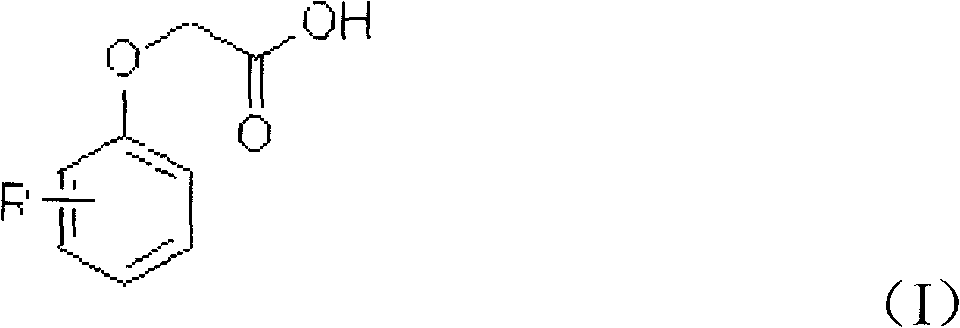
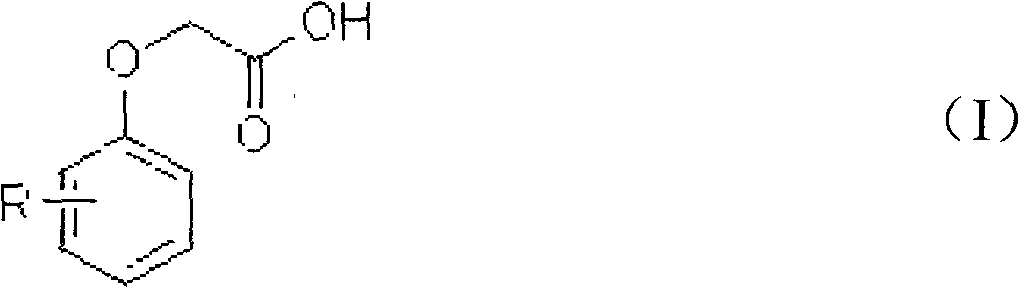Chloration method for phenoxyacetic acid and derivatives thereof
A chlorination agent and compound technology, applied in the field of chlorination of phenoxyacetic acid and its derivatives, can solve the problems of large waste water, difficult control of chlorination depth, unsuitable for industrial production, etc., and achieve the effect of easy industrialization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Add 100 g of dichloroethane, 15.2 g of phenoxyacetic acid, 0.1 g of boron trifluoride, and 0.2 g of sulfurous acid into a 250 ml four-necked bottle equipped with a thermometer, stirring, reflux condenser, and tail gas recovery device, and heat up to 50°C 14.0 g of sulfuryl chloride was slowly and uniformly added, and the addition was completed in 2 hours. After the reaction was completed, the temperature was lowered and filtered to obtain 17.8 g of 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid with a purity of 99.23% and a yield of 94.9%.
[0028] Adopt the same condition as embodiment 1, just change catalyst, the results are shown in Table 1.
[0029] Chlorination of phenoxyacetic acid under different catalysts in table 1
[0030] experiment number
Embodiment 2
[0032] Add 100g of chloroform, 15.2g of phenoxyacetic acid, 0.1g of boron trifluoride, and 0.2g of sulfurous acid into a 250ml four-necked bottle equipped with a thermometer, stirring, reflux condenser, and tail gas recovery device, heat up to 50°C, and slowly Add 14.0 g of sulfuryl chloride at a uniform speed and complete the addition in 2 hours. After the reaction, cool down and filter to obtain 17.1 g of 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid with a purity of 99.15% and a yield of 91.2%.
[0033] Using the same conditions as in Example 2, only changing the solvent, the results are shown in Table 2.
[0034] Chlorination of phenoxyacetic acid under different solvents in table 2
[0035] experiment number
Embodiment 3
[0037] Add 100 g of dichloroethane, 15.2 g of phenoxyacetic acid, 0.1 g of boron trifluoride, and 0.2 g of sulfurous acid into a 250 ml four-necked bottle equipped with a thermometer, stirring, reflux condenser, and tail gas recovery device, and heat up to 50°C , slowly and uniformly added 29.0 g of sulfuryl chloride, and the addition was completed in 4 hours. After the reaction was completed, the temperature was lowered and filtered to obtain 19.8 g of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid with a purity of 98.05% and a yield of 90.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com