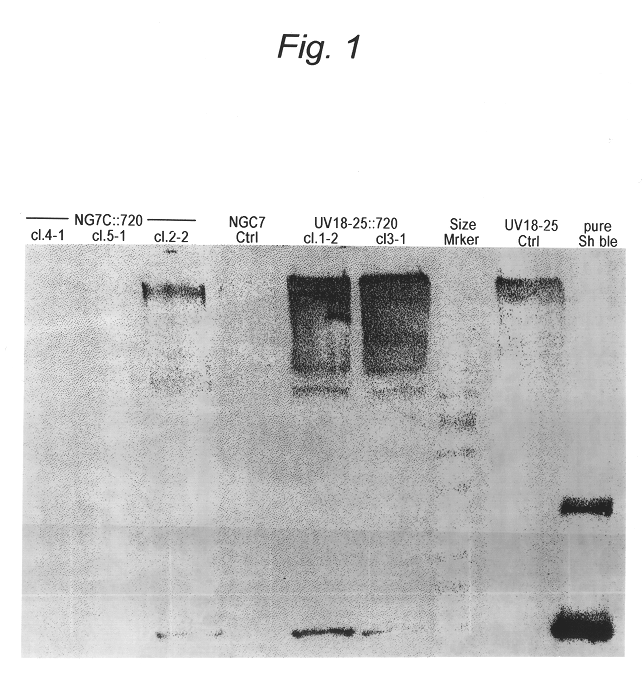
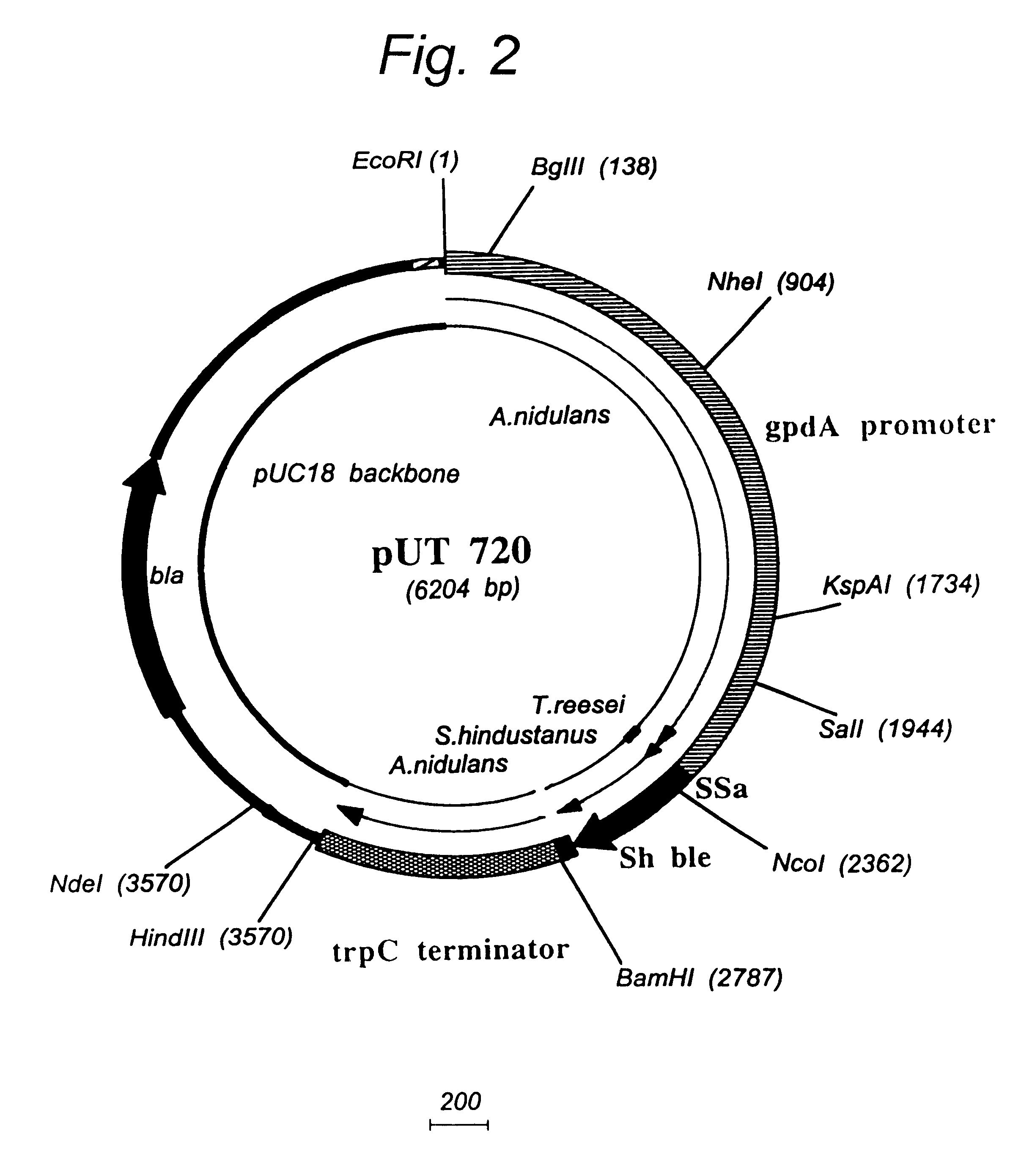
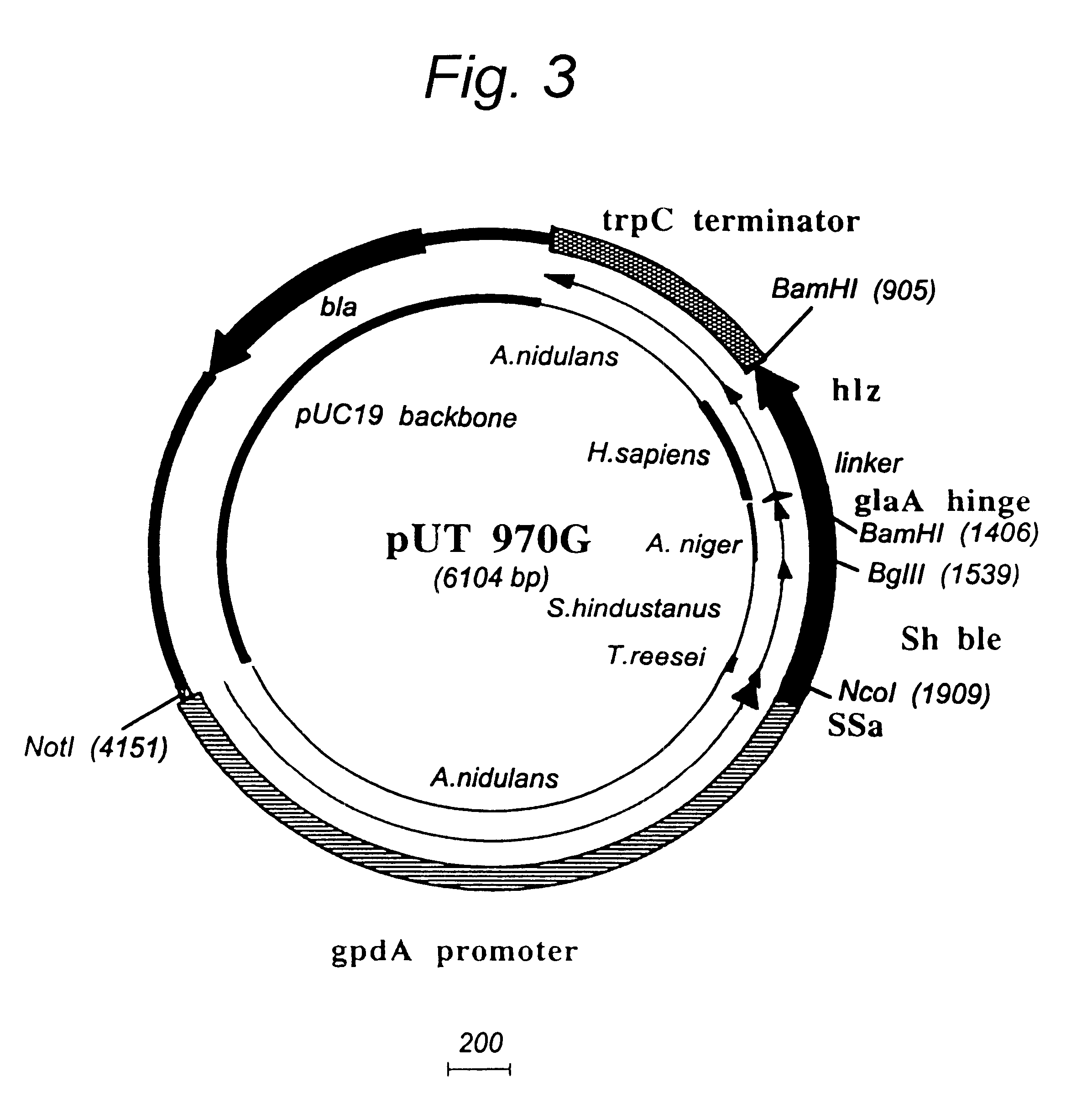
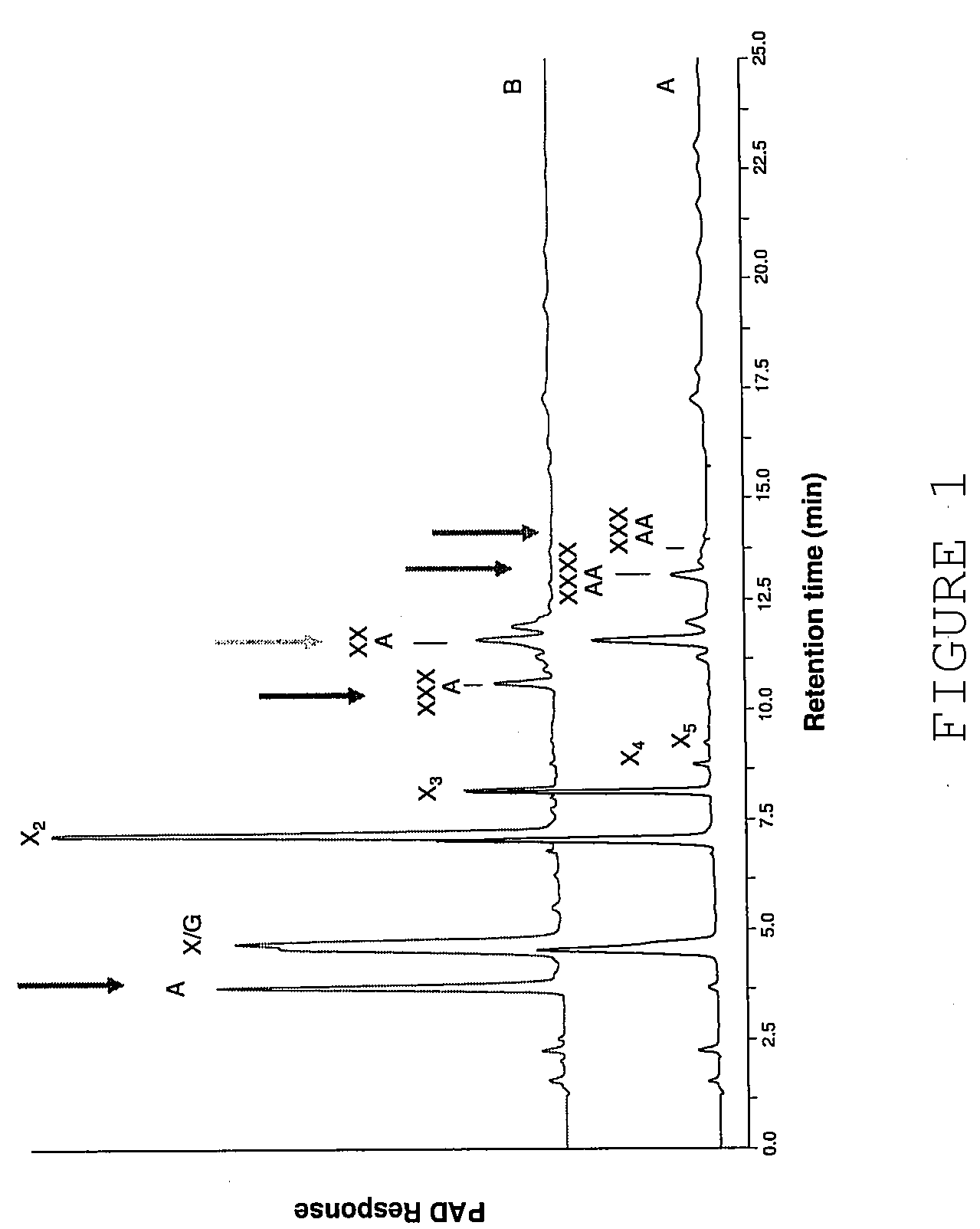
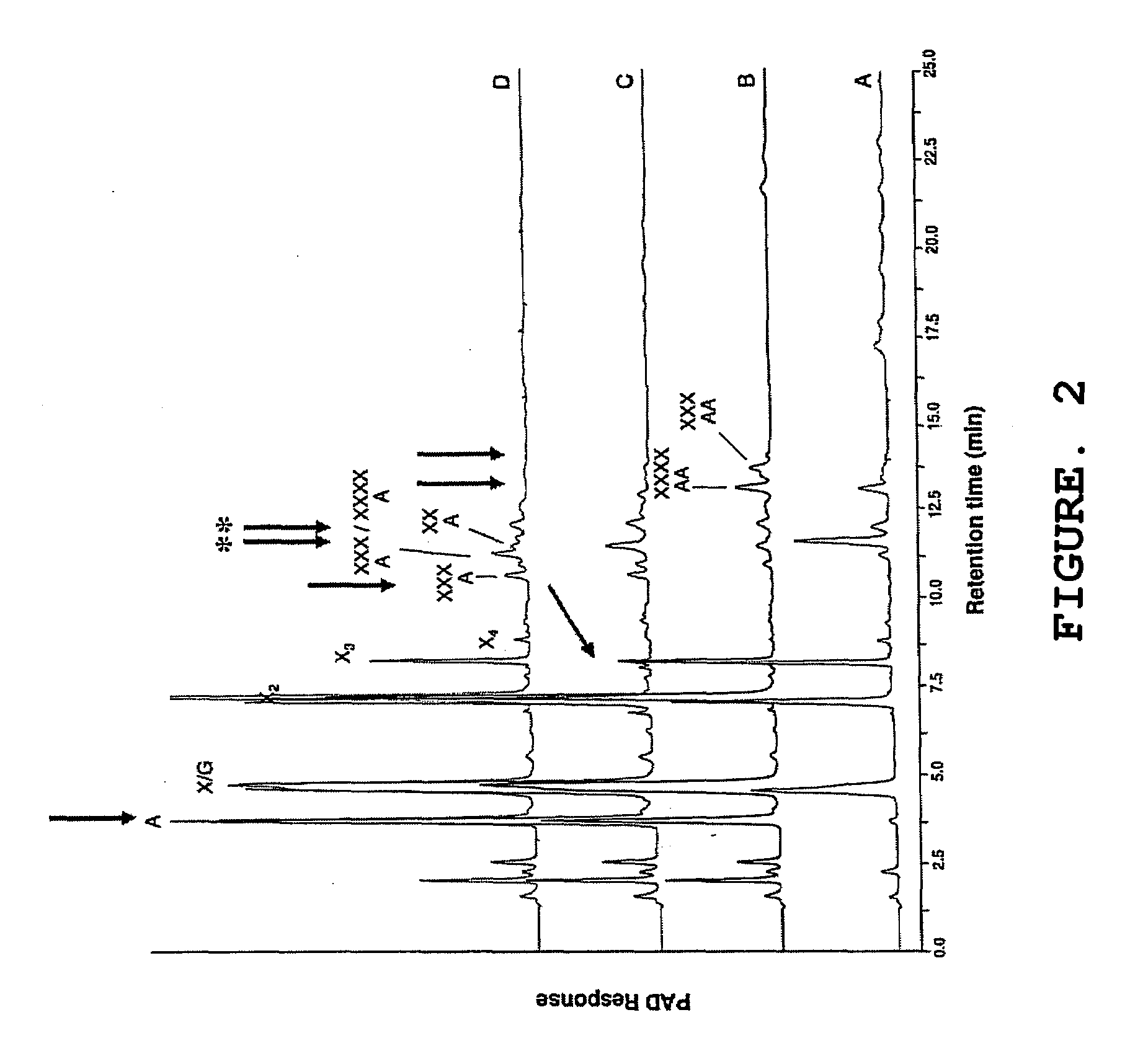
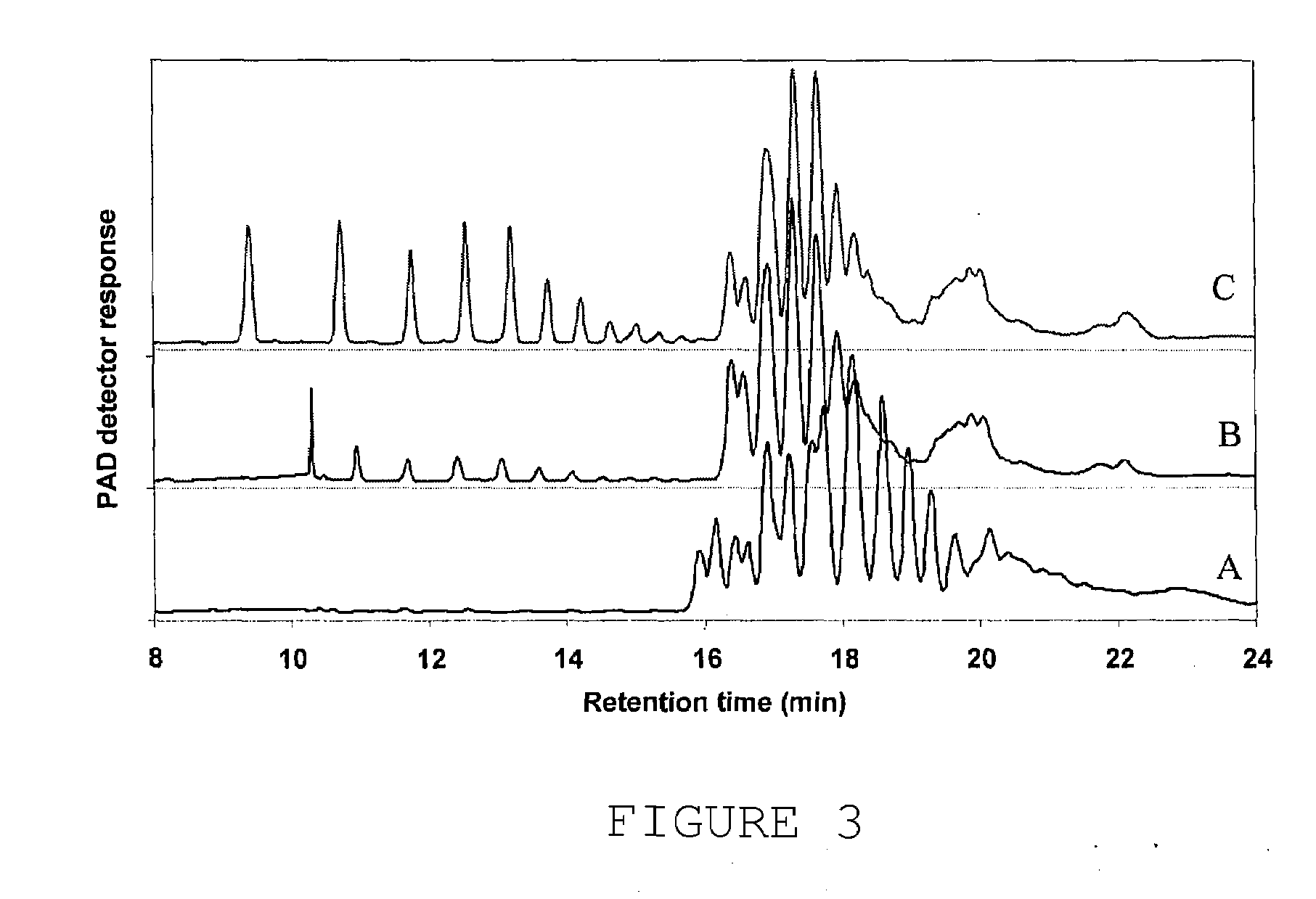
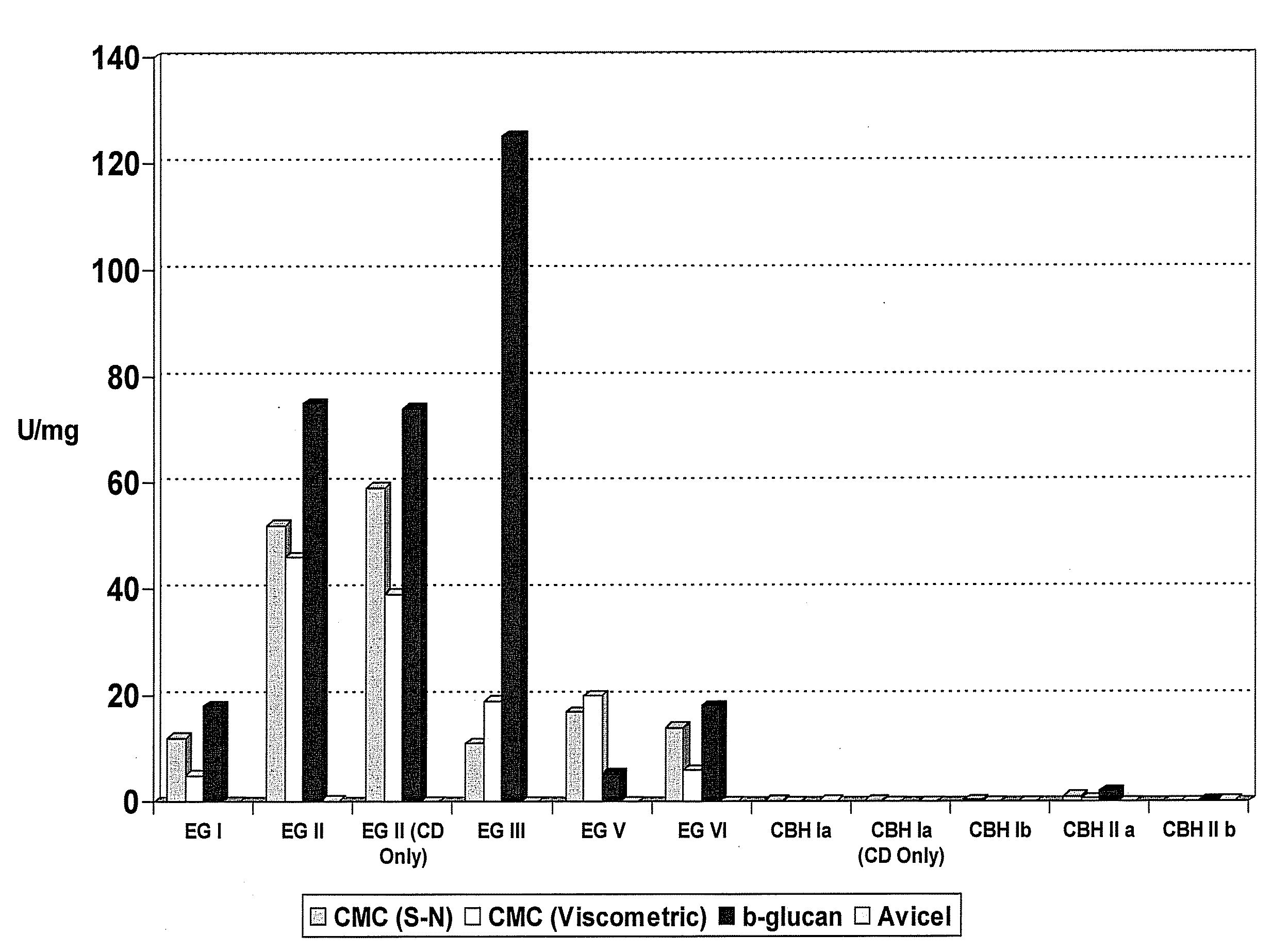
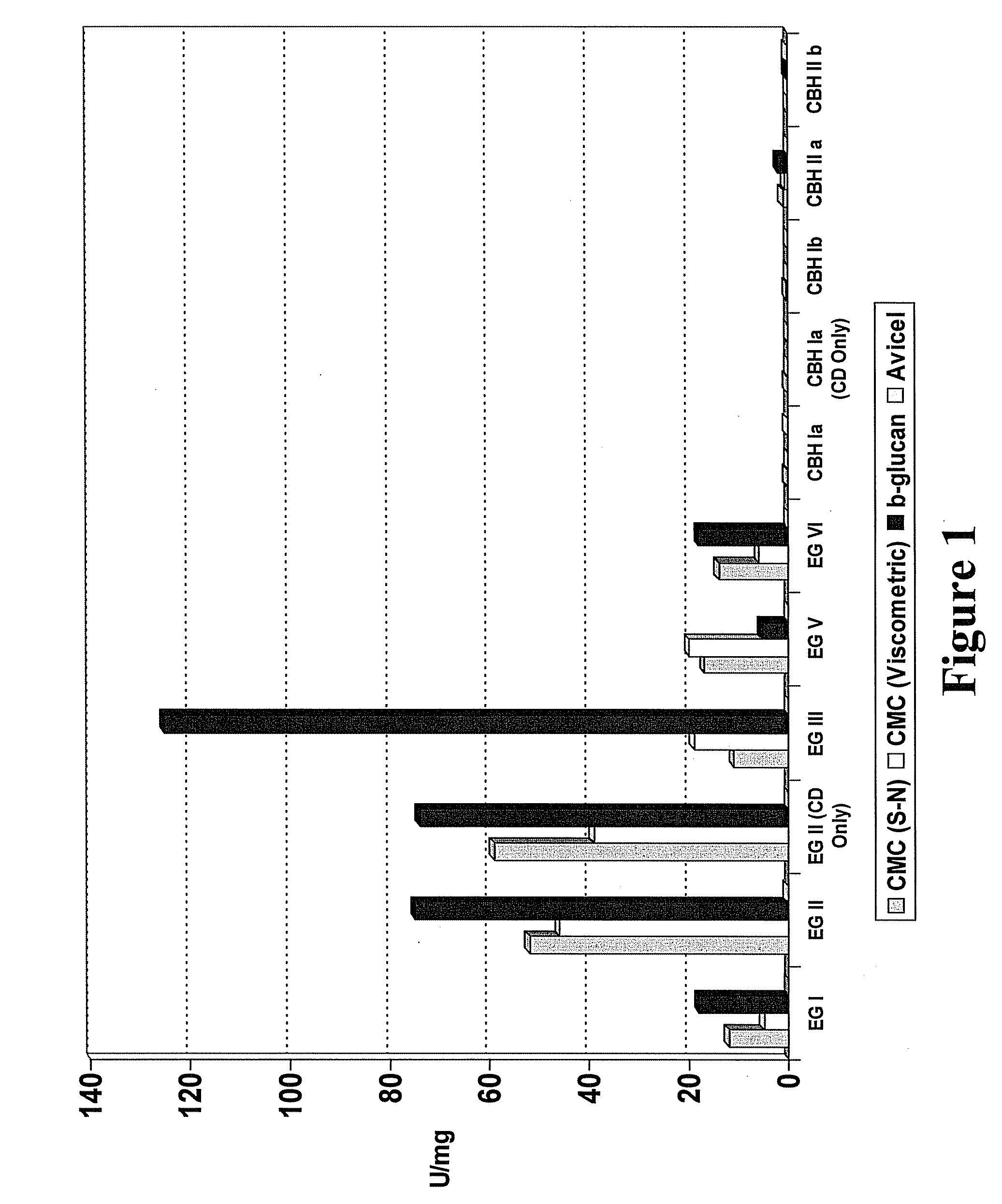
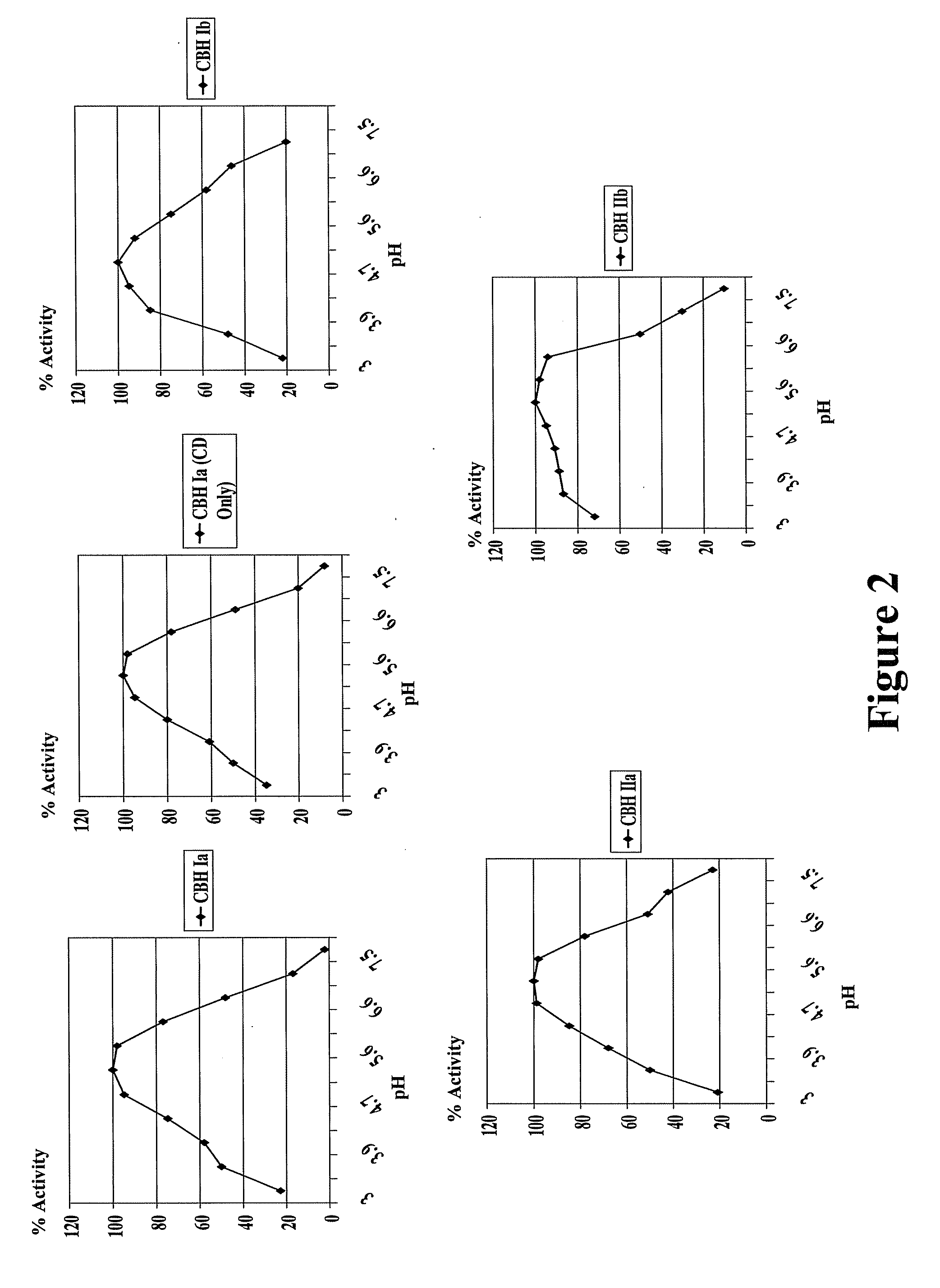
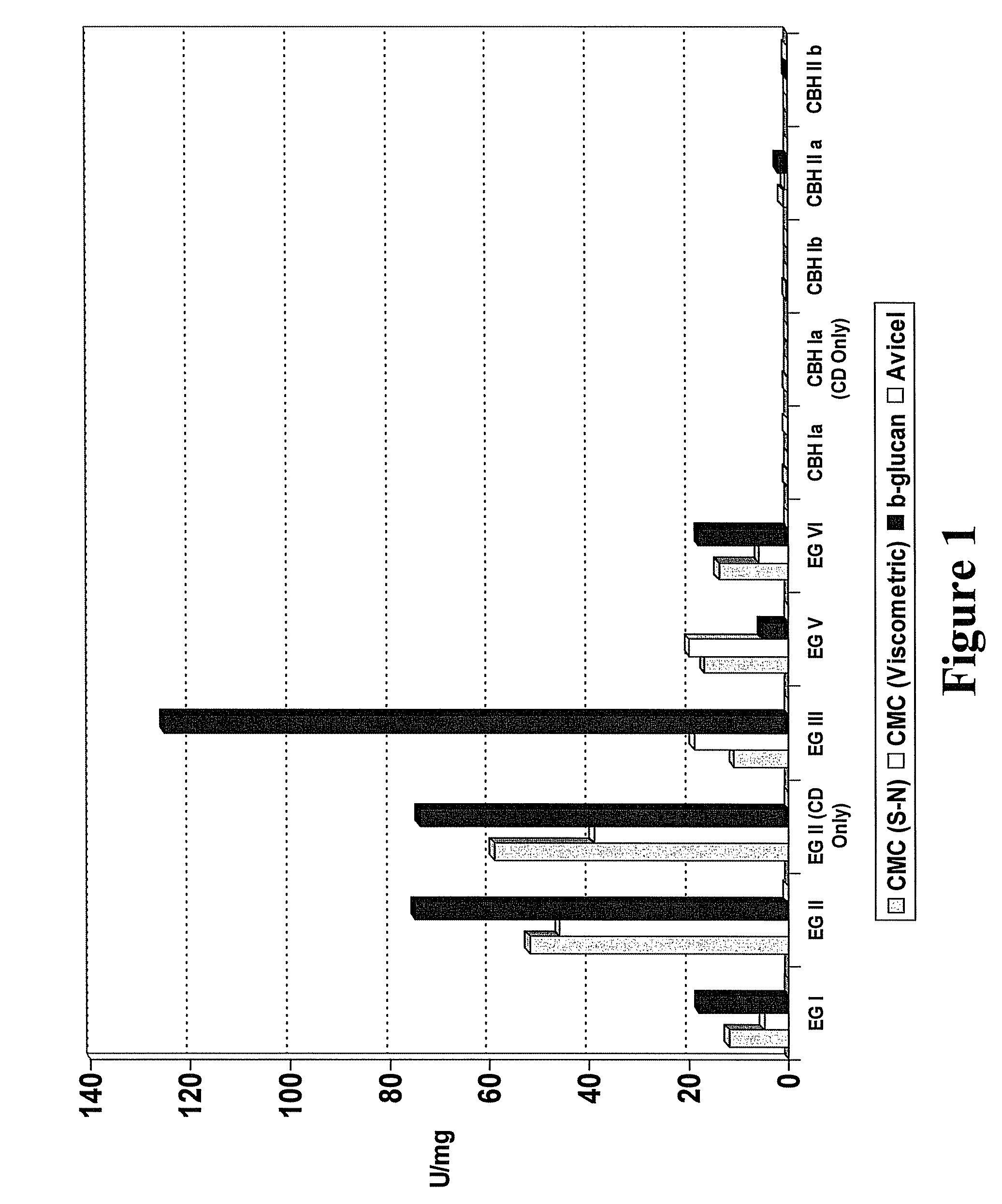
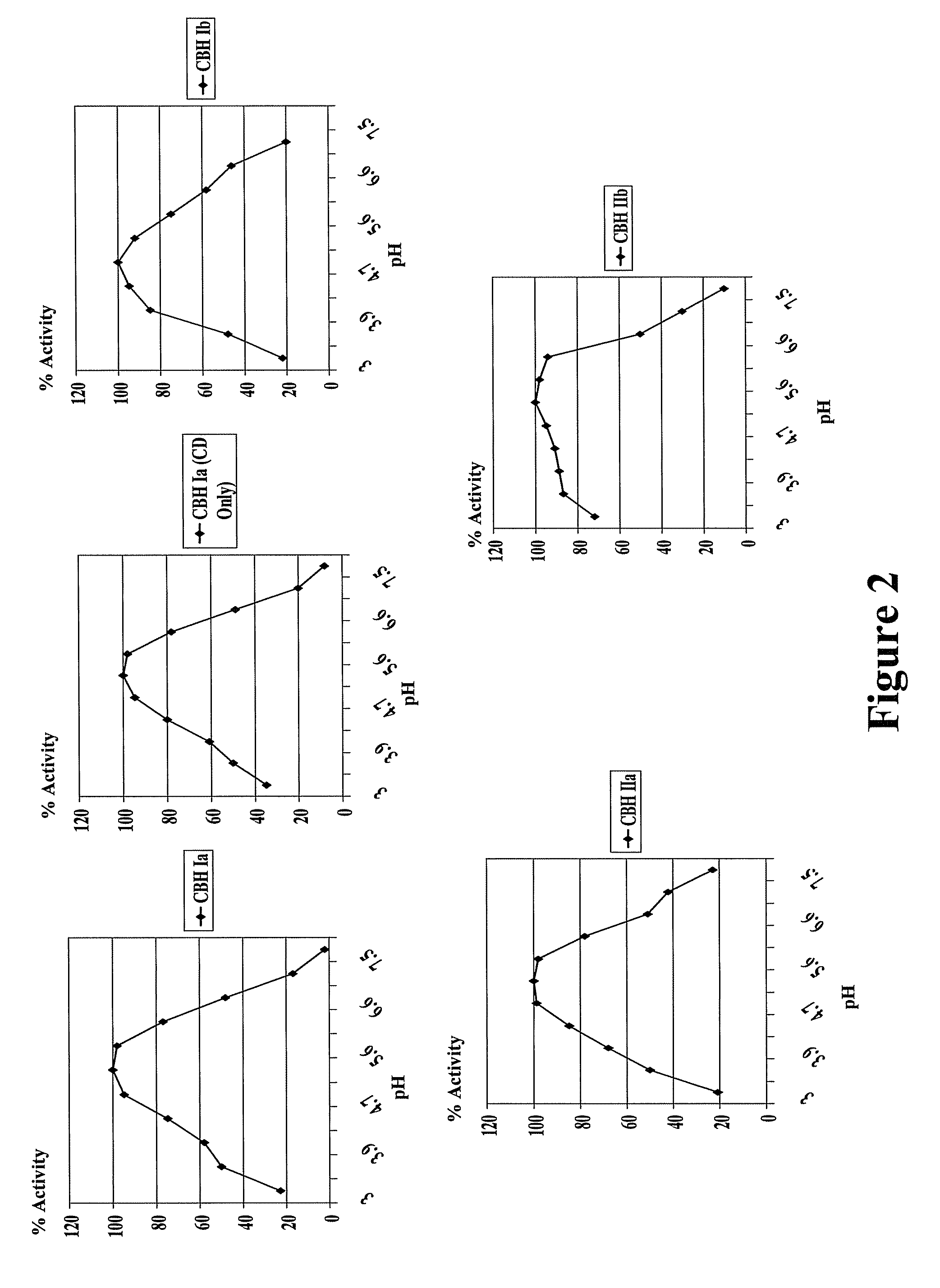
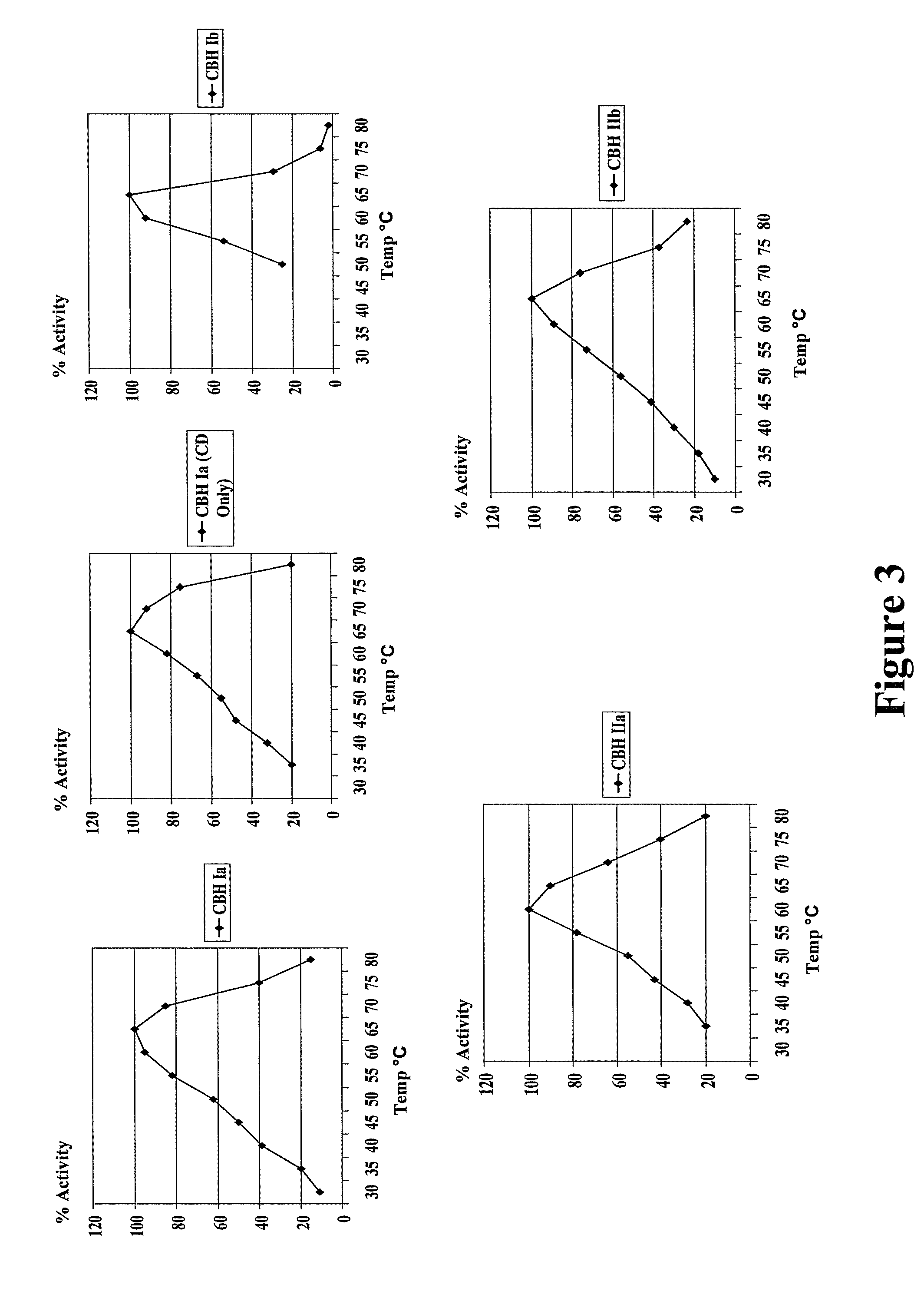
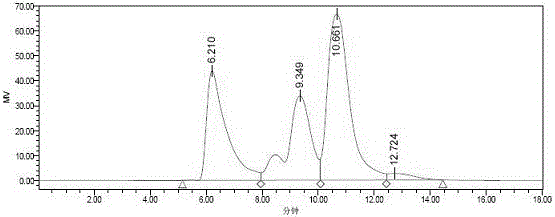
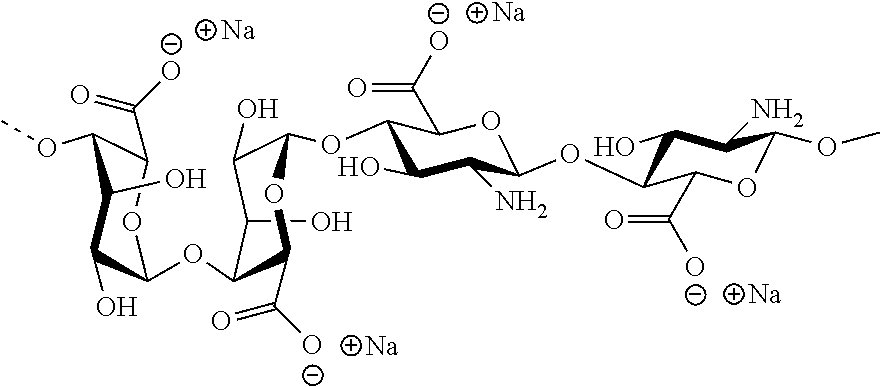
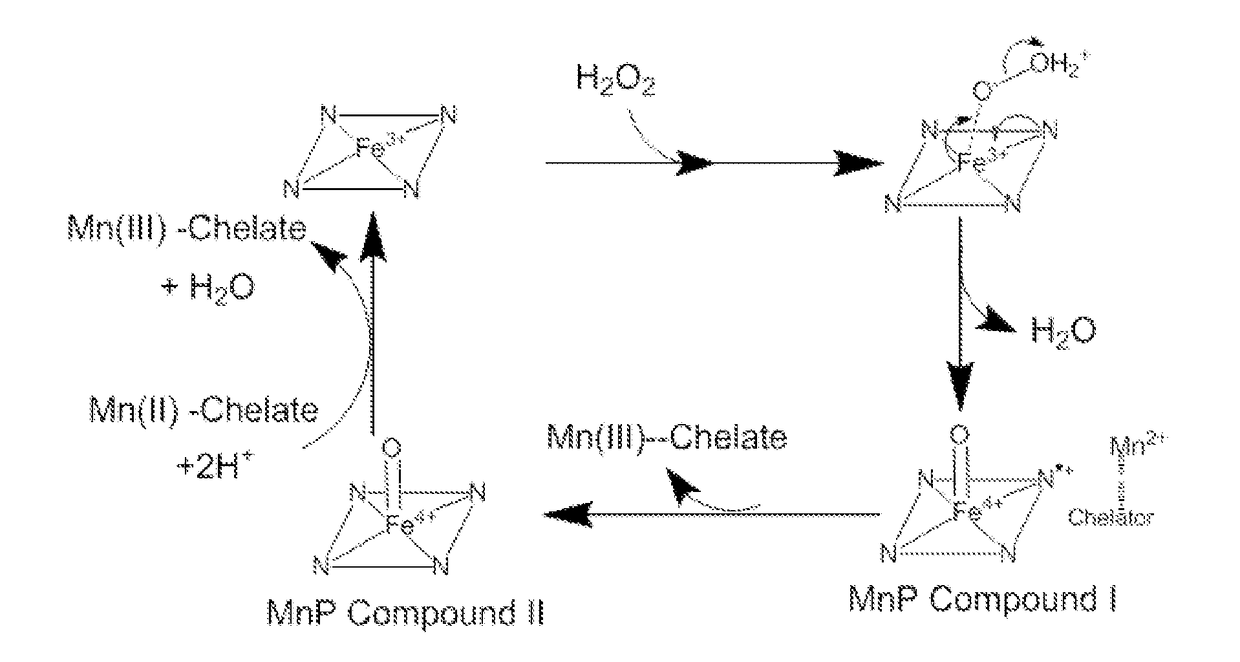
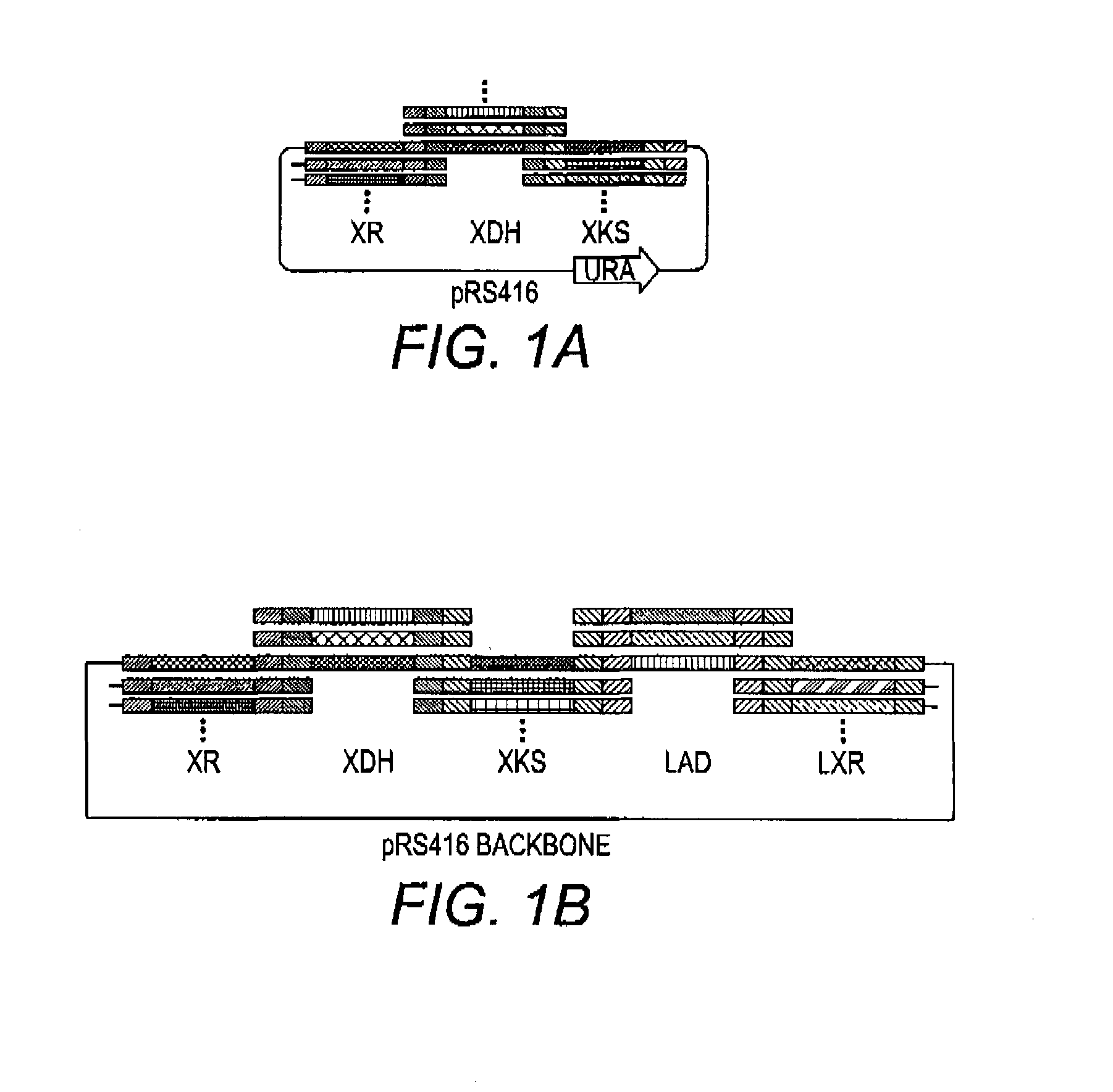
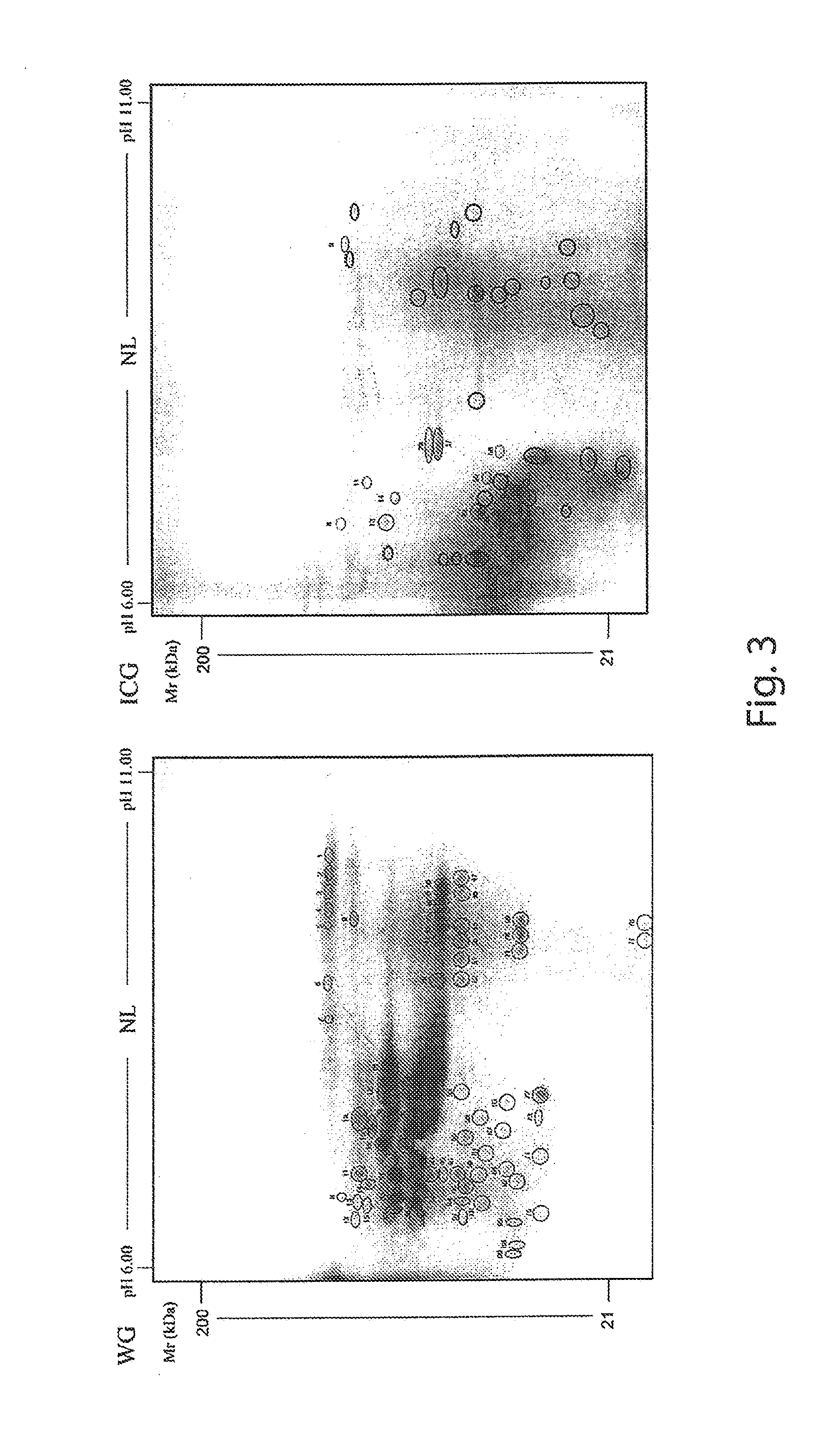
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Fungal enzymes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fungi can contain a variety of enzymes, such as protease, amylase, lipase, cellulase and tilactase (supports lactose absorption). Like plant enzymes, fungal enzymes are acid stable and can survive within the pH range of the stomach. They are also suitable for a vegetarian diet, unlike animal-sourced enzymes.
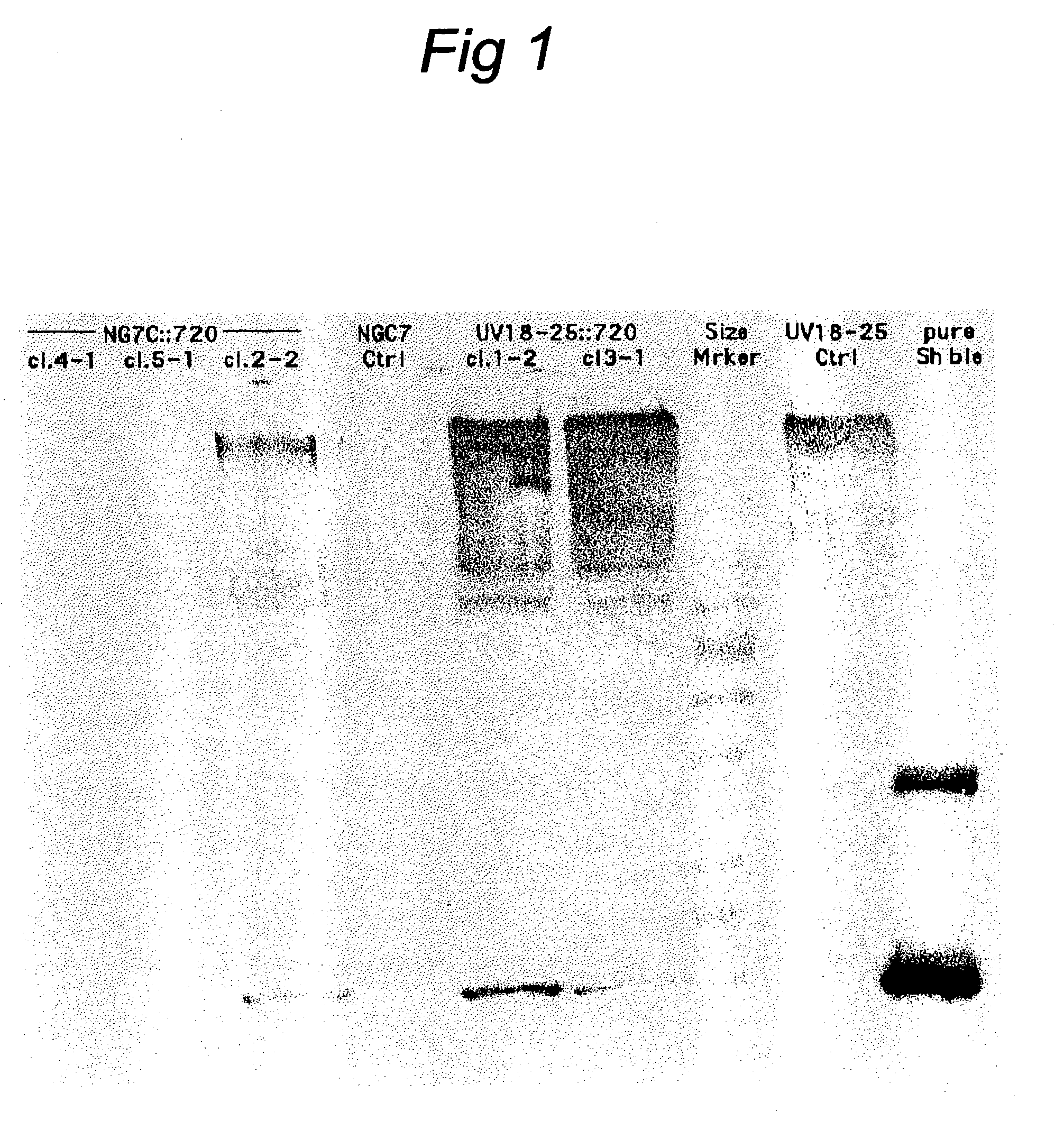
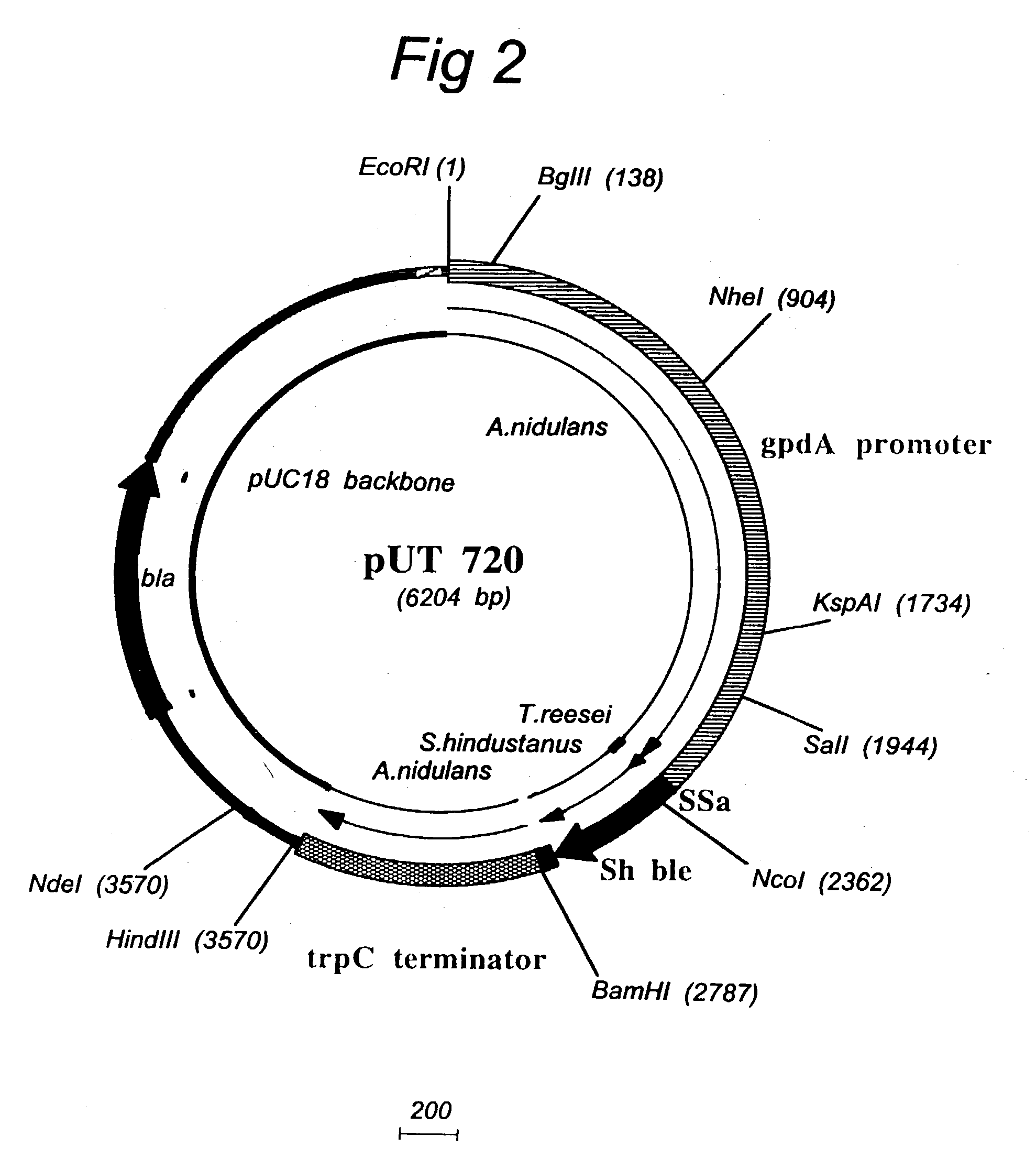
Transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts
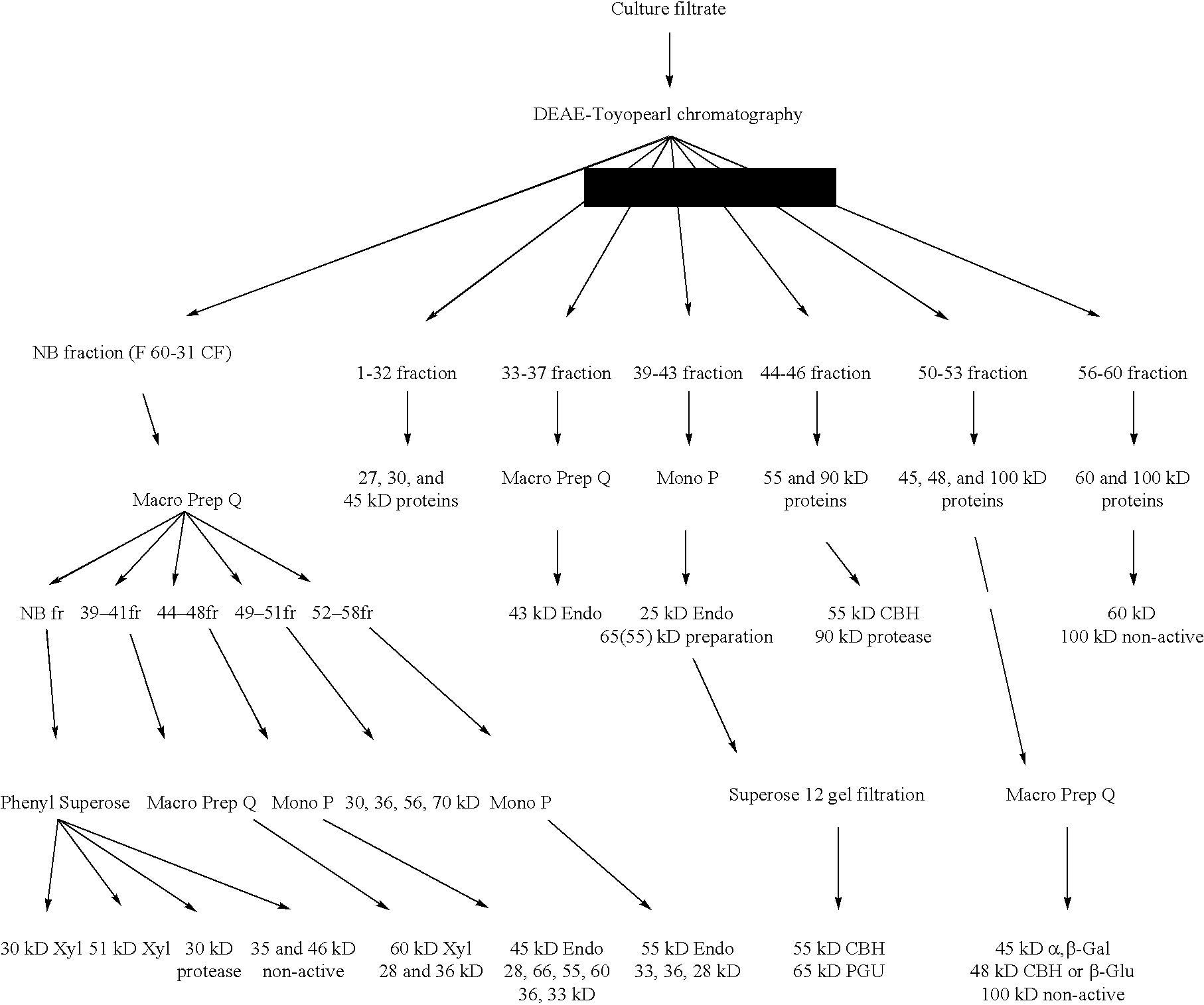
A novel transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts for expressing and secreting heterologous proteins or polypeptides is described. The invention also covers a process for producing large amounts of polypeptide or protein in an economical manner. The system comprises a transformed or transfected fungal strain of the genus Chrysosporium, more particularly of Chrysosporium lucknowense and mutants or derivatives thereof. It also covers transformants containing Chrysosporium coding sequences, as well expression-regulating sequences of Chrysosporium genes. Also provided are novel fungal enzymes and their encoding sequences and expression-regulating sequences.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Novel Fungal Enzymes
This invention relates to novel enzymes and novel methods for producing the same. More specifically this invention relates to a variety of fungal enzymes. Nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, compositions, recombinant and genetically modified host cells, and methods of use are described. The invention also relates to a method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars with enzymes that degrade the lignocellulosic material and novel combinations of enzymes, including those that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. The invention also relates to a method to release cellular content by degradation of cell walls. The invention also relates to methods to use the novel enzymes and compositions of such enzymes in a variety of other processes, including washing of clothing, detergent processes, biorefining, deinking and biobleaching of paper and pulp, and treatment of waste streams.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Novel Fungal Enzymes
InactiveUS20090280105A1Easy to cleanOrganic active ingredientsNon-fibrous pulp additionCelluloseWaste stream
This invention relates to novel enzymes and novel methods for producing the same. More specifically this invention relates to a variety of fungal enzymes. Nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, compositions, recombinant and genetically modified host cells, and methods of use are described. The invention also relates to a method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars with enzymes that degrade the lignocellulosic material and novel combinations of enzymes, including those that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. The invention also relates to methods to use the novel enzymes and compositions of such enzymes in a variety of other processes, including washing of clothing, detergent processes, deinking and biobleaching of paper and pulp, and treatment of waste streams.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Fungal enzymes
InactiveUS7923236B2Easy to cleanOrganic active ingredientsNon-fibrous pulp additionCelluloseWaste stream
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts
InactiveUS20040002136A1Minimise risk of degradationAvoid necessityFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyMutant
A novel transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts for expressing and secreting heterologous proteins or polypeptides is described. The invention also covers a process for producing large amounts of polypeptide or protein in an economical manner. The system comprises a transformed or transfected fungal strain of the genus Chrysosporium, more particularly of Chrysosporium lucknowense and mutants or derivatives thereof. It also covers transformants containing Chrysosporium coding sequences, as well expression-regulating sequences of Chrysosporium genes. Also provided are novel fungal enzymes and their encoding sequences and expression-regulating sequences.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Zymocyte mixture containing lucid ganoderma, preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a zymocyte mixture containing lucid ganoderma. A mycoplasm mixture containing hypha and culture matrix components is obtained by fermenting the lucid ganoderma in a solid fermentation mode in a nutritional culture matrix which at least comprises a carbon source and a nitrogen source needed by the growth of fungi, wherein medical raw materials salvia miltiorrhiza are mixed in the culture matrix. A mycoplasm fermentation final product having both the effects of the salvia miltiorrhiza and the ganoderma fungi is obtained after bidirectional solid fermentation including influence of medical raw materials on the growth and metabolism process of ganoderma mycelium and transformation of a ganoderma fungal enzyme system on the medical materials compositions, and the invention can be applied to preparing a medicament and / or a cosmetic with the effects of promoting blood circulation by removing blood stasis and antioxidation.
Owner:成都宇泽生物基因化妆品有限公司
Fungal cell wall degrading enzyme
ActiveUS7635470B2Convenient ligationCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method for producing low DE value malt oligosaccharide syrup by potato starch
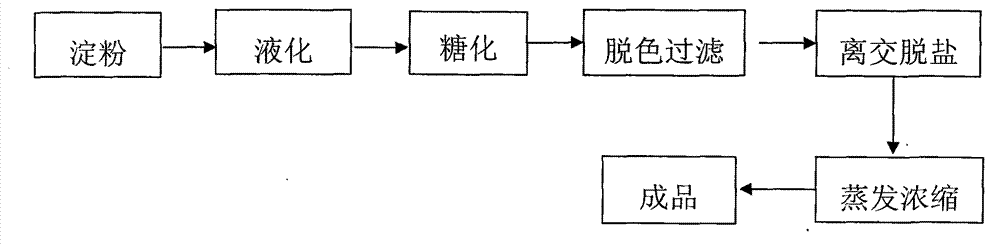
The invention relates to a method for producing low DE value malt oligosaccharide syrup by potato starch, which takes the potato starch as raw material and sequentially leads liquefaction and saccharification to be carried out. The method comprises the steps of: adding 0.03-0.06wt% of calcium chloride and 30-40mu / g of starch high temperature resistant alpha-amylase into starch slurry with the specific weight of 10-15 OBe and the pH value of 5.0-6.5, and carrying out liquefaction by a jet liquefier at the temperature of 105-115 DEG C; then, carrying out heat preservation on the liquefied material for 25-35min at the temperature of 95-98 DEG C; after that, adding 2-8mu / g of starch fungal enzyme and 0.3-1.0mu / g of starch pullulanase into the starch liquefied material, carrying out saccharification for 2-3h at the temperature of 55-65 DEG C, and obtaining starch saccharified liquid; and finally, decoloring and concentrating the saccharified liquid, and obtaining the low DE value malt oligosaccharide syrup with the solid material content of 60-65wt%. Therefore, the malt oligosaccharide syrup has the DE value of 30-40 and the main content of malt polysaccharide with the polymerization degree of 2-7, and can be used for preparing phosphate oligosaccharide.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing phosphoryl oligosaccharide by holoenzyme method
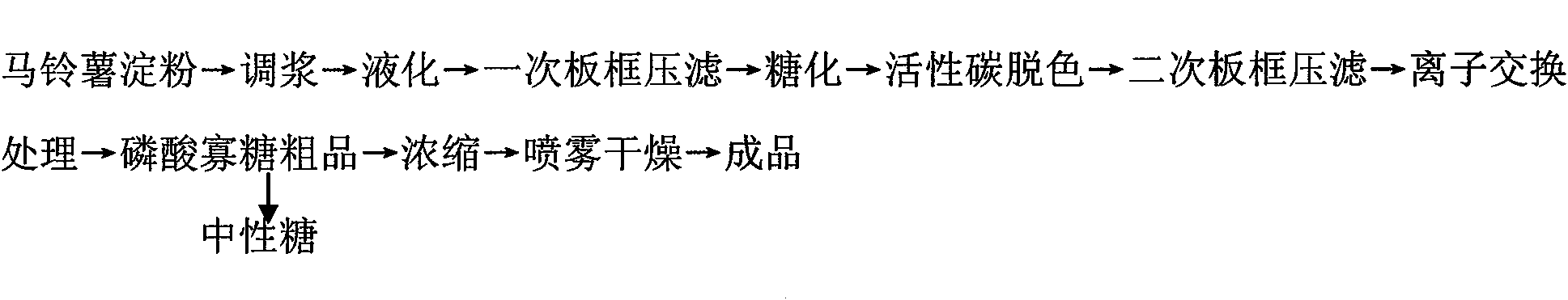
InactiveCN101792785ALarge exchange capacityBig economic interestsFermentationPotato starchFiltration
The invention discloses a method for preparing functional oligosaccharide, i.e. phosphoryl oligosaccharide by a holoenzyme method, which takes potato starch as the raw material. The invention adopts a novel high temperature resistant alpha-amylase to combine with the low-pressure steam injection and liquefaction technology to liquefy the potato starch; CaCl2 is added to serve as an erzyme activity accelerator; after the mixture is fully liquefied, liquefied liquid is saccharified by fungal enzyme after plate-frame pressure filtration; pullulanase is added for synergy to ensure that starch conversion rate is more than or equal to 98%; and malt oligosaccharide syrup with low DE value is prepared; 001*7 strong acidic styrene cation exchange resin is used for processing the syrup to remove parts of impurities with positive charges and coluring matters; then, 7170 strong-basicity styrene anion exchange resin is adopted for processing to remove natural sugar to obtain the phosphoryl oligosaccharide with negative charges; and finally, sugar liquor obtained by separation is concentrated and dried to obtain the target product.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing acarbose
ActiveCN102559814AReduce manufacturing costRaise the level of fermentationMicroorganism based processesFermentationEmulsionPullulanase
The invention discloses a method for preparing acarbose, which adopts four enzymes to cooperatively carry out starch liquefaction and saccharification, and comprises the following steps that: (1) starch emulsion is liquefied with alpha-amylase at appropriate pH and temperature, and the DE (Dextrose Equivalent) value is controlled between 11 and 18; (2) the starch liquefied liquid is cooled to an appropriate temperature, the appropriate pH is adjusted, pullulanase, fungal enzyme and beta-amylase are added, certain time is maintained, and the composite maltose conversion rate can reach 85-95%; and (3) the liquefied starch is used for acarbose fermentation after being sterilized. According to the starch liquefaction method provided by the invention, the compound maltose content is high, and the high yield and the low impurities of acarbose fermentation are ensured. The method is simple, is easy to operate and is low in cost, and is suitable for the industrial production of acarbose fermentation.
Owner:LIVZON NEW NORTH RIVER PHARMA
Compositions for enhancing biological functions in organisms
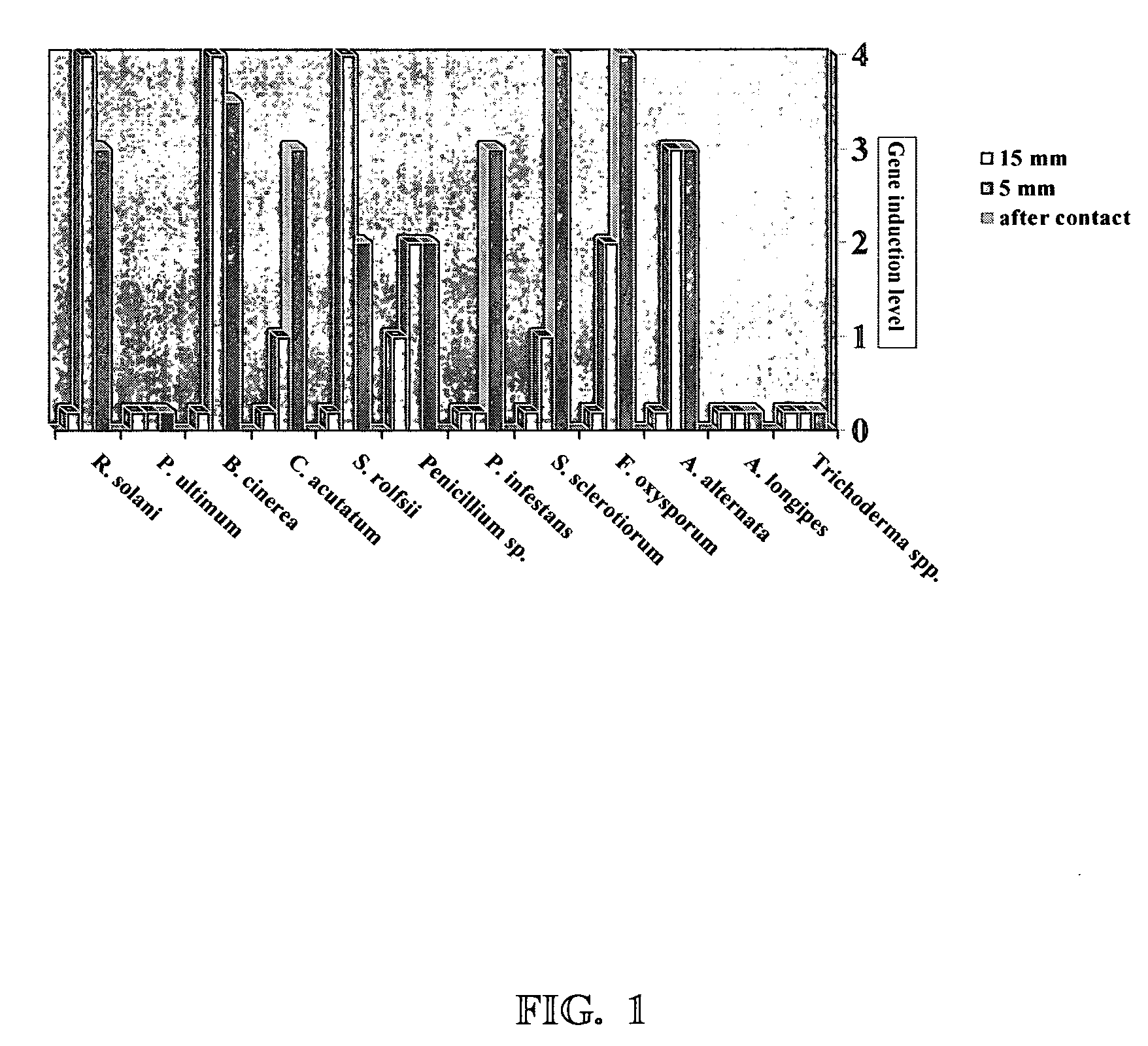
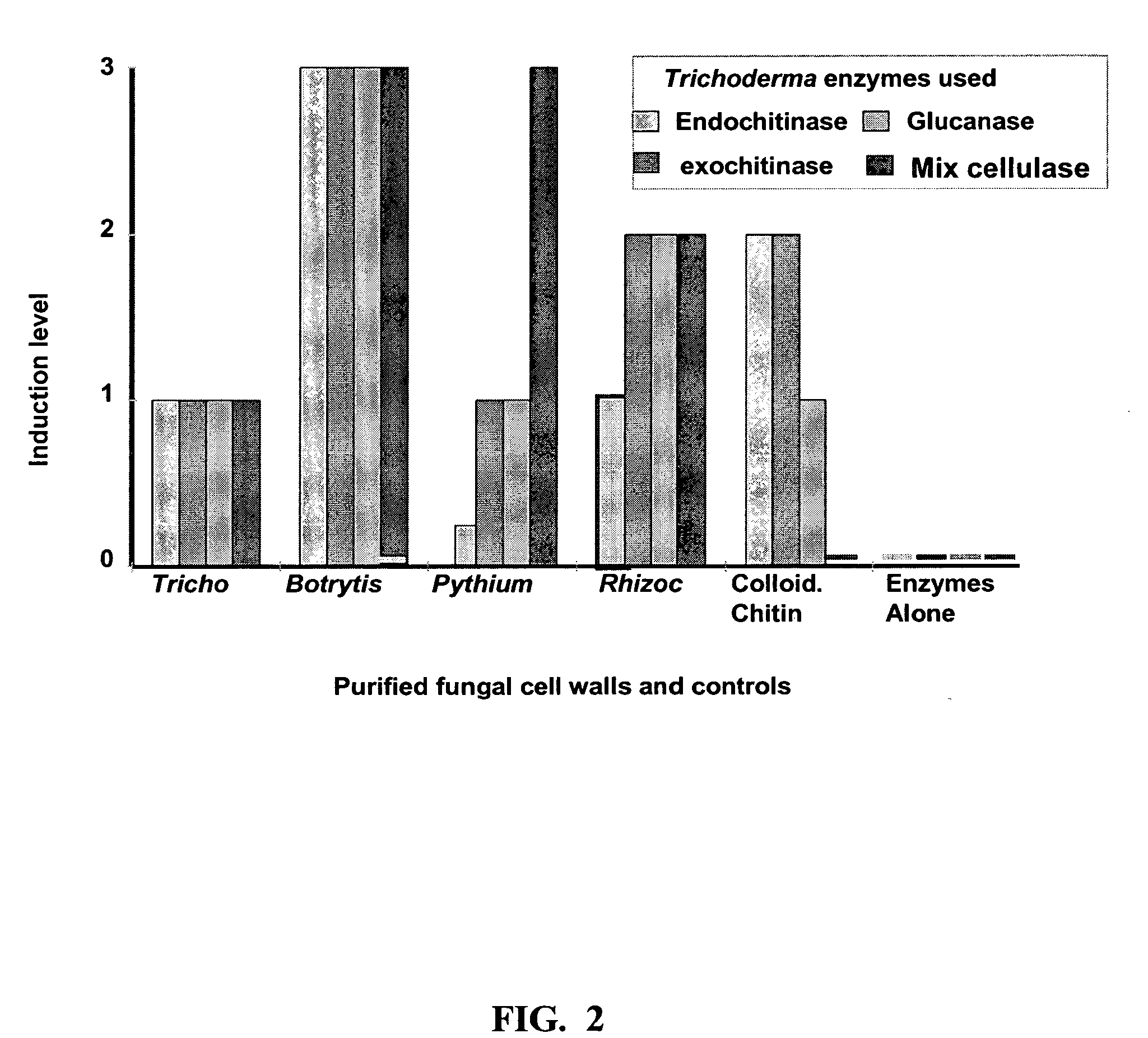
The present invention provides a composition which includes elicitor compounds selected from the group consisting of: (N,N′diacetylhexobiose)n; (N,N′diacetylhexobiose)n having one or more associated amino acid residues, wherein the amino acid residues are valine or ornthine; (N,N′diacetylhexosamine)n having an associated (dihexobiose)n; (N,N′diacetylhexosamine)n having an associated (dihexobiose)n and one or more associated amino acid residues, wherein the amino acid residues are valine or ornithine; or combinations thereof. The (N,N′diacetylhexobiose)n and (N,N′diacetylhexosamine)n comprise N-acetylglucosamine or other amino hexosamines, while the (N,N′diacetylhexobiose)n and (dihexobiose)n are any D-hexoaldose or N-acetylamino derivative of D-hexoaldoses. In this aspect of the present invention, n=1 to 5 and the compounds are all 3 kDa or less. Also provided are a method for increasing the rate of fungal growth, a method for increasing extracellular fungal enzyme production, a method for increasing biological control of plant and animal diseases, a method for increasing a method for increasing resistance of plants to diseases, and a method of alleviating pain and increasing resistance to, or recovery from, diseases in animals, using the composition of the present invention.
Owner:LORITO MATTEO +3
Isolation of SU1, a starch debranching enzyme, the product of the maize gene sugary1
InactiveUS20050204425A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesGMO PlantsAmino acid
SU1, a starch debranching enzyme active in maize endosperm (Zea mays), and the cDNA and genomic sequences encoding SU1 are disclosed. The amino acid sequence is significantly similar to that of bacterial isoamylases, enzymes that hydrolyze α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds. Amino acid sequence similarity establishes SU1 as a member of the α-amylase superfamily of starch hydrolytic enzymes. Also disclosed are antibodies reactive with the SU1 protein, methods of producing antibodies to the SU1 protein, methods of producing fusion proteins including SU1 as well as recombinant SU1 and methods of producing transgenic plants with a modified Su1 gene. The native or expressed SU1 protein can serve as a replacement for the bacterial and fungal enzymes currently used in the starch processing industry.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Fungal Cell Wall Degrading Enzyme
ActiveUS20080227147A1Convenient ligationCosmetic preparationsHydrolasesNucleotideEukaryotic plasmids
A novel fungal enzyme having lysozyme activity has been isolated. The invention further relates to a fungal polypeptide having lysozyme activity and belonging to the GH25 family, wherein the enzyme is selected from the group consisting of (a) a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence, which has at least 80% identity with amino acids 1 to 233 of SEQ ID NO:2; (b) a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence, which has at least 80% identity with the polypeptide encoded by the lysozyme encoding part of the nucleotide sequence inserted into a plasmid present in strain DSM 16084; (c) a polypeptide which is encoded by a nucleotide sequence which hybridizes under high stringency conditions with a polynucleotide probe consisting of the complementary strand of nucleotides 84 to 782 of SEQ ID NO:1; or (d) a fragment of (a), (b) or (c) that has lysozyme activity.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Isolation of SU1, a starch debranching enzyme, the product of the maize gene sugary1
InactiveUS6995300B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAlpha-amylaseGMO Plants
SU1, a starch debranching enzyme active in maize endosperm (Zea mays), and the cDNA and genomic sequences encoding SU1 are disclosed. The amino acid sequence is significantly similar to that of bacterial isoamylases, enzymes that hydrolyze α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds. Amino acid sequence similarity establishes SU1 as a member of the α-amylase superfamily of starch hydrolytic enzymes. Also disclosed are antibodies reactive with the SU1 protein, methods of producing antibodies to the SU1 protein, methods of producing fusion proteins including SU1 as well as recombinant SU1 and methods of producing transgenic plants with a modified Su1 gene. The native or expressed SU1 protein can serve as a replacement for the bacterial and fungal enzymes currently used in the starch processing industry.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method for partial degradation of gluten
InactiveUS20150223506A1Reduced gluten contentReduce contentDough treatmentDough/pre-mixesGlutenCereal grain
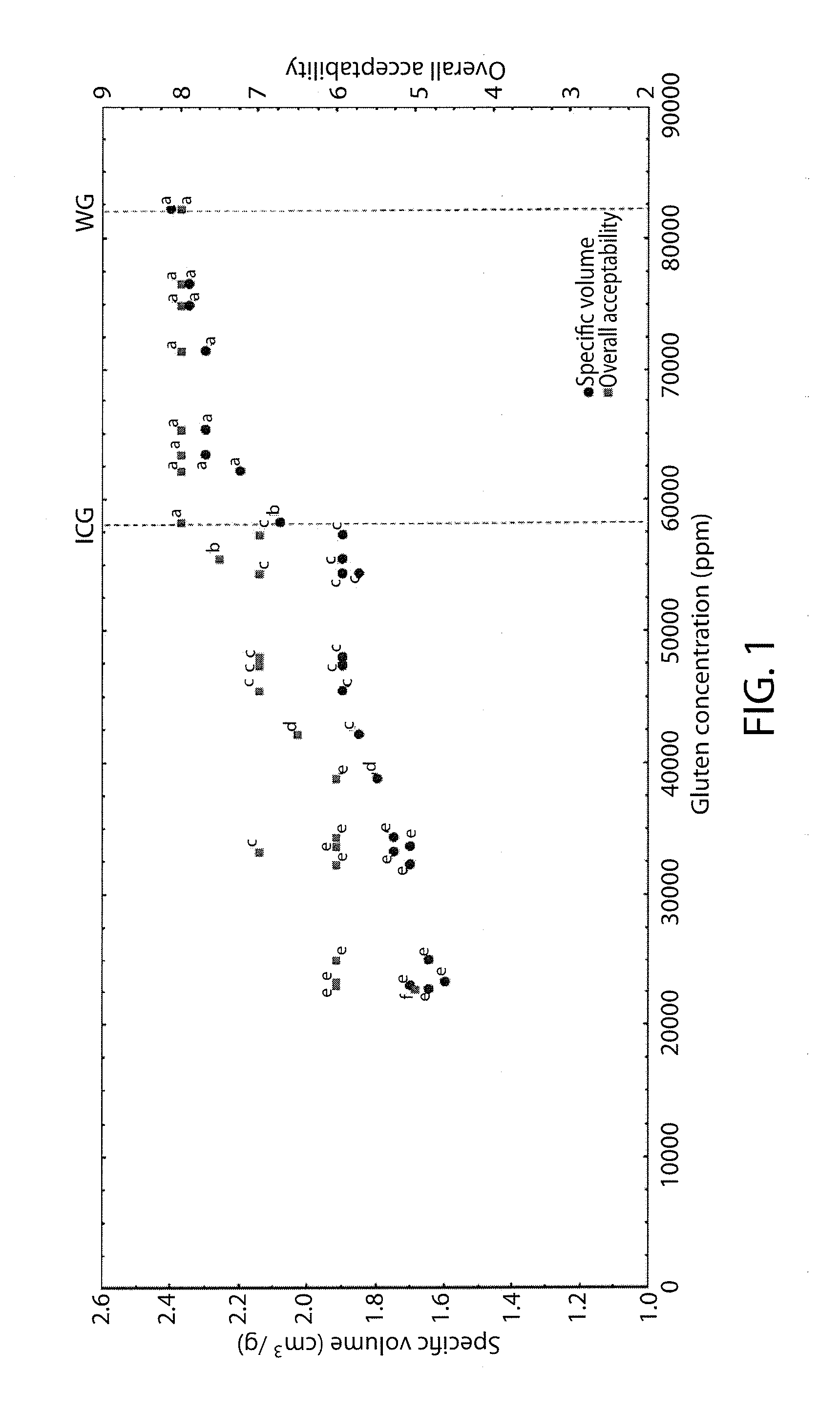
The present invention is directed to a method for preparing flour dough with reduced content of gluten starting from gluten containing cereals flours. In particular, the invention is directed to the use of lactic acid bacteria and fungal enzymes for the partial degradation of gluten in wheat flour in order to obtain flour dough with residual gluten concentration from 20,000-80,000 ppm. The flour dough obtained by the method of the invention can be used to prepare food products with reduced gluten content.
Owner:GIULIANI SPA
Moisture-proof paint slurry and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106281012AStrong adhesionHigh hardnessNatural resin coatingsArtist's paintsTectorial membraneSurface layer
Provided are moisture-proof paint slurry and a preparation method thereof. The moisture-proof paint slurry is prepared from, by weight, 30-40 parts of refined raw lacquer, 25-35 parts of mica powder, 20-25 parts of gypsum powder, 15-22 parts of kaolin powder, 5-12 parts of cattle bone powder, 10-15 parts of moisture proof agent and 8-12 parts of adhesive; preparation of the moisture-proof paint slurry comprises the following processes of 1 mixed powder preparation, 2 moisture proof agent preparation and 3 mixing. According to the moisture-proof paint slurry and the preparation method thereof, the raw lacquer is refined with a fungal enzyme, the rheological property can be effectively adjusted, the produced paint slurry is high in adhesive force and hardness and has the functions of resisting corrosion, resisting abrasion and preventing moisture, the paint slurry is smeared to a wood base, coating is convenient, the hardness and strength of the wood base can be effectively improved, holes and gaps in a board can be well filled up and smoothed, a layer of protective film can be formed on the surface layer of the board, the effective moisture-proof function is achieved, the quality of a bottom plate is improved, and therefore the quality of a finished lacquer painting product is guaranteed.
Owner:哈尔滨漆艺之星科技发展有限公司
Preparation method of baking syrup
The invention provides a preparation method of baking syrup. The method comprises the following steps: 1) liquefying bio-enzyme: liquefying starch milk with a certain concentration by using alpha-thermostable amylase to form liquefied liquid with DE value of 10-15%; b) saccharifying bio-enzyme: under the actions of fungal enzyme and compound saccharifying enzyme, reacting the liquefied liquid to generate saccharified liquid containing glucose, maltose and maltotriose, wherein the contents of the glucose, the maltose and the maltotriose are respectively 18-24%, 16-20% and 12-18%; c) refining: performing active carbon discoloring filtering, ion exchange desalting and vacuum concentrating on the obtained saccharified liquid to obtain the baking syrup with a certain concentration. The baking syrup prepared by the method provided by the invention not only can keep the excellent physiological functional characteristics of malt syrup, but also is capable of improving the browning reaction, the surface color of the food is darkened, and the unique burnt can be produced.
Owner:SHANDONG BAILONG CHUANGYUAN BIO TECH
BX11 enzymes having xylosidase activity
This invention relates to novel enzymes and novel methods for producing the same. More specifically this invention relates to a variety of fungal enzymes. Nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, compositions, recombinant and genetically modified host cells, and methods of use are described. The invention also relates to a method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars with enzymes that degrade the lignocellulosic material and novel combinations of enzymes, including those that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. The invention also relates to a method to release cellular content by degradation of cell walls. The invention also relates to methods to use the novel enzymes and compositions of such enzymes in a variety of other processes, including washing of clothing, detergent processes, biorefining, deinking and biobleaching of paper and pulp, and treatment of waste streams.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Anti-moth paint mortar and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN106318208AStrong adhesionHigh hardnessAntifouling/underwater paintsNatural resin coatingsStalactiteLacquer
The invention relates to an anti-moth paint mortar and preparing method thereof. The raw material of anti-moth paint mortar comprises refined raw lacquer, quartz powder, quicklime powder, wood powder, stalactite powder, insect repellent, adhesive. The materials is prepared from, by weight, 30-40 parts of refined raw lacquer, 25-35 parts of quartz powder, 20-25 parts of quicklime powder, 15-22 parts of wood powder, 5-12 parts of stalactite powder, 10-15 parts of insect repellent and 8-12 parts of adhesive. The preparing steps are as follows: (1) preparing the mixed powder; (2) preparing the insect repellent; (3) mixing. The anti-moth paint mortar adopts fungal enzyme for refining processing of raw lacquer, and can effectively adjust the rheology of the raw lacquer. The produced paint mortar has strong adhesion and high hardness, with corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, and anti-moth function. It is easy to be smeared on the wood embryo to improve the hardness and strength of wood embryo and to fill the holes as well as the gaps on the board. The anti-moth agent is made by the extraction of active ingredients from Chinese medicine, and enhances the pest control effect on the board.
Owner:哈尔滨漆艺之星科技发展有限公司
Fungal enzyme for improving content of gasifiable oil in crude oil as well as preparation method and application method thereof
PendingCN109486775ARaise saturated hydrocarbonsIncrease aromatics contentMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesCulture mediumsCoal
The invention discloses a fungal enzyme for improving the content of gasifiable oil in crude oil as well as a preparation method and an application method thereof. The fungal enzyme is prepared from the following raw materials: an oil displacement fungus and an enzyme-production culture medium, wherein the enzyme-production culture medium is prepared from wheat bran, a salt solution and the crudeoil. The fungal enzyme disclosed by the invention is used for carrying out enzymatic conversion on the crude oil and a macromolecular component including asphalt in the crude oil is degraded and converted into a small molecular gasifiable component; the content of saturated hydrocarbon and aromatic hydrocarbon in an enzymatic conversion product of the crude oil is remarkably improved; the preparation method is simple and easy to operate and implement; and the fungal enzyme can provide theoretical support for improving the quality of the crude oil by utilizing the fungal enzyme and also provides scientific evidence for a technological deign for improving the yield of gasoline and low-boiling-point coal diesel in a refining process of the crude oil by utilizing a fungal enzyme method.
Owner:陕西博秦生物工程有限公司 +1
Isomaltose hypgather cleaning and production method
InactiveCN103555794AIncrease profitReduce the burden onFermentationIsomaltooligosaccharideNeutral protease
The invention belongs to the technical field of starch sugar and especially relates to an isomaltose hypgather cleaning and production method. The isomaltose hypgather cleaning and production method comprises the following steps: using peeled and degermed corn flour as a raw material, dissolving the corn flour by adding water, adding alpha-amylase in the dissolved solution, and adjusting pH value and keeping warm; cooling the dissolved solution and adding fungal enzyme for thermal insulation, adding alpha-transglucosidase and keeping warm, adjusting pH to neutral, and adding neutral protease to carry out enzymolysis so as to obtain an enzymatic hydrolysate; filtering, decolouring and refining the enzymatic hydrolysate and finally concentrating to obtain a concentrate; separating the concentrate by a sequential simulated moving bed, respectively collecting effluents of isomaltose hypgather, glucose and polysaccharide, concentrating the isomaltose hypgather eluant, and drying to obtain the product. The method provided by the invention has advantages of simple step and stable reaction, is easy to carry out, is adopted to effectively raise production efficiency and utilization rate of raw materials, reduce energy consumption and production cost and mitigate environmental burden, and is beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG BAILONG CHUANGYUAN BIO TECH
Preparation method for improving fermentation efficiency of citric acid
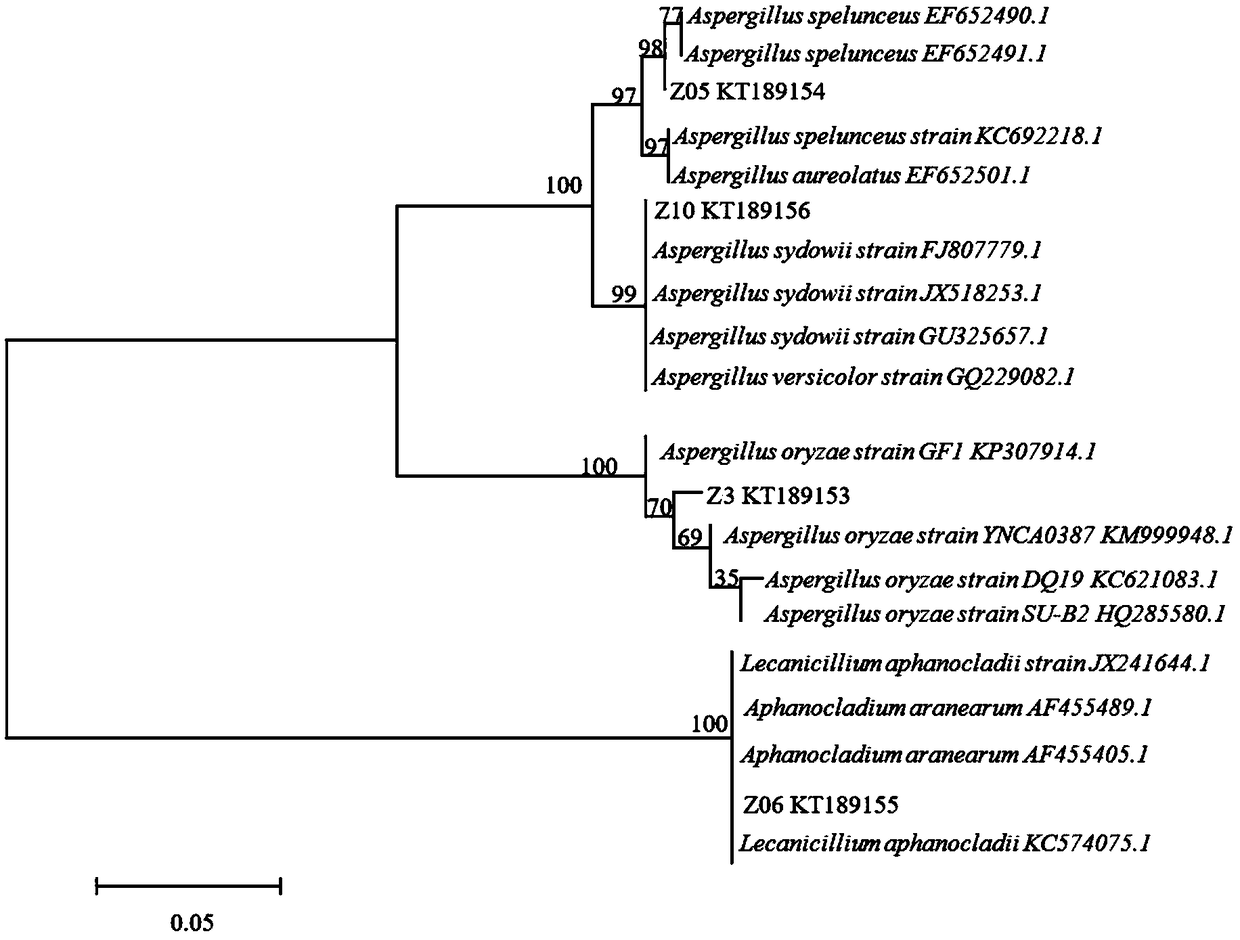
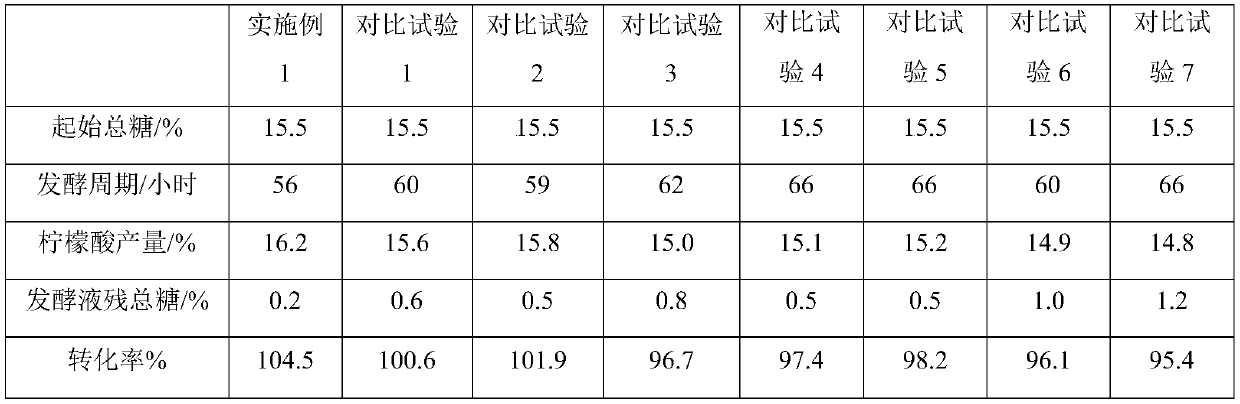
ActiveCN111172204AImprove conversion rateReduce production food consumptionMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydrolysateXylanase
The invention relates to a preparation method for improving fermentation efficiency of citric acid. According to the preparation method, a starch raw material is liquefied, a saccharifying enzyme, a fugal enzyme, xylanase and acid proteinase are added to implement enzymolysis, then dextrin and oligosaccharides can be converted into reducing sugar as much as possible, a part of corn proteins are converted into amino acids, the obtained saccharification hydrolysate is adopted to produce aspergillus niger fermented citric acid, and in addition, at a front stage of fermentation, the saccharifyingenzyme, the fugal enzyme, the xylanase and the acid proteinase are further added. When the citric acid is produced through fermentation by using the method, the fermentation conversion rate can be effectively increased, residual total sugar of a fermentation broth can be reduced, the production energy consumption can be reduced, and the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:合肥五粮泰生物科技有限公司
Process for preparing maltose by high-temperature liquification method
The invention provides a process for preparing maltose by a high-temperature liquification method. The process comprises the following steps: performing pulp conditioning on starch and water until 18 to 20 baume degrees to obtain mixed starch pulp; adjusting the pH value of the mixed starch pulp to be 3.0 to 3.5 by using sulfuric acid, performing primary jetting at the temperature of 150 to 160 DEG C, and adding fungal enzyme into liquefied liquid to obtain saccharified liquid; adding diatomite into the saccharified liquid, filtering by using a sheet frame, adding activated carbon into the filtrate, and performing decoloring treatment by an Amar filtering machine to obtain decolored saccharified liquid; passing through ion exchange resin, wherein the discharging conductivity of the saccharified liquid after ion exchange is less than or equal to 20 us / cm; pumping the saccharified liquid after ion exchange into a quintuple-effect evaporator and performing evaporation and concentration, wherein the concentration after concentration is 75 percent. The aim of the process is as follows: the enzyme preparation is saved by the high-temperature liquification method under the condition of not adopting amylase.
Owner:河南飞天生物科技股份有限公司
Enzyme Formulation and Method for Degradation
ActiveUS20180142229A1Efficient degradationContaminated soil reclamationOxidoreductasesPerfluorinated compoundSynthetic rubber
An enzyme formulation includes an encapsulated fungal enzyme which is effective for degrading at least one material selected from the group consisting of hydrocarbons, vulcanized rubber, synthetic rubber, natural rubber, vulcanized polymers and perfluorinated compounds. A degradation method includes treating one of the above-mentioned materials with an encapsulated fungal enzyme to degrade the material.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Antifouling paint and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN106318207AStrong adhesionHigh hardnessAntifouling/underwater paintsNatural resin coatingsResistWear resistant
The invention discloses an anti-moth paint mortar and a preparing method thereof, wherein the raw materials of said anti-moth paint mortar are refined raw lacquer, emery powder, tile powder, zeolite powder, yuhua stone powder, insect-resist agent, and adhesive powder. The said raw materials shall be counted by weight, including 30-40 parts of refined raw lacquer, 25-35 parts of emery powder, 20-25 parts of tile powder, 15-22 parts of zeolite powder, 5-12 parts of yuhua stone powder, 10-15 parts of insect-resist agent and 8-12 parts of adhesive powder; the preparing steps are as follows: (1) prepare the mixed powder; (2) prepare the insect-resist agent; (3) mixing. The anti-moth paint mortar adopts fungal enzyme for refining processing of raw lacquer, and can effectively adjust the rheology of the raw lacquer. The produced paint mortar has strong adhesion and high hardness, with corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, and anti-moth function. It is easy to be smeared on the wood embryo to improve the hardness and strength of wood embryo and to fill the holes as well as the gaps on the board. The anti-moth agent is made by the extraction of active ingredients from Chinese medicine, and enhances the pest control effect on the board.
Owner:哈尔滨漆艺之星科技发展有限公司
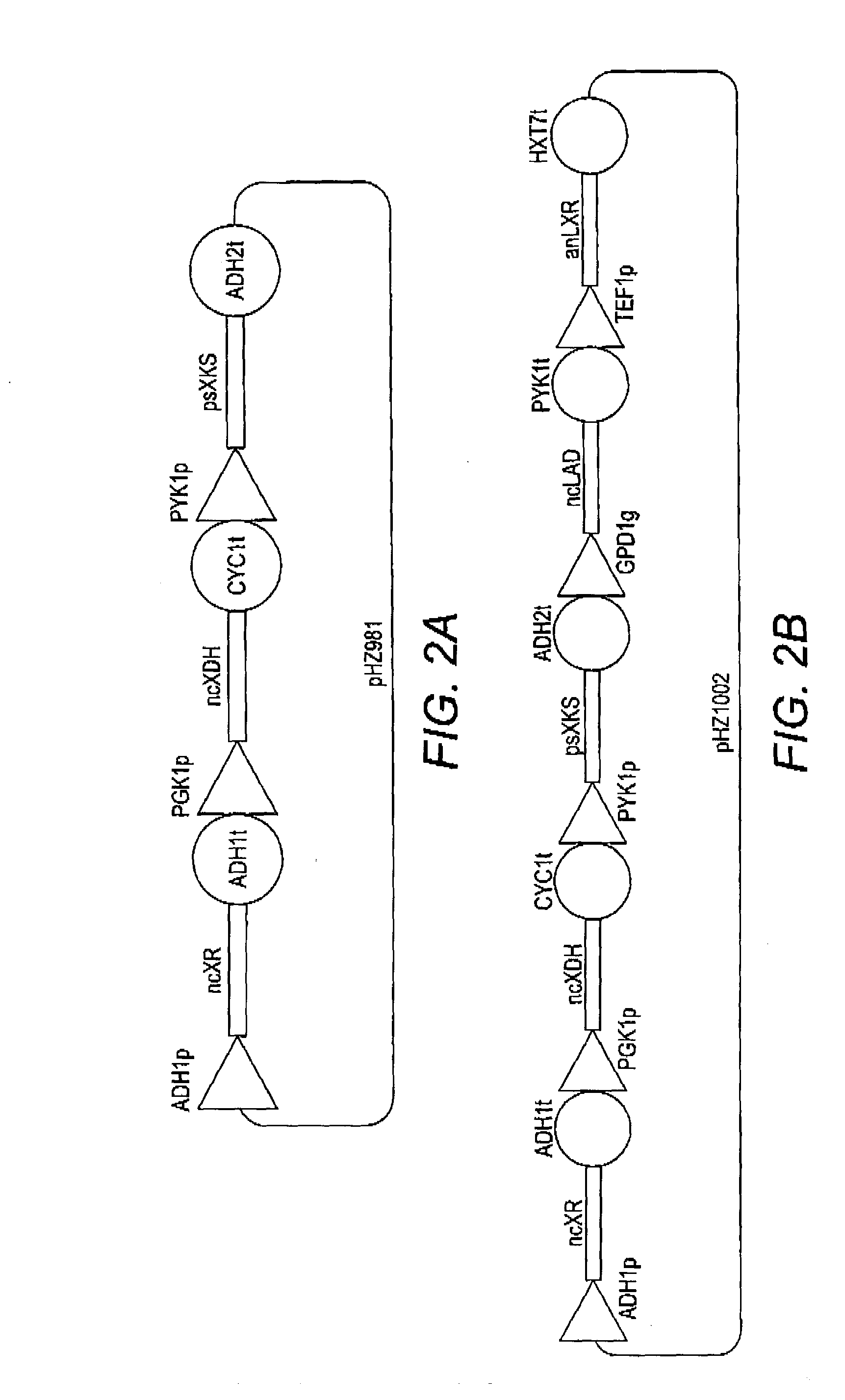
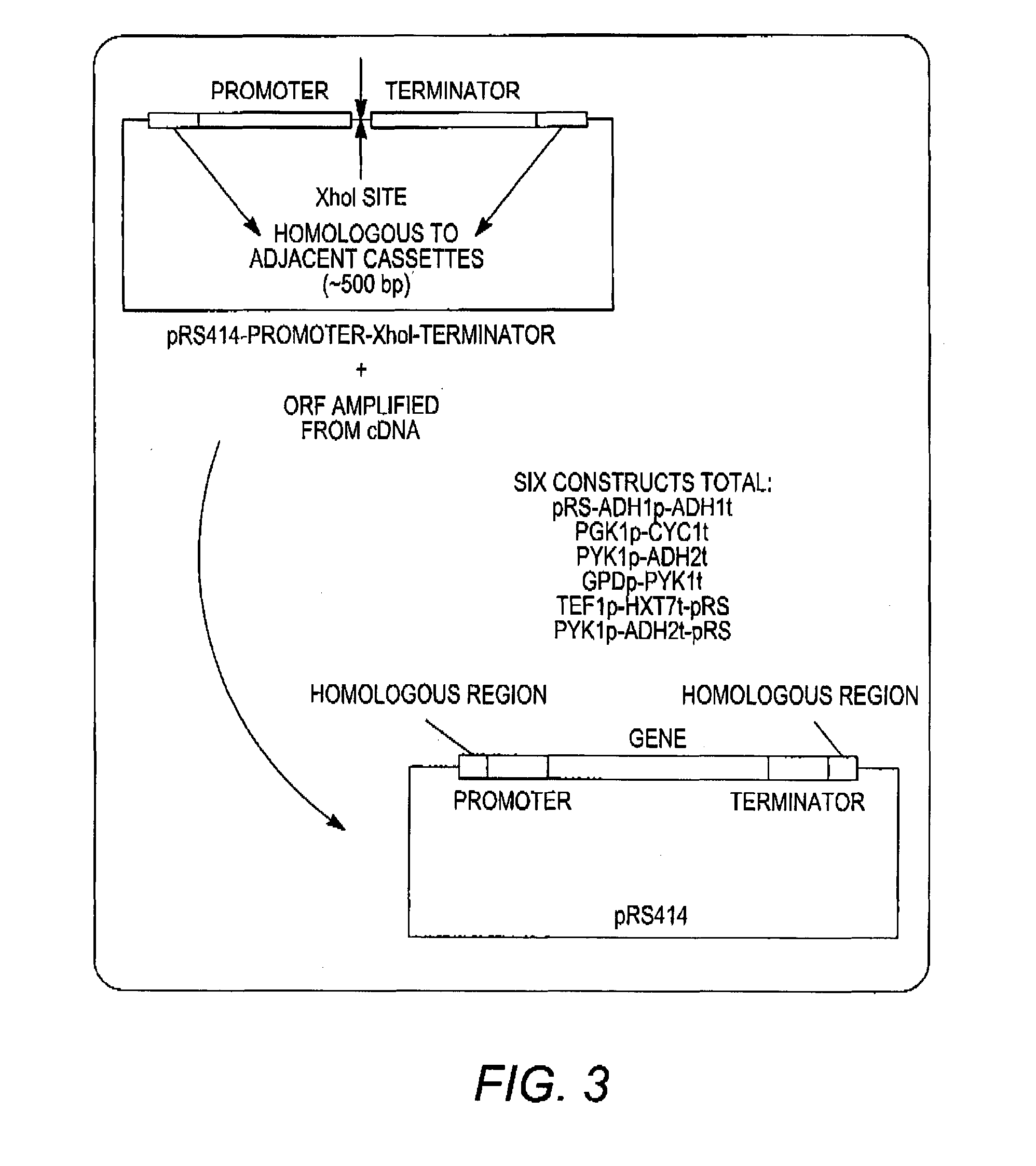
Combinatorial design of highly efficient heterologous pathways
InactiveUS20130295631A1Efficient productionImprove bindingMicroorganismsTransferasesHeterologousBiotechnology
The present disclosure relates to the production of highly efficient heterologous pathways in host cells by identifying favorable enzyme and / or promoter combinations. In particular the present disclosure provides methods for assembly and selection of multi-step xylose and arabinose / xylose utilization pathways from a library of fungal enzymes. The present disclosure further provides compositions containing favorable enzyme combinations, as well as recombinant yeast expressing such combinations, and methods of use for bioconversion of pentose sugars. Also provided are compositions and methods involving favorable expression patterns identified by utilization of combinations of promoters of varying strengths. Provided herein are methods for assembly and selection of multi-step xylose, arabinose / xylose, and cellobiose utilization pathways from a library of promoters of varying strengths. The present disclosure further provides compositions containing heterologous enzyme-coding polynucleotides under the control of favorable promoters, as well as recombinant yeast expressing such enzymes, and methods of their use for bioconversion of pentose and / or hexose sugars.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method for partial degradation of gluten
InactiveUS20140065262A1Reduced gluten contentReduce contentDough treatmentDough/pre-mixesGlutenCereal grain
The present invention is directed to a method for preparing flour dough with reduced content of gluten starting from gluten containing cereals flours. In particular, the invention is directed to the use of lactic acid bacteria and fungal enzymes for the partial degradation of gluten in wheat flour in order to obtain flour dough with residual gluten concentration from 20,000-80,000 ppm. The flour dough obtained by the method of the invention can be used to prepare food products with reduced gluten content.
Owner:GIULIANI SPA
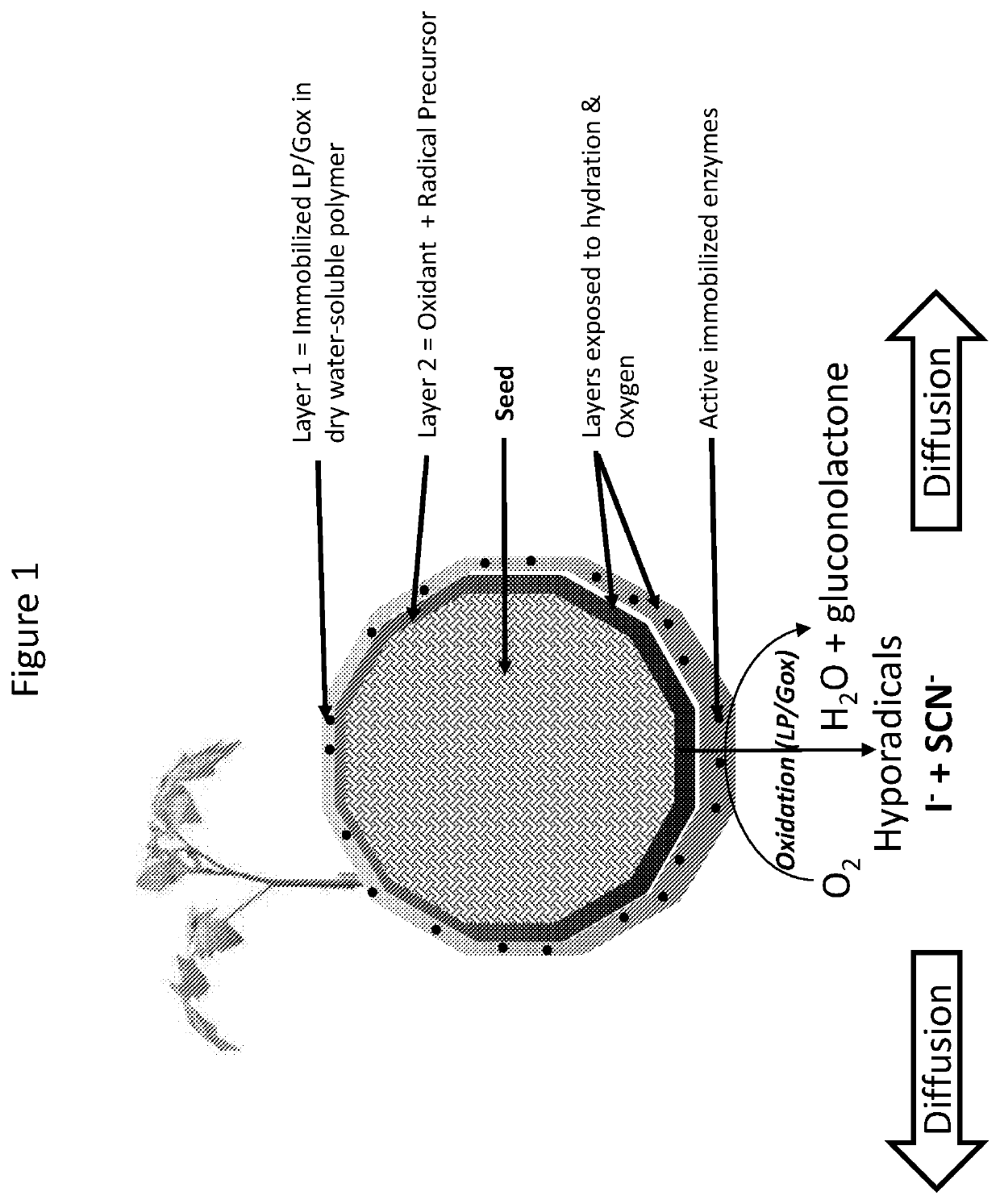
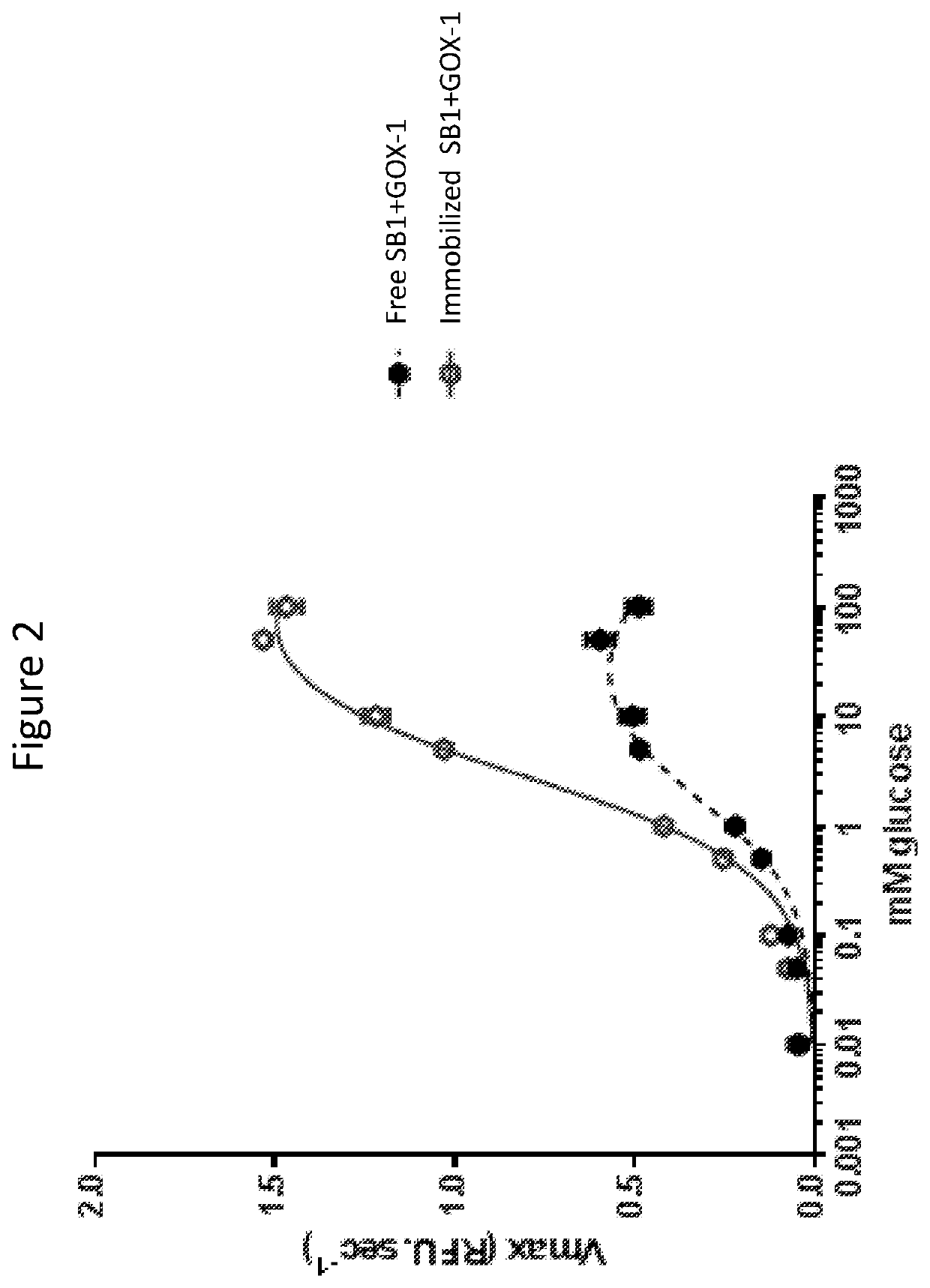
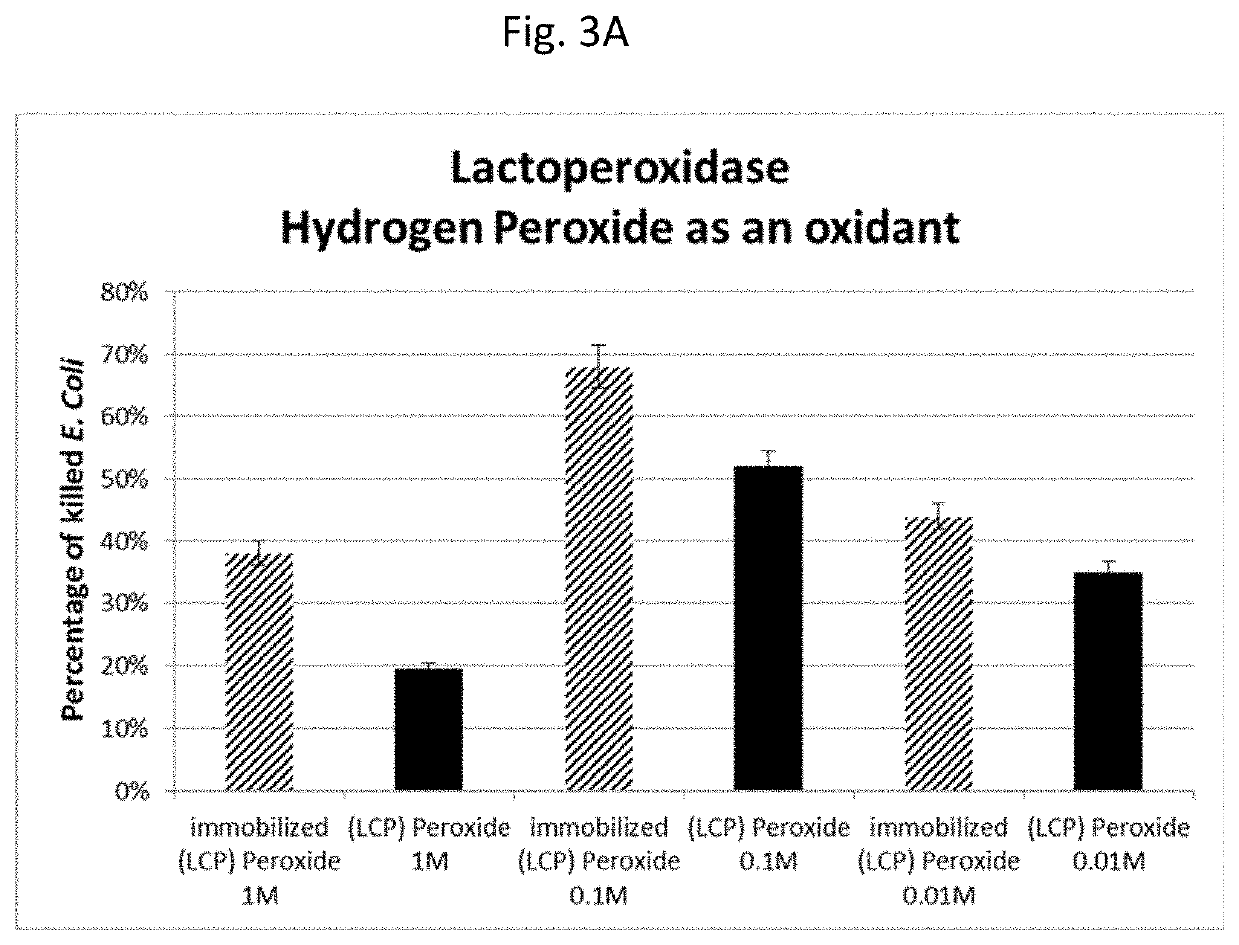
Magnetically immobilized microbiocidal enzymes
The present invention provides compositions and methods for reducing microbial contamination or infection in plants, animals, fabrics, and products therefrom. The present invention also provides compositions and methods for reducing human infections. In particular, it provides solid magnetic nanoparticles comprising bacteriostatic, bactericidal, fungistatic, or fungicidal enzymes in one component, and substrates for the enzymes in another component. The compositions are dormant and become active upon exposure to hydration and oxygen.
Owner:ZYMTRONIX LLC
DNA encoding protein and methods of using same
InactiveUS8420378B2The fermentation process is simpleFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyDna encoding
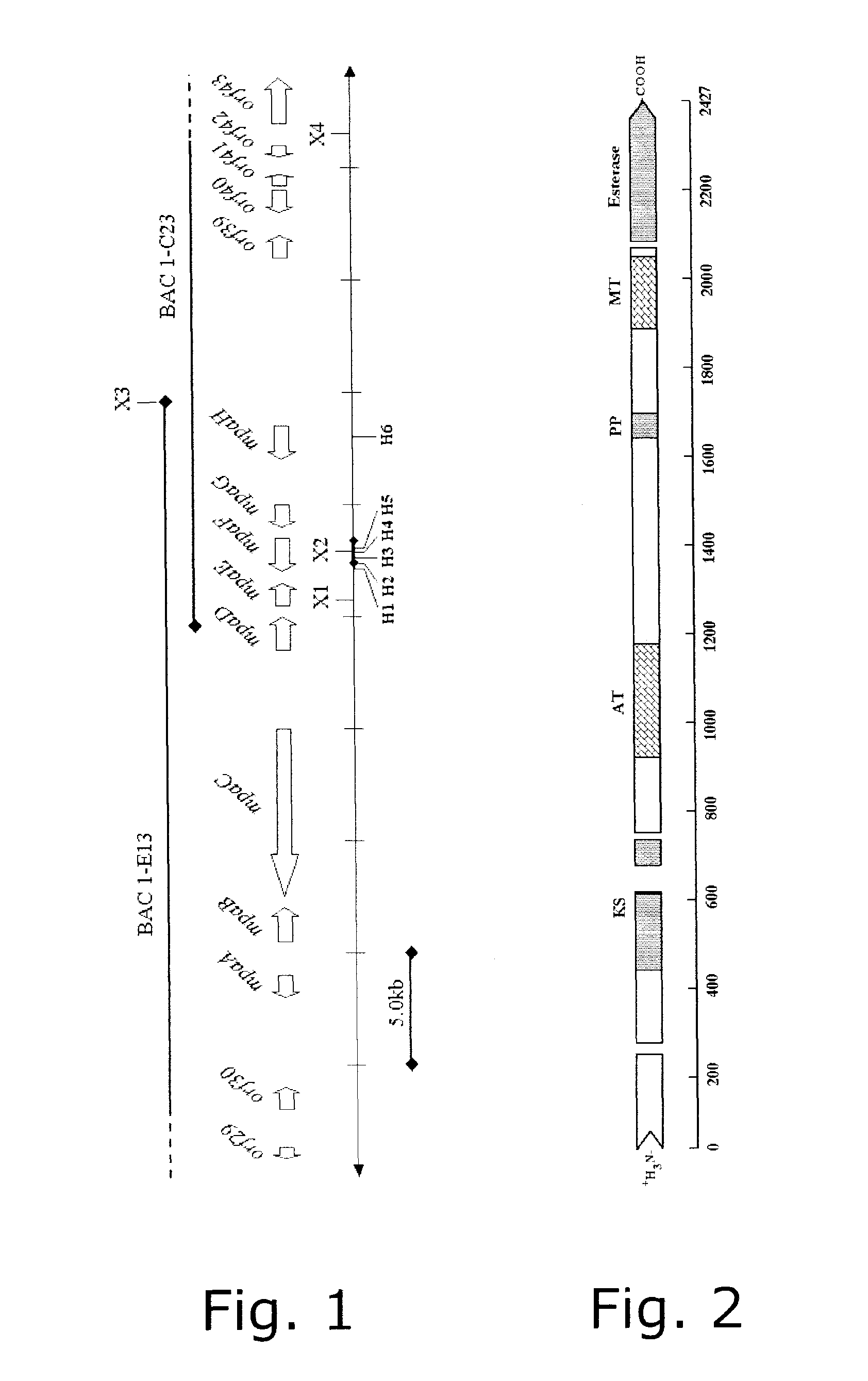
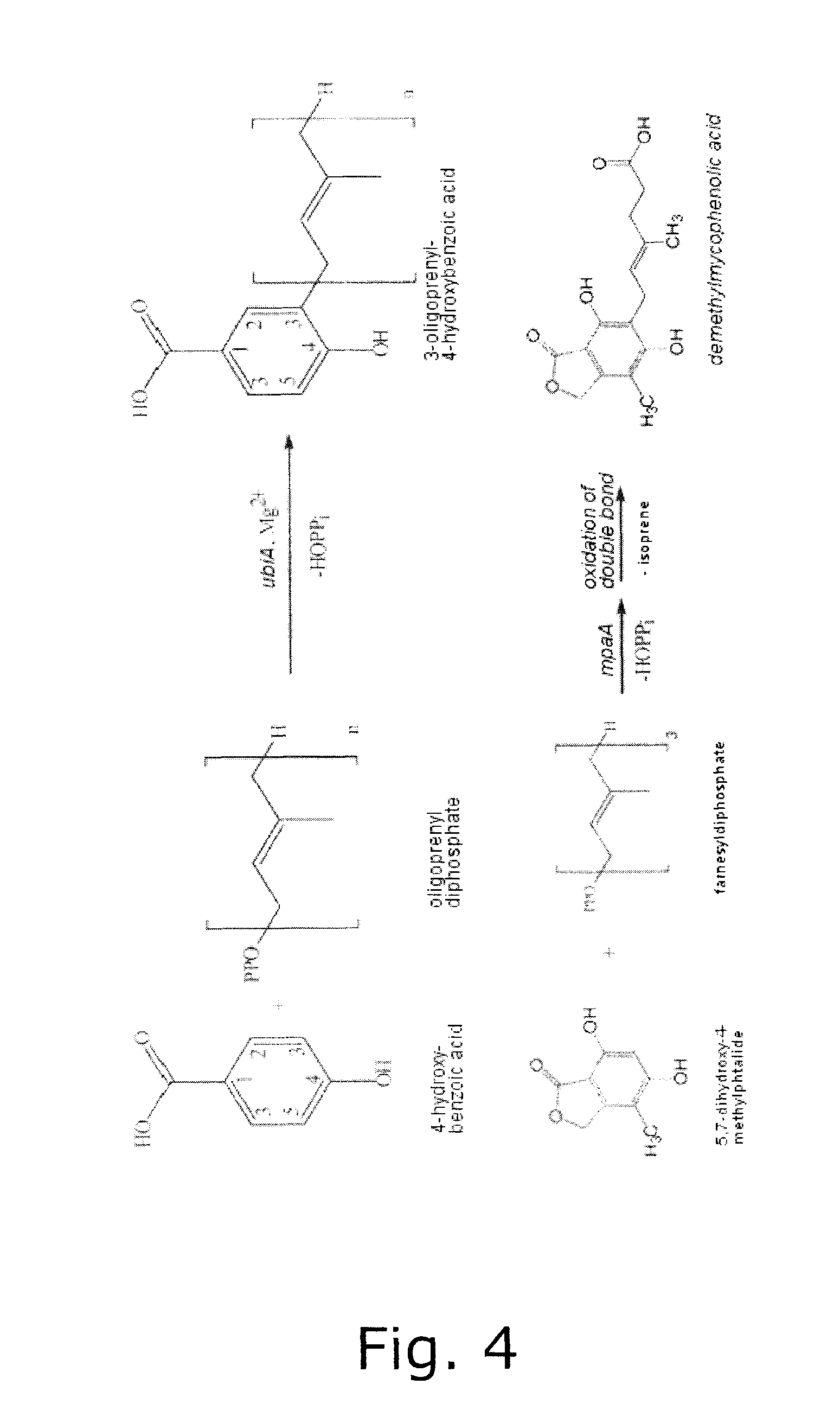
The present invention relates to novel tools for improving MPA production. In particular, the present invention relates to fungal enzymes that are specific for MPA synthesis.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
A kind of method for preparing acarbose
ActiveCN102559814BReduce manufacturing costRaise the level of fermentationMicroorganism based processesFermentationEmulsionPullulanase
The invention discloses a method for preparing acarbose, which adopts four enzymes to cooperatively carry out starch liquefaction and saccharification, and comprises the following steps that: (1) starch emulsion is liquefied with alpha-amylase at appropriate pH and temperature, and the DE (Dextrose Equivalent) value is controlled between 11 and 18; (2) the starch liquefied liquid is cooled to an appropriate temperature, the appropriate pH is adjusted, pullulanase, fungal enzyme and beta-amylase are added, certain time is maintained, and the composite maltose conversion rate can reach 85-95%; and (3) the liquefied starch is used for acarbose fermentation after being sterilized. According to the starch liquefaction method provided by the invention, the compound maltose content is high, and the high yield and the low impurities of acarbose fermentation are ensured. The method is simple, is easy to operate and is low in cost, and is suitable for the industrial production of acarbose fermentation.
Owner:LIVZON NEW NORTH RIVER PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com