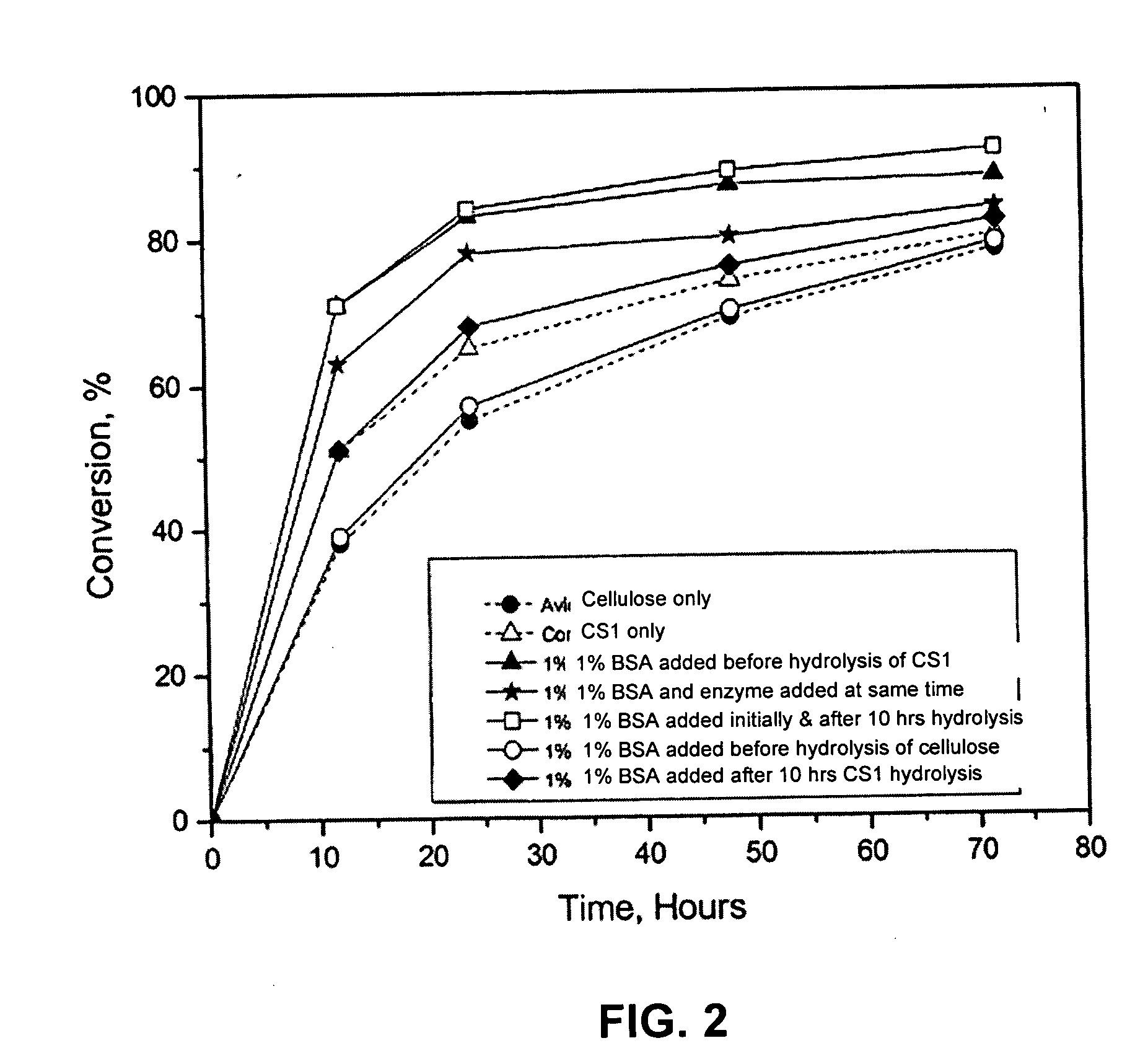
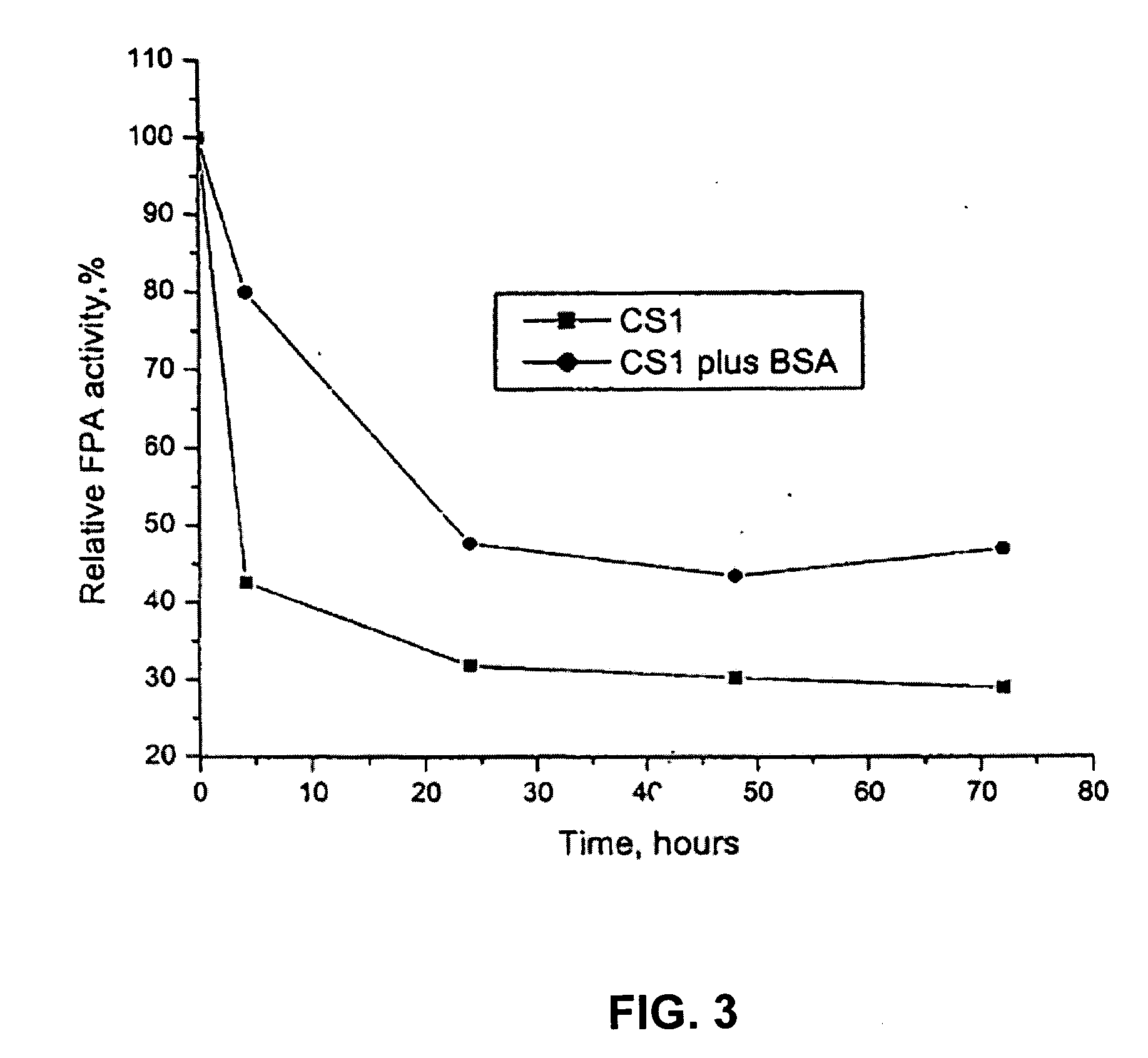
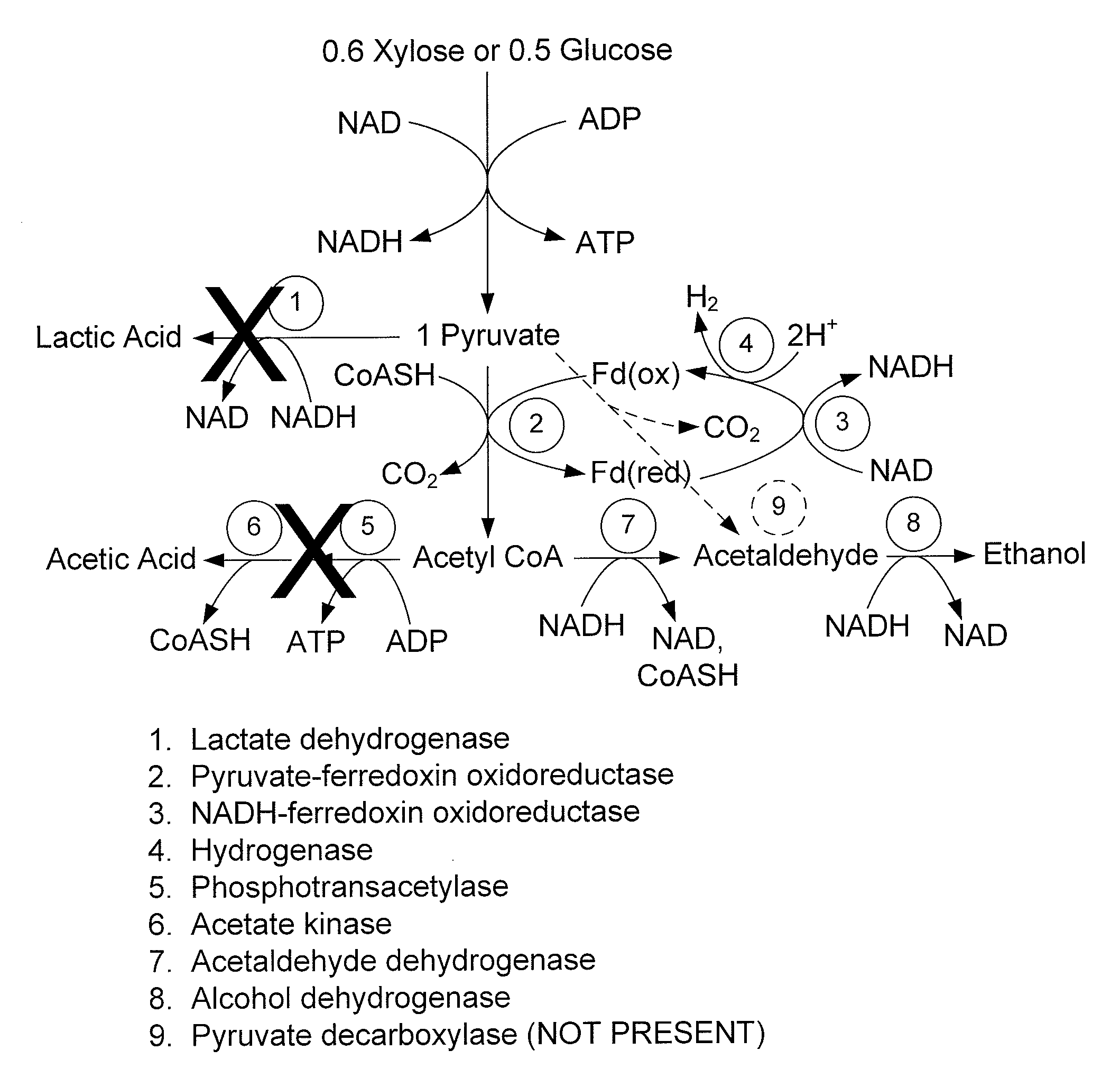
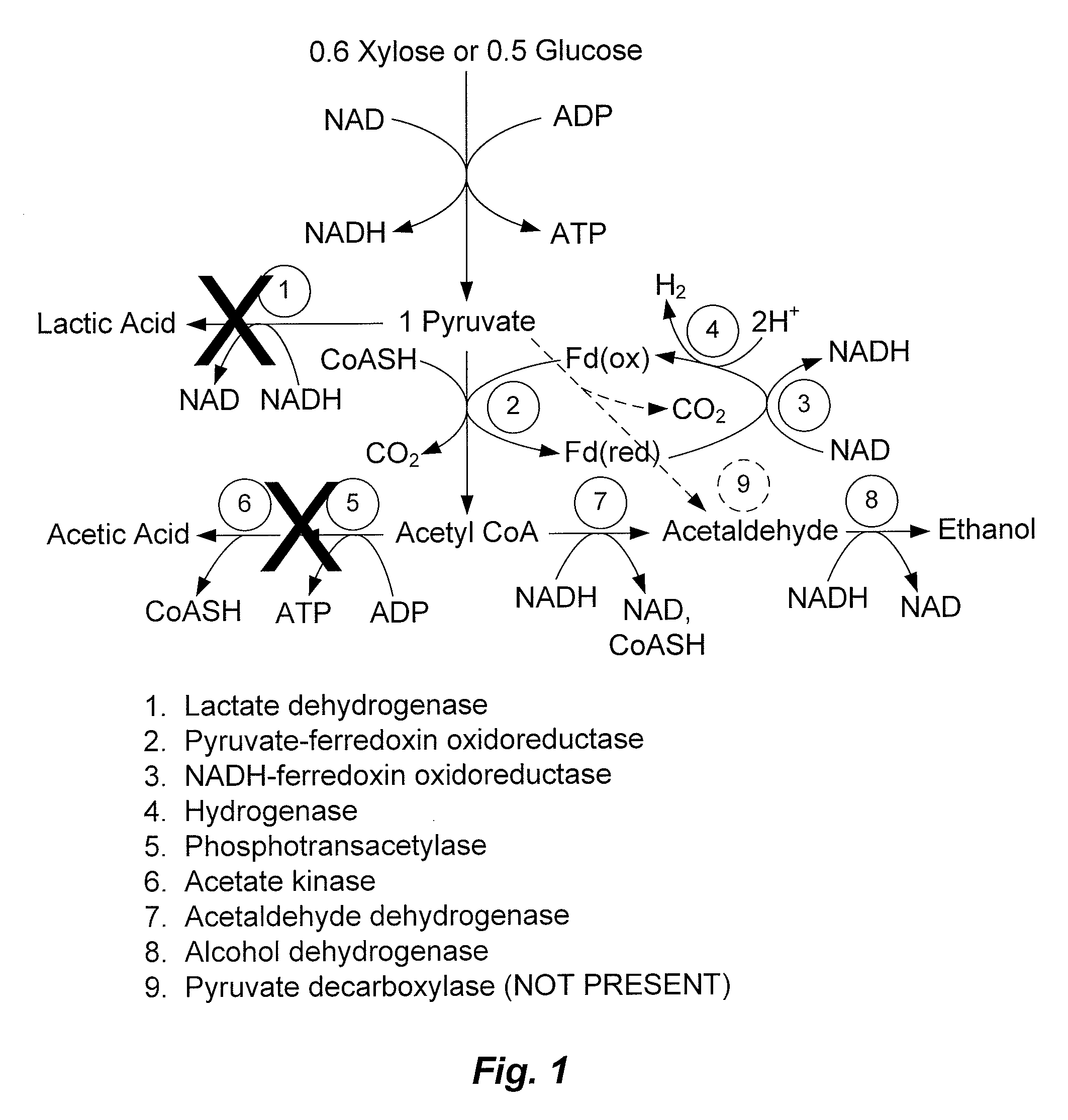
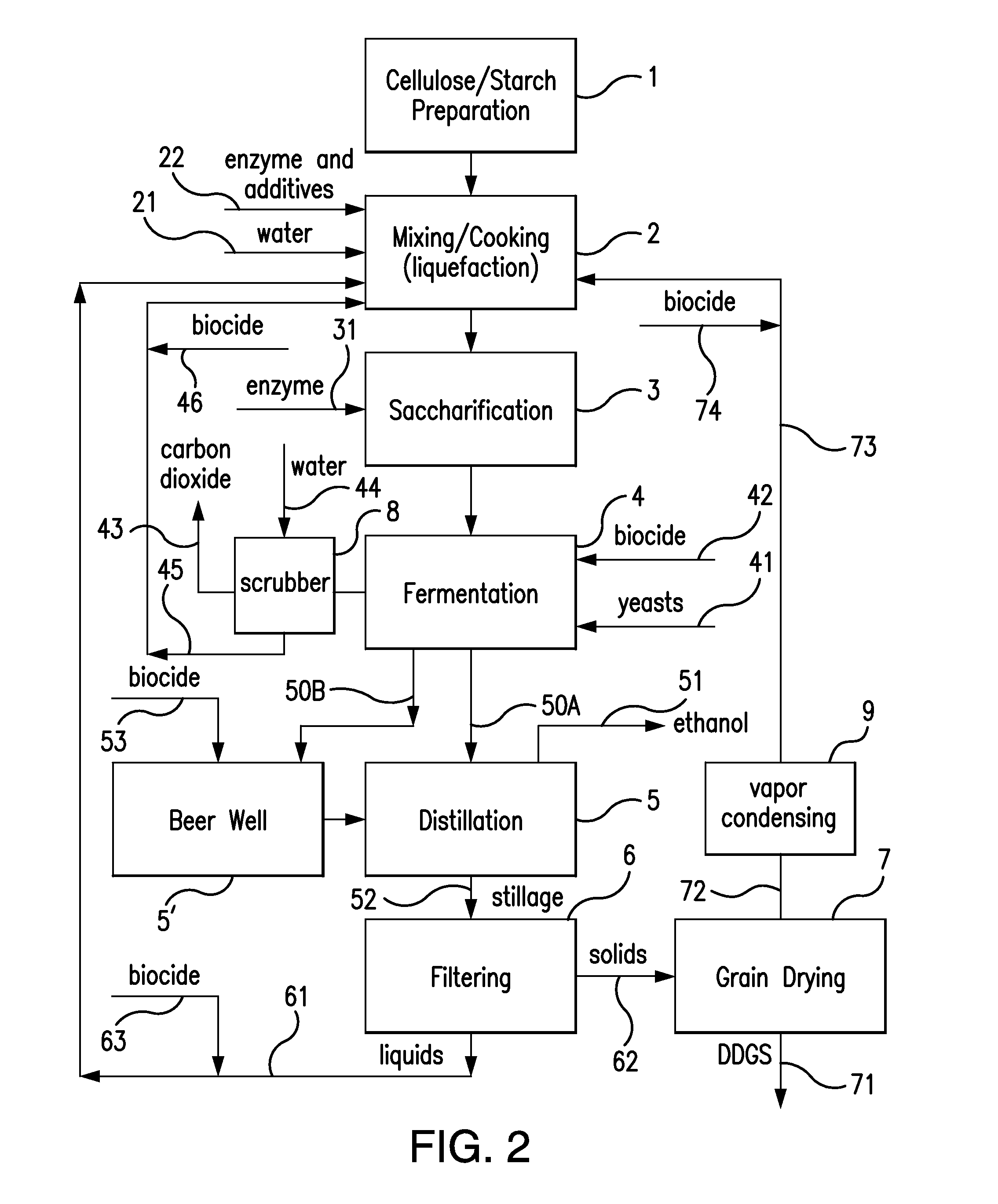
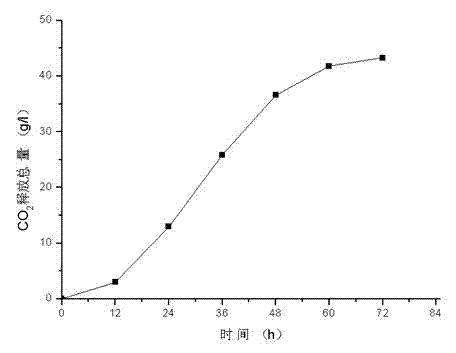
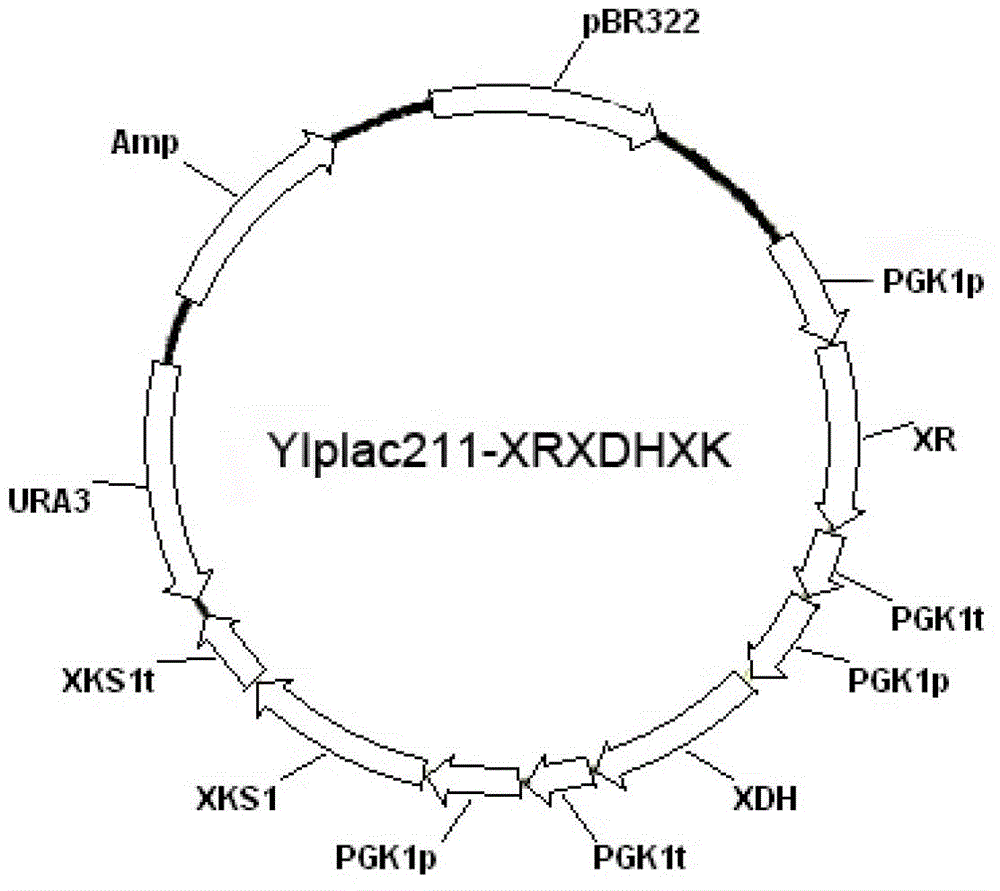
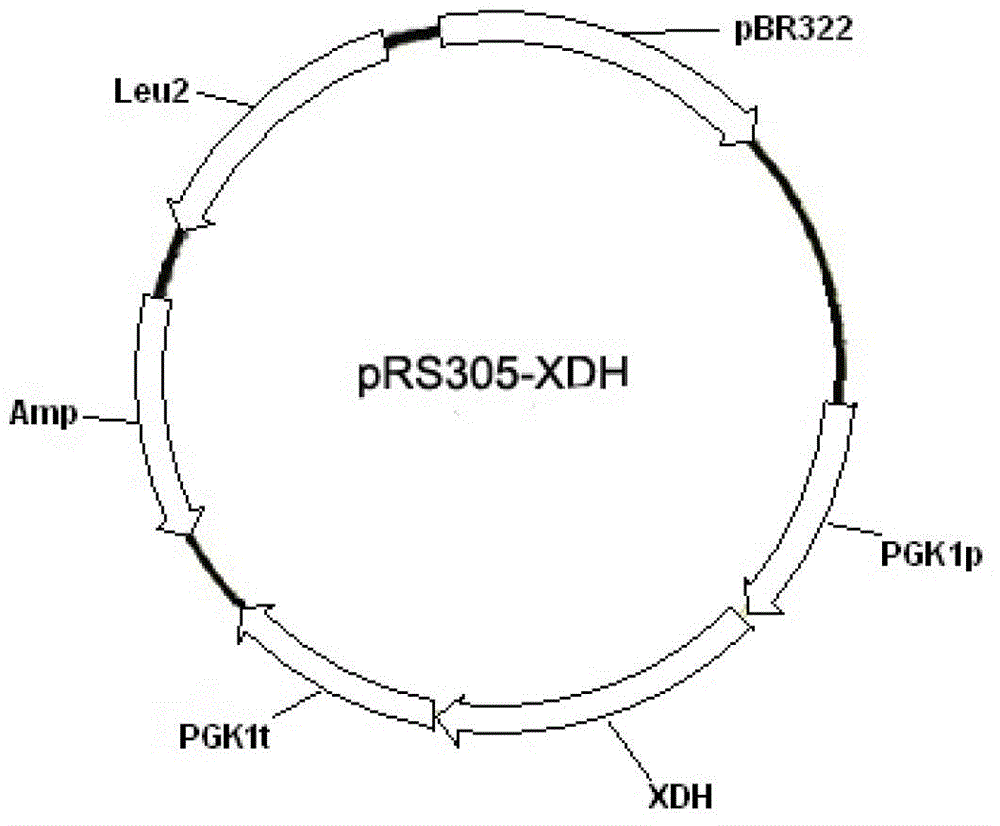
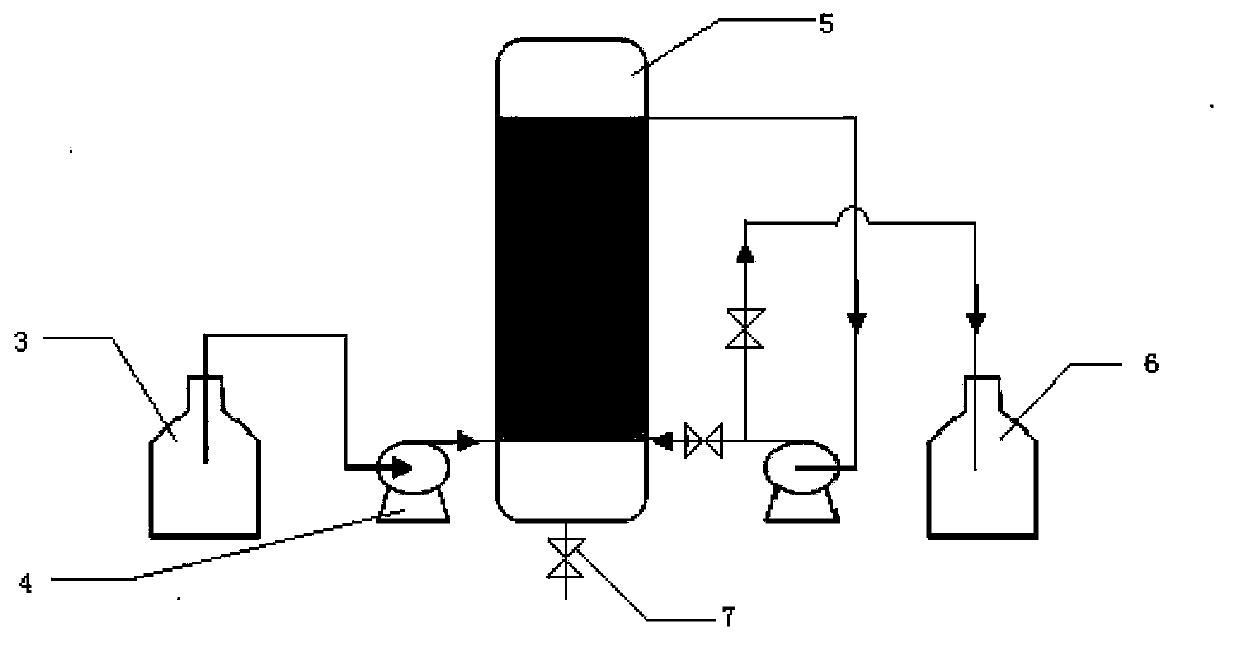
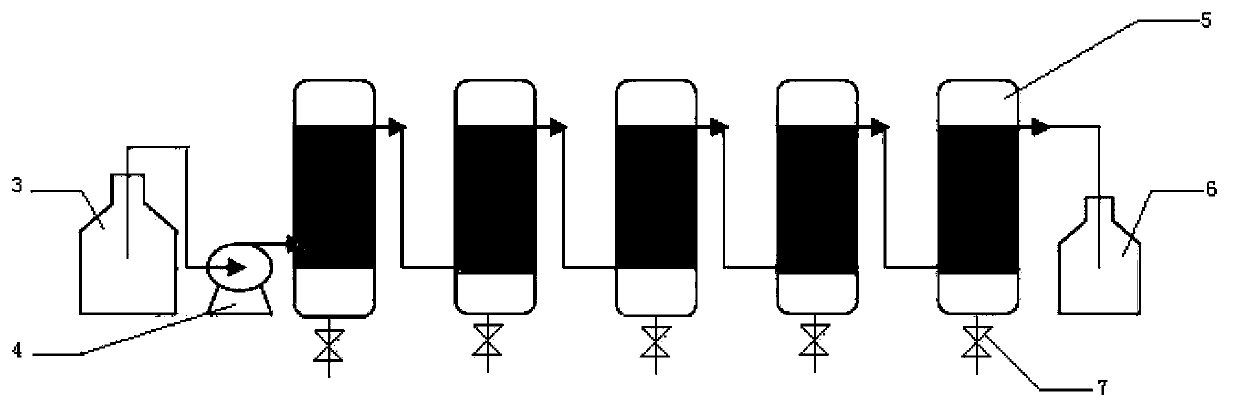
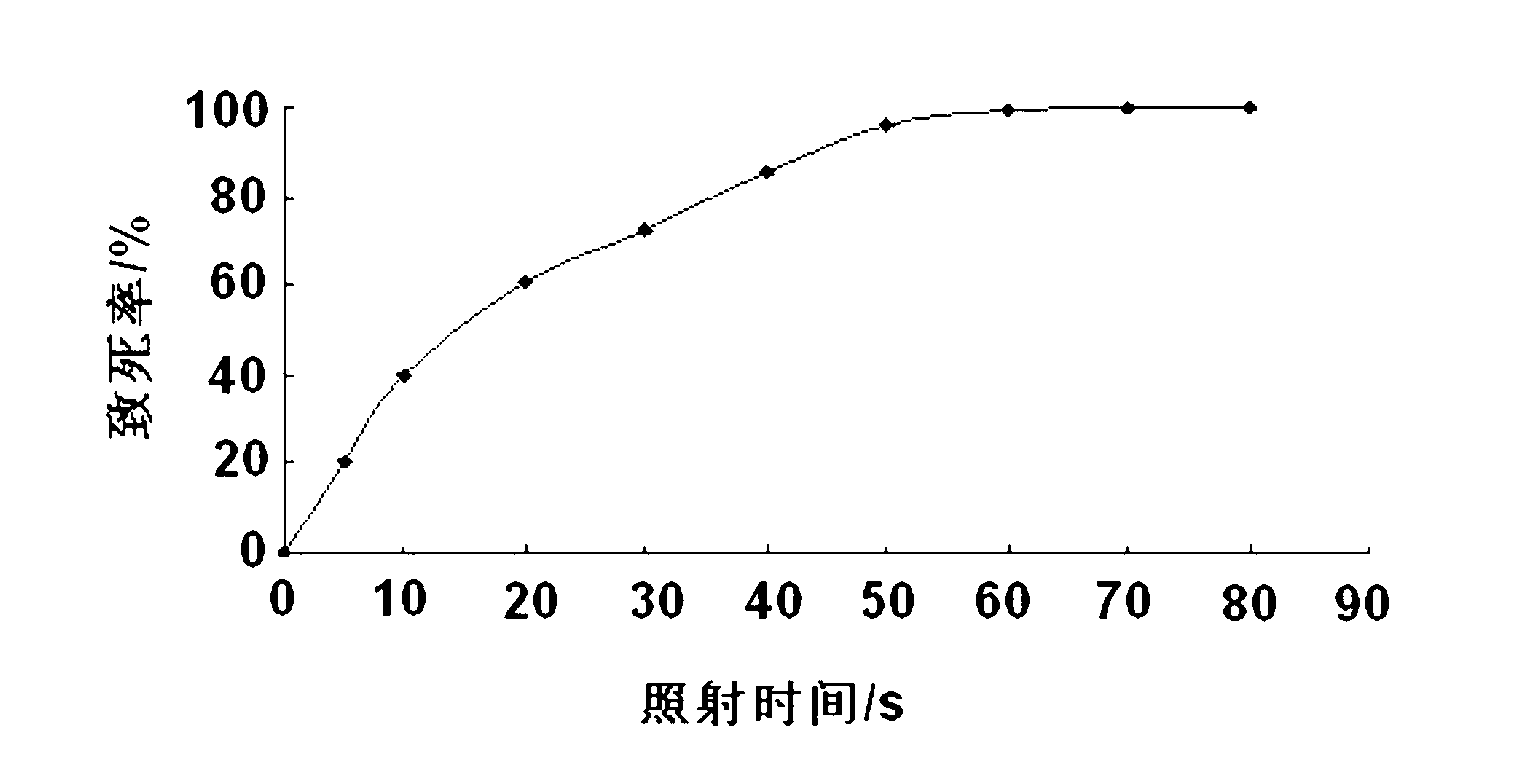
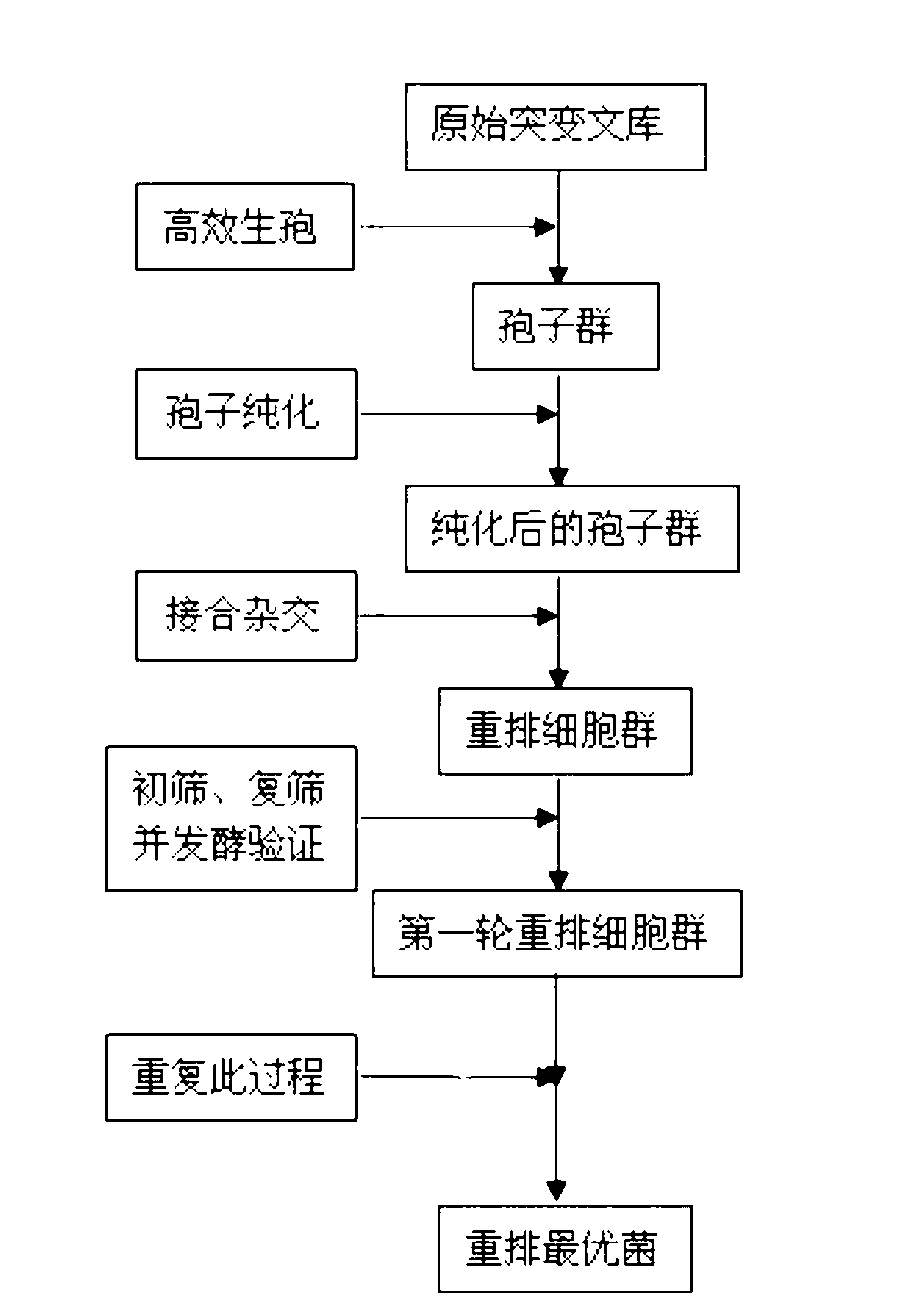
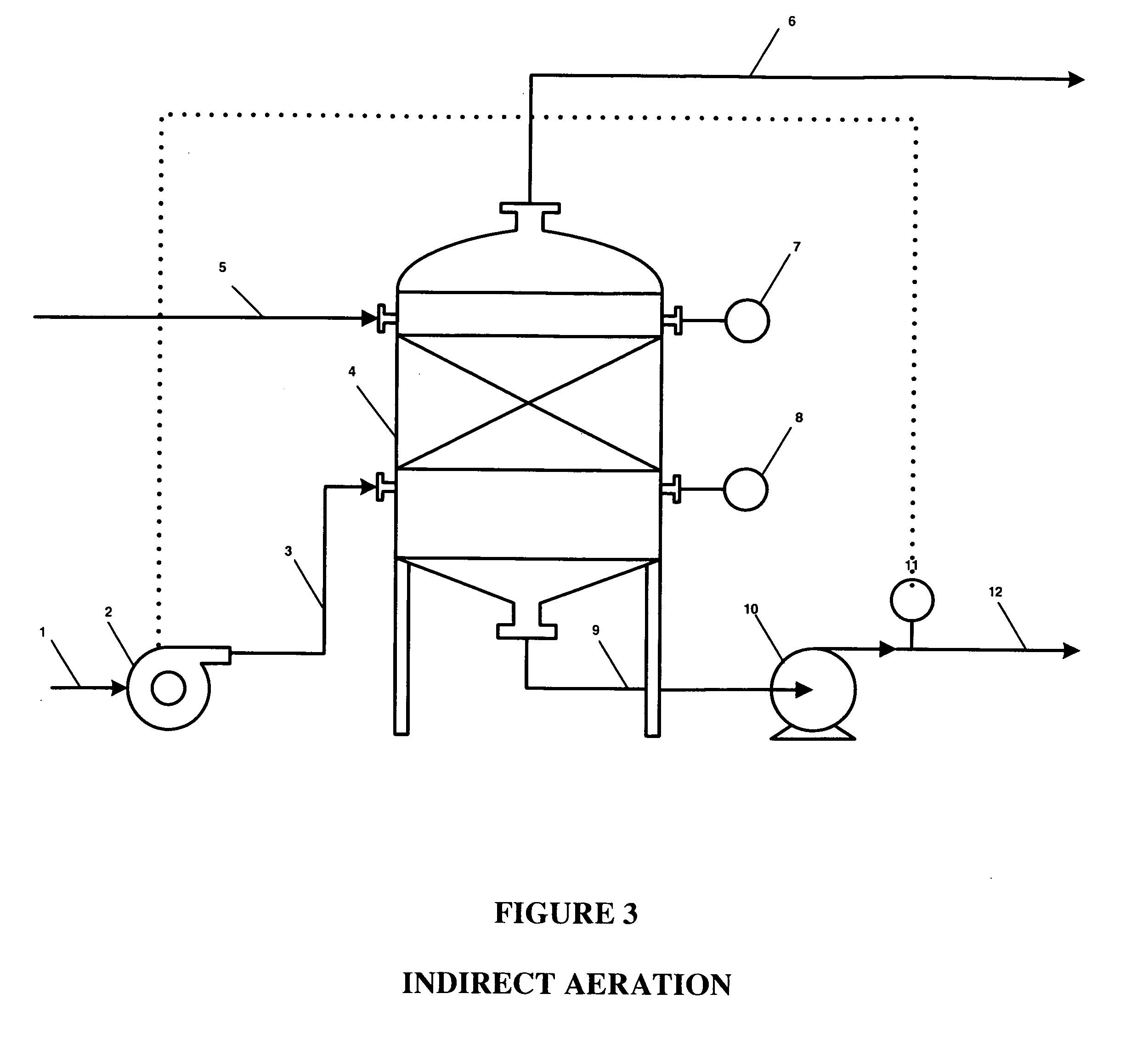
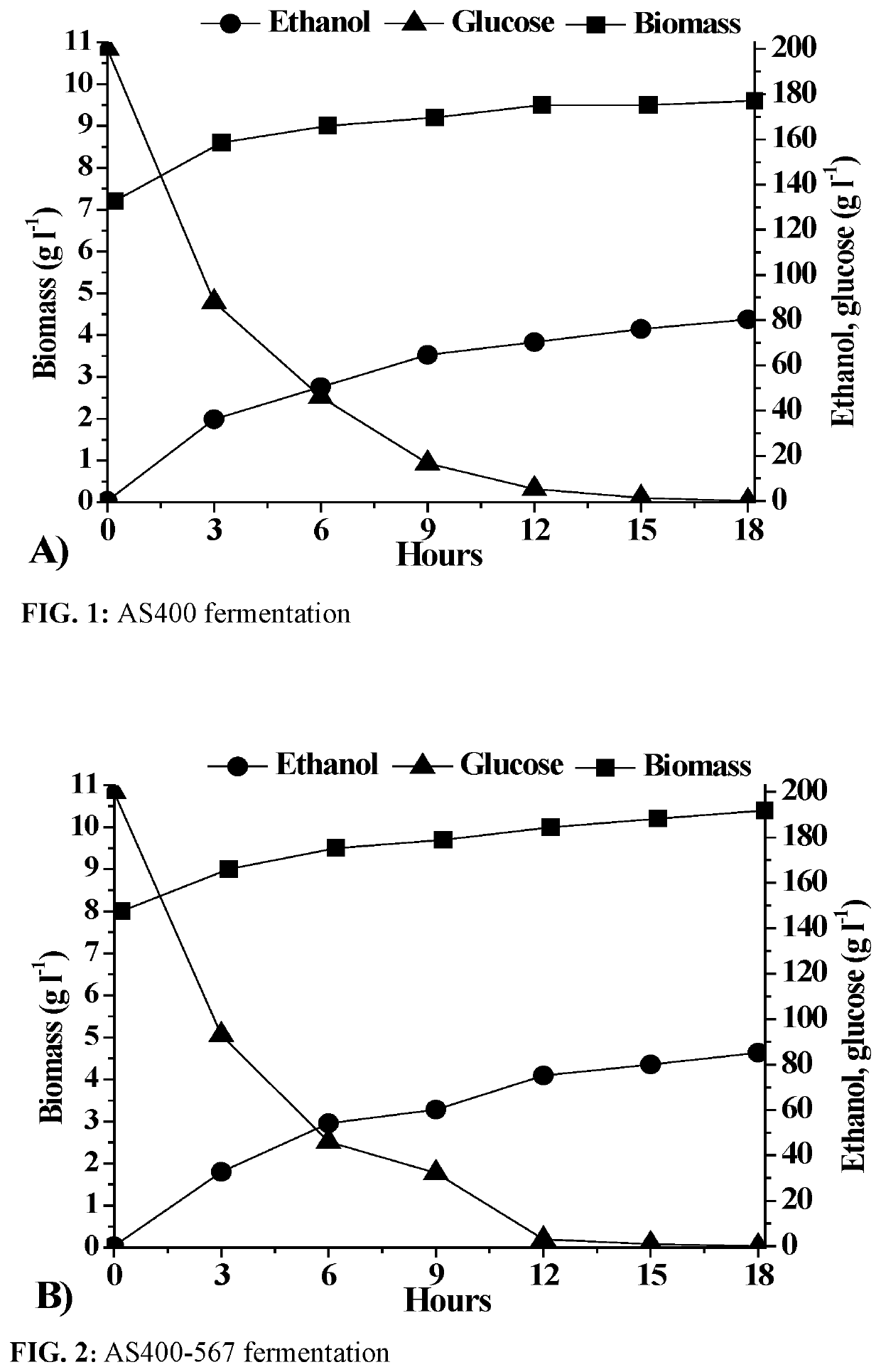
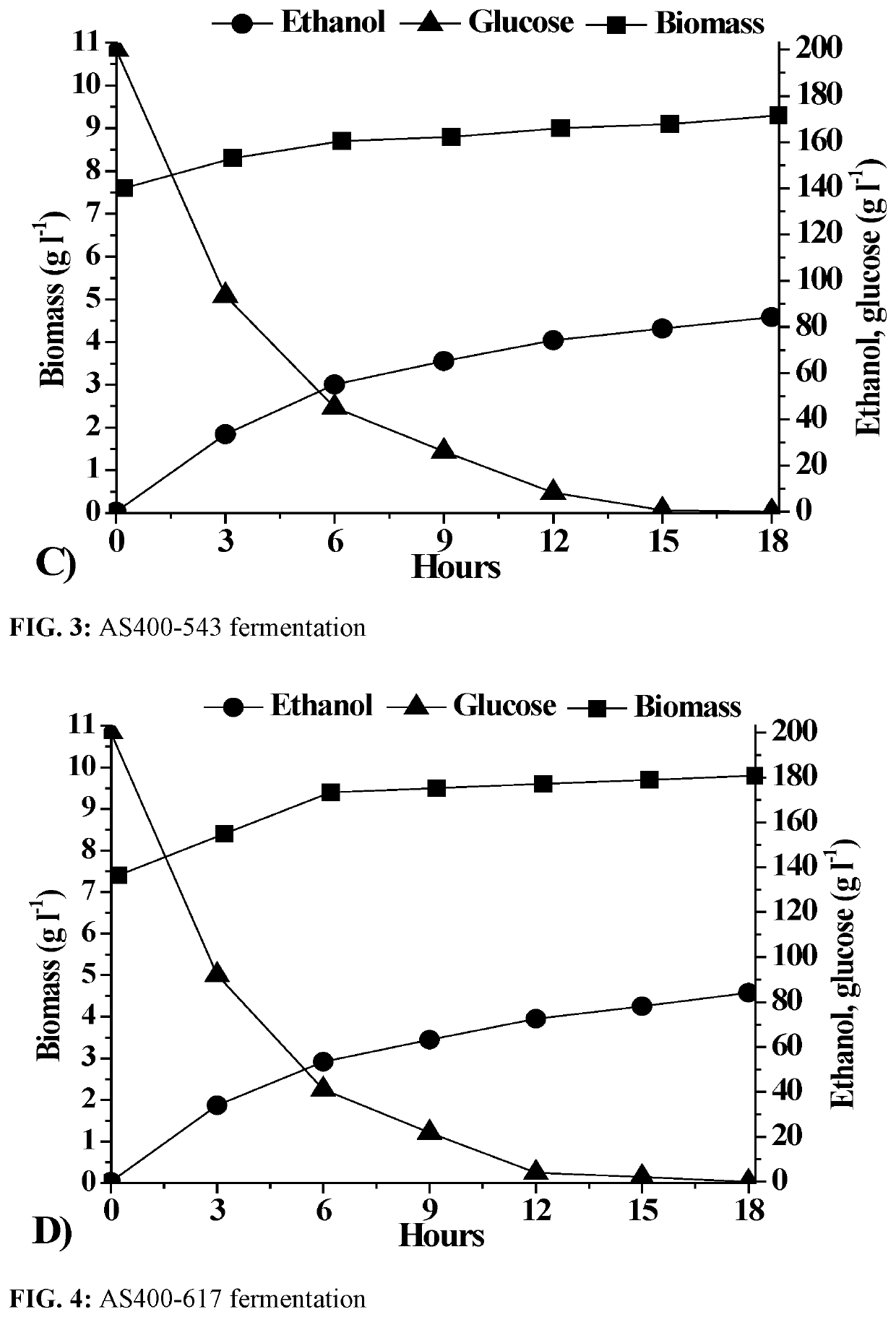
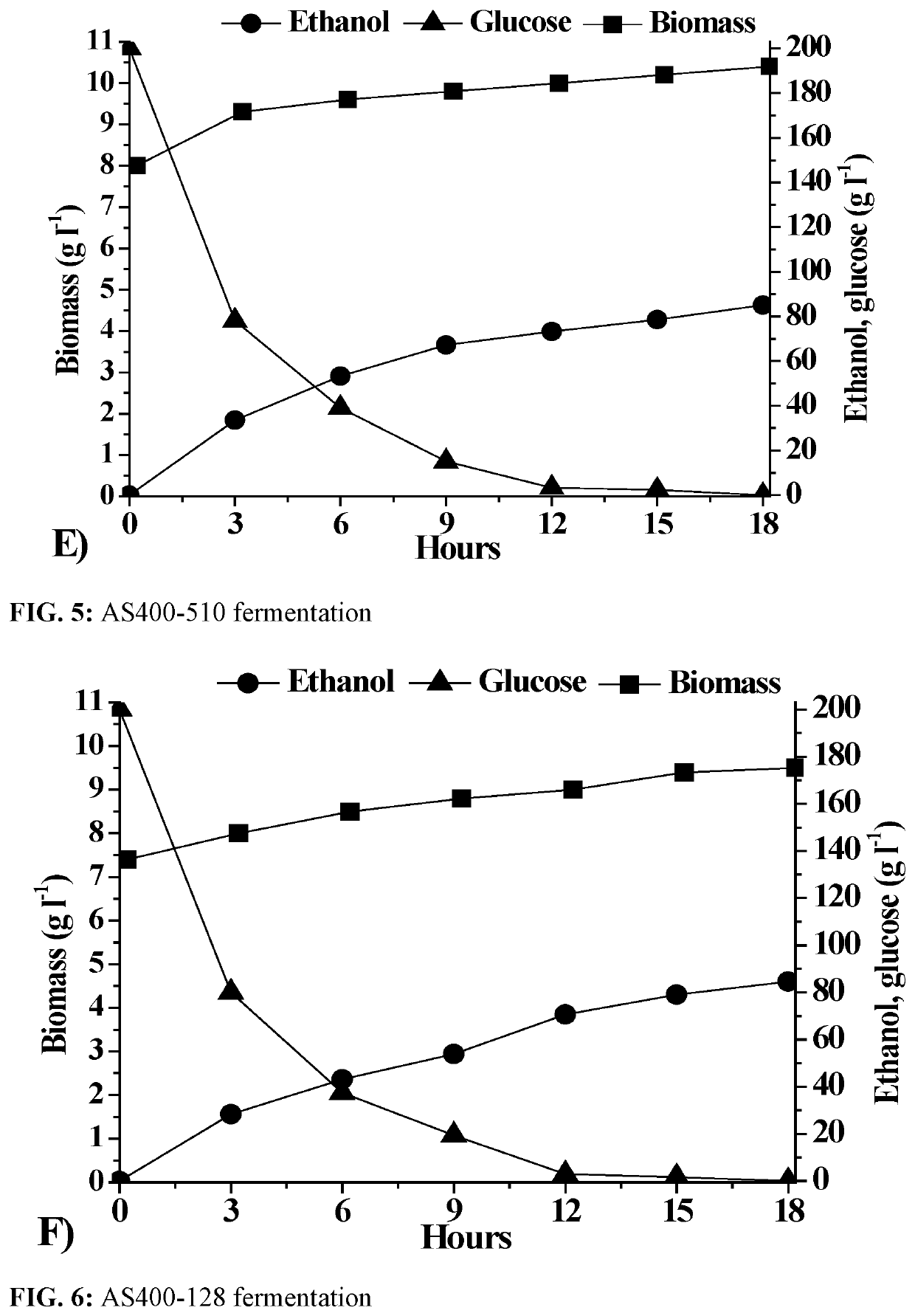
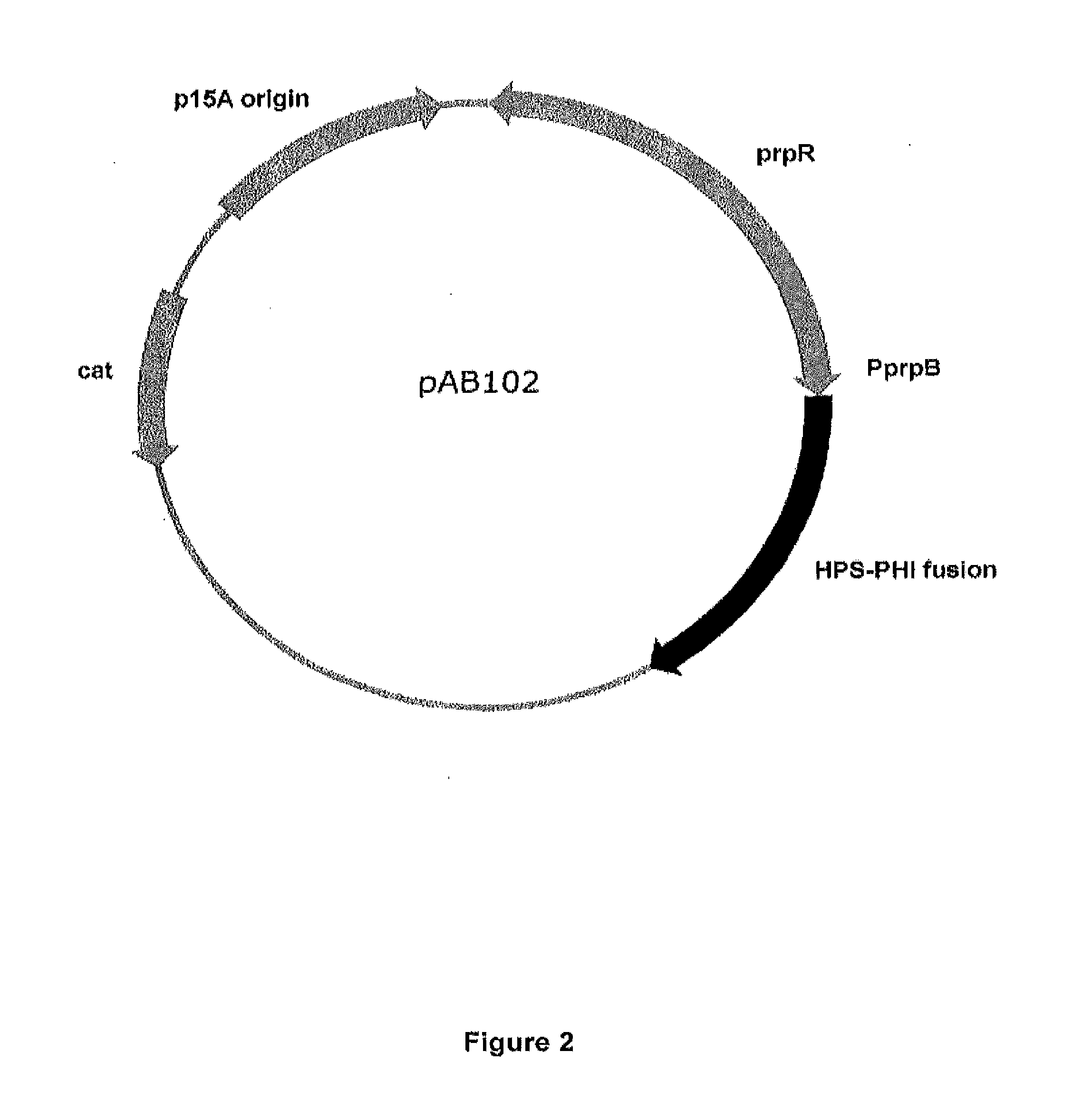
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
281 results about "Ethanol yield" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
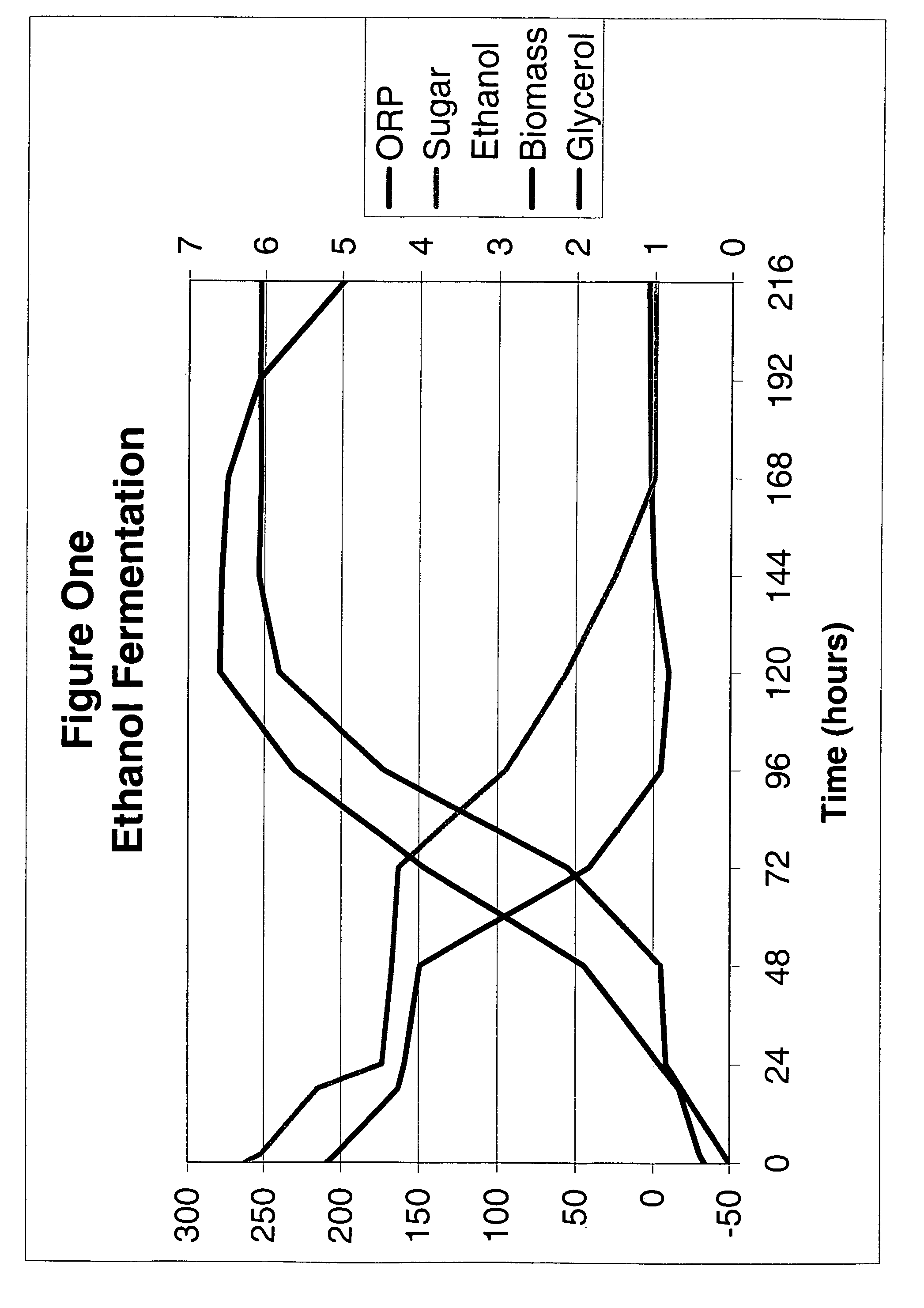
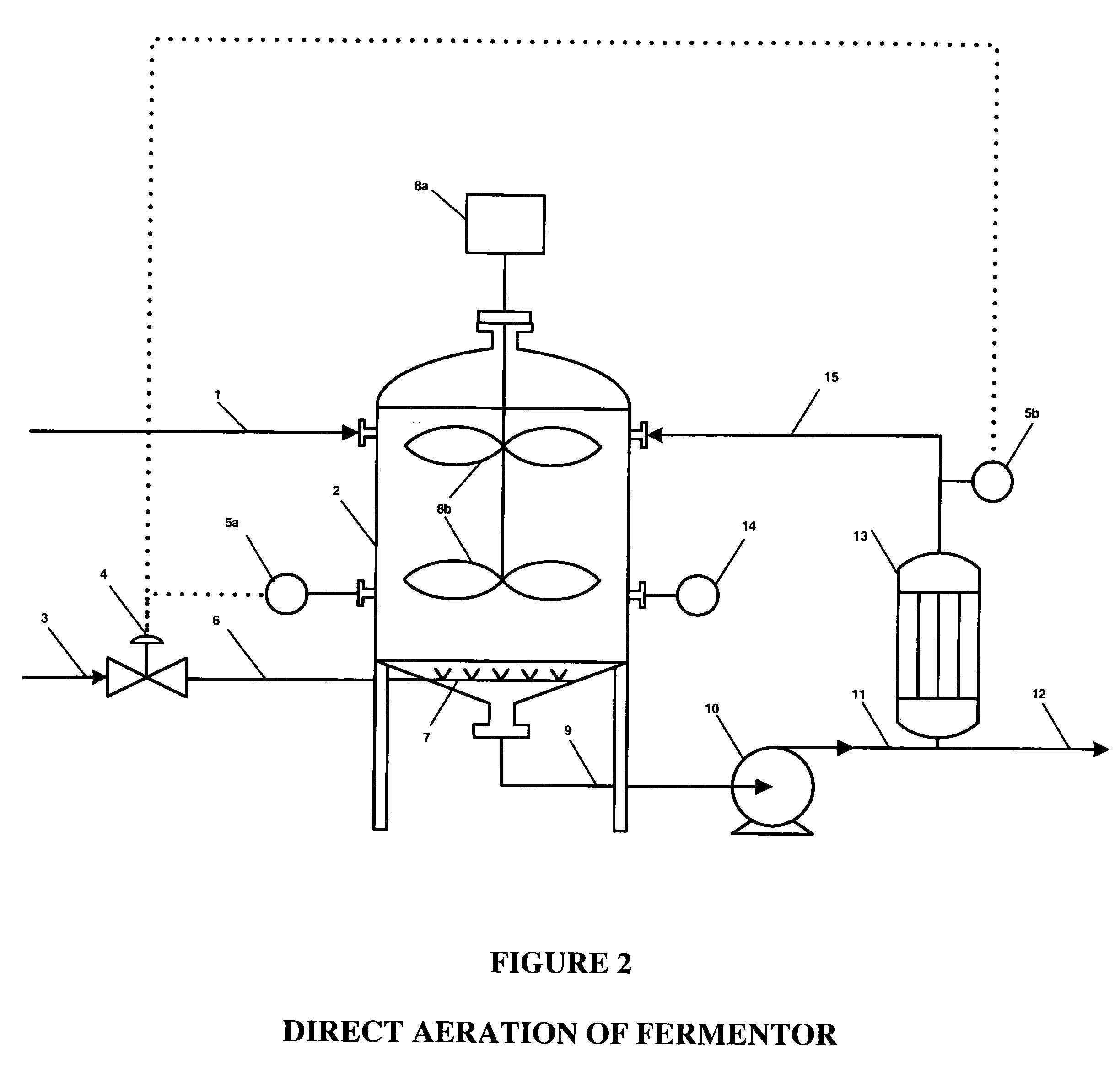
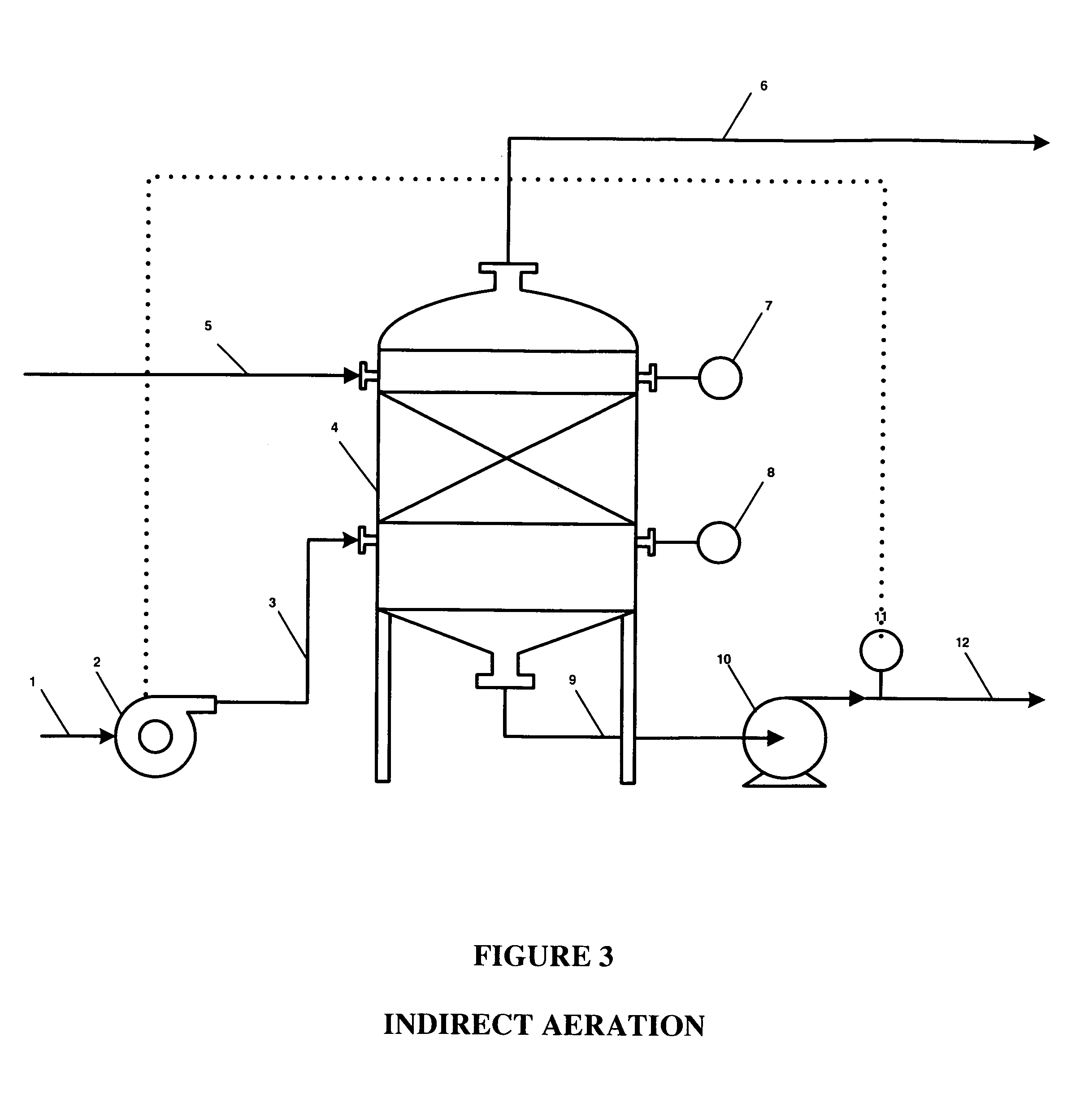
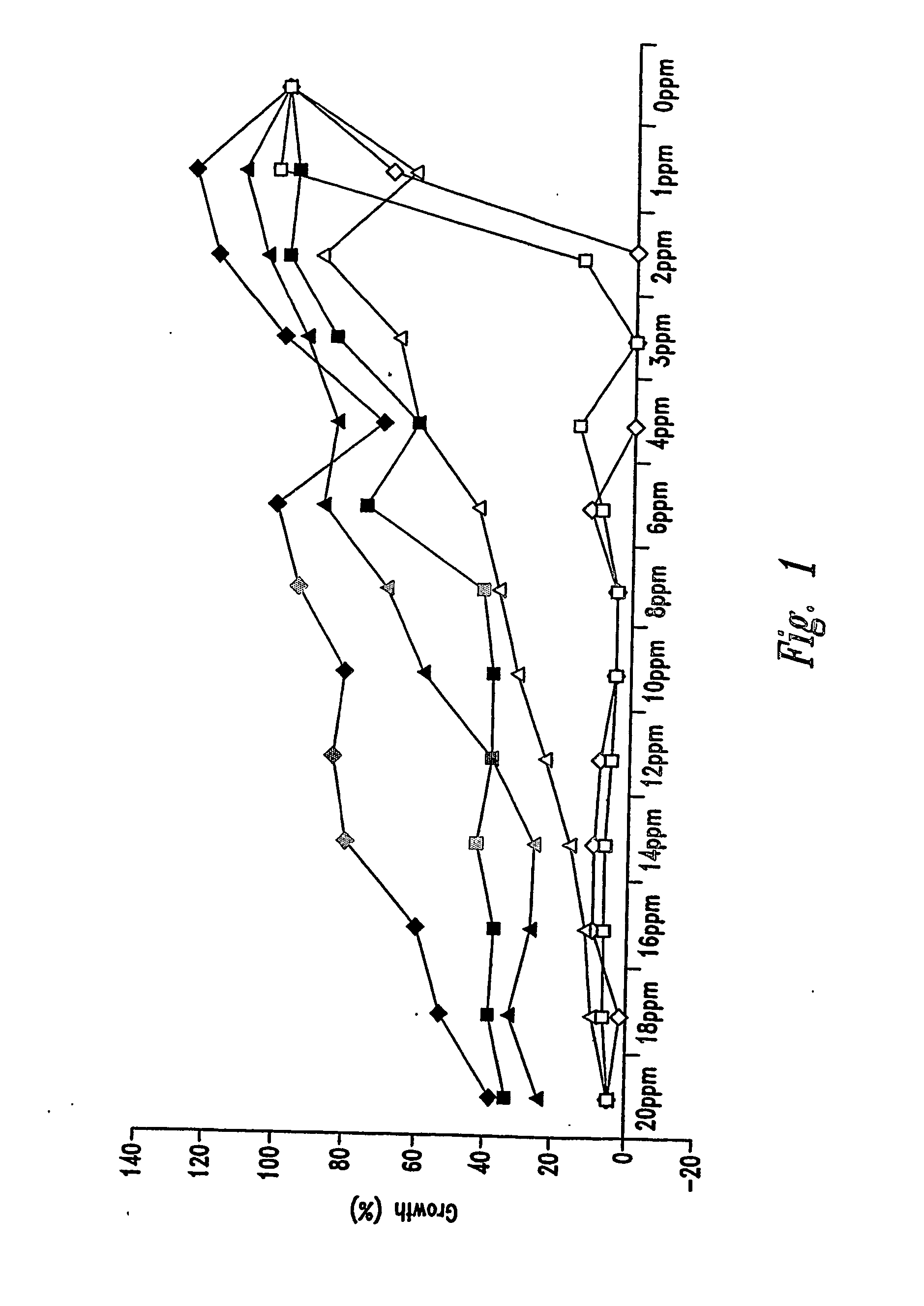
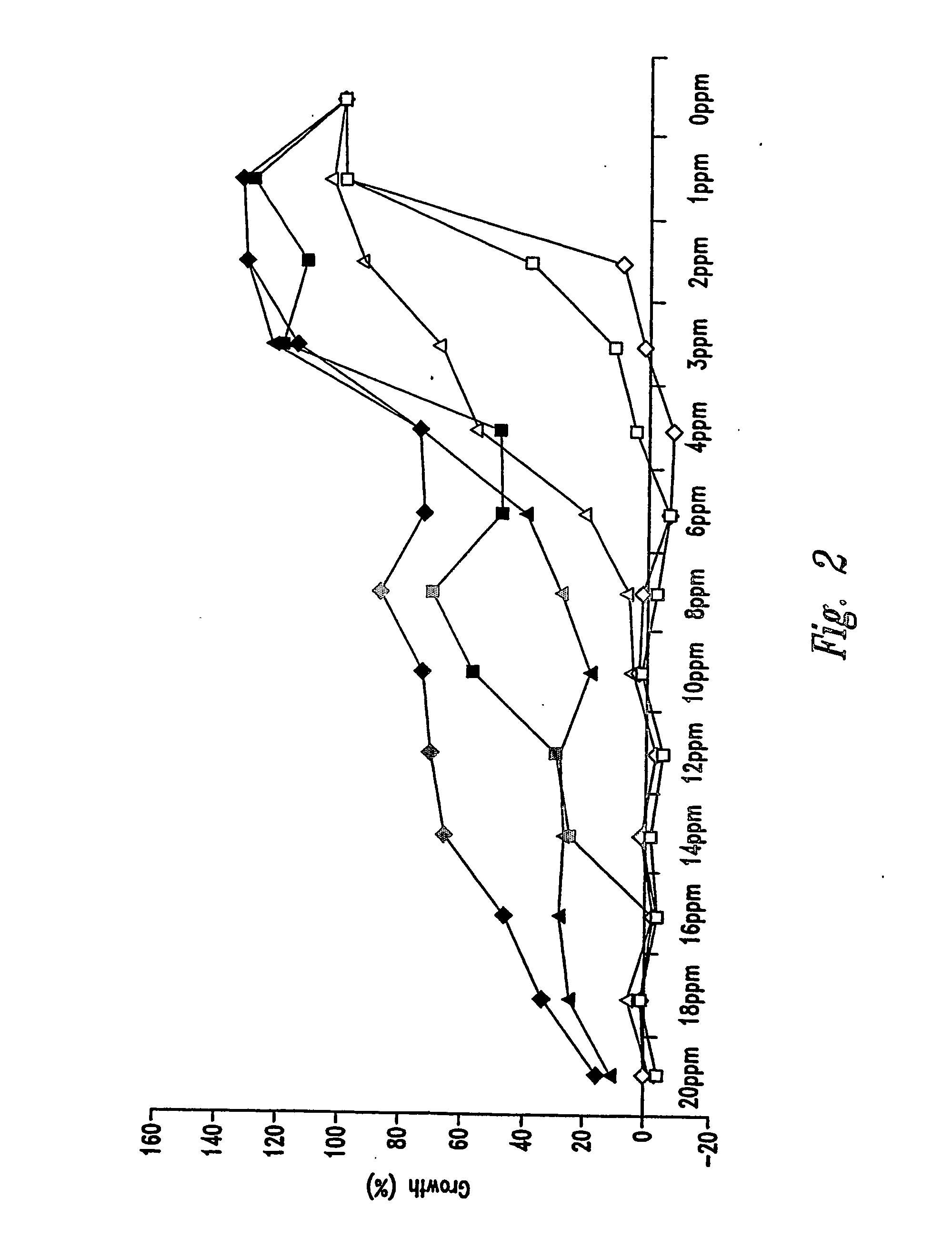
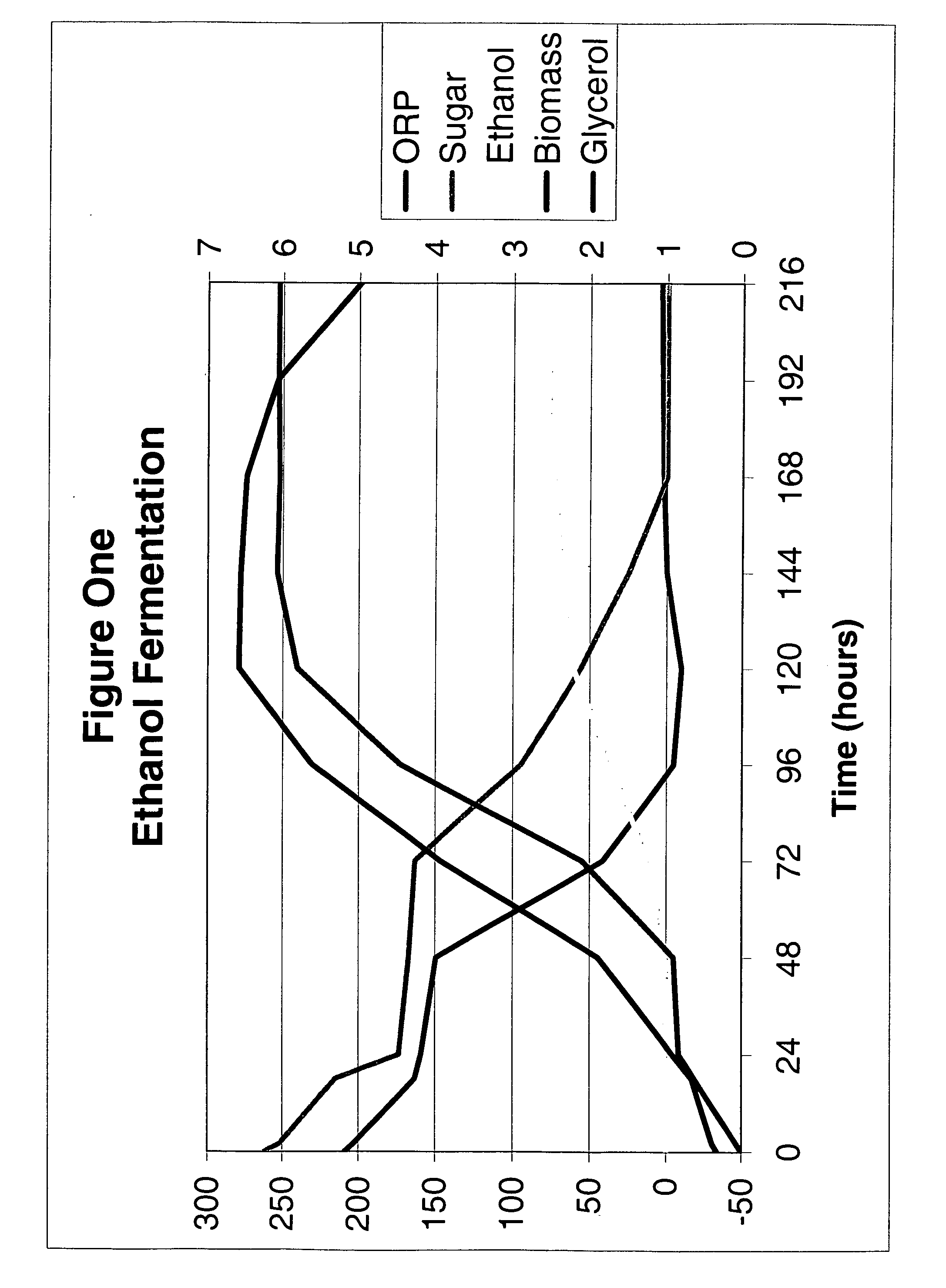
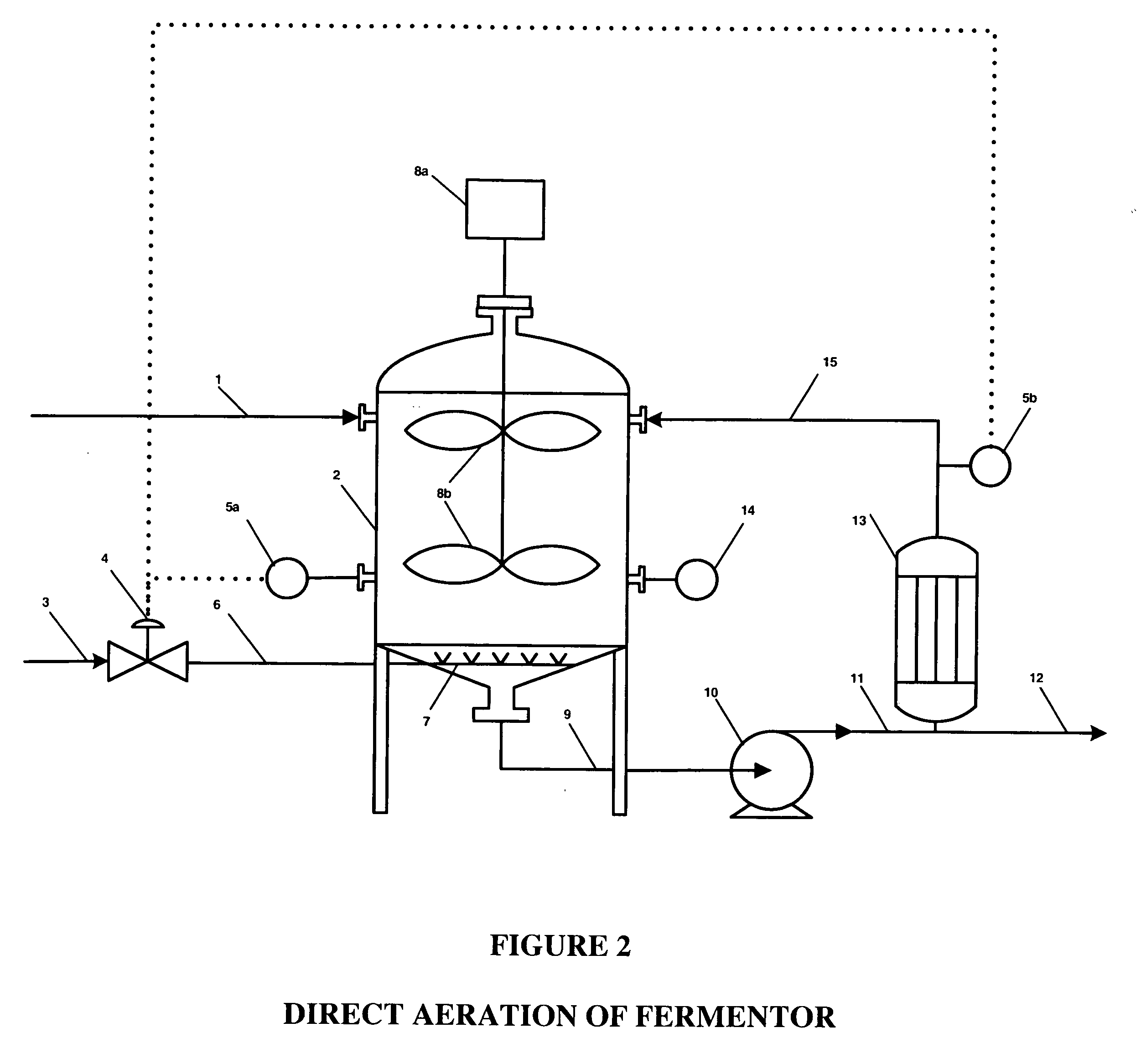
Ethanol fermentation using oxidation reduction potential
InactiveUS7078201B2Increased ethanol productionReduce formationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiofuelsOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
A process to improve ethanol yield, decrease fermentation time and reduce byproduct formation by monitoring and controlling oxidation reduction potential (redox) of the fermentor is disclosed.
Owner:BURMASTER BRIAN M
Lignin blockers and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060088922A1High efficiency in cellulose conversionLess of advantageProtein composition from vegetable seedsBiofuelsLignin degradationLignocellulosic biomass
Disclosed is a method for converting cellulose in a lignocellulosic biomass. The method provides for a lignin-blocking polypeptide and / or protein treatment of high lignin solids. The treatment enhances cellulase availability in cellulose conversion and allows for the determination of optimized pretreatment conditions. Additionally, ethanol yields from a Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation process are improved 5-25% by treatment with a lignin-blocking polypeptide and / or protein. Thus, a more efficient and economical method of processing lignin containing biomass materials utilizes a polypeptide / protein treatment step that effectively blocks lignin binding of cellulase.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
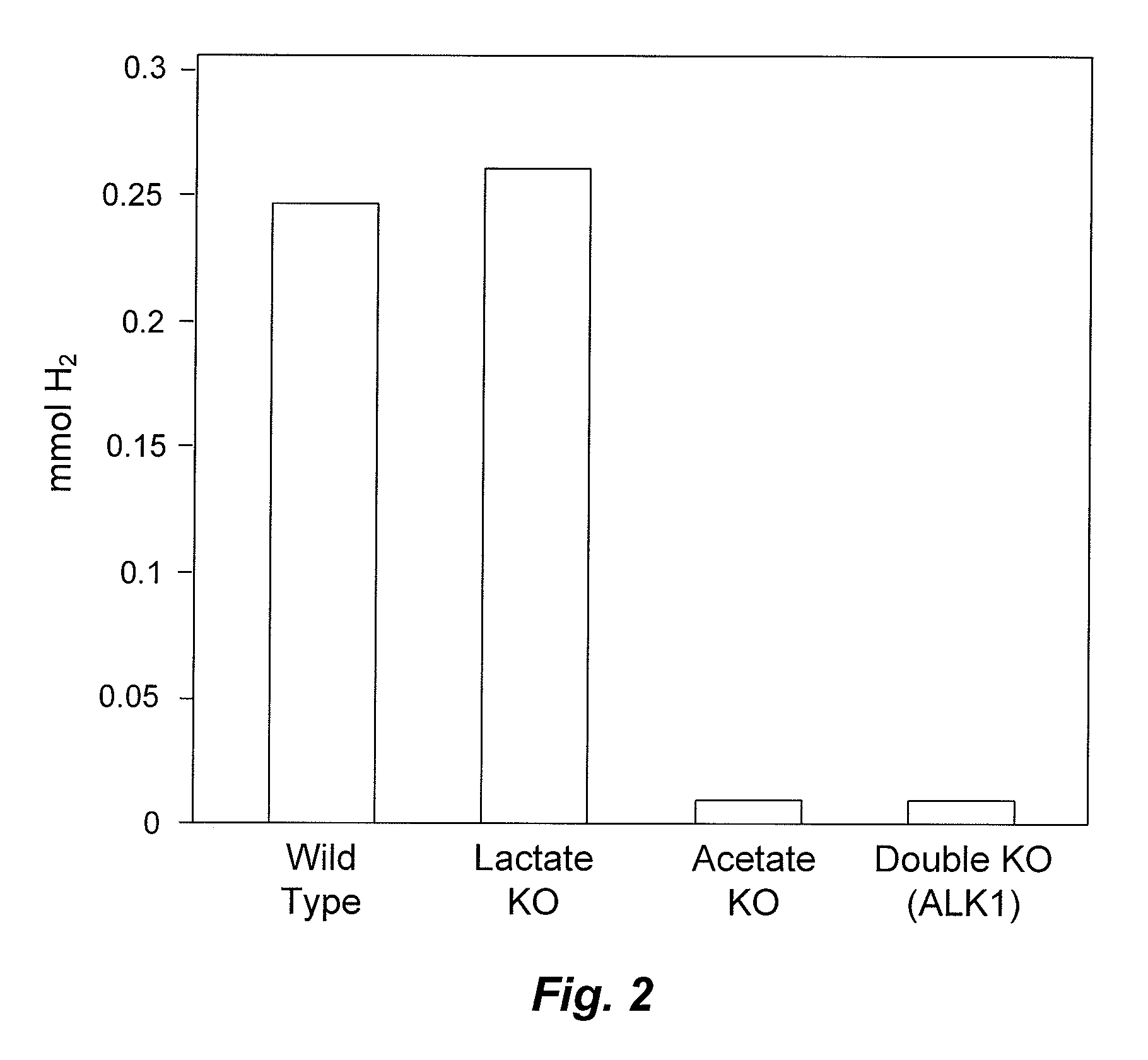
Thermophilic Organisms For Conversion Of Lignocellulosic Biomass To Ethanol
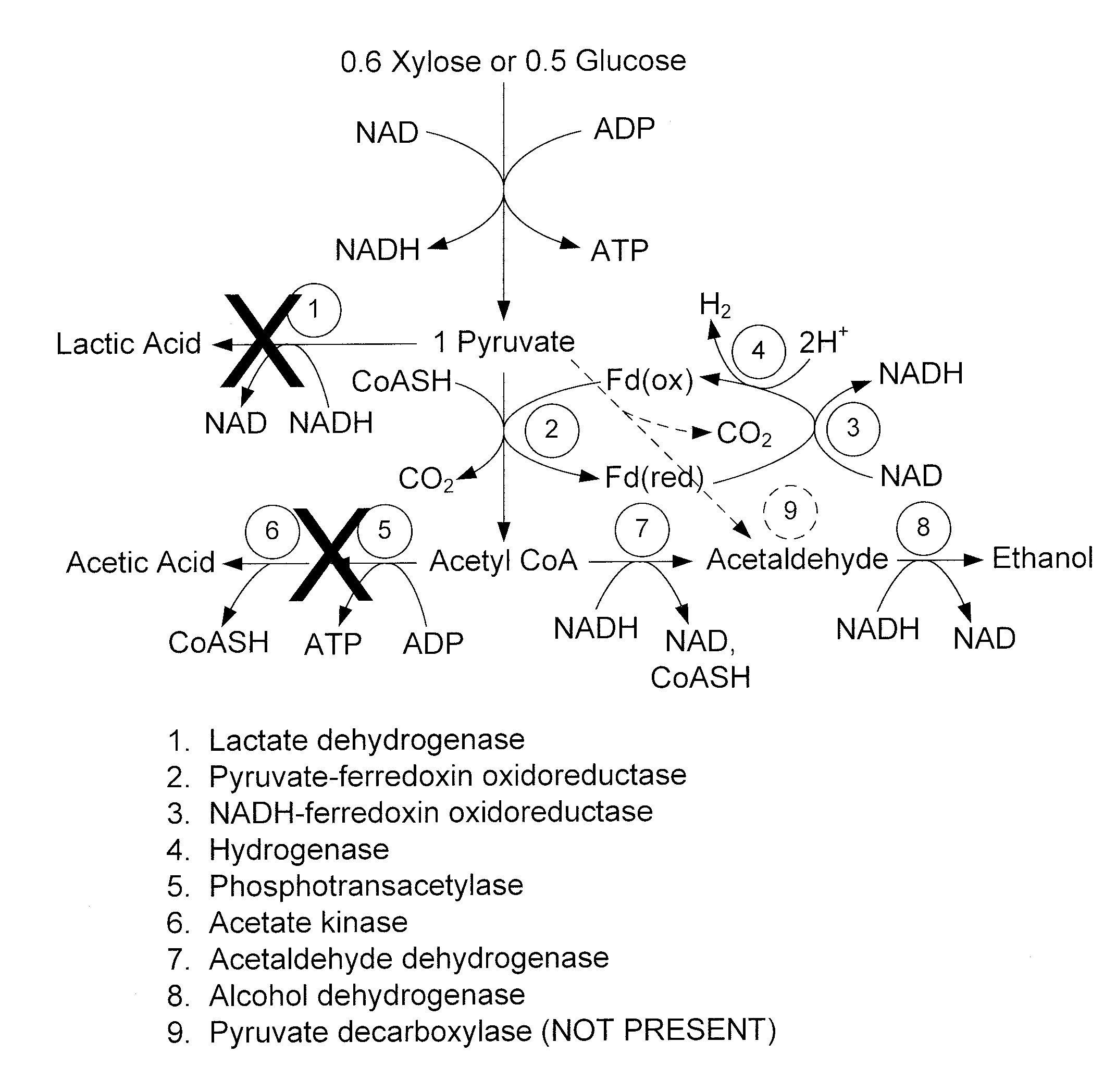
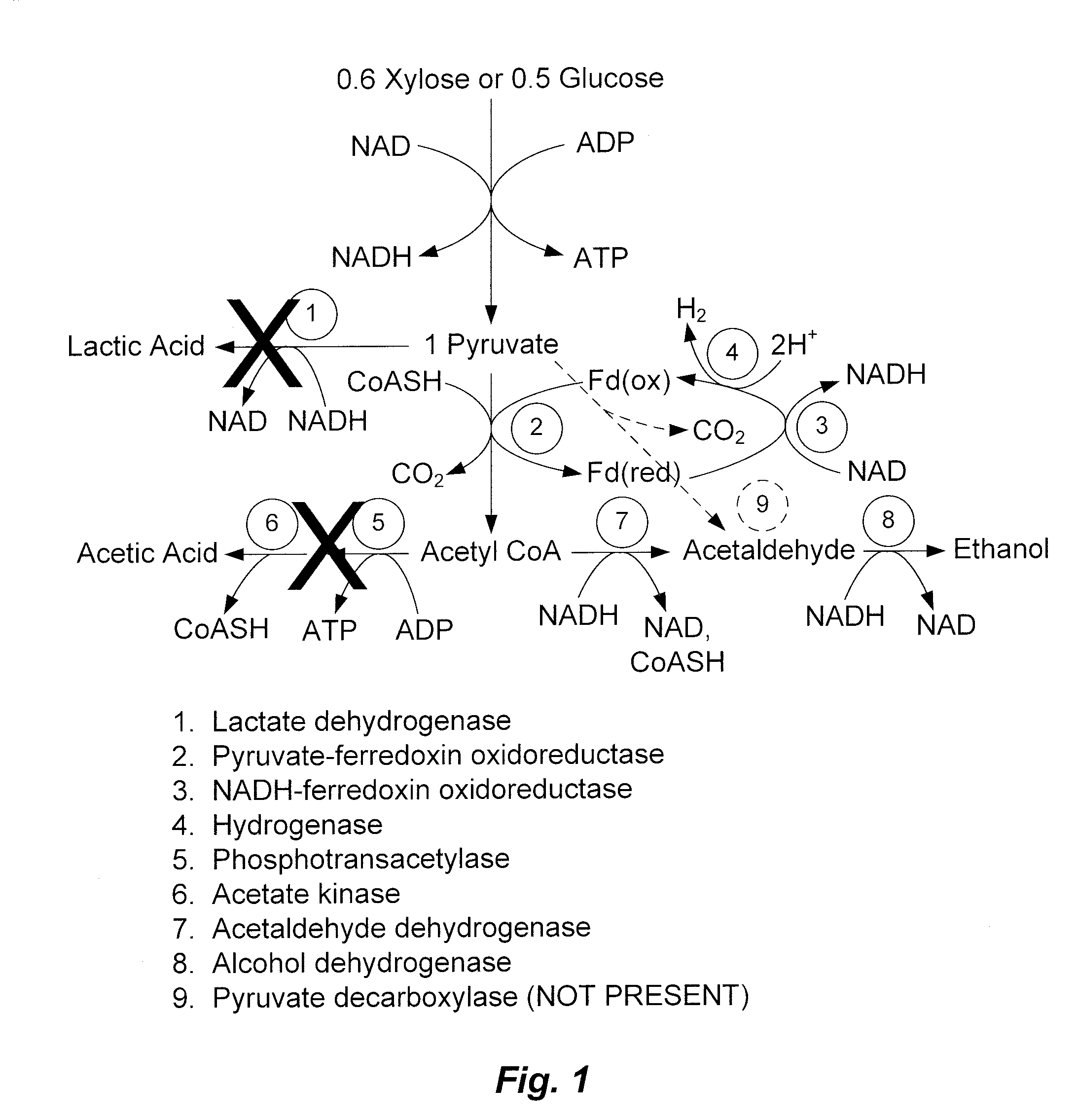
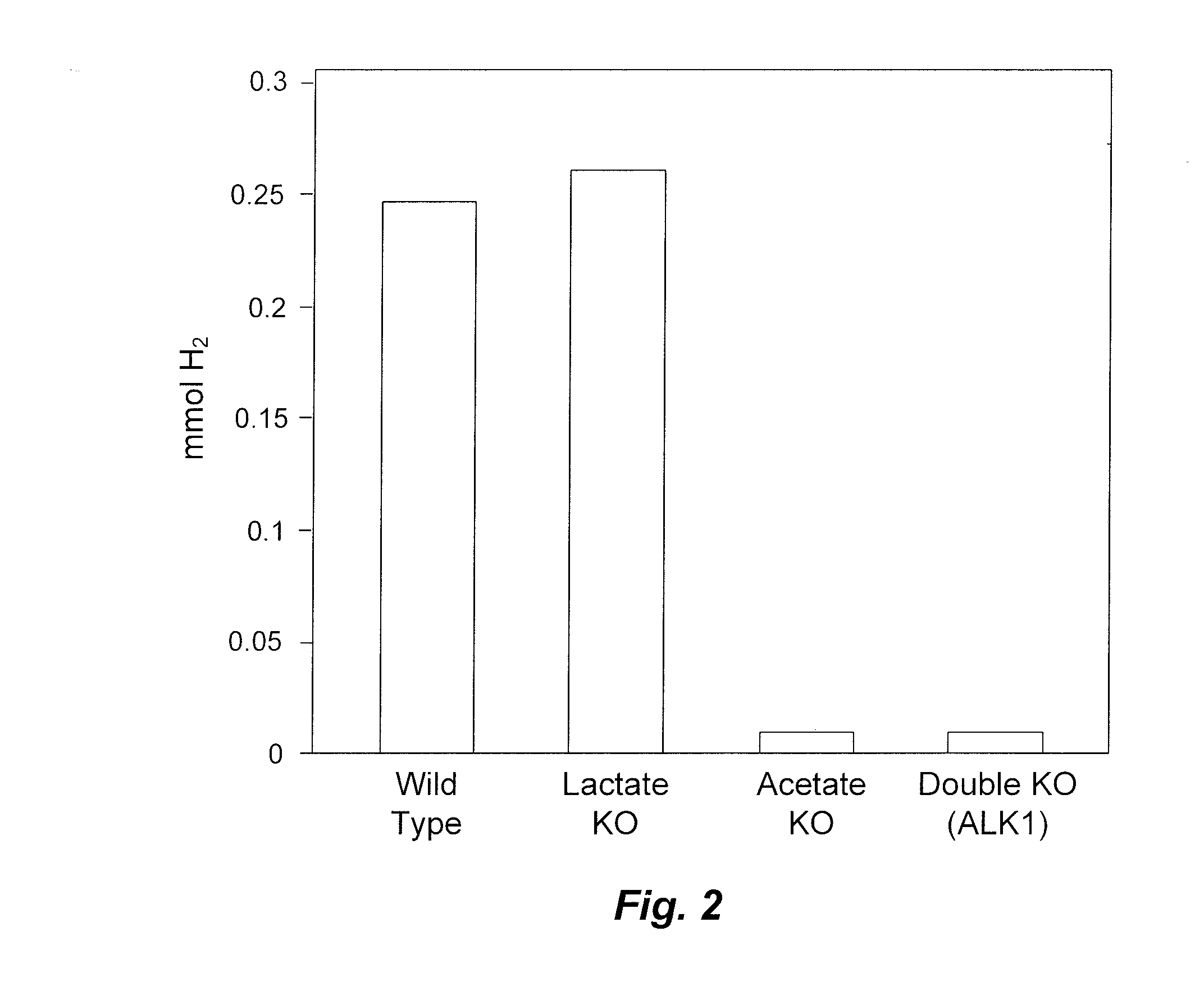
Mutant thermophilic organisms that consume a variety of biomass derived substrates are disclosed herein. Strains of Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum with acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase expression eliminated are disclosed herein. Further, strain ALK1 has been engineered by site directed homologous recombination to knockout both acetic acid and lactic acid production. Continuous culture involving a substrate concentration challenge lead to evolution of ALK1, and formation of a more robust strain designated ALK2. The organisms may be utilized for example in thermophilic SSF and SSCF reactions performed at temperatures that are optimal for cellulase activity to produce near theoretical ethanol yields without expressing pyruvate decarboxylase.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Wine brewing yeast strain and method for producing ethanol by efficient stalk fermentation
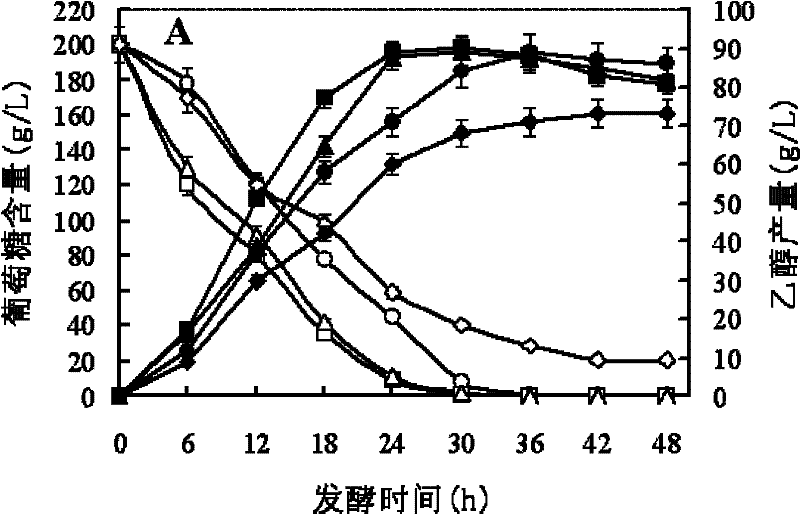
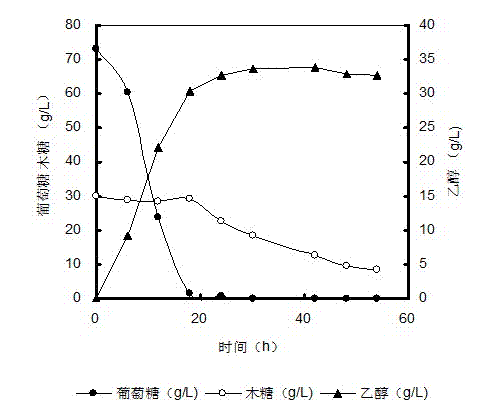
The invention discloses a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a method for producing ethanol by fermenting stalks, the strain is Saccharomyces cerevisiae DQ1, the collection No. is CGMCC No.2528, the strain can tolerate methanoic acid, acetic acid and furfural type inhibitors in hydrolyzate of the stalks, tolerate high glucose concentration and ethanol concentration and have wide growth temperature, and the strain is fermented at high temperature; the method for producing the ethanol by fermenting the stalks comprises two-stage culture of seeds, wherein the first stage culture is carried out in a synthetic culture medium for 16-24 hours, the second stage culture is that a mixed culture medium containing 30-70 percent of hydrolyzate is inoculated into with the inoculation amount of 5-10 percent for culture for 15-20 hours, and the inoculation into the hydrolyzate with the inoculation amount of 10 percent or simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of the stalks is further carried out for producing the ethanol. The invention has the advantages of being applicable to high-solid-content stalk enzyme hydrolysis and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation, with short fermentation period, high ethanol yield, and low production cost, thereby having great industrial application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Processes Using Antibiotic Alternatives In Bioethanol Production
ActiveUS20110230394A1Increase productionLow and no adverse environmental impactAntibacterial agentsBiocideEthanol yieldAntibacterial peptide
Methods for controlling the growth of bacteria in ethanol fermentation systems with antibiotic alternatives, which can be nonoxidizing biocides, stabilized oxidizers, or any combinations thereof, are described. As an option, a process or composition of the present invention can include one or more polycyclic antibacterial peptides. The methods can provide improvements, such as increased ethanol yields with minimal carryover of biocide into co-products of the processes.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Screening and application of yeast with high ethanol yield and low fusel oil yield in Chinese Maotai-flavor liquor production
InactiveCN102226155AReduce manufacturing costSimple production processFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementDistillationScreening method
Screening and application of yeast with high ethanol yield and low fusel oil yield in Chinese Maotai-flavor liquor production belong to the technical field of biological engineering. The strain is any one strain selected from pichia anomala CGMCC4740, schizosaccharomyces pombe CGMCC4744, zygosaccharomyces bailii CGMCC4745, trichosporon asahii CGMCC4746, saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC4747, kazachstania exigua CGMCC4748, pichia fermentans CGMCC4750. The strain is separated from various Daqu, fermented grains, brewing raw materials and brewing environment of several Chinese famous distilleries; the screening method comprises the following steps: diluting distiller yeast samples, fermented grains, brewing raw materials or brewing environment substances, coating on a TTC primary screening plate, selecting a colony with an obvious red color, inoculating the colony in a shake flask for culture, performing secondary screening, determining the contents of ethanol and fusel oil of the fermentation broth by a distillation specific gravity method and HS-SPME-GC-MS respectively, screening the strain with high ethanol concentration and low fusel oil concentration. The strain is applicable to food industry and brewed wine industry.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
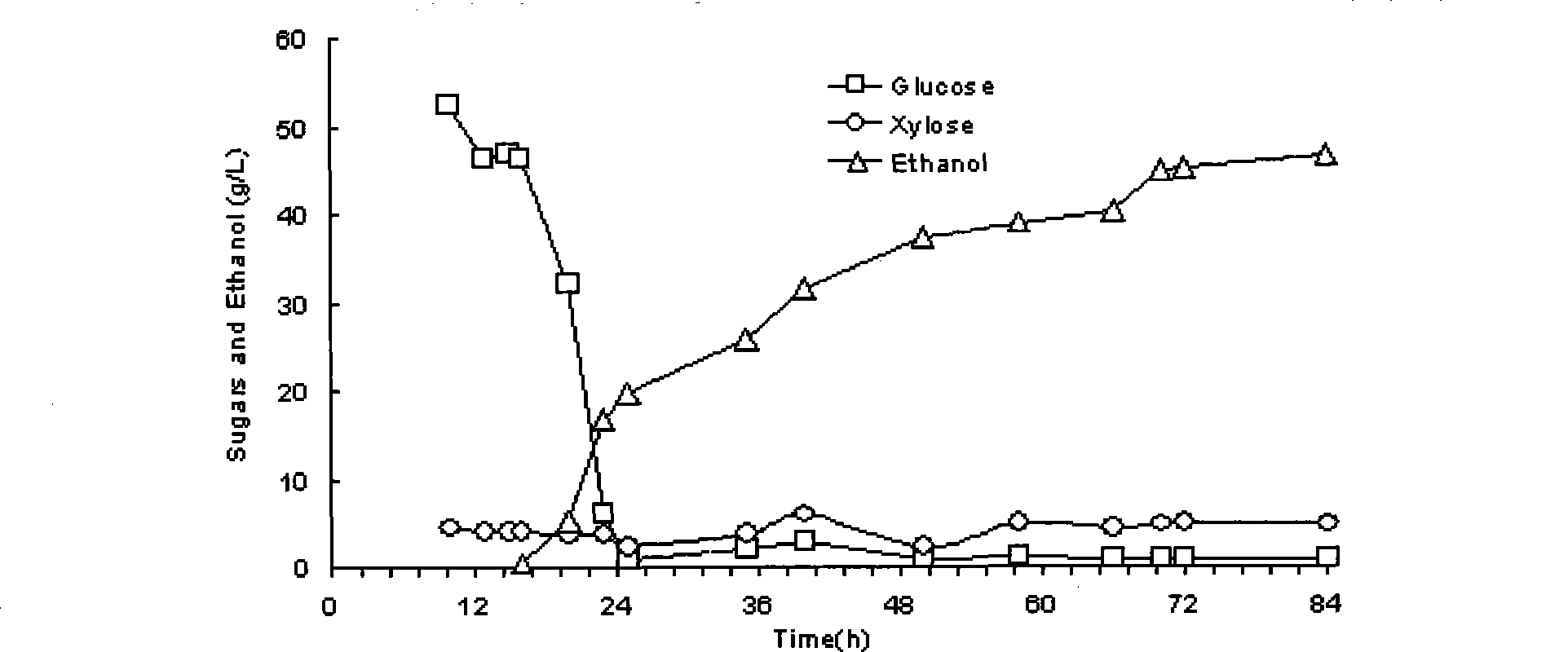
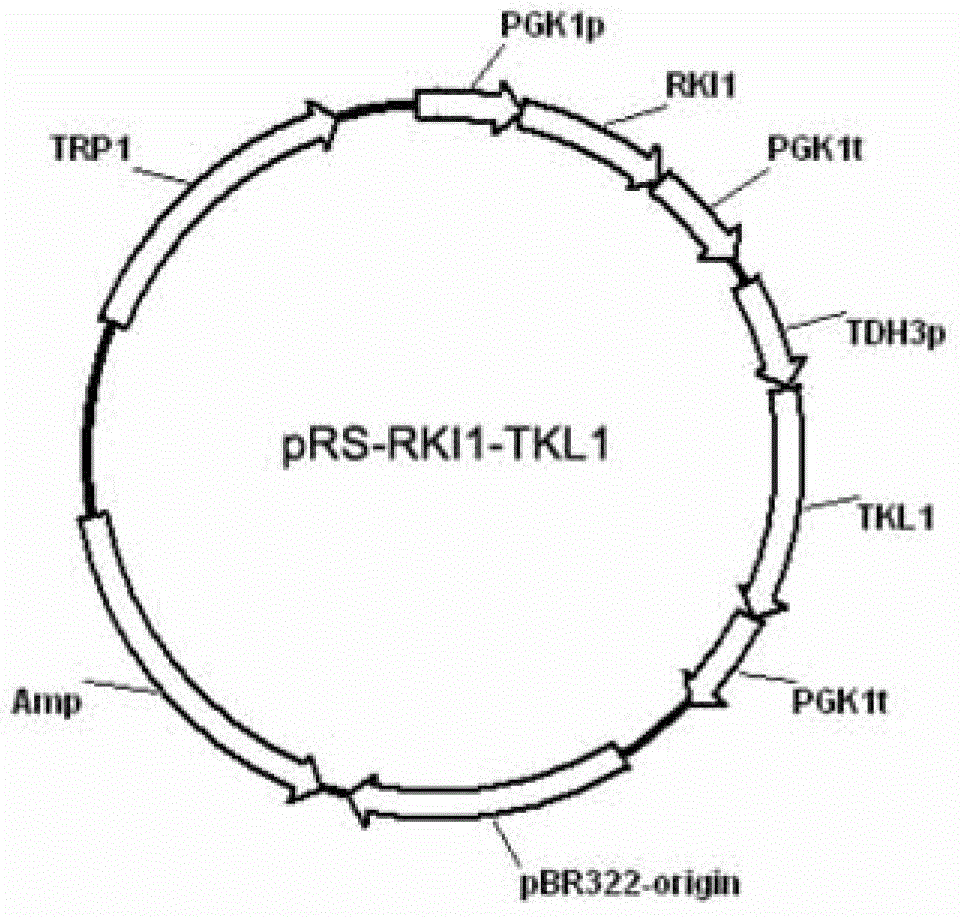
Recombinant yeast strain capable of efficiently metabolizing xylose and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant yeast strain (Saccharomyces cerevisiae)) capable of efficiently metabolizing xylose, which is named SyBE005. The recombinant yeast strain has been collected in Common Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the collection number is CGMCC No.6634, and the recombinant yeast strain has the capacity of efficiently metabolizing xylose to produce ethanol. The recombinant yeast strain SyBE005 can effectively ferment xylose to generate ethanol. The ethanol yield reaches 64% of the theoretical yield, and the yield of the byproduct xylitol is lower than 12%; and thus, the recombinant yeast strain can efficiently convert xylose into ethanol, and is an excellent strain utilizing cellulose hydrolysate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Ethanol resistant and furfural resistant strains of E. coli FBR5 for production of ethanol from cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20090053793A1Concentration maximizationHigh yieldBacteriaBiofuelsCelluloseResistant strain
Owner:ROWAN UNIVERSITY
Method for production of ethanol by continuous fermentation of immobilized yeast cells
The invention provides a method for production of ethanol by continuous fermentation of immobilized yeast cells, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) a fiber material is attached to a support frame, and is filled into a bioreactor; (2) yeast cells are immobilized in the fiber material in the bioreactor; (3) a fermentation medium is added into the bioreactor to begin ethanol fermentation; (4) when glucose in the fermentation medium is consumed, a fermentation liquid flows out of the bioreactor, the ethanol is collected, the fermentation medium is added, and then the step (4) is repeated. The method uses the fiber material for immobilization of the yeast cells for continuous fermentation to produce the ethanol, the fiber material as an immobilization material is stably in property, non-toxic, and good in adsorption and mass transfer effects, can be repeatedly used, is easy to achieve continuous production of the ethanol, and in a continuous fermentation process can greatly improve the ethanol yield.
Owner:NANJING HIGH TECH UNIV BIOLOGICAL TECH RES INST CO LTD
Method for producing ethanol by high-efficiency simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation
InactiveCN102251010AReduce pollutionNo pollution in the processBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesEthanol yieldHemicellulose
The invention discloses a method for producing ethanol by high-efficiency simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation, which comprises the following steps: pretreating; concentrating and detoxifying; preparing yeast seed solution; performing simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation; and distilling / rectifying. When the method provided by the invention is used, the inhibition action of a monosaccharide component formed by hydrolysis of cellulose on cellulose is relieved, the enzymolysis saccharification efficiency and fermentation yield are improved, the recovery rate of hemicelluloses in bagasse is about 60 percent, the cellulose recovery rate is about 86 percent, and the total ethanol yield of dry bagasse can reach about 20 percent.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YOURUI BIOSCI
High-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and breeding method thereof
ActiveCN103232948AHigh genetic stabilityBack mutationFungiMutant preparationBiotechnologyEthanol yield
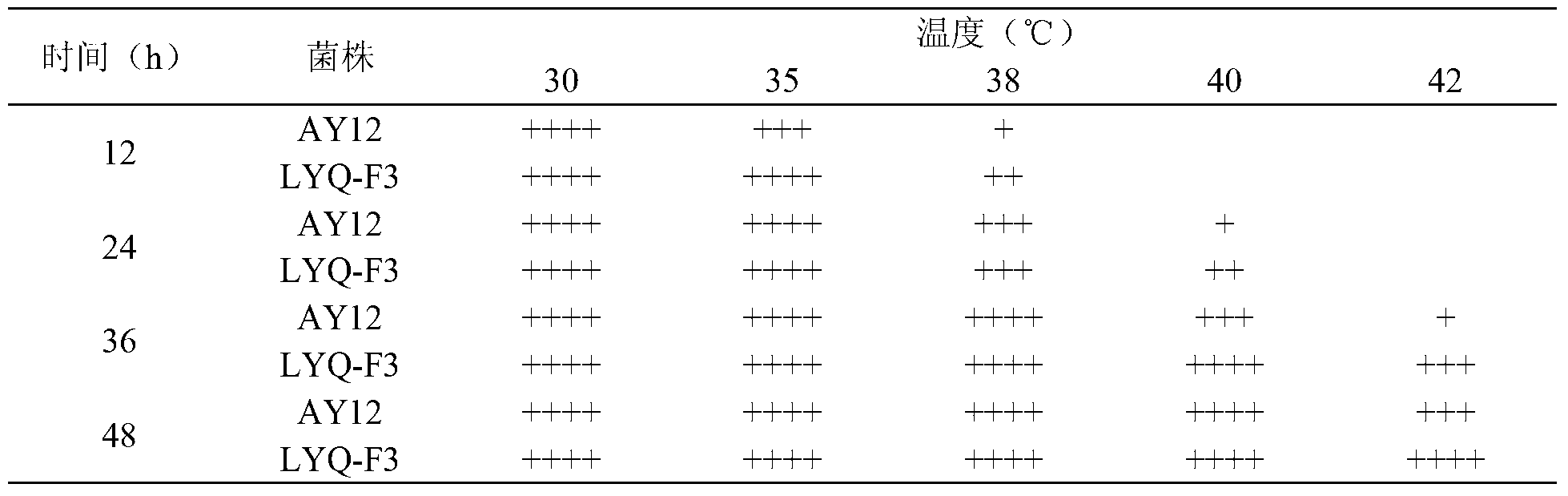
The invention provides a high-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a breeding method of the high-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. The saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) SY-5-11L has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7377. The strain is characterized in that the ethanol yield is 13.9% (v / v) at a condition of fermenting at high temperature of 38 DEG C on the premise that other fermenting performances are not influenced, the yield is improved by 17.8% as compared with that of a parent strain. The ethanol output at the condition of fermenting at high temperature of 40 DEG C is 12.2% (v / v), and is improved by 34.1% as compared with that of the parent strain. The breeding method comprises the following steps of: performing artificial ultraviolet mutagenesis on an initial strain of the saccharomyces cerevisiae; screening out 23 forward mutant strains as a genome rearrangement library, wherein the ethanol output of the forward mutant strains are obviously raised on the condition of fermenting at a high temperature; and performing the genome rearrangement at three rounds, thus gaining the mutant strains with the maximum ethanol output under the high-temperature fermenting condition. The finally bred saccharomyces cerevisiae strain can be subjected to alcoholic fermentation at the high-temperature fermenting condition, brings no special requirements to fermenting equipment and technological conditions, and can be put into service with the equipment and conditions of general plants, thus having a wide application prospect.
Owner:贵州钓鱼台国宾酒业有限公司
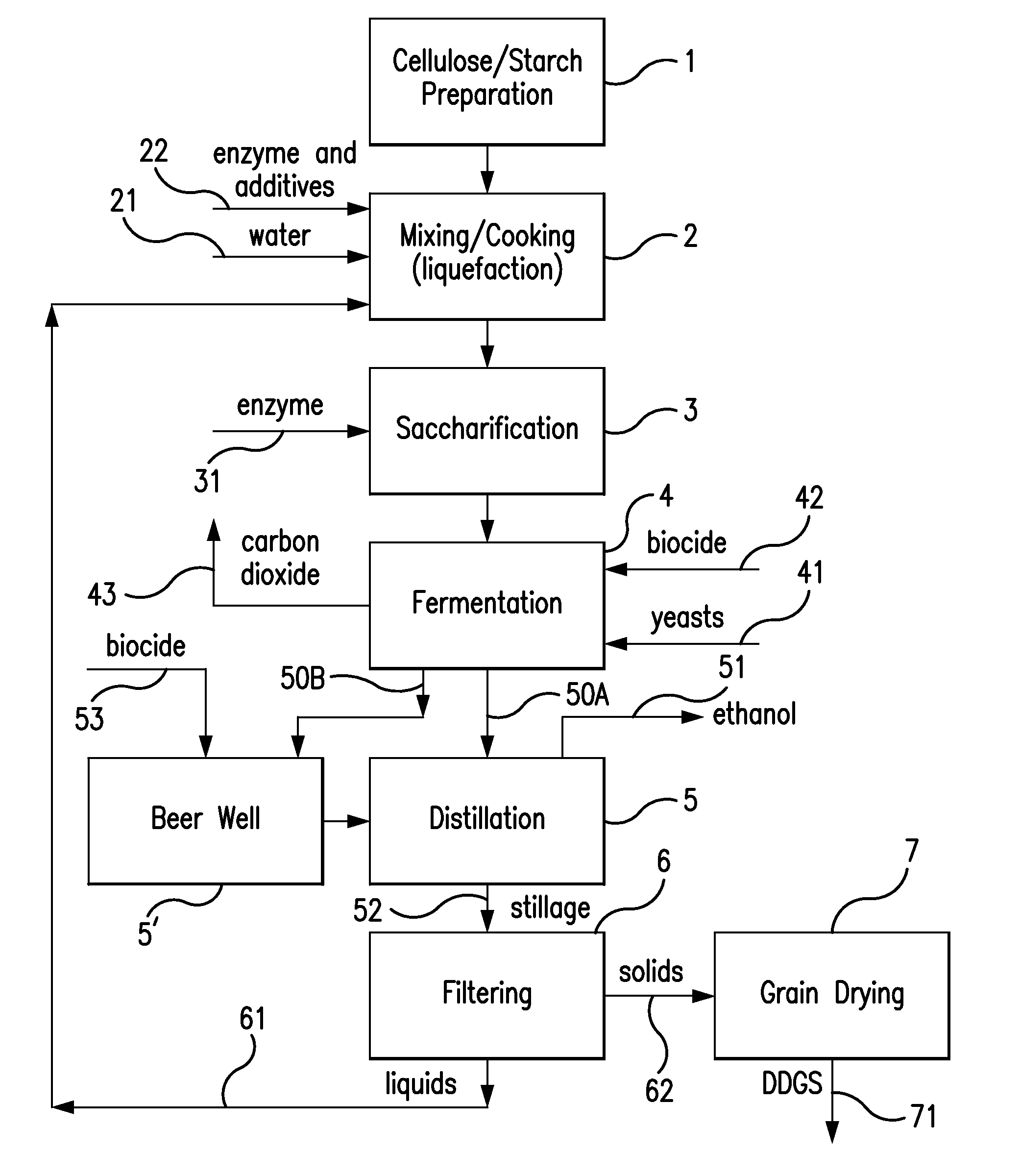
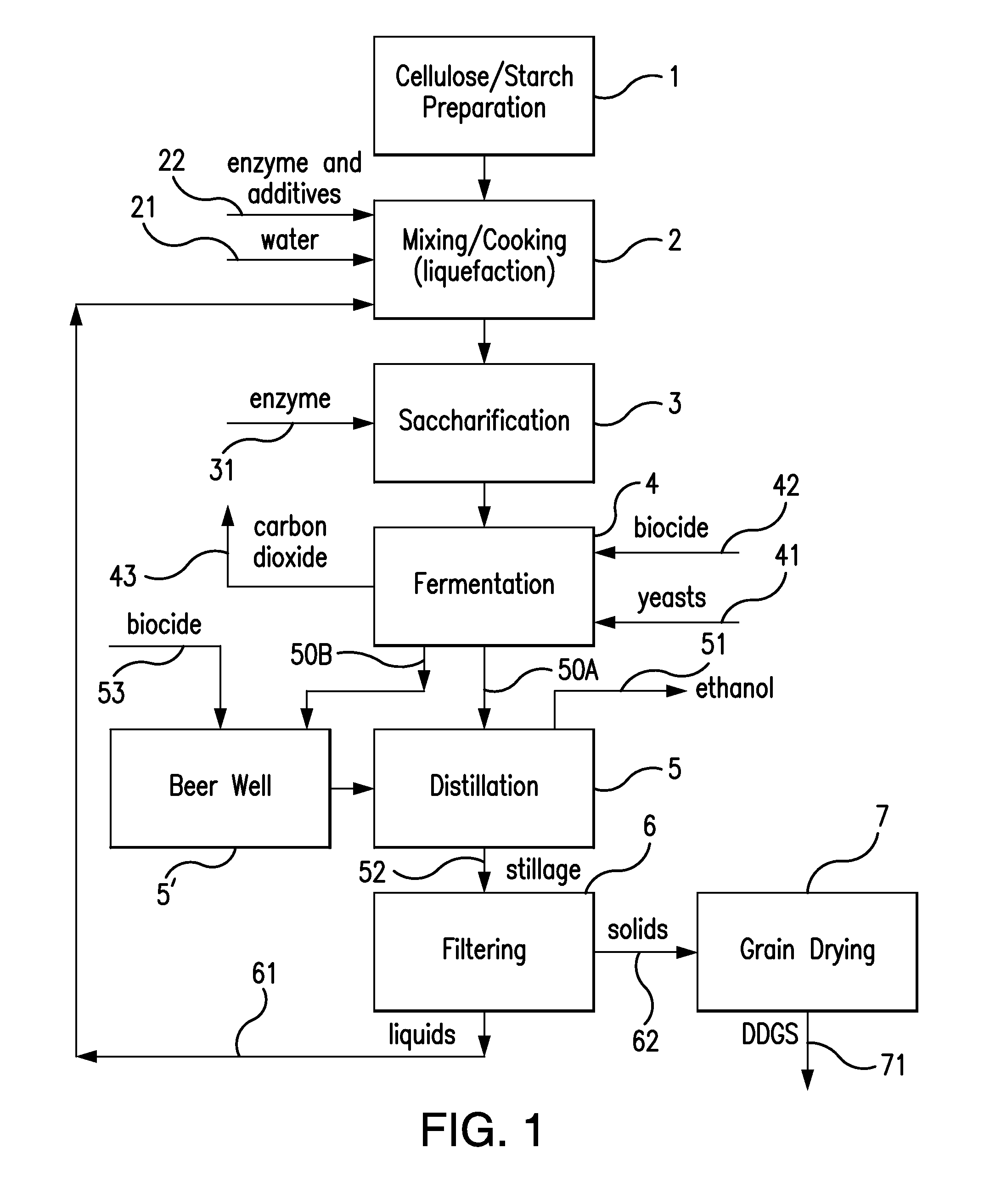
Production method for fuel ethanol
ActiveCN103103217AIncrease concentrationReduce energy consumptionBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesFiberEthanol yield
The invention relates to a production method for fuel ethanol. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating a fiber raw material and a cheap carbon source raw material; (2) mixing the pretreated fiber raw material and the pretreated cheap carbon source raw material and carrying out pre-enzymatic hydrolysis, wherein a weight ratio of the cheap carbon source raw material to the fiber raw material is 1: 3 to 3: 1 on a dry basis, an obligate hydrolase preparation is used in the process of pre-enzymatic hydrolysis, and the obligate hydrolase preparation contains cellulase and comprises diastase and / or inulase at the same time; and (3) selectively adding a fermentable sugar raw material in the fiber raw material having undergone pre-enzymatic hydrolysis, adjusting a temperature to 24 to 44 DEG C, adding saccharomyces cerevisiae and carrying out synchronous saccharification and joint fermentation for production of ethanol. The method provided by the invention can effectively increase the concentration of ethanol in the fermentation broth of the fiber raw material and reduce energy consumption in the phase of concentration of ethanol and has the advantages of simple production flow and high ethanol yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with multiple-stress resistance, and application thereof in cellulose alcohol fermentation
InactiveCN102199554AImprove toleranceEfficient conversionFungiMicroorganism based processesHydrolysateAlcohol production
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with multiple-stress resistance, and the application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain in cellulose alcohol fermentation. The invention provides a saccharomyces cerevisiae T43 CGMCC No. 4642. The saccharomyces cerevisiae T43 has strong temperature adaptability (such that cooling and heating cost is reduced during fermentation processes) and good tolerance with inhibitors in cellulose hydrolysate (such that production processes can be simplified, and fermentation time can be shortened). Therefore, the saccharomyces cerevisiae has good prospect to be adopted in industrial application. According to the present invention, the efficient conversion of glucose in corn stalk hydrolysate to ethanol can be achieved, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be directly used in present fuel ethanol production technologies and new lignocellulose ethanol technologies. With the technical scheme of the present invention, ethanol production theorugh cerevisiae fermentation of cellulose hydrolysate can be started at a high temperature. According to the present invention, low energy consumption, low material consumption, low cost and high ethanol yield can be achieved in the cerevisiae fermentation process of cellulose alcohol production. With the present invention, huge economic benefits and good social benefits are brought in.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing fuel ethanol by using straw fiber materials
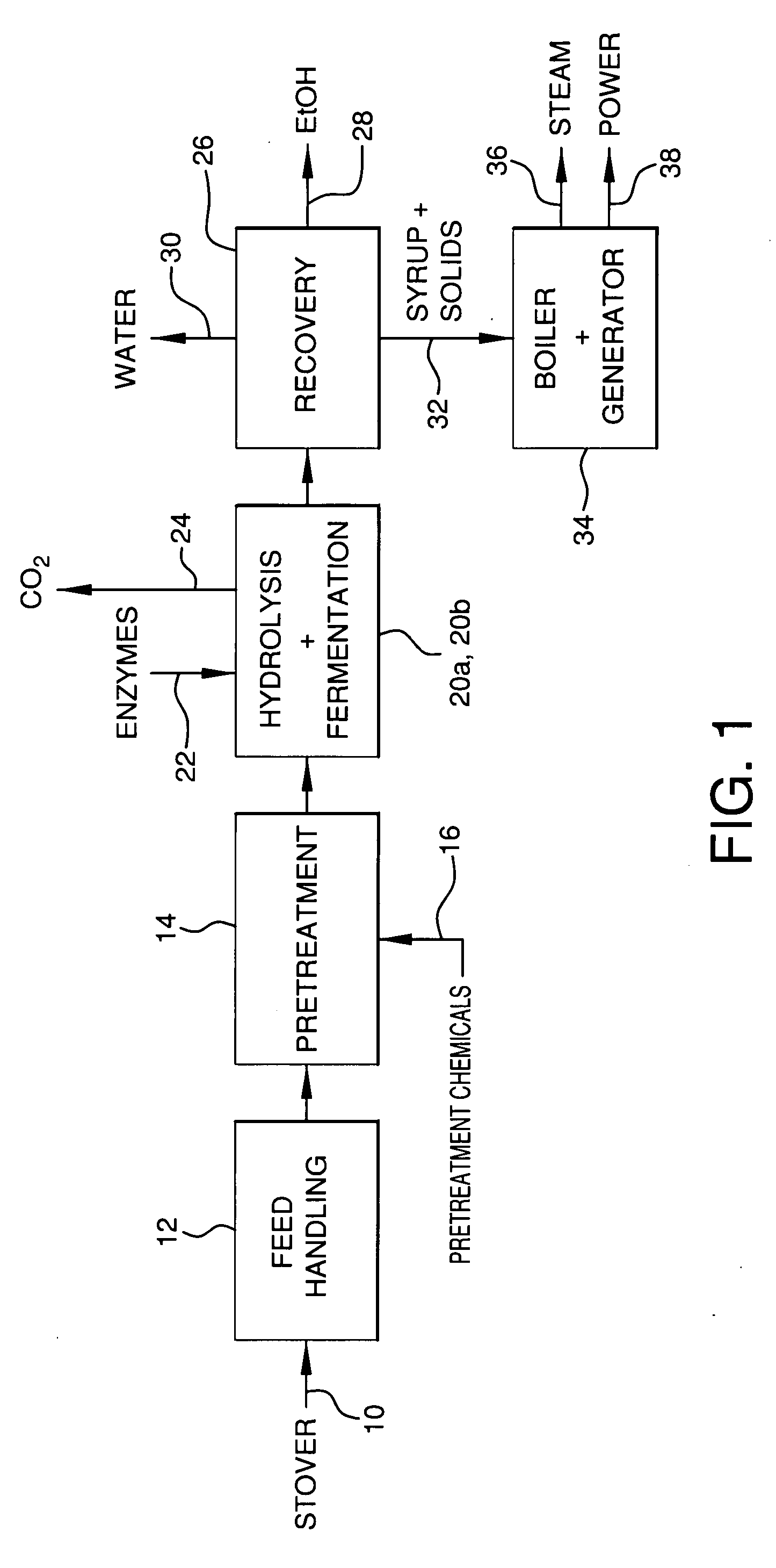
This invention discloses a method for producing fuel ethanol from a straw fibre raw material, comprising: (1) raw material selection; (2) disintegration; (3) pre-processing; (4) double-enzyme saccharifying; (5) sterilization; (6) enlargement culture and application of Pachysolen tannophilus P-01; (7) fermentation; (8) distillation; characterizing: the pre-processing employs white-rot fungi solid culture to decompose lignin. The procedures comprise: (1) bacterium: Coridus versicolor; (2) crude laccase production: (1) culture media producing condition,(2) fermentation: inoculate 6 parti-color Coriolus versicolor seed stopper per 1000ml, 28-30Deg C, 150rpm shake culture for 7d, remove the hypha by filtration so as to obtain the crude laccase; (3) crude peroxidase production: i. culture media, ii. fermentation: inoculate 6 rings of Phanerochete chrysosporium spores per 100ml, 37-39Deg C, static culture for 9d, remove hypha by filtration so as to obtain crude peroxidase; (4) conditions of enzyme liquid decomposing straw: add 1ml crude peroxidase and crude laccase respectively to the straw powder and mix homogenously, and then decompose the straw at 45Deg C, pH 4.5 for 72h. This invention can improve the ethanol yield and decease cost.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Ethanol resistant and furfural resistant strains of E. coli FBR5 for production of ethanol from cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20080090283A1Maximizing ethanol concentrationIncreased ethanol yieldBacteriaBiofuelsCelluloseResistant strain
Owner:ROWAN UNIVERSITY
Use of hop acids in fuel ethanol production
InactiveUS20060263484A1Accurate doseEffective controlMilk preparationBeer fermentationBacteroidesMinimum inhibitory concentration
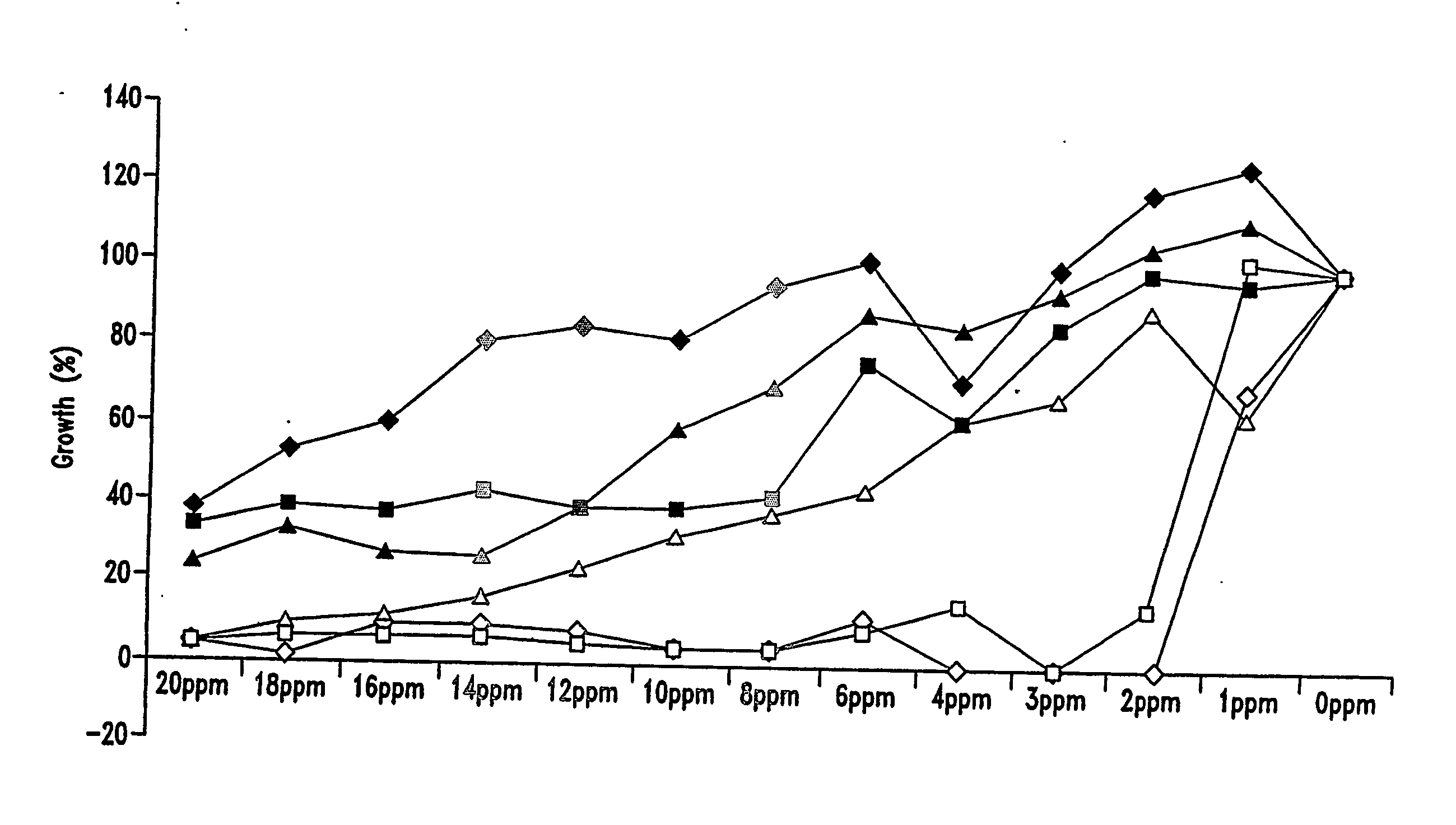
Six hop acids are common to hops and beer: alpha acid, beta acids, isoalpha acids, rho-isoalpha acids, tetrahydro-isoalpha acids, and hexahydro-isoalpha acids. The six hop acids were tested to determine which were the most effective in inhibiting the growth of bacteria common to fuel ethanol production. The bacteria used in the tests were Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus fermentum. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of the hop acids were determined using MRS-broth. Molasses mash and wheat mashes were used as the growth media for the fermentations. In all cases the hop acids controlled the growth of these two lactobacillus bacteria with tetrahydroisoalpha acid, hexahydroisoalpha acid, and isoalpha acid killing the most bacteria at the lowest MIC. Treating yeast propagators, steep tanks, and fermenters with a minimum inhibitory concentration of hop acids will stop bacteria growth, increase ethanol yields and avoid the need for antibiotics.
Owner:JOHN I HAAS
Ethanol fermentation using oxidation reduction potential
InactiveUS20060115884A1Increased ethanol productionReduce glycerol formationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiofuelsOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
A process to improve ethanol yield, decrease fermentation time and reduce byproduct formation by monitoring and controlling oxidation reduction potential (redox) of the fermentor is disclosed.
Owner:BURMASTER BRIAN M
Methods for the positive selection of ethanol overproducing mutants from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveUS10577580B2Produced in advanceIncreased ethanol productionFungiMutant preparationBromopyruvic acidGlyoxylic acid
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Method for preparing ethyl alcohol with potatoes
ActiveCN101319233AEasy to separateReduce wasteBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlcoholThree stage
The invention relates to the ethanol preparation field, and discloses a method for preparing ethanol through tuber crops. The method is based on an ethanol preparation device. The invention is characterized in that: the preparation method comprises the following steps of preprocessing; mixing materials; liquefying; desanding; and generating ethanol. The method arranges the desanding step behind the liquefying step and adopts a three-stage desanding process with reasonable process layout, obvious desanding effect and high ethanol yield.
Owner:CHINA LIGHT IND XIAN DESIGN ENG
Process for preparing fuel ethanol by using straw fiber materials
This invention discloses a method for producing fuel ethanol from a straw fibre raw material, comprising: (1) raw material selection; (2) disintegration; (3) pre-processing; (4) double-enzyme saccharifying; (5) sterilization; (6) enlargement culture and application of Pachysolen tannophilus P-01; (7) fermentation; (8) distillation; characterizing: the pre-processing employs white-rot fungi solid culture to decompose lignin. The procedures comprise: (1) bacteria selection: Phanerochete chrysosporium, which is donated by Shanghai hydnology institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, is a fugus, and can produce lignin decomposing enzymes under specific culture conditions, comprising lignin peroxidase, manganese dependent peroxidase, laccase, and so on; (2) specific culture media producing conditions: i. add 2g glucose, 0.3g ammonium chloride and 100g water to dry straw per 100g and mix homogenously, sterilize at 121Deg C for 2h, inoculate Phanerochete chrysosporium for culture decomposition; ii. conditions of culture decomposition: inoculation 5%, 37-39Deg C, pH normal, material to volume: 1:5 ( dry material weight: container volume), cycle 30 days. This invention can improve the ethanol yield and decease cost.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing fuel ethanol by low-energy consumption wood raw material
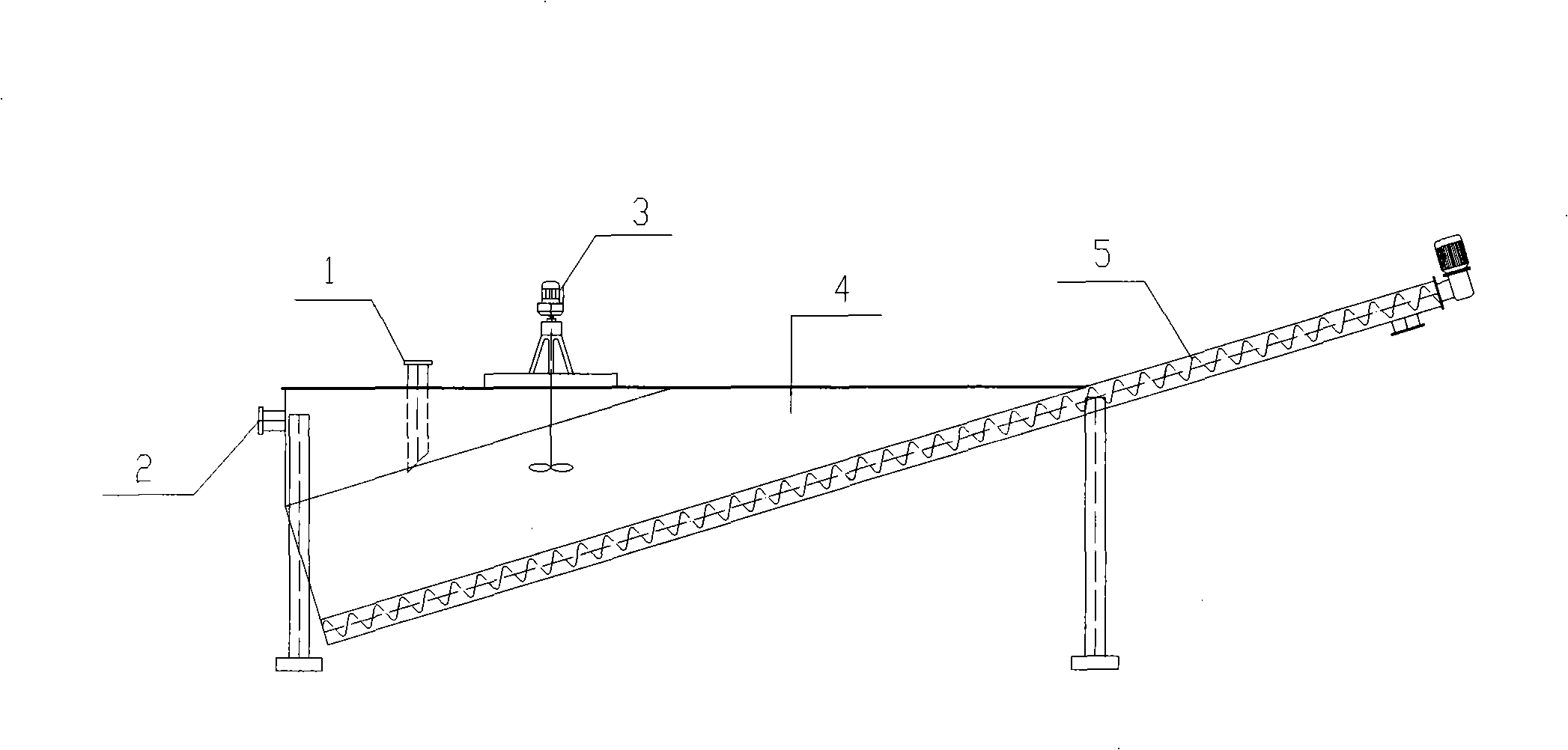
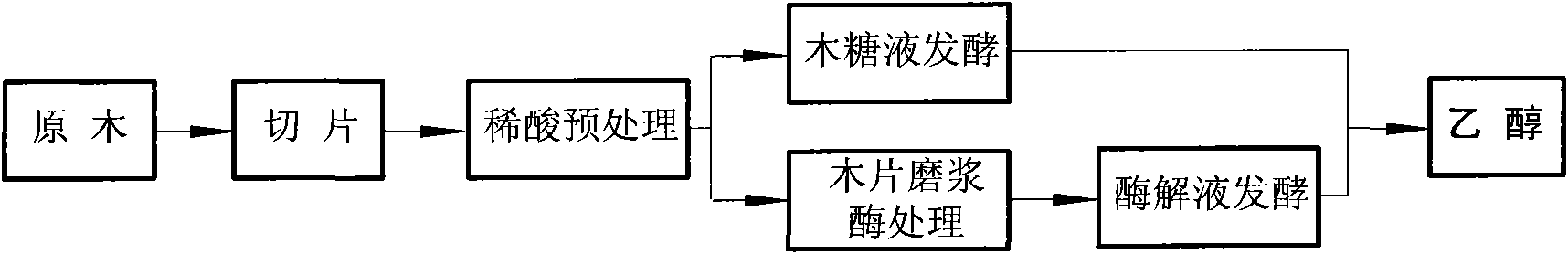
InactiveCN101597625AReduce energy consumptionBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesCelluloseHigh concentration
The invention relates to a method for preparing fuel ethanol by adopting a respective fermentation technology of xylose solution and woodpulp enzymolysis solution after completing slicing and dilute acid pretreatment of wood. Due to the adoption of novel processes including dilute sulphuric acid pretreatment and high-concentration jordaning / enzymolysis, the method simplifies production equipment, remarkably saves electricity consumption, operation man hour and production cost during raw material pretreatment and increases the utilization efficiency of xylans; meanwhile, the recovery rate of xylose is over 80.0 percent, and the enzyme hydrolysis yield of cellulose exceeds 65.0 percent. The method realizes efficient utilization of the xylose and glucose and quick fermentation of ethanol, and ensures that the sugar utilization rate and ethanol yield of the xylose and glucose ethanol fermentation respectively reach 82.5 percent, 85.0 percent, 90.0 percent and 92.0 percent.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Process for preparing ethanol from synthesis gas via methyl alcohol
ActiveCN102690171AHigh selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationEthanol synthesisAcetic acid
The invention relates to a process for preparing ethanol from synthesis gas via methyl alcohol. The synthesis gas is divided into two parts, one part of the synthesis gas is used for methanol synthesis, and the other part is separated as CO (carbon monoxide) and H2 (hydrogen); the synthesis gas and methanol synthesis circulating tail gas are mixed into methanol synthesis material gas; the methanol synthesis material gas is subjected to methanol synthesis reaction under the action of a methanol synthesis catalyst to obtain the methyl alcohol and methanol synthesis circulating tail gas; the CO separated from the synthesis gas and acetic acid synthesis circulating tail gas are mixed and then subjected to carbonylation together with methyl alcohol; acetic acid synthesis reaction is carried out to obtain acetic acid and acetic acid synthesis circulating tail gas; the H2 separated from the synthesis gas is mixed with ethanol synthesis circulating tail gas to enter a reactor; the mixed gas and acetic acid contact the catalyst to carry out the ethanol synthesis reaction by hydrogenation so as to obtain ethanol and by-product and ethanol synthesis circulating tail gas, and a crude product at the outlet of the reactor is separated to obtain ethanol. The process disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high ethanol yield, high energy utilization rate of overall process, low cost and feasibility in mass production.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
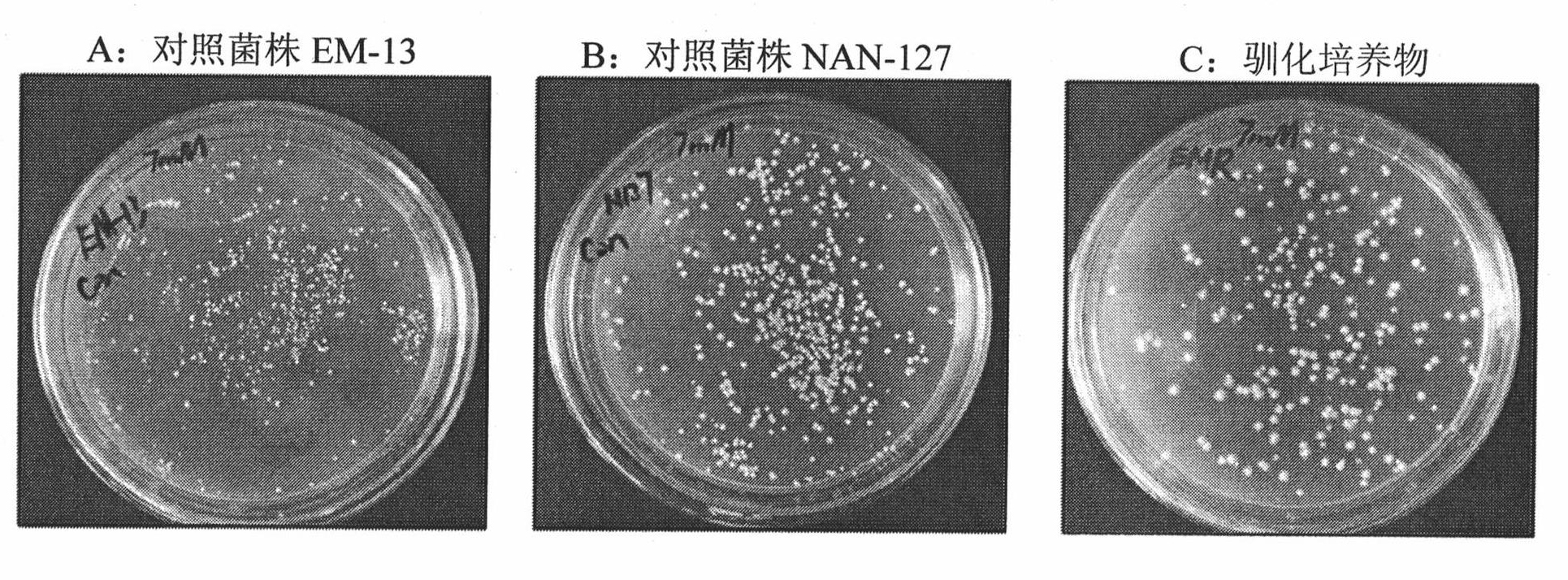
Vanillin-tolerant saccharomyces cerevisiae
InactiveCN101928675AShortened growth lagImprove toleranceFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCellulose
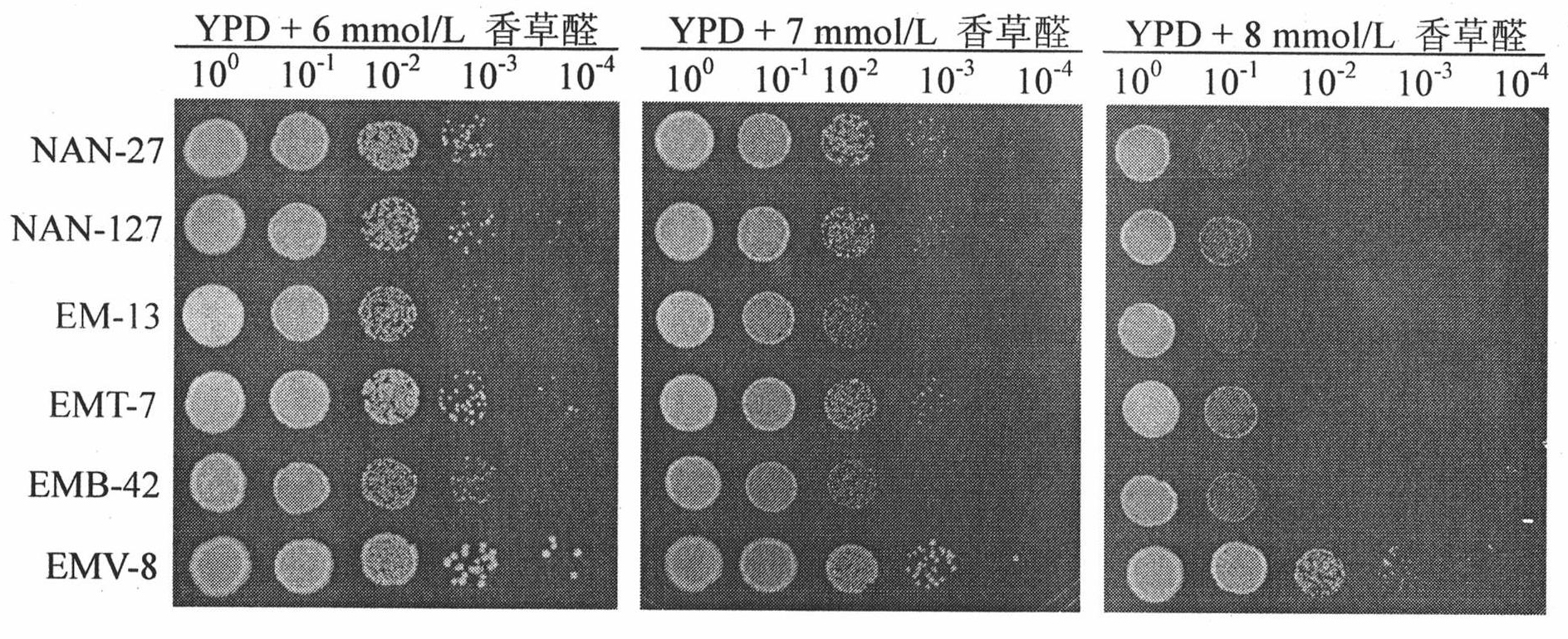
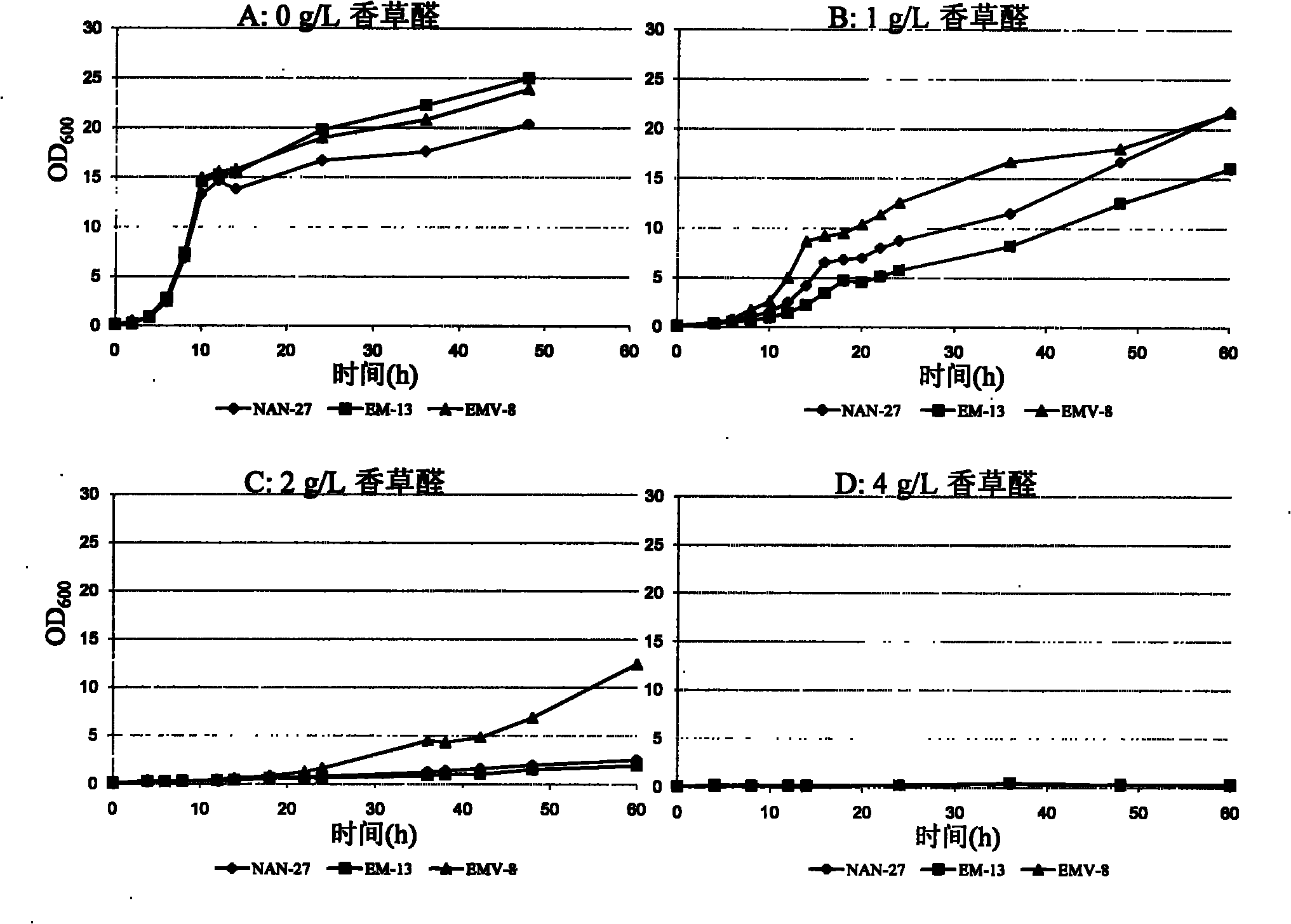
The invention discloses vanillin-tolerant saccharomyces cerevisiae. The strain is named as saccharomyces cerevisiae EMV-8 and collected in CGMCC on July 16th, 2010 with a collection number CGMCC No.4012. The strain is obtained by domesticating saccharomyces cerevisiae EM-13 in a YEPD liquid culture medium prepared from corn straw steam blackout extraction solution of different concentrations and screening; compared with the original strain EM-13, the strain can consume all glucose faster and has high ethanol yield when cultured in the YEPD liquid culture medium containing 1g / L of vanillin,; when cultured in the YEPD liquid culture medium containing 2g / L of vanillin, the strain has the growth delay period shortened by about 20 hours compared with the original strain; and the strain has good application value for further breeding the inhibitor tolerant saccharomyces cerevisiae in lignocellulose hydrolysis solution, and meanwhile has certain theoretical value for researching the phenolic compound tolerance mechanism of the saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
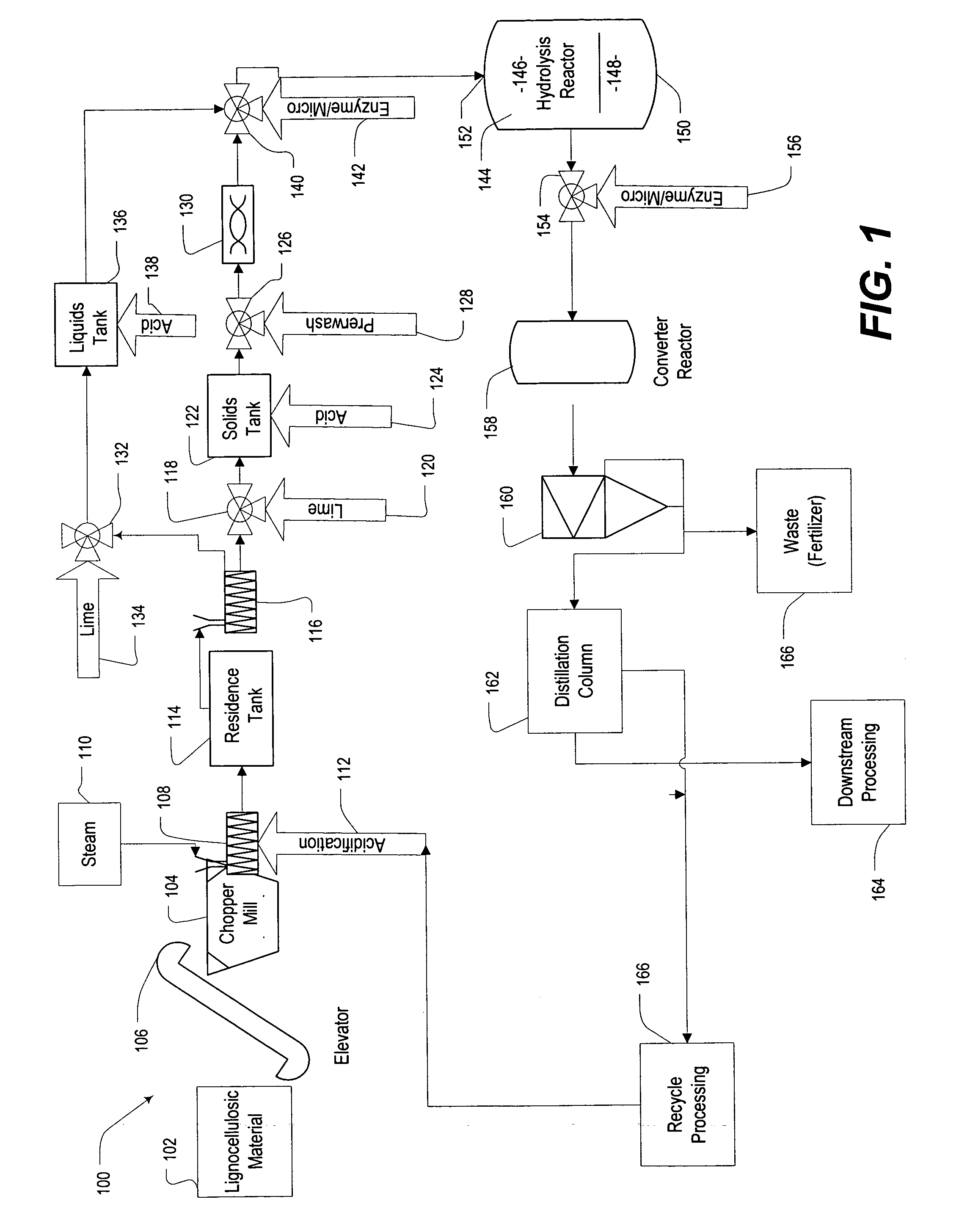
Method for carrying out alkaline pretreatment on plant fiber raw materials for preparing ethanol through enzymolysis and fermentation
ActiveCN102827883ARequirements to reduce dosageGuaranteed costBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesFiberHydrolysate
The invention discloses a method for carrying out alkaline pretreatment on plant fiber raw materials for preparing ethanol through enzymolysis and fermentation. According to the method, firstly, green liquid is used for carrying out alkaline treatment on the air dried plant fiber raw materials; then, under the condition that the substrate w / v concentration being 5 to 15 percent, the cellulose is adopted for batch type hydrolysis for 48 to 72 hours; and after the hydrolysis completion, hydrolysate is subjected to solid-liquid separation, the obtained clear liquid is concentrated to a state that the glucose concentration in the sugar liquid is 100 to 200g / L, hexose in the concentrated sugar liquid is converted into the ethanol through brewer's yeast, the ethanol mash is removed through distillation, and then, the pichia stipitis is used for converting pentose into the ethanol. The method realizes the goals that the mature process and equipment of the paper pulp process are utilized for recovering chemical medicine and heat energy, the consumption of chemicals and the loss of heat energy are reduced, the environment pollution is reduced, the clean production of the ethanol is realized, the efficient proceeding of the enzymolysis and the hexose and pentose fermentation are respectively ensured through the low-substrate-concentration enzyme hydrolysis and the sequential fermentation, particularly, through the pentose fermentation, the ethanol yield of each ton of plant fiber raw materials is improved, and the raw material cost of the ton ethanol is reduced.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Thermophillic Organisms For Conversion Of Lignocellulosic Biomass To Ethanol
Mutant thermophilic organisms that consume a variety of biomass derived substrates are disclosed herein. Strains of Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum with acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase expression eliminated are disclosed herein. Further, strain ALK1 has been engineered by site directed homologous recombination to knockout both acetic acid and lactic acid production. Continuous culture involving a substrate concentration challenge lead to evolution of ALK1, and formation of a more robust strain designated ALK2. Both organisms produce near theoretical ethanol yields without expressing pyruvate decarboxylase
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Reducing Carbon Dioxide Production and Increasing Ethanol Yield During Microbial Ethanol Fermentation
InactiveUS20120052542A1Reduce productionMinimization requirementsFungiBacteriaMicroorganismCarbon dioxide production
The present invention provides compositions and methods for producing ethanol wherein the amount of CO2 by-product is reduced during the fermentation process. The invention includes the use of oxidized lignin during the fermentation process.
Owner:ATHENA BIOTECH INC
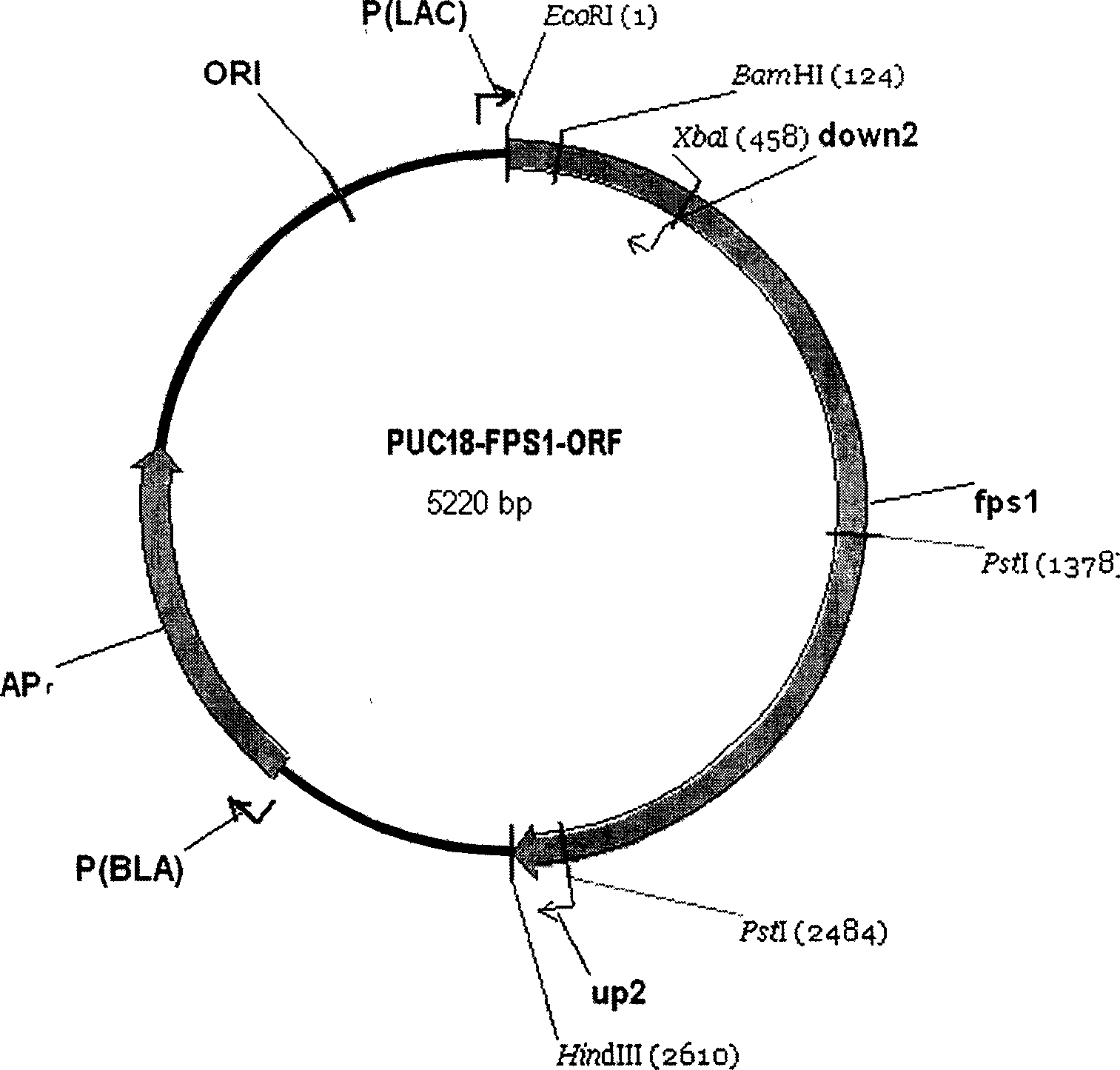
Glycerol channel protein gene deleted brewing microzyme strain capable of reducing glycerol output and increasing ethanol output and construction method thereof
ActiveCN1763175AGood physical propertiesIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGlycerol
The present invention discloses one kind of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with glycerin passage protein gene deficiency and resulting in lowered glycerin generation and raised ethanol yield and its construction process. The construction process includes the following steps: 1. obtaining Saccharomyces cerevisiae monoploid and deleting of URA3 gene; 2. constructing PUC18-FPS1-ORF plasmid; 3. constructing PUC18-FUF plasmid; and 4. constructing KAM-21 strain. The present invention deletes glycerin passage protein FPS1 gene code embedded on cell membrane and loses the expression of FPS1 gene by means of gene engineering technology, so as to inhibit glycerin synthesizing way, convert from glycerin metabolism to ethanol metabolism, increase ethanol yield, and solve serial problems in ethanol production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for creating distiller's yeast ethanol high yield bacterial strain
InactiveCN101323837AIncrease productionLow residual sugarFungiMutant preparationEthylmethane SulfonateSpore
The invention discloses a method for constructing the ethanol high-yield strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which comprises the following steps: (1) ethylmethane sulfonate is utilized to carry out random mutagenesis to the amphiploid strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to cause the final concentration of the volume of the ethylmethane sulfonate in the bacteria liquid to be processed to be 2 to 4 percent and the concentration of the amphiploid strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to be 2 multiplied by 10<6> to 6 multiplied by 10<6> cell / ml; (2) 3 to 5 rounds of the sexual recombination of high efficient sporulation, spore purification and full integration cause genome recombination between strains in a library to construct the ethanol high-yield strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The ethanol output of the recombinant strains constructed by the method of the invention is increased by 8.88 percent compared with that of contrast strains, residual sugar is reduced by 64.37 percent, the fermentation cycle is shortened by 10 hours and ethanol and high osmotic resistance are 5.10 times of that of the contrast strains, thus providing excellent strains for the industrial production of fuel ethanol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Compound enzymatic hydrolysis method for straw raw materials
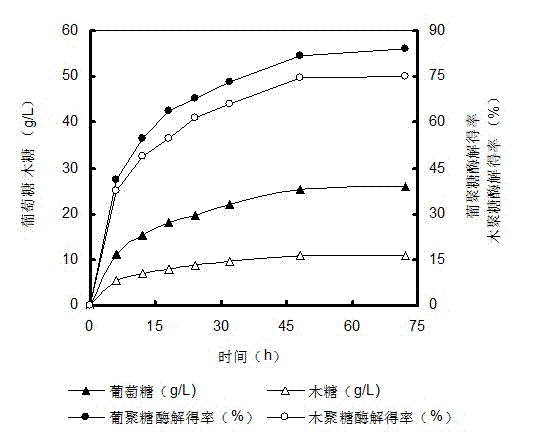
The invention discloses a compound enzymatic hydrolysis method for straw raw materials, which comprises: hydrolyzing the straw raw materials by diluted acid to decompose lignin; adding xylanase, cellulose, amylase, pectinase and beta-glucanase, and adjusting the pH value of the mixture to 4.3 to 5.5 by using an acidic matter or alkaline matter; and performing enzymatic hydrolysis at 40 to 55 DEG C for 24 to 72 hours. In the invention, a compound enzyme method is used to perform enzymatic hydrolysis on straw to convert the straw into reducing sugar, a proper mixing ratio of compound enzymes is selected to allow enzymes to interact to maximize the hydrolysis, the concentration of the reducing sugar generated by the enzymatic hydrolysis is high, the yield of sugar is high, the enzymatic hydrolysis conditions are mild, adverse influences on fermentation in a later period are avoided, the growth of a strain for fermentation in the later period is not inhibited, the ethanol yield during fermentation is high, the investment and cost are small, and thus, the method is suitable for large-scale use in industry.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing high-concentration ethanol by mixed fermentation of starch and molasses
InactiveCN102080105AIncrease profitIncrease total sugar concentrationBiofuelsFermentationHigh concentrationDistillation
The invention discloses a method for producing high-concentration ethanol by the mixed fermentation of starch and molasses which are used as raw materials. The method comprises the following steps of: adding water to the raw material of starch and stirring to constant volume, liquefying at low temperature and simultaneously fermenting and saccharifying, and then adding the raw material of molasses for mixed fermentation through the batch or continuous flow feeding supplement way. The mixing ratio of the raw materials of starch and molasses is 1:2-8:1 (W / V), the temperature of fermentation is 30-37 DEG C, the time of fermentation lasts for 40-48h, the percentage of ethanol yield is 12.43-16.67% (V / V). The invention changes the traditional single raw material fermentation way, and not only improves the total sugar concentration of the fermented mash, but also reduces the viscosity of starch raw mash and improves the liquidity, so the concentration of ethanol in the fermentation mash is increased, and the raw material utilization rate is improved, and ethanol distillation energy consumption and production cost are decreased, the amount of sewage discharge is reduced, the load of sewage treatment is lowered and the ethanol production process is more economical and environmentally friendly.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com