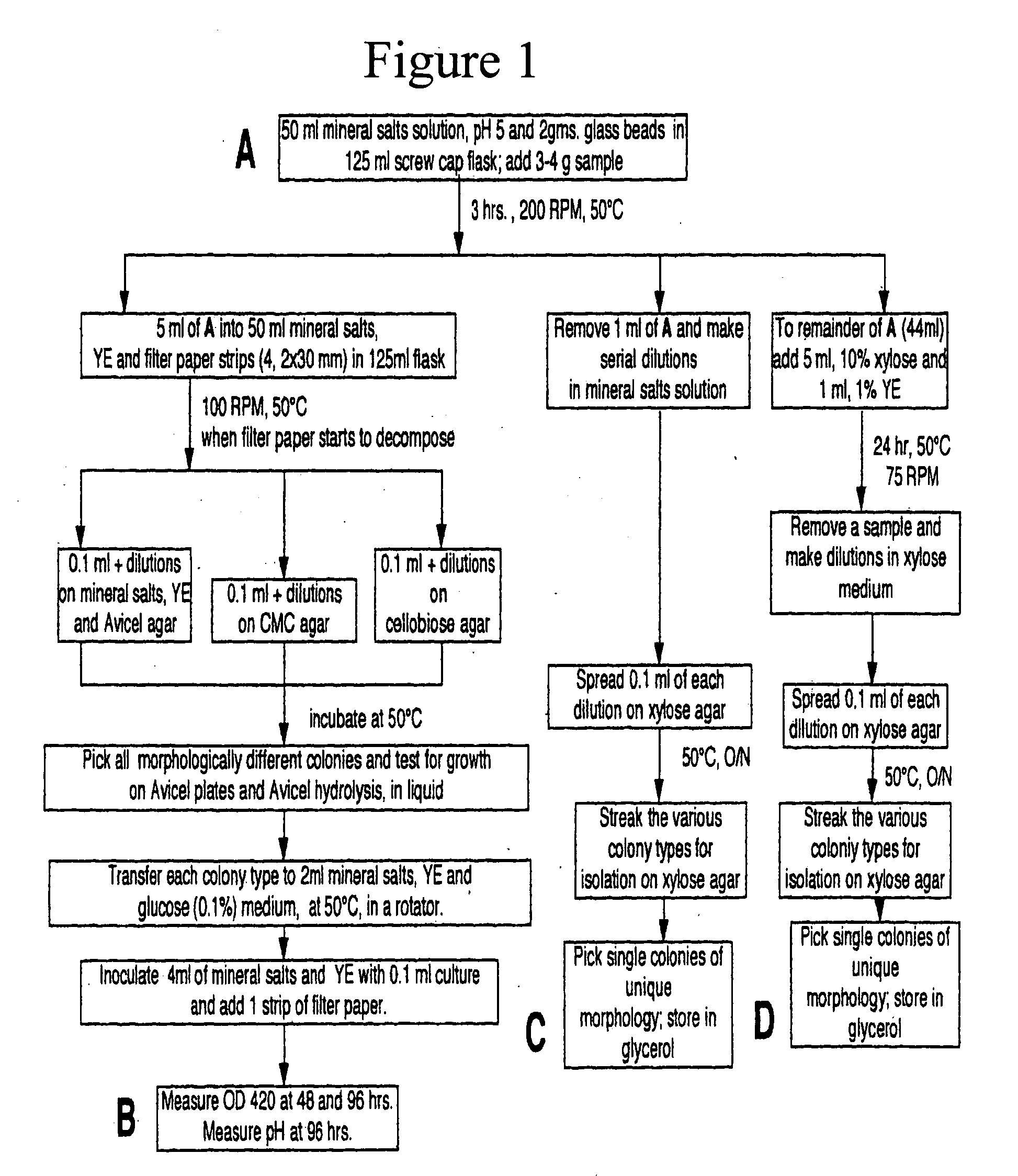
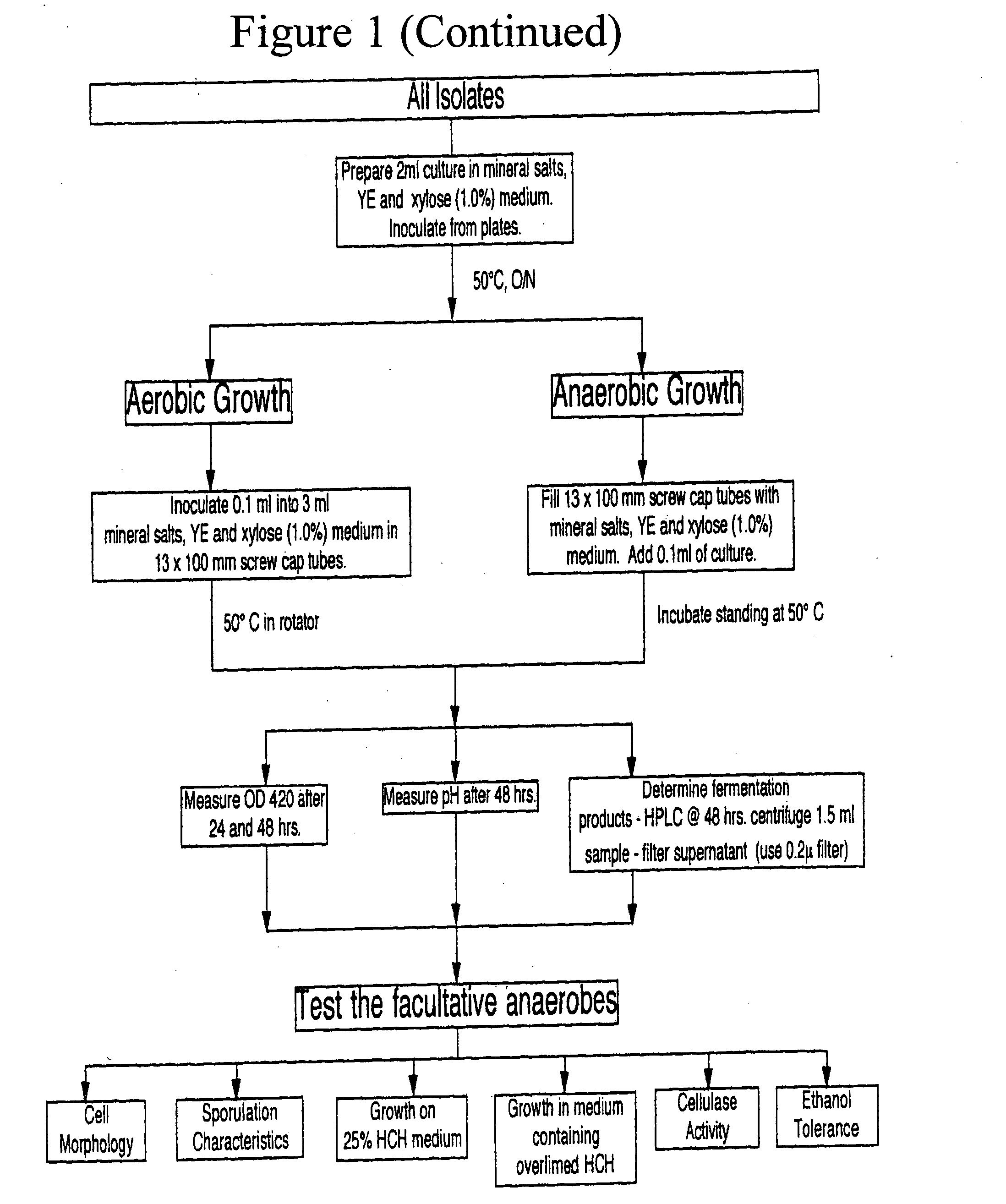
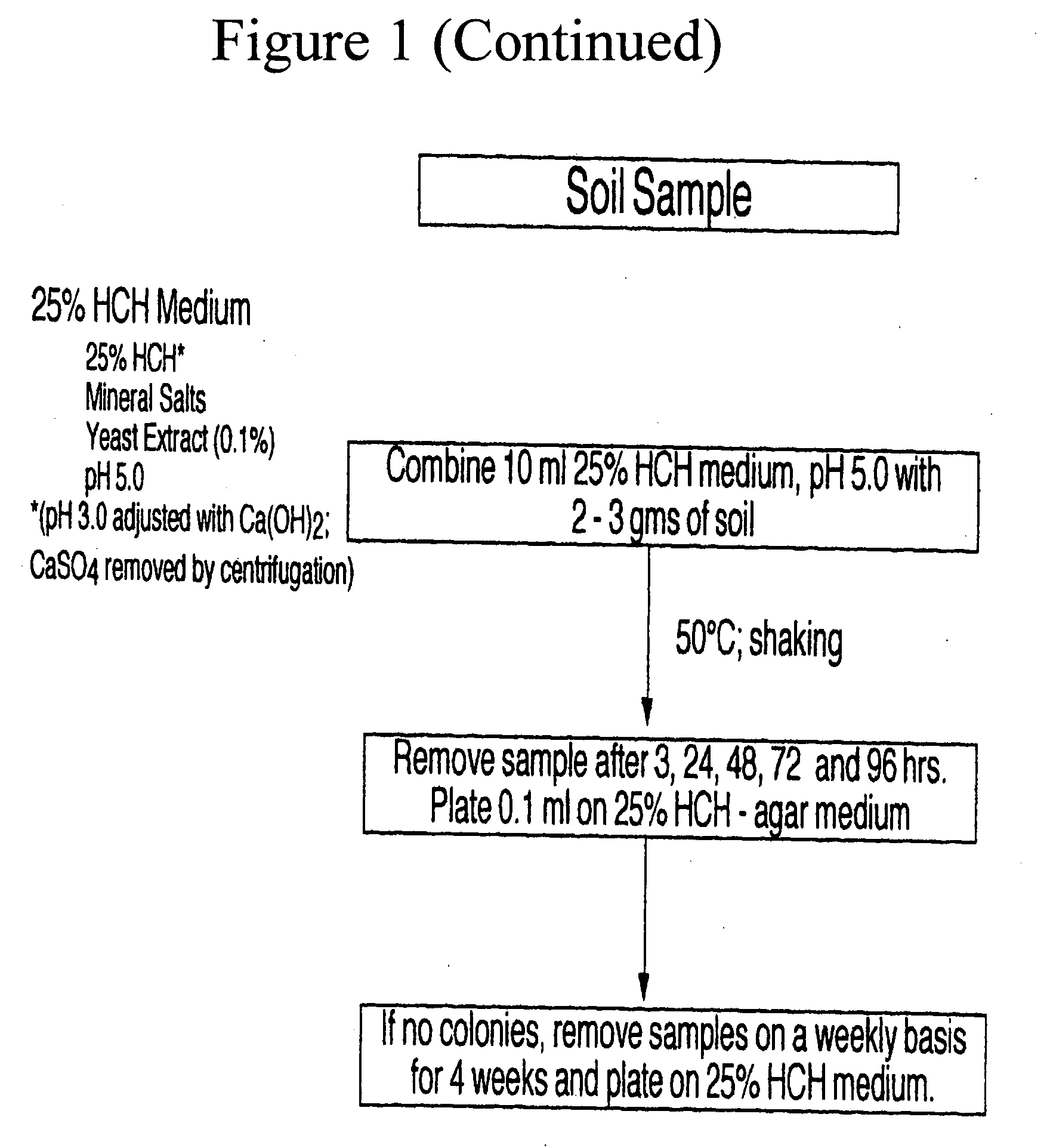
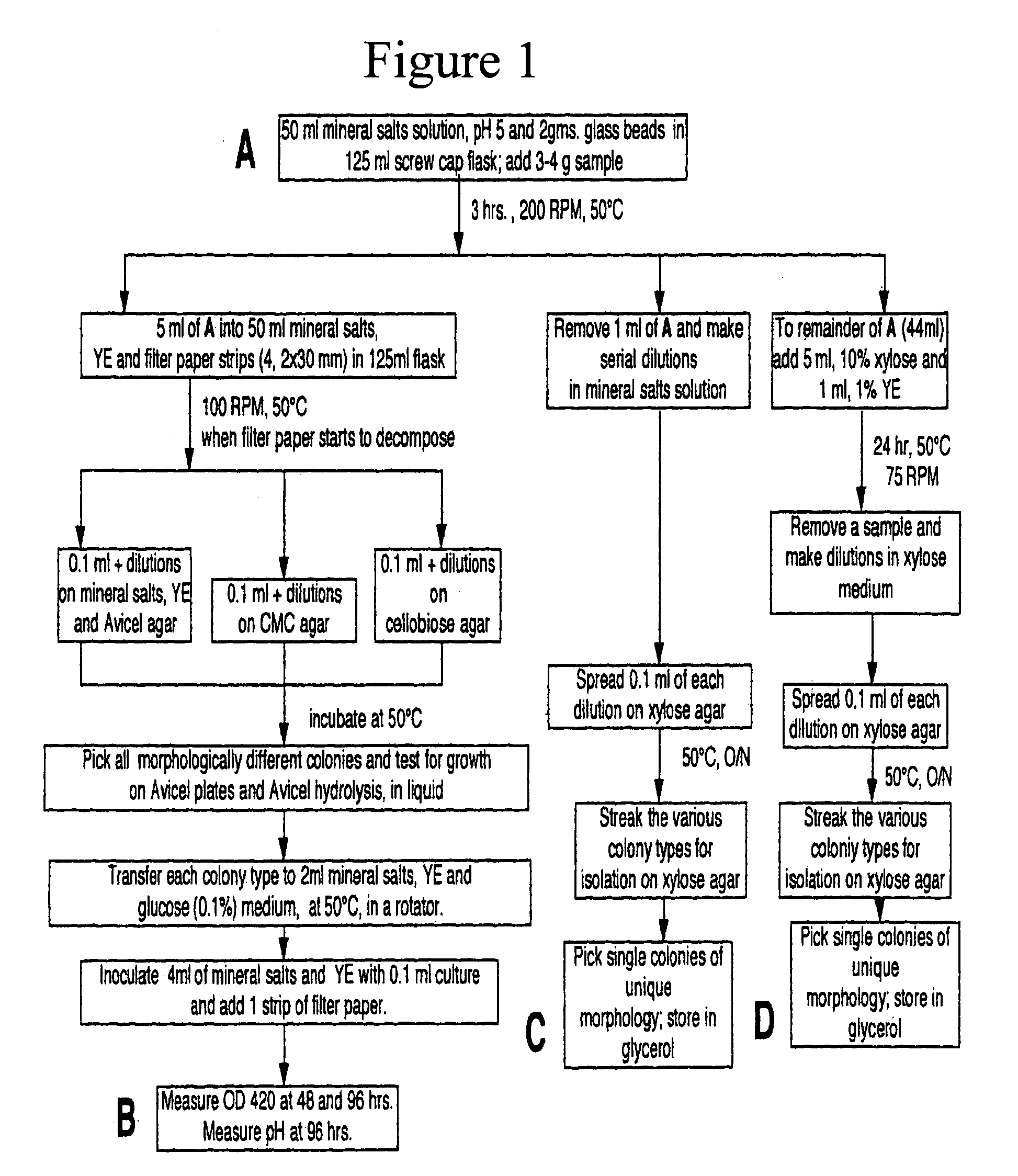
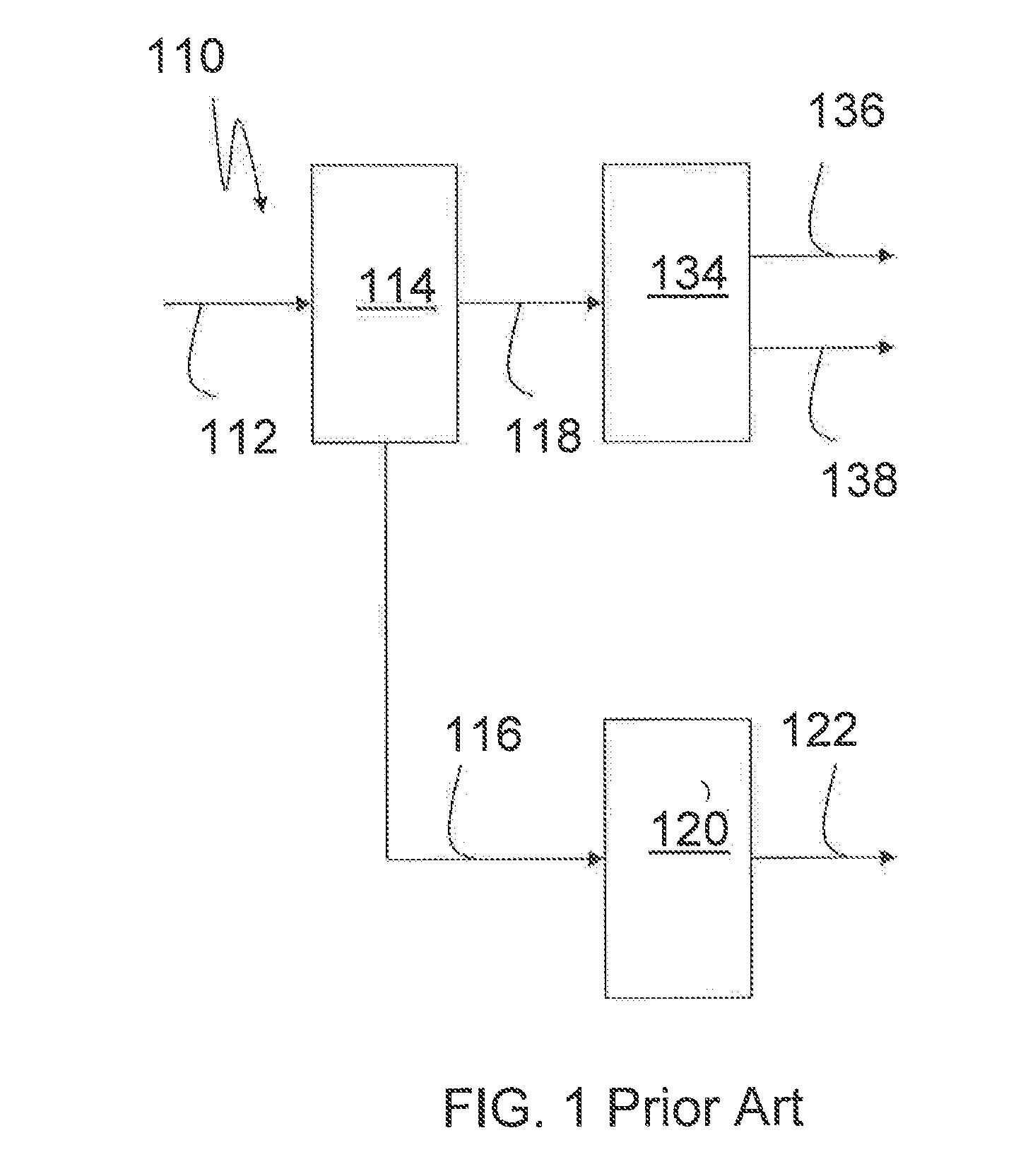
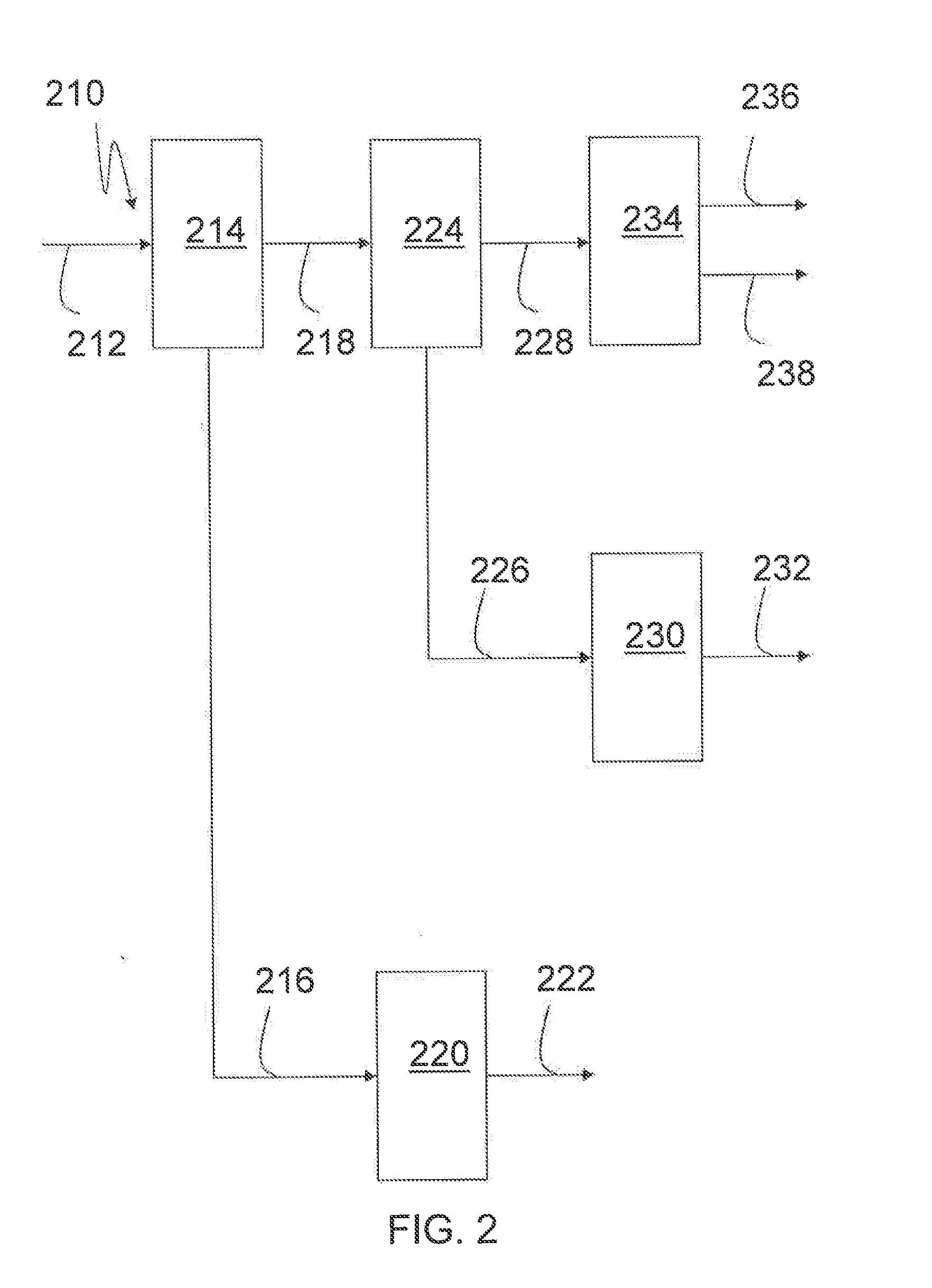
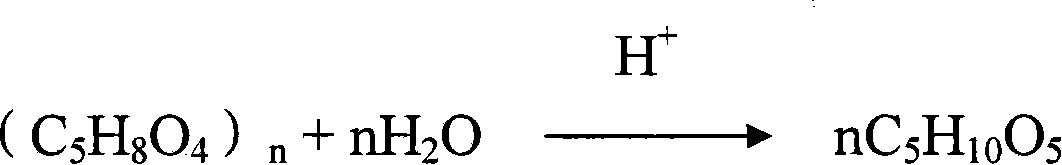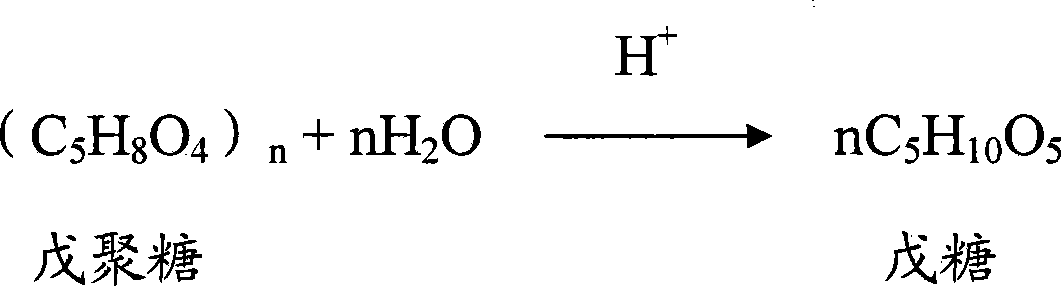Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
553 results about "Pentose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
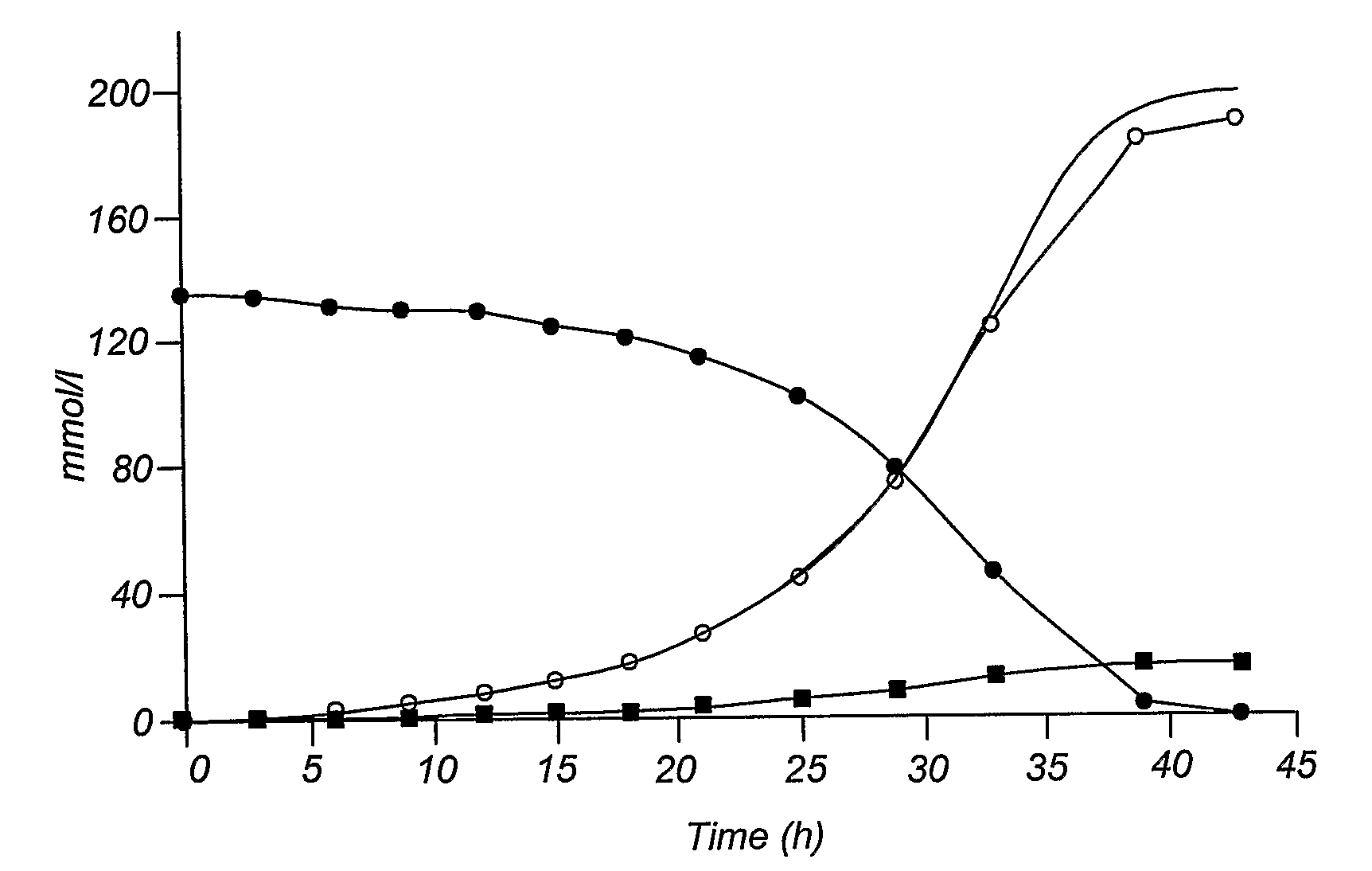
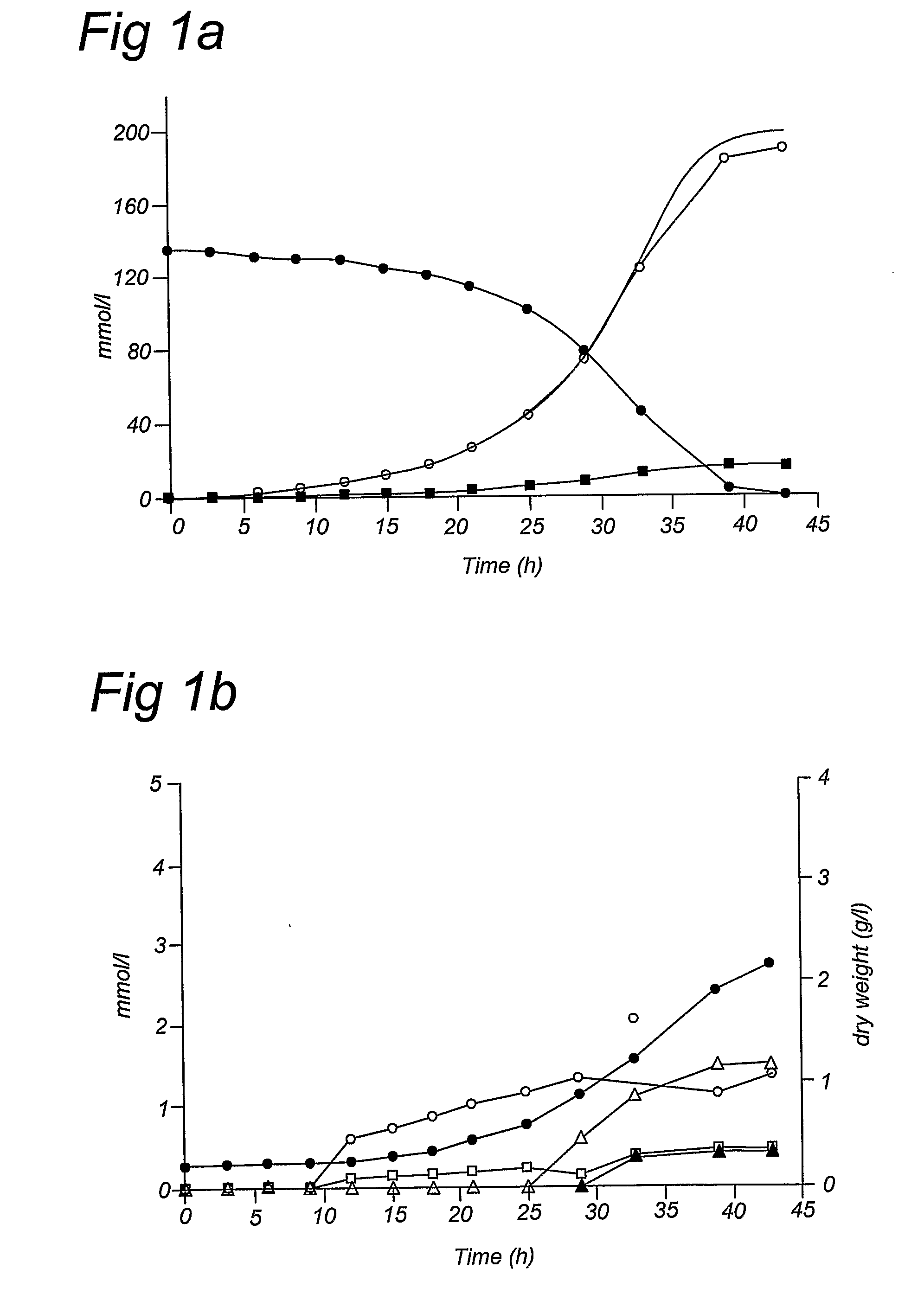
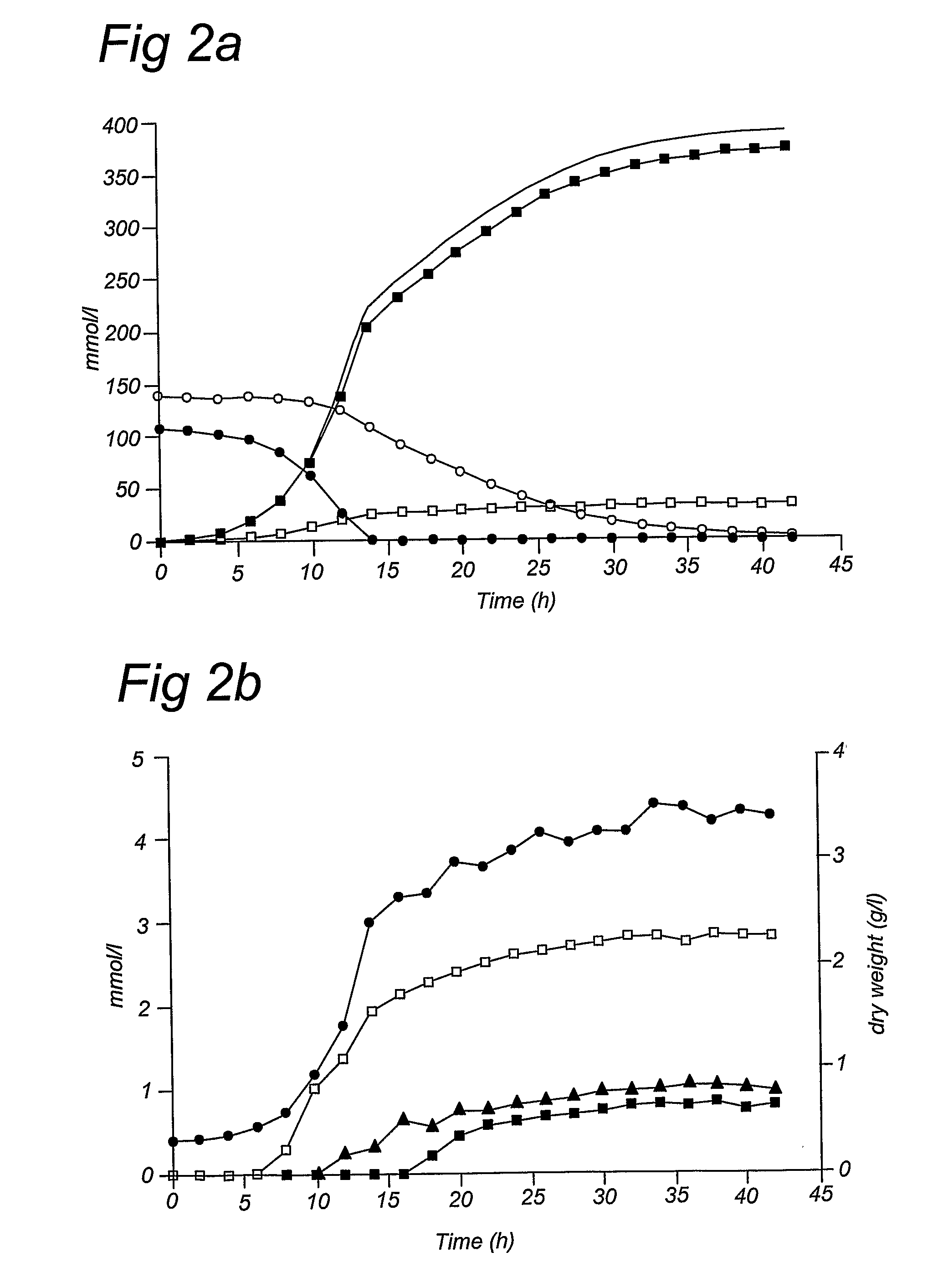
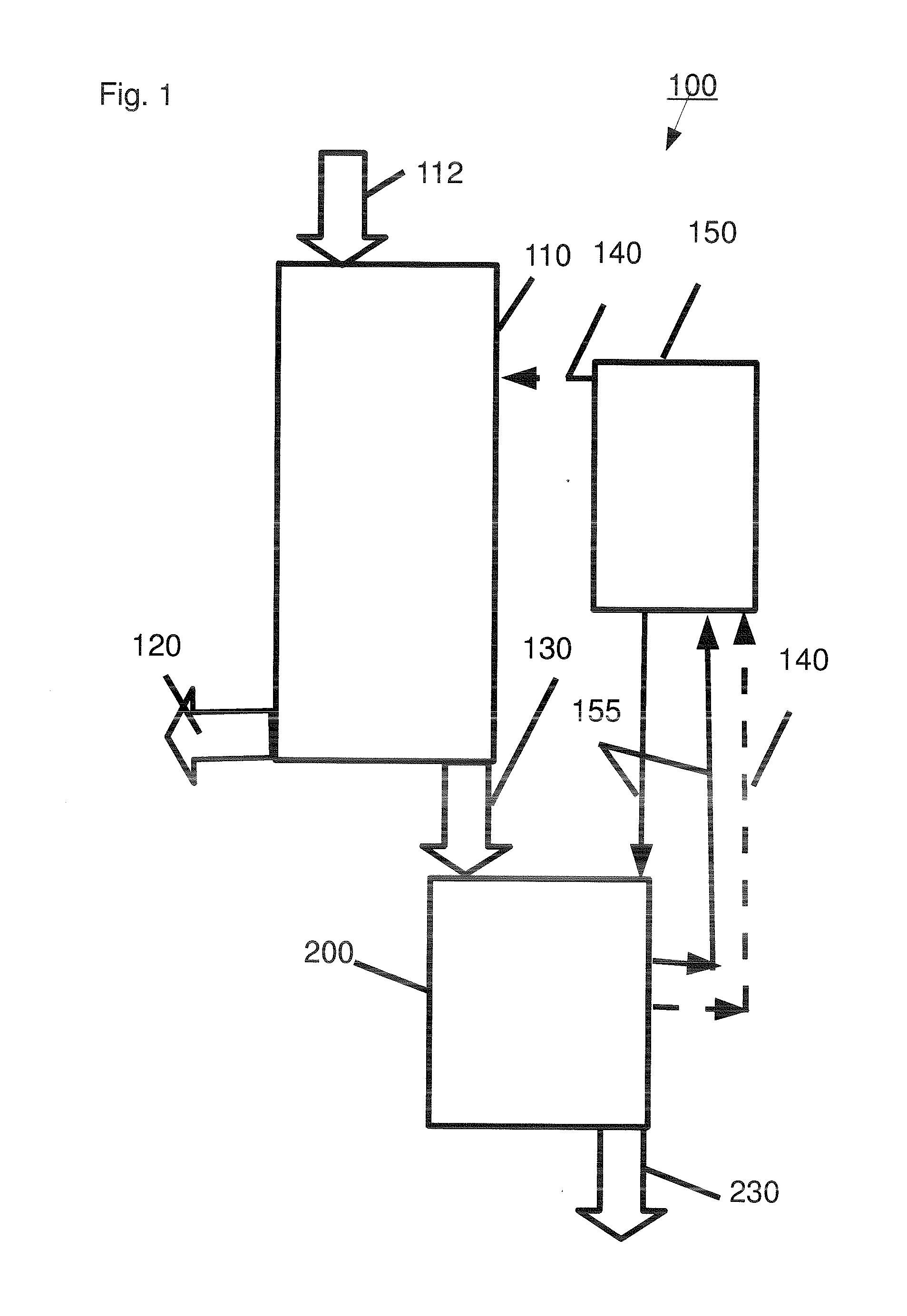
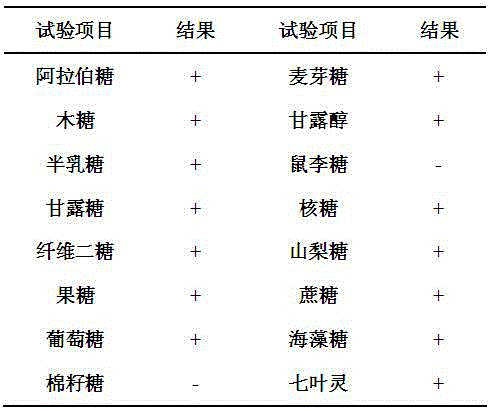
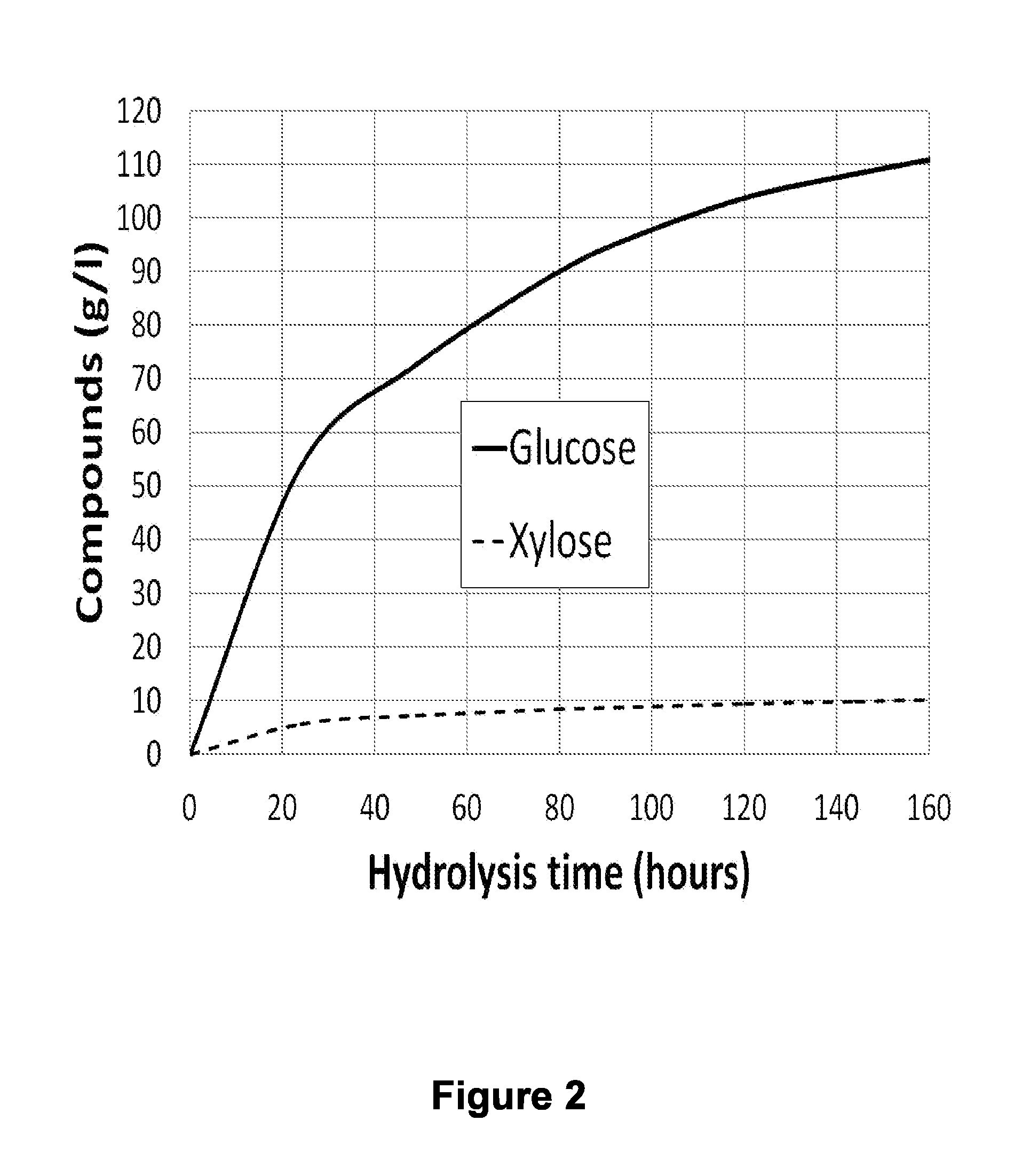
A pentose is a monosaccharide with five carbon atoms. Pentoses are organized into two groups: Aldopentoses have an aldehyde functional group at position 1. Ketopentoses have a ketone functional group at position 2 or 3. In the cell, pentoses have a higher metabolic stability than hexoses.
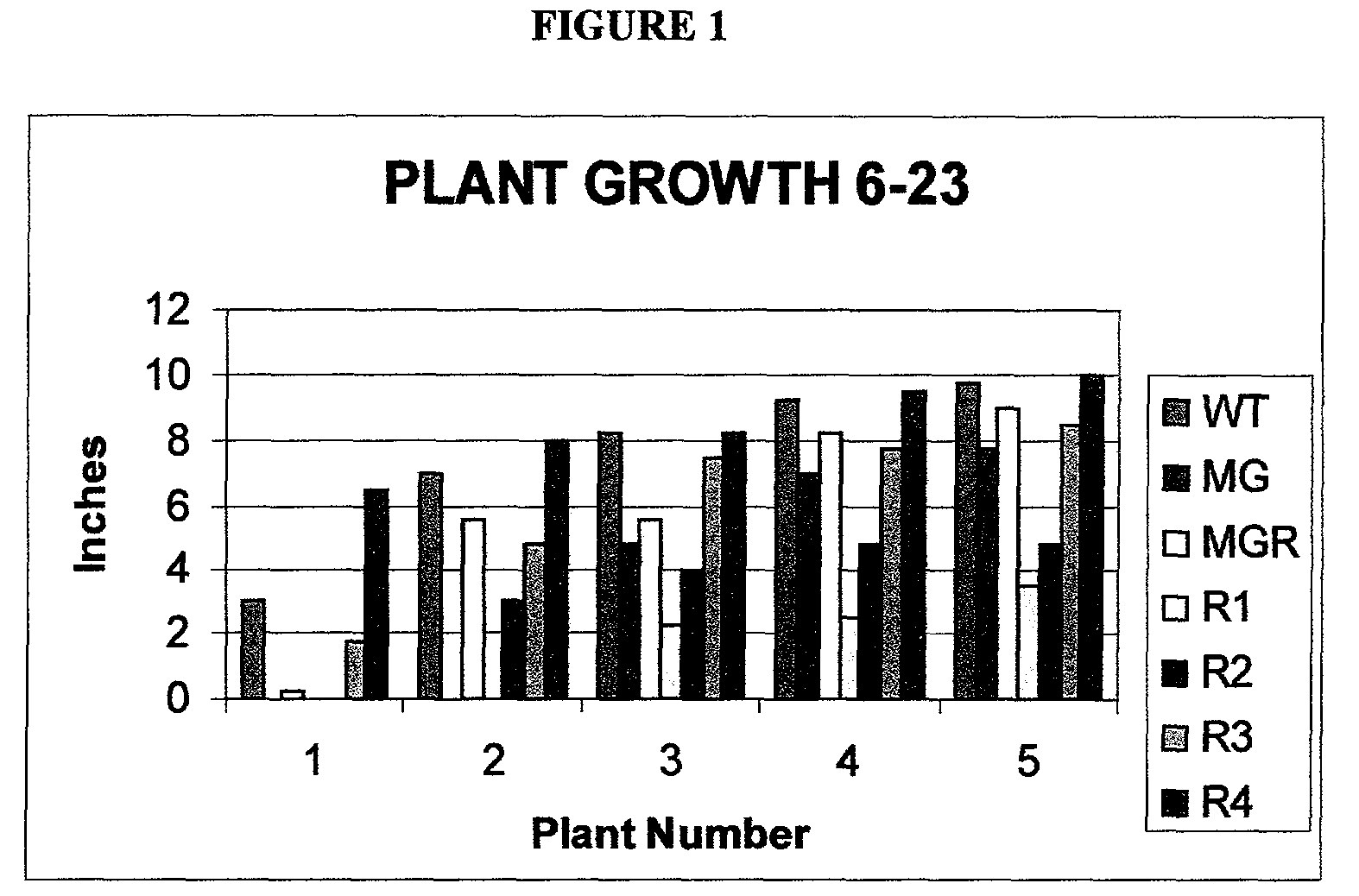
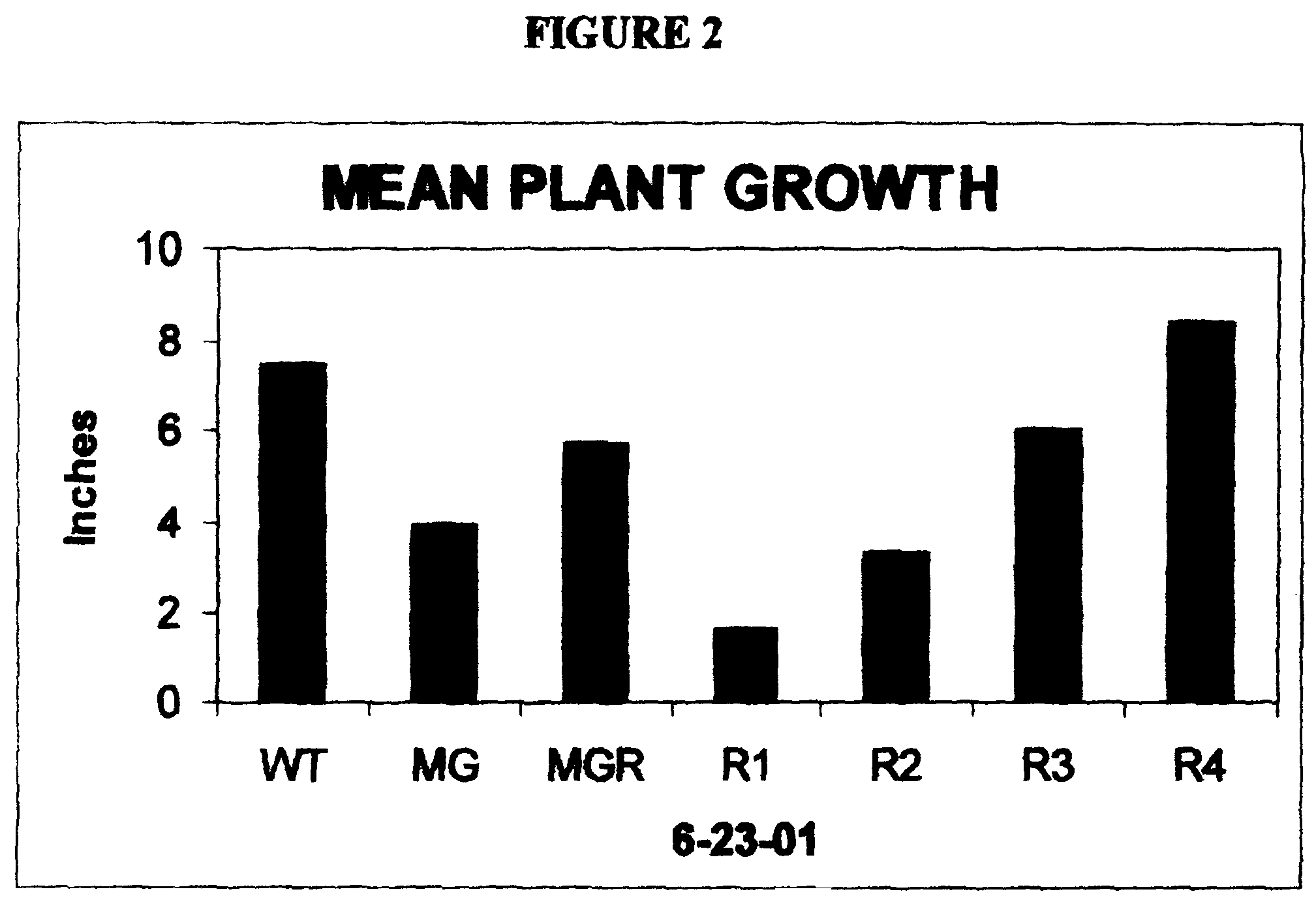
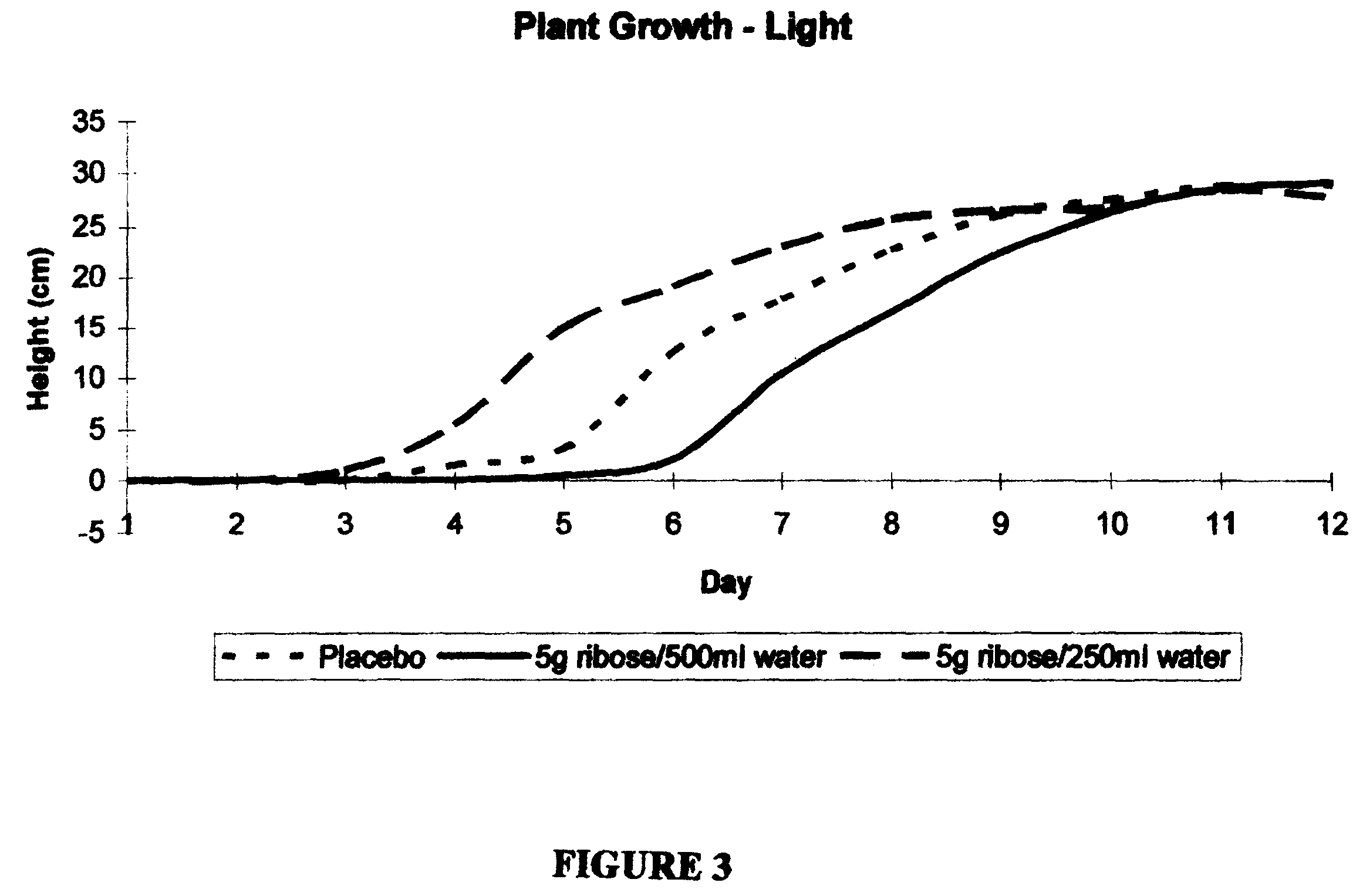
Use of ribose to enhance plant growth
Owner:BIOENERGY INC
Fermentation of pentose sugars
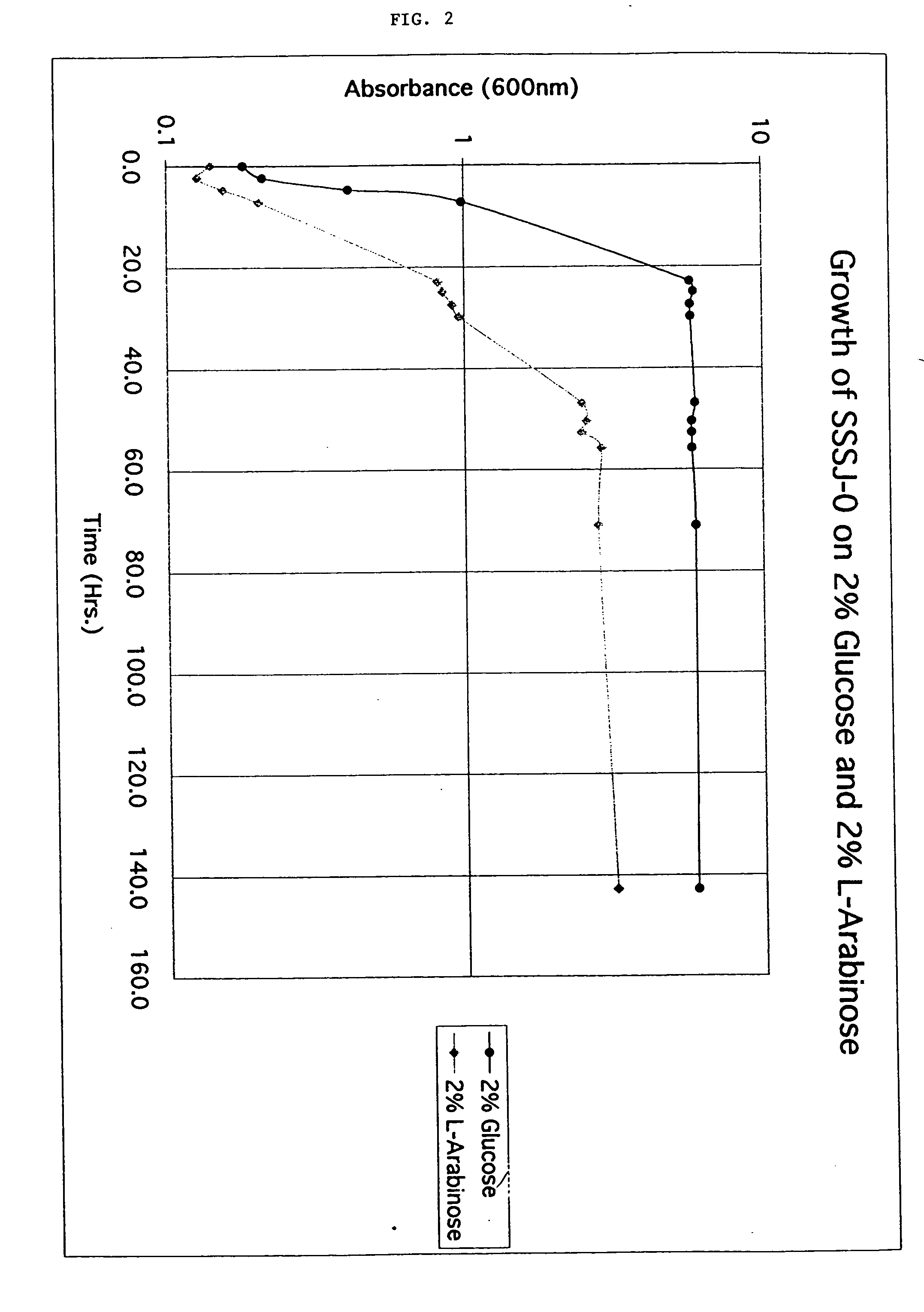
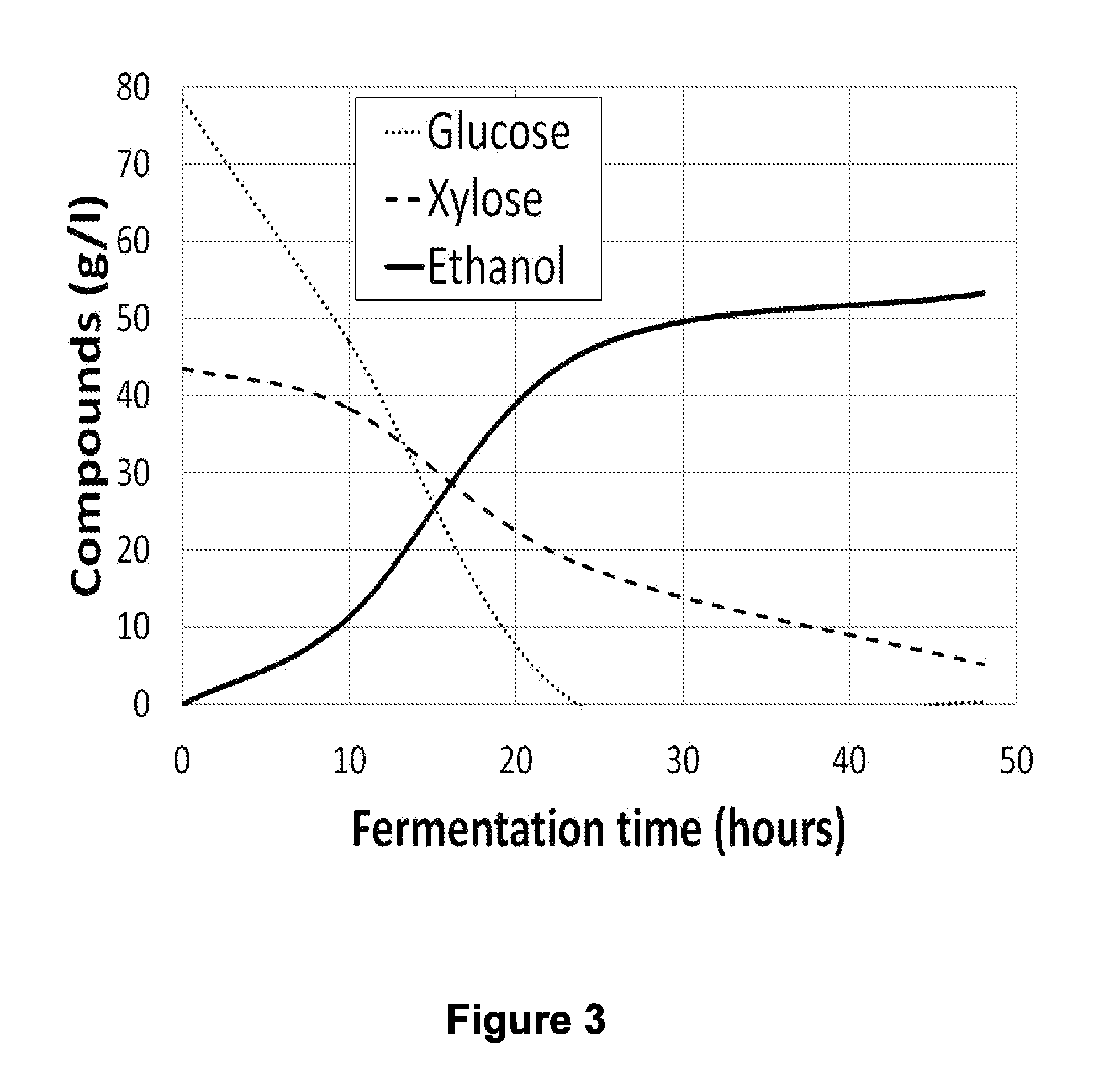
The present invention relates to host cells transformed with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a eukaryotic xylose isomerase obtainable from an anaerobic fungus. When expressed, the sequence encoding the xylose isomerase confers to the host cell the ability to convert xylose to xylulose which may be further metabolised by the host cell. Thus, the host cell is capable of growth on xylose as carbon source. The host cell preferably is a eukaryotic microorganism such as a yeast or a filamentous fungus. The invention further relates to processes for the production of fermentation products such as ethanol, in which a host cell of the invention uses xylose for growth and for the production of the fermentation product. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding eukaryotic xylose isomerases and xylulose kinases as obtainable from anaerobic fungi.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Medical stent provided with inhibitors of atp synthesis
A stent provided with a composition having at least one type of inhibitor of ATP synthesis, optionally together with at least one inhibitor of the pentose phosphate pathway is disclosed. The medical stent is useful for treating stenosis and preventing restenosis in vascular ducts and for treating cancerous tumors present in ducts, resectioned cavities and scars and any disorder arising from the proliferation of cells in ducts or cavities.
Owner:INTERSTITIAL THERAPEUTICS
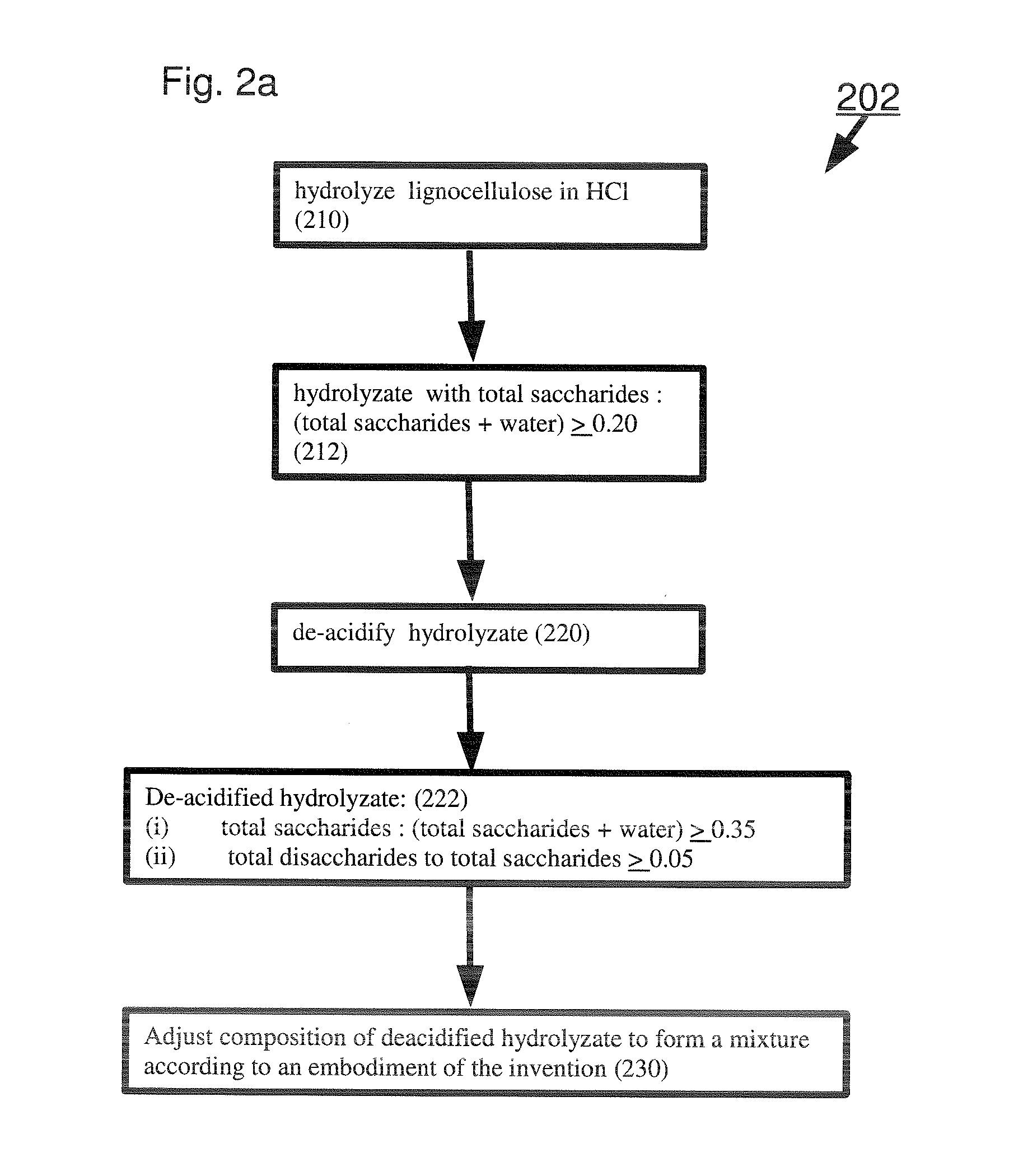
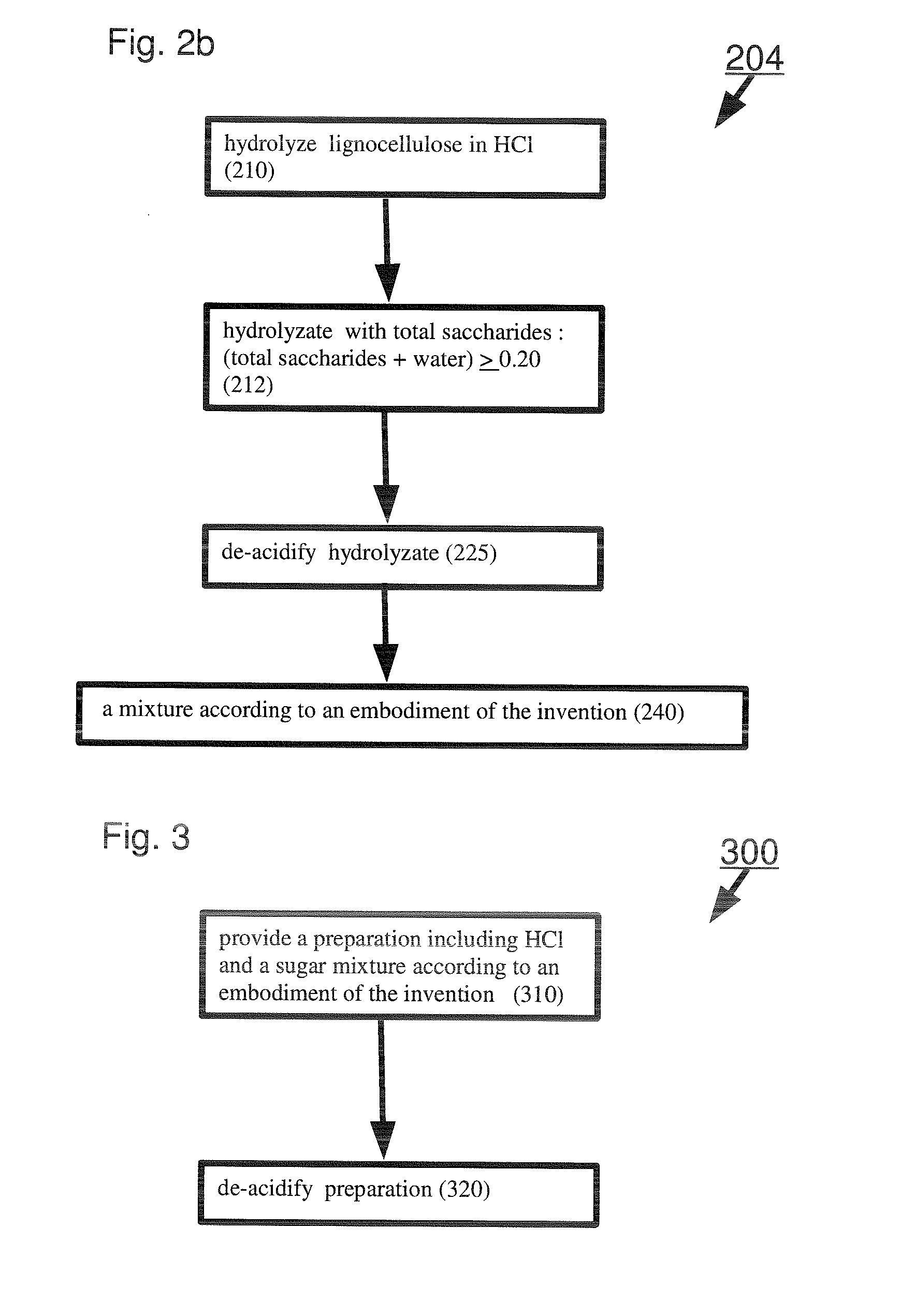
Production of chemicals from lignocellulose, biomass or sugars
InactiveUS20050250192A1High yieldLow costBacteriaUnicellular algaeBiological bodyCompound (substance)
The subject invention relates to newly isolated organisms from nature that produce L(+)-lactic acid high yield from hexose and pentose sugars found in biomass. Organisms and processes or methods for the production of lactic acid and other industrially important chemicals from cellulose and hemicellulose are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA
Production of chemicals from lignocellulose, biomass or sugars
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for producing wood sugar product
ActiveCN101659681AHigh purityFermentation went wellIon-exchange process apparatusSugar derivativesChromatographic separationHydrolysis
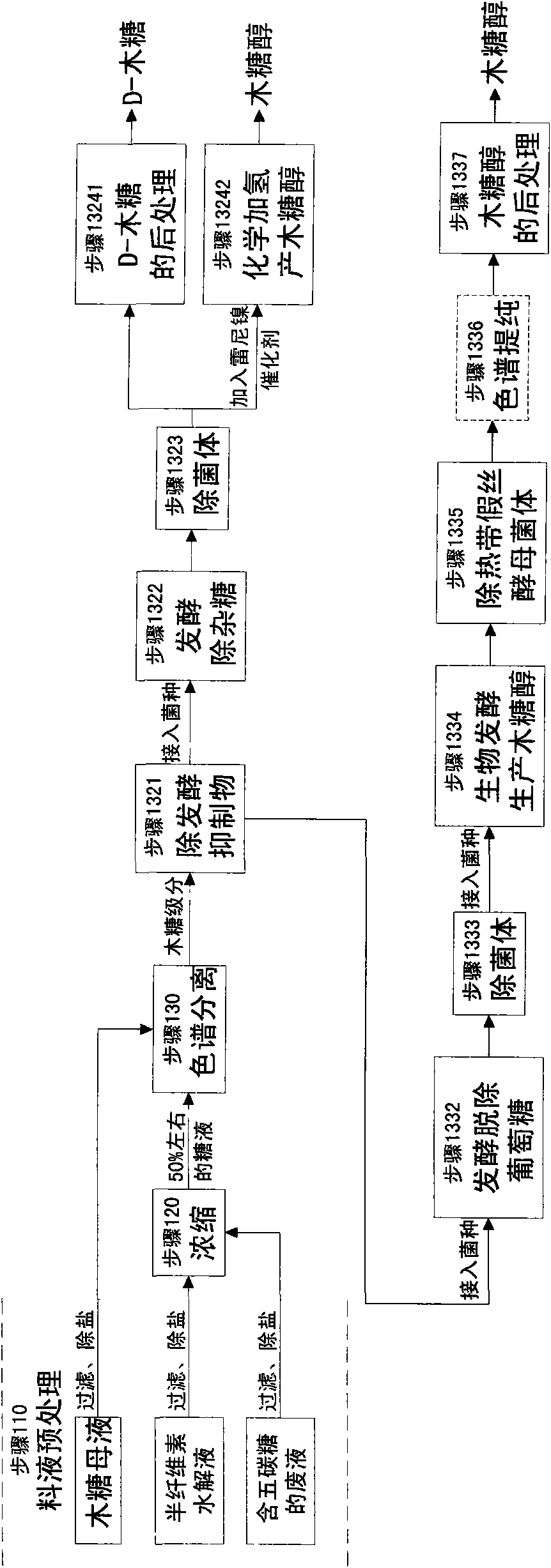
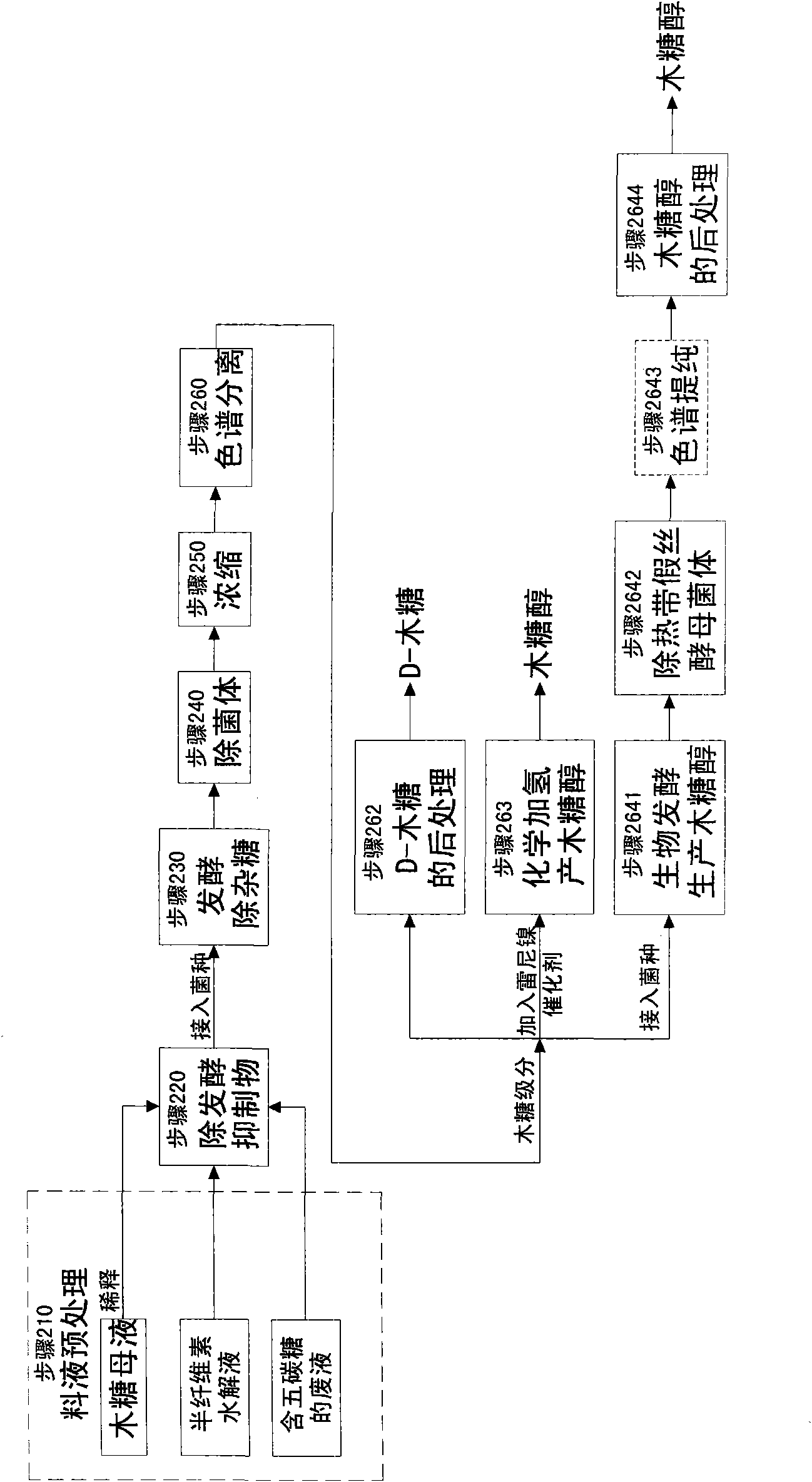
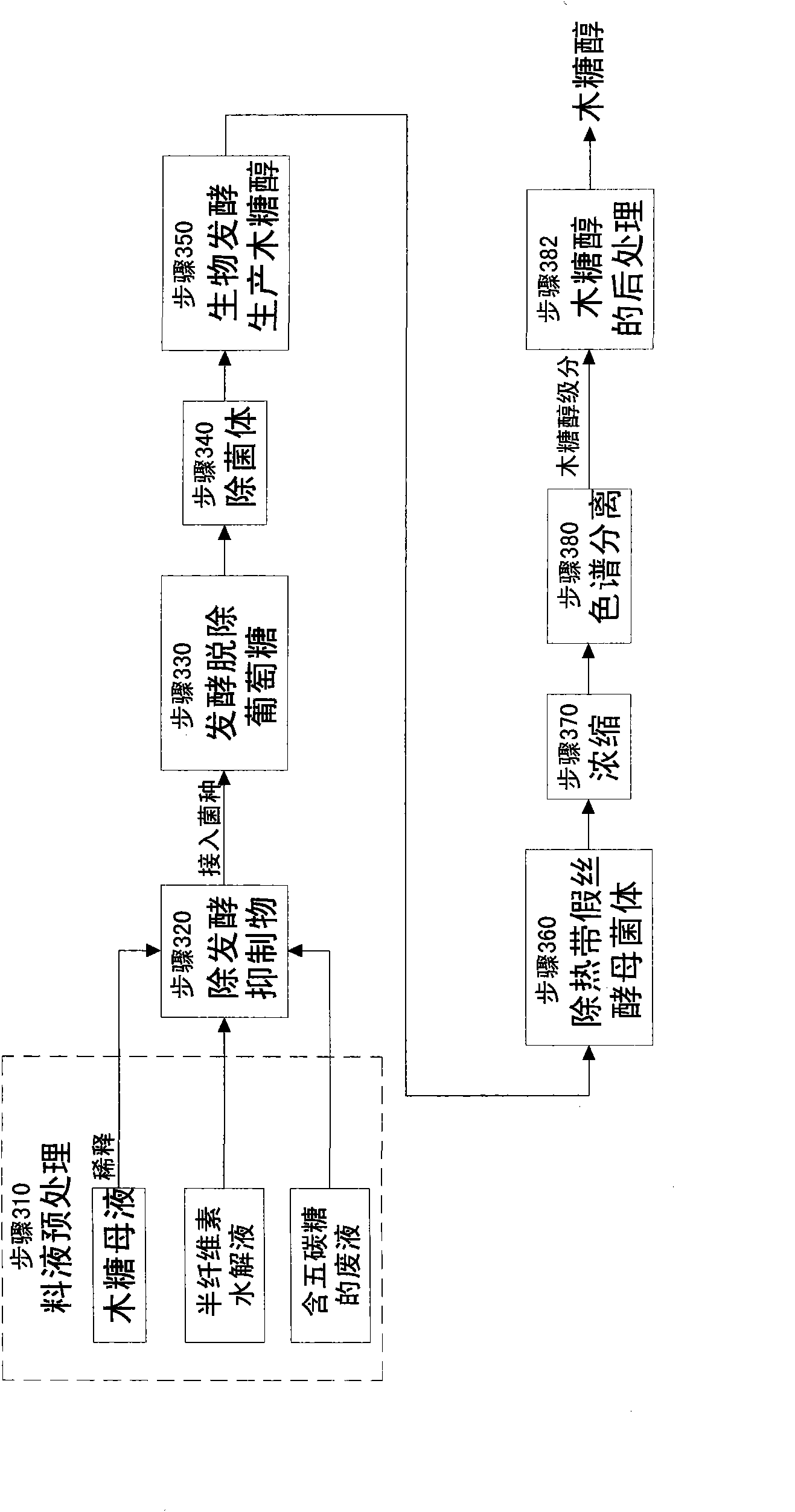
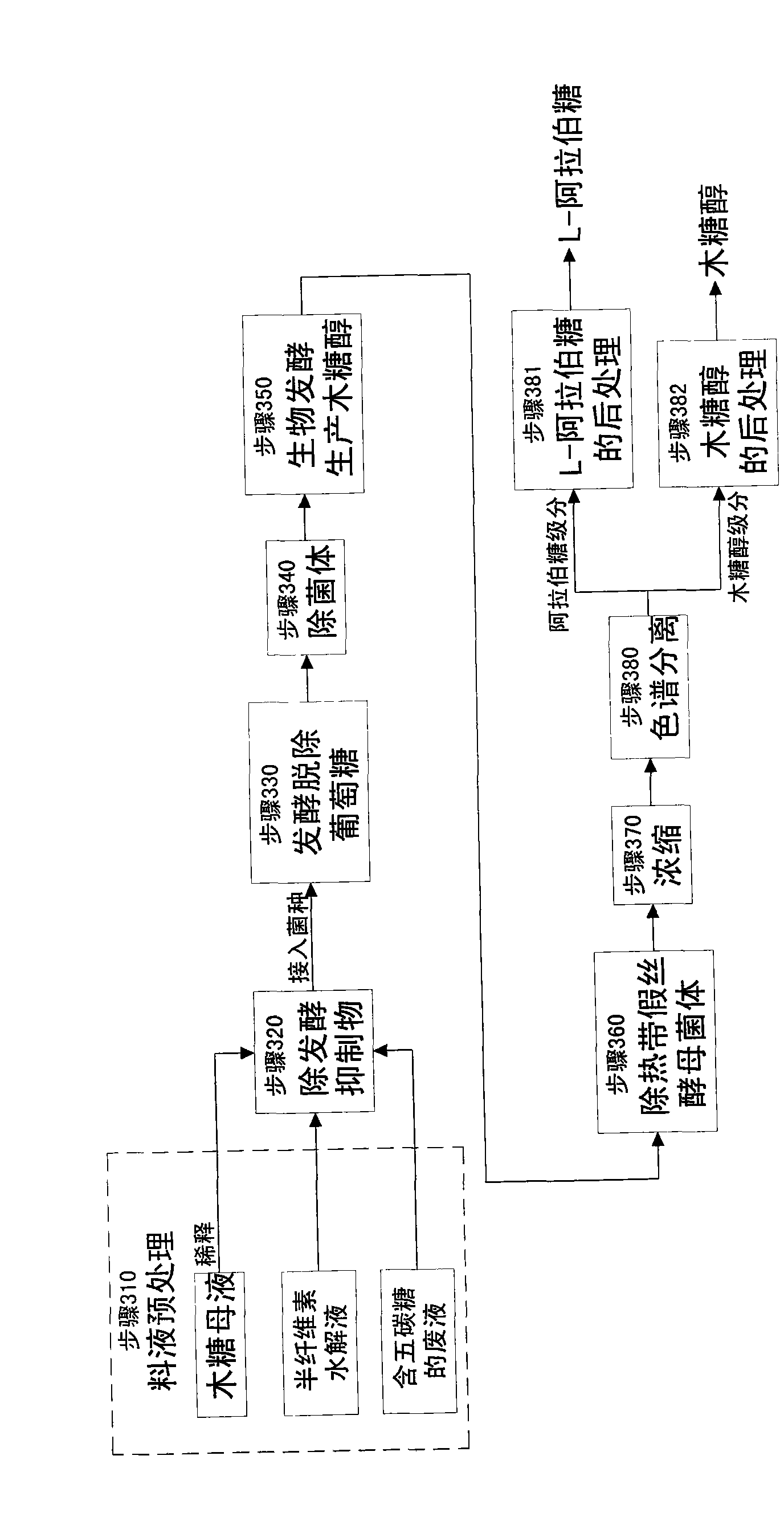
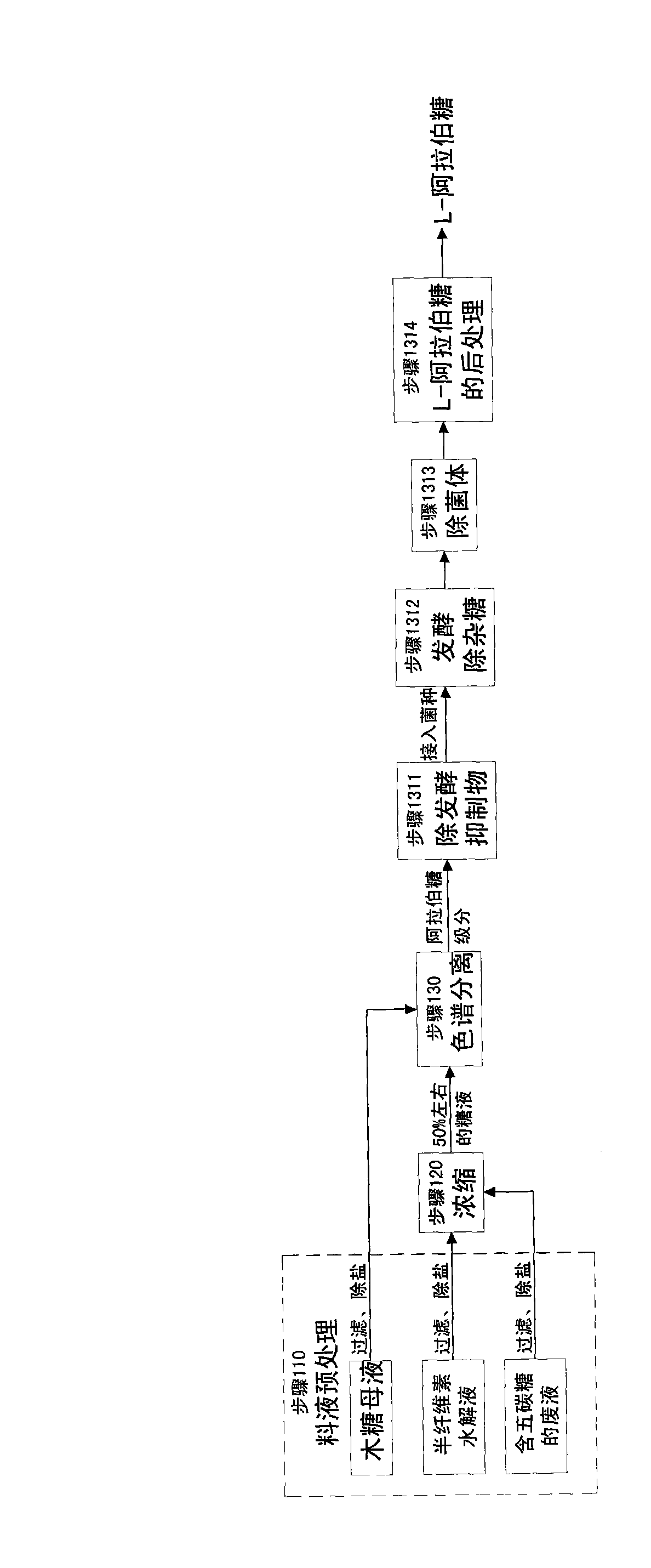
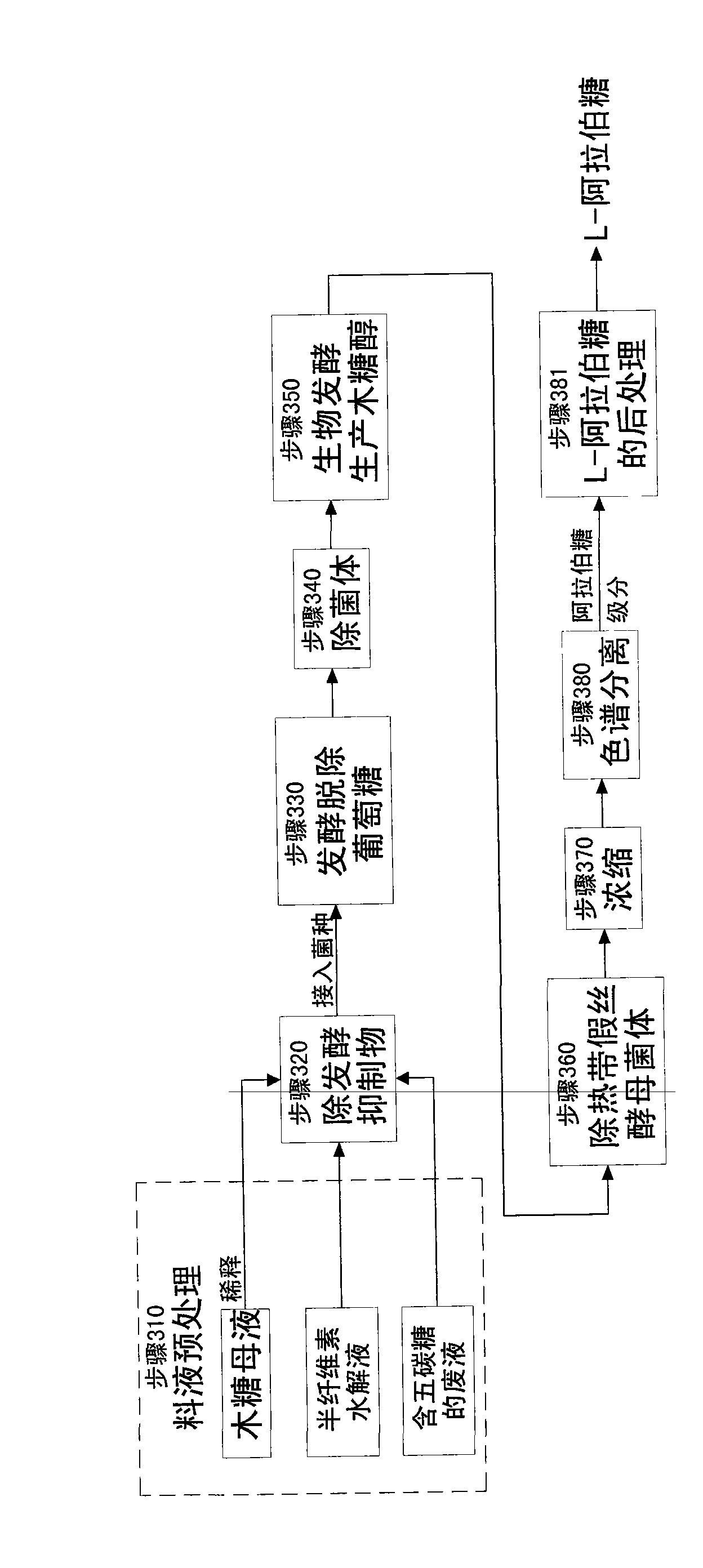
The invention relates to a method for producing a wood sugar product and a byproduct of ethanol or D-ribose or citric acid. The method takes hydrolysis liquid, wood sugar mother liquor and / or production waste liquid containing pentose of agricultural or forestry waste as the raw materials, comprising the following steps: (a) preprocessing feed liquid; (b) colour spectrum separation: separating thefeed liquid into arabinose fraction feed liquid and wood sugar fraction feed liquid; (c) removing mixed sugar at least containing glucose and galactolipin; and (d) carrying out aftertreatment on thewood sugar fraction feed liquid to obtain the wood sugar product. The wood sugar product comprises xylitol and D-wood sugar. The invention has low production cost and high efficiency and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHENGQUAN HEALTANG
Method for producing L-arabinose and D-xylose
ActiveCN101665523AHigh purityFermentation went wellIon-exchange process apparatusSugar derivativesBiotechnologyChromatographic separation
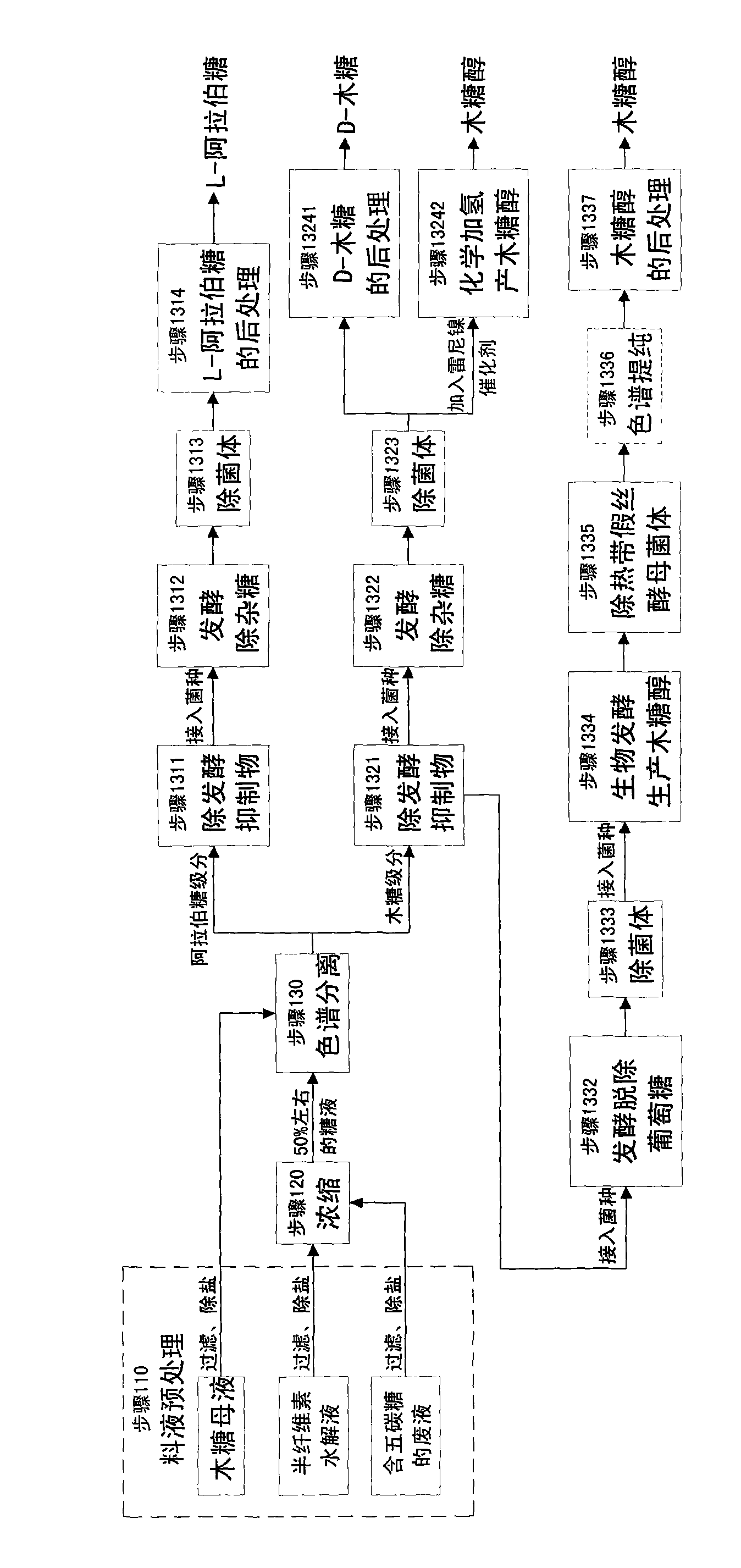
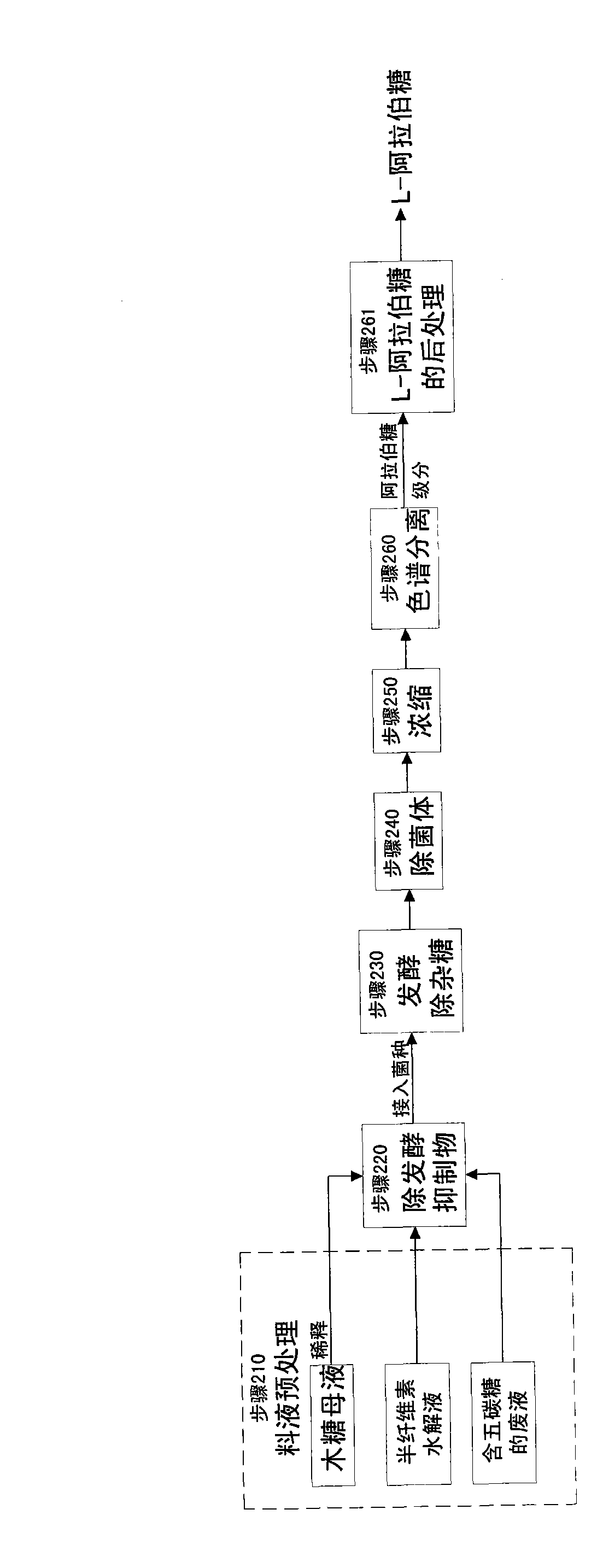
The invention relates to a method for producing L-arabinose and D-xylose, which can simultaneously produce ethanol or D-ribose or citric acid as a byproduct. The method utilizes a hydrolyzate of agricultural waste, a xylose mother liquor and / or a production waste liquor containing pentose as the raw materials and comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating the raw materials; (b) carrying out the chromatographic resolution to separate the raw materials into an arabinose-stage liquor and a xylose-stage liquor; (c1) removing fermentation inhibitors which are impurities and unwanted bacteria, which have an inhibiting effect on the fermentation; (c2) fermenting to remove unwanted saccharides at least comprising glucose and galactose; (d) and finally, respectively carrying out the post treatment on the arabinose-stage liquor and the xylose-stage liquor to obtain the L-arabinose and the D-xylose. Steps (c1) and (c2) are arranged before the chromatographic resolution in step (b) or after step (b). The method has the advantages of low production cost and high efficiency, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHENGQUAN HEALTANG
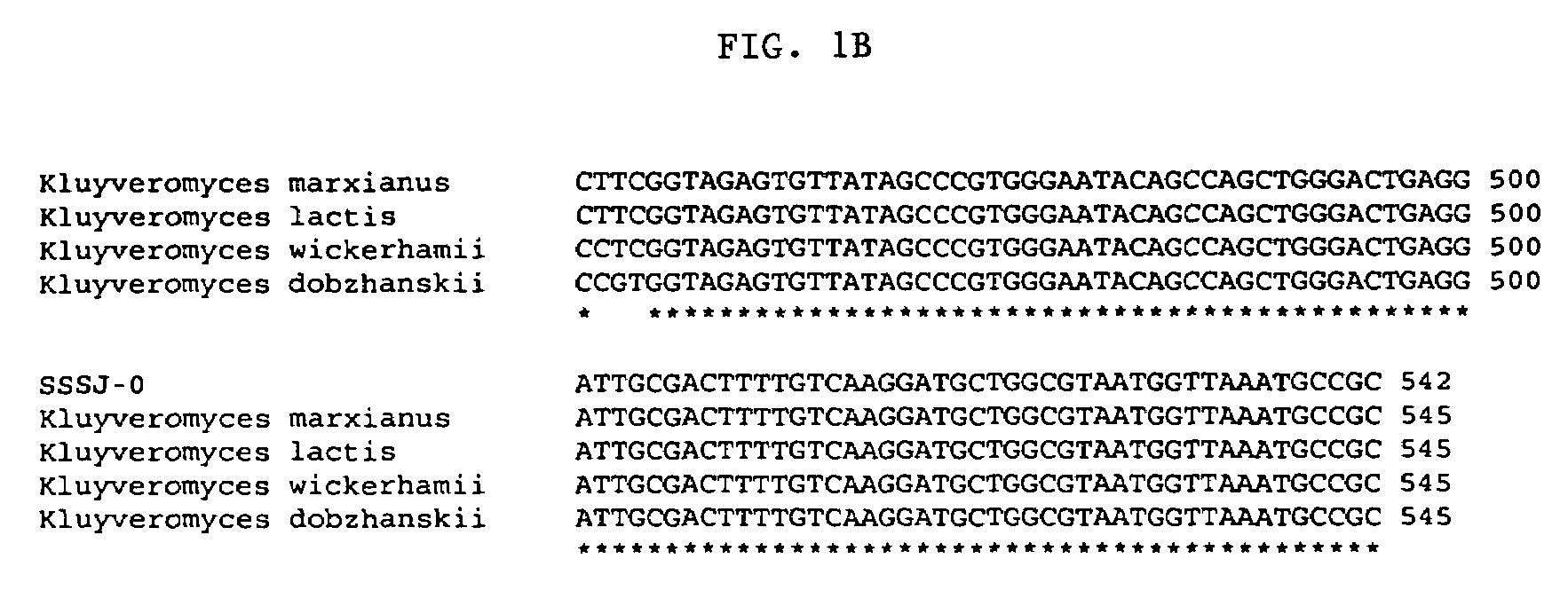
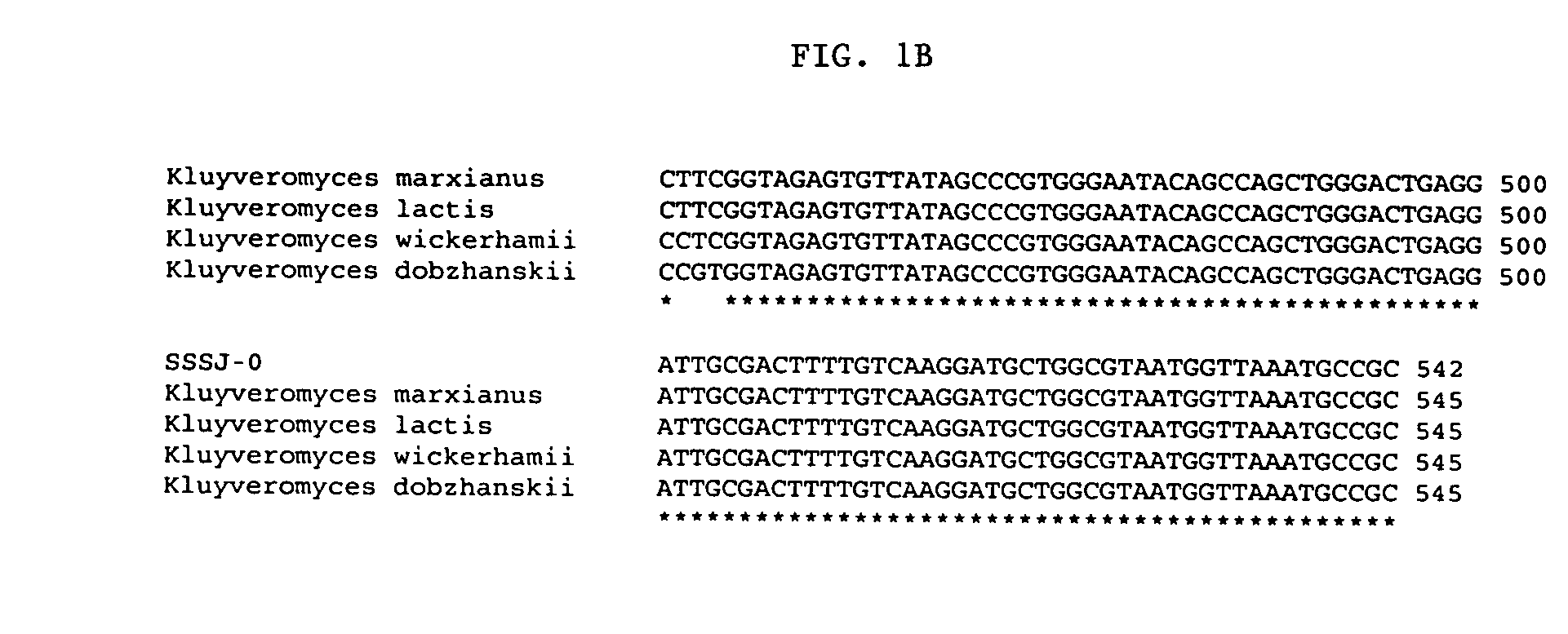
Kluyveromyces strains metabolizing cellulosic and hemicellulosic materials
This invention relates to the use of microorganisms for the generation of ethanol from lignocellulosic waste materials. Yeast strains of the genus Kluyveromyces which have the capability to ferment cellulose, hexose sugars to ethanol are provided. Also provided are methods for converting cellulose, hexoses, or mixed hydrolysates of hexoses to ethanol by fermentation with Kluyveromyces strains. The invention also provides methods to isolate yeast strains which metabolize cellulose, pentoses, or hemicelluloses from waste materials.
Owner:NEW TECH HLDG
Process for the manufacture of anhydro sugar alcohols with the assistance of a gas purge
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
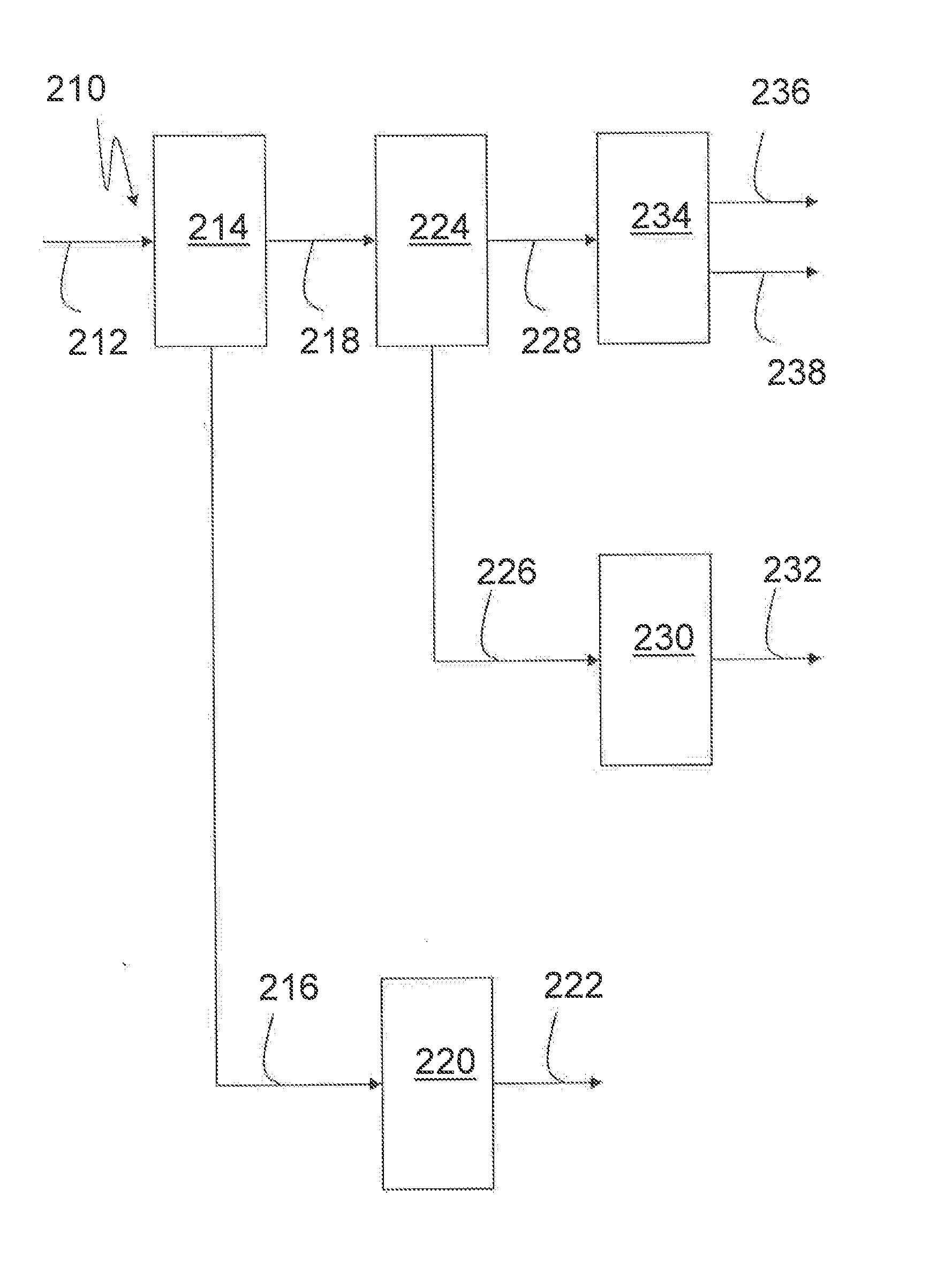
Process, Plant, and Biofuel For Integrated Biofuel Production
InactiveUS20110126448A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseBiodiesel
This invention relates to a process, a plant, and a biofuel for integrated biofuel production, such as with biogasoline, biodiesel, and / or sugar product. The integrated process includes the step of removing hexose from a feedstock to form a lignocellulosic material. The process also includes the step of converting the hexose to a biogasoline and / or a biodiesel material, and the step of depolymerizing lignocellulosic material to form pentose and a residue. The process also includes the step of converting the pentose to a biogasoline and / or a biodiesel material.
Owner:BP BIOFUELS UK
Organic material production system using biomass material and method
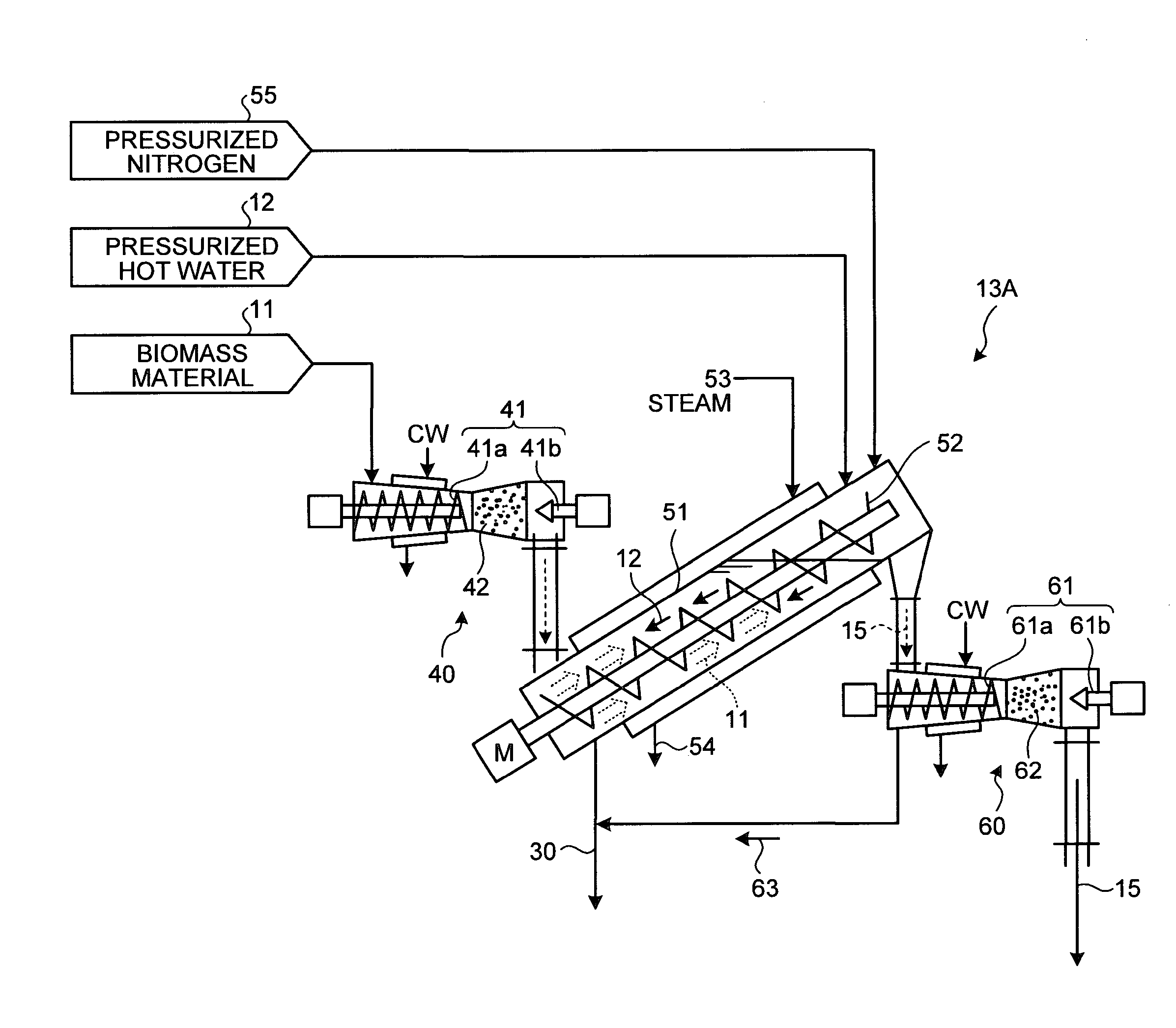
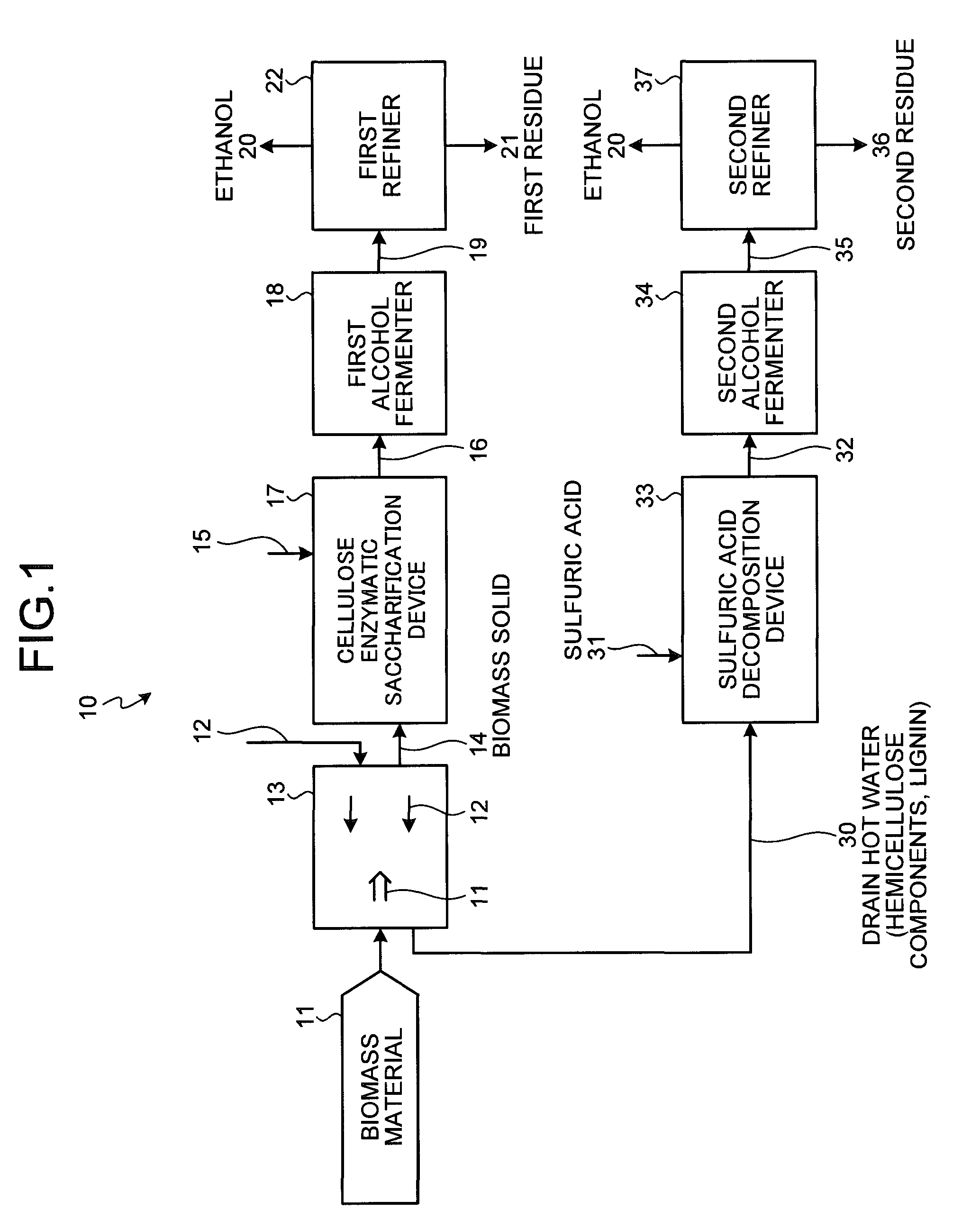
ActiveUS20110124057A1Efficiently saccharifyingImprove efficiencyPretreatment with water/steamBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAlcoholDecomposition
An organic material production system using biomass material includes: a hydrothermal decomposition apparatus (13) that causes the biomass material (11) and hot compressed water (12) to countercurrently contact with each other and undergo hydrothermal decomposition, and that transfers a lignin component and a hemicellulose component into the hot compressed water, so as to separate the lignin component and the hemicellulose component from a biomass solid residue; a cellulose enzymatic saccharification device (17) that treats, with an enzyme, cellulose in the biomass solid residue, so as to enzymatically saccharify the cellulose to a first sugar solution containing hexose; an alcohol fermenter (18) that produces alcohols by fermentation using the obtained first sugar solution; a sulfuric acid decomposition device (33) that decomposes, with sulfuric acid, the hemicellulose component in hot water (30) discharged from the hydrothermal decomposition apparatus, which contains the eluted lignin component and the eluted hemicellulose component, so as to decompose the hemicellulose component to a second sugar solution containing pentose; and a second alcohol fermenter (34) that produces, using the second sugar solution containing pentose, alcohols by fermentation.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHI POWER SYSTEMS ENVIRONMENTAL SOLUTIONS LTD
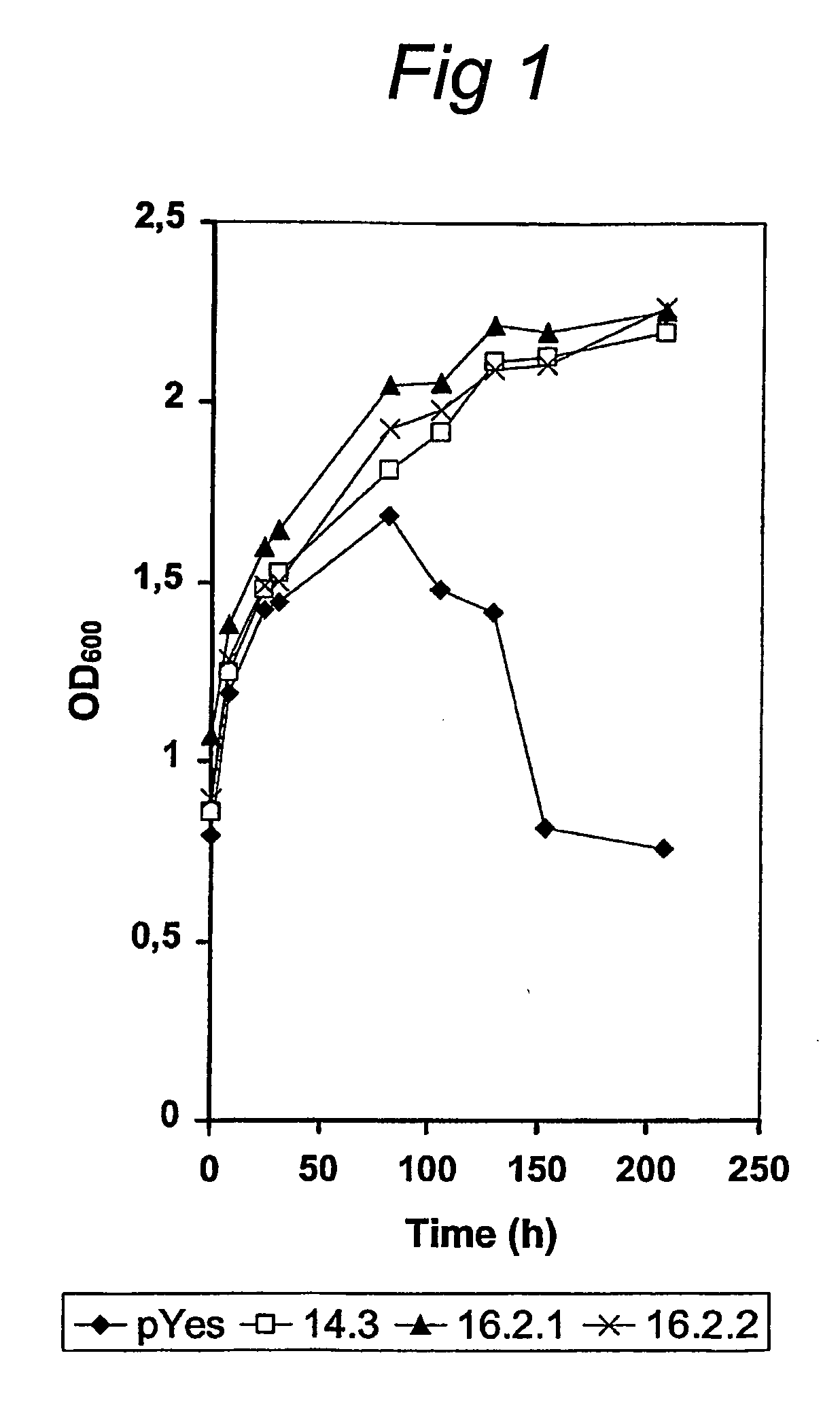
Metabolic Engineering of Xylos Fermentation
The present invention relates to further genetic modifications in eukaryotic host cells that have been transformed to express a xylose isomerase that confers the host cell the ability of isomerising xylose to xylulose. The further genetic modifications are aimed at improving the efficiency of xylose metabolism and include e.g. reduction of unspecific aldose reductase activity, increased xylulose kinase activity and increased flux of the pentose phosphate pathway. The modified host cells of the invention are suitable for the production of a wide variety of fermentation products, including ethanol, in fermentation processes in which a source of xylose or a source of xylose and glucose are used as carbon source.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Sugar mixtures and methods for production and use thereof
A sugar mixture comprising: monosaccharides; oligosaccharides in a ratio ≧0.06 to total saccharides; disaccharides in a ratio to total saccharides ≧0.05; pentose in a ratio to total saccharides ≧0.05; at least one alpha-bonded di-glucose; and at least one beta-bonded di-glucose. Also disclosed are methods to make and / or use such mixtures.
Owner:VIRIDA
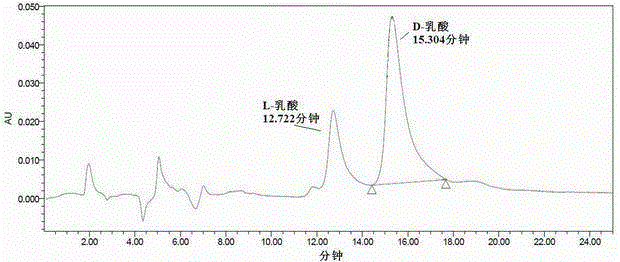
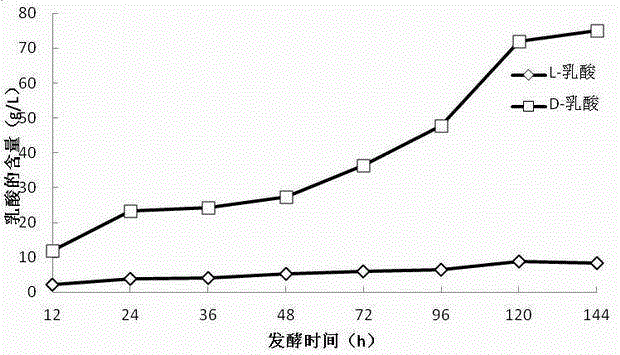
Lactobacillus and method for producing D-lactic acid by fermenting using lactobacillus
ActiveCN102978134AGood nutritional needsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactobacillusMicrobiology
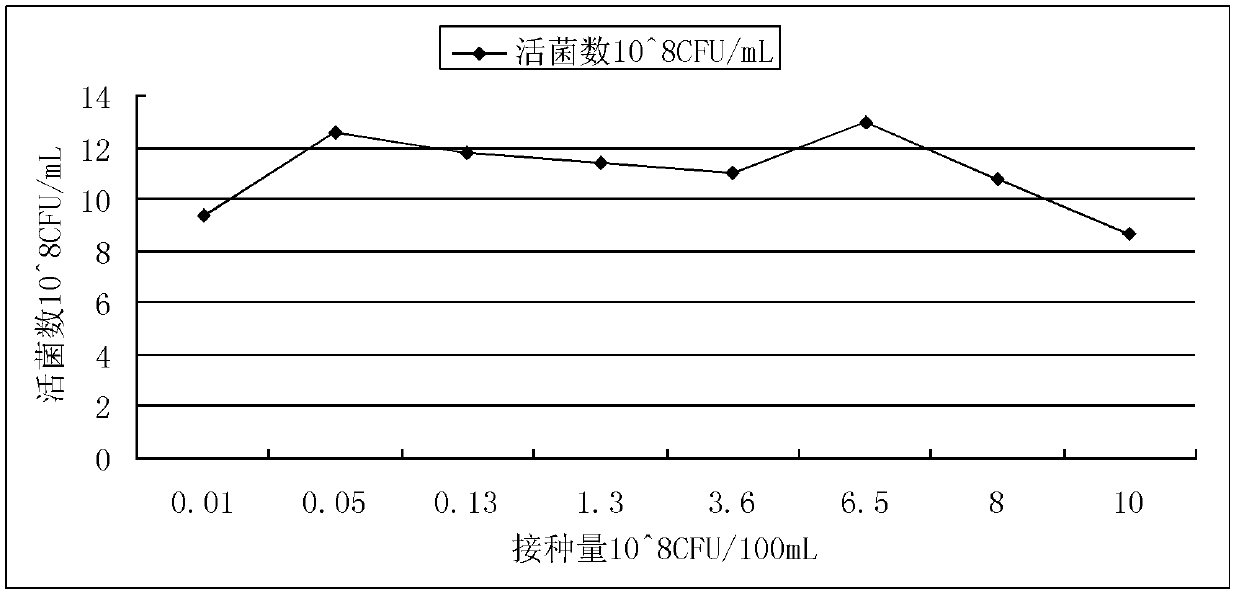
The invention discloses lactobacillus and a method for producing D-lactic acid by fermenting using the lactobacillus. A strain for the lactobacillus is lactobacillus (Lactobacillussp.) DMDL9010, and preservation number is CGMCC No.5172. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out three-time activation culture on the strain; and then, fermenting for 108-144 hours at the temperature of 20 DEG C-35 DEG C to obtain D-lactic acid which is high in optical purity. According to the lactobacillus DMDL9010, D-lactic acid can be produced by fermenting pentose and hexose, and D-lactic acid is stable and high in yield, and the yield is 65-85g / L; produced D-lactic acid is high in optical purity which reaches 80-90%; the raw material adopted in the fermentation is wide in source and low in cost, and the fermenting cycle of the strain is just 108-144 hours; and D-lactic acid is produced by using the method, thus cost is saved, production efficiency is improved. The method disclosed by the invention has an important industrial application value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for increasing lignocellulose saccharification yield through multi-step enzymolysis
InactiveCN102191299AHigh yield of enzymatic hydrolysisReduce generationFermentationHydrolysateCellobiose
The invention relates to a method for increasing the lignocellulose saccharification yield through multi-step enzymolysis. The method comprises the following main steps: 1) pretreating wood fiber raw material; 2) adding one or more of bio-degrading enzymes in the pretreated wood fiber stepwise or simultaneously, removing the extract component or lignin in the raw material to change the fiber structure of the raw material; 3) adding one or more of hemicellulose degrading enzymes in the lignocellulose which is removed extract or lignin through enzymolysis stepwise or simultaneously, extracting pentose in the raw material; and 4) filtering fiber residue obtained in the step 3) through the enzymolysis, and adding cellulase and / or cellobiase to hydrolyze continuously and obtain glucose hydrolysate. By adopting the method, each component can be recycled and the total reducing sugar yield can be increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Kluyveromyces strains metabolizing cellulosic and hemicellulosic materials
This invention relates to the use of microorganisms for the generation of ethanol from lignocellulosic waste materials. Yeast strains of the genus Kluyveromyces which have the capability to ferment cellulose, hexose sugars to ethanol are provided. Also provided are methods for converting cellulose, hexoses, or mixed hydrolysates of hexoses to ethanol by fermentation with Kluyveromyces strains. The invention also provides methods to isolate yeast strains which metabolize cellulose, pentoses, or hemicelluloses from waste materials.
Owner:NEW TECH HLDG
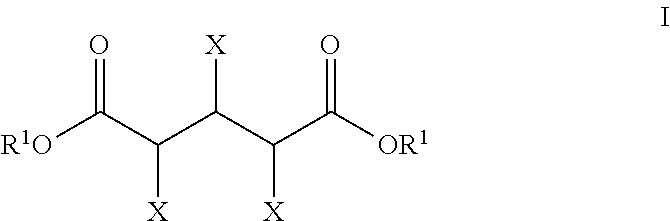
Production of glutaric acid and derivatives from carbohydrate-containing materials
ActiveUS8785683B2Low costCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationGlutaric acidHydrodeoxygenation
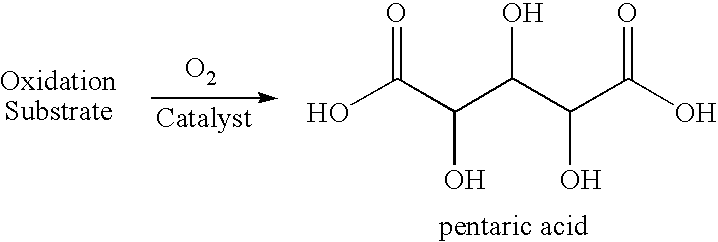
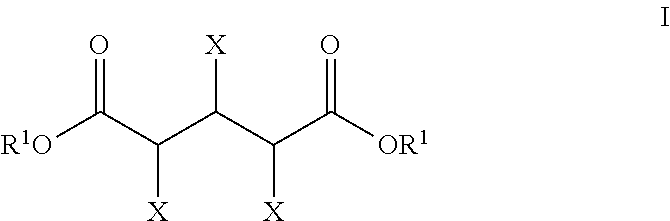
The present invention generally relates to processes for the chemocatalytic conversion of a pentose source to a glutaric acid product. The present invention includes processes for the conversion of pentose to a glutaric acid product via pentaric acid or derivatives thereof. The present invention also includes processes comprising the catalytic oxidation of pentose to pentaric acid and catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of pentaric acid or derivatives thereof to a glutaric acid product.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
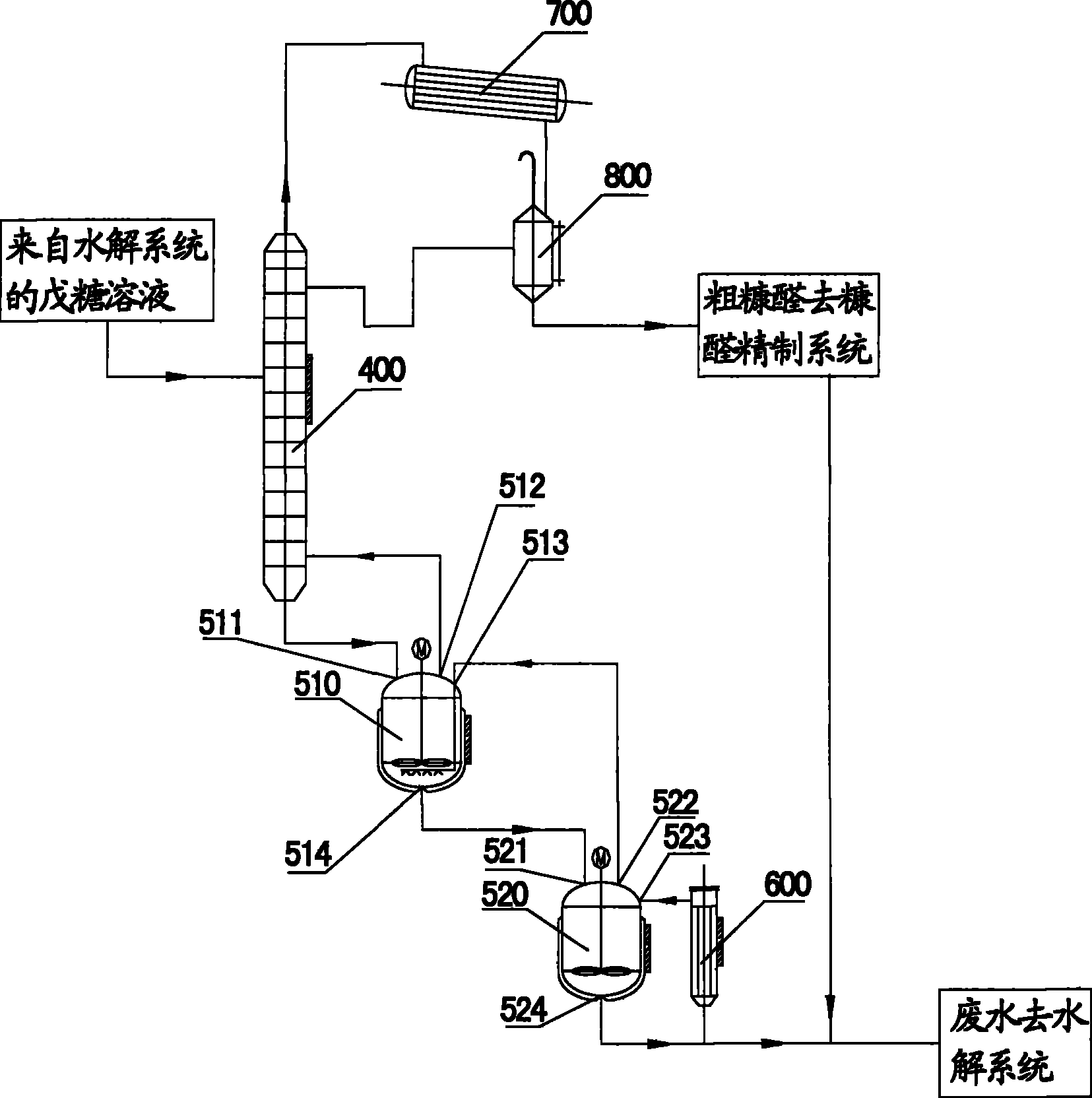
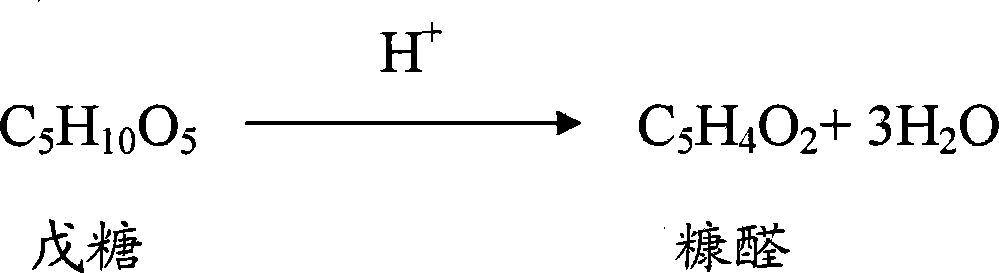
System and method for producing furol by using agricultural and forestry castoff
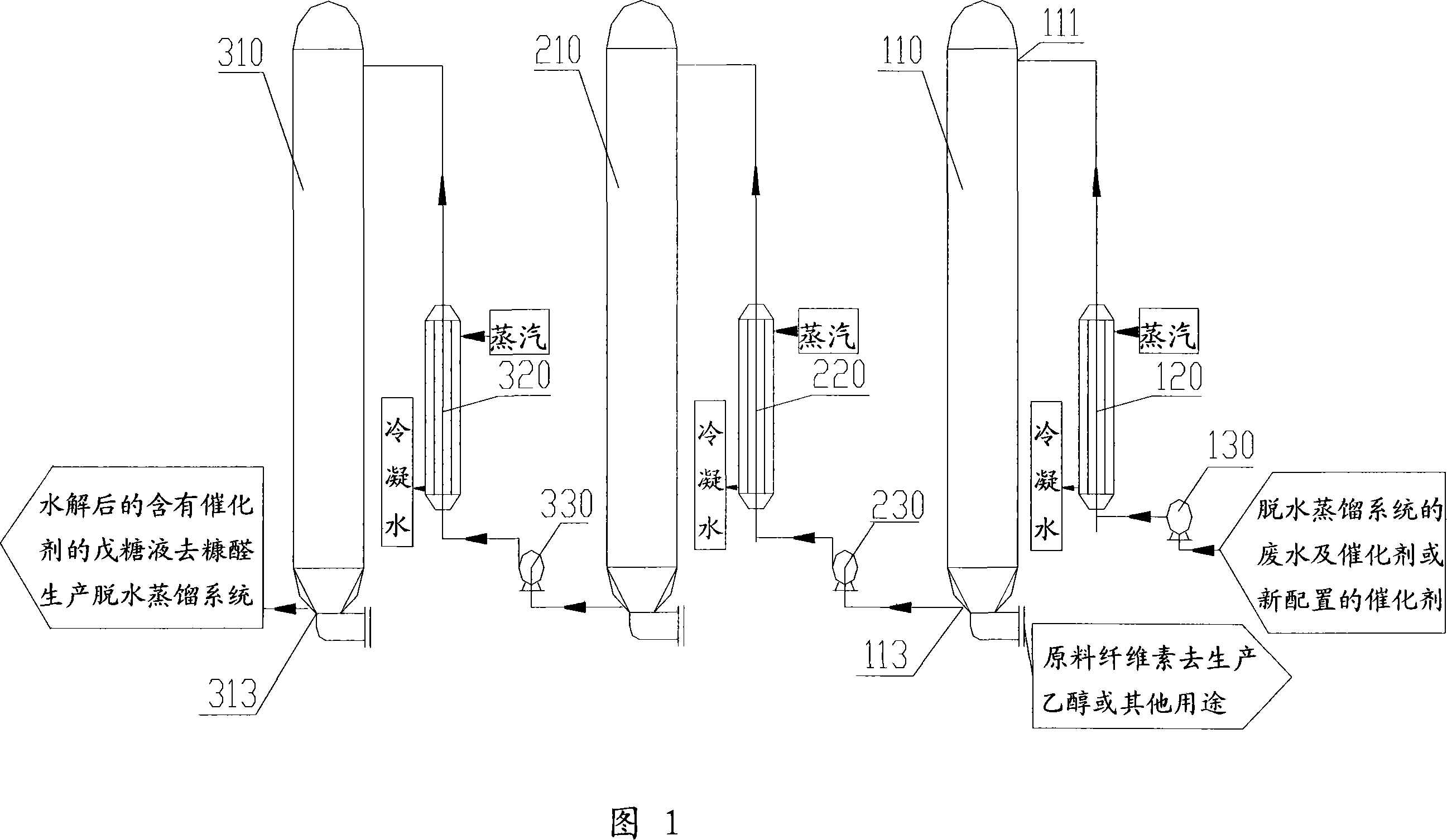
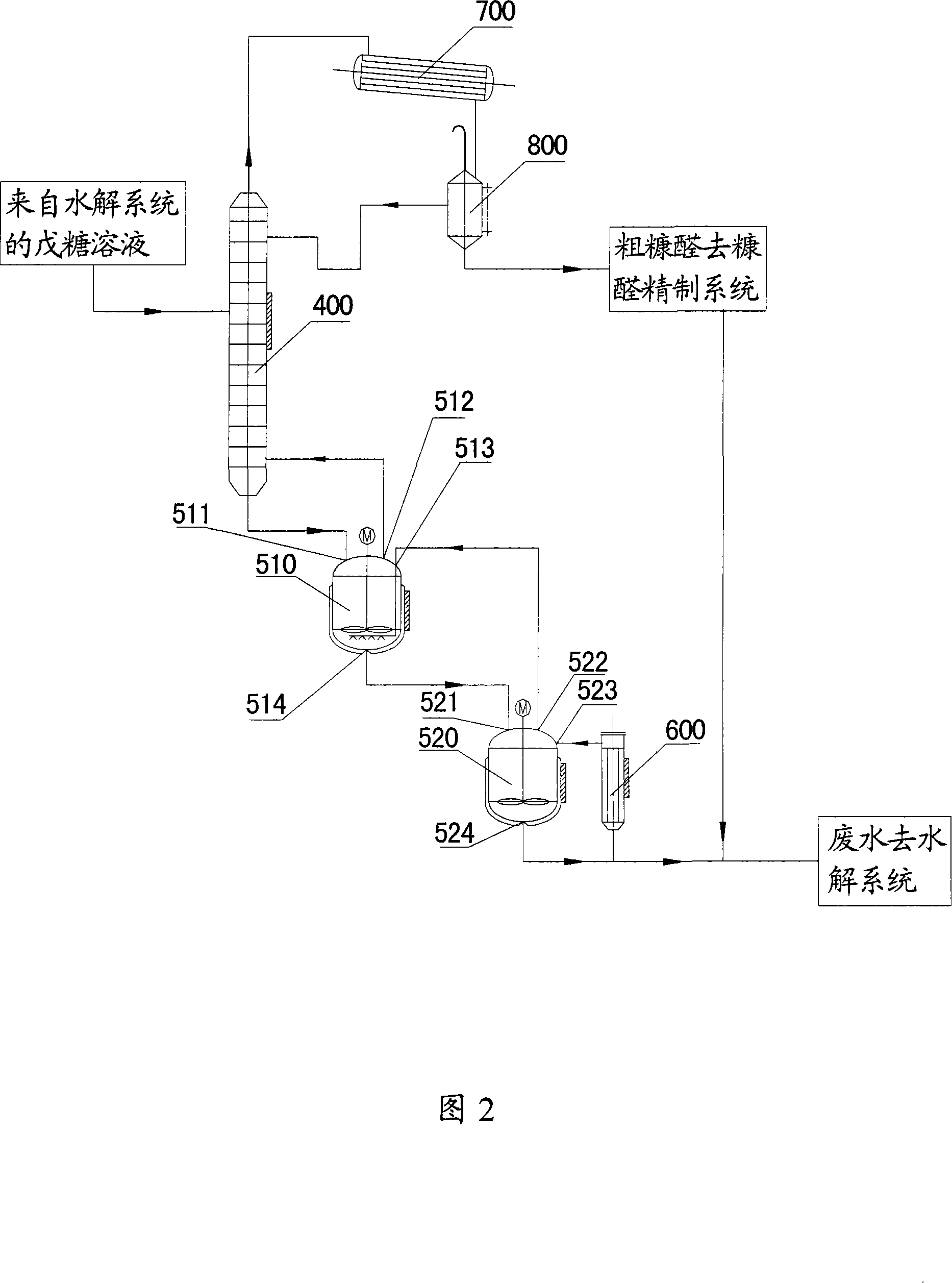
The invention discloses a system and method to produce furfural with agricultural wastes, which is characterized by the following: choosing two-step method; comprising hydrolysis system and dehydration distilling system; setting the hydrolysis system as N grade hydrolysis autoclave with end-to-end; proceeding continuous hydrolysis for the agricultural wastes; generating pentose solution; setting the dehydration distilling system as dehydration distilling unit and dehydration reclaiming unit; dewatering and distilling for the pentose solution with the dehydration distilling unit; getting furfural steam; setting the dehydration reclaiming unit as at least one grade dewatering reactor; further-dewatering; generating furfural steam; sending into dehydration distilling tower; distilling continuously; sending the waste water from the dehydration reclaiming unit back to dehydration system; realizing zero discharge for waste water. This invention possesses high productivity, low energy consumption and warm reacting condition, which can be used as raw material to produce alcohol.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
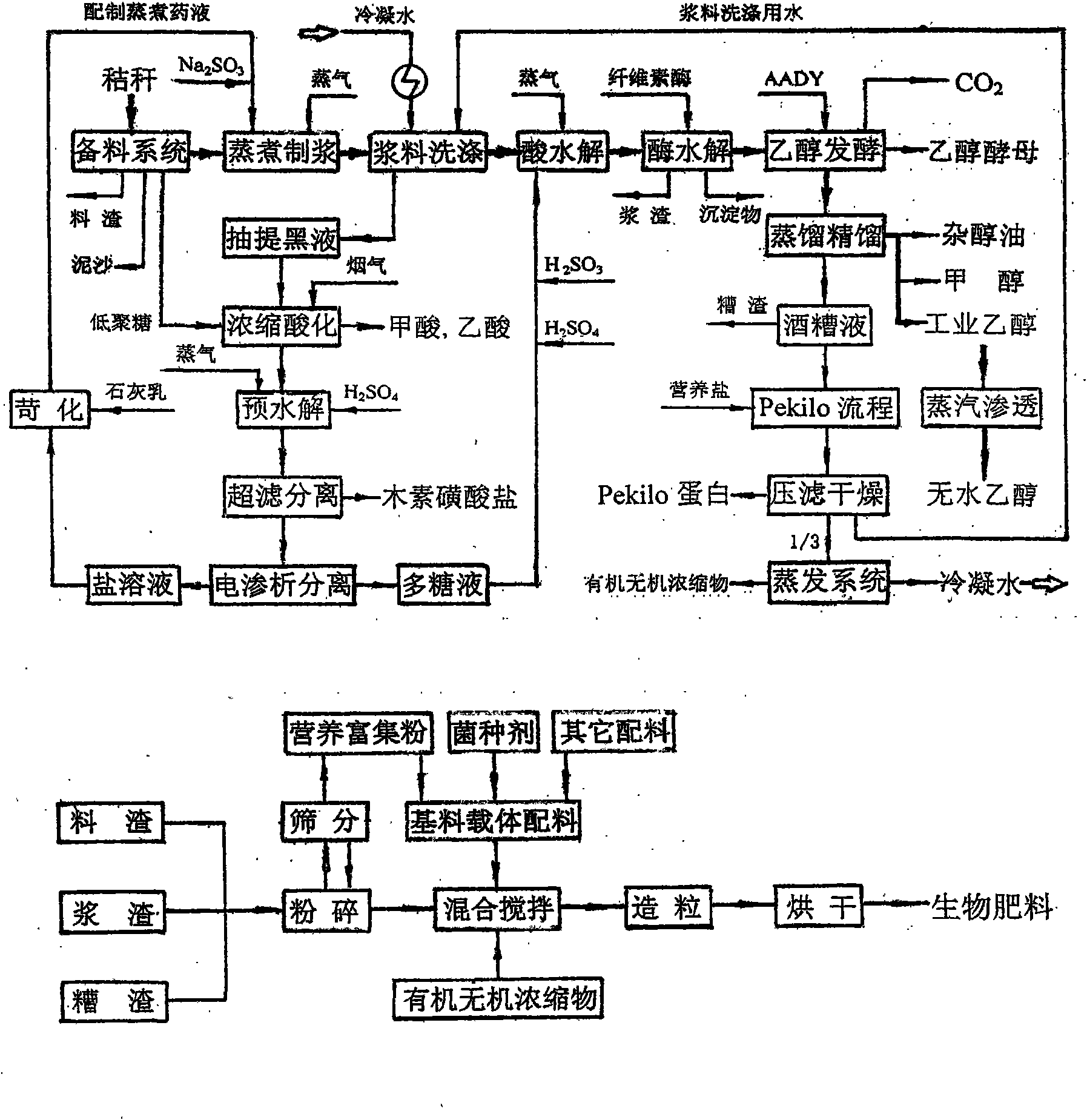
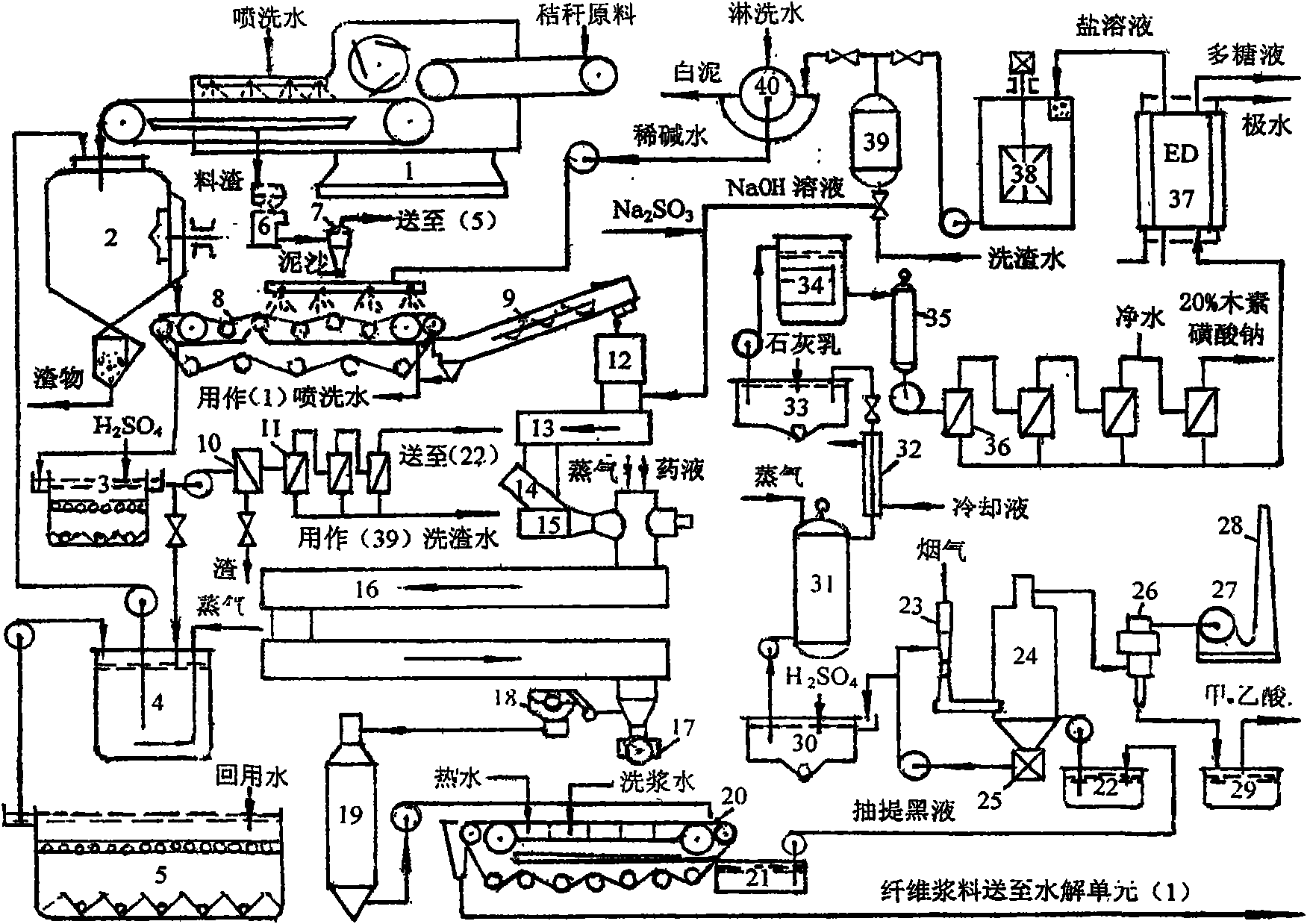
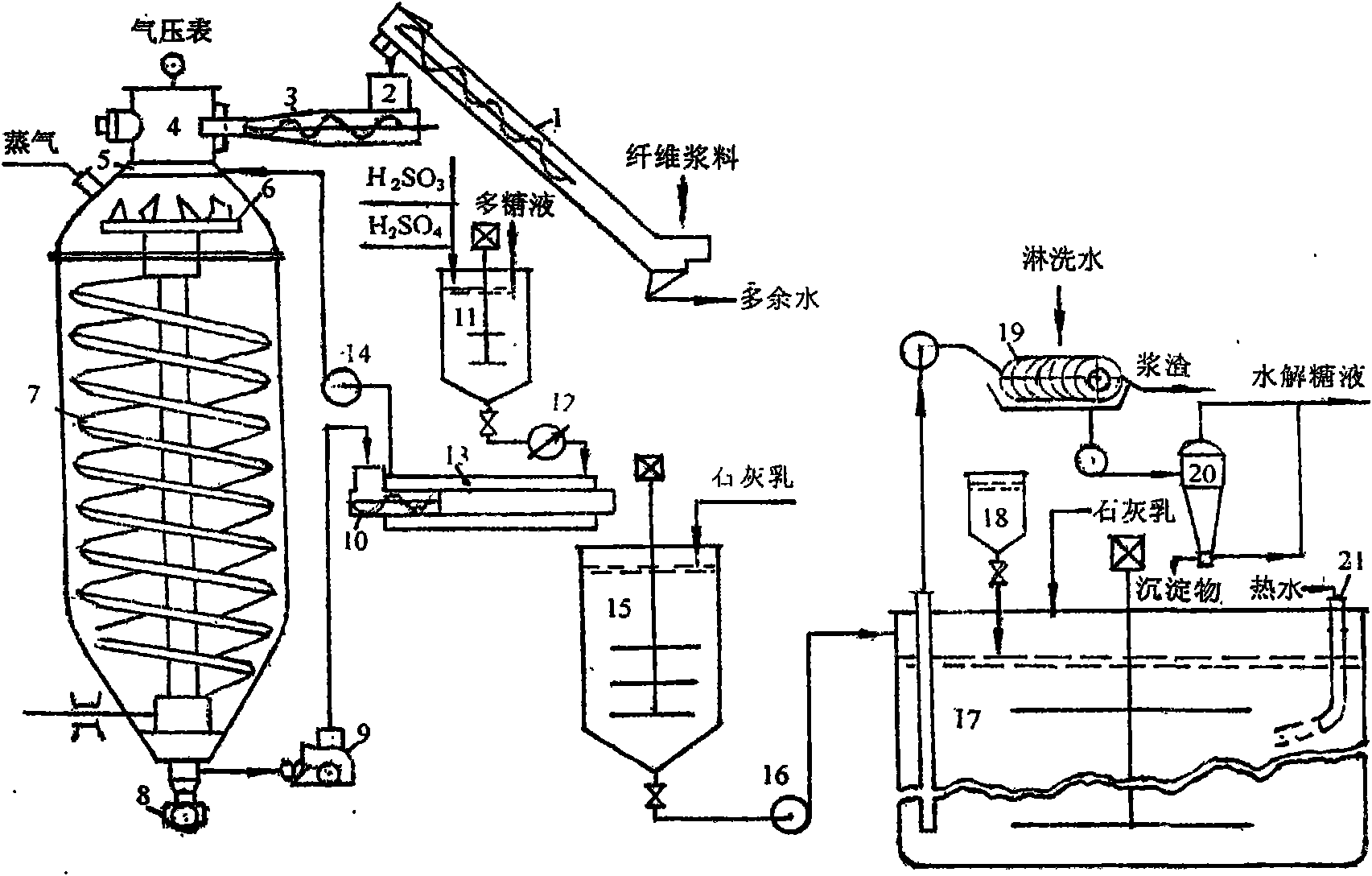
Production method of dissolving pulp
The invention relates to a production method of dissolving pulp. The method comprises the steps of pre-hydrolyzing plant fibrous raw materials by water, steam or diluted acid, then digesting the materials by peroxy acid, and processing the materials by hemicellulase, thus obtaining the dissolving pulp. The dissolving pulp produced by the method has the whiteness more than 90% ISO (International Standards Organization), and the content of Alpha-cellulose is more than 92%, and the content of pentosan is less than 2.0%. The method is applicable to wood and non-wood fibrous raw materials.
Owner:济南绿泉新材料科技有限公司
Method for producing L-arabinose
ActiveCN101665524AHigh purityFermentation went wellIon-exchange process apparatusSugar derivativesChromatographic separationImpurity
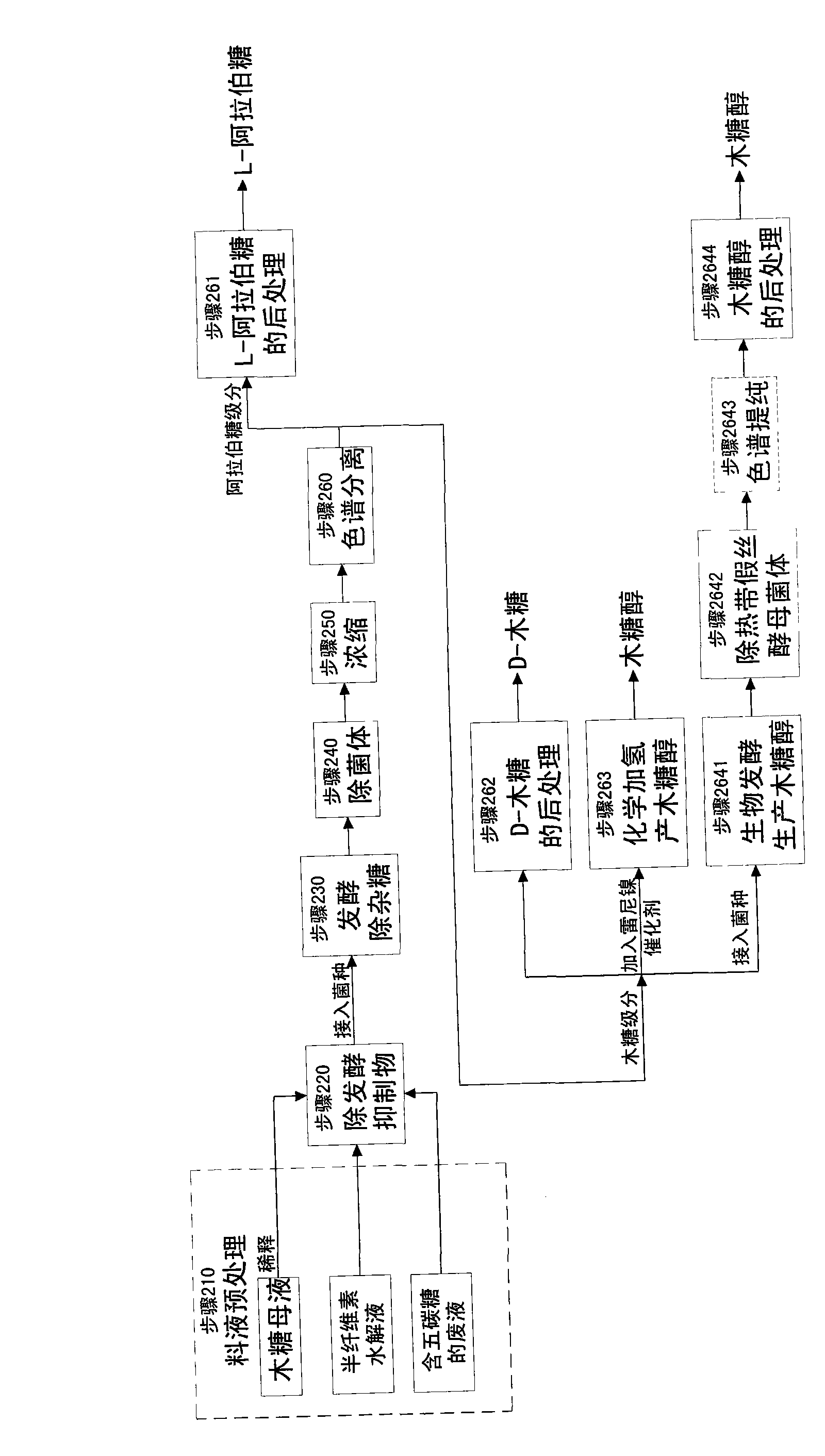
The invention relates to a method for producing L-arabinose, which can simultaneously produce ethanol, D-ribose and citric acid as byproducts. The method utilizes a hydrolyzate of agricultural waste, a xylose mother liquor and / or a production waste liquor containing pentose as the raw materials and comprises the following steps: (a) pretreating the raw materials; (b) carrying out the chromatographic resolution to separate the raw materials into an arabinose-stage liquor and a xylose-stage liquor; (c) removing impurities and unwanted bacteria, which have an inhibiting effect on fermentation, as well as unwanted saccharides at least comprising glucose and galactose; (d) and carrying out the post treatment on the arabinose-stage liquor to obtain the L-arabinose. Steps (c1) and (c2) are arranged before the chromatographic resolution in step (b) or after step (b). The invention has the advantages of low production cost and high efficiency, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHENGQUAN HEALTANG
Lactic acid bacteria semi-solid fermentation product for increasing growth performance of animals and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN102599348AEasy feedingLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSemi solidGlucose polymers
The invention discloses a lactic acid bacteria semi-solid fermentation product. The product is prepared by the following processes: inoculating lactic acid bacteria in raw materials and fermenting at a temperature of 24-44 DEG C for 24-40h to obtain the product. The raw materials comprise 4.0-5.0g of wheat bran, 1.2-1.8g of soybean meal, 0.8-1.2g of glucose or brown sugar, and water, wherein water is added until the total amount of the raw materials is up to 100mL. The inoculation amount of the lactic acid bacteria is 1.0-2.0*10<7>cfu / 100mL, wherein the lactic acid bacteria is composed of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus pentosaceus with a strain viable count ratio of (3:10)-(10:3). The lactic acid bacteria semi-solid fermentation product for increasing growth performance of animals provided by the invention is the first fluid fermentation feed independently developed in China according to the national conditions for culture, inherits the advantages of the traditional solid fermentation feeds, and at the same time has the advantages of being more convenient, fresher, more significant in feeding effects, lower in cost and the like.
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司
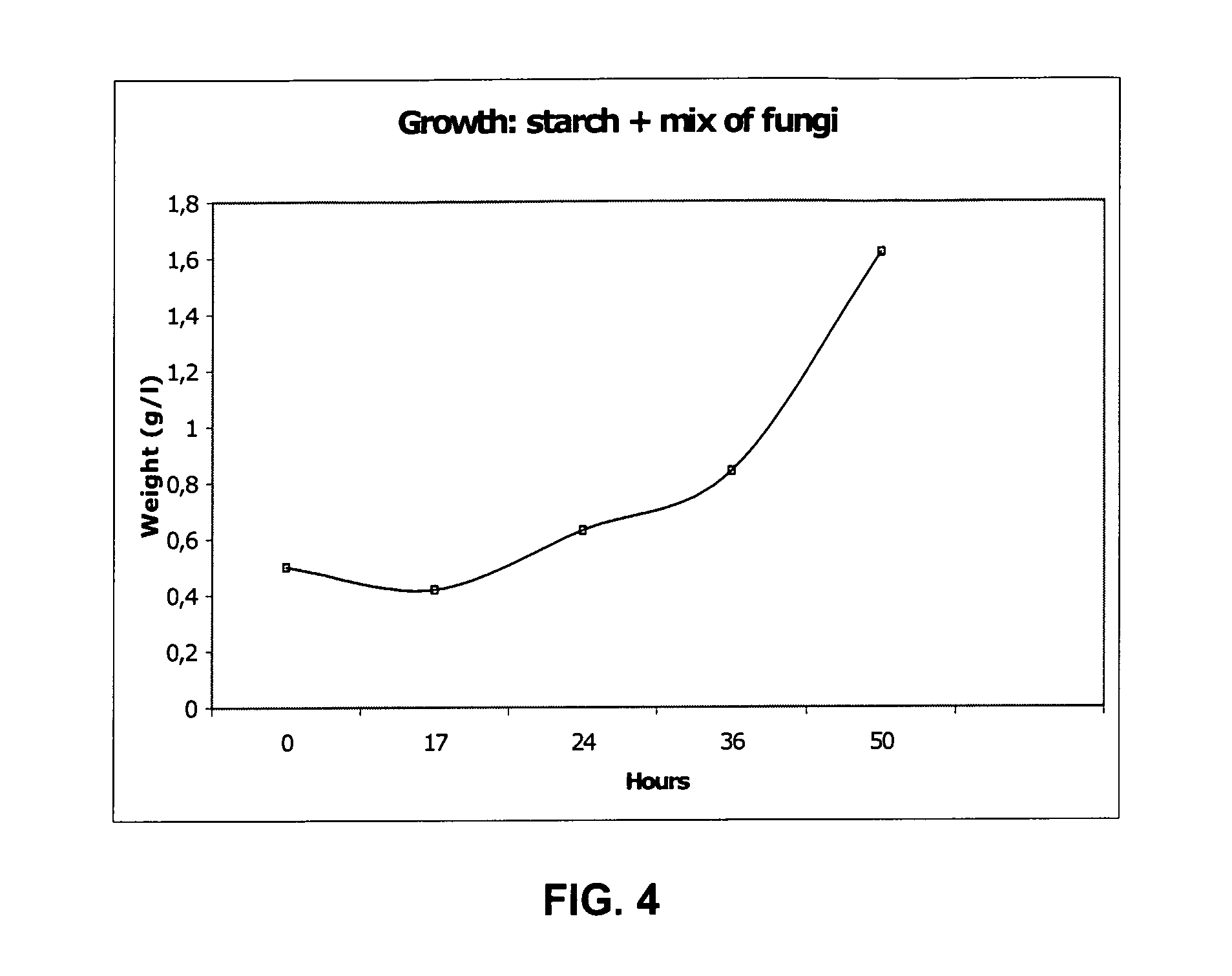
Fermentation Process, Starter Culture and Growth Medium
InactiveUS20070231869A1High economicHigh environmental interestFungiBiofuelsMicroorganismCell culture media
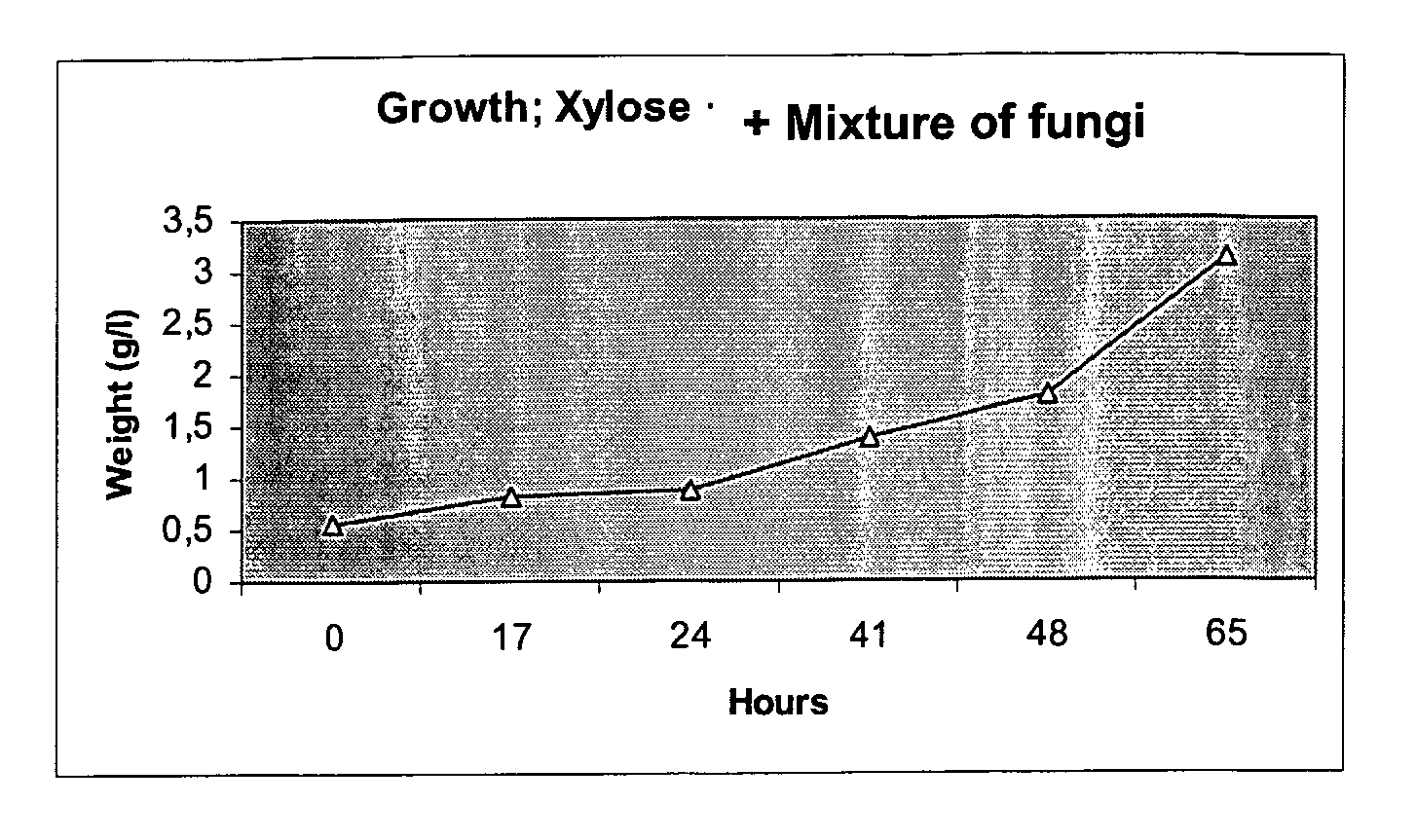
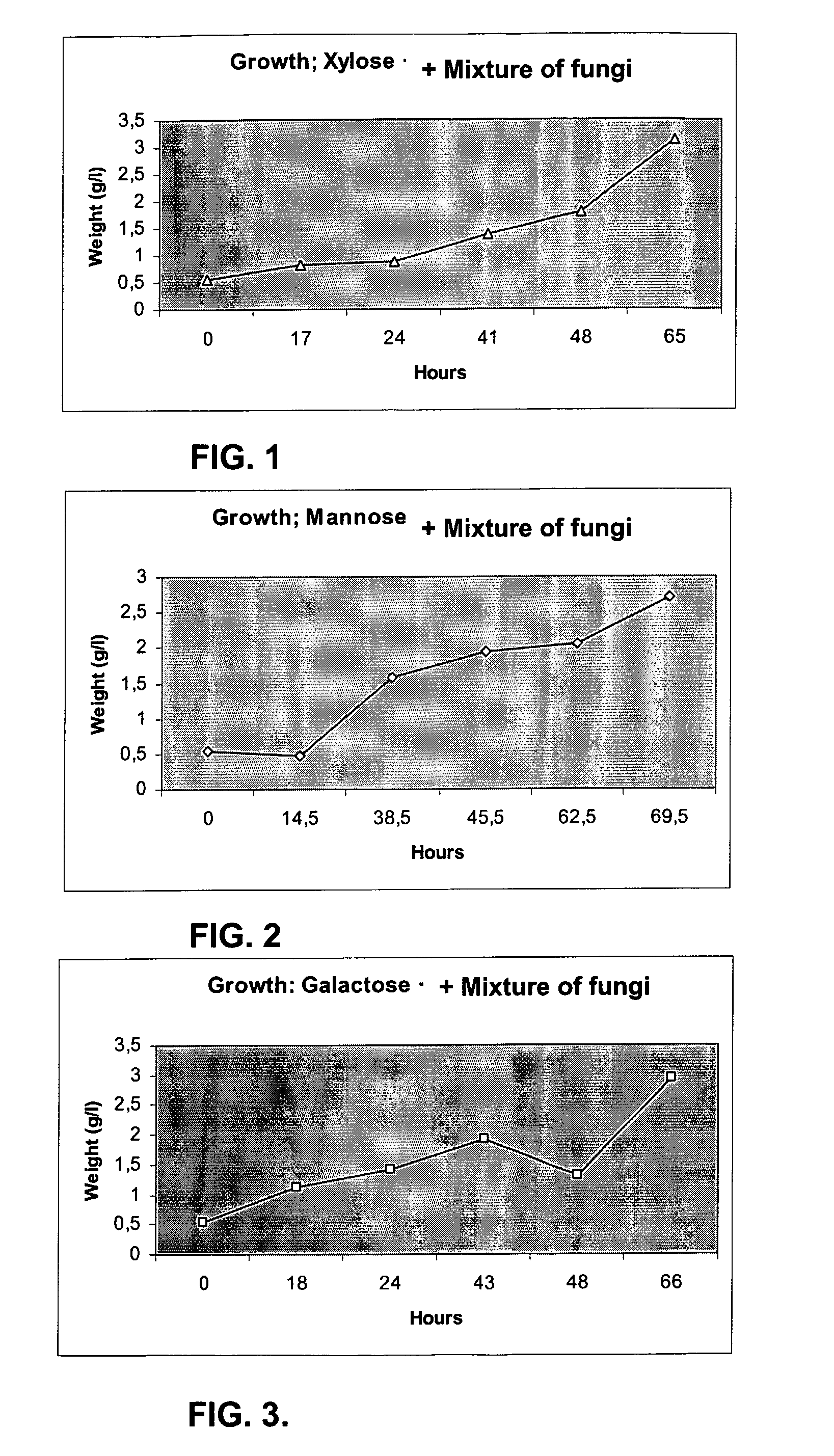
Ethanol production from biomass can be rendered more effective by the use of at least one fungus or a mix of fungi capable of fermenting pentose compounds, or both pentose as well as hexose compounds. Preferably said at least one fungus is a fungus belonging to the species Chalara sp., optionally used in combination with a second fungus belonging to the species Trametes sp. Preferably said fungus or fungi is / are used in combination with other fermenting microorganisms, such as a yeast, e.g. Saccaromyces cerevisiae.
Owner:SWETREE TECHOLOGIES AB
System and method for producing furol by using agricultural and forestry castoff
The invention discloses a system and method to produce furfural with agricultural wastes, which is characterized by the following: choosing two-step method; comprising hydrolysis system and dehydration distilling system; setting the hydrolysis system as N grade hydrolysis autoclave with end-to-end; proceeding continuous hydrolysis for the agricultural wastes; generating pentose solution; setting the dehydration distilling system as dehydration distilling unit and dehydration reclaiming unit; dewatering and distilling for the pentose solution with the dehydration distilling unit; getting furfural steam; setting the dehydration reclaiming unit as at least one grade dewatering reactor; further-dewatering; generating furfural steam; sending into dehydration distilling tower; distilling continuously; sending the waste water from the dehydration reclaiming unit back to dehydration system; realizing zero discharge for waste water. This invention possesses high productivity, low energy consumption and warm reacting condition, which can be used as raw material to produce alcohol.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Ethanol-guiding straw bio-refining full-sealing integration system
InactiveCN101555495AImprove productivityStrong profitabilityBy-product recoveryFungiFiberLiquid waste
The invention relates to a fiber biomass refining technology, in particular to an ethanol-guiding straw bio-refining full-sealing integration system. Based on the clean pulping of the straw, a chemical and biological combined method is used for totally hydrolyzing amylose separated from a cellulose and a hemicellulose separated into pulps and braised waste liquid to prepare a hexose and a pentose;and the hexose and the pentose are converted into series of chemical and biological products which taking ethanol as dominant product. As a firstly separated and subsequently disposed straw bio-refin ing integration system, the cellulose and the hemicellulose in the straw raw material are utilized effectively; furthermore, 20-25% of the lignin in the raw material and the material slag, slurry slag, trough slag and ashes (mineral matter) produced in the production process are totally converted into the product with high additional values, thus realizing the environment objects of full sealing and zero draining and controlling the production cost (apportionment cost after the straw biomass is totally utilized) of the fuel ethanol within 1800-2000RMB / t.
Owner:徐守才
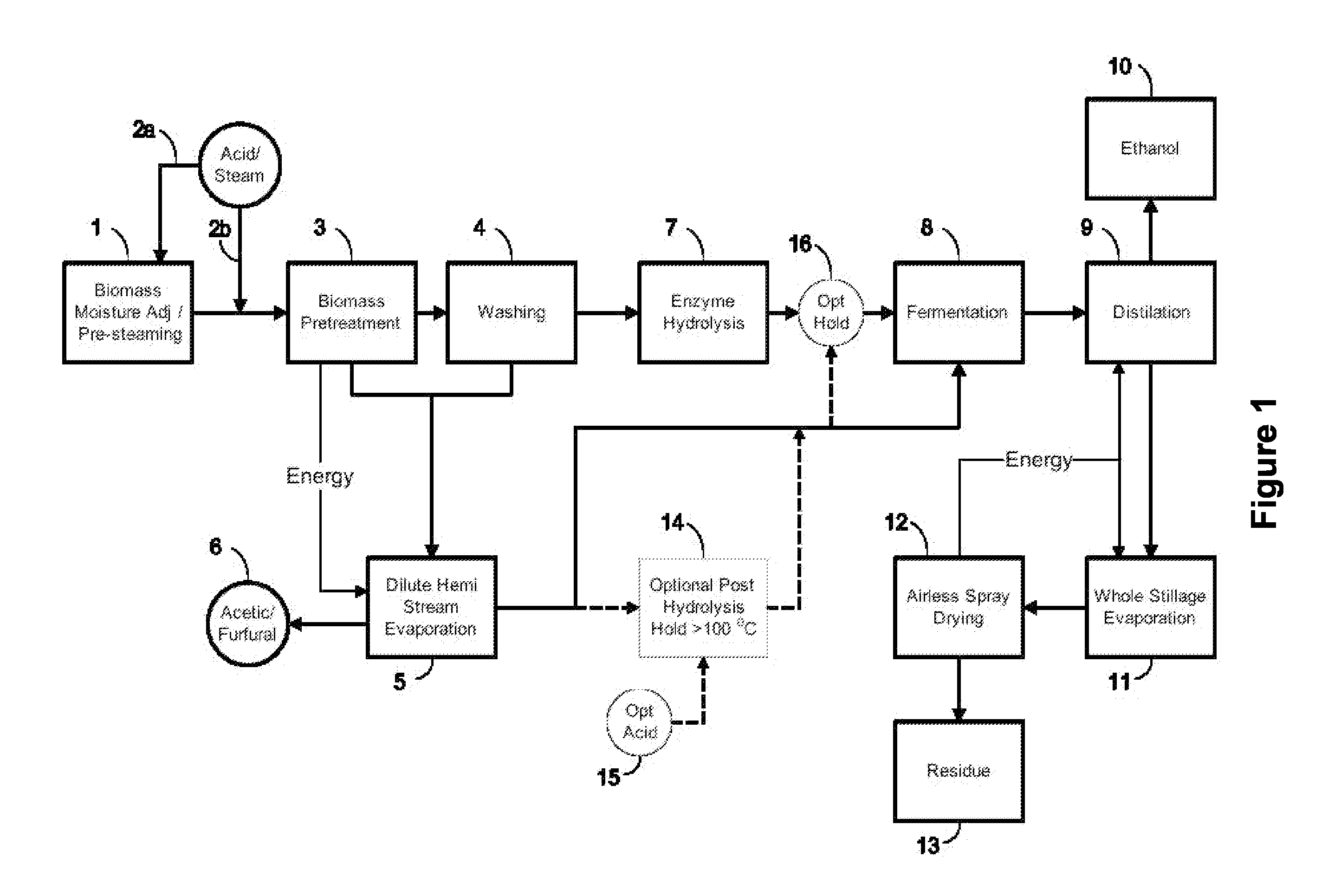
Continuous process for the production of ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass
A continuous process for the recovery of ethanol from hemicellulose and cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass. Yield of fermentable sugars can be maximized by continuous operation of the pre-treatment system and careful selection of pretreatment conditions including the addition of only small amounts of dilute mineral acid and low pressure. With this approach, the xylose component that is mainly present in its unfermentable oligomeric form in known pre-hydrolysis Kraft processes can be recovered more efficiently and as a monomer that can be fermented by xylose fermenting yeasts and bacteria. Due to the use of only dilute acids, there is a very low loss of glucose and xylose hence very low production of toxic chemicals (e.g. HMF, furfural) in the pretreatment step. The resulting overall fermentation efficiency of both hexose and pentose sugars is 90% of the theoretical maximum.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
Apparatus and method for hydrolysis of cellulosic material in a multi-step process to produce c5 and c6 sugars using a single vessel
InactiveUS20090308383A1Undesirable effectFructose productionSugar juice extraction using extracting agentsCelluloseSingle vessel
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Process, Plant And Biofuel For Integrated Biofuel Production
InactiveUS20100146843A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseBiodiesel
This invention relates to a process, a plant, and a biofuel for integrated biofuel production, such as with butanol, biodiesel, and / or sugar product. The integrated process includes the step of removing hexose from a feedstock to form a lignocellulosic material. The process also includes the step of converting the hexose to butanol and / or a biodiesel material, and the step of depolymerizing lignocellulosic material to form pentose and a residue. The process also includes the step of converting the pentose to butanol and / or a biodiesel material.
Owner:BP BIOFUELS UK
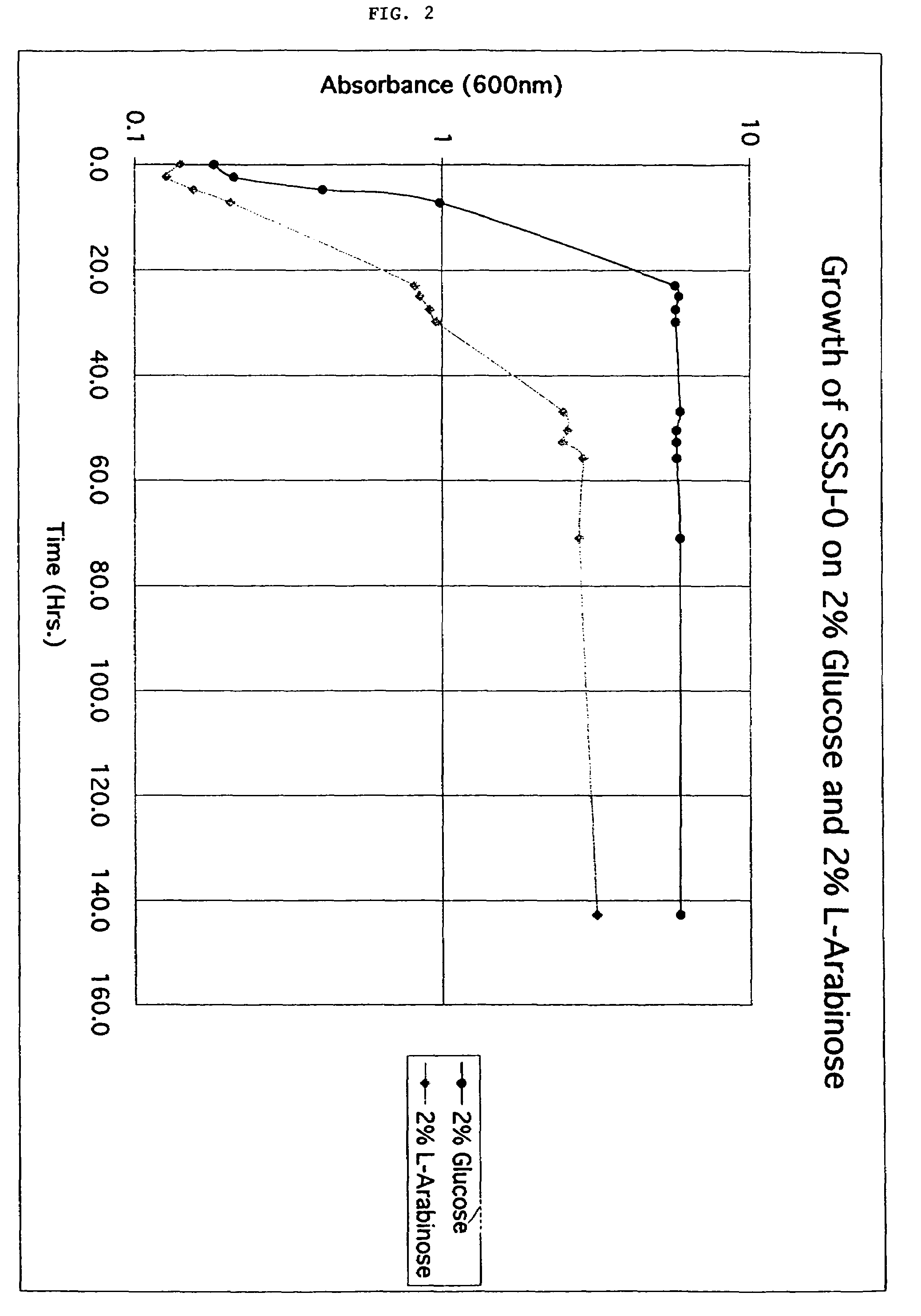
Pentose fermentation of normally toxic lignocellulose prehydrolysate with strain of Pichia stipitis yeast using air
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
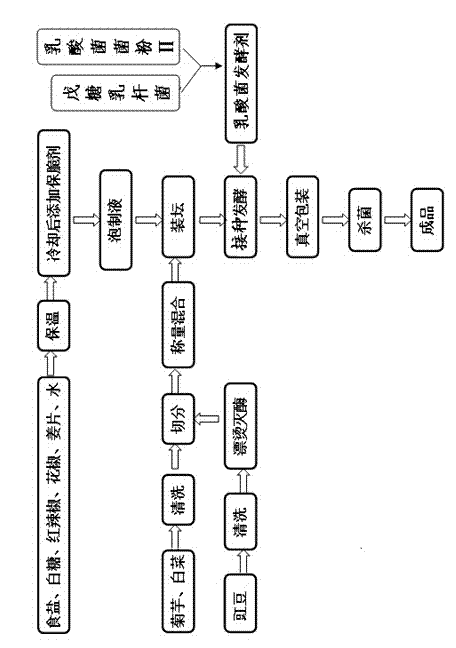
Low-salt compound flavored pickle of jerusalem artichoke and preparation method of low-salt compound flavored pickle
ActiveCN104738480AMeet \"greenMeeting nutritional needsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPectinase
The invention relates to a low-salt compound flavored pickle of jerusalem artichoke and a preparation method of the low-salt compound flavored pickle, belonging to the technical field of food processing. The method comprises the following steps: with certain quality of jerusalem artichoke, Chinese cabbage and cowpea as main raw materials, preparing a pickling liquid from water, salt, white sugar, chilli, pricklyash peels and ginger slices; adding a brittleness-keeping agent prepared from CaCl2, gelatin and pectinase, inoculating a leavening agent prepared from lactobacillus pentosus and lactobacillus plantarum, and producing the low-salt compound flavored pickle of the jerusalem artichoke; and packing, sterilizing, cooling to prepare the low-salt compound flavored pickle. According to the method, rapid production of the low-salt and high-quality flavored pickle of the jerusalem artichoke is realized; peeling is not needed; a color retention agent or a preservative is not added; the process is simple; the cost is low; the bioactive substances such as synanthrin and fructo-oligosaccharide are preserved to the maximal extent; meanwhile, new functional factors such as functional terpene compounds are generated by fermentation; the low-salt compound flavored pickle is bright in color and luster, sour, crisp and refreshing, and unique in flavor, and has the healthcare efficacies of appetizing, helping digestion, improving digestion, preventing decayed tooth, preventing obesity, lowering blood glucose and improving the immunity.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
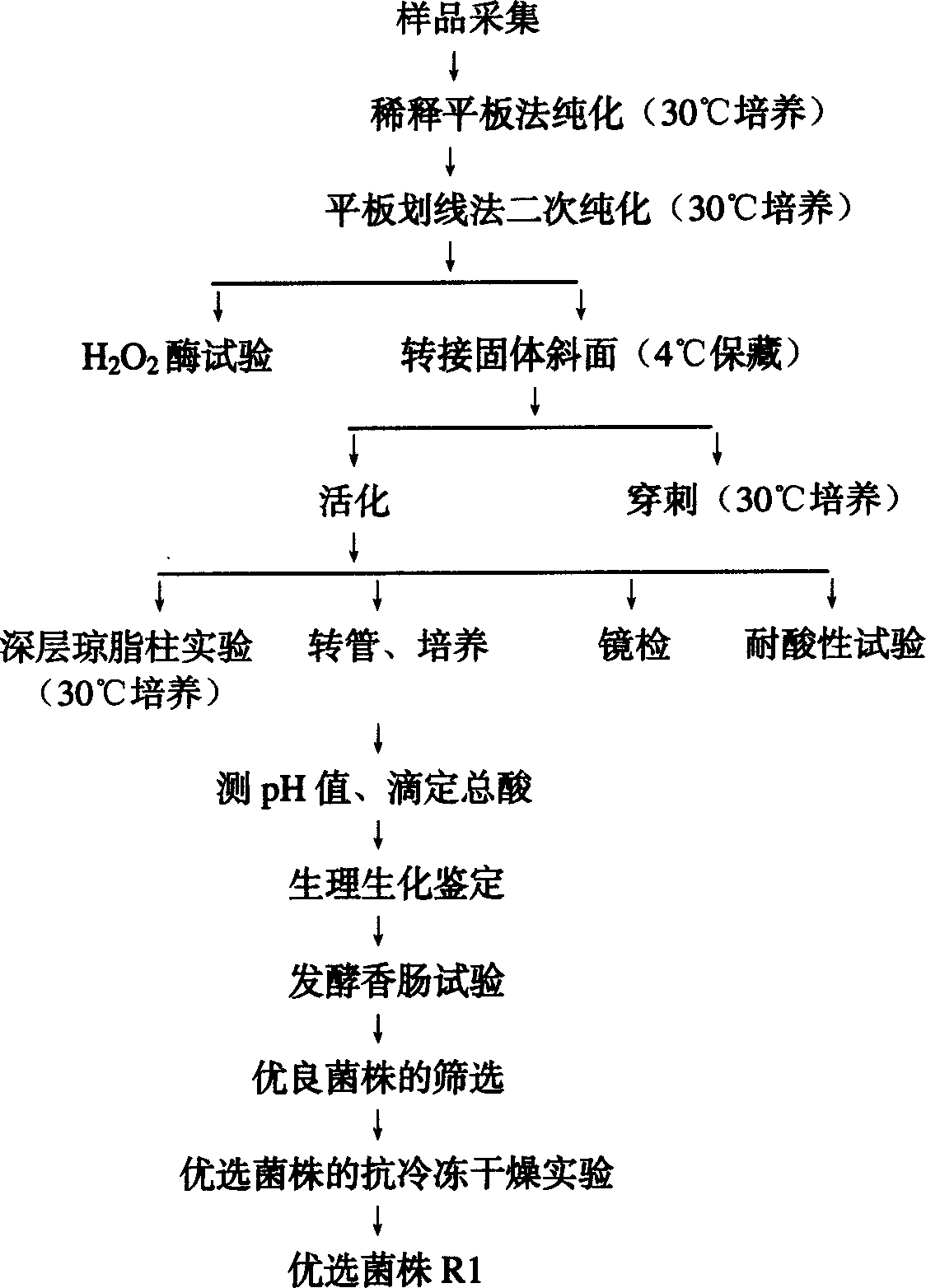
Lactobacillus pentosus strain, ferment produced thereby and the use of ferment in meat ware
The invention discloses a lactobacillus pentosus strain and ferment produced thereby, wherein the docket number of the R1(Lactobacillus pentosus R1) strain in the Chinese Microbiological Culture Preservation Administration Commission Common Microbiological Center is CGMCC No.0917. The pentose lactobacillus R1 strain of the invention can endure 4.0% salt solution and nitrite solution whose concentration is 80-100mg / L. The leaven prepared from the bacterial can be applied into the fermentation production of meat food.
Owner:河南双汇投资发展股份有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com