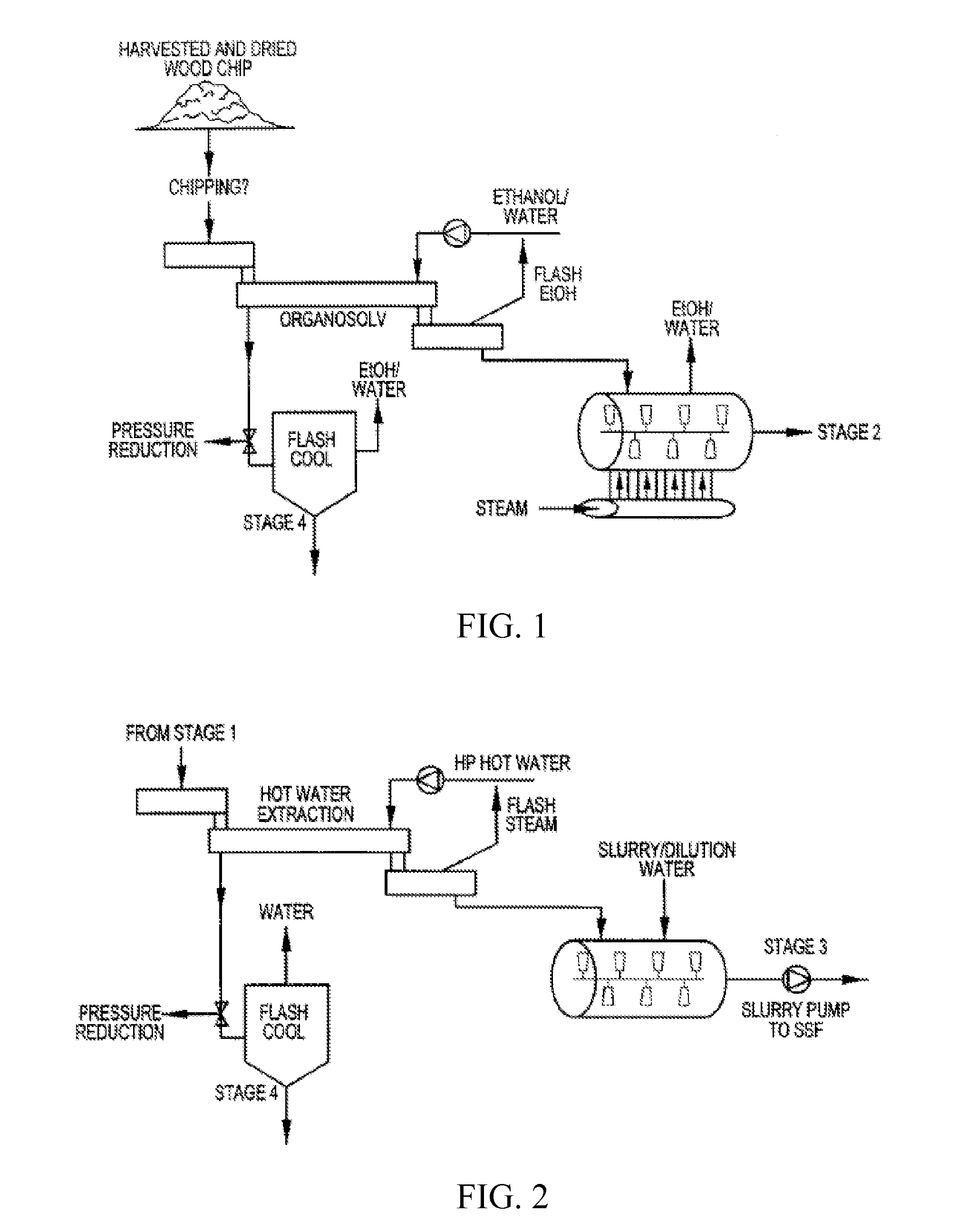
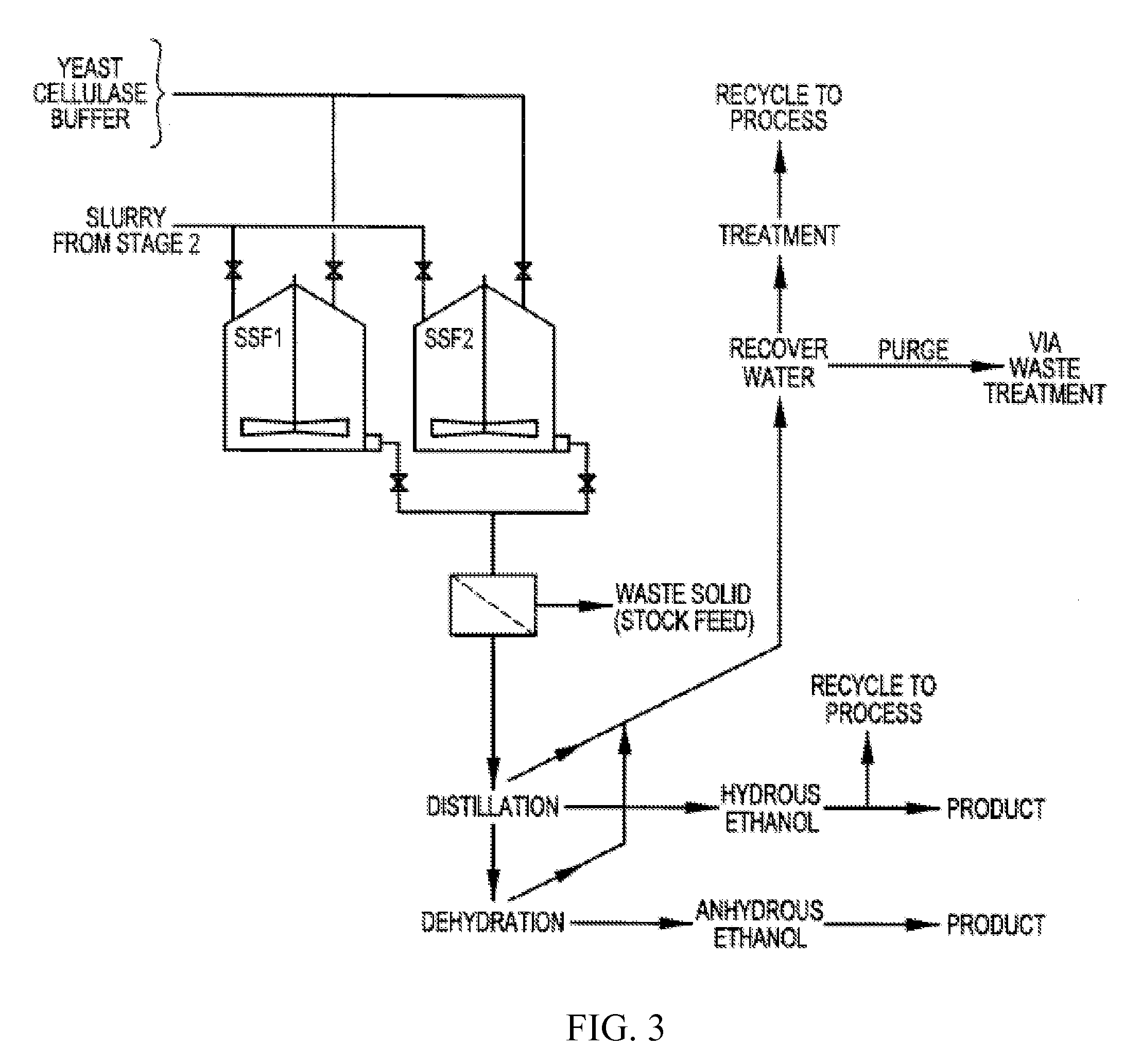
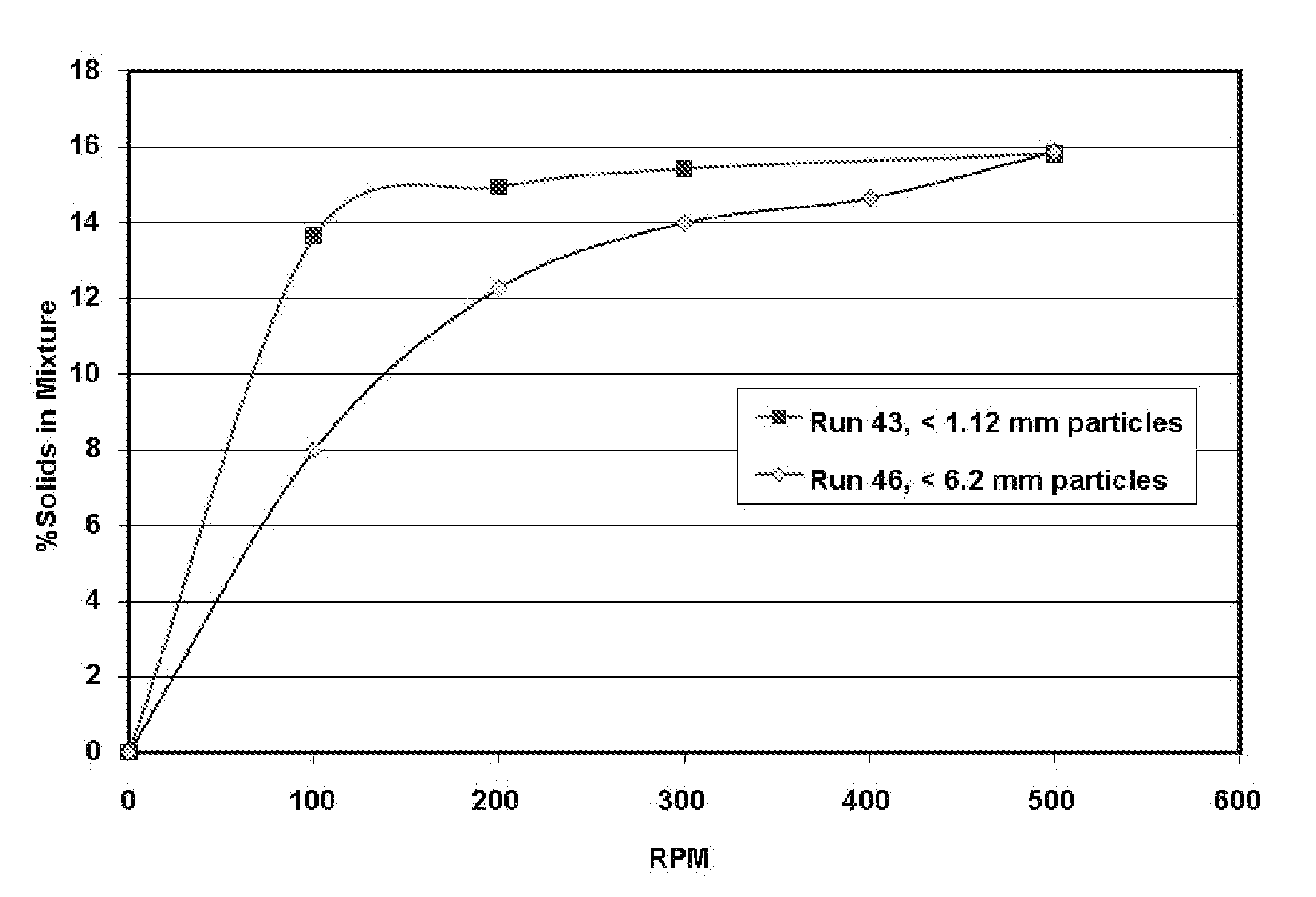
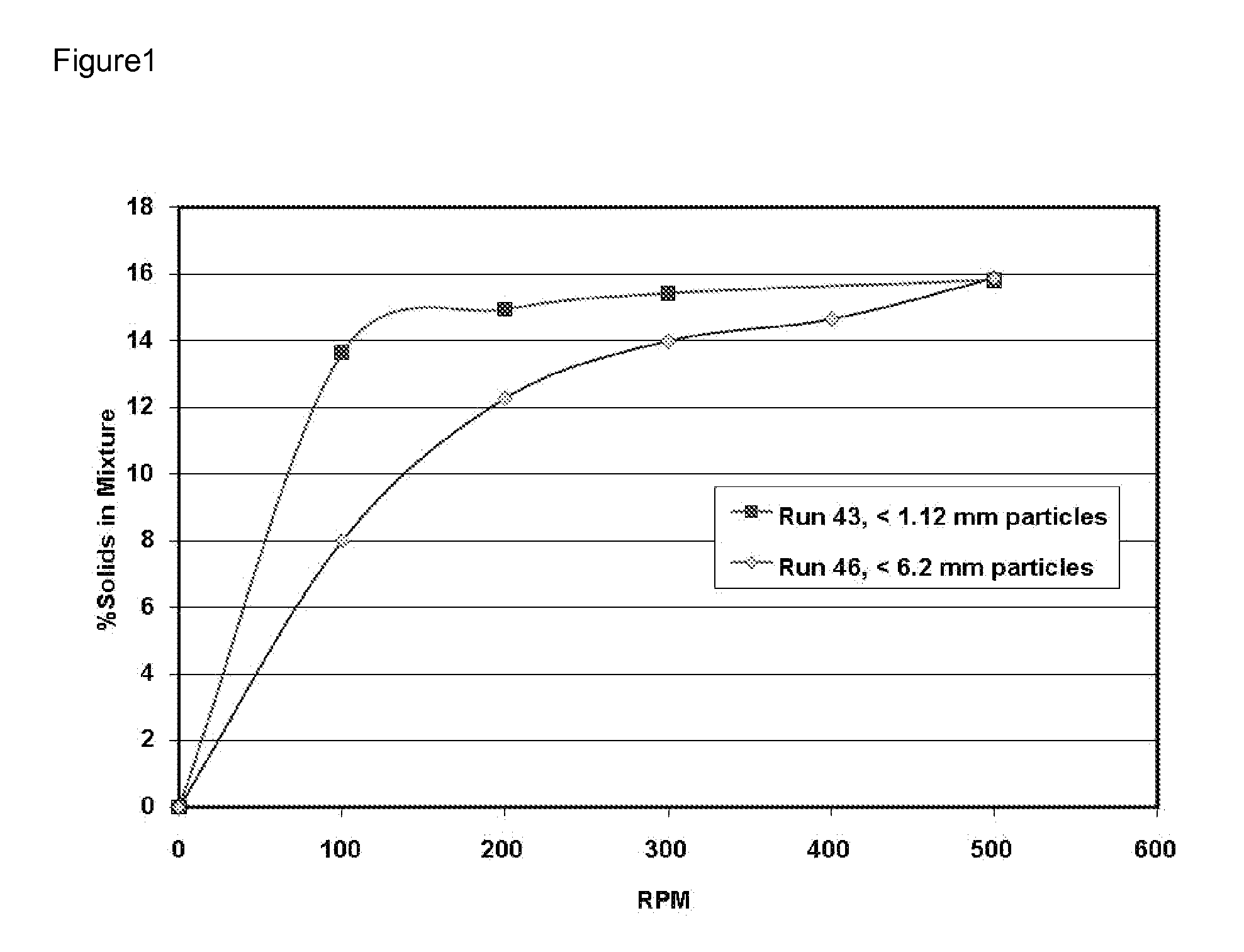
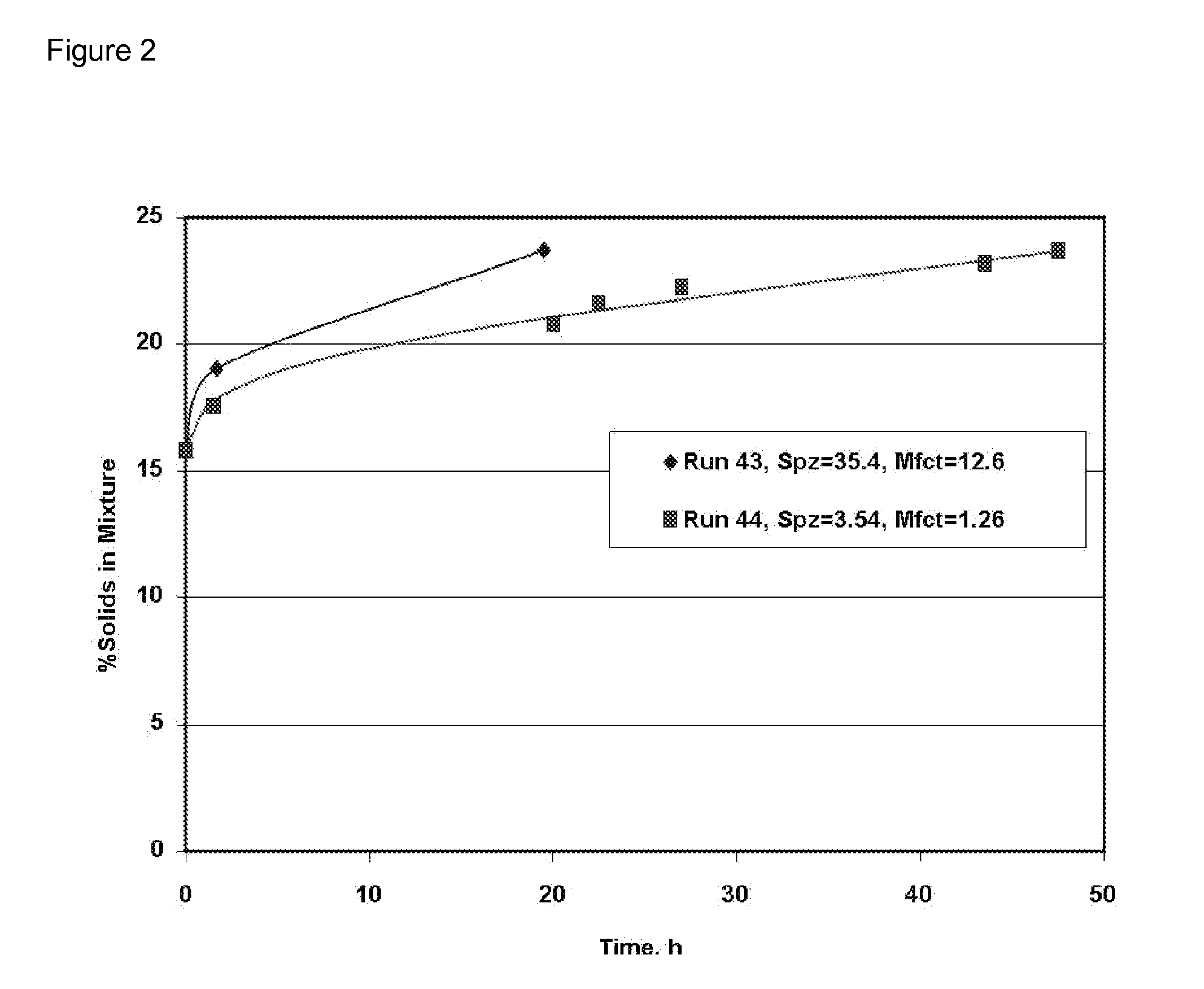
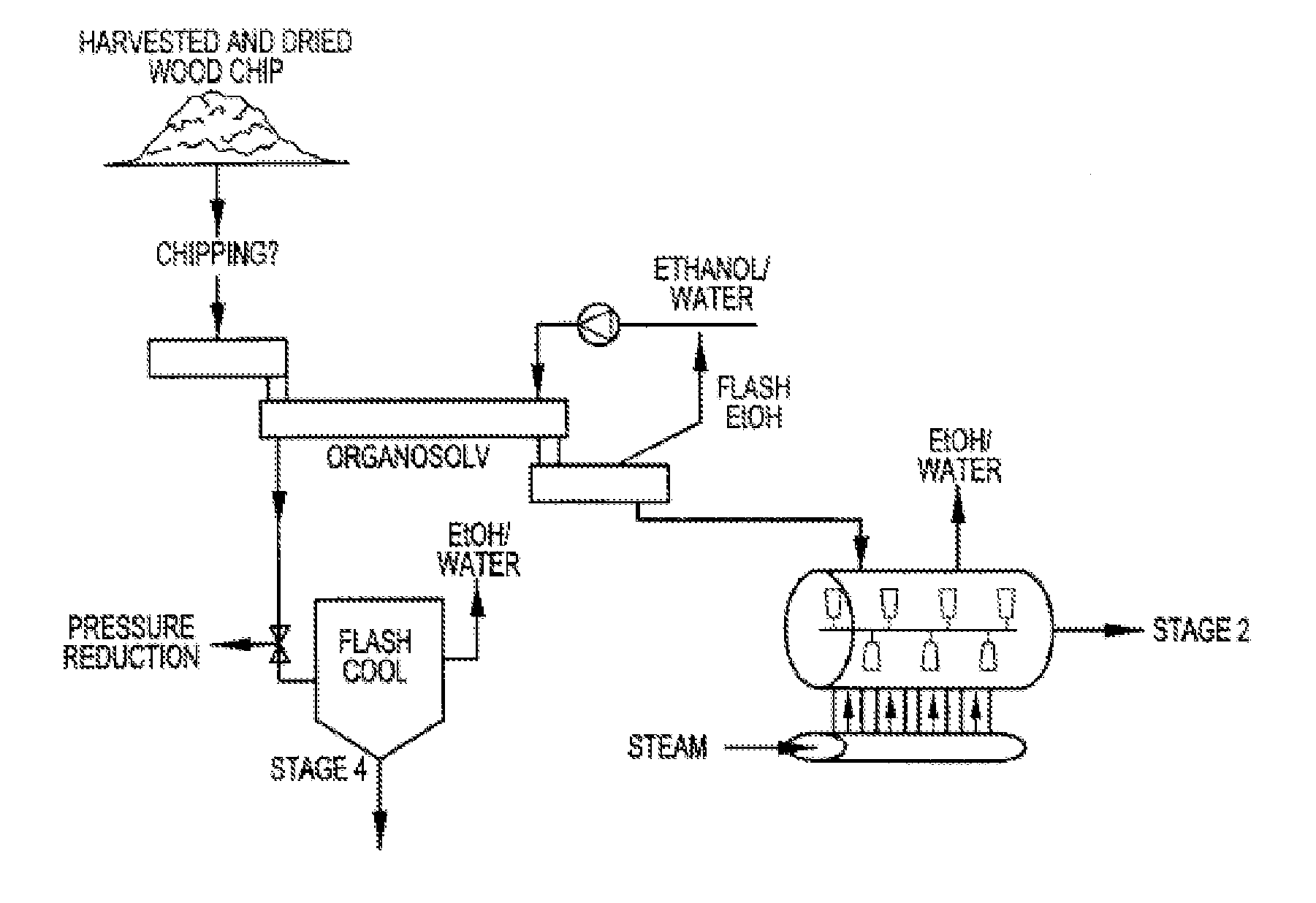
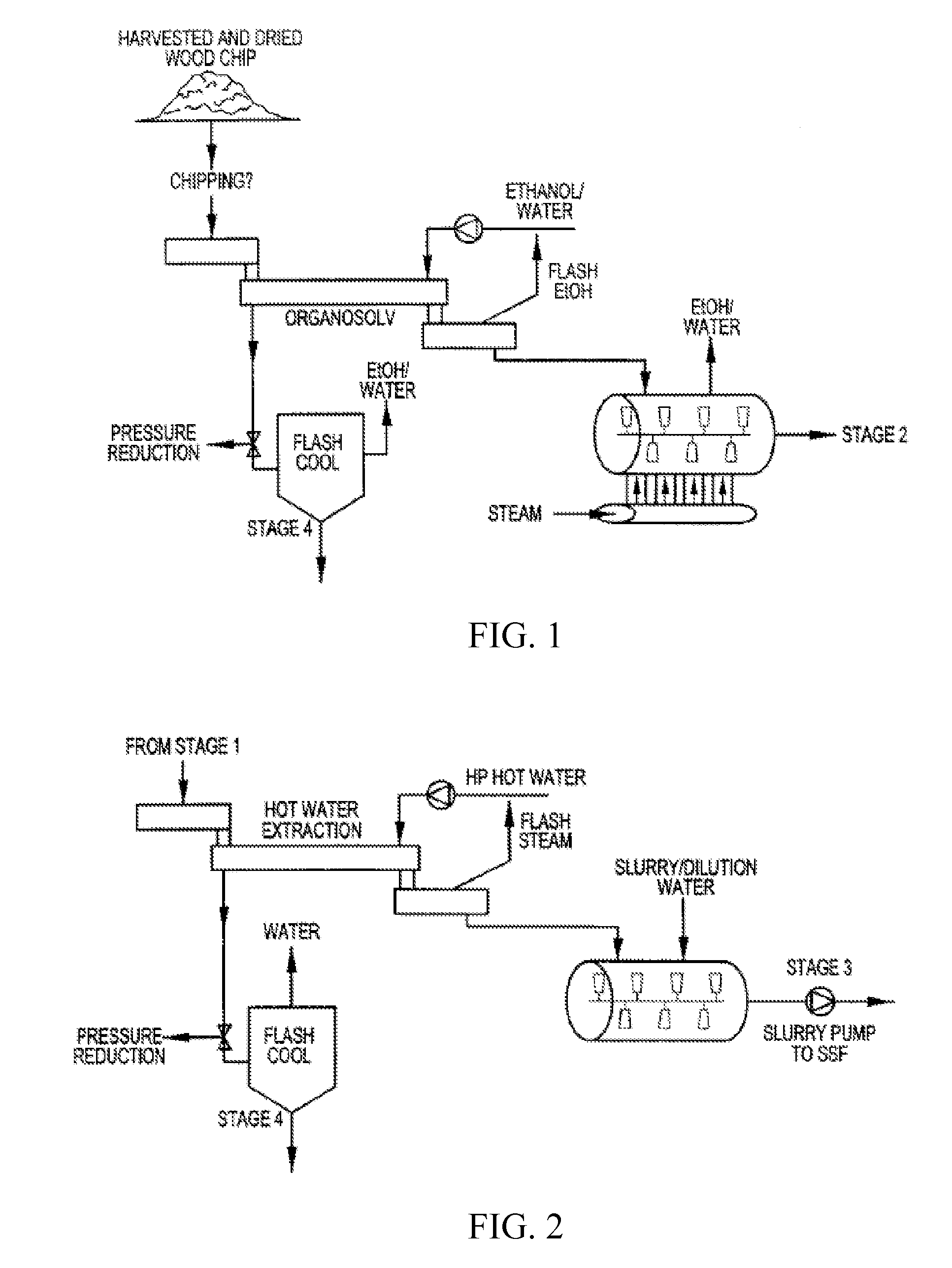
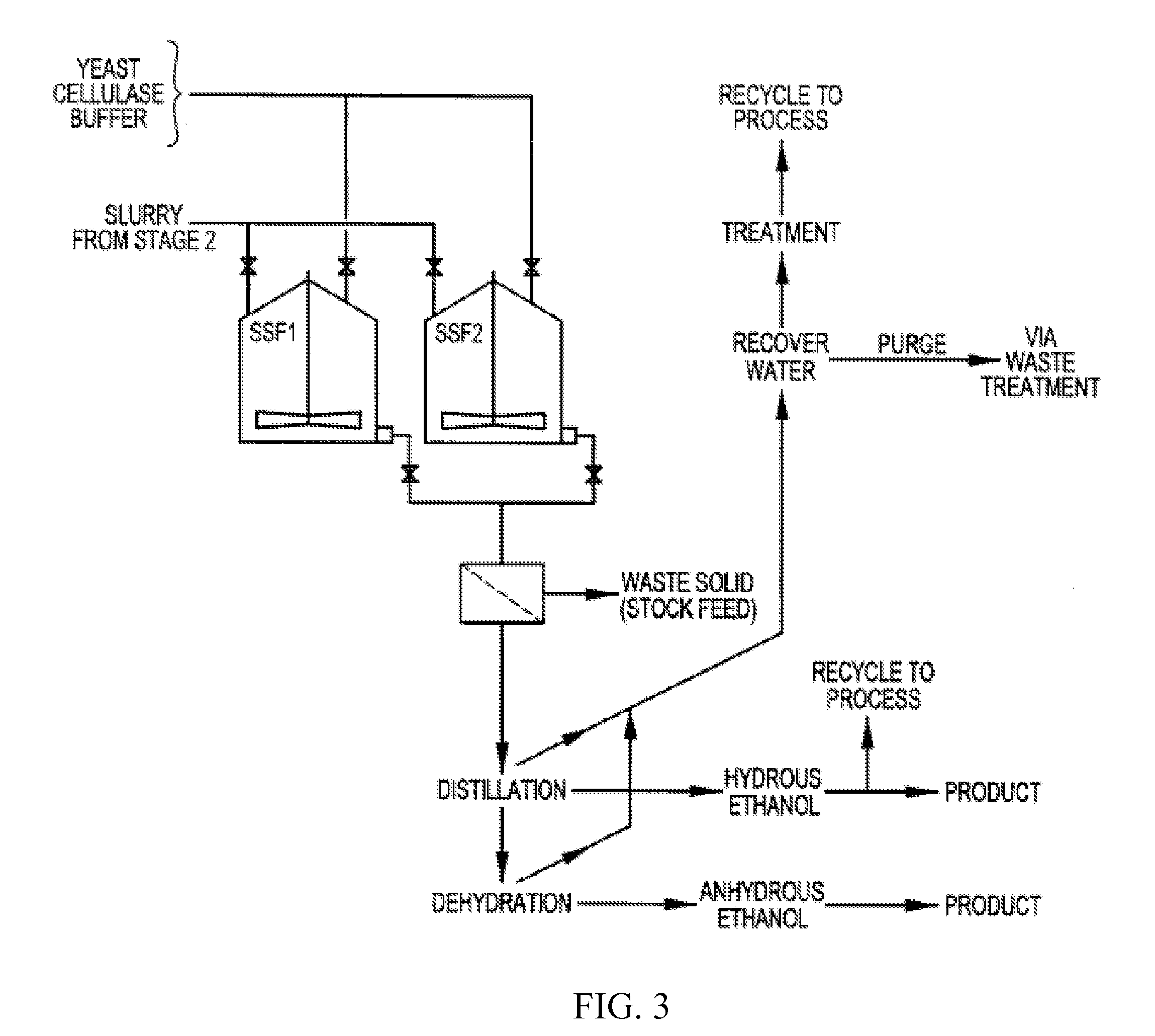
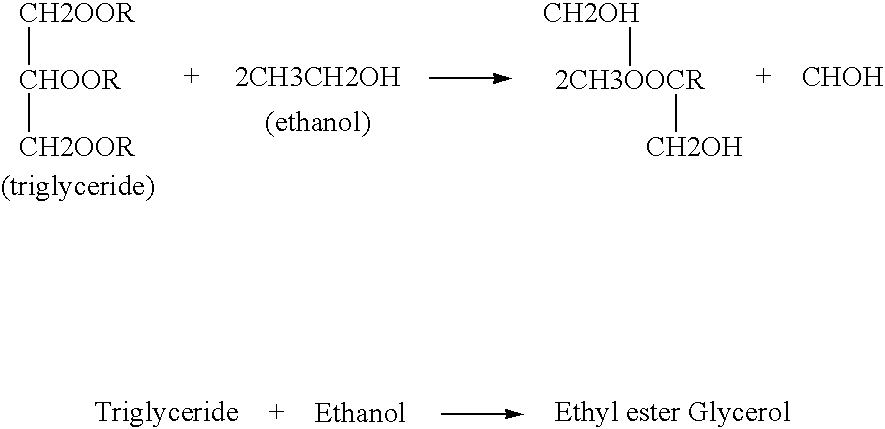
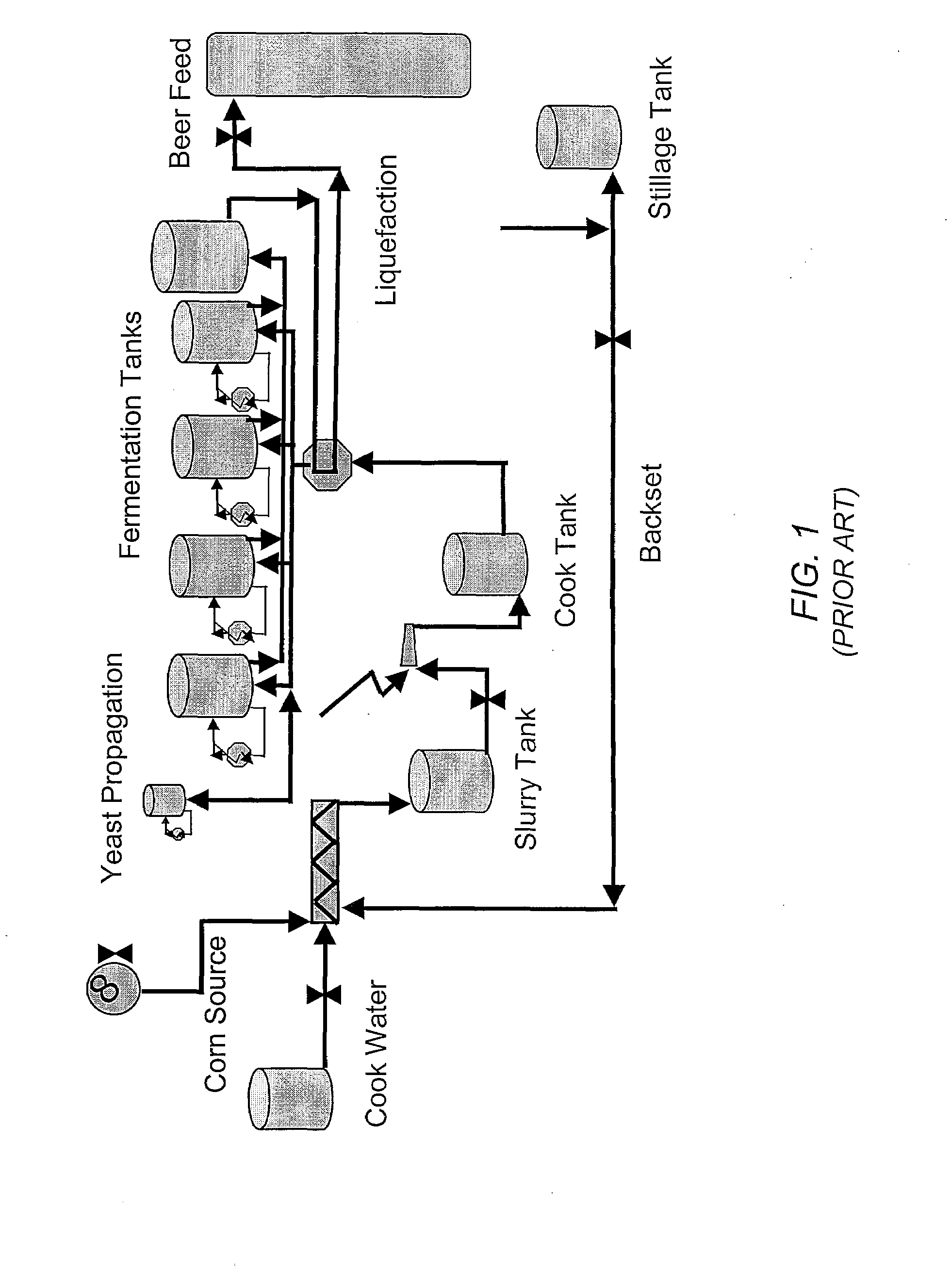
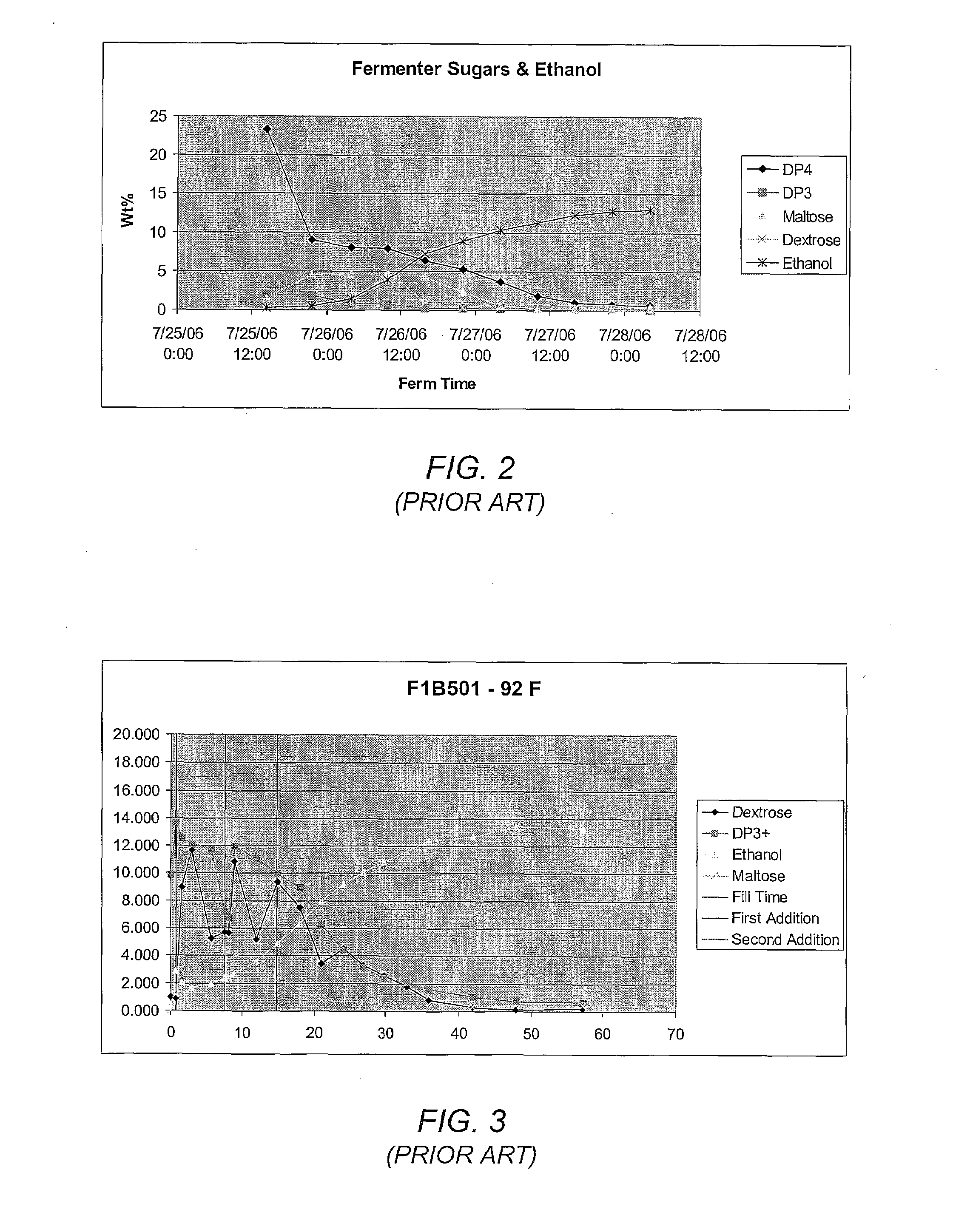
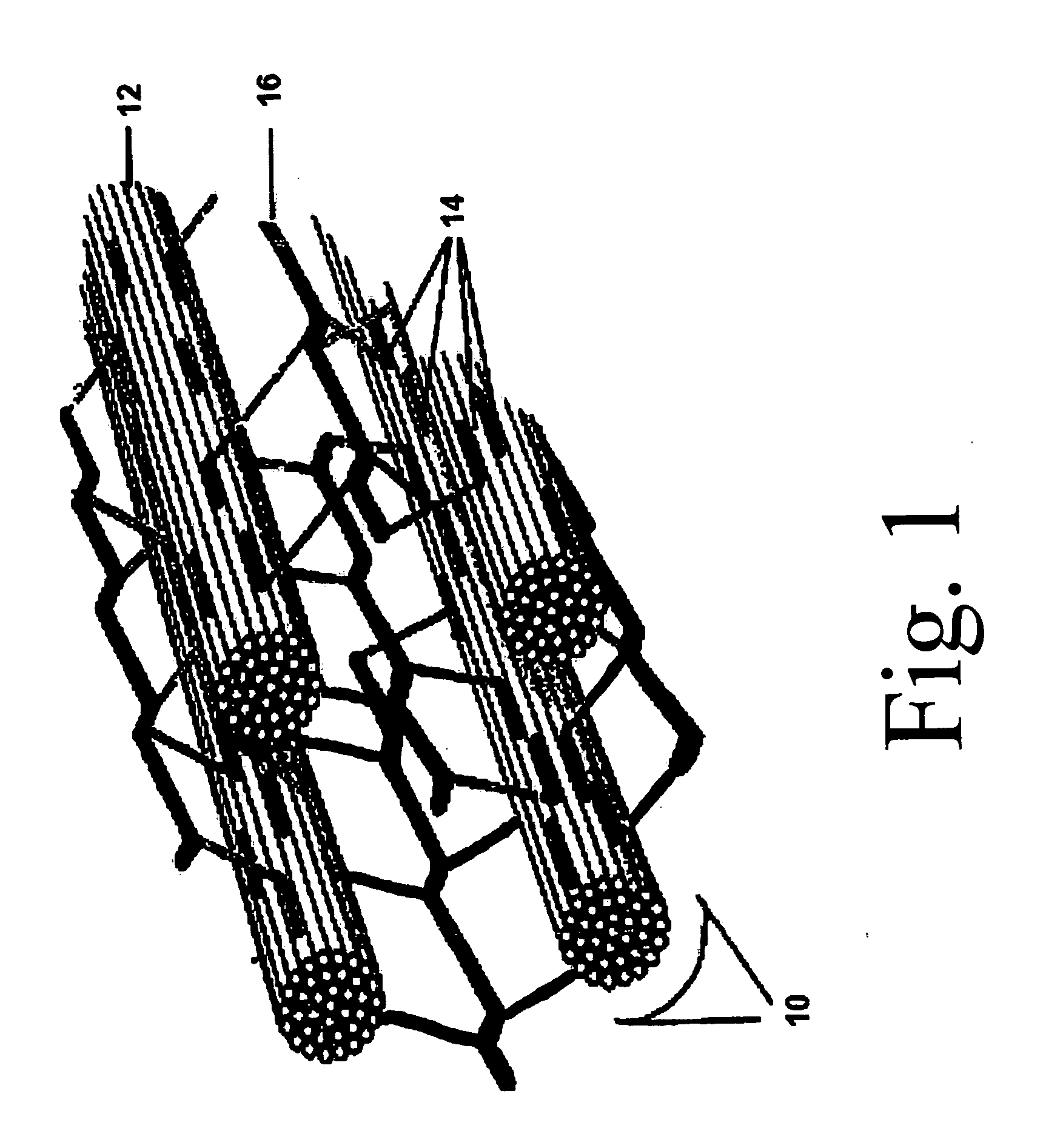
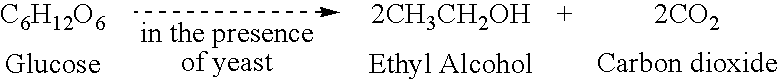Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
528 results about "Fermentable sugar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fermentable carbohydrates are the sugars that are easily fermented in your digestive system, which include oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols. They are composed of short chains of sugar molecules, making them easy to break down. Once these sugars reach your large intestine,...
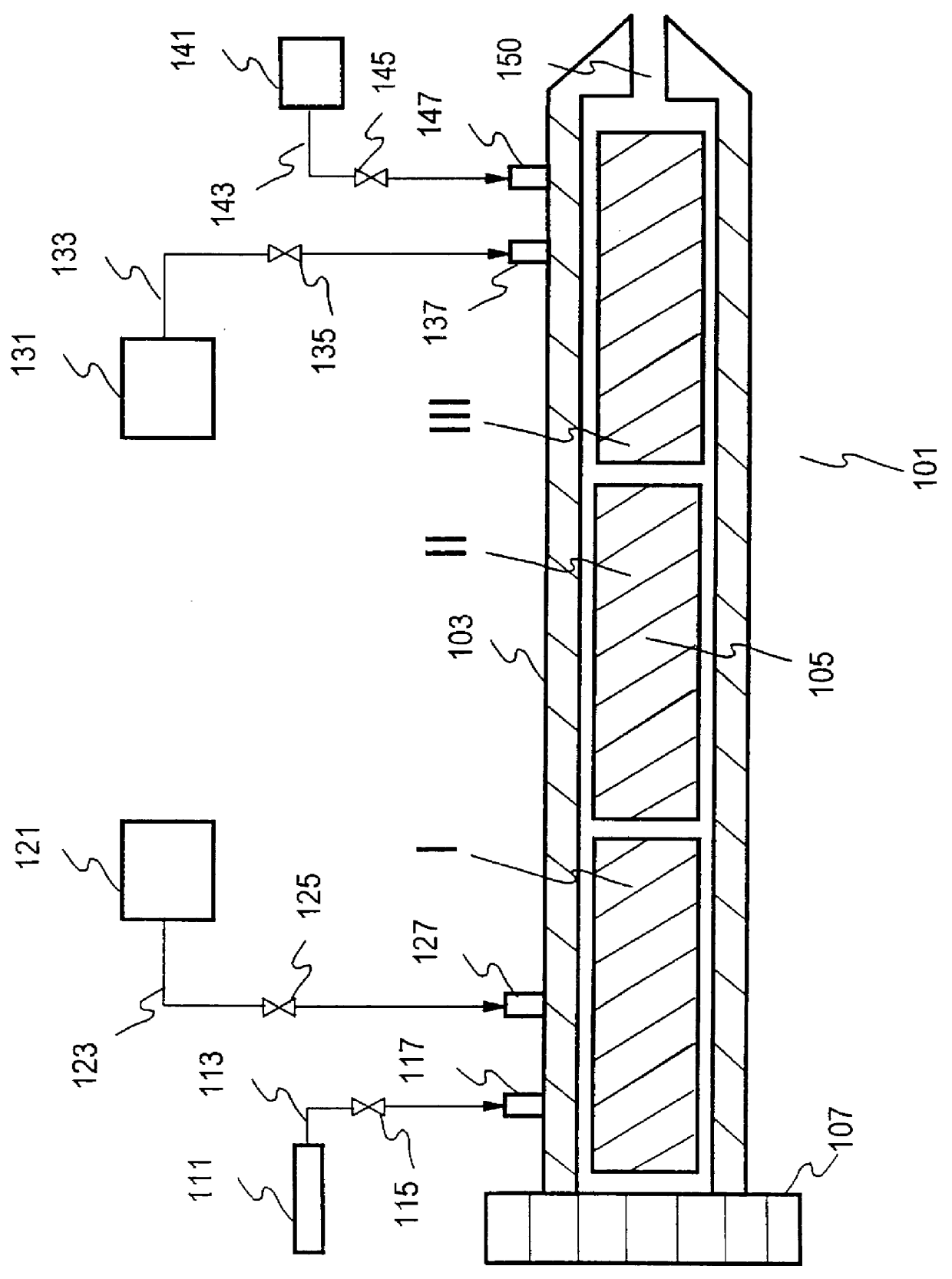
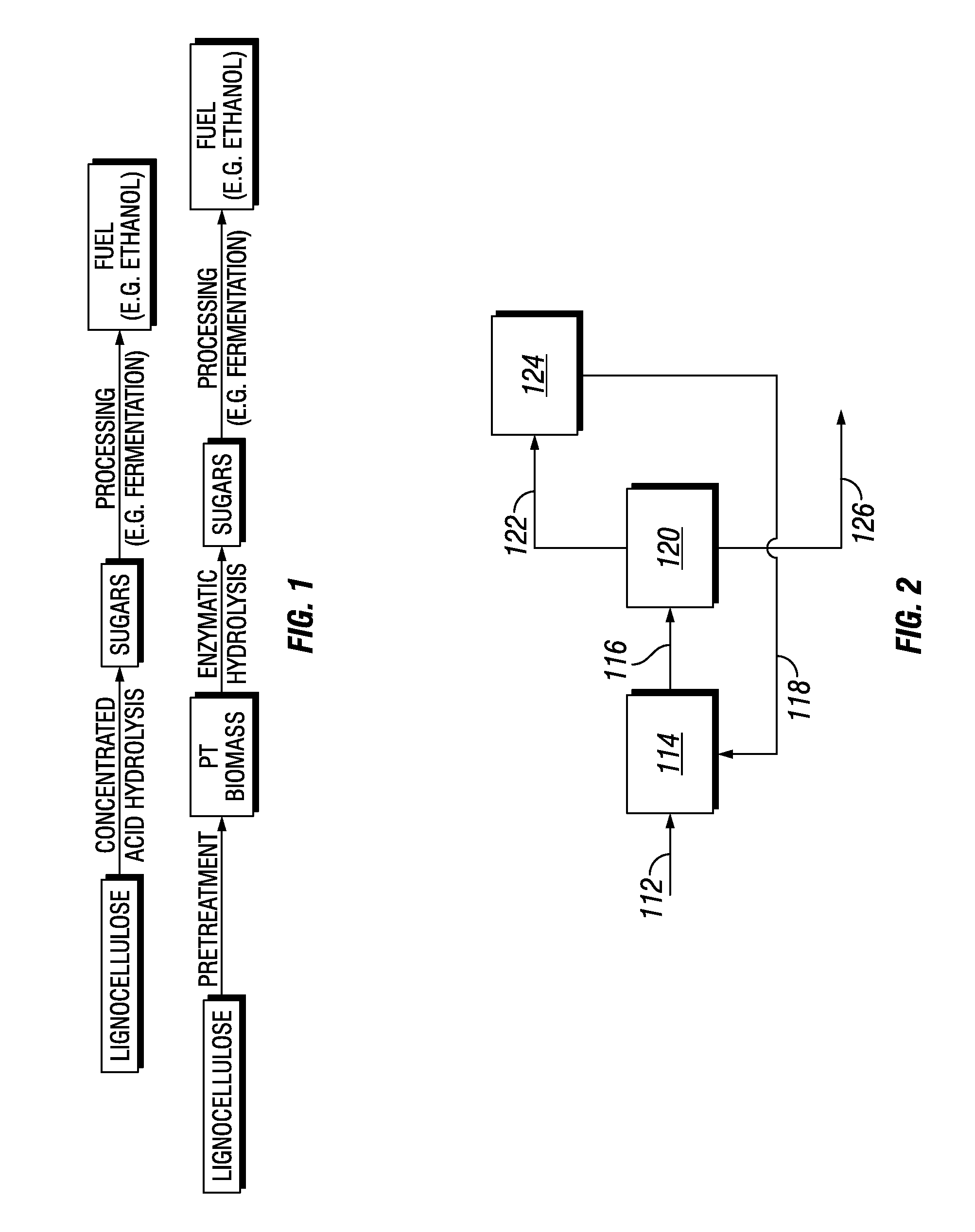
Treatment of biomass to obtain fermentable sugars
InactiveUS20070031918A1Toxic reductionReduce needBiological substance pretreatmentsByproduct vaporizationFermentable sugarCompound (substance)
Biomass is pretreated using a low concentration of aqueous ammonia at high biomass concentration. Pretreated biomass is further hydrolyzed with a saccharification enzyme consortium. Fermentable sugars released by saccharification may be utilized for the production of target chemicals by fermentation.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
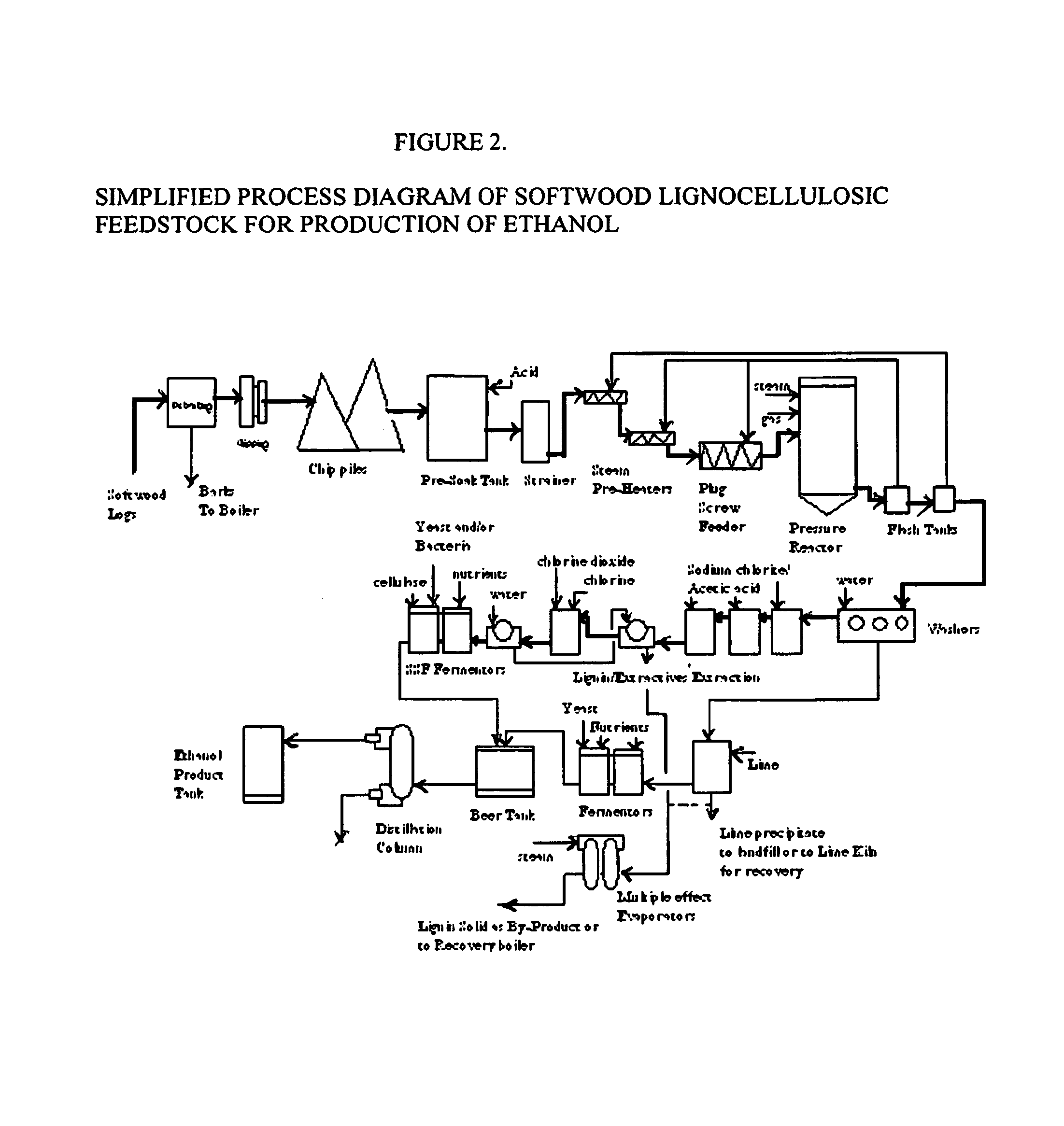
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS20080057555A1Robust and cost-effectiveImprove responseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentButanediol
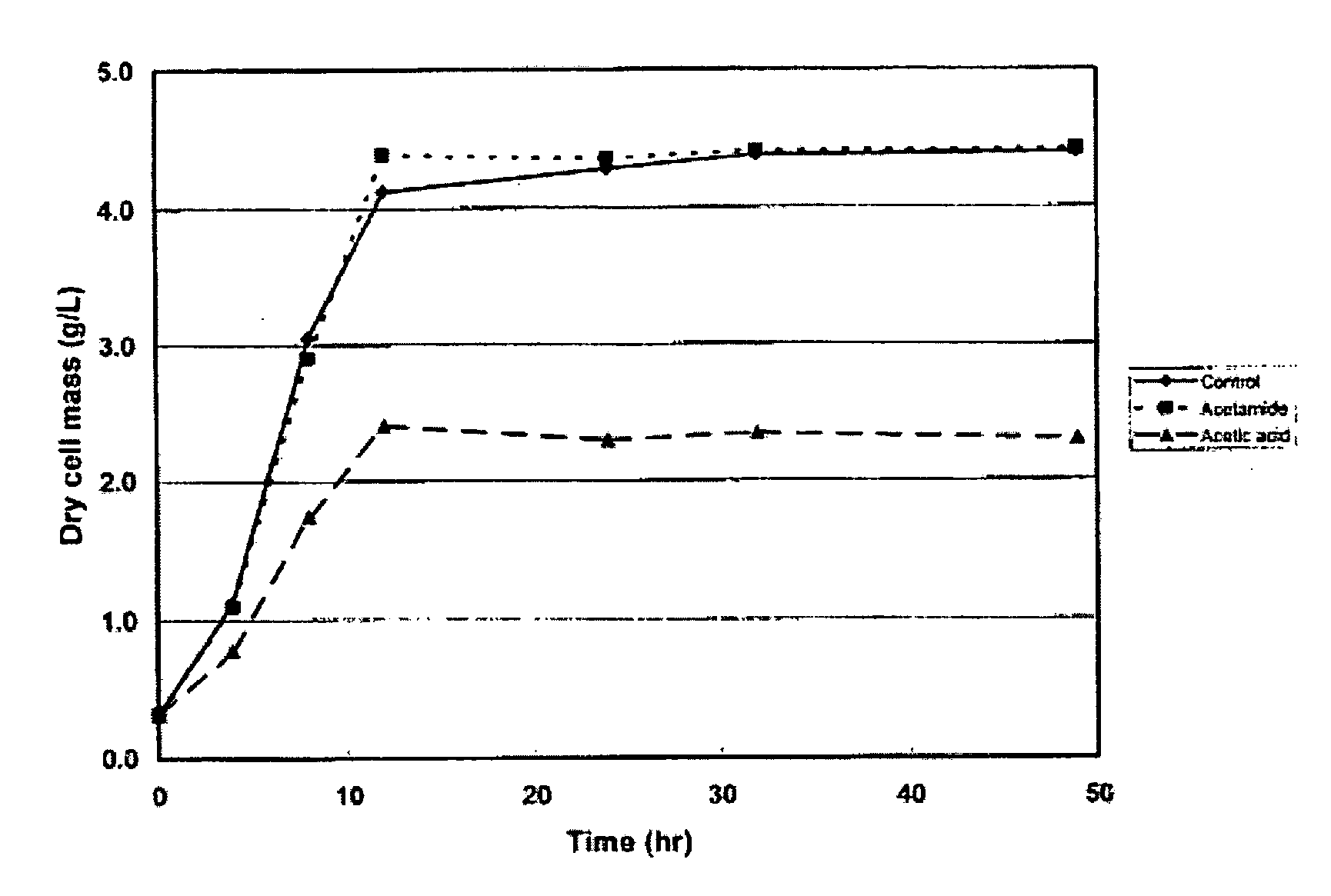
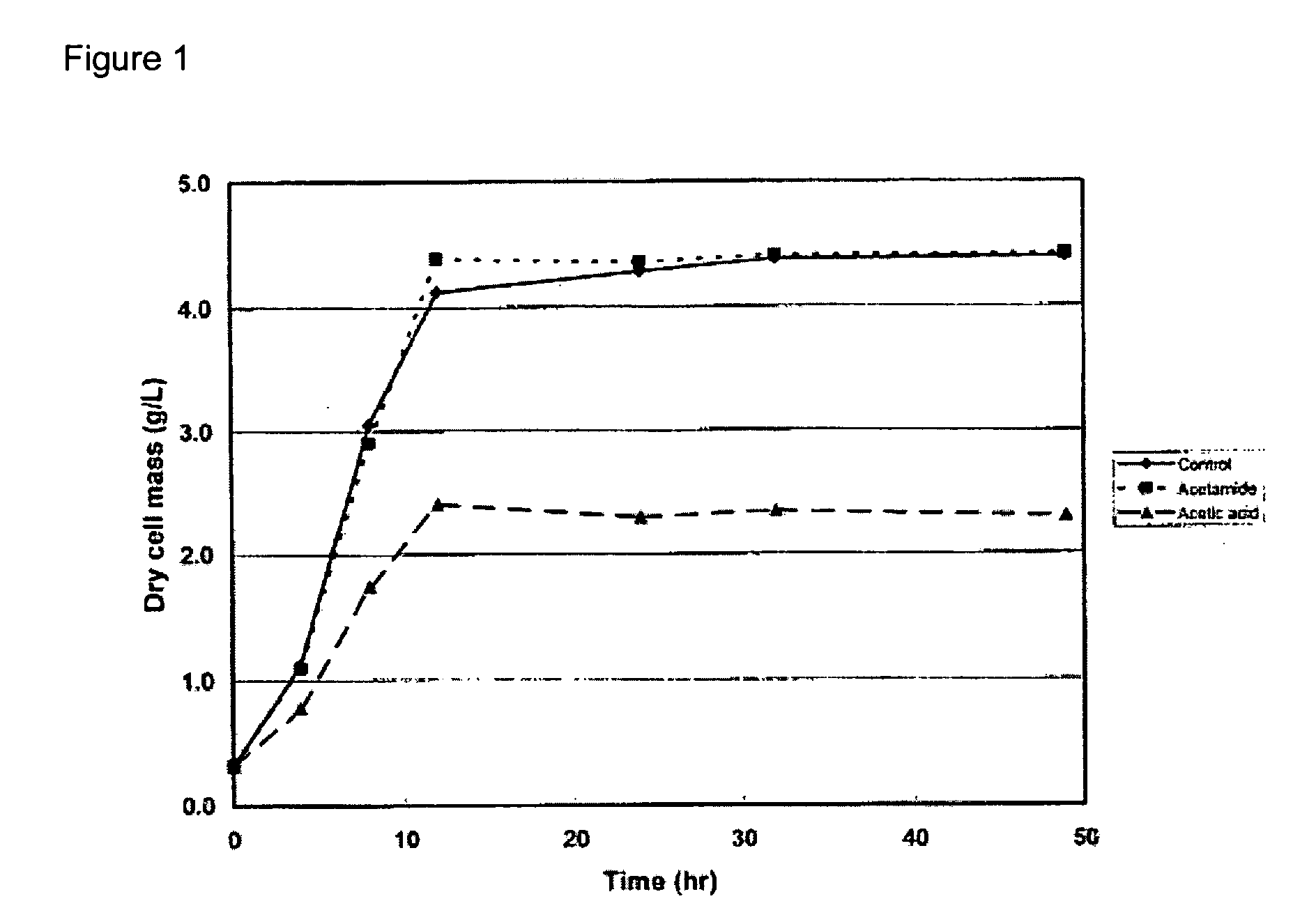
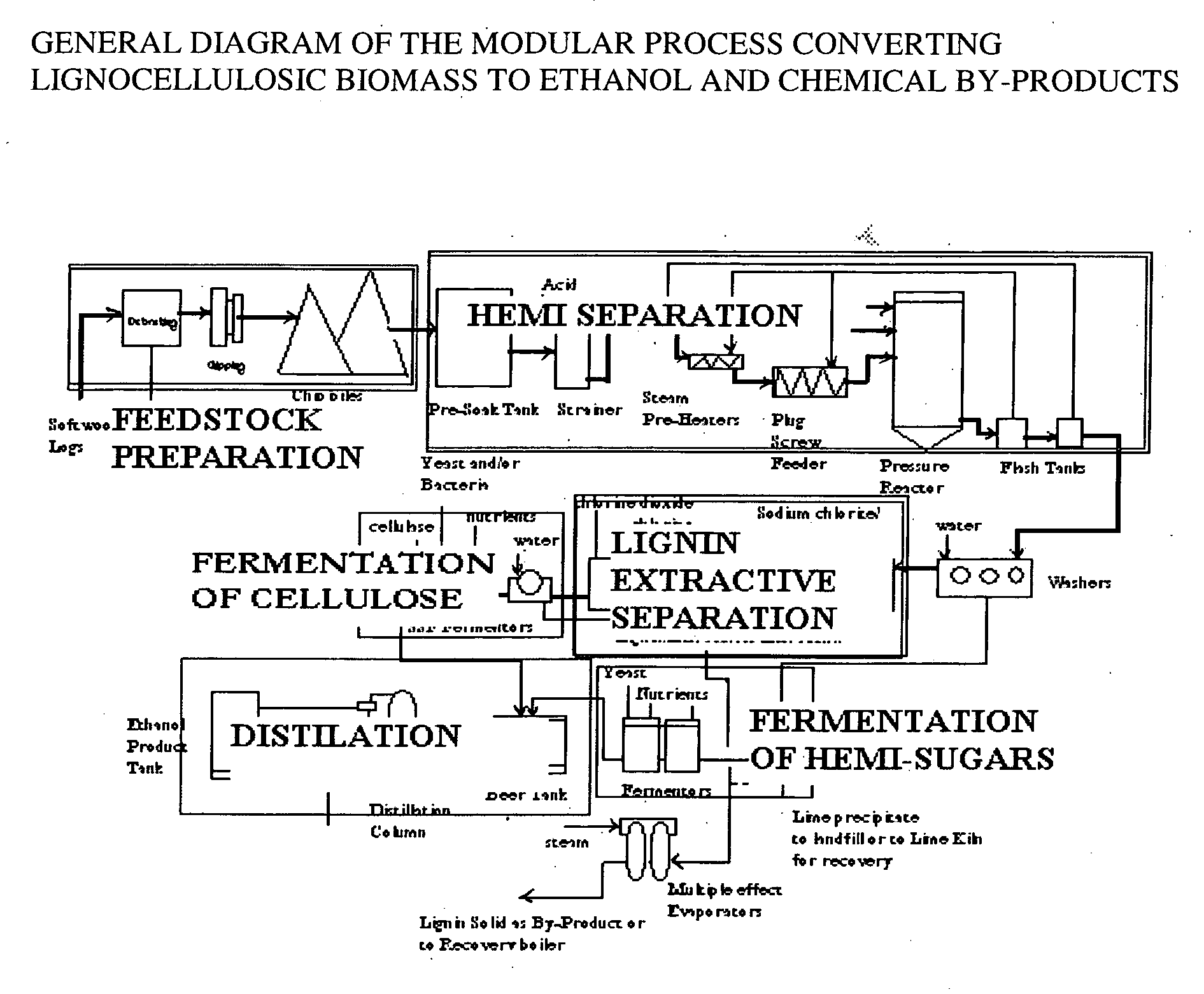
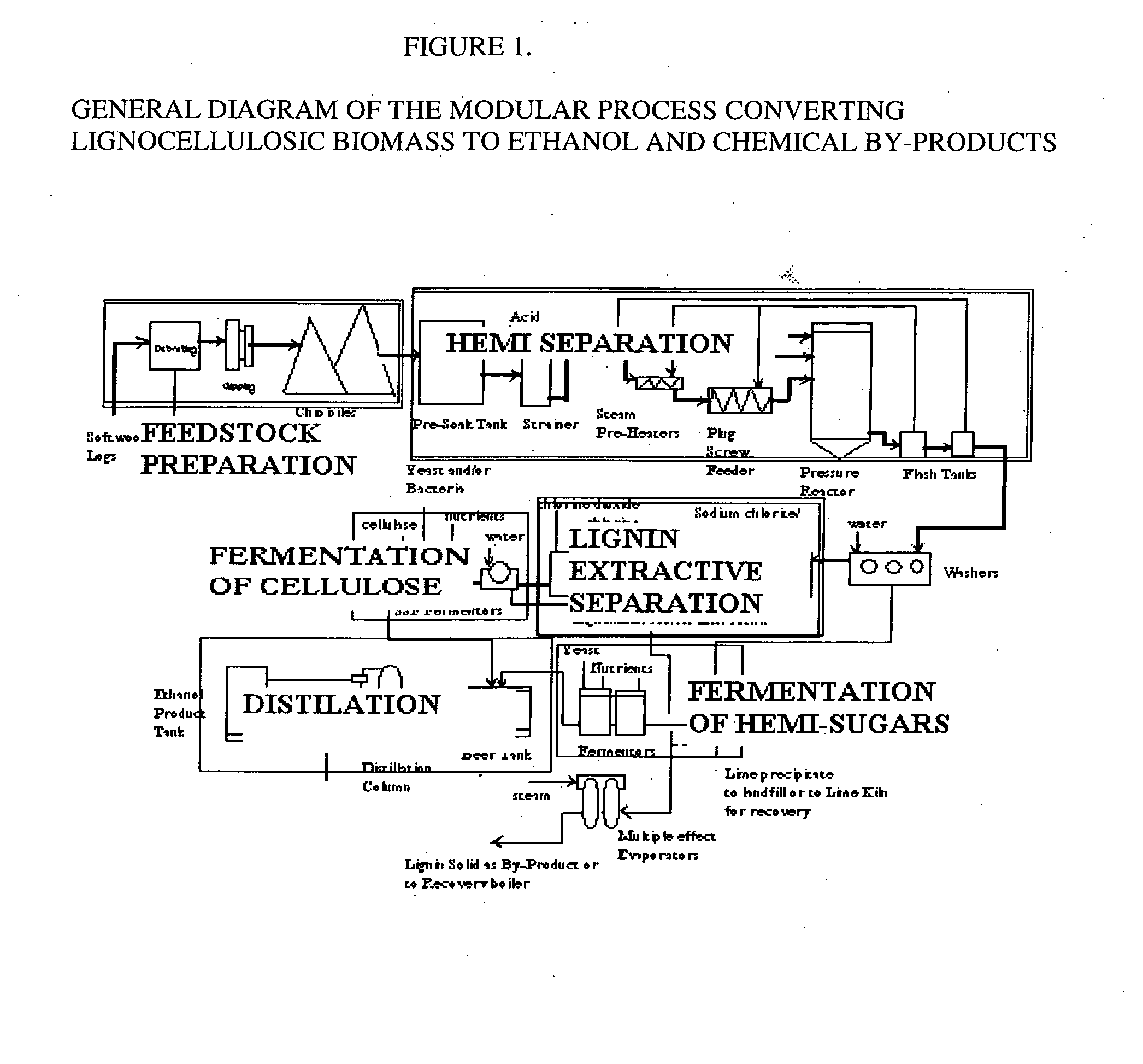
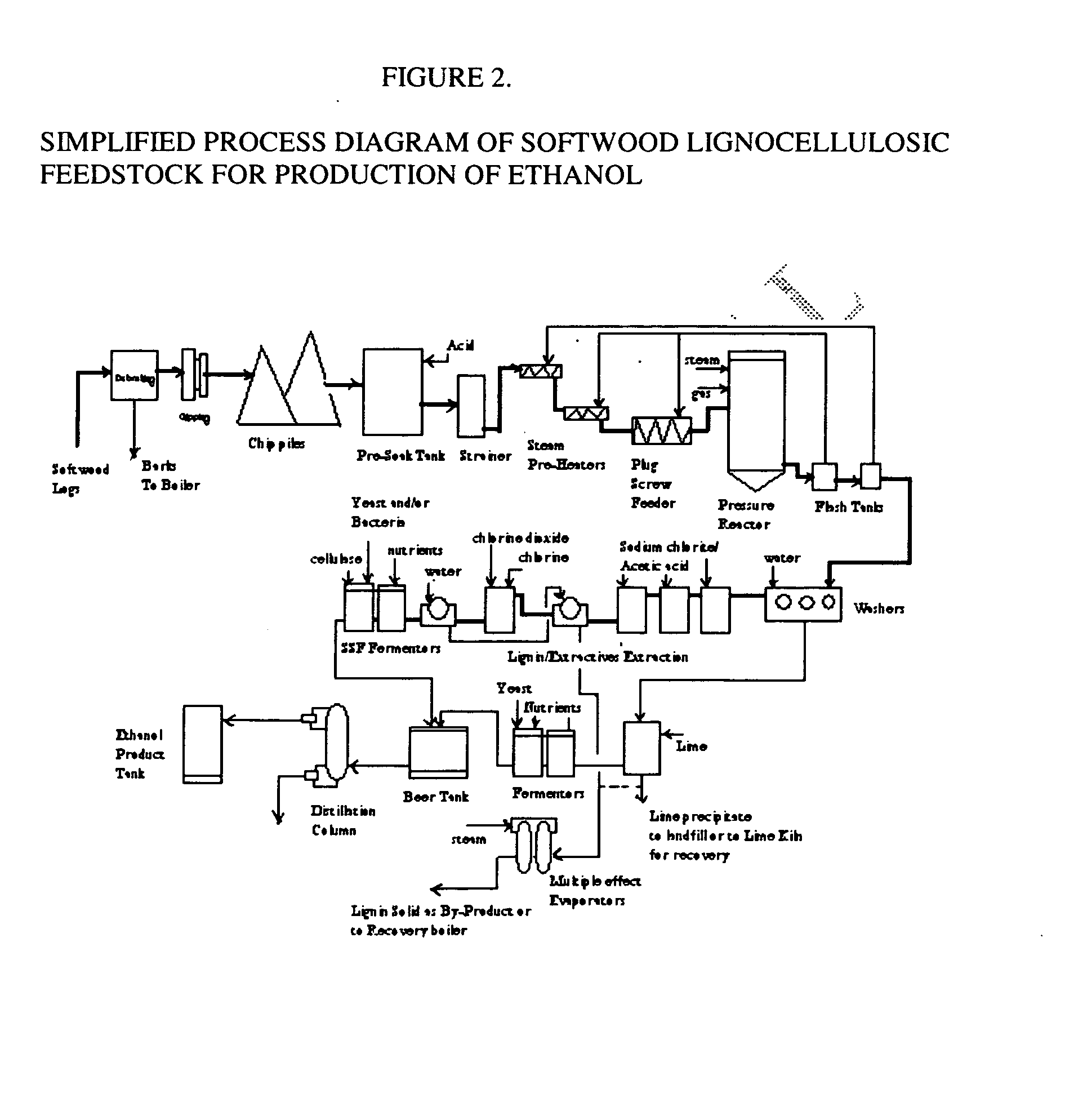
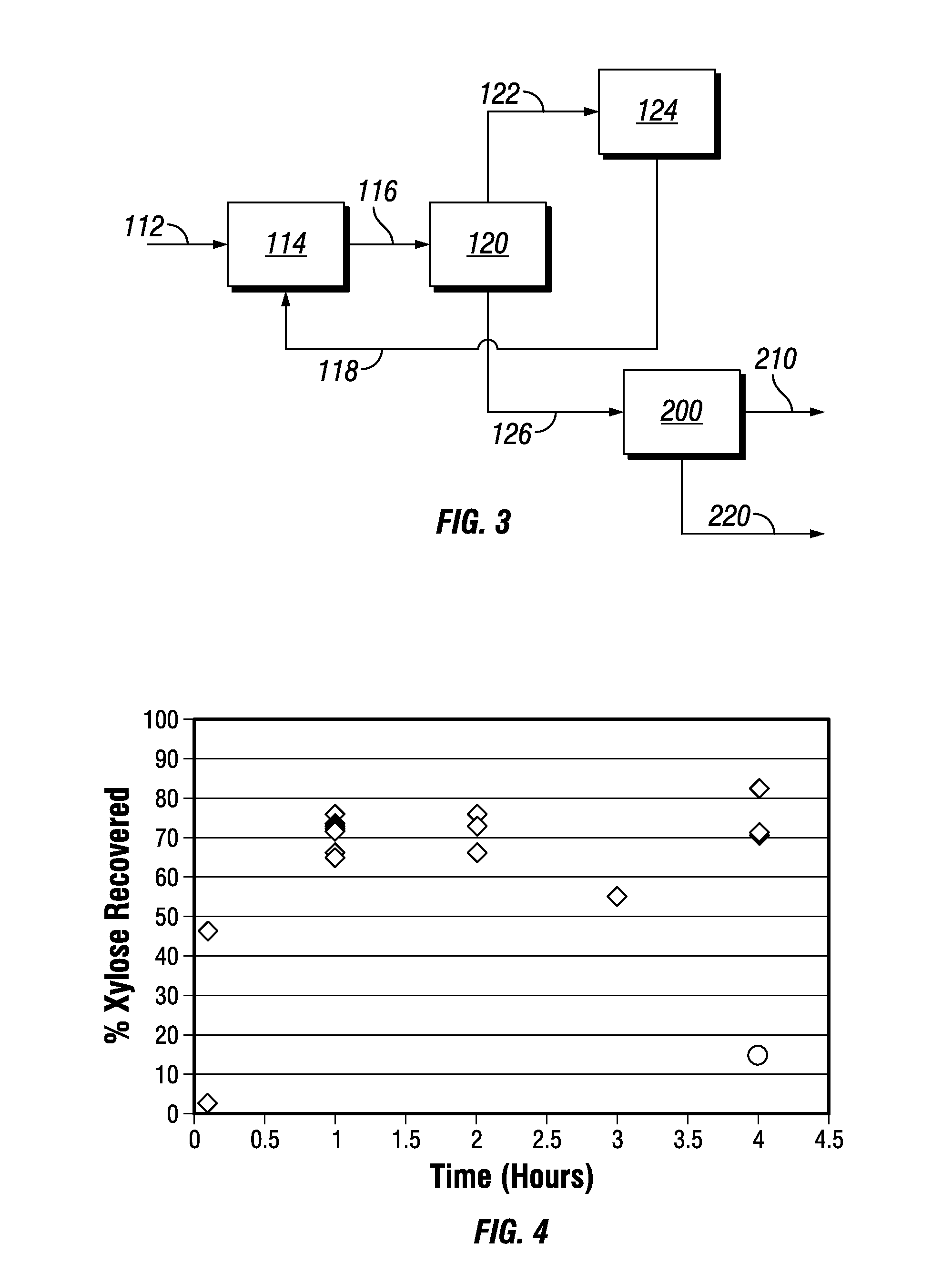
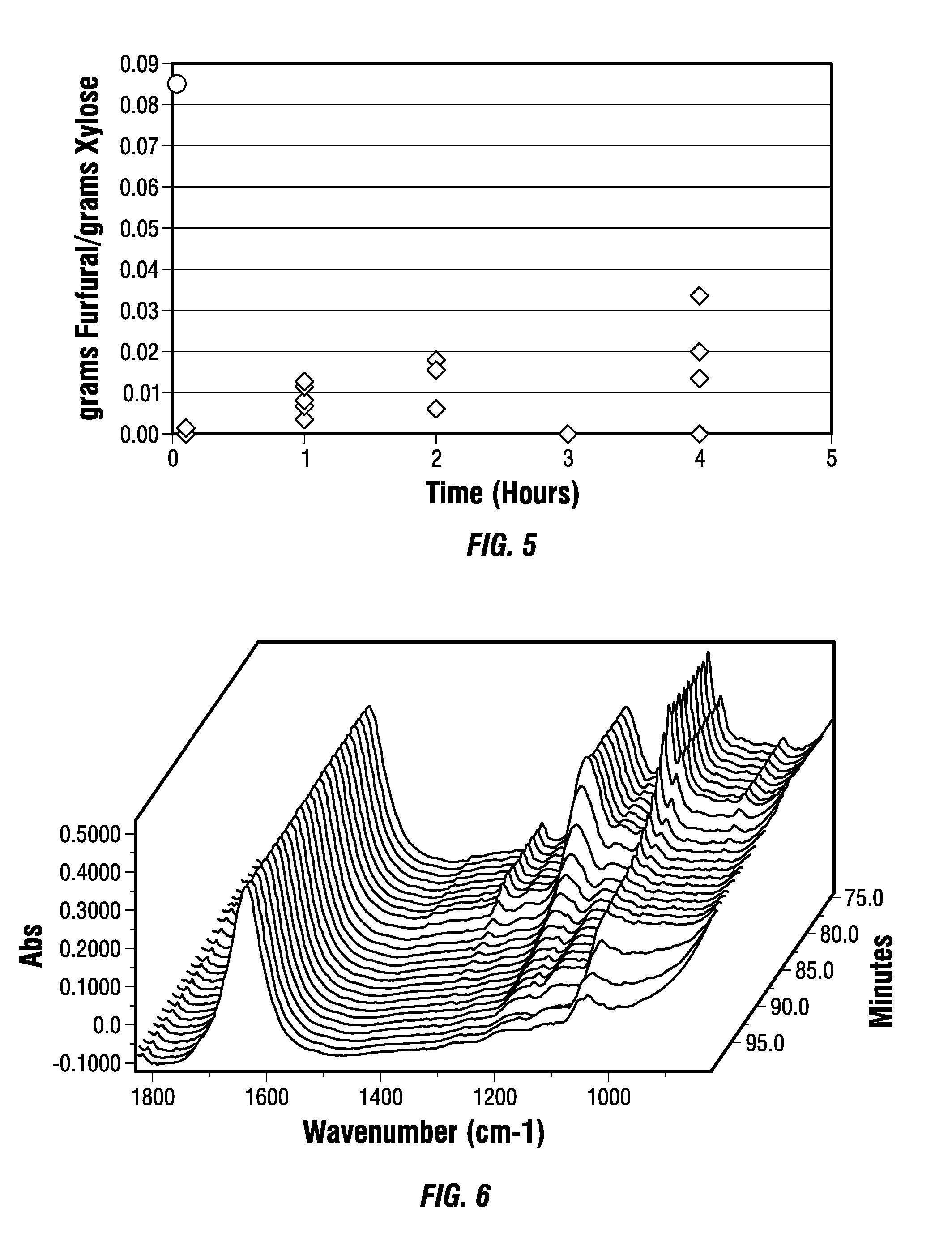
A continuous and modular process converts lignocellulosic materials for the production of ethanol principally and / or chemicals such as methanol, butanediol, propanediol, hydrocarbon fuel, etc. Renewable lignocellulosic biomass such as but not all inclusive hardwoods (gum, beech, oak, sweet gum, poplar, eucalyptus, etc.), soft woods (pines, firs, spruce, etc.), corn stovers, straws, grasses, recycled papers, waste products from pulp and paper mills, etc can be used as feedstock. The process is designed to be modular and the feed entry point can be selected to adapt to different biomass feedstock. Lignocellulosic biomass such as hardwood and softwood are subjected to chemical / pressure treatment stages using potent and selective chemicals such as sodium chlorite / acetic acid (anhydrous) and chlorine / chlorine dioxide to separate the main components—lignin, cellulose (glucose) and hemicelluloses (xylose, arabinose, galactose)—into three process streams. The separated carbohydrates are further subjected to washing, cleaning, neutralization, and / or mild hydrolysis and subsequently fermented to produce ethanol. Residual lignin and extractives remained with the cellulose are removed by chemical treatment steps to enhance the fermentations of cellulose. Pre-hydrolysate after neutralization to neutralize and remove toxic components such as acetic acid, furfural, phenolics, etc. containing (xylose, arabinose, galactose) and hexoses (glucose) can be either separately or together with the purified cellulosic fraction fermented to produce ethanol. Approximately 100 gallons of ethanol, suitable to be used as a fuel, can be produced from one dried ton of wood. Significant amount of lignin are separated as a by-product and can be converted to hydrocarbon fuel, surfactant, drilling aid, or can be incinerated for generation of power and steam.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
Integration of alternative feedstreams for biomass treatment and utilization
InactiveUS20070037259A1High solid contentBiological substance pretreatmentsByproduct vaporizationHigh concentrationDry weight
The present invention provides a method for treating biomass composed of integrated feedstocks to produce fermentable sugars. One aspect of the methods described herein includes a pretreatment step wherein biomass is integrated with an alternative feedstream and the resulting integrated feedstock, at relatively high concentrations, is treated with a low concentration of ammonia relative to the dry weight of biomass. In another aspect, a high solids concentration of pretreated biomass is integrated with an alternative feedstream for saccharifiaction.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
Novel Fungal Enzymes
This invention relates to novel enzymes and novel methods for producing the same. More specifically this invention relates to a variety of fungal enzymes. Nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, compositions, recombinant and genetically modified host cells, and methods of use are described. The invention also relates to a method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars with enzymes that degrade the lignocellulosic material and novel combinations of enzymes, including those that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. The invention also relates to a method to release cellular content by degradation of cell walls. The invention also relates to methods to use the novel enzymes and compositions of such enzymes in a variety of other processes, including washing of clothing, detergent processes, biorefining, deinking and biobleaching of paper and pulp, and treatment of waste streams.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Ethanol production with dilute acid hydrolysis using partially dried lignocellulosics
InactiveUS20030199049A1Increase sugar yieldImprove digestibilityBiofuelsWaste based fuelCelluloseGrowth phase
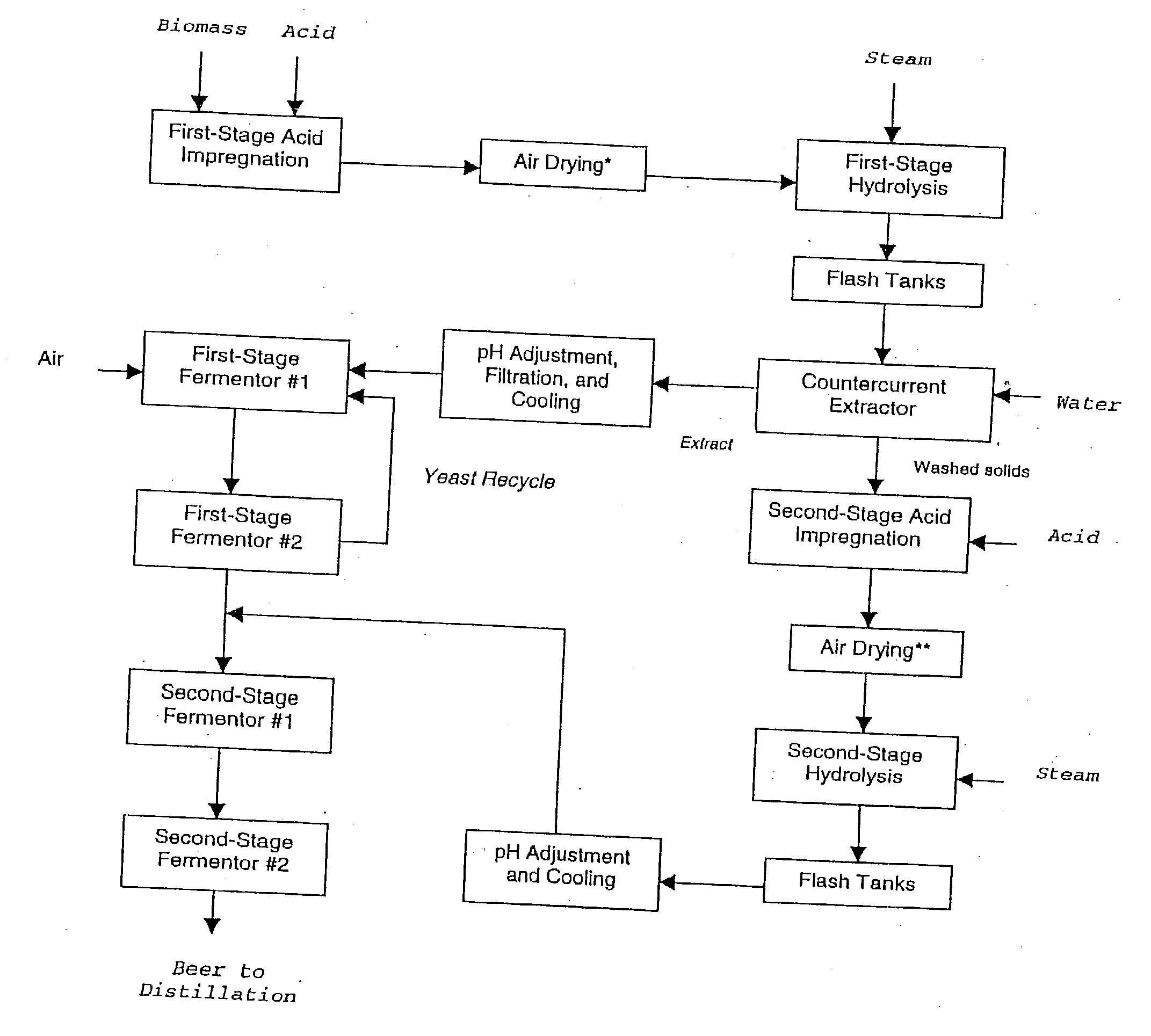
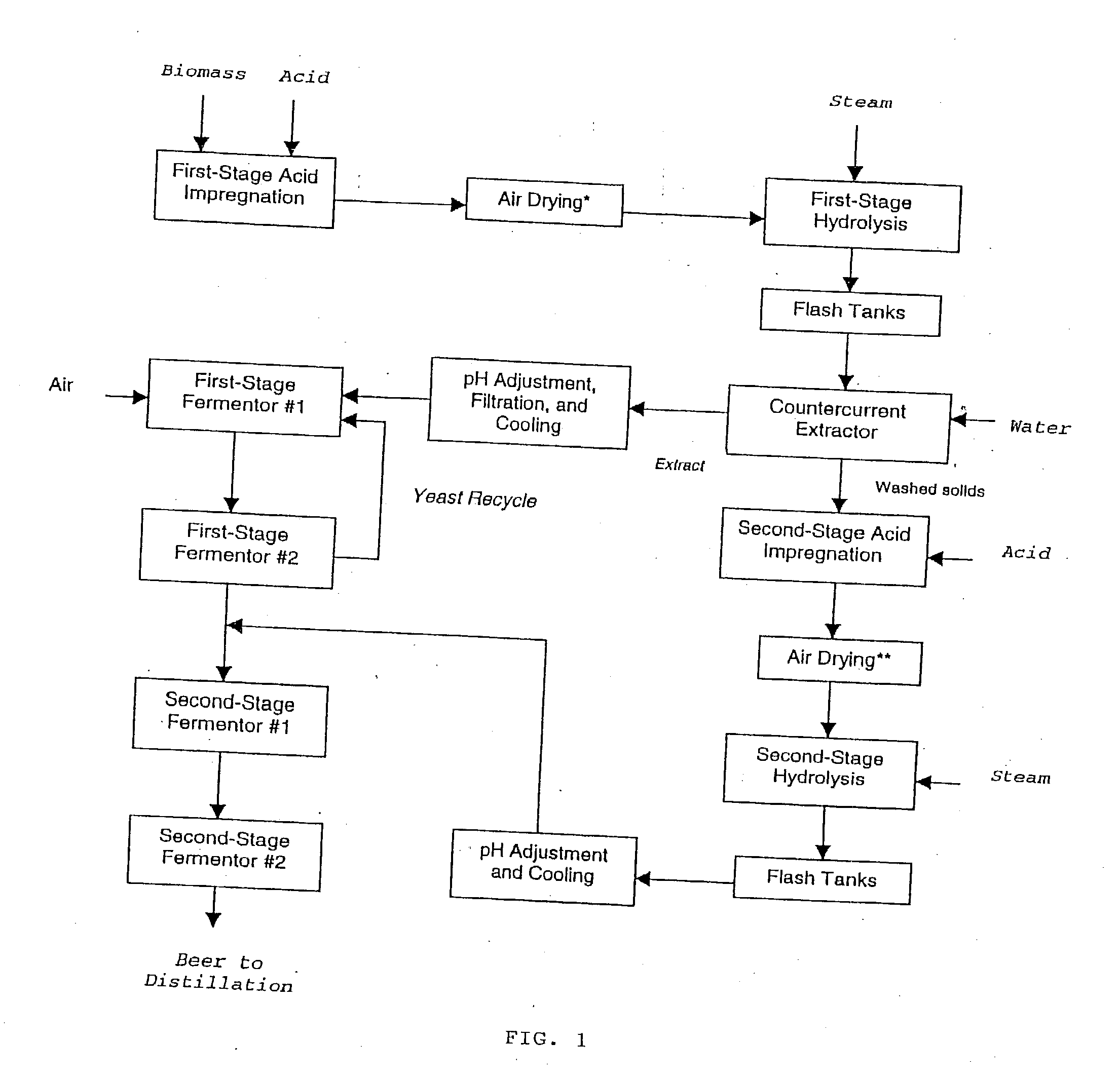
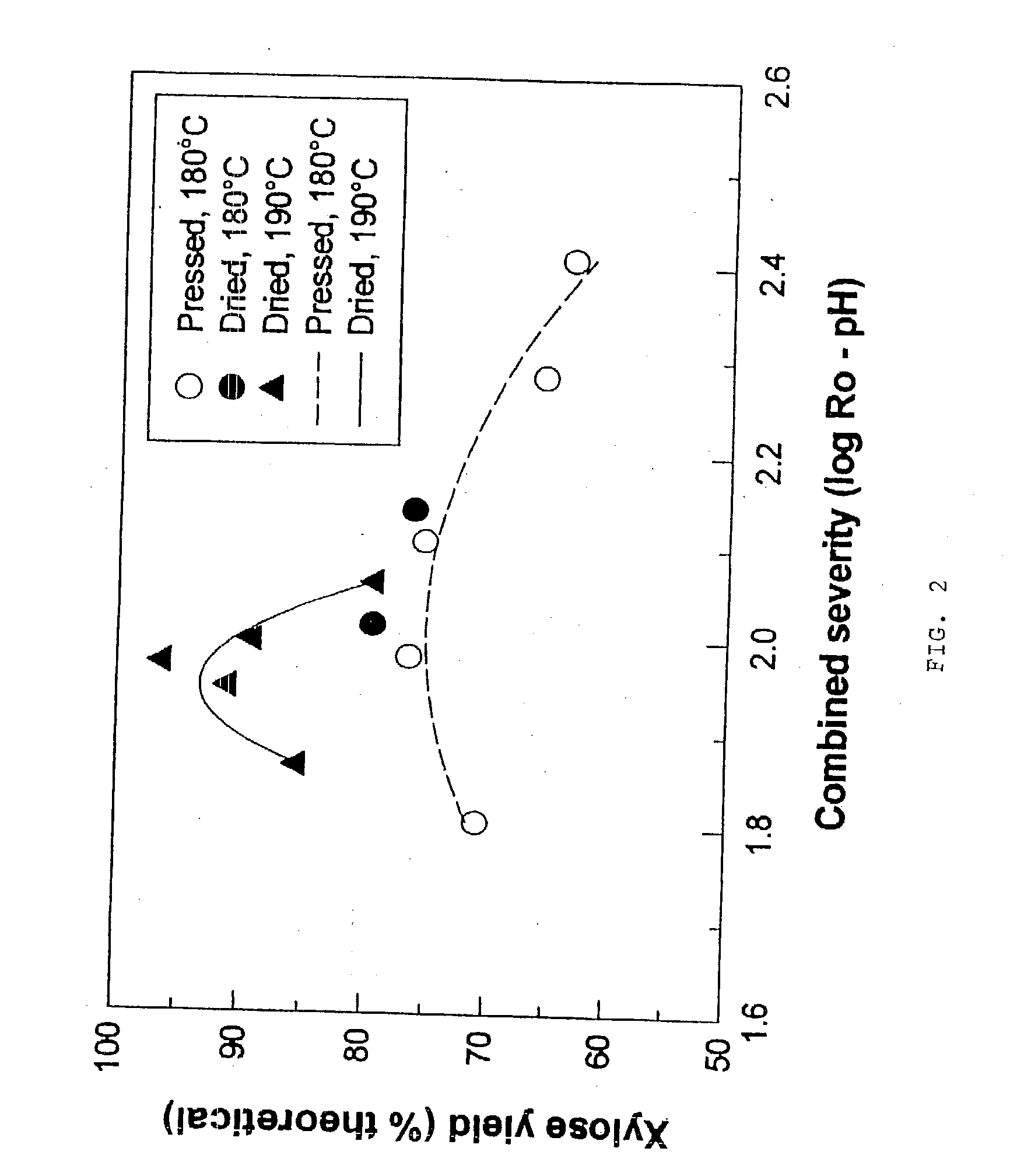
In a process for converting lingnocellulosic biomass to ethanol, the improvement of obtaining higher fermentable soluble sugar yields by drying acid impregnated biomass particles, comprising: a) feeding moist lignocellulosic biomass into an acid impregnator to render it acid-soaked and draining the acid-soaked biomass to about 30% to 35% by weight solids; b) dewatering the acid-soaked biomass by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of the biomass and arrive at about 40% to 60% by weight solids; c) subjecting the acid-impregnated biomass to a first-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature of from 130° C. to 220° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars, and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank-the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for a counter-current extractor; d) washing the hydrolysate, adjusting the pH of the sugar extract to about 5, and recovering more than 95% of the soluble sugars in the first-stage hydrolysate slurry by a counter-current extractor; e) subjecting remaining washed-first stage solids of pretreated biomass to a second-stage acid and metal salt impregnator and dewatering by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of biomass to arrive at 40% to 60% by weight solids; f) subjecting the acid and metal salt-impregnated biomass to a second-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature from 190° C. to 240° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank, at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank, the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for second-stage fementors; g) cooling pH-adjusted extract from the counter-current extractor, feeding the extract to a first-stage fermentor and air sparging the first-stage fermentor at a rate sufficient to promote enough yeast growth to compensate for loss through second-stage fermentors; h) pH adjusting second-stage hydrolysate slurry to 4.5, cooling the slurry and adding it into the top of the first fermentor of a two-fermentor train in the second stage fermentors, pumping broth from the bottom of the first stage fermentors to the second stage fermentors while the yeast is in the growth phase for a period sufficient to consume over 95% of fermentable sugars; and i) recovering ethanol.
Owner:MIDWEST RES INST
Lignin and other products isolated from plant material, methods for isolation and use, and compositions containing lignin and other plant-derived products
InactiveUS20090062516A1Good for healthImprove responseSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationFiberElastomer
Lignin polymers having distinctive properties, including a generally high molecular weight and generally homogeneous size distribution, as well as preservation of native reactive side groups, are isolated by solvent extraction of plant materials. Methods for isolation of lignin polymers, and for use of the isolated lignin polymers are disclosed. Compositions containing lignin isolated from plant materials, such as carbon fiber composites, resins, adhesive binders and coatings, polyurethane-based foams, rubbers and elastomers, plastics, films, paints, nutritional supplements, food and beverage additives are disclosed. Xylose and xylose derivatives, furfural, fermentable sugars, cellulose and hemi-cellulose products may be used directly or further processed. The lignin polymers and other plant-derived products disclosed herein may be produced in abundance at low cost, and may be used as substitutes for feedstocks originating from fossil fuel or petrochemical sources in the manufacture of various products.
Owner:VERTICHEM CORP
Process For Concentrated Biomass Saccharification
Processes for saccharification of pretreated biomass to obtain high concentrations of fermentable sugars are provided. Specifically, a process was developed that uses a fed batch approach with particle size reduction to provide a high dry weight of biomass content enzymatic saccharification reaction, which produces a high sugars concentration hydrolysate, using a low cost reactor system.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Lignin and other products isolated from plant material, methods for isolation and use, and compositions containing lignin and other plant-derived products
InactiveUS20090069550A1Great potentialTotal calories lowLignin derivativesPulp by-products recoveryFiberElastomer
Lignin polymers having distinctive properties, including a generally high molecular weight and generally homogeneous size distribution, as well as preservation of native reactive side groups, are isolated by solvent extraction of plant materials. Methods for isolation of lignin polymers, and for use of the isolated lignin polymers are disclosed. Compositions containing lignin isolated from plant materials, such as carbon fiber composites, resins, adhesive binders and coatings, polyurethane-based foams, rubbers and elastomers, plastics, films, paints, nutritional supplements, food and beverage additives are disclosed. Xylose and xylose derivatives, furfural, fermentable sugars, cellulose and hemi-cellulose products may be used directly or further processed. The lignin polymers and other plant-derived products disclosed herein may be produced in abundance at low cost, and may be used as substitutes for feedstocks originating from fossil fuel or petrochemical sources in the manufacture of various products.
Owner:VERTICHEM CORP
Production of biodiesel from combination of corn (maize) and other feed stocks
InactiveUS20070099278A1Increase Biodiesel production outputStable year round productionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOrganic compound preparationProcess systemsSodium Bentonite
A method and system to produce biodiesel from a combination of corn (maize) and other agro feedstock may be simarouba, mahua, rice, pongamia etc. Germ is separated (either by wet process or dry process) from corn, crude corn oil extracted from germ and corn starch milk / slurry is heated and cooked in jet cooker to about 105 degree Celsius, enzymes added to convert starch into fermentable sugars in liquification and saccharification process and rapidly cooled down to about 30 degree Celsius. Simarouba fruits syrup, mahua syrup is mixed with corn starch milk (after saccharification). When yeast is added the fermentation takes place for about 72 hours. Thereafter the fermented wash is distilled to produce ethanol. Water consumed in dry process is very less compared to traditional wet process system. Corn oil and mixture of other oils is fed into transesterification (reaction) vessels where ethanol with catalyst, usually sodium hydroxide is added and reaction takes place for about a period of 2-8 hours. Crude biodiesel and crude glycerin as by-products is produced. Excess ethanol removed by distillation process. Crude biodiesel washed with warm water to remove residual soaps or unused catalyst, dried and biodiesel stored for commercial use. Oil extracted from spent bleach mud (used sodium bentonite), a waste product of edible oil refineries may also be utilized for economical production of biodiesel in combination of corn oil and ethanol.
Owner:AARE PALANISWAMY RAMASWAMY
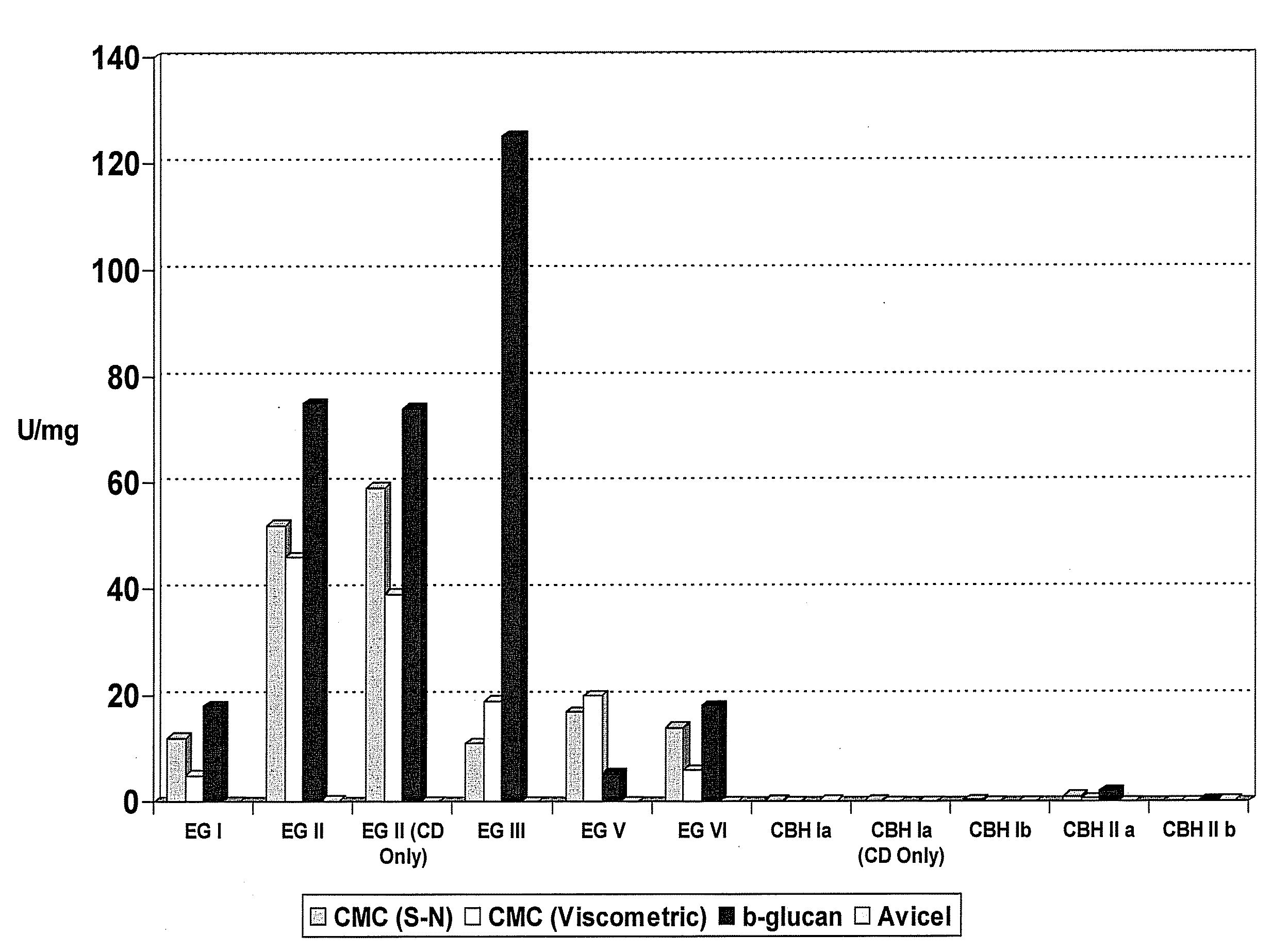
Treatment of cellulosic material and enzymes useful thererin
The present invention relates to the production of sugar hydrolysates from cellulosic material. The method may be used e.g. for producing fermentable sugars for the production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic material. Cellulolytic enzymes and their production by recombinant technology is described, as well as uses of the enzymes and enzyme preparations.
Owner:ROAL O Y (FI)
Process for concentrated biomass saccharification
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
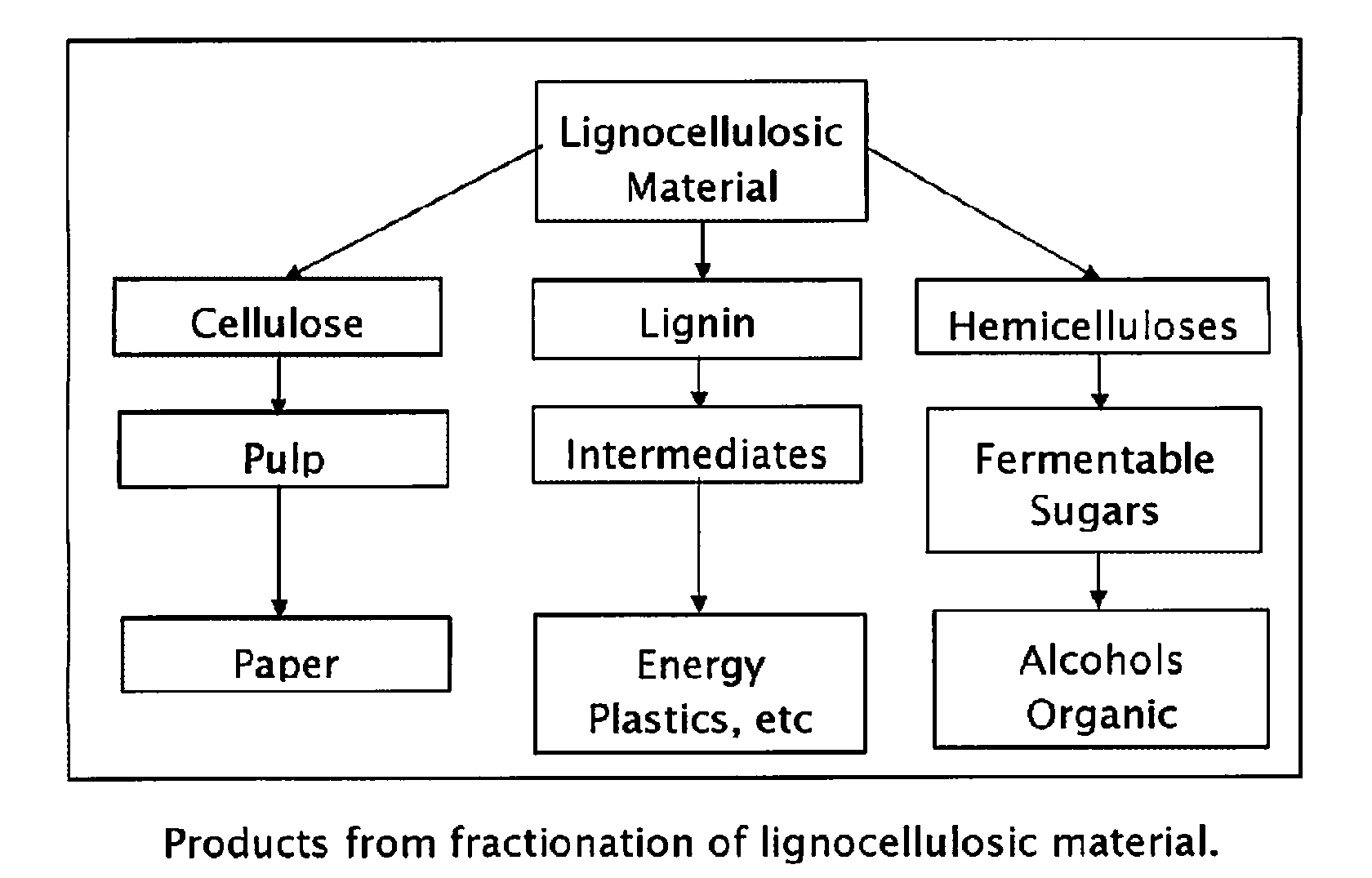
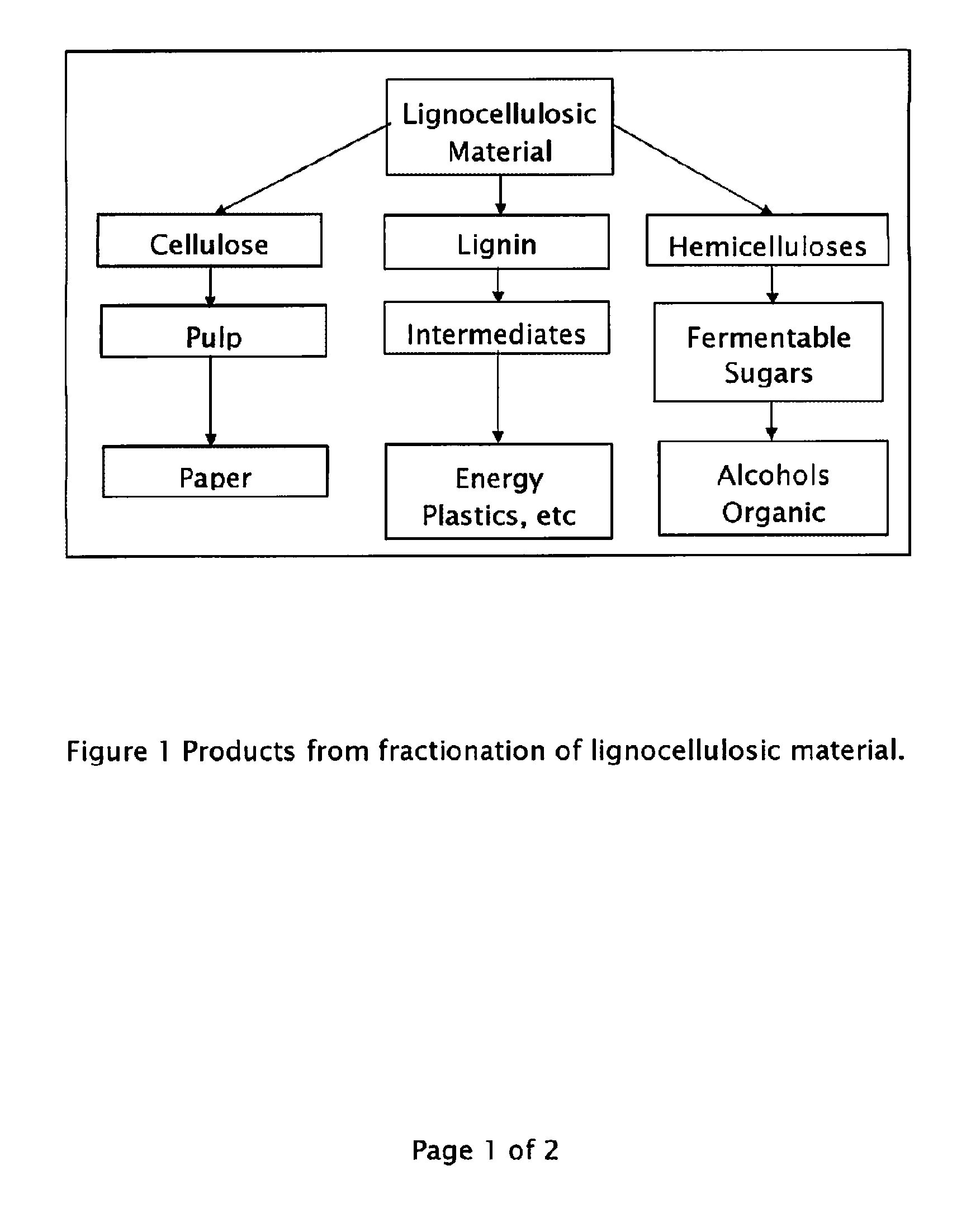
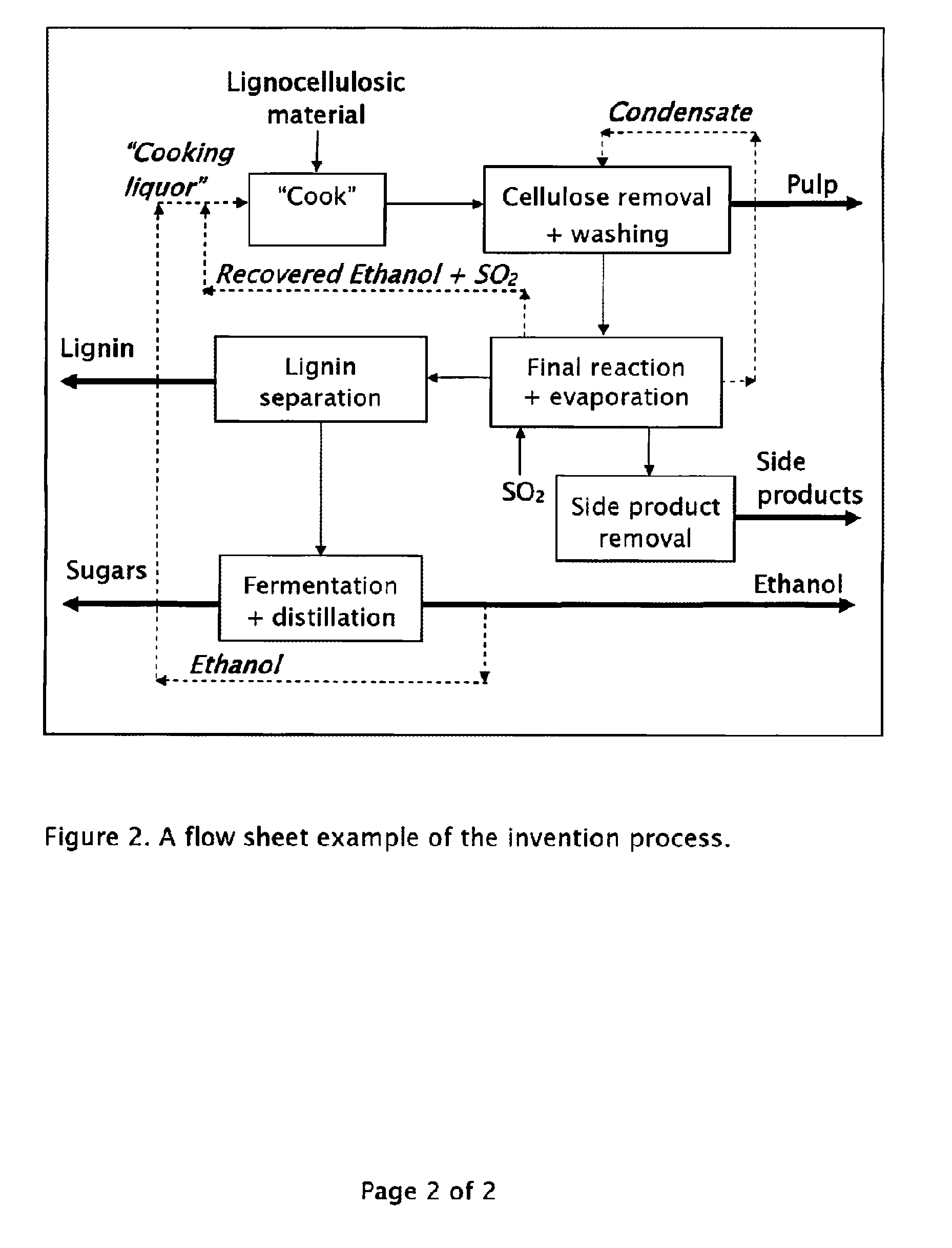
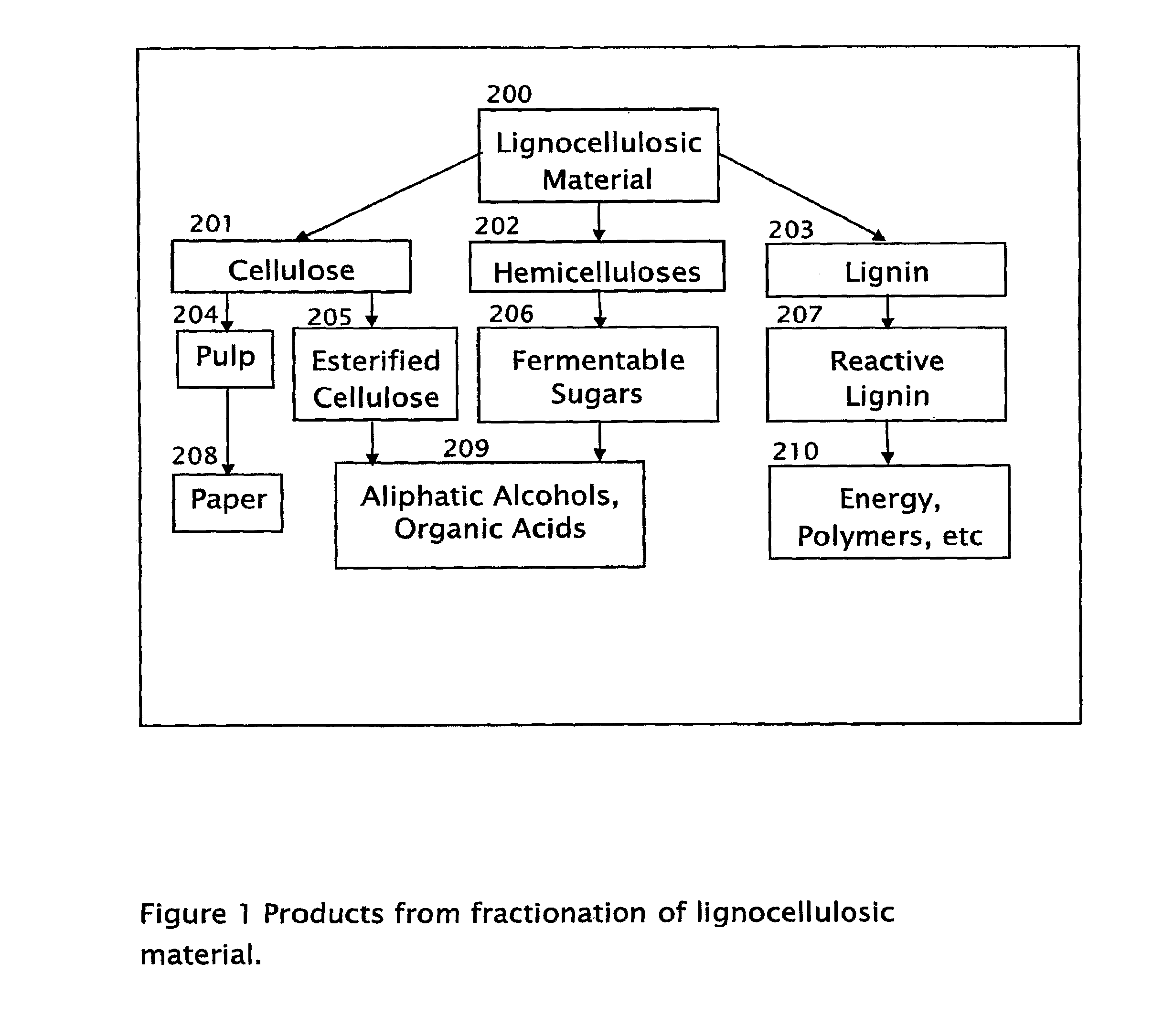
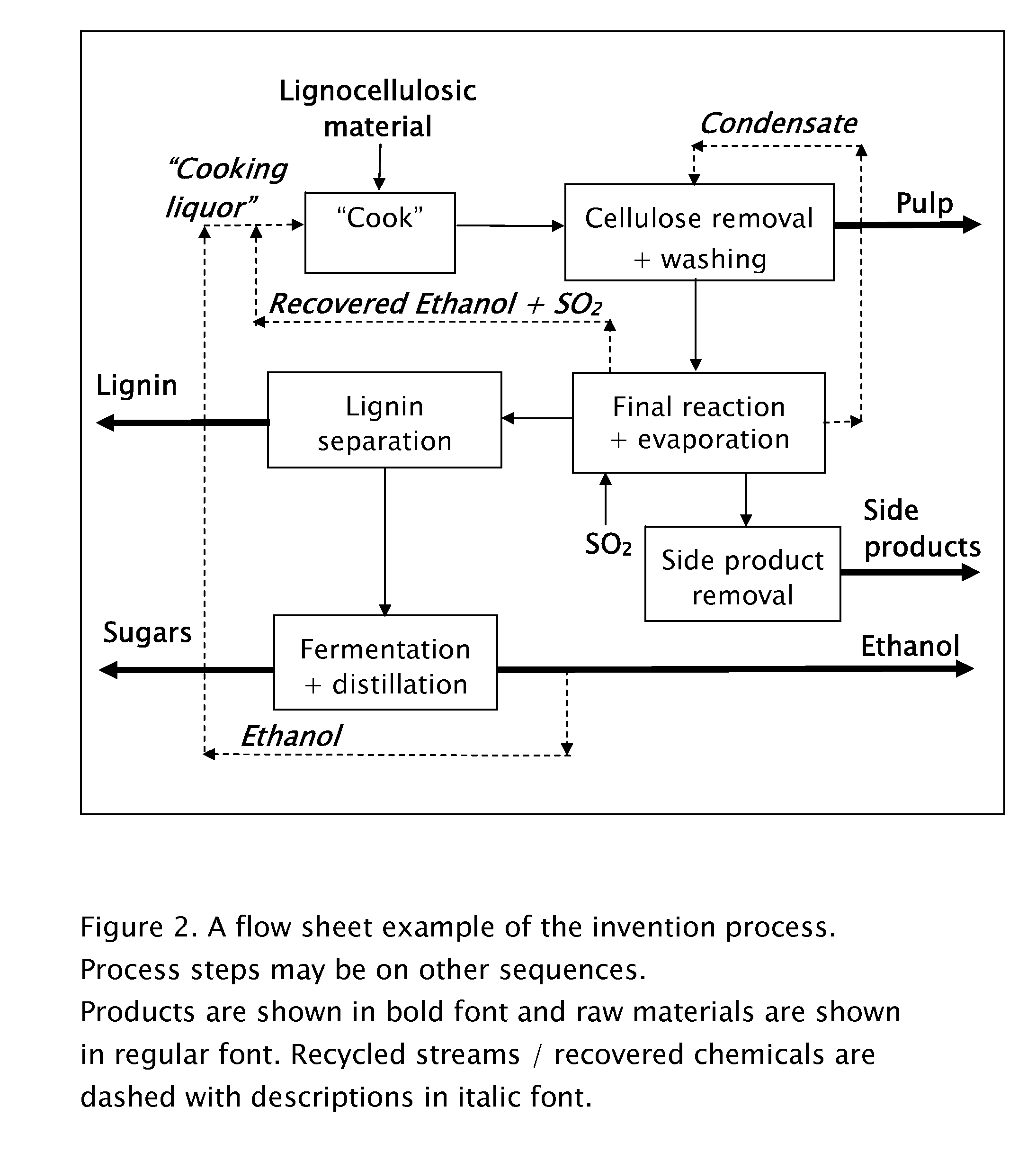
Method for the production of fermentable sugars and cellulose from lignocellulosic material
ActiveUS8030039B1High yieldIncreased ethanol yieldFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPulping with organic compoundsOrganic acidAlcohol
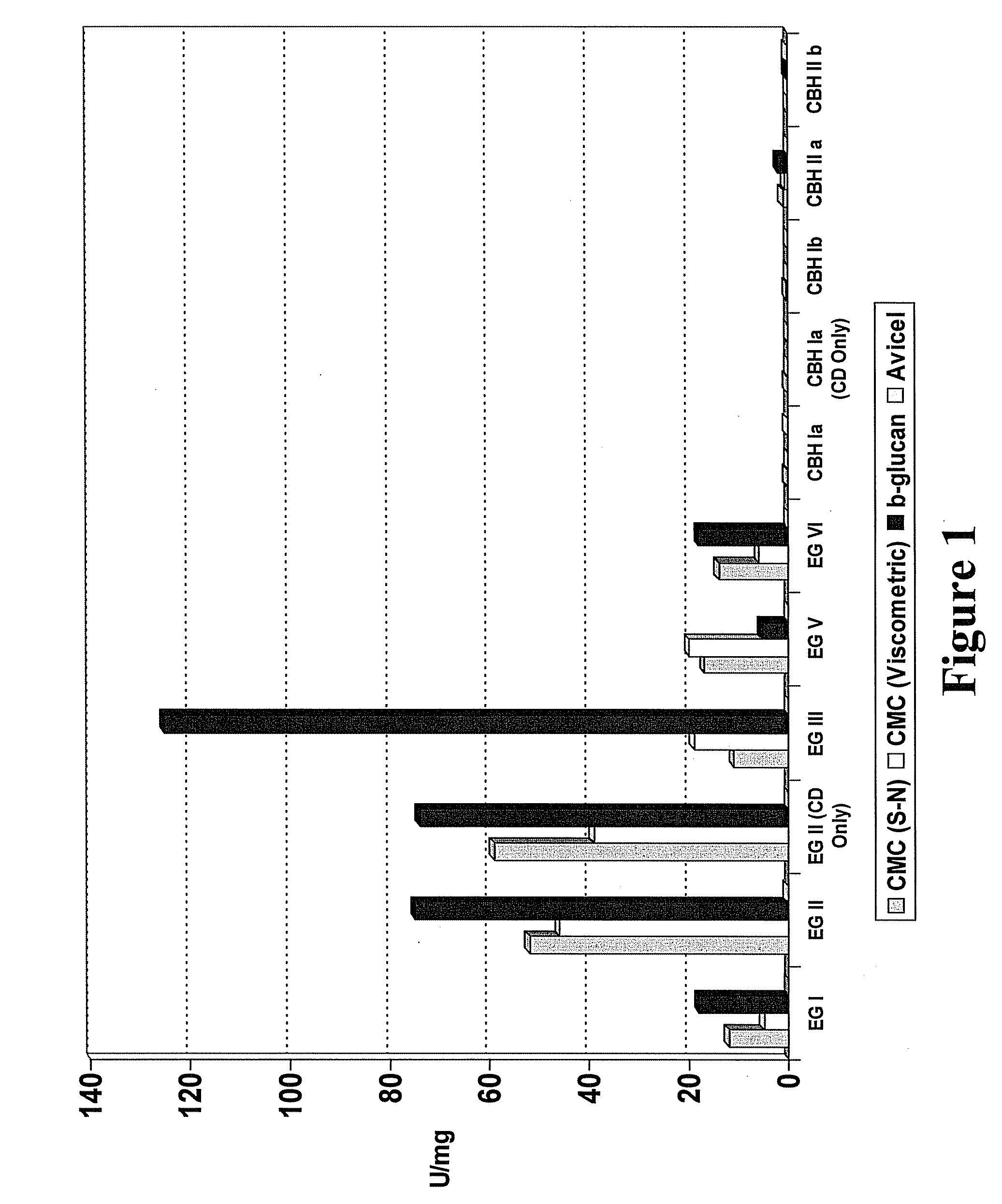
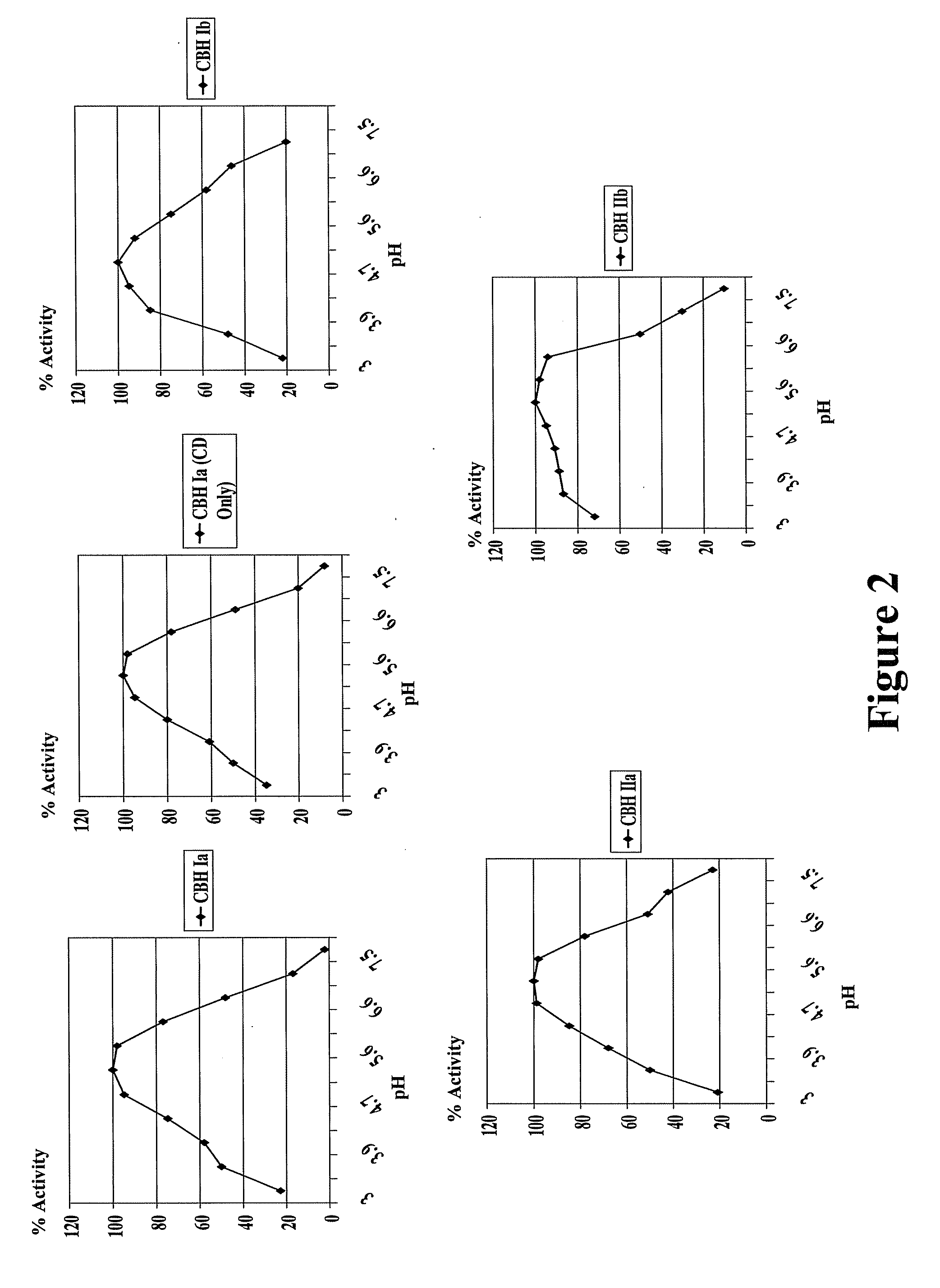
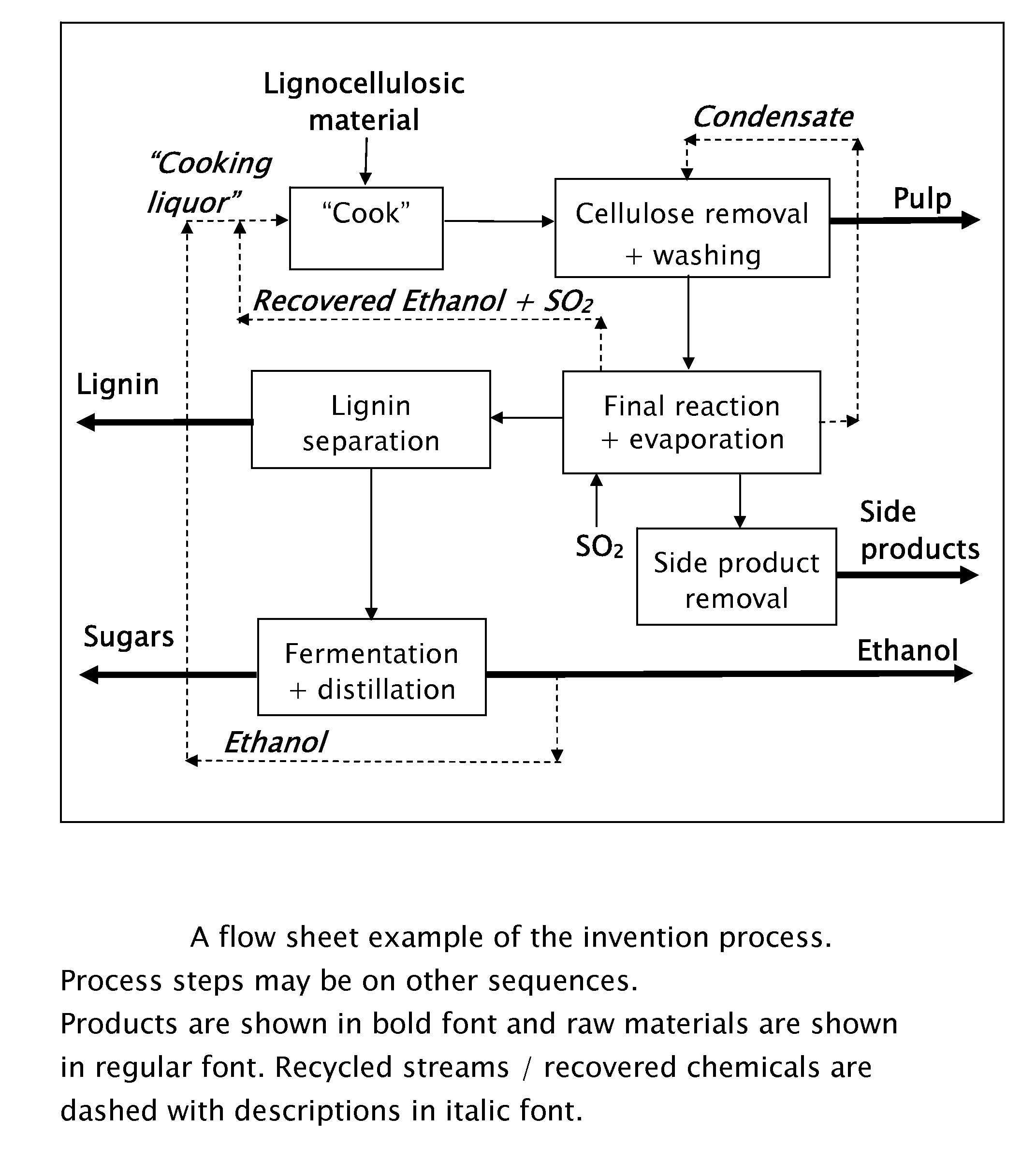
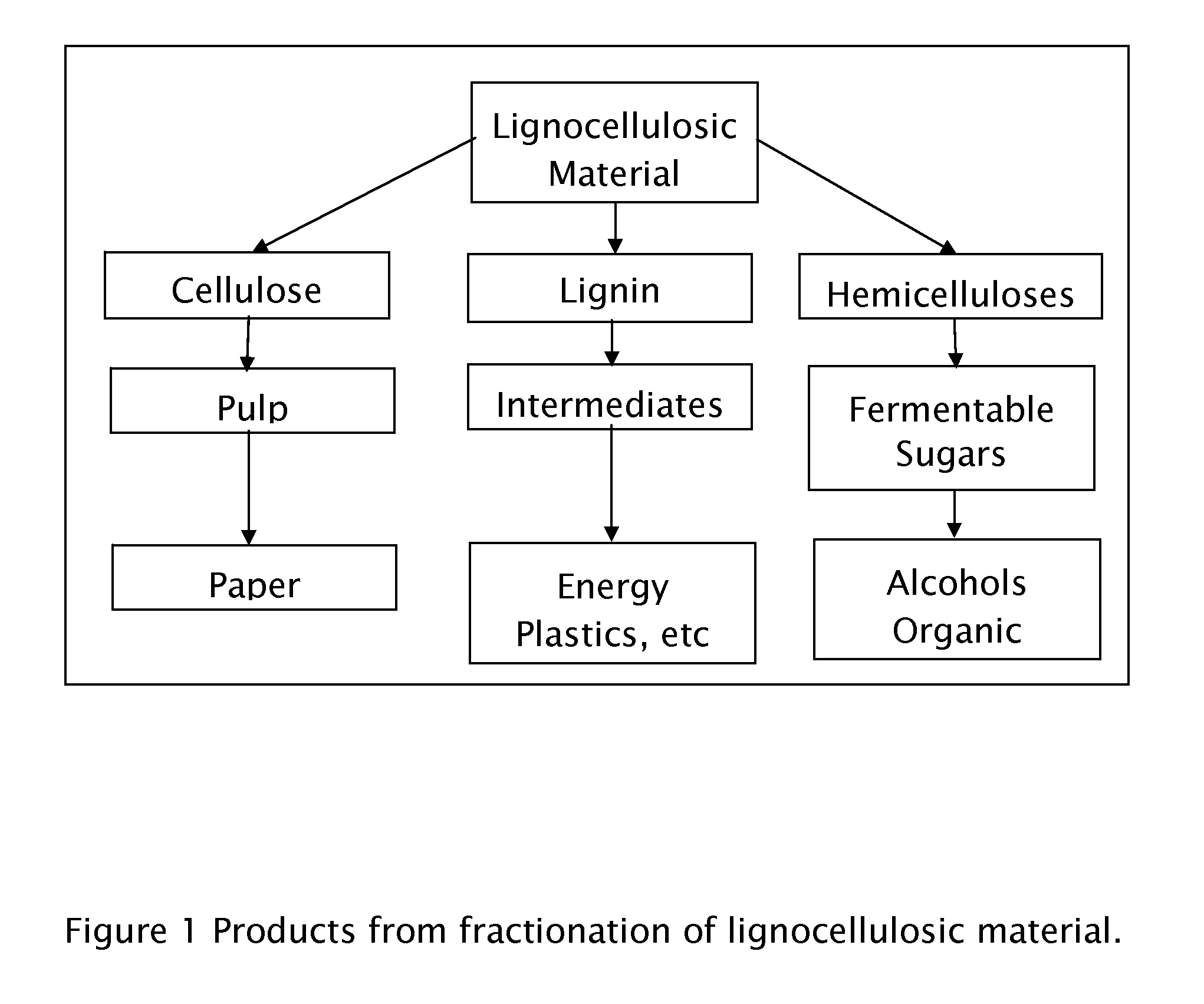
A method for the production of fermentable sugars and high viscosity cellulose from lignocellulosic material in a batch or continuous process is provided. Lignocellulosic material is fractionated in a fashion that cellulose is removed as pulp, cooking chemicals can be reused, lignin is separated for the production of process energy, and hemicelluloses are converted into fermentable sugars, while fermentation inhibitors are removed. High yield production of alcohols or organic acids can be obtained from this method using the final reaction step.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
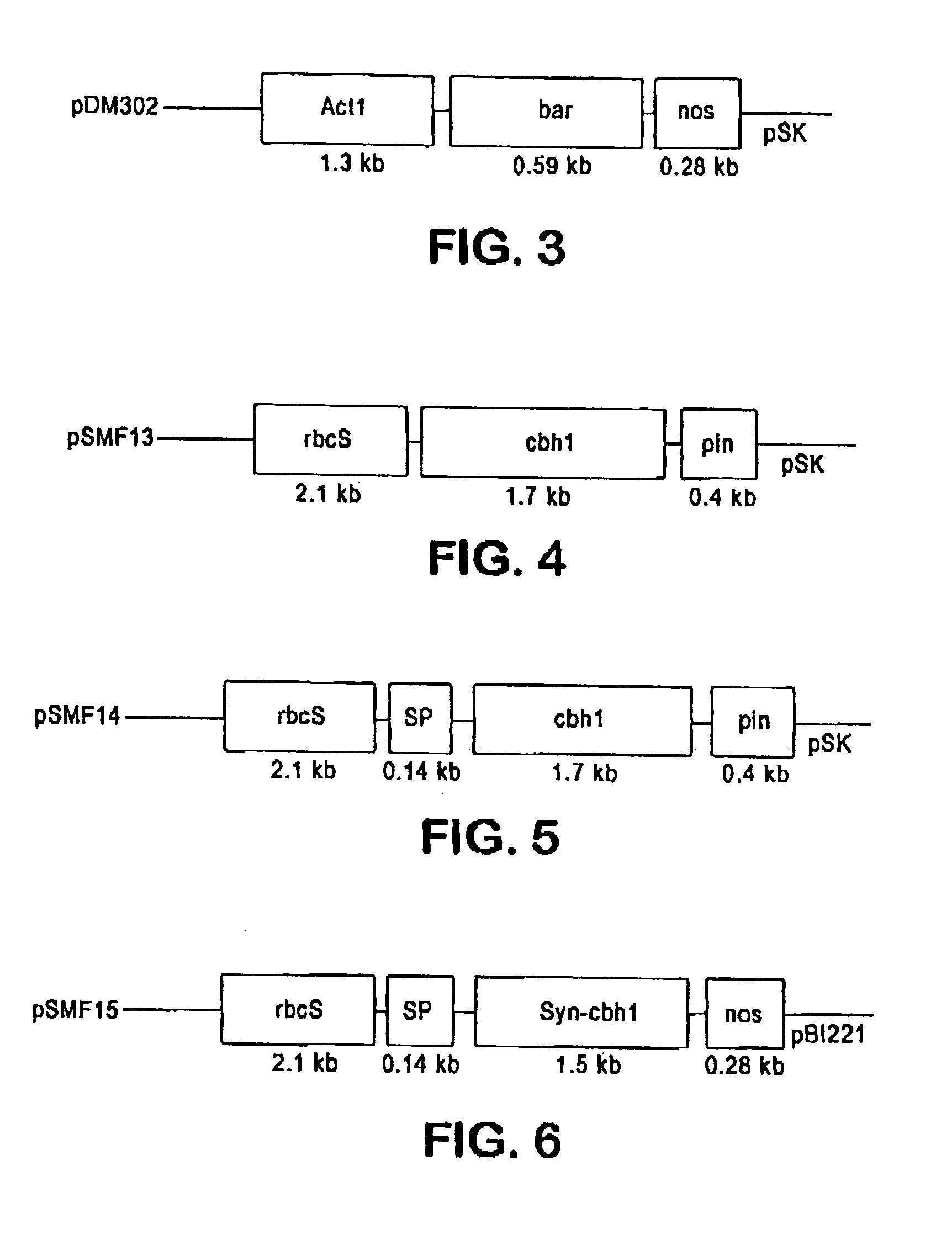
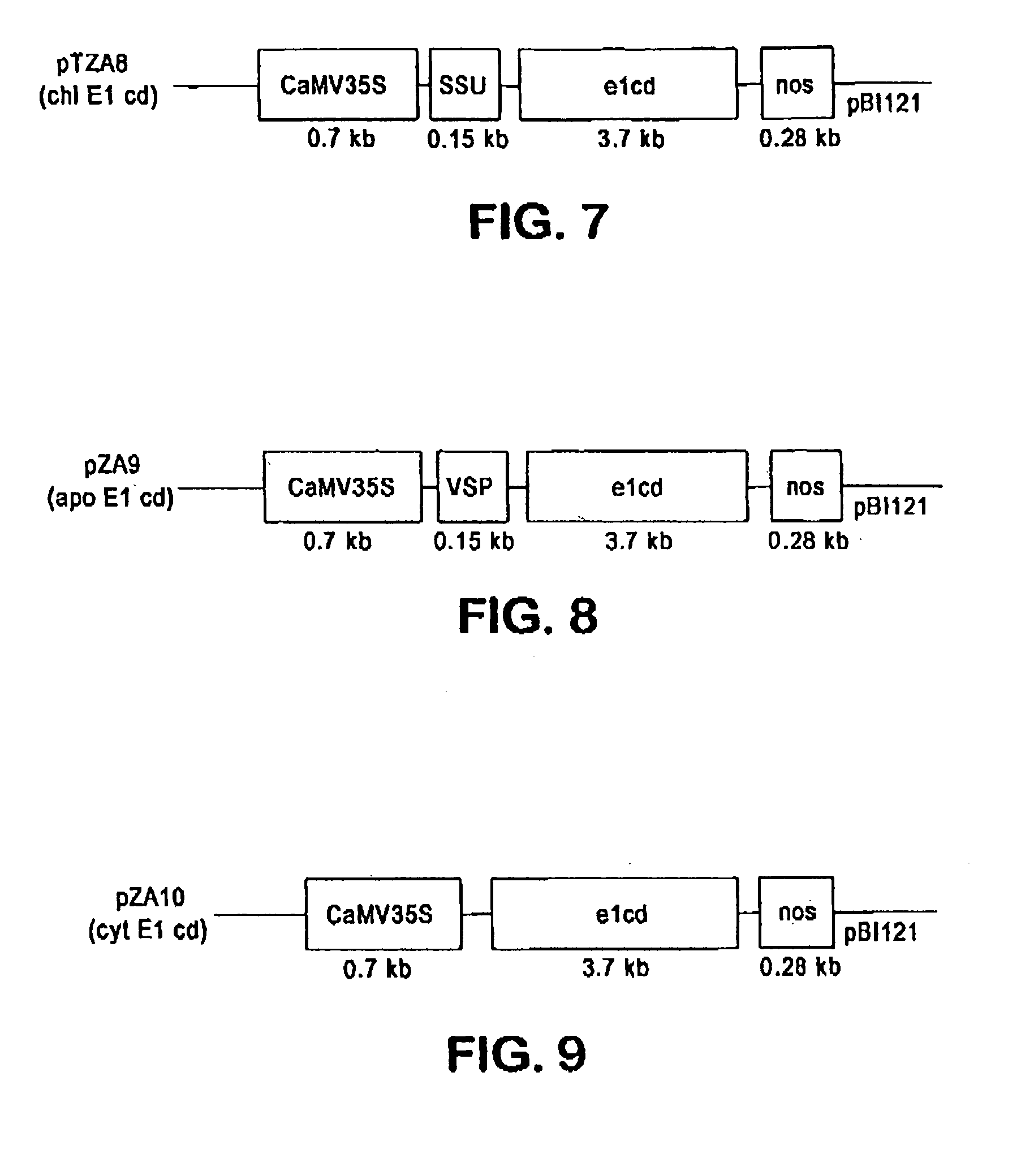
Production of beta-glucosidase, hemicellulase and ligninase in E1 and FLC-cellulase-transgenic plants
InactiveUS20070192900A1Increase biomassReduce the amount of solutionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesAlgluceraseBeta-glucosidase
The present invention provides transgenic plants expressing one or more cell wall degrading enzymes that can degrade lignocellulose to fermentable sugars. These fermentable sugars can further be fermented to ethanol or other products. The enzymes are directed to the plastids or the apoplasts or the transgenic plant for storage. When the transgenic plants are harvested, the plants are ground to release the enzymes which then are used to degrade the lignocellulose of plant material to produce the fermentable sugars. The transgenic plants express the flowering locus c gene so that flowering is delayed and the plant biomass is increased.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
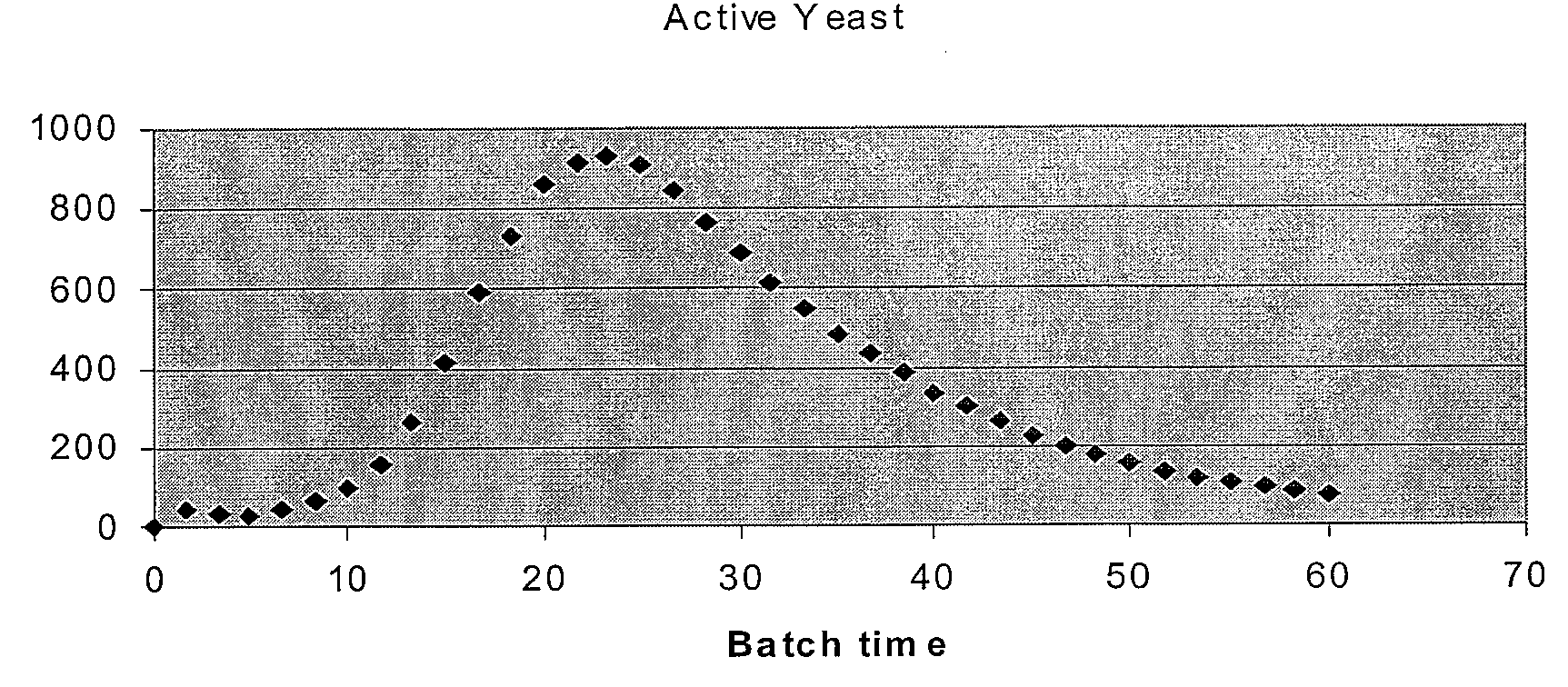
Nonlinear Model Predictive Control of a Biofuel Fermentation Process
ActiveUS20080167852A1Maximizing yeast growthMaximize productionBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperatue controlBiotechnologyLinear control
System and method for managing batch fermentation in a biofuel production process. A nonlinear control model of yeast growth and fermentable sugar concentration for biofuel (e.g., fuel ethanol) production in a batch fermentation process (pure and / or fed-batch fermentation) of a biofuel production process is provided. Process information for the batch fermentation process is received, and the nonlinear control model executed using the process information as input to determine values of one or more fermentation process variables for the batch fermentation process, e.g., fermentation temperature and / or enzyme flow, for substantially maximizing yeast growth and achieving target fermentable sugar concentrations. The batch fermentation process is then controlled in accordance with the determined values for the one or more fermentation process variables to substantially maximize yeast growth and achieve target fermentable sugar concentrations, where substantially maximizing yeast growth and achieving target fermentable sugar concentrations substantially maximizes biofuel production in the batch fermentation process.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Biomass Treatment Method
InactiveUS20090050134A1Small sizeIncrease surface areaPressurized chemical processSugar productsFermentable sugarAmmonia
A method for treating biomass was developed that uses an apparatus which moves a biomass and dilute aqueous ammonia mixture through reaction chambers without compaction. The apparatus moves the biomass using a non-compressing piston. The resulting treated biomass is saccharified to produce fermentable sugars.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
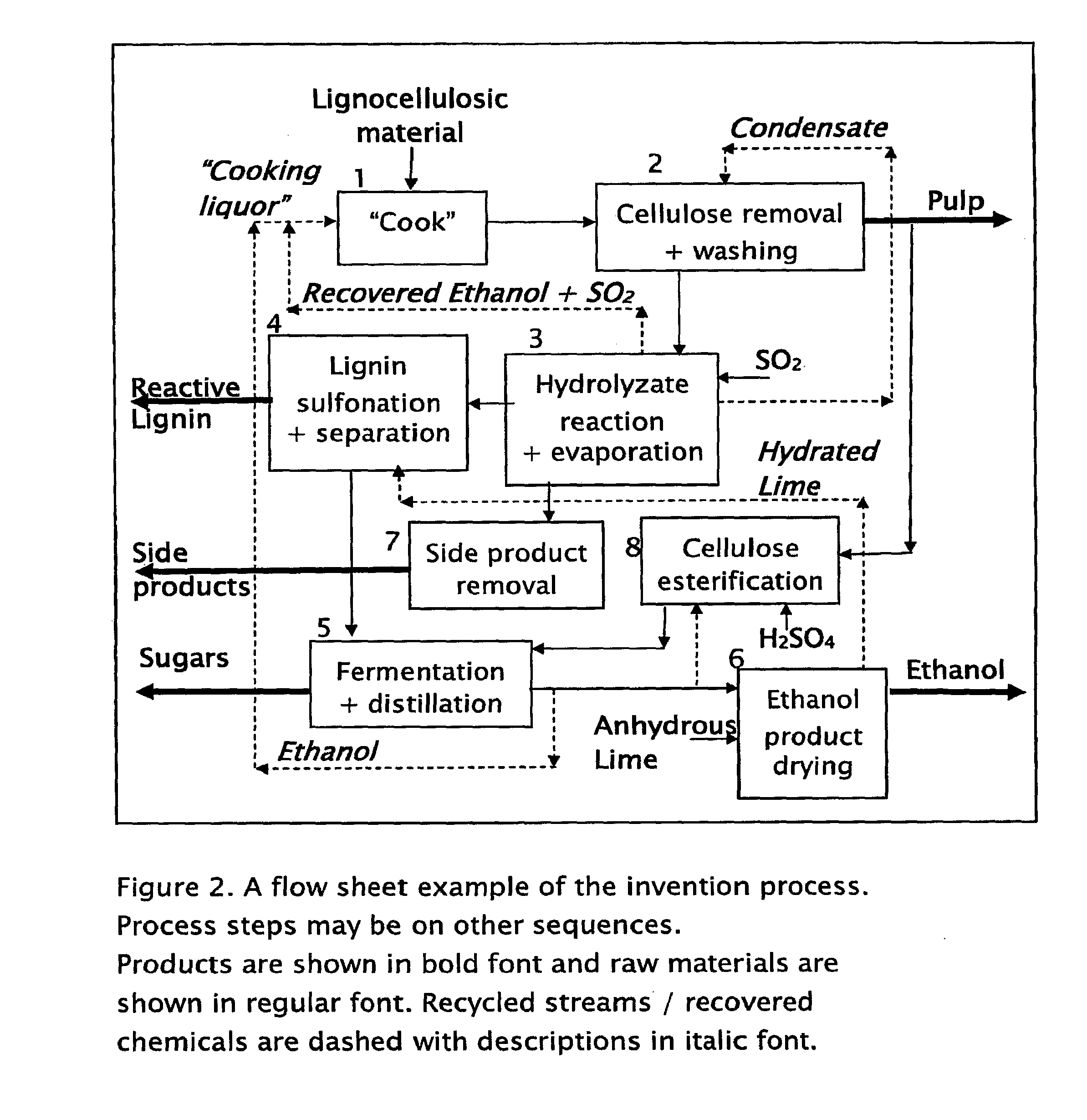
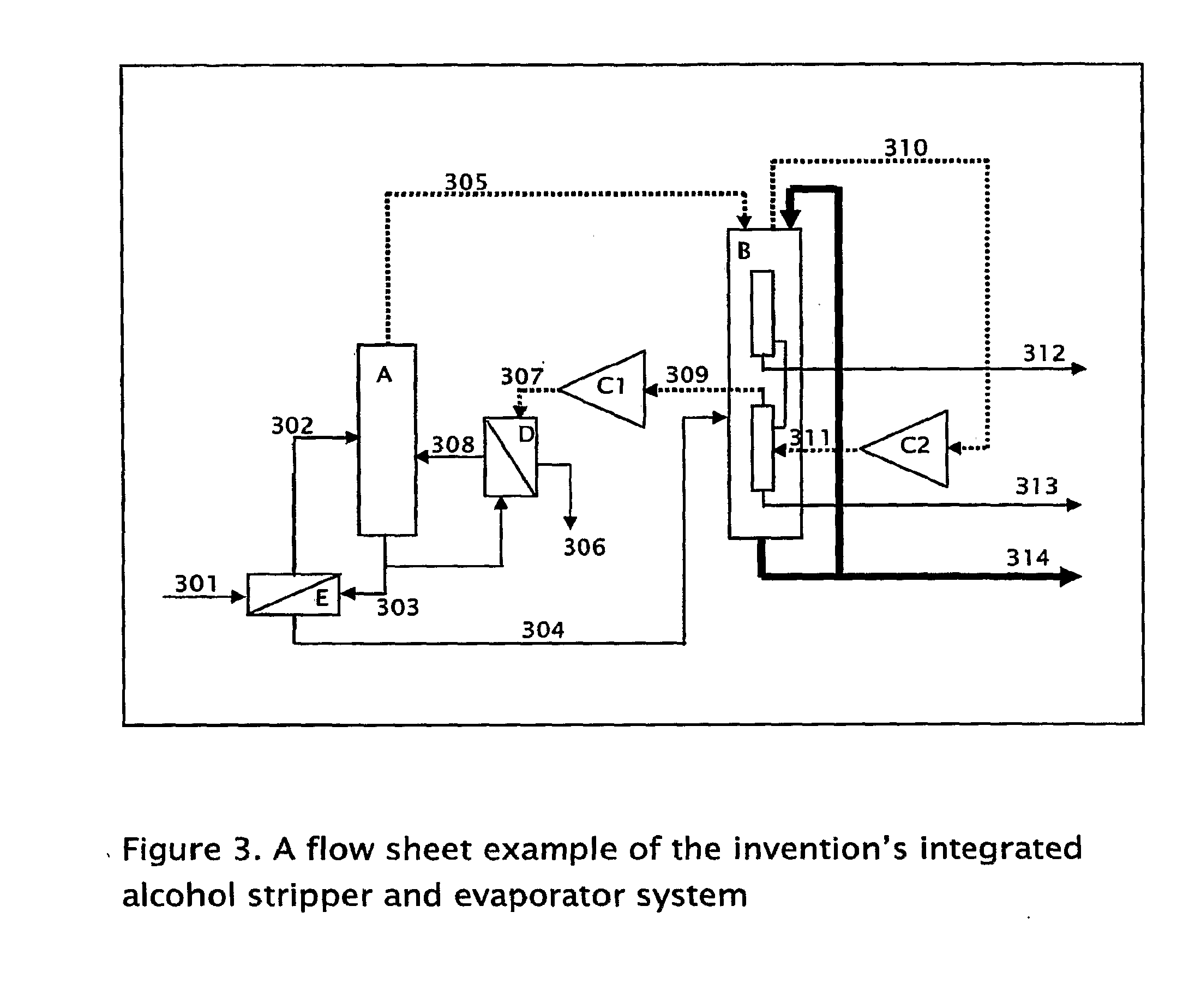
Process for the stepwise treatment of lignocellulosic material to produce reactive chemical feedstocks
InactiveUS20110003352A1Using liquid separation agentCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesSulfonateLignosulfonates
A method for the fractionation of lignocellulosic materials into reactive chemical feedstock in a batch or semi continuous process by the stepwise treatment with aqueous aliphatic alcohols in the presence of sulfur dioxide or acid. Lignocellulosic material is fractionated in a fashion that cellulose is removed as pulp, or converted to esterified cellulose, cooking chemicals are reused, lignin is separated in the forms of reactive native lignin and reactive lignosulfonates and hemicelluloses are converted into fermentable sugars, while fermentation inhibitors are removed. In an integrated vapor compression stripper and evaporator system, aliphatic alcohol is removed from a liquid stream and the resulting stream is concentrated for further processing.
Owner:API INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC +1
Novel Fungal Enzymes
InactiveUS20090280105A1Easy to cleanOrganic active ingredientsNon-fibrous pulp additionCelluloseWaste stream
This invention relates to novel enzymes and novel methods for producing the same. More specifically this invention relates to a variety of fungal enzymes. Nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, compositions, recombinant and genetically modified host cells, and methods of use are described. The invention also relates to a method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars with enzymes that degrade the lignocellulosic material and novel combinations of enzymes, including those that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. The invention also relates to methods to use the novel enzymes and compositions of such enzymes in a variety of other processes, including washing of clothing, detergent processes, deinking and biobleaching of paper and pulp, and treatment of waste streams.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Method for the production of fermentable sugars and cellulose from lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS20070254348A1Pulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulp by-products recoveryOrganic acidAlcohol
A method for the production of fermentable sugars and cellulose from lignocellulosic material in a batch or continuous process. Lignocellulosic material is fractionated in a fashion that cellulose is removed as pulp, cooking chemicals reused, lignin is separated for the production of process energy, hemicelluloses are converted into fermentable sugars, while fermentation inhibitors are removed. High yield production of alcohols or organic acids can be obtained from this method using the final reaction step.
Owner:RETABINA THEODORA +1
Transgenic plants containing ligninase and cellulase which degrade lignin and cellulose to fermentable sugars
InactiveUS7049485B2Stress resistantConfer resistanceBiofuelsOther foreign material introduction processesLignin-modifying enzymeFermentable sugar
The present invention provides transgenic plants which after harvest degrade the lignin and cellulose therein to fermentable sugars which can further be fermented to ethanol or other products. In particular, the transgenic plants comprise ligninase and cellulase genes from microbes operably linked to a DNA encoding a signal peptide which targets the fusion polypeptide produced therefrom to an organelle of the plant, in particular the chloroplasts. When the transgenic plants are harvested, the plants are ground to release the ligninase and cellulase which then degrade the lignin and cellulose of the transgenic plants to produce the fermentable sugars.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
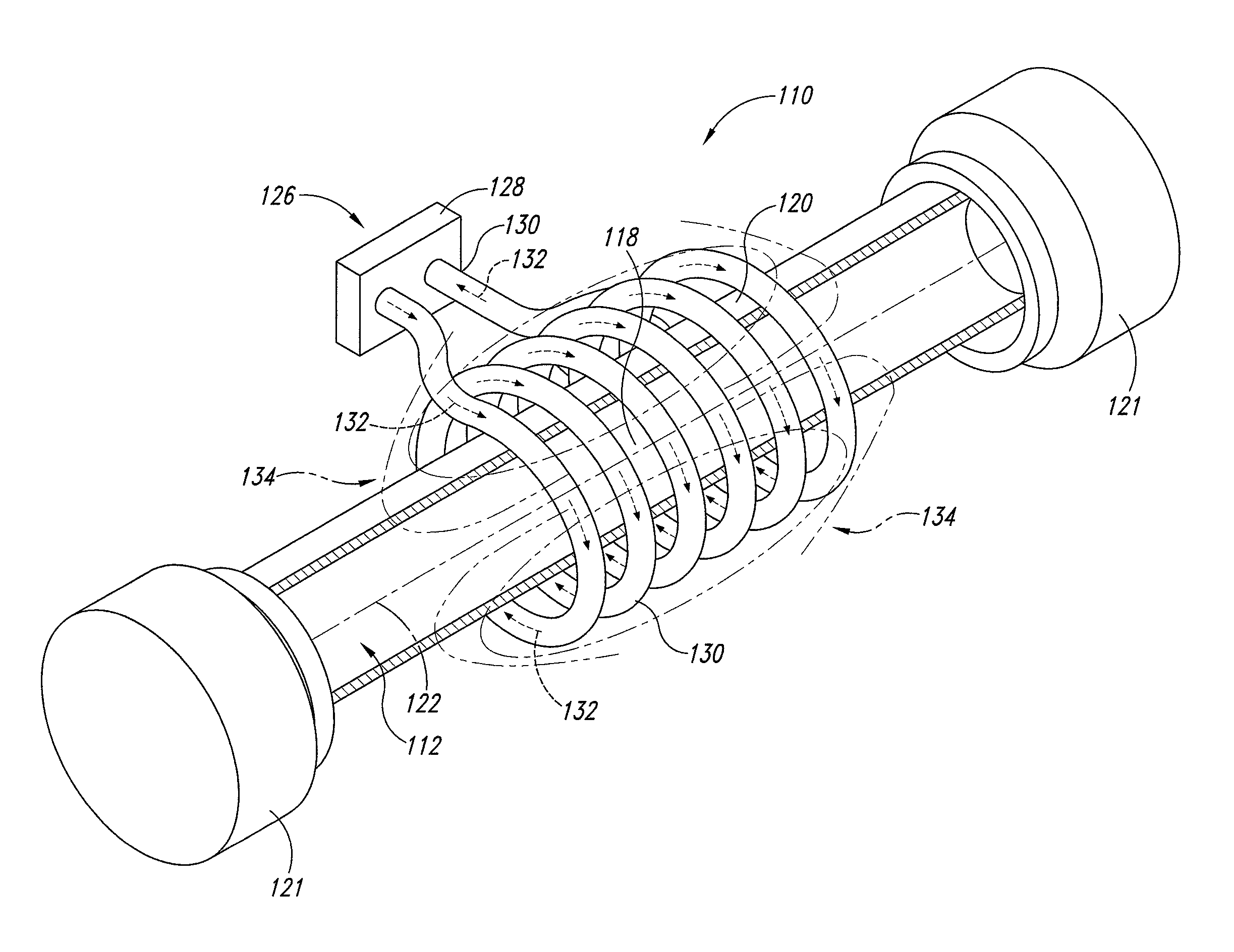
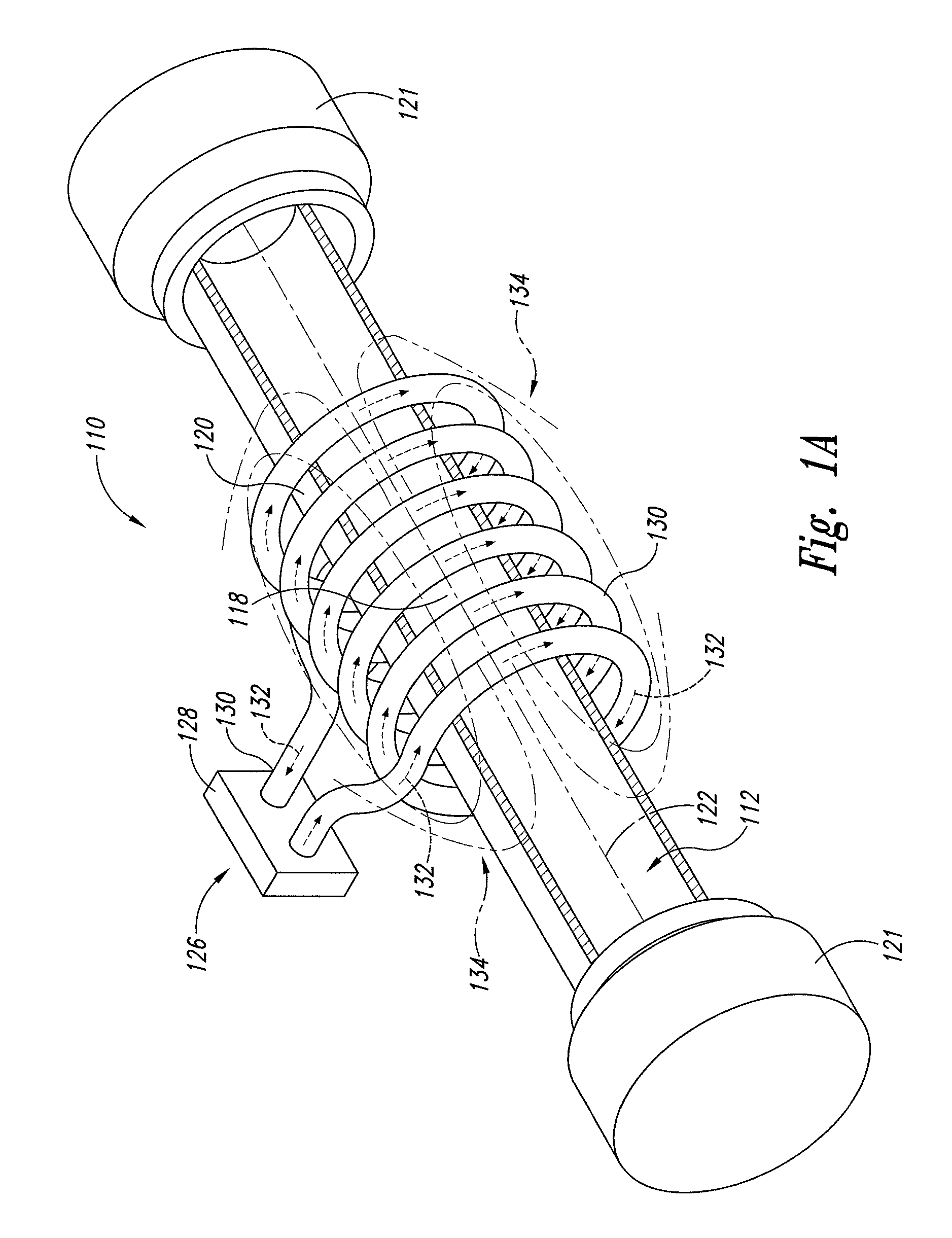
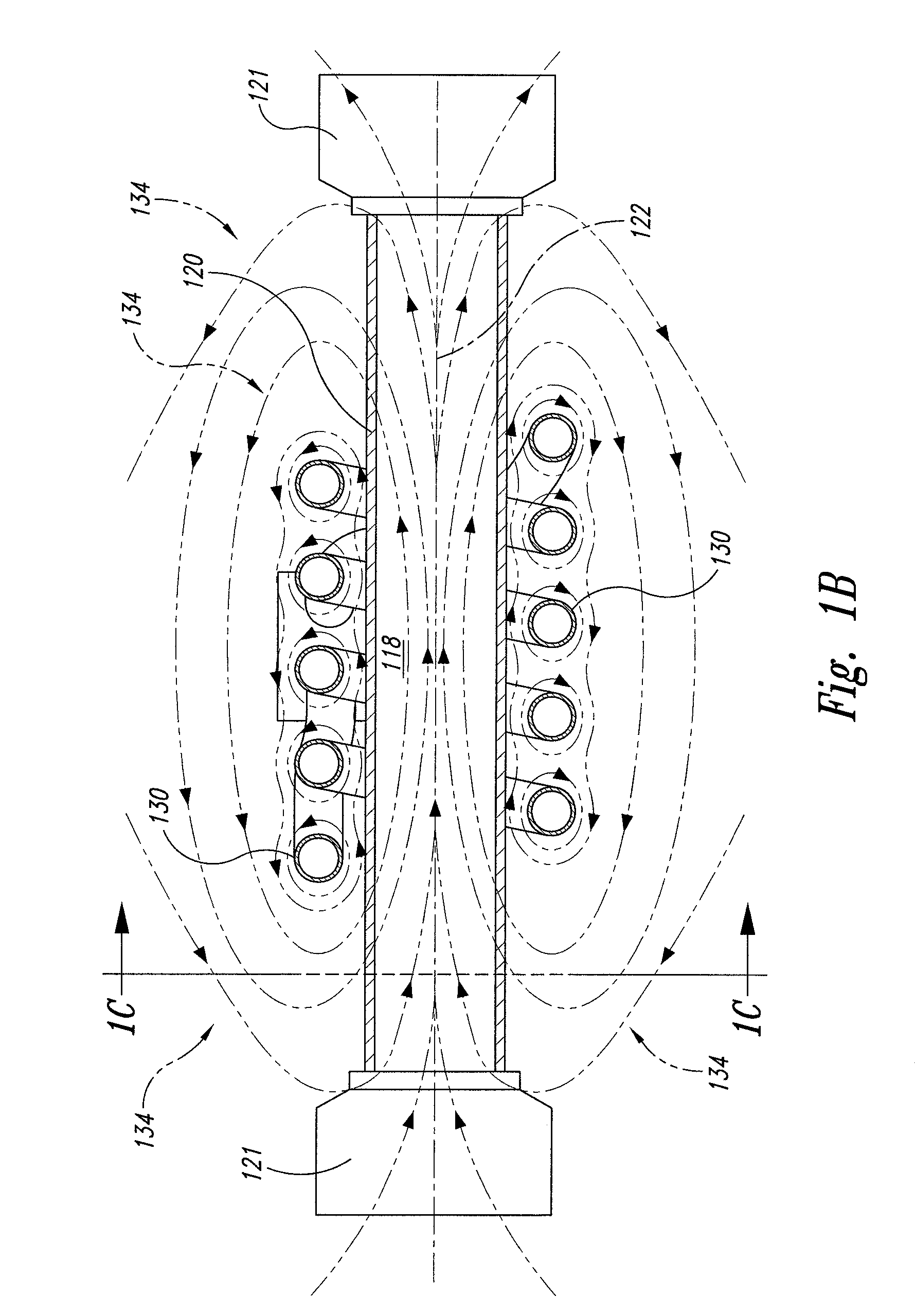
Supercritical fluid biomass conversion systems
ActiveUS7955508B2Enhances rapid cleavage and depolymerizationIndirect heat exchangersWater/sewage treatment by substance additionThermal energyOrganic solvent
Disclosed herein are supercritical fluid biomass conversion machines, systems, and methods for converting a wide range of biomass materials into a plurality of reaction products including fermentable sugars and various aromatic substances. In one embodiment, a method is disclosed that comprises the steps of: providing an extruder; conveying a mixture of the selected biomass material and water through the extruder and into a supercritical fluid biomass conversion zone; heating and further pressurizing the mixture within the supercritical fluid biomass conversion zone to yield at least supercritical water, wherein heat energy is supplied by means of an induction heating coil positioned circumferentially about the supercritical fluid biomass conversion zone; retaining the mixture within the supercritical fluid biomass conversion zone for a period of time sufficient to yield the plurality of reaction products; and separating the plurality of reaction products into at least a water soluble fraction and an organic solvent soluble fraction.
Owner:XTRUDX TECH
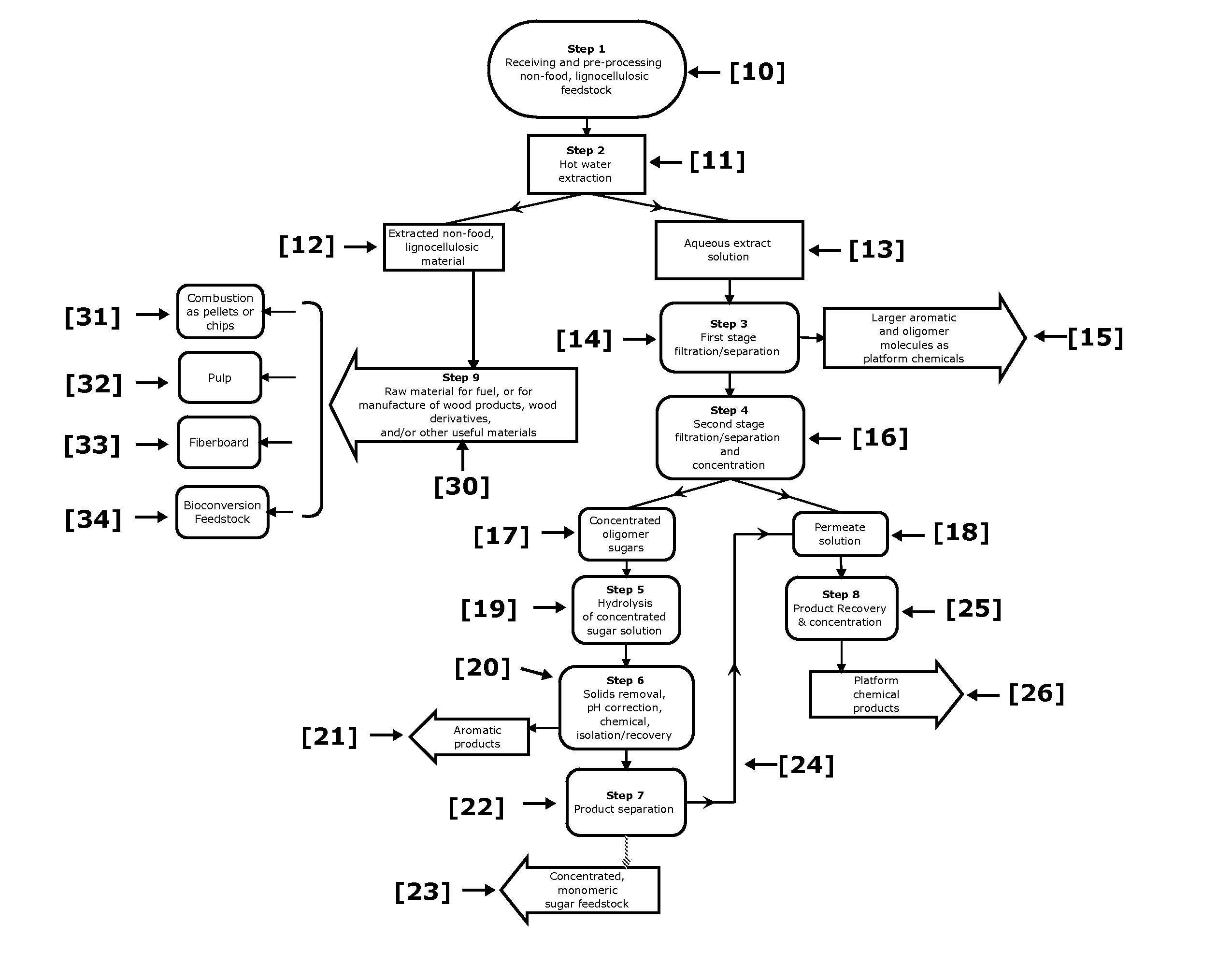
Biorefinery Process for Extraction, Separation, and Recovery of Fermentable Saccharides, other Useful Compounds, and Yield of Improved Lignocellulosic Material from Plant Biomass
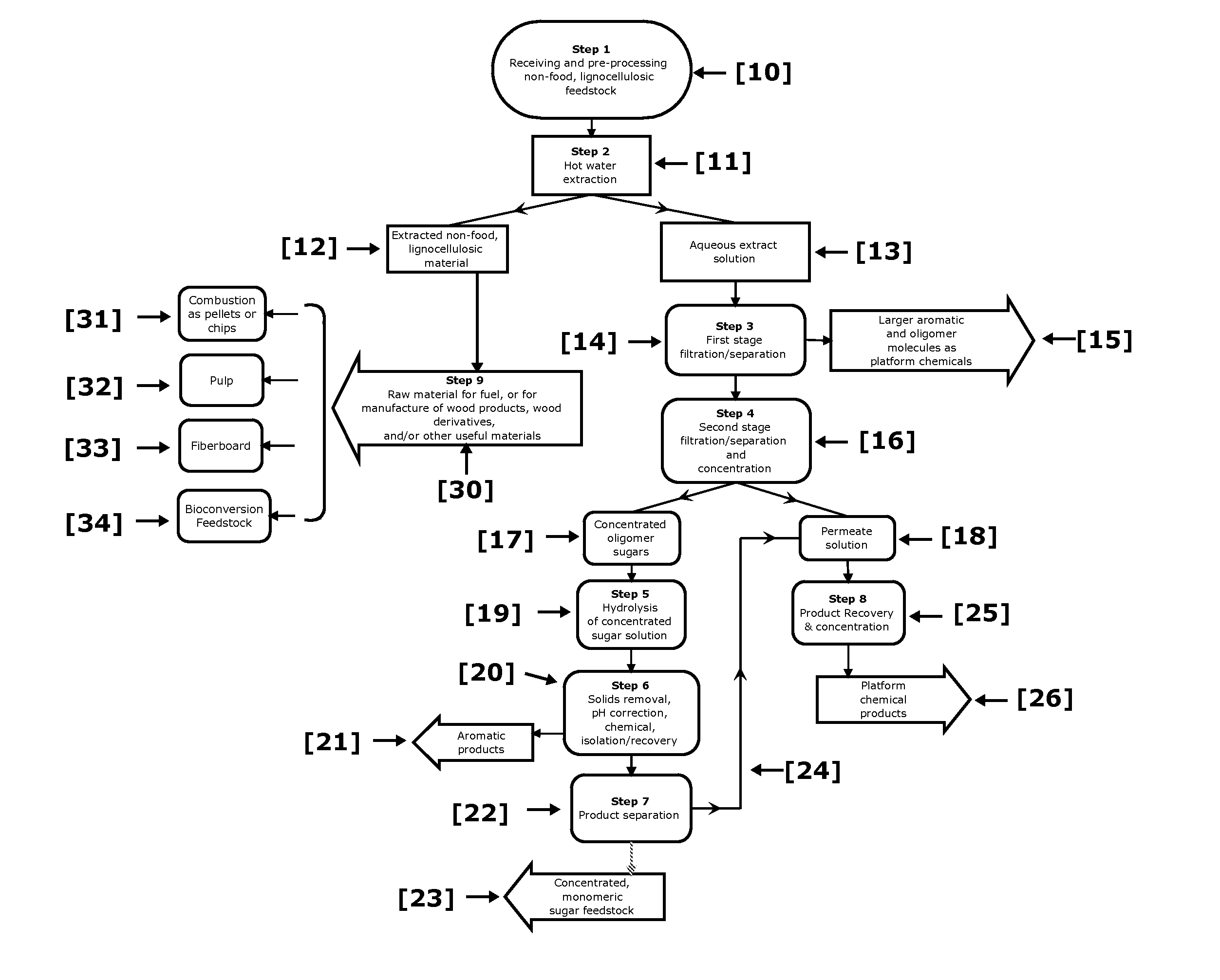
ActiveUS20110129886A1Increase diversityIncrease probabilityCellulosic pulp after-treatmentBiofuelsFurfuralAqueous extract
Non-food plant biomass is subjected to hot-water extraction in a pressurized vessel at an elevated temperature up to about 250° C. and at a pH below about 7.0, to yield an aqueous extract containing hemicellulosic components, other wood-derived compounds, and a lignocellulosic residue. The separated aqueous extract or liquor is purified and concentrated through a multi-step process producing fermentable sugars. At each stage, inhibitory chemicals such as acetic acid, lignin, and furfural are separated and eventually recovered as commercial chemicals. The lignocellulosic residue may be further processed, as a material with enhanced resistance to sorption of water, for manufacture of improved pulp and paper, construction materials, pellet fuel, and / or other useful products.
Owner:APPLIED BIOREFINERY SCI
Ozone treatment of biomass to enhance enzymatic saccharification
InactiveUS20100159521A1Reduce yieldReduction in yieldSugar derivativesBiofuelsCelluloseFermentable sugar
Methods for treating lignocellulosic biomass to produce readily saccharifiable carbohydrate-enriched biomass are provided. In one method, lignocellulosic biomass comprising lignin is treated with aqueous ammonia, then contacted with a gas comprising ozone at a temperature of about 0° C. to about 50° C. In another method, lignocellulosic biomass comprising lignin is contacted with a gas comprising ozone at a temperature of about 0° C. to about 50° C., then treated with aqueous ammonia. The readily saccharifiable carbohydrate-enriched biomass may be saccharified with an enzyme consortium to produce fermentable sugars.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Corn fractionation method
InactiveUS20070184541A1Avoid fermentationContributing to air pollutionMicroorganismsBiofuelsFractionationFermentable sugar
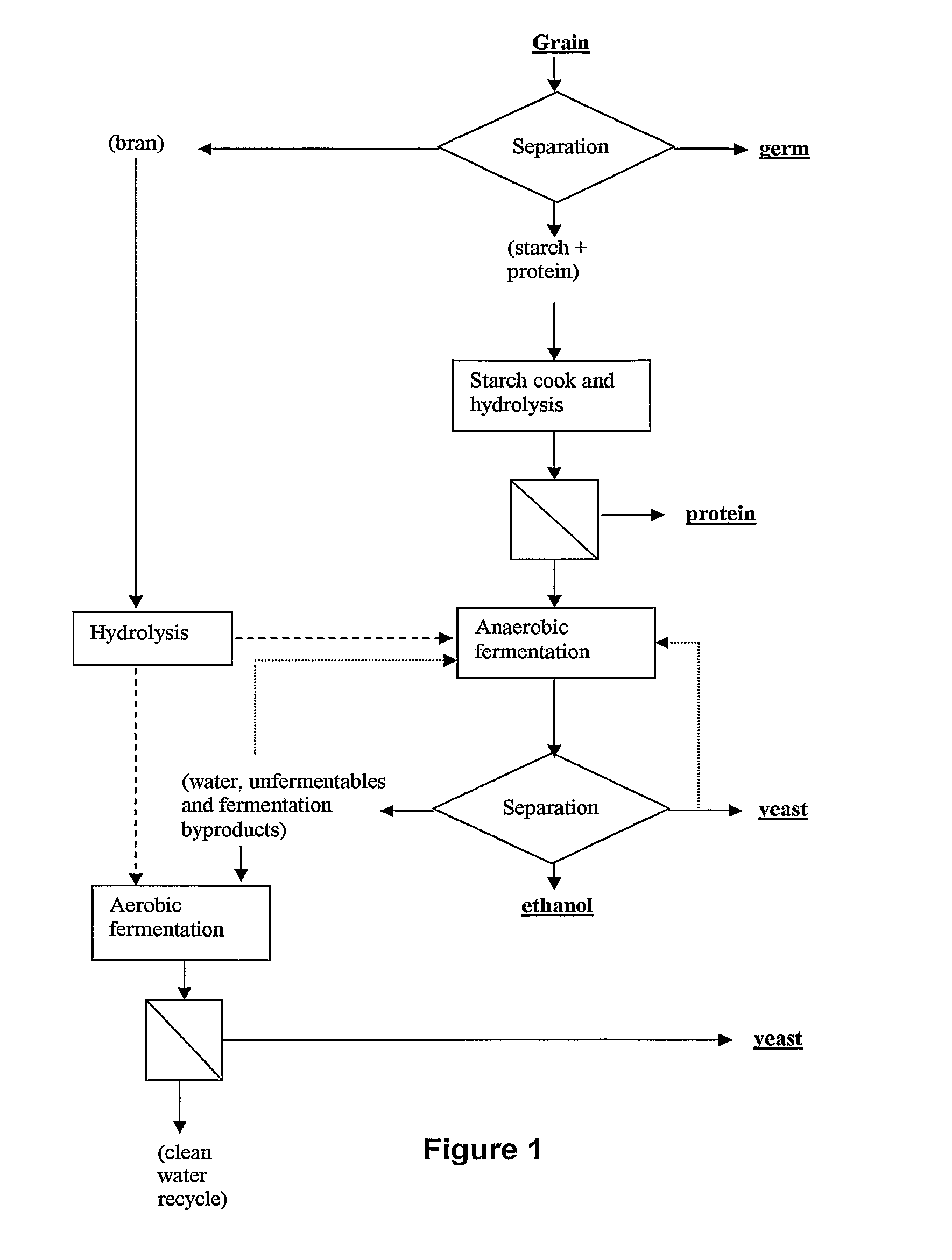
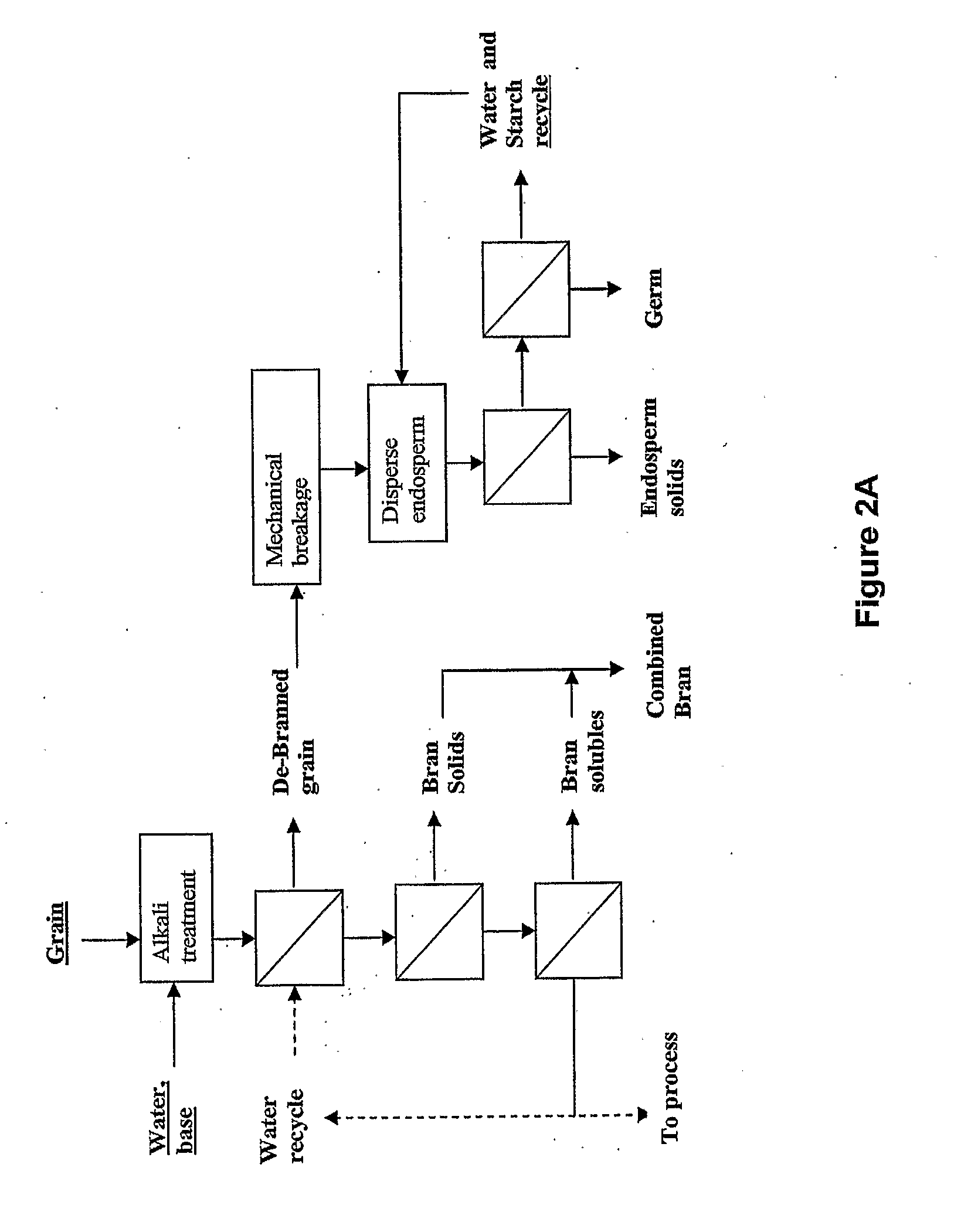
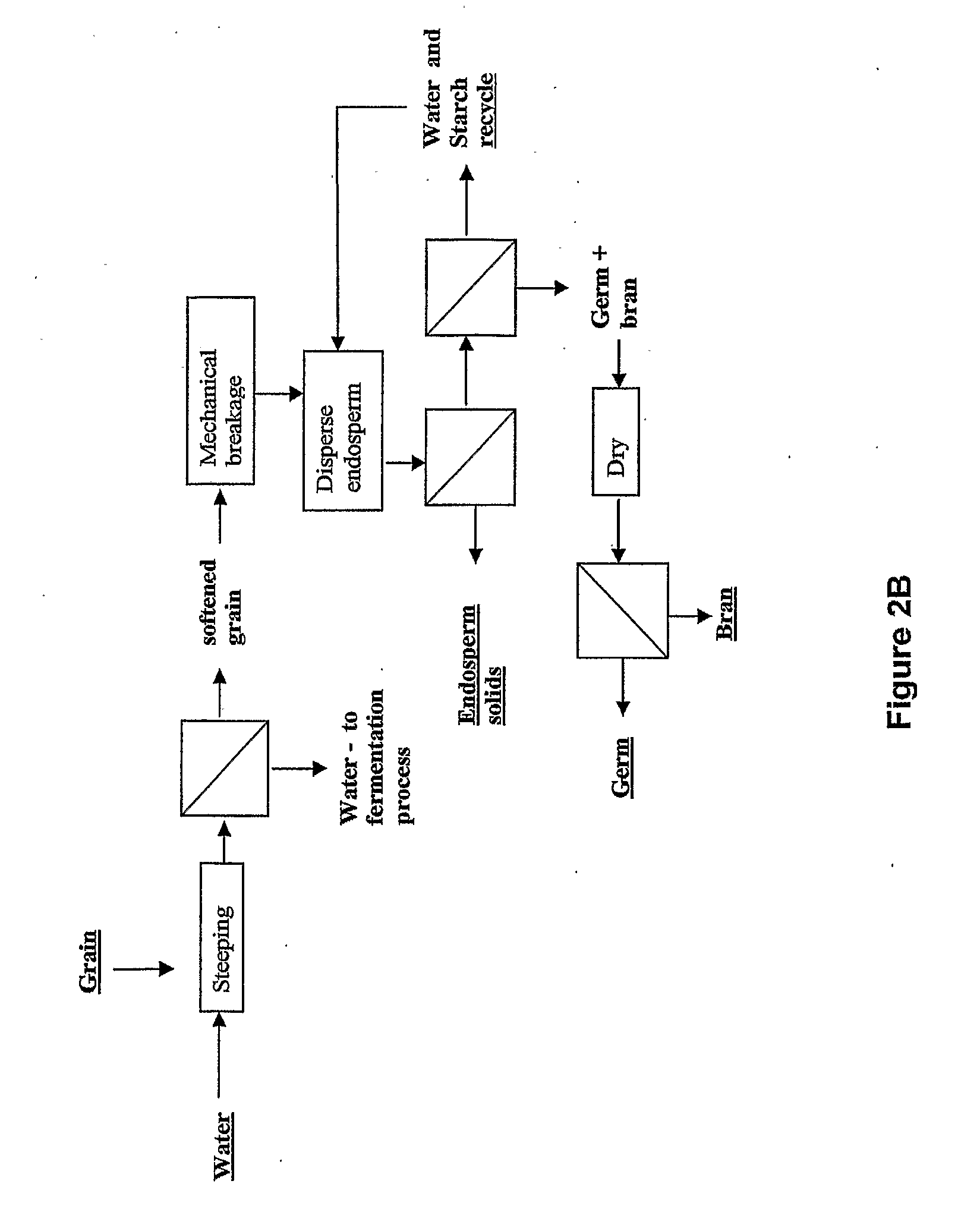
An improved method for processing corn into ethanol and other valuable co-products. The invention generally involves a multi-step process which produces germ (or oil), protein, and feed yeast as its co-products while maintaining or enhancing the provision of fermentable sugar to ethanol fermentation. This is accomplished by fundamentally altering the way the corn is fractionated, disrupting the cell walls rather than the protein matrix as is done in conventional wet milling.
Owner:GRAINVALUE
Concentrated sulfuric acid hydrolysis of lignocellulosics
InactiveUS6063204AMinimize and preclude potential backflowEliminate requirementsPressurized chemical processOther chemical processesUnit operationFermentable sugar
A process, system, and apparatus for effectively and economically producing fermentable sugars from cellulosic feedstocks is described. The economic viability of using wood and / or agricultural waste, containing large fractions of cellulose and hemicellulose is highly dependent on the method used for hydrolysis. Underlying the gist of this invention are newly discovered methods, means, and techniques by which both the pentosans and hexosans comprising the hemicellulose fraction of the selected feedstock and the hexosans comprising the cellulose fraction of the selected feedstock can be quickly and efficiently converted in a single pass through a single device to fermentable sugars containing minimal quantities of degradation products known to inhibit fermentation. Successful operation of this new hydrolysis process employing a new reactor design can produce fermentable sugars at rates and efficiencies previously thought unattainable by reducing the number of processing steps, pieces of equipment, and unit operation previously used.
Owner:FARINA GEORGE E
Treating biomass to produce materials useful for biofuels
Fermentable sugar useful for the production of biofuels can be produced from biomass by contacting the biomass with a solution containing at least one α-hydroxysulfonic acid. The α-hydroxysulfonic acid can be easily removed from the product and recycled.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS7666637B2Robust and cost-effectiveImproving biological reactivity of celluloseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentHydrolysate
The invented process separates main components in lignocellulosic biomass, specifically hardwoods, softwoods into lignin and fractions of high purity sugars which are used for ethanol production. The invented process comprises of treatment stages at high temperature and high pressure with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. Residual lignin and extractives in the cellulosic solid fraction are selectively removed by chemical treatments of sodium chlorite, anhydrous acetic acid, chlorine and chlorine dioxide to enhance the purity and biological conversion of cellulose to ethanol. The pre-hydrolysate generated from the acid treatment stage, containing xylose, arabinose, galactose, glucose and the purified cellulosic fraction are enzymatically hydrolyzed and fermented to produce ethanol. Significant amount of lignin from the process is recovered as a by-product.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
Integrated biorefineries for production of sugars, fermentation products, and coproducts
InactiveUS20140356915A1Minimize cooling water requirementRequires minimizationChemical industryBiofuelsSolventMonomer
Processes are described for fractionating lignocellulosic biomass into cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, comprising fractionating lignocellulosic biomass in the presence of a solvent for lignin (such as ethanol), a hydrolysis catalyst (such as sulfur dioxide), and water, to produce a liquor containing hemicellulose, cellulose-rich solids, and lignin; hydrolyzing the hemicellulose to produce hemicellulosic monomers; saccharifying the cellulose-rich solids to produce glucose; recovering the hemicellulosic monomers and the glucose, separately or in a combined stream, as fermentable sugars; and fermenting the fermentable sugars to a fermentation product having a higher normal boiling point than water. Process integration of mass and / or energy is disclosed in many specific embodiments. The fermentation product may include an organic acid, an alcohol, a diol, or combinations thereof.
Owner:API INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
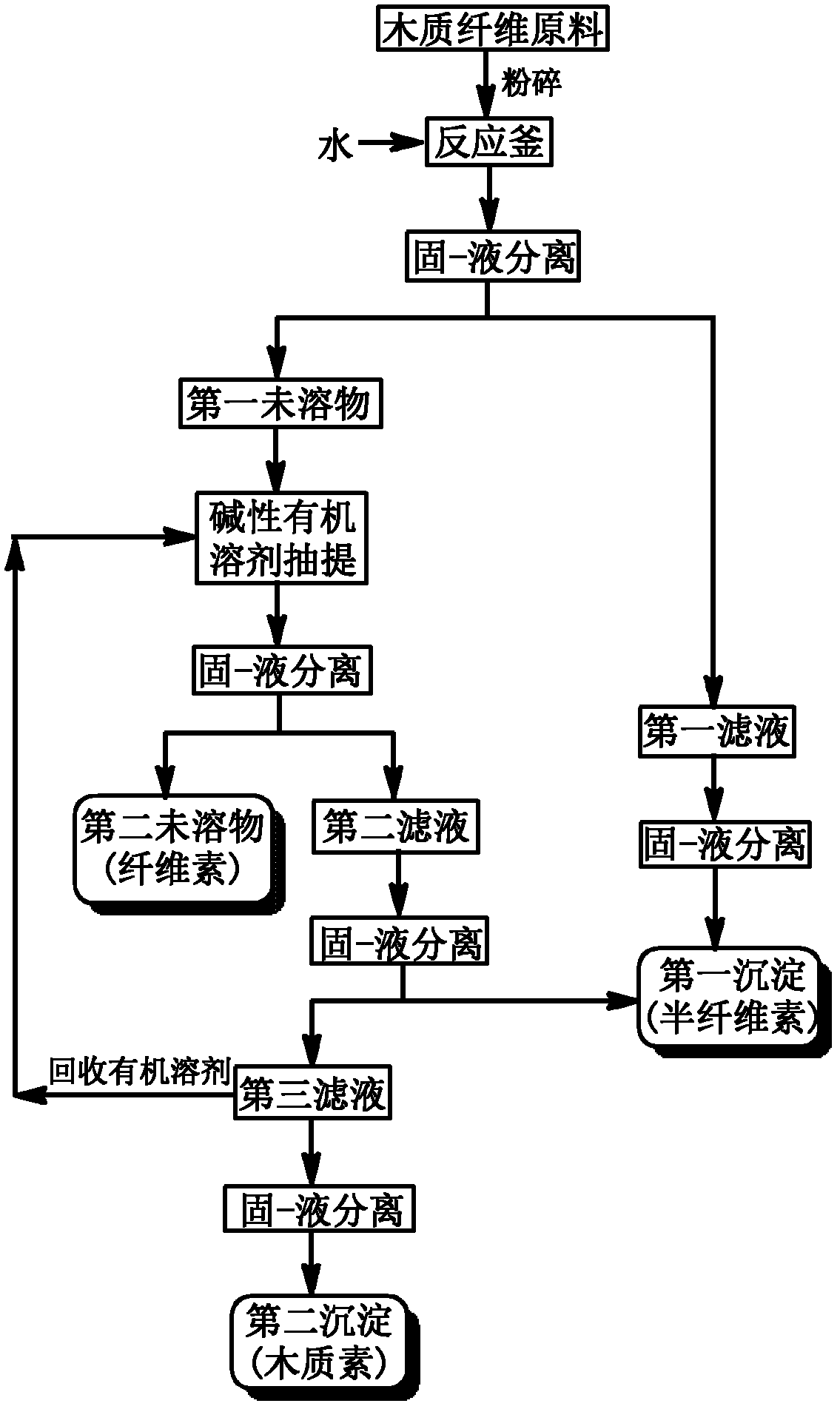
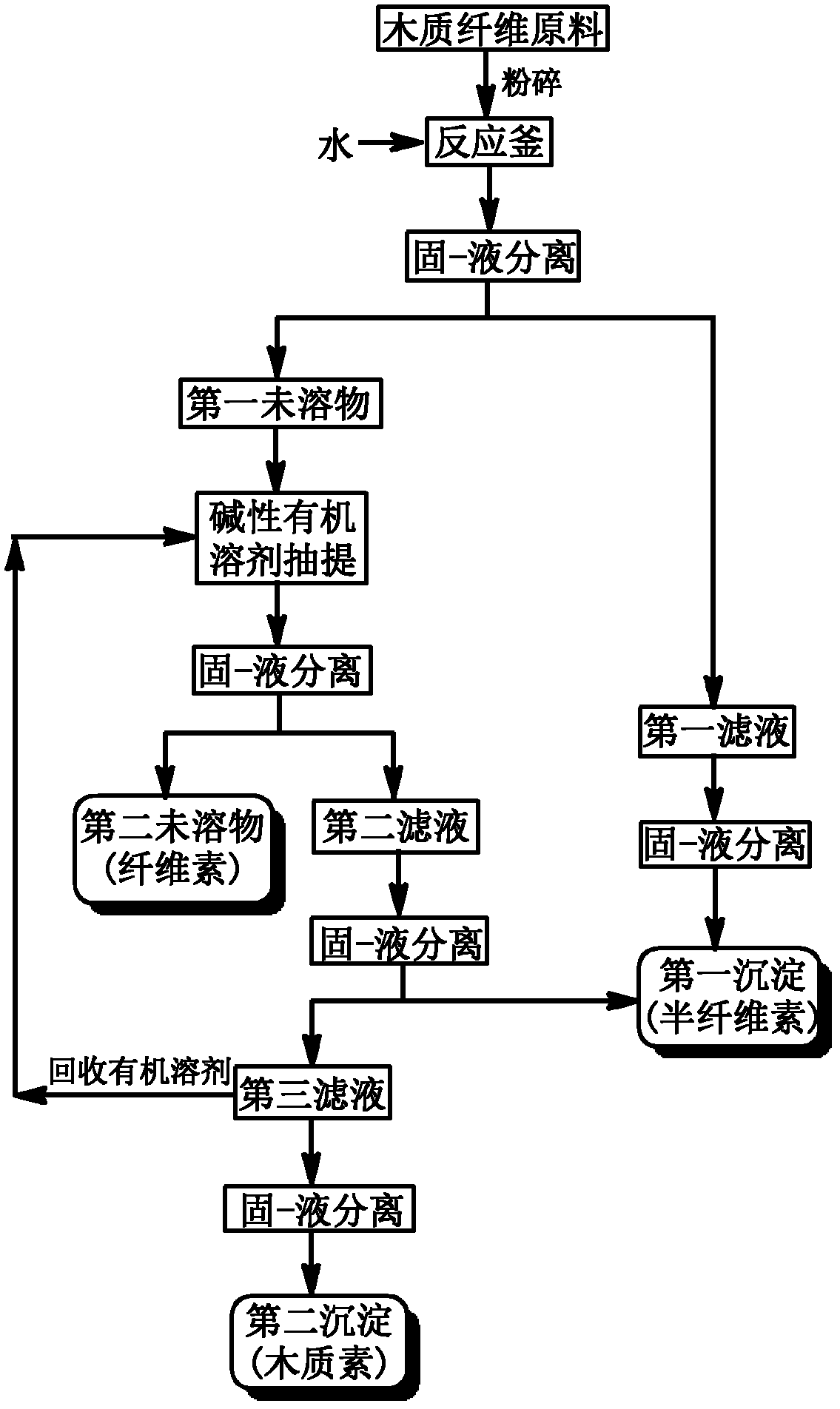
Method of extracting hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin from wood fiber raw materials
The invention relates to a method of extracting hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin from wood fiber raw materials and belongs to the field of utilization and technology of biomass resources of agriculture and forestry. In the method, the hemicellulose is extracted from the wood fiber raw materials by using hot water, then the lignin is extracted by using alkaline organic solvent under mild conditions; and residual ingredients rich in the cellulose are further used for enzyme hydrolysis to prepare fermentable sugar solution, thereby achieving full-ingredient utilization of the hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin in the biomass resources of the agriculture and forestry. The method has simple process, and is environmentally friendly, the organic solvent can be recycled, thereby promoting the development of the green agriculture and forestry, and the method has wide social and economic benefits.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
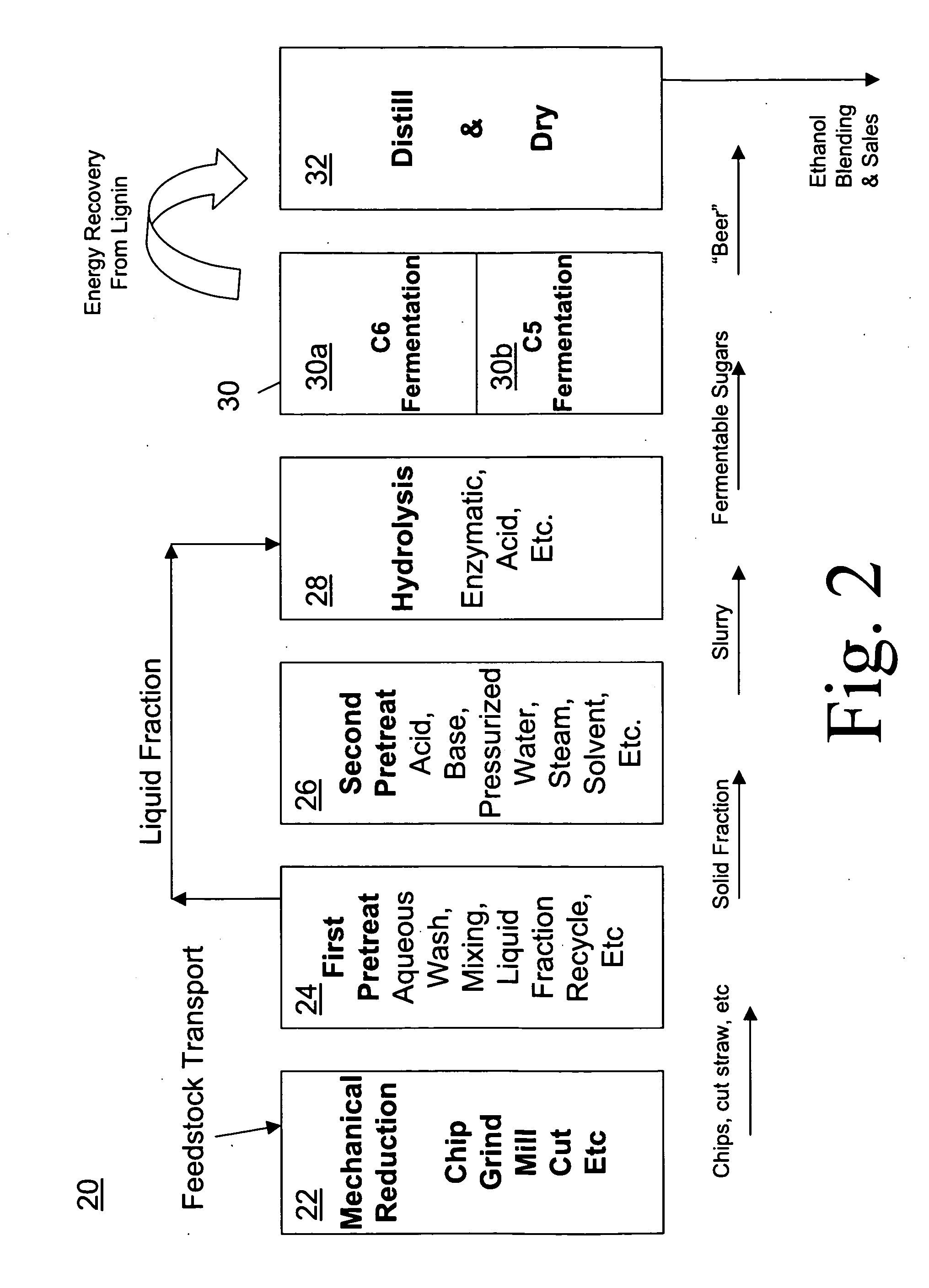
Treatment Systems and Processes for Lignocellulosic Substrates that Contain Soluble Carbohydrates
InactiveUS20090061495A1Lowering capital cost per unit of ethanol producedImprove throughputBiofuelsFermentationDistillationPolymer
A biorefining process used to convert lignocellulosic biomass into ethanol via a fermentation pathway. In a first pretreatment process step, the biomass is mixed with an aqueous wash solution to remove soluble carbohydrates from the biomass structure. Next, the solid fraction is separated from a liquid fraction. In a second pretreatment process, the solid fraction is pre-treated to make the fiber bundles and complex polysaccharides more amenable to enzymatic hydrolysis. Following the second pretreatment process, the pre-treated biomass is subjected to one or more enzymes in a hydrolysis process. The liquid fraction isolated from the first pretreatment process is diverted past the second pretreatment process and is recombined with the solid fraction in the hydrolysis process. The enzyme cocktail in the hydrolysis process breaks down the alpha- and hemicellulose polymers into fermentable sugars. Finally, a fermentation process produces a “beer” that is further processed in a distillation and dehydration process.
Owner:BEATTY CHRIS +2
Production of gasoline from fermentable feedstocks
ActiveUS20100137647A1High speedHigh oil contentOrganic compound preparationBiofuelsBiodieselKetonic acids
Methods are disclosed for forming heptan-4-one, and, optionally, heptan-4-ol, from fermentable sugars. The sugars are fermented using a bacteria or yeast that predominantly forms butyric acid. The butyric acid is subjected to catalytic ketonization conditions to form heptan-4-one, with concomitant loss of water and carbon dioxide. The heptan-4-one can be subjected to catalytic hydrogenation to form heptan-4-ol, an either of these can be included in gasoline compositions. In one aspect, the fermentable sugars are derived from lignocellulosic materials such as wood products, switchgrass, or agricultural wastes, which are delignified to form lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose. The cellulose and hemicellulose can be depolymerized to form glycose and xylose, either or both of which can be fermented by the bacteria. Thus, the methods described herein can convert biomass to a fuel composition or fuel additive, which can be used in a conventional gasoline engine, unlike traditional fuels such as ethanol or biodiesel.
Owner:CPS BIOFUELS INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com