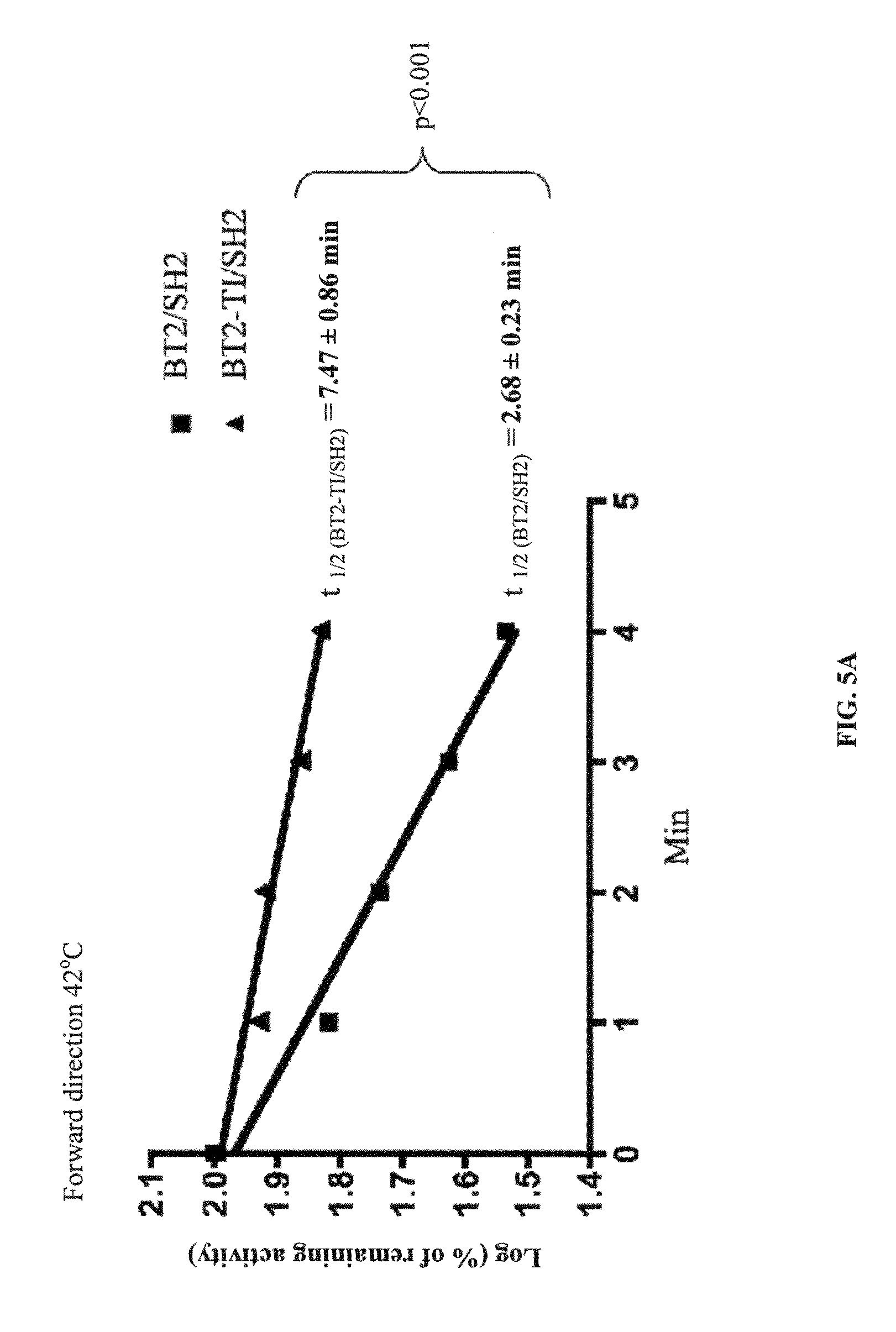
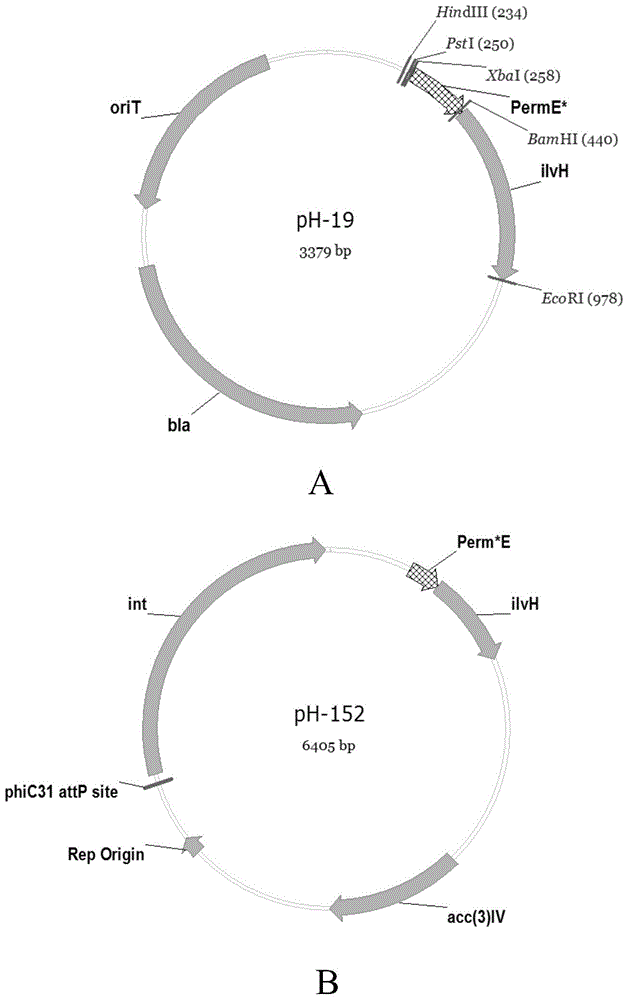
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Small subunit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Small Subunit. The structure of the small subunit is available in the PDB entries 1fka and 1fjg . The small subunit is in charge of information flow during protein synthesis.
Cotton promoter
A promoter isolated from a cotton gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase is described. The isolated promoter is operably linked to a coding sequence of interest to make a chimeric gene.
Owner:NOVARTIS FINANCE
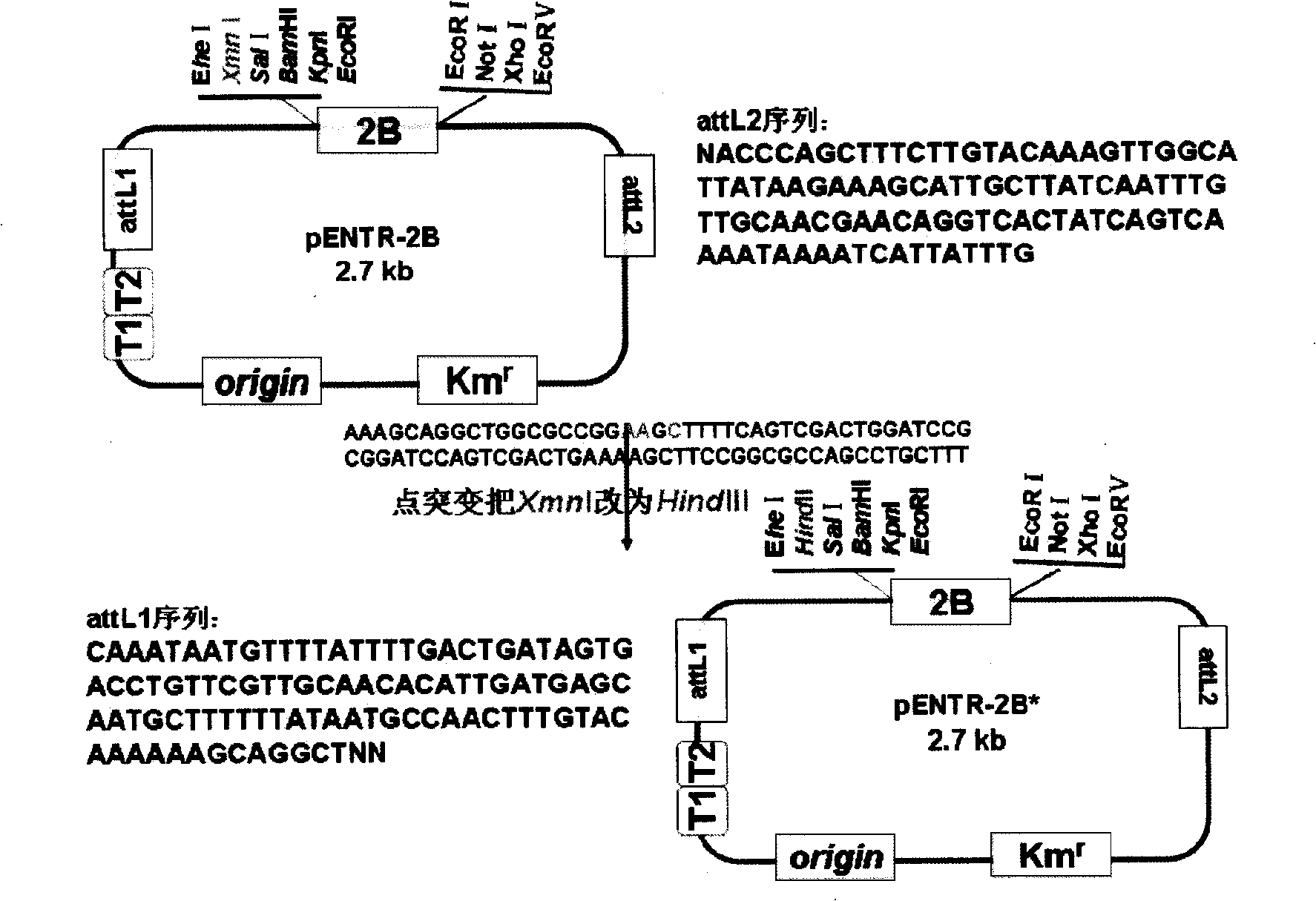
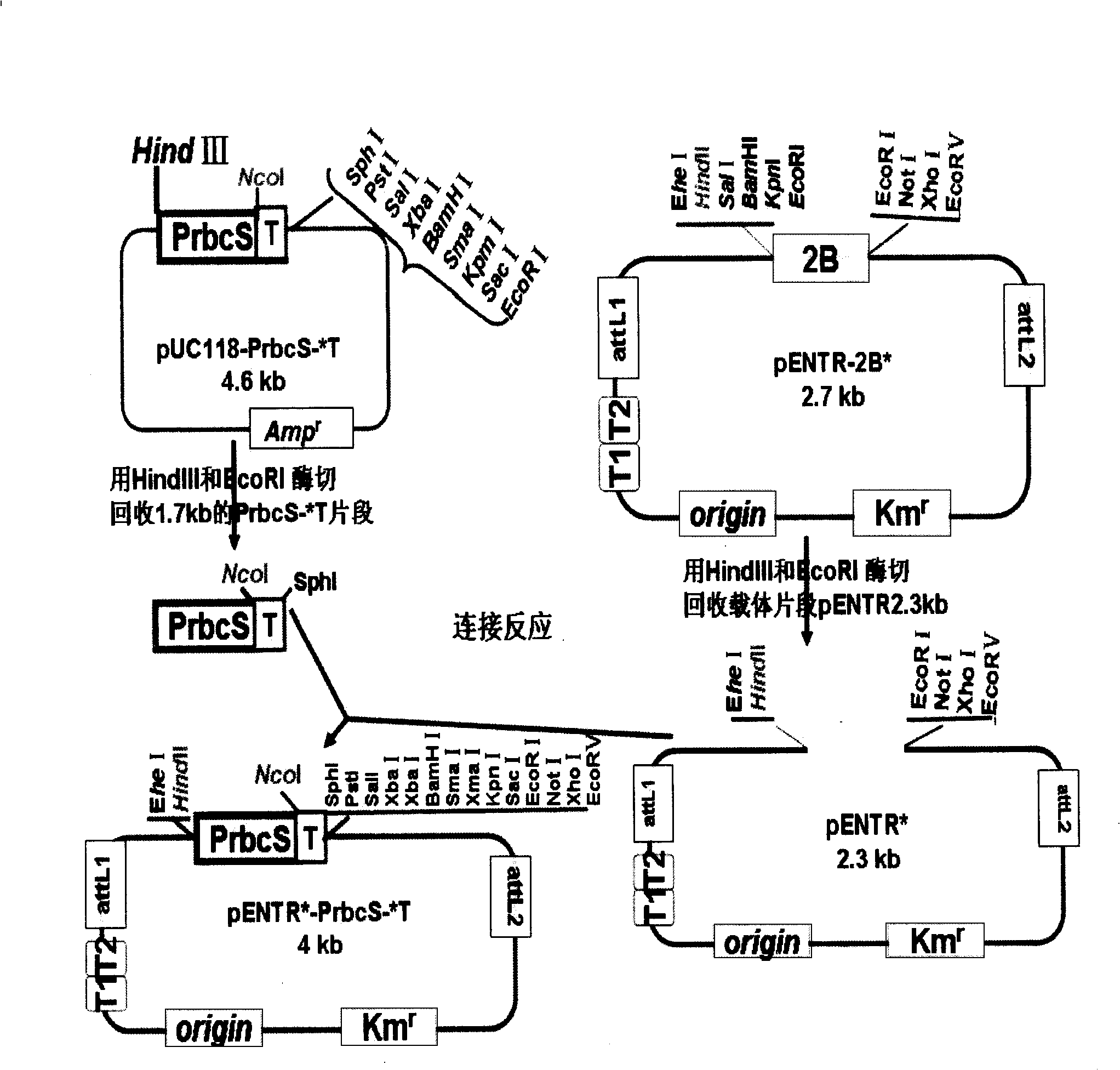
Gateway cloning entry vector, construction method and use thereof
The invention discloses a gateway cloning technology entry plasmid vector. The vector contains a photoinducible promoter (Prbcs) of a small subunit gene of 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) and a green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter gene. The invention also discloses a construction method and application of the vector. Through the vector, the gateway cloning technology can be utilized to quickly construct a photoinducible plant expression vector of a target gene to realize the high level expression of the target gene in plant leaves, the expression of the target gene is adjusted by light intensity, and expressed target protein can be positioned into chloroplast or cytoplasm.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
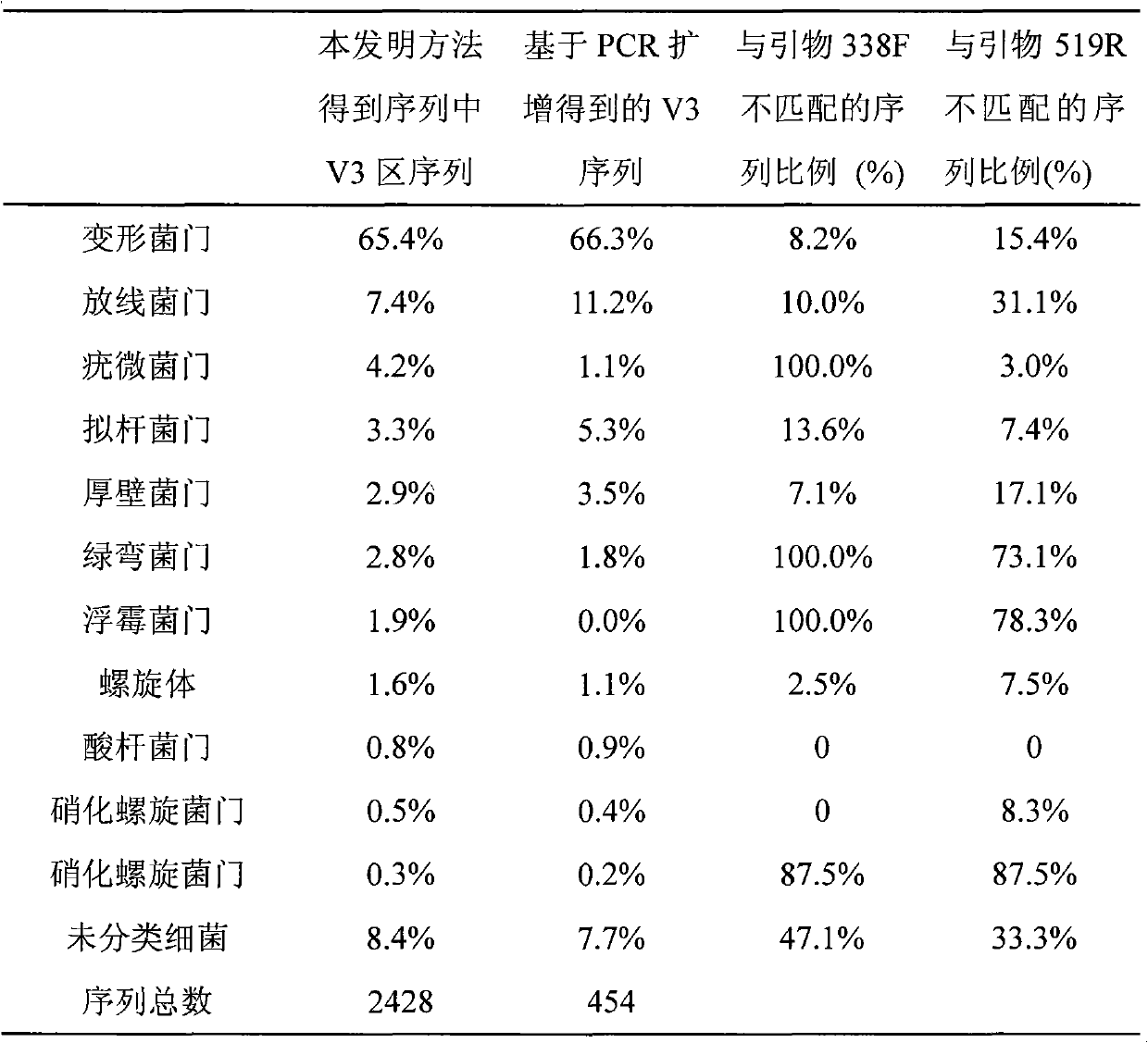
Method for analyzing microbial community structures
InactiveCN101792807ASimple and fast operationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBiocoenosis
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioanalysis, and particularly relates to a method for analyzing microbial community structures. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting total RNA in an environment sample; separating small-subunit rRNA from the total RNA; carrying out reverse transcription on the small-subunit rRNA by random primer for sequencing; extracting the small-subunit rRNA sequence from the results of sequencing; and confirming category message according to the obtained small-subunit rRNA sequence, and acquiring the characteristics of the microbial community structure. The method does not use specific PCR amplification so as to avoid various deviations in the PCR process; and meanwhile, the method can be used for analyzing the community structure of bacteria, archimycetes and eukaryotic microorganism, thus truly and completely reflecting the characteristics of the microbial community structure in the environment sample.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Goat pox vaccine strain expression vector
The invention provides an expression vector used for expressing foreign protein in the recombination of goat pox virus. A foreign gene is inserted in the down stream of a VVI1L promoter or a VVP11 promoter in the expression vector, by the homologous recombination with the parent plant of the goat pox virus, 12 recombined sheep pox viruses for expressing the foreign protein are obtained, a flanking sequence in the vector, which can make the homologous recombination with the parent plant of the goat pox virus, is a sheep pox virus G14-STV-44-55 vaccine strain which contains TK gene, IFNR-gamma gene or RR small subunit gene, by utilizing the expression vectors, the recombined goat pox viruses expressing different foreign proteins can be constructed by different methods, and the recombined goat pox viruses can be used as recombined live vector vaccines to prevent and treat diseases and study relations of expression, processing, structure and function of different biological active proteins.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
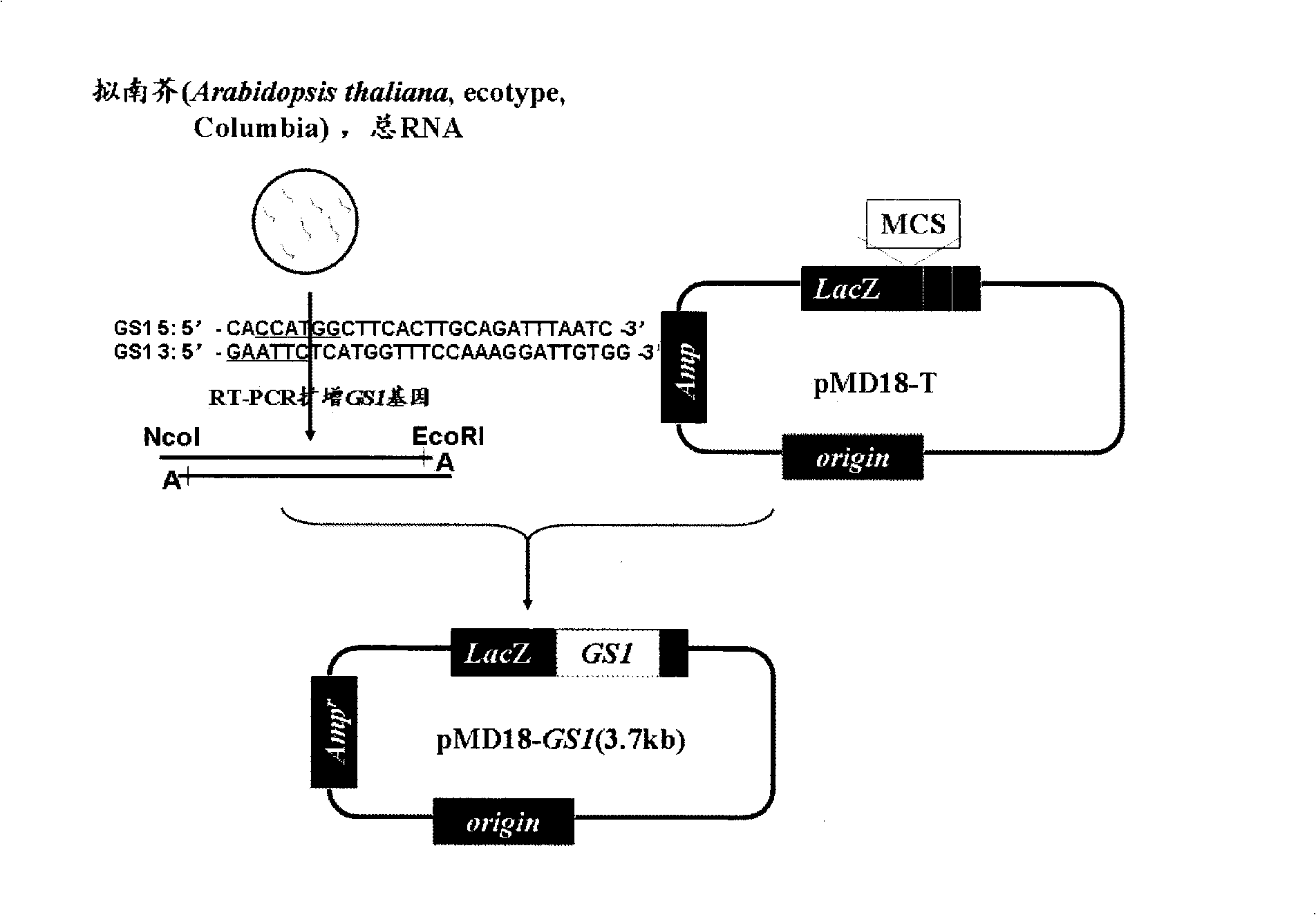
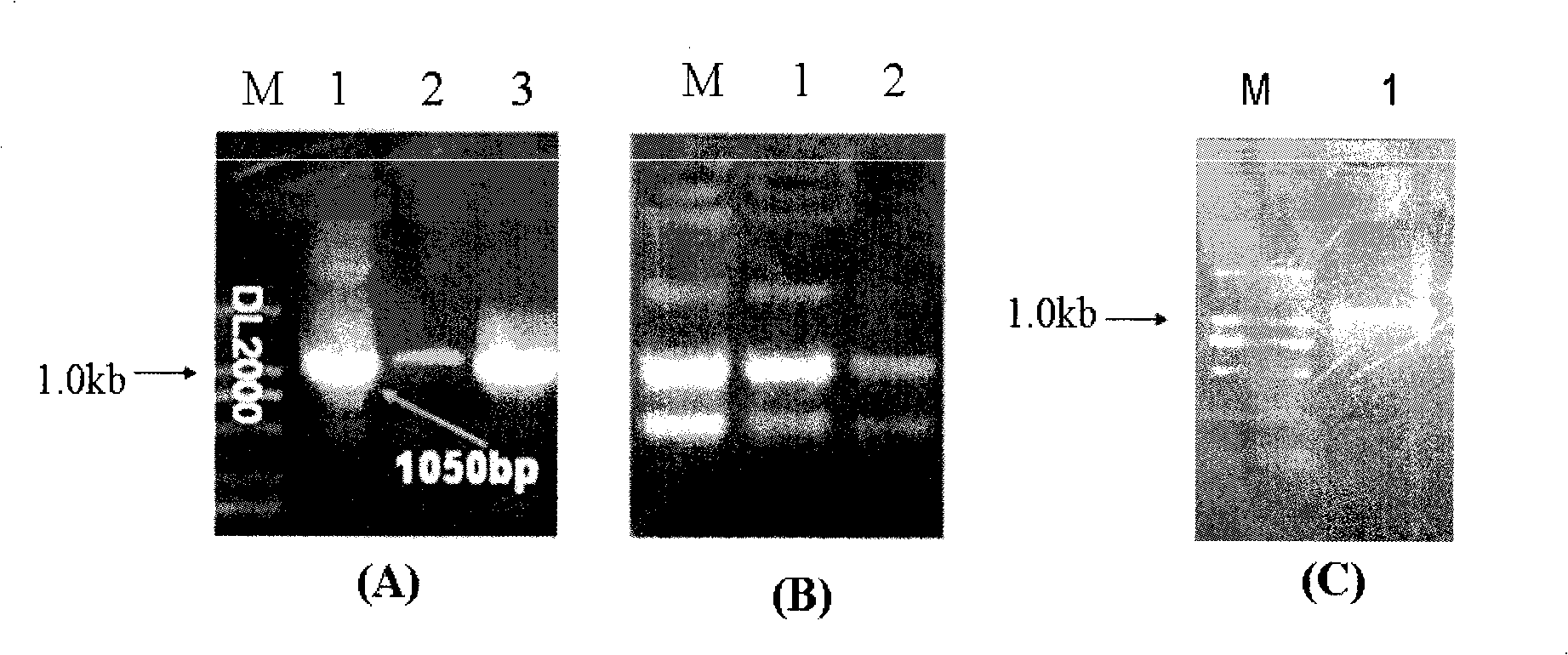
Construction and use of plant expression vector of Arabidopsis thaliana cytoplasm type glutamine synthetase gene
InactiveCN101407824AImprove nitrogen use efficiencyIncreased reassimilation capacityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsNicotiana tabacumLow nitrogen
The invention relates to a special plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-GS1 which comprises an arabidopsis thaliana cytoplasm glutamine synthetase gene GS1 and can improve the utilization rate of a plant nitrogen element. A method of RT-PCR is used for cloning the GS1 gene from the arabidopsis thaliana of a model plant, a photoinduction type promotor (the promotor of a a small subunit Rubisco) is used for controlling the excessive expression of the GS1 gene in a plant leaf and a leaf disc conversion method is used for transferring the GS1 gene into a pPZP221-PrbcS-Dof1 type transgene tobacco. An experiment result shows that the GS1 gene can be normally transferred in the transgene tobacco; under the nutrition condition of low nitrogen and the growing conditions of indoor irradiation for 24 hours of 2000LUX and 25 DEG C, the growing situation of the plant transferred with the single gene of Dof1 is (the expression of the gene is controlled by the photoinduction type promotor Prbcs) is a little better than that of a contrast tobacco (a wild type without transgene); after being transferred under the natural growing condition of a green house, the growing situation of the tobacco which is simultaneously transferred with the GS1 gene and the Dof1 gene shows remarkable growing advantages than that of the contrast plant; and therefore, simultaneously and excessively expressing the GS1 gene and the Dof1 gene, can improve the efficiency of the GS / GOGAT (glutamine synthetase / glutamic acid synthetase) approaches in the leaf more extensively, thereby improving the utilization rate of the plant nitrogen element. The vector can be broadly applied to the molecule breeding of crops, improving the utilization rate of the plant nitrogen element thereof and the durability to the nutrition condition of low nitrogen and being capable of obtaining a higher yield under the conditions of applying less fertilizers and even not applying the fertilizers.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
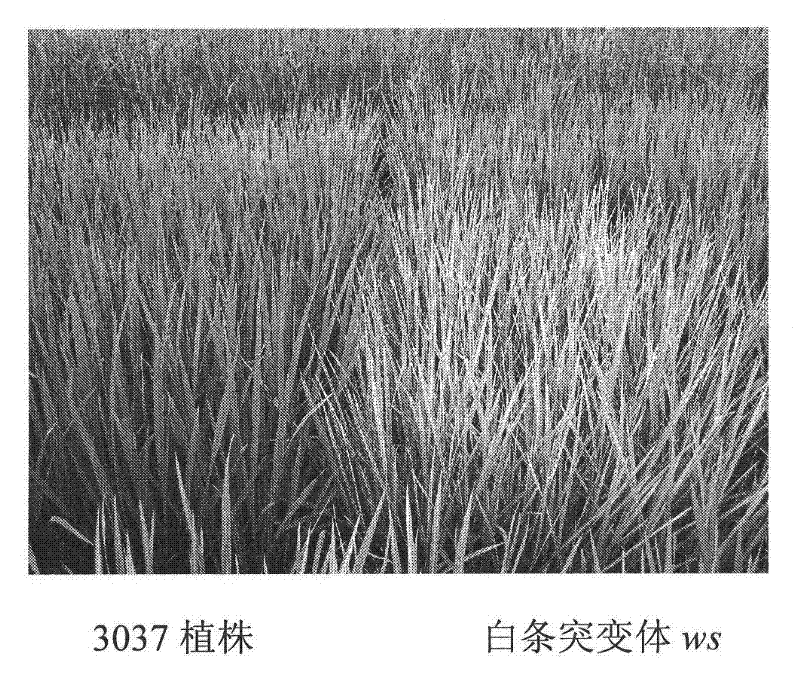
Protein capable of promoting chloroplast development and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102477090APromote photosynthesisIncrease productionViruses/bacteriophagesPlant peptidesRibonucleotide reductaseBiotechnology
The invention discloses a rice protein capable of promoting chloroplast development and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein is one of 1) a protein formed by amino acid residue sequences of the SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence table or 2) a protein which is formed after one or more amino acid residues in the amino acid residue sequences of the SEQ ID No.2 in the sequence table are substituted and / or deleted and / or added and has the same activities as the amino acid residue sequences of the SEQ ID No.2. The gene is used for coding the small subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, and the development of rice chloroplast is affected after the gene is mutated so that white stripes are distributed on the rice leaves in the vein direction.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
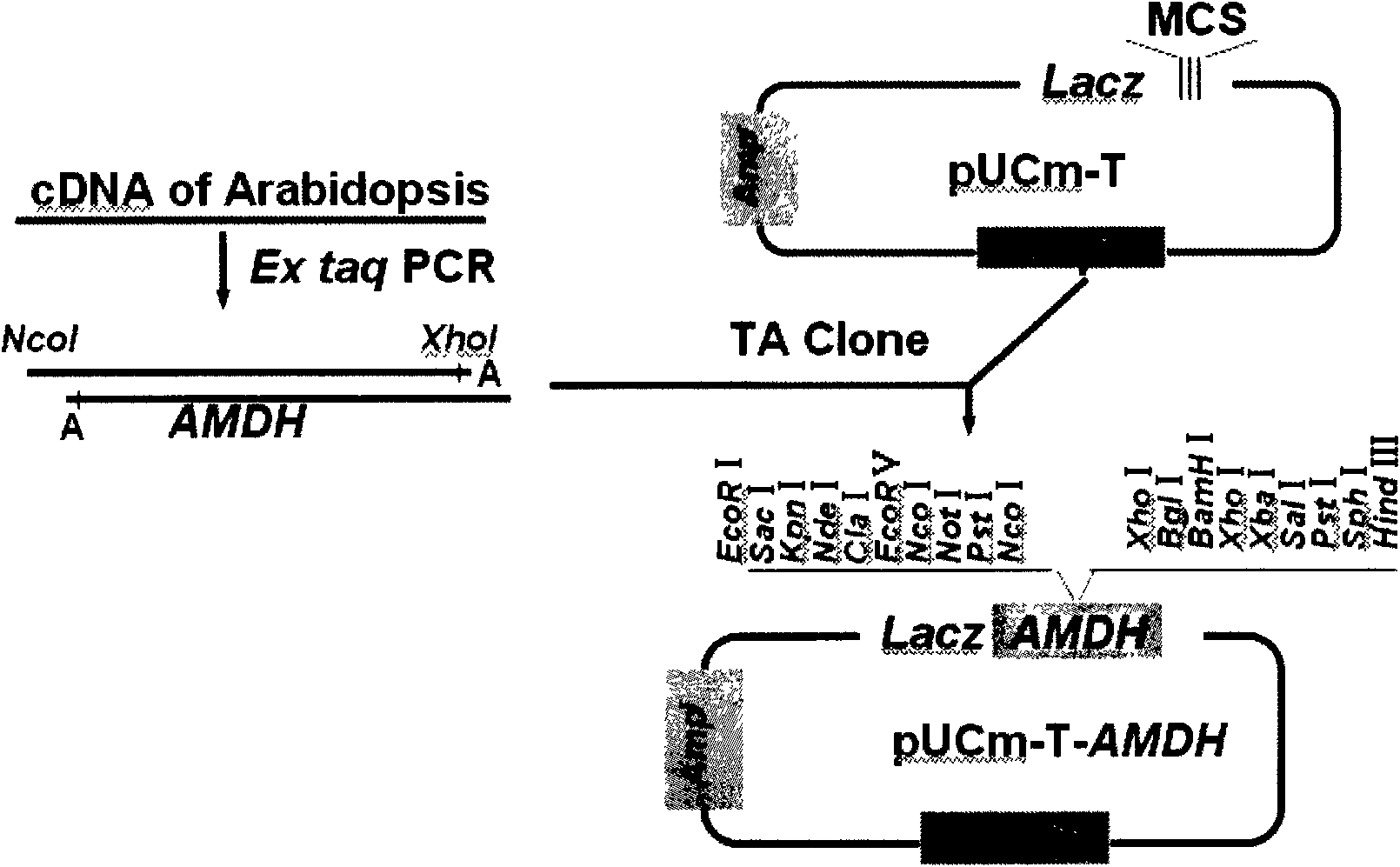
Plant expression vector of arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic malate dehydrogenase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101586116ADetoxifyImprove the ability to resist aluminum poisoningFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumWild type
The invention in particular relates to a plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-AMDH for improving the aluminum toxicity resistance of plants, a construction method and application thereof, which belong to the field of plant gene engineering. The special vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-AMDH for improving the aluminum toxicity resistance of the plants is the plant expression vector containing a photoinducible promoter (PrbcS) of a rubulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RubIsco) small subunit gene and an arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic malate dehydrogenase gene (AMDH). The AMDH gene is cloned from arabidopsis thaliana, the photoinducible promoter is used to control the overexpression of the AMDH gene in tobacco, malic acid is synthesized, and the malic acid is secreted out of cells so as to strengthen the resistance of the plants on aluminum toxicity in acid soil. Experimental results show that the activity of malate dehydrogenase of trans-AMDH genic tobacco leaves is 1.4 times of that of wild tobacco. Under the stress of 30 mu M of aluminum toxicity, trans-AMDH genic tobacco can secrete more organic acid, and has better root system growth; and the growth condition under the stress of the aluminum toxicity shows that the plant height and the green leaf number of the trans-AMDH genic tobacco are higher than those of the wild tobacco.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Xanthine dehydrogenase intercepting body and application thereof
ActiveCN105985935AAvoid limited enzymatic processesSimple production processOxidoreductasesFermentationNucleotidasePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a xanthine dehydrogenase intercepting body and an application thereof. The protein comprises xanthine dehydrogenase intercepting body small subunit, xanthine dehydrogenase intercepting body intermediate subunit, and xanthine dehydrogenase intercepting body large subunit. The affinity of xanthine dehydrogenase intercepting body is increased by 19% by comparing a wild substrate (xanthine), the conversion number is increased by 115%, the catalysis efficiency is increased by 166%, and the temperature toleration is increased by 11 DEG C. The xanthine dehydrogenase intercepting body is in favor of developing the novel application field by combining with other enzymes, and is suitable for sample detection for detecting xanthine and hypoxanthine, the xanthine dehydrogenase intercepting body can be used for detecting inorganic phosphoric acid by combining with PNP enzyme, can be used for detecting adenosine deaminase by combining with PNP, XOD and POD enzymes and detecting 5'-nucleotidase, and is suitable for industrial application. The xanthine dehydrogenase intercepting body is in favor of increasing enzyme catalysis efficiency and reducing cost, and is in favor of industrial application.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for cultivating starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation
InactiveCN103173485AImprove conversion rateHigh total starch contentTransferasesFermentationGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseSucrose synthetase
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation. According to the transgenic plant cultivation method provided by the invention, a selection marker gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase large subunit gene, a sucrose synthase gene, and a granule-bound starch synthase gene are introduced into a target plant, such that a transgenic plant is obtained. The total starch content of the transgenic plant is higher than that of the target plant. As a result of experiment of the invention, a plurality of genes can be simultaneously transferred in one-time through one time of gene gun bombardment, such that transgenic material cultivation period and work load can be greatly shortened. Specifically, the 4 genes related to starch metabolism are simultaneously transferred in, such that the total starch content of a transgenic regenerated plant is higher than that of wild-type plant.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Heat resistant plants and plant tissues and methods and materials for making and using same
InactiveUS20090260101A1Improve heat resistanceReduce yield lossSugar derivativesTransferasesPlant tissueSmall subunit
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for providing plants or plant tissue with increased resistance to heat conditions. Increased resistance of a plant or plant tissue to heat conditions provides for decreased yield losses generally observed at elevated temperatures. One aspect of the invention concerns polynucleotides that encode a mutant plant small subunit of AGPase. The subject invention also comprises a mutant plant small subunit of AGPase encoded by a polynucleotide of the invention. The subject invention also concerns plants comprising a polynucleotide of the invention and method for making the plants.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Cyanobacterial nucleic acid fragments encoding proteins useful for controlling plant traits via nuclear or plastome transformation
InactiveUS7285701B2Improve methodEasy to identifySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
This invention provides cyanobacteria as an alternative source of ahas and pds genes for plant transformations and for selectable markers. In particular, it provides for cyanobacteria, for example, Synechocystis, as a source of genes encoding herbicide insensitive proteins, and elements of genes for control of expression in plastids. Nucleic acid fragments, both the acetolactate synthase (ahas) large subunit and the ahas small subunit, were found to provide herbicide resistance. Also, the present invention provides novel Synechocystis mutant phytoene desaturase (PDS) gene conferring resistance to 4′-fluoro-6[(alpha,alpha,alpha,-trifluoro-m-tolyl)oxy]-picolinamide, a bleaching herbicide. The present invention provides improvements to method involving cyanobacteria for the screening of compounds, including a new high-through-put protocol that is a rapid and cost effective way to identify target site genes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
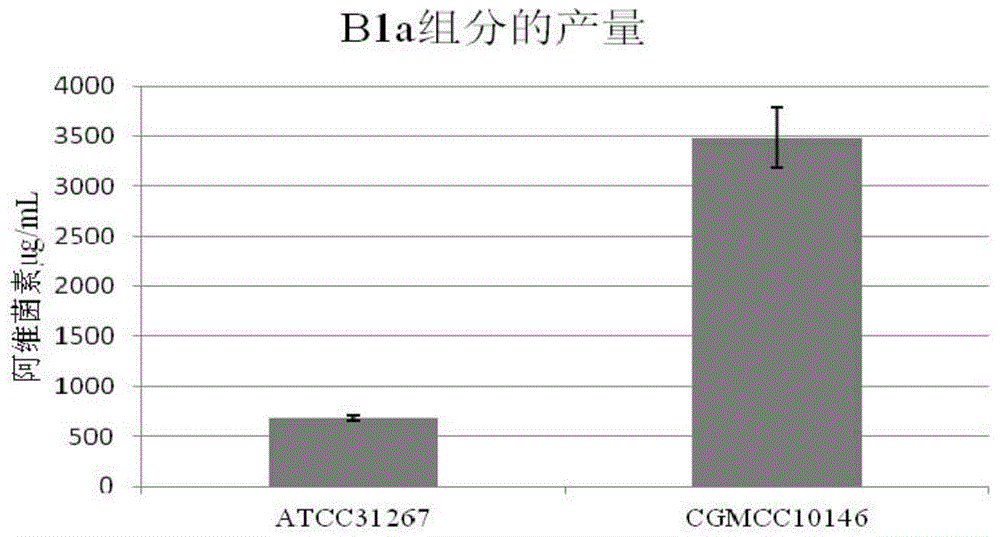
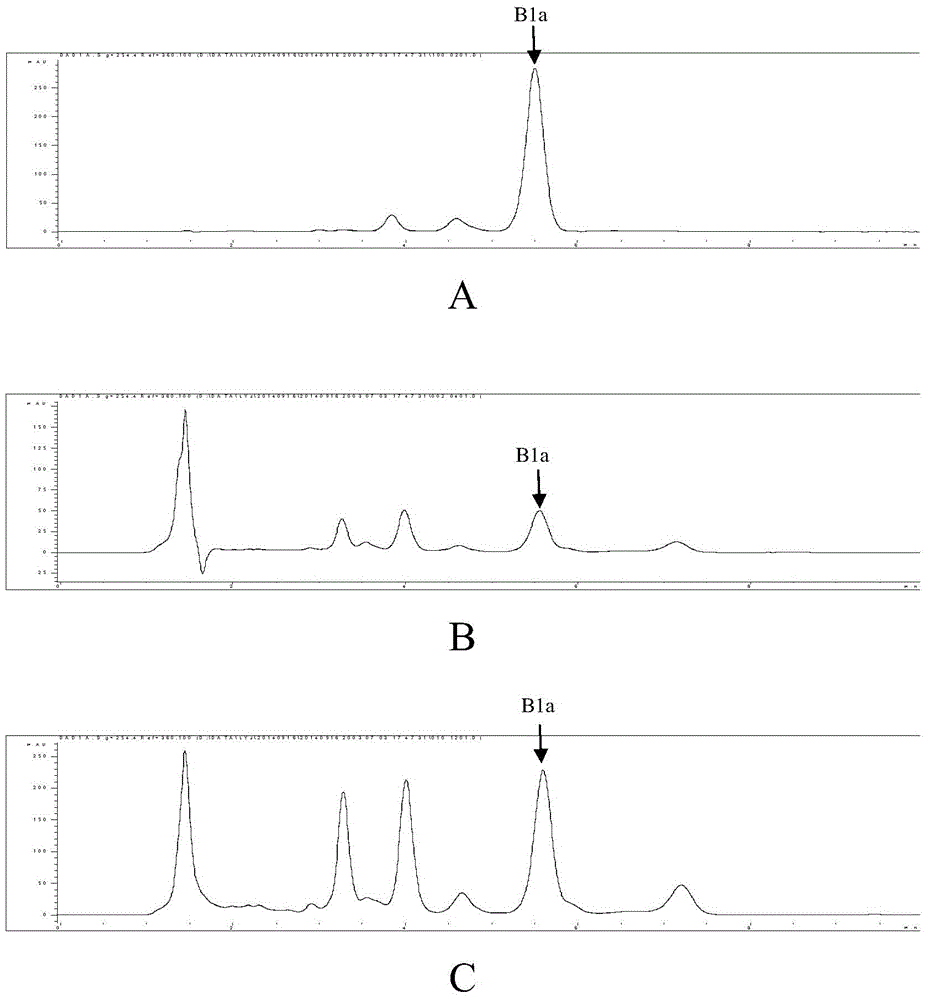
Recombined streptomycete, construction method thereof and method for increasing antibiotic yield
ActiveCN104531598AIncrease productionIncrease the amount of enzymeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetolactic acidAcetolactate synthase
The invention discloses a recombined streptomycete, a construction method of the recombined streptomycete and a method for increasing the antibiotic yield. The recombined streptomycete over-expresses acetolactic acid synthase small subunit ilvH. The recombined streptomycete over-expresses acetolactic acid synthase to adjust subunit genes, and the yield of products such as antibiotics for conducting secondary metabolism with L-isoleucine and / or L-valine and / or L-leucine as precursors / a precursor can be remarkably increased.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods to screen for antibiotic agents and their use in treatment of opportunistic infections
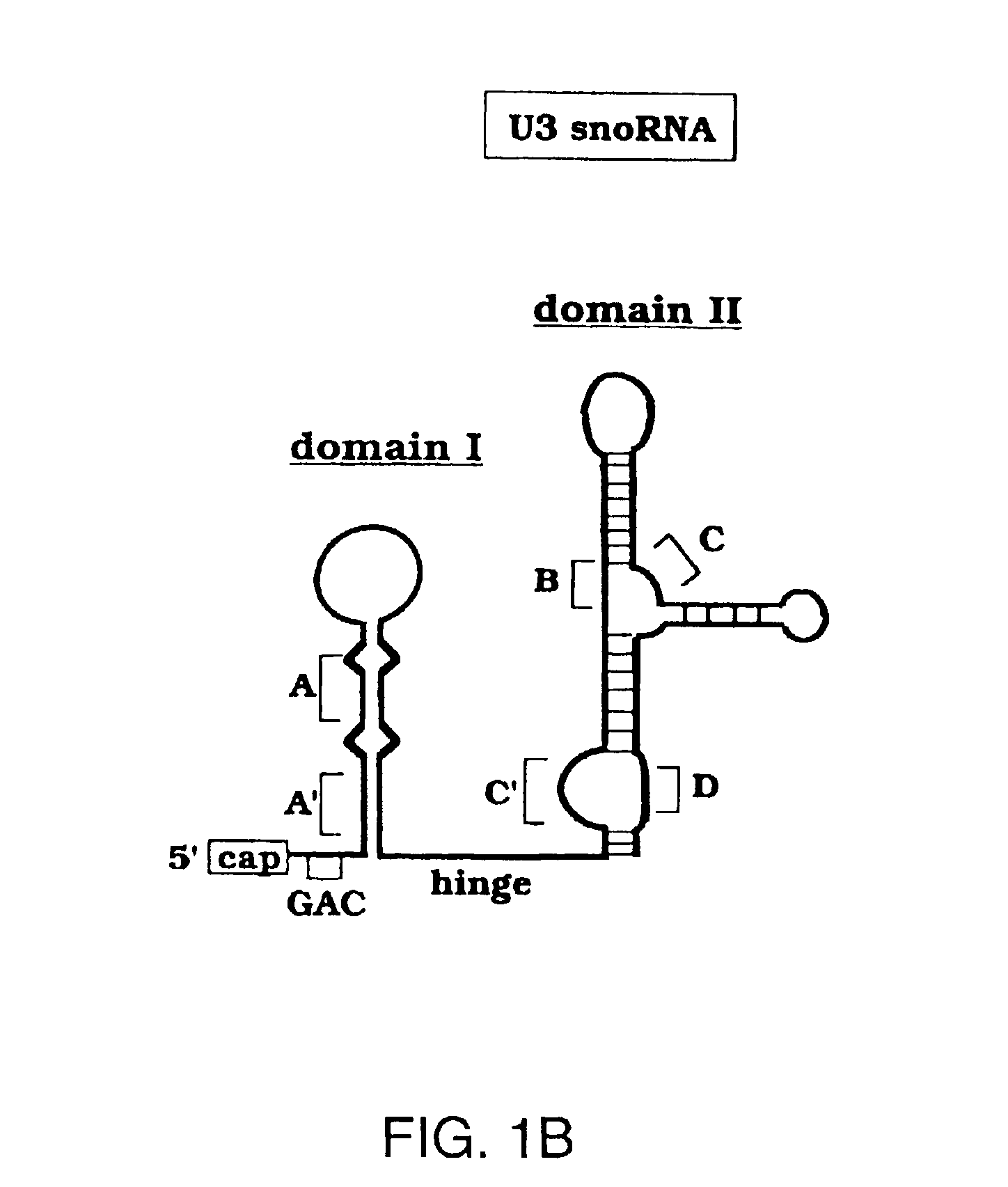
InactiveUS6913889B2Sufficient distanceReduce cell viabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiparasitic agentsAntibiotic AgentsRibosome Subunits
The present invention provides novel targets in eukaryotic cells for antibiotic agents and methods for identification of antibiotic agents affecting such targets and the use of the identified antibiotic agents in treatment of opportunistic infections in eukaryotic hosts. The invention is based upon the identification of species specific 5′ hinge and 3′ hinge regions of U3 small nucleolar ribonucleic acid (snoRNA). The present invention discloses that the external transcribed spacer (ETS) of the ribosomal RNA precursor (pre-rRNA) comprises sequences that are complementary to the 5′ and 3′ hinge regions of U3 snoRNA. The invention further discloses that sequence substitutions of the 5′ hinge or 3′ hinge region of U3 snoRNA severely compromise or fully inhibit the cleavage events at sites 1 and 2 in rRNA processing necessary to form mature 18S rRNA which is a vital component of the small subunit of ribosomes of all eukaryotes.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
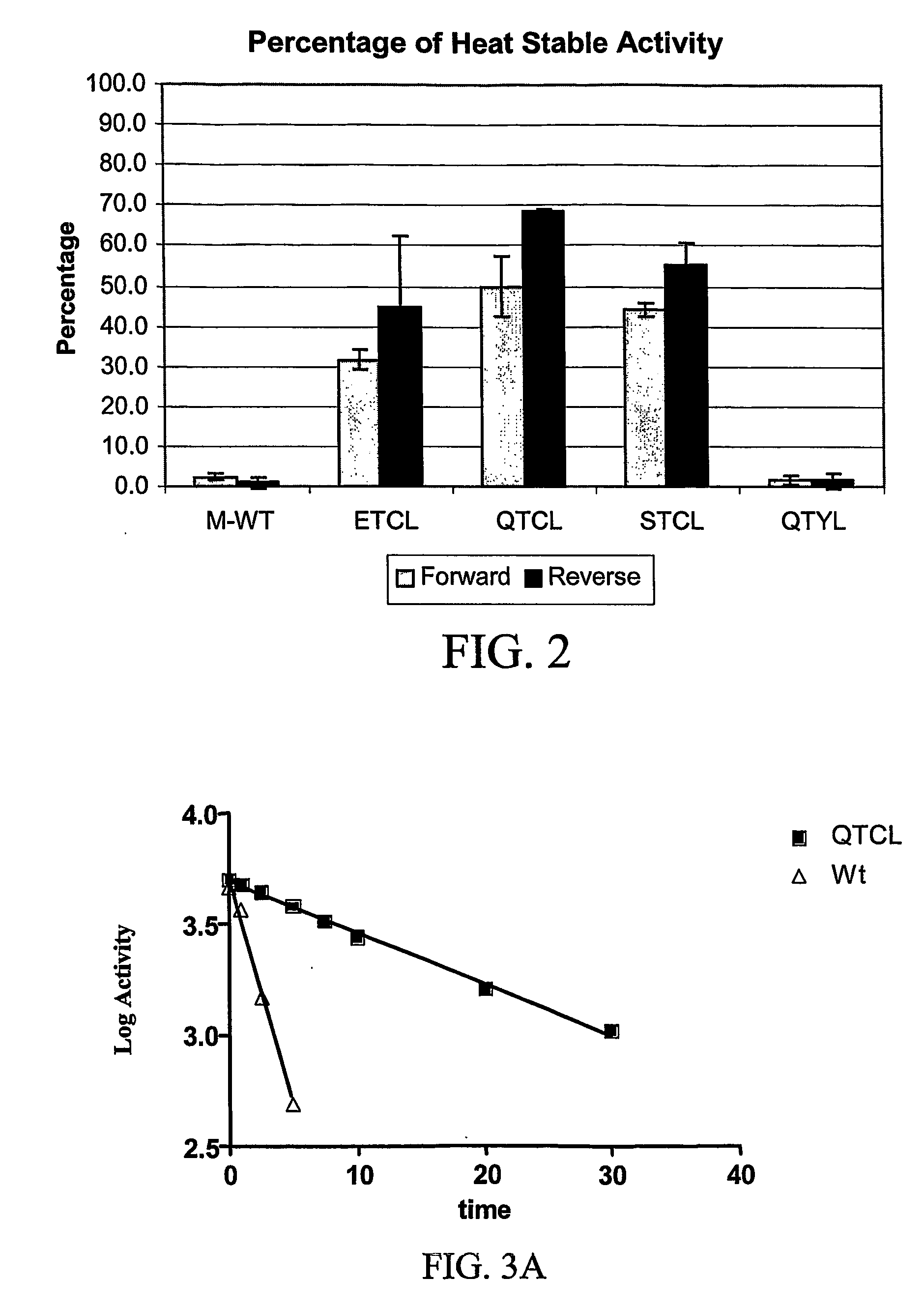
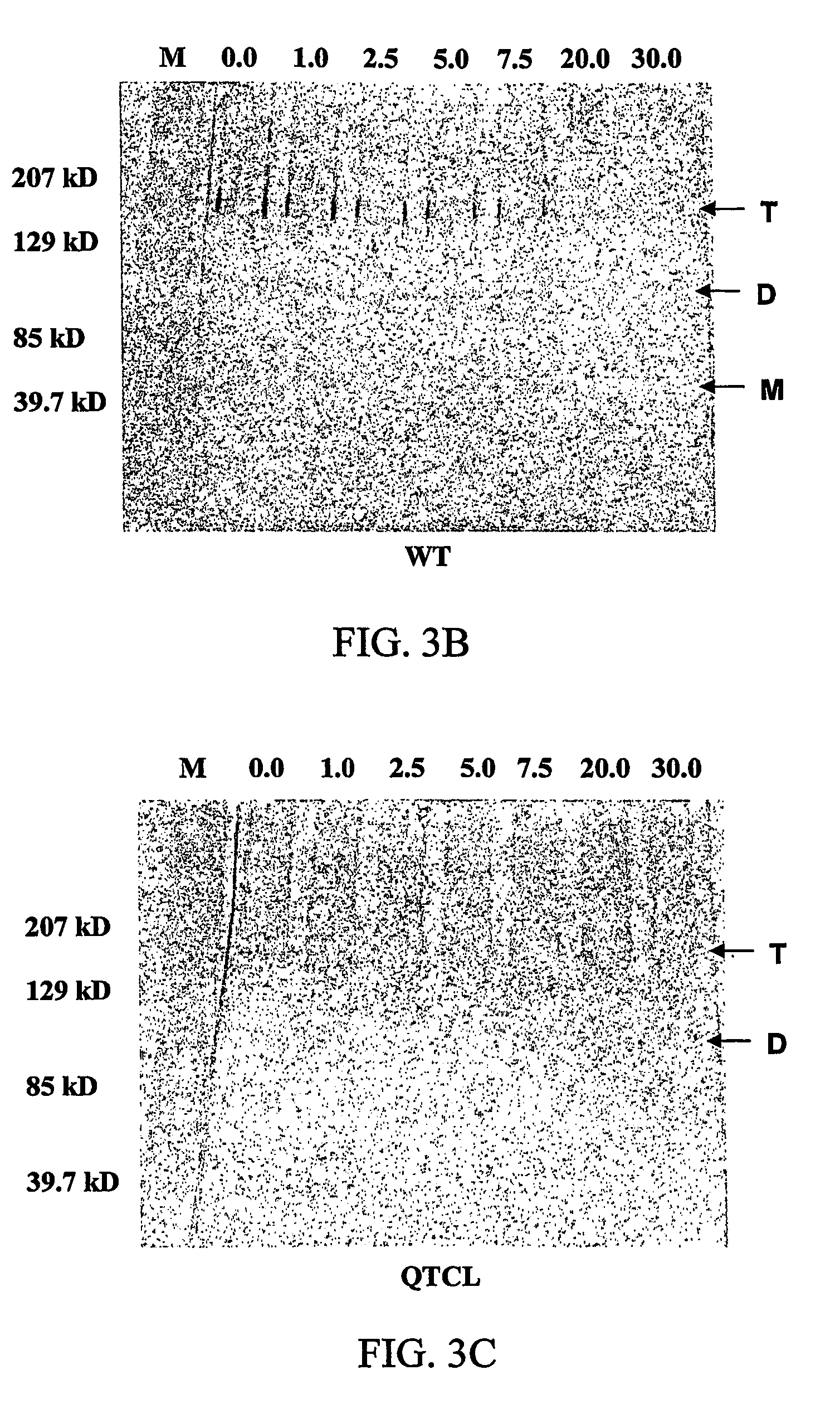
Heat stable variants of plant adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit
InactiveUS20110167519A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove heat resistanceSugar derivativesHydrolasesNucleotideWild type
The subject invention concerns polynucleotides encoding a small subunit of plant AGP having one or more mutations in the amino acid sequence wherein the mutation confers increased heat stability to the expressed AGP enzyme. Mutations in the N-terminus of the small subunit of heat labile plant AGP results in AGP enzymes that are significantly more heat stable compared to wild type AGP in that the mutant AGP retains significant levels of enzymatic activity following exposure to heat treatment. In one embodiment, the polynucleotide encodes a mutant small subunit of maize AGP. The subject invention also concerns methods for providing a plant with increased resistance to heat conditions. Plants with heat labile AGP can be transformed with a polynucleotide of the present invention. The subject invention also concerns these transformed plants and transgenic progeny thereof. The subject invention also concerns mutant polypeptides encoded by polynucleotides of the present invention.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
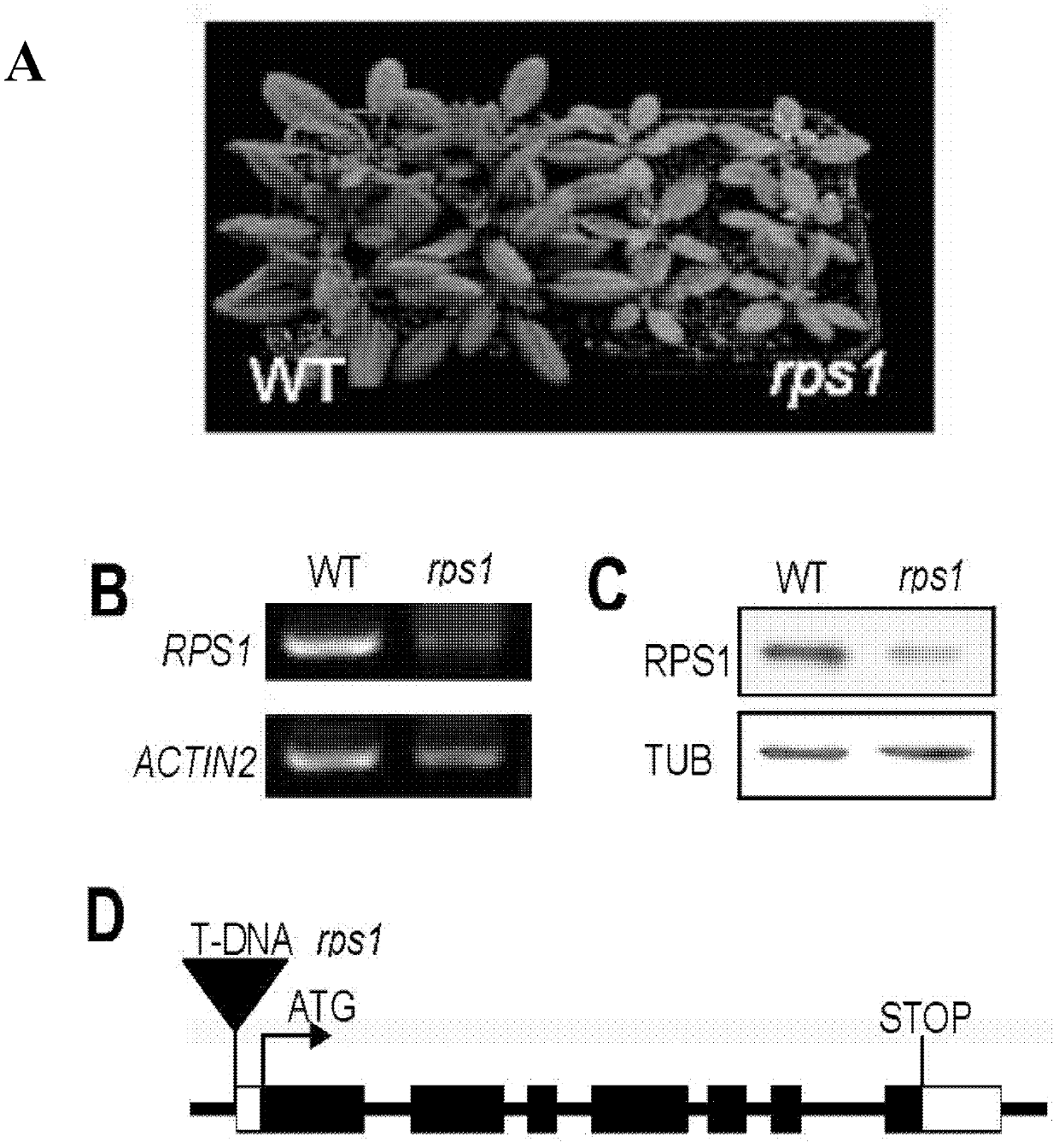
Related protein capable of adjusting translation efficiency of chloroplast protein and improving heat resistance of plants, and application thereof
InactiveCN103288941AImprove heat resistancePlant peptidesFermentationHeat resistanceChloroplast thylakoids
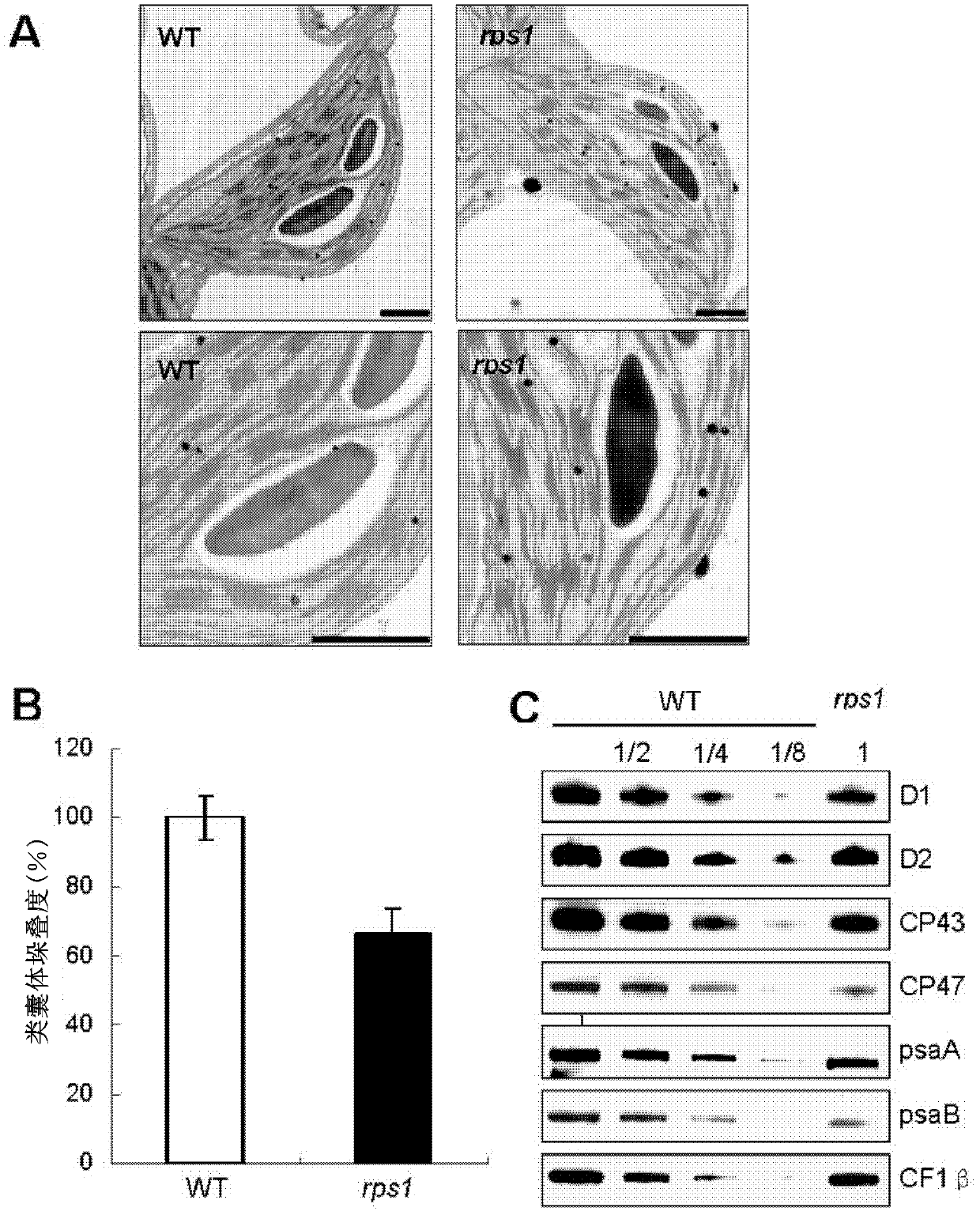
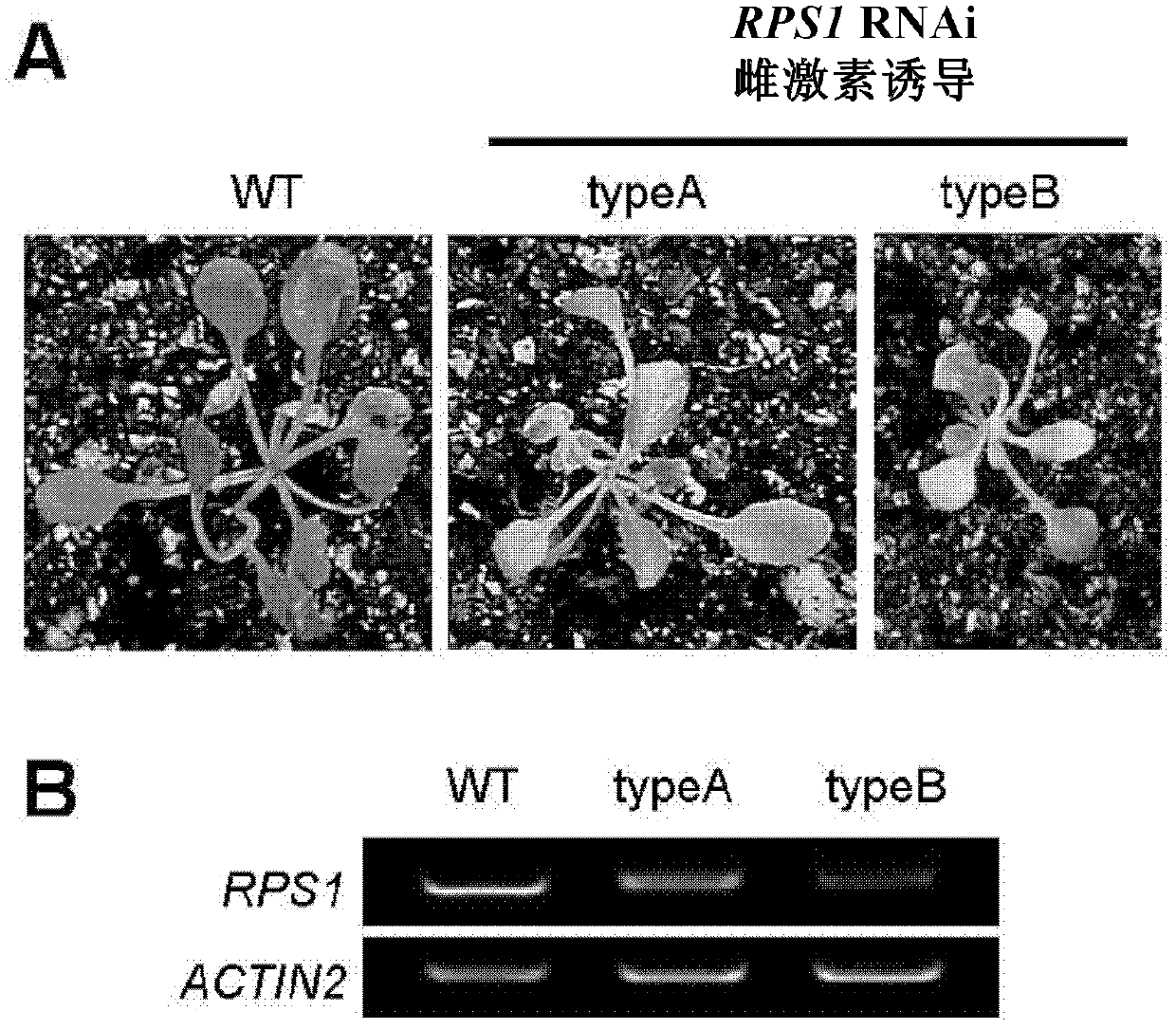
The invention relates to related protein capable of adjusting translation efficiency of chloroplast protein and improving heat resistance of plants, and application thereof. In particular, the inventor screens one mutant rps1 related to the translation efficiency of the chloroplast protein and the heat resistance of the plants from various different arabidopsis mutants, and identifies a plant chloroplast ribosome small subunit S1 (RPS1) gene from the mutant; and the gene and polypeptide can effectively maintain the heat stability of a thylakoid membrane, can improve the translation efficiency of the chloroplast protein of the plants, can improve the survival ability and the photosynthesis efficiency of the plants under heat stress, and can effectively avoid and reduce adverse influence of high temperature on the plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting TaAGPS gene allelic variation relevant to thousand kernel weight
InactiveCN105907862AValid identificationRapid and effective separation and identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a method for detecting wheat cytoplasmic adp glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit (TaAGPS) gene excellent allelic variation relevant to thousand kernel weight by using CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) marks. According to the method, the corresponding basic groups of two allelic variations (TaAGPS-7A-T and TaAGPS-7A-G) in the 5092 site of the TaAGPS-7A exon region III are respectively T and G; the corresponding amino acid is Ser and Ala; firstly, a primer is used for performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on SEQ ID No: 1 and SEQ ID No: 2; after the enzyme digestion by using DdeI incision enzyme, electrophoresis detection is performed; the authentication of different allelic variations of the TaAGPS genes in wheat germplasm resources and later generation breeding can be conveniently and efficiently realized. The operation can be completed through conventional PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis methods; the operation is convenient; stability and feasibility are realized.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gateway inlet vector pEn-L4*-PrbcS-*T-GFP-L3*, construction method thereof and application thereof
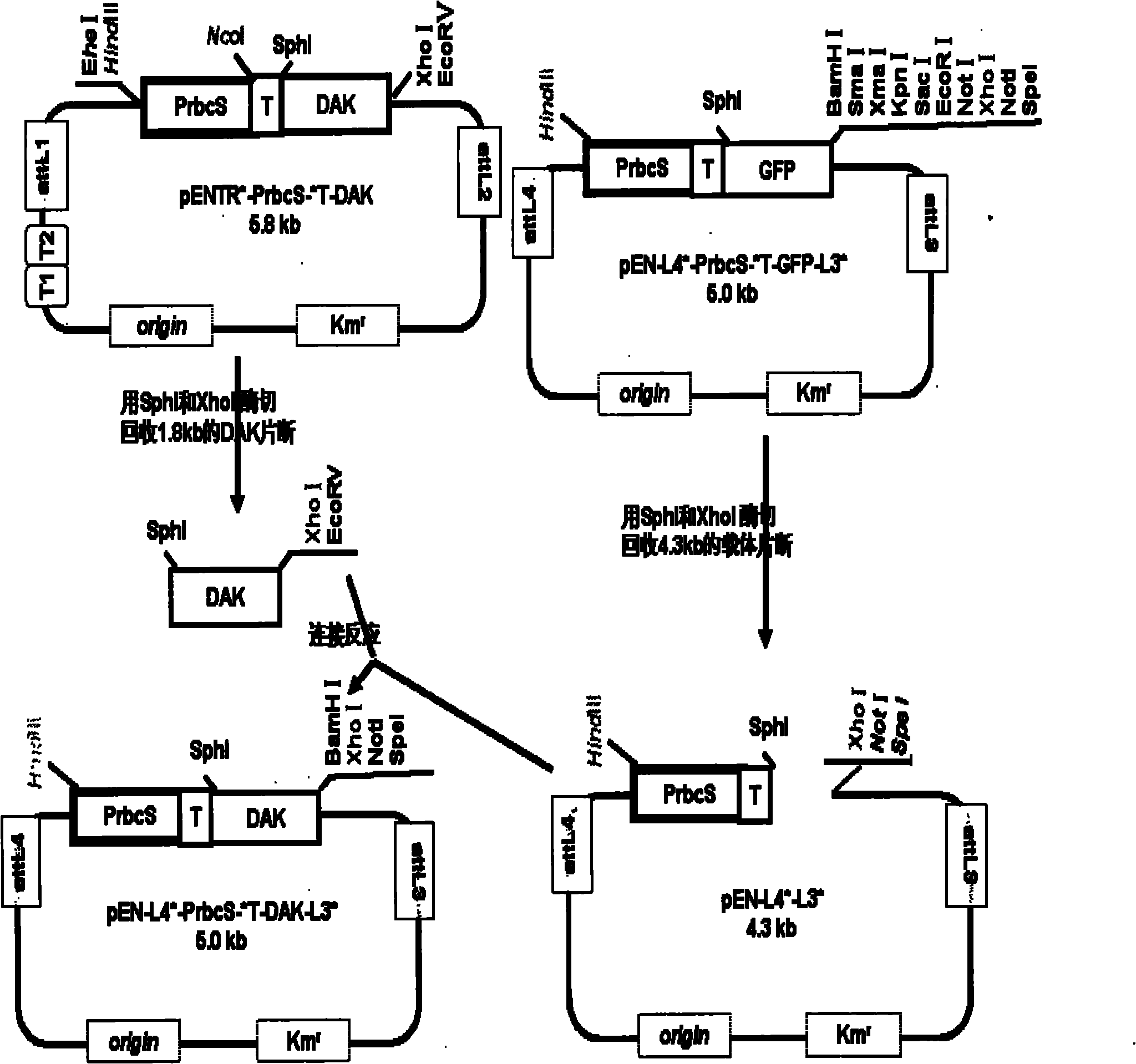
The invention relates to a gateway inlet vector for the gateway technology, and in particular to a gateway inlet plasmid vector (pEn-L4*-PrbcS-*T-GFP-L3*). The vector comprises sequences L4 and L3, rubisco, a small subunit gene photo-inductive promoter (PrbcS), a chloroplast stroma positioning sequence (T*) and a green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter gene, which are required for the LR recombination reaction in the gateway technology. A construction method and application of the vector are that: one plant expression vector connected in series with two target gene expression boxes can be quickly constructed by using the vector and another gateway inlet vector containing L1 and L2 sequences through the LR recombination reaction so as to realize conversion operation of two target genes through one conversion event. The expression of the target gene can be controlled with the PrbcS promoter in the vector and high-level expression of the target gene in the leaves of a plant can be realized by substituting the GFP gene in the vector with the target gene.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN105087516AImprove controllabilitySimple screening methodTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention provides an ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant and a screening method and application thereof. The screening method includes the steps of firstly, synthesizing first chain cDNA; secondly, performing PCR amplification; thirdly, building AGPase large and small subunit cDNA prokaryotic expression vectors; fourthly, performing active screening. The method has the advantages that distant hybridization is performed on AGPase large subunit genes and small subunit genes from different species, and the recombinant gene expression vectors are obtained in a highly-controllable manner; escherichia coli glgC mutant strains are converted and inoculated to a Conberg enrichment solid culture medium, and iodine-potassium iodide dyeing is used to screen the high-activity ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant. The screening method is simple and practical and stable and reliable. The enzyme activity and glycogen content of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant are evidently higher than those of wild corn AGPase, evident change of the substrate affinity of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant is avoided, and the sensitivity of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant to activating agent is increased.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Corn embryosperm ADP- glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant and its screening method and application
InactiveCN1970744AHigh affinityIncrease enzyme activityTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliAgricultural science
The invention discloses a maize-endosperm ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylas mutant and sieving method and application, which comprises the following steps: 1) mutating cDNA of large and small subunit of maize-endosperm AGPase through alcaine hydroxylamine mutation agent randomly; 2) transmitting mutated cDNA and wild-type cDNA into escherichia coli glgC mutation germ; sieving positive monoclonal; 3) seeding positive monoclonal line on the Conberg rich solid board to culture under 35-39 deg.c; 4) dyeing; comparing the color; obtaining deep color mutation as maize-endosperm ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylas mutant.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Electrophoresis method for removing Rubisco enzyme interference of watermelon leaves and separating residual low-abundance proteins
InactiveCN102584972AEfficient removalQuick removalPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesProtein spotSmall subunit
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and discloses an electrophoresis method for removing Rubisco from plant leaves and enriching and separating residual proteins. The method comprises the following steps of: removing Rubisco from watermelon leaves by using 18 percent PEG-4000; leaching residual proteins through a TCA-acetone precipitation method; and performing two-dimensional electrophoresis to separate residual proteins from watermelon leaves. Compared with a holoprotein two-dimensional electrophoretogram, the method has the advantages that: after Rubisco in watermelon leaves is precipitated by adopting the 18 percent PEG, most large and small subunits of Rubisco disappear, the expression levels of most residual proteins are raised, the quantity of proteins obtained by separating is increased by 48.4 percent, and a large quantity of new protein spots (65+ / -15) appear in a region of which the molecular weight is smaller than 25.0kDa. As proved by repeated experiments, the electrophoresis method has the advantages of high repeatability, clear spectra and reliable result.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
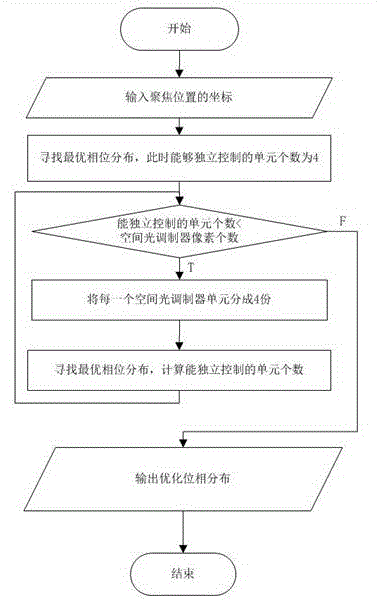
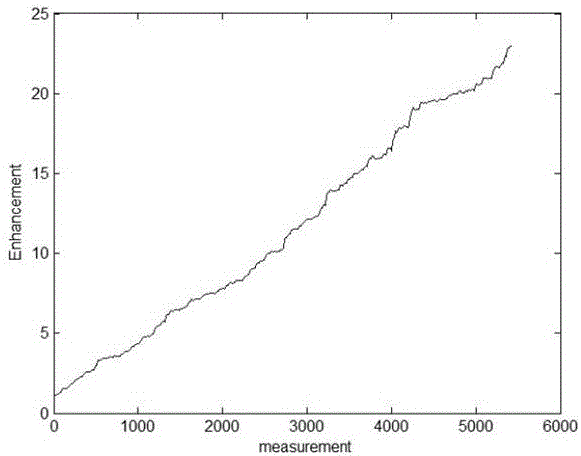
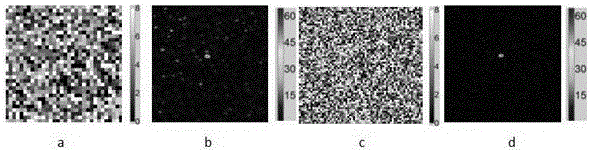
Unit splitting modulation method for focusing light through scattering medium
ActiveCN106725319AFast convergenceImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSpatial light modulatorSpeckle pattern
The invention discloses a unit splitting modulation method for focusing light through a scattering medium and relates to the field of bioimaging. The method is characterized by including the step of finding an optimal phase and the step of quaternary splitting method modulation. In the step of finding the optimal phase, the phase change of 0-2pi is conducted on a spatial light modulator, phase modulation is conducted on incident plane waves, a CCD is adopted to receive a corresponding speckle pattern, the light intensity at the focusing position is calculated, comparison is conducted, and the phase value corresponding to the maximum light intensity is stored; In the step of quaternary splitting method modulation, a phase (optimal phase) making the output strength at the focusing position maximum is found in each unit, then the units are equally and sequentially divided into four parts, each unit adopts a previous optimized phase while continuing to search for better phase distribution, and in this way, the units can be subdivided and optimized into smaller subunits, even pixels of the spatial light modulator.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Plant expression vector for improving capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of plant and application thereof
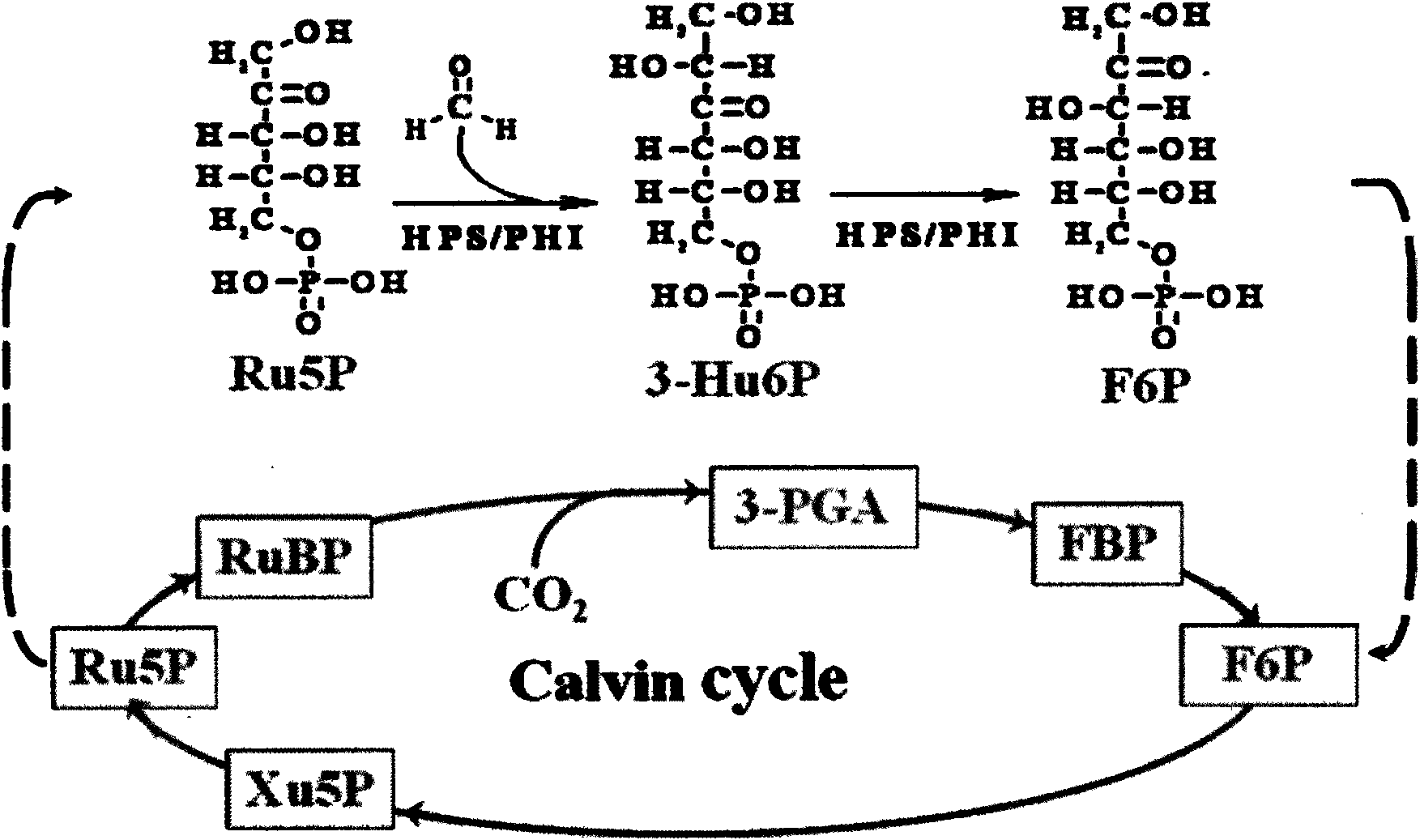
InactiveCN101629185AEnhanced efficiency of formaldehyde assimilationPromote absorptionVector-based foreign material introductionHigh concentrationWild type
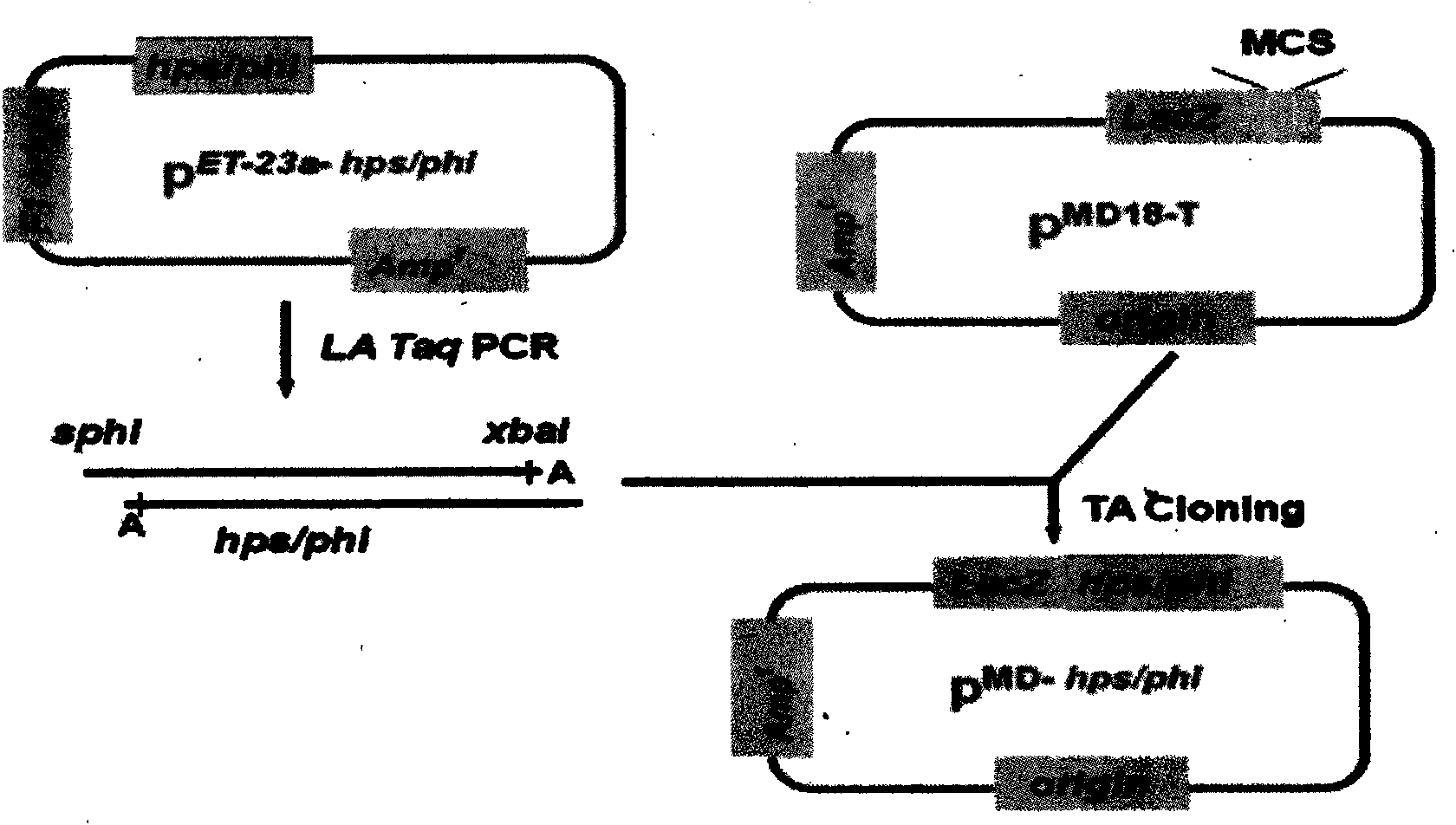
The invention discloses a plant expression vector pK2-35S-PrbcS-*T-hps / phi for improving the metabolic capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of plants, and the plant expression vector is a plant expression vector of a bifunctional enzyme HPS / PHI gene formed by integrating a PrbcS containing a Rubisco 3C small subunit gene and a transfer peptide sequence thereof as well as 6-phosphonate hexulose synthetase and 6-osphofructose isomerase of Mycobacteriumgastri MB19. A procaryon expression vector pET-23a-hps / phi plasmid of HPS / PHI is used as a template and is amplified to acquire an hps / phi gene, and the PrbcS and a chloroplast transfer peptide are used for controlling the expression of the hps / phi gene in the chloroplast of plant leaves, thereby improving the capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of the plants. An experiment indicates that the growing condition of transgenic plants is better than that of wild plants, and the transgenic plants have a lighter phenomenon of leaf chlorosis when the transgenic plants grow in the environments of high-concentration extrinsic gas and liquid formaldehyde. Transgenic plant leaves can completely eliminate the formaldehyde in 4mM of formaldehyde treatment fluid within 90 hours, but wild leaves have slower absorption efficiency, and 17 percent of formaldehyde still remains.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Transient expression vector carrying NtRBSC1 gene
InactiveCN107058373APrecise positioningEasy for in-depth developmentVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and in particular relates to a recombinant transient expression vector carrying a small subunit gene of tobacco ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. One transient expression vector NtRBSC1-pFF19-GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) is constructed by utilizing a tobacco NtRBSC1 gene; after tobacco cells are transformed through the vector, fused protein of fluorescence labeled gene GFP and NtRBSC1 can be transformed into tobacco protoplasts, so that NtRBSC1 protein is subjected to sub-cellular localization by detecting the position of the fused protein through a laser confocal microscope; the position of chloroplast is displayed. Overall, the manner is a simple and accurate method for localizing in living cells and accurate reference evidence can be provided for research on the chloroplast of the tobacco cells and related genes; research on the tobacco NtRBSC1 gene and deep development of functions of the tobacco NtRBSC1 gene are convenient to realize.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Cyanobacterial nucleic acid fragments encoding proteins useful for controlling plant traits via nuclear or plastome transformation
InactiveUS7083967B1Easy to identifyImprove methodBacteriaTransferasesPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
This invention provides an alternative source of ahas and pds nucleic acids for plant transformation and selection. In particular, the invention provides ahas and pds nucleic acids from cyanobacteria, for example, Synechocystis, and expression elements of these genes for control of expression in plastids. The invention further provides nucleic acids encoding the acetolactate synthase (ahas) large subunit and the ahas small subunit which were found to provide herbicide resistance to plants. The present invention also provides a novel Synechocystis mutant phytoene desaturase (PDS) gene conferring resistance to 4′-fluoro-6-[(alpha, alpha, alpha,-trfluoro-m-tolyl)oxy]-picolinamide, a bleaching herbicide. The present invention provides improved methods involving cyanobacteria for the screening of compounds, including a new high throughput protocol that is a rapid and cost effective way to identify target site genes.
Owner:BASF CORP
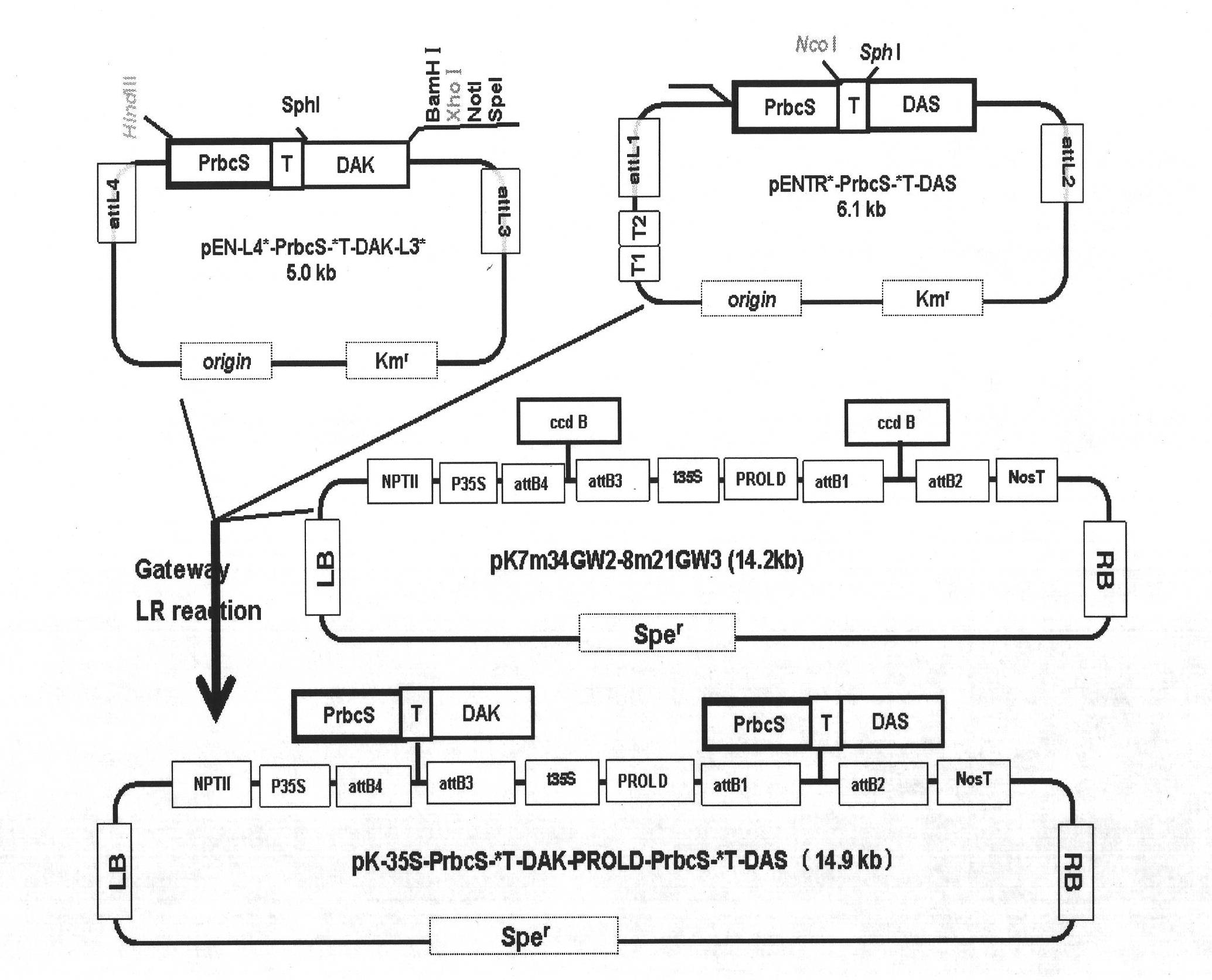
Plant expression vector constructed by dihydroxy acetone synthetase and dihydroxy acetone kinase gene expression cassette in series as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN101838666AEnhanced efficiency of formaldehyde assimilationPromote absorptionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPichia pastorisDihydroxyacetone kinase
The invention particularly relates to a plant expression vector, namely pK-35S-PrbcS-*T-DAK-PROLD-PrbcS-*T-DAS, for improving the capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of plants, as well as a construction method thereof and application thereof in improving the capability of absorbing and resisting exogenous formaldehyde of plants. The plant expression vector, namely pK-35S-PrbcS-*T-DAK-PROLD-PrbcS-*T-DAS, for improving the capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of plants is formed by an optical inducible promoter (PrbcS) containing a tomato 1,5 ribulose diphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) 3C small subunit gene and a transfer peptide sequence (*T) thereof, a dihydroxy acetone synthetase (DAS) gene of candida boidinii and a dihydroxy acetone kinase (DAK) gene (two genes) of Pichia pastoris. The conversion operation of both the DAS gene and the DAK gene can be completed by performing a conversion test by using the vector for one time.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mapping new sites for antibiotic action in the ribosome
InactiveUS20090042186A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismSmall subunit
The present invention provides a method of mapping and identifying new sites for antibiotic action in the ribosome of a microorganism. The method comprises: (a) providing a random mutant library of the rRNA genes of the microorganism prepared by randomly mutating the rRNA genes of the microorganism; (b) enriching the library in clones with deleterious rRNA mutants by negative selection; (c) screening for clones with deleterious rRNA mutations; (d) mapping the deleterious rRNA mutations in the clones obtained from step (c) to identify sites in the rRNA which are important functional sites in the ribosome; and (e) selecting functional sites identified in the rRNA in step (d) which are not targeted by a known antibiotic as new sites for antibiotic action for the microorganism. The rRNA gene can be the 16S rRNA of the small subunit or the 23S rRNA or the 5S rRNA of the large subunit of the ribosome of the microorganism.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Viral nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6204045B1Improved vaccineOrganic active ingredientsFungiHeterologousLaryngotracheitis virus
Various genes of herpes virus of turkeys (HVT), Marek's disease virus (MDV) and infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) have been identified as non-essential regions (and candidates for insertion sites for foreign genes) and / or as antigen-encoding regions. The former include the HVT homologue of the HSV (herpes simplex virus) gC gene, the TX (thymidine kinase) region of MDV or ILTV, ORF3 of ILTV (as defined herein), the ribonucleotide reductase (large subunit) gene of ILTV, MDV or HVT and the ribonucleotide reductase (small subunit) gene of MDV. The antigen-encoding regions include the HVT homologues of the HSV gB, gC and gH genes, the ILTV homologue of HSV gB, ORF2 of ILTV, and the HVT homologue of the HSV-1 immediate early genes IE-175 and IE-68. Manipulation of these genes allows vaccines to be prepared comprising attenuated virus or virus carrying heterologous antigen-encoding sequences.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
Engineering bacteria based on nitrite reductase and implementation method of engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104152393AGuaranteed purityStable biological activityBacteriaClimate change adaptationNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention relates to engineering bacteria based on nitrite reductase and an implementation method of the engineering bacteria in the technical field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the following steps: by taking streptomyces griseorubens genome DNA as a template, performing PCR amplification with a primer containing enzyme cutting sites to sequentially obtain nucleotide sequences for encoding nitrite reductase large-subunits and nitrite reductase small subunits; sequentially connecting the gene sequences obtained by amplification to a coexpression vector pETDuet-1, and finally obtaining a recombinant coexpression vector pETDuet-NC-ND; and transforming the nitrite reductase expression vector into an Escherichia coli expression strain. Aiming at the defects that the application range and effect are severely limited because most of the nitrite reductases are intracellular enzymes in a living body and the expression quantity is low in the prior art, the engineering bacteria can realize great in-vitro expression synthesis of the nitrite reductase by using genetic engineering means and has high significance for rapidly repairing secondary salinization soil and realizing precision agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Rapid detection method for trichina nucleic acid and rapid detection kit thereof
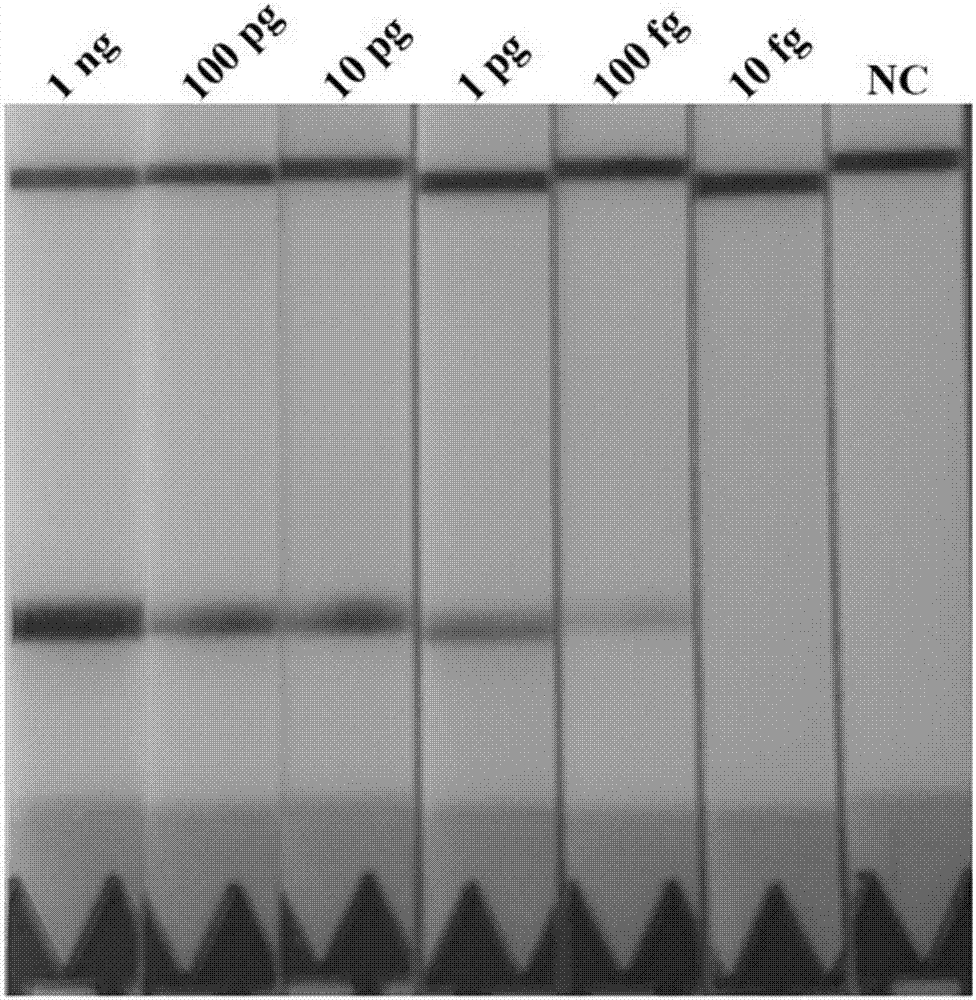
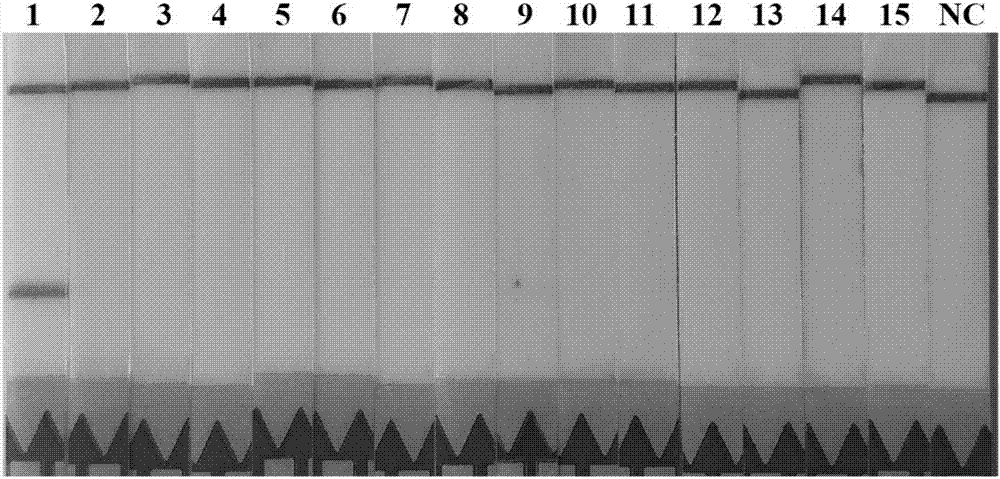
PendingCN107385054AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyNucleic acid
The invention discloses a rapid detection kit for trichina nucleic acid. The kit comprises the following components: an RPA primer probe mixed solution, a PBST solution, a flow measurement chromatographic test strip, RPA lyophozyme and an RPA reaction premixed solution. The invention also provides a rapid detection method for the trichina nucleic acid. The rapid detection method and the rapid detection kit have the beneficial effects that on the basis of molecular biology, a specific primer and a probe are firstly designed on the basis of trichina mitochondrion small subunit rRNA (rrnS) genes, then the kit for rapidly detecting the trichina nucleic acid is prepared by utilizing a recombinant enzyme polymeric enzyme amplification-flow measurement chromatography method, the sensitivity is higher than that of traditional PCR, the specificity is high, a whole process only needs 30 minutes, and a result is extremely simple and convenient to determine; and after a nucleic acid sample is obtained, the whole reaction process can be carried out in a non-laboratory environment, and the rapid detection method and the rapid detection kit not only are suitable for clinical diagnosis, but also can be applied to various fields such as food safety detection, farm on-site detection and wild animal environmental assessment.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
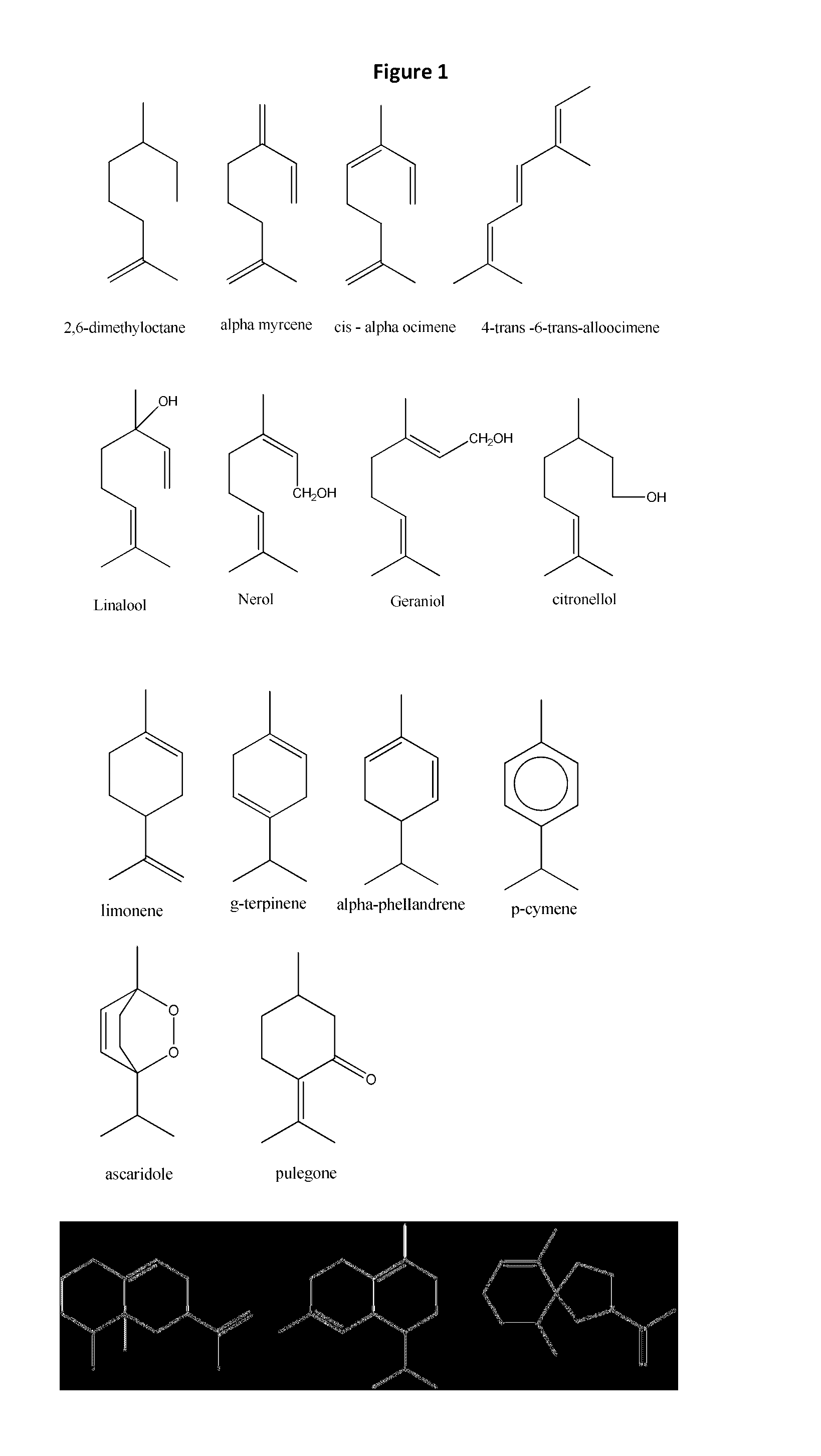
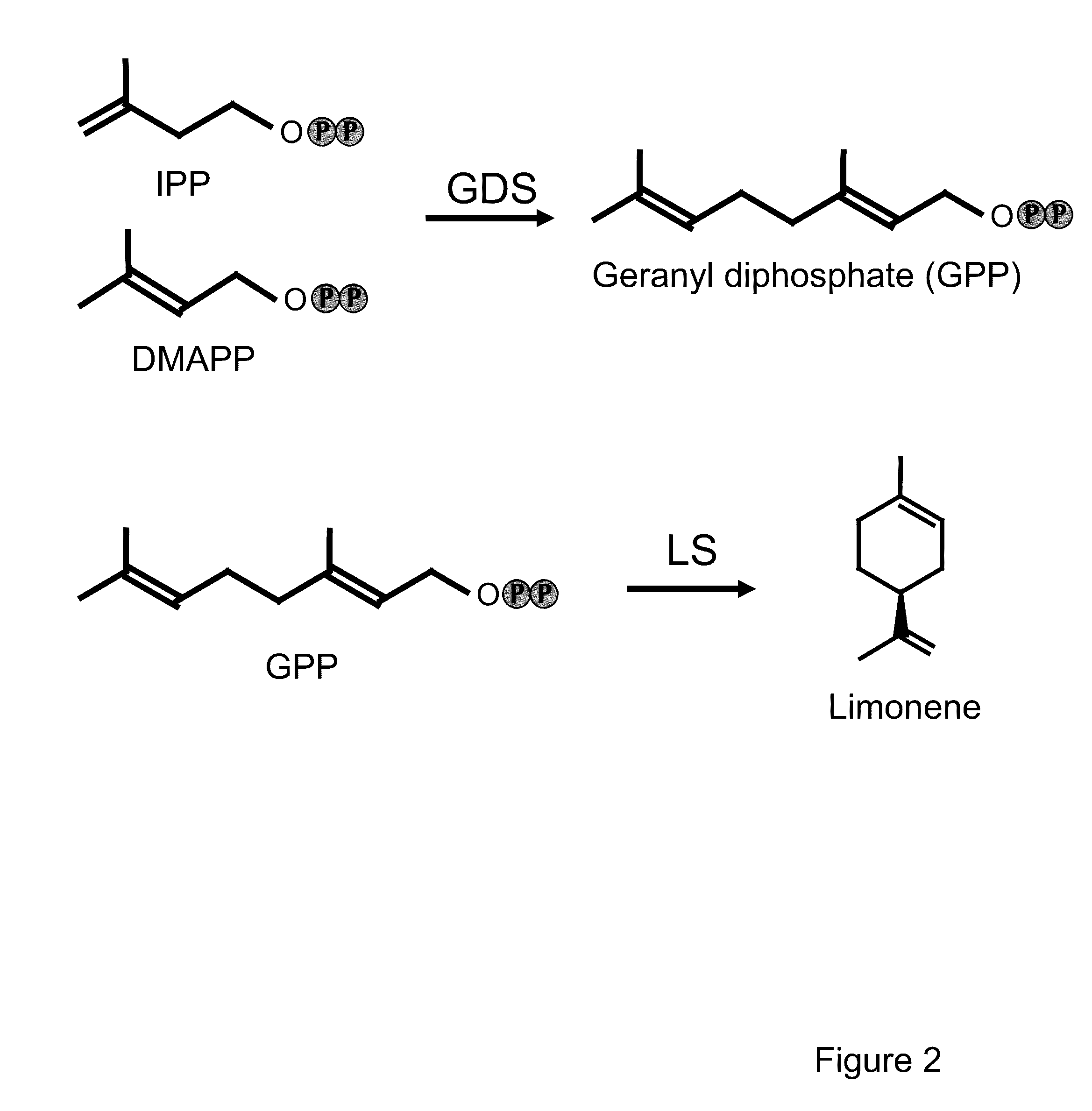
Methods for high yield production of terpenes
InactiveUS9534227B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic compound preparationBiofuelSmall subunit
Provided are enhanced high yield production systems for producing terpenes in plants via the expression of fusion proteins comprising various combinations of geranyl diphosphate synthase large and small subunits and limonene synthases. Also provided are engineered oilseed plants that accumulate monoterpene and sesquiterpene hydrocarbons in their seeds, as well as methods for producing such plants, providing a system for rapidly engineering oilseed crop production platforms for terpene-based biofuels.
Owner:DONALD DANFORTH PLANT SCI CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com