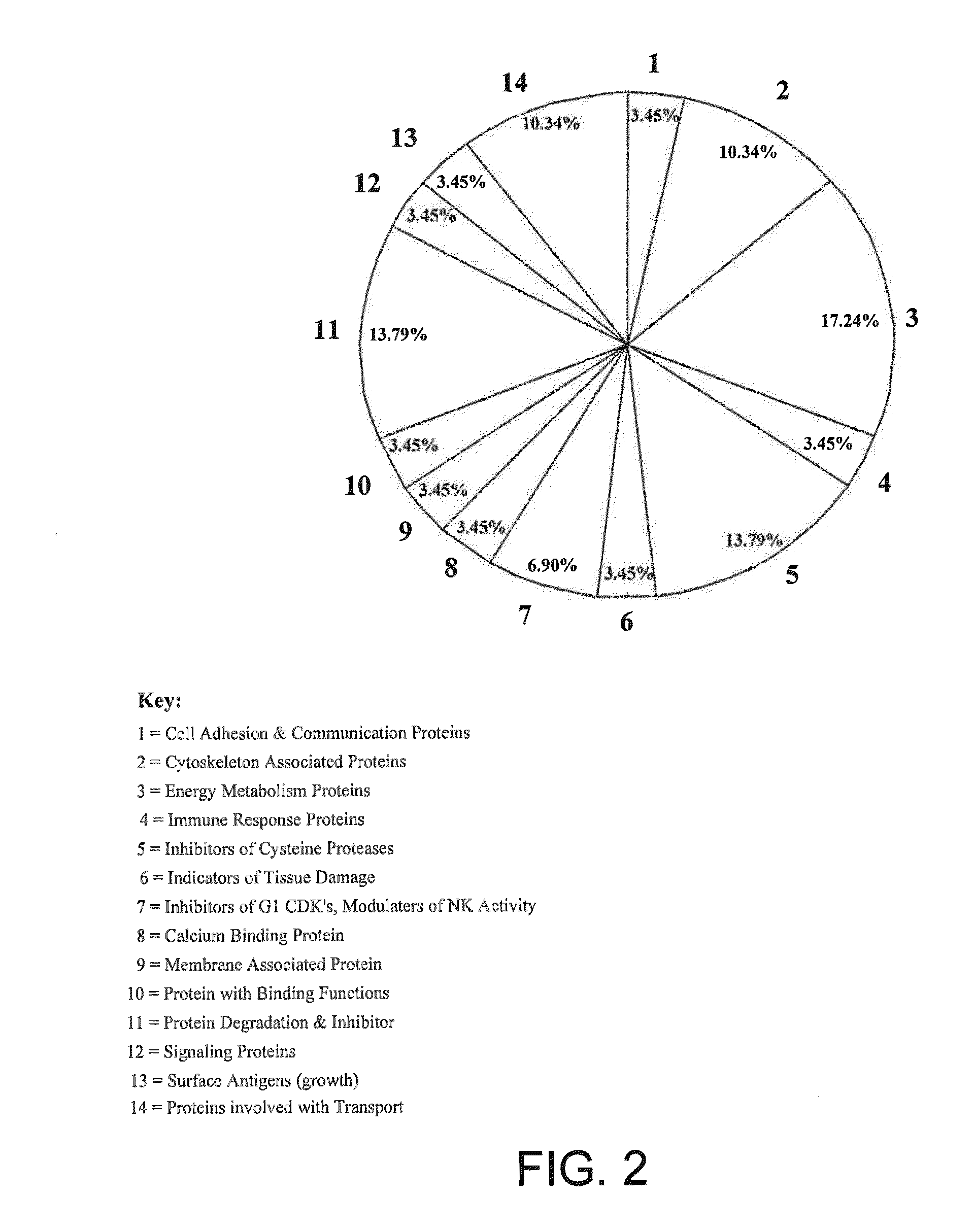
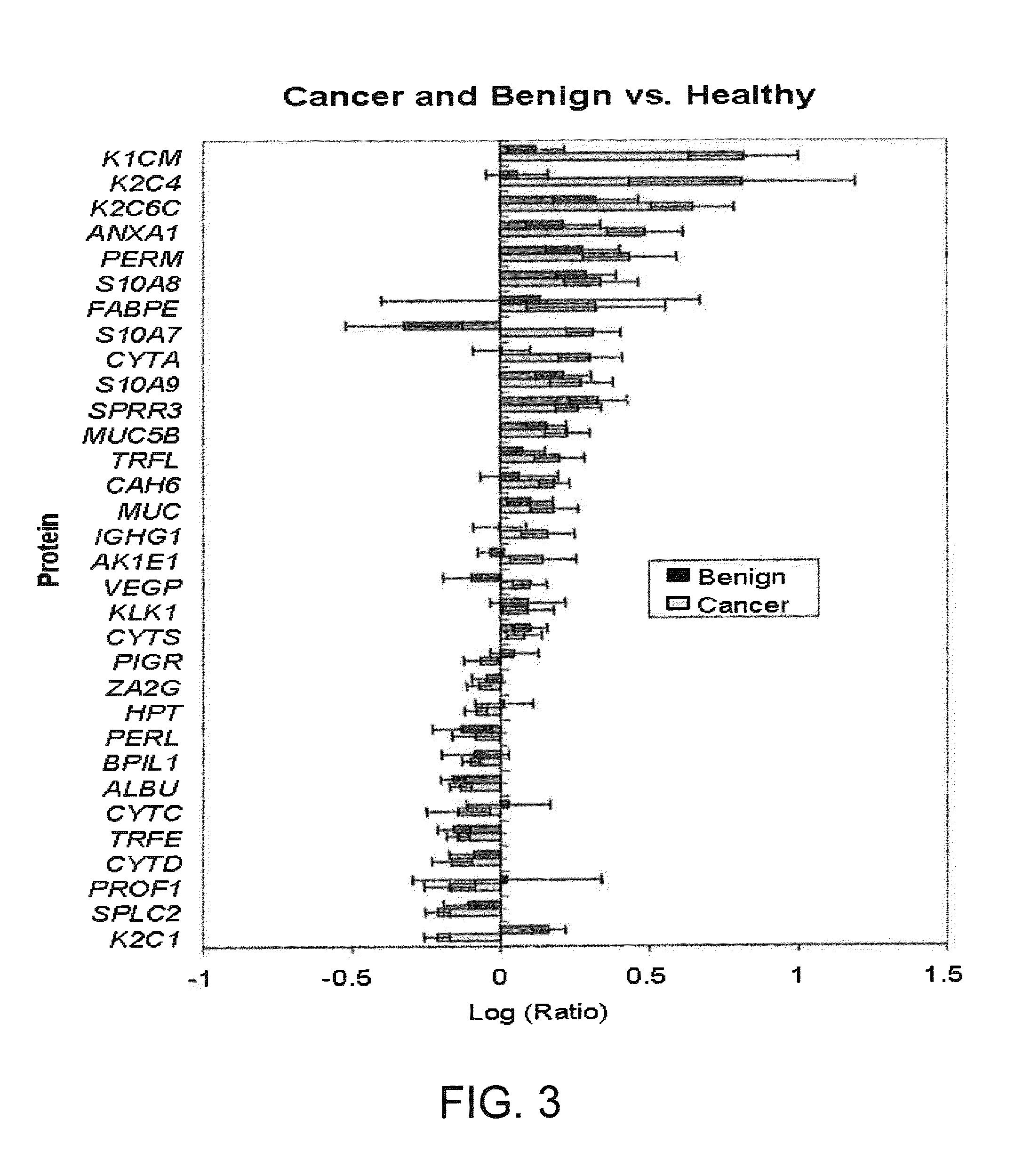
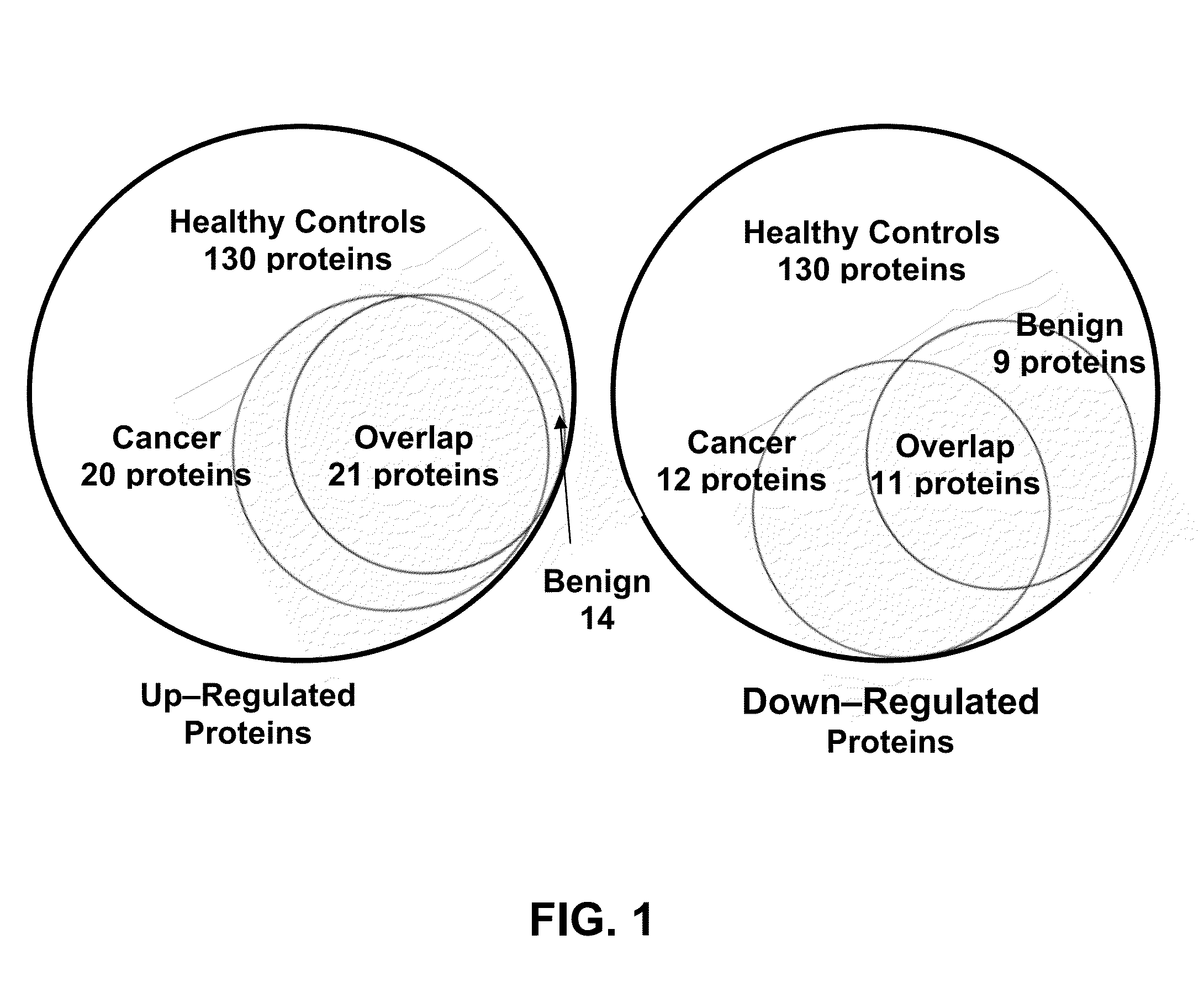
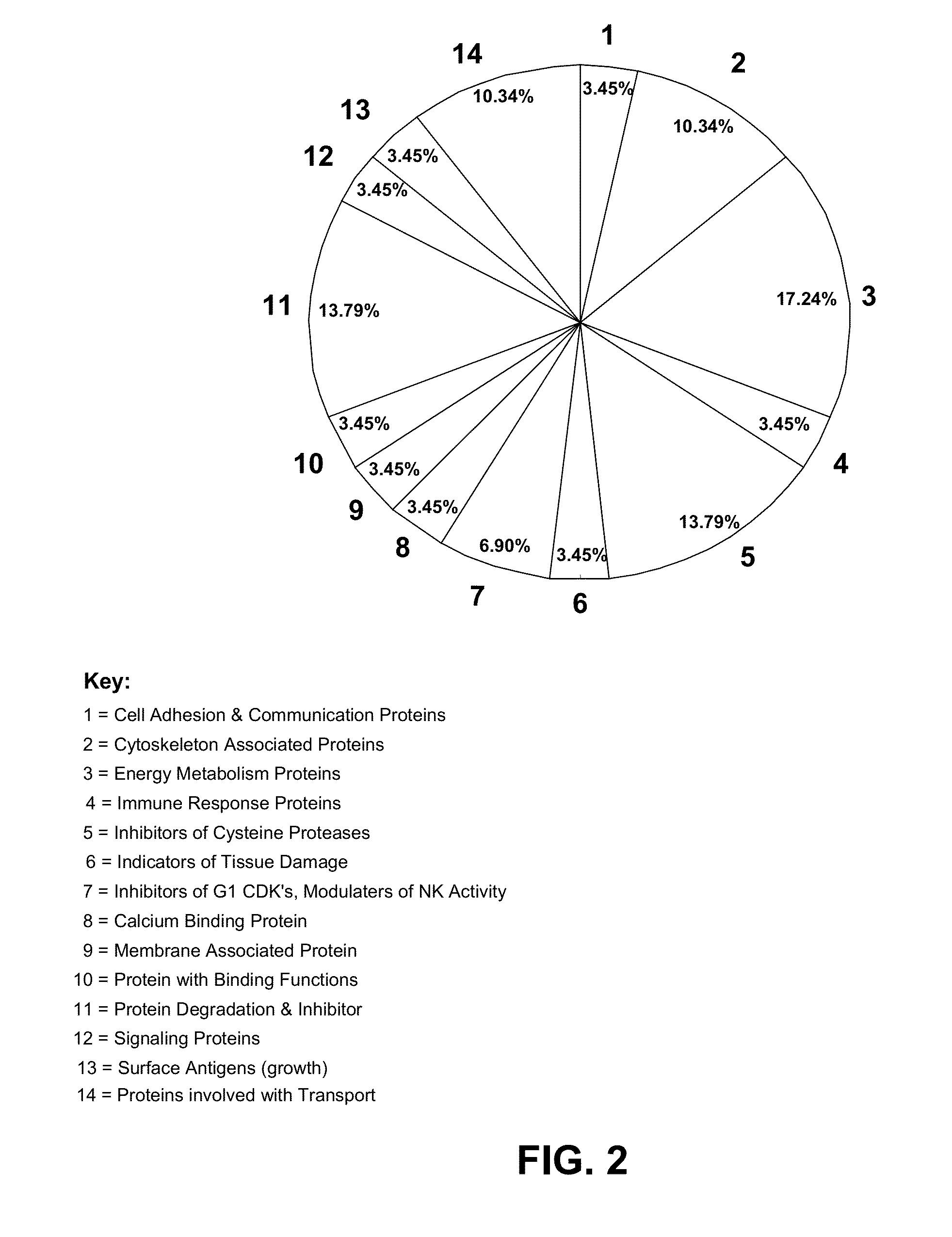
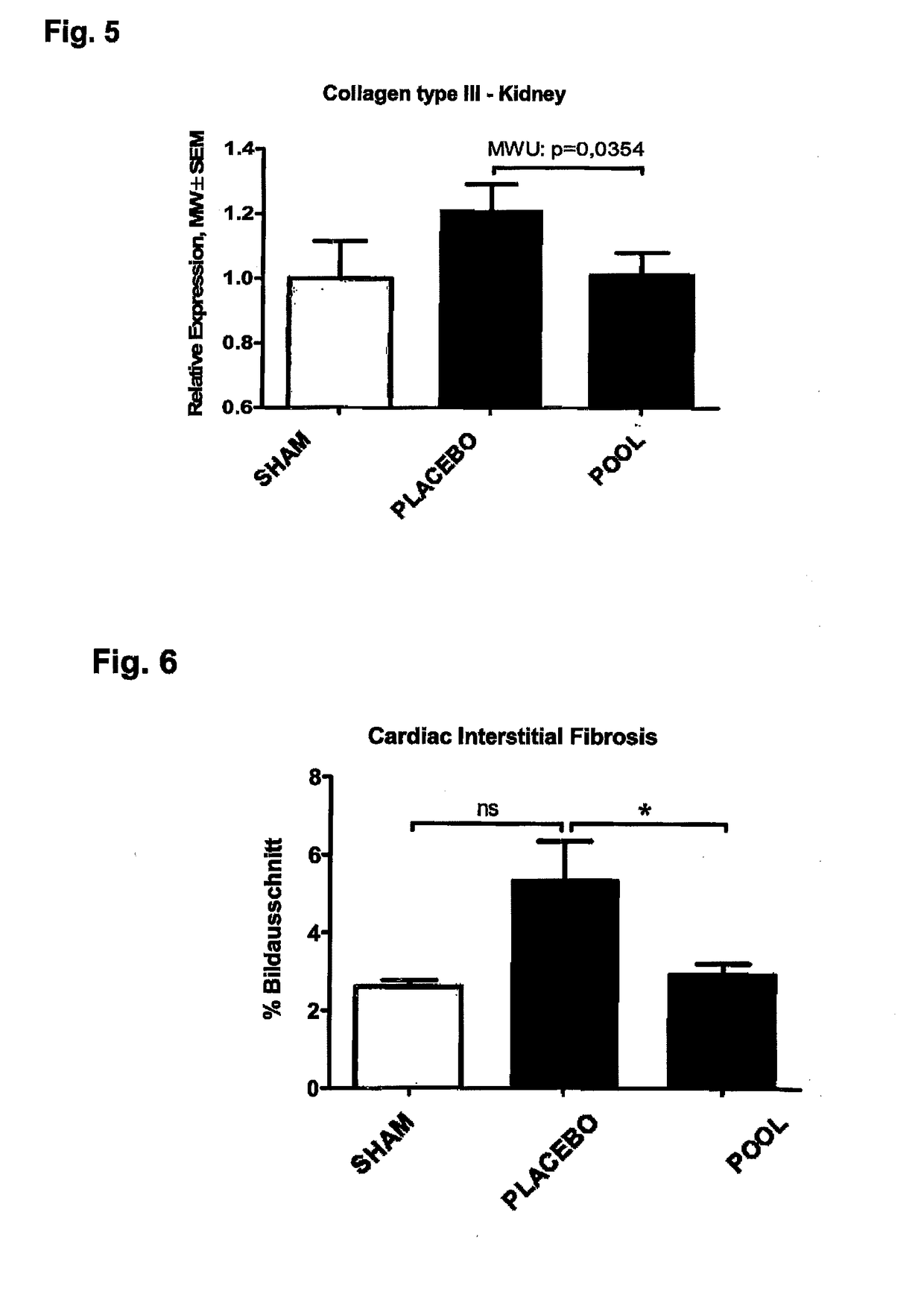
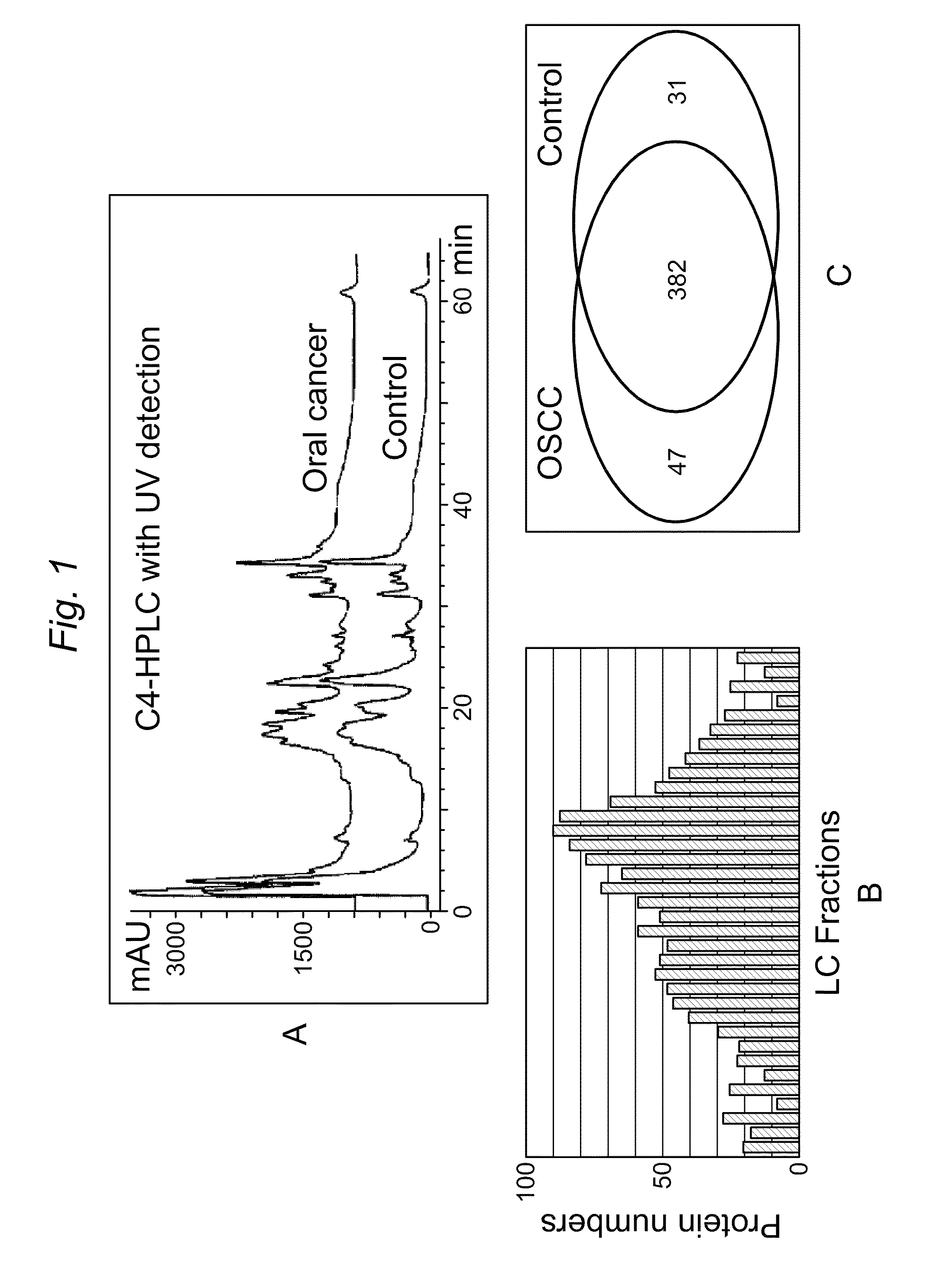
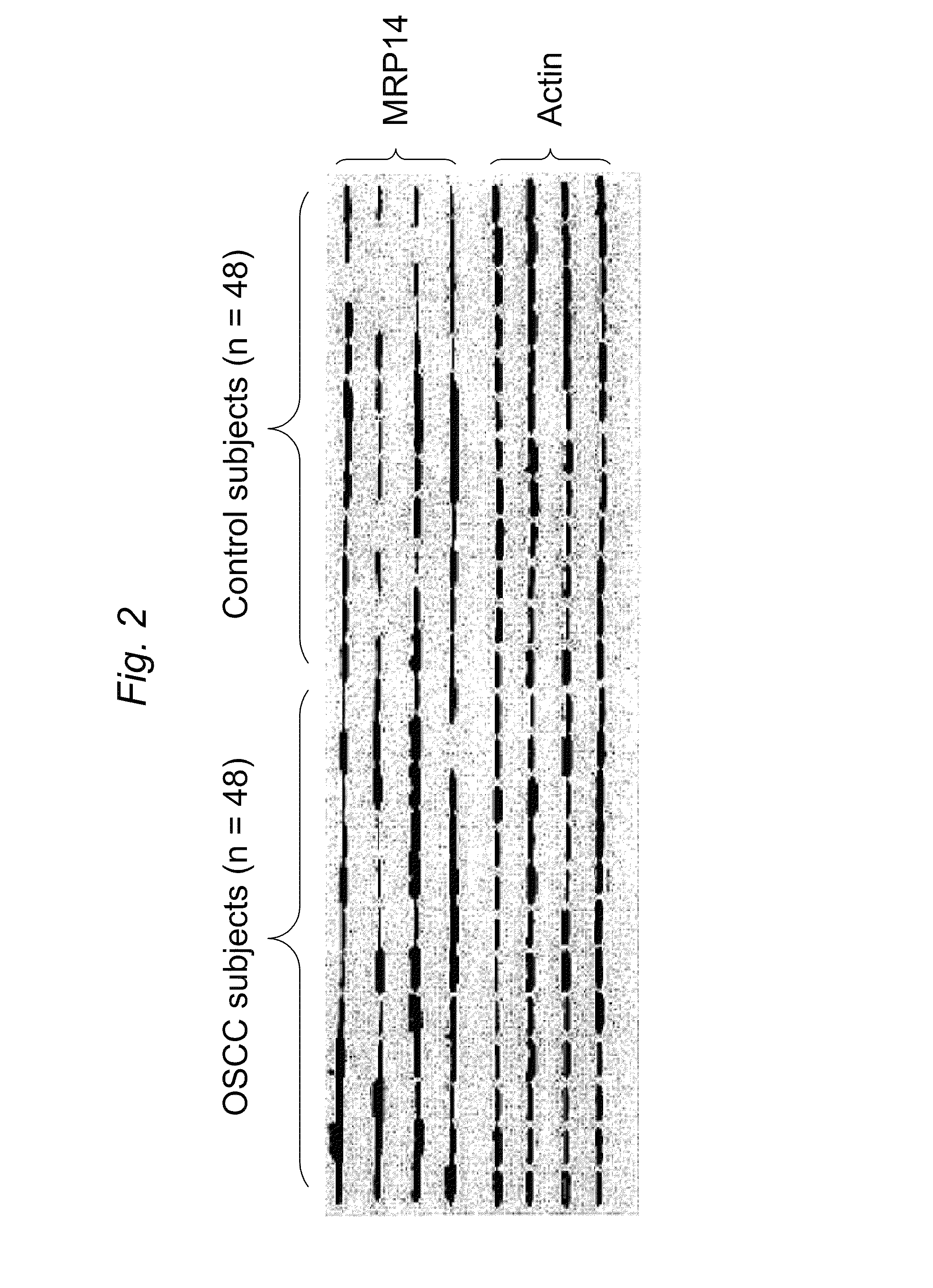
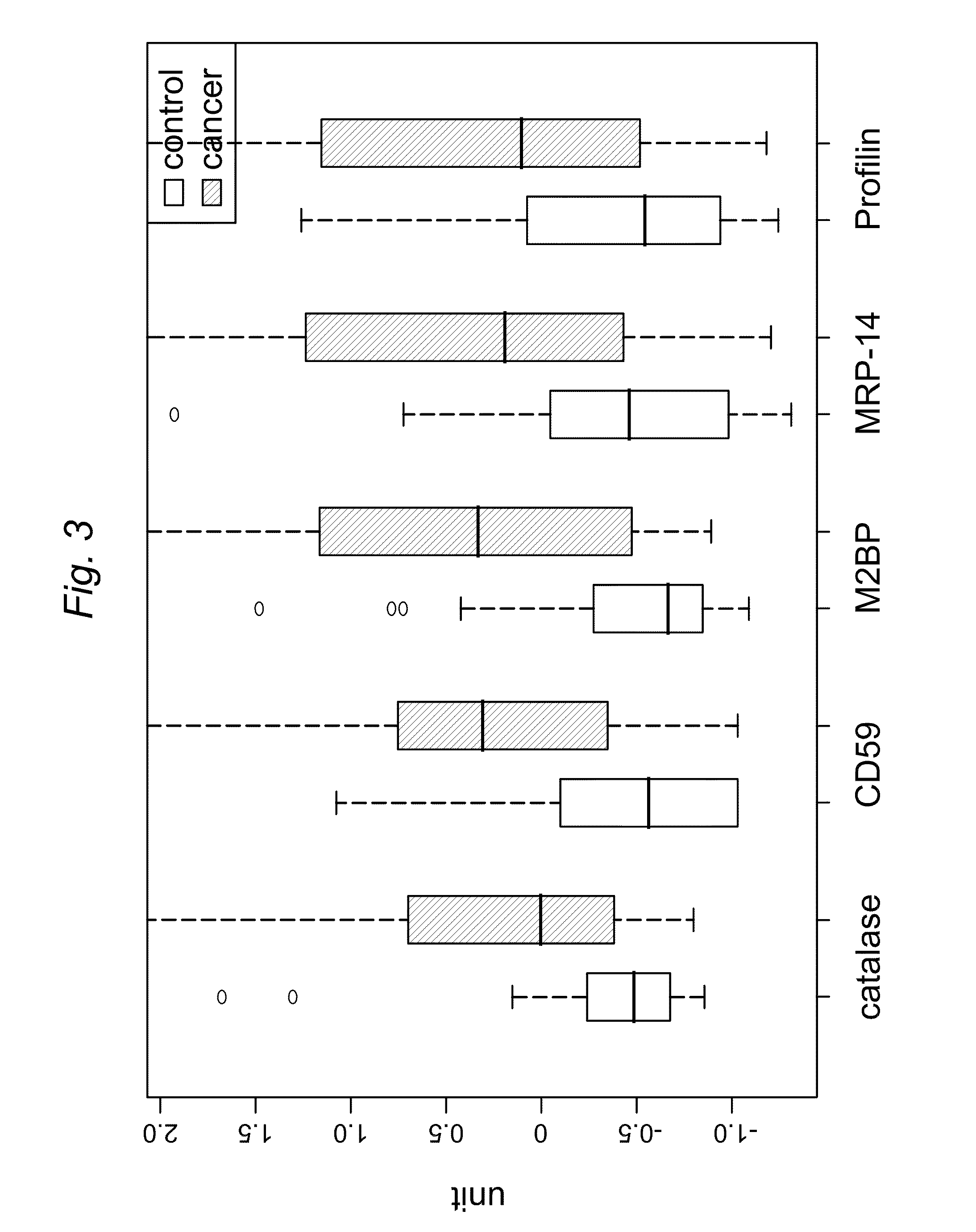
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Salivary Proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
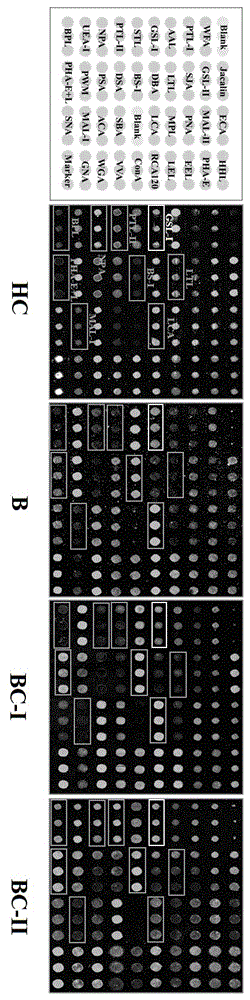
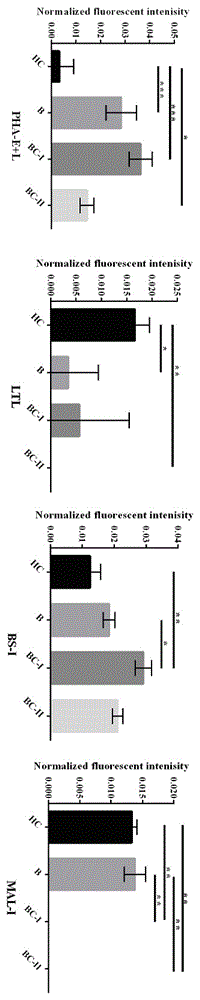
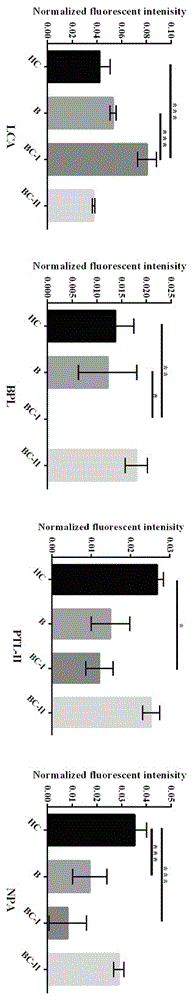
Agglutinin chip for identifying breast cancer based on sialoprotein, reagent kit and application of reagent kit
The relates to an agglutinin chip used for identifying cancer, in particular to an agglutinin chip for identifying breast cancer based on sialoprotein, a reagent kit and application of the reagent kit, and aims at providing an agglutinin chip for identifying breast cancer in a non-destructive mode through the change of carbohydrate chains in saliva, a reagent kit and application of the reagent kit. The agglutinin chip for identifying breast cancer based on sialoprotein comprises an agglutinin testing probe set. The agglutinin testing probe set at least comprises a combination of PHA-E+L, LTL, BS-I, MAL-I, LCA, BPL, PTL-II, NPA and GSL-I, or at least comprises a combination of LTL, BS-I, MAL-I, LCA, BPL, NPA and GSL-I. By means of the agglutinin chip, differentially-expressed glycoprotein carbohydrate chain structures in a patient saliva sample can be rapidly detected, whether a corresponding person suffers from a breast tumor or not is detected, and whether the breast tumor is breast cancer or not is determined; besides, saliva is adopted as an object to be detected and is easy and convenient to collect, and health risks existing when a serum sample is collected for detection in the prior art are avoided.
Owner:深圳格道糖生物技术有限公司
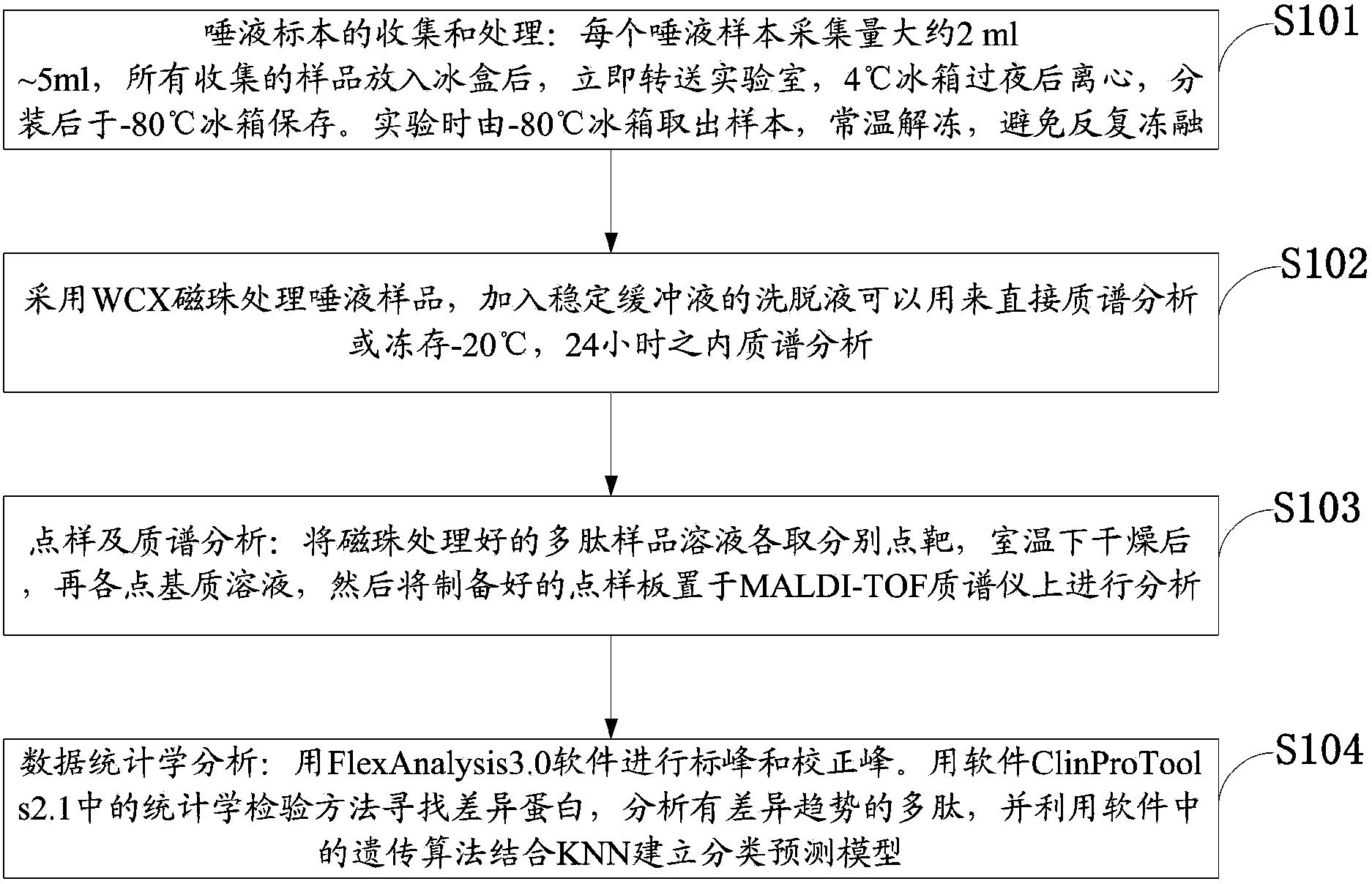
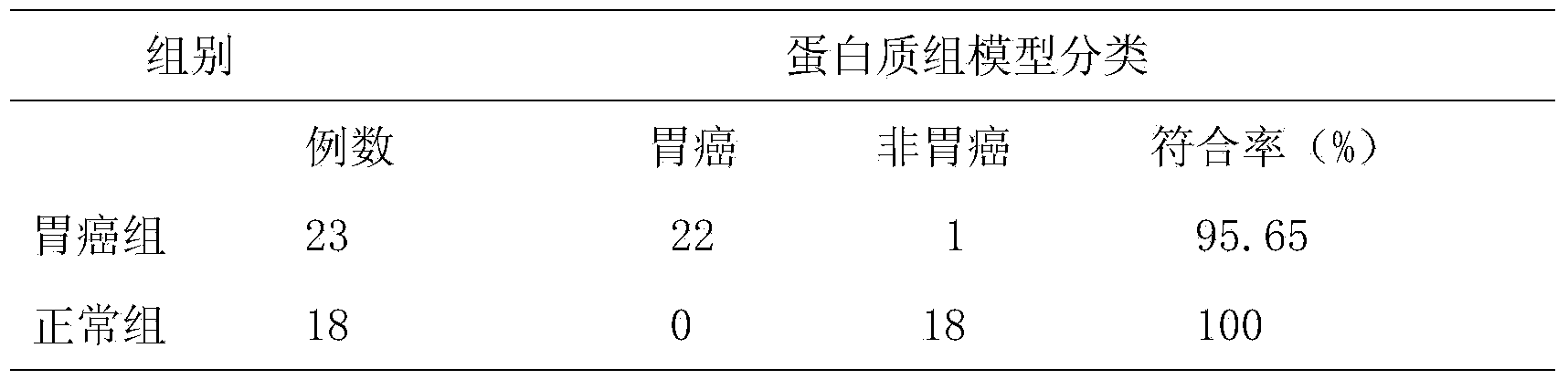
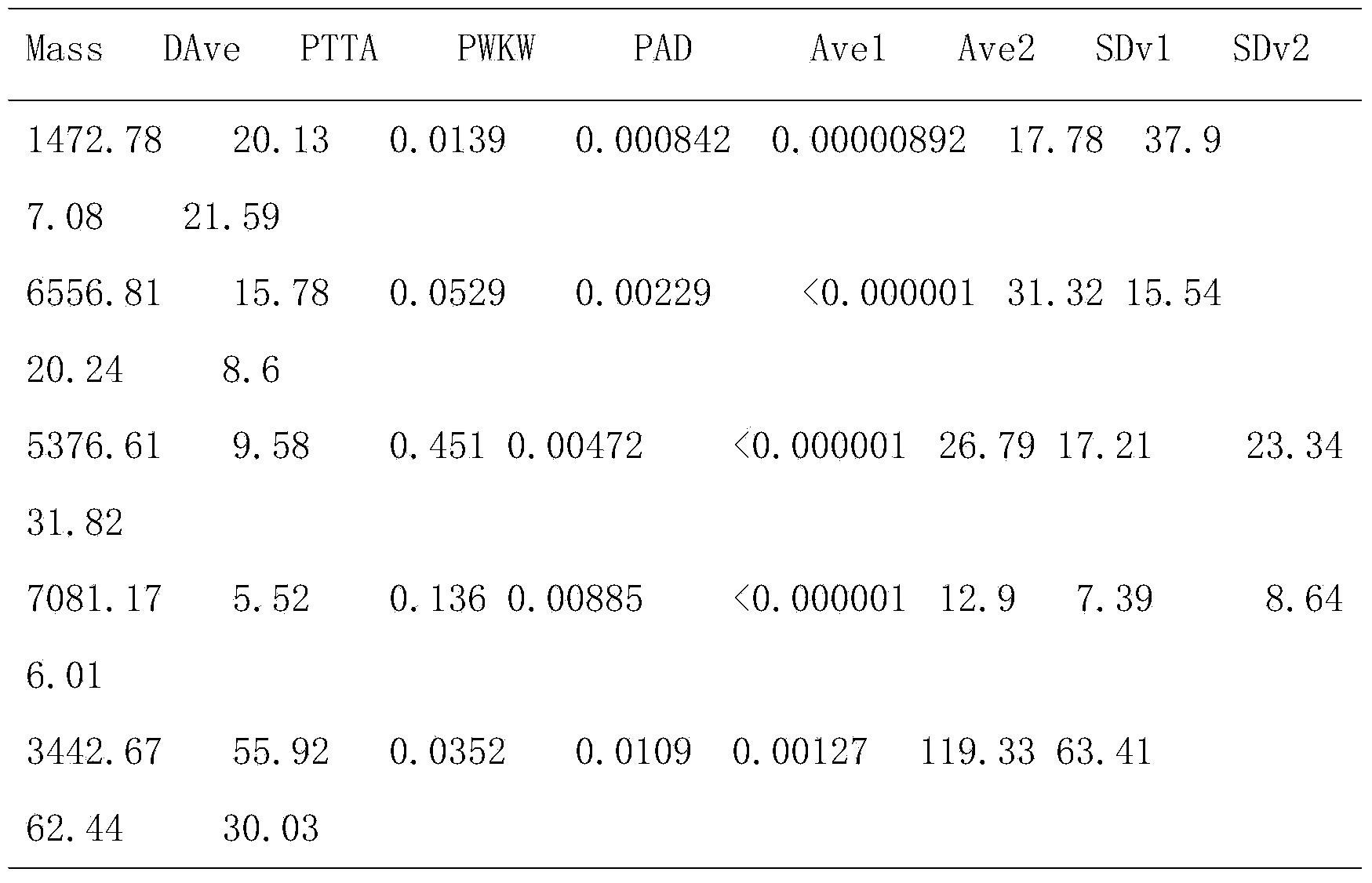
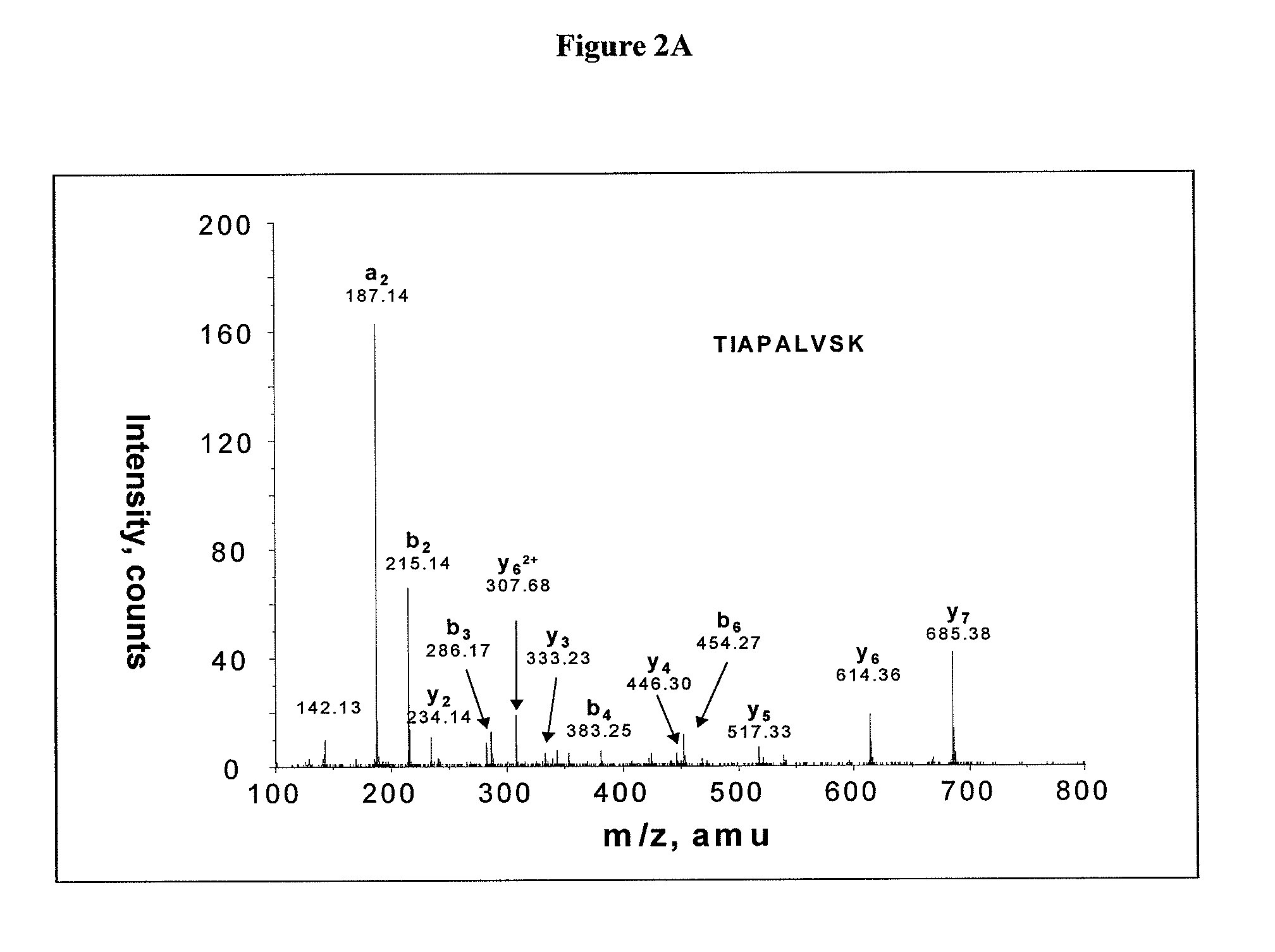
Salivary protein diagnosis model for gastric cancer and establishment method for salivary protein diagnosis model
InactiveCN104007169AEasy to buildEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBatch processingSaliva sample
The invention discloses a salivary protein diagnosis model for gastric cancer and an establishment method for the salivary protein diagnosis model. The establishment method for the salivary protein diagnosis model for gastric cancer comprises the following steps of collecting and processing a saliva sample; processing the saliva sample by adopting WCX magnetic balls; performing sample application and mass spectrometry; and performing data statistical analysis. The salivary protein diagnosis model for gastric cancer mainly comprises four salivary protein peaks, and mass-to-charge (m / z) ratios of the salivary protein peaks in human salivary proteins are 1,472.78Da, 2,936.49Da, 6,556.81Da and 7,081.17Da respectively. According to the salivary protein diagnosis model for gastric cancer and the establishment method for the salivary protein diagnosis model, by a classification prediction model established by the four protein peaks of which the mass-to-charge ratios (m / z) in the human salivary proteins are 1,472.78Da, 2,936.49Da, 6,556.81Da and 7,081.17Da respectively, the m / z of the corresponding proteins in human saliva and the model are analyzed to preliminarily judge gastric cancer, the identification rate is 97.83 percent, and the predication capability is 79.82 percent. Clinical back substitution test results show that the accuracy rate of the diagnosis model is 97.56 percent, the sensitivity of the diagnosis model is 95.65 percent and the specificity of the diagnosis model is 100 percent. The establishment method is simple, and has the characteristics of reasonability, feasibility, convenience in operation and batch processing capability.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Detection of saliva proteins modulated secondary to ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast
InactiveUS20100279419A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansDisease diagnosisFibroadenomaSalivary Proteins
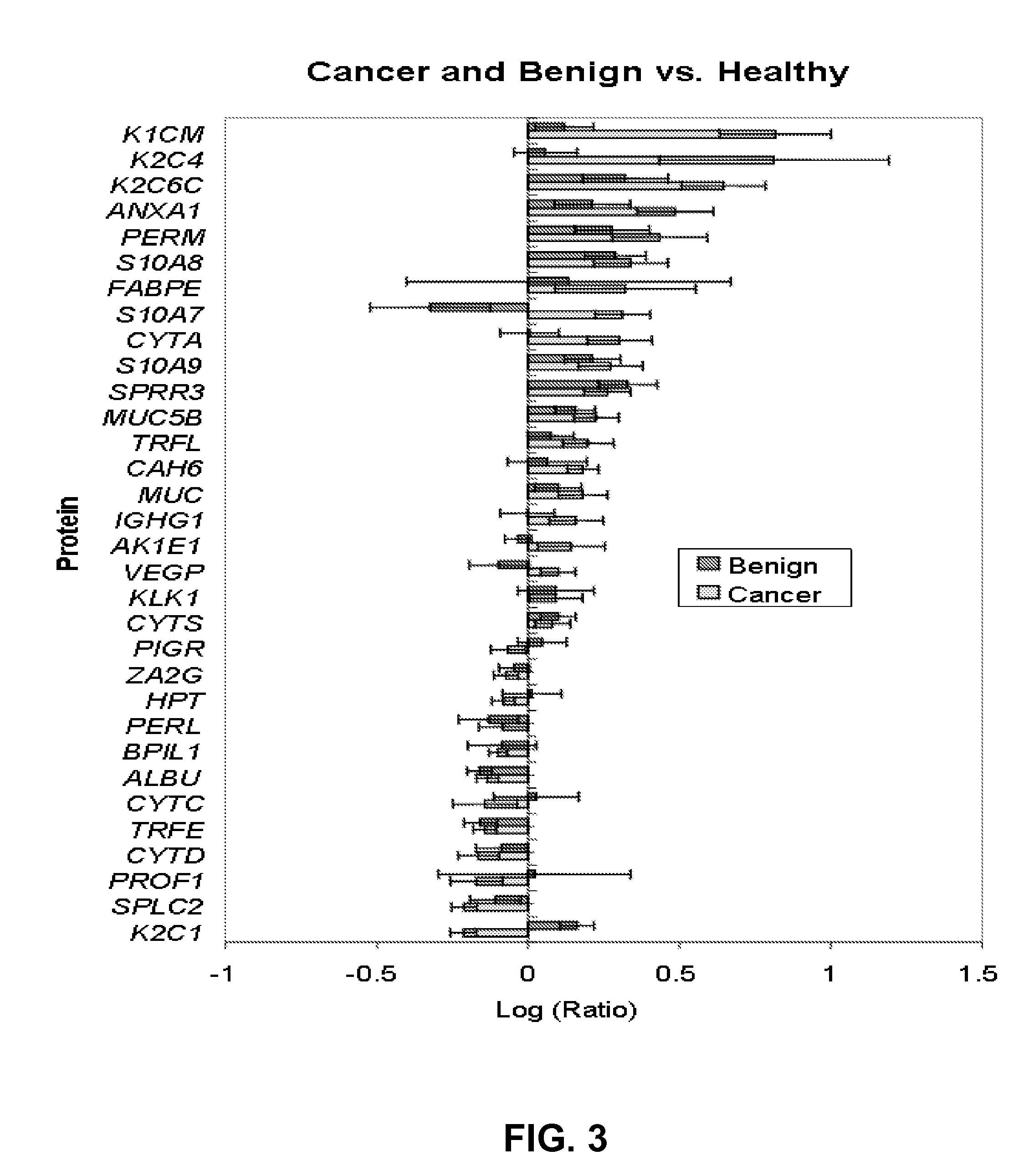
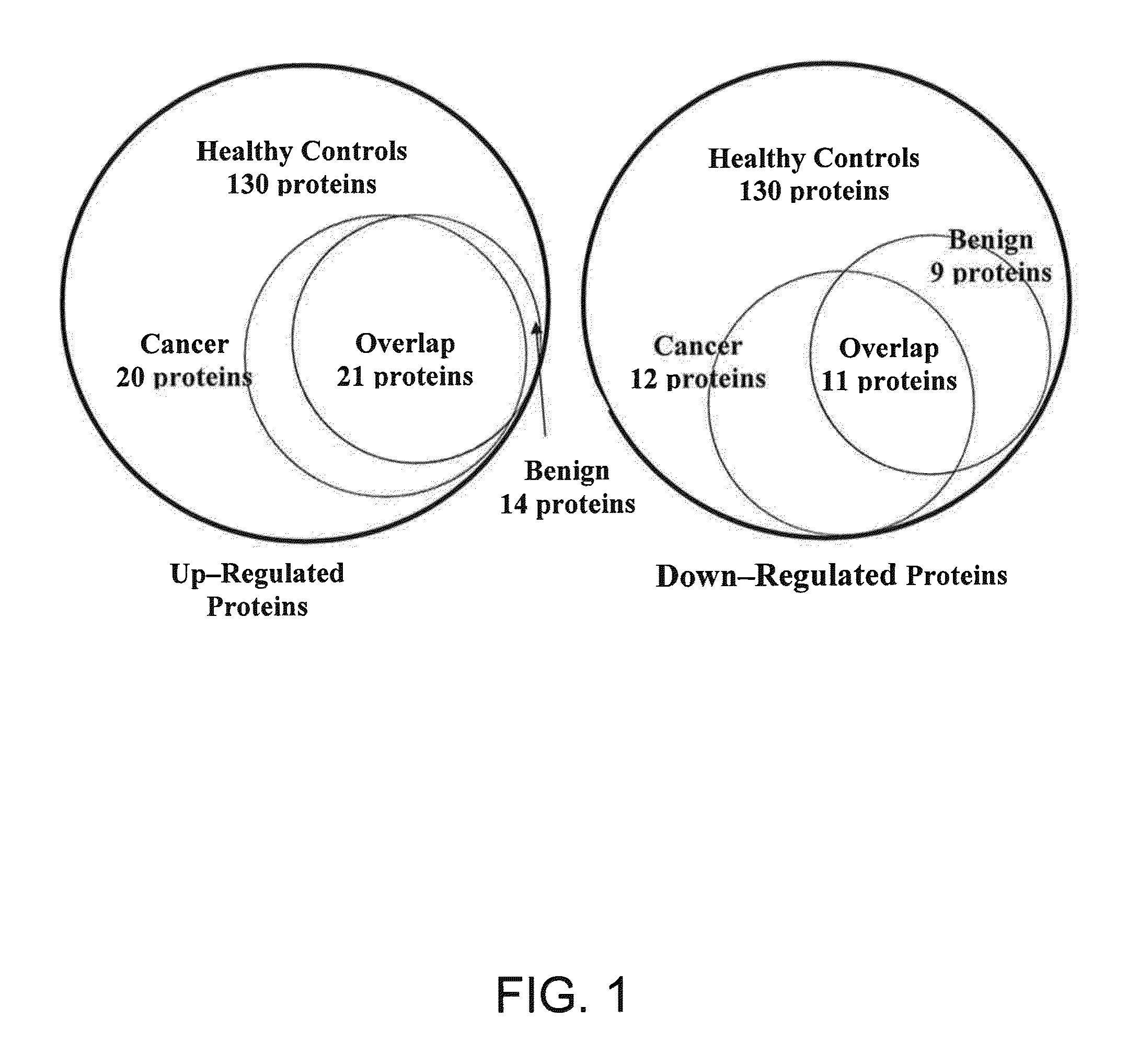
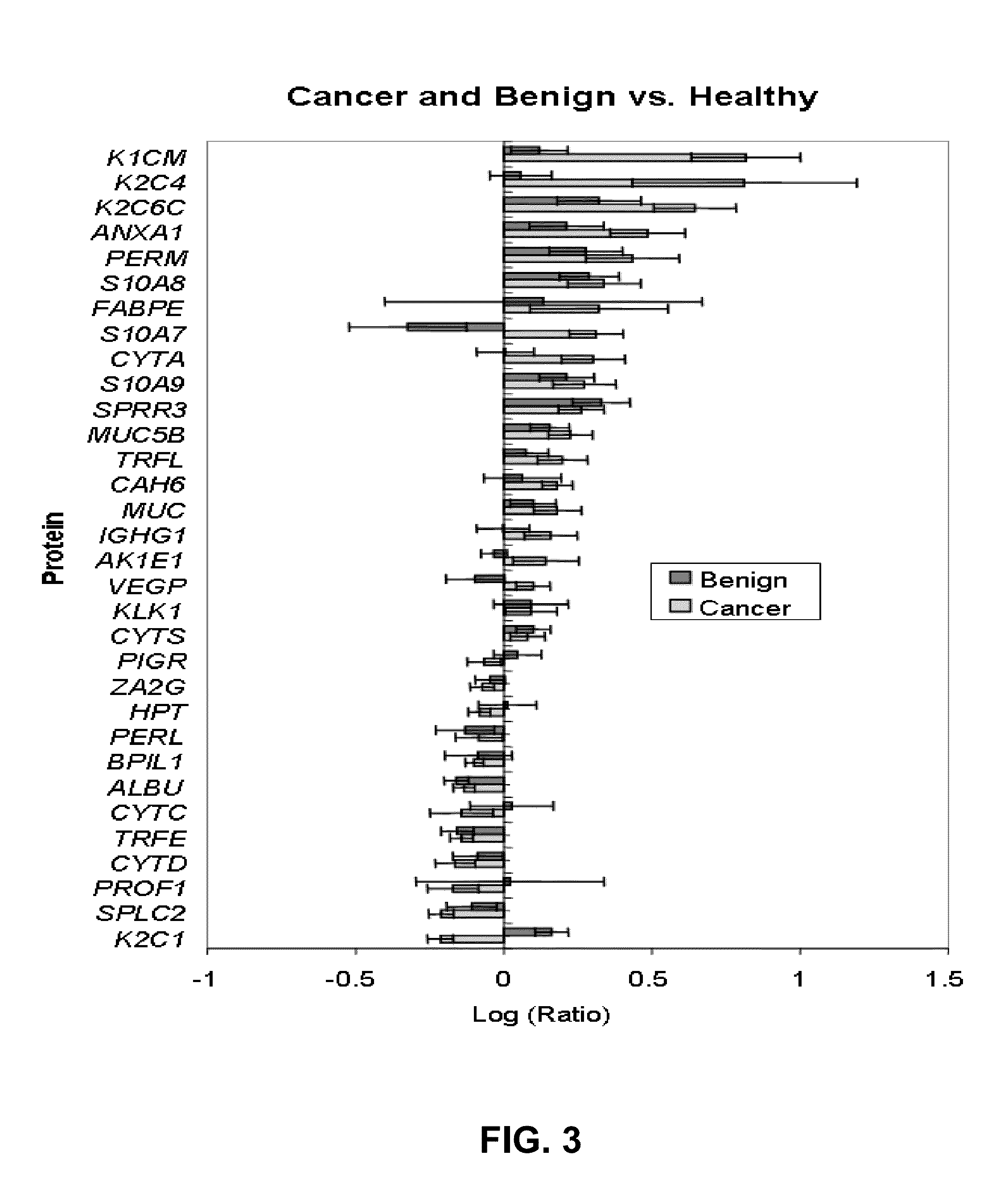
A method of differentiating among the presence of ductal carcinoma in situ in the breast, benign fibroadenoma of the breast, and non-cancerous breast tissue in a subject is disclosed. The method comprises: measuring the concentration of at least one protein biomarker selected from a group of forty-nine differentially expressed proteins in the saliva of persons with DCIS, or benign fibroadenoma, or in persons who are cancer-free. The resulting test data is compared to a reference panel. From the comparison the presence in the subject of either ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast, or benign fibroadenoma of the breast is determined.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
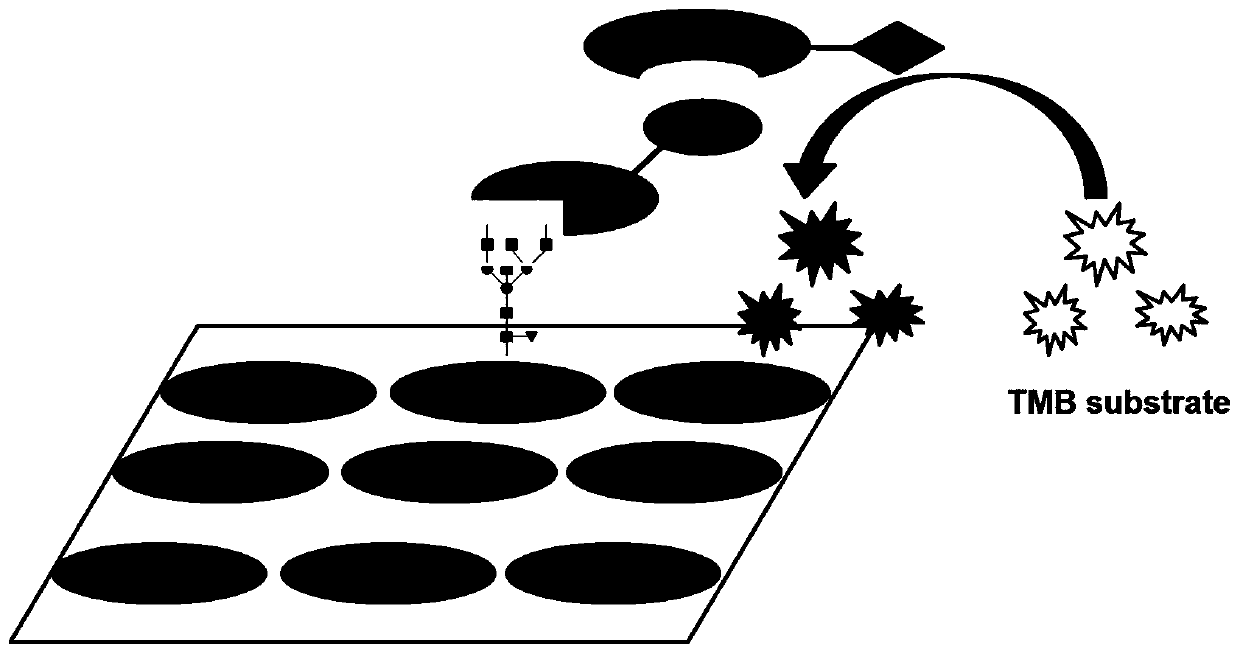
Lectin chip for detecting carbohydrate chain markers based on blood serum and commonly based on protein in blood serum and saliva as well as kit and application of lectin chip
InactiveCN105675893ARapid determination of specific bindingBiological testingSaliva sampleSalivary Proteins
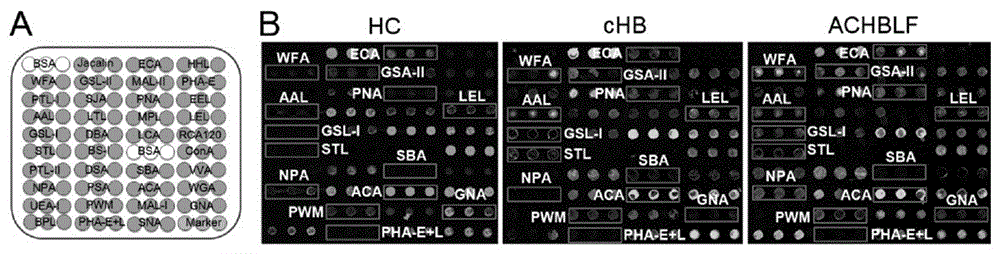
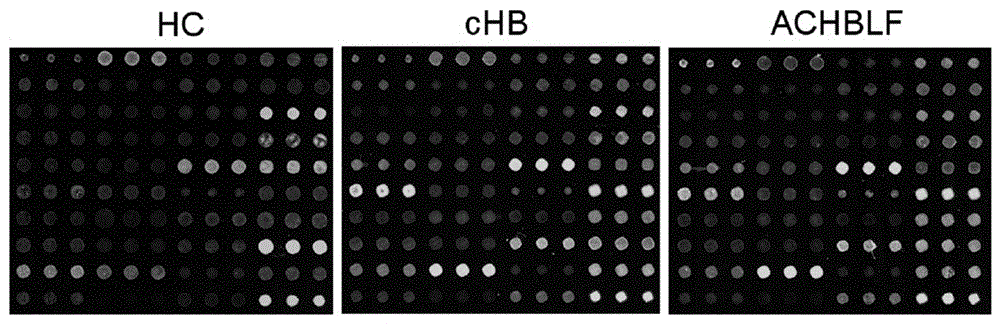
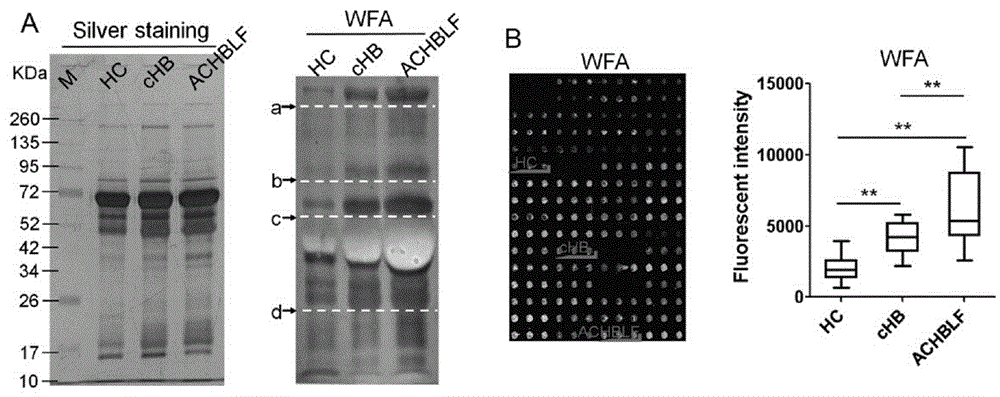
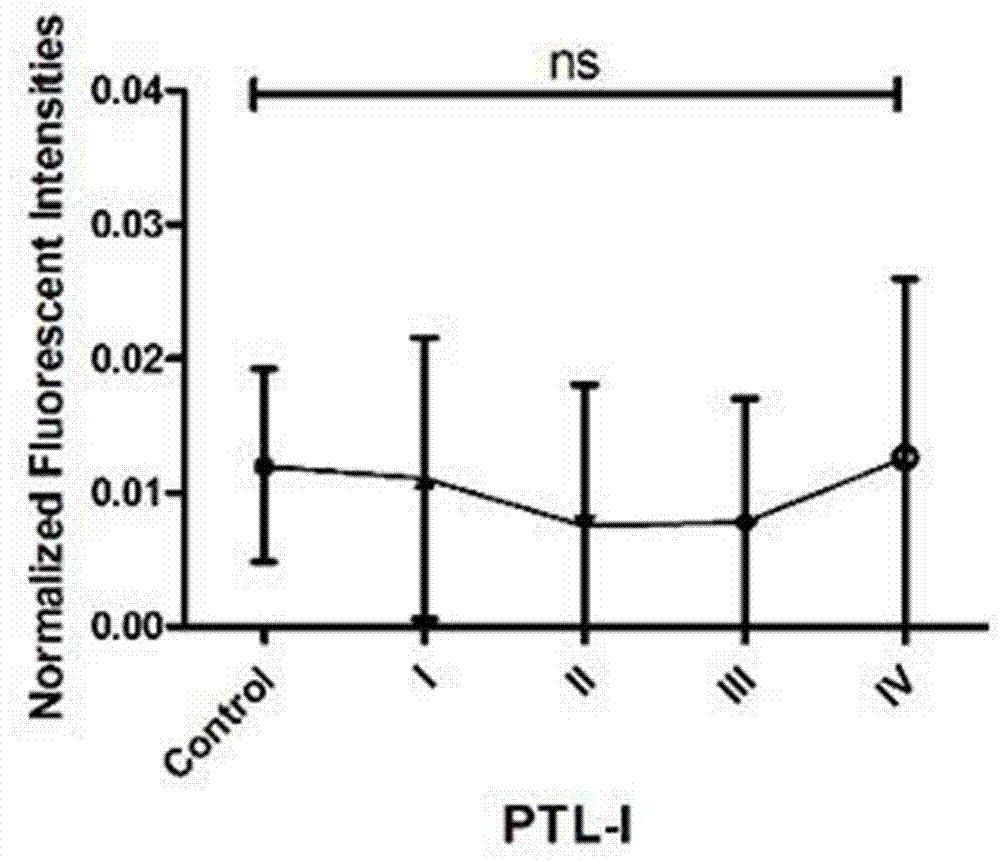
The invention provides a lectin chip for detecting carbohydrate chain markers based on protein in blood serum or saliva as well as a kit and application of the lectin chip, relates to the lectin chip for detecting the carbohydrate chain markers in blood serum or saliva, and particularly relates to the lectin chip for detecting the carbohydrate chain markers based on protein in blood serum and saliva as well as a kit and application of the lectin chip. The invention aims at providing a non-injury lectin chip for detecting the carbohydrate chain markers by identifying protein in saliva or blood serum and a method thereof. The lectin chip for detecting the carbohydrate chain markers based on serum carbohydrate binding protein, provided by the invention, comprises a testing lectin probe set, wherein the testing lectin probe set at least comprises PTL-I, PNA, AAL, LTL, STL, BS-I, PTL-II, SBA, ACA, UEA-I, MAL-I and PHA-E+L. The lectin chip can be used for rapidly detecting a specific carbohydrate protein chain structure in blood serum and saliva samples, and rapidly judging the specific combination of carbohydrate chains in the samples, so as to determine whether corresponding people have hepatitis or not and determine whether people are ACHBLF patients or not.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
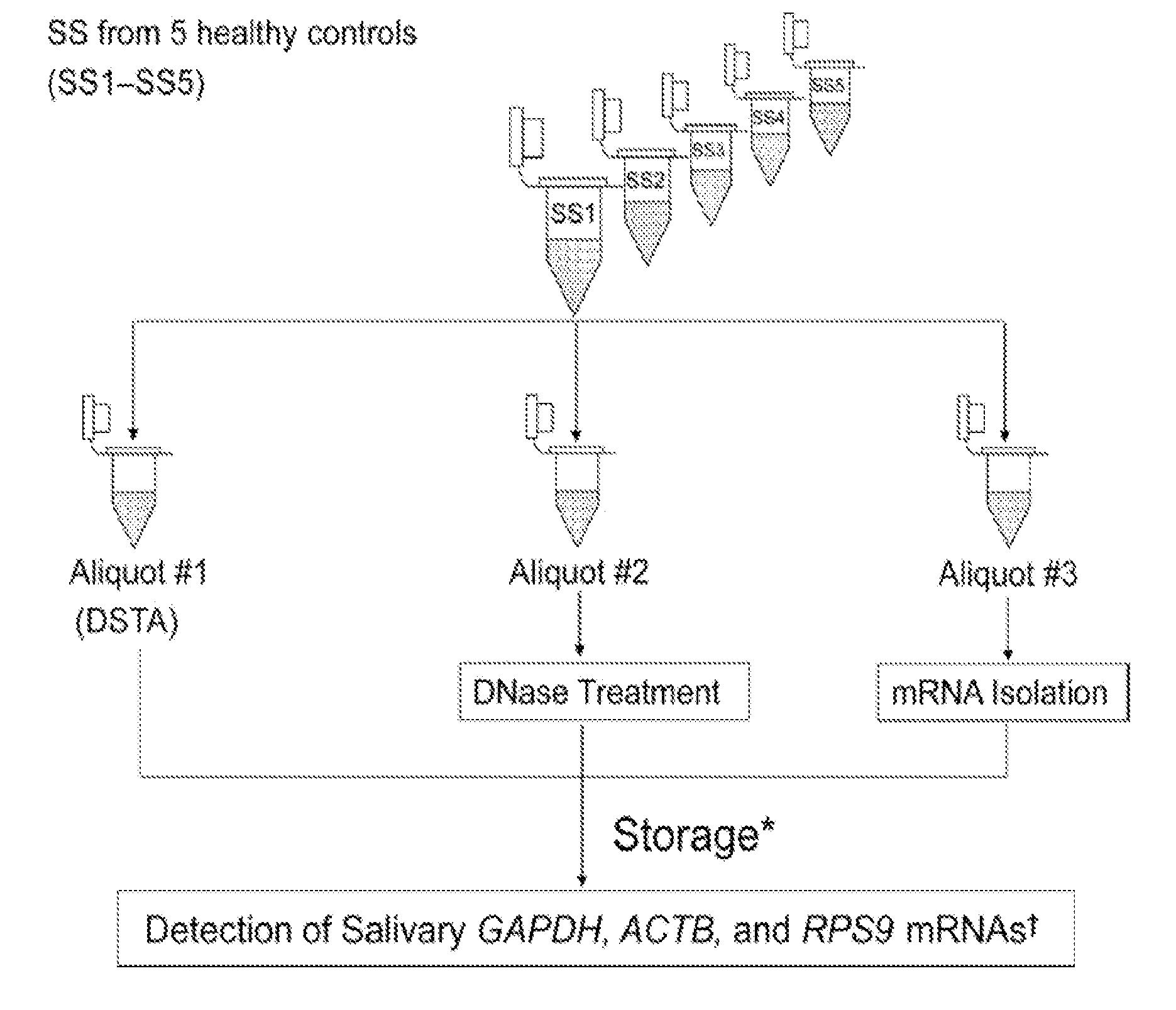
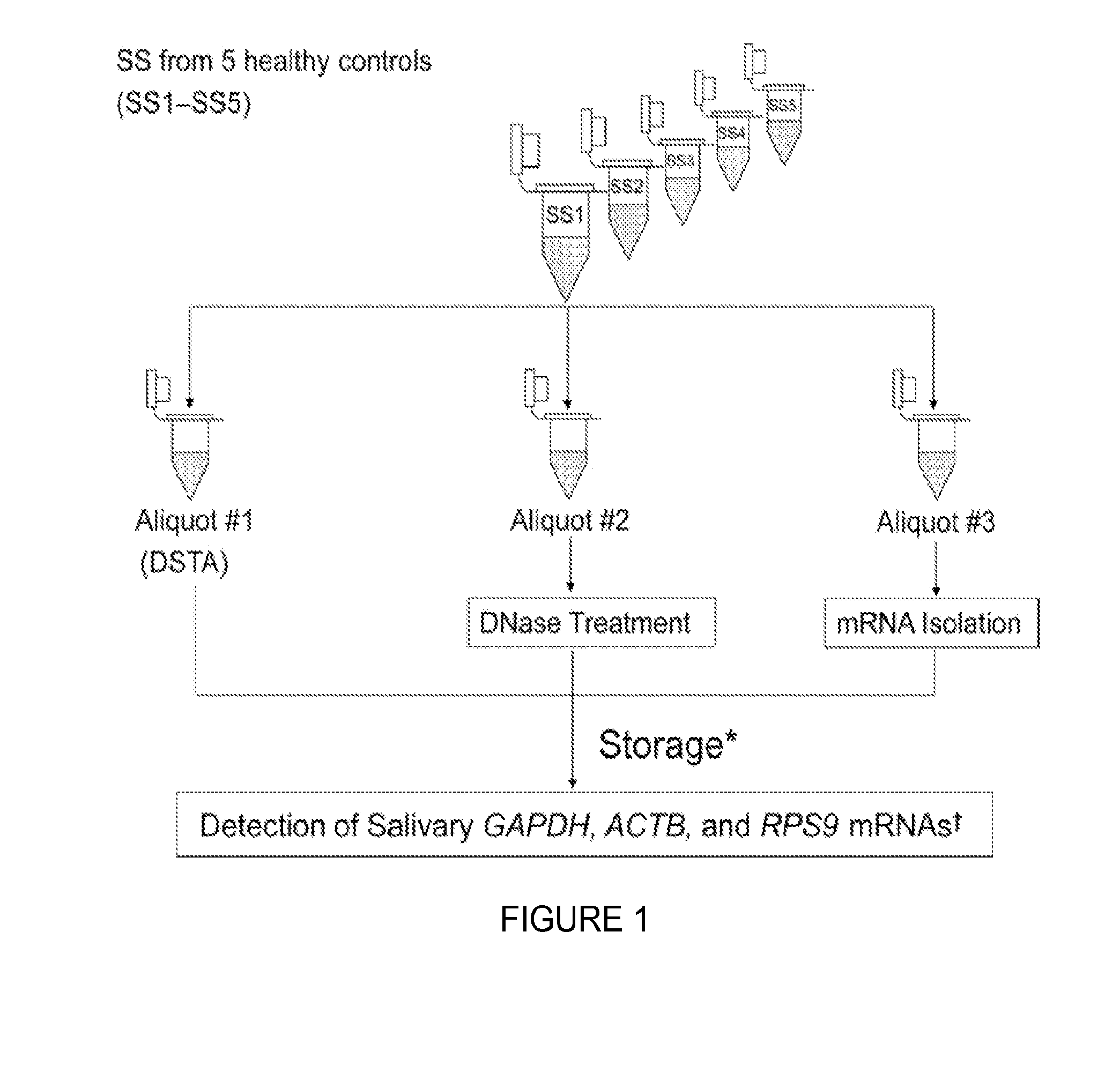
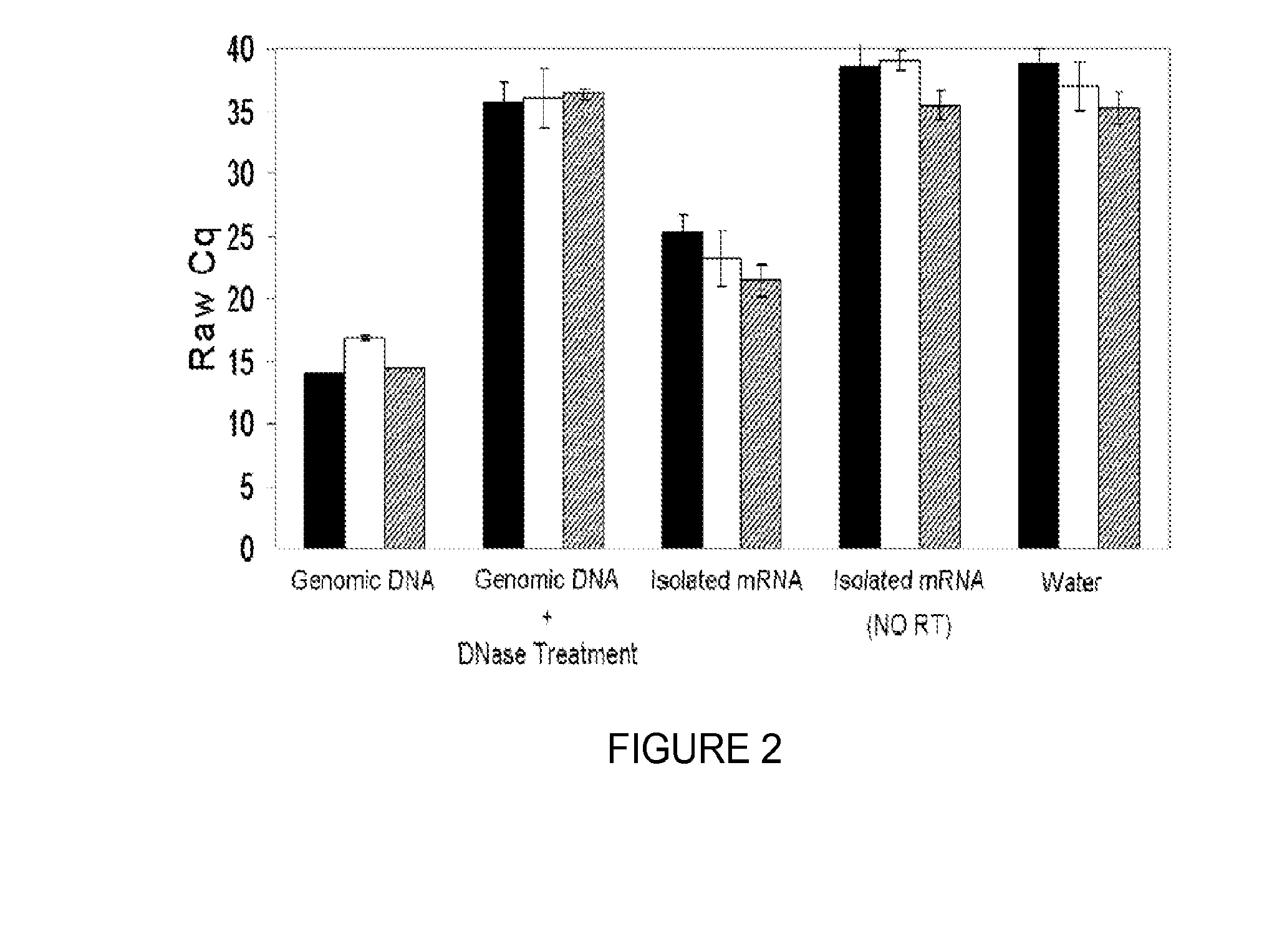
Saliva collection, processing, stabilization, and storage method
ActiveUS20140329705A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationSaliva sampleCell free
Provided herein is an all-in-one saliva collection apparatus that collects saliva to allow for the filtration of saliva in order to separate saliva components, such as extracellular proteins and nucleic acids that are not present in intact cells, from the intact cells and debris remaining in the extracted sample. The filtered saliva samples can be aliquoted into two fractions for protein and / or nucleic acid analysis. The present invention further describes long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary nucleic acids, and long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary proteins added to an ethanol solution. The filtered cell-free saliva samples have diagnostic usefulness.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
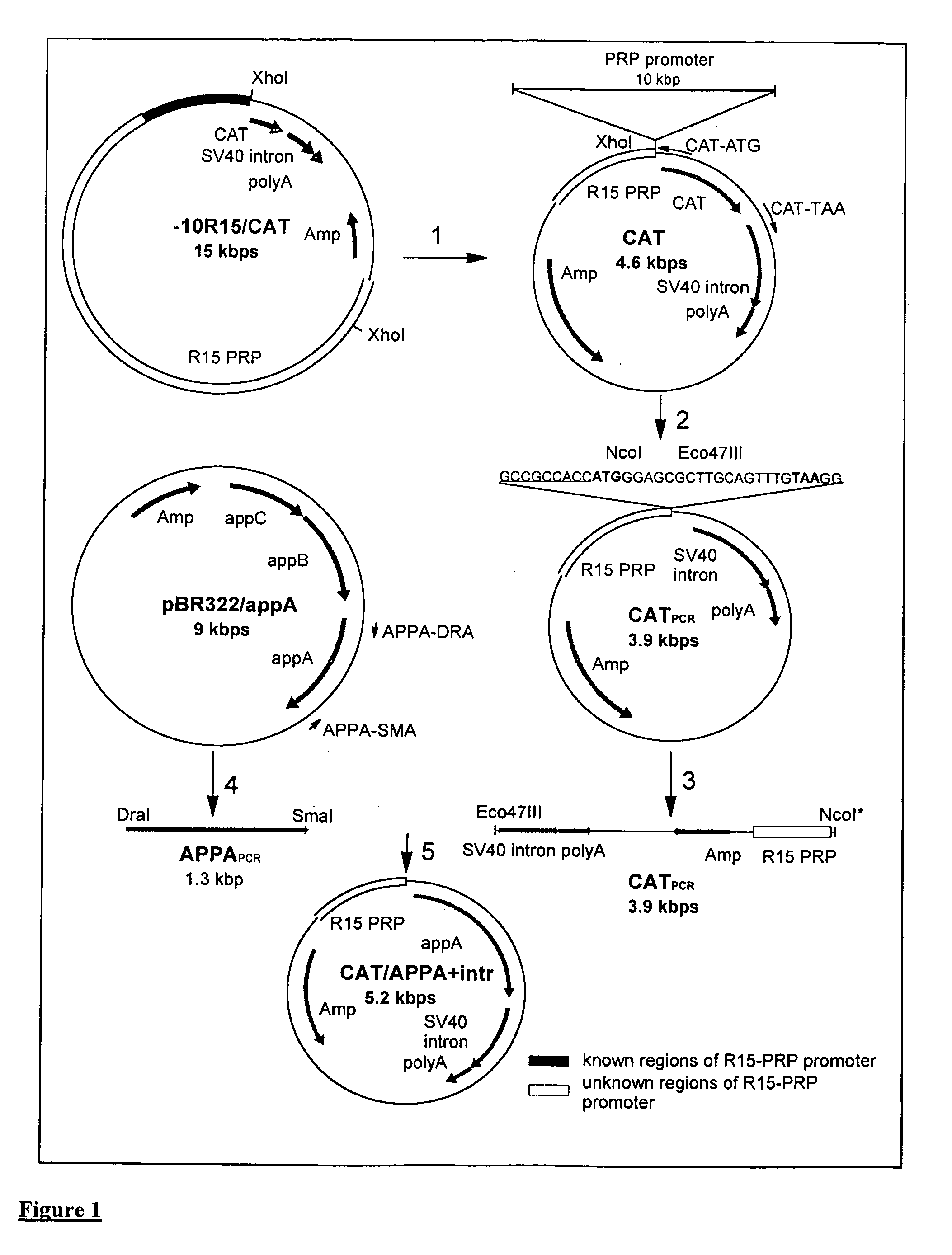
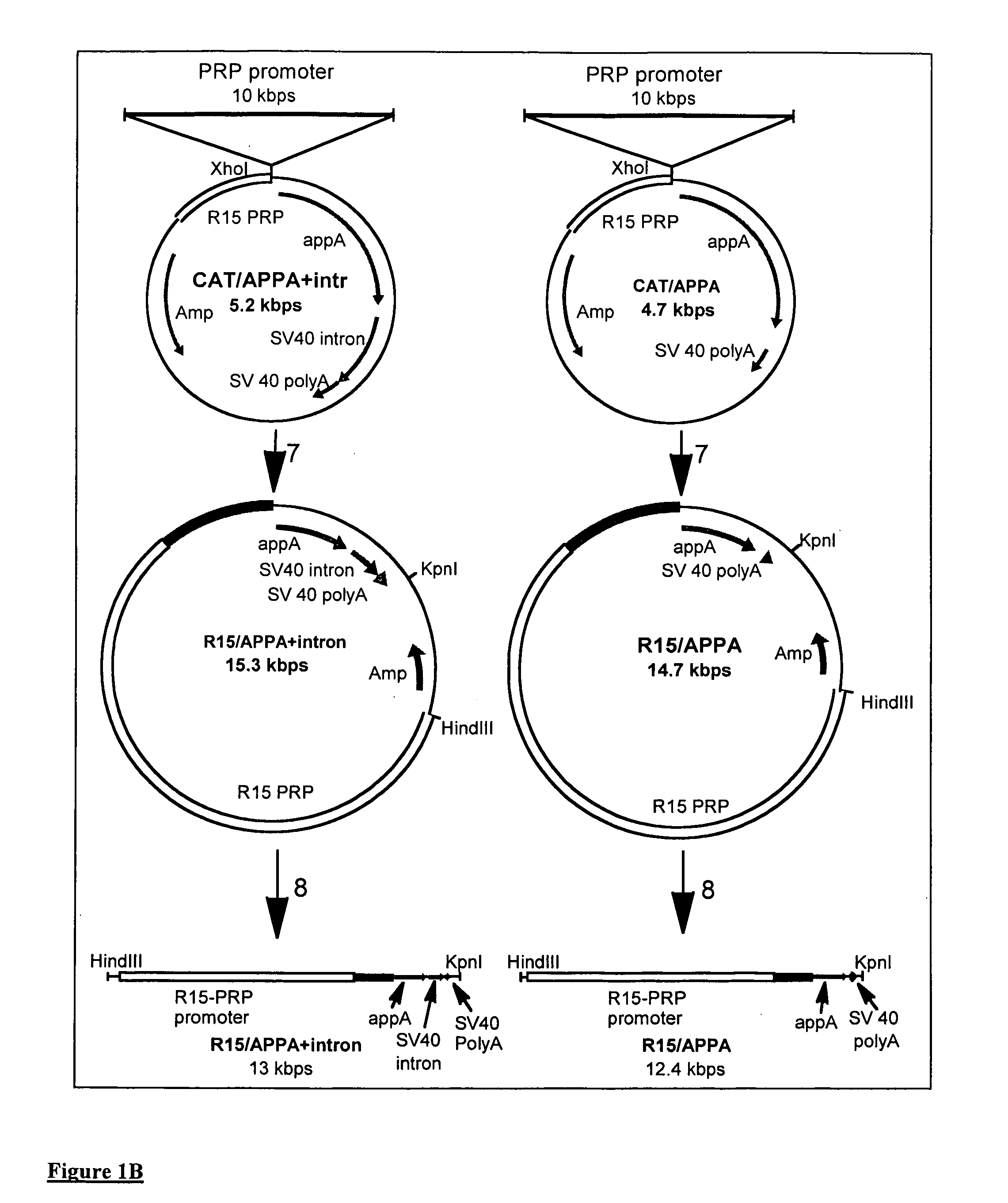
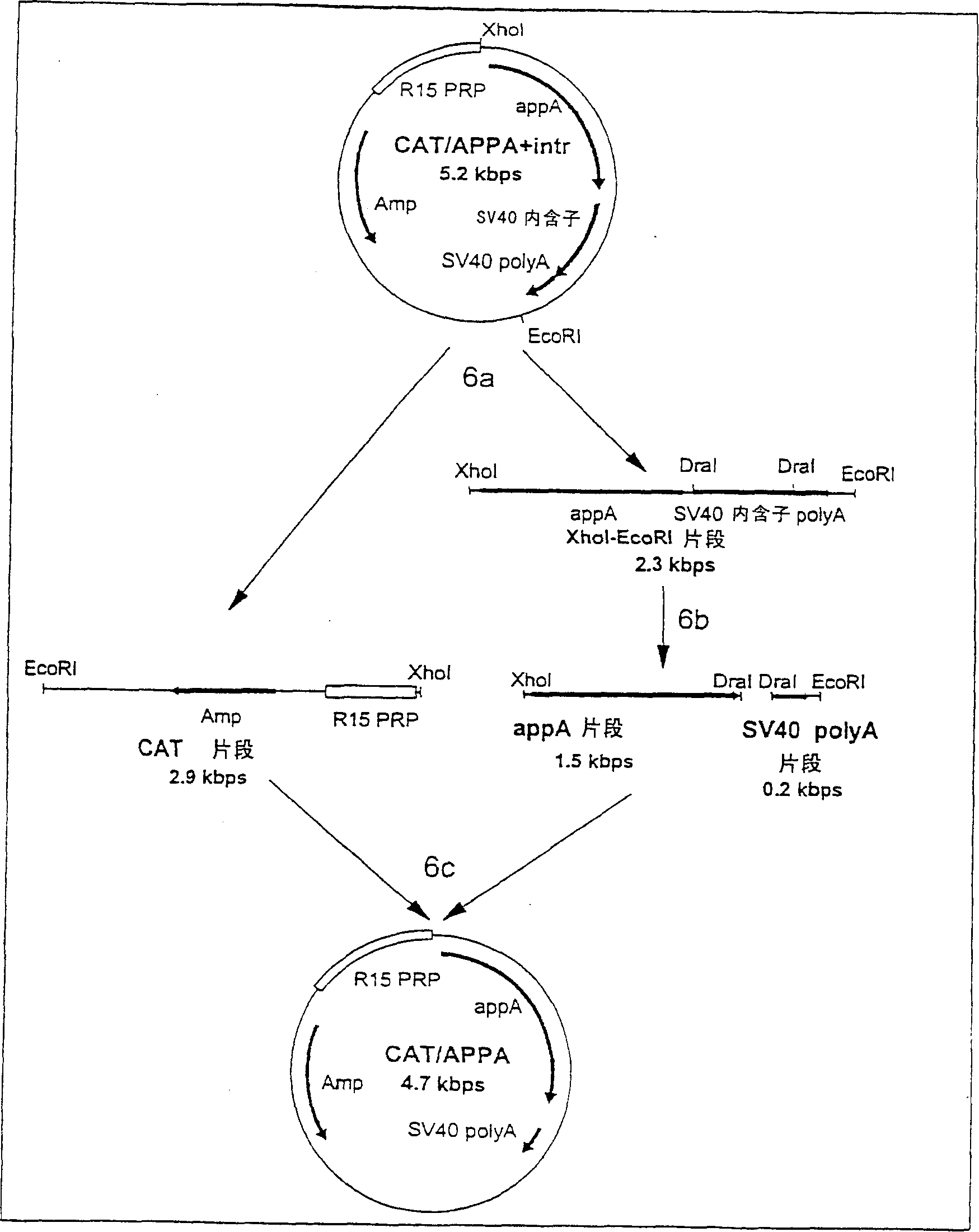
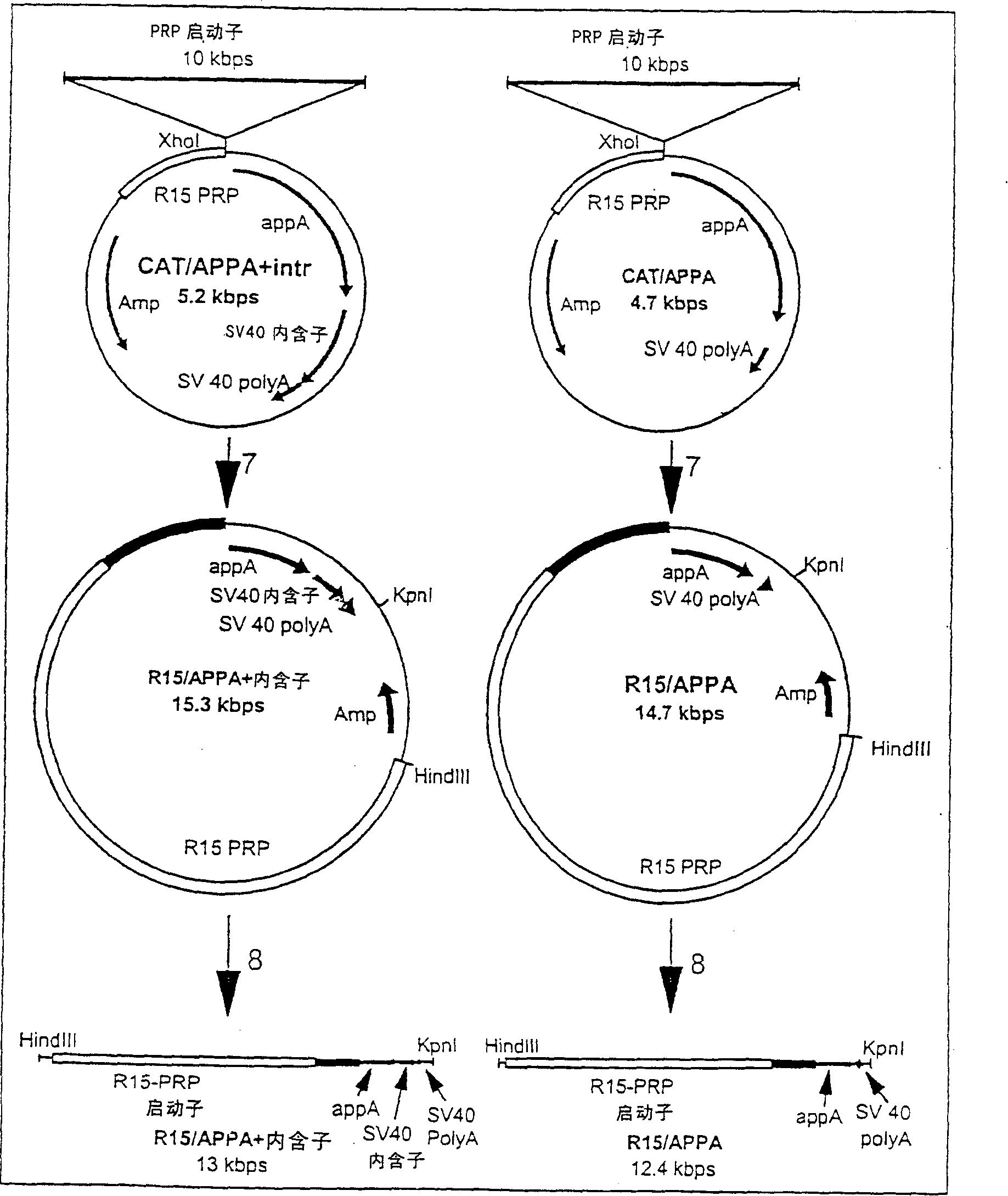
Transgenic animals expressing salivary proteins
The invention provides a transgenic animal having within its genome a transgene construct for gastrointestinal tract specific expression of a protein. In a preferred embodiment, the protein is a phytase or a homologue thereof. Such proteins may be heterologous and may be specifically expressed in the salivary gland of the animal by operably linking the nucleic acid sequence encoding the protein with regulatory sequence including a salivary gland protein promoter / enhancer. Also provided are methods of expressing and producing proteins using such nucleic acid constructs. Further, antibodies specific to such proteins and immunological diagnostic kits are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
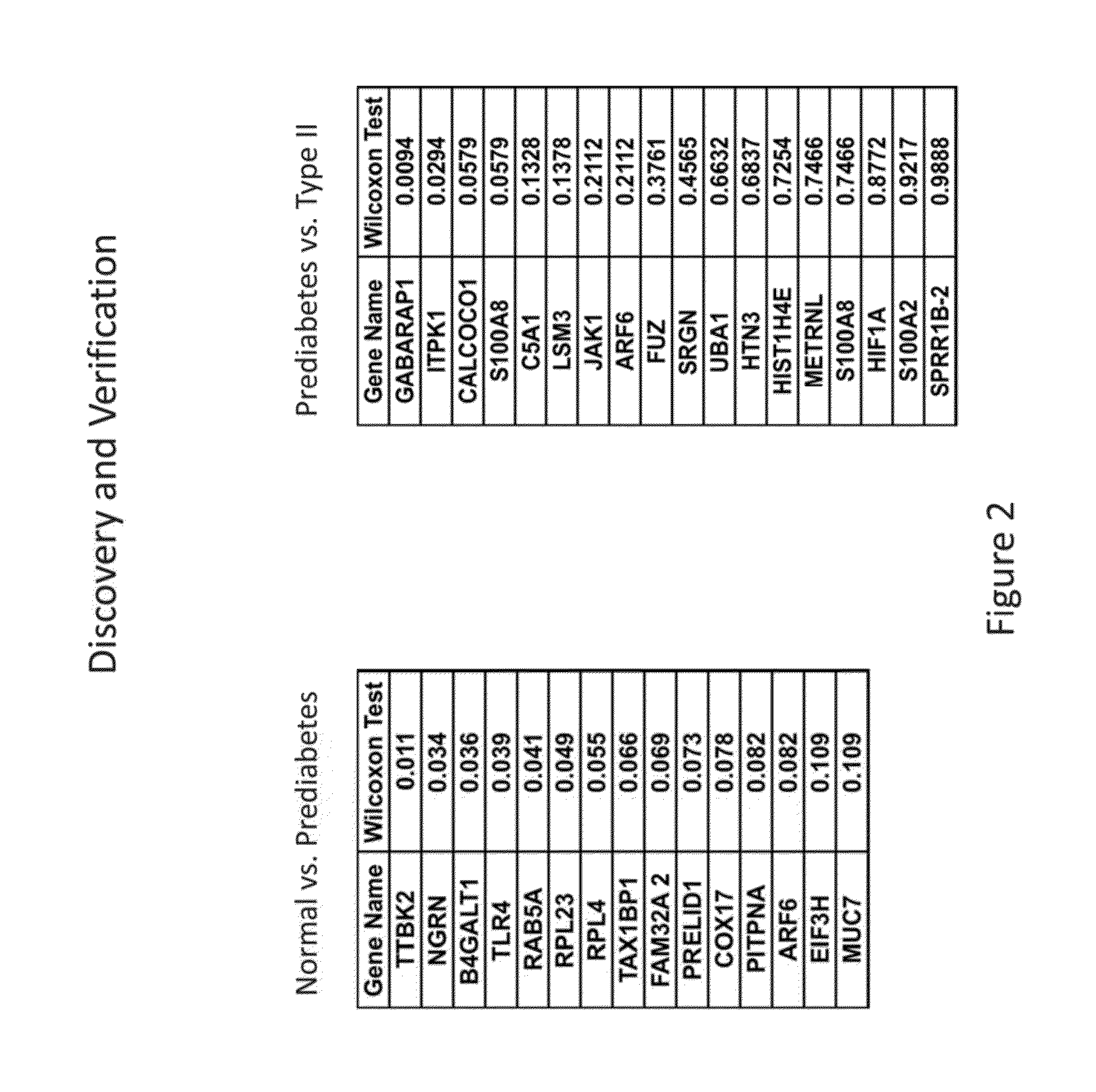
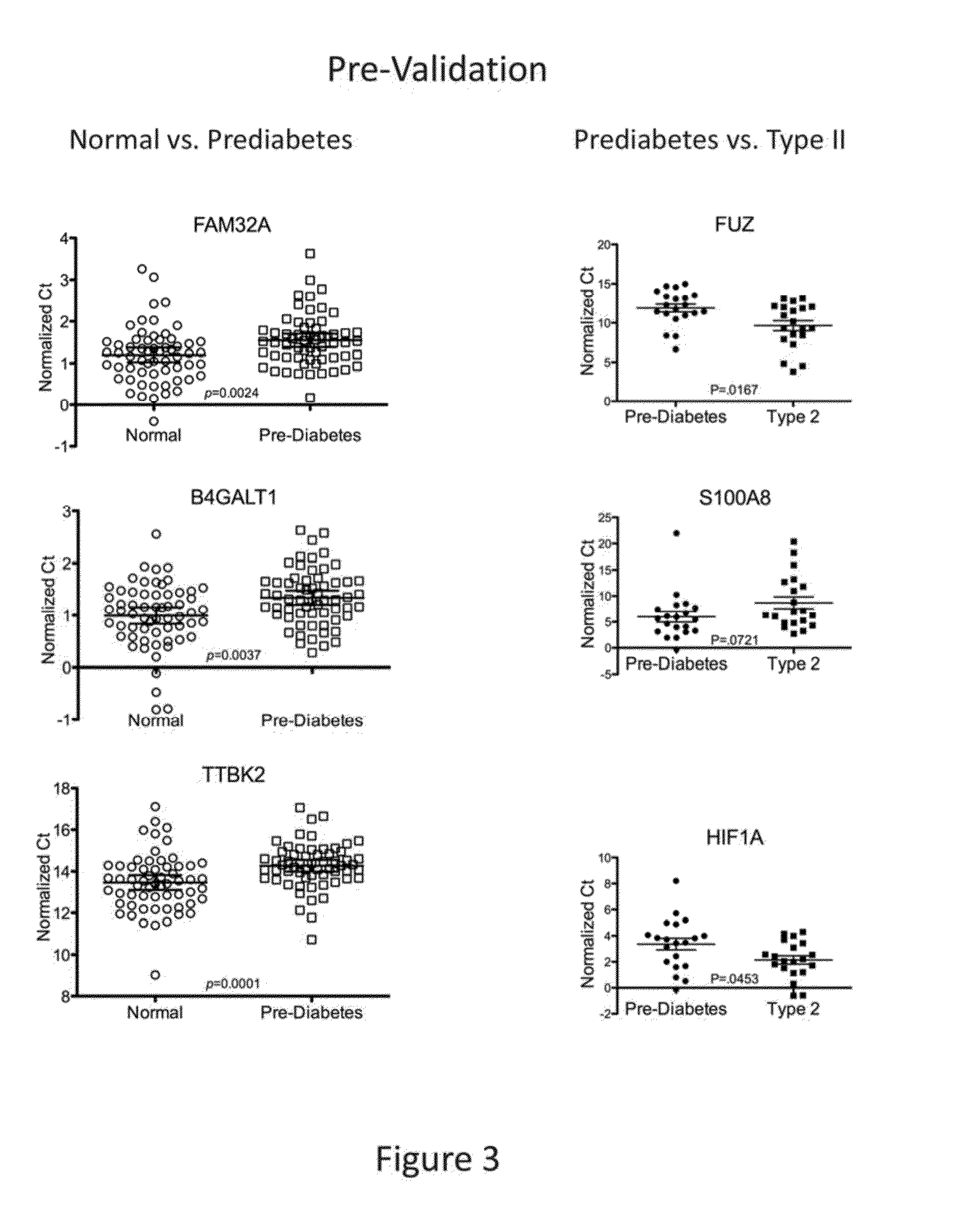
Salivary biomarkers for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes
The present invention provides for the first time the identification of salivary protein and RNA factors that can be used in the detection of diabetes. The present invention therefore provides methods of diagnosing and providing a prognosis for diabetes, by examining relevant proteins and RNA in a patient's saliva.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
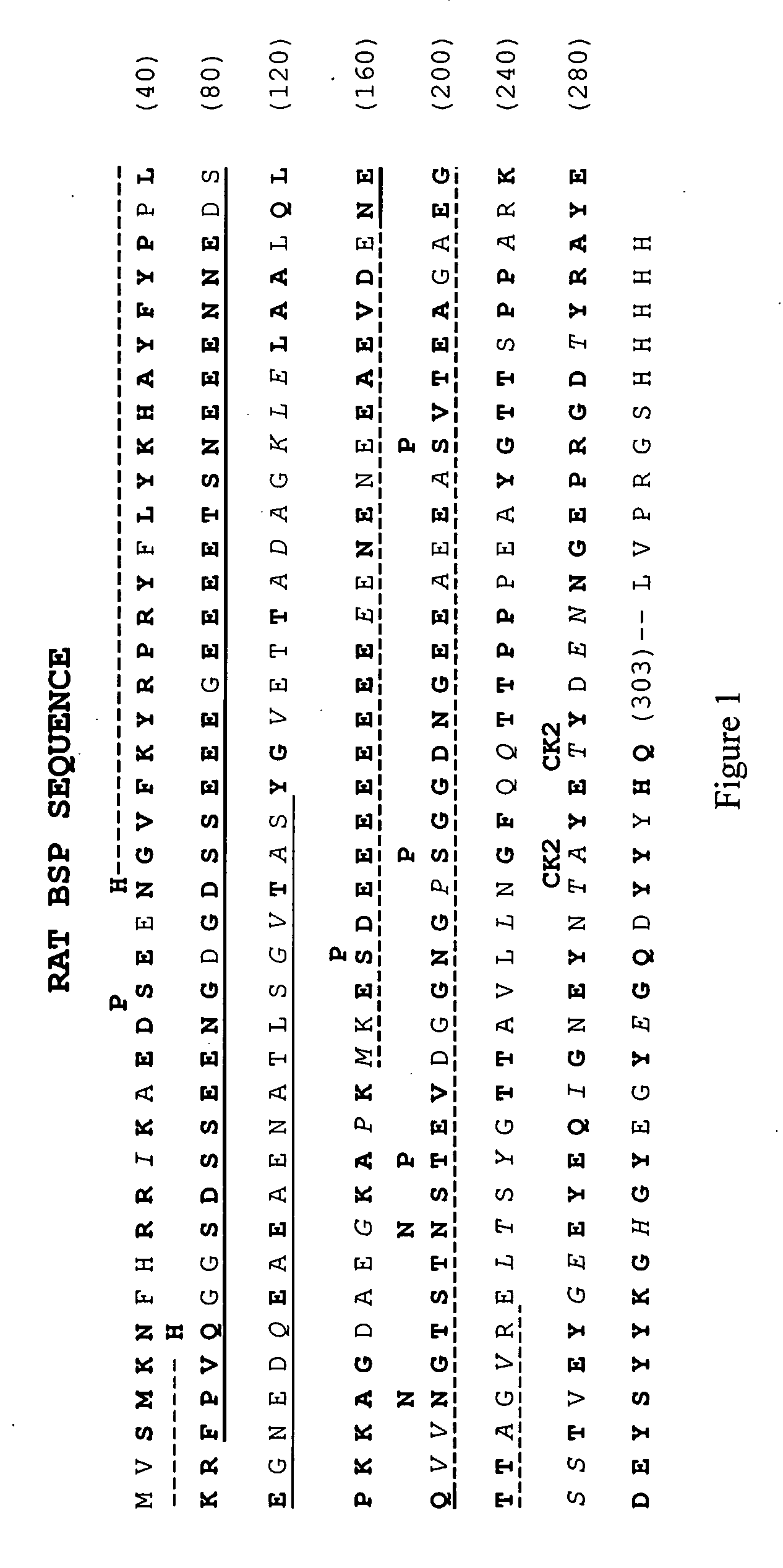
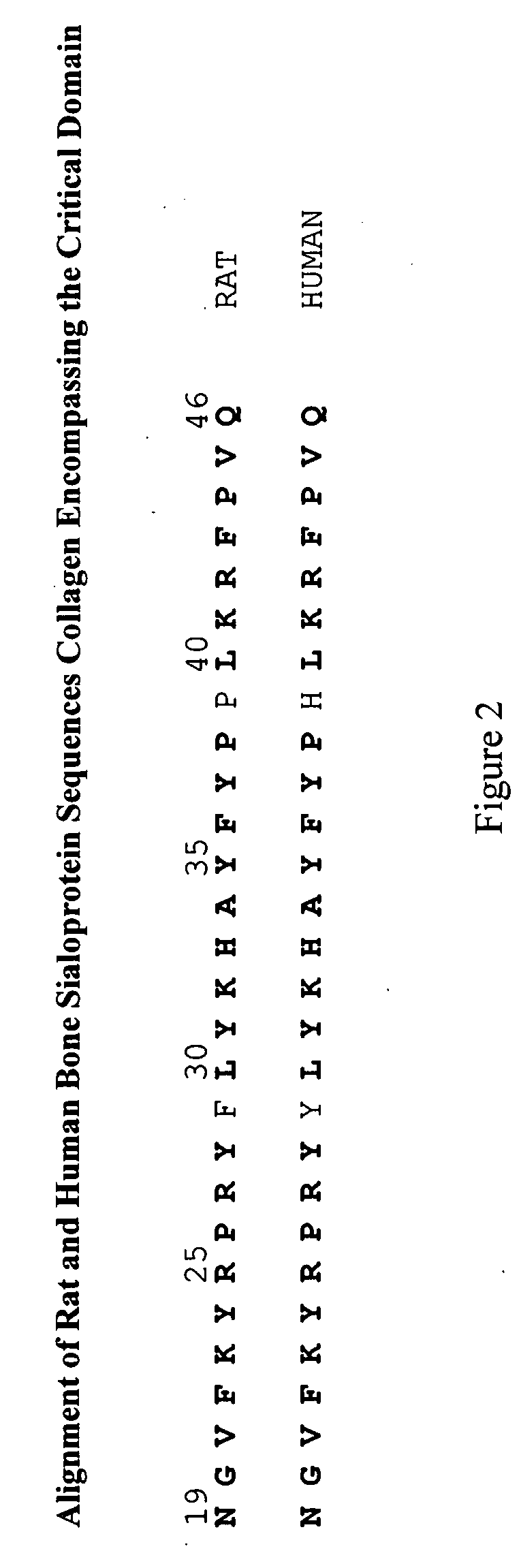
Bone Sialoprotein Collagen-Binding Peptides
InactiveUS20090005298A1Connective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsBone sialoproteinMedicine
The present invention provides Novel collagen-binding peptides of bone sialoprotein (BSP). Peptides comprising a portion of the N-terminal collagen binding domain of BSP (residues 1-100) are used to stimulate mineralization, nucleate hydroxyapatite, and promote bone formation in collagen expressing tissues. Medicaments for use in the same are also contemplated. Chimeric and conjugate peptides comprising said collagen-binding BSP peptides are also included.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Bionic anti-caries polypeptide based on casein-rich saliva, derivative, salt and application thereof
ActiveCN107353334ASimple manufacturing methodReduce manufacturing costPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemCalcium EDTAAmino acid
The invention discloses a bionic anti-caries functional polypeptide based on casein-rich saliva, a polypeptide derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt and an application in pharmacy thereof. The bionic anti-caries functional polypeptide is based on an anti-caries functional segment of the casein-rich saliva, the adjustment and improvement for the amino acid sequence are performed on the anti-caries functional segment and the bionic anti-caries functional polypeptide contains the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The polypeptide mainly utilizes the 'DpSpSEEK' amino acid sequence to realize the adsorption combination of polypeptide and de-mineralized enamel and the 'DpSpSEEK' amino acid sequence thereof can react with calcium phosphate ions so as to induce hydroxyapatite nucleation, so that the in-situ mineralizing repairing function for early enamel caries can be realized. The polypeptide is characterized by lower molecular weight, convenience in compound, low cost, better anti-caries effect, structure stability, safety and reliability. The invention utilizes the bionic thought to simulate natural saliva protein, designs the anti-caries polypeptide with a re-mineralization function and provides an ideal new method for preventing and controlling caries.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Saliva collection, processing, stabilization, and storage method
ActiveUS10023903B2Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationSaliva sampleCell free
Provided herein is an all-in-one saliva collection apparatus that collects saliva to allow for the filtration of saliva in order to separate saliva components, such as extracellular proteins and nucleic acids that are not present in intact cells, from the intact cells and debris remaining in the extracted sample. The filtered saliva samples can be aliquoted into two fractions for protein and / or nucleic acid analysis. The present invention further describes long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary nucleic acids, and long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary proteins added to an ethanol solution. The filtered cell-free saliva samples have diagnostic usefulness.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Transgenic animals expressing salivary proteins
The invention provides a transgenic animal having within its genome a transgene construct for gastrointestinal tract specific expression of a protein. In a preferred embodiment, the protein is a phytase or a homologue thereof. Such proteins may be heterologous and may be specifically expressed in the salivary gland of the animal by operably linking the nucleic acid sequence encoding the protein with regulatory sequence including a salivary gland protein promoter / enhancer. Also provided are methods of expressing and producing proteins using such nucleic acid constructs. Further, antibodies specific to such proteins and immunological diagnostic kits are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
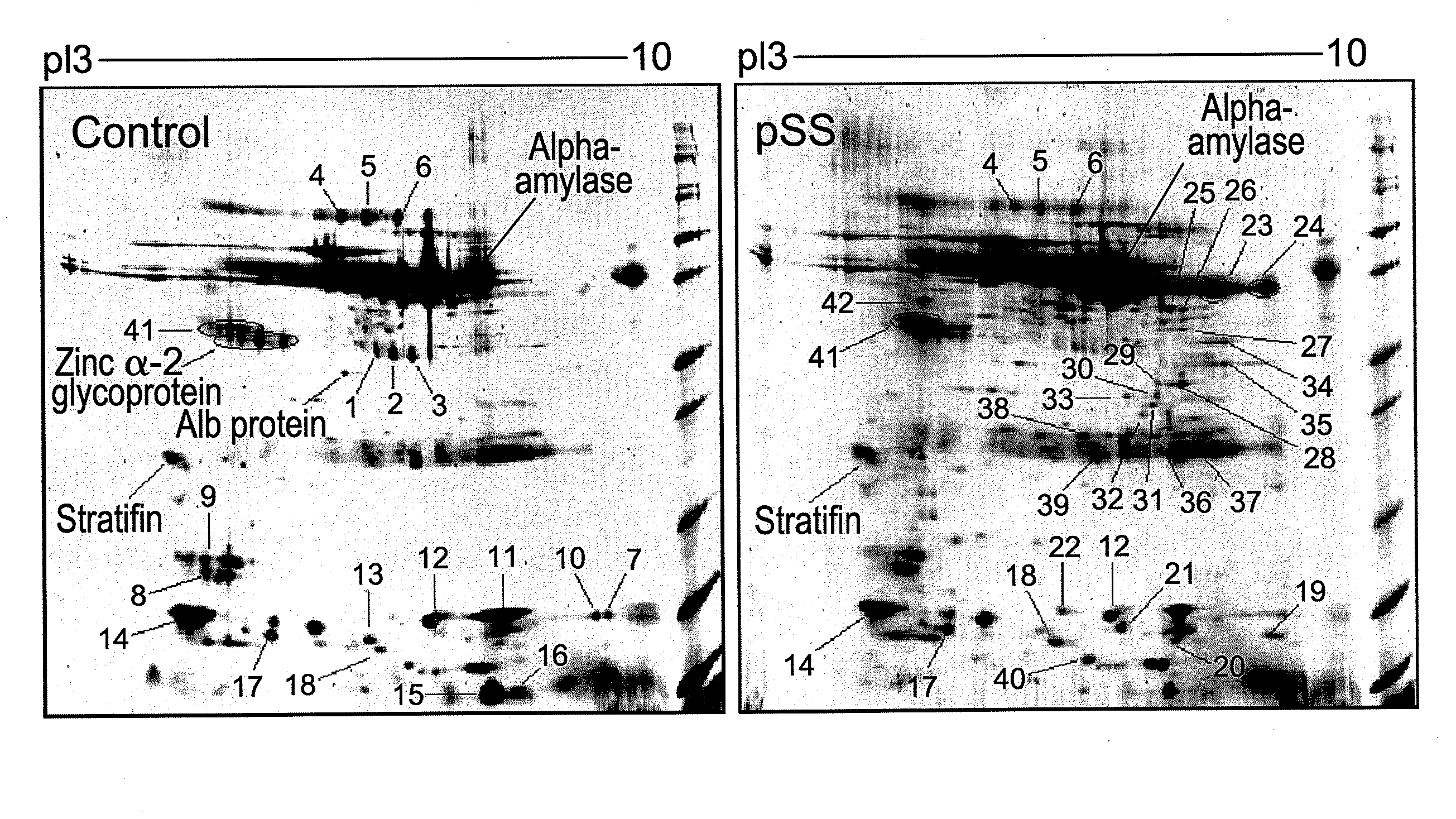
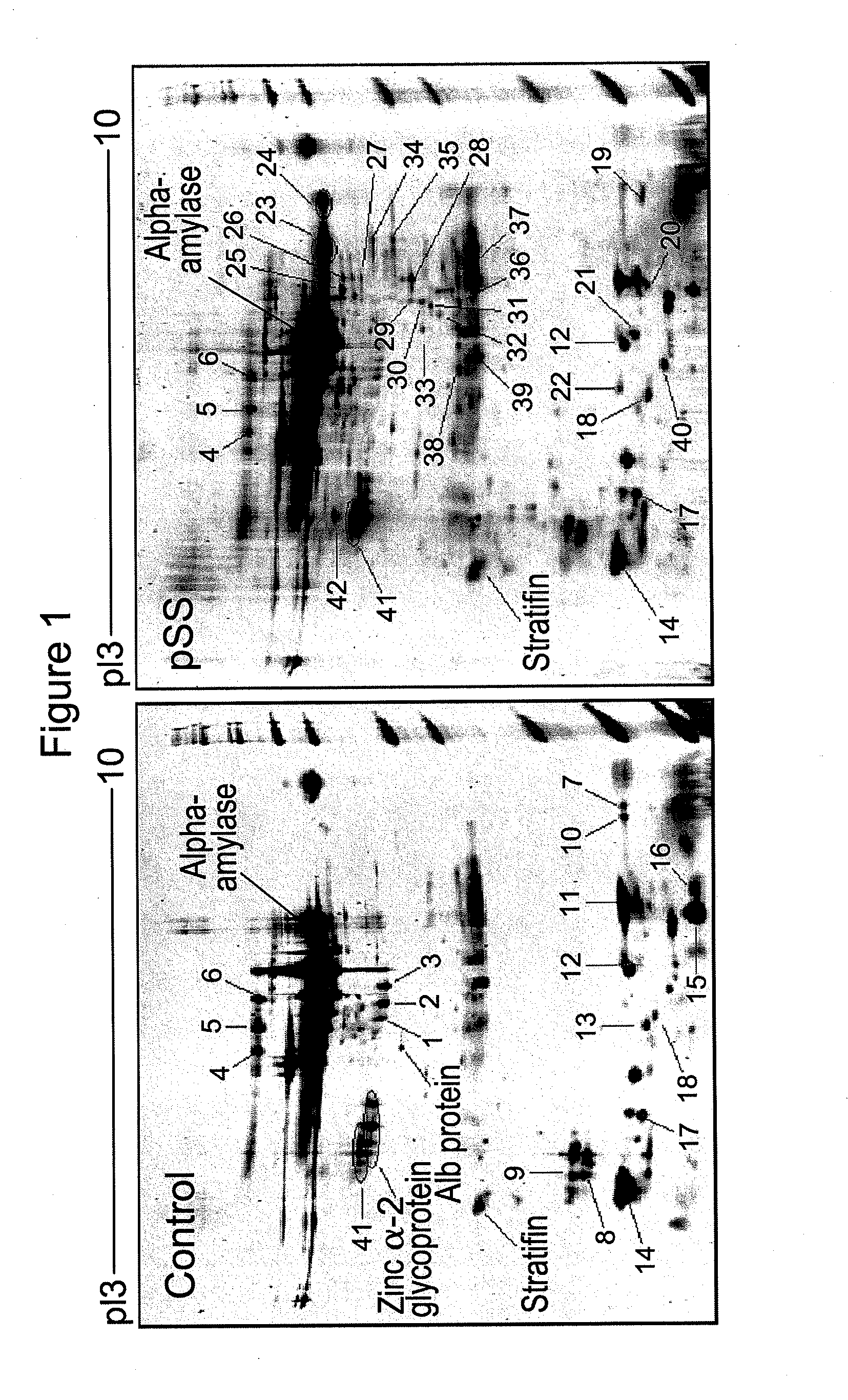
Salivary biomarkers for Sjögren's syndrome
The present invention provides for the first time the identification of salivary protein and RNA factors that can be used in the detection of primary Sjögren's Syndrome. The present invention therefore provides methods of diagnosing and providing a prognosis for Sjögren's Syndrome, by examining relevant proteins (including certain autoantigens and autoantibodies) and RNA in a patient's saliva.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
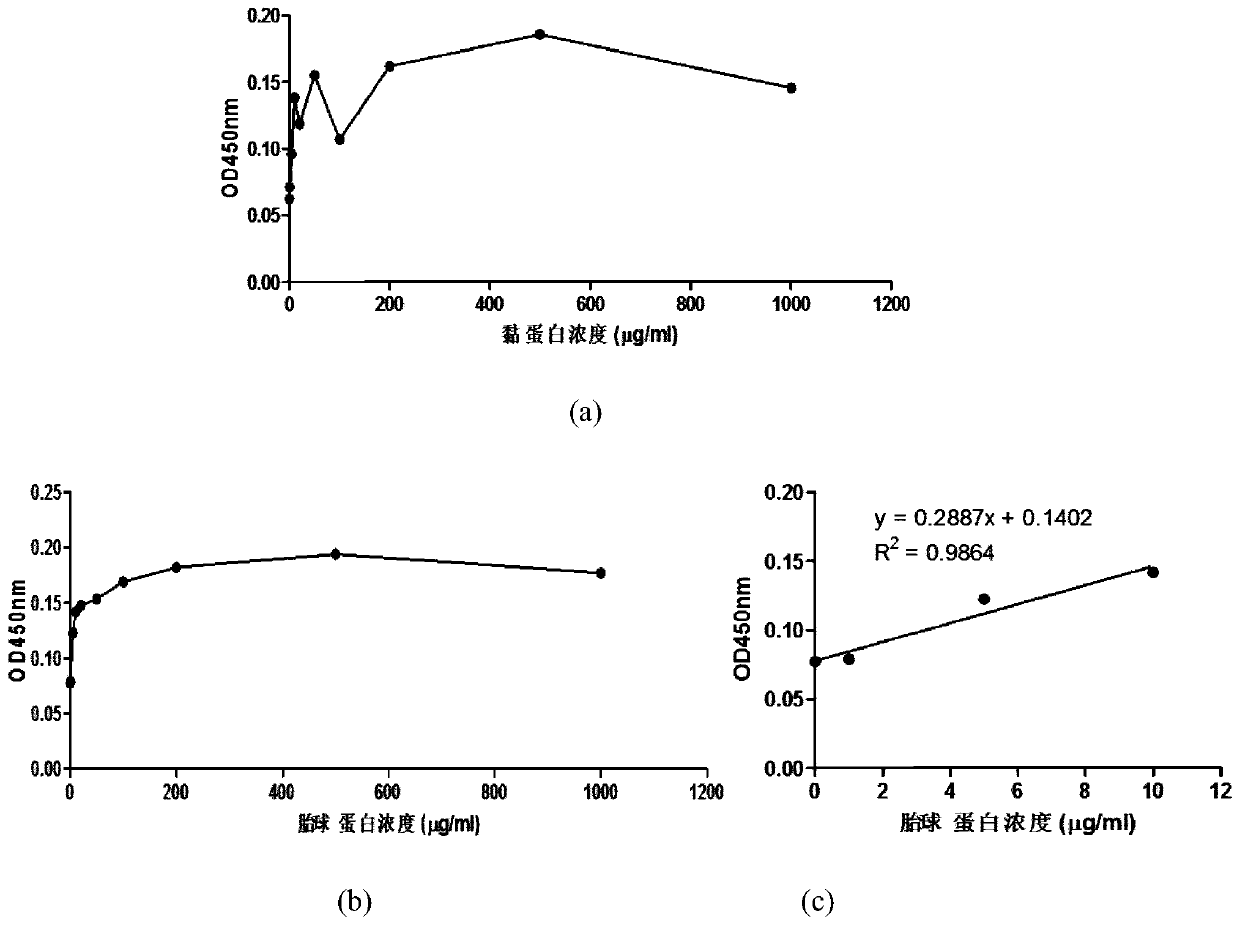
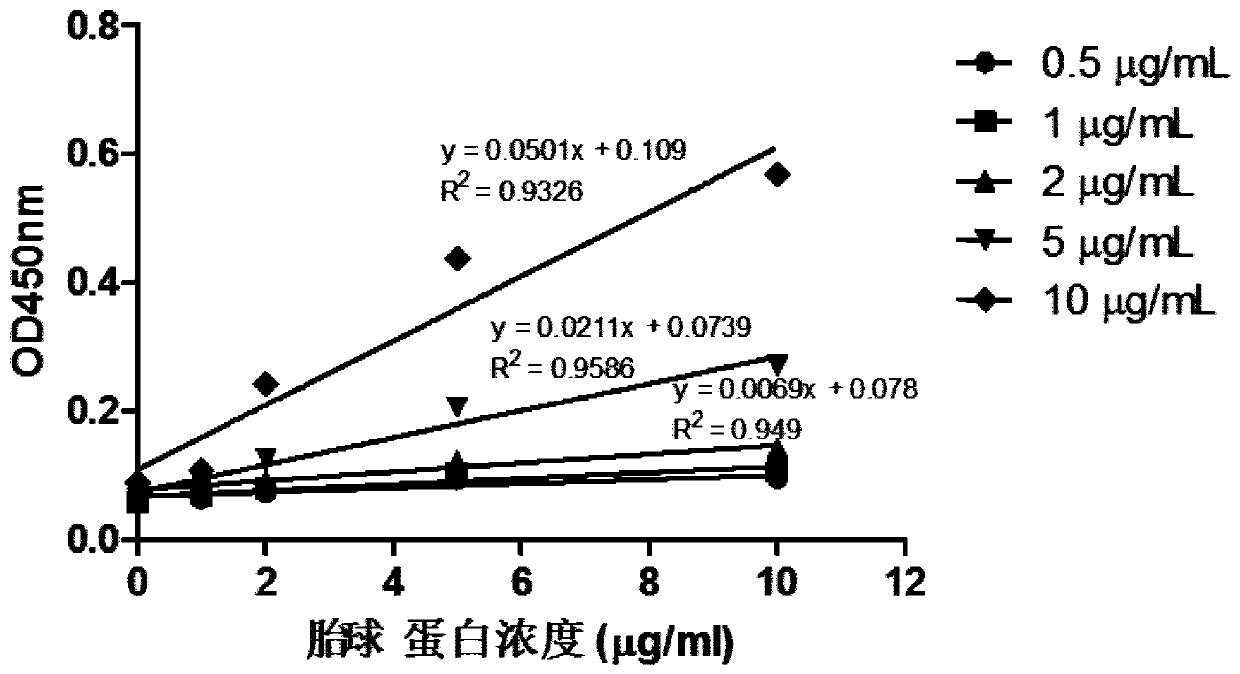
Method for detecting content of SA alpha 2-3Gal sugar chain in saliva sample by ELISA
ActiveCN110763849AQuantitative results are accurateHigh detection sensitivityBiological material analysisBiological testingSaliva sampleSalivary Proteins
The invention discloses a method for detecting the content of an SA alpha 2-3Gal sugar chain in a saliva sample by ELISA. According to the method, a fetal globulin is used as a standard substance, andthe content of the fetal globulin which has the same content as the SA alpha 2-3Gal sugar chain in the saliva sample under a certain saliva protein coating concentration can be calculated by utilizing a standard curve, so that the content of the SA alpha 2-3Gal sugar chain in the saliva sample can be calculated, and the quantitative result is accurate.
Owner:陕西医药控股医药研究院有限公司
Detection method of diabetes B kidney deficiency salivary protein markers
InactiveCN107976544ANon-invasive detection and evaluation meansSimple detection and evaluation meansDisease diagnosisBiological testingReversed-Phase Liquid ChromatographyProteomic Profile
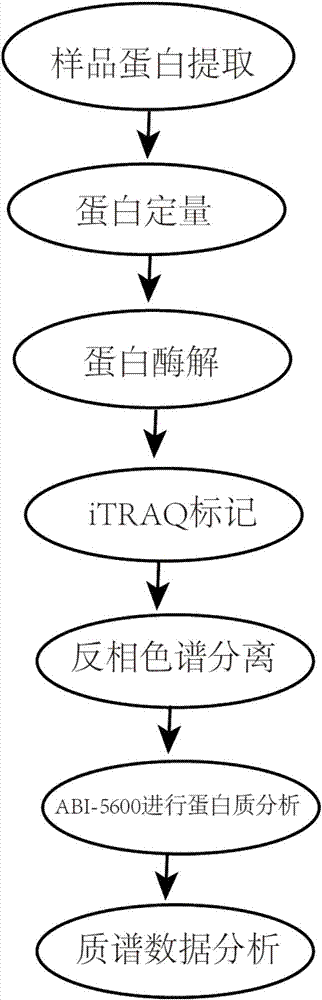
The invention discloses a detection method of diabetes B kidney deficiency salivary protein markers. The method comprises the following concrete steps of extracting sample protein; determining the extracted protein concentration by a Bradford method; performing proteolysis, iTRAQ marking, vacuum freeze centrifugation drying and reversed-phase chromatography separation under high pH conditions; performing protein analysis on ABI-5600; performing mass spectrometric data analysis; during database selection, if organisms are sequenced organisms, directly selecting the species databases; if the organisms are non-sequenced organisms, selecting main category proteome database most relevant to the tested sample; using an ABI-5600 type mass spectrograph to perform iTRAQ mass spectrograph analysis.The specific protein marker in the diabetes B kidney deficiency can be fast and reliably discovered by a proteomic technological scheme. A noninvasive, simple, convenient, fast and practical detectionand evaluation measure is built for the early diagnosis and treatment, postoperative recurrence, transfer and prognosis observation of the diabetes B kidney deficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN ELDERLY MEDICAL RES INST +1
Salivary Protein Markers for Detection of Breast Cancer
InactiveUS20130116343A1Increased and decreased riskIncreased riskBiocideDisease diagnosisSaliva sampleMedicine
A method of diagnosing a patient's risk of breast cancer comprises measuring in a saliva sample from the patient a concentration of at least a first protein marker, wherein the first protein marker is either ubiquitin or cytochrome p450, to provide a set of test data comprising a concentration value of each protein marker in the saliva sample. The test values are then compared to a reference panel comprising a Reference Control Value and a Reference Breast Cancer Value, and a diagnosis of either increased or decreased risk of breast cancer is determined for the patient based on a result of that comparison. A test kit for identifying a person at increased risk of breast cancer is also provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Detection of saliva proteins modulated secondary to ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast
InactiveUS20130280743A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOncologyBreast Duct
A method of differentiating among the presence of ductal carcinoma in situ in the breast, benign fibroadenoma of the breast, and non-cancerous breast tissue in a subject is disclosed. The method comprises: measuring the concentration of at least one protein biomarker selected from a group of forty-nine differentially expressed proteins in the saliva of persons with DCIS, or benign fibroadenoma, or in persons who are cancer-free. The resulting test data is compared to a reference panel. From the comparison the presence in the subject of either ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast, or benign fibroadenoma of the breast is determined.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for preparing saliva protein sample
ActiveCN101871857BHigh recovery rateShort preparation timePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAcetic acidSalivary Proteins
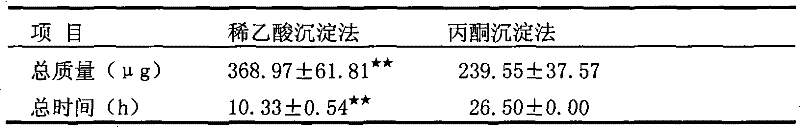
The invention discloses a method for preparing a saliva protein sample, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of saliva protein samples. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) collecting saliva; 2) centrifuging 800g of collected saliva at 4 DEG C for 15 minutes, and sucking supernate; 3) adding 0.05 to 5 volume percent acetic acid and uniformly mixing; 4)centrifuging 14,000g of the mixed solution at 4 DEG C for 60 minutes, and sucking supernate; 5) putting the supernate in a dialysis bag, and dialyzing by using double distilled water for 5 hours; and6) condensing to obtain the saliva protein sample. The method has the advantages of high protein recovery rate, short preparation time, safety, nontoxicity, increase of loading quantity of low abundance proteins, clear and easily analyzed maps and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
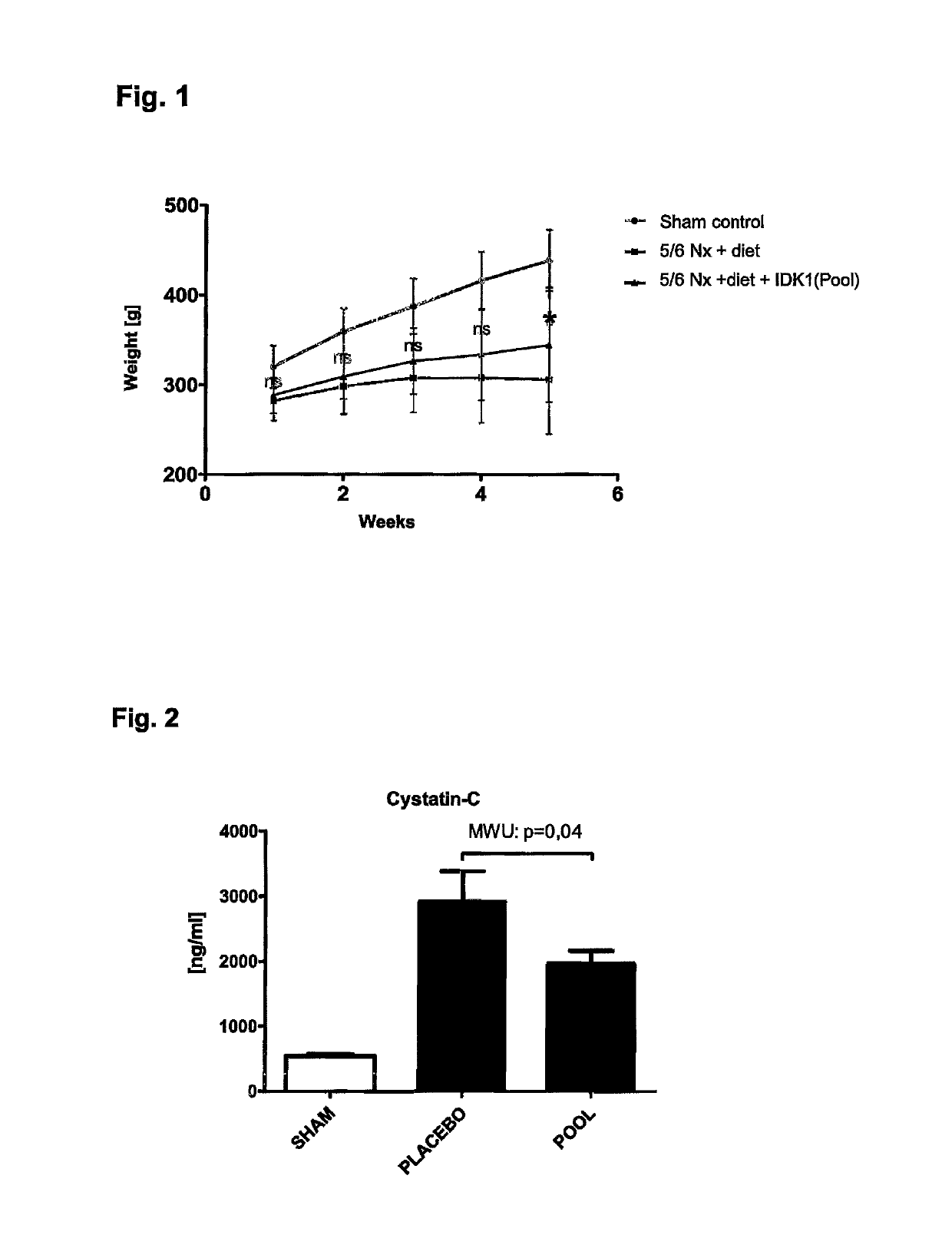
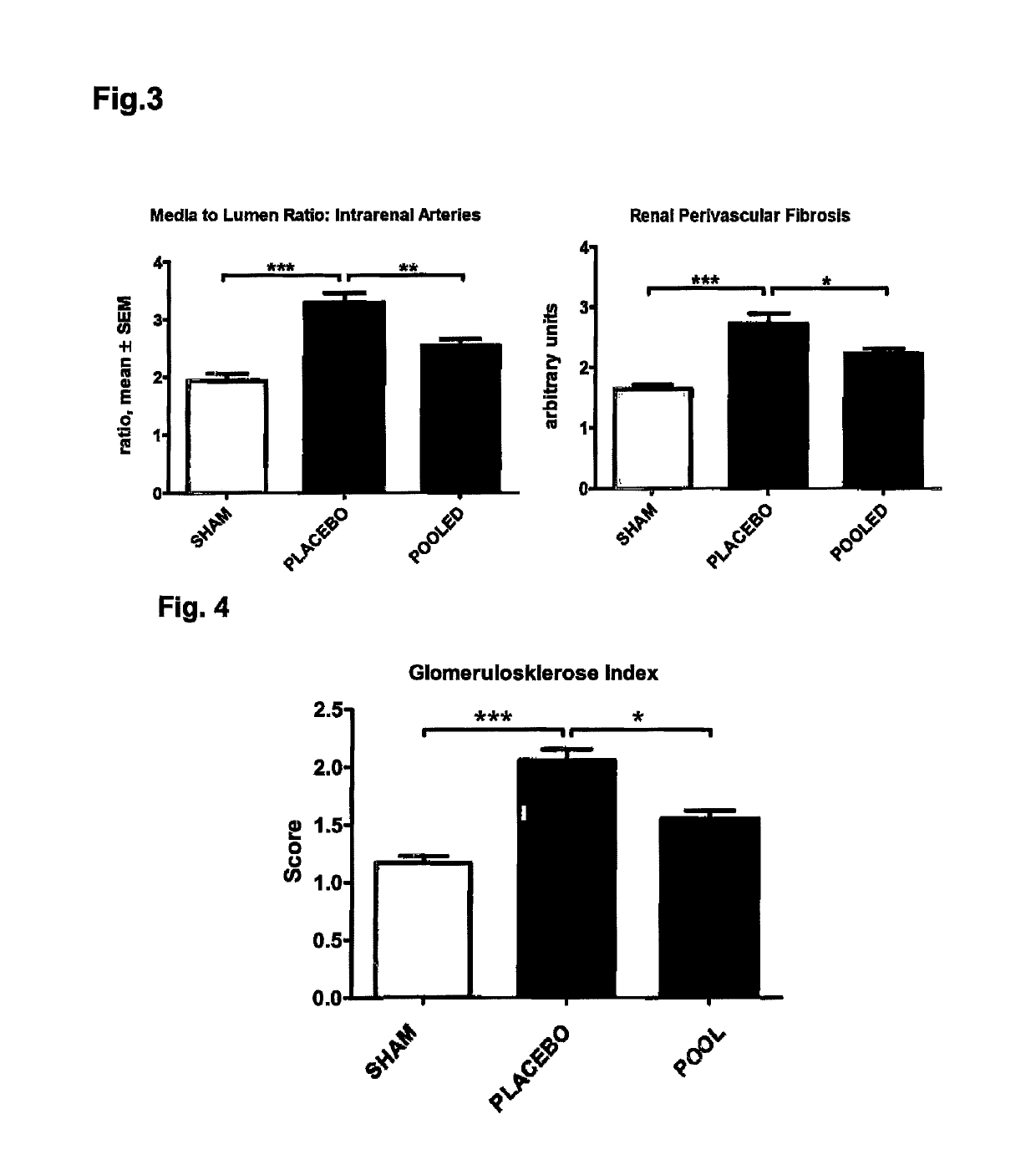
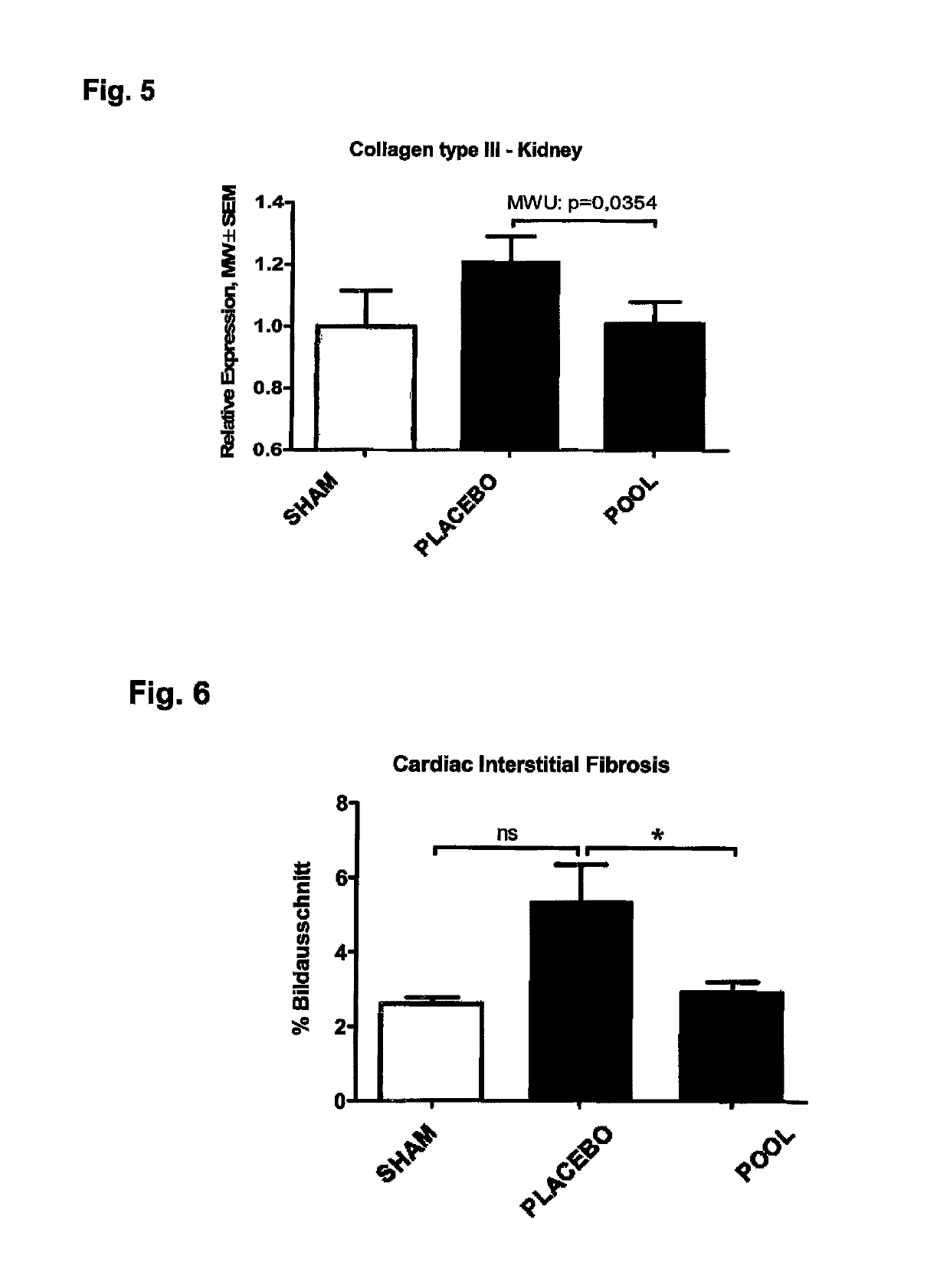
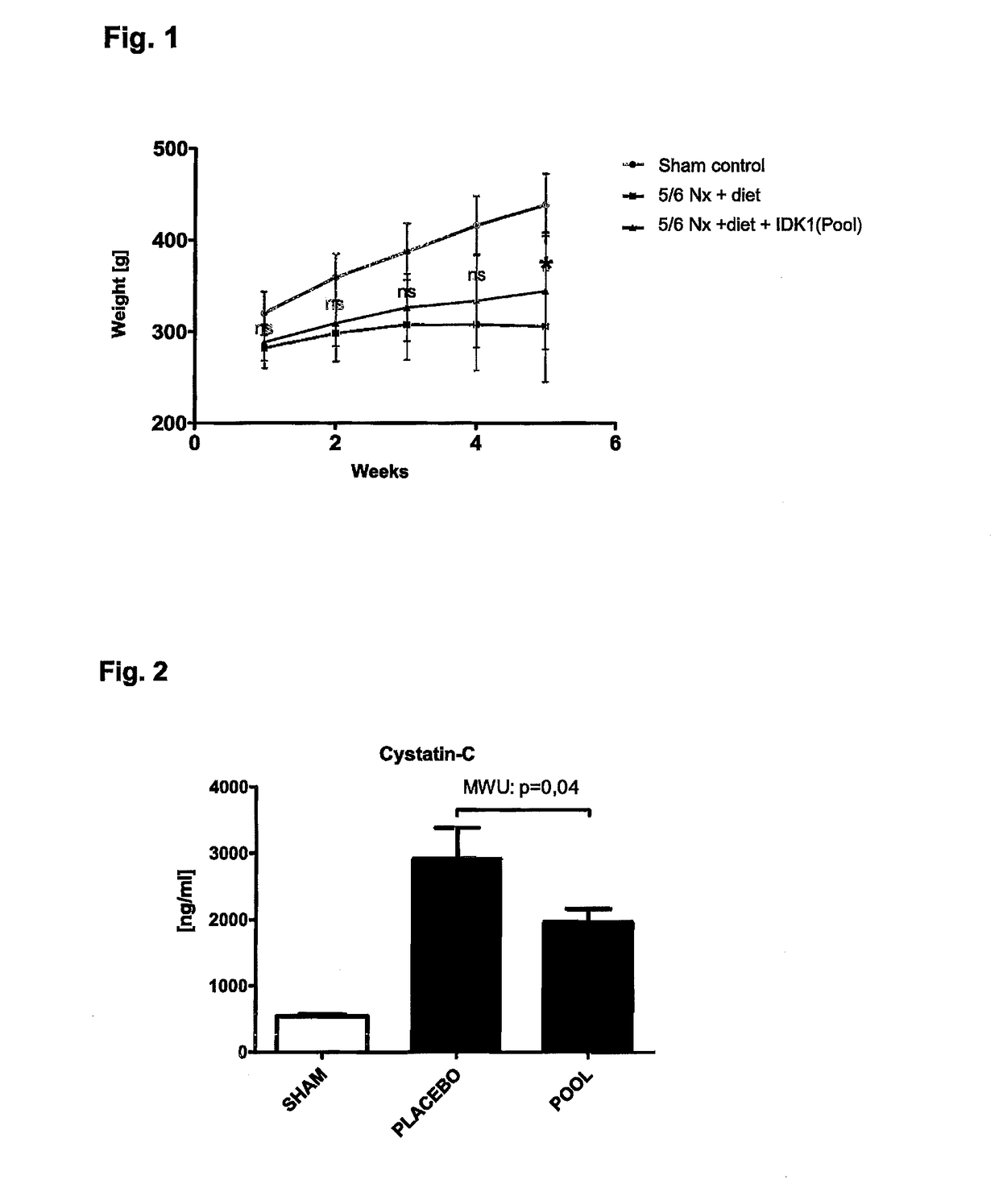
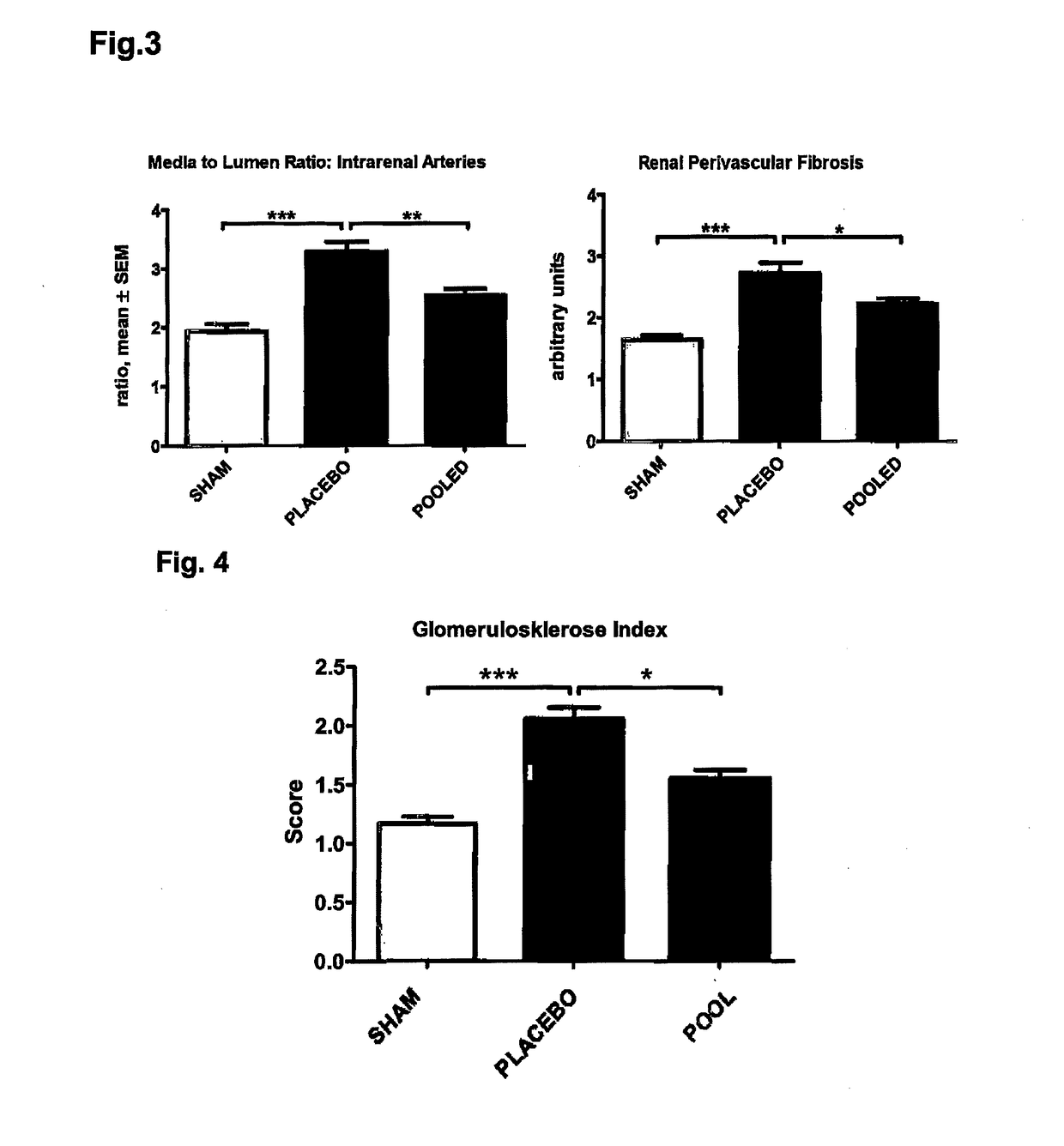
Medicament and apparatus for treating chronic kidney disease
ActiveUS10253092B2Reduce concentrationReduce calcium concentrationHaemofiltrationImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBone sialoproteinMortality rate
Owner:IMMUNDIAGNOSTIK AG
Medicament and apparatus for treating chronic kidney disease
ActiveUS20170204172A1Reduce concentrationReduce calcium concentrationHaemofiltrationImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBone sialoproteinSalivary Proteins
The present invention provides a novel therapy concept based on a removal of circulation BSP (bone sialoprotein) from the plasma of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), preferably by plasmapheresis or an administration of antibodies against BSP in plasma. The present invention further provides a BSP absorber material for plasmapheresis and a pharmaceutical composition namely in form of anti-BSP antibodies for direct administration which are biocompatible in humans. The beneficial effects of this therapy have been proven by the observed correspondence between levels of circulating free BSP levels and mortality of CKD patients.
Owner:IMMUNDIAGNOSTIK
Salivary protein biomarkers for human oral cancer
ActiveUS8728744B2Particle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman cancerSalivary Proteins
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for diagnosing degenerative joint disease
The invention provides methods for diagnosing degenerative joint disease in an animal by collecting a saliva sample from an animal; determining the amount of at least one diagnostic agent selected from the group consisting of interferon gamma, interferoninducible protein-10, interleukin-2, and total saliva protein in the saliva sample; comparing the amount of diagnostic agent found in the saliva sample to a corresponding amount of the same diagnostic agent found in a saliva sample from one or more comparable control animals that do not suffer from degenerative joint disease; and diagnosing that the animal is susceptible to or suffering from degenerative joint disease if the amount of diagnostic agent in the saliva sample from the animal is greater than the amount of same diagnostic agent found in the saliva sample from the one or more comparable control animals.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
A dsrna inhibiting the expression of wheat aphid gland protein mys2 gene and its application
The invention discloses dsRNA (double-strand ribose nucleic acid) capable of inhibiting wheat aphid salivary protein MYS2 gene expression and application thereof. The invention provides the double-stranded RNA molecule shown in the sequence 2 in a sequence table. The DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule encoding the RNA molecule and the application of the RNA molecule or DNA molecule are protected in the invention, and the application of RNA molecule or DNA molecule includes at least one of the following: (1) preventing and treating aphid; (2) promoting death of aphid; (3) inhibiting growth of aphid; and (4) inhibiting expression of in vivo salivary protein MYS2 gene of aphid. The dsRNA has important application value in prevention and control of aphid in agriculture production.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
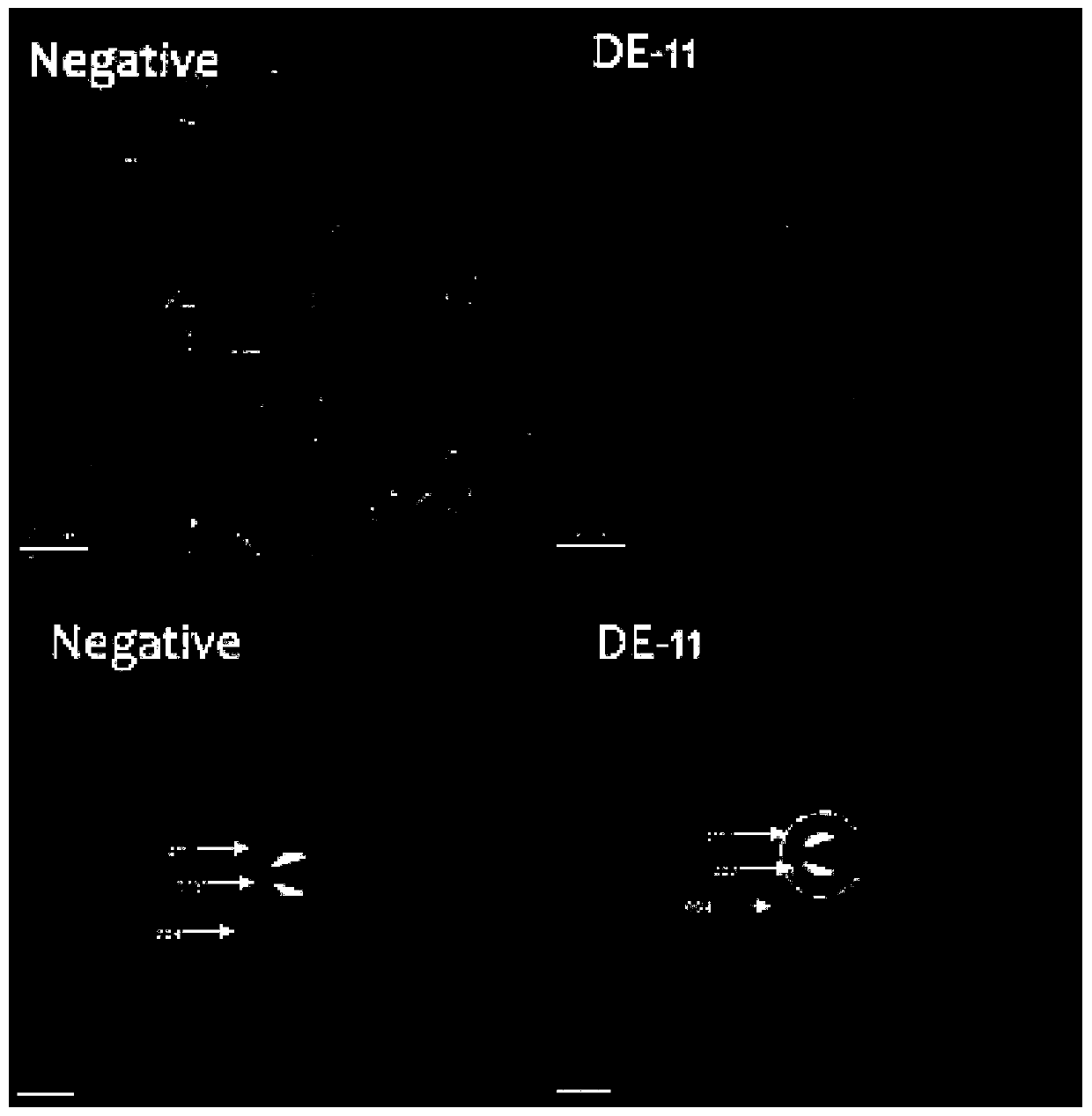
A lectin chip and method for detecting sugar chain markers based on salivary protein
A lectin chip for detecting sugar chain markers based on salivary protein and a method thereof, relating to a lectin chip for detecting sugar chain markers, in particular to a lectin chip for detecting sugar chain markers based on protein and its method. The purpose is to provide a non-damaging lectin chip and method for detecting sugar chain markers by identifying proteins in saliva. The lectin chip for detecting sugar chain markers based on salivary protein includes a test lectin probe set, and the test lectin probe set includes faba bean lectin, Reticula aurantia lectin, pea lectin, square bean Lectin-II and lentil bean lectin-I, wherein lentil lectin-II and lentil bean lectin-I were used as internal reference lectins. Using the lectin chip to detect sugar chain markers has the advantages of no damage to the human body, less sample consumption, fast detection results and high sensitivity, and can be applied to identify whether there is gastric cancer.
Owner:深圳格道糖生物技术有限公司
Biomimetic anti-caries polypeptide based on salivary statherin, its derivative and salt and application
ActiveCN107353334BSmall molecular weightStable structurePeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemCalcium biphosphateSalivary Proteins
The invention discloses a bionic anti-caries functional polypeptide based on casein-rich saliva, a polypeptide derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt and an application in pharmacy thereof. The bionic anti-caries functional polypeptide is based on an anti-caries functional segment of the casein-rich saliva, the adjustment and improvement for the amino acid sequence are performed on the anti-caries functional segment and the bionic anti-caries functional polypeptide contains the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The polypeptide mainly utilizes the 'DpSpSEEK' amino acid sequence to realize the adsorption combination of polypeptide and de-mineralized enamel and the 'DpSpSEEK' amino acid sequence thereof can react with calcium phosphate ions so as to induce hydroxyapatite nucleation, so that the in-situ mineralizing repairing function for early enamel caries can be realized. The polypeptide is characterized by lower molecular weight, convenience in compound, low cost, better anti-caries effect, structure stability, safety and reliability. The invention utilizes the bionic thought to simulate natural saliva protein, designs the anti-caries polypeptide with a re-mineralization function and provides an ideal new method for preventing and controlling caries.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
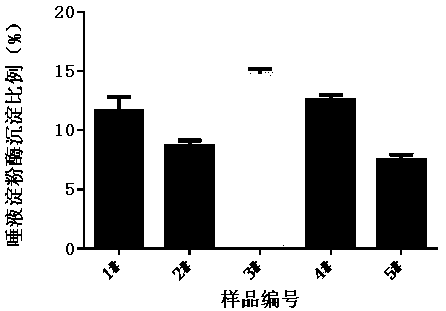
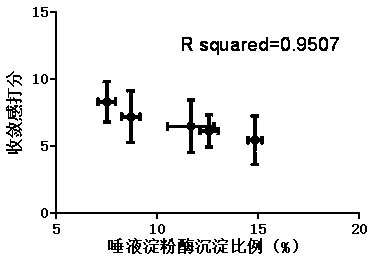
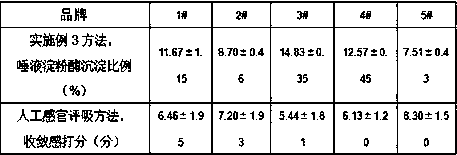
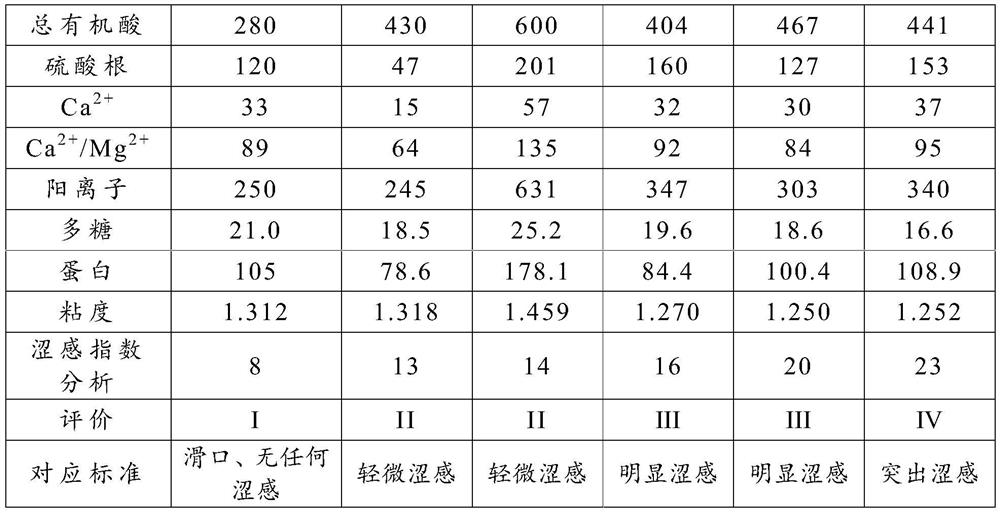
In-vitro method for representing influence of cigarette smoke on oral astringency
The invention relates to an in-vitro method for representing the influence of cigarette smoke on oral astringency, and belongs to the technical field of biological application. The method includes thesteps of cigarette main stream smoke total particulate matter extraction, artificial saliva preparation, TPM supernatant preparation, dyeing, protein content measurement and the like. The method is simple in operation, a protein environment in saliva is simulated by salivary amylase according to the principle that astringency can be generated by salivary protein precipitation, and astringency isquantitatively represented by precipitation proportion. Moreover, smoke total particulate matters are gathered by in-vitro suction and then react with the salivary amylase, the influence of smoke on the salivary amylase is amplified by the concentration process, subtle differences of different cigarette smoke are compared, and the method can be used for quantitative representing the influence of the cigarette smoke on oral astringency and provides a reference for sensory evaluation of the cigarette smoke.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Use of the salivary protein CD14 as an indicator of the low risk to developing dental caries
It is generally accepted that salivary components are important for dental health, but till now no clear correlation has been found between one or more of said components and the onset of dental caries. The present invention relates to an assay method comprising analysing the presence and / or the content of the salivary soluble CD14 protein from a saliva sample of the individual subjected to examination; the absence of said protein from the salivary sample, or its presence in a reduced amount compared to a predetermined threshold value in caries-free individuals, is considered as a marker of susceptibility to developing caries and / or as a diagnostic element for the existence of ongoing carious lesions.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI TORINO
Attractant for promoting salivary protein secretion of mycophagous flour mites, and salivary protein collection method
The invention provides an attractant for promoting salivary protein secretion of mycophagous flour mites, and a salivary protein collection method. The attractant comprises a solvent and an attractant component dissolved in the solvent; the solvent comprises a sucrose aqueous solution; and the attractant component is prepared from 3-octanone and alpha-terpinene. According to the attractant for promoting salivary protein secretion of the mycophagous flour mites, provided by the invention, through the synergistic effect of the sucrose aqueous solution, the 3-octanone and the alpha-terpinene, the mycophagous flour mites are attracted by utilizing the volatility of the 3-octanone and the alpha-terpinene; and 3-octanone, alpha-terpinene and the sucrose aqueous solution are used for stimulating the lured mycophagous flour mites to secrete salivary proteins, so that the secretion amount of the salivary proteins is increased, and the difficulty of obtaining the flour mite salivary protein is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Astringency Evaluation Method Based on Beer Components
The invention proposes a method for evaluating astringency based on beer components, which belongs to the technical field of beer brewing. In this method, the astringency degree of the beer components is characterized by an astringency index, and the astringency index=(beer astringency factor+beer astringency masking factor)ⅹ100+53. Compared with sensory evaluation, this method is quantifiable, accurate, and not affected by human factors; in addition, when this method is used for the evaluation of beer astringency, it not only takes into account the factors that can precipitate salivary protein and cause astringency, but also takes into account Conceal the astringent factor, more realistic and practical sensory evaluation.
Owner:TSINGTAO BREWERY
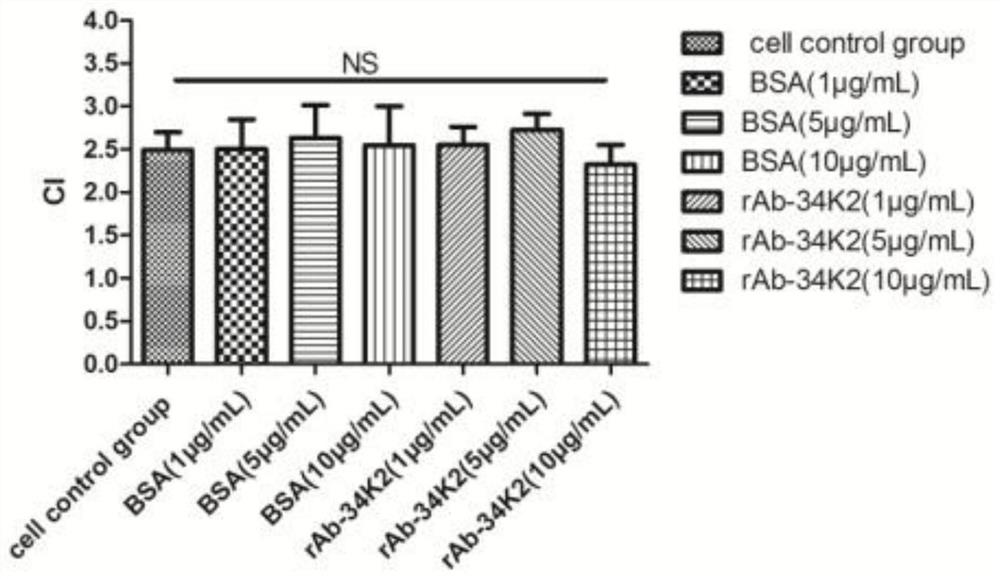
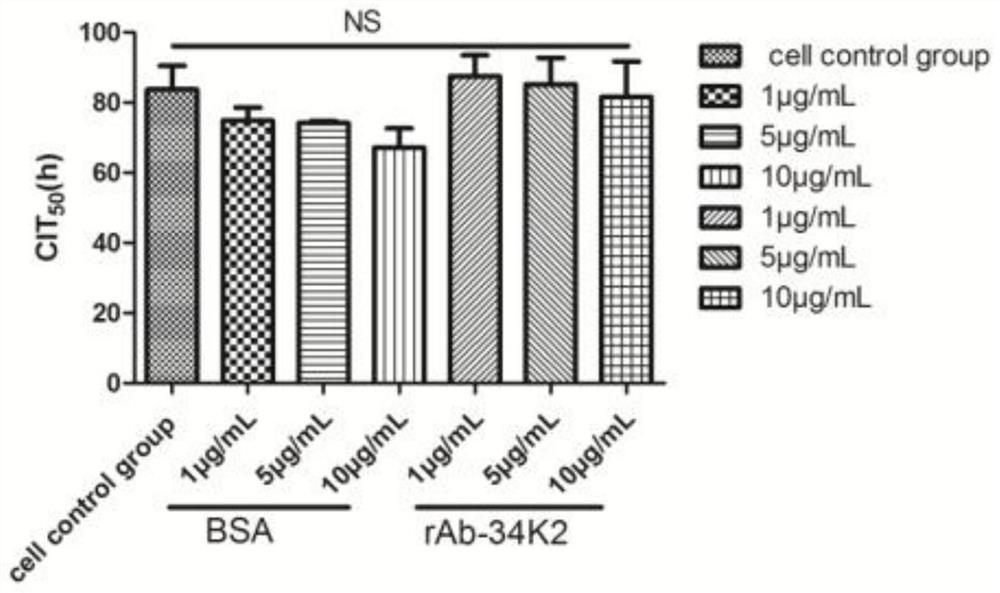
Application of Aedes albopictus salivary 34k2 recombinant protein in hacat cells infected by denv2
ActiveCN107236028BPromote proliferationFacilitated DiffusionSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicroorganism based processesVirus multiplicationAedes albopictus
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to an application of a recombinant aedes albopictus salivary 34K2 (short for rAb-34K2DENV2) protein to promotion of DENV (Dengue virus) multiplication. A preparation method comprises the step that the rAb-34K2DENV2 protein can promote multiplication of DENV2 in HaCaT cells. The mechanism is that theDENV2-infectedHaCaT cells are inhibited from expressing type-I interferon IFN-alpha / beta to promote virus multiplication, meanwhile, the rAb-34K2protein can induce apoptosis of the DENV2-infectedHaCaTcells, and great significance in study of the function of aedes albopictus salivary protein components in a disease transmission mechanism of mosquitos is realized.
Owner:GUIZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Salivary protein fingerprint spectrum molecular diagnosis model establishing method of type II diabetes mellitus
InactiveCN105699663AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityDisease diagnosisBiological testingSaliva sampleMagnetic bead
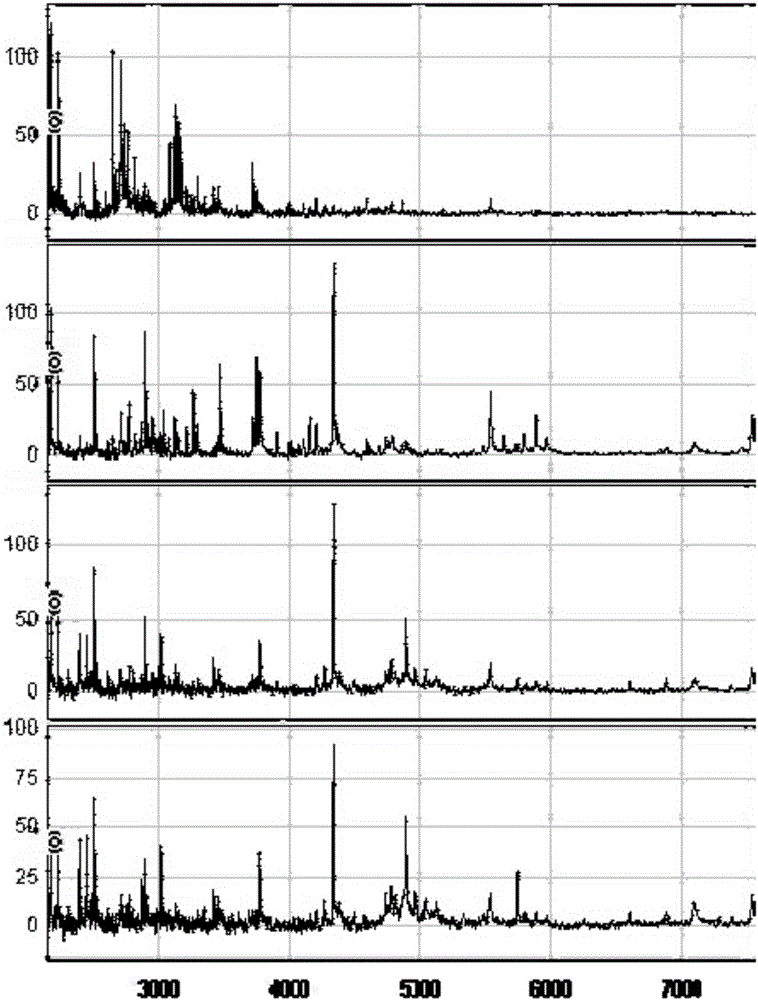
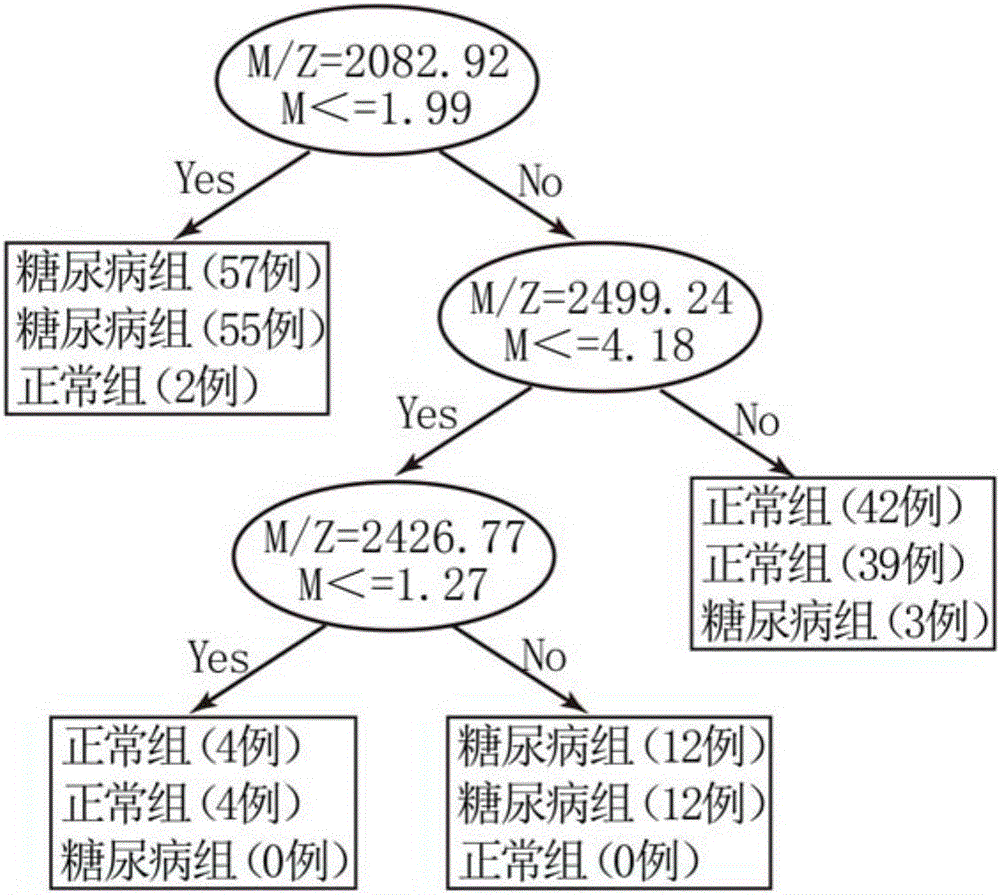
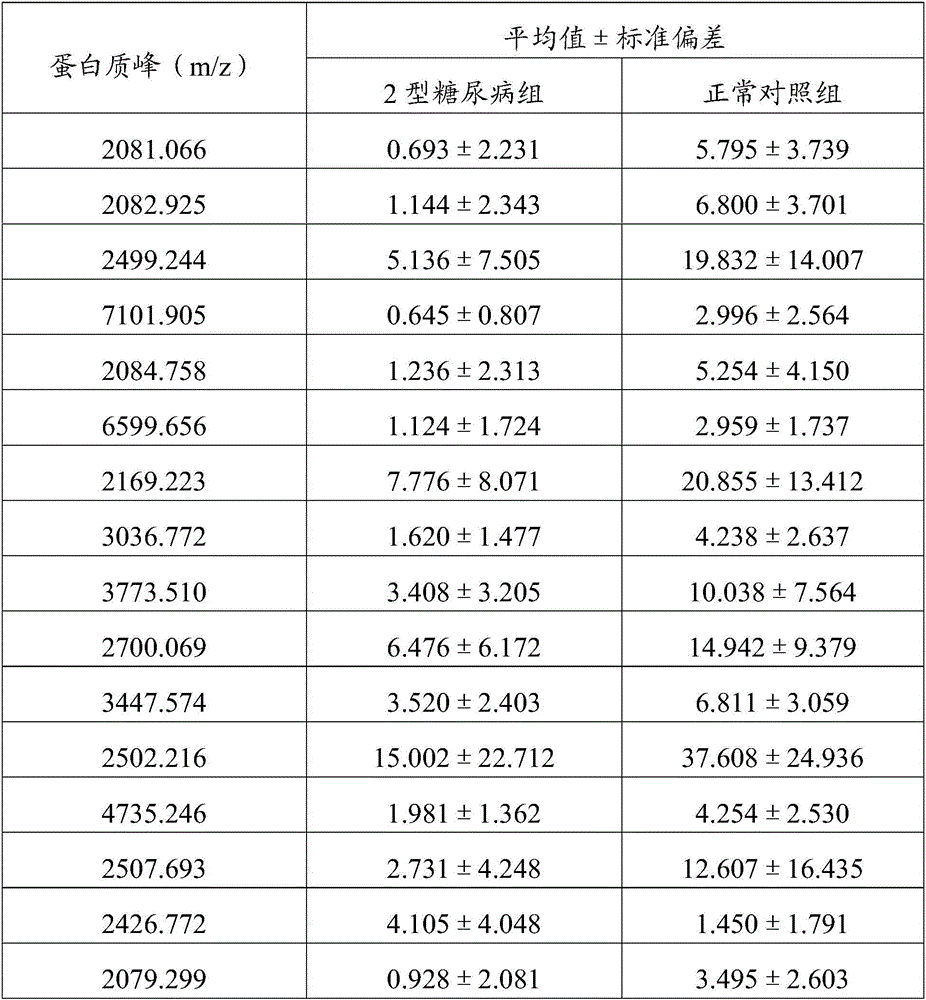
The invention discloses a method for establishing a type 2 diabetes salivary protein fingerprint molecular diagnostic model, comprising the following steps: sample collection; sample pretreatment; nano magnetic beads activation; saliva sample loading; nano magnetic beads elution; data collection; analysis; building diagnostic models. The present invention uses a liquid chip combined with MALDI technology to detect the saliva protein fingerprints of patients with type 2 diabetes, screens out 80 highly significant statistically significant differential protein peaks from the saliva proteins, and selects mass-to-charge ratios of 2082.92, 2499.24 and 2426.77 Differential protein peaks were modeled, with a recognition rate of 94.3% and a predictive ability of 93.3%. The results of clinical back substitution test showed that the sensitivity of the diagnostic model was 88.6%, and the specificity was 77.8%. It shows that the model has excellent diagnostic efficiency, high sensitivity and strong specificity for type 2 diabetes.
Owner:SHENZHEN ELDERLY MEDICAL RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com