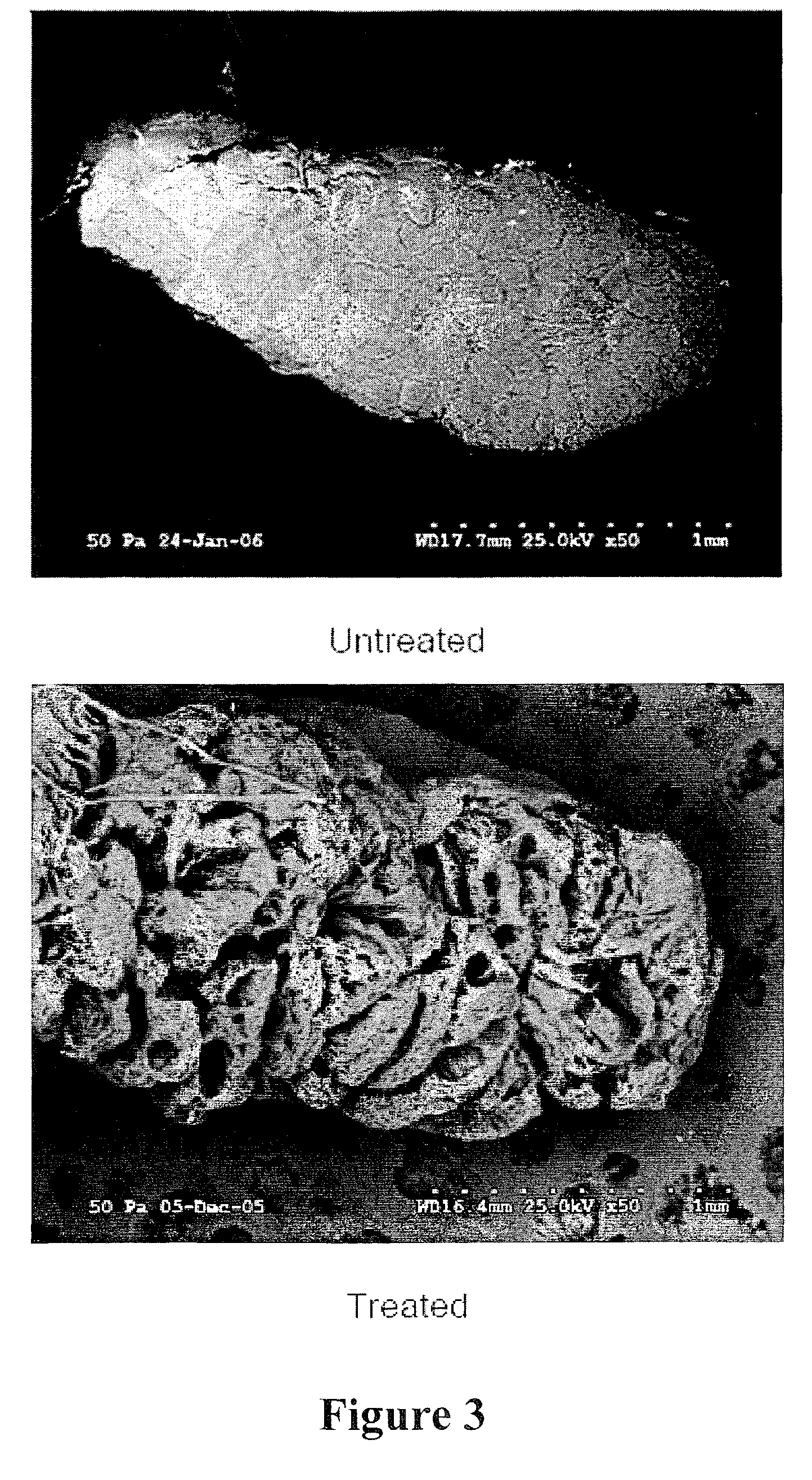
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Intact cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The administration has kept intact most of President Obama’s plan to modernize America’s deterrent force. ... and functionally complete the sense of touch was intact intact cell membranes: as. a: physically virginal ...
Devices and processes for analysing individual cells
InactiveUS20090098541A1Easy to separateCompared rapidly and convenientlyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell trappingEngineering
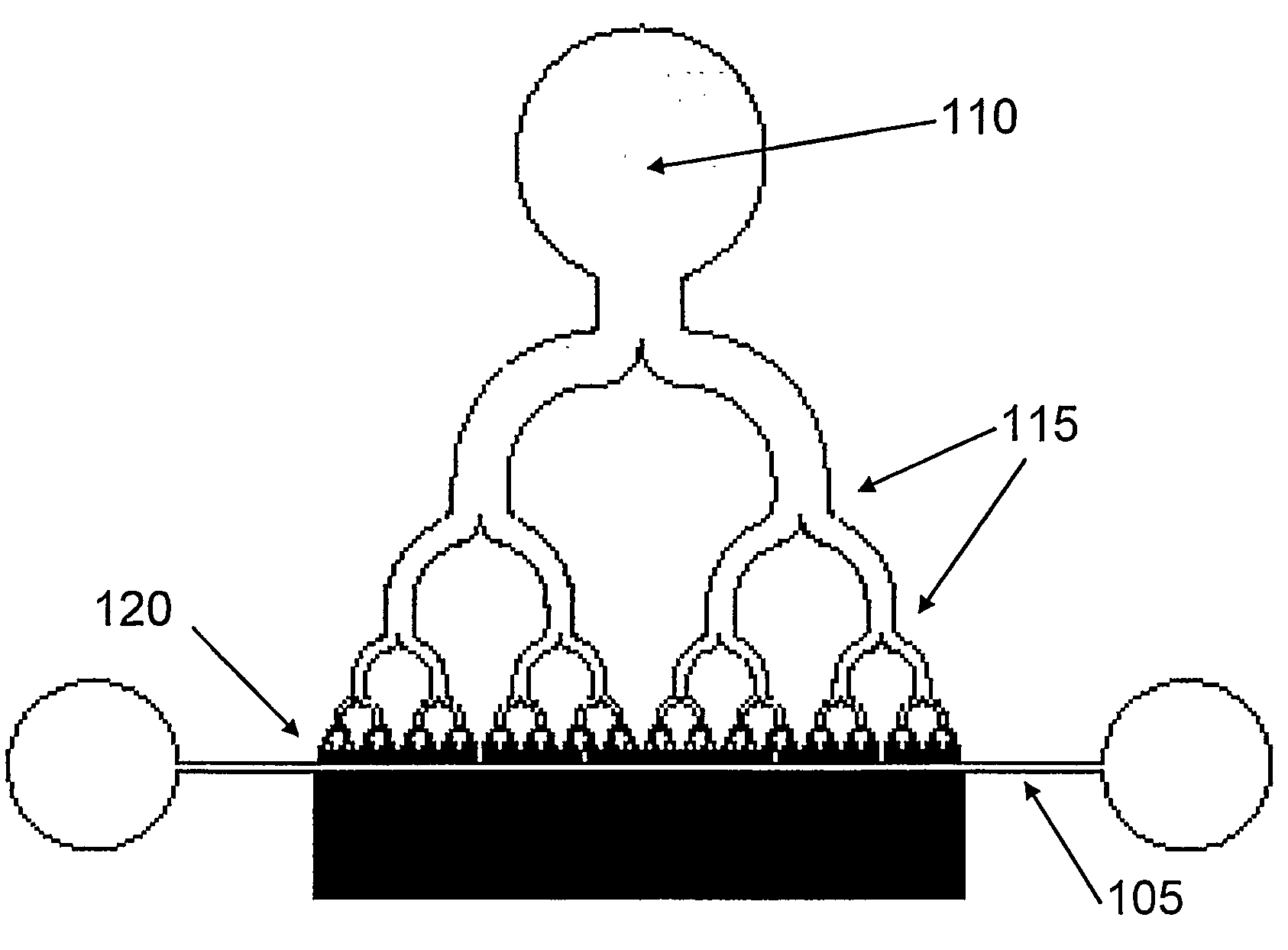
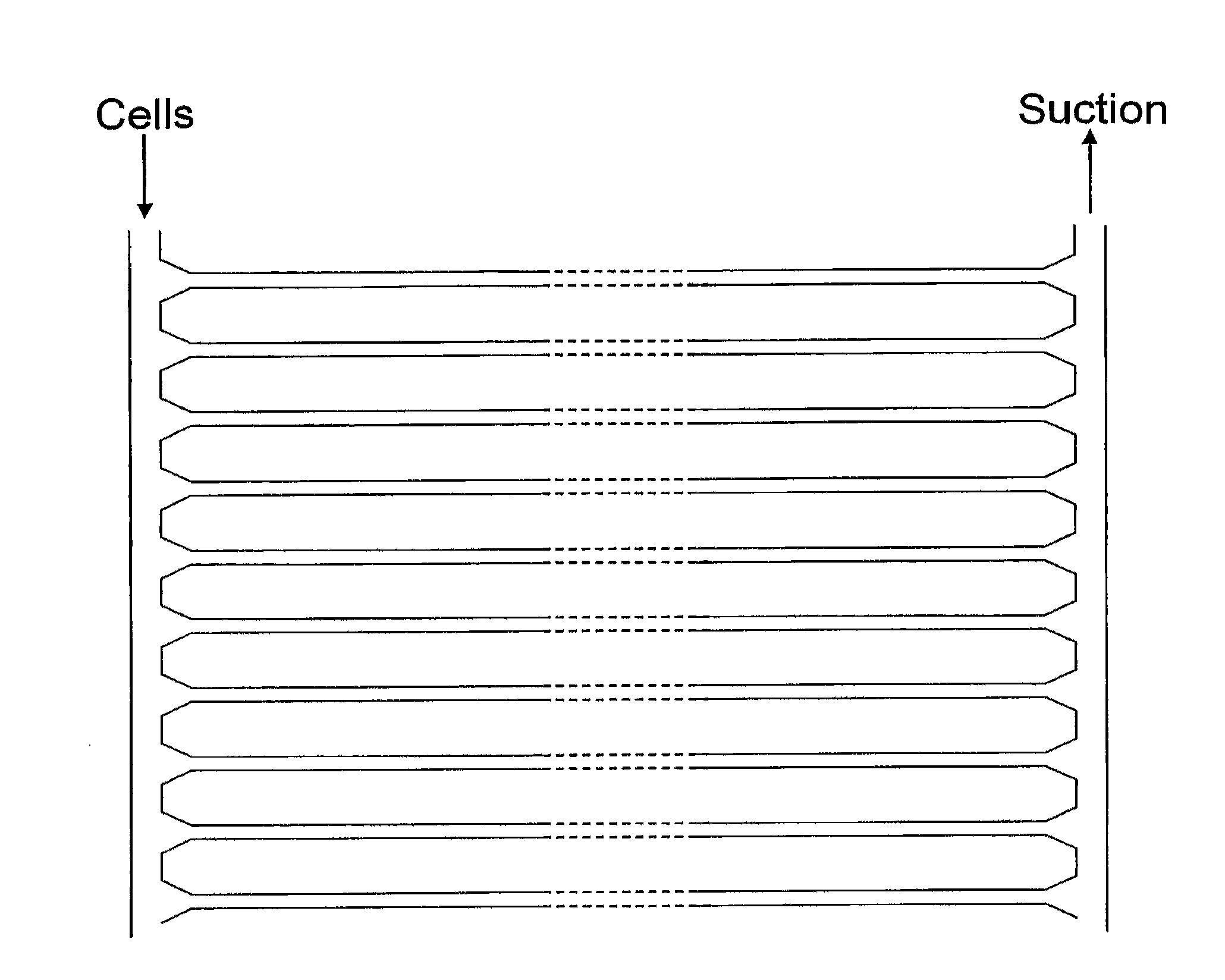
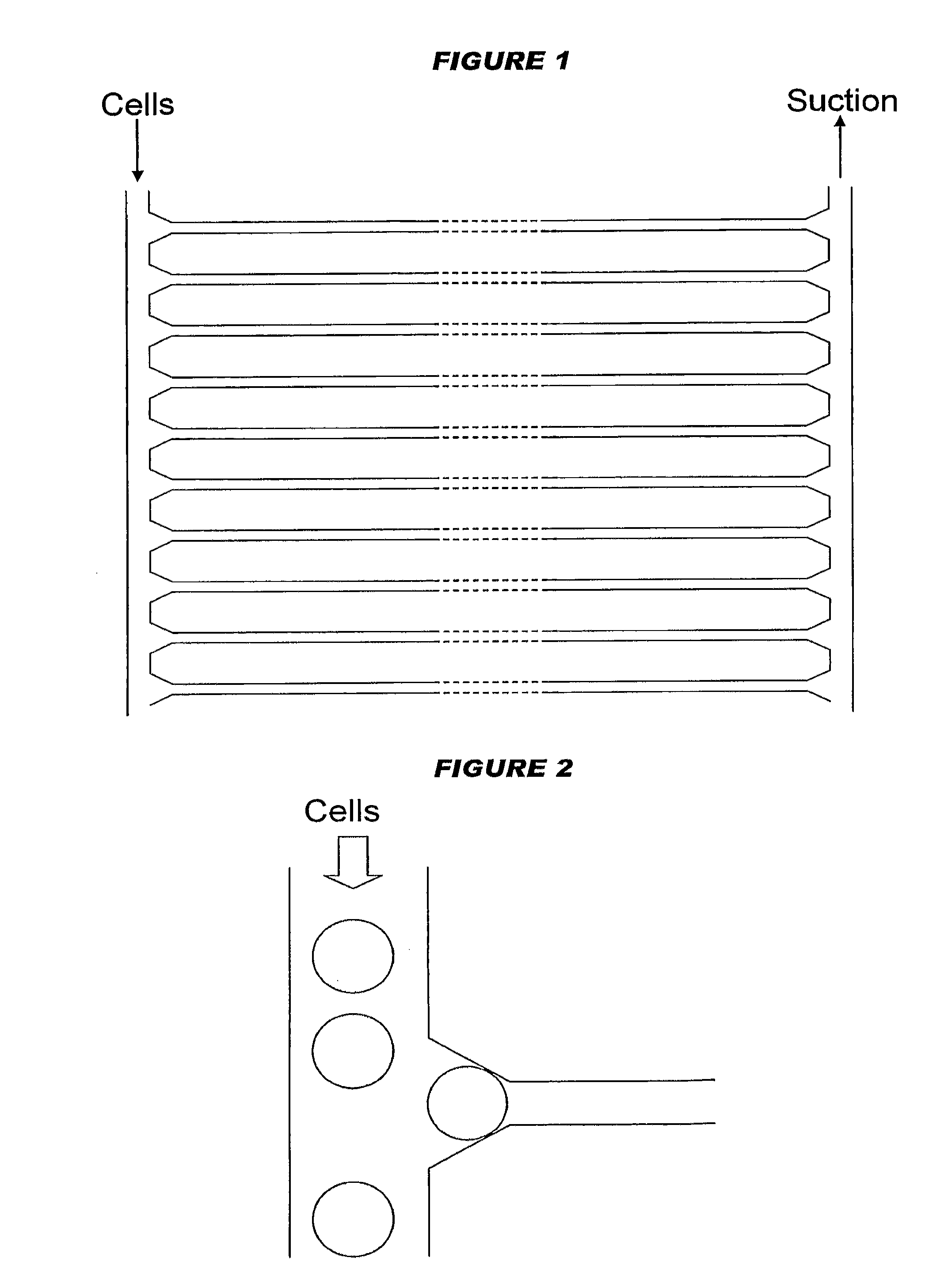
A device for individually analysing cells of interest, comprising (a) a channel for receiving the contents of a cell of interest, wherein the channel has an input end and an output end, and (b) a cell trapping site in proximity to the input end of the channel, wherein (i) the input end of the channel is adapted such that an intact cell of interest cannot enter the channel; and (ii) the channel contains one or more analytical components for analysing the contents of the cell of interest. In use, a cell is applied to the device, where it is trapped by the cell trapping means. The cell cannot enter the channel intact, but its contents can be released in situ to enter the channel's input end. The contents can then move down the channel, towards the output end, and they encounter the immobilised reagents, thereby permitting analysis of the cell contents.
Owner:OXFORD GENE TECH IP
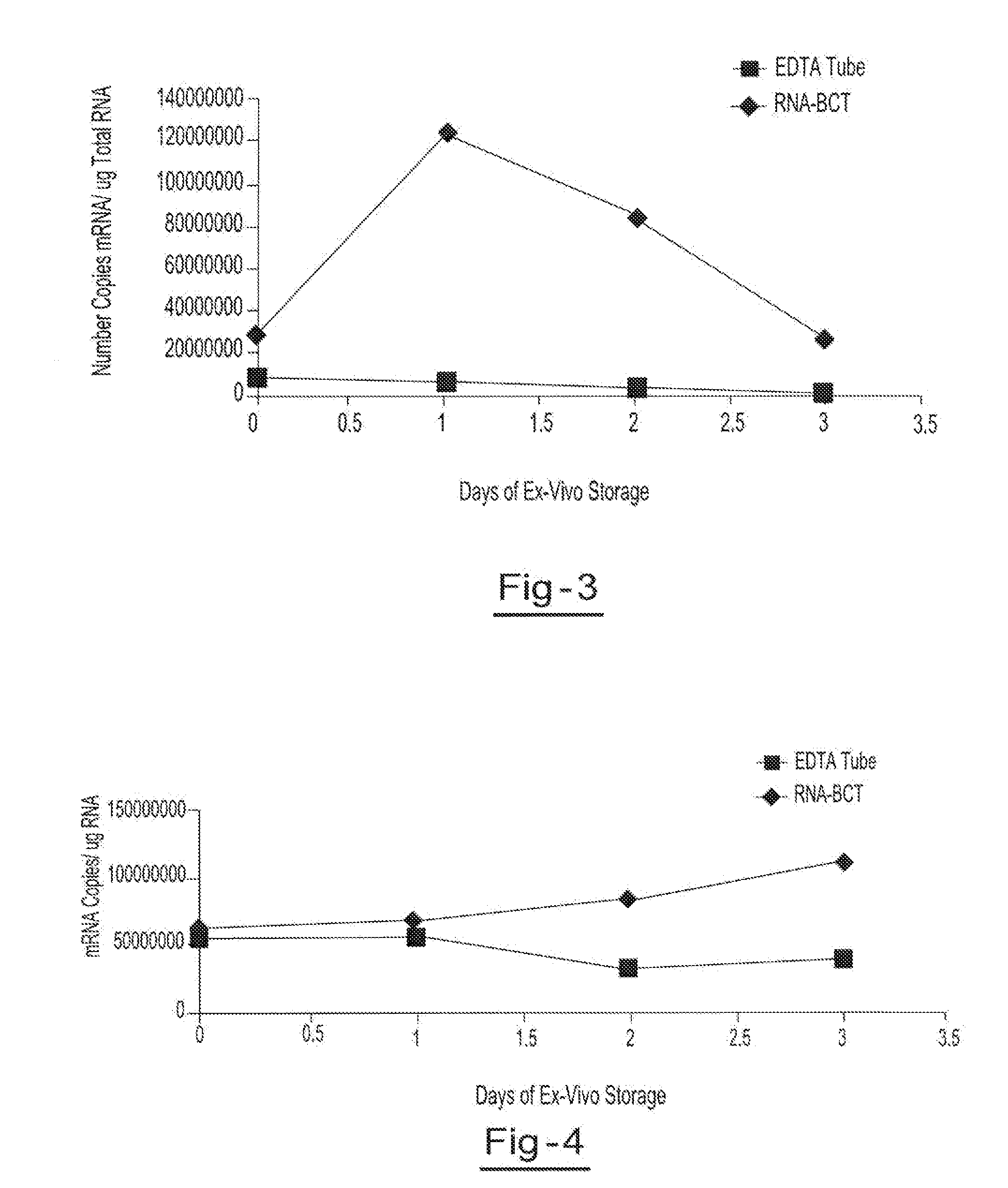
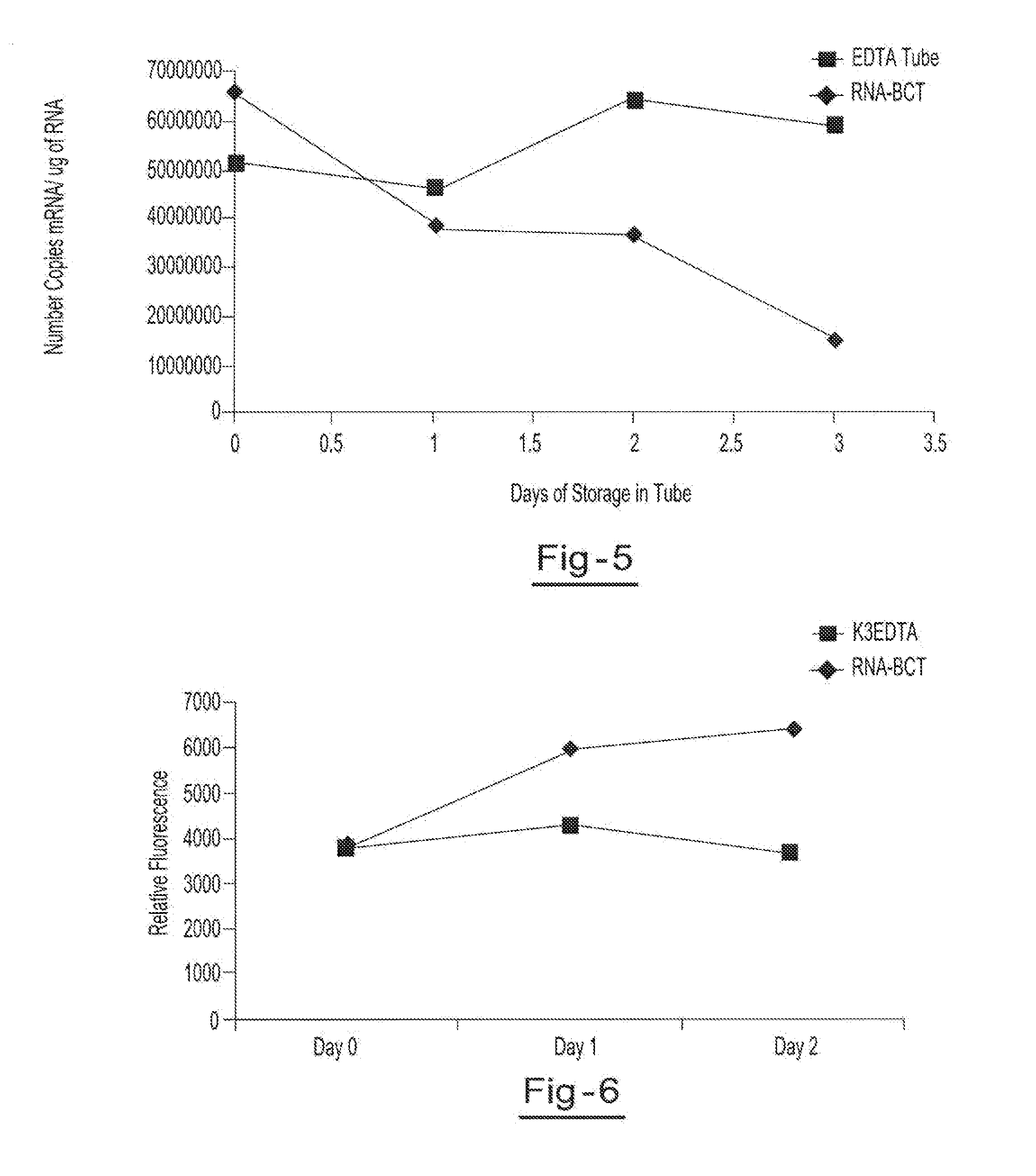
Stabilization of RNA in intact cells within a blood sample
InactiveUS20110111410A1Effective isolationEfficient testingMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureLysisNuclease
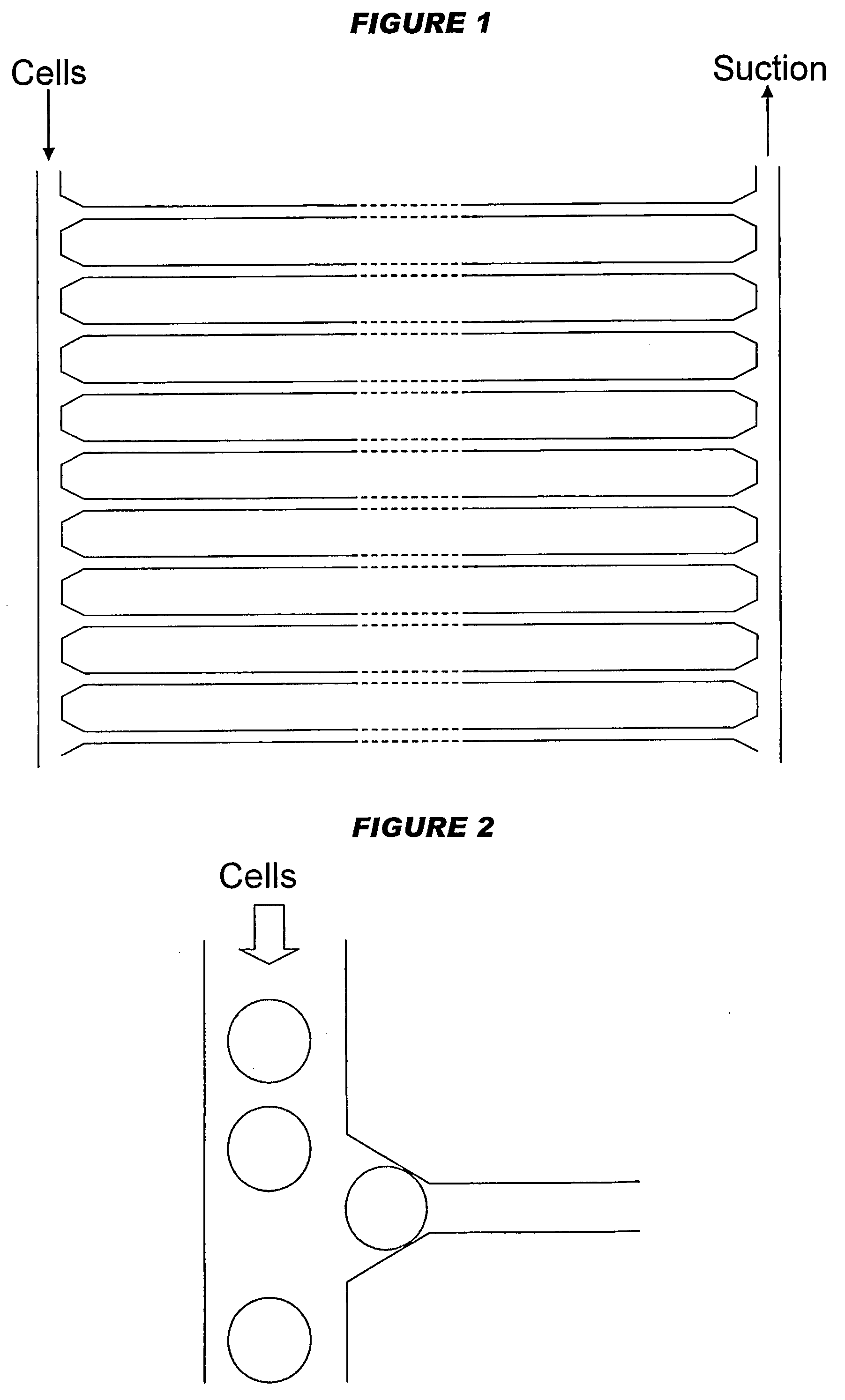
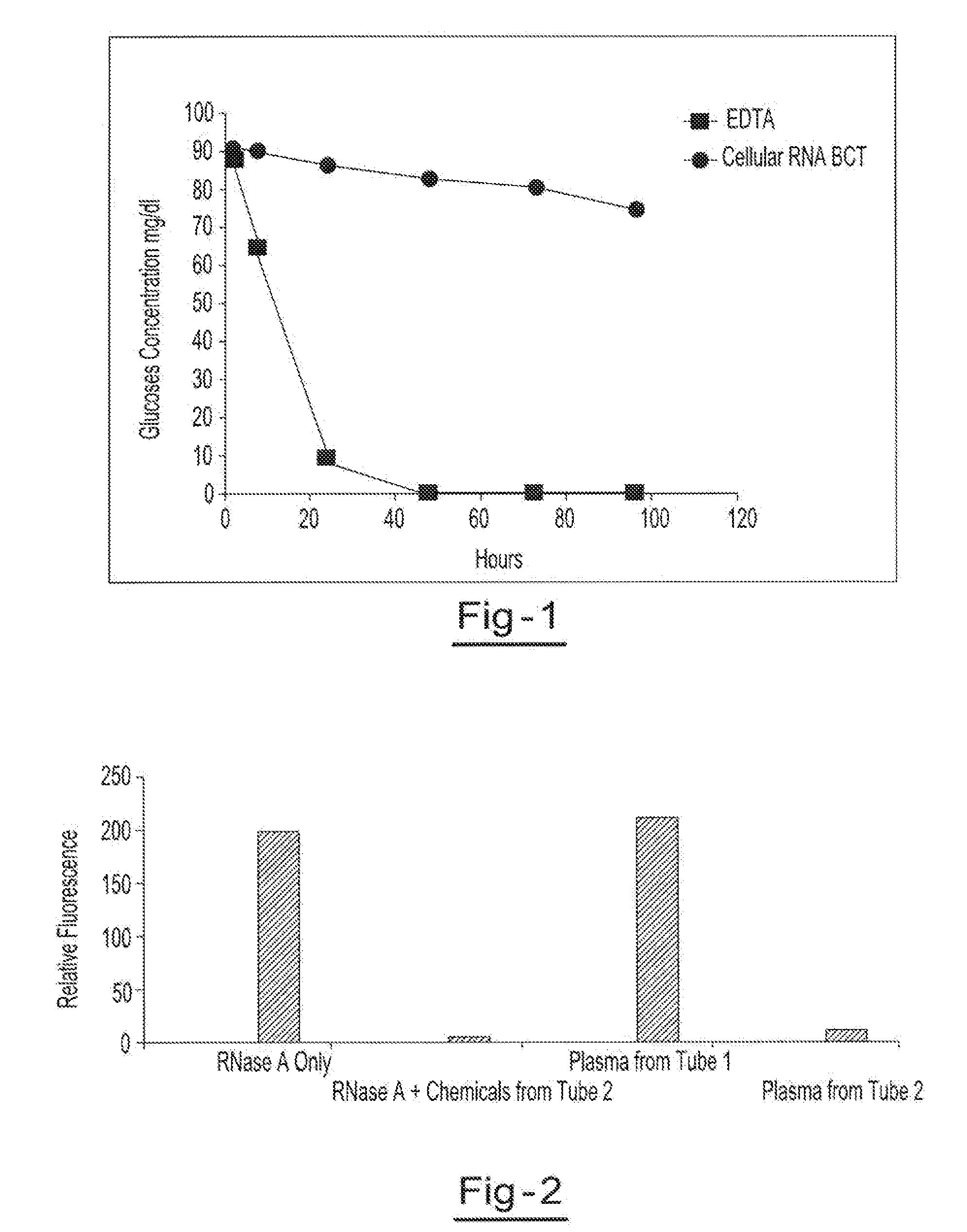
A method for preserving and processing nucleic acids located within a blood sample is disclosed, wherein a blood sample containing nucleic acids is treated to reduce both blood cell lysis and nuclease activity within the blood sample. The treatment of the sample aids in increasing the integrity and amount of cellular nucleic acids that can be identified and tested while avoiding contamination of the isolated nucleic acids with cell-free nucleic acids.
Owner:STRECK INC
Cell Transport Compositions and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090232891A1Enhance intracellular deliveryReduce deliveryPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiketopiperazinesImmune Stimulation
Compositions and methods have been developed for transporting compounds across membranes with little or no toxicity and, when targeted through the appropriate routes of administration (i.e., lung, gastrointestinal (GI) tract), little or no immune stimulation. The compositions can mediate cellular delivery of compounds that would otherwise not enter cells and enhance the intracellular delivery of compounds that would otherwise enter cells inefficiently. The methods are carried out by contacting a proximal face of a lipid bilayer or membrane (e.g. the surface of an intact cell) with a complex containing a compound (e.g., a therapeutic agent) and a diketopiperazine (DKP). DKP and the compound are non-covalently associated with each other or covalently bound to each other.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Lipid mediated screening of drug candidates for identification of active compounds
InactiveUS20030198664A1Reduce solubilityMicroencapsulation basedMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid formationSolubility
The subject invention provides liposome formulations that are capable of specifically targeting cell types. The subject invention also provides for the encapsulation of new chemical entities (NCE) or other drug candidate molecules (DCM) within liposomes that specifically target a particular cell type. The subject invention, advantageously, solubilizes compounds, with low solubility in aqueous environments, and permits screening of these compounds against intact cells for biological activity in the absence of detergents that can damage cell membranes. Also provided are methods of preparing liposome formulations that target a specific cell type and methods of delivering therapeutic agents to target cells.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO +1
Pharmacological profiling of drugs with cell-based assays
InactiveUS20060040338A1Enable optimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningPost translationalAssay
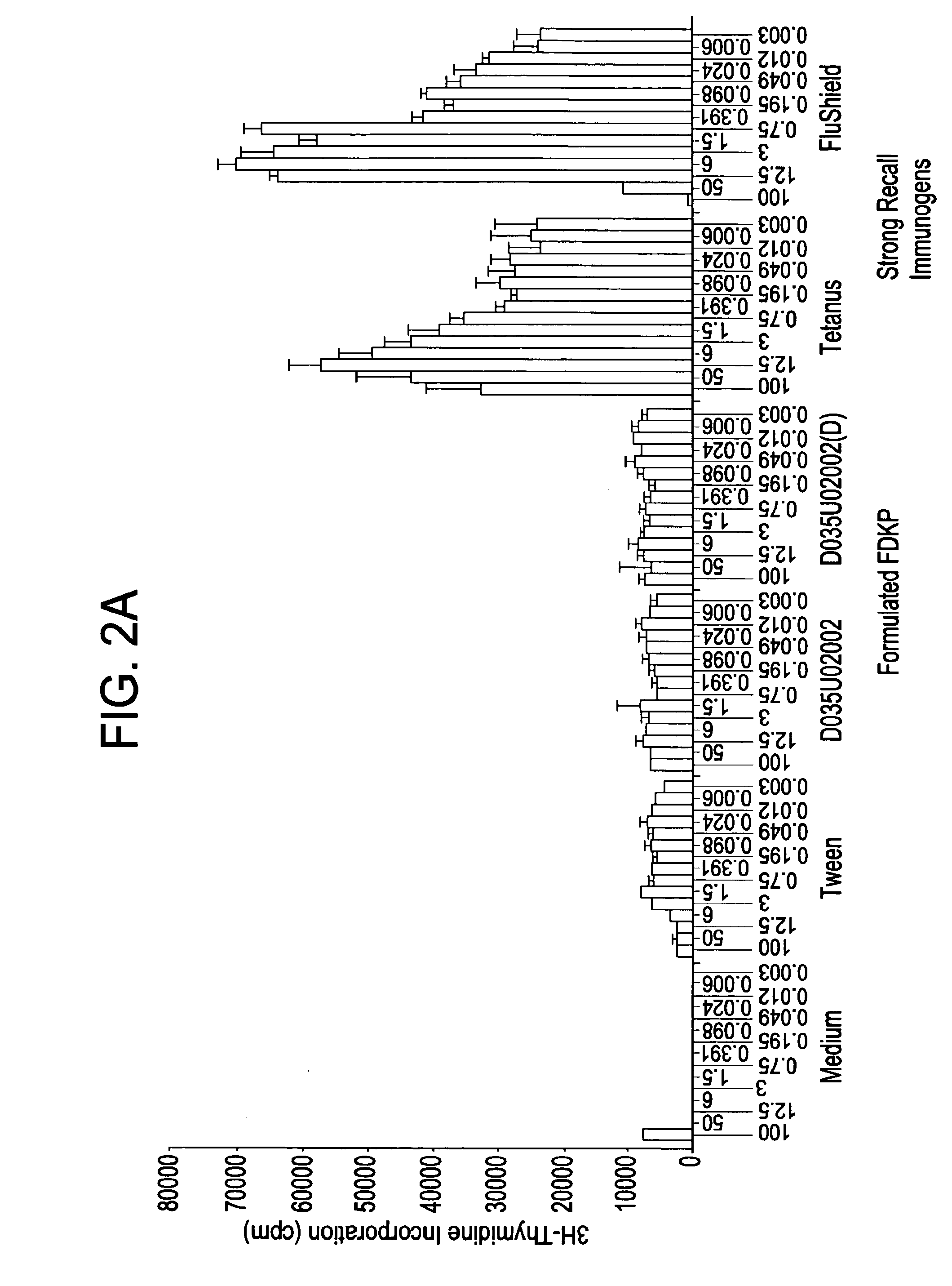
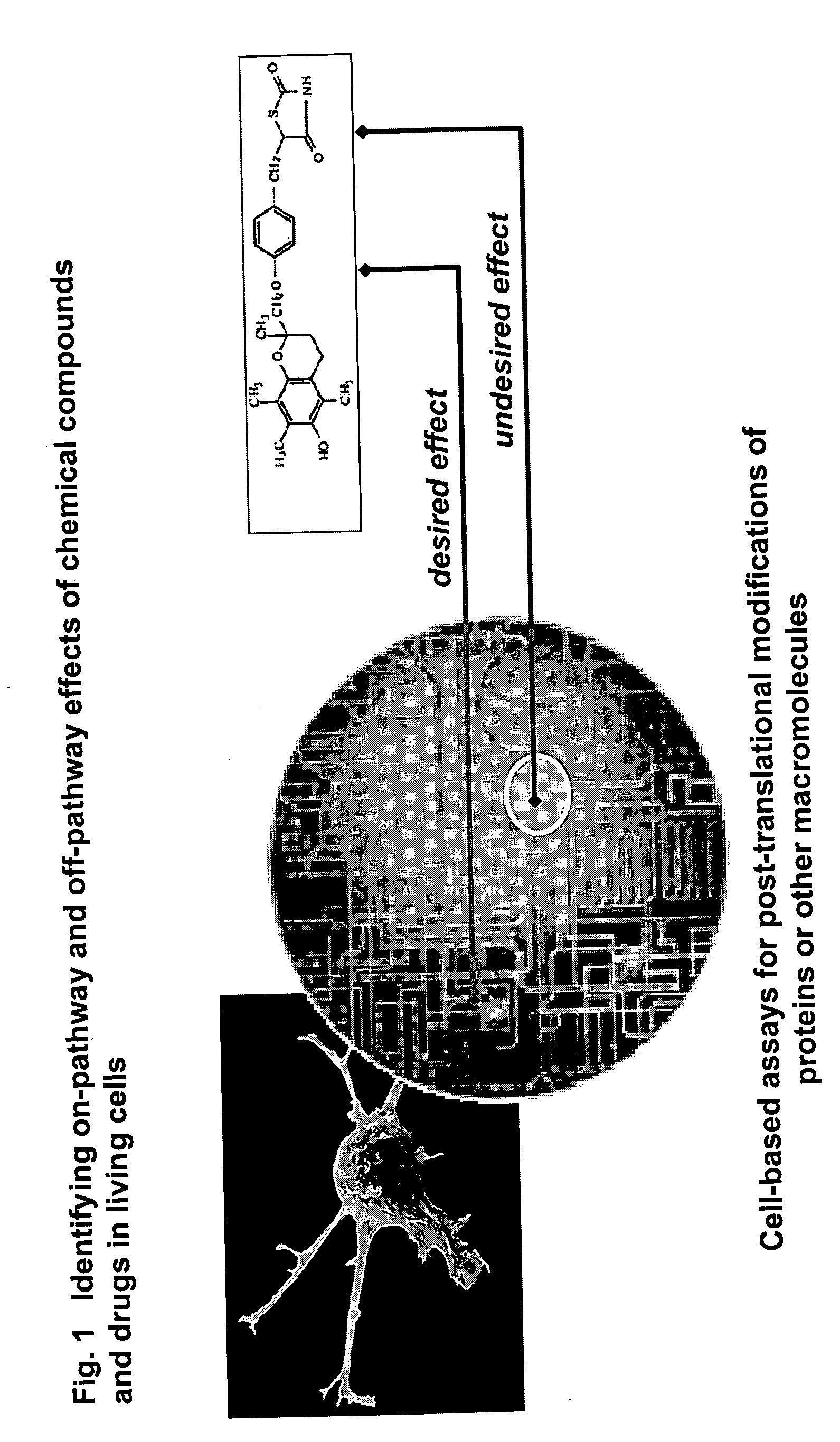
The instant invention provides a method for establishing safety profiles for chemical compounds, as well as pharmacological profiling said method comprising (A) testing the effects of said chemical compounds on the amount and / or post-translational modifications of two or more macromolecules in intact cells; (B) constructing a pharmacological profile based on the results of said tests; and (C) comparing said profile to the profile(s) of drugs with established safety characteristics. Additionally, the invention is also directed to a composition comprising an assay panel, said panel comprising at least one high-content assay for the amount and / or post-translational modification of a protein and at least one high-content assay for the amount and / or subcellular location of a protein-protein interaction.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Methods for control of flux in metabolic pathways through protease manipulation
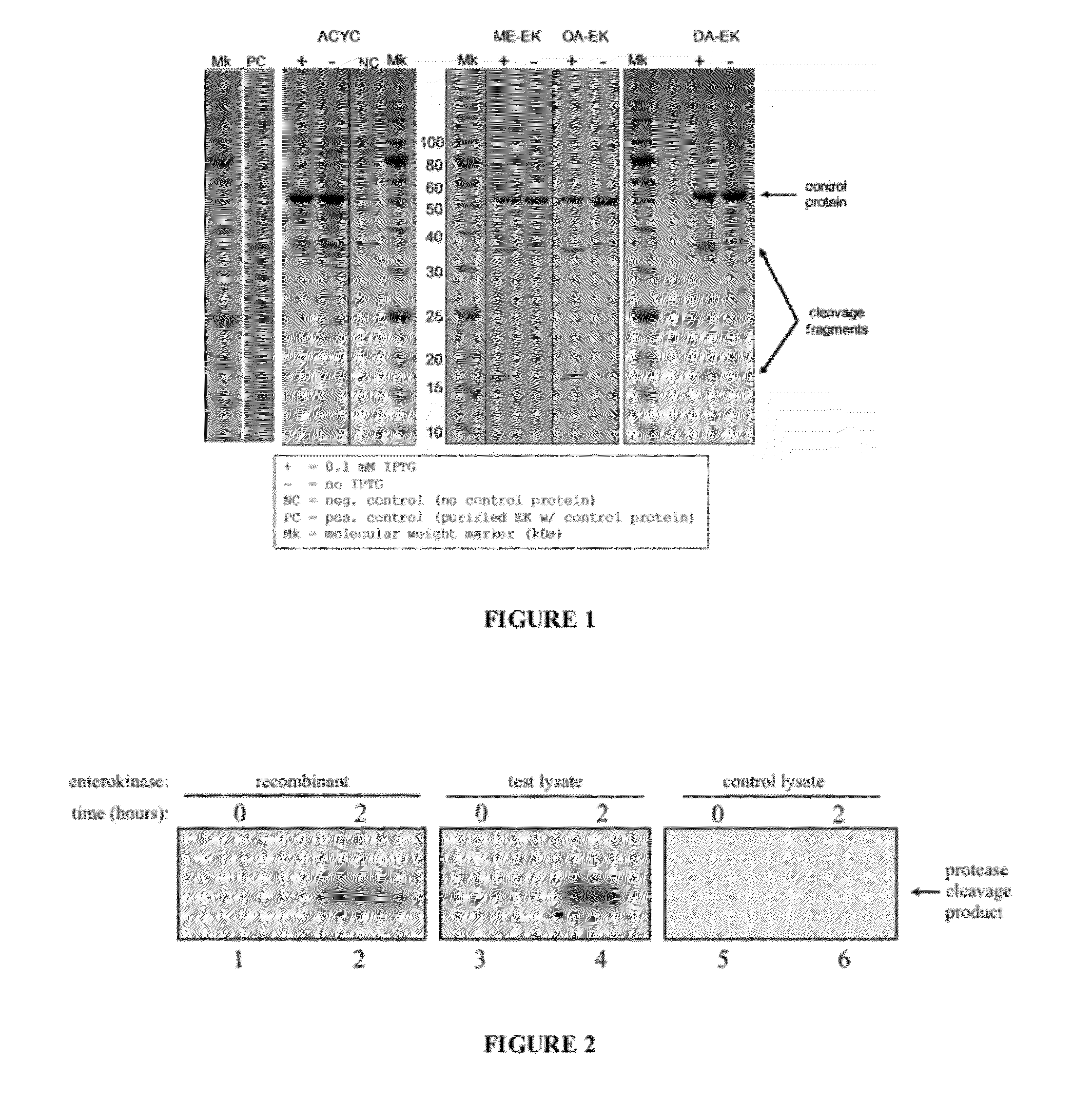
The embodiments described herein pertain to cells, and methods for preparing cells, that can be used as biocatalysts by altering enzymes that compete for a substrate or product of a pathway of interest such that the targeted enzyme is sensitive to a site-specific protease, which protease is expressed but relocated in the cell to a site where it is not in contact with the targeted enzyme in the intact cell. Upon cell lysis, the protease contacts the target enzyme, which is then inactivated by protease cleavage.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Cell Transport Compositions and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20150290132A1Reduce deliveryPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiketopiperazinesImmune Stimulation
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Methods for preparing and analyzing cells having chromosomal abnormalities
InactiveUS20060257884A1Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescenceFluorescence in situ hybridization
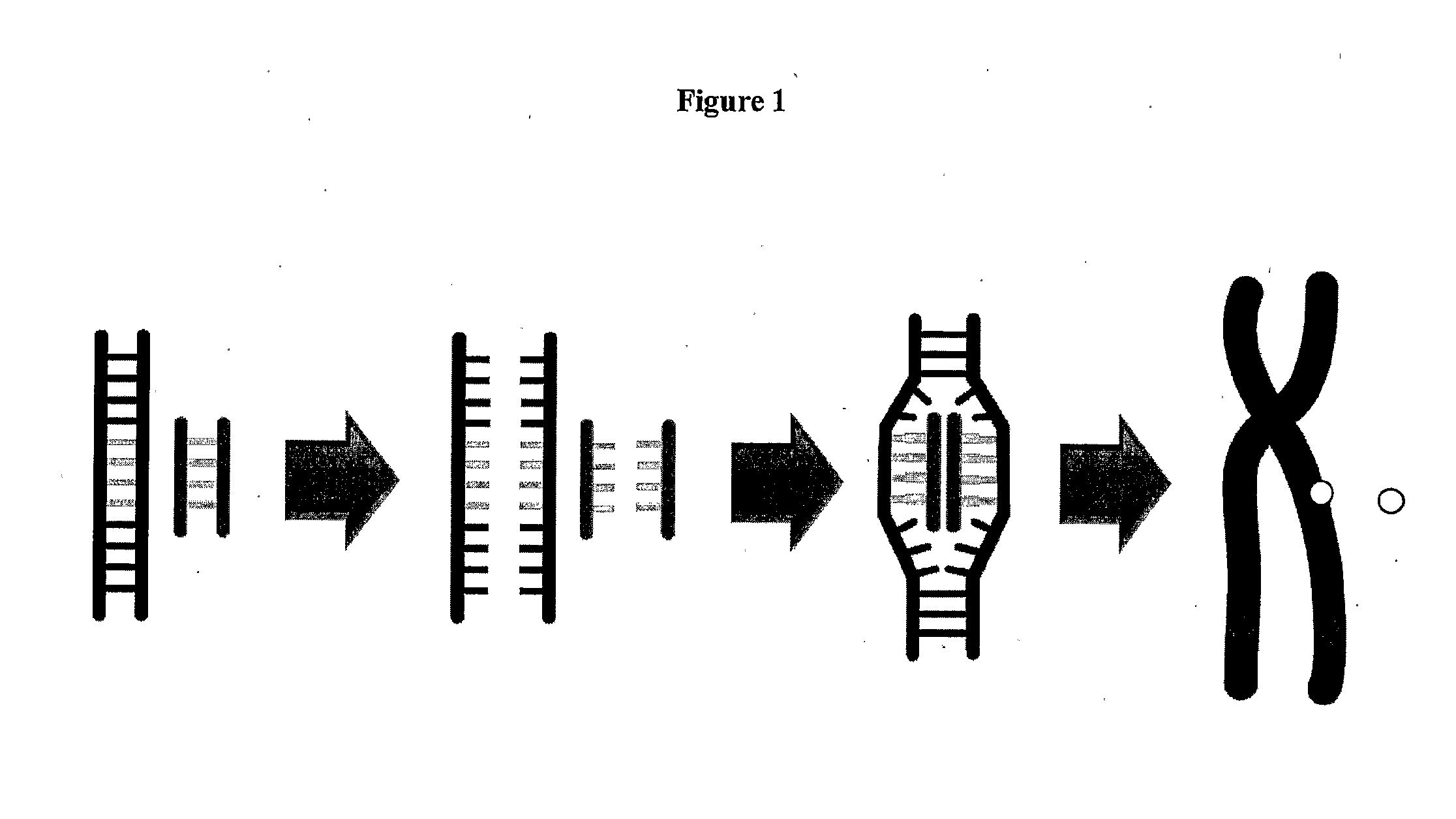
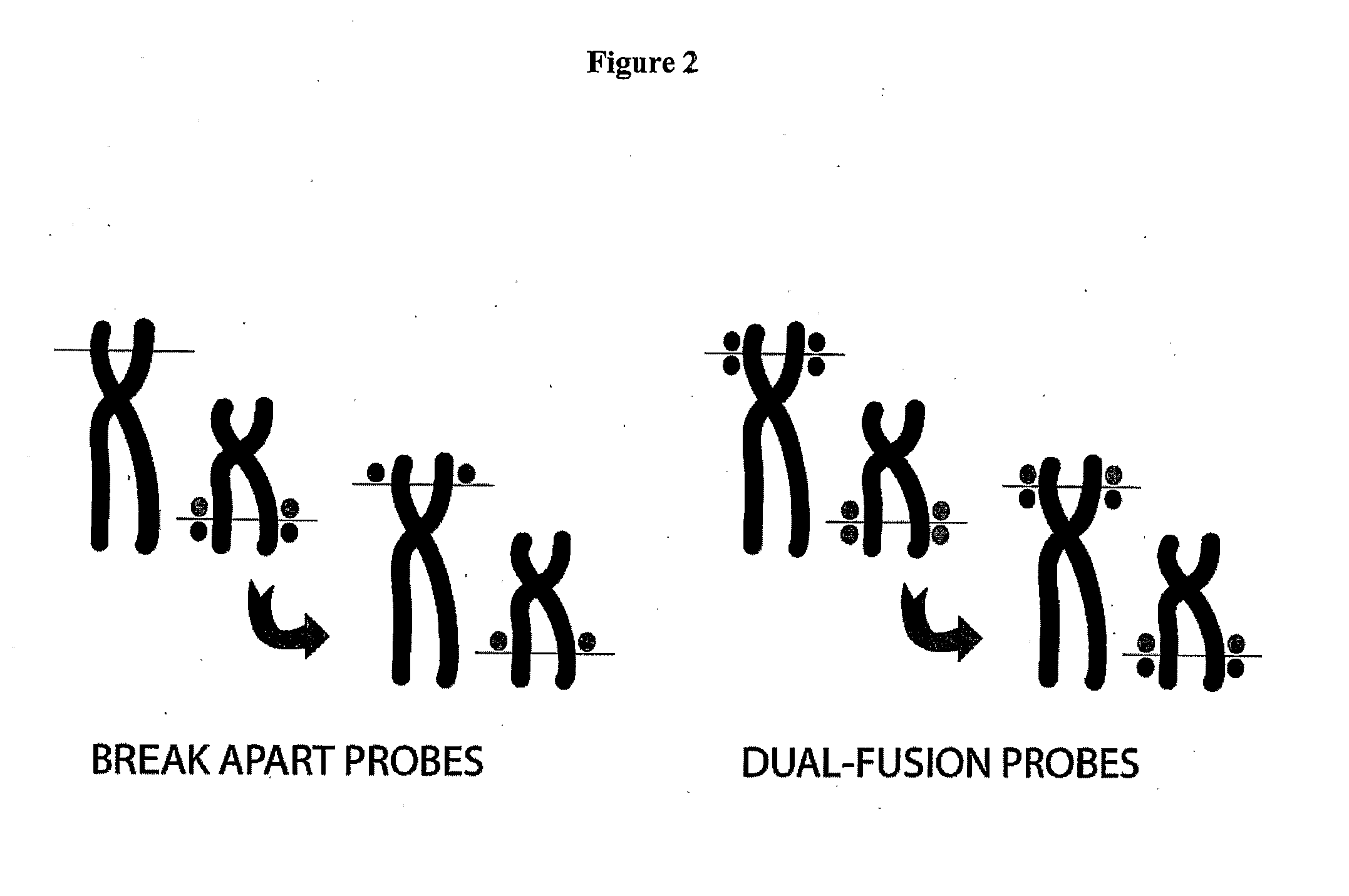
The present invention provides methods for preparing cells with highly condensed chromosomes, such as sperm, and methods for detecting and quantifying specific cellular target molecules in intact cells. Specifically, methods are provided for detecting chromosomes and chromosomal abnormalities, including aneuploidy, in intact cells using fluorescence in situ hybridization of cells in suspension, such as sperm cells.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
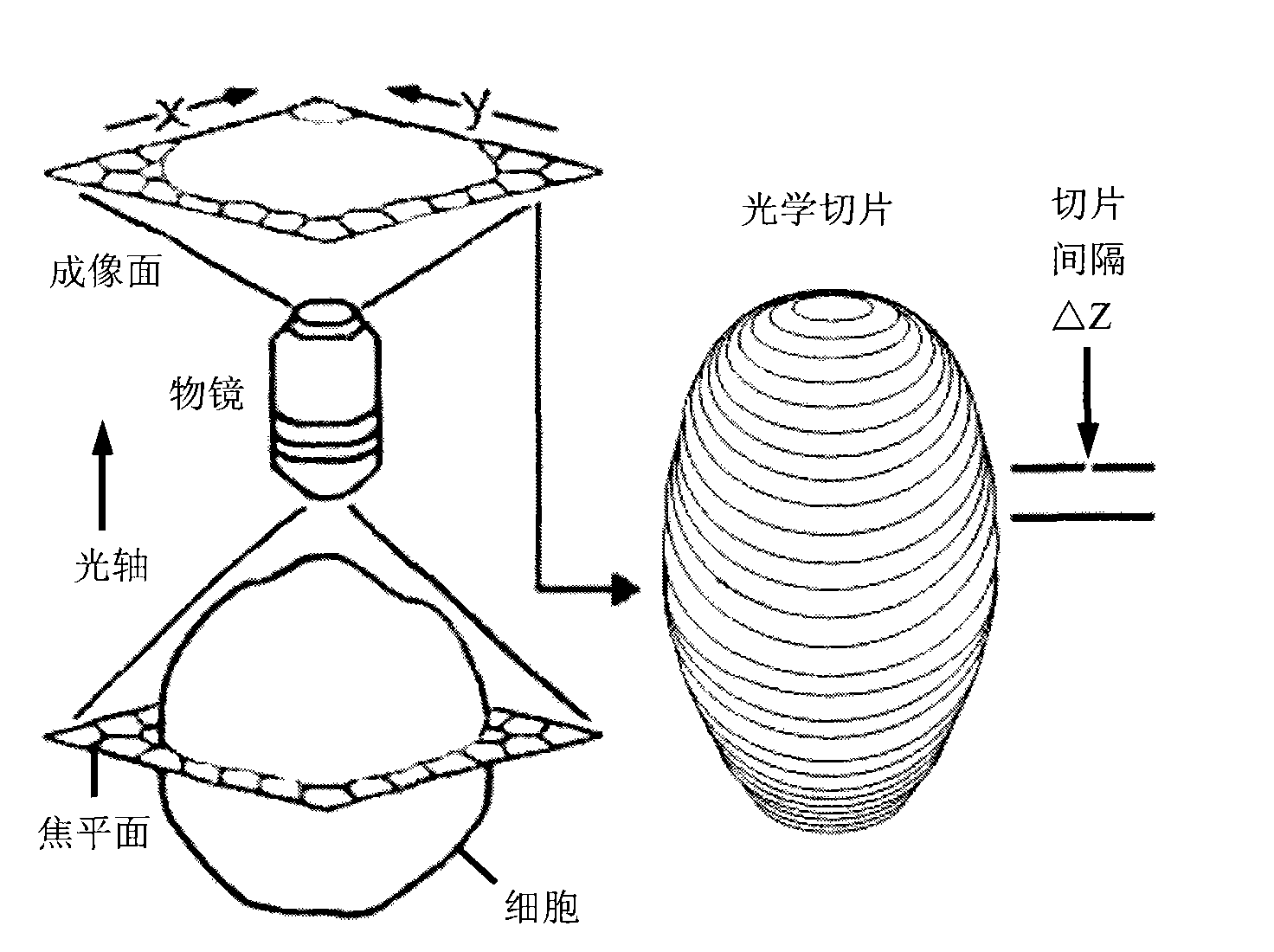
Digital confocal microscope optical section collecting device
The invention provides a driver of a digital confocal microscope optical section collecting device. The driver comprises a single-chip system, a sub-division driver, a stepping motor and a displacement driving device, and the driver arranged on the microscope and controlled by a computer drives a stage to acquire the sequenced optical section images of cells on the stage by an image detector. The method for the driver to acquire the optical section images is to carry out the submicron equidistant stepping control on the stage of the microscope by setting the section distance, collected section number and other parameters. By using the definition-based evaluation for the function value and the change rate thereof as the evaluation standards, the method of the invention is capable of automatically focusing on cells and locating the upper and lower edges, and acquiring the sequenced optical section images of intact cells.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Methods of identifying cellular target molecules
InactiveUS20060246481A1Easy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionFlow cytometryIntact cell
The present invention provides methods of detecting and / or quantifying specific cellular target molecules in intact cells. The present invention further provides methods of processing an intact cell to facilitate in situ hybridization for use in flow cytometry.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
Precision optical intracellular near field imaging/spectroscopy technology
InactiveUS7129454B2Facilitates molecular analysisMore powerSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseaseMolecular analysis
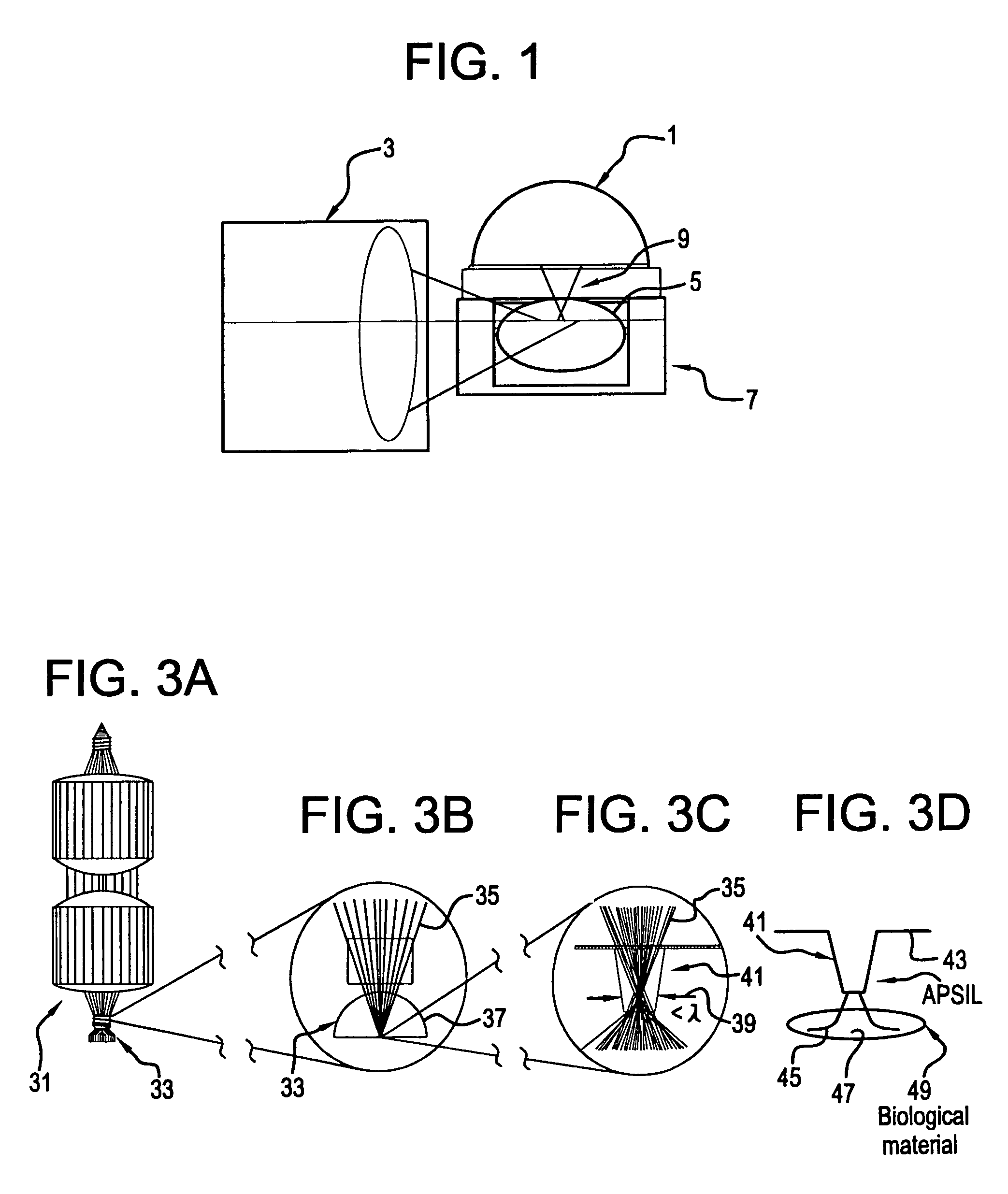
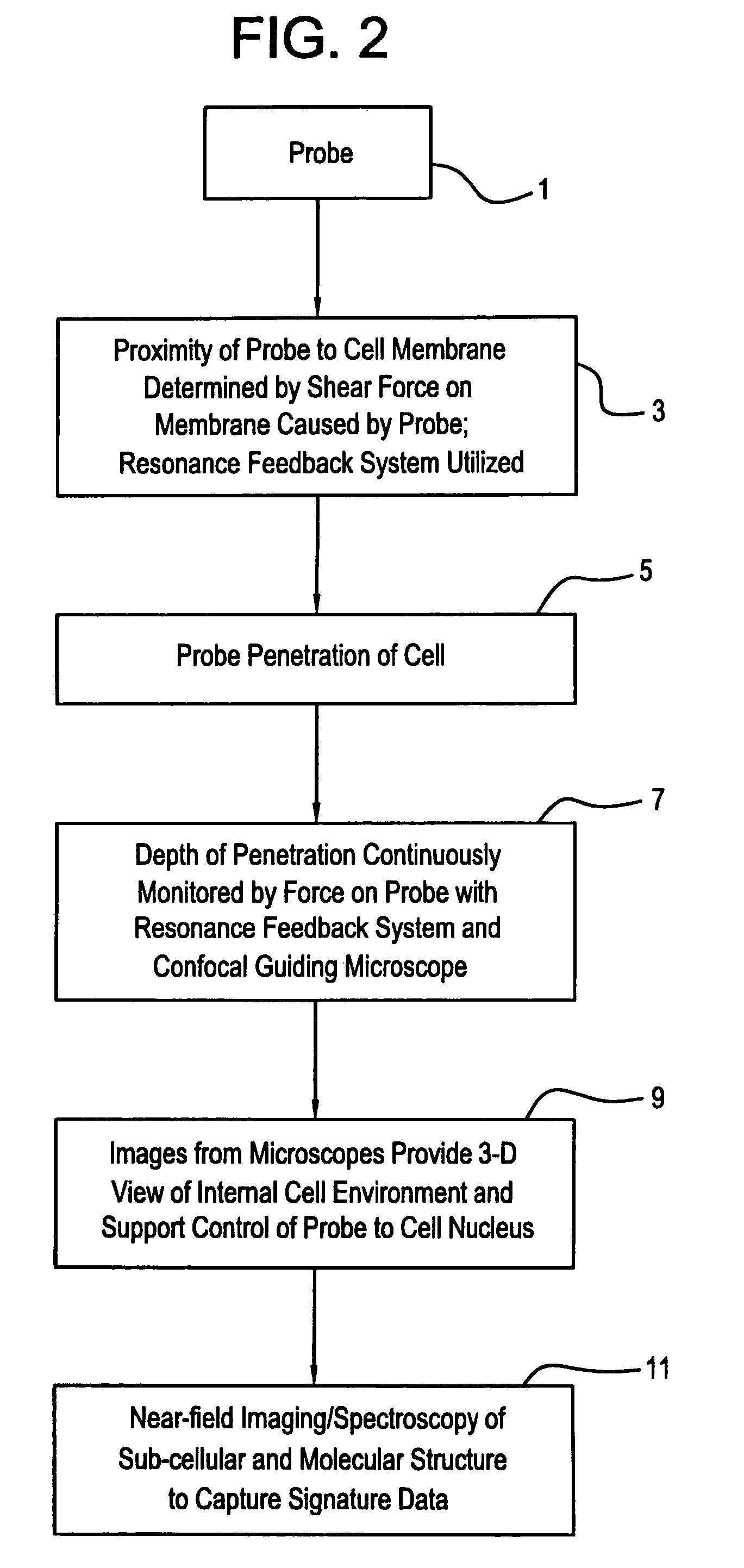
A Precision Optical Intracellular Near Field Imaging / Spectroscopy Technology (POINT / NANOPOINT) is a high-resolution instrument for analyzing and comparing molecular characteristics of cells. A nanosensor array is provided which is capable of imaging inner regions of living cells without destroying its natural environment and providing new information about molecular makeup of cells. The POINT probe collects data from high-resolution imagery, providing an imaging tool for investigating cells at sub-cellular and molecular levels. Data are then incorporated into a signature facilitating molecular analysis of diseases. The POINT probe non-invasively penetrates cell membranes to image insides of intact cells allowing the POINT probe to collect data without destroying cell structures. The probe provides cellular imaging to enable the viewing of both imaging and spectroscopy of internal regions of cells. The POINT system may be attached to existing microscopes to achieve a very high resolution.
Owner:NANOPOINTS
Strain of micro-organism Lactobacillus fermentum ME-3 as novel anti-microbiol and anti-oxidative probiotic
The strain of micro-organism Lactobacillus fermentum ME-3 is a novel anti-microbial and anti-oxidative probiotic. It has a high anti-microbial effect on Escherichia coli, Shigella sonnei, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhimurium, and moderate activity against Helicobacter pylori strains. The strain of micro-organism possesses Mn-superoxide dismutase and both its lysates and intact cells have high anti-oxidative activity, increasing the glutathione red-ox ratio in blood sera and able to capture toxic hydroxyl radicals. The strain of micro-organism could be used as a probiotic for the production of functional food (yoghurt, cheese) and non-comestibles (tablets, capsules) for the prophylaxis of intestinal and uroinfections, both for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases, caused by prolonged oxidative stress.
Owner:UNIV OF TARTU
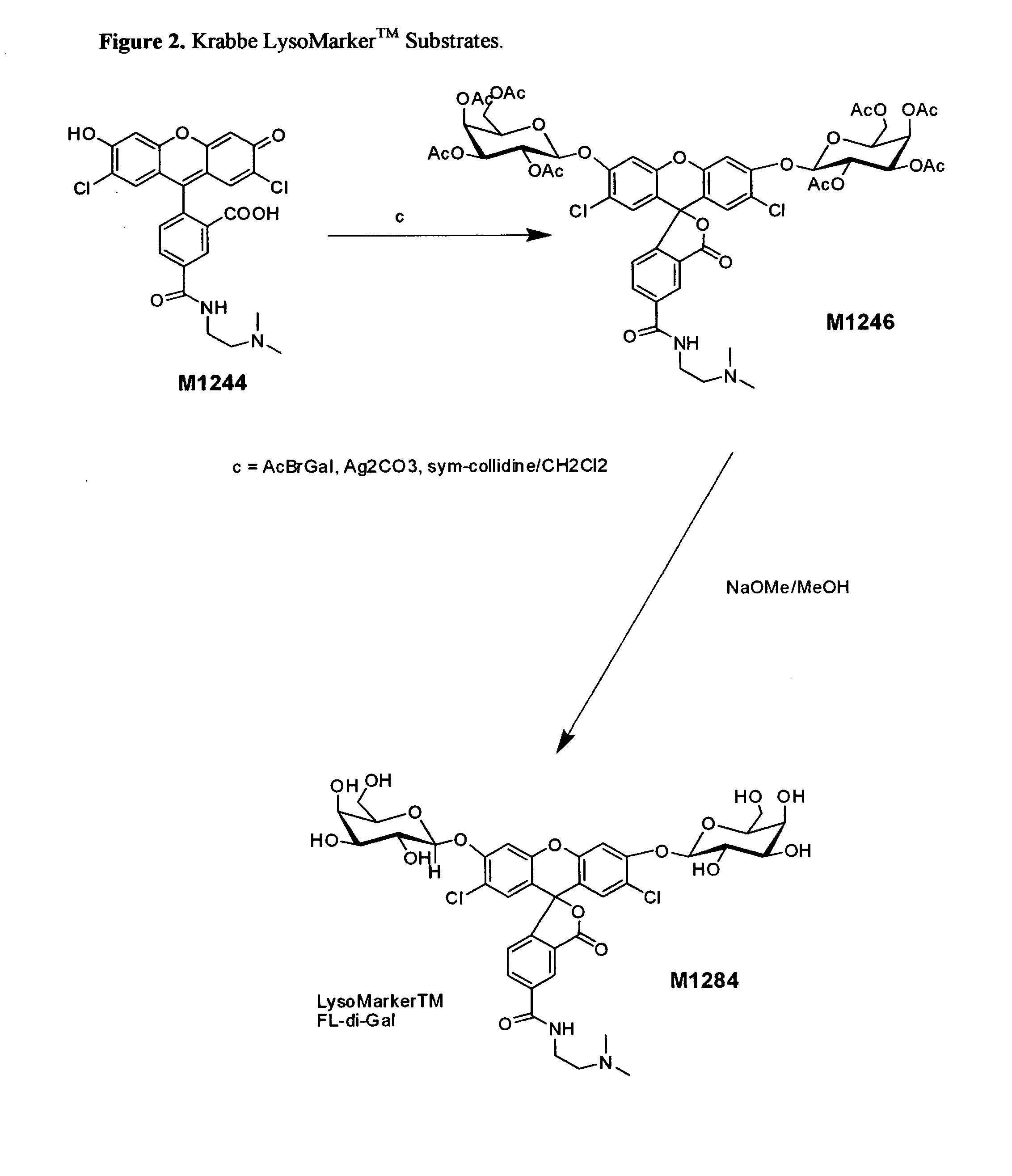
Enzyme substrates for visualizing acidic organelles
ActiveUS20100233744A1Enough timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisLysosomeFluorescence
The present invention relates to the visualization of acidic organelles based upon organelle enzyme activity. The organelle substrates of the invention are specific for enzyme activity of the organelle and label these organelles, such as lysosomes, rendering them visible and easily observed. Substrates of the present invention include substrates that produce a fluorescent signal. The fluorogenic acidic organelle enzyme substrates of this invention are designed to provide high fluorescence at low pH values and are derivatized to permit membrane permeation through both outer and organelle membranes of intact cells and can be used for staining cells at very low concentrations. They can be used for monitoring enzyme activity in cells at very low concentrations and are not toxic to living cells or tissues.
Owner:MARKER GENE TECH
Method and kit for assessing viable cells
ActiveUS20110312012A1Fast resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh concentrationThiol
The present invention provides simple, rapid methods and procedures for analyzing cells, hereunder quantitative and qualitative assessment of cells, such as viability. The present invention relates to the use of various optionally substituted reporter compounds particularly detectable upon their reaction with thiol-containing species present in higher concentrations in intact (e.g., living) cells than in non-intact (e.g., dead, stressed and apoptotic) cells. The present invention also relates to the use of various optionally substituted reporter compounds particularly detectable upon their reaction with species present in intact and / or non-intact cells. Moreover, the present invention relates to the use of measuring techniques and / or instruments coupled with the use of various optionally substituted reporter compounds. The invention further relates to compositions used in methods for analyzing cells, such as a composition comprising N-(7-dimethylamino-4-methyl-3-coumarinyl)-maleimide (DACM).
Owner:CHEMOMETEC AS
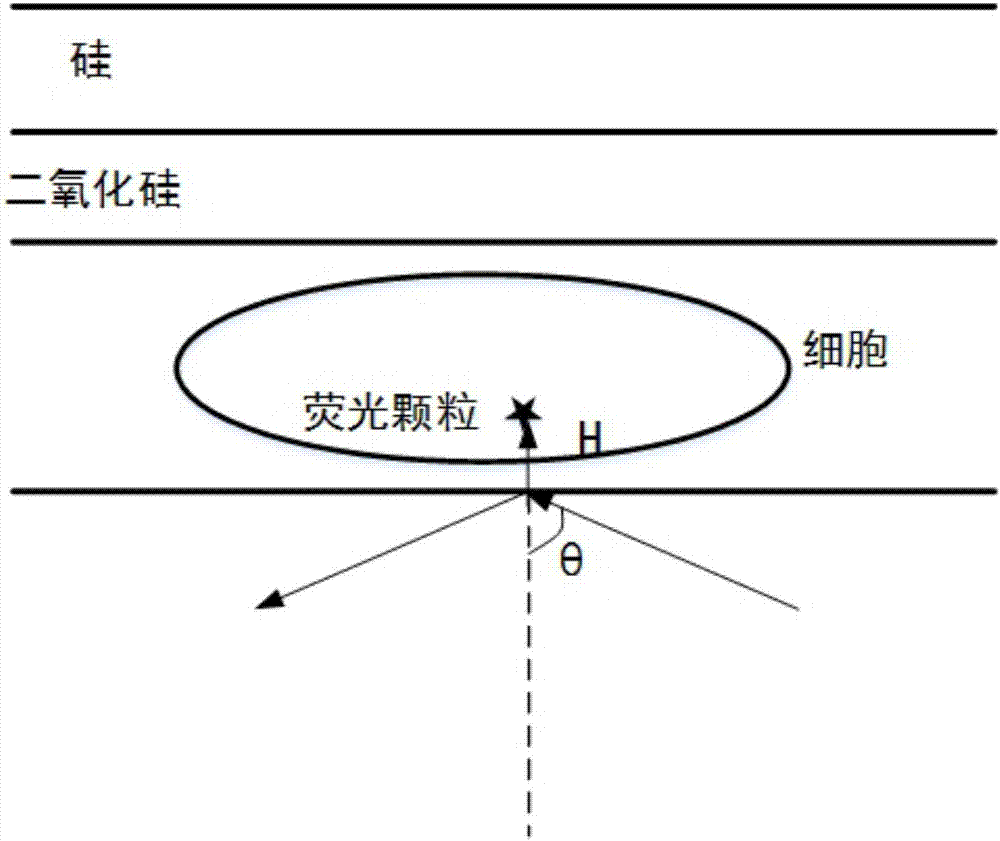
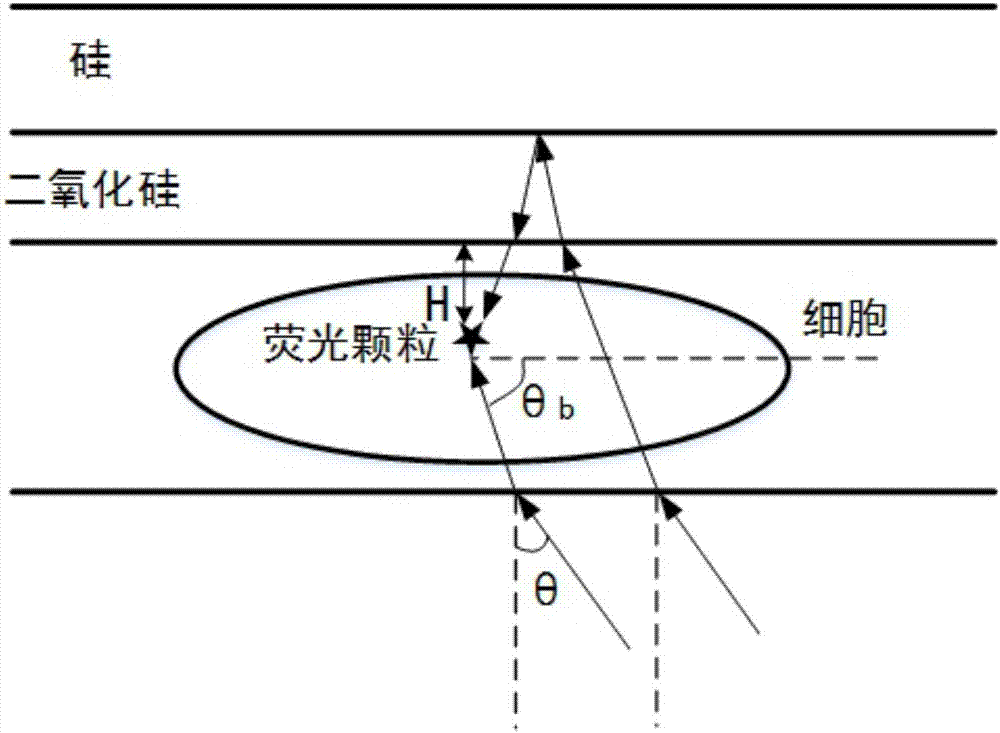
Method and apparatus for carrying out wide-field three-dimensional ultra-high resolution positioning and imaging on intact cell
The invention discloses a method for carrying out wide-field three-dimensional ultra-high resolution positioning and imaging on an intact cell. The method comprises: modulating the polarization state of incident light into P-polarized light or S-polarized light; illuminating a sample after the modulated light beam becomes into tangential polarized light or radial polarized light; illuminating the lower surface of the cell by using the evanescent wave generated by light having an incident angle of more than a total internal reflection critical angle; illuminating the upper surface of the cell by using a pattern, wherein transmitted light having an incident angle of less than a total internal reflection critical angle and the reflected light generated after one reflection with the upper surface of the cell are subjected to interference to generate the pattern; and according to the fluorescence information emitted by the collected sample, re-constructing the three-dimensional super-resolution image of the intact cell. The invention further discloses an apparatus for carrying out wide-field three-dimensional ultra-high resolution positioning and imaging on an intact cell. According to the present invention, the method and the apparatus have characteristics of rapid imaging, simple equipment, convenient operation and the like, and can be well used for the detection of fluorescent samples.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
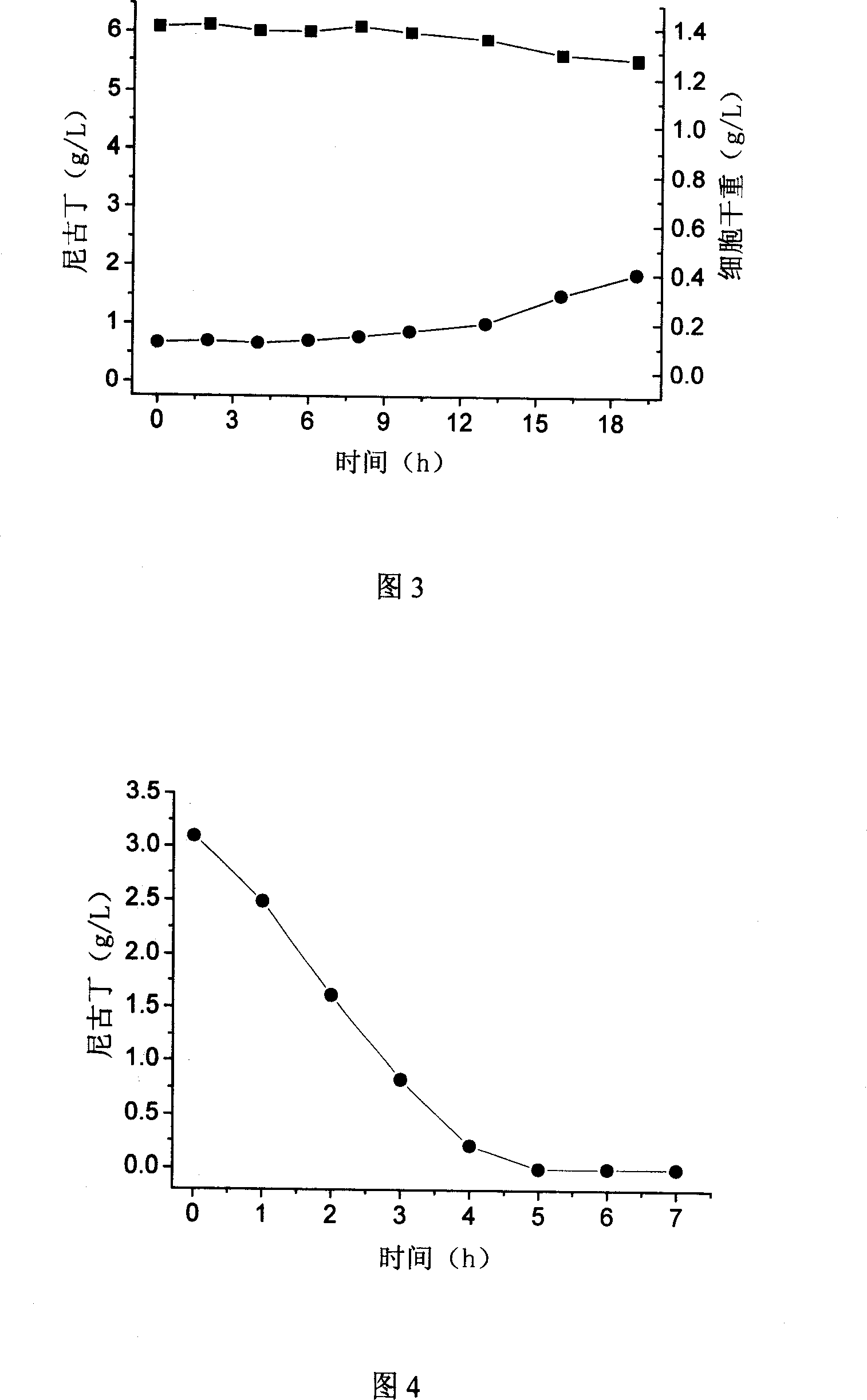
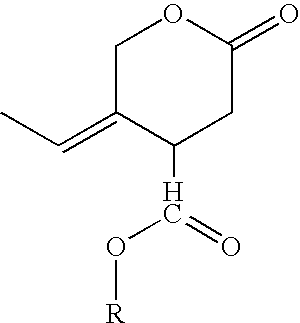
Pseudomonas putida capable of metabolizing nicotine and application thereof
InactiveCN101016528ALow costGood cell permeabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a pseudomonas putida to metabolite nicotine, which is characterized by the following: preserving in China Typical Culture Preservation Center (Wuhan university, china Wuhan) with keeping number as CCTCC NO.M 205038; possessing stronger nicotine metabolic ability and nicotine toxin immunity ability; growing highest at 6g / L nicotine density; culturing a good deal of bacterial strain; using intact cell as biological activator; degrading nicotine from tobacco industrial waste water completely. This bacterium possesses simple operation and quick disposing waste water speed, which can be used to dispose the waste water from tobacco industrial widely.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Compounds and compositions derived from olives and methods of use thereof
The preparation of extracts from olive fruits, olive tree leaves, olive oil as well as olive-press waste. The isolation of natural products from these extracts and the evaluation of the DNA protective antioxidant activity of the extracts and the purified compounds on intact cells.
Owner:LAVIPHARM +1
Devices and processes for analysing individual cells
InactiveUS8372629B2Easy to readBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell trappingReagent
Owner:OXFORD GENE TECH IP
Cell Analysis On Microfluidic Chips
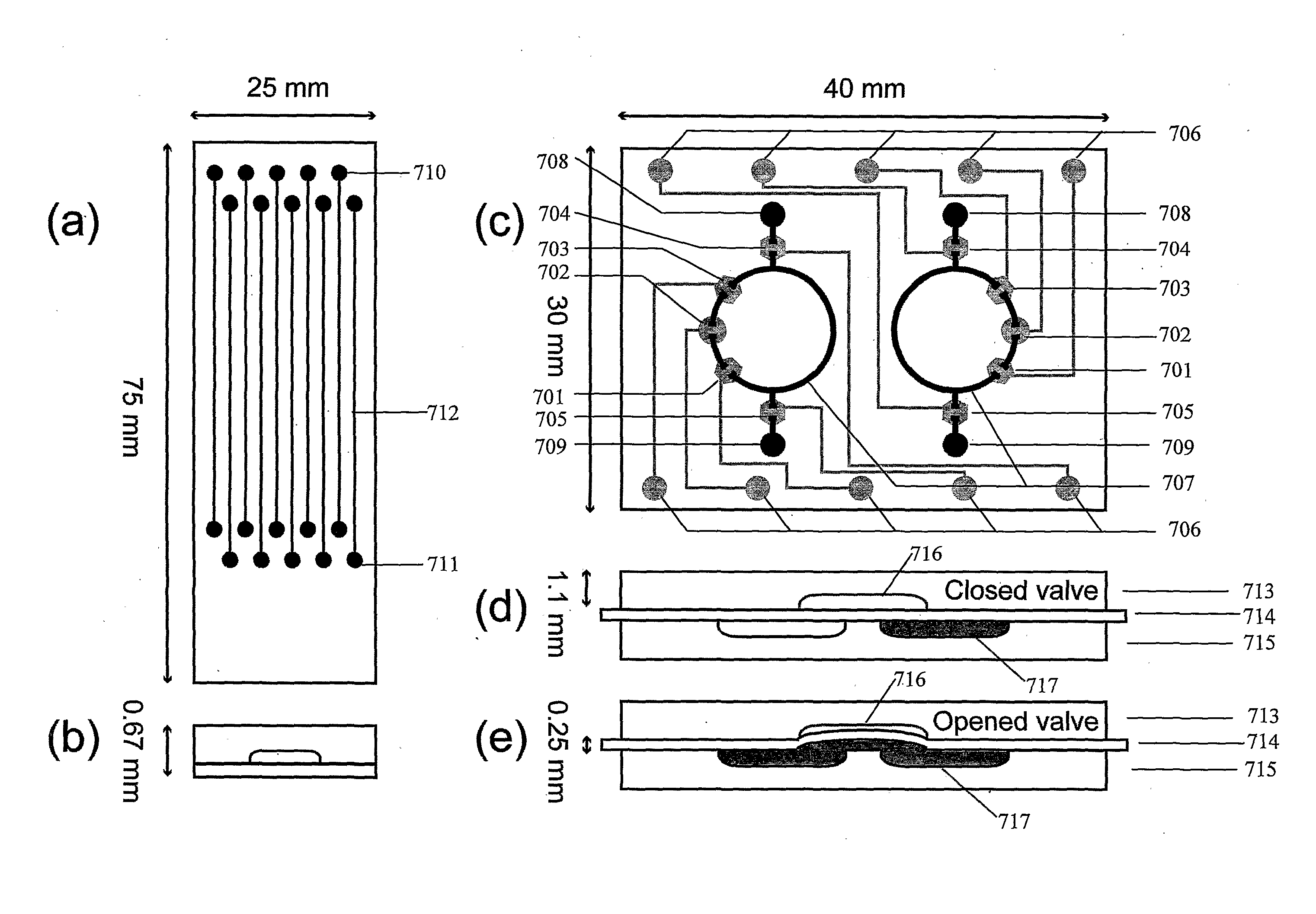
InactiveUS20120082978A1Suitable shapeReduce sizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyIntact cell
The present invention provides for a method of implementing fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) or other cellular analysis processes using intact cells within a microfluidic, chip-based, apparatus. The invention further provides for a method of cellular immobilization within a microfluidic device. Also provided is a method for automated analysis of FISH or other cellular analysis using discrete colormetric probes.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Protein-protein interactions for pharmacological profiling
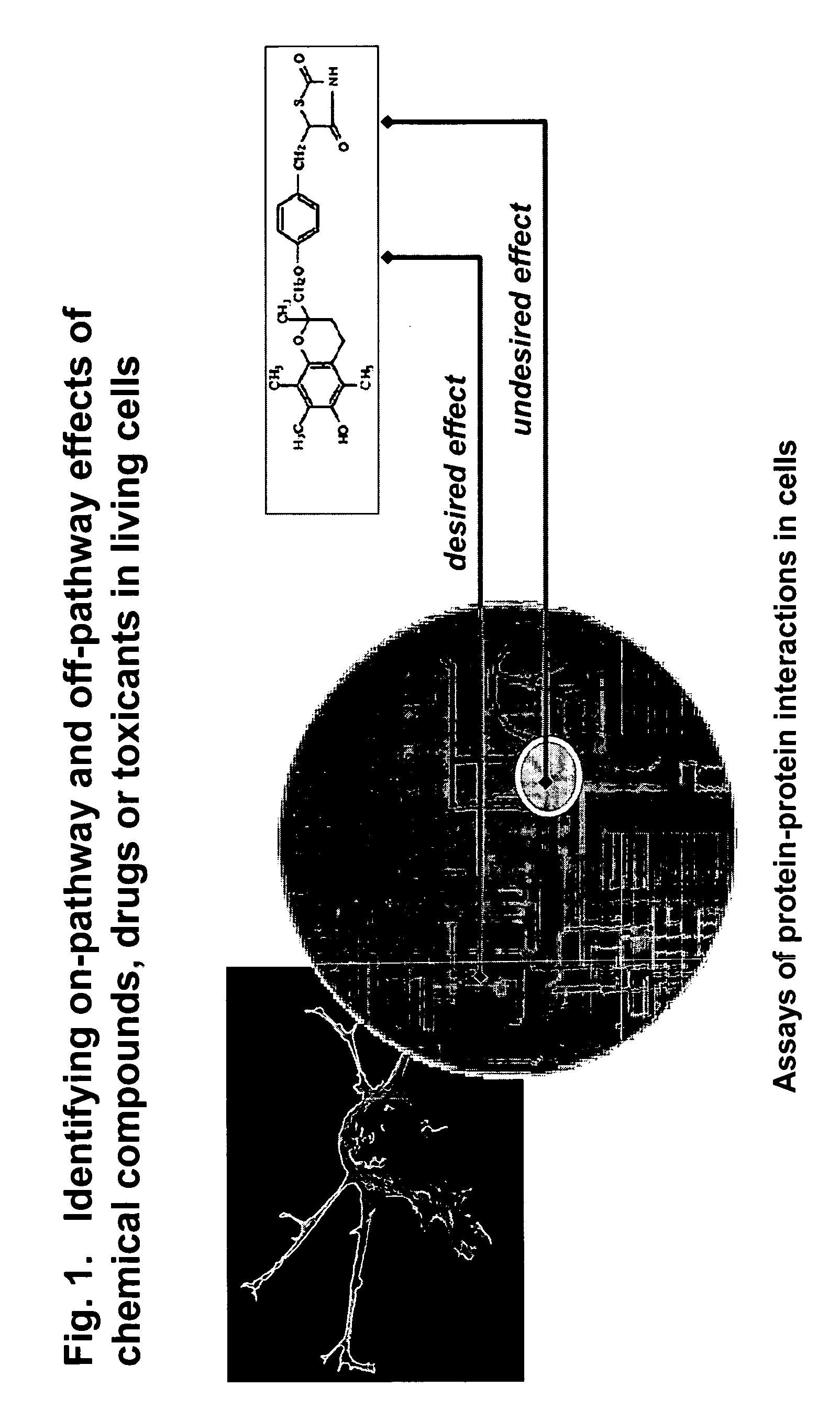
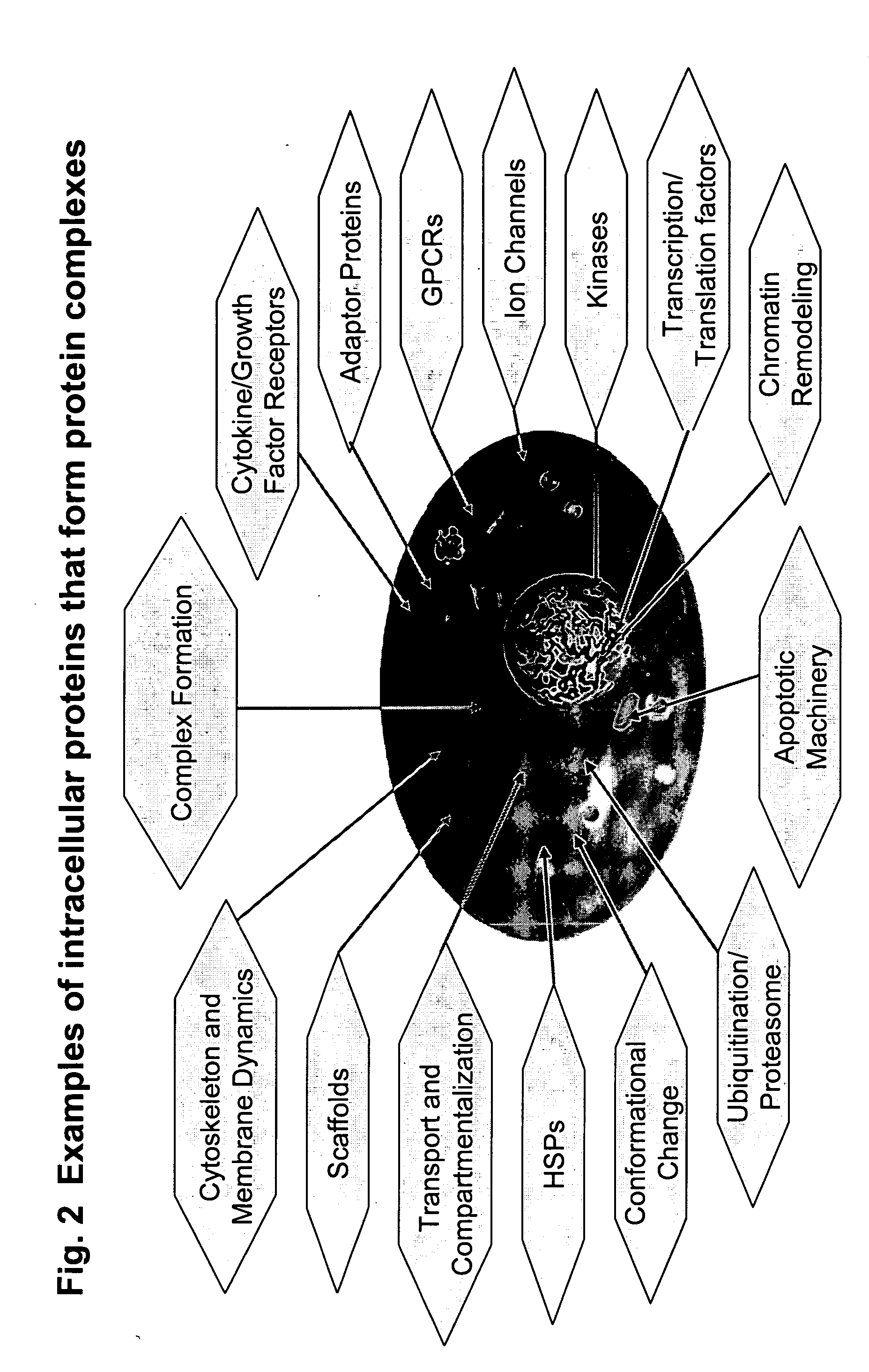
InactiveUS20050221280A1Enable optimizationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningToxicantEfficacy
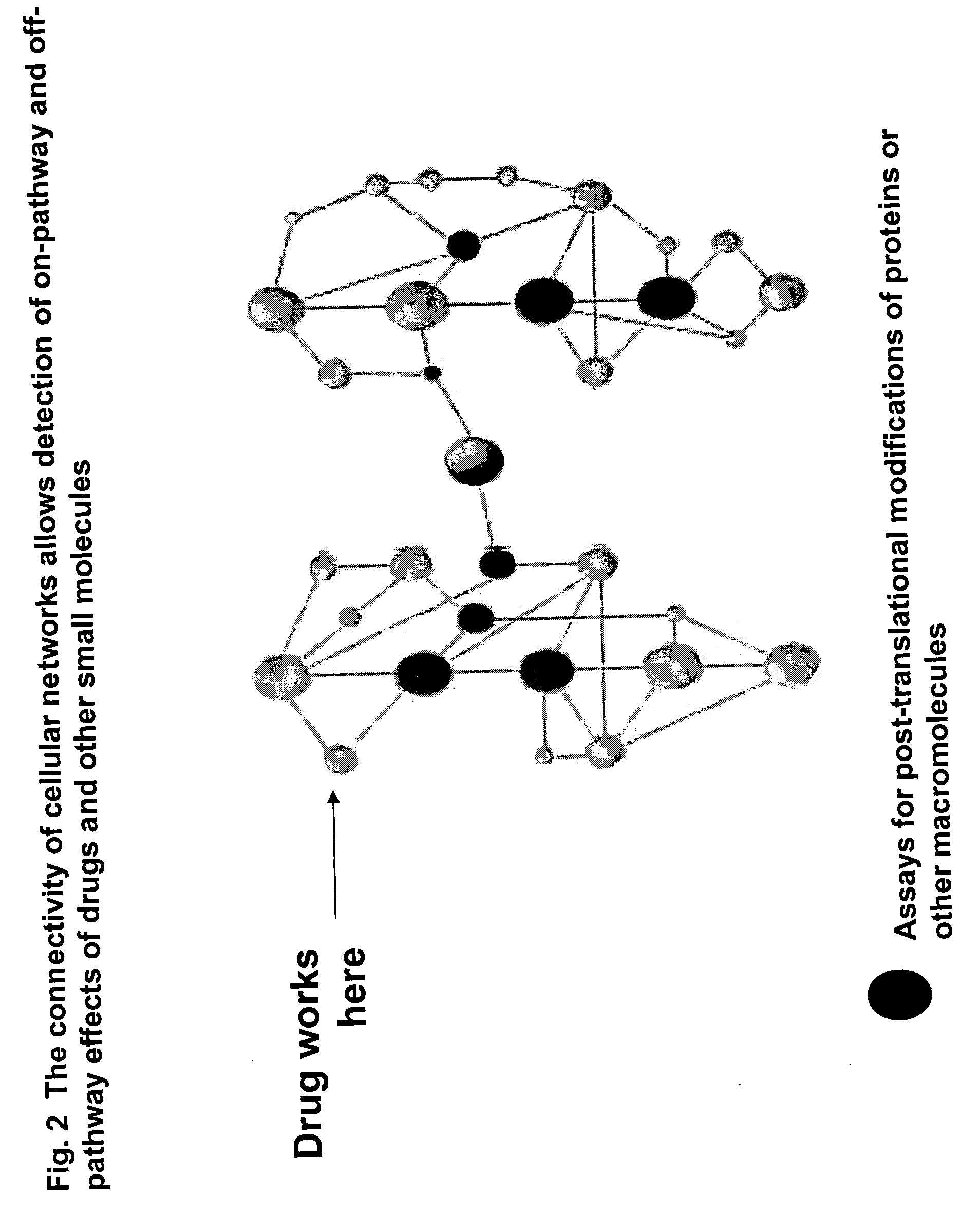
The present invention provides methods for performing pharmacological profiling of a chemical compound, in particular to improve drug safety and efficacy at an early stage in the drug development process. The chemical compound may be a test compound, drug lead, known drug or toxicant. The compound is profiled against a panel of assays. Preferred embodiments of the invention include high-content assays for protein-protein interactions. The compositions and methods of the invention can be used to identify pathways underlying drug efficacy, safety, and toxicity; and to effect attrition of novel compounds with undesirable or toxic properties. The compositions and methods of the invention can also be used to identify new uses of therapeutic agents, to screen libraries of chemical compounds, to perform lead optimization, and to perform studies of structure-activity relationships in the context of intact cells. The compositions and methods of the invention can be applied to any test compound, drug, drug target, pathway, and therapeutic indication.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
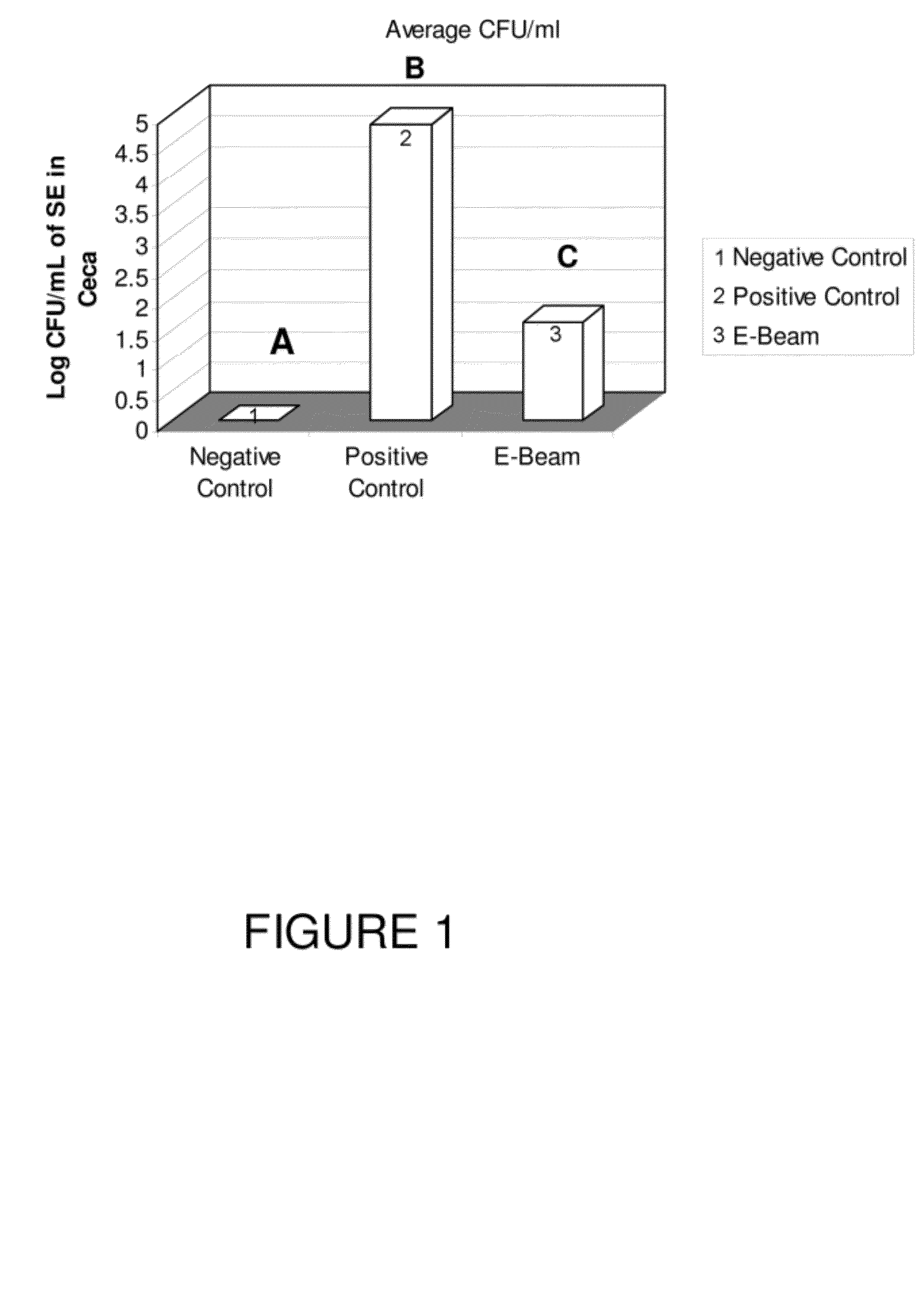
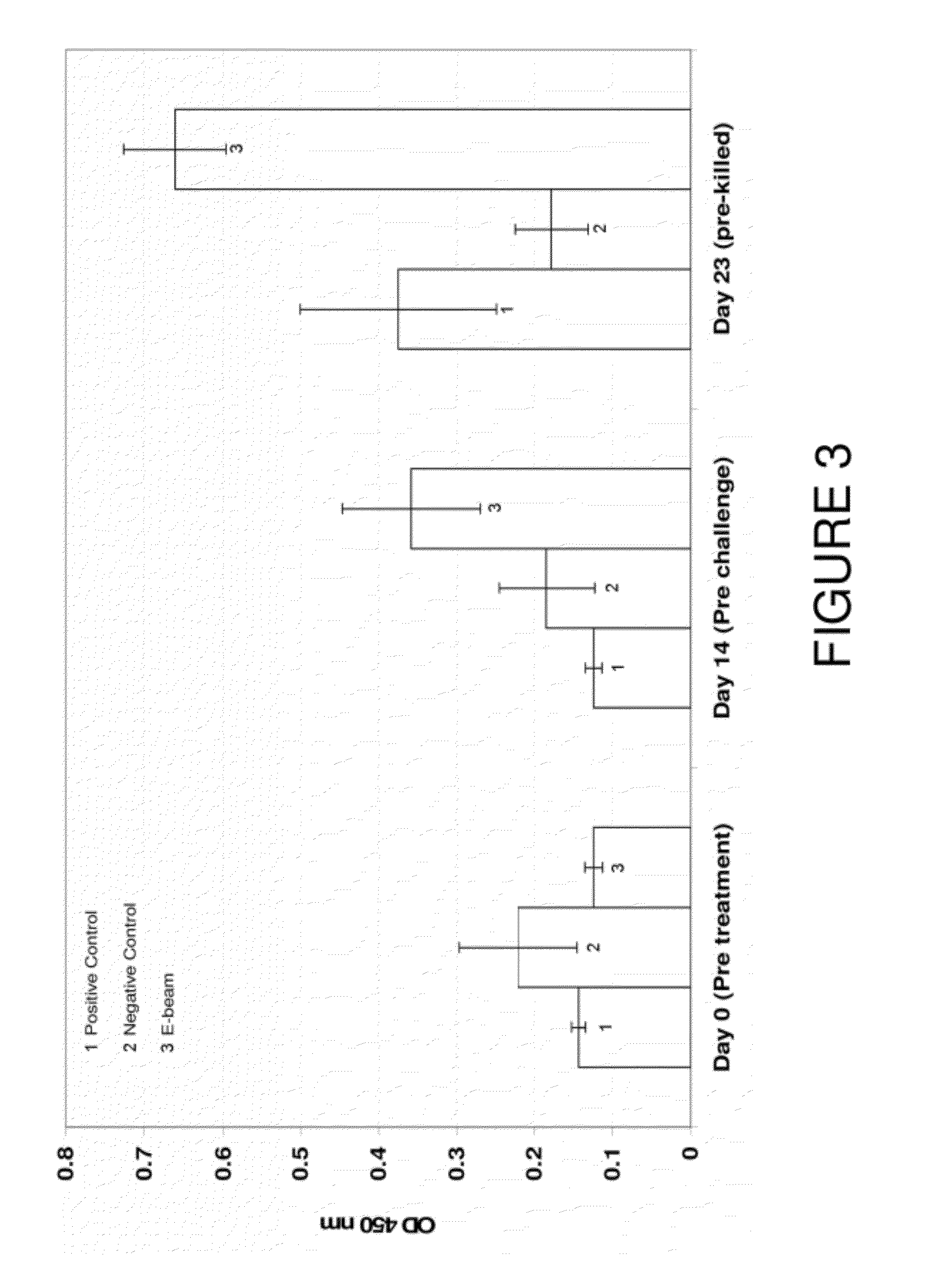
High energy electron beam irradiation for the production of immunomodulators in poultry
InactiveUS8173139B1Controlling and inhibiting Salmonella colonizationStimulating protective immune responseBacterial antigen ingredientsLaser detailsProtection sexIrradiation
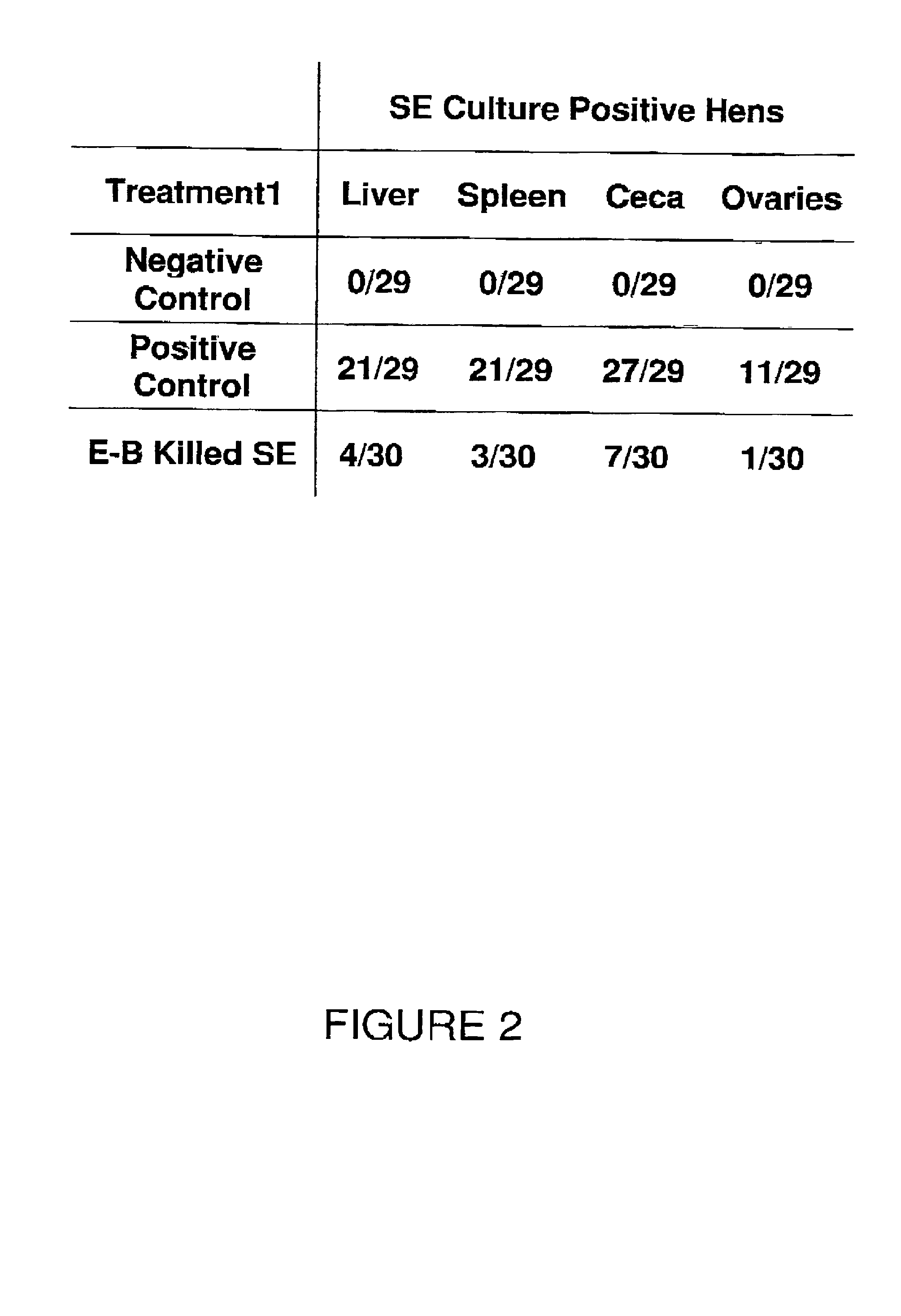
Populations of Salmonella in animals may be substantially reduced by treatment with a vaccine composition which has been produced by exposing whole, intact cells of a Salmonella species to irradiation with an electron beam under conditions effective to kill the cells. The electron beam irradiated cells of Salmonella are effective for stimulating protective immune responses in the animals against the Salmonella. Induction of these immune responses significantly reduces or eliminates the colonization of the animal by the Salmonella, and consequently reduces or eliminates the shedding of Salmonella in the feces of the animals.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Methods for treating hormone disorders
InactiveUS6410715B1Sugar derivativesBiological material analysisCellular componentTherapeutic Hormone
Method for screening for a non-hormone agent potentially useful to treat a hormone disorder The method involves contacting a potential agent with a system containing a cellular component and a translation factor. The component and factor interact with one another in an intact normal cell in a manner responsive to the hormone to cause a modulation of translation in the cell. The method involves determining whether the agent causes a modulation of translation by the component and the factor analogous to that which occurs in intact cells in response to the hormone.
Owner:QUESTCOR PHARMA
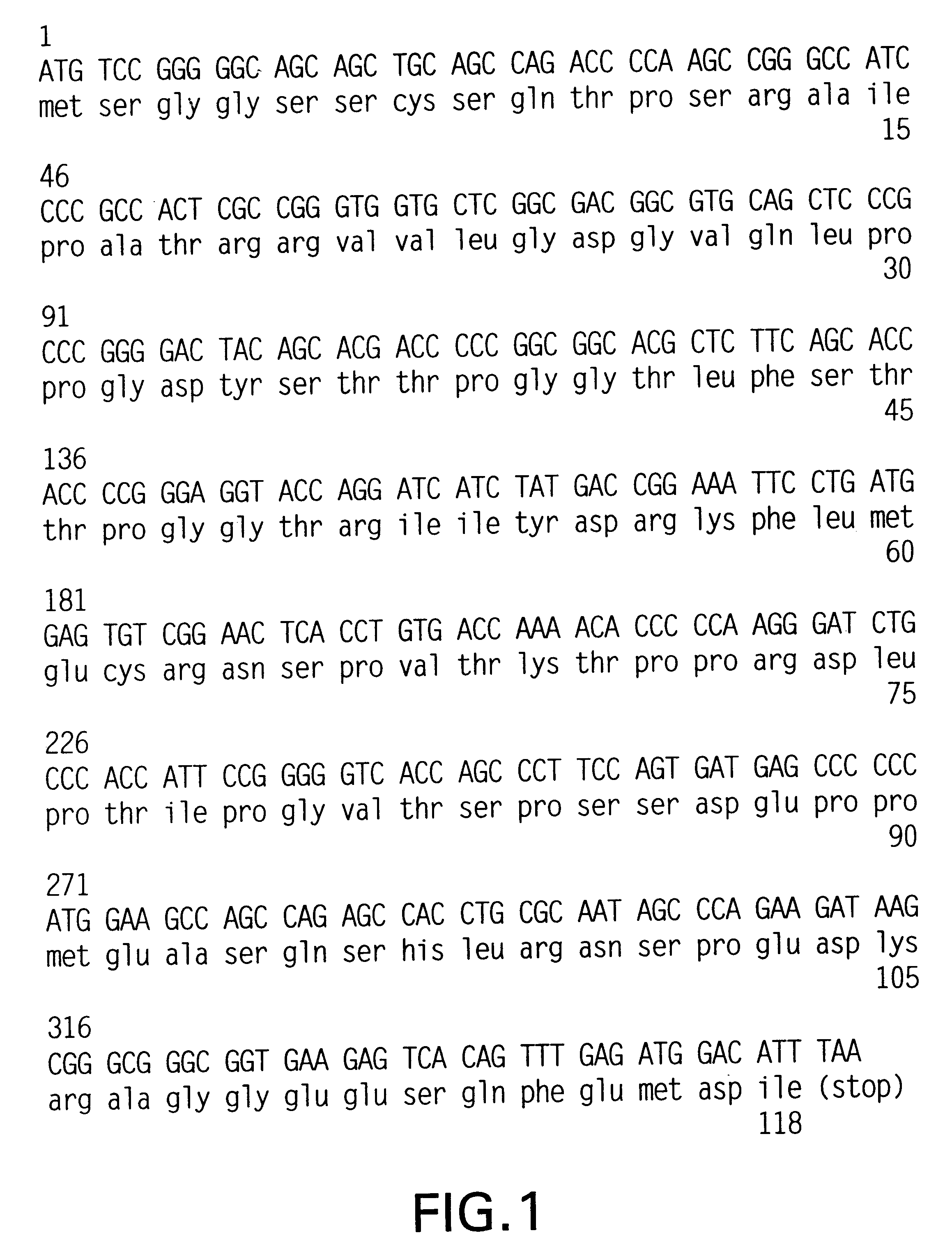
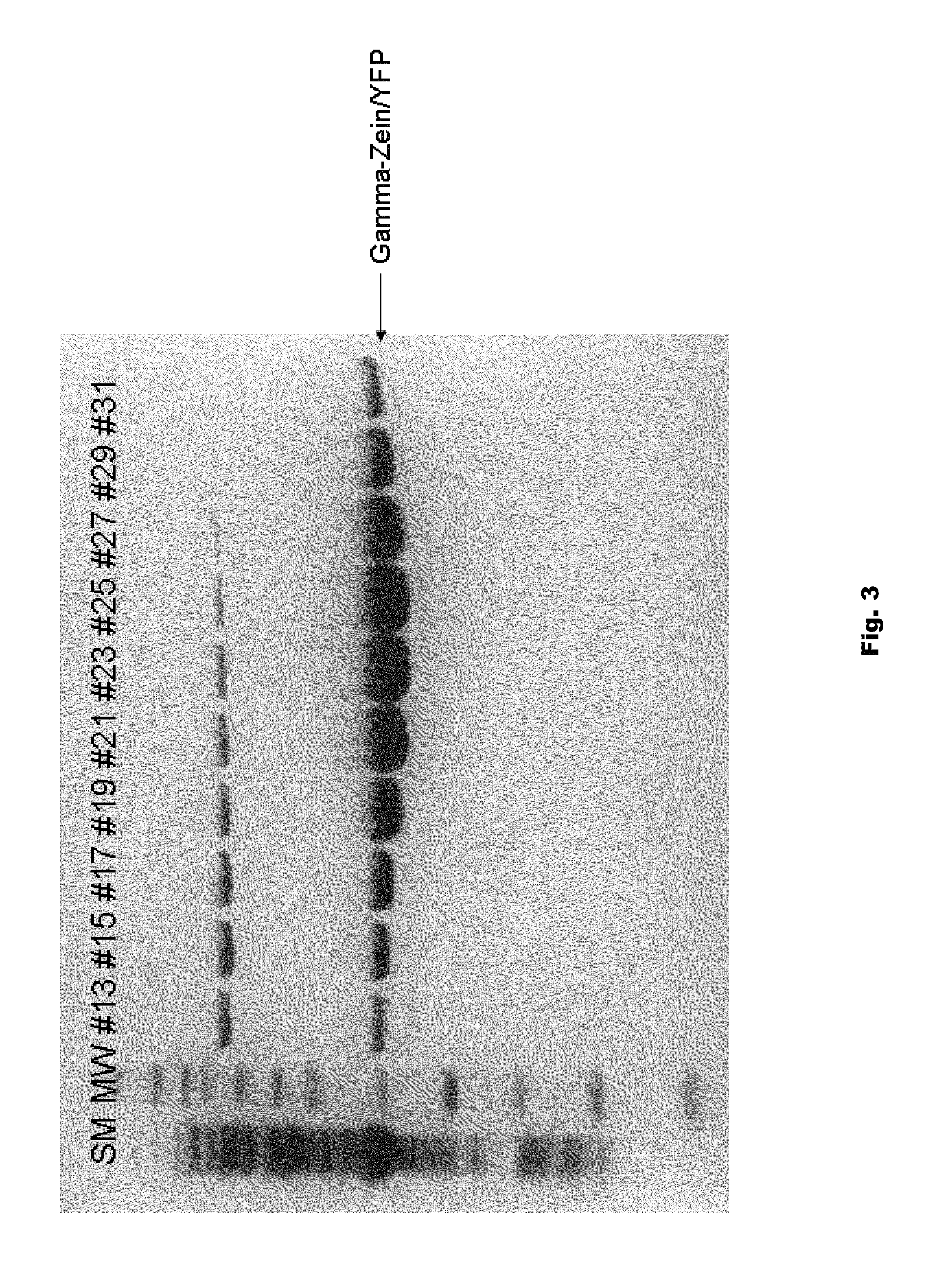
Plant peptide gamma-zein for delivery of biomolecules into plant cells
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
A pluripotent vaccine against enveloped viruses
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods for the induction of immune responses in mammals against enveloped animal viruses. More particularly, the invention provides vaccine compositions containing multiple MHC allotypes. By generating an immune response against these MHC molecules, virus or virus-infected cells expressing foreign MHC molecules can be attacked prior to infection of cells in the immunized host. In some embodiments, the vaccine compositions contain viral antigens and adjuvants as well. The vaccine compositions may comprise intact cells, cell-derived membrane preparations or recombinantly or chemically produced MHC molecules or fragments thereof.
Owner:JOHN WAYNE CANCER INST
Structurally modified acellular tissue engineering scaffolds and methods of production
ActiveUS7829108B2Improve seeding efficiencyCell culture supports/coatingUnknown materialsPorosityFreeze-drying
Methods are provided for producing a bioscaffold from natural tissues by oxidizing a decellularized tissue to produce a bioscaffold having pores therein. The pore size and porosity is increased to better accommodate intact cells so that live cells can better infiltrate and inhabit the bioscaffold. The bioscaffold may be freeze-dried or lyophilized, sterilized and (optionally) aseptically packaged for subsequent use. A further aspect of the present invention is a bioscaffold produced by the processes described herein. Methods of treatment using the bioscaffold as a graft or as a biomedical implant for implantation are also provided. Also provided are methods of seeding a bioscaffold with mammalian cells, wherein the seeding carried out either in vitro or in vivo, and wherein a bioscaffold produced as described herein is utilized for said seeding.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
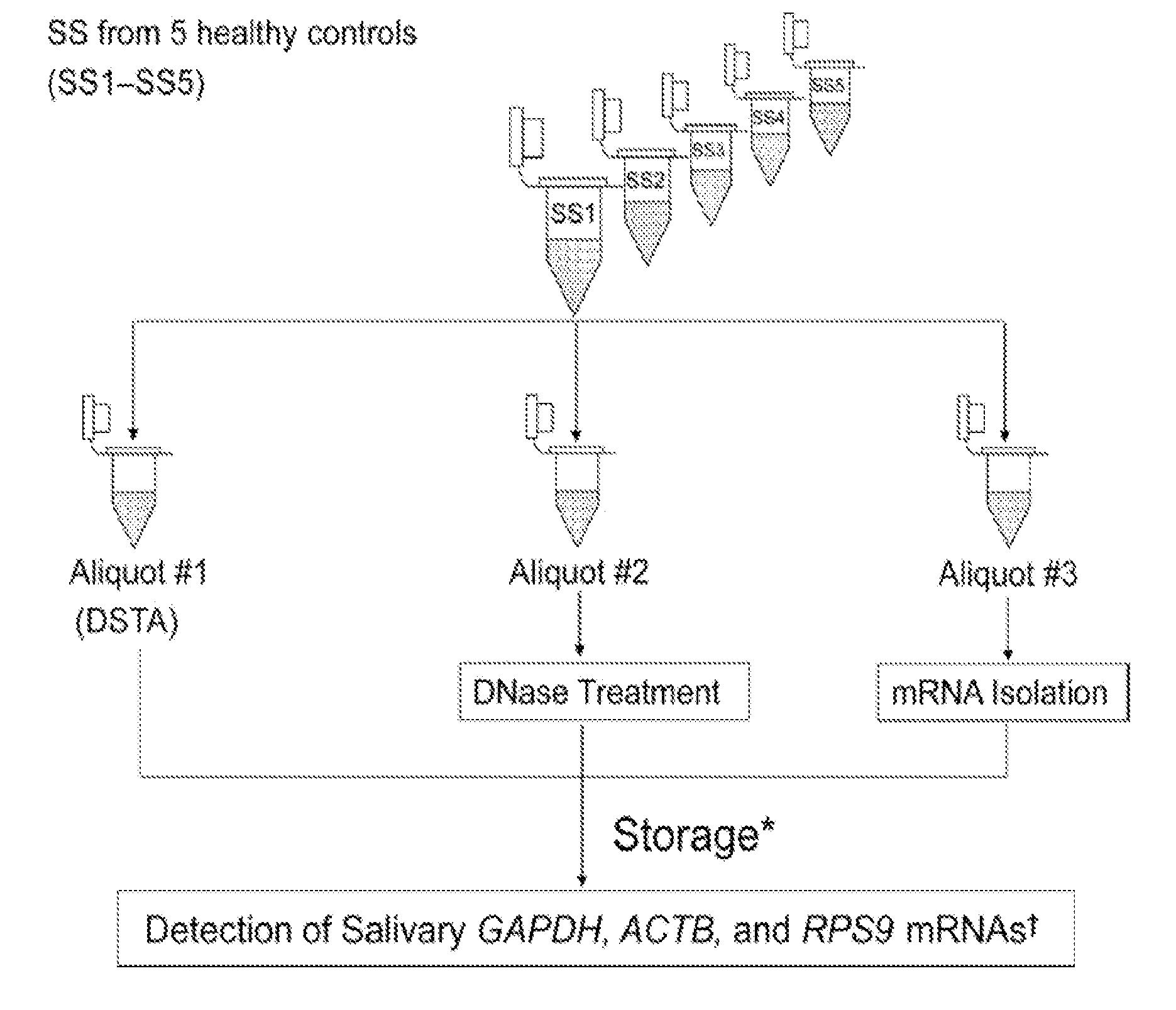
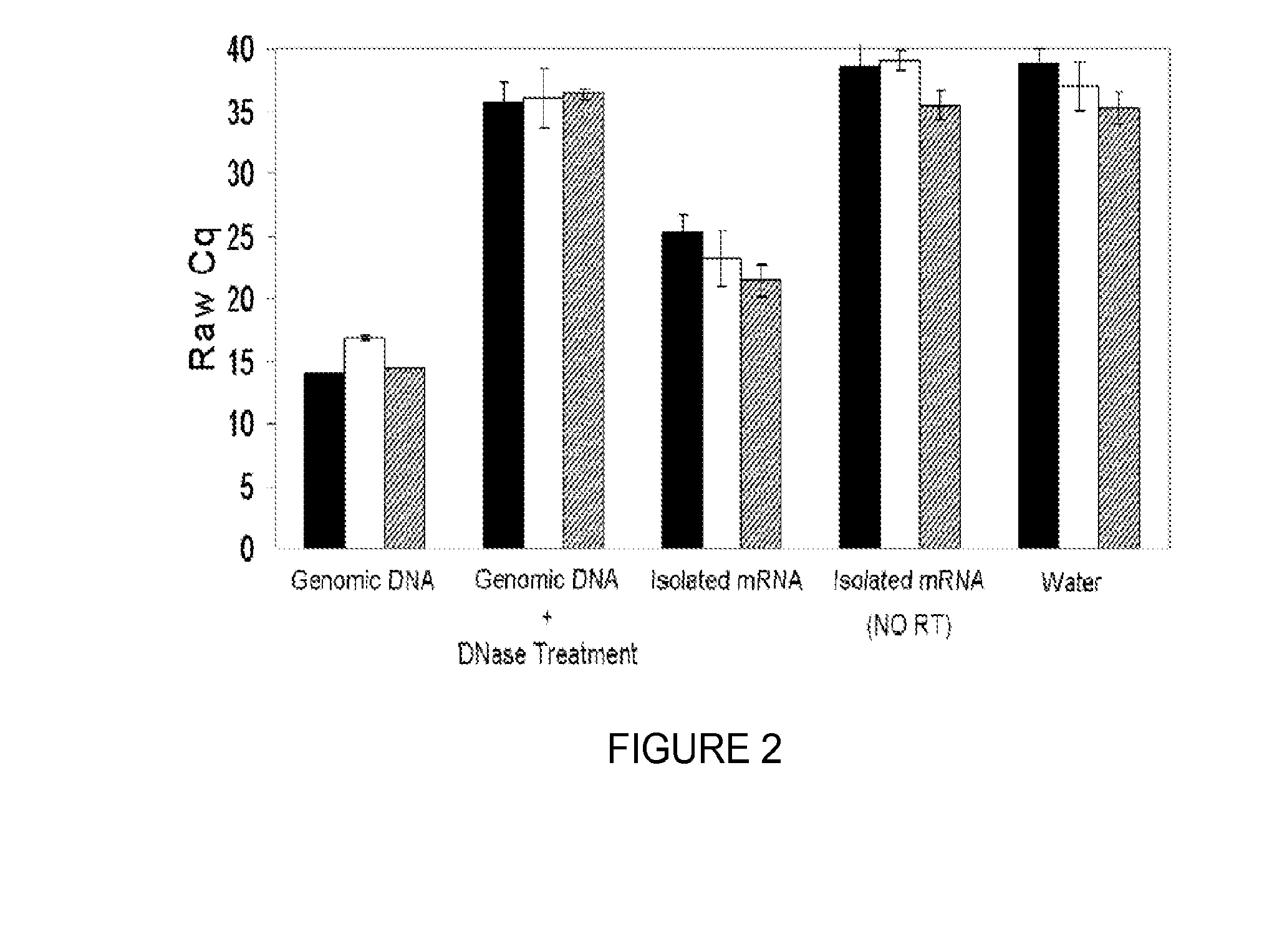
Saliva collection, processing, stabilization, and storage method
ActiveUS20140329705A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationSaliva sampleCell free
Provided herein is an all-in-one saliva collection apparatus that collects saliva to allow for the filtration of saliva in order to separate saliva components, such as extracellular proteins and nucleic acids that are not present in intact cells, from the intact cells and debris remaining in the extracted sample. The filtered saliva samples can be aliquoted into two fractions for protein and / or nucleic acid analysis. The present invention further describes long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary nucleic acids, and long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary proteins added to an ethanol solution. The filtered cell-free saliva samples have diagnostic usefulness.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
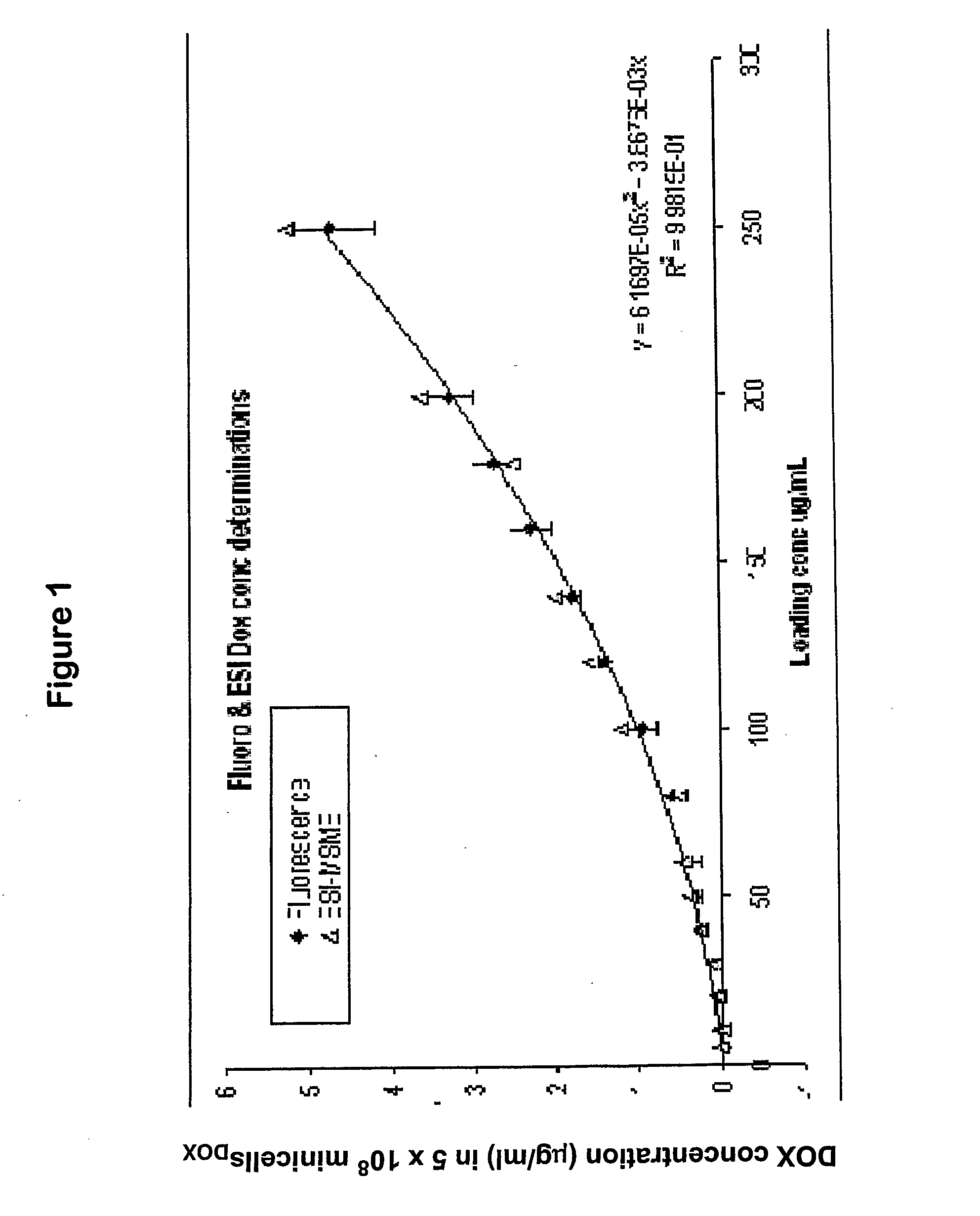
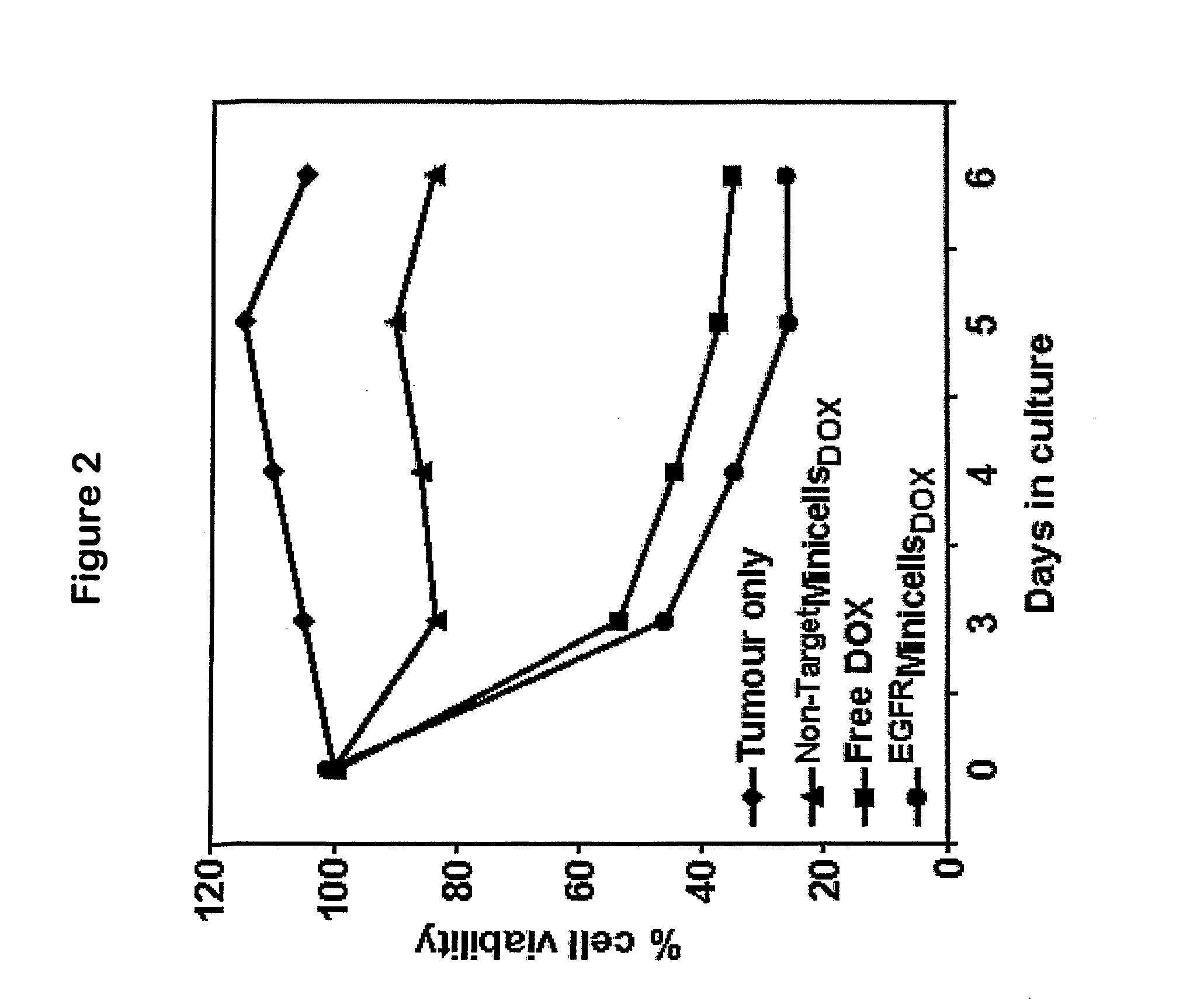
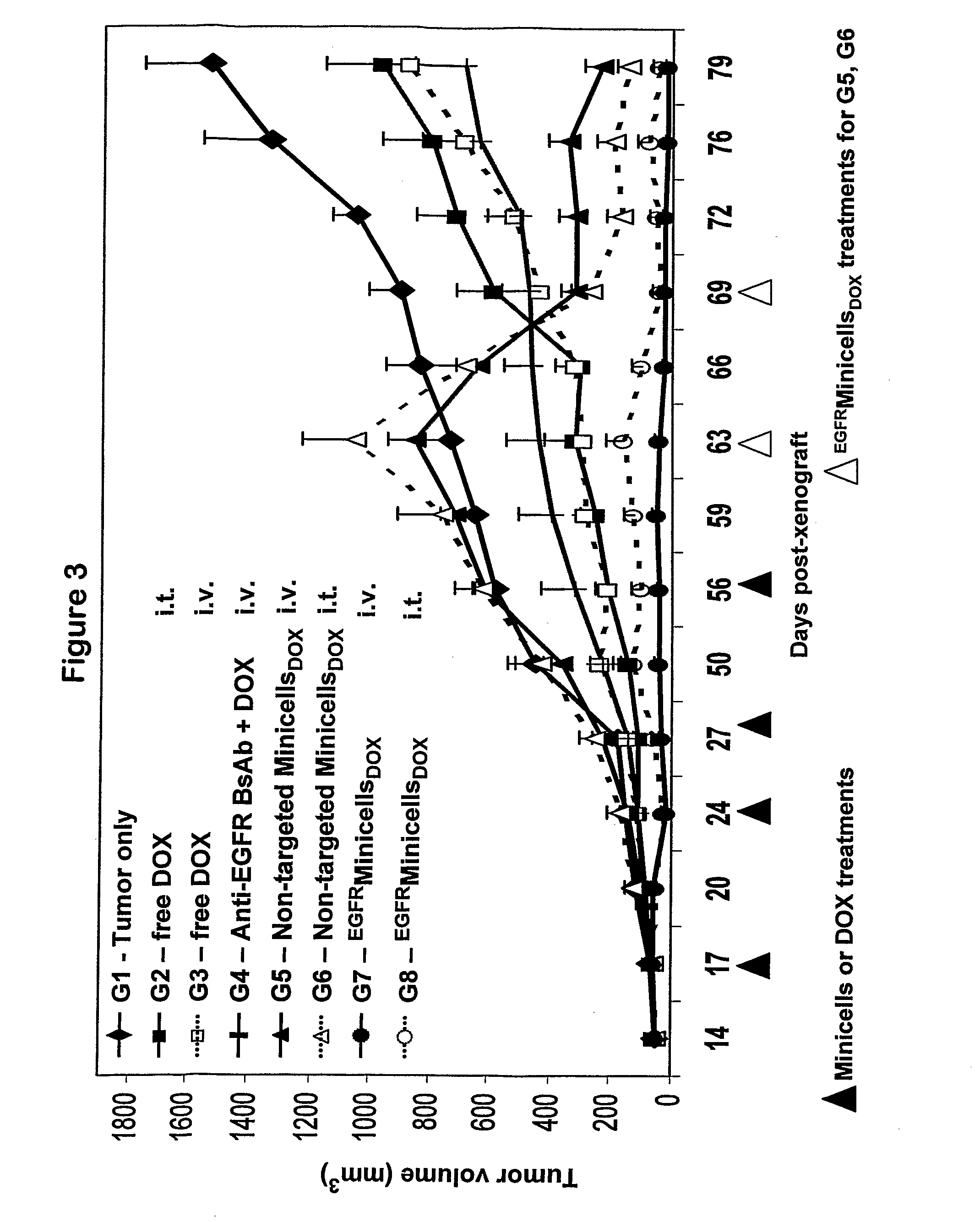
Methods for targeted in vitro and in vivo drug delivery to mammalian cells via bacterially derived intact minicells
A composition comprising intact minicells that contain a drug molecule is useful for targeted drug delivery. One targeted drug delivery method employs bispecific ligands, comprising a first arm that carries specificity for a bacterially derived minicell surface structure and a second arm that carries specificity for a mammalian cell surface receptor, to target drug-loaded minicells to specific mammalian cells and to cause endocytosis of the minicells by the mammalian cells. Another drug delivery method exploits the natural ability of phagocytic mammalian cells to engulf minicells without the use of bispecific ligands.
Owner:ENGENEIC MOLECULAR DELIVERY PTY LTD
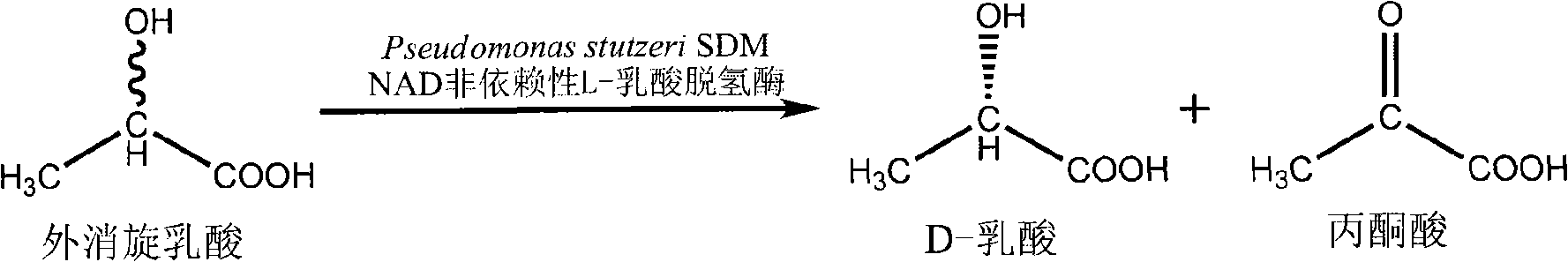
Method for producing D-lactic acid by enzyme resolution of D,L-lactic Acid
InactiveCN101333554AShorten the growth cycleLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationThermal denaturationD-lactic acid dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a method for producing D-lactic acid by splitting racemized lactic acid by adopting an enzyme method, comprising steps of: (1) preparation of an intact cell suspension or a crude enzyme liquid containing NAD independent lactic acid dehydrogenase, (2) inactivating the NAD independent D-lactic acid dehydrogenase by a thermal denaturation method, (3) splitting the racemized lactic acid, (4) preprocessing of transformation liquid, (5) separation of D-lactic acid and pyruvic acid, (6) refining the D-lactic acid and the pyruvic acid, etc. The method has advantages of simple culture medium, short growth cycle, low cost, low expenses of the follow-up separation and extraction, high substrate concentration resistance and high enantiomeric excess value of the product D-lactic acid, and lays the foundation for the development and application of low-priced racemized lactic acid and the high-efficient production of D-lactic acid.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
In vitro methods for the induction and maintenance of plant cell lines as single suspension cells with intact cell walls, and transformation thereof
InactiveUS8012752B2Cell culture mediaOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellPrimary cell
The subject invention provides simple and consistent methods to break suspension cell aggregates to single cells with intact primary cell walls. The subject invention relates in part to cell separation of suspension cell aggregates cultured in medium containing pectin-degrading enzymes or tubulin de-polymerizing compounds including colchicine. The subject invention also relates to novel uses of compounds for such purposes. Another aspect of the subject invention relates to transformation of the subject, isolated cells. Such processes simplify and integrate single-cell-based transformation and selection processes into transgenic and transplastomic event-generation work processes. The subject invention also removes technical constraints and produces marker-free and uniformly expressing transgenic lines in a high throughput fashion to support various needs of animal health, biopharma, and trait and crop protection platforms.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Actinomycetes strain and application thereof in preparation of aromatic hydroxylamine
InactiveCN101735961AImprove conversion rateHigh selectivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxylamineD-Glucose
The invention relates to an actinomycetes (Streptomyces thioluteus) strain CGMCC No. 2725 and application thereof in the preparation of aromatic hydroxylamine. The strain CGMCC No. 2725 is easy to obtain and culture, and has a complete coenzyme regeneration system exists in a cell body of the strain, the spontaneous cyclic regeneration of coenzyme can be performed only by adding an appropriate quantity of auxiliary substrates (such as glucose or ethanol and the like) without additionally adding expensive reduced coenzyme. In addition, the use of intact cells can leave out the process of extracting and purifying enzyme, so the strain is more suitable for large-scale commercial application.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com