Method for extracting platinum, palladium, rhodium from automotive catalyst of ore phase reconstruction
A catalyst, platinum and palladium technology, applied in the field of effective recovery of platinum group metals, can solve the problems of short service life of plasma gun, difficulty in separating metal and slag, and limitation of practical application, so as to shorten production process, reduce loss of precious metals, and material adaptability strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
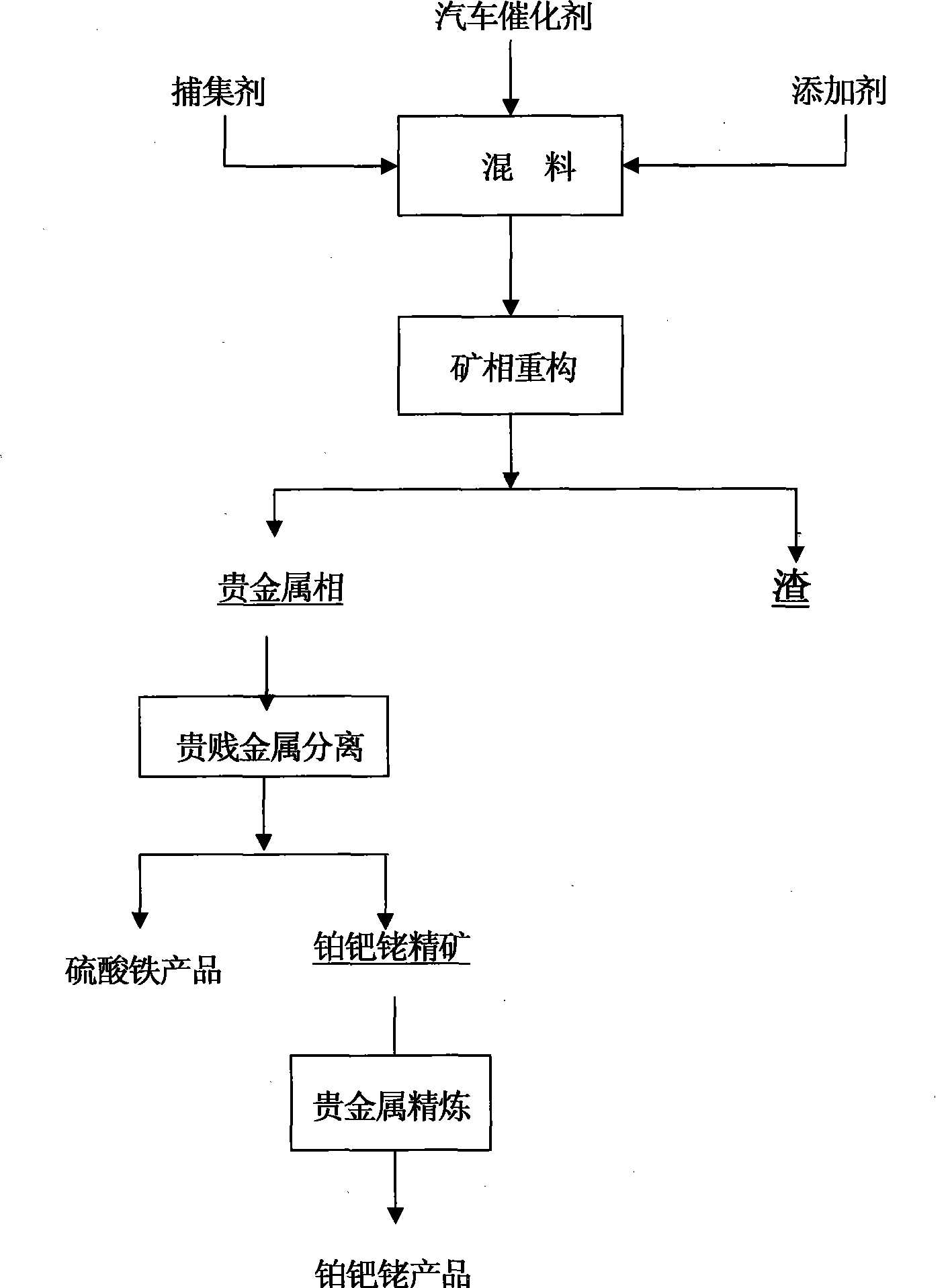
[0029] Embodiment 1. Ore phase reconstruction
[0030] Take the exhausted catalyst of the automobile, add the trapping agent and additive, the trapping agent is iron ore or iron oxide, and the dosage is 50-120% of the weight of the residue leached from the exhausted catalyst; the additive is iron ore, lime, carbon powder and quartz sand, and the additive The dosage is 30-300% of the weight of the spent catalyst raw material, and the crushing particle size is 40-200 mesh.
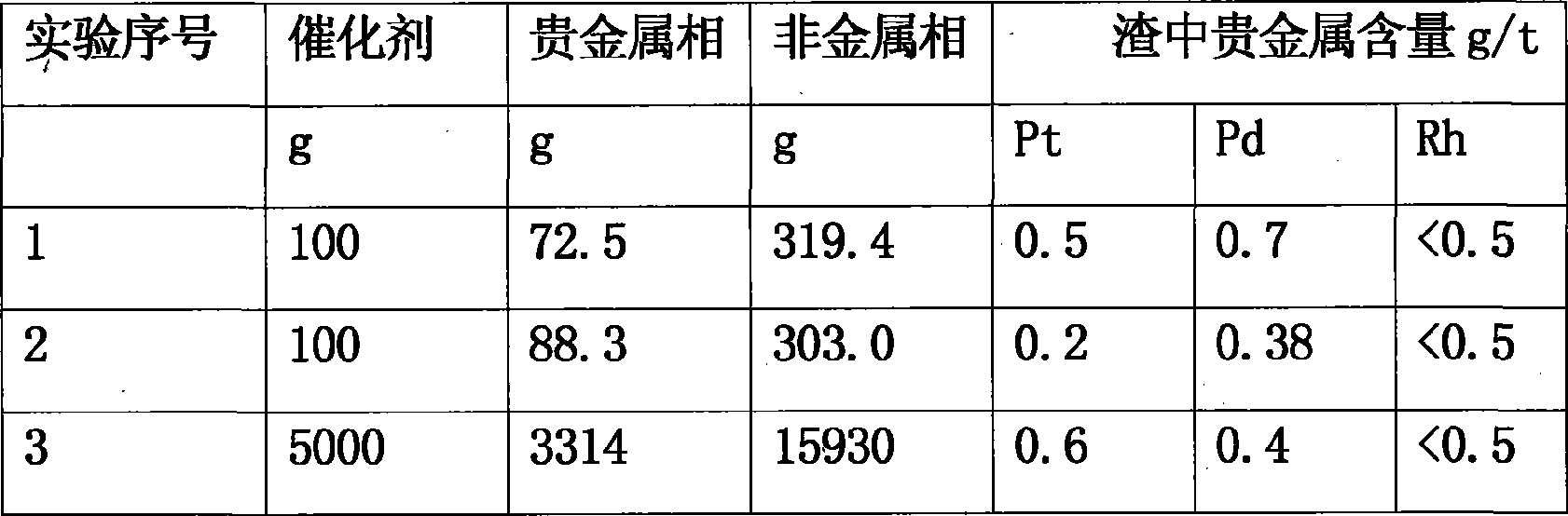
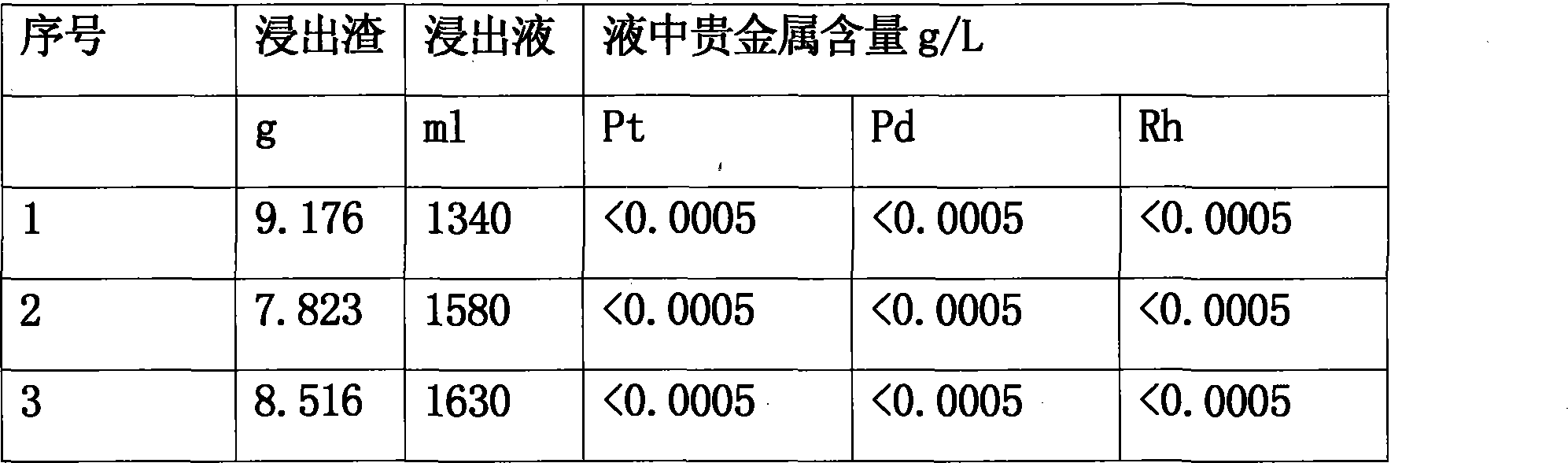
[0031] After mixing with a mixer, put it into a clay graphite crucible, place it in a high-temperature resistance furnace, and keep the temperature at 1400°C for 0.5 hours. After the melting is completed, take it out, cool it to room temperature, and pour out the melted material. Divided into two phases of precious metal alloy and smelting slag, the slag phase is prepared in a sample maker, and the sample is sent for analysis to detect the content of platinum, palladium and rhodium.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com