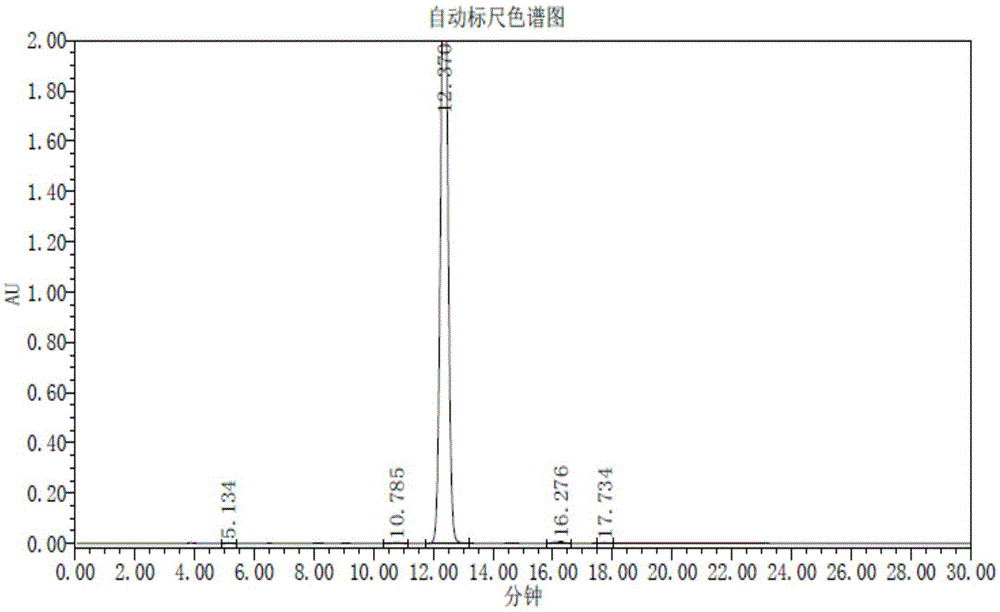
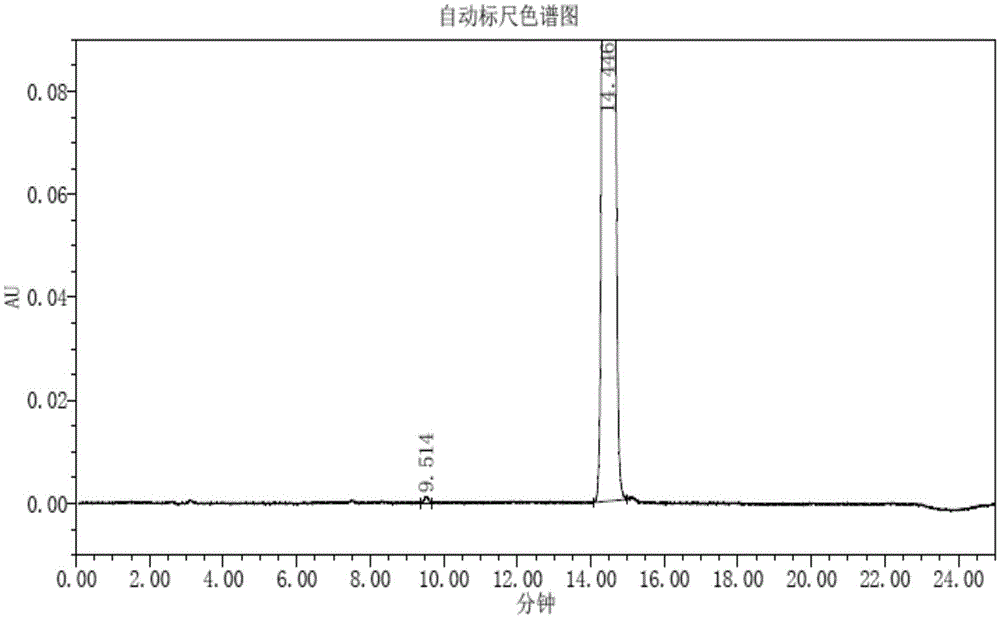
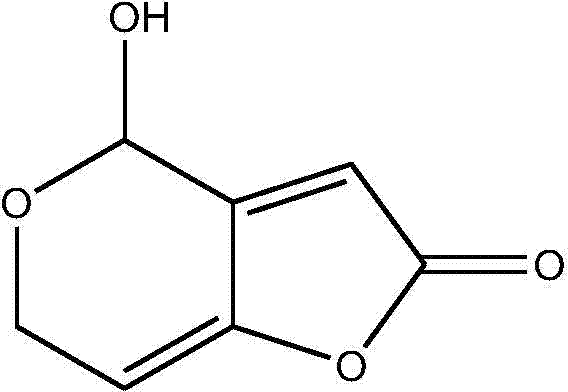
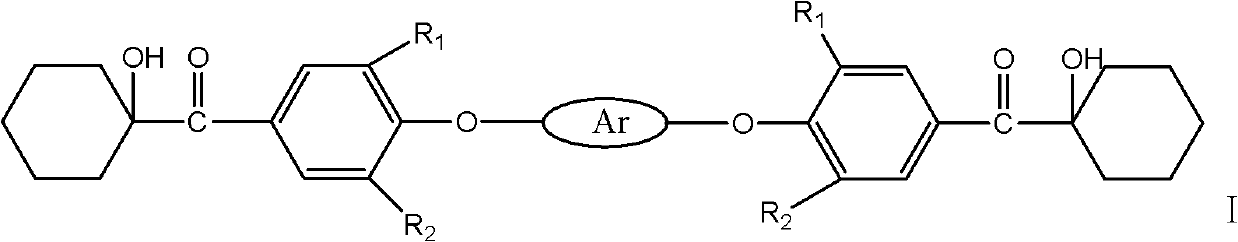
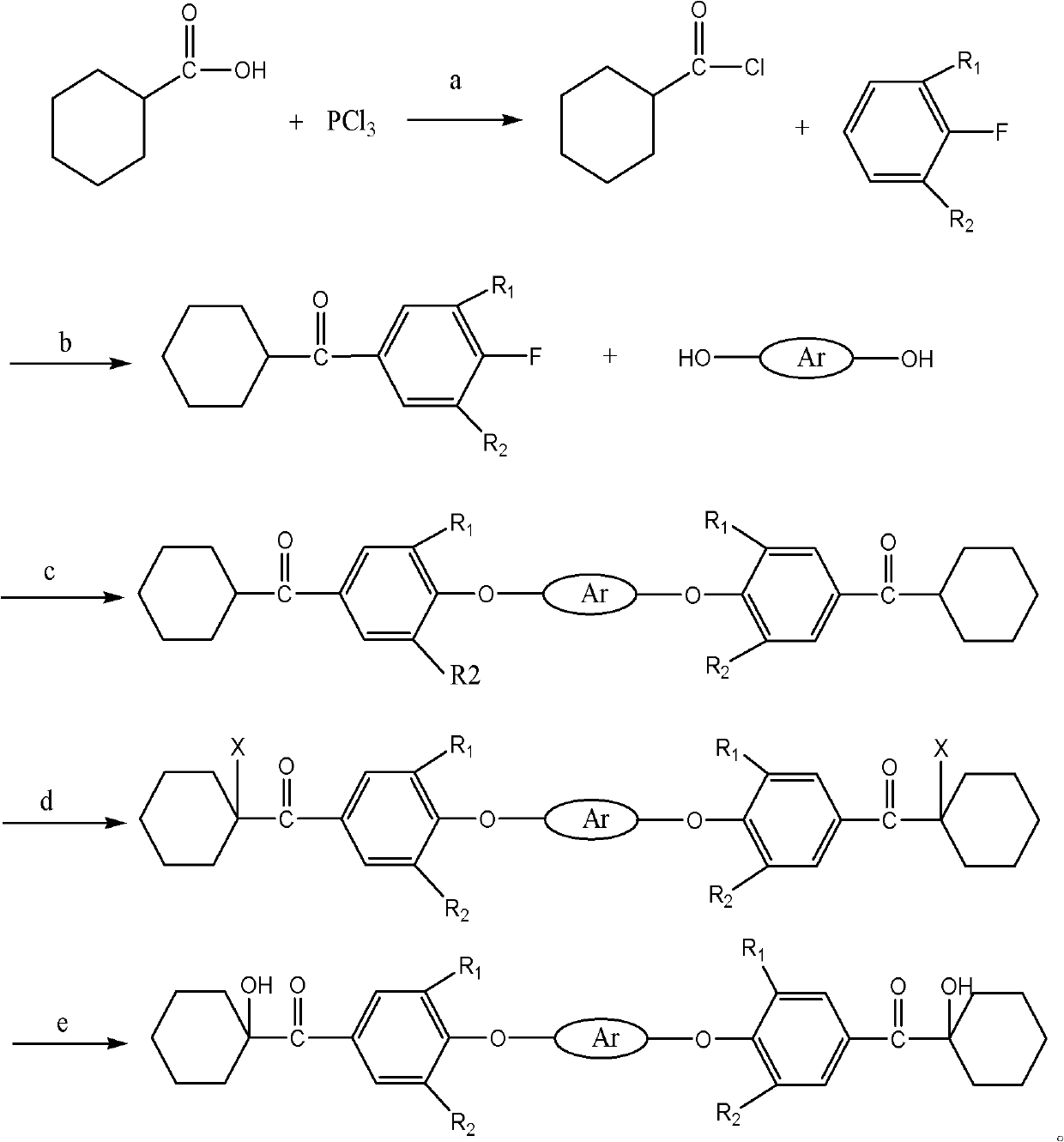
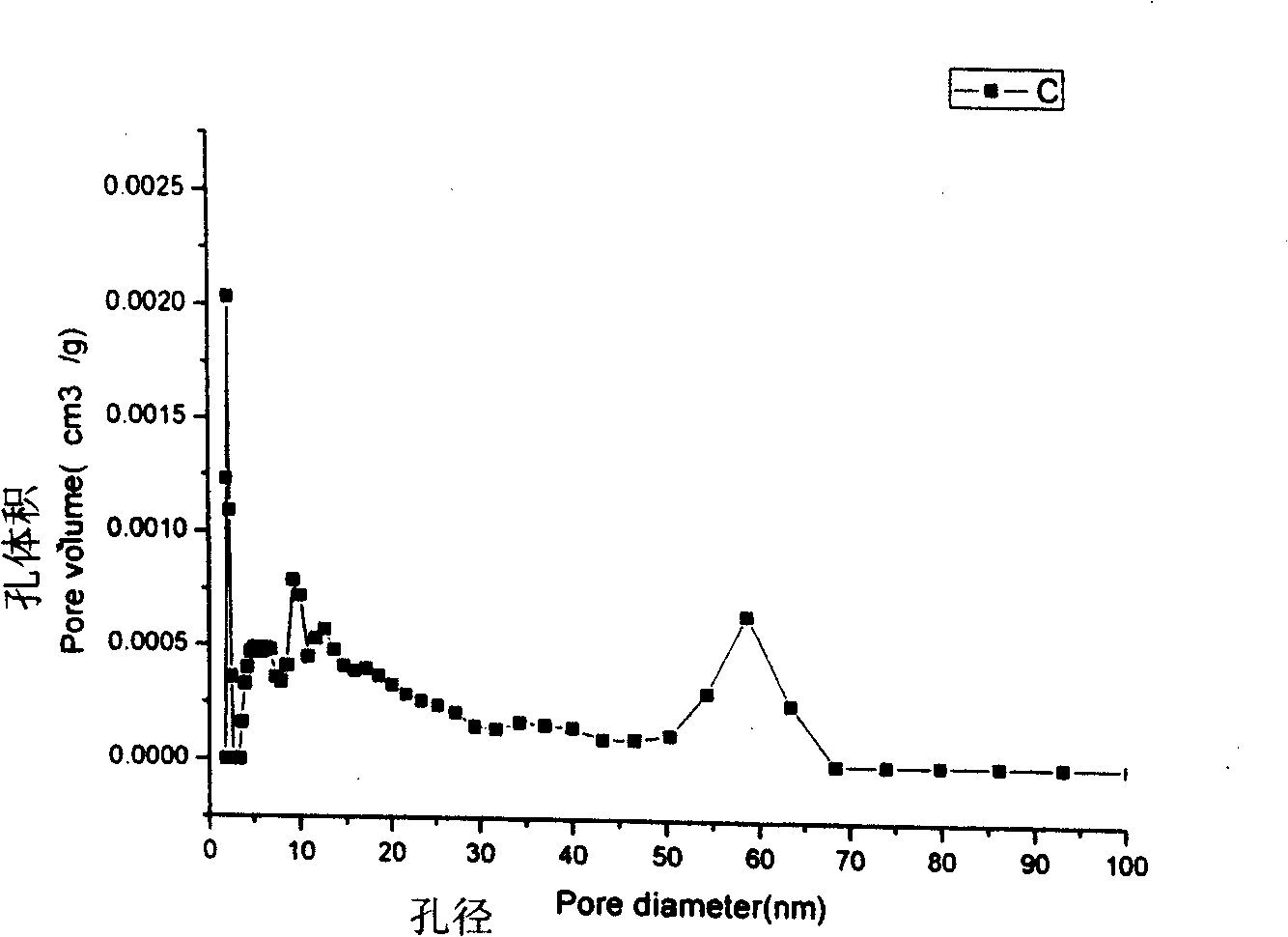
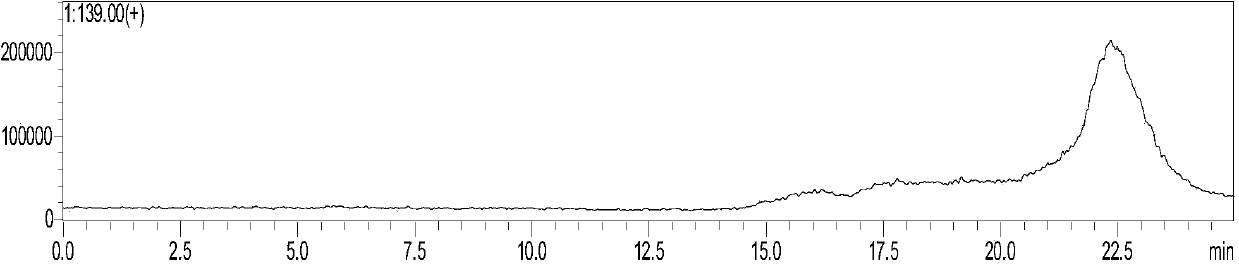
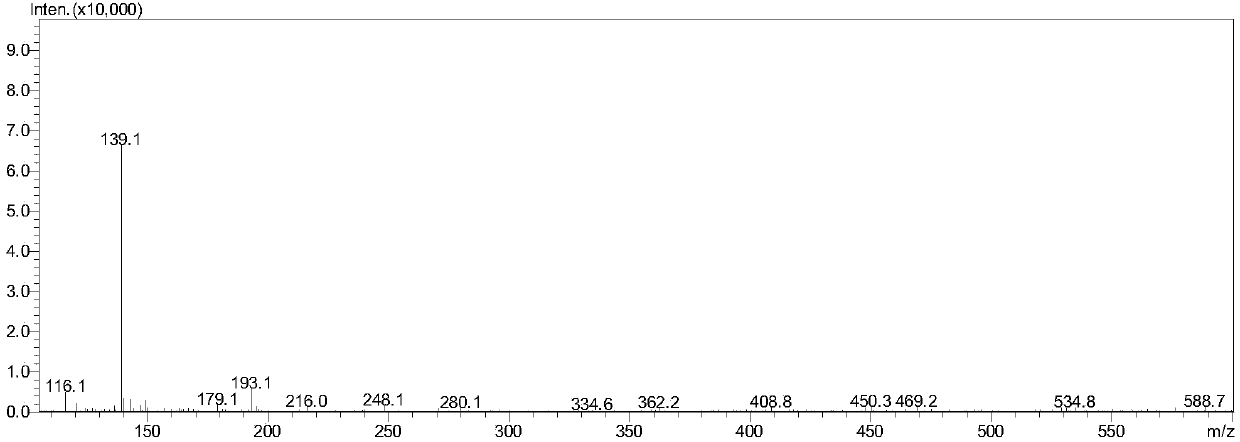
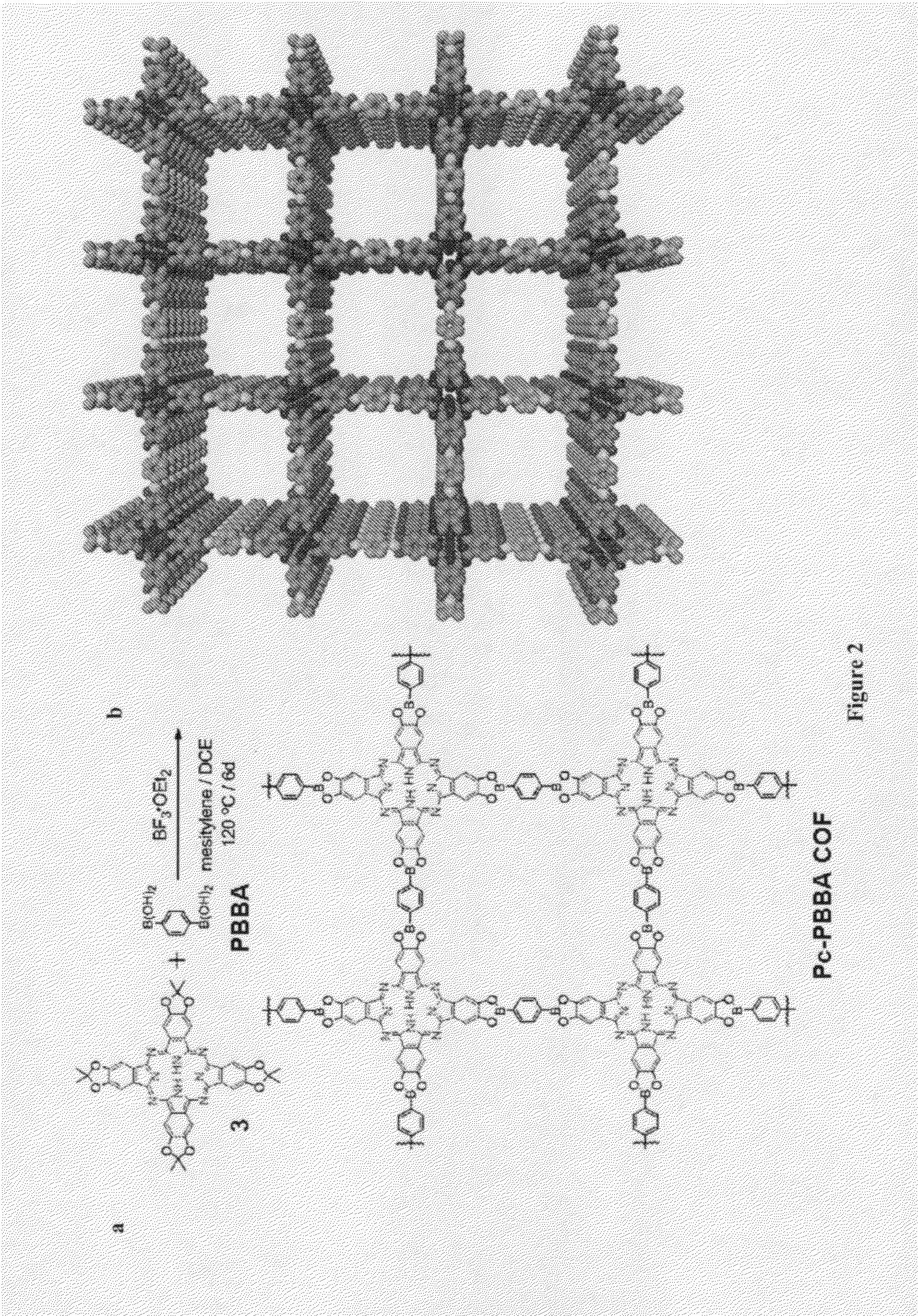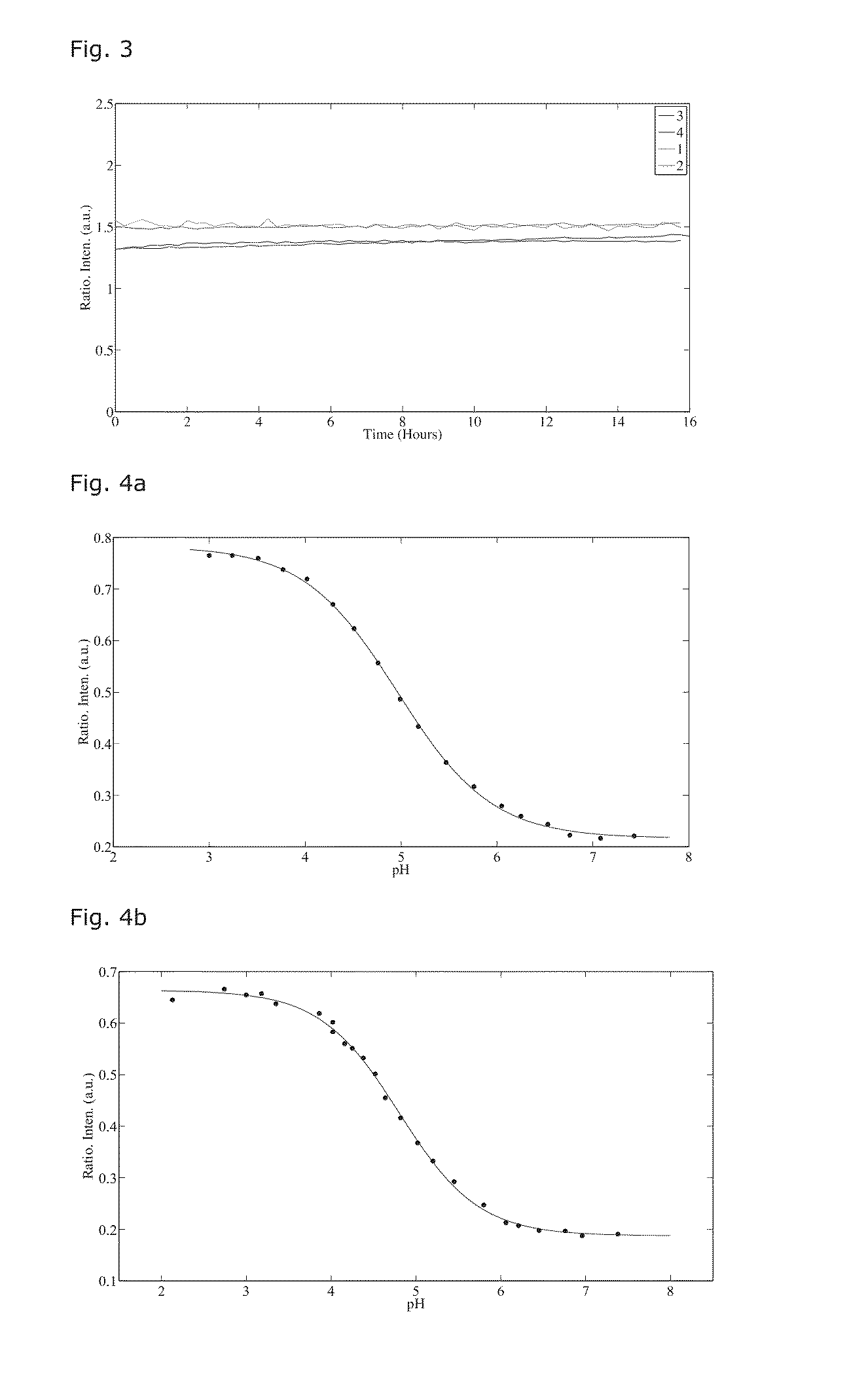Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
750 results about "Lewis acid catalysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp² or sp³), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.
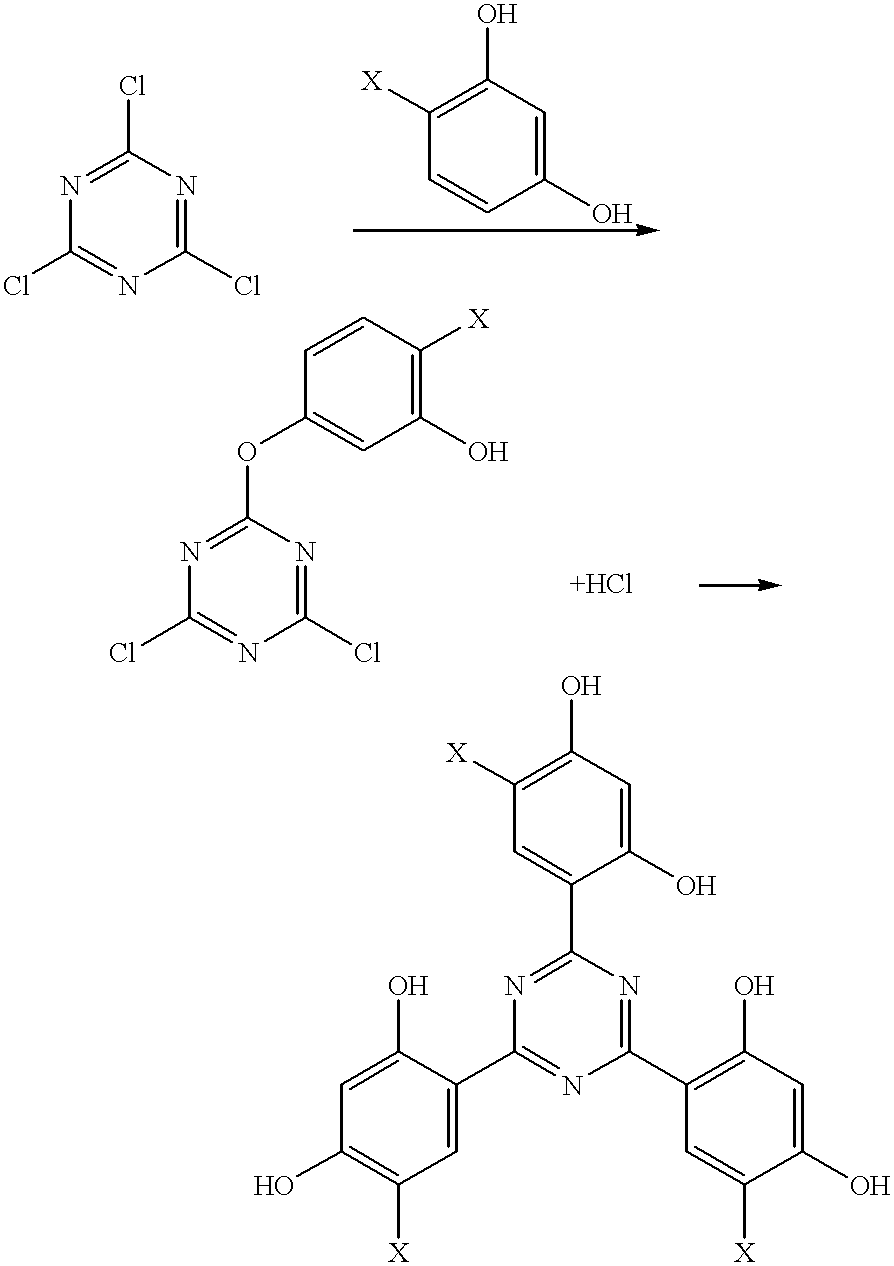
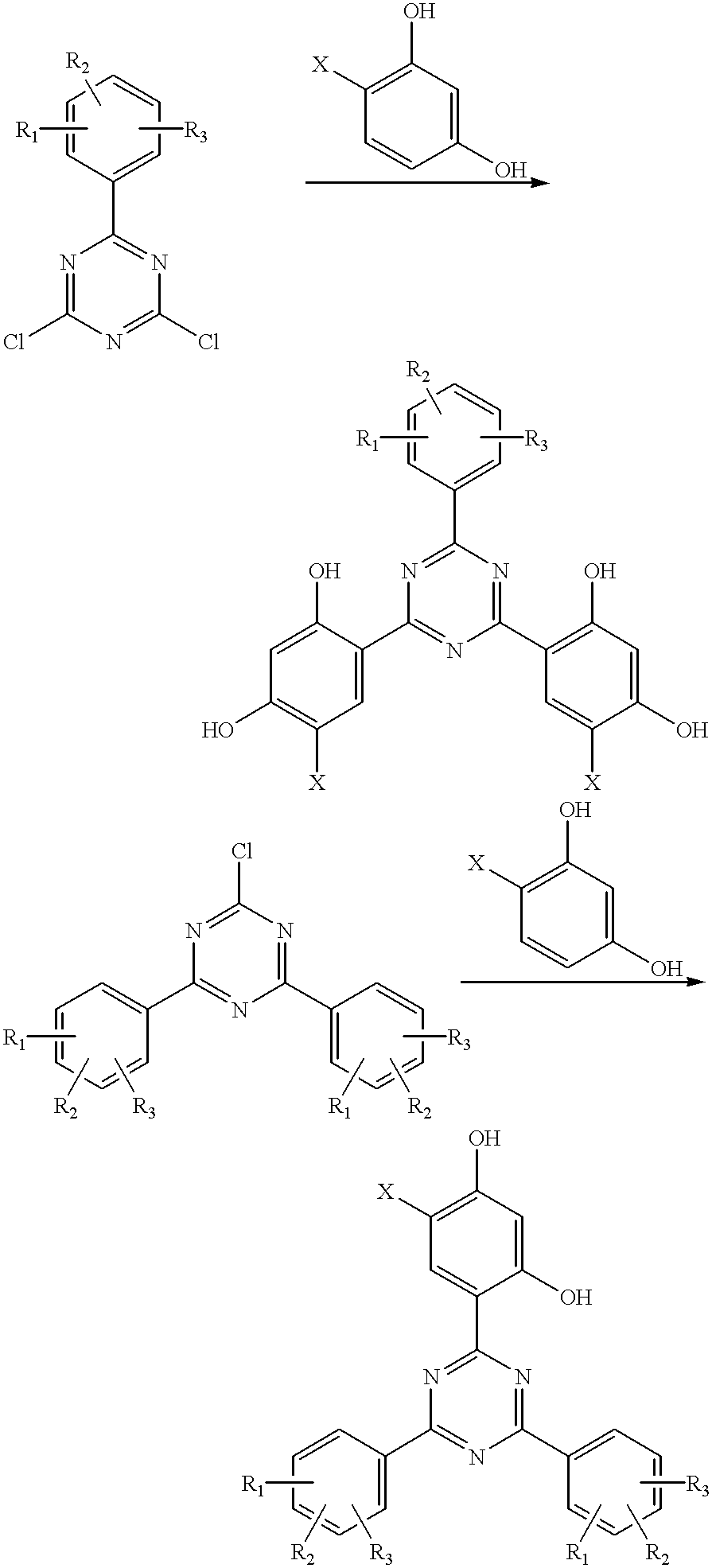
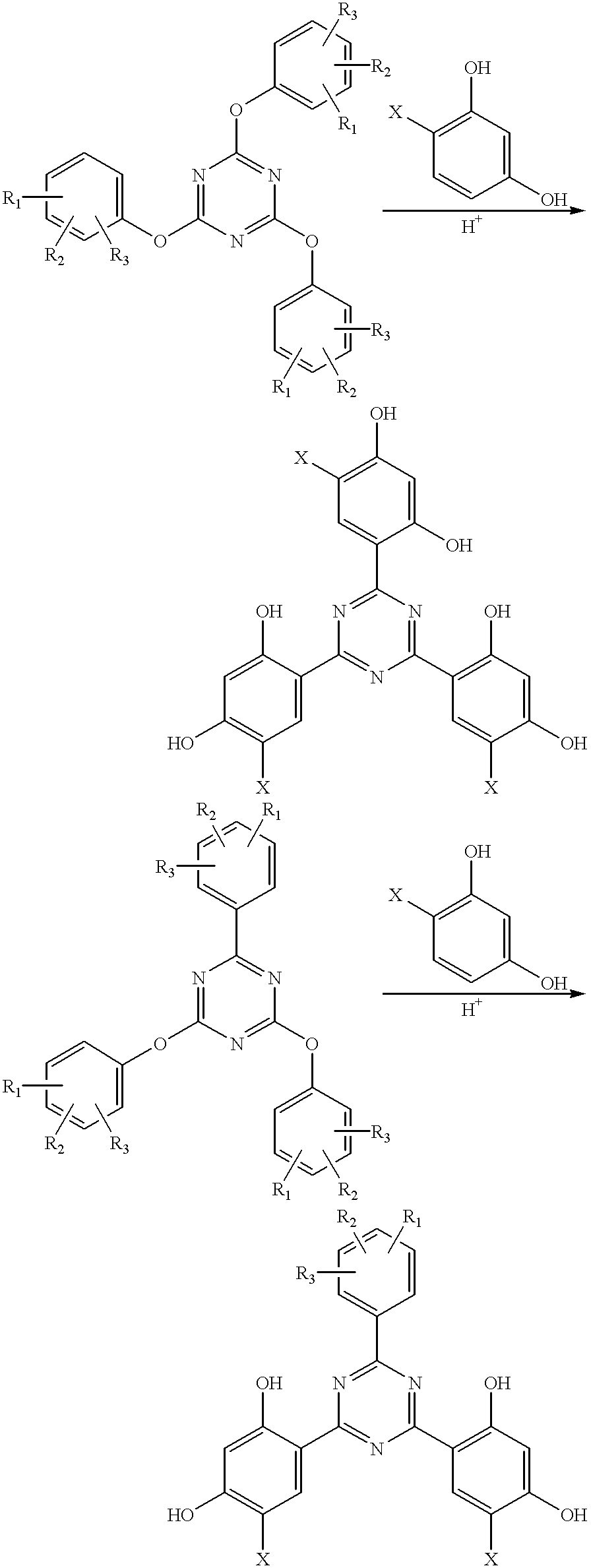
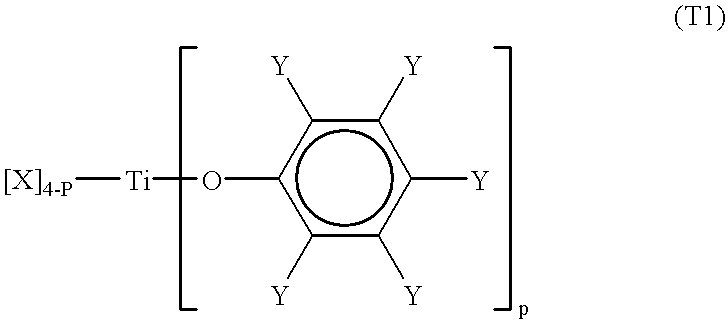
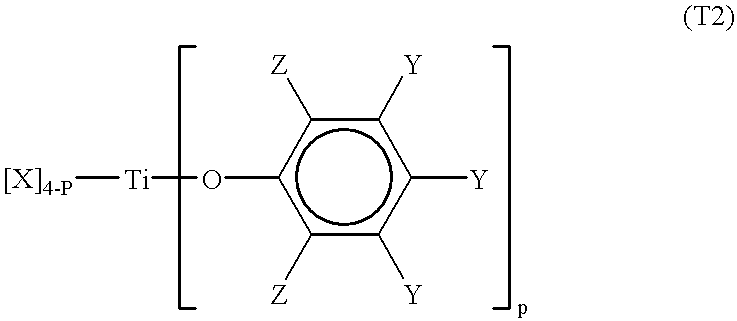
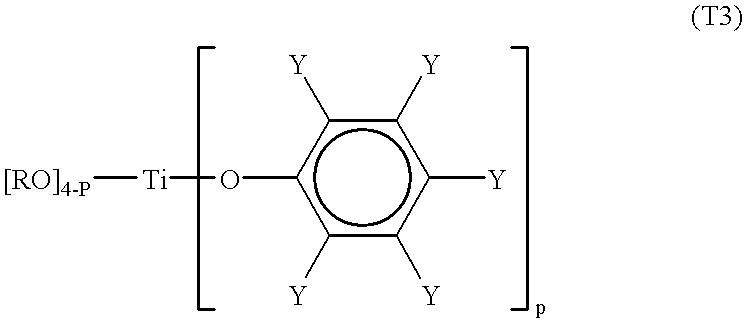
Methods for the preparation of tris-aryl-o-hydroxyphenyl-s-triazines
InactiveUS6242598B1Reduce in quantityPoor leaving groupOrganic chemistryLewis acid catalysisResorcinol
A process for preparing 2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-4.6-diaryl-s-triazines in three steps starting with cyanuric chloride is described. Step 1 involves the nucleophilic (basic) displacement of one chlorine atom with a phenolic moiety. Step 2 involves a Friedel-Crafts reaction using a Lewis acid catalyst (preferably aluminum chloride) to replace the remaining two chlorine atoms with aryl groups such as xylyl. Finally, step 3 involves replacing the phenolic moiety with resorcinol using either a Lewis acid or protic acid catalyst or combinations thereof. Some additional processes only peripherally related to the three-step process outlined above are also described for the preparation of various s-triazine compounds. The s-triazines prepared are useful as UV absorbers for the stabilization of organic substrates against the adverse effects of actinic light.
Owner:CIBA SPECIALTY CHEM CORP
Process for preparing halogenated alkanes
InactiveUS7094936B1High selectivityBig advantagePreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation by halogen replacementAlkaneLewis acid catalysis
Methods and materials are provided for the production and purification of halogenated compounds and intermediates in the production of 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane. In a preferred embodiment, the process steps include: (1) reacting carbon tetrachloride with vinyl chloride to produce 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane; (2) dehydrochlorinating the 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane with a Lewis acid catalyst to produce 1,1,3,3-tetrachloropropene; (3) fluorinating the 1,1,3,3-tetrachloropropene to produce 1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene; (4) fluorinating the 1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene to produce a product mixture containing 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane; and (5) separating 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane from by-products.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for producing fluorinated organic compounds
ActiveUS20060258891A1Cheap purificationSeparation economicalPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPhysical/chemical process catalystsSimple Organic CompoundsGas phase
A method for preparing fluorinated organic compounds wherein at least one fluorinated olefin is reacted with methyl fluoride in the gas-phase and in the presence of a Lewis Acid catalyst to form at least one product having at least 3 carbon atoms.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Processes for the preparation of a monodisperse polymers, processes for the continuous polymerization of cyclic monomers, and polymers prepared thereby
The present invention relates to a method for preparing lactone polymers, carbonate polymers, lactone-carbonate block copolymers and lactone-arbonate random copolymers via a ring-opening addition reaction of a lactone monomer, a cyclic carbonate monomer or a mixture thereof using an initiator and in the presence of a specific titanium-type Lewis acid catalyst. The resulting polymers have a molecular weight distribution (Mw / Mn) approximately equal to 1 or a extremely high purity of single-structure components. The polymer molecules range in an oligomer region to a molecular weight of approximately 200,000. The present invention also relates to a method for preparing lactone polymers, carbonate polymers and lactone-carbonate copolymers having a narrow molecular weight distribution and which can be obtained via a continuous polymerisation of a lactone monomer and / or a cyclic carbonate monomer using an initiator in an extruder in the presence of a specific titanium-type Lewis acid catalyst or an aluminium-type Lewis acid catalyst. The present invention also relates to these resulting polymers.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
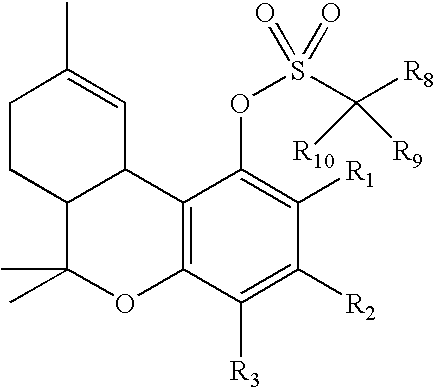
Process for production of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol
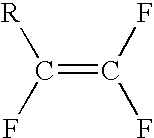
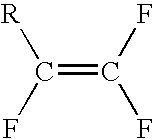
InactiveUS7674922B2High selectivityLower overall renovationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationArylPtru catalyst
The present invention relates to a process for preparation of a delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol compound or derivative thereof involving treating a first intermediate compound with an organoaluminum-based Lewis acid catalyst, under conditions effective to produce the delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol compound or derivative thereof. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a process for preparation of a cannabidiol or cannabidiolate compound involving reacting a first starting compound with a second starting compound in the presence of a metal triflate catalyst, under conditions effective to form the cannabidiol or cannabidiolate compound. The present invention also relates to a compound of the formula:where R8, R9, and R10 are the same or different and independently selected from the group consisting of H, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted aryl, substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl, or halo, with R1, R2, and R3 defined herein.
Owner:ALBANY MOLECULAR RESEARCH INC
Methods of making alkyl lactates and alkyl levulinates from saccharides
InactiveUS20150045576A1Organic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionLevulinic acidAlcohol
Unique methods have been developed to convert saccharides into value-added products such as alkyl lactates, lactic acid, alkyl levulinates, levulinic acid, and optionally alkyl formate esters and / or hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). Useful catalysts include Lewis acid catalysts and Brønsted acid catalysts including mineral acids, metal halides, immobilized heterogeneous catalysts functionalized with a Brønsted acid group or a Lewis acid group, or combinations thereof. The saccharides are contacted with the catalyst in the presence of various alcohols.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Synthetic process for efficiently and continuously producing 4,4-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone
InactiveCN108047101AAvoid cross usageAvoid pollutionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationChlorobenzeneFiltration
The invention discloses a synthetic process for efficiently and continuously producing 4,4-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone, which comprises the following steps: carrying out Friedel-Crafts acylation on thionyl chloride and excessive chlorobenzene under the action of a lewis acid catalyst, carrying out pyrohydrolysis and adding chlorobenzene to carry out layering after the reaction is finished, adding anoxidizing agent into a sulfoxide organic layer to carry out oxidization, adding activated carbon to carry out decoloration and filtering; cooling filtrate and carrying out rejection filtration to obtain 4,4-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone. The synthetic process has the advantage that chlorobenzene not only is a raw material, but also is a reaction solvent, so that cross use of various solvents is avoided. Particularly, use of a great amount of acetic acid used as an oxidation reaction solvent is avoided, and corrosion to equipment and environmental pollution are avoided. In the integral process flow,separation and extraction of an intermediate 4,4-dichlorodiphenyl sulfoxide are avoided, so that production time of the product is greatly shortened, and production cost is saved. By using hydrogen peroxide, acetic acid and concentrated sulfuric acid as mixed oxidizing agents, oxidization capacity of hydrogen peroxide is greatly improved, yield and purity of the product are greatly improved, yield of the product reaches 90% or more, and purity of the product is greater than 99.8%.
Owner:九江中星医药化工有限公司
Process for preparing taxoids from baccatin derivatives using lewis acid catalyst
The present invention relates to a process of preparing a taxoid (X) by reacting a protected baccatin derivative (B) with a β-lactam (C) in the presence of one or more Lewis acids and a base agent. The present invention also relates to a process of preparing the protected baccatin derivative (B) from a baccatin derivative (A) comprising a protection reaction catalyzed by one or more Lewis acids with an optional base agent.
Owner:YUNG SHIN PHARMACEUTICALS INDUSTRIAL CO LTD
POLYSILOXANES CONTAINING (METH)ACRYLIC ESTER GROUPS ATTACHED VIA SiOC GROUPS, PROCESSES FOR PREPARING THEM AND THEIR USE AS A RADIATION-CURABLE ADHESIVE COATING
The present invention accordingly provides new organopolysiloxanes having (meth)acrylic ester groups attached pendent and terminally or only pendent via SiOC groups, of the general average formula (I) and also provides a process for preparing the compounds by reacting polysiloxanes containing SiH groups with (meth)acrylated monoalcohols and / or (meth)acrylated polyalcohols using Lewis-acid catalysts or catalysts comprising an acid and salts thereof.
Owner:EVONIK GOLDSCHMIDT GMBH
Epoxy resins and processes for preparing the same
InactiveUS20110039982A1Improve responseReduces potential corrosivityEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyCyclohexanedimethanol
Epoxy resins comprising a cis, trans-1,3- and -1,4-cyclohexanedimethylether moiety and processes for preparing the epoxy resins. The process of preparation of the epoxy resins comprises reacting (a) a mixture of a cis-1,3-cyclohexanedimethanol, a trans-1,3-cyclohexanedimethanol, a cis-1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol, and a trans-1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol, (b) an epihalohydrin, (c) a basic acting substance, (d) optionally, a solvent, (e) optionally, a catalyst, and / or (f) optionally, a dehydrating agent. The process may be a slurry epoxidation process, an anhydrous epoxidation process, or a Lewis acid catalyzed coupling and epoxidation process.
Owner:BLUE CUBE IP
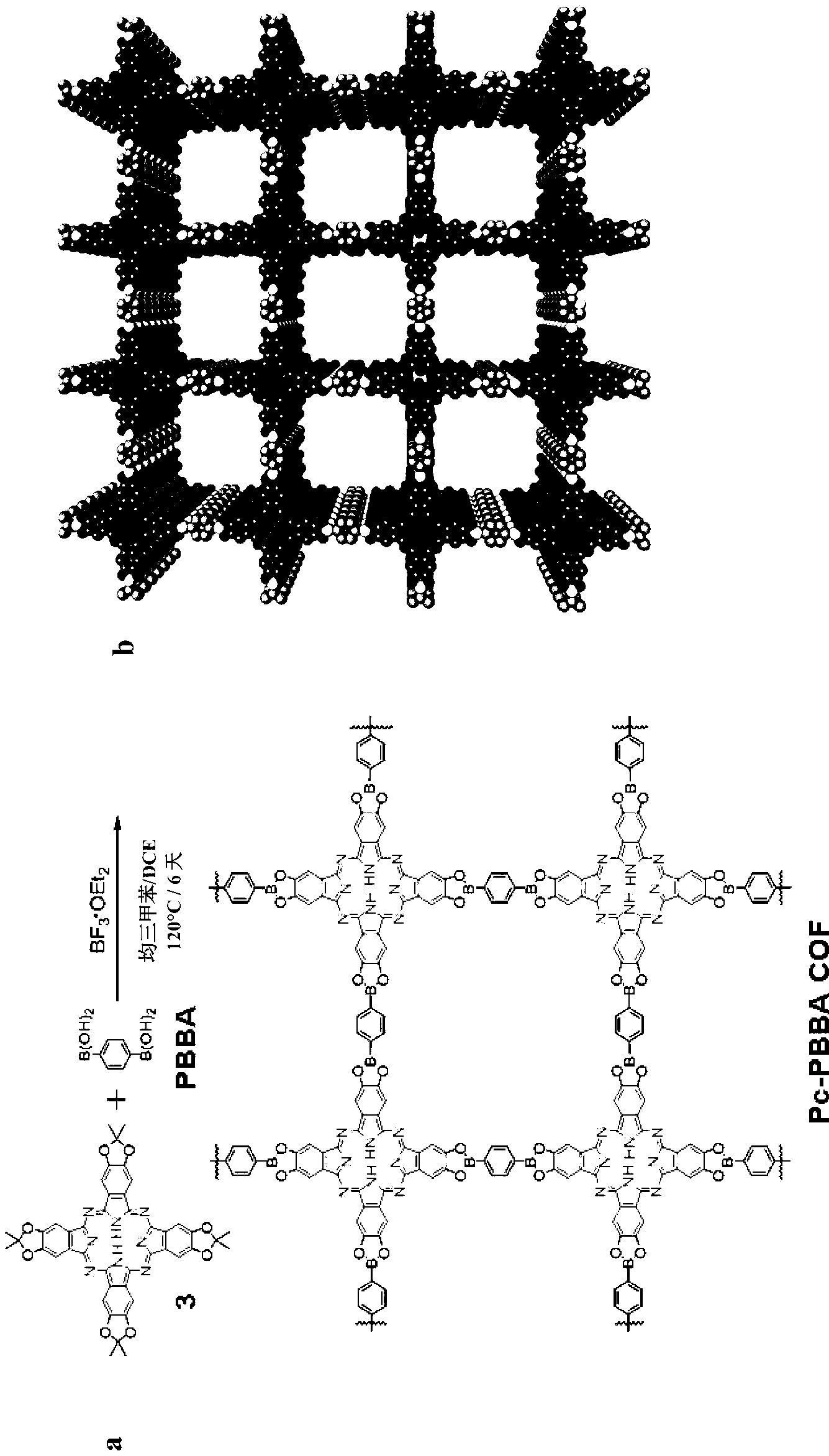
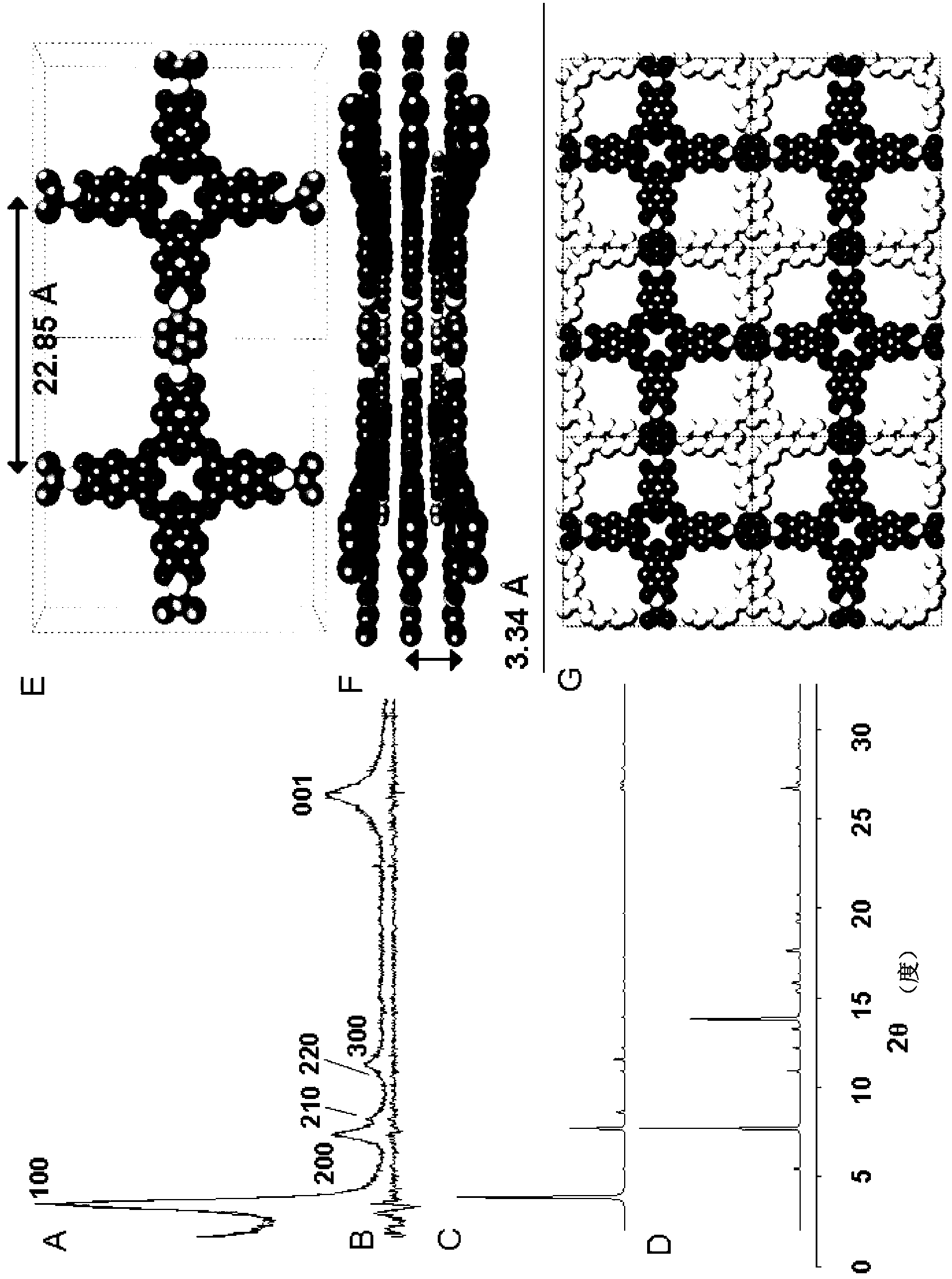
Covalent Organic Frameworks and Methods of Making Same
InactiveUS20140148596A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBoron containingAcid catalyzed
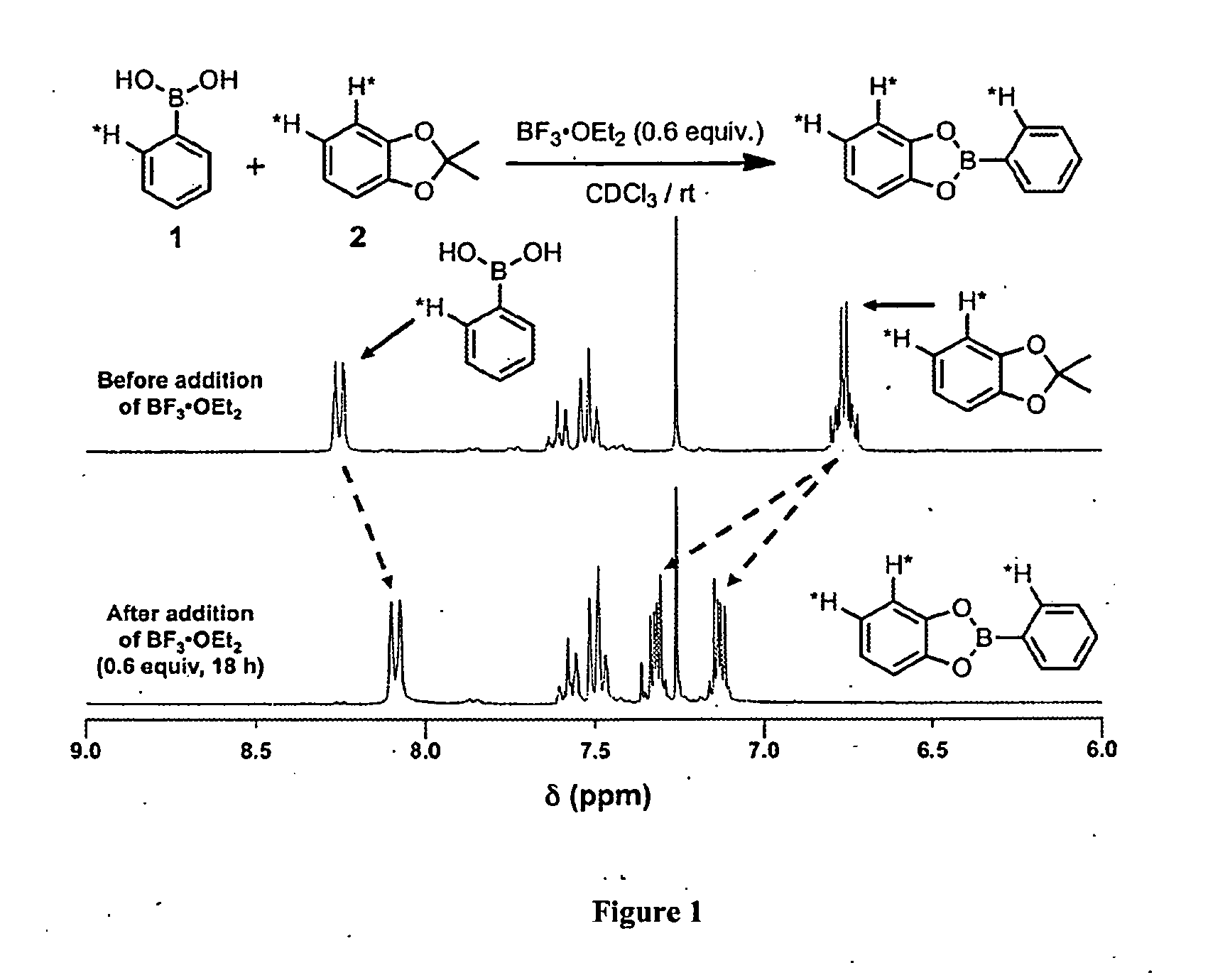
Crystalline COFs comprising a phthalocyanine moiety and a boron-containing multifunctional linking group joined by boronate ester bonds. A method for making crystalline COFs comprising Lewis acid catalyzed formation of boronate ester bonds between protected catechol subunits and multifunctional linkers comprising boronic acid groups. The COFs can be used in applications such as, for example, electronic devices.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Sol-Gel Based Matrix
ActiveUS20160251516A1Short response timeLower the volumeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiaryl/thriaryl methane dyesPorosityAnalyte
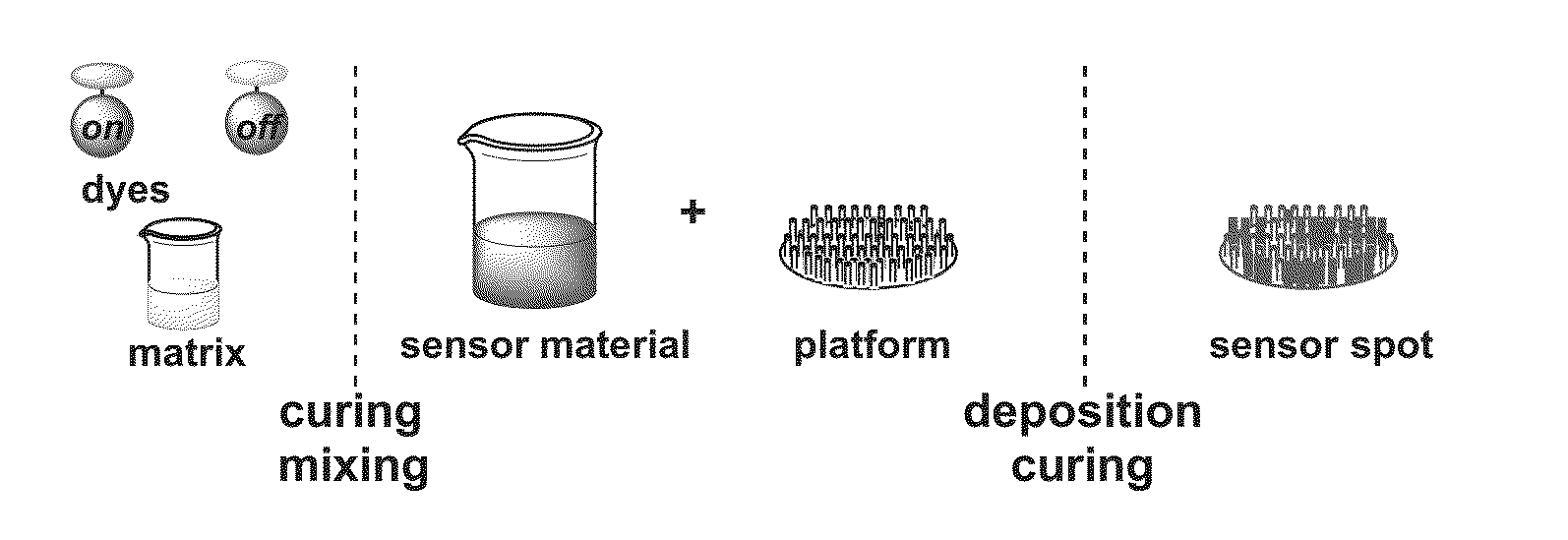
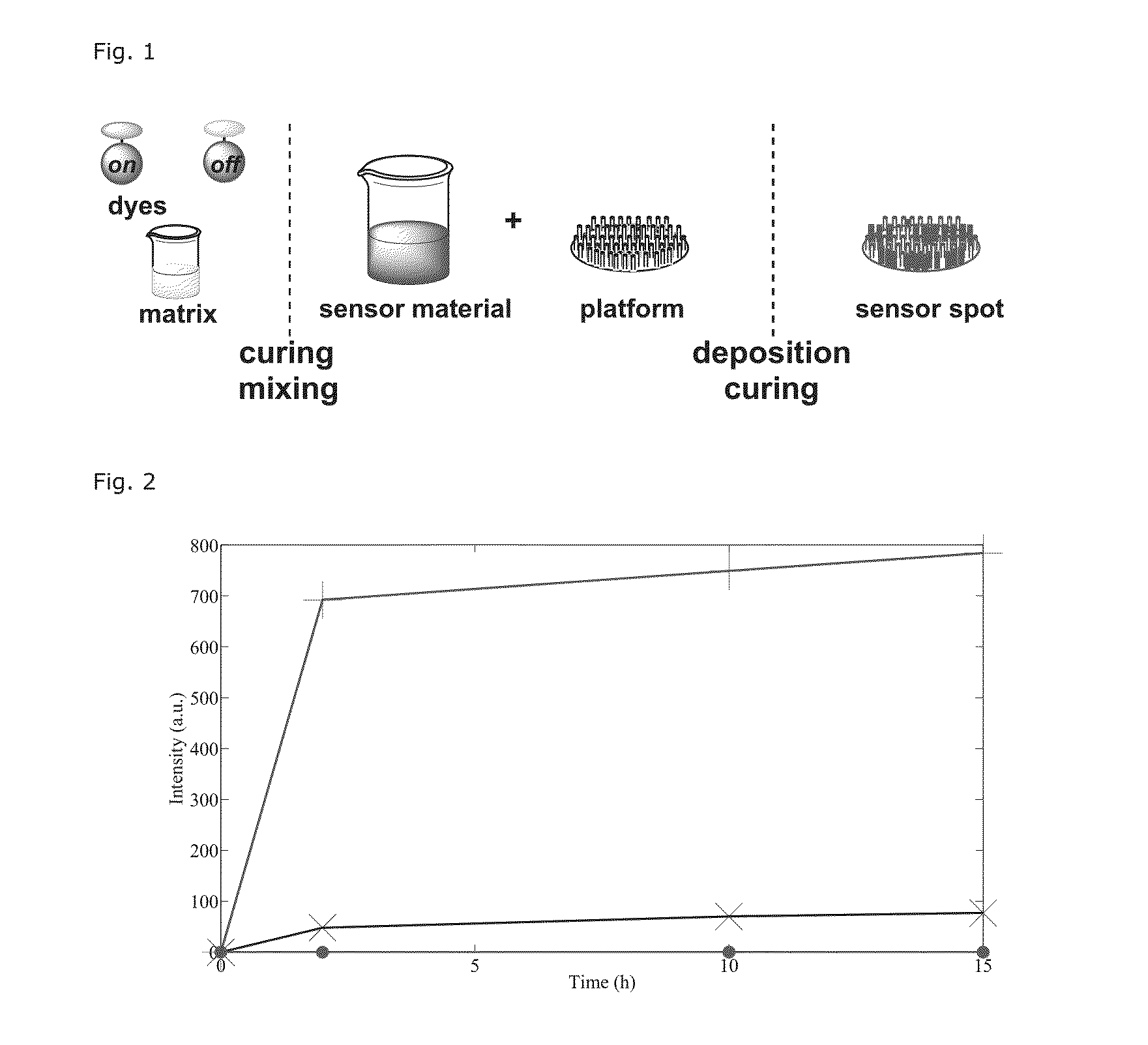
The present invention relates to a method for the production of a sol-gel based matrix. The method comprises the steps of: a) providing a first alkoxysilane of the general formula: R1—Si(OR2)3 and a second alkoxysilane of the general formula (I): b) preparing a first sol-gel component by polymerisation of the first alkoxysilane in the presence of an acid catalyst, c) preparing a second sol-gel component by polymerisation of the second alkoxysilane in the presence of an Lewis acid catalyst, d) Mixing the first sol-gel component and the second sol-gel component for the preparation of a sol-gel based matrix. The above method results in a sol-gel based matrix with high stability and high porosity. The sol-gel based material may be used for the production of a composite or sensor suitable for monitoring analytes. Methods for preparing these composites or sensors are provided as well.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN
Method for preparing biological diesel oil by esterifying, ester interchanging greases in high acid number
InactiveCN1760335AImprove responseReduce the impactBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionOil and greaseBiodiesel
A process for preparing biologic diesel oil from the fat with high acid number by esterifying and ester exchange includes such steps as proportionally loading said fat and methanol into high-pressure reactor, proportionally adding Lewis acid as catalyst, reation, distilling the resultant to separate methanol, centrifugal separation or filter to remove part of catalyst, water washing to remove residual glycerin and catalyst, and refining.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Trifluridine intermediate and preparation method of trifluridine
ActiveCN105461772ASolve pollutionSolve productivitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationLewis acid catalysisHomogeneous catalysis
The invention provides a preparation method of a trifluridine intermediate. Under the action of an acidic resin catalyst, 1-chloro-2-deoxy-3,5-di-O-p-chlorobenzoyl-D-ribose and 5-trifluoromethyl-2,4-bis(trimethylsilaneoxy)pyrimidine undergo a condensation reaction so as to obtain the trifluridine intermediate. According to the invention, a heterogeneous catalysis technology is utilized, acidic resin is used as a catalyst, and a traditional Lewis acid catalyst is replaced. Under the precondition of guaranteeing that product quality is controllable, a production technology is greatly improved. Catalytic efficiency is high, and conditions are mild. Purity of the prepared 1-(2'-deoxy-3,5-di-O-p-chlorobenzoyl-beta-D-furanose)-5-trifluoromethyluracil is greatly raised, and the problem that the use of the Lewis acid catalyst leads to severe post-treatment emulsification and environmental pollution and is not beneficial to industrial production is also effectively solved.
Owner:SINOPHARM A THINK PHARMA
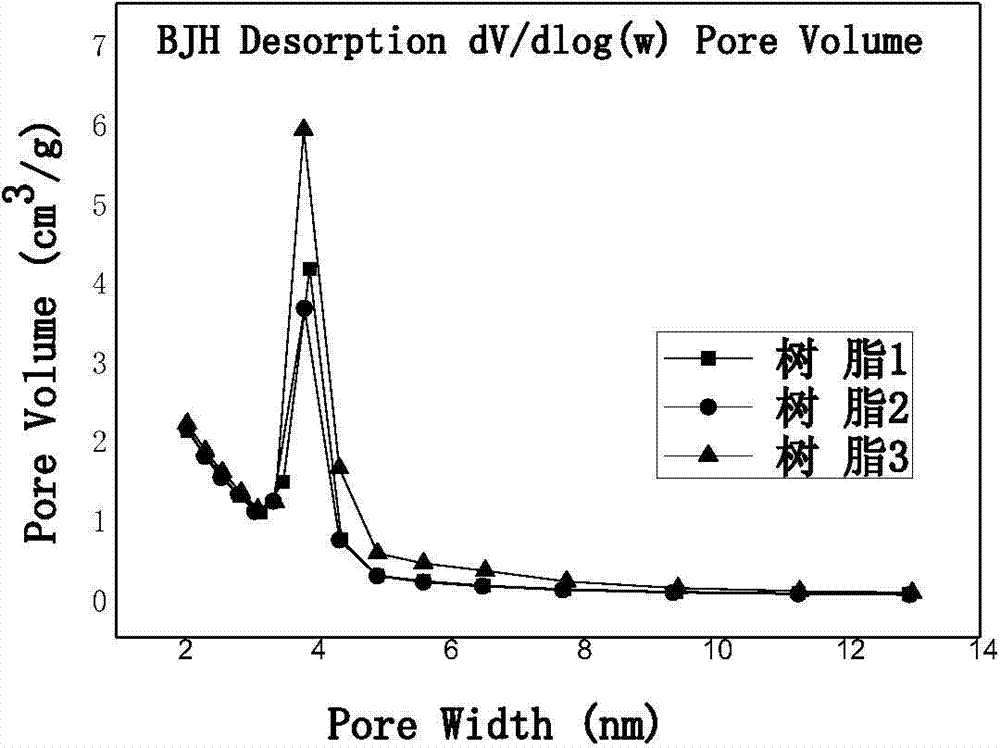
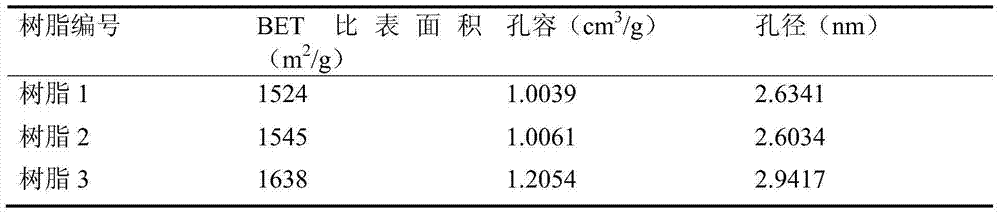
Ultrahigh cross-linked macro-porous adsorption resin applicable to removal of patulin
ActiveCN103772573ADense channelsUnique Pore Size DistributionIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesCross-linkFunctional monomer
The invention provides ultrahigh cross-linked macro-porous adsorption resin which is obtained by taking a styrene monomer as a functional monomer, taking a multi-vinyl monomer as a cross-linking agent, suspending and polymerizing in the presence of a pore forming agent to obtain low-cross-linked macro-porous polystyrene white ball, reacting the obtained white ball with chloromethyl ether under the catalysis of lewis acid to obtain chloromethylation macro-porous polystyrene resin, and carrying out a Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction on the obtained chloromethylation macro-porous polystyrene resin in the presence of a swelling agent by taking the lewis acid as a catalyst. Through adopting a novel cross-linking agent and pore forming agent system, the obtained resin has the advantages of high specific surface area and uniform pore diameter; the specific surface area is up to 1500-1800m<2> / g, the pore diameter distribution is uniform, a pore channel is dense and the average pore diameter is small; the pore diameter of the obtained macro-porous resin is rightly applicable to removal of patulin in juice and the removing efficiency is high; the resin can be used for pointedly removing the patulin which stably exists in the juice and the potential hazards on the human health, caused by the patulin in the juice, are solved; the ultrahigh cross-linked macro-porous adsorption resin has great social and economic benefits.
Owner:AMICOGEN CHINA BIOPHARM CO LTD
Covalent organic frameworks and methods of making same
Crystalline COFs comprising a phthalocyanine moiety and a boron-containing multifunctional linking group joined by boronate ester bonds. A method for making crystalline COFs comprising Lewis acid catalyzed formation of boronate ester bonds between protected catechol subunits and multifunctional linkers comprising boronic acid groups. The COFs can be used in applications such as, for example, electronic devices.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
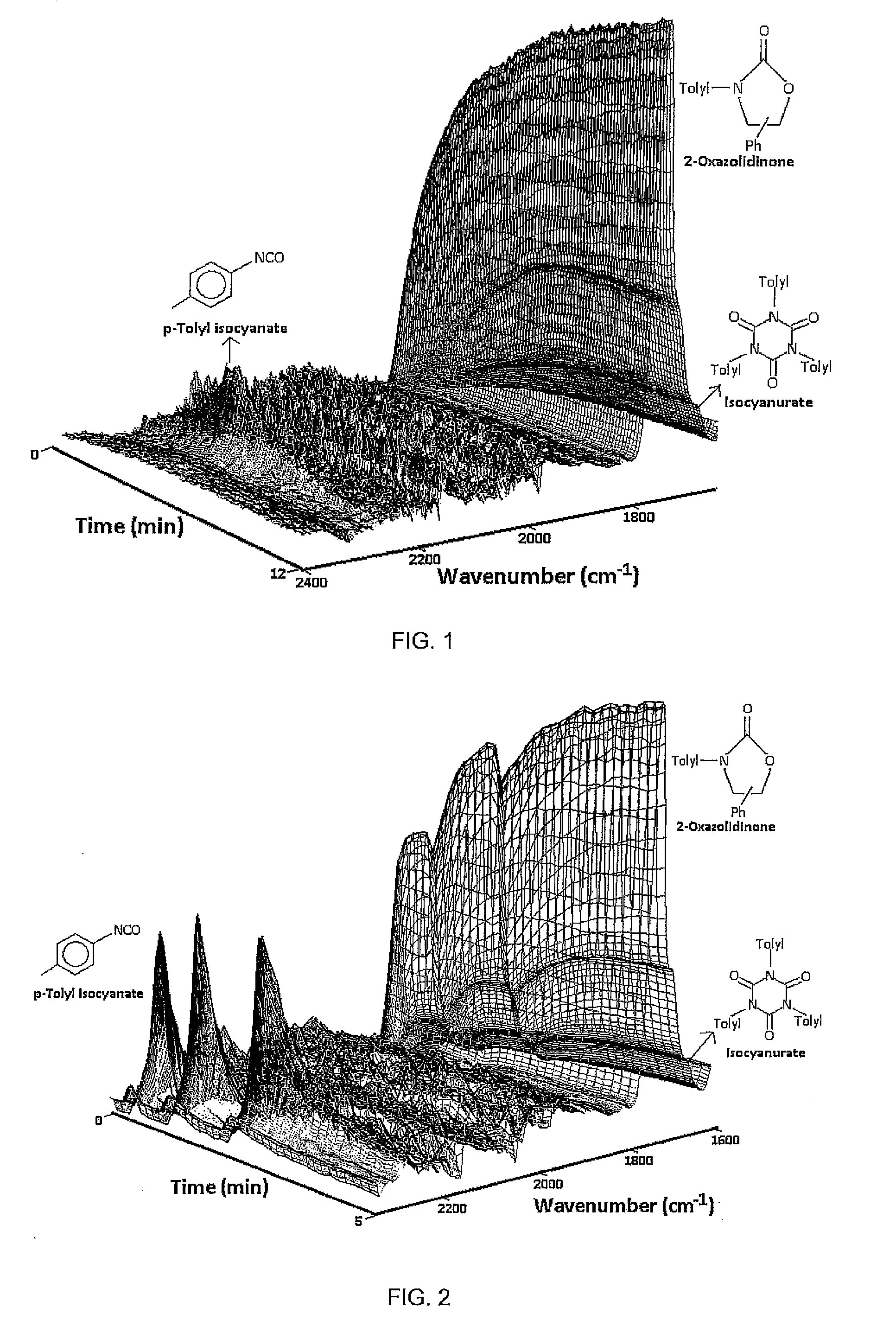
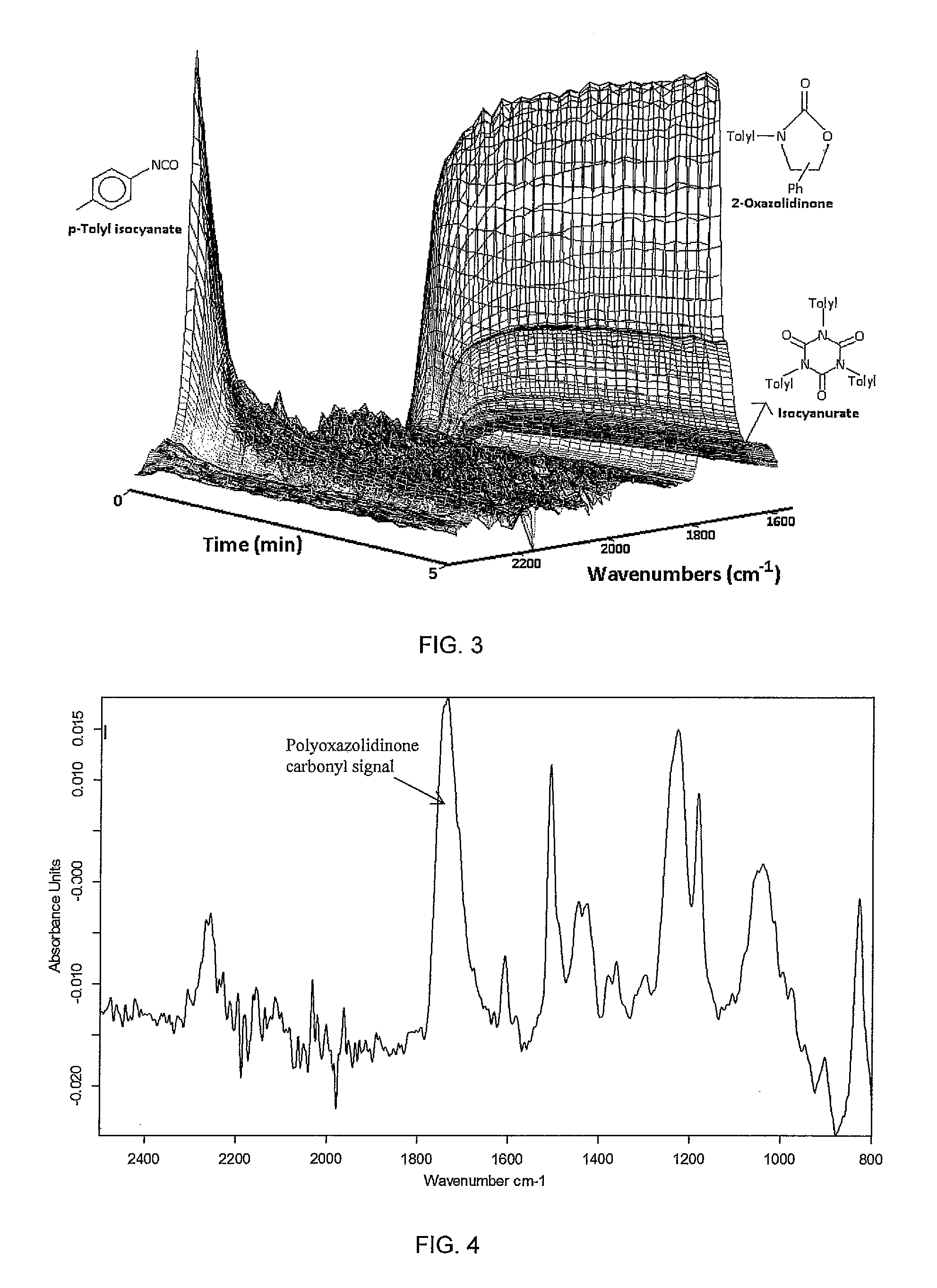
Method for the production of oxazolidinone compounds
The present invention relates to a method for the production of oxazolidinone compounds, comprising the step of slowly reacting an isocyanate compound with an epoxide compound in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst. The invention further relates to an oxazolidinone compound, obtainable by a method according to the invention, with a colour as determined according to ASTM D1209-05 (2011) of ≦200 and a molar ratio of the oxazolidinone compound to isocyanurate by-product o / i of ≧85 / 15. Lastly, the invention relates to an oligomeric or polymeric oxazolidinone compound, obtainable by a method according to the invention using an isocyanate compound with two or more NCO groups per molecule and an epoxide compound with two or more epoxy groups per molecule, comprising at least two units derived from the isocyanate compound and at least two units derived from the epoxide compound, with a colour as determined according to ASTM D1209-05 (2011) of ≦200.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Method for improving dispersibility of graphene in polymer matrix
The invention provides a method for improving dispersibility of graphene in a polymer matrix. The method comprises the following steps: fusing and mixing a polymer, graphene and a Lewis acid catalyst according to a ratio of 100: 3-10: 0.1-2 so as to obtain polymer / graphene composite material master batch; and then removing the Lewis acid and mixing the prepared master batch with the polymer so as to obtain a nanocomposite with low graphene content. Compared with a polymer / graphene composite material prepared without treatment with the Lewis acid catalyst, the polymer / graphene composite material obtained in the invention has the following advantages: dispersion of graphene in the polymer matrix is more uniform; aggregate is obviously reduced; and more uniform dispersion of graphene is beneficial for further improvement of thermal oxidative stability of the composite material.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Method for producing fluorinated organic compounds
ActiveUS7396965B2Cheap purificationSeparation economicalPhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offGas phaseLewis acid catalysis
A method for preparing fluorinated organic compounds wherein at least one fluorinated olefin is reacted with methyl fluoride in the gas-phase and in the presence of a Lewis Acid catalyst to form at least one product having at least 3 carbon atoms.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Alkylbenzene sulfonate Gemini surfactant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102452966ALow critical micelle concentrationReduce surface tensionTransportation and packagingSulfonic acids salts preparationAlkaneChlorosulfuric acid
The invention relates to an alkylbenzene sulfonate Gemini surfactant and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: undergoing a substitution reaction: undergoing a substitutive etherification reaction at the temperature of 65-70 DEG C for 6 hours on phenol and dihalogenated alkane under the action of a phase transfer catalyst to generate bisether, wherein the molar ratio of the phenol to saturated dihalide is 1:3, the saturated dihalide is head-to-end dibromoalkane, the quantity of atoms C of the dibromoalkane is larger than 2, and the phase transfer catalyst is tetrabutylammonium bromide; performing Fourier alkylation: making the bis-ether react with an alkyl halide at the temperature of 80 DEG C and under the pressure of 0.3 MPa under the action of a Louis acid catalyst to generate dialkyl phenylate, wherein the molar ratio of the bis-ether to the alkyl halide is 1:2; undergoing a sulfonation reaction: undergoing a sulfonation reaction on the dialkyl phenylate and a chlorosulfonic acid in the molar ratio of 1:4 by taking dichloromethane as a solvent at the temperature of 0 DEG C; and undergoing a salt-forming reaction: adding an alkali to generate a target product. The alkylbenzene sulfonate Gemini surfactant has very high interfacial activity and a very low critical micelle concentration.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for preparing bromination polystyrene
The invention discloses a method for preparing bromination polystyrene, which includes (1) adding 10-30 parts by weight of styrene into 100 parts by weight of dichloroethane and adding 0.1 to 0.5 parts by weight of BPO or AIBN to obtain polystyrene dichloroethane solution; (2) adding 0.1 to 3 parts by weight of lewis acid catalyst and 0.1 to 3 parts by weight of backbone protective agent in the above prepared solution and then dropping 30 to 90 parts of bromine chloride dichloroethane solution to obtain bromination polystyrene dichloroethane solution; (3) adding 00.5 to 0.1 parts by weight ofneutralizer into the above prepared solution, conducting washing and static layering, adding 0.1 to 3 parts by weight of fat removing bromine preventing agent in the layered organic layers, conducting flash evaporation, cooling, centrifugation and drying on the organic layer to obtain the product. The process is capable of manufacturing polystyrene with narrow molecular weight distribution, and the polystyrene can obtain bromination polystyrene with controllable molecular weight after bromination.
Owner:SHANDONG RUNKE CHEM
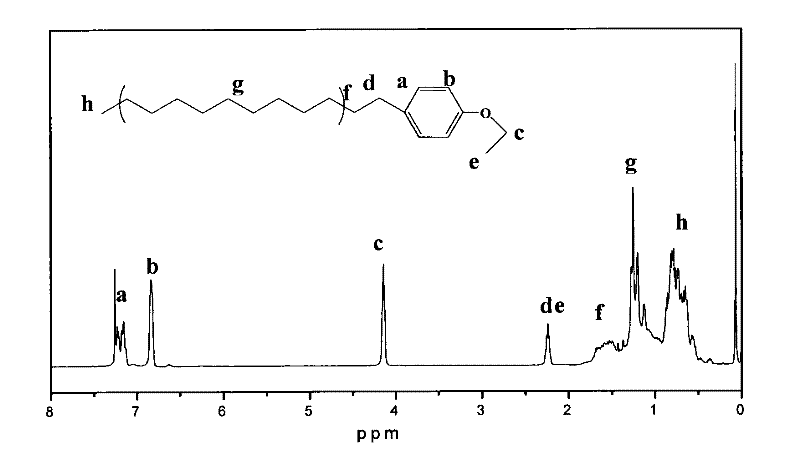
Method for producing low molecular polyamide from tung oi
The method of preparing low molecular polyamide by china wood oil relates to a different method to prepare epoxide resin curing agent. Firstly, china wood oil and methyl alcohol have ester interchange with the inorganic alkali or Louis catalyst which is 0:1%-5% of china wood oil, generating methyl jasmonate, then have addition reaction of methyl jasmonate it and unsaturated binary acid with Louis, generating which finally has amidation with polybasic amine in 150-230deg.C; then clear away the material did not react, acquiring low molecular polyamide. The invention has no pollution to the environment, low energy cost, the epoxide resin and its solified product have good resistance to heat and high mechanical strength.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Process for preparing self-dispersible coloring agent using lewis acids and ink composition comprising the coloring agent
InactiveUS7393403B2Good colorIncreased durabilityPreparation by hydrocarbon radical introductionDuplicating/marking methodsArylDispersion stability
A self-dispersible coloring agent represented by formula (II) below is prepared by incorporating a hydrophilic group into a coloring agent through a reaction of a hydrophilic group-containing halide represented by formula (I) below and the coloring agent in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst:X-L-R1 (I)(the coloring agent)-L-R1 (II)wherein L represents a single bond or —C(═O)—; R1 is selected from the group consisting of a substituted or unsubstituted C1-C20 alkyl group containing a hydrophilic group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C20 aryl group containing a hydrophilic group a substituted or unsubstituted C2-C20 heteroaryl group containing a hydrophilic group and a substituted or unsubstituted C7-C20 arylalkyl group containing a hydrophilic group; and X is one of: —F, —Br, —I and —Cl. may be obtained conveniently through a one-step process. The ink composition containing the self-dispersible coloring agent provides effective long-term storage stability and dispersion stability using a one-step process.
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
Macromolecule difunctional group alpha-hydroxy-ketone photoinitiator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102020726AIncrease the relative molecular massReduce volatilityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationLewis acid catalysisKetone
The invention discloses a macromolecule difunctional group alpha-hydroxy-ketone photoinitiator shown in the following formula and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: firstly, preparing acyl chloride by hexahydrobenzoic acid; carrying out Friedel-Crafts acylations reaction on the acyl chloride and halogeno benzene in the presence of catalysis by lewis acid; then, in the presence of the catalysis, synthetizing a diketone midbody by ketone and bisphenol; and carrying out alpha-site halogenating and hydrolyzing on the diketone midbody to obtain a target product by. The macromolecule difunctional group alpha-hydroxy-ketone photoinitiator has good compatibility with resin, the volatility of the difunctional group alpha-hydroxy-ketone photoinitiator is greatly improved if compared with corresponding micromolecule photoinitiato, but the photo-initiation activity is not obviously reduced. Most importantly, because of the influence by conjugation, the photoinitiator disclosed by the invention has obvious red shift of absorption wavelength, has higher light absorption efficiency and has good application prospect in the material industries of paint, ink and the like.
Owner:CHANGSHANG NEWSUN CHEM IND
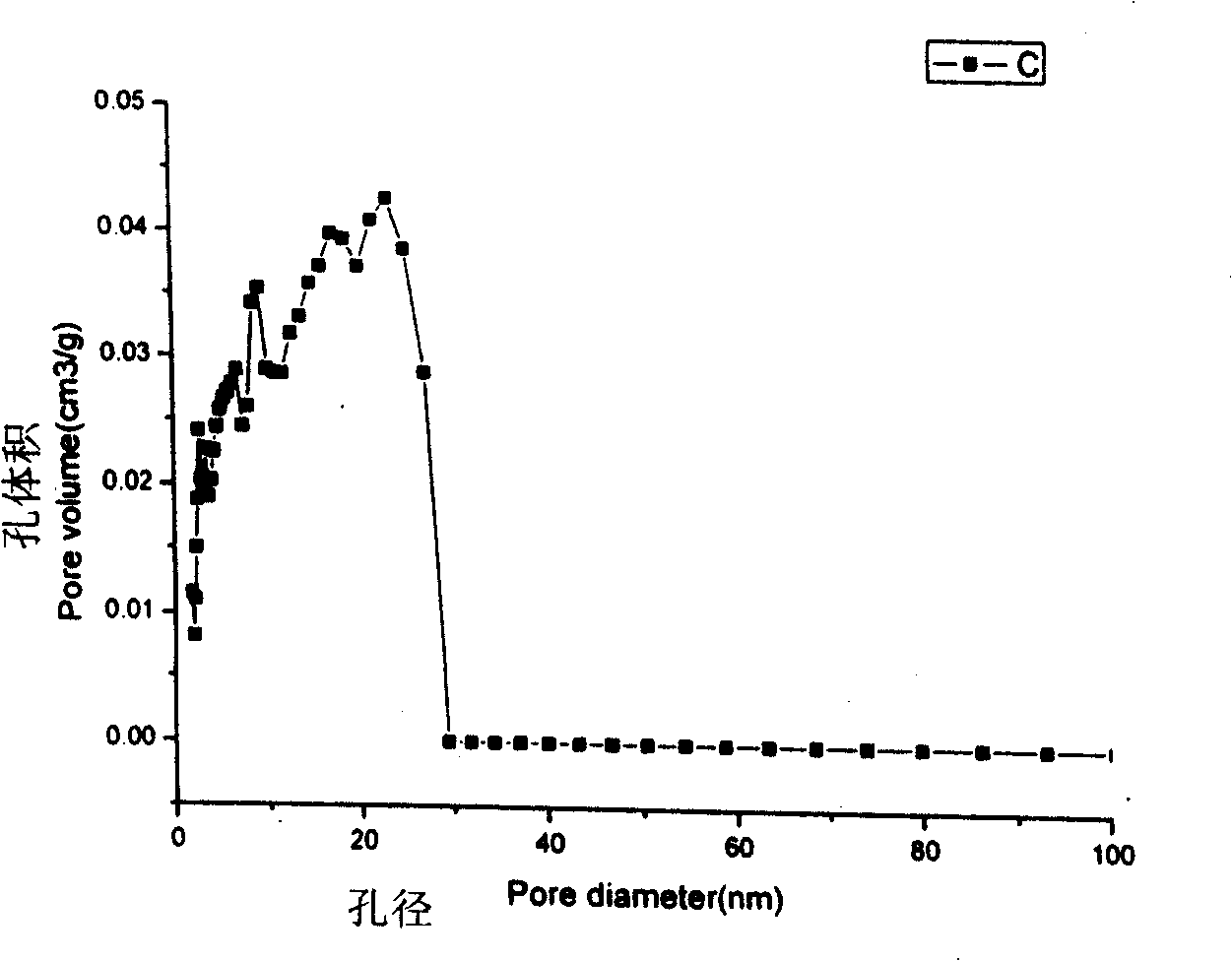
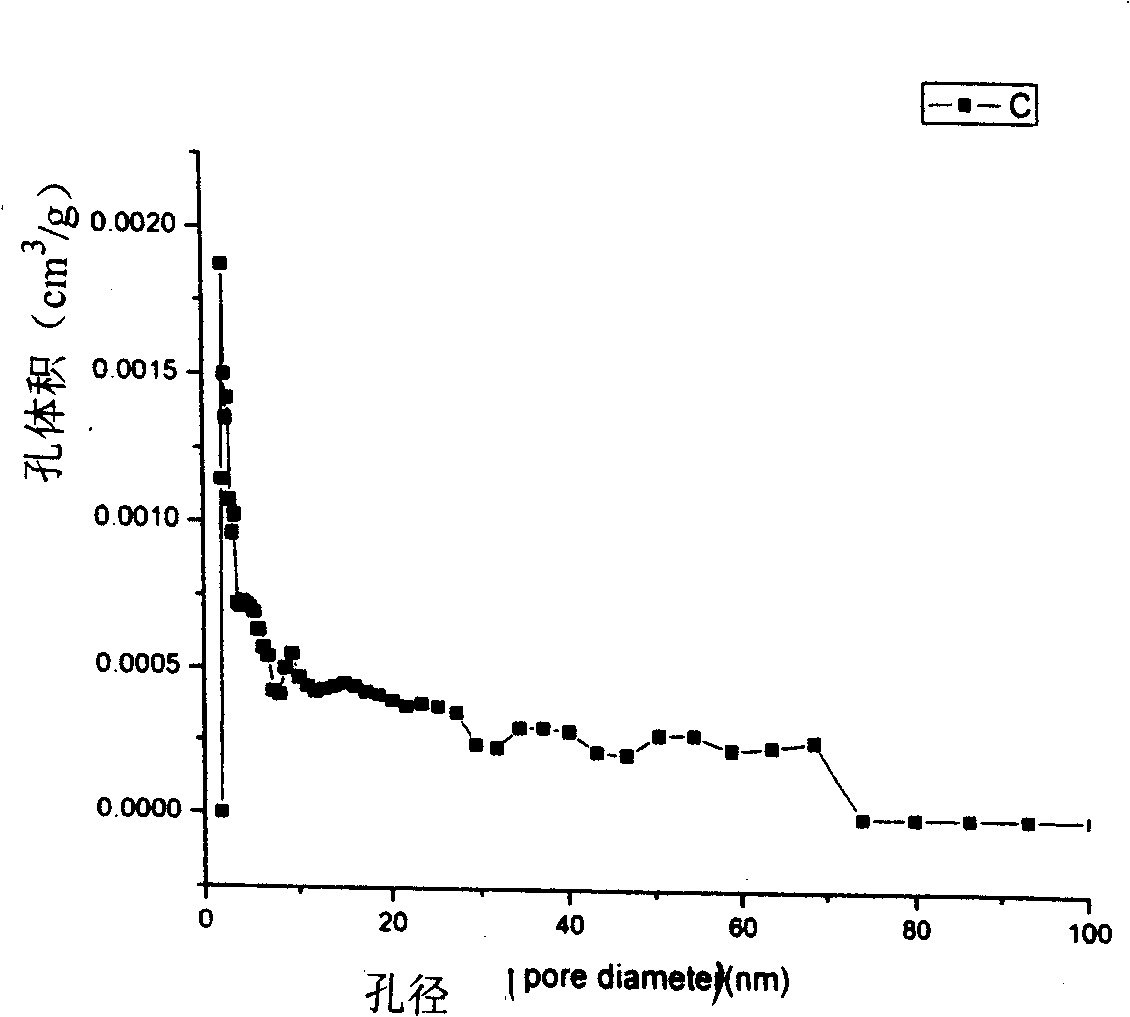
Adsorption resin with centralized pore diameter and large Micropore specific surface area and method for producing the same
ActiveCN101274269AHigh adsorption selectivityEasy to handleOther chemical processesChemical structureWastewater
The invention discloses an adsorption resin with concentrated aperture and larger micro-hole area compared with a superficial area and a preparation method of the adsorption resin. The resin apertures are concentrated and distributed in the area of 1.5-2.5nm; the micro-hole proportion is more than 60%. The preparation method of the resin has the steps as follows: (1) synthesis of narrow distribution micro-hole low crosslinking polystyrene resin; (2) chloromethylation of the narrow distribution micro-hole low crosslinking polystyrene resin under the catalysis of lewis acid catalyst; (3) subsequent crosslinking reaction of chloromethylated low crosslinking polystyrene resin under the catalysis of lewis acid catalyst. The microporosity of the resin prepared by the invention achieves 60-95%; the micro-hole has uniform distribution and has obvious single peak characteristic and obvious separation effect on the organic matters with identical chemical structure type and different molecule sizes, and can be effectively used for disposing and recycling corresponding organic wastewater. The reagent used by the method provided by the invention is relatively simple and easy to buy, and the required equipment is simple and easy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
High-molecular weight long-chain branched crystalline polylactic acid material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-molecular weight long-chain branched crystalline polylactic acid material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1) adding 0.1 to 1 percent of protonic acid catalyst into aqueous solution of lactic acid or mixed solution of the aqueous solution of the lactic acid and silicon dioxide nano particle silica sol containing 0.1 to 10 weight percent of lactic acid, and dehydrating to obtain a product I; 2) adding 0.4 to 2 molar percent of dibasic acid or anhydride into the product I, and reacting to obtain a product II; 3) adding 0.1 to 1 weight percent of lewis acid catalyst into the product II, performing melt polycondensation, and adding 0.1 to 5 weight percent of crystallization accelerator to obtain terminal carboxyl group crystalline polylactic acid prepolymers; and 4) reacting diglycidyl ester and the terminal carboxyl group crystalline polylactic acid prepolymers in a molar ratio of 0.8:1-1.2:1 to obtain the high-molecular weight long-chain branched crystalline polylactic acid material. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, short reaction time, high efficiency, low cost and environmental friendliness and capability of contributing to realizing commercialization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing melamine phosphate (borate) fire retardant
InactiveCN101143876AHarm reductionAvoid corrosionGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsPhosphorus organic compoundsPhosphateMelamine phosphate
The present invention discloses a method which can prepare a phosphate (borate) melamine salt flame retardant by a dry process. According to the molar ratio of 1:2 to 4, small molecular polyol and inorganic acid containing phosphor or boron are uniformly mixed with lewis acid catalyst with one to one point five percent of the weight of the small molecular polyol, the temperature of the produced solution is raised to 100 to 150 DEG C, reaction lasts two to five hours, after melamine with the molar ratio of 1:1.5 to 2.5 of inorganic acid containing phosphor or boron is added, the produced solid is smashed into fine powder which can pass through a sieve with one hundred and twenty meshes, under a reaction temperature between 180 DEG C and 230 DEG C, reaction lasts one point five to four hours, and after the generated product is washed until the filtrate is neutral, the phosphate (borate) melamine salt flame retardant is produced by filtration, drying and smash. Because the dry process is applied, the present invention avoids the problem that the organic solvents used by the prior art harm environment and erode equipment, reduces energy consumption and production cost and avoids the problem of the hydrolysis of phosphate, which is caused by a reaction under the water phase; moreover, the present invention has the advantages of simple technique and convenient operation and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:应急管理部四川消防研究所
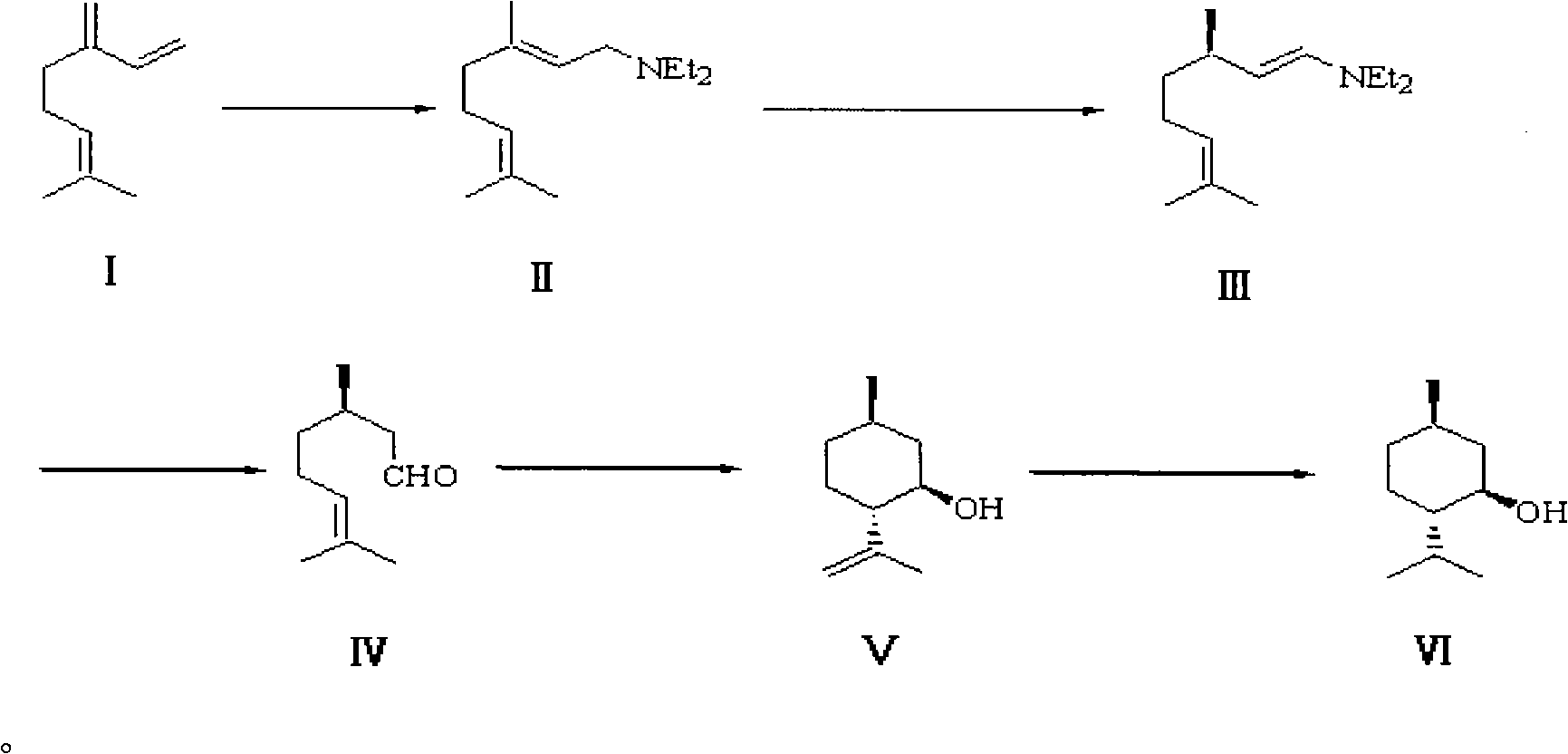
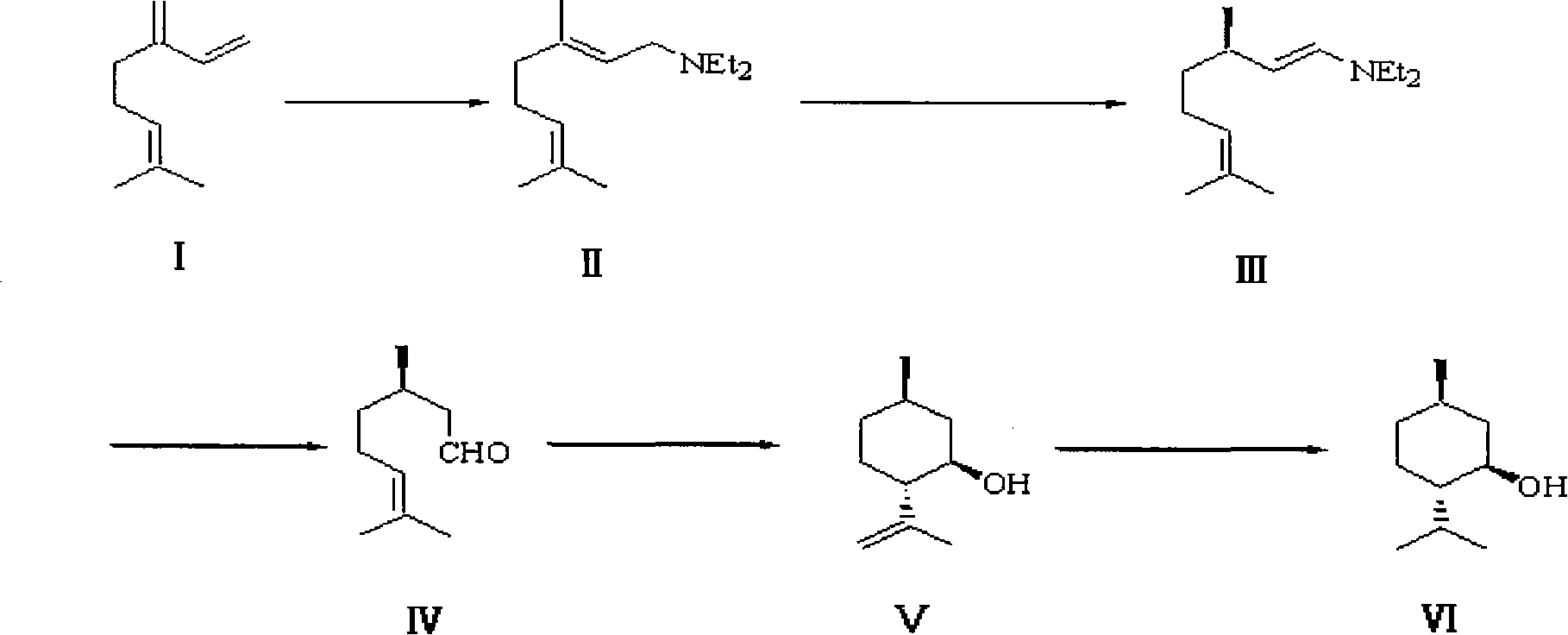
Method for synthesizing L-menthol
InactiveCN101602651AWide variety of sourcesLow pricePreparation by isomerisationPreparation by hydrogenationIsomerizationOrganic synthesis
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis, in particular to a method for synthesizing L-menthol. The method for synthesizing L-menthol takes myrcene as an initial raw material and comprises the following steps: amination reaction: diethylamine and myrcene carry out amination reaction to obtain geranylamine; isomerization reaction: the geranylamine carries out isomerization reaction under the catalytic action of chiral catalyst to obtain intermediate enamine; hydrolysis reaction: the enamine carries out hydrolysis reaction in an acidic medium to produce intermediate D-citronellal; cyclization reaction: the D-citronellal generates L-isopulegol by lewis acid catalyst and organic solvent; and hydrogenation reaction: the L-isopulegol is hydrogenated to obtain L-menthol. The method for synthesizing L-menthol has the yield of more than 90 percent, the GC purity of higher than 99.0 percent and the specific rotation of -49 degrees to -50 degrees, the raw material myrcene has wide sources and lower cost, and the whole method has simple technology, good repeatability and high yield and is quite suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:SHANGHAI WANXIANG FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
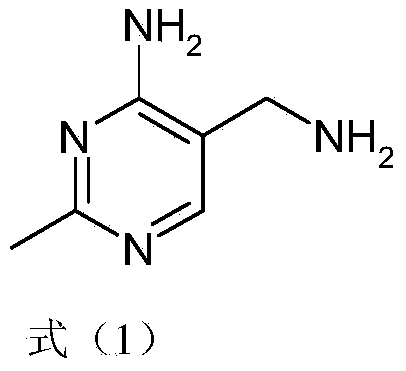
Simple and quick method for synthesizing improved vitamin B1 intermediate 2-methyl-4-amino-5-aminomethylpyrimidine
ActiveCN103435556AReduce concentrationReduce decompositionOrganic chemistryAminopropionitrilePropionitrile
The invention relates to a simple and quick method for synthesizing an improved vitamin B1 intermediate 2-methyl-4-amino-5-aminomethylpyrimidine. The method comprises the following steps: condensing 3-alkyl (aryl) formamido-propionitrile serving as a raw material with acetamidine in the catalytic action of lewis acid; cyclizing with trimethyl orthoformate, and hydrolyzing under an alkaline condition to prepare the vitamin B1 key intermediate 2-methyl-4-amino-5-aminomethylpyrimidine. The four reacting processes are performed in sequence by a one-pot reaction, and the product in each step does not need to be separated and purified. According to the method, highly carcinogenic o-chloroaniline or other small molecular aniline compounds are not used, residues of o-chloroaniline compounds in the vitamin B1 product can be eliminated. Furthermore, the preparation process is short and convenient in flow, small in wastewater amount and high in yield.
Owner:XINFA PHARMA
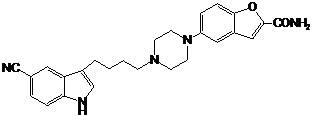
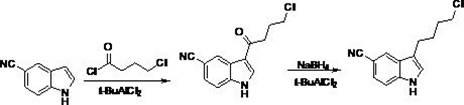
Preparation method of vilazodone
The invention provides a preparation method of vilazodone, which comprises the following steps: reacting 5-cyanoindole, which is used as the initial raw material, with substituted phenylsulfonyl chloride under alkaline conditions, carrying out Friedel-Crafts reaction under the catalytic action of Lewis acid, reducing the product, and carrying out substitution reaction with 5-(1-piperazino)-benzofuryl-2-formamide to obtain the vilazodone. The invention also provides three intermediate compounds related to the vilazodone preparation method. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of low cost, high yield and simple after-treatment, and is easy to operate and convenient for industrial production; and all the reagents are conventional reagents.
Owner:上海泛凯生物医药科技有限公司 +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com