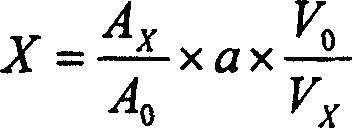Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
471 results about "Pseudomonas putida" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
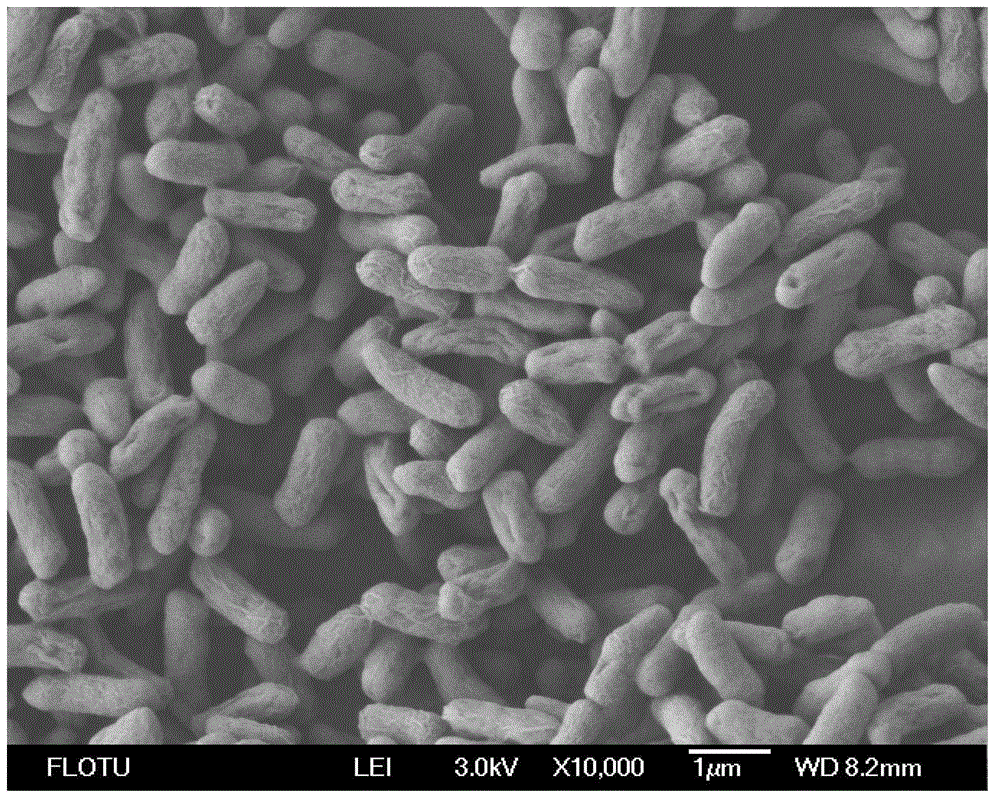
Pseudomonas putida is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, saprotrophic soil bacterium. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, P. putida was taxonomically confirmed to be a Pseudomonas species (sensu stricto) and placed, along with several other species, in the P. putida group, to which it lends its name.
Heterotrophic nitrification microbial preparation, cultivation method and use thereof
ActiveCN101302485AWide range of substratesEasy to trainImmobilised enzymesBacteriaHigh concentrationMicroorganism
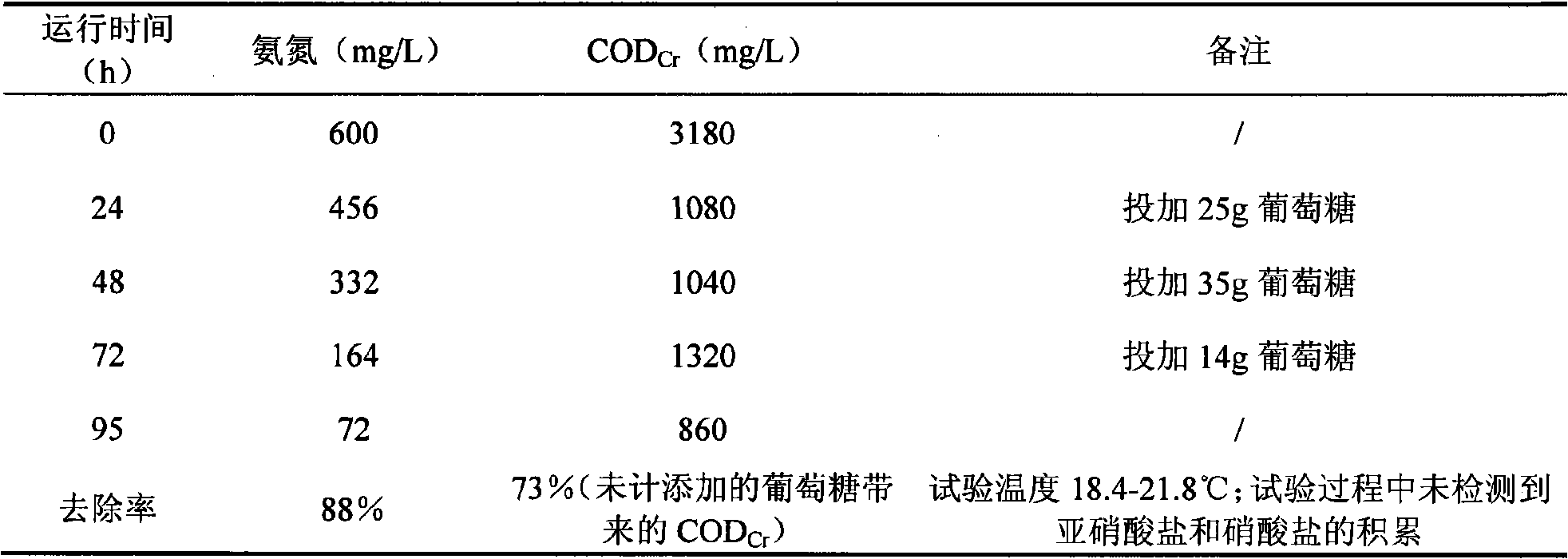
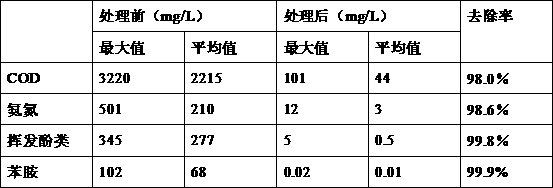
The invention belongs to the environmental microorganism field, and in particular relates to a heterotrophic nitrification microorganism agent, a method for cultivating the same, and a use of the same in culture wastewater treatment. The microorganism agent contains Stenotrophomonas maltophilias strain DN1.1 and Pseudomonas putida strain DN1.2 which have the preservation registration numbers respectively as CCTCC M 207074 and CCTCC M 207075. The microorganism agent can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in a water body, accumulates no nitrite or nitrate during denitrification, and can simultaneously remove CODCr in organic wastewater, which is applicable to the treatment of high-concentration culture wastewater. The use of the microorganism agent in treating culture wastewater is simple in process and stable in effect.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Biocontrol for plants with Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas putida, and Sporobolomyces roseus
The present invention is directed to isolated Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas putida, and Sporobolomyces roseus which are useful as a biocontrol agent. These organisms are useful in a method of imparting to plants protection against plant pathogens by applying them to plants, plant seeds, or soil surrounding plants under conditions effective to impart disease protection to the plants or plants produced from the plant seeds. The biocontrol agents are also useful in a method of enhancing plant growth which involves applying them to plants, plants seeds, or soil surrounding plants under conditions effective to enhance growth in the plants or plants produced from the plant seeds.
Owner:EMBRAPA TRIGO +1
Regulation of heterologous recombinant protein expression in methylotrophic and methanotrophic bacteria
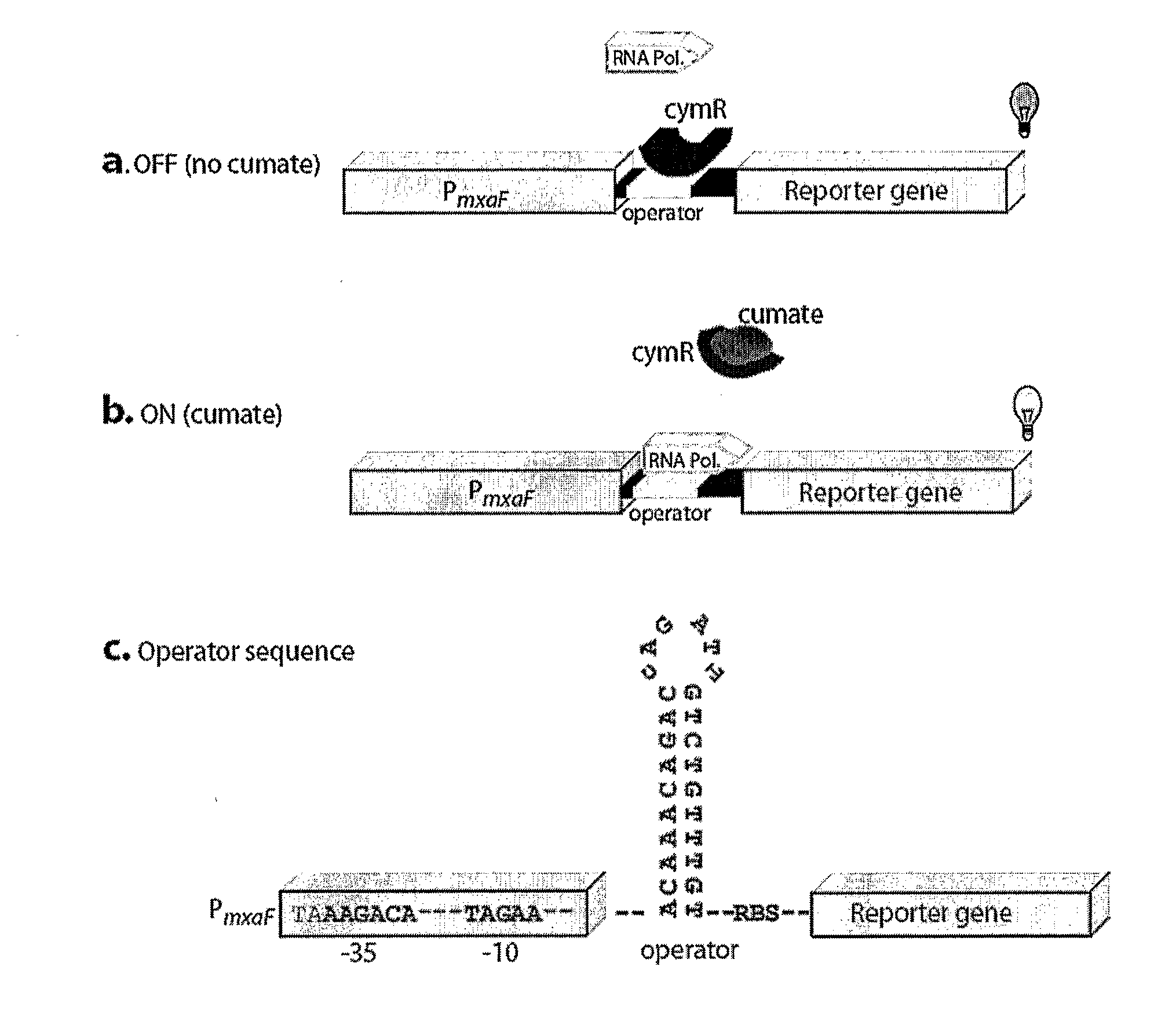
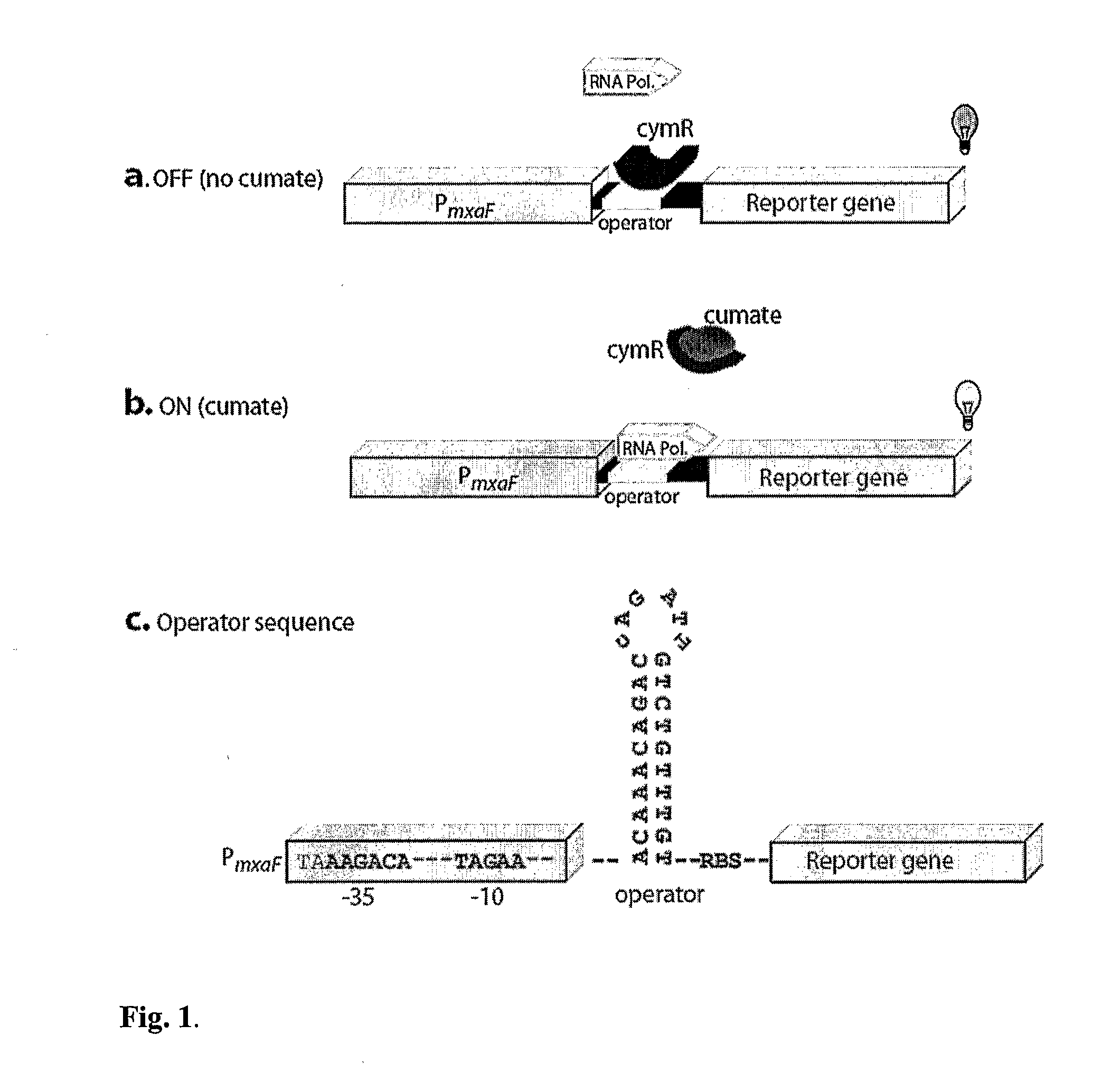
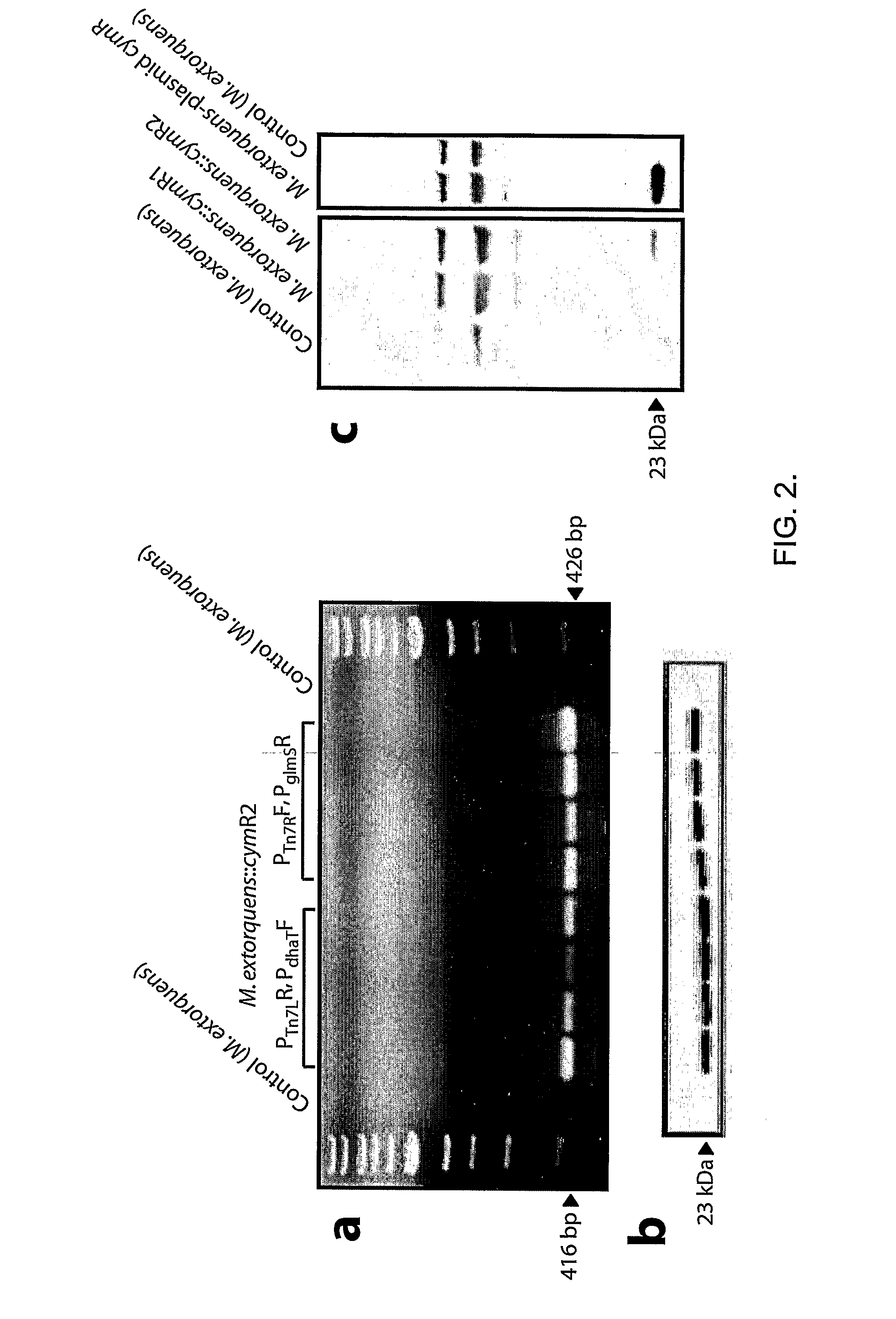
Methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria such as Methylobacterium are transformed with a gene of interest, and expression of the gene is regulated by means of a cumate repressor protein and an operator sequence which is operatively linked to the gene of interest, and the addition of an external agent. Specifically, the cymR repressor and cmt operator from Pseudomonas putida may serve to regulate gene expression in methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria with the addition of cumate.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Preparation method and application for compound fungus agent for degrading organic matter
InactiveCN102344899AImprove biological activityImprove adsorption capacityBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyBenzoic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method for a compound fungus agent for specifically degrading an organic matter for a biological enhancing water treatment system. The compound fungus agent is added into a biological treatment process, has high biological activity, a stable effect and low cost, is easy to adsorb on the surface of a carrier and is difficult to lose. The preparation method issimple and practical, and has a short preparation period and low cost. The compound fungus agent comprises the following four strains: 20 to 30 percent of pseudomonas-stutzeri, 20 to 30 percent of pseudomonas putida, 10 to 20 percent of pseudomonas-pertucinogena and 30 to 50 percent of bacillus subtilis. The compound fungus agent is prepared by combining and screening the strains, performing slant culture and primary culture, mixing according to the proportion, and performing secondary cycle culture. The preparation method is widely used in a biological enhancing water treatment process, has a long-term and stable operation period, and has specific degradation ability for toxic and harmful organic pollutants such as halogenated hydrocarbons, phenol, benzoic acid, aromatics, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, heterocyclic compounds, phthalic acid ester and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Compound microbial bacterial preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101864362AOvercoming the problem of only targeting a single organic wastePromote enrichmentFungiBacteriaCelluloseBacillus licheniformis
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection and discloses a compound microbial bacterial preparation and application thereof. The compound microbial bacterial preparation consists of fermentation liquor of four bacteria, i.e. Bacillus licheniformis, Pseudomonas putida, Enterobacter cloacae and Candida valida. The compound microbial bacterial preparation provided by the invention has strong digestion power for various types of cellulose, proteins and fat macromolecules. The addition of the compound microbial bacterial preparation into excess sludge and / or kitchen waste can quicken enrichment of methanogen, shorten anaerobic digestion time and improve methane yield. Moreover, the synergetic effect of the four microbial strains is superior to the effect of any one, two or three strains of microorganisms.
Owner:江苏加德绿色能源有限公司
Heterotrophic nitrification aerobic denitrifying bacteria, culturing method thereof and uses
ActiveCN101338282AWide range of substratesEasy to trainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesHigh concentration
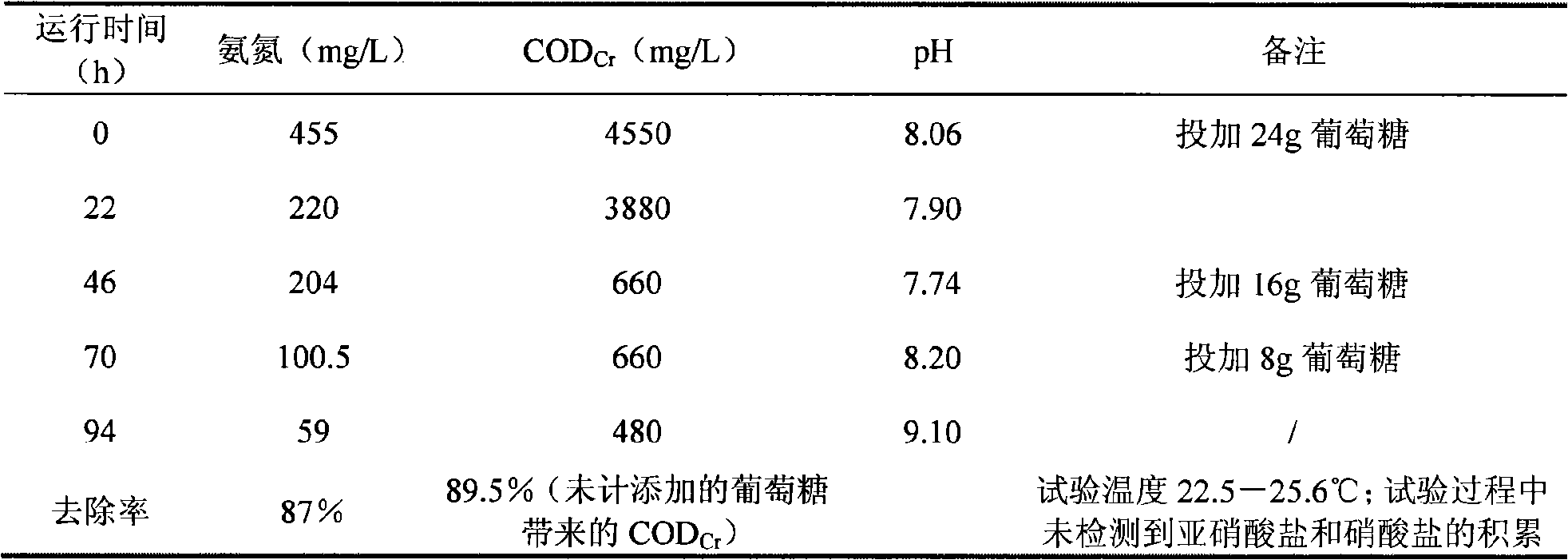
The invention belongs to the environmental microorganism field, relates to a high efficiency heterotrophic nitration aerobic denitrifying bacteria and the culture method and the purpose. The bacterium is Pseudomonas putida DN1.2 with the preservation and registration number of CCMCC M207075, which can effectively remove the ammonia nitrogen, nitrous acid and the mixture in water. At the same time, the bacterium also can remove the CODCr in the organic waste water. The bacterium is suitable for being used in the treatment of organic nitrogenous effluent with high concentration and inorganic nitrogenous effluent. The nitrite and nitrate can not be produced in the denitrification process. The waste water treatment process is simple by using the strain and the denitrification effect is stable.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
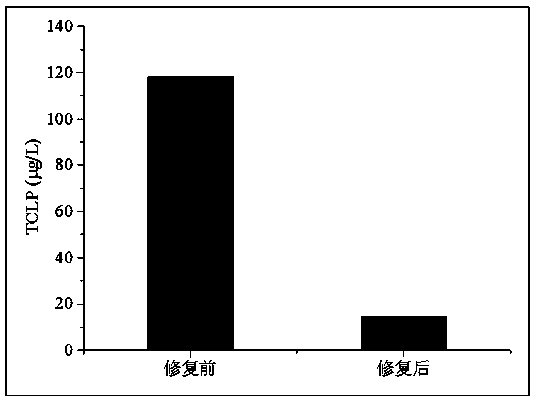
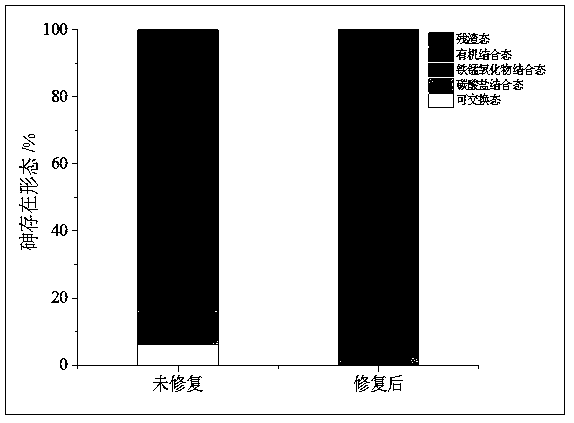
Method for remedying acidified arsenic contaminated soil by biochar-loaded nano-scale zero-valent iron cooperated with bacteria
ActiveCN109570227AReduce dosageAvoid destructionContaminated soil reclamationChemical reactionPseudomonas putida
The invention relates to a method for remedying acidified arsenic contaminated soil by biochar-loaded nano-scale zero-valent iron cooperated with bacteria. The method includes selecting Pseudomonas putida strain MnB1 (ATCC23483); carrying out enrichment culture on the Pseudomonas putida strain in enrichment culture media; inoculating strains in culture media with divalent manganese and carrying out culture on the strains to obtain active metabolites; adding the active metabolites and the green synthetic biochar-loaded nano-scale zero-valent iron into the acidified arsenic contaminated soil anduniformly stirring the active metabolites, the biochar-loaded nano-scale zero-valent iron and the acidified arsenic contaminated soil; carrying out a series of physical-chemical reaction on active manganese oxide, zero-valent iron, biochar and trivalent arsenic or pentavalent arsenic in the soil; converting the arsenic in exchangeable forms into arsenic in residual forms. The method has the advantages that the arsenic in the soil can be effectively immobilized, the pH (potential of hydrogen) of the soil can be increased, and the double purposes of remedying soil acidification and arsenic contamination can be simultaneously achieved; the method is short in remediation time, high in efficiency, wide in treatment range and free of secondary pollution, and stable effects can be realized.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Microbe-enzyme composite preparation used for restoring water in urban and rural polluted river, and its preparation method
ActiveCN102815792AImprove metabolic activityHigh degradation activityWater resource protectionBacteriaBacillus licheniformisAmylase
The invention provides a microbe-enzyme composite preparation used for restoring water in an urban and rural polluted river, and its preparation method. The urban and rural polluted river restoration microbe-enzyme composite preparation is characterized in that the microbe mainly comprises 30-60% of Bacillus licheniformis, 25-35% of a nitrobacterium, and 15-35% of pseudomonas putida; and the composite enzyme mainly comprises 40-60% of a protease, 15-25% of an amylase and 25-35% of a cellulase. The optimized microbe is compounded with the composite enzyme to prepare the microbe-enzyme composite preparation against water of different pollution degrees, the addition amount of the microbe is 1-5g / m<3>, and the addition amount of the composite enzyme is 0.01-0.05g / m<3>. The microbe-enzyme composite preparation is added to the urban and rural polluted river to carry out microbial reinforced restoration with aeration as an auxiliary measure, can effectively improve defects of low microbe metabolism activity, low environmental tolerance, short retention time in the polluted water and the like existing in the prior art, and has a substantial water purifying effect.
Owner:浙江绿凯环保科技股份有限公司
Microorganism bacterium agent for straw and excrement mixed composting
ActiveCN103232944AWell mixedPromote the process of mixed aerobic compostingFungiBio-organic fraction processingFecesPseudomonas putida
The invention discloses a microorganism bacterium agent for straw and excrement mixed composting. The microorganism bacterium agent is composed of the following strains: (2-6)*10<10>cfu of hair mould per gram, (2-6)*10<10>cfu of trichoderma virens per gram, (2-6)*10<10>cfu of geotrichum candidum per gram, (2-8)*10<9>cfu of saccharomyces cerevisiae per gram, (3-5)*10<11>cfu of bacillus thermophilus per gram, (2-6)*10<11>cfu of lactobacillus thermophilus per gram, (2-8)*10<10>cfu of white rot fungi per gram, (2-8)*10<10>cfu of monilinia fructicola per gram, (3-7)*10<8>cfu of pseudomonas putida per gram, (2-6)*10<11>cfu of nitrosococcus per gram, (1-4)*10<6>cfu of green algae per gram and (2-5)*10<7>cfu of blue-green algae per gram. The microorganism bacterium agent can promote a straw and excrement mixed aerobatic composting progress, shorten a composting period, improve a composting rotten degree, accelerate biodegradation of organic matters, alleviate ozone generation and diffusion during composting and reduce loss of nutrient substances such as nitrogen, can be applied to composting of different straw and excrement raw materials for composting enterprises and is used for producing bio-organic fertilizers.
Owner:山东土木启生物科技有限公司
Pseudomonas putida with aerobic denitrifying capability and method of treating waste water by the same
InactiveCN101016524AStrong toleranceRealize simultaneous nitrification and denitrificationBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesNitritePseudomonas putida
The invention discloses a pseudomonas putida (Pseudomonas putida) WXZ-4 CGMCC No.1798 strain with aerobic denitrifying property and a method to denitrify the waste water; which is characterized by the following: possessing strong tolerance degree for dissolved oxygen; deacidizing nitrate and nitrite with distinctive speed under the condition of 50-98% saturated dissolved oxygen; seeding to active sludge; proceeding enriched culture; realizing the aerobic anti-nitration.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Complex endophytic bacterial inoculant and application thereof in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil
ActiveCN105950502AOvercoming Weaknesses of RepairImprove repair efficiencyBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacteroidesSedum alfredii
The invention discloses a complex endophytic bacterial inoculant and an application thereof in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. The complex inoculant is composed of acinetobactercalcoaceticus, pseudomonas fluorescens, bacillusmegaterium, stenotrophomonasmaltophilia, bacillus pumilus and pseudomonas putida. The complex inoculant disclosed by the invention, when applied to heavy metal pollution remediation, integrates advantages of various endophytic bacteria and overcomes disadvantages of phytoremediation; and the complex inoculant can promote the growth of sedum alfredii hance, enhance the absorbing capacity of the sedum alfredii hance to heavy metals and improve the efficiency of phytoremediation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
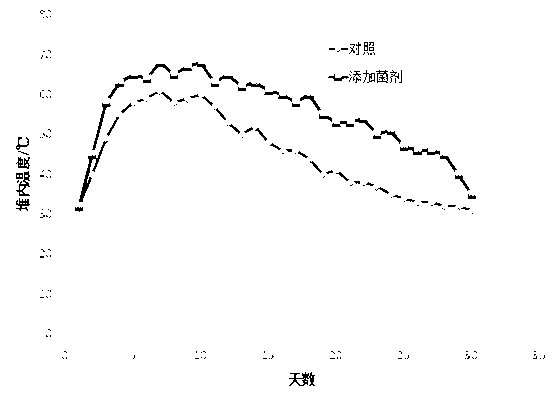
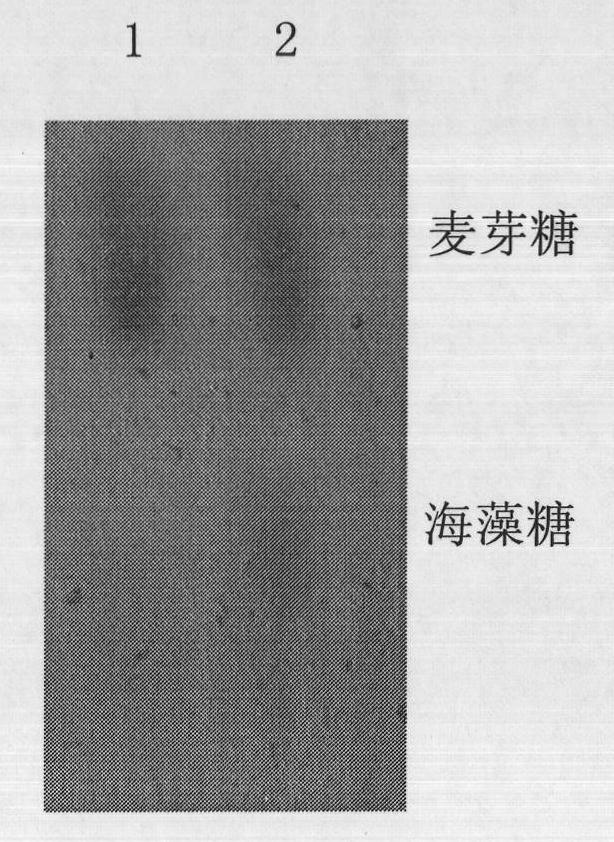
Production method of trehalose
The invention relates to a production method of trehalose, in particular to a method for producing trehalose by utilizing pseudomonas putida, belonging to the technical field of fermentation engineering and microorganism. The method for producing trehalose by utilizing pseudomonas putida comprises the following steps of: culturing the pseudomonas putida, treating beta-mercaptoethanol and fermenting. In the method, maltose is used as a substrate, and then the maltose is transformed to the trehalose in one step through preparing the permeable cells of pseudomonas putida by utilizing trehalose synthase in the cells of the pseudomonas putida. Through determination, about 3-5% of trehalose is generated in the permeable cell solution of the pseudomonas putida treated by using the beta-mercaptoethanol.
Owner:ZHUCHENG DONGXIAO BIOTECH
Microorganism bacterium agent for treating industrial wastewater pollution
ActiveCN105505841AEasy to prepareSimple and fast operationFungiBacteriaOperational costsPseudomonas putida
The invention relates to a microorganism bacterium agent for treating industrial wastewater pollution. The microorganism bacterium agent is prepared from pseudomonas putida, candida utilis, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, clostridium papyrosolvens, nitrosomonas europaea, paracoccus denitrificans and auxiliary materials. The microorganism bacterium agent has the advantages that various bacteria in mutualistic symbiosis are compatible reasonably without antagonism and are effective in degradation of phenyl amines degradation-resistant compounds when being thrown into a wastewater treatment system, thereby being suitable for industrial wastewater treatment and being capable of increasing treatment water quantity, improving treatment water quality, reducing operational cost and promoting up-to-standard discharge.
Owner:芜湖市科邦新能源科技有限公司
Microbial sludge deodorizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106520627AIncrease the rate of catalytic reactionsReduced Pollution ChancesFungiBacteriaBacteroidesSludge
The invention discloses a microbial sludge deodorizer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: conducting high-density culture on strains of streptococcus thermophilus, bacillus subtilis, aspergillus oryzae, photosynthetic bacteria, saccharomyces cerevisiae, lactobacillus casei and pseudomonas putida; dehydrating and drying the various single strains which are subjected to high-density culture, so that hypopus microbial dry powder is prepared; and mixing the streptococcus thermophilus, the bacillus subtilis, the aspergillus oryzae, the photosynthetic bacteria, the saccharomyces cerevisiae, the lactobacillus casei and the pseudomonas putida according to weight ratio of 10-20 parts of the streptococcus thermophilus, 10-15 parts of the bacillus subtilis, 20-30 parts of the aspergillus oryzae, 10-15 parts of the photosynthetic bacteria, 10-20 parts of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, 10-15 parts of the lactobacillus casei and 10-20 parts of the pseudomonas putida, so that the microbial sludge deodorizer is obtained. The microbial sludge deodorizer provided by the invention is applicable to garbage deodorization; and in comparison with the prior art, the microbial sludge deodorizer is low in production investment, low in production cost and convenient to use, and moreover, the microbial sludge deodorizer is good in deodorizing effect.
Owner:YANCHENG FUHUA ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION IND DEV CO LTED
Microbial cell sensor for detecting toluene organic pollutants
The invention discloses a microbial cell sensor for detecting toluene organic pollutants and a detection method thereof, and relates to a microbial cell sensor for detecting toluene organic pollutants, which is constructed by using a regulatory sequence of pseudomonas putida degradation genes and a plasmid sequence of regulatory protein genes and commercial report genes, and a detection method thereof. The bacterial host is Escherichia coli, and is used for detecting toluene organic matters. The lowest detection concentration on the toluene is 40 micromoles per liter, and the highest detection concentration on the toluene is 1,000 micromoles per liter.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving oil sludge separating and processing efficiency and bacterial strain used for method
The invention belongs to the environment-friendly field, and discloses a method for improving oil sludge separating and processing efficiency and a bacterial strain used for the method. The method for improving the oil sludge separating and processing efficiency comprises the following steps: (1), sampling and analyzing processed oil sludge; (2), determining microorganism nutrients to be added according to components and content of a nitrogen element and a phosphor element in the processed oil sludge; (3), adding a mixed culture of candida lipolytica Y-57 and pseudomonas putida P-101 and the microorganism nutrients into the to-be-processed oil sludge, stirring, ventilating and culturing for over 8 hours under the condition with pH of 6-10 under a temperature of 8 DEG C-45 DEG C to separate oil and mud in the oil sludge. According to the invention, a microorganism treatment method is adopted for separating the oil and the mud in the oil sludge to achieve an effect of an oil resource recovery rate; moreover, a chemical agent which generates influence to the environment is not added, so that secondary pollution is not generated. Resourceful treatment is carried out on oil-containing mud to obtain a certain economic benefit, and therefore, the method is an economical and effective oil sludge treating technology.
Owner:JIANGSU BODA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Heterotrophic nitrification aerobic granule sludge, culture method thereof and use
ActiveCN101306870APre-fixed validCultivate successBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActivated sludgeMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the environmental microorganism field, in particular relating to heterotrophic nitrification aerobic granular sludge and a cultivation method and an application thereof. An inoculated strain of the aerobic granular sludge is stenotrophomonas maltophilia and pseudomonas putida. Activated carbon is adopted to prefix a functional strain culture, ordinary activated sludge is not inoculated, and the heterotrophic nitrification aerobic granular sludge can be cultivated. The aerobic granular sludge can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and a mixture thereof in a water body, can also simultaneously remove CODCr in organic wastewater, is applicable to the treatment of high concentrated organic nitrogen-containing wastewater and inorganic nitrogen-containing wastewater, and does not produce the accumulation of nitrite and nitrate during the denitrification. The application of the aerobic granular sludge for wastewater treatment has simple process and steady denitrification effect.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
High-concentration chemical sewage composite inocula and use thereof
ActiveCN105621626AThe method of treating sewage is simple and easyImprove survival rateBiological water/sewage treatmentSynechococcusBacillus cereus
The invention discloses high-concentration chemical sewage composite inocula. The high-concentration chemical sewage composite inocula comprise, by weight, 180-220 parts of bacillus cereus, 150-160 parts of bacillus circulans, 75-85 parts of Exiguobacterium acetylicum, 90-120 parts of bacillus coagulans, 150-170 parts of pseudomonas aeruginosa, 20-25 parts of micrococcus luteus, 120-140 parts of thiobacillus thiooxidans, 180-230 parts of rhodococci, 20-30 parts of lactobacillus brevis, 50-65 parts of paracoccus denitrificans, 95-112 parts of alcaligenes faecalis, 110-125 parts of pseudomonas putida, 100-130 parts of enterobacter aerogenes, 280-320 parts of beer yeast and 140-160 parts of lactobacillus fermenti. All strains of the composite inocula reasonably cooperate with each other, produce synergistic effects, do not produce antagonism, have a high survival rate, is suitable for one step addition and fast forms dominant bacterial community. The high-concentration chemical sewage composite inocula have unique treatment effects on high-concentration chemical sewage, have a COD clearance rate of 94.17%, reduce an operation cost and promote qualified discharge.
Owner:江苏元捷环境科技有限公司
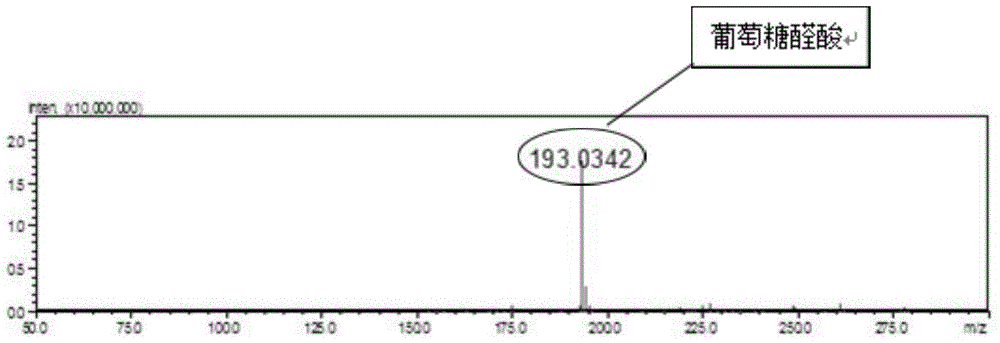
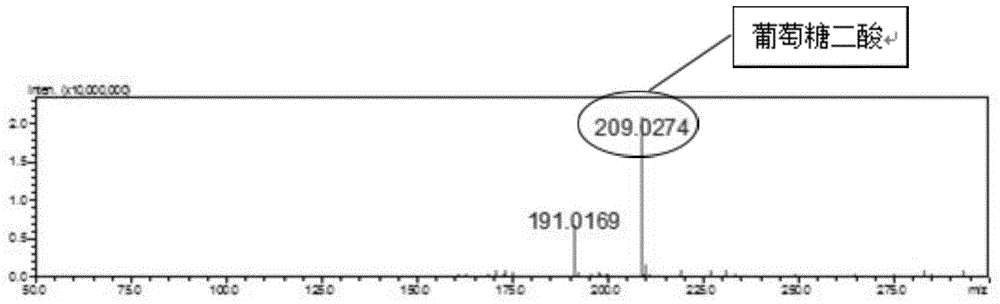
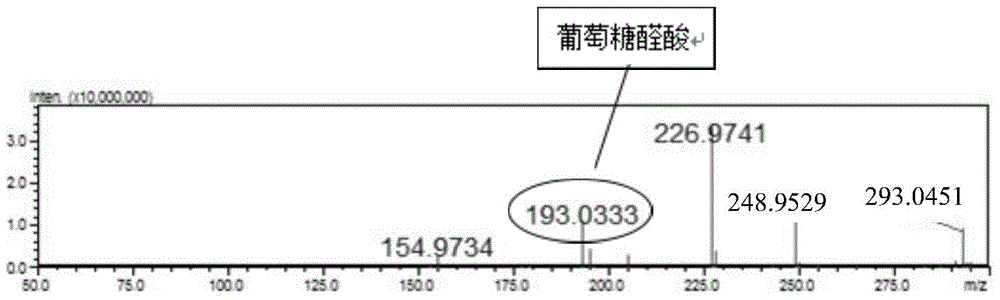
Biosynthesis method of glucuronic acid and glucuric acid
ActiveCN104312987AEfficient yieldEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method of glucuronic acid and glucuric acid, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The biosynthesis method is characterized by expressing myo inositol oxygenase (MIOX) from pichia pastoris in Escherichia coli to convert myo inositol into glucuronic acid, and expressing aldehyde acid dehydrogenase (Udh) from pseudomonas putida to convert produced glucuronic acid into glucuric acid, thereby successfully establishing a synthesis path from myo inositol to glucuric acid. Recombinant Escherichia coli established by the method has very great application prospect, and a new idea is provided for generating glucuronic acid and glucuric acid through conversion by the biological method.
Owner:江苏弘康未来营养科技有限公司
Chromium slag processing method for chemical-biological coupling reduction of hexavalent chrome
The invention relates to a chromium slag treatment when coupling and reducing hexavalent chromium from chromium slag, wherein said method comprises using wet method to break, and adding the solution with acid and reducer, controlling the pH value, reducing the density of hexavalent chromium; transferring the liquid-solid mixture to another reactor, adding acid and reducer, mixing to reduce the hexavalent chromium; adding anaerobe, emerging. The acid can be sulfuric acid, etc; the reducer can be sulfite, etc; the anaerobe can be the mixture of SRB, Pseudomonas putida and Escherichia coli.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
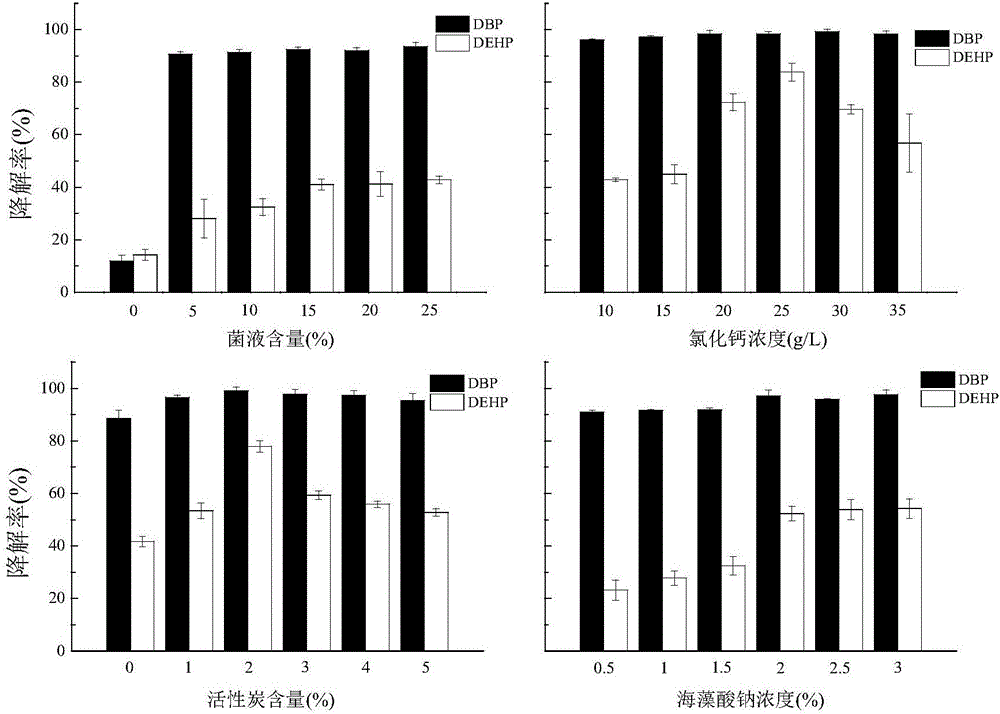
Immobilized microspheres for degrading bacteria of PAEs (phthalic acid esters) and preparation method and application of such immobilized microspheres
ActiveCN106834269AEasy to operateEasy to fixContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganism based processesActivated carbonPseudomonas putida
The invention relates to immobilized microspheres for degrading bacteria of PAEs (phthalic acid esters) in farmland soil and a preparation method of such immobilized microspheres. The preparation method includes (1), preparing a bacterial suspension, namely culturing pseudomonas putida RXX-01 (preservation number: CGMCC No.13224) to a logarithmic phase, cleaning bacteria with normal saline, and mixing the bacteria into the bacterial suspension with the normal saline so as to enable OD600 of the bacterial suspension to equal 0.8-1.2; (2), preparing mixed bacterial liquid, namely preparing a sodium alginate solution with sterile water, adding activated carbon into the sodium alginate solution with mixing uniformly to obtain mixed liquid, and adding the bacterial suspension obtained in the step (1) into the mixed liquid with mixing uniformly so as to obtain the mixed bacterial liquid, wherein the mixed bacterial liquid comprises, by weight, 15-25% of bacterial suspension, 2-3% of sodium alginate and 2-4% of activated carbon; (3) preparing the immobilized microspheres, namely preparing a 20-30 g / L calcium chloride solution with sterile water, dropwise adding the mixed bacterial liquid into the calcium chloride solution, and crosslinking for 20-30 hours so as to obtain the immobilized microspheres, wherein a volume ratio of the mixed bacterial liquid to the calcium chloride solution is 1:1.5-1:2. The preparation method is simple, and the immobilized microspheres are high in efficiency of degrading the phthalic acid esters in the soil.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV +1
High-activity high-tolerance formaldehyde degrading bacteria and application thereof
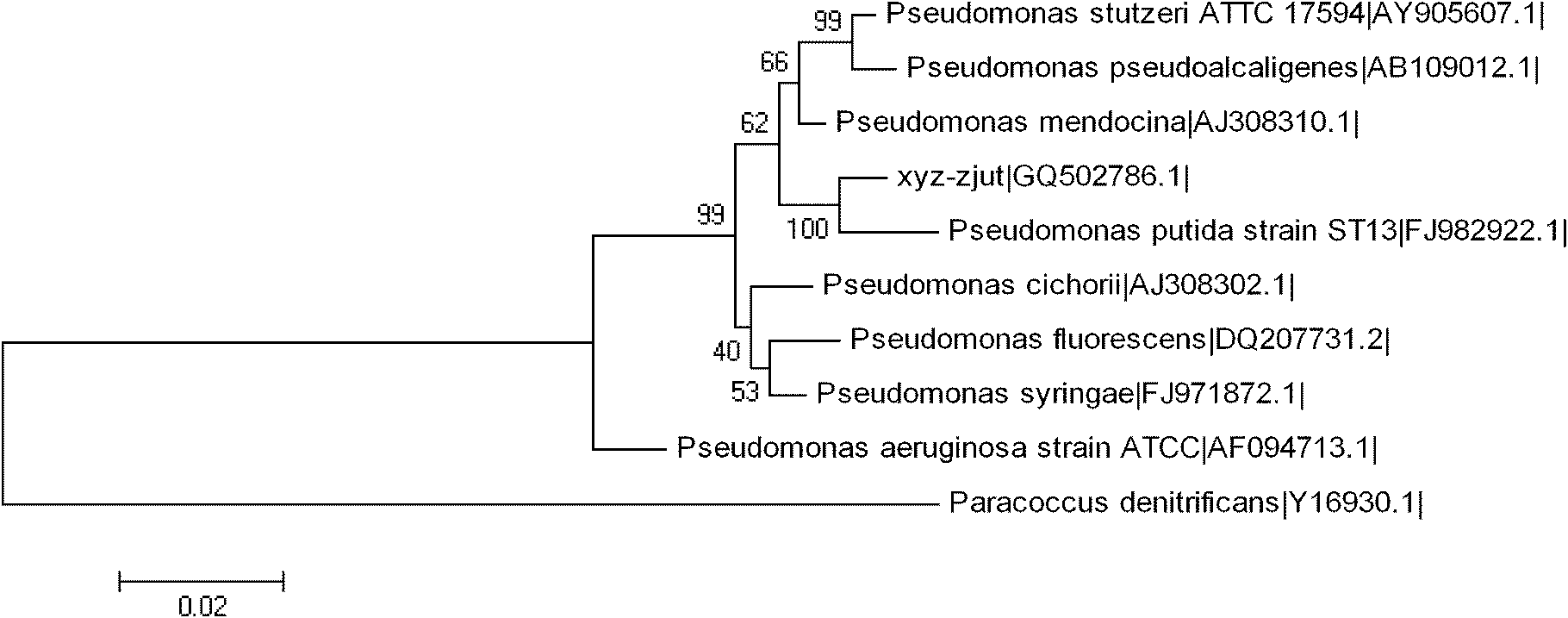
The invention provides high-activity high-tolerance formaldehyde degrading bacteria and an application thereof in micro-biological degradation of formaldehyde. In the invention, Pseudomonas putida xyz-zjut is conserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection; the address is Wuhan University, Luojia Mountain, Wuhan City, Hubei Province, 430072; the conservation date is May 23, 2010; and the conservation number is CCTCC No: M 2010125. The invention has the beneficial effects that the high-activity high-tolerance formaldehyde degrading bacteria and the application thereof provide a basis for biological control and treatment of formaldehyde and have wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and application thereof
ActiveCN110184246AHigh catalytic activitySolve the problem of low enzyme activityOxidoreductasesFermentationPseudomonas putidaThreonine
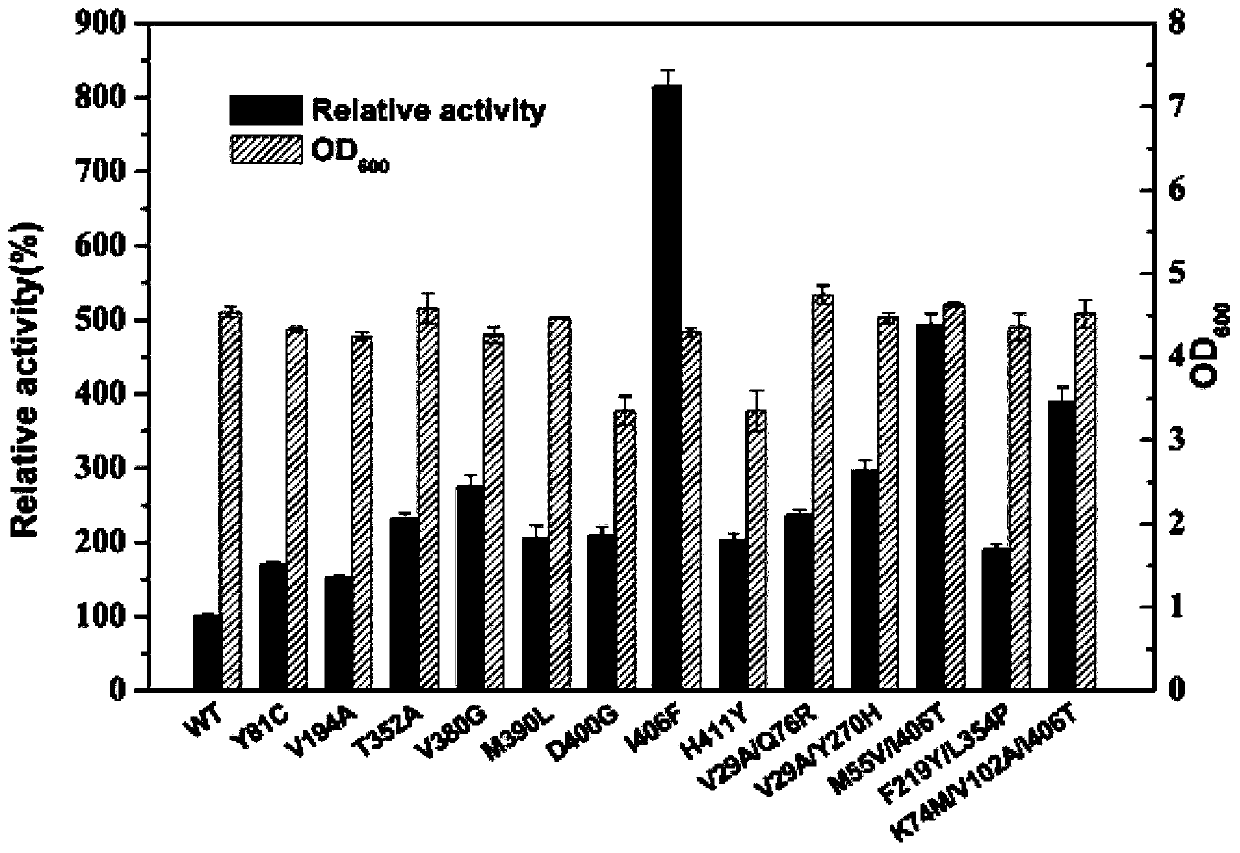
The present invention discloses glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and an application thereof. The glutamate dehydrogenase mutants are one of the following: mutating 402th lysine of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 to phenylalanine or aspartic acid; mutating 406th isoleucine to phenylalanine or threonine; conducting combined mutation of 121th threonine and 123th leucine; and conducting combined mutation of 379th alanine and 383th leucine. A molecular transformation method combining directed evolution with semi-rational design significantly improves catalytic activity of glutamate dehydrogenase derived from pseudomonas putida to 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphono)butyric acid (PPO) and solves a problem of low glutamate dehydrogenase activity in preparation of L-glufosinate by a reductive amination method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bacterium of degrading residual of organophorus pespared agent of bacterium
InactiveCN1563356AWill not affect the use effectEasy to useBacteriaPesticide residuePseudomonas putida
A bacterial strain for eliminating organophosphorous residue is Granis staining reaction negative bacteria DLL-1 identified as pseudomonas putida. Its biological feature is G- with thallus being short bar shape, tail end being oval and single end being grown thickly with flagellum. The Genbank landing number of 16S rDNA for the bacterial strian is AF 447394.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
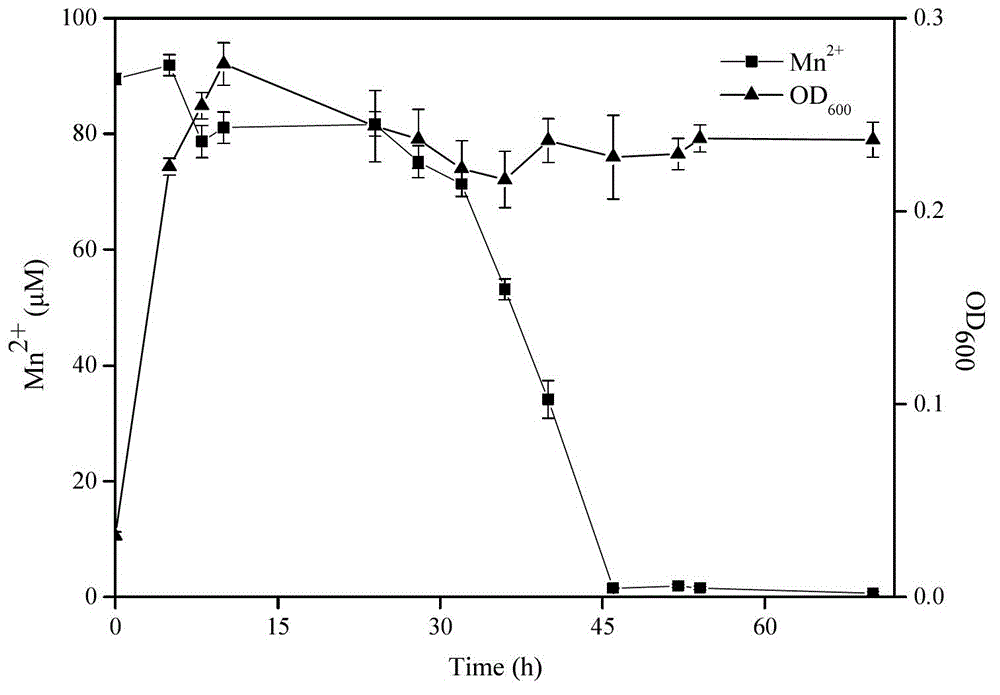
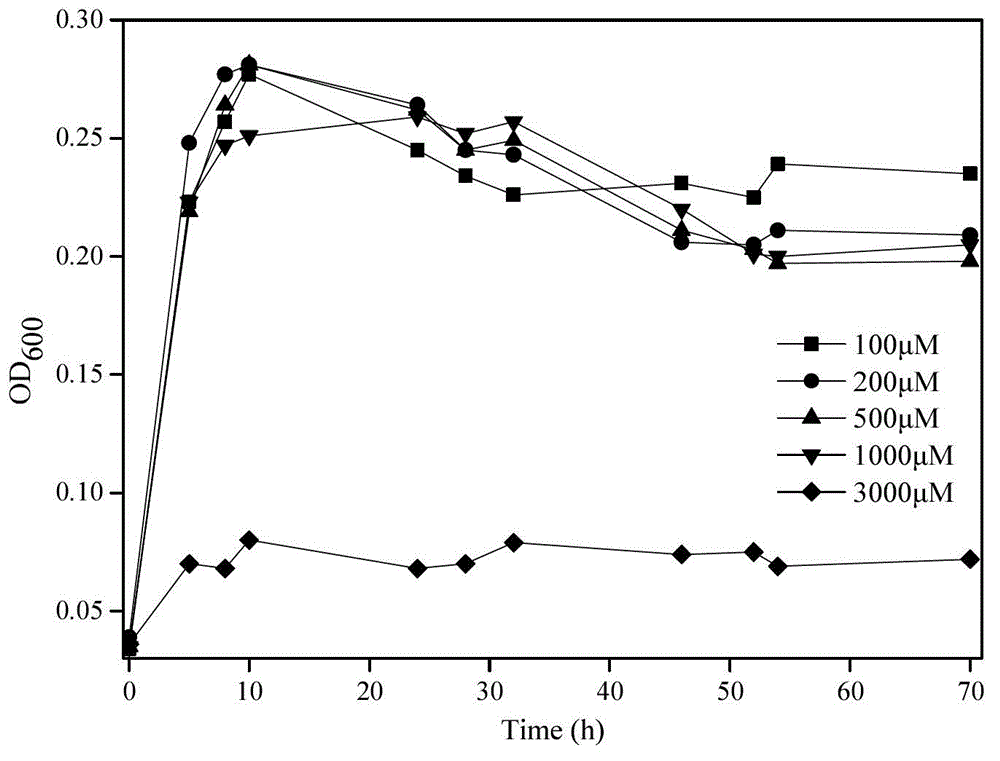
Manganese oxidizing bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN103333826AMaintain growth activityBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPseudomonas putidaWater insoluble
The invention discloses manganese oxidizing bacteria capable of oxidizing Mn<2+>. The bacteria can oxide the Mn<2+> in a water body to generate water-insoluble manganese oxide. The Mn<2+> oxidizing bacteria are a pseudomonas putida QJX 1 strain with a preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.6630. The pseudomonas putida QJX 1 strain provided by the invention is used for oxidizing the Mn<2+> in natural water bodies, wherein the operating temperature (10-30 DEG C) is within a normal temperature range, the pH value (6.5-8.5) is within a neutral range, and the pseudomonas putida QJX 1 strain has high Mn<2+> oxidation efficiency. The invention also relates to a method for removing Mn<2+> in water bodies or solid matrixes. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating the manganese oxidizing bacteria or a microbial agent containing the manganese oxidizing bacteria into the water bodies or solid matrixes, and culturing for a proper time under conditions of 10-35 DEG C and pH of 6.5-8.5.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
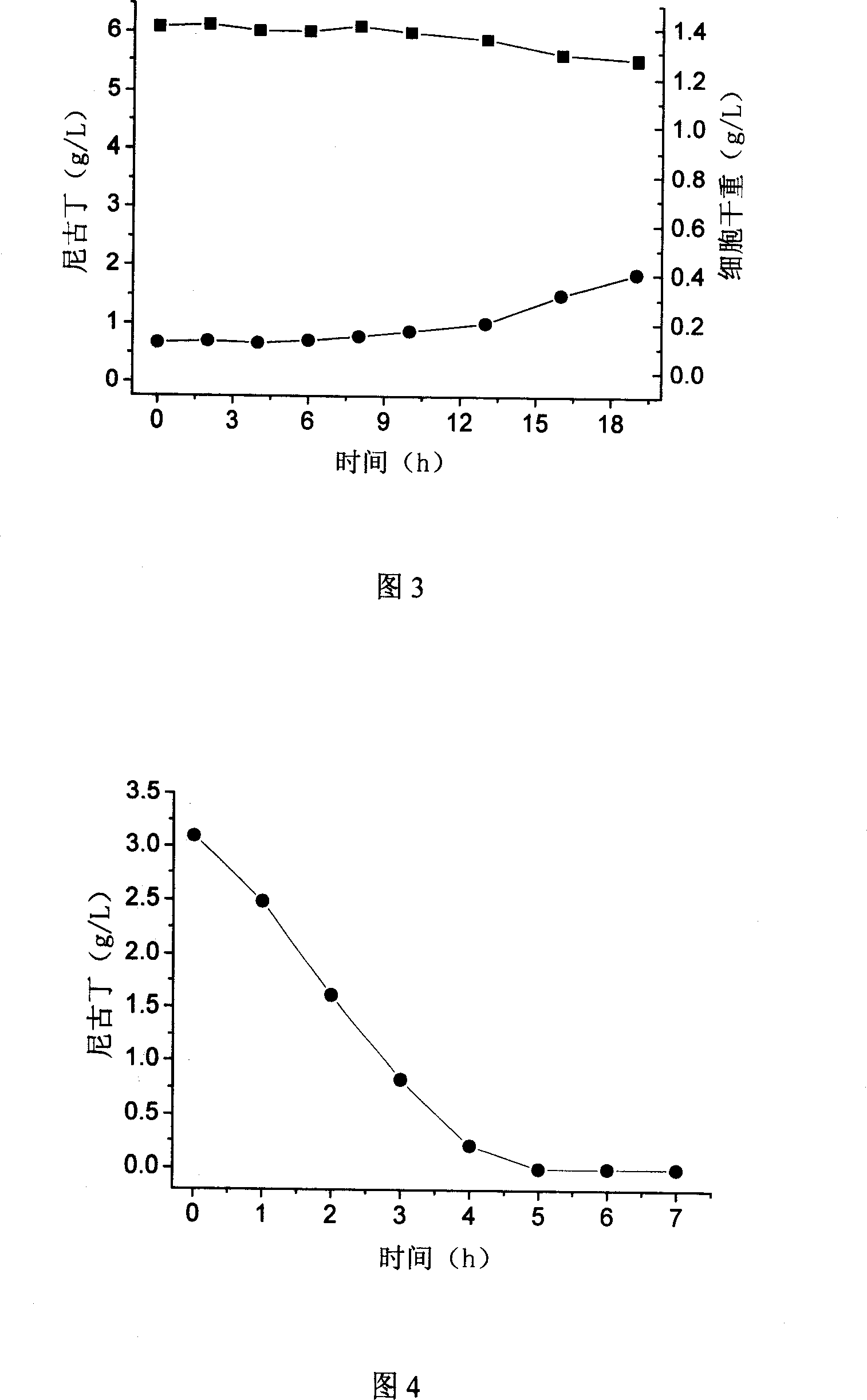
Pseudomonas putida capable of metabolizing nicotine and application thereof
InactiveCN101016528ALow costGood cell permeabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a pseudomonas putida to metabolite nicotine, which is characterized by the following: preserving in China Typical Culture Preservation Center (Wuhan university, china Wuhan) with keeping number as CCTCC NO.M 205038; possessing stronger nicotine metabolic ability and nicotine toxin immunity ability; growing highest at 6g / L nicotine density; culturing a good deal of bacterial strain; using intact cell as biological activator; degrading nicotine from tobacco industrial waste water completely. This bacterium possesses simple operation and quick disposing waste water speed, which can be used to dispose the waste water from tobacco industrial widely.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer and special bacteria thereof
ActiveCN101845414AHigh purityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas putidaCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a method for preparing hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer and special bacteria thereof. Recombinant pseudomonas putida is prepared by the method comprising the following steps of: depriving coding functions of 3-hydroxyfatty acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase coding gene and 3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase coding gene in pseudomonas putida to obtain recombinant pseudomonas putida, and recording the recombinant pseudomonas putida as recombinant pseudomonas putida I. Experiments prove that the hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer, particularly medium and long-chain hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer (C4-C14), can be obtained by using the recombinant bacteria organism to synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoate. The obtained hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer has high purity and high yield. The method of the invention can synthesize the medium and long-chain hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer with random length, and overcomes the defect that only one 3-hydroxybutyrate (HB) homopolymer can be obtained by biosynthesis in the prior art. Therefore, the method of the invention has broad application prospect in the biosynthesis field of the hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Bacterial biological fungicide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101953377ANo pollutionNot easy to develop resistanceBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyPseudomonas putida
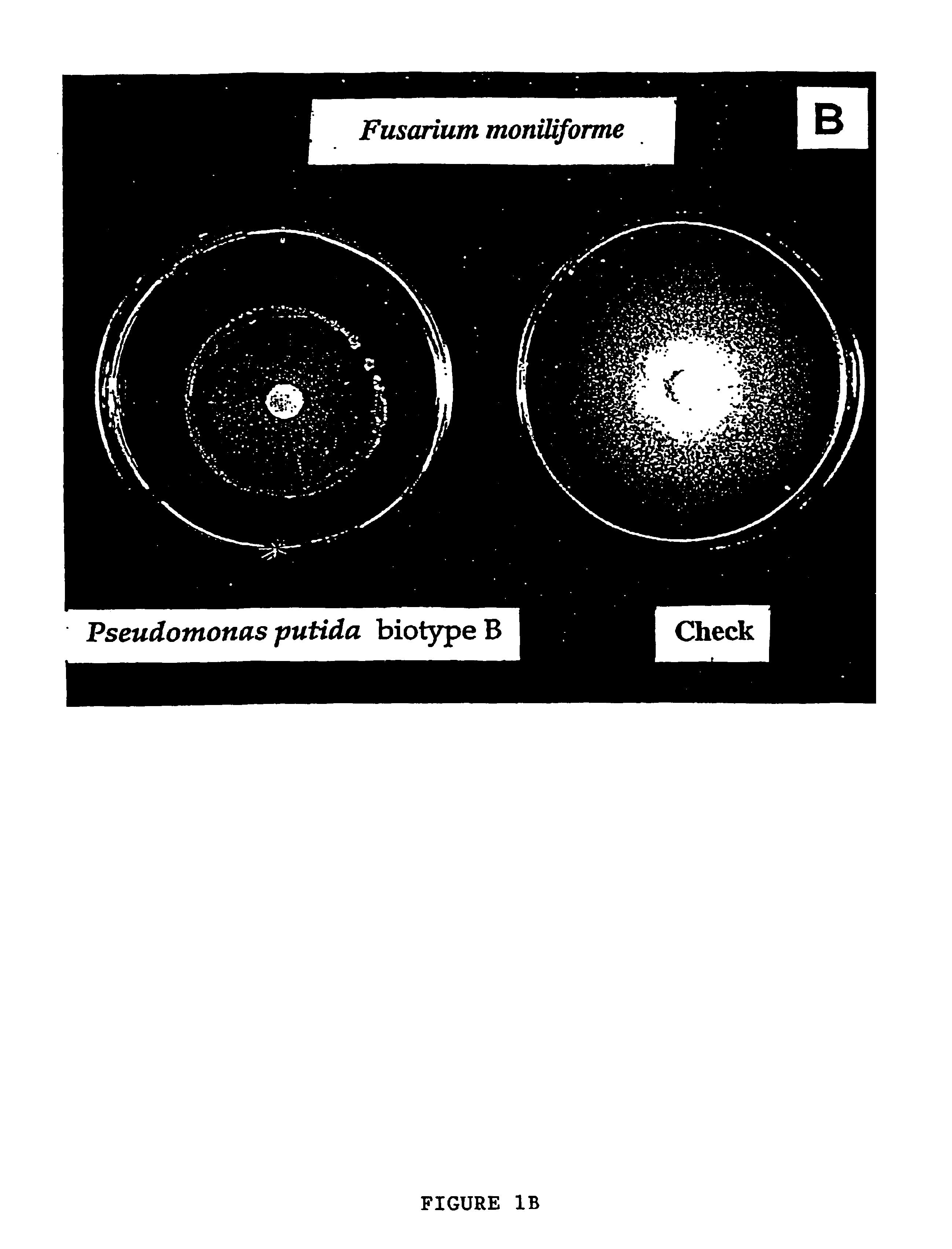
The invention provides a bacterial biological fungicide and a preparation method thereof. Microbial pesticide living Pseudomonas putida is used as a starting strain; and the bacterial biological fungicide is obtained after fermentation and reproduction. The bacterial biological fungicide can be used for nearly all crops infected by Pythium, Rhizoctonia and Fusarium, is safe for the crops, and has good effect on the crops such as cucumber, tomato, scallion, eggplant, green pepper, cotton, watermelon, sesame and the like. The bacterial biological fungicide has the greatest advantages that the bacterial biological fungicide is all nature, harmless, safe to people and livestock and environment-friendly; the pathogenic bacteria are not easy to produce resistance; and the bacterial biological fungicide is favorable for production of green vegetables, and has huge economic, ecological and social benefits.
Owner:王文夕
Soil conditioner for degrading pesticides in soil with microorganisms
InactiveCN106478288ARepair pollutionRich in organic matterExcrement fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersCompound organicBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a soil conditioner for degrading pesticides in soil with microorganisms. The soil conditioner is prepared from, by mass, 100-200 parts of organic fermented manure, 3-5 parts of trace fertilizer, 2-5 parts of bentonite, 5-7 parts of phosphate rock powder, 3-5 parts of amino acid and 0.1-1 part of microbial flora, wherein the microbial flora is composed of pseudomonas fluorescens, rhodopseudomonas palustris, alcaligenes faecalis, pseudomonas putida, bacillus licheniformis, spherical lysine bacillus, bacillus subtilis and bacillus cereus. The soil conditioner is prepared by compounding various microbial strains, the organic fermented manure, the trace fertilizer, amino acid, the bentonite and the phosphate rock powder, and can degrade the chemical pesticides in the soil, such as organic phosphorus pesticides, heterocyclic pesticides, phenol pesticides and aromatic pesticides, and remedy the pesticide-contaminated soil.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
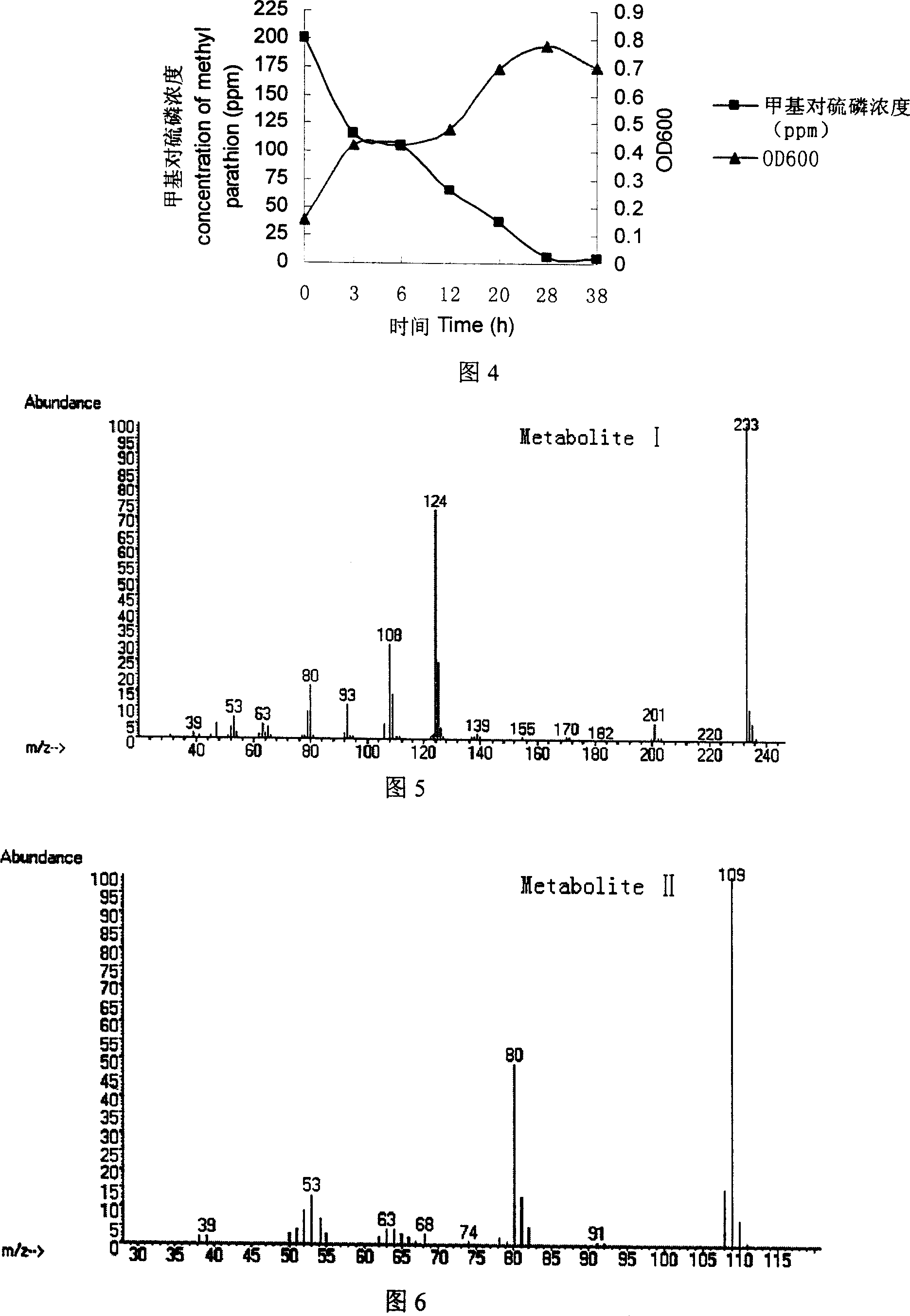
DU-E4LP seudomonas putida and use in degradating parathionmethyl
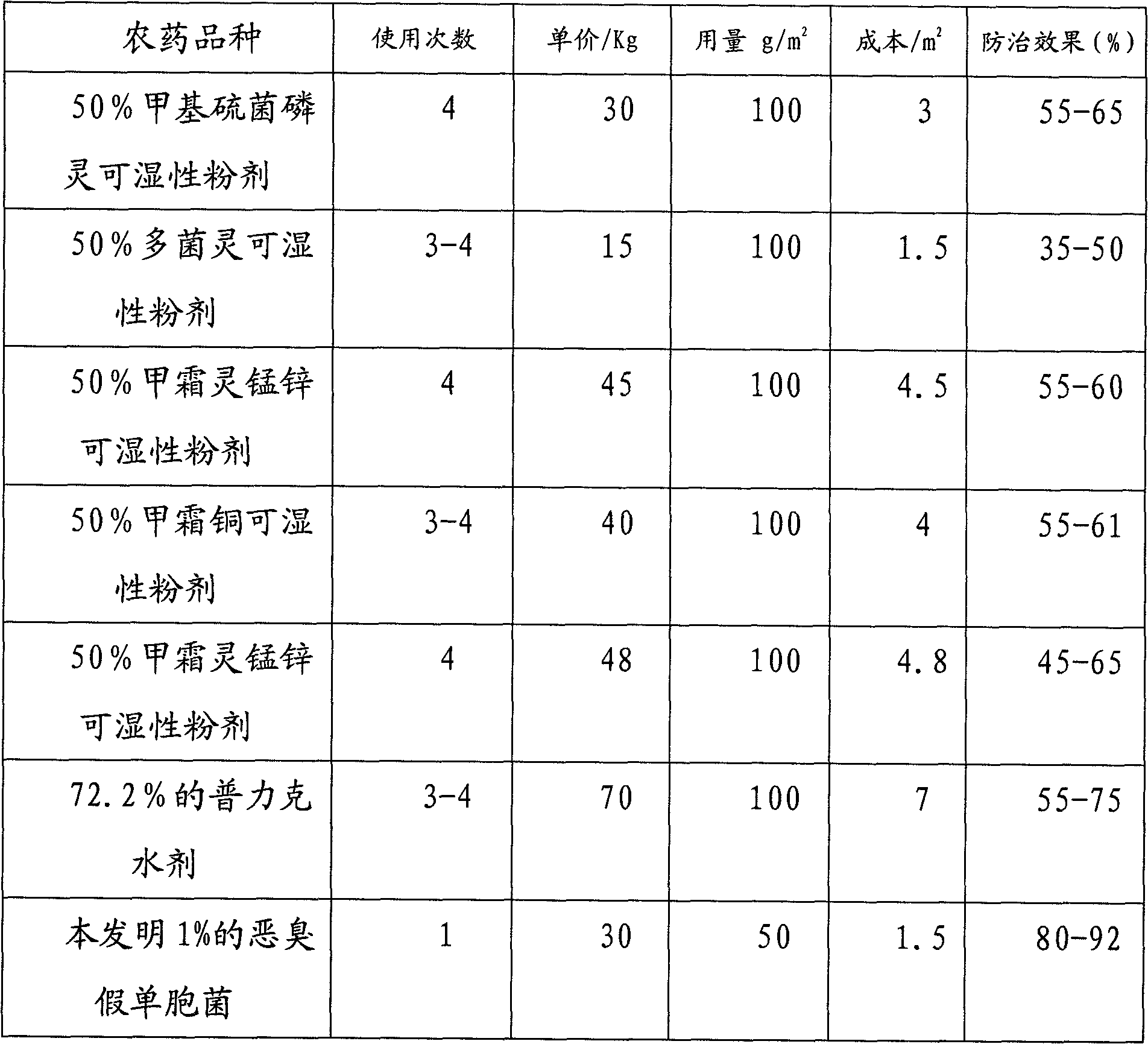
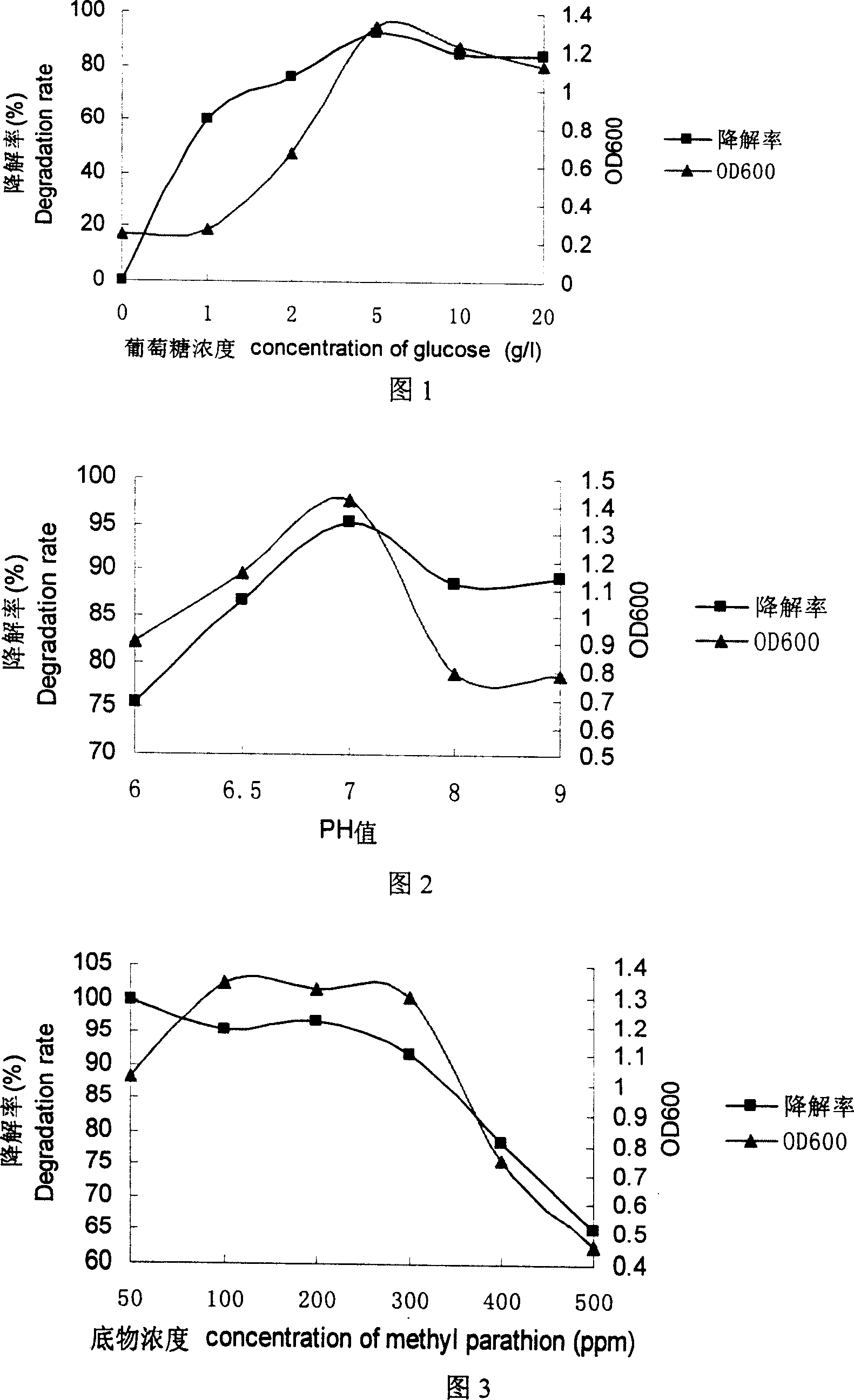
The invention supplies a methyl parathion degradation fungus DM-1 that the preservation NO is CGMCC No.1620. The classification designation is Bacillus subtilis. It is separated and selected from soil polluted by agricultural chemical. The fungus has good degradation effect to 50-500ppm methyl parathion at 30 degree centigrade.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com