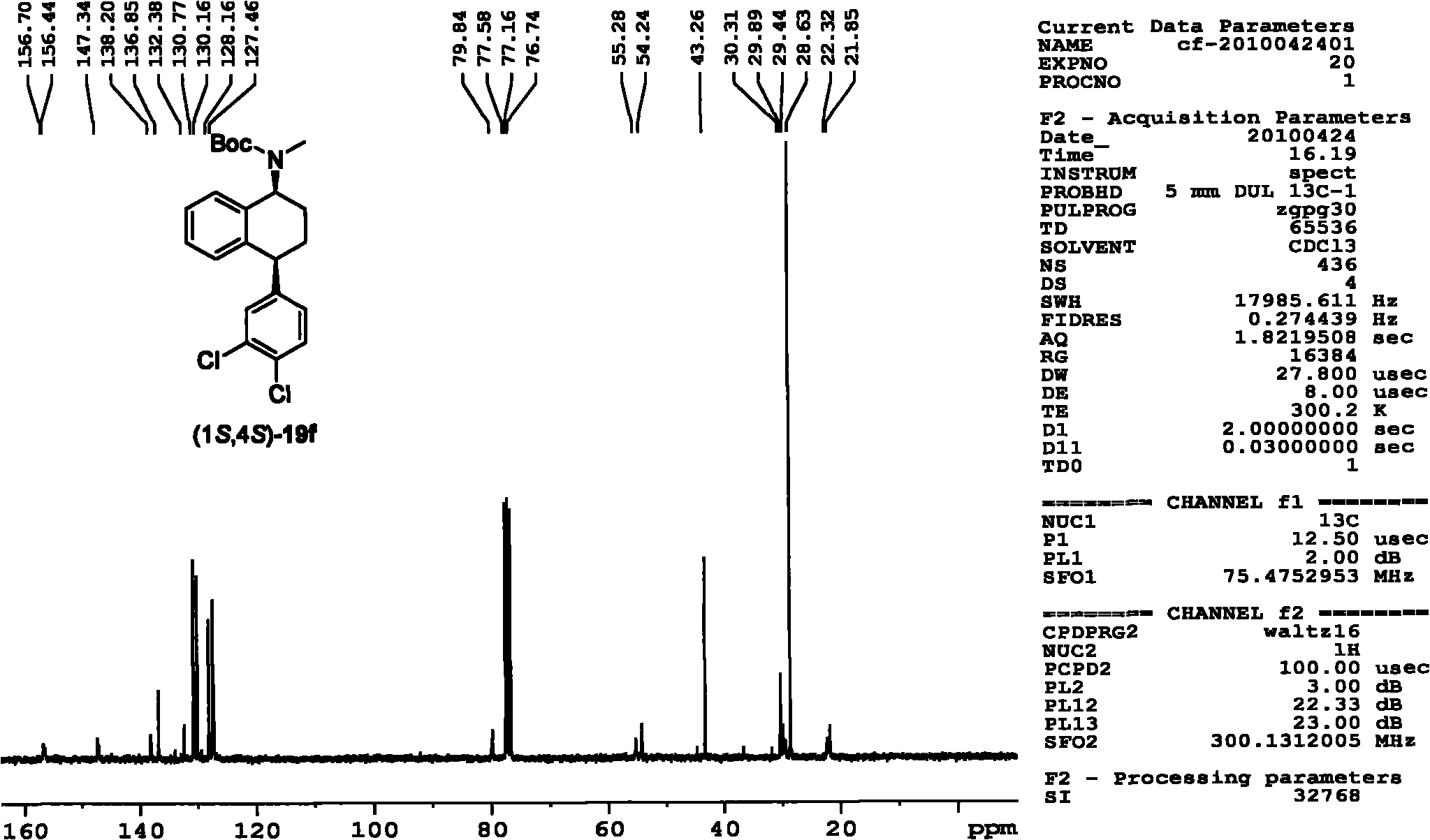
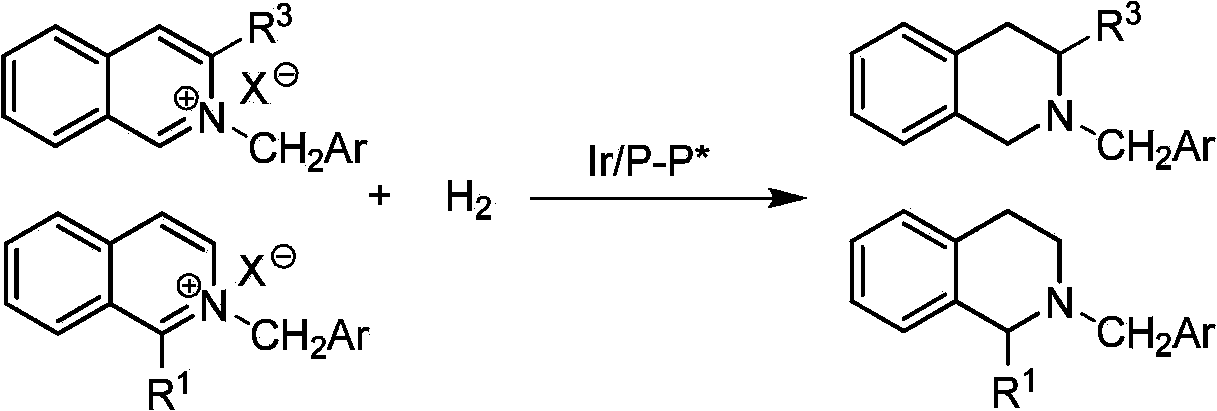Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
536 results about "Enantiomeric excess" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enantiomeric excess (ee) is a measurement of purity used for chiral substances. It reflects the degree to which a sample contains one enantiomer in greater amounts than the other. A racemic mixture has an ee of 0%, while a single completely pure enantiomer has an ee of 100%. A sample with 70% of one enantiomer and 30% of the other has an ee of 40% (70% − 30%).
Bimetallic catalyst for synthetizing vertical structure regular makrolon
ActiveCN103102480AMild reaction conditionsThe process is simple and convenientActivated carbonPolycarbonate
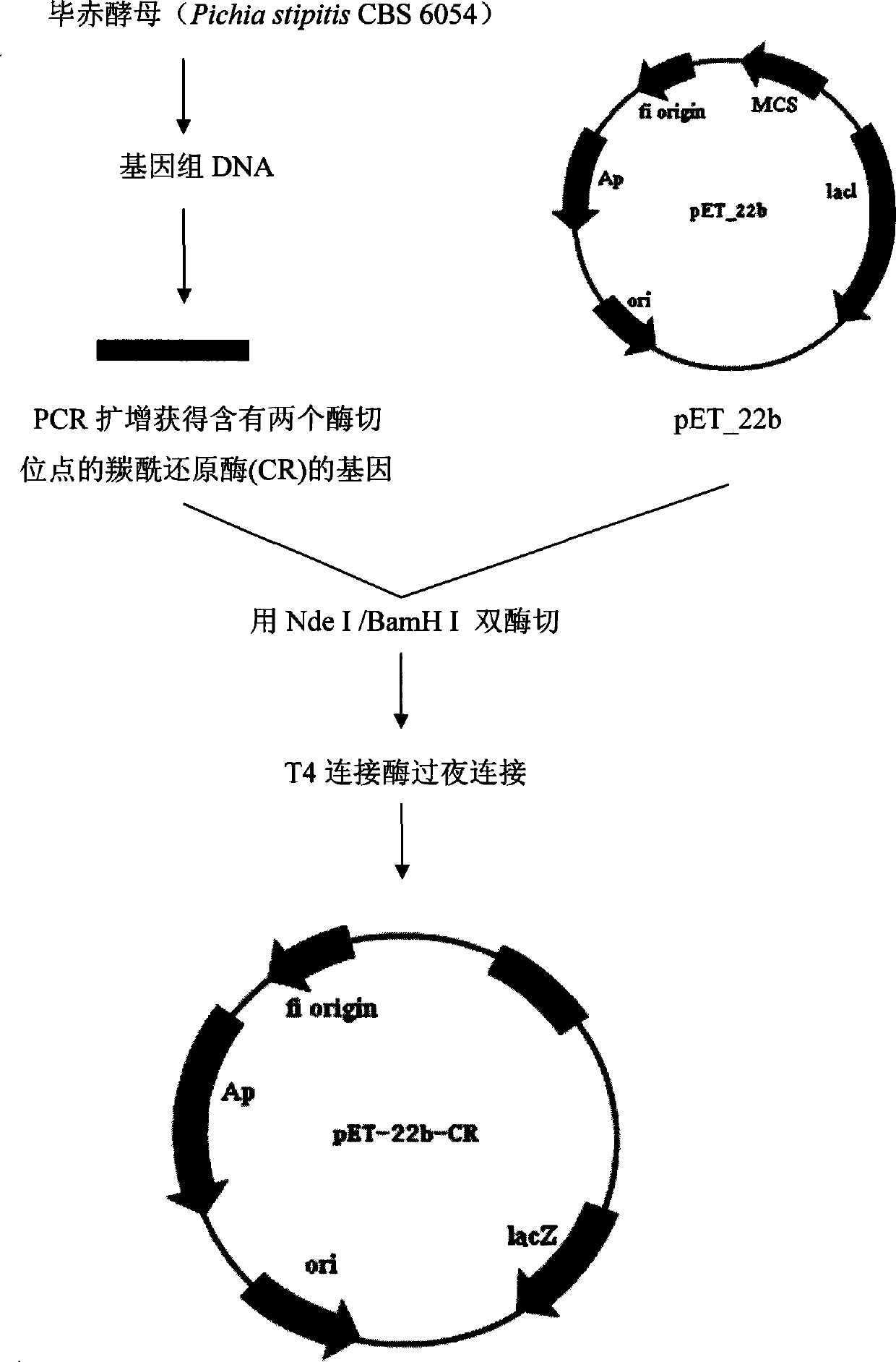
The invention relates to a bimetallic catalyst for synthetizing vertical structure regular makrolon through catalyzing and activating carbon dioxide to be copolymerized with internal compensation alkyleneoxide. The catalyst is a dual four-tooth or dual three-tooth Schiff alkali complex, of which two metal centers are connected through a biphenyl skeleton. Under the action of single or nucleophilicity co-catalyst, the catalyst can be used for catalyzing the carbon dioxide efficiently to be copolymerized with the internal compensation alkyleneoxide under mild condition and lower concentration of the catalyst to prepare the makrolon, the makrolon can be regulated when the catalyst efficiency is 104-106g polymer / mole catalyst and the polymer molecular weight is between 103 and 105, the makrolon can be regulated when the molecular weight distribution is less than 2 and the vertical structure regularity is between 60-100%, an alternate structure exceeds 98% and the makrolon can be degraded into a small molecular compound. The product selectivity and structure selectivity of the polymer compounds of the catalyst system using a chiral ligand are all above 98%, the enantiomer excess value of the mellow obtained by degradation reaches as high as 99%, so that the bimetallic catalyst provides a broad prospect for industrial application.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing (S)-(4-chlorphenyl)-(pyridine-2-yl)-methanol by utilizing microbial catalysis
ActiveCN102559520AHigh excessLess side effectsFungiMicroorganism based processesPhosphateReaction temperature
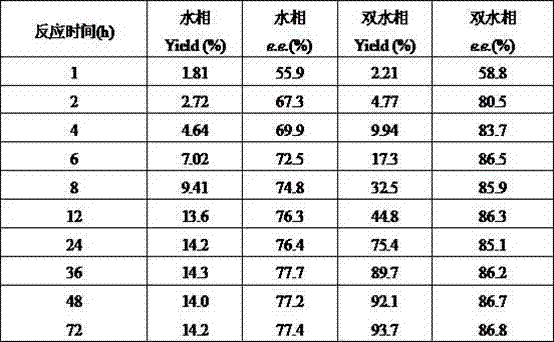
The invention relates to a method for preparing (S)-(4-chlorphenyl)-(pyridine-2-yl)-methanol by utilizing microbial catalysis, and belongs to the technical field of biological catalysis. According to the method, 4-chlorphenyl-(pyridine-2-yl)-ketone is subjected to asymmetrical reduction by utilizing kluyveromycessp (CCTCCM 2011385) whole cells to synthesize the (S)-(4-chlorphenyl)-(pyridine-2-yl)-methanol. The method comprises the following steps of: sieving a microbe which has high-stereoselectivity carbonyl reductase activity on a prochiral ketone substrate, determining a series of conditions of asymmetrical reduction reaction, such as reaction temperature, pH, the concentration of cells, the concentration of the substrate and reaction time and additives (including various secondary solvents, polyethyleneglycol (PEG), phosphates and the like), wherein the enantiomer excess value and yield of the (S)-(4-chlorphenyl)-(pyridine-2-yl)-methanol serving as a product can reach 86.7 percent e.e and 92.1. The product is separated and extracted initially by silicagel column chromatography, so that the purity of the separated product is 99.2 percent, and the extraction yield is 56.7 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing high-purity esomeprazole
ActiveCN102584792AShort preparation timeReduce the difficulty of operationOrganic chemistryBiochemical engineeringCombinatorial chemistry
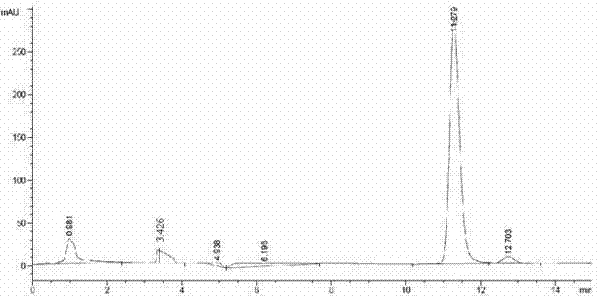
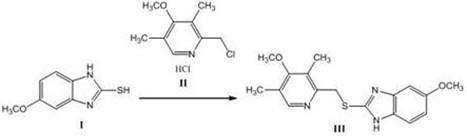
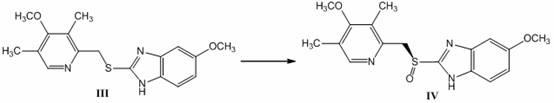
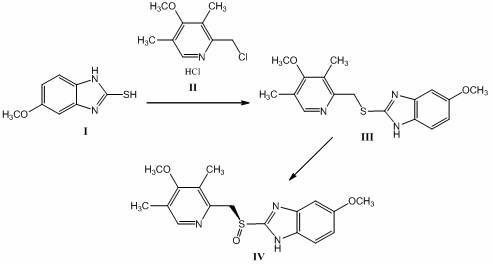
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing and refining salt of esomeprazole. According to the method, 2-sulfydryl-5-methoxyl-1H-benzimidazole is used as an initiative raw material for reaction, and a reaction condition is optimized, so that reaction is performed under a mild condition, and the content of impurities in the product is reduced effectively. After the synthesized product is refined further, the purity and enantiomer excess of the product are over 99 percent, so that the effect and safety of administration are improved.
Owner:NANJING YOUKE BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL RES
Application of alcohol dehydrogenase in catalytic generation of ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate
InactiveCN103160547AHigh yieldHigh optical activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses application of alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction. By using alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 as a catalyst, ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate as a substrate and NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) as a cofactor, asymmetric reduction is carried out to prepare the ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate. The invention applies the alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction for the first time, and has favorable effect. The enzyme activity is up to 5.6 U / mg, the yield of the substrate is up to 94%, and the enantiomeric excess value of the product is 100%. The yield is high, and the production cost is greatly lowered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
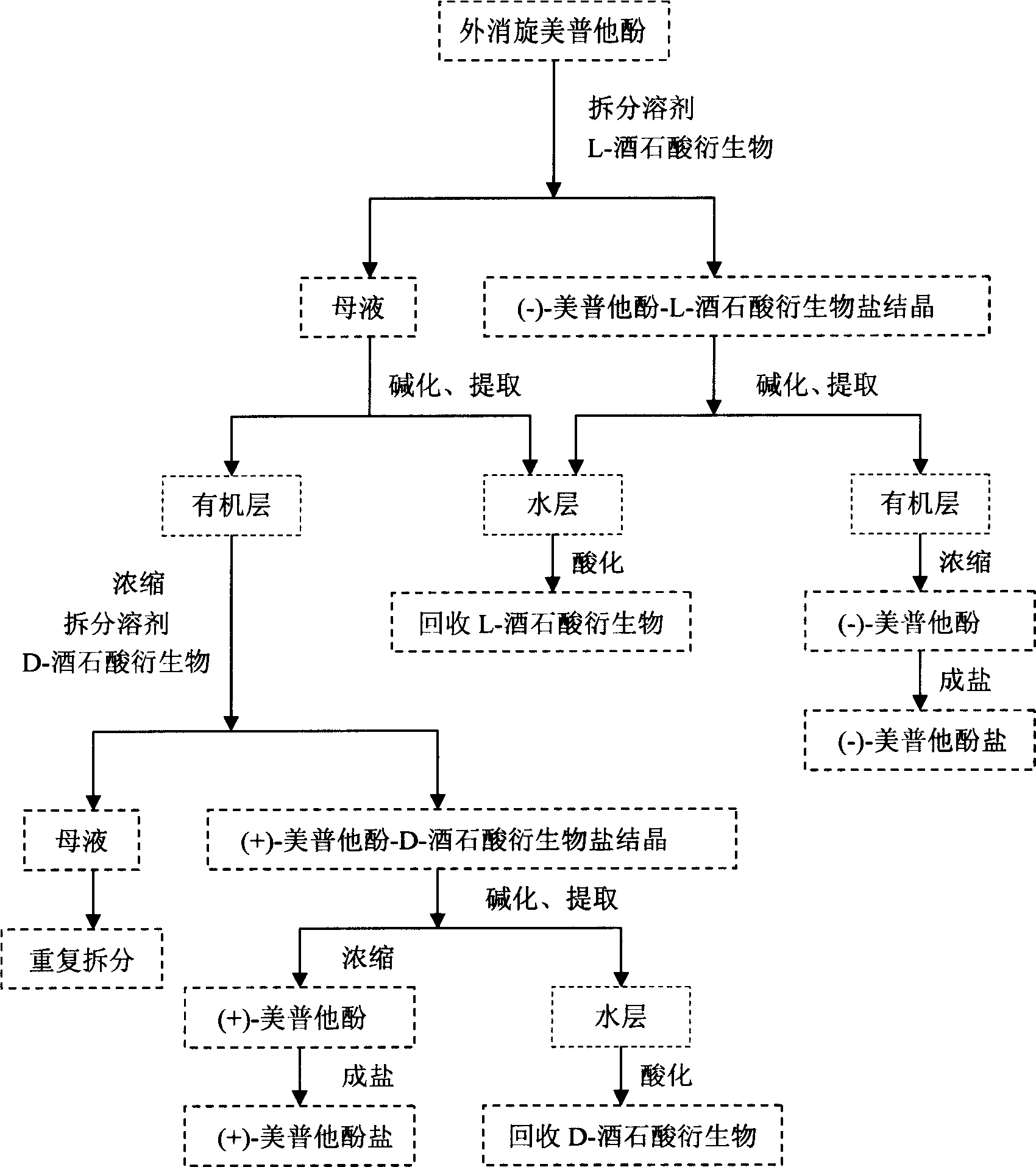
Optical-purity meptazinol orits salts, and preparing method
InactiveCN1850804APharmacologically activeNervous disorderOrganic chemistryAbsolute configurationSingle crystal
This invention belongs to pharmacy field, it relates optical pure mei pu ta fen and its preparation method and application. Racemation mei pu ta fen is splited by optical pure tartaric acid evolving object to get optical pure monomer, enantiomeric excess testing is done through capillary electrophoresis method, their e.e.valude are both excess 99 percent. Laevorotation and dextrorotation mei put a fen absolute configuration is decided by single crystal X-diffraction method as S and R. the R(+)mei pu ta fen has srong activity in analgesia activity testing, but S(-)mei pu ta fen has more stronger activity in acetylcholine esterase restrain activity testing, analgesic medicine and senile dementia medicine can be further prepared.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
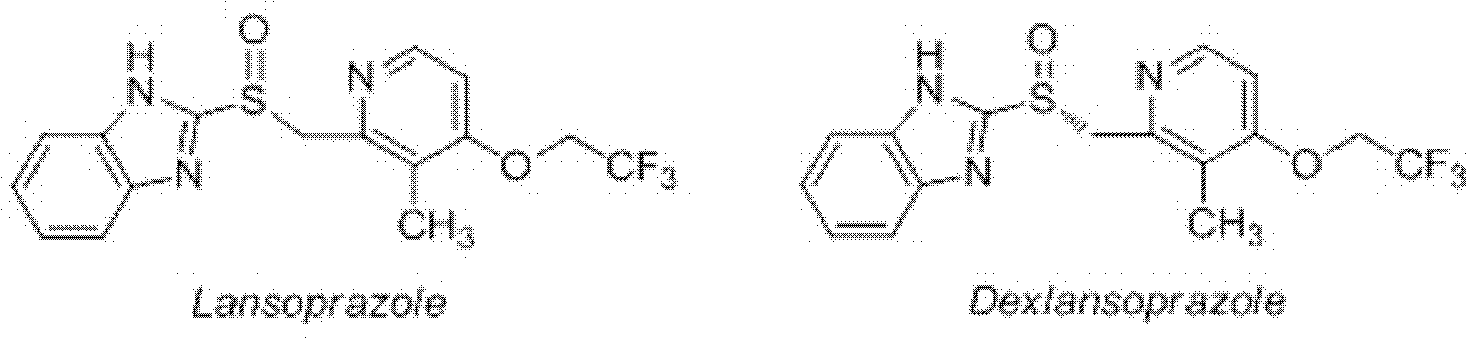
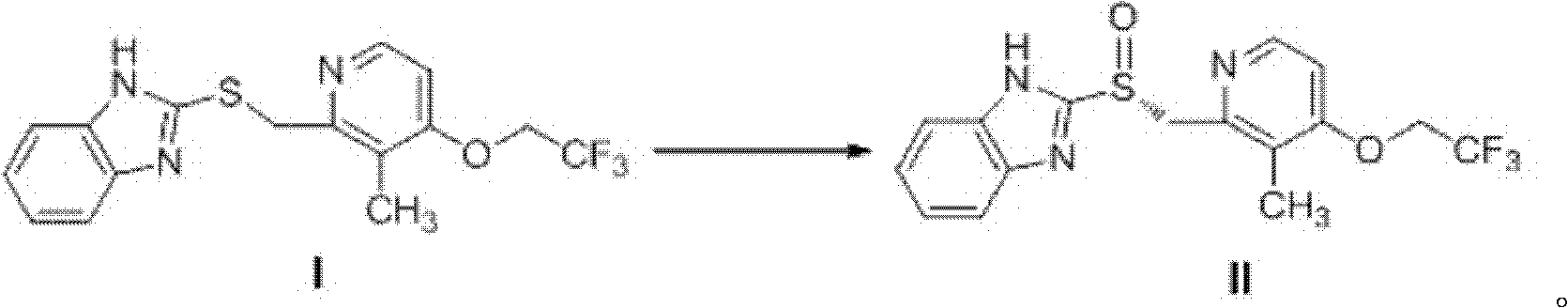
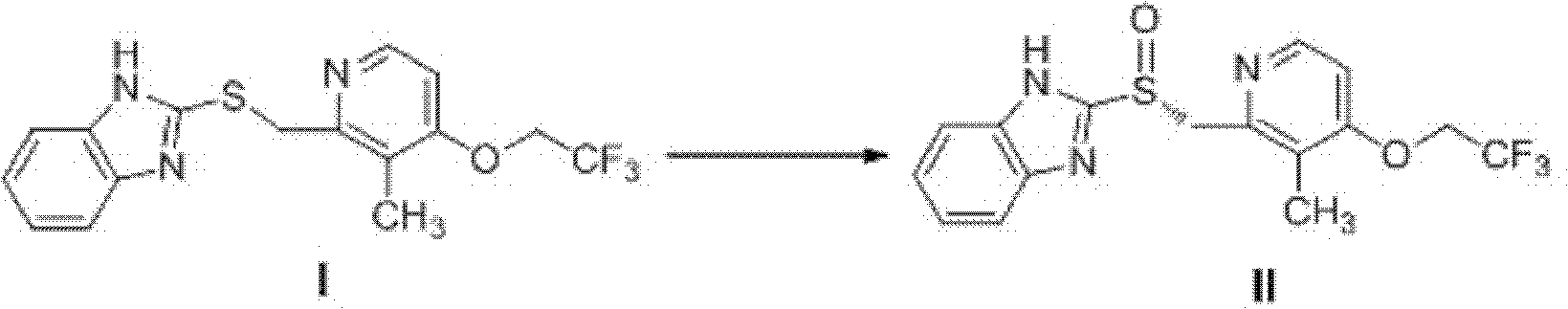
Method for synthesizing and purifying dexlansoprazole
ActiveCN102659763AHigh purityAvoid heating operationsOrganic chemistryDexlansoprazoleImproved method
The invention mainly relates to an improved method for synthesizing dexlansoprazole by utilizing a Sharpless asymmetric oxidation method and an optimized method for purifying dexlansoprazole. According to the method, the total yield is above 40% and the purity of the product and the enantiomeric excess (e.e.) are both above 99.5%. The preparation method is simple, is low in cost and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:南京博德生物制药有限公司
Chiral compounds and compositions containing the same
The invention relates to a novel class of compounds useful as chiral dopants, which compounds are available in both enantiomeric forms. Another aspect of the invention relates to such compounds having a enantiomeric excess of one enantiomeric form, which are useful in liquid crystal formulations. Such formulations are advantageous in displays and various other products.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for the Production of Enriched Isopulegol
ActiveUS20080214877A1Easy to disassembleIncrease in the enantiomeric excessOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationMentholPolymer science
The present invention relates to a process for preparing enriched isopulegol by crystallization from a melt comprising isopulegol. The invention relates specifically to a process for preparing enantiomerically enriched n-isopulegol proceeding from optically active isopulegol having a relatively low enantiomeric excess by crystallization from the melt. The invention further relates to a process for preparing menthol proceeding from enantiomerically and / or diastereomerically enriched n-isopulegol prepared by crystallization from the melt.
Owner:BASF AG
Processes and intermediates for preparing steric compounds
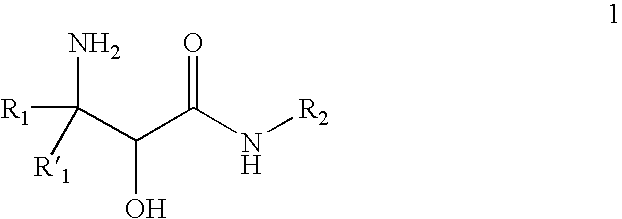
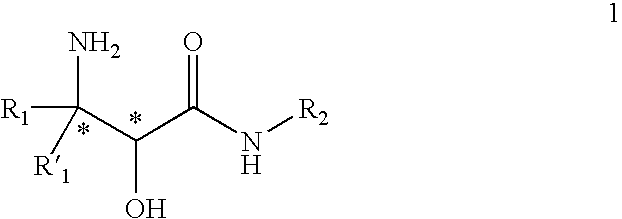
InactiveUS20070244334A1Organic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsBeta hydroxy acidStereochemistry
This invention relates to processes and intermediates for the preparation of an alpha-amino beta-hydroxy acid of Formula 1 wherein the variables R1, R′1 and R2 are defined herein and the compound of Formula 1 has an enantiomeric excess (ee) of 55% or greater.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Use of carbonyl reductase in (S)-4-chloro-3 hydroxy butyric ether production
The invention discloses an application of carbonyl reductase with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 to prepare (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic ethyl ester by asymmetric reduction of 4-chloracetyl ethyl acetate. The carbonyl reductase with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 is taken as a catalyst, the ethyl 4-chloracetyl ethyl acetate is taken as a substrate, and NADPH is taken as a cofactor, and the (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic ethyl ester is prepared by the asymmetric reduction. The carbonyl reductase with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 is applied to preparing the (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic ethyl ester by the asymmertric reduction of the 4-chloroacetyl ethyl acetate for the first time, which produces good effect; the yield of the substrate is up to 95%, and the enantiomer excess value of the product is 100%, the yield is high, and the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Application of Chryseobacterium sp. and carbonyl reductase thereof in production of aprepitant chiral intermediate
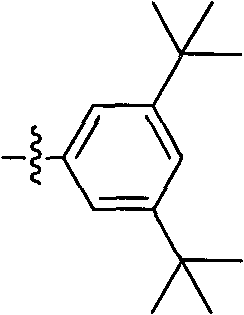
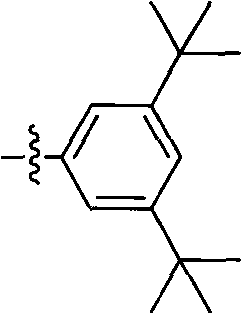
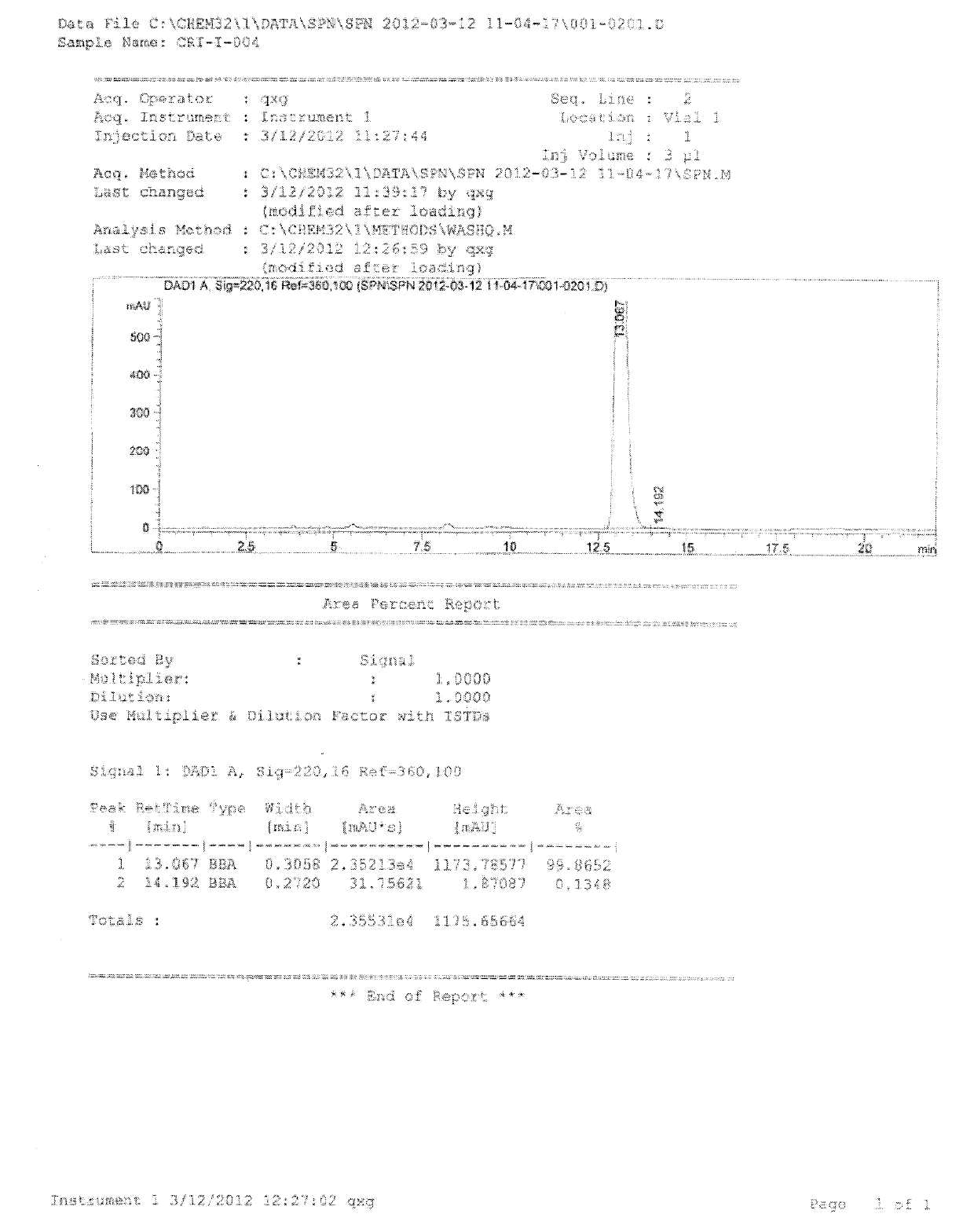
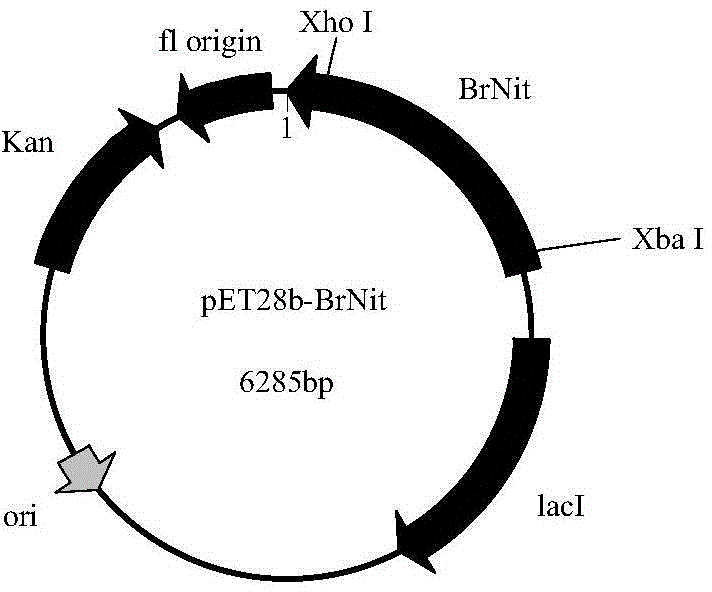
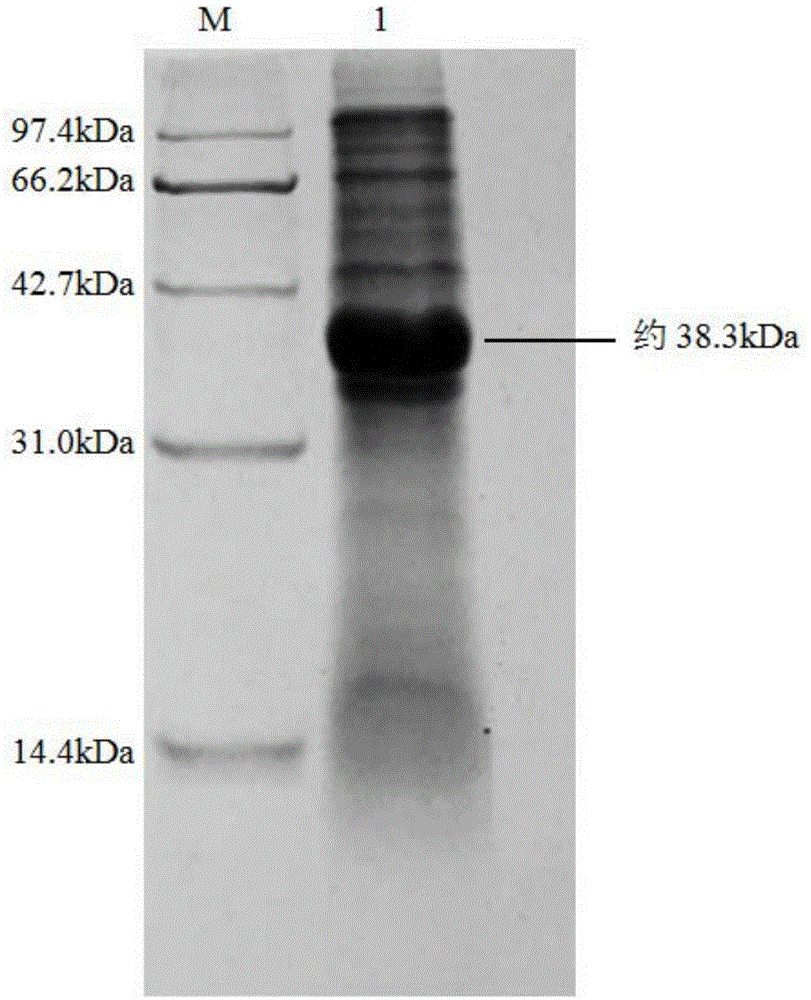
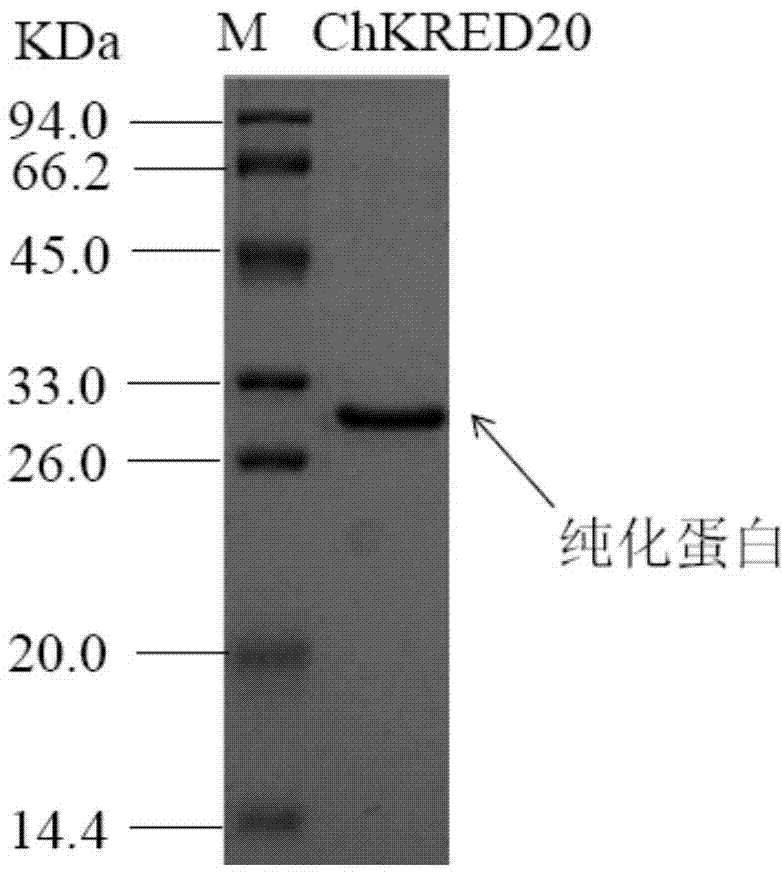
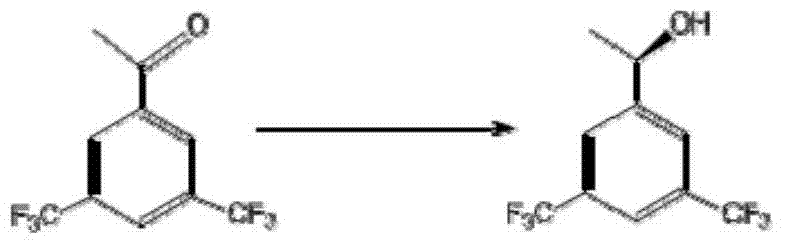
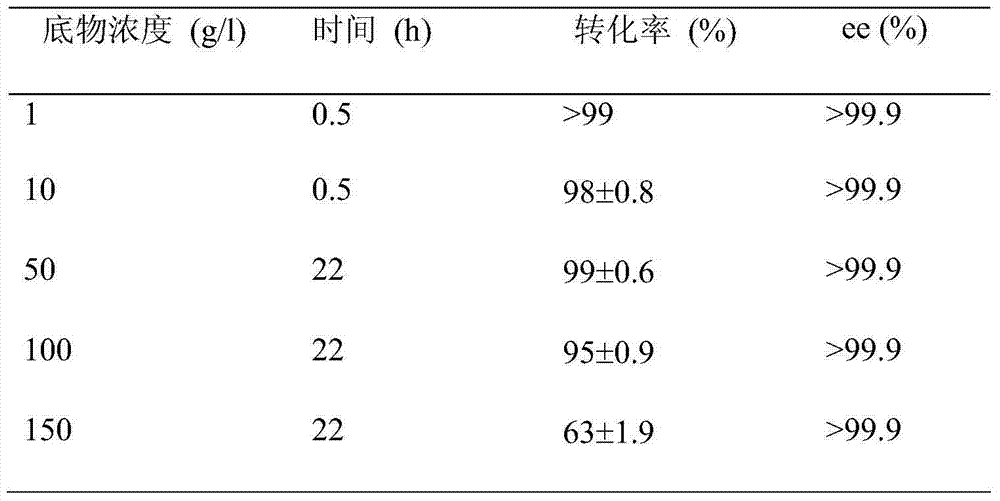
The invention discloses a strain of Chryseobacterium sp. CA49 (with an accession number of CCTCC M2012484), carbonyl reductase ChKRED20 coded by the genome of the strain and preparation of an aprepitant chiral intermediate (R)-1-[3,5-di(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol by using the original strain of Chryseobacterium sp. or the carbonyl reductase as a biocatalyst. The enantiomeric excess value of the produced intermediate is greater than 99.9%. Crude ChKRED20 enzyme powder can catalyze up to 200 g / L of a substrate and enables a conversion rate of more than 99% to be obtained in 24 h; a coenzyme circulating system is simple and cheap, the produced intermediate is easy to separate and purify, and a high recovery rate and good industrial application prospects are obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
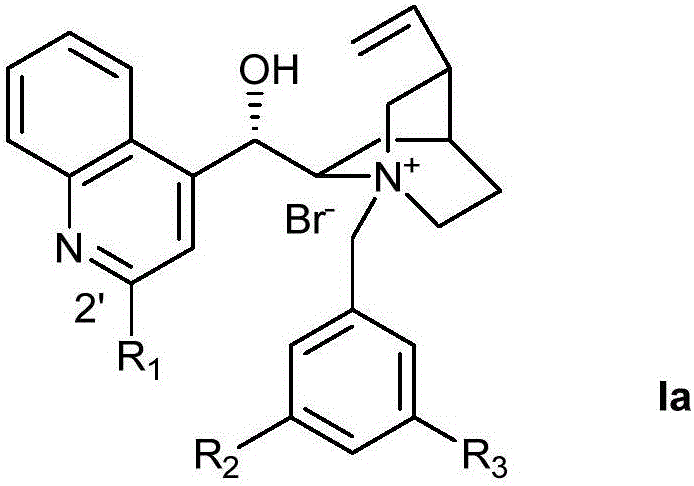
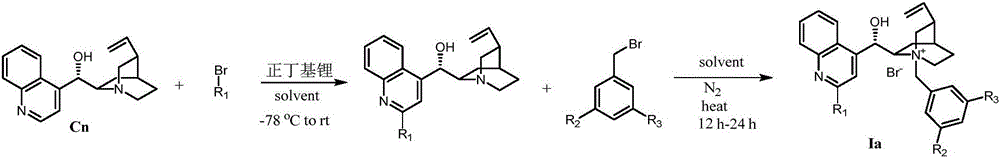
Novel method for preparing chiral alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound by using quinine C-2' derivative as catalyst
ActiveCN105152958AHigh catalytic activityAchieve asymmetric α-hydroxylationOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAlkaneHalohydrocarbon
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis, and provides a novel method for preparing a chiral alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound by using quinine C-2' derivative as a catalyst. The quinine C-2' derivative, of which the amount is 0.5-50 mol%, is used as the catalyst to react with a substrate and an oxidizer in an inert reaction solvent to prepare the chiral alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound, wherein the maximum yield is 99%, and the maximum enantiomeric excess value is 98%. The inert solvent comprises halohydrocarbon, aromatic hydrocarbon, alkane and the like. The oxidizer is common organic peroxide. The ratio of the oxidizer to the beta-dicarbonyl compound is 1-20, and the reaction temperature is -70 to 50 DEG C. The organic peroxide or oxydol can be used as the oxidizer to respectively obtain two alpha-hydroxylation products in different configuration.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing with recombinant carbonyl reductase
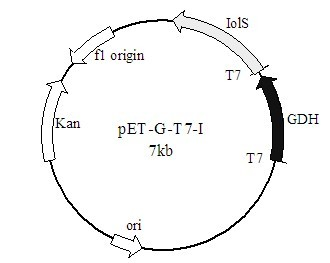
InactiveCN102618590AAvoid inhibitionImprove conversion abilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliEthyl butyrate
The invention discloses a method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing recombinant carbonyl reductase, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning gene segments of carbonyl reductase (IolS) and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) from bacillus subtilis CGMCC NO.1.1508, expressing an IolS gene and a GDH gene in series by adopting a dual-starter method to construct a recombinant plasmid pET24a-G-T7-I, and introducing the plasmid into escherichia coli BL21(DE3); and under the condition of not adding or adding a small amount of NADP+cofactors, performing biotransformation by taking a cell-free extract of the escherichia coli recombinant plasmid as a catalyst, 2-oxo-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate as a substrate and glucose as a substrate to obtain (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, wherein the enantiomeric excess value of the product is higher than 99.5 percent. In the method, IolS and GDH are co-expressed, so that efficient regeneration of an intra-cellular cofactor NADP(H) is realized, production cost is lowered, and a good industrial application prospect is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for synthesizing chiral cyclic amine through catalyzing asymmetric hydrogenation of quinolin-3-amine by iridium
ActiveCN104710406AEasy to separateHigh reactivityOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDiphosphinesIridium chloride
A catalysis system used by a method for synthesizing chiral cyclic amine through catalyzing asymmetric hydrogenation of quinolin-3-amine by iridium is a chiral diphosphine complex of iridium. A reaction is carried out under the following conditions: the temperature is 25-70DEG C; a solvent is a toluene / tetrahydrofuran mixed solvent (V / V=3:1); the pressure is 2-14atm; a ratio of a substrate to a catalyst is 25:1; and the catalyst is a (1,5-cyclooctadiene)iridium chloride dimer and chiral diphosphine ligand complex. A corresponding chiral cyclic amine derivative is prepared from quinolin-3-amine, and the enantiomeric excess value can reach 94%. The method has the advantages of simple and practical operation, easily available raw material, high enantioselectivity, good yield, and green, atom-economic and environmentally-friendly reaction.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
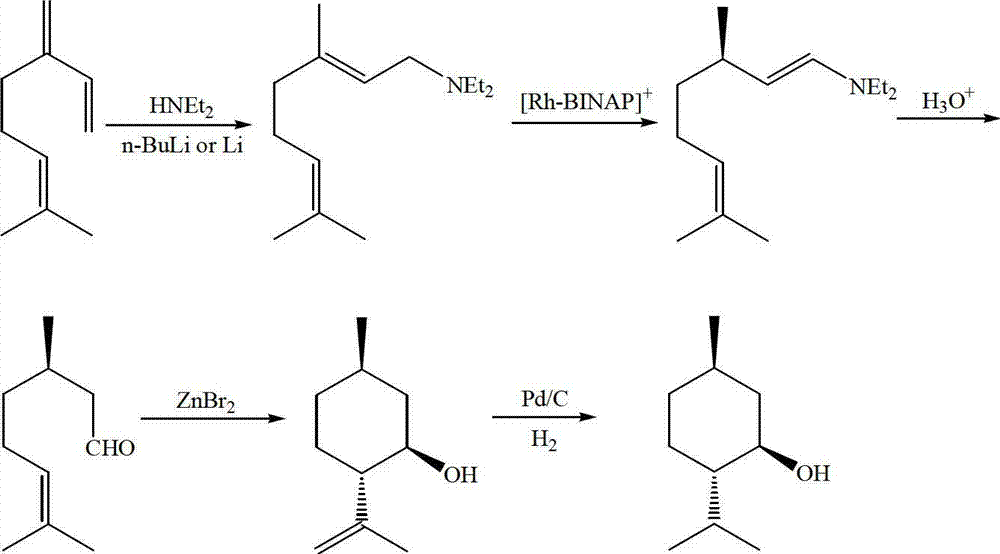
Method for asymmetric synthesis of levorotation menthol
InactiveCN103044204AEasy to makeMild reaction conditionsPreparation by hydrogenationLewis acid catalysisDihydropyridine derivatives
The invention discloses a method for asymmetric synthesis of levorotation menthol. The method comprises the following steps: citral is taken as an initial raw material, a dihydropyridine derivant is taken as a negative hydrogen source, chiral amine serves as a chiral auxiliary agent for catalytic and asymmetric hydrogenization synthesis of dextrorotation citronellal, the dextrorotation citronellal is catalyzed by Lewis acid for ring-closing synthesis of levorotation isopulegol, and the levorotation isopulegol is subject to catalytic hydrogenation to finally produce the levorotation menthol. The total yield of the levorotation menthol produced by adopting the method is larger than 60 percent, and the ee (enantiomeric excess) value is larger than 90 percent. The method has the characteristics of mild reaction conditions, simple synthetic process, simplicity in catalyst preparation, convenience in catalyst recovery and the like and is suitable for large-scale industrial production of levorotation menthol.
Owner:GUANGDONG FOOD IND INST +1
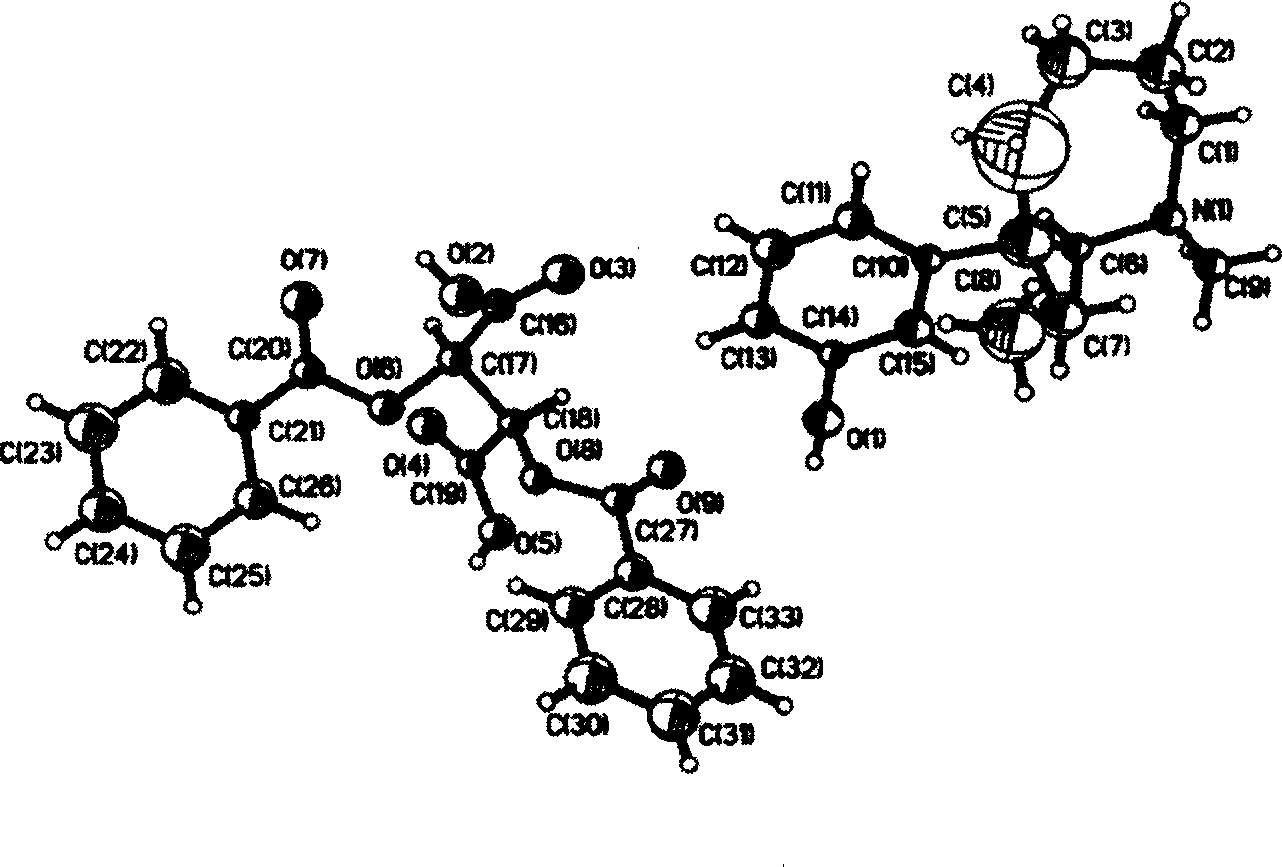
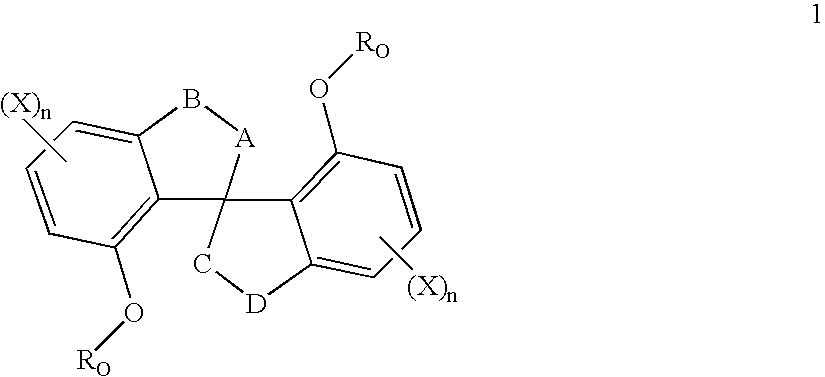
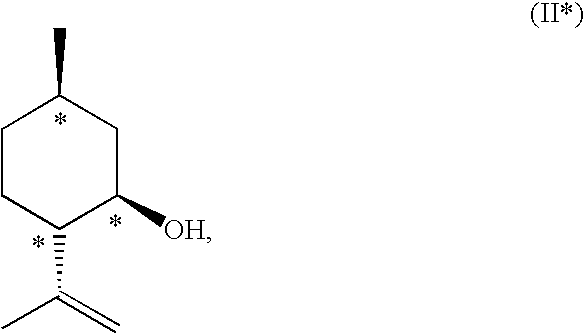
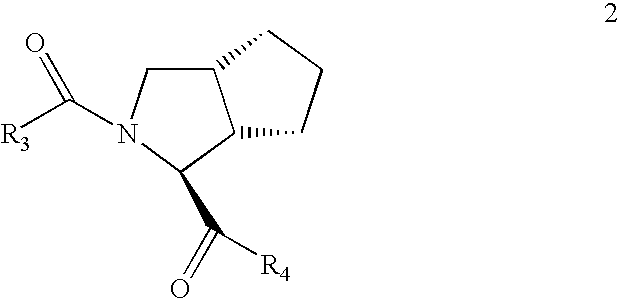
Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof
The present invention provides for a process for preparing racemic methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate, its corresponding salt: (2S, 3R, 4S)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate di-p-toluoyl-D-tartaric acid (“D-DTTA”) salt or a (2R, 3S, 4R)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric acid salt (“L-DTTA”) in a high enantiomeric excess. This invention also provides for a process for preparing a (2S, 3R, 4S)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate dibenzoyl-D-tartaric acid (“D-DBTA”) salt or a (2R, 3S, 4R)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate L-tartaric acid (“L-DBTA”) salt in a high enantiomeric excess. Further, this invention provides a process for preparing intermediates II, IIB, III, IV, IV salt, V, VI, and VII.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
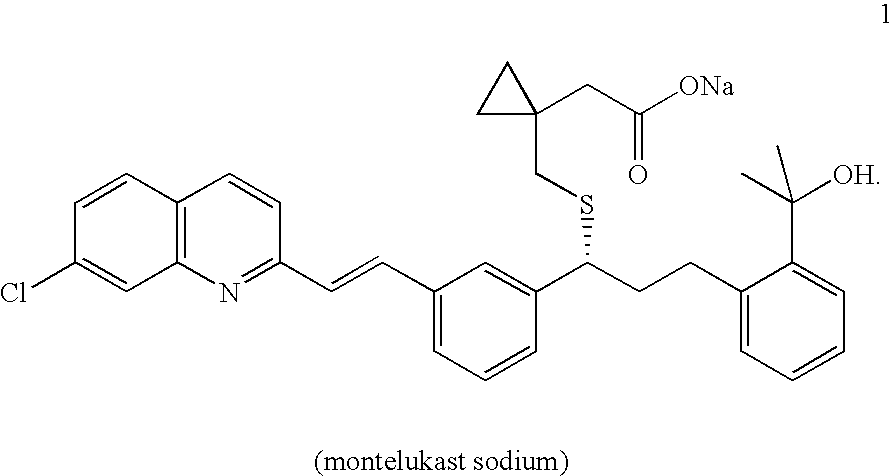
Process for preparing montelukast and precursors thereof
The present invention provides a process for stereoselectively reducing 2-[3-[3-[2-(7-chloro-2-quinolinyl)ethenyl]-phenyl]-3-oxopropyyl]benzoic-acid methyl ester, to produce to produce methyl 2-[3-(S)-[3-[2-(7-chloro-2-quinolinyl)-ethenyl]phenyl]-3-hydroxypropyl]benzoate, and a process for producing montelukast or a salt thereof. The present invention further provides a process for purifying methyl 2-[3-(S)-[3-[2-(7-chloro-2-quinolinyl)-ethenyl]phenyl]-3-hydroxypropyl]benzoate. The reduction process of the present invention uses a chiral reagent and can produce the desired reduction product in high enantiomeric excess (ee).
Owner:CHEMAGIS
Method for biologically preparing (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyric acid ethyl ester with recombinant escherichia coli expressed ketoreductase
InactiveCN103173503AHigh optical purityGenerate efficientlyMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a method for biologically preparing (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyric acid ethyl ester with recombinant escherichia coli expressed ketoreductase and application thereof in preparing (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyric acid ethyl ester through asymmetric reduction of 4-chloroacetoacetic acid ethyl ester. The recombinant escherichia coli for expressing the gene of the ketoreductase (KRED) is coupled with glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) so that the escherichia coli cell is recombined into a catalyst; efficient preparation of (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyric acid ethyl ester through asymmetric reduction of 4-chloroacetoacetic acid ethyl ester in a single water phase is realized no matter in the presence of or in the absence of coenzyme NAD(P)H; and the molar transformation rate is higher than 92% and the enantiomer excess (e.e.) of the product is 100%.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV +1
Process for the preparation of galanthamine
PCT No. PCT / GB97 / 00023 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 2, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 2, 1998 PCT Filed Jan. 6, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 25330 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 17, 1997The subject invention concerns a process for the preparation of enantiomerically-enriched galanthamine from racemic galanthamine, and a process for increasing the enantiomeric excess of enantiomerically-enriched galanthamine, by direct crystallization of galanthamine salts.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Method for asymmetrically synthesizing chiral beta-acetenyl ketone from beta-ketonic acid
InactiveCN104513146AHigh reactivityHigh stereoselectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsKetonic acidsKetone
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing chiral beta-acetenyl ketone by catalytic intermolecular decarboxylation from beta-ketonic acid and a propargyl compound. A chiral copper catalyst adopted in the invention is synthesized in stiu from a copper salt and a chiral P,N,N-tridentate ligand in various polar solvents and nonpolar solvents. According to the invention, various chiral beta-acetenyl ketone compounds with substituent groups can be synthesized conveniently, and can obtain a percent enantiomeric excess as high as 95%. The method in the invention is advantaged by operational simplicity, available raw materials, wide substrate application range, high enantioselectivity, and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for synthesizing chiraltetrahydro naphthalenederivate through asymmetric hydrogenation on isoquinoline by means of iridium catalyst
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a chiraltetrahydro naphthalenederivate through asymmetric hydrogenation on isoquinoline by means of an iridium catalyst. A catalysis system applied in the method is a chiral bi-phosphine complex of metal iridium. The reaction is carried out under the conditions that the temperature is 25-60 DEG C; the volume ratio of tetrahydrofuran to dichloromethane in a solvent, namely a mixed solvent of tetrahydrofuran and dichloromethane is 1:1; the pressure is 13-50 Mpa; the ratio of a substrate to a catalyst is 50:1; the catalyst is a coordination compound of a (1,5-cyclooctadiene) iridium chloridedipolymer and a chiral bi-phosphine ligand. The corresponding chiral 1-position or 3-position substituted tetrahydro naphthalenederivate through hydrogenation on isoquinoline, and the enantiomeric excess of the derivate can reach 96%. The method is simple and practical in operation, raw materials are easy to obtain, the enantioselectivity is high, the yield is high, the reaction has atom economy, and the environment is friendly.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and methods for two-dimensional chromatography
ActiveUS20160238573A1Reduce the amount requiredComponent separationSolid sorbent liquid separationAnalyteDrug compound
Provided are two-dimensional chromatography systems and methods for separating and / or analyzing complex mixtures of organic compounds. In particularly, a two-dimensional reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC)-supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) system is described including a trapping column at the interface which collects the analytes eluted from the first dimension chromatography while letting the RPLC mobile phase pass through. The peaks of interest from the RPLC dimension column are effectively focused as sharp concentration pulses on the trapping column, which is subsequently injected onto the second dimension SFC column. The system can be used for simultaneous achiral and chiral analysis of pharmaceutical compounds. The first dimension RPLC separation provides the achiral purity result, and the second dimension SFC separation provides the chiral purity result (enantiomeric excess).
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Preparation method of crizotinib intermediate (1S)-1-(2, 6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethanol
ActiveCN103319311AHigh optical purityGood choiceOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogenMedicinal chemistry
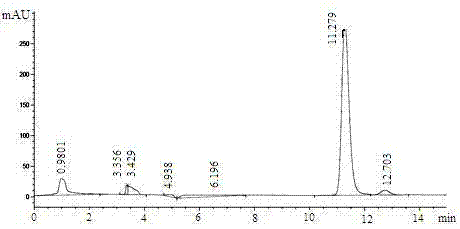
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical synthesis, and more specifically relates to a preparation method of a crizotinib intermediate (1S)-1-(2, 6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethanol. 1-(2, 6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl) ethanone is taken as a raw material, and the crizotinib intermediate (1S)-1-(2, 6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethanol is obtained in the presence of a chiral catalyst, an alkali and hydrogen, wherein the chiral catalyst is a compound having the general structure shown in formula (I). The high purified (1S)-1-(2, 6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethanol is produced with the chiral catalyst, and the enantiomeric excess (ee) value of the product is determined to be more than 99% by chiral HPLC. When the mole ratio of the chiral catalyst to a reaction substrate is in a range of 1 / 100000 to 1 / 1000000, the optical purity can be achieved, the reaction substrate can be converted completely, and reaction yield is almost qualified.
Owner:浙江瑞博制药有限公司
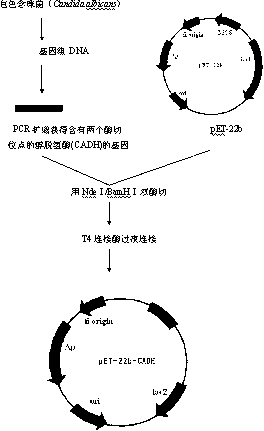
Nitrilase, encoding genes, carrier and application
InactiveCN104962540AAtom economy is highHigh potential for industrial applicationHydrolasesFermentationBrassica rapaBirdsrape Mustard
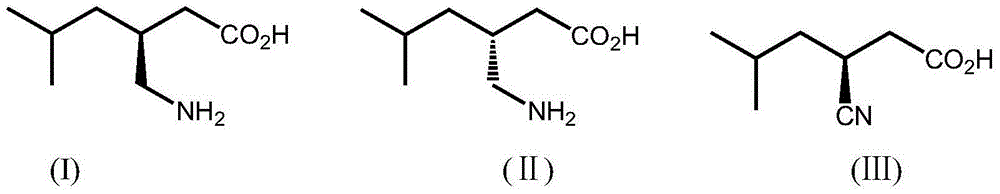
The invention discloses nitrilase from brassica rapa, encoding genes and an application of the encoding genes to the preparation of pregabalin chiral intermediate (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid through biocatalysis, and an amino acid sequence of the nitrilase is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention provides novel nitrilase for preparing the (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid with high region and high stereoselectivity through hydrolysis, the concentration of hydrolysis substrates of the nitrilase can reach more than 1 M, and an ee (enantiomeric excess) value is kept more than 99 percent. The pregabalin important chiral intermediate (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid can be prepared through the nitrilase; a preparation method of the (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid has the advantages of high atom economy, mild conditions, environmental friendliness and the like and has high industrial application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Application of aldo-keto reductase in catalytic generation of (R)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate
InactiveCN104726507ADisinhibition effectImprove conversion abilityBacteriaOxidoreductasesHydroxybutyric acidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses an application of aldo-keto reductase in catalytic generation of (R)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate. With aldo-keto reductase of which an amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 as a catalyst, with 4-ethyl acetoacetate as a substrate and NADPH as a cofactor, the (R)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate is prepared by asymmetric reduction. The aldo-keto reductase of which the amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 is applied to the 4-ethyl acetoacetate to prepare the (R)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate in an asymmetric reduction manner for the first time, so that a good effect is obtained; the enzyme activity can be up to 8.1U / mg; the conversion ratio of the aldo-keto reductase on the substrate can be up to 99.8%; the enantiomer excess value of the product is greater than 995; the yield is high; and the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation method for ketone-derived N-alkylimine
InactiveCN102050688AHigh enantioselectivityCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationAsymmetric hydrogenationKetone
The invention discloses a method for performing the asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation of ketone-derived N-alkylimine. In the method disclosed by the invention, the catalytic hydrogenation of the ketone-derived N-alkylimine is performed in the presence of a chiral catalyst formed by a chiral diamine ligand and a transitional metal to obtain a chiral amine product with high yield and high enantioselectivity. The enantiomeric excess of a chiral amine product formed by the hydrogenation of an acyclic N-alkylimine substrate may reach 98 percent ee; and the enantiomeric excess of a chiral amine product formed by the hydrogenation of an exocyclic N-alkylimine substrate may reach over 99 percent ee. The method disclosed by the invention realizes the asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation of ketone-derived N-alkylimine with high enantioselectivity, and the obtained chiral amine product is an important medicinal and material intermediate and has a bright actual application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing an intermediate of sitagliptin via enzymatic conversion
The invention provides a process for preparing 3-hydroxy-1-(3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one (Formula I), into its racemic (R / S) form or any of its optically active (S) or (R) forms or enantiomeric excess mixture of any of the forms comprising: a) reacting 4-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-one of formula (III) with a suitable oxidoreductase enzymes or its suitable variants in the presence of suitable conditions and co-factor; and b) isolating 3-hydroxy-1-(3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one, into its racemic (R / S) form or any of its optically active (S) or (R) forms or enantiomeric excess mixture of any of the forms.
Owner:CADILA HEALTHCARE LTD
Method for biological catalysis of unsymmetrical reduction carbon based compound in water/ion liquid diphasic system
InactiveCN101319236AEasy to separateEasy to recycleMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidBiocompatibility Testing
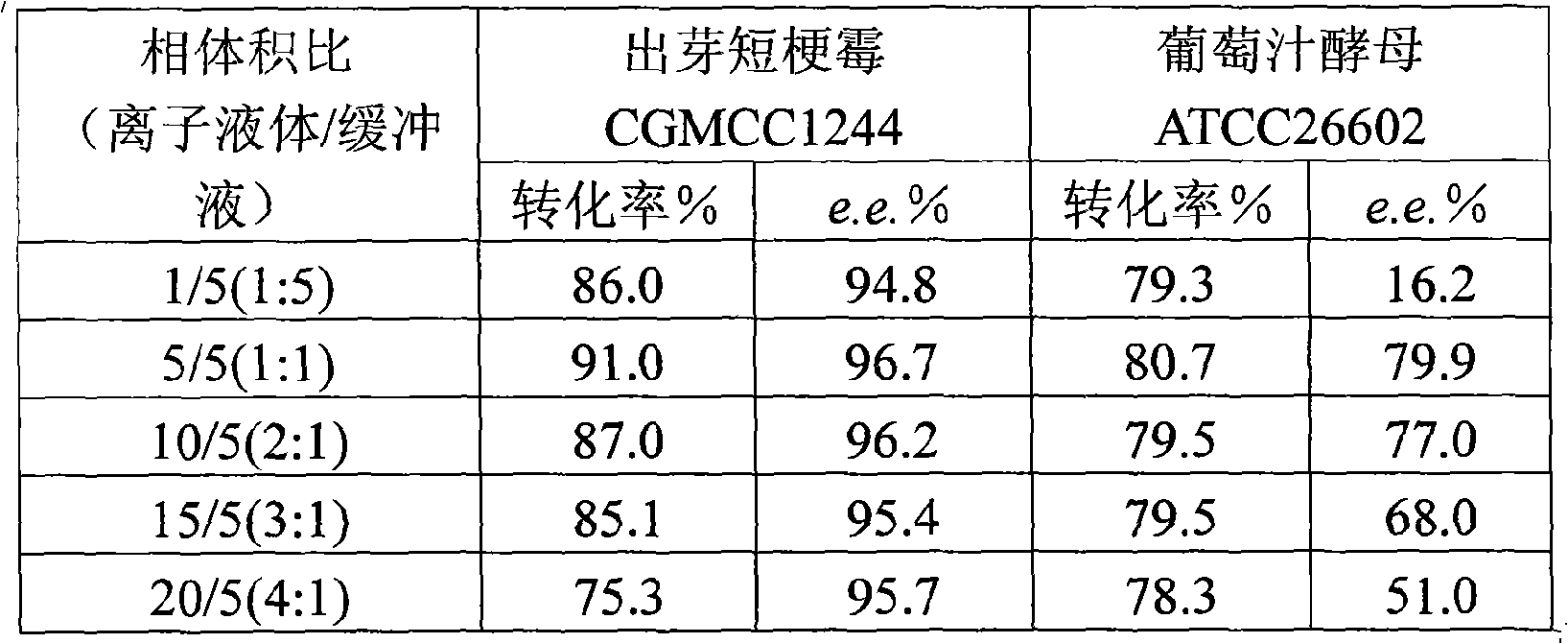
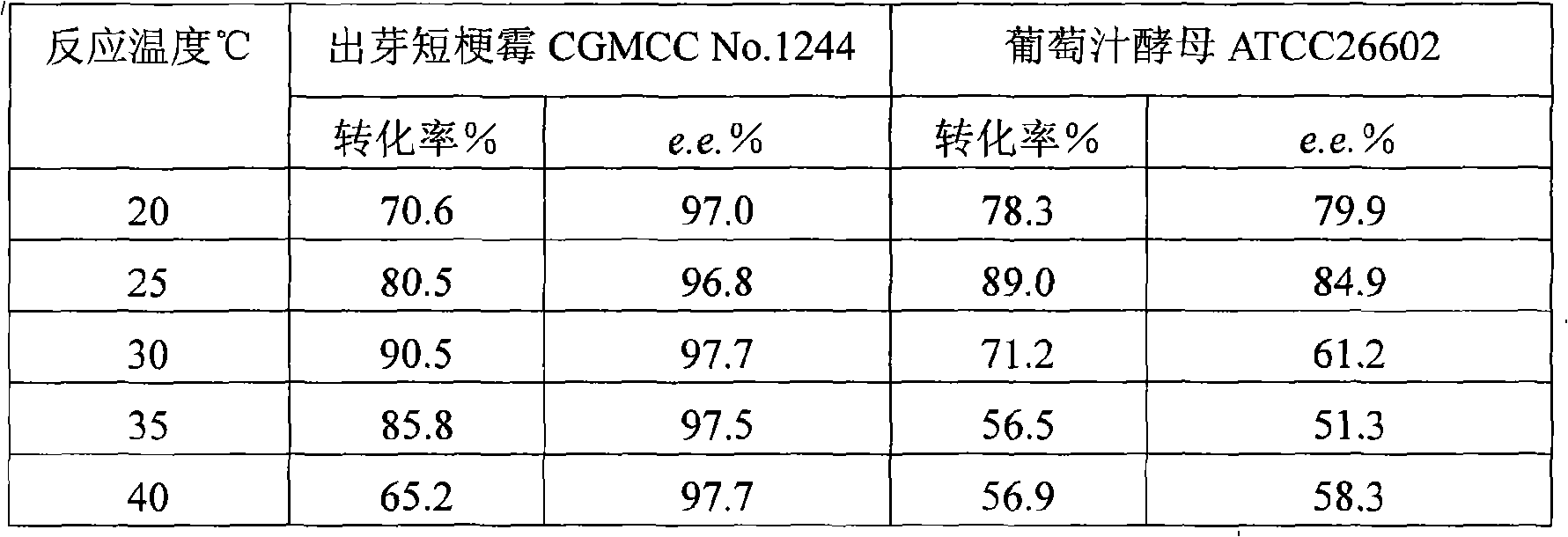
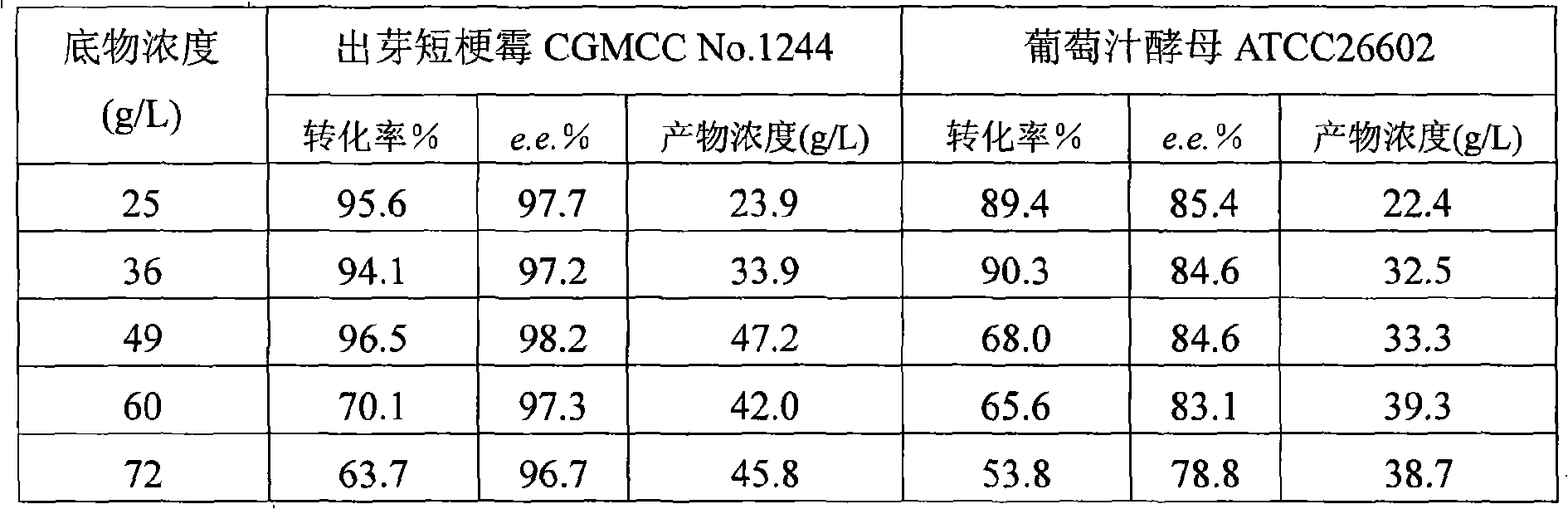
The invention discloses a method for asymmetrically reducing a carbonyl compound by biocatalysis in a water / ion liquid biphasic system, which belongs to the biochemical engineering technical field. The method takes a selective strain producing carbonyl reductase as a starting strain, and prochiral ketone as a substrate to perform reducing preparation of corresponding chiral alcohol in the water / ion liquid biphasic system; the method comprises the following steps that: Aureobasidium pullulans CGMCC No.1244 is used to catalyze 4-chloro-acetoacetic acid ethyl ester to perform the asymmetrical reduction preparation of (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyric acid ethyl ester, and Saccharoinyces uvarum ATCC 26602 is used to catalyze 4,4,4-trifluoroacetoacetate to perform the asymmetrical reduction preparation of (R)-4, 4, 4-trilfluoro-3-hydroxybutyrate. The method shows the advantages of no toxicity, no smell, difficult volatilization, good biocompatibility, no environmental pollution, simple product separation, easy recovery, repeated use and so on, of ion liquid. At the same time, the method improves the transformation rate, the concentration and an enantiomeric excess value of a reaction product, and quickens the process of the reaction.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for synthesizing derivatives of chiral tetrahydroquinoline by catalyzing asymmetric hydrosilylation with iridium
InactiveCN101845016AReduce usageHigh reactivityOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIridiumQuinoline
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
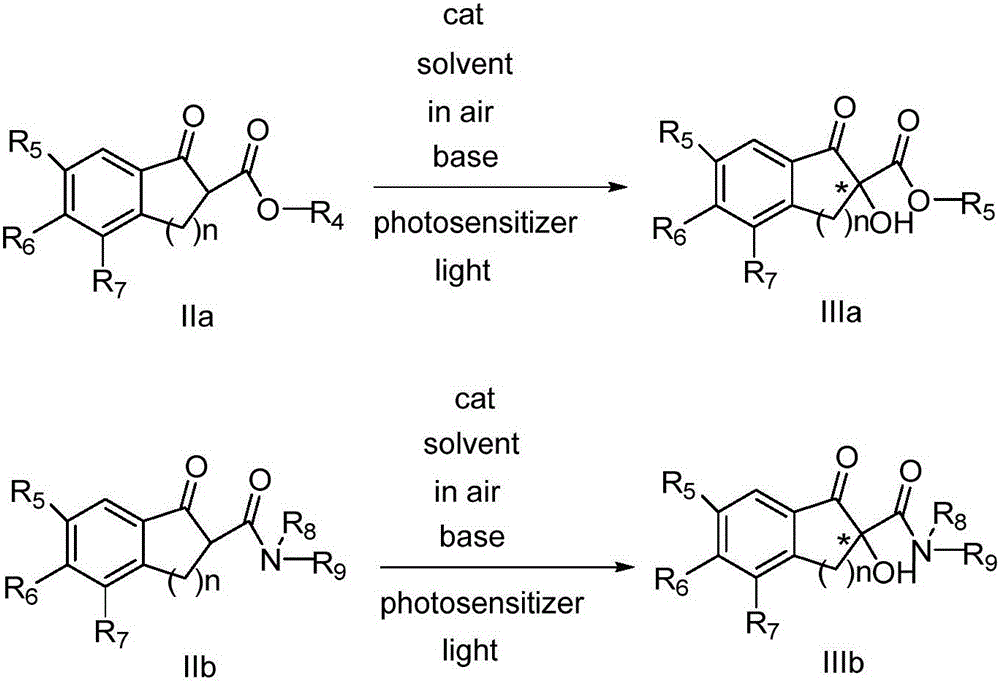
Novel method for asymmetric alpha-hydroxylation of photo-oxygenation beta-dicarbonyl compound based on C-2' phase transfer catalyst
InactiveCN105732387AHigh catalytic activityGood substrate applicabilityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPhotosensitizerOrganic synthesis
The invention belongs to the technical fields of organic synthesis and provides a novel method for asymmetric alpha-hydroxylation of a photo-oxygenation beta-dicarbonyl compound based on a C-2' phase transfer catalyst.The beta-dicarbonyl compound, the cinchona alkaloid C-2' phase transfer catalyst and an organic photosensitizer are stirred in a solvent, alkali is added, strong stirring reaction is performed in the air under the condition of visible light, the reaction temperature is 50-70 DEG C, the reaction time is 1-4 hours, and a chiral alpha-hydroxyl-beta-dicarbonyl compound with the yield no lower than 70% and the enantiomeric excess selectivity no lower than 60% ee is obtained; derivatization is conducted on a cheap cinchona alkaloid C-2' potential easy to obtain a series of chiral phase transfer catalysts having higher catalytic activity, molecules are successively oxidized into an oxidant, and the asymmetric alpha-hydroxylation of the photo-oxygenation beta-dicarbonyl compound is achieved.The method has good substrate applicability and environmental friendliness.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




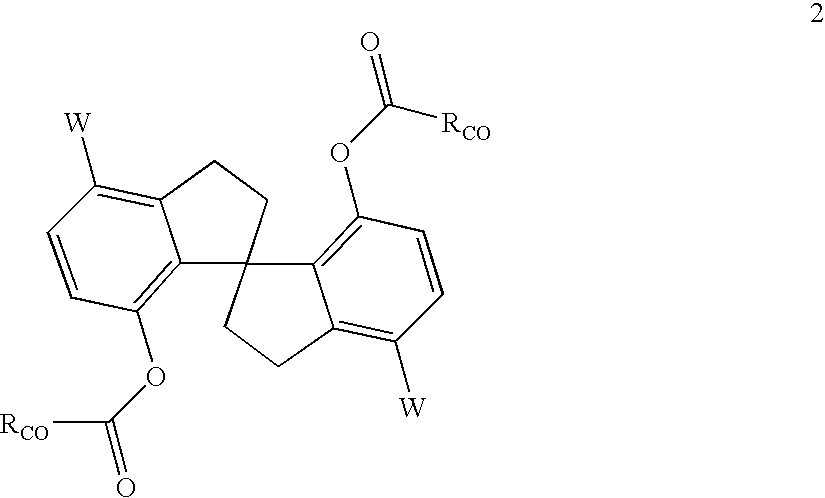







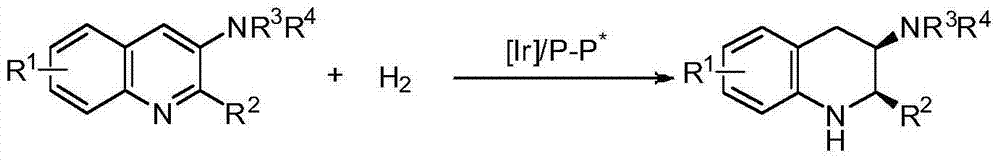



![Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/616865f1-32fc-4a7d-a092-5502ba2d7d9f/US07723531-20100525-C00001.png)
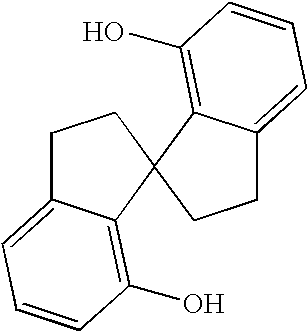
![Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/616865f1-32fc-4a7d-a092-5502ba2d7d9f/US07723531-20100525-C00002.png)
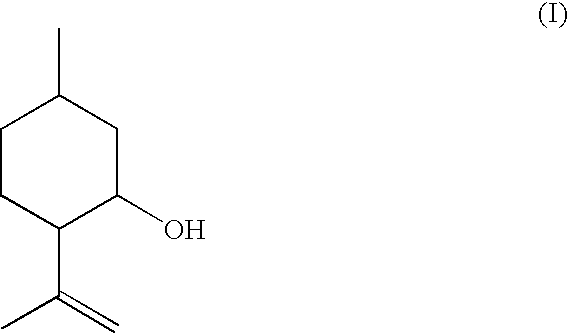
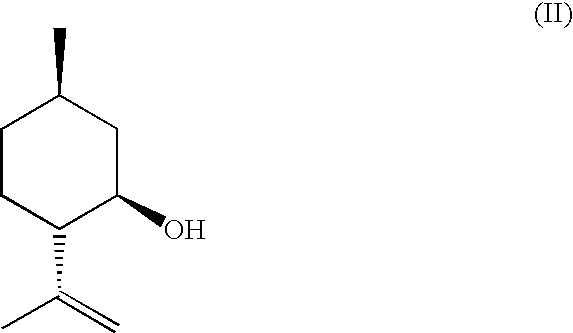
![Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/616865f1-32fc-4a7d-a092-5502ba2d7d9f/US07723531-20100525-C00003.png)