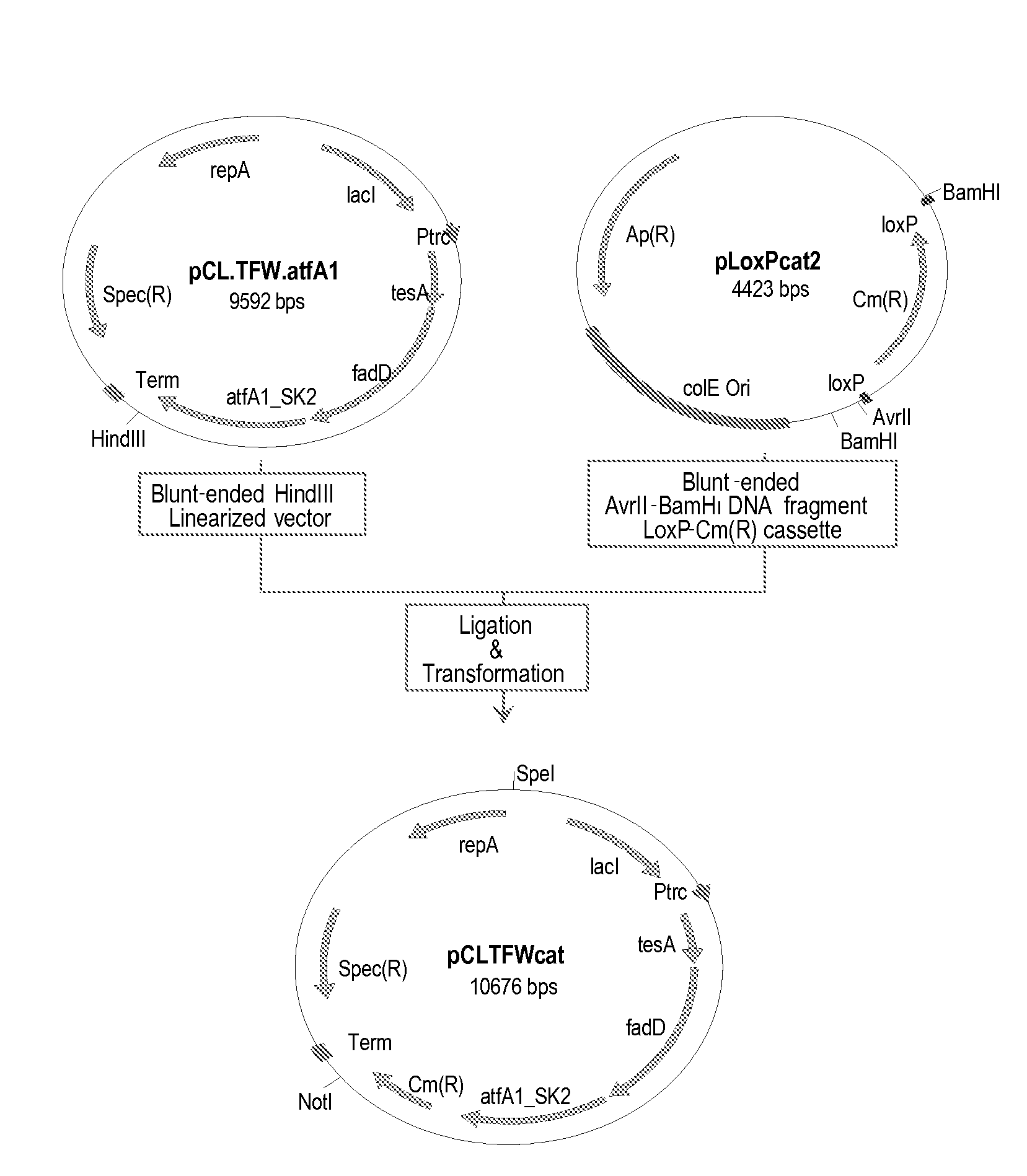
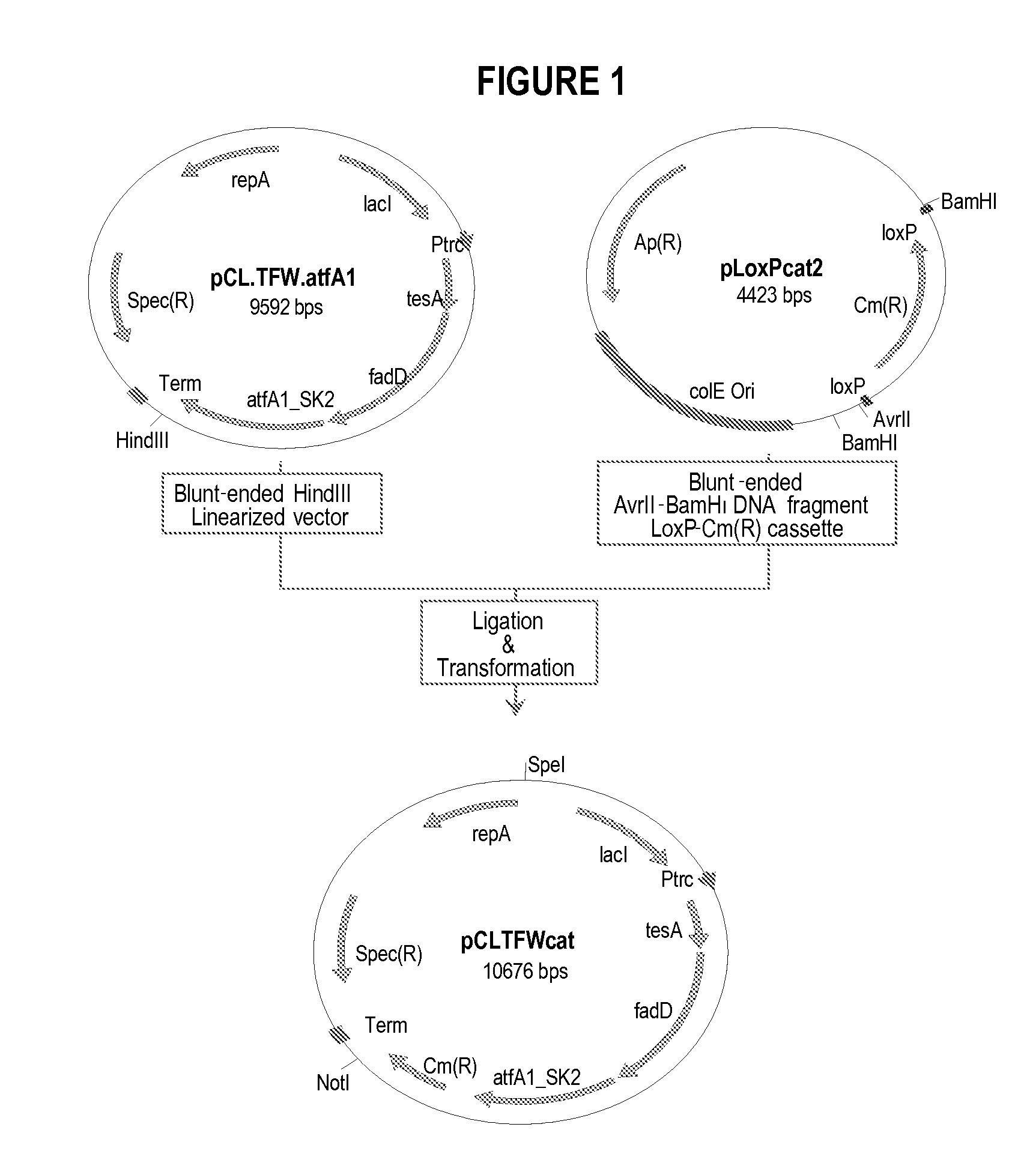
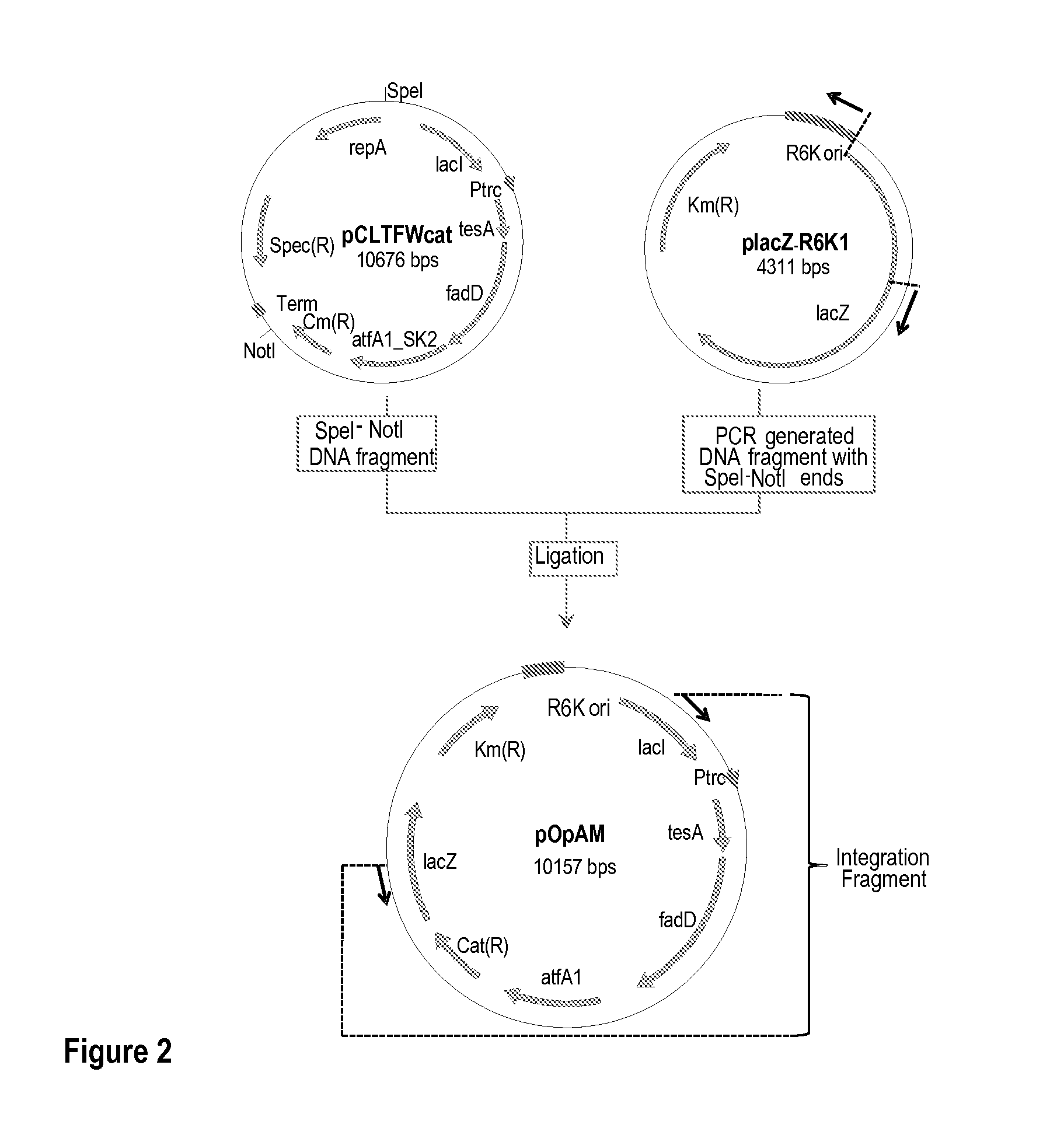
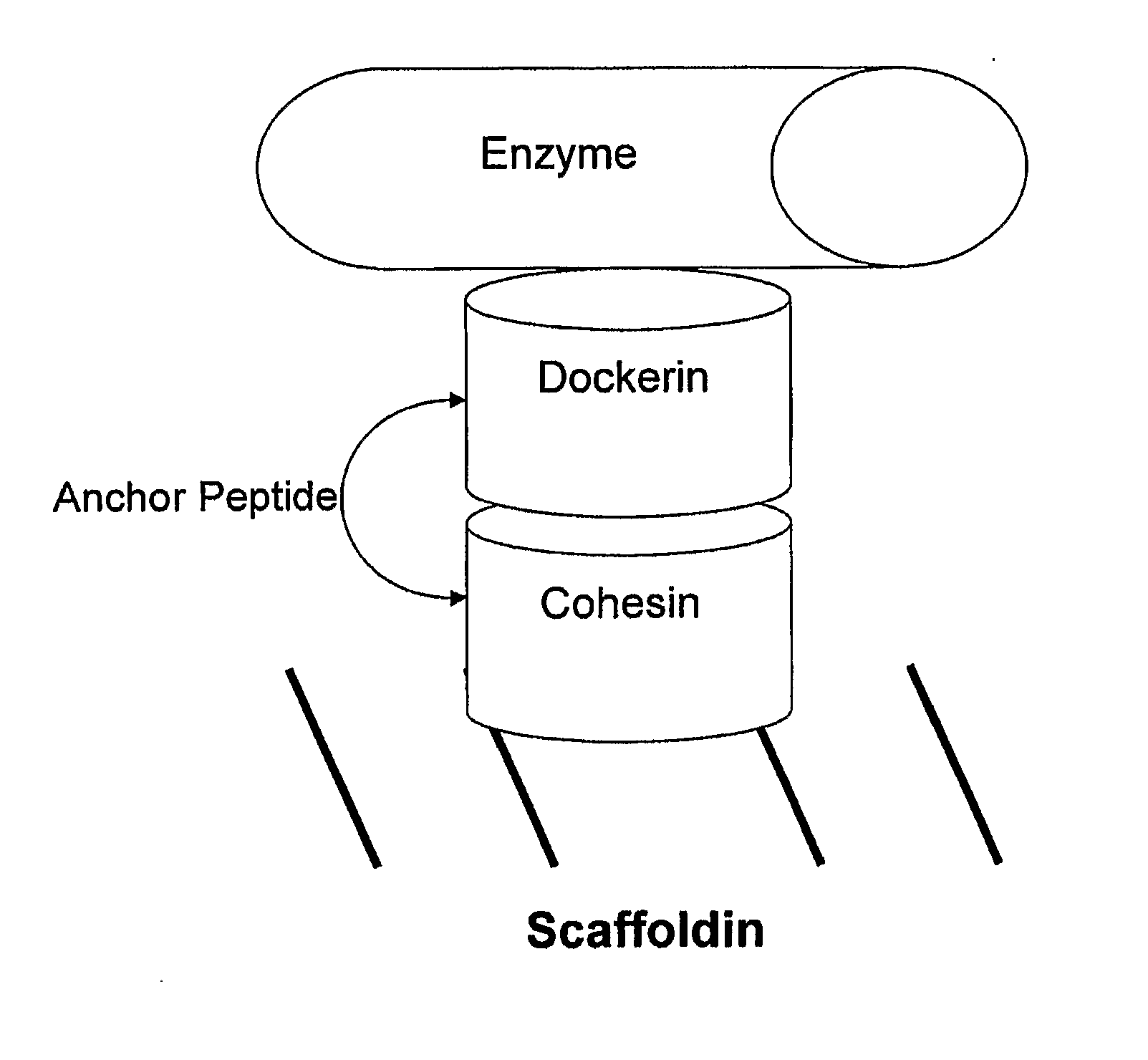
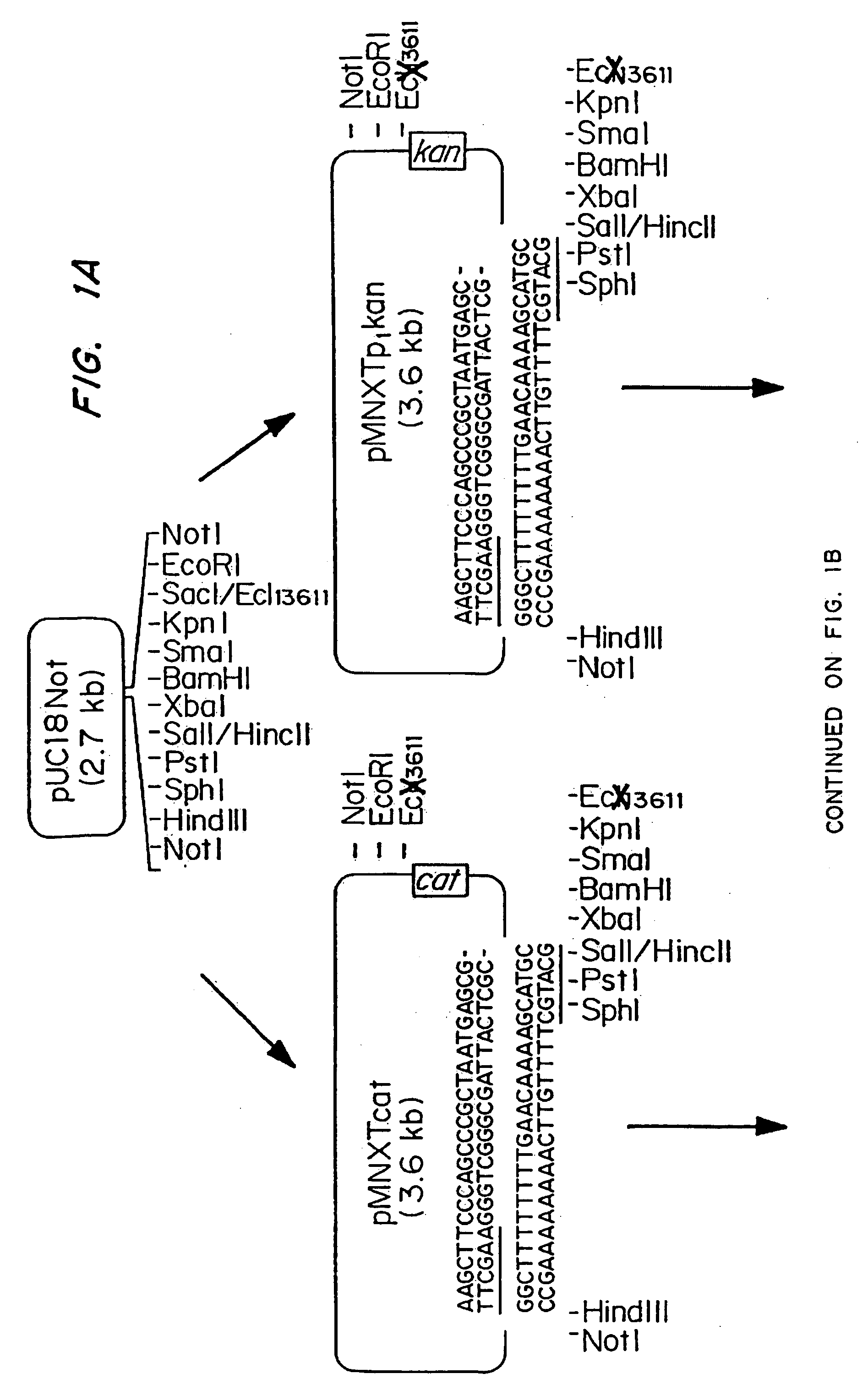
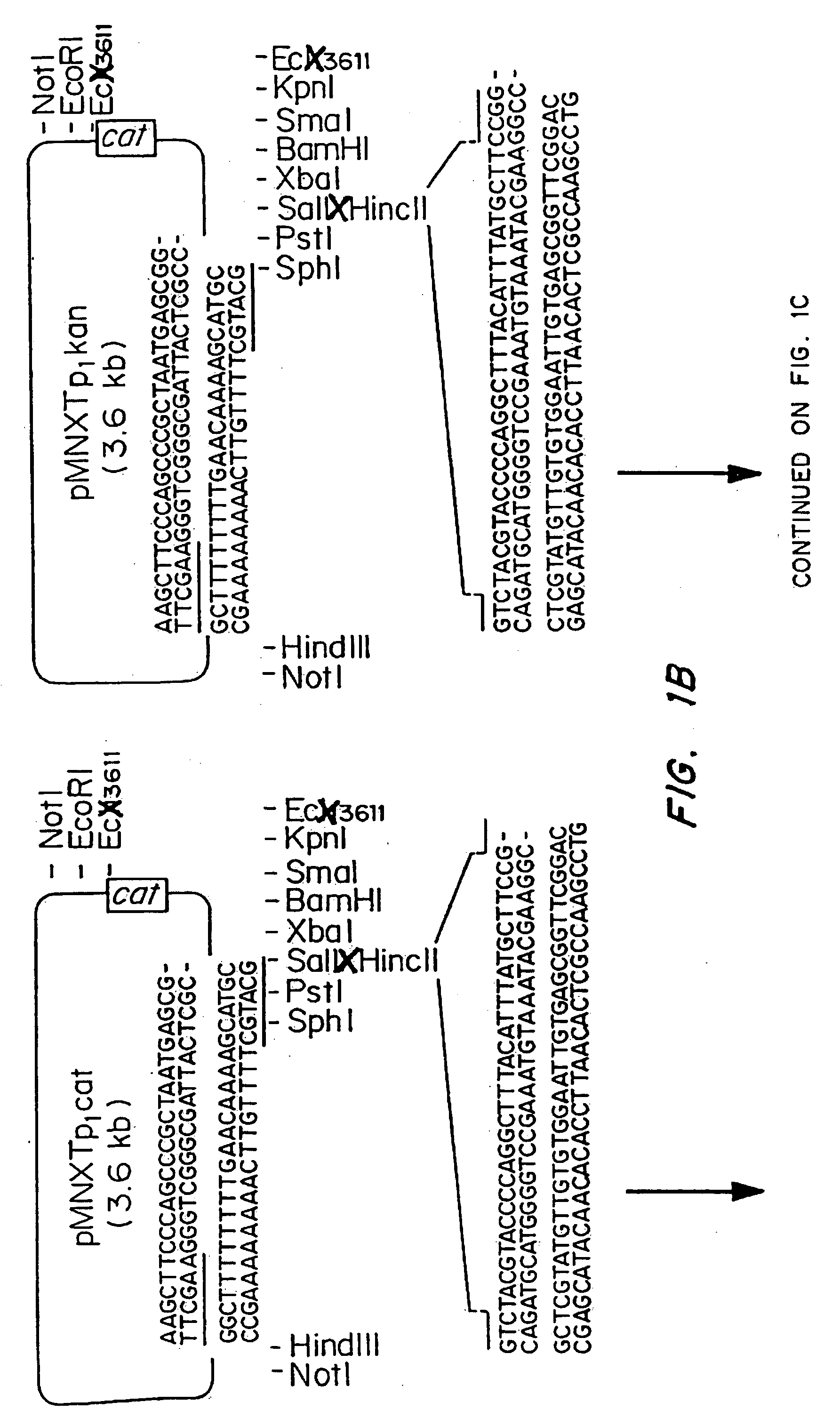
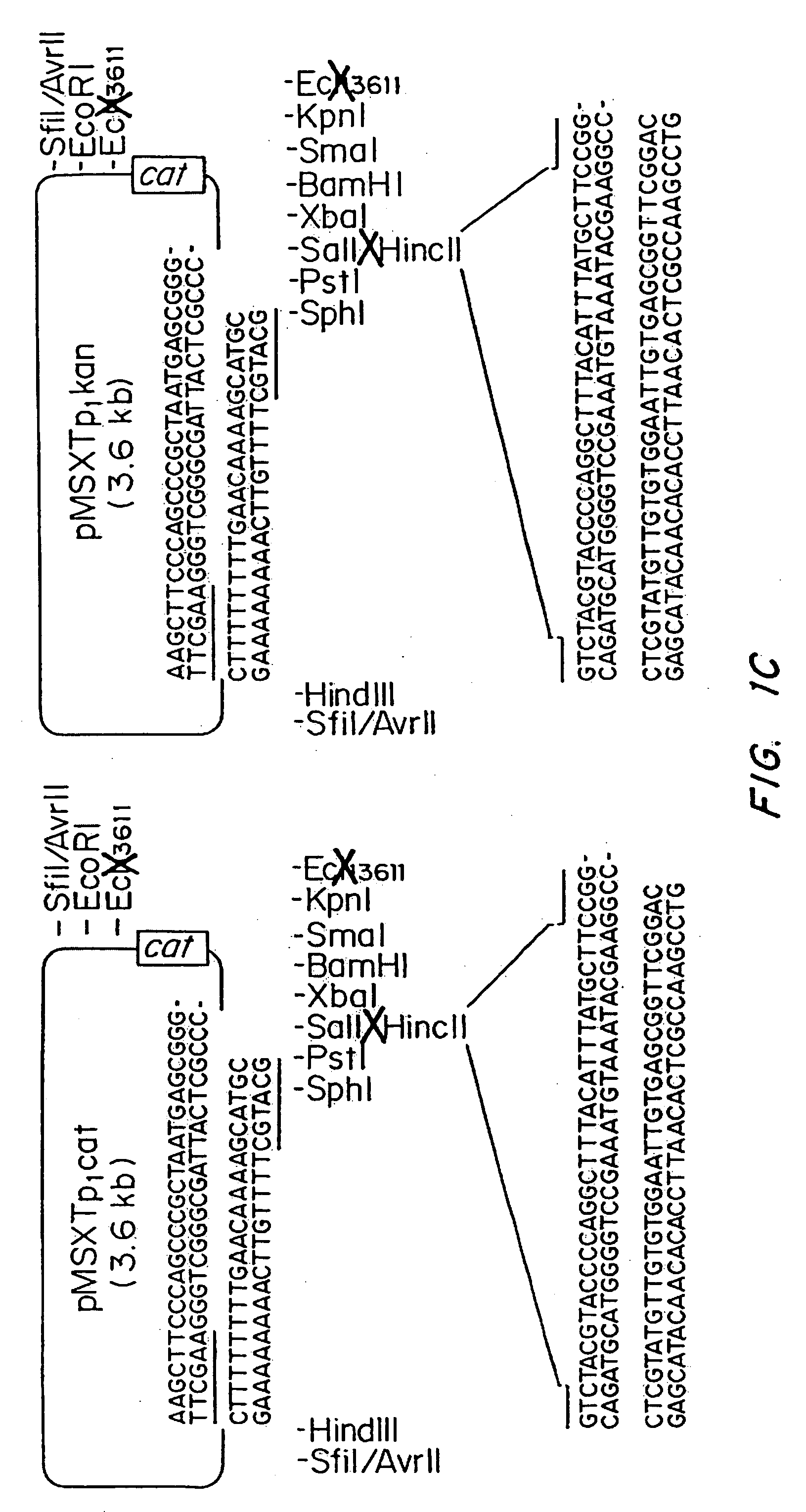
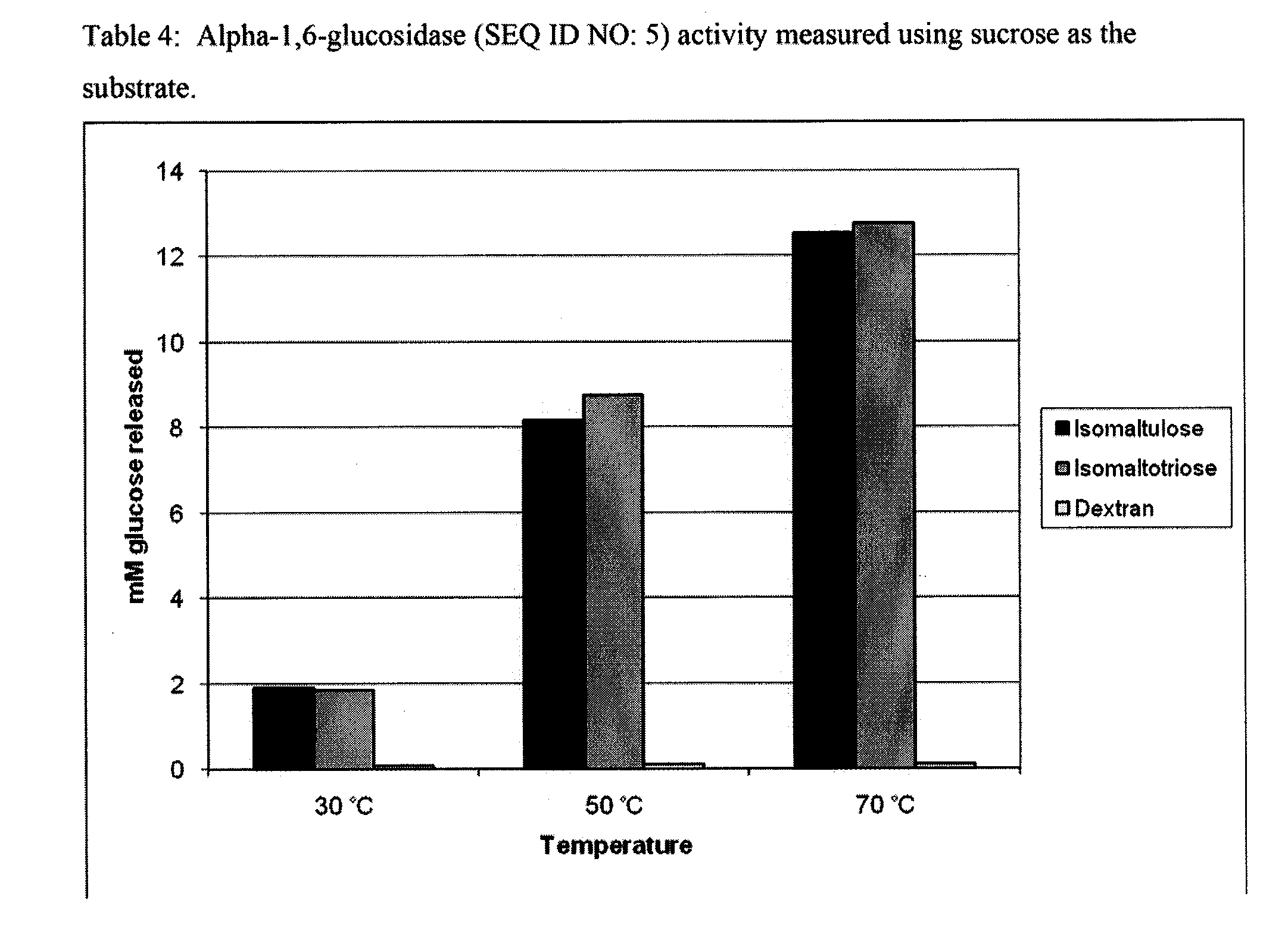
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
236 results about "Genetically modified microorganisms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetically modified micro-organisms (GMMOs) and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are micro-organisms and organisms in which genetic material has been purposely altered through genetic engineering in a way that does not occur naturally.
Methods and materials for making and using transgenic dicamba-degrading organisms
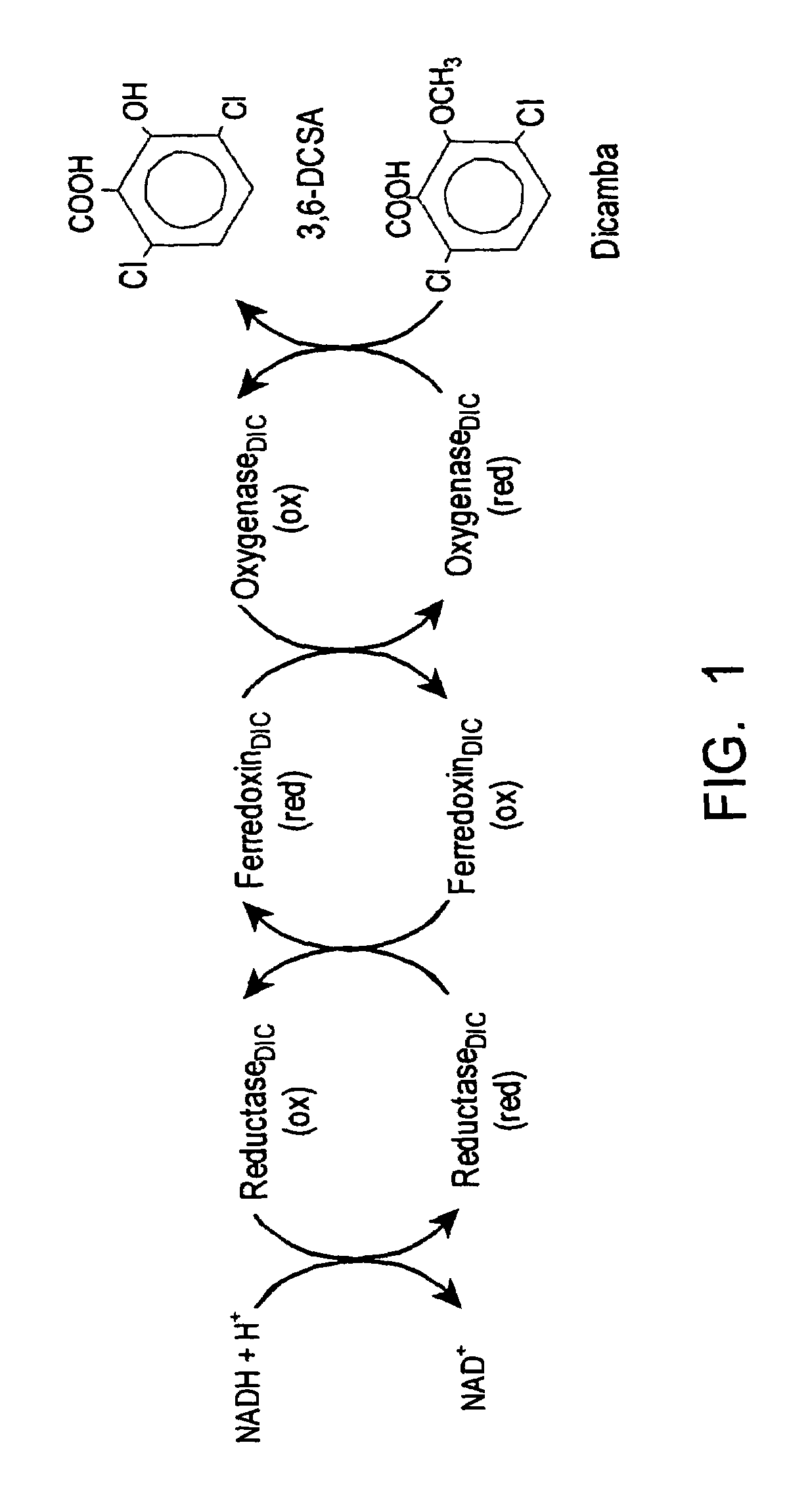
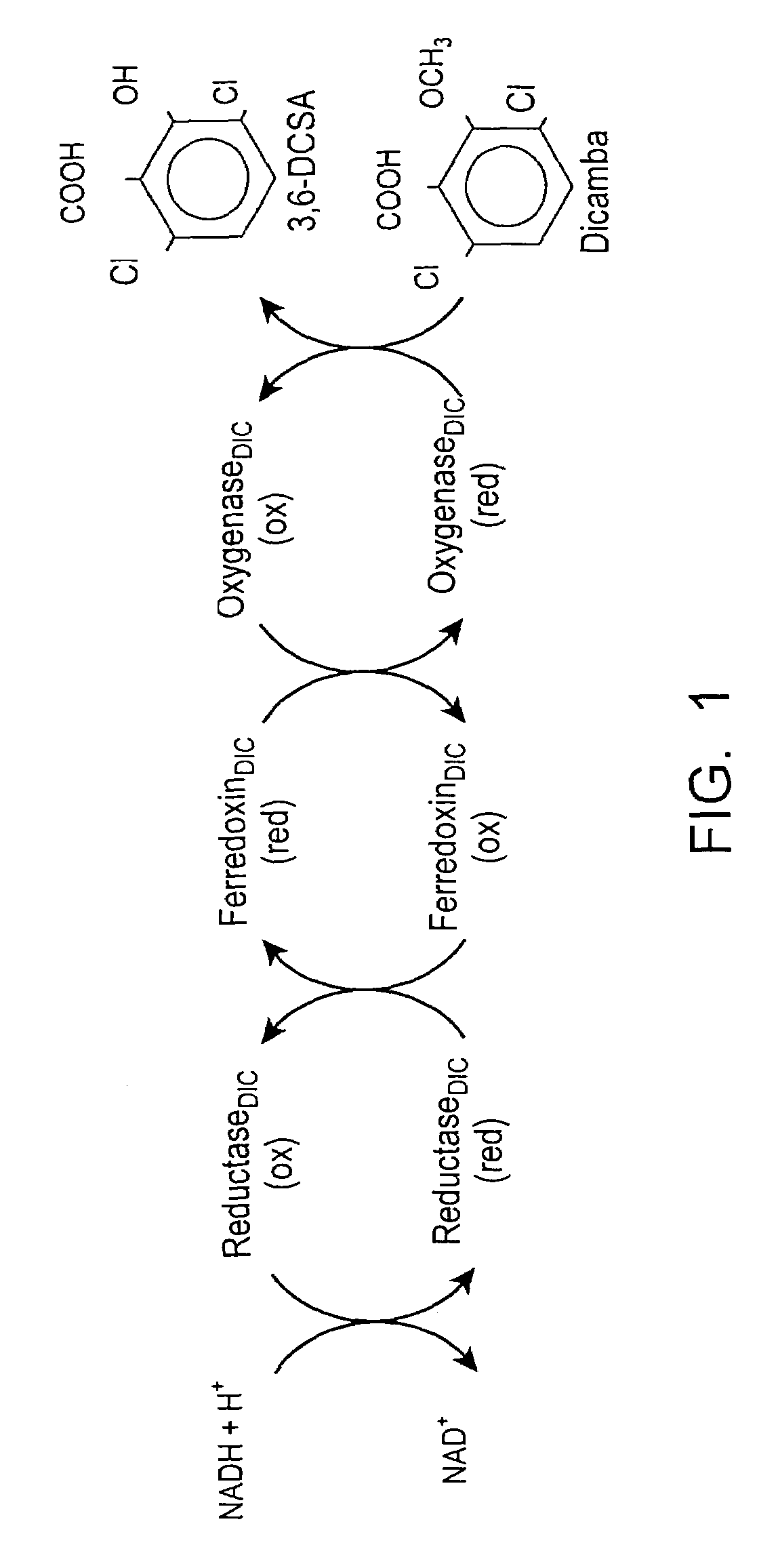
The invention provides isolated and at least partially-purified dicamba-degrading enzymes, isolated DNA molecules coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, DNA constructs coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, transgenic host cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, and transgenic plants and plant parts comprising one or more cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes. Expression of the dicamba-degrading enzymes results in the production of dicamba-degrading organisms, including dicamba-tolerant plants. The invention further provides a method of controlling weeds in a field containing the transgenic dicamba-tolerant plants of the invention and a method of decontaminating a material containing dicamba comprising applying an effective amount of a transgenic microorganism or dicamba-degrading enzyme of the invention to the material. Finally, the invention provides a method of selecting transformed plants and plant cells based on dicamba tolerance and a method of selecting or screening transformed host cells, intact organisms and parts of organisms based on the fluorescence of 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid produced as a result of dicamba degradation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Methods and materials for making and using transgenic dicamba-degrading organisms
The invention provides isolated and at least partially-purified dicamba-degrading enzymes, isolated DNA molecules coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, DNA constructs coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, transgenic host cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, and transgenic plants and plant parts comprising one or more cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes. Expression of the dicamba-degrading enzymes results in the production of dicamba-degrading organisms, including dicamba-tolerant plants. The invention further provides a method of controlling weeds in a field containing the transgenic dicamba-tolerant plants of the invention and a method of decontaminating a material containing dicamba comprising applying an effective amount of a transgenic microorganism or dicamba-degrading enzyme(s) of the invention to the material. Finally, the invention provides a method of selecting transformed plants and plant cells based on dicamba tolerance and a method of selecting or screening transformed host cells, intact organisms and parts of organisms based on the fluorescence of 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid produced as a result of dicamba degradation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Recombinant microorganism and methods of production thereof
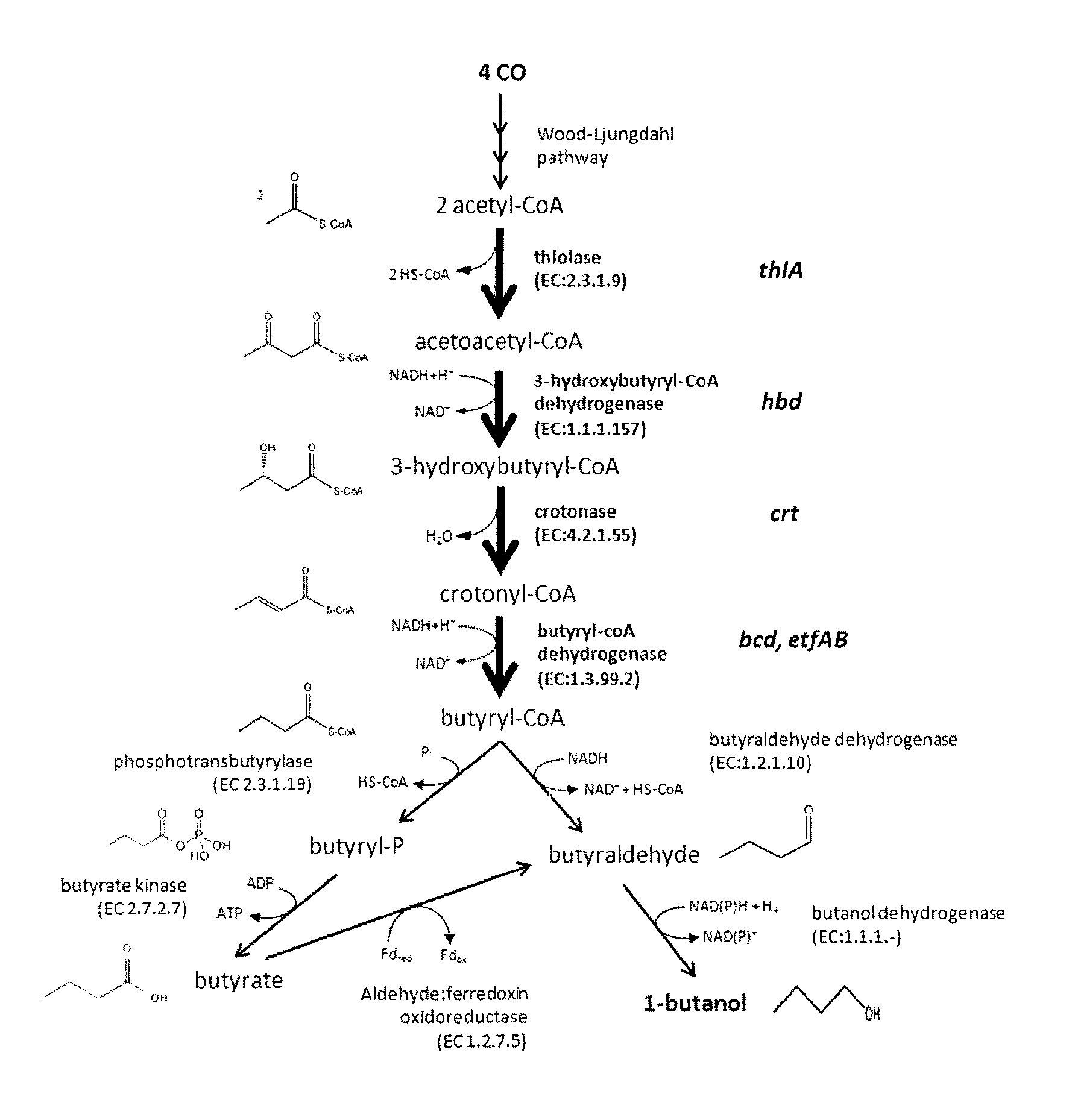
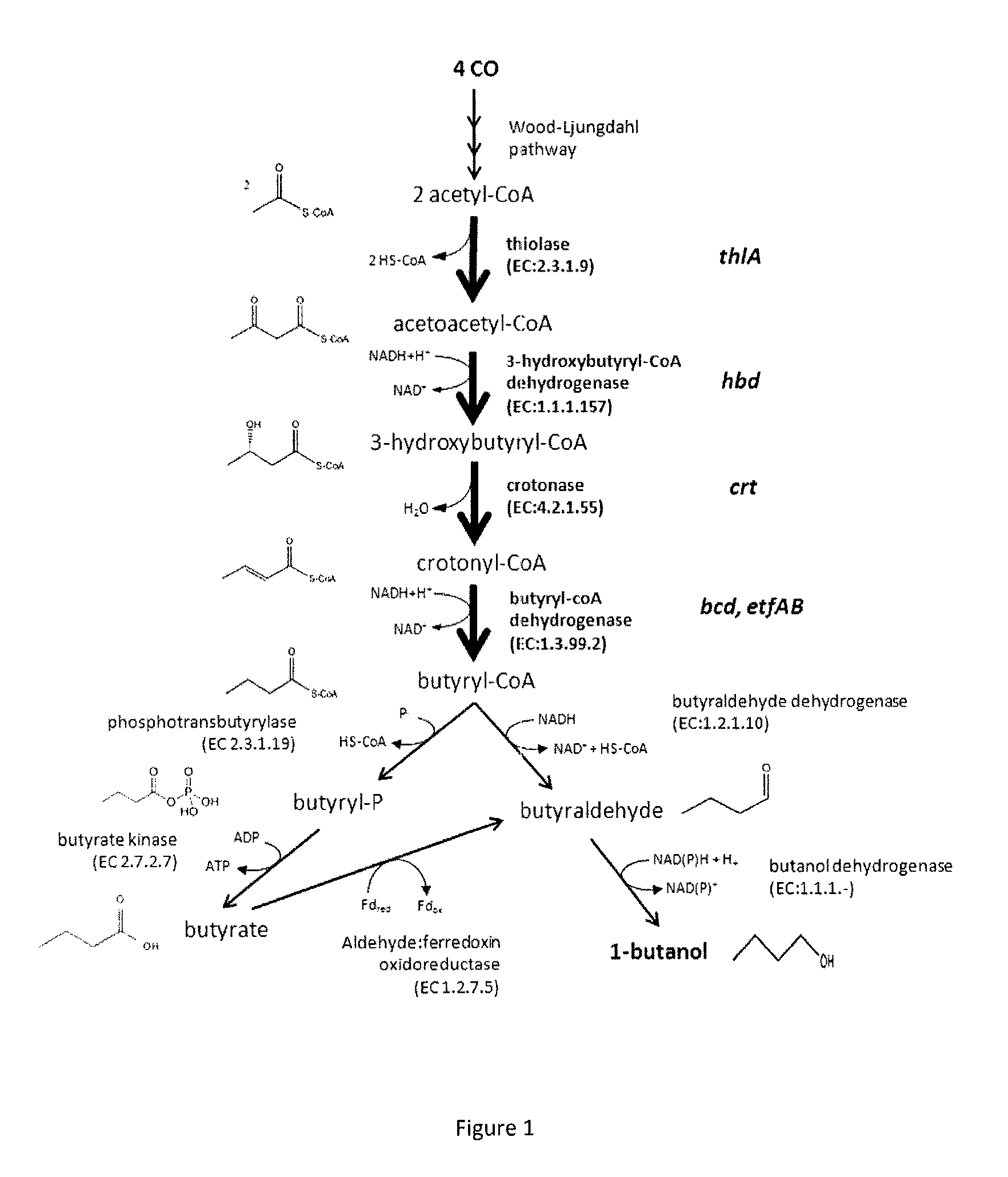
A novel genetically modified microorganisms capable of using CO to produce 1-butanol and / or a precursor thereof, novel methyltransferases and nucleic acids encoding same, methods for producing genetically modified microorganisms using said novel methyltransferases, and methods of producing 1-butanol and / or a precursor thereof by microbial fermentation.
Owner:LANZATECH NZ INC
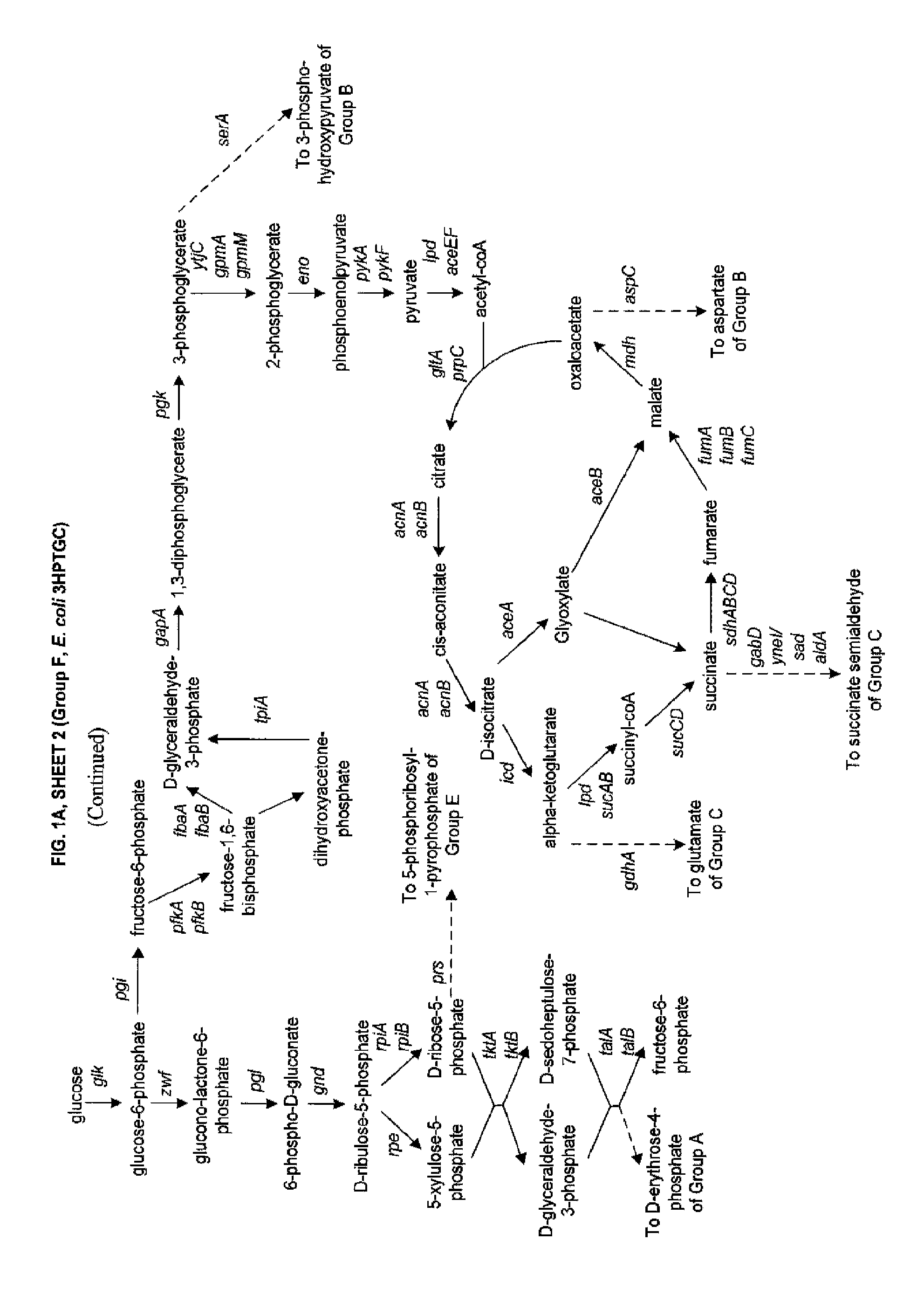
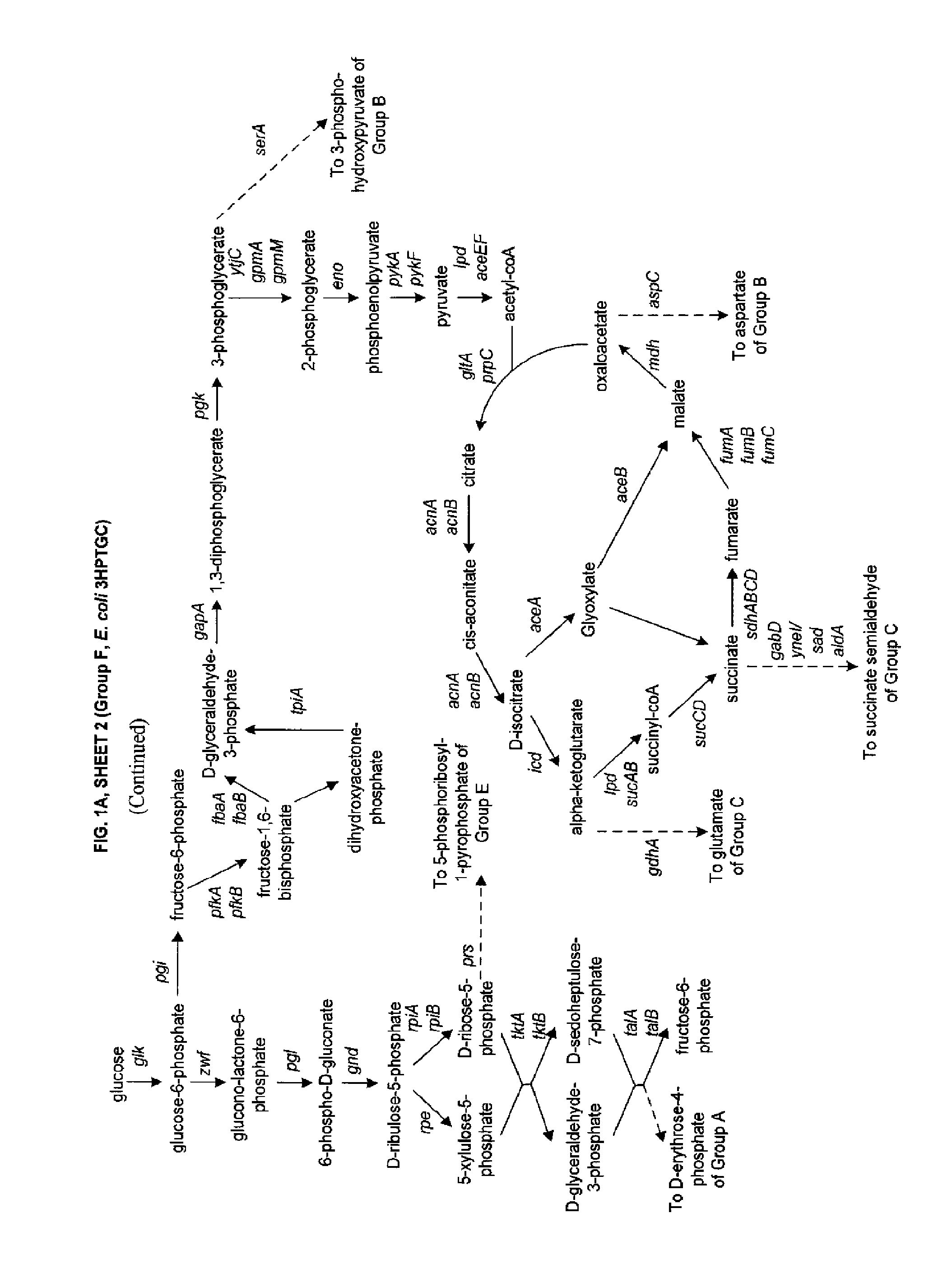
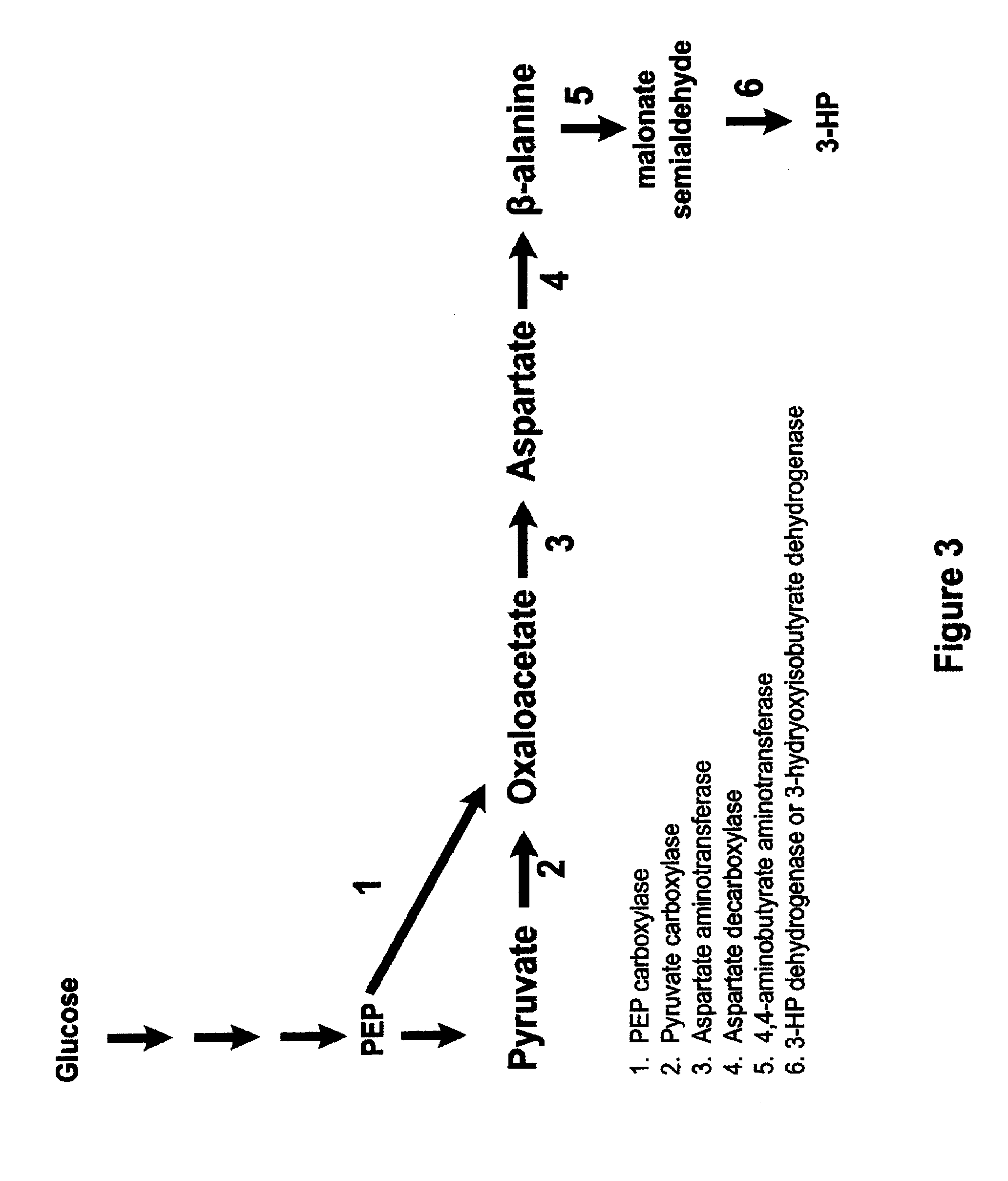
Methods, systems and compositions for increased microorganism tolerance to and production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-hp)
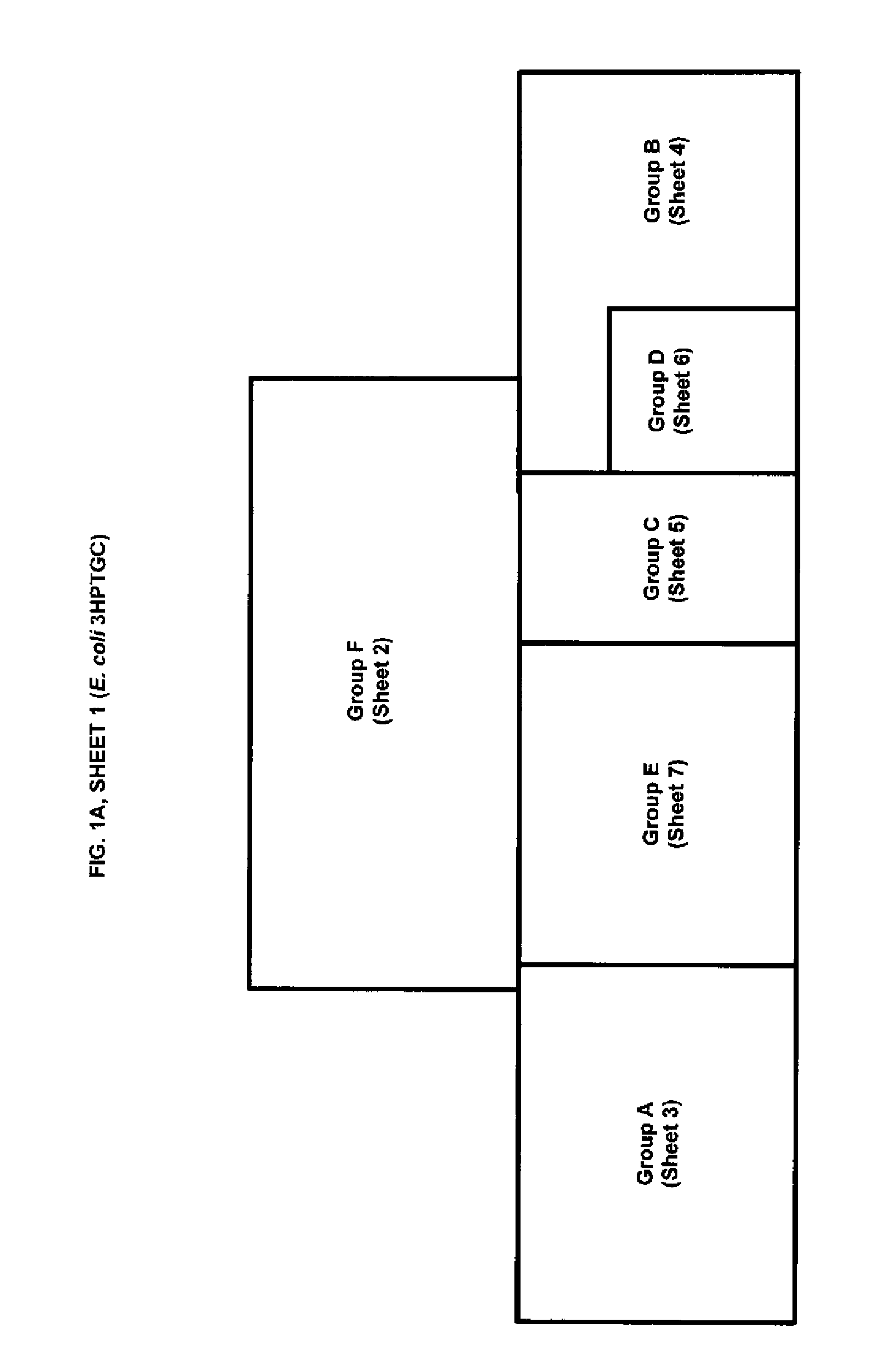
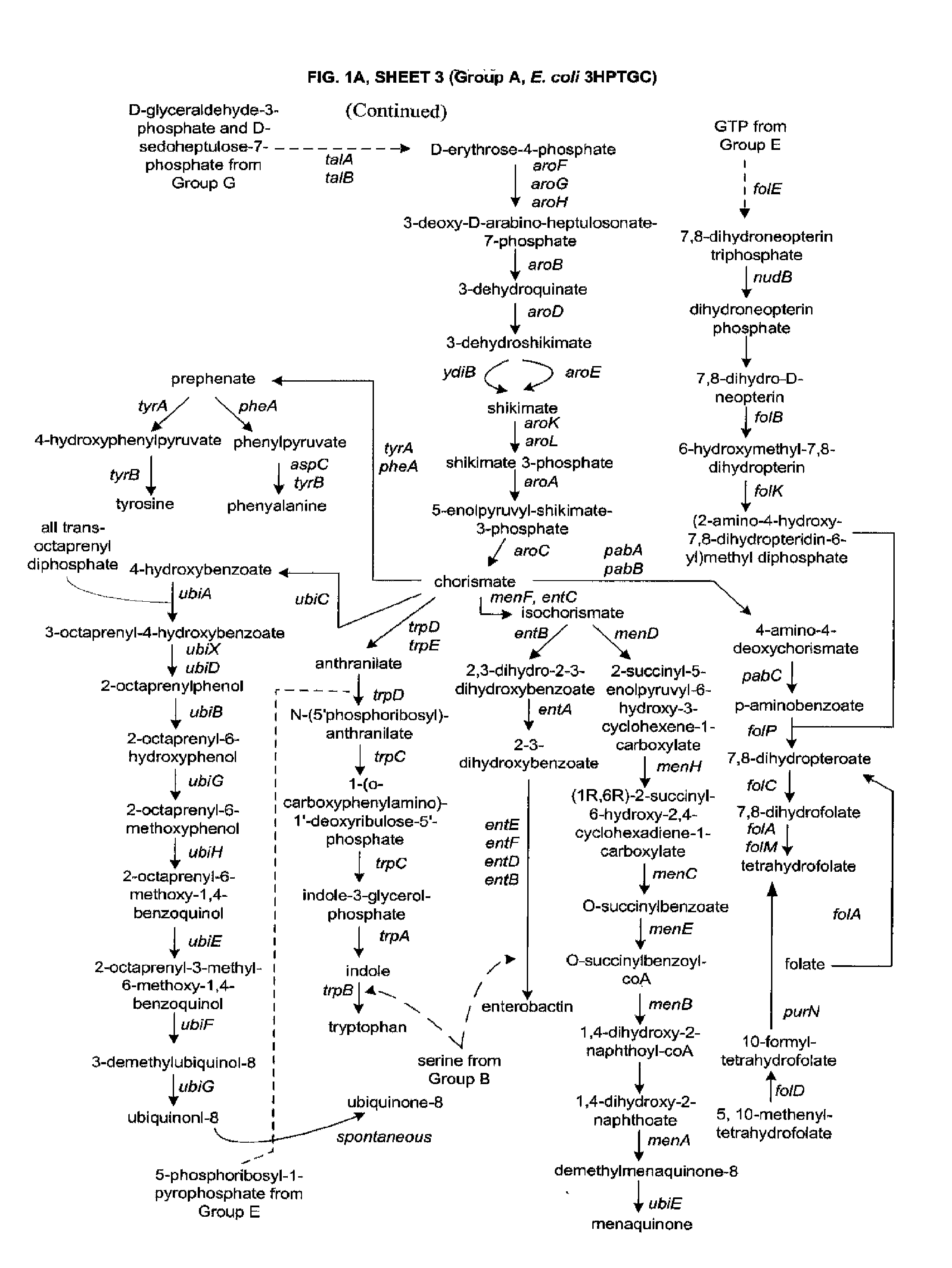
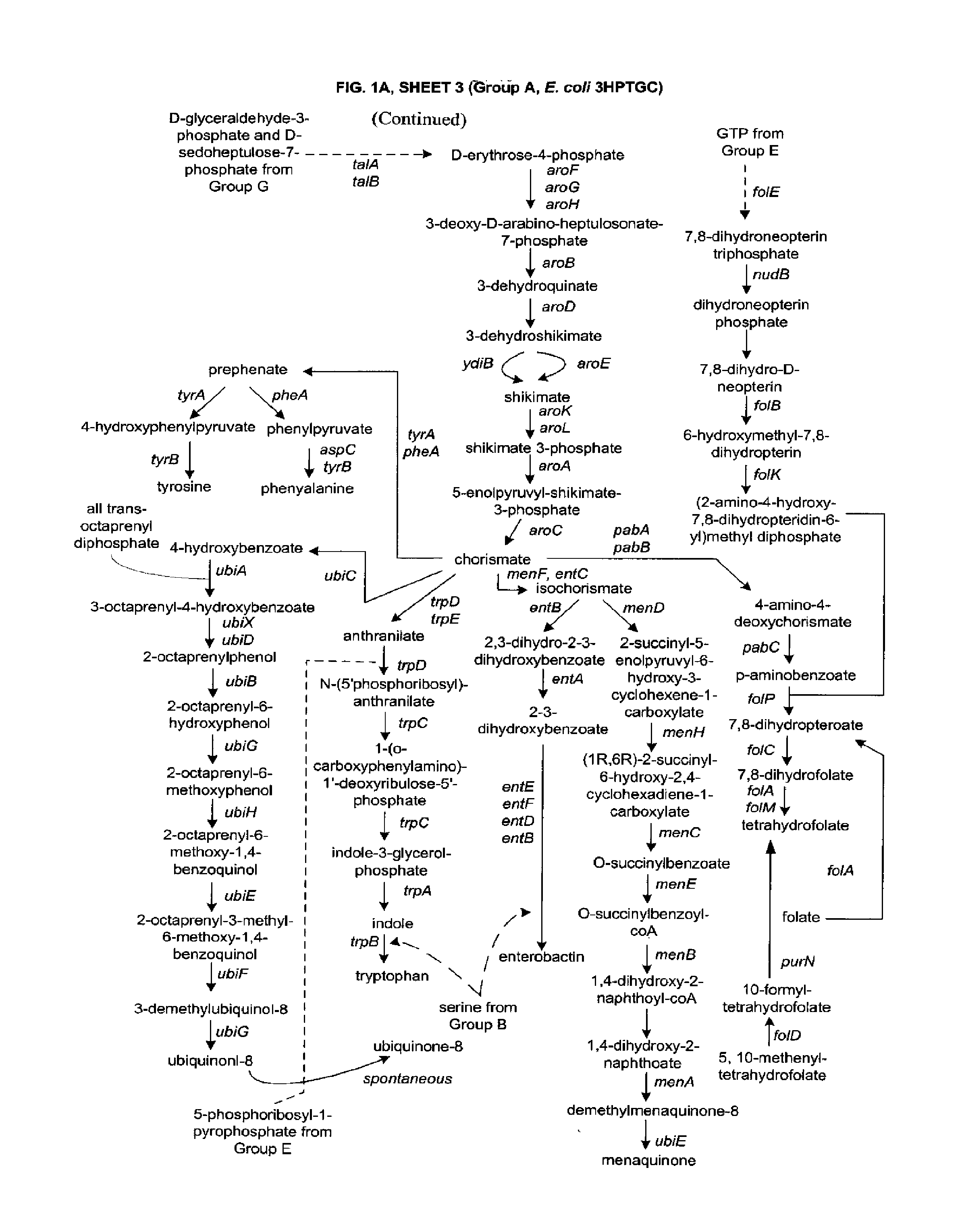
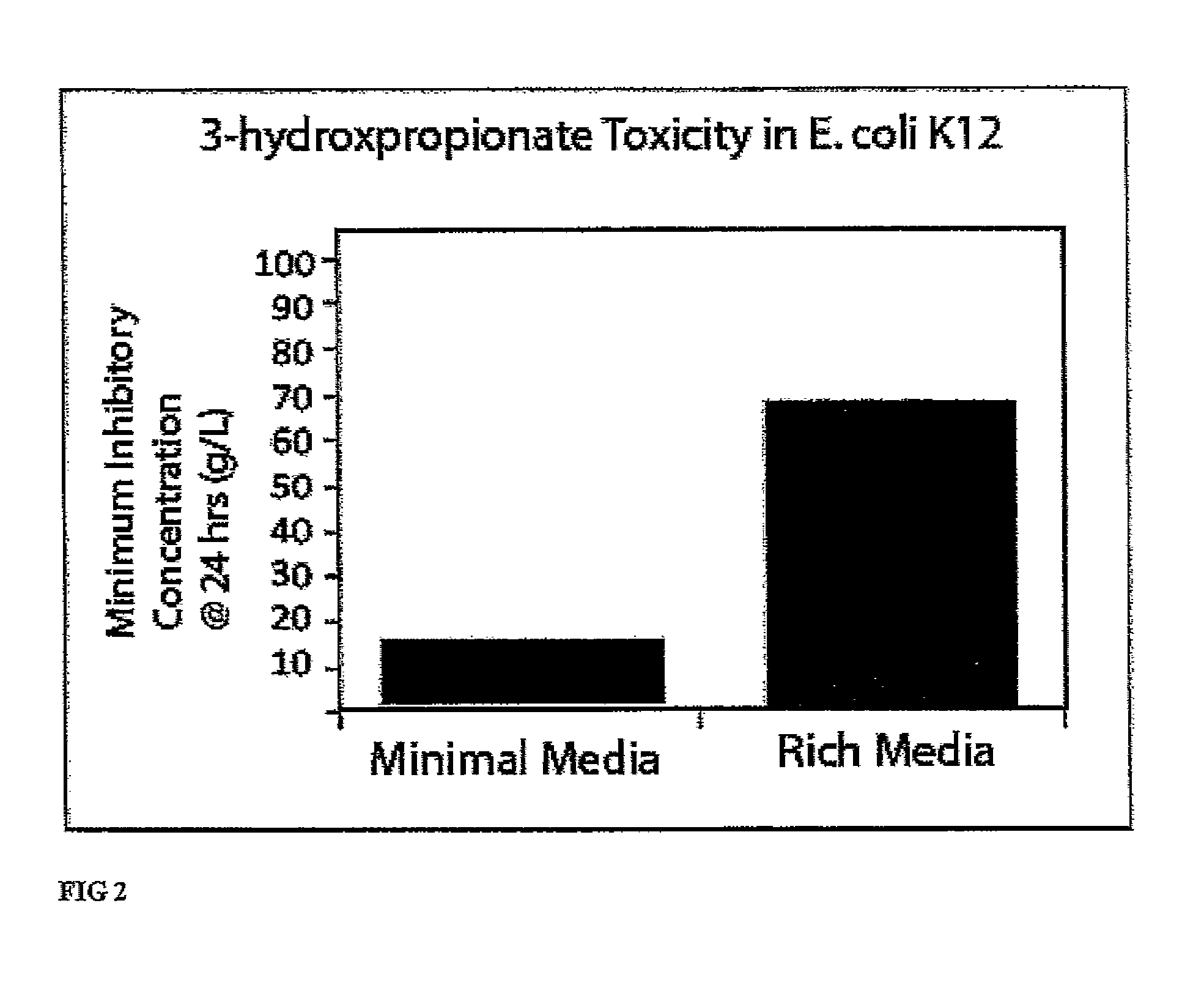
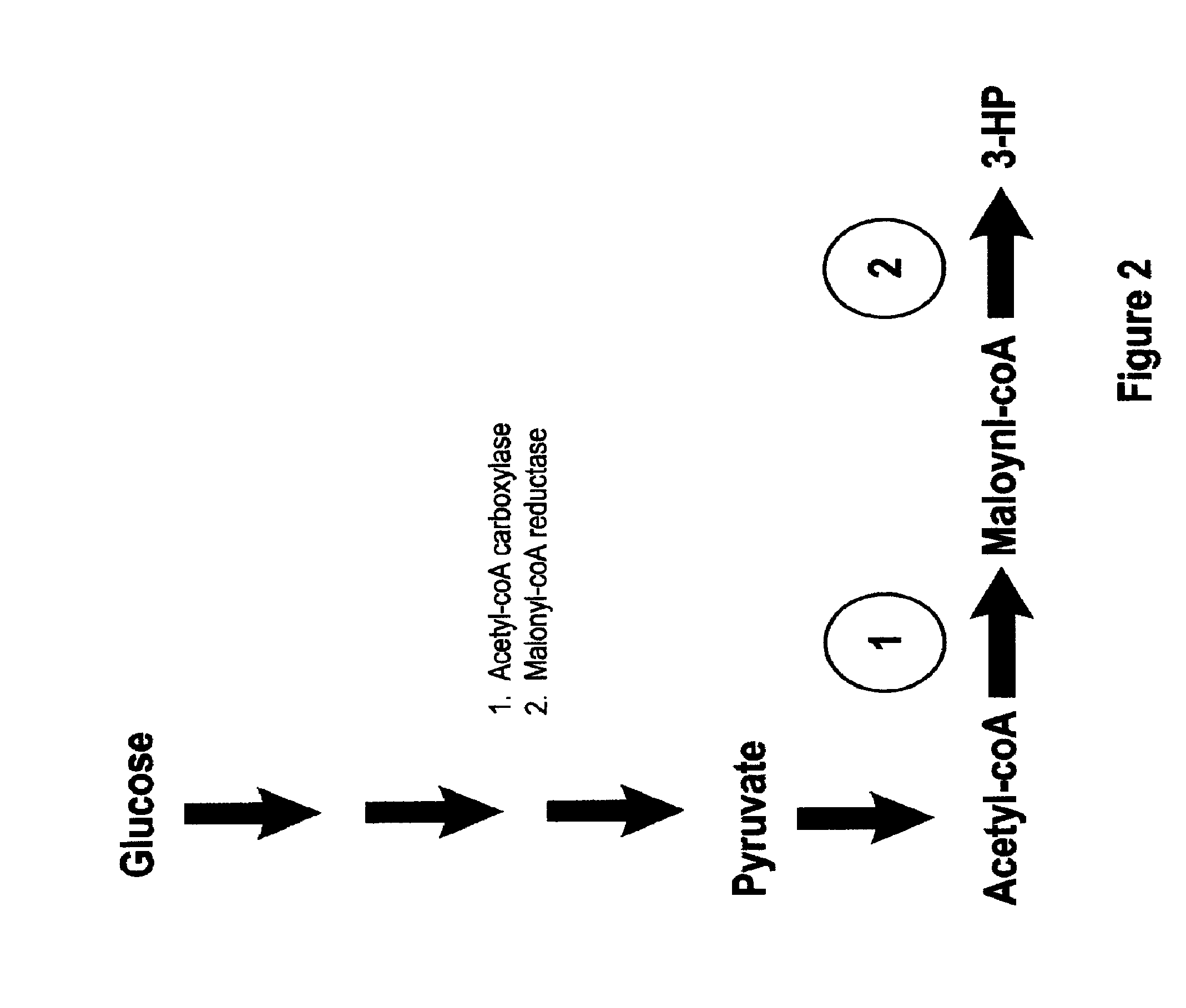
The present invention relates to methods, systems and compositions, including genetically modified microorganisms, adapted to exhibit increased tolerance to 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP), particularly through alterations to interrelated metabolic pathways identified herein as the 3-HP toleragenic pathway complex (“3HPTGC”). In various embodiments these organisms are genetically modified so that an increased 3-HP tolerance is achieved. Also, genetic modifications may be made to provide at least one genetic modification to any of one or more 3-HP biosynthesis pathways in microorganisms comprising one or more genetic modifications of the 3HPTGC.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Products and Methods for In Vivo Secretion of Monatin
Products and methods for the in vivo production of monatin sweetener are provided. The products include microorganisms that are genetically modified to secrete or to improve secretion of monatin; microorganisms that are genetically modified to produce monatin; and microorganisms that are genetically modified to both secrete or improve secretion of monatin and produce monatin. The methods include producing monatin in such genetically engineered microorganisms.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Transgenic microbial polyhydroxyalkanoate producers
InactiveUS6913911B2Simple production processInduce expressionSugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyTransposon mutagenesis
Transgenic microbial strains are provided which contain the genes required for PHA formation integrated on the chromosome. The strains are advantageous in PHA production processes, because (1) no plasmids need to be maintained, generally obviating the required use of antibiotics or other stabilizing pressures, and (2) no plasmid loss occurs, thereby stabilizing the number of gene copies per cell throughout the fermentation process, resulting in homogeneous PHA product formation throughout the production process. Genes are integrated using standard techniques, preferably transposon mutagenesis. In a preferred embodiment wherein mutiple genes are incorporated, these are incorporated as an operon. Sequences are used to stabilize mRNA, to induce expression as a function of culture conditions (such as phosphate concentration), temperature, and stress, and to aid in selection, through the incorporation of selection markers such as markers conferring antibiotic resistance.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Compositions and methods for 3-hydroxypropionate bio-production from biomass
ActiveUS8048624B1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurement3-Hydroxypropionic acidDecarboxylase activity
Methods of obtaining mutant nucleic acid sequences that demonstrate elevated oxaloacetate α-decarboxylase activity are provided. Compositions, such as genetically modified microorganisms that comprise such mutant nucleic acid sequences, are described, as are methods to obtain the same.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
Production of commercial biodiesel from genetically modified microorganisms
InactiveUS20100257777A1Clean emission profileReduce the amount requiredBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsBiodieselGlycerol
The invention provides a fermentation and recovery process for the production of biodiesel of commercial grade quality according to commercial and environmental standards (e.g., ASTM ANP, or EPA trace elements and emissions standards), by fermentation of carbohydrates using a genetically modified microorganism. The process provides a direct route for the production of fatty esters, without the need for producing oils which are later chemically transesterified with the concomitant production of large quantities of glycerin and other undesirable side-products.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
Modified microorganism uses therefor
ActiveUS20110097769A1Increasing production of fatty acidImprove production yieldBacteriaBiofuelsMicroorganismBiological body
The invention provides a genetically modified microorganism that acquires the ability to consume a renewable feedstock (such as cellulose) and produce products. This organism can be used to ferment cellulose, one of the most abundant renewable resources available, and produce products.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
Transgenic microbial polyhydroxyalkanoate producers
Transgenic microbial strains are provided which contain the genes required for PHA formation integrated on the chromosome. The strains are advantageous in PHA production processes, because (1) no plasmids need to be maintained, generally obviating the required use of antibiotics or other stabilizing pressures, and (2) no plasmid loss occurs, thereby stabilizing the number of gene copies per cell throughout the fermentation process, resulting in homogeneous PHA product formation throughout the production process. Genes are integrated using standard techniques, preferably transposon mutagenesis. In a preferred embodiment wherein mutiple genes are incorporated, these are incorporated as an operon. Sequences are used to stabilize mRNA, to induce expression as a function of culture conditions (such as phosphate concentration), temperature, and stress, and to aid in selection, through the incorporation of selection markers such as markers conferring antibiotic resistance.
Owner:METABOLIX
Compositions and methods for producing fermentable carbohydrates
InactiveUS20110201059A1Increasing total locked carbohydrate contentGenetic engineeringFermentationMicroorganismYeast
Provided herein are methods for producing fermentable sugar obtained from a plant tissue. The methods include providing transgenic plant material comprising one or more locked carbohydrates and contacting plant material with an enzyme capable of converting the locked carbohydrate into a fermentable sugar. The methods are useful for providing sugar or sugar pre-cursors for several industrial purposes including ethanol production. The invention also encompasses plants and plant parts that produce a lock enzyme to yield a locked carbohydrate, with the consequence of accumulating the locked carbohydrate in the plant. The invention also encompasses providing a key enzyme able to convert locked carbohydrates to fermentable sugars. Key enzymes can be provided by transgenic plants or plant parts, transgenic microbes, transgenic yeast, microbes or yeast.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Methods, Systems and Compositions for Increased Microorganism Tolerance to and Production of 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid (3-HP)
InactiveUS20120264902A1Increase productionImprove the level ofOrganic chemistryFermentationMicroorganism3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The present invention relates to methods, systems and compositions, including genetically modified microorganisms, adapted to exhibit increased tolerance to 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP), particularly through alterations to interrelated metabolic pathways identified herein as the 3-HP toleragenic pathway complex (“3HPTGC”). In various embodiments these organisms are genetically modified so that an increased 3-HP tolerance is achieved. Also, genetic modifications may be made to provide at least one genetic modification to any of one or more 3-HP biosynthesis pathways in microorganisms comprising one or more genetic modifications of the 3HPTGC.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Modified microorganisms and uses therefor
ActiveUS8535916B2Improve production yieldUndesirable side reactionBacteriaBiofuelsBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention provides a genetically modified microorganism that acquires the ability to consume a renewable feedstock (such as cellulose) and produce products. This organism can be used to ferment cellulose, one of the most abundant renewable resources available, and produce products.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
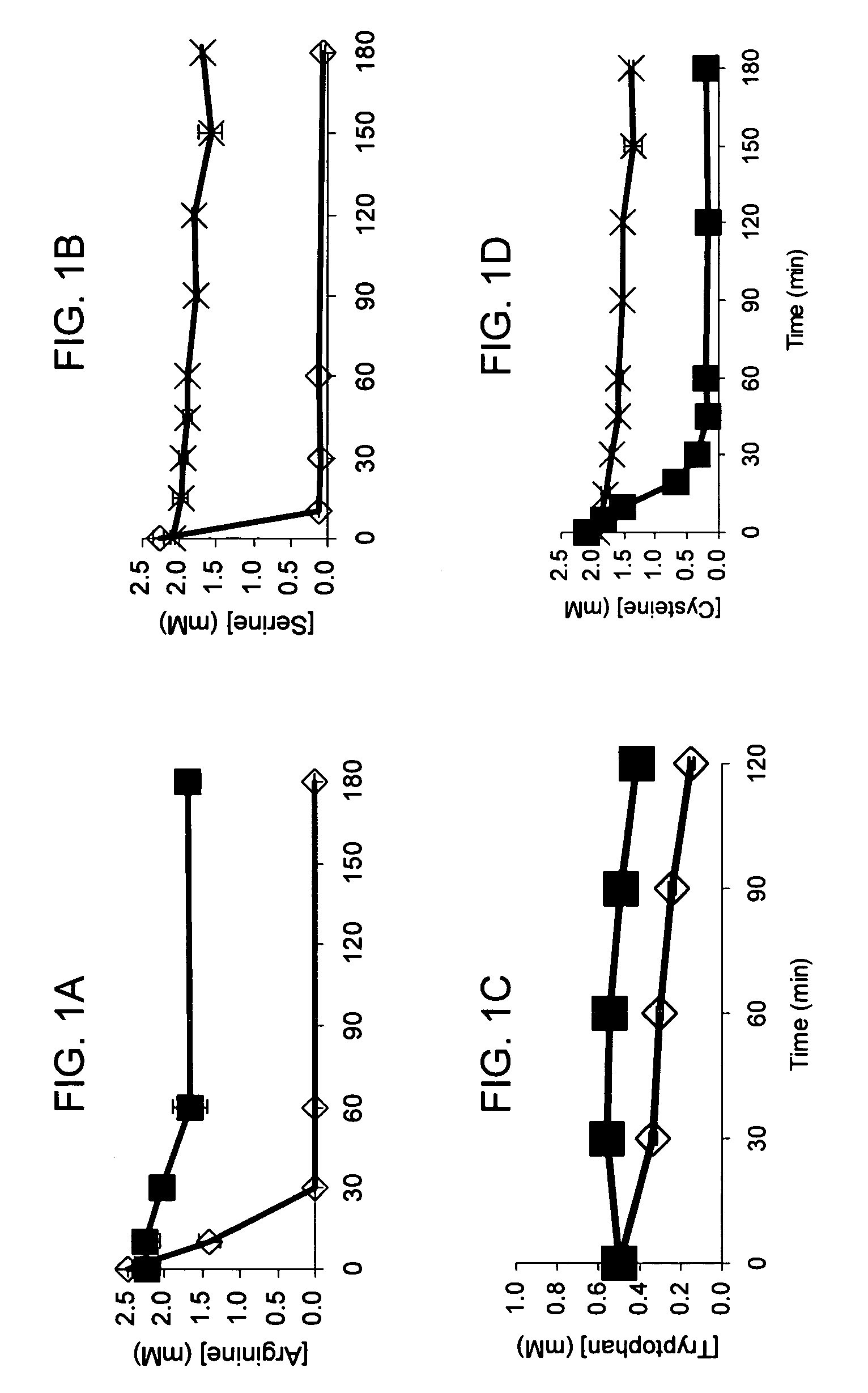
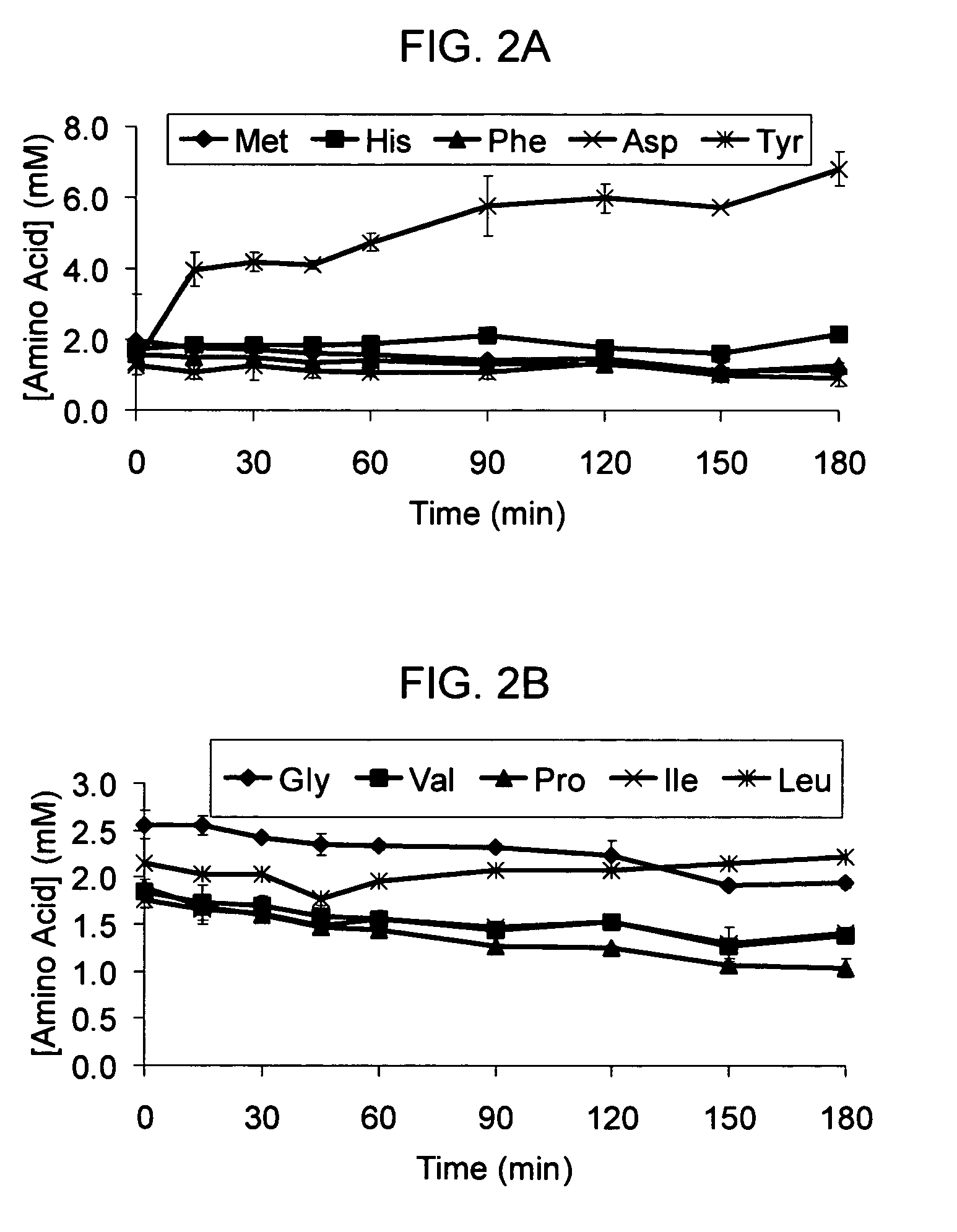
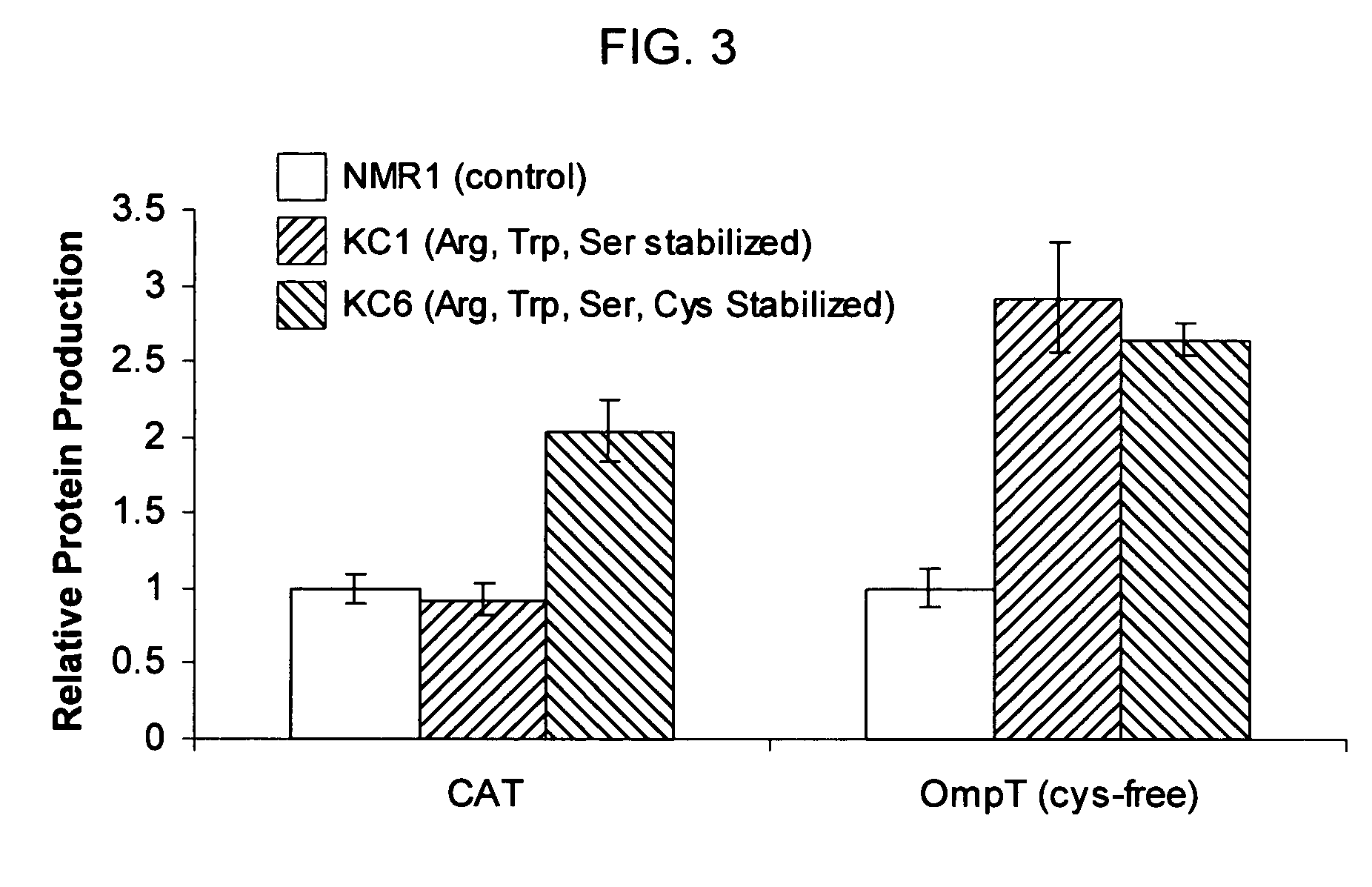
Total amino acid stabilization during cell-free protein synthesis
Compositions and methods are provided for the enhanced in vitro synthesis of protein molecules, by optimizing the metabolism of amino acids present in the reaction mix, preferably all amino acids in the reaction mixture. By performing synthesis with extracts from genetically modified microbial strains that are deficient in multiple amino acid metabolizing enzymes reduces the enzymatic activities responsible for catalyzing these reactions and improves the overall yield of synthesis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
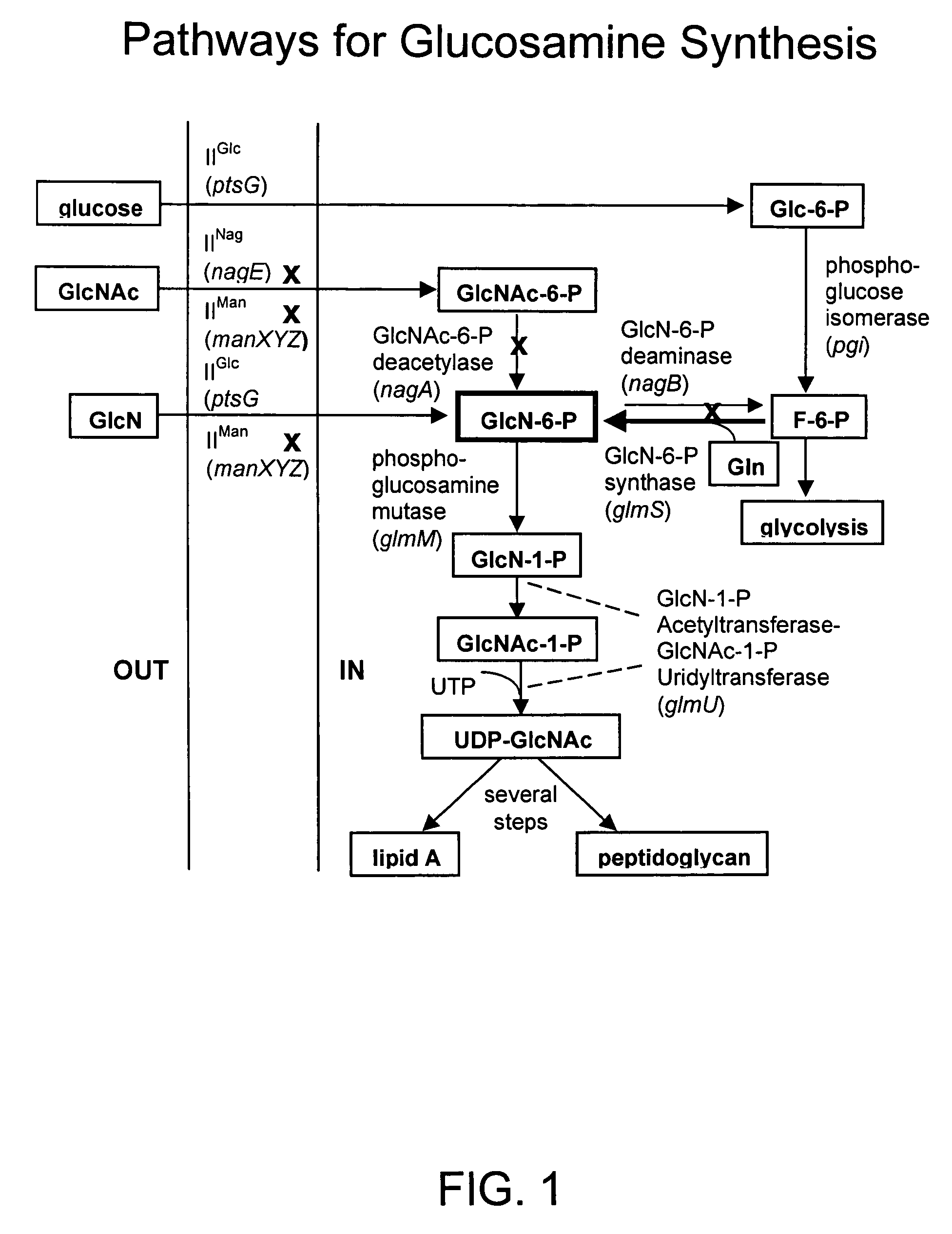
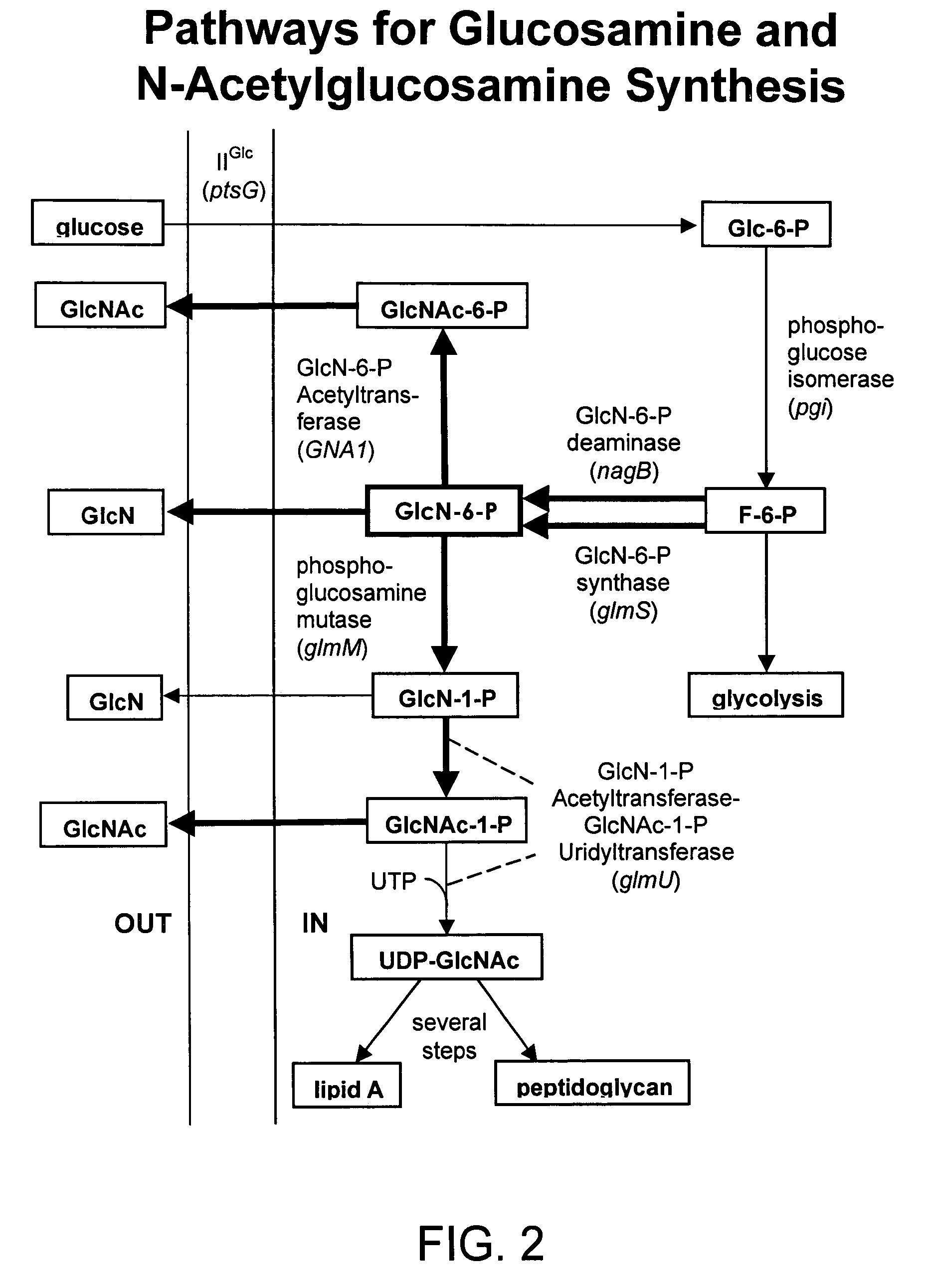
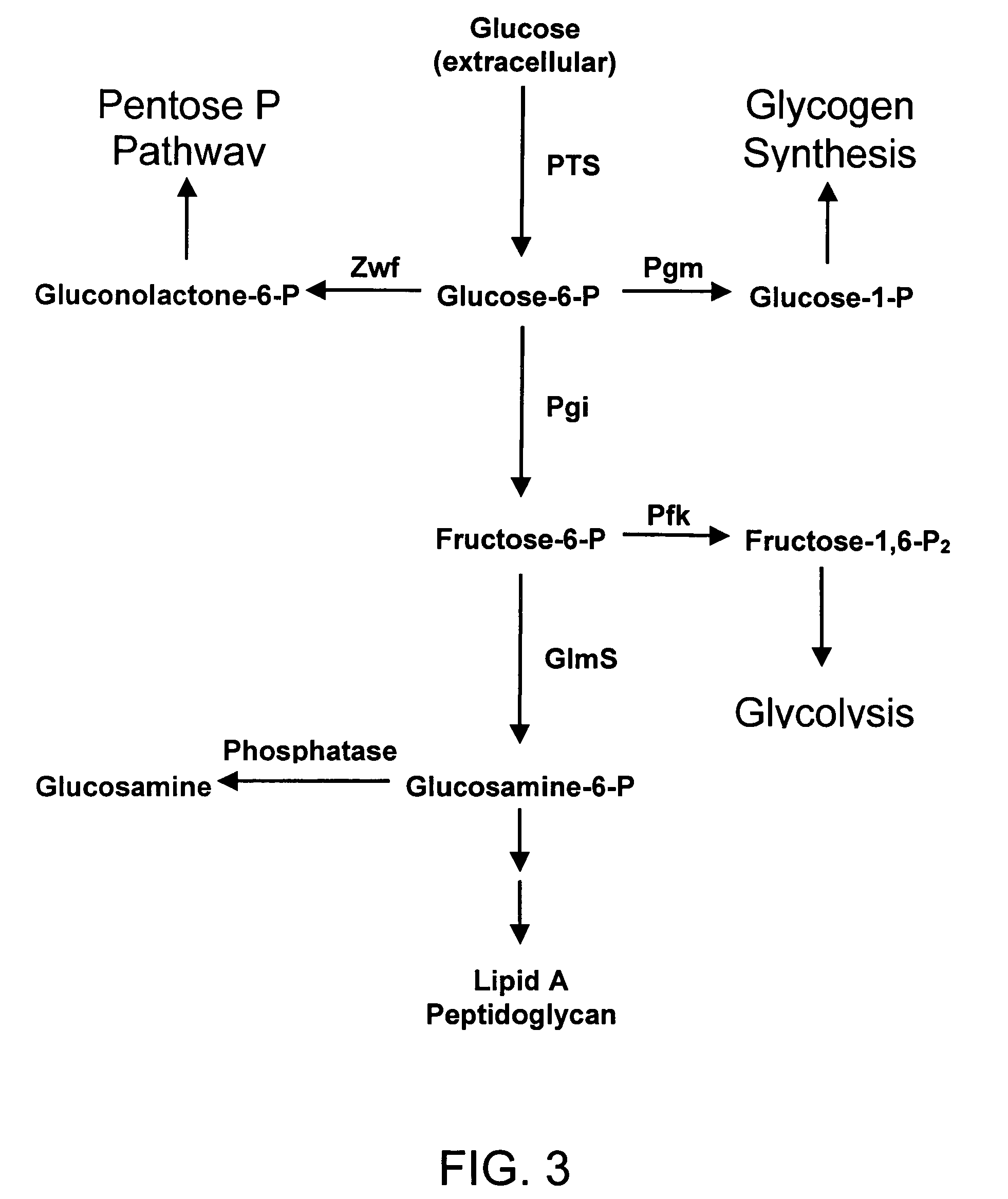
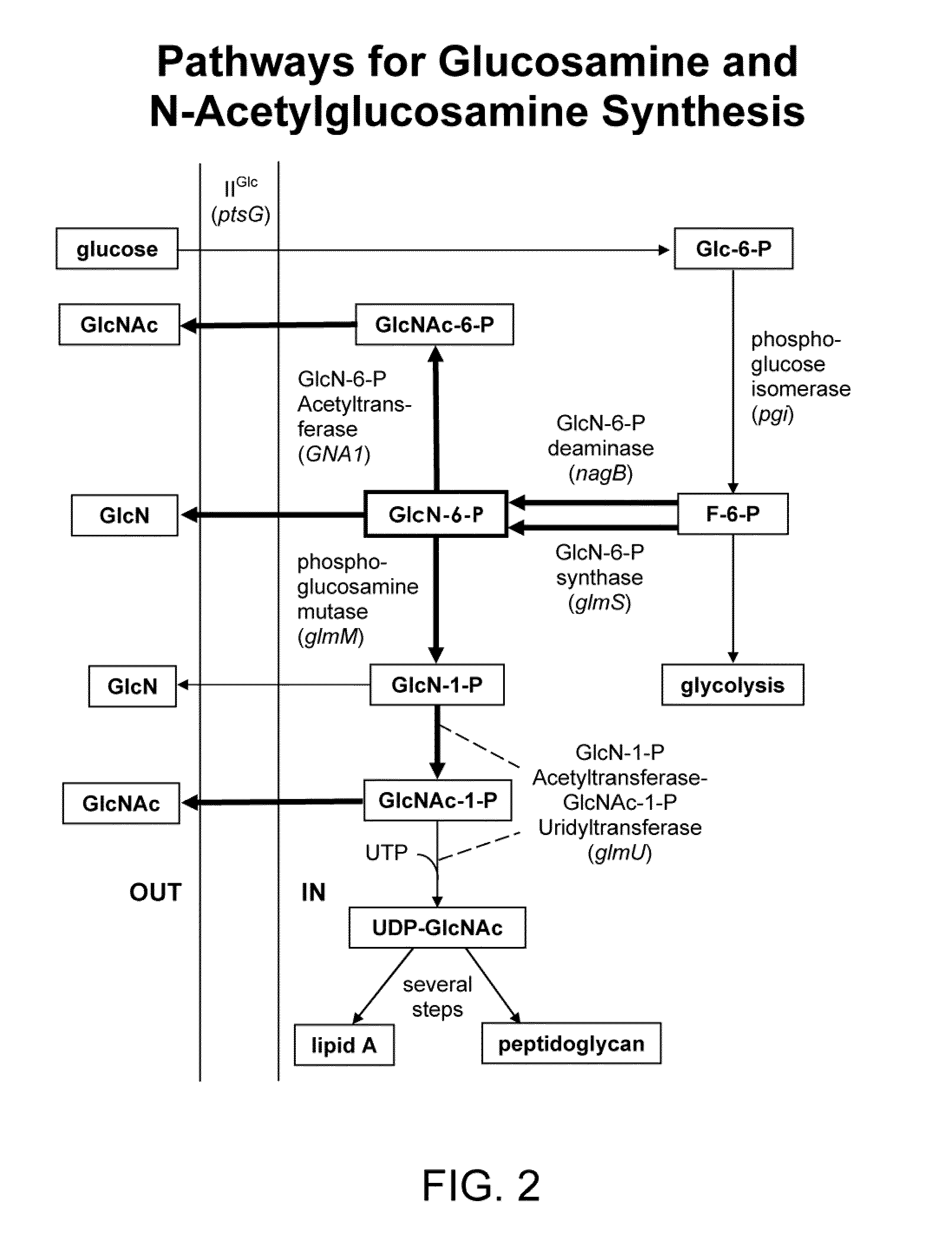
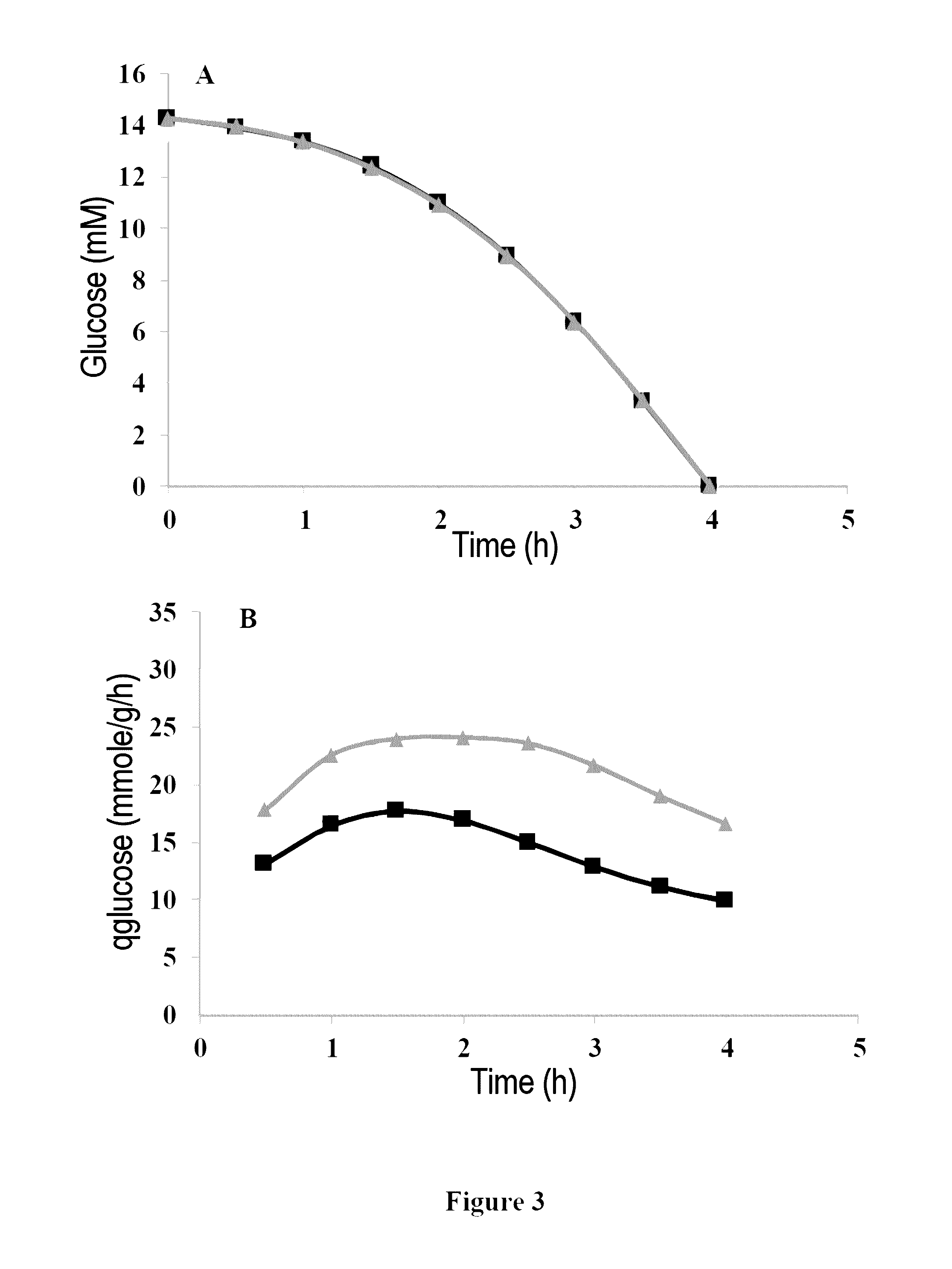
Process and materials for production of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine
A biosynthetic method for producing glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine is disclosed. Such a method includes the fermentation of a genetically modified microorganism to produce glucosamine and / or N-acetylglucosamine. Also disclosed are genetically modified microorganisms that are useful for producing glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine. In addition, methods of recovering N-acetylglucosamine that has been produced by a fermentation process, including methods that result in N-acetylglucosamine of high purity, are described. Also disclosed is a method to produce glucosamine from N-acetylglucosamine.
Owner:ARKION LIFE SCI LLC
Methods, systems, and compositions for increased microorganism tolerance to and production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-hp)
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Methods for stabilizing production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived compounds
ActiveUS20160177341A1Increase probabilityLonger sustained non-catabolic compound productionFungiBacteriaMicroorganismHeterologous
The present disclosure relates to the use of a switch for the production of heterologous non-catabolic compounds in microbial host cells. In one aspect, provided herein are genetically modified microorganisms that produce non-catabolic compounds more stably when serially cultured under aerobic conditions followed by microaerobic conditions, and methods of producing non-catabolic compounds by culturing the genetically modified microbes under such culture conditions. In another aspect, provided herein are genetically modified microorganisms that produce non-catabolic compounds more stably when serially cultured in the presence of maltose followed by the reduction or absence of maltose, and methods of producing non-catabolic compounds by culturing the genetically modified microbes under such culture conditions.
Owner:AMYRIS INC +1
L-carnitin dehydrogenases, their derivatives and method for producing substituted (s) alkanols
The present invention relates to proteins having an enzymatic activity of reducing substituted alkanones such as 3-methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-propan-1-one. The invention furthermore relates to nucleic acids coding for said proteins, nucleic acid constructs, vectors, genetically modified microorganisms and to methods for preparing substituted (S)-alkanols, such as, for example, (S)-3-methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-(S)-propanol.
Owner:BASF AG
Microbial production of fatty alcohols
Genes and strains of recombinant microorganisms are provided that are engineered to produce fatty alcohols and fatty alcohol derivatives. The organisms can include one, two, three or more transgenes that direct the biosynthesis of one or more fatty alcohols or derivatives. Methods of producing fatty alcohols using transgenic microorganisms are also provided.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
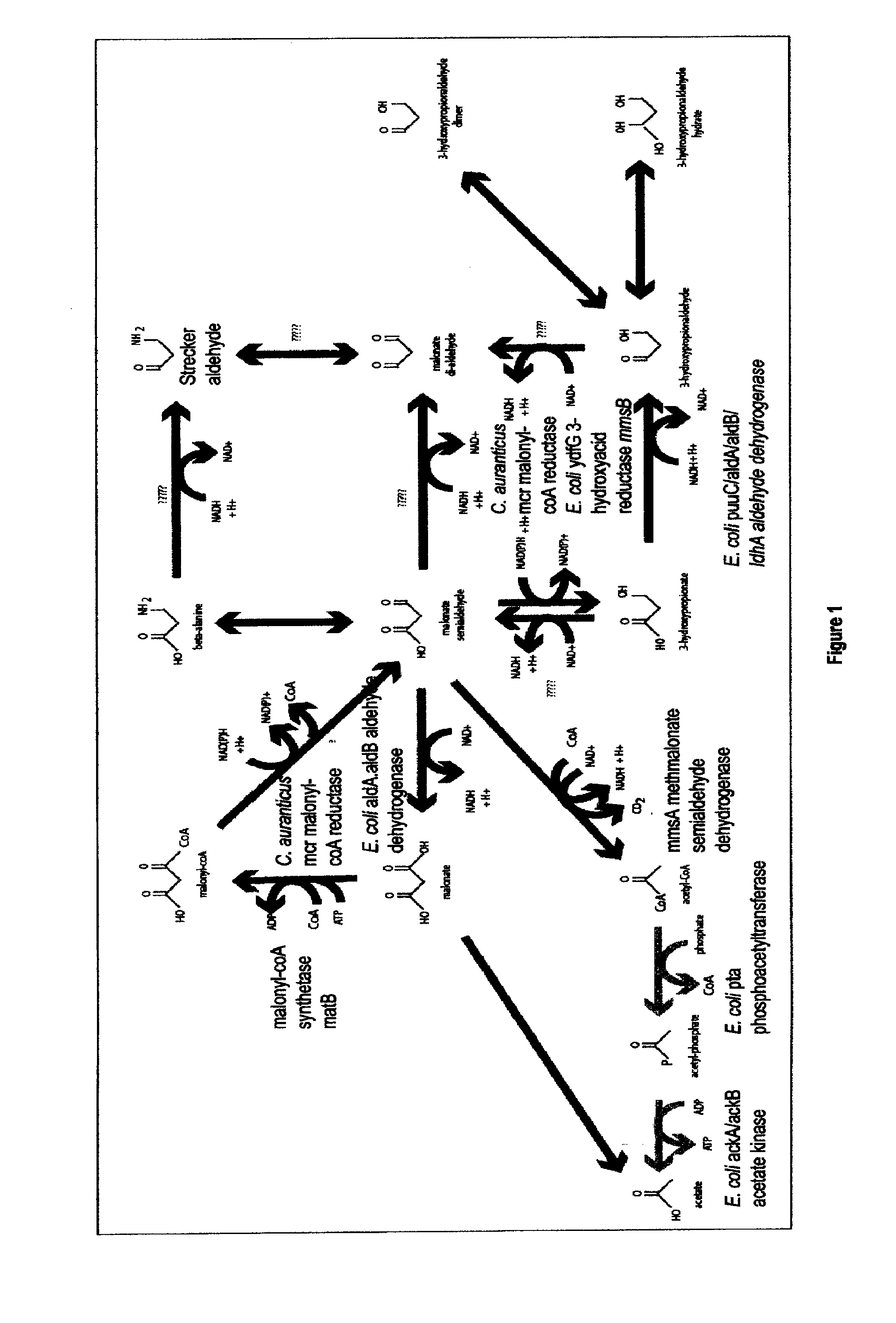
Methods, Systems And Compositions Related To Reduction Of Conversions Of Microbially Produced 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid (3-HP) To Aldehyde Metabolites
Owner:CARGILL INC
Novel Dehydrogenases, the Derivatives thereof, and Method for the Production of Optically Active Alkanols
The present invention relates to proteins having an enzymatic activity of reducing substituted alkanones such as 3-methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-propan-1-one. The invention furthermore relates to nucleic acids coding for said proteins, nucleic acid constructs, vectors, genetically modified microorganisms and to methods for preparing optically active substituted alkanols, such as, for example, (S)-3-methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-(S)-propanol.
Owner:BASF AG
Recombinant microorganisms and uses therefor
The invention provides, inter alia, methods for the production of acetone, isopropanol and / or precursors of acetone and / or isopropanol by microbial fermentation of substrates comprising CO, genetically modified microorganisms of use in such methods, nucleic acids suitable for preparation of genetically modified microorganisms, a novel alcohol dehydrogenase and nucleic acids encoding same.
Owner:LANZATECH NZ INC
Expression of an active carrier from xylose in genetically modified saccharomyces cerevisae
InactiveUS20090053784A1High affinity towards xyloseFaster xyloseFungiCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCelluloseBiotechnology
The present invention confers to the ferementative yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, genetically modified by insertion of a nucleic acid sequence encoding a xylose and a glucose active transporter, the ability to assimilate xylose using a system of co-transport with protons exhibiting a high affinity for xylose. The invention is useful for the production of bioethanol from plant biomass and other lignocellulosic materials, using genetically modified microorganisms for assimilating and fermenting xylose in mixtures of hexoses and pentoses resulting from raw material of industrial interest.
Owner:FUNDACAO FACULDADE DE CIENCIAS E TECNOLOGIA
Methods, Systems And Compositions Related To Reduction Of Conversions Of Microbially Produced 3-Hydroxyproplonic Acid (3-HP) To Aldehyde Metabolites
InactiveUS20130189787A1Lower metabolismDecrease microbial enzymatic conversionBacteriaUnicellular algaeEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
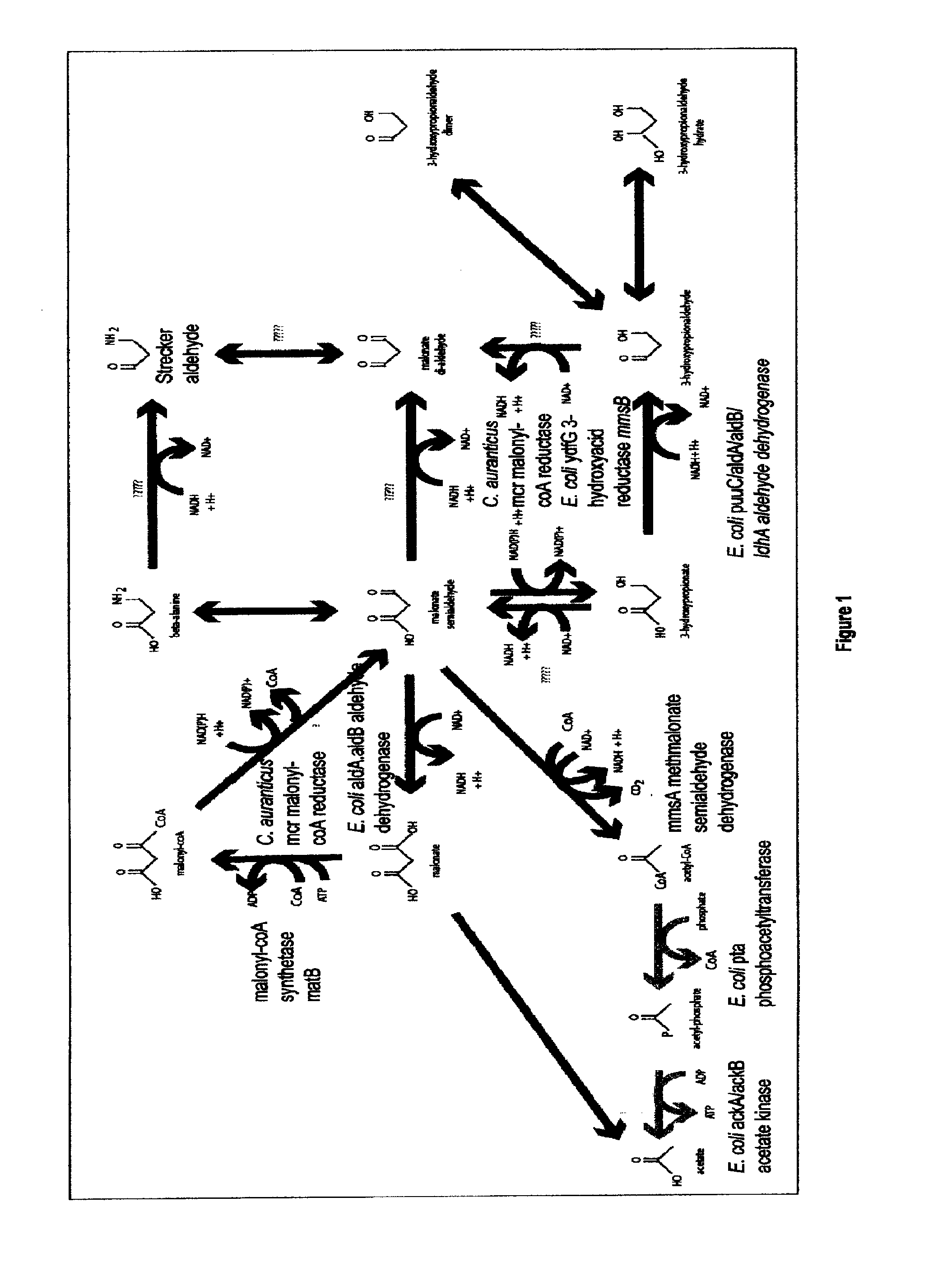
The present invention relates to methods, systems and compositions, including genetically modified microorganisms, directed to achieve decreased microbial conversion of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP) to aldehydes of 3-HP. In various embodiments this is achieved by disruption of particular aldehyde dehydrogenase genes, including multiple gene deletions. Among the specific nucleic acids that are deleted whereby the desired decreased conversion is achieved are aldA, aldB, puuC), and usg of E. coli. Genetically modified microorganisms so modified are adapted to produce 3-HP, such as by approaches described herein.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
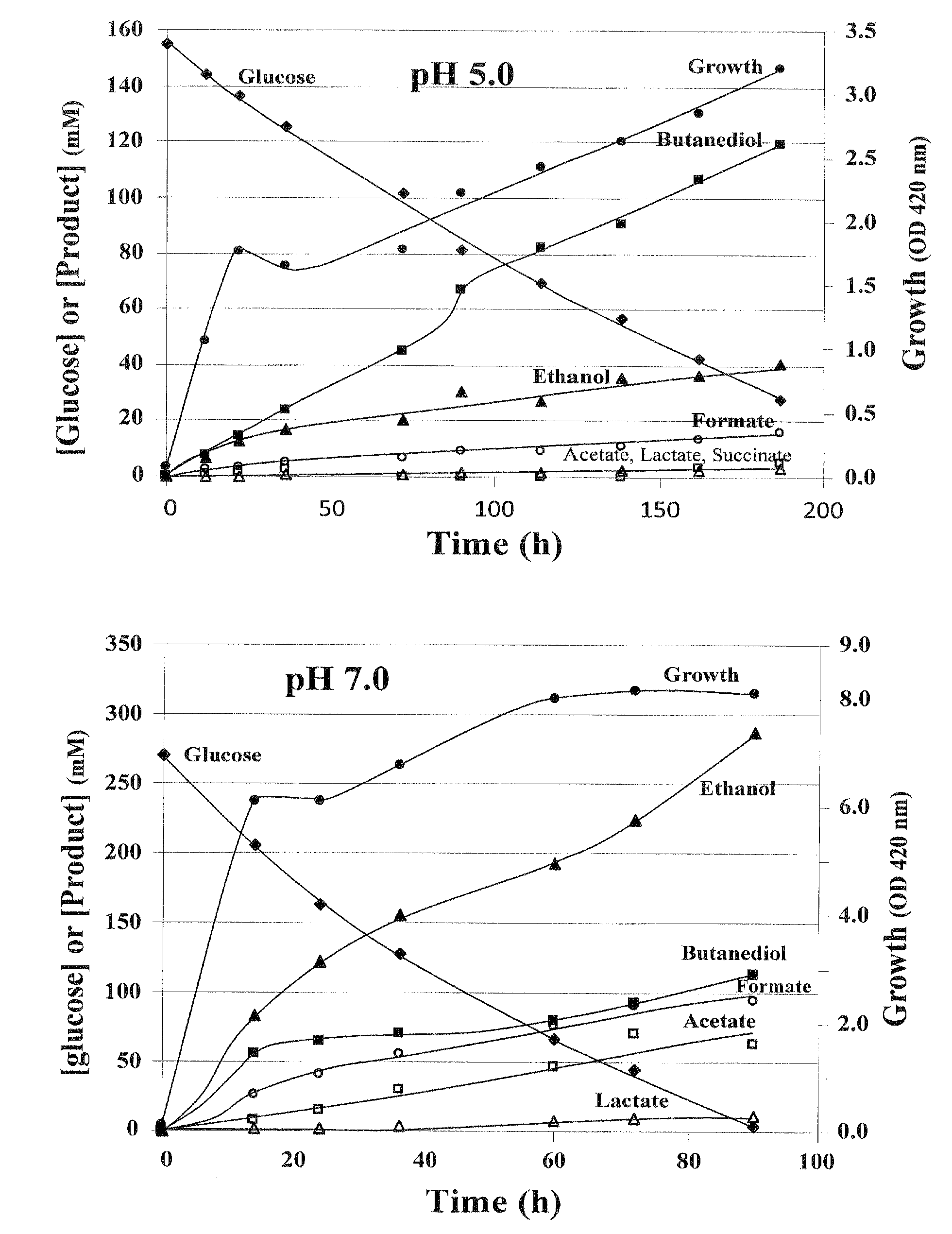
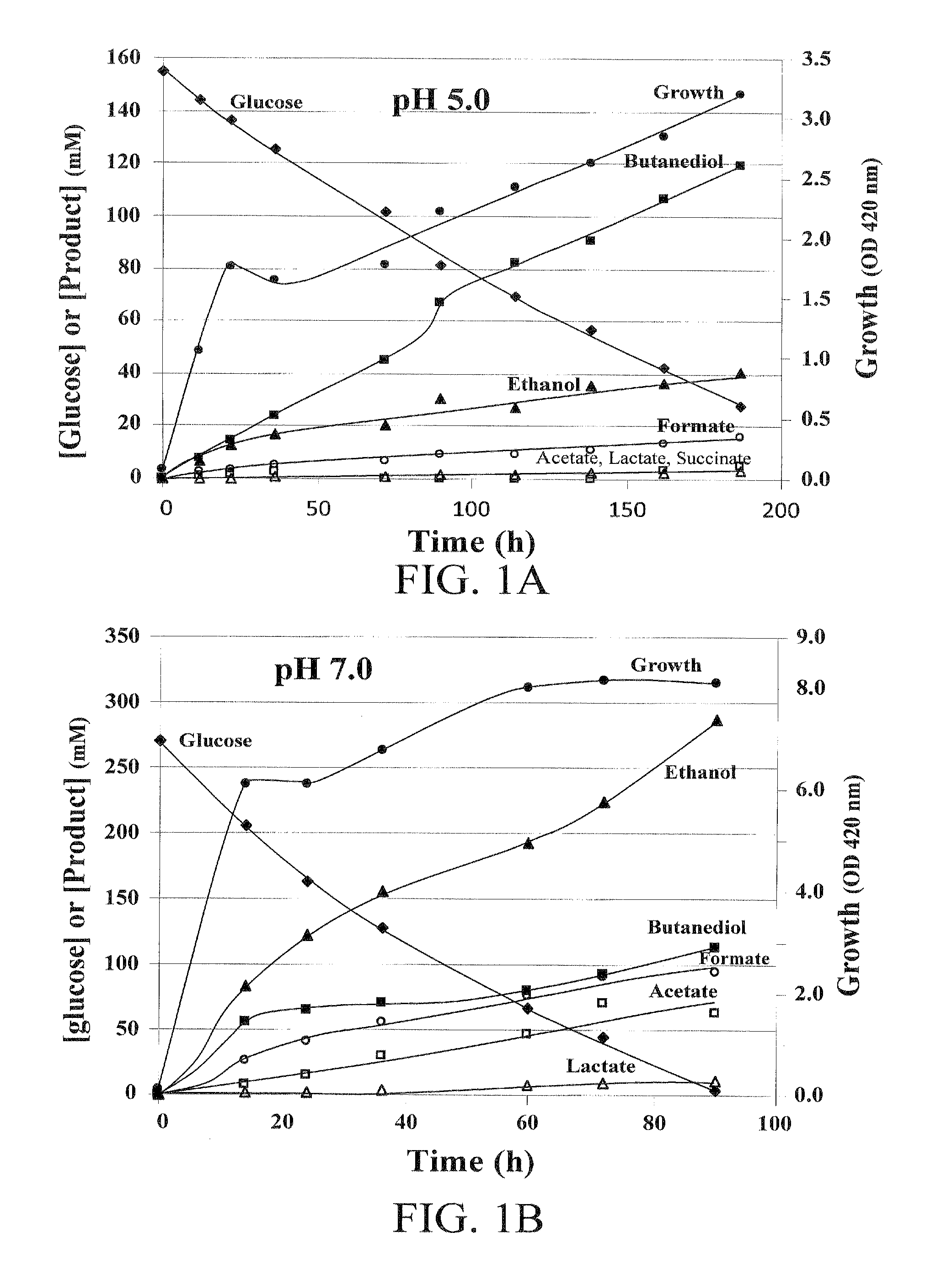
Engineering of thermotolerant bacillus coagulans for production of d(-)-lactic acid
Genetically modified microorganisms having the ability to produce D(−)-lactic acid at temperatures between 30° C. and 55° C. are provided. In various embodiments, the microorganisms may have the chromosomal lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) gene and / or the chromosomal acetolactate synthase (alsS) gene inactivated. Exemplary microorganisms for use in the disclosed methods are Bacillus spp., such as Bacillus coagulans.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Delta6-desaturases from Primulaceae, expressing plants and PUFA-containing oils
The present invention relates to an improved method for the specific production of unsaturated ω-3 fatty acids and a method for the production of triglycerides having an increased content of unsaturated fatty acids, in particular ω-3 fatty acids having more than three double bonds. The invention relates to the production of a transgenic organism, preferably a transgenic plant or a transgenic microorganism, having an increased content of fatty acids, oils or lipids having Δ6 double bonds due to the expression of a Δ6-desaturase from Primulaceae. The invention additionally relates to expression cassettes containing a nucleic acid sequence, a vector and organisms containing at least one nucleic acid sequence or an expression cassette. The invention further relates to unsaturated fatty acids and triglycerides having an increased content of unsaturated fatty acids and use thereof.
Owner:IACR ROTHAMSTED
Process and materials for production of glucosamine and n-acetylglucosamine
A biosynthetic method for producing glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine is disclosed. Such a method includes the fermentation of a genetically modified microorganism to produce glucosamine and / or N-acetylglucosamine. Also disclosed are genetically modified microorganisms that are useful for producing glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine. In addition, methods of recovering N-acetylglucosamine that has been produced by a fermentation process, including methods that result in N-acetylglucosamine of high purity, are described. Also disclosed is a method to produce glucosamine from N-acetylglucosamine.
Owner:ARKION LIFE SCI LLC
Recombinant microorganism
The invention concerns a microorganism which is genetically modified so as to i) synthesize an organic monomer by fermentation of a carbon source, and ii) depolymerize a polymer constituted at least by an organic monomer which it is capable of synthesizing. The invention also concerns a method for producing an organic monomer using a genetically modified microorganism of this type, as well as the coculture of this microorganism with another microorganism which is capable of synthesizing a polymer of interest.
Owner:CARBIOS
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids, novel biosynthesis genes, and novel plant expression constructs
The present invention relates to a method for the production of unsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds. The invention furthermore relates to the use of nucleic acid sequences SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 11 encoding polypeptides having desaturase activity in the method and for generating a transgenic organism, preferably a transgenic plant or a transgenic microorganism, with an increased content of fatty acids, oils or lipids with unsaturated C18-, C20-, or C22-fatty acids, and to their homologs or derivatives, to gene constructs encompassing these genes, and to their use alone or in combination with biosynthesis genes of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The invention also relates to multiexpression cassettes for seed-specific expression, and to vectors or organisms which encompass a desaturase gene alone or in combination with further desaturases and / or elongase genes or homologs using said expression cassettes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com