Ligand-directed covalent modification of protein
a covalent modification and protein technology, applied in the field of enzyme inhibitors, can solve the problems of protein target modification, other undesirable effects, and difficulty in developing reversible inhibitors that selectively inhibit one or more desired kinases, and achieve irreversible inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
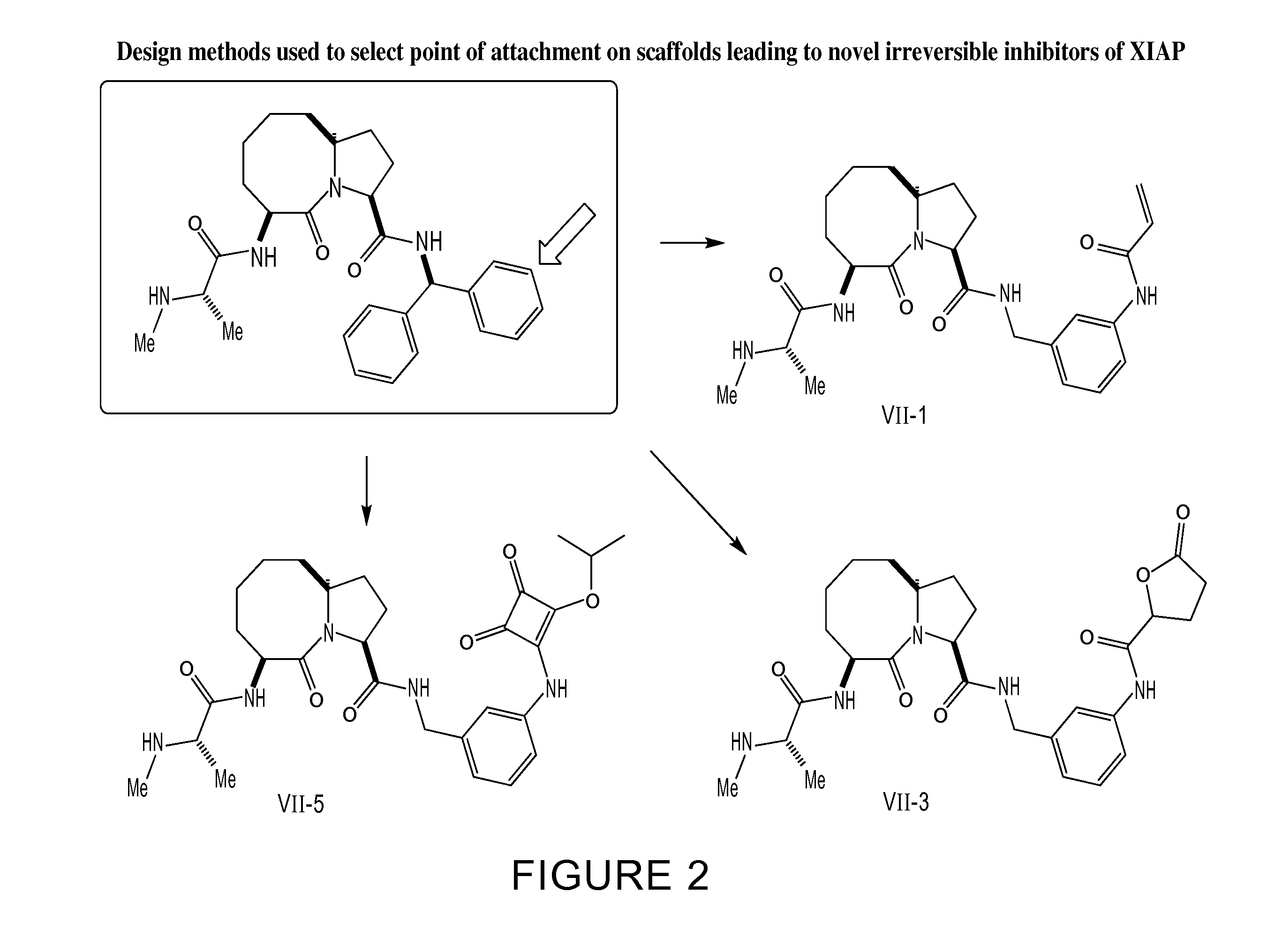
[0756](3S,6S,10aR)-6-((S)-2-(methylamino)propanamido)-5-oxo-N-((R)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)decahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]azocine-3-carboxamide (Compound A) is a reversible inhibitor of XIAP (Ki 26 nM) (Sun et al., J. Med. Chem. 52, 593-596 (2009). Using the structure-based design algorithm described herein, Compound A was converted from a reversible inhibitor into Compound VII-1, a potent and irreversible inhibitor of XIAP. The process for the conversion of Compound A to Compound VII-1 is described below.
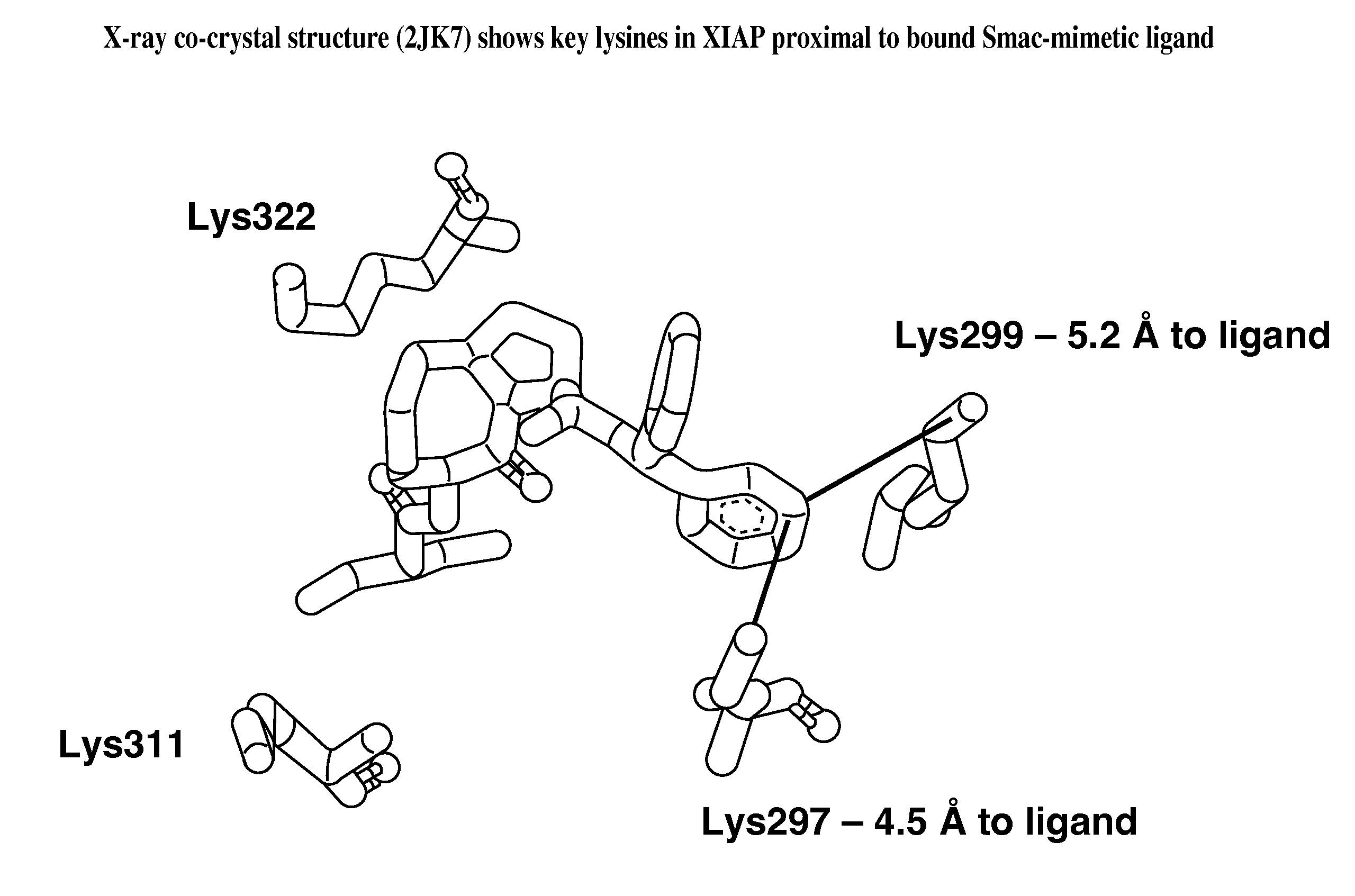
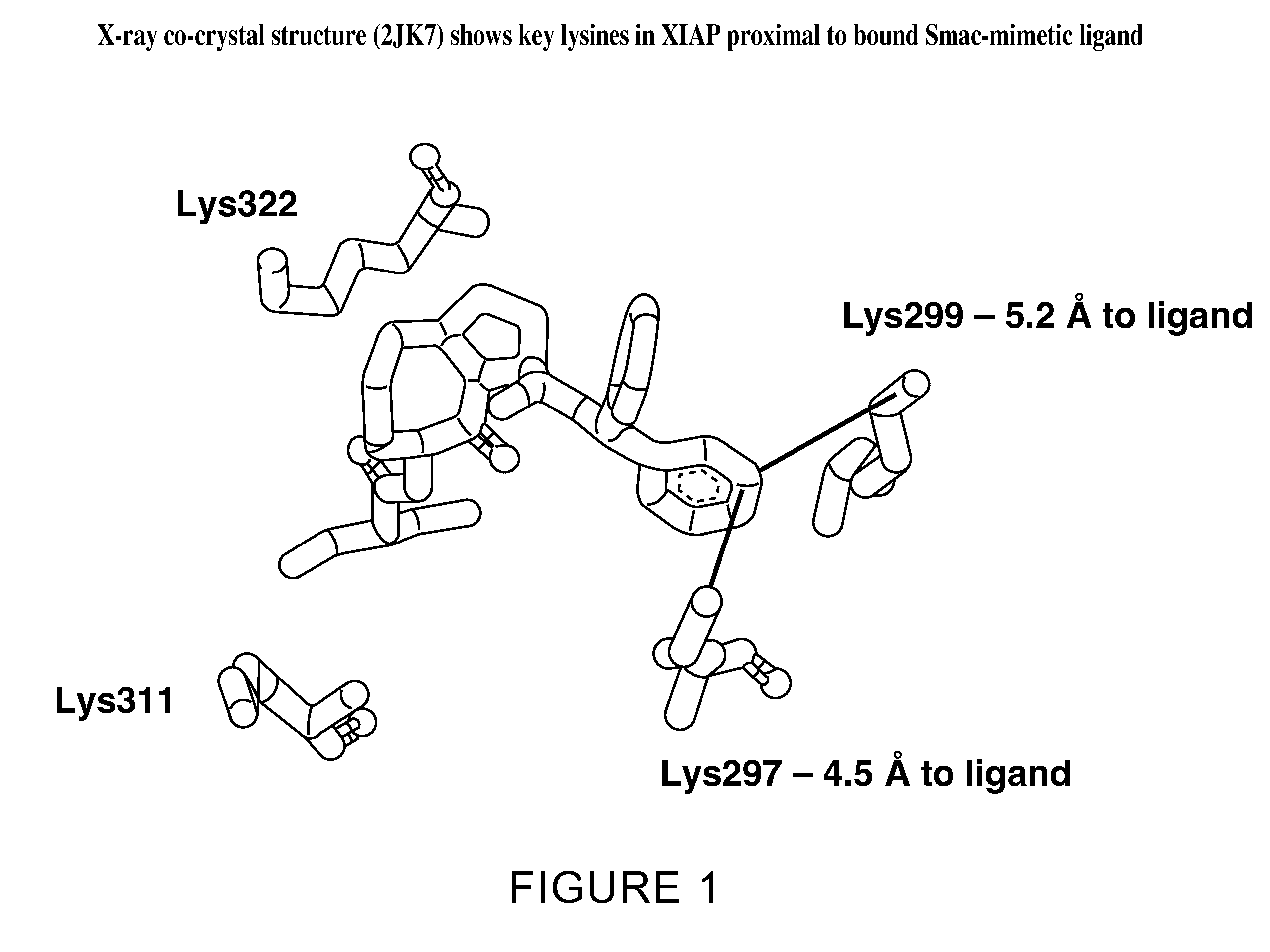
[0757]The X-ray crystal structure of XIAP complexed with Compound B, a related compound to Compound A, has been reported (Sun, H., et al., J. Med. Chem. 51, 7169-7180 (2008)) and was obtained from the protein databank (pdbcode 2JK7 at www.resb.org). The X-ray complex of Compound B bound to XIAP was used to
design covalent inhibitors of XIAP using the design algorithm described herein. The three-dimensional structure of Compound B was docked into the XIAP ligand-binding site using ...
example 1a
[0761]
[0762](3S,6S,10aS)-N-(3-acrylamidobenzyl)-6-(S)-2-(methylamino)propanamido)-5-oxodecahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]azocine-3-carboxamide: The title compound was prepared according to the steps and intermediates as described below.
(S)-2-benzyl 1-tert-butyl 5-oxopyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxylate (1a)
[0763]
[0764]To a stirred solution of L-pyroglutamic acid (75 g, 0.58 mol) and N,N-diisopropyl-ethylamine (87.3 g, 0.676 mol) in dry dichloromethane (1.0 L) at 0° C. was added benzyl bromide (98.84 g, 0.58 mol) dropwise. The reaction mixture was heated under reflux for 5 h, cooled to RT and washed with aqueous NaH2PO4. The aqueous layer was extracted with CH2Cl2; the combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue obtained was then taken in acetonitrile (1.5 L) and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (7.09 g, 58.0 mmol) and Boc-anhydride (150.0 g, 0.688 mol) were added and stirred at RT for 3 hrs. The reaction mixture was concentra...
example 2
[0787]
[0788]tert-Butyl (S)-1-(3S,6S,10aS)-3-(3-acrylamidobenzylcarbamoyl)-5-oxodecahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]azocin-6-ylamino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl(methyl)carbamate: The title compound was prepared according to the steps and intermediates as described below.
[0789]To a mixture of the aniline 1k (60 mg) and triethylamine (80 μl) in dry dichloromethane (2 mL) was added acryloyl chloride (19 μl) dropwise at 0° C. The reaction mixture was concentrated and the residue was purified using semi-prep HPLC (TFA modifier) to give a white solid. LCMS: m / e 470.3 (M+1-tBu).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| non-covalent interactions | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| global energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com