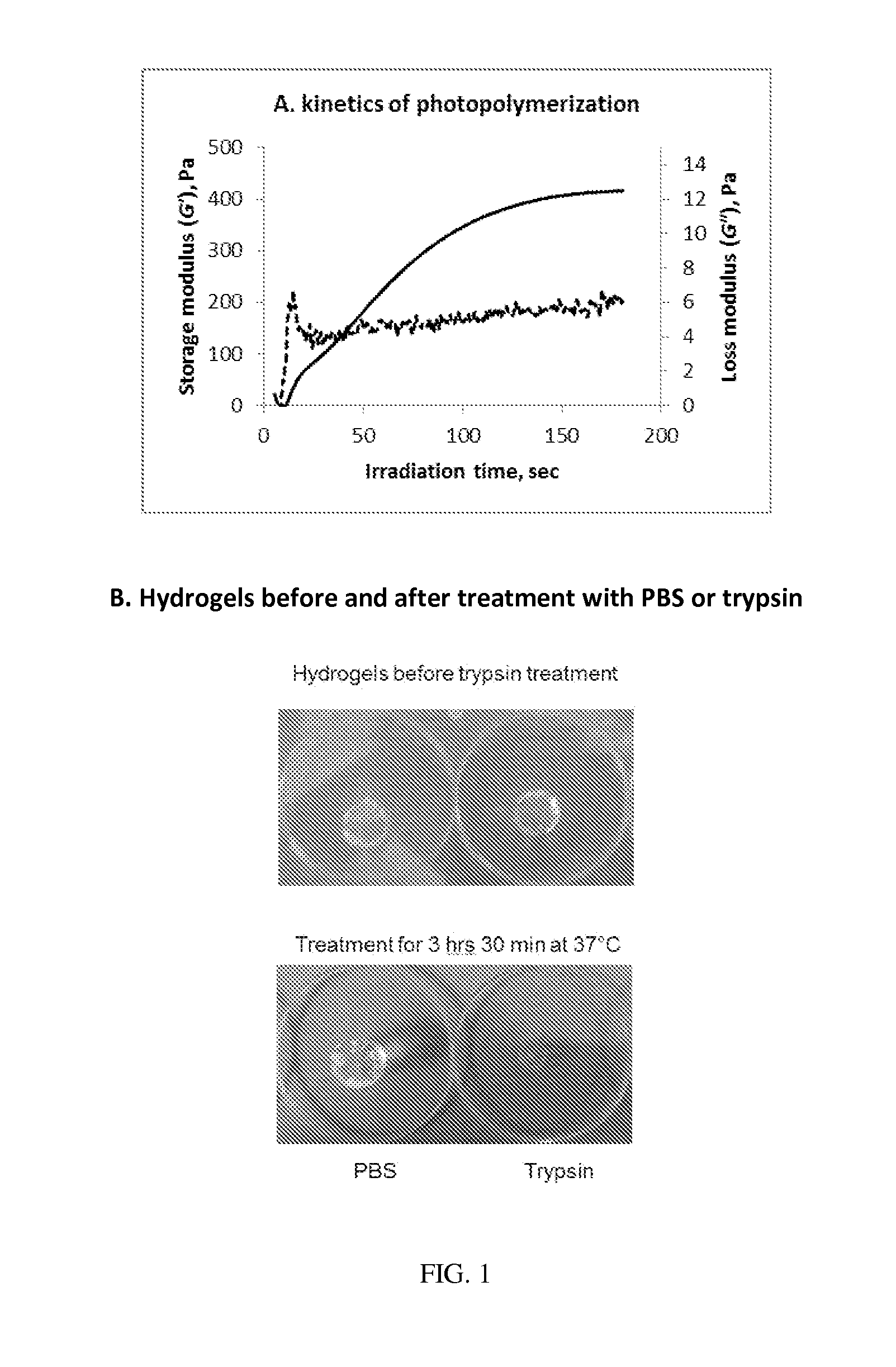
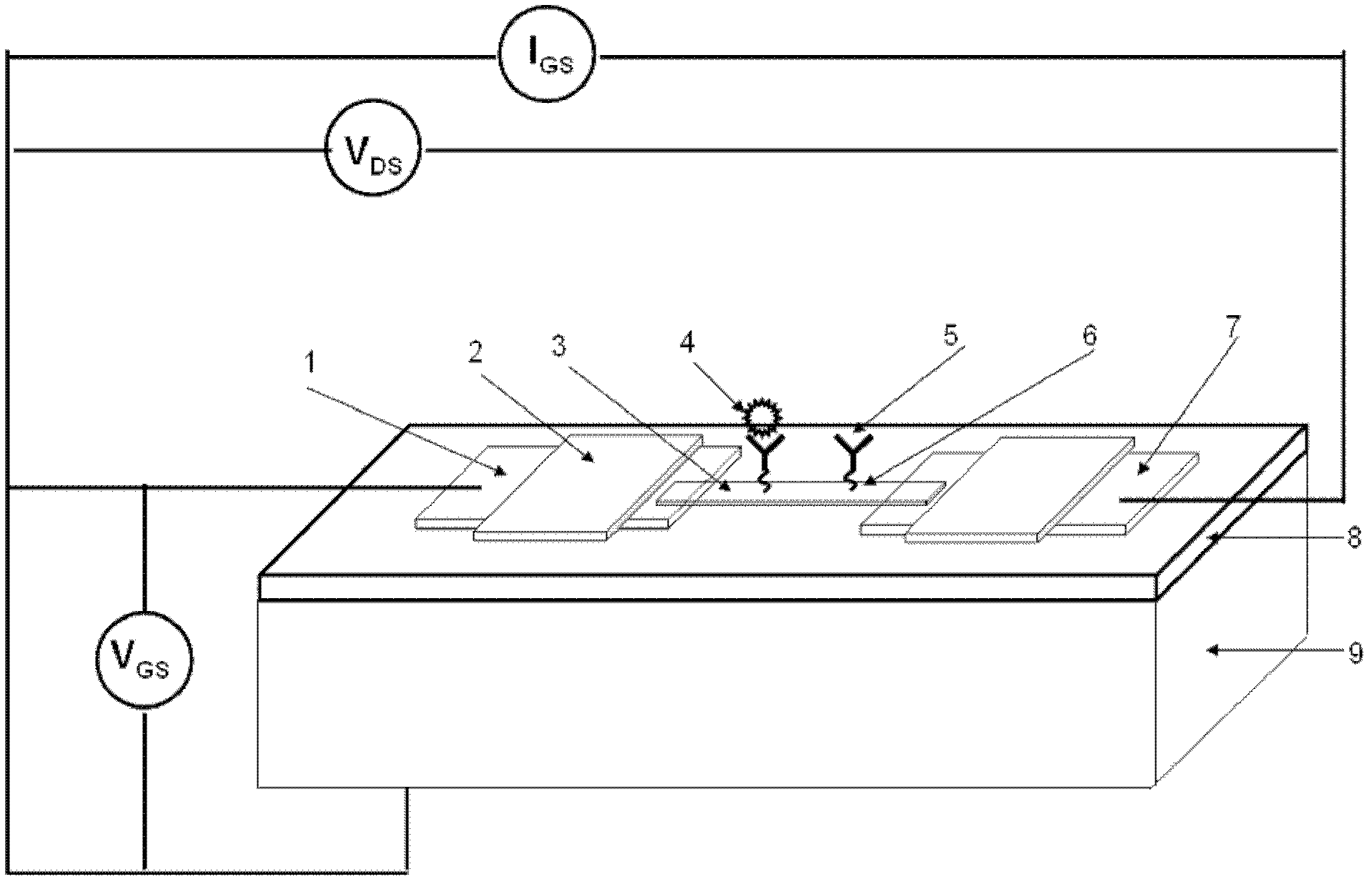
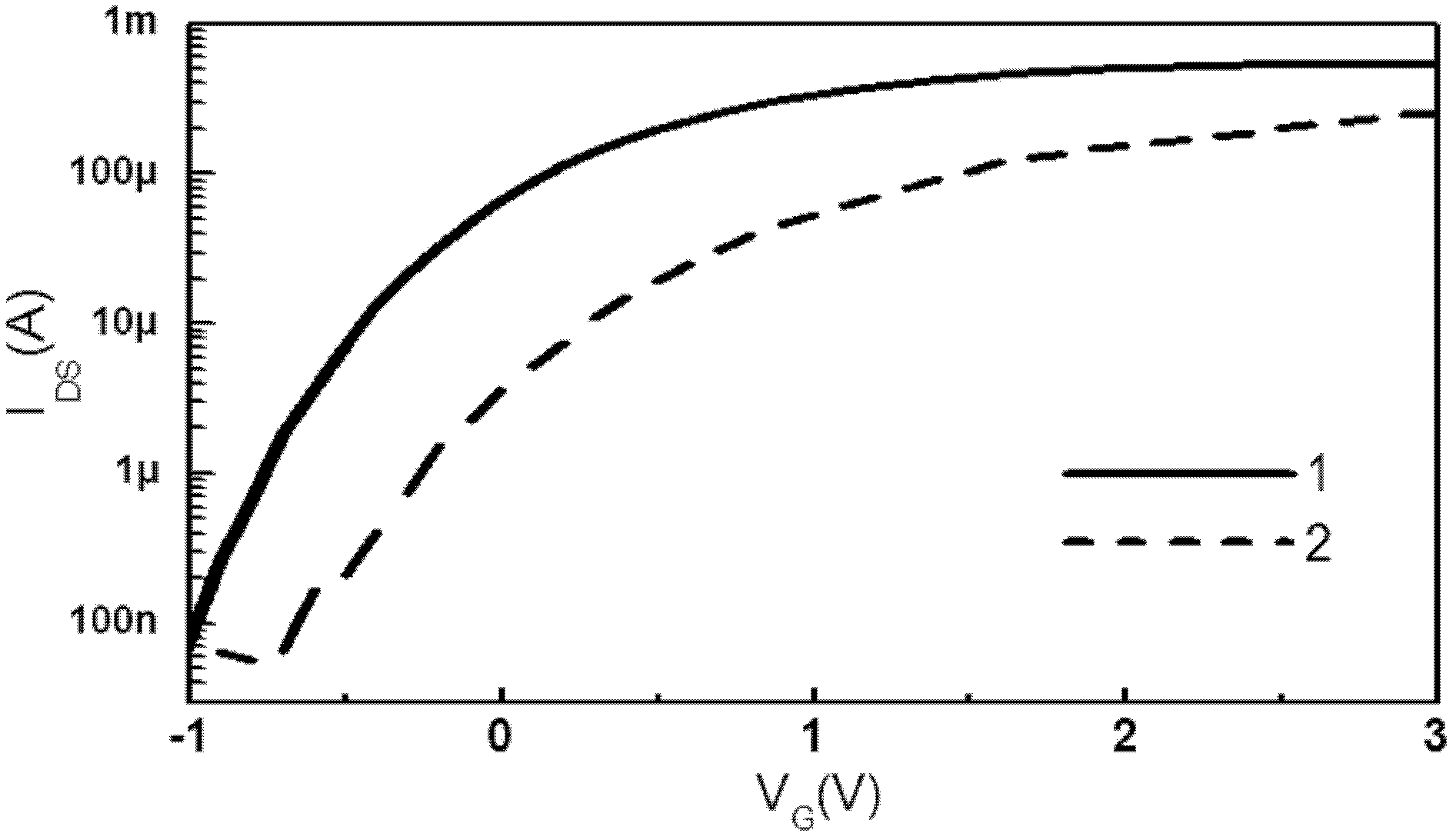
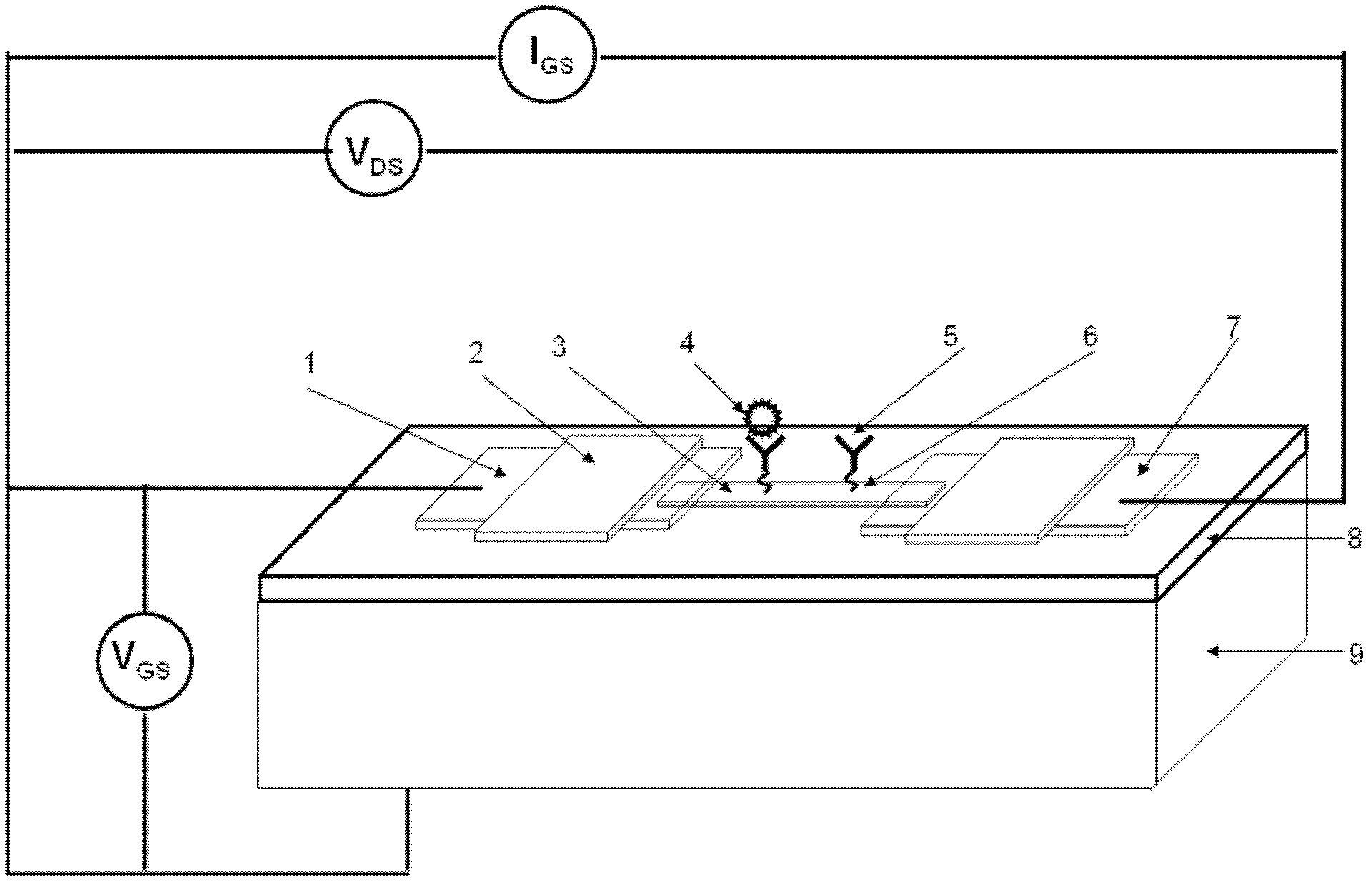
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
220 results about "Covalent modification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
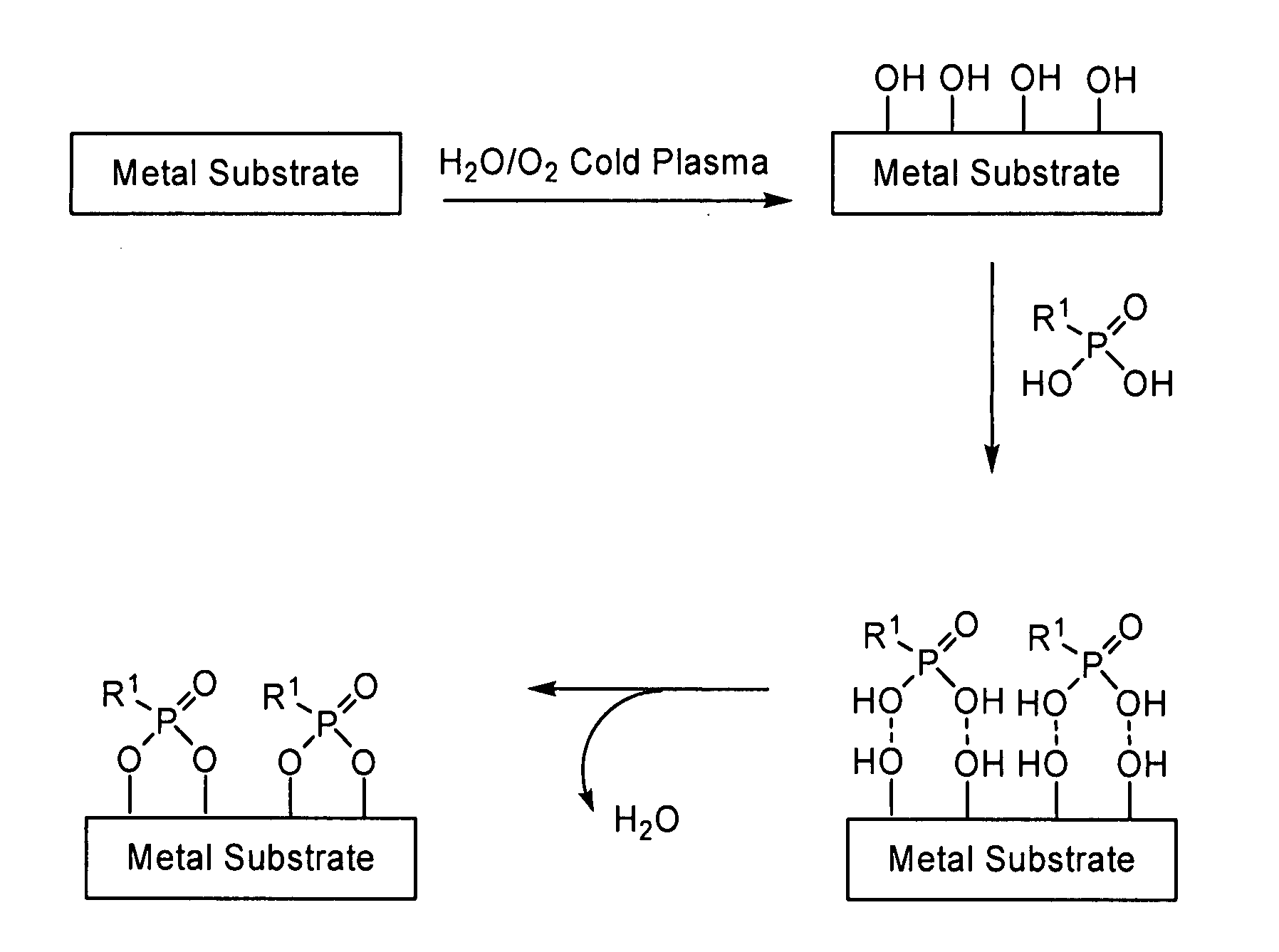
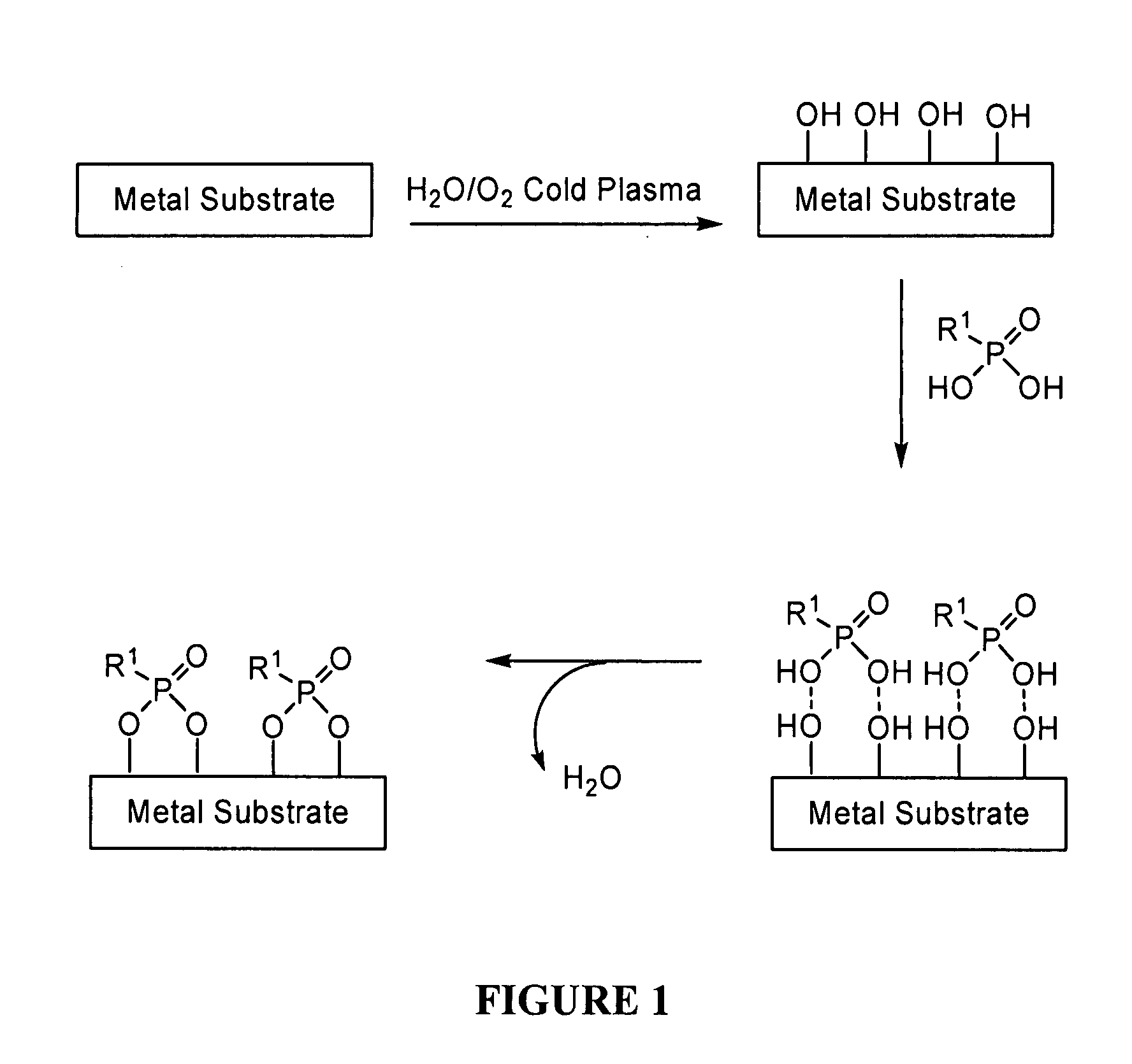
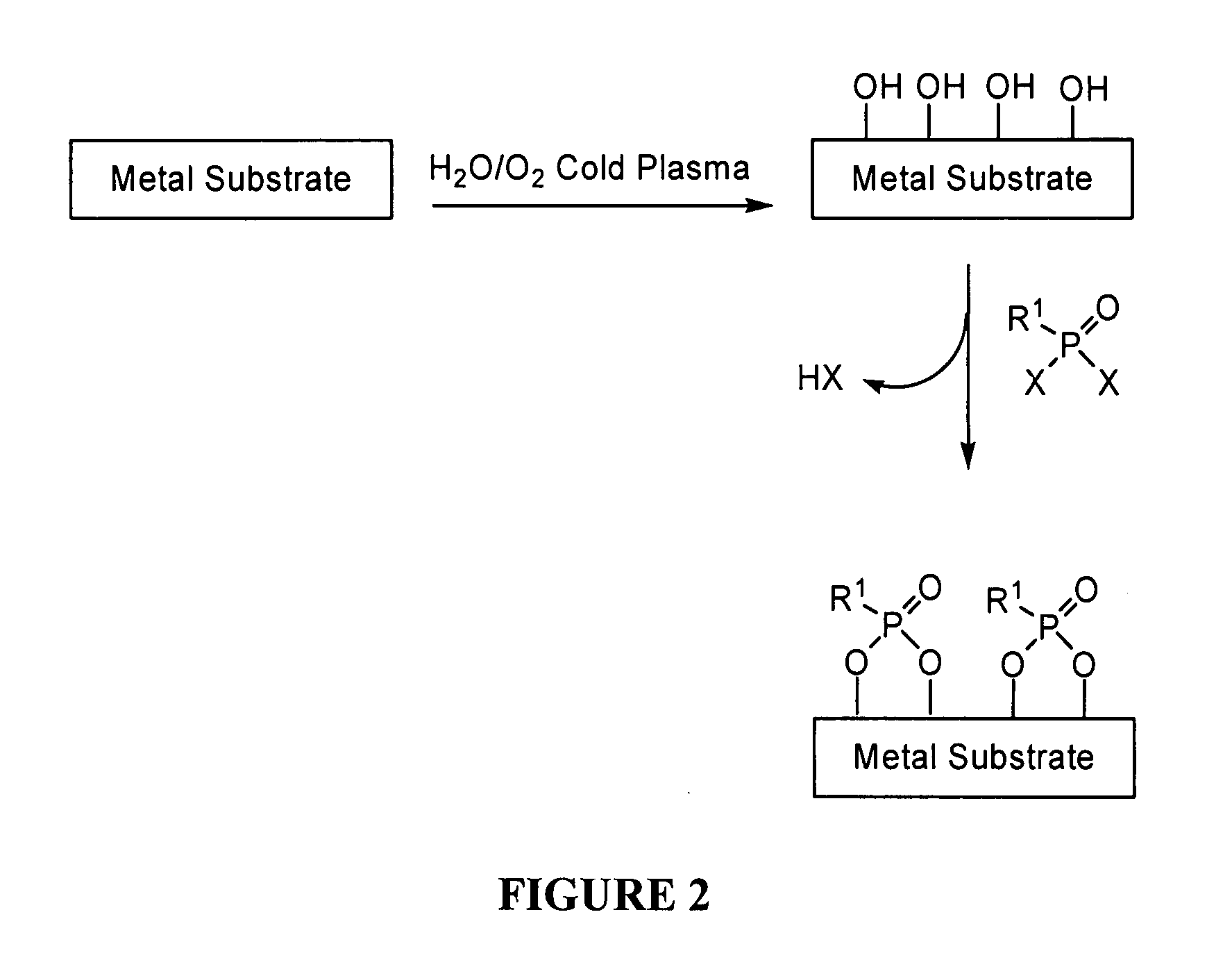
Covalent modification of metal surfaces
The present invention provides modified metal surfaces, methods of preparing the same, and intermediates thereto. These materials are useful in a variety of applications including biomaterials.
Owner:INTEZYNE TECH INC
Ligand-directed covalent modification of protein
InactiveUS20110269244A1Easily assumeMolecular designTransferasesCovalent modificationPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention relates to enzyme inhibitors. More specifically, the present invention relates to ligand-directed covalent modification of proteins; method of designing same; pharmaceutical formulation of same; and method of use.
Owner:CELGENE CAR LLC
Methods and Kits for Detection of Antibiotic Resistance
InactiveUS20120196309A1Promotes bacterial resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometric analysisResistant bacteriaMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention relates to a method of detecting antibiotic resistant bacteria in a sample. The method includes the steps of analyzing a sample derived from bacteria via mass spectrometry to produce a data set, and determining from the data set the presence or absence of a covalently modified antibiotic compound in the sample, wherein the presence of a covalently modified antibiotic compound in the sample is indicative that the bacteria are resistant to the antibiotic. The present invention also relates to a kit for determining the presence or absence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in a sample. The kit includes reagents for preparing and performing the assay, and instructions for the set-up, performance, monitoring, and interpretation of the assay.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Modified polynucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS6867290B2Improve stabilityReduce potential blockSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligoribonucleotidesPolyribonucleotides
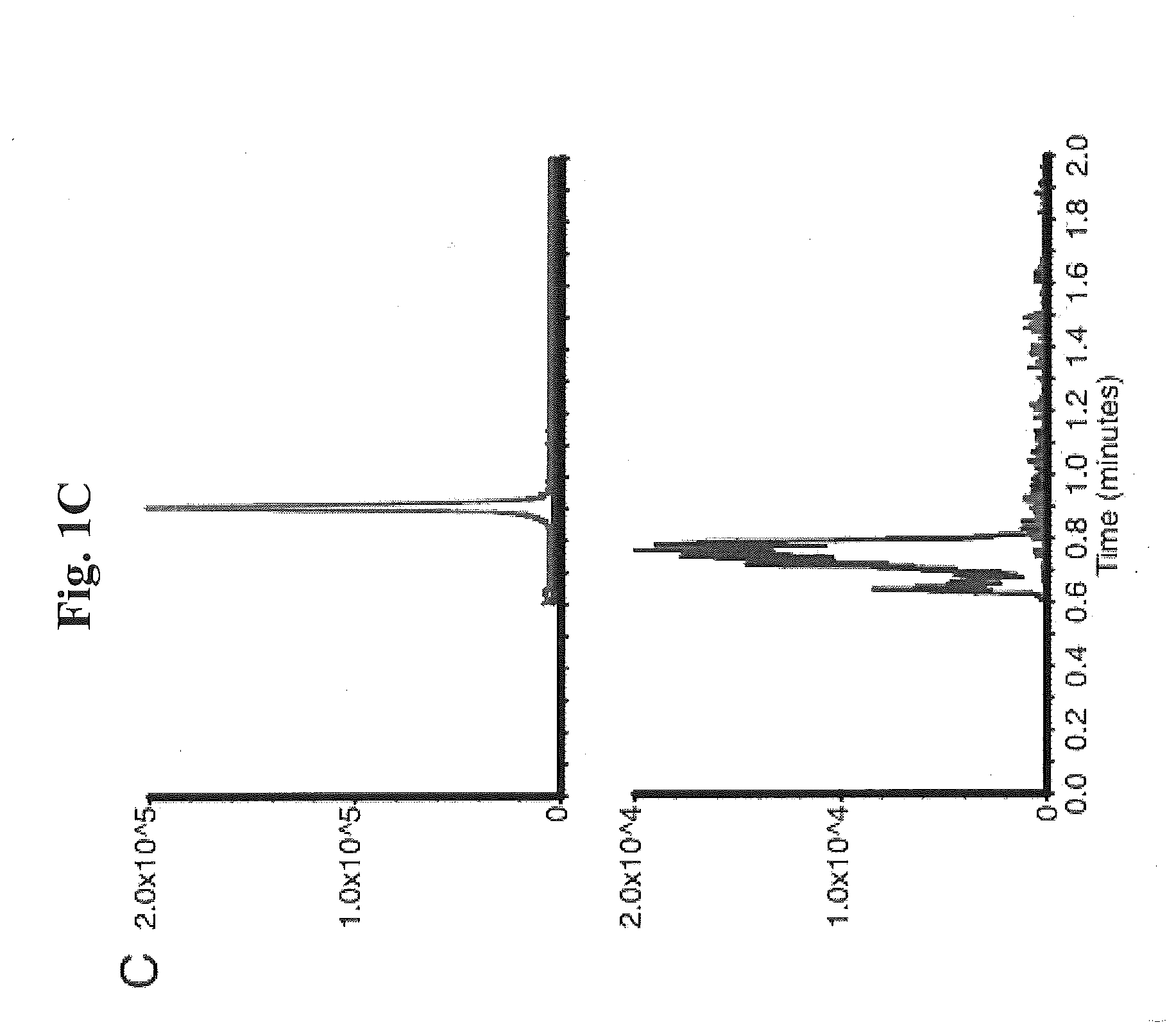
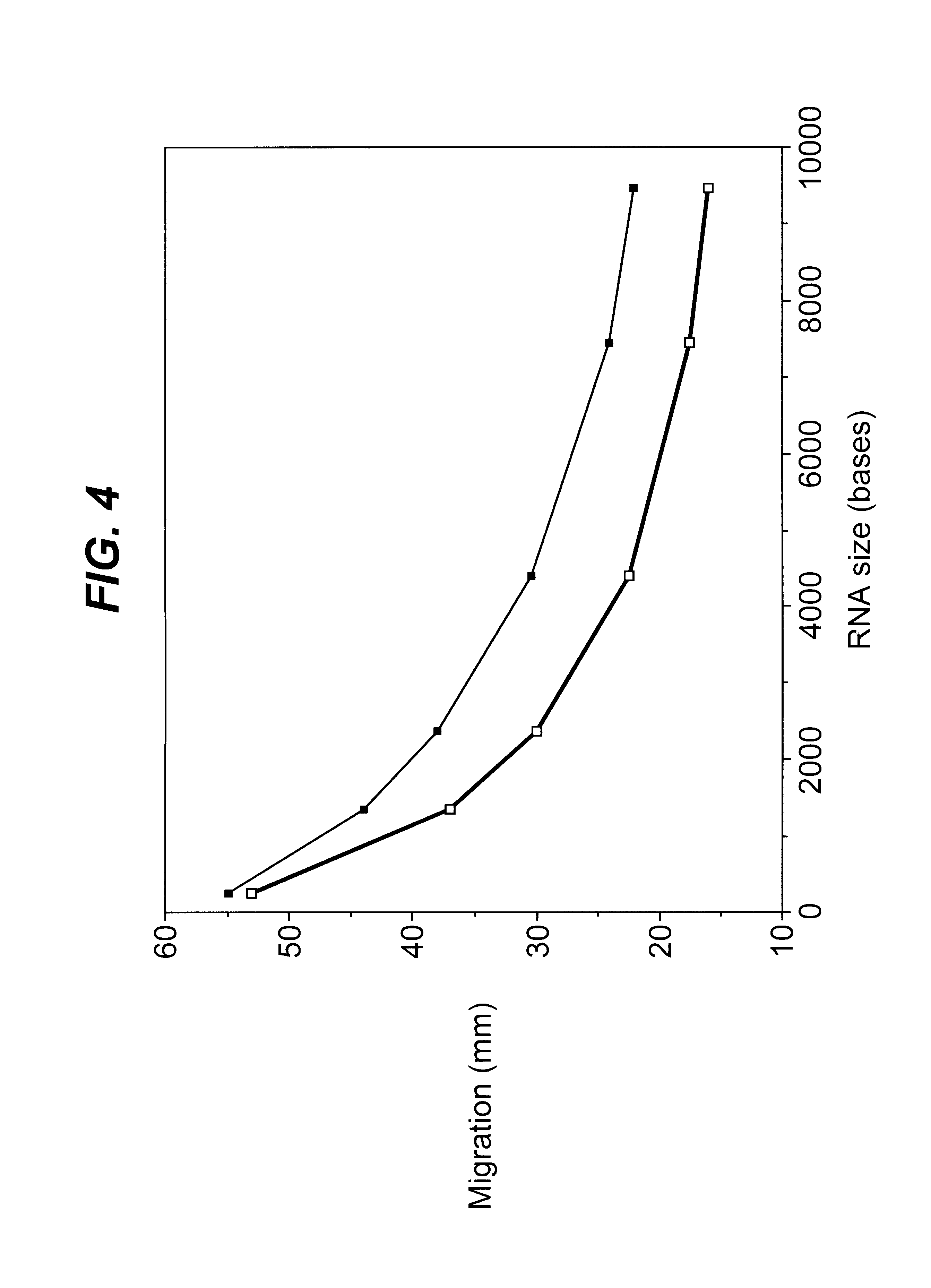
Provided is a polynucleotide comprising mRNA, rRNA or viral RNA, comprising ribose rings that are covalently modified at the 2′-OH position. Further provided are methods for producing a double-stranded oligo- or polynucleotide from a template comprising an oligo- or polyribonucleotide, a proportion of the ribose rings of which are covalently modified at the 2′-OH position to bear a substituent which enables replication of the template by the nucleic acid polymerase. Also provided is use of a poly-nucleotide comprising mRNA, rRNA or viral RNA, a proportion of the ribose rings of which are covalently modified at the 2′-OH position, in a hybridisation reaction.
Owner:CYCLOPS GENOME SCI
Methods and compositions for wound healing
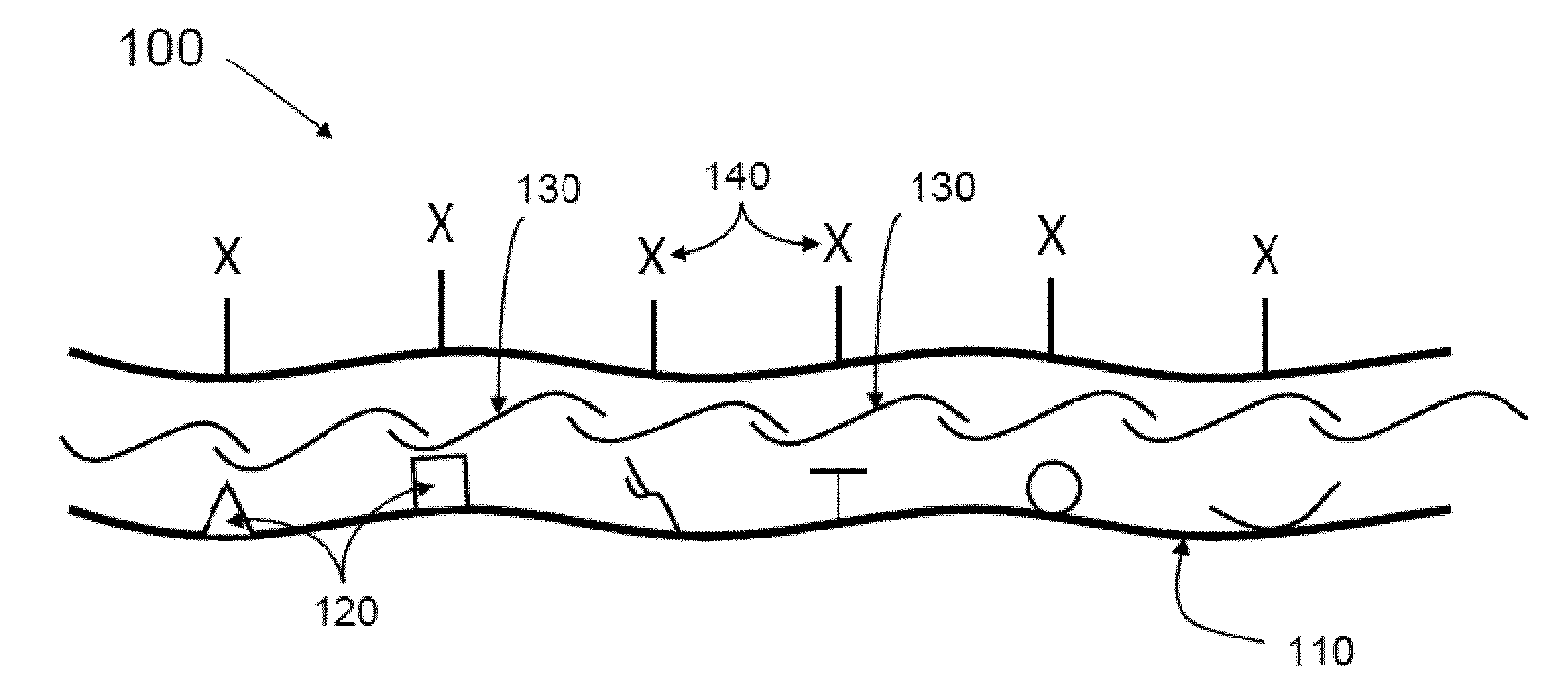
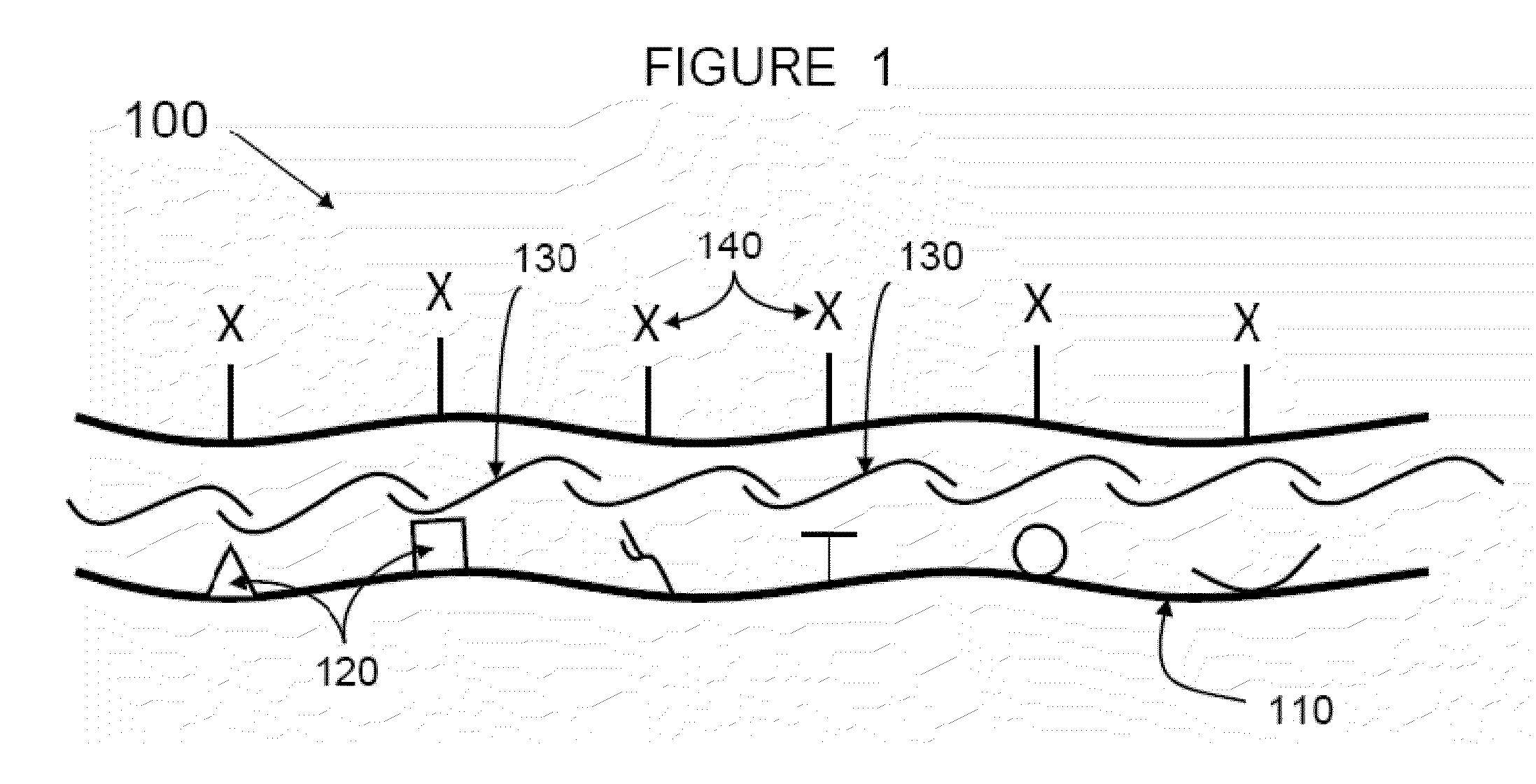
ActiveUS20110189287A1Promoting and enhancing wound healingSignificant positive effectBiocidePowder deliveryPolyelectrolyteWound healing
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for wound healing. In particular, the present invention relates to promoting and enhancing wound healing by utilizing cross-linker covalent modification molecules to attach and deliver wound active agents to a wound. In addition, the present invention provides methods and compositions utilizing oppositely charged polyelectrolytes to form a polyelectrolyte layer on a wound surface. The invention further relates to incorporating wound active agents into a polyelectrolyte layer for delivery to a wound.
Owner:IMBED BIOSCI
Methods and compositions for wound healing
PendingUS20150283287A1Promoting and enhancing wound healingSignificant positive effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideWound healingPolyelectrolyte
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for wound healing. In particular, the present invention relates to promoting and enhancing wound healing by utilizing cross-linker covalent modification molecules to attach and deliver wound active agents to a wound. In addition, the present invention provides methods and compositions utilizing oppositely charged polyelectrolytes to form a polyelectrolyte layer on a wound surface. The invention further relates to incorporating wound active agents into a polyelectrolyte layer for delivery to a wound.
Owner:IMBED BIOSCI
Pharmaceutical compositions for sustained release delivery of peptides
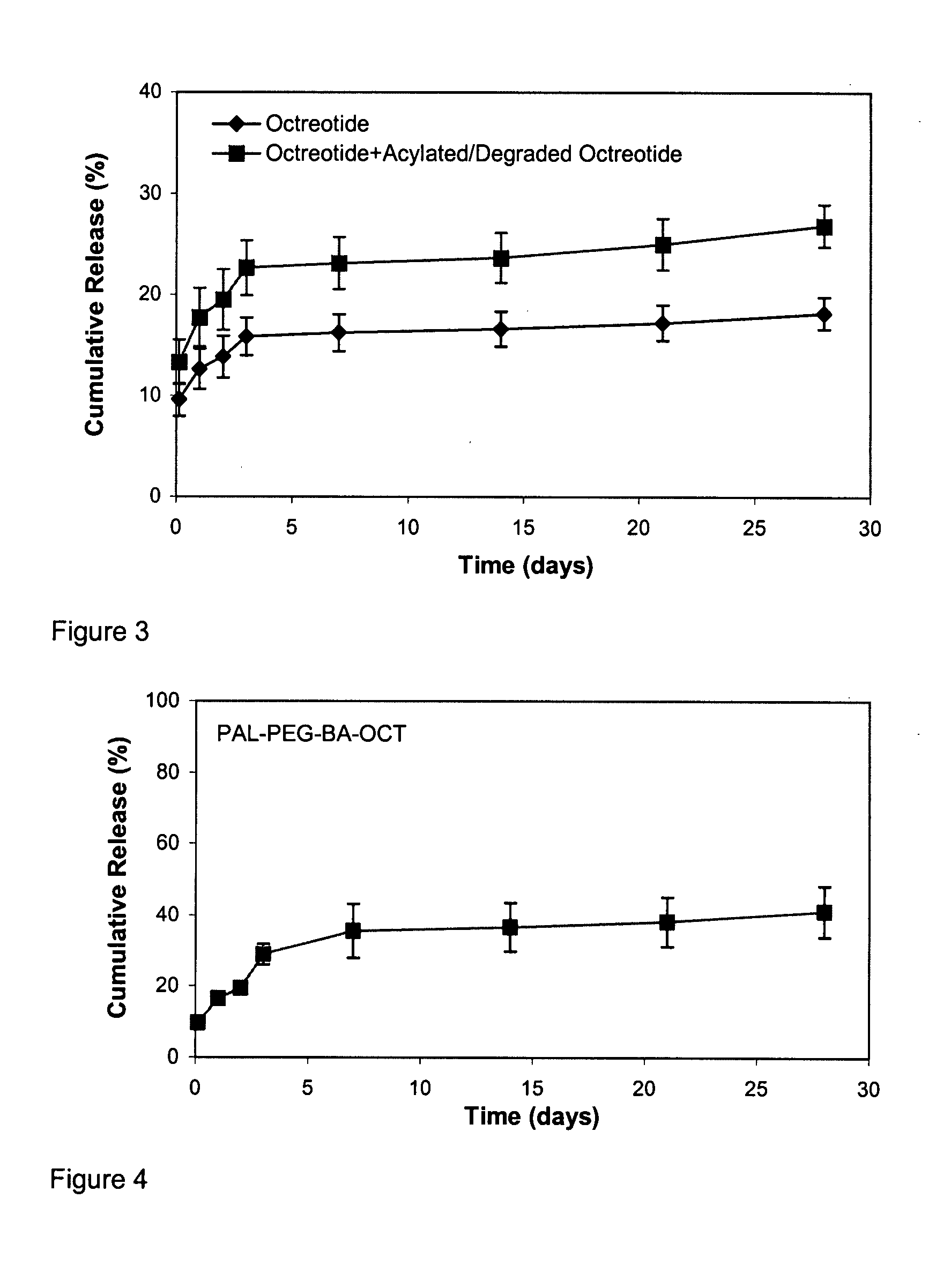
ActiveUS20080020016A1Reduce undesired initial burst releaseImproved profileAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic solventMedicine
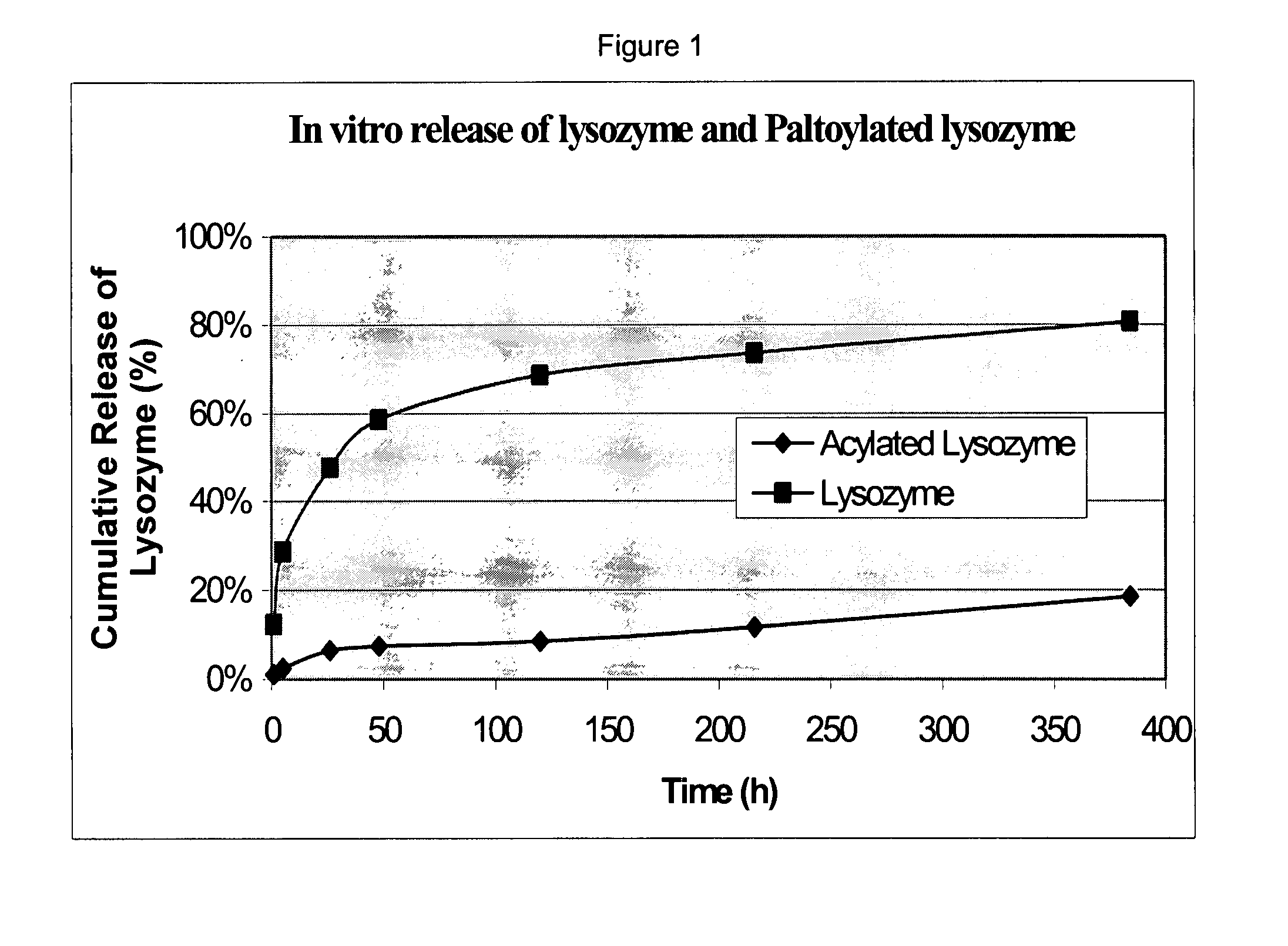
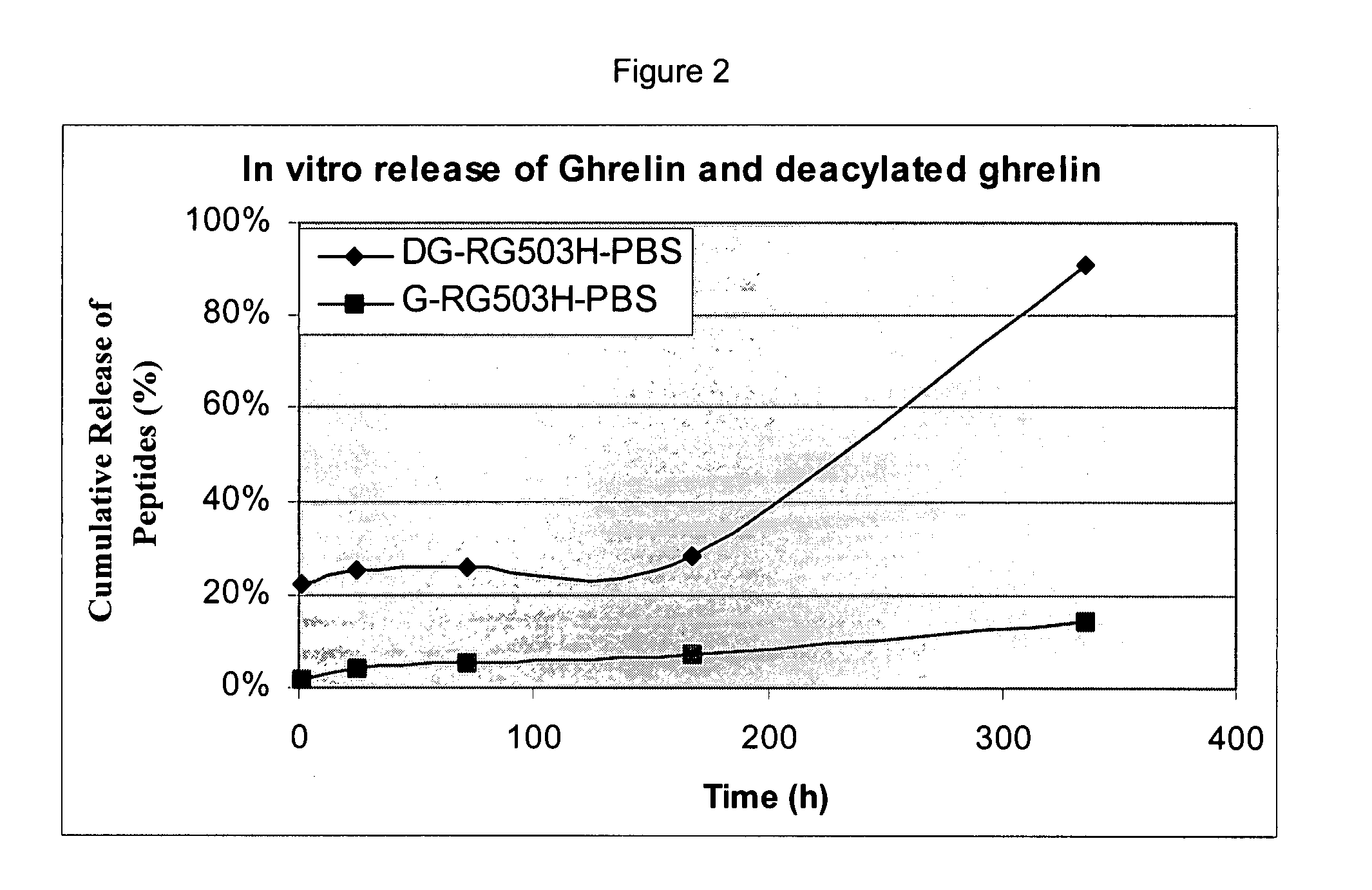
The present invention provides methods of forming a solid, biodegradable implant in-situ in a body by administering a liquid pharmaceutical composition comprising an effective amount of a biocompatible, water-insoluble, biodegradable polymer and an effective amount of a therapeutic peptide covalently modified with one or more lipophilic or amphiphilic moieties, which are dissolved or dispersed in a biocompatible, water-soluble organic solvent. This invention also provides related compositions and methods.
Owner:FORESEE PHARMA CO LTD
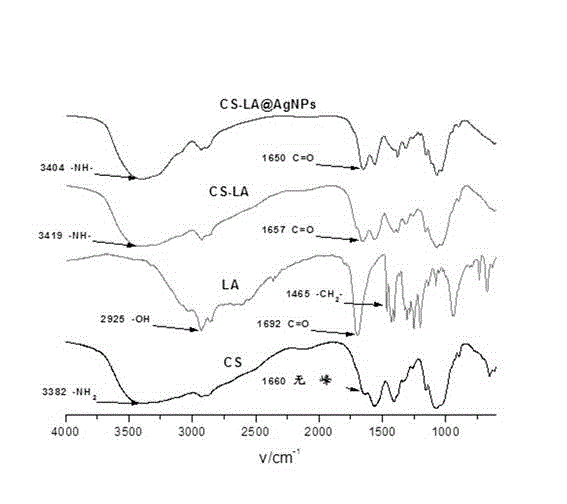
Nano-silver antibacterial composite decorated by modified chitosan, preparing method and application
ActiveCN104128602AWide variety of sourcesLow priceMaterial nanotechnologyAntimicrobial actionCovalent modification
The invention discloses a nano-silver antibacterial composite modified by modified chitosan and a preparing method of the nano-silver antibacterial composite. According to the nano-silver antibacterial composite and the preparing method of the nano-silver antibacterial composite, the chitosan with the small molecule quantiy and good water solubility is selected and used as a raw material, chemical modification is conducted on the chitosan by using small molecules which are capable of having chelation with nano-silver particles, the modified chitosan is arranged on the surfaces of the nano-silver particles in a covalent modification mode, and the novel nano-silver antibacterial composite is prepared. The prepared nano-silver antibacterial composite modified by the modified chitosan has good water solubility and dispersibility and can be stably dispersed in a water solution in a long term without aggregation under the conditions of high salinity and wide pH. The prepared nano-silver antibacterial composite modified by the modified chitosan enables the antibacterial property of the chitosan and the antibacterial property of nano-silver to be in effective synergy, the antibacterial performance is good, and the nano-silver antibacterial composite can serve as a water coating agent to perform the surface antibacterial function on the surfaces of materials and can also permeate into fiber type materials to perform the deep internal antibacterial function.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Covalent functionalization graphene and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses covalent functionalization graphene and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the covalent functionalization graphene comprises the following steps of: adding 1 part by weight of graphene oxide and 0.1-100 parts by weight of azido substances to a reactor; reacting for 0.1-72 hours in a hot bath at 100-220 DEG C; filtering, centrifugalizing, and washing to obtain the covalent functionalization graphene. In the invention, the graphene oxide is used as a raw material to directly react with an azido compound to prepare a covalently-modified functionalization graphene material based on nitrene chemistry by adopting a one-step method. The preparation method has simple and convenient method, simple process and large-scale production, is a general method and can enable multiple functional groups (such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, bromo and long alkyl group) and high polymers (such as polyethylene glycol and polystyrene) to be covalently connected to the graphene. The obtained covalent functionalization graphene has good solvent dispersity and conductivity, and can be processed in a solvent and widely used in the fields of micro-nano electron, machinery, chemical engineering, high performance materials, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
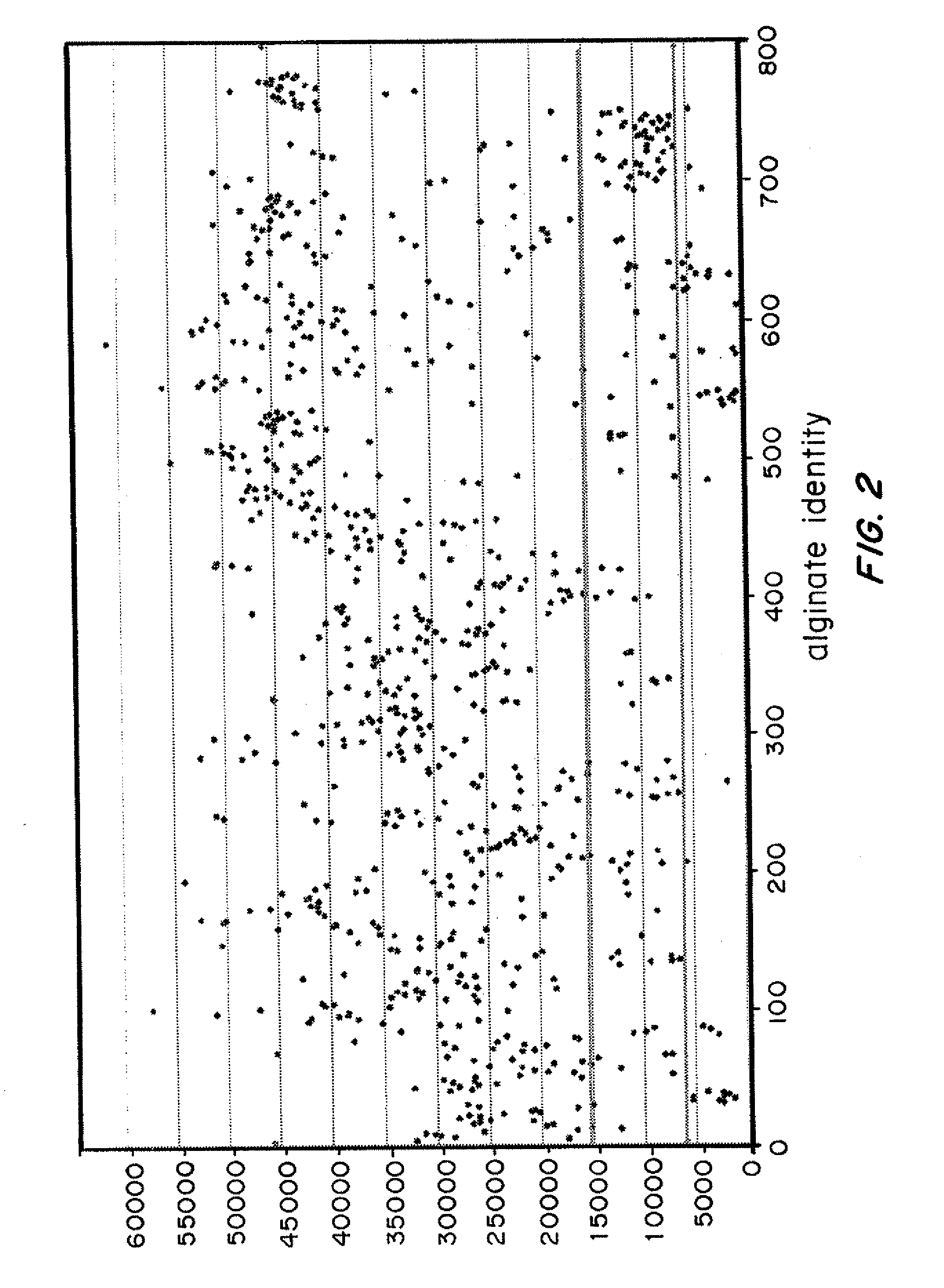
Modified alginates for cell encapsulation and cell therapy
ActiveUS20120308650A1Avoid encapsulationImprove propertiesPowder deliveryBiocideBiocompatibility TestingBiochemistry
Covalently modified alginate polymers, possessing enhanced biocompatibility and tailored physiochemical properties, as well as methods of making and use thereof, are disclosed herein. The covalently modified alginates are useful as a matrix for the encapsulation and transplantation of cells. Also disclosed are high throughput methods for the characterizing the biocompatibility and physiochemical properties of modified alginate polymers.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
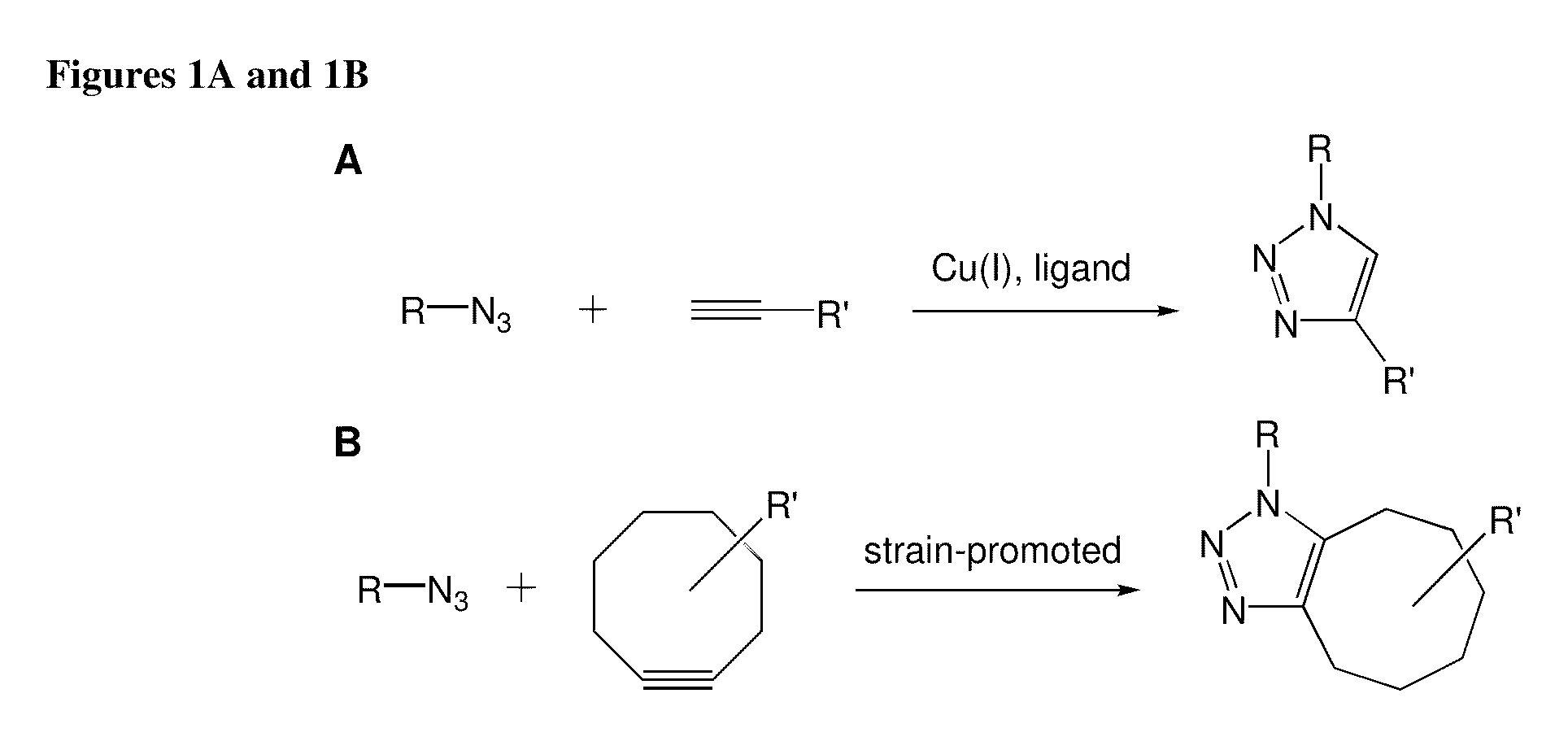
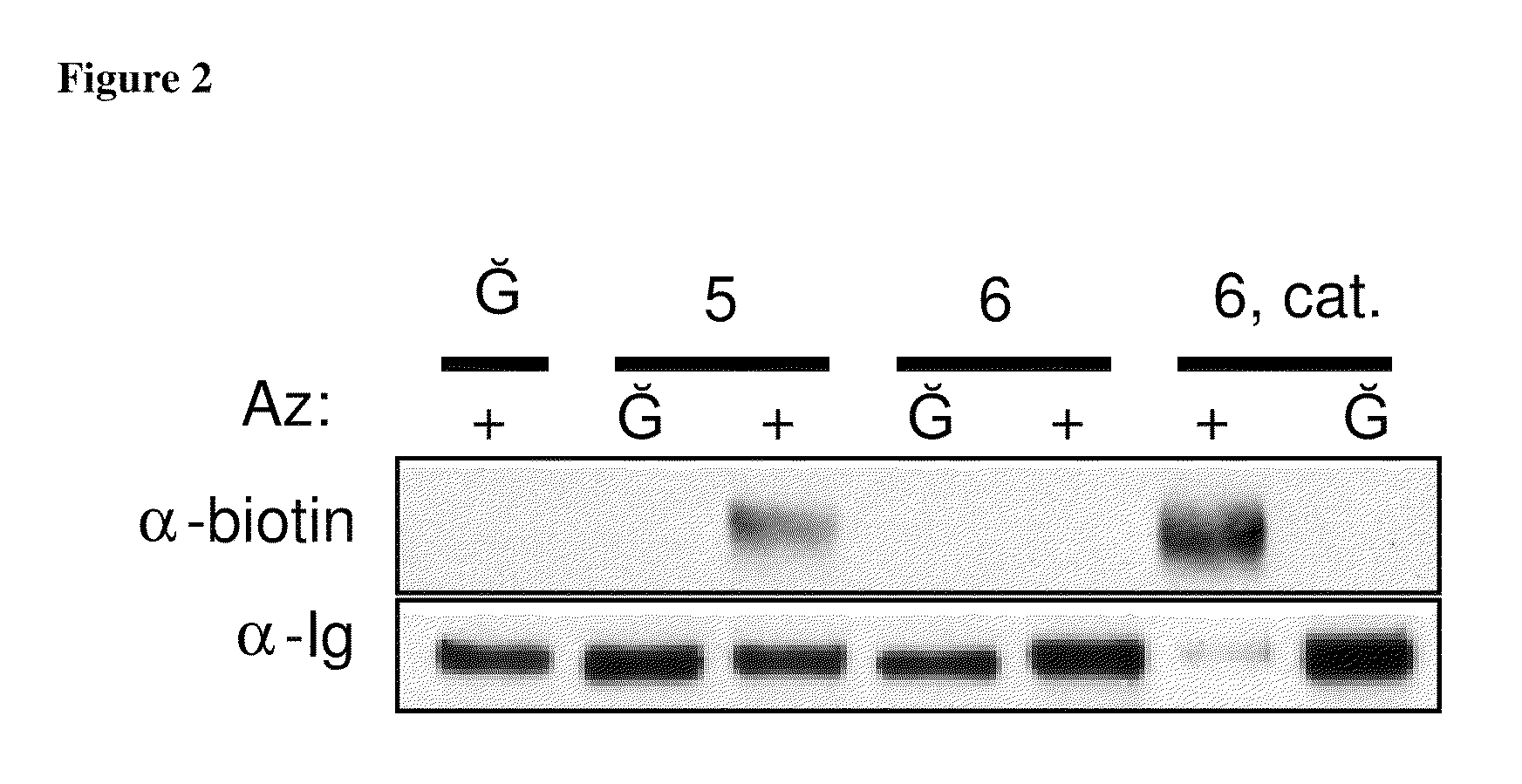
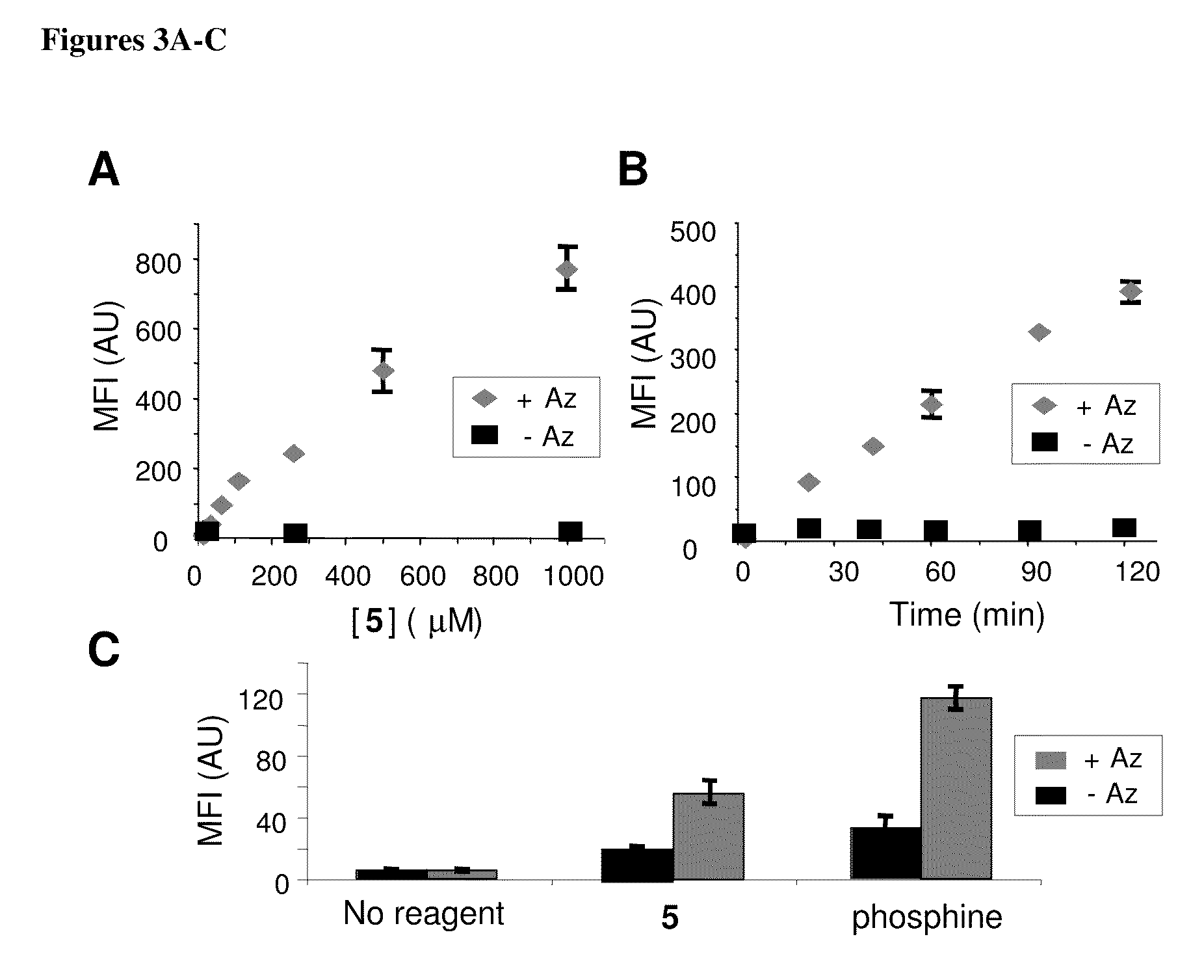
Compositions and methods for modification of biomolecules
The present invention provides modified cycloalkyne compounds; and method of use of such compounds in modifying biomolecules. The present invention features a cycloaddition reaction that can be carried out under physiological conditions. In general, the invention involves reacting a modified cycloalkyne with an azide moiety on a target biomolecule, generating a covalently modified biomolecule. The selectivity of the reaction and its compatibility with aqueous environments provide for its application in vivo (e.g., on the cell surface or intracellularly) and in vitro (e.g., synthesis of peptides and other polymers, production of modified (e.g., labeled) amino acids).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
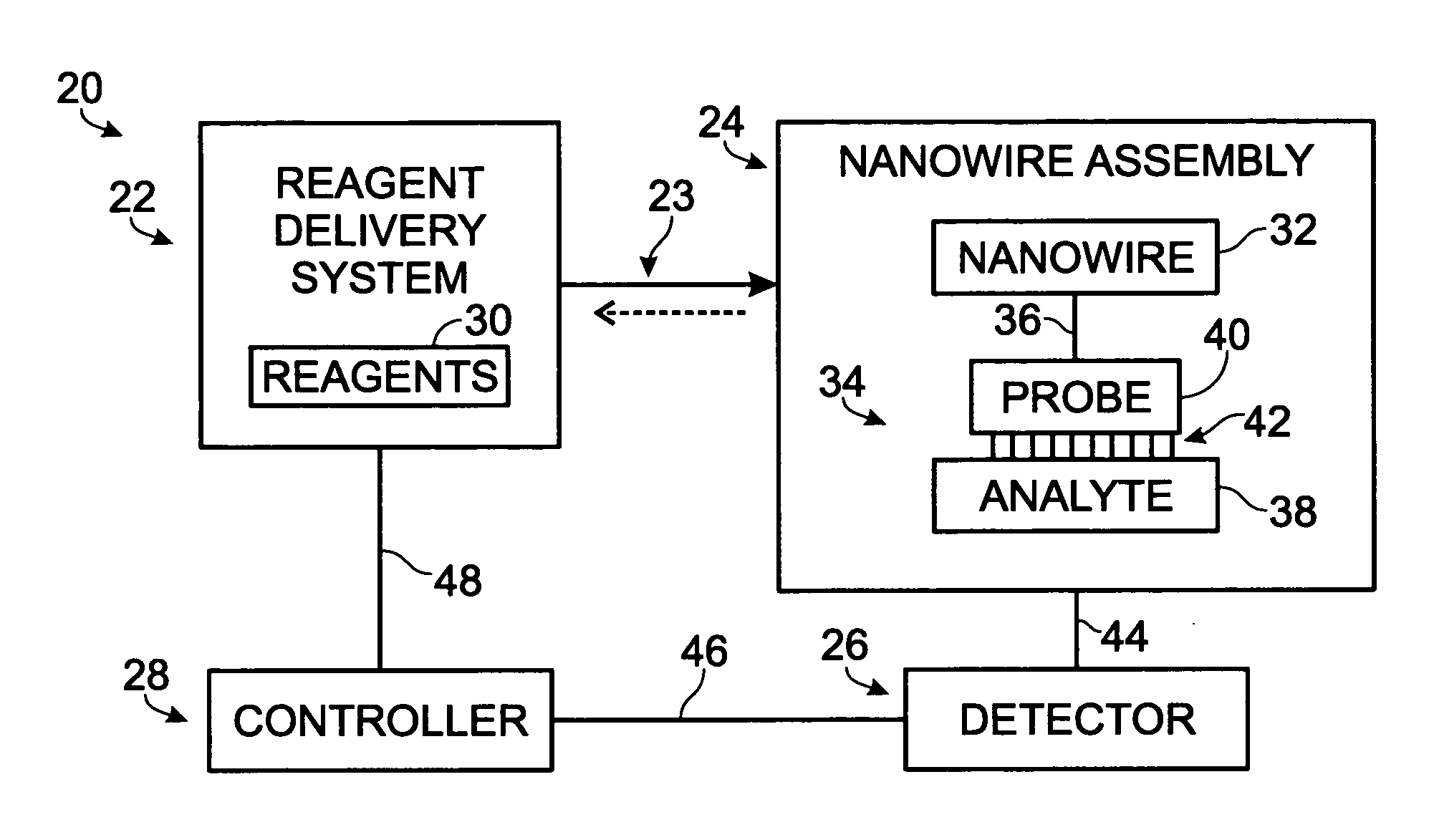
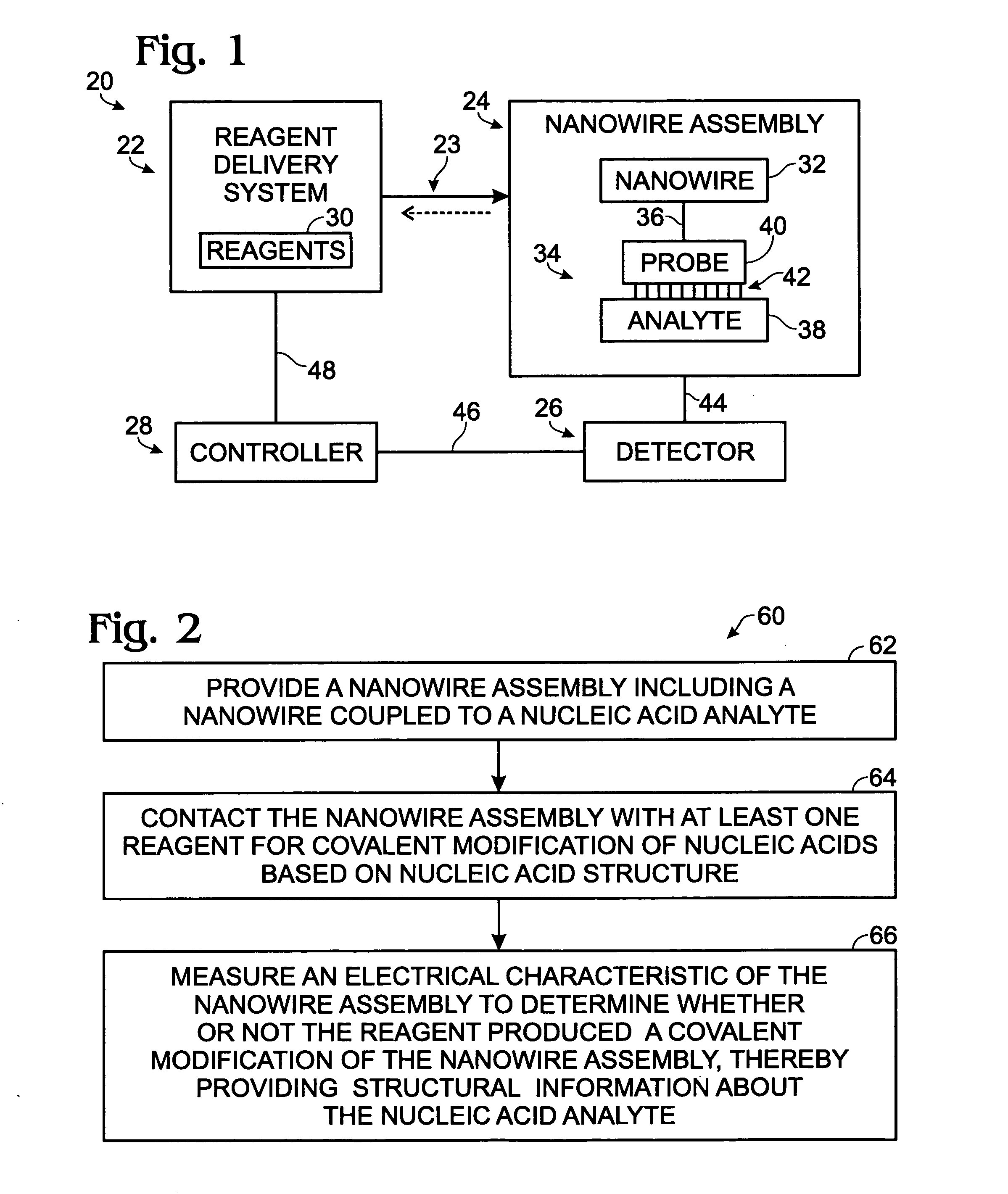
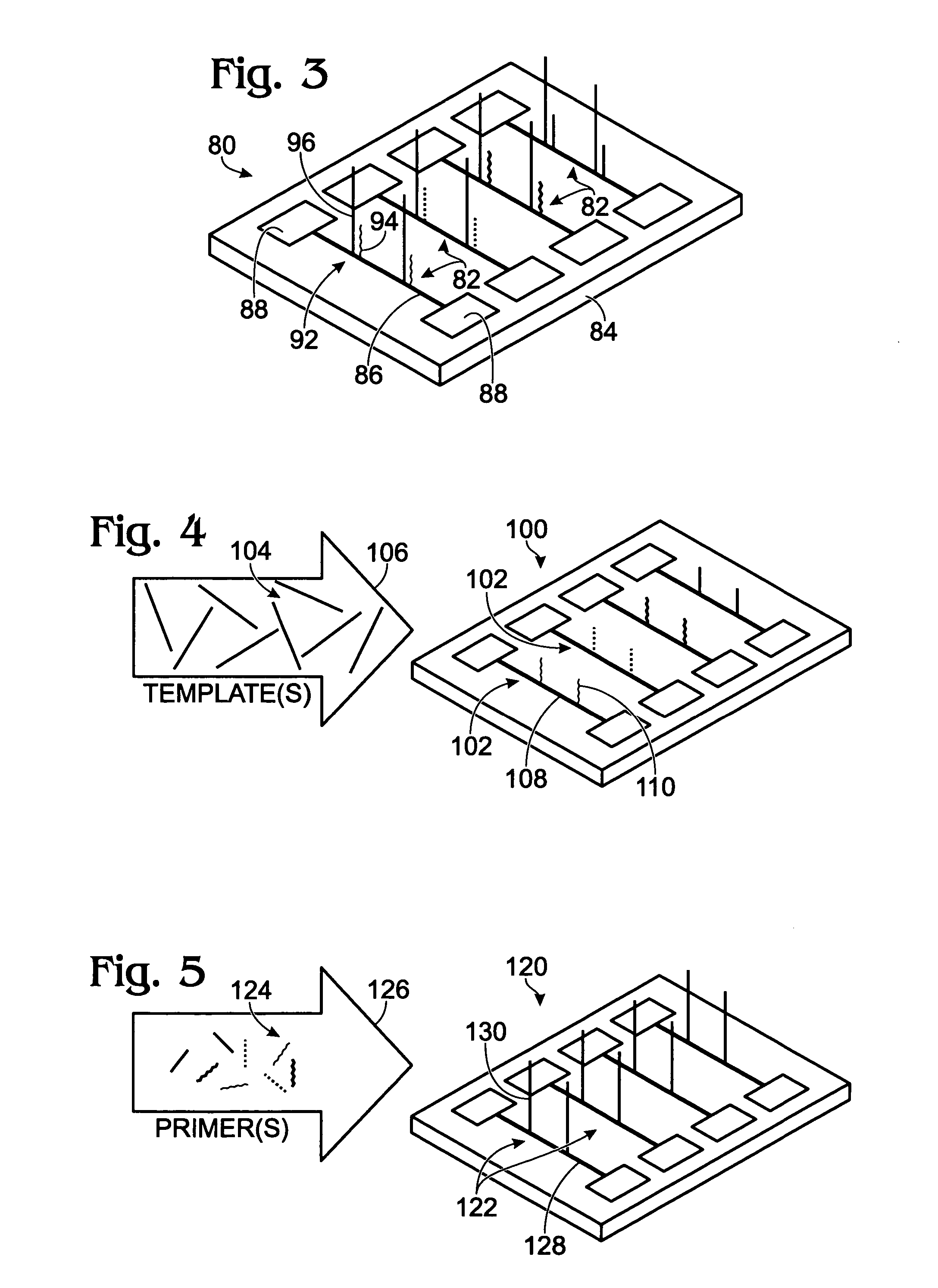
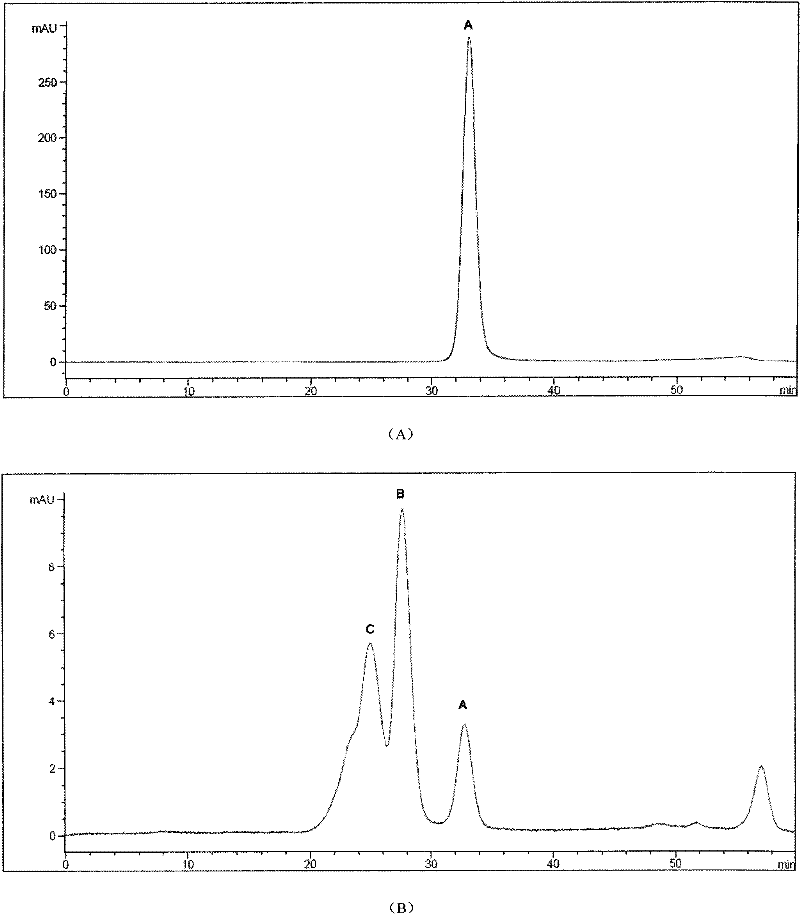
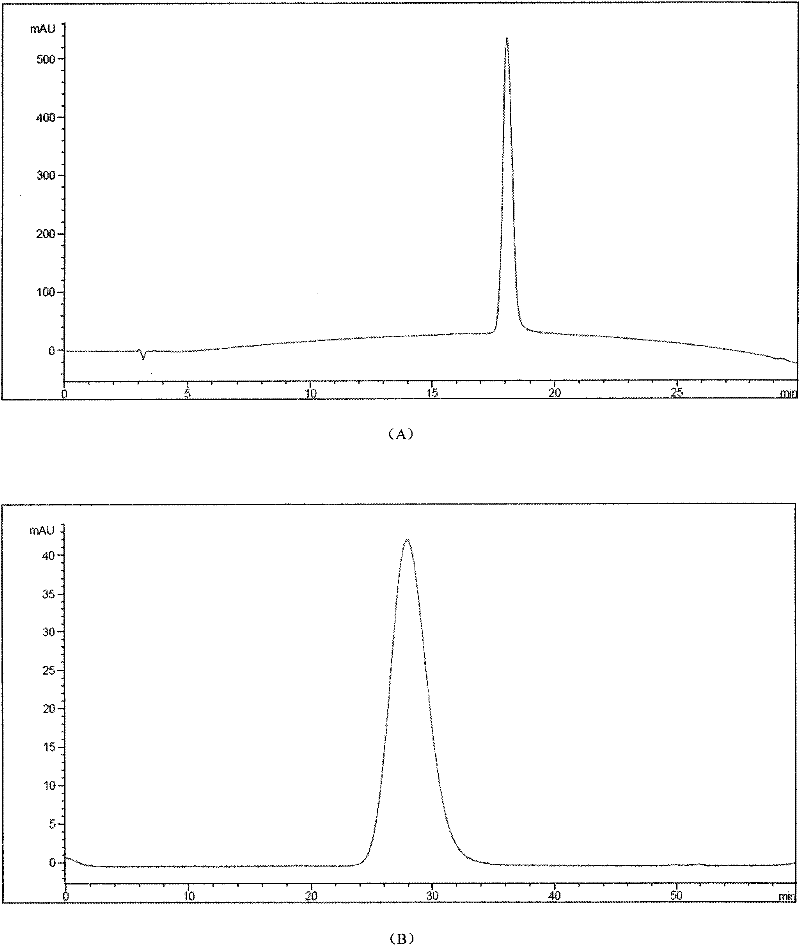
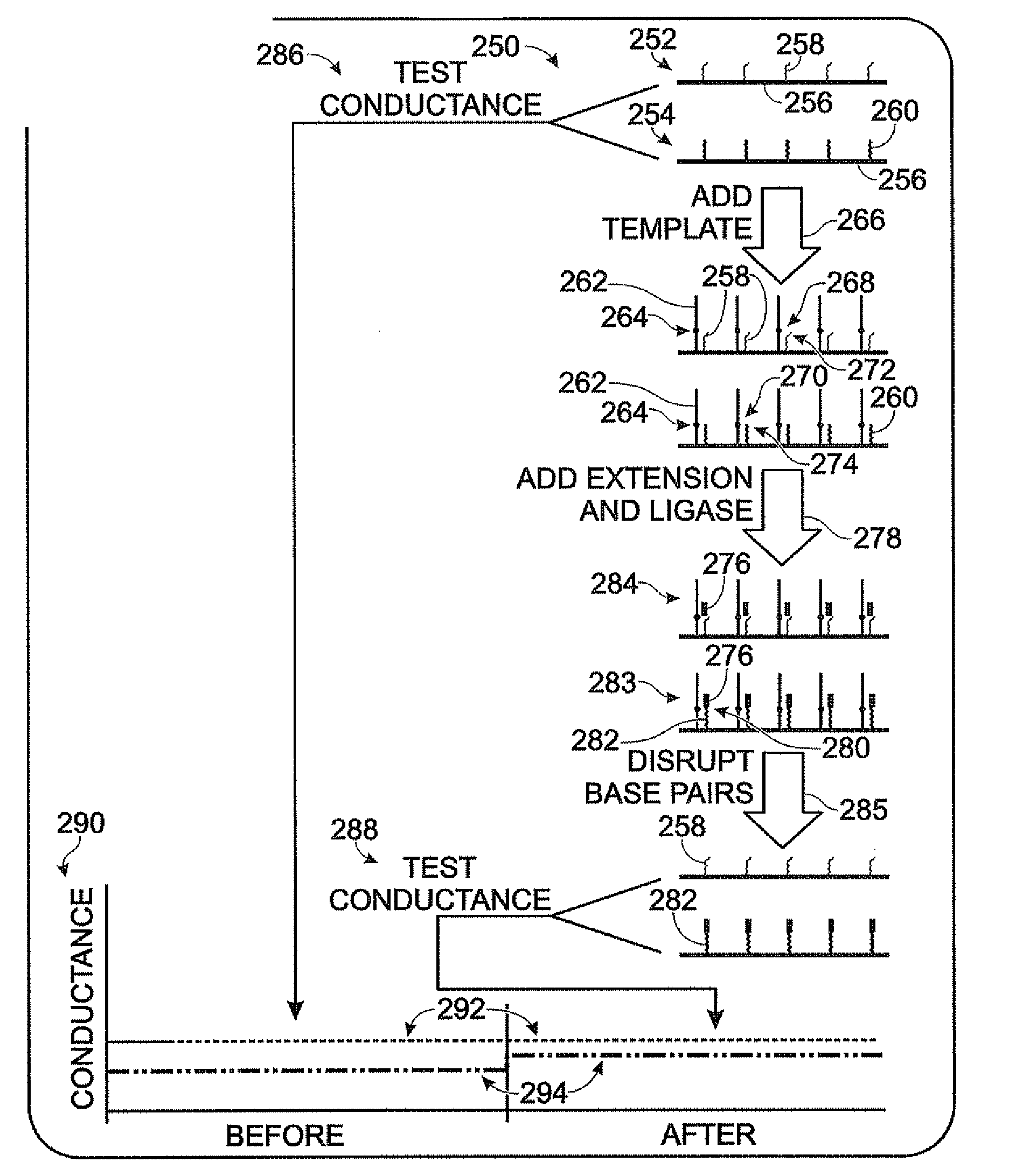
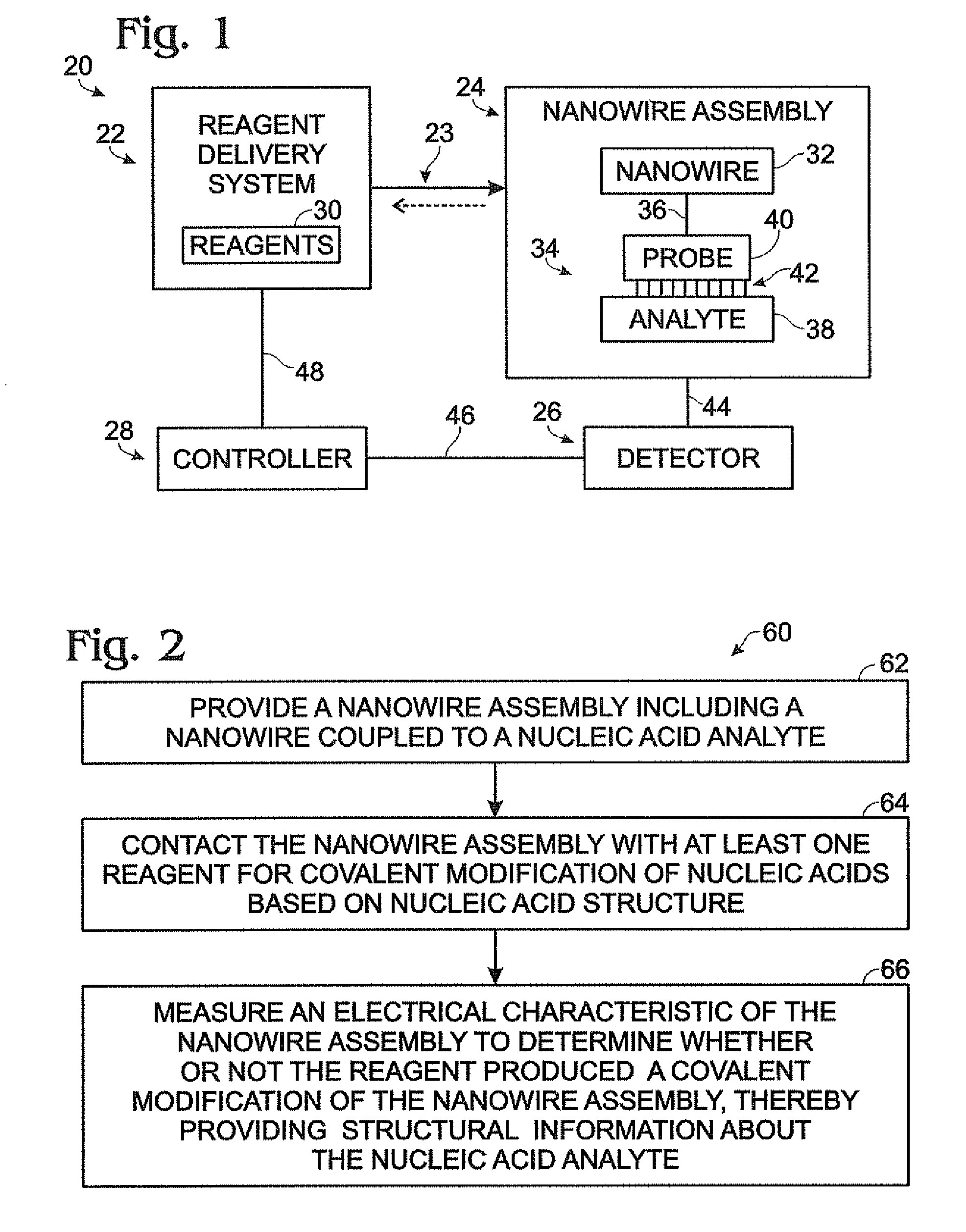
Nanowire-based system for analysis of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20070238186A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanowireCovalent modification
System for detection and / or analysis of nucleic acids using nanowires to detect covalent modification of nucleic acids.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
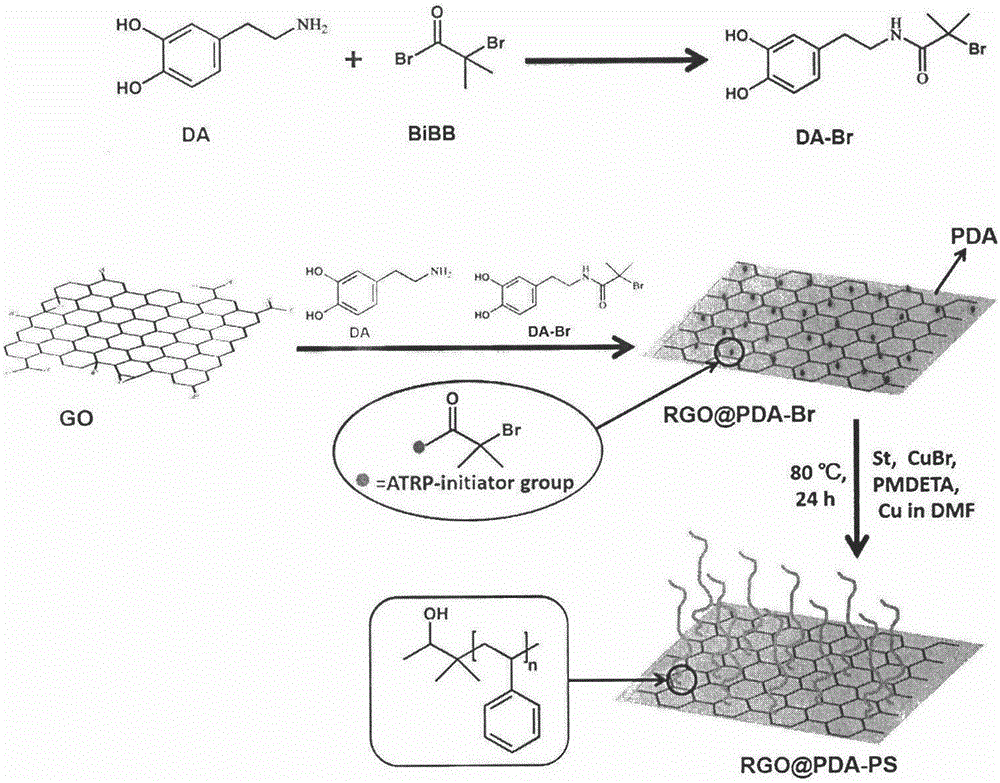
Novel method for modifying graphene with polymer
The invention discloses a novel method for modifying graphene with polymer. By introducing polydopamine and combining covalent modification with non-covalent modification, the method increases the stability of the modified product structure under the premise of ensuring the integrity of the graphene structure. Firstly, by utilizing the strong adhesion of dopamine, the dopamine is self-polymerized to form a film on the surface of a graphene sheet, moreover, 2-Bromo-2-methylpropionyl bromide (BiBB) as common initiator for atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) is grafted on the dopamine by amidation, at the same time, graphene oxide (GO) is partially reduced by the dopamine (DA), and thereby graphene macroinitiator RGO@PDA-Br is obtained. Polymeric monomer is then added, so that the ATRP of the polymeric monomer is initiated on the surface of the graphene, and thereby a polymer-modified graphene material is obtained. By controlling conditions such as monomer concentration and reaction time, the novel method can obtain modified graphene materials with different densities and chain lengths of polymer grafted on the surfaces, meeting the characteristics of controllable / living ATRP. In addition, the feasibility and universality of the novel method for modifying graphene with polymer put forward by the invention are applicable to various monomers suitable for ATRP.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
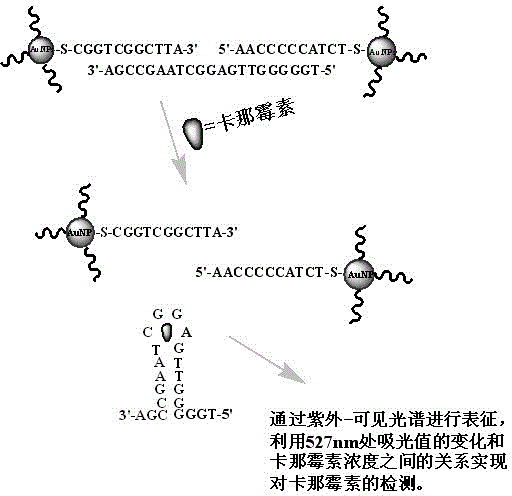
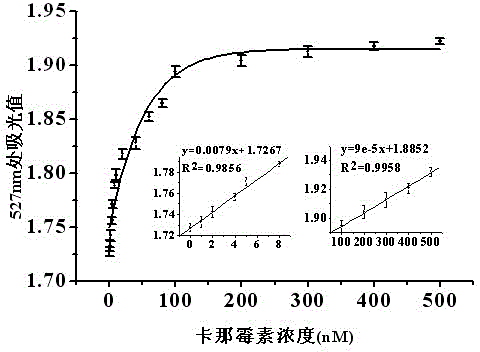
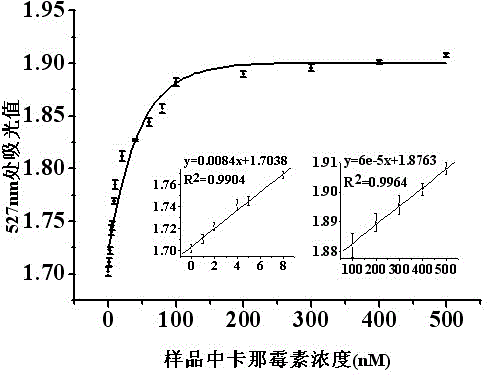
Detection method of kanamycin residue based on nucleic acid aptamer
InactiveCN103335972ASimple methodHigh sensitivityColor/spectral properties measurementsAptamerNanoparticle
The invention discloses a detection method of a kanamycin residue based on a nucleic acid aptamer, and belongs to the technical field of analytic chemistry. The method comprises the steps that by using a sulfydryl covalent modification mode, ssDNA (single-stranded Deoxyribonucleic Acid) complementary with the two ends of a kanamycin aptamer is modified on the surfaces of AuNPs (Gold Nanoparticles) respectively; two kinds of functionalized AuNPs are obtained; the kanamycin aptamer is added and pairwise bound with ssDNA on the surfaces of the functionalized AuNPs; spatial distances among the AuNPs are closed; the AuNPs are mediated to be aggregated; after the AuNPs are mixed with kanamycin samples with different concentrations, specific binding between kanamycin and the aptamer allows an aggregation to be disaggregated, which is manifested by a change of an AuNPs characteristic absorption peak in an ultraviolet-visible spectrum; and the kanamycin residue is detected by using a relation between a change of the absorbency at a 527-nanometer part and the concentration of the kanamycin. The method is good in repeatability and stability, easy to operate and high in sensitivity, and can be used for directly determining the kanamycin residues in samples such as pretreated milk.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing nano-antibiotic materials
The process for preparing nano-class antibacterial material features that nanoparticles is linked with antibacterial moleculae by co-valent modification, and includes such steps as mixing nanoparticles with double-function active groups, reacting while stirring to obtain activated nano particles, reacting on nitrogen-contained polymer in organic solvent, and reacting on alkylating reagent in organic solvent. Its advantages are high effect and durability, and no environmental pollution.
Owner:邱树毅
Porous inorganic material with insecticidal and mothproof function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102210302AIncrease loadChange drug loadingBiocideArthropodicidesCovalent modificationInorganic materials
The invention discloses a porous inorganic material with insecticidal and mothproof functions and a preparation method thereof. The porous inorganic material with insecticidal and mothproof functions takes porous inorganic material as a carrier, the outer surface of the carrier is grafted with cationization reagent, the inner surface of the duct of the porous inorganic material is grafted with silane coupling agent, and micromolecule mothproof drug is loaded in a pore. The preparation method for the porous inorganic material with insecticidal and mothproof functions comprises the following steps: carrying out covalent modification on the porous inorganic material; grafting a functional group with a cation electric charge on the surface of the porous inorganic material; and loading the micromolecule insecticide into the pore of the porous inorganic material. The porous inorganic material with insecticidal and mothproof functions, which is prepared by using the preparation method disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of excellent insecticidal and mothproof functions, low cost, simple preparation technology and good commercial application prospect and can be used for fields,such as buildings, papermaking, coating, hygiene products and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Nano-fluorescent probe with quantum dots and application of nano-fluorescent probe with quantum dots on tumor targeting detection
InactiveCN102879364ALarge particle sizeDodge clearFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsTumor targetMda mb 231
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine detection, in particular to a method for preparing a nano-fluorescent probe with the quantum dots and an application of the nano-fluorescent probe with the quantum dots on tumor detection. According to the method, aiming at the defects that the traditional preparation method of the quantum dots is complicate to operate and high in cost, a simple and cheap water phase synthetic technique with the quantum dots is provided. The specific synthetic process comprises the synthesis of the water soluble quantum dots, the synthesis of a biocompatible modifier (mPEG) and a tumor cell targeting modifier (cRGD) with the sulfydryl functional groups and a direction reaction between the quantum dots and the two modifiers with the sulfydryl functional groups. According to the method provided by the invention, the preparing raw materials are easy to obtain, the whole preparation process is covalent modification under the conventional condition and the properties of the quantum dots and the modifiers are not changed, and the functions of in vivo long circulation and special cell targeting are simultaneously given for the quantum dots through a one-step reaction, so that the cost is effectively reduced. The modified fluorescent and bright quantum dots obtained by the method are about 5nm in particle size, strong in anti-photo-bleaching property, and have good biocompatibility. The transfection efficiency of the quantum dots on human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells can be effectively regulated and controlled by further adjusting the mole ratio of mPEG to cRGD on the surfaces of the quantum dots, so that the nano-fluorescent probe with quantum dots can be applied to the cell fluorescent imaging detection of the tumor targeting.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Conductive composite material containing carbon nano tubes and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102911446AWill not damage the structureGood dispersionNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCarbon nanotubeCovalent modification
The invention relates to a conductive composite material comprising carbon nano tubes and a preparation method thereof. The conductive composite material containing the carbon nano tubes comprises the following components: carbon nano tubes (CNTs), dispersant polymer and matrix polymer. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) evenly mixing the CNTs with polymer sections serving as a dispersant by mass percent of (5-50):(95-50), and carrying out melt blending, extrusion and granulation by a double-screw extruder to obtain masterbatches, wherein the polymer sections contain benzene rings and nitrile groups; and (2) adding the prepared masterbatches and pure thermoplastic polymer sections into the double-screw extruder in mass ratio of (2-40):(98-60), and then carrying out melt blending and extrusion to obtain the conductive composite material. The preparation process disclosed by the invention has simple process, does not need to perform covalent modification on the CNTs and does not destroy the structure of the CNTs, the CNTs have good dispersibility, and the prepared composite material has high content of CNTs and good conductibility.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
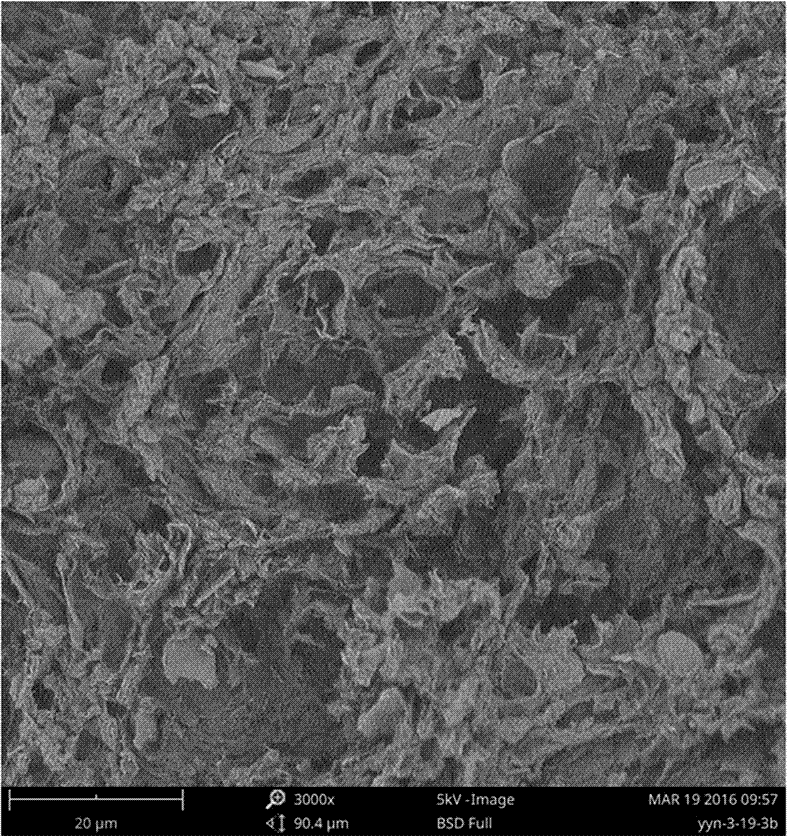
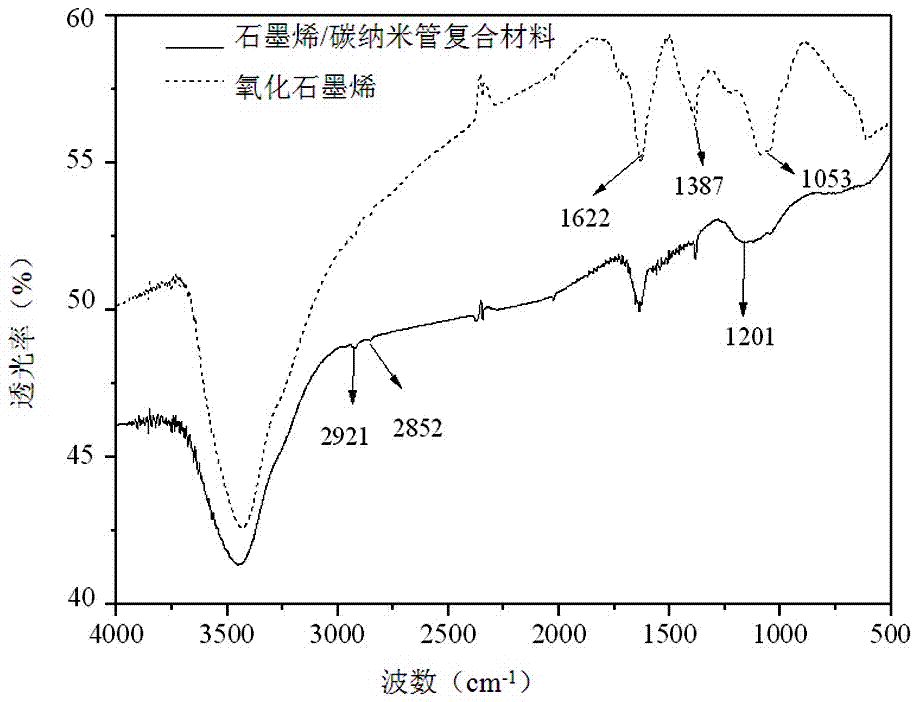
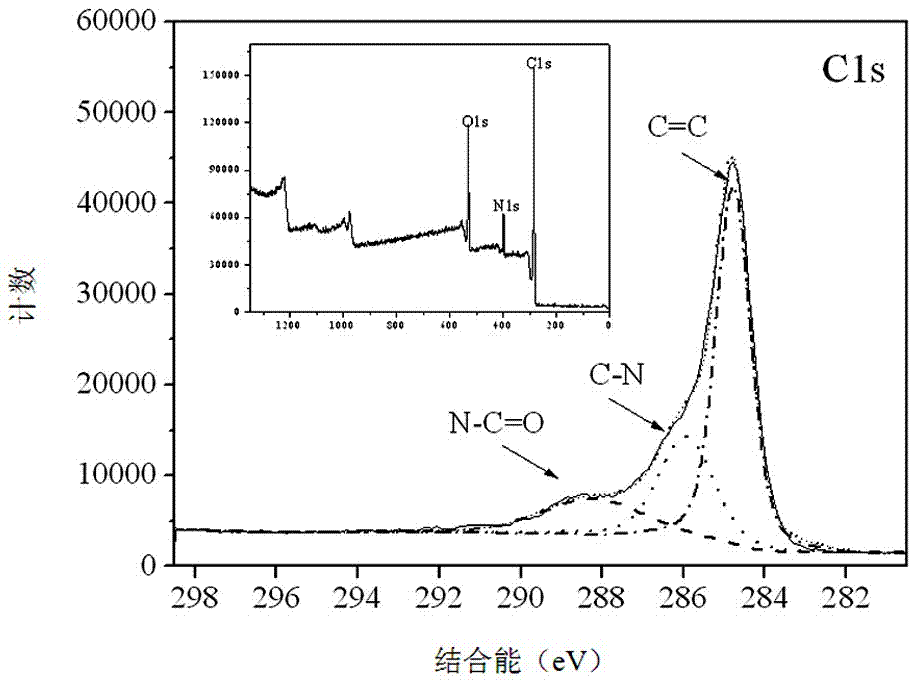
Preparation method and application of graphene/carbon nano-tube composite
ActiveCN106861617AAvoid clumpingLarge specific surface areaOther chemical processesComponent separationEthylenediamineCLORPRENALINE
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a graphene / carbon nano-tube composite. The preparation method comprises the following steps: oxidizing graphene powder and a multiwalled carbon nano-tube together to obtain graphene oxide and an oxidized carbon nano-tube; carrying out ultrasonic peeling and dispersion on the graphene oxide and the oxidized carbon nano-tube; carrying out modification connection and reduction on the graphene oxide and the oxidized carbon nano-tube with ammonia water and ethylenediamine; and filtering, washing and drying a product after reaction to obtain the graphene / carbon nano-tube composite. The preparation method is simple and convenient, and reaction conditions are mild; in the preparation method, the graphene is connected with the carbon nano-tube through covalent modification, and the carbon nano-tube is connected between graphene slice layers. The graphene / carbon nano-tube composite prepared by the method has a fluffy and porous three-dimensional skeleton structure, and can be used for extracting and detecting melamine, clenbuterol, sulfadimidine sodium, indoleacetic acid, bambuterol, clorprenaline, dicofol, 2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,1-dichloroethane or chlorofluoro thiochromanone.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Micro-nano material, product of covalent modification of hydrophilic substances for surface of micro-nano material, and preparation method
ActiveCN106519147AReduce non-specific adsorptionIncrease coverageCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationMicro nanoHydrophilic polymers
The invention discloses a micro-nano material, a product of covalent modification of hydrophilic substances for the surface of the micro-nano material, and a preparation method. Carboxyl groups or potential carboxyl groups are contained on the surface of the micro-nano material and transformed into active esters; the product of covalent modification of the hydrophilic substances for the surface is obtained through taking a hydrophilic compound or / and a hydrophilic polymer containing aliphatic primary amines or / and aliphatic secondary amines as a modifier, forming amido bonds from the active esters for the surface and the hydrophilic compound or / and the hydrophilic polymer, and carrying out covalent modification; during preparation, enough carboxyl groups or potential carboxyl groups are generated on the surface of a polymeric material from monomers containing carboxyl groups or / and potential carboxyl groups and transformed into active esters, then amido bonds are formed from the active esters and a modifier with aliphatic primary amines and / or aliphatic secondary amines, potential facultative ionic groups and hydrophilic connection arms, and having a moderate volume, and covalent modification layers are obtained; and multilayer covalent modification is realized during a process of repeatedly generating the active esters on the surface of the product of covalent modification and then forming the amido bonds from the active esters and the hydrophilic modifier, and the surface of the micro-nano material is efficiently covered with the hydrophilic modifier having a medium volume, thus the non-specific adsorption of the modification product for biological molecules is remarkably reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING FARSIGHTED BLUE DRAGON FBD BIOTECH CO LTD CHINA
Graphene composite conductive ink for ink-jet printing and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses graphene composite conductive ink for ink-jet printing and a preparation method thereof. The graphene composite conductive ink comprises the following ingredients (by weight): 1-30 parts of graphene, 0.1-15 parts of multi-walled carbon nanotube, 0-7.5 parts of conductive carbon black, 290-320 parts of a mixed solvent, 0.2-10 parts of a surfactant, and 0.2-15 parts of a binder. The preparation technology is simple and feasible. According to the preparation technology, a series of steps that are hard to operate, such as tedious covalent modification, dipolar addition reaction, diazonium salt coupling, solvent exchange, etc. in the prior art are omitted; but by direct one-step grinding and mixing, the surface of a conductive filler is coated with the surfactant to prepare graphene ink with good dispersion. No poisonous reagents are used during the preparation process. The preparation method is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Utilization of Wolinella succinogenes asparaginase to treat diseases associated with asparagine dependence
InactiveUS6251388B1Highly efficaciousLess immunosuppressive activitySugar derivativesBacteriaHomotetramerAutoimmune condition
Described herein are methods for producing recombinant forms of asparaginase derived from Wolinella succinogenes. In addition, methods for covalent modification of proteins, including asparaginases, by acylation are also provided. Certain embodiments provide for epitopic-labeling of the amino terminus of W. succinogenes asparaginase. Additional embodiments concern methods for the therapeutic utilization of the native, homotetrameric form of W. succinogenes asparaginase, as well as the use of epitopically-labeled or non-epitopically-labeled recombinant W. succinogenes asparaginase (or a covalently modified analog thereof) in the therapeutic treatment of malignant and non-malignant hematological disease and other diseases where asparagine depletion or deprivation would be efficacious or which respond to asparagine depletion or deprivation, as well as their potential utilization in the therapeutic treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, AIDS, and SLE.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES
Electrochemical sensor and its prepn process and use
InactiveCN101046461AHigh mutation rateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCarboxyl radicalCarbon nanotube
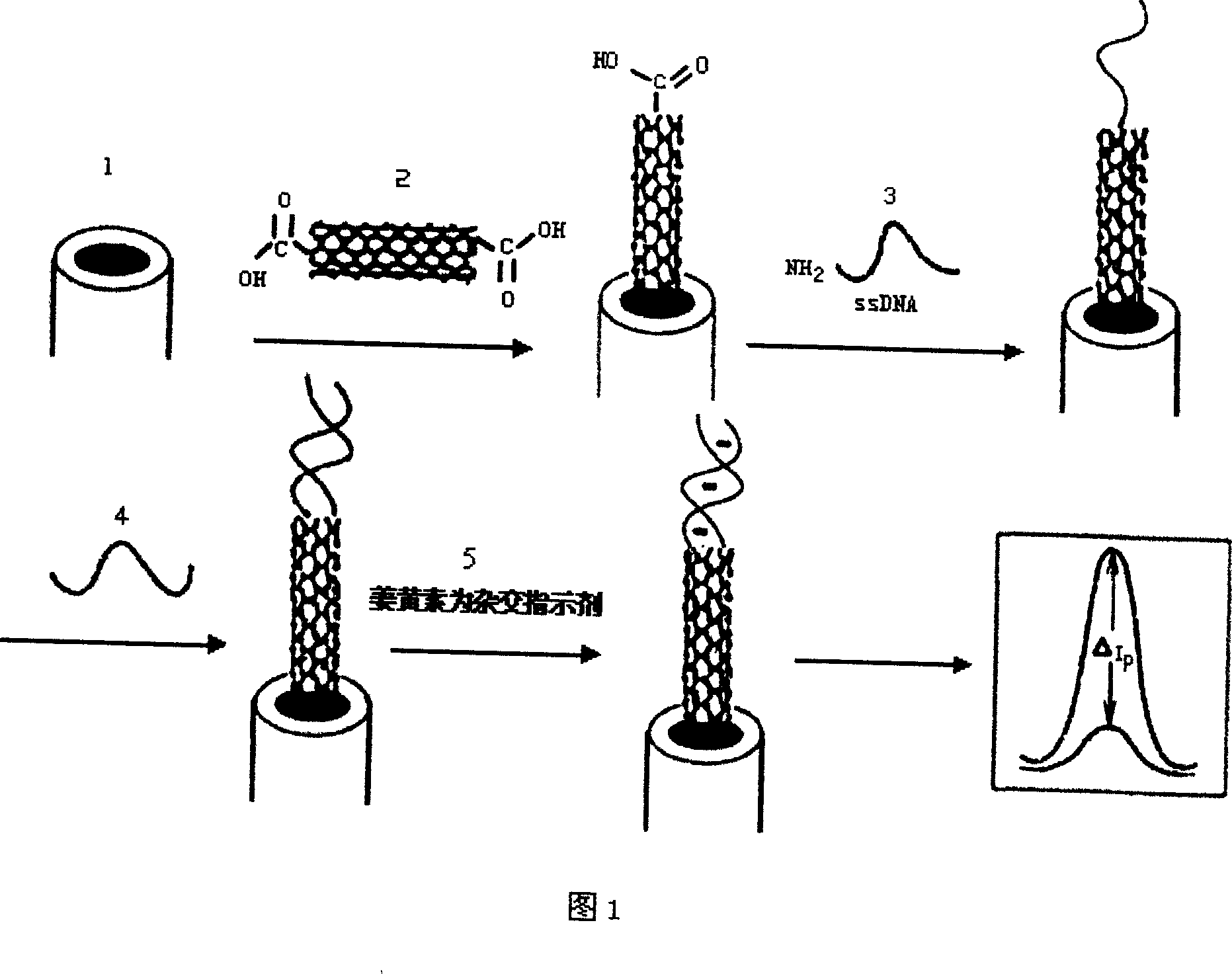
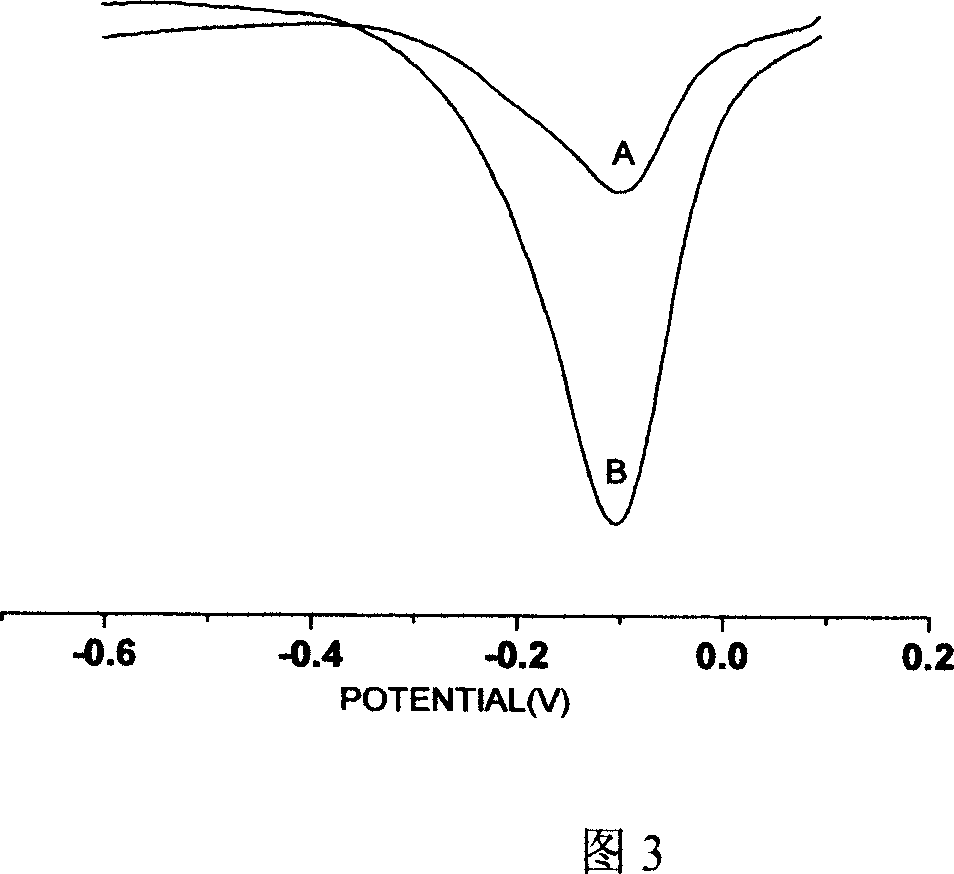
The present invention discloses one kind of electrochemical sensor and its preparation process and use. The electrochemical sensor is prepared through decorating the surface of glass-carbon electrode with open-mouthed multi-wall carbon nanotube possessing carboxylated end, fixing BCR / ABL b3-a2 type gene probe through covalent decoration onto the end carboxyl radical of carbon nanotube, hybridizing the probe DNA and the target DNA and adopting curcumin as hybridization indicator for researching the recognizing capacity of single strand fixed on the decorated electrode on complementary DNA. The carbon nanotube has great specific surface area favoring the fixing of DNA on the electrode and excellent electron transferring characteristic for high detection sensitivity of sensor. The sensor is used in detecting chronic granulocytic leukemia gene and has high selectivity and high sensitivity.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Fluorescent magnetic nanoparticle for hypochlorous acid detection and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN103952147ASimple preparation processLow costOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a fluorescent magnetic nanoparticle for hypochlorous acid detection and a synthetic method thereof. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: preparing a ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticle as a magnetic core material by adopting a solvent thermal method, coating the outer part of the magnetic core with a layer of nonporous silicon dioxide and a layer of mesoporous silicon dioxide in sequence by adopting a sol-gel method, and finally covalently modifying a magnetic mesoporous material obtained in the previous two steps with an organic fluorescent molecule capable of specifically identifying hypochlorous acid through a silane coupling agent, thus obtaining the fluorescent magnetic nanoparticle for the hypochlorous acid detection. The nanoparticle is simple in a preparation process and low in cost; the detection of high sensitivity and high selectivity of the hypochlorous acid can be realized by utilizing the remarkable enhancement of a fluorescent signal of the nanoparticle before and after recognition; and the magnetic control and separation of the magnetic nanoparticle can be realized by additionally arranging a magnetic field. The fluorescent magnetic nanoparticle and the synthetic method thereof have an important application prospect in the fields of visual tracing and imaging of the hypochlorous acid in living organisms, quantitative detection of hypochlorous acid in environmental water, clearing and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Live cell biosensors
InactiveUS20060029946A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningPhosphorylationBinding domain
The invention provides dyes, biosensors, and methods for using the dyes and biosensors to detect selected target molecules. The biosensors have a binding domain and a dye, or a dye which is attached directly to the target of interest. Binding domains contemplated by the invention include biomolecules or fragments of biomolecules that interact with target molecules of interest and can be specific to a given conformational state or covalent modification of the molecule (e.g. phosphorylation). In one embodiment, the binding domain of a biosensor is a single chain variable fragment (scFv) with a dye of the invention linked to a CDR3 region. The invention also provides environmentally sensitive dyes useful for detecting changes in the binding, conformational change, or posttranslational modification of the selected target.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method for preparing antibiosis (coating) film
InactiveCN1563156AHas broad-spectrum antibacterial propertiesImprove antibacterial propertiesBiocideAnimal repellantsAntibiosisPolymer science
In the preparing method, nanoantibiotic powder is prepared by connecting germicide covalency of quaternary ammoium salt or quaternary phosphorus salt polymer on nanopowder through covalent decoration method in utilizing nanopowder with functional perssad of antibiosis, prepared powder is disposed to be antibiotic solution containing 0.01-0.1% nanogermicide and then the colution is added into four sorts of film forming materials for making film with conventional process.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
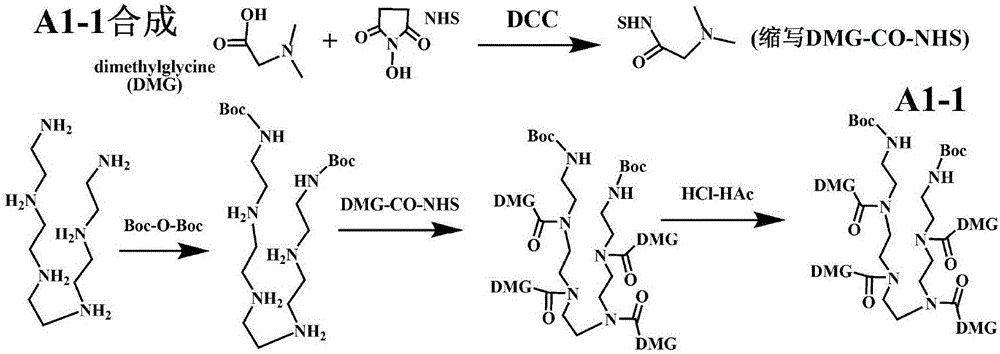
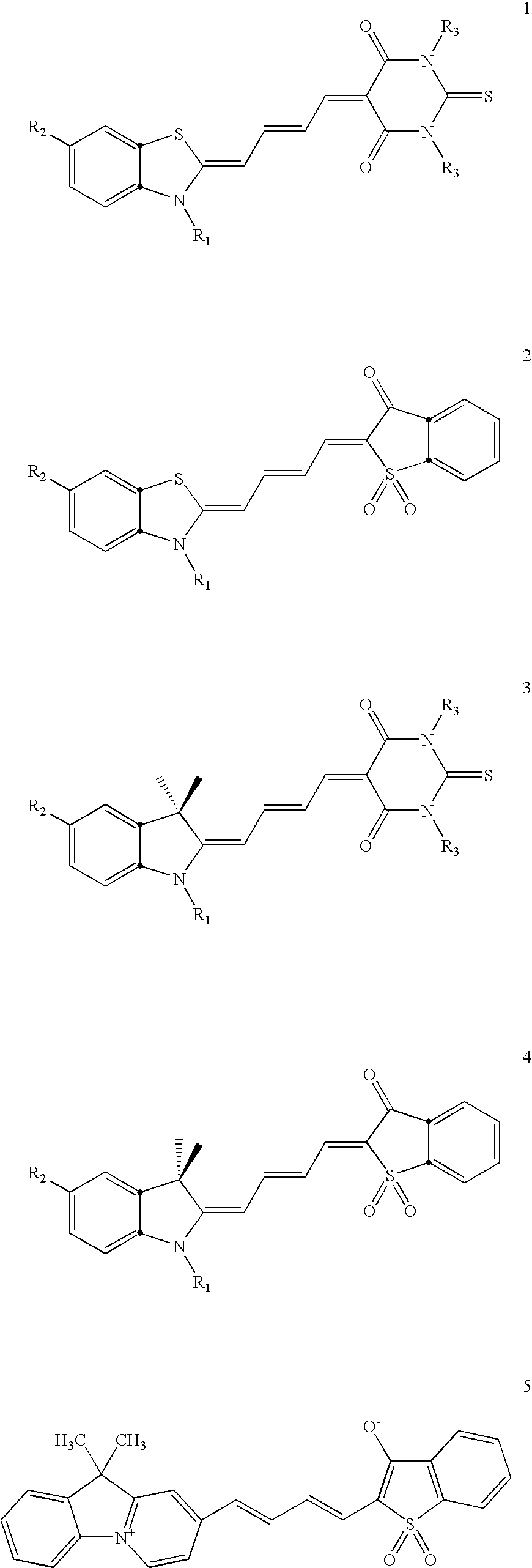
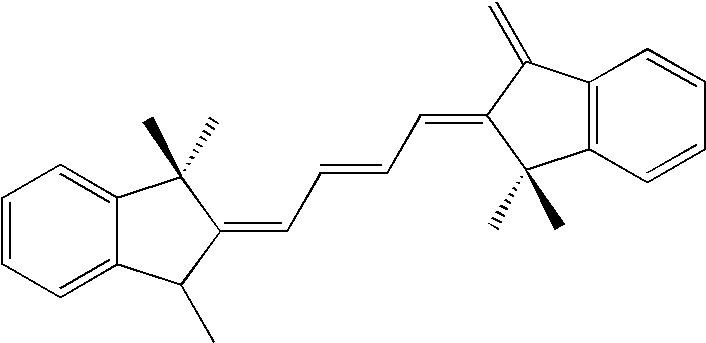
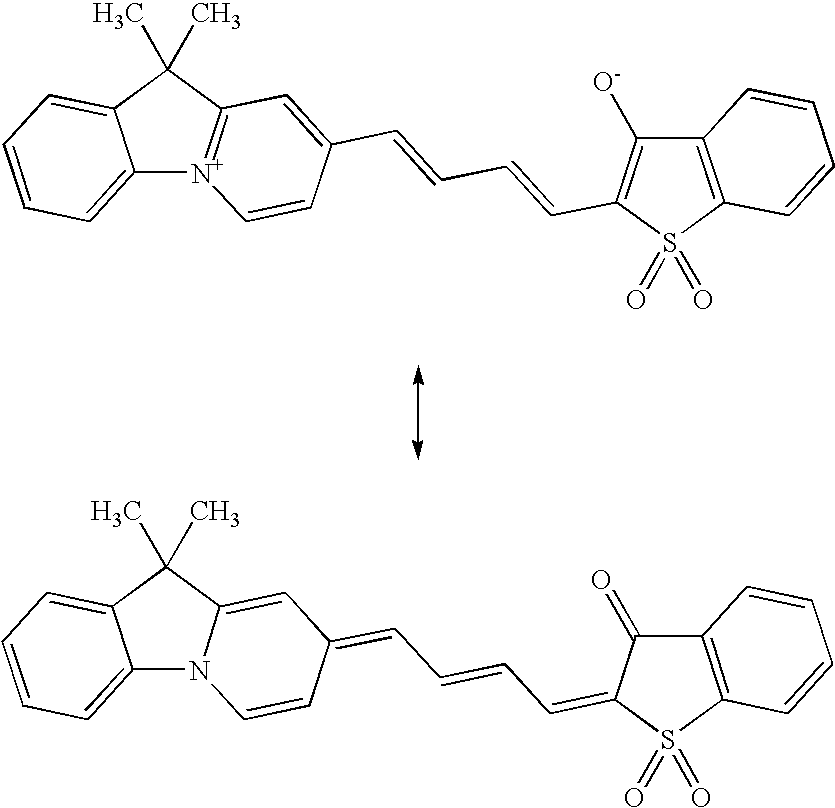
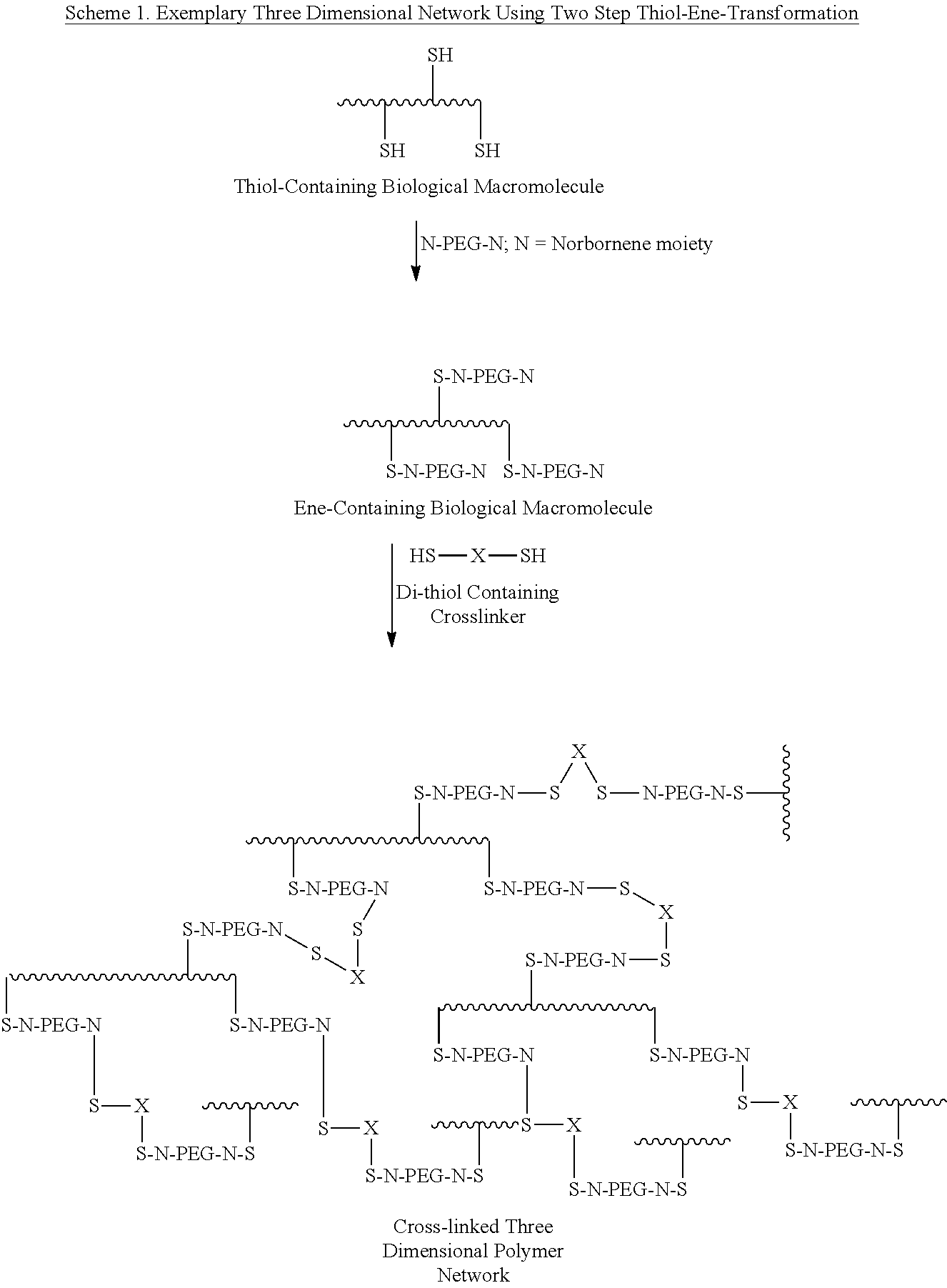
Covalent modification of biological macromolecules
The present disclosure provides a method of covalently modifying a biological macromolecule, the method comprising subjecting a reaction mixture comprising: (a) a biological macromolecule comprising one or more thiol groups; and (b) a molecule comprising one or more olefin or alkyne moieties to a radical reaction under conditions sufficient to produce the covalently modified biological macromolecule. The present disclosure also provides a method of covalently modifying a biological macromolecule, the method comprising subjecting a reaction mixture comprising: (a) a molecule comprising one or more thiol groups; and (b) a biological macromolecule comprising one or more olefin or alkyne moieties to a radical reaction under conditions sufficient to produce the covalently modified biological macromolecule. The present disclosure further provides a covalently modified biological macromolecule prepared by any of the disclosed methods. The covalently modified biological macromolecules may be further crosslinked to form a scaffold.
Owner:MOSAIC BIOSCI
Viral disease diagnosis device and method based on field effect transistor
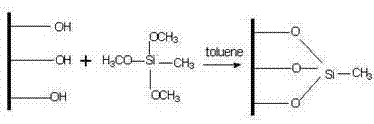
InactiveCN102435654AMiniaturizationEasy to integrateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansViral antibodySilanes
The invention discloses a quick diagnosis device for a viral communicable disease based on a field effect transistor, which is composed of three parts, i.e., a field effect transistor biological chip, a microfluid channel sample introduction encapsulation system and an electronic detection system. A source electrode, a drain electrode and a semiconductor channel between the source electrode and the drain electrode are constructed on a silicon substrate by utilizing a semiconductor manufacturing process; and a covalent modification silane reagent on the channel is taken as a connection molecule for connecting viral antibodies; then a microfluid channel made from polydimethylsiloxane is used to be encapsulated in tight fit with the silicon substrate; finally the source electrode and the drain electrode are connected with a set of a signal detection system, so that a person or an animal can be diagnosed whether to be infected with the viral disease quickly, accurately and sensitively. The quick diagnosis device is a portable epidemic communicable disease detection instrument.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Polyethylene glycol dog source urate oxidase analogue, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN102634492AImprove enzyme activity retentionStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderMutated proteinChronic gout
The invention discloses a polyethylene glycol (PEG) dog-source urate oxidase analogue, wherein the dog-source urate oxidase analogue is natural dog-source urate oxidase and chimeric protein and mutant protein containing part of dog-source and human-source urate oxidase amino acid sequences, the average molecular weight of polyethylene glycol is about 1kDa-40kDa, and each urate oxidase monomer is coupled with 2-15 polyethylene glycol molecules in average. According to the method for preparing mammal-source urate oxidase subjected to covalent modification by the polyethylene glycol, the enzyme activity retention rate is higher than 85.0%, and the purification is higher than 95.0%. According to the method, the dog-source urate oxidase analogue subjected to covalent modification by the polyethylene glycol and drug compositions thereof can be used for preventing and / or treating acute hyperuricemia caused by hematologic tumor chemotherapy and hyperuricemia and chronic gout caused by metabolic disorders.
Owner:SHANDONG NEWTIME PHARMA
Nanowire-Based System for Analysis of Nucleic Acids
ActiveUS20090226927A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanowireCovalent modification
System for detection and / or analysis of nucleic acids using nanowires to detect covalent modification of nucleic acids.
Owner:SUN HONGYE +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com