Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
108 results about "Chrysosporium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chrysosporium is a type of hyaline hyphomycetes fungi in the family Onygenaceae. Chrysosporium colonies are moderately fast-growing, flat, white to tan to beige in color; they often have a powdery or granular surface texture. Hyaline, one-celled (ameroconidia) are produced directly on vegetative hyphae by non-specialized conidiogenous cells. Conidia are typically pyriform to clavate with truncate bases (6 to 7 by 3.5 to 4 um) and are formed either intercalary (arthroconidia), laterally (often on pedicels), or terminally.
Preparation method for sludge aerobic composting composite inoculum
ActiveCN104293694APromote degradationPromote growth and reproductionFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisSludge
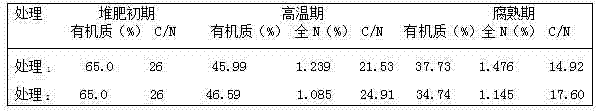
The invention discloses a preparation method for a sludge aerobic composting composite inoculums. According to the method, the Bacillus subtilis (No. 10066), the Bacillus licheniformis (No. 10103), the Lactobacillus acidophilus (No. 6075), the Candida utilis (No. 31272), and the Phanerochaete chrysosporium (No. 40719) that are preserved in China Center of Industrial Culture Collection (CICC) are subjected to individual culture, and are then mixed in proportion and inoculated into a fermentation culture to perform expanded culture, thus obtaining the composite inoculum. At the initial stage of inoculating the composite inoculums to sludge aerobic composting, the time for the compost body to reach a high temperature period is advanced by 4-6 days, the compositing period is shortened by 11-14 days, the stack moisture content is decreased by 18%-25%, and the total nitrogen content of the compost body is increased by 15%-20%, thus improving the composting effect.
Owner:GUANGXI BOSSCO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Crop straw decomposing inoculant and using method and effect thereof
ActiveCN103966150APromote repairImprove disease resistanceBio-organic fraction processingFungiBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a crop straw decomposing inoculant and application in straw bioreactor and water-logged compost. The inoculant is compounded of 0.5-2 parts of phanerochaete chrysosporium, 0.5-2 parts of trichoderma aureoviride, 0.5-2 parts of bacillus subtilis and 0.5-2 parts of bacillus mucilagimosus krassilm, wherein the effective viable count is 6*10<8> per gram. The straw decomposing inoculant is applied to a tomato stalk bioreactor planting technology, and the average ground temperature is 18.3 DEG C and is increased by 2.2 DEG C as compared with that of contrast without use of the inoculant; the average greenhouse temperature is 14.3 DEG C and is increased by 2.0 DEG C as compared with the average greenhouse temperature of the contrast; the average CO2 concentration is 956ppm and is 2.17 times higher than that of the contrast; the harvest time is 15 days earlier than the harvest time of the contrast; the acre yield is 5881kg and is increased by 22.7 percent as compared with the acre yield of the contrast; the occurrence rate of plant diseases and insect pests is lower as compared with that of the contrast. The inoculant is applied to wheat straw retting and decomposing, is high in decomposition speed, high in compost flexibility, the straws are basically decomposed, and the fermentation time is shorter than that of an inoculant purchased in the market.
Owner:天津市农业科学院
Immobilized biological adsorbent, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102423697AEasy to handleImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesOn/in inorganic carrierPhanerochaete sp.Liquid medium
The invention discloses an immobilized biological adsorbent containing phanerochete chrysosporium, the surface of which is uniformly wrapped by a layer of carrier Fe3O4 nanoparticles for fixation. The method comprises the steps of: first adding Fe3O4 nanoparticles into a phanerochete chrysosporium liquid medium containing tween 80, then inoculating a phanerochete chrysosporium spore suspension, conducting shaking cultivation so as to obtain the immobilized biological adsorbent. The invention also discloses application of the adsorbent in dye wastewater treatment. The biological adsorbent of the invention has high adsorption efficiency and large adsorption capacity, and can be effectively used for treating neutral red and lead in dye wastewater. The preparation technology and treatment technology in the invention are characterized by simplicity and low cost.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Vegetable waste composting bacterial agent, using method thereof and organic substrate prepared from vegetable waste composting bacterial agent
ActiveCN103966148AIncrease contentPromote repairPlant growth regulatorsBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a vegetable waste composting bacterial agent, a using method thereof and an organic substrate prepared from the vegetable waste composting bacterial agent. The vegetable waste composting bacterial agent is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 1-3 parts of phanerochaete chrysosporium, 1-3 parts of trichoderma harzianum, 1-3 parts of bacillus subtilis and 1-3 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus, wherein the effective viable count of the complex bacterial agent is up to 4*10<8> / g. The vegetable waste composting bacterial agent can be used for fermenting and composting vegetable wastes and resisting to cucumber fusarium wilt and has the fermentation period of 25 days for treating vegetable wastes and more than 50 days for treating uninoculated vegetable wastes. The organic substrate is prepared through fermenting by using a special process after adding 1kg of composting bacterial agent into every 5 cubic meters of vegetable wastes, wherein the vegetable wastes comprise the following components in parts by weight: 40-60 parts of eggplant straw, 20-40 parts of cucumber vine, 5-15 parts of Chinese cabbage leaves and 5-15 parts of brown coal, wherein the organic substrate can be used as a seedling substrate of tomatoes, has the emergence rate of 92% and has the same effect as a seedling substrate sold on the market.
Owner:天津市农业科学院
Straw decomposing inoculant
InactiveCN102146341AEasy to operateLow costMicroorganismsOrganic fertilisersBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to a straw decomposing inoculant which comprises the following components of 0.2-1.5 billion / g of bacillus subtilis, 0.2-1.5 billion / g of bacillus licheniformis, 20-150 million / g of thermophilic sporotrichosis, 20-150 million / g of Trichoderma Koningii and 20-150 million / g of Phanerochete chrysosporium. Therefore, the straw decomposing inoculant has the advantages of low cost and short decomposing time and is practical and easy to operate.
Owner:东莞市天盛生物科技有限公司
Composite microbial agent used for degradation of garden waste, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a composite microbial agent used for degradation of garden waste. The composite microbial agent is composed of composite bacterial liquid and a carrier, wherein the composite bacterial liquid comprises Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus siamensis, Bacillus tequilensis and Phanerochaete chrysosporium. The bacterial strains of the composite microbial agent produce synergism, so the composite microbial agent can substantially degrade a variety of macro-molecular components in the garden waste, improve the decomposition degree of the waste, enhance the nutrient structure and microfloras of compost and reduce heavy metal pollution. The invention also relates to a preparation method for the composite microbial agent, a method for degrading and converting the garden waste by using the composite microbial agent and fertilizer prepared from products obtained after degradation and conversion of the garden waste with the composite microbial agent.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for removing heavy metal pollutant from water body by using phanerochete chrysosporium
InactiveCN102101729ASimple operating conditionsEasy to implementWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSporelingPhanerochaete sp.
The invention discloses a method for removing a heavy metal pollutant from a water body by using phanerochete chrysosporium. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing spore suspension by using phanerochete chrysosporium spore powder; inoculating into a liquid culture medium for shake culture; filtering to obtain phanerochete chrysosporium pellets; adding the pellets into wastewater, adjusting the pH value of the wastewater, performing adsorption reaction under a constant temperature condition, filtering the wastewater after the reaction, and recovering the pellets to finish a removal process one time; cleaning the recovered pellets by using deionized water and then adding the cleaned pellets into culture solution for continuous culture so as to obtain phanerochete chrysosporium regenerative pellets; and adding the phanerochete chrysosporium regenerative pellets into heavy metal wastewater to be treated for cycling. By the method, hyphae are not required to be modified and pretreated and can be repeatedly used, the reaction condition is simple, and the water body of a complex composition can be treated.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Compound microbial preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104313008AToxicAnti-bacteriaWater contaminantsOn/in organic carrierBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a compound microbial preparation as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation comprises phanerochaete chrysosporium balls, polyvinyl alcohol, silicon dioxide, activated carbon, sodium alginate and zeolite powder, which form the compound microbial preparation through crosslinking by a solution with sodium dihydrogen phosphate. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing a gel liquid with the polyvinyl alcohol, sodium alginate, silicon dioxide and zeolite powder, mixing with a phanerochaete chrysosporium spore suspension with the activated carbon, then gradually dripping into the solution with the sodium dihydrogen phosphate so as to prepare embedded balls, and cultivating by a Kirk inorganic culture solution so as to prepare the compound microbial preparation. The compound microbial preparation has many gaps, high adsorption efficiency and good selectivity, the adsorbent has strong stability, the preparation method has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, affordability and so on, and the compound microbial preparation can be used for eliminating cadmium and 2, 4-dichlorophen in waste water.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Complex microbial agent for stabilizing treatment of stock garbage in cities and towns as well as preparation method and application of complex microbial agent
ActiveCN109852557APromote degradationAltered ion valence diseaseFungiBacteriaMicrobial agentPseudomonas putida
The invention provides a complex microbial agent for stabilizing treatment of stock garbage in cities and towns as well as a preparation method and an application of the complex microbial agent. The complex microbial agent contains sporotrichum thermophile, pseudomonas alcaligenes, halobacillus sp, bacillus subtilis, pseudomonas putida, candida utilis, saccharomyces cerevisiae, phanerochaete chrysosporium and lactobacillus plantarum. Growth metabolism, degradability and activity of all microbial strains in the complex microbial agent can effectively complement and cooperate with one another, the microbial strains can grow and propagate quickly in a landfill system to promote the temperature of a garbage treatment environment to increase quickly, meanwhile, organic matter, BDM and toxic andharmful substances in a landfill can be quickly and efficiently degraded, the stabilizing time of the garbage landfill is greatly shortened, stable harmless treatment of landfill is promoted, and thecomplex microbial agent can be applied to aerobic stabilizing treatment of garbage in cities and towns in practice.
Owner:BEIJING GUOHUAN TSINGHUA ENVIRONMENT ENG DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD BEIJING CHINA
Biosynthesis method of cadmium sulfide quantum dot
InactiveCN102965406AGood biocompatibilityGood monochromaticityFungiMicroorganism based processesPhanerochaeteThio-
The invention discloses a Biosynthesis method of a cadmium sulfide quantum dot. The method comprises the following steps of: on the basis of taking thioacetamide as an S source, water soluble cadmium salt as a Cd source, a sulfhydryl compound as a stabilizer and a phanerochaete chrysosporium mycelium pellet as an adsorbent, adding the S source, the Cd source and the sulfhydryl compound into a culture solution which contains the phanerochaete chrysosporium mycelium pellet to carry out shake cultivation on a shaking table, and carrying out filtration, cleaning in deionized water, ultrasonication, centrifuging and purification after the cultivation to obtain the cadmium sulfide quantum dot. The method provided by the invention is simple in operation, low in cost and good in reproducibility; and the prepared cadmium sulfide quantum dot has the characteristics of low toxicity, good biocompatibility and excellent optical property.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Specific bacterial strain for fusing two fungi and a protoplast and constructing method thereof
InactiveCN1405307ALow costSimple and fast operationFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyPseudomonas
The invention refers to a specific bacterium plant fused by the protoplast of two epiphytes and one bacterium and its structuring method which fuses the protoplast of true nucleus cell of white rotten epiphyte (phanerochaete chrysosporium), original nucleus cell (Pseudomonas) of aboriginal bacterium YZ1 and real nucleus cell of vintage yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), and by three relative genes' reformation and conformity in a same cell, structures the gene-engineering specific bacterium. The technique consists of parent and three-parent transboundary fusion.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Cultural method for improving degradation performance of phanerochaete chrysosporium
InactiveCN103168619AControl growth patternIncrease exposureHorticultureFertilizer mixturesPhanerochaete sp.Mycelium
The invention relates to a cultural method for improving degradation performance of phanerochaete chrysosporium, and belongs to the bioengineering field. Silicon substrate nanometer particles are added to a phanerochaete chrysosporium fluid medium to conduct fermental cultivation, due to functions among the silicon substrate nanometer particles and spore and mucelium, and meanwhile the silicon substrate nanometer particles enter the interior of mycelium pellets, and a spherical phanerochaete chrysosporium group which has excellent application effect in dye degradation aspect is acquired.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Compound microbial inoculant as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105969669AIncreased reducing sugar contentIncrease enzyme activityFungiMicroorganism based processesFiberTrichoderma koningii
The invention provides a compound microbial inoculant for vinegar residue fermentation; the inoculant comprises mixed fungi, wherein the mixed fungi are formed by mixing phanerochaete chrysosporium, trichoderma koningii, aspergillus niger and aspergillus ficuum. The invention also provides a preparation method of the inoculant and an application of the inoculant in vinegar residue fermentation. With the application of the inoculant, the content of coarse fibers in vinegar residue is reduced, the content of reducing sugar, which is easy to digest in the vinegar residue, is increased, the activity of hydrolase in the vinegar residue is improved and the feed value of the vinegar residue is improved.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Biological preparation for treating sodium glutamate fermentation sewage
ActiveCN105906169AReduce dosageShorten the timeTreatment using aerobic processesWater contaminantsBiotechnologyMonosodium glutamate
The invention relates to a biological preparation for treating sodium glutamate fermentation sewage. The biological preparation comprises a physical preparation and a complex microbial agent, wherein the complex microbial agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 4-5 parts of Azotobacter chroococcum, 4-5 parts of phanerochaete chrysosporium, 5-6 parts of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 4-6 parts of Clostridium papyrosolvens, 3-4 parts of penicillium ochrochlorron, 3-4 parts of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and 2-3 parts of bacillus cereus. The biological preparation contains multiple microorganisms having excellent degradation capacity to non-biodegradable pollutants, and by virtue of reasonable compatibility of the strains, the good degradation effect is achieved, and the application prospect of the biological preparation is wide.
Owner:内蒙古阜丰生物科技有限公司
Method for promoting complex enzyme to catalyze degradation of straws by using active mediator combination
InactiveCN102559763AIncreased CorruptionPromote catalysisMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a method for promoting complex enzyme to catalyze degradation of straws by using active mediator combination, which includes the following steps: (1) preprocessing the straws: smashing the straws to obtain straw powder and sieving to be reserved; (2) preparing complex enzyme liquid: cultivating phanerochaete chrysosporium in liquid state to obtain the complex enzyme liquid; and (3) catalyzing degradation: adding the complex enzyme liquid into the straw powder, adding active mediator combination simultaneously, keeping warm, preserving moisture, and standing to finish degradation catalyzing. The method for degrading the straws improves enzymolysis rate of lignin in the straws, is favorable for decomposing and transforming and resource utilization of the straws, and is low in cost, simple in operation, low in operation cost, clean and free of pollution.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Structure capable of being used for treating heavy metals in bottom mud dredging tail water and construction method thereof
InactiveCN103539266ALow process costSimple operating conditionsBiological water/sewage treatmentPhanerochaete sp.Microsphere
The invention discloses a structure capable of being used for treating heavy metals in bottom mud dredging tail water. The structure comprises a settling pond and a reaction pool, wherein the reaction pool comprises an adjusting column and at least one absorption column. The adjusting column and the absorption columns use a grating cylinder mould as a frame, the adjusting column is filled with a solid particle filler and the absorption columns are filled with compounds consisting of Fe3O4-calcium alginate-phanerochaete chrysosporium microspheres. The adjusting column and the absorption columns are sequentially arranged along a water flow direction. A construction method of the structure comprises the following steps: constructing the settling pond and the reaction pool; digging more than two grooves in the reaction pool; placing the grating cylinder mould in a direction vertical to the water follow; filling the solid particle filler to the most upstream groove, filling compound biological absorption materials in the balance of grooves, and ensuring that the filler is higher than the water line of the reaction pool. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low cost, simple preparation process, high absorption efficiency and the like, and can be used for treating heavy metal pollutants in the bottom mud dredging tail water.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
High-efficiency aerobic composting inoculant for livestock and poultry manure and method for aerobic composting thereof
ActiveCN110029073AReduce contentDrain controlFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisFeces
The invention discloses a high-efficiency aerobic composting inoculant for livestock and poultry manure and a method for aerobic composting thereof. The inoculant is composed of the following bacterial species by following volume proportion: the ratio of Bacillus licheniformis: Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Aspergillus niger is 1:4 to 5:5-6. The aerobic composting comprises the following steps: S1.adding agricultural and forestry waste to the manure of livestock and poultry, adjusting the C / N of livestock manure to 28-30 and the water content being 55%-60%; and S2. adding a sugar source to thelivestock and poultry manure regulated in S1, then adding the above-mentioned inoculant, and uniformly mixing the materials and performing the aerobic composting. After aerobic composting, the degradation of antibiotics in livestock manure is significant, and the content of available heavy metals and resistance genes in livestock manure is greatly reduced, and nitrogen loss is effectively controlled, so that the inoculant has great application prospects.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Complex microbial agent and application thereof in aerobic repair of landfill
ActiveCN108504604AImprove microenvironmentRich functional strainsFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisMicrobial agent
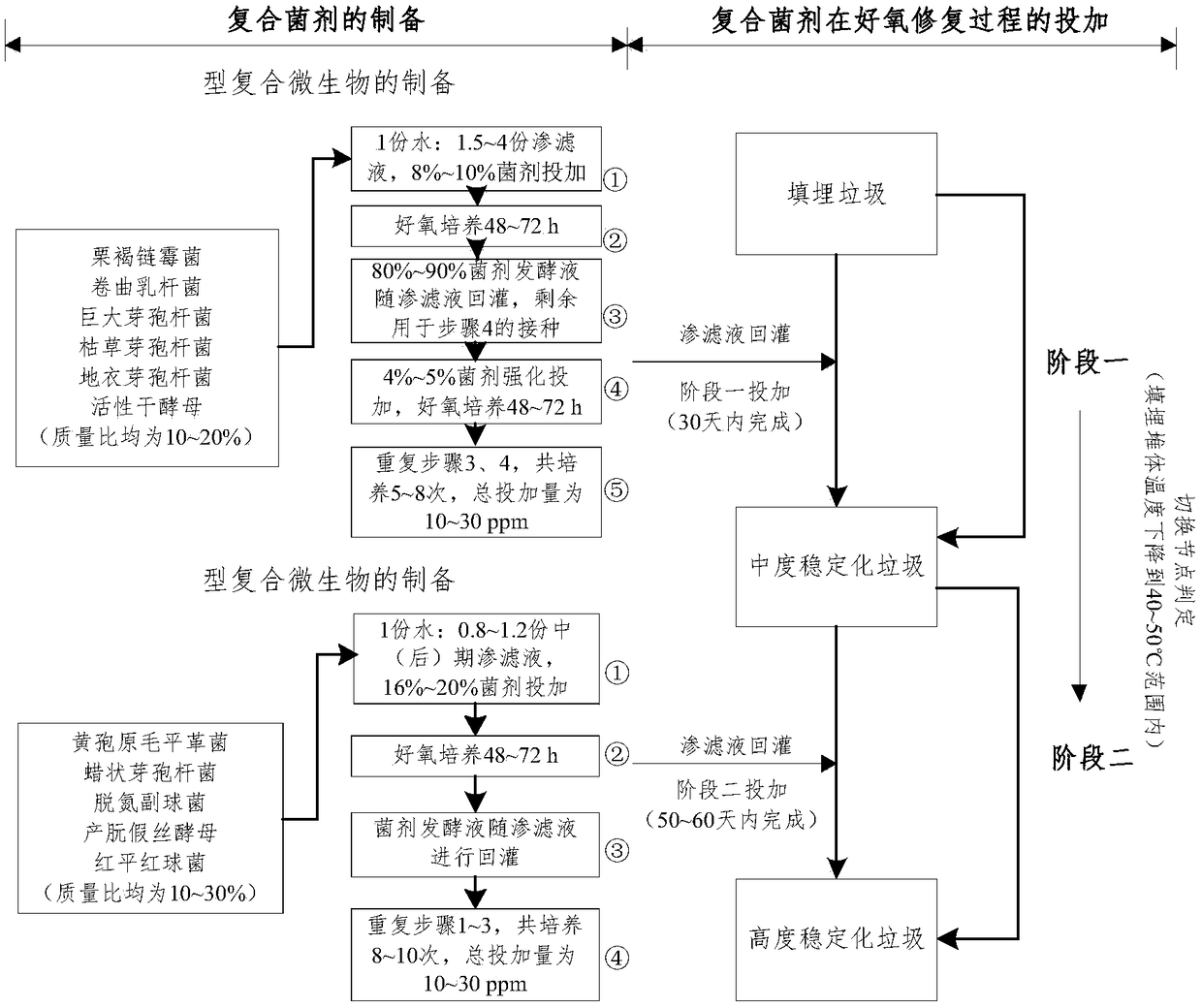
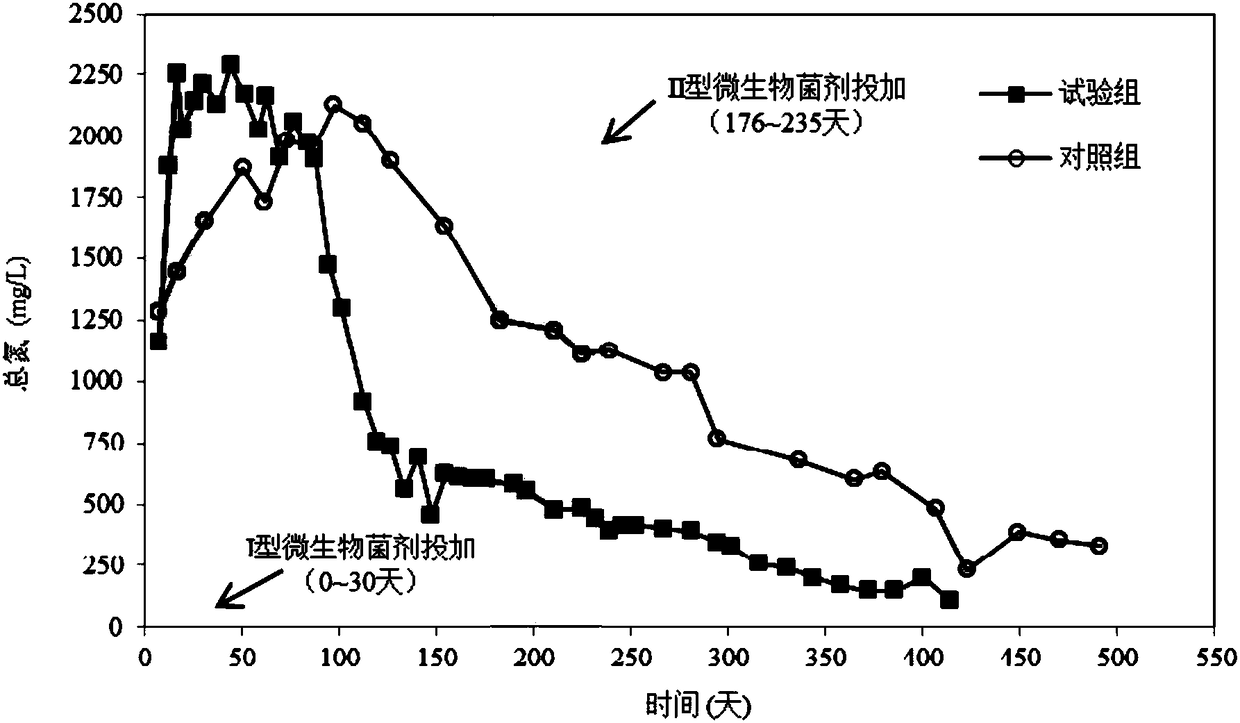
The invention relates to the field of garbage disposal, in particular to a complex microbial agent and an application thereof in aerobic repair of landfill. The complex microbial agent contains an type-I complex microbial agent and / or a type-II complex microbial agent, wherein the type-I complex microbial agent is prepared from streptomyces badius, lactobacillus crispatus, bacillus megatherium, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis and active dry yeast; the type-II complex microbial agent is prepared from phanerochaete chrysosporium, bacillus cereus, paracoccus denitrificans, candida utilis and rhodococcus erythropolis. The complex microbial agent is an efficient microbial agent prepared by massive screening and compounding according to specificity of nature change of garbage components, environmental factors and pollutants in the aerobic repair process of the landfill. The two types of microbial agents are added selectively in the aerobic repair process of the landfill by stages,and by means of function specificity of the microbial agents, the aerobic repair operating effect of the landfill is enhanced, the treatment cycle is shortened, and the operating cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING GEOENVIRON ENG & TECH
Compound bacterial agent applied to high-efficiency quick straw decomposition and application of compound bacterial agent
InactiveCN104293701AShorten the maturity timeEfficient decompositionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of comprehensive utilization of crop straws and relates to a compound bacterial agent applied to high-efficiency quick straw decomposition. The compound bacterial agent applied to the high-efficiency quick straw decomposition is composed of a dewaxing bacterial agent and an enamelysin bacterial agent, wherein the dewaxing bacterial agent is a compound bacterial agent of Bacilluscereus, Bacillussubtilis and Clostridiumpasteurianum, and the enamelysin bacterial agent is a compound bacterial agent of P.chrysosporium, Aspergilusoryzae and Trichodermaviride. The compound bacterial agent applied to the high-efficiency quick straw decomposition can realize high-efficiency quick straw decomposition, straws are converted into an environmental-friendly organic fertilizer, and cyclic regeneration of biological energy sources is realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of porous nitrogen-doped graphene/carbon nanotube composite conductive agent
InactiveCN107039656AMild reaction conditionsNo pollution in the processCell electrodesSecondary cellsDoped grapheneCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous nitrogen-doped graphene / carbon nanotube composite conductive agent. The preparation method comprises the steps of inoculating phanerochaete chrysosporium into a seed expansion culture solution for aerobic culture to obtain a seed liquid; adding the seed liquid and a graphene suspension liquid into a nutrition limitation culture solution, and dispersing the product subjected to constant-temperature shaking culture and processing in deionized water to obtain a nanopore graphene oxide suspension liquid; mixing the product and a carbon nanotube suspension liquid, performing ultrasonic processing, adding the mixed suspension liquid to an anaerobic denitrifying bacteria culture solution, and inoculating denitrifying bacteria seed liquid for anaerobic culture to obtain the porous nitrogen-doped graphene / carbon nanotube composite conductive agent. A two-step green preparation method is employed, a toxic reagent is not used, the preparation method has the advantages of moderate and controllable reaction process and low cost, and is easy to promote, and the prepared porous nitrogen-doped graphene / carbon nanotube composite conductive agent can be widely applied into the fields of a lithium ion battery and the like.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Microorganism combination and degradation method for degrading heavy metal-enriched plants
InactiveCN109055263AImprove leaching rateIncreased average leaching rateFungiBacteriaCelluloseMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism, in particular to a microorganism combination and a degradation method for degrading heavy metal-enriched plants. The microorganism combination consists of B.subtilis, P.chrysosporium, T.ressei and Pterulasp.strain QD-1 accoriding to a ratio of (0.5 to 1.5):(0.5 to 1.5):(0.5 to 1.5):(0.5 to 1.5):(0.5 to 1.5). The microorganism combination has theadvantages that the microorganism degrading and capacity reduction with low cost, low energy consumption and green and safe effects are realized; the good effect is realized on the degrading effect of enriched plant and the extracting of heavy metals; the lignocellulose is highly and efficiently degraded so as to reach the high-efficiency degrading and high-flux capacity reduction of biomass; thebacterial strain has good uranium tolerance, and the antagonism is avoided between the bacterial strains.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genetically engineered bacterium and applications thereof
InactiveCN104593279AHighly soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase 10320 secretion capacityFacilitated releaseFungiMicroorganism based processesSolubilityCellulose
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium which comprises a host cell and a target gene transferred into the host cell, and the genetically engineered bacterium is characterized in that the target gene is an encoding gene of phanerochaete chrysosporium LPMO (lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases). The invention also discloses a construction method of the genetically engineered bacterium and an application of the genetically engineered bacterium in degrading raw materials such as celluloses. The genetically engineered bacterium provided by the invention has a high CBM module containing LPMO (LPMO10320) secretion capacity, and the secretion capacity can reach 1.39mg / ml; and when the genetically engineered bacterium is applied to the degradation treatment of raw materials such as celluloses, the degradation velocity and degree of the celluloses can be improved, the generation amount of glucose can be increased, and compared with endogenously expressed phanerochaete chrysosporium, the generation amount is increased by nearly 100 times.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Compound microbial agent for river regulation, preparation method of compound microbial agent and river sewage treatment method
InactiveCN106987535AAdaptableGrowth inhibitionFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisSuspended particles
The invention discloses a compound microbial agent for river regulation, a preparation method of the compound microbial agent and a river sewage treatment method. In the compound microbial agent, a microbial agent A is made by mixing of five fermentation liquors formed by single culture of bacillus megaterium CCTCC NO.M2012352, bacillus subtillis CGMCC NO.1.2162, bacillus licheniformis CGMCC NO.1.6510, bacillus amyloliquefaciens CGMCC NO.1.7463 and phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F1767; a microbial agent B is made by mixing of two fermentation liquors formed by single culture of debaryomyces hansenii CGMCC NO.5770 and saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC NO.3003. The compound microbial agent has advantages that amino nitrogen and nitro nitrogen in water can be degraded, phosphorus concentration is decreased, and precipitation of solid suspended particles, bacterial cells and colloid particles in water is realized.
Owner:XIANGTAN ZHILIAN TECH MATASTASIS PROMOTE CO LTD
Method for treating landfill leachate with photocatalytic biosorbent
ActiveCN106045058BGood adsorption and degradation effectSimple processPhysical/chemical process catalystsOther chemical processesLitterSorbent
The invention discloses a method for treating landfill leachate with a photocatalytic biological adsorbent, which includes the following steps: mixing the photocatalytic biological adsorbent with the landfill leachate to perform light oscillation adsorption and degradation to complete the treatment of the landfill leachate; photocatalytic biological adsorbent Adsorbents include P. chrysosporium pellets, graphite type C 3 N 4 and calcium alginate, graphite type C 3 N 4 Calcium alginate is used to coat the hyphae of P. chrysosporium cocci. The method of the present invention has the advantages of low cost, simple operation, short cycle, easy separation, etc., and has a good adsorption and degradation effect on organic pollutants in landfill leachate.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Technology for degrading anthraquinone compounds in wastewater by use of phanerochaete chrysosporium
The invention discloses a technology for degrading anthraquinone compounds in wastewater by use of phanerochaete chrysosporium, and relates to the field of bioengineering. The phanerochaete chrysosporium is used as an original strain; after liquid shake-flask culture and liquid strain enlarge culture, the bacterial liquid is transferred to the wastewater containing anthraquinone compounds, and certain nutrient substances are supplemented to perform fermentation culture. By adopting the technology, the removal rate of anthraquinone compounds can reach 60-100%.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for promoting composite enzymes by utilizing resveratrol and oxalic acid to catalytically degrade rice straws
InactiveCN102559764AIncreased CorruptionImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATE
The invention discloses a method for promoting composite enzymes by utilizing resveratrol and oxalic acid to catalytically degrade rice straws, which comprises the following steps of: (1) straw pretreatment: crushing the rice straws to obtain straw powder and screening for standby; (2) composite enzyme liquid preparation: culturing phanerochaete chrysosporium in a liquid state to obtain composite enzyme liquid; and (3) catalytic degradation: adding the composite enzyme liquid in the straw powder, simultaneously adding resveratrol solution, oxalic acid solution and H2O2 solution, heat-insulating, moisturizing and standing to finish the catalytic degradation. The method for degrading the rice straws has the beneficial effects that the corruption speed of the rice straws is accelerated, the corruption degree of the rice straws is improved, the enzymolysis efficiency of lignin is improved, the usage amount of the composite enzymes can be effectively reduced, and the industrial production can be realized; and meanwhile, the method has the advantages of low cost, simplicity in operation, low running expense, cleanness and no pollution.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Composite microbial agent for river treatment and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a composite microbial agent for river treatment and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the composite microbial agent, an agent A is formed by mixing five fermentation liquids formed by individual cultivation of a bacillus megatherium CCTCC No.M2012352, a bacillus subtillis CGMCC No.1.2162, a bacillus licheniformis CGMCC No.1.6510, a bacillus amyloliquefaciens CGMCC No.1.7463 and a phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F1767; and an agent B is a fermentation liquid formed by individual cultivation of a debaryomyces hansenii CGMCC No.5770. The composite microbial agent is capable of degrading amino nitrogen and nitro nitrogen in water, reducing the phosphorus concentration and precipitating solid suspended particles, somatic cells and colloid particles in water.
Owner:XIANGTAN ZHILIAN TECH MATASTASIS PROMOTE CO LTD
Soil remediation method based on pleurotus ostreatus and phanerochaete chrysosporium
InactiveCN110814018ANo secondary pollutionIncrease productionContaminated soil reclamationOxidoreductasesPentachlorophenolPhanerochaete
The invention belongs to the technical field of restoration of contaminated soil by a microbial method, and particularly relates to a soil remediation method based on pleurotus ostreatus and phanerochaete chrysosporium. In the soil remediation method, sterilized pine wood is used as a culture medium to cultivate pleurotus ostreatus and phanerochaete chrysosporium, and then a soil sample to be treated is added to continue the cultivation. The method cannot cause secondary pollution; the induction effect is good, and the laccase yield is significantly increased; and the content of pentachlorophenol in the soil can be significantly reduced.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Complex microbial inoculant for efficient degradation of straw and preparation method and application of complex microbial inoculant
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, in particular to a complex microbial inoculant for efficient degradation of straw and a preparation method and application of the complex microbial inoculant. The complex microbial inoculant comprises a flora A, a flora B and a flora C; the flora A comprises aspergillus fumigatus, aspergillus versicolor, trichoderma harzianum, phanerochaete chrysosporium and auricularia polytricha; the flora B comprises bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis and bacillus amyloliquefaciens; and the flora C comprises depubyomyces hansenii, pichia guilliermondii, bacillus subtilis, bacillus cereus and aneurinibacillus. The flora A is used for preparing a microbial agent I, the flora A and the flora B are used for preparing a microbial agent II, the flora A and the flora C are used for preparing a microbial agent III, and the flora A, the flora B and the flora C are used for preparing a microbial agent IV. According to the complex microbial inoculant, the flora A which is close to the environment and has a lignocellulose degradation function is preferably selected from the natural environment by a traditional microbiological method, and the flora B and the flora C are combined to achieve a synergistic effect, so that the straw degradation efficiency is effectively improved, and the complex microbial inoculant has important guiding significance on straw resource utilization.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
A vegetable waste decomposing bacterial agent and its use method and prepared organic substrate
ActiveCN103966148BIncrease contentPromote repairPlant growth regulatorsBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a vegetable waste decomposing bacterial agent, a use method thereof and an organic matrix prepared therefrom. The decomposed bacterial agent is composed of 1-3 parts of Phaneroderma chrysosporium, 1-3 parts of Trichoderma harzianum, 1-3 parts of Bacillus subtilis and 1-3 parts of Bacillus peptone-like in parts by weight; The number of effective viable bacteria reached 4×108 / g. It can ferment decomposed vegetable waste and resist cucumber wilt bacteria. The fermentation cycle of vegetable waste treatment is 25 days, while the uninoculated one needs more than 50 days. The organic matrix is fermented by adding 1 kg of the decomposing bacteria agent to every 5 cubic meters of vegetable waste, and the parts by weight of the vegetable waste are as follows: 40-60 parts of eggplant stalks, 20-40 parts of cucumber seedlings , 5-15 parts of Chinese cabbage leaves and 5-15 parts of lignite, the organic substrate can be used as the seedling-raising substrate of tomato, and the emergence rate reaches 92%, reaching the effect of the seedling-raising substrate sold in the market.
Owner:天津市农业科学院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com