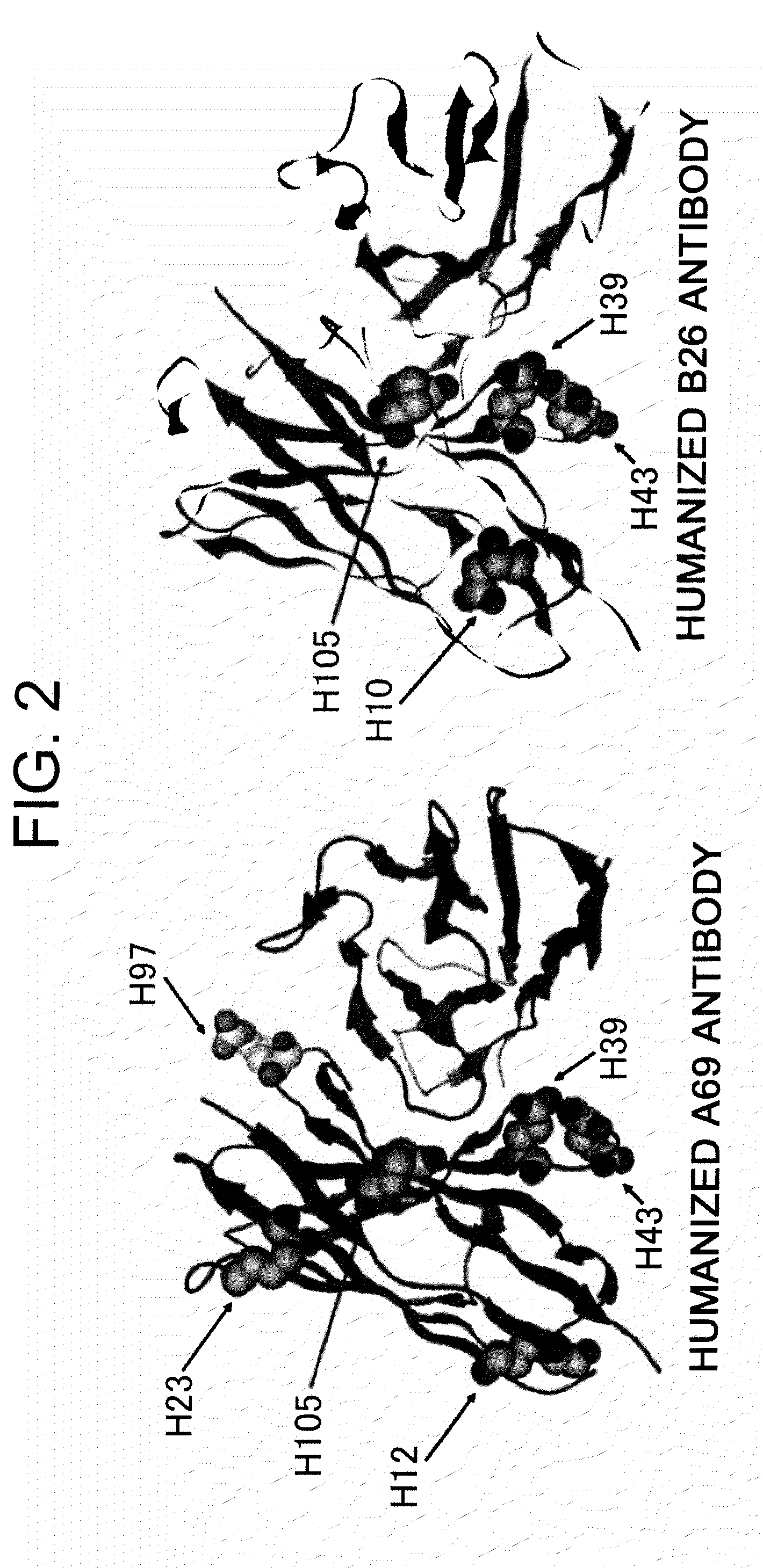
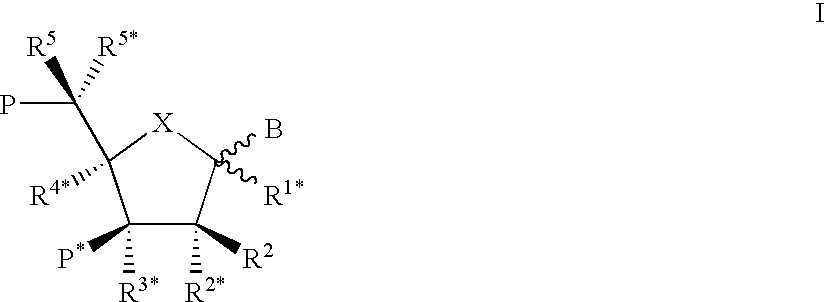Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
15856results about "Tissue culture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
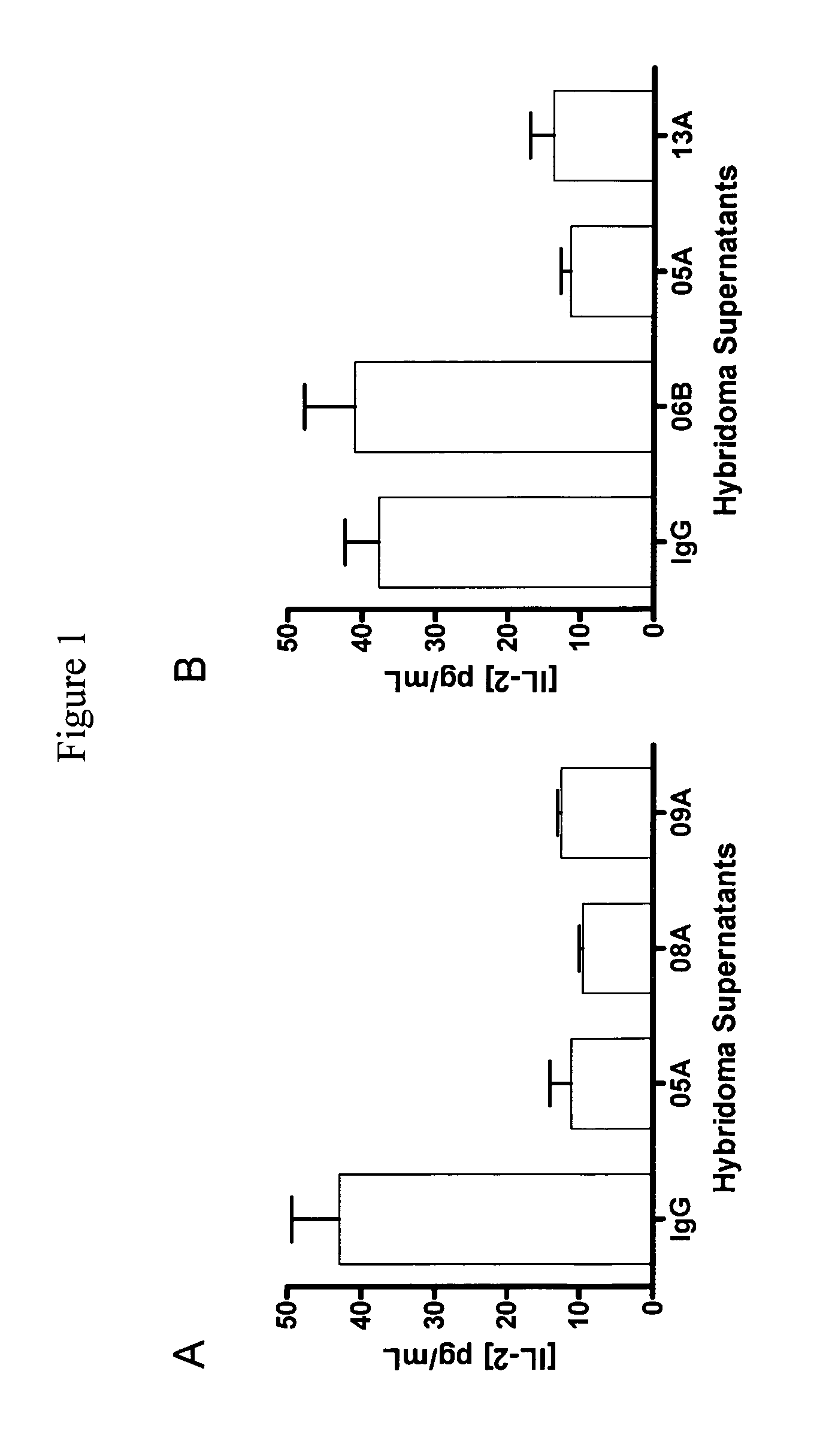
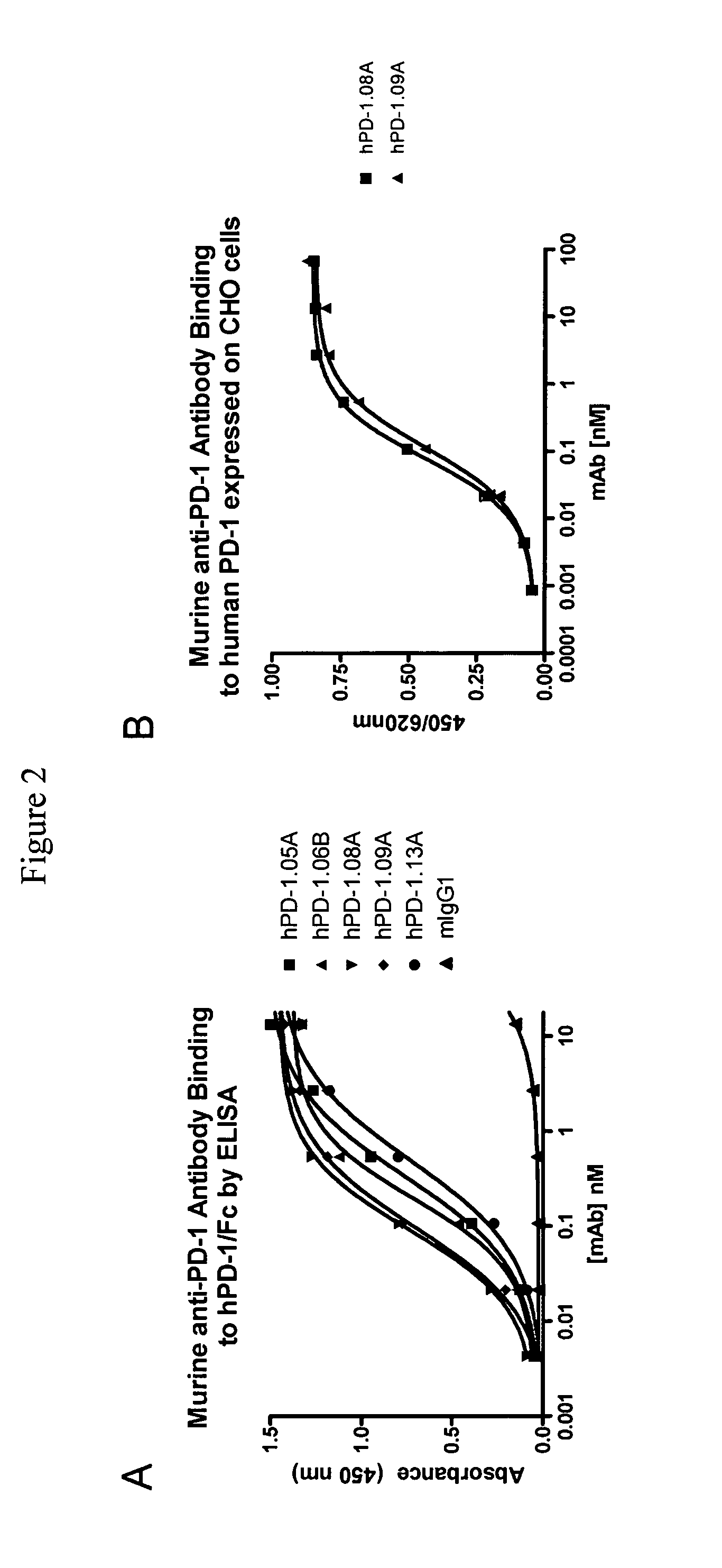
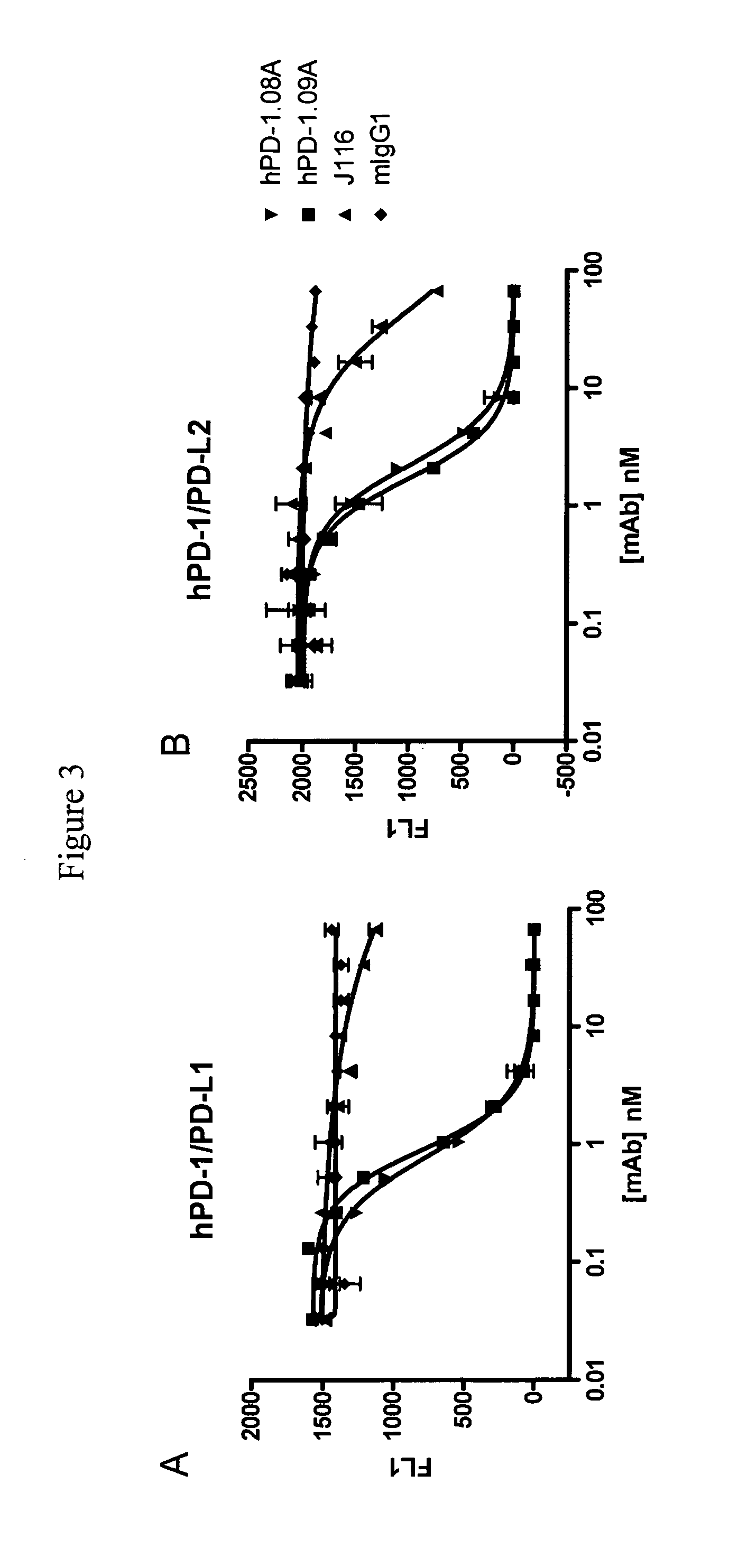
Antibodies to human programmed death receptor PD-1
ActiveUS8354509B2Increased activationIncreased proliferationSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsProgrammed deathReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Antibodies which block the binding of human Programmed Death Receptor 1 (hPD-1) to its ligands (hPD-L1 or hPD-L2) and their variable region sequences are disclosed. A method of increasing the activity (or reducing downmodulation) of an immune response through the PD-I pathway is also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME BV
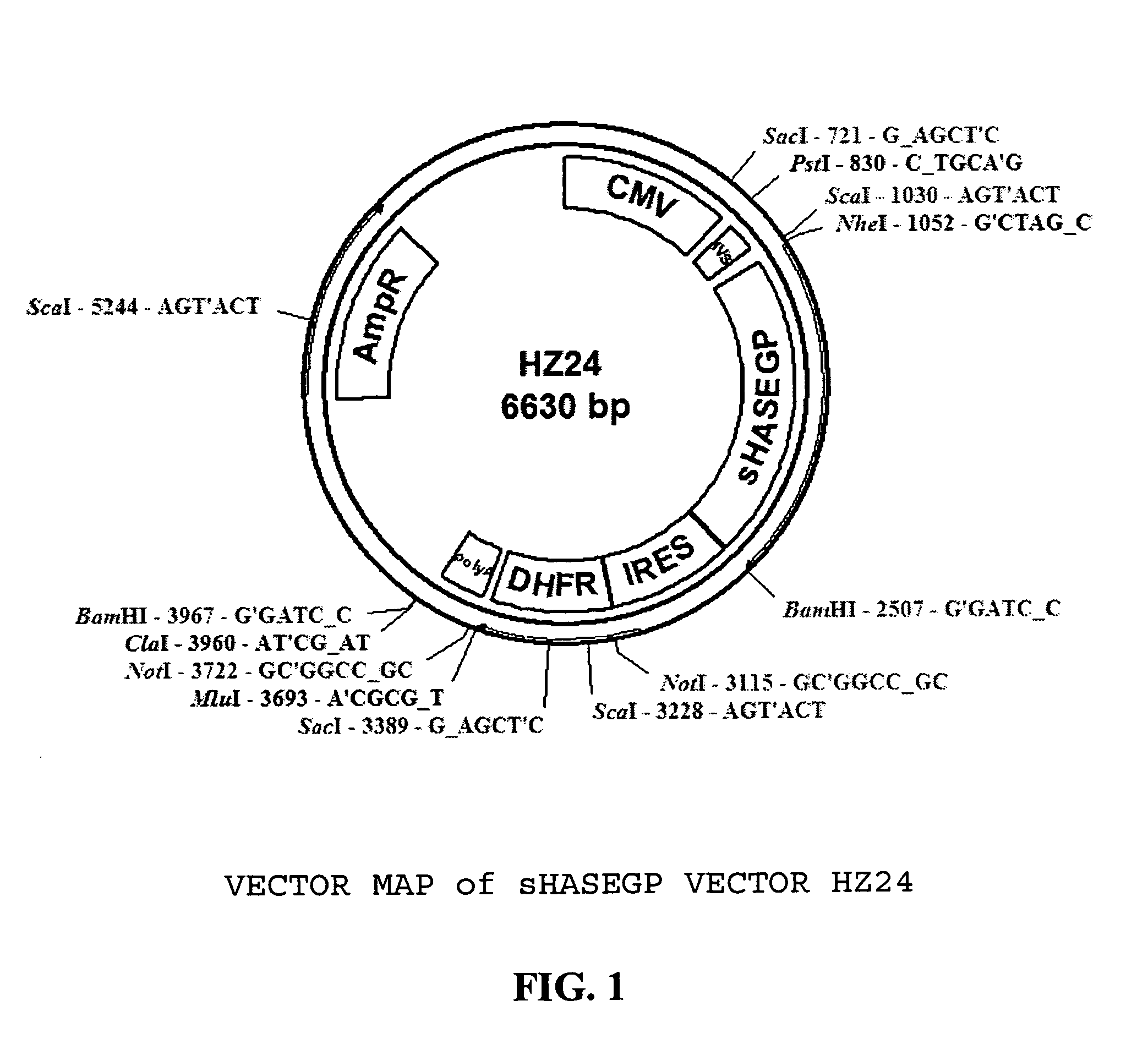
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
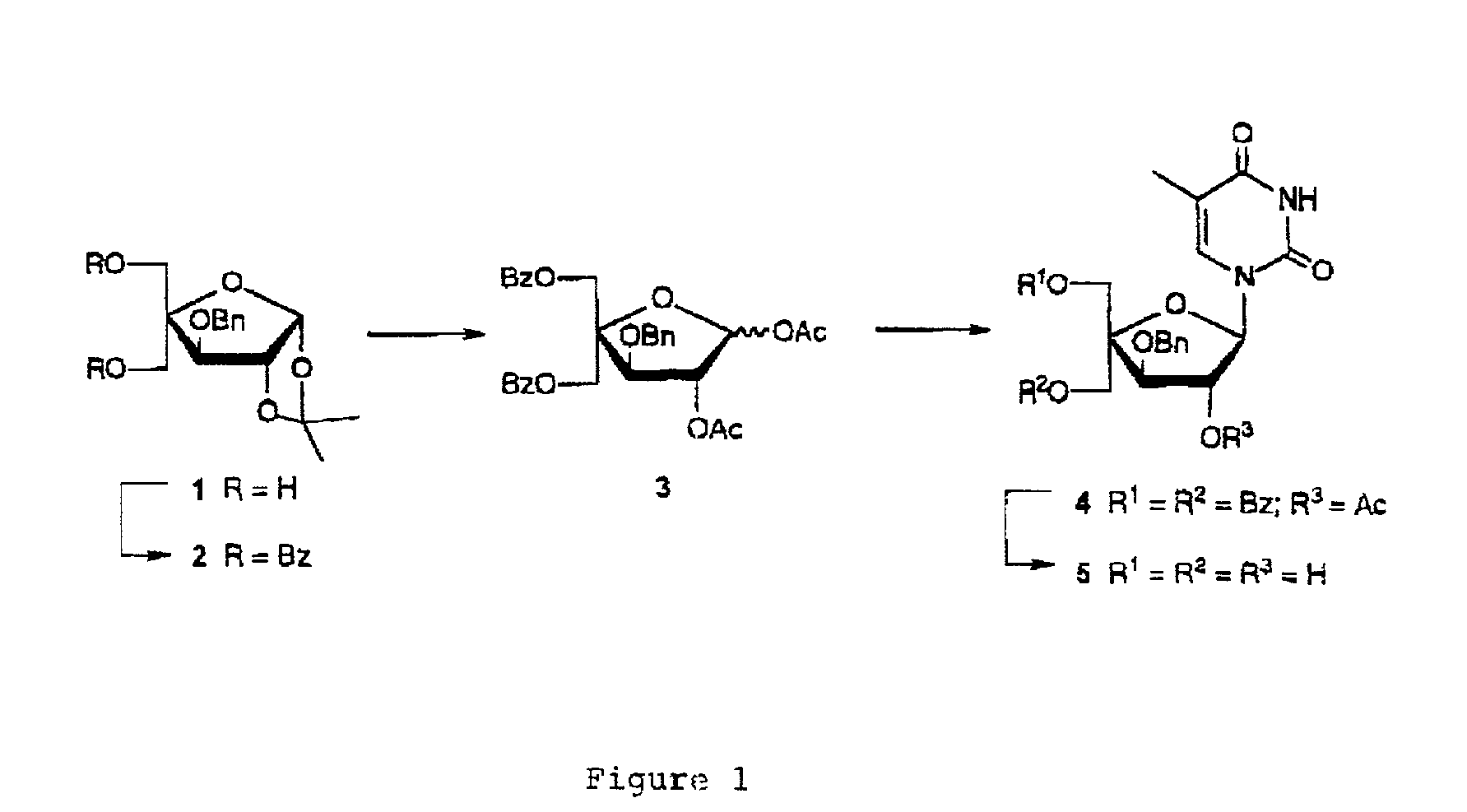
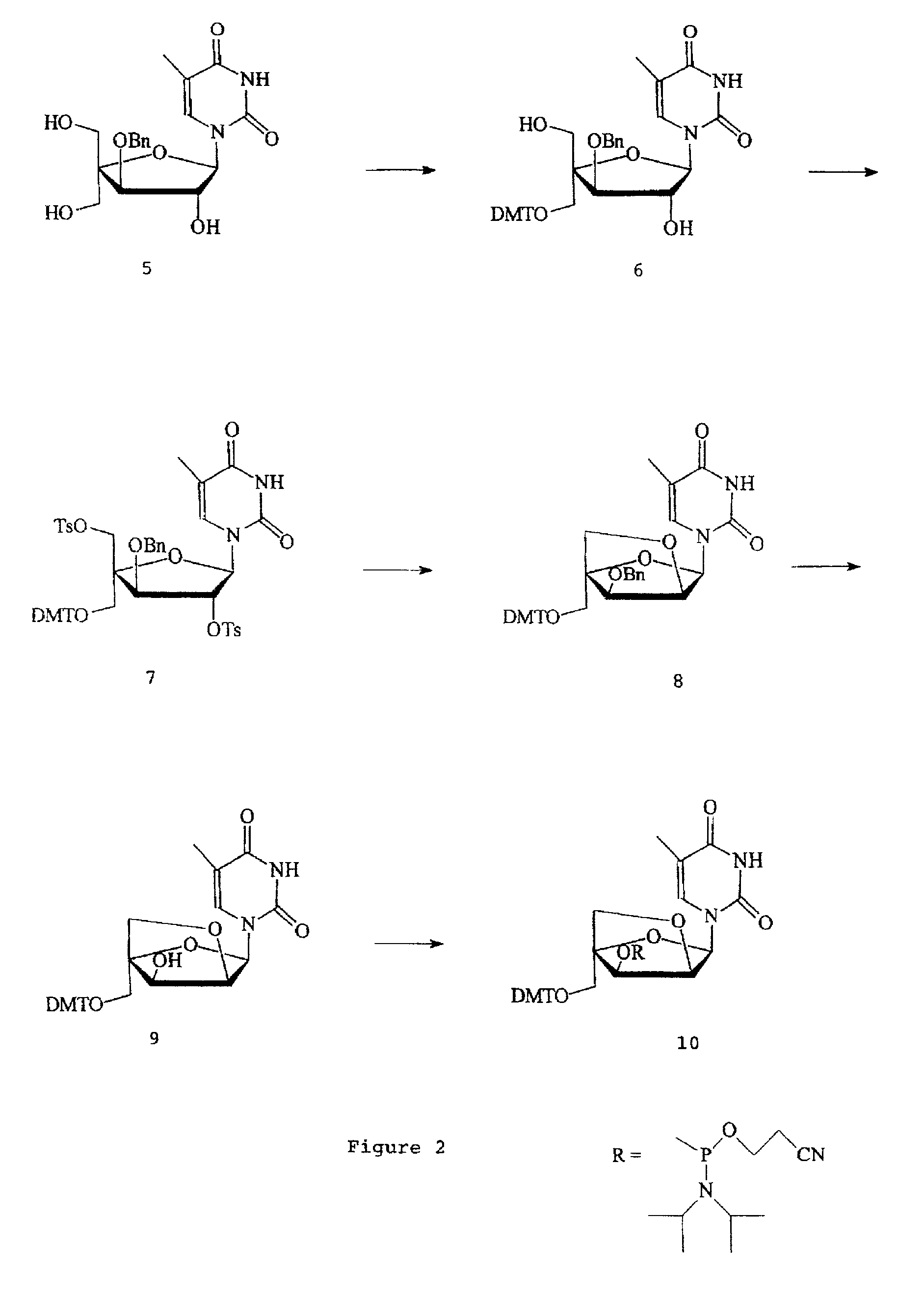
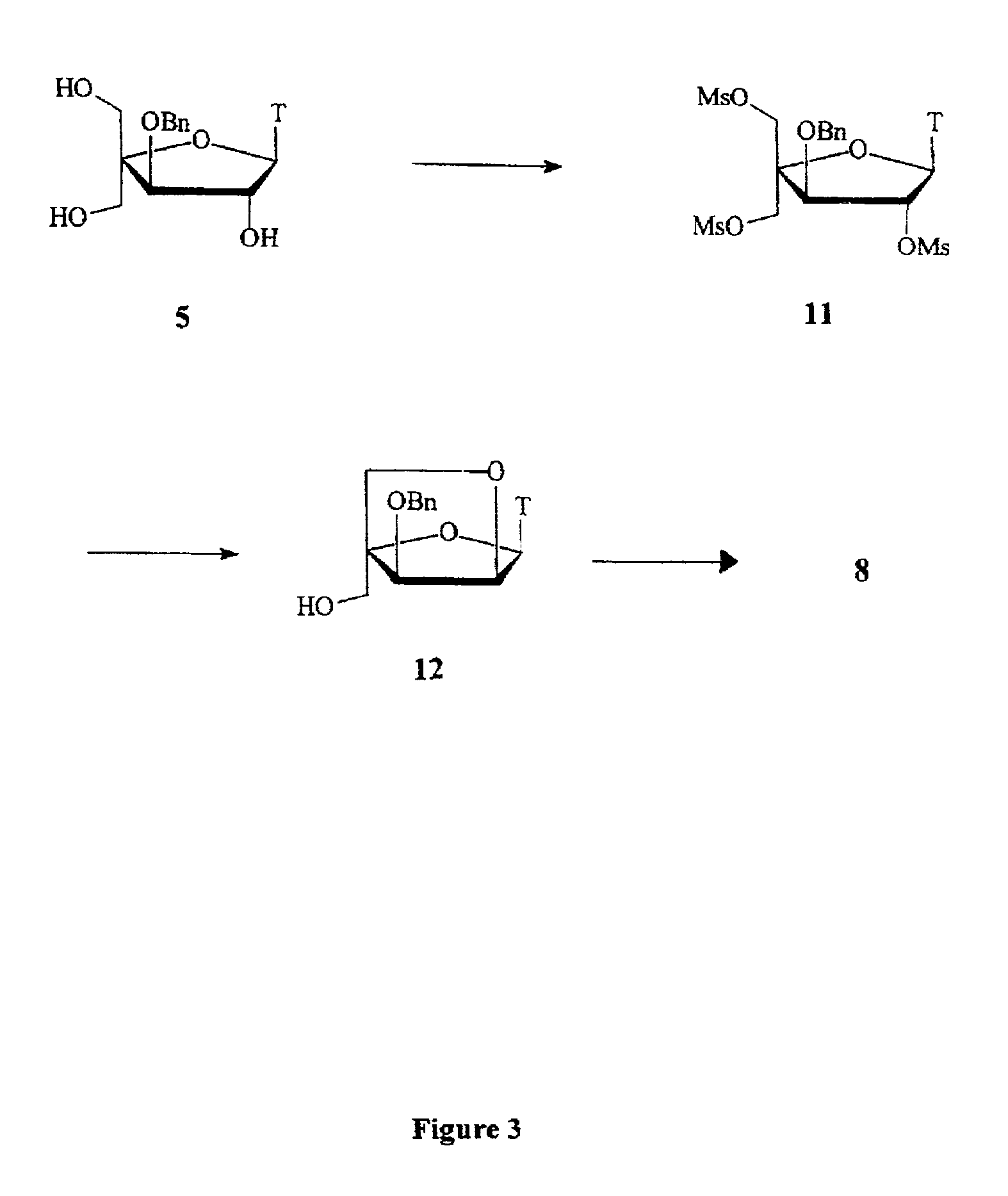
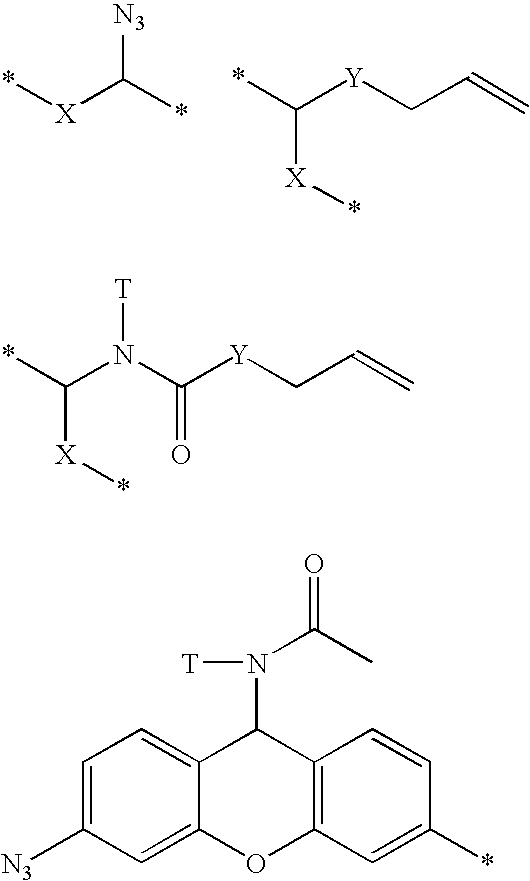
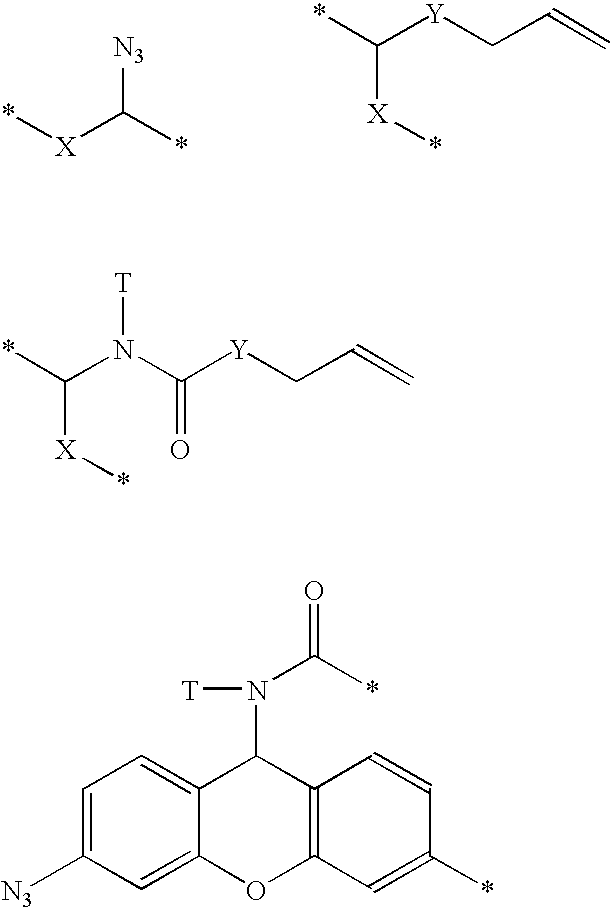
L-ribo-LNA analogues
Provided are L-ribo bicyclic nucleotide compounds as well as syntheses of such compounds. The nucleoside compounds of the invention are useful in forming oligonucleotides that can produce nucleobase specific duplexes with complementary single stranded and double stranded nucleic acids.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Genetic constructs for delaying or repressing the expression of a target gene
The present invention relates generally to synthetic genes for modifying endogenous gene expression in a cell, tissue or organ of a transgenic organism, in particular a transgenic animal or plant. More particularly, the present invention provides novel synthetic genes and genetic constructs which are capable of repressing delaying or otherwise reducing the expression of an endogenous gene or a target gene in an organism when introduced thereto.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method for preparing two-layer bicomposite collagen material for preventing post-operative adhesions
InactiveUS6596304B1Improve propertiesAvoid stickingPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgerySurgical operationPost operative
A bicomposite material based on collagen is prepared which has two closely bound layers and is biocompatible, non-toxic, hemostatic and biodegradable in less than a month, and can be used in surgery to achieve hemostasis and prevent post-surgical adhesion. To prepare the material, a solution of collagen or gelatin, which may contain glycerine and a hydrophilic additive such as polyethylene glycol or a polysaccharide, is poured onto an inert support to form a layer 30 .mu.m to less than 100 .mu.m thick. Then a polymeric porous fibrous layer is applied during gelling of the collagen or gelatin, and the resultant material is dried. The polymeric porous fibrous layer may be made of collagen or a polysaccharide, and have a density of not more than 75 mg / cm.sup.2, a pore size from 30 .mu.m to 300 .mu.m and a thickness of 0.2 cm to 1.5 cm.
Owner:IMEDEX BIOMATERIAUX CHAPONOST
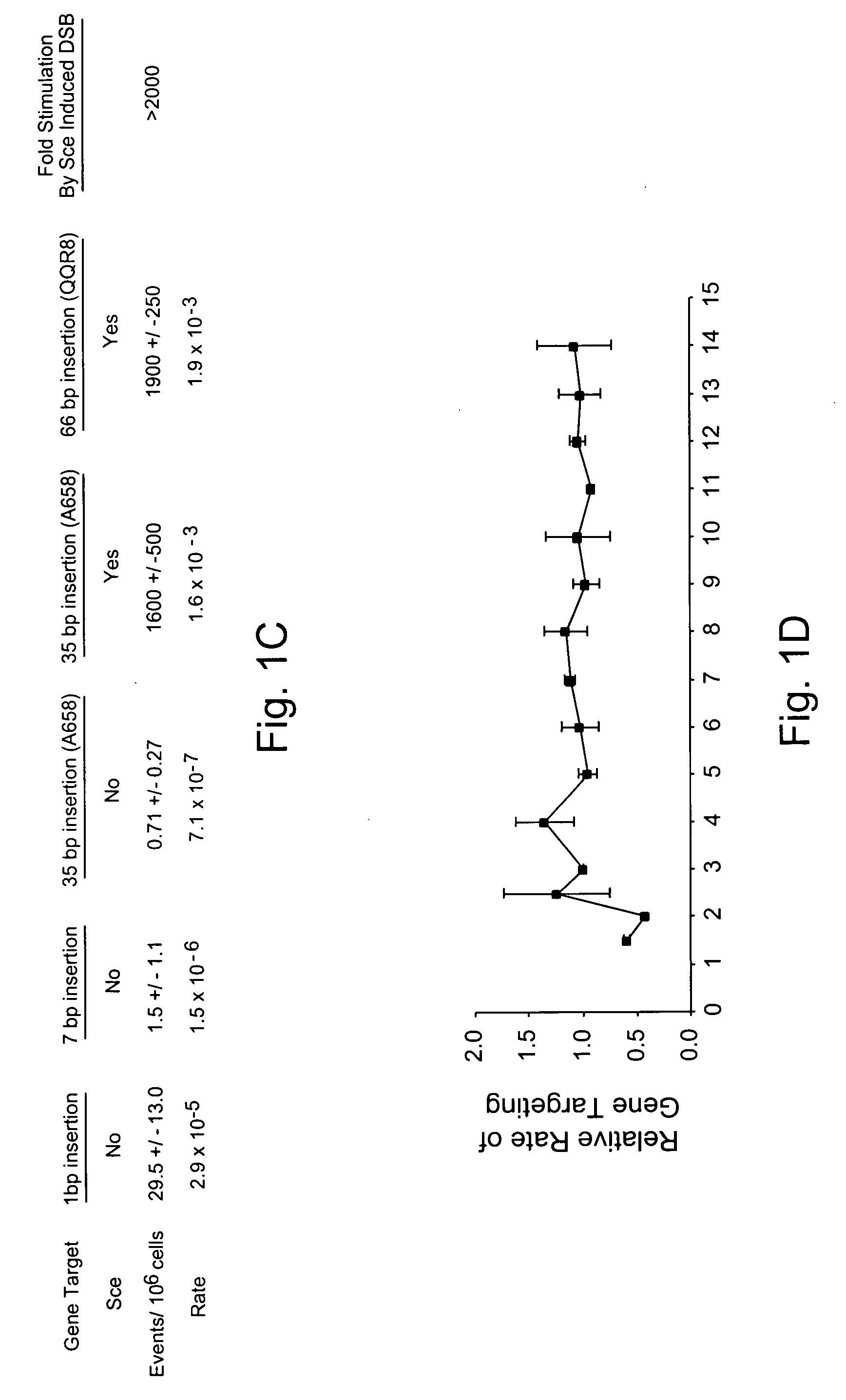
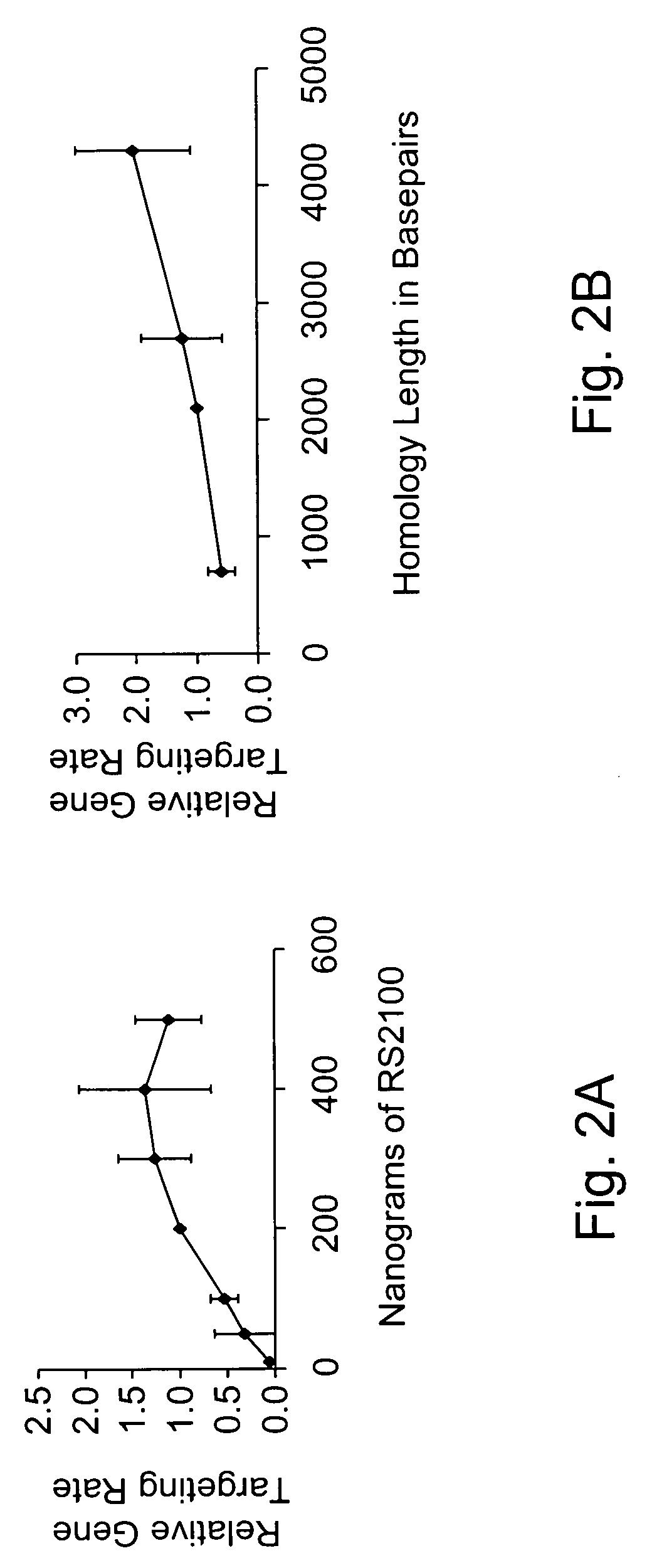
Use of chimeric nucleases to stimulate gene targeting
ActiveUS20050026157A1Ameliorate genetic disorderIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsFusion with DNA-binding domainGene targetsGenetic Change
Gene targeting is a technique to introduce genetic change into one or more specific locations in the genome of a cell. For example, gene targeting can introduce genetic change by modifying, repairing, attenuating or inactivating a target gene or other chromosomal DNA. In one aspect, this disclosure relates to methods and compositions for gene targeting with high efficiency in a cell. This disclosure also relates to methods of treating or preventing a genetic disease in an individual in need thereof. Further disclosed are chimeric nucleases and vectors encoding chimeric nucleases.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
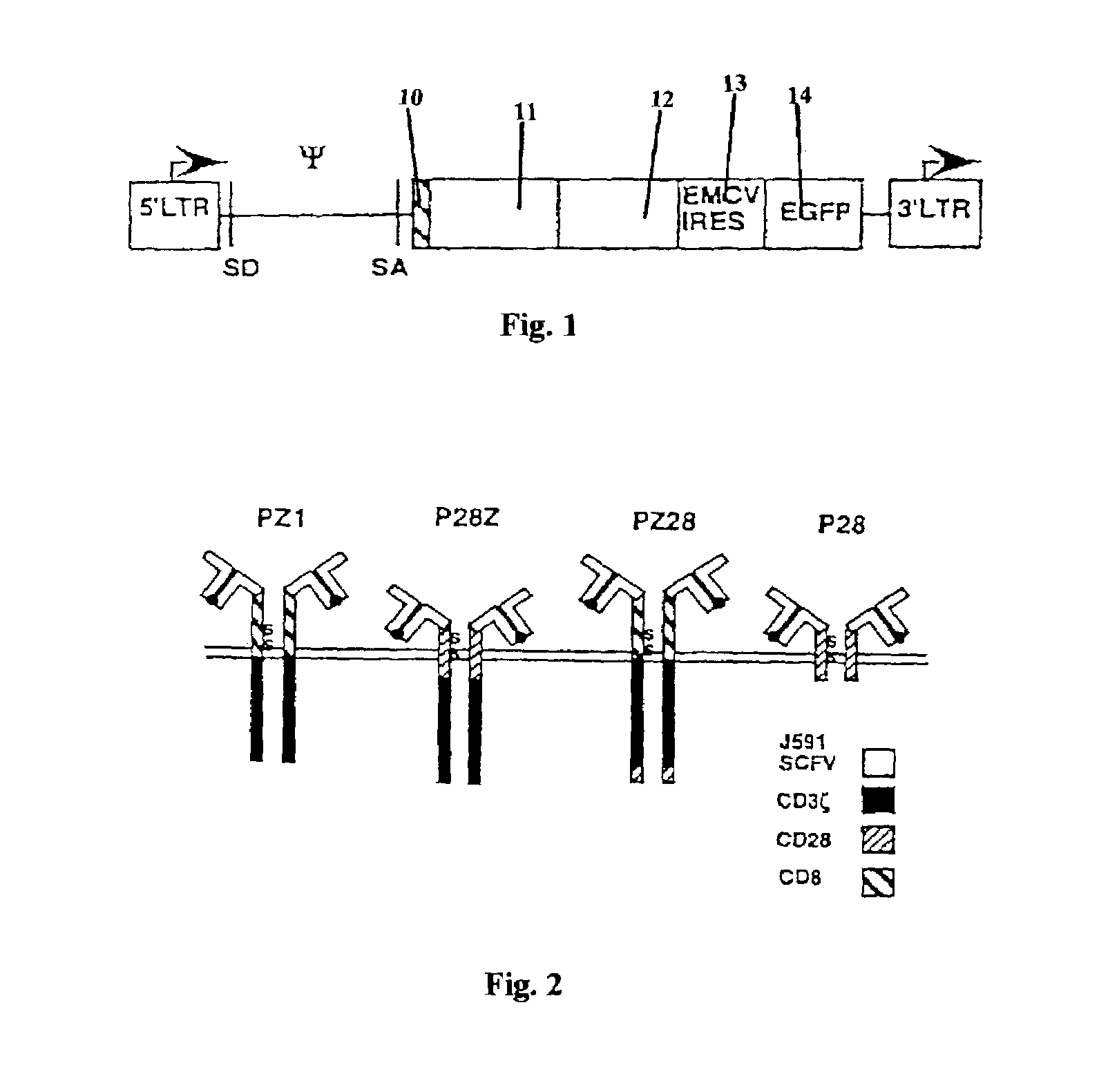
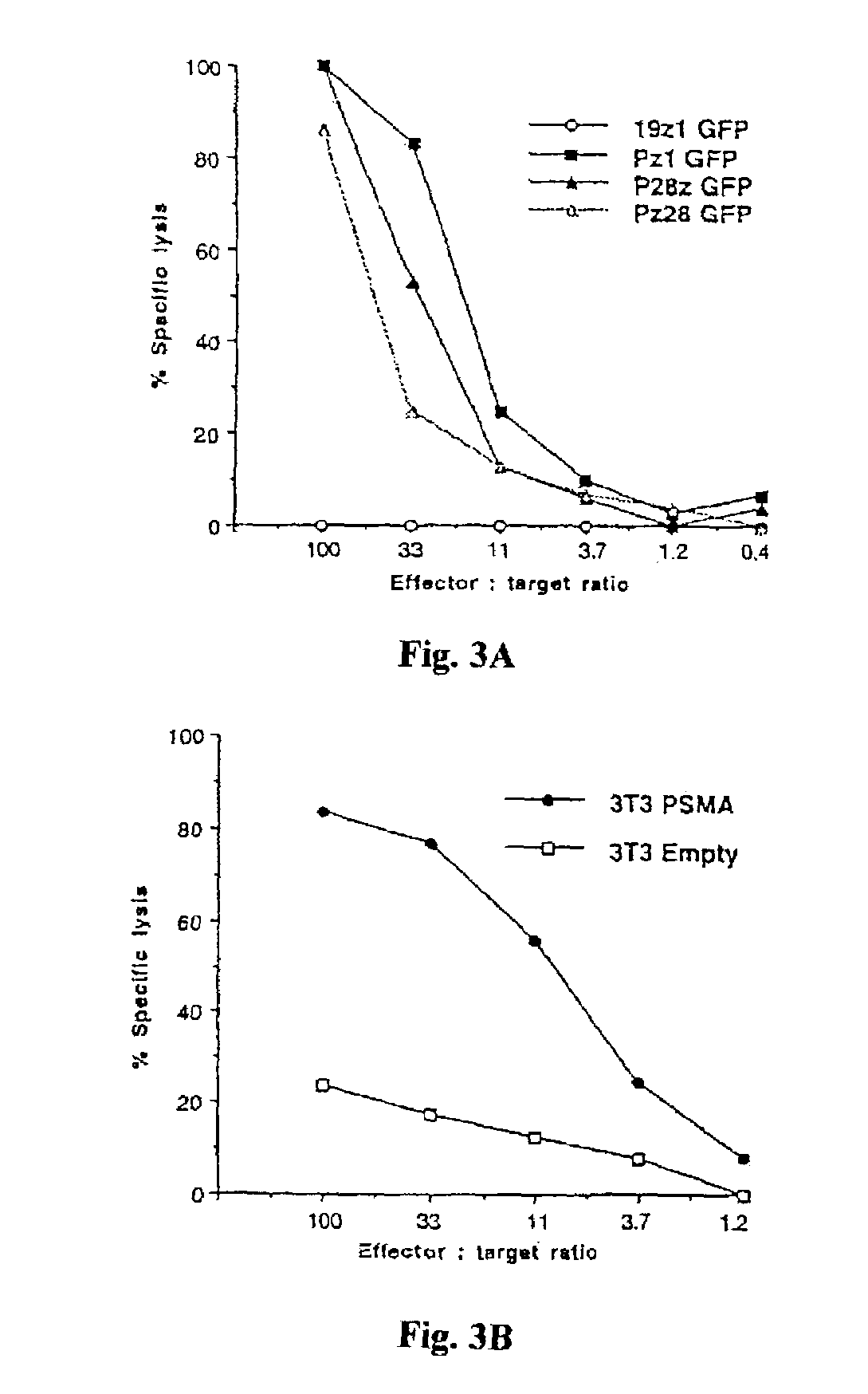
Nucleic acids encoding chimeric T cell receptors
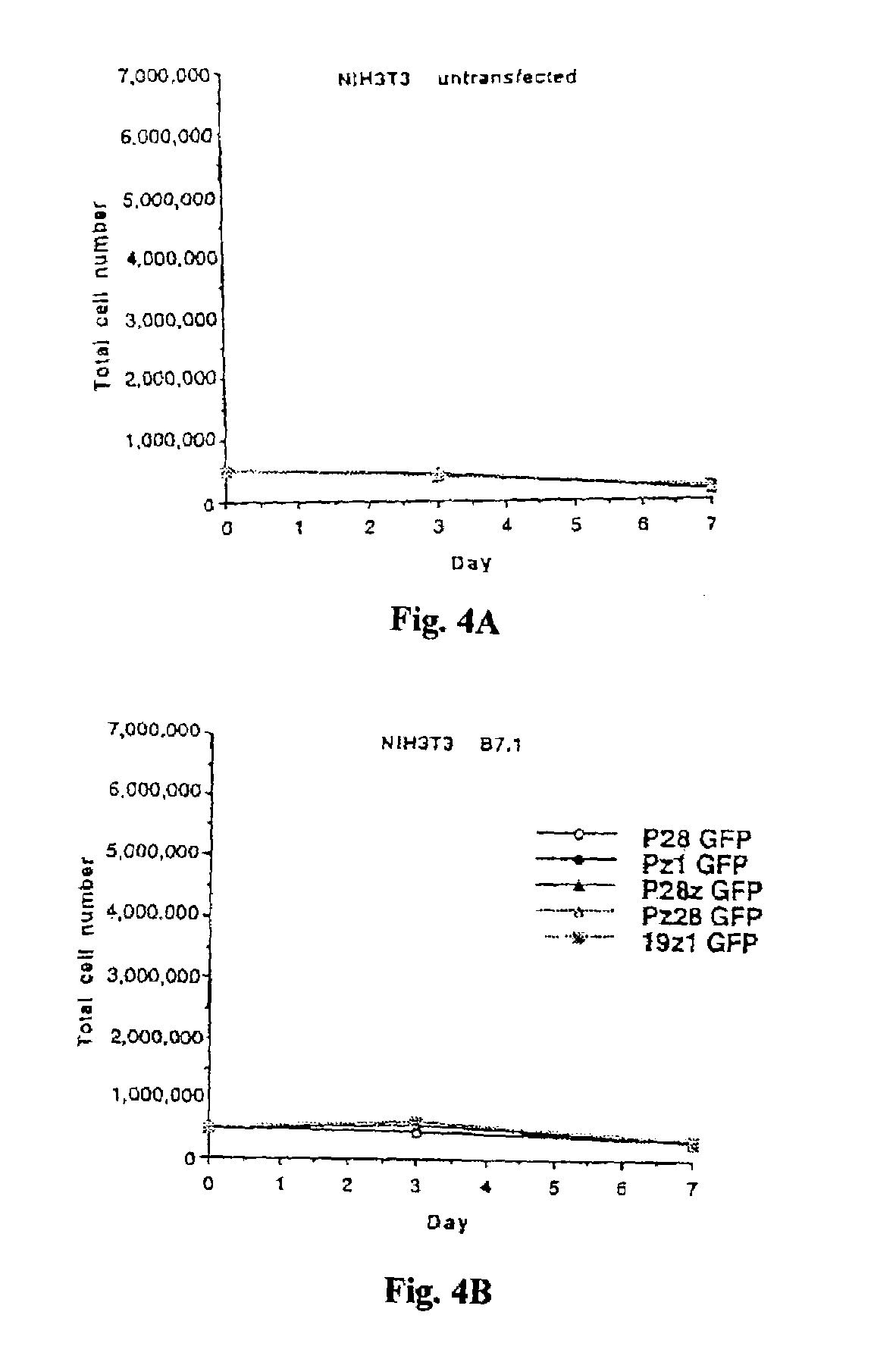
ActiveUS7446190B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCytotoxicityBiological activation
Chimeric T cell receptors (TCR) are provided that combine, in a single chimeric species, the intracellular domain of CD3 ζ-chain, a signaling region from a costimulatory protein such as CD28, and a binding element that specifically interacts with a selected target. When expressed, for example in T-lymphocytes from the individual to be treated for a condition associated with the selected target, a T cell immune response is stimulated in the individual to the target cells. The chimeric TCR's are able to provide both the activation and the co-stimulation signals from a single molecule to more effectively direct T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity against the selected target and T-lymphocyte proliferation.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
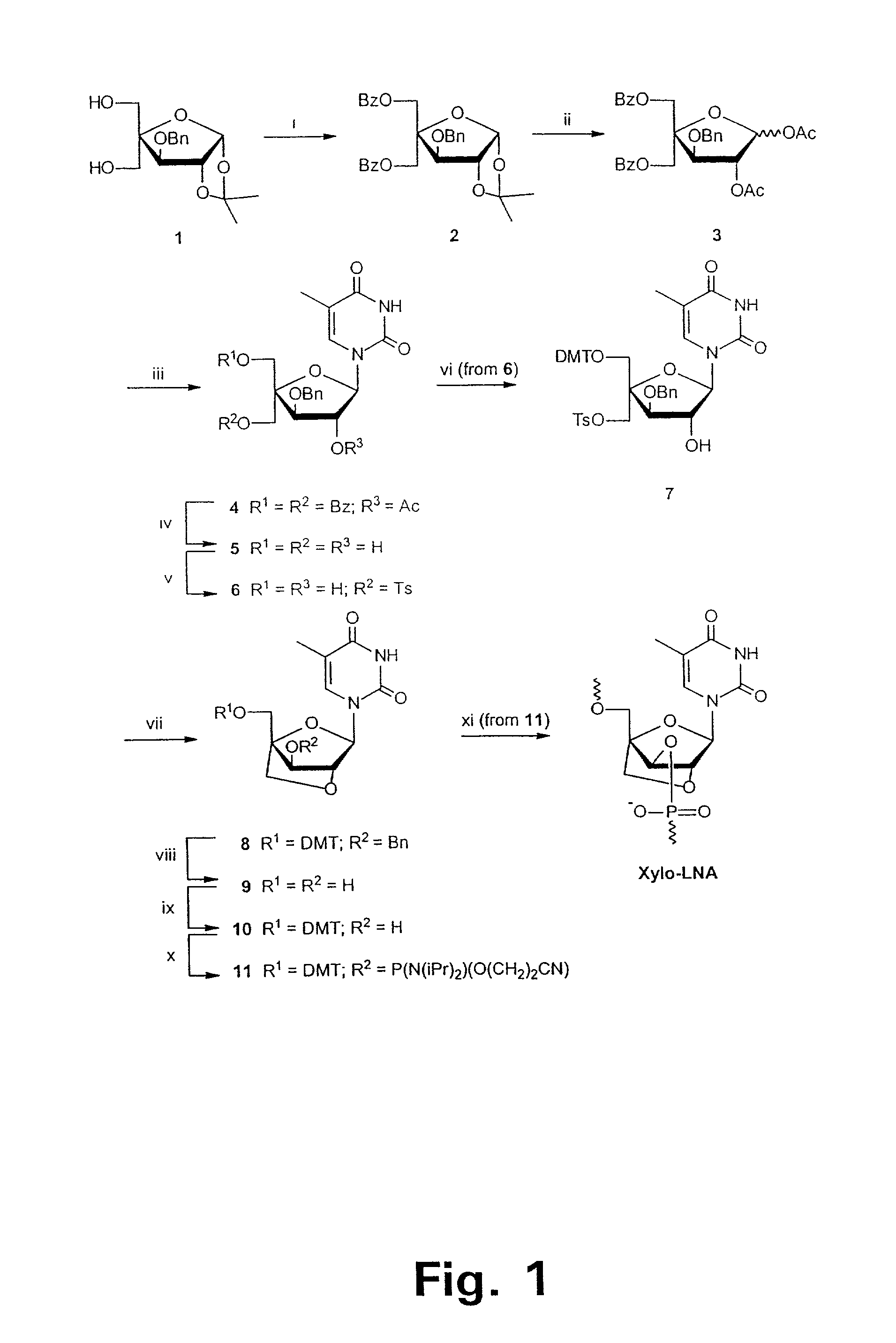
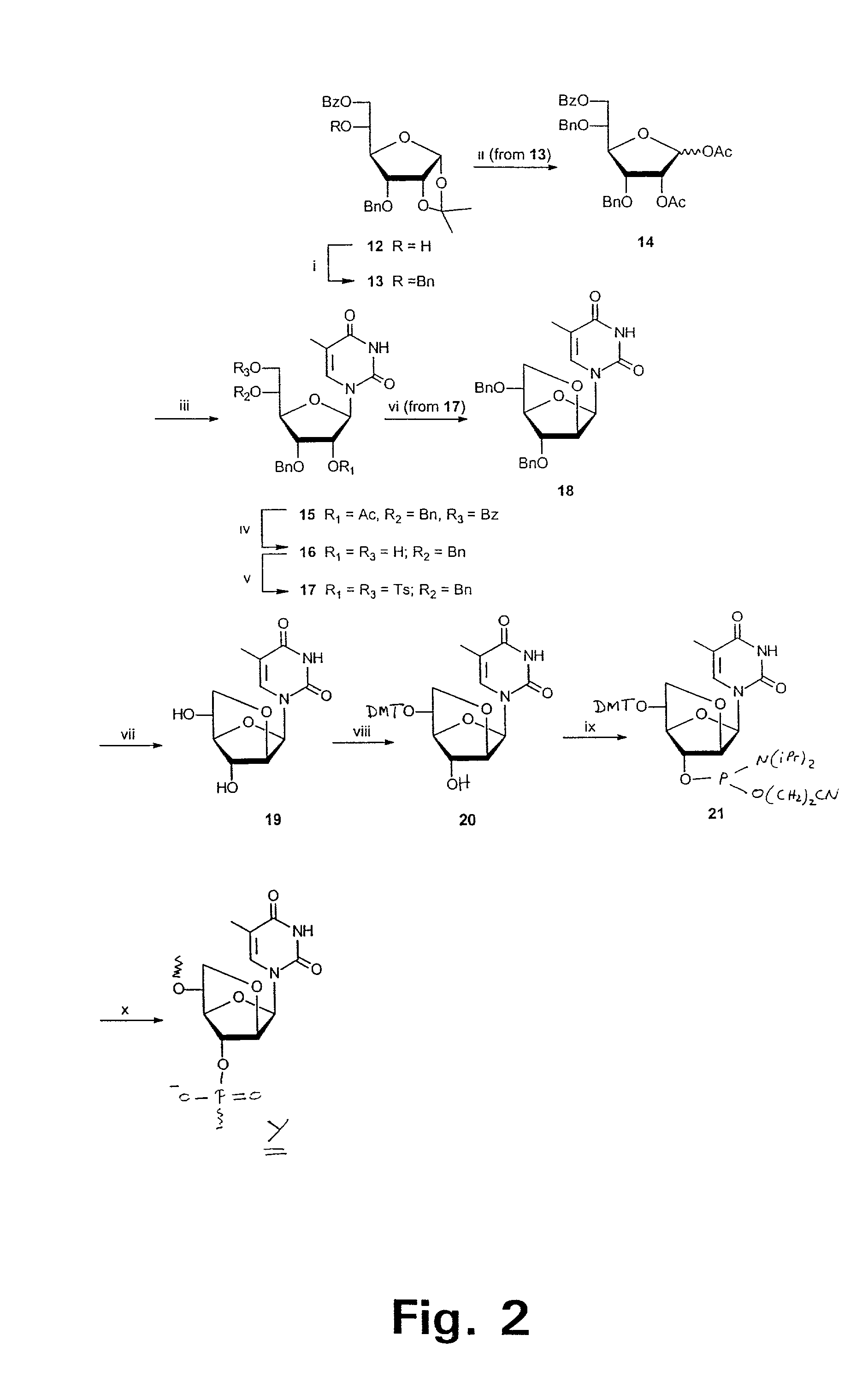
Xylo-LNA analogues
Based on the above and on the remarkable properties of the 2′-O,4′-C-methylene bridged LNA monomers it was decided to synthesise oligonucleotides comprising one or more 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer(s) as the first stereoisomer of LNA modified oligonucleotides. Modelling clearly indicated the xylo-LNA monomers to be locked in an N-type furanose conformation. Whereas the parent 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleosides were shown to adopt mainly an N-type furanose conformation, the furanose ring of the 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl monomers present in xylo-DNA were shown by conformational analysis and computer modelling to prefer an S-type conformation thereby minimising steric repulsion between the nucleobase and the 3′-O-phopshate group (Seela, F.; Wömer, Rosemeyer, H. Helv. Chem. Acta 1994, 77, 883). As no report on the hybridisation properties and binding mode of xylo-configurated oligonucleotides in an RNA context was believed to exist, it was the aim to synthesise 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer and to study the thermal stability of oligonucleotides comprising this monomer. The results showed that fully modified or almost fully modified Xylo-LNA is useful for high-affinity targeting of complementary nucleic acids. When taking into consideration the inverted stereochemistry at C-3′ this is a surprising fact. It is likely that Xylo-LNA monomers, in a sequence context of Xylo-DNA monomers, should have an affinity-increasing effect.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Methods and agents for screening for compounds capable of modulating gene expression
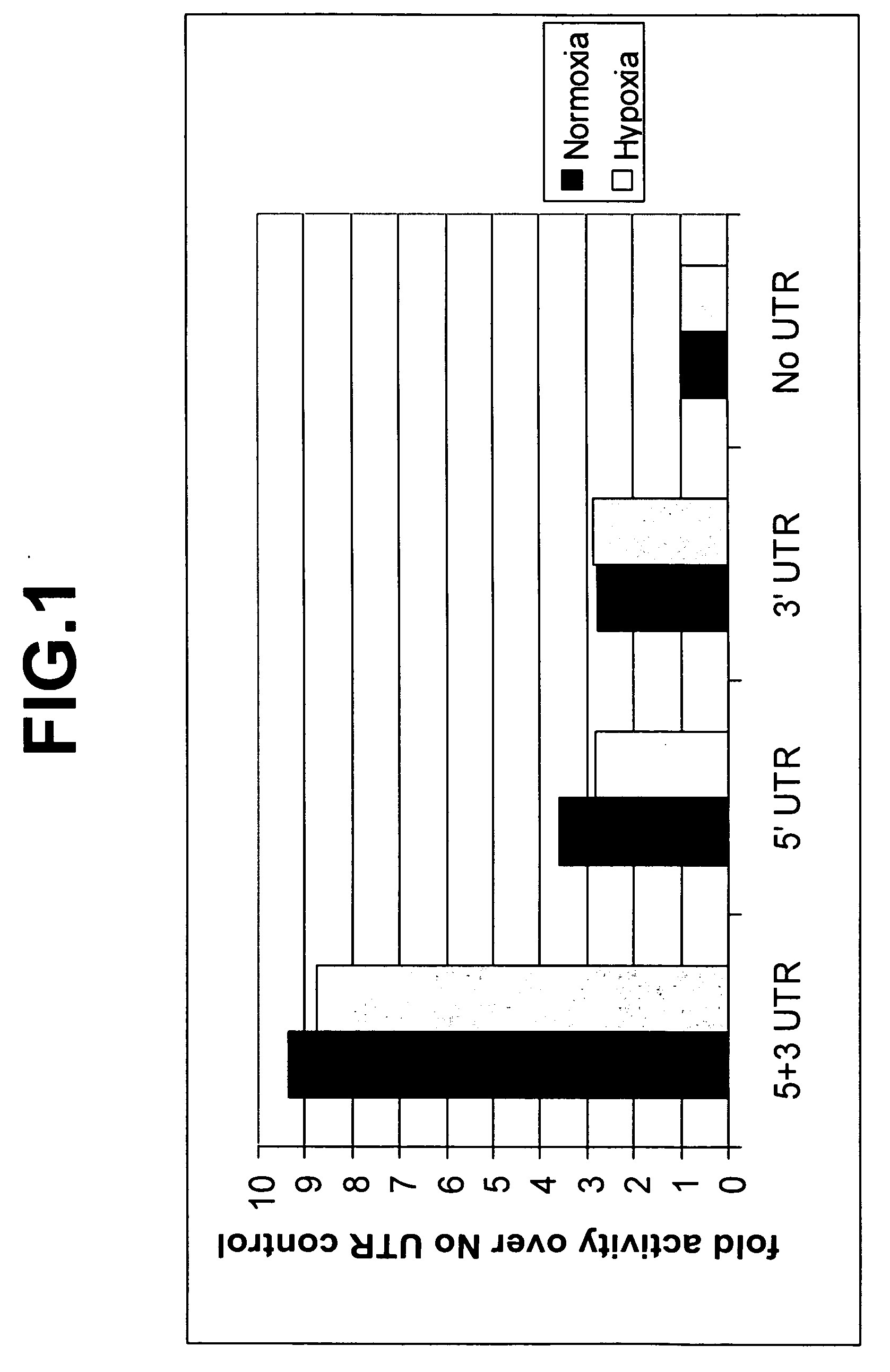
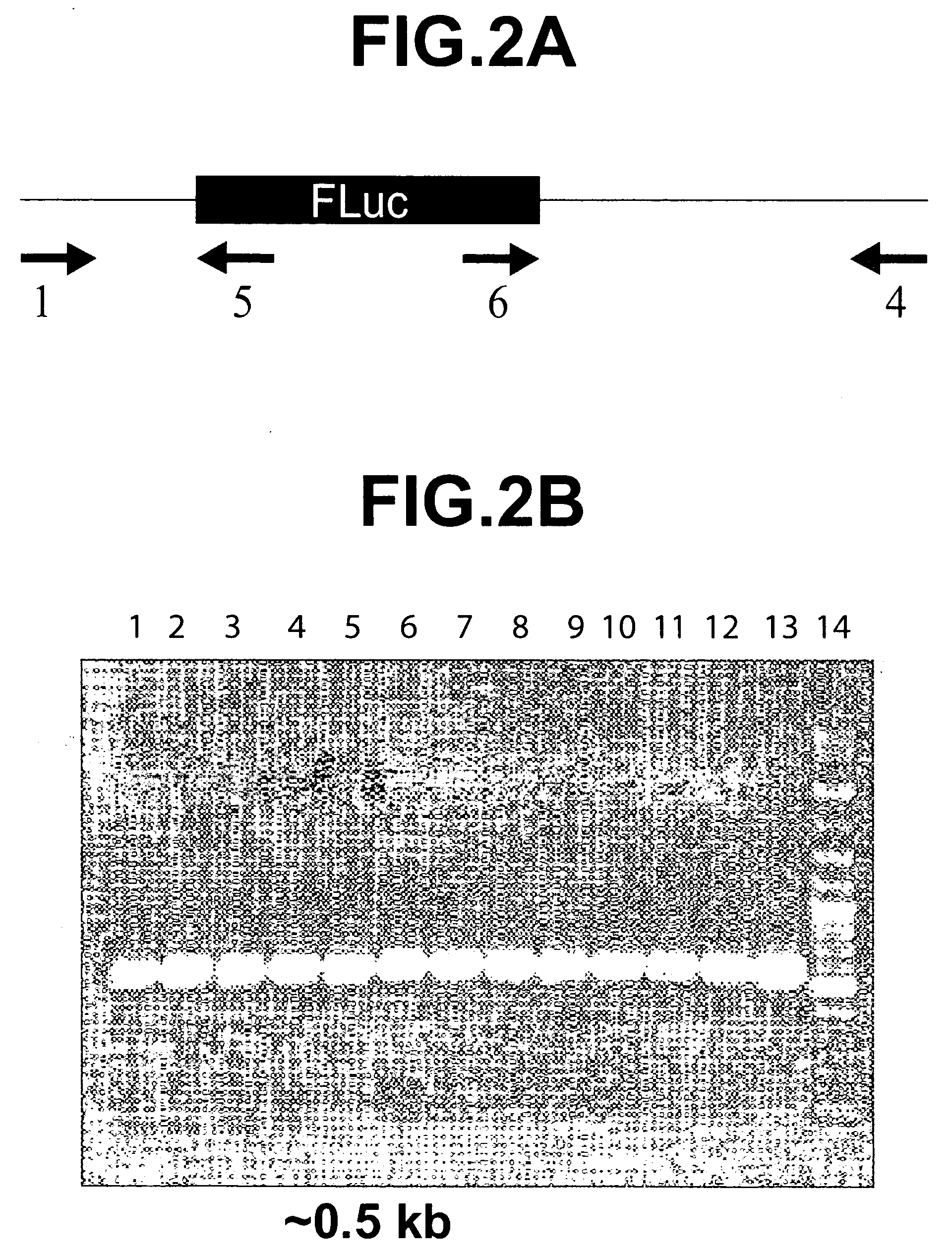
InactiveUS20050048549A1Modulate expressionLibrary screeningTissue cultureRegulator geneProtein level
The invention relates to the fields of screening assays, compounds, and methods for altering gene expression and protein levels. In particular, the invention includes assays to screen for agents capable of modulating gene expression in a UTR-dependent manner and agents capable of modulating gene expression.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
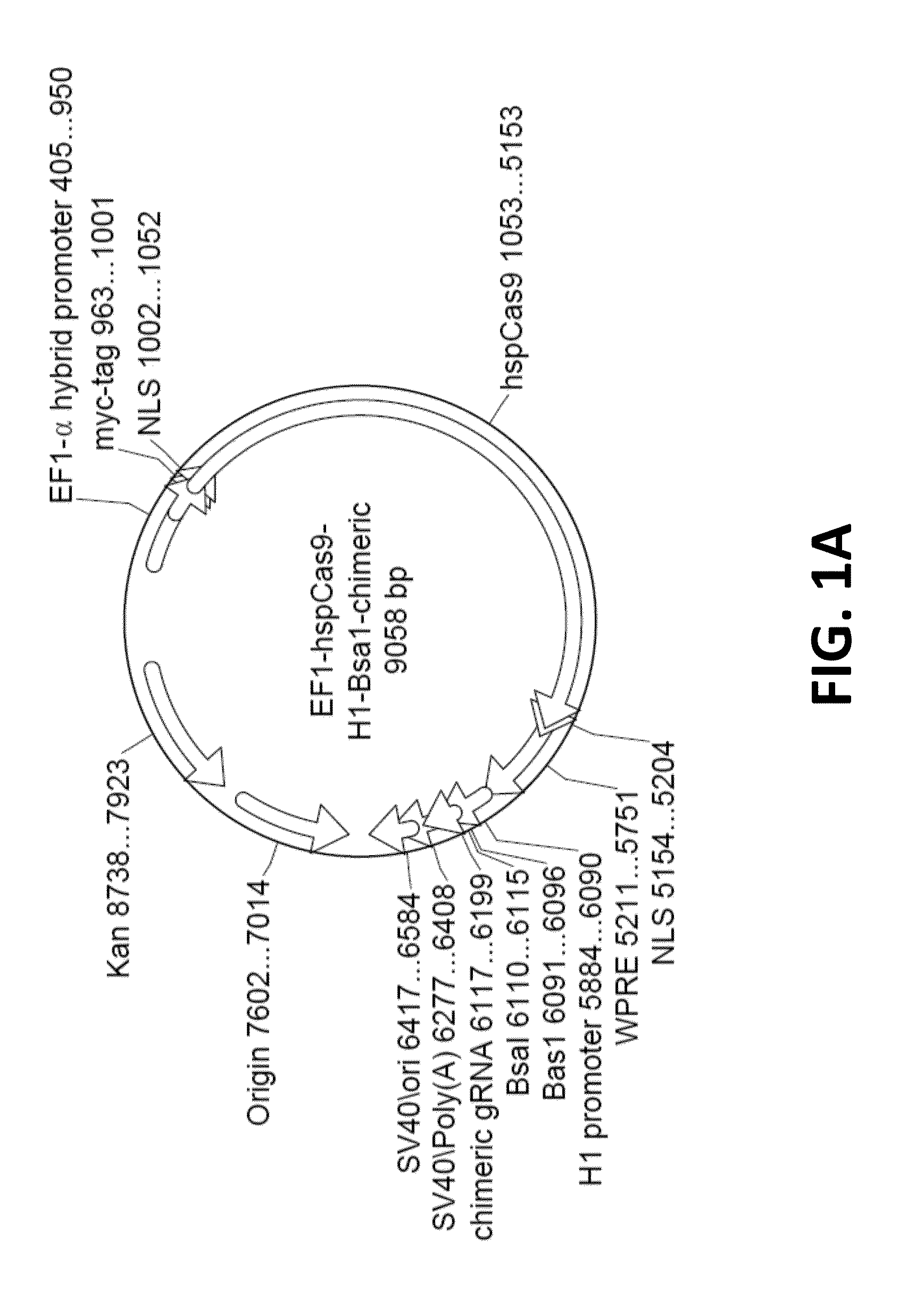
Crispr/cas systems for genomic modification and gene modulation
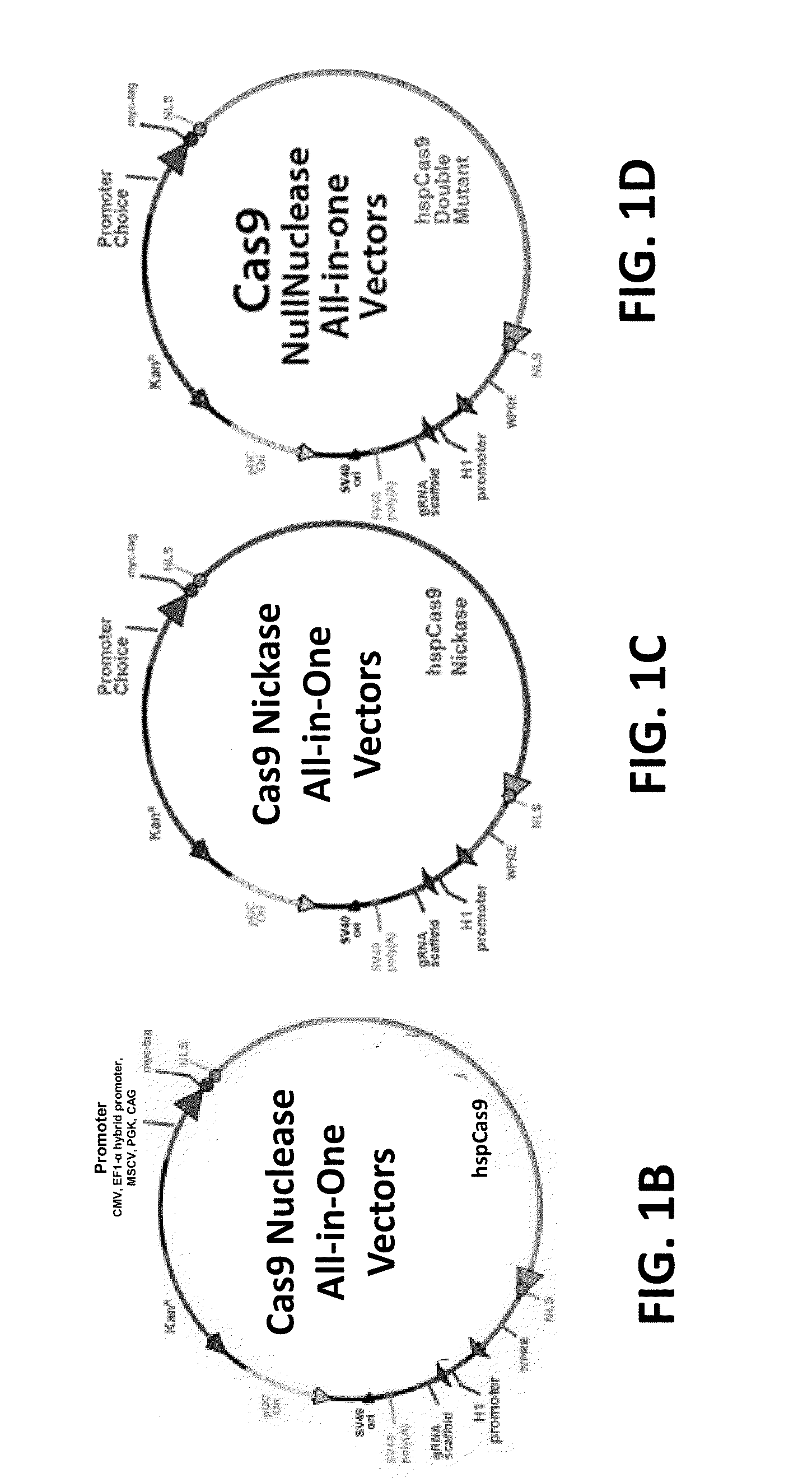
The invention relates to engineered CRISPR / Cas9 systems for genomic modification and regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells. The specification describes the design and validation of polynucleotides encoding the Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes) Cas9 gene and protein and variants of that protein, where the nucleotide sequence has been optimized for expression in mammalian cells, and also modified by fused sequences that enhance various aspects of the CRISPR / Cas system. The specification also describes systems for RNA-guided genome engineering and gene regulation in mammalian cells, including human cells.
Owner:SYST BIOSCI
Polymerases
ActiveUS20060281109A1Improve the level ofProceed efficientlySugar derivativesHydrolasesModified dnaPolymerase L
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
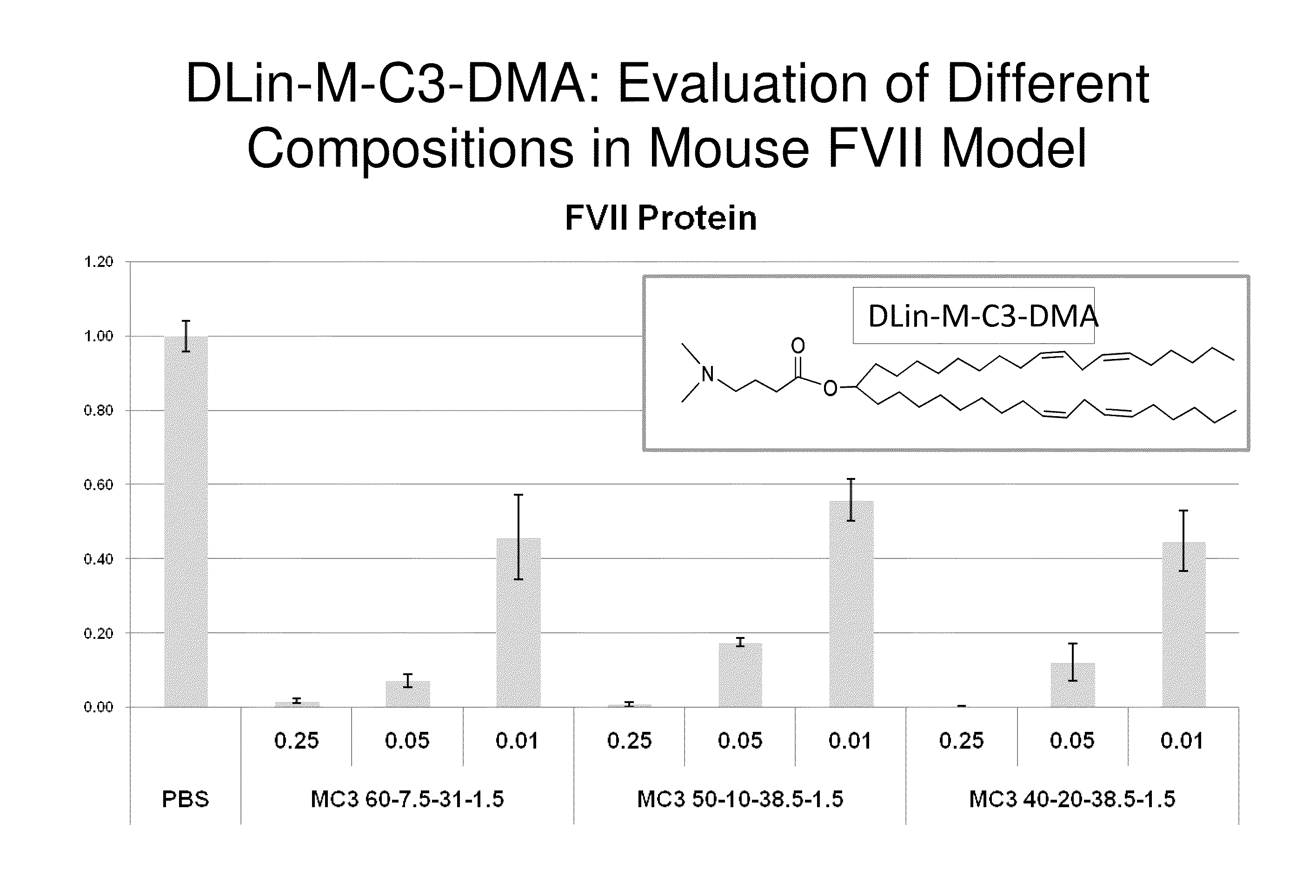
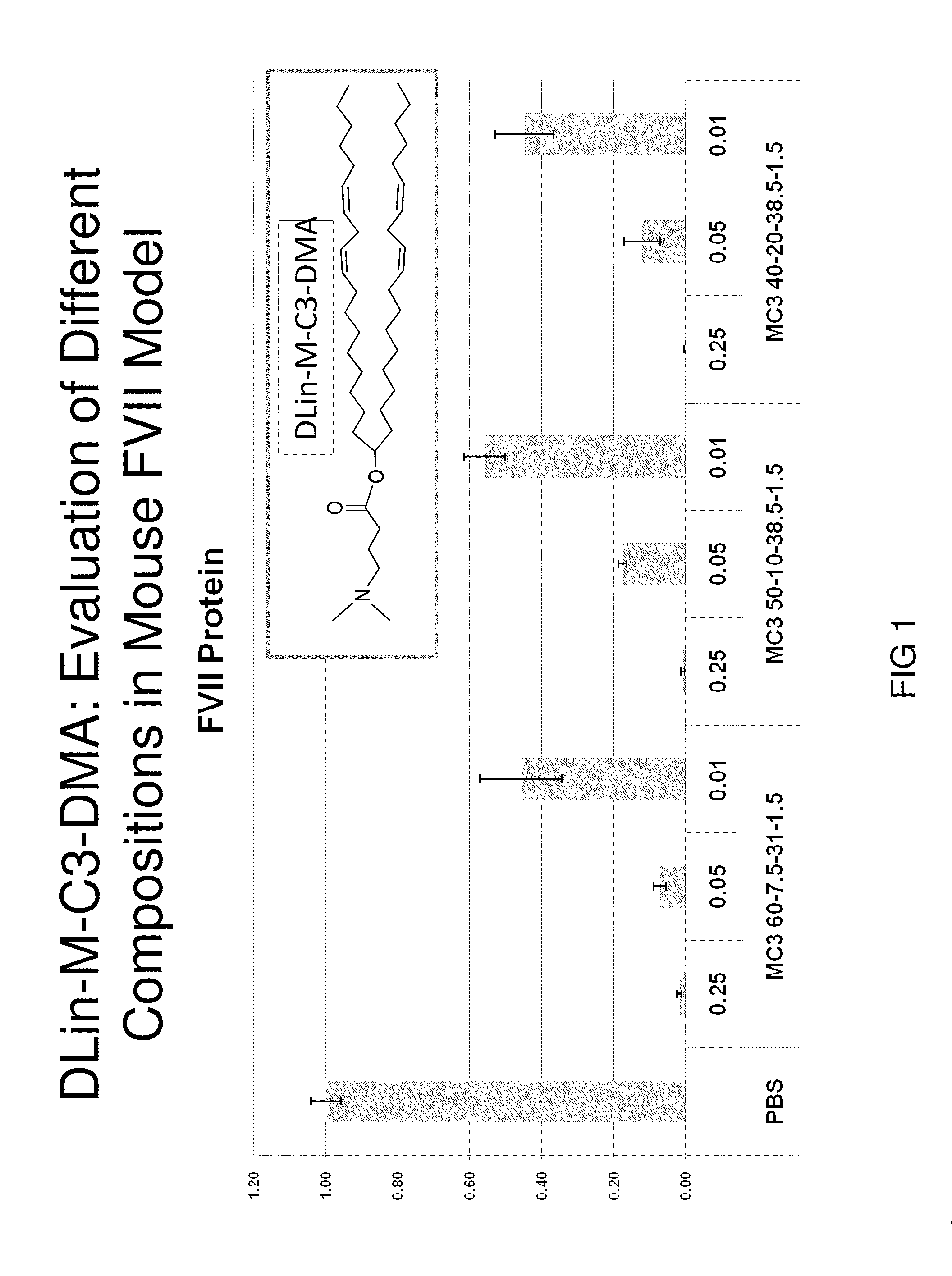
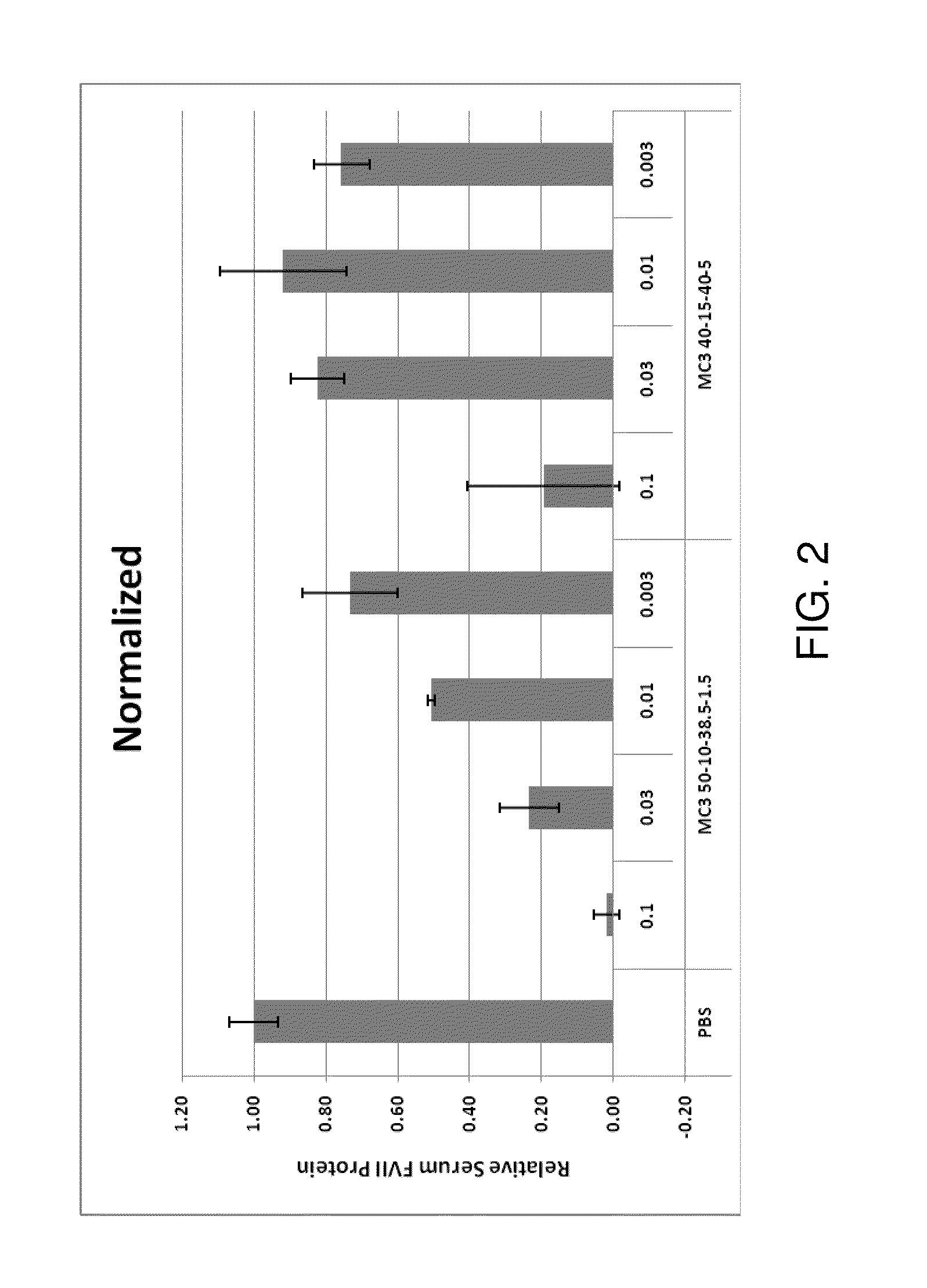
Lipid formulation
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
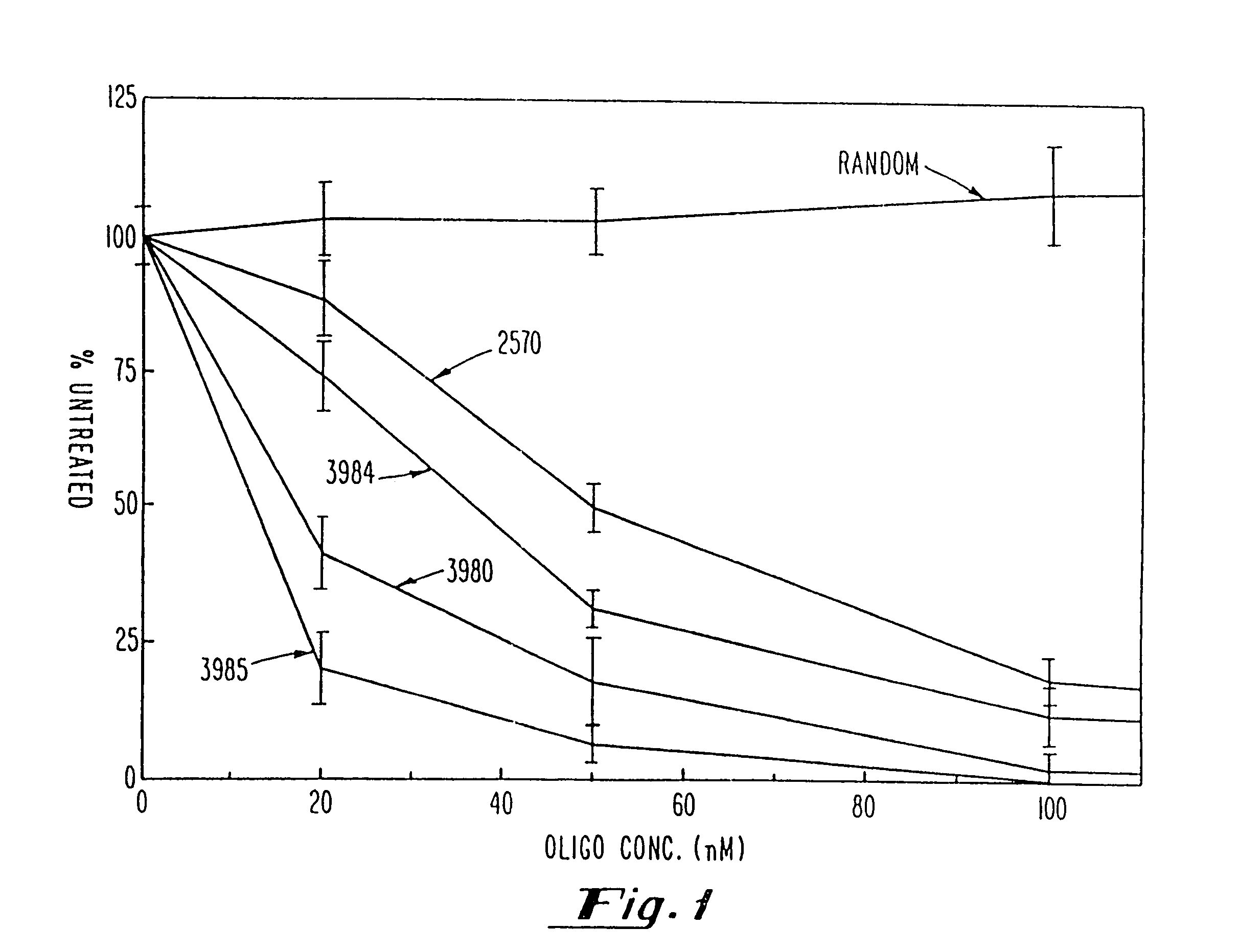
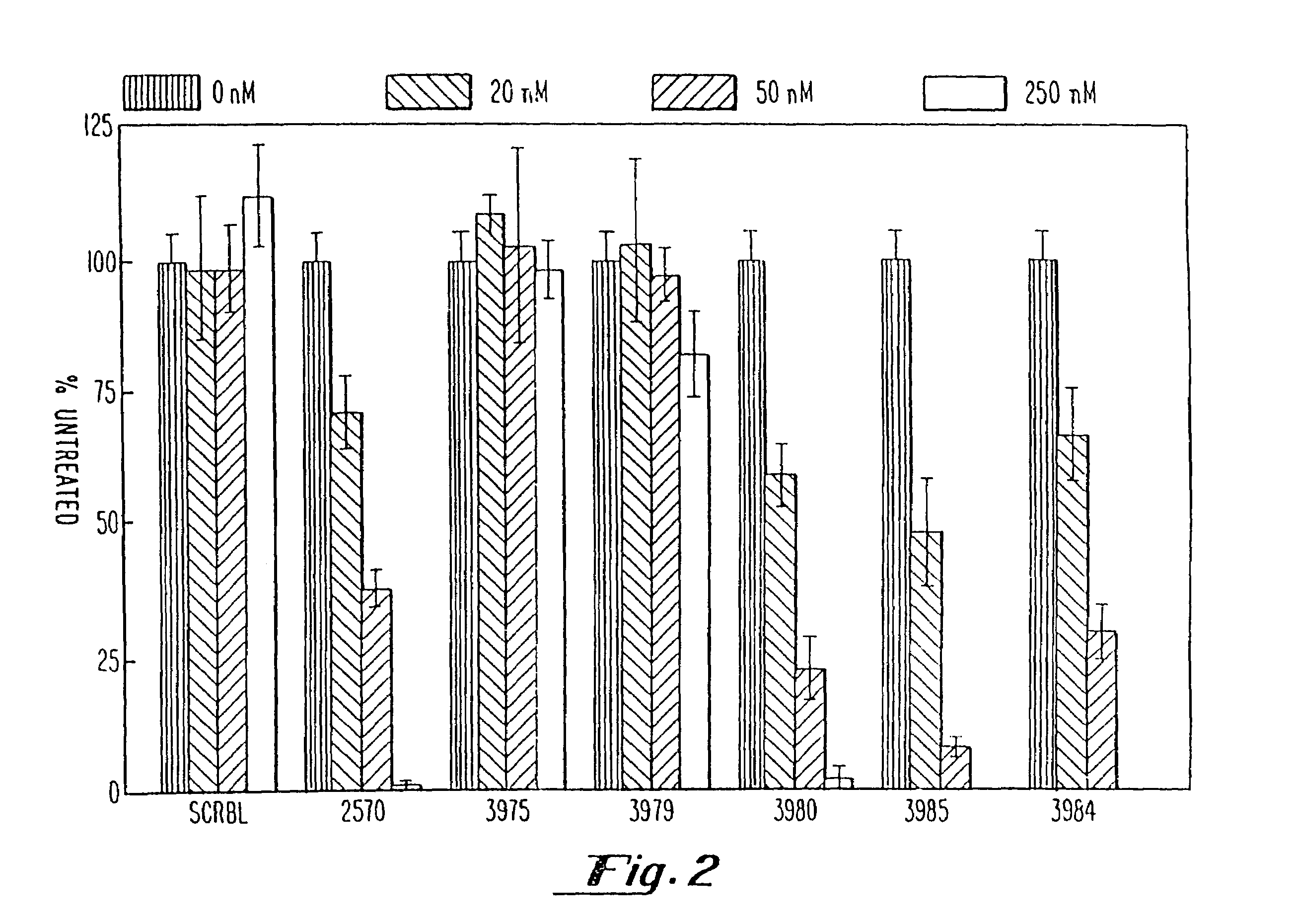
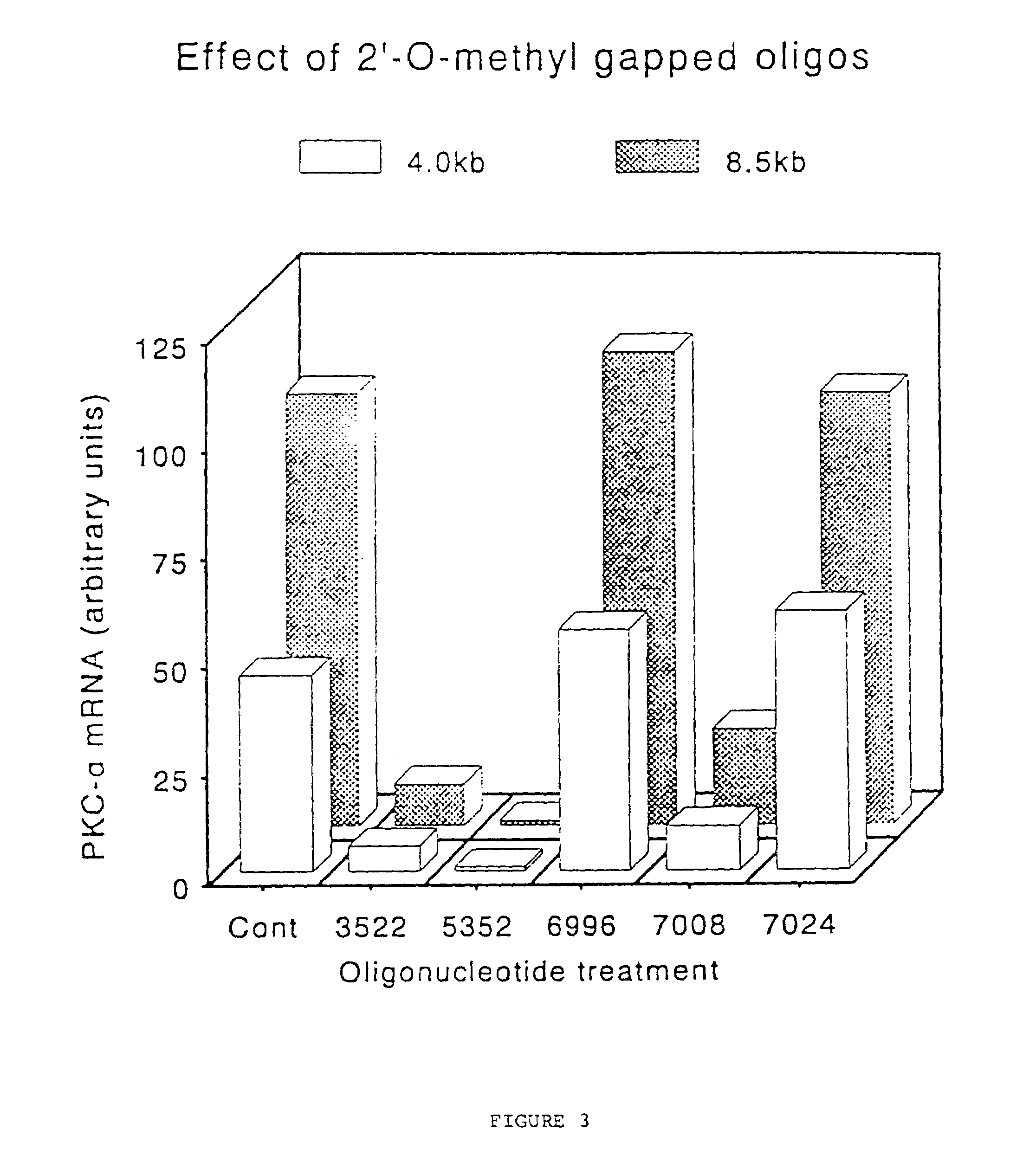
Gapped oligonucleotides
InactiveUS7015315B1Increased nuclease resistanceHigh binding affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsNuclease
Oligonucleotides and other macromolecules are provided which have increased nuclease resistance, substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary strand, and subsequences of 2′-deoxy-erythro-pentofuranosyl nucleotides that activate RNase H. Such oligonucleotides and macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
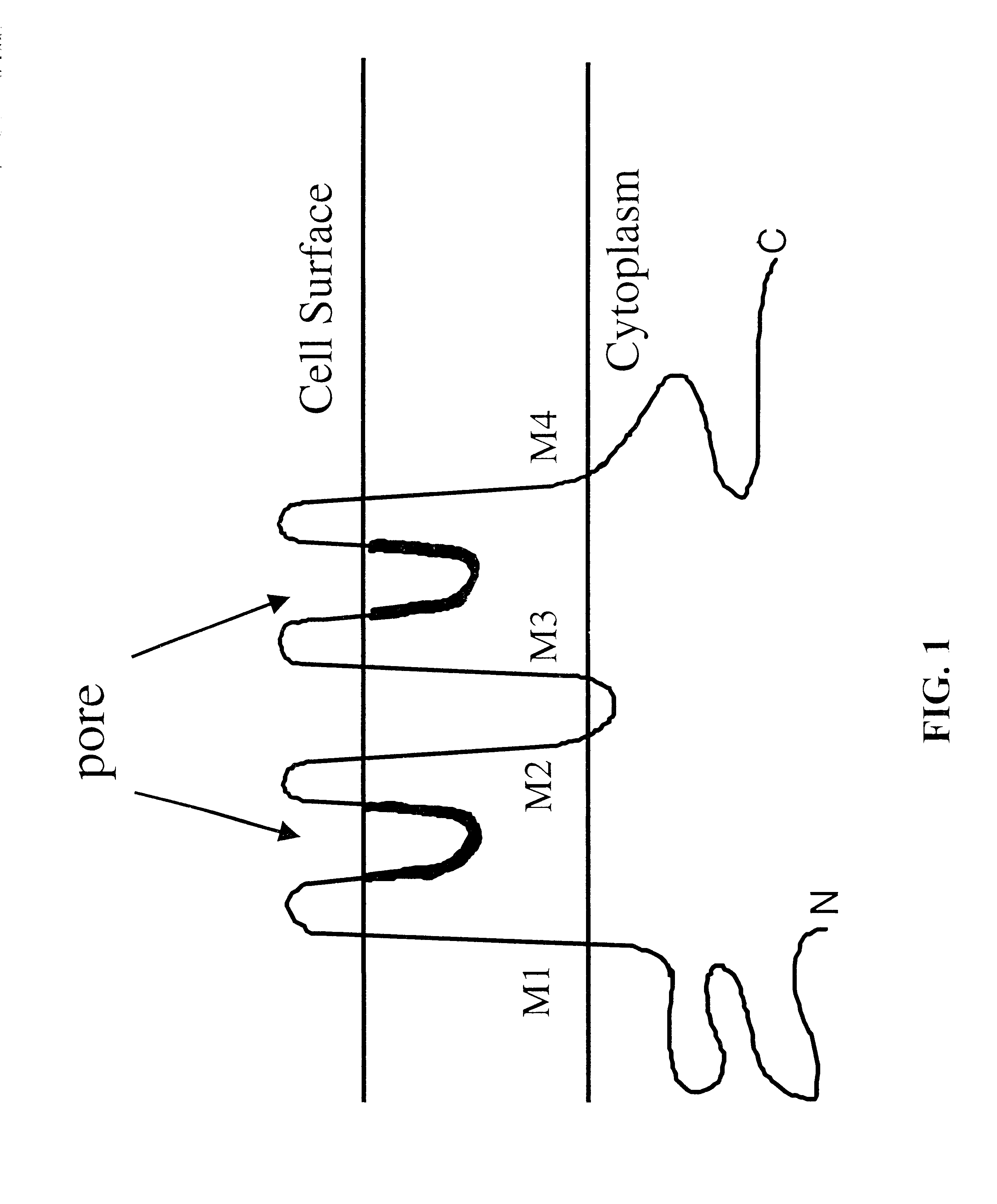
Nucleic acids and polypeptides of invertebrate TWIK channels and methods of use
Tandem pore domain weak inward rectifying K+ (TWIK) channel nucleic acids and proteins that have been isolated from Drosophila melanogaster and Leptinotarsa are described. The TWIK channel nucleic acids and proteins can be used to genetically modify metazoan invertebrate organisms, such as insects, coelomates, and pseudocoelomates, or cultured cells, resulting in TWIK channel expression or mis-expression. The genetically modified organisms or cells can be used in screening assays to identify candidate compounds which are potential pesticidal agents or therapeutics that interact with TWIK channel proteins. They can also be used in methods for studying TWIK channel activity and identifying other genes that modulate the function of, or interact with, the TWIK channel gene.
Owner:EXELIXIS PHARMA
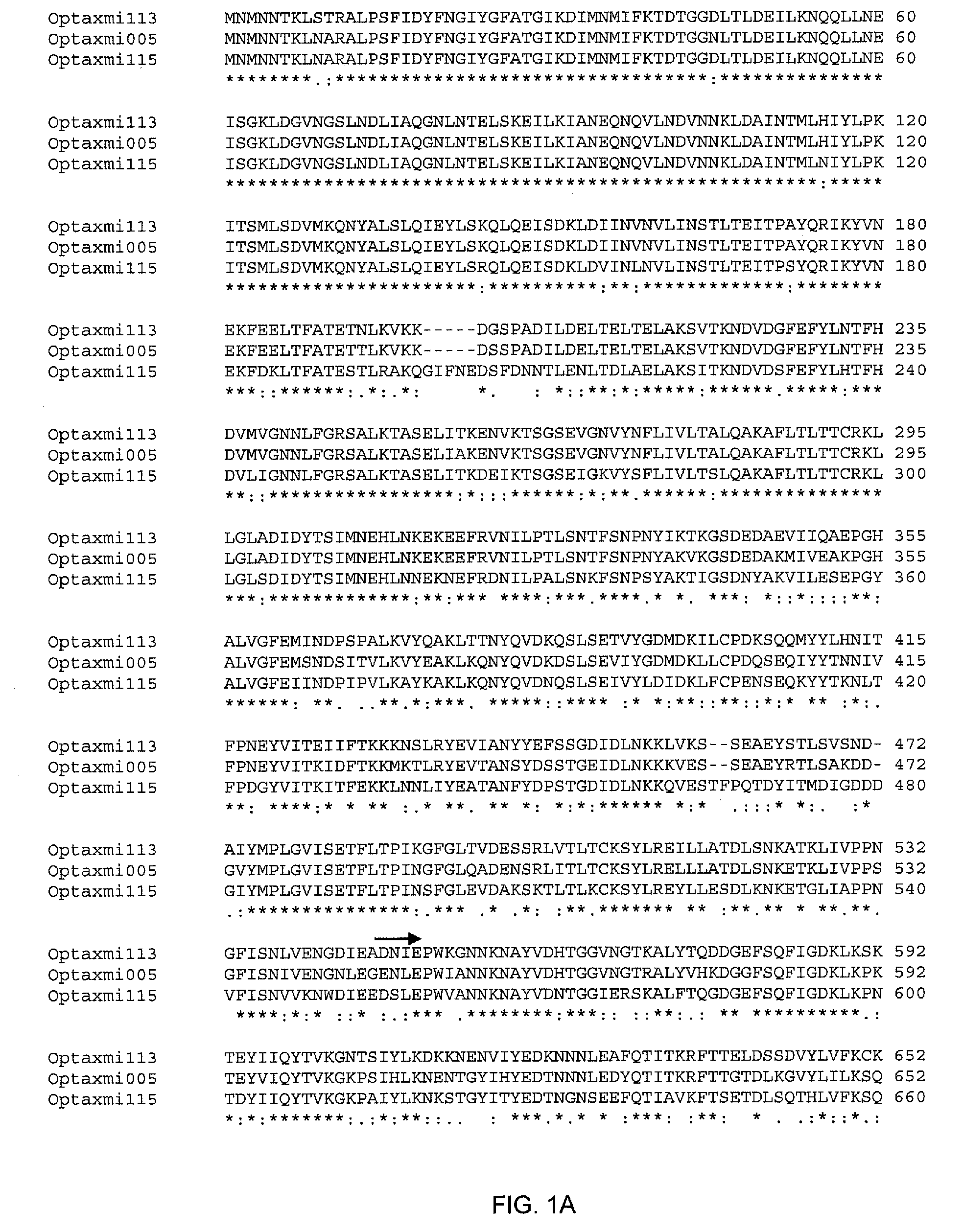
Axmi-115, axmi-113, axmi-005, axmi-163 and axmi-184: insecticidal proteins and methods for their use
ActiveUS20100004176A1Confer resistanceProduct can be usedBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDelta endotoxinDNA construct
Compositions and methods for conferring insecticidal activity to host cells are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a delta-endotoxin polypeptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in host cells. Compositions also comprise transformed host cells. In particular, isolated delta-endotoxin nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed, and antibodies specifically binding to those amino acid sequences. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:4, 5, 6, 13, or 14, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 2, 3, 11, or 12, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Biocompatible implant and use of the same
InactiveUS20060252981A1Good biological affinityStrong enoughImpression capsEye implantsRough surfaceBiological body
The present invention provides an implant capable of being cellularized in treatment of an injured organ or tissue in organisms. The present inventors found that a biocompatible implant comprising a biological molecule and a support is capable of being cellularized. The implant can be used instead of conventional implants which essentially comprise cells. The present invention provides a biocompatible implant comprising A) a biological molecule and B) a support. The present invention also provides A) a first layer having a rough surface, B) a rough surface; B) a second layer having a strength which allows the support to resist in vivo shock. The first layer is attached to the second layer via at least one point.
Owner:CARDIO
Gapped 2' modified oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6326199B1High affinityAvoid degradationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideNuclease
Oligonucleotides and other macromolecules are provided that have increased nuclease resistance, substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary strand, and sub-sequences of 2'-deoxy-erythro-pentofuranosyl nucleotides that activate RNase H enzyme. Such oligonucleotides and macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to antisense therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
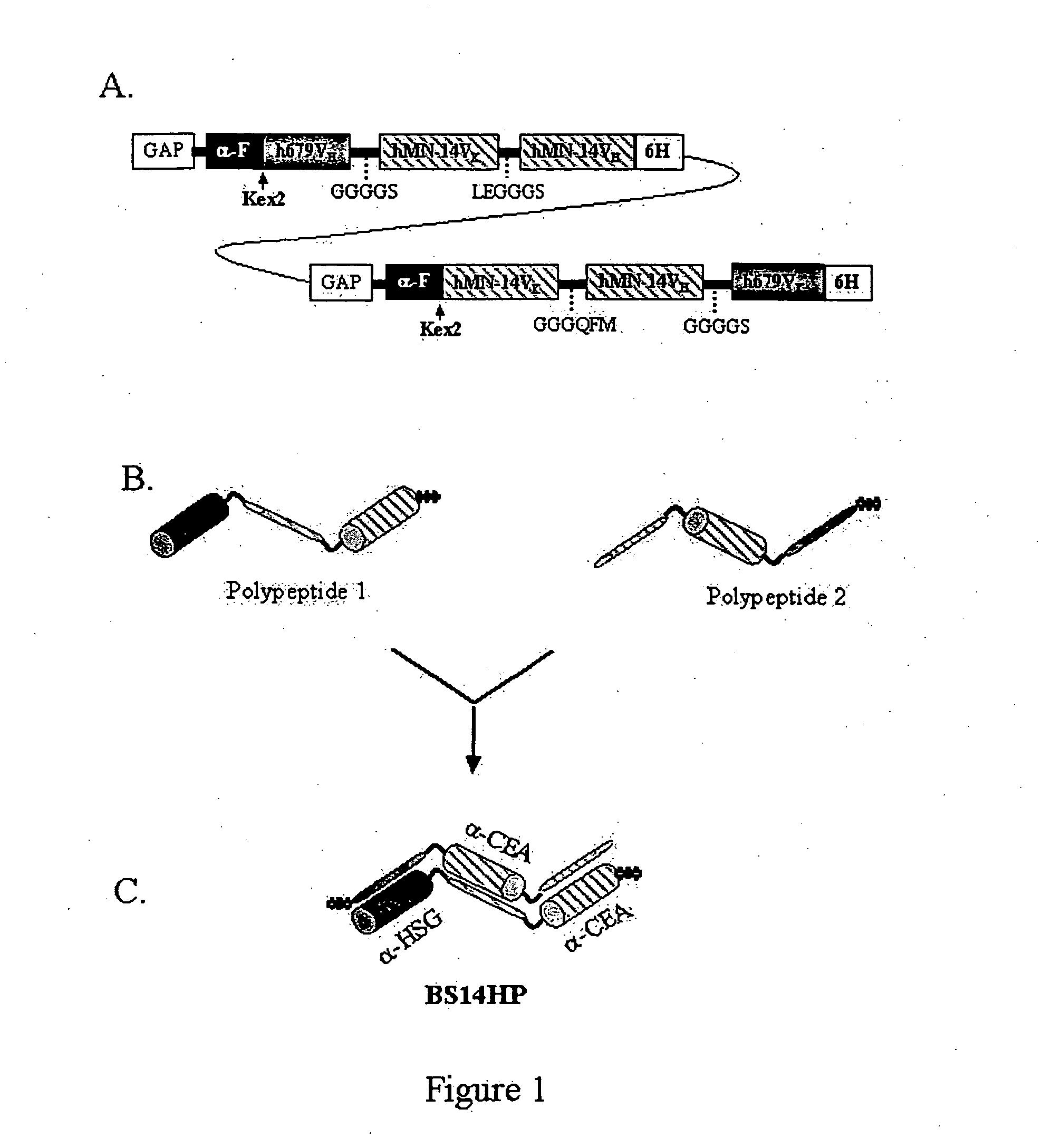
Polyvalent protein complex
The invention provides for a polyvalent protein complex (PPC) comprising two polypeptide chains generally arranged laterally to one another. Each polypeptide chain typically comprises 3 or 4 “v-regions”, which comprise amino acid sequences capable of forming an antigen binding site when matched with a corresponding v-region on the opposite polypeptide chain. Up to about 6 “v-regions” can be used on each polypeptide chain. The v-regions of each polypeptide chain are connected linearly to one another and may be connected by interspersed linking regions. When arranged in the form of the PPC, the v-regions on each polypeptide chain form individual antigen binding sites.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Antisense modulation of Smad6 expression
Antisense compounds, compositions and methods are provided for modulating the expression of Smad6. The compositions comprise antisense compounds, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding Smad6. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of Smad6 expression and for treatment of diseases associated with expression of Smad6 are provided.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
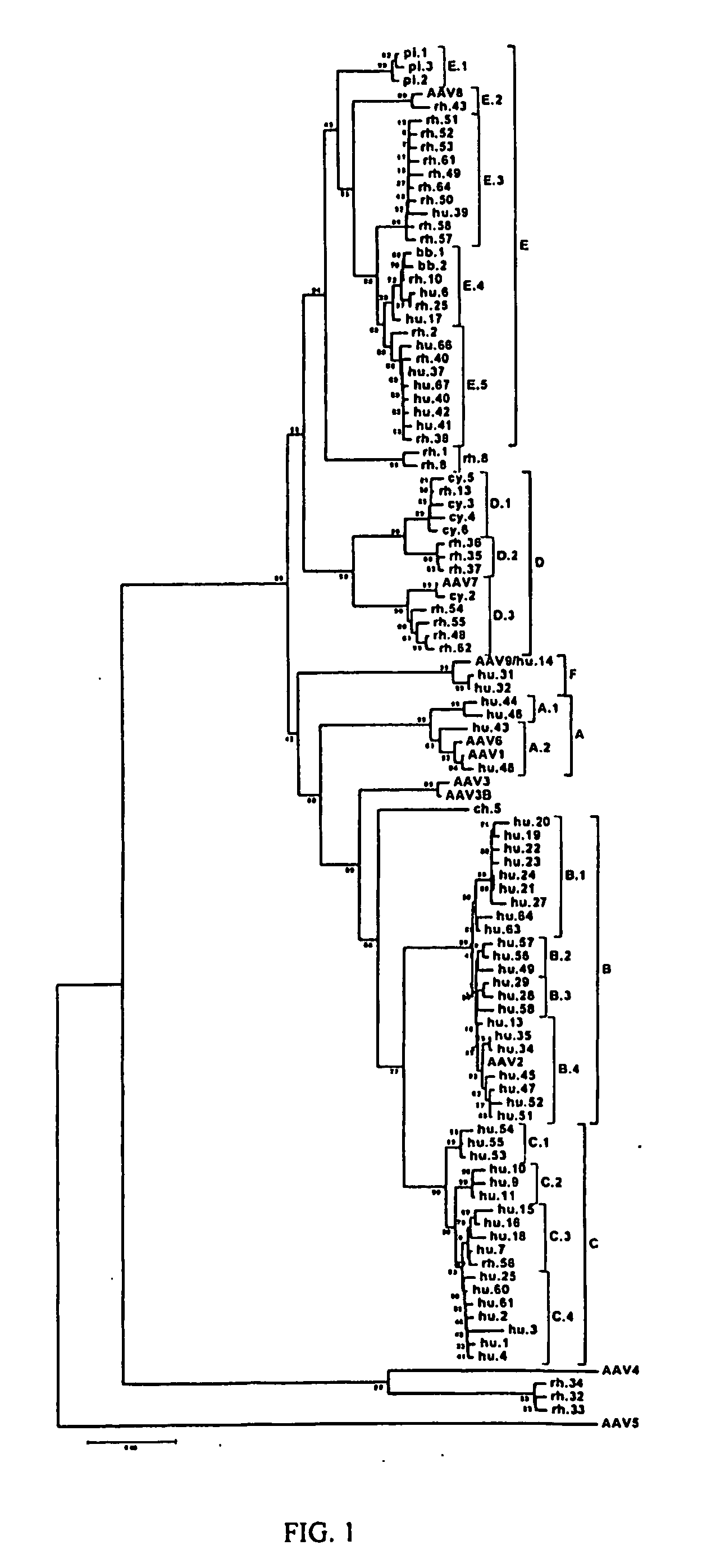
Adeno-associated virus (aav) clades, sequences, vectors containing same, and uses therefor
Sequences of novel adeno-associated virus capsids and vectors and host cells containing these sequences are provided. Also described are methods of using such host cells and vectors in production of rAAV particles. AAV-mediated delivery of therapeutic and immunogenic genes using the vectors of the invention is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
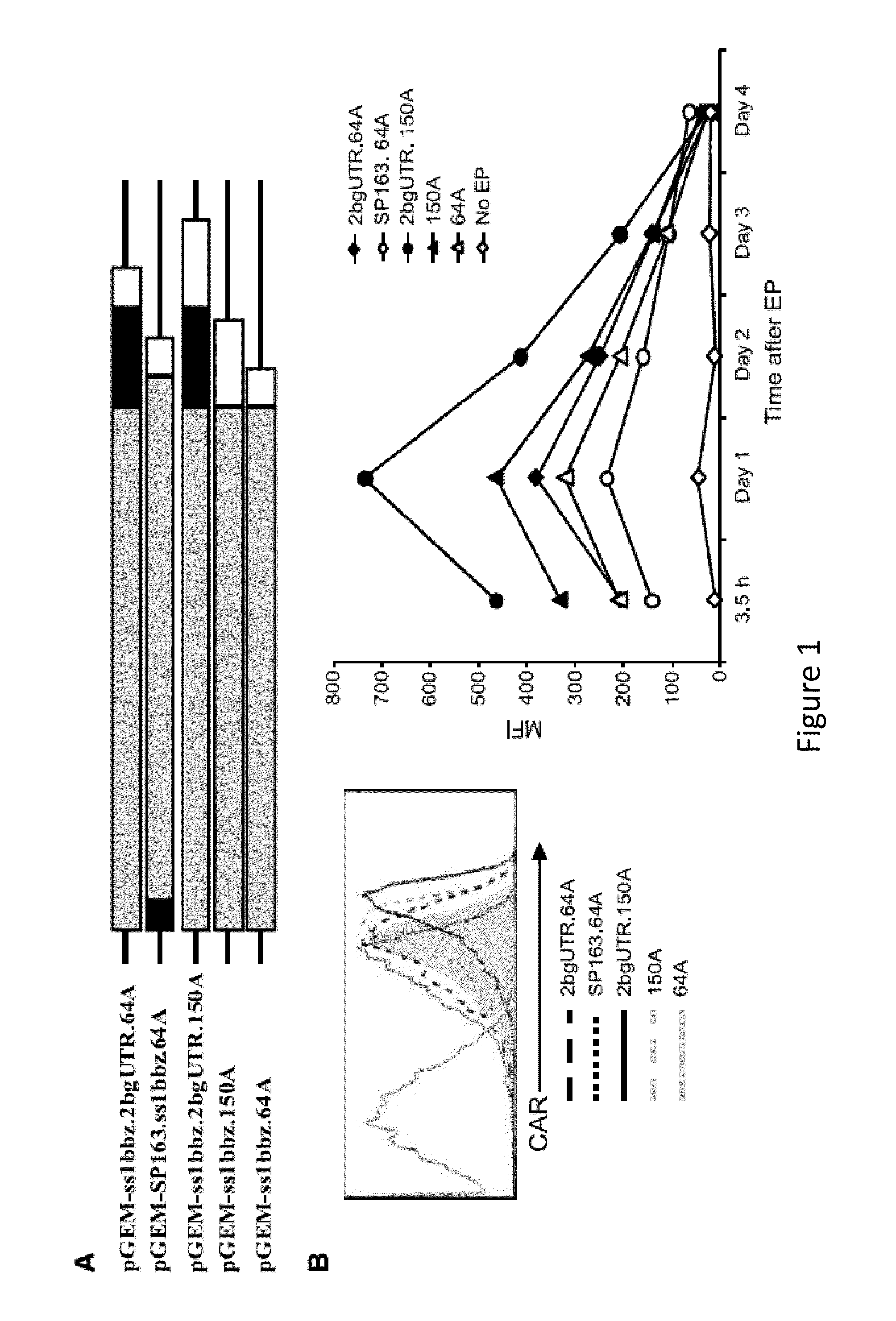
RNA engineered t cells for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20140227237A1Reduce riskLimited half-lifeBiocideVirusesAntigen receptorChimeric antigen receptor
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for generating RNA Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) transfected T cells. The RNA-engineered T cells can be used in adoptive therapy to treat cancer.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
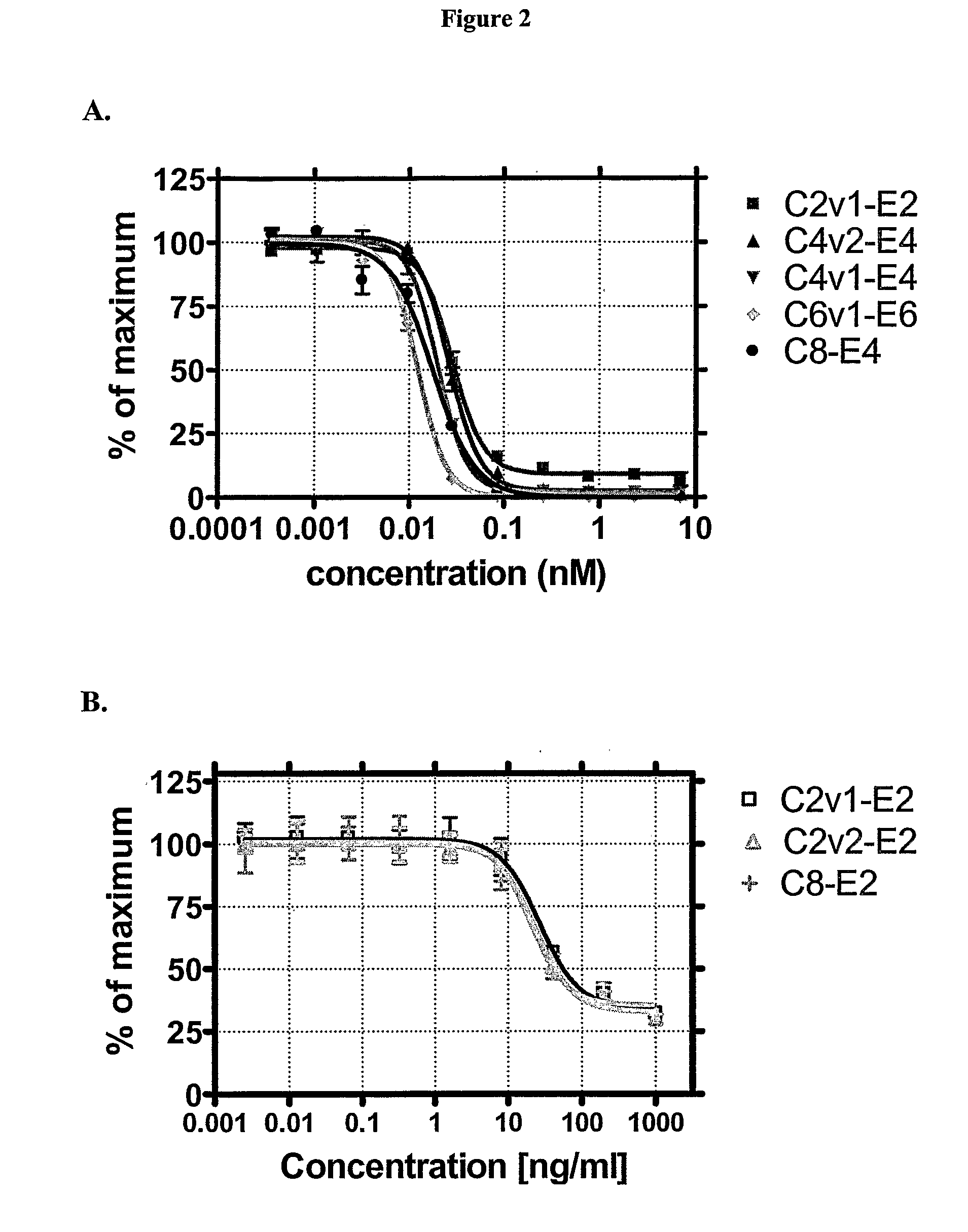
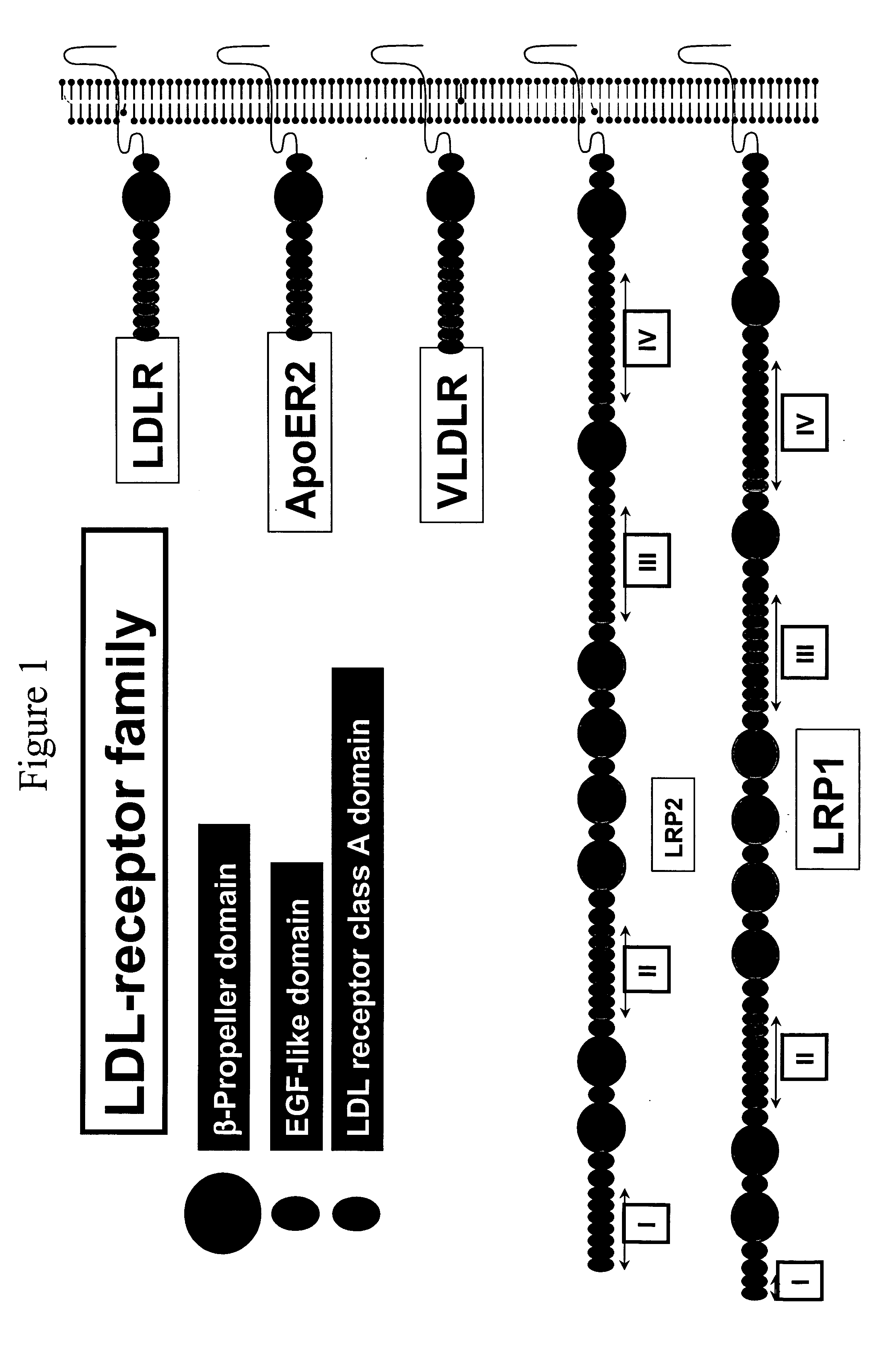
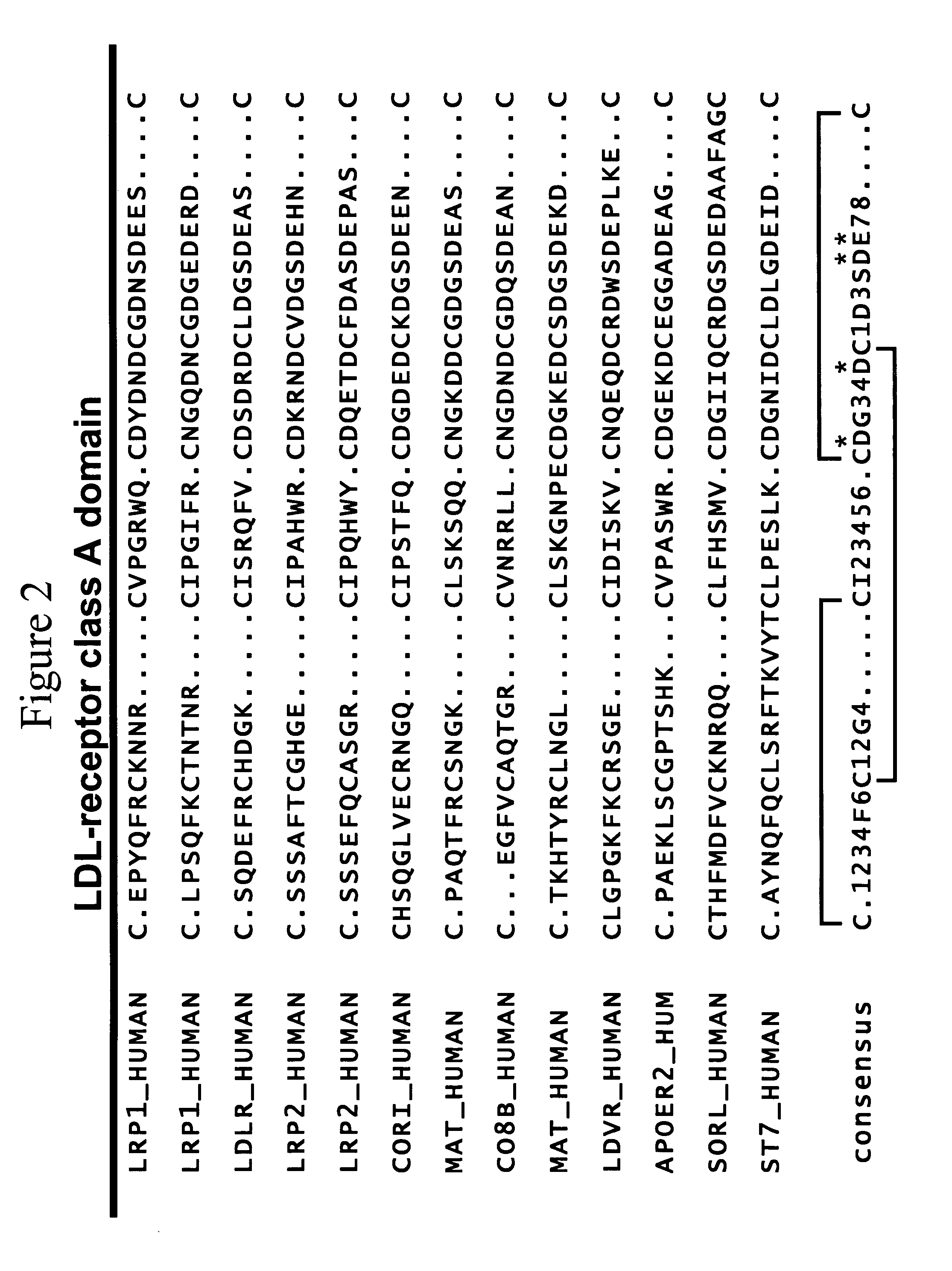
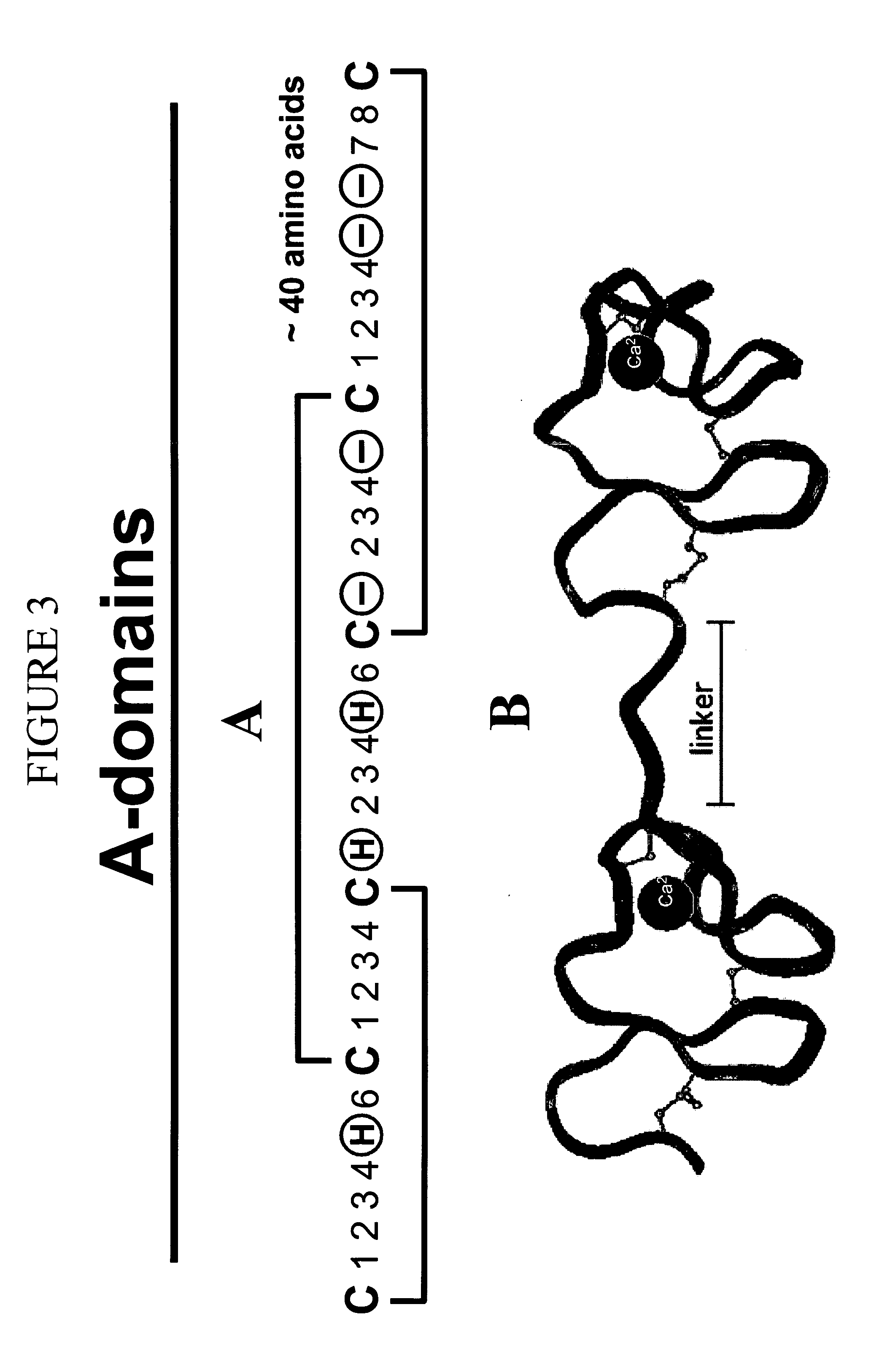
LDL receptor class A and EGF domain monomers and multimers
InactiveUS20050164301A1High affinityStimulate and inhibit activityPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsMonomerIntegrated systems
Specific monomer domains and multimers comprising the monomer domains are provided. Methods, compositions, libraries and cells that express one or more library member, along with kits and integrated systems, are also included in the present invention.
Owner:AMGEN MOUNTAIN VIEW
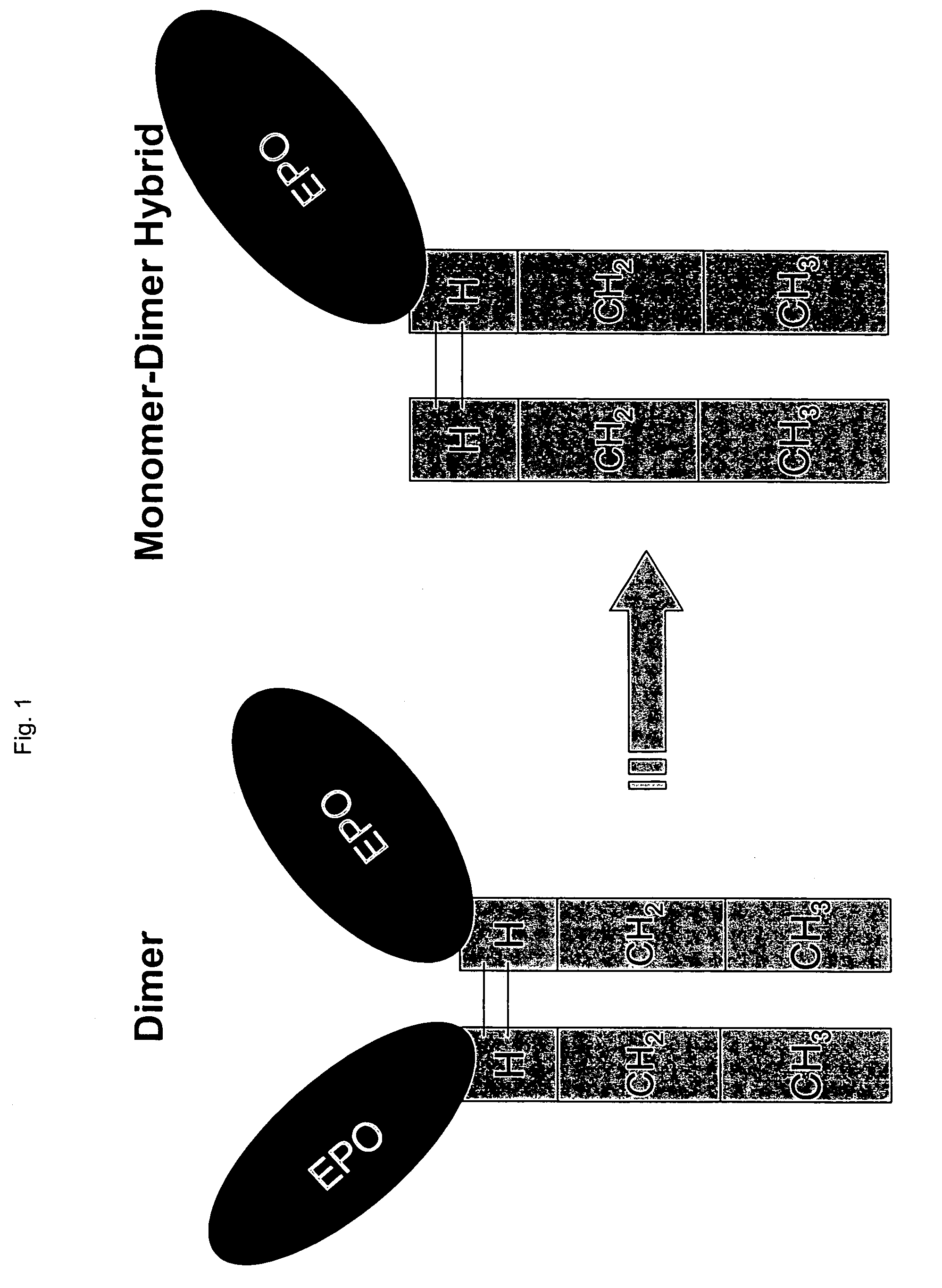
Glycosylation analogs of erythropoietin
ActiveUS7217689B1Increase the number ofHigh sialic acid contentPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue culturePlasmidDNA
Erythropoietin analogs having at least one additional site for glycosylation, or a rearrangement of at least one site for glycosylation are disclosed. The invention also relates to DNA sequences encoding said erythropoietin analogs, and recombinant plasmids and host cells for analog expression.
Owner:AMGEN INC
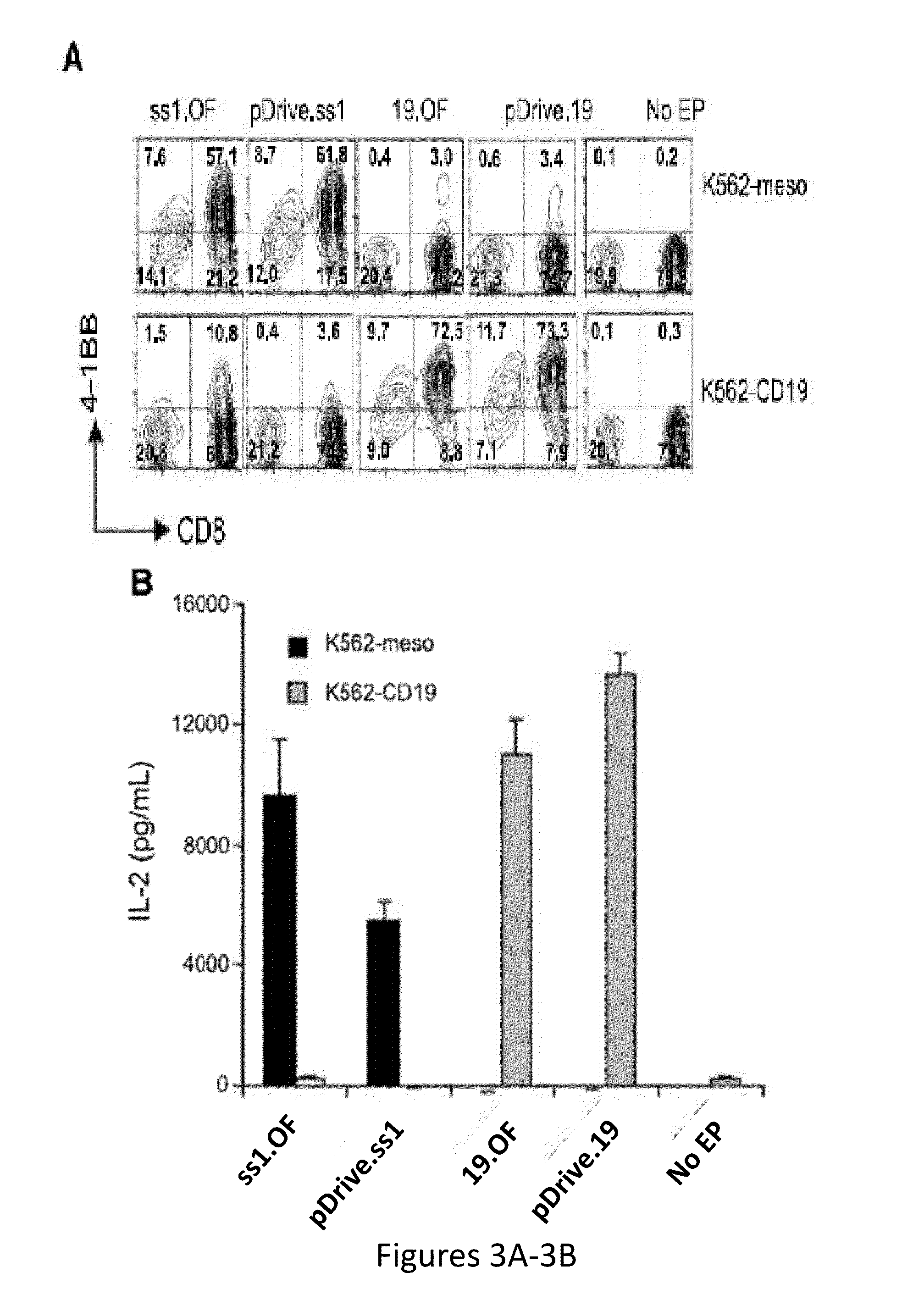
Antibody for 4-1BB
The present invention includes the receptor protein 4-1BB and the cDNA gene encoding for receptor protein 4-1BB. The nucleotide sequence of the isolated cDNA is disclosed herein along with the deduced amino acid sequence. The 4-1BB protein and fragments and derivatives can be used: 1) as a probe to isolate ligands to receptor protein 4-1BB, 2) to stimulate proliferation of B-cell's expressing 4-1BB, or 3) to block 4-1BB ligand binding. A monoclonal antibody against 4-1BB was developed which specifically recognizes an epitope on the extracellular domain of receptor protein 4-1BB. The monoclonal antibody can be used enhance T-cell proliferation and activation by treating T-cells that have expressed receptor protein 4-1BB with the monoclonal antibody. The effectiveness of the treatment was enhanced when conducted in the presence of protein tyrosinase kinase. A fusion protein for detecting cell membrane ligands to receptor protein 4-1BB was developed. It comprises the extracellular portion of the receptor protein 4-1BB and a detection protein bound to the portion of the receptor protein 4-1BB.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Methods of modifying antibodies for purification of bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS20090263392A1Efficient purificationFunction increaseSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesBinding site
The present inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column based on the difference in isoelectric points between the H chains of two types of antibodies, wherein the difference is introduced by modifying the amino acids present on the surface of the antibody variable regions of two types of antibodies that constitute a bispecific antibody. Furthermore, the inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column by linking respective antigen binding sites (heavy chain variable regions) to the antibody constant regions having different isoelectric points, and then coexpressing these antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
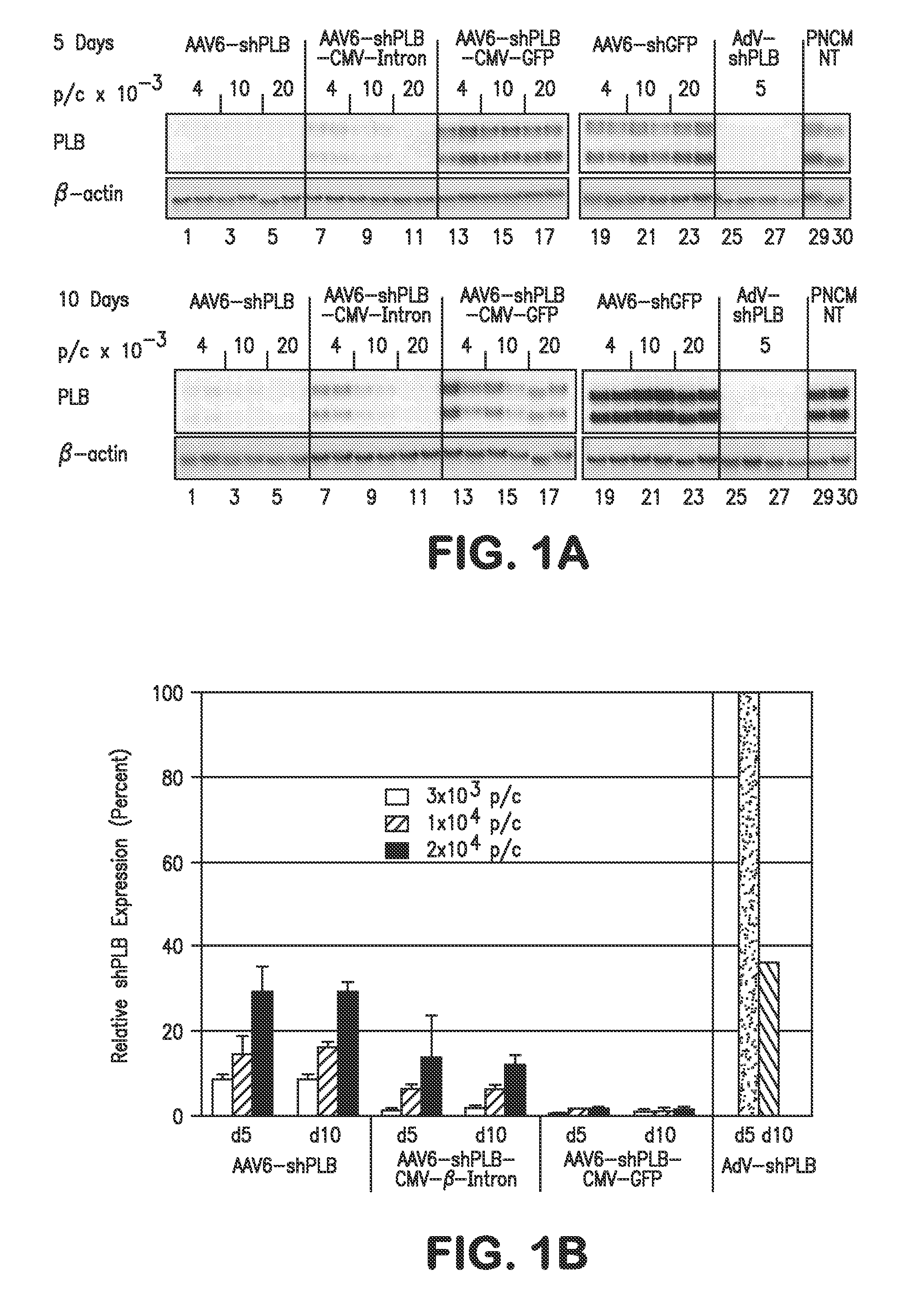
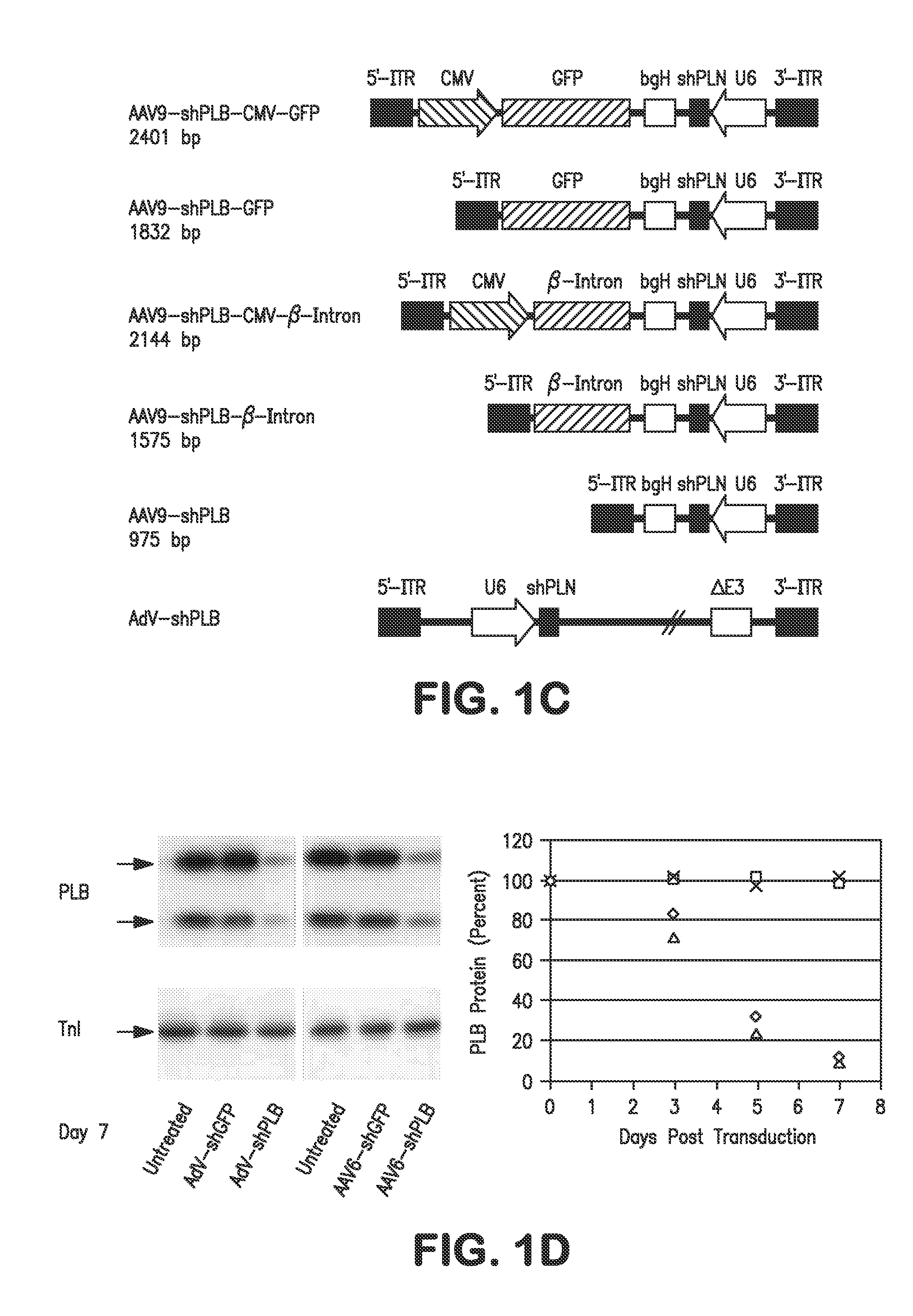
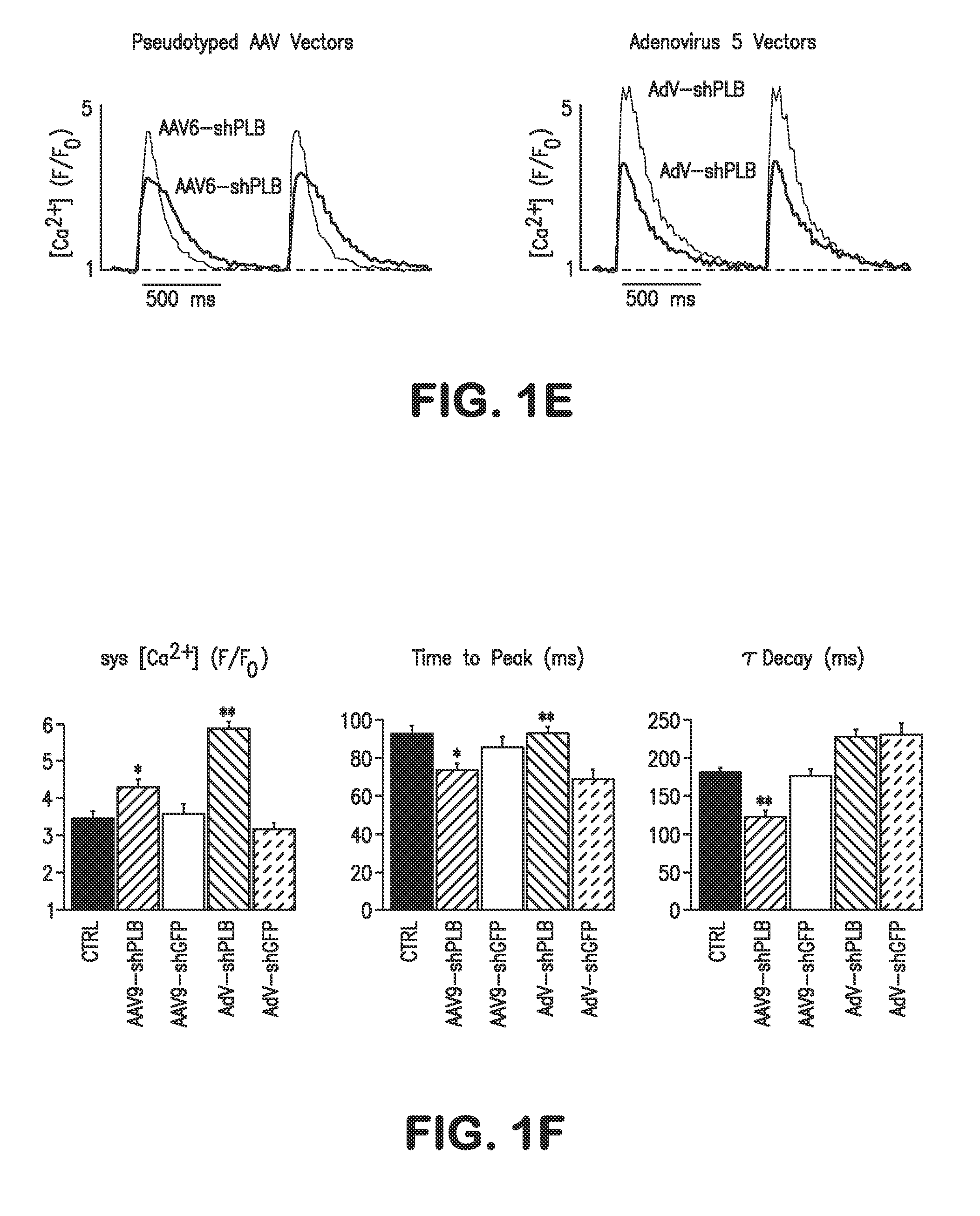
RNA interference for the treatment of heart failure
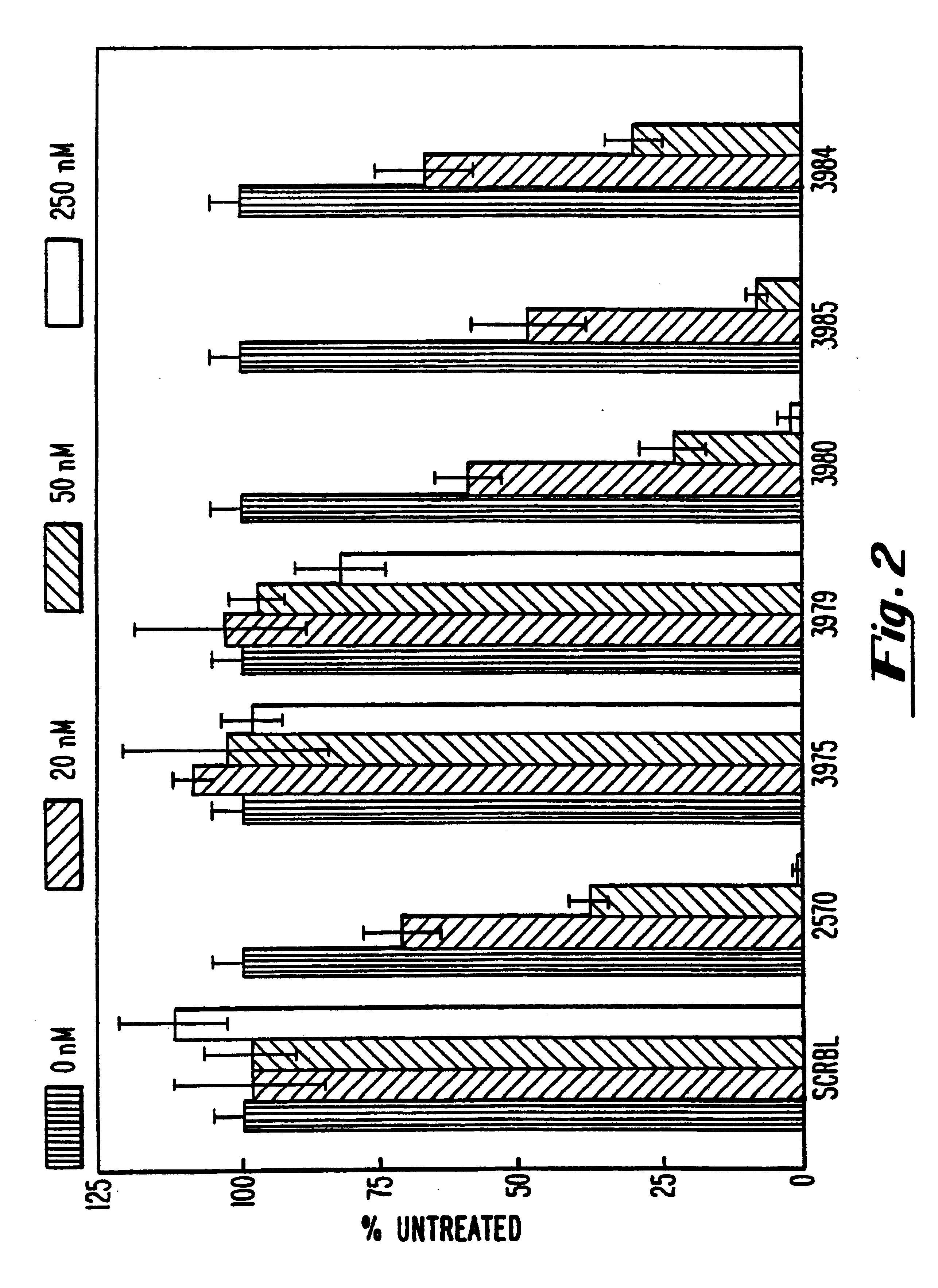
InactiveUS8404658B2Reduce expressionDecreasing ventricular arrhythmiasOrganic active ingredientsTissue culturePhospholambanTransfection
The present invention relates to targeted RNAi for the treatment of heart failure by modulating defective cardiac Ca2+ homeostasis via decreasing expression or activity of phospholamban (PLB) using adeno-associated virus (AAV) transfection of cardiomyocytes. Methods for decreasing ventricular arrhythmias, as well as methods for overall improvement of survival from heart failure in subjects are also disclosed. Further, the present invention provides methods which can be used to diagnose susceptibility to treatment by RNAi, and includes pharmaceutical compositions, kits and vectors including an RNAi sequence.
Owner:NANOCOR THERAPEUTICS +1
Antisense modulation of connective tissue growth factor expression
Antisense compounds, compositions and methods are provided for modulating the expression of connective tissue growth factor. The compositions comprise antisense compounds, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding connective tissue growth factor. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of connective tissue growth factor expression and for treatment of diseases associated with expression of connective tissue growth factor are provided.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
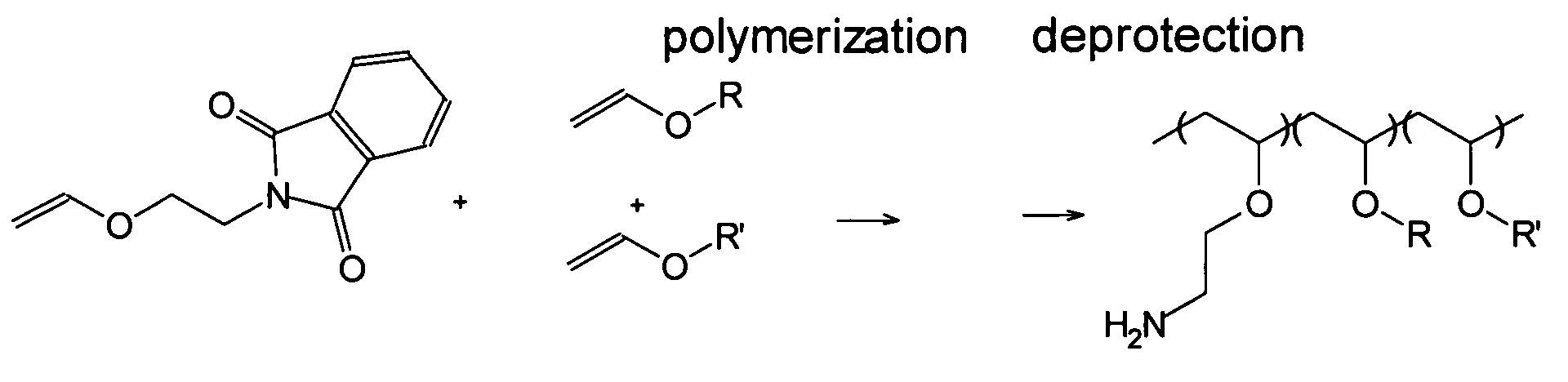
Polyconjugates for In Vivo Delivery of Polynucleotides
ActiveUS20080152661A1Reduce aggregationEnhances transfection activityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDelivery vehicleNucleotide
The present invention is directed to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for delivering polynucleotides or other cell-impermeable molecules to mammalian cells. Described are polyconjugates systems that incorporate targeting, anti-opsonization, anti-aggregation, and transfection activities into small biocompatible in vivo delivery vehicles. The use of multiple reversible linkages connecting component parts provides for physiologically responsive activity modulation.
Owner:ARROWHEAD MADISON
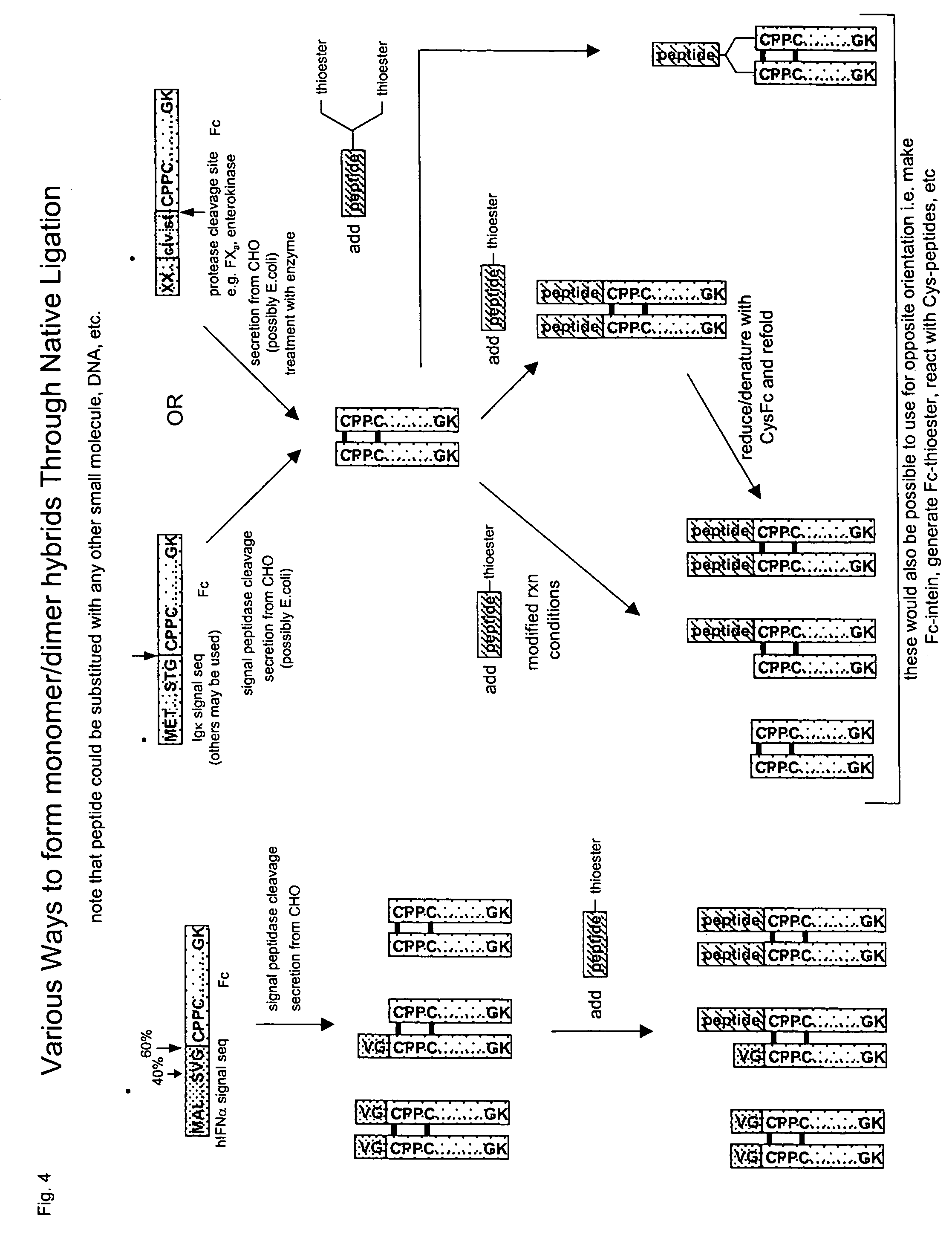
Methods for chemically synthesizing immunoglobulin chimeric proteins
ActiveUS7381408B2Prolong lifeEasy to purifyHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsChimera ProteinBiochemistry
The invention provides methods of chemically synthesizing chimeric proteins comprising at least a portion of an immunoglobulin constant region and a biologically active molecule.
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com