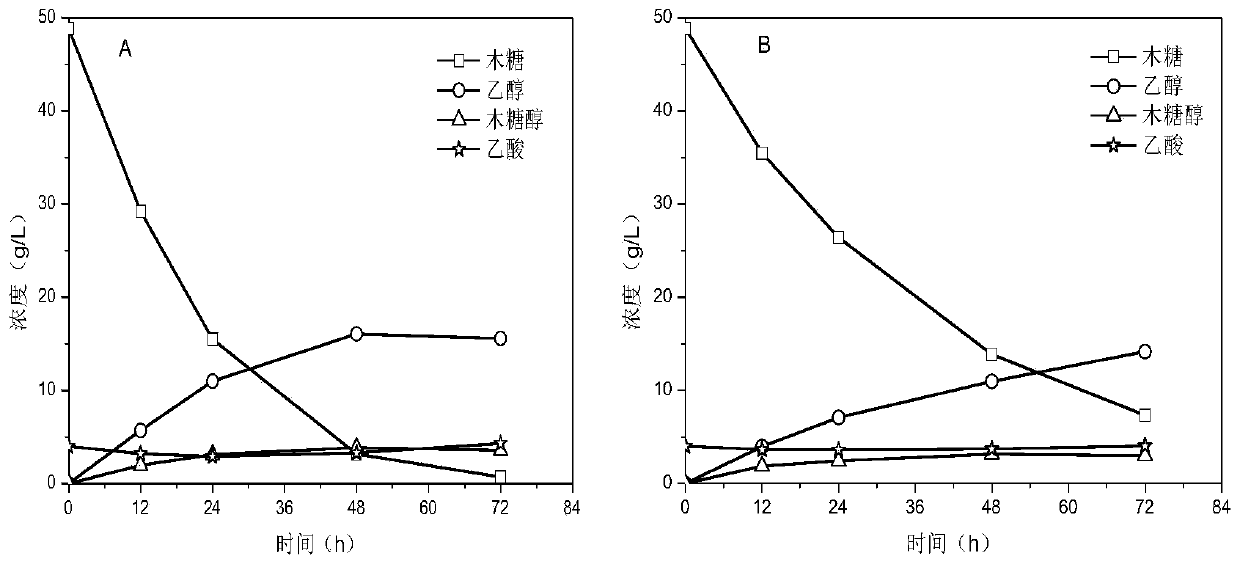
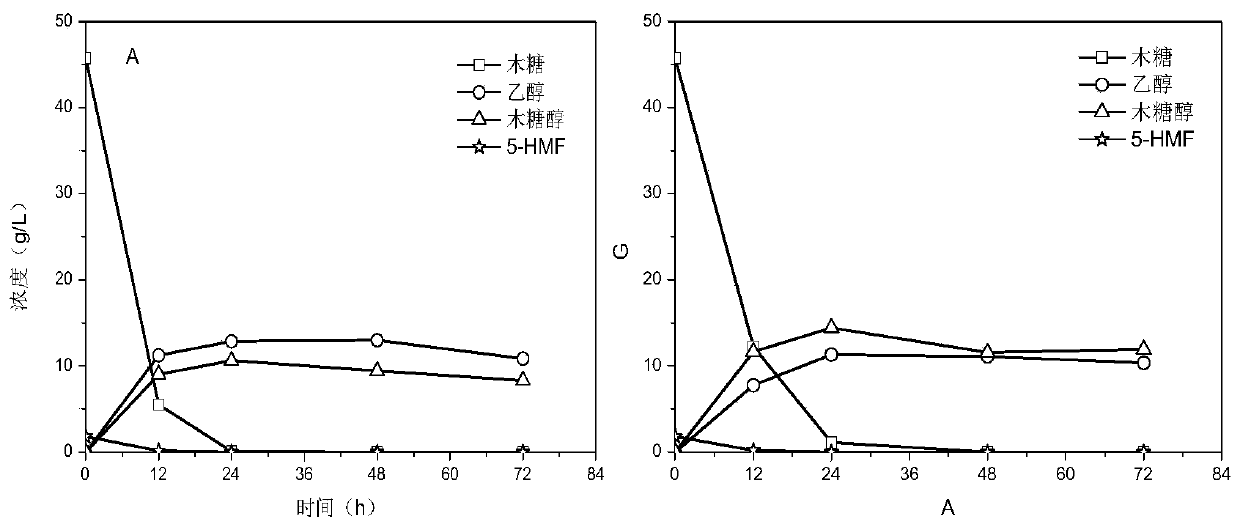
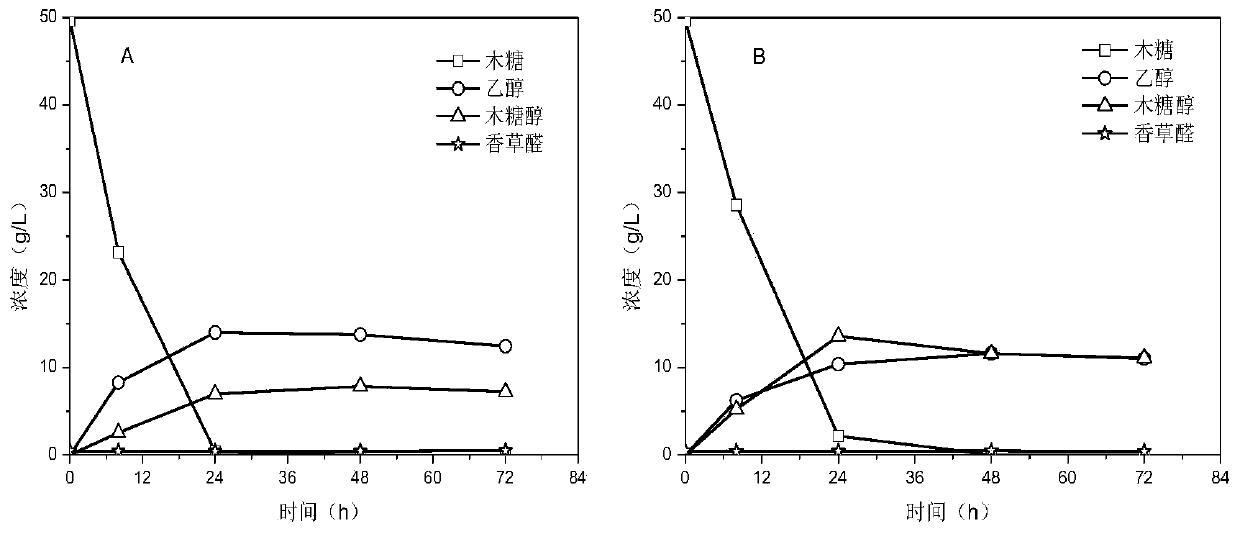
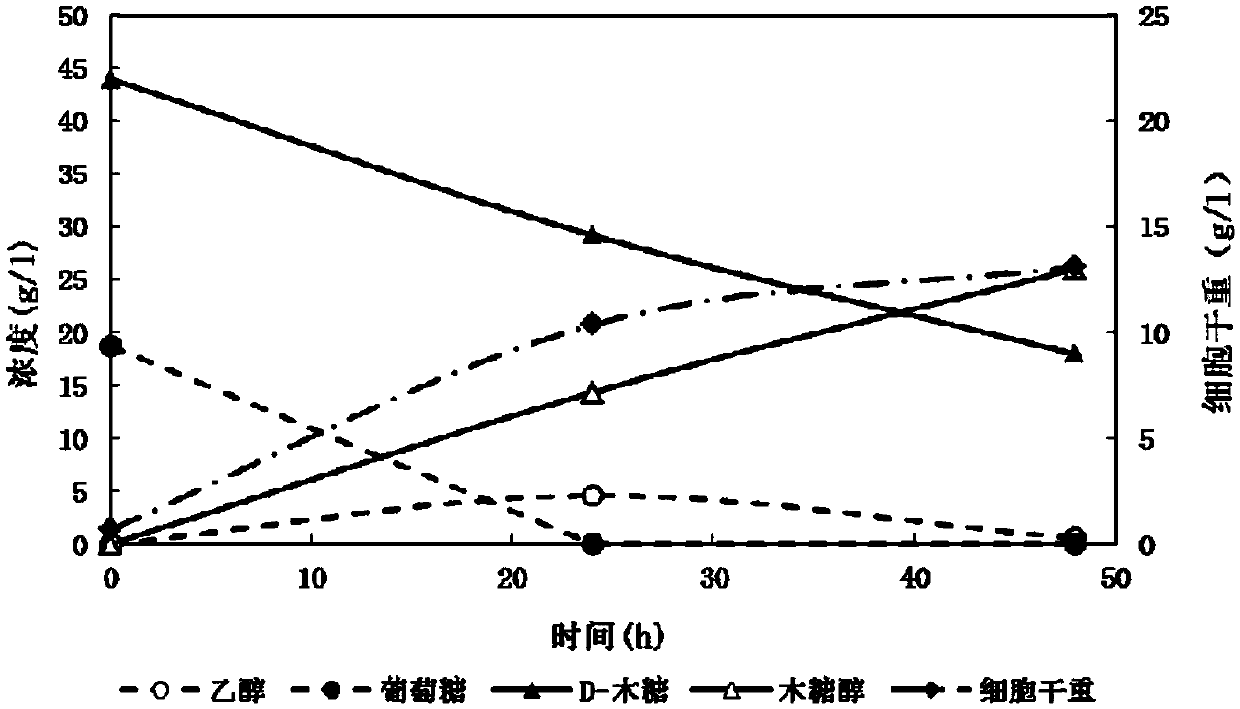
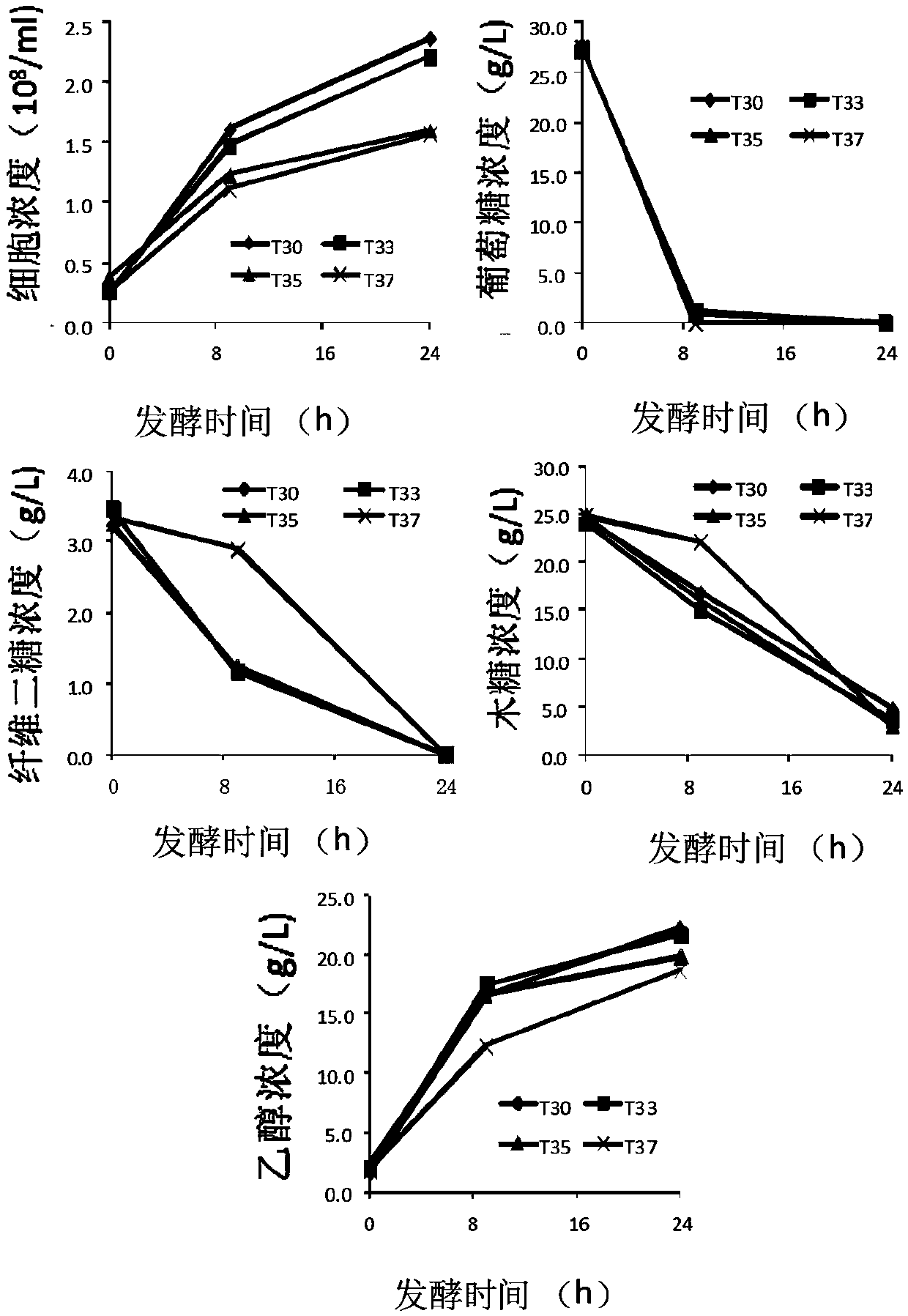
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
96 results about "Xylose fermentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
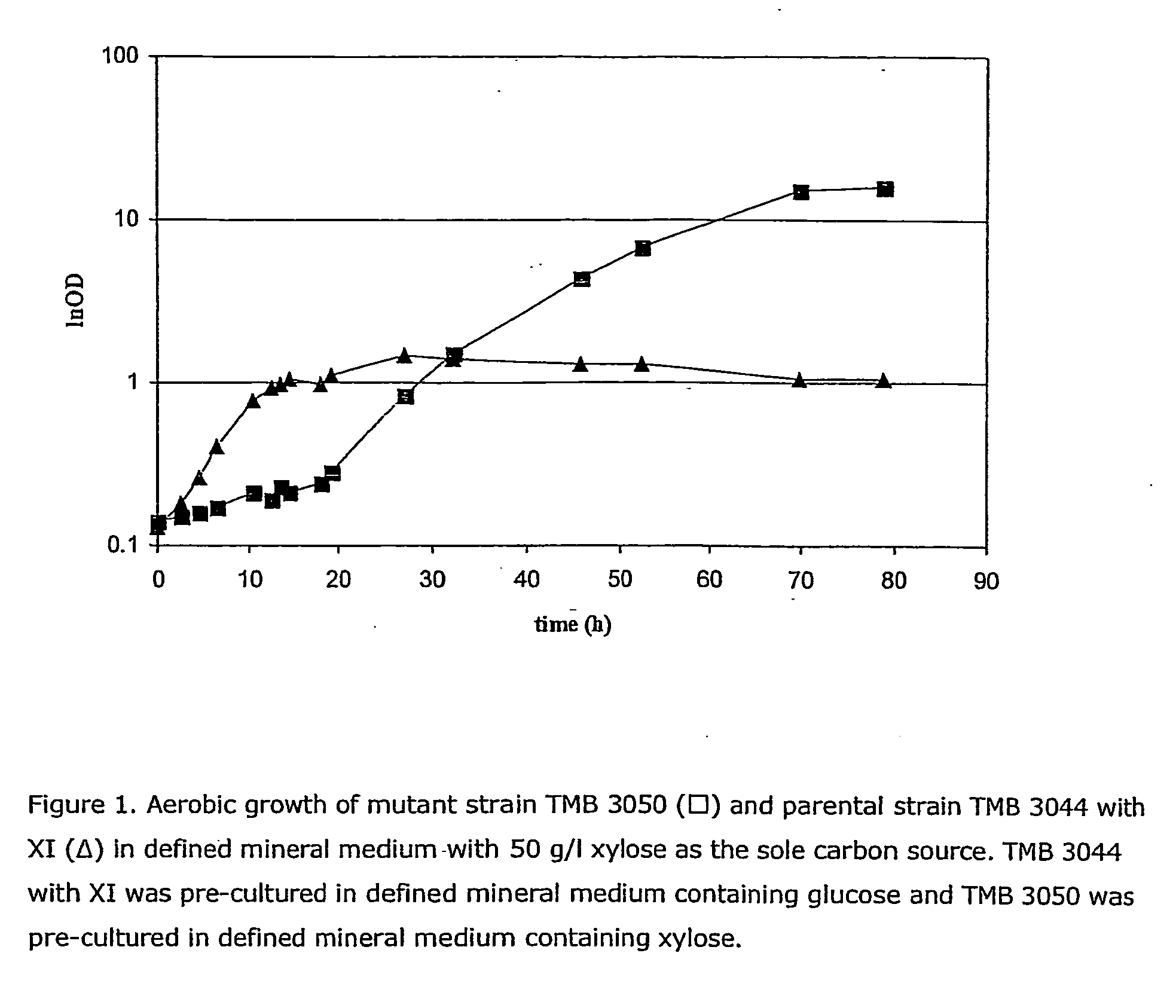
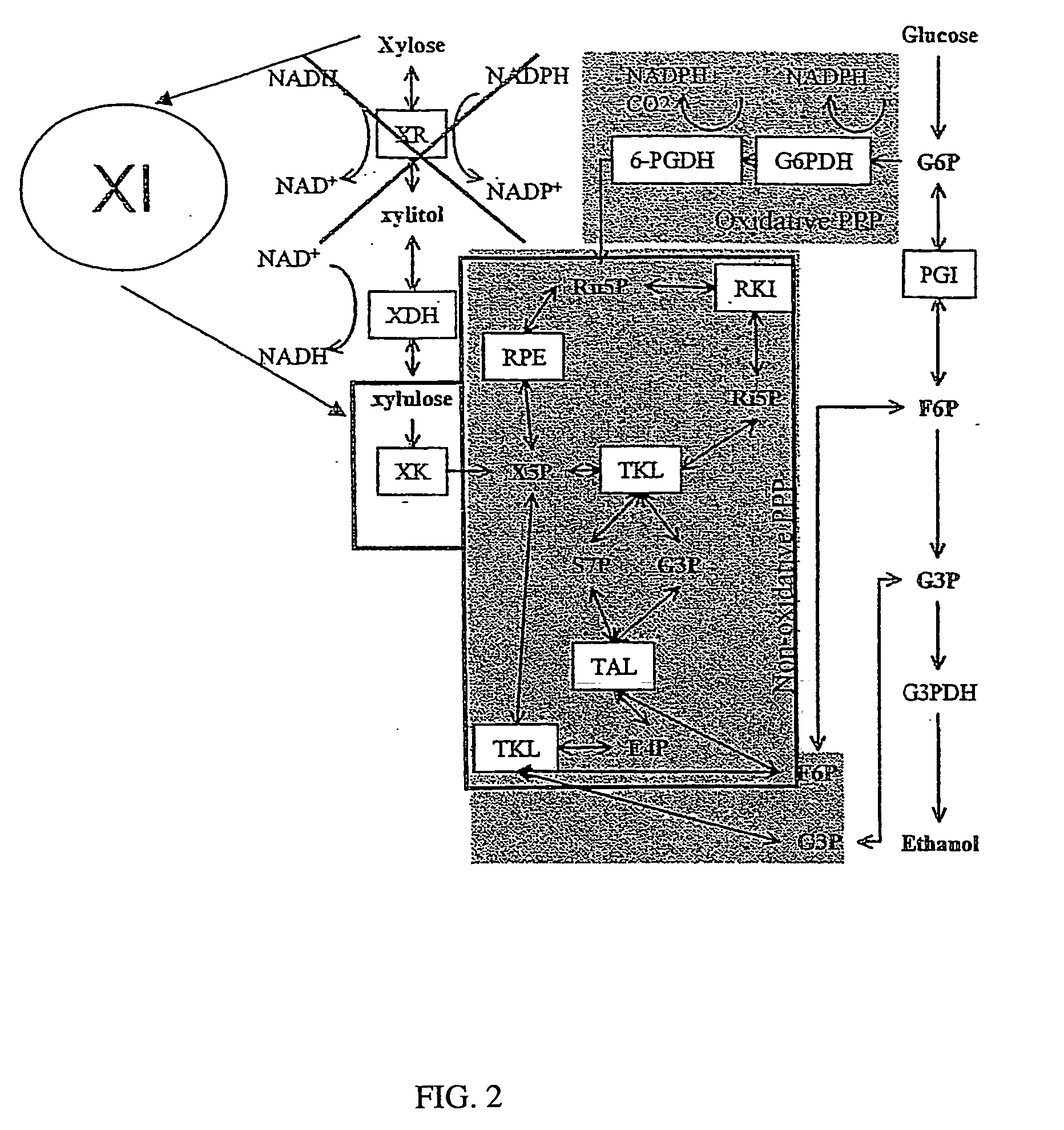
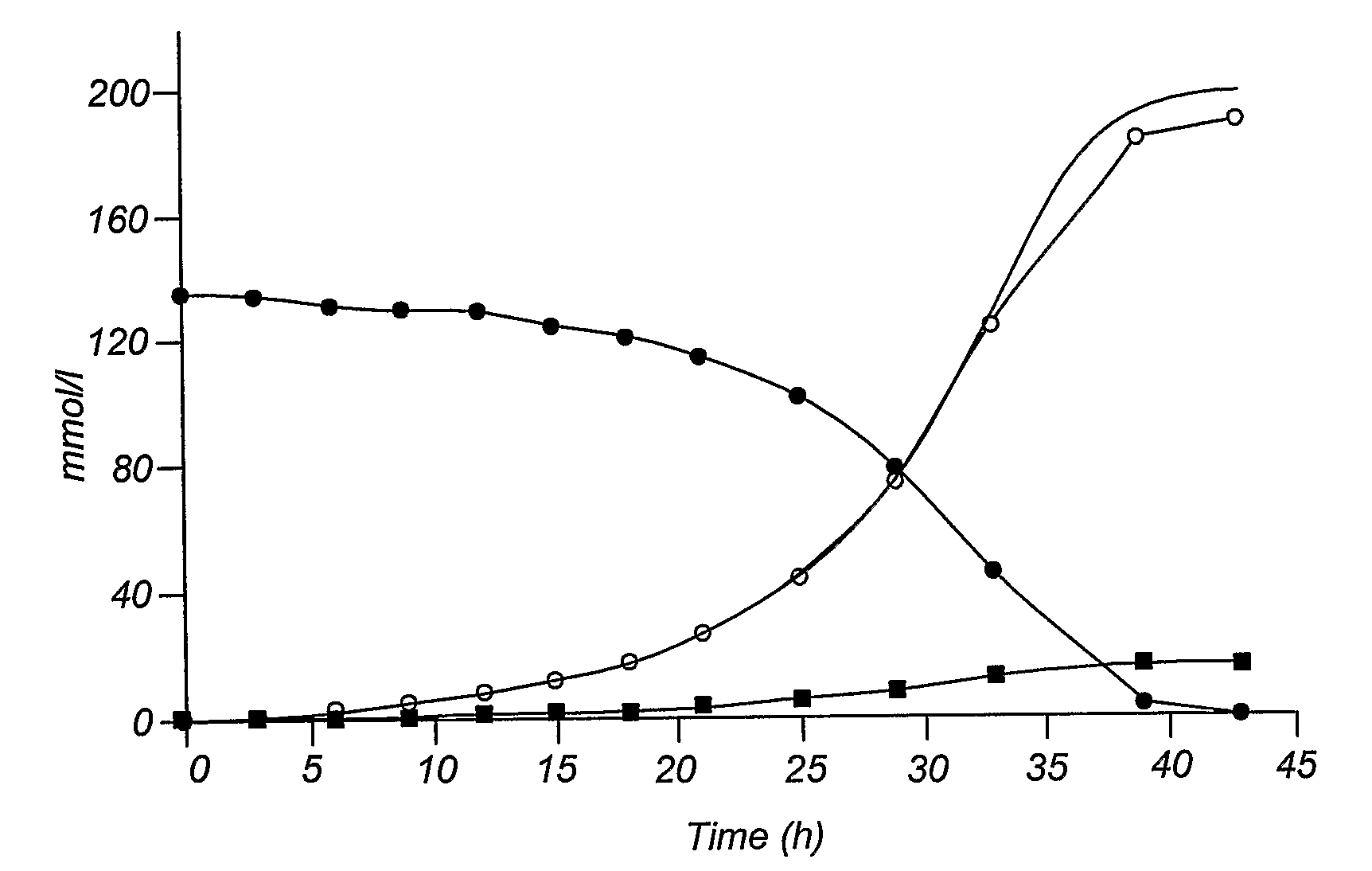
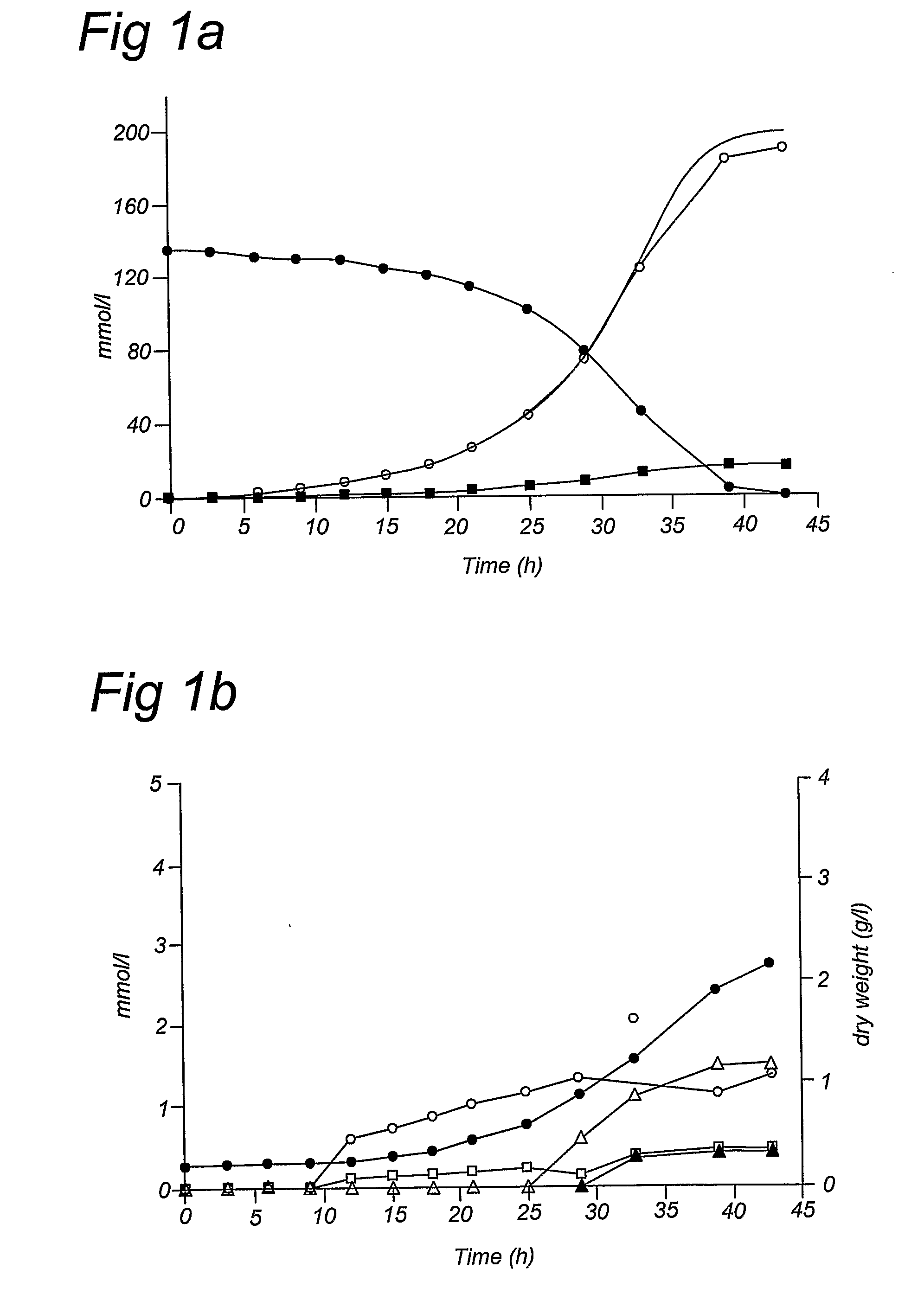
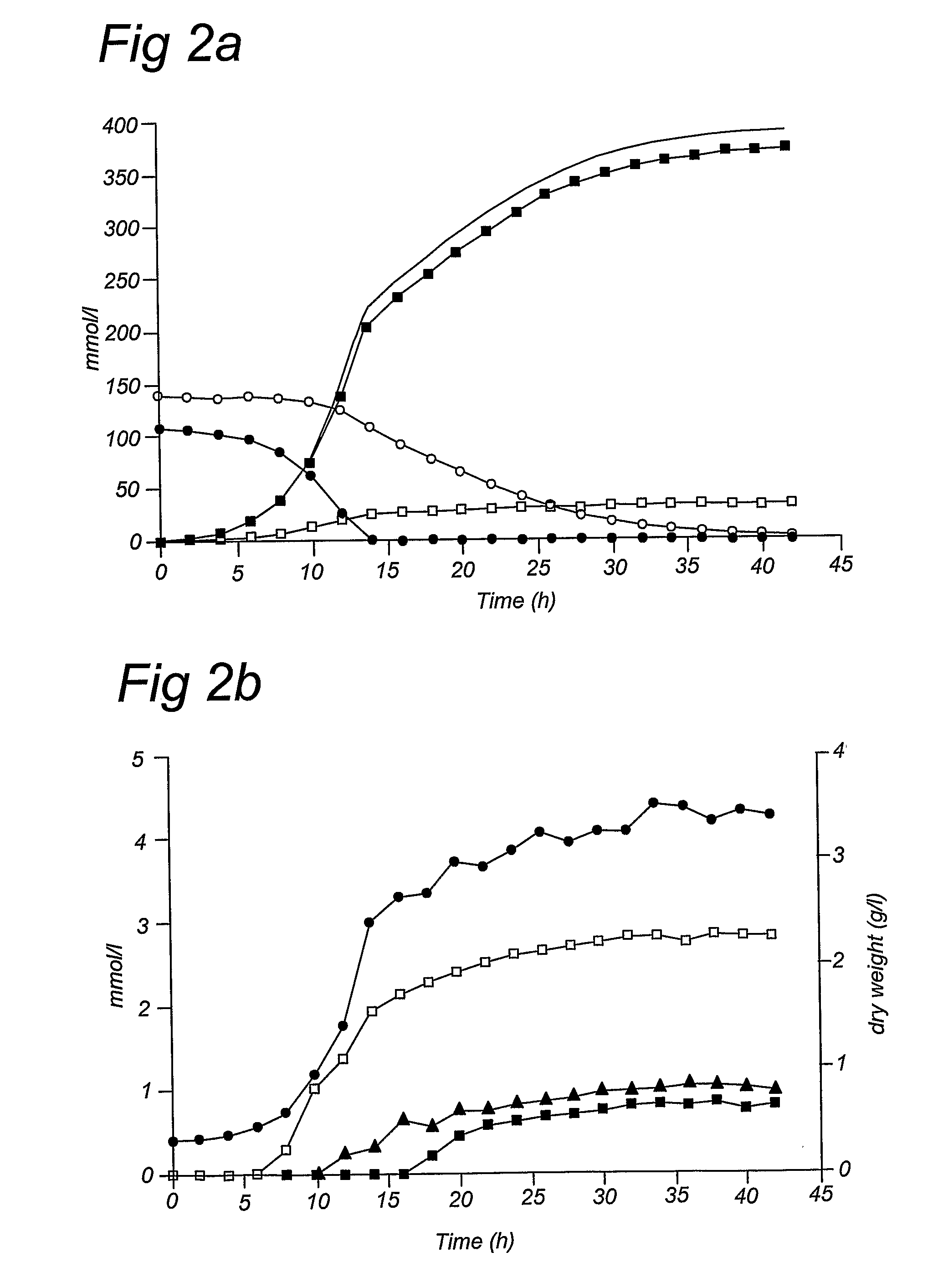
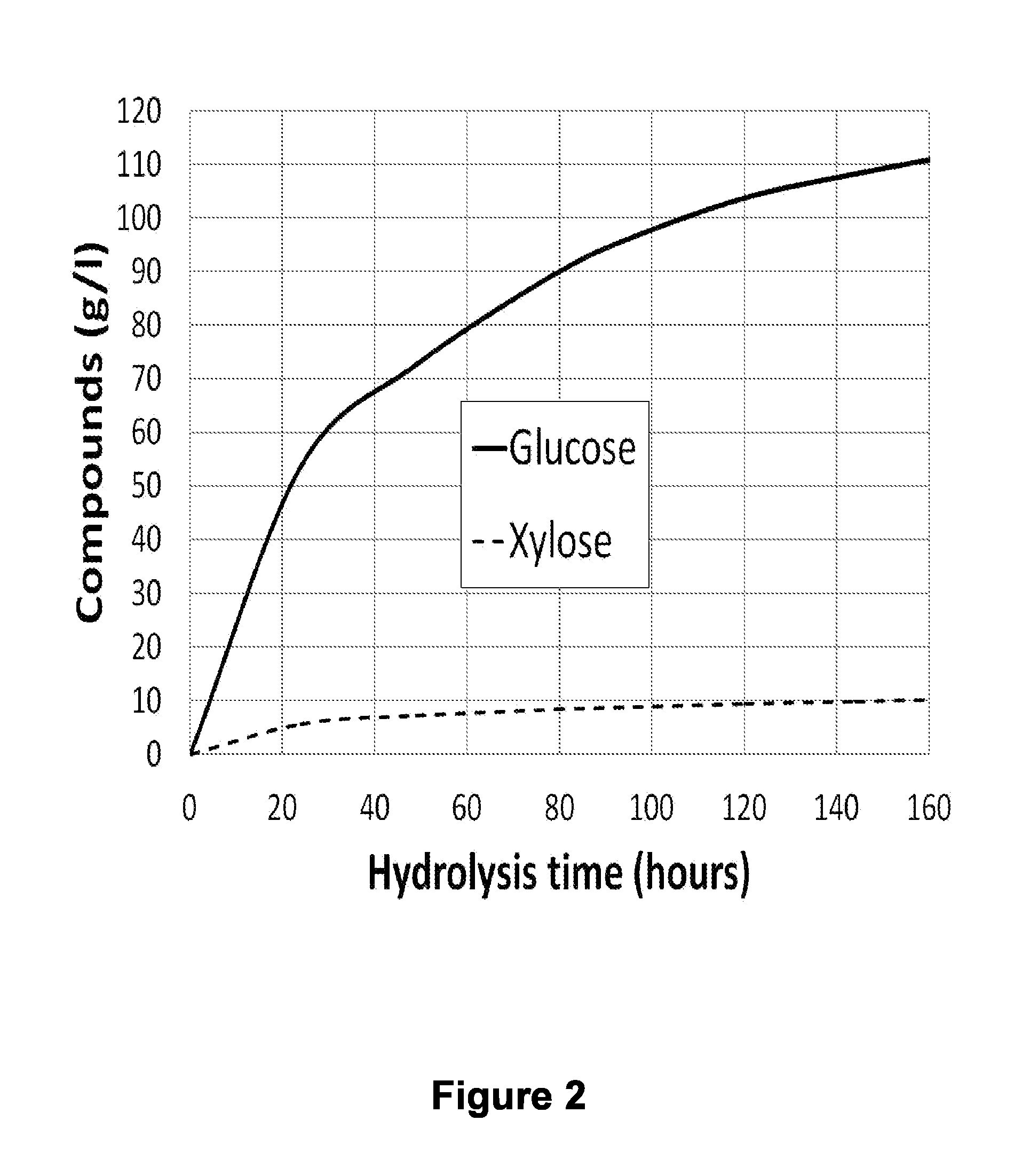
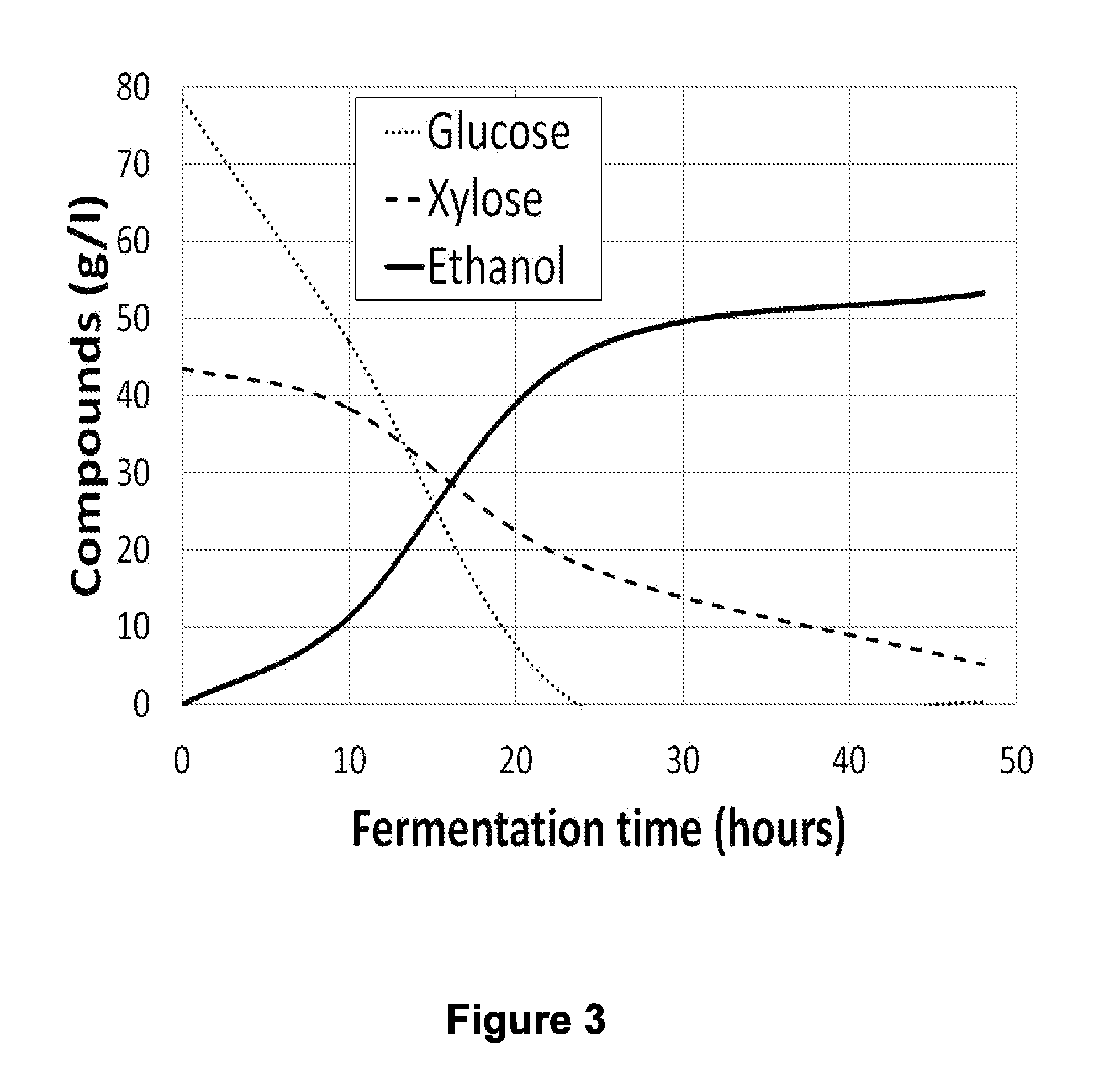
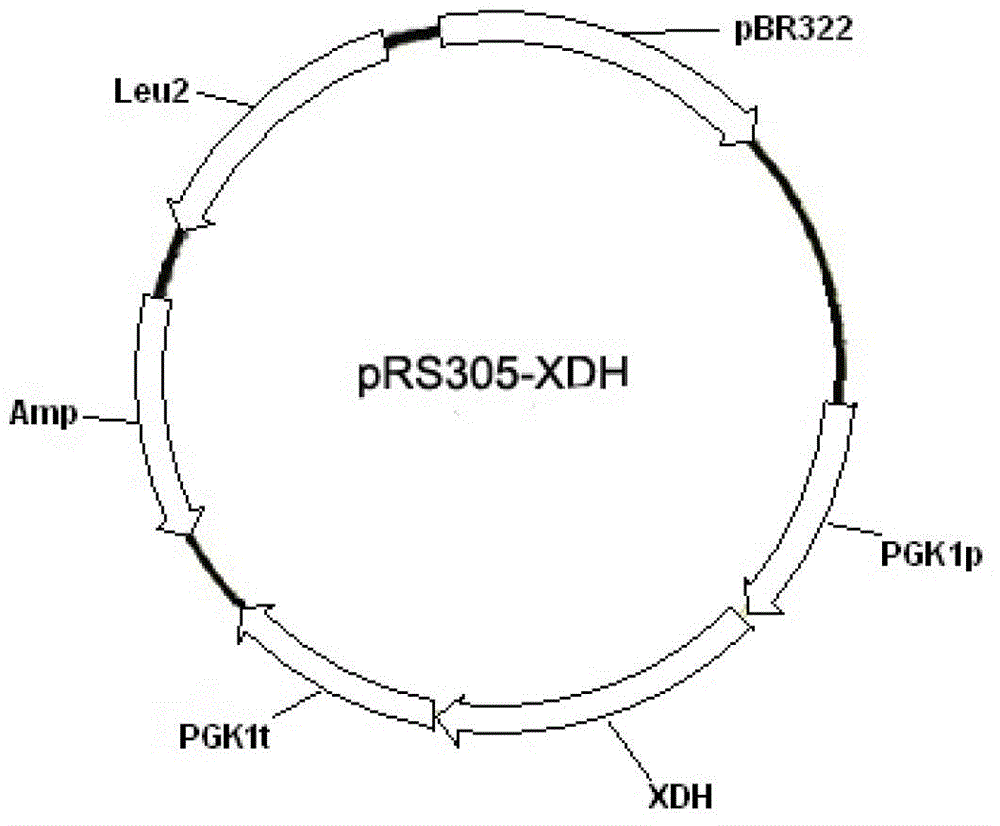
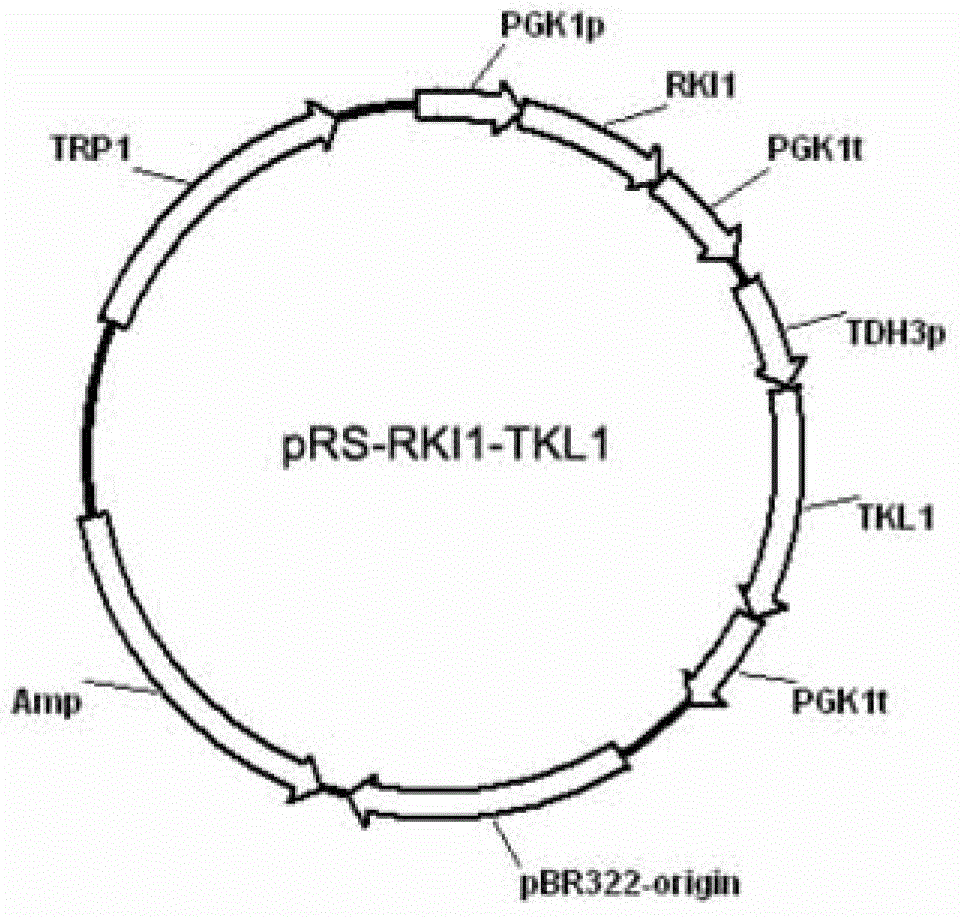
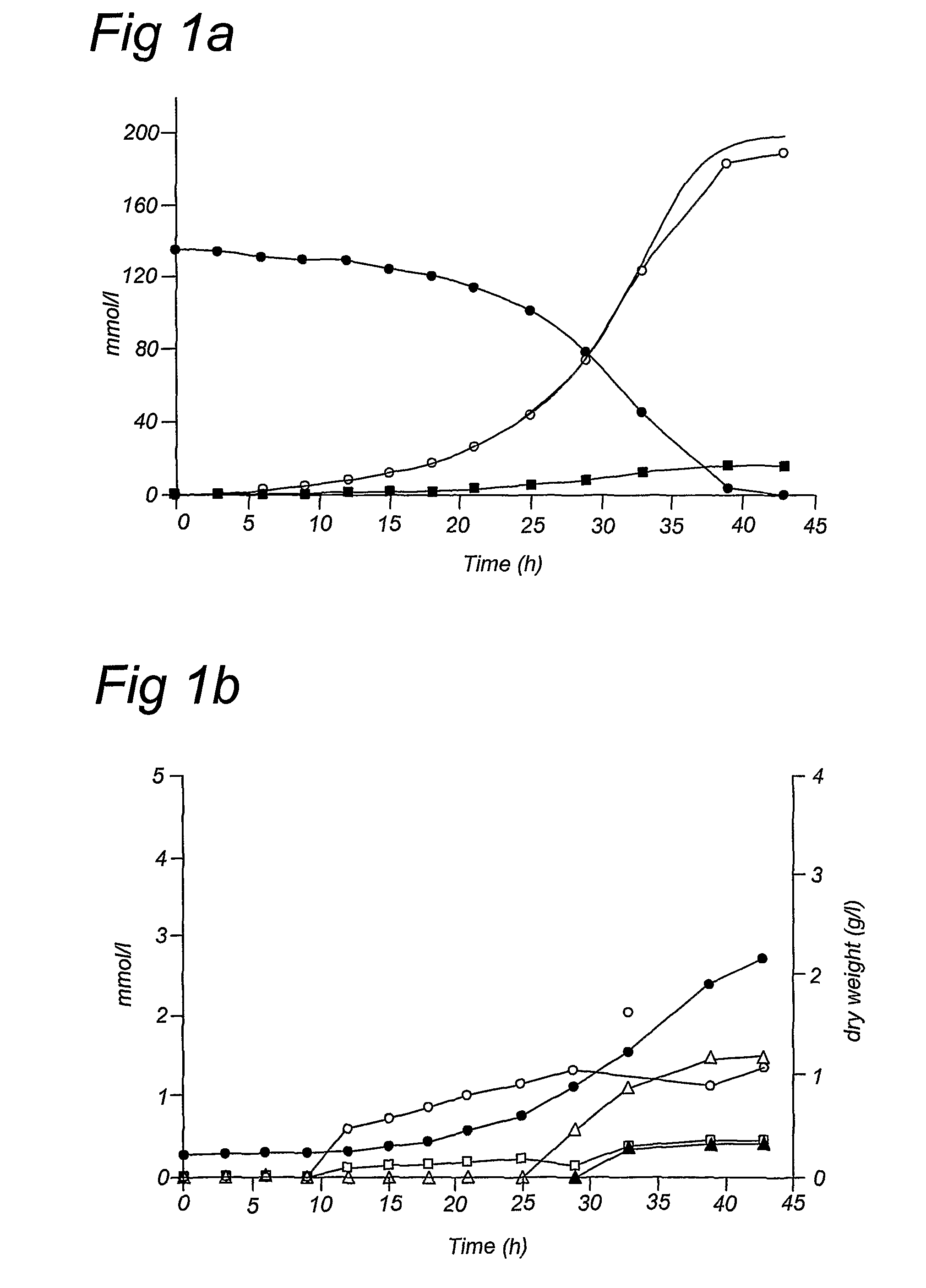
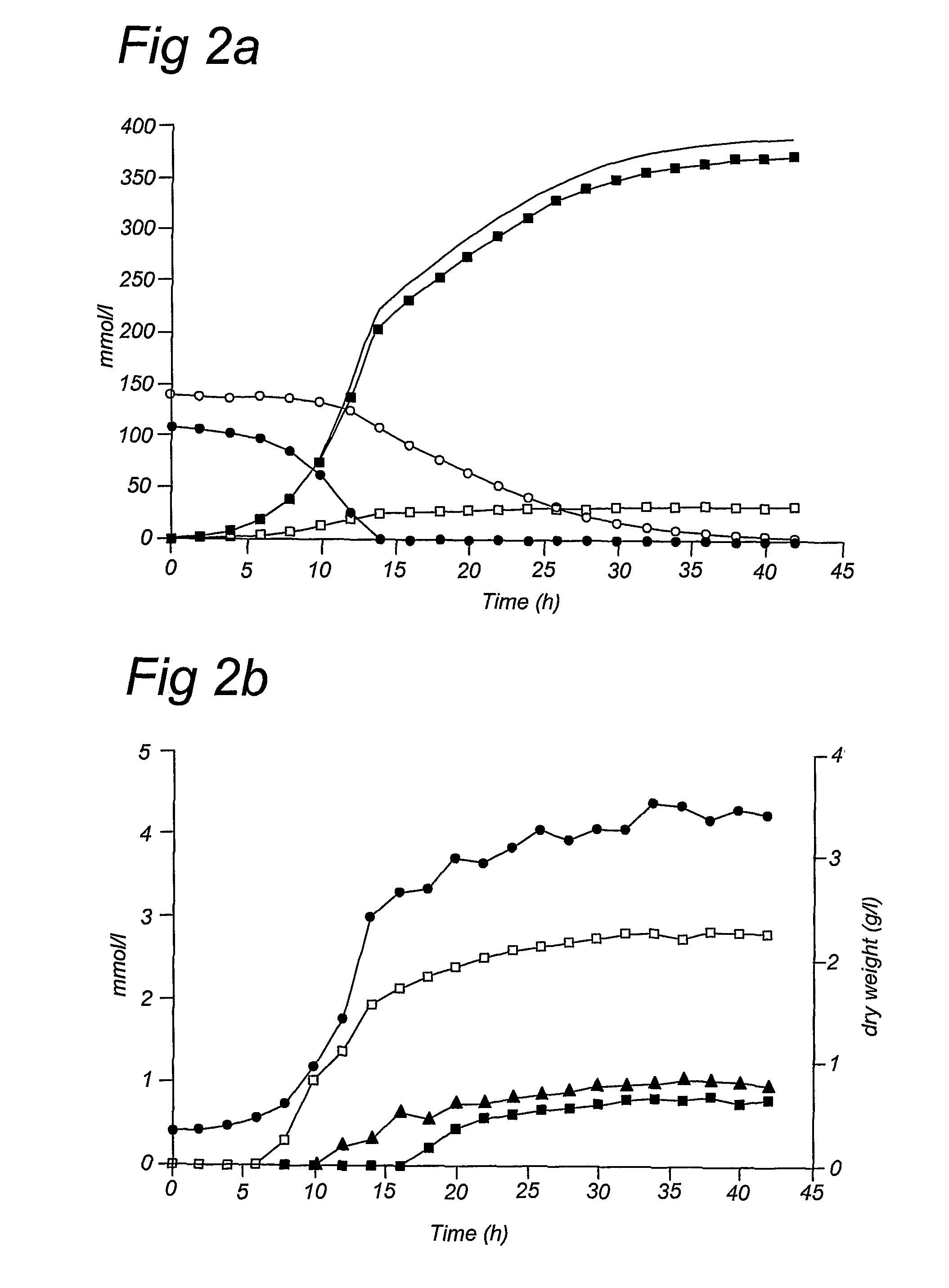
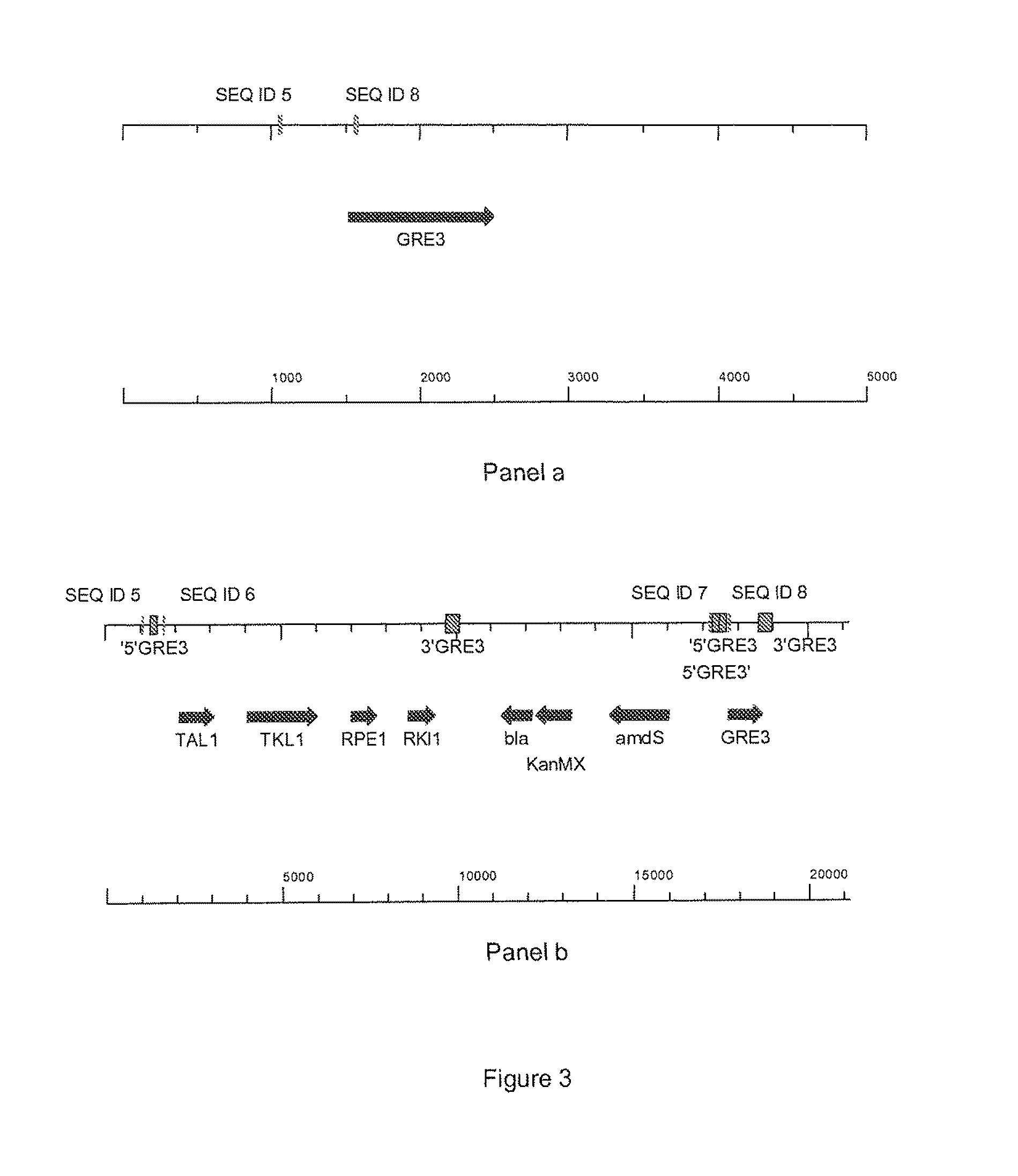
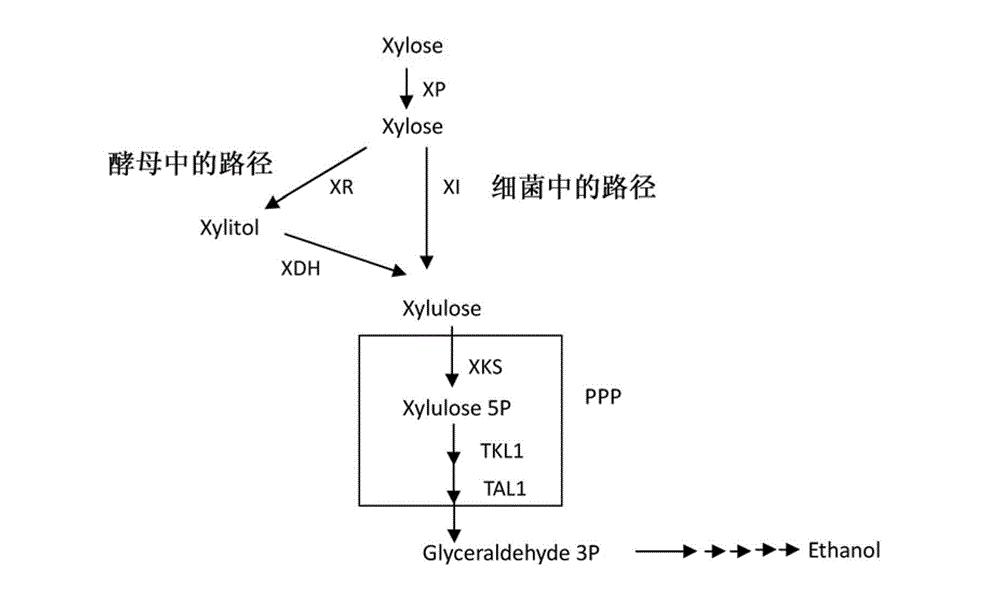
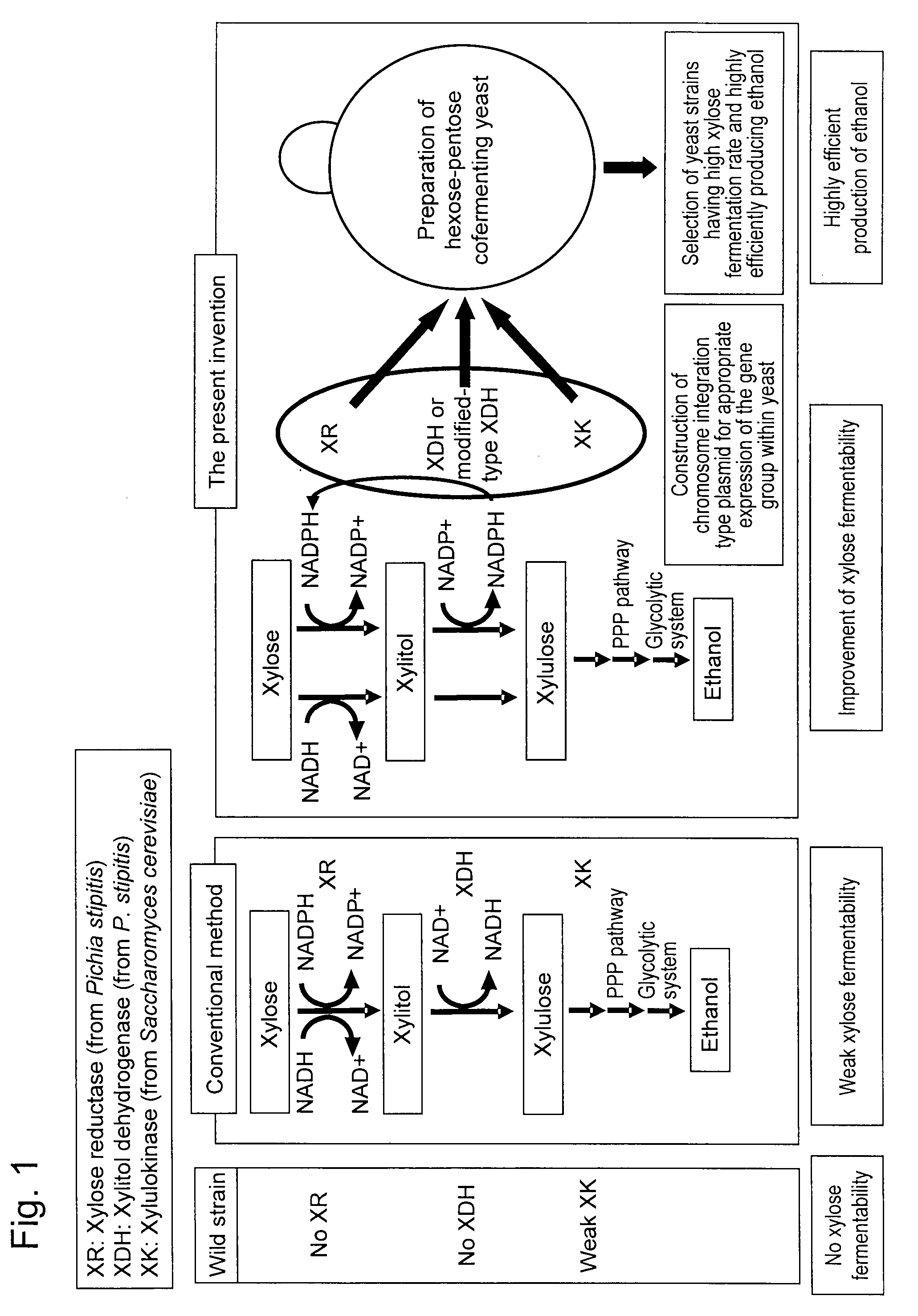
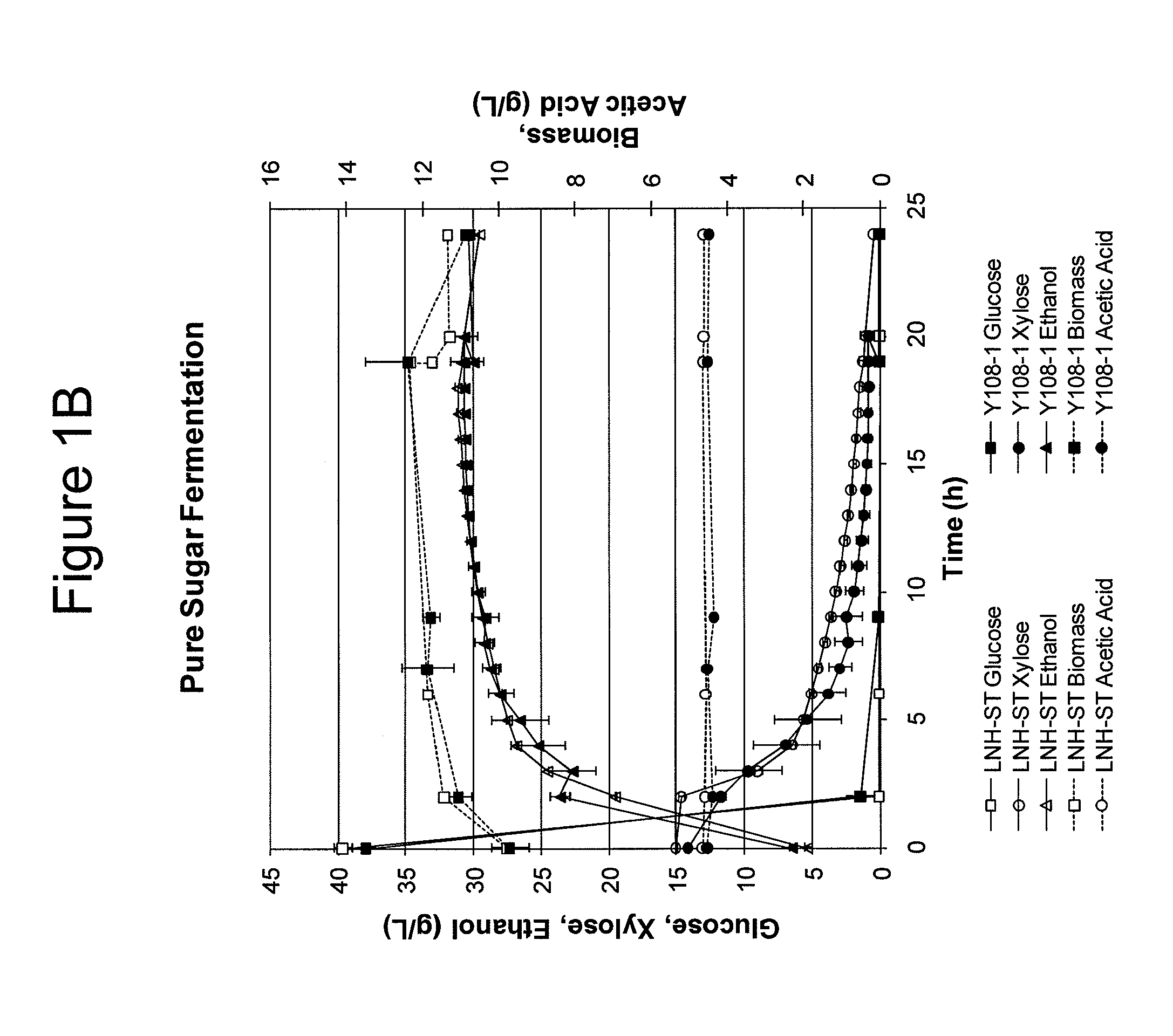
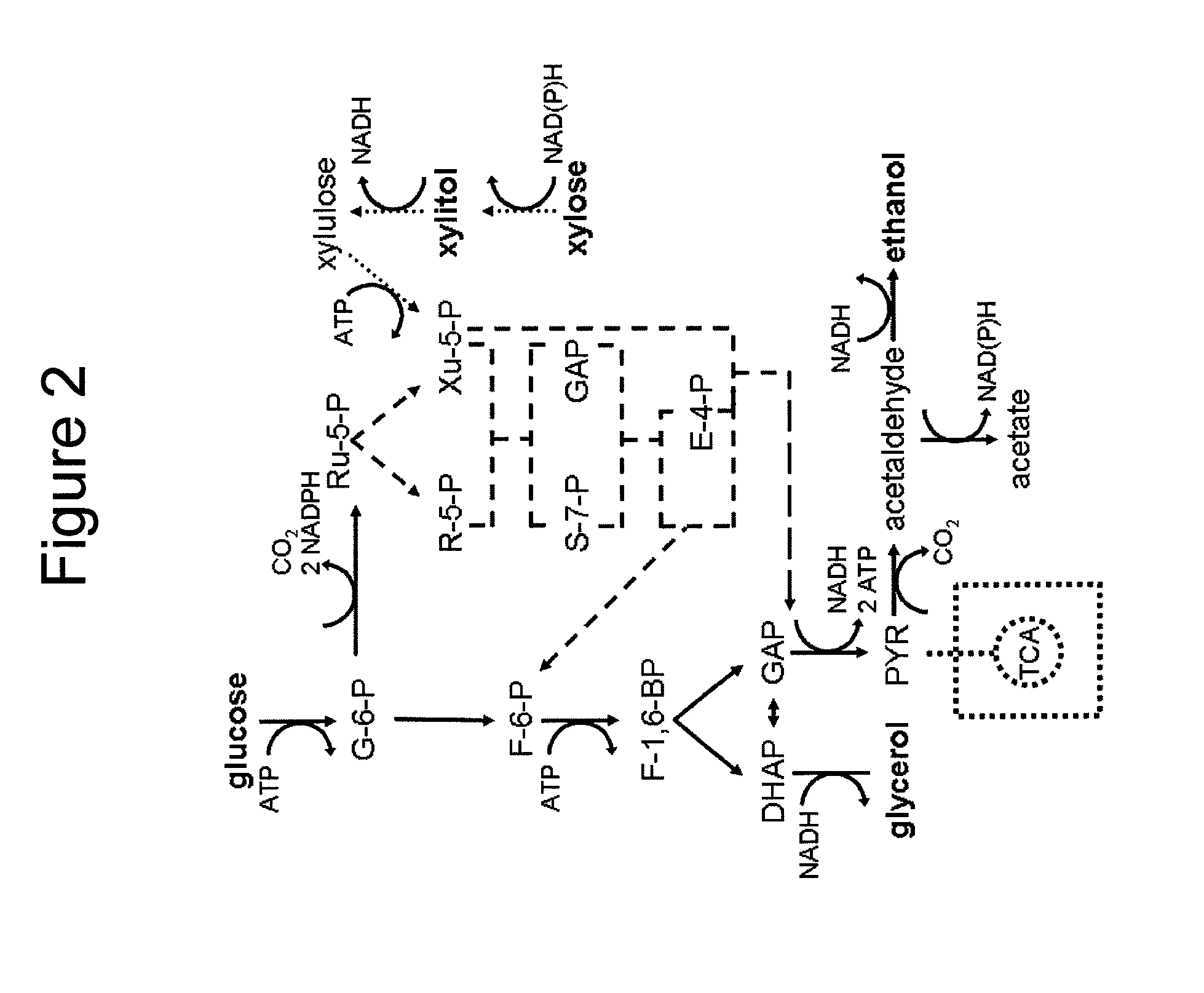
Xylose fermentation in S. cerevisiae. The fungal pathway uses xylose reductase (XR) and xylitol dehydrogenase (XDH,) whereas the bacterial pathway uses xylose isomerase (XI).
Construction of new xylose utilizing saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
The present invention relates to a novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain utilizing xylose for fermenting ethanol expressing xylose isomerase (XI), overexpressing xylulokinase (XK), overexpressing the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), and non-expressing aldose reductase (AR) and being adapted to growth in mineral defined medium with xylose as sole carbon source.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Metabolic Engineering of Xylos Fermentation
The present invention relates to further genetic modifications in eukaryotic host cells that have been transformed to express a xylose isomerase that confers the host cell the ability of isomerising xylose to xylulose. The further genetic modifications are aimed at improving the efficiency of xylose metabolism and include e.g. reduction of unspecific aldose reductase activity, increased xylulose kinase activity and increased flux of the pentose phosphate pathway. The modified host cells of the invention are suitable for the production of a wide variety of fermentation products, including ethanol, in fermentation processes in which a source of xylose or a source of xylose and glucose are used as carbon source.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
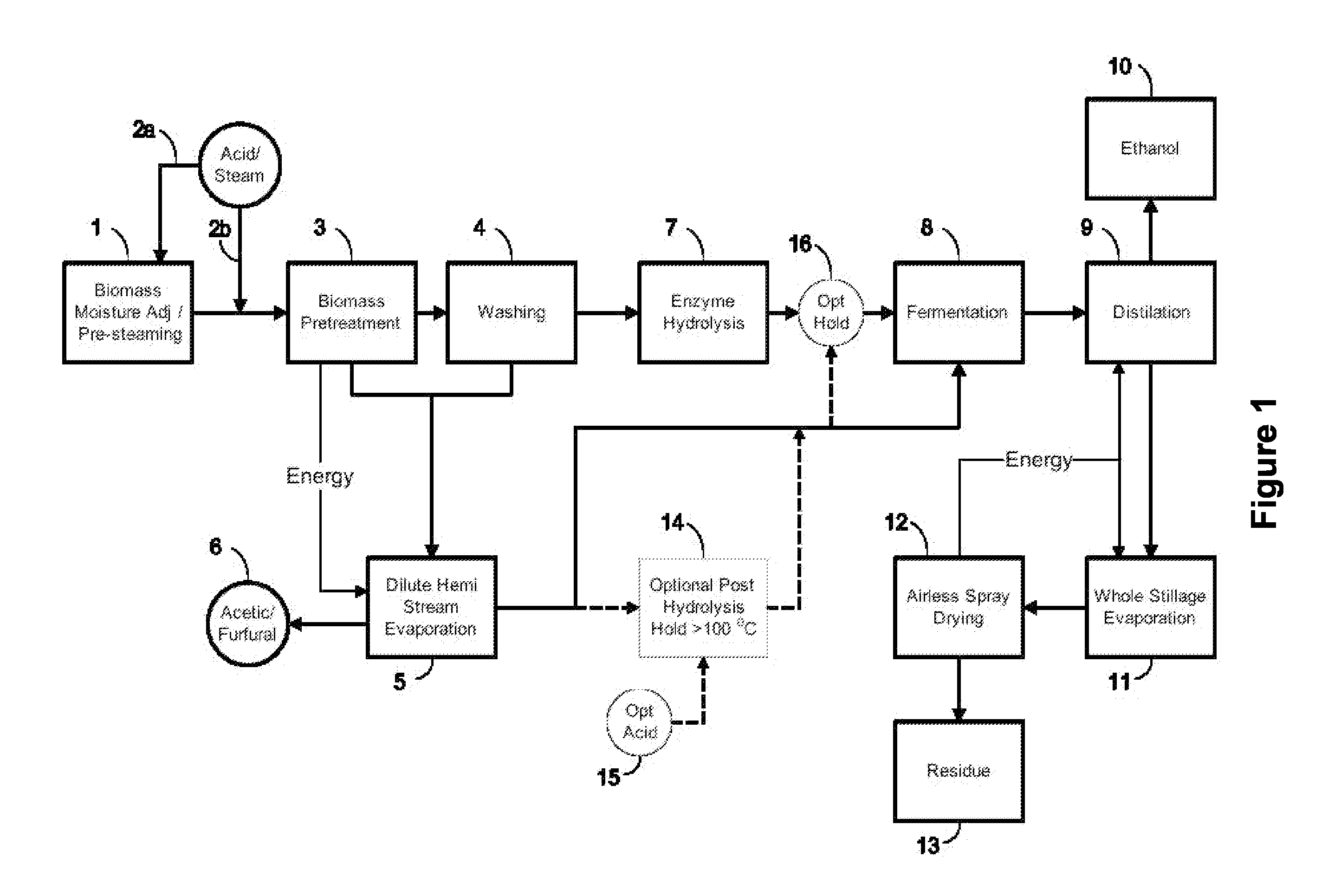
Continuous process for the production of ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass
A continuous process for the recovery of ethanol from hemicellulose and cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass. Yield of fermentable sugars can be maximized by continuous operation of the pre-treatment system and careful selection of pretreatment conditions including the addition of only small amounts of dilute mineral acid and low pressure. With this approach, the xylose component that is mainly present in its unfermentable oligomeric form in known pre-hydrolysis Kraft processes can be recovered more efficiently and as a monomer that can be fermented by xylose fermenting yeasts and bacteria. Due to the use of only dilute acids, there is a very low loss of glucose and xylose hence very low production of toxic chemicals (e.g. HMF, furfural) in the pretreatment step. The resulting overall fermentation efficiency of both hexose and pentose sugars is 90% of the theoretical maximum.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
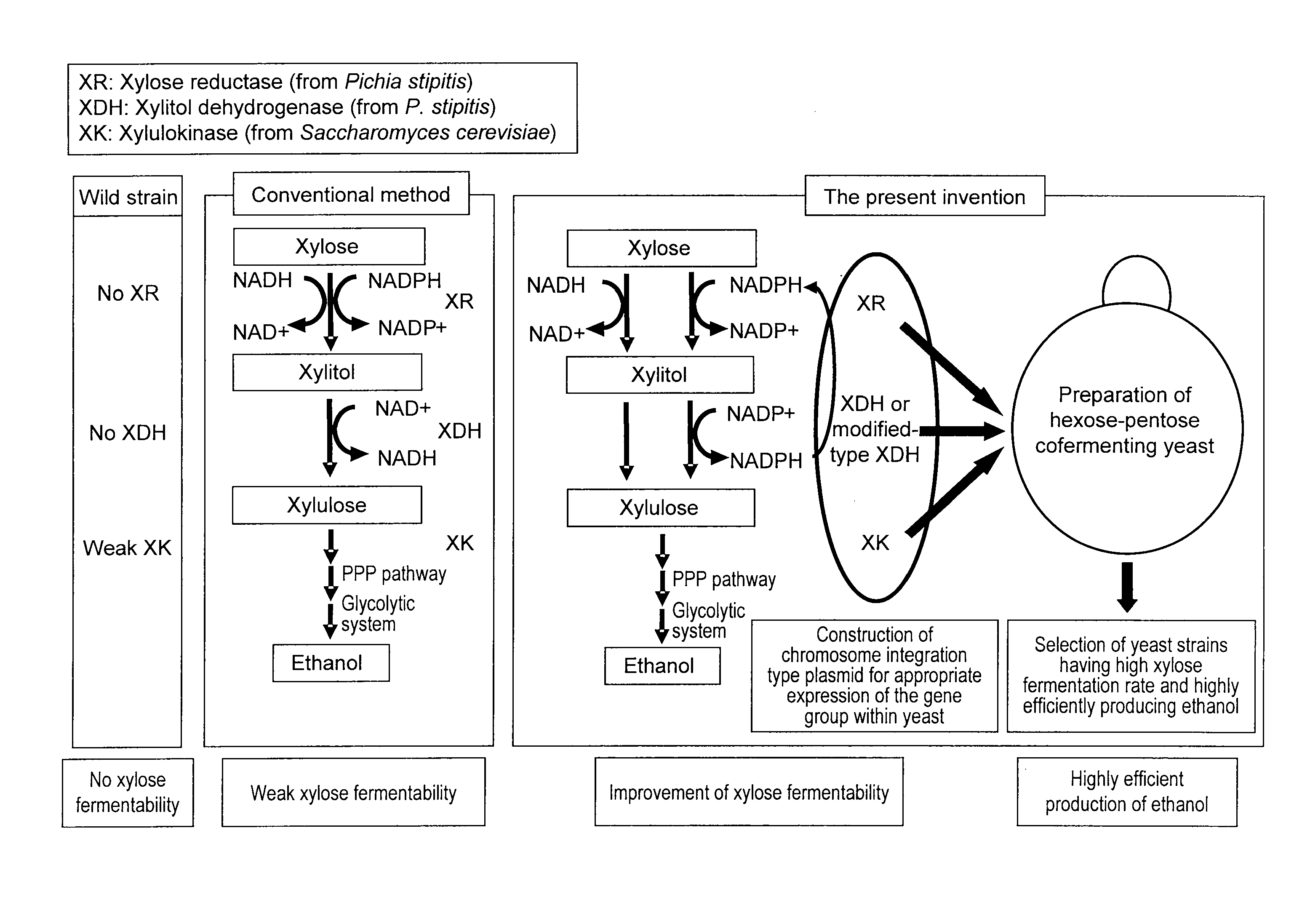
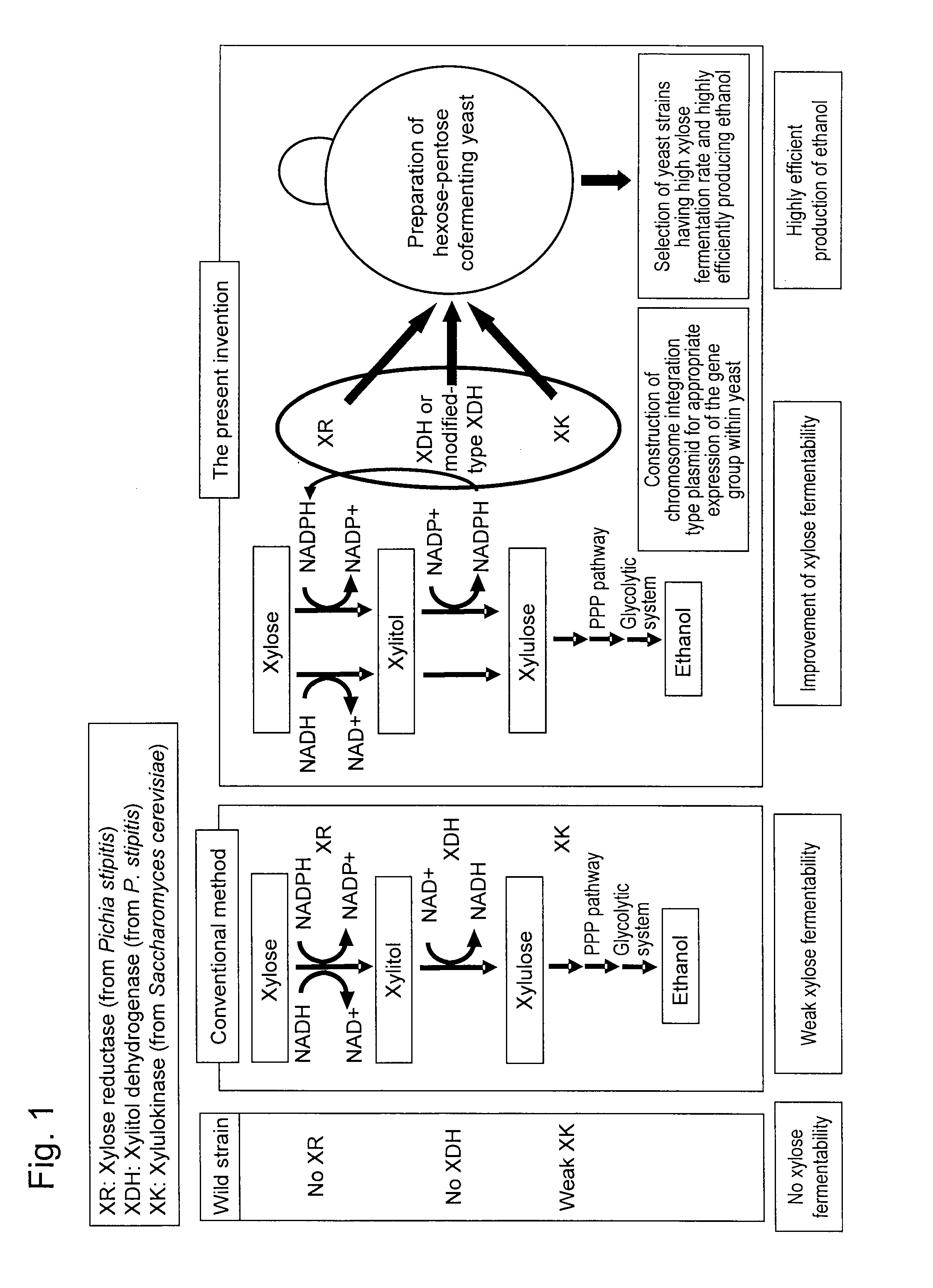
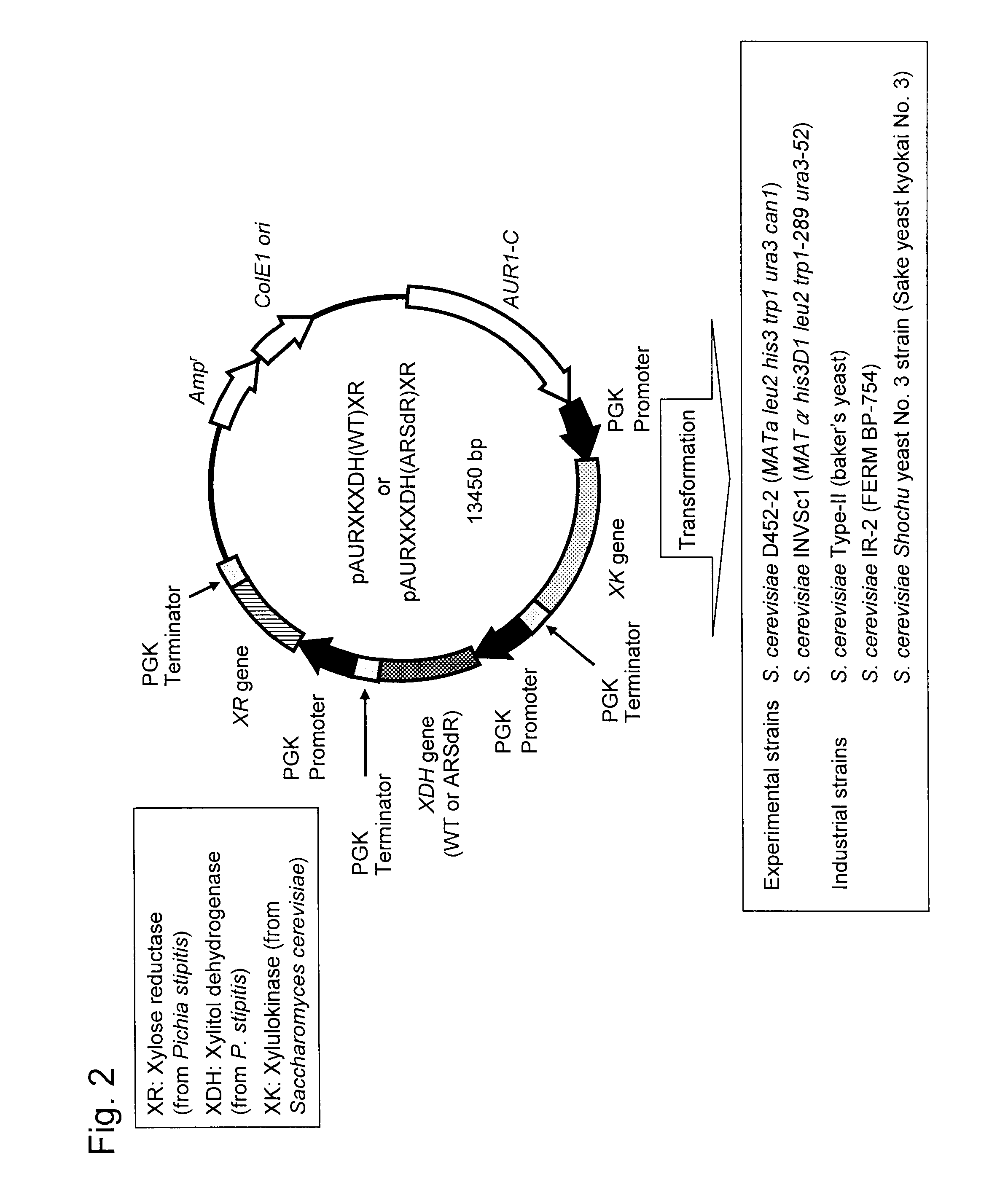
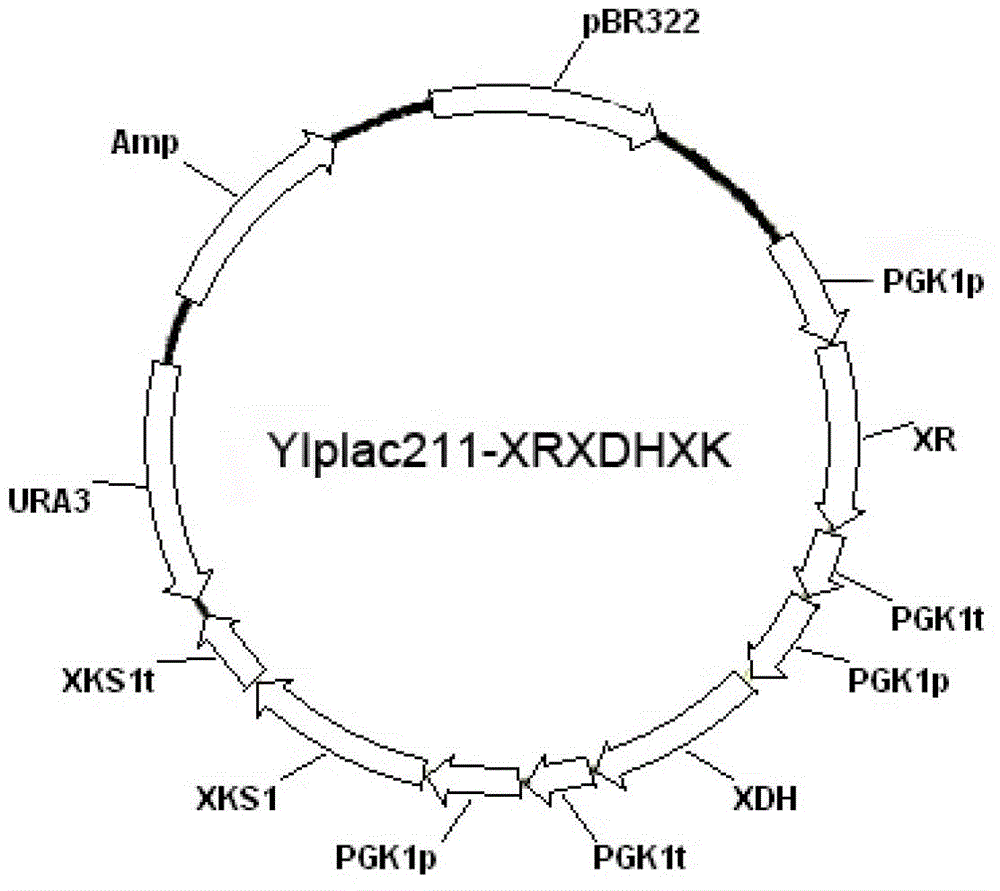
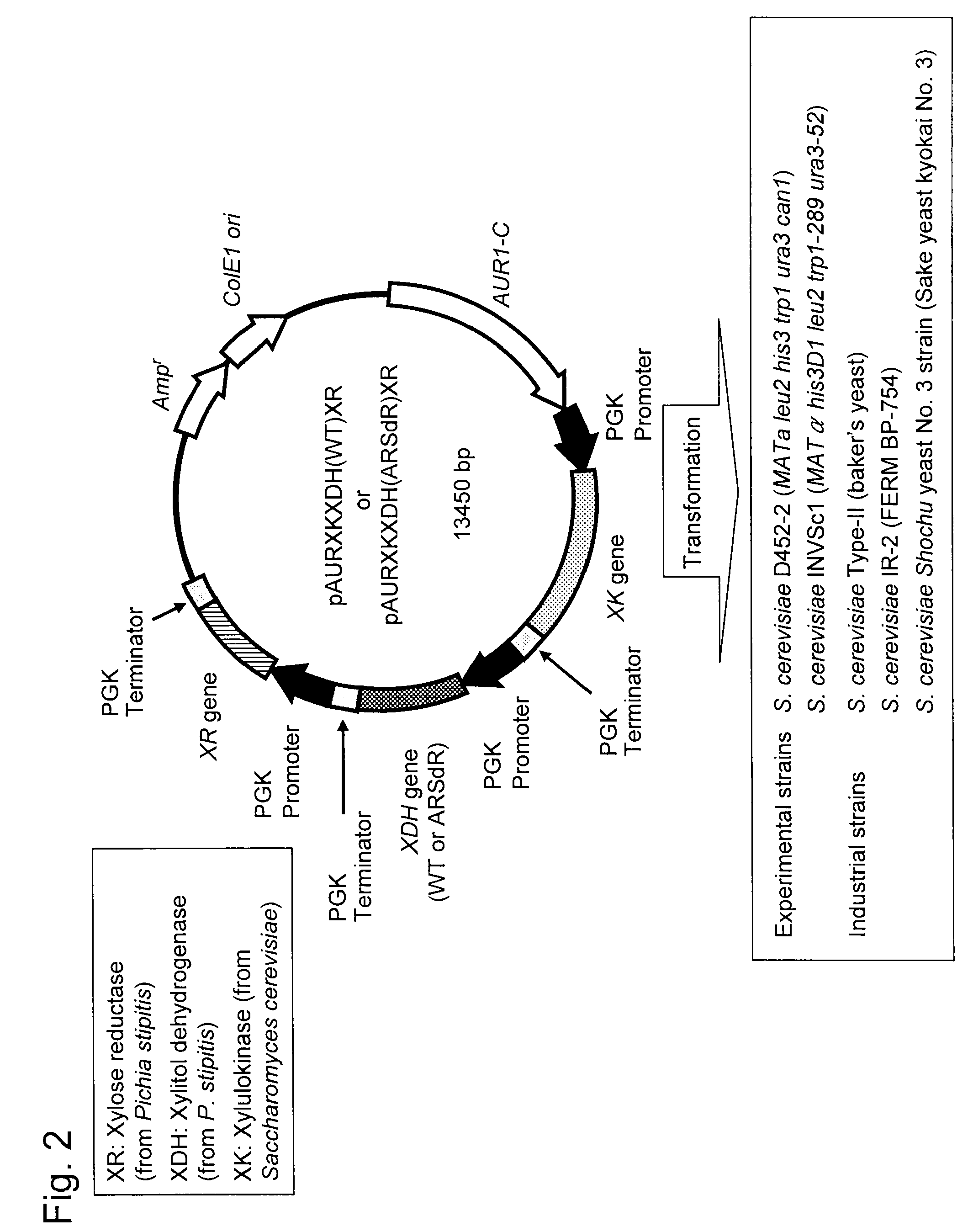
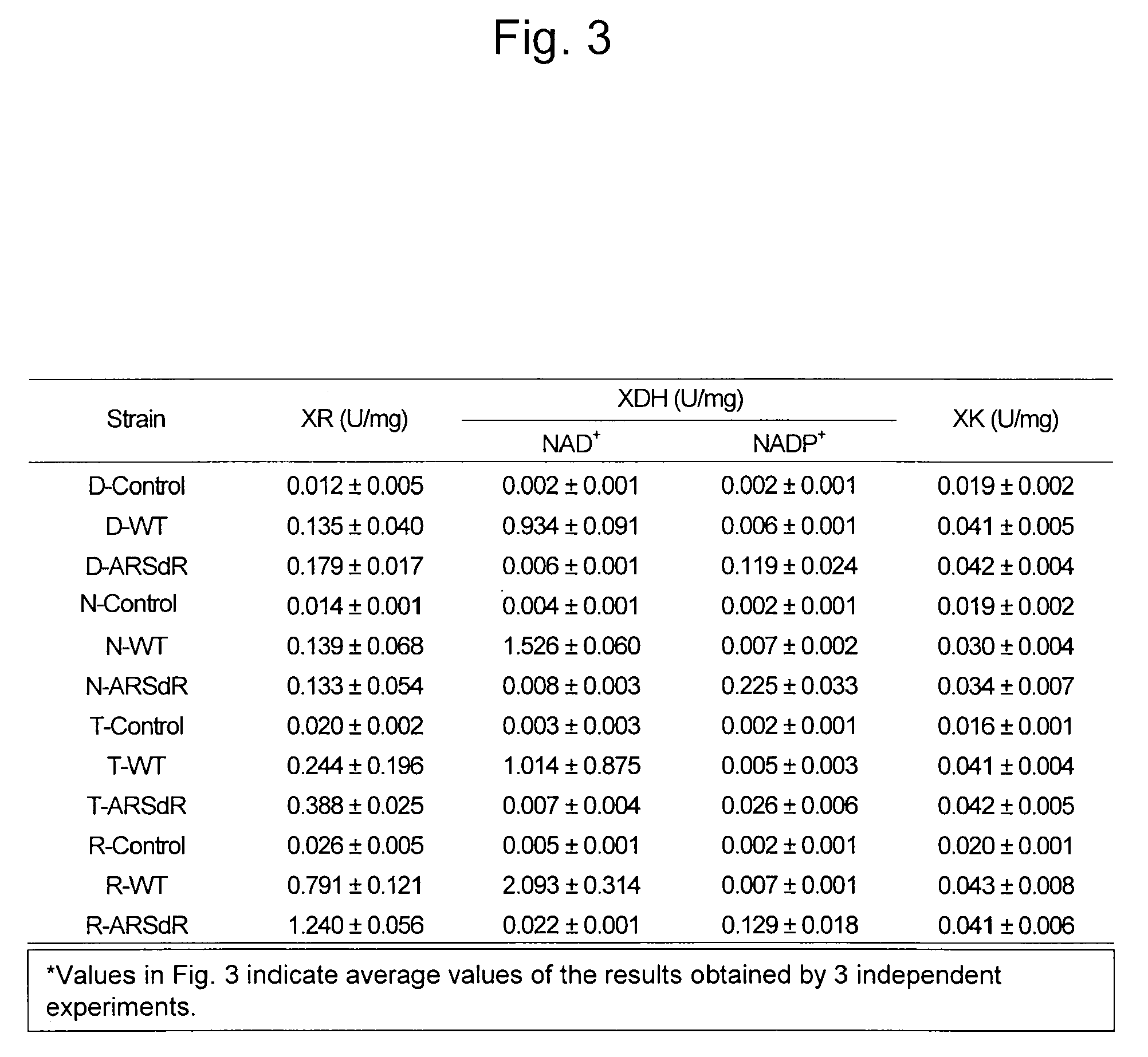
Hexose-pentose cofermenting yeast having excellent xylose fermentability and method for highly efficiently producing ethanol using the same
InactiveUS20110027847A1Efficient conversionValid conversionFungiTransferasesXylose fermentationPichia stipitis
Genetic recombinant yeast expressing xylose reductase (XR), (wild-type or mutant) xylitol dehydrogenase (XDH), and xylulokinase (XK) and a method for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose using the yeast are provided. Pichia stipitis-derived XR and (wild-type or modified-type) XDH genes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived XK gene were introduced via chromosomal integration. Thus, a genetic recombinant yeast having a high xylose fermentation rate, being capable of producing ethanol from xylose in high yields, and having high xylose fermentability in the presence of glucose, as well as a method using the recombinant yeast for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose or a saccharified solution from lignocellulose-based biomass are provided. Furthermore, a method for improving the xylose fermentability of the genetic recombinant yeast of the present invention via acclimatization treatment is also provided herein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Recombinant yeast strain capable of efficiently metabolizing xylose and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant yeast strain (Saccharomyces cerevisiae)) capable of efficiently metabolizing xylose, which is named SyBE005. The recombinant yeast strain has been collected in Common Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the collection number is CGMCC No.6634, and the recombinant yeast strain has the capacity of efficiently metabolizing xylose to produce ethanol. The recombinant yeast strain SyBE005 can effectively ferment xylose to generate ethanol. The ethanol yield reaches 64% of the theoretical yield, and the yield of the byproduct xylitol is lower than 12%; and thus, the recombinant yeast strain can efficiently convert xylose into ethanol, and is an excellent strain utilizing cellulose hydrolysate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Xylose-fermenting yeast engineered to increase flux of the pentose phosphate pathway
The present invention relates to further genetic modifications in eukaryotic host cells that have been transformed to express a xylose isomerase that confers the host cell the ability of isomerizing xylose to xylulose. The further genetic modifications are aimed at improving the efficiency of xylose metabolism and include e.g. reduction of unspecific aldose reductase activity, increased xylulose kinase activity and increased flux of the pentose phosphate pathway. The modified host cells of the invention are suitable for the production of a wide variety of fermentation products, including ethanol, in fermentation processes in which a source of xylose or a source of xylose and glucose are used as carbon source.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Recombinant yeast having enhanced xylose fermentation capabilities and methods of use
The present invention relates to the production of biofuels and chemical feedstocks. The present invention provides recombinant yeast having enhanced xylose fermentation capabilities. Methods of using such recombinant yeast for improved biofuel and chemical feedstock production are also provided.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for producing acetone butanol by steam explosion straw xylose fermentation and extracting remainder
ActiveCN101942485AImprove use valueRealize graded conversionPretreatment with water/steamPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsFiberCellulose
The invention relates to a method for producing acetone butanol by steam explosion straw xylose fermentation and extracting remainder, which comprises the following steps of: performing solid and liquid separation after steam explosion straws are soaked into water, and obtaining furfural, organic acid and xylose from the steam explosion straw liquid; producing the acetone butanol by the steam explosion straw xylose fermentation, wherein the yield of the total solvent is 12 to 22g / L; and extracting the steam explosion straw solid by using alkali, wherein the alkali extraction liquid is used for preparing lignin and the alkali extraction residue is used for making paper and producing feed by fermentation. The method transforms cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the straws by stages, canproduce furfural, organic acid, xylose, lignin and papermaking fiber, and can produce fermentation products such as acetone, butanol, feed protein and the like by biotransformation. The method realizes comprehensive utilization of straw resources, has no waste and pollutant discharge during production, achieves pollution-free production, and has good social benefit and economic benefit.
Owner:北京中科百瑞能工程技术有限责任公司
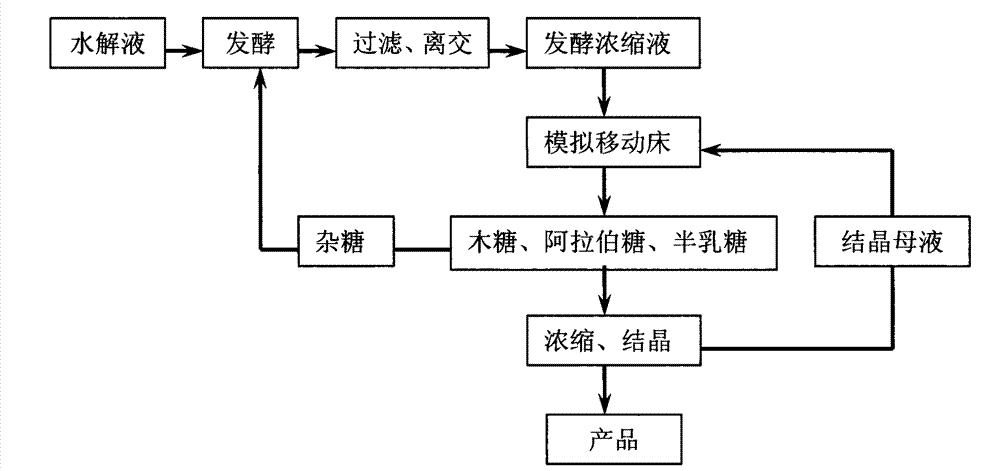
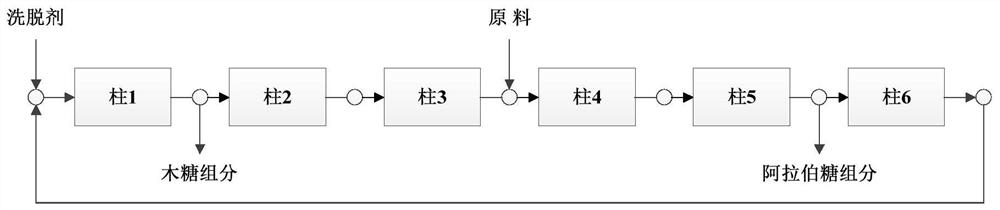
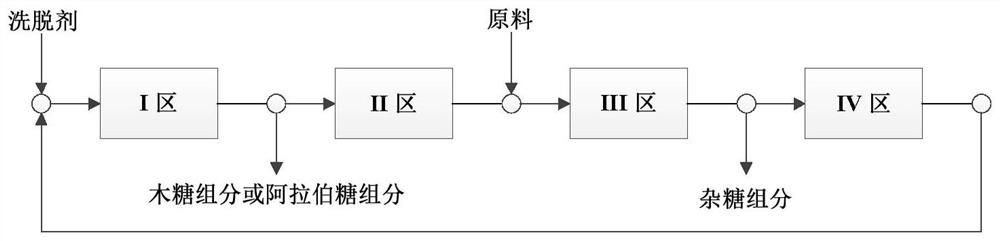
Method for extracting xylose, arabinose and galactose from xylose fermentation broth or xylose mother liquor
InactiveCN102924538AEasy to operateAchieve separationSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationXylose fermentationChromatographic separation
The invention provides a method for extracting xylose, arabinose and galactose from xylose fermentation broth or xylose mother liquor. According to the method, a simulated moving bed chromatographic separation device of sugar alcohol separating resin special for filling is adopted, water serves as an eluent, the separation temperature is 30-90DEG C, the flow rate of feed liquid is controlled at 2-50cm / min, continuous separation and purification of the xylose, the arabinose and the galactose in the xylose fermentation broth or the xylose mother liquor is achieved, and high-purity xylose, arabinose and galactose products are obtained through concentration and crystallization. The method has the advantages of being wide in application range, good in separation effect, high in product purity, environment-friendly and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Pentose sugar fermenting cell
ActiveUS8399215B2Reduce the amount of solutionMicroorganismsBiofuelsBiotechnologyXylose fermentation
The invention relates to a cell which comprises a nucleotide sequence encoding a xylose isomerase, wherein the amino acid sequence of the xylose isomerase has at least about 70% sequence identity to the amino acid sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 3 and wherein the nucleotide sequence is heterologous to the host. The cell of the invention may be used in a process for producing a fermentation product, such as ethanol. Such a process may comprise fermenting a medium containing a source of xylose with a cell of the invention such that the cell ferments xylose to the fermentation product.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Carbonyl reductase, mutant and application thereof in preparation of antifungal drug intermediates
ActiveCN106701698AHigh catalytic activityEasy to getOxidoreductasesFermentationXylose fermentationAntifungal drug
The invention relates to carbonyl reductase, a mutant and application thereof in preparation of antifungal drug intermediates. The invention specifically discloses xylose fermentation yeast carbonyl reductase and a mutant with improved activity thereof, encoding genes and amino acid sequences, recombinant expression vectors and recombinant expression transformants containing the gene sequences, as well as application of catalyzing asymmetric reduction of prochiral carbonyl compounds by taking the xylose fermentation yeast carbonyl reductase or corresponding recombinant expression transformants as catalysts, particularly catalyzing reduction of 2-chloro-2',4'-difluoroacetophenone and 2,2',4'-trichloroacetophenone for preparing antifungal compound precursors (R)-2-chloro-1-(2',4'-difluorophenyl)ethanol and (R)-2-chloro-1-(2',4'-dichlorophenyl)ethanol. Compared with the existing other asymmetric reduction methods, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high enzymatic reaction substrate concentration, mild reaction condition, environment friendliness, high yield, high optical purity of products and the like and has excellent application prospects.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
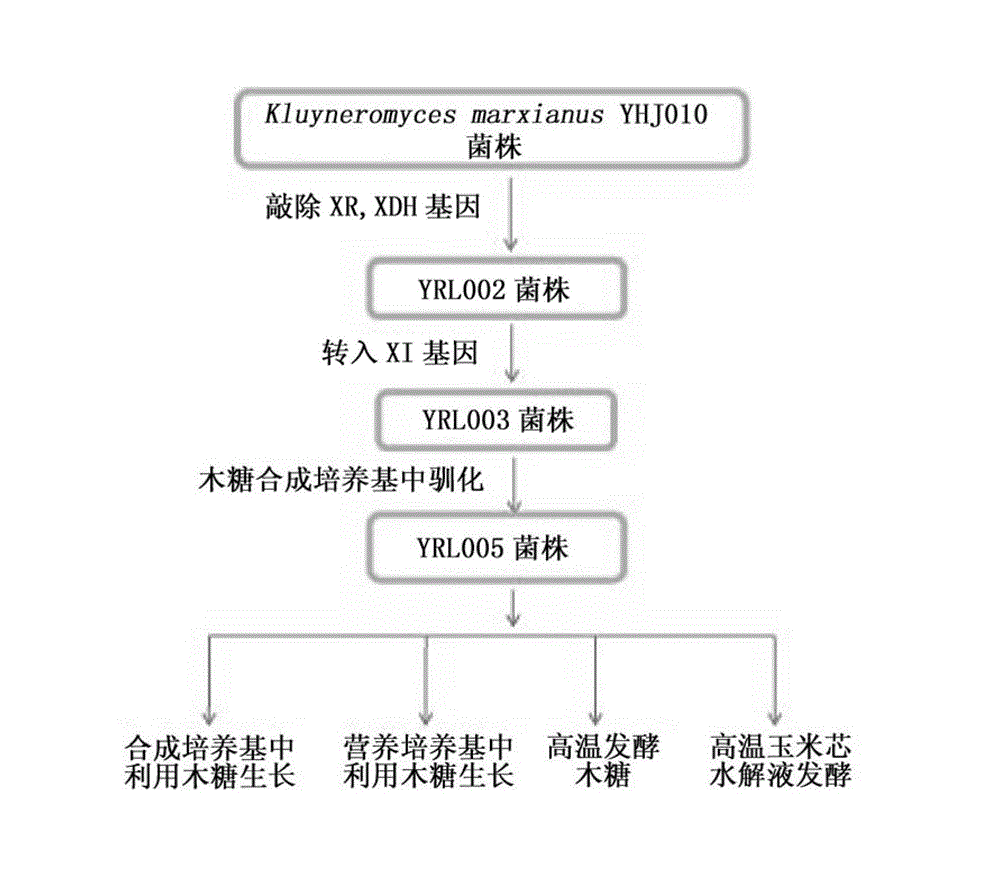
Heat-resistant engineered yeast strains for high-temperature high-efficiency xylose fermentation and application of heat-resistant engineered yeast strains
The invention relates to heat-resistant engineered yeast strains for xylose fermentation. A heat-resistant yeast strain Kluyveromyces marxianus in which xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase genes are knocked out is taken as a host, and a heat-resistant yeast expression vector containing a xylose isomerase gene of which a codon is optimized is transformed into the host. The invention also relates to domesticated strains of the heat-resistant engineered yeast strains for the xylose fermentation, a preparation method for the domesticated strains and application of the domesticated strains.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Prokaryotic Xylose Isomerase for the Construction of Xylose Fermenting Yeasts
The present invention relates to the use of nucleic acid molecules coding for a bacterial xylose isomerase (XI), preferably coming from Clostridium phytofermentans, for reaction / metabolization, particularly fermentation, of recombinant microorganisms of biomaterial containing xylose, and particularly for the production of bioalcohols, particularly bioethanol, by means of xylose fermenting yeasts. The present invention further relates to cells, particularly eukaryotic cells, which are transformed utilizing a nucleic acid expression construct which codes for a xylose isomerase, wherein the expression of the nucleic acid expression construct imparts to the cells the capability to directly isomerize xylose into xylulose. Said cells are preferably utilized for reaction / metabolization, particularly fermentation, of biomaterial containing xylose, and particularly for the production of bioalcohols, particularly bioethanol. The present invention also relates to methods for the production of bioethanol, and to methods for the production of further metabolization products, comprising the metabolization of media containing xylose.
Owner:LESAFFRE & CIE
Xylose fermentation strain resistant to inhibitors and construction method and applications thereof
ActiveCN109706089AIncreased ability to tolerate inhibitorsSuperior ability to tolerate inhibitorsFungiMutant preparationXylose fermentationCellulose
The invention discloses a xylose fermentation strain resistant to inhibitors. The strain is named as SEB11 and has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 16570. The invention also relates to a construction method of the above-mentioned xylose fermentation strain, and the method comprises the steps of: selecting a starting strain SEB5; performing plasma mutagenesis treatment on the starting strain, andpicking out bacterial colonies which are better or similar to the starting strain in growth situation; and subjecting the picked strains to plate initial screening and actual saccharification liquidrescreening so as to obtain the xylose fermentation strain SEB11 resistant to inhibitors. The present invention also relates to applications of the above xylose fermentation strain in producing ethanol by using xylose in lignocellulose. The method adopts an industrial strain of the xylose as a starting strain, adopts a normal-pressure room-temperature plasma mutagenesis technique for mutagenesis,and obtains the xylose fermentation mutant strain SEB11 with excellent inhibitor tolerance according to the growth condition in a plate medium containing inhibitors and the actual saccharification liquid fermentation rescreening. The xylose consumption rate is significantly increased, and a better fermentation result exhibits.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Industrial saccharomyces cerevisiae strain capable of producing xylitol and construction method of industrial saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
ActiveCN105368732AQuick and easy to getImprove performanceFungiMicroorganism based processesXylose fermentationDNA
The invention relates to an industrial saccharomyces cerevisiae strain capable of producing xylitol and a construction method of the industrial saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. The preservation number of the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain is CGMCC 11326. The construction method comprises the following steps: taking pK-XR-Ct plasmids as a template, taking delta-pB-F and delta-pB-R as primers, and carrying out PCR amplification to obtain DNA fragments A, taking the DNA fragments A as a template, and carrying out amplification to obtain DNA fragments B; screening the G418 optimal tolerance concentration of a saccharomyces cerevisiae fusion strain; converting the saccharomyces cerevisiae fusion strain; and screening unicellular converters to obtain the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. The saccharomyces cerevisiae SEB6 strain prepared by the construction method provided by the invention has excellent performances of producing xylitol through xylose fermentation, and the yield of xylitol is high; and meanwhile, the problems that exogenous genes get lost and the expression level is low existing in the expression of the existing saccharomyces cerevisiae strains are avoided.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Hexose-pentose cofermenting yeast having excellent xylose fermentability and method for highly efficiently producing ethanol using the same
InactiveUS8445243B2Efficient conversionValid conversionFungiTransferasesXylose fermentationPichia stipitis
Genetic recombinant yeast expressing xylose reductase (XR), (wild-type or mutant) xylitol dehydrogenase (XDH), and xylulokinase (XK) and a method for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose using the yeast are provided. Pichia stipitis-derived XR and (wild-type or modified-type) XDH genes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived XK gene were introduced via chromosomal integration. Thus, a genetic recombinant yeast having a high xylose fermentation rate, being capable of producing ethanol from xylose in high yields, and having high xylose fermentability in the presence of glucose, as well as a method using the recombinant yeast for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose or a saccharified solution from lignocellulose-based biomass are provided. Furthermore, a method for improving the xylose fermentability of the genetic recombinant yeast of the present invention via acclimatization treatment is also provided herein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Metabolic Engineering yeast using xylose fermentation for producing ethanol
Xylose fermentation ethanol is one of the key technologies utilizing biomass to produce ethanol. A saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterial strain is set up by a method of metabolic engineering. The bacterial strain not only can ferment the ethanol produced by the xylose, but also can automatically balance oxido-reduction cofactor, so as to be a metabolic engineering microzyme which has little by-product and can effectively use xylose fermentation for producing the ethanol. The conversion rate of xylose fermentation ethanol of bacterial strain reaches 88%, thus laying the foundation for utilizing the biomass to produce fuel ethanol.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ethanol by xylose fermentation and construction method thereof
The invention provides recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ethanol by xylose fermentation and a construction method thereof. In the invention, candida boidinii is led to the saccharomyces cerevisiae to metabolize a DNA fragment of a coding gene of related enzymes of the xylose, so that the saccharomyces cerevisiae can secrete and express xylose isomerase the enzymatic reaction conditions of which are close to growth conditions of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, so the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae can effectively utilize the xylose to produce the ethanol, thus solving the technical problem that the saccharomyces cerevisiae can not utilize the xylose to produce the ethanol. The invention lays a foundation for industrial application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing the ethanol by using xylose fermentation, thus having great economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Pentose sugar fermenting cell
The invention relates to a cell which comprises a nucleotide sequence encoding a xylose isomerase, wherein the amino acid sequence of the xylose isomerase has at least about 70% sequence identity to the amino acid sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 3 and wherein the nucleotide sequence is heterologous to the host. A cell of the invention may be used in a process for producing a fermentation product, such as ethanol. Such a process may comprise fermenting a medium containing a source of xylose with a cell of the invention such that the cell ferments xylose to the fermentation product.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Continuous process for the production of ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveUS9434961B2Yield maximizationCheap productionBiofuelsFermentationXylose fermentationFurfural
A continuous process for the recovery of ethanol from hemicellulose and cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass. Yield of fermentable sugars can be maximized by continuous operation of the pre-treatment system and careful selection of pretreatment conditions including the addition of only small amounts of dilute mineral acid and low pressure. With this approach, the xylose component that is mainly present in its unfermentable oligomeric form in known pre-hydrolysis Kraft processes can be recovered more efficiently and as a monomer that can be fermented by xylose fermenting yeasts and bacteria. Due to the use of only dilute acids, there is a very low loss of glucose and xylose hence very low production of toxic chemicals (e.g. HMF, furfural) in the pretreatment step. The resulting overall fermentation efficiency of both hexose and pentose sugars is 90% of the theoretical maximum.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for expressing xylose isomerase and construction method
ActiveCN105368731AImprove ethanol yieldFast filtrationFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousXylose fermentation
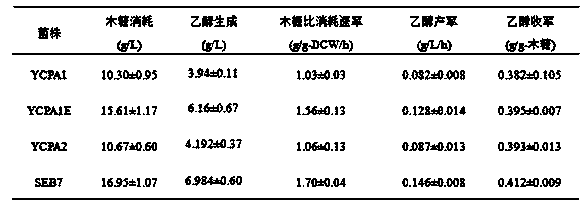
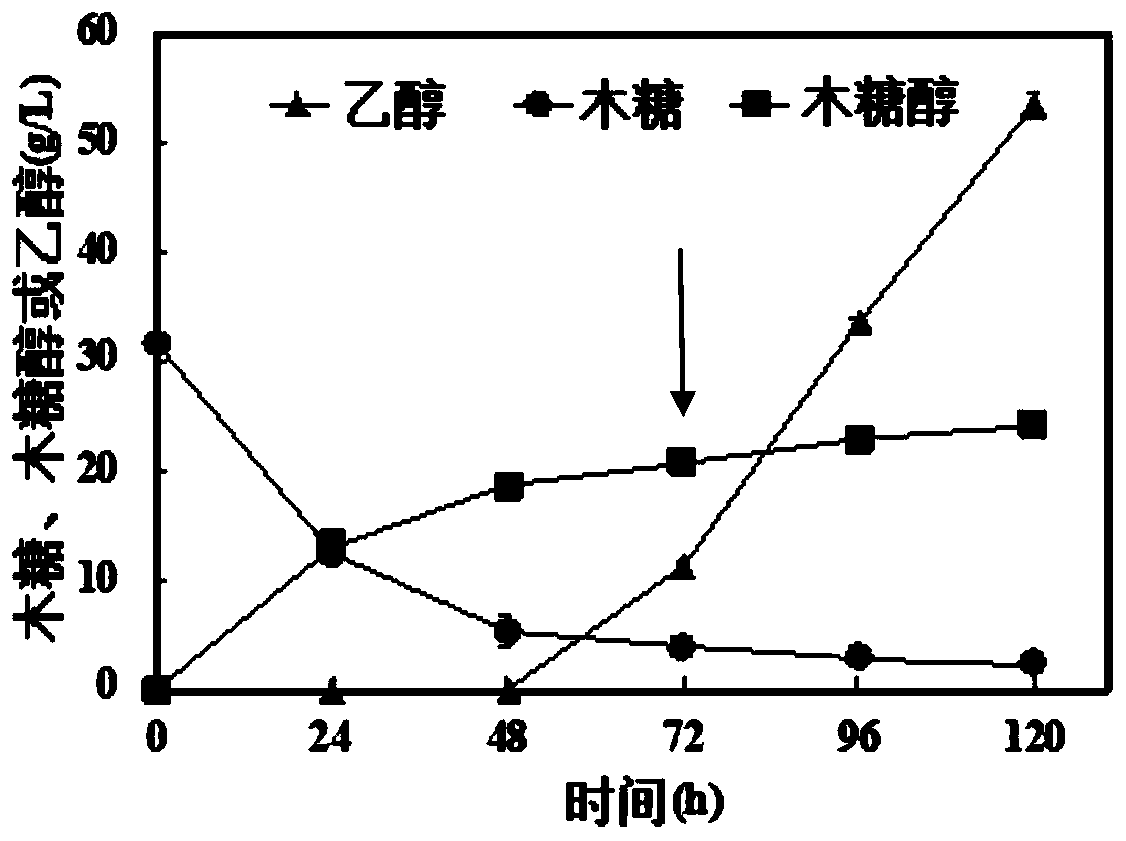
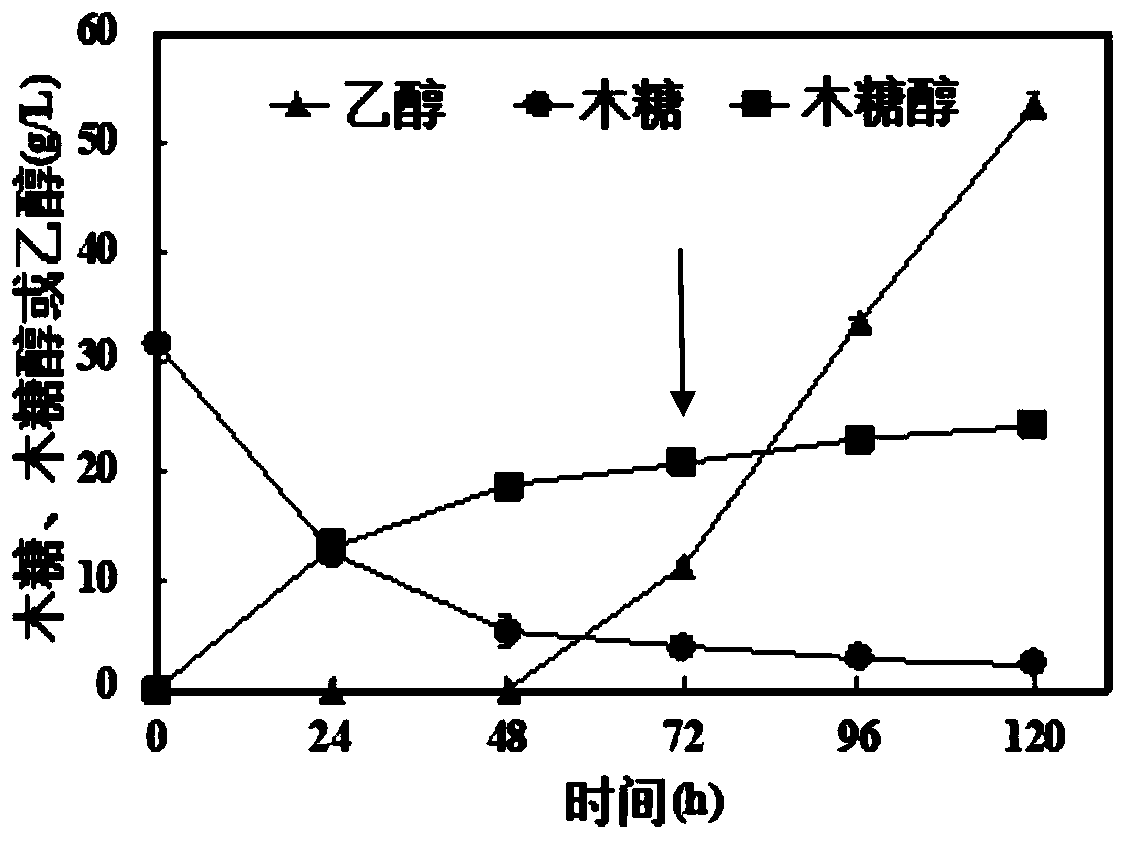
The invention discloses a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for expressing xylose isomerase and a construction method and solves the problem that after heterogenous expression of xylA gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a recombinant bacterium constructed thereby has a low growth rate in xylose, causing the fermentation requirement to be not met. The invention includes a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain SEB7, collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center under CGMCC11327. The invention also provides a construction method of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain SEB7. The strain SEB7 obtained by the invention can generate ethanol 6.98 g / L within a fermenting time of 48 h by using xylose 16.95 g / L, with ethanol yield up to xylose 0.412 g / g; the strain has the advantages such as high xylose fermentation speed and high ethanol yield.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Fermentation method for producing xylitol and ethanol by using undetoxified cellulose raw materials
ActiveCN111118071AReduce dosageImprove sugar utilizationBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyXylose fermentation
In view of problems in the existing cellulose ethanol preparation technologies that inhibitors in a cellulose hydrolyzate inhibit fermentation, xylose cannot be completely converted, glucose inhibitsfermentation of the xylose, and a cellulase acting temperature and a microbe fermentation temperature are non-uniform, the invention provides a fermentation method for producing xylitol and ethanol byusing undetoxified cellulose raw materials. The fermentation method comprises the steps of inoculum culture, xylose fermentation, cellulase adding, synchronous diastatic fermentation and the like. According to the method, simultaneous utilization of the xylose and the inhibitors is achieved by adopting an acetic acid and xylose co-utilization based Kluyveromyces marxianus strain, and thus, the problem in inhibitor removal is avoided; by adopting high-temperature synchronous diastatic fermentation, the problem that the cellulase is unmatched with a fermentation temperature is avoided; and compared with the existing cellulose ethanol fermentation technologies, the production cost can be remarkably reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
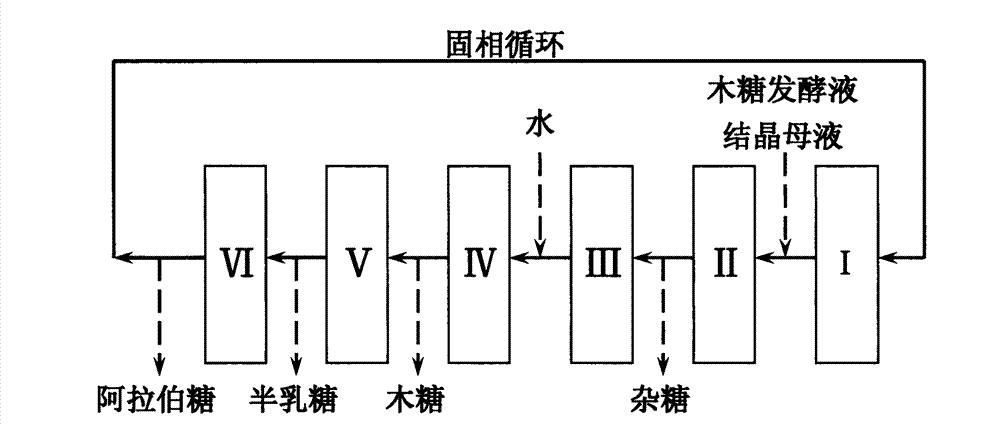
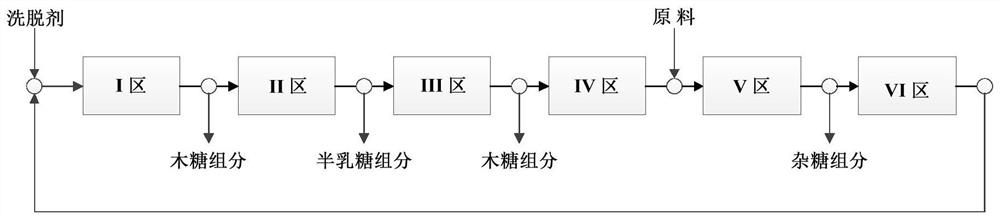
Method for simultaneously preparing xylose, arabinose and galactose by utilizing intermittent simulated moving bed chromatography
ActiveCN111747997AFully tap the valueHigh yieldSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationXylose fermentationBiochemical engineering
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously preparing xylose, arabinose and galactose by utilizing intermittent simulated moving bed chromatography, and belongs to the technical field of foodindustry separation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating xylose mother liquor; and (2) separating xylose, arabinose and galactose by intermittent simulated moving bed chromatography. According to the invention, xylose, arabinose and galactose can be simultaneously prepared from xylose mother liquor or xylose fermentation liquor with high purity and high yield; the problems that the sugar component recovery rate is not high, the conventional chromatography does not meet the separation requirement, the existing chromatography multi-component separation system is complex, the fixed phase demand is large, the separation function area is subjected to cross contamination and the like are solved; the problems that the crystallization yield of xylose and arabinose is relatively low due to galactose, galactose is difficult to consume by a fermentation method and the like are also solved, full recovery of high-value saccharides is realized, and the resource utilization rateis increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
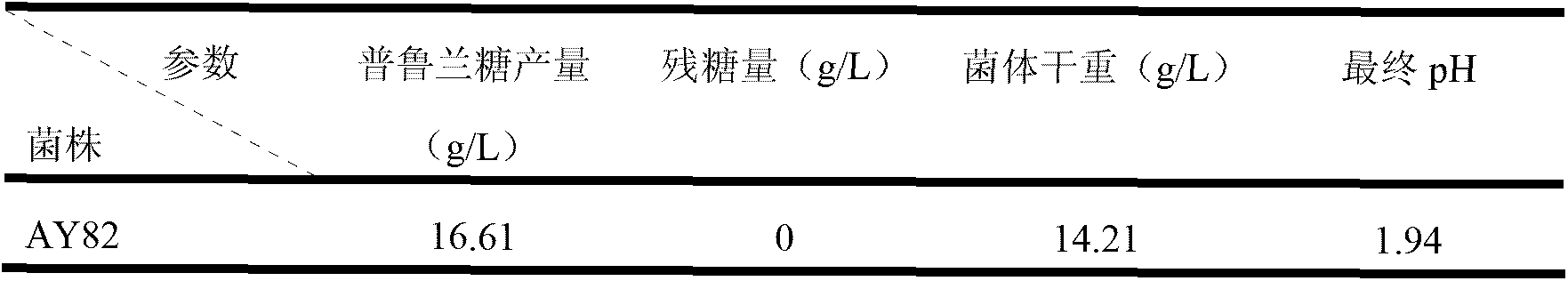
Aureobasidium Pullulan producing pullulan with high yield by utilizing xylose and application of Aureobasidium Pullulan
ActiveCN103255067ALess pigmentEasy to separate and purifyFungiMicroorganism based processesXylose fermentationPullulan
The invention discloses an Aureobasidium Pullulan producing pullulan with high yield by utilizing xylose and a production method of pullulan. The Aureobasidium Pullulan is taken as an original strain and subjected to ultraviolet mutagenesis to obtain a mutated strain which produces pullulan with high yield and secretes less pigment. The Aureobasidium Pullulan mutated strain AY82 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Center with the data of Jan 18th, 2013 and the preservation number of CGMCC No.7154. The Aureobasidium Pullulan mutated strain AY82 can produce pullulan by utilizing fermentation of xylose, yield of pullulan is higher, after shake-flask culture is carried out on xylose fermentation culture medium for seven days, the yield of pullulan is 16.61g / L, and after culture by virtue of a 5L fermentation tank is carried out for seven days, the yield is 16.23g / L. Study on the Aureobasidium Pullulan producing pullulan by utilizing xylose can provide a new method for reasonably utilizing xylose, and additional value of xylose can be effectively enhanced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing ethanol by quick fermentation of xylose and construction method
ActiveCN105368730AStrong fermentation abilityConsumption rate is fastFungiMicroorganism based processesXylose fermentationBrevibacterium saccharolyticum
The invention relates to a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing ethanol by quick fermentation of xylose and a construction method, discloses a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain capable of producing ethanol by fermenting glucose, xylose and cellobiose at the same time, and solves the problem that existing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cannot be used for producing ethanol by using xylose and cellobiose. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain SEB3 is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center under CGMCC11323. The invention also provides a construction method of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain SEB3. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain has the advantages of high xylose fermenting capacity, high xylose consumption speed, high ethanol yield and the like; meanwhile, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain SEB3 is better in acid resistance and temperature tolerance, and both pH not lower than 3 and temperature not higher than 35 DEG C have no significant impact on the fermenting speed and efficiency of xylose and cellobiose.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN106434772AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMalate synthaseXylose fermentation
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for producing malic acid efficiently by means of xylose fermentation and a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. In the recombinant bacterium, hosphopentose isomerase, L-fuculokinase, L-fucose-1-phosphate aldolase, aldehyde dehydrogenase, glycolate oxidase and malate synthase are overexpressed, and meanwhile xylulokinase, malate dehydrogenase and fumarate hydratase are knocked out, so that a malic acid synthesis route is obtained. According to the recombinant bacterium, the malic acid yield and the xylose conversion rate in shake flask culture and fermentation tank culture can reach ideal levels, and a good industrialized application prospect is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method and device for removing salt in xylose fermentation liquor
InactiveCN102909105AAchieve separationReduce loss rateIon-exchange column/bed processesSaccharides productionXylose fermentationImpurity ions
The invention relates to a method for removing salt in xylose fermentation liquor. By utilizing an ion exchange column series technology, impurity ions in solution are separated to obtain xylose liquor without salt. The method comprises the following specific execution steps: taking the pretreated xylose fermentation liquor as a raw material, quickly carrying out series connection after cation exchange columns are penetrated, realizing the saturated adsorption of cation exchange resin through the series connection of the cation exchange columns in sequence and obtaining qualified cation exchange solution; and taking the qualified cation exchange solution as a raw material, quickly carrying out series connection after anion exchange columns are penetrated, realizing the saturated adsorption of anion exchange resin through the series connection of the anion exchange columns in sequence and obtaining xylose liquor without salt.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Industrial Applications of A Novel Aldo/Keto Reductase Of Zymomonas Mobilis
InactiveUS20120196342A1Reducing xylitol productionIncreased ethanol yieldBacteriaBiofuelsXylose fermentationFurfural
The present invention relates to methods of reducing the toxicity of lignocellulosic hydrolysates which comprise one or more inhibitors. One method reduces the amount of furfural inhibitor leading to a more effective process. Another method reduces the amount of xylitol produced during the fermentation of xylose present in lignocellulosic hydrolysates. Naturally occurring aldo / keto reductase enzymes, as well as, enzymes produced by recombinant cells or by selective adaptation may be employed.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Prevotella ruminicola xylose isomerase and co-expression with xylulokinase in yeast for xylose fermentation
A xylose isomerase (XI) enzyme which exhibits increased activity and affinity for xylose is produced by strain TC2-24 of the rumen bacterium, Prevotella ruminicola. The gene encoding this enzyme may be used to produce improved recombinant yeast capable of utilizing xylose. The recombinant yeast are preferably transformed with heterologous polynucleotide sequences coding both the P. ruminicola XI, and the xylulokinase (XKS) of a Prevotella species. Yeast transformed with the polynucleotide sequences coding both of these XI and XKS exhibit significantly increased xylose utilization and cell growth on a culture medium containing xylose as the sole carbon source, in comparison to yeast transformed with XKS and XI from other sources.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Modified yeast strains exhibiting enhanced fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates
InactiveUS8603788B2High copy numberIncreasing expression and activitySugar derivativesBacteriaCelluloseBiotechnology
The present invention relates to novel xylose-fermenting yeast strains (for example, yeast of the genus Saccharomyces, e.g., S. cerevisiae) with an enhanced ability to ferment the xylose (and / or another pentose sugar) present in a lignocellulosic hydrolysate to a fermentation product(s) (for example, an alcohol (e.g., ethanol) or a sugar alcohol (e.g., xylitol)).
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com