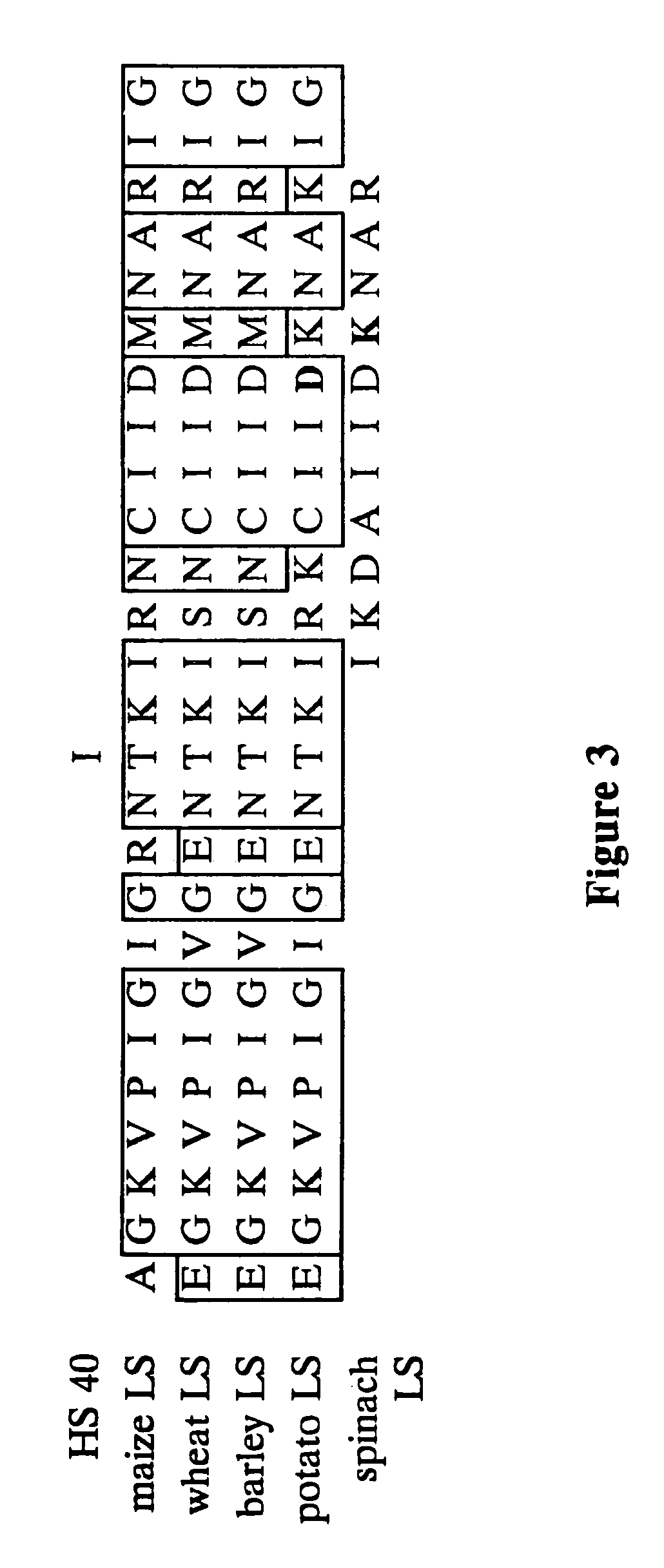
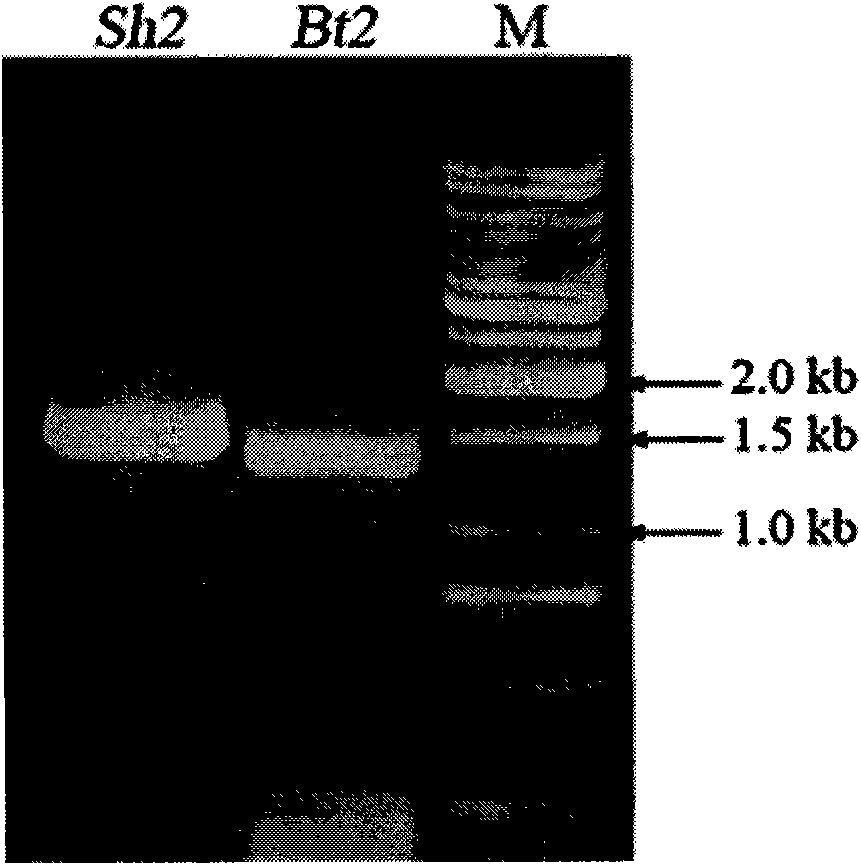
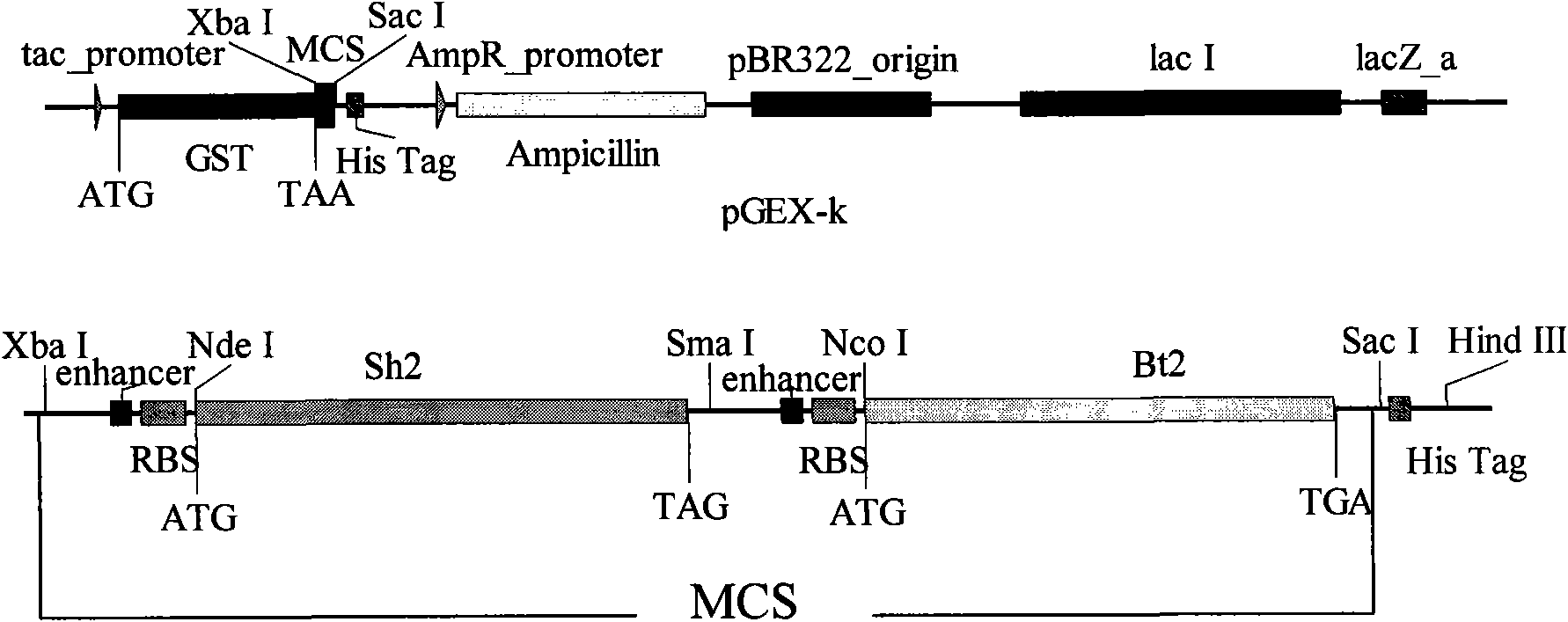
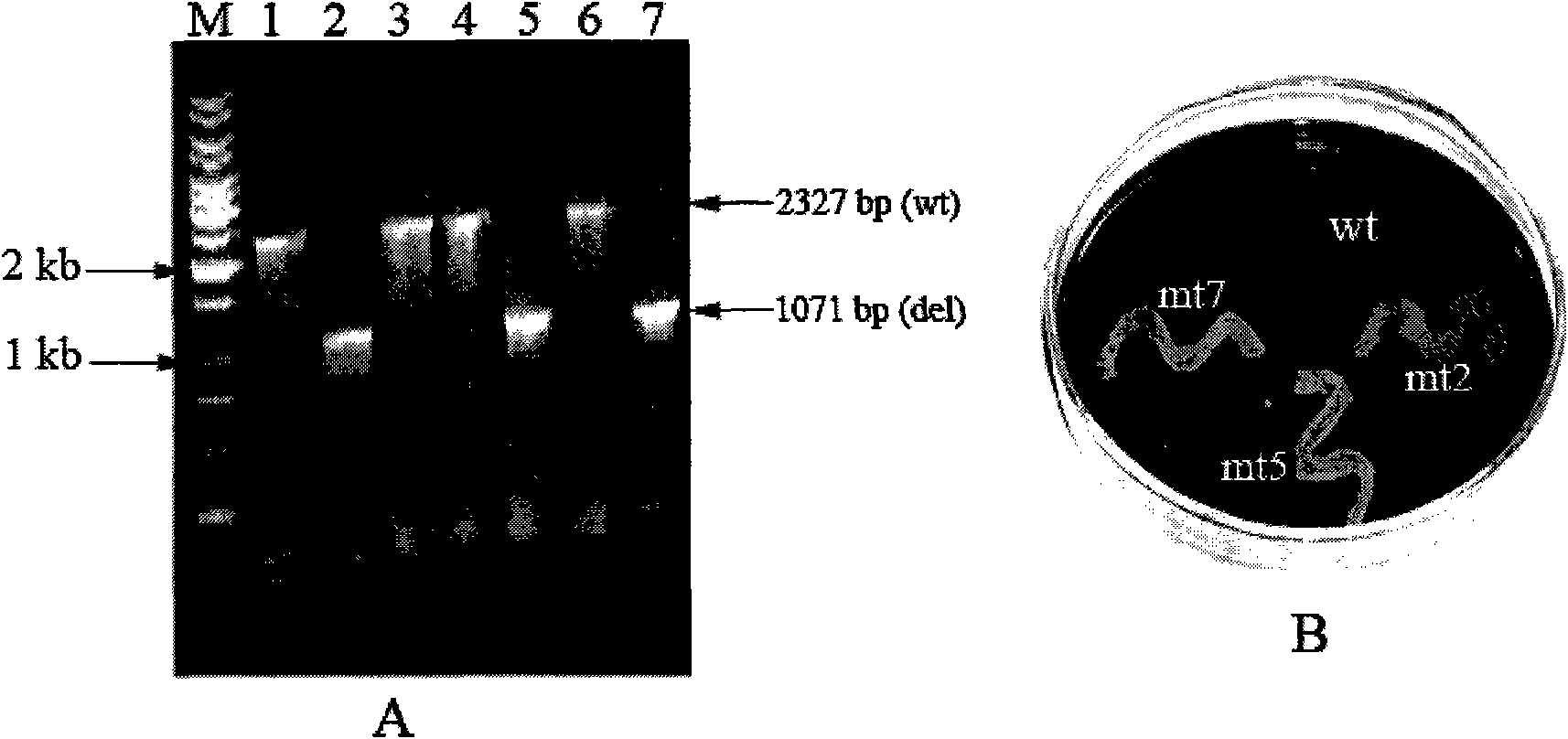
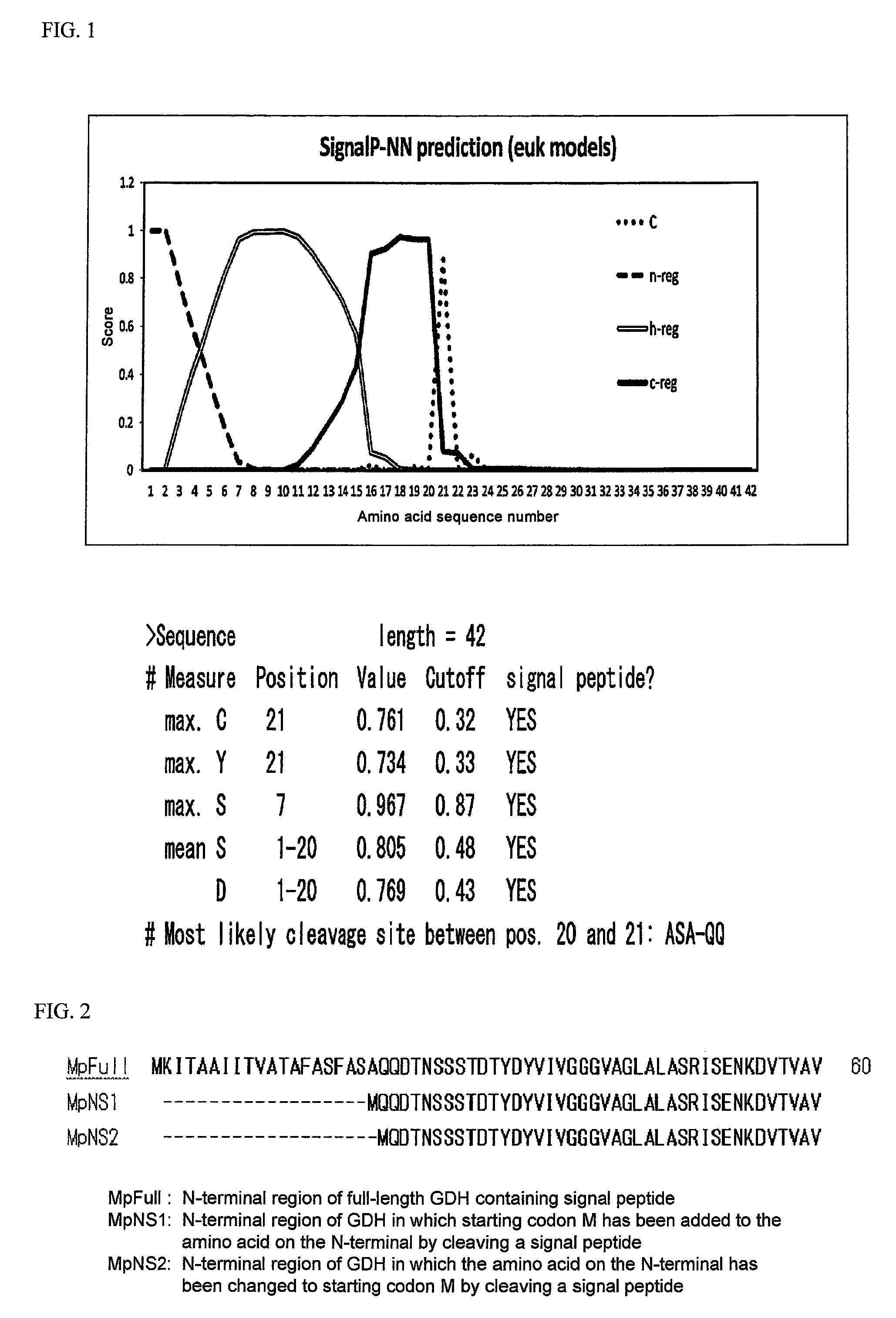
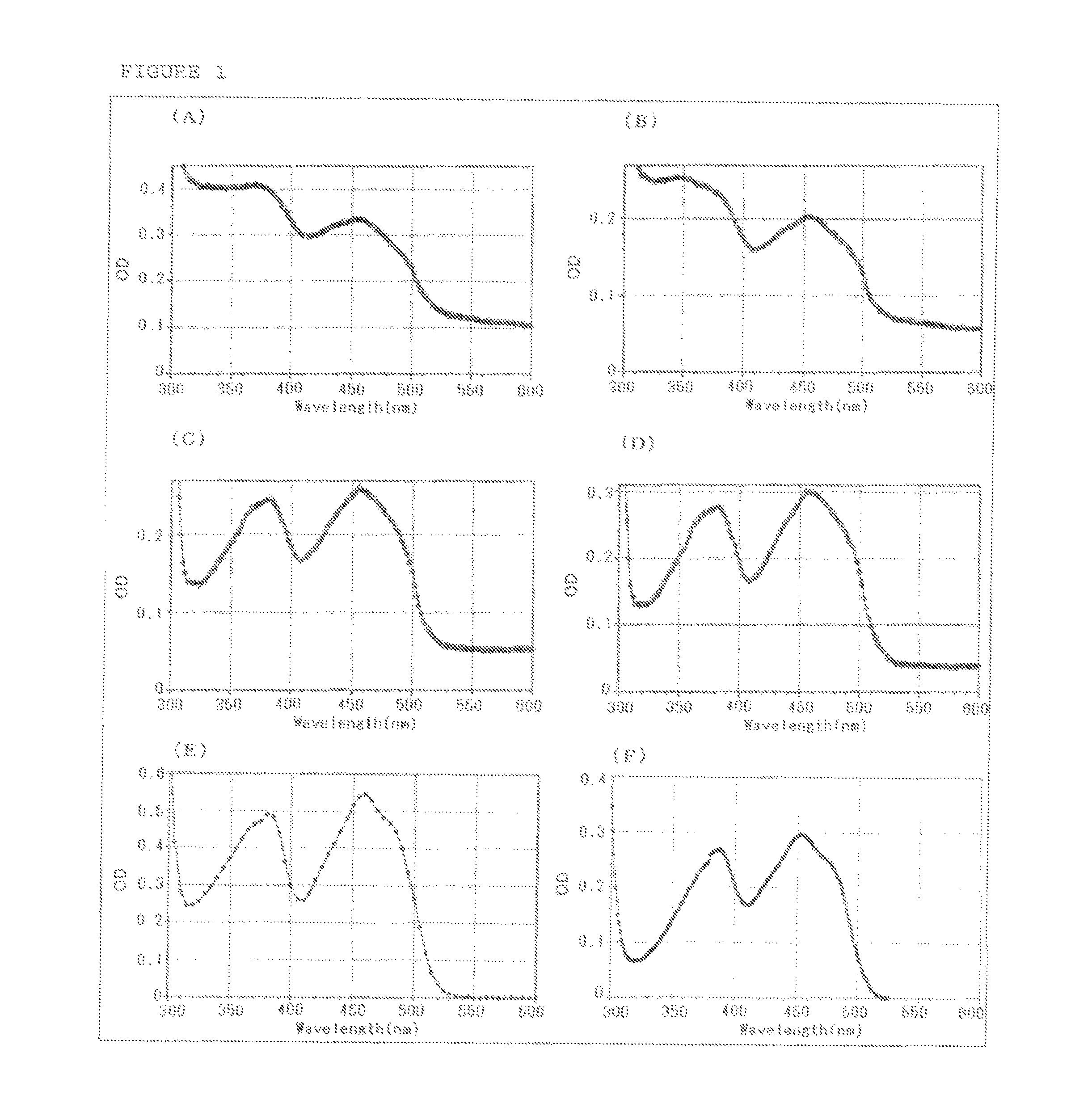
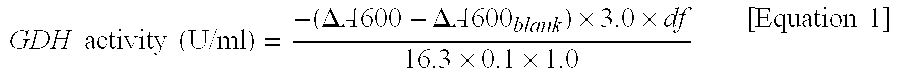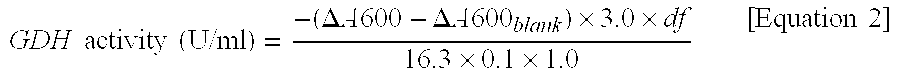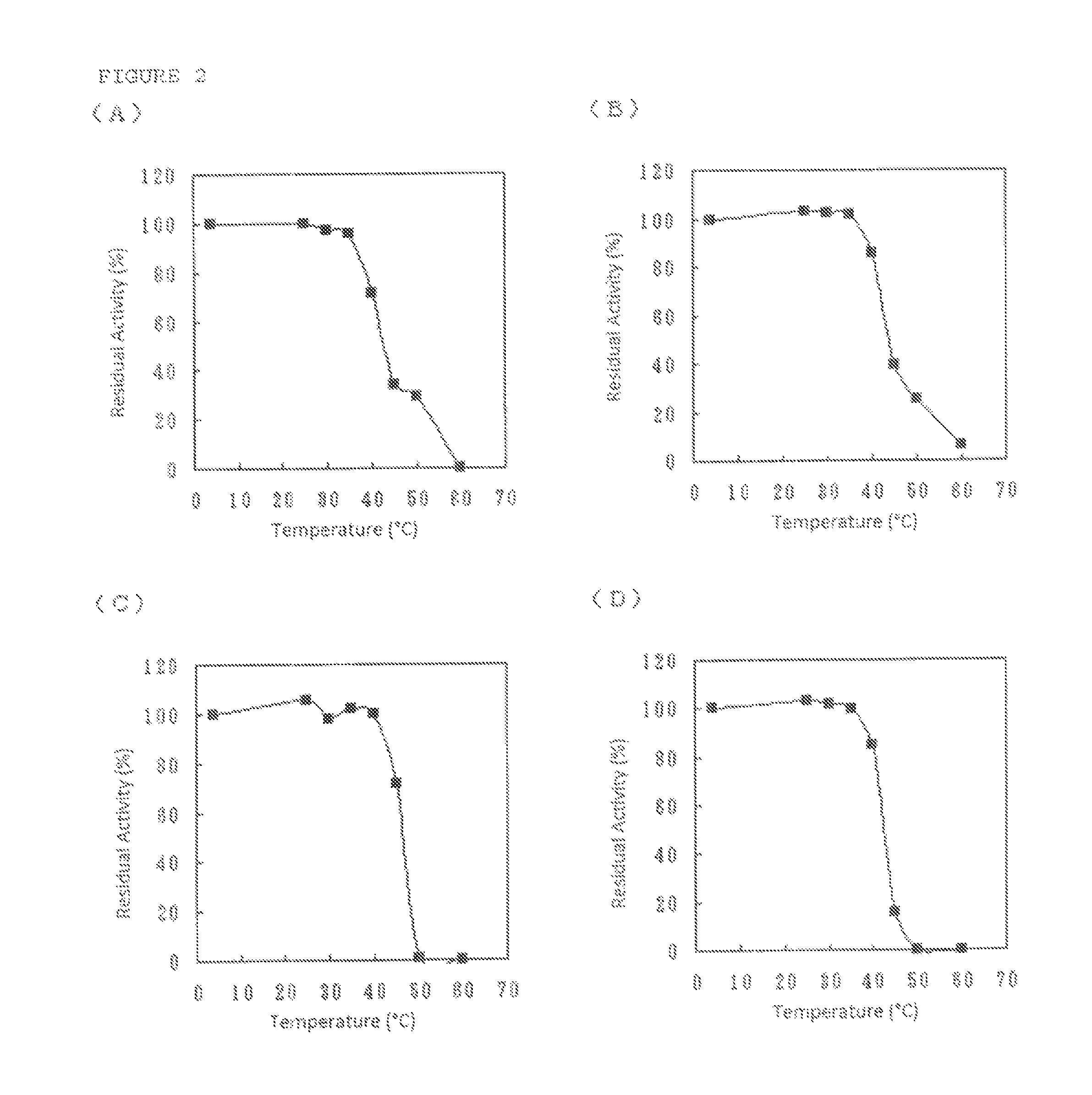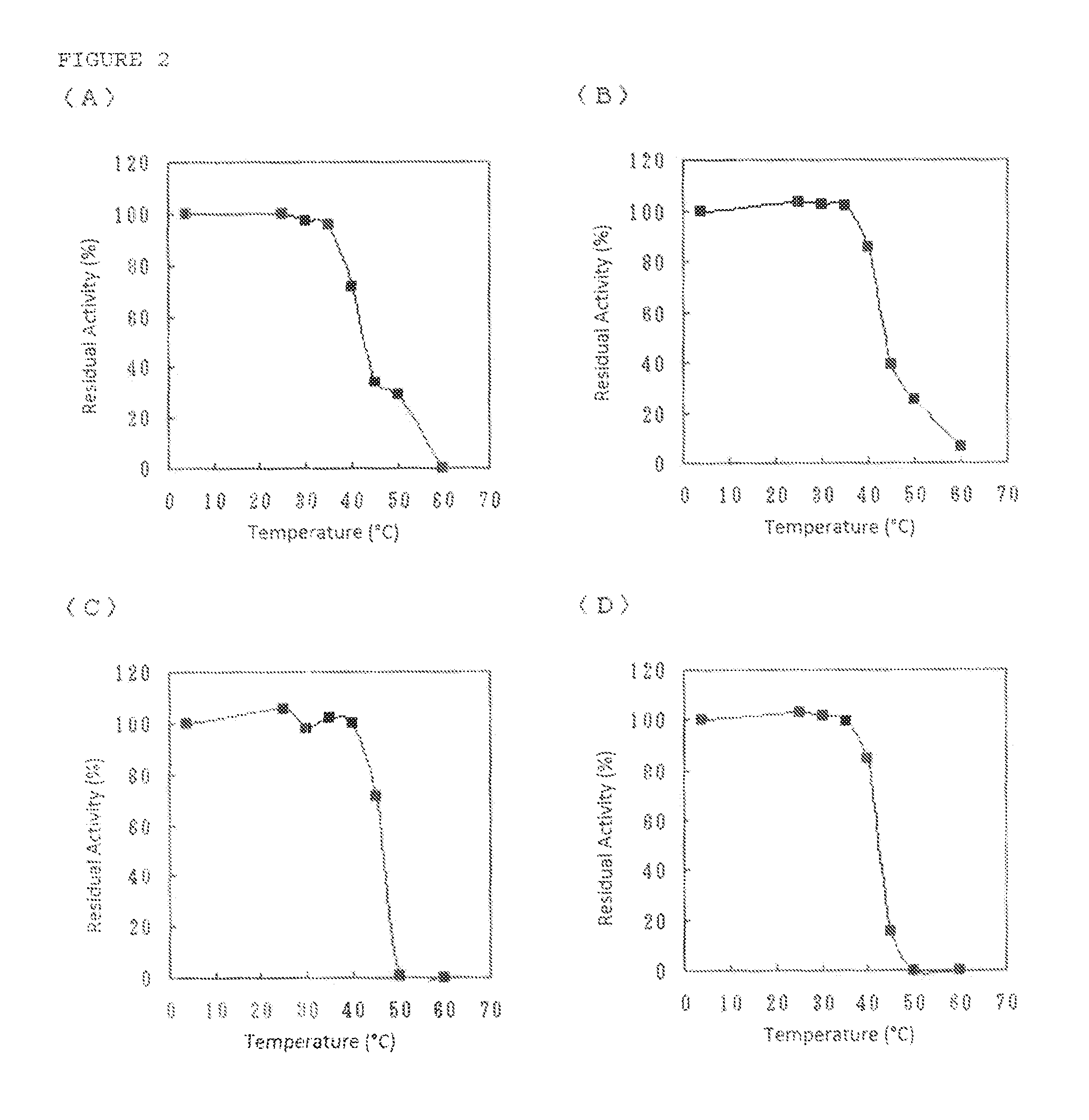Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
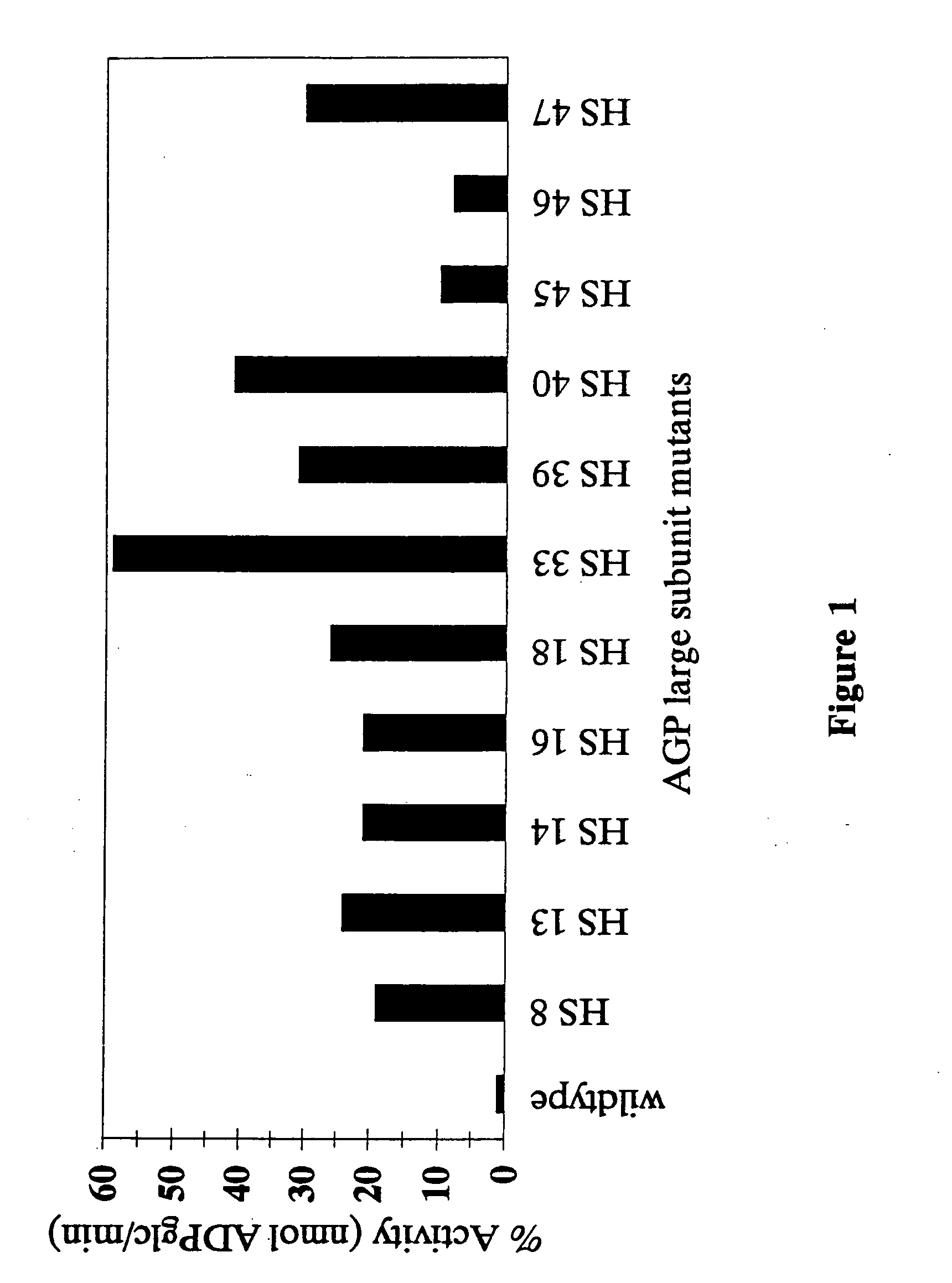
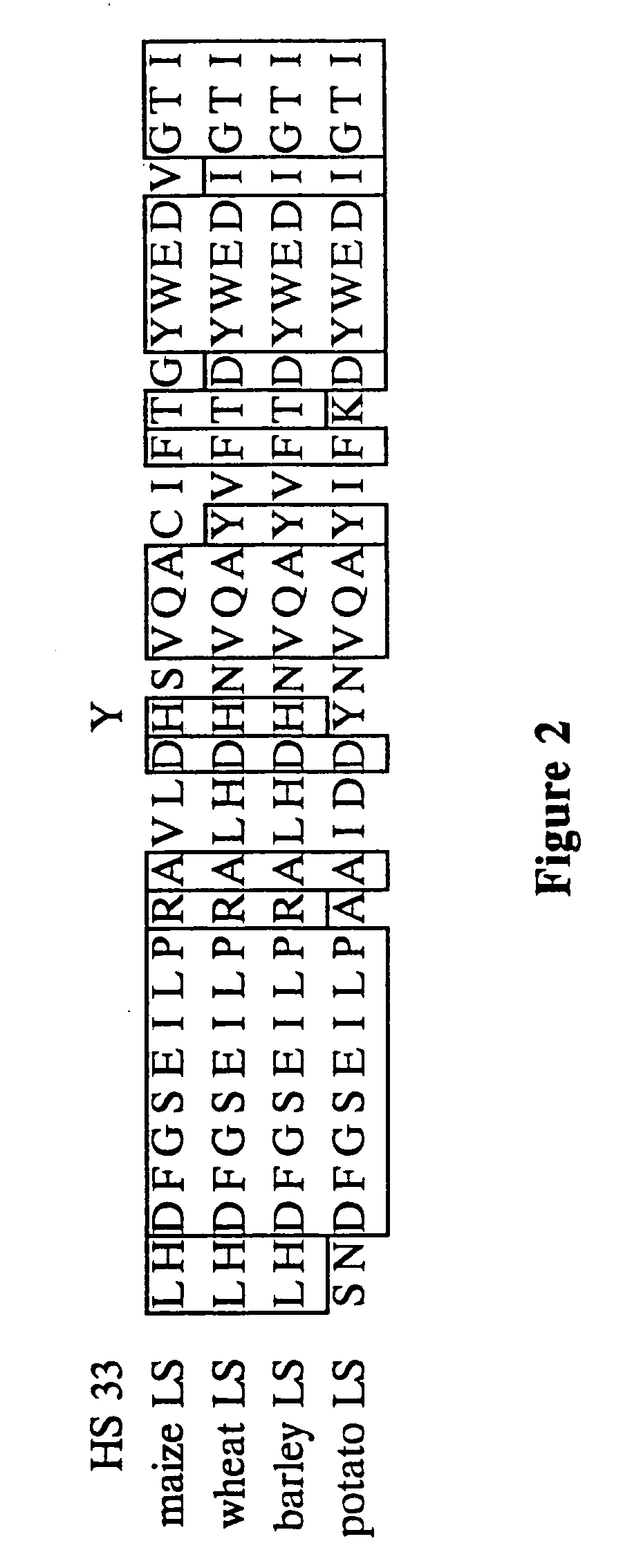
53 results about "ADP Glucose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Li J, Baroja-Fernandez E, Bahaji A, Munoz FJ, Ovecka M, Montero M, Sesma MT, Alonso-Casajus N, Almagro G, Sanchez-Lopez AM, Hidalgo M, Zamarbide M, Pozueta-Romero J: Enhancing sucrose synthase activity results in increased levels of starch and ADP-glucose in maize (Zea mays L.) seed endosperms. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013 Feb;54(2):282-94. doi: 10 ...
Pentose phosphate pathway upregulation to increase production of non-native products of interest in transgenic microorganisms
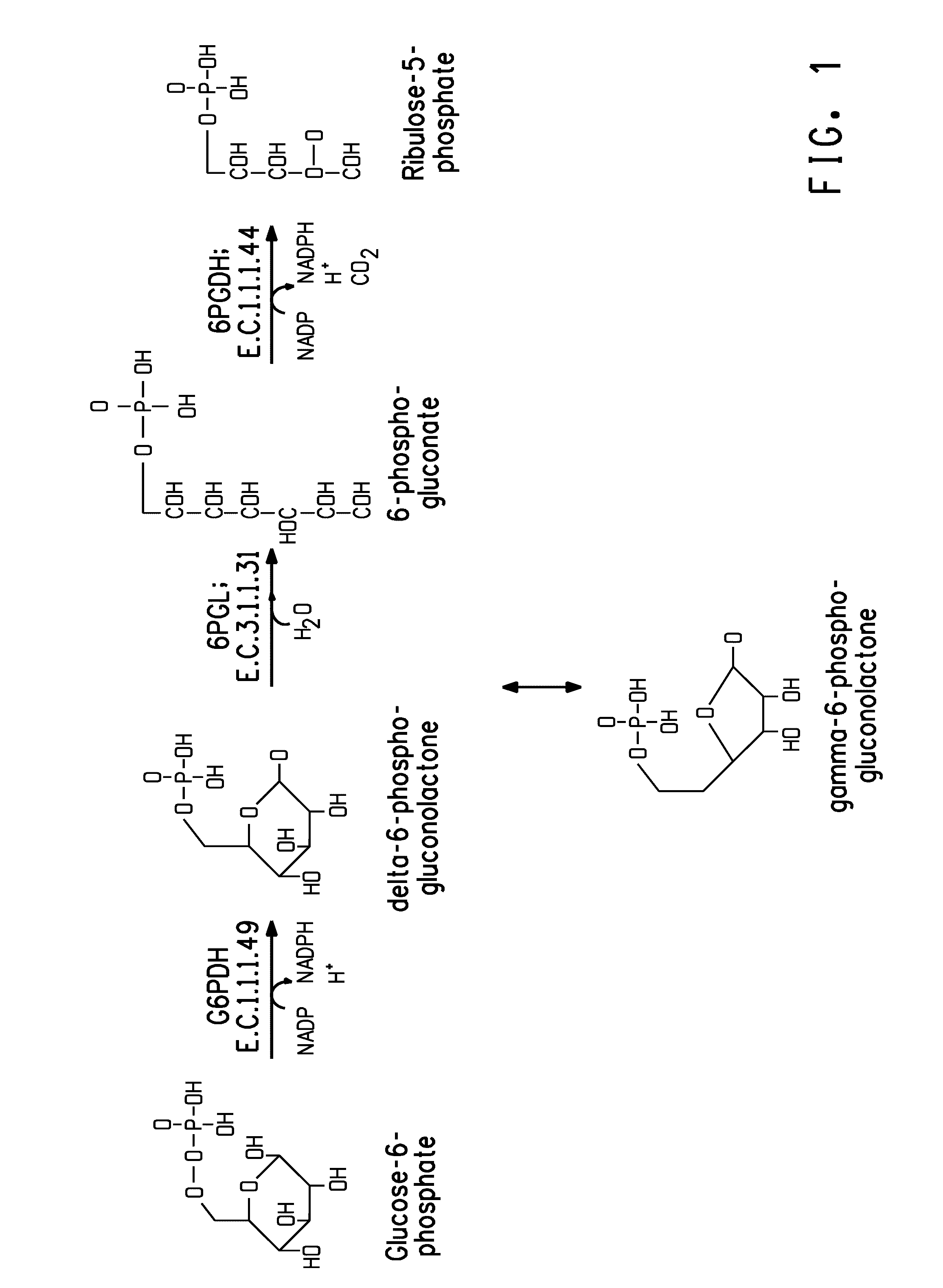
Coordinately regulated over-expression of the genes encoding glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase [“G6PDH”] and 6-phospho-gluconolactonase [“6PGL”] in transgenic strains of the oleaginous yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica, comprising a functional polyunsaturated fatty acid [“PUFA”] biosynthetic pathway, resulted in increased production of PUFAs and increased total lipid content in the Yarrowia cells. This is achieved by increased cellular availability of the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate [“NADPH”], an important reducing equivalent for reductive biosynthetic reactions, within the transgenic microorganism.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
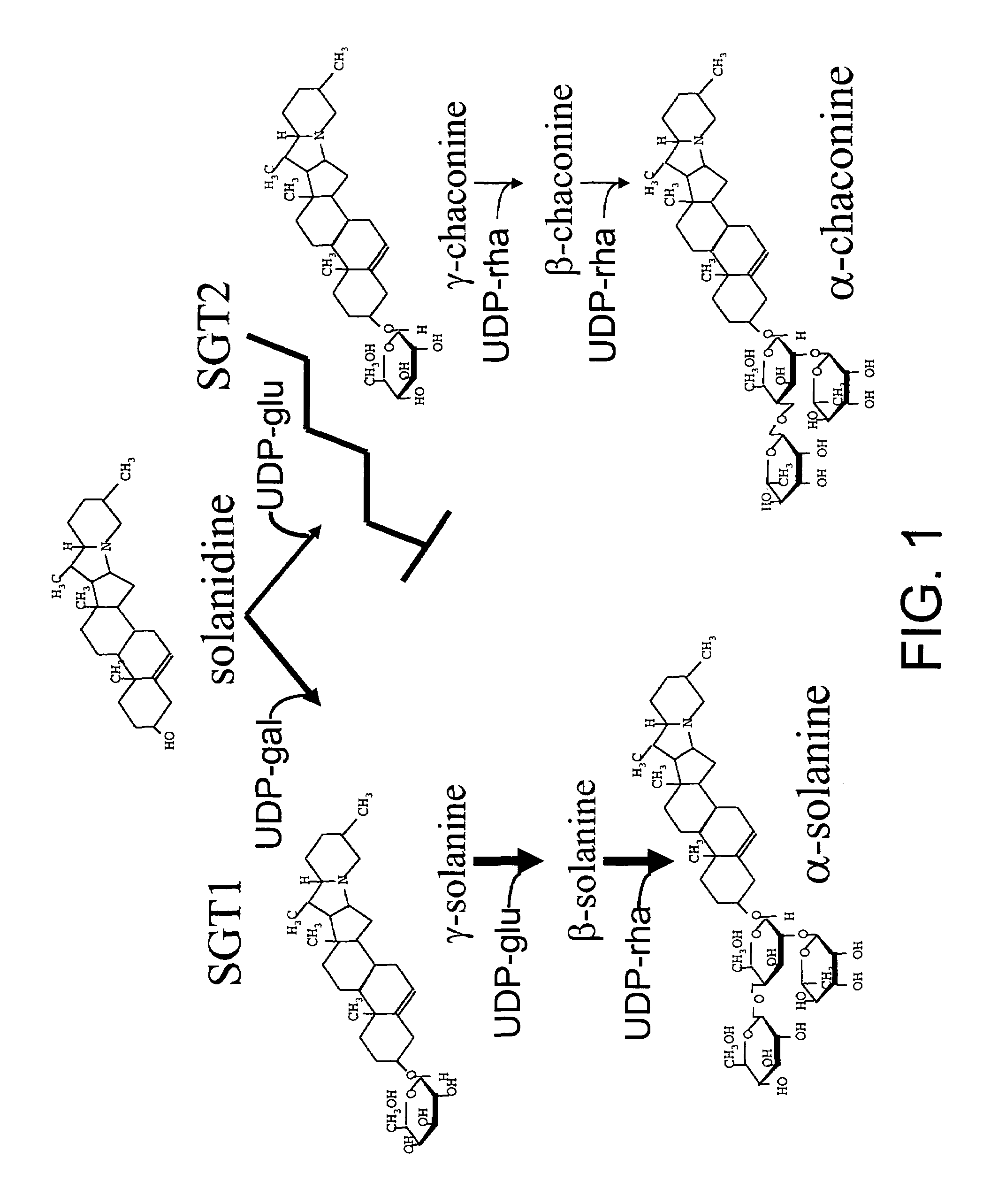
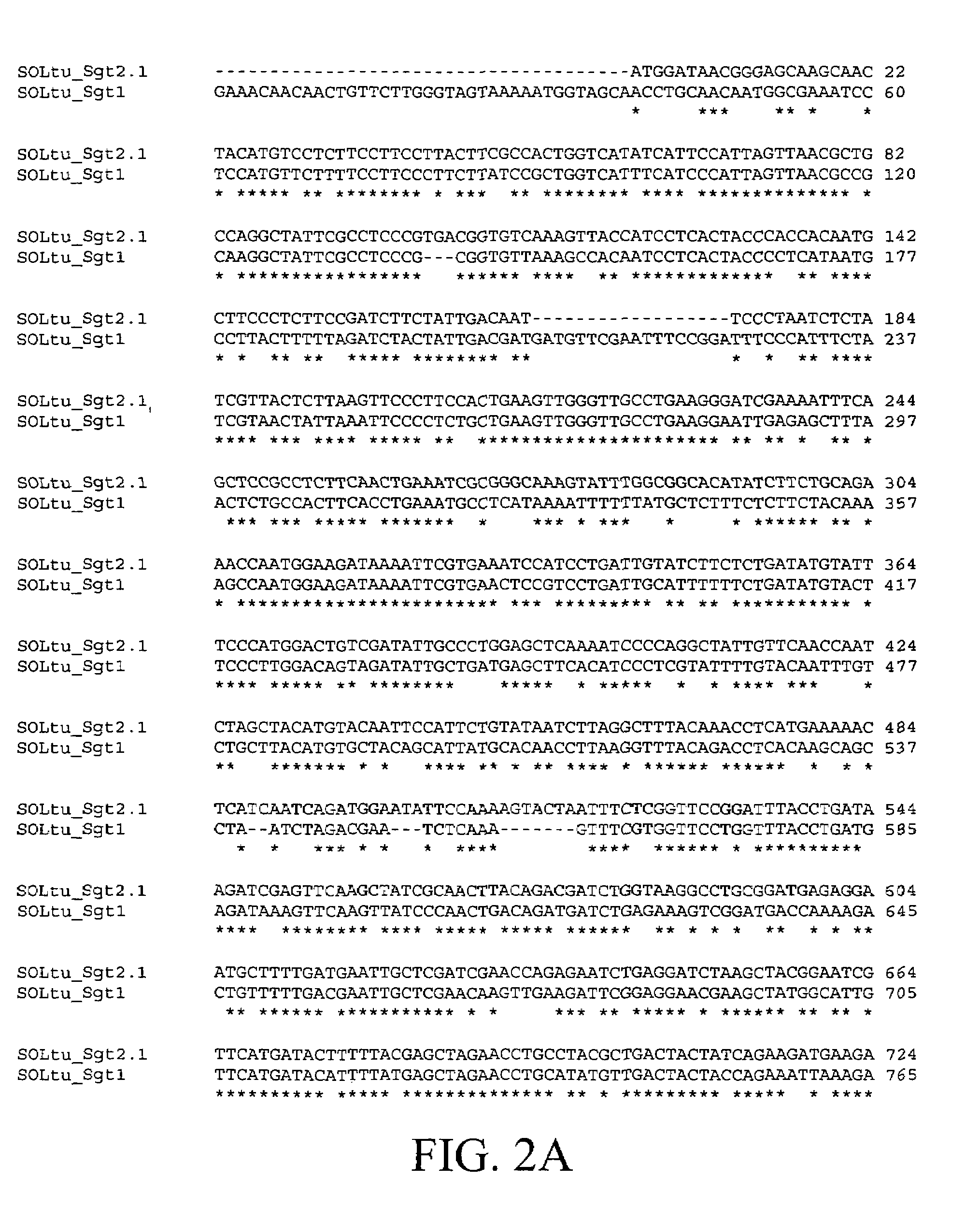
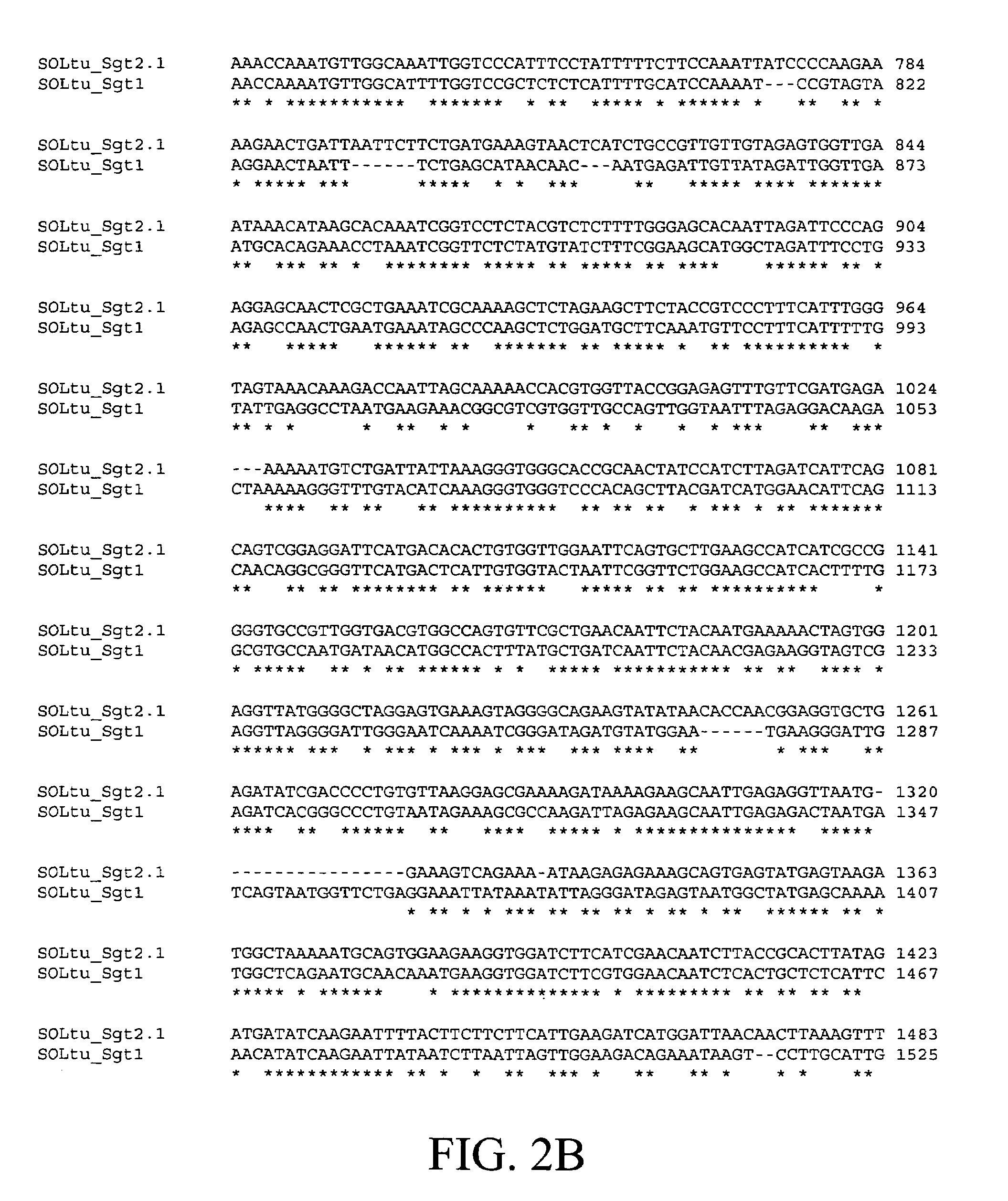
Solanum tuberosum sterol alkaloid glycosyltransferase (SGT) a novel solanidine glucosyltransferase SGT2 and uses thereof
InactiveUS7375259B1Increased glycoalkaloid biosynthesisReduce or eliminate glycoalkaloid biosynthesisBacteriaLibrary member identificationSterolSolanidine glucosyltransferase
Nucleic acid sequences from potato that encode the enzyme UDP-glucose:solanidine glucosyltransferase (SGT2) are disclosed. Recombinant DNA molecules containing the sequences, and use thereof, in particular, use of the sequences and antisense constructs to inhibit the production of SGT2 and thereby reduce the level of the more human-toxic of the two predominant steroidal glycoalkaloids α-chaconine and / or increase the level of the more insect-toxic α-solanine in Solanaceous plants such as potato are described.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
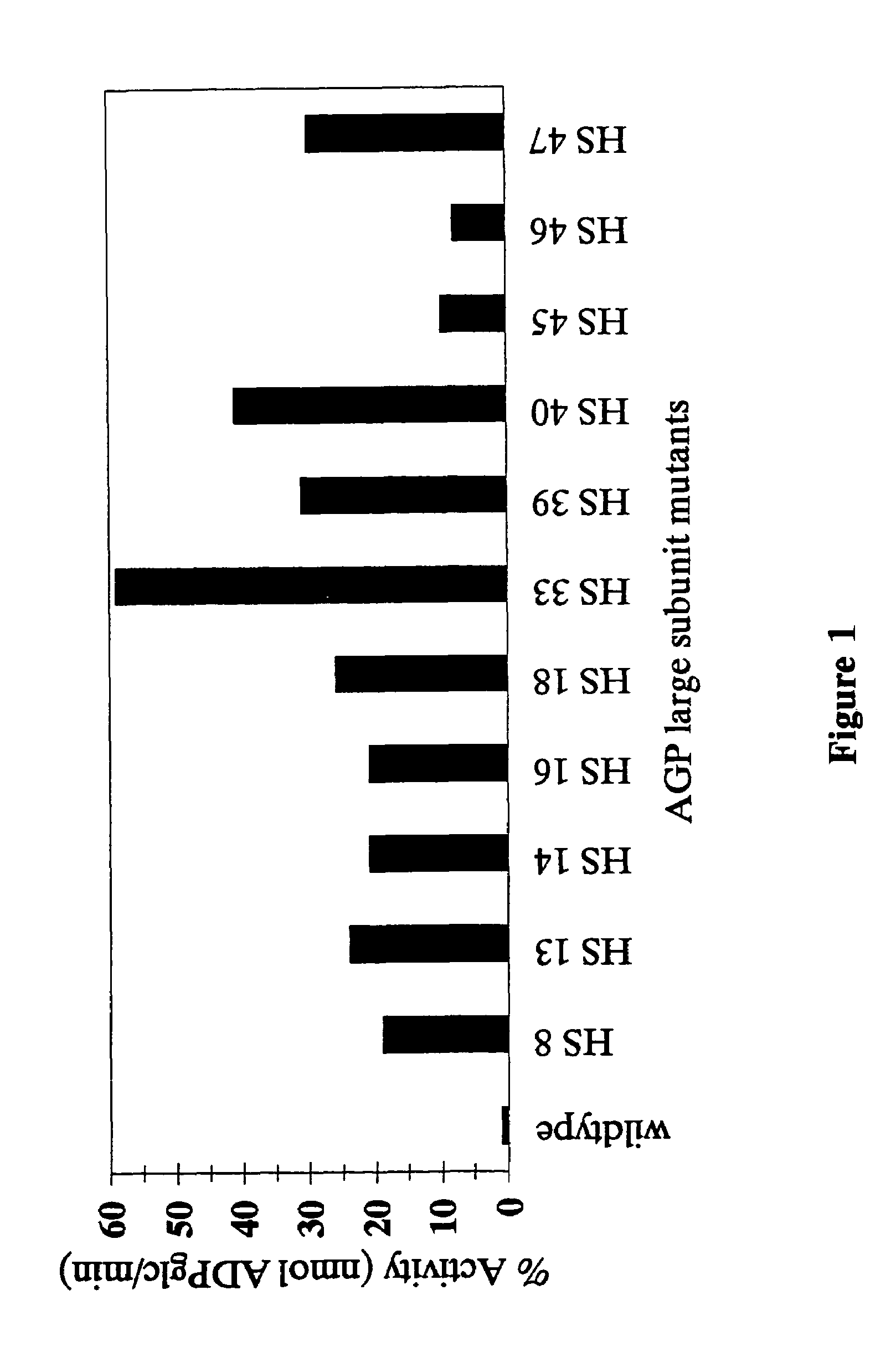
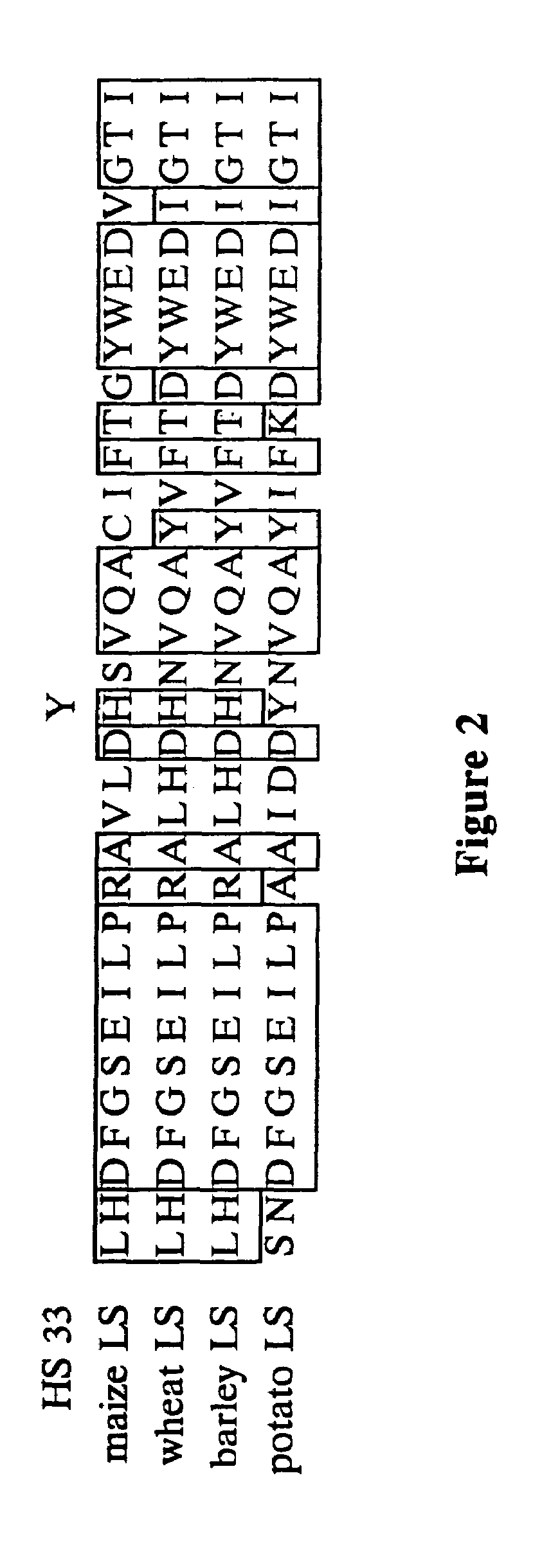
Nucleic acids encoding heat stable mutants of plant ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
InactiveUS7312378B2Increase crop yieldImprove toleranceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideHeat stability
The subject invention pertains to novel mutant polynucleotide molecules that encode enzymes that have increased heat stability. These polynucleotides, when expressed in plants, result in increased yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress. The polynucleotide molecules of the subject invention encode maize endosperm ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGP) and soluble starch synthase (SSS) enzyme activities. Plants and plant tissue bred to contain, or transformed with, the mutant polynucleotides, and expressing the polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides, are also contemplated by the present invention. The subject invention also concerns methods for isolating polynucleotides and polypeptides contemplated within the scope of the invention. Methods for increasing yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN109777763AIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCitrate synthase
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Heat stable mutants of starch biosynthesis enzymes
InactiveUS6969783B2Increase crop yieldImprove toleranceSugar derivativesHydrolasesPlant tissueNucleotide
The subject invention pertains to novel mutant polynucleolide molecules that encode enzymes that have increased heat stability. These polynucleotides, when expressed in plants, result in increased yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress. In one embodiment, the polynucleotide molecules of the subject invention encode maize endosperm ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGP) activity. Plants and plant tissue bred to contain, or transformed with, the mutant polynucleotides, and expressing the polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides, are also contemplated by the present invention. The subject invention also concerns methods for isolating polynucleotides and polypeptides contemplated within the scope of the invention. Methods for increasing yield in plants grown under conditions or heat stress are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant, encoding genes thereof and application of same two
The invention discloses a corn endosperm ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant, encoding genes thereof and application of the same two. The protein can be the protein (1) formed by the first amino acid sequences showed as in a sequence table and can also be the protein (2) which is formed by substituting and / or deleting the first amino acid residue sequences showed as in a sequence table and / or adding one or several amino acid residues to the first amino acid residue sequences, has ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase activity and is derived from the protein (1). The corn endosperm ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant and the encoding thereof play important roles in the corn variety improvement.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, method for producing flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, and glucose measurement method
ActiveUS9074239B2Increased substrate specificityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEscherichia coliAmino acid substitution
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH), which in addition to having high substrate specificity and adequate desirable heat stability, is suitable for efficient production, preferably using E. coli, yeast or molds and the like as host cells. The FAD-GDH has amino acid substitutions at positions equivalent to one or more locations selected from the group consisting of position 213, position 368 and position 526 in the amino acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 8. The FAD-GDH is acquired from a culture by inserting a gene encoding the FAD-GDH into host cells such as E. coli. A preferable example of the FAD-GDH is FAD-GDH, in which a signal peptide region present in an N-terminal region has been deleted from the amino acid sequence of Mucor-derived FAD-GDH, and which has the aforementioned amino acid substitutions. The FAD-GDH can be preferably used in clinical diagnosis.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS8945359B2Good reproducibilityImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConcentrations glucoseMaltose
The invention provides a flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase exhibiting reduced fluctuation of activity depending on temperature environment, and a method for measuring glucose concentration using the flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has the following properties (1) to (3): (1) activity: which exhibits glucose dehydrogenase activity in the presence of an electron acceptor; (2) substrate specificity: which exhibits an activity of 10% or less against maltose, D-galactose, D-fructose, sorbitol, lactose and sucrose when the activity against D-glucose is defined as 100%; and (3) temperature characteristics: which exhibits lower fluctuation of activity in a wide temperature range of 10 to 50° C.
Owner:IKEDA SHOKKEN KK
Protein having flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent glucose dehydrogenase activity
InactiveUS20150267178A1Improve thermal stabilityMaintain good propertiesAnimal cellsBacteriaFlavin adenine dinucleotideGlucose dehydrogenase activity
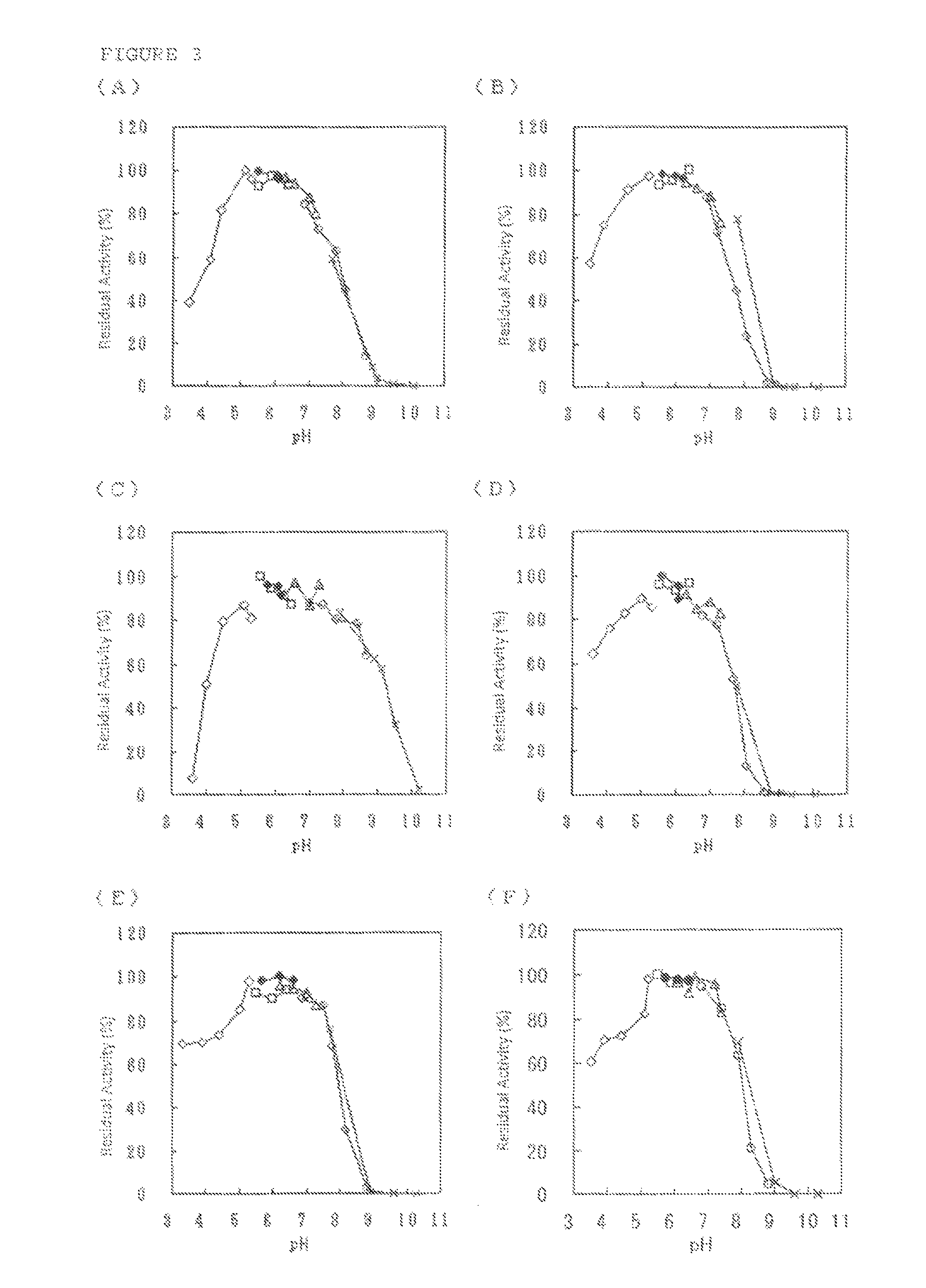
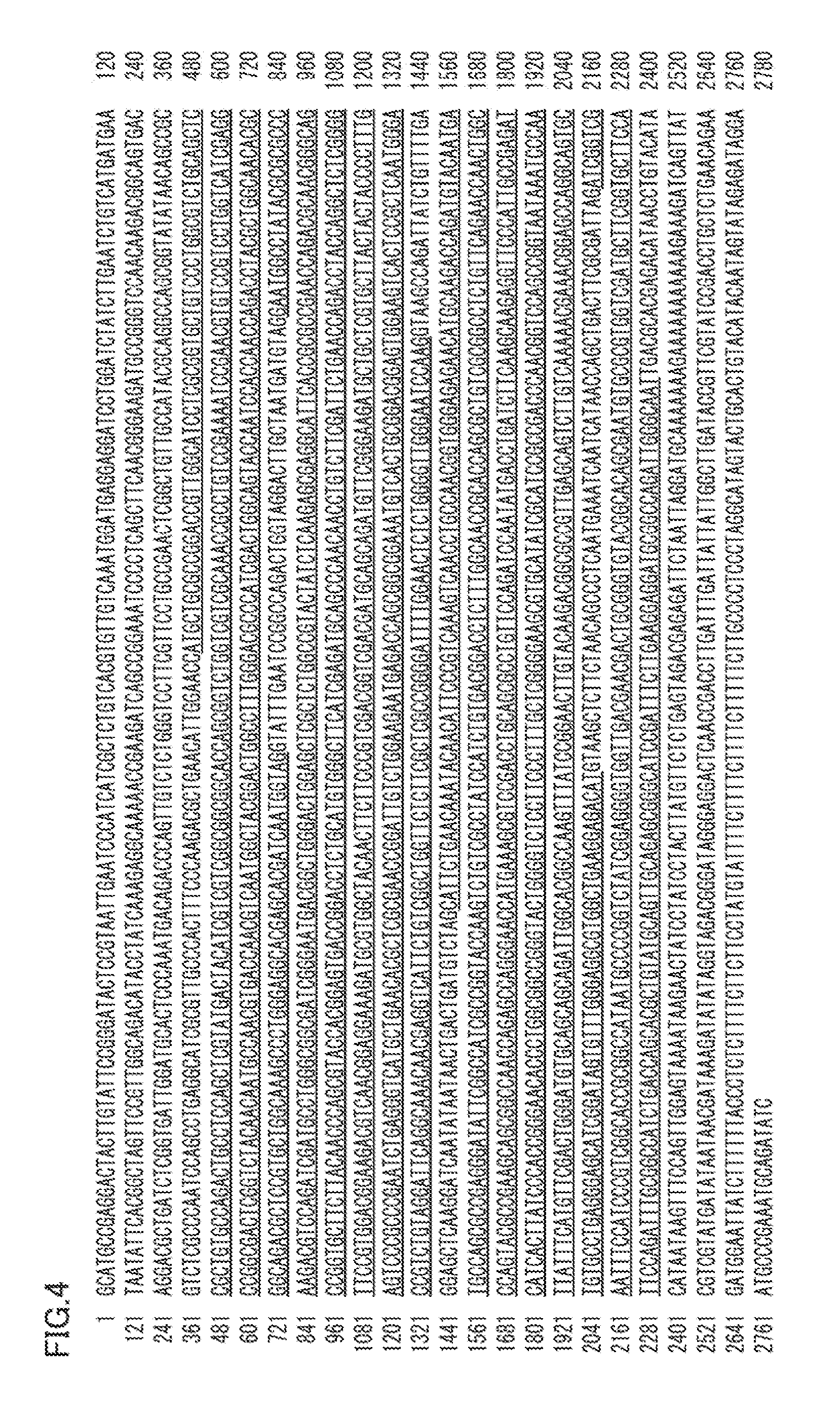
The present invention provides a protein derived from a thermophilic filamentous fungus having flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent glucose dehydrogenase activity. The present invention provides an enzyme for glucose measurement that has better thermal stability than that of conventional enzymes while being unaffected by dissolved oxygen, not requiring the addition of a coenzyme, and maintaining the excellent properties of FADGDH in terms of having excellent substrate specificity (particularly low reactivity with maltose).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Heat stable mutants of starch biosynthesis enzymes
InactiveCN1503842AIncrease productionImprove toleranceHydrolasesMutant preparationPlant tissueNucleotide
The present invention relates to novel mutant polynucleotide molecules encoding enzymes with enhanced thermostability. When expressed in plants, these polynucleotides lead to increased yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress. In one embodiment, the polynucleotide molecule of the present invention encodes maize endosperm ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGP) and soluble starch synthase (SSS) enzyme activities. Also contemplated by the present invention are plants and plant tissues grown to contain or transformed with such mutant polynucleotides and expressing a polypeptide encoded by such polynucleotides. The invention also relates to methods for isolating polynucleotides and polypeptides within the scope of the invention. The present invention also provides methods of increasing yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20130203093A1Good reproducibilityImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicroorganismsConcentrations glucoseMaltose
The invention provides a flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase exhibiting reduced fluctuation of activity depending on temperature environment, and a method for measuring glucose concentration using the flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has the following properties (1) to (3): (1) activity: which exhibits glucose dehydrogenase activity in the presence of an electron acceptor; (2) substrate specificity: which exhibits an activity of 10% or less against maltose, D-galactose, D-fructose, sorbitol, lactose and sucrose when the activity against D-glucose is defined as 100%; and (3) temperature characteristics: which exhibits lower fluctuation of activity in a wide temperature range of 10 to 50° C.
Owner:IKEDA SHOKKEN KK
Method for detecting TaAGPS gene allelic variation relevant to thousand kernel weight
InactiveCN105907862AValid identificationRapid and effective separation and identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a method for detecting wheat cytoplasmic adp glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit (TaAGPS) gene excellent allelic variation relevant to thousand kernel weight by using CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) marks. According to the method, the corresponding basic groups of two allelic variations (TaAGPS-7A-T and TaAGPS-7A-G) in the 5092 site of the TaAGPS-7A exon region III are respectively T and G; the corresponding amino acid is Ser and Ala; firstly, a primer is used for performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on SEQ ID No: 1 and SEQ ID No: 2; after the enzyme digestion by using DdeI incision enzyme, electrophoresis detection is performed; the authentication of different allelic variations of the TaAGPS genes in wheat germplasm resources and later generation breeding can be conveniently and efficiently realized. The operation can be completed through conventional PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis methods; the operation is convenient; stability and feasibility are realized.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
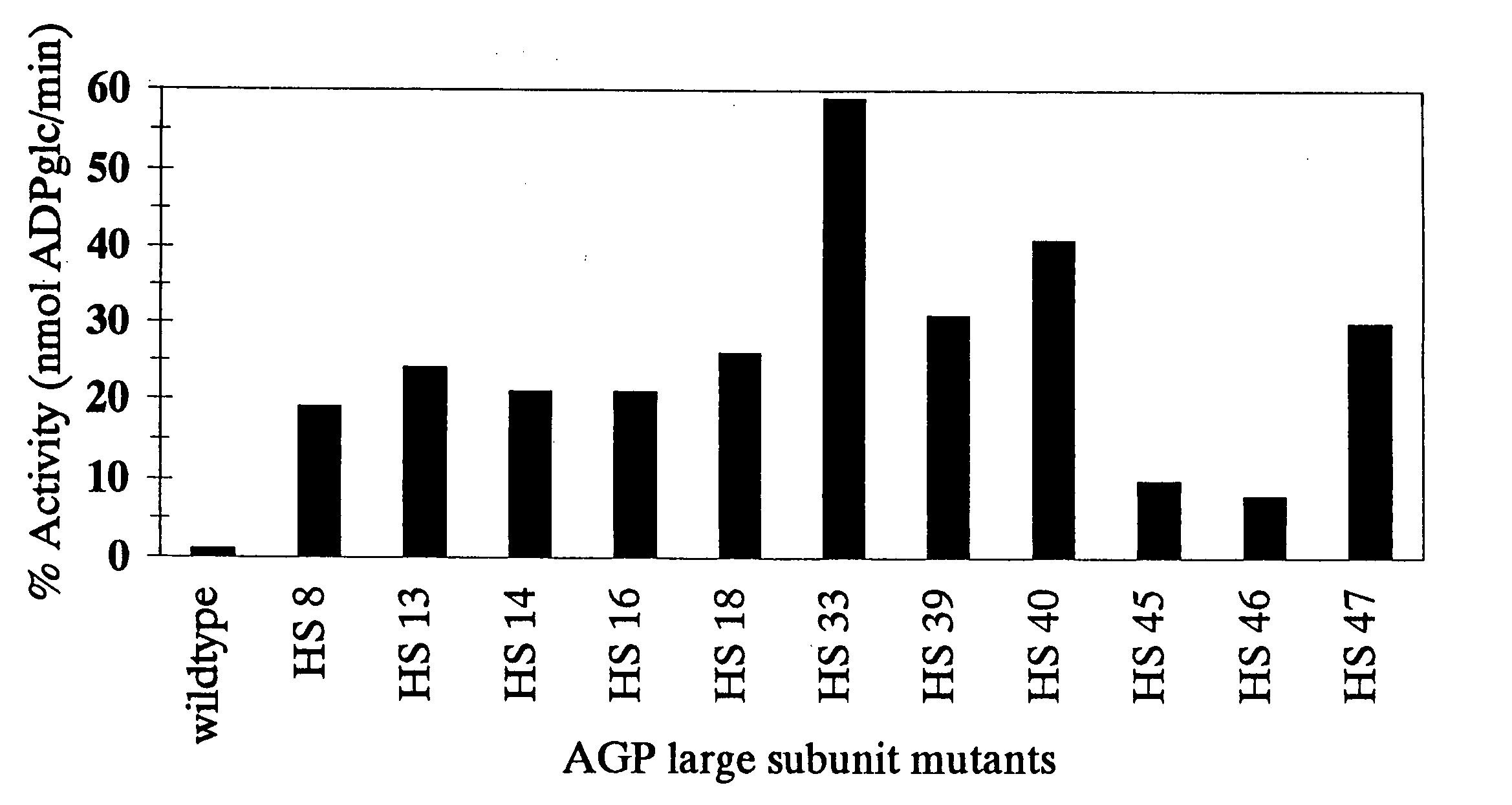
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN105087516AImprove controllabilitySimple screening methodTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention provides an ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant and a screening method and application thereof. The screening method includes the steps of firstly, synthesizing first chain cDNA; secondly, performing PCR amplification; thirdly, building AGPase large and small subunit cDNA prokaryotic expression vectors; fourthly, performing active screening. The method has the advantages that distant hybridization is performed on AGPase large subunit genes and small subunit genes from different species, and the recombinant gene expression vectors are obtained in a highly-controllable manner; escherichia coli glgC mutant strains are converted and inoculated to a Conberg enrichment solid culture medium, and iodine-potassium iodide dyeing is used to screen the high-activity ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant. The screening method is simple and practical and stable and reliable. The enzyme activity and glycogen content of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant are evidently higher than those of wild corn AGPase, evident change of the substrate affinity of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant is avoided, and the sensitivity of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant to activating agent is increased.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Trehalose synthase with increased maltose conversion rate, method for preparing trehalose synthase and application thereof
Owner:HUNAN JINDAI TECH DEV CO LTD
Corn embryosperm ADP- glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant and its screening method and application
InactiveCN1970744AHigh affinityIncrease enzyme activityTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliAgricultural science
The invention discloses a maize-endosperm ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylas mutant and sieving method and application, which comprises the following steps: 1) mutating cDNA of large and small subunit of maize-endosperm AGPase through alcaine hydroxylamine mutation agent randomly; 2) transmitting mutated cDNA and wild-type cDNA into escherichia coli glgC mutation germ; sieving positive monoclonal; 3) seeding positive monoclonal line on the Conberg rich solid board to culture under 35-39 deg.c; 4) dyeing; comparing the color; obtaining deep color mutation as maize-endosperm ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylas mutant.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Expressing acid invertase or ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase in floral tissue for enhanced floral sink strength and increased stability of seed in plants
InactiveUS7193130B2Improve abilitiesEnhances sink strengthClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesUltimate tensile strengthTransgene
The invention discloses a transgenic method for enhancing sink strength in female reproductive organs. It involves the expression of nucleic acids encoding acid invertase or ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase floral tissue. The invention also includes expression constructs used in the method.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
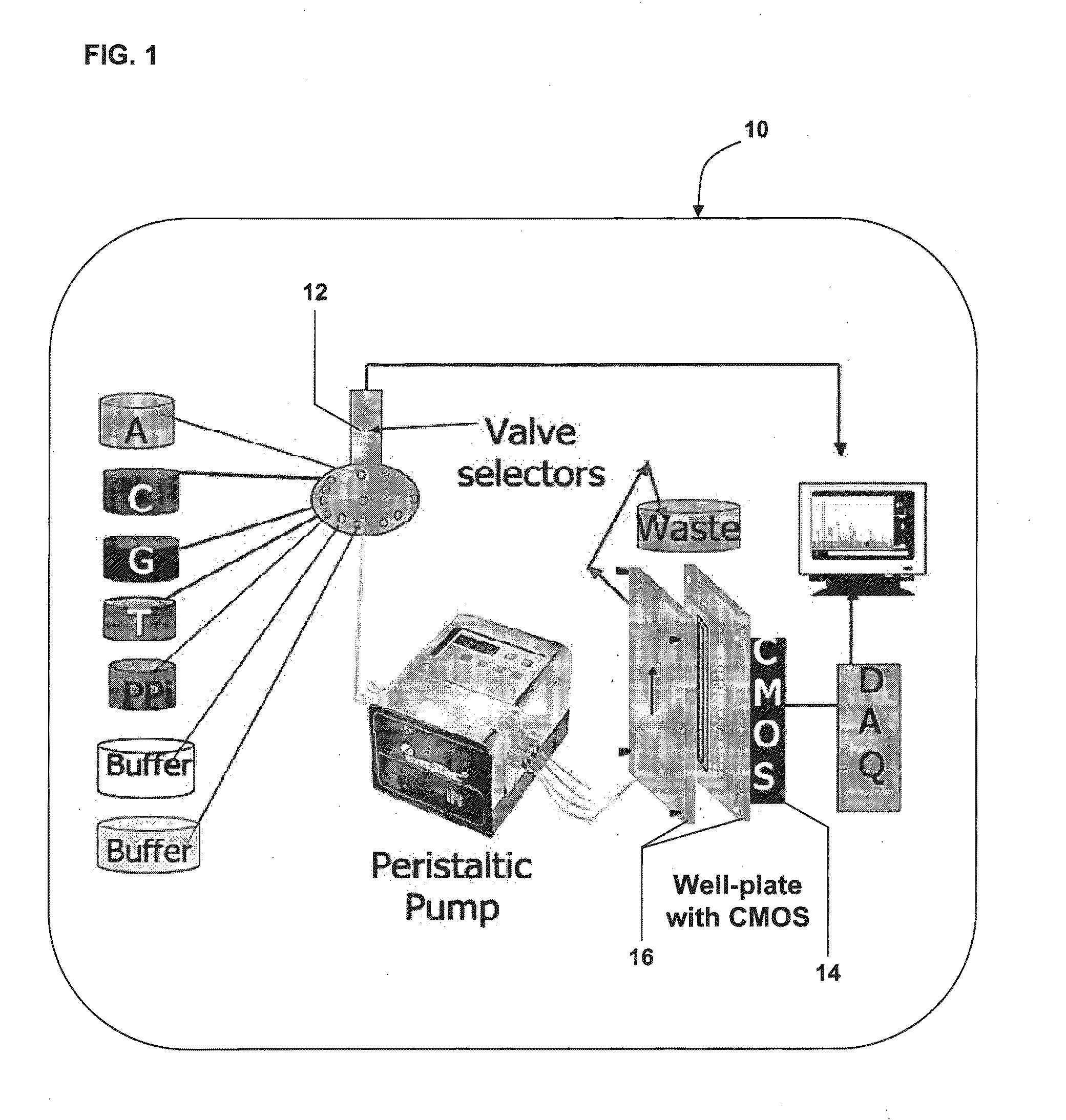
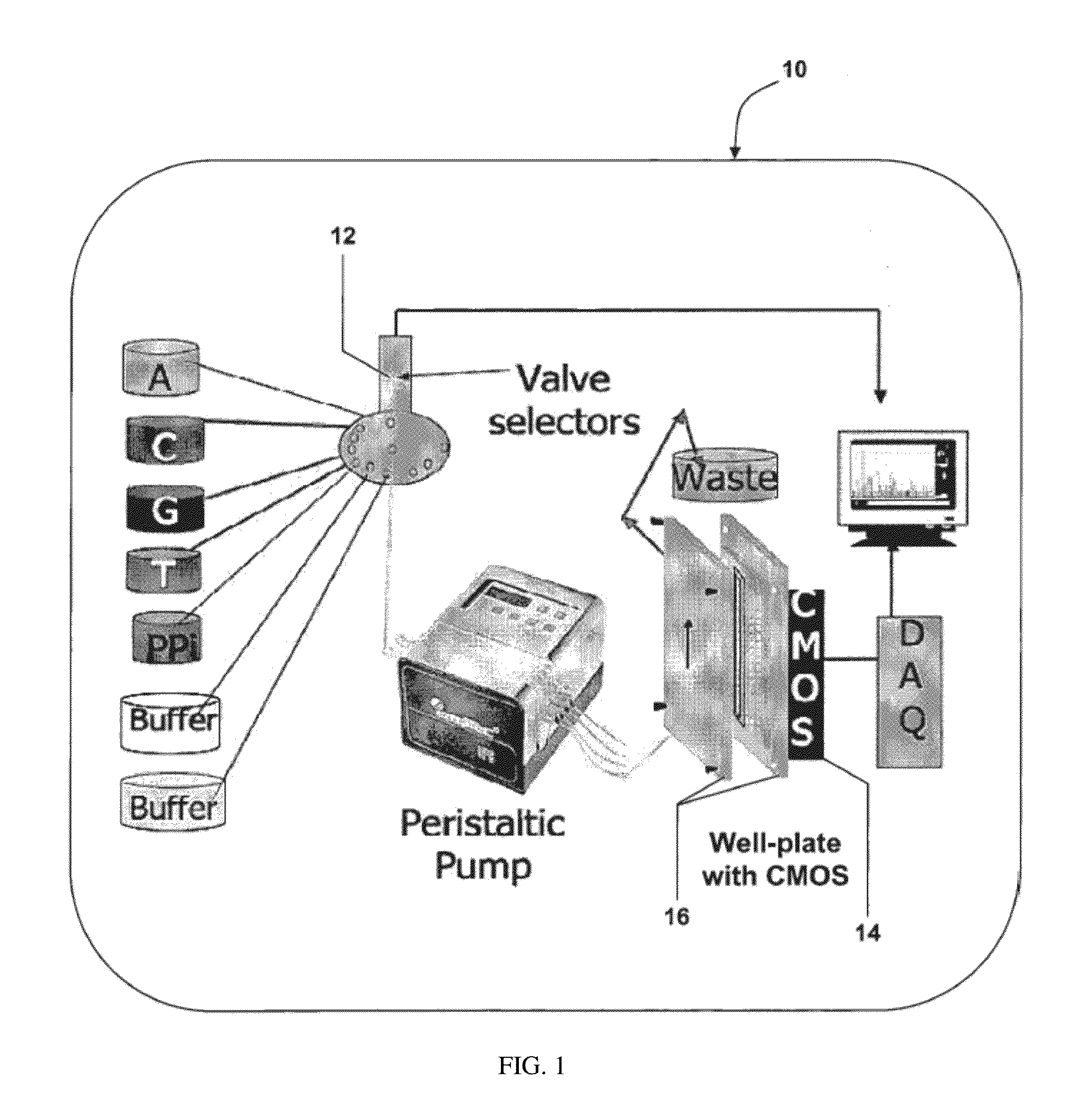
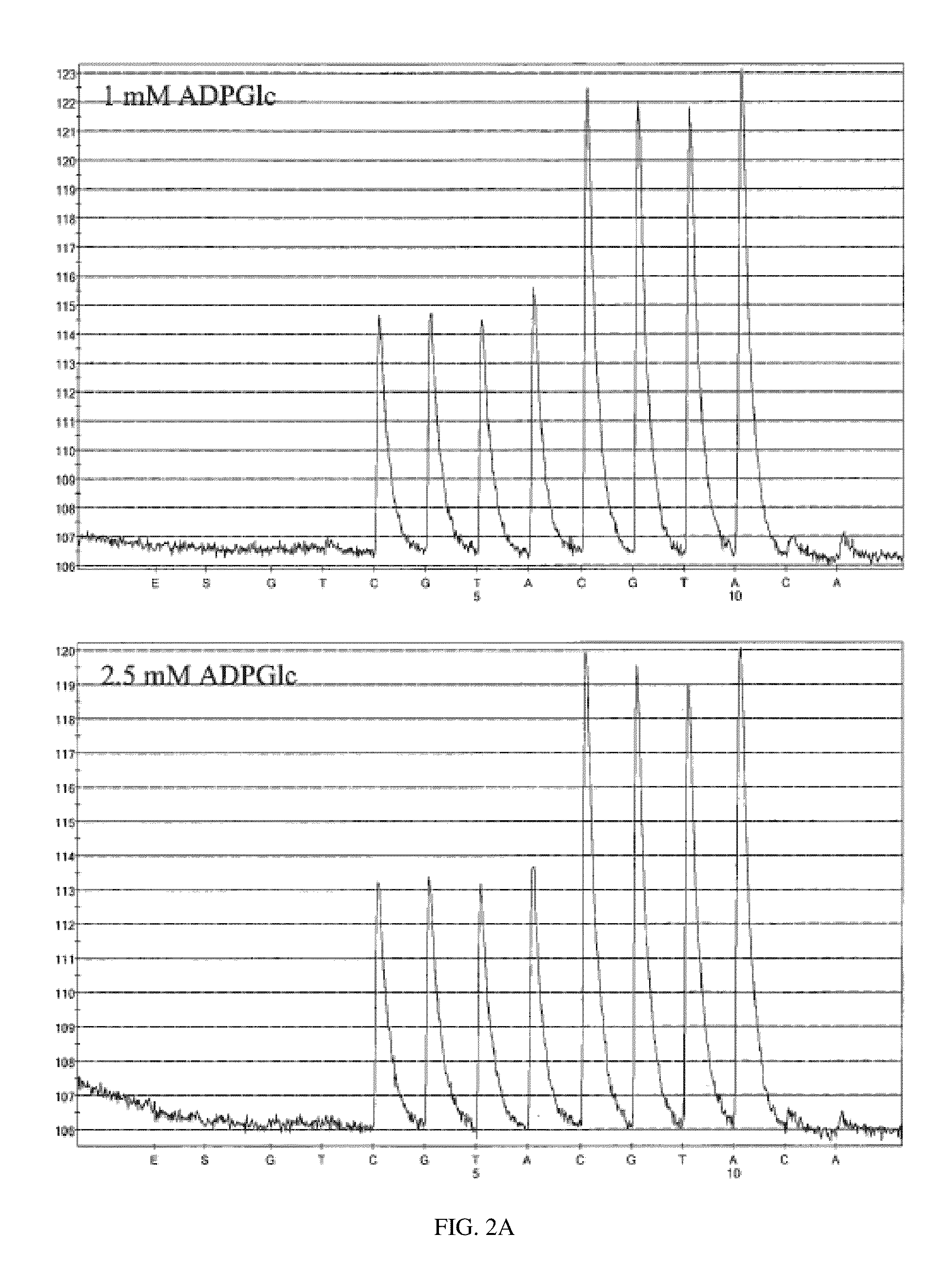
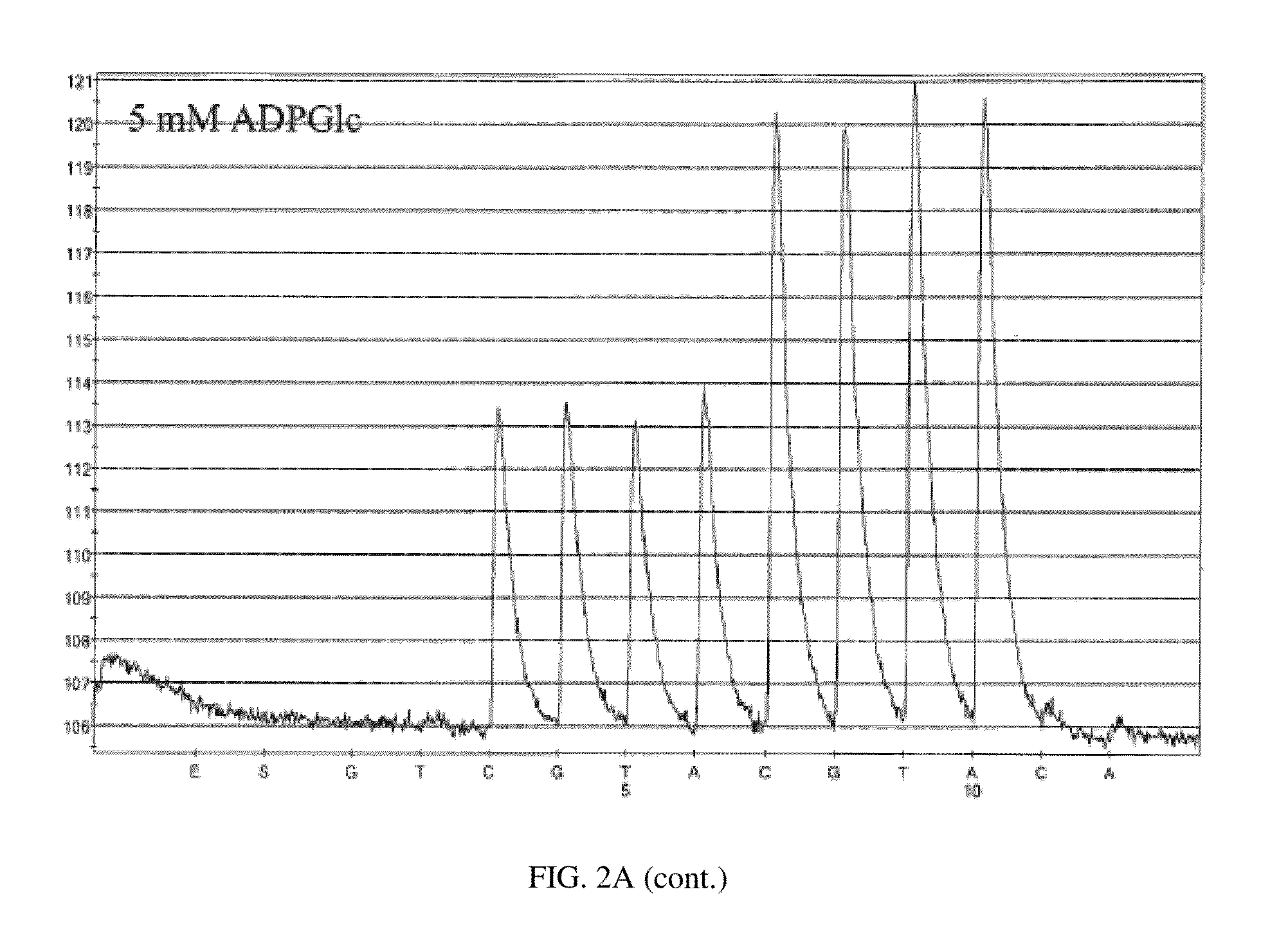
Integrated microfluidic and solid state pyrosequencing systems
InactiveUS20130045876A1Reduce layeringBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnzyme systemPyrophosphate
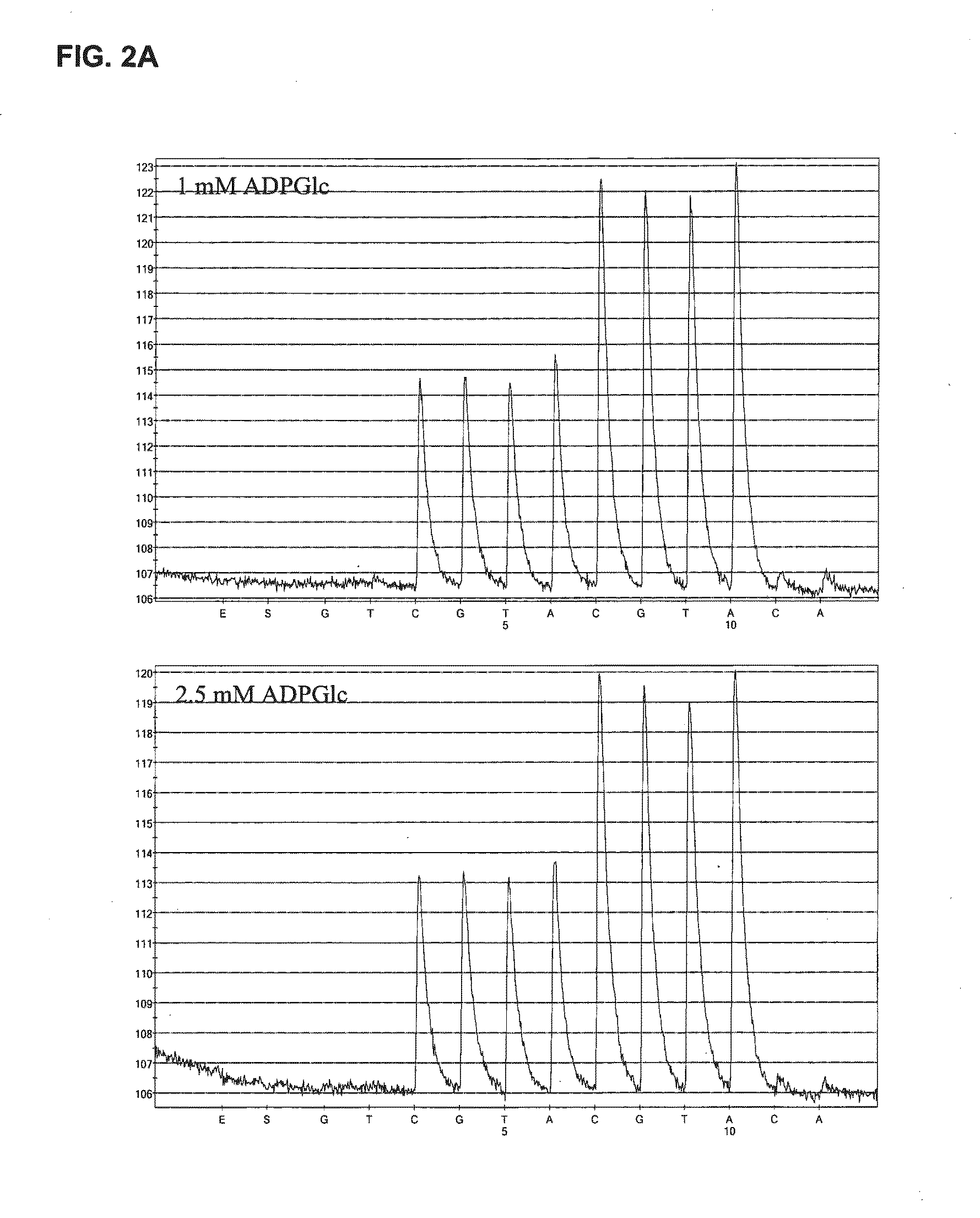
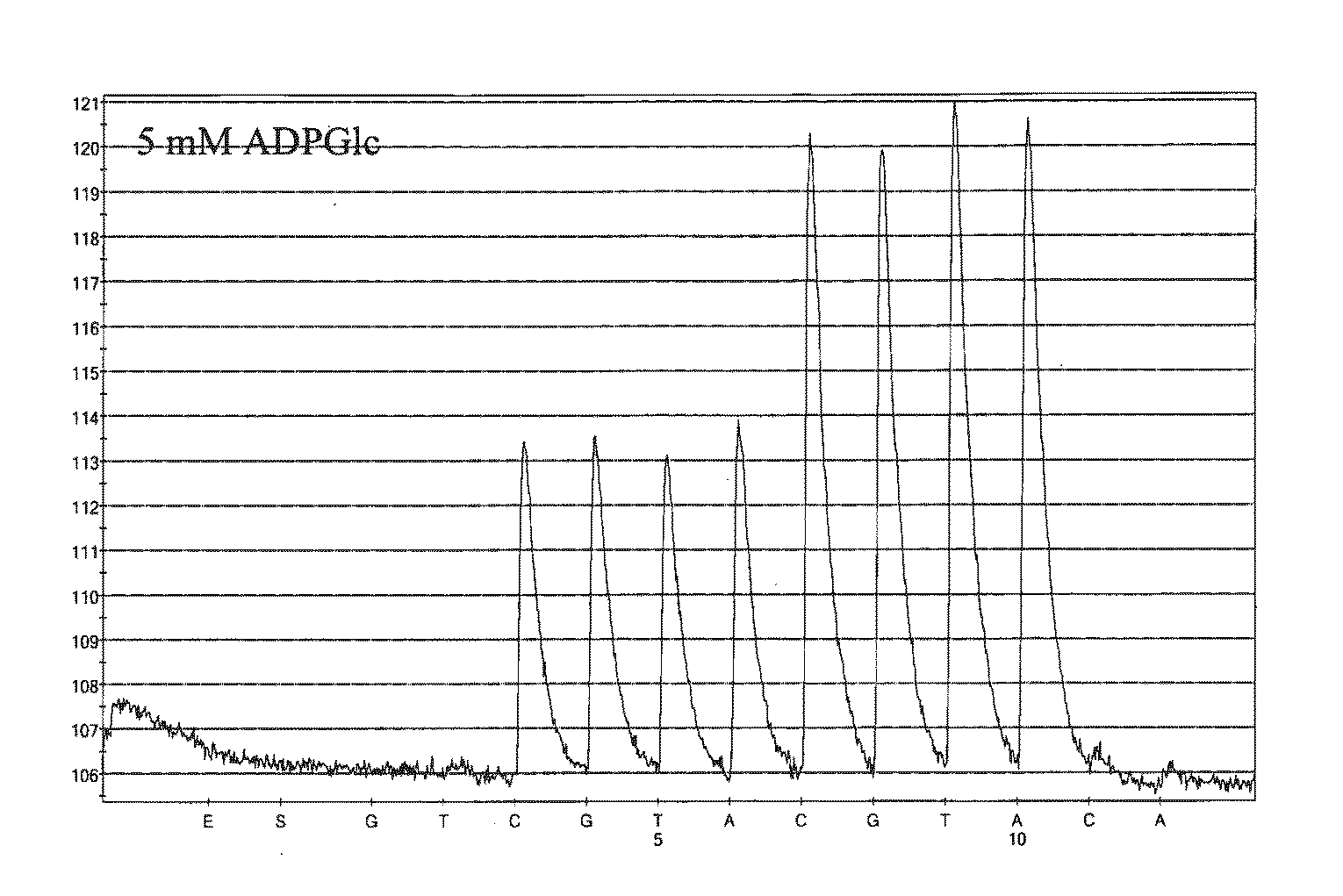
The invention provides for sequencing a nucleic acid molecule based on the detection of base incorporation by the release of pyrophosphate (PPi) using a new enzyme system comprising adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) and its substrate ADP-glucose.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Heat stable mutants of starch biosynthesis enzymes
InactiveUS20080109921A1Increase crop yieldImprove toleranceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideENCODE
The subject invention pertains to novel mutant polynucleotide molecules that encode enzymes that have increased heat stability. These polynucleotides, when expressed in plants, result in increased yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress. The polynucleotide molecules of the subject invention encode maize endosperm ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGP) and soluble starch synthase (SSS) enzyme activities. Plants and plant tissue bred to contain, or transformed with, the mutant polynucleotides, and expressing the polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides, are also contemplated by the present invention. The subject invention also concerns methods for isolating polynucleotides and polypeptides contemplated within the scope of the invention. Methods for increasing yield in plants grown under conditions of heat stress are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Cells producing antibody compositions
Cells to be used in producing antibody compositions, for example, an antibody having a high antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic activity which is useful in various diseases, an antibody fragment or a fused protein having the Fc domain of the antibody; a process for producing an antibody composition by using these cells; antibody compositions; and uses thereof. In the above-described antibody compositions, the ratio of sugar chains, which are free from fucose bonded to N-acetylglucosamine at the sugar chain reducing end, to the total N-glycoside linkage complex sugar chains bonded to the Fc domain amounts to 20% or more. Moreover, novel GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydrogenase, GDP-keto-6-deoxymannose 3,5-epimerase 4-reductase, GDP-beta-L-fucose pyrophosphorylase, alpha-1,6-fucosyltransferase and DNAs encoding the same are provided.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Integrated microfluidic and solid state pyrosequencing systems
InactiveUS8916347B2Reduce layeringBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnzyme systemPyrophosphate
The invention provides for sequencing a nucleic acid molecule based on the detection of base incorporation by the release of pyrophosphate (PPi) using a new enzyme system comprising adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) and its substrate ADP-glucose.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
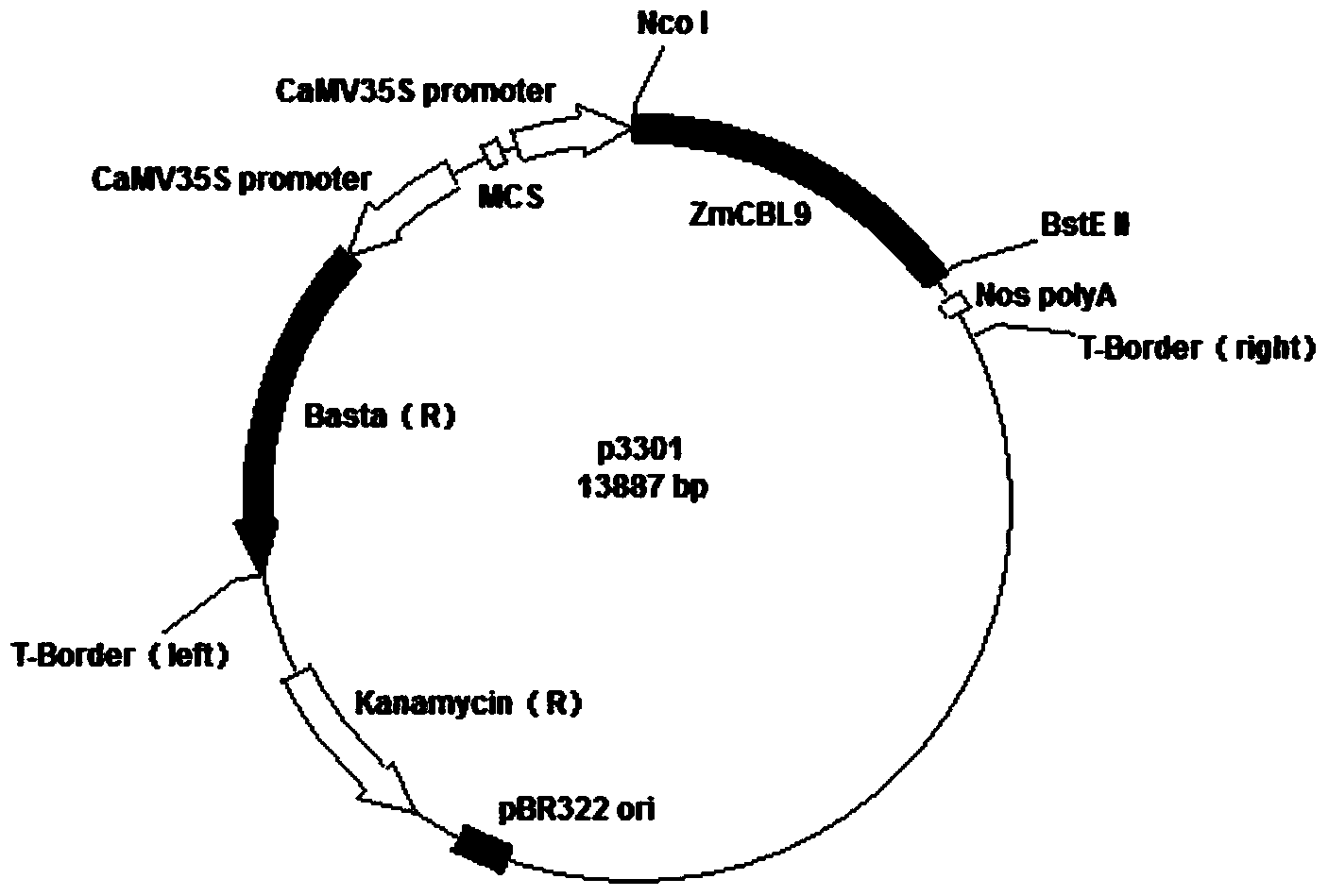
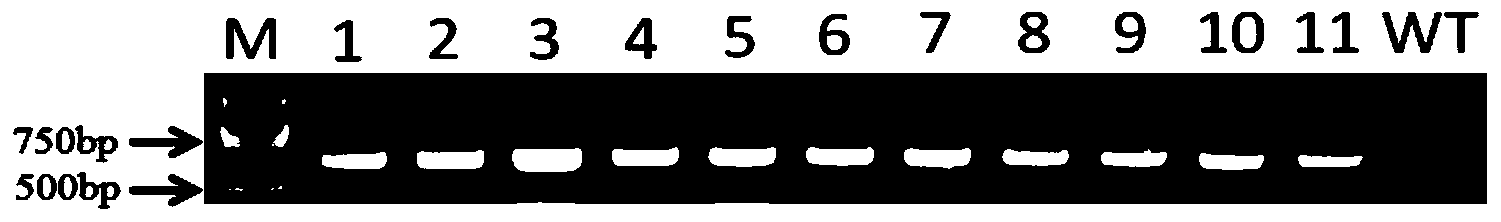
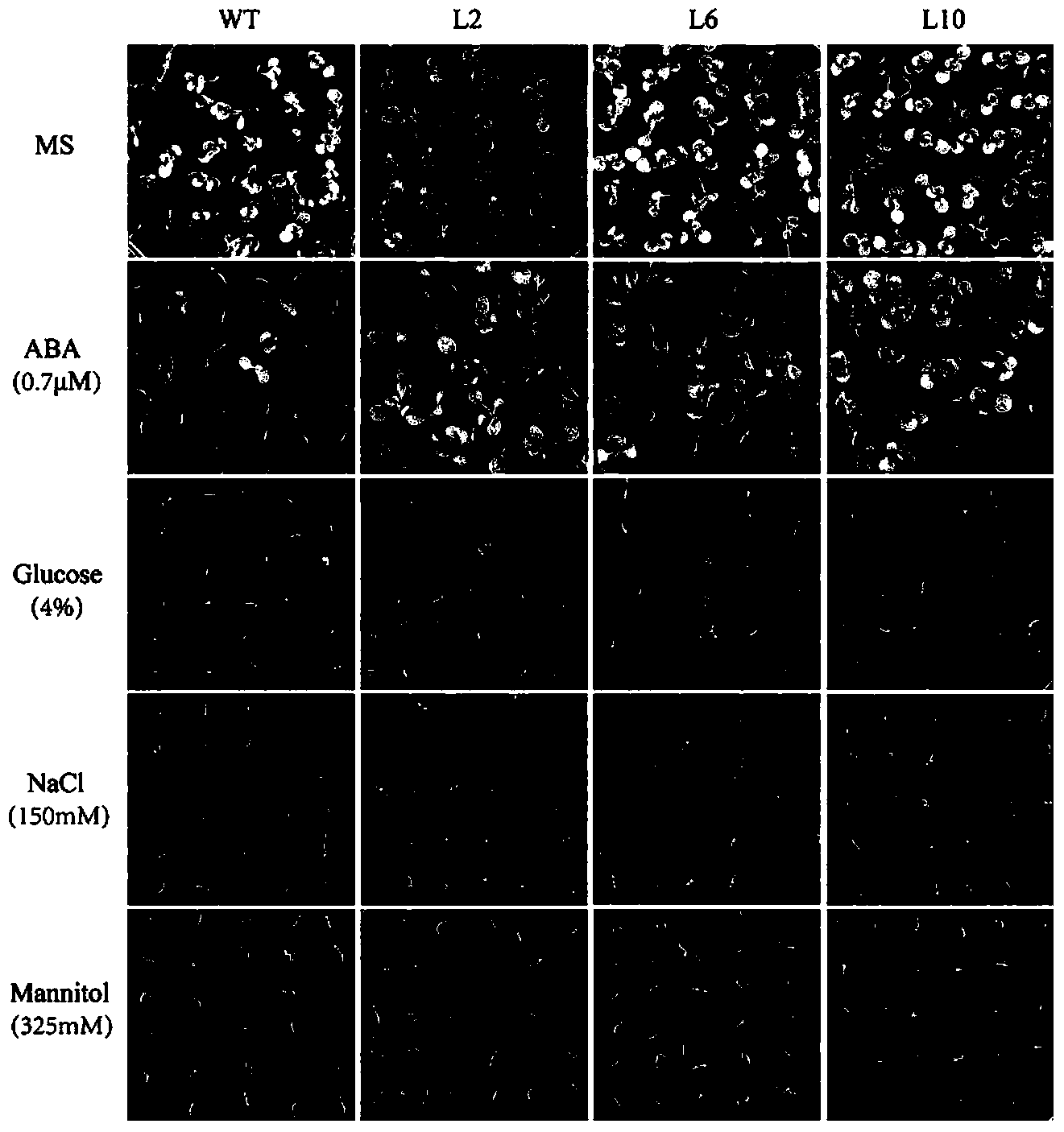
Application of CDS (Coding Sequence) sequence of CBL9 (Calcineurin B-Like) gene of corn
The invention relates to an application of a CDS (Coding Sequence) sequence of a CBL9 (Calcineurin B-Like) gene of corn. The invention provides the function of the CDS sequence of the CBL9 gene of corn for the first time. The CDS sequence of the CBL9 gene of corn is cloned to a plant expression vector and the vector is transferred to a plant body, so that the obtained transgenetic plant is saline-alkaline tolerant, osmotic stress resistant, high glucose resistant and ABA (Abscisic Acid) stress resistant. ZmCBL9 protein takes part in the salt tolerant and osmotic stress resistant process by regulating the downstream related gene and has important meaning for cultivating high yield transgenetic crops.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cross-linked starch biosynthesis recombinant gene YXI and application thereof
The invention discloses a cross-linked starch biosynthesis recombinant gene YXI and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, glgC55 of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase coding gene is separated out from a mutant strain of escherichia coli JM109-3, and an ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) small subunit coding gene (SSU cDNA) and a starch grain-combined starch synthase coding gene GBSSI promoter are respectively separated out from potatoes. An AGPase subunit composed of 431 amino acids is coded by glgC55, wherein four specific mutations, which are K39E, V71A, I248V and K304E, exist, the first two appear in the Rossmann fold regions of the oligomeric subunit N-terminal metabolic groups, and the latter two appear in oligomeric subunit C-terminal heterogeneously regulated and oligomerized LbH groups.
Owner:宁夏晨曦农业科技服务有限公司
Method for producing starch by Monoraphidium
ActiveCN106554980AHigh in starchSimple processMicroorganism based processesFermentationPyrophosphatasesMonoraphidium
The invention discloses a method for producing starch by Monoraphidium. The method comprises (1) preparing a microalgae seed liquid, wherein the microalgae is Monoraphidium sp. SS-06 and has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 10765, (2) inoculating an N element-rich microalgae culture medium with the Monoraphidium seed liquid, carrying out culture until a logarithmic growth phase, carrying out standing and sedimentation, discharging the supernatant and acquiring microalgae cells, (3) inoculating a low N element content microalgae culture medium with the microalgae cells, adding an ADP glucose pyrophosphatase inhibitor into the culture medium and carrying out continuous illumination culture until a stable period to obtain starch-rich microalgae cells. The method is conducive to proliferation of microalgae cells and accumulation of starch, can produce microalgae cells with high starch content and has the characteristics of simple processes, low cost and high yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
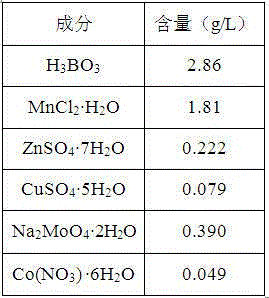
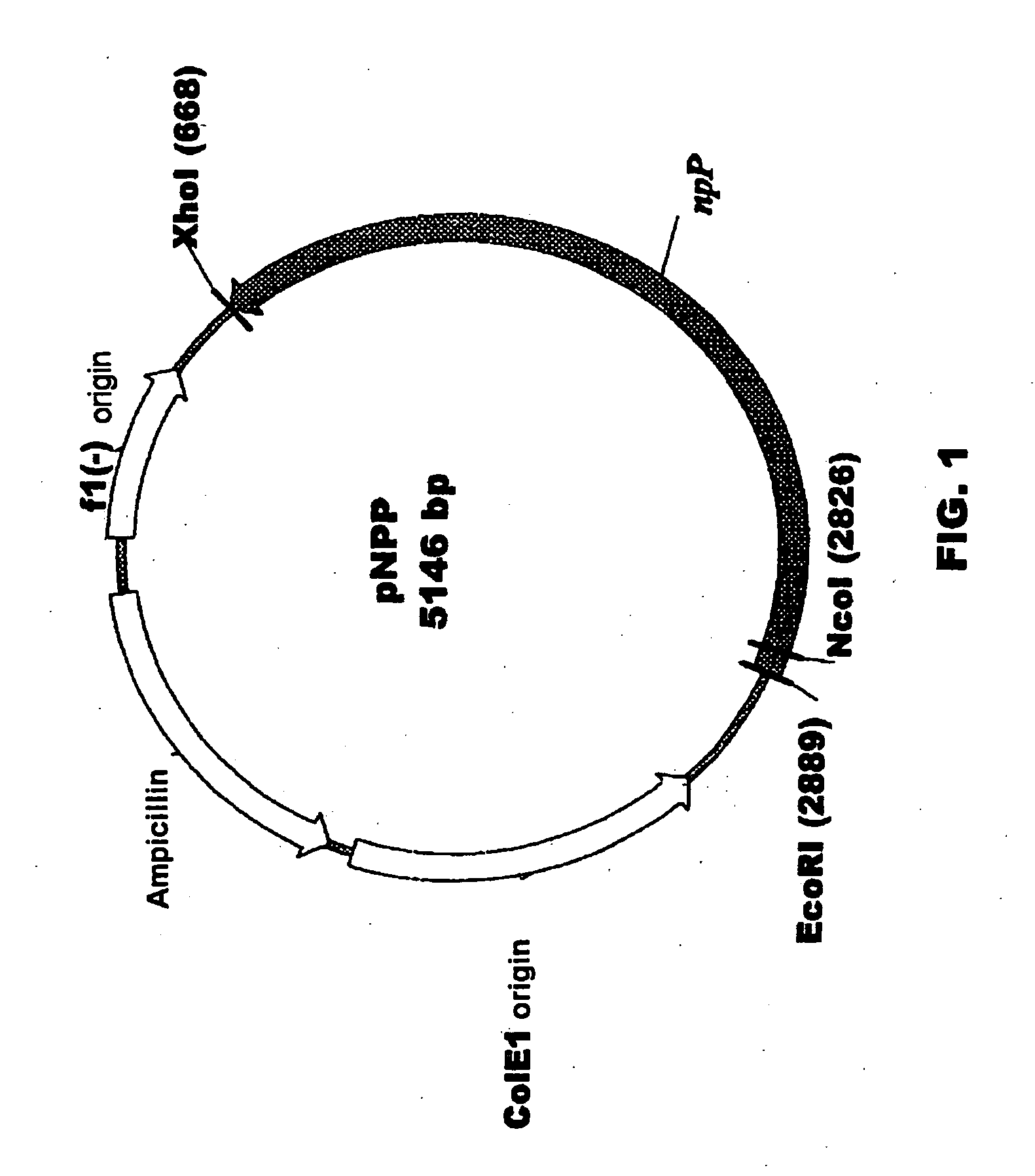
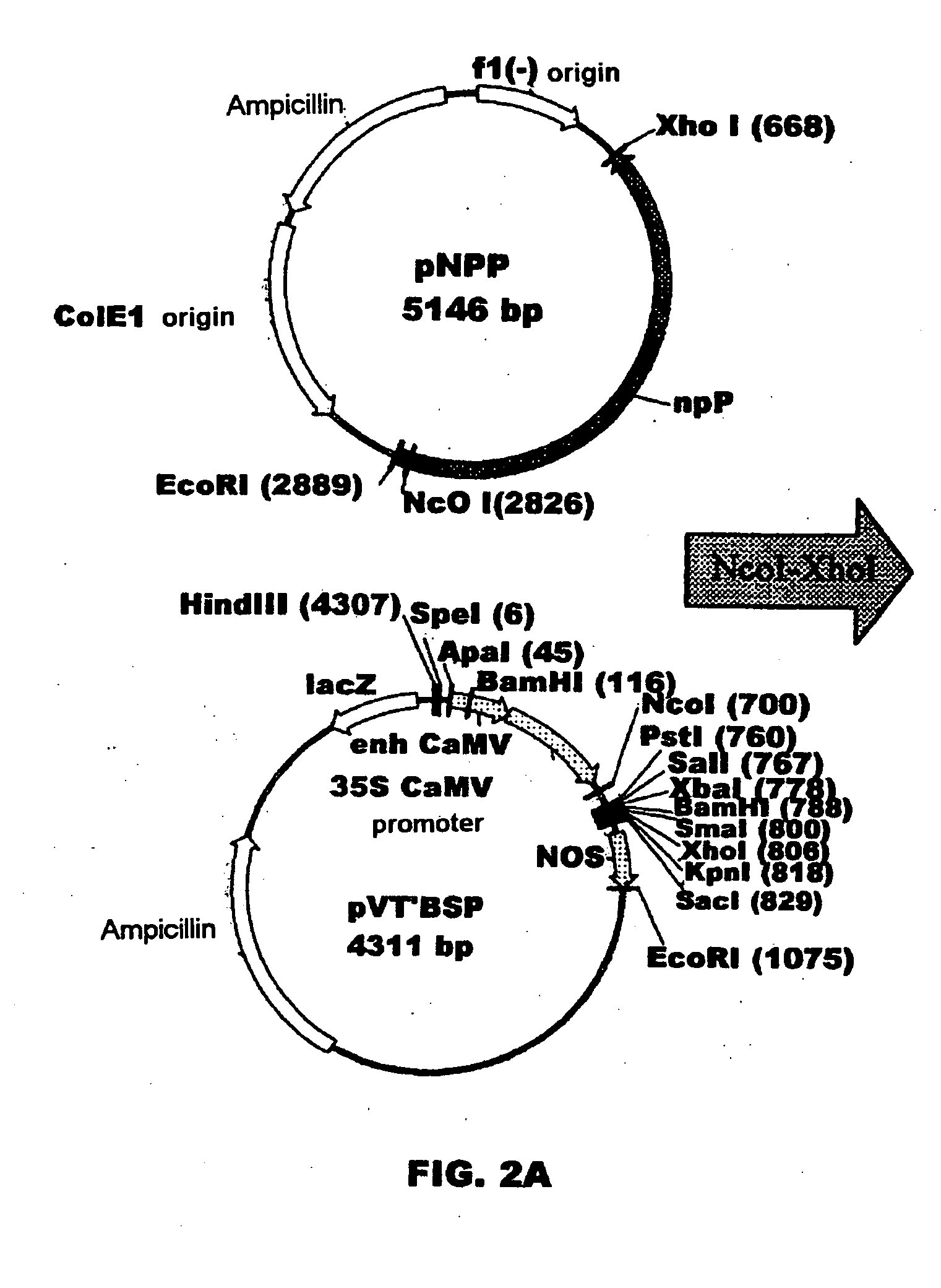
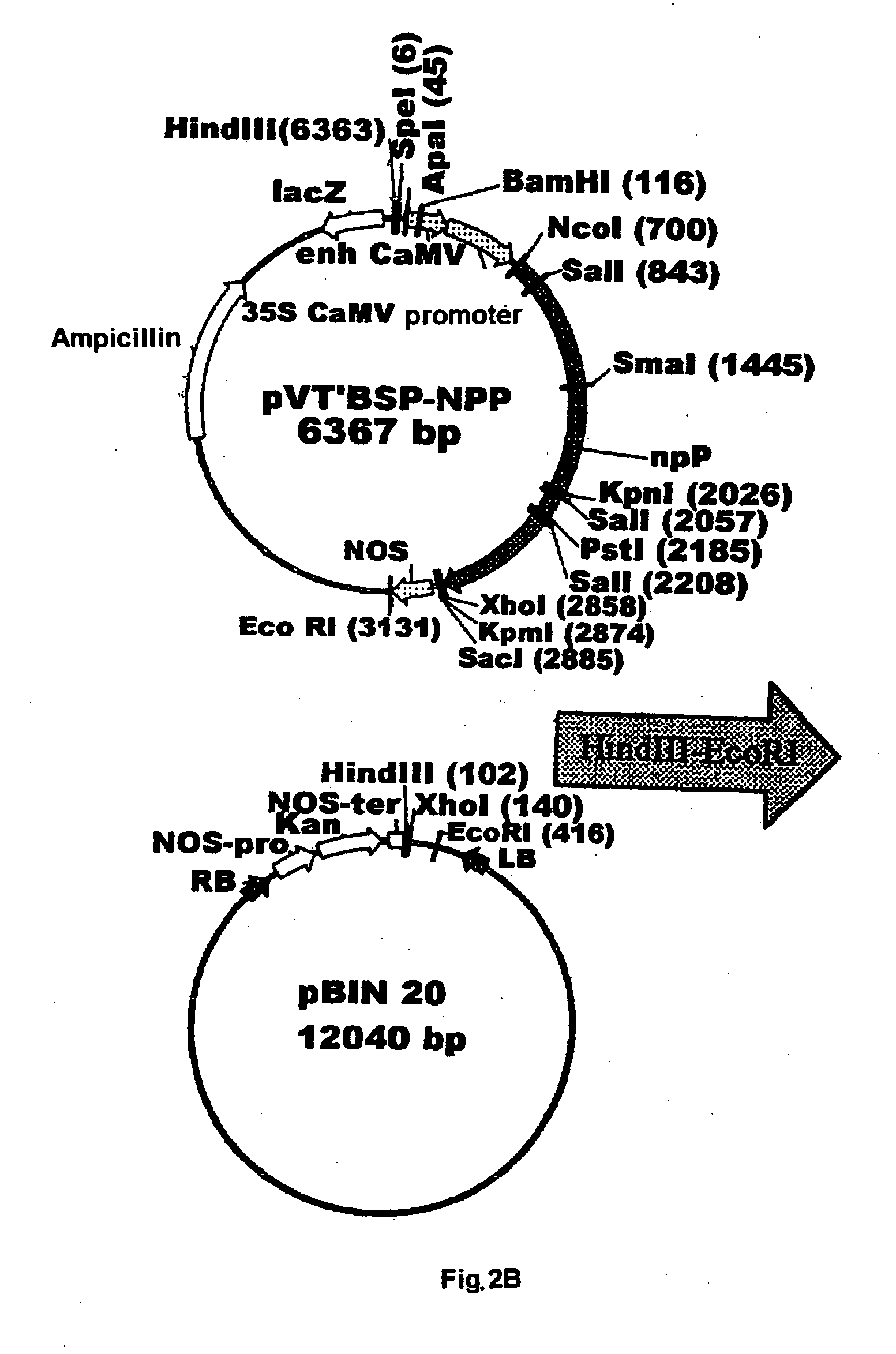
Plant nucleotide-sugar pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (nppase), method of obtaining same and use of same in the production of assay devices and in the production of transgenic plants
InactiveUS20060242739A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh resistancePhosphate
Plant nucleotide pyrophosphatase / phosphodiesterase (NPPase), method of production, use in the manufacture of testing devices and in the production of transgenic plants. NPPase is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of a wide range of small molecules with phosphodiester and phosphosulphate bonds, in particular ADPG (adenosine diphosphate glucose) and APS (adenosine 5′-phosphosulphate). The enzyme obtained from plant extracts is used in assay devices for determining levels of nucleoside diphosphate sugars, based either on the sugar-1-phosphate released, or on the nucleoside monophosphate, both of which are products formed by the reaction catalysed by NPPase, as well as the detection of sulphonucleotides such as 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulphate (PAPS) and APS. The amino acid sequence of the enzyme is also described, as well as the nucleotide sequence of a complete cDNA and another incomplete cDNA. Finally, it describes the production of transgenic plants that overexpress NPPase and that have a high content of sugars, low content of starch and cell-wall polysaccharides and high resistance to high concentrations of salts and high temperature.
Owner:UNIV PUBLICA DE NAVARRA PAMPLONA +1
Glucose oxidase mutant
ActiveCN109207446AImprove heat resistanceAccessory food factorsOxidoreductasesAfter treatmentBiochemistry
The invention relates to the technical field of protein engineering, in particular to a glucose oxidase mutant. The glucose oxidase three-point mutant GOD-K has residual enzyme activity of 68.20% after processing at 70 DGE C for 2.5 min, after treatment at 75 DEG C for 2.5 min, the residual enzyme activity is 42.76%, which are 19.3% and 38.1% higher than that of the two point mutant GOD11, respectively. The results showed that the mutant GOD11 had unexpected effect and was more suitable for application in industrial production, so its market prospect was broad.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Microscale Glucose Sensor Microelectrodes
ActiveCN103462615BSimple structureReduce manufacturing costDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGlucose sensorsMaximum diameter
The invention relates to the field of detecting instruments, in particular to a micrometer-scale glucose sensor microelectrode. The micrometer-scale glucose sensor microelectrode comprises a substrate, a working electrode and a counter electrode, the front portion of the substrate is a working area, the working electrode and the counter electrode are located in the working area, the maximum diameter of the cross section of the working area is less than or equal to 1 millimeter, PADs in one-to-one correspondence to the electrodes are arranged at the tail of the substrate, and each of the working electrode and the counter electrode is connected with the corresponding PAD through a lead. The electrodes are reasonably distributed on the planar or columnar insulating substrate and width of each electrode or cross-sectional diameter of each columnar electrode is limited to effectively reduce size of the electrode, so that rejection reaction of receptors is reduced.
Owner:MEDTRUM TECH
Sucrose-inducible promoter from sweetpotato
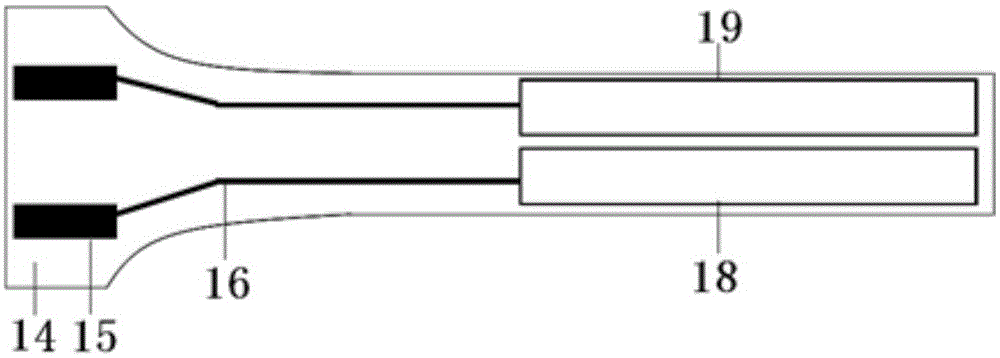
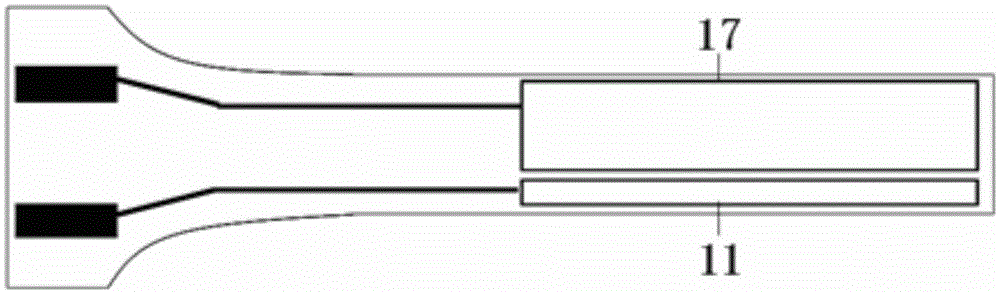
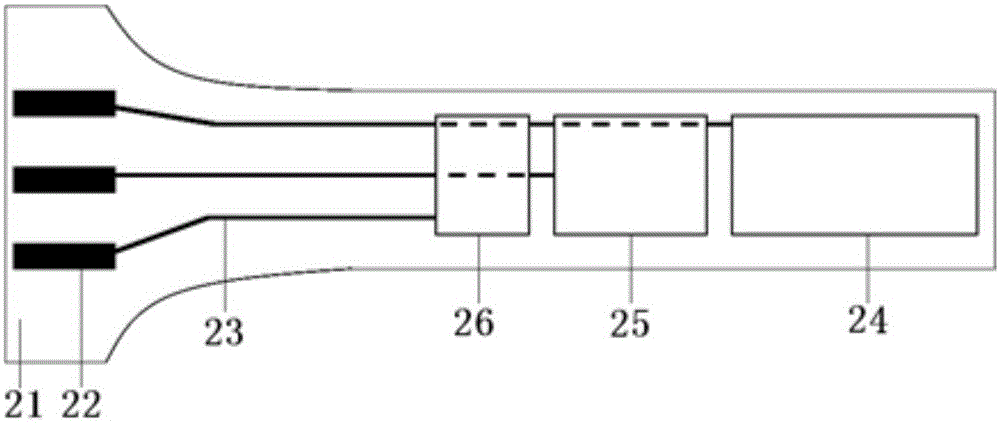
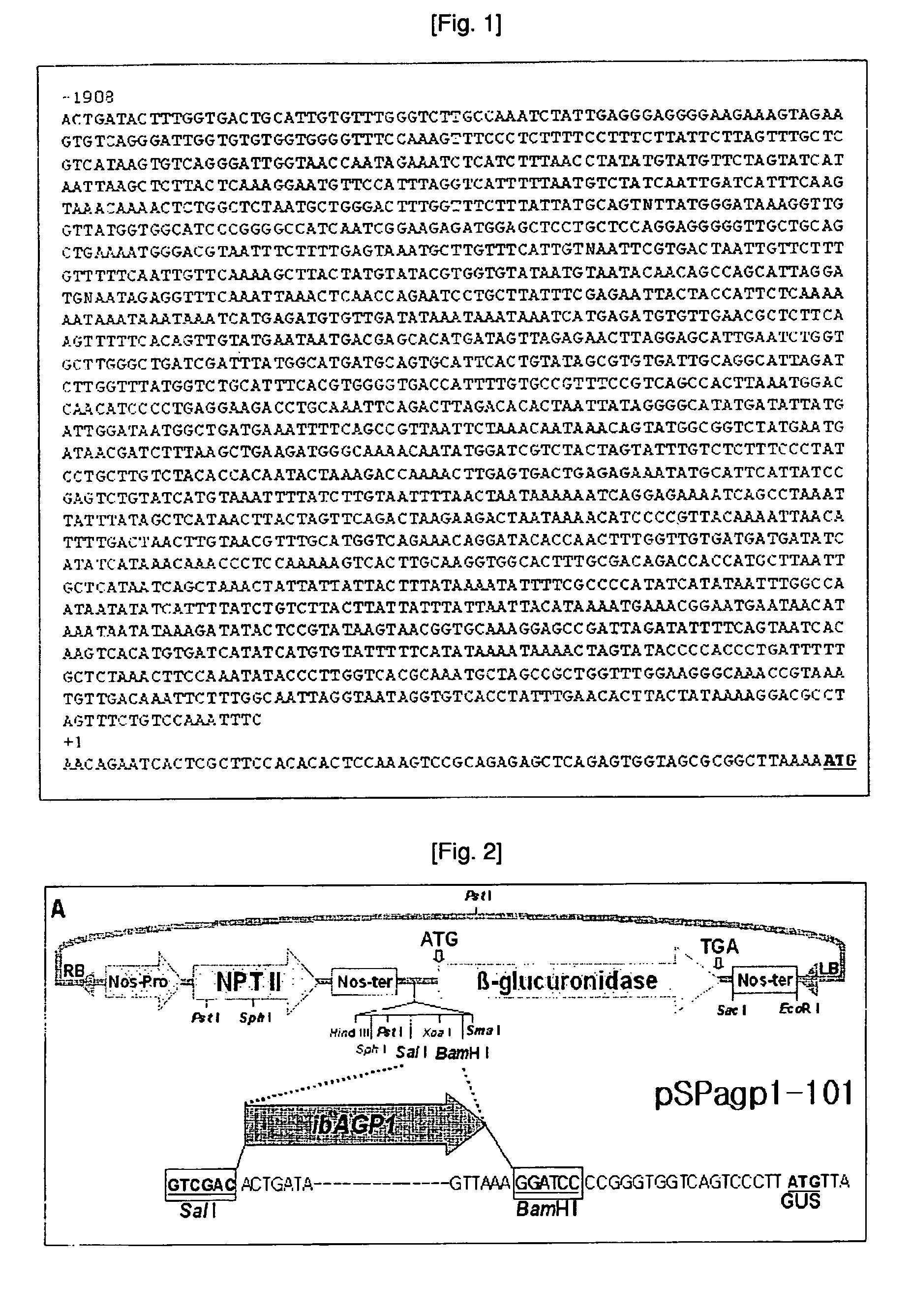
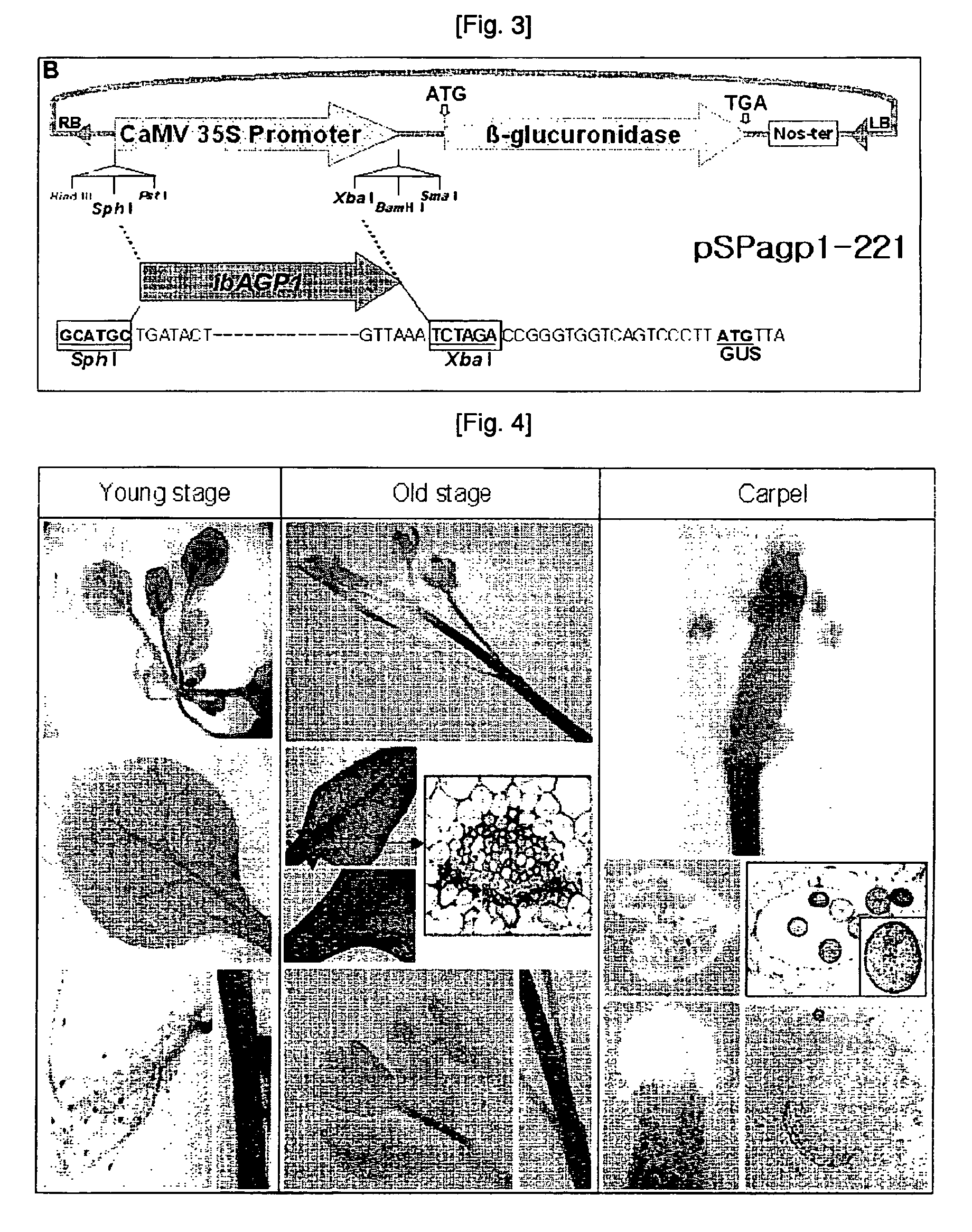
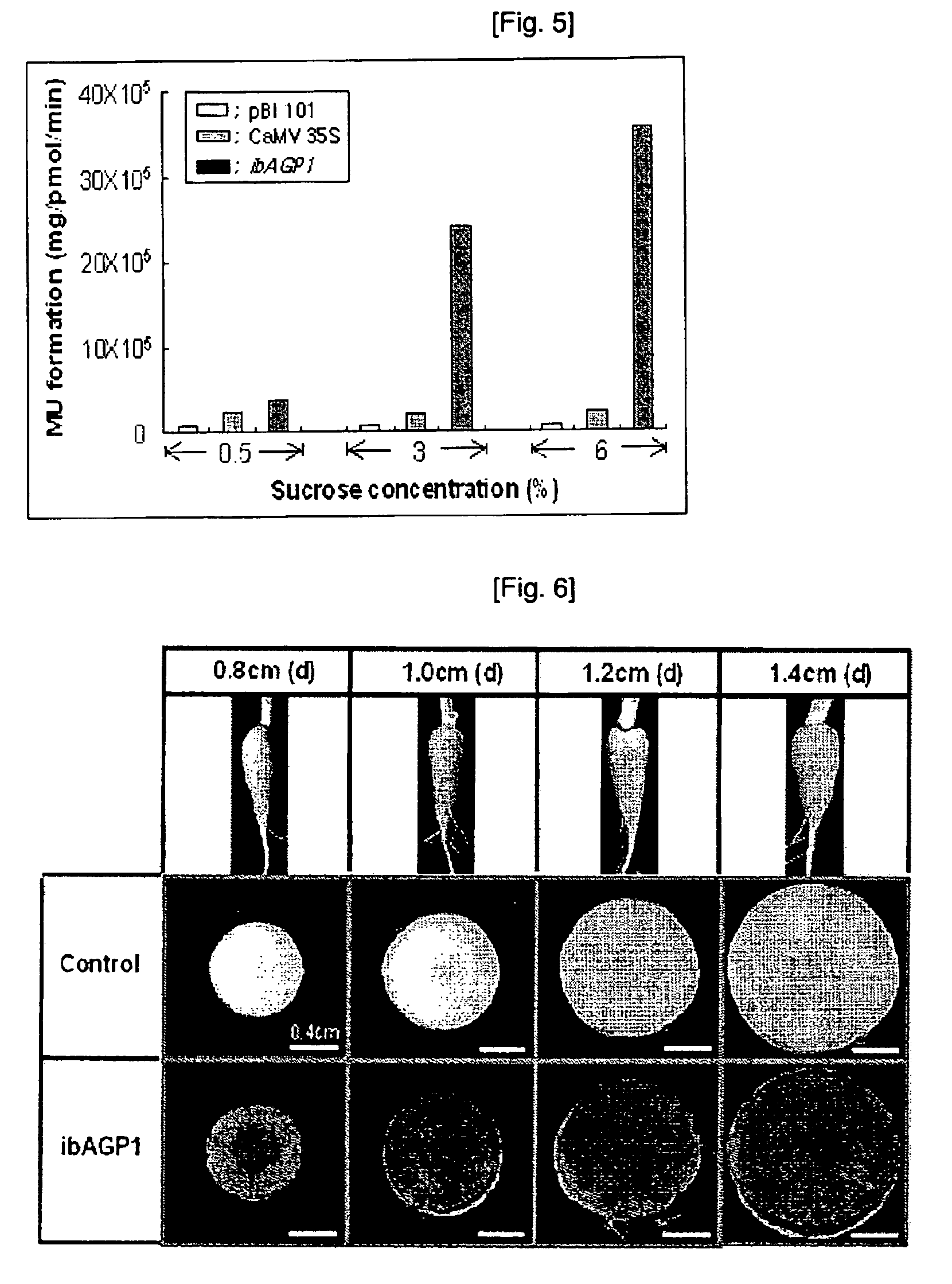
Disclosed herein are a novel sucrose-inducible promoter sequence and a 5′ untranslated region which are derived from sweetpotato ADP-glucose pyrophosphorlyase gene (ibAGPl) (SEQ ID NO: 1). Also disclosed are expression vectors using the same sequences and a transgenic plant using the same vectors. The promoter and 5′ untranslated region according to the present invention can confer a high level of sucrose-inducible expression in plants, particularly in plant storage roots which contain sucrose in relatively large quantities to accumulate starch in large quantities in plants. Therefore the present invention may be useful for the generation of transgenic plants to produce useful proteins in large quantities in plant storage roots.
Owner:HANBAT NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
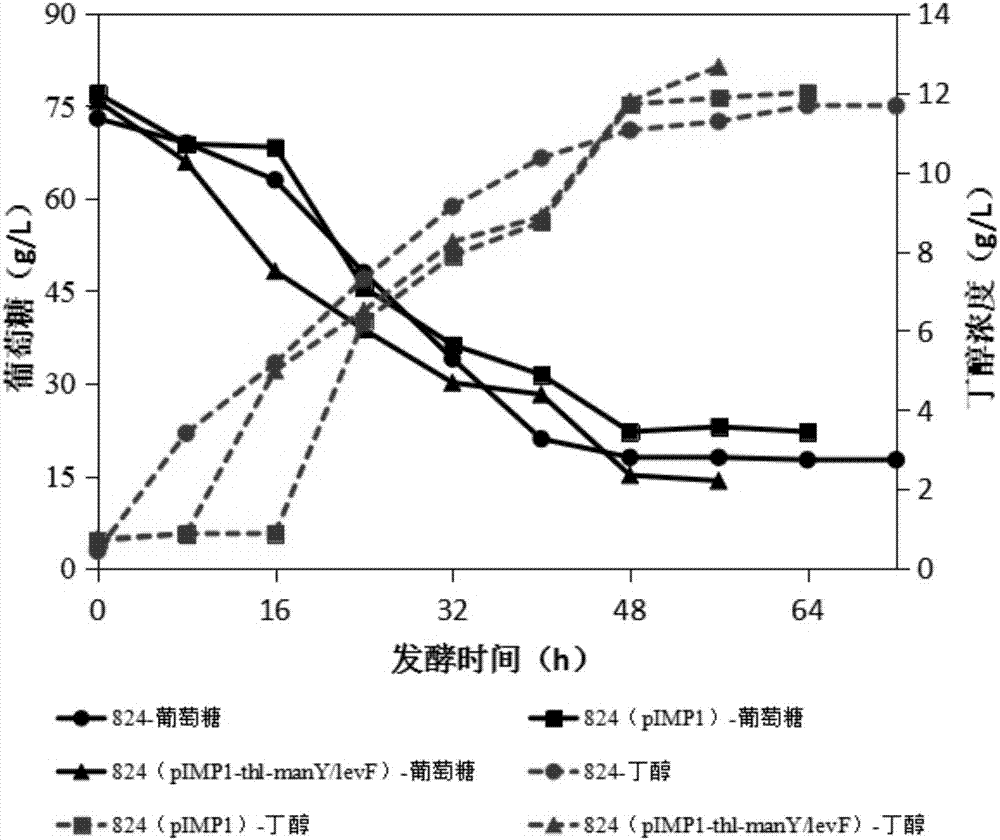
Application of manY/levF gene segment to butanol production
The invention discloses application of a manY / levF gene segment to butanol production, and particularly relates to overexpression recombination clostridium for producing butanol at high yield as wellas a building method and application thereof. The manY / levF gene sequence is SEQ ID NO.1. The building method of the overexpression recombination clostridium comprises the following steps of (1) manY / levF gene overexpression recombination plasmid building; (2) overexpression recombination plasmid amplification; (3) overexpression recombination plasmid methylation; (4) manY / levF gene overexpressionrecombination bacterial strain building; (5) overexpression recombination bacterial strain butanol fermentation performance detection. The invention also comprises fermentation application of the overexpression recombination clostridium to butanol production. When the manY / levF gene is overexpressed in C.acetobutylicum ATCC 824, the utilization rate of glucose, fructose and jerusalem artichoke hydrolysate in ABE fermentation and the butanol yield can be obviously improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
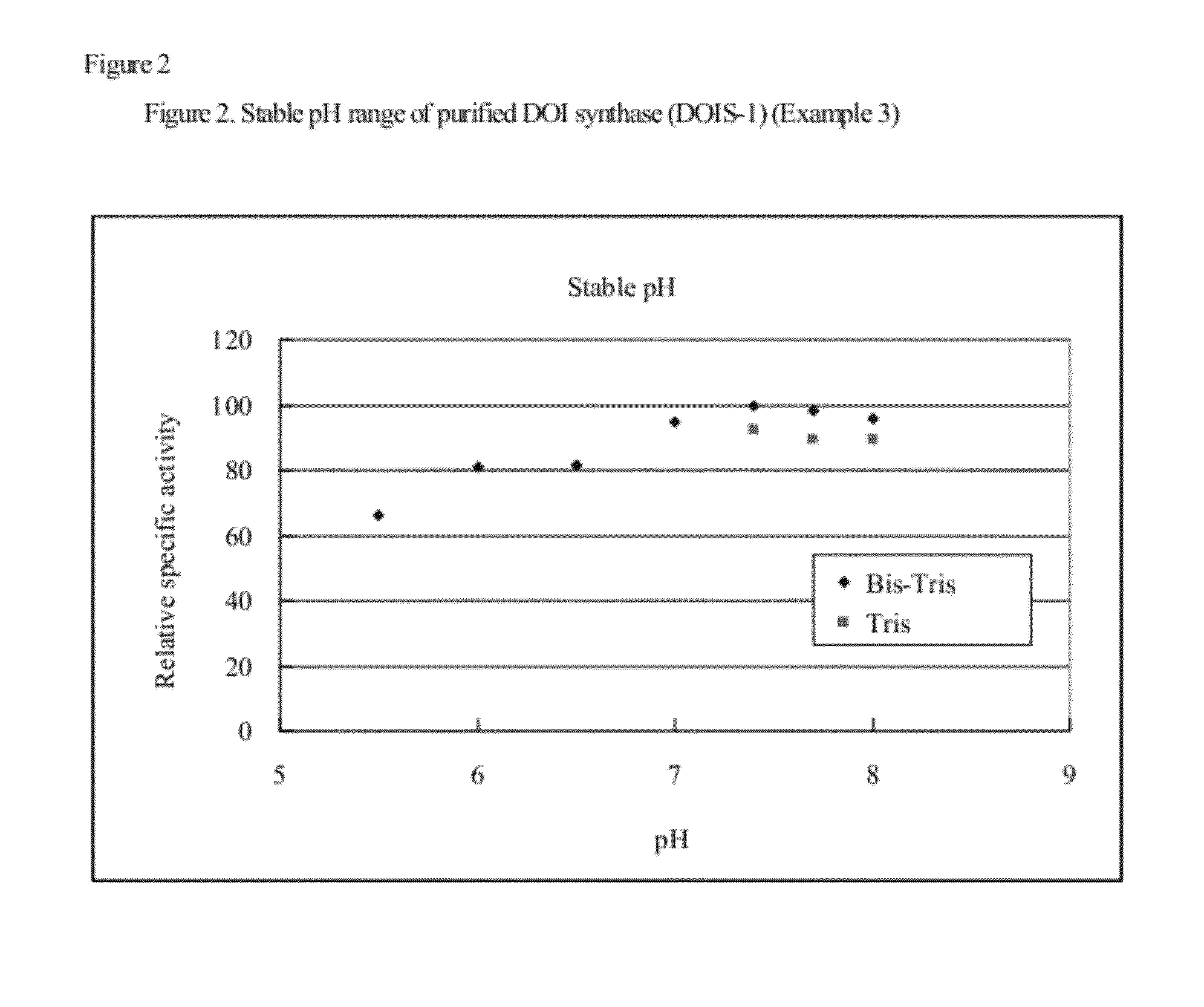
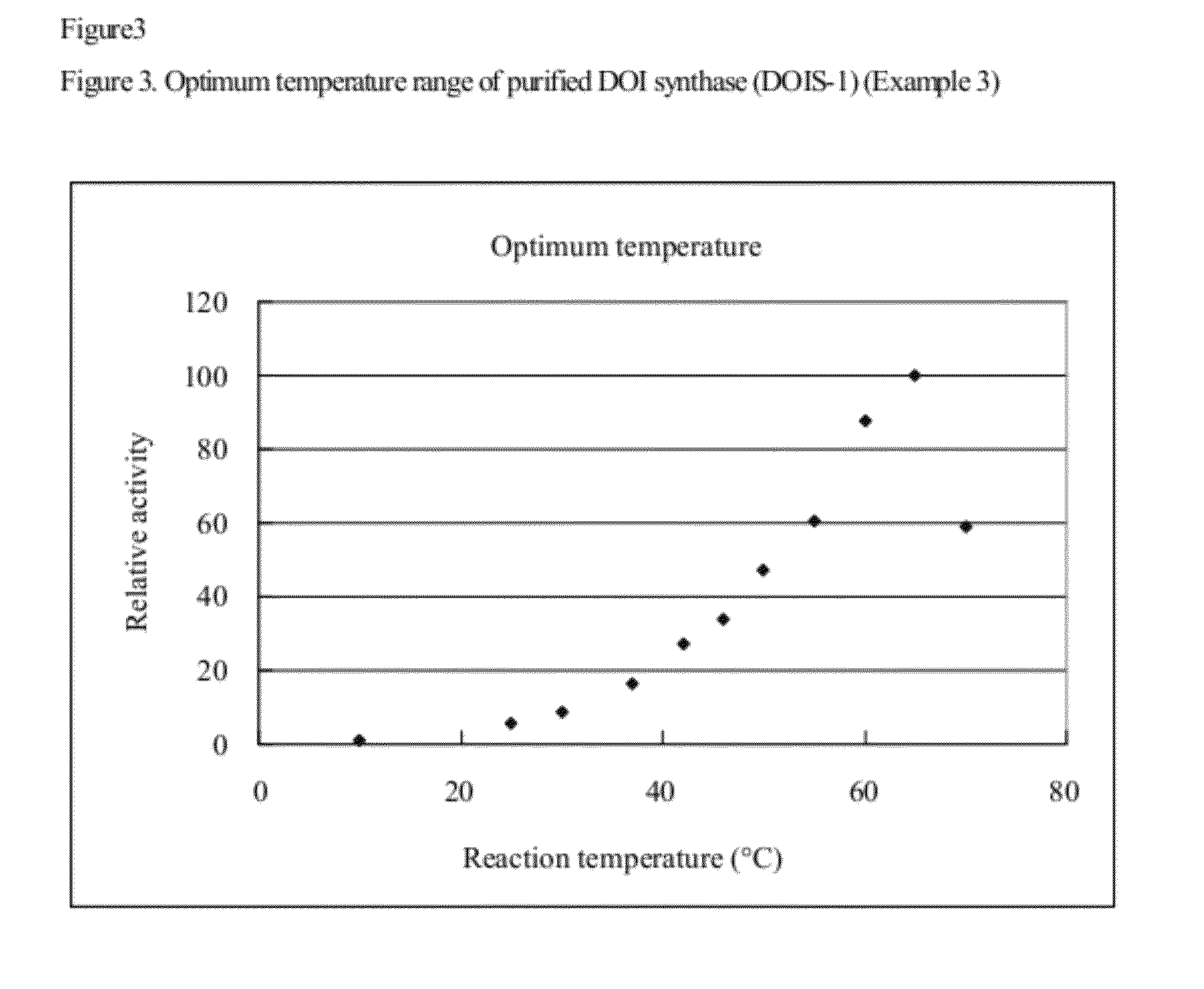
2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose synthase
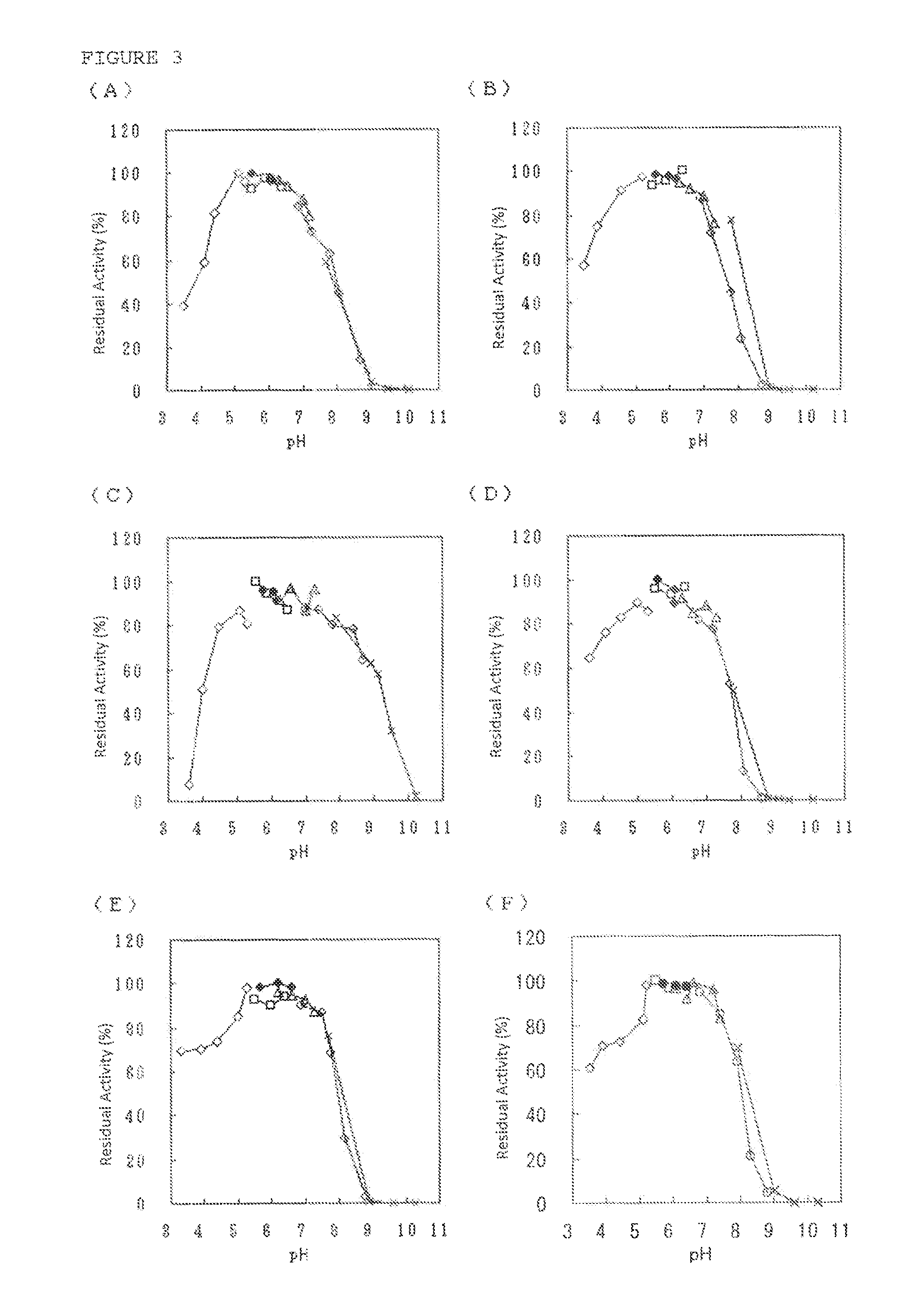
An object of the present invention is to provide a DOI synthase having properties such as stability to heat and pH, which are superior to those of conventional enzymes, and a method for producing DOI using the above-mentioned enzyme. The present invention provides a 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose synthase having the properties described in the following (1), (2), (4), (6) and (7), and also having the properties described in the following (3) and / or (5):(1) action: the enzyme has a function to convert glucose-6-phosphate to 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose;(2) optimum pH range: pH 7.0 to 7.7;(3) stable pH range: pH 6.0 to 8.0;(4) optimum temperature range: 55° C. to 70° C.;(5) stable temperature range: 20° C. to 46° C.;(6) coenzyme used: NAD+; and(7) molecular weight: 39,000 to 42,000.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
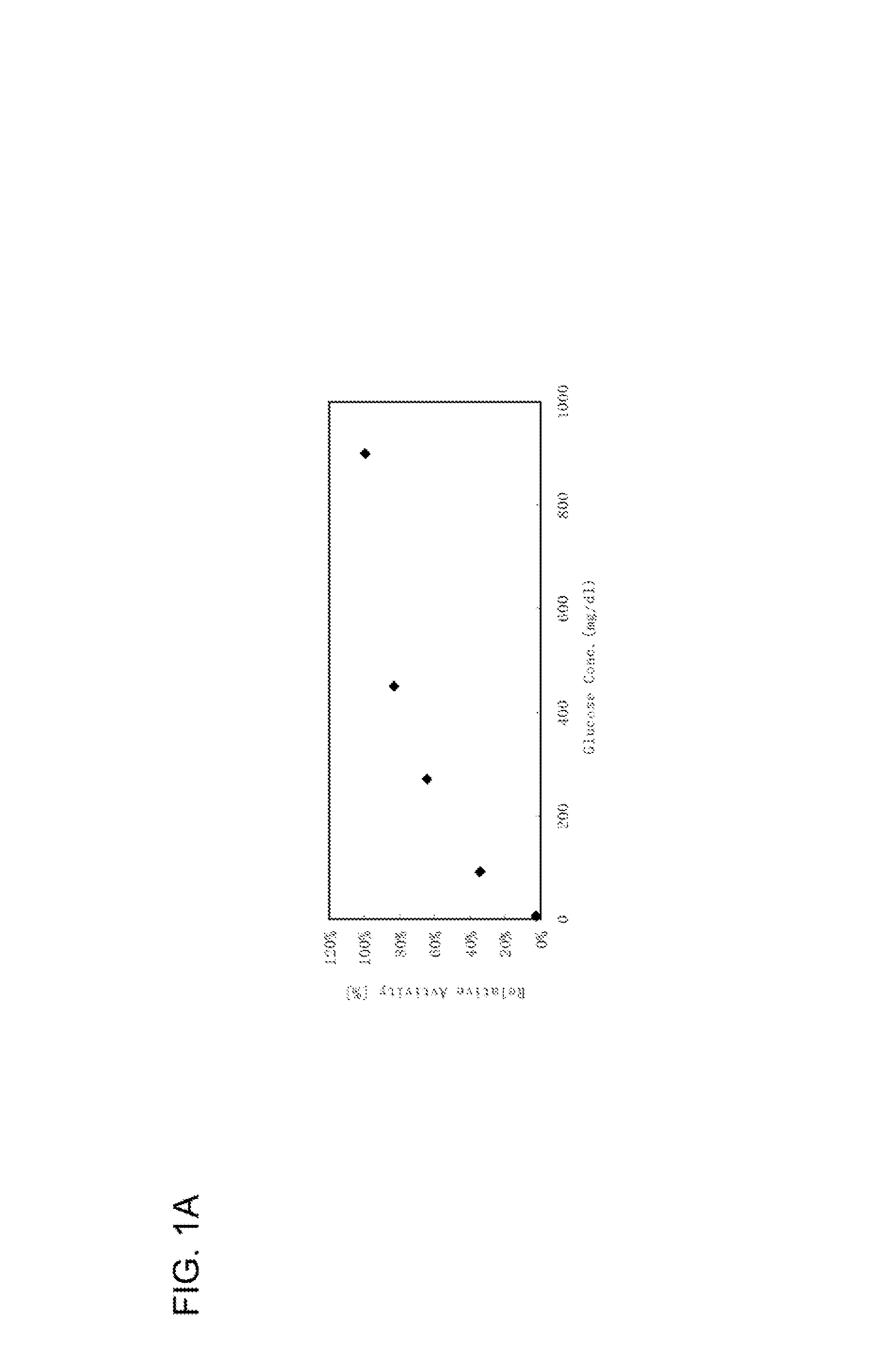
Modified glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS8969060B2Reduce sensitivityAccurately determineBacteriaSugar derivativesPhenanthrolineWild type
The purpose of the present invention is to provide an FAD-conjugated glucose dehydrogenase that is hard to be inhibited by the inhibitors such as 1,10-phenanthroline.The present invention relates to a modified glucose dehydrogenase (GLD), comprising an amino acid sequence of a wild-type FAD-conjugated glucose dehydrogenase (GLD) represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 having a substitution of at least one amino acid residue selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues at positions 298, 338, 340, 341, 343, 352, 354, 424, 426, 431 and 432, wherein the modified GLD has a reduced susceptibility to an inhibitor, as compared with the wild-type GLD, especially to said modified GLD, which has 40% or more of a relative activity when determined in a system wherein the inhibitor coexists at a final concentration of 1 mM based on an enzymatic activity when determined in a system wherein the inhibitor does not coexist.
Owner:IKEDA SHOKKEN KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com