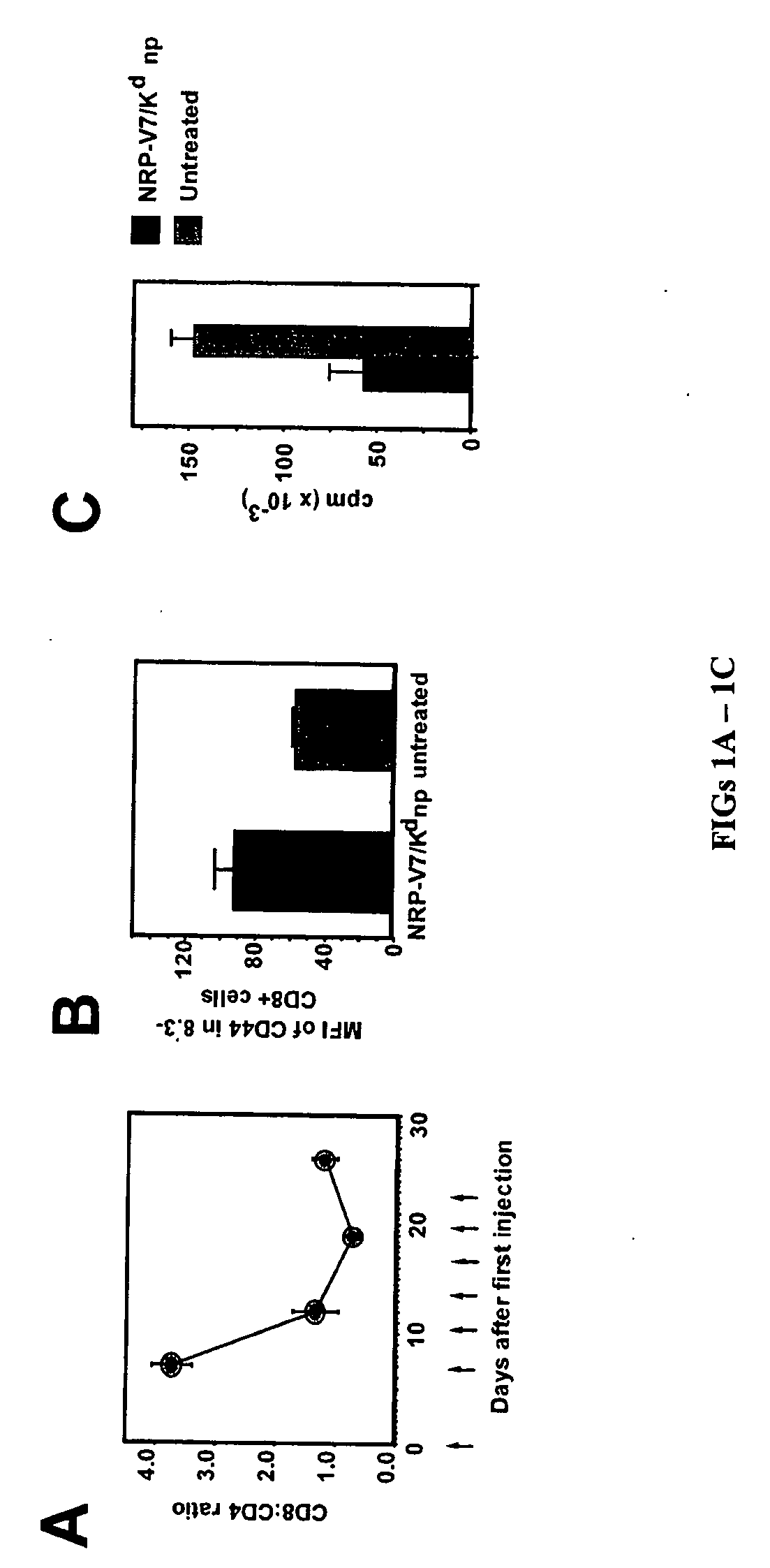
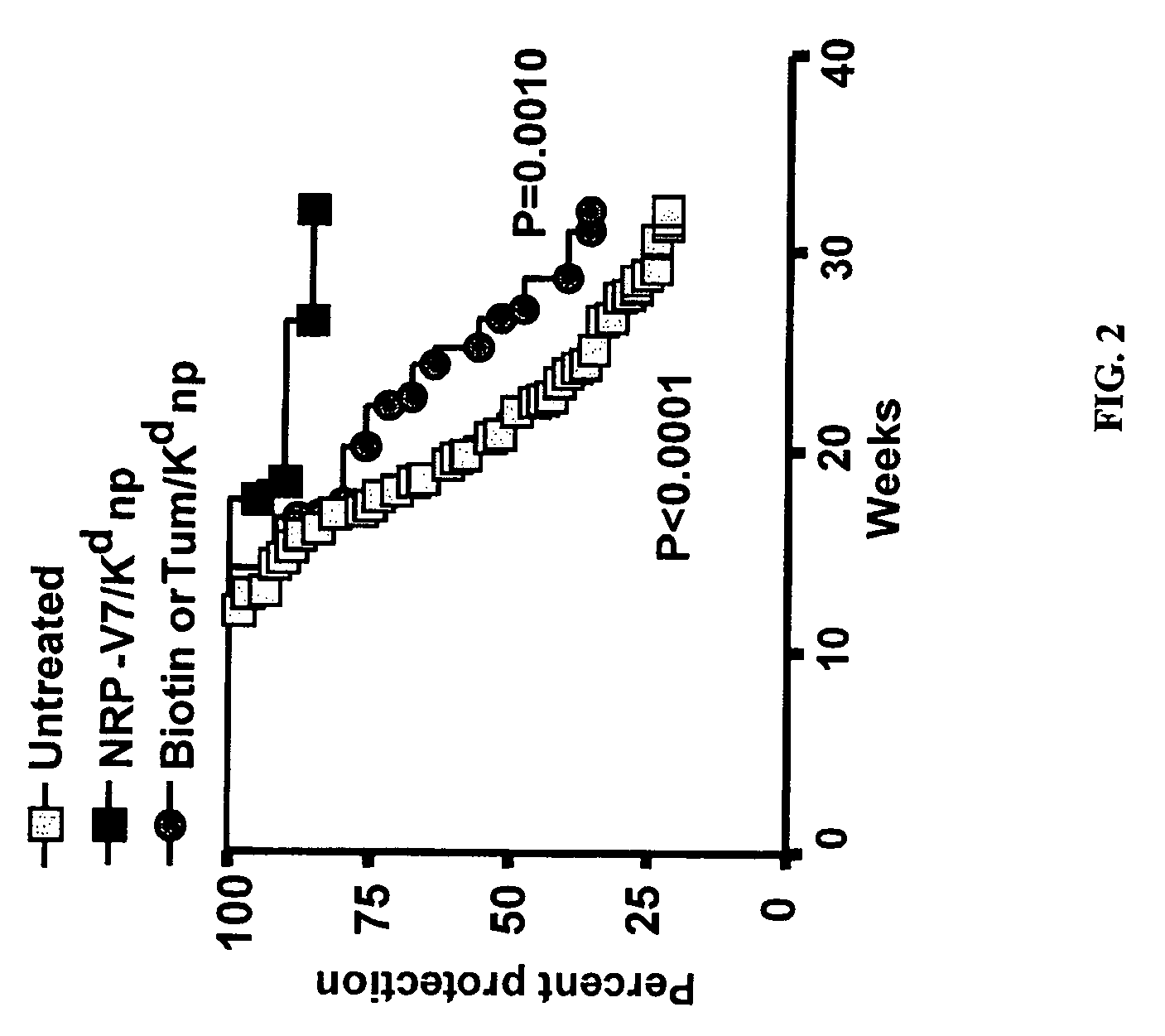
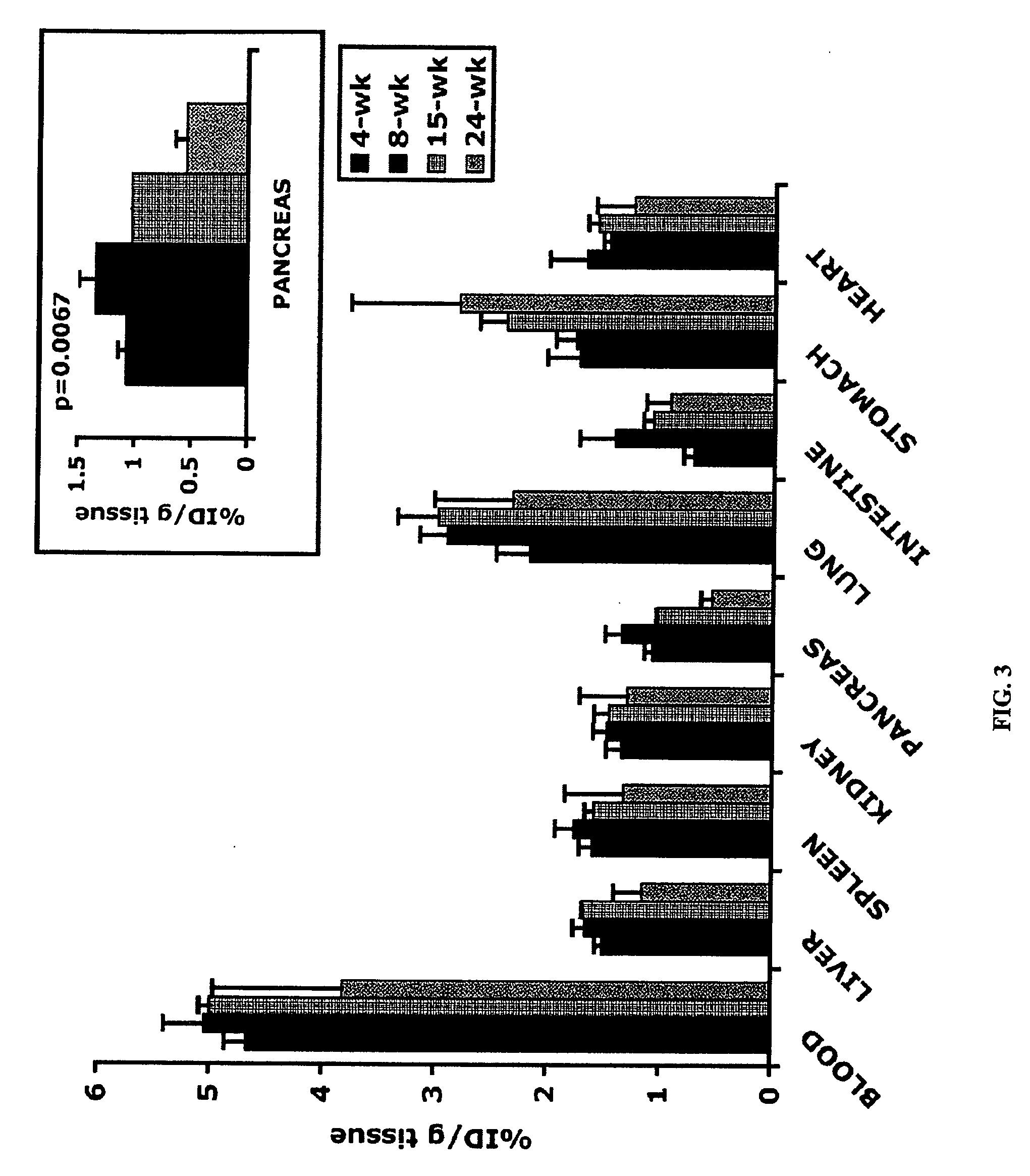
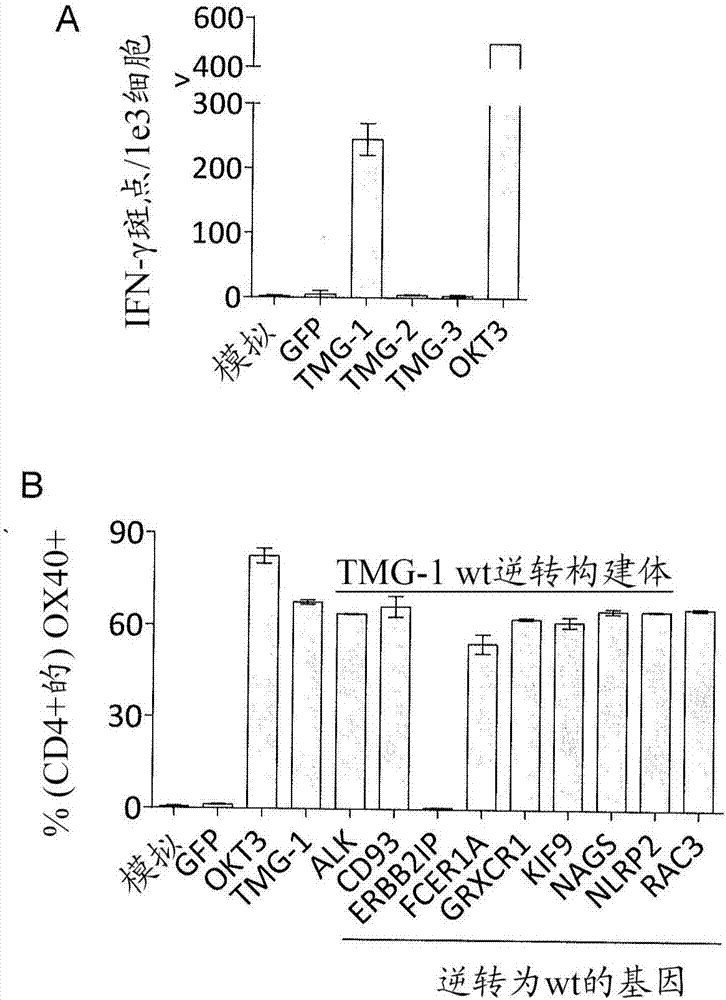
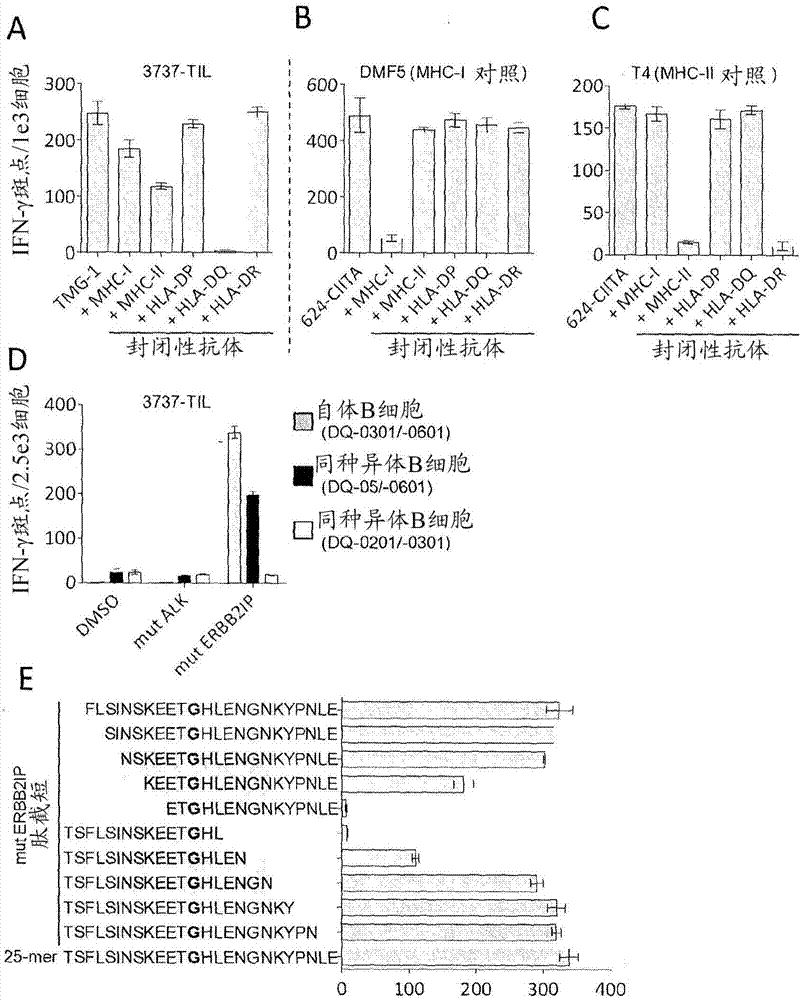
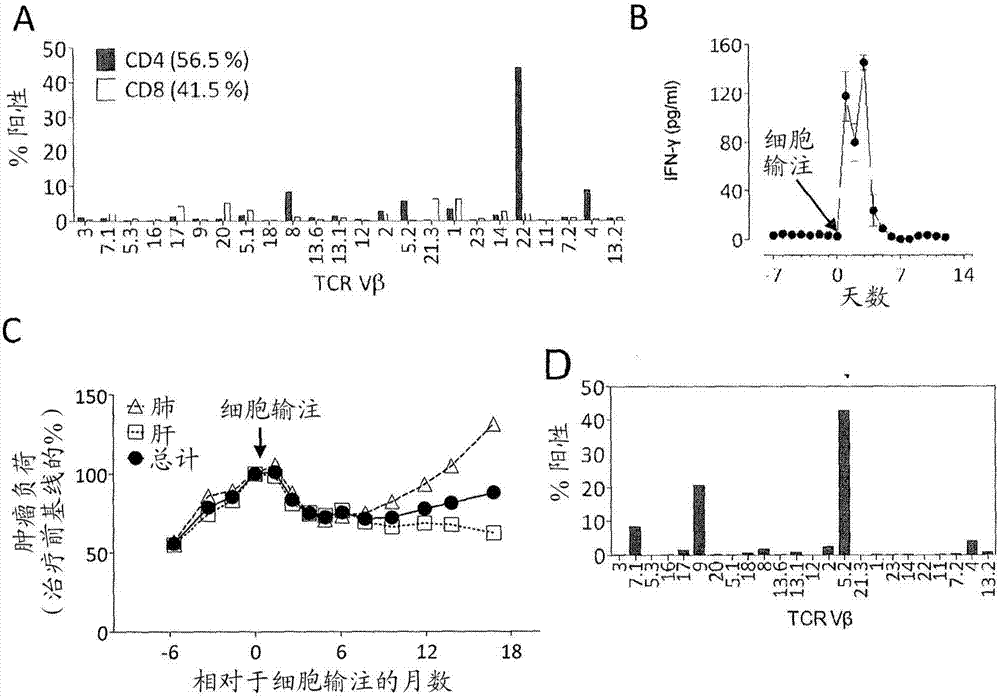
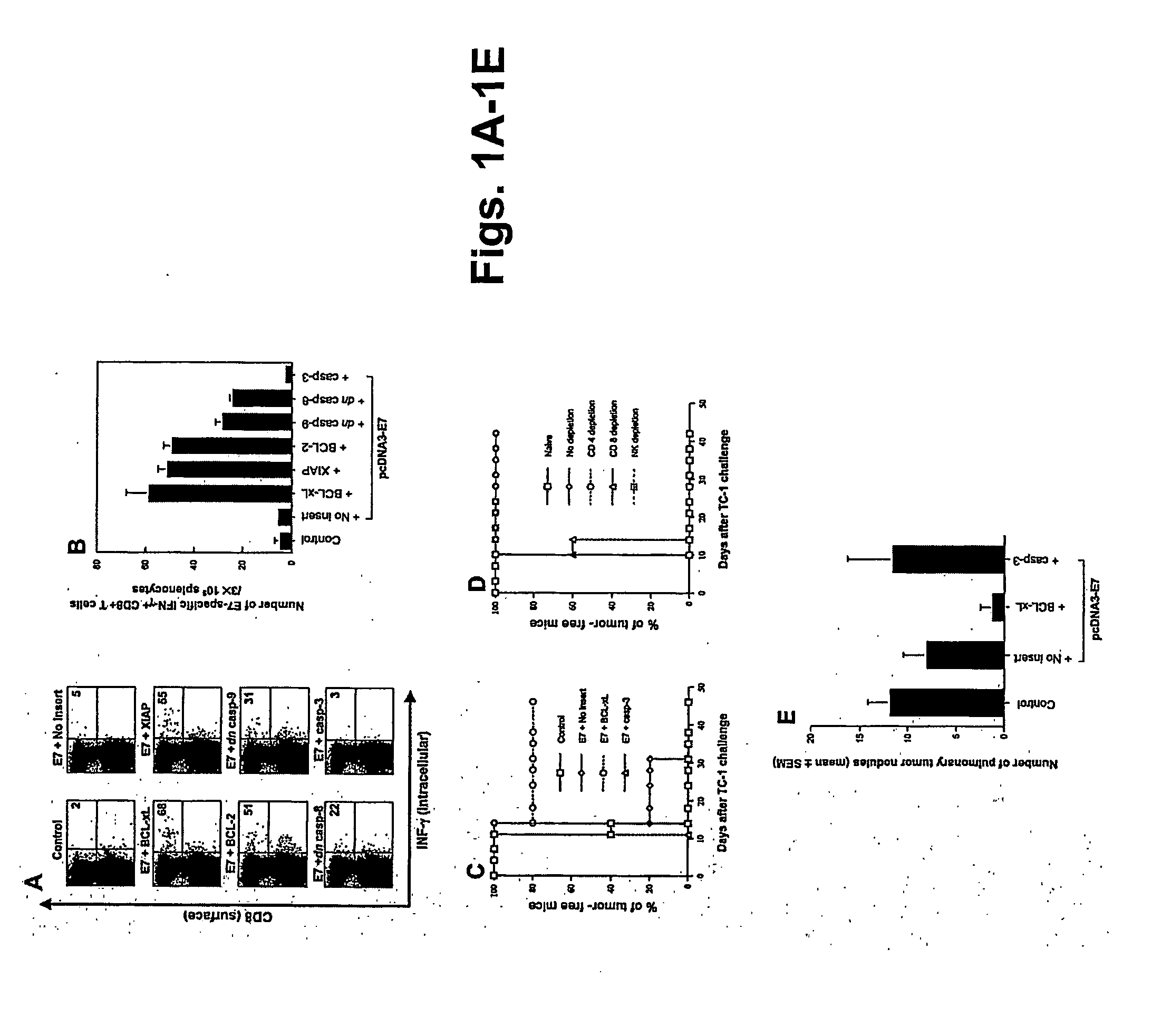
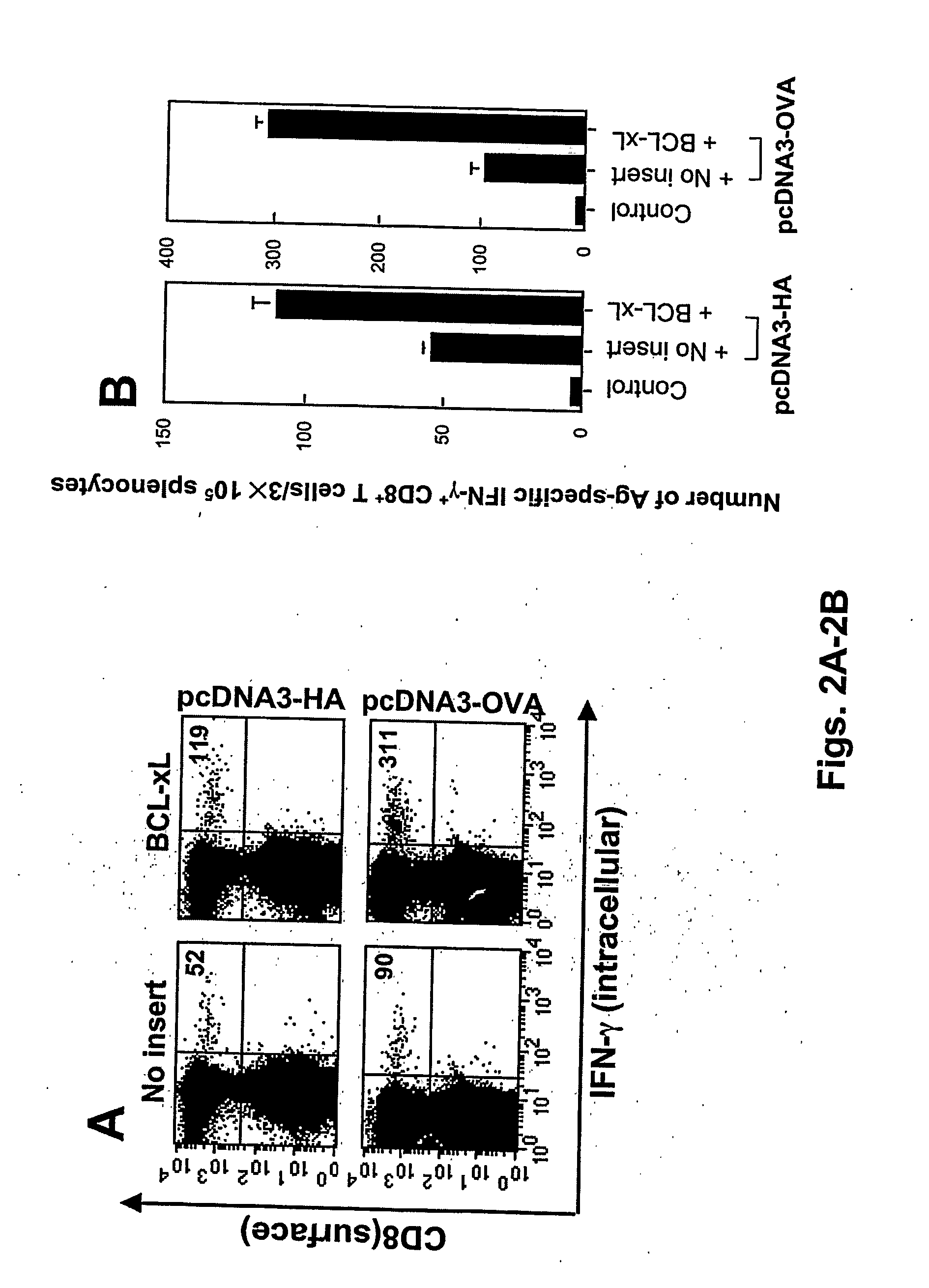
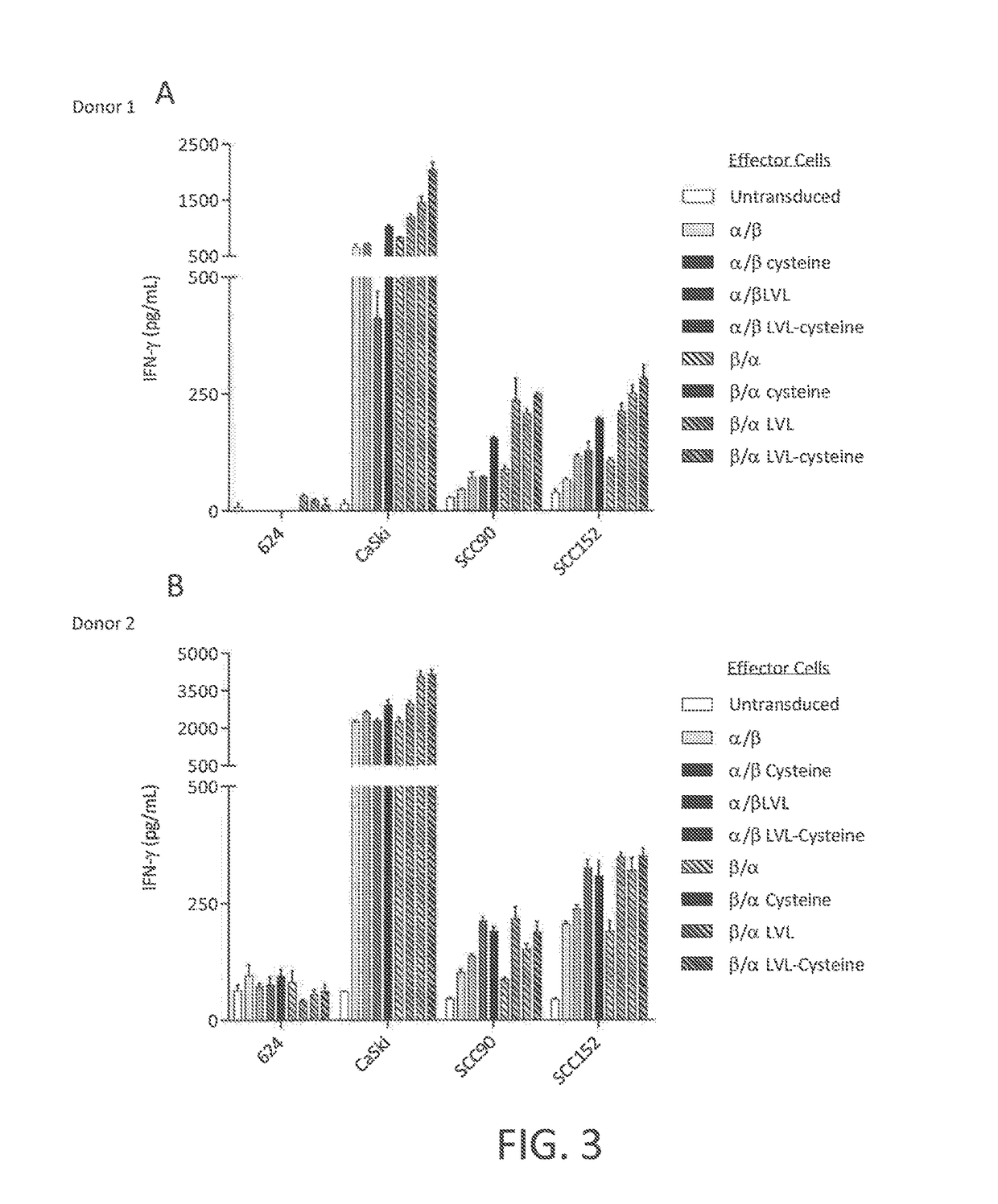
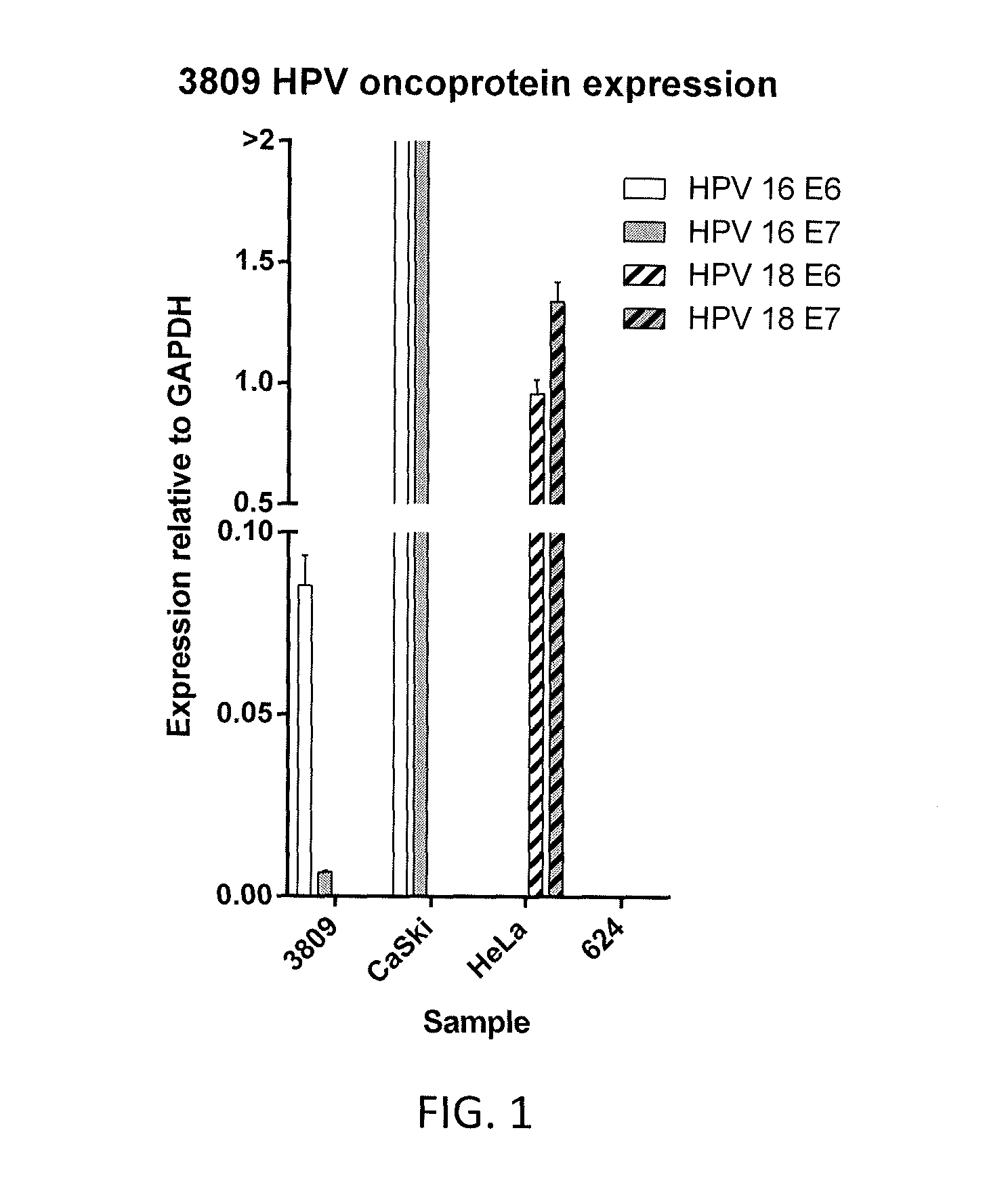
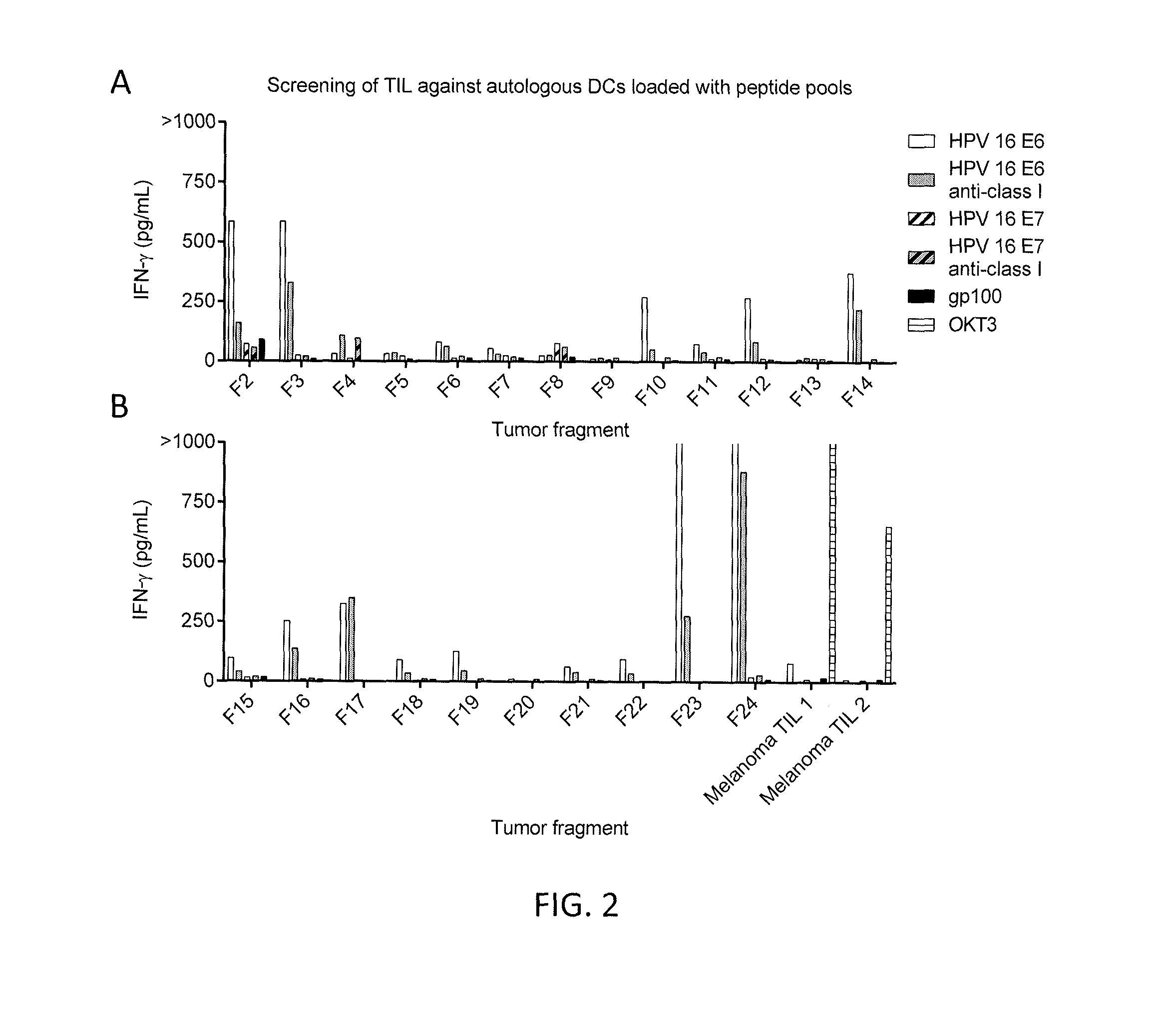
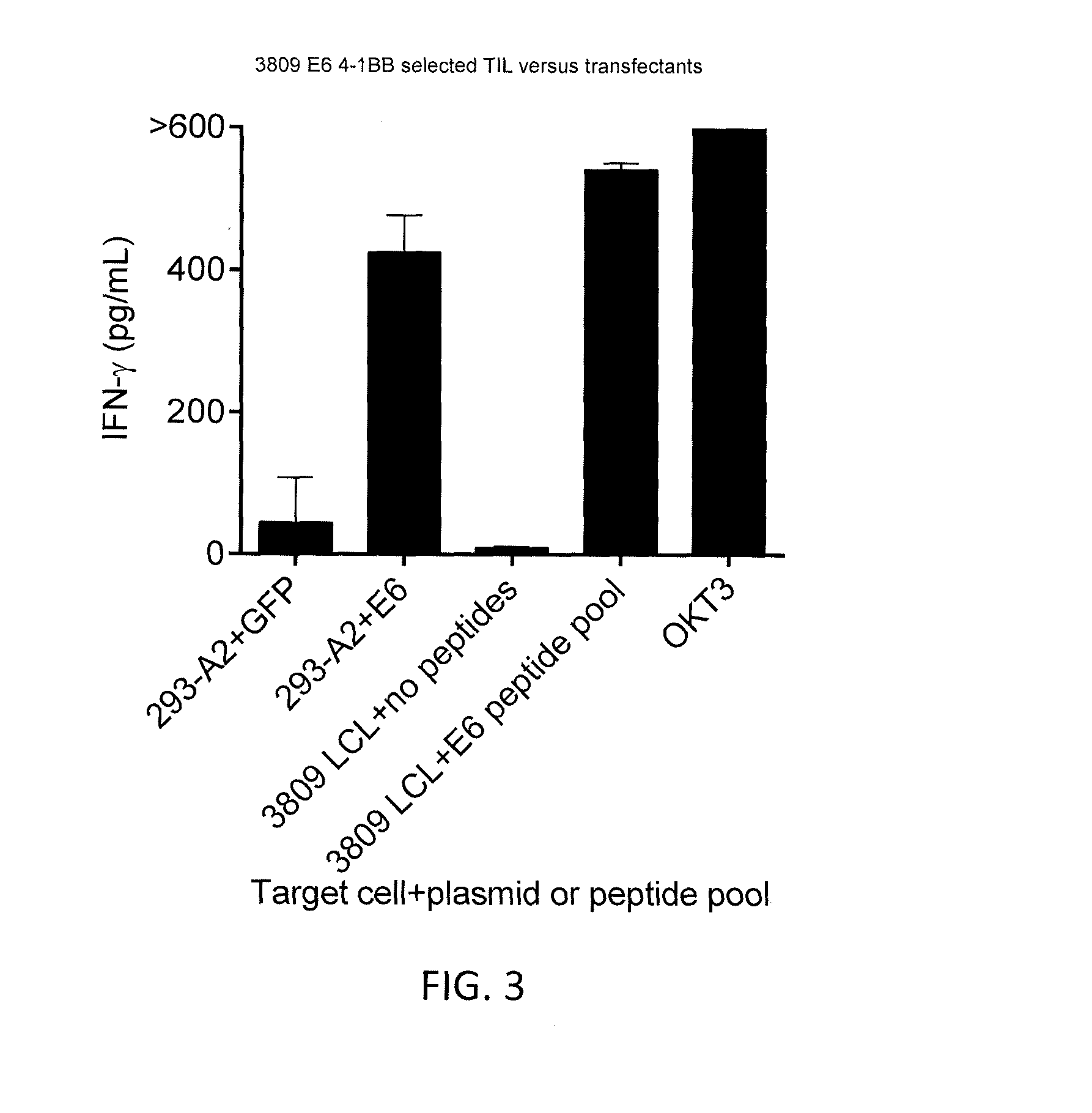
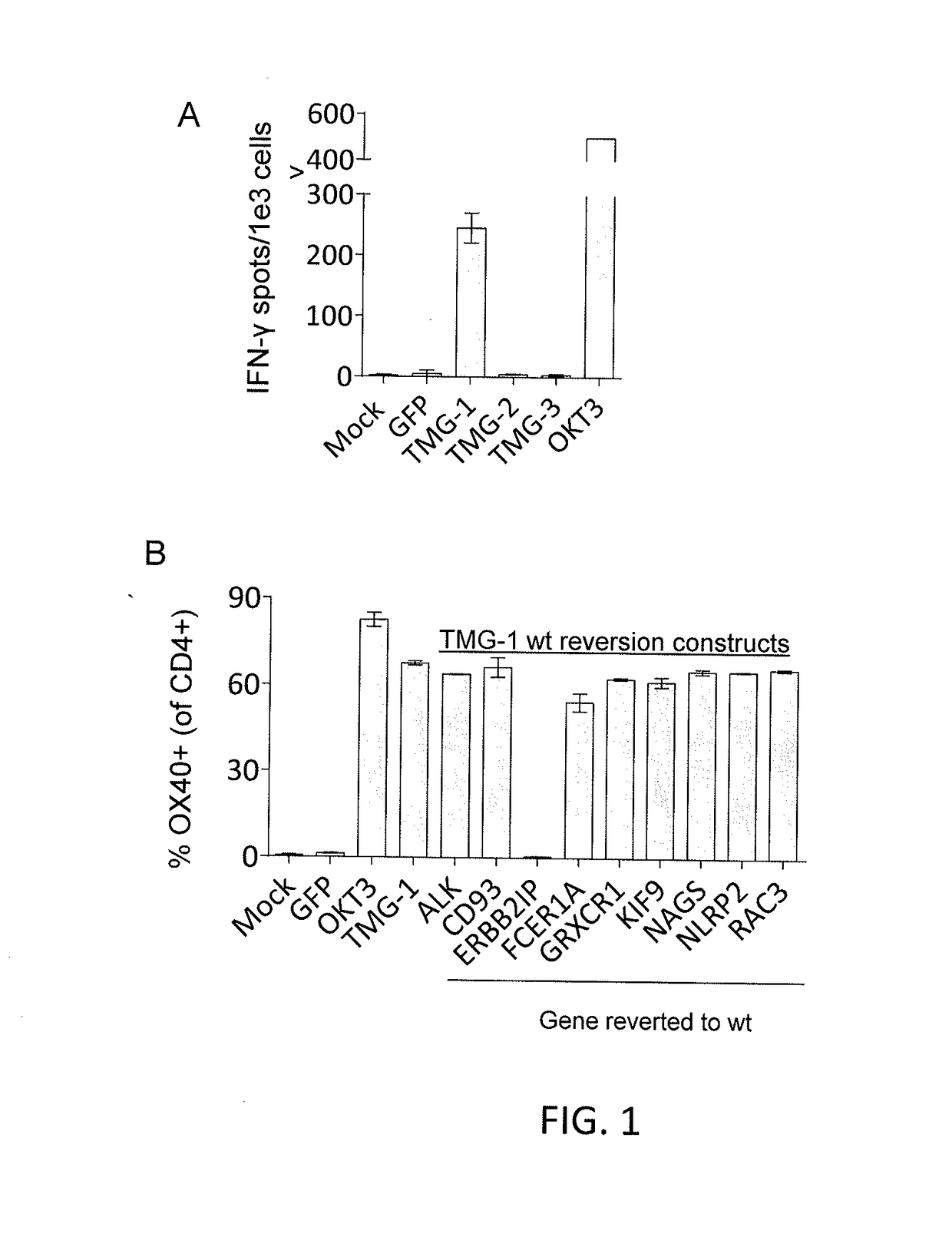
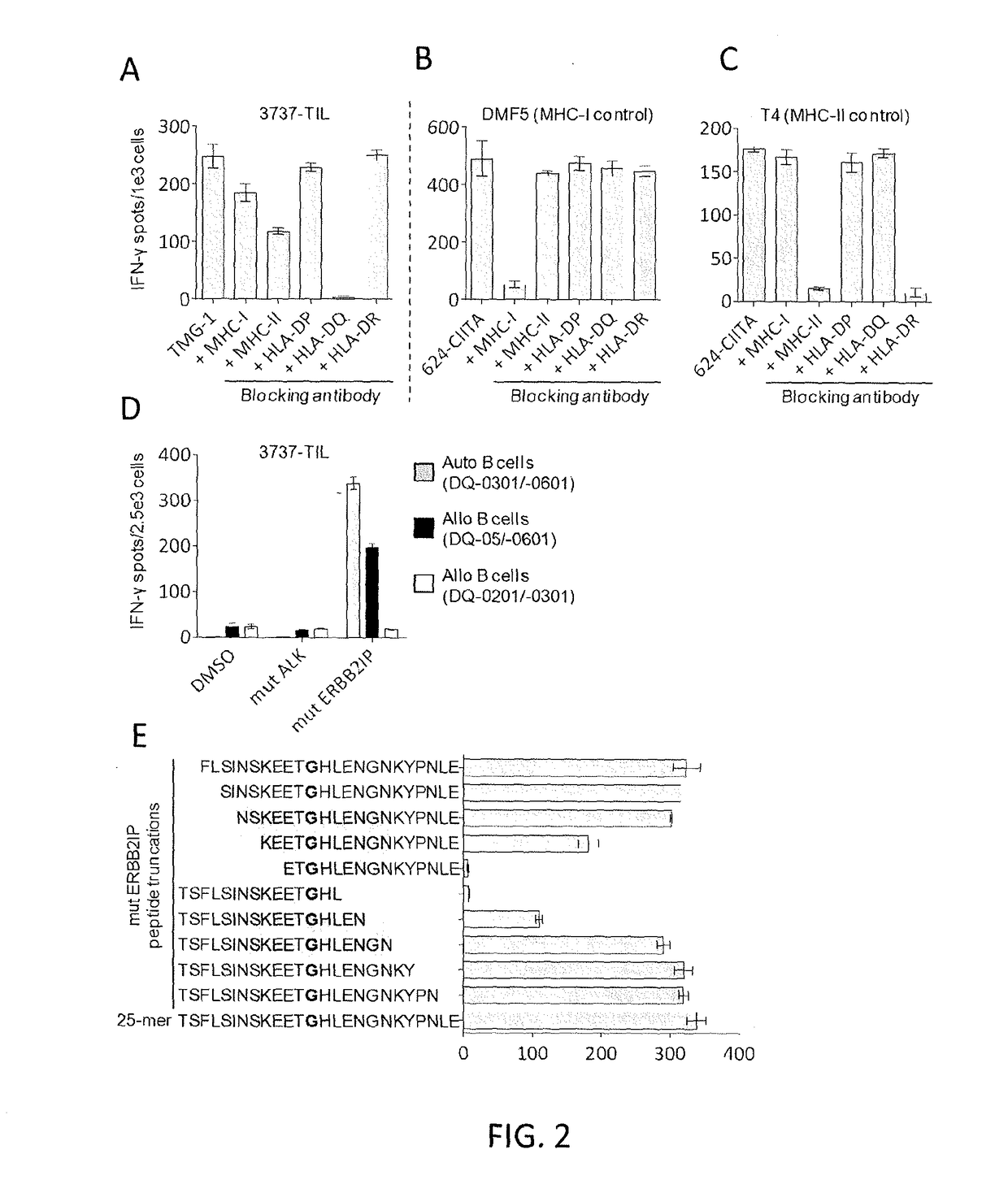
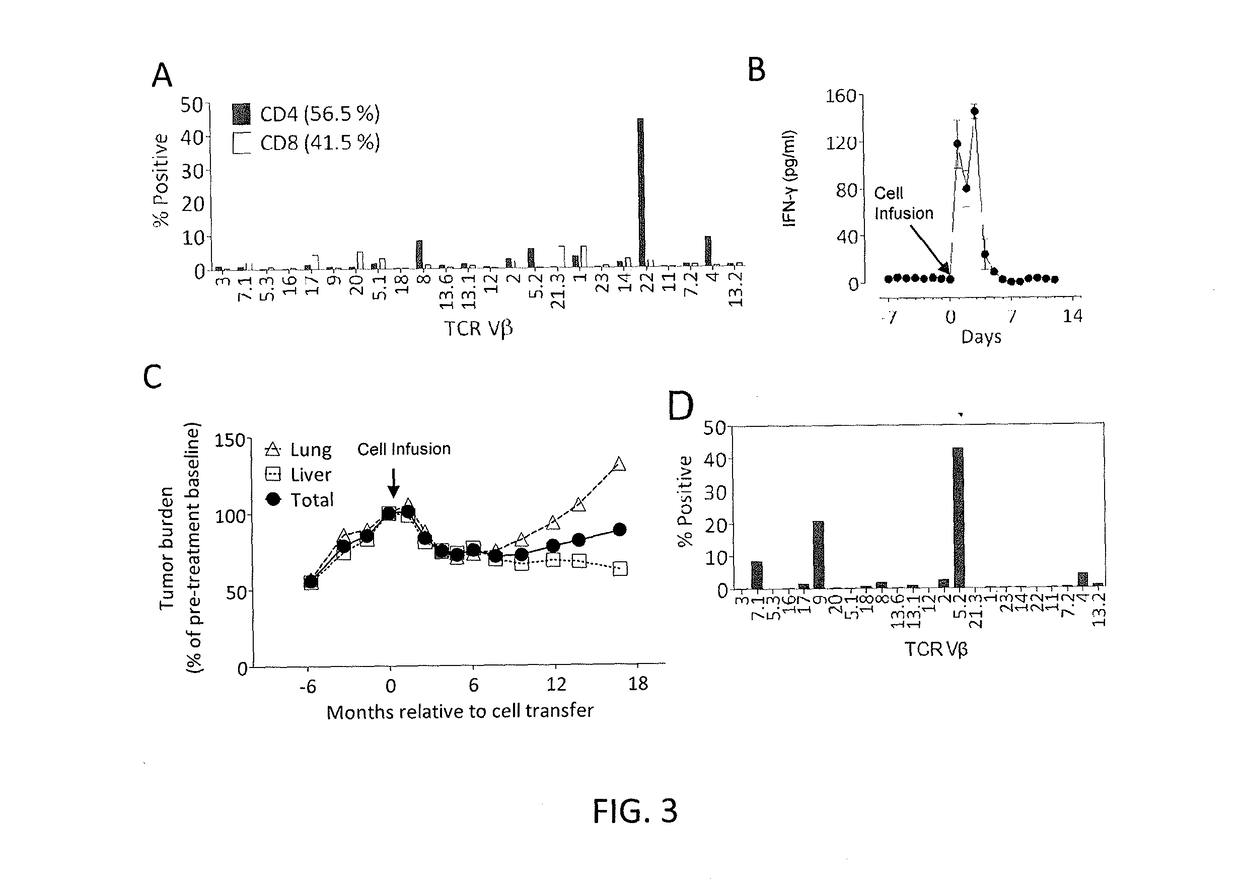
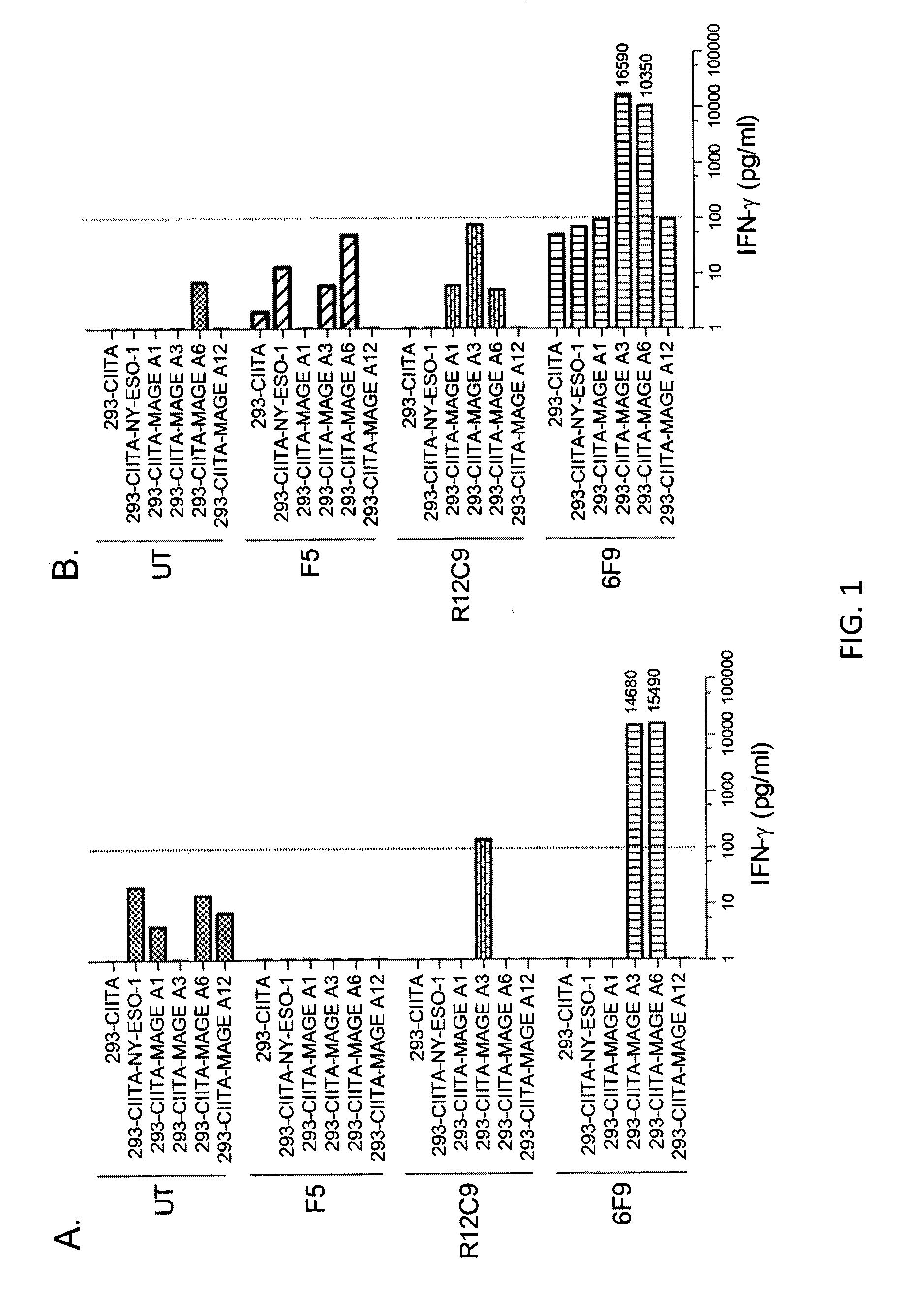
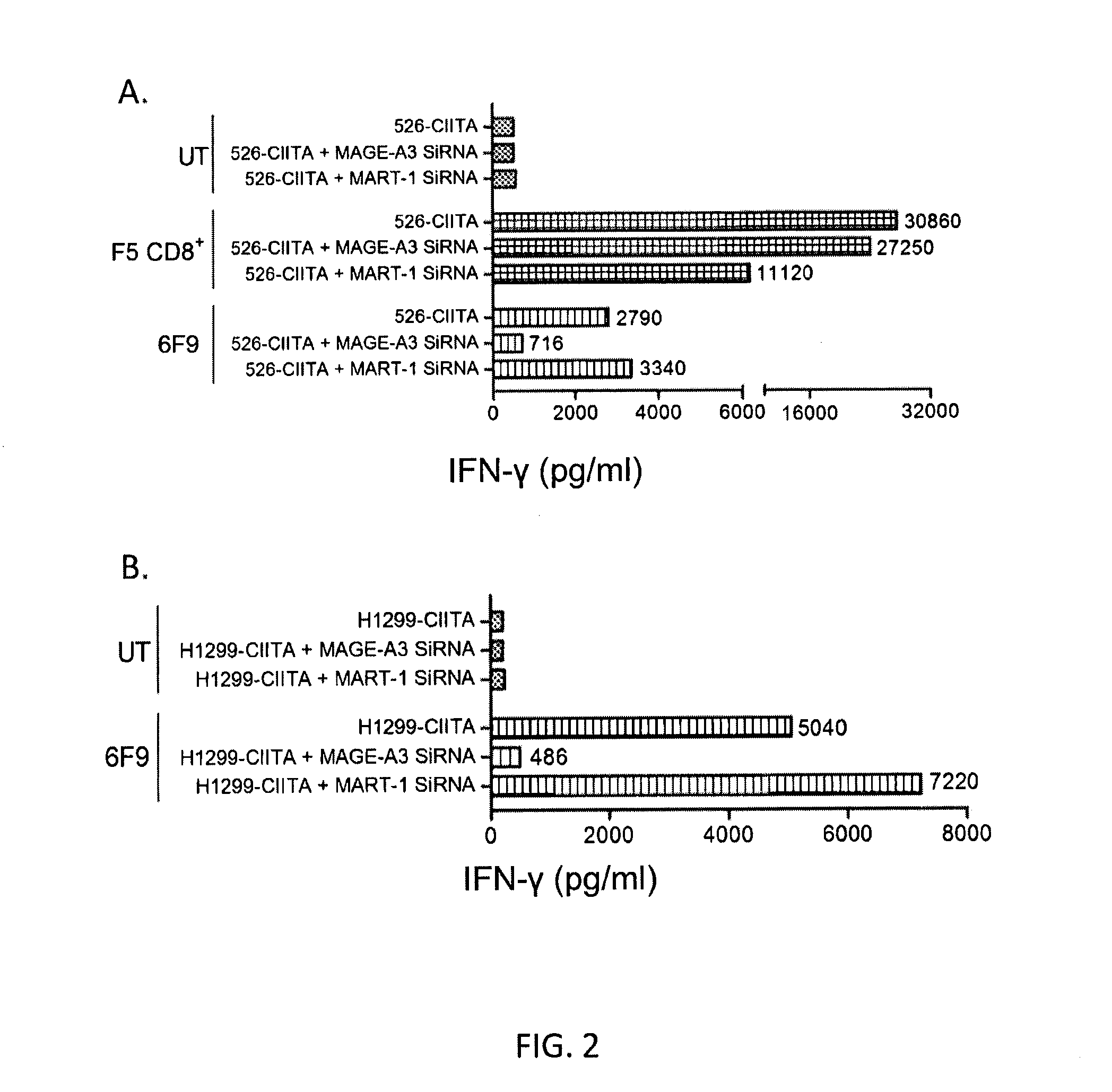
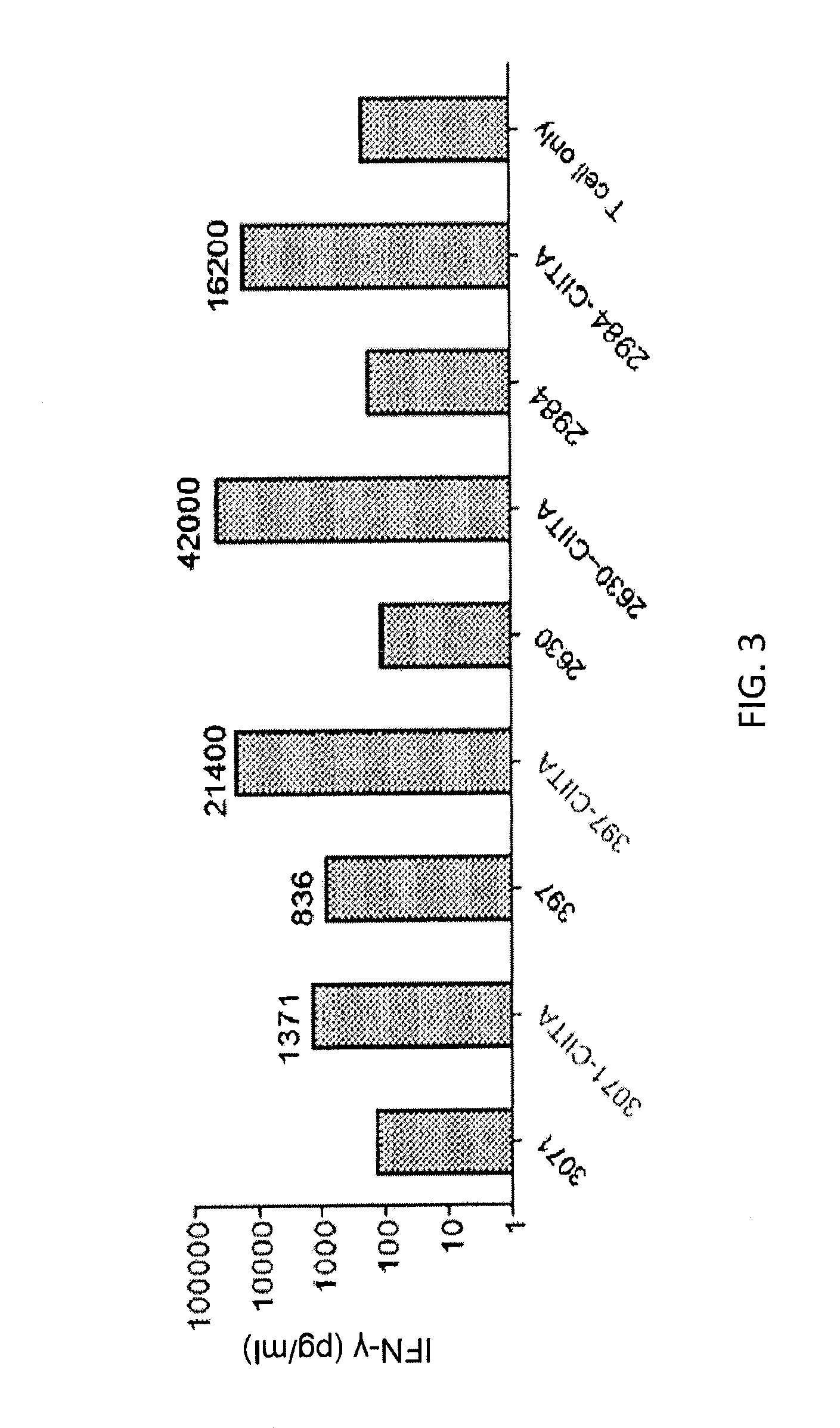
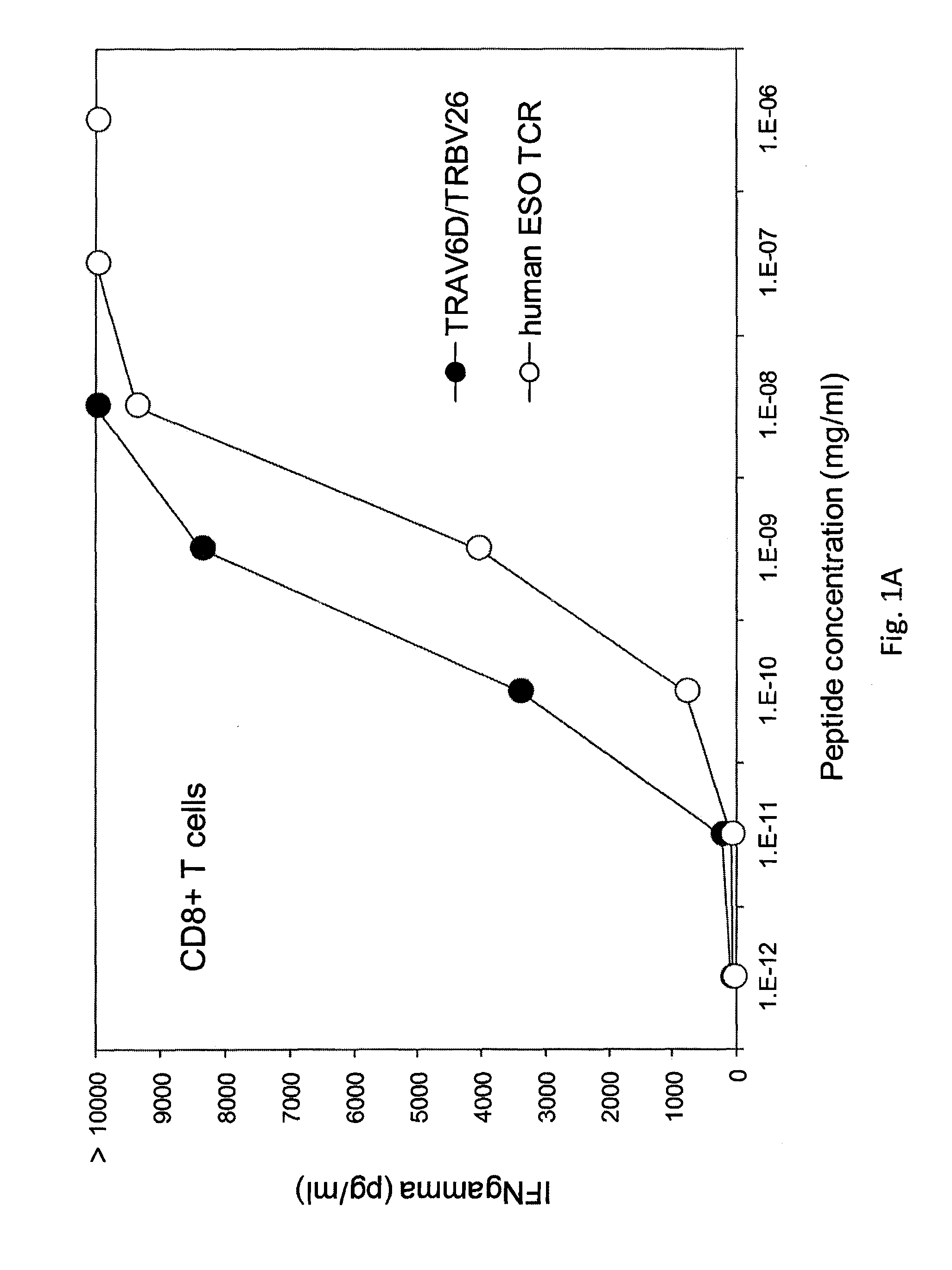
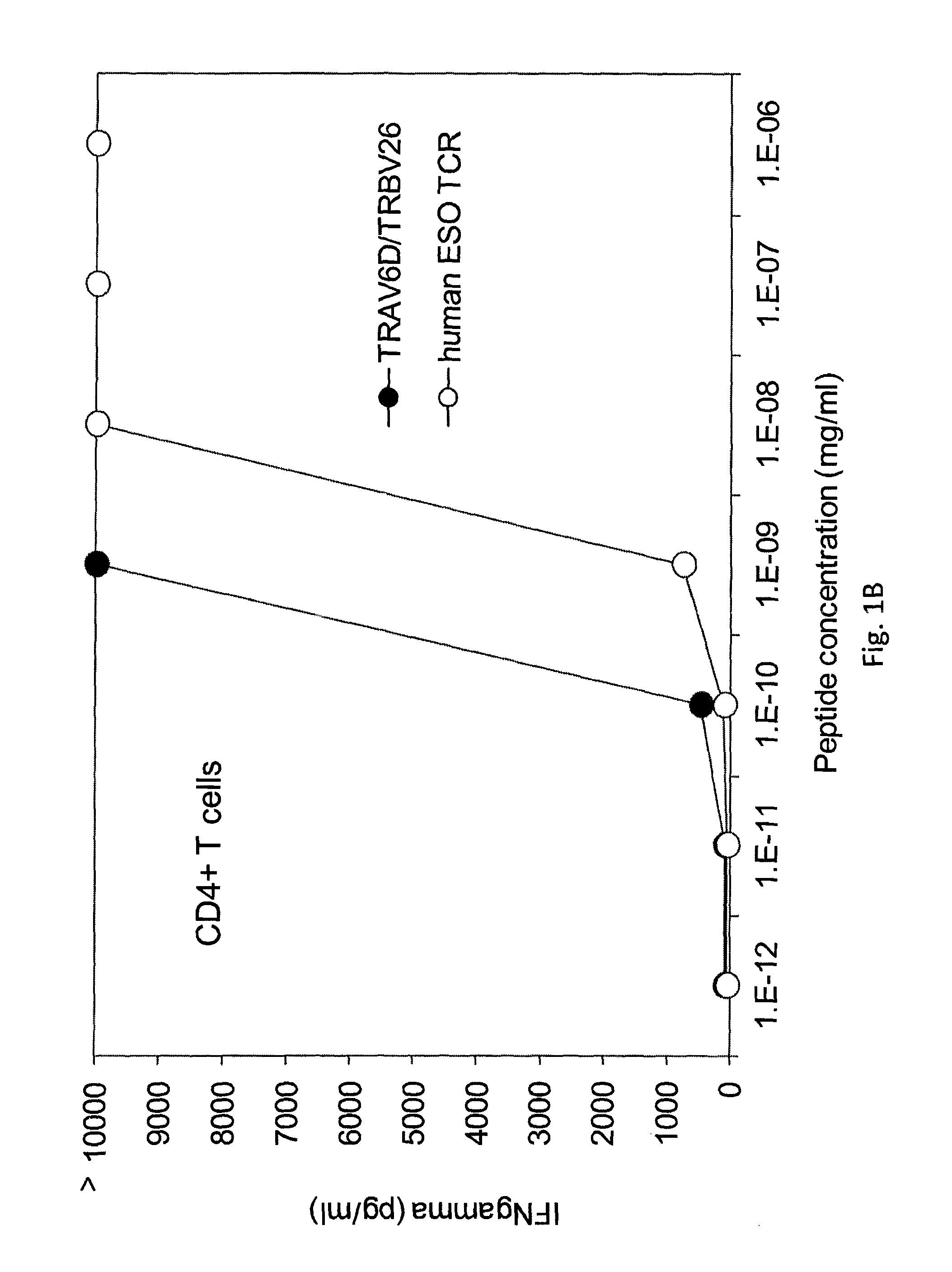
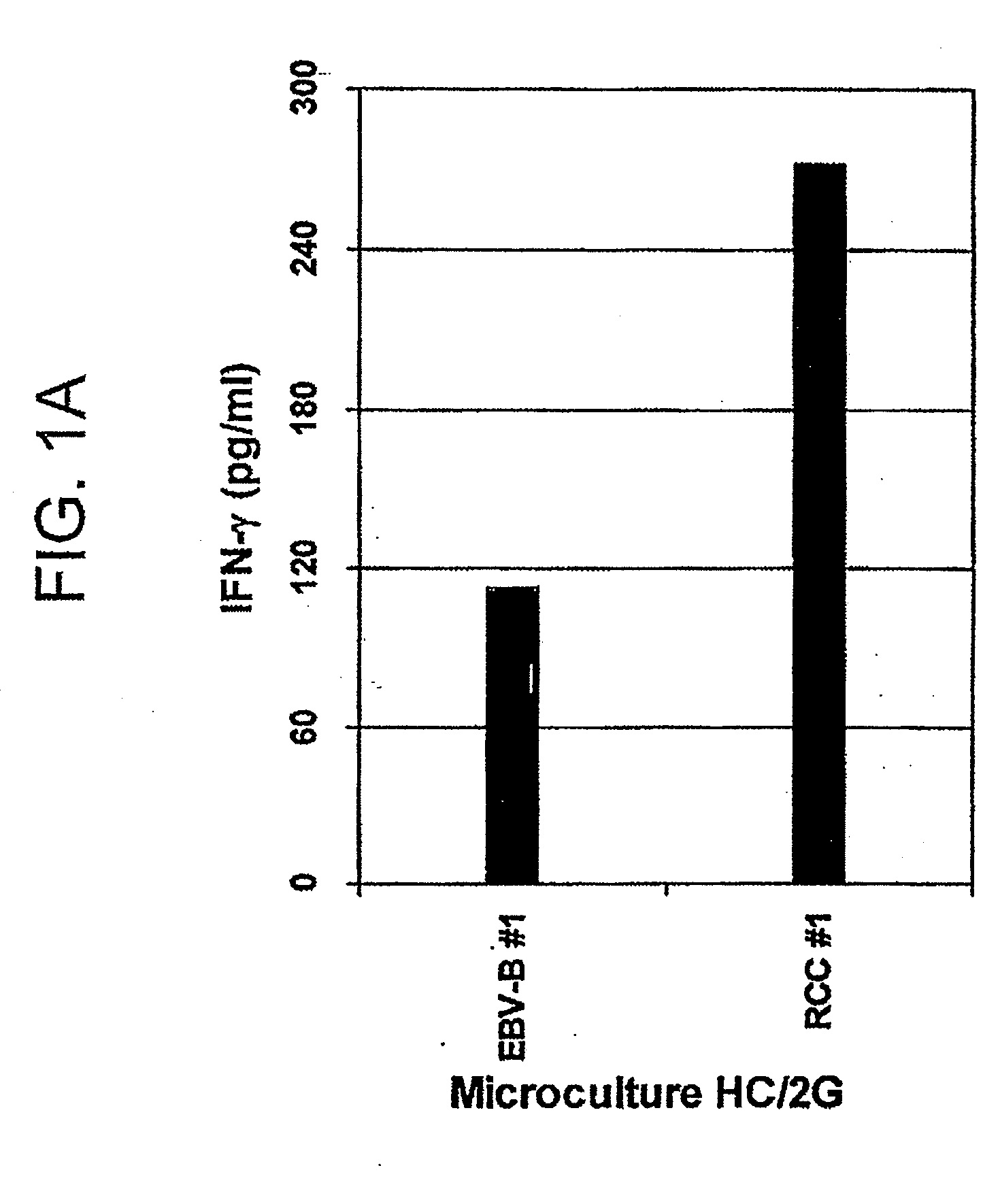
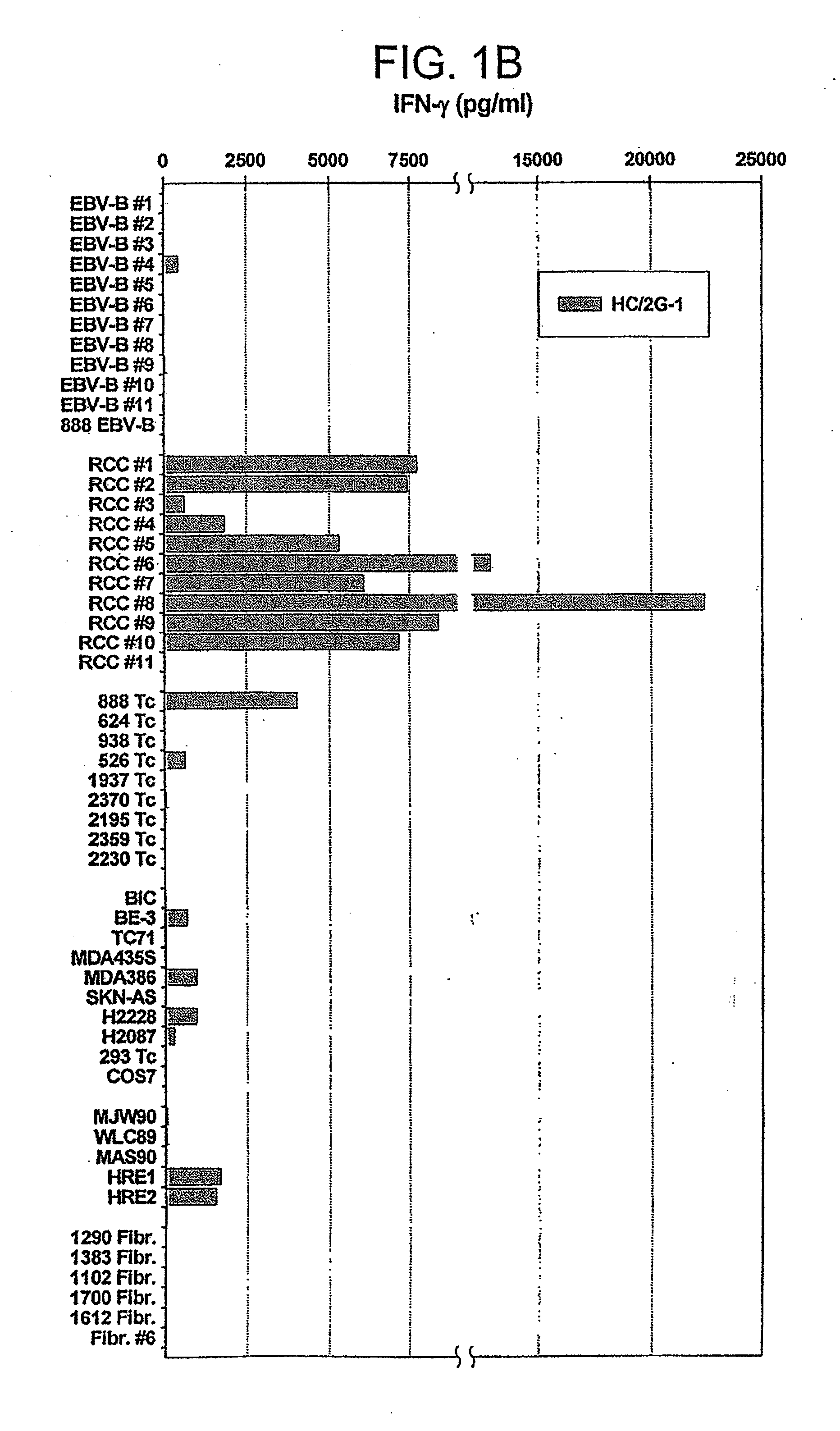
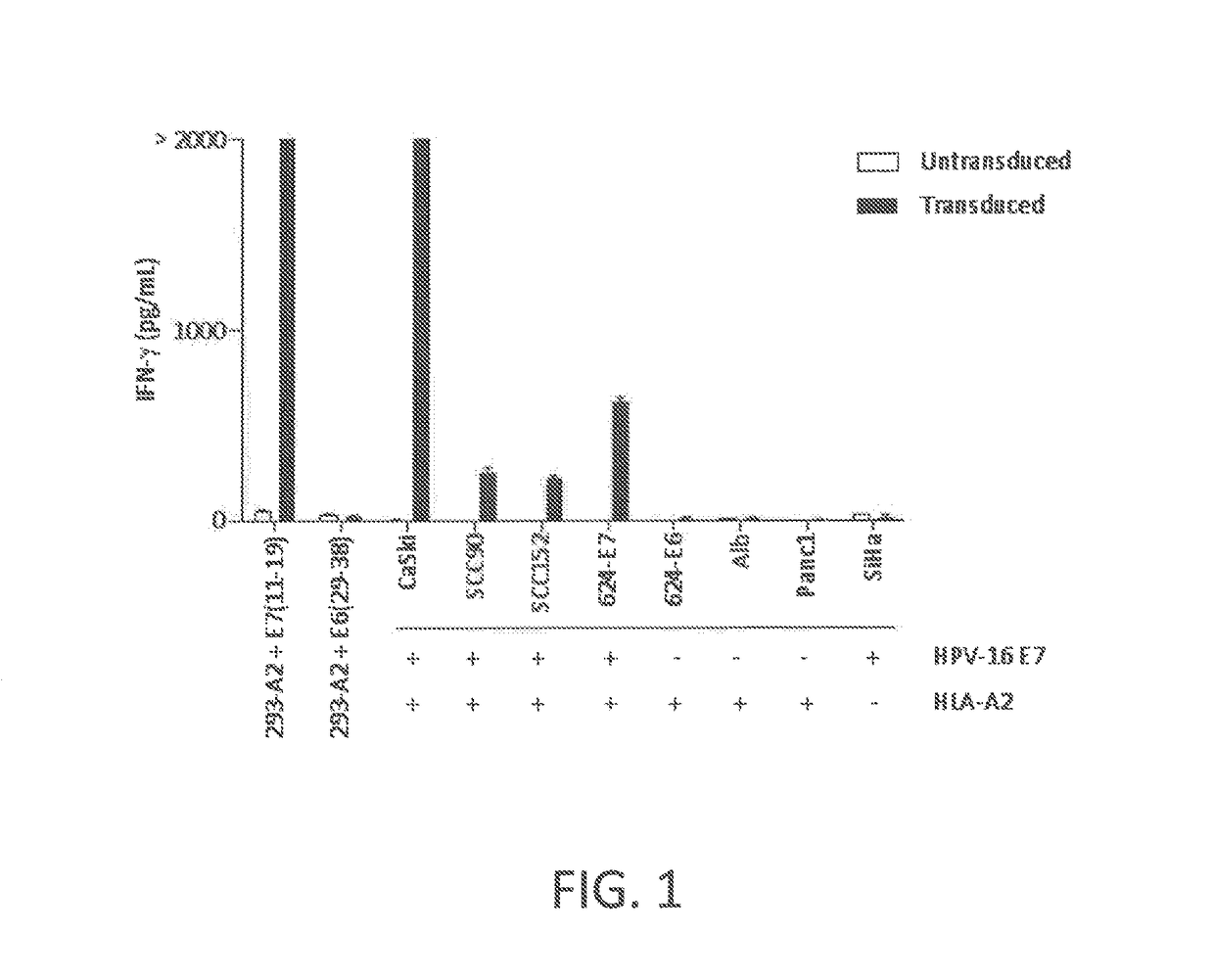
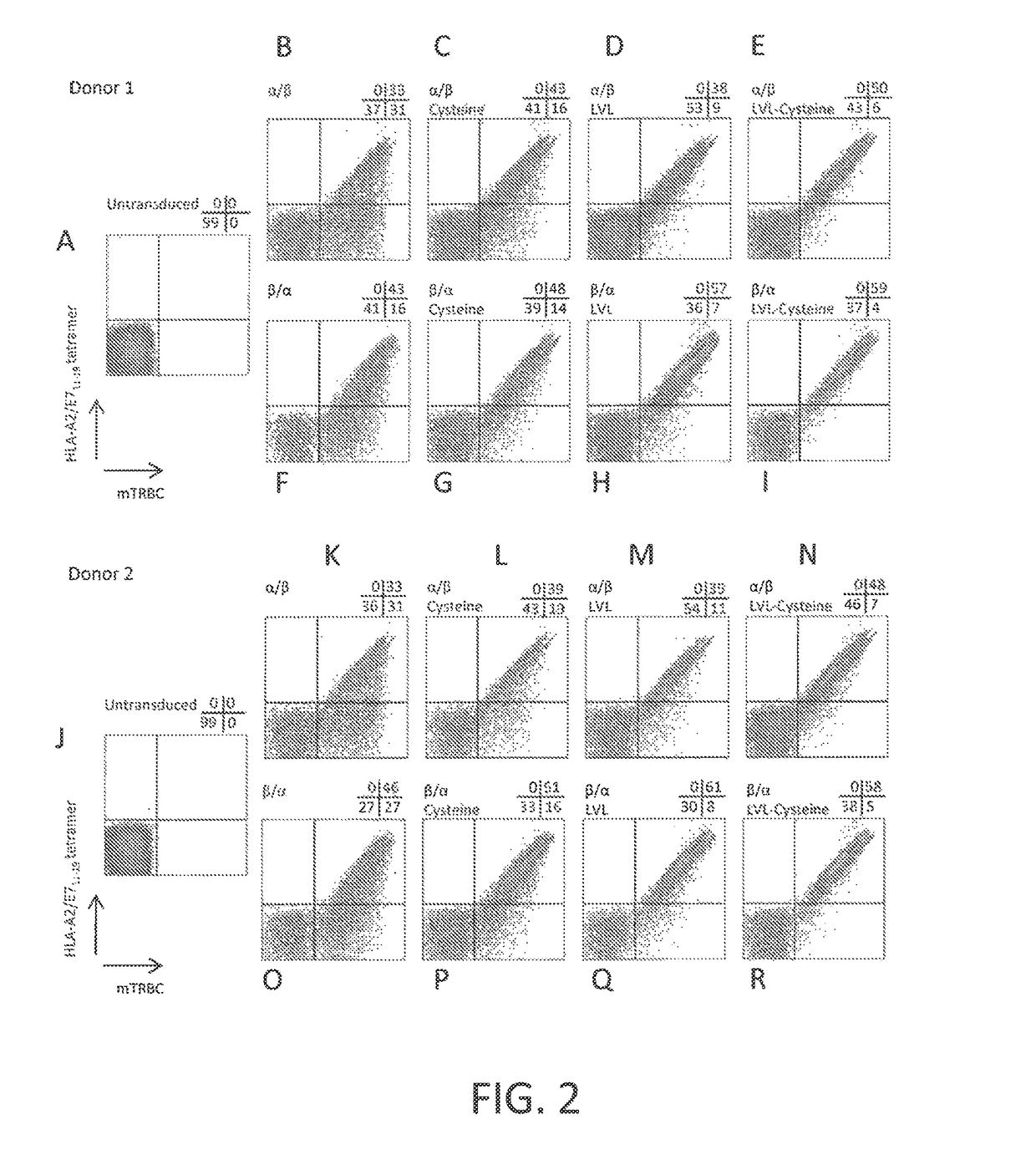
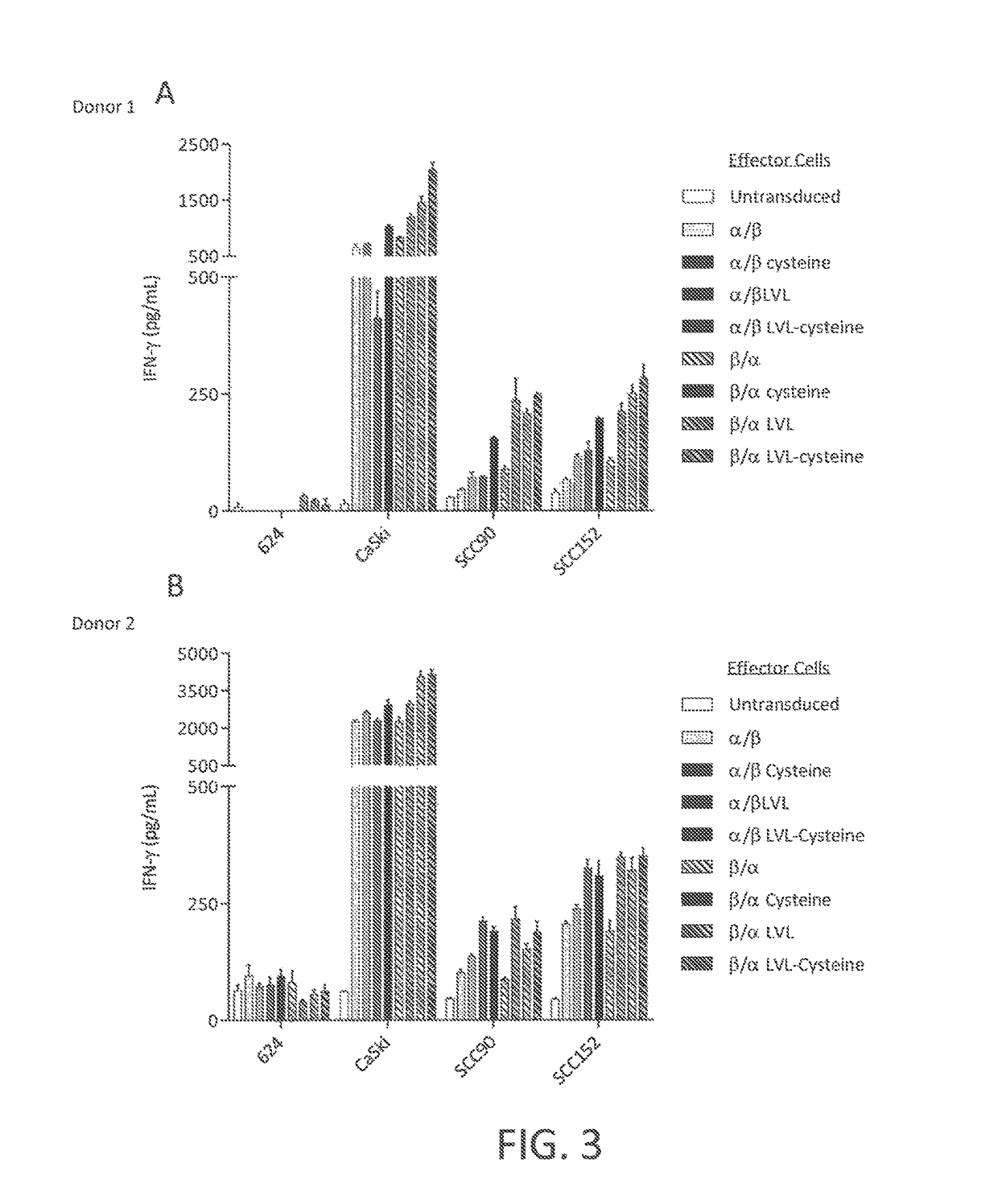
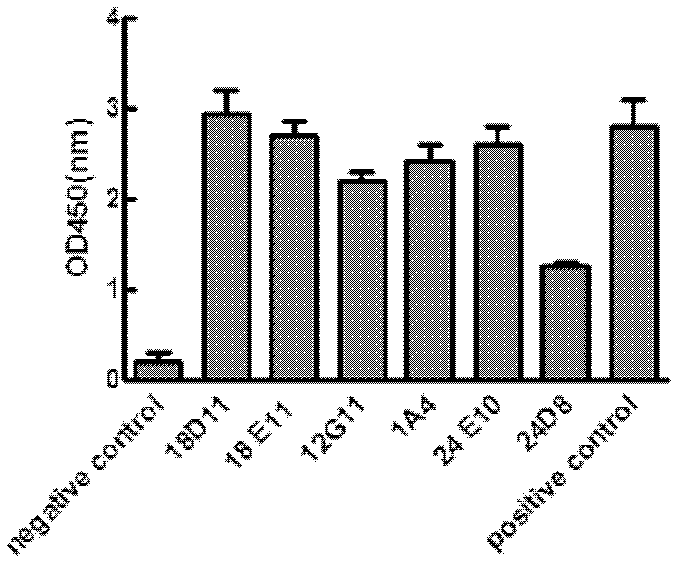
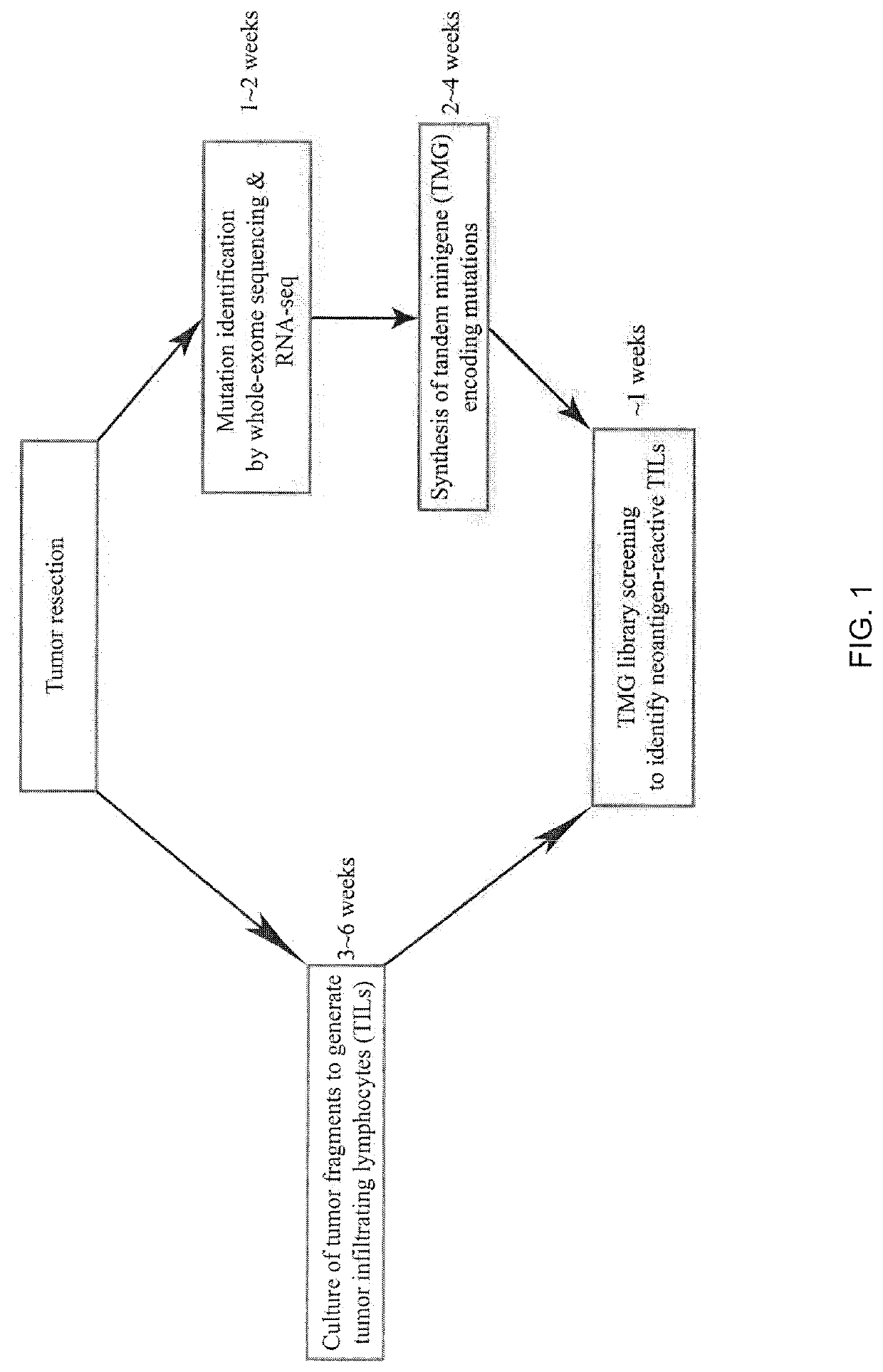
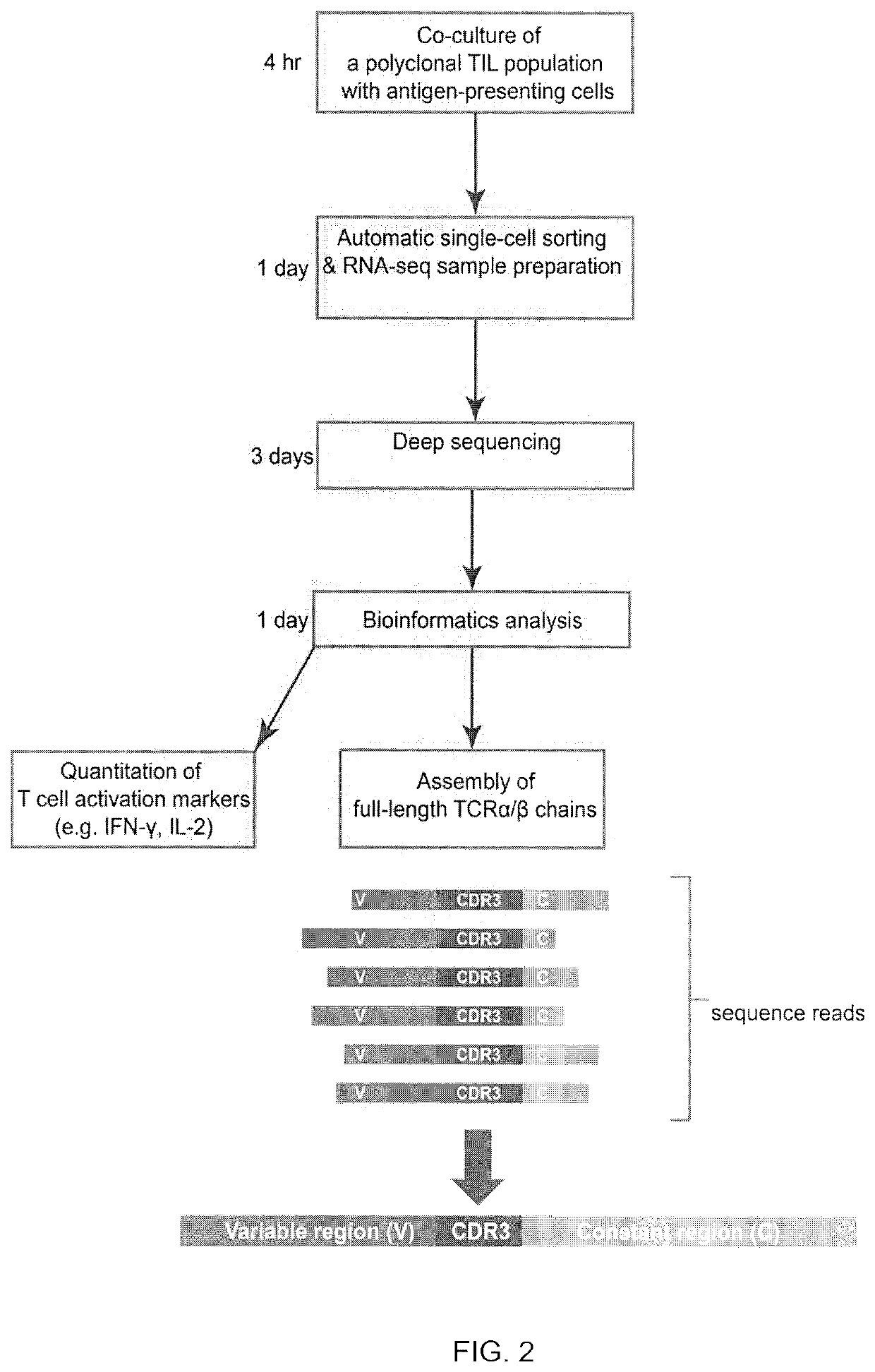
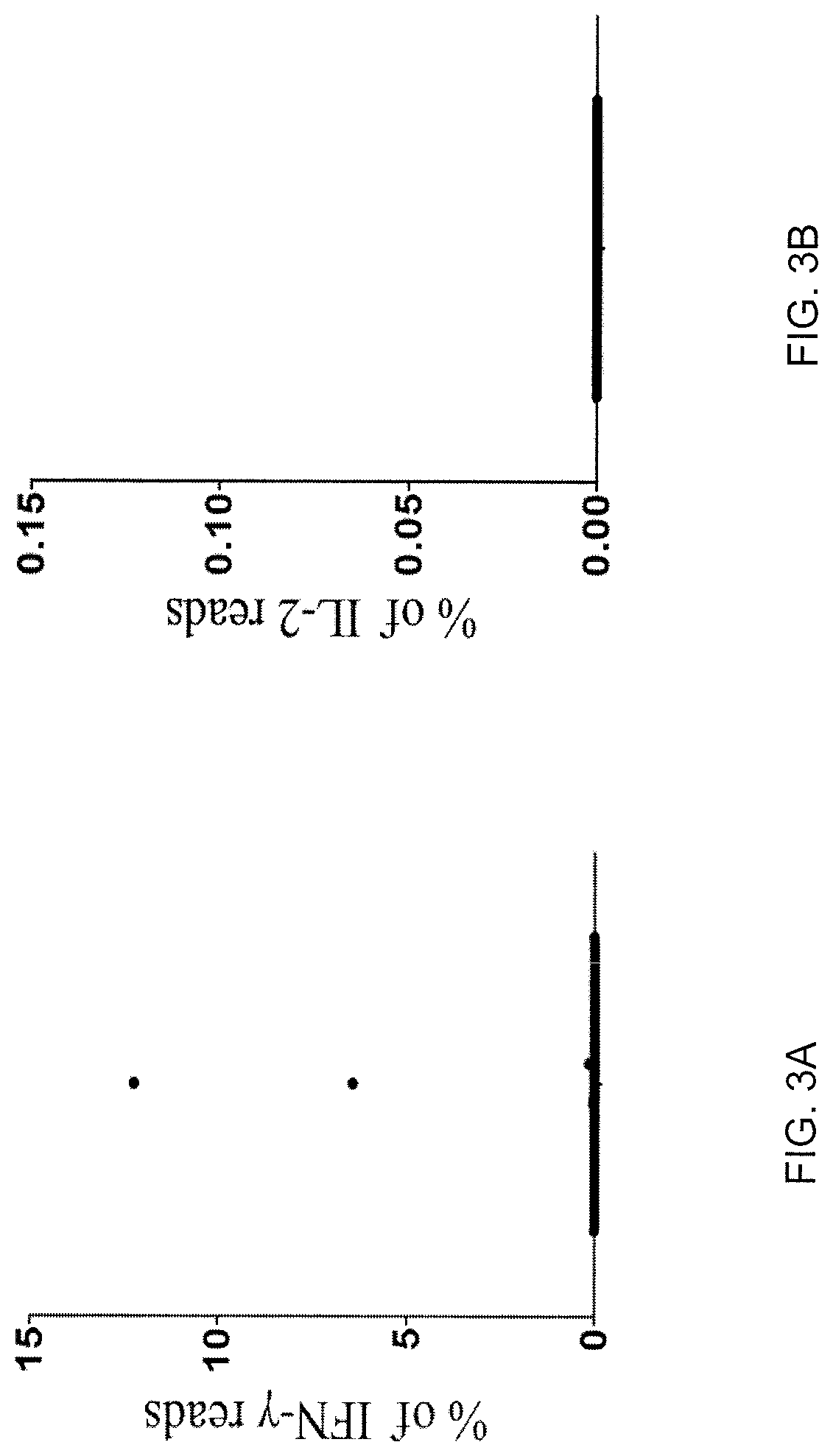
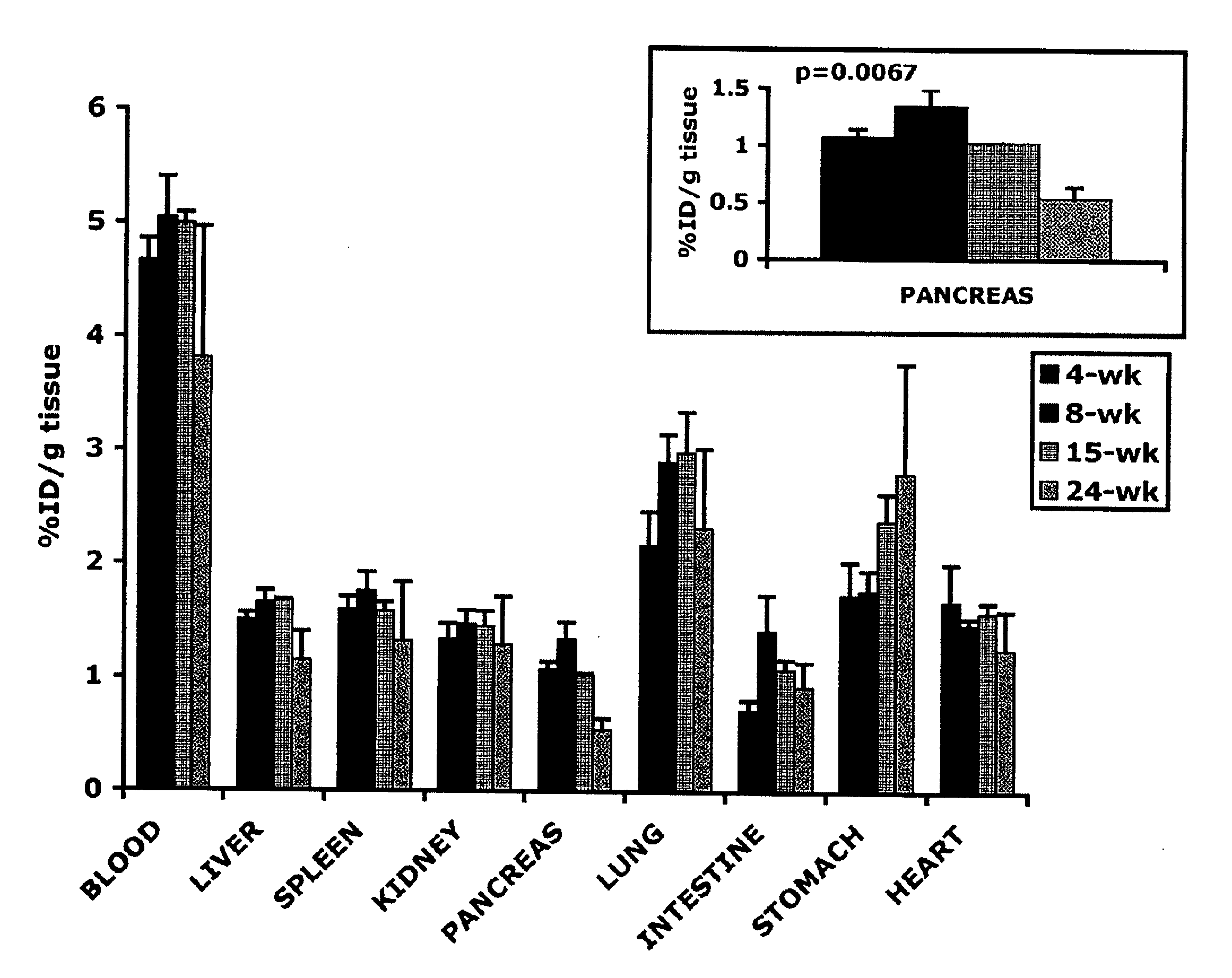
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
164 results about "Antigenic Specificity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antigenic specificity The property of mature B and T lymphocytes that enables them to respond to specific foreign antigens entering the body. Antigen specificity requires mature B and T cells that have been previously exposed to the antigen and, therefore, are able to recognize it again and respond by neutralizing or destroying it. The exact process by ...
Compositions and methods for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune conditions
ActiveUS20090155292A1Suppress autoreactive T-cell responsesPrevent and ameliorate T1DPowder deliveryAntipyreticDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The methods include selectively reducing or expanding T cells according to the antigenic specificity of the T cells. Therefore, the present invention can be used to reduce or eliminate pathogenic T cells that recognize autoantigens, such as beta cell specific T cells. As such, the present invention can be used to prevent, treat or ameliorate autoimmune diseases such as IDDM. Furthermore, the present invention can be used to expand desirable T cells, such as anti-pathogenic T cells to prevent, treat and / or ameliorate autoimmune diseases.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods of isolating t cell receptors having antigenic specificity for a cancer-specific mutation
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Molecular vaccines employing nucleic acid encoding anti-apoptotic proteins
InactiveUS20070026076A1Increase the number ofEasy to demonstratePowder deliveryVirusesDendritic cellVaccine Potency
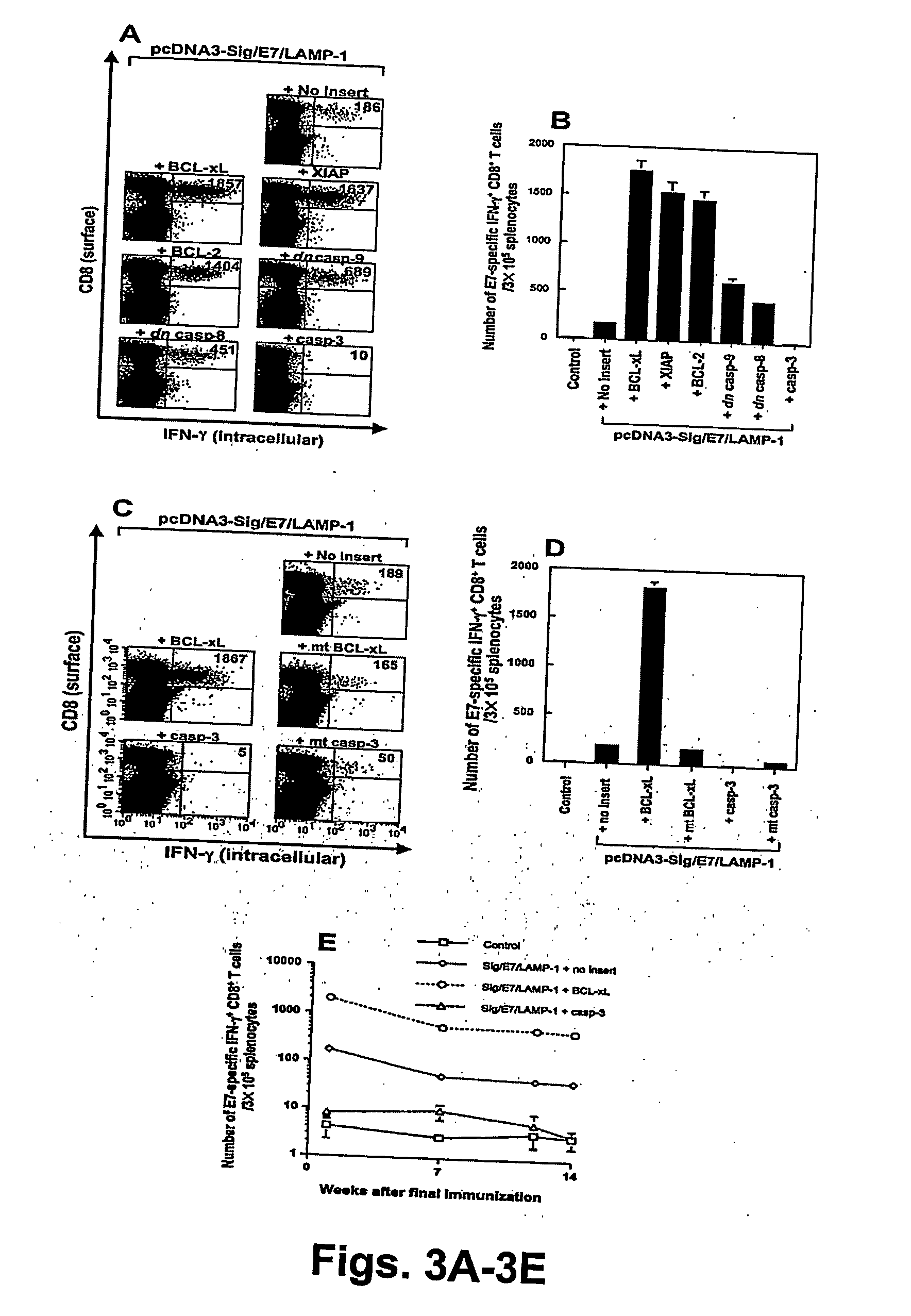
T cell immune responses are enhanced by presentation of antigen to CD8+ T cells using a chimeric nucleic acid immunogen or vaccine that links DNA encoding an antigen with DNA encoding a polypeptide that targets or translocates the antigenic polypeptide to which it is fused (immunogenicity-potentiating polypeptides or “IPP”). By inhibiting apoptosis in the vicinity of a T cell responses to such a nucleic acid immunogen, even more potent immune responses are attained. The present strategy prolongs the survival of DNA-transduced cells, including dendritic cells (DCs), thereby enhancing the priming of antigen-specific T cells and increase potency. Co-delivery of DNA encoding an inhibitor of apoptosis, including (a) BCL-xL, (b) BCL-2, (c) XIAP, (d) dominant negative caspase-9, or (e) dominant negative caspase-8, or (f) serine protease inhibitor 6 (SPI-6) which inhibits granzyme B, with DNA encoding an antigen, prolongs the survival of transduced DCs and results in significant enhancement of antigenspecific T cell immune responses that provide potent antitumor effects. Thus, co-administration of a DNA vaccine encoding antigen linked to an IPP along with one or more DNA constructs encoding an anti-apoptotic protein provides a novel way to enhance vaccine potency.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
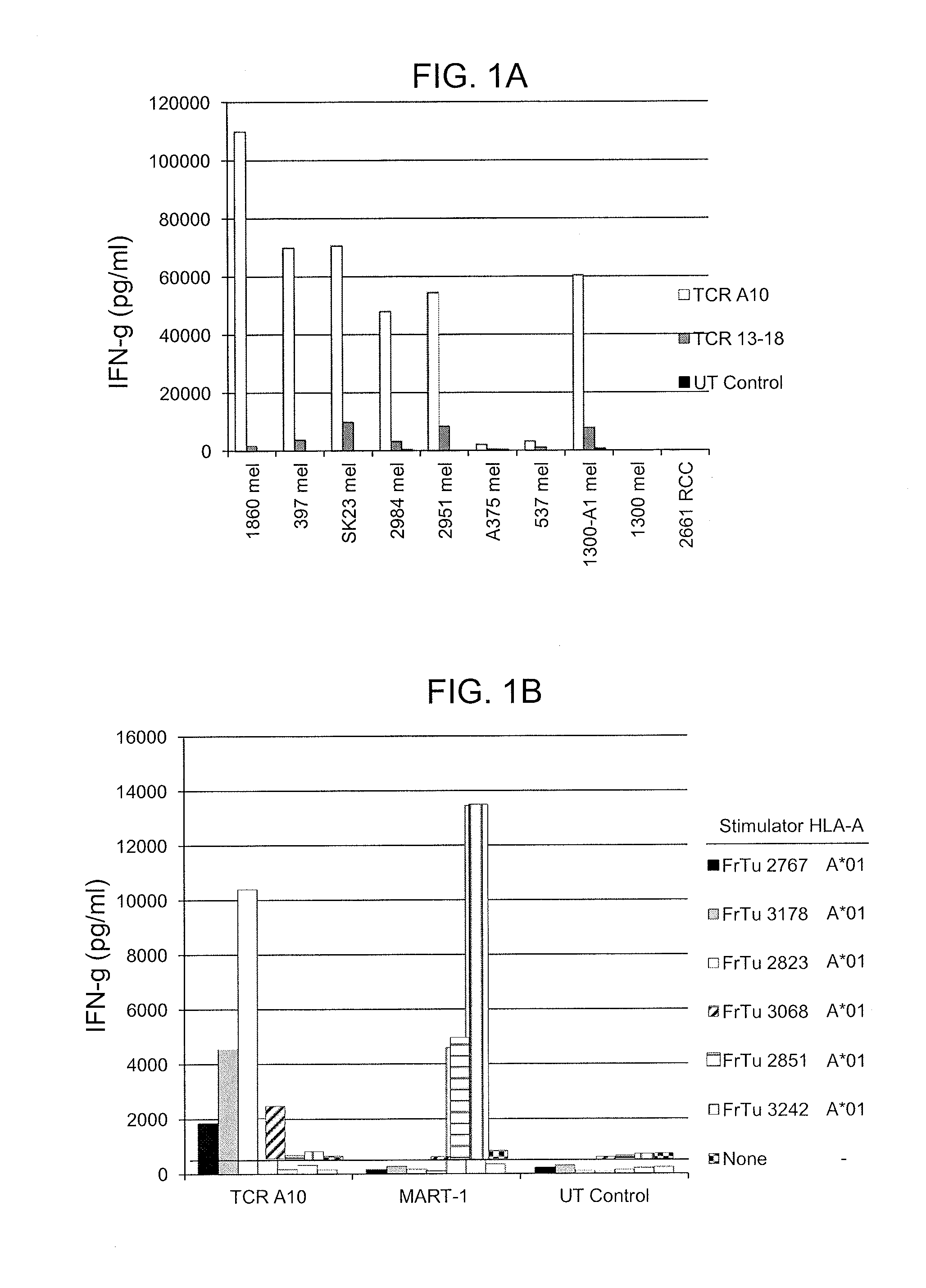
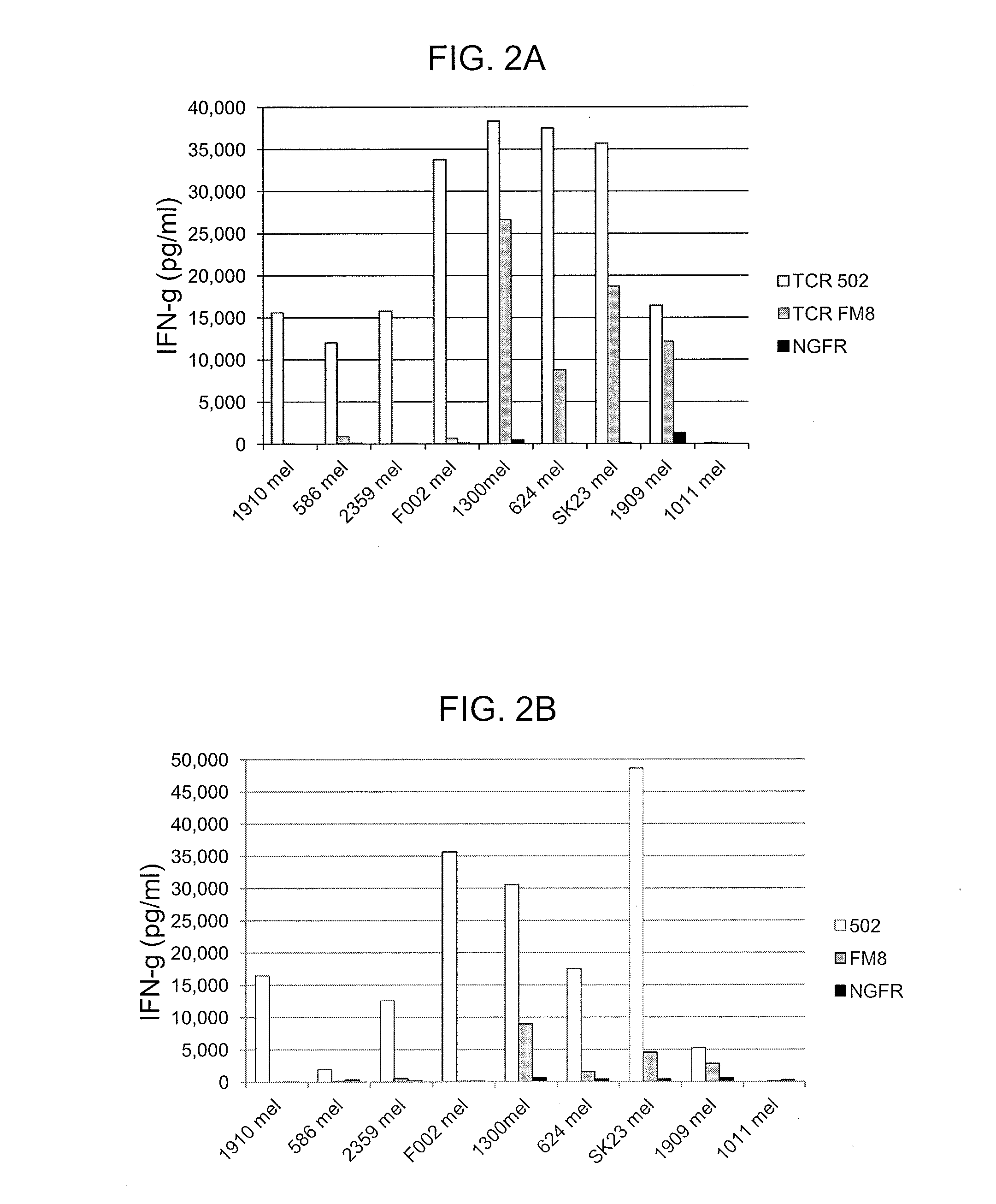
T cell receptors and related materials and methods of use
InactiveUS7820174B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsMajor histocompatibilityCancer antigen
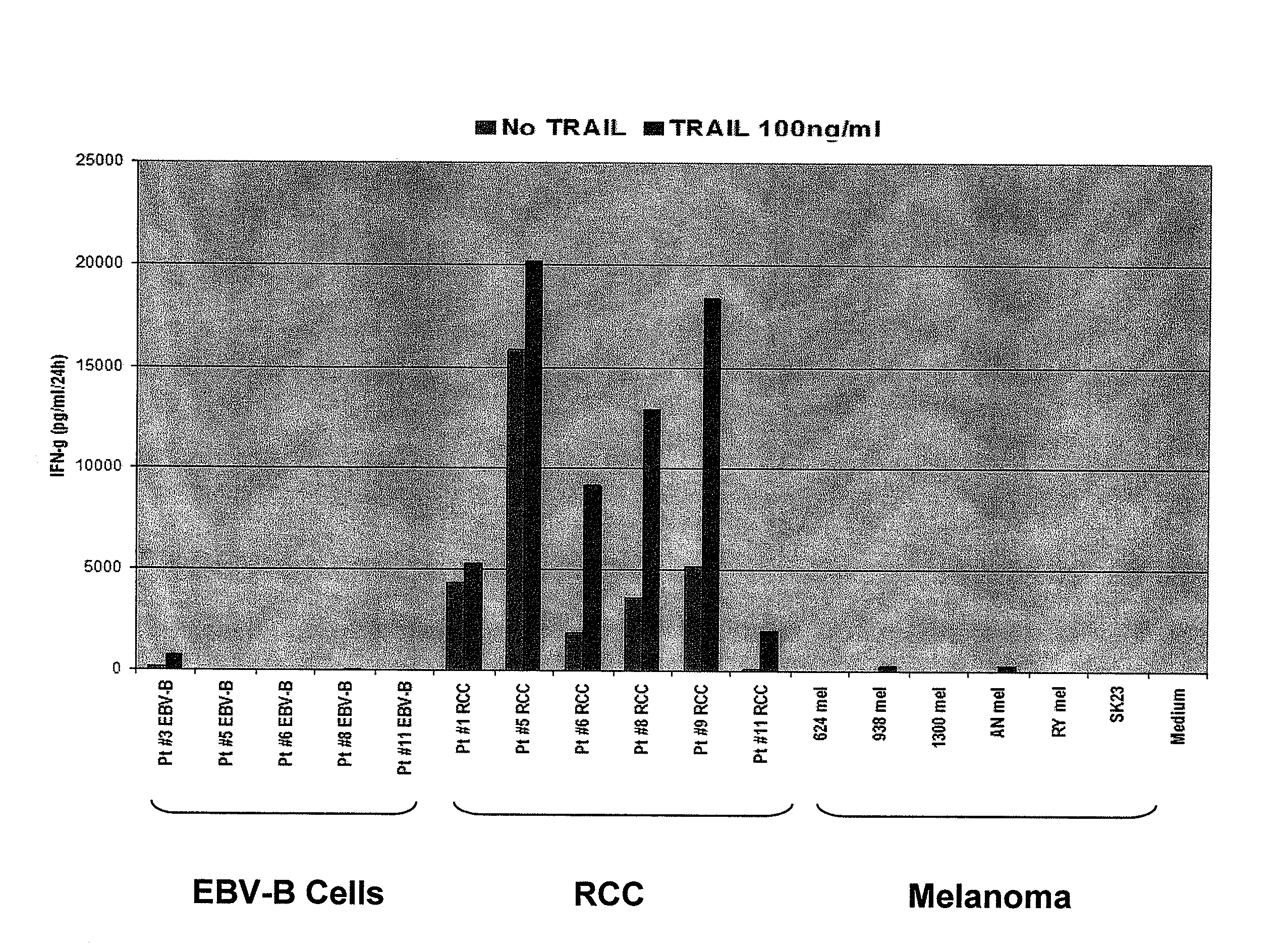
The invention provides an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for a cancer antigen, e.g., a renal cell carcinoma antigen, wherein the TCR recognizes the cancer antigen in a major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-independent manner. Also provided are related polypeptides, proteins, nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, isolated host cells, populations of cells, antibodies, or antigen binding portions thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions. The invention further provides a method of detecting the presence of cancer in a host and a method of treating or preventing cancer in a host using the inventive TCRs or related materials.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
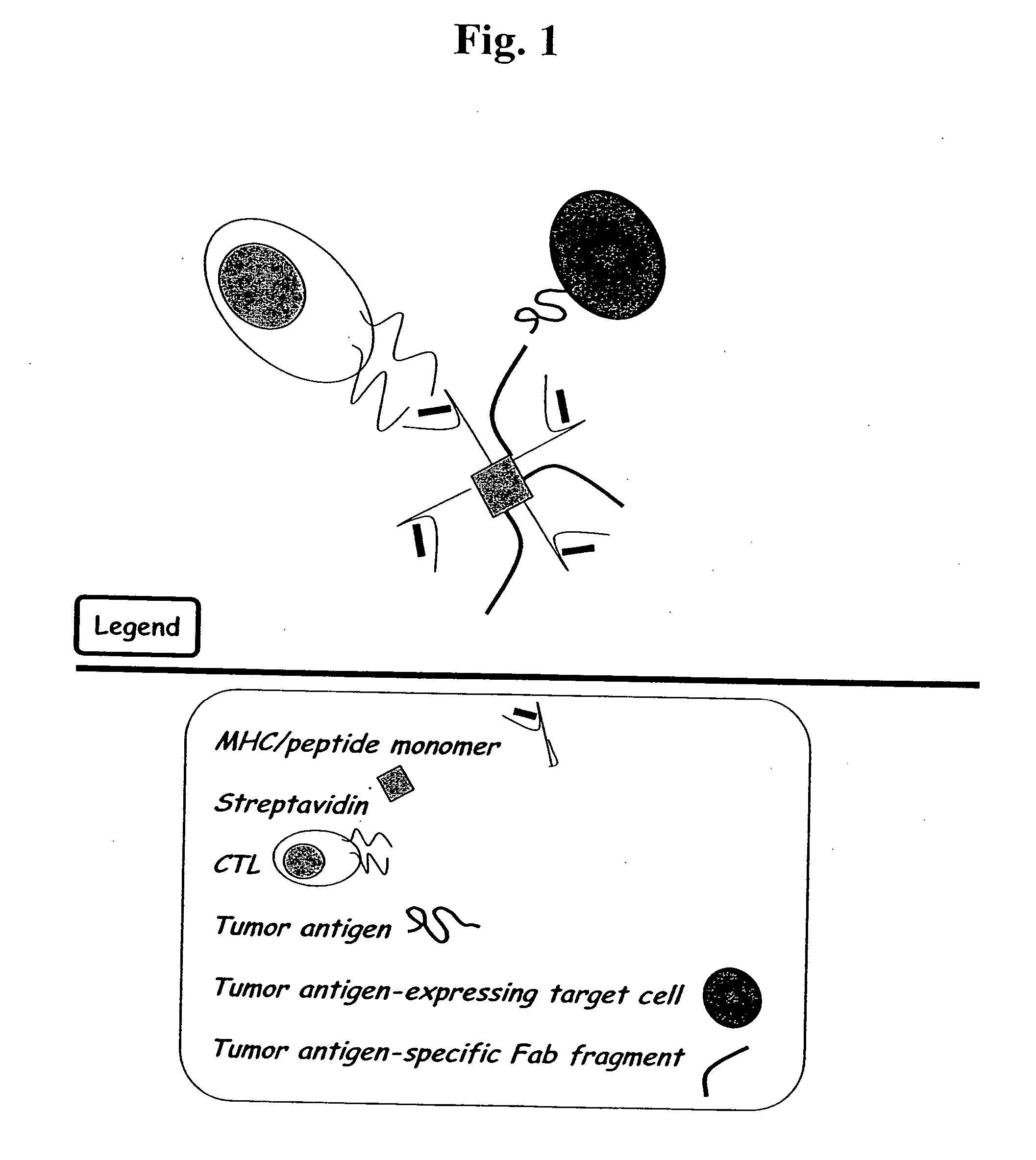
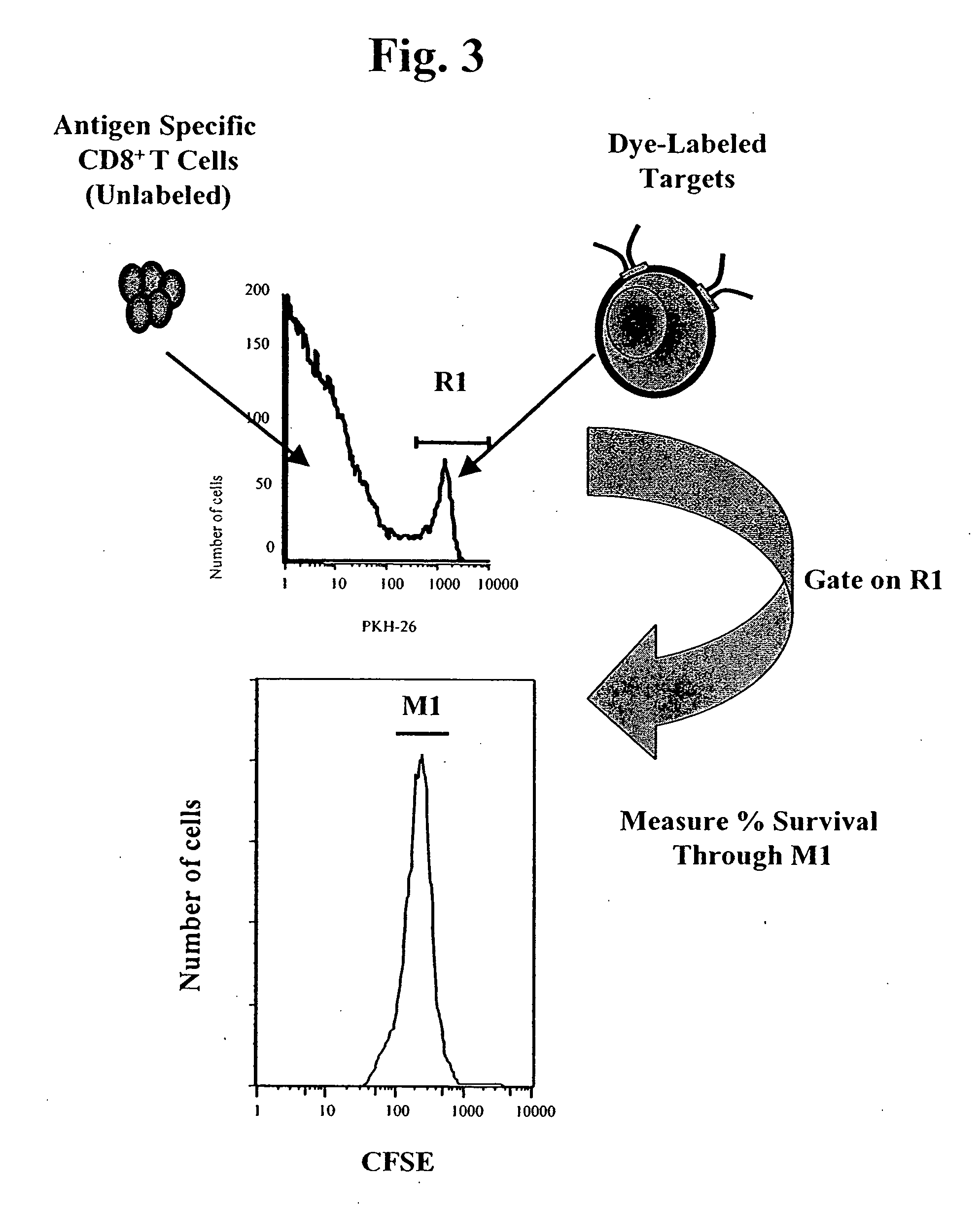
MHC bridging system for detecting CTL-mediated lysis of antigen presenting cells
InactiveUS20050287611A1Reduce signalingBiological material analysisBlood/immune system cellsLysisFluorescence
A bridging assay that utilizes a multivalent MHC binding molecule to enumerate the number of antigen-specific CTLs in a particular sample and also determines the functional capability of the CTL population in the sample is provided. In one embodiment, the assay is used to measure the effector function of any tetramer-positive CTL using a single non-MHC-containing target cell line that is adapted to form an antibody bridge with the tetramer. Furthermore, effector function and enumeration can be measured by flow cytometry, and additional markers residing on either effector or target cell populations may be detected using antibodies coupled with other fluorochromes. The tetramer bridging assay will allow investigators to easily determine the lytic capacity and antigenic specificity of CTLs using a commercially available reagent in a non-radioactive assay.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
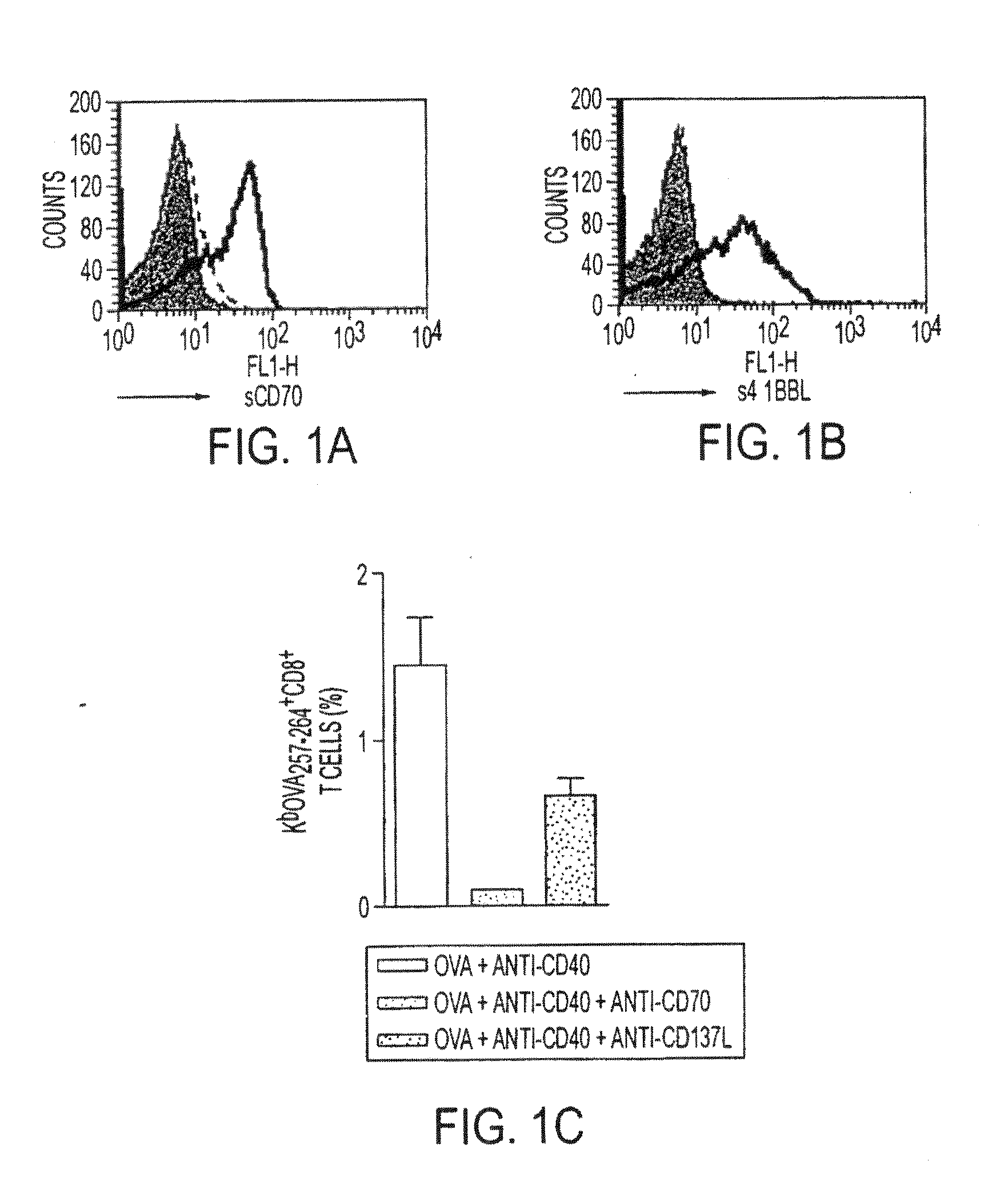
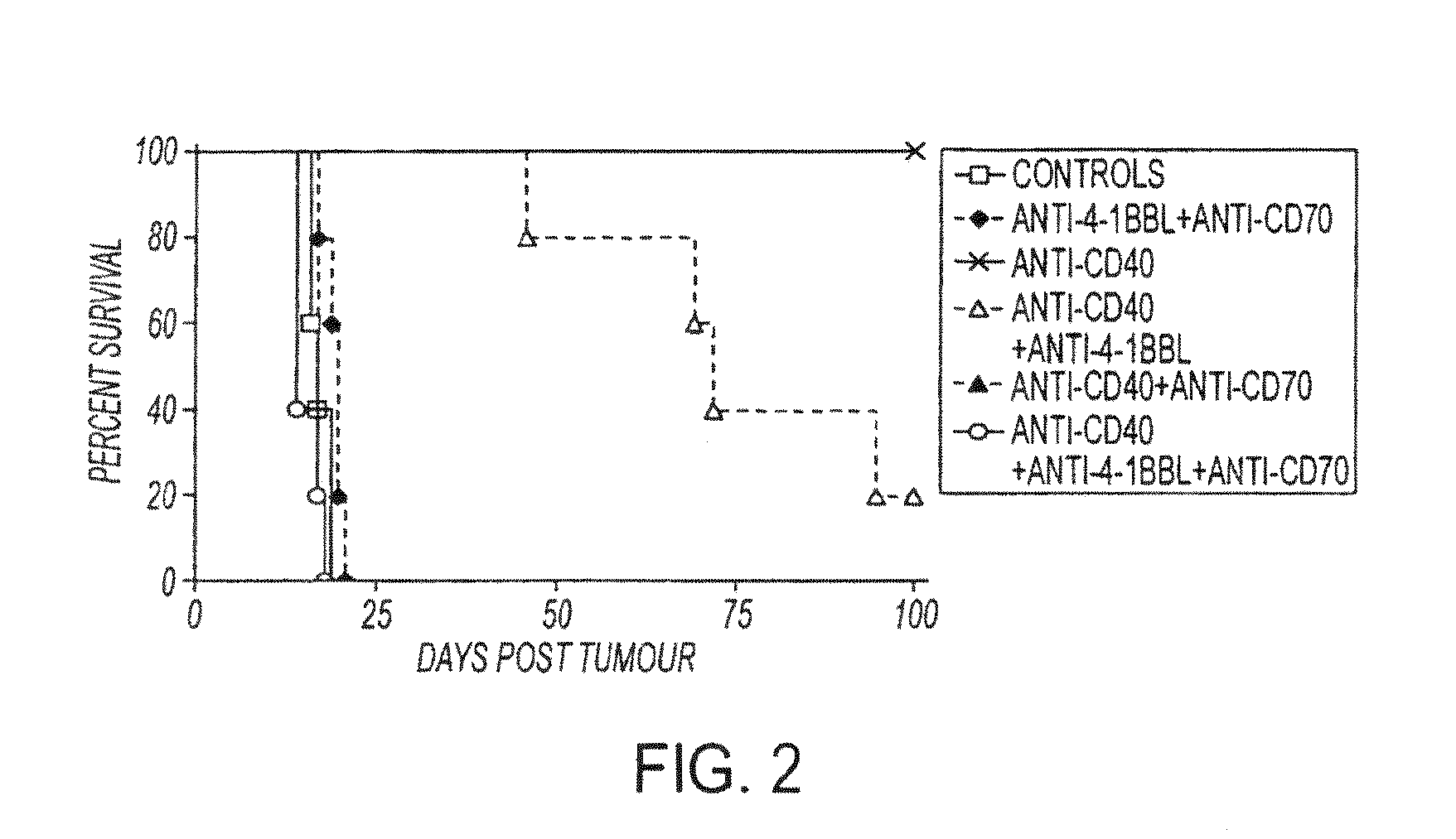
Human immune therapies using a cd27 agonist alone or in combination with other immune modulators
InactiveUS20130336976A1Promotes strong expression of 4-1BBImprove responseAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsIMMUNE STIMULANTSCD8
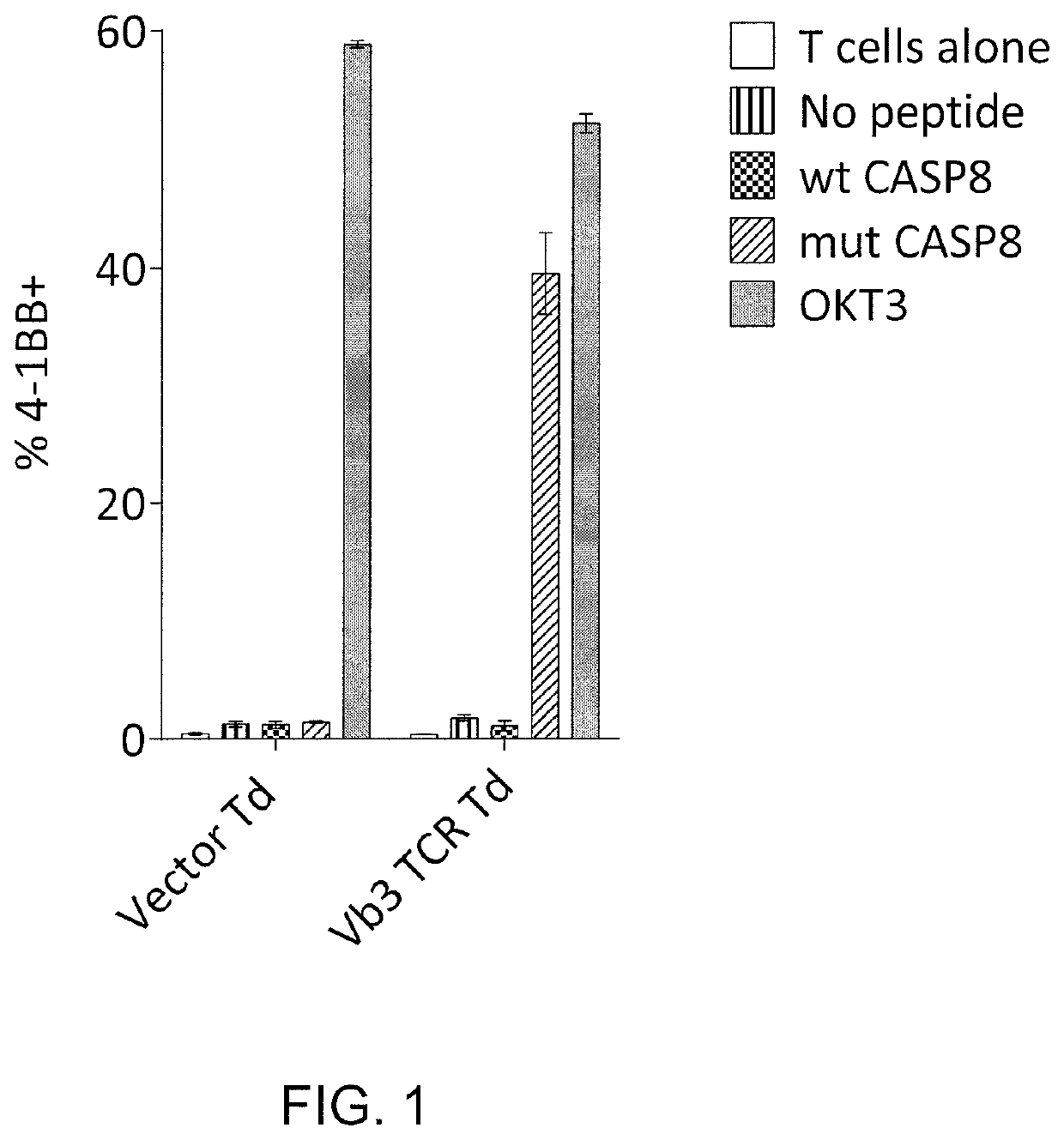
Methods of inducing T cell proliferation and expansion in vivo for treating conditions wherein antigen-specific T cell immune response are therapeutically desirable such as cancer, infection, inflammation, allergy and autoimmunity and for enhancing the efficacy of vaccines are provided. These methods comprise the administration of at least one CD27 agonist, preferably an agonistic CD27 antibody, alone or in association with another moiety such as immune stimulant or immune modulator such as an anti-CD40, OX-40, 4-1BB, or CTLA-4 antibody or an agent that depletes regulatory cells, or a cytokine. These mono and combination therapies may also optionally include the administration of a desired antigen such as a tumor antigen, an allergen, an autoantigen, or an antigen specific to an infectious agent or pathogen against which a T cell response (often CD8+) is desirably elicited.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
T cell receptors and related materials and methods of use
The invention provides T cell receptors (TCRs) having antigenic specificity for a cancer antigen, e.g., tyrosinase. Also provided are related polypeptides, proteins, nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, isolated host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions. The invention further provides a method of detecting the presence of cancer in a host and a method of treating or preventing cancer in a host using the inventive TCRs or related materials.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
GP100-specific T cell receptors and related materials and methods of use
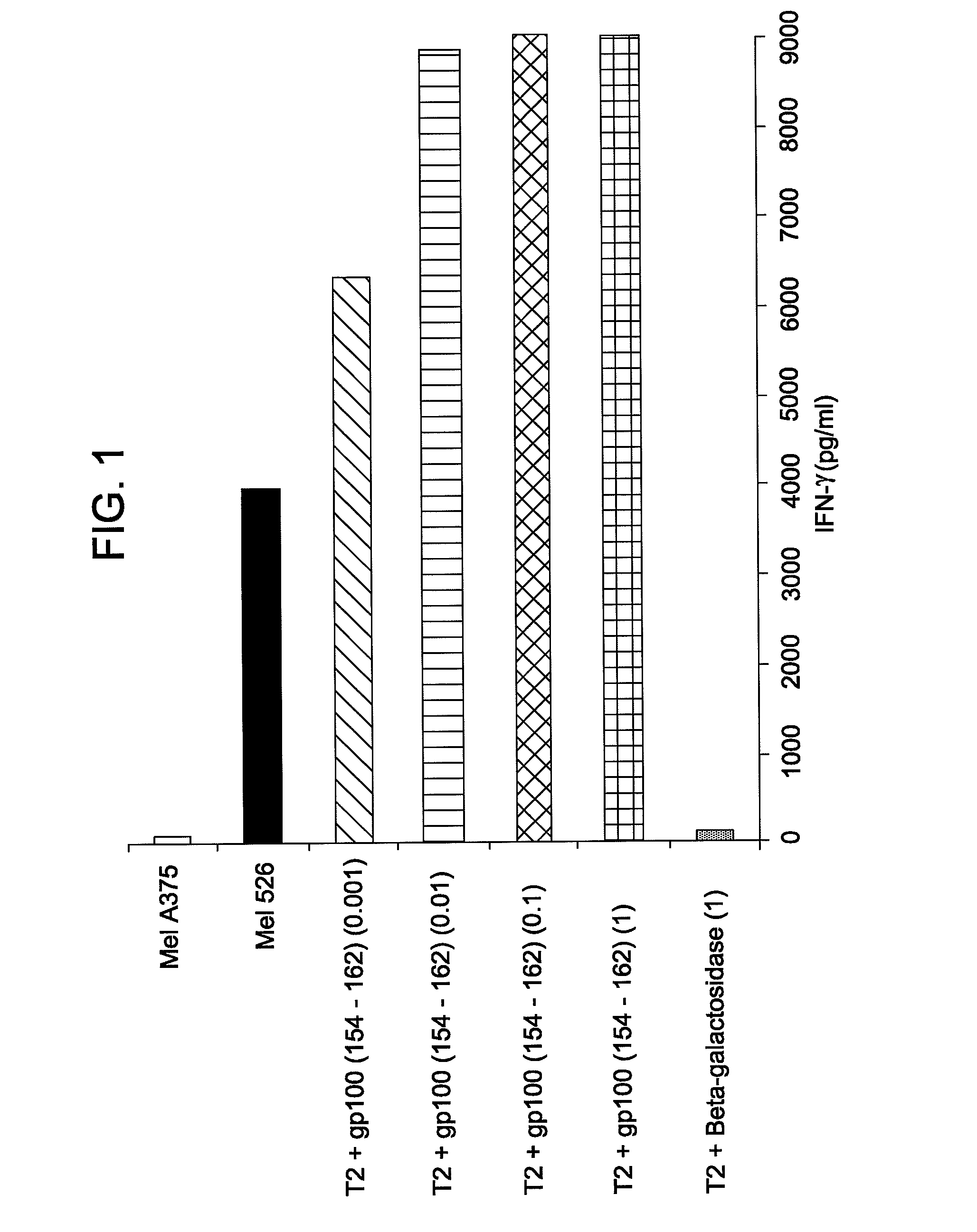
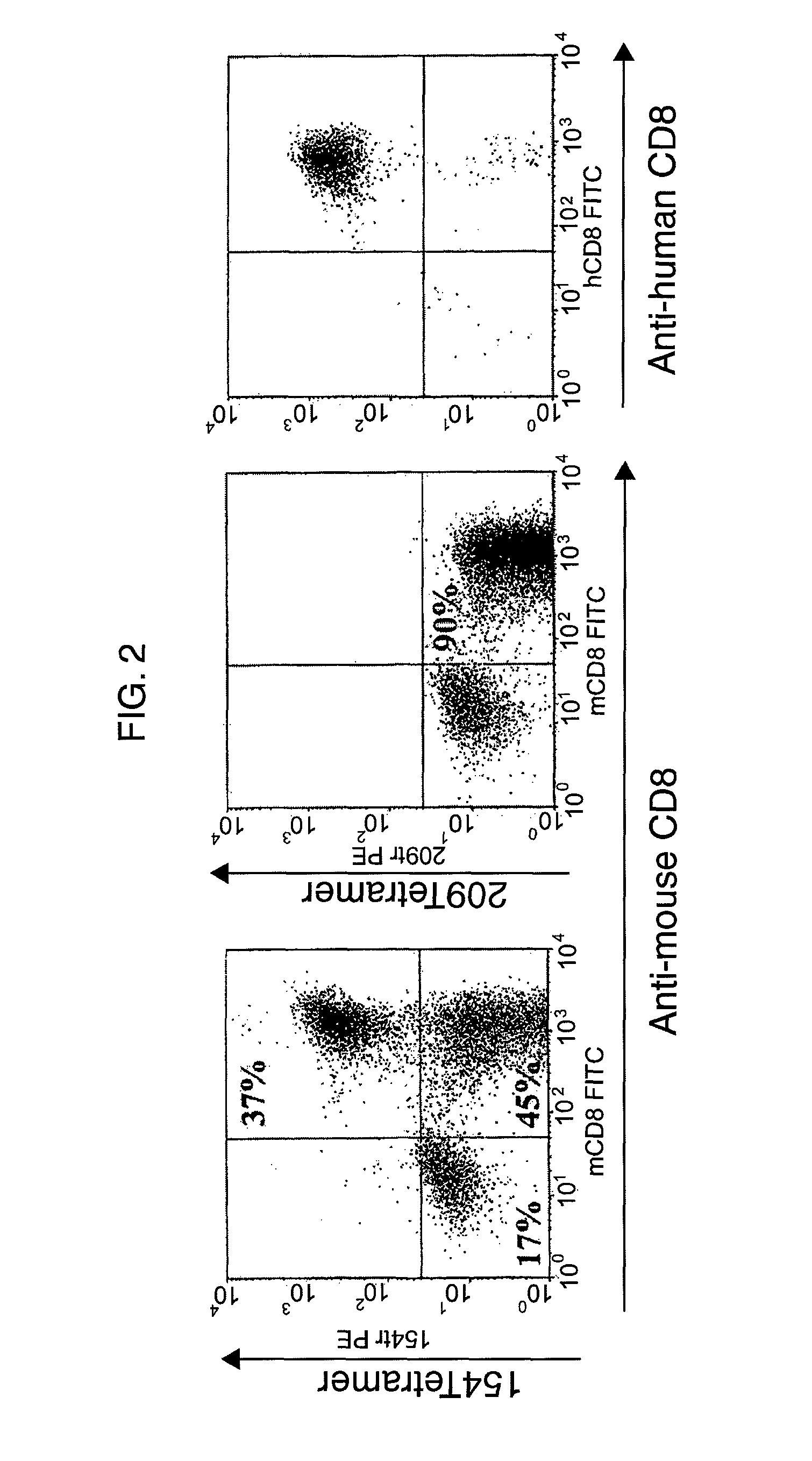
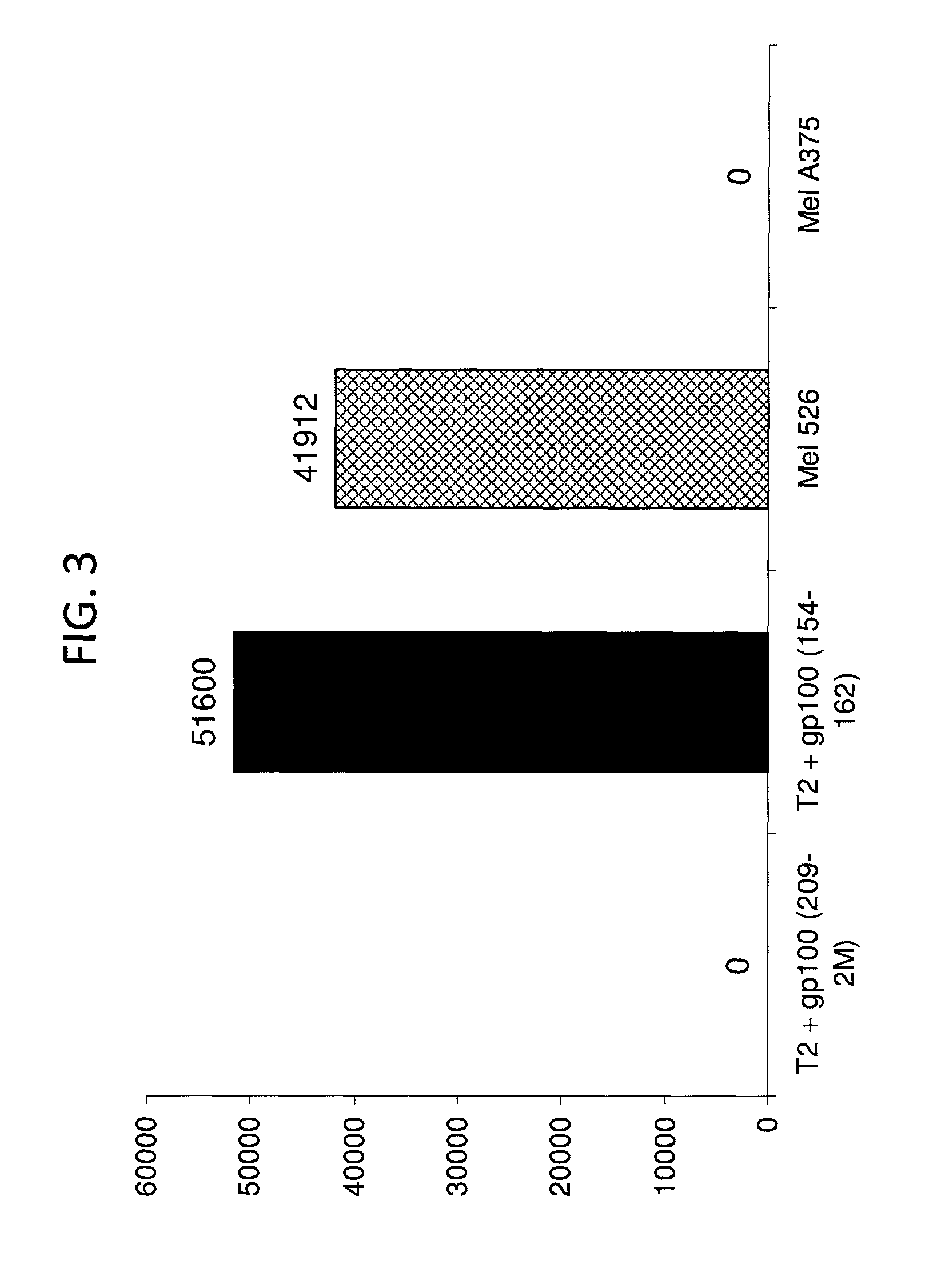
The invention provides human cells, particularly human T cells, comprising a murine T Cell Receptor (TCR) having antigen specificity for the cancer antigen gp100. Isolated or purified TCRs having antigenic specificity for amino acids 154-162 of gp100 (SEQ ID NO: 1), as well as related polypeptides, proteins, nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, antibodies, or antigen binding fragments thereof, conjugates, and pharmaceutical compositions, are further provided. The invention further provides a method of detecting the presence of cancer in a host and a method of treating or preventing cancer in a host comprising the use of the inventive materials described herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
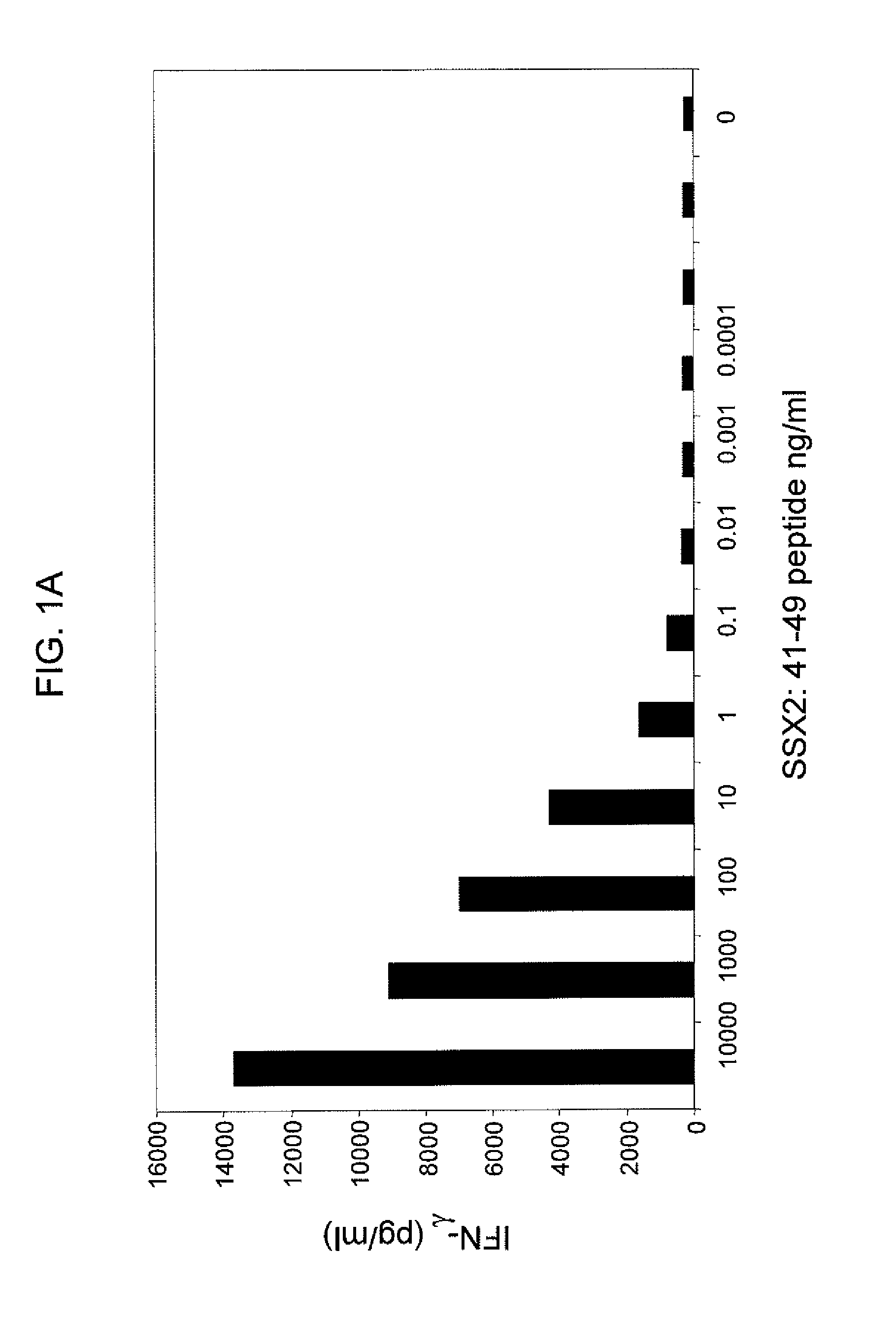
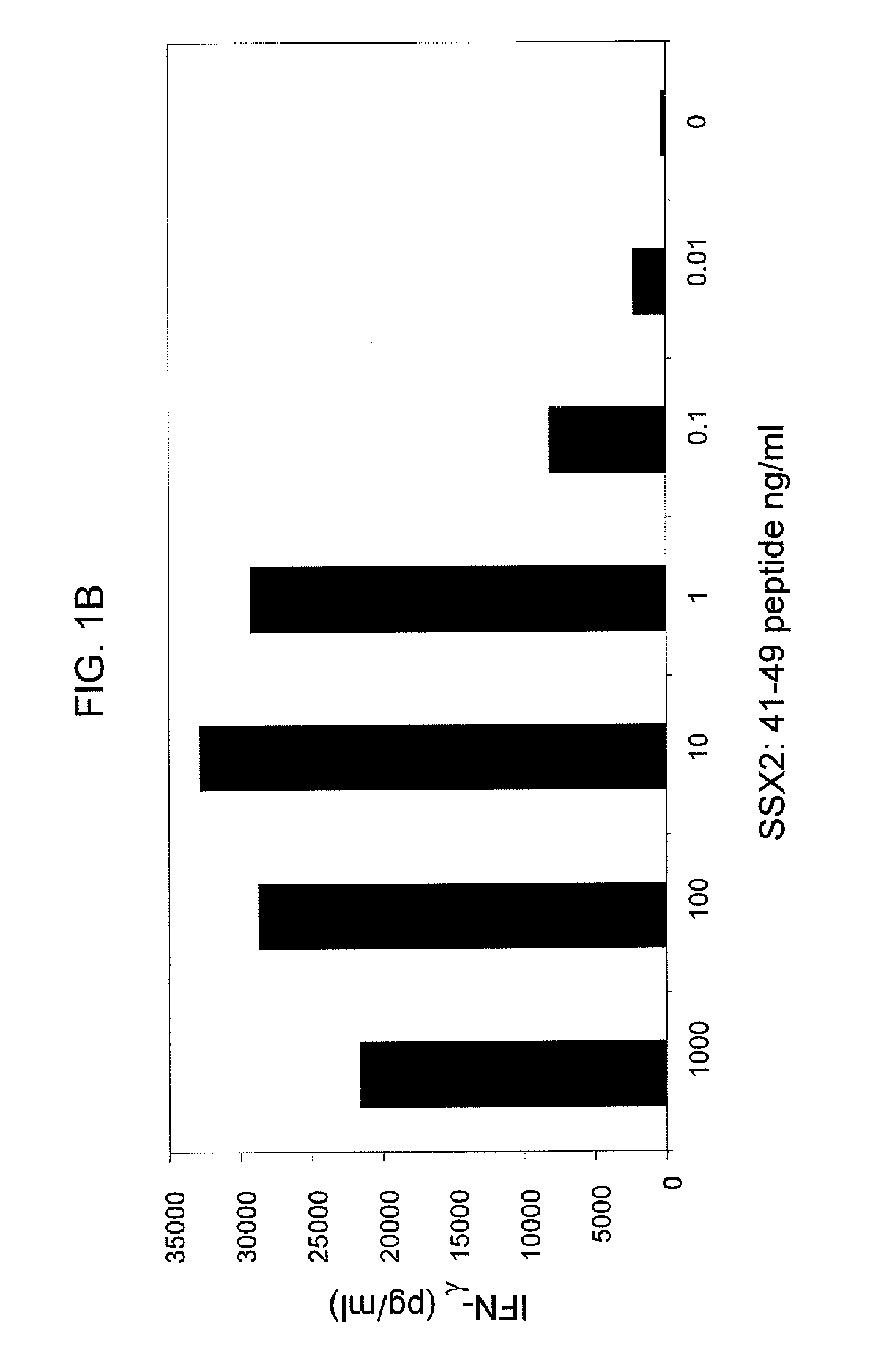
Anti-SSX-2 T cell receptors and related materials and methods of use
ActiveUS9345748B2Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderSynovial sarcomaAntiendomysial antibodies
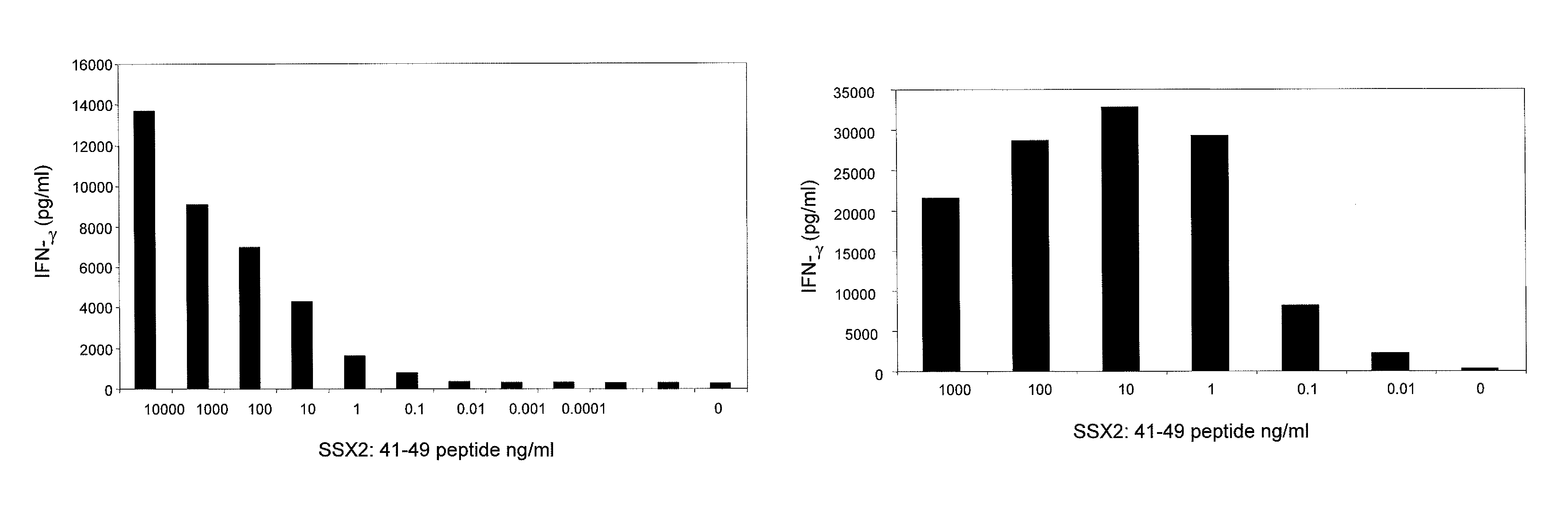
The invention provides an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for synovial sarcoma X Breakpoint (SSX)-2. The invention further provides related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, and populations of cells. Further provided by the invention are antibodies, or an antigen binding portion thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions relating to the TCRs of the invention. Methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a host and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a host are further provided by the invention.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
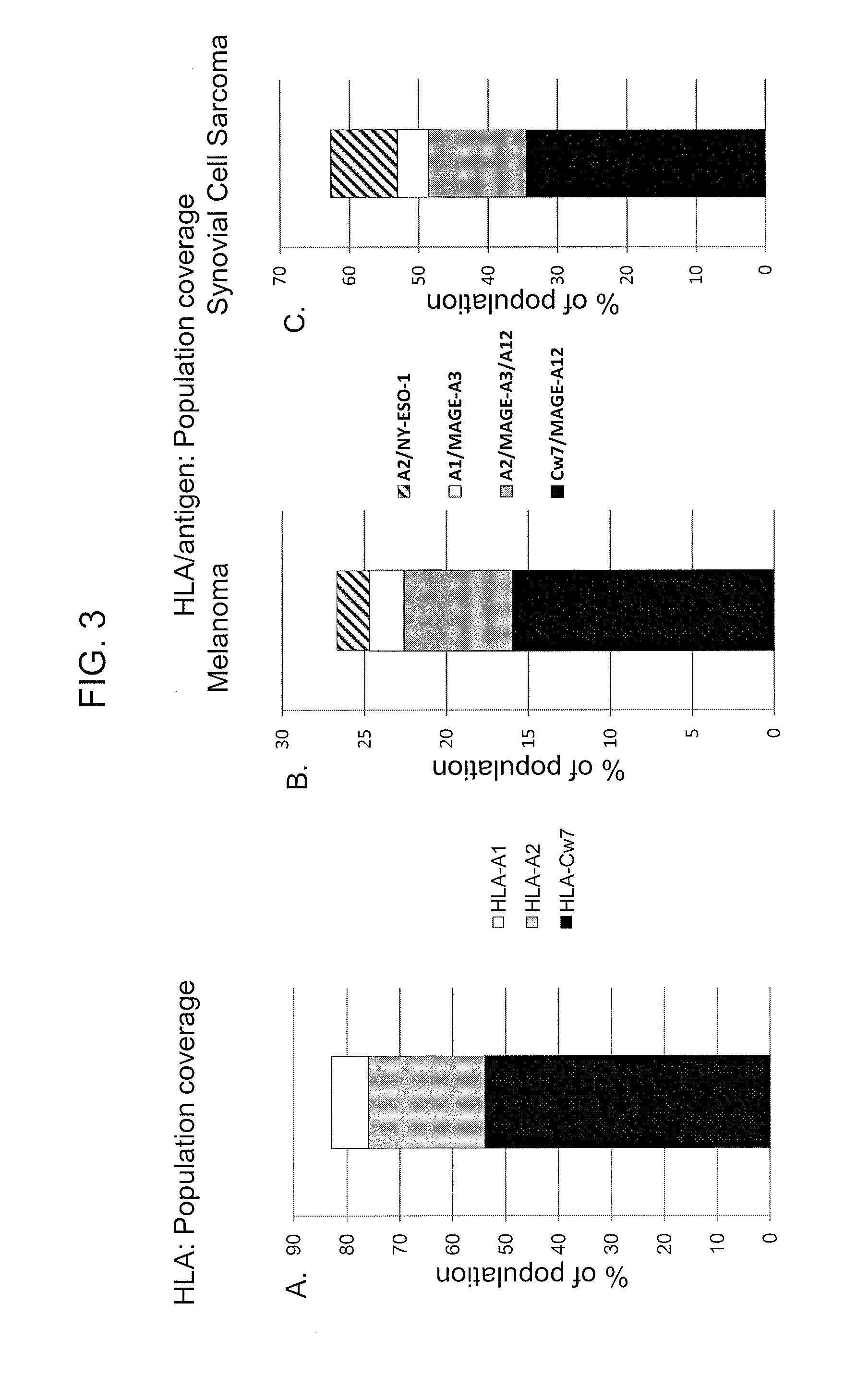
T cell receptors recognizing hla-a1- or hla-cw7-restricted mage
InactiveUS20140378389A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigen bindingRecombinant expression
The invention provides an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for a) melanoma antigen family A (MAGE A)-3 in the context of HLA-A1 or b) MAGE-A12 in the context of HLA-Cw7. The invention further provides related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, and populations of cells. Further provided by the invention are antibodies, or an antigen binding portion thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions relating to the TCRs of the invention. Methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a host and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a host are further provided by the invention.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Methods for treating autoimmune disease using biocompatible bioabsorbable nanospheres
InactiveUS20120093934A1Sufficient amountIncreasing and maintaining numberPowder deliveryAntipyreticAutoimmune diseaseSelf-Antigens
The methods include selectively reducing or expanding T cells according to the antigenic specificity of the T cells using biocompatible bioabsorbable nanospheres. Therefore, the present invention can be used to reduce or eliminate pathogenic T cells that recognize autoantigens, such as beta cell specific T cells. As such, the present invention can be used to prevent, treat or ameliorate autoimmune diseases such as IDDM. Furthermore, the present invention can be used to expand desirable T cells, such as anti-pathogenic T cells to prevent, treat and / or ameliorate autoimmune diseases.
Owner:UTI LLP
Autoantibody detection systems and methods
InactiveUS20100204055A1Improve throughputMultiplex well-controlled assay performancePeptide librariesLibrary screeningDiseaseProtein
Autoantibodies in biological samples such as serum can result from changes to biomolecules (e.g., proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids) that are associated with disease. Such autoantibodies are useful biomarkers because they frequently appear early in disease and are readily accessible, particularly in biological fluids such as blood and serum. CT antigens are particularly useful for detecting autoantibodies correlated with cancer. Numerous population-based profiles for pluralities of different autoantibody species, at least some of which are specifically reactive with CT antigens, allow for simultaneous assessment of multiple disease-associated analytes is a single test, which can be more effective in diagnostics and drug development than individual profiles. The instant invention provides autoantibody detection array devices that include a plurality of independently selected autoantibody-reactive reagent species, such as full-length CT antigens or the antigenic portions thereof, disposed on a substrate. Such arrays can be used to screen biological samples taken from patients or other subjects for diagnostic, drug development, and other applications.
Owner:BONNER FERRABY PHOEBE W +2
Regulatory T cells suppress autoimmunity
The invention provides methods for producing an autoantigen-specific regulatory T cell enriched composition, and resultant compositions and methods of use.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Anti-human papillomavirus 16 e7 t cell receptors
ActiveUS20170145070A1Minimize ToxicityImprove abilitiesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeHuman papillomavirus
Disclosed is a synthetic T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for an HLA-A2-restricted epitope of human papillomavirus (HPV) 16 E7, E711-19. Related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, and populations of cells are also provided. Antibodies, or an antigen binding portion thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions relating to the TCRs of the invention are also provided. Also disclosed are methods of detecting the presence of a condition in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing a condition in a mammal, wherein the condition is cancer, HPV 16 infection, or HPV-positive premalignancy.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Anti-human papillomavirus 16 e6 t cell receptors
ActiveUS20160152681A1Highly avid recognitionMinimize destructionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeHuman papillomavirus
Disclosed is a T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for an HLA-A2-restricted epitope of human papillomavirus (HPV) 16 E6, E629-38. Related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, and populations of cells are also provided. Antibodies, or an antigen binding portion thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions relating to the TCRs of the invention are also provided. Also disclosed are methods of detecting the presence of a condition in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing a condition in a mammal, wherein the condition is cancer, HPV 16 infection, or HPV-positive premalignancy.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
TCR (T Cell Receptor) for identifying S183-91 epitope of hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen and application of TCR
ActiveCN107827959AGood killing effectSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeHepatitis B virus
The invention discloses a method for separating an antigen-specificity T cell and cloning and encoding an antigen-specificity TCR gene from the antigen-specificity T cell. The invention also providesa nucleic acid molecule of the TCR for encoding the specificity of an HBV surface antigen S183-91, and a carrier containing the nucleic acid molecule. The TCR disclosed by the invention can be combined with an HBV S183-91 antigen short peptide complex FLLTRILTI-HLA*A0201; meanwhile, a cell of the TCR disclosed by the invention is transduced, can be specifically activated, and has a strong killingeffect on target cells.
Owner:许嘉峰
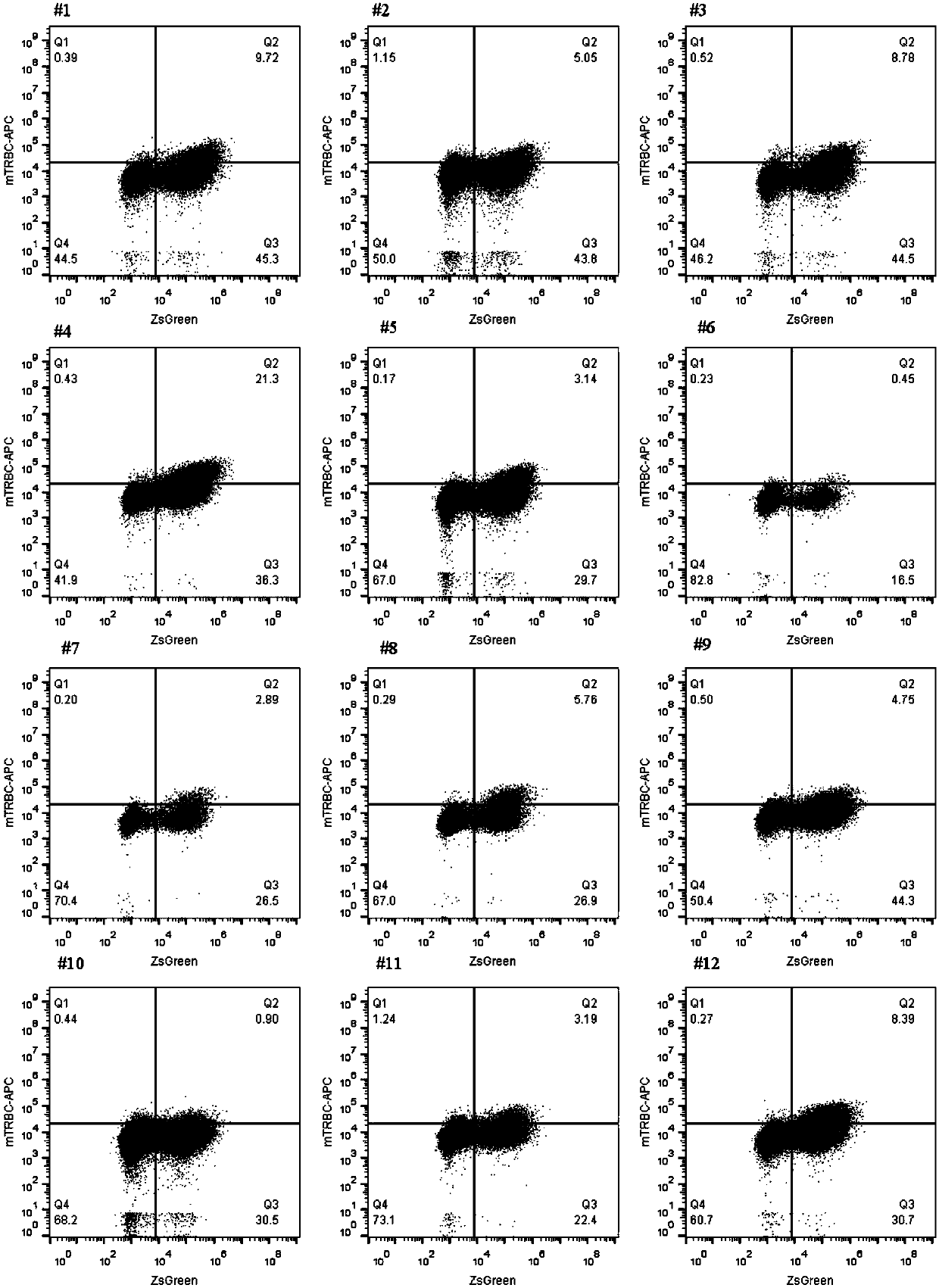
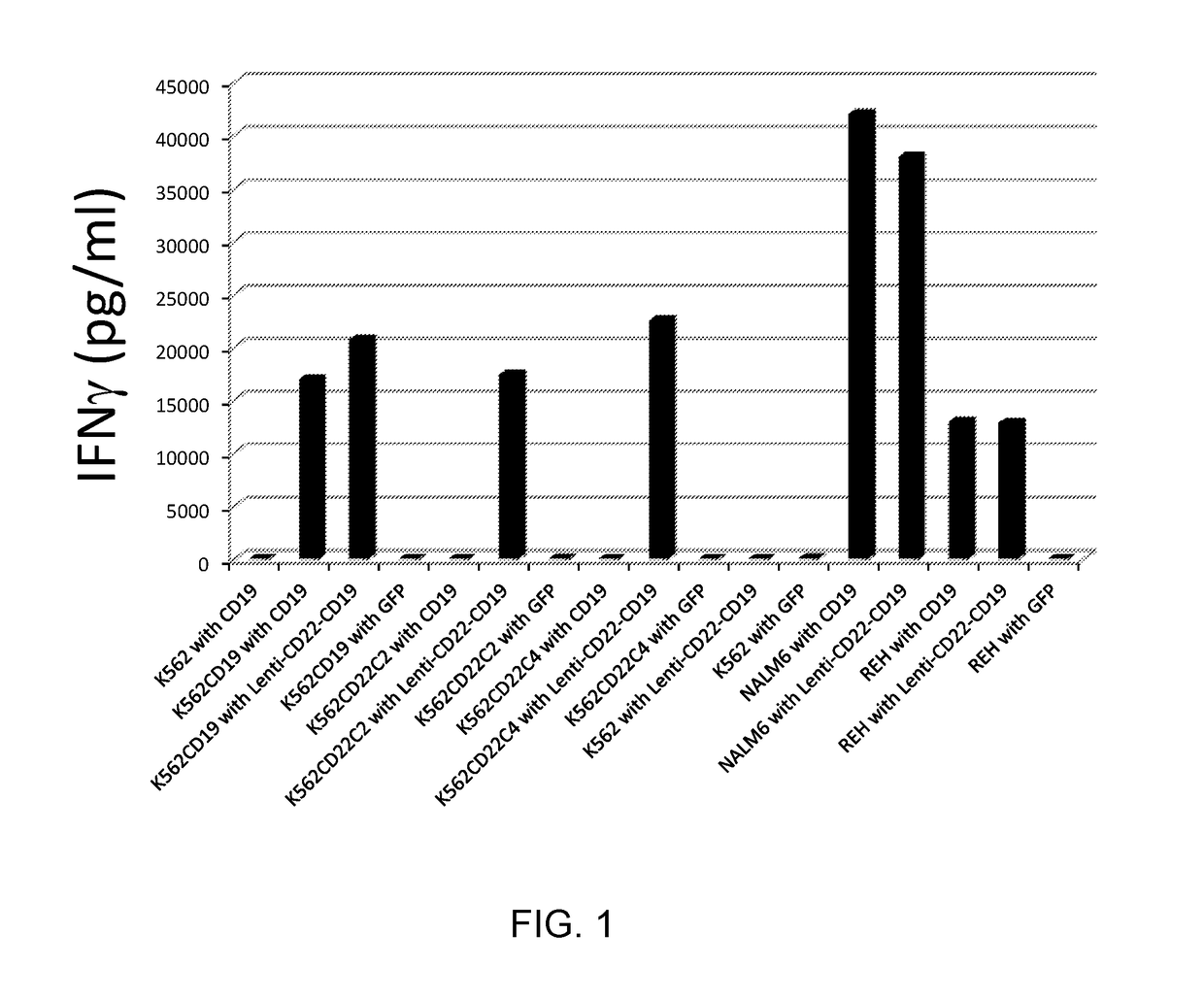
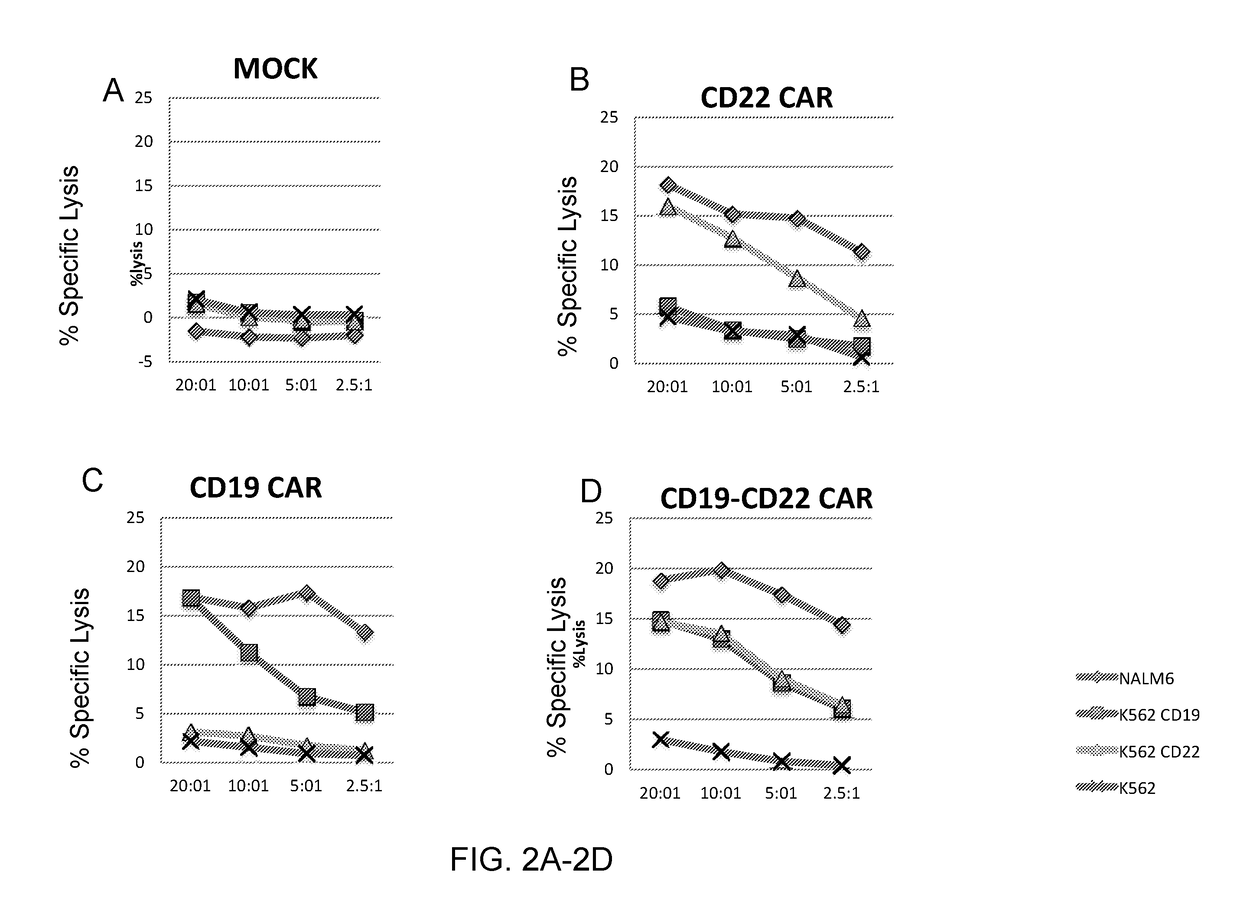
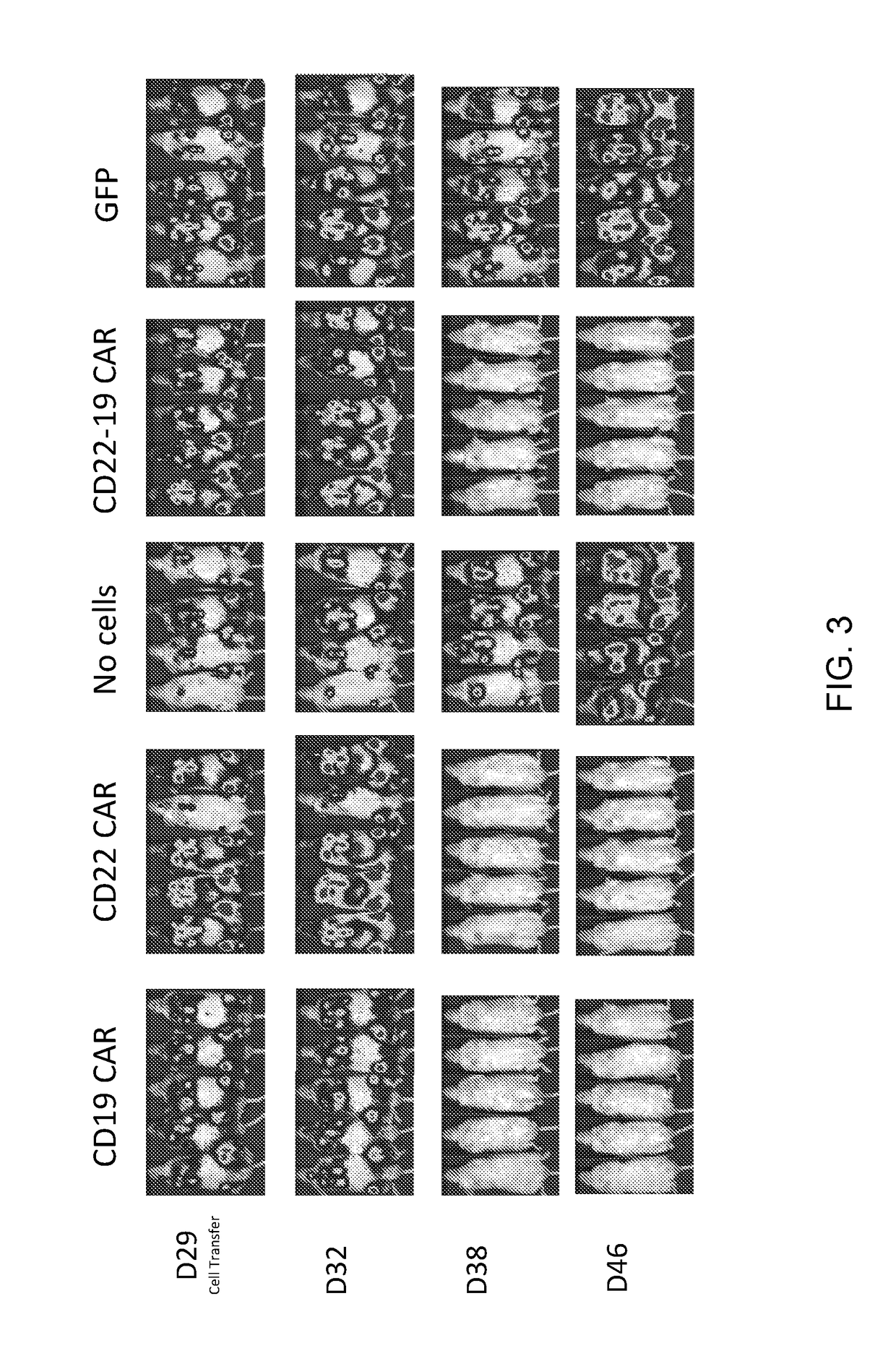
Dual specific Anti-cd22-Anti-cd19 chimeric antigen receptors
ActiveUS20180111992A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorsAnti cd19
The invention provides dual specific chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) having antigenic specificity for CD19 and CD22. Nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions relating to the CARs are disclosed. Methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods of isolating t cell receptors having antigenic specificity for a cancer-specific mutation
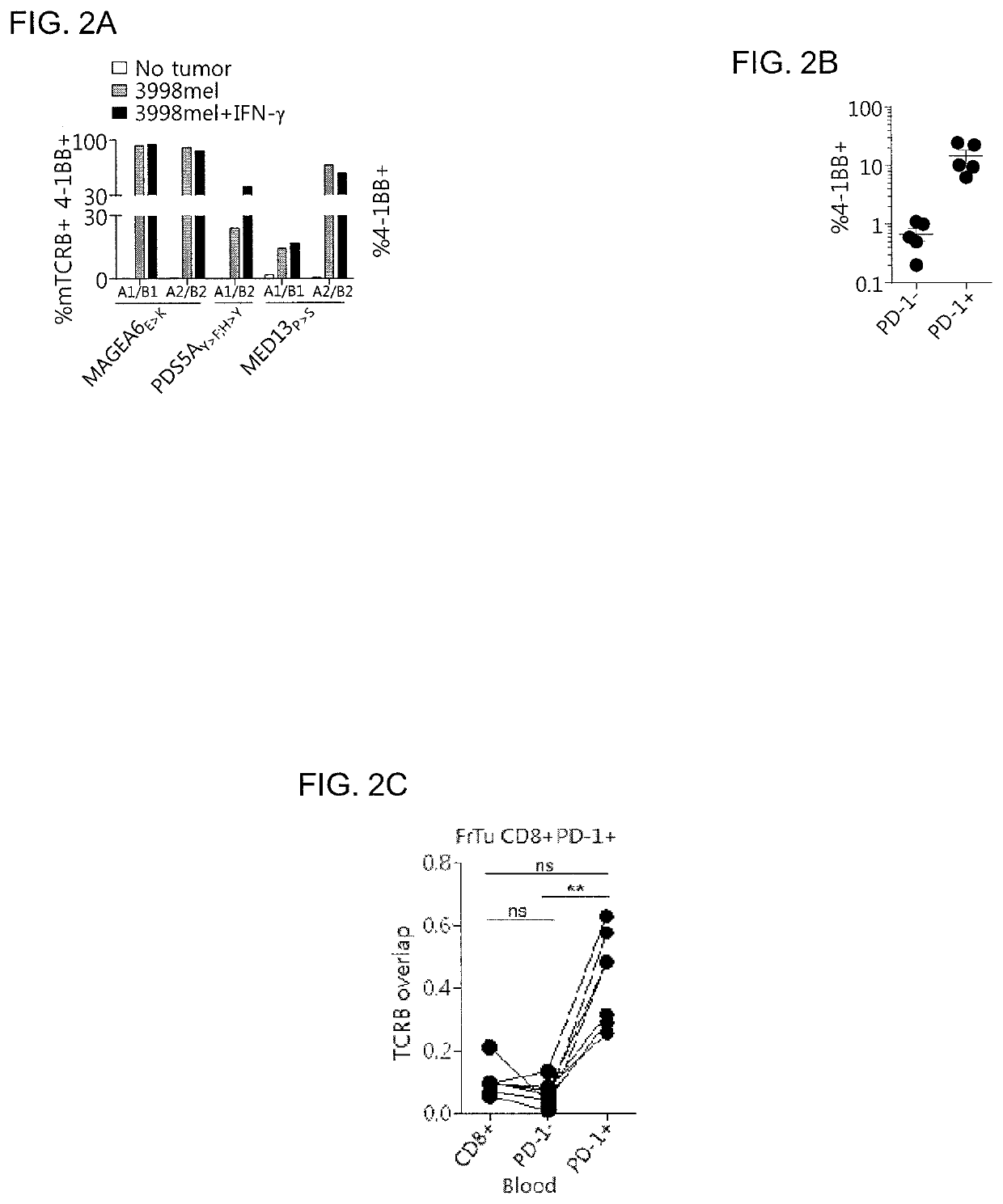
Disclosed are methods of isolating a TCR having antigenic specificity for a mutated amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific mutation, the method comprising: identifying one or more genes in the nucleic acid of a cancer cell of a patient, each gene containing a cancer-specific mutation that encodes a mutated amino acid sequence; inducing autologous APCs of the patient to present the mutated amino acid sequence; co-culturing autologous T cells of the patient with the autologous APCs that present the mutated amino acid sequence; selecting the autologous T cells; and isolating a nucleotide sequence that encodes the TCR from the selected autologous T cells, wherein the TCR has antigenic specificity for the mutated amino acid sequence encoded by the cancer-specific mutation. Also disclosed are related methods of preparing a population of cells, populations of cells, TCRs, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating or preventing cancer.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
T cell receptors recognizing mhc class ii-restricted mage-a3
The invention provides an isolated or purified T-cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for MHC Class II-restricted MAGE-A3. The invention further provides related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, and populations of cells. Further provided by the invention are antibodies, or an antigen binding portion thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions relating to the TCRs of the invention. Methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a host and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal are further provided by the invention.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Murine anti-NY-ESO-1 T cell receptors
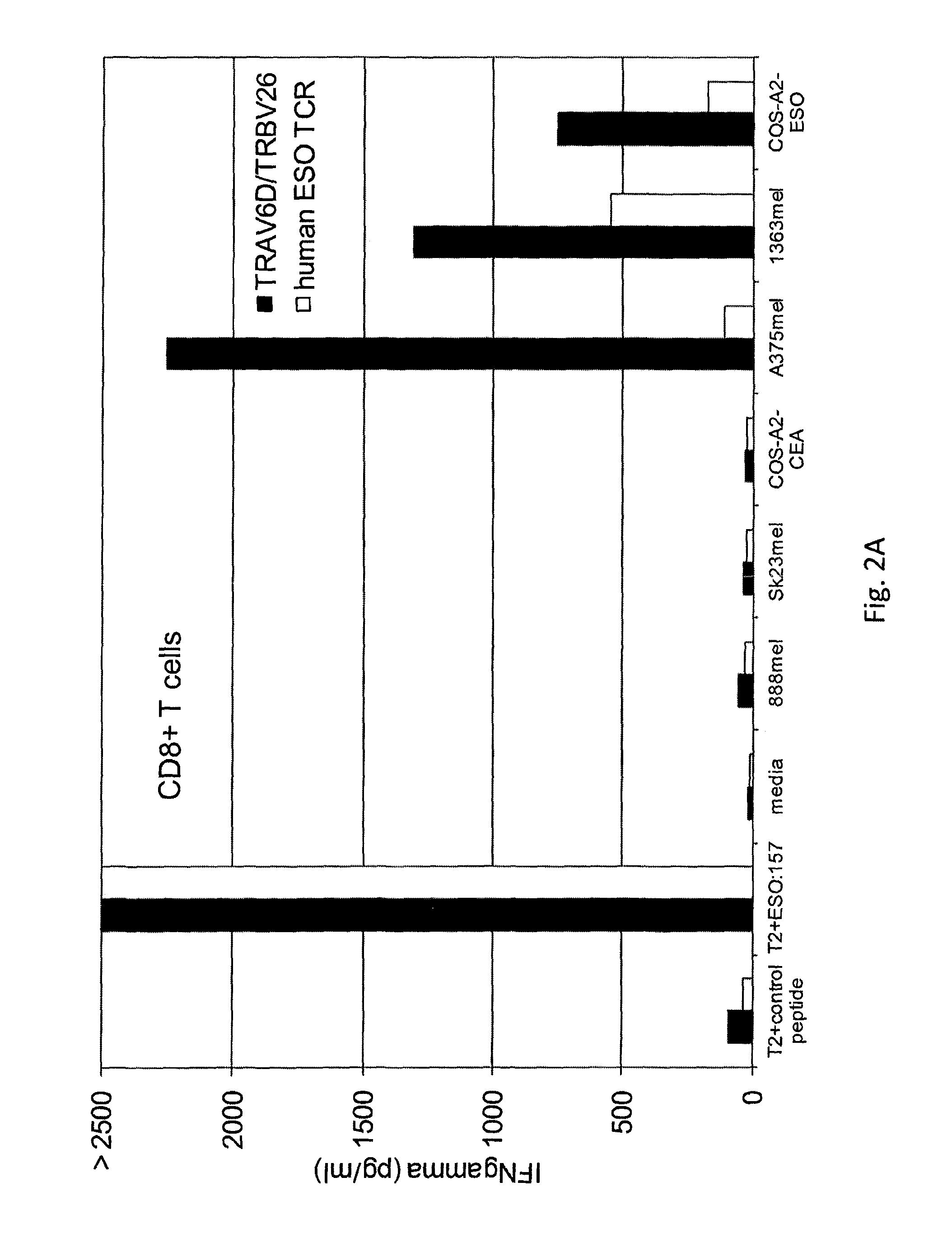
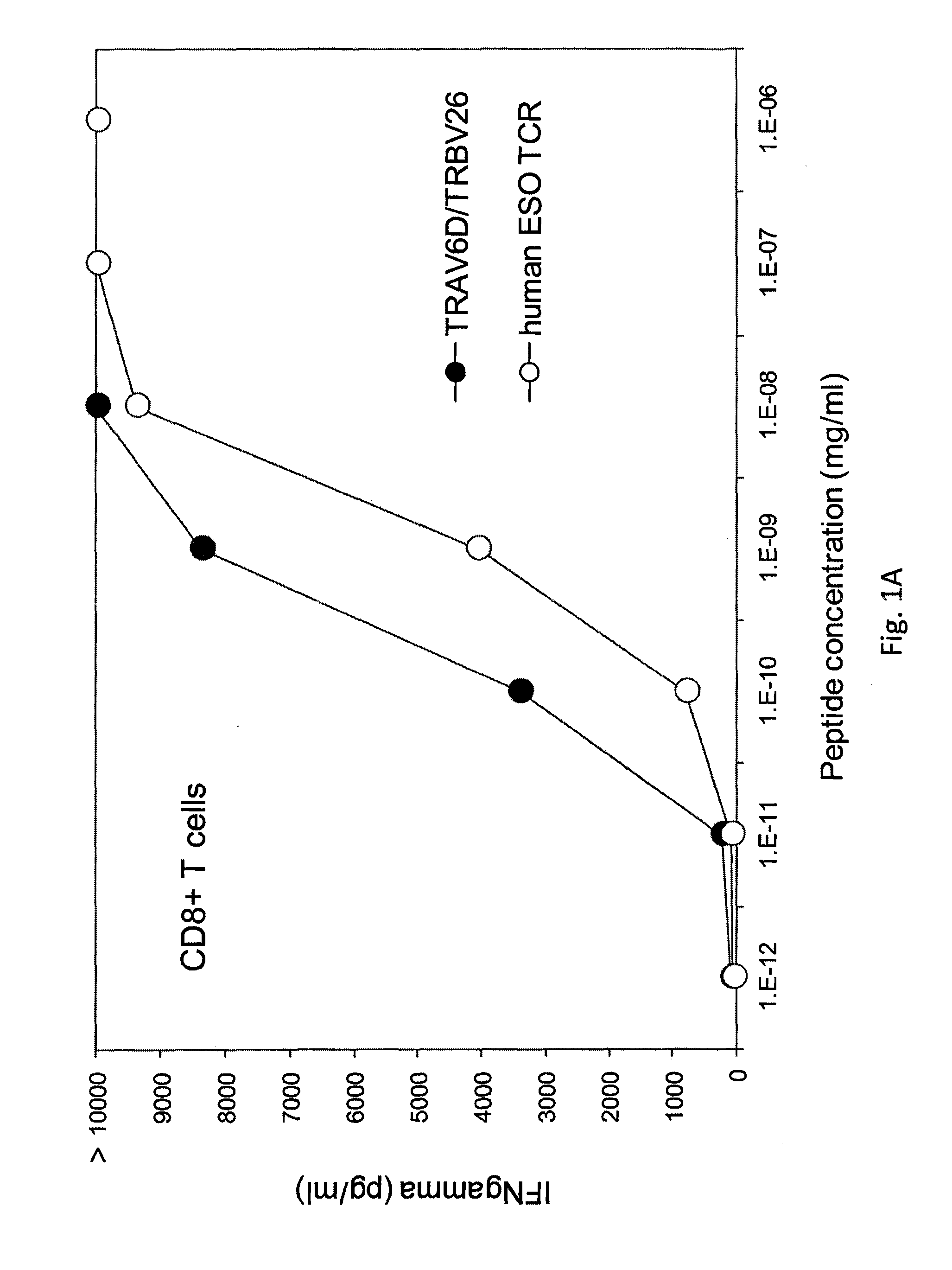
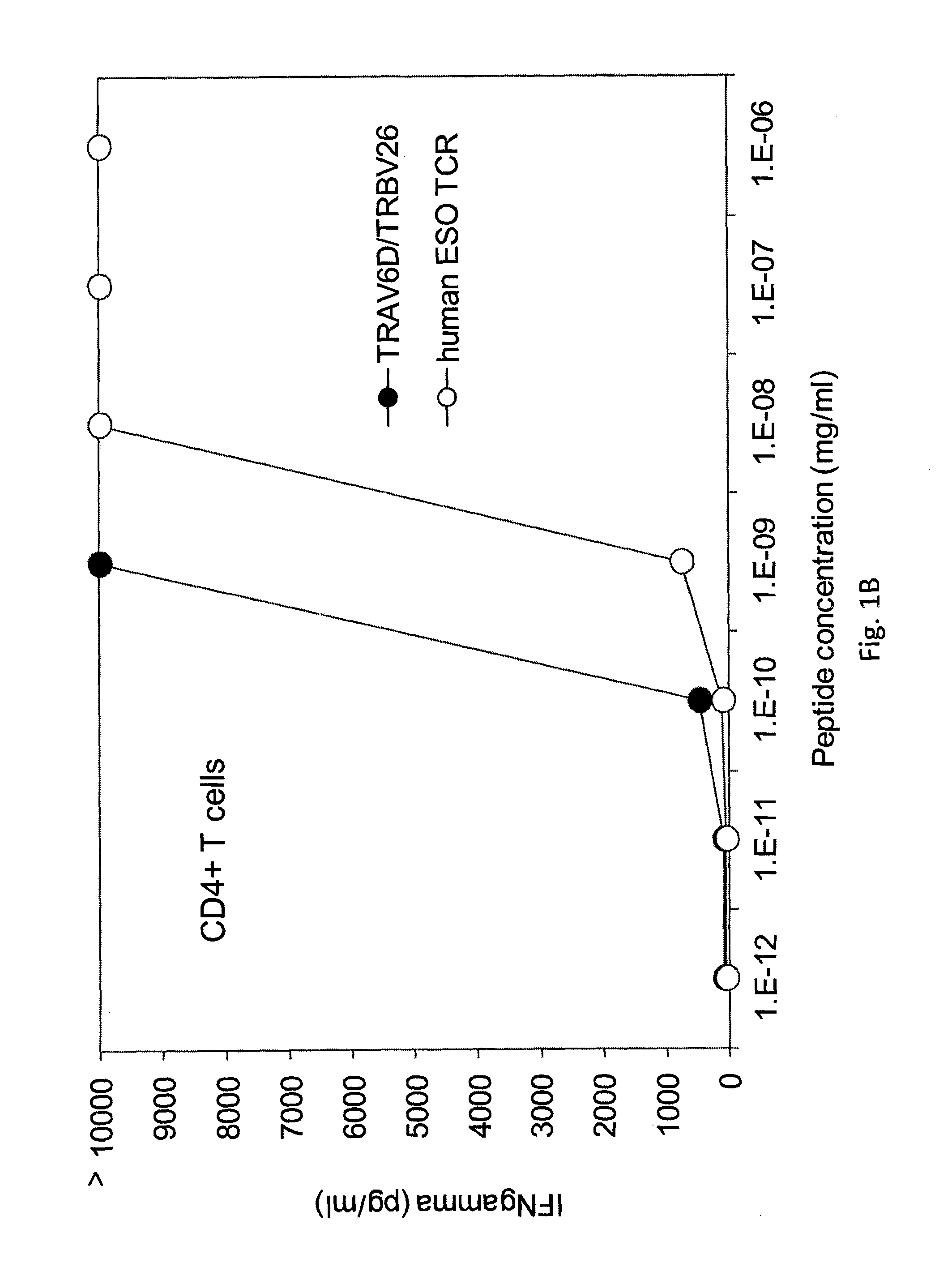
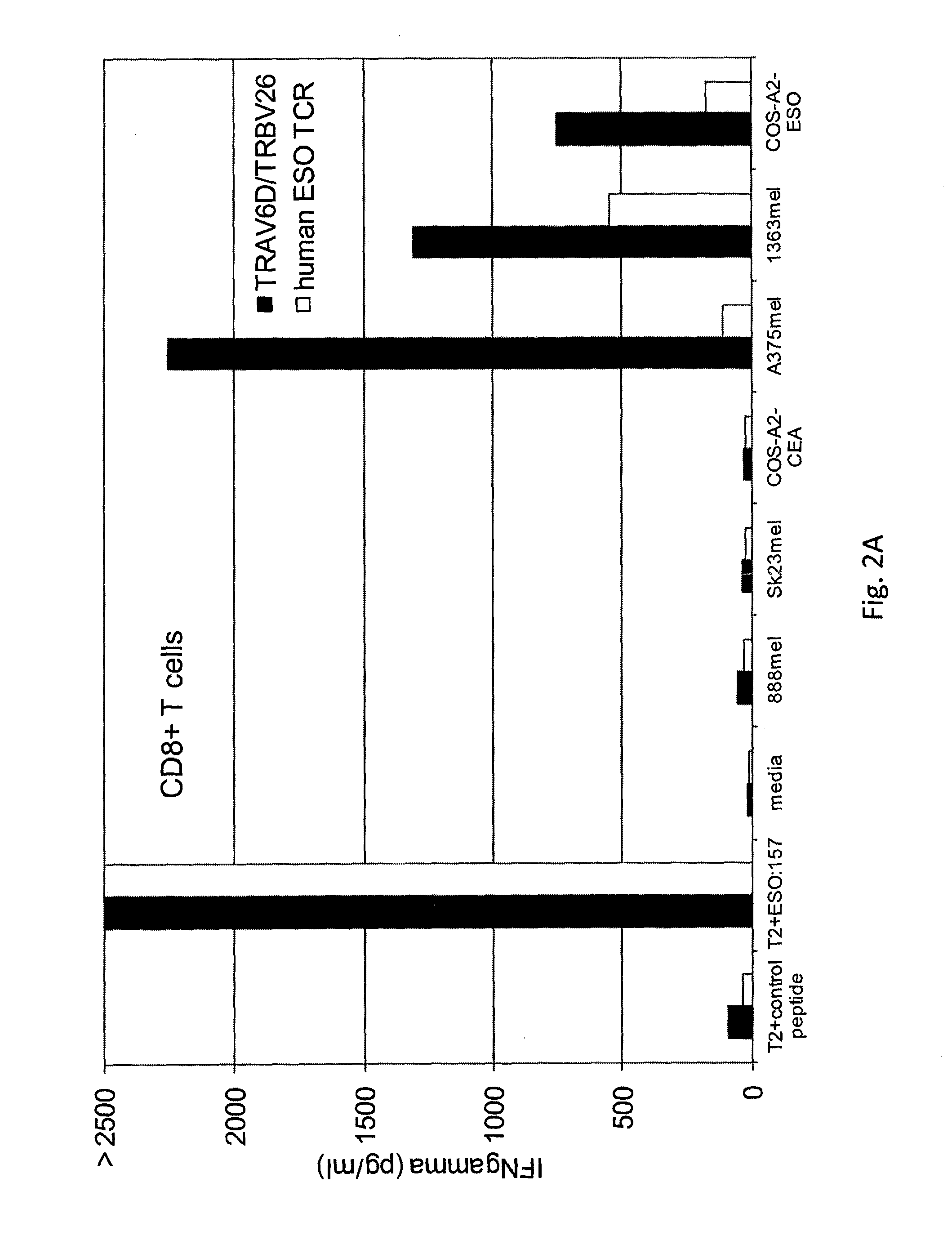
The invention provides an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for NY-ESO-1. Also provided are related polypeptides, proteins, nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, isolated host cells, populations of cells, antibodies, or antigen binding portions thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions. The invention further provides a method of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and a method of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal using the inventive TCRs or related materials.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Preparation method and application of a new tumor dendritic cell therapeutic vaccine
ActiveCN102258772APrevent relapseAvoid diversionBlood/immune system cellsAntibody medical ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthTumor therapy
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a new therapeutic vaccine for dendritic tumor cells. The therapeutic tumor vaccine is chemotherapeutic drug induced tumor antigen, wherein, the dendritic cells are loaded and activated. The chemotherapeutic medicament induced tumor antigen contains a plurality of immunostimulation molecules as well as tumor-associated and specific antigen, which can remarkably carry out chemotaxis and activation on immunocytes such as the dendritic cells, T-cells (thymus-dependent lymphocytes) and the like, stimulate the dendritic cells to be mature and express a plurality of cell factors and chemotactic factors, effectively induce immune response reaction with antigenic specificity and non-specificity and strengthen body immune function. The therapeutic vaccine provided by the invention can be used for preventing and treating tumors and has the characteristics of simple preparation process, low cost, strong specificity, obvious curative effect and the like.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Murine Anti-ny-eso-1 t cell receptors
ActiveUS20150141347A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen bindingB-cell receptor
The invention provides an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for NY-ESO-1. Also provided are related polypeptides, proteins, nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, isolated host cells, populations of cells, antibodies, or antigen binding portions thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions. The invention further provides a method of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and a method of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal using the inventive TCRs or related materials.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods of isolating T cells and T cell receptors having antigenic specificity for a cancer-specific mutation from peripheral blood
ActiveUS10544392B2Peptide/protein ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsCancer preventionPharmaceutical drug
Disclosed are methods of isolating T cells and TCRs having antigenic specificity for a mutated amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific mutation. Also disclosed are related methods of preparing a population of cells, populations of cells, TCRs, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating or preventing cancer.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
T cell receptors and related materials and methods of use
InactiveUS20090042798A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsMajor histocompatibilityCancer antigen
The invention provids an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for a cancer antigen, e.g., a renal cell carcinoma antigen, wherein the TCR recognizes the cancer antigen in a major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-independent manner. Also provided are related polypeptides, proteins, nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, isolated host cells, populations of cells, antibodies, or antigen binding portions thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions. The invention further provides a method of detecting the presence of cancer in a host and a method of treating or preventing cancer in a host using the inventive TCRs or related materials.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Anti-human papillomavirus 16 E7 T cell receptors
ActiveUS10174098B2Minimize ToxicityImprove abilitiesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeHuman papillomavirus
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
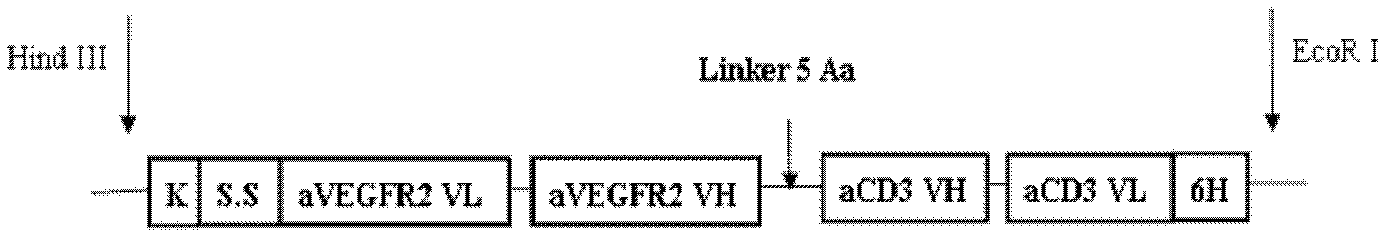
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) acceptor 2/CD3 bispecific single-chain antibody
ActiveCN102219856AImprove hydrophilic abilityImprove flexibilityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesVascular endothelium
The invention relates to a genetic engineering antibody, in particular to a vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) acceptor 2 / CD3 bispecific single-chain antibody. The bispecific single-chain antibody comprises two binding sites respectively having antigenic specificity on the VEGF acceptor 2 and CD3. The invention further relates to nucleotide sequence coding the bispecific antibody, a carrier containing nucleotide sequence, and a host cell transfected by the carrier. The VEGF2 / CD3 bispecific single-chain antibody has small molecular weight and immunogenicity, is easy to penetrate throughcompact tumor barrier and enters the microcirculation around solid tumor, thus having application prospects in preparing tumor treatment drugs.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of completely humanized antibody of infectious disease pathogen
InactiveCN103045607AFully humanizedNo rejectionImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHumanized antibodyInfectious illness
The invention relates to a preparation method of the completely humanized antibody of a infectious disease pathogen, which mainly comprises the following steps of: preparing an infectious disease pathogen antigen; fluorescently labeling an infectious disease pathogen antibody; concentrating and purifying the peripheral B cells of an infectious disease patient; combining the labeled pathogen antigen and the antigenic-specificity B cells; screening antigenic-specificity single B cells through a flow cytometer; carrying out single cell RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on genes positioned in the heavy chain and light chain variable region of the infectious disease pathogen antibody; connecting with a heavy chain and light chain constant region to construct the eukaryotic expression vector of the humanized antibody; and carrying out the high-efficiency expression and purification of a recombined antibody in an eukaryotic cell. The humanized monoclonal antibody prepared through the method disclosed by the invention can be used for the infectious disease diagnosis and the infectious disease treatment.
Owner:李福胜
Methods of isolating neoantigen-specific t cell receptor sequences
PendingUS20200056237A1Efficient identificationLow costImmunoglobulin superfamilyMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingAmino acid
Disclosed are methods of isolating paired T cell receptor (TCR) alpha and beta chain sequences, or an antigen-binding portion thereof. Also disclosed are methods of automatically identifying the TCR alpha and beta chain V segment sequences and CDR3 sequences of a TCR having antigenic specificity for a mutated amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific mutation. Methods of preparing a population of cells that express paired TCR alpha and beta chain sequences, or an antigen-binding portion thereof, are also disclosed. Isolated pairs of TCR alpha and beta chain sequences and isolated populations of cells prepared by the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Compositions and methods for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune conditions
InactiveUS20110059121A1Suppress autoreactive T-cell responsesPrevent and ameliorate T1DPowder deliveryAntipyreticDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The methods include selectively reducing or expanding T cells according to the antigenic specificity of the T cells. Therefore, the present invention can be used to reduce or eliminate pathogenic T cells that recognize autoantigens, such as beta cell specific T cells. As such, the present invention can be used to prevent, treat or ameliorate autoimmune diseases such as IDDM. Furthermore, the present invention can be used to expand desirable T cells, such as anti-pathogenic T cells to prevent, treat and / or ameliorate autoimmune diseases.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods of isolating t cells and t cell receptors having antigenic specificity for a cancer-specific mutation from peripheral blood
Disclosed are methods of isolating T cells and TCRs having antigenic specificity for a mutated amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific mutation. Also disclosed are related methods of preparing a population of cells, populations of cells, TCRs, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating or preventing cancer.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com