Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1638 results about "Dichloroethane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dichloroethane can refer to either of two isomeric organochlorides with the molecular formula C₂H₄Cl₂: 1,1-Dichloroethane 1,2-Dichloroethane
Cement compositions containing flexible, compressible beads and methods of cementing in subterranean formations
Cement compositions comprising flexible, compressible beads, processes for preparing such cement compositions, and methods of cementing in subterranean formations using such cement compositions. One or more flexible, compressible beads are mixed with the cement before pumping the cement into a well bore. The flexible, compressible beads are preferably composed of an elastomeric material such as a copolymer of methylmethacrylate and acrylonitrile; a terpolymer of methylmethacrylate, acrylonitrile, and dichloroethane; a styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer; and polystyrene. The flexible, compressible beads may be heated to expand the beads before mixing with the cement such that the ensuing cement composition will have a desired density. Non-flexible beads such as spherulites may also be added to the cement compositions.
Owner:REDDY B RAGHAVA +2
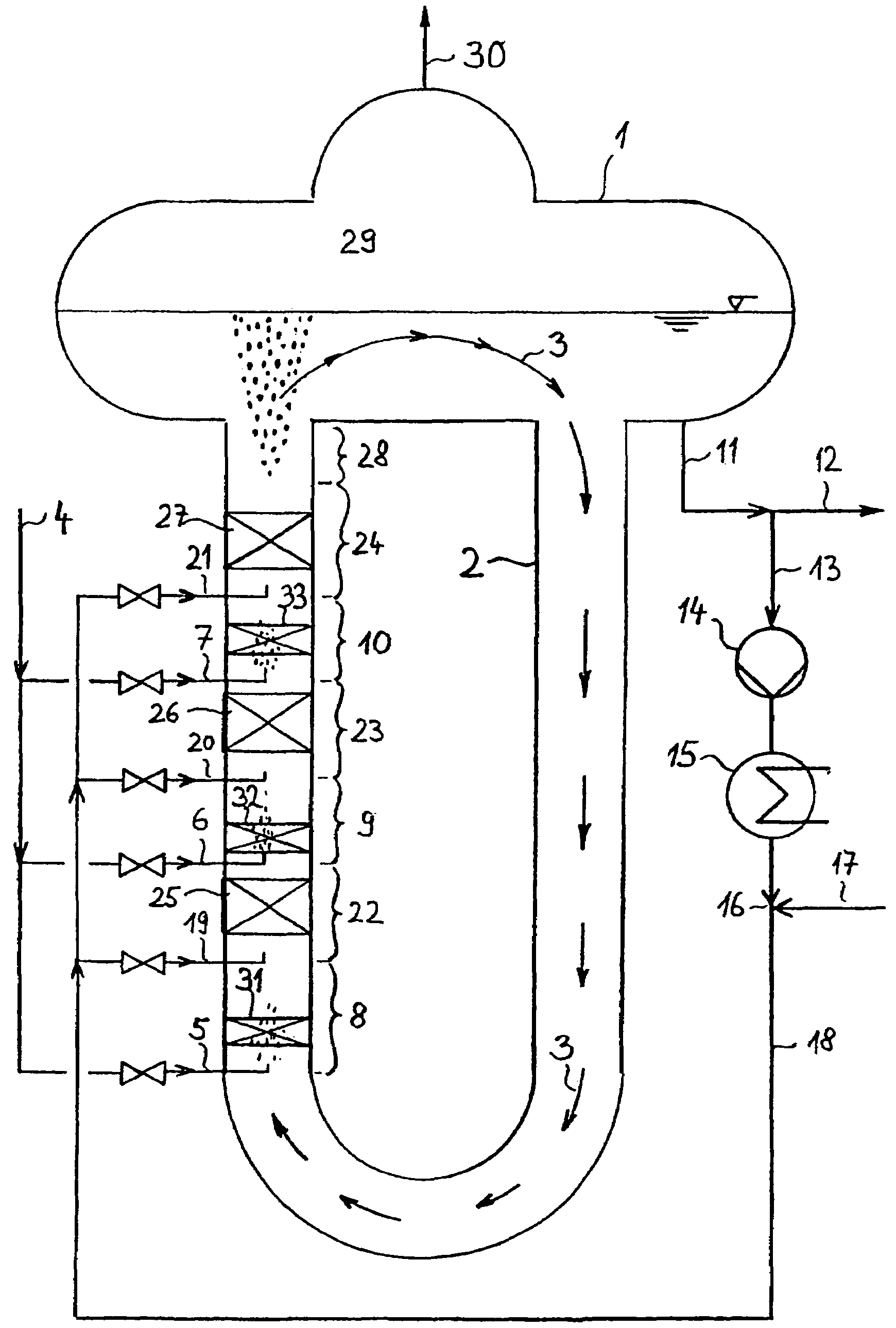
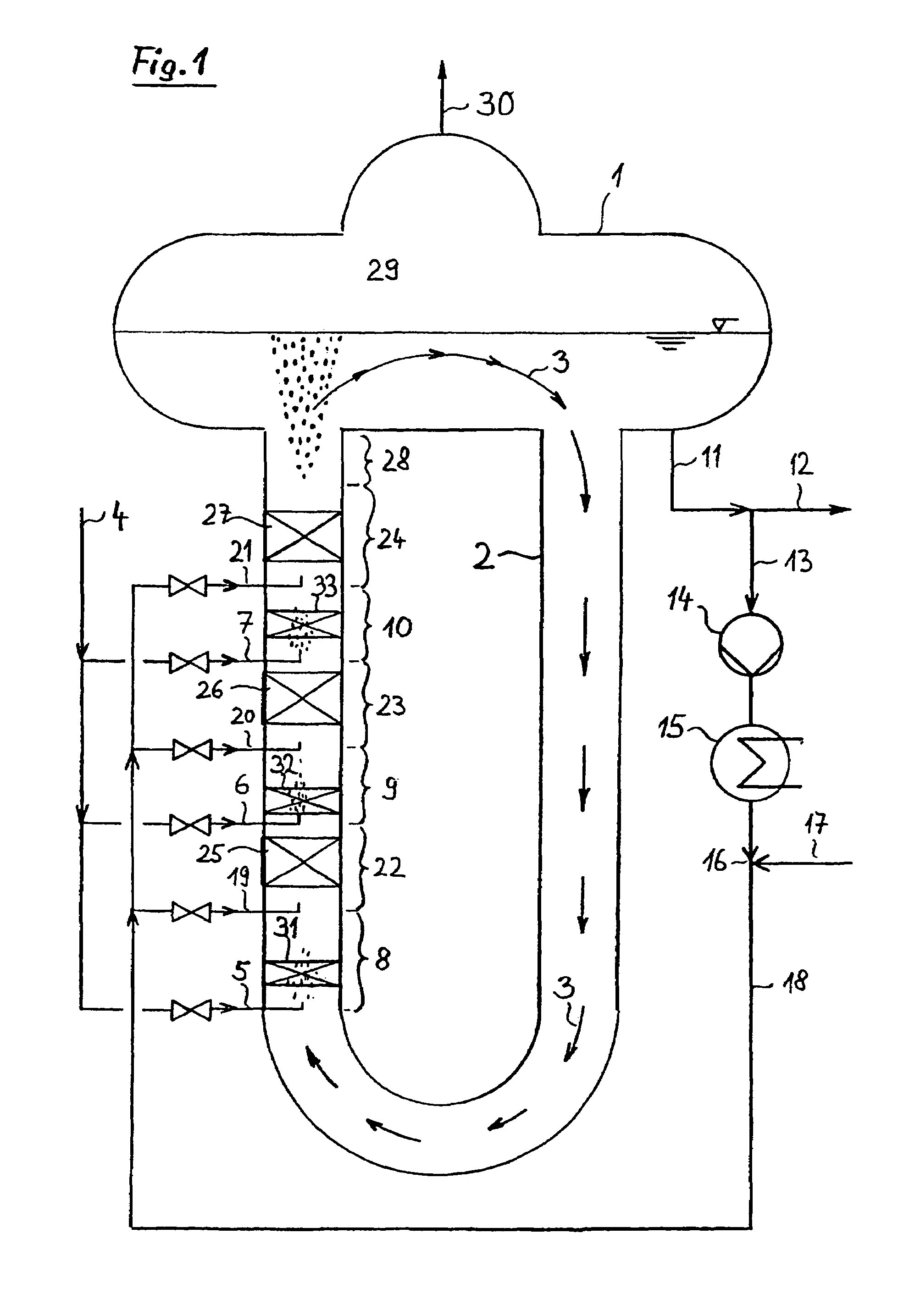
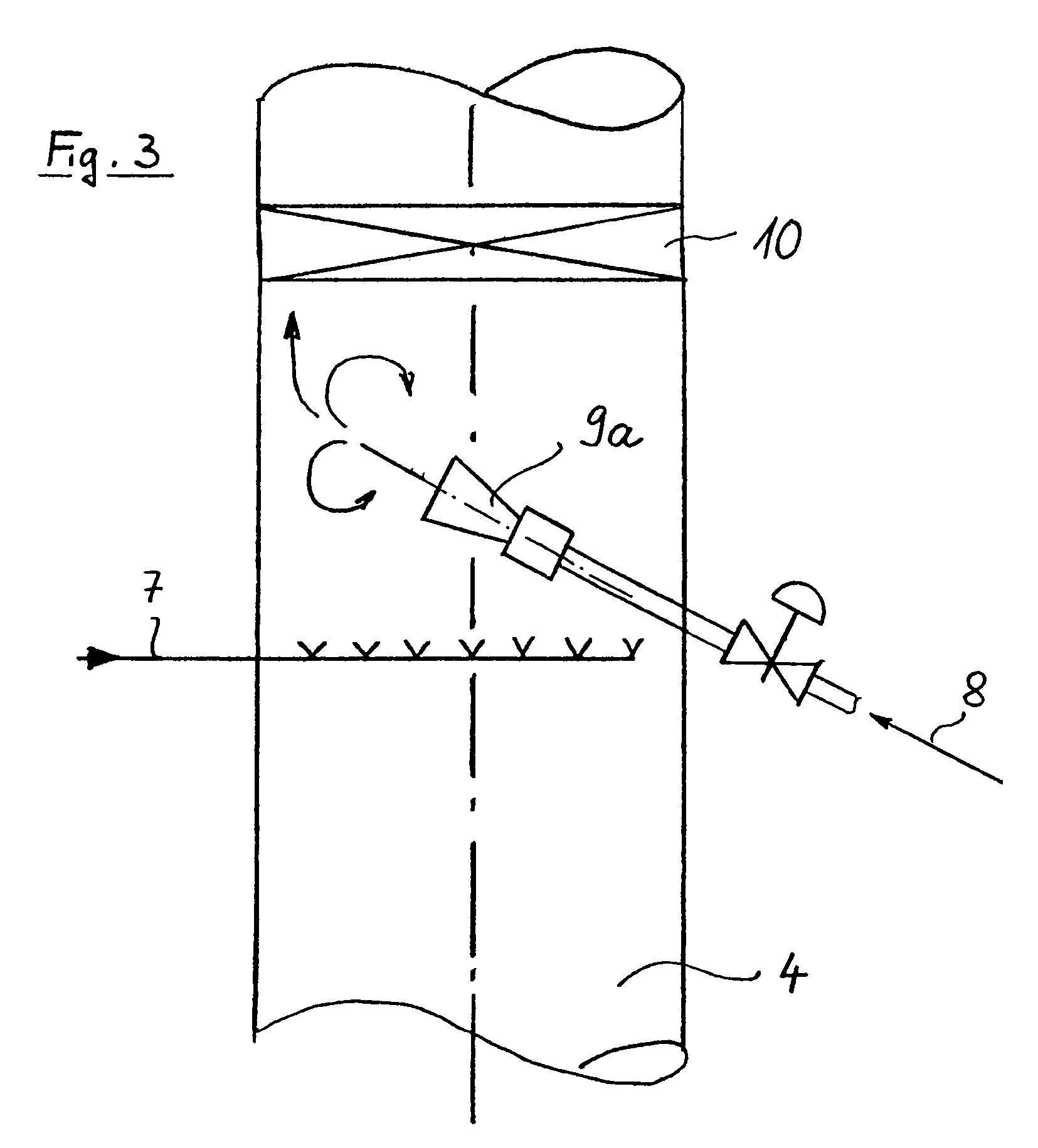
Method and device for producing 1,2-dichlorethane by means of direct chlorination
ActiveUS7579509B2Excellent part-load performanceReduce stressFlow mixersMixing methodsLiquid stateStatic mixer
The invention refers to a process for the production of high-purity 1,2-dichloroethane from dissolved chlorine and dissolved ethylene, which are brought into contact with each other in a circulating liquid reaction fluid, which mainly consists of 1,2-dichlorethane and a catalyst and flows through at least one vertically arranged loop-type reaction section, both legs of the loop being connected to an overhead degassing vessel from where the reaction product is withdrawn either in gaseous or in liquid state or in both gaseous and liquid state, and numerous admixing sections being arranged in the leg of the loop in which the liquid rises, and each of these admixing sections having one upstream feed point for dissolved or gaseous ethylene and one downstream feed point for dissolved chlorine and, if required, the admixing sections featuring static mixers.
Owner:UHDE GMBH +1
Gold-based catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination
InactiveUS20140213437A1Molecular sieve catalystsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrogenChemical compound
Powder catalysts that comprise particles of chemical compounds of Au and Cu deposited on acid-washed carbon-based supports are effective catalysts in ethyne hydrochlorination to produce vinyl chloride monomers (VCMs). They give a high selectivity and productivity of VCM and decreased amounts of the byproducts of chloroethane, dichloroethane and others. Thiocyanates are used as complexing agents to extend the catalyst lifetime. The activity of the catalyst is enhanced by doping nitrogen atoms into the support.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for producing 1,2-dichloroethane by means of direct chlorination
ActiveUS7671244B2Increase capacityDouble the conversion rate according to reactionGaseous chemical processesPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offGas phaseEthane Dichloride
The invention relates to a method for producing high-purity 1,2-dichloroethane from dissolved chlorine and dissolved ethylene which are brought into contact with each other using a circulating liquid reaction medium which essentially consists of 1,2-dichloroethane and a catalyst and passes through at least one reaction loop. The two limbs of the loop are connected to a gas-phase stripping container which is arranged at the top and from which the reaction product is outwardly transferred either in a gaseous or liquid form or both in a gaseous form and in a liquid form. The addition points for the addition of chlorine and dissolved ethylene are arranged in the limb of the loop in which the liquid rises. The addition point for dissolved chlorine is always arranged downstream of the ethylene addition point. At least one addition point for liquid 1,2-dichloroethane follows each chlorine addition point, and the addition of the liquid 1,2-dichloroethane is carried out under kinetic energy which is high enough to enable a vigorous mixture of 1,2-dichloroethane, dissolved chlorine and ethylene to be carried out. Preferably, the liquid 1,2-dichloroethane is added by means of at least one jet mixer.
Owner:UHDE GMBH
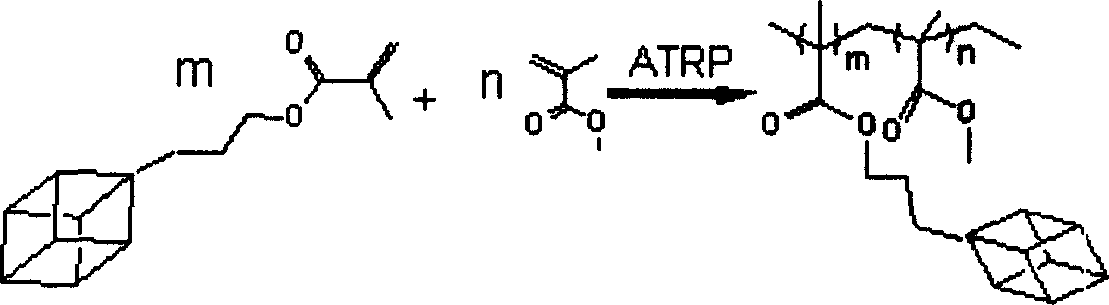
Fluoride POSS acrylic ester block multipolymer resin and its synthesis
InactiveCN101029137AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove hydrophobicityCyclohexanonePolymer science
A fluoride POSS acrylic resin block copolymer resin and its synthesis are disclosed. The molecular-weight of copolymer Mn is 20000-60000, Mn / Mw is 1.1-1.5, contact angle between coating and water is 85-120degree. The process is carried out by adding components into reactor to obtain methyl acrylate performed polymer with Br end capping, reacting with CuBr, PMDETA and F-POSS, removing catalyst from reactant, depositing while filtering by methanol, vacuum drying to constant weight to obtain the final product. The polymer powders can be dissolved into acetic ether, acetone, 1,2-dichloroethane, dioxane and cyclohexanone or their mixtures, then it can be used for coating or filming.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
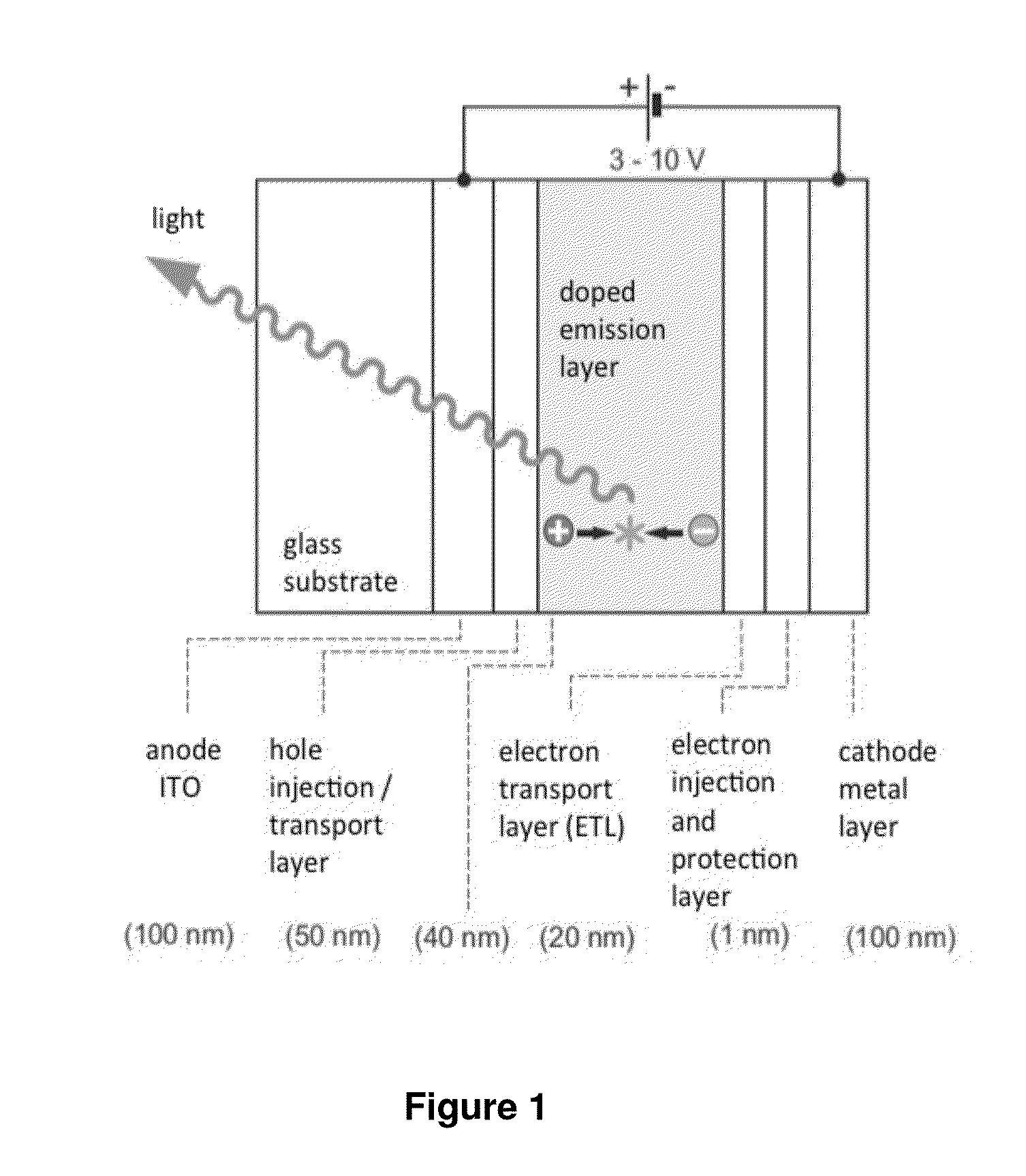
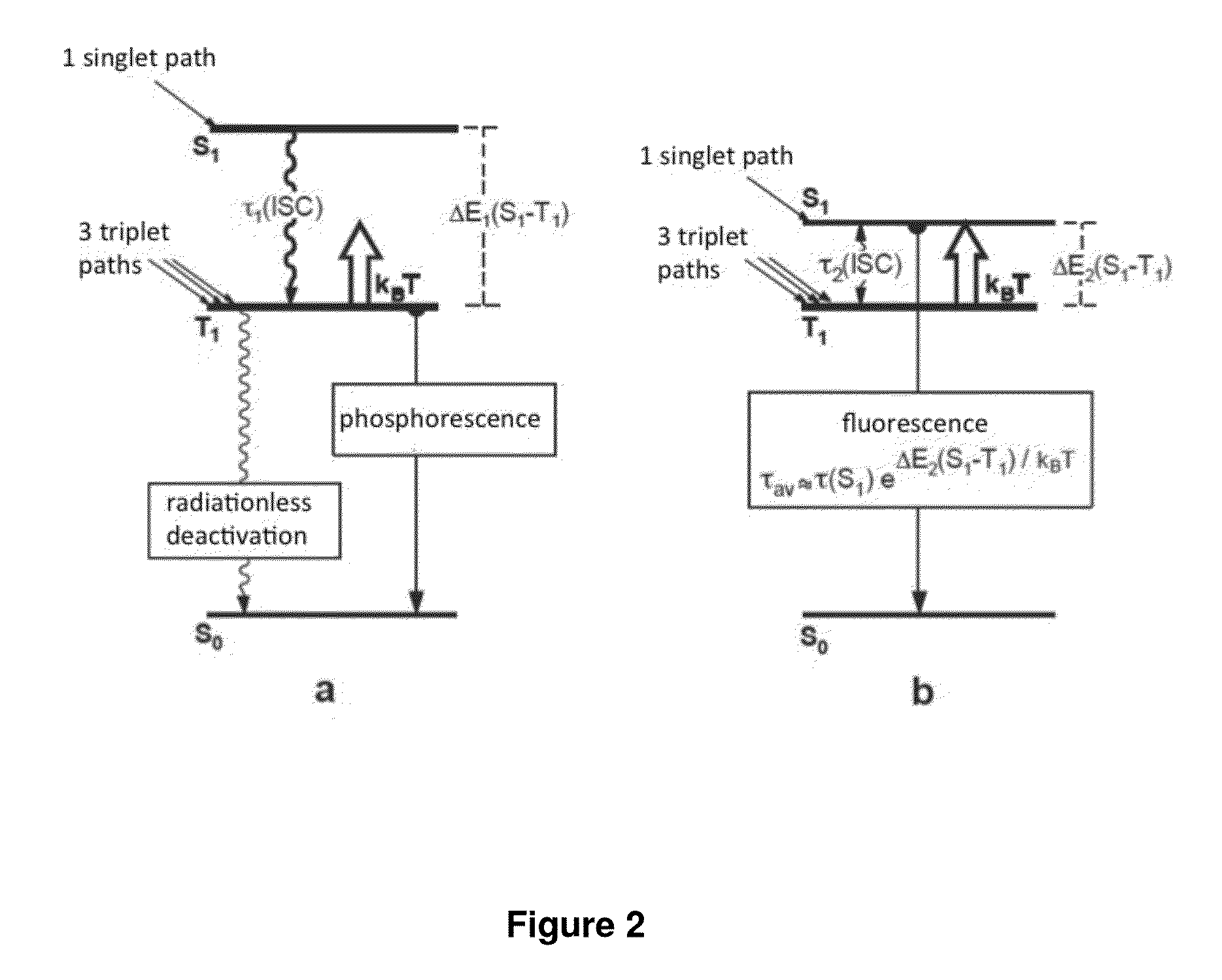
Copper (i) complexes for optoelectronic devices
ActiveUS20130150581A1Short possible emission decay timeDiminished roll-off behaviorFinal product manufactureGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolubilityChlorobenzene
The invention relates to neutral mononuclear copper (I) complexes for emitting light and with a structure according to formula (A) in which: M represents: Cu(I); L∩L represents: a single, negatively charged, bidentate ligand; N∩N represents: a diimine ligand (substituted with R and FG), in particular a substituted 2,2′-bipyridine derivative (bpy) or a substituted 1,10-phenanthroline derivative (phen); R represents: at least one sterically demanding substituent for preventing the planarisation of the complex in the excited state; FG=functional group, and represents: at least one second substituent for increasing solubility in organic solvents. The substituent can also be used for electron transport or alternatively for hole transport, said functional group being bound to the diimine ligands either directly or by means of suitable bridges; and the copper (I) complex: having a ΔE(S1−T1) value of less than 2500 cm−1 between the lowest excited singlet state (S1) and the triplet state (T1) which lies below; having an emission lifespan of at most 20 μs; having an emission quantum yield of greater than 40%, and a solubility of at least 1 g / L in organic solvents, in particular polar organic hydrocarbons such as acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, benzene, toluene, chlorobenzene, dichlorobenzene, dichloromethane, chloroform, dichloroethane, tetrachloroethylene, alcohols, acetonitrile or water.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method for preparing chloroethylene by catalytic reforming
InactiveCN101817723ASolve the problem of high temperature energy consumptionSolve pollutionPhysical/chemical process catalystsHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationCatalytic reformingActivated carbon
The invention discloses a method for preparing chloroethylene by catalytic reforming, which relates to a method for preparing the chloroethylene. The method comprises: a step of preparing a catalyst by using active carbon as a carrier, in which a barium salt is used as a catalyst, the active carbon is used as the catalyst carrier, and the barium salt is dissolved in water, absorbed by the active carbon and dried to obtain the catalyst carried by the active carbon; and a step of synthesizing the chloroethylene, in which acetylene gas and dichloroethane vapour are mixed and introduced to a reactor containing the catalyst carried by the active carbon to react, the reaction effluent is cooled to room temperature, unreacted dichloroethane is condensed to be separated out, and the remaining gas is compressed and frozen to give liquid chloroethylene. In the invention, a mercury free catalyst is adopted, the mercury pollution of the chloroethylene production industry is eliminated, and the reaction is performed spontaneously with little energy consumption.
Owner:ZHONGKE YIGONG SHANGHAI CHEM TECH CO LTD
Cement compositions containing flexible, compressible beads and methods of cementing in subterranean formations
Cement compositions comprising flexible, compressible beads, processes for preparing such cement compositions, and methods of cementing in subterranean formations using such cement compositions. One or more flexible, compressible beads are mixed with the cement before pumping the cement into a well bore. The flexible, compressible beads are preferably composed of an elastomeric material such as a copolymer of methylmethacrylate and acrylonitrile; a terpolymer of methylmethacrylate, acrylonitrile, and dichloroethane; a styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer; and polystyrene. The flexible, compressible beads may be heated to expand the beads before mixing with the cement such that the ensuing cement composition will have a desired density. Non-flexible beads such as spherulites may also be added to the cement compositions.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
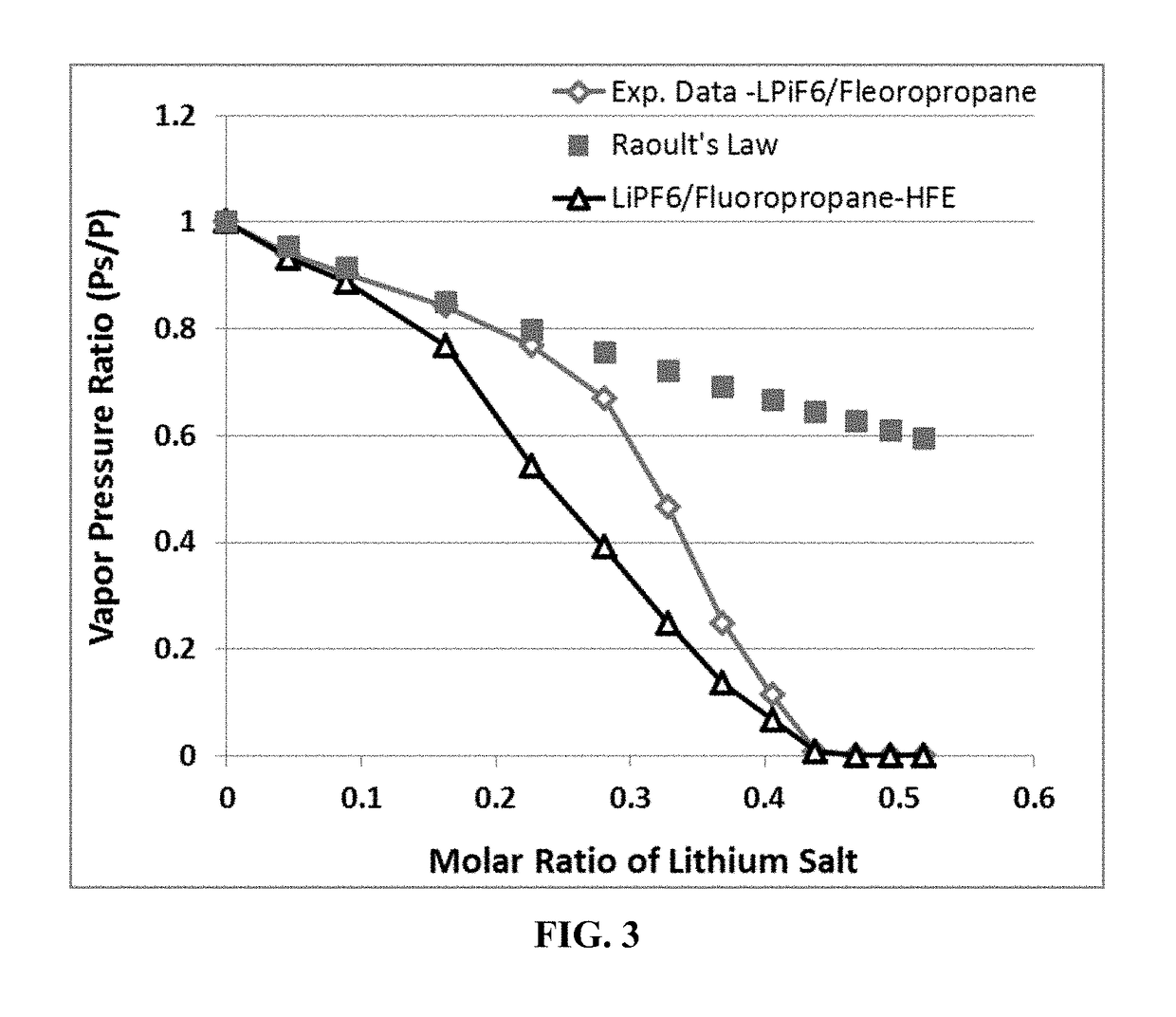
Non-flammable Electrolyte Containing Liquefied Gas and Lithium Secondary Batteries Containing Same
ActiveUS20180375156A1Flammability of any liquefied gas solvent can be effectively suppressedImprove solubilityOrganic chemistryCell electrodesElectrolytic agentDifluoroethyne
A rechargeable lithium cell comprising a cathode, an anode, an optional ion-permeable membrane disposed between the anode and the cathode, a non-flammable salt-retained liquefied gas electrolyte in contact with the cathode and the anode, wherein the electrolyte contains a lithium salt dissolved in or mixed with a liquefied gas solvent having a lithium salt concentration greater than 1.0 M so that the electrolyte exhibits a vapor pressure less than 1 kPa when measured at 20° C., a vapor pressure less than 60% of the vapor pressure of the liquefied gas solvent alone, a flash point at least 20 degrees Celsius higher than a flash point of the liquefied gas solvent alone, a flash point higher than 150° C., or no flash point, wherein the liquefied gas solvent is selected from methane, fluoromethane, difluoromethane, chloromethane, dichloromethane, ethane, fluoroethane, difluoroethane, tetrafluoroethane, chloroethane, dichloroethane, tetrachloroethane, propane, fluoropropane, chloropropane, ethylene, fluoroethylene, chloroethylene, or a combination thereof.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Ionic liquid functionalized ultra-crosslinking polymer as well preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel functionalized organic porous polymer and particularly relates to an ionic liquid functionalized ultra-crosslinking polymer and a preparation method thereof. The ionic liquid functionalized ultra-crosslinking polymer is prepared by reacting the following components in a molar ratio: 0.5-10% of a crosslinking agent, 10-70% of an imidazole ionic liquid and 10-80% of a monomer, wherein the used solvent is 1,2-dichloroethane; the monomer used in the ionic liquid functionalized ultra-crosslinking polymer is one or a combination of two or more of benzene, biphenyl, pyrrole, thiophene, furan, 1,3,5-triphenyl benzene or p-chloromethyl styrene, preferably, p-chloromethyl styrene. The porous polymer can be applicable to gas adsorption, especially capture and separation of CO2 gas.
Owner:HANGZHOU REWARD TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Composite functional super high cross-linked adsorption resin containing quaternary amine group, and its preparation method
ActiveCN1865302AHighlight hydrogen bondsProminent electrostatic effectOther chemical processesDibenzoyl PeroxideDisperser
The invention discloses a super high cross-linking adsorption resin with quaternary amines base composite function and making method, which comprises the following steps: utilizing phenylethene as monomer, diphenyl ethylene as cross linking agent, liquid wax as hole-sealing agent, magnesium carbonate as disperser, benzoyl peroxide as initiator; adopting nitrobenzene, substituted nitrobenzene, dichloroethanes or orthodichlorobenzene as swelling agent in the cross-linking reaction course of chloromethylation low cross-linking large-hole polyphenylacetylene; using zinc chloride, ferric chloride or tin tetrachloride as catalyst to produce different cross linking composite functional resin priority in the preset time and temperature condition; adding trimethylamine to aminate to produce the product. The resin possesses double functions of adsorption and ion exchanging, which can be applied in drug separation, little polluted water source and organic chemical waste water harnessing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
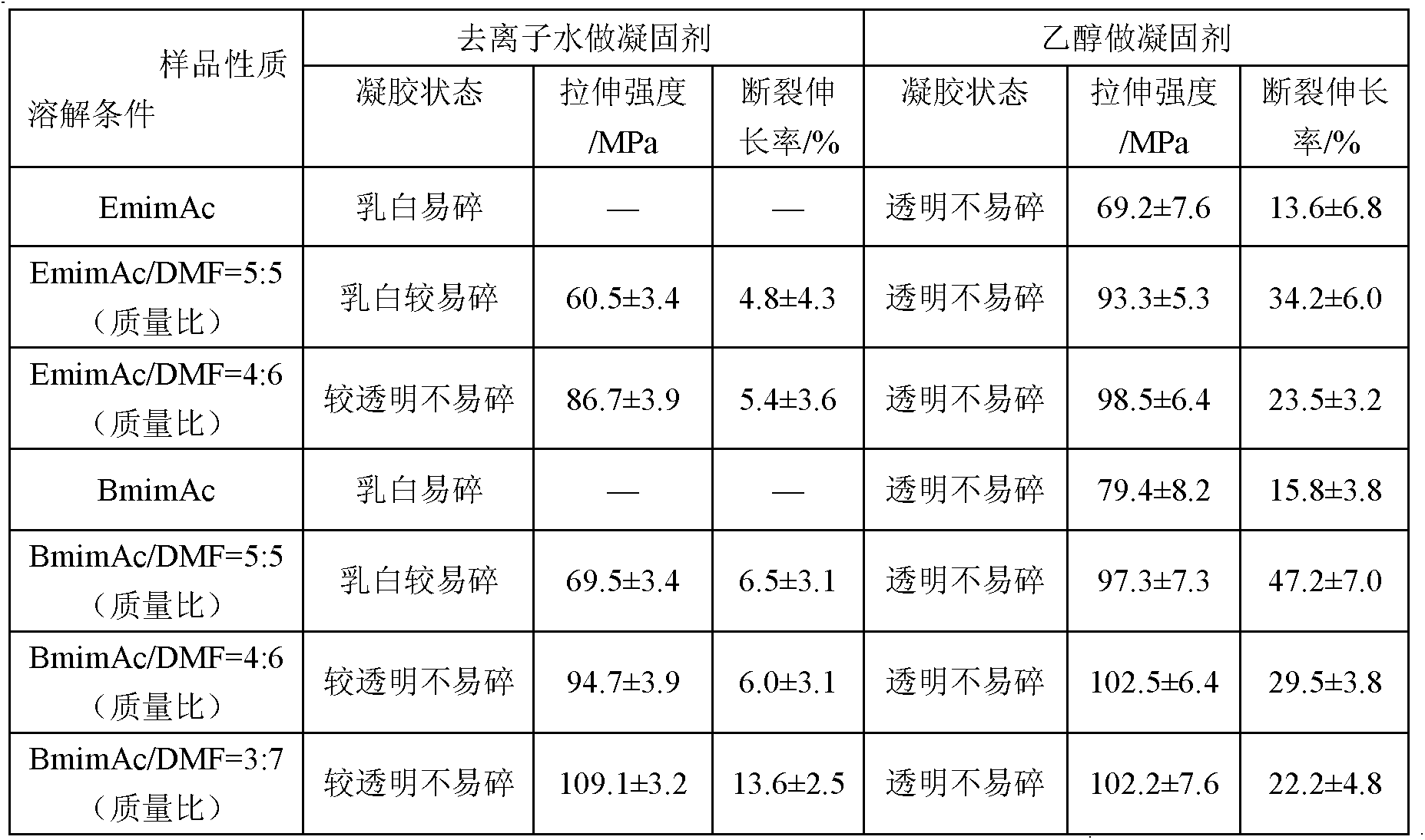
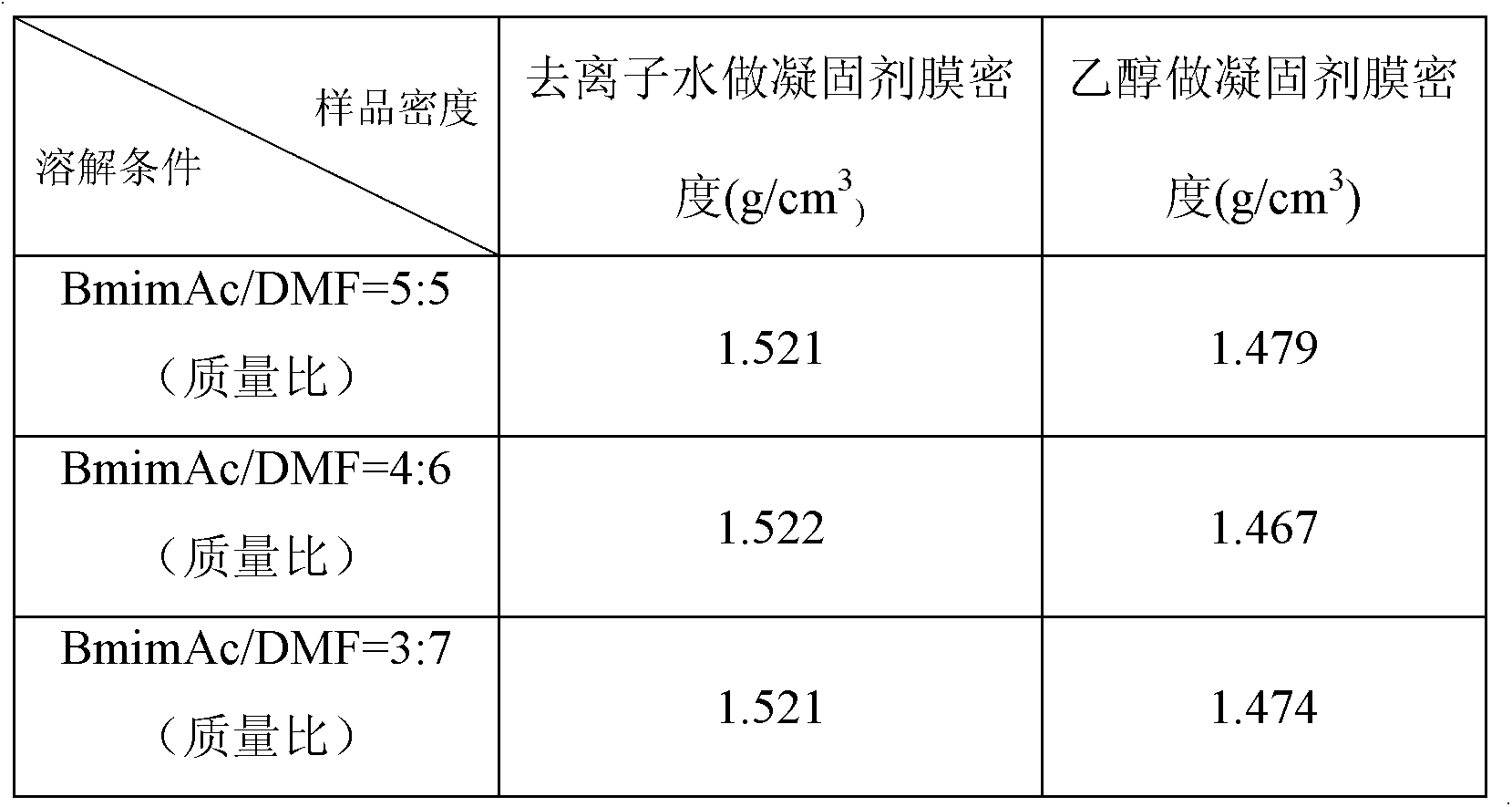
Preparation method of regenerated cellulose material
ActiveCN104130425AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove toughnessBulk chemical productionCarboxylic acidEthane Dichloride
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of a regenerated cellulose material and discloses a preparation method of the regenerated cellulose material. A employed solvent is a carboxylic acid type ionic liquid or is a co-solvent which is composed of the carboxylic acid type ionic liquid and an active-proton-free polar organic solvent, wherein the carboxylic acid type ionic liquid is preferably selected from 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole acetate, 1-propyl-3-methylimidazole acetate or 1-butyl-3- methylimidazole acetate; an auxiliary solvent is selected from one or more of DMF, DMAc, DMI, DMSO, pyrrodine, acetone, dichloromethane and dichloroethane; and a solidifying agent is preferably selected from alcohol organic solvents. The carboxylic acid type ionic liquid is most preferably selected from the 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole acetate and the 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole acetate; the auxiliary solvent is most preferably DMF; and the solidifying agent is preferably ethanol; wherein a mass ration of the carboxylic acid type ionic liquid to the auxiliary solvent is 5:5. By means of the preparation method, mechanical performances of a regenerated cellulose product can be significantly improved and environmental pollution can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,2-dichloroethane
InactiveUS7053252B2Good choicePreparation by halogen halide additionOrganic chemistry methodsHydrogen fluoridePolymer science
The invention relates to a process for preparing 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,2-dichloroethane (F123).This process consists in placing 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane (F133a) in contact with chlorine in the presence of hydrogen fluoride and a fluorination catalyst.F133a may be obtained by fluorination of trichloroethylene, and the F123 may be subsequently fluorinated to F125.
Owner:ATOFINA
Fireproof flame-retardant polyurethane external wall thermal-insulation system material
InactiveCN101851993AImprove fire and flame retardant performanceImprove heat resistanceFireproof paintsCovering/liningsFoaming agentPolyol
The invention relates to a fireproof flame-retardant polyurethane external wall thermal-insulation system material, which is characterized by comprising a moistureproof primer paint, a flame-retardant rigid polyurethane foam material, an interface agent, anti-crack mortar, a fireproof coating and a decorating coating which are arranged sequentially from inside to outside, wherein the flame-retardant rigid polyurethane foam material consists of an component A and a component B; the component A is prepared by mixing 80 to 50 parts by weight of phosphorous flame-retardant polyether polyol, 20 to 50 parts by weight of heterocyclic amine polyether polyol, 2 parts by weight of organic silicon foam stabilizer, 2 parts by weight of dimethylethanolamine catalyst, 1 part by weight of dibutyltin dilaurate catalyst, 20 to 50 parts by weight of flame retardant and 20 to 40 parts by weight of fluoro dichloroethane; the component B is a flame-retardant polyisocyanates curing agent; in the using process, the component A and the component B are mixed and foamed and an isocyanate index is between 1.05 and 1.10. The fireproof flame-retardant polyurethane external wall thermal-insulation system material of the invention has the advantage of having higher fireproof flame-retardant property.
Owner:SHANGHAI COLLODIN MATERIAL TECH DEV CO LTD
Process for the manufacture of 1,2-dichloroethane
InactiveUS8058490B2Low costHigh purityPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offChemical recyclingCatalytic oxidationEthane Dichloride
Process for the manufacture of 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) starting from a stream of ethane which is subjected to a catalytic oxydehydrogenation (ODH) thus producing a gas mixture containing ethylene which is then dried and conveyed to a chlorination reactor supplied with a flow of chlorine so that at least 10% of the ethylene is converted to DCE. The stream of products derived from the chlorination reactor is then conveyed to an oxychlorination reactor in which the majority of the balance of ethylene is converted to DCE.
Owner:SOLVAY SA
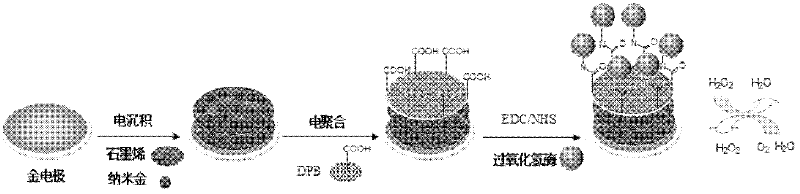
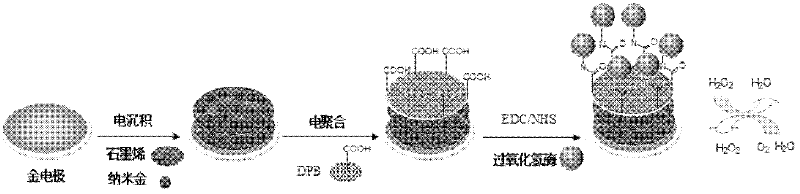
Method for preparing graphene biosensor
ActiveCN102520038ASensitive electrochemical responsePrecise size controlMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSupporting electrolyteConductive polymer
The invention relates to a method for preparing a graphene biosensor, belonging to the technical field of electrochemistry. The method comprises the following steps of: immersing a processed gold electrode into graphene oxide and a sodium sulphate solution, electrically depositing the electrode through a control electric potential, taking out the electrode, washing the electrode by using water, after drying the electrode at room temperature, putting the electrode in a chloroauric acid solution, electrically depositing the electrode through the control electric potential, taking out the electrode, washing the electrode by using water, and drying the electrode at room temperature; putting a modified electrode in a conductive polymer monomer and a supporting electrolyte solution, polymerizing the electrode through the control electric potential by adopting a cyclic voltammetry, taking out the electrode, washing the electrode by using water, and drying the electrode at room temperature; and activating the modified electrode in an EDC / NHS (Dichloroethane / N-Hydroxysuccinimide) solution, and immersing the modified electrode in a vomiting toxin antibody. The method disclosed by the invention is used for fixing graphene, gold nanoparticles and conducting polymers through electro-deposition; therefore, the method is very green and environment-friendly; furthermore, the thickness of a coating and sizes and distribution densities of the gold nanoparticles can be precisely controlled, thus, the batch production repeatability of the modified electrode is good.
Owner:盐城福万家保温板有限公司
Catalyst applied to preparation of vinyl chloride by catalytic cracking of 1,2-dichloroethane as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
InactiveCN104289247AGood dispersionLow cracking temperaturePreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPhysical/chemical process catalystsActivated carbonEthane Dichloride
The invention relates to a nitrogen-doped active carbon catalyst applied to preparation of vinyl chloride by catalytic cracking of 1,2-dichloroethane and in particular relates to active carbon, wherein the inner surface and the outer surface of the active carbon are doped with nitrogen; the doping content of nitrogen is 0.1-10wt%; furthermore, meal is loaded on the nitrogen-doped active carbon catalyst and exists in the form of a metal compound; the loading content of the metal compound is 0.1-10wt%. According to the catalyst, the preparation method is simple, the process is short, materials are easily available, and the cost is relatively low; the nitrogen doped in the active carbon has a small possibility of losing and inactivating; the nitrogen is doped in the nitrogen-doped active carbon catalyst loaded with the metal compound, so that the dispersion of the metal component on the active carbon can be effectively improved; the catalytic activity is improved; the cracking temperature of dichloroethane can be greatly reduced under the catalytic action of the catalyst prepared by the method.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Ethylene oxychlorination catalyst and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN100998942AIncrease throughputIncrease profitCatalyst activation/preparationHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationMicrosphereRare earth
A catalyst for the oxychlorinating reaction of ethene to prepare dichloroethane is composed of the carrier (aluminum oxide-titanium oxide microballs), primary active component (Cu) and secondary active component consisting of at least one of La, Ce, Nd, Pr and Y, one transition metal and at least one alkali metal. Its preparing process includes preparing carrier by codeposition, and dipping in active components.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Chloration method for phenoxyacetic acid and derivatives thereof
InactiveCN102336654AEasy to industrializeOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationChlorobenzeneIndustrial waste water
The invention provides a chloration method for phenoxyacetic acid and derivatives thereof, which comprises the following steps that: raw materials of the phenoxyacetic acid or the derivatives of the phenoxyacetic acid and chlorinating agents take reaction at a certain temperature in organic solvents under the effect of catalysts, wherein the chlorinating agents can be chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite, calcium hypochlorite and sulfuryl chloride, the catalysts can be lewis acid and sulfurated substances, and solvents can be dichloromethane, dichloroethane, trichloromethane, carbon tetrachloride, formic acid, ethyl acetate, benzene, toluene, dimethylbenzene, chlorobenzene and o-dichlorobenzene. The method has the advantages that the operation can be carried out under the waterless condition, the generation of a large amount of industrial waste water is avoided, the used catalysts are safe and are easy to obtain, the solvents can be cyclically used, and the industrialization is easy.
Owner:DALIAN RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
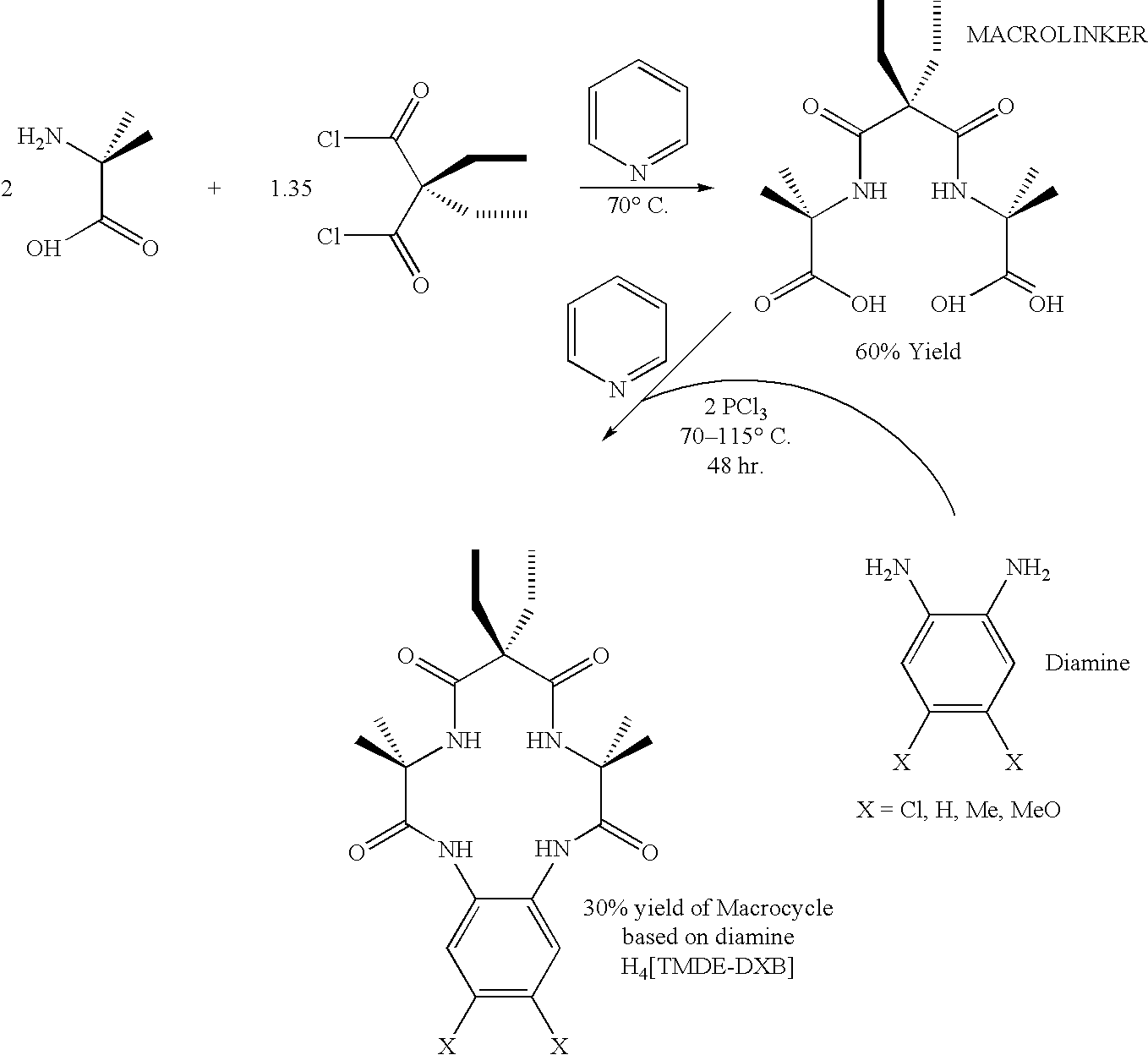
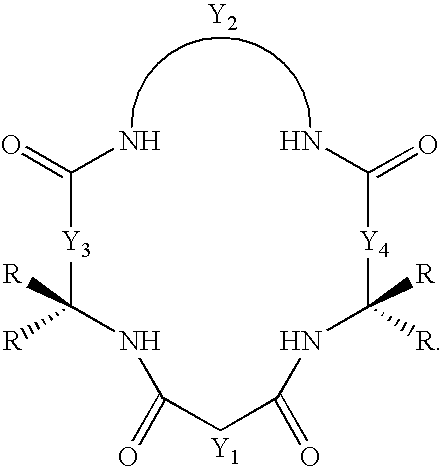
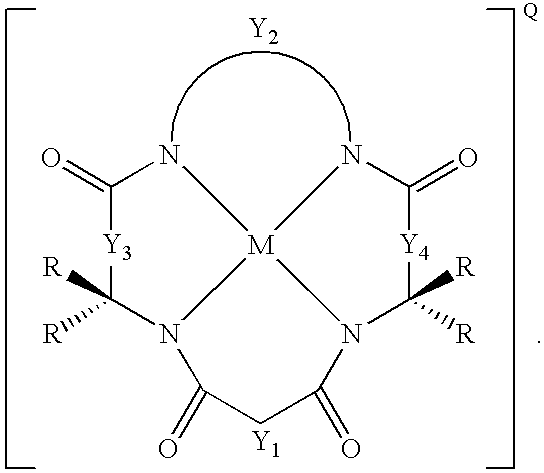
Synthesis of macrocyclic tetraamido compounds and new metal insertion process
An improved method of synthesizing a macrocyclic tetraamido compound includes protecting the amino portion of an amino carboxylic acid to form a protected amino carboxylic acid; exposing the protected amino carboxylic acid to a first solvent, preferably a hydrocarbon solvent, such as toluene or 1,2-dichloroethane, dichloromethane, dibromomethane and 1,2-dibromoethane. The carboxylic acid portion of the protected amino carboxylic acid is then converted to an activated carboxylic acid by one of esterification or acid halide formation, to form a protected amino activated carboxylic acid derivative. The protected amino activated carboxylic acid derivative is reacted with a diamine in the presence of a second solvent, such as THF or ,2-dichloroethane, dichloromethane, dibromomethane and 1,2-dibromoethane, to form a protected diamide diamine intermediate. Following deprotection, the diamide diamine intermediate is reacted with an activated diacid, such as an activated malonate, oxalate or succinate derivative to form the macrocyclic tetraamido compound. The macrocyclic tetraamido compound may further be complexed with a transition metal.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Preparation method of rare earth element modified and aldehyde removed resin and application of rare earth element modified and aldehyde removed resin in ethylene glycol refining
ActiveCN104356258AImprove removal effectStable physical and chemical propertiesCation exchangersBenzoyl peroxidePolyvinyl alcohol
The invention relates to a preparation method of rare earth element modified and aldehyde removed resin and an application of the rare earth element modified and aldehyde removed resin in ethylene glycol refining. According to the preparation method, styrene is taken as a monomer, divinylbenzene is taken as a crosslinking agent, benzoyl peroxide is taken as an initiator, polyvinyl alcohol is taken as a suspending agent, water is taken as a reaction medium, and the components react in a suspension polymerization manner at the temperature of 85-95 DEG C; a polymer obtained after reaction is dissolved in dichloroethane for swelling, sulfuric acid is added for a sulfonation reaction, and cation exchange resin is obtained; and a nitric acid solution of the rare earth element is added into the cation exchange resin, and the rare earth element is chemically bonded to the resin to obtain the spherical modified and aldehyde removed resin. A fixed bed reactor is filled with the aldehyde removed resin, ethylene glycol is refined at the temperature of 60-70 DEG C, the density of a resin packing layer heap is 400-600 kg / m<3>, the reaction pressure is 0.4 MPa, under the catalytic action of the modified and aldehyde removed resin, impurity aldehyde and ethylene glycol have a condensation polymerization reaction and produce a product that does not influence an ethylene glycol product, and obtained ethylene glycol has high purity.
Owner:JIANGSU SUQING WATER TREATMENT ENG GROUP +1
Metal cleaner
The invention discloses a metal cleaner. The metal cleaner is prepared from, by weight, 50%-90% of halohydrocarbon cleaners, 0%-10% of ester additives, 2%-30% of hydrocarbon additives, 0%-20% of alcohol additives, 0%-25% of alcohol ether additives and 0%-5% of amine additives, wherein the halohydrocarbon cleaners are chlorohydrocarbon and / or chloro-fluoro-hydrocarbon, chlorohydrocarbon is tetrachloroethylene and / or dichloromethane, and chloro-fluoro-hydrocarbon is 1-fluoro-1,1-dichloroethane. The metal cleaner is large in cleaning force, high in permeability and dispersity, capable of cleaning wax, ink, punching oil, cutting oil and lubricating oil, small in smell and free of toxicity.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINJUNXIANG TECHCAL
Compositions Containing 1-Chloro-3,3,3 Trifluoropropene And 1-Fluoro-1,1 Dichloroethane
InactiveUS20120043492A1Easy to adaptReduce pressureOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesBlowing agent1,1-Dichloro-1-fluoroethane
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
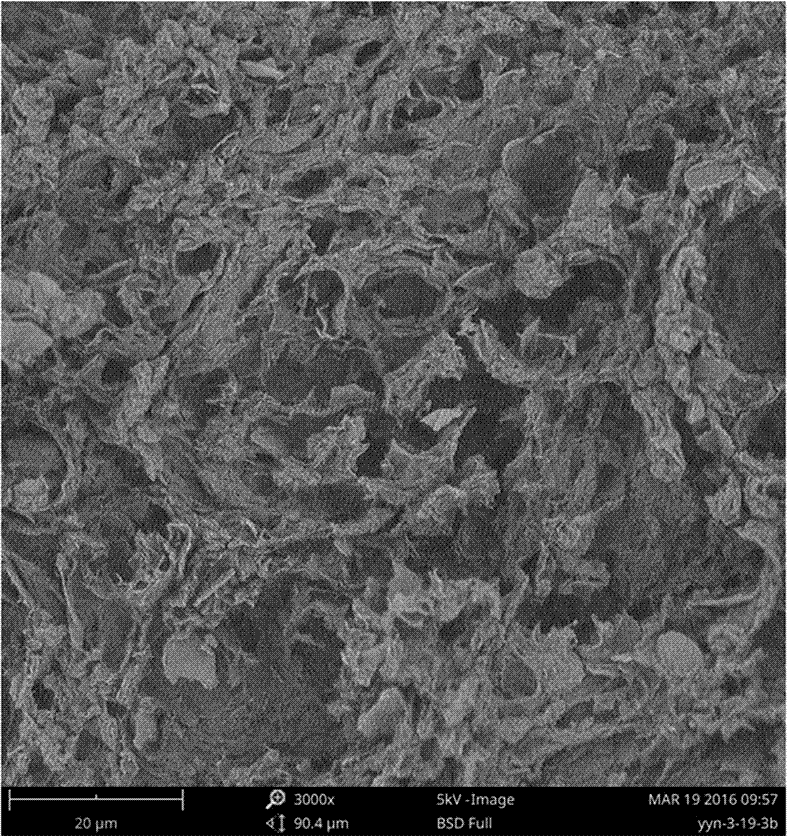
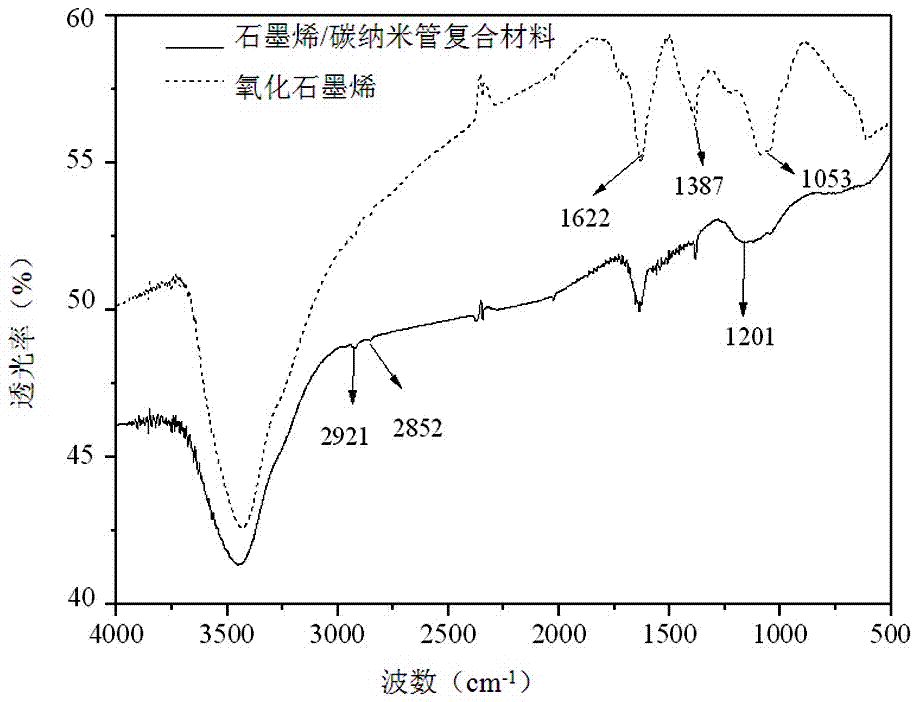
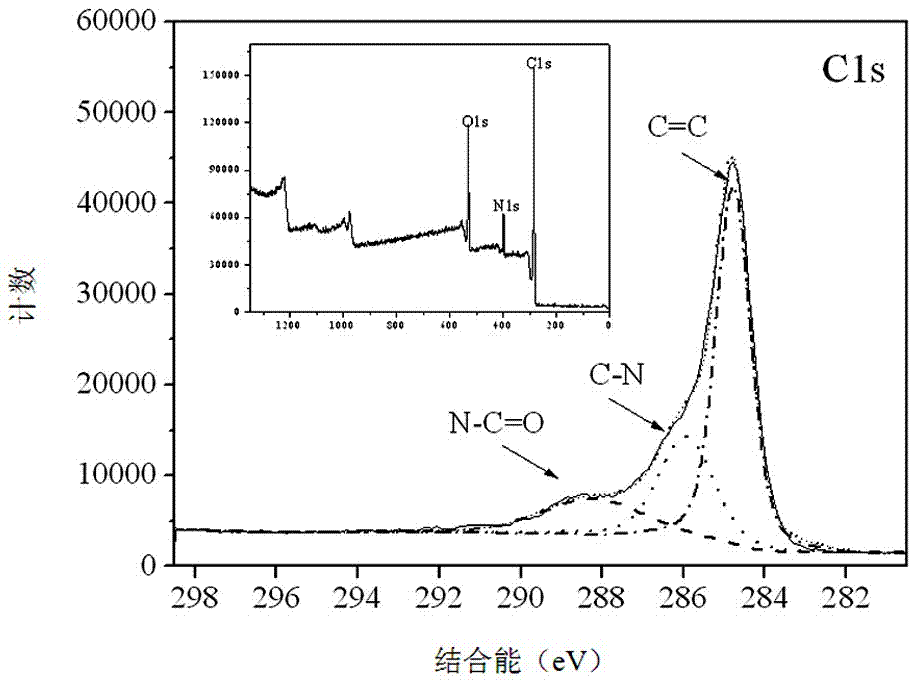
Preparation method and application of graphene/carbon nano-tube composite
ActiveCN106861617AAvoid clumpingLarge specific surface areaOther chemical processesComponent separationEthylenediamineCLORPRENALINE
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a graphene / carbon nano-tube composite. The preparation method comprises the following steps: oxidizing graphene powder and a multiwalled carbon nano-tube together to obtain graphene oxide and an oxidized carbon nano-tube; carrying out ultrasonic peeling and dispersion on the graphene oxide and the oxidized carbon nano-tube; carrying out modification connection and reduction on the graphene oxide and the oxidized carbon nano-tube with ammonia water and ethylenediamine; and filtering, washing and drying a product after reaction to obtain the graphene / carbon nano-tube composite. The preparation method is simple and convenient, and reaction conditions are mild; in the preparation method, the graphene is connected with the carbon nano-tube through covalent modification, and the carbon nano-tube is connected between graphene slice layers. The graphene / carbon nano-tube composite prepared by the method has a fluffy and porous three-dimensional skeleton structure, and can be used for extracting and detecting melamine, clenbuterol, sulfadimidine sodium, indoleacetic acid, bambuterol, clorprenaline, dicofol, 2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,1-dichloroethane or chlorofluoro thiochromanone.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of secondarily-crosslinked adsorption resin
The invention relates to a preparation method of secondarily-crosslinked adsorption resin. The preparation method includes a secondary crosslinking step in which polystyrene resin chloromethylated bead is subjected to a secondary crosslinking reaction to obtain the secondarily-crosslinked adsorption resin. The secondary crosslinking step includes a still-standing and swelling process, in which 1 part by weight of the polystyrene resin chloromethylated bead, 0.5-4 parts by weight of an alcohol substance and 4-6 parts by weight of 1,2-dichloroethane are added to perform the still-standing and swelling process. The secondarily-crosslinked adsorption resin is used for blood purification. Through the preparation method, residual chloromethyl groups in ultrahigh-crosslinked polystyrene-divinylbenzene resin, thereby increasing chemical stability and blood compatability of the adsorption resin.
Owner:JAFRON BIOMEDICAL
Method for preparing bromination polystyrene
The invention discloses a method for preparing bromination polystyrene, which includes (1) adding 10-30 parts by weight of styrene into 100 parts by weight of dichloroethane and adding 0.1 to 0.5 parts by weight of BPO or AIBN to obtain polystyrene dichloroethane solution; (2) adding 0.1 to 3 parts by weight of lewis acid catalyst and 0.1 to 3 parts by weight of backbone protective agent in the above prepared solution and then dropping 30 to 90 parts of bromine chloride dichloroethane solution to obtain bromination polystyrene dichloroethane solution; (3) adding 00.5 to 0.1 parts by weight ofneutralizer into the above prepared solution, conducting washing and static layering, adding 0.1 to 3 parts by weight of fat removing bromine preventing agent in the layered organic layers, conducting flash evaporation, cooling, centrifugation and drying on the organic layer to obtain the product. The process is capable of manufacturing polystyrene with narrow molecular weight distribution, and the polystyrene can obtain bromination polystyrene with controllable molecular weight after bromination.
Owner:SHANDONG RUNKE CHEM
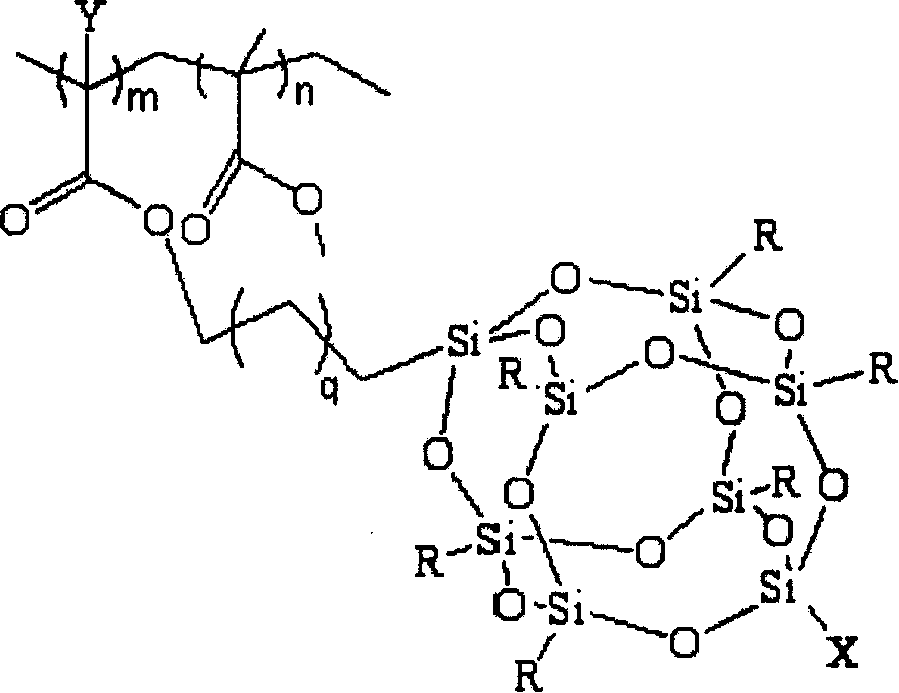
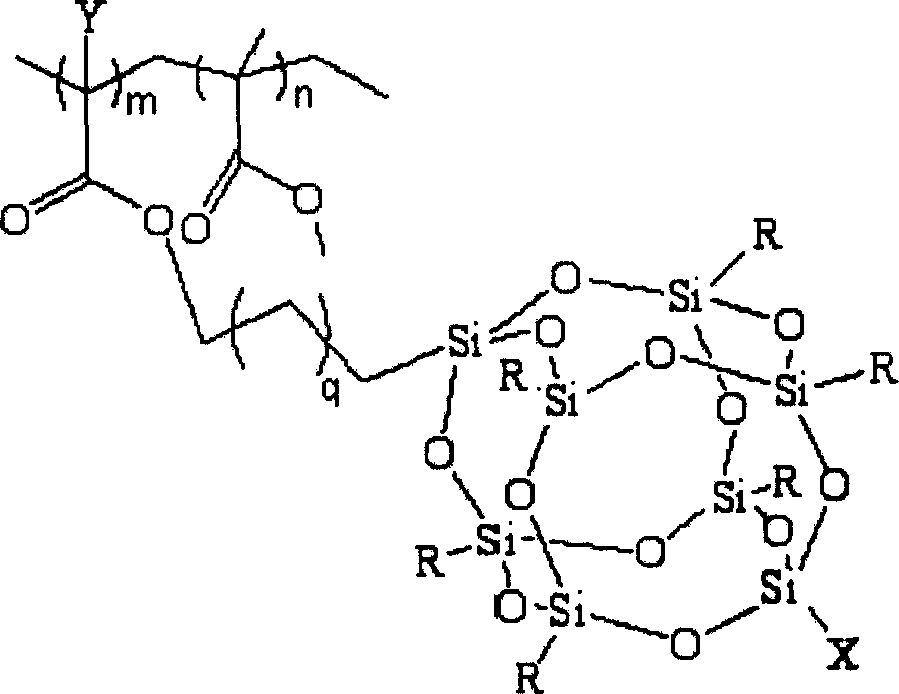
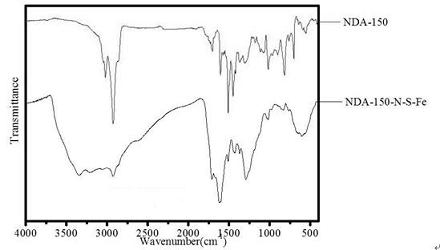
A kind of composite functional fluoride removal resin and its preparation method
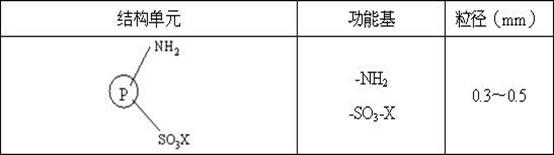
InactiveCN102268114AEfficient and deep defluorinationImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionChemistryDichloroethane
The invention discloses a composite functional fluorine-removing resin, which belongs to the field of resins. The resin is based on styrene-divinylbenzene resin, the structural unit is , contains functional groups -NH2 and -SO3-X (Fe / Al), the particle size is 0.3-0.5mm, and the saturated adsorption capacity for F- is 2.16~8.10mg / g. The preparation method is: take styrene-divinylbenzene resin as the matrix, add 60-80% concentrated nitric acid and 75-98% concentrated sulfuric acid to react at 40-80°C, and stir for 0.5-3 hours to obtain the loaded nitro Resin R-NO2; use dichloroethane as swelling agent, add 80-98% concentrated sulfuric acid to react at 70-120°C, stir and react for 8-16 hours to get nitro-sulfonic acid resin R-NO2 -SO3H; at 60-100°C, add SnCl2·2H2O, concentrated hydrochloric acid, ethanol, and reflux for 8-16 hours to obtain amino-sulfonic acid resin R-NH2-SO3H; at 20-60°C, add 0.1-1.0 mol / L iron salt or aluminum salt solution, stirred and reacted for 18-30 hours, and the composite functional fluorine removal resin R-NH2-SO3-X (Fe / Al) modified by amino groups and supported by metals was prepared. The composite functional fluorine removal resin prepared by the invention can be used for high-efficiency and deep fluorine removal.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Catalyst for preparing vinyl chloride by cracking 1,2-dichloroethane as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
InactiveCN105833892AImprove catalytic performanceRaw materials are cheap and easy to getPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPhysical/chemical process catalystsActivated carbonNitrogen
The invention relates to a catalyst for cracking 1,2-dichloroethane to prepare vinyl chloride and its preparation method and application. The catalyst uses activated carbon as a carrier and supports nitrogen-containing compounds. The catalyst is based on the total mass of the catalyst. The mass percentage of nitrogen-containing compounds is 16.7% to 44.4%. The catalyst prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention has better catalytic performance, can reduce the temperature for preparing vinyl chloride from 450-500°C in the current industrial pyrolysis to 280-300°C, and increase the single-pass conversion rate of dichloroethane from 50%. The selectivity of vinyl chloride can reach 93%, and the selectivity of vinyl chloride can also reach 99.3%, and has a long service life of nearly 100 hours, and the catalyst raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, and the preparation process is simple. The catalyst is not only suitable for the cracking of dichloroethane, but also suitable for the reforming of acetylene dichloroethane to prepare vinyl chloride.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Process for preparing brominated polystyrene
The invention provides a preparation method of bromized polystyrene. The method is characterized in that sulfur is taken as the scavenging agent of a small amount of water in the electrophilic bromination reaction of the polystyrene and as the quencher of free radical in the electrophilic bromination reaction of the polystyrene, and the mass of the sulfur is 0.1 to 12 percent of that of the polystyrene. In the organic solvent of dichloroethane, chloroform, bromochloromethane, carbon tetrachloride or tetrachloroethane, the anhydrous aluminium trichloride, the anhydrous ferric chloride, the titanium tetrachloride, the antimonous chloride, the aluminum powder, the zinc powder or the iron powder is taken as the catalyst, the sulfur is taken as the scavenging agent of the small amount of water and as the quencher of the free radical, and the bromized polystyrene is prepared by the electrophilic bromination reaction between the polystyrene and the bromine.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
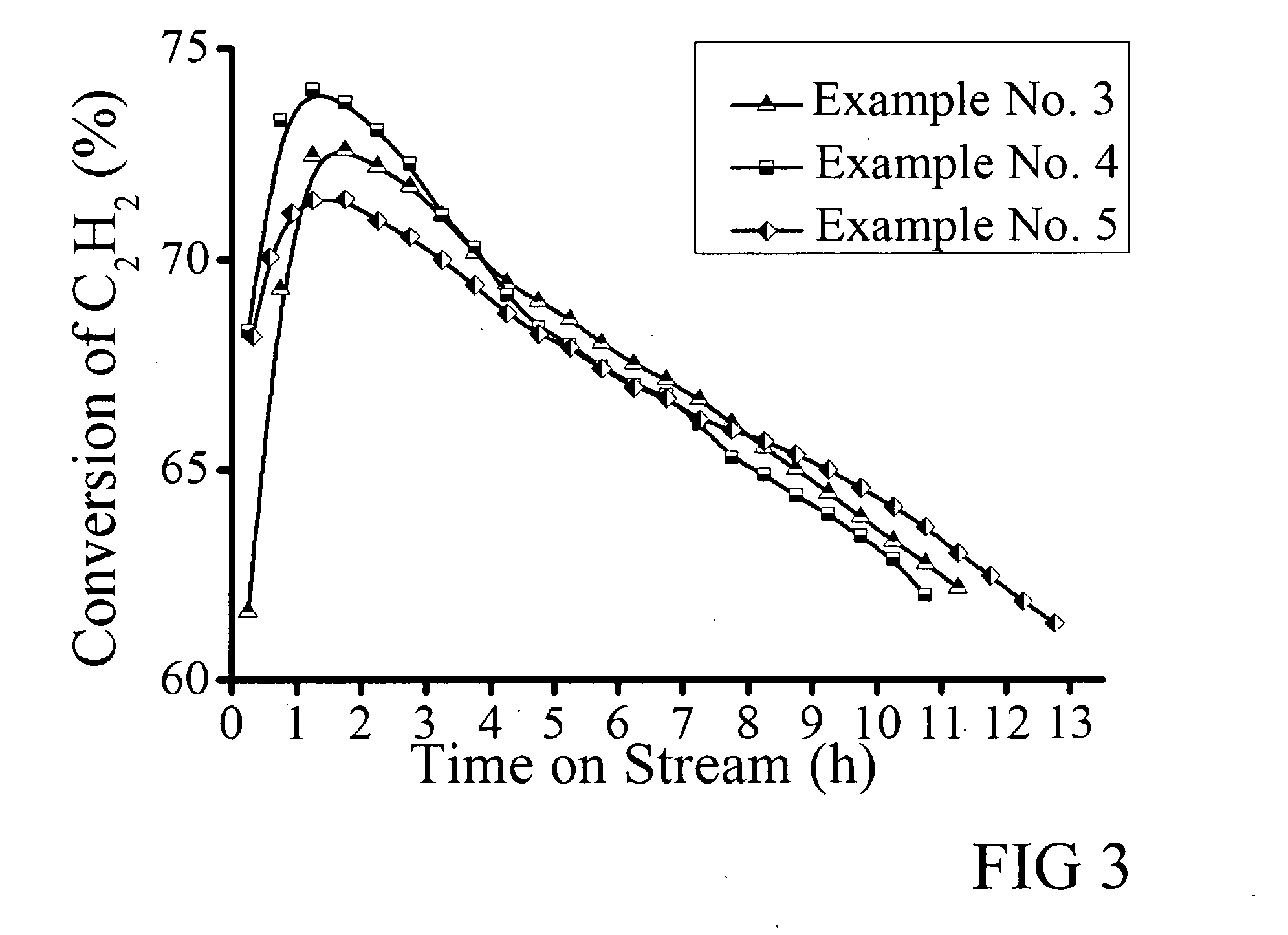
Method for preparing vinyl chloride through catalyzing acetylene and dichloroethane
ActiveCN104326865AHigh conversion rate of acetyleneHigh selectivityPhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offActivated carbonNitrogen
The invention discloses a method for preparing vinyl chloride through catalyzing acetylene and dichloroethane to react. The method comprises the steps: mixing acetylene and dichloroethane steam according to a molar ratio of 1:1-1:4, then introducing into a fixed bed reactor provided with a nitrogen modified catalyst, and carrying out a reaction with the reaction temperature of 180-300 DEG C and the air speed of 20-120 h<-1>. The nitrogen modified catalyst takes active carbon as a carrier, and is loaded with a metal salt compound and a nitrogen-containing compound; based on the total mass of the catalyst, the mass percentage of the metal salt compound is 0.01-10%, and the mass percentage of the nitrogen-containing compound is 0.01-10%. Vinyl chloride prepared by the method has the characteristics of high acetylene conversion rate and high vinyl chloride selectivity; and the nitrogen modified catalyst preparation process adopted in the process method is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com