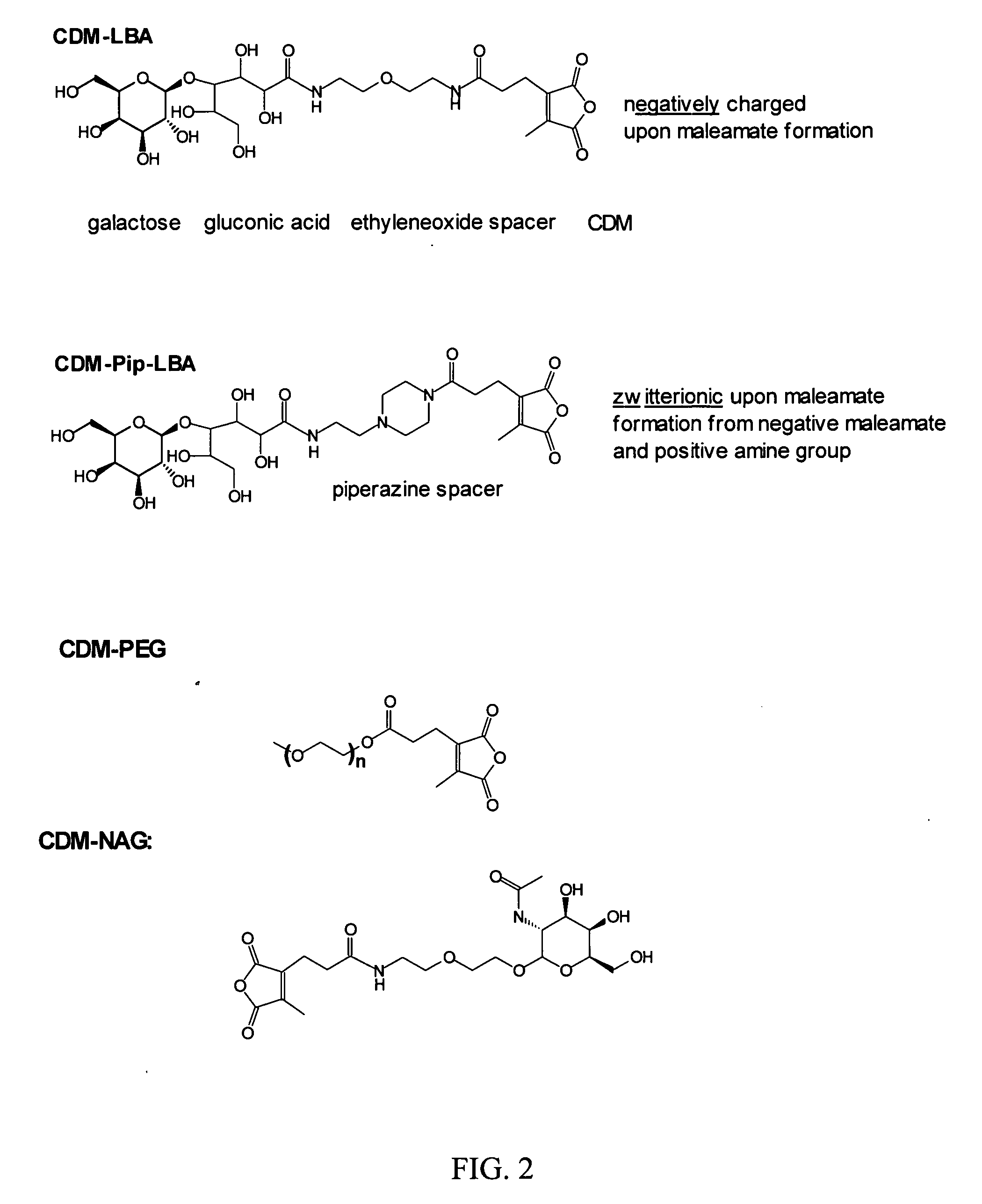
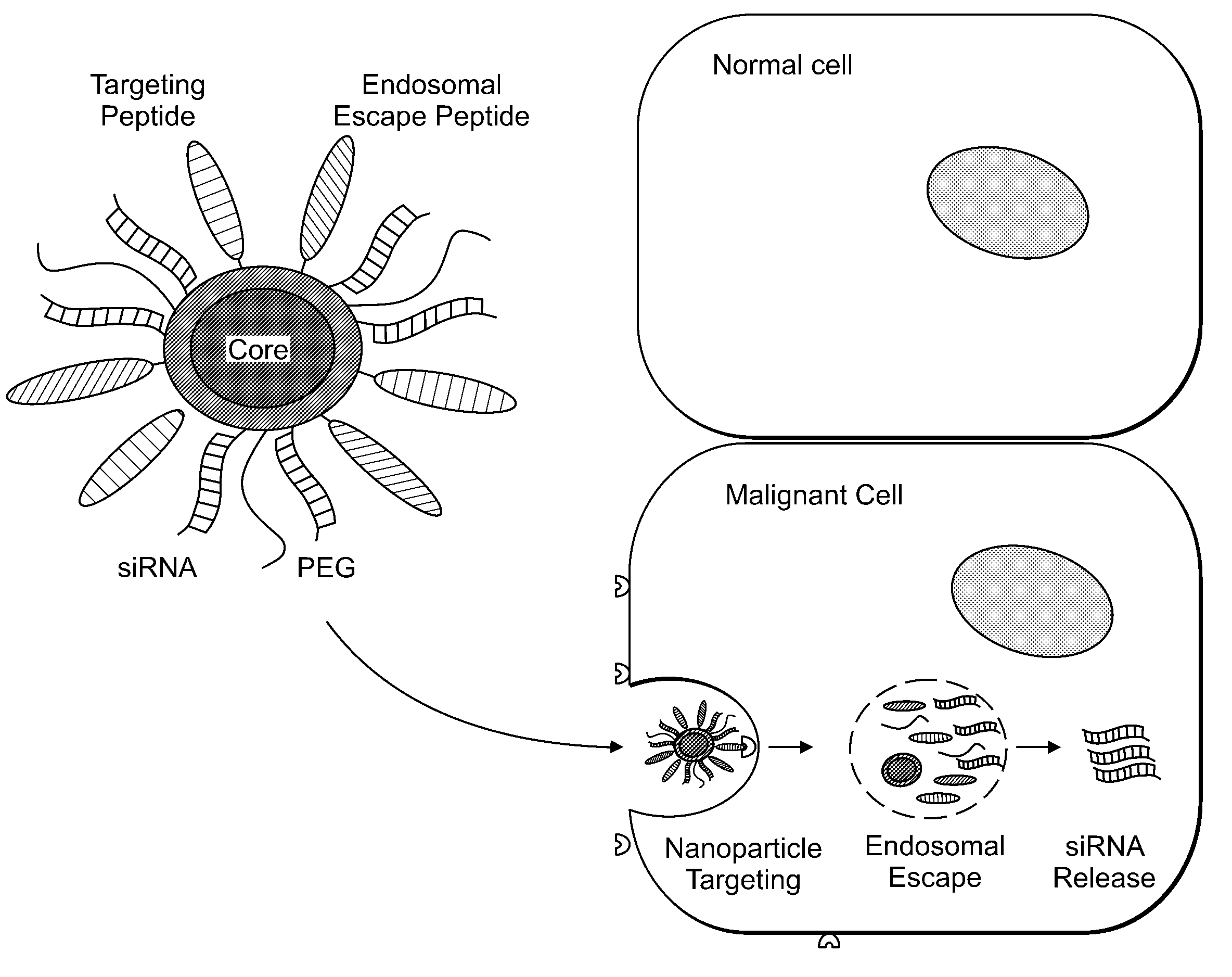
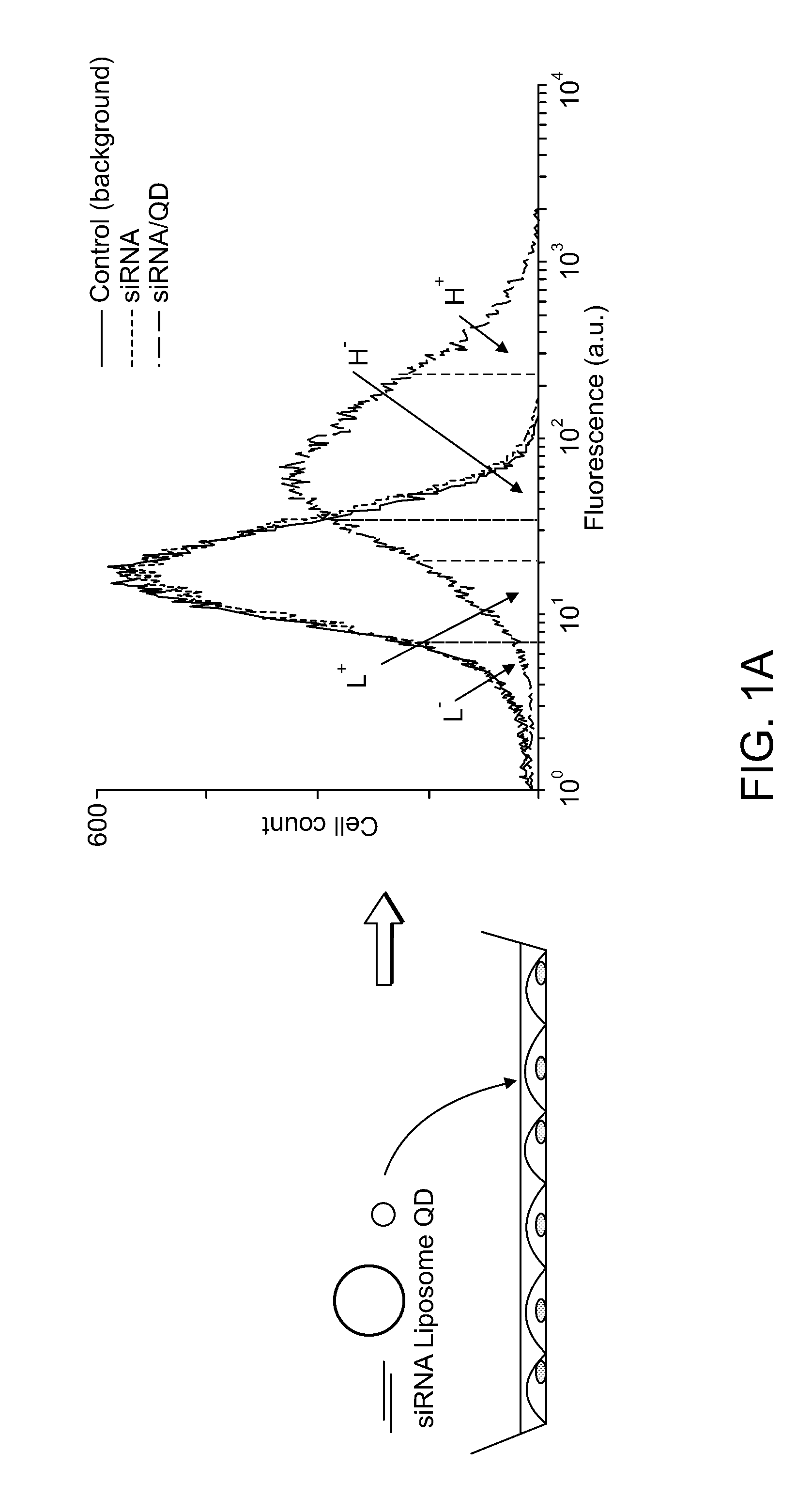
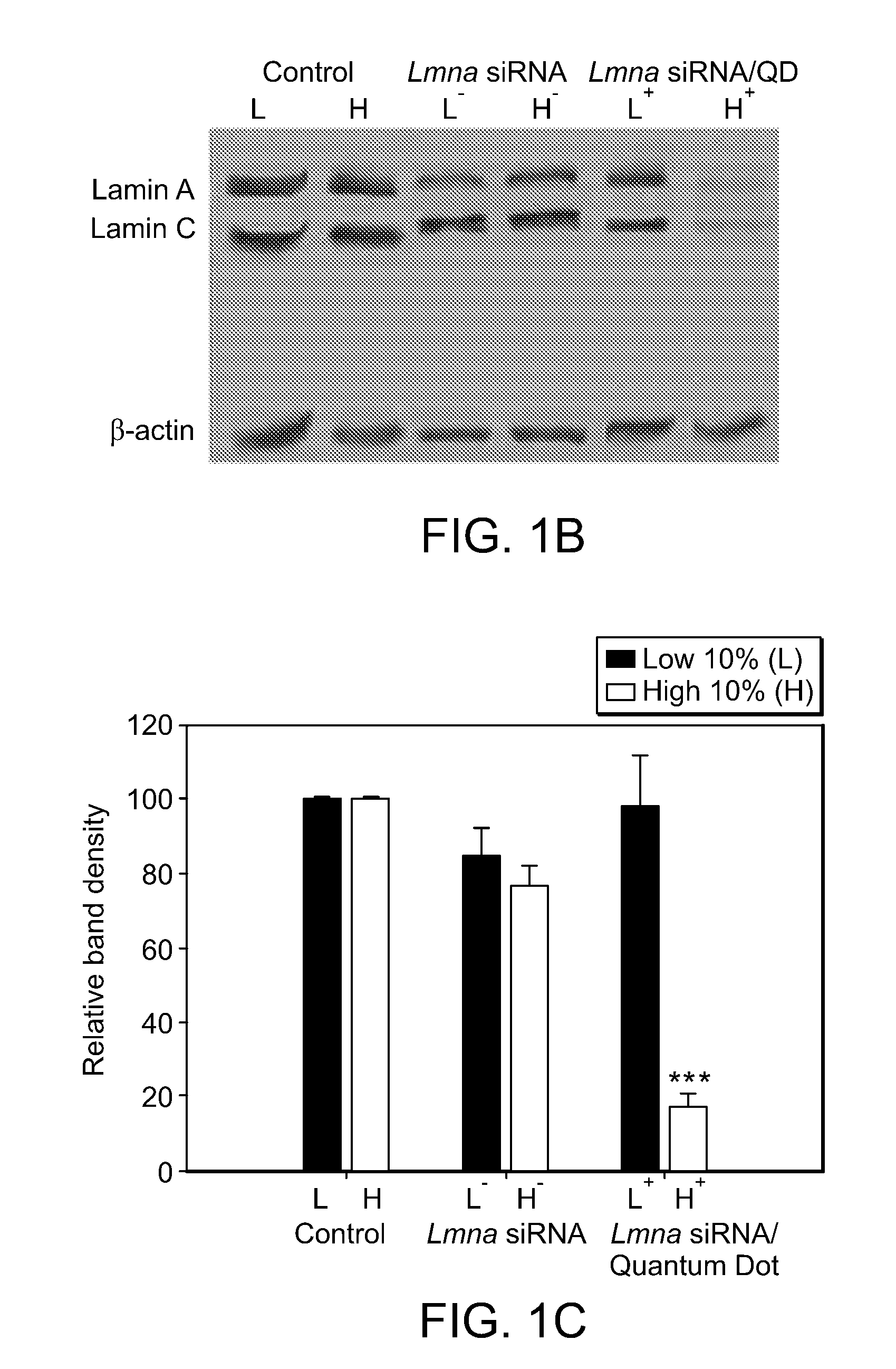
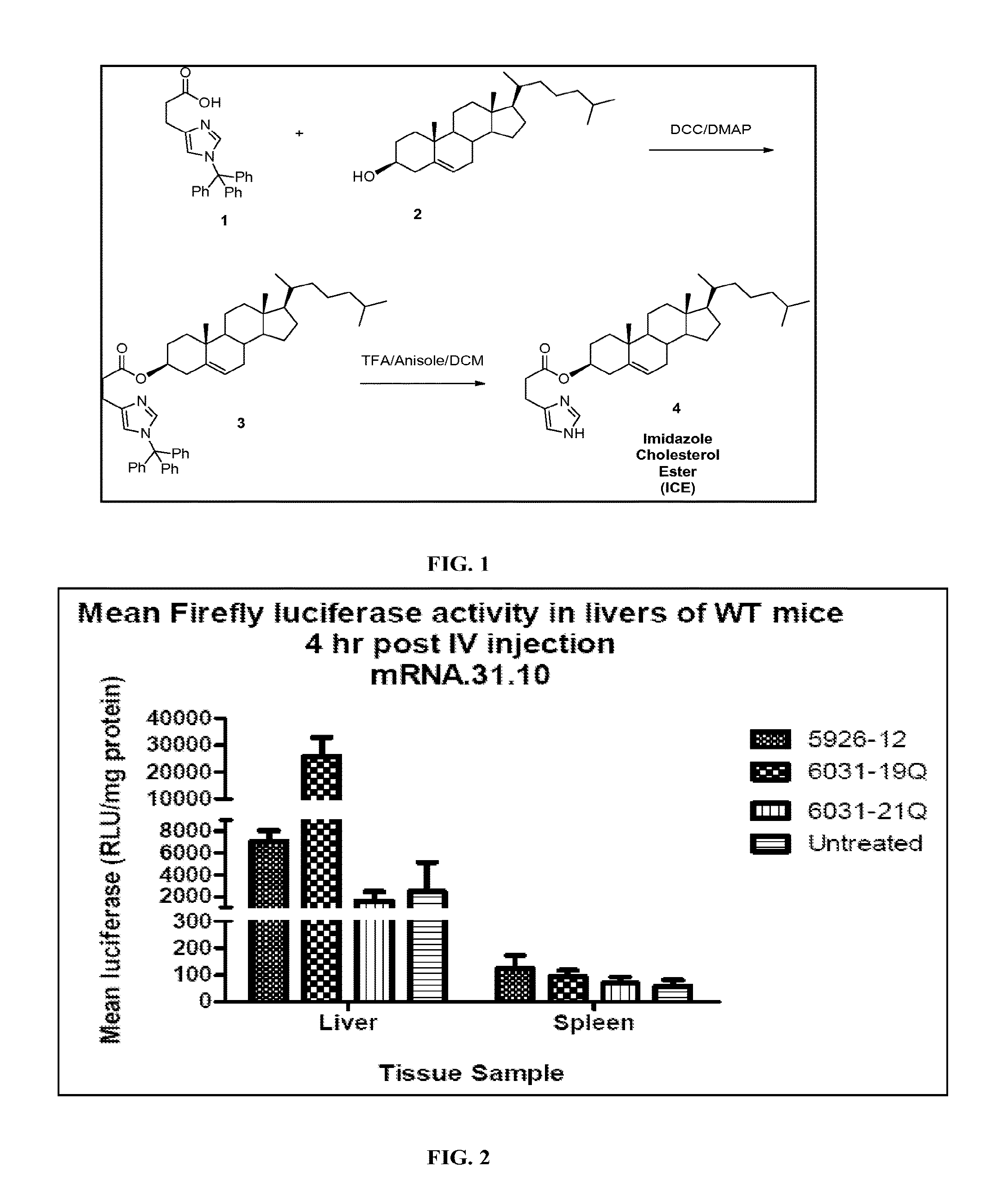
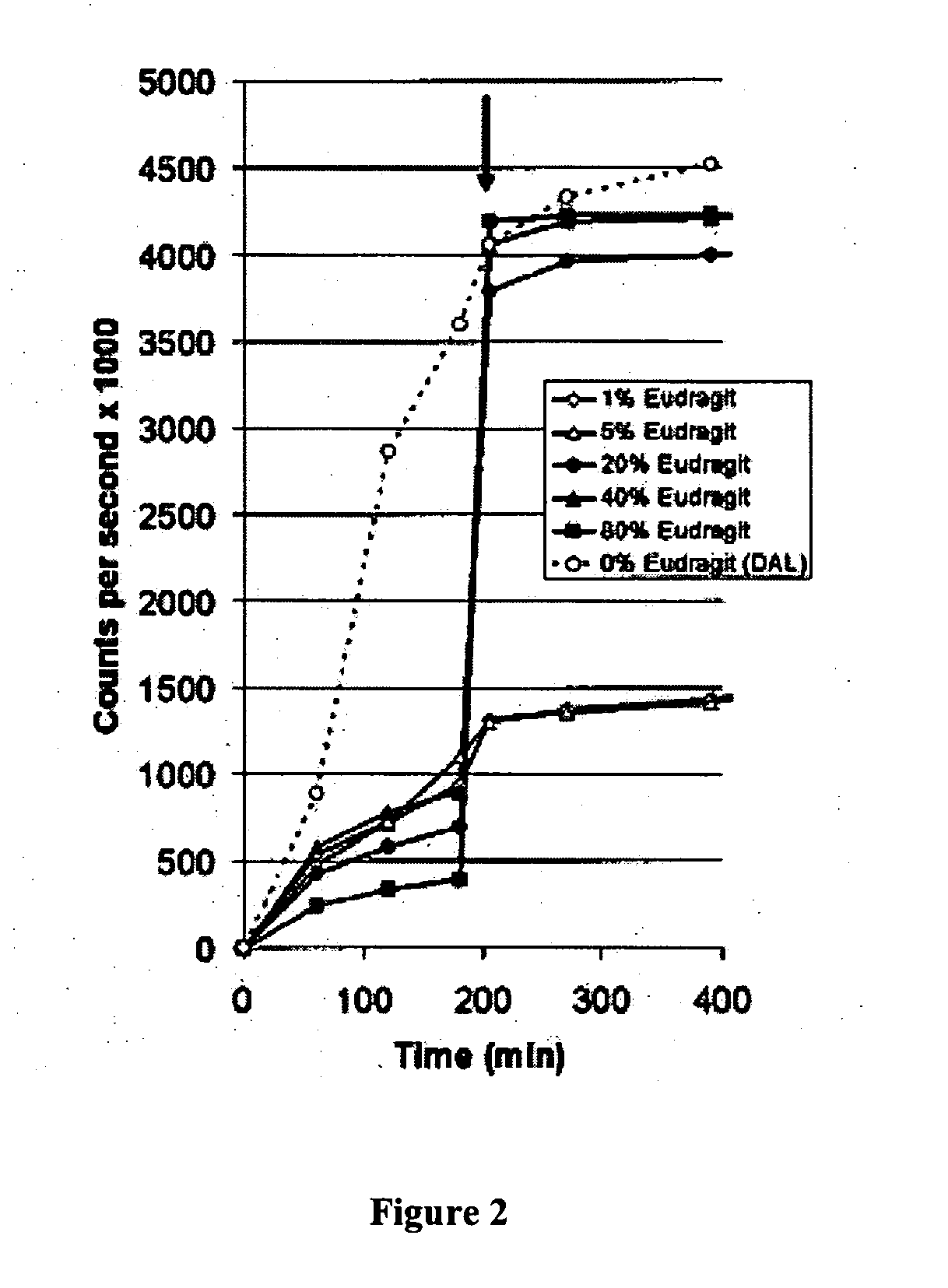
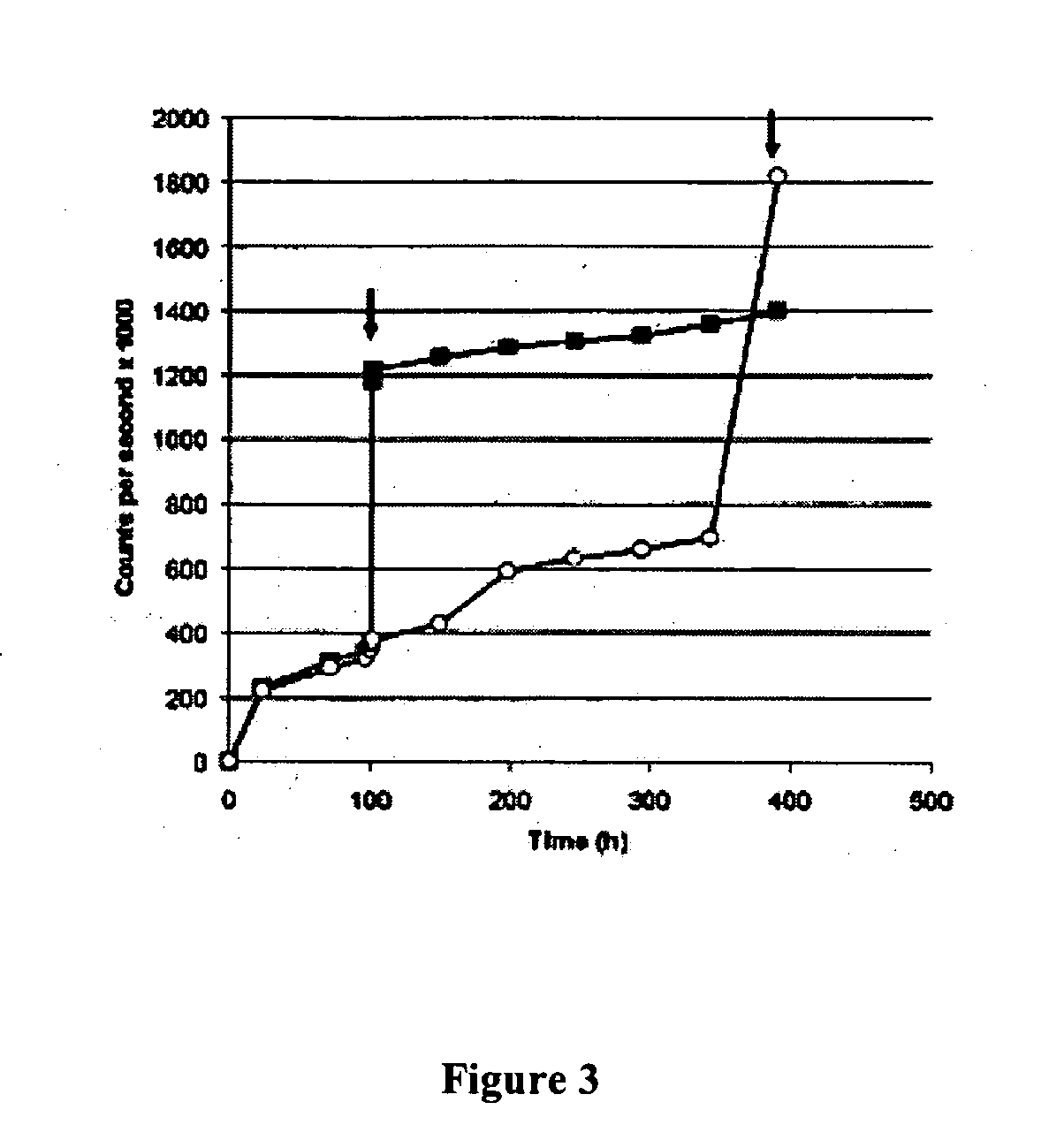
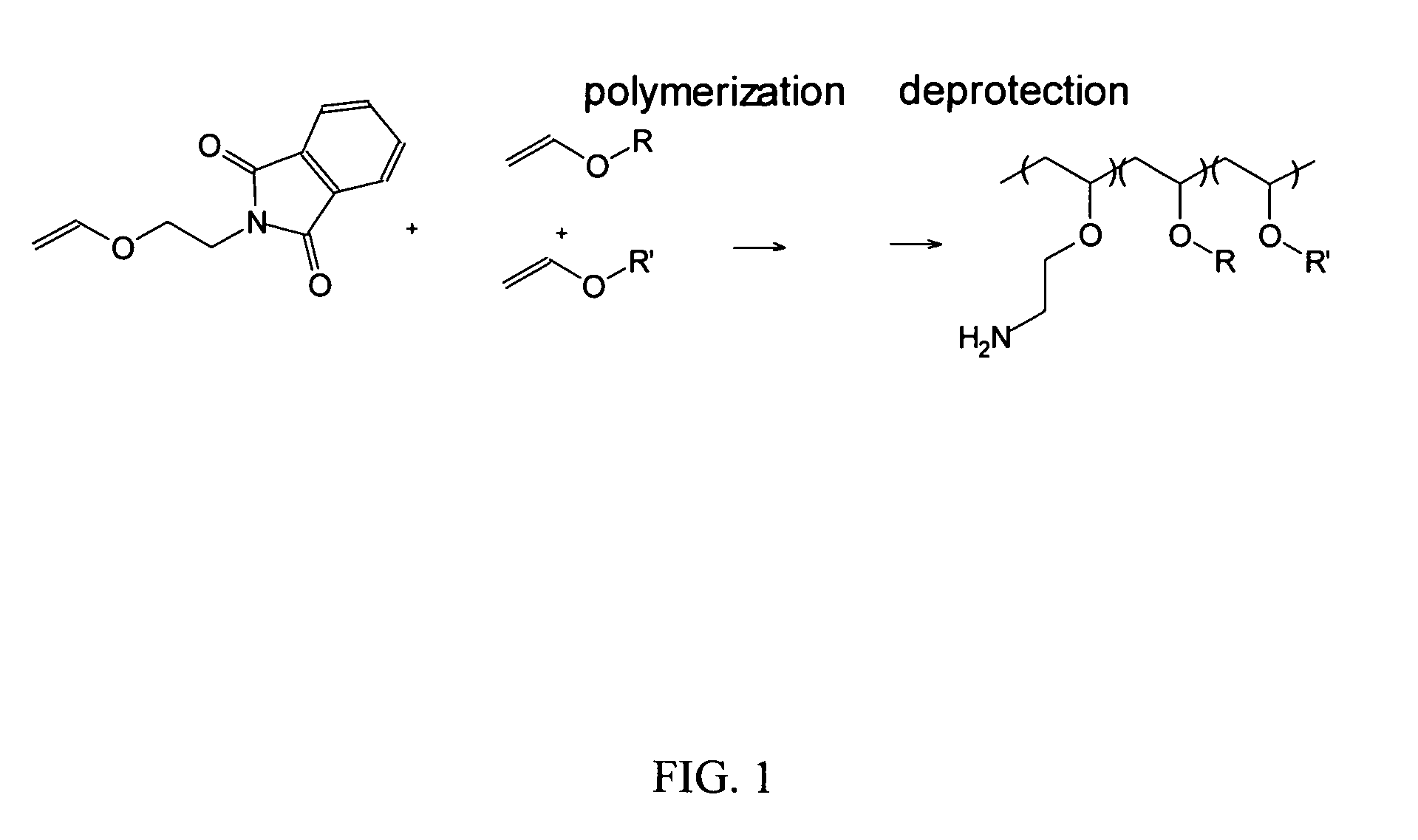
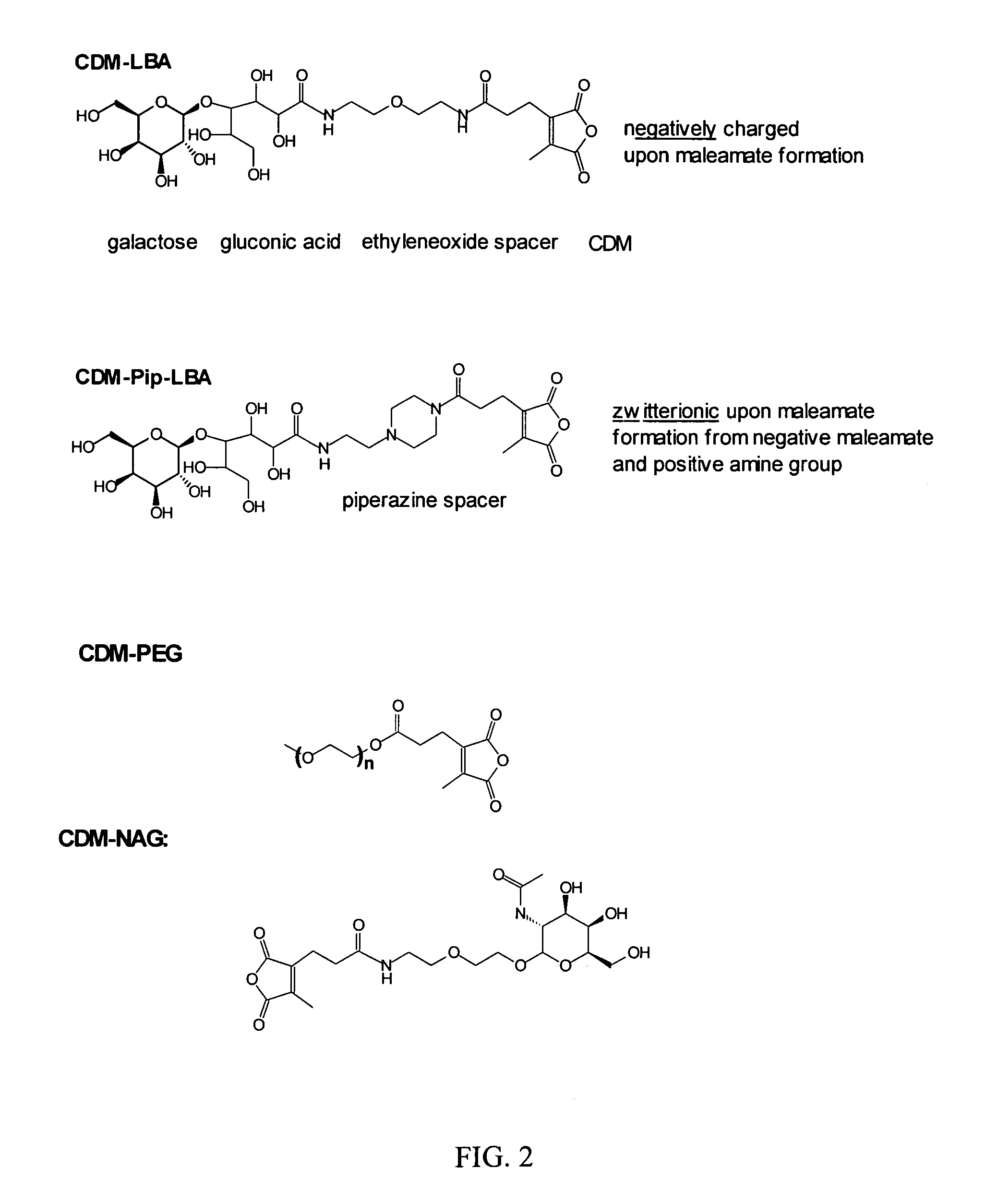
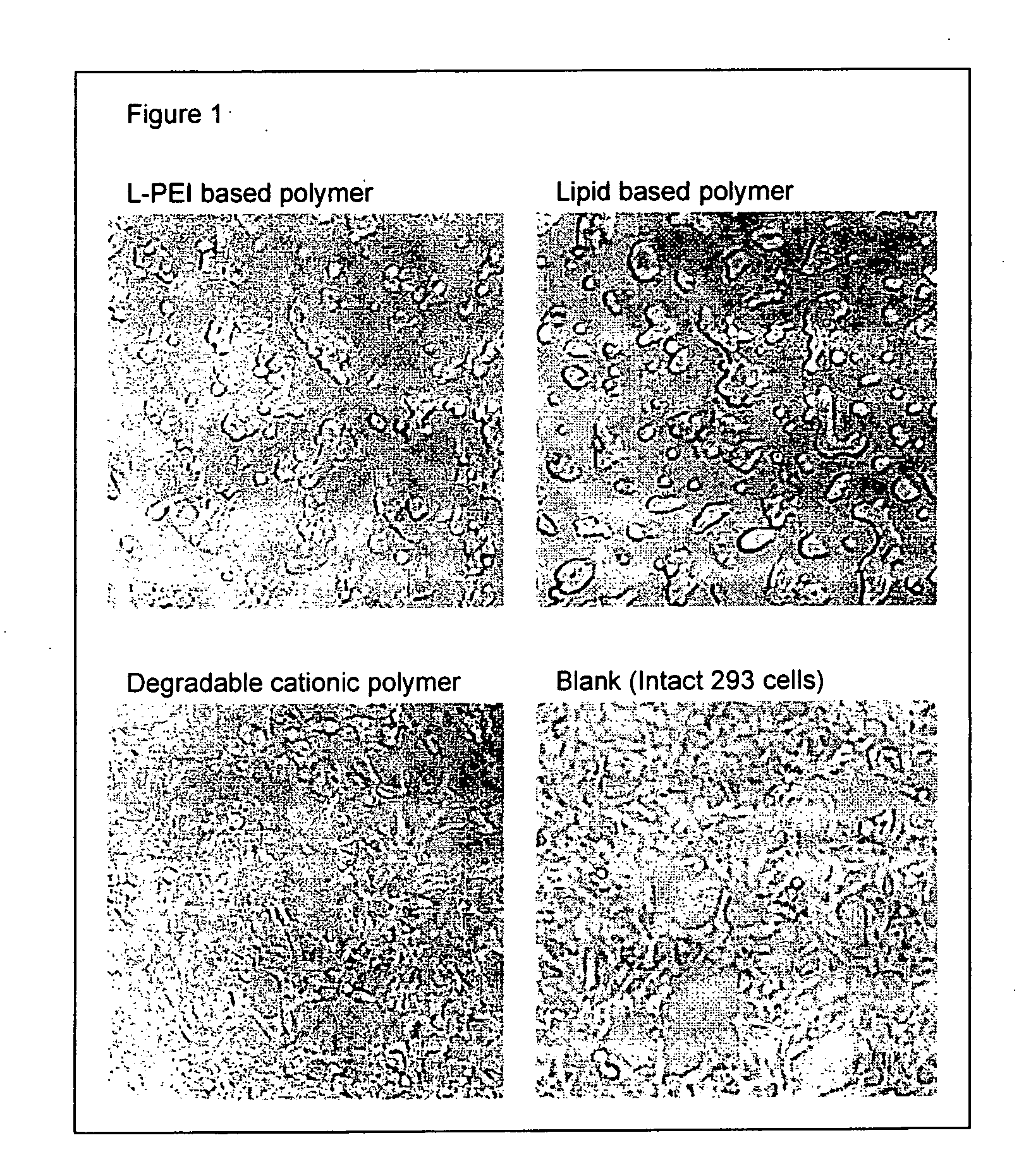
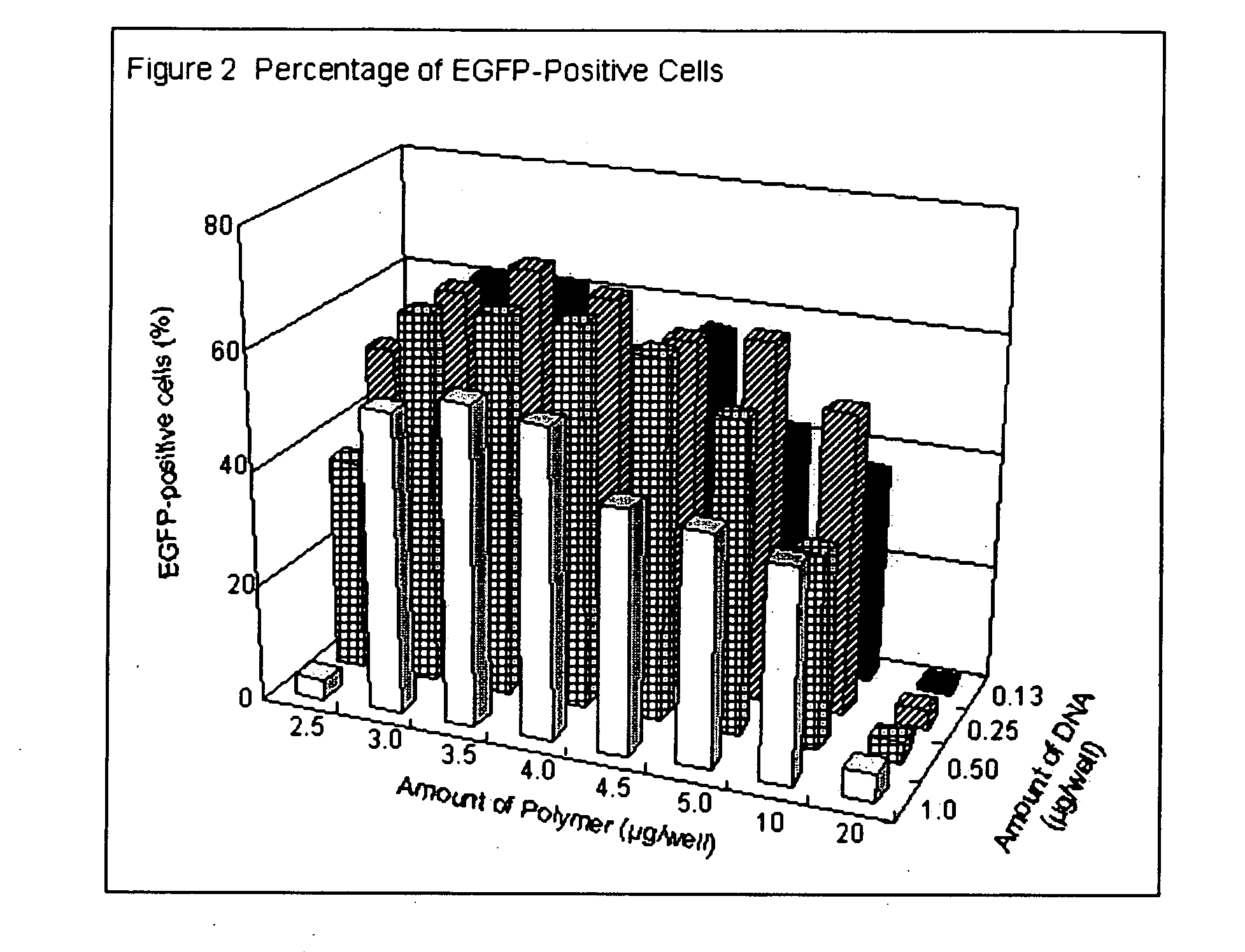
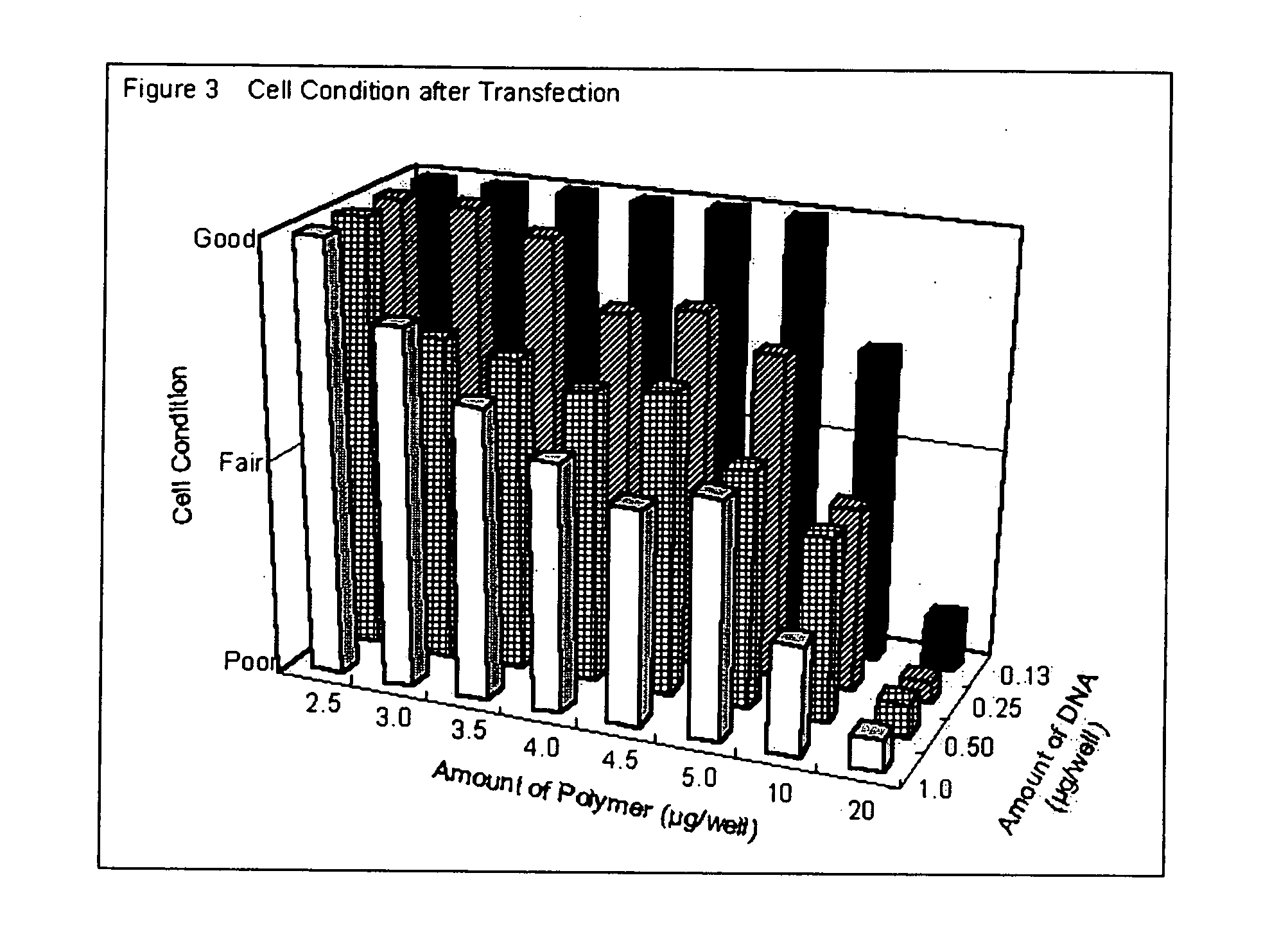
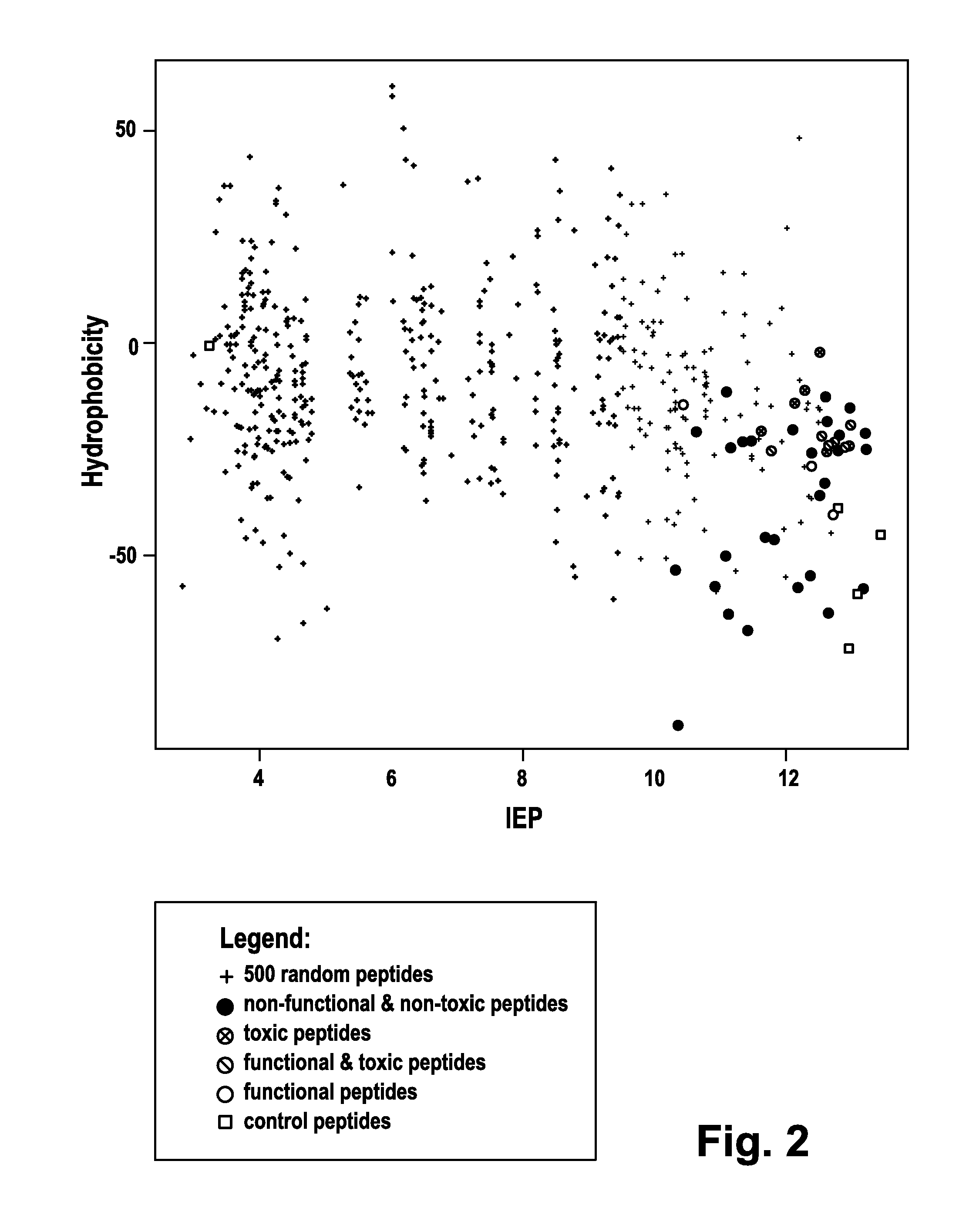
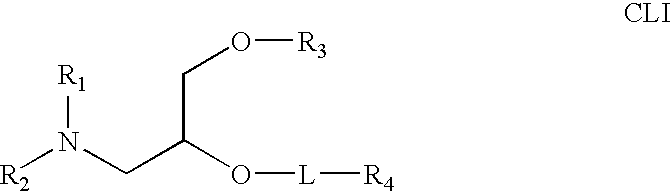Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2076 results about "Transfection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
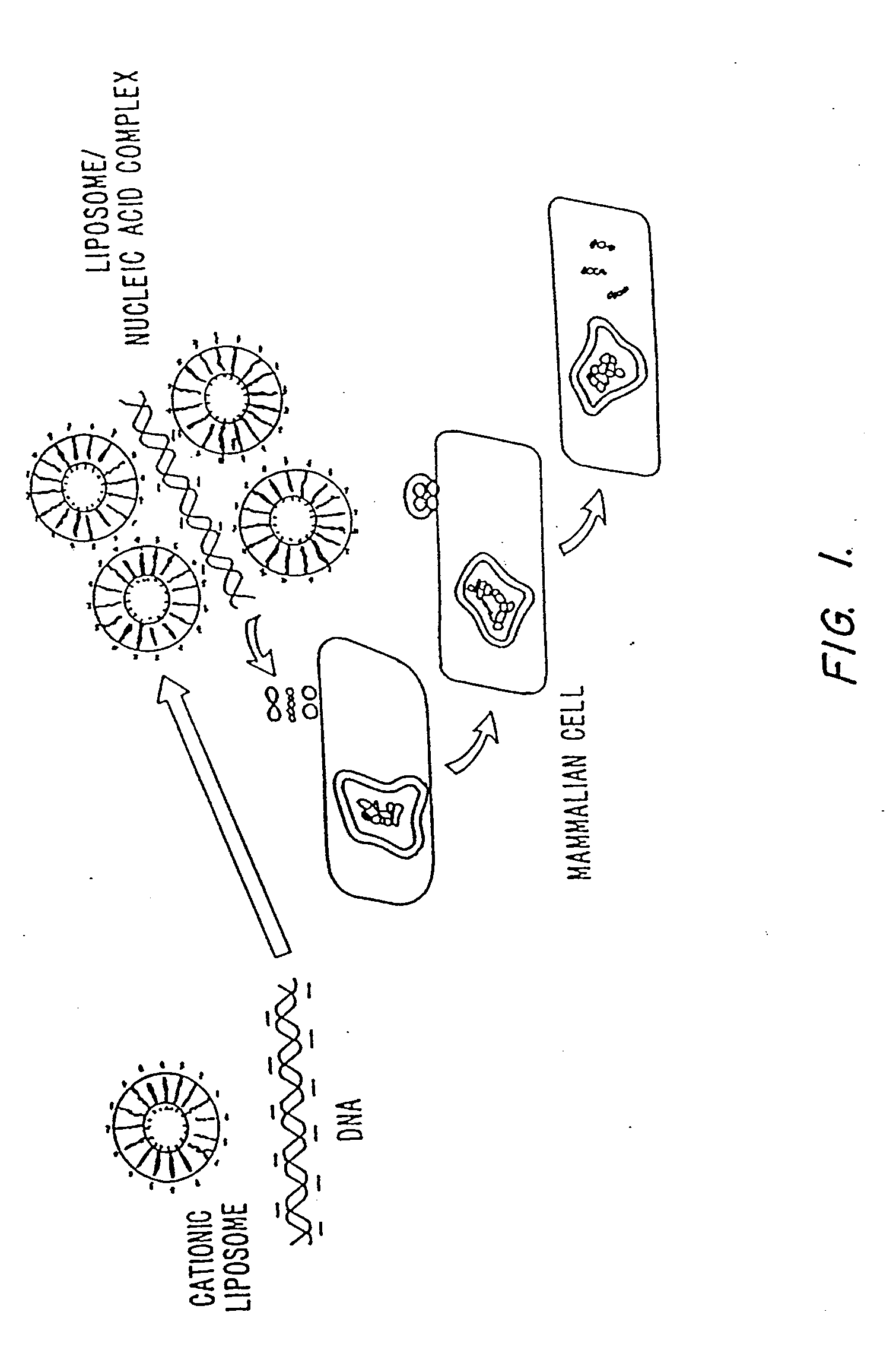
Transfection is the process of deliberately introducing naked or purified nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. It may also refer to other methods and cell types, although other terms are often preferred: "transformation" is typically used to describe non-viral DNA transfer in bacteria and non-animal eukaryotic cells, including plant cells. In animal cells, transfection is the preferred term as transformation is also used to refer to progression to a cancerous state (carcinogenesis) in these cells. Transduction is often used to describe virus-mediated gene transfer into eukaryotic cells.
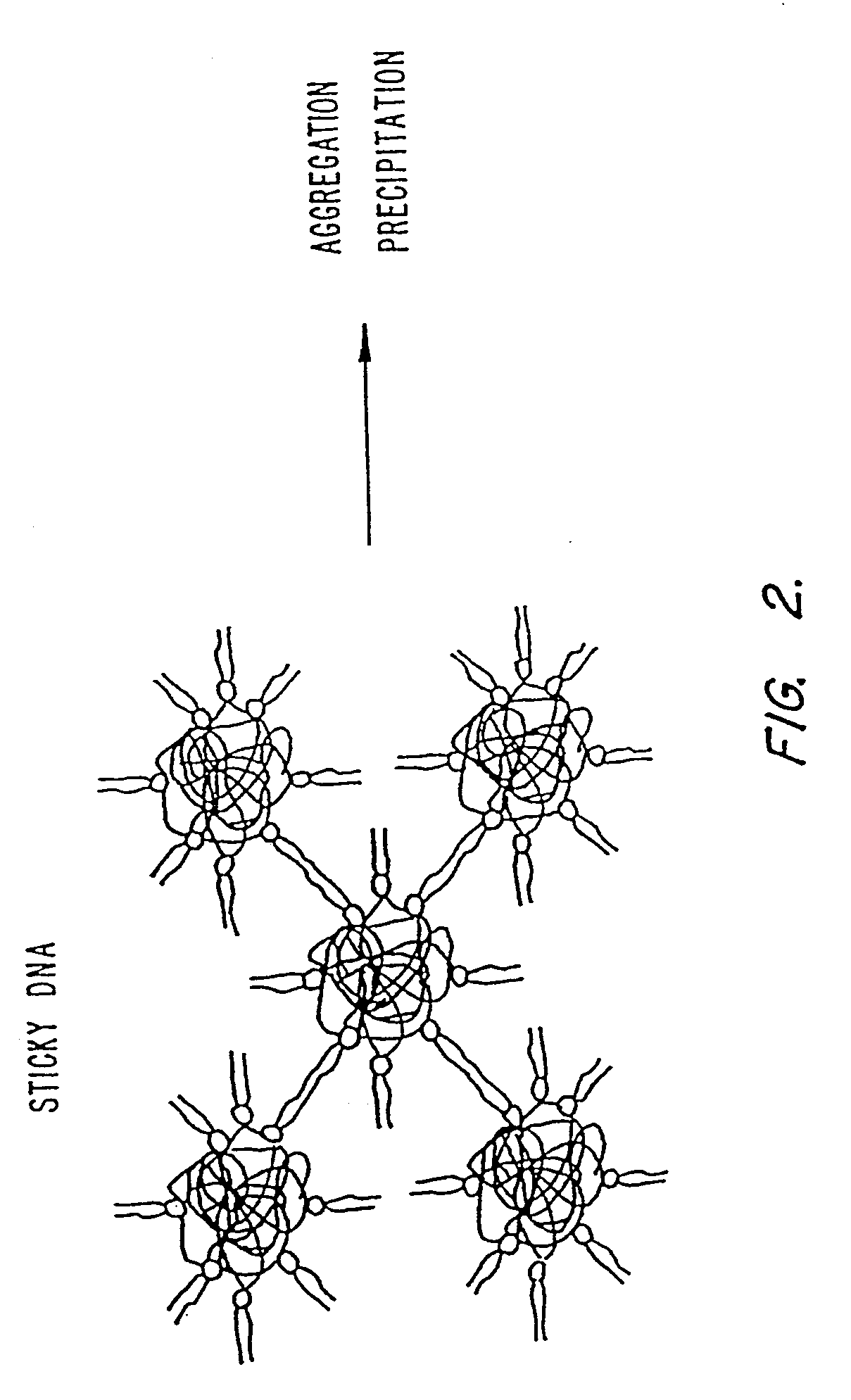
Nucleic Acid-Lipopolymer Compositions
InactiveUS20090042829A1Increase efficiency and dosing flexibilityEfficiently be lyophilizedSpecial deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCholesterolFiller Excipient
Compositions, methods, and applications that increase the efficiency of nucleic acid transfection are provided. In one aspect, a pharmaceutical composition may include at least about 0.5 mg / ml concentration of a nucleic acid condensed with a cationic lipopolymer suspended in an isotonic solution, where the cationic lipopolymer includes a cationic polymer backbone having cholesterol and polyethylene glycol covalently attached thereto, and wherein the molar ratio of cholesterol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10, and the molar ratio of polyethylene glycol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10. The composition further may include a filler excipient.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
ActiveUS7404969B2Reduce deliveryAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationMolecular composition
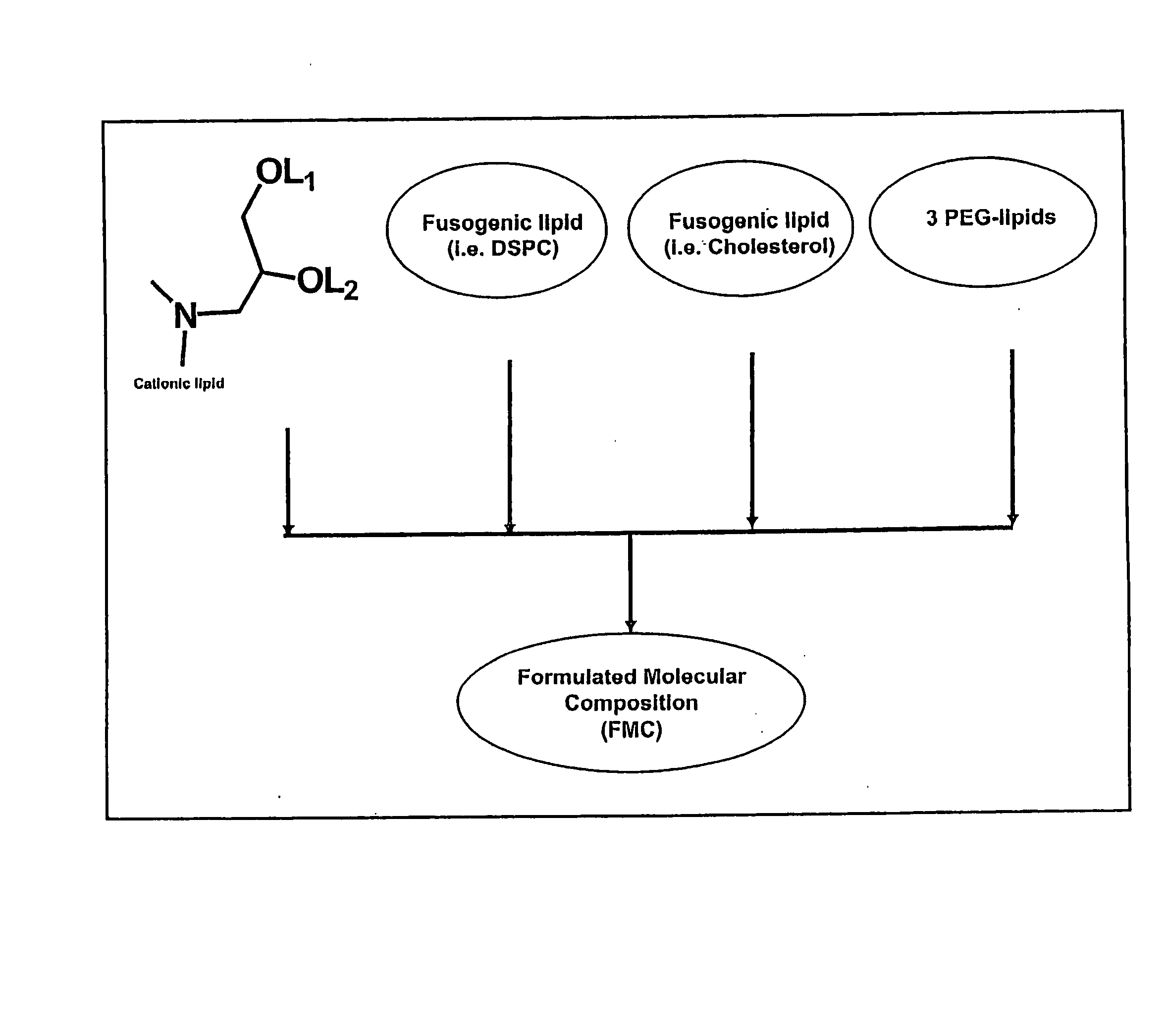
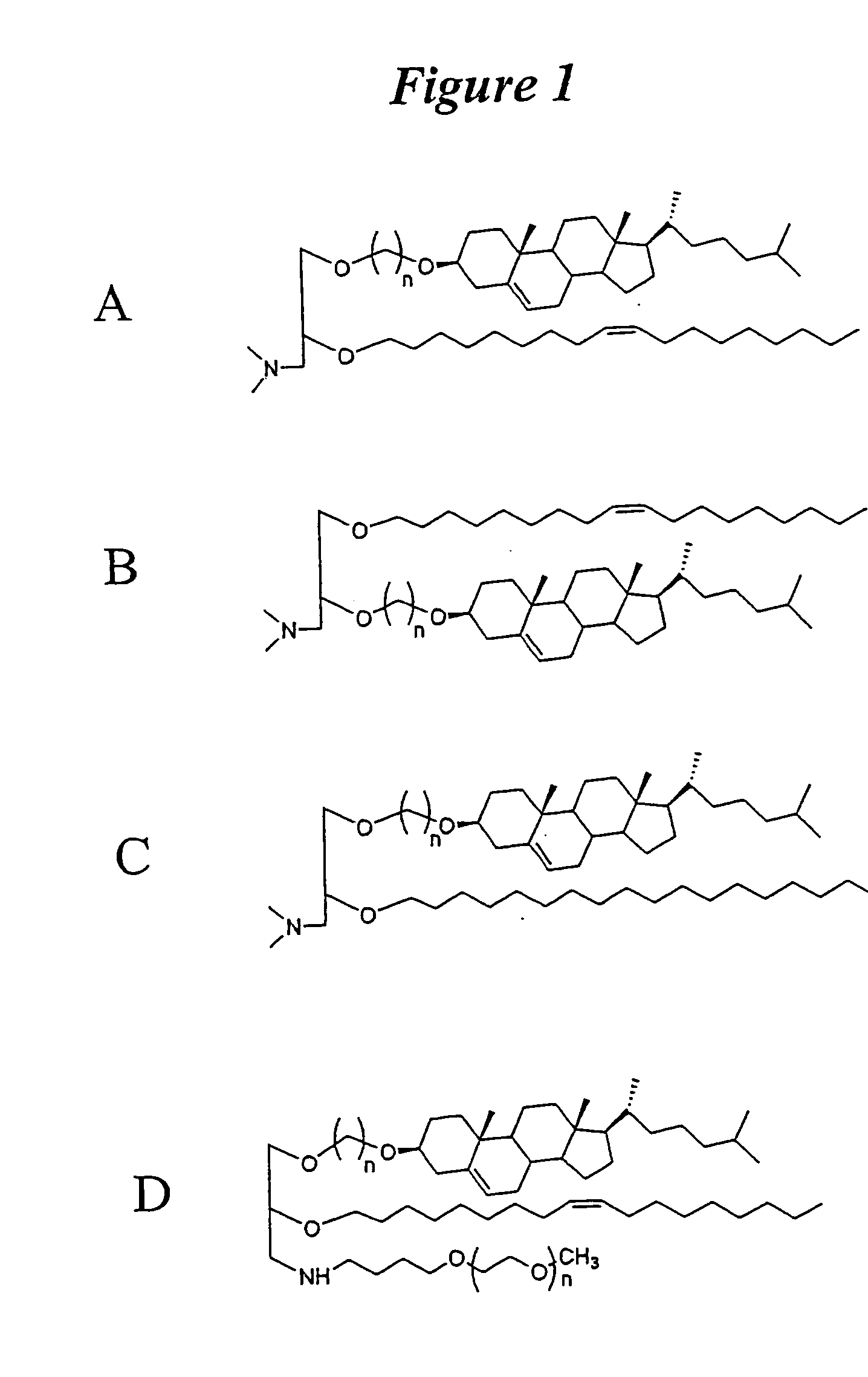
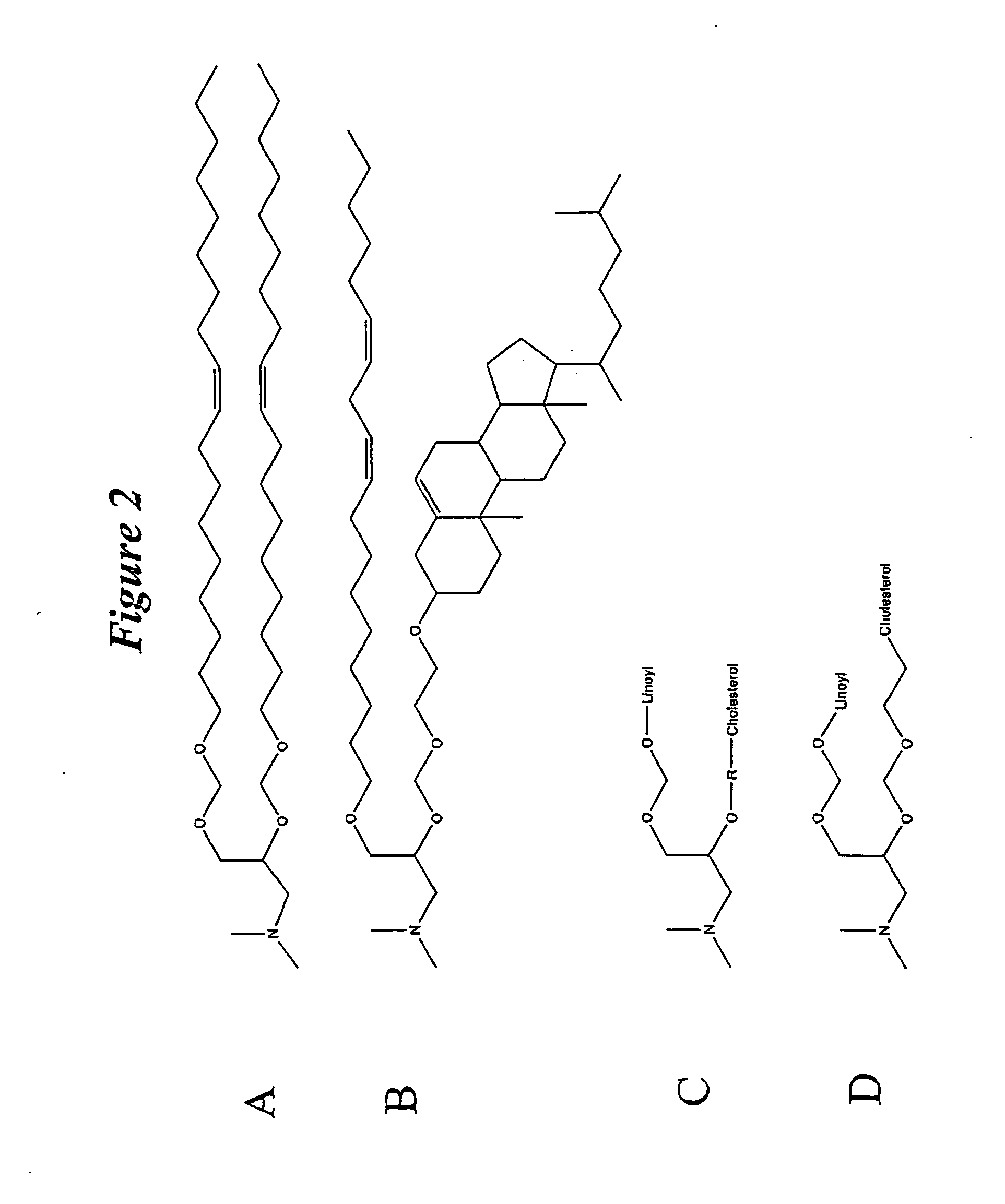
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver short interfering nucleic acid (siNA). The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
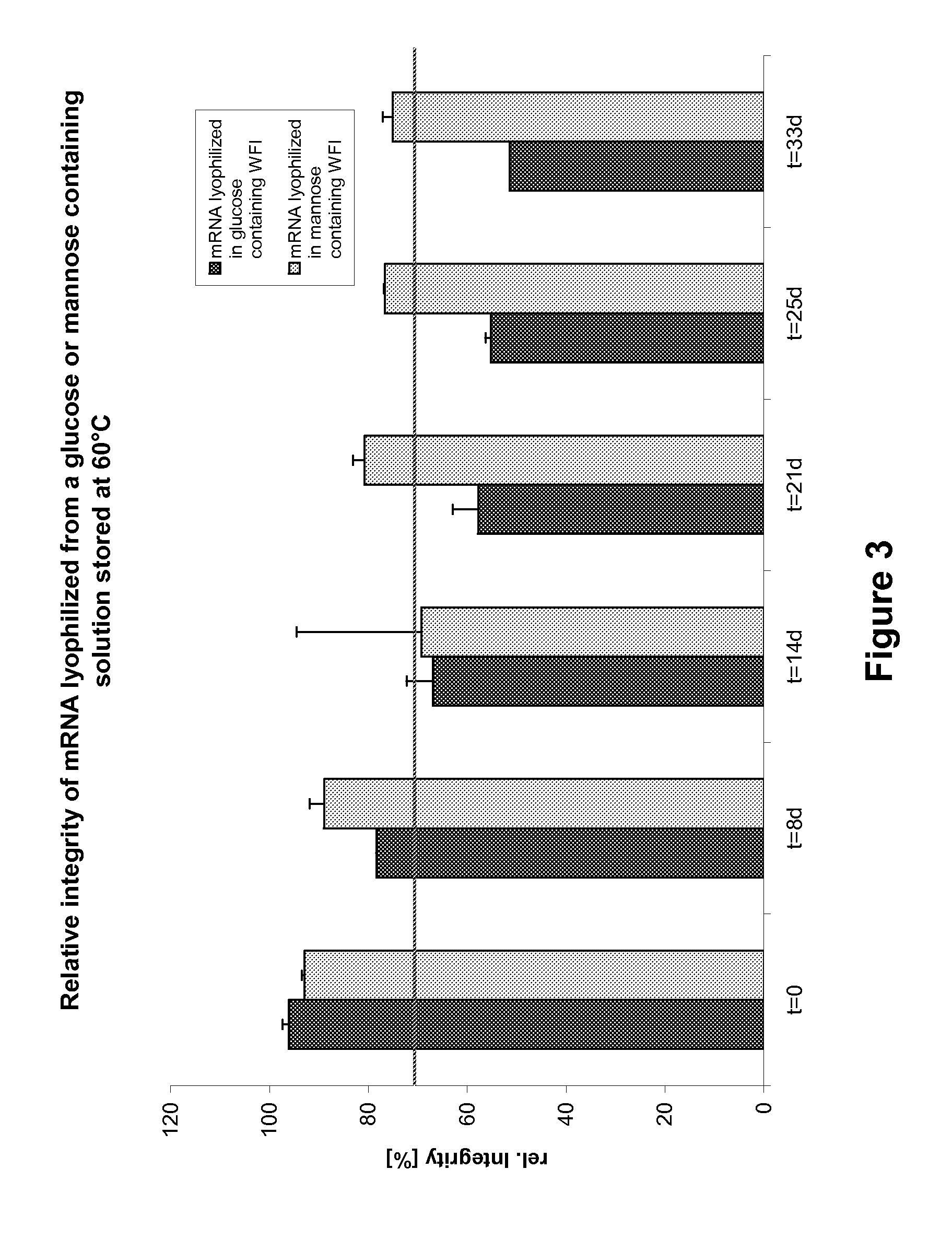
Mannose-containing solution for lyophilization, transfection and/or injection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20120258046A1High transfection efficiencyEnhance protein expressionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoTransfection
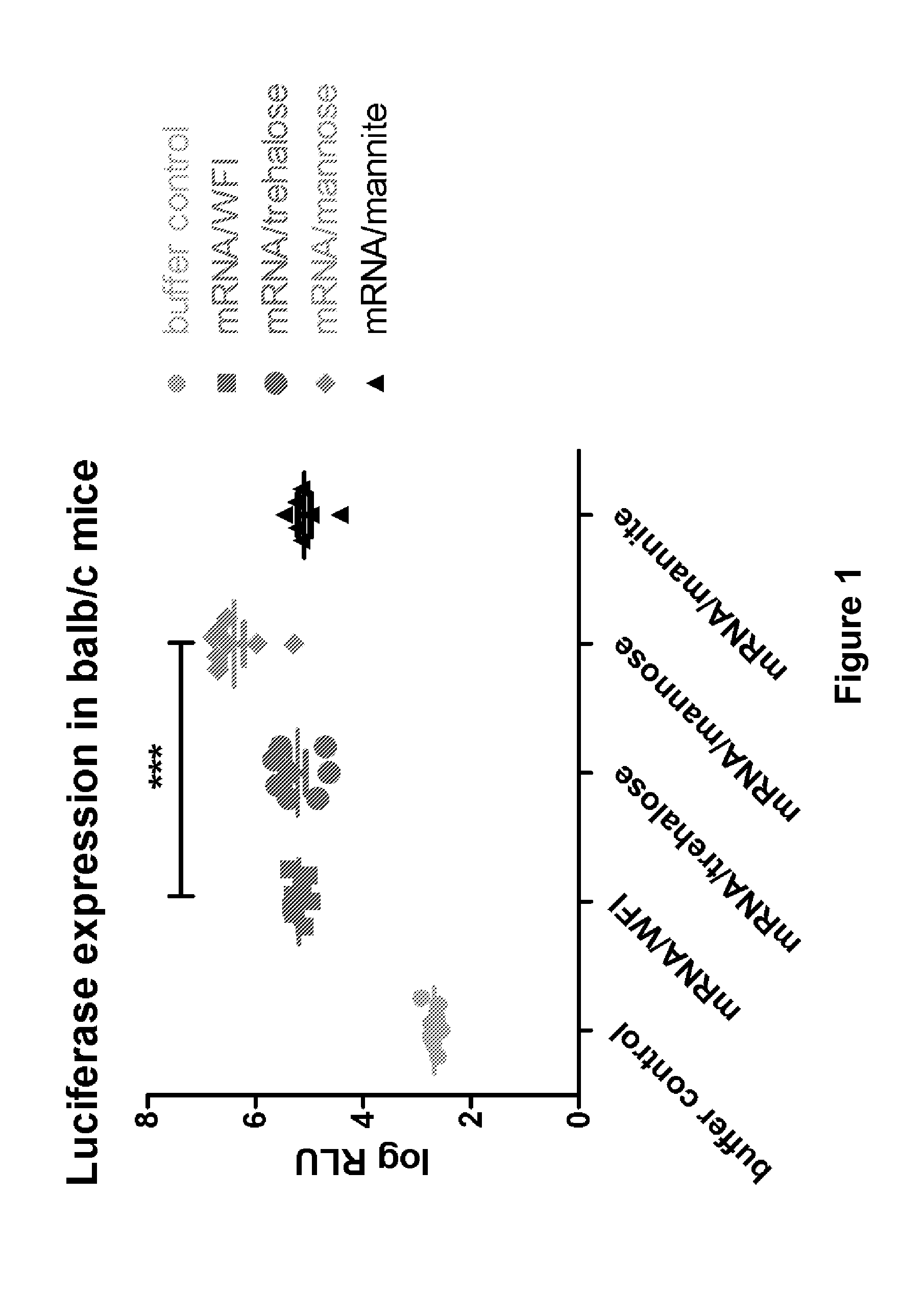
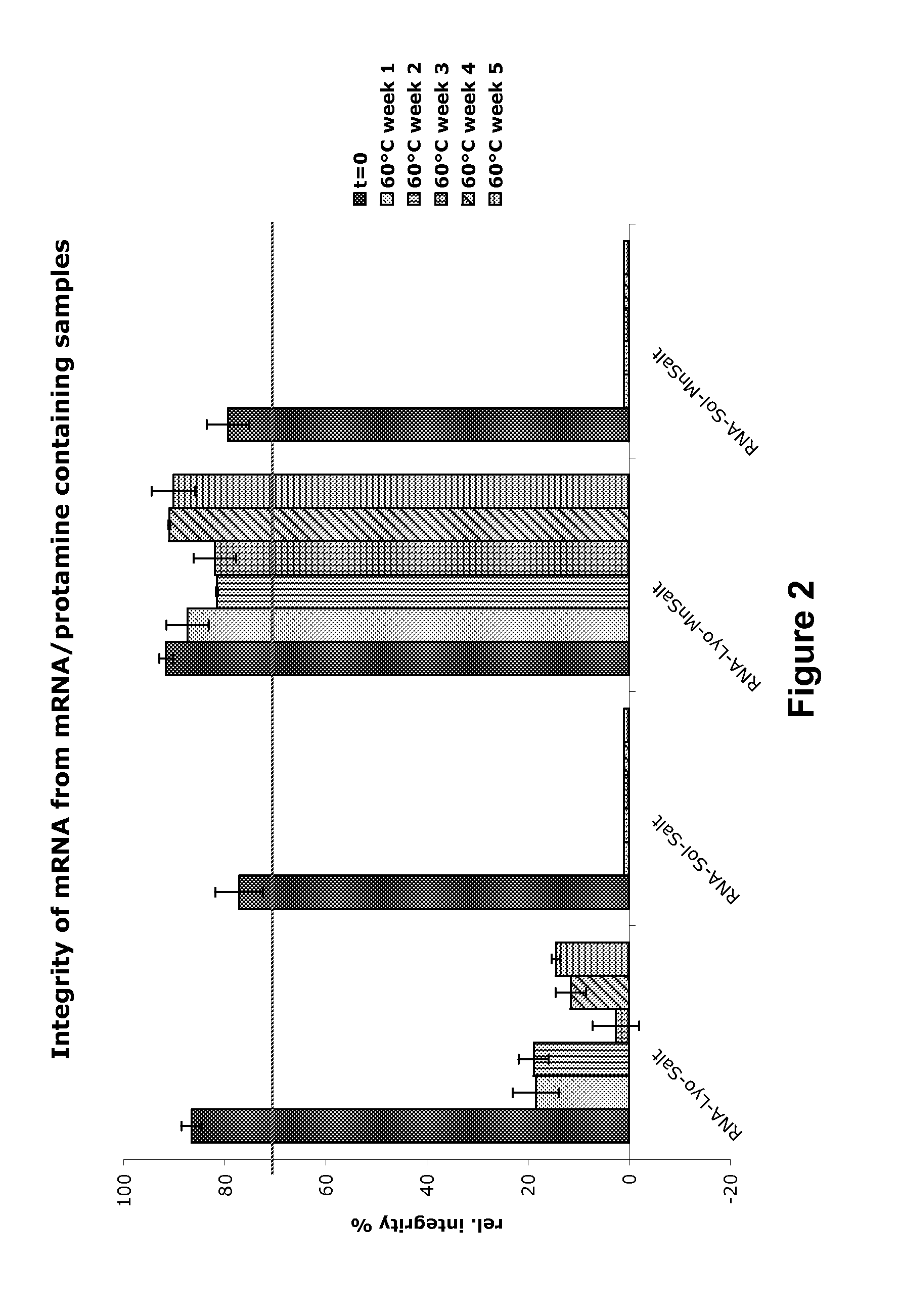
The present invention is directed to (the use of) a solution containing at least one nucleic acid (sequence) and free mannose for lyophilization, transfection and / or injection, particularly of RNA and mRNA. The inventive solution exhibits a positive effect on stabilization of the nucleic acid (sequence) during lyophilization and storage but also leads to a considerable increase of the transfection efficiency of a nucleic acid. It thus also increases in vivo expression of a protein encoded by such a nucleic acid upon increased transfection rate. The present invention is furthermore directed to a method of lyophilization using the mannose-containing solution, to pharmaceutical compositions, vaccines, kits, first and second medical uses applying such a mannose-containing solution and / or a nucleic acid (sequence) lyophilized or resuspended with such a solution.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
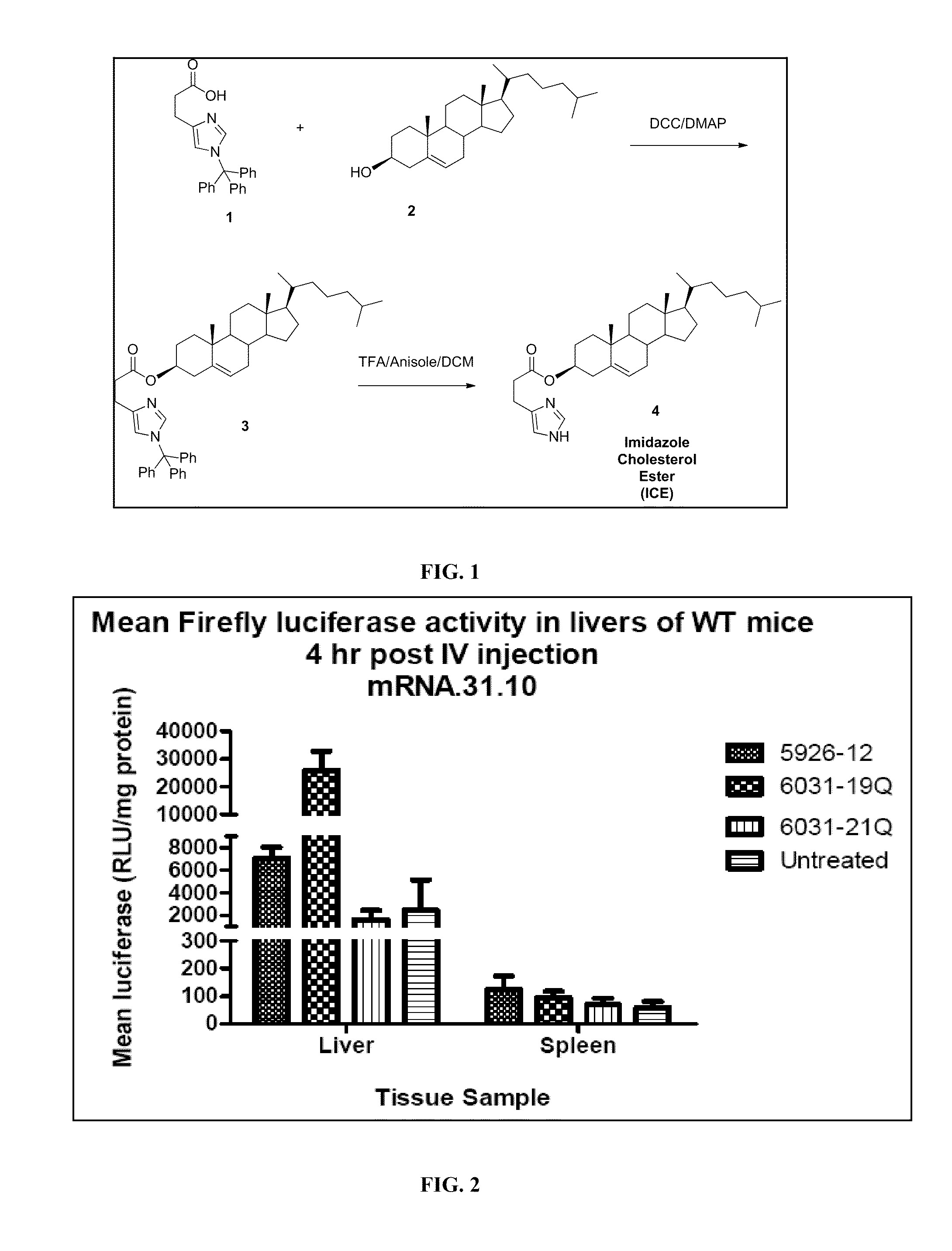
Delivery of mRNA for the augmentation of proteins and enzymes in human genetic diseases
InactiveUS20110244026A1Facilitating transfectionReduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseADAMTS Proteins
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods of modulating the expression of gene or the production of a protein by transfecting target cells with nucleic acids. The compositions disclosed herein demonstrate a high transfection efficacy and are capable of ameliorating diseases associated with protein or enzyme deficiencies.
Owner:TRANSLATE BIO INC
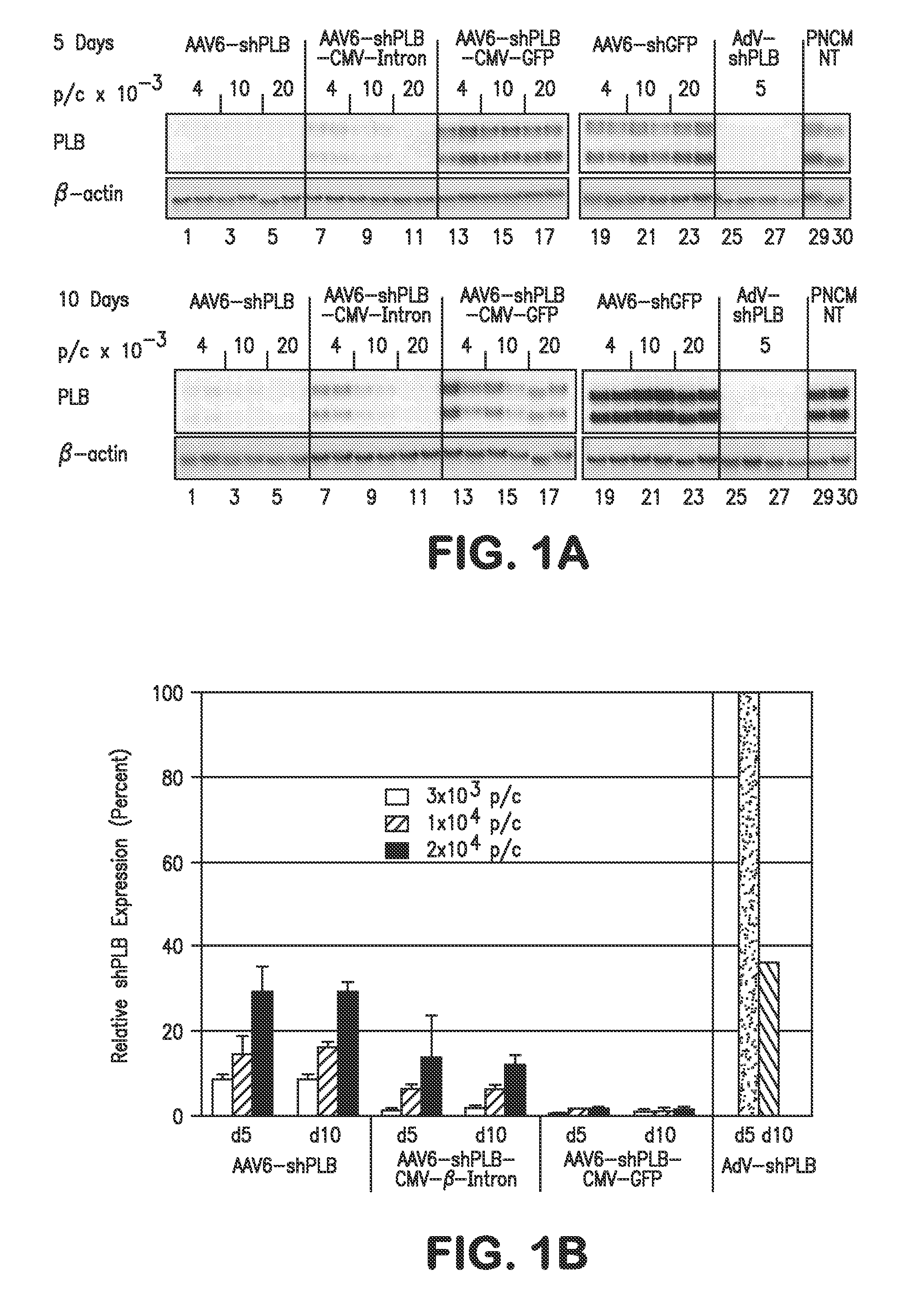
RNA interference for the treatment of heart failure
InactiveUS8404658B2Reduce expressionDecreasing ventricular arrhythmiasOrganic active ingredientsTissue culturePhospholambanTransfection
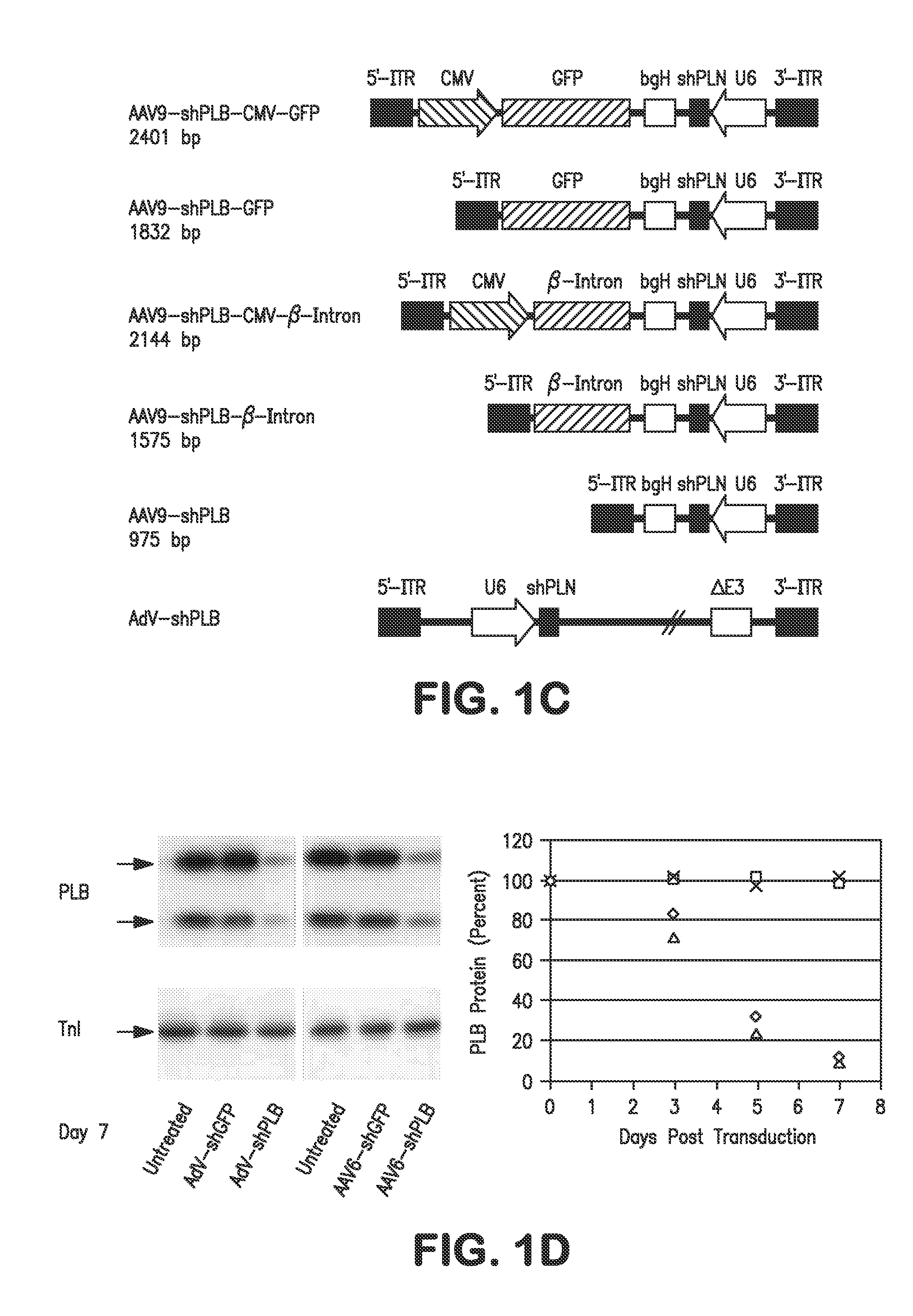
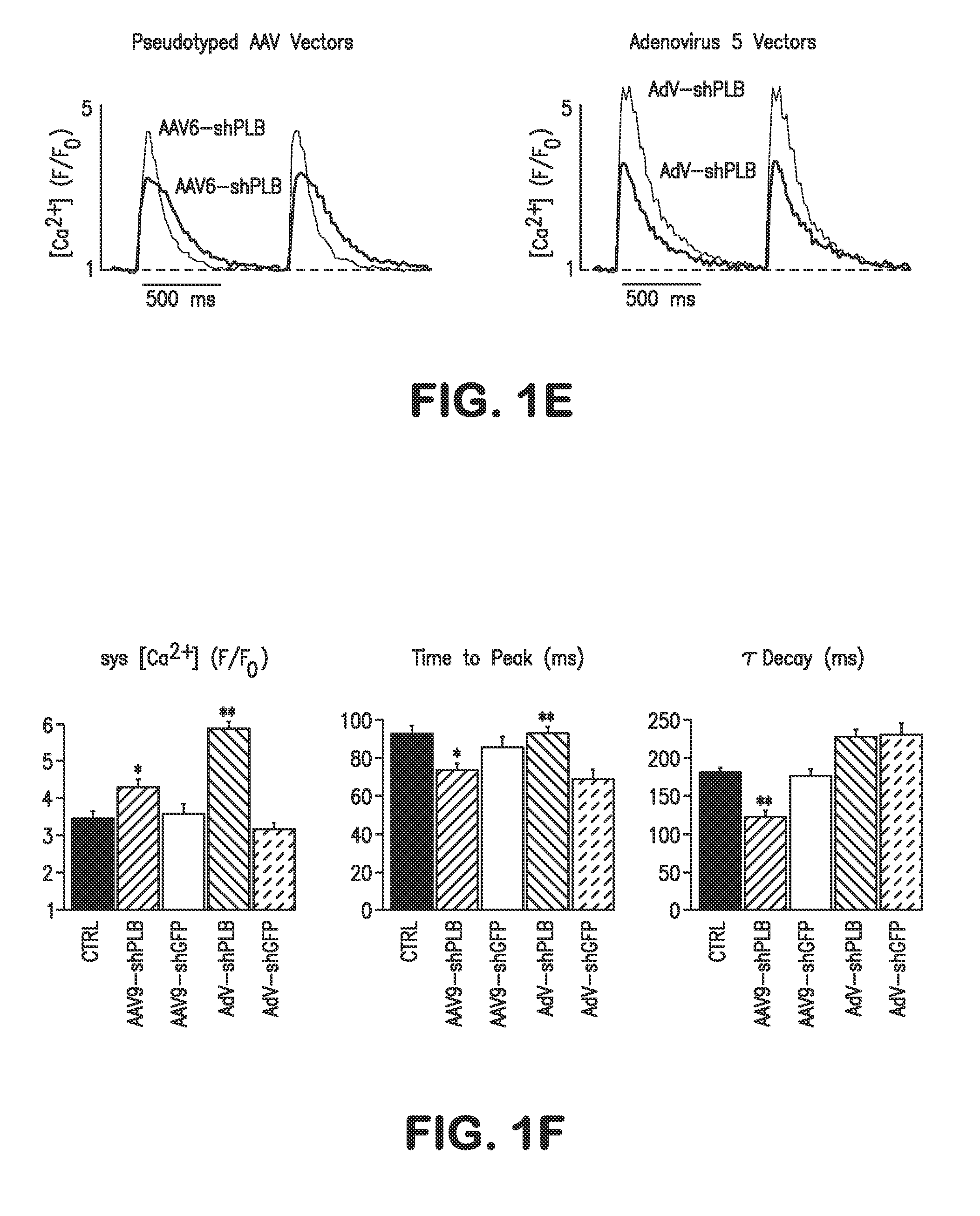
The present invention relates to targeted RNAi for the treatment of heart failure by modulating defective cardiac Ca2+ homeostasis via decreasing expression or activity of phospholamban (PLB) using adeno-associated virus (AAV) transfection of cardiomyocytes. Methods for decreasing ventricular arrhythmias, as well as methods for overall improvement of survival from heart failure in subjects are also disclosed. Further, the present invention provides methods which can be used to diagnose susceptibility to treatment by RNAi, and includes pharmaceutical compositions, kits and vectors including an RNAi sequence.
Owner:NANOCOR THERAPEUTICS +1
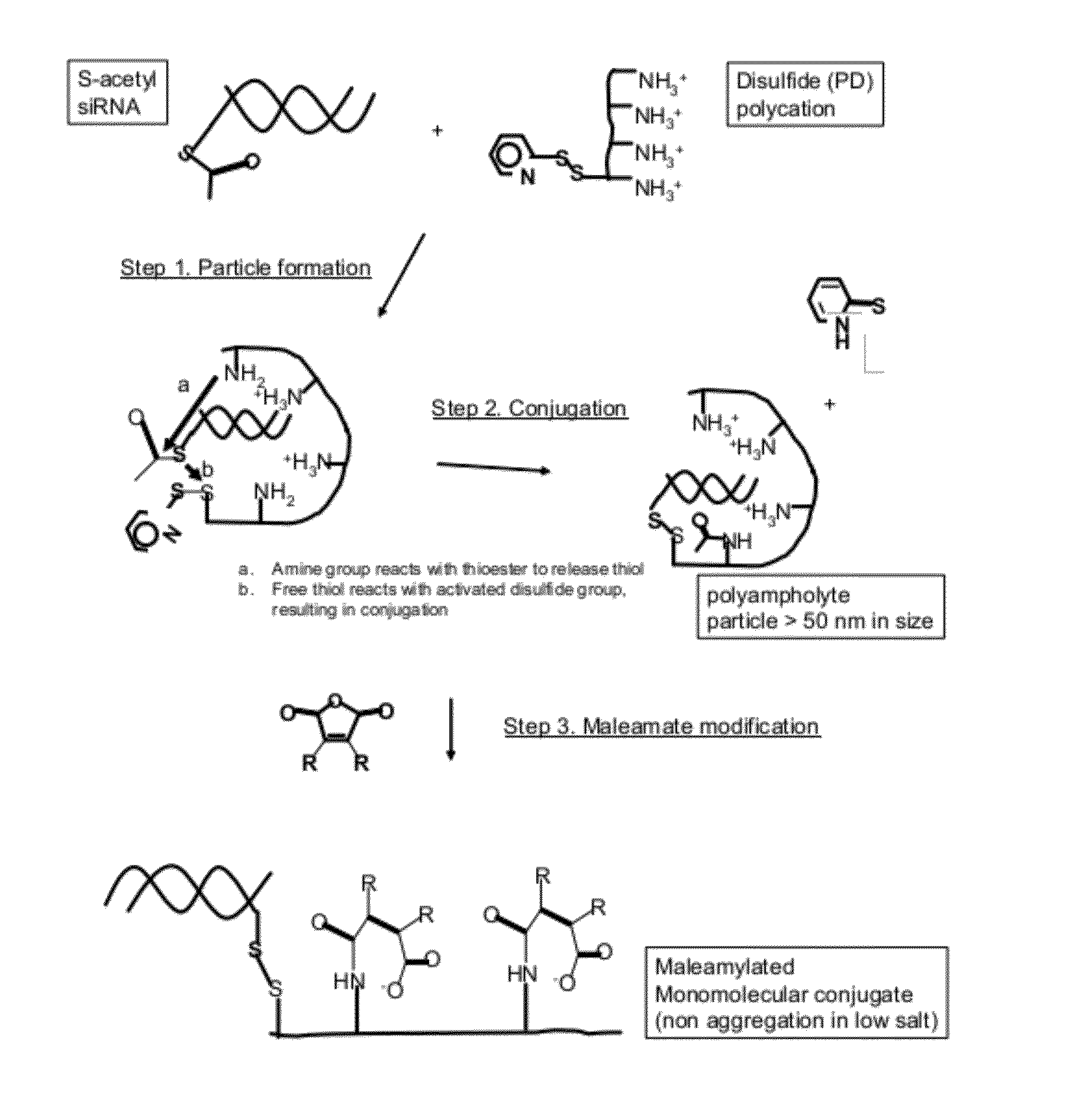
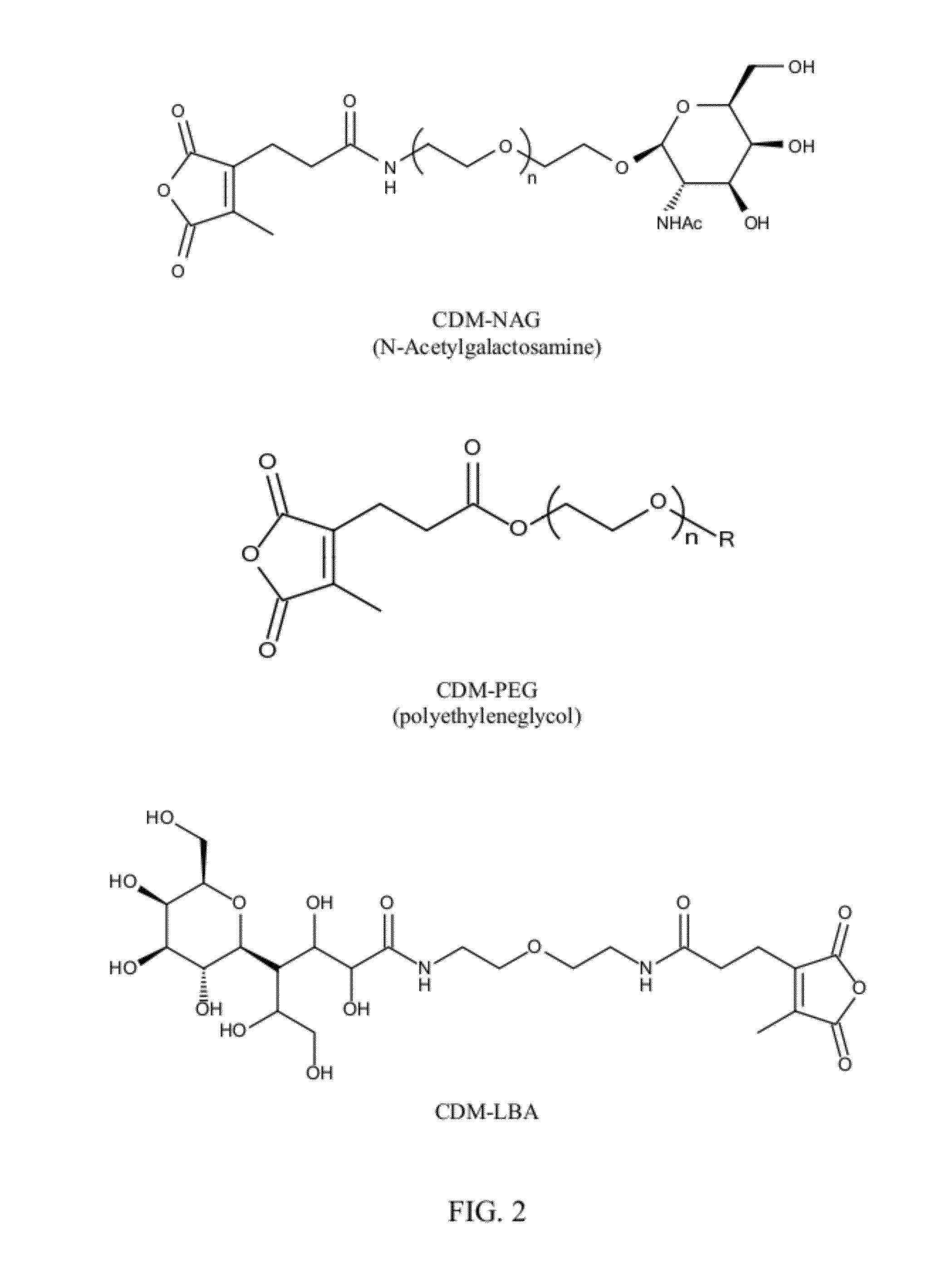
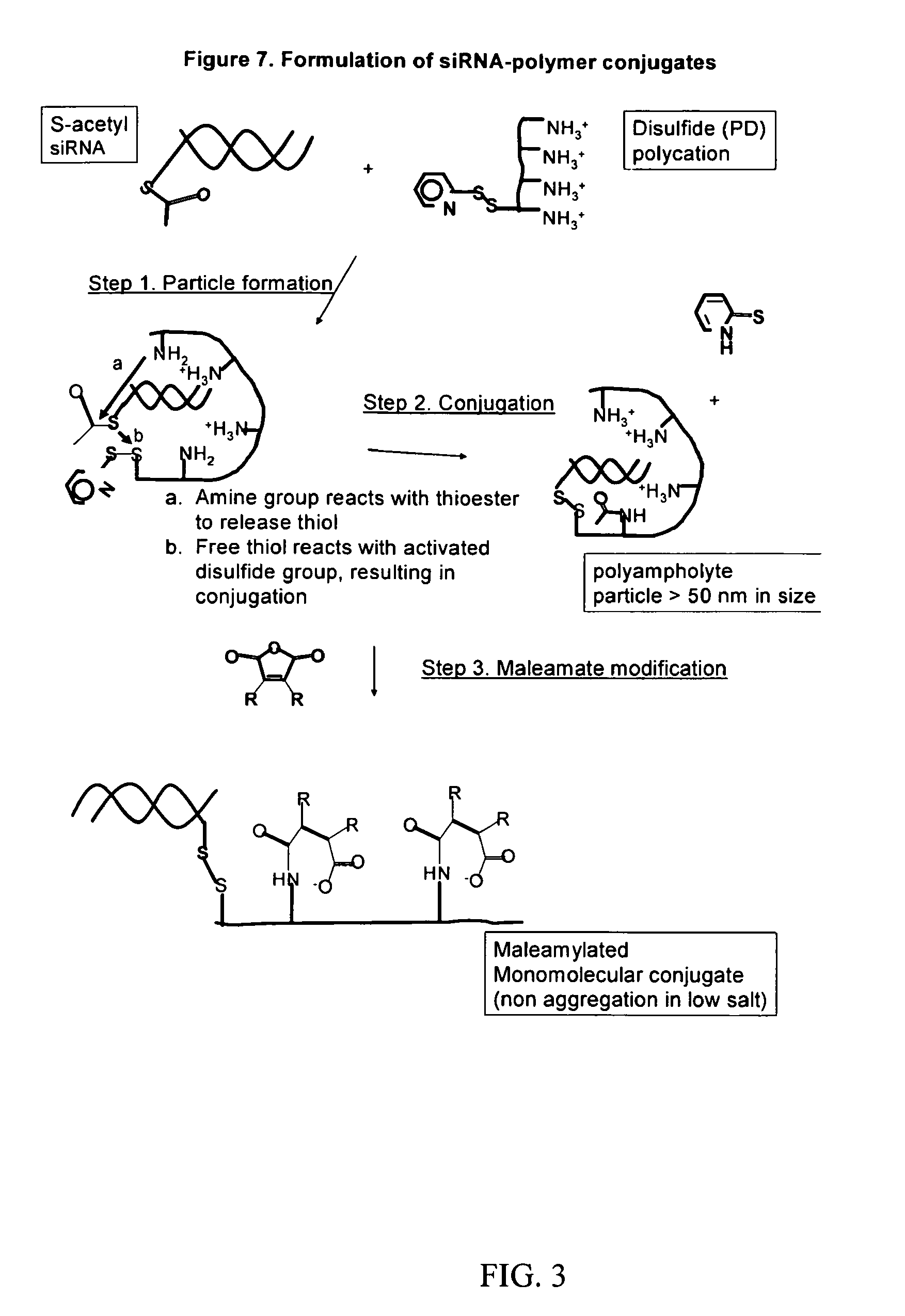
Polyconjugates for In Vivo Delivery of Polynucleotides
ActiveUS20080152661A1Reduce aggregationEnhances transfection activityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDelivery vehicleNucleotide
The present invention is directed to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for delivering polynucleotides or other cell-impermeable molecules to mammalian cells. Described are polyconjugates systems that incorporate targeting, anti-opsonization, anti-aggregation, and transfection activities into small biocompatible in vivo delivery vehicles. The use of multiple reversible linkages connecting component parts provides for physiologically responsive activity modulation.
Owner:ARROWHEAD MADISON
Delivery of Nanoparticles and/or Agents to Cells
InactiveUS20080213377A1Extended circulation timeReduce degradationPowder deliverySugar derivativesDiagnostic agentNanoparticle
The present invention provides systems, methods, and compositions for targeted delivery of nanoparticles and / or agents to tissues, cells, and / or subcellular locales. In general, compositions comprise a nanoparticle (e.g. quantum dot, polymeric particle, etc.), at least one modulating entity (such as a targeting moiety, transfection reagent, protective entity, etc.), and at least one agent to be delivered (e.g. therapeutic, prophylactic, and / or diagnostic agent). The present invention provides methods of making and using nanoparticle entities in accordance with the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
ActiveUS20080020058A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryLipid formationCholesterol
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), short hairpin RNA (shRNA), and RNAi inhibitor molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
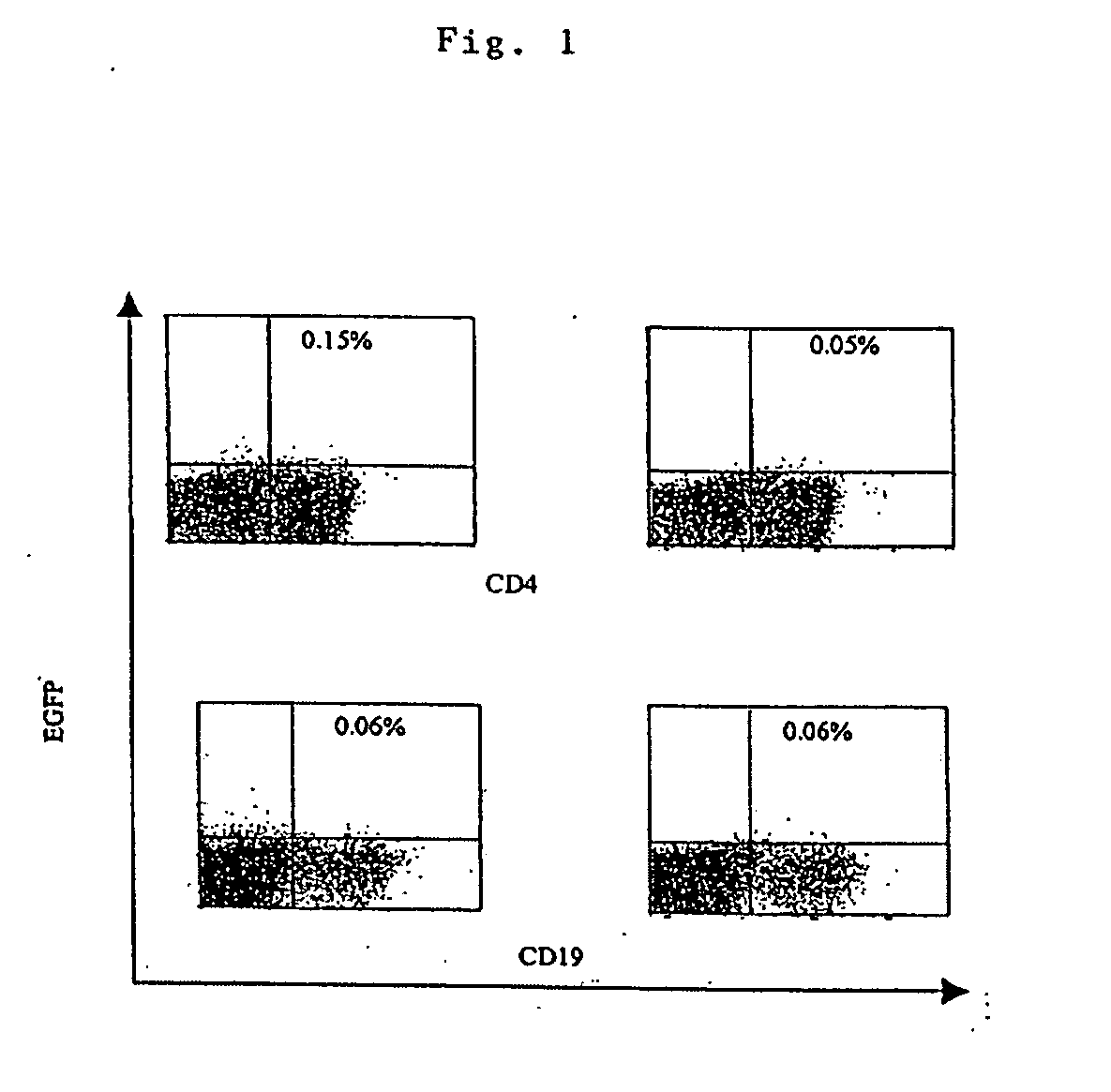
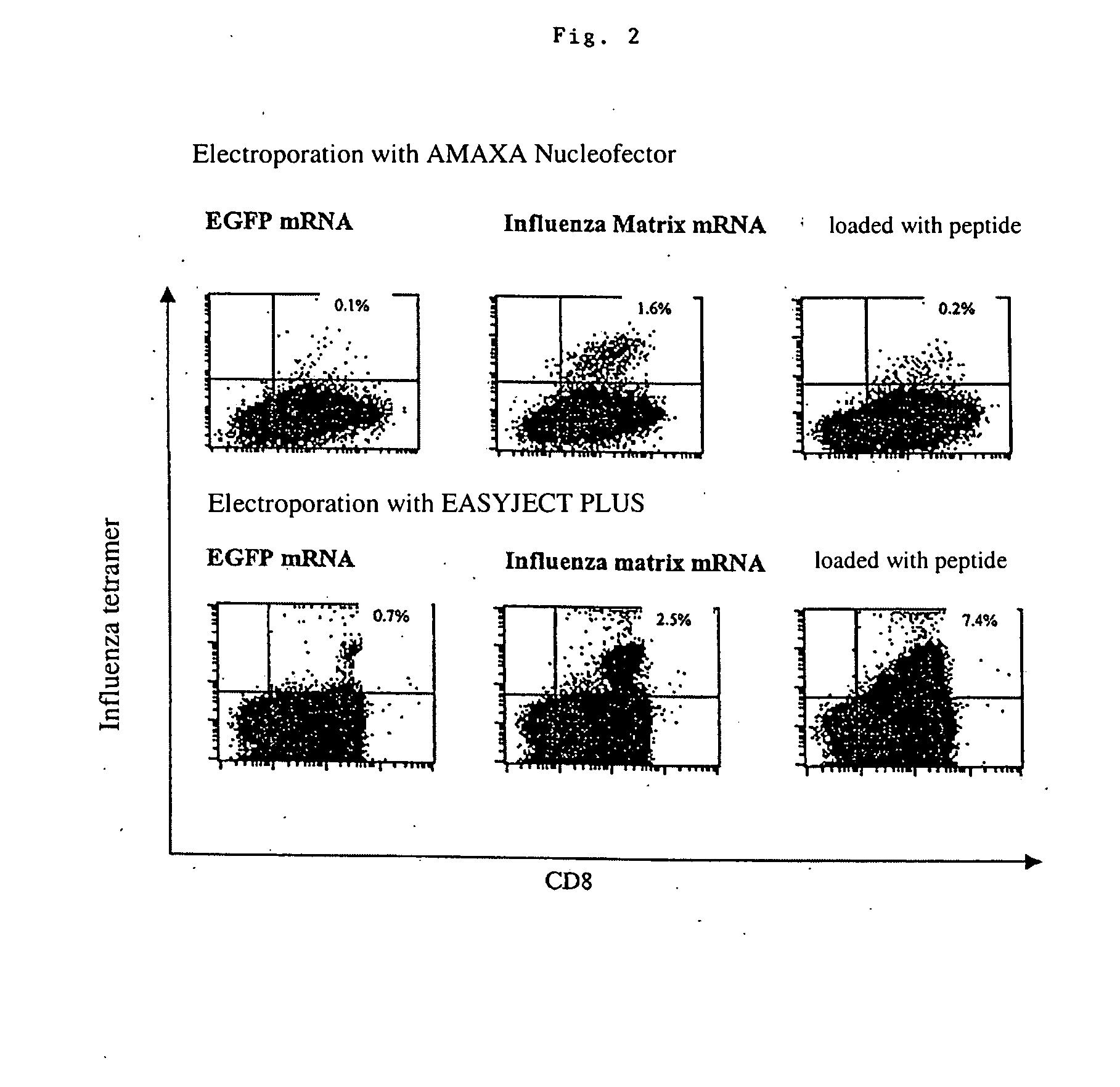
Transfection of blood cells with mRNA for immune stimulation and gene therapy
InactiveUS20060188490A1Improve stabilityIncrease transfectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideAntigenCancer prevention
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing blood cells or haemopoietic cells, e.g. red blood cells (erythrocytes), granulocytes, mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and / or blood platelets, in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient and / or vehicle, wherein the cells are transfected with at least one mRNA comprising at least one region coding for at least one antigen. The invention further discloses a method of preparing the aforesaid pharmaceutical composition and the use of blood cells transfected in this way for the preparation of drugs or pharmaceutical compositions for immune stimulation against the antigens encoded by the mRNA. The subjects according to the invention are used especially for the therapy and / or prophylaxis of carcinoses or infectious diseases and can also be employed in gene therapy.
Owner:CUREVAC AG
Liver specific delivery of messenger RNA
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods of modulating the expression of gene or the production of a protein by transfecting target cells with nucleic acids. The compositions disclosed herein demonstrate a high transfection efficacy and are capable of ameliorating diseases associated with protein or enzyme deficiencies.
Owner:TRANSLATE BIO INC
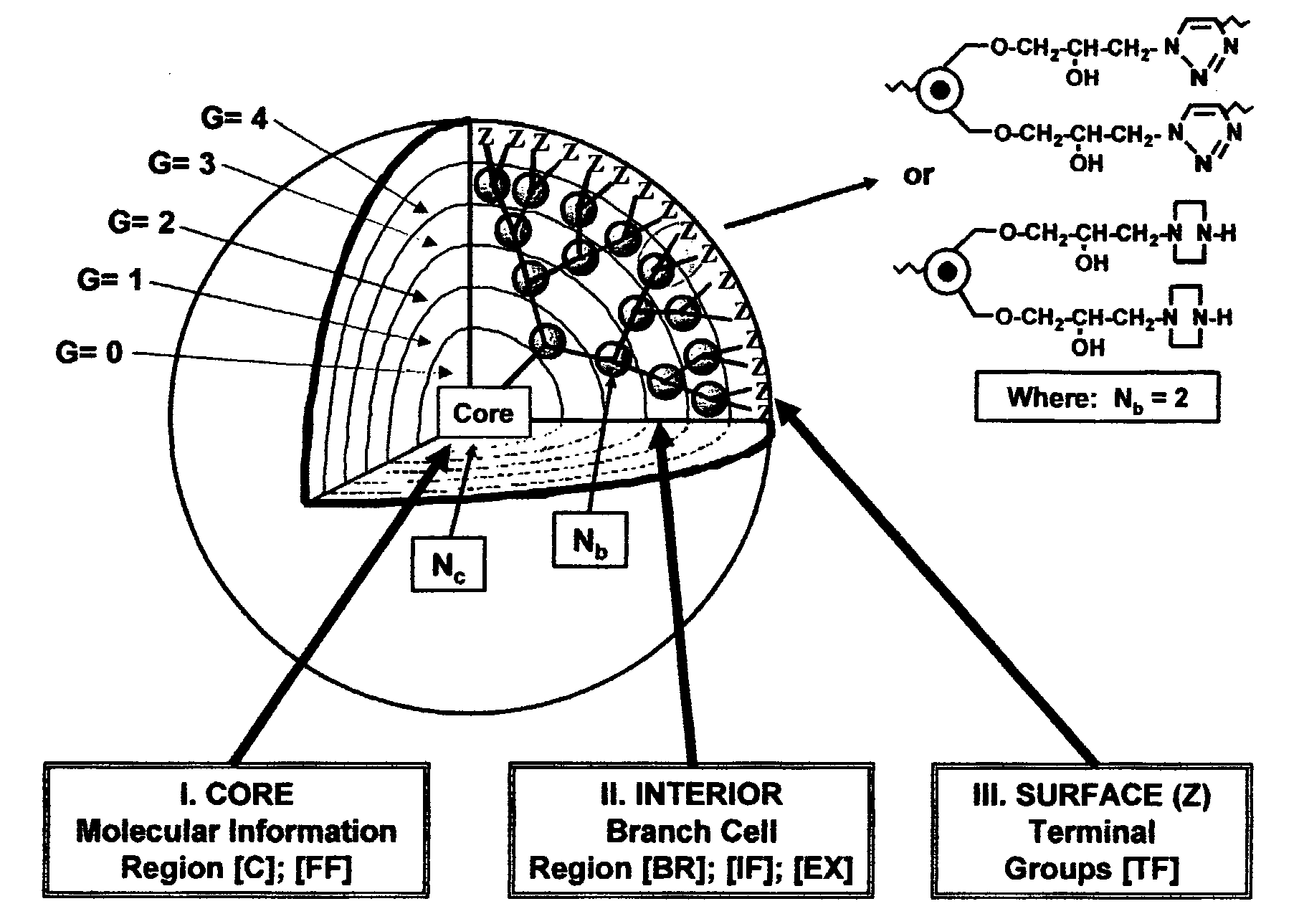
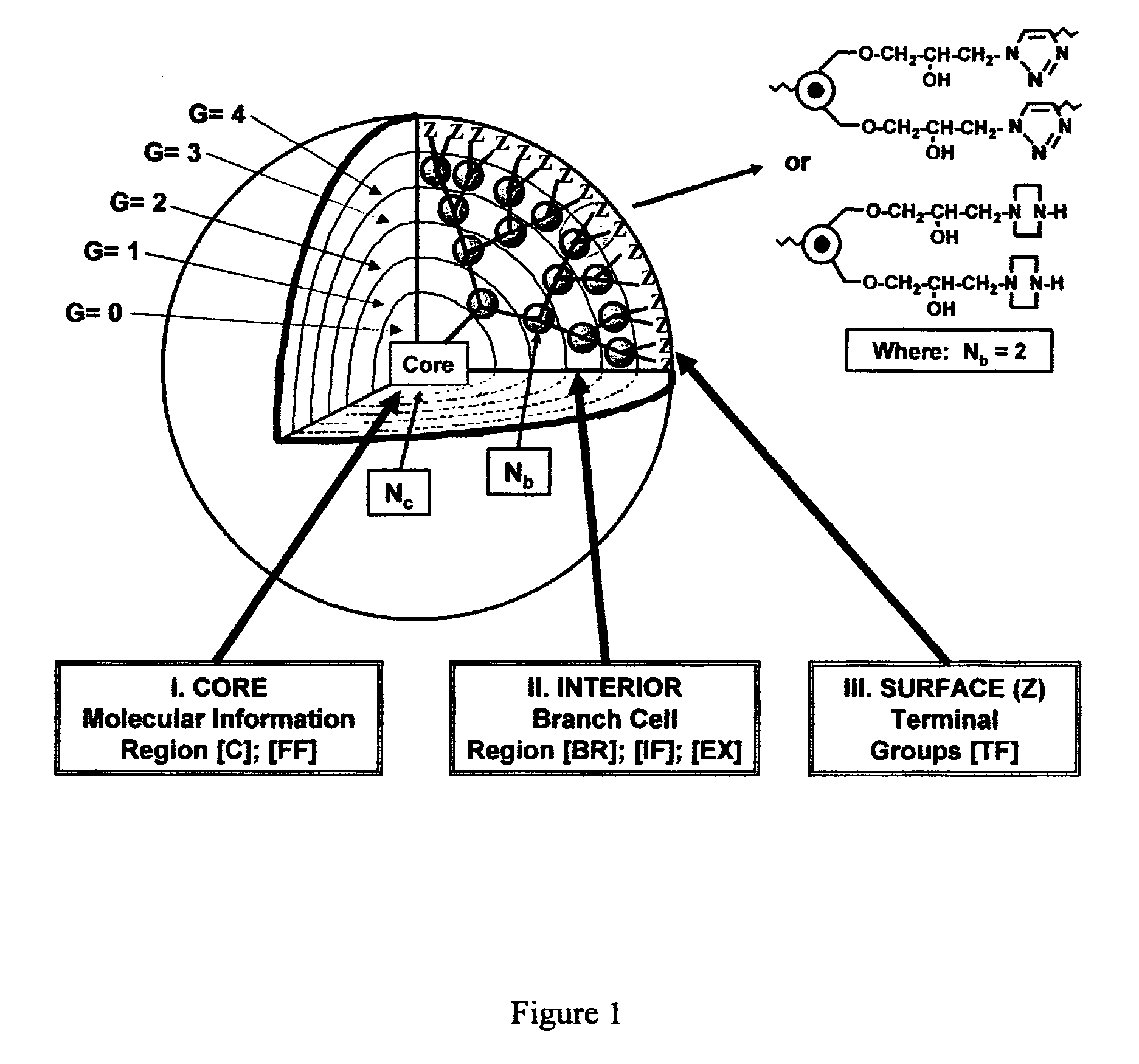
Dendritic Polymers With Enhanced Amplification and Interior Functionality
ActiveUS20070298006A1Reduced responseSizePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkScavenger
Dendritic polymers with enhanced amplification and interior functionality are disclosed. These dendritic polymers are made by use of fast, reactive ring-opening chemistry (or other fast reactions) combined with the use of branch cell reagents in a controlled way to rapidly and precisely build dendritic structures, generation by generation, with cleaner chemistry, often single products, lower excesses of reagents, lower levels of dilution, higher capacity method, more easily scaled to commercial dimensions, new ranges of materials, and lower cost. The dendritic compositions prepared have novel internal functionality, greater stability (e.g., thermal stability and less or no reverse Michael's reaction), and reach encapsulation surface densities at lower generations. Unexpectedly, these reactions of polyfunctional branch cell reagents with polyfunctional cores do not create cross-linked materials. Such dendritic polymers are useful as demulsifiers for oil / water emulsions, wet strength agents in the manufacture of paper, proton scavengers, polymers, nanoscale monomers, calibration standards for electron microscopy, making size selective membranes, and agents for modifying viscosity in aqueous formulations such as paint. When these dendritic polymers have a carried material associated with their surface and / or interior, then these dendritic polymers have additional properties for carrying materials due to the unique characteristics of the dendritic polymer, such as for drug delivery, transfection, and diagnostics.
Owner:DENDRITIC NANO TECH INC
Isolation of bone marrow fraction rich in connective tissue growth components and the use thereof to promote connective tissue formation
InactiveUS20050130301A1Peptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderConnective tissue fiberTissue defect
A bone marrow isolate rich in one or more connective tissue growth components, methods of forming the isolate, and methods of promoting connective tissue growth using the isolate are described. A biological sample comprising bone marrow is centrifuged to separate the sample into fractions including a fraction rich in connective tissue growth components. The fraction rich in connective tissue growth components is then isolated from the separated sample. The isolate can be used directly or combined with a carrier and implanted into a patient at a tissue (e.g., bone) defect site. The biological sample can comprise bone marrow and whole blood. The isolate can be modified (e.g., by transfection with a nucleic acid encoding an osteoinductive polypeptide operably linked to a promoter) prior to application to the tissue defect site. The isolate can be made and applied to the tissue defect site in a single procedure (i.e., intraoperatively).
Owner:MCKAY WILLIAM F +1
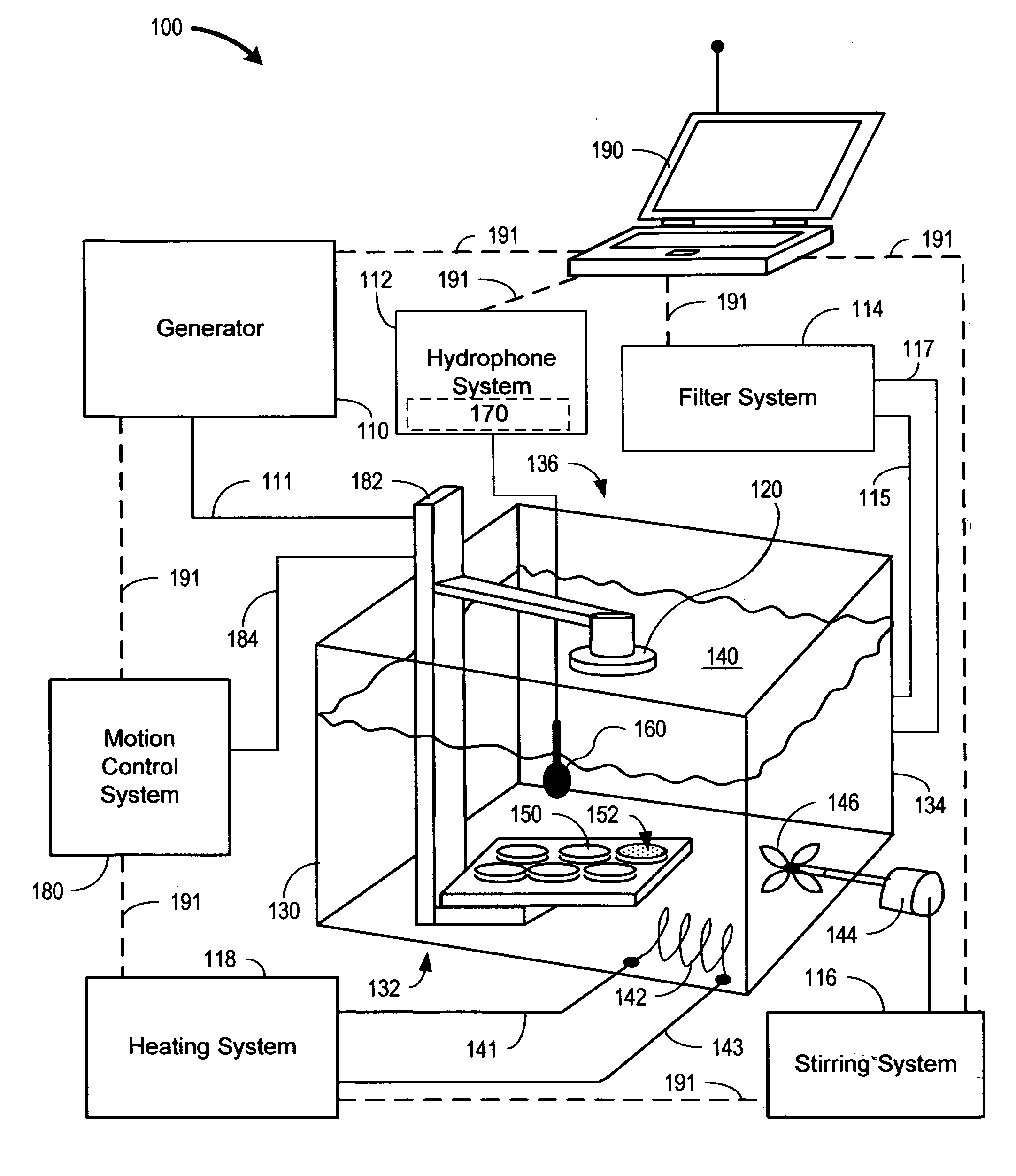
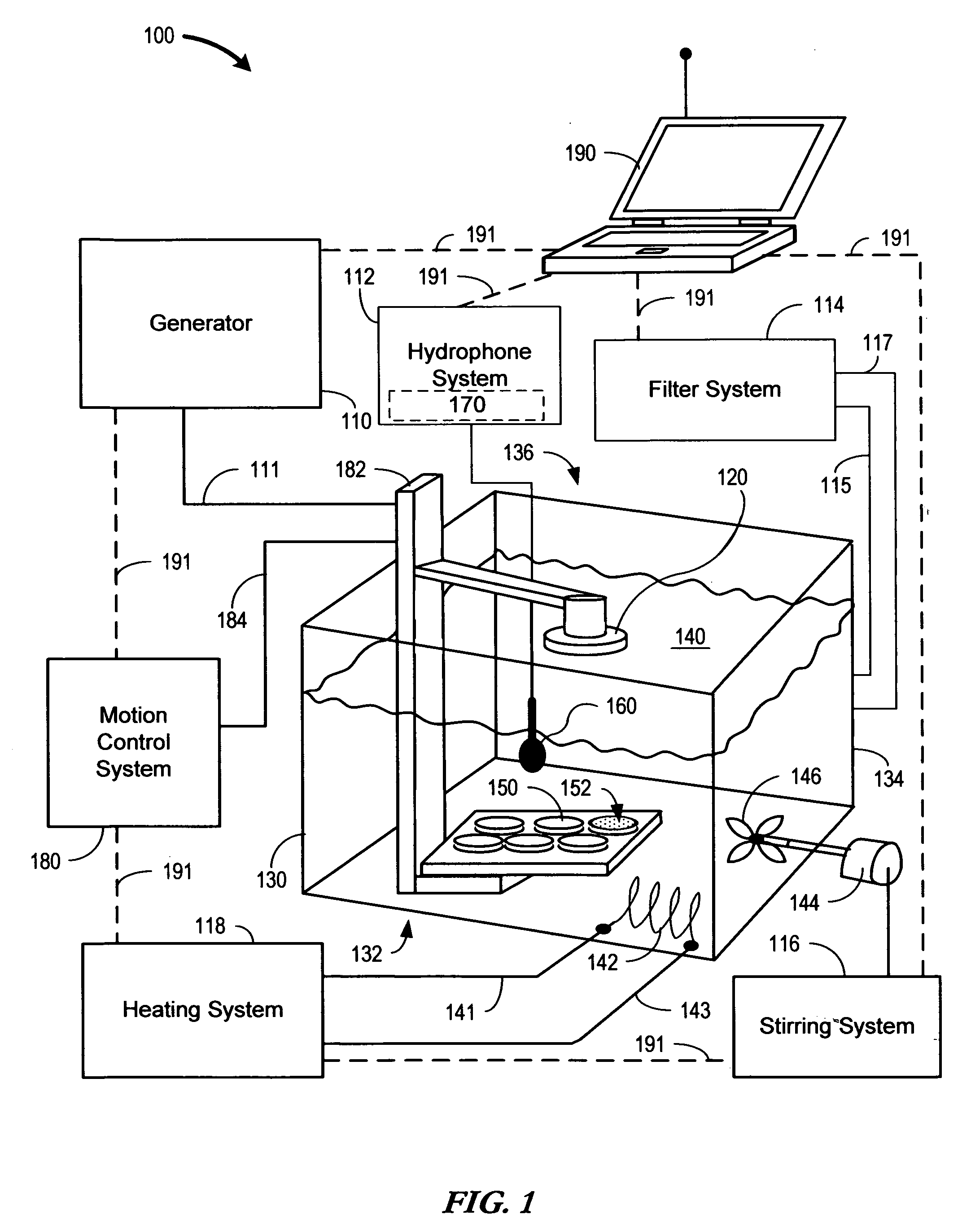
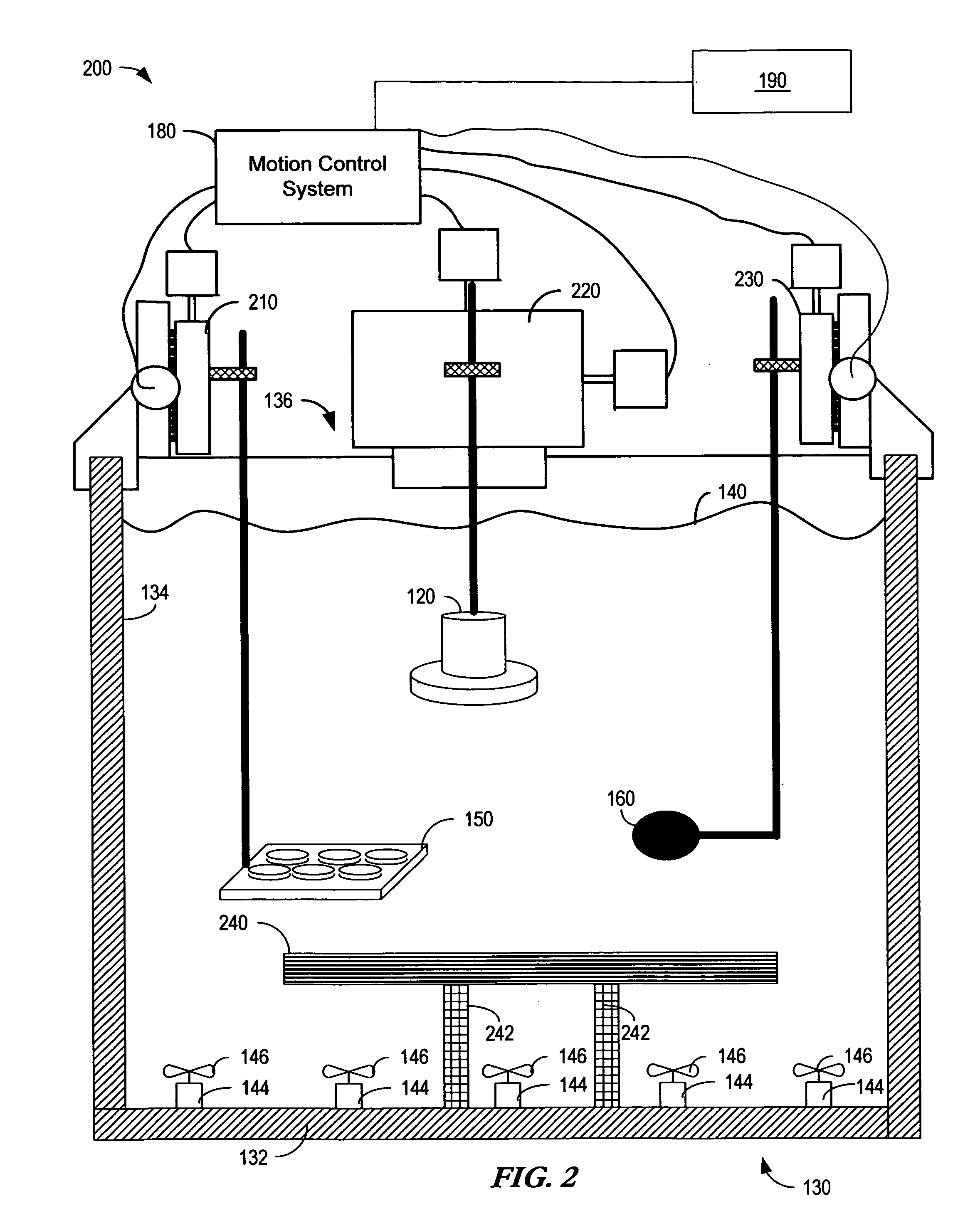
Sonoporation systems and methods
InactiveUS20100009424A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityHydrophone
The present invention is directed to devices and methods that apply ultrasonic energy for the purpose of inducing transfection and cell transformation. A sonoporation system in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes an ultrasonic electrical energy generator connected to an ultrasonic transducer producing stress waves. The ultrasonic transducer is connected to a fluid containment tank configured to accept at least a portion of the ultrasonic transducer whereby the ultrasonic stress waves may be delivered into the fluid medium. A cell holder is configured to hold one or more cells desirable for transfection. A hydrophone may be electrically connected to an acoustic stress wave intensity detection circuit. A motion control system having an arm configured to receive one or both of the cell holder and the hydrophone is configured to provide motion of one or both of the cell holder and the hydrophone within the fluid medium.
Owner:ARTISON
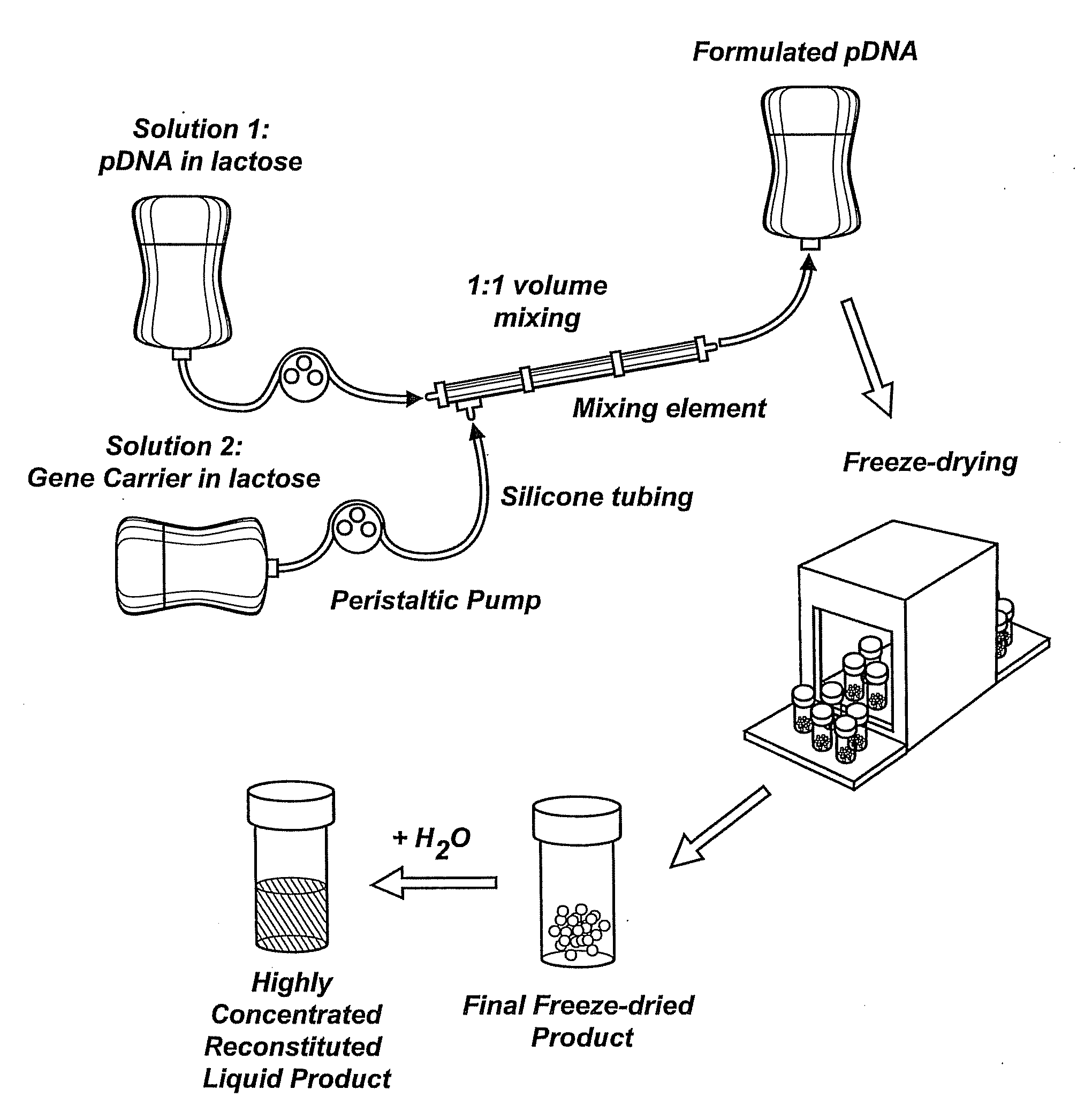
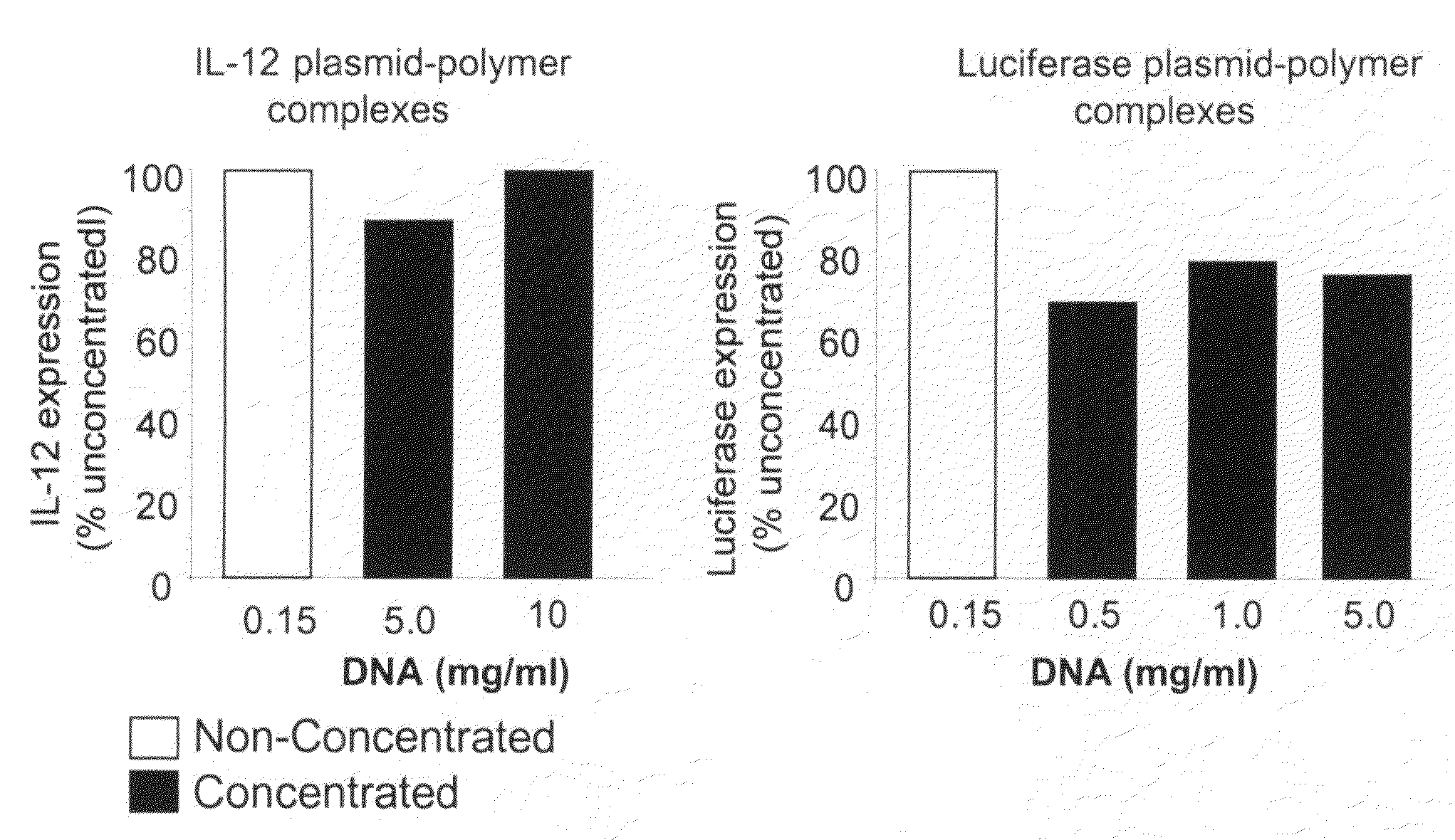
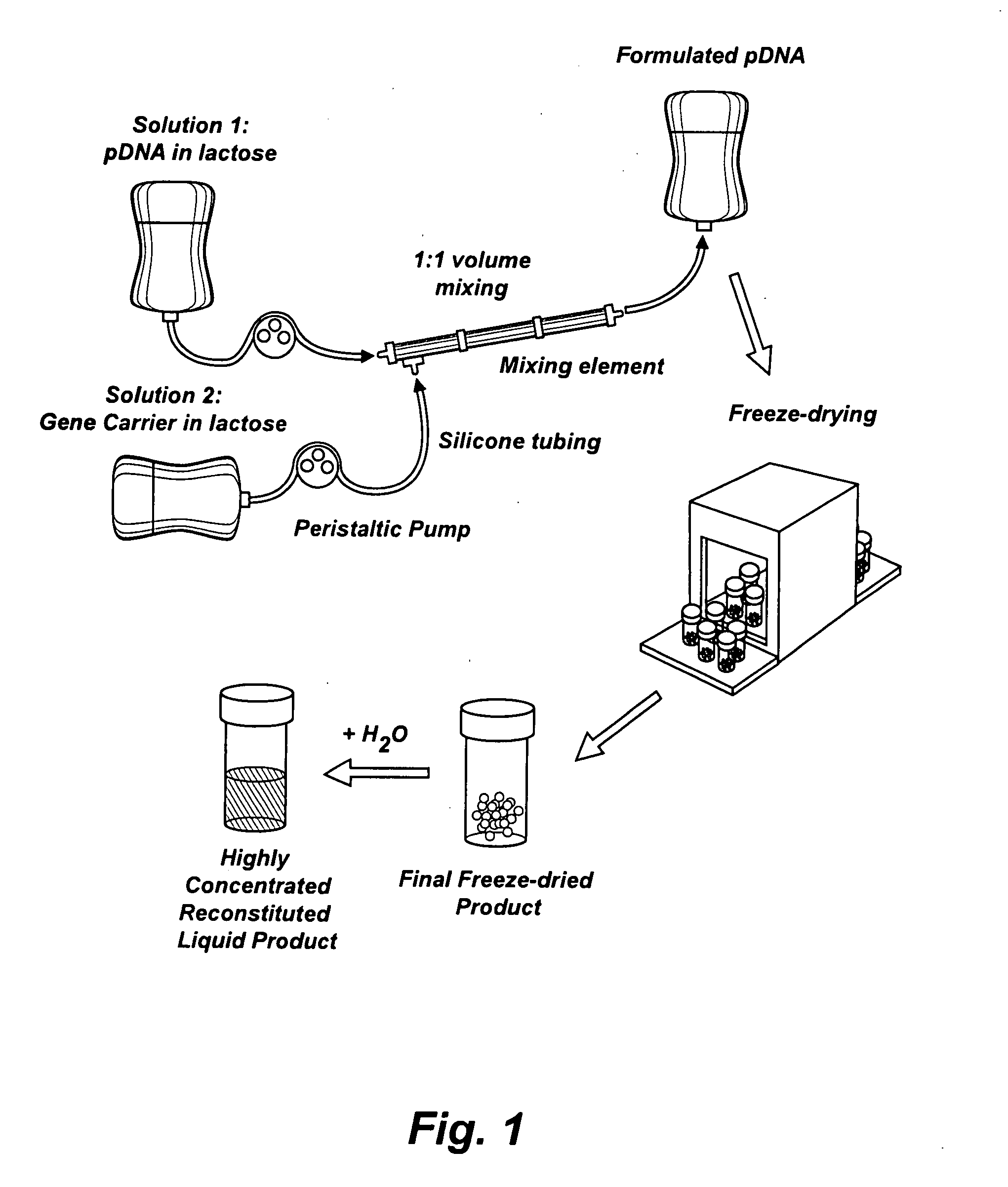
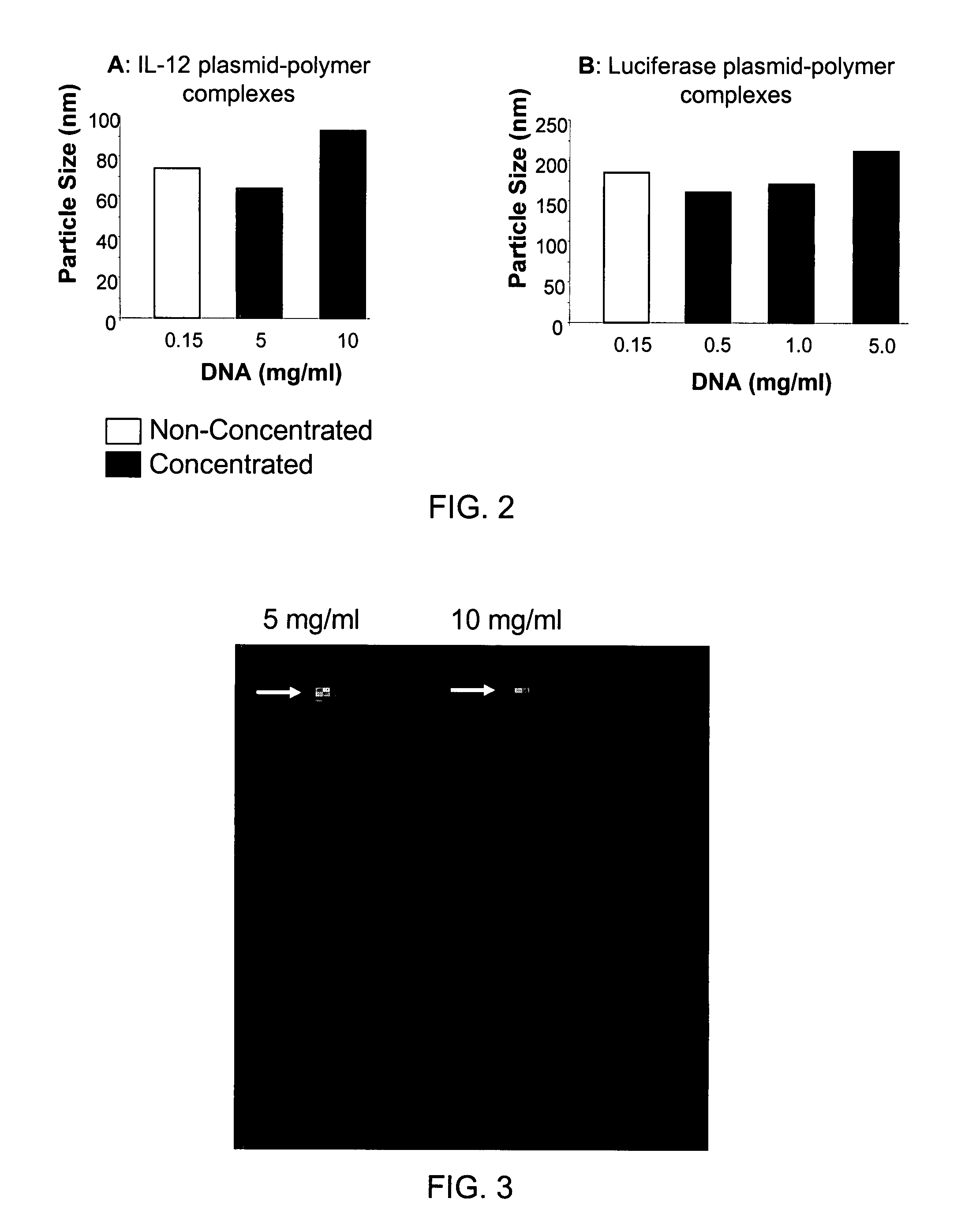
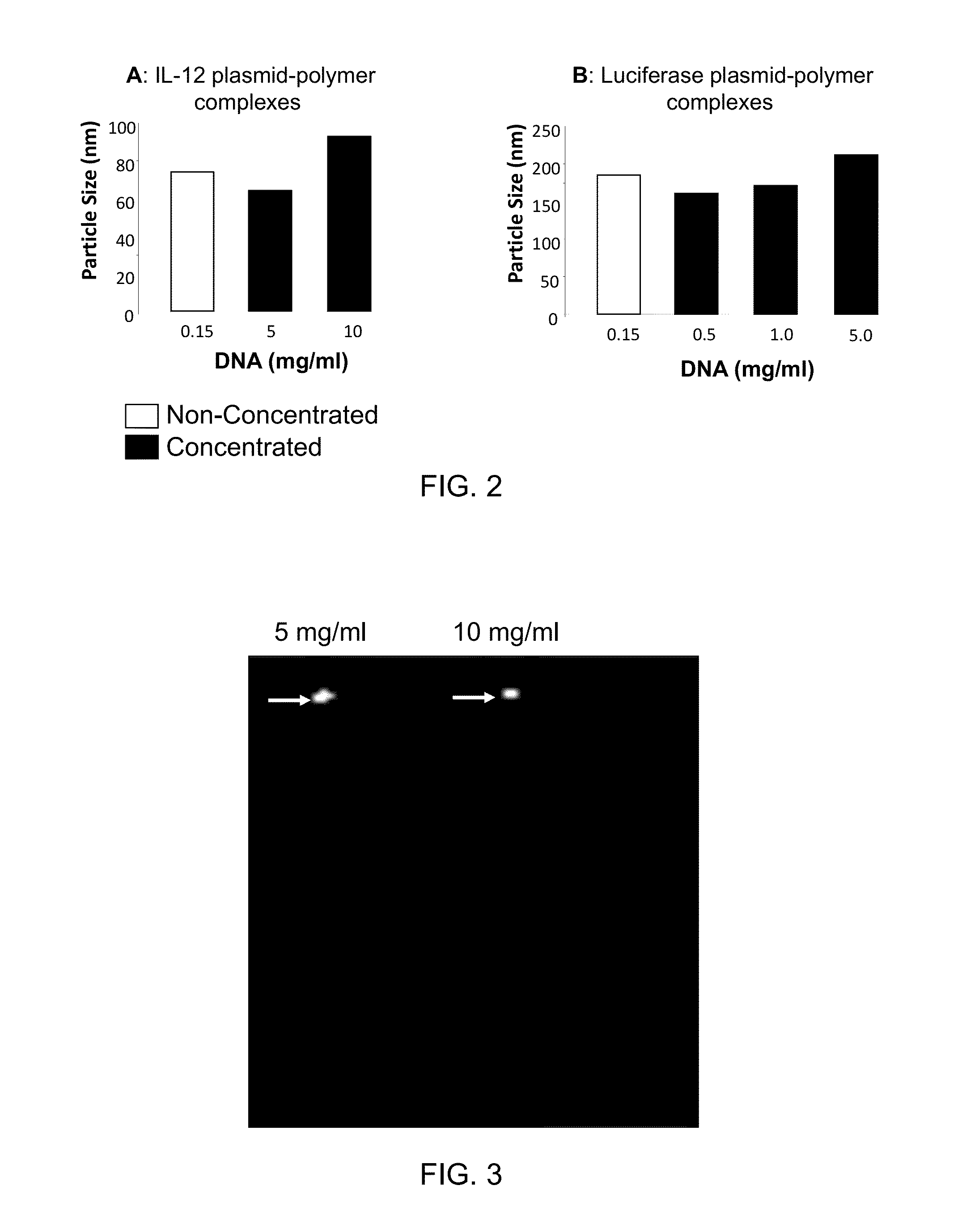
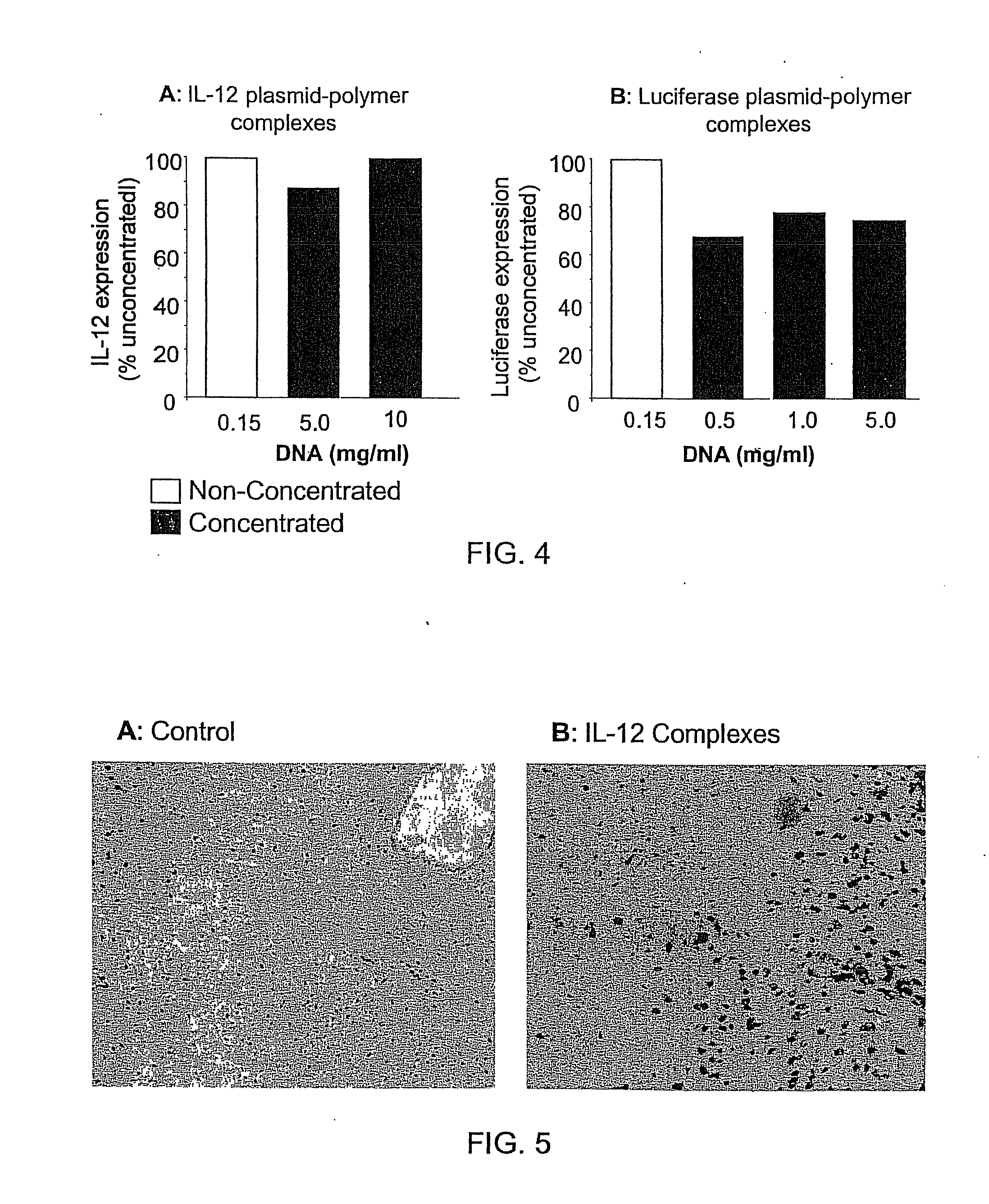
Composition, method of preparation & application of concentrated formulations of condensed nucleic acids with a cationic lipopolymer
UndeterminedUS20090042825A1Increase efficiency and dosing flexibilitySpecial deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsFiller ExcipientCholesterol
Compositions, methods, and applications that increase the efficiency of nucleic acid transfection are provided. In one aspect, a pharmaceutical composition may include at least about 0.5 mg / ml concentration of a nucleic acid condensed with a cationic lipopolymer suspended in an isotonic solution, where the cationic lipopolymer includes a cationic polymer backbone having cholesterol and polyethylene glycol covalently attached thereto, and wherein the molar ratio of cholesterol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10, and the molar ratio of polyethylene glycol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10. The composition further may include a filler excipient.
Owner:EXPRESSION GENETICS INC
Transfection of blood cells with mRNA for immune stimulation and gene therapy
InactiveUS20120009221A1Improve stabilityIncrease transfectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntigenPharmaceutical medicine
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing blood cells or haemopoietic cells, e.g. red blood cells (erythrocytes), granulocytes, mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and / or blood platelets, in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient and / or vehicle, wherein the cells are transfected with at least one mRNA comprising at least one region coding for at least one antigen. The invention further discloses a method of preparing the aforesaid pharmaceutical composition and the use of blood cells transfected in this way for the preparation of drugs or pharmaceutical compositions for immune stimulation against the antigens encoded by the mRNA. The subjects according to the invention are used especially for the therapy and / or prophylaxis of carcinoses or infectious diseases and can also be employed in gene therapy.
Owner:CUREVAC AG
Polyconjugates for In Vivo Delivery of Polynucleotides
The present invention is directed to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for delivering polynucleotides or other cell-impermeable molecules to mammalian cells. Described are polyconjugates systems that incorporate targeting, anti-opsonization, anti-aggregation, and transfection activities into small biocompatible in vivo delivery vehicles. The use of multiple reversible or labile linkages connecting component parts provides for physiologically responsive activity modulation.
Owner:ARROWHEAD MADISON
pH-triggered microparticles
InactiveUS20050123596A1Efficient deliveryGood biocompatibilityPowder deliveryMicroencapsulation basedPolyesterLipid formation
Microparticles that are designed to release their payload when exposed to acidic conditions are provided as a vehicle for drug delivery. Any therapeutic, diagnostic, or prophylatic agent may be encapsulated in a lipid-protein-sugar or polymeric matrix including a pH triggering agent to form pH triggerable microparticles. Preferably the diameter of the pH triggered microparticles ranges from 50 nm to 10 micrometers. The matrix of the particles may be prepared using any known lipid (e.g., DPPC), protein (e.g., albumin), or sugar (e.g., lactose). The matrix of the particles may also be prepared using any synthetic polymers such as polyesters. Methods of preparing and administering the particles are provided. Methods of immunization, transfection, and gene therapy are also provided by administering pH triggerable microparticles.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +2
Compounds and methods for reversible modification of biologically active molecules
The present invention is directed compounds for reversibly modification of biologically active molecules. Described are polyconjugates systems that incorporate targeting, anti-opsonization, anti-aggregation, and transfection activities into small biocompatible in vivo delivery conjugates. The use of reversible modification provides for physiologically responsive activity modulation.
Owner:ARROWHEAD MADISON
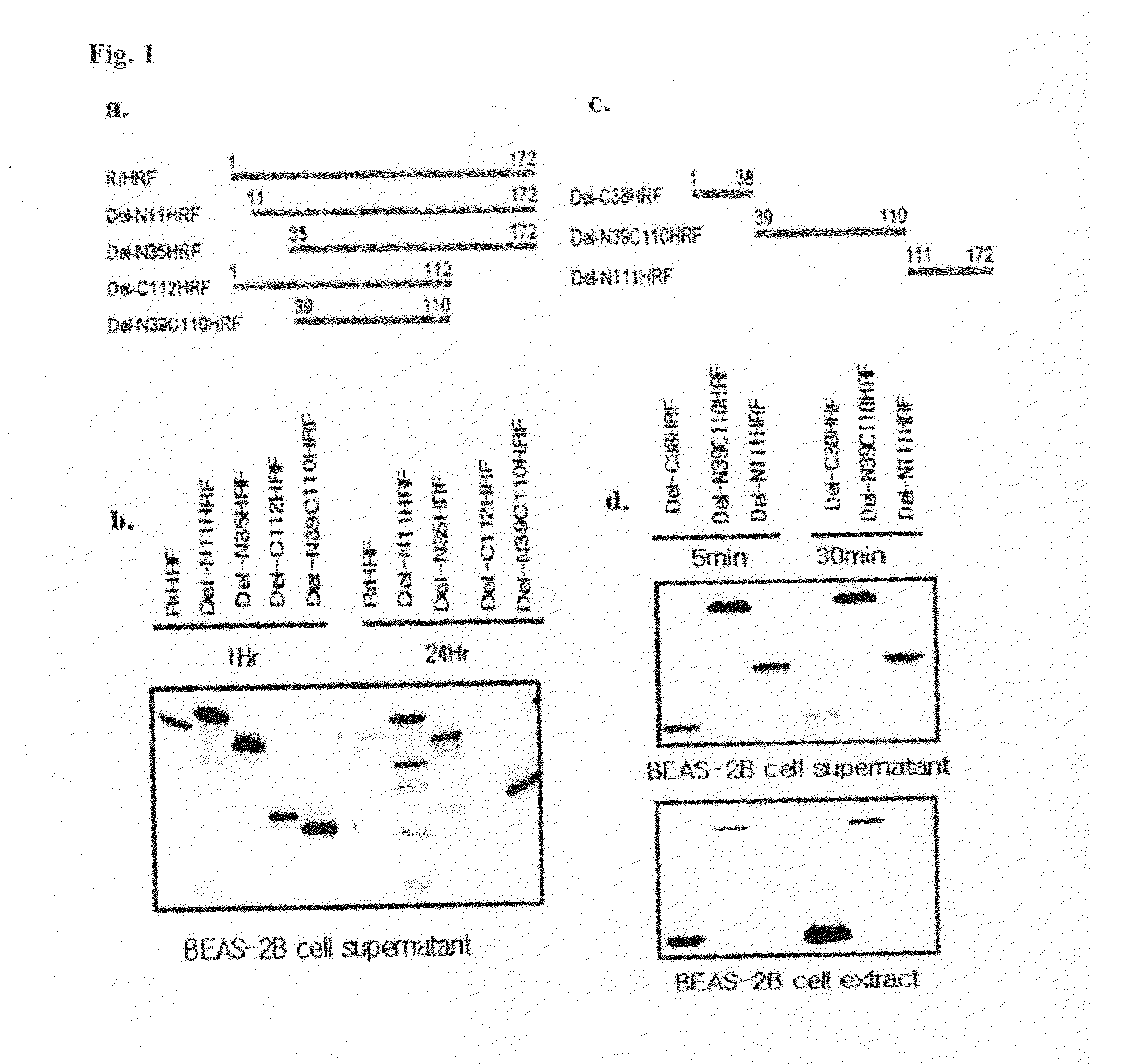
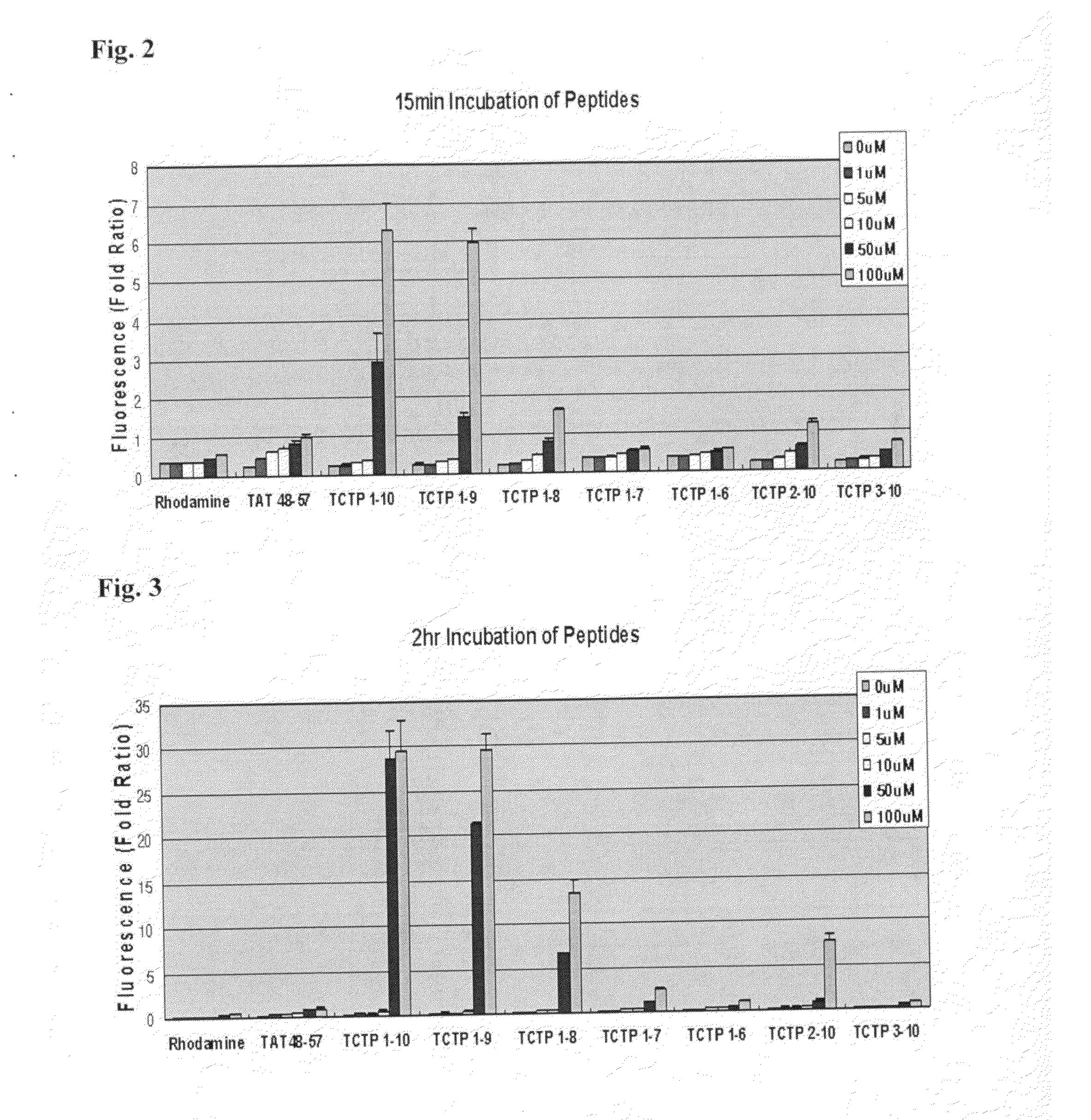
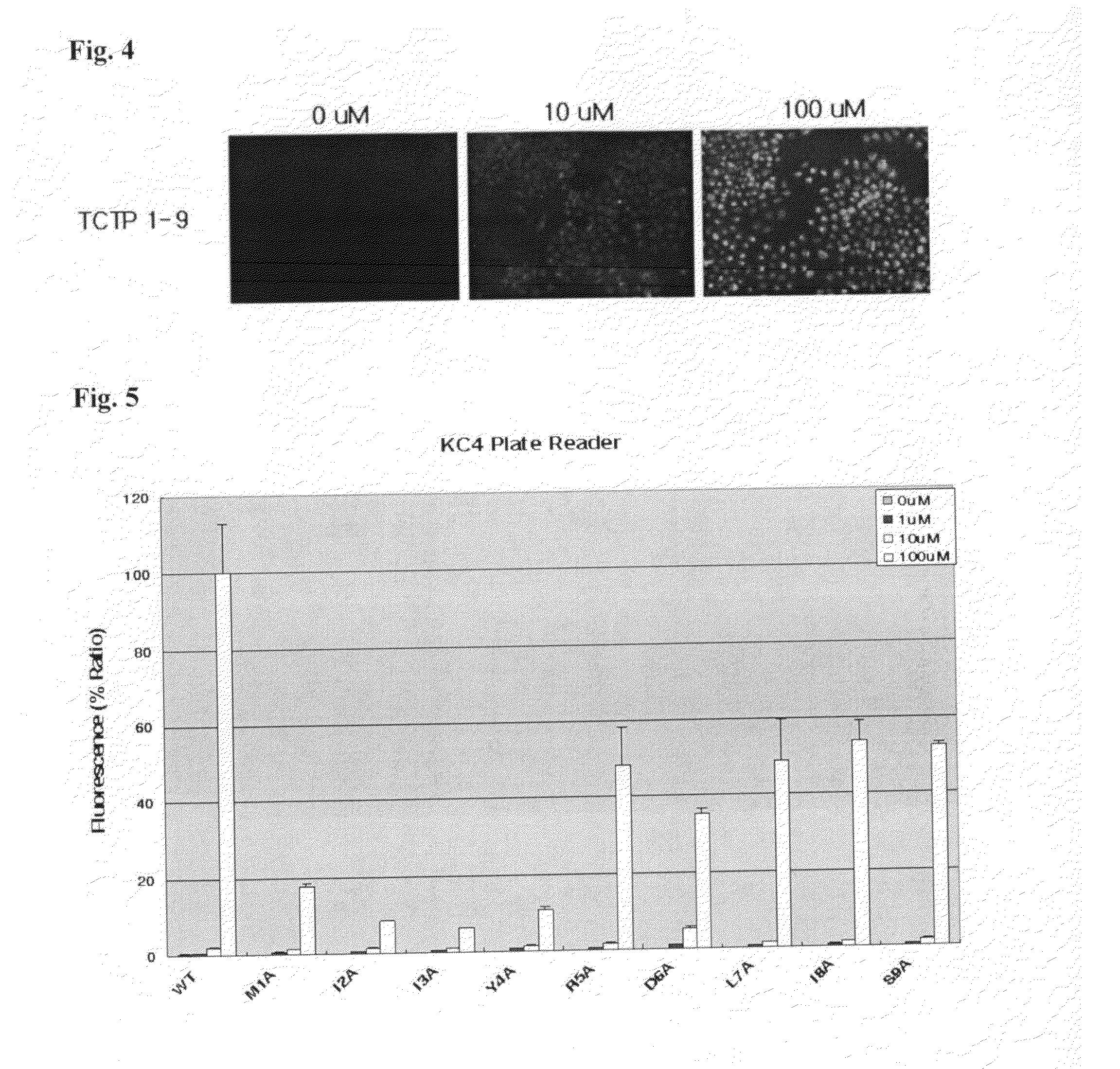
Peptide having cell membrane penetrating activity
InactiveUS20130129726A1Prominent penetrating efficiencyTargeting of drugs is required high efficientlyPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug compositionsHistamine releasing factorProtein transduction domain
Provided are transmembrane complexes that contain a protein transduction domain (PTD) from the N-terminus of IgE-dependent histamine-releasing factor (HRF) and a target substance that is to be delivered into a cell. Also provided are nucleic acid molecules encoding the transmembrane complex, and methods of delivering the target substance into a cell interior by contacting the transmembrane complex with a cell. Also provided are transfection kits containing the PTD and the target substance.
Owner:EWHA UNIV IND COLLABORATION FOUND
Solid surface with immobilized degradable cationic polymer for transfecting eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20060134790A1Without significant loss of transfection activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRoom temperatureTransfection
A cell transfection / culture device is disclosed which includes a solid support coated with a degradable polymer cation as a transfection reagent. The transfection / culture device is conveniently stored at room temperature until use. Cell transfection is accomplished easily by adding the nucleic acid of interest and the cells to be transfected to the transfection / culture device. Cell transfection is completed in less than one hour by using the transfection / culture device described herein.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Cell-penetrating peptides and uses thereof
The present invention relates to the identification and functional characterization of human cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) and their use; in particular as transfection vehicles.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Buffer solution for electroporation and a method comprising the use of the same
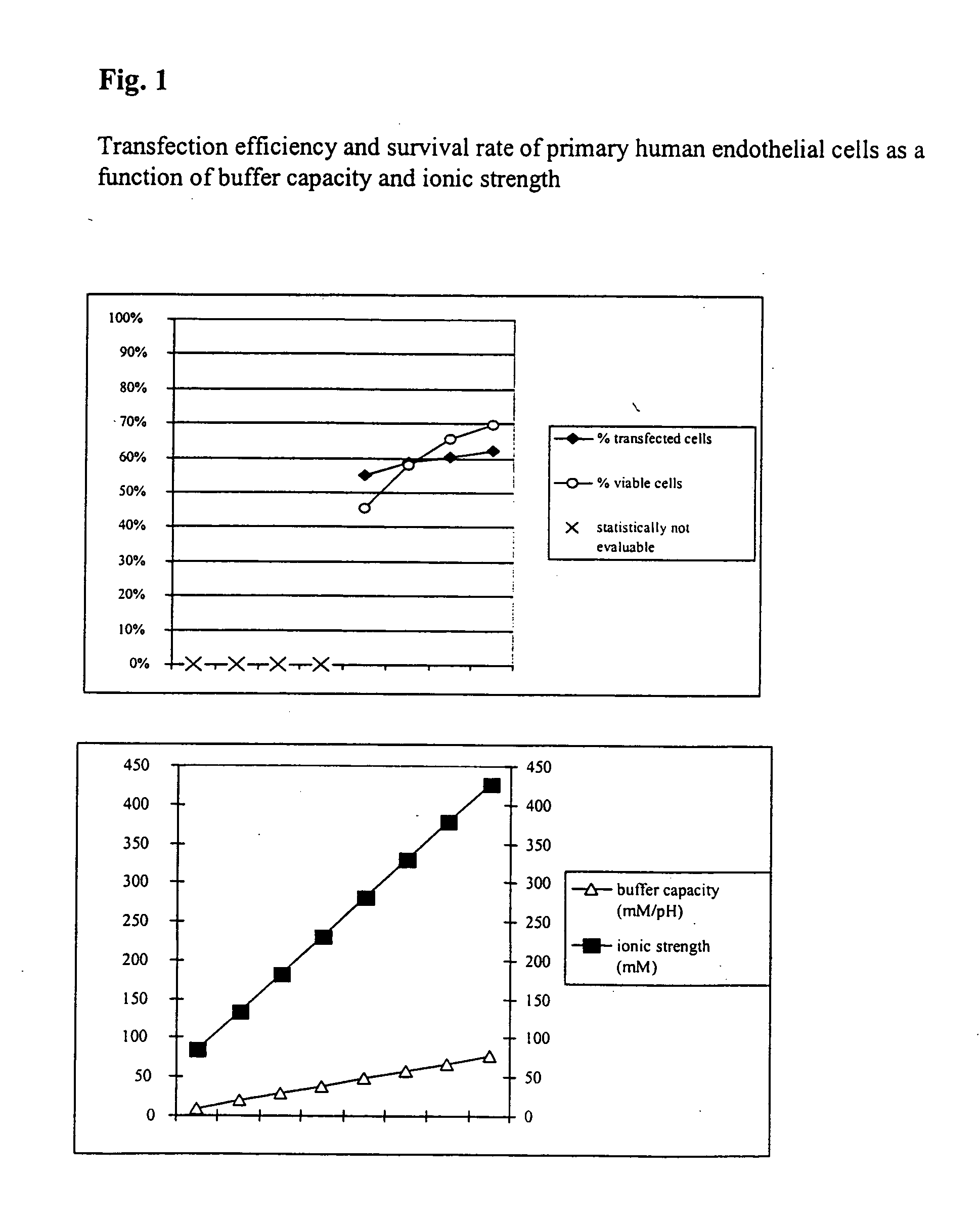
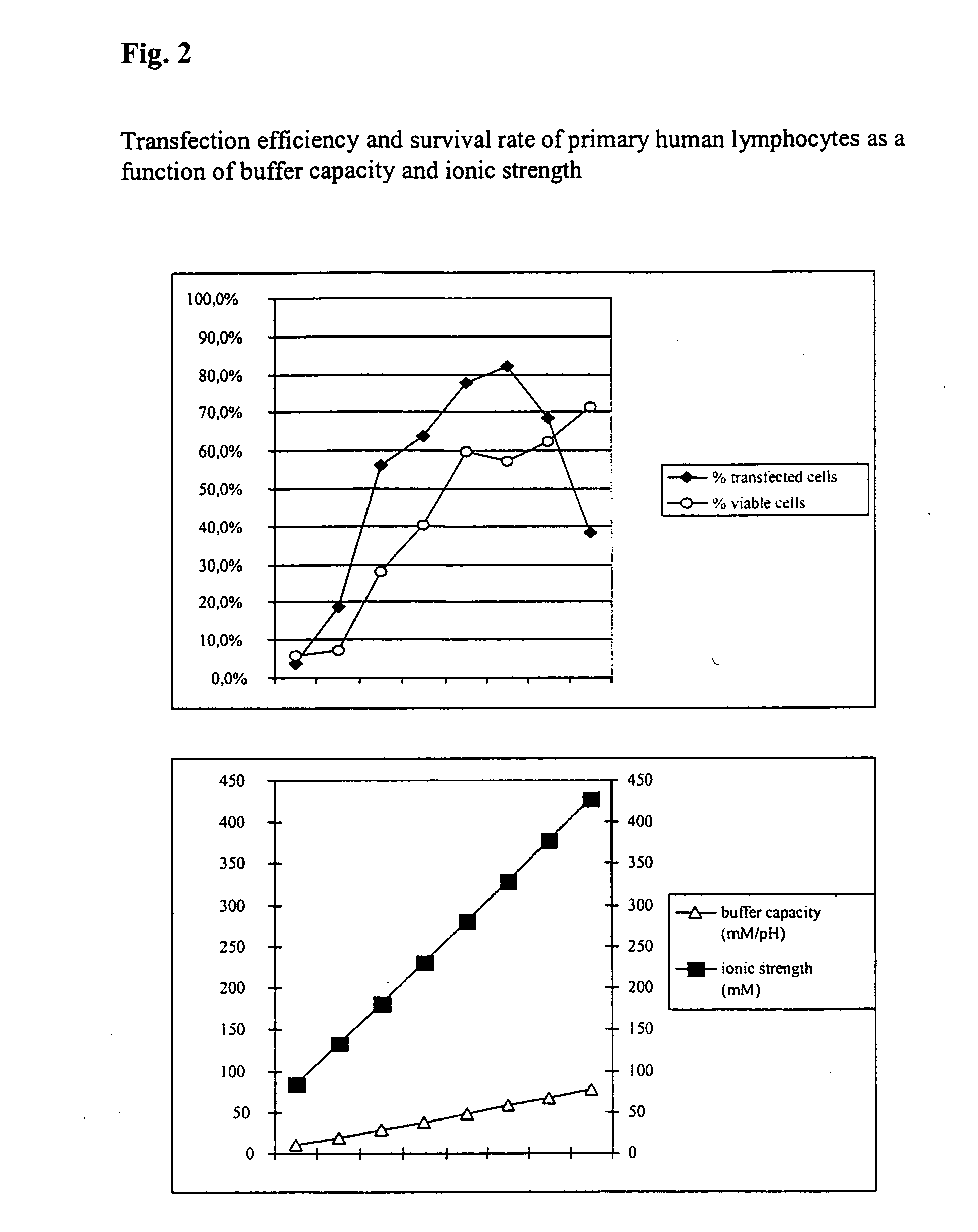
InactiveUS20050064596A1High transfection efficiencyReduce cell deathPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsElectroporationIon
The invention relates to a buffer solution for suspending animal or human cells and for dissolving biologically active molecules in order to introduce said biologically active molecules into the cells using an electric current and to a method for introducing biologically active molecules into animal or human cells using an electric current and a buffer solution. The inventive buffer solution has a buffering capacity of at least 20 mmol*I−1*pH−1 and an ionic strength of at least 200 mmol*I−1 during a change to the pH value from pH 7 to pH 8 and at a temperature of 25° C. The use of a buffer solution of this type in the corresponding method allows biologically active molecules to be introduced into animal and human cells with a high degree of transfection efficiency and at the same time a low cell mortality. Different cell types, in particular dormant and actively dividing cells of low activity, can be successfully transfected in said buffer solution.
Owner:LONZA COLOGNE
Methods for treating cancer using cytokine-expressing polynucleotides
InactiveUS7268120B1Improved in vivo polypeptide expressionMinimizing adverse side effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMammalSodium phosphates
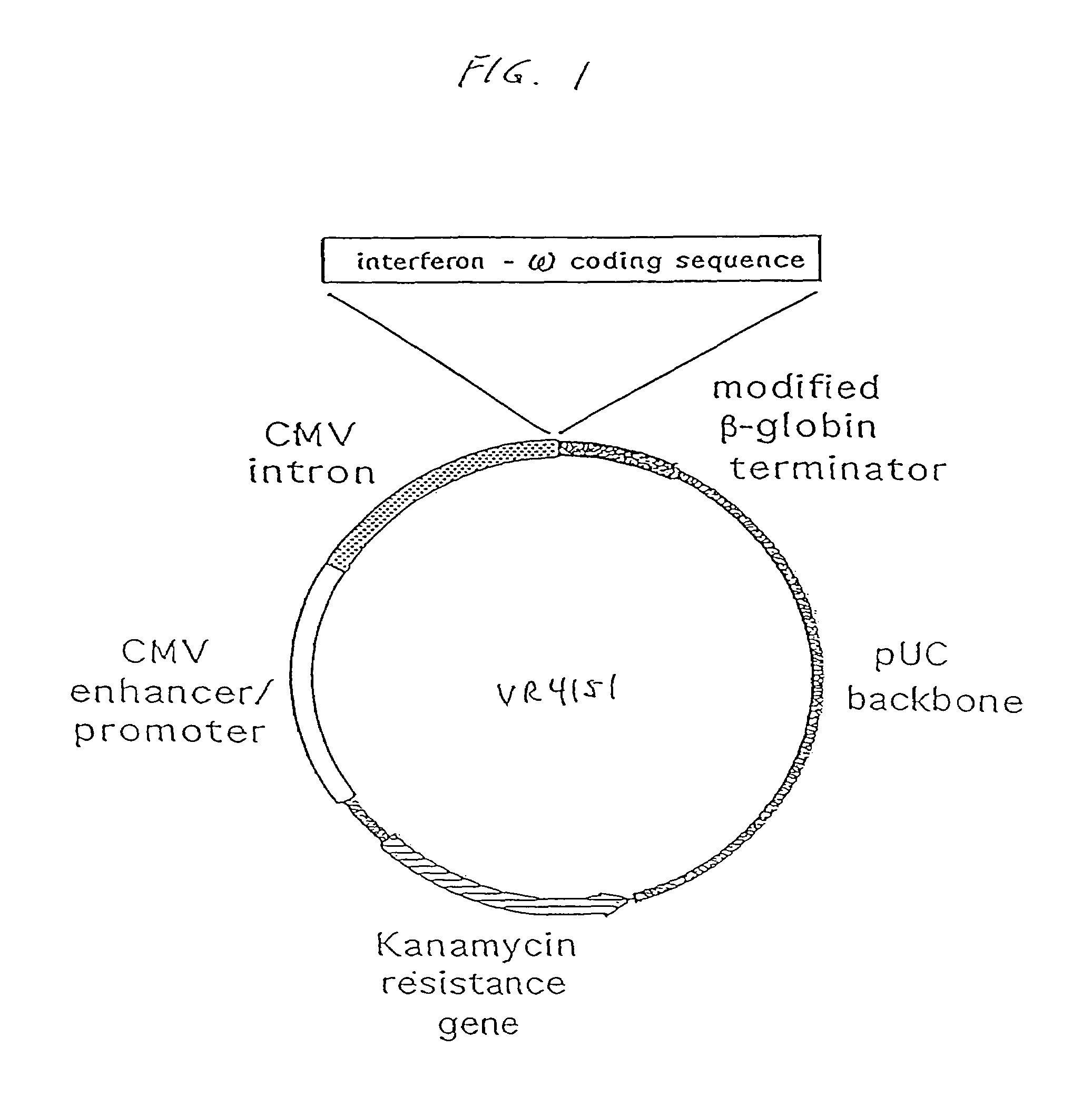
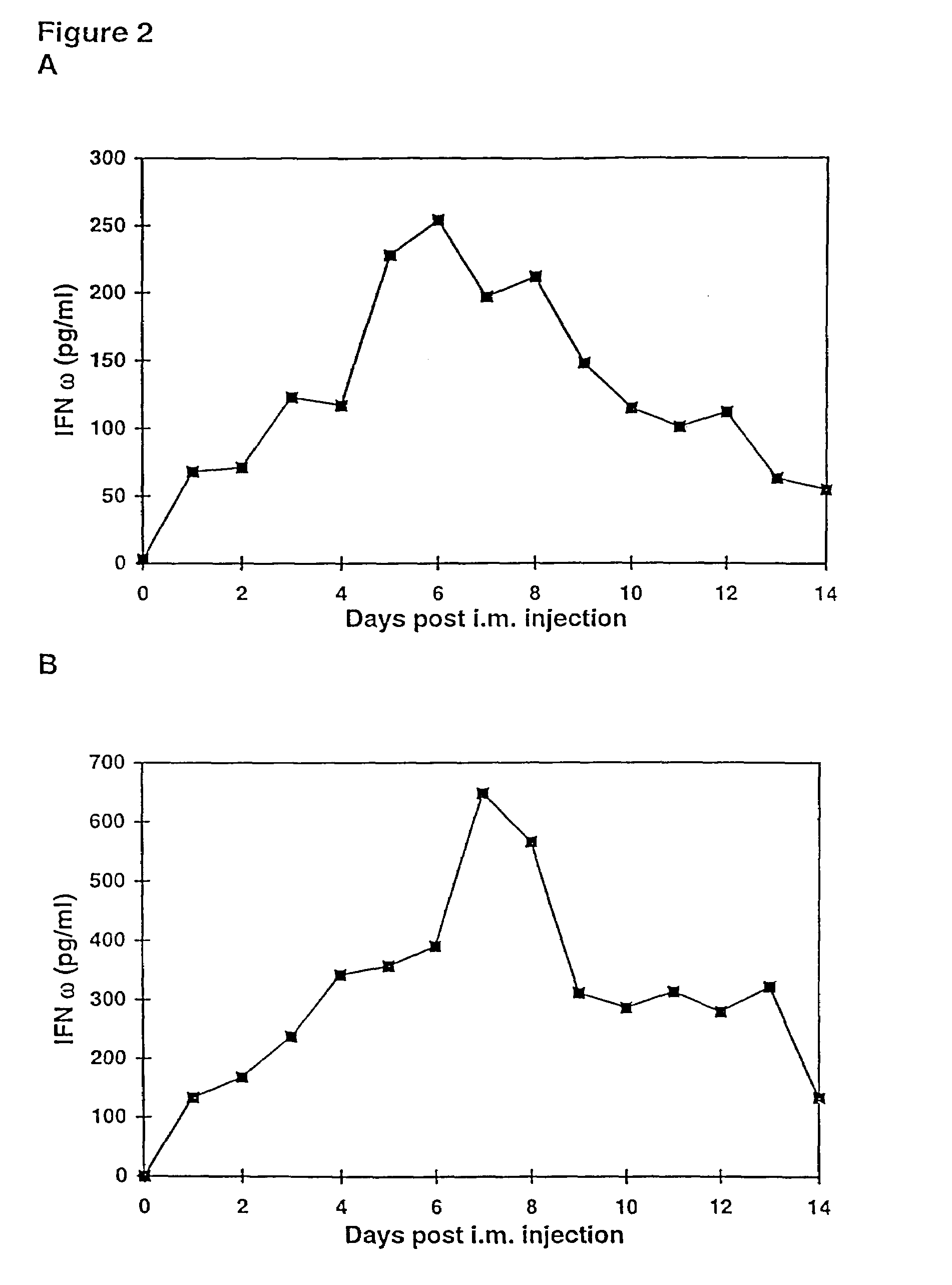
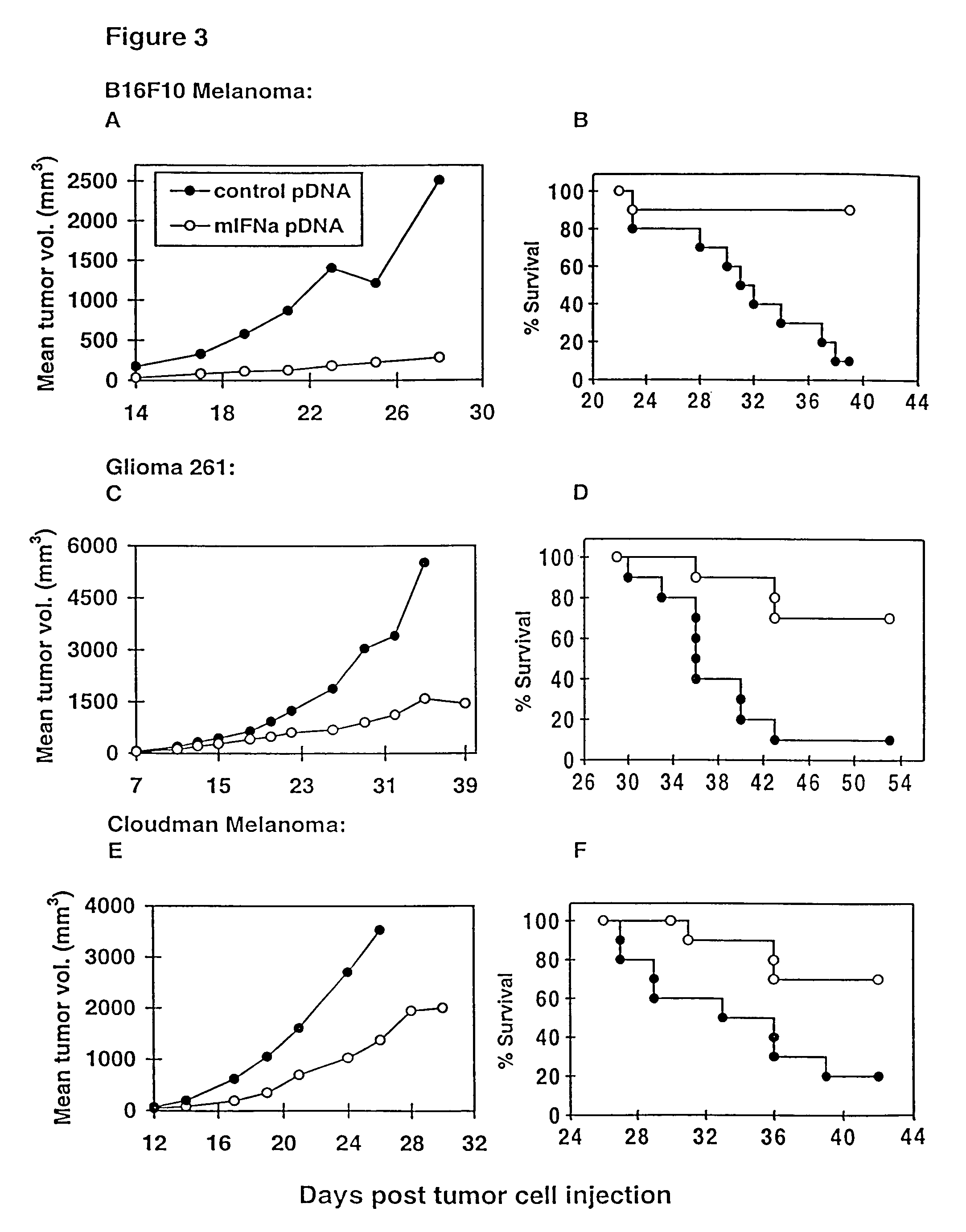
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition, comprising a non-infectious, non-integrating polynucleotide construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding an interferon ω and one or more cationic compounds. The present invention also provides methods of treating cancer in a mammal, comprising administering into a muscle of the mammal a non-infectious, non-integrating DNA polynucleotide construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding a cytokine. In addition, the present invention also relates to the methodology for selective transfection of malignant cells with polynucleotides expressing therapeutic or prophylactic molecules in intra-cavity tumor bearing mammals. More specifically, the present invention provides a methodology for the suppression of an intra-cavity dissemination of malignant cells, such as intraperitoneal dissemination. Furthermore, the invention relates to compositions and methods to deliver polynucleotides encoding polypeptides to vertebrate cells in vivo, where the composition comprises an aqueous solution of sodium phosphate.
Owner:VICAL INC
Optimization of determinants for successful genetic correction of diseases, mediated by hematopoietic stem cells
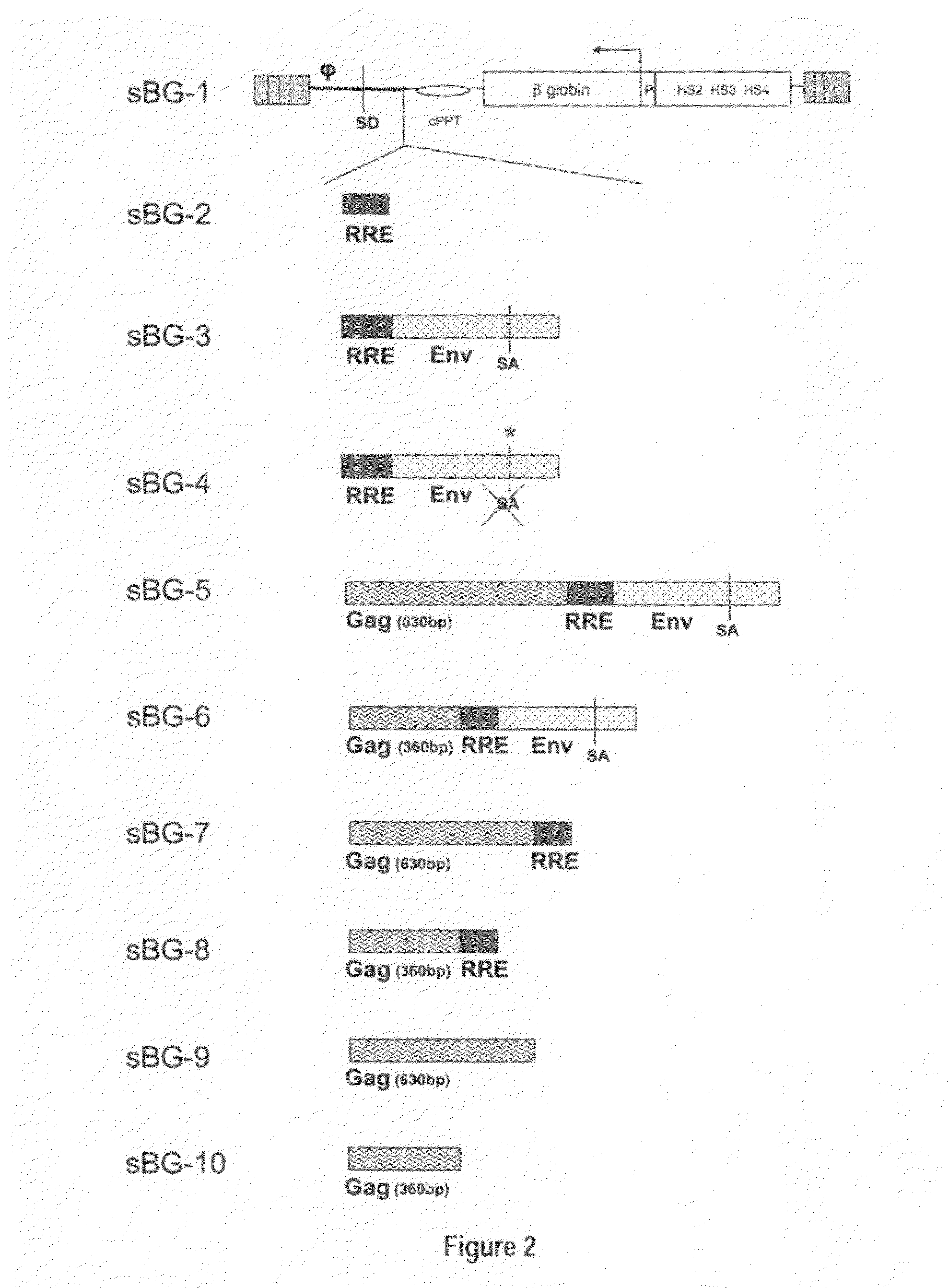
InactiveUS20110294114A1Improve stabilityImprove securityVectorsSugar derivativesNervous systemSickle cell anemia
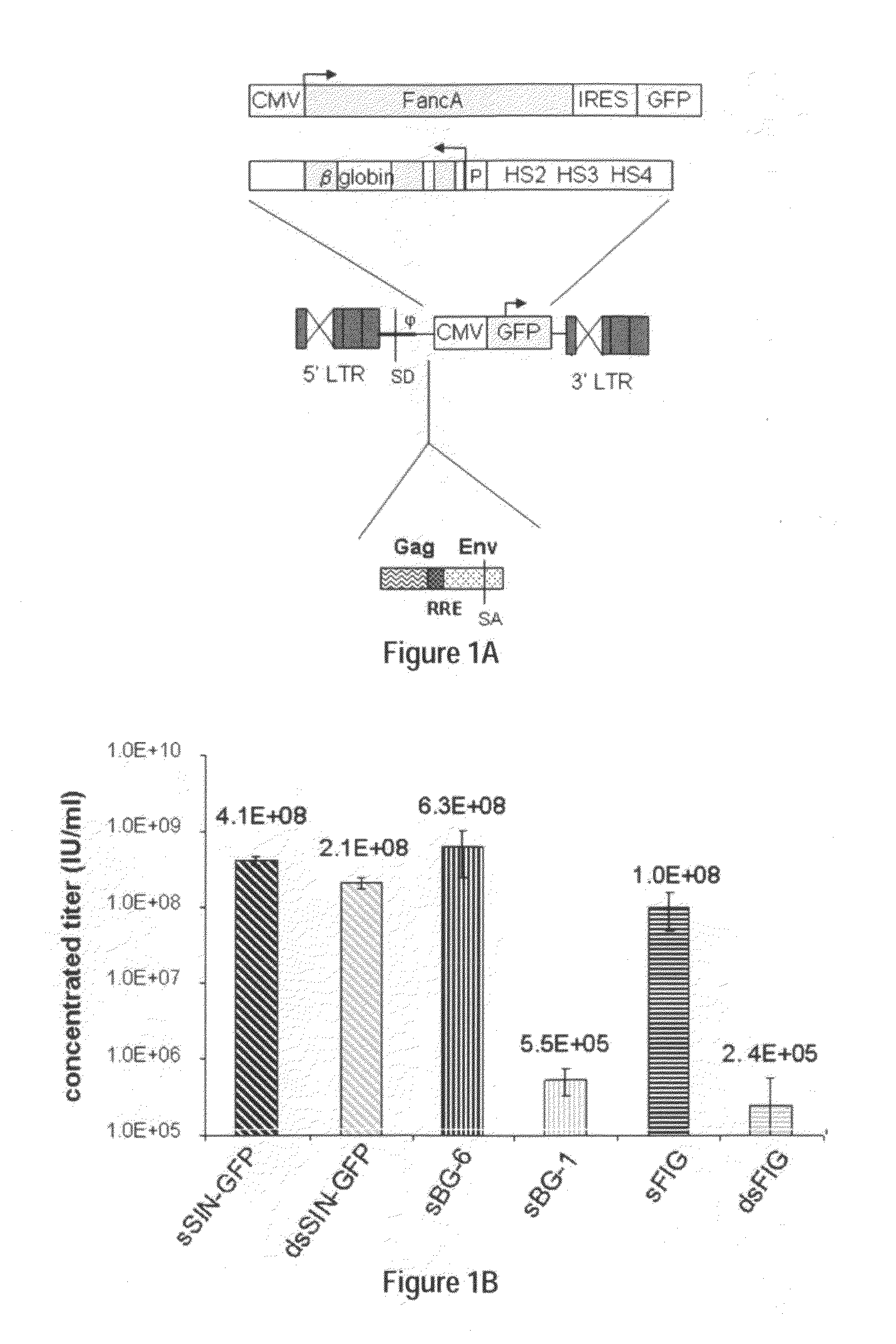
Methods and compositions disclosed herein generally relates to methods of determining minimum hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) chimerism and gene dosage for correction of a hematopoietic disease; in particular, in in vivo models. The invention also relates to modified lentiviral expression vectors for increase a viral titer and various methods for increasing such titers as well as expression vectors capable of enhancing such titers. The invention also relates to CHS4 chromatin insulator-derived functional insulator sequences. The invention further relates to methods for genetic correction of diseases or reducing symptoms thereof, such as sickle cell anemia, a lysosomal storage disease. The invention further relates to a method of improving and / or correcting one or more central nervous system (CNS) abnormalities caused by one or more lysosomal storage disease. The invention further relates to methods of improving titer in transfection-based bioreactor culture production or transfection-based production systems using eukaryotic cells.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Nucleic Acid-Lipopolymer Compositions
ActiveUS20130065942A1Increase efficiency and dosing flexibilityEfficiently be lyophilizedSpecial deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsFiller ExcipientCholesterol
Compositions, methods, and applications that increase the efficiency of nucleic acid transfection are provided. In one aspect, a pharmaceutical composition may include at least about 0.5 mg / ml concentration of a nucleic acid condensed with a cationic lipopolymer suspended in an isotonic solution, where the cationic lipopolymer includes a cationic polymer backbone having cholesterol and polyethylene glycol covalently attached thereto, and wherein the molar ratio of cholesterol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10, and the molar ratio of polyethylene glycol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10. The composition further may include a filler excipient.
Owner:CLSN LAB
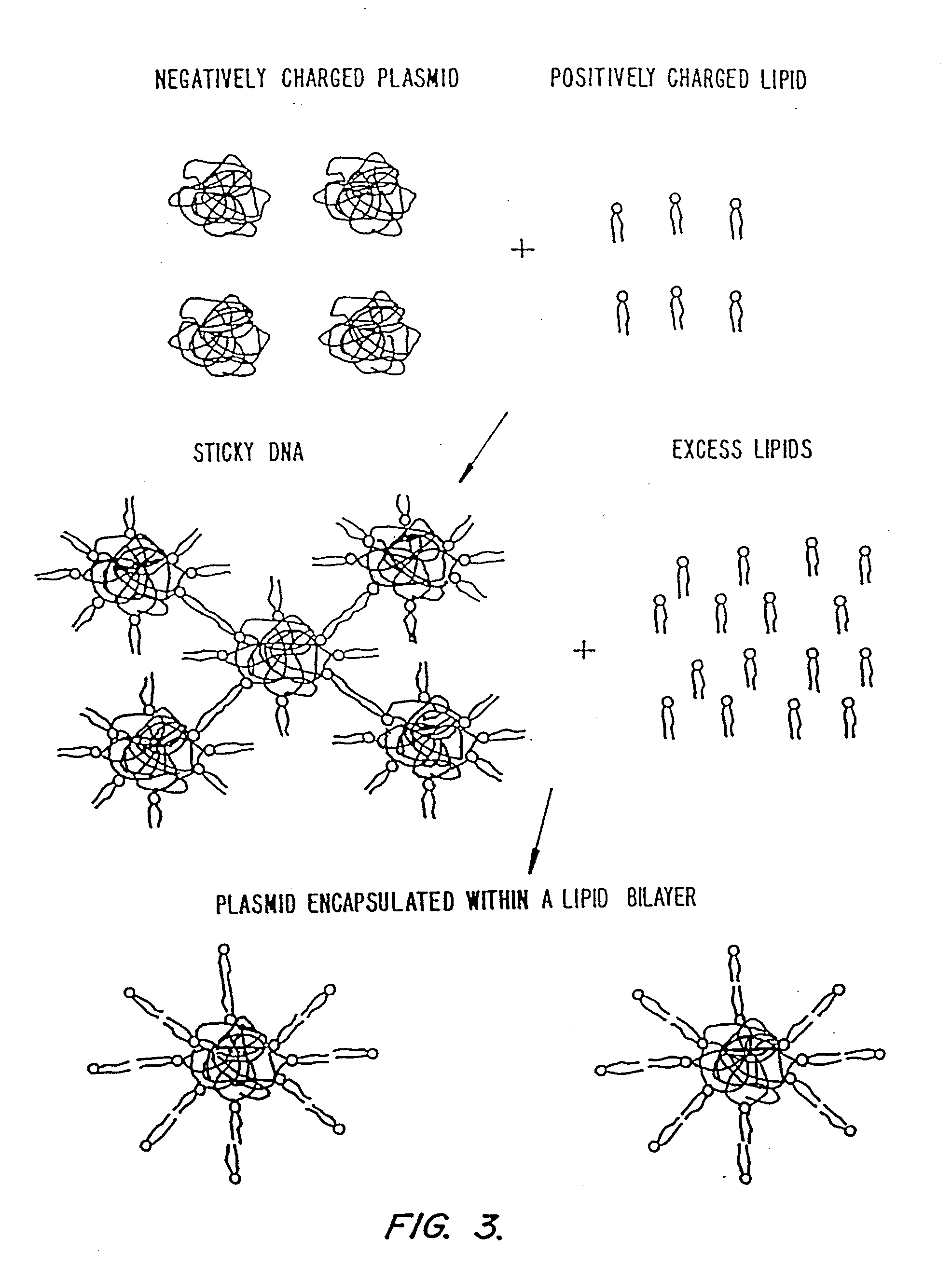
Methods for encapsulating plasmids in lipid bilayers
Plasmid-lipid particles which are useful for transfection of cells in vitro or in vivo are described. The particles can be formed using either detergent dialysis methods or methods which utilize organic solvents. The particles are typically 65-85 nm, fully encapsulate the plasmid and are serum-stable.
Owner:TEKMIRA PHARMA CORP +1
T-cell epitope identification
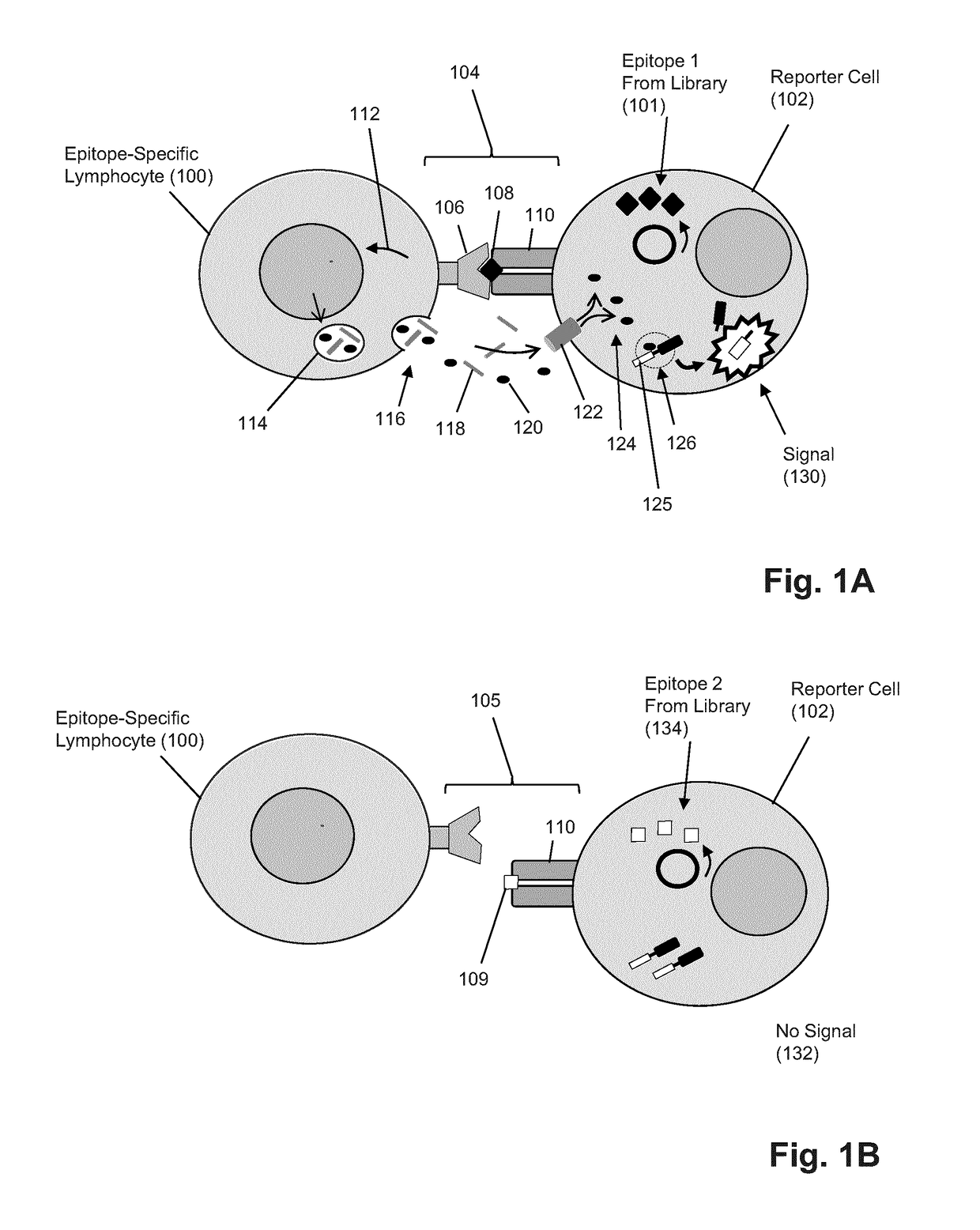
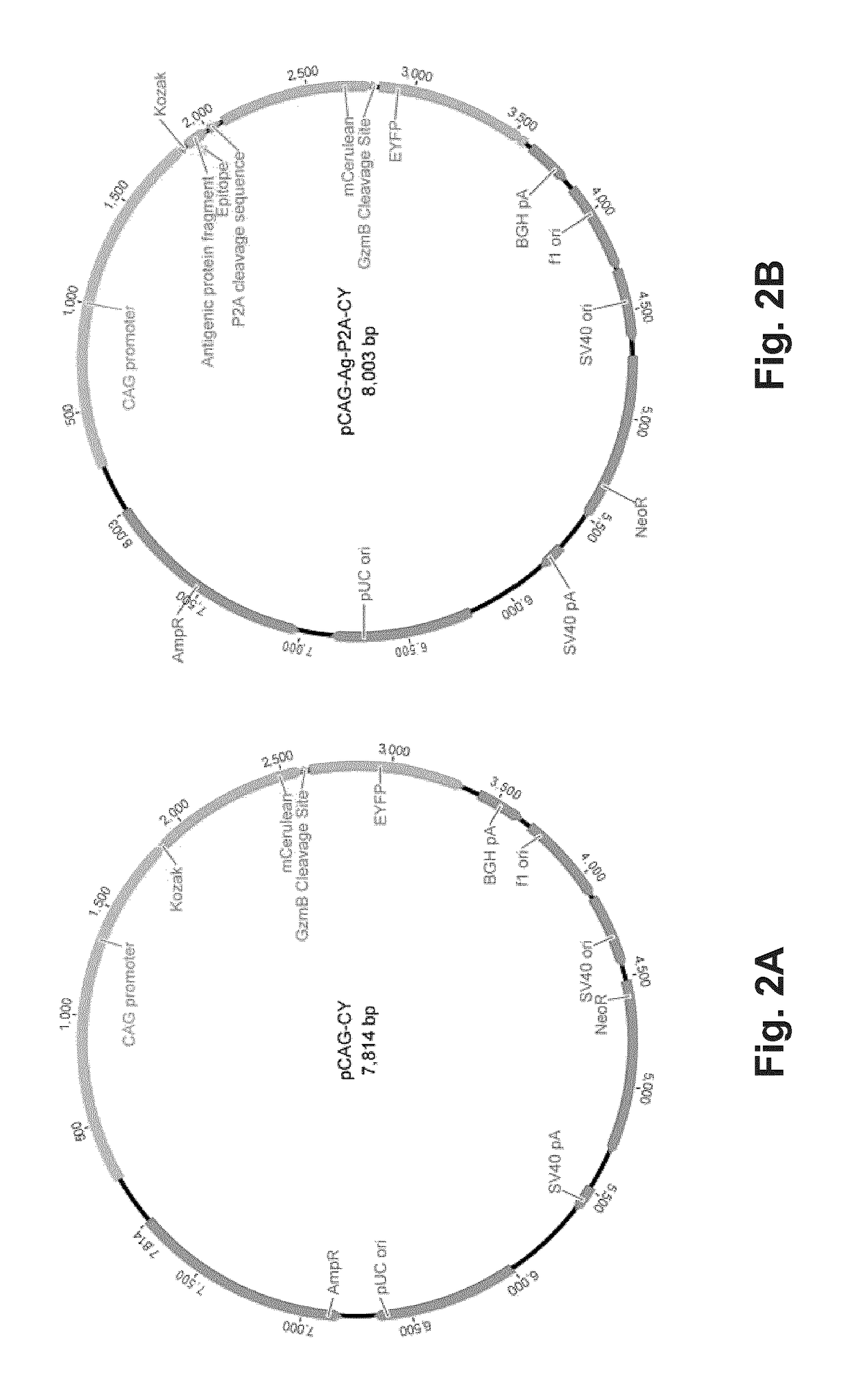
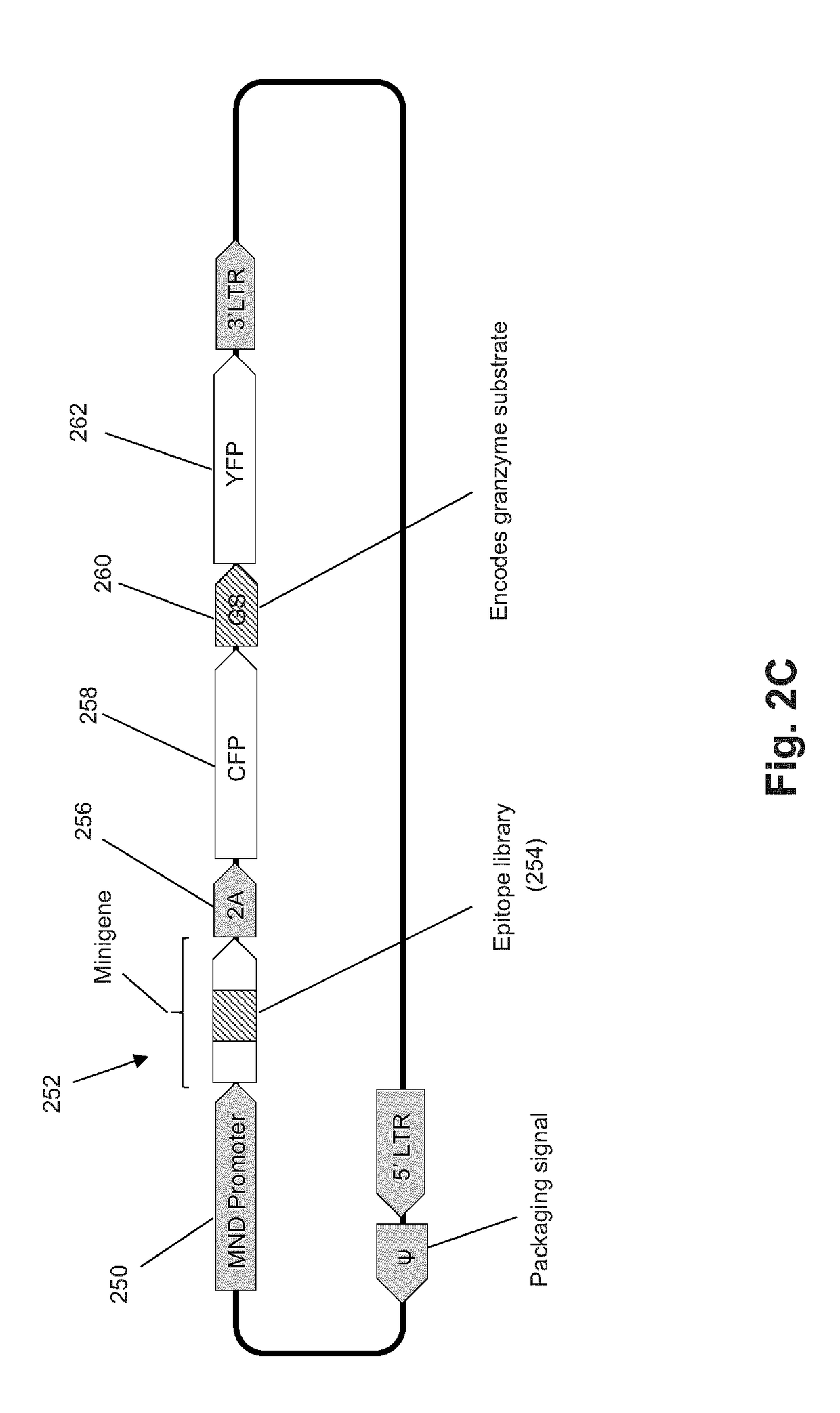
ActiveUS20180052176A1Efficient removalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotideMembrane bound
The present invention is a method for determining the identity of the epitopes recognized by T-cells. The method consists of expressing an encoded library of candidate epitope sequences in a recipient reporter cell capable of providing a detectable signal upon cytotoxic attack from a single cognate T-cell followed by contacting the reporter cells with T-cells of interest. The reporter cells with a single indicating cytotoxic attack from a T-cell are isolated and then analyzed by next-generation sequencing in order to identify the epitope sequences. Specifically disclosed is a method in which a library of candidate epitope-encoding nucleic acids are expressed in cells which feature a membrane-bound major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein, said library produced by transfection of plasmids featuring both a nucleotide encoding the candidate epitope and a nucleotide encoding a FRET-based fluorescent protein cleaved by granzyme.
Owner:PROVINCIAL HEALTH SERVICES AUTHORITY
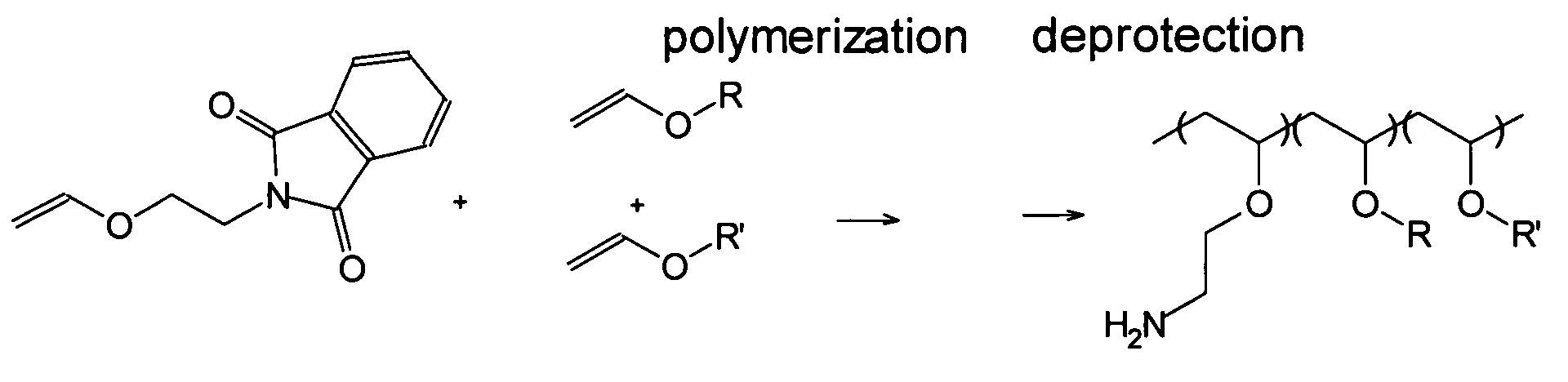
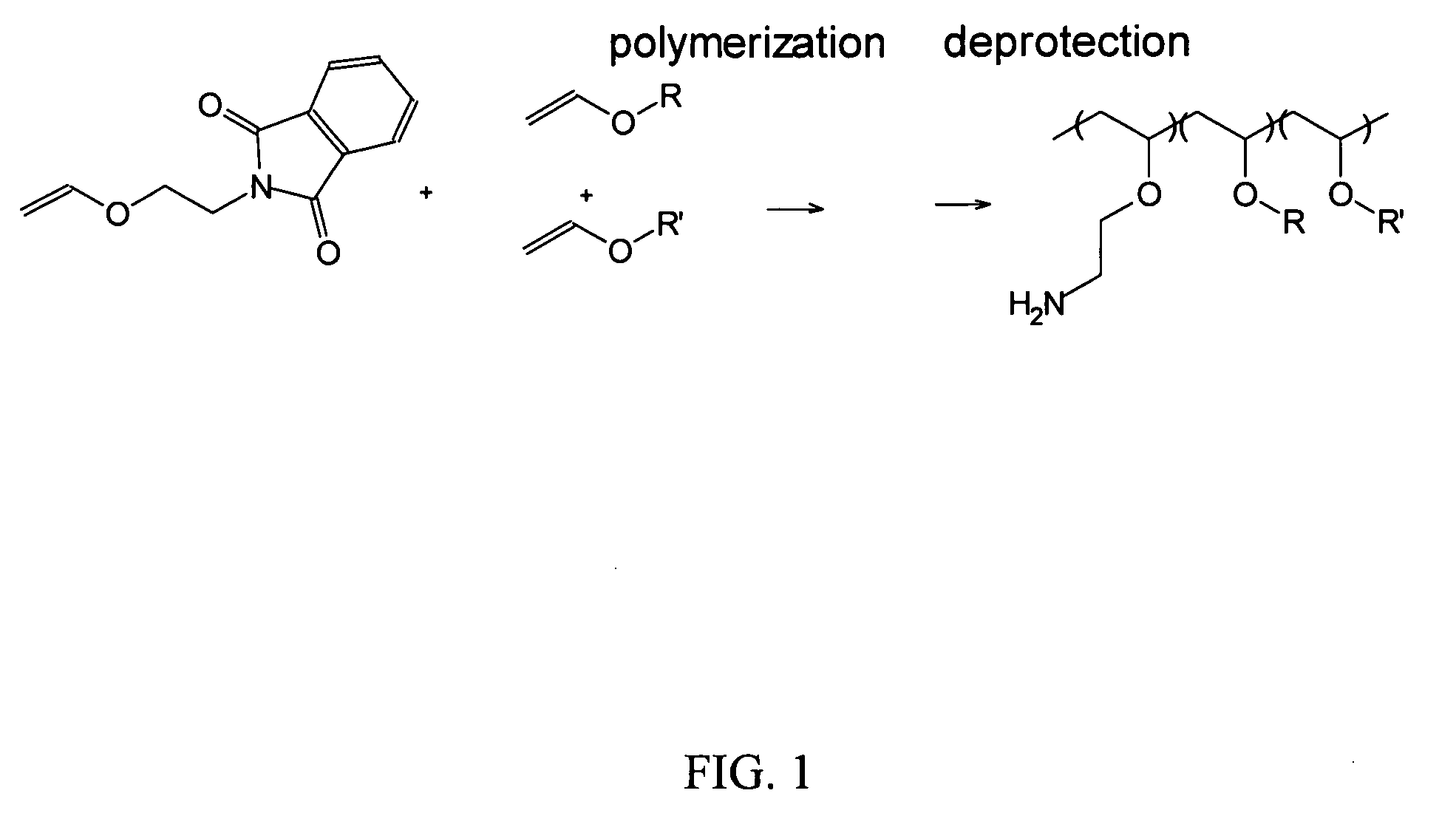
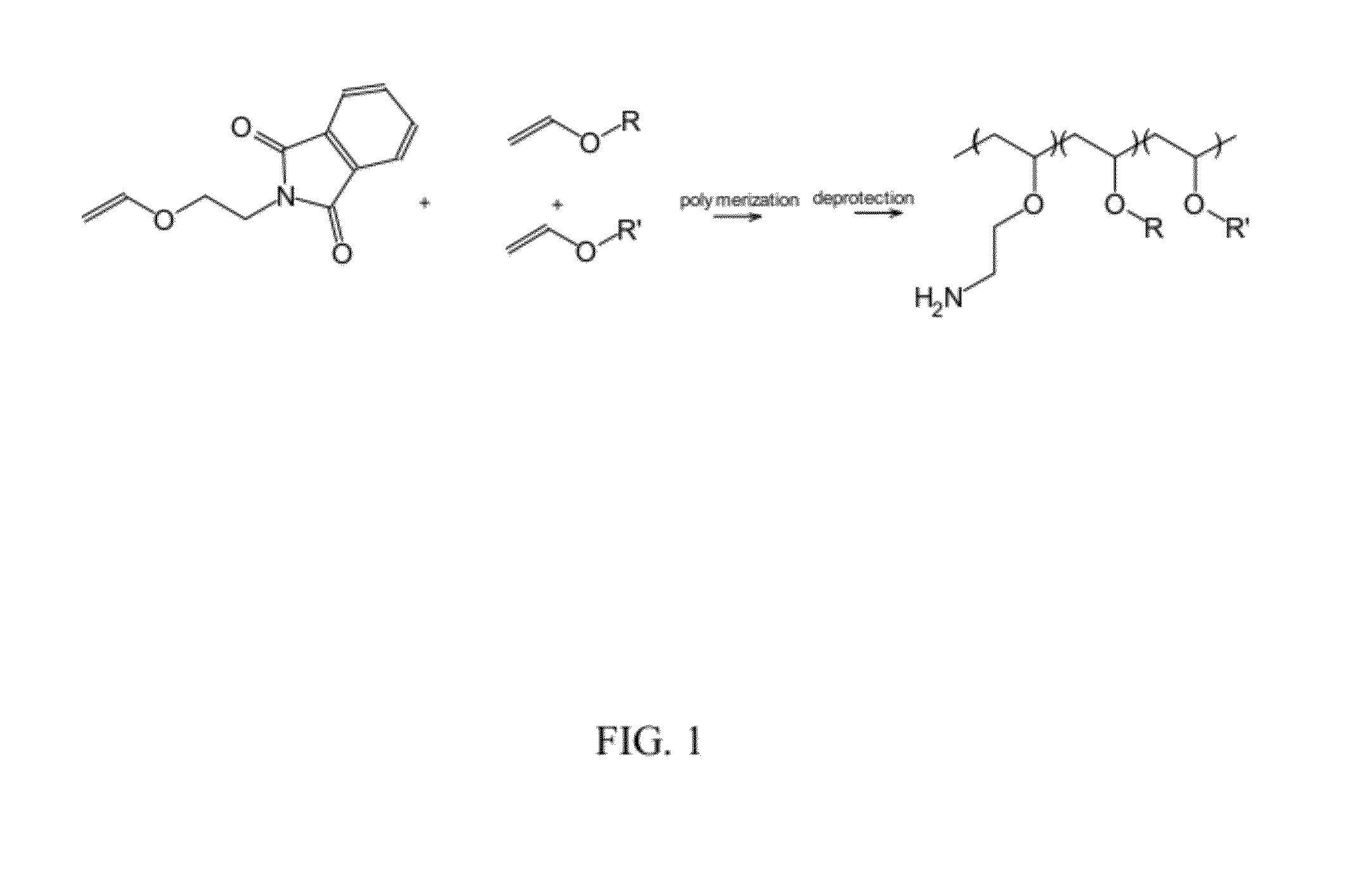
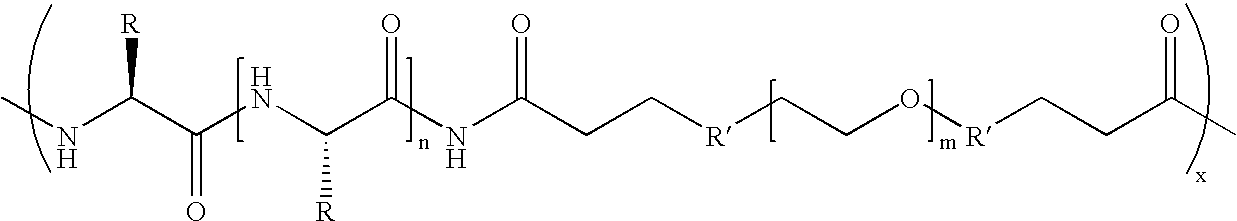
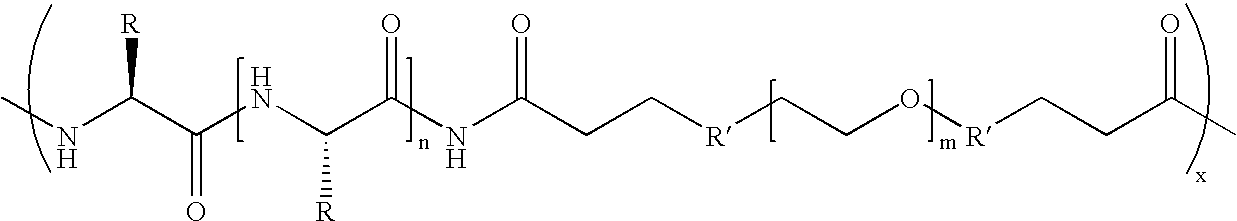
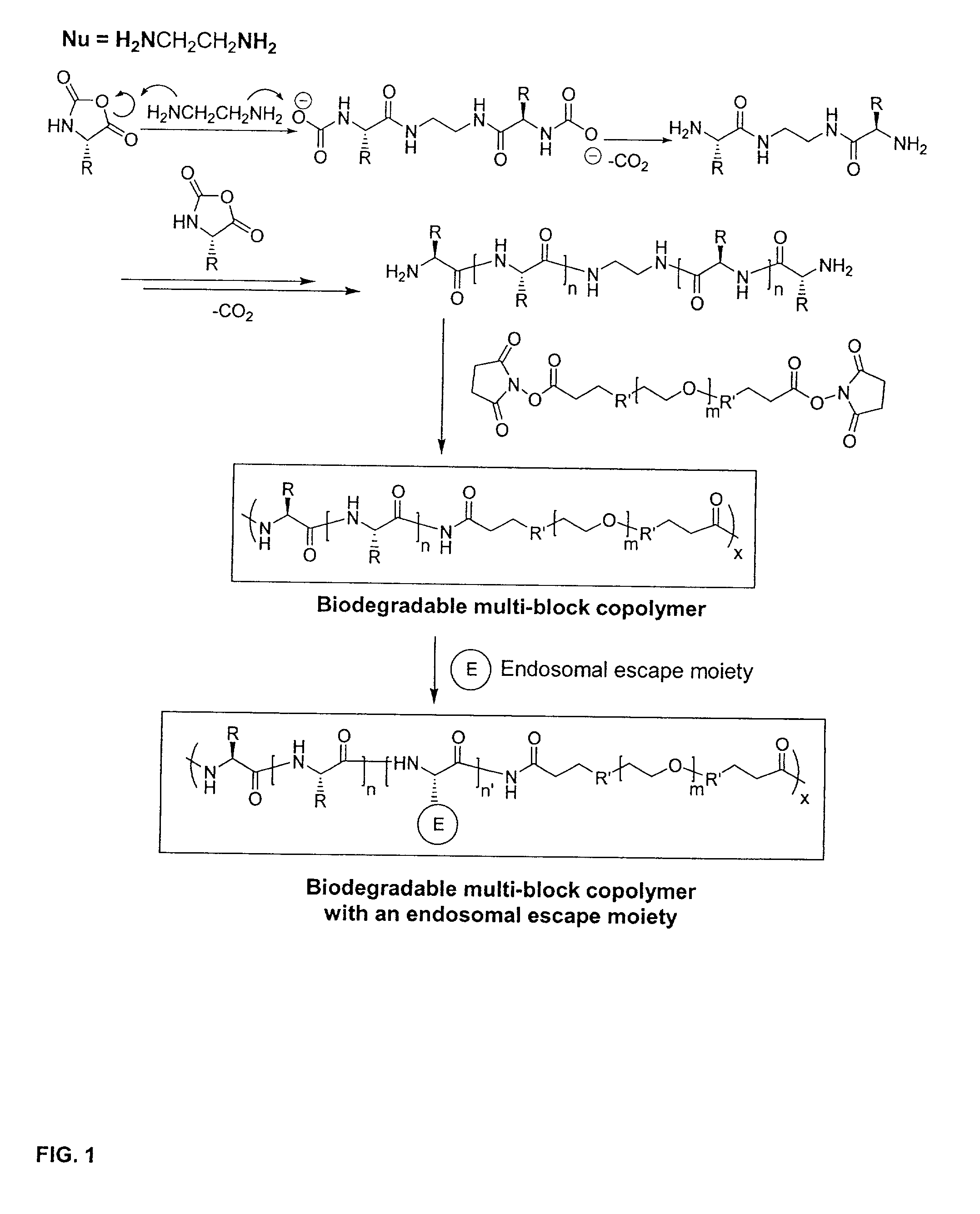
Biodegradable multi-block copolymers of poly(amino acid)s and poly(ethylene glycol) for the delivery of bioactive agents
InactiveUS20030147958A1Easy to chargeSmall sizePowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsCarbamateHydrophilic polymers
This patent discloses the synthesis of a multi-block copolymer containing poly(amino acids) (PAA) and a hydrophilic polymer which are degradable under physiological conditions. Control over the degradation rate of the obtained copolymers is achieved by introducing ester, amide or urethane groups as a biodegradable linkage connecting the PAA and the hydrophilic polymer. The biodegradable multi-block copolymers display high transfection efficiency in plasmid delivery with low cytotoxicity.
Owner:EXPRESSION GENETICS INC
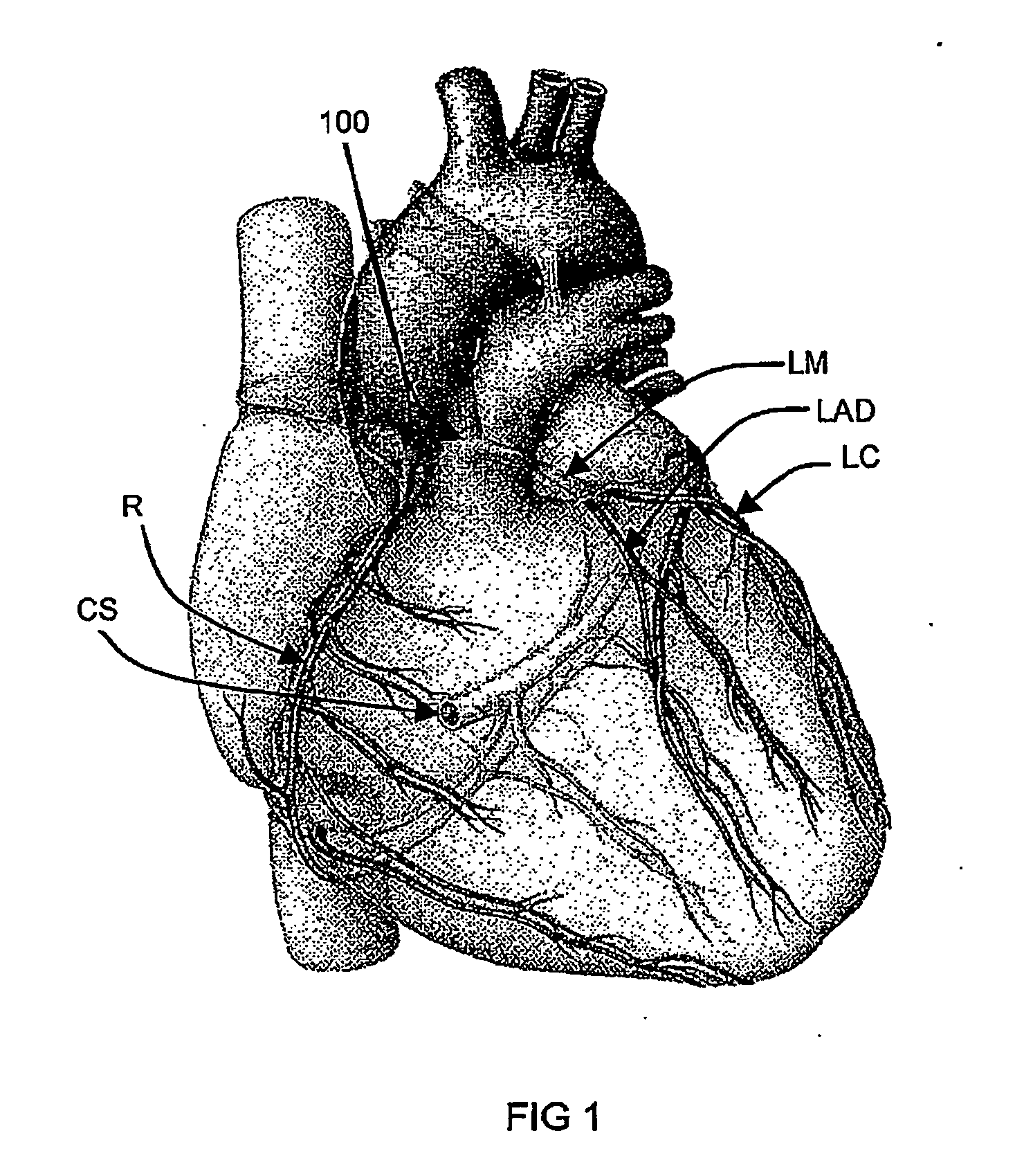
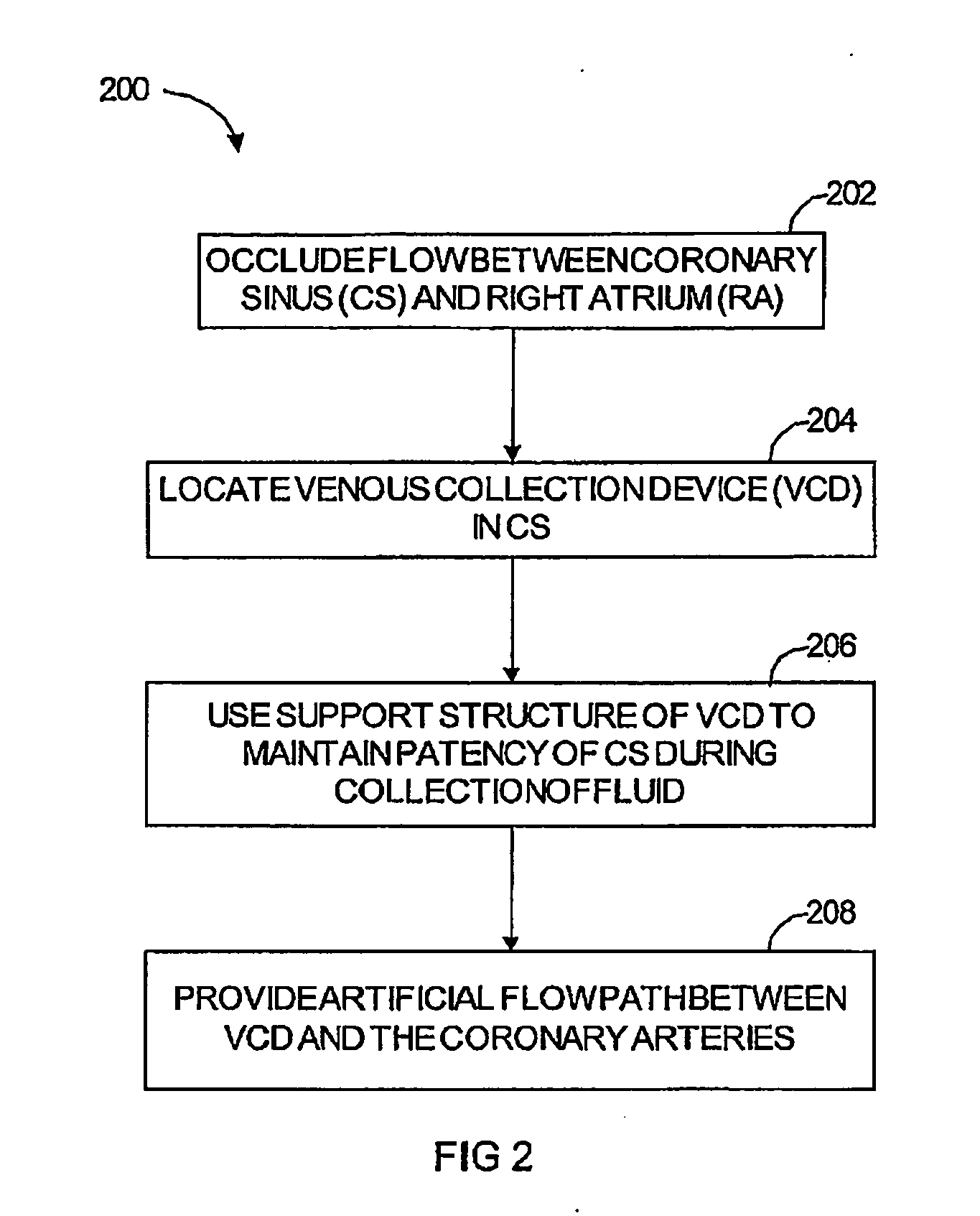
Polynucleotide delivery to cardiac tissue
InactiveUS20060148742A1Improve ejection fractionReduce probabilityVirusesBalloon catheterCoronary arteriesVein
A method for delivering a polynucleotide to cardiac tissue, including substantially isolating the coronary venous circulation from systemic circulation, and introducing a polynucleotide into the isolated coronary venous circulation to effect localized transfection of cardiac tissue. The polynucleotide advantageously produces a therapeutic effect, such as increasing or decreasing the expression level of a protein in the cardiac tissue.
Owner:OSPREY MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com