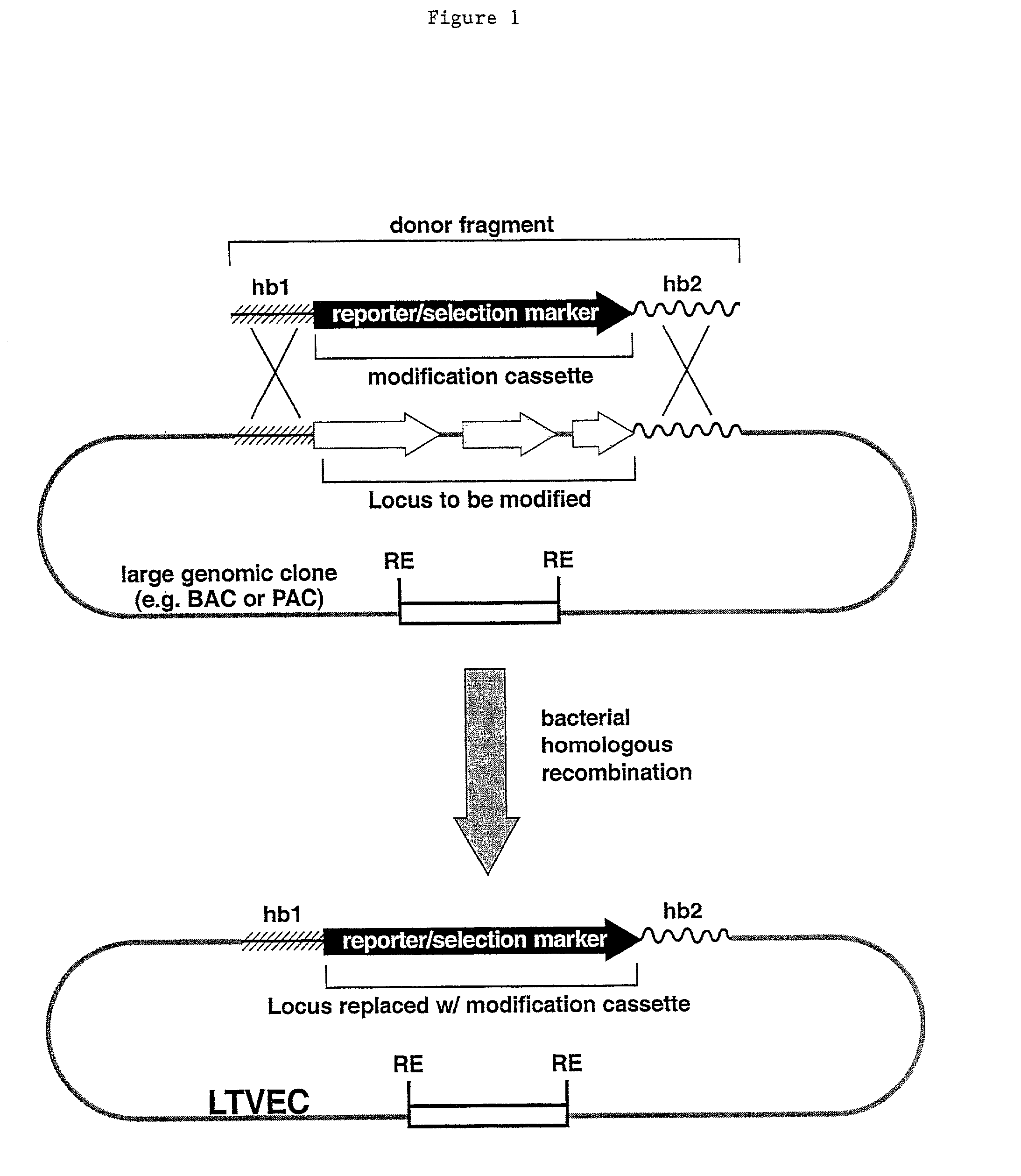
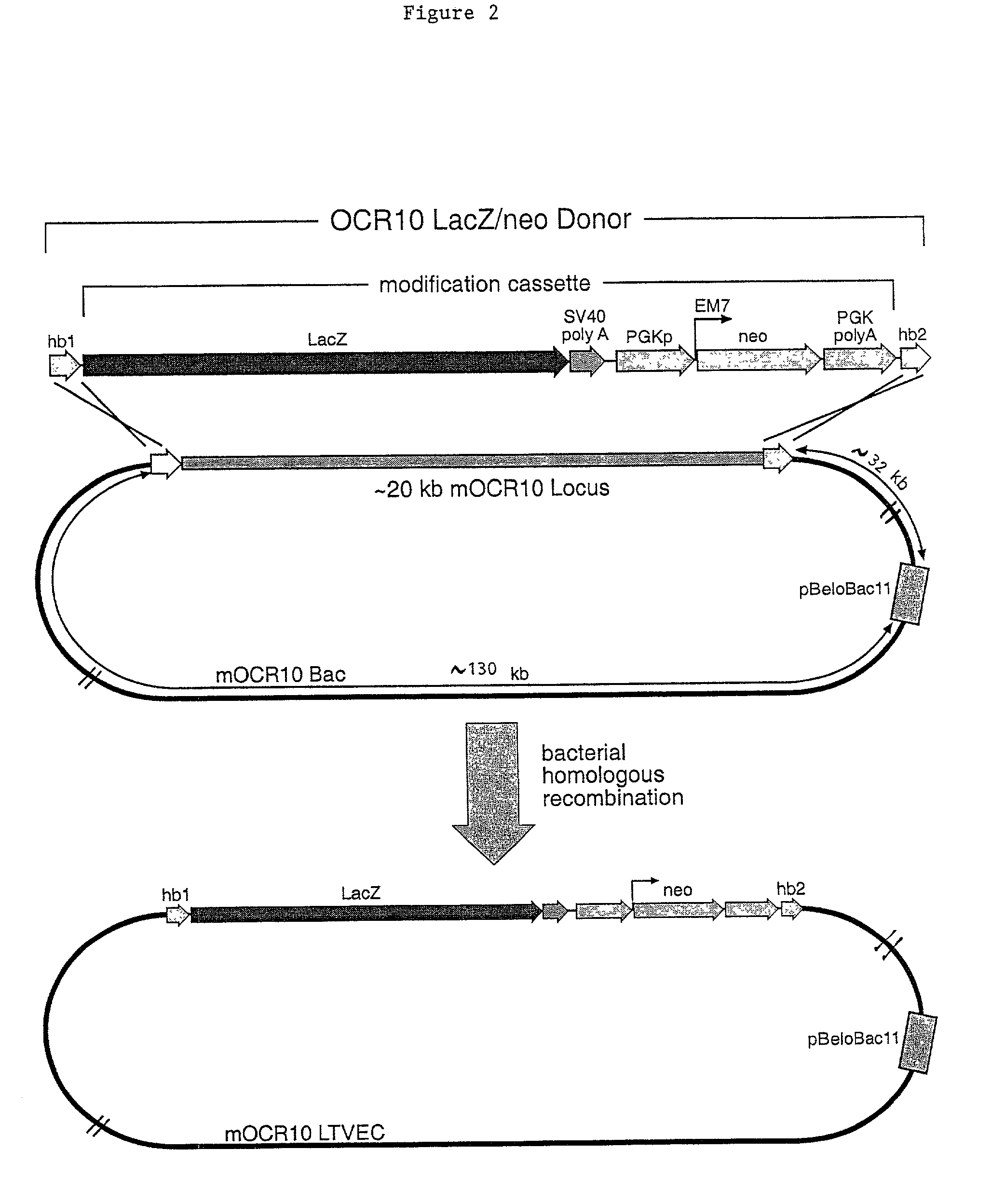
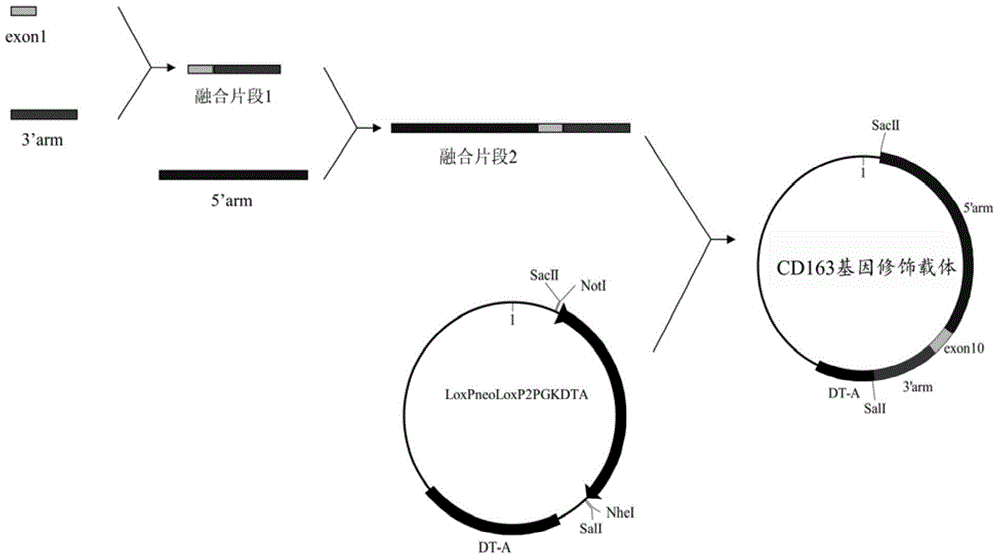
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
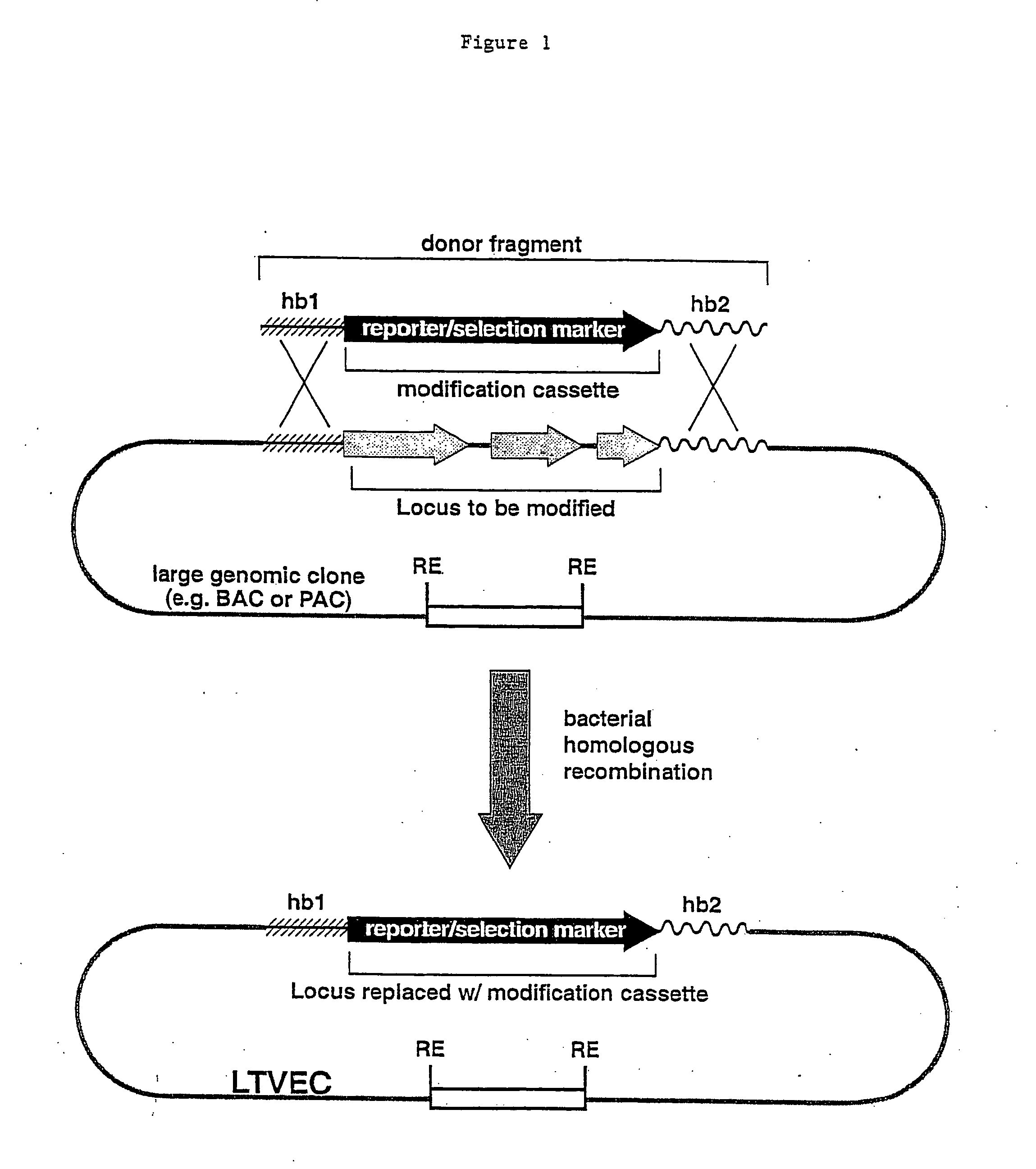
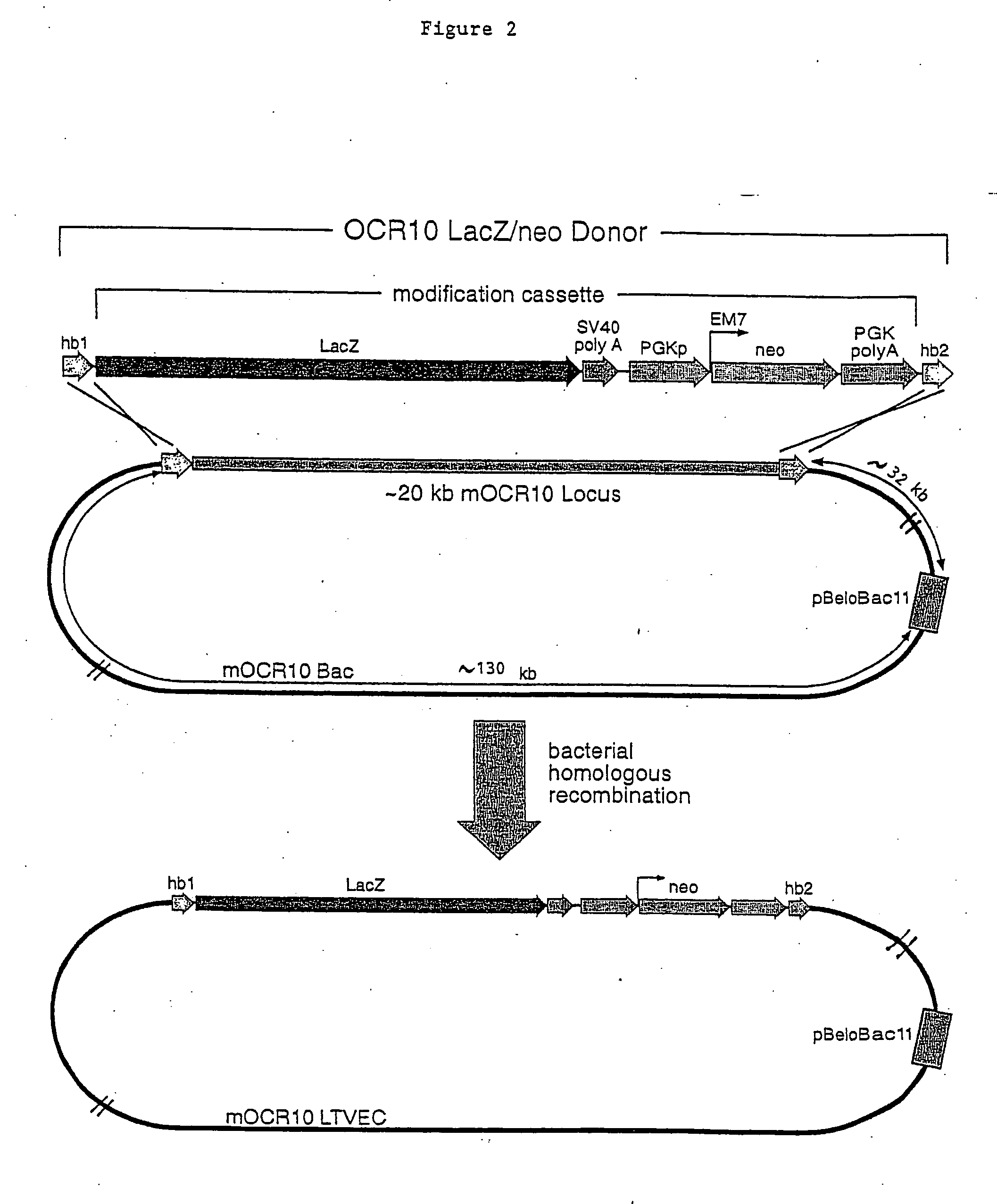
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Systems for in vivo site-directed mutagenesis using oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20040171154A1Large deletionImprove applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousSite-directed mutagenesis
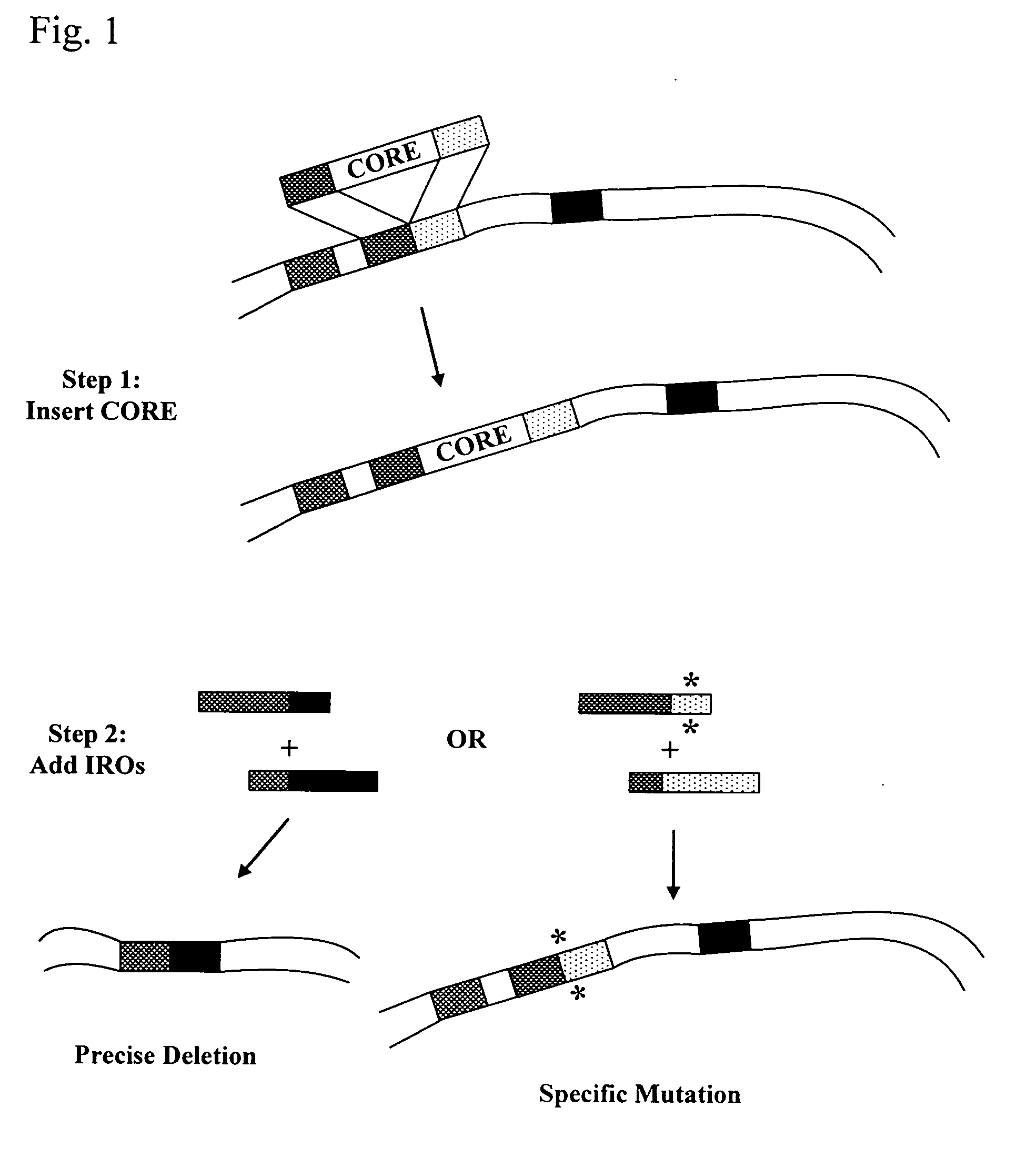
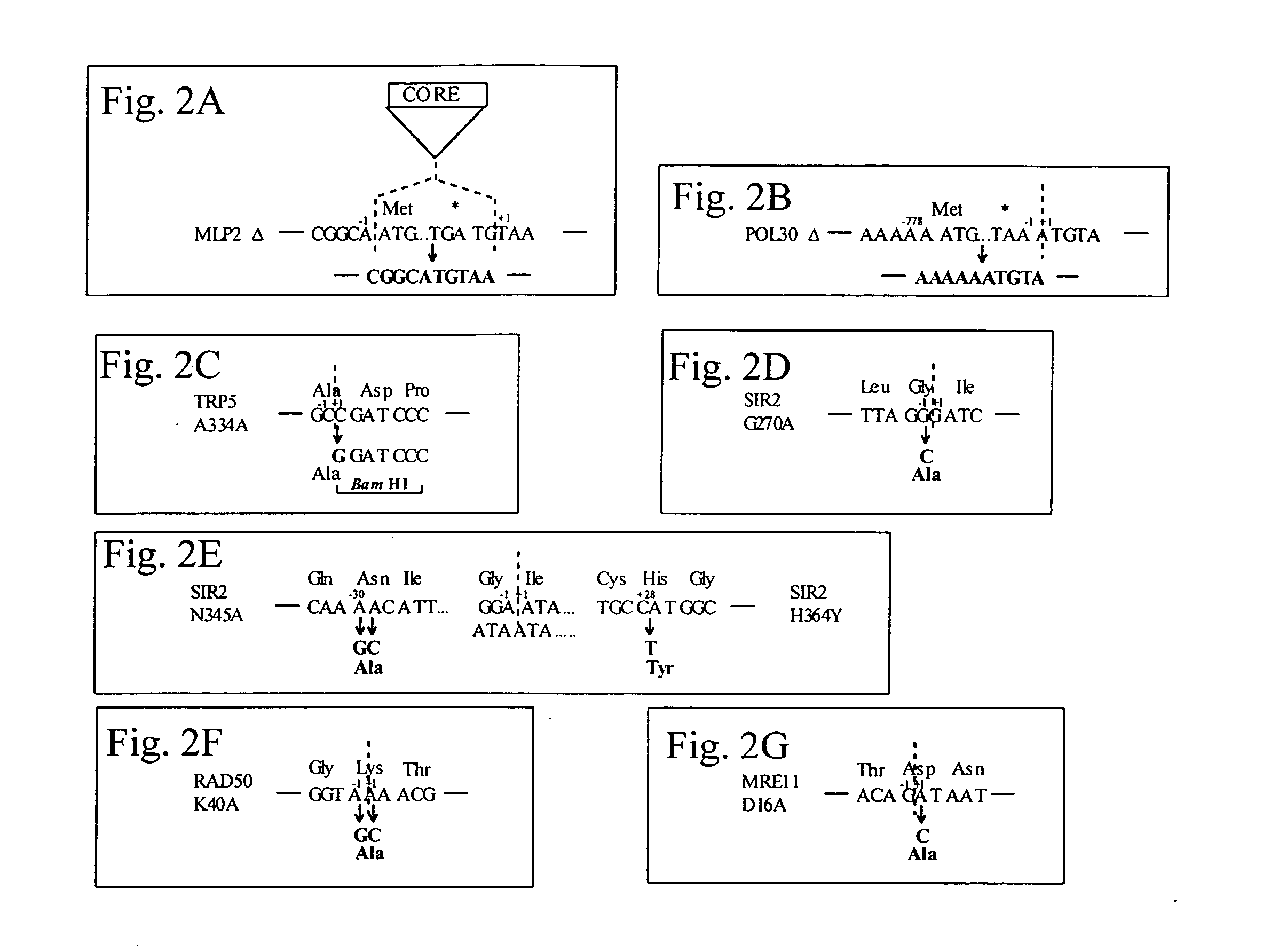
This disclosure provides several methods to generate nucleic acid mutations in vivo, for instance in such a way that no heterologous sequence is retained after the mutagenesis is complete. The methods employ integrative recombinant oligonucleotides (IROs). Specific examples of the described mutagenesis methods enable site-specific point mutations, deletions, and insertions. Also provided are methods that enable multiple rounds of mutation and random mutagenesis in a localized region. The described methods are applicable to any organism that has a homologous recombination system.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Method for integrating genes at specific sites in mammalian cells via homologous recombination and vectors for accomplishing the same
InactiveUS6413777B1Reduce in quantityImprove the level ofPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMammalReactive site
A method for achieving site specific integration of a desired DNA at a target site in a mammalian cell via homologous recombination is described. This method provides for the reproducible selection of cell lines wherein a desired DNA is integrated at a predetermined transcriptionally active site previously marked with a marker plasmid. The method is particularly suitable for the production of mammalian cell lines which secrete mammalian proteins at high levels, in particular immunoglobulins. Novel vectors and vector combinations for use in the subject cloning method are also provided.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous genes(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
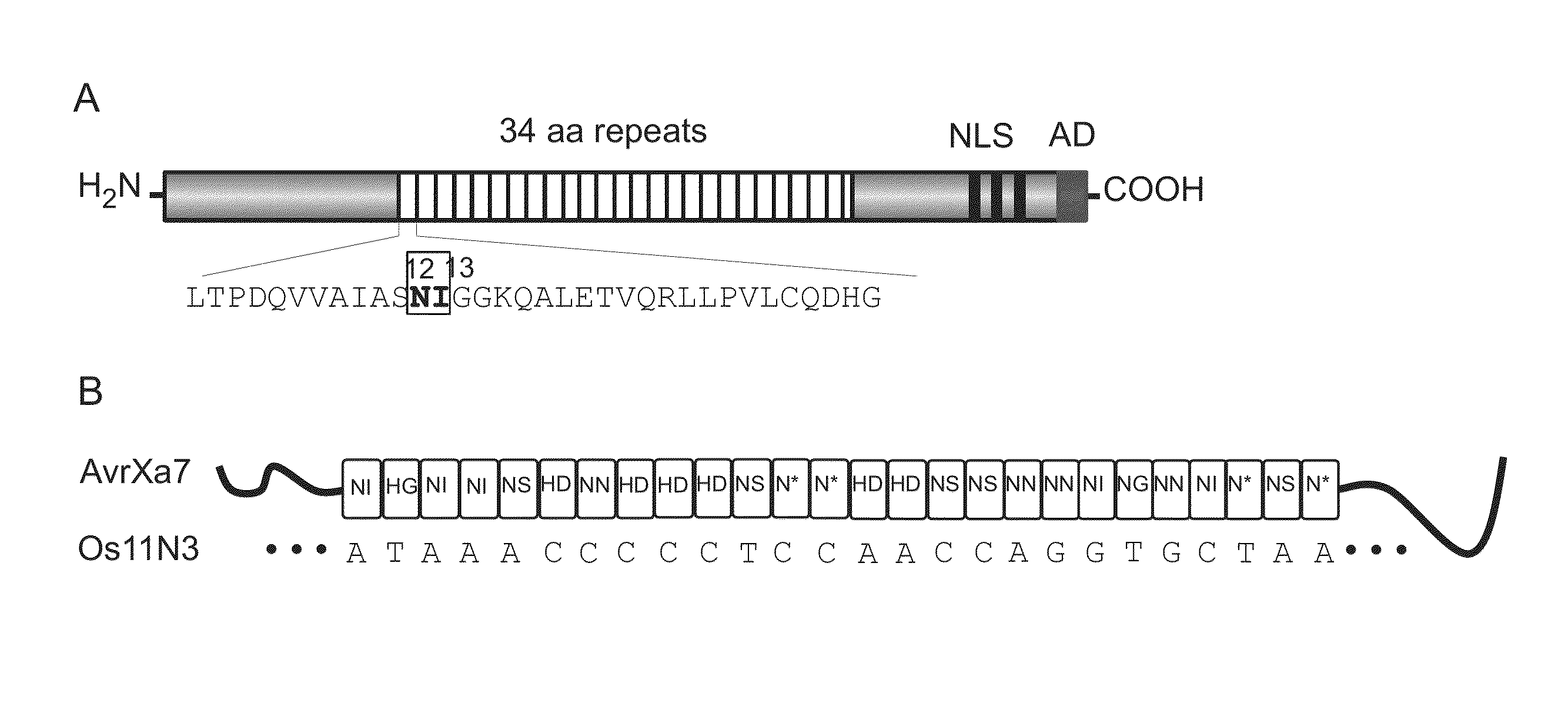
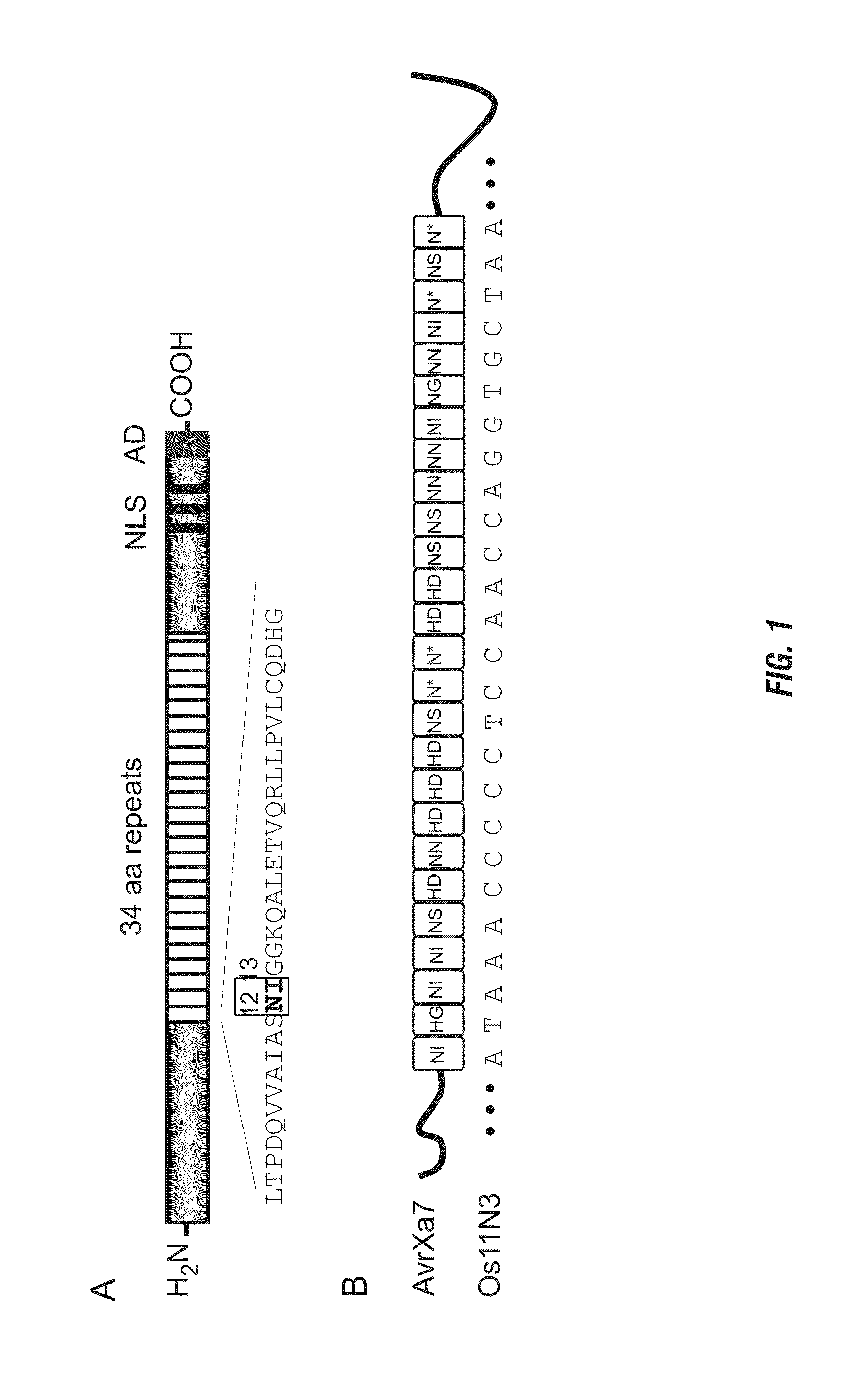
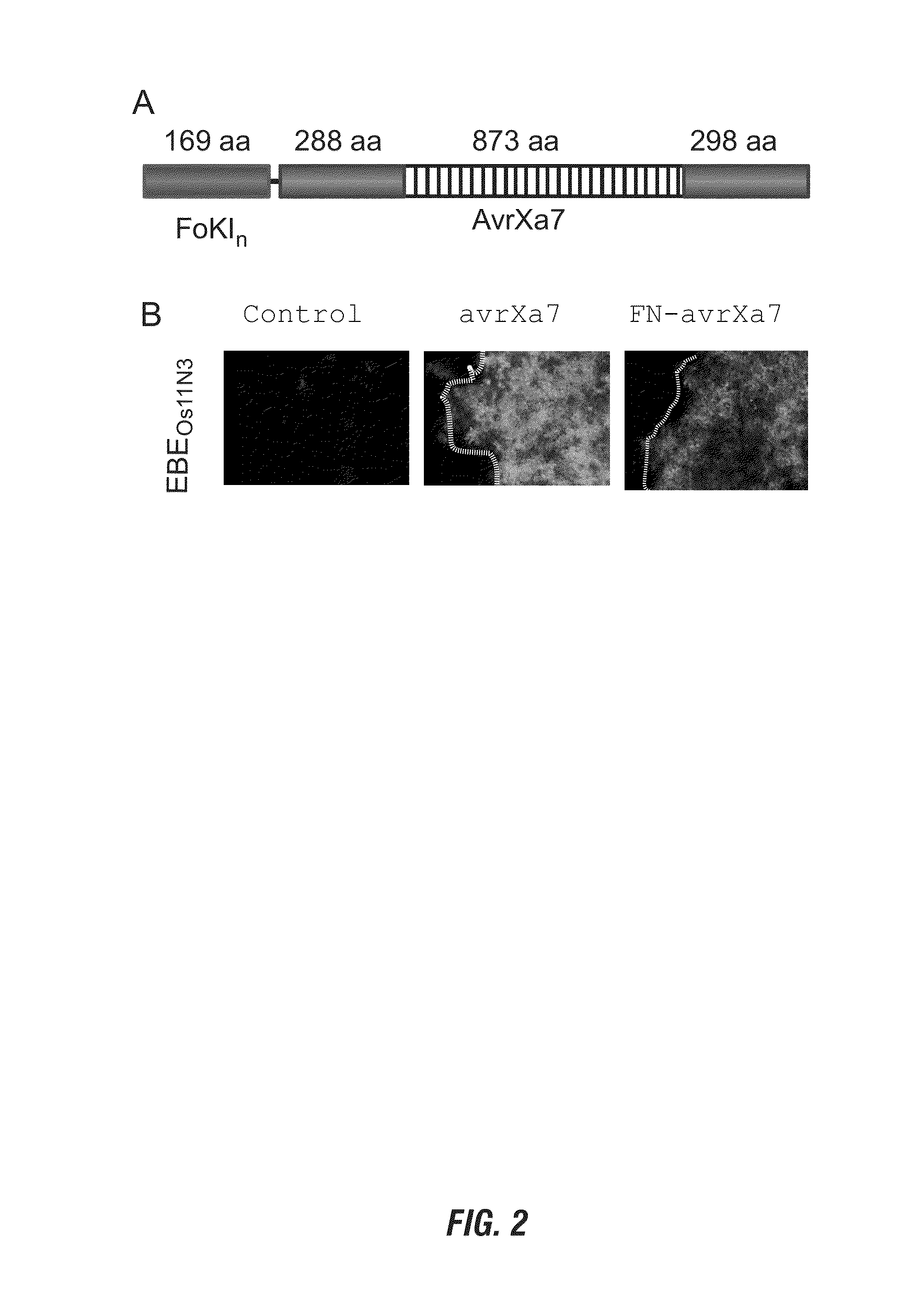
Nuclease activity of tal effector and foki fusion protein
The present invention provides compositions and methods for targeted cleavage of cellular chromatin in a region of interest and / or homologous recombination at a predetermined site in cells. Compositions include fusion polypeptides comprising a TAL effector binding domain and a cleavage domain. The cleavage domain can be from any endonuclease. In certain embodiments, the endonuclease is a Type IIS restriction endonuclease. In further embodiments, the Type IIS restriction endonuclease is FokI.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method for constructing gene site-directed mutation
ActiveCN103388006AEfficient constructionRaise the ratioVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsMulti siteEmbryo
Owner:BIORAY LABORATORIES INC
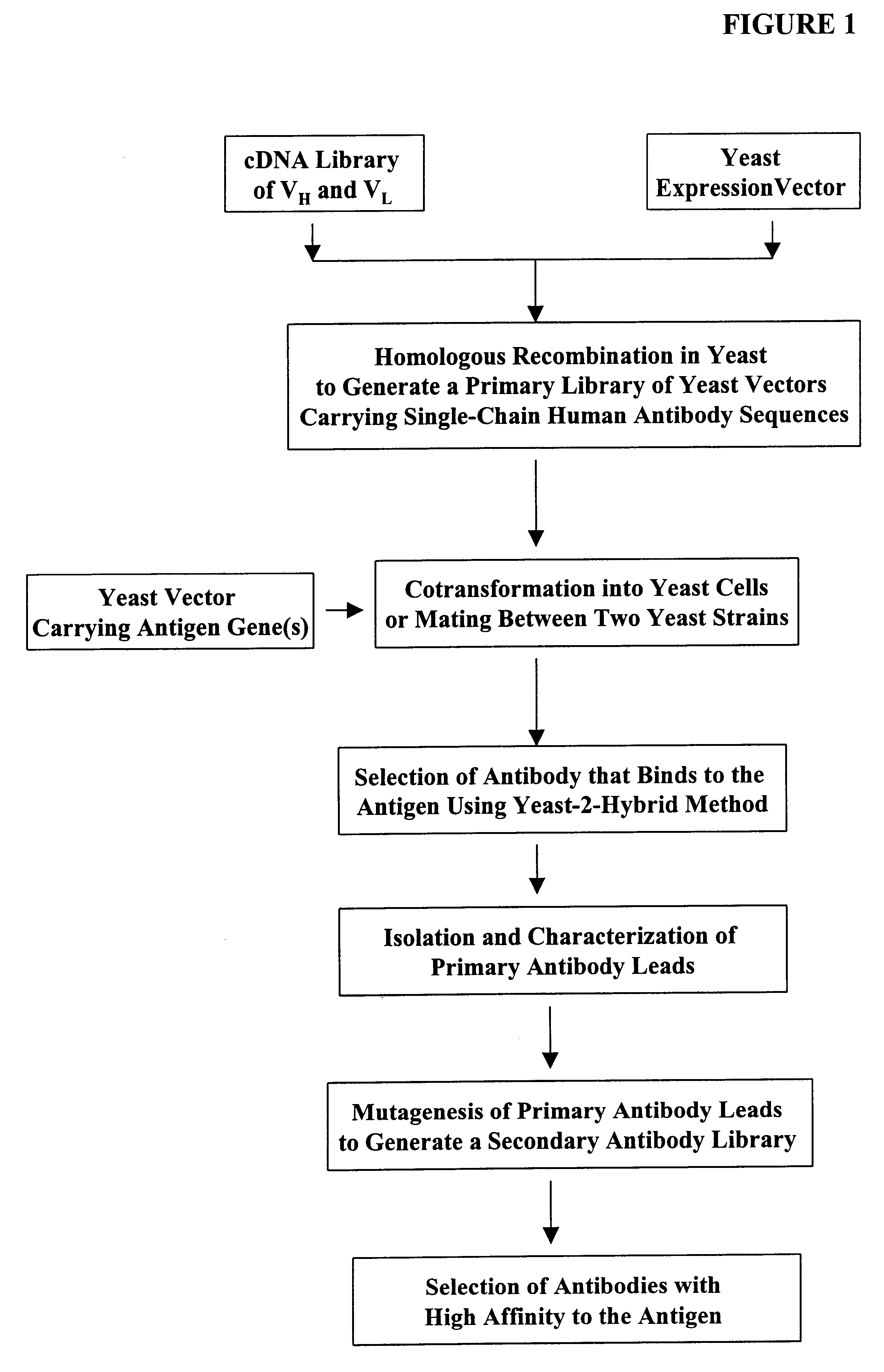
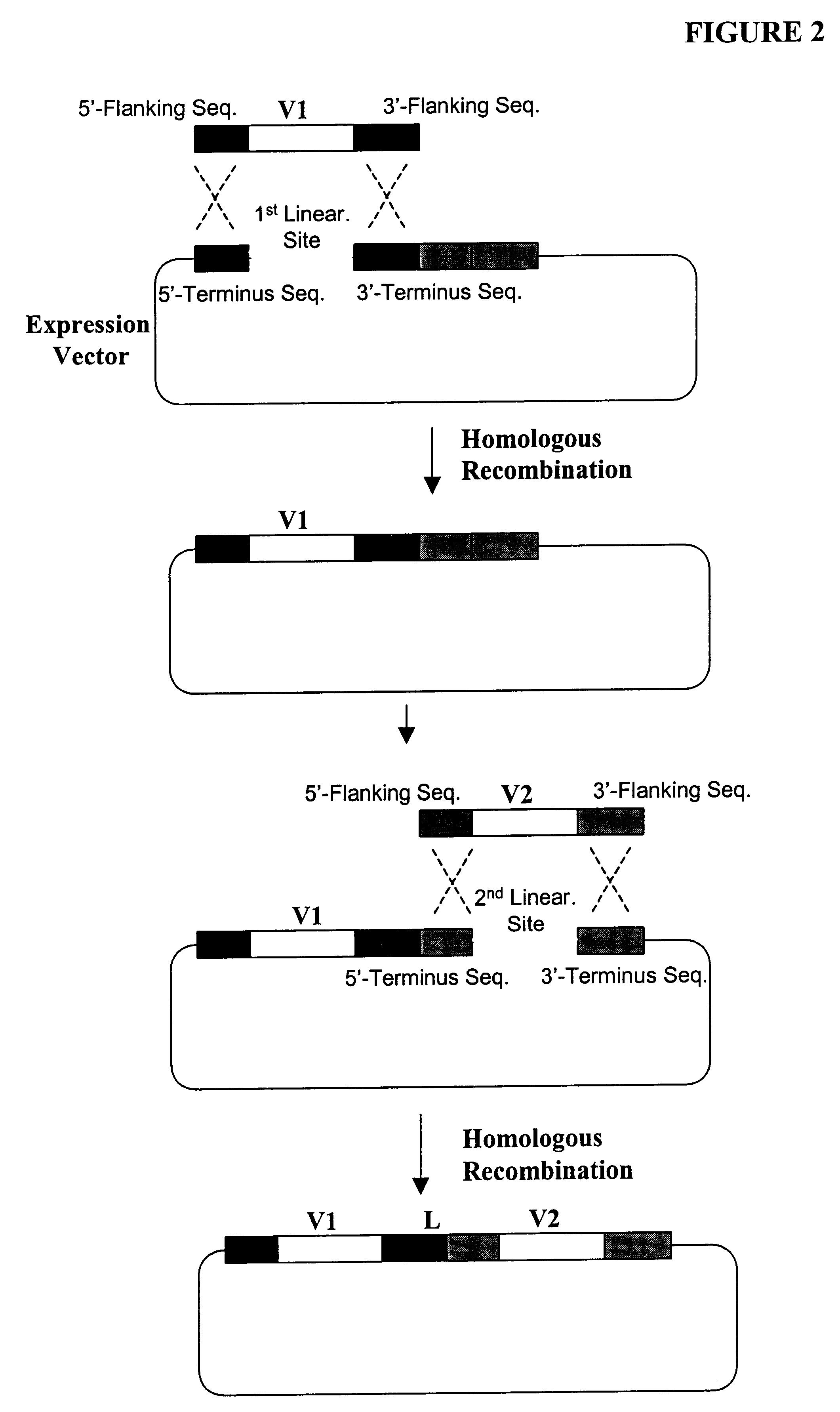
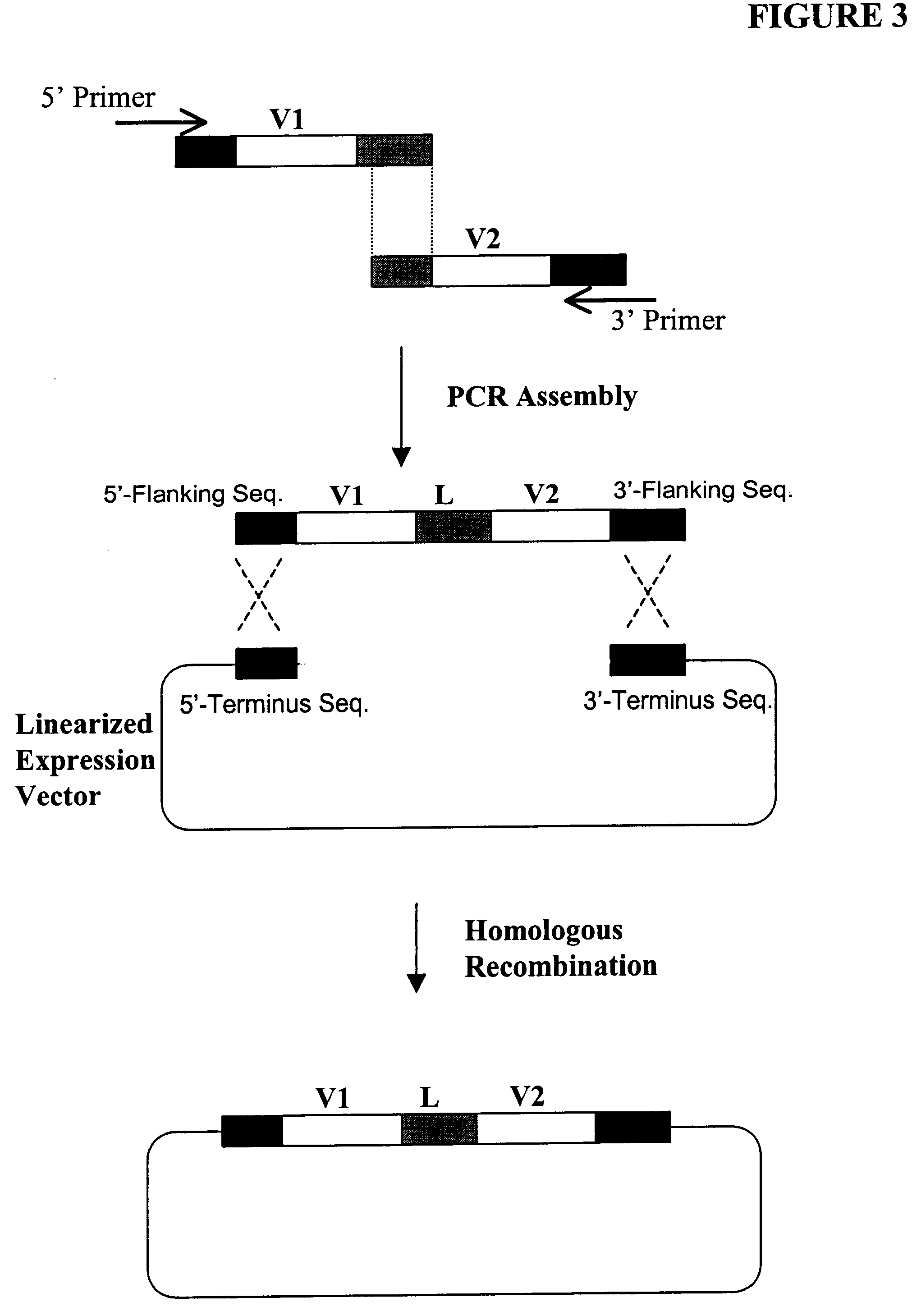
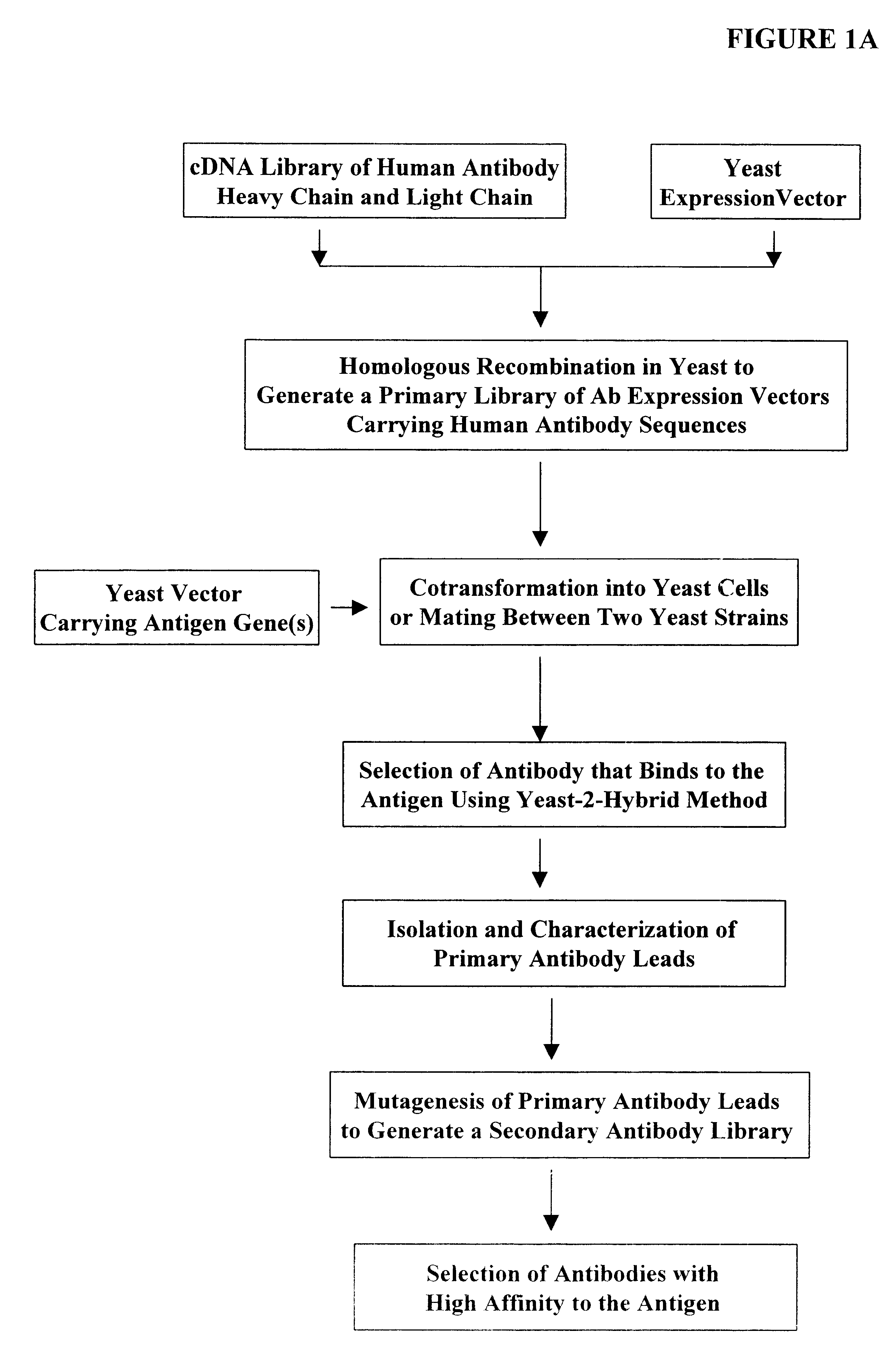
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6406863B1High affinityEasy to assembleMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsTarget peptideIn vivo
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Method of targeted gene disruption, genome of hyperthermostable bacterium and genome chip using the same
It is intended to provide an efficient and sure gene targeting method embodied at an arbitrary position in the genome of an organism and a kit therefor. It is also intended to provide a method for targeted-disruption of an arbitrary gene in the genome of an organism which comprises: 1) the step of providing the whole sequencial data of the genome of the organism; 2) the step of selecting at least one arbitrary region in the sequence; 3) the step of providing a vector containing a sequence homologous with the region selected above and a marker gene; 4) the step of transforming the organism by the vector; and 5) the step of providing the organism under such conditions as allowing homologous recombination. Moreover, the genome of a hyperthermostable bacterium and its array are provided.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
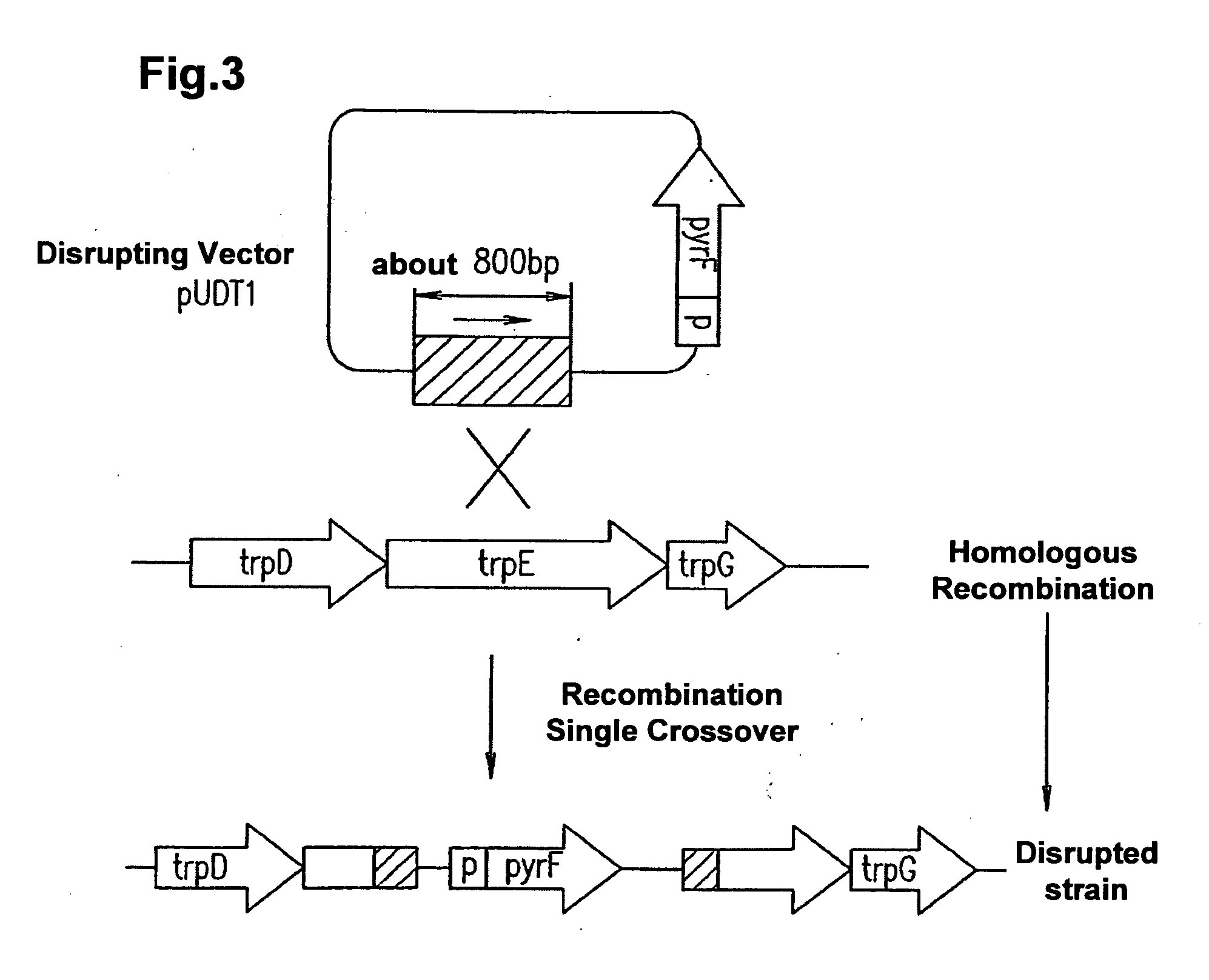
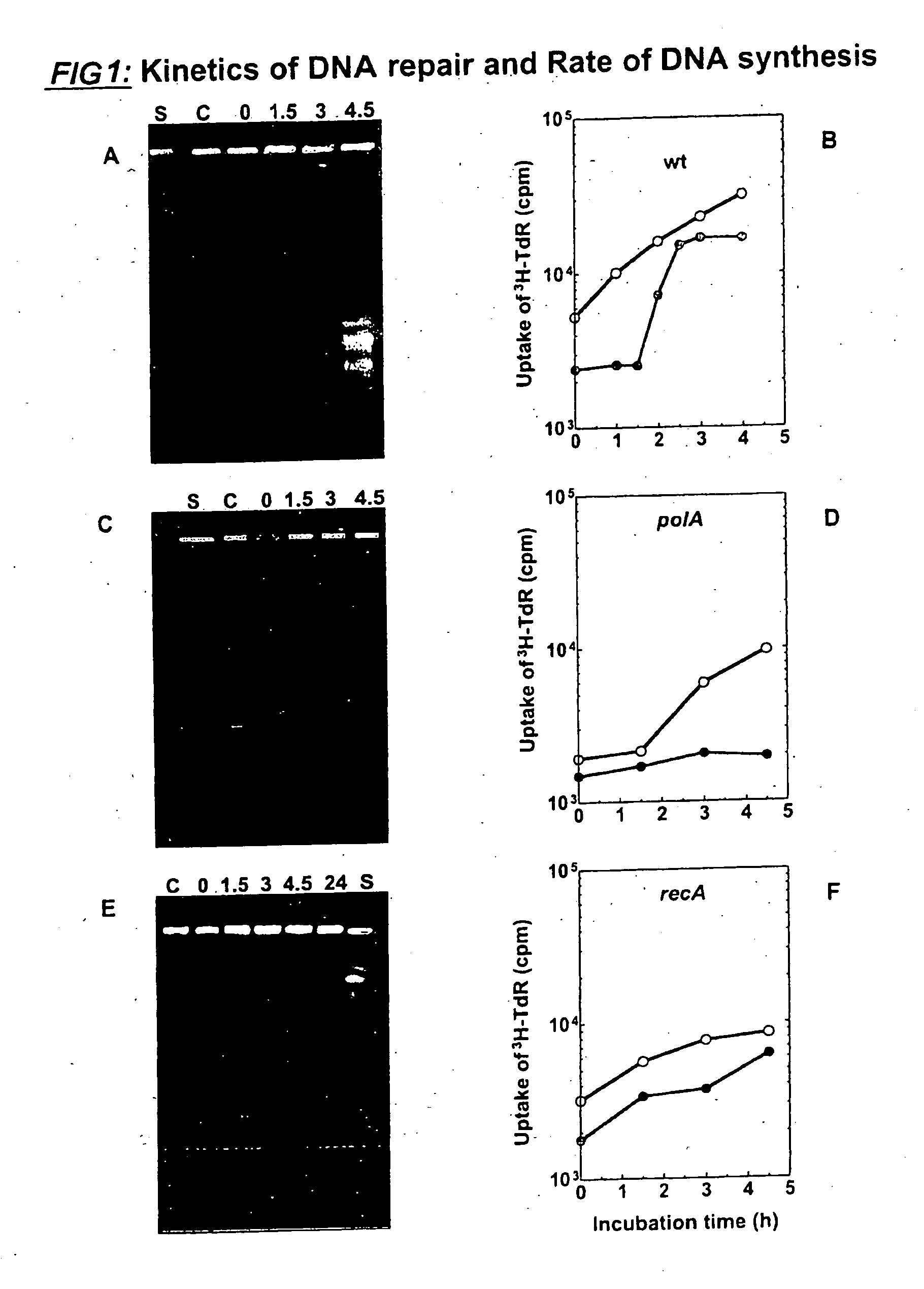
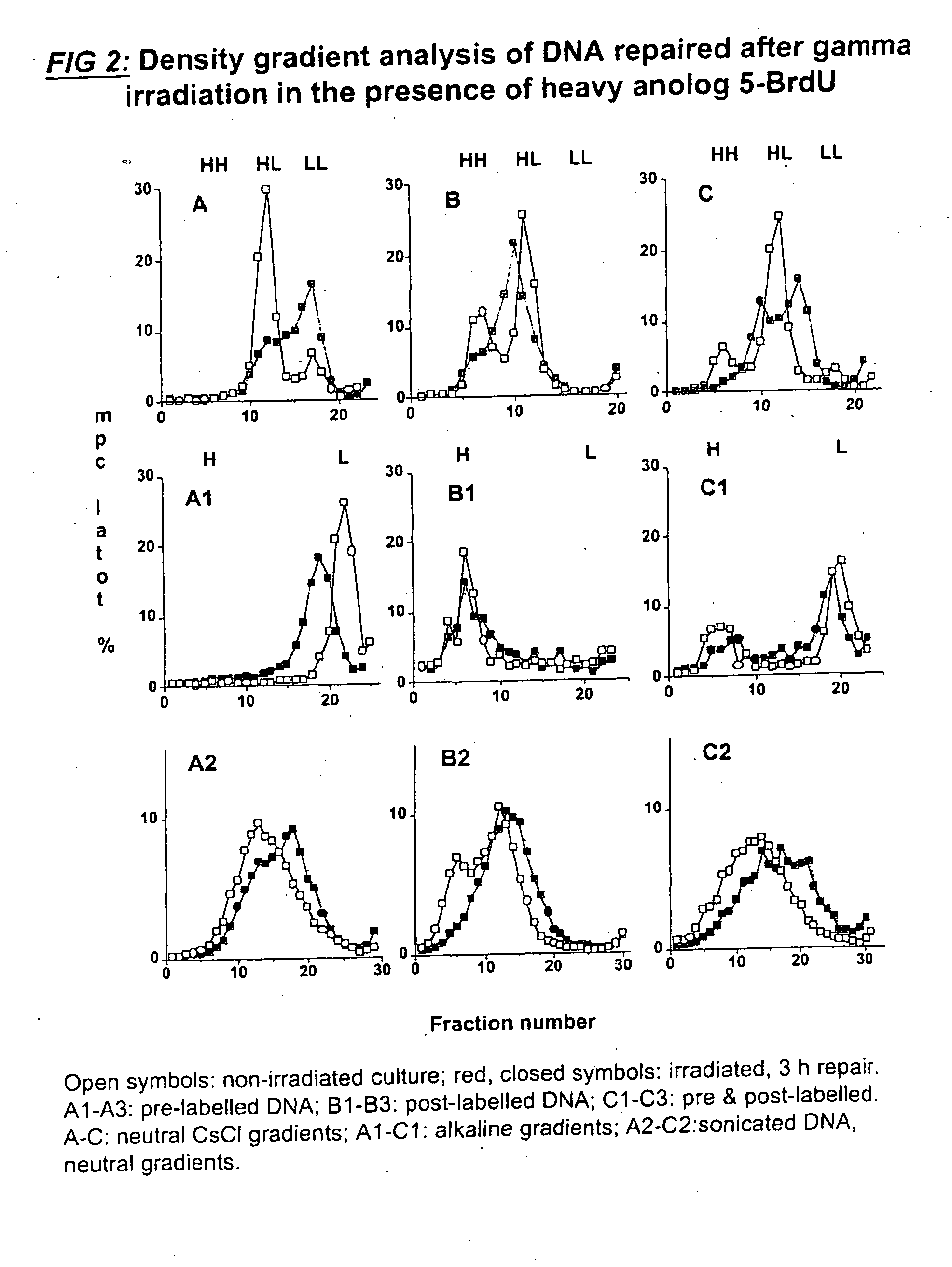
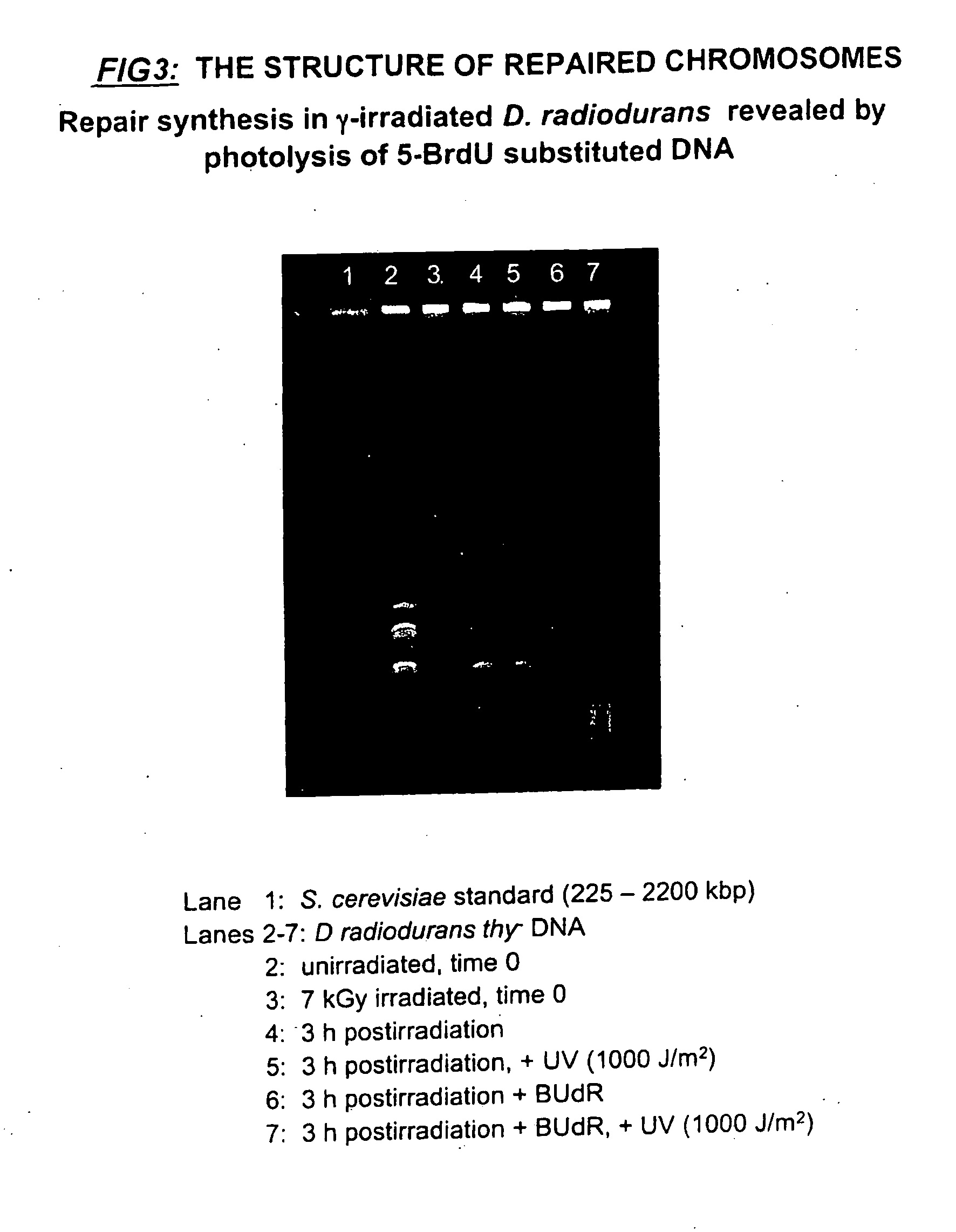
Process for Chromosomal Engineering Using a Novel Dna Repair System
This invention relates to chromosomal engineering via DNA repair process. The process of the invention comprises the steps of: 1) submitting at least one source of biological activity, e.g. Deinococcus radiodurans, to radiation, desiccation and / or chemical treatment liable to damage the DNA, so as to substantially shatter its chromosomes into short fragments; 2) annealing complementary single strand tails extended by the synthesis templated on partially overlapping DNA fragments of said shattered chromosomes; 4) converting the resulting long linear DNA intermediates into intact circular chromosomes, by means of a RecA dependent homologous recombination; whereas at least one foreign source of genetic material, e.g. DNA, can be introduced during steps 2 and / or 3; and 4) optionally separating and collecting the recombined chromosomes thus obtained.
Owner:DEINOVE SA
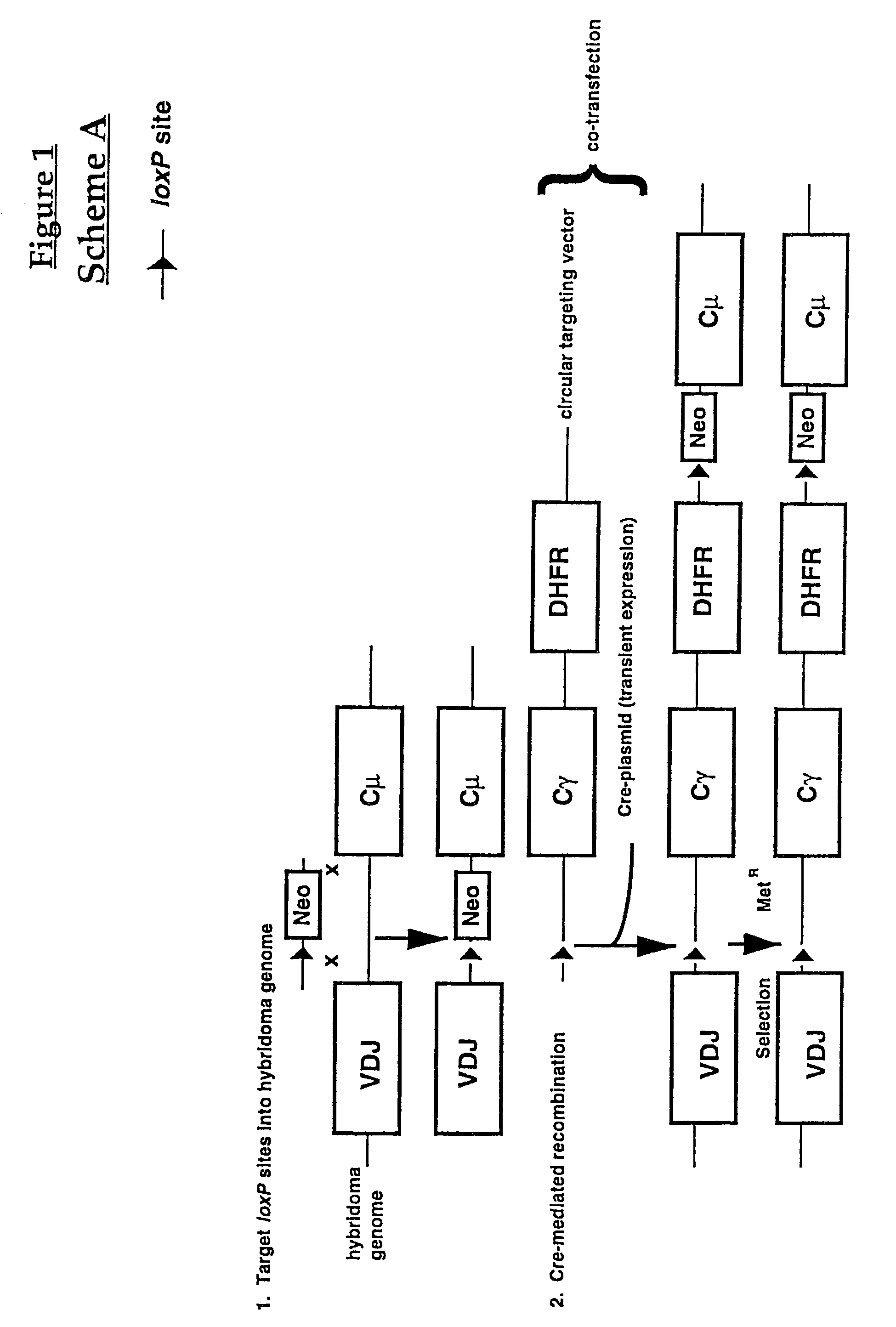
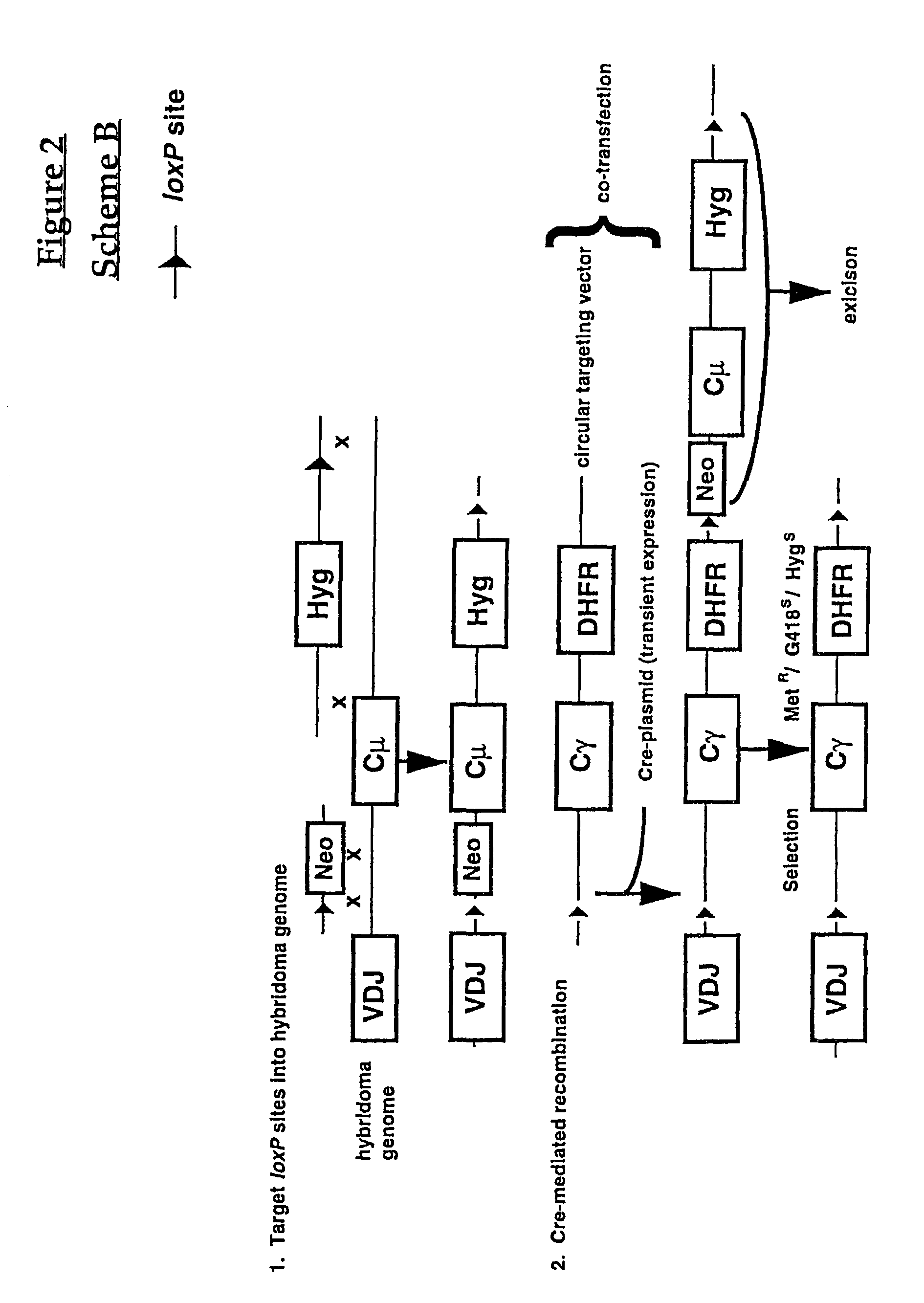
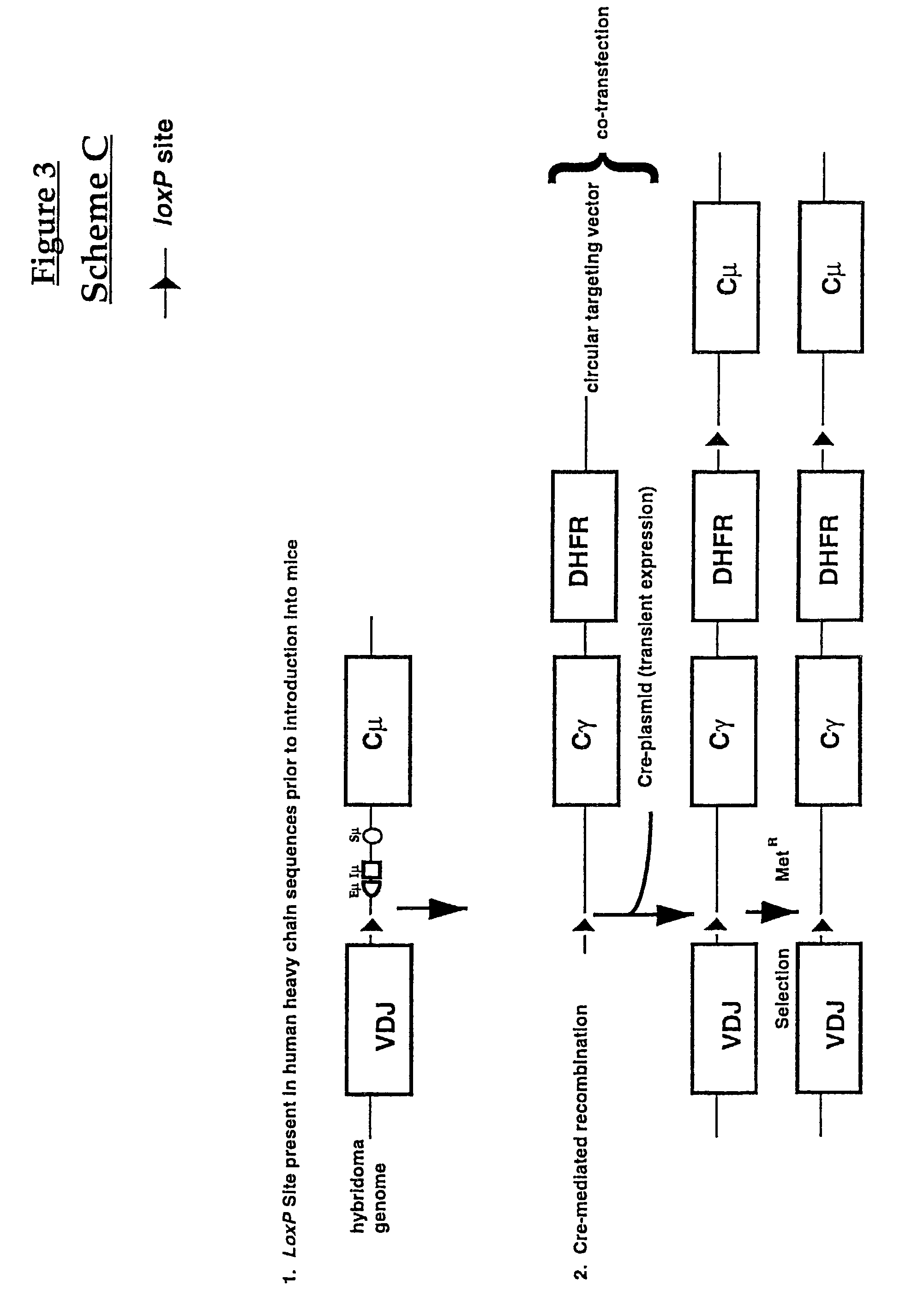
Production of antibodies using cre-mediated site-specific recombination
InactiveUS7145056B2Improve recombination efficiencyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesSite-specific recombinationAntibody-Producing Cells
A method to produce a cell expressing an antibody from a genomic sequence of the cell comprising a modified immunoglobulin locus using Cre-mediated site-specific recombination is disclosed. The method involves first transfecting an antibody-producing cell with a homology-targeting vector comprising a lox site and a targeting sequence homologous to a first DNA sequence adjacent to the region of the immunoglobulin loci of the genomic sequence which is to be converted to a modified region, so the first lox site is inserted into the genomic sequence via site-specific homologous recombination. Then the cell is transfected with a lox-targeting vector comprising a second lox site suitable for Cre-mediated recombination with the integrated lox site and a modifying sequence to convert the region of the immunoglobulin loci to the modified region. This conversion is performed by interacting the lox sites with Cre in vivo, so that the modifying sequence inserts into the genomic sequence via Cre-mediated site-specific recombination of the lox sites. Also disclosed are a form of the method used to produce a cell expressing a modified antibody molecule using Cre-mediated site-specific recombination, and antibody-producing cells obtainable by the disclosed methods. Class-switching modifications of human antibodies produced in murine hybridoma cells are exemplified.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC +1
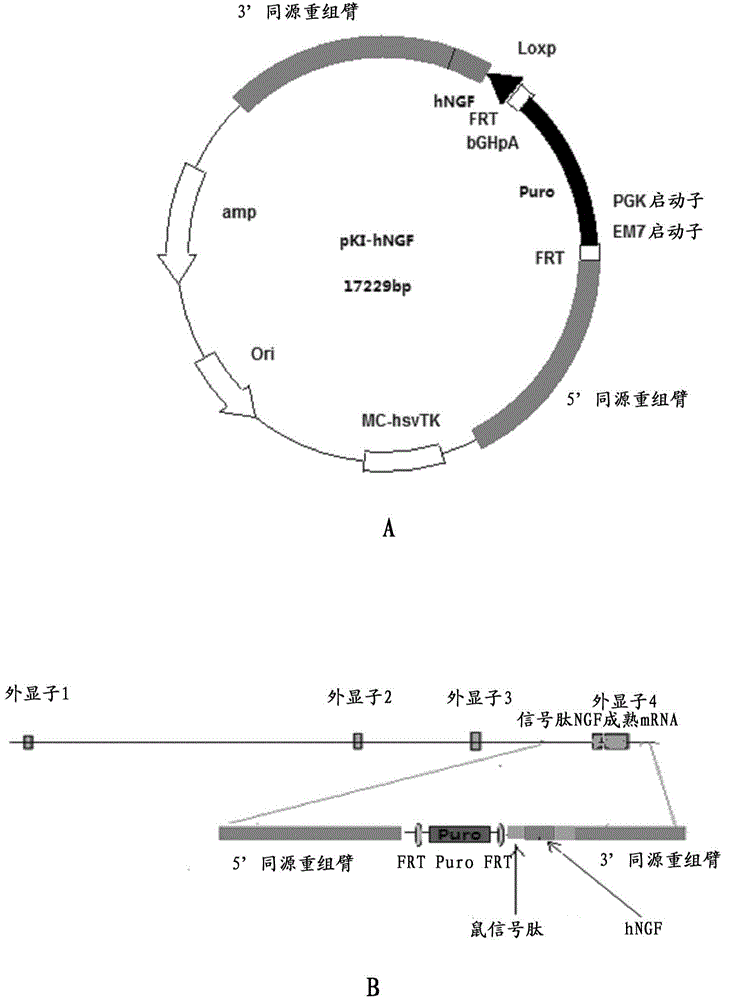
Preparation method for transgenic mice capable of producing human nerve growth factor
ActiveCN104561095AEasy to operateIncrease success rateAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionPlasmid dnaGenetically modified mouse
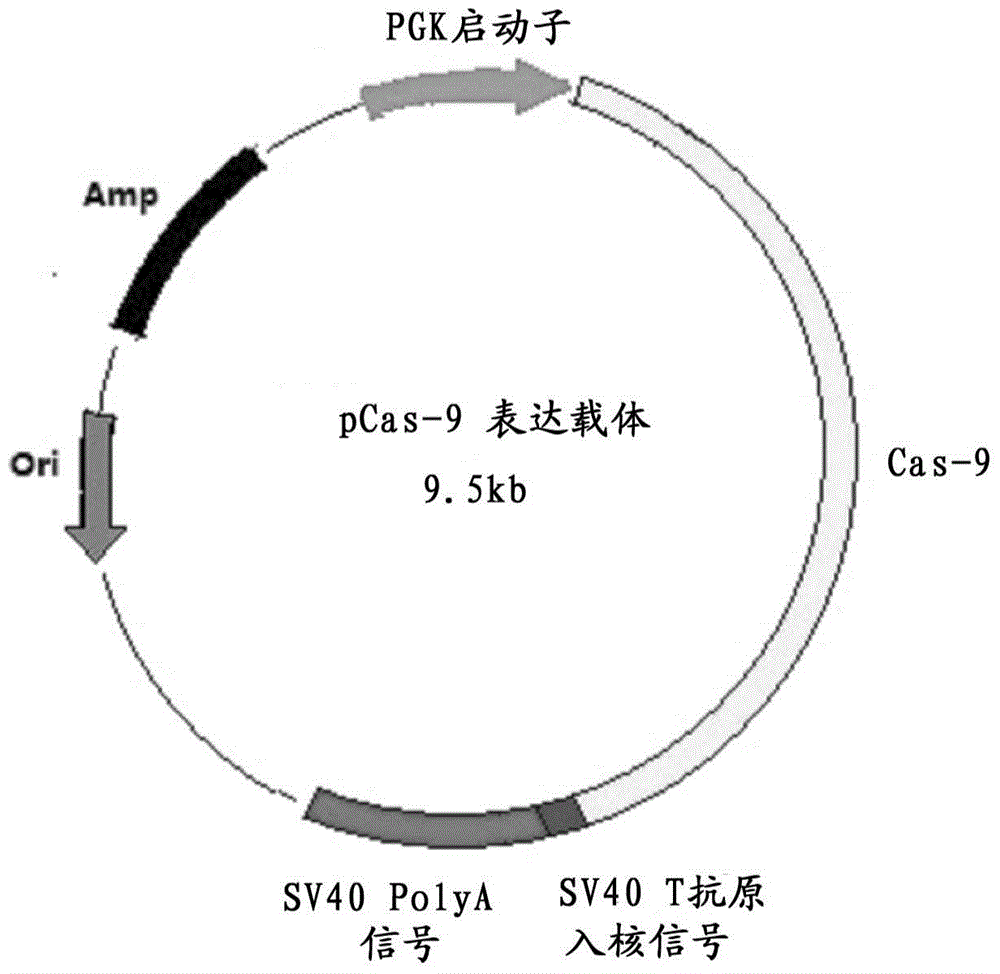
The invention discloses a method for producing transgenic mice through a homologous recombination technology. The method comprises the following steps: replacing mouse NGF genes on mouse chromosomes by human NGF genes through a Cas-9 / CRISPR gene knock-in technology, and obtaining the genes with homozygous human NGF genes through breeding and knocking the genes in mice, thus obtaining filial generation mice with salivary glands capable of secreting human NGF. Compared with the conventional targeting technology utilizing positive and negative double screening homologous recombination genes, the method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, capable of being realized only by transfecting mouse embryonic stem cells by three plasmid DNAs or carrying out pronucleus injection on the zygotes of mice, and high in success rate which is up to 2-5% and remarkably higher than the mouse embryonic stem cell positive rate of 0.1% of the common gene targeting technology.
Owner:深圳市国创纳米抗体技术有限公司
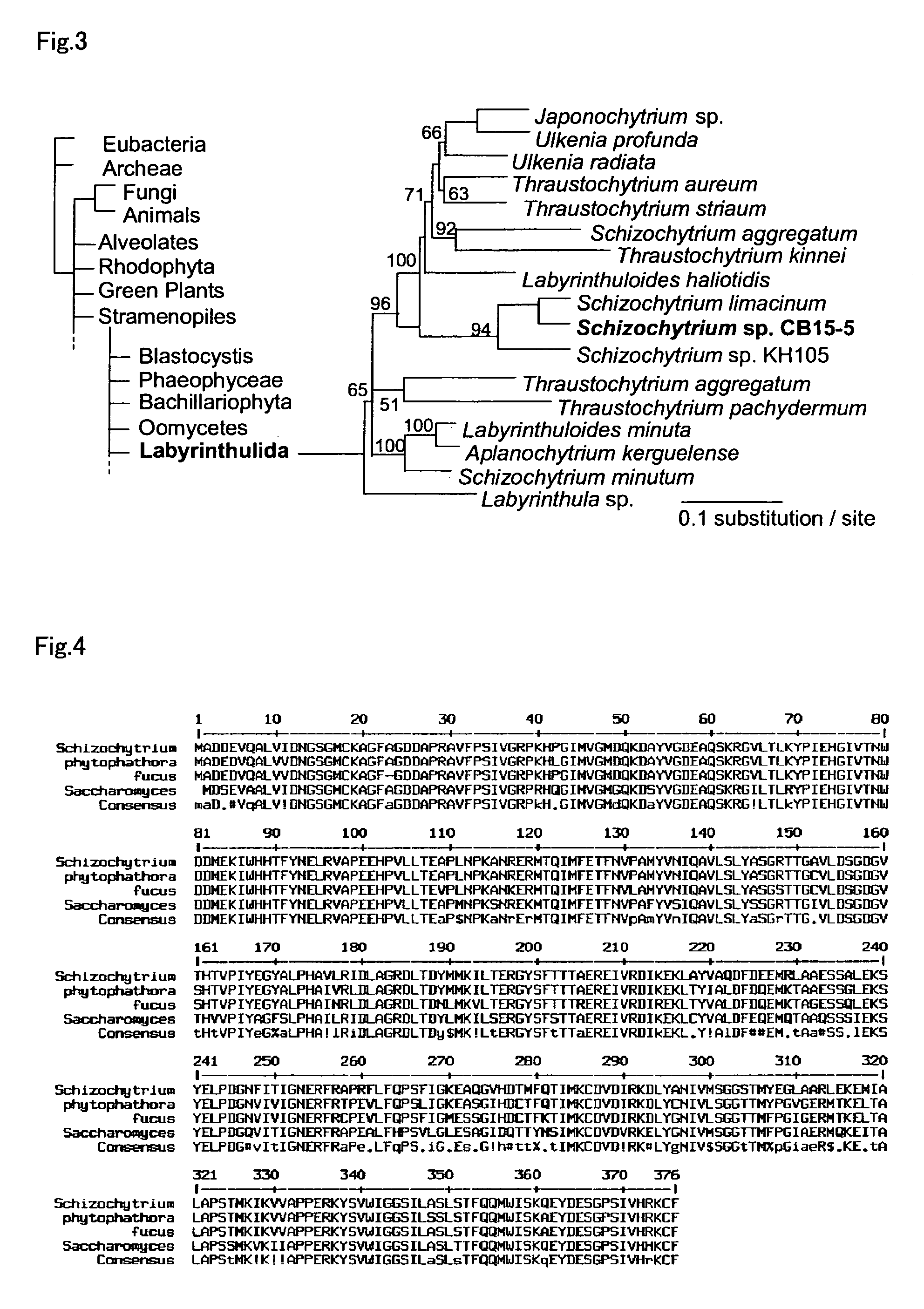
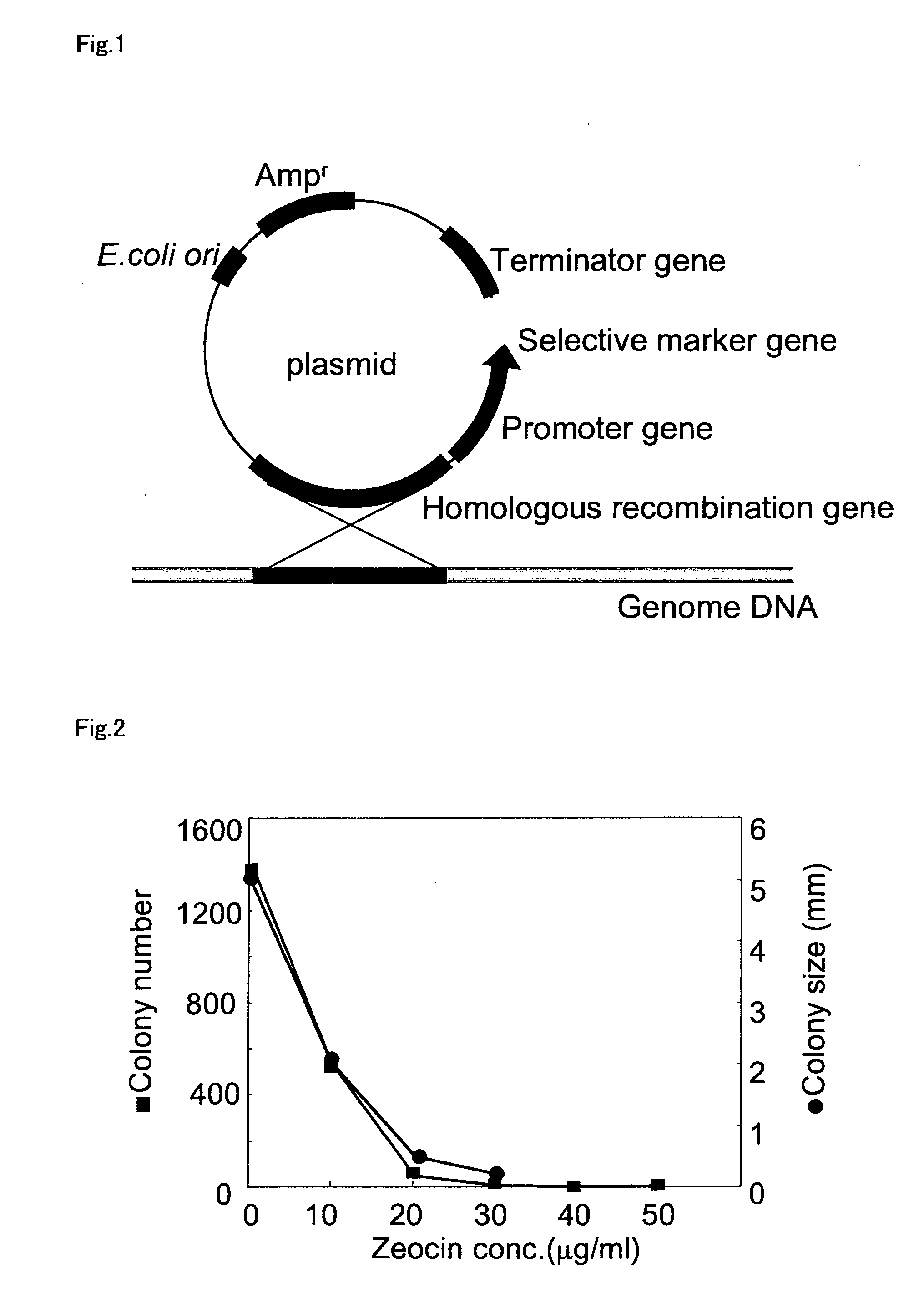
Method for introducing a gene into Labyrinthulomycota
An object of the present invention is to provide a transformation system for Labyrinthulomycota that allows the elucidation of biosynthetic mechanisms of lipids such as PUFA and carotenoids as well as for the construction of a high production system and the design and development of novel functional lipid molecules by the control of the mechanisms. The present invention provides a method for introducing a transgene into a cell of Labyrinthulomycota, which comprises introducing into a cell of Labyrinthulomycota a recombinant vector comprising a transgene and a nucleotide sequence which is homologous to a part of chromosomal DNA of Labyrinthulomycota and is capable of homologous recombination with the chromosomal DNA, and then inducing homologous recombination in this homologous nucleotide sequence.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY +1
Method of cloning reproductive and respiratory syndrome resisting pig
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
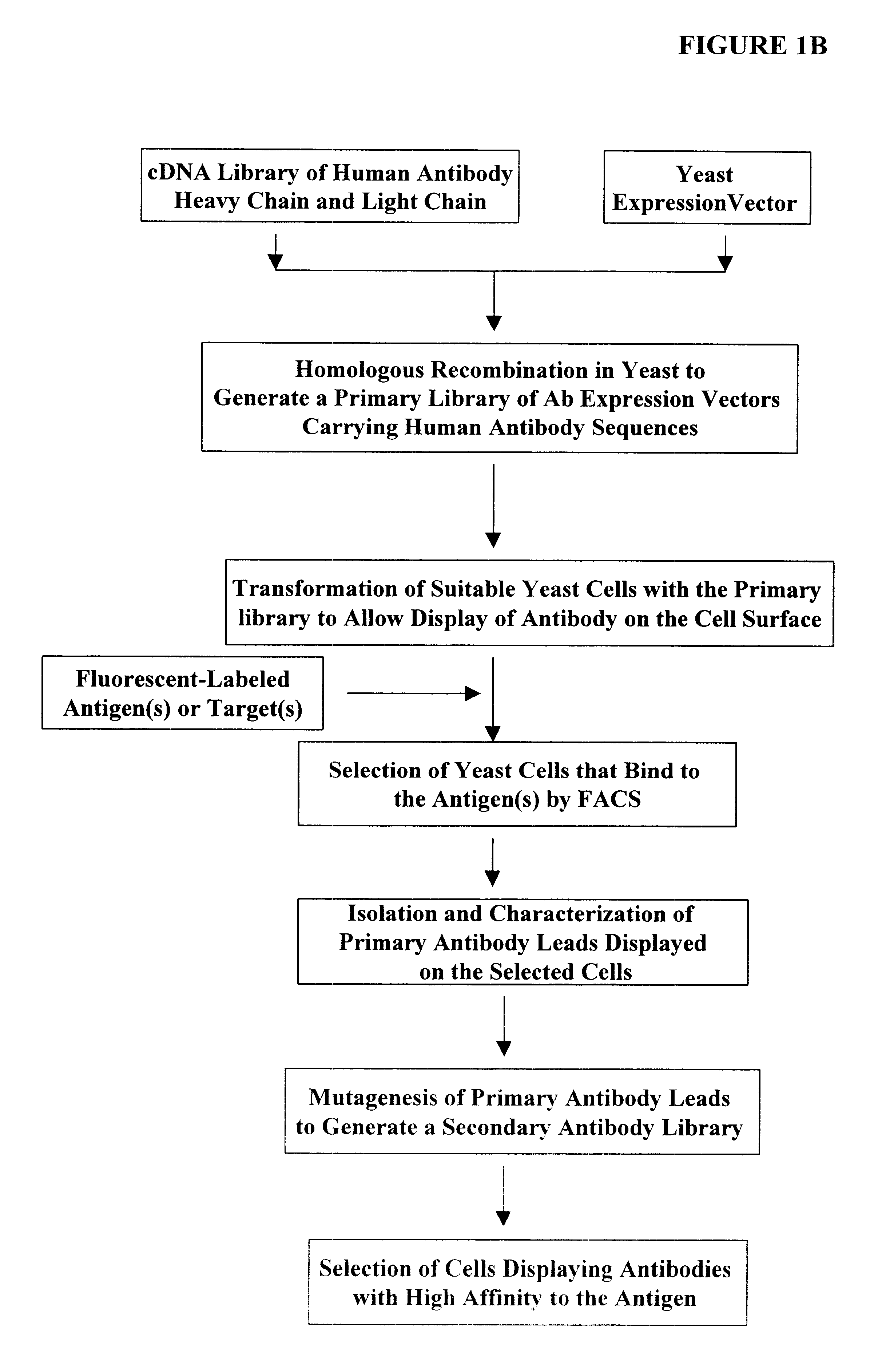
Assembly and screening of highly complex and fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6610472B1High affinityEasy to assembleFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNucleotide
Compositions, methods, and kits are provided for efficiently generating and screening a library of highly diverse protein complexes for their ability to bind to other proteins or oligonucleotide sequences. In one aspect of the invention, a library of expression vectors is provided for expressing the library of protein complexes. The library comprises a first nucleotide sequence encoding a first polypeptide subunit; and a second nucleotide sequence encoding a second polypeptide subunit. The first and second nucleotide sequences each independently varies within the library of expression vectors. In addition, the first and second polypeptide subunit are expressed as separate proteins which self-assemble to form a protein complex, such as a double-chain antibody fragment (dcFv or Fab) and a fully assembled antibody, in cells into which the library of expression vectors are introduced. The library of expression vectors can be efficiently generated in yeast cells through homologous recombination; and the encoded proteins complexes with high binding affinity to their target molecule can be selected by high throughput screening in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Vector capable for transformation of labyrinthulomycota
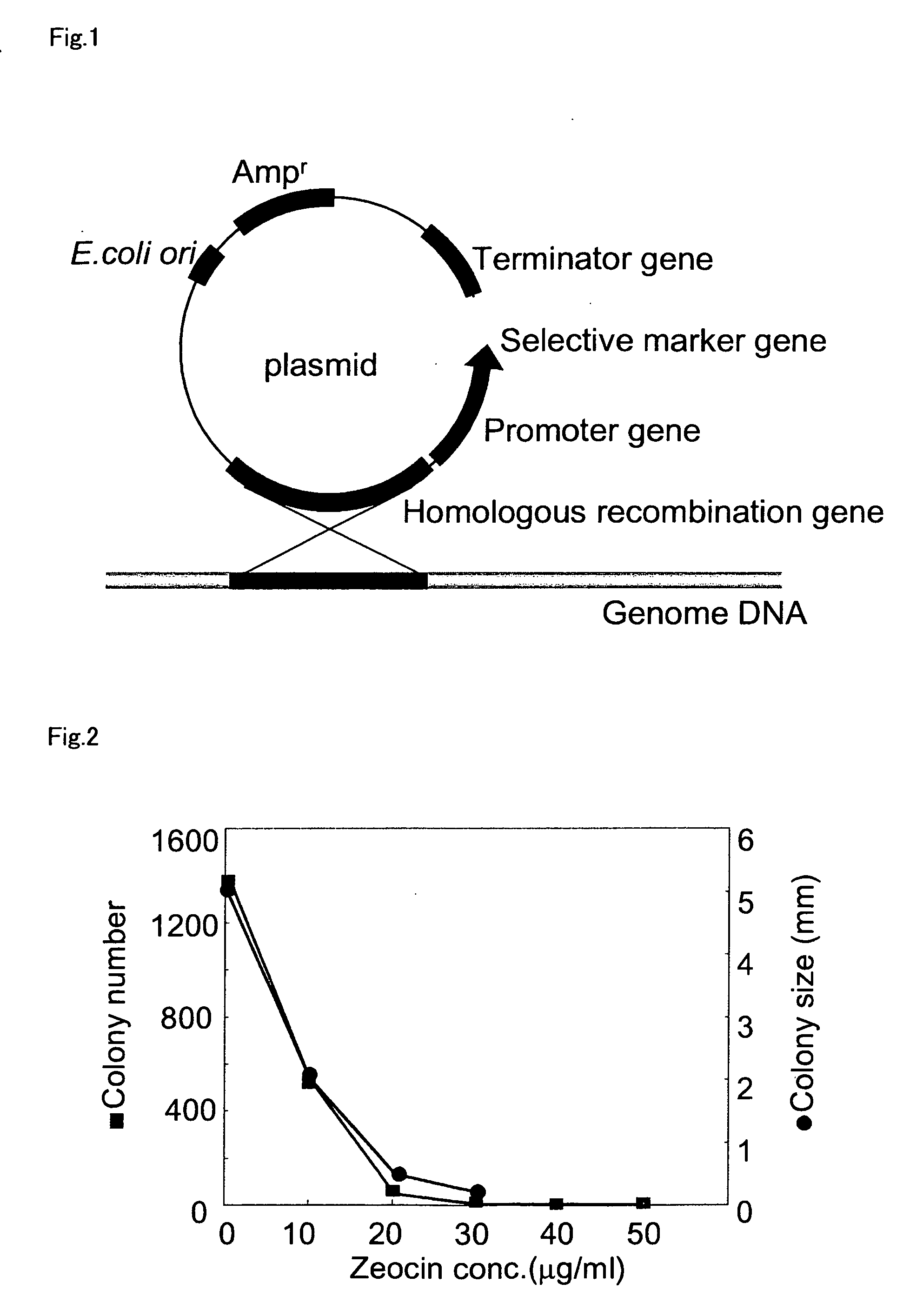
An object of the present invention is to provide a transformation system for Labyrinthulomycota that allows the elucidation of biosynthetic mechanisms of lipids such as PUFA and carotenoids as well as for the construction of a high production system and the design and development of novel functional lipid molecules by the control of the mechanisms. The present invention provides a vector for the transformation of Labyrinthulomycota with a transgene, which comprises at least (1) a nucleotide sequence which is homologous to a part of chromosomal DNA of Labyrinthulomycota and is capable of homologous recombination with the chromosomal DNA, (2) a selection marker gene having a promoter sequence located upstream and a terminator sequence located downstream, and (3) a cloning site for transgene insertion having a promoter sequence located upstream and a terminator sequence located downstream.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Use of meganucleases for inducing homologous recombination ex vivo and in toto in vertebrate somatic tissues and application thereof
A single chain homing endonuclease, comprising a first variant of I-CreI having the amino acid sequence of accession number pdb 1g9y (SEQ ID NO: 23 is residues 1-153 of pdb Ig9y) and a second variant of I-CreI variant having the amino acid sequence of accession number pdb 1g9y (SEQ ID NO: 23 is residues 1-153 of pdb Ig9y) in a single polypeptide.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
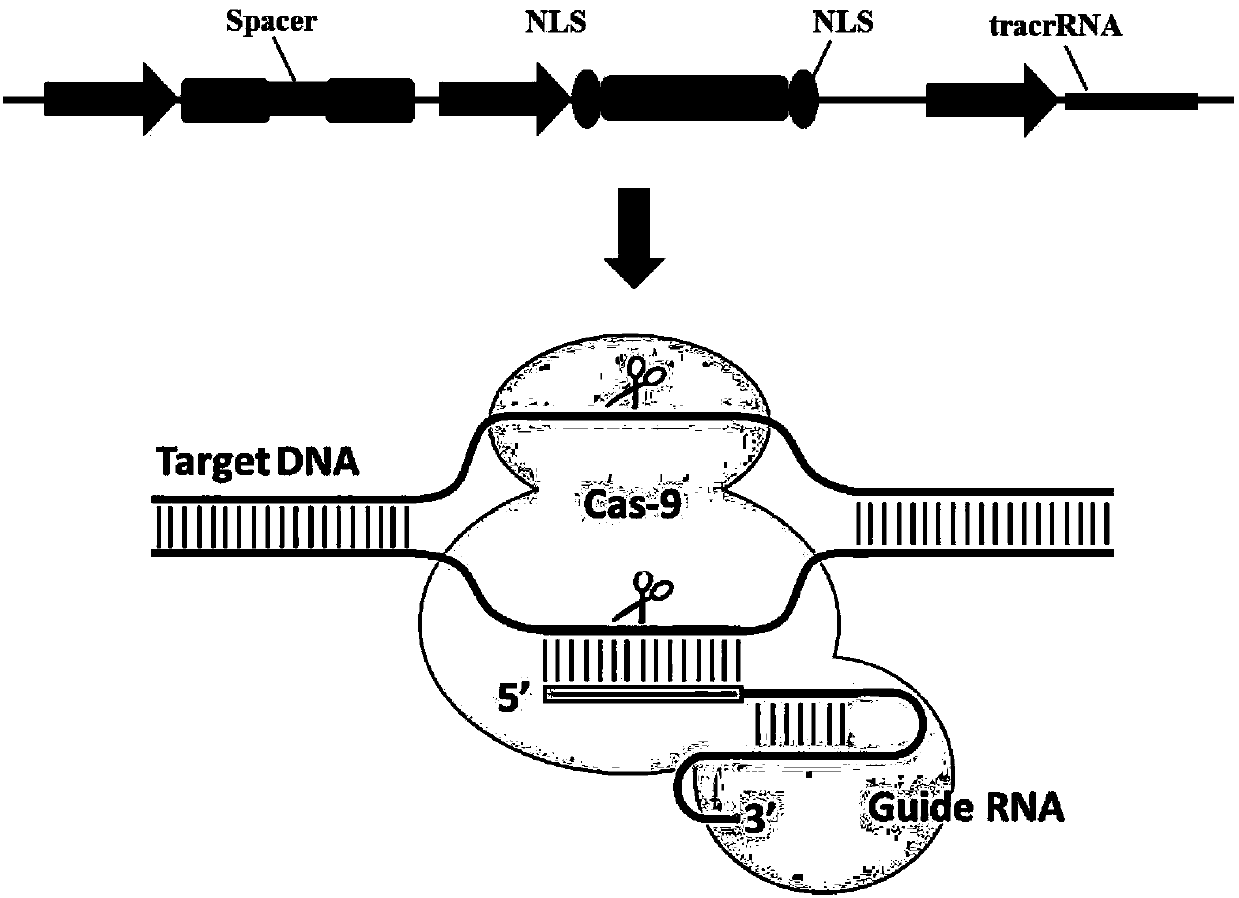
Compounds and methods for crispr/cas-based genome editing by homologous recombination
The present invention relates to guide RNAs comprising adaptor segments having one or more modifications, and their use in homologous recombination by CRISPR:Cas systems. The modified adaptor segments are resistant to degradation by RNaseH. The present invention also relates to a dual guide RNA strategy in which a first guide RNA directs a Cas enzyme to make a double-strand break at a first target sequence, and a second guide RNA comprises an adaptor segment attached to a donor polynucleotide, and binds a second target sequence that is offset from the first target sequence.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Enhanced homologous recombination mediated by lambda recombination proteins
InactiveUS20030224521A1Reduce chanceNormal EcoRV digestion pattern is restoredFungiBacteriaMammalKnockout animal
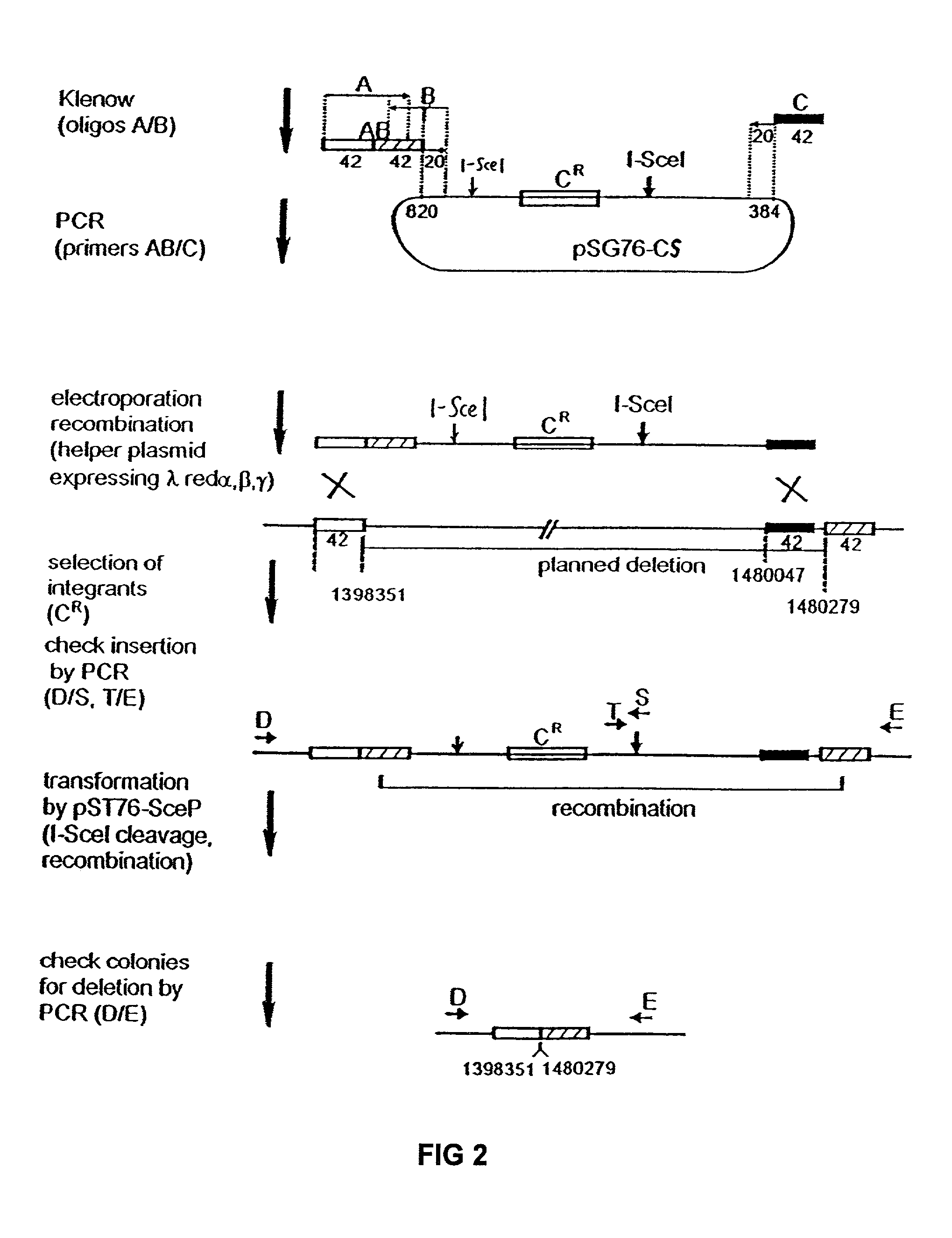
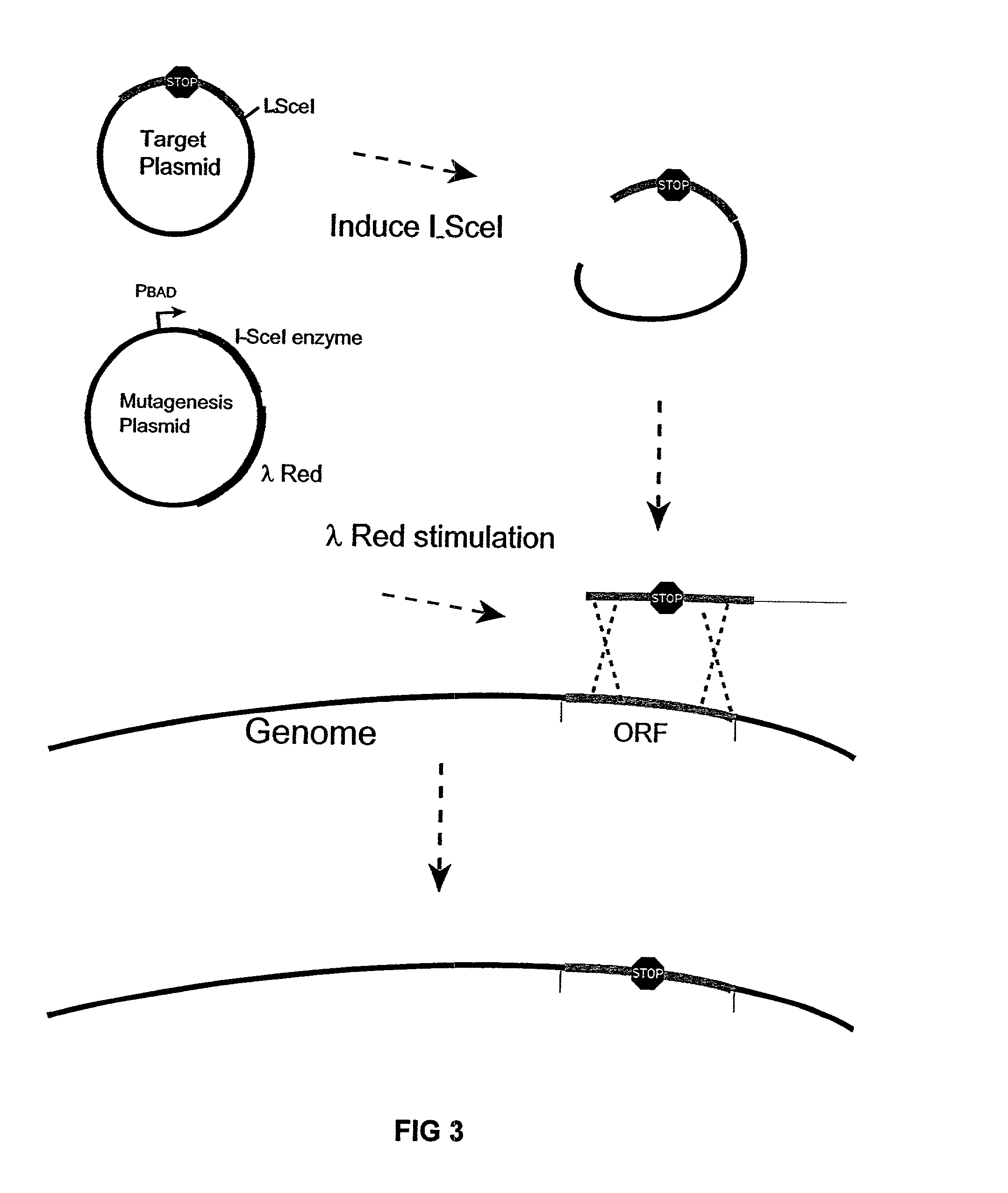
Disclosed herein are methods for generating recombinant DNA molecules in cells using homologous recombination mediated by recombinases and similar proteins. The methods promote high efficiency homologous recombination in bacterial cells, and in eukaryotic cells such as mammalian cells. The methods are useful for cloning, the generation of transgenic and knockout animals, and gene replacement. The methods are also useful for subcloning large DNA fragments without the need for restriction enzymes. The methods are also useful for repairing single or multiple base mutations to wild type or creating specific mutations in the genome. Also disclosed are bacterial strains and vectors which are useful for high-efficiency homologous recombination.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Molecular cloning method based on CRISPR/Cas9 and homologous recombination of saccharomyces cerevisiae cell endogenous genes
ActiveCN105624146AStrong specificityEasy to fragmentFungiVector-based foreign material introductionTime transformationDNA fragmentation
The invention relates to a novel molecular cloning method, and in particular to a method for obtaining recombinant vectors by modifying initial vectors through combined utilization of a CRISPR / Cas9 system and a saccharomyces cerevisiae cell endogenous gene homologous recombination system; only through one-time transformation and selection operations, the method can simultaneously complete insertion of ore or more target DNA fragments into the initial vectors, deletion of one or more DNA fragments from the initial vectors and / or substitution of one or more DNA fragments on the vectors for one or more target DNA fragments. The invention further relates to a reagent kit for conveniently and effectively applying the method provided by the invention.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
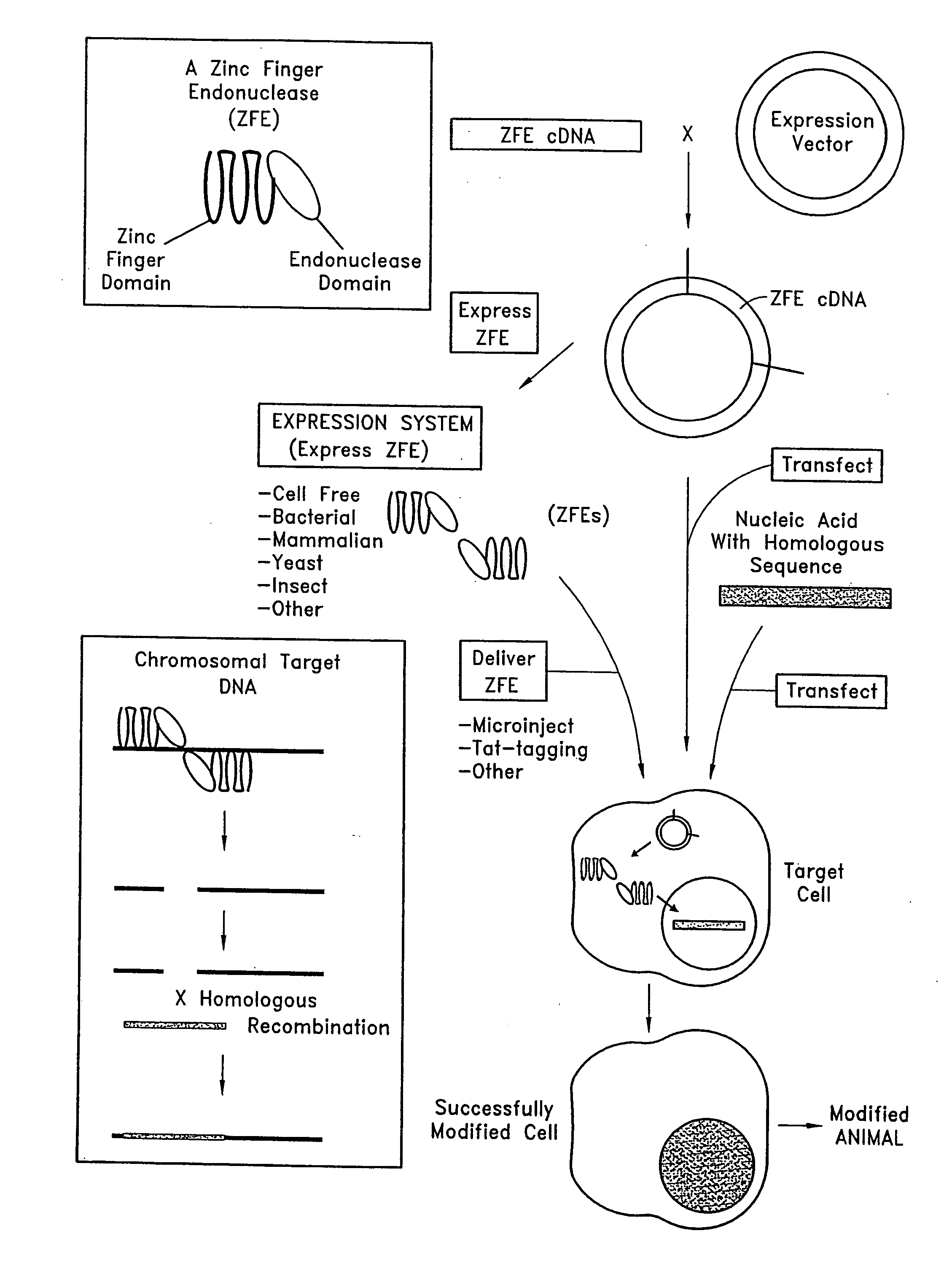
Targeted chromosomal mutagenasis using zinc finger nucleases
The present invention provides for a method or methods of targeted genetic recombination or mutagenesis in a host cell or organism, and compositions useful for carrying out the method. The targeting method of the present invention exploits endogenous cellular mechanisms for homologous recombination and repair of double stranded breaks in genetic material. The present invention provides numerous improvements over previous mutagenesis methods, such advantages include that the method is generally applicable to a wide variety of organisms, the method is targeted so that the disadvantages associated with random insertion of DNA in-to host genetic material are eliminated, and certain embodiments require relatively little manipulation of the host genetic material for success. Additionally, it provides a method that produces organisms with specific gene modifications in a short period of time.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Methods and compositions for using zinc finger endonucleases to enhance homologous recombination
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
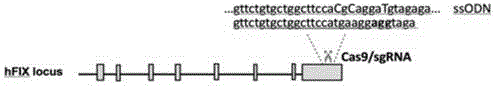
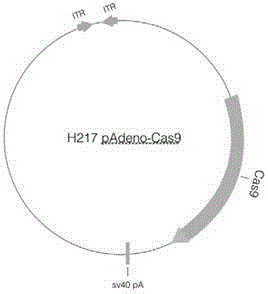
Site specific repairing carrier system and method of blood coagulation factor genetic mutation
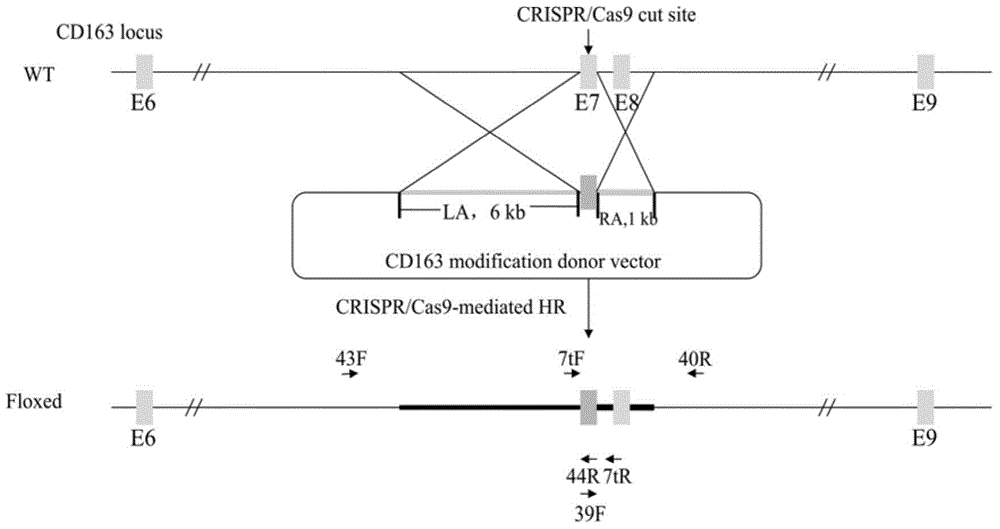
The invention discloses a method for carrying out in-situ repairing on blood coagulation factor F8 / F9. The method comprises the following steps: in a target genome sequence, selecting the mutation sites of blood coagulation factor as the gene sites for in-situ repairing; designing the binding sites of nuclease of sgRNA sequence of a CRISPR / Cas system; designing a homologous recombinant repairing donor sequence for in-situ repairing; delivering nuclease protein and / or sgRNA and the nucleotide sequence of the homologous recombinant repairing donor to the gene sites of in-situ repairing by a delivering carrier; generating damages to the genome DNA by the nuclease on the gene in-situ repairing sites; and inserting the homologous recombinant repairing donor sequence into the gene in-situ repairing sites so as to repair the gene or supplement the expression of gene. The in-situ repairing of mutation sites of blood coagulation factor can be applied to the clinic, and the method has the advantages of precise induction, safer and controllable process, and definite target.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
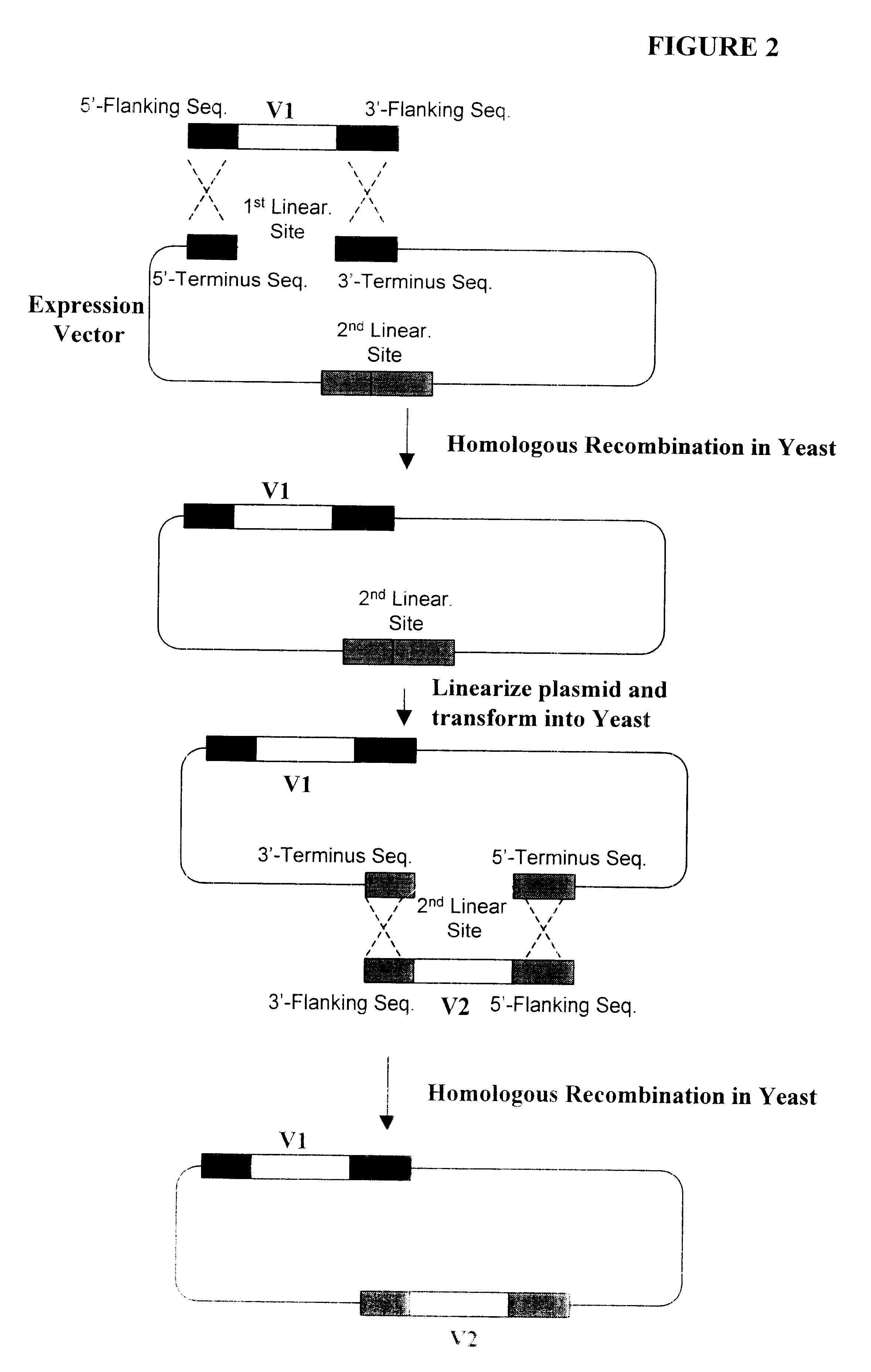
Generation of recombinant DNA by sequence-and ligation-independent cloning
InactiveUS20070292954A1Efficient conversionGenerate efficientlyTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesRecombinant DNAEnzyme
The present invention is directed methods for cloning DNA by homologous recombination. The methods can be used without a need for ligases or restriction enzymes and allow for the rapid alignment of multiple DNA fragments.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
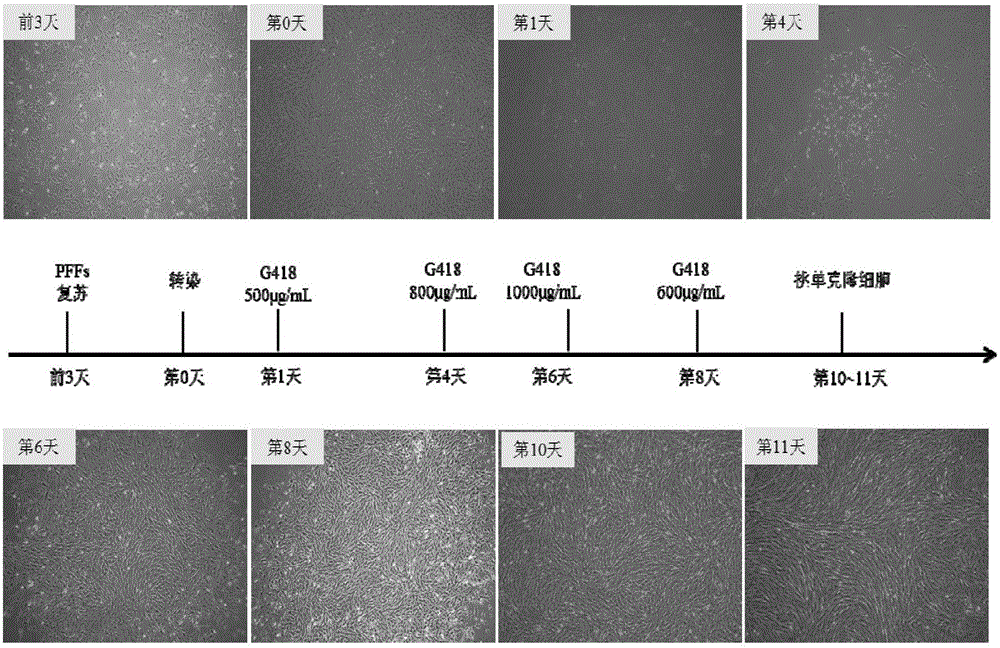
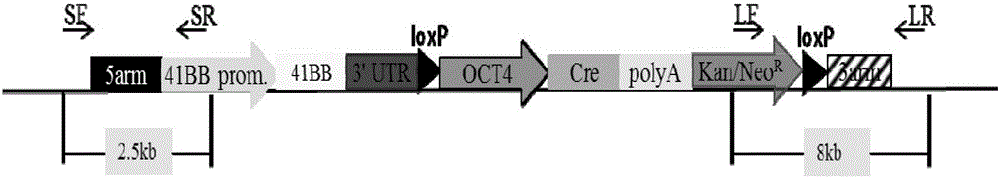
Overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof
InactiveCN105087620AHigh copy numberLower activation thresholdVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryInteinEmbryo
The invention provides an overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed on a left homologous arm and a right homologous arm of an intron 1 of a rosa26 gene, a 4-1BB regulatory sequence and an OCT4 specific promoter; the left homologous arm, a 4-1BB expression cassette, LoxP locus-contained Cre and Neo expression cassettes, the right homologous arm and negative selection DTA diphtheria toxin are connected in sequence to obtain a 4-1BB homologous recombinant vector p4BOCNDR; the vector and a CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR-associated) targeting vector of sgRNA (small guide ribonucleic acid) containing the intron 1 of the specific targeting porcine rosa26 gene are transferred together into a porcine fetus fibroblast; by taking a positive cell as a donor cell and an oocyte as a recipient cell, a cloned embryo is obtained through a somatic cell nuclear transfer technique; the cloned embryo is transplanted into a porcine uterus for fetation to obtain a transgenic pig integrating a 4-1BB gene at the fixed point of a first intron of the rosa26 gene and automatically deleting a marker gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
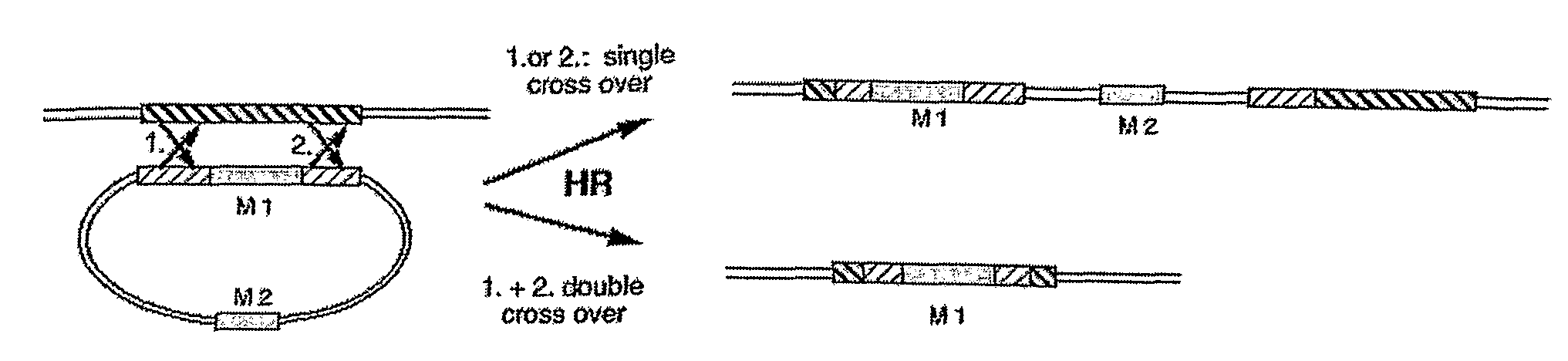
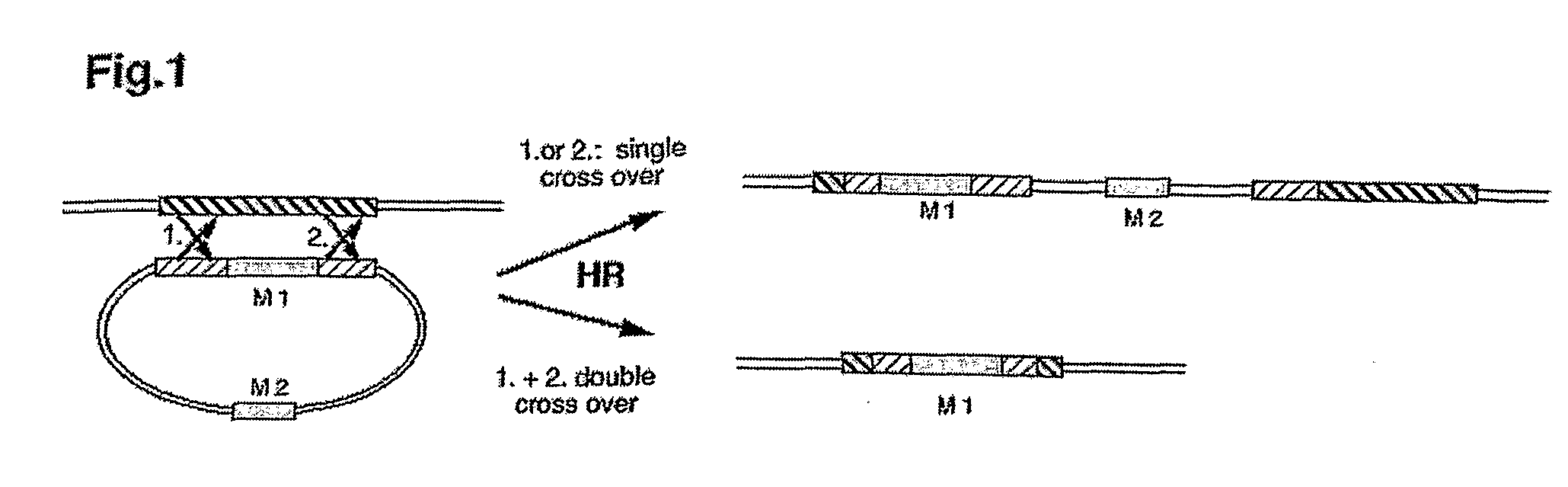
Method for Increasing the Ratio of Homologous to Non-Homologous Recombination
InactiveUS20080194029A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideSingle-Stranded DNA Binding Proteins
Gene targeting allows the deletion (knock out), the repair (rescuing) and the modification (gene mutation) of a selected gene and the functional analysis of any gene of interest. Targeting of nuclear genes has been a very inefficient process in most eukaryotes including plants and animals due to the dominance of illegitimate integration of the applied DNA into non-homologous regions of the genome. The present invention provides a method for increasing the ratio of homologous to non-homologous recombination of a polynucleotide into a host cell's DNA by suppressing non-homologous recombination. Surprisingly, the number of non-homologous recombination events can be reduced if the polynucleotide is applied as a purified single-stranded DNA, preferably coated with a single strand binding protein.
Owner:HEGEMANN PETER +1
Thermophilic Organisms For Conversion Of Lignocellulosic Biomass To Ethanol
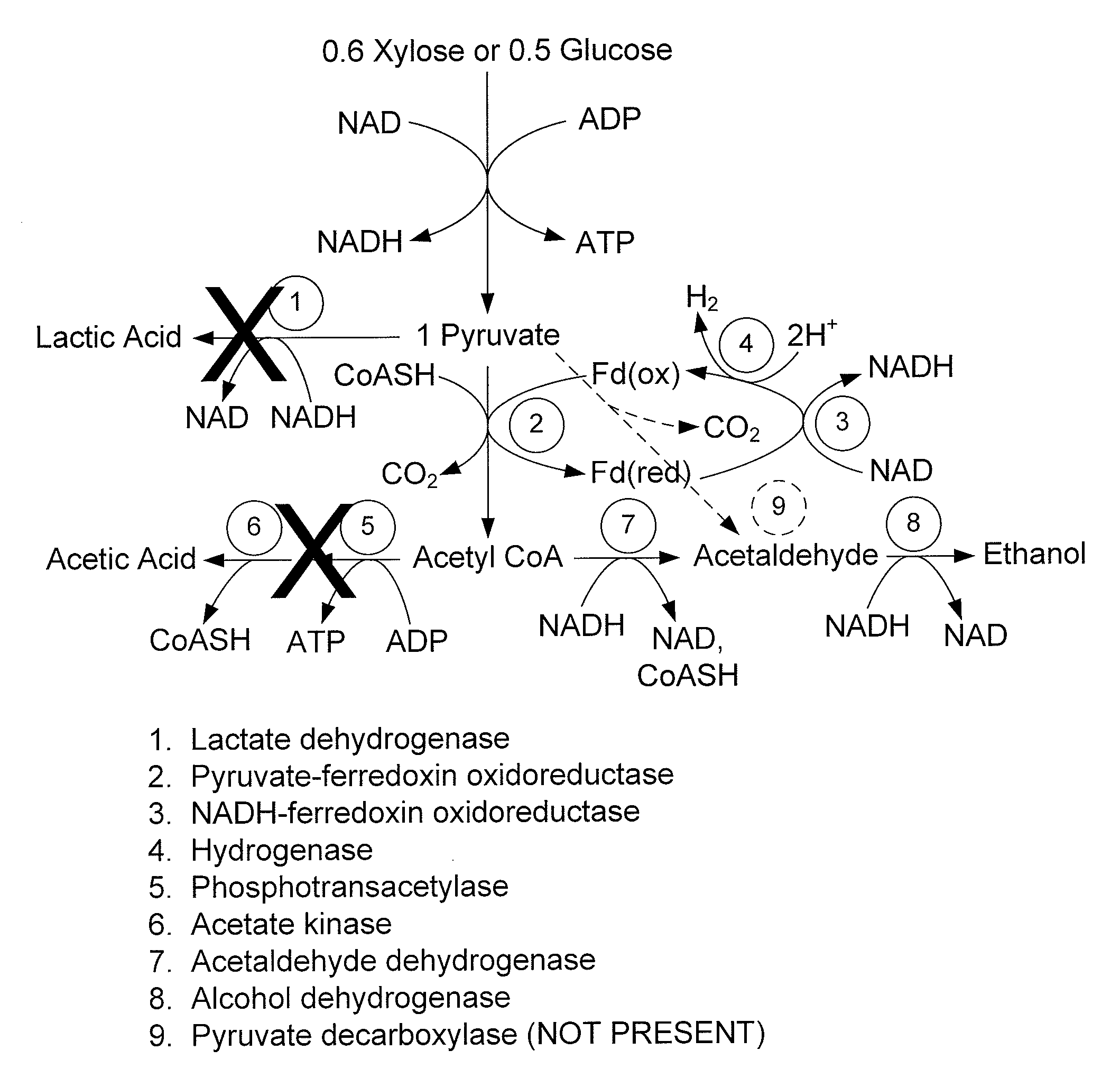
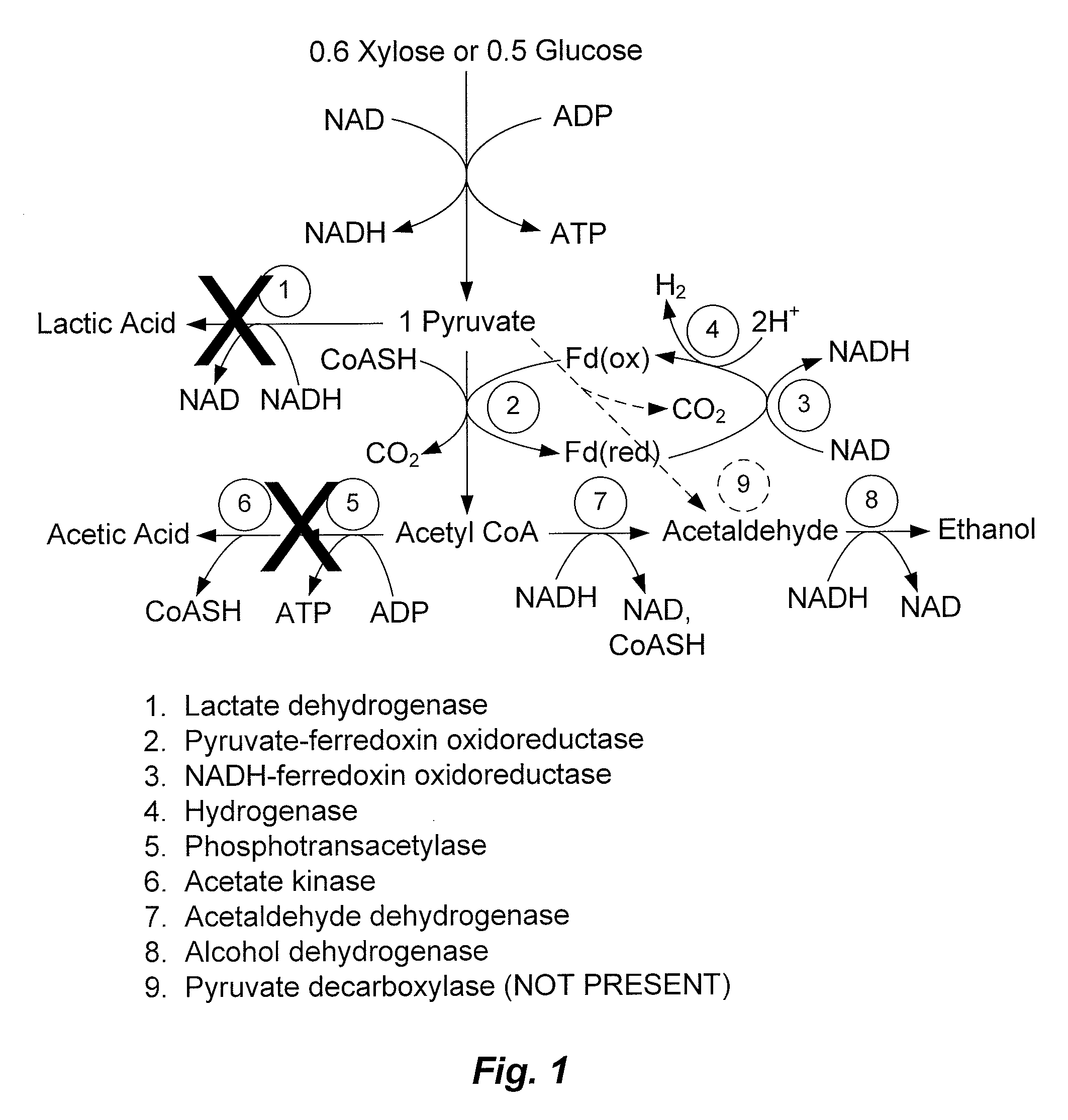
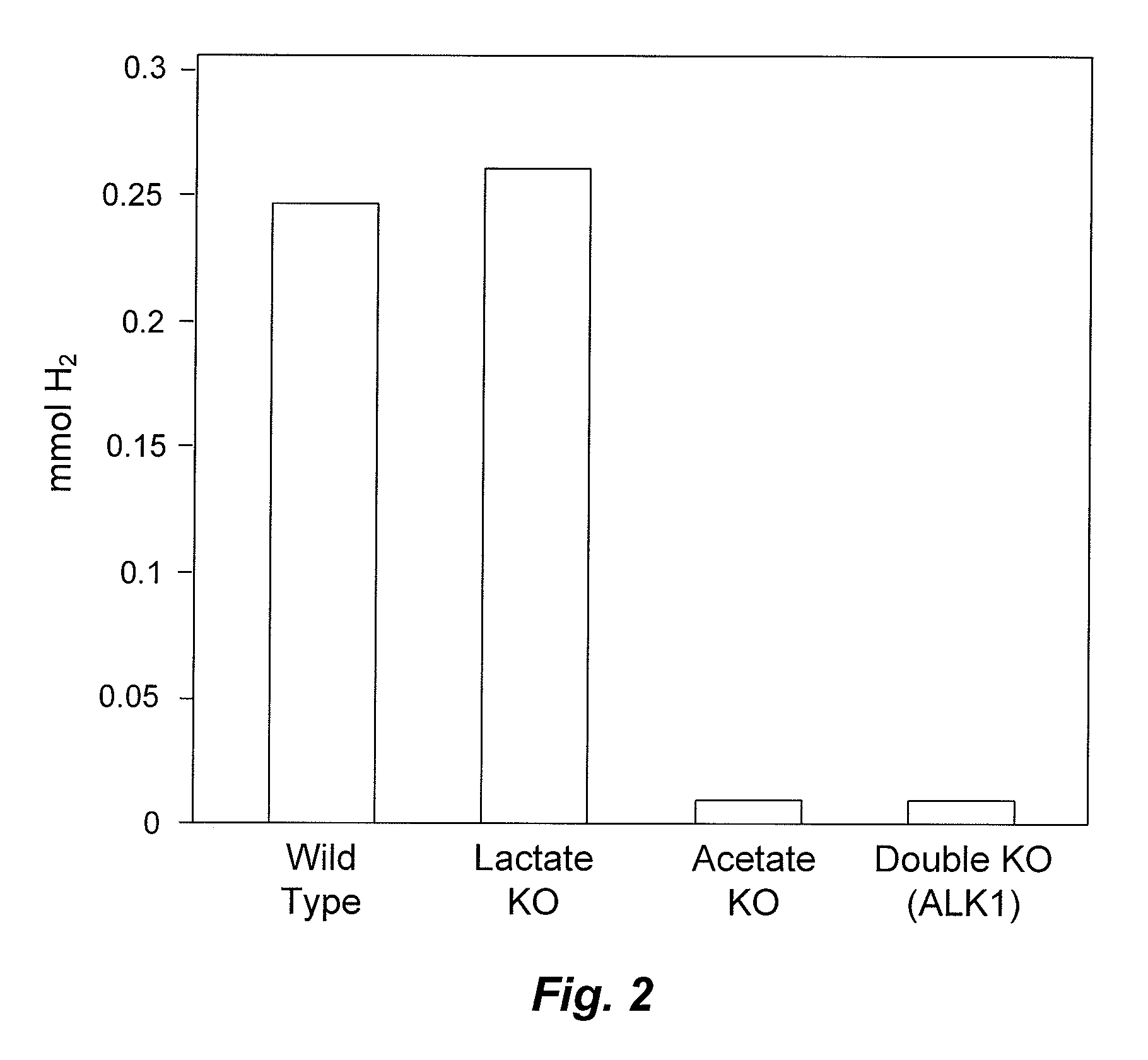
Mutant thermophilic organisms that consume a variety of biomass derived substrates are disclosed herein. Strains of Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum with acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase expression eliminated are disclosed herein. Further, strain ALK1 has been engineered by site directed homologous recombination to knockout both acetic acid and lactic acid production. Continuous culture involving a substrate concentration challenge lead to evolution of ALK1, and formation of a more robust strain designated ALK2. The organisms may be utilized for example in thermophilic SSF and SSCF reactions performed at temperatures that are optimal for cellulase activity to produce near theoretical ethanol yields without expressing pyruvate decarboxylase.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Embryonic or stem-like cell lines produced by cross species nuclear transplantation
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of a species different from the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for the production of isogenic embryonic stem cells, in particular human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. These embryonic or stem-like cells are useful for producing desired differentiated cells and for introduction, removal or modification, of desired genes, e.g., at specific sites of the genome of such cells by homologous recombination. These cells, which may contain a heterologous gene, are especially useful in cell transplantation therapies and for in vitro study of cell differentiation.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Bacteria with reduced genome
InactiveUS6989265B2Efficient processingEasy to purifyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGenetically engineered
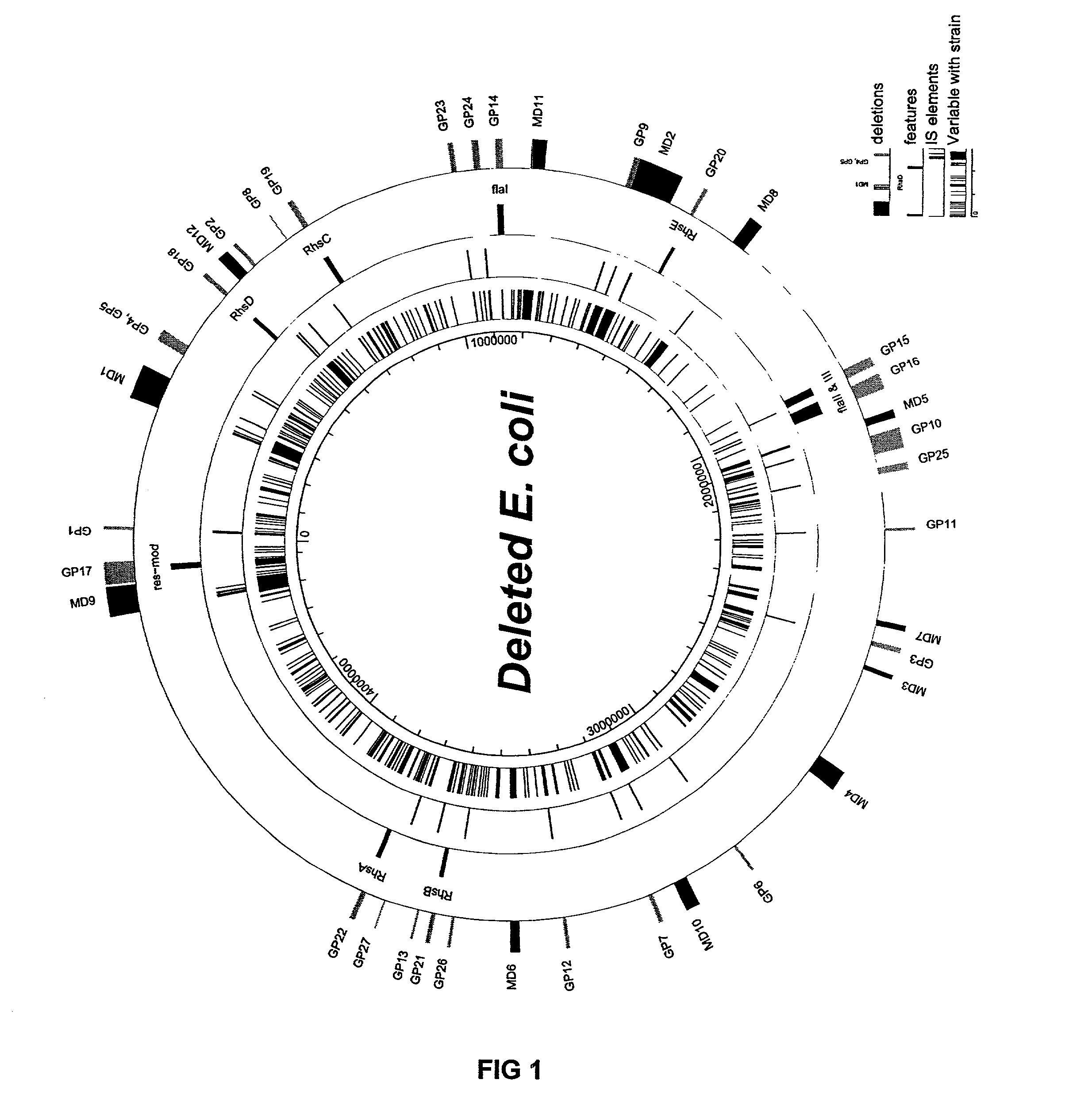
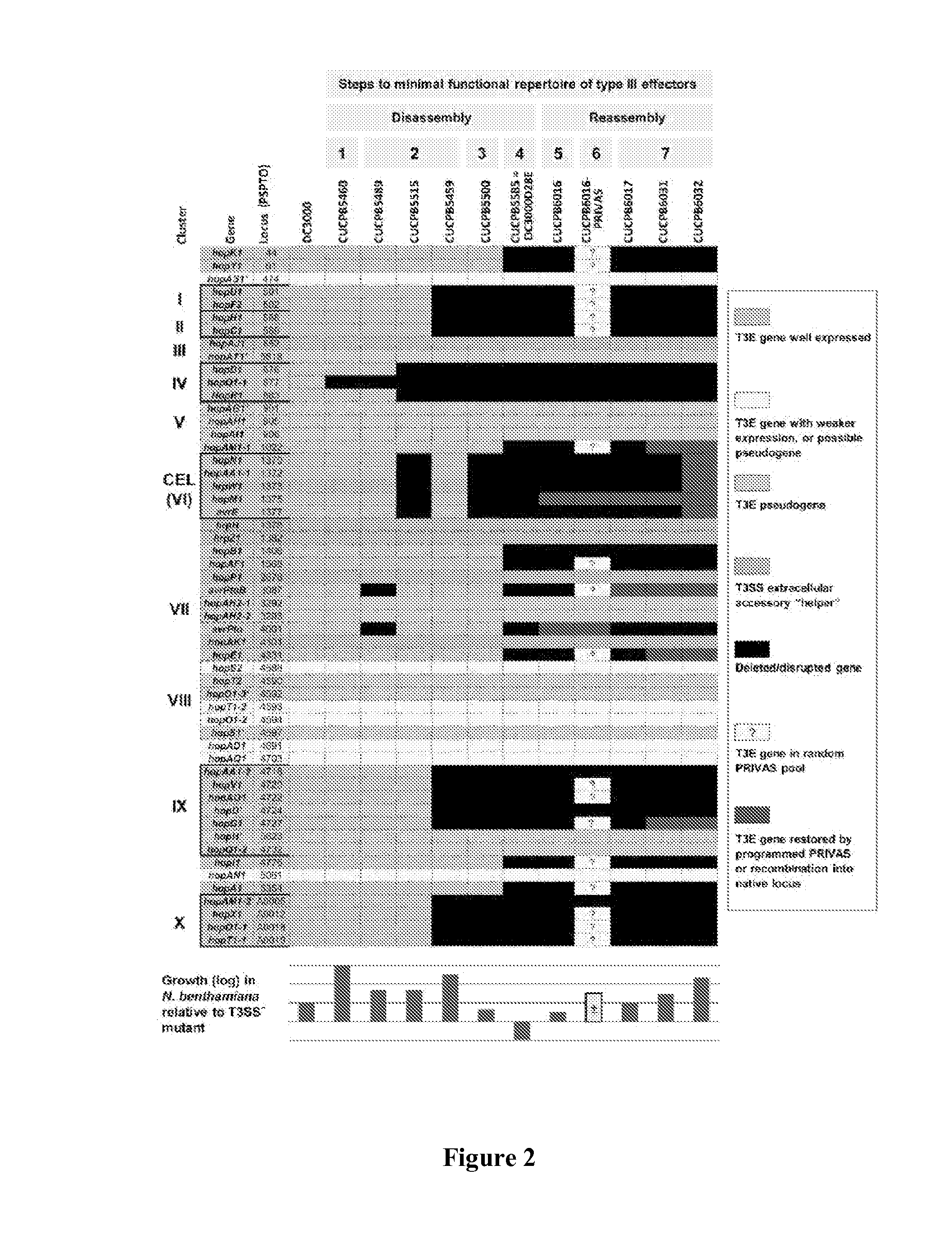
The present invention provides a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be at least 2 to 14% smaller than the genome of its native parent strain. A bacterium with a smaller genome can produce a commercial product more efficiently. The present invention also provides methods for deleting genes and other DNA sequences from a bacterial genome. The methods provide precise deletions and seldom introduces mutations to the genomic DNA sequences around the deletion sites. Thus, the methods can be used to generate a series of deletions in a bacterium without increasing the possibility of undesired homologous recombination within the genome. In addition, some of the methods provided by the present invention can also be used for replacing a region of a bacterial genome with a desired DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method of dual-adapter recombination for efficient concatenation of multiple DNA fragments in shuffled or specified arrangements
ActiveUS20130298265A1Good adhesionEasy to assembleSugar derivativesBacteriaOligonucleotideBioinformatics
The present invention relates to methods of assembling a plurality of genetic units to form synthetic genetic constructs. This method involves appending universal adapter oligonucleotides and flexible adapter oligonucleotides to the 5′ and 3′ ends of separate genetic units to be assembled to form separate dual extended genetic units. The dual extended genetic units are assembled together via homologous recombination between the flexible adapter oligonucleotide portions of the dual extended units to form synthetic genetic constructs. The present invention further relates to synthetic genetic constructs formed using the methods of the present invention, and vectors, cells, and organisms containing such synthetic genetic constructs.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com