Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
250 results about "Major histocompatibility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
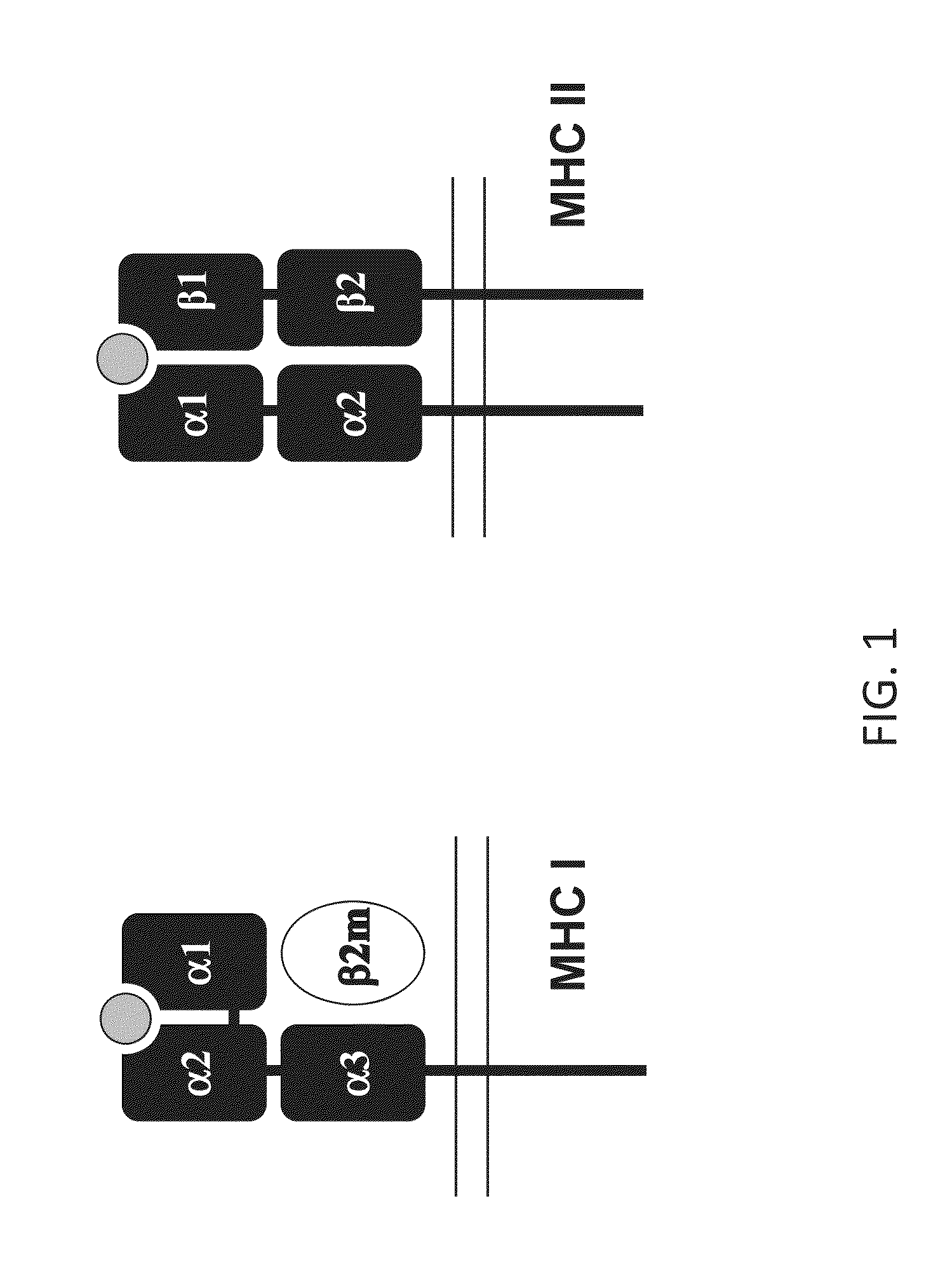
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC), group of genes that code for proteins found on the surfaces of cells that help the immune system recognize foreign substances. MHC proteins are found in all higher vertebrates. In human beings the complex is also called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system.
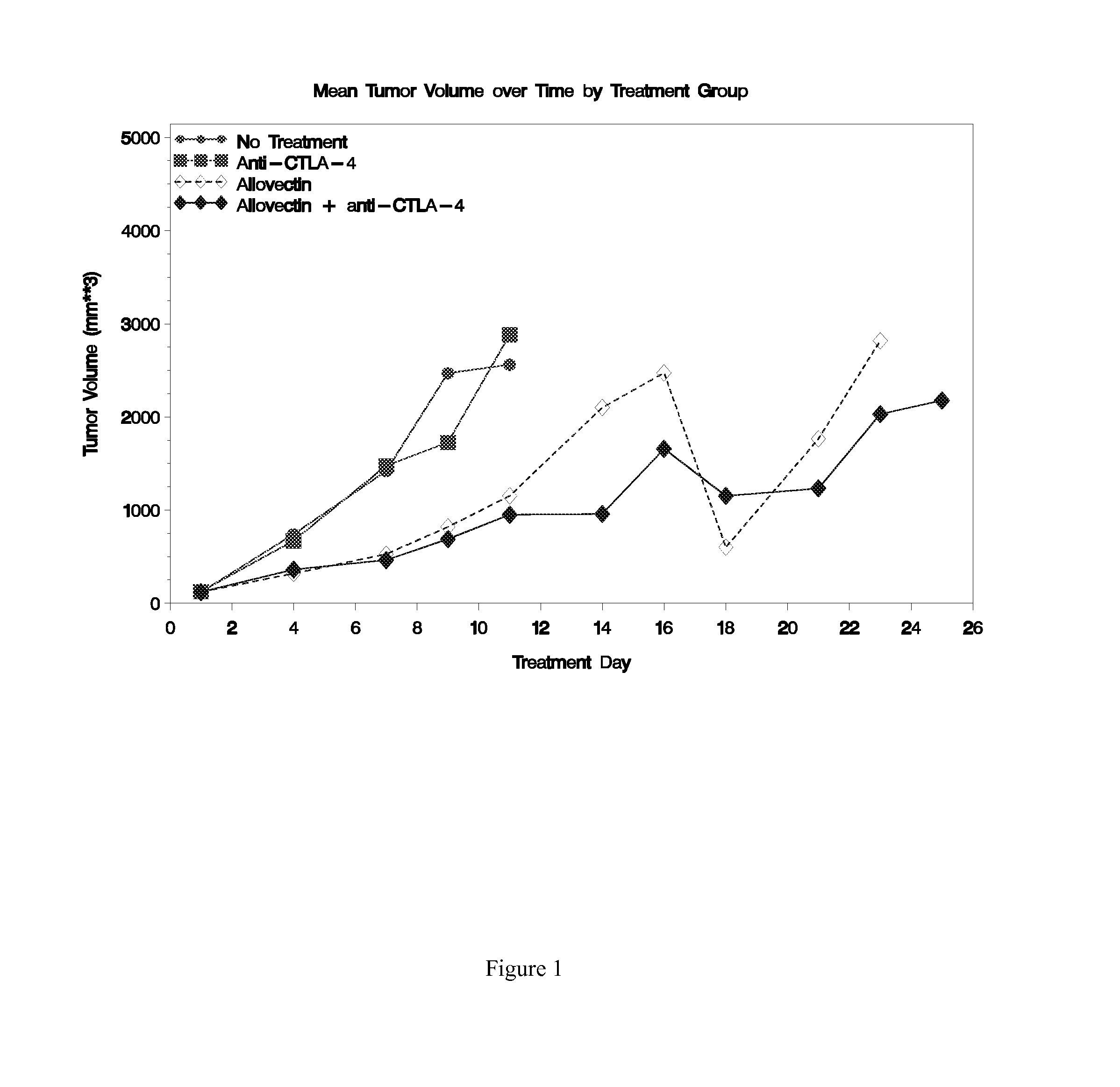
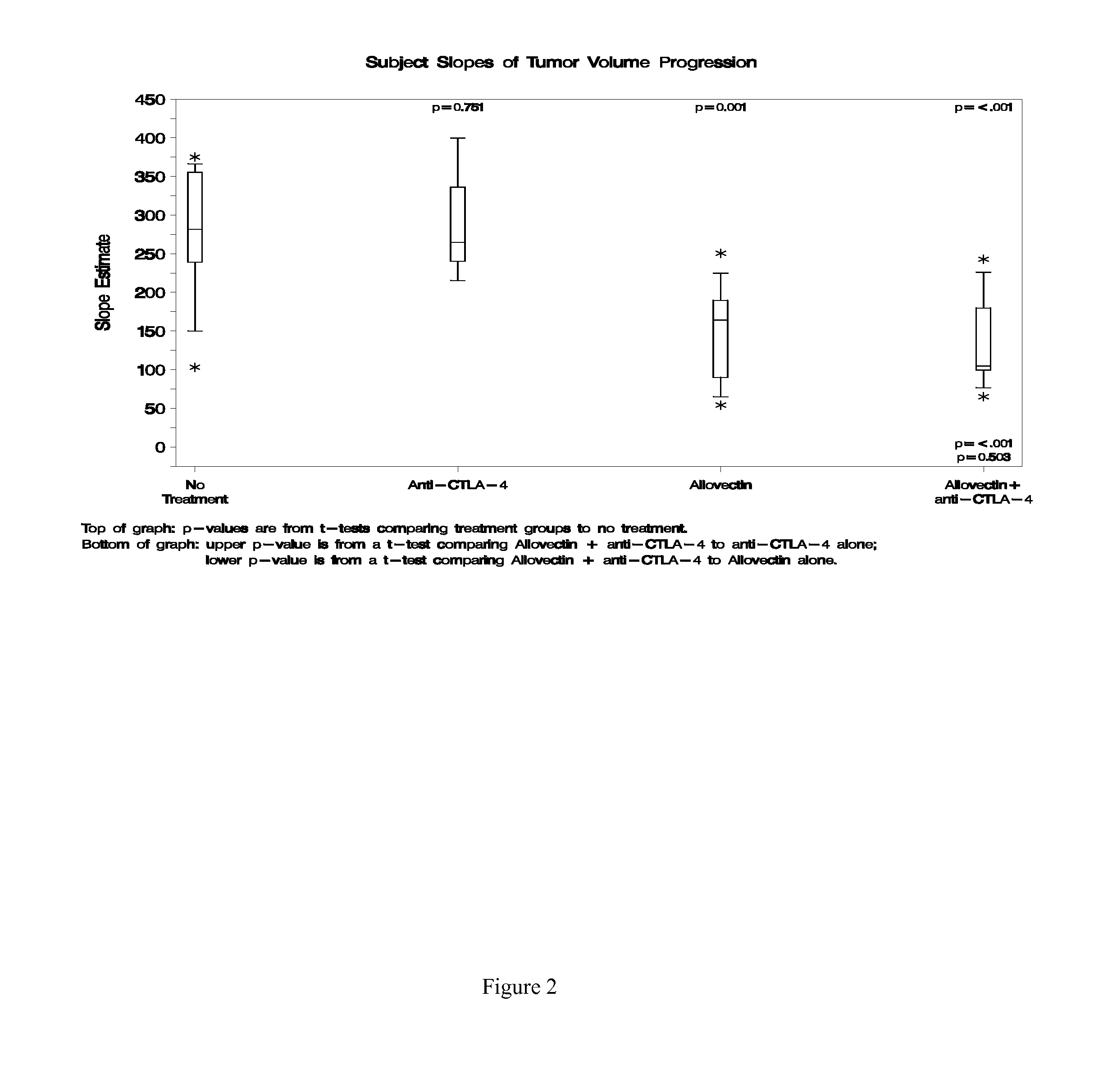
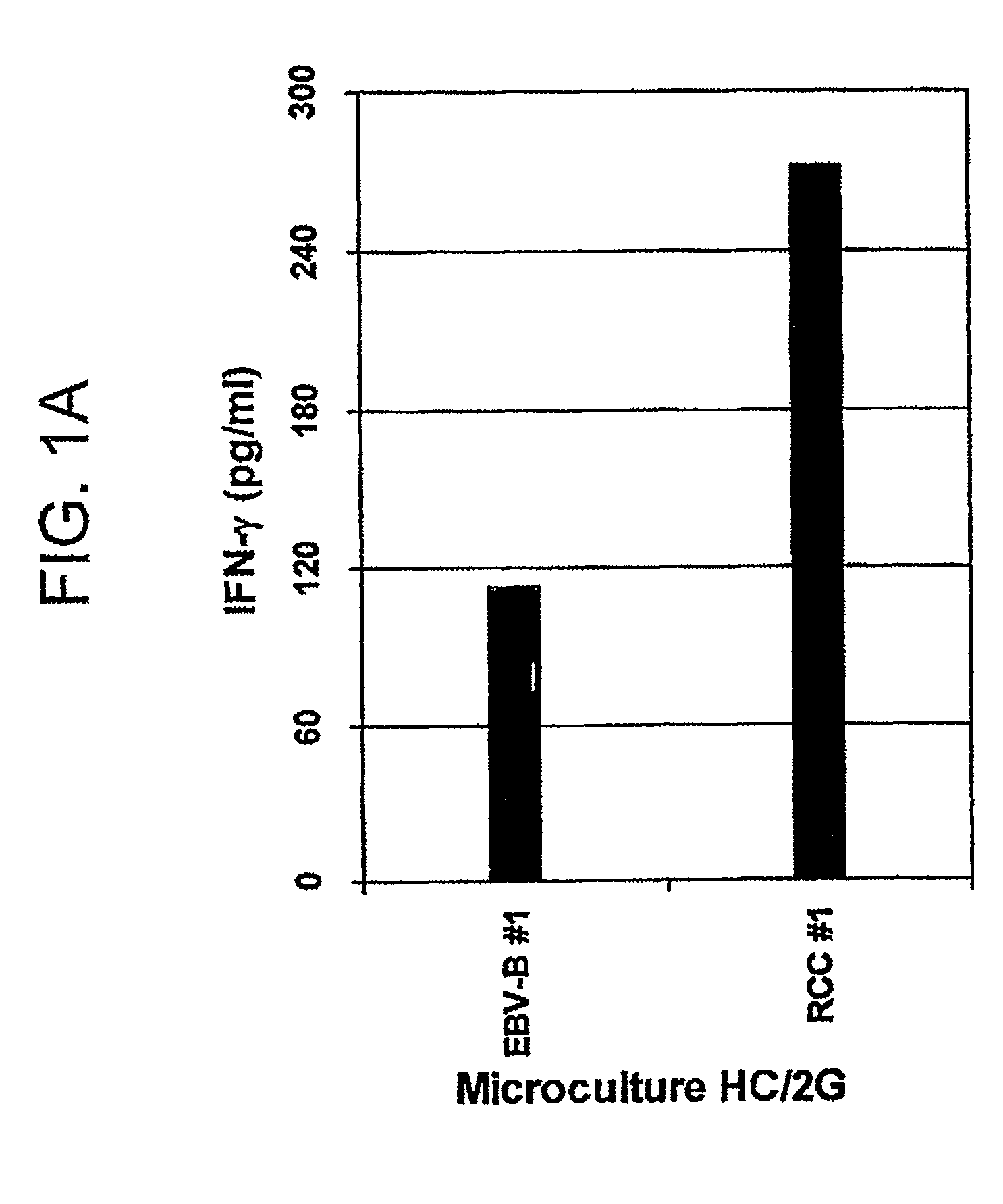
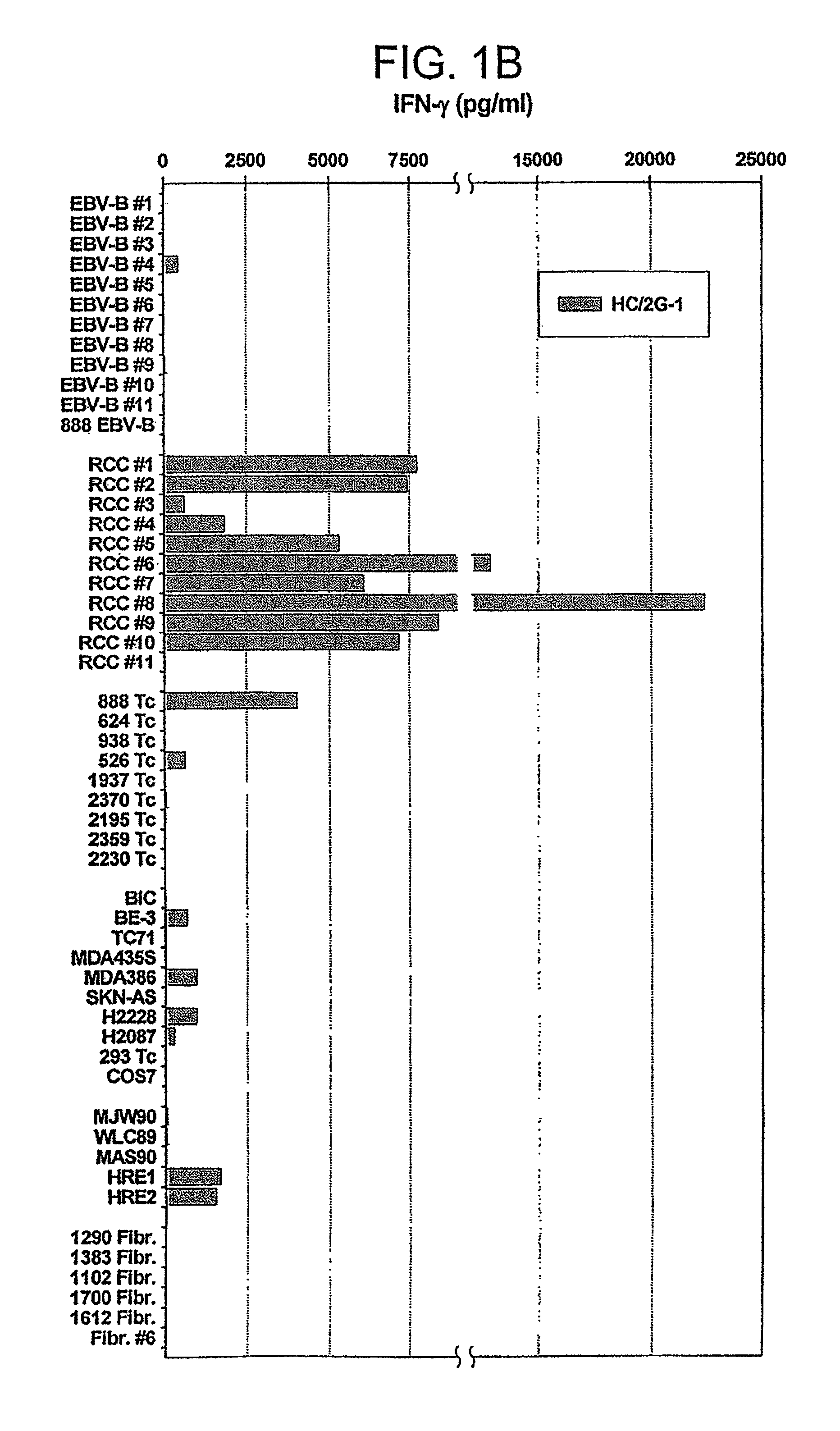
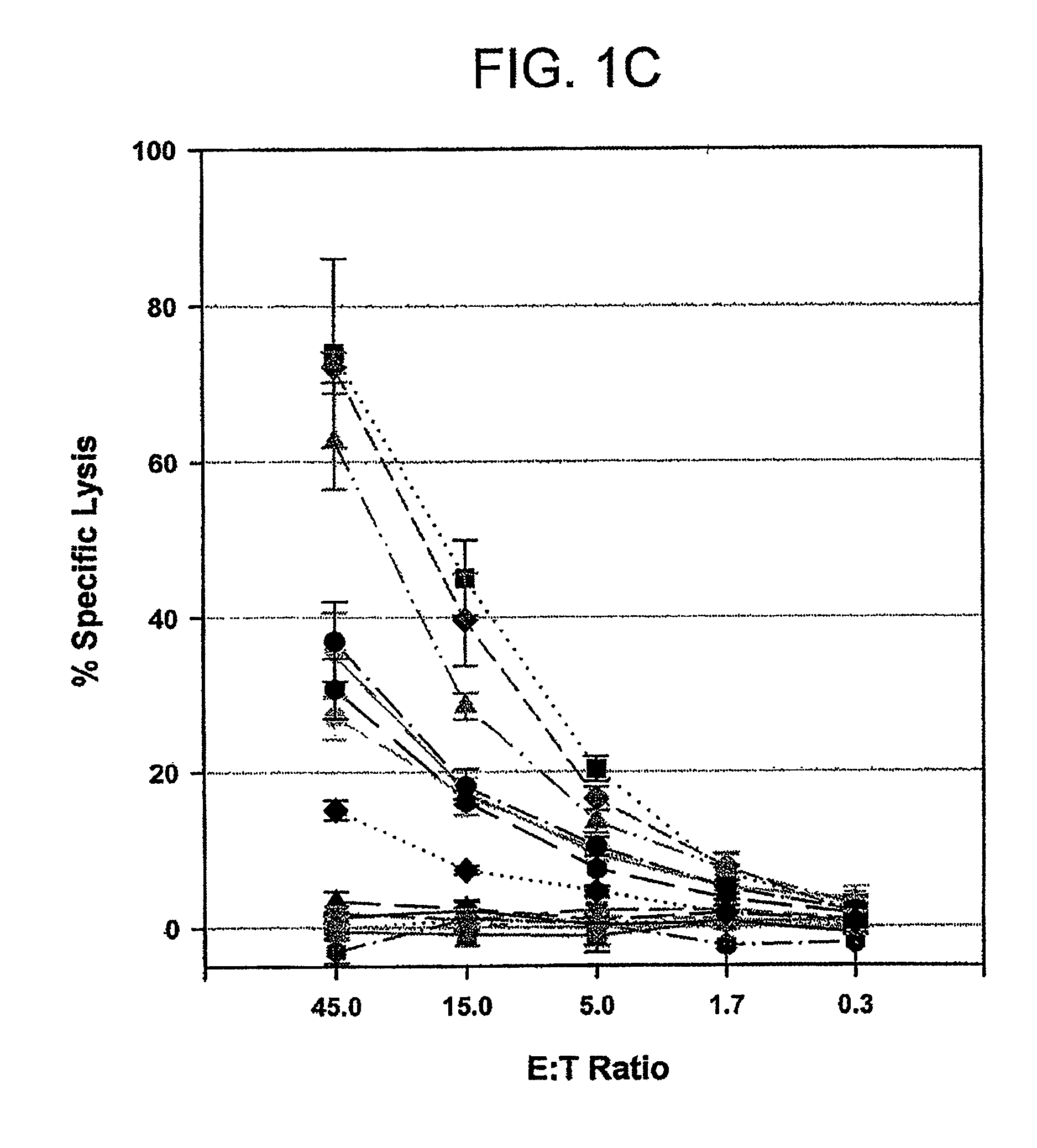
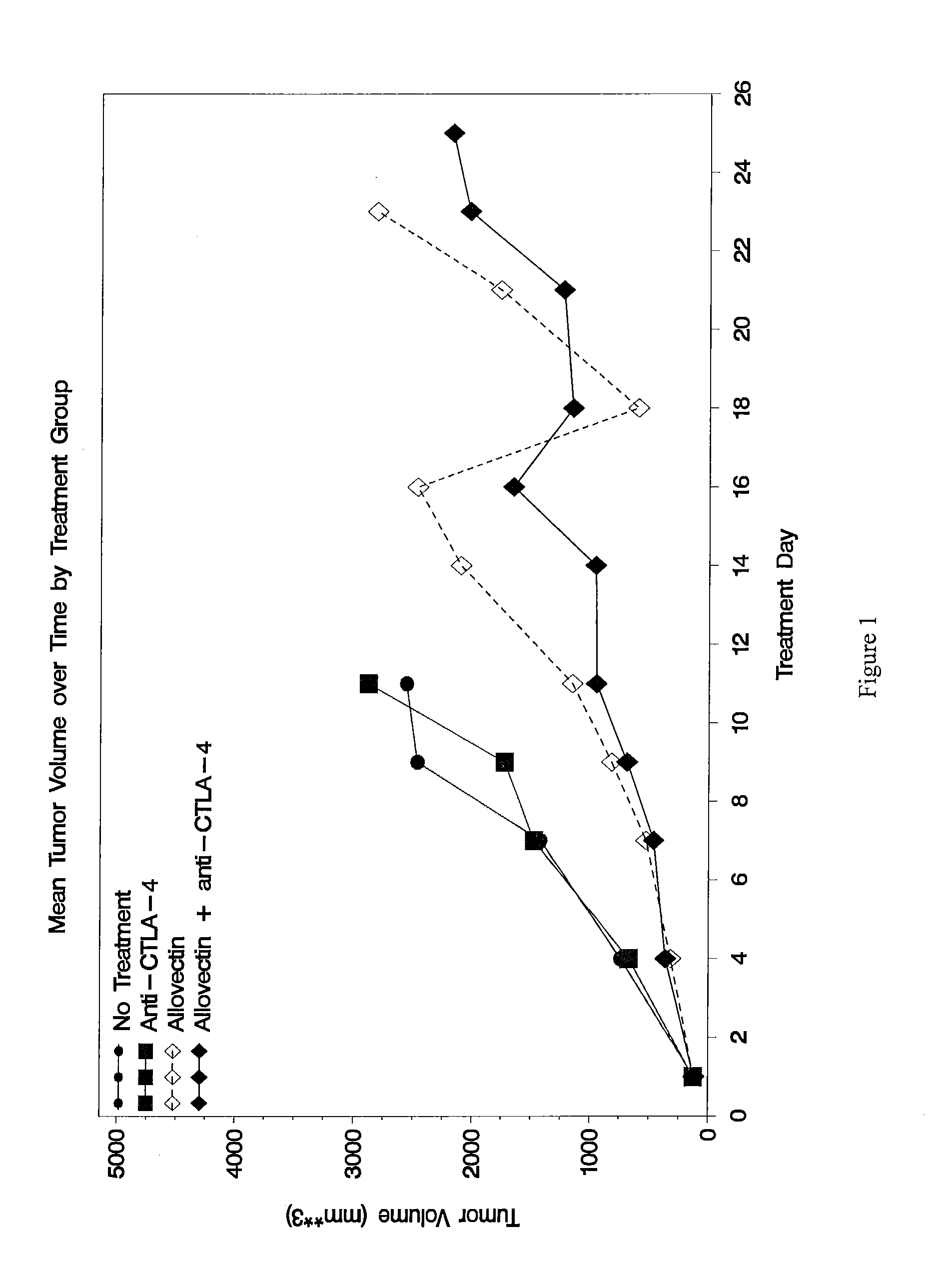
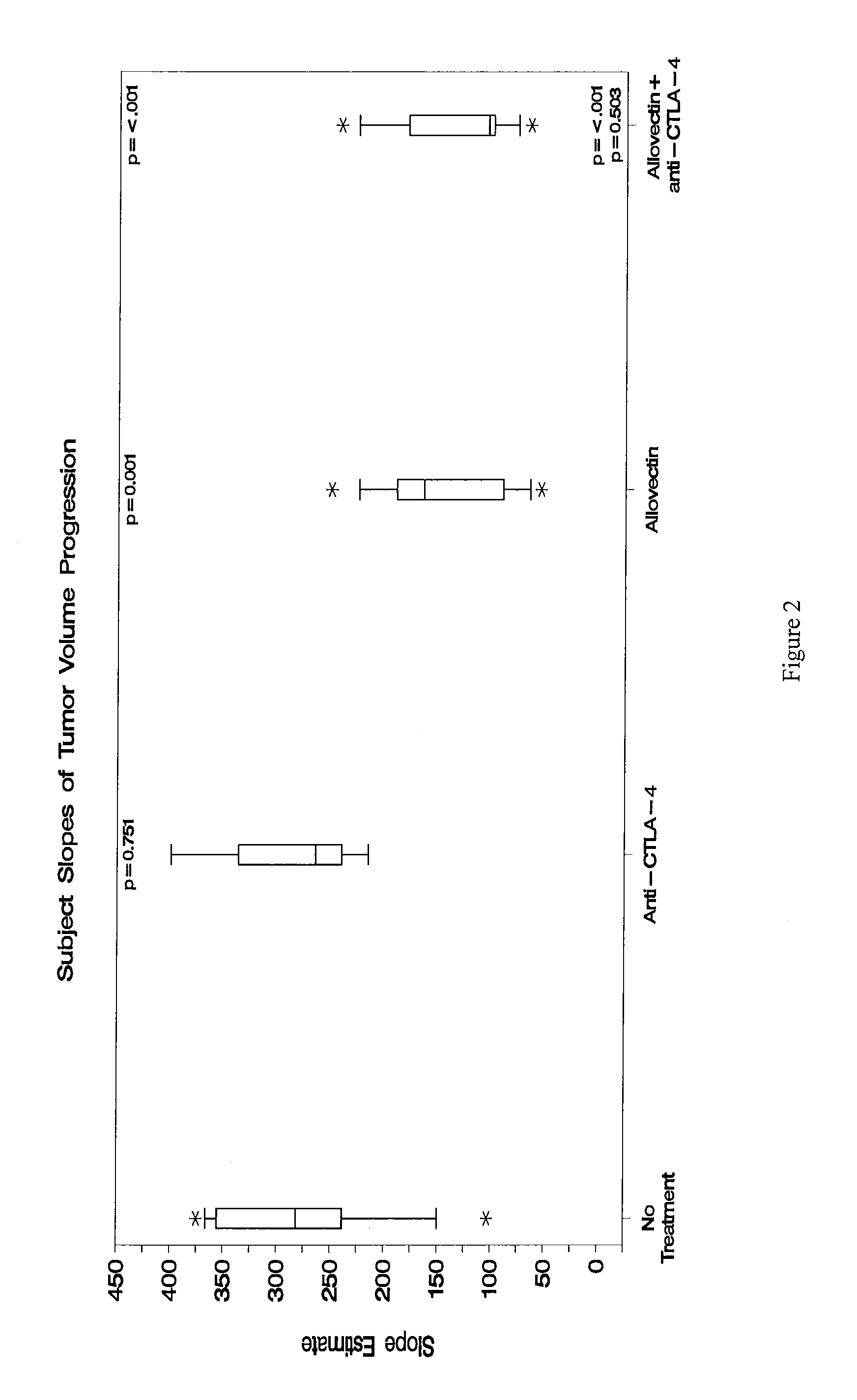
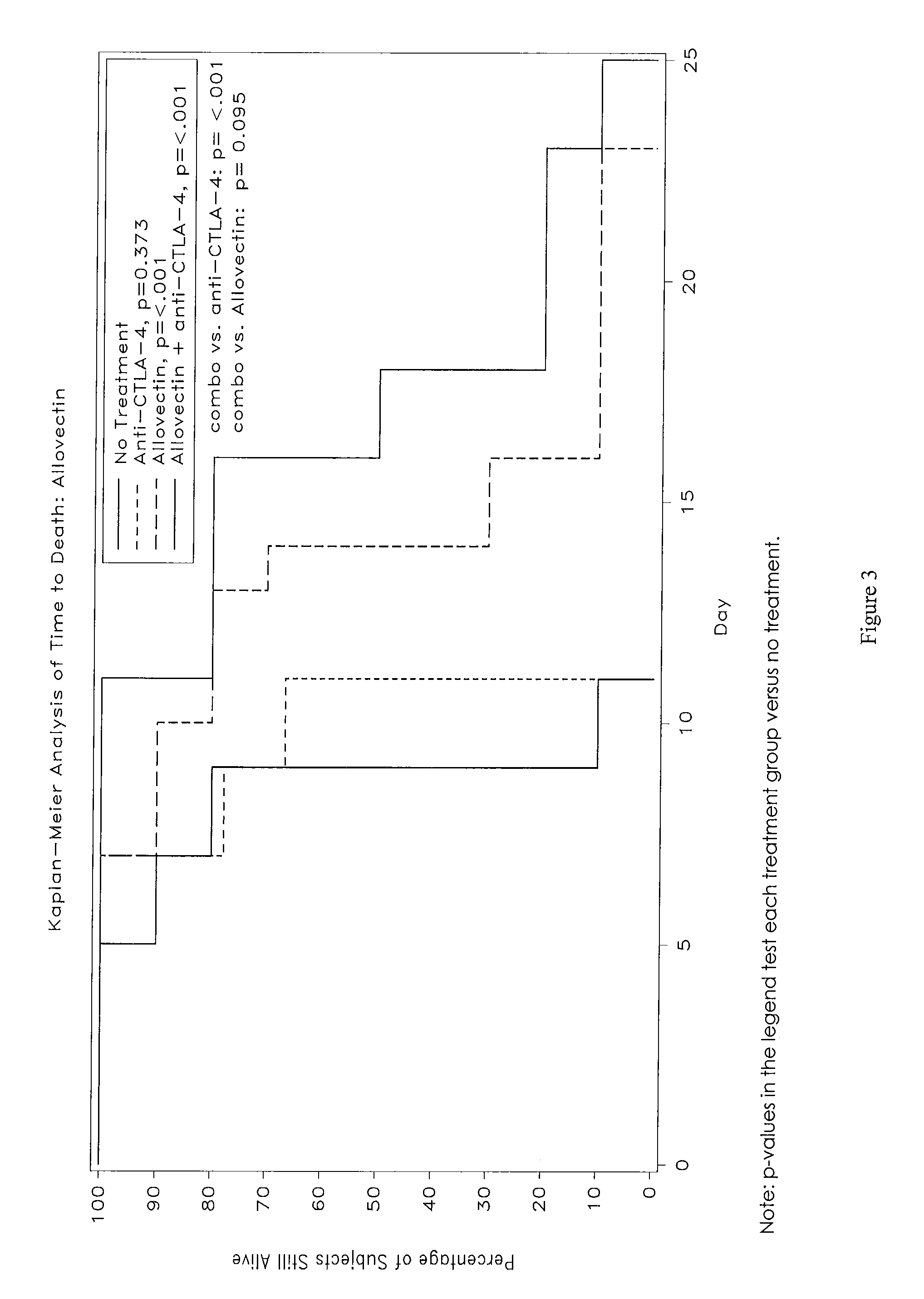
Synergistic Anti-tumor efficacy using alloantigen combination immunotherapy
InactiveUS20130071403A1Increased activationOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsImmunotherapeutic agentIrritation
The present disclosure provides combinations of immunotherapeutics and methods for treating medical conditions that are characterized by the lack of an effective immune response, for example as would result following a down-regulation of MHC class I, such as in cancer. The immunotherapeutic compositions of the invention, which can be used to treat the medical conditions, include one or more immunostimulatory antibodies or molecules having specificity for CTLA-4, PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2, CD40, OX40, CD137, GITR, ILT2, or ILT3, or ligands for these molecules (e.g., an isolated fully-human monoclonal antibody) in association with one or more alloantigens, such as, vector(s) capable of expressing protein(s) or peptide(s) that stimulate T-cell immunity against tissues or cells, formulated in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The proteins or peptides may comprise class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens, β2-microglobulins, or cytokines. The MHC antigen may be foreign to the subject. The MHC antigen may be HLA-B7.
Owner:VICAL INC
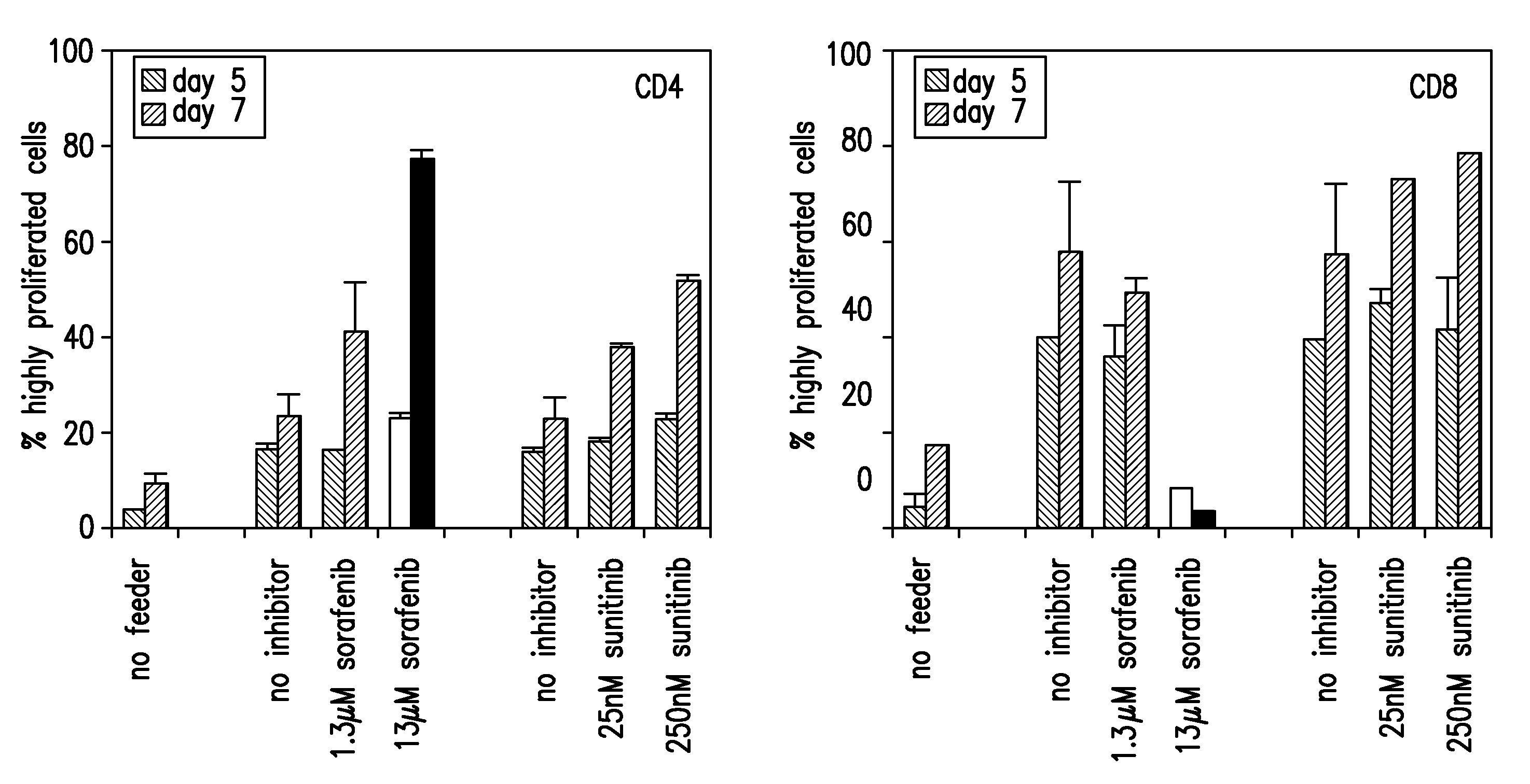
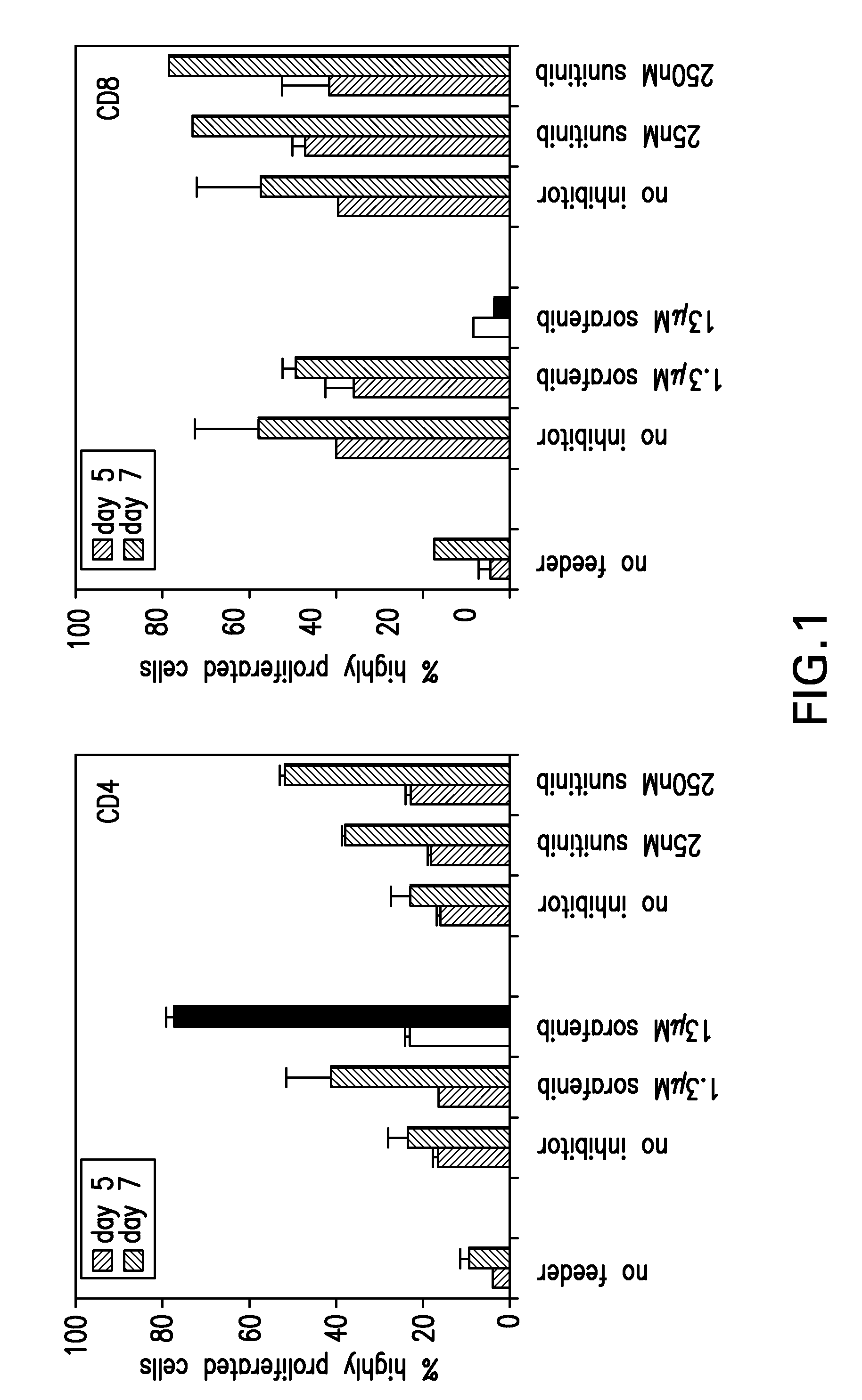
Combination therapy using active immunotherapy
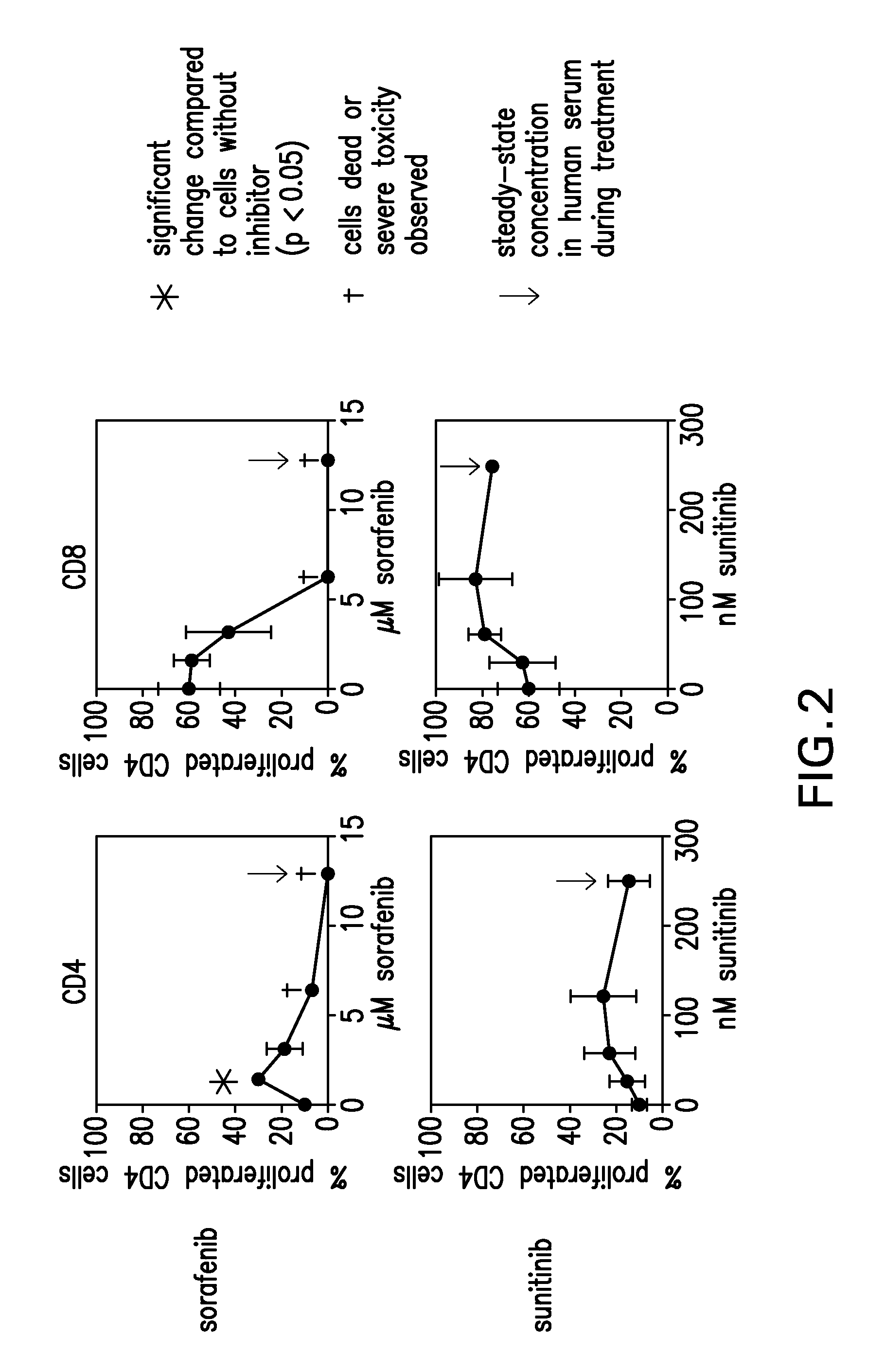
InactiveUS20090004213A1Organic active ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsSunitinib malateMajor histocompatibility
The present invention relates to methods of treating cancer in a mammal comprising administering to the mammal a combination therapy comprising a vaccine and a multi-kinase inhibitor, wherein the vaccine comprises an isolated tumor associated peptide having the ability to bind to a molecule of the human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class-I or class-II. Preferably the multi-kinase inhibitor is sunitinib malate and / or sorafenib tosylate or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
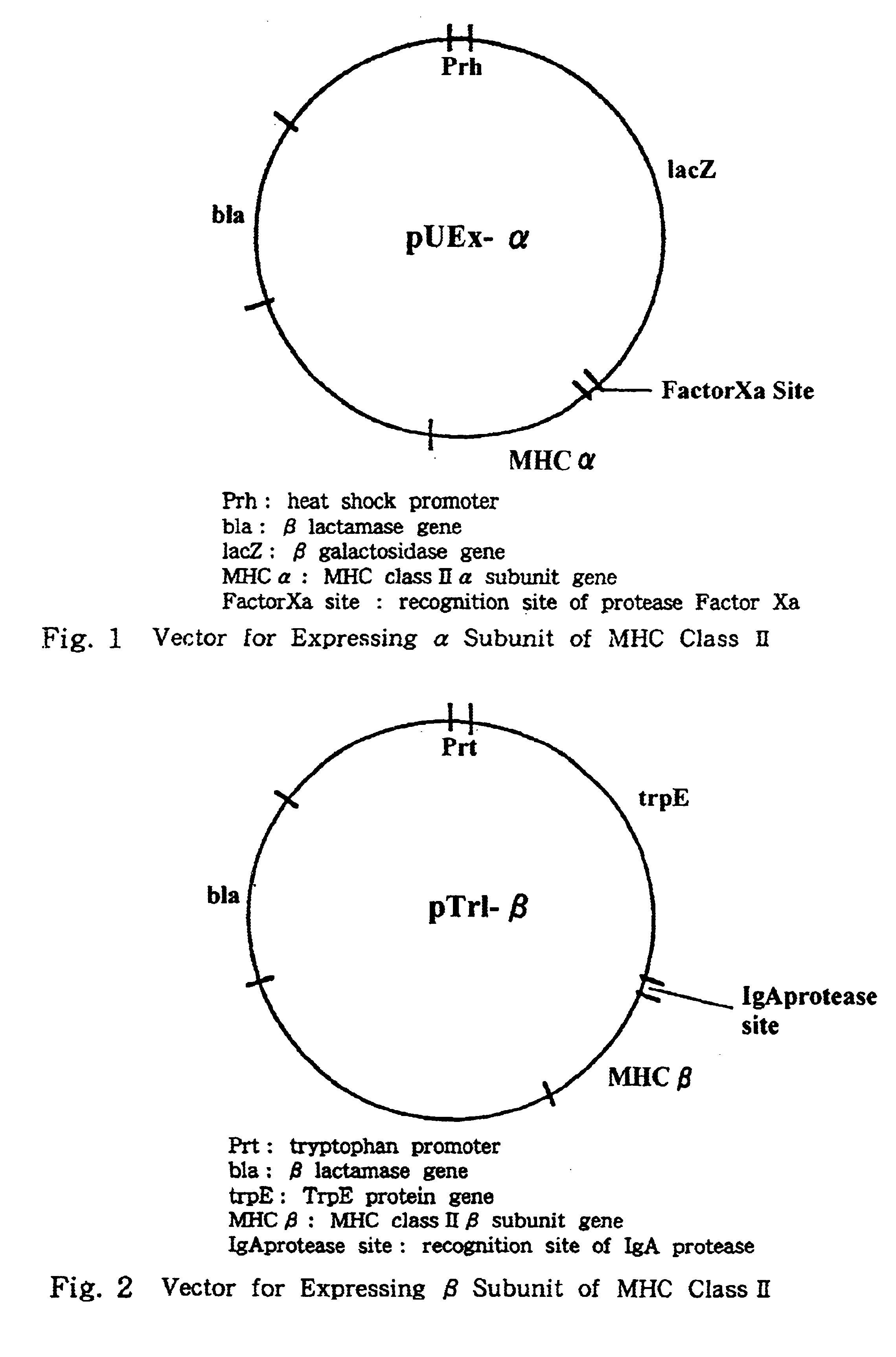
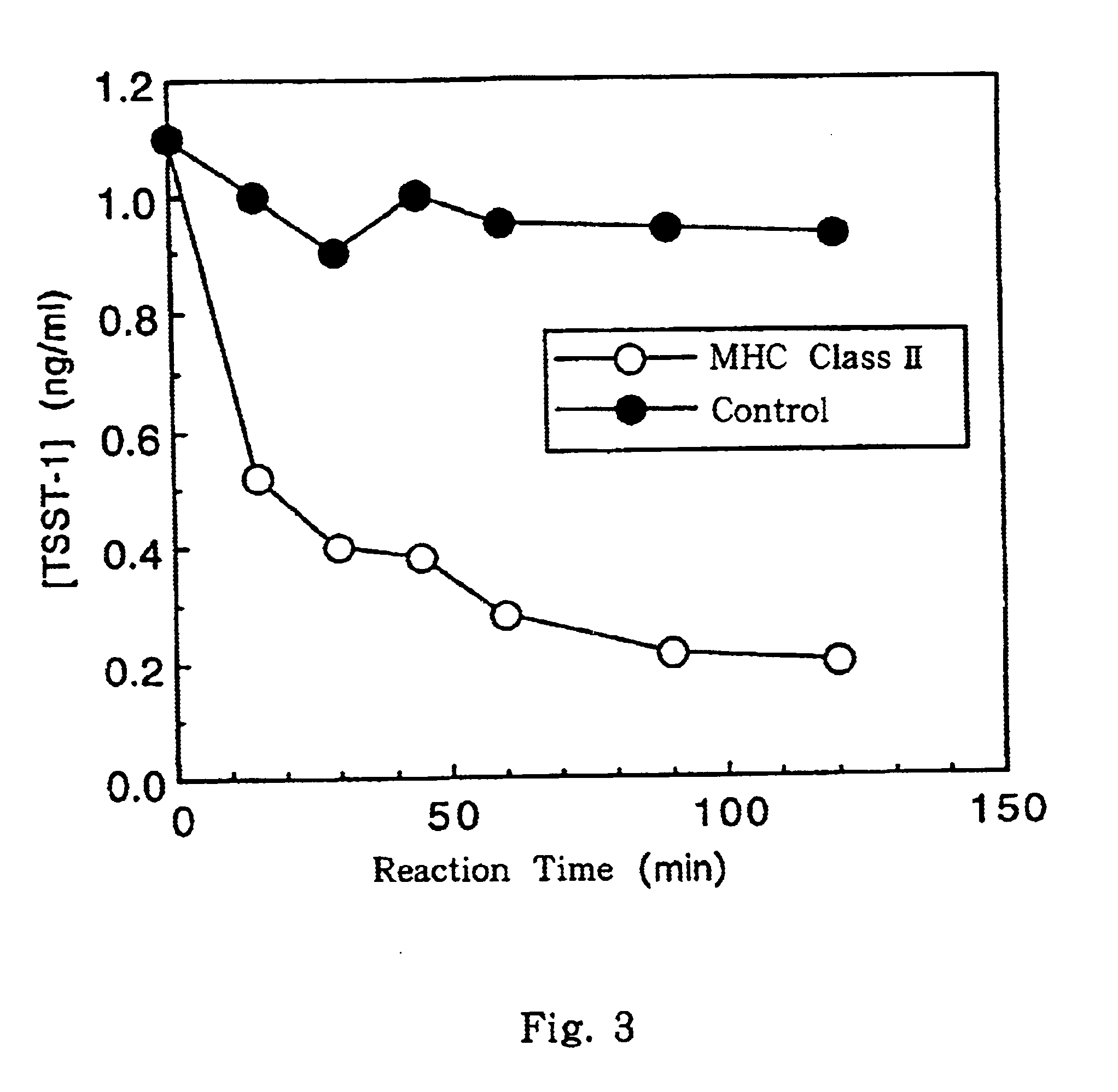
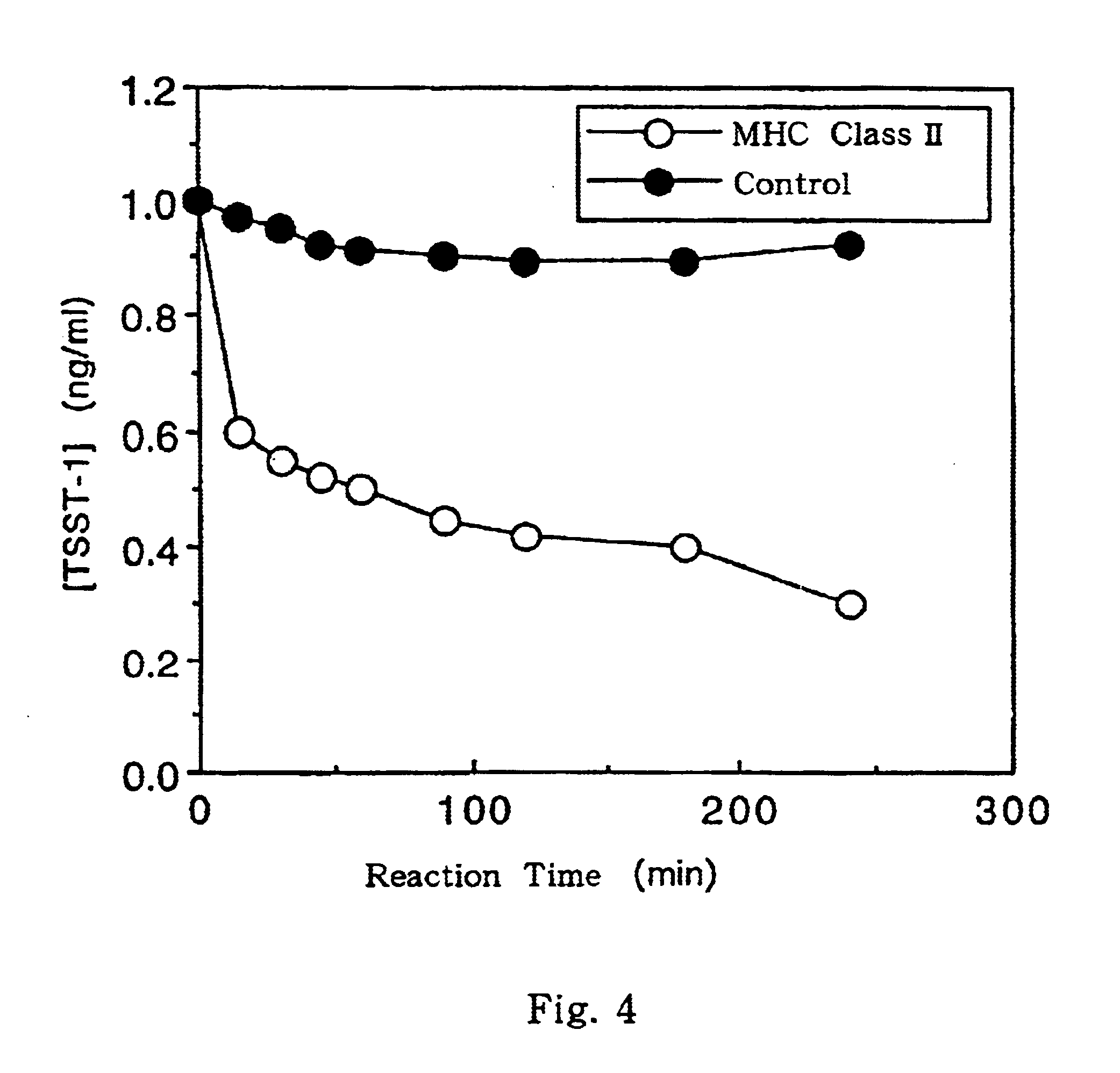
Process for preparing major histocompatibility antigen class II protein and materials in which the same is bound
InactiveUS6630315B1Produce significantIon-exchanger regenerationMicroorganism based processesFiberMajor histocompatibility
This invention provides a process for producing major histocompatibility antigen class II protein (hereinafter referred to as "MHC class II" for short) which occurs on the surfaces of antigen-presenting cells and the like, and MHC class II-bound materials in which MHC class II, alpha and / or beta subunit of MHC class II, or a part thereof is bound to a carrier such as beads, fibers and hollow fibers via covalent bond, as well as a module for removing superantigen using the same. This invention also provides a method for detecting or quantifying superantigens using MHC class II or a part thereof having an affinity to the superantigens, as well as an assay kit therefor.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Peptides and combination of peptides for use in immunotherapy against small cell lung cancer and other cancers
ActiveUS10253077B2Increase in motilityAid in diagnosisPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAbnormal tissue growthAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients. Peptides bound to molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or peptides as such, can also be targets of antibodies, soluble T-cell receptors, and other binding molecules.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Tumor antigen based on products of the tumor suppressor gene WT1
Owner:INT INST OF CANCER IMMUNOLOGY INC
Novel peptides and combination of peptides and scaffolds thereof for use in immunotherapy against colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and other cancers
ActiveUS20160346371A1Reduce releaseImprove discriminationImmunoglobulin superfamilyTumor rejection antigen precursorsEpitopeMajor histocompatibility
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Universal CAR-T cell and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107723275AImprove expression rateImprove effectiveness and safetyMammal material medical ingredientsNucleic acid vectorAbnormal tissue growthDisease
The invention belongs to the field of immunotherapy and relates to a universal CAR-T cell and a preparation method and application thereof. In the universal CAR-T cell, the functions of a T cell antigen receptor (TCR) and major histocompatibility complexes (MHC I and MHC II) in the T cell are inhibited while multi-gene knockout is performed; a gene encoding the TCR includes TRAC and / or TRBC; genesencoding the major histocompatibility complexes include HLA-A, B2MH and CIITA. The universal CAR-T cell can target relevant markers of specific tumors and inactivate the functions of the TCR and theMHC on the cell surface, can reduce immunological rejection caused by allogeneic cell therapy and safely and effectively remove tumor cells in the diseased human body, is not affected by the disease or a treatment mode of a patient in use and can be prepared at any time, treatment can be provided at the optimum time, and treatment effectiveness is ensured.
Owner:CHONGQING PRECISION BIOTECH CO LTD
Genetically modified major histocompatibility complex mice
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express chimeric human / non-human MHC I and MHC II polypeptides and / or human or humanized β2 microglobulin polypeptide, as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the same. Also provided are constructs for making said genetically modified animals and methods of making the same. Methods of using the genetically modified animals to study various aspects of human immune system are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Novel peptides and combination of peptides for use in immunotherapy against prostate cancer and other cancers
ActiveUS20170037089A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAdditive ingredientProstate cancer
The present invention relates to peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients. Peptides bound to molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or peptides as such, can also be targets of antibodies, soluble T-cell receptors, and other binding molecules.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Novel peptides and combination of peptides and scaffolds for use in immunotherapy against Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) and other cancers
ActiveUS20160287687A1High error rateIncreased riskPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeMajor histocompatibility
The present invention relates to peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients. Peptides bound to molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or peptides as such, can also be targets of antibodies, soluble T-cell receptors, and other binding molecules.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
T cell receptors and related materials and methods of use
InactiveUS7820174B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsMajor histocompatibilityCancer antigen
The invention provides an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for a cancer antigen, e.g., a renal cell carcinoma antigen, wherein the TCR recognizes the cancer antigen in a major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-independent manner. Also provided are related polypeptides, proteins, nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, isolated host cells, populations of cells, antibodies, or antigen binding portions thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions. The invention further provides a method of detecting the presence of cancer in a host and a method of treating or preventing cancer in a host using the inventive TCRs or related materials.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Synergistic Anti-tumor efficacy using alloantigen combination immunotherapy
InactiveUS20130280265A1Increased activationOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsImmunotherapeutic agentEfficacy
The present disclosure provides combinations of immunotherapeutics and methods for treating medical conditions that are characterized by the lack of an effective immune response, for example as would result following a down-regulation of MHC class I, such as in cancer. The immunotherapeutic compositions of the invention, which can be used to treat the medical conditions, include one or more immunostimulatory antibodies or molecules having specificity for CTLA-4, PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2, CD40, OX40, CD137, GITR, ILT2, or ILT3, or ligands for these molecules (e.g., an isolated fully-human monoclonal antibody) in association with one or more alloantigens, such as, vector(s) capable of expressing protein(s) or peptide(s) that stimulate T-cell immunity against tissues or cells, formulated in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The proteins or peptides may comprise class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens, β2-microglobulins, or cytokines. The MHC antigen may be foreign to the subject. The MHC antigen may be HLA-B7.
Owner:VICAL INC
Method of epitope discovery
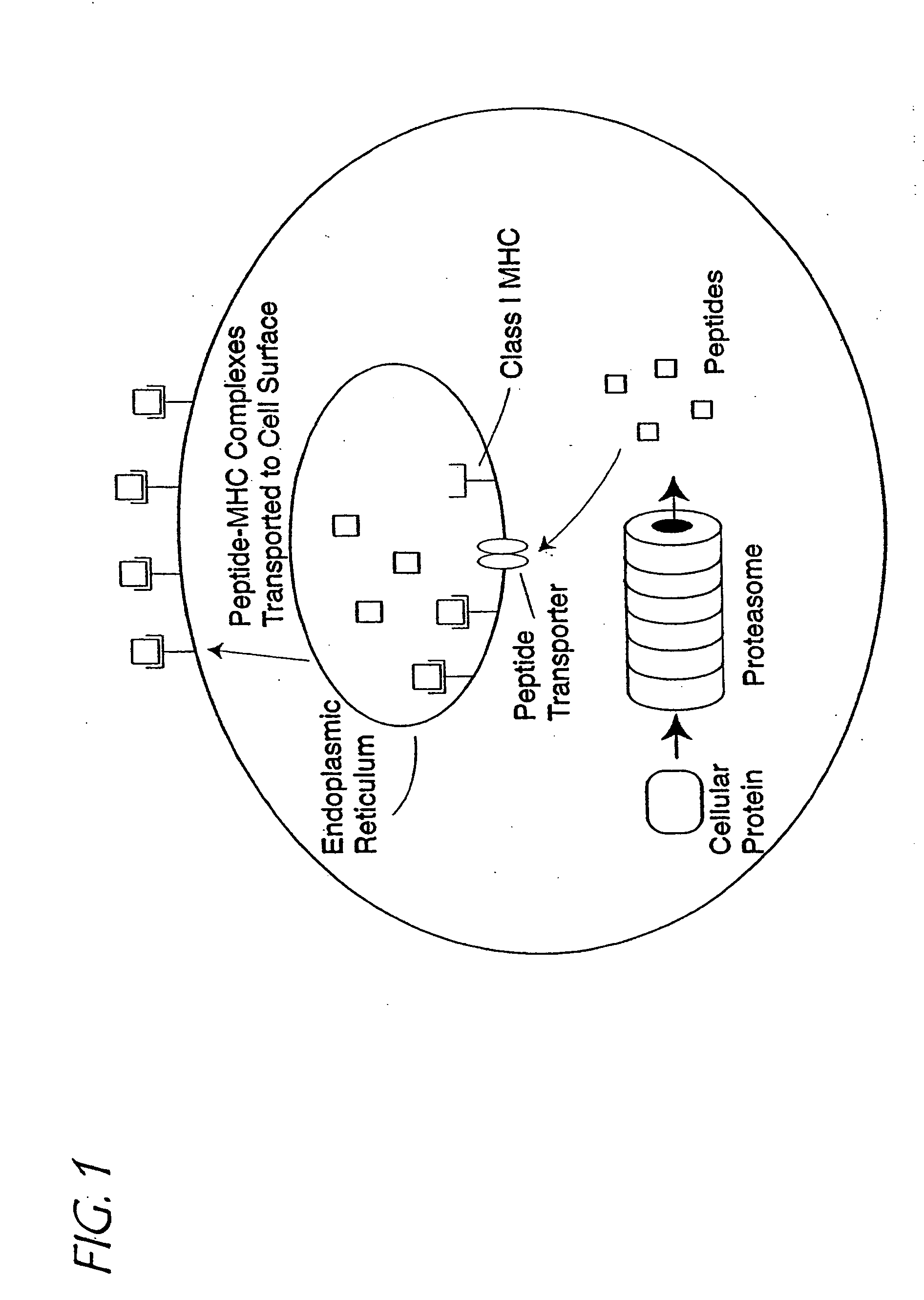
A method of epitope discovery comprising the step of selecting an epitope from a population of peptide fragments of an antigen associated with a target cell, wherein the fragments have a known or predicted affinity for a major histocompatibility complex class I receptor peptide binding cleft, wherein the epitope selected corresponds to a proteasome cleavage product of the target cell.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Novel peptides and combination of peptides for use in immunotherapy against pancreatic cancer and other cancers
The present invention relates to peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients. Peptides bound to molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or peptides as such, can also be targets of antibodies, soluble T-cell receptors, and other binding molecules.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Product and process for T lymphocyte immunosuppression
InactiveUS6264950B1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMajor histocompatibilityActivation cells
The present invention relates to a product and process for suppressing an immune response using a T lymphocyte veto molecule capable of blocking cell surface molecules responsible for T cell activation. Disclosed is a CD4 or CD2 molecule, associated with an immunoglobulin molecule capable of binding to a major histocompatibility antigen. Also disclosed is a method to produce a T lymphocyte veto molecule, a therapeutic composition comprising a T lymphocyte veto molecule and methods to use T lymphocyte veto molecules in therapeutic processes requiring suppression of an immune response.
Owner:NAT JEWISH MEDICAL & RES CENT
Novel peptides and combination of peptides for use in immunotherapy against breast cancer and other cancers
ActiveUS20170173132A1High error rateImmunoglobulin superfamilyTumor rejection antigen precursorsAdditive ingredientNeoplasm
The present invention relates to peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients. Peptides bound to molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or peptides as such, can also be targets of antibodies, soluble T-cell receptors, and other binding molecules.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Novel peptides and combination of peptides for use in immunotherapy against NHL and other cancers
ActiveUS20170296640A1High error ratePromote cell proliferationTumor rejection antigen precursorsTumor specific antigensEpitopeMajor histocompatibility
The present invention relates to peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients. Peptides bound to molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or peptides as such, can also be targets of antibodies, soluble T-cell receptors, and other binding molecules.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Universal donor cells
InactiveUS6916654B1Inhibition of activationHigh degreePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsClass II major histocompatibility complex geneT cell
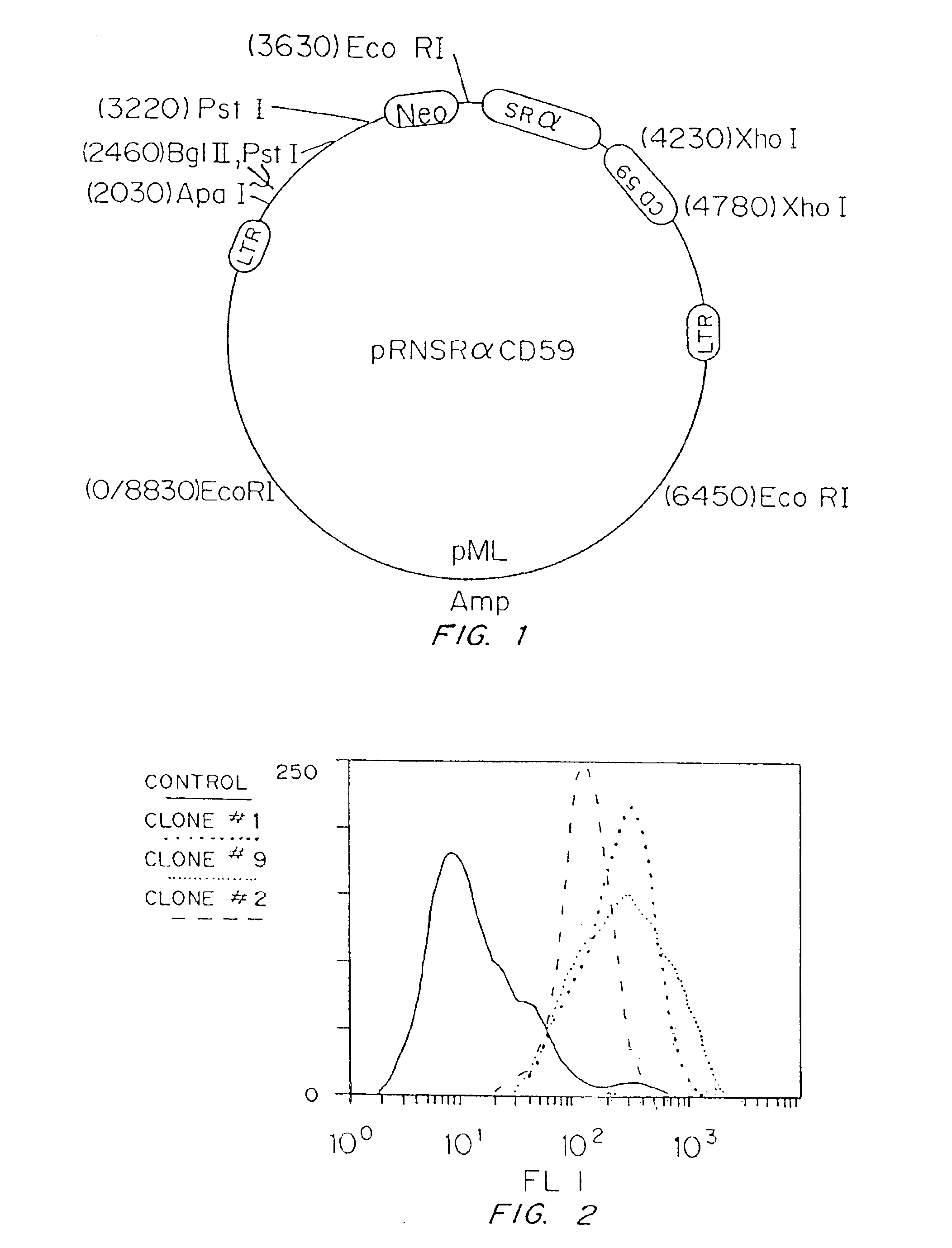
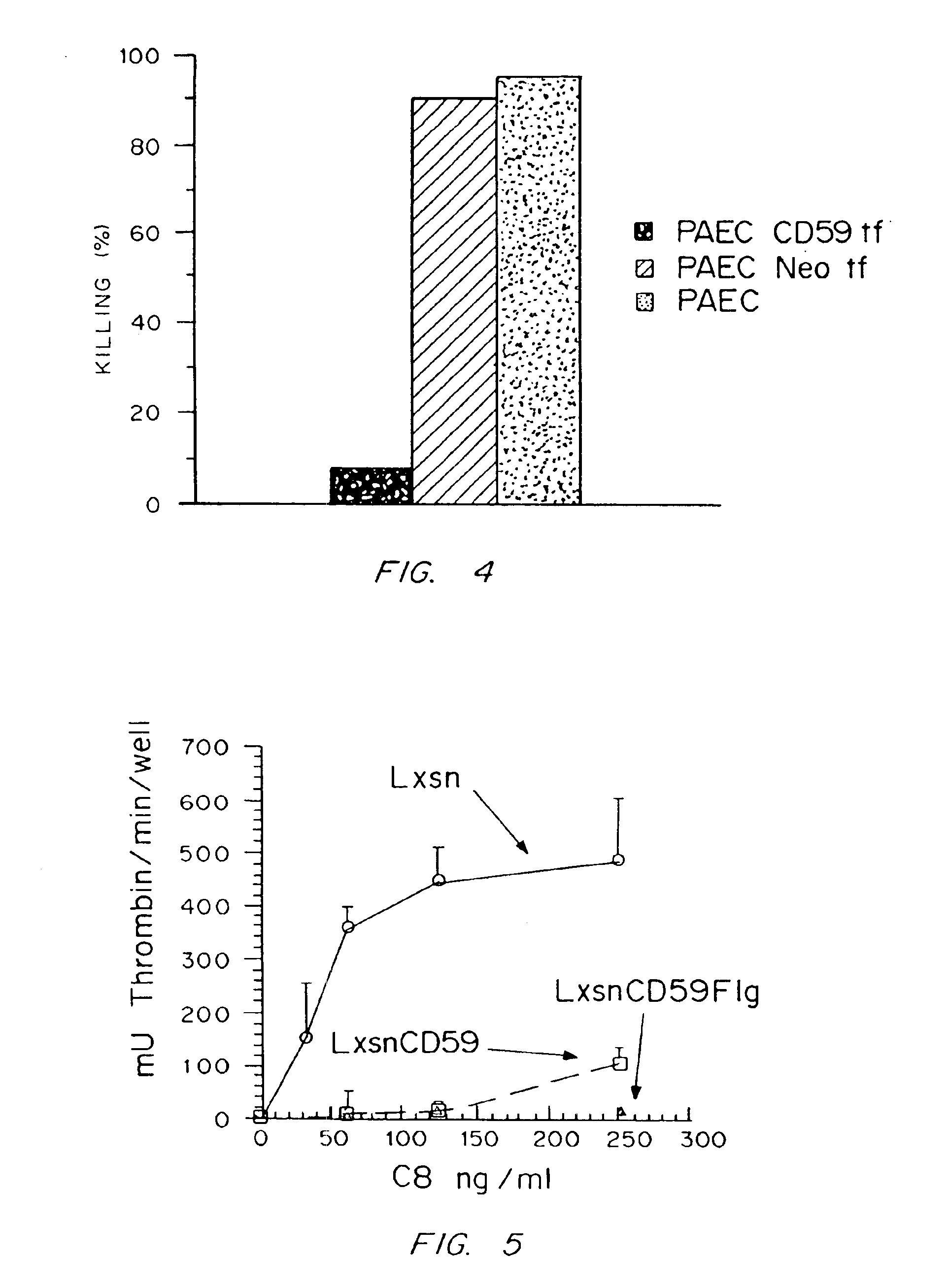
Genetically engineered cells are provided which can serve as universal donor cells in such applications as reconstruction of vascular linings or the administration of therapeutic agents. The cells include a coding region which provides protection against complement-based lysis, i.e., hyperacute rejection. In addition, the cell's natural genome is changed so that functional proteins encoded by either the class II or both the class I and the class II major histocompatibility complex genes do not appear on the cell's surface. In this way, attack by T-cells is avoided. Optionally, the cells can include a self-destruction mechanism so that they can be removed from the host when no longer needed.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND +1
Immunogenic peptides and their use in immune disorders
ActiveUS20100303866A1High expressionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAuto antigenAutoimmune disease
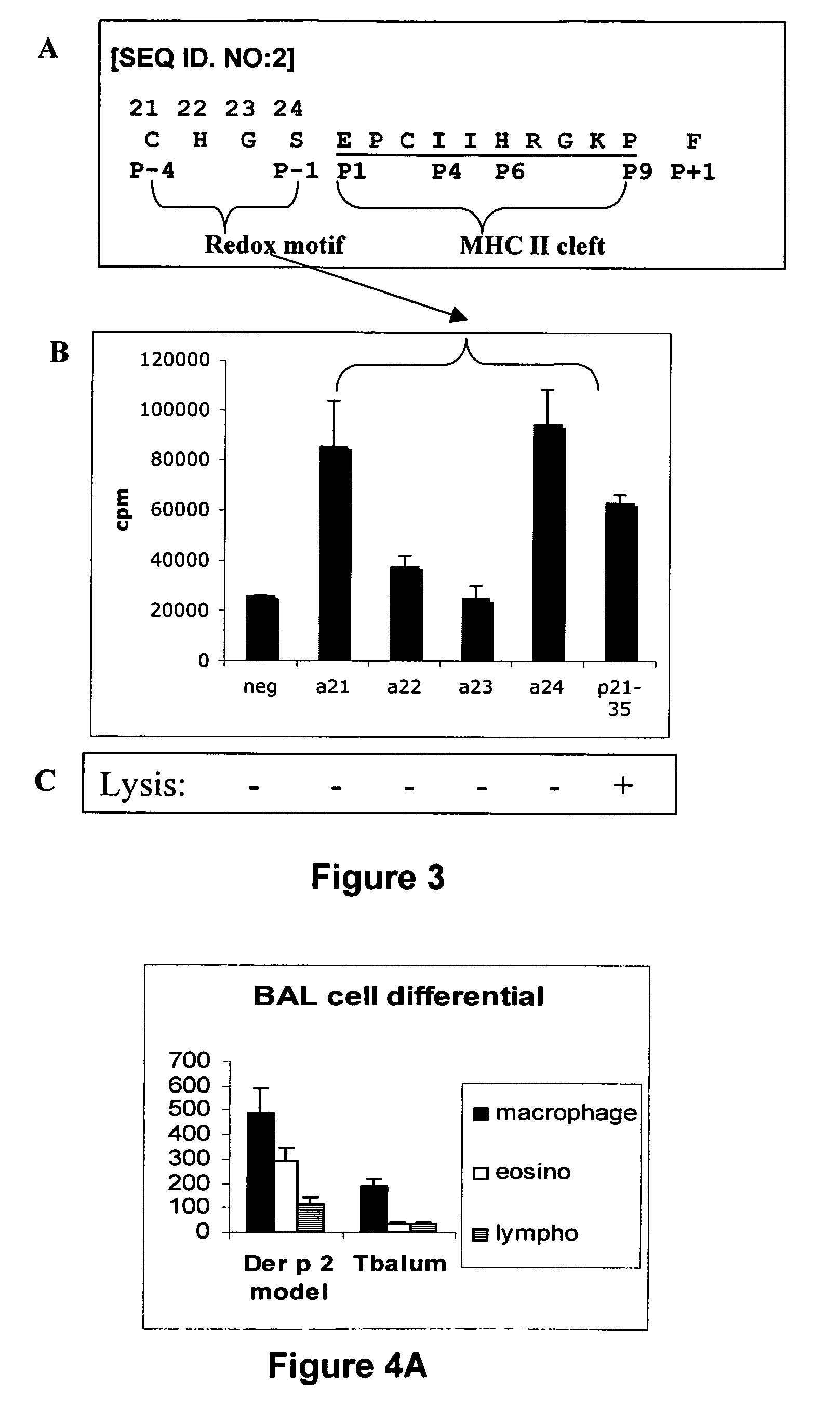
The present invention provides novel peptides and homologues thereof. The peptides of the invention comprise (i) a T-cell epitope of an antigen (self or non-self) with a potential to trigger an immune reaction presented by a class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) determinant and recognised by CD4+ T cell more specifically of an allergen or auto-antigen, coupled, optionally through the use of a linker to (ii) an amino acid sequence having a reducing activity, such as a thioreductase sequence. The peptides of the invention have been shown to be useful a medicine, more in particular for the prevention or treatment of immune disorders, more specifically of allergic disorders or autoimmune diseases. The present invention thus provides for the use of said peptides for the manufacture of a medicament for the prevention or treatment of an immune disorder and further provides for methods of treatment or preventing immune disorders by using said peptides. The present invention also provides for compositions comprising said peptides.
Owner:IMCYSE
Engineering t cell receptors
InactiveUS20150191524A1Immunoglobulin superfamilySugar derivativesMajor histocompatibilityPeptide ligand
The use of model T cell receptors (TCRs) as scaffolds for in vitro engineering of novel specificities is provided. TCRs with de novo binding to a specific peptide-major histocompatibility complex (MHC) product can be isolated by: 1) mutagenizing a T cell receptor protein coding sequence to generate a variegated population of mutants (a library), 2) selection of the library of TCR mutants with the specific peptide-MHC, using a process of directed evolution and a “display” methodology (e.g., yeast, phage, mammalian cell) and the peptide-MHC ligand. The process can be repeated to identify TCR variants with improved affinity for the selecting peptide-MHC ligand.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Tumor antigen based on products of the tumor suppressor gene WT1
InactiveUS20050266014A1Effect be exertPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureTumour suppressor geneMajor histocompatibility
A tumor antigen that comprises, as an active ingredient, a product of the Wilms' tumor suppressor gene WT1 or a peptide composed of 7-30 contiguous amino acids containing an anchor amino acid for binding to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I in said amino acid sequence, and a vaccine comprising said antigen.
Owner:INT INST OF CANCER IMMUNOLOGY INC
Antibody having a t-cell receptor-like specificity, yet higher affinity, and the use of same in the detection and treatment of cancer, viral infection and autoimmune disease
InactiveUS20050255101A1High affinityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementAutoimmune conditionMajor histocompatibility
An isolated molecule which comprises an antibody specifically bindable with a binding affinity below 20 nanomolar, preferably below 10 nanomolar, to a human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I being complexed with a HLA-restricted antigen and optionally further comprises an identifiable or therapeutic moiety conjugated to the antibody.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
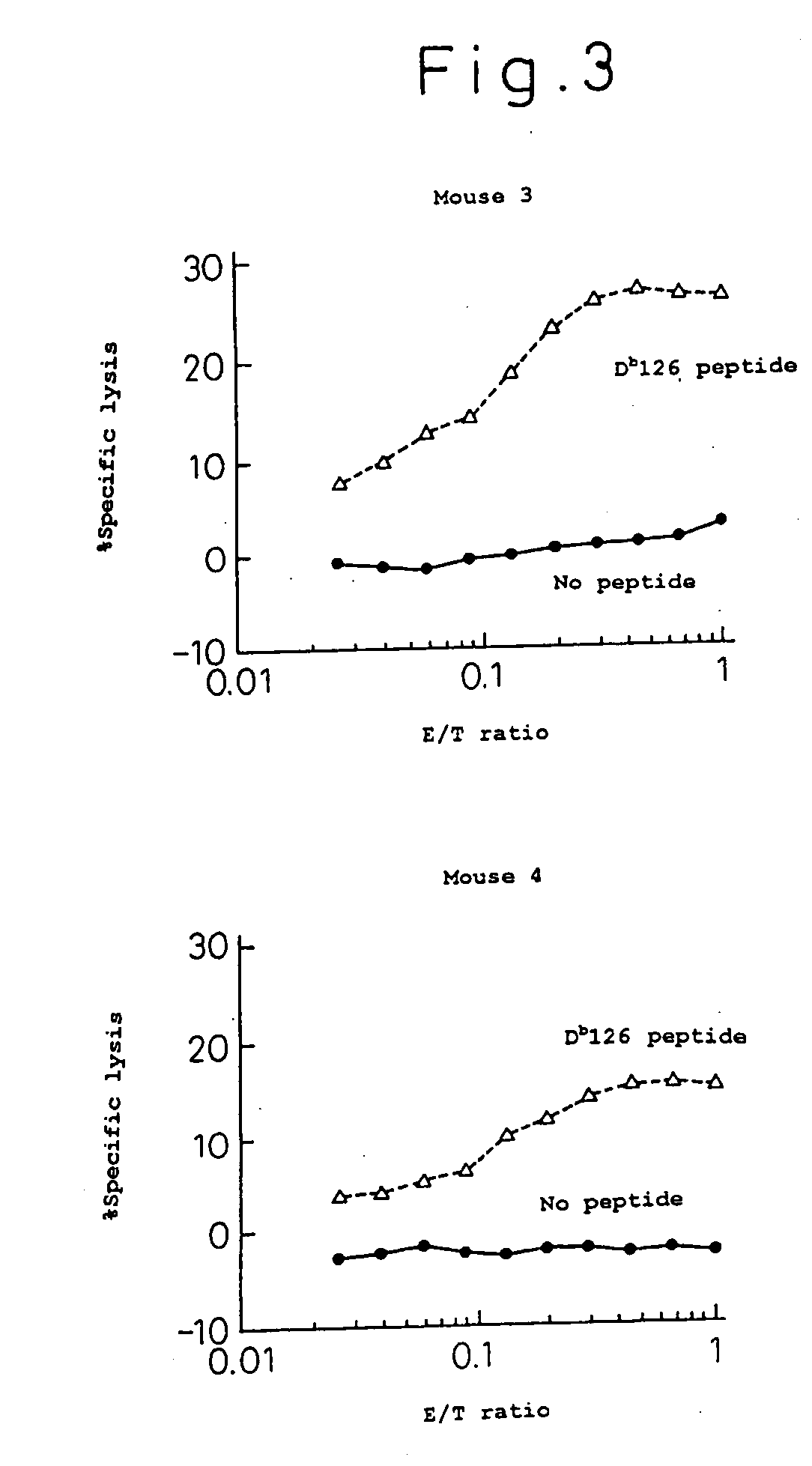
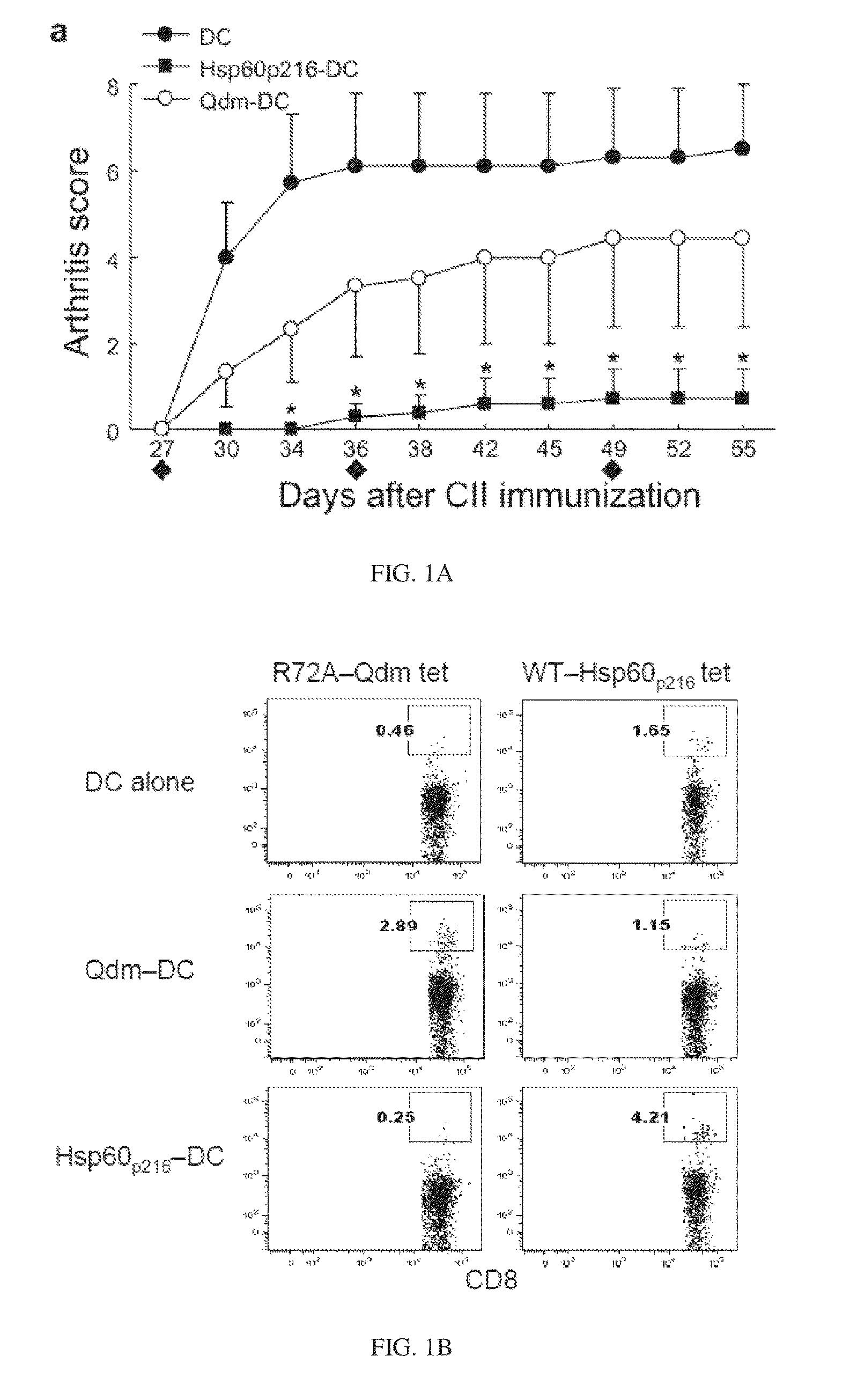
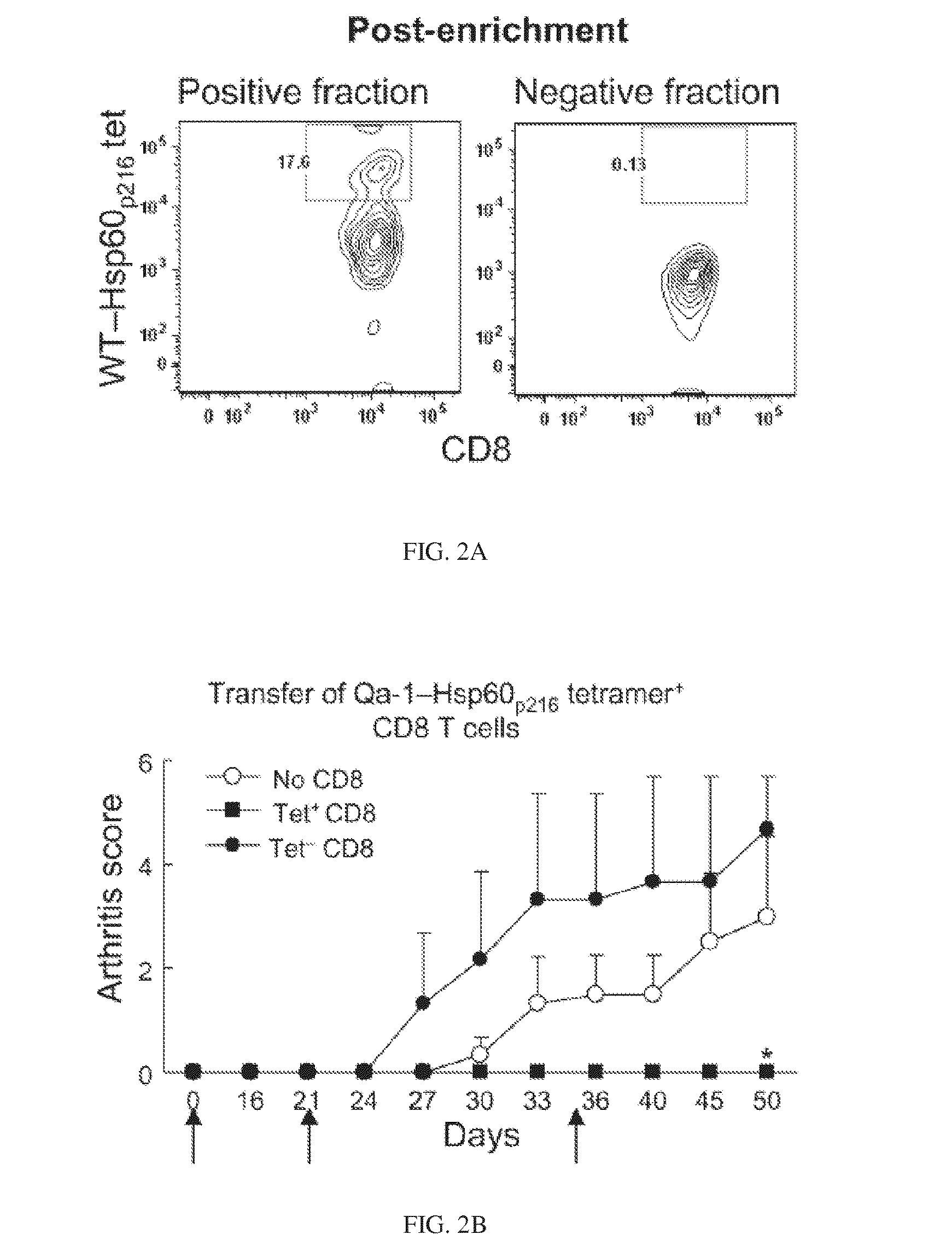
Targeted expansion of qa-1-peptide-specific regulatory cd8 t cells to ameliorate arthritis
ActiveUS20150250862A1Symptoms improvedEffective to ameliorateMammal material medical ingredientsDepsipeptidesAutoimmune responsesAutoimmune disease
Nanoparticles to treat autoimmune diseases and HIV infection are provided. The nanoparticles comprise a biocompatible polymer and a complex, wherein the complex is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I antigen E (HLA-E) linked to a peptide, and wherein the HLA-E-peptide complex is linked to the surface of the nanoparticle. The present invention also relates to methods for treating autoimmune diseases and HIV infection.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
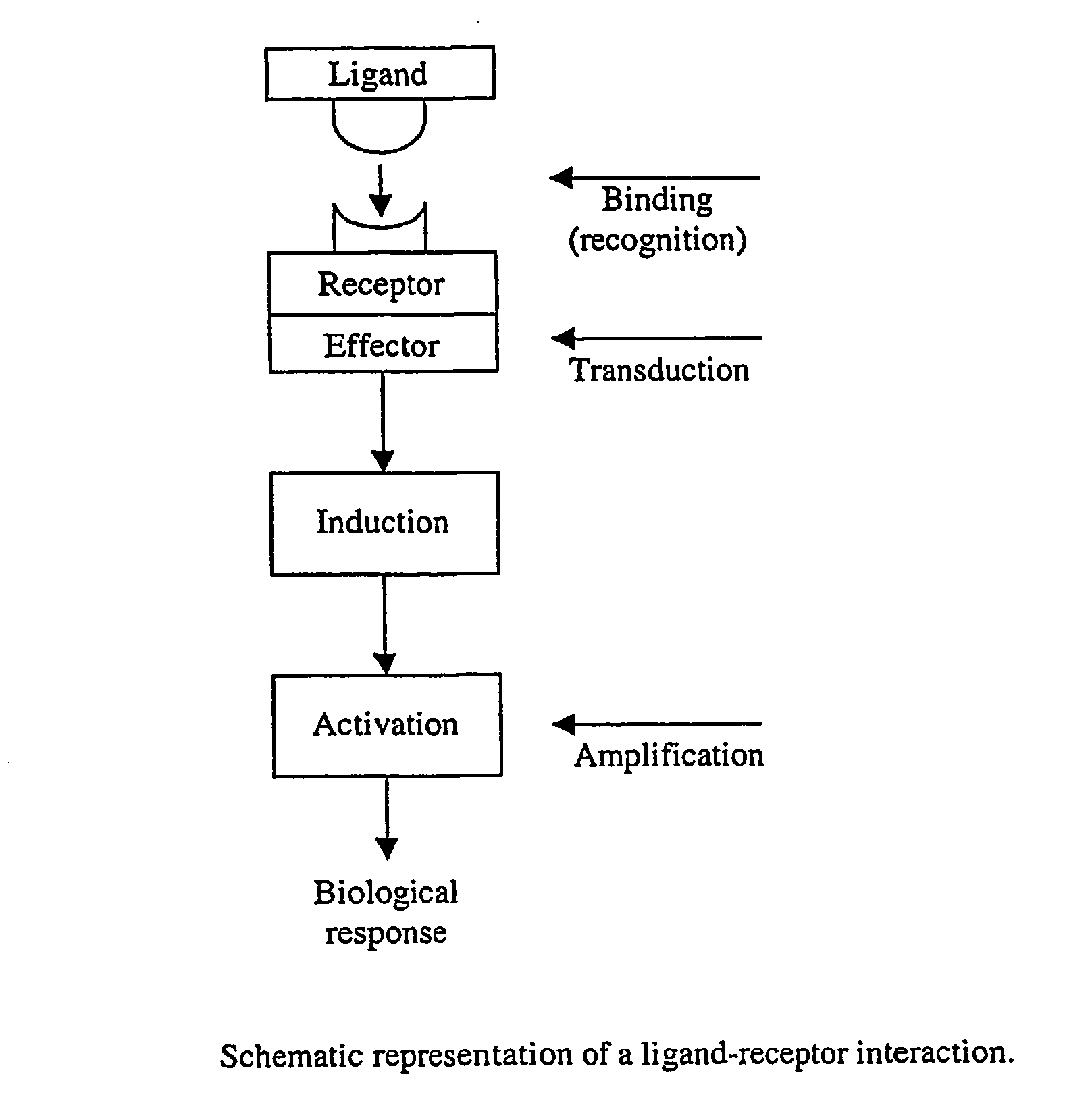
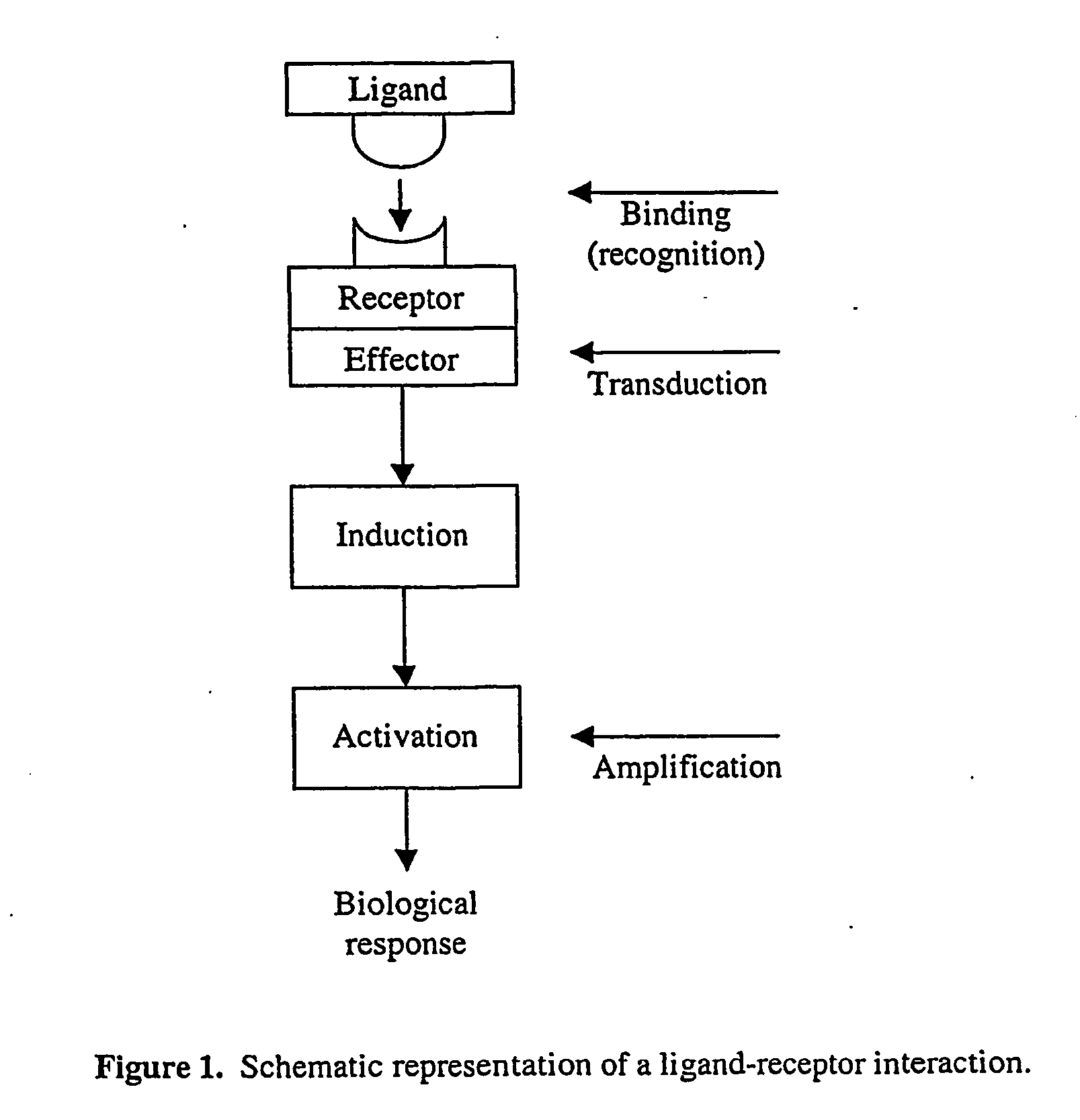
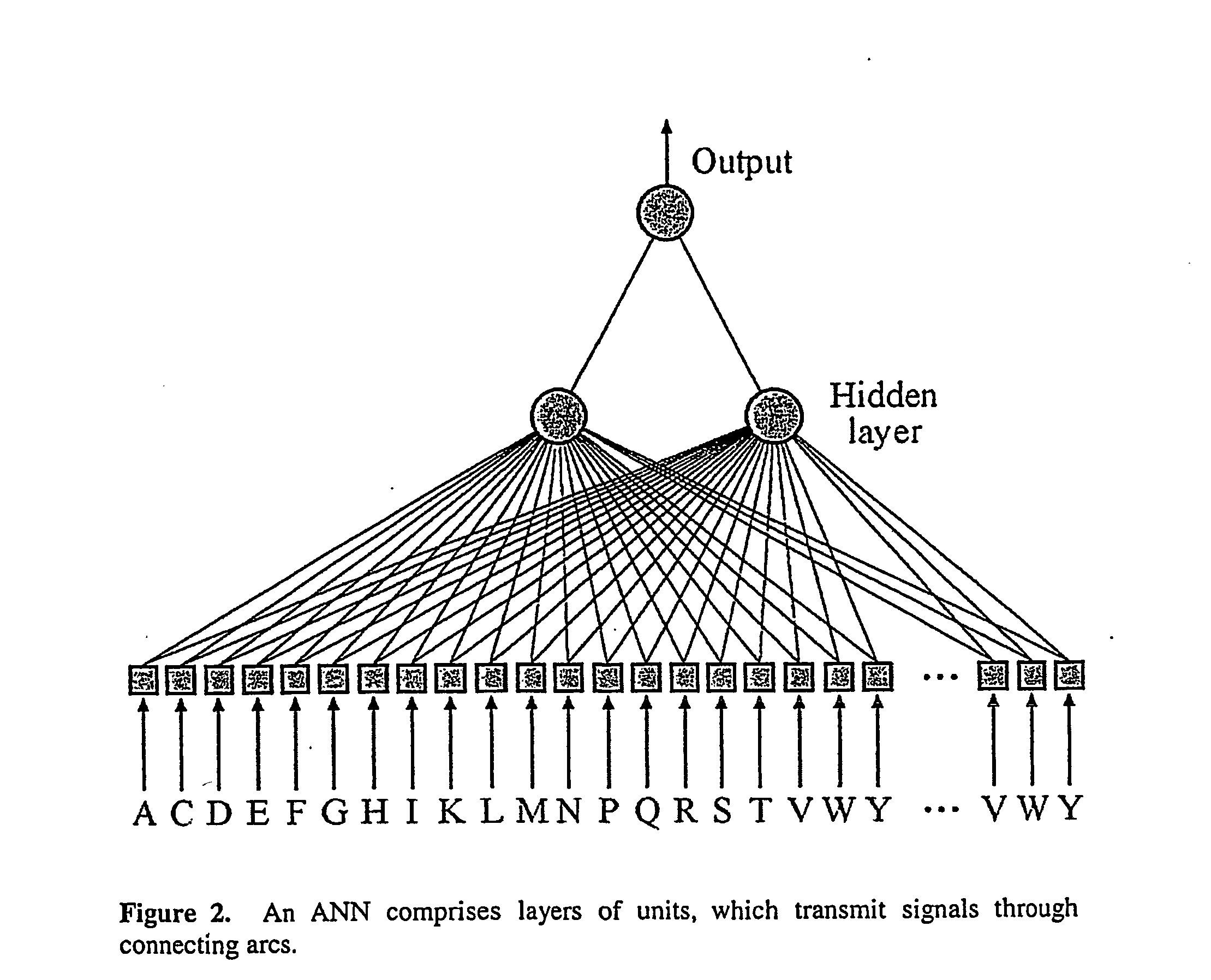
System and method for systematic prediction of ligand/receptor activity
InactiveUS20050074809A1Easy to useAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingMajor histocompatibilityComputer science
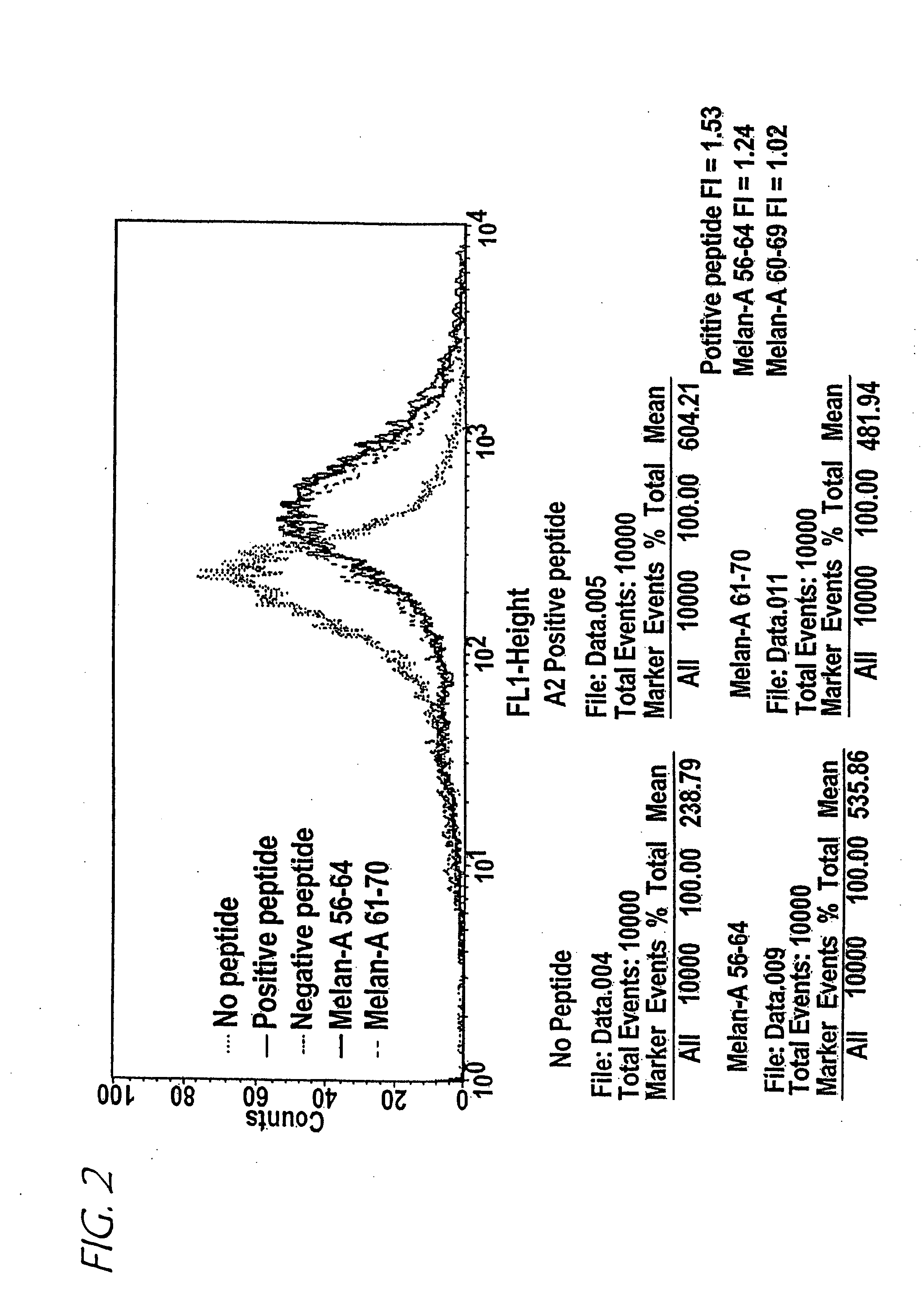
Disclosed is a general system and method, for prediction of binding of peptide-like ligands (peptides) to peptide-like receptors (receptors). Specifically this invention uses non-linear prediction models (including, but not limited to, artificial neural networks), sequence data form ligands and their respective receptors, and known ligand-receptor binding affinities. The representation of ligand-receptor interaction used along with the binding affinity of said interaction is used to train a determining means in a form of a predictive model. Prediction of binding affinity of a novel (not used for training of a predictive model) ligand-receptor interaction, involving a peptide and a particular receptor, involves the combining of representations of both peptide and receptor and presenting that representation to a previously trained predictive model. The system and method can be used as a single predictive model for determination of ligand binding to an individual receptor, or to a group of related receptors. This system and method was validated using data on peptide binding to major histocompatibility complex molecules (MHC) and artificial neural networks (ANN).
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
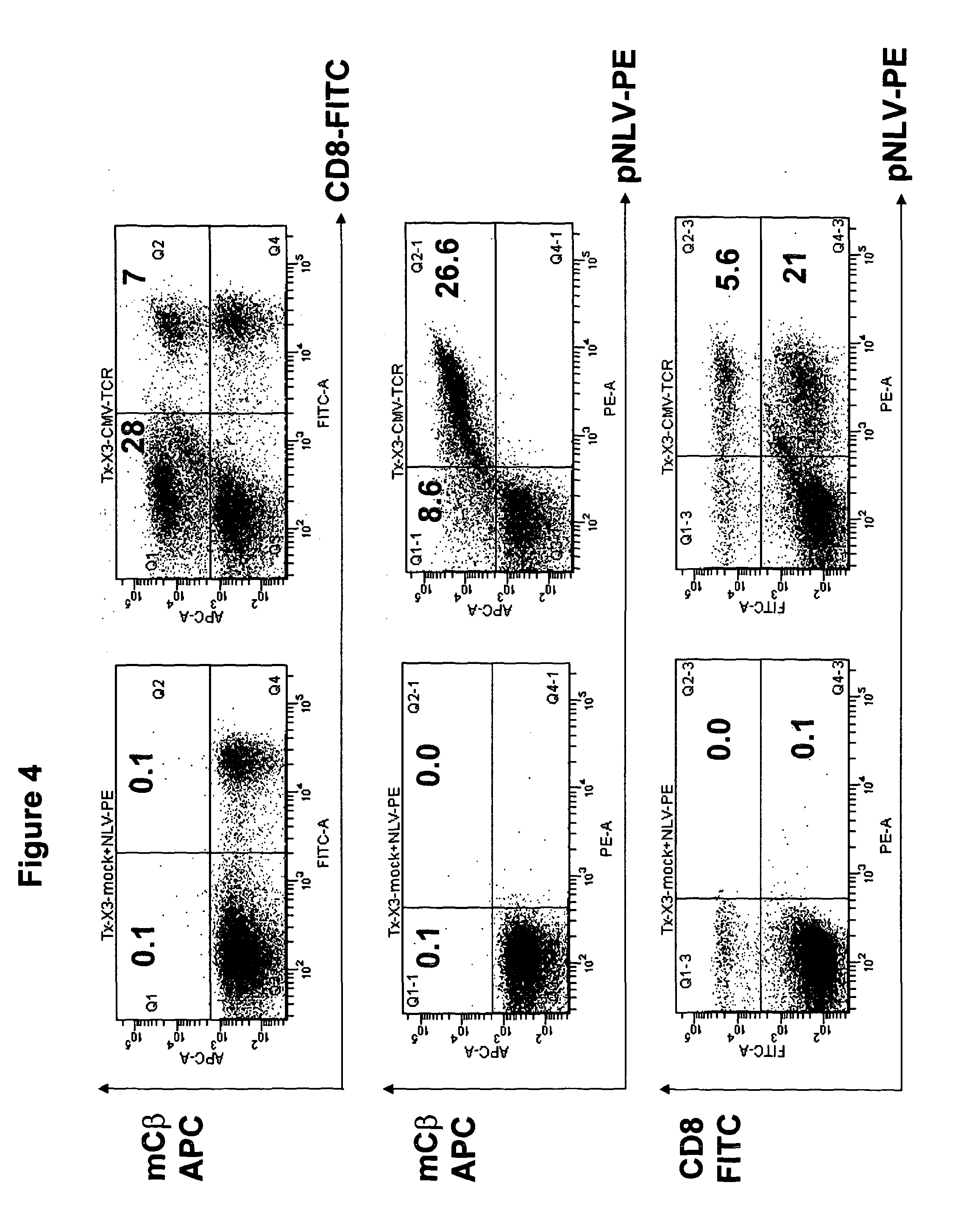
T-cell receptor capable of recognising an antigen from cytomegalovirus
The present invention provides a T-cell receptor (TCR) which binds to a peptide from the cytomegalovirus (CMV) phosphoprotein pp65 having the amino acid sequence NLVPMVATV (SEQ ID No. 1) when presented by a major histocompatability complex (MHC) molecule. The present invention also provides a nucleotide sequence encoding such a TCR, a vector comprising such a nucleotide sequence and its use to produce a CMV-specific T-cell. The present invention also provides the use of CMV-specific T-cell for cellular immunotherapy.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Cancer immunotherapy with a viral antigen-defined, immunomodulator-secreting cell vaccine
A human cell line, which lacks major histocompatibility class I (MHC-I) antigens and major histocompatibility class II (MHC-II) antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express (i) a nucleotide sequence encoding an immunomodulator and (ii) a nucleotide sequence encoding a viral antigen, and a method of inducing or stimulating an immune response in a human to a viral-associated disease or cancer comprising administering to the human (i) the aforementioned human cell line in an amount sufficient to induce or stimulate an immune response to the viral associated disease or cancer, (ii) a human cell line, which lacks MHC-I and MHC-11 antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express a nucleotide sequence encoding an immunomodulator, and a human cell line, which lacks MHC-I and MHC-II antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express a nucleotide sequence encoding an antigen of EBV, simultaneously or sequentially in either order, by the same or different routes, in amounts sufficient to induce or stimulate an immune response to the viral-associated disease or cancer, or (iii) an immunomodulator and a human cell line, which lacks MHC-I and MHC-II antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express a nucleotide sequence encoding an antigen of EBV, simultaneously or sequentially in either order, by the same or different routes, in amounts sufficient to induce or stimulate an immune response to the viral associated disease or cancer.
Owner:JOHNS HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Compositions and methods to initiate or enhance antibody and major-histocompatibility class I or class II-restricted t cell responses by using immunomodulatory, non-coding rna motifs
InactiveUS20050222060A1Effectively turningPotent and differential impact on the adaptive immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsRNA MotifsMajor histocompatibility
Owner:BOT ADRIAN L +4
Therapeutic and diagnostic cloned MHC-unrestricted receptor specific for the MUC1 tumor associated antigen
The invention provides an isolated nucleic acid encoding a receptor, other than an immunoglobulin, wherein the receptor binds to a MUC1 tumor antigen independently of an major histocompatibility complex (MHC). The invention provides a method of activating a signaling pathway and / or killing a cancer cell using a receptor that is similar to or is a T cell receptor
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Transgenic mice having a human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) phenotype, experimental uses and applications
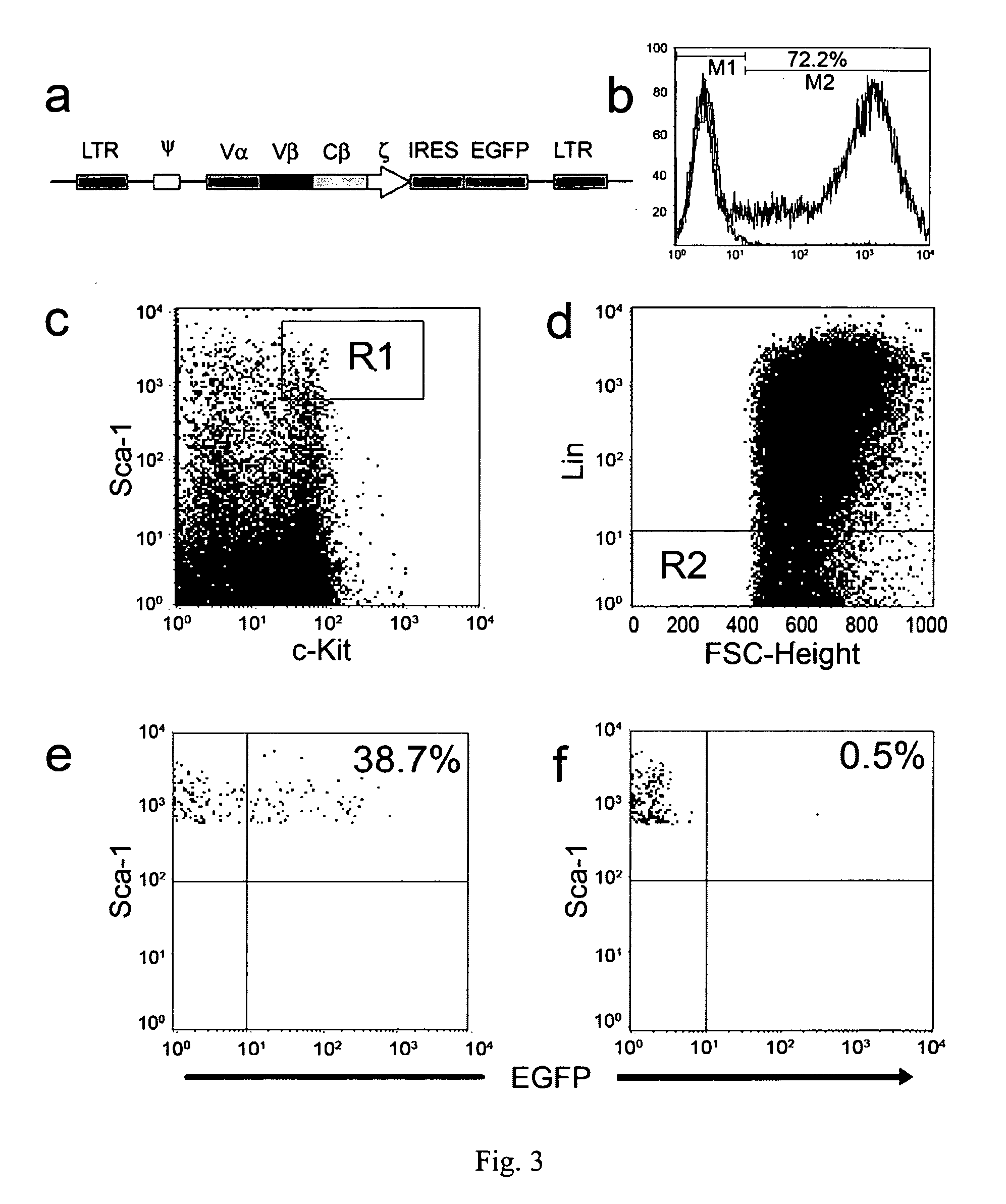
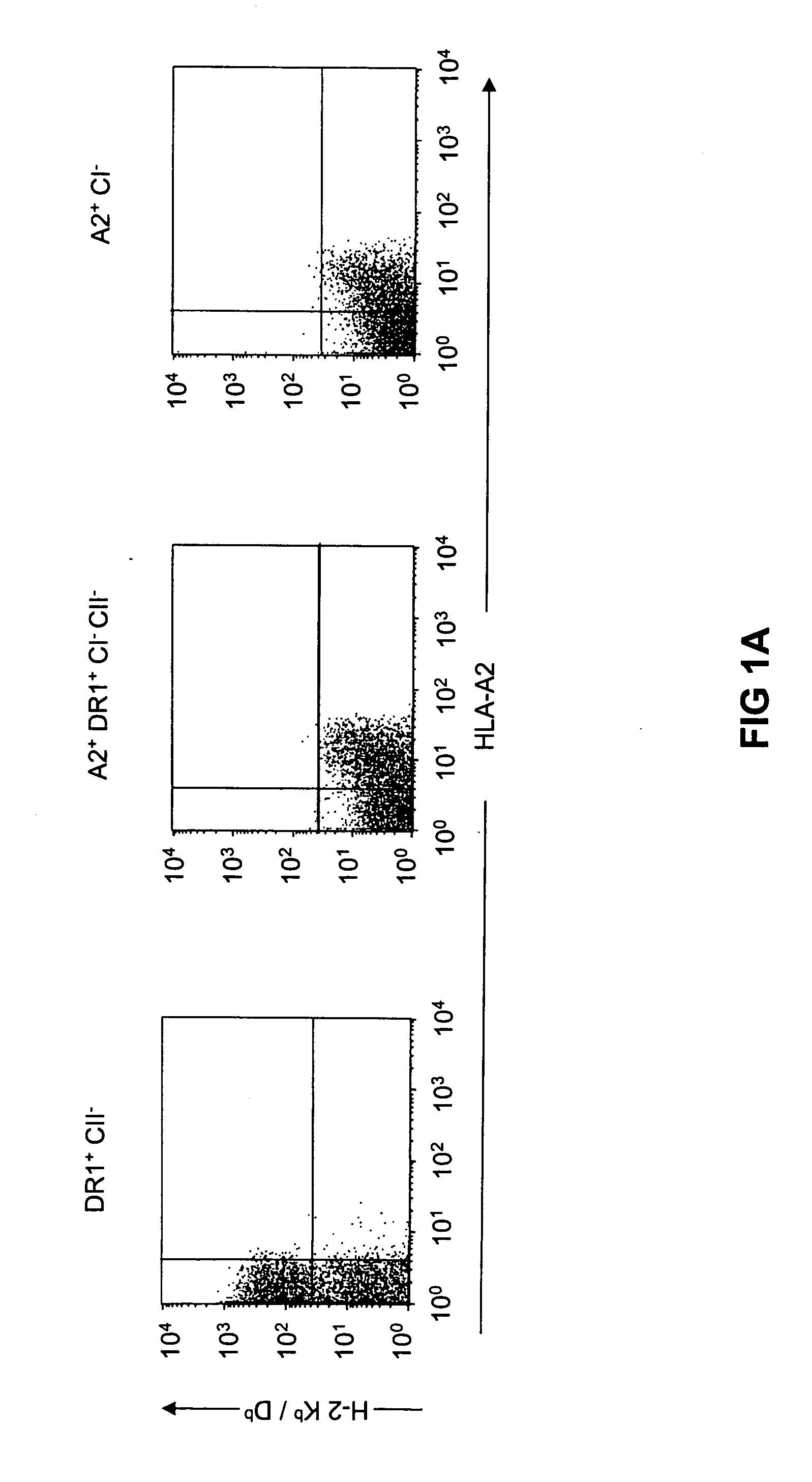
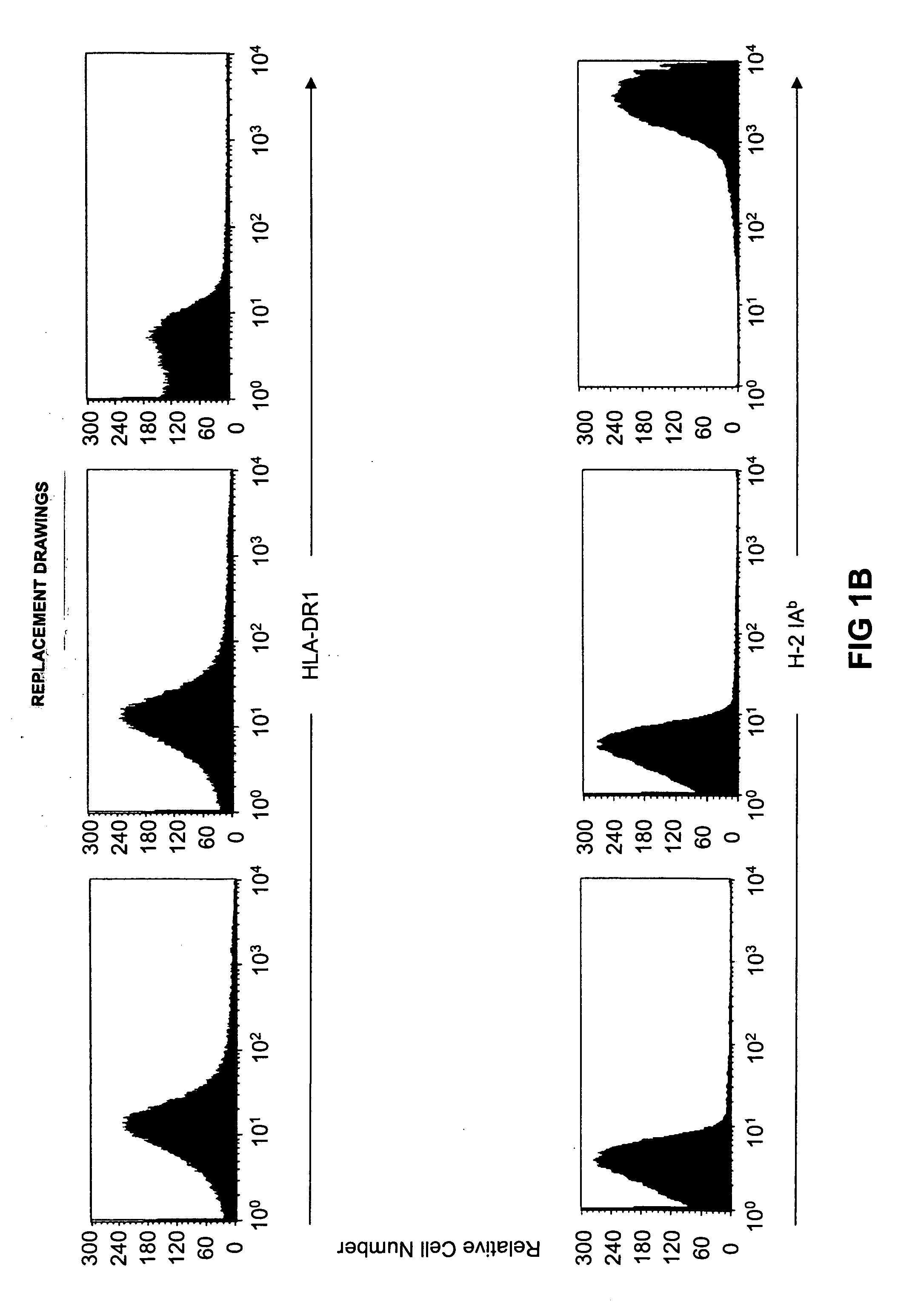
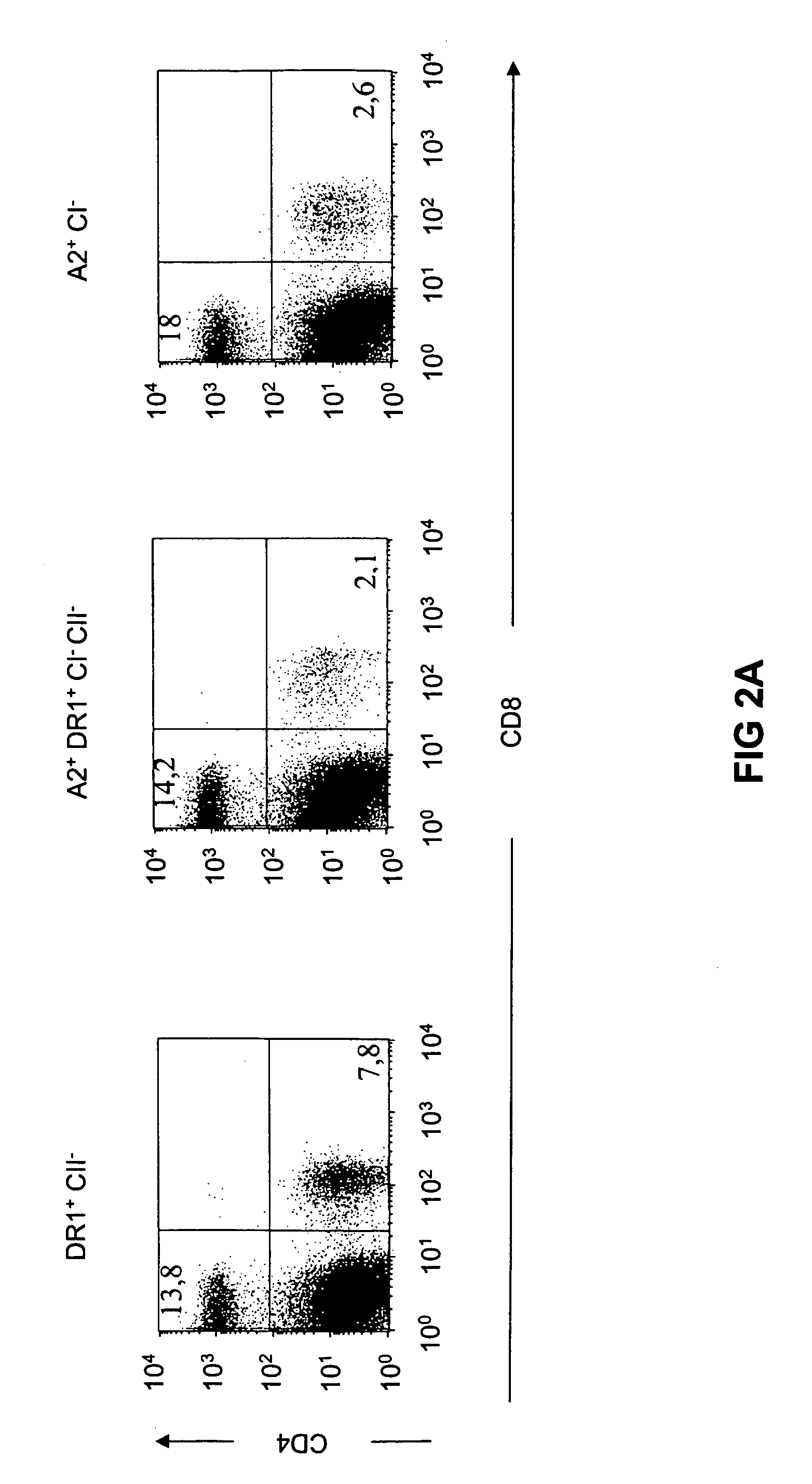
The present invention relates to transgenic mice and isolated transgenic mouse cells, the mice and mouse cells comprising a disrupted H2 class I gene, a disrupted H2 class II gene, a functional HLA class I transgene, and a functional HLA class II transgene. In embodiments, the transgenic mouse or mouse cells are deficient for both H2 class I and class II molecules, wherein the transgenic mouse comprises a functional HLA class I transgene and a functional HLA class II transgene. In embodiments, the transgenic mouse or mouse cell has the genotype HLA-A2+HLA-DR1+β2m°IAβ°. The invention also relates to methods of using a transgenic mouse of the invention.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Genetically modified major histocompatibility complex mice
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express chimeric human / non-human MHC I and MHC II polypeptides and / or human or humanized β2 microglobulin polypeptide, as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the same. Also provided are constructs for making said genetically modified animals and methods of making the same. Methods of using the genetically modified animals to study various aspects of human immune system are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com