Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Malate dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Malate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.37) (MDH) is an enzyme that reversibly catalyzes the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate using the reduction of NAD⁺ to NADH. This reaction is part of many metabolic pathways, including the citric acid cycle. Other malate dehydrogenases, which have other EC numbers and catalyze other reactions oxidizing malate, have qualified names like malate dehydrogenase (NADP⁺).
Malic Acid Production in Recombinant Yeast
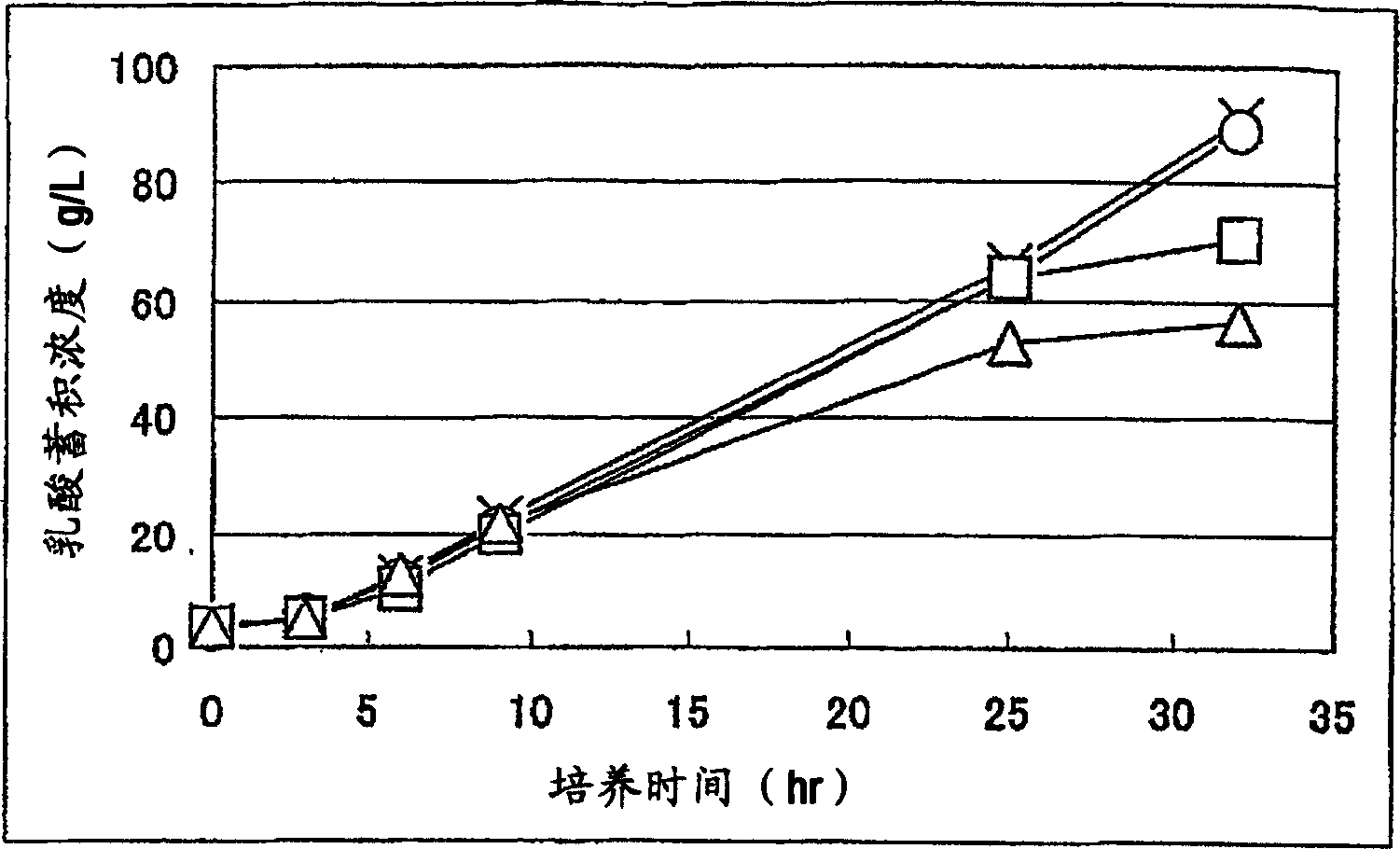
We disclose a recombinant yeast, wherein the yeast is pyruvate decarboxylase enzyme (PDC) activity negative (PDC-negative) and is functionally transformed with a coding region encoding a pyruvate carboxylase enzyme (PYC) wherein the PYC is active in the cytosol, a coding region encoding a malate dehydrogenase enzyme (MDH) wherein the MDH is active in the cytosol and is not inactivated in the presence of glucose, and a coding region encoding a malic acid transporter protein (MAE). We also disclose a method of producing malic acid by culturing such a yeast in a medium comprising a carbon source and a carbon dioxide source and isolating malic acid from the medium.
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
Rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102796675AImprove the lubrication effectImprove securityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLipid formation
The invention relates to a rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the genetic engineering strain is mainly as follows: utilizing rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) of rhodotorula glutinis as a target sequence for homologous integration, using strong promoter genes PGK1 of saccharomyces cerevisiae and malate dehydrogenase genes ME of chaetomium cochloides to construct an expression vector to be introduced into rhodotorula glutinis, and enabling ME genes to obtain high-efficient expression in a rhodotorula glutinis body, wherein the content of lipid in a transformant is improved by 2.5 times in comparison with a wild strain. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, key enzyme genes and a strong promoter for anabolism of the lipid are introduced on the basis that the anabolism of microbial oil is known, so that the lipid metabolism is regulated and controlled, and the yield of oil is improved. The genetic engineering strain can be applied to production of the microbial oil and development of functional oil related products, such as medicaments, health care products and the like.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
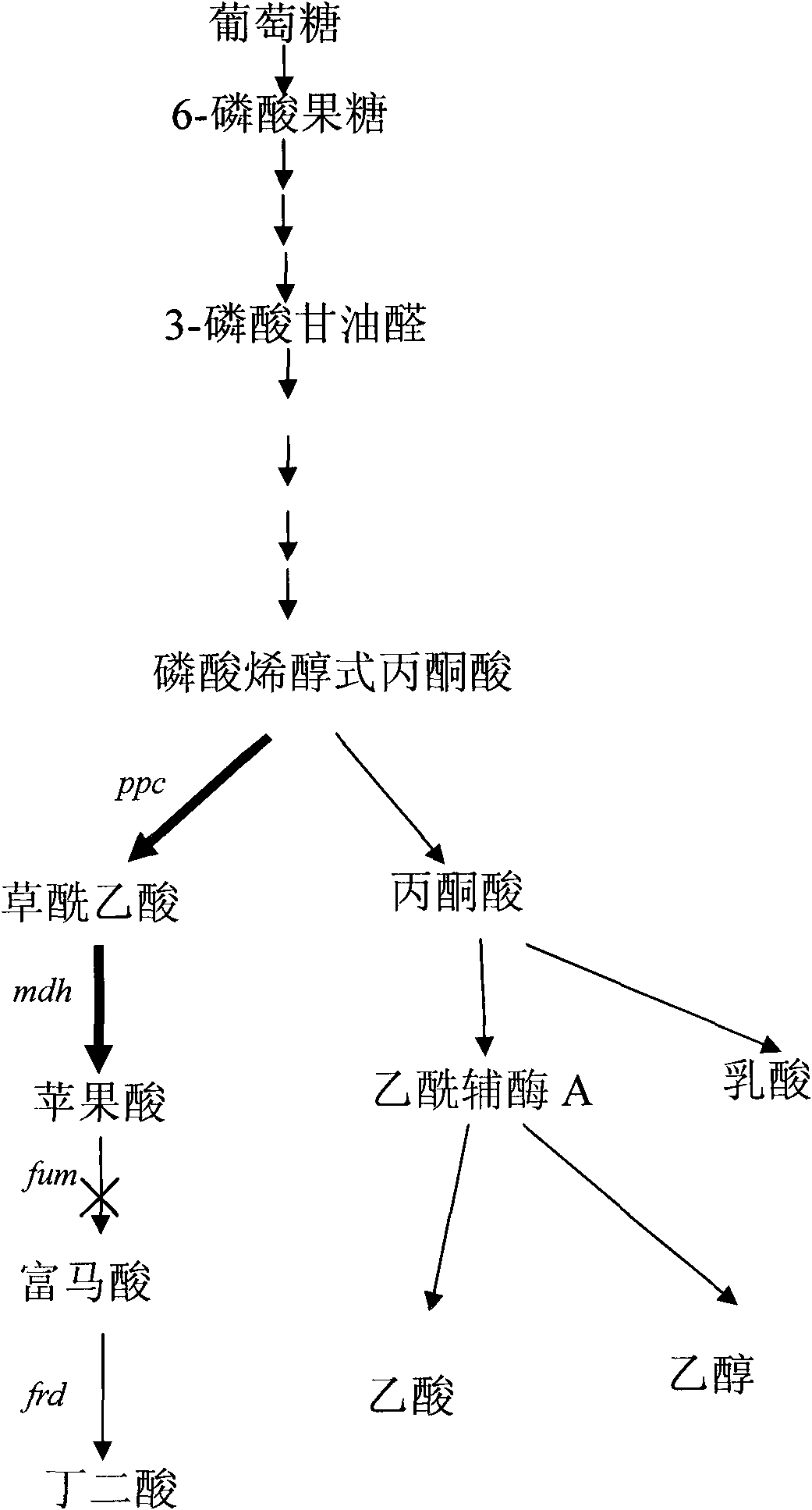
Gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application thereof
The invention provides a gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid as well as a construction method and application thereof. In the invention, key phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase(PEPCK) related to the L-malic acid, malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and fumarase (FumC) are transformed to obtain the gene engineering bacterial strain; a deactivation mutation is carried out on the fumCto cause the interruption of a metabolic flux at the converting position from the malic acid to the fumaric acid so as to accumulate the target product L-malic acid; before the mdh, the promoter of aninner source pepck gene is added to generate the metabolic flux biased towards the malic acid; in addition, through the inducement of monofluorine sodium acetate, the activity of the PEPCK is improved, and the product feedback inhibition is greatly reduced. The bacterial strain applied to the fermentative production of the L-malic acid so as to obviously improve the yield of L-malic acid. The invention has advantages of simple technology, obvious effect and low cost and can satisfy the demand of markets.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Plant expression vector for improving aluminum-tolerance of plant
InactiveCN101230357AIncrease resistancePromote growthSugar derivativesFermentationEscherichia coliAgricultural science
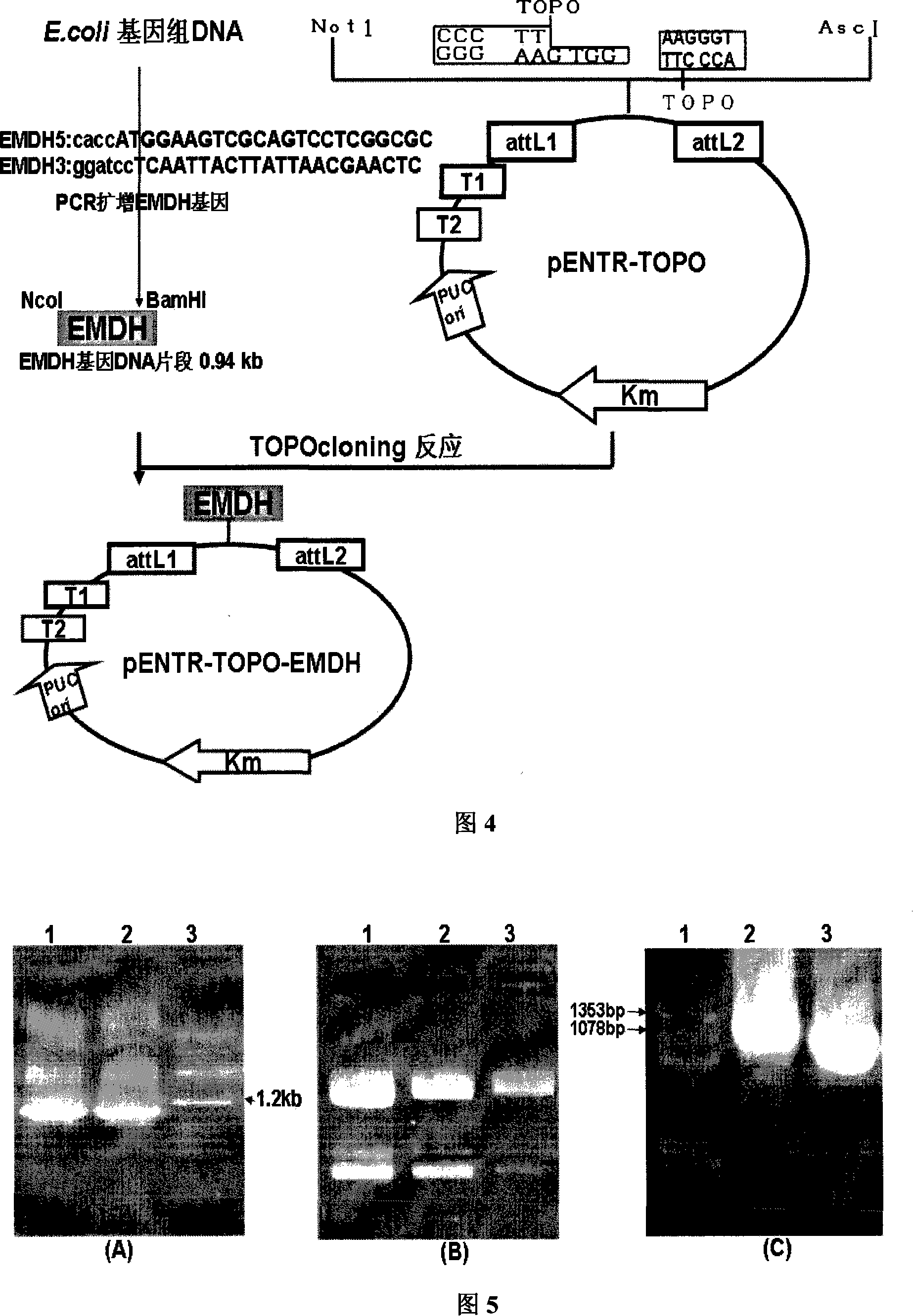
The invention discloses a plane expression vector for increasing the ability of resisting the aluminum toxicity and the application thereof, which belongs to plant genetic engineering field. The vector contains the Escherichia coli malate dehydrogenase (EMDH); the upstream of the malate dehydrogenase (EMDH) is Rubisco small subunit photoinduced promoter. The test shows that, the activity of EMDH of transgene tobacco obtained by transforming the tobacco by the vector is 1 to 3.3 times of that of the wild tobacco. Under the stress of 100 to 300uM aluminum toxicity, the EMDH transferred tobacco can secrete more malic acid; the root grows well, which has an enhanced tolerance for aluminum toxicity. The specific vector of the invention can increases the tolerance for aluminum toxicity of the plant, and has a great potential of application in improving the crops in particular in the acid soil of South China.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
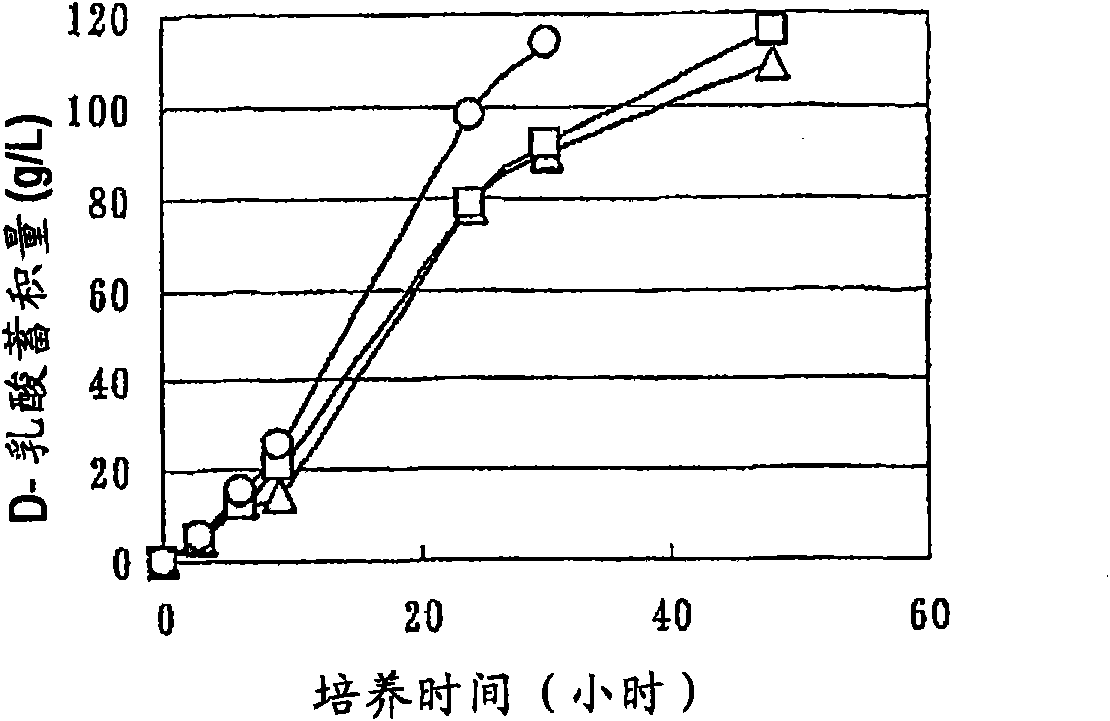
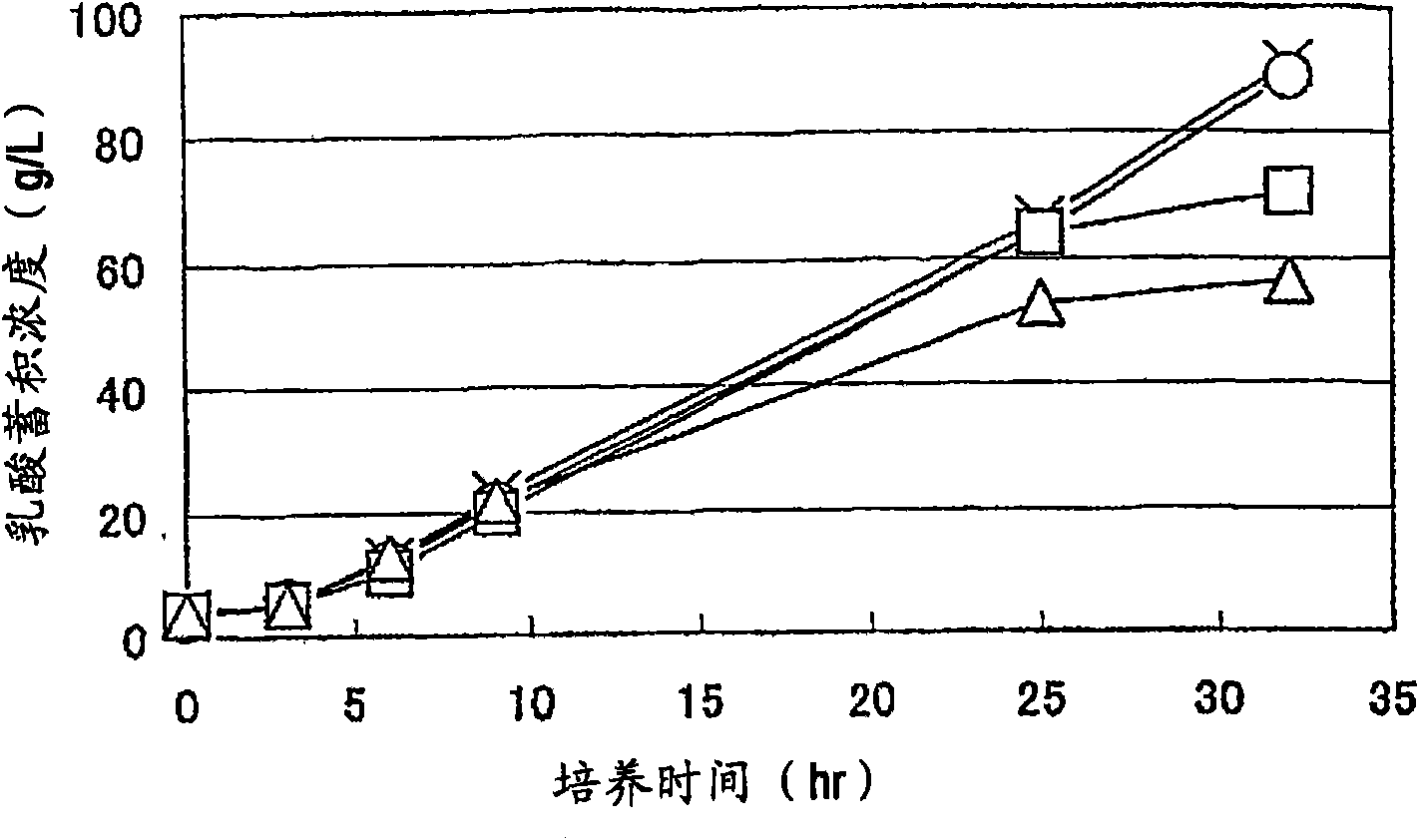
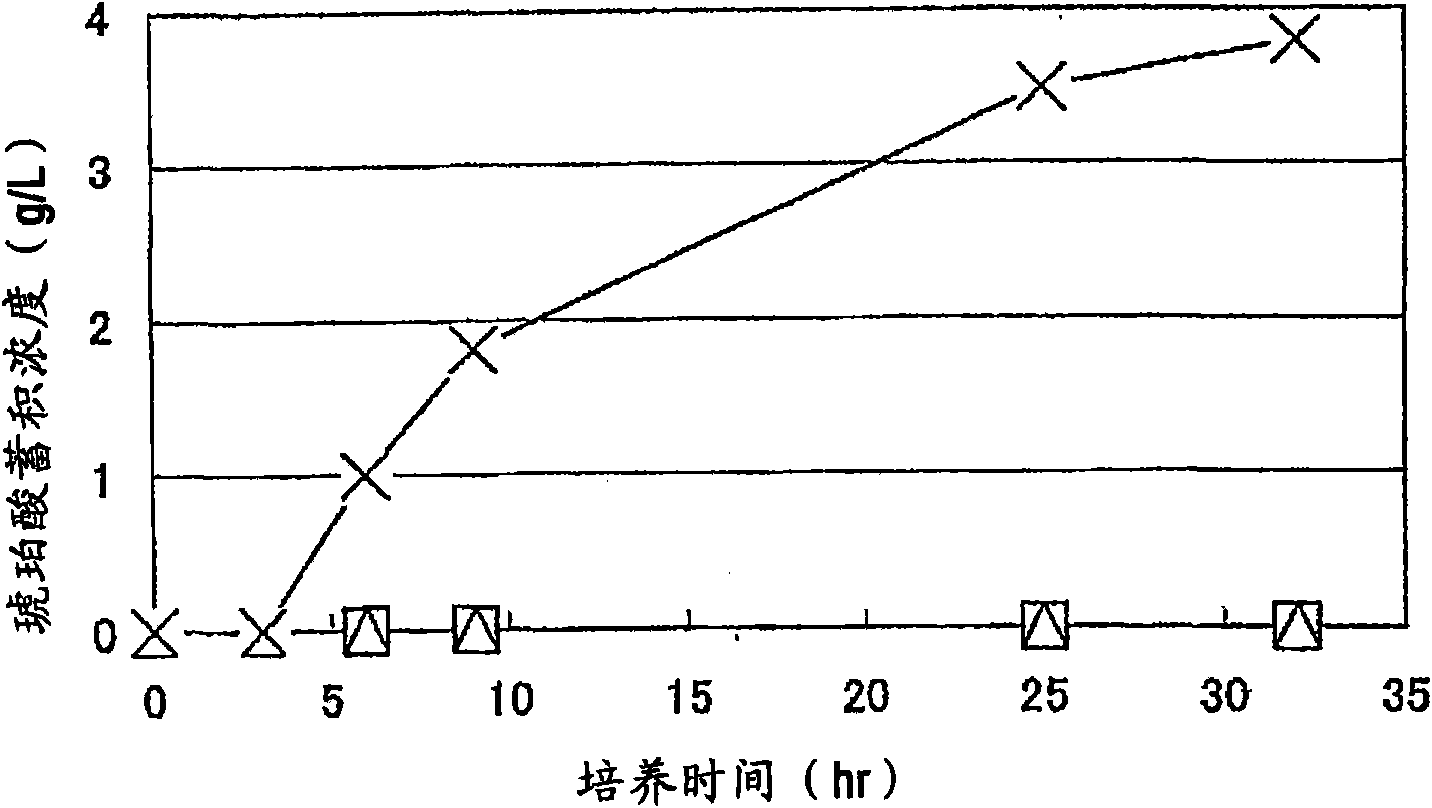
Biocatalyst for producing d-lactic acid
ActiveCN1856577AImprove productivityHigh purityBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyD-lactic acid dehydrogenase activityEscherichia coli
It is intended to provide a process for highly producing D-lactic acid. It is also intended to provide a process for highly selectively producing D-lactic acid having a high optical purity with the formation of little organic acids as by-products. D-Lactic acid is produced by culturing a microorganism having inactivated or lowered pyruvate formate-lyase activity and elevated Escherichia coli-origin NADH-dependent D-lactic acid dehydrogenase (ldhA) activity, a microorganism having inactivated or lowered FAD-dependent D-lactic acid dehydrogenase activity, or a microorganism as described above having a TCA cycle, inactivated or lowered malic acid dehydrogenase activity and inactivated or lowered aspartic acid ammonia-lyase activity. The ldhA activity is elevated by ligating a gene encoding ldhA to a promoter of a gene controlling the expression of a protein, which participates in a glycolysis system, a nucleic acid biosynthesis system or an amino acid biosynthesis system, on genome.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Plant expression vector of arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic malate dehydrogenase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101586116ADetoxifyImprove the ability to resist aluminum poisoningFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumWild type
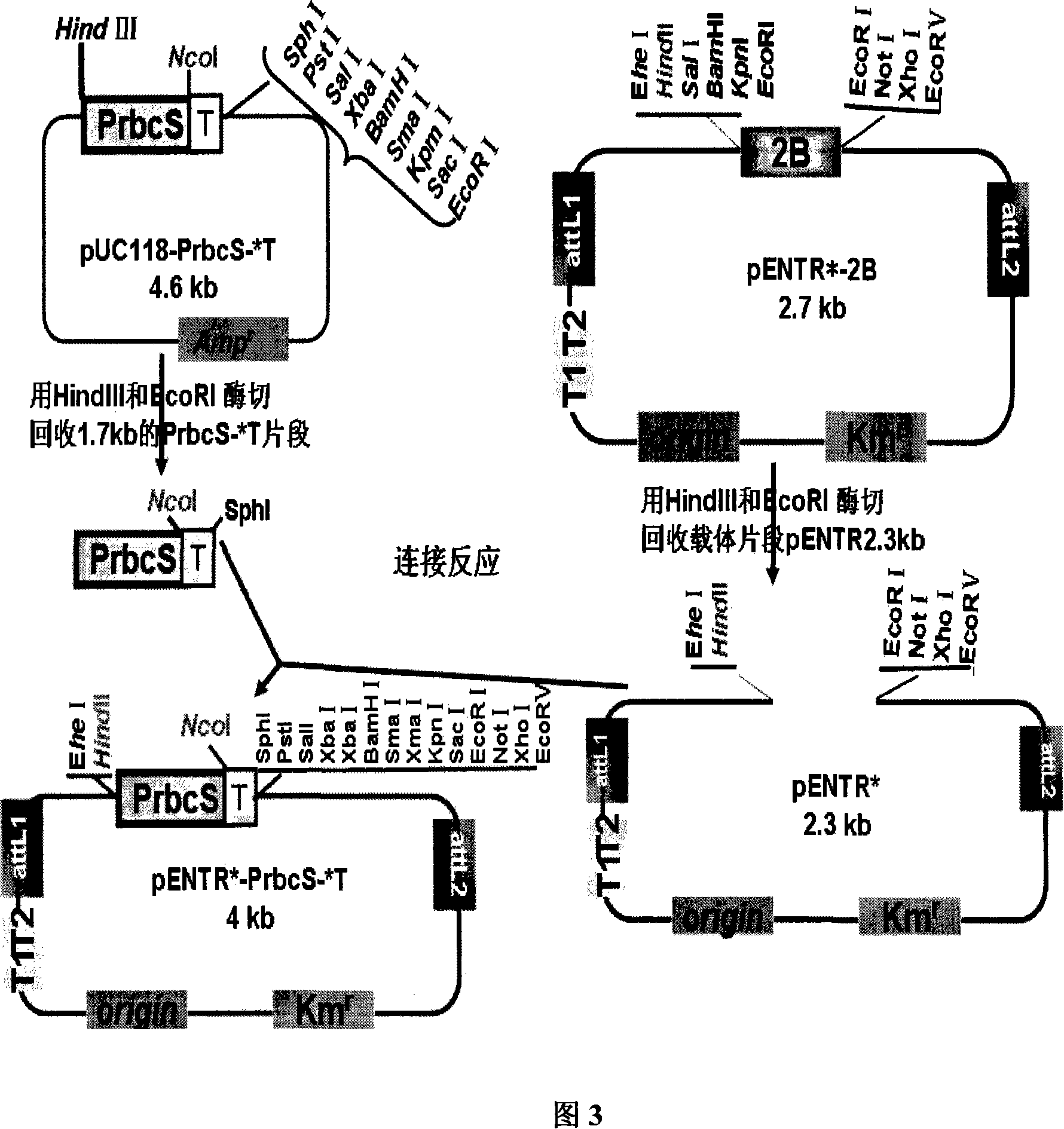
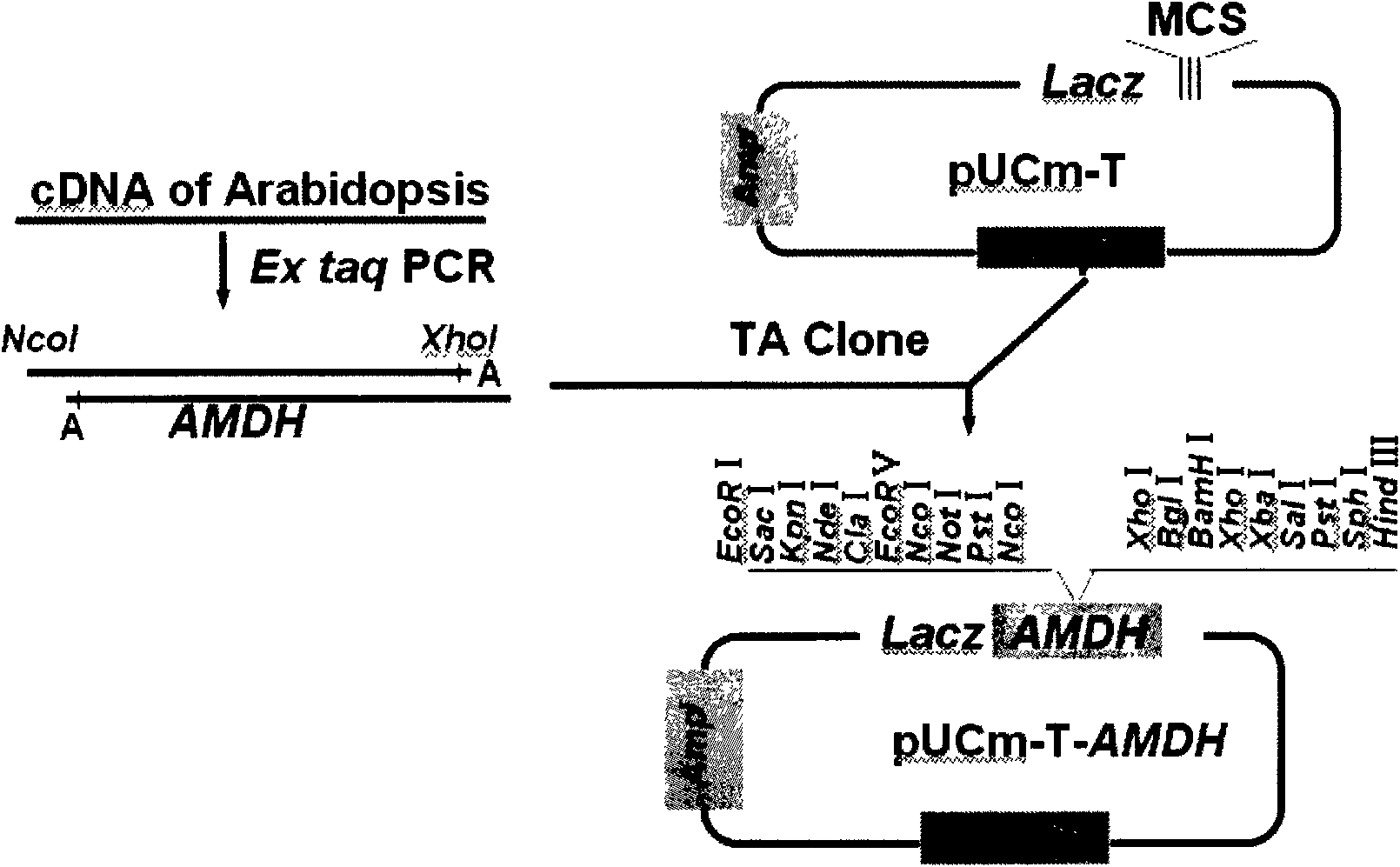
The invention in particular relates to a plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-AMDH for improving the aluminum toxicity resistance of plants, a construction method and application thereof, which belong to the field of plant gene engineering. The special vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-AMDH for improving the aluminum toxicity resistance of the plants is the plant expression vector containing a photoinducible promoter (PrbcS) of a rubulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RubIsco) small subunit gene and an arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic malate dehydrogenase gene (AMDH). The AMDH gene is cloned from arabidopsis thaliana, the photoinducible promoter is used to control the overexpression of the AMDH gene in tobacco, malic acid is synthesized, and the malic acid is secreted out of cells so as to strengthen the resistance of the plants on aluminum toxicity in acid soil. Experimental results show that the activity of malate dehydrogenase of trans-AMDH genic tobacco leaves is 1.4 times of that of wild tobacco. Under the stress of 30 mu M of aluminum toxicity, trans-AMDH genic tobacco can secrete more organic acid, and has better root system growth; and the growth condition under the stress of the aluminum toxicity shows that the plant height and the green leaf number of the trans-AMDH genic tobacco are higher than those of the wild tobacco.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
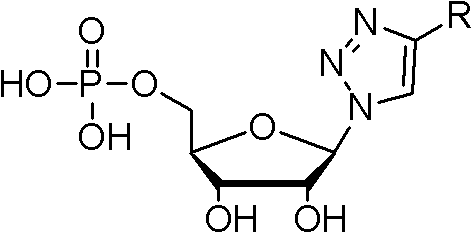
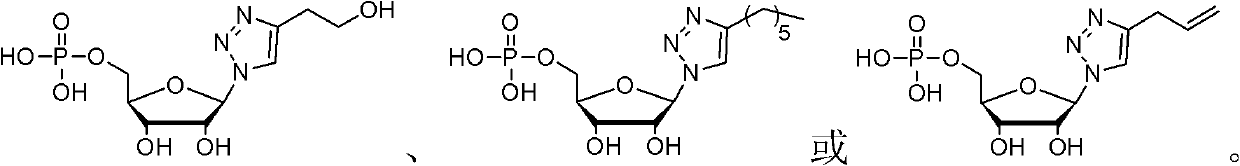
Nucleotide analogue and synthesis and application thereof
InactiveCN102558261AConducive to synthetic structural diversityConducive to structural diversityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliMalic enzyme
The invention discloses a nucleotide analogue and a synthesis and a application thereof. The constitutional formula of the nucleotide analogue is that: Tetra-O-Acetyl-D-Ribose is adopted as a raw material and generates the nucleotide analogue containing a triazole ring formwork through four steps of reaction, wherein R is C2-C15 saturated or unsaturated alkyl, or C2-C10 saturated or unsaturated alkyl containing hetero atoms; or R is R1 which is hydroxyl, alkoxy, amino or substituent amido; or R is R2 which is aryl or saturated or unsaturated alkyl; or R is R3 which is halogen, amono, methoxyl, methyl or other substituent. The nucleotide analogue can restrain the growth of microorganism such as escherichia coli, and can be used as an inhibitor of dehydrogenase such as malate dehydrogenase.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
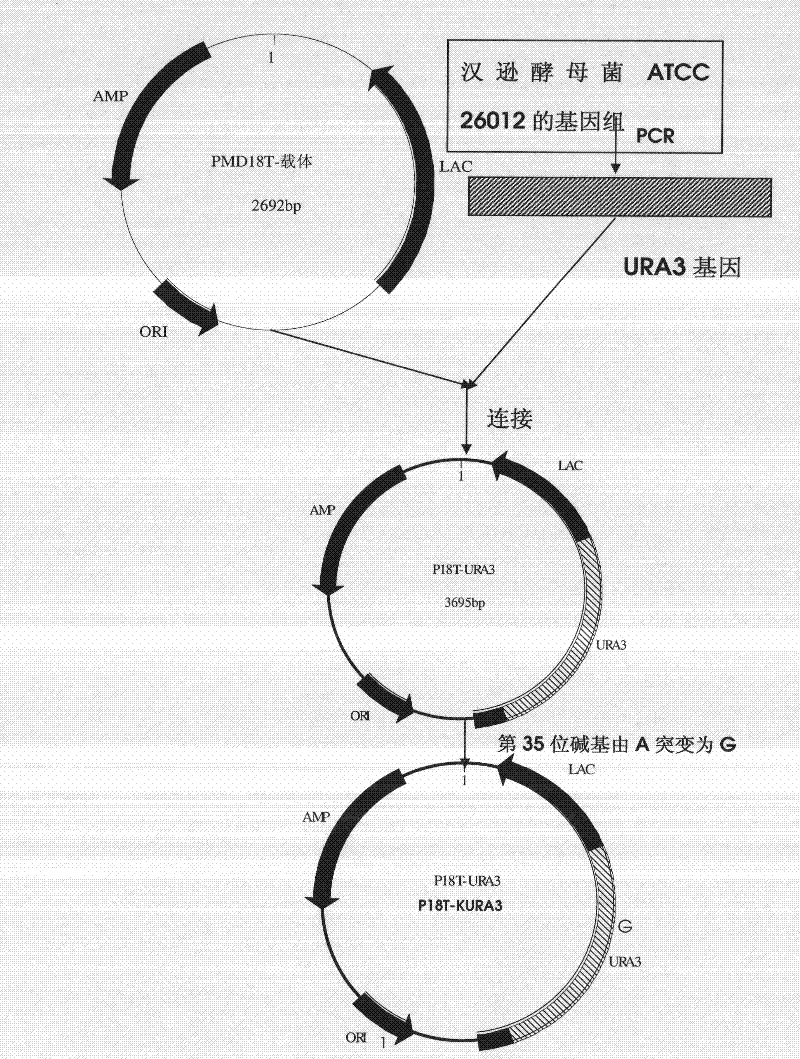
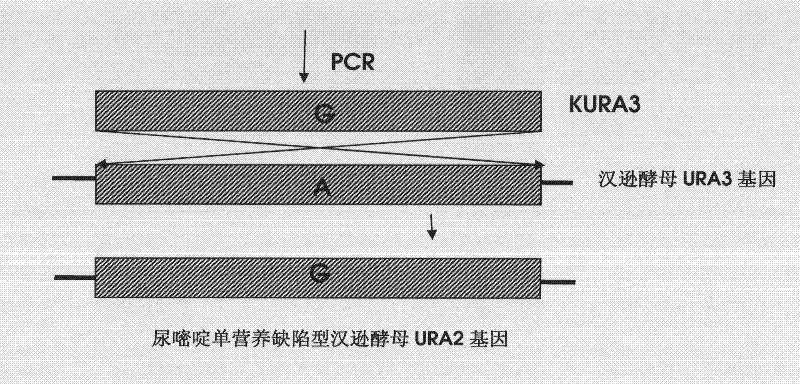
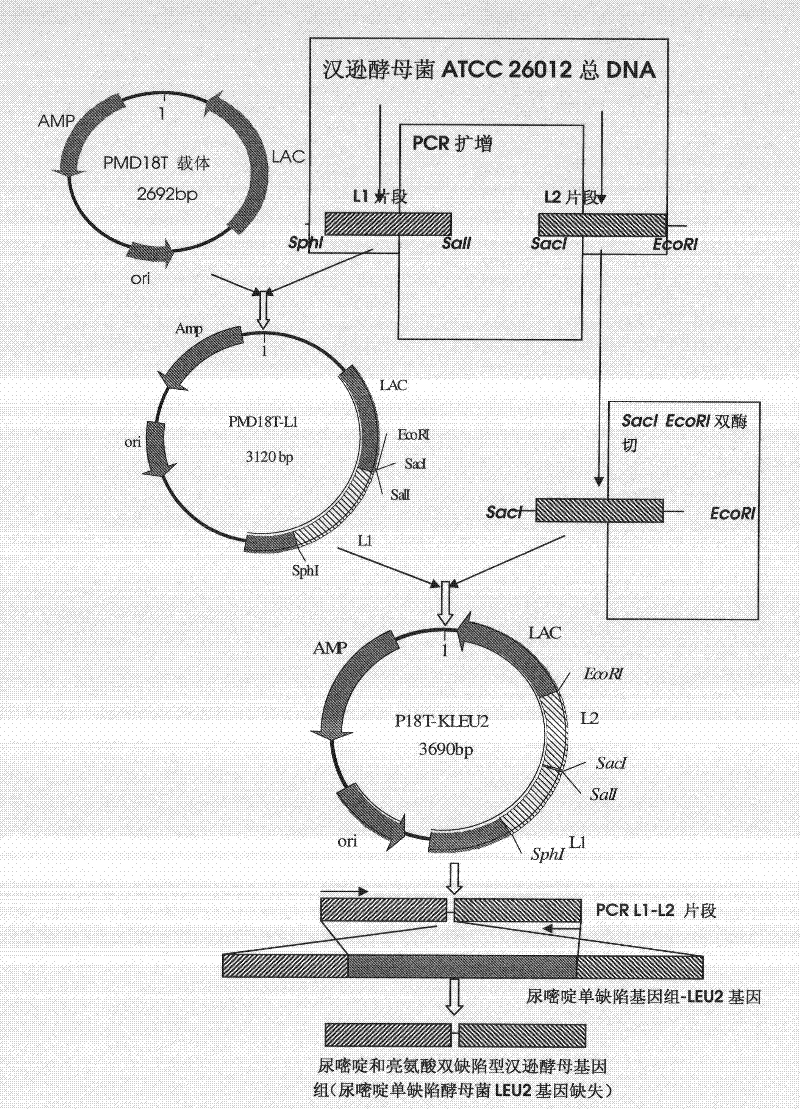
DNA sequence, recombinant vector, single and double auxotrophic Hansenula polymorpha, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102234620AConvenient sourceSuitable for researchFungiMicroorganism based processesVaccine ProductionPhosphate
The invention relates to a double auxotrophic yeast, wherein the yeast is Hansenula polymorpha, and the orotic glycoside-5-phosphate decarboxylase gene and the beta-isopropyl malate dehydrogenase gene of the Hansenula polymorpha are blocked. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the double auxotrophic yeast. In addition, the invention also provides a DNA sequence and a recombinant vector used to prepared the double auxotrophic yeast. The double auxotrophic yeast of the invention has the advantages of low reverse mutation, high genetic stability, high biomass, and the like, and plays an important role in genetic engineering vaccine production; for example, HPV16-type L1 and 58L2 protein have double expression with high efficiency in the yeast.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF BIOLOGICAL PROD
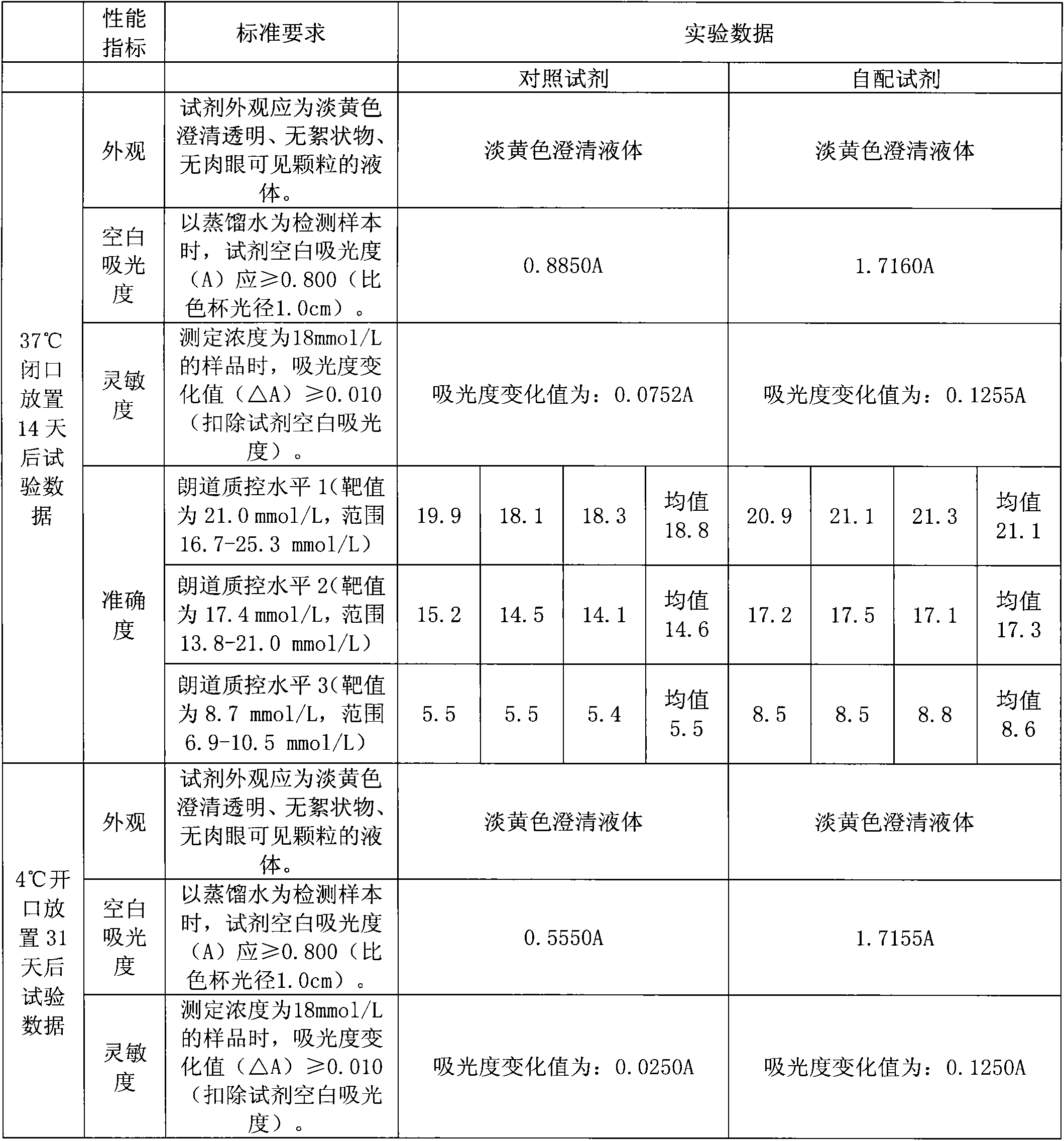
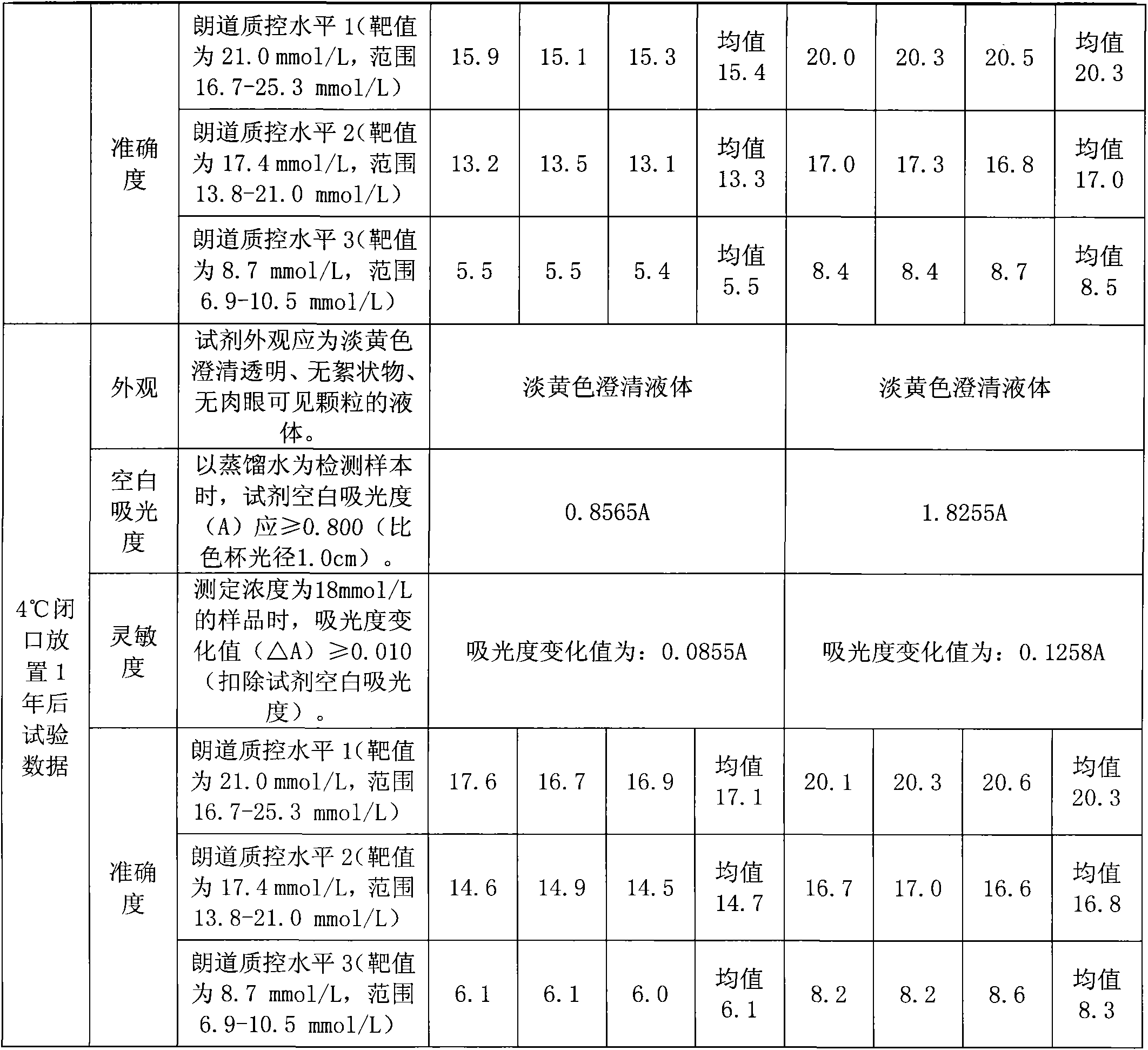
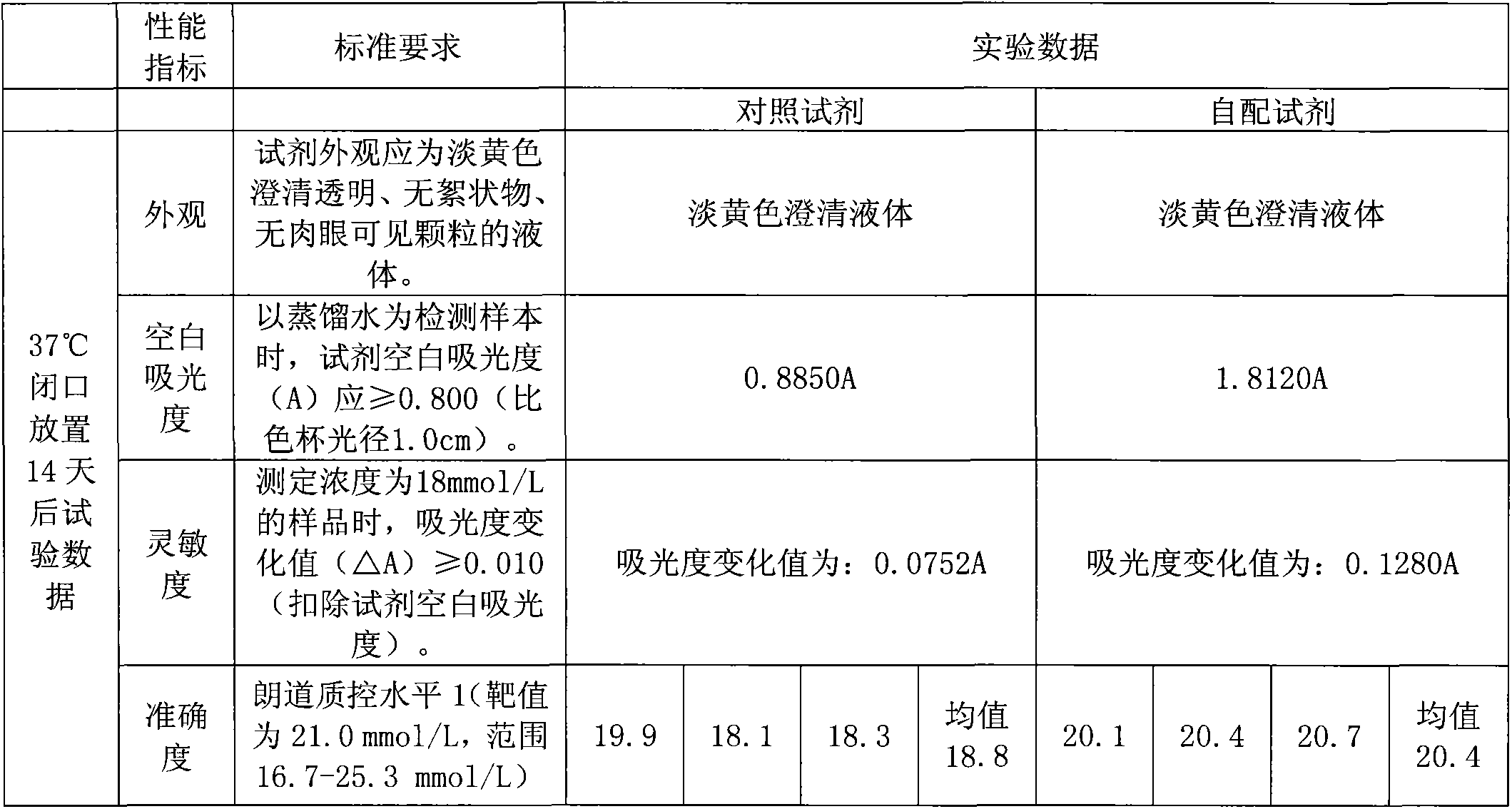
Kit for determining mitochondria aspartate aminotransferase
InactiveCN102010890AUndisturbedThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementLactate dehydrogenaseActivity ratios
The invention discloses a kit for determining mitochondria aspartate aminotransferase, containing a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 contains aspartic acid protease, alpha- ketoglutaric acid, L-aspartic acid, malate dehydrogenase, lactate dehydrogenase, a preservative and PEG6000. The enzyme activity ratio of the aspartic acid protease to the malate dehydrogenase to the lactate dehydrogenase in the reagent 1 is (0.1-50):(0.1-50):(0.1-10); the ratio of the alpha- ketoglutaric acid to the malate dehydrogenase is (0.1-60)g:(0.1-50)KU; the mass ratio of the alpha- ketoglutaric acid to the L-aspartic acid to the preservative to the PEG6000 is (0.1-60):(5-200):(0.2-10):(1-100); and the mass ratio of NADH (Reduced Form of Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotid) to a preservative to EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid).2Na is (0.5-10):(0.2-10):(1-50). The kit for determining the mitochondria aspartate aminotransferase is used for determining the activity of the determining mitochondria aspartate aminotransferase, is free from the interference of high cell plasma aspartate aminotransferase and obtains accurate result.
Owner:北京迪迈医学诊断技术有限公司
Carbon dioxide measurement kit
InactiveCN103558370AEasy to useEasy to operateBiological testingFlavin adenine dinucleotidePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention provides a carbon dioxide measurement kit. The carbon dioxide measurement kit mainly comprises the following components: 50 to 200mM of a buffer solution, 10 to 50% of a stabilizer, 0.1 to 5% of a surface active agent, 0.1 to 5g / L of a preservative, 1 to 20mM of a reaction accelerator, 2 to 10mM of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide (reduction type), 5 to 50g / L of phosphoenolpyruvic acid, 50 to 500U / L of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, and 1 to 3KU / L of malate dehydrogenase; a recycling system of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide (reduction type) comprises (1) 2 to 20g / L of glucose substrate, (2) 100 to 2,000U / L of corresponding glucose dehydrogenase, and (3) 1 to 5mM of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide. The carbon dioxide measurement kit is convenient to use and simple to operate; the components participating in coupling reaction are extra added, so that no pollution caused by endogenous and allogenic substances are introduced; the rate of the recycling system is below the main reaction rate, thus the main reaction cannot be interfered; the carbon dioxide measurement kit is high in stability and can be used for a long time.
Owner:QINGDAO JINYANG BIOTECH
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN106434772AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMalate synthaseXylose fermentation
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for producing malic acid efficiently by means of xylose fermentation and a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. In the recombinant bacterium, hosphopentose isomerase, L-fuculokinase, L-fucose-1-phosphate aldolase, aldehyde dehydrogenase, glycolate oxidase and malate synthase are overexpressed, and meanwhile xylulokinase, malate dehydrogenase and fumarate hydratase are knocked out, so that a malic acid synthesis route is obtained. According to the recombinant bacterium, the malic acid yield and the xylose conversion rate in shake flask culture and fermentation tank culture can reach ideal levels, and a good industrialized application prospect is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method, reagent and kit for quantitative determination of mitochondrial AST activity in human serum
InactiveCN104865214AAccurate detectionSimple and fast operationColor/spectral properties measurementsLactate dehydrogenaseAminotransferase activity
The invention relates to a reagent for the quantitative determination of mitochondrial AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase) activity in human serum. The reagent comprises a reagent I and a reagent II which are placed separately, wherein the reagent I contains Tris buffer, L-aspartic acid, malate dehydrogenase, lactate dehydrogenase, a c-AST goat anti-human antibody and an enzyme stabilizer; the reagent II contains alpha-ketoglutaric acid and reductive coenzyme. A kit and a detection method adopted in the invention only require tens of microlitres of serum, need no centrifugation or electrophoresis and other separation treatments, are easy to operate, can meet the requirements of automatic analysis, and are applicable to the timely and accurate detection of large-scale samples.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LANSEN BIOTECH
The Method for Enhancement of Photosynthesis and Biomass of Plant by Plastid Transformation of Malate Dehydrogenase
InactiveUS20100043096A1Increase biomassPromote photosynthesisRoot feedersClimate change adaptationOrganismGMO Plants
The present invention relates to a method for enhancement of photosynthesis and biomass of a plant by plastid transformation with MDH gene, more precisely a method for enhancement of photosynthesis and biomass of C3 plant by plastid transformation system with MDH gene. The MDH plastid transgenic plant prepared by the method of the present invention exhibits not only increased photosynthesis efficiency but also increased growth rate, leaf area, stem diameter and biomass of the plant, compared with the control plant. Therefore, the plastid transformed C3 plant prepared by C4 type gene introduction can be effectively used for enhancing photosynthesis and biomass of the plant.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Hydrophilic domain protein gene
InactiveCN106117323AReduce aggregationAvoid structural changesEnzyme stabilisationBacteria peptidesCrystallographyLactate dehydrogenase
The present invention finds the protective effect of the hydrophilic domain on the enzyme in the Dhp(DR1172) protein. The present invention expresses a core protein containing a complete hydrophilic domain. The experimental results showed that the protein was repeatedly frozen and thawed in liquid nitrogen and H 2 O 2 Both can protect the activities of malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) under shock stress conditions, and both can reduce the aggregation of LDH and prevent its structure from changing to protect its activity.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cloning and application of promoter sequence of corn malate dehydrogenase gene
InactiveCN101979551AExcellent inbred homozygousVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsPlant cellGermplasm
The invention discloses cloning and application of a promoter sequence of a corn malate dehydrogenase gene. In a method, the promoter sequence of the cytoplasmic corn malate dehydrogenase gene is cloned in a corn genome and fused with a target gene coding region or a ribose nucleic acid interfere (RNAi) structure to construct a plant expression structure; recombination genes are imported into plant cells by using transgene technology so as to obtain transgenic plants; the transgenic plants and later generations thereof with obviously improved stress resistance or economic characteristic are selected by detecting transgenic expression or goal characteristic to create a novel germplasm with application prospect in plant breeding.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Determination of blood ammonia content and blood ammonia diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1778946AStrong specificityImprove test accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention is about a method of measuring the content of blood ammonia, and it also concerns the reagent box of blood ammonia diagnosis. This invention belongs to the field of medical testing and measuring technology. The reagent box is consisted of buffer solution, 2ú¡ketoglutarate, reduced coenzyme, phosphoenolpyruvate, glutamate dehydrogenase, glutamate decarboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, malate dehydrogenase and stabilizer. Firstly, we cause an enzyme-coupled reaction through mixing the sample and the reagent according to a certain proportion of volume; secondly, put the final reactant under the biochemical analyzer and test the absorbance variational situation (speed) of dominant wavelength; then we can get the content ofblood ammonia. By using this invention, we can get the necessary measuring result with high sensitiveness and fine precision through biochemical analyzer, and the result would not be contaminated by material of internal and exogenous sources. Thus, this method can be conveniently promoted and applied.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
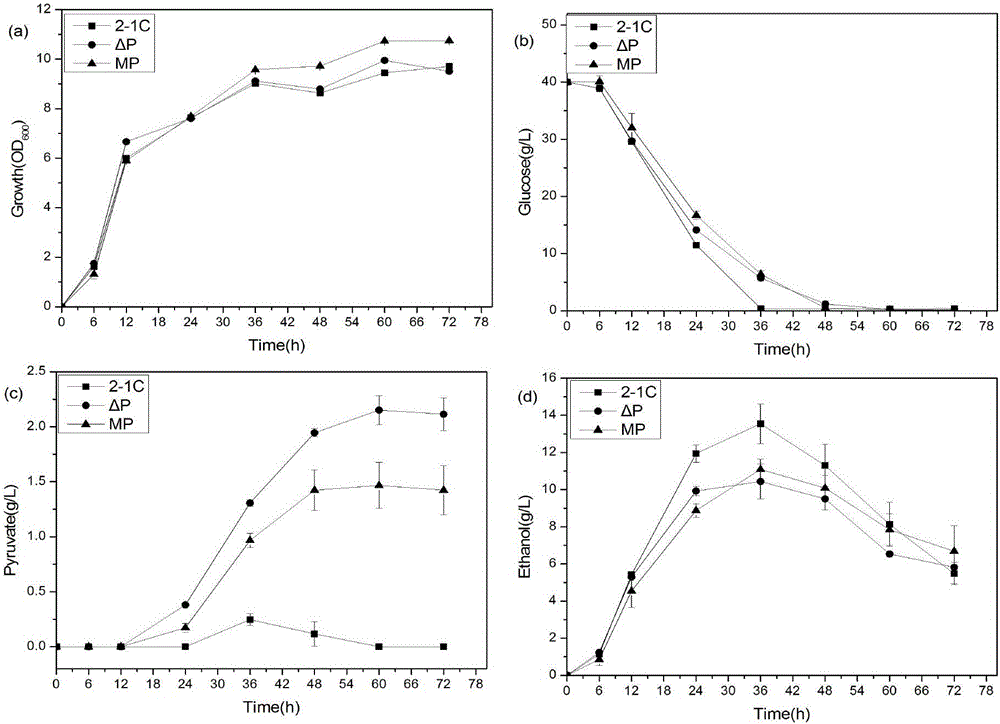
Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene engineering bacteria for producing succinic acid and application thereof
ActiveCN105838632ARealize accumulationReduce lossesFungiMicroorganism based processesWild typeSuccinic acid
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae gene engineering bacteria for producing succinic acid and application thereof, and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering. Malate dehydrogenase gene RoMDH from rhizopus oryzae is adopted to replace PDC1, the yield of ethanol obtained by fermentation of wild saccharomyces cerevisiae reaches the maximum value 13.55 plus or minus 1.062g / L, and the yield of improved strain MP ethanol is 11.09 plus or minus 0.539g / L, and compared with the yield obtained by adopting the wild type, the yield is reduced by 18.15 percent. On the basis, SDH2 gene is knocked out. After culture medium optimization, MP Delta S deleted strain can accumulate succinic acid by 0.698 plus or minus 0.0285g / L, and by contrast, the wild saccharomyces cerevisiae does not accumulate succinic acid. The saccharomyces cerevisiae gene engineering bacteria can effectively reduce the loss of a carbon flow, creates a condition for the engineering yeast to efficiently produce succinic acid, and has a good industrial application value and prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Biocatalyst for production of d-lactic acid
ActiveCN101654666AImprove productivityHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSuccinic acid
The subject of the present invention is to provide a method for producing D-lactic acid in high yield, and to provide a method for producing D-lactic acid with high selectivity, in which optical purity is high and a by-product organic acid is small. A microorganism, wherein activity of pyruvate formate-lyase (pfl-) is inactivated or decreased, and further activity of Escherichia coli-derived NADH-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase (ldhA) is enhanced, is cultured to produce a remarkable amount of D-lactic acid in a short time. With regard to a method for enhancing ldhA activity, by linking, on agenome, a gene encoding 1dhA with a promoter of a gene which controls expression of a protein involved in a glycolytic pathway, a nucleic acid biosynthesis pathway or an amino acid biosynthesis pathway, suitable results are obtained compared to the method for enhancing expression of the gene using an expression vector. In addition, a microorganism in which a did gene is substantially inactivatedor decreased is cultured to produce high quality D-lactic acid with reduced concentration of pyruvic acid. Furthermore, it is possible to suppress by-production of succinic acid and fumaric acid whilemaintaining high D-lactic acid productivity by using the above-mentioned microorganism having a TCA cycle, wherein activity of malate dehydrogenase (mdh) is inactivated or decreased, and further activity of aspartate ammonia-lyase (aspA) is inactivated or decreased.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Method for screening bacterial strains with high output of low-temperature MDH (malate dehydrogenase)
InactiveCN108977386AQuick filterPrecise screeningBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBromocresol greenMethyl thiazolyl tetrazolium
The invention relates to the field of fermenting engineering, in particular to a method for screening bacterial strains with high output of low-temperature MDH (malate dehydrogenase). The MDH is a keyenzyme for cell center oxidizing channels, and is closely related with the movement of bacterial flagellum in related reports. The method has the advantages that the bromocresol green is used for primary screening, and the bacterial strain with stronger acid production property is screened out; the power property of the bacterial strain is detected by MTT (methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium), the screening is performed for the second time, and the bacterial strain with stronger power property is selected to test the activity of the enzyme; the low-temperature bacterial strain with high output of MDHs can be accurately screened out by double screening; finally, the activity of the enzyme is detected to finally determine the high-output bacterial strain; the bacterial strains with high output oflow-temperature intracellular MDH can be conveniently and accurately screened out within 20 days, and the blank in the related field of screening of culture mediums by the MDH is filled.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
Detection kit for aspartate aminotransferase with good repeatability
InactiveCN109724933AHigh activityEliminate distractionsColor/spectral properties measurementsLactate dehydrogenaseLithium chloride
The invention relates to the technical field of biochemical detection, in particular to a detection kit for aspartate aminotransferase with good repeatability and a preparation and application methodthereof. The kit comprises a reagent R1 and a reagent R2. The reagent R1 comprises a buffer solution, a PH value adjusting agent, L-aspartic acid, potassium ferrocyanide, an AP5A, an EGTA, lithium chloride, a surfactant, levoglucosides, lactate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase, and a preservative component. The reagent R2 comprises a buffer solution, a PH value adjusting agent, a BSA, a preservative, a-ketoglutarate, and NADH components. The kit is optimized in terms of removing reflection interference, increasing the activity of the reacted enzyme, improving the uniformity of the reactionsystem, and preferably selecting the excellent sub-wavelength. The kit remarkably improves the repeatability of reagents, especially the repeatability of low-value samples so as to improve the accuracy of clinical diagnosis results and achieve great clinical practical value.
Owner:BIOBASE BIODUSTRY (SHANDONG) CO LTD
Stable reagent for determining glutamic oxalacetic transaminase
The invention provides a stable reagent for determining glutamic oxalacetic transaminase. The reagent is a dual reagent and comprises TRIS (tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane), NADH (reduced form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotid), LDH (lactate dehydrogenase), MDH (malate dehydrogenase), EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid), TritonX-100, BSA (bovine serum albumin) and Proclin. According to the reagent, the heat stability, onboard stability and transportation stability of an in-vitro diagnosis reagent of an NADH indicating system are effectively improved; and the shelf life of a reagent kit can be prolonged effectively.
Owner:BEIJING BEIJIAN XINCHUANGYUAN BIOLOGICAL TECH
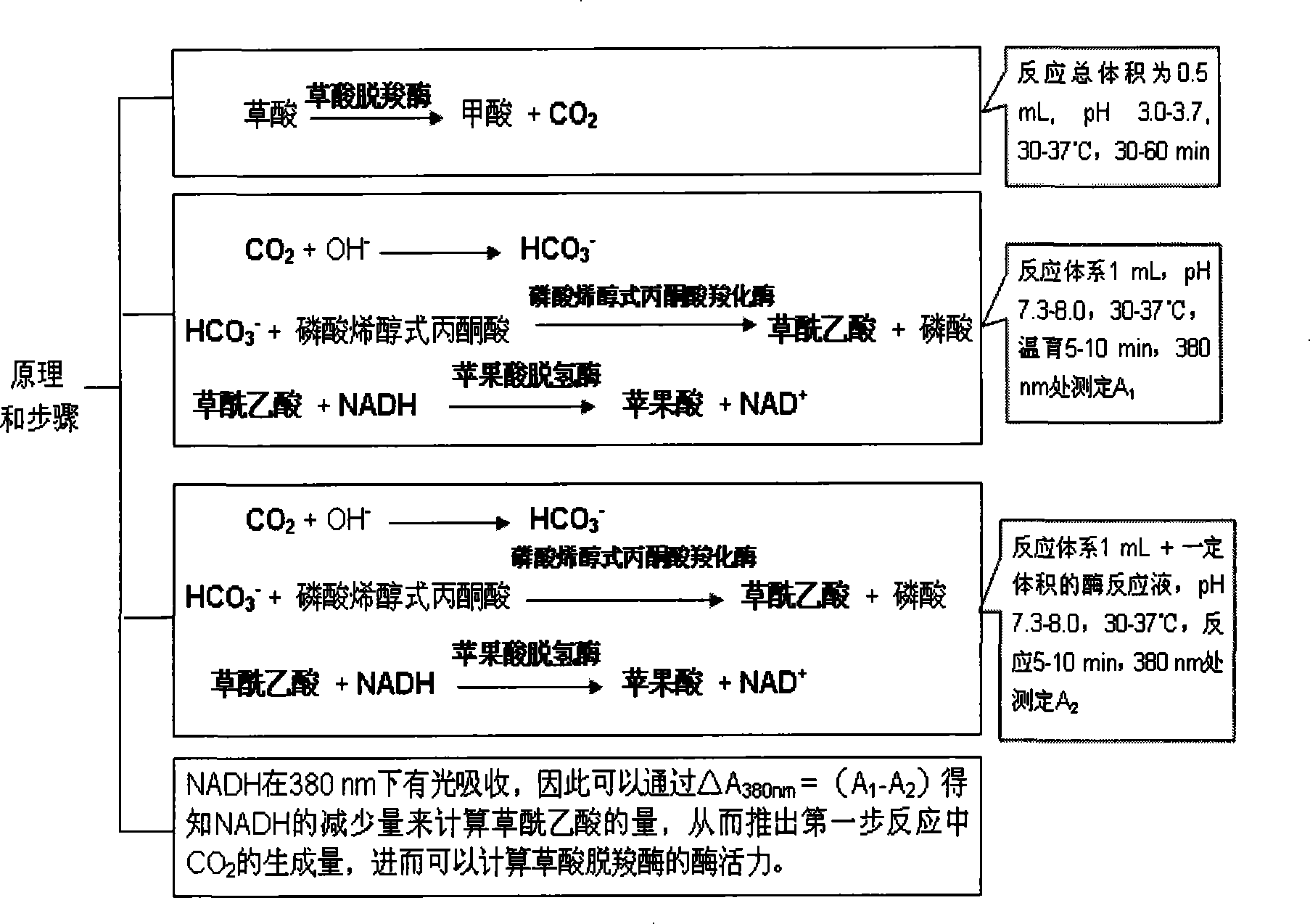
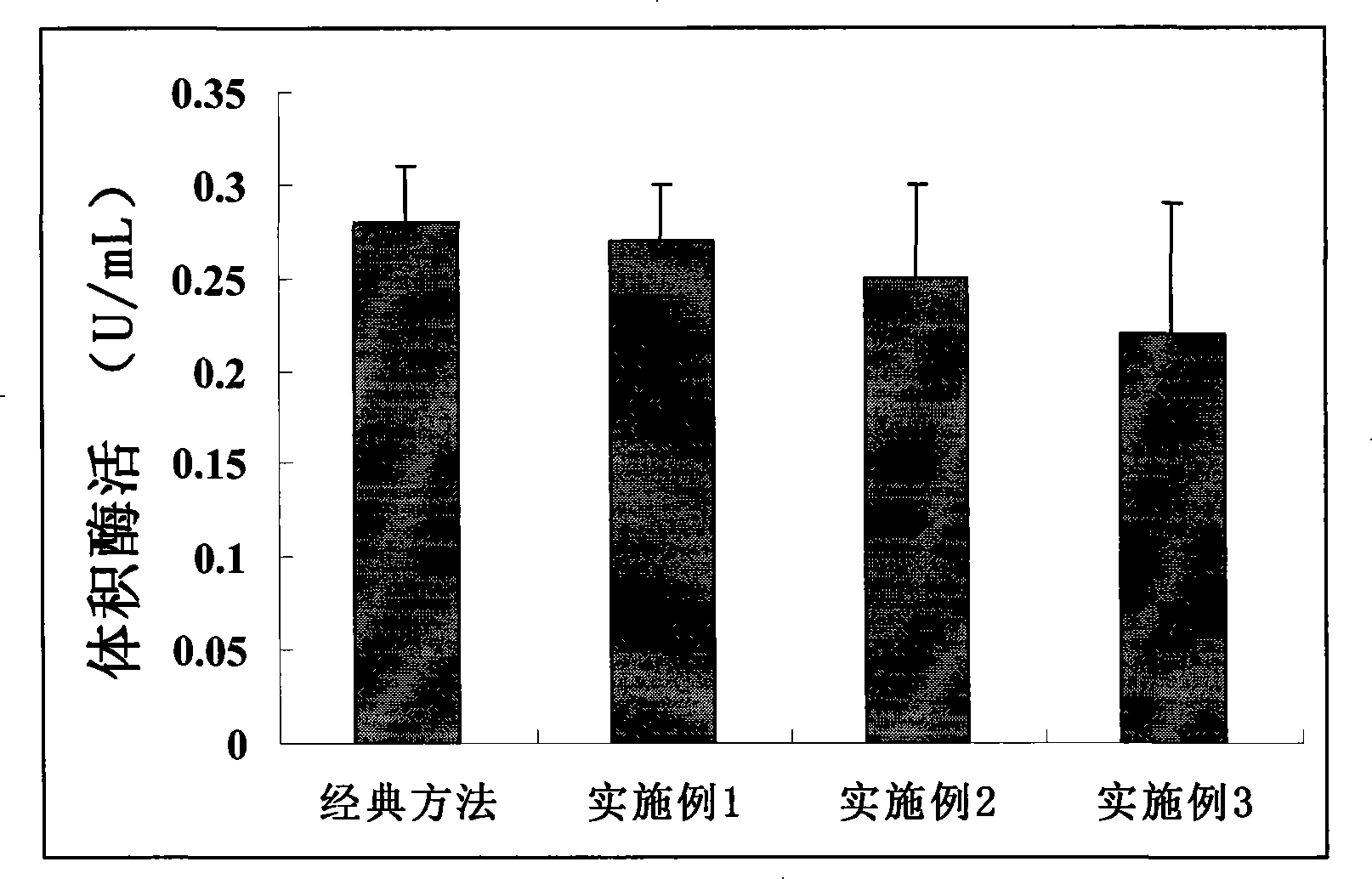
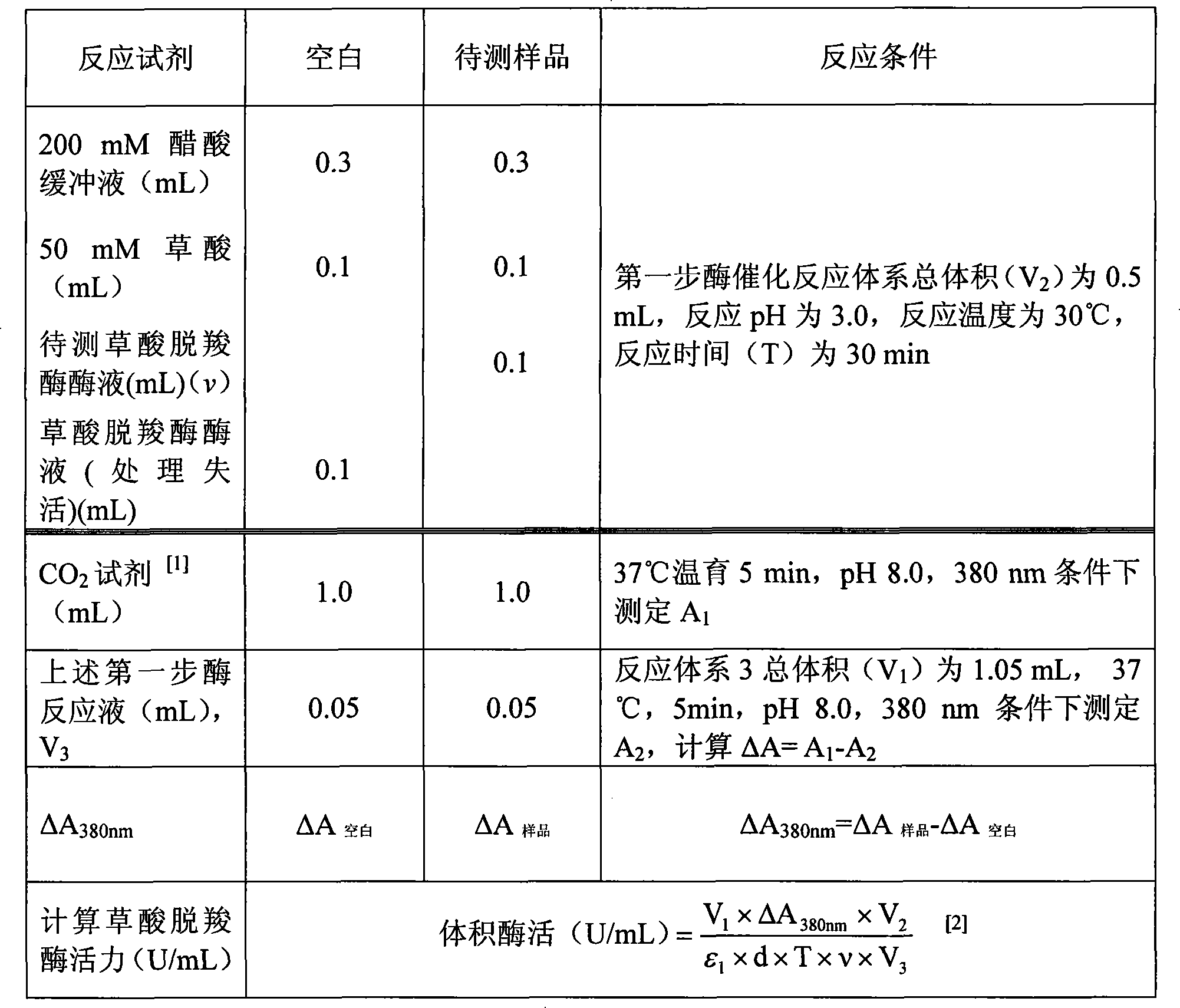
Method for calculating oxalate decarboxylase activity by determining carbon dioxide concentration
InactiveCN101241073AEasy to measureShort reaction timeAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylasePhosphate
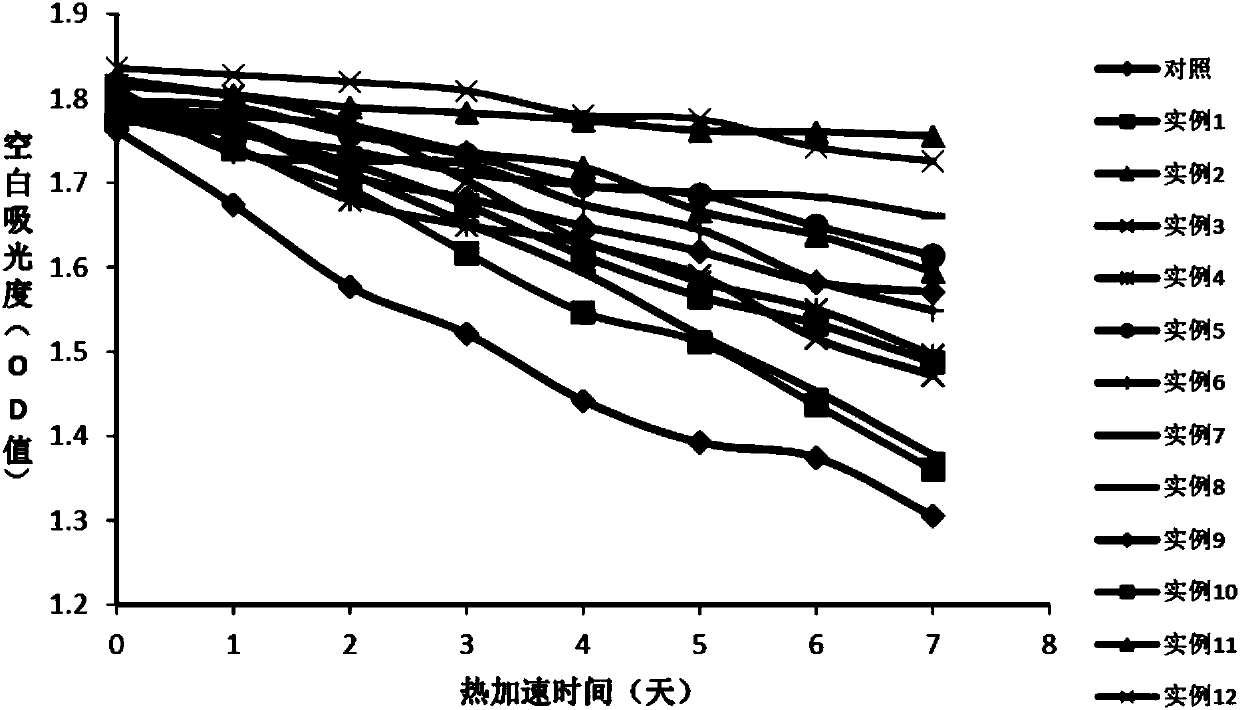
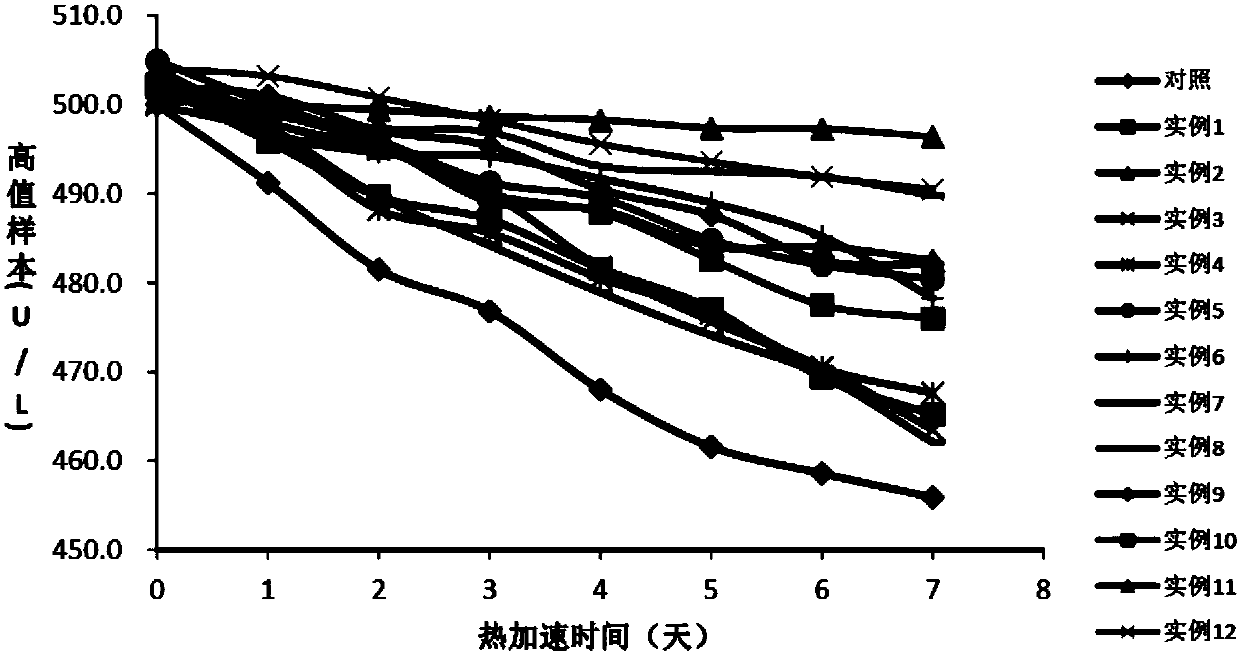
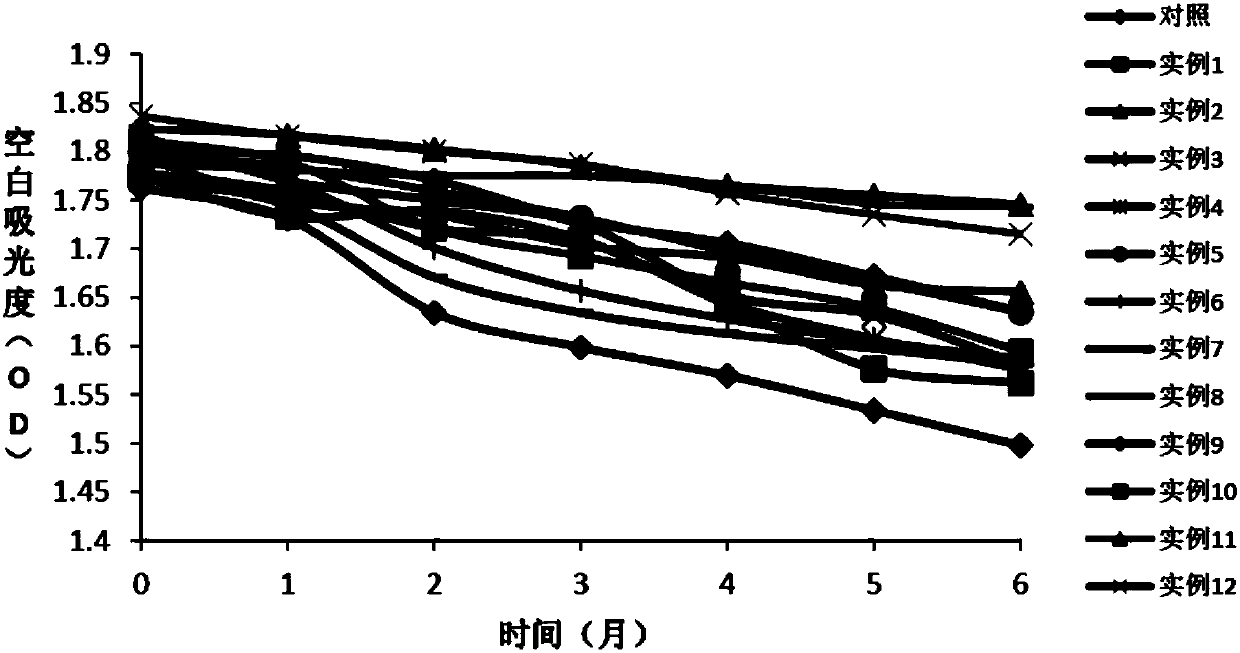
The present invention relates to a method to calculate oxalate decarboxylase activity by detecting carbon dioxide concentration, which comprises 1) mixing substrate, oxalate decarboxylase, and HAC buffer at a temperature between of 30-37 degree C for 0.5 to 1 hour; 2) confecting Tris-HCl buffer at pH values between 7.3-8.5 containing phosphate enol type pyruvate, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, NADH, malate dehydrogenase at a temperature between of 30-37 degree C, after incubation, detecting A1 at 380 nm location; 3) adding the reaction solution of step 1) into the solution of step 2), reacting at a temperature between of 30-37 degree C and detecting A2 at 380 nm location; 4) calculating NADH decrement according to the formula of delta A380nm=A1-A2, and calculating the generated carbon dioxide consistence according to the reaction principles to calculate oxalate decarboxylase activity. The said method is a good method for dectecting oxalate decarboxylase which is credibility, high sensitivity, and the valve detected thereby is close to the value detected by the classical method for detecting oxalate decarboxylase.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Malate dehyrogenases
Owner:TECHNIP ENERGIES FRANCE
Tea tree cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase gene and encoding protein thereof
The invention discloses a tea tree cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase gene and an encoding protein thereof, wherein the enzyme has an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO: 1. Compared with the prior art, the malate dehydrogenase containing a Cam-cyMDH gene can be widely used for separating D, L-malic acid and be applied to the tea tree F1 hybrid.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Synthesis method of 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid
The invention discloses a synthesis method of 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid. The method takes allochenodeoxycholic acid as an initial raw material and includes the following steps: adding phosphate buffer, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, lactate dehydrogenase, 7-[alpha]hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and sodium pyruvate, performing reaction, and performing cooling after enzyme was inactivated through high temperature; additionally adding L-sodium malate, malate dehydrogenase and 7-[beta]hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase to react, and performing cooling to room temperature after the enzyme was inactivated through high temperature; and obtaining the 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid through filtration, washing and drying. The overall process of the method includes the oxidation and reduction steps of the allochenodeoxycholic acid and the synthesis of the 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid. The whole reaction of the method is conducted in an aqueous solution without using organic solvents; the method is simple in technology and easy to operate; and the purity of the obtained 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid can reach more than 98.5%, and the obtained 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid can be used as samples of pharmaceutical properties such as toxicology and pharmacology in pharmaceutical research institutions and can also be used as impurity reference substances during quality research of ursodeoxycholic acid.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN BAILING BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Malate dehydrogenase electrode as well as preparation method and application thereof
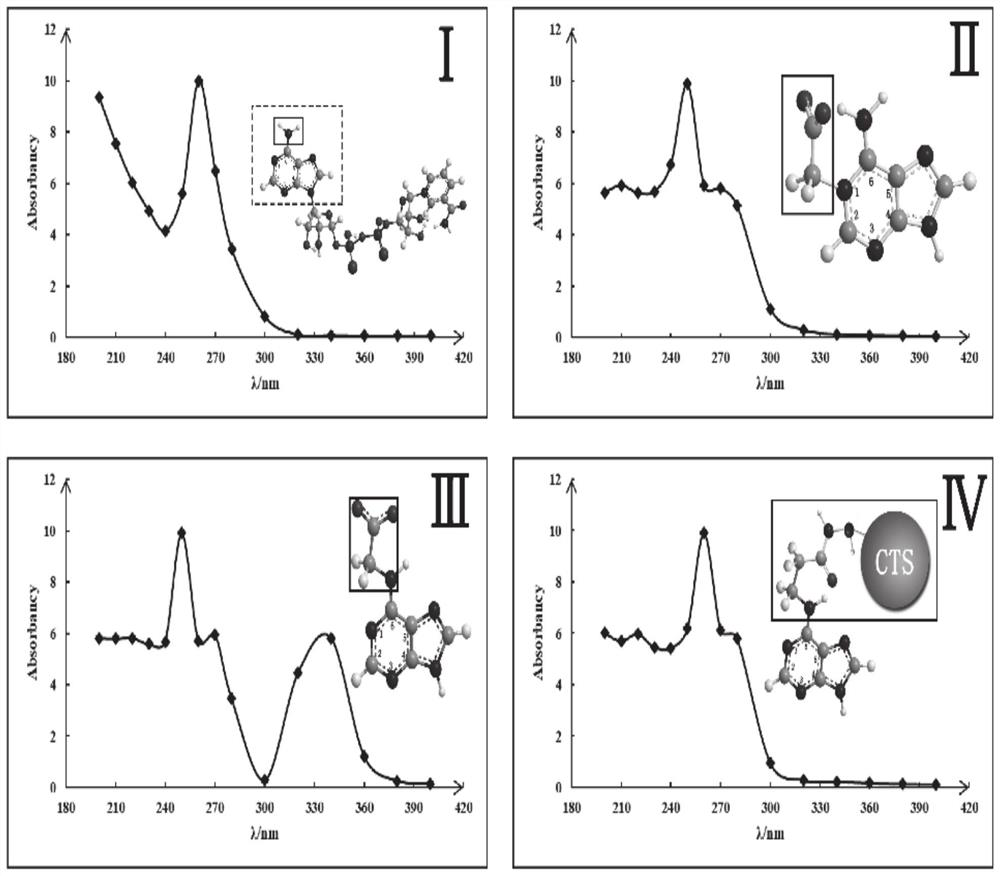
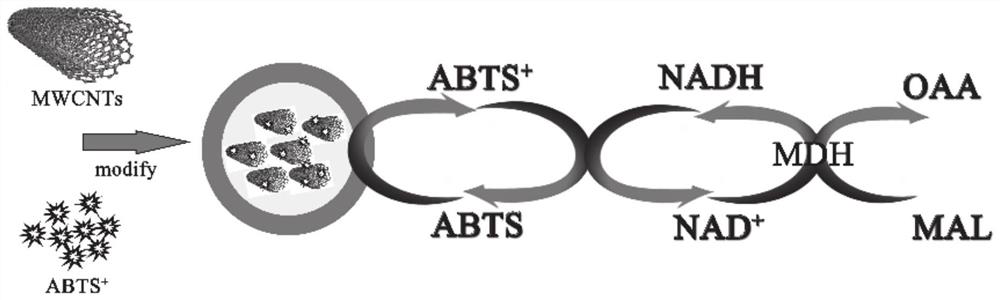
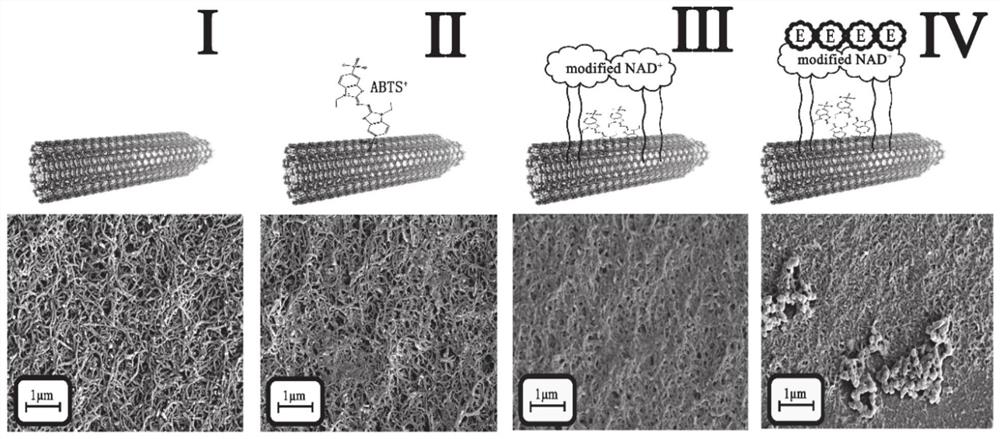
ActiveCN111896599AHigh activityPerformance is not affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesCarbon nanotubeCombinatorial chemistry
The invention provides a malate dehydrogenase electrode as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: chemically modifying a coenzyme factor smallmolecule NAD < + > non-active part through a chemical means, covalently connecting the chemically modified NAD < + > with a chitosan carrier to obtain an NAD < + >- chitosan compound, modifying a carbon nanotube on the surface of a substrate electrode, and detecting NADH by using the carbon nanotube as a substrate material; electrically depositing ABTS on the electrode, and achieving NAD <+> in-situ regeneration by using the ABTS as an electron mediator; dropwise adding an NAD < + >- chitosan compound to realize fixation of NAD < + > on the surface of the electrode; connecting dehydrogenase tothe chitosan carrier through glutaraldehyde cross-linking action to obtain a dehydrogenase electrode; the immobilization and regeneration method of NAD < + > can be combined with different types of dehydrogenases to prepare various dehydrogenase electrodes / biosensors. The method has wide practical application value in the field of biosensor preparation.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
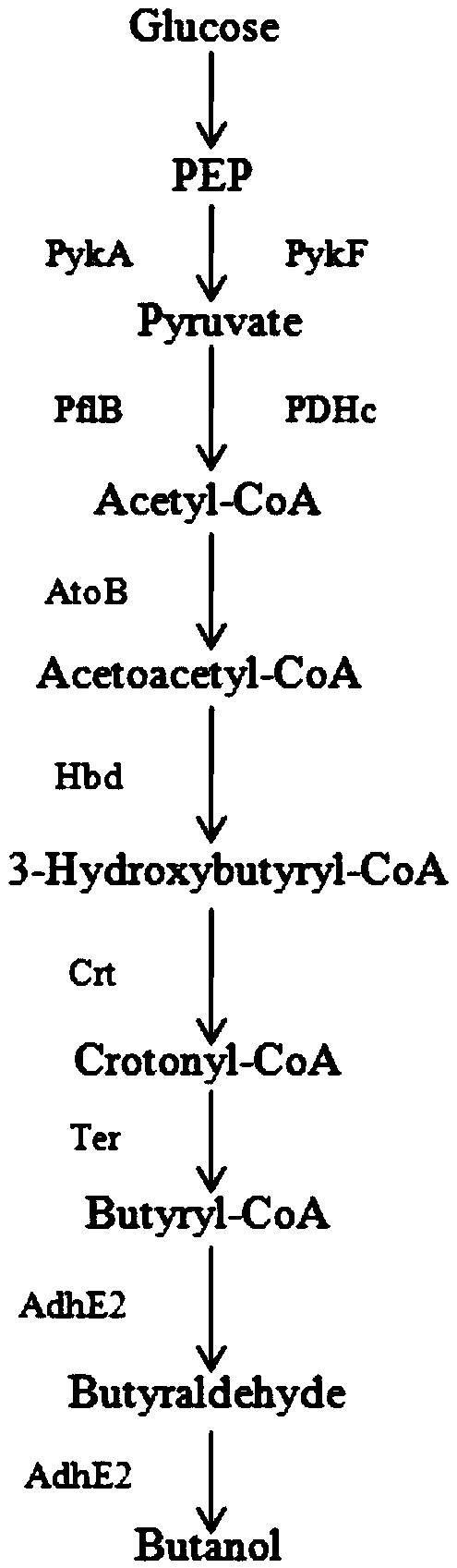
Method for improving yield of butanol produced by escherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for improving yield of butanol produced by escherichia coli. According to the method for constructing recombinant bacteria, expression of a malate dehydrogenase gene (mdh) on the genome of an original strain for producing butanol is inhibited or silenced to obtain the recombinant bacteria. Experiments prove that the modified target capable of promoting escherichia coli to produce butanol is the malate dehydrogenase gene (Genbank: mdh gene (b3236) in the NC_000913.3 sequence). By a lembda-red homogenous recombinant system knockout technology, after the mdh gene of the engineering strain of escherichia coli for producing butanol is knocked out, the butanol output can be increased by 283 percent, and the yield can be increased by 89 percent.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for performing secretory expression of glucose oxidase based on optimization of metabolic engineering, recombinant bacterium and application thereof
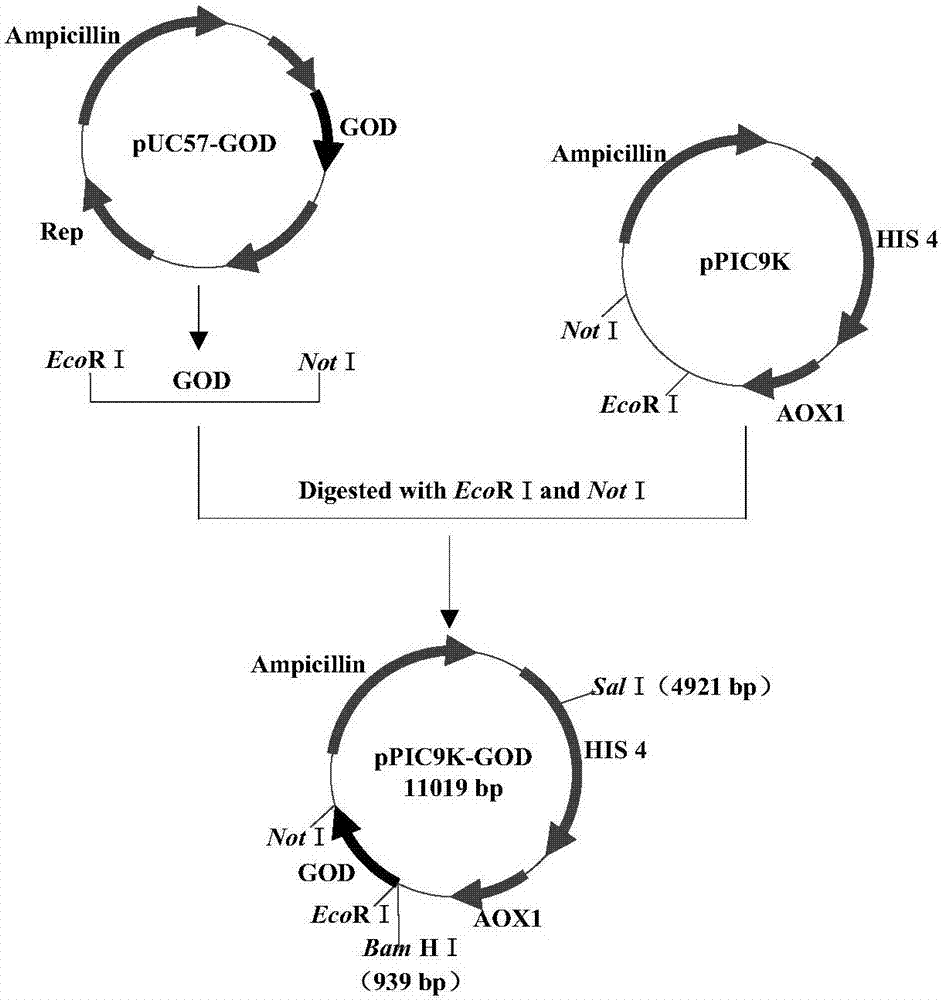
The invention relates to a method for performing secretory expression of glucose oxidase (GOD) based on the optimization of metabolic engineering, a recombinant bacterium and application thereof. The invention provides a method which can efficiently secretorily express GOD and improve the enzyme activity thereof. The GOD and malic acid dehydrogenase 1 coding gene (mdh1) or 6-phosphogluconolactonase coding gene (sol3) is co-expressed in a yeast strain, so that the efficient expression of the GOD is realized. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a recombinant bacterium for efficiently secreting the GOD built by adopting pichia pastoris as a host.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Use of sugar phosphates, sugar phosphate analogs, amino acids and/or amino acid analogs for modulating the glucolysis-enzyme complex, the malate asparate shuttle and/or the transaminases
InactiveUS20090163591A1Prevent proliferationSuppressing defensive over-reactionsBiocideAntipyreticSugar phosphatesEnzyme complex
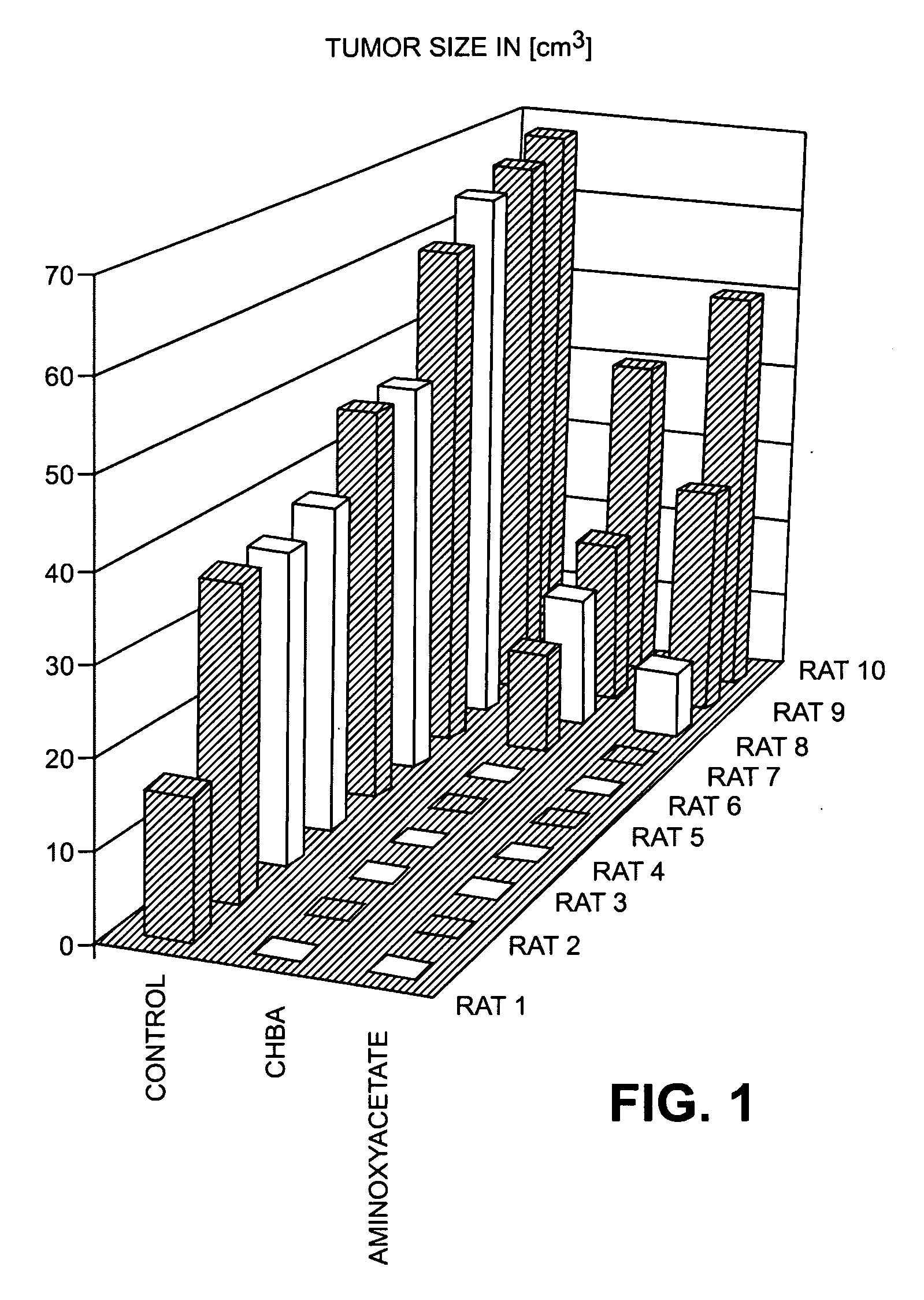
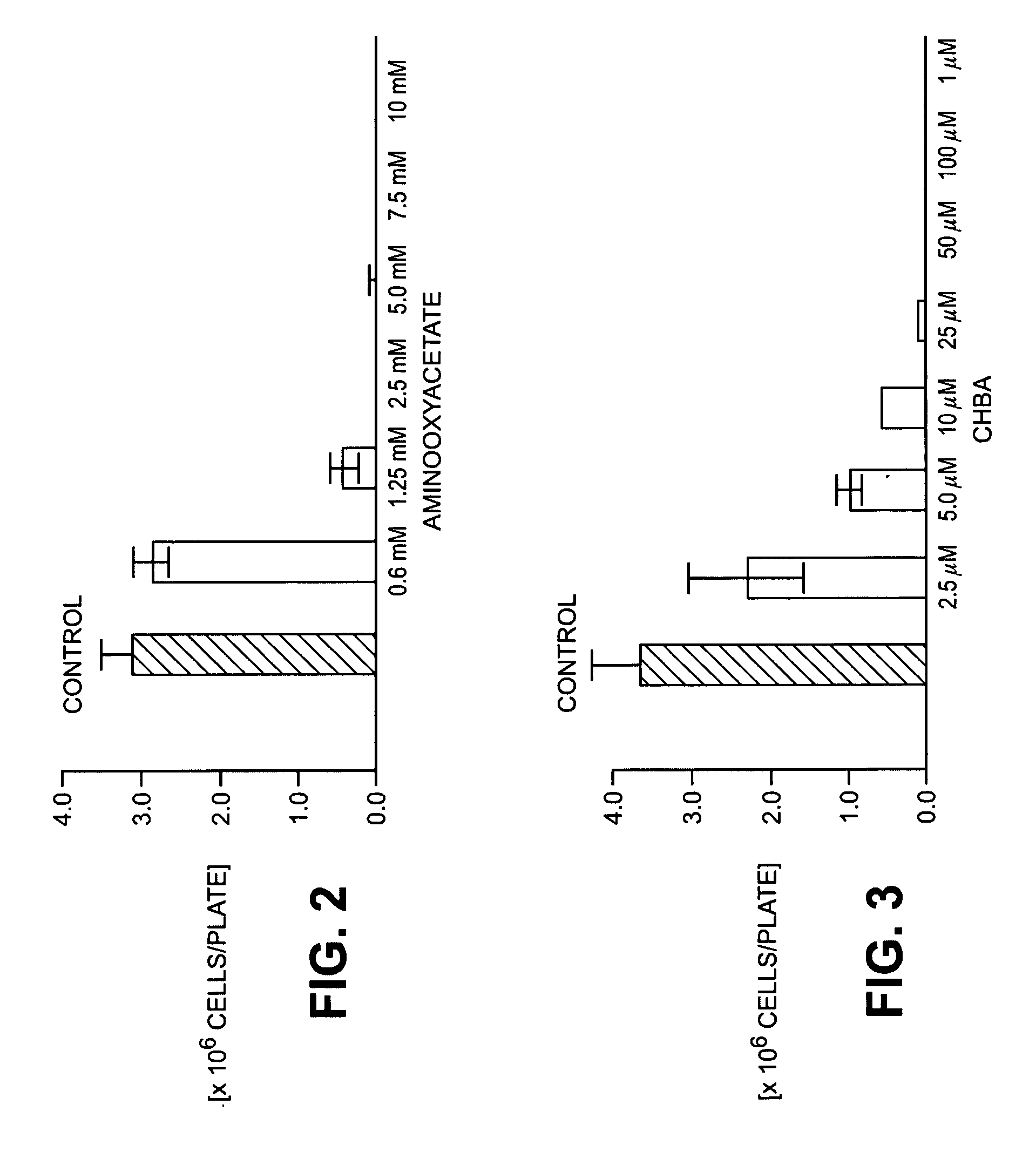
The invention relates to methods for the treatment of tumors and / or for immune suppression and / or sepsis by modulating the association of the glycolysis enzyme complex / M2-PK and / or by inhibition of transaminases and / or separation of the binding of the malate dehydrogenase to p36 comprising administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a substance selected from the group consisting of amino acids, amino acid analogs, sugar phosphates, sugar phosphate analogs, and mixtures of said substances.
Owner:EIGENBRODT ERICH +2
Carbon dioxide diagnosis/ determination reagent kit and carbon dioxide concentration determination method
InactiveCN101169439AFast measurementImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementCodecarboxylaseEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a carbon dioxide diagnosing / testing reagent box which utilizes the enzyme color method, and also relates to a method for testing the consistence of carbon dioxide, and the elements and the components of reagent. The invention belongs to the technical field of the medicine / food / environment check. The reagent box of the invention mainly comprises cushion fluid, pyruvic acid, malate dehydrogenase (codecarboxylase), reduced enzyme and stabilizer. A series of enzyme reactions occur by mixing the sample and the reagent according to a certain volume rate. Then the reactant is arranged under an ultraviolet and visible light analysis instrument to test the reduction extend and the speed of the absorbency at the 340nm of the main wavelength, thereby testing the consistence of the carbon dioxide. By adopting the invention, the testing result can be obtained by the ultraviolet and visible light analysis instrument, and the promotion and the application are convenient.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com










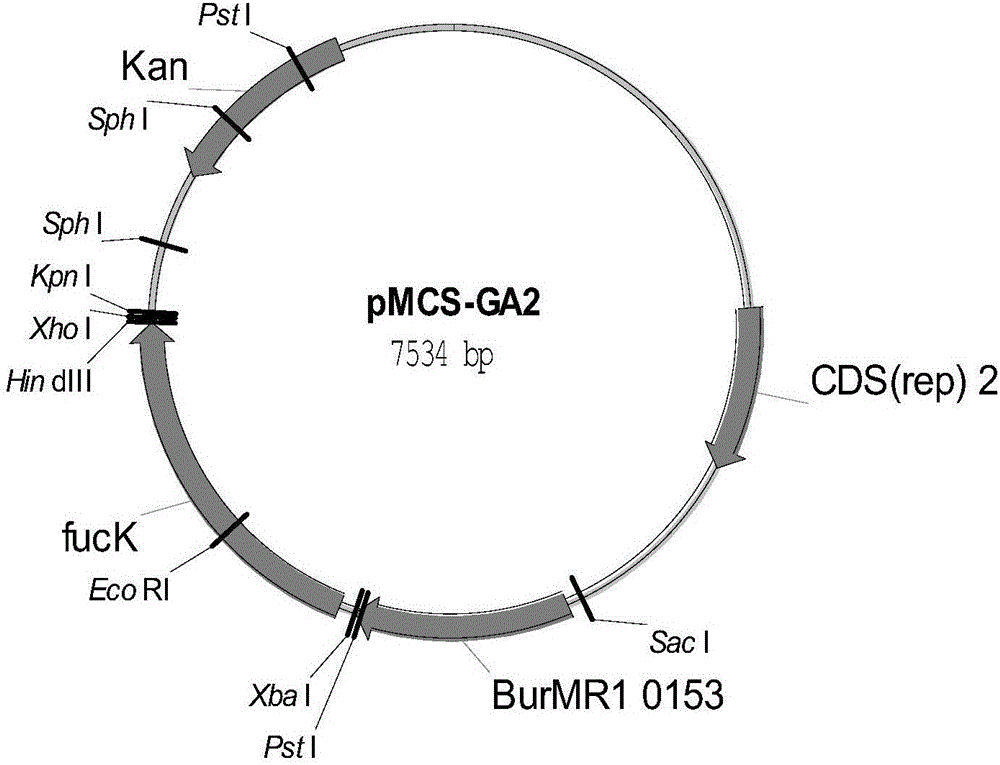
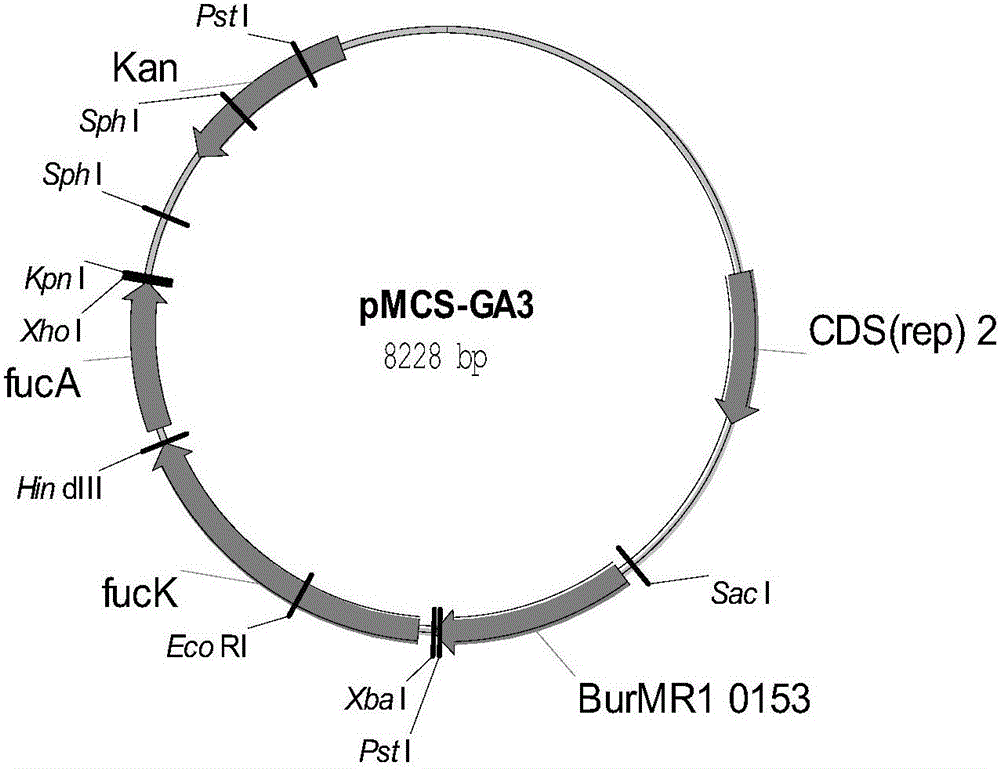



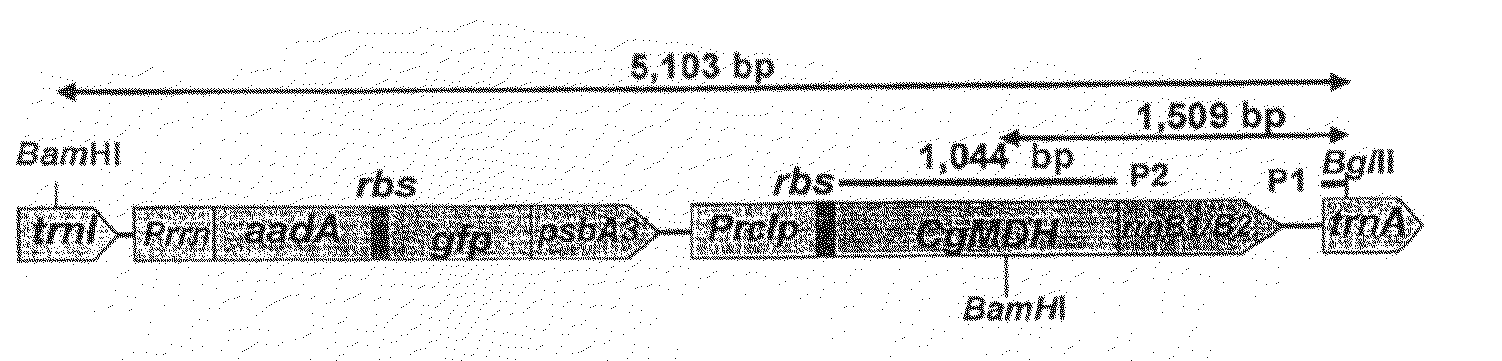














![Synthesis method of 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid Synthesis method of 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1b315145-f6d9-4f90-a1e5-9e6dc92b0acb/HDA0002893083090000011.png)