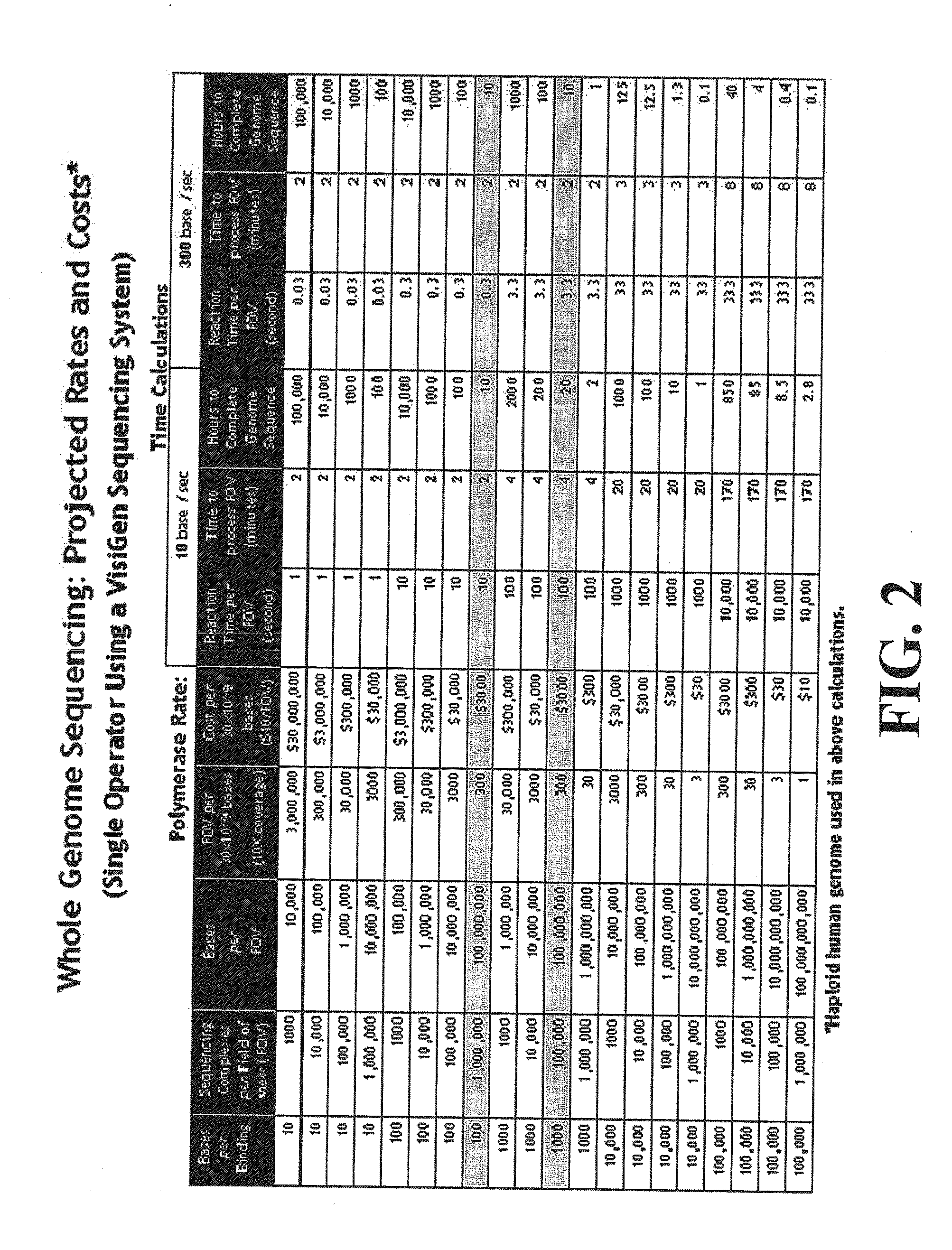
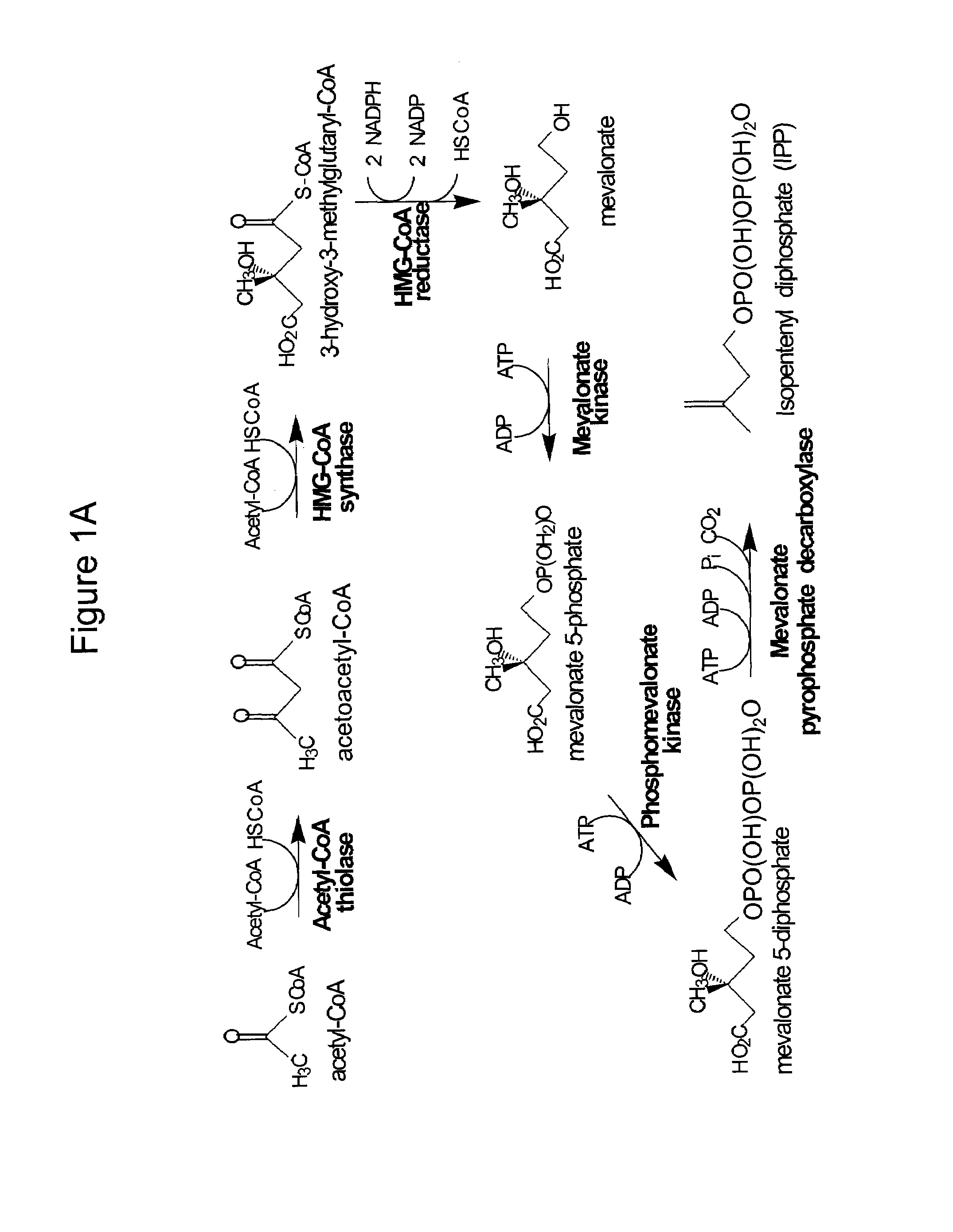
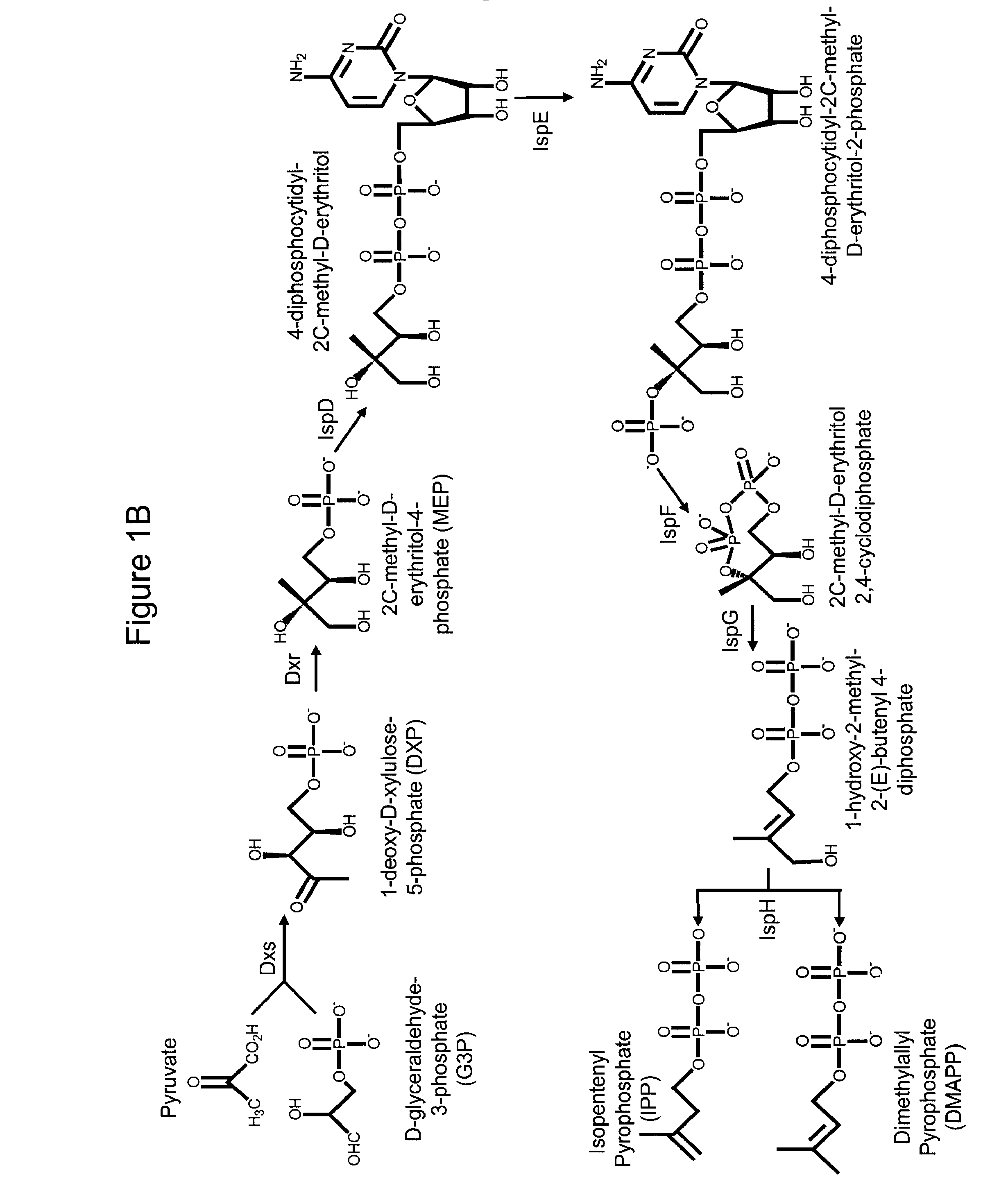
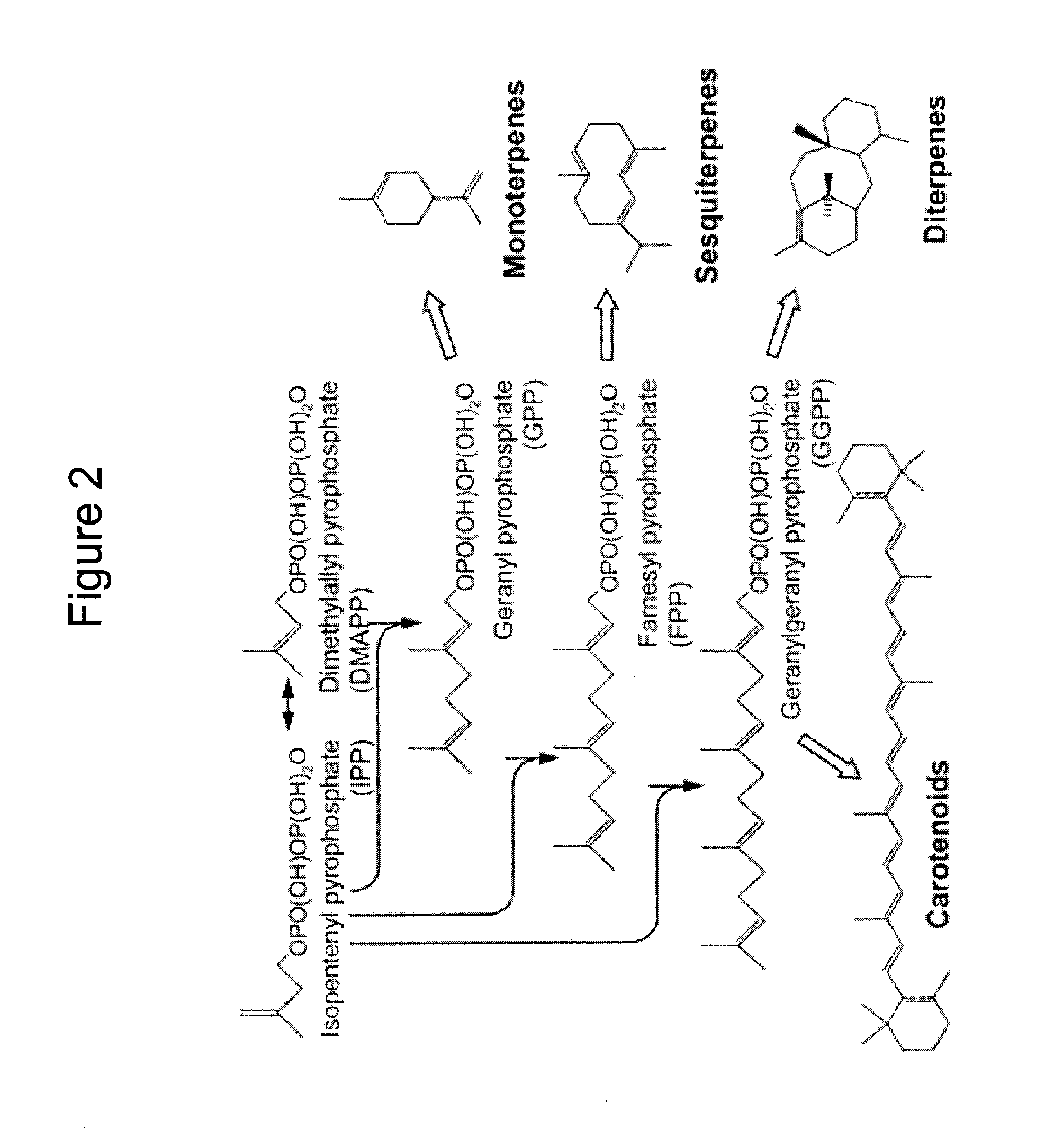
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2212 results about "Genetically modify" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
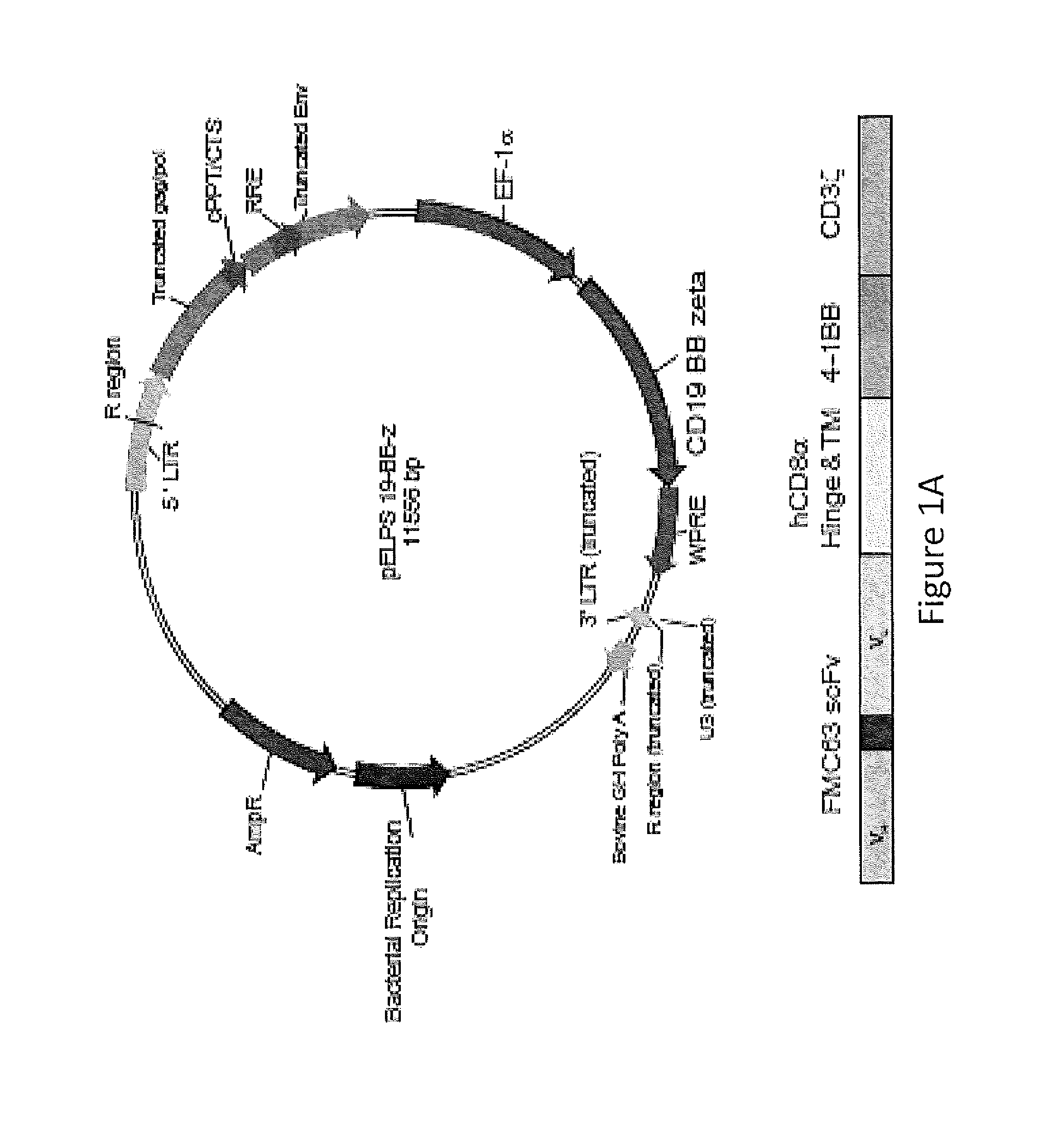
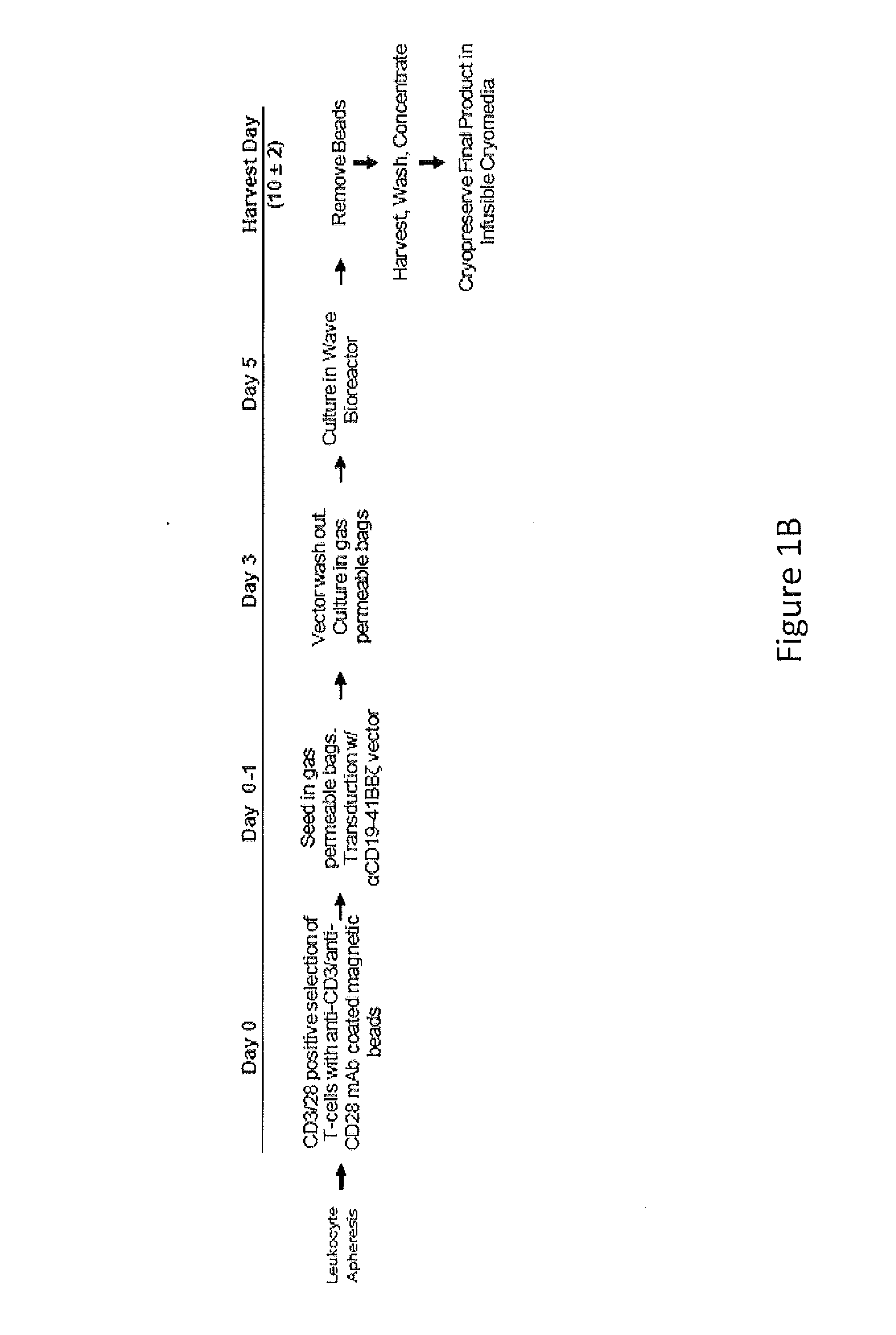
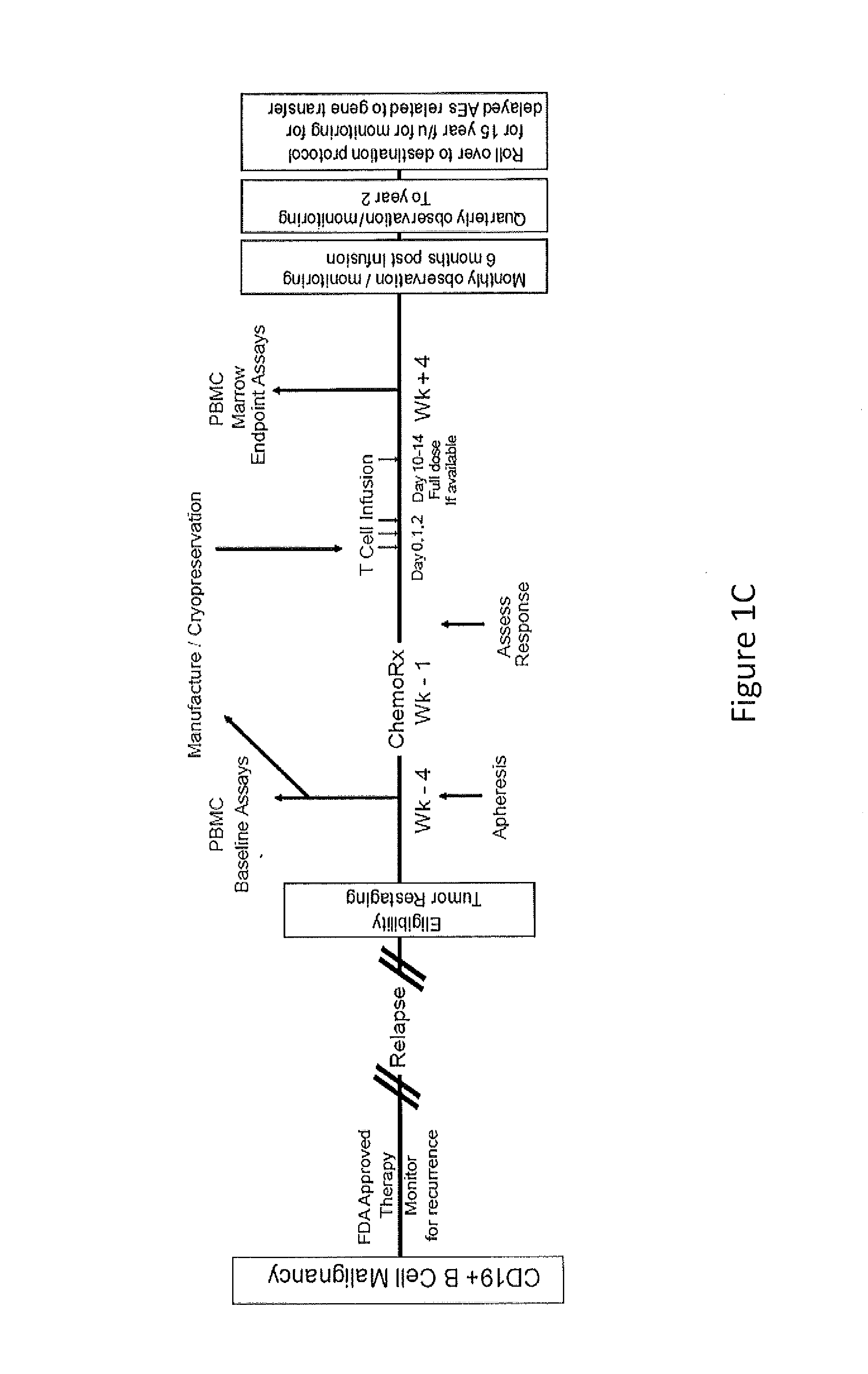
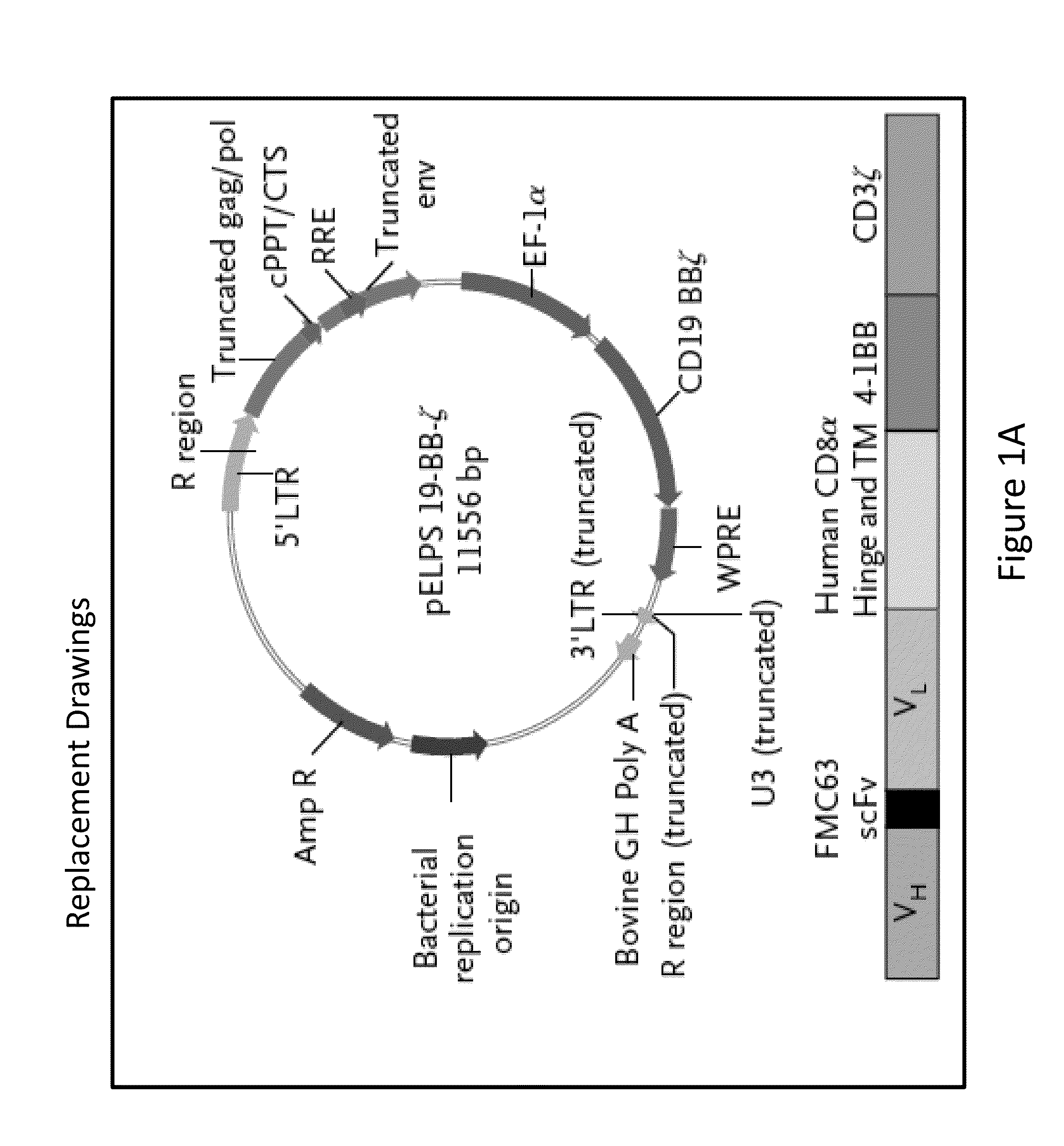
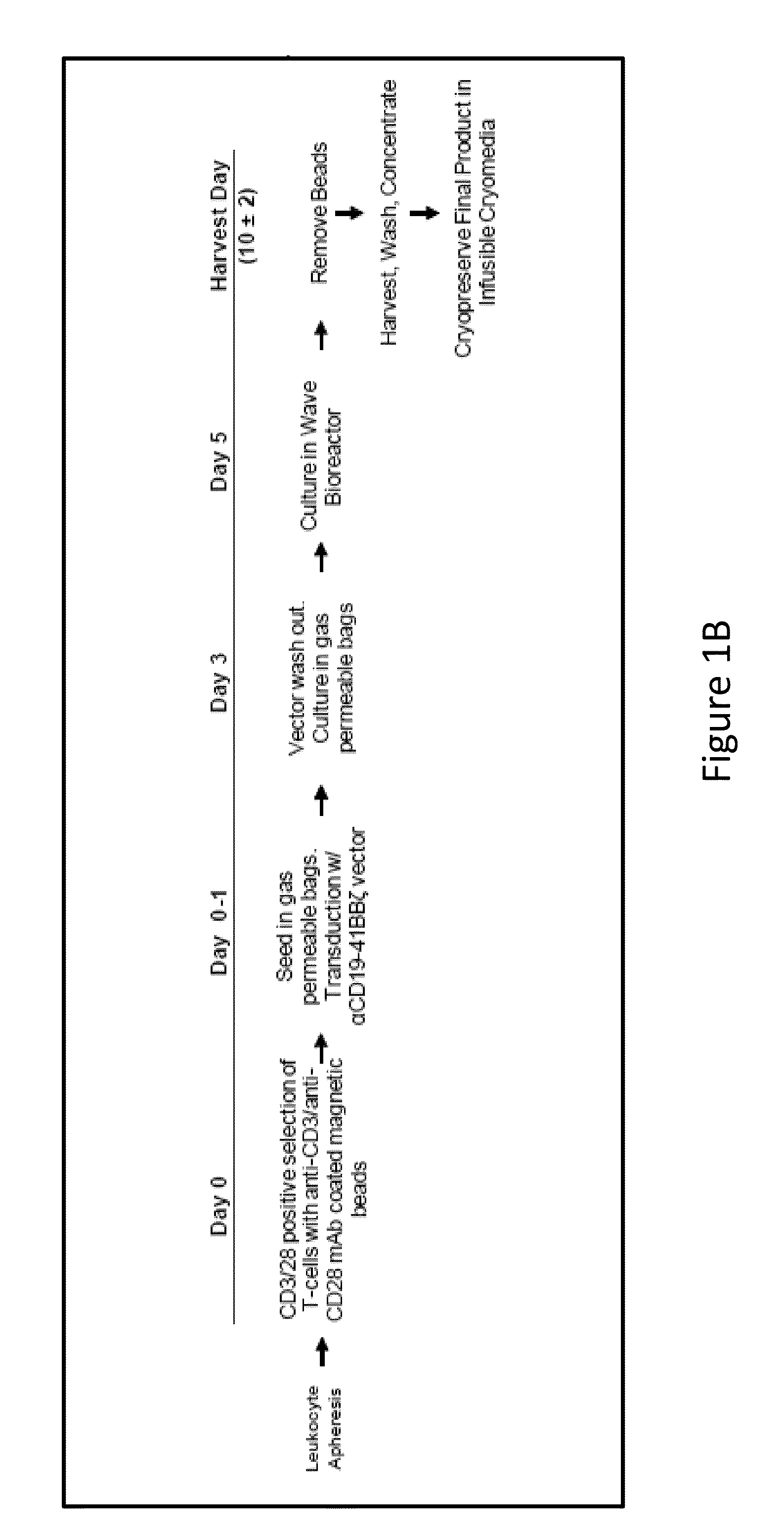
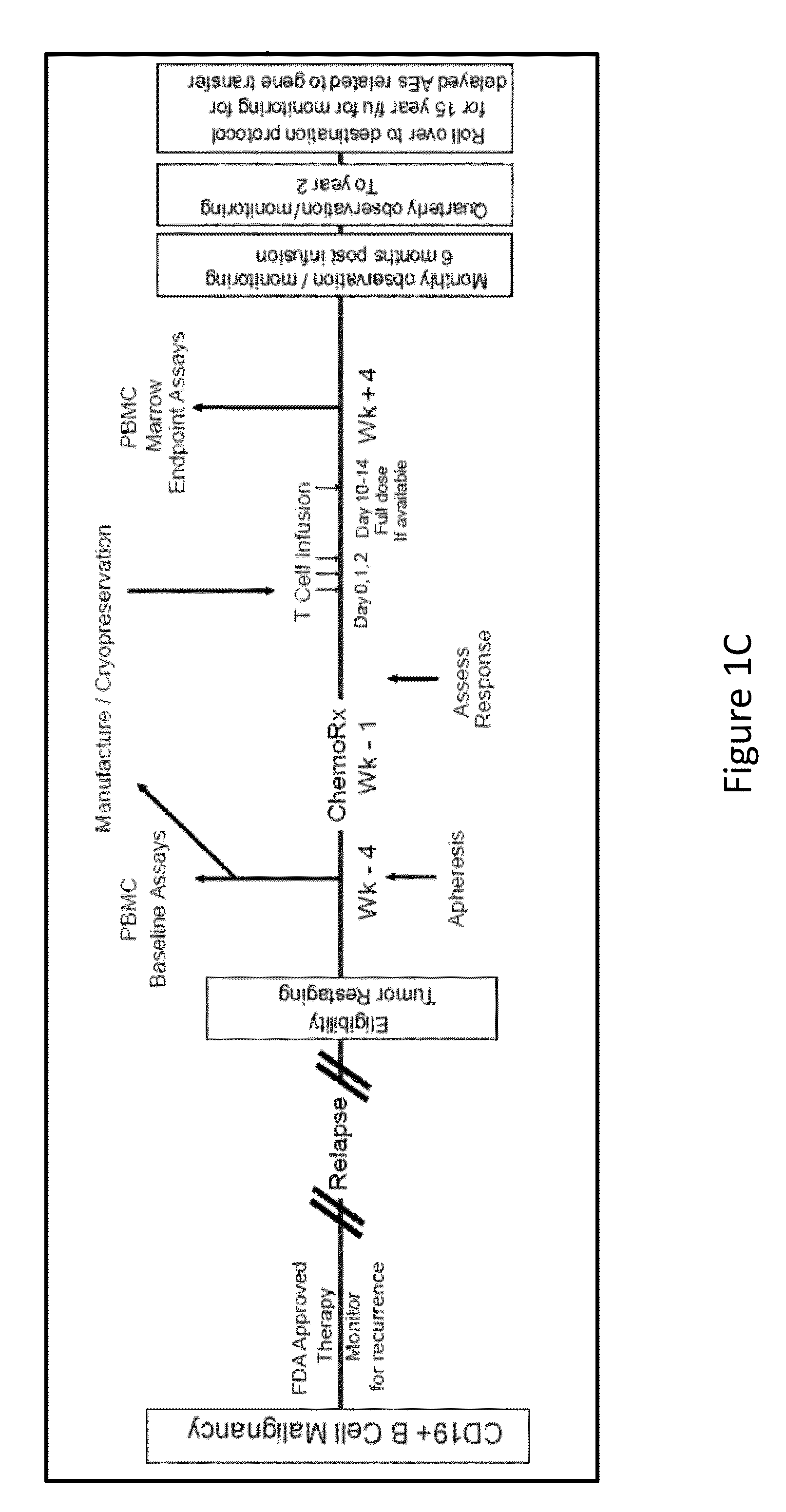
Use of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T-Cells to Treat Cancer
ActiveUS20130287748A1Stimulate immune responseVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding domainAntigen binding
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancer in a human. The invention includes relates to administering a genetically modified T cell to express a CAR wherein the CAR comprises an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain, a costimulatory signaling region, and a CD3 zeta signaling domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods of making conditioned cell culture medium compositions
InactiveUS6372494B1Eliminate wrinklesEliminate frown lineCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsReserve CellCell culture media
Novel products comprising conditioned cell culture medium compositions and methods of use are described. The conditioned cell medium compositions of the invention may be comprised of any known defined or undefined medium and may be conditioned using any eukaryotic cell type. The medium may be conditioned by stromal cells, parenchymal cells, mesenchymal stem cells, liver reserve cells, neural stem cells, pancreatic stem cells and / or embryonic stem cells. Additionally, the cells may be genetically modified. A three-dimensional tissue construct is preferred. Once the cell medium of the invention is conditioned, it may be used in any state. Physical embodiments of the conditioned medium include, but are not limited to, liquid or solid, frozen, lyophilized or dried into a powder. Additionally, the medium is formulated with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier as a vehicle for internal administration, applied directly to a food item or product, formulated with a salve or ointment for topical applications, or, for example, made into or added to surgical glue to accelerate healing of sutures following invasive procedures. Also, the medium may be further processed to concentrate or reduce one or more factors or components contained within the medium.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Nucleic acids and polypeptides of invertebrate TWIK channels and methods of use
Tandem pore domain weak inward rectifying K+ (TWIK) channel nucleic acids and proteins that have been isolated from Drosophila melanogaster and Leptinotarsa are described. The TWIK channel nucleic acids and proteins can be used to genetically modify metazoan invertebrate organisms, such as insects, coelomates, and pseudocoelomates, or cultured cells, resulting in TWIK channel expression or mis-expression. The genetically modified organisms or cells can be used in screening assays to identify candidate compounds which are potential pesticidal agents or therapeutics that interact with TWIK channel proteins. They can also be used in methods for studying TWIK channel activity and identifying other genes that modulate the function of, or interact with, the TWIK channel gene.
Owner:EXELIXIS PHARMA
Targeted modification of rat genome
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a rat genomic locus of interest using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified rat comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided. Compositions and methods are provided which comprise a genetically modified rat or rat cell comprising a targeted genetic modification in the rat interleukin-2 receptor gamma locus, the rat ApoE locus, the rat Rag2 locus, the rat Rag1 locus and / or the rat Rag2 / Rag1 locus. The various methods and compositions provided herein allows for these modified loci to be transmitted through the germline.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods and Compositions for the Targeted Modification of a Genome
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a genomic locus of interest in a eukaryotic cell, a mammalian cell, a human cell or a non-human mammalian cell using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Further methods combine the use of the LTVEC with a CRISPR / Cas system. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified non-human animal comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Method for facilitating pathogen resistance
InactiveUS20030150017A1Convenient researchImprove developmentClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesDNA constructNucleotide
Methods are provided for the genetic control of pathogen infestation in host organisms such as plants, vertebrate animals and fungi. Such methods utilize the host as a delivery system for the delivery of genetic agents, preferably in the form of RNA molecules, to a pathogen, which agents cause directly or indirectly an impairment in the ability of the pathogen to maintain itself, grow or otherwise infest a host plant, vertebrate animal or fungus. Also provided are DNA constructs and novel nematode nucleotide sequences for use in same, that facilitate pathogen resistance when expressed in a genetically-modified host. Such constructs direct the expression of RNA molecules substantially homologous and / or complementary to an RNA molecule encoded by a nucleotide sequence within the genome of a pathogen and / or of the cells of a host to effect down-regulation of the nucleotide sequence. Particular hosts contemplated are plants, such as pineapple plants, and particular pathogens are nematodes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND +1
Endoribonuclease compositions and methods of use thereof
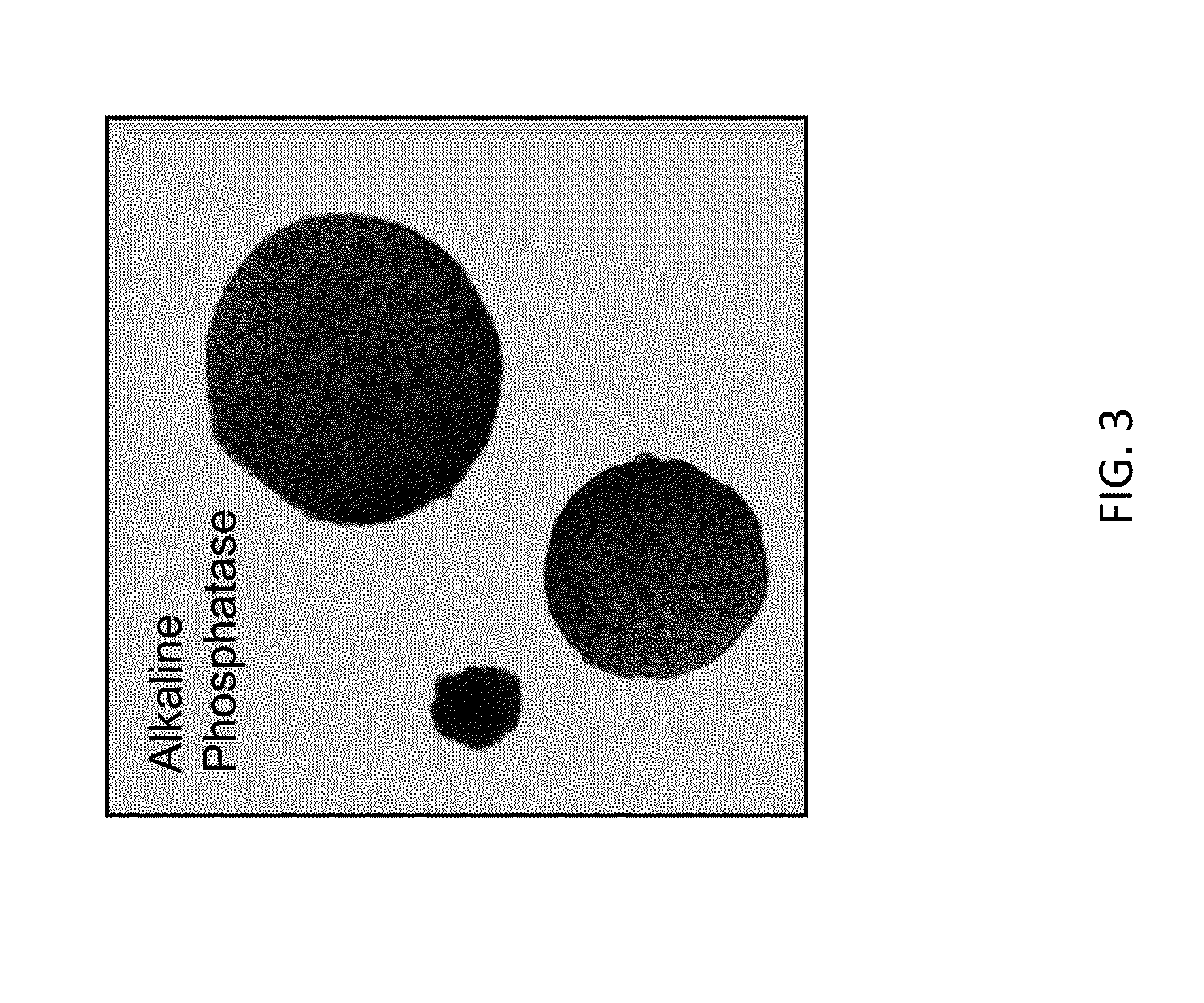
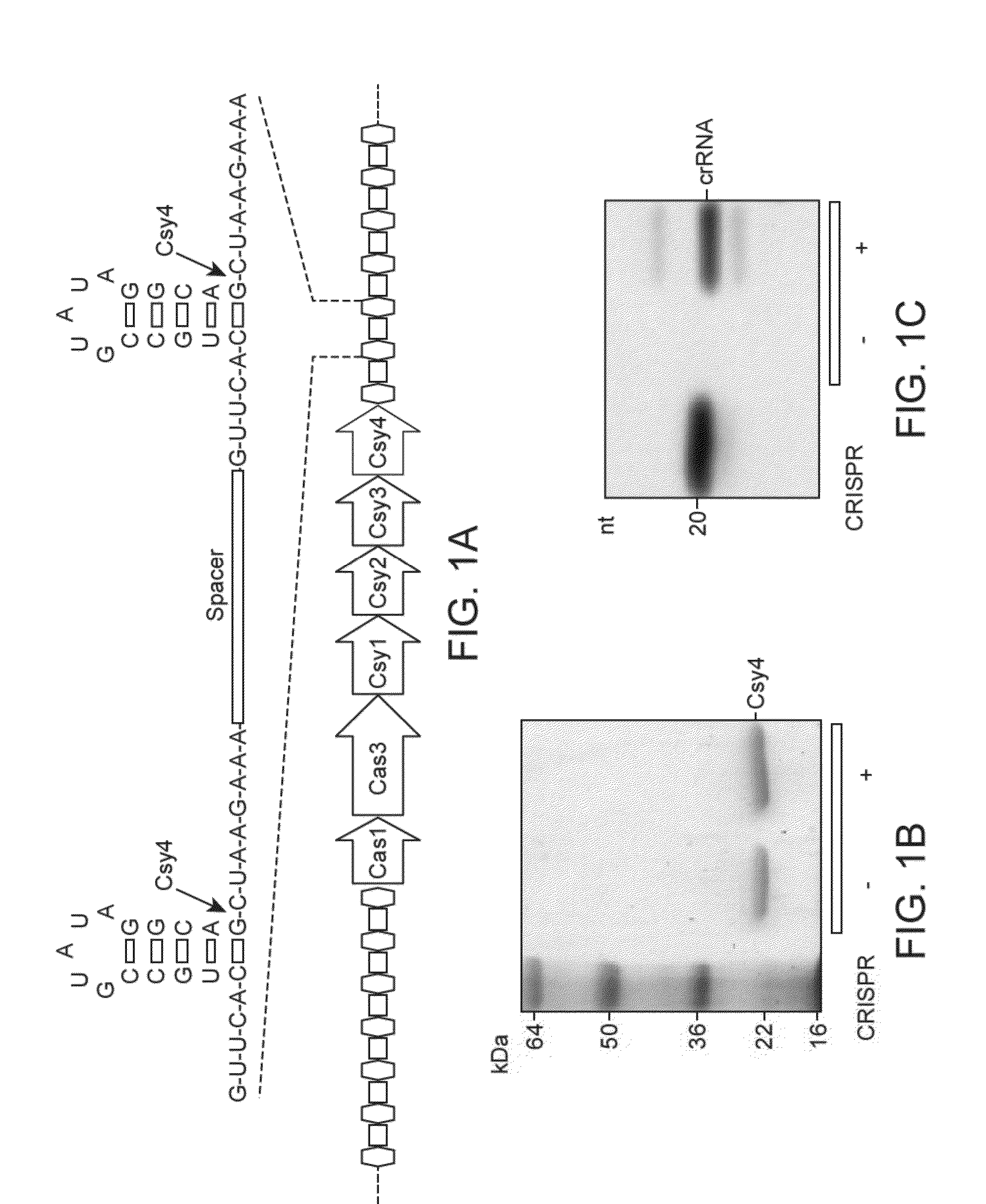
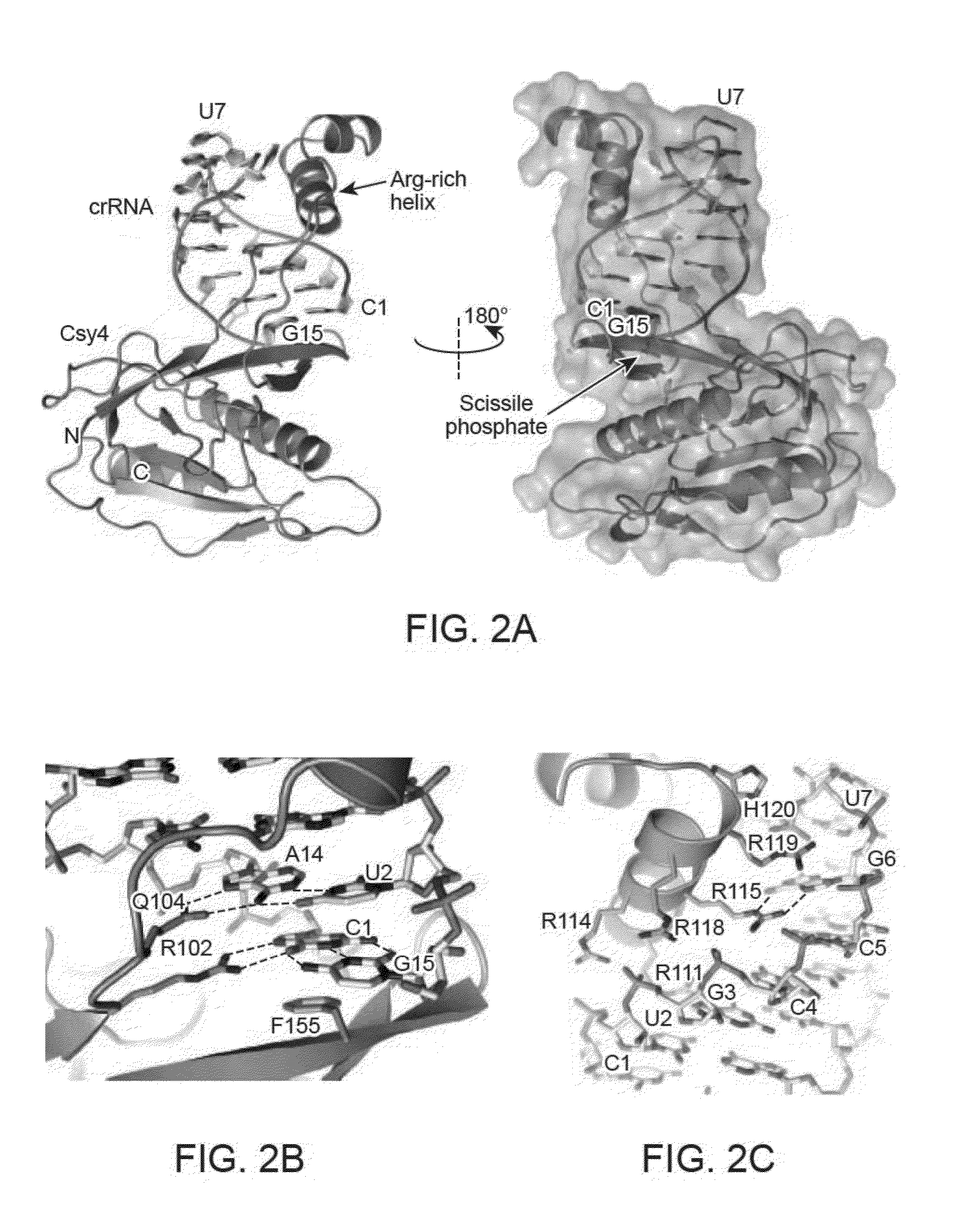
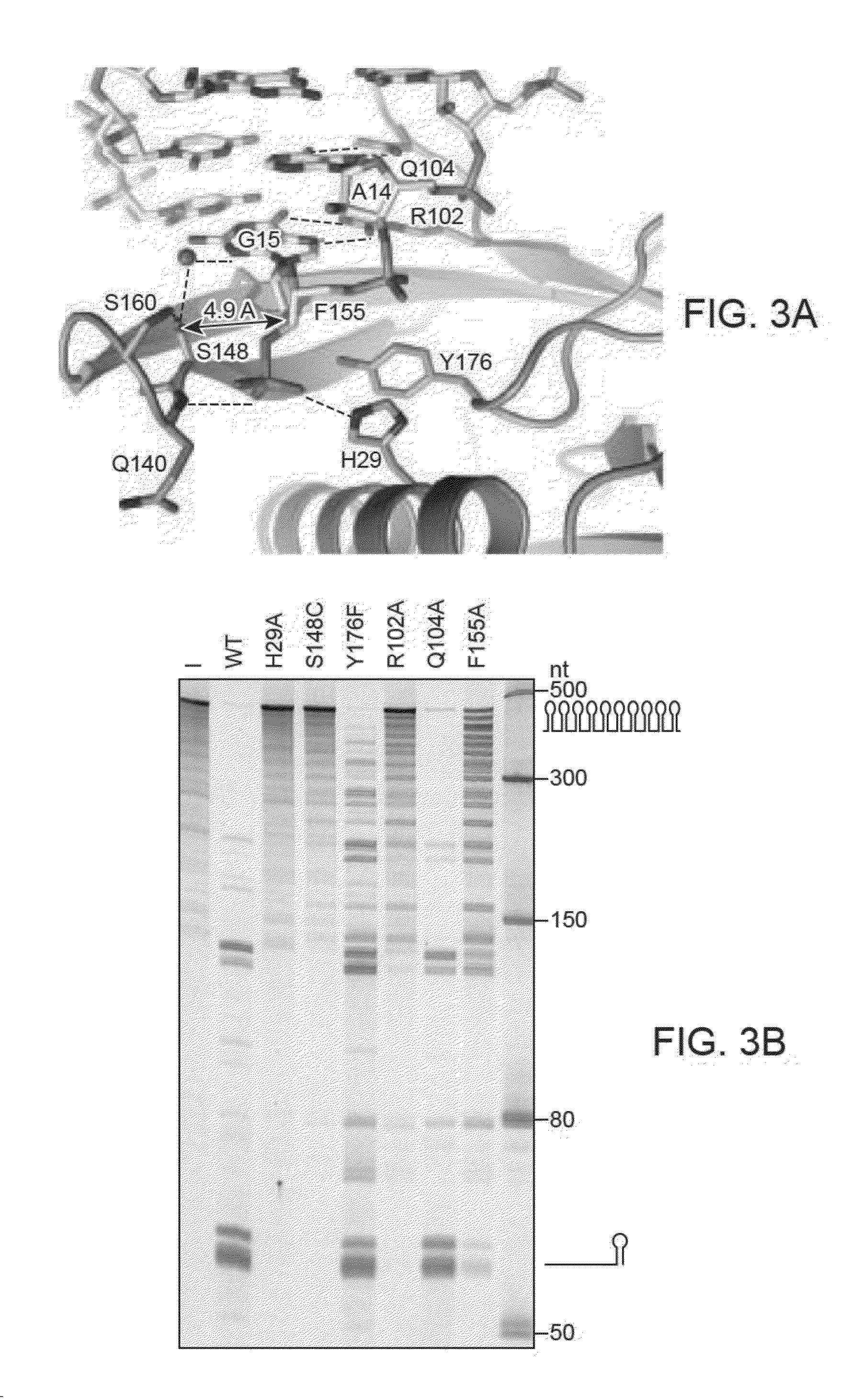
The present disclosure provides variant Csy4 endoribonucleases, nucleic acids encoding the variant Csy4 endoribonucleases, and host cells genetically modified with the nucleic acids. The variant Csy4 endoribonucleases find use in a variety of applications, which are also provided. The present disclosure also provides methods of detecting a specific sequence in a target polyribonucleotide; and methods of regulating production of a target RNA in a eukaryotic cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Targeted modification of rat genome
InactiveUS20140309487A1Enhance homologous recombinationAnimal reproductionApolipeptidesRAG2Nucleic acid sequencing
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a rat genomic locus of interest using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified rat comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided. Compositions and methods are provided which comprise a genetically modified rat or rat cell comprising a targeted genetic modification in the rat interleukin-2 receptor gamma locus, the rat ApoE locus, the rat Rag2 locus, the rat Rag1 locus and / or the rat Rag2 / Rag1 locus. The various methods and compositions provided herein allows for these modified loci to be transmitted through the germline.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
TREATMENT OF CANCER USING HUMANIZED ANTI-EGFRvIII CHIMERIC ANTIGEN RECEPTOR
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating diseases associated with expression of EGFRvIII. The invention also relates to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific to EGFRvIII, vectors encoding the same, and recombinant T cells comprising the anti-EGFRvIII CAR. The invention also includes methods of administering a genetically modified T cell expressing a CAR that comprises an anti-EGFRvIII binding domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +2
CICM cells and non-human mammalian embryos prepared by nuclear transfer of a proliferating differentiated cell or its nucleus
InactiveUS6235970B1Simple procedureSimplifying and facilitating procedureNervous disorderMuscular disorderPresent methodNuclear transfer
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of the same species as the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring, and for production of isogenic CICM cells, including human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic mammalian embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST
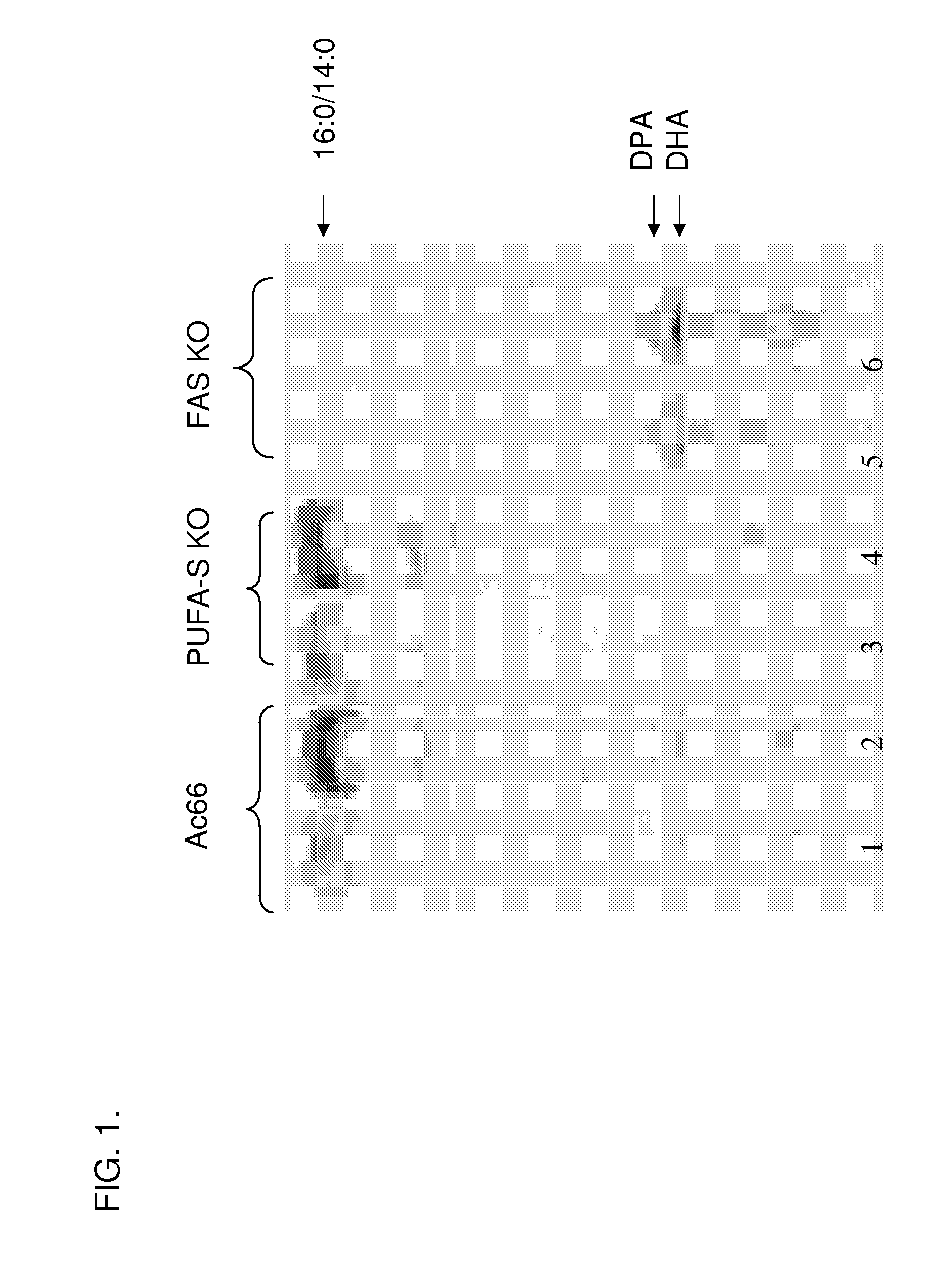
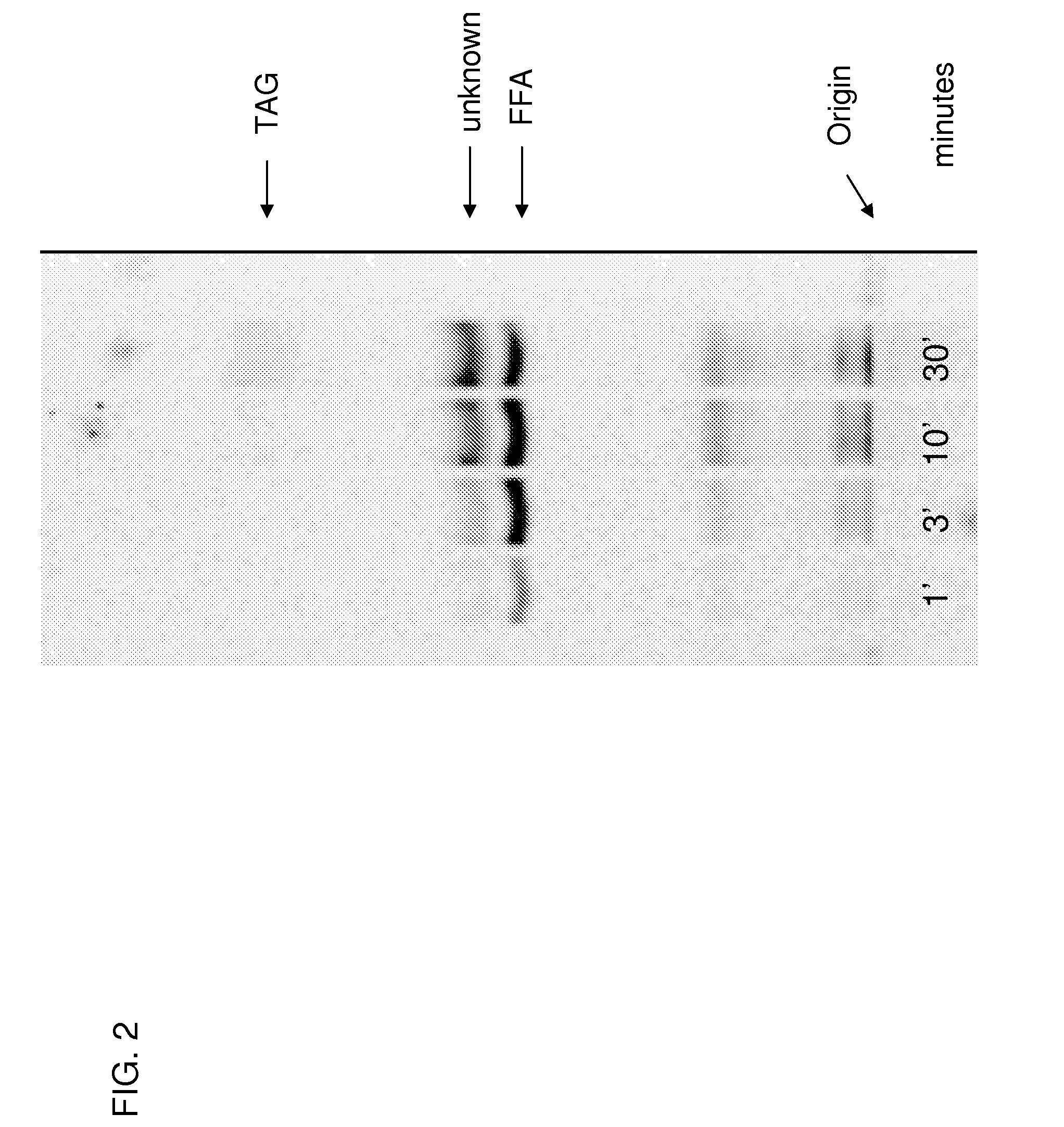
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using PUFA polyketide synthase systems
InactiveUS20070245431A1Improve the level ofReduce competitionOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or to increase the level of malonyl CoA in the plant or plant cell, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils obtained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:SEMBIOSYS GENETICS INC +1
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
InactiveUS7271315B2BryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesLipid formationBiotechnology
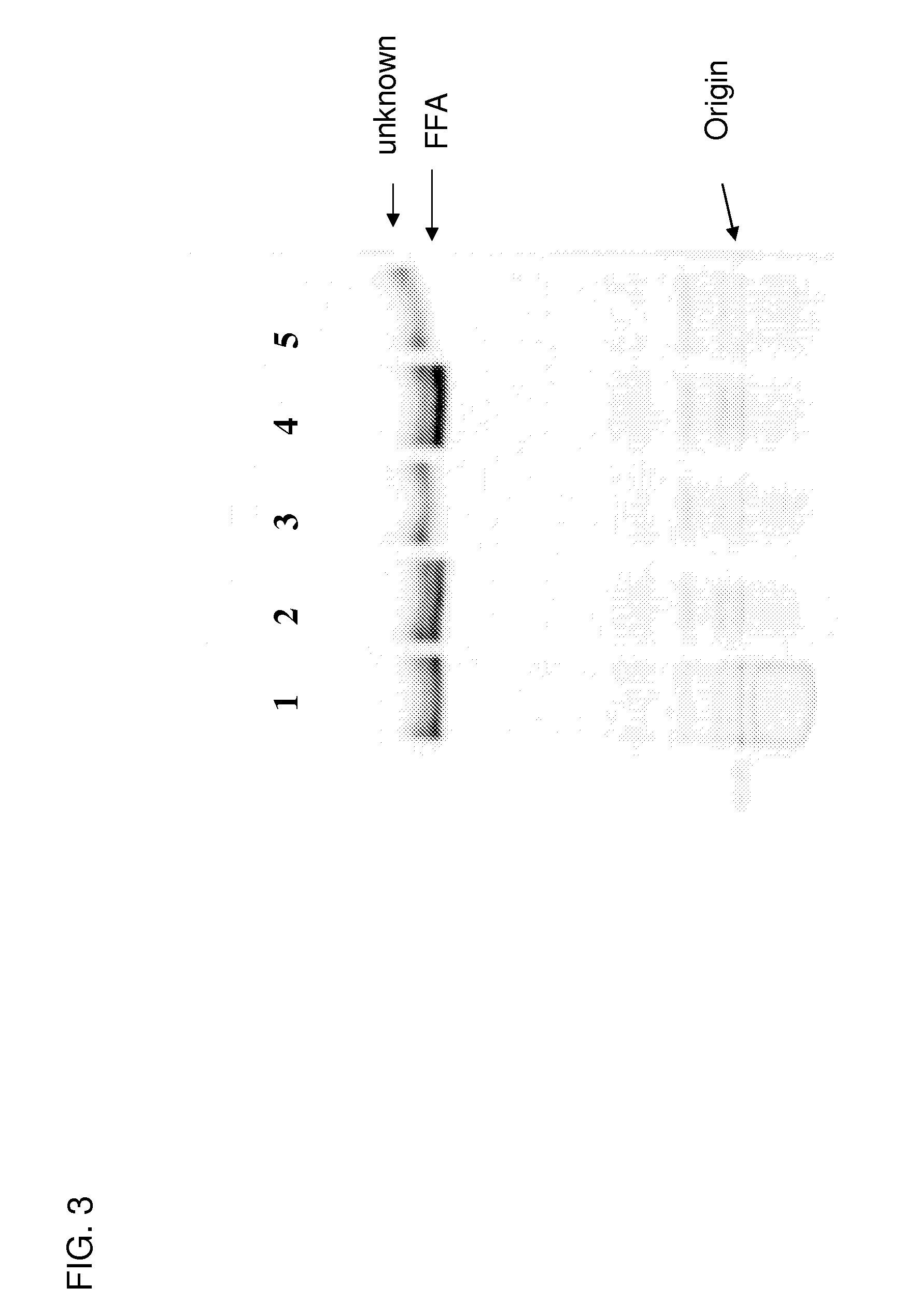
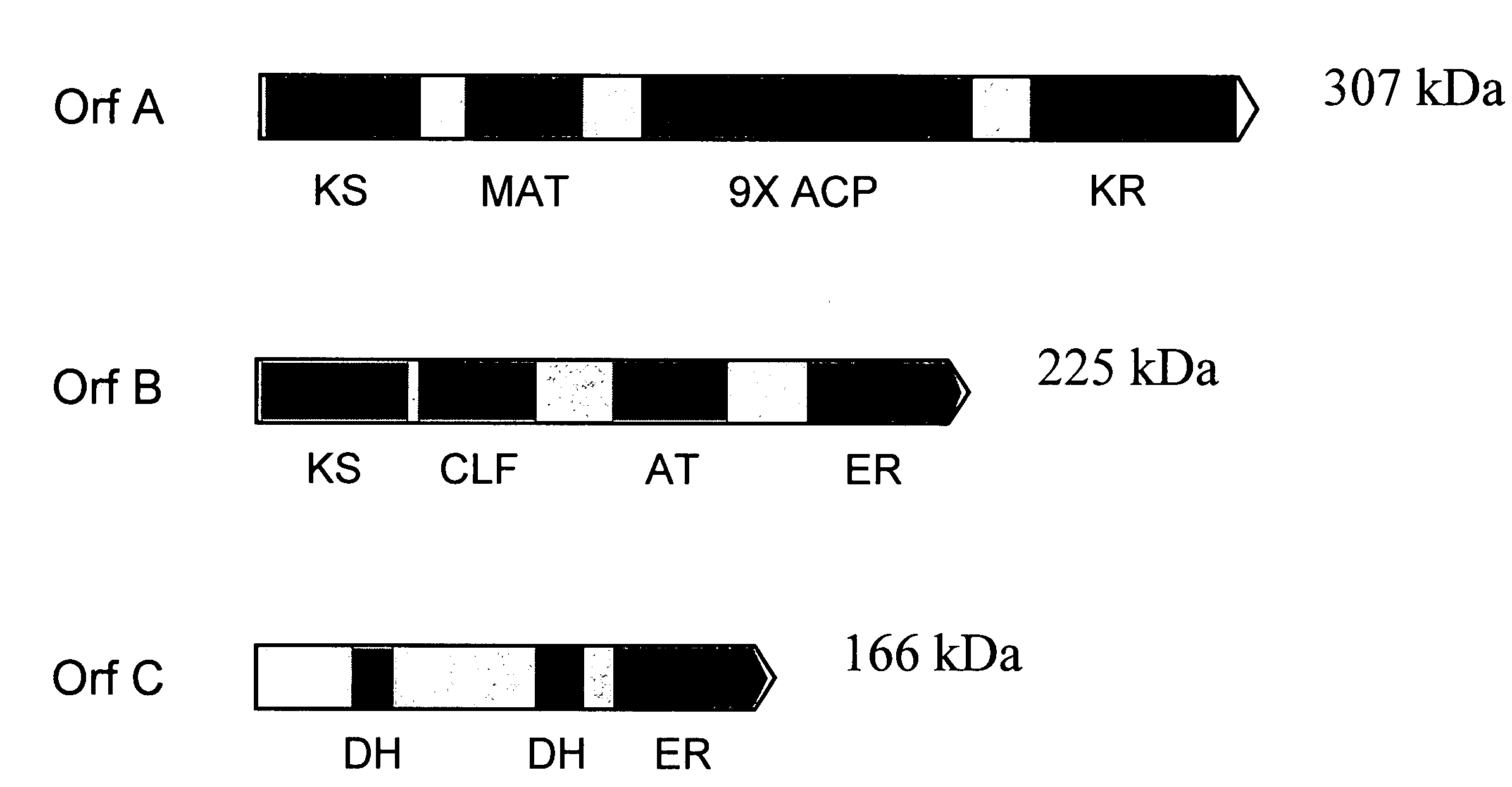
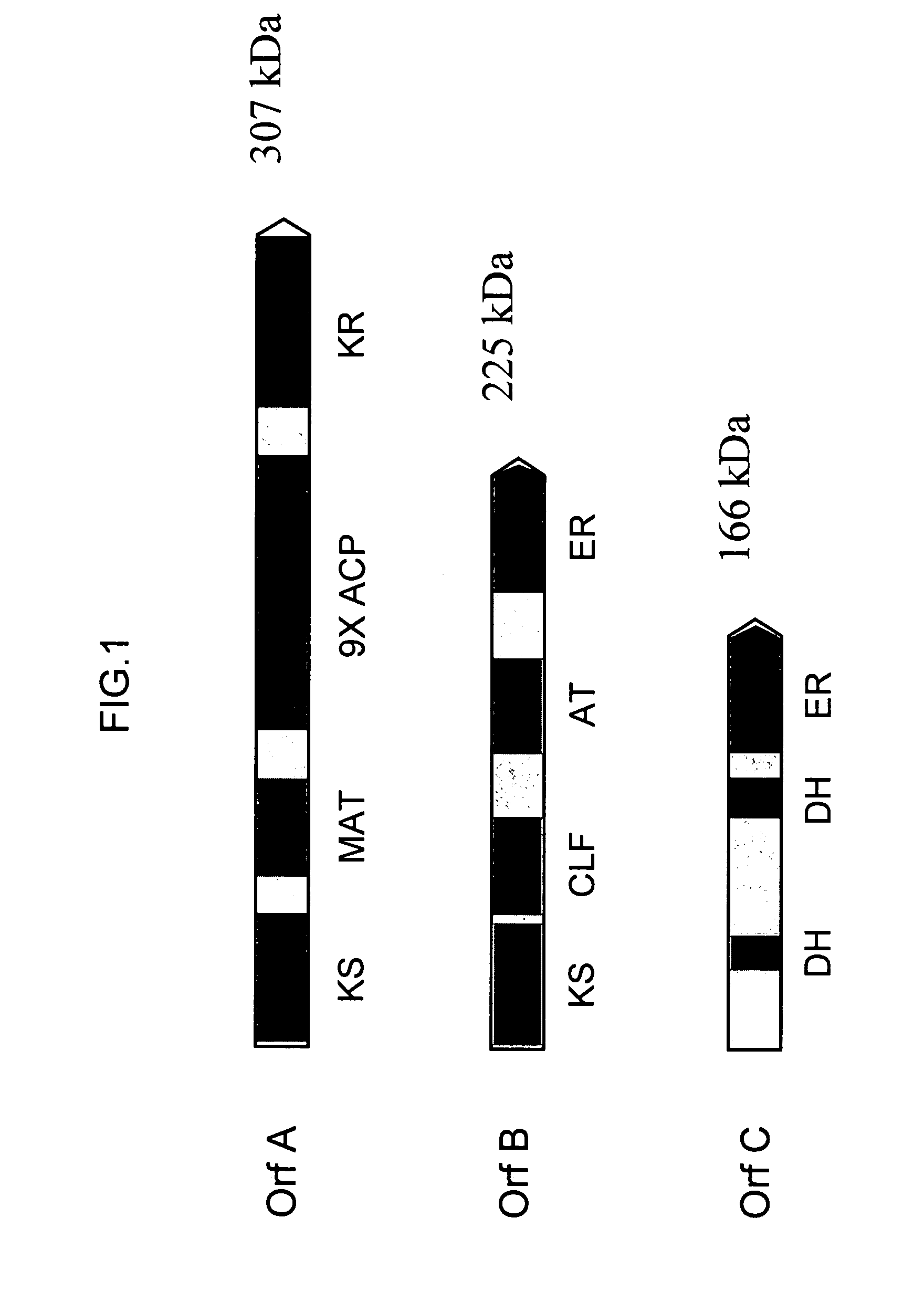
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from Schizochytrium, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
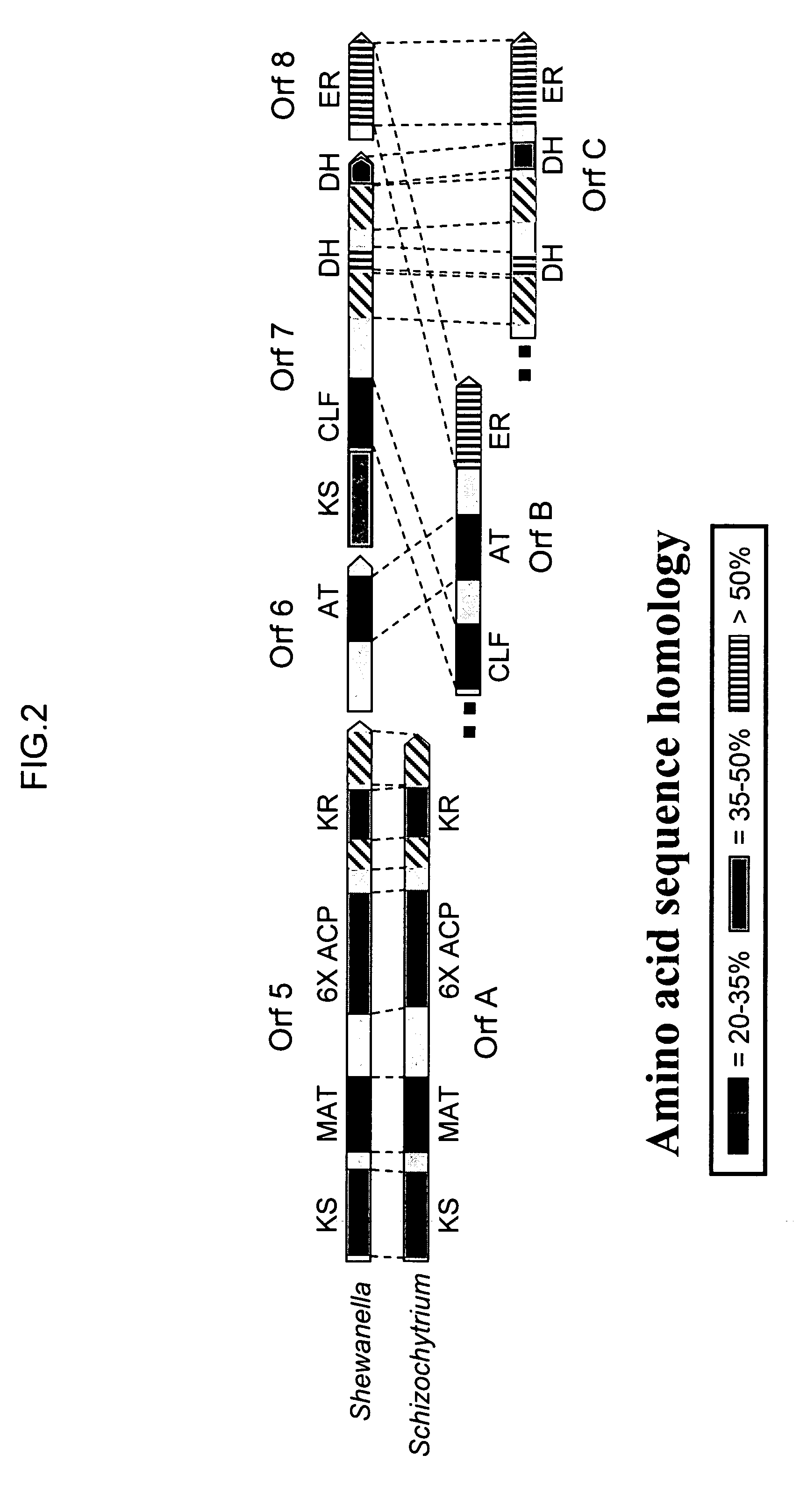
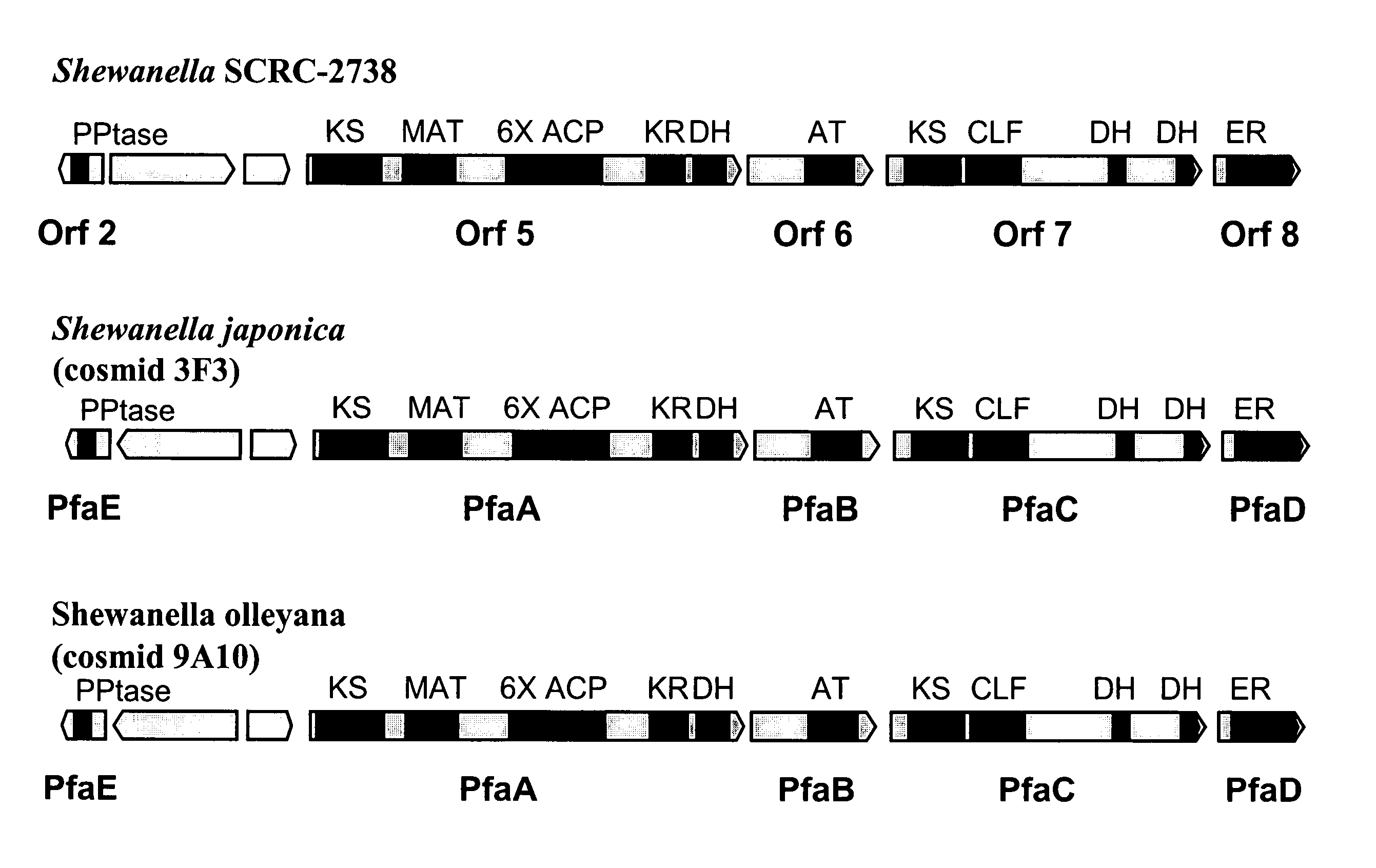
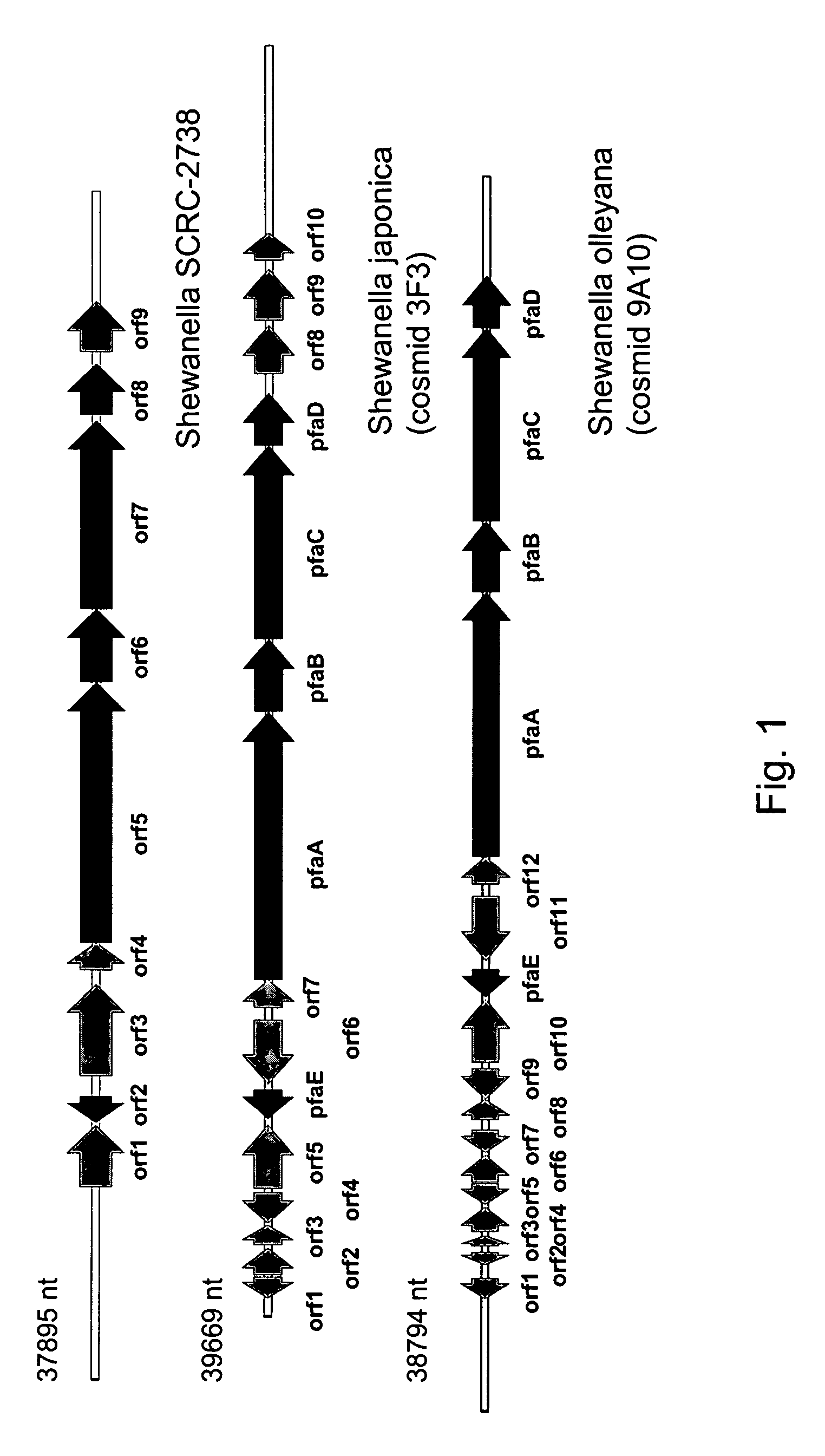
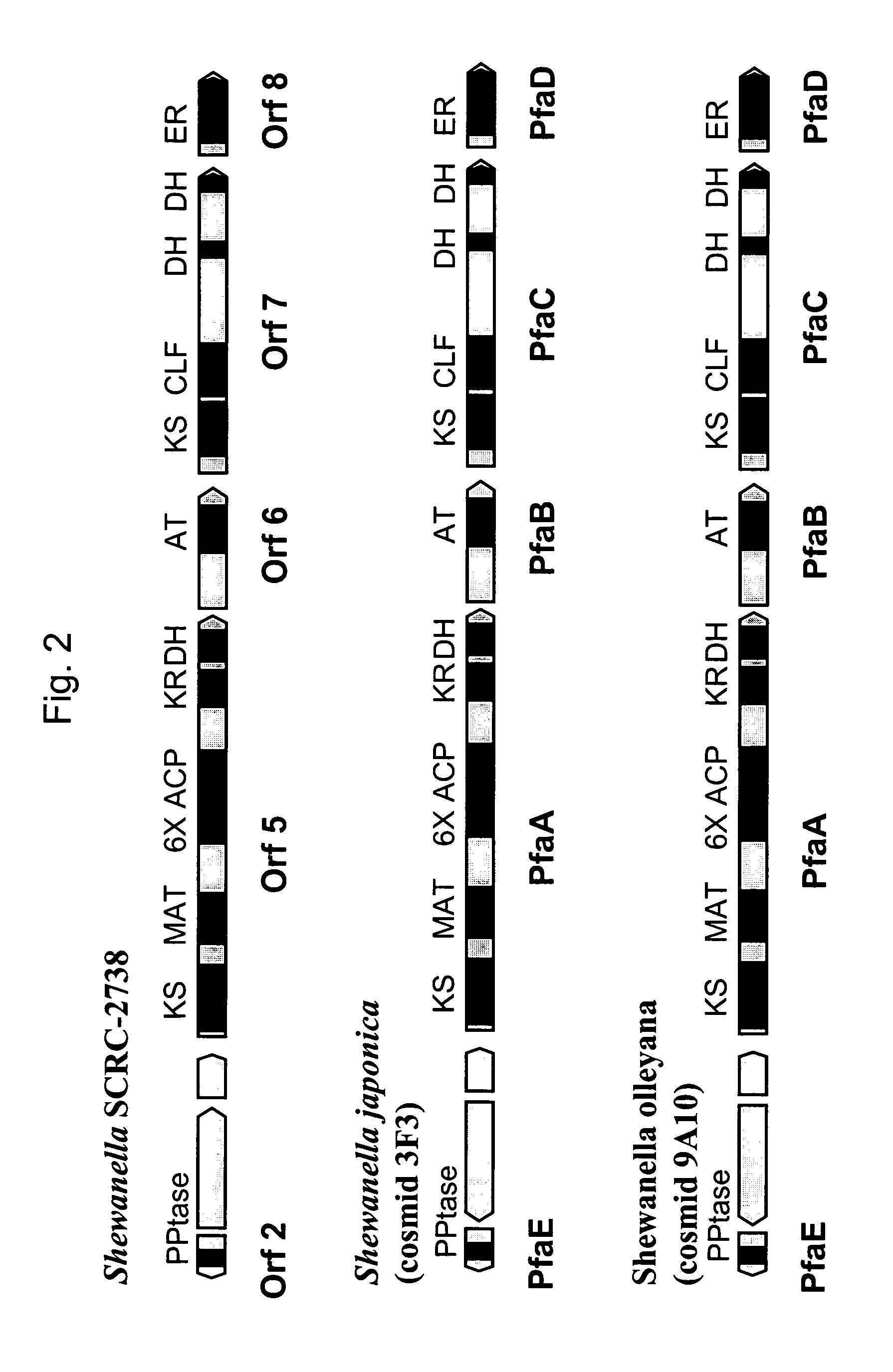
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from the bacterial microorganisms Shewanella japonica and Shewanella olleyana, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Methods and compositions for the targeted modification of a genome
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a genomic locus of interest in a eukaryotic cell, a mammalian cell, a human cell or a non-human mammalian cell using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Further methods combine the use of the LTVEC with a CRISPR / Cas system. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified non-human animal comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Compositions, methods and systems for single molecule sequencing
InactiveUS20110165652A1Enhanced signalReduce background noiseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSynthesis methods
Compositions, systems and methods of sequencing are disclosed, where the compositions and systems include polymerase enzymes that have been genetically modified to more efficiently incorporate nucleotides including labels having a detectable properties that are released during incorporation, to augment a rate of labeled nucleotide incorporation, to augment a rate of pyrophosphate release, or to augment two or more of these properties and rates. Also disclosed are terminally labeled and dual labeled nucleotides, and click-chemistry based methods of synthesizing the same.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
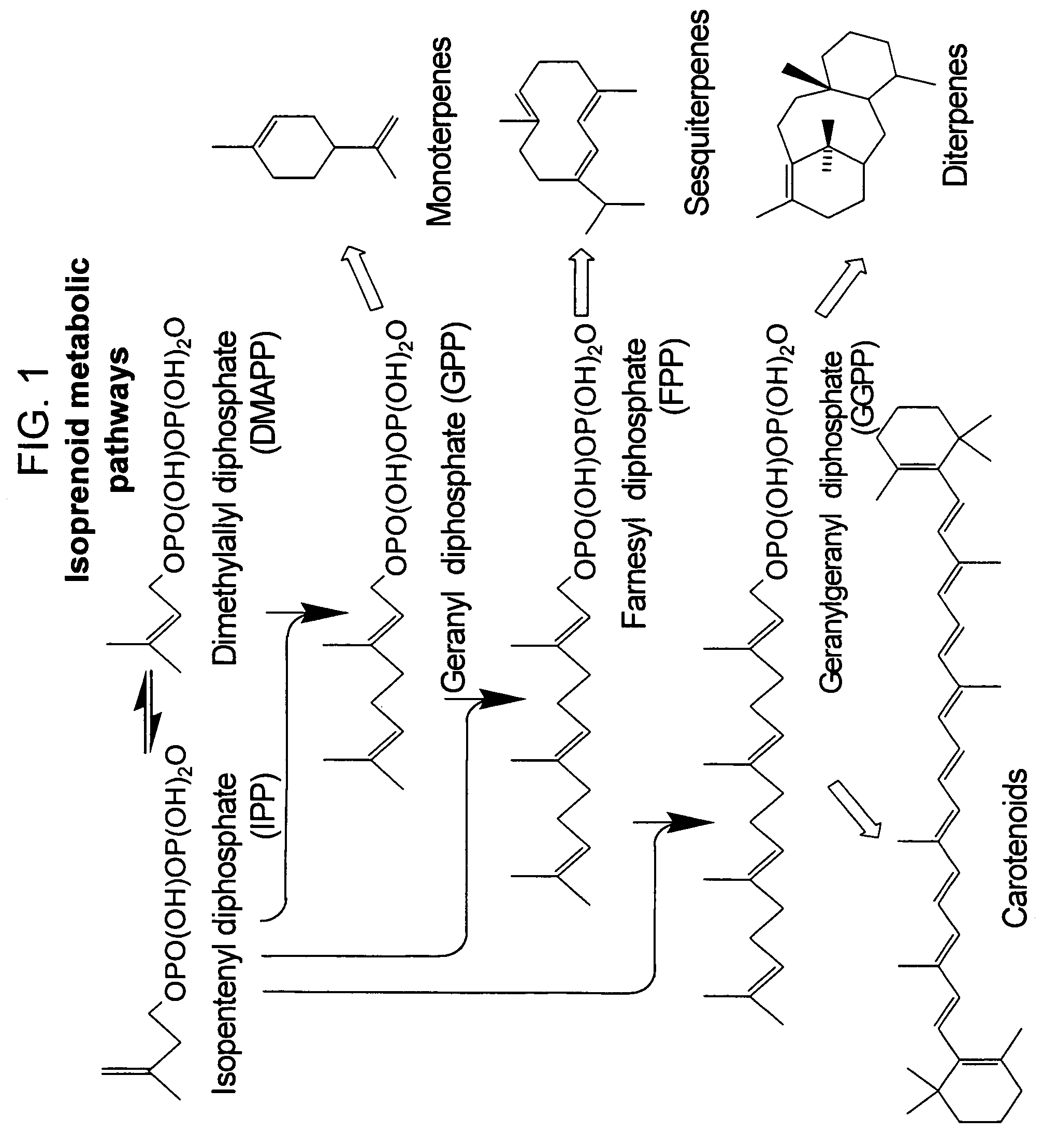
Production of isoprenoids
The present invention provides methods for a robust production of isoprenoids via one or more biosynthetic pathways. The invention also provides nucleic acids, enzymes, expression vectors, and genetically modified host cells for carrying out the subject methods. The invention also provides fermentation methods for high productivity of isoprenoids from genetically modified host cells.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
ActiveUS20070270494A1Improve the level ofReduce competitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHeterologousAcyl-CoA synthetase
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or to increase the level of malonyl CoA in the organism, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils obtained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
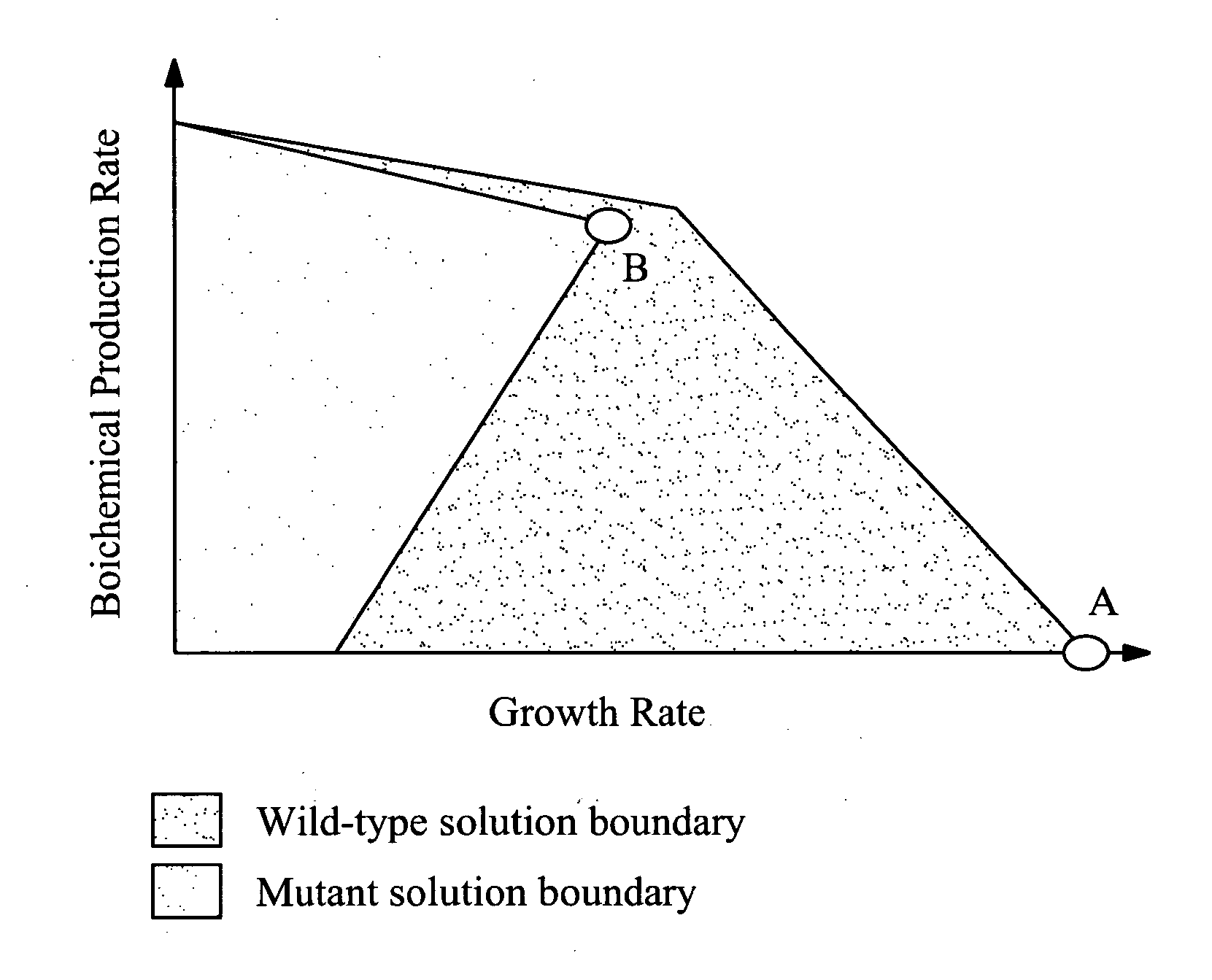
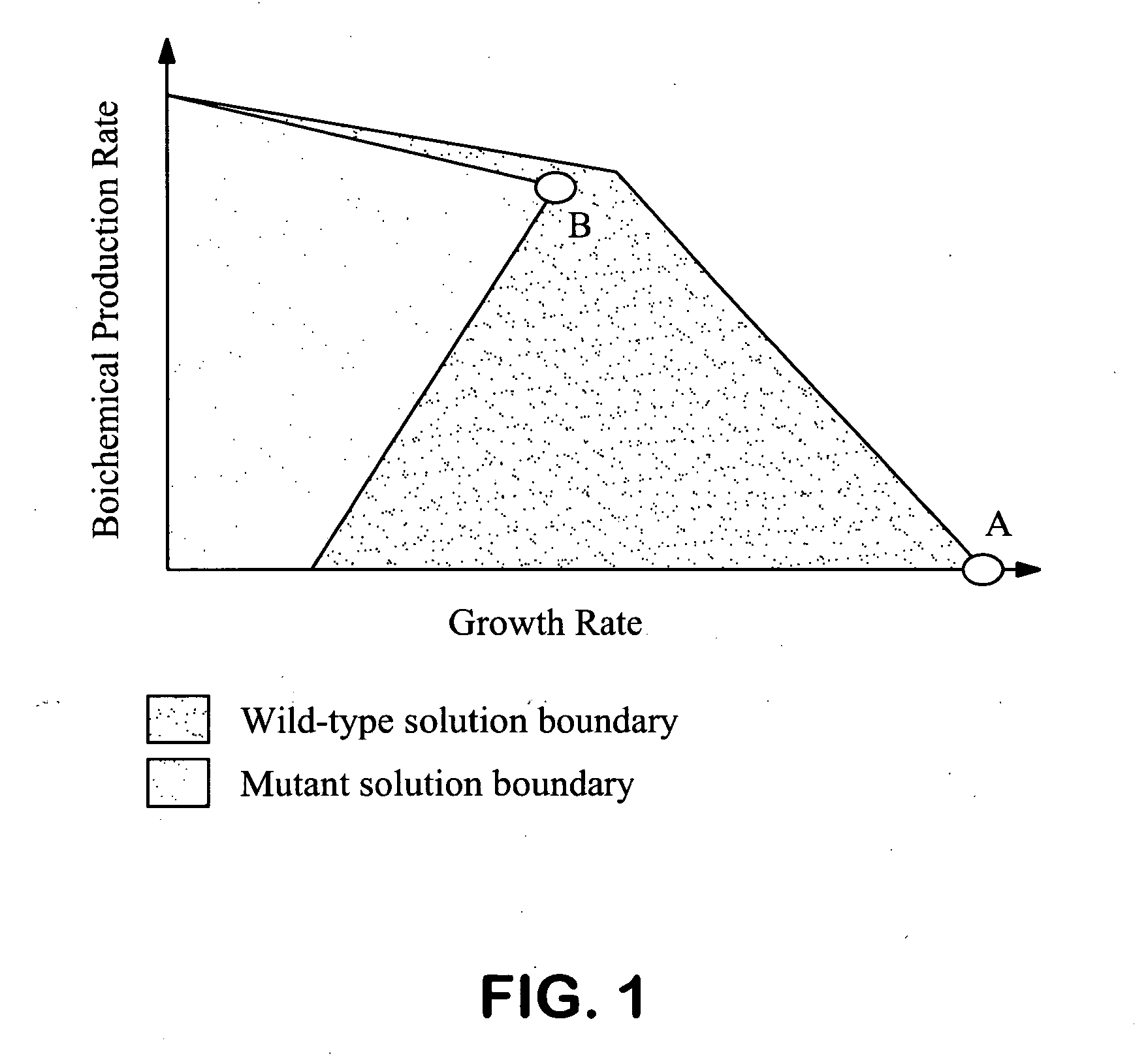
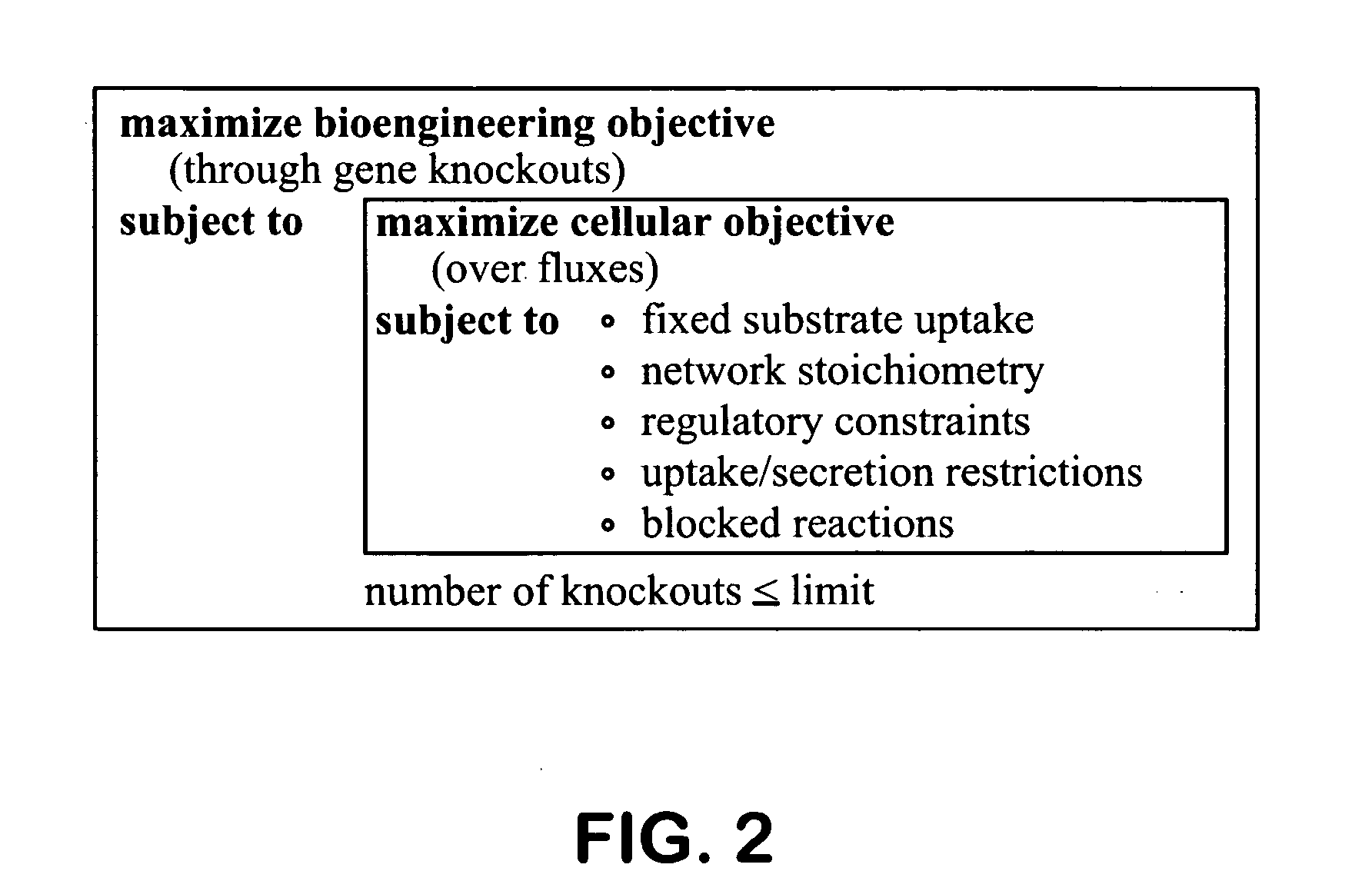
Methods and organisms for the growth-coupled production of succinate
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism comprising one or more gene disruptions encoding an enzyme associated with growth-coupled production of succinate when an activity of the enzyme is reduced, whereby the one or more gene disruptions confers stable growth-coupled production of succinate onto the non- naturally occurring microorganism. Also provided is a non-naturally occurring microorganism comprising a set of metabolic modifications obligatory coupling succinate production to growth of the microorganism, the set of metabolic modifications comprising disruption of one or more genes selected from the set of genes comprising: (a) adhE, ldhA; (b) adhE, ldhA, acka-pta; (c) pfl, ldhA; (d) pfl, ldhA, adhE; (e) acka-pta, pykF, atpF, sdhA; (f) acka-pta, pykF, ptsG, or (g) acka-pta, pykF, ptsG, adhE, ldhA, or an ortholog thereof, wherein the microorganism exhibits stable growth-coupled production of succinate. Additionally provided is a non-naturally occurring microorganism having the genes encoding the metabolic modification (e) acka-pta, pykF, atpF, sdhA that further includes disruption of at least one gene selected from pyka, atpH, sdhB or dhaKLM; a non-naturally occurring microorganism having the genes encoding the metabolic modification (f) ackA-pta, pykF, ptsG that further includes disruption of at least one gene selected from pykA or dhaKLM, or a non-naturally occurring microorganism having the genes encoding the metabolic modification (g) ackA-pta, pykF, ptsG, adhE, ldhA that further includes disruption of at least one gene selected from pykA or dhaKLM. The disruptions can be complete gene disruptions and the non-naturally occurring organisms can include a variety of prokaryotic or eukaryotic microorganisms. A method of producing a non-naturally occurring microorganism having stable growth-coupled production of succinate also is provided. The method includes: (a) identifying in silico a set of metabolic modifications requiring succinate production during exponential growth, and (b) genetically modifying a microorganism to contain the set of metabolic modifications requiring succinate production.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
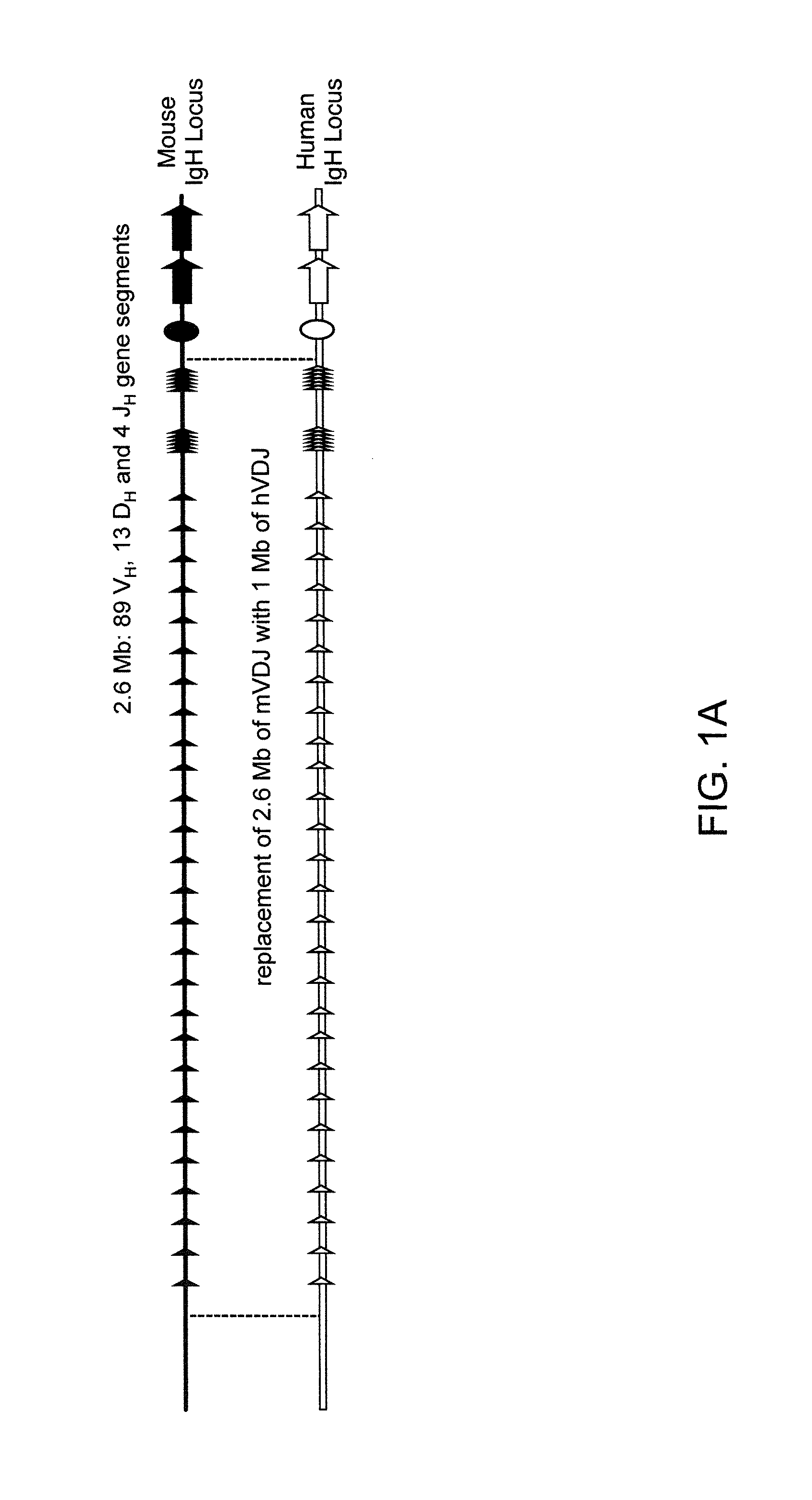
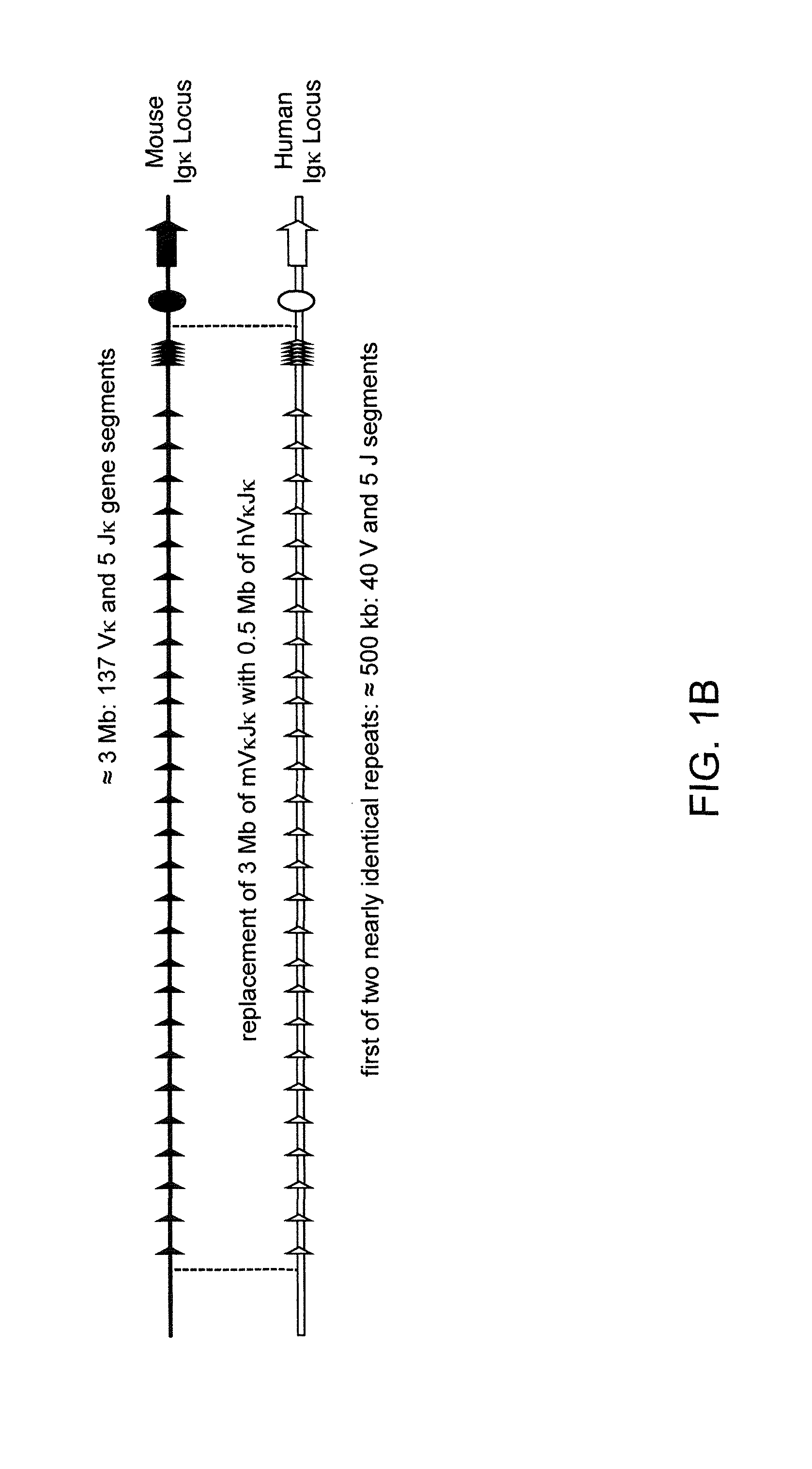
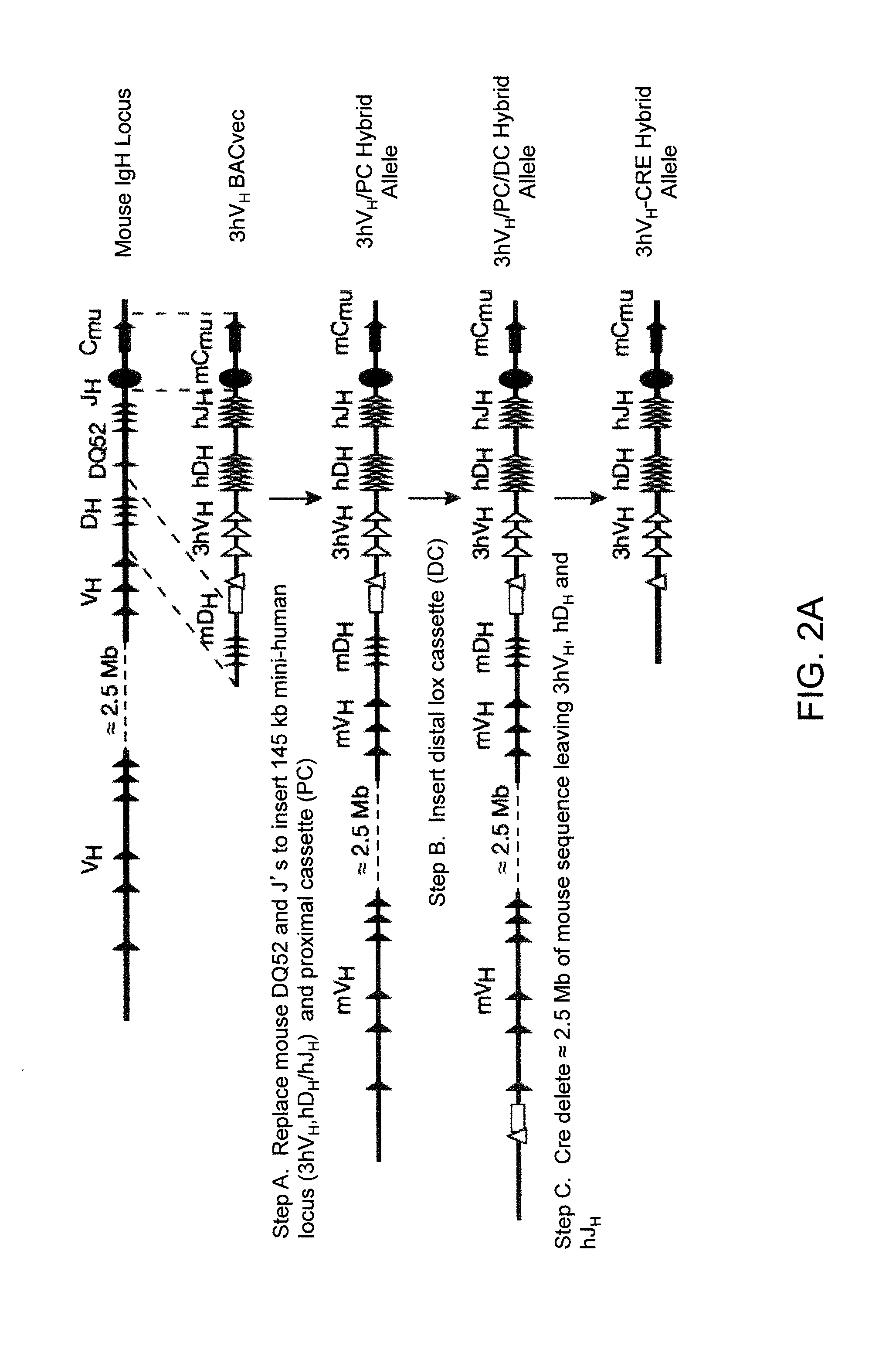
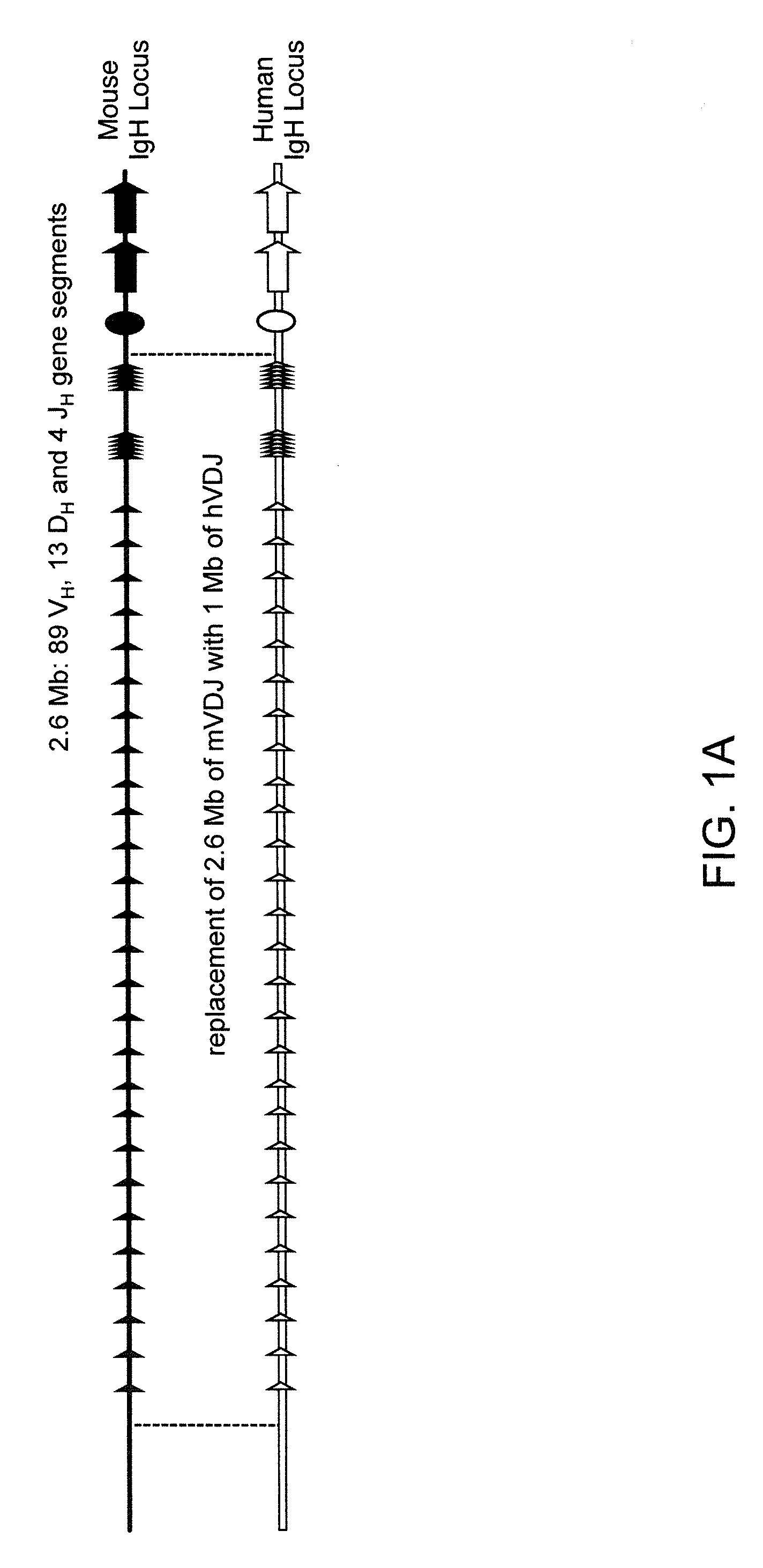
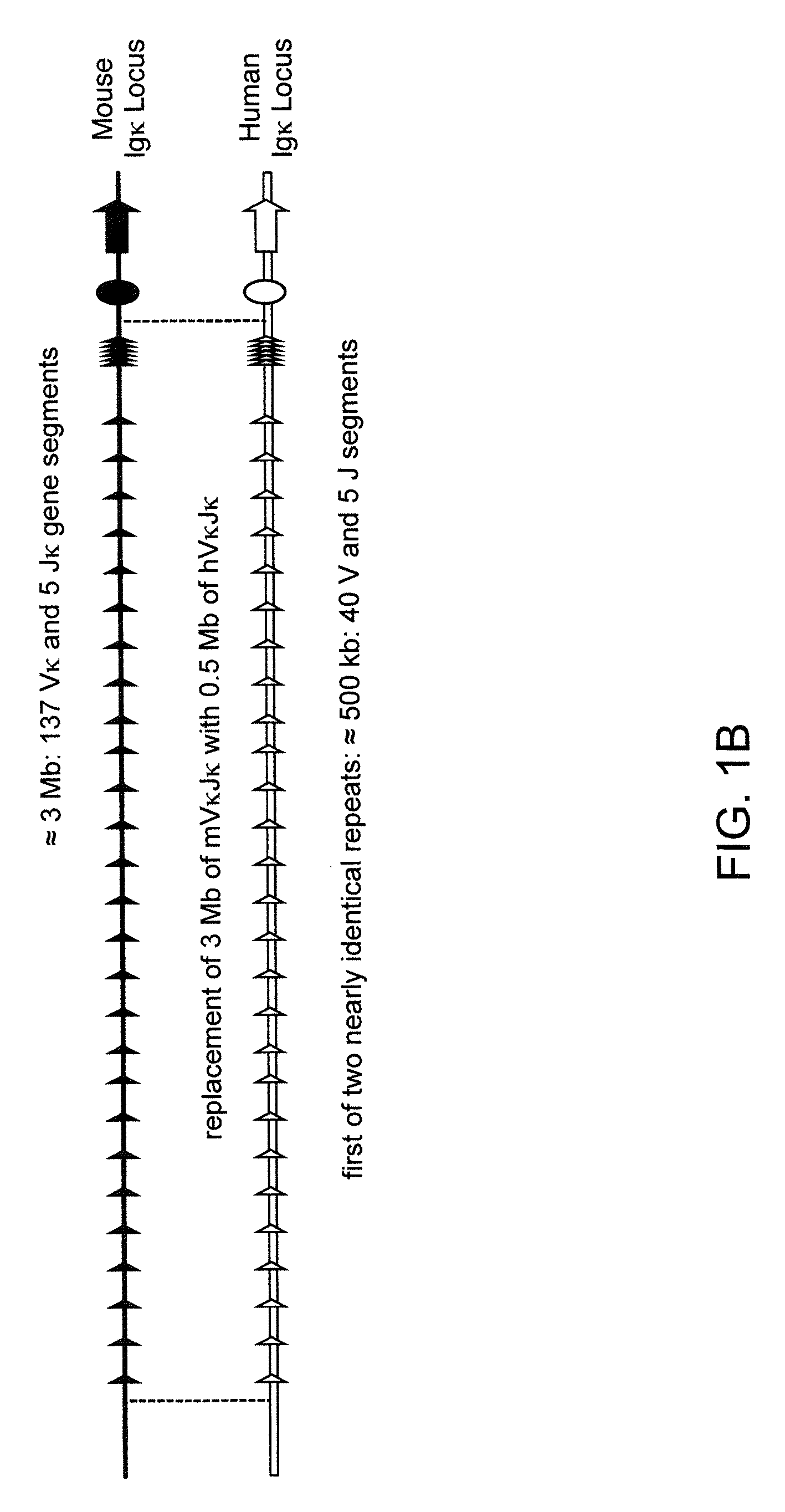
ADAM6 mice
ActiveUS8642835B2Reduces and eliminates ADAM activityImprove fertilityHydrolasesImmunoglobulins against growth factorsMatingNucleotide sequencing
Mice are provided that comprise a reduction or deletion of ADAM6 activity from an endogenous ADAM6 locus, or that lack an endogenous locus encoding a mouse ADAM6 protein, wherein the mice comprise a sequence encoding an ADAM6 or ortholog or homolog or fragment thereof that is functional in a male mouse. In one embodiment, the sequence is an ectopic ADAM6 sequence or a sequence that confers upon a male mouse the ability to generate offspring by mating. Mice and cells with genetically modified immunoglobulin heavy chain loci that comprise an ectopic nucleotide sequence encoding a mouse ADAM6 or functional fragment or homolog or ortholog thereof are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Genetically modified cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, the constructs and method thereof
The invention provides a genetically modified Cyanobacteria having a construct comprising DNA fragments encoding pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase (adh) enzymes obtained from the Zymomonas mobilis plasmid pLOI295. The Cyanobacteria are capable of producing ethanol in recoverable quantities of at least 1.7 mumol ethanol per mg of chlorophyll per hour.
Owner:ENOL ENERGY
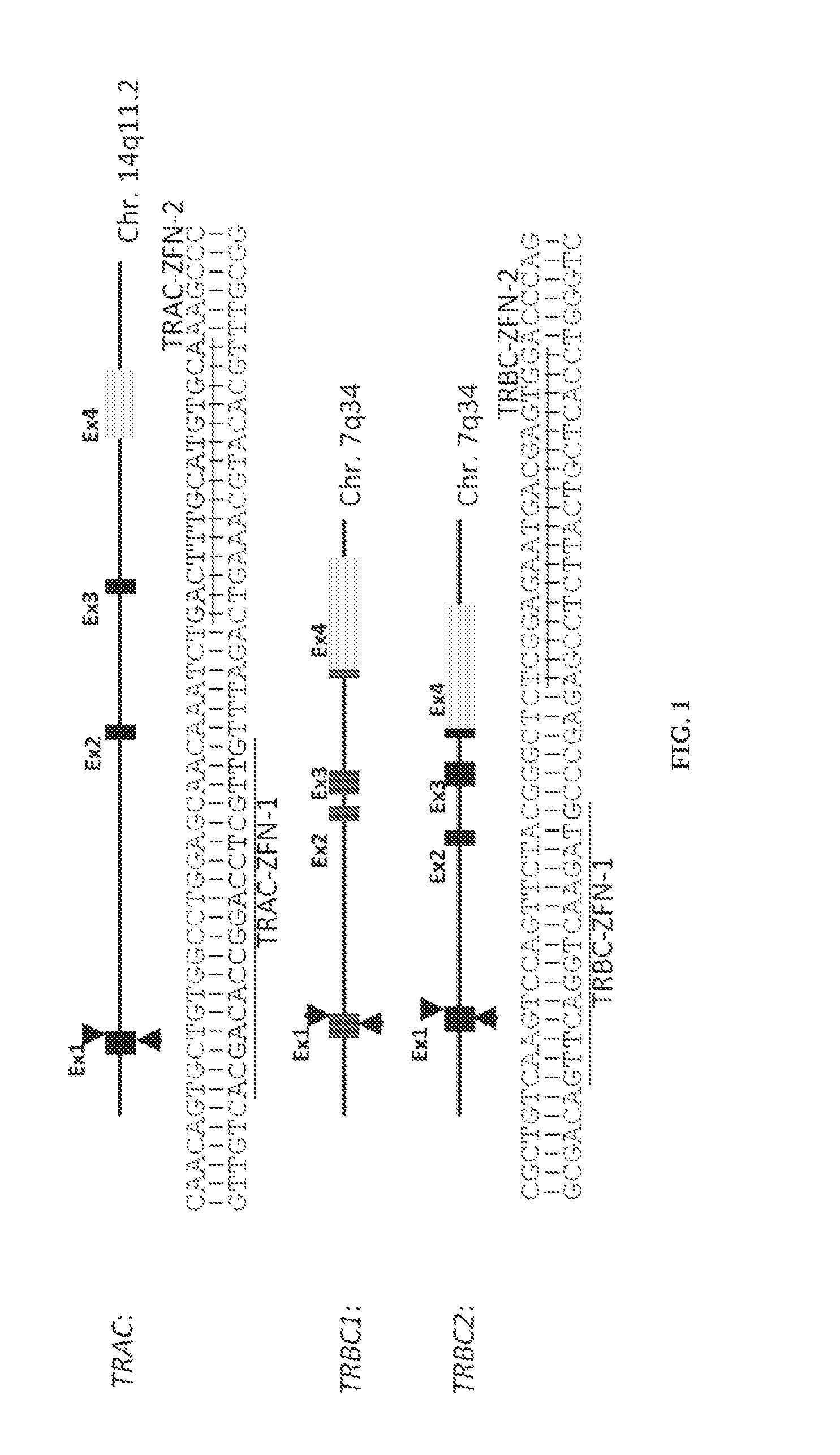
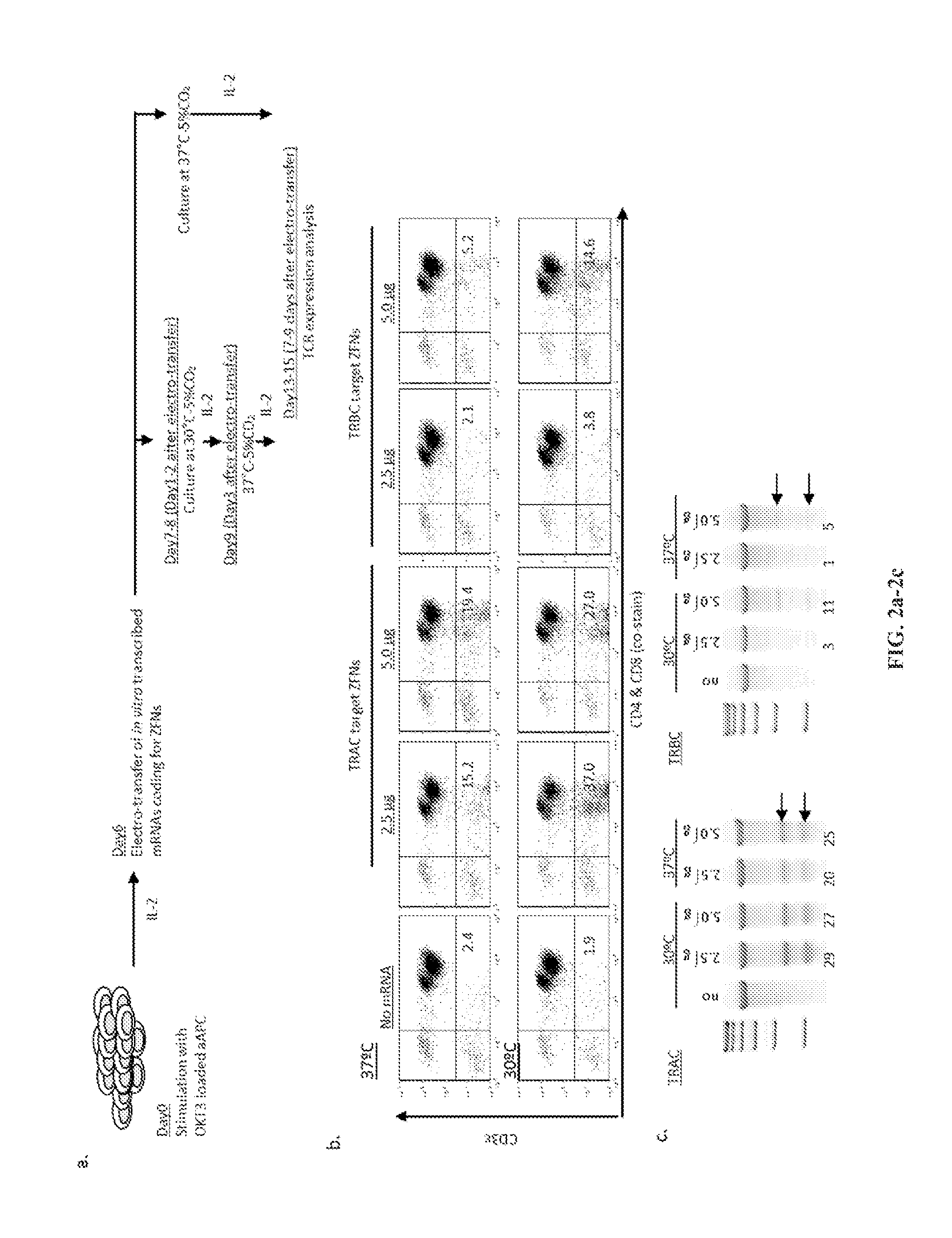
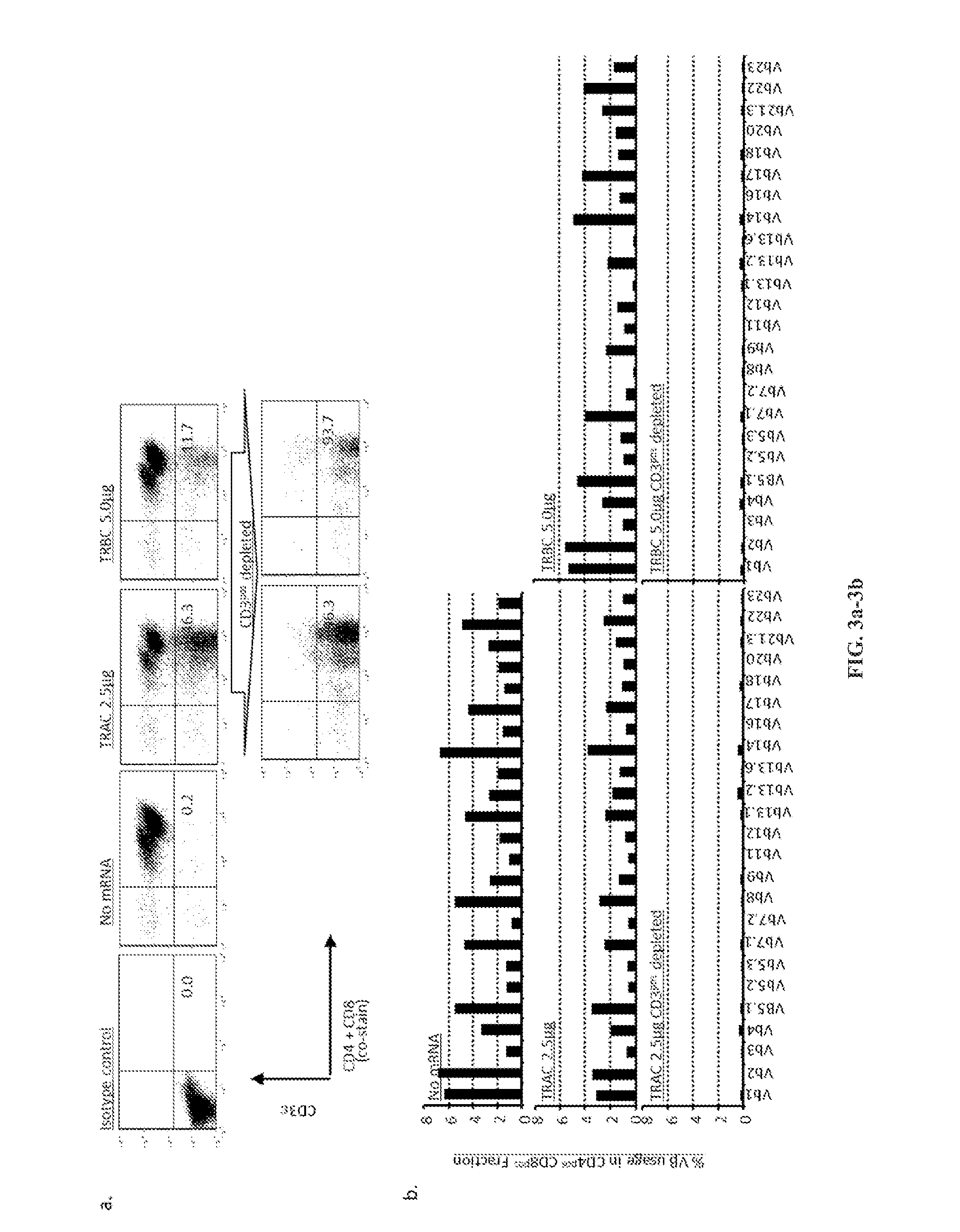
Car+ t cells genetically modified to eliminate expression of t-cell receptor and/or HLA
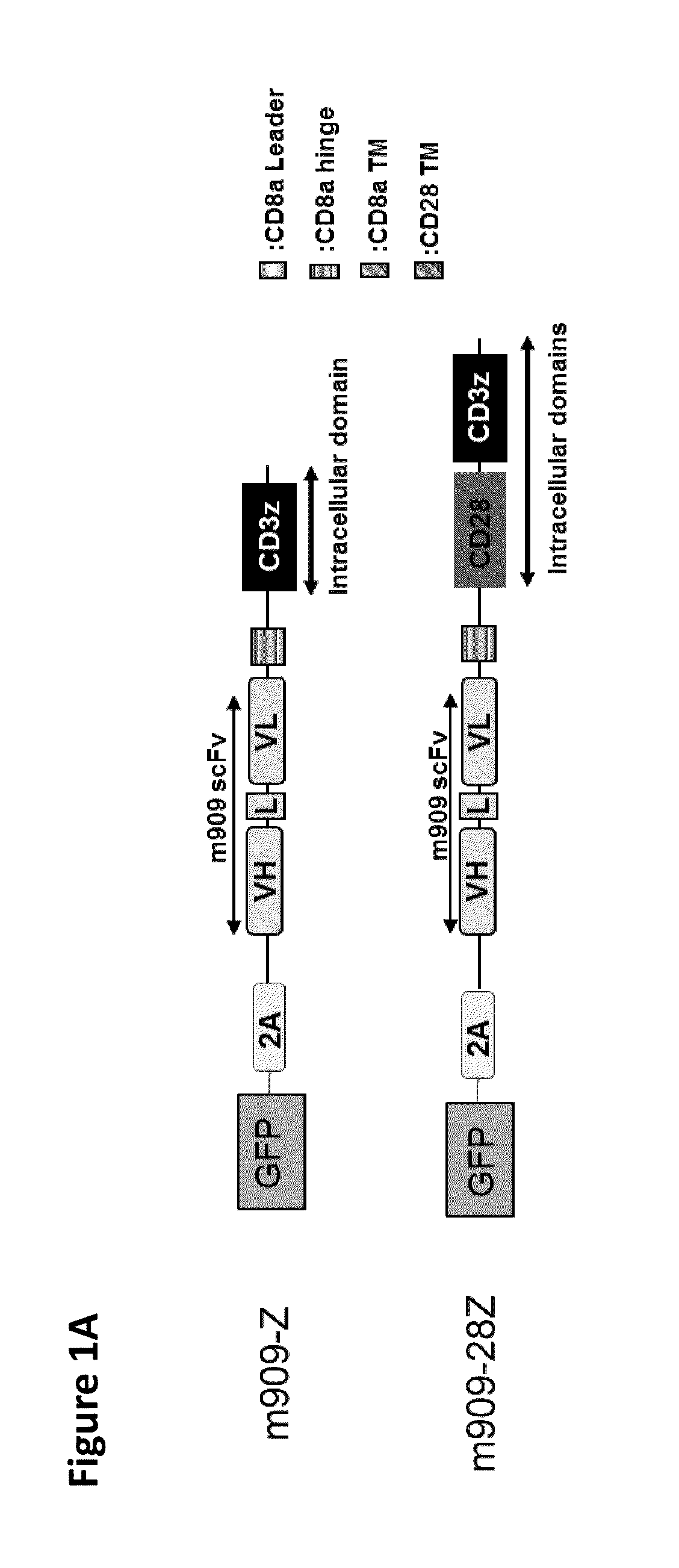
ActiveUS20140349402A1Suitable for storageReduce/eliminate T cellsGenetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsAntigen receptorsAutoimmunity
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for immunotherapy employing a modified T cell comprising disrupted T cell receptor and / or HLA and comprising a chimeric antigen receptor. In certain embodiments, the compositions are employed allogeneically as universal reagents for “off-the-shelf treatment of medical conditions such as cancer, autoimmunity, and infection. In particular embodiments, the T cell receptor-negative and / or HLA-negative T cells are generated using zinc finger nucleases, for example.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
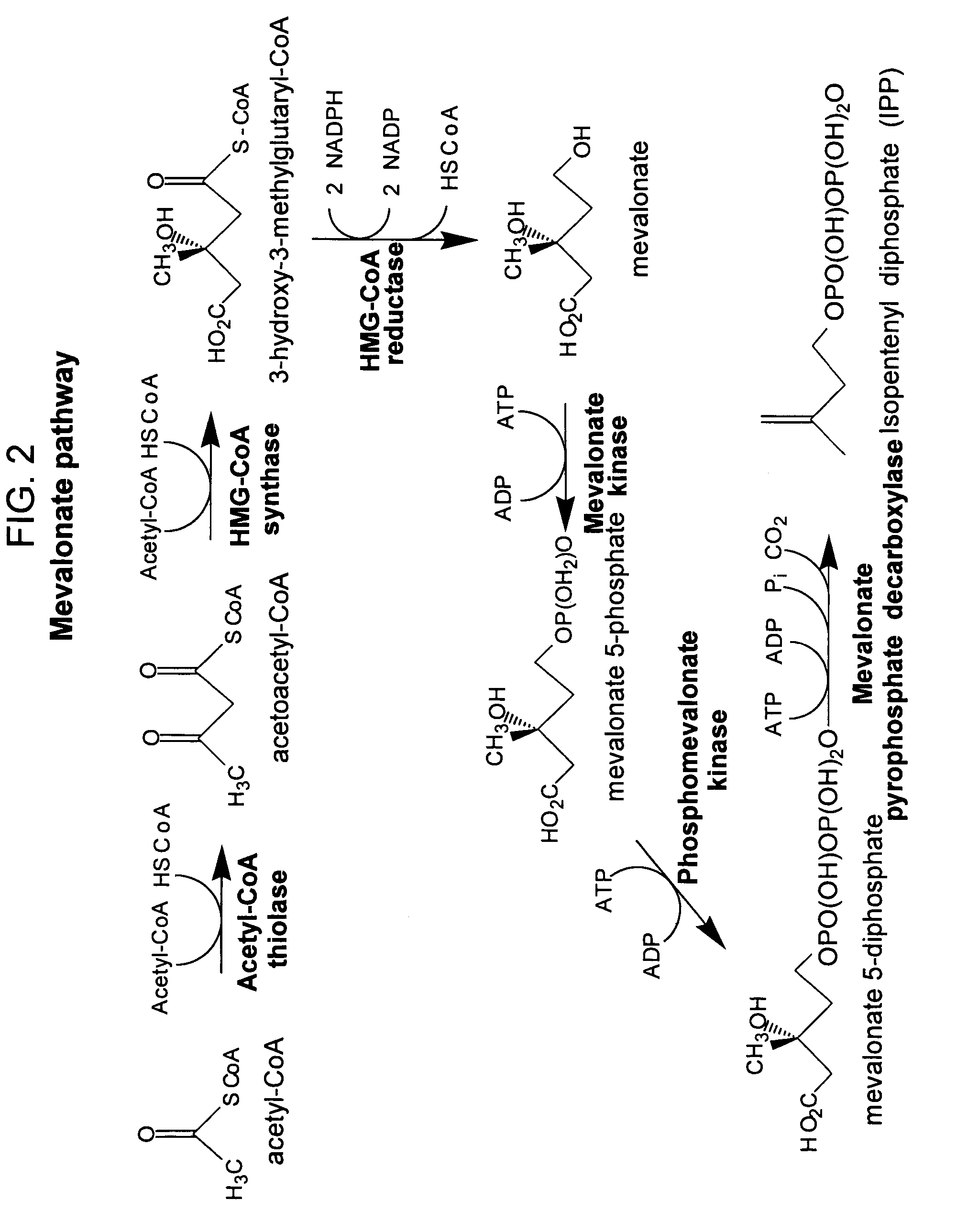
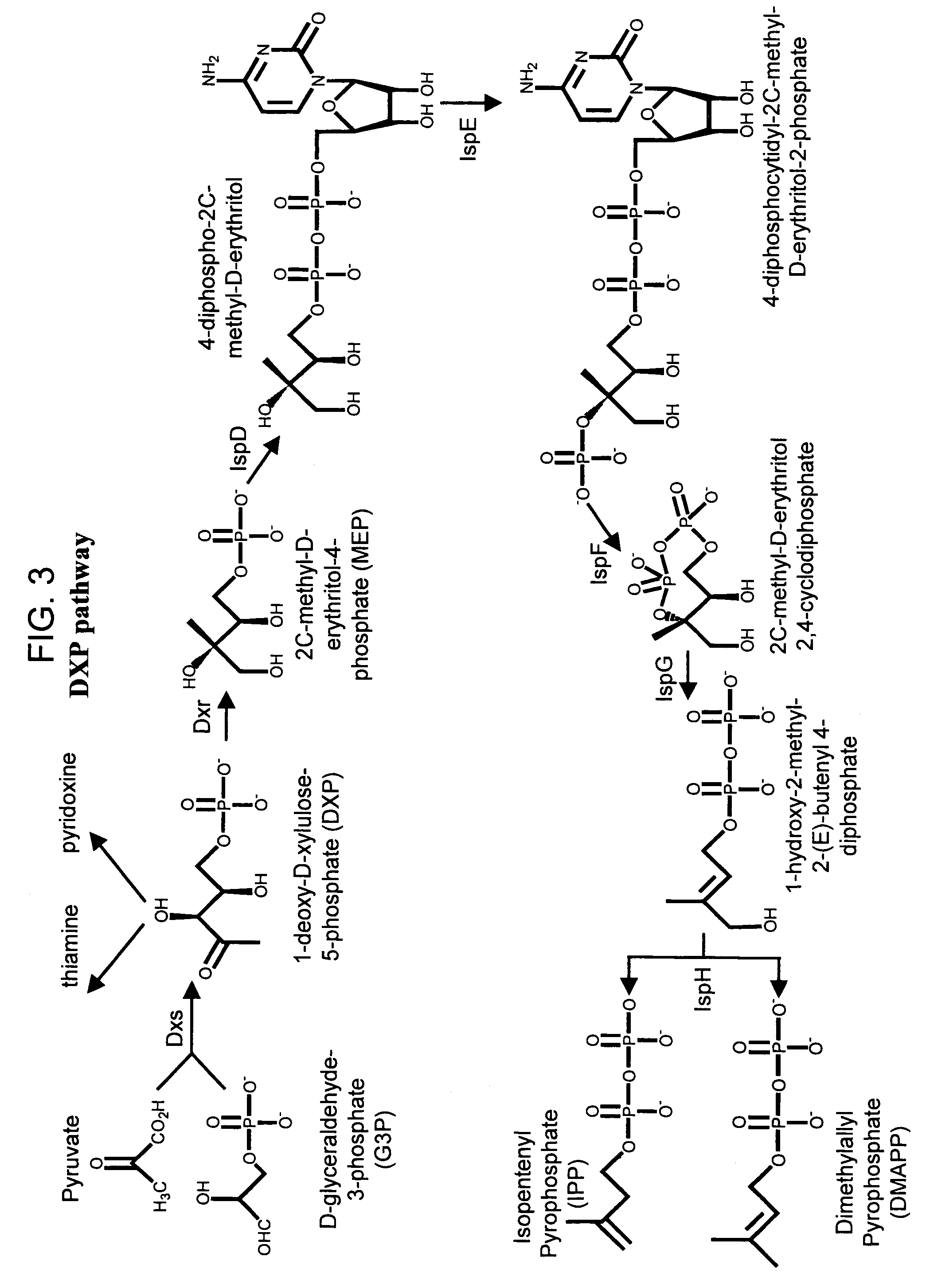
Method for enhancing production of isoprenoid compounds
The present invention provides methods of producing an isoprenoid or an isoprenoid precursor in a genetically modified host cell. The methods generally involve modulating the level of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) in the cell, such that the level of HMG-CoA is not toxic to the cell and / or does not substantially inhibit cell growth, but is maintained at a level that provides for high-level production of mevalonate, IPP, and other downstream products of an isoprenoid or isoprenoid pathway, e.g., polyprenyl diphosphates and isoprenoid compounds. The present invention further provides genetically modified host cells that are suitable for use in a subject method. The present invention further provides recombinant nucleic acid constructs for use in generating a subject genetically modified host cell, including recombinant nucleic acid constructs comprising nucleotide sequences encoding one or more mevalonate pathway enzymes, and recombinant vectors (e.g., recombinant expression vectors) comprising same. The present invention further provides methods for identifying nucleic acids that encode HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR) variants that provide for relief of HMG-CoA accumulation-induced toxicity. The present invention further provides methods for identifying agents that reduce intracellular accumulation of HMG-CoA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Processes for the preparation of novel collagen-based supports for tissue engineering, and biomaterials obtained
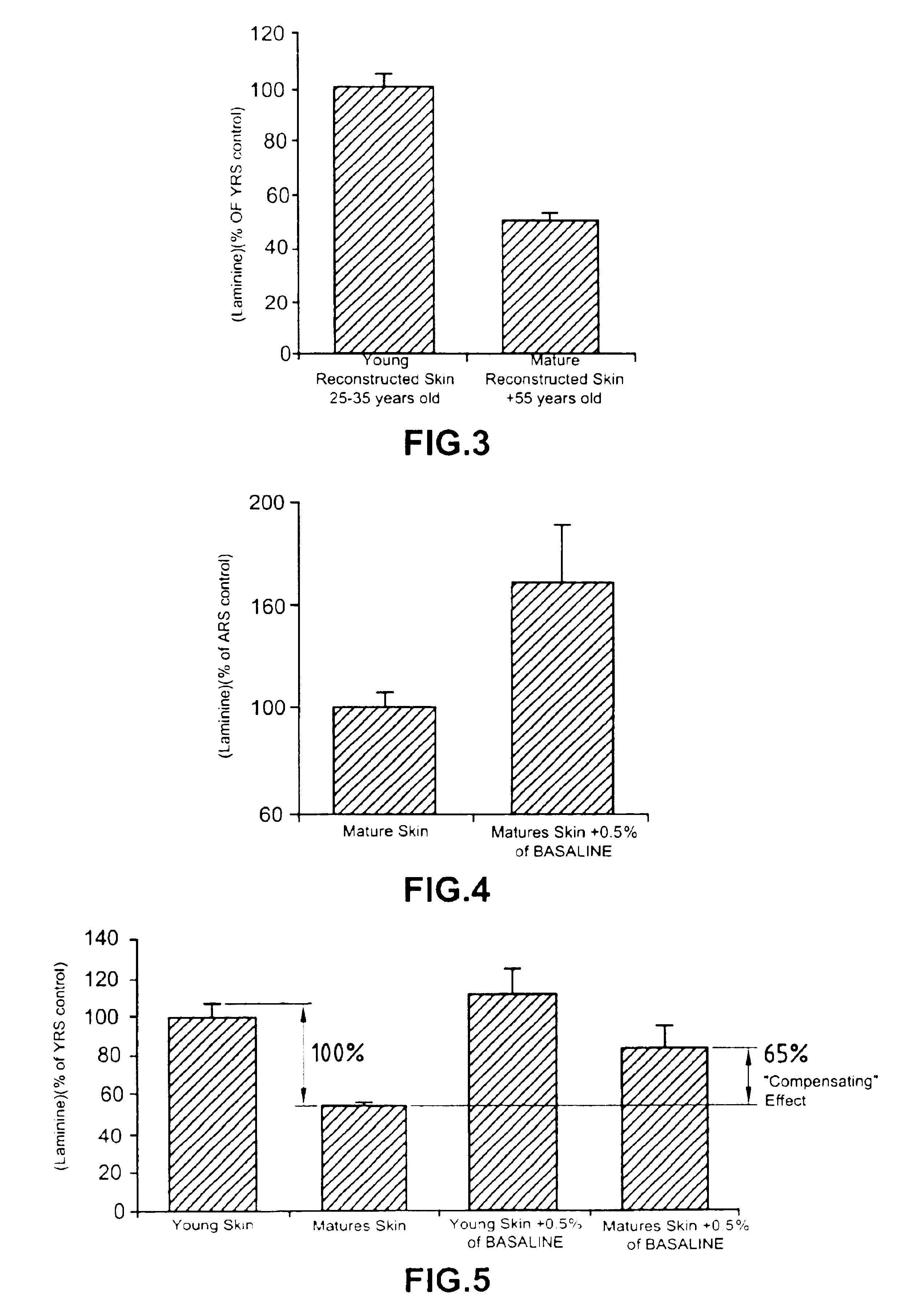
A composite product is disclosed as a collagen support comprising at least one porous collagen layer covered on at least one side with an essentially compact collagen membrane consisting either of a collagen film prepared by drying a collagen gel, preferably in air or a gaseous fluid, or of a very highly compressed collagen sponge. At least one of the two layers, i.e. the porous layer and the essentially compact membrane, may comprise normal, genetically modified or malignant living cells originating particularly from young or elderly subjects. This composite product is used as a collagen support for the manufacture of artificial skin intended especially for performing in vitro tests on the efficacy of potentially active substances or for reconstructing damaged areas of skin in vivo.
Owner:BASF BEAUTY CARE SOLUTIONS FRANCE SAS
Novel Fungal Enzymes
This invention relates to novel enzymes and novel methods for producing the same. More specifically this invention relates to a variety of fungal enzymes. Nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, compositions, recombinant and genetically modified host cells, and methods of use are described. The invention also relates to a method to convert lignocellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars with enzymes that degrade the lignocellulosic material and novel combinations of enzymes, including those that provide a synergistic release of sugars from plant biomass. The invention also relates to a method to release cellular content by degradation of cell walls. The invention also relates to methods to use the novel enzymes and compositions of such enzymes in a variety of other processes, including washing of clothing, detergent processes, biorefining, deinking and biobleaching of paper and pulp, and treatment of waste streams.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Method for the production of polypeptides
The present invention relates to a novel method for the production of short chain polypeptides, including polypeptides having up to 3 disulfide bonds and / or structures rich in basic amino acid residues, and open structured short chain polypeptides, e.g. glucagon, glucagon like peptides and their functional analogues, in genetically modified yeast cells, said genetically modified yeast cells, and a method for the preparation of said yeast cells.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
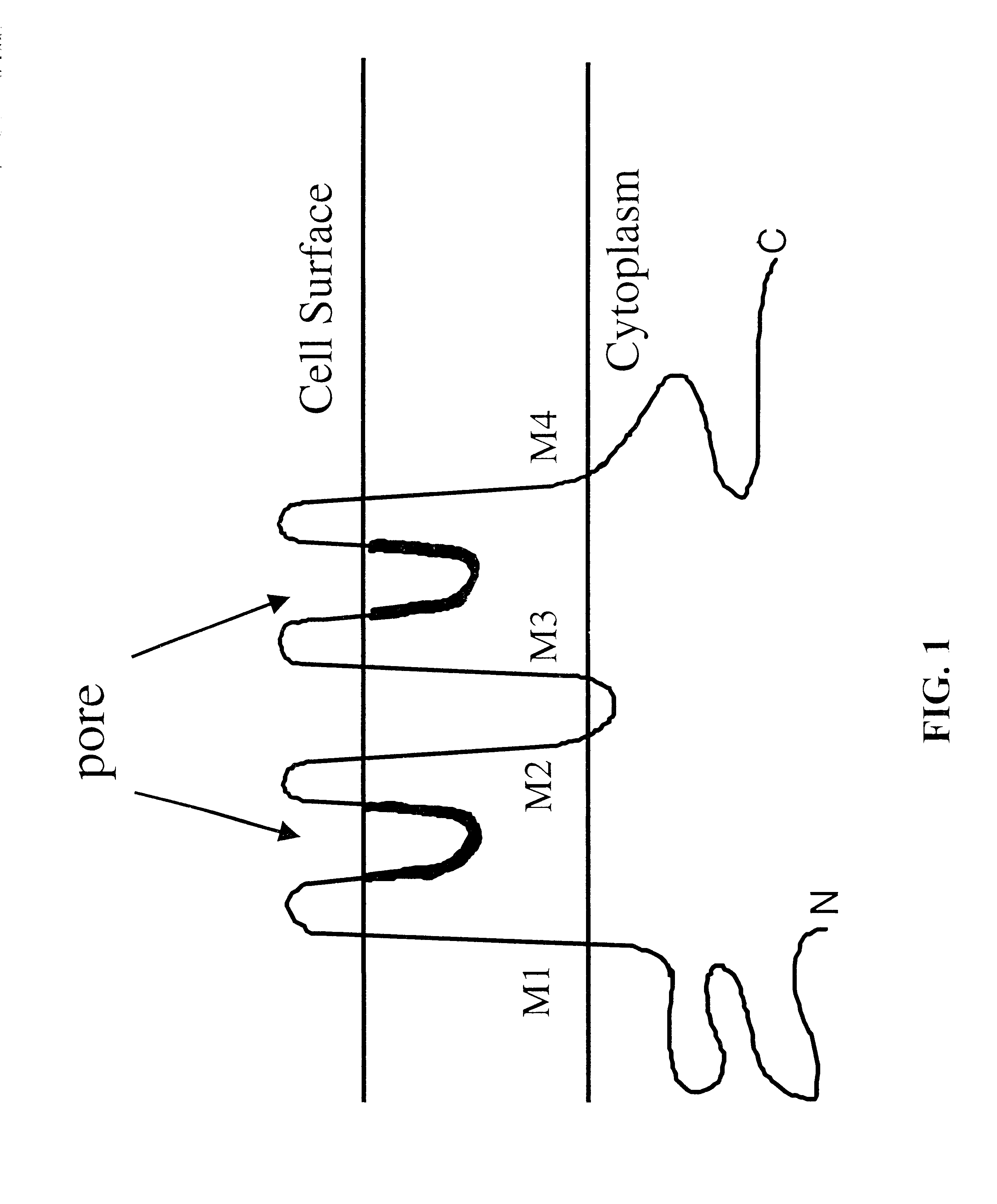
System and Method for Localization of Large Numbers of Fluorescent Markers in Biological Samples
ActiveUS20120193530A1Reduce respective collection solid angleExtensive collectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesFluorescenceQuantum dot
A method and system for the imaging and localization of fluorescent markers such as fluorescent proteins or quantum dots within biological samples is disclosed. The use of recombinant genetics technology to insert “reporter” genes into many species is well established. In particular, green fluorescent proteins (GFPs) and their genetically-modified variants ranging from blue to yellow, are easily spliced into many genomes at the sites of genes of interest (GoIs), where the GFPs are expressed with no apparent effect on the functioning of the proteins of interest (PoIs) coded for by the GoIs. One goal of biologists is more precise localization of PoIs within cells. The invention is a method and system for enabling more rapid and precise PoI localization using charged particle beam-induced damage to GFPs. Multiple embodiments of systems for implementing the method are presented, along with an image processing method relatively immune to high statistical noise levels.
Owner:FEI CO
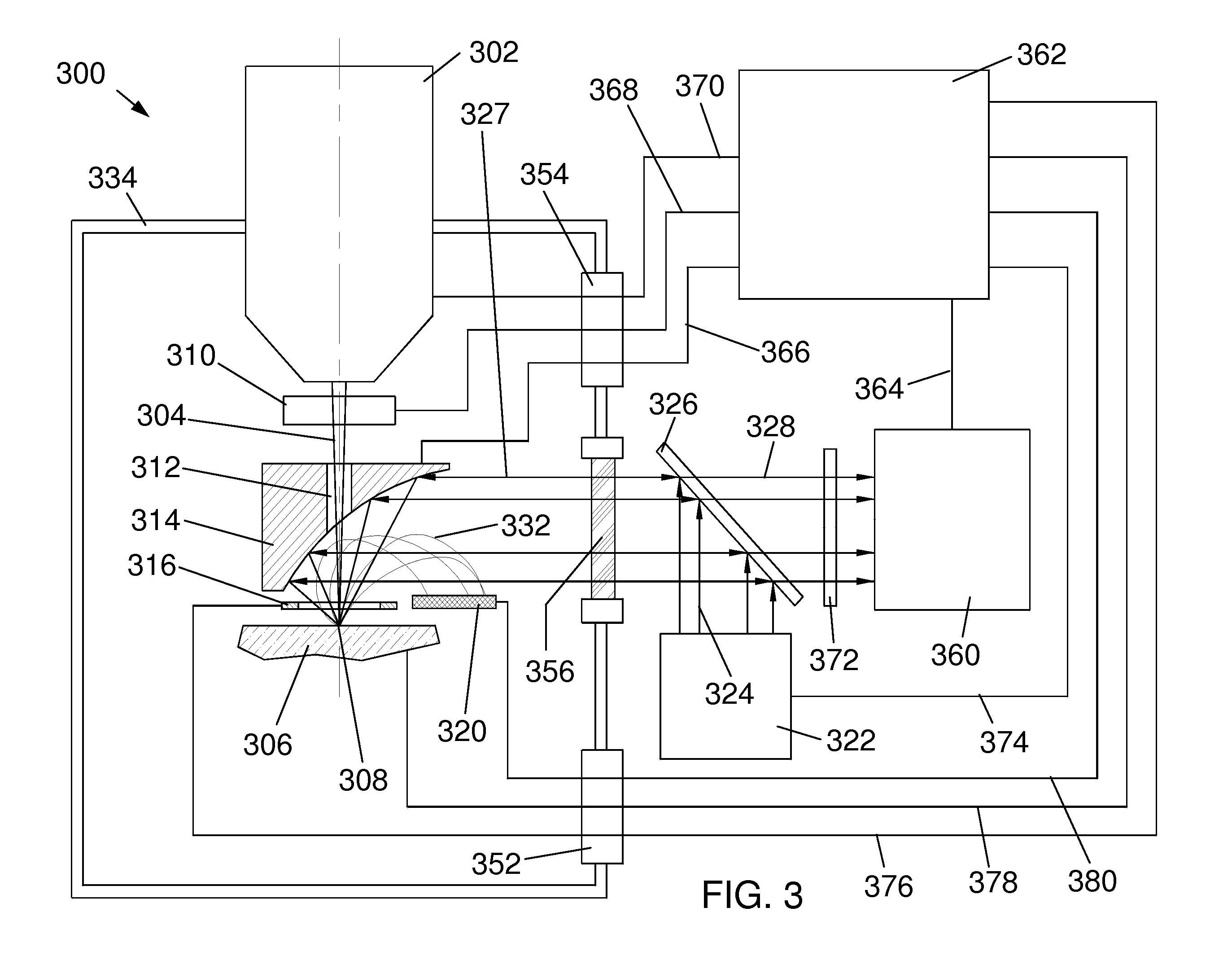
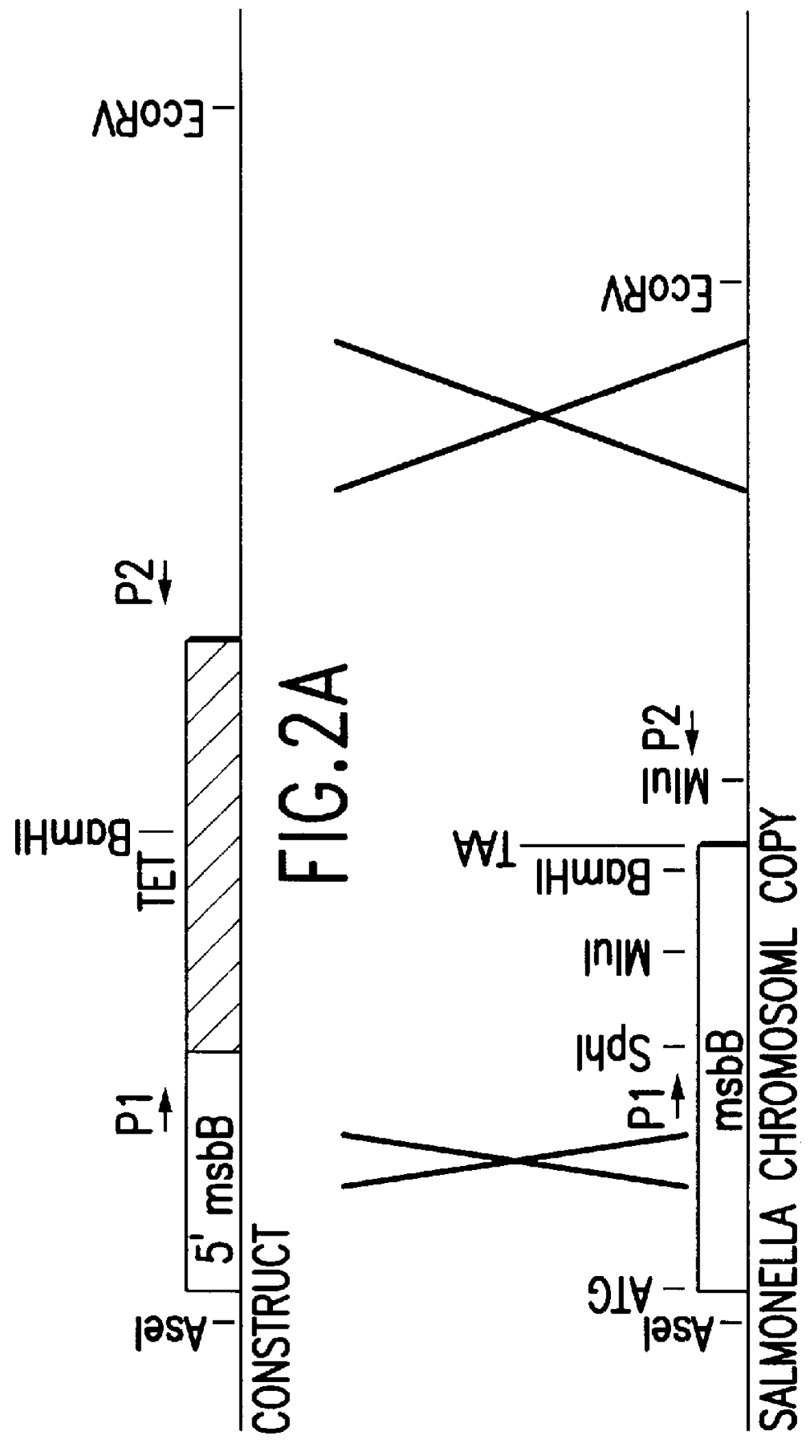
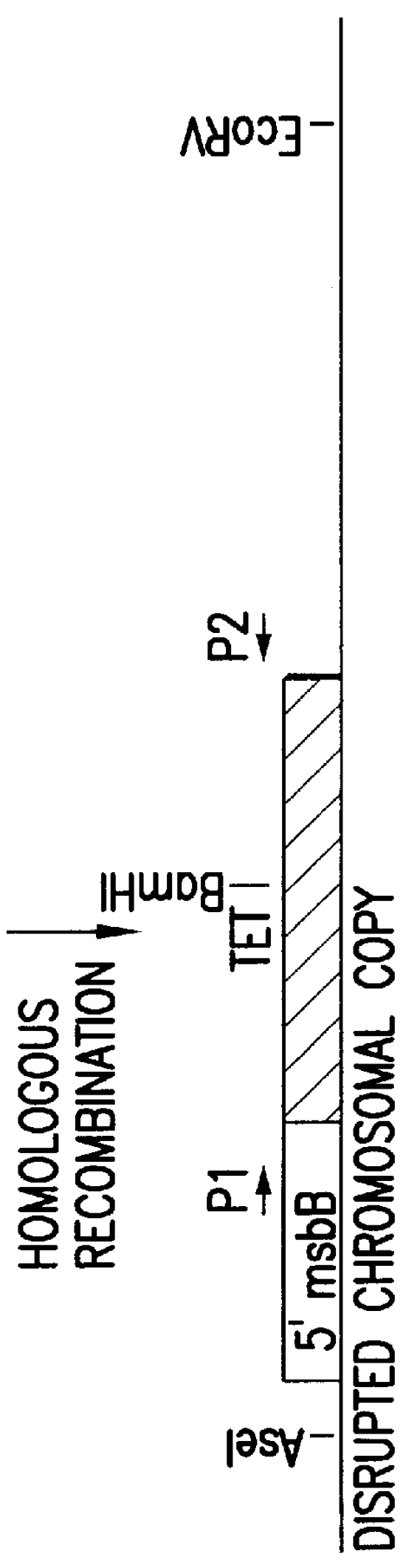
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS6080849AImprove securityReduce capacityBiocideBacteriaTumor targetVirulent characteristics
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Methods for Treatment of Cancer
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancer in a human. The invention includes relates to administering a genetically modified T cell to express a CAR wherein the CAR comprises an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain, a costimulatory signaling region, and a CD3 zeta signaling domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
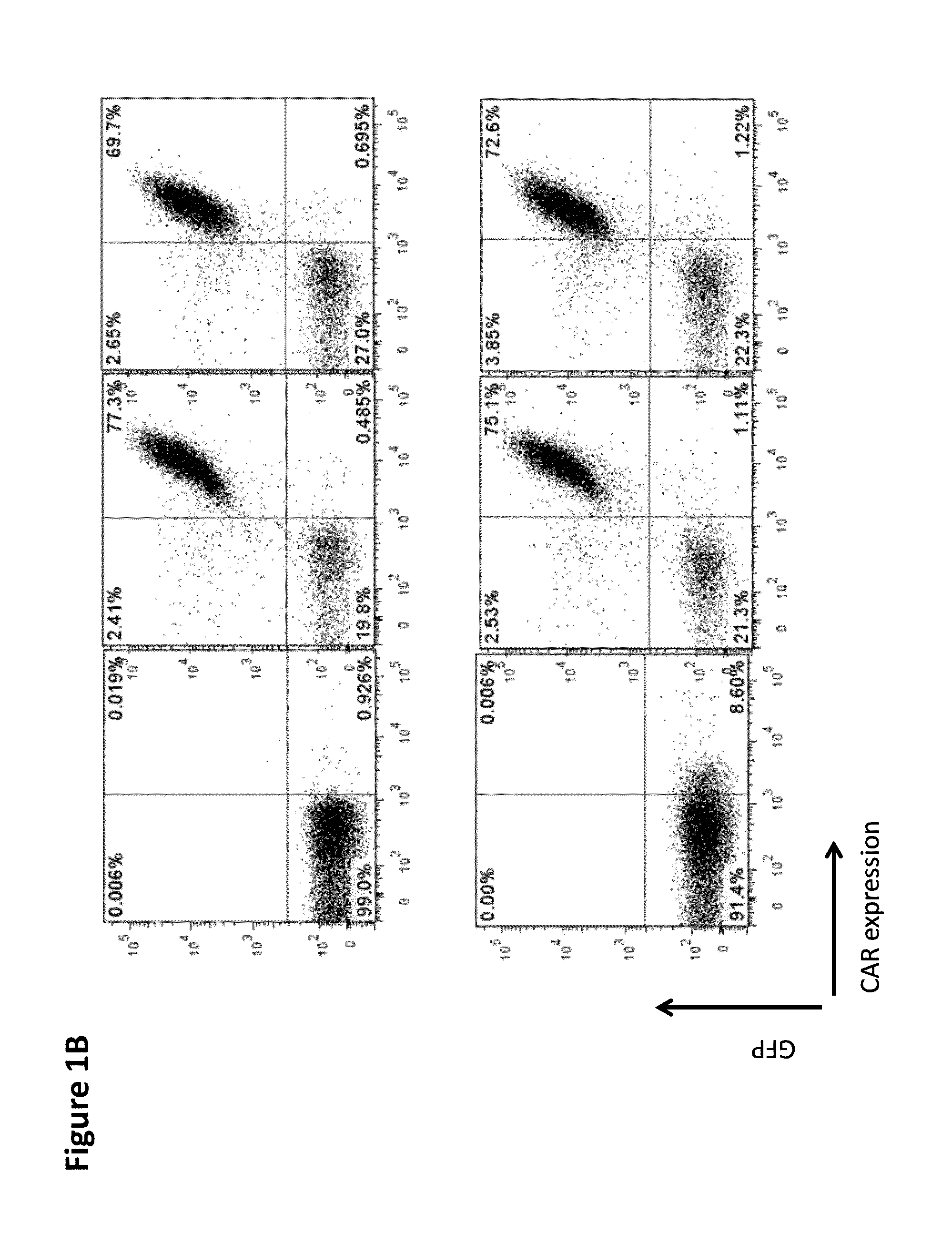
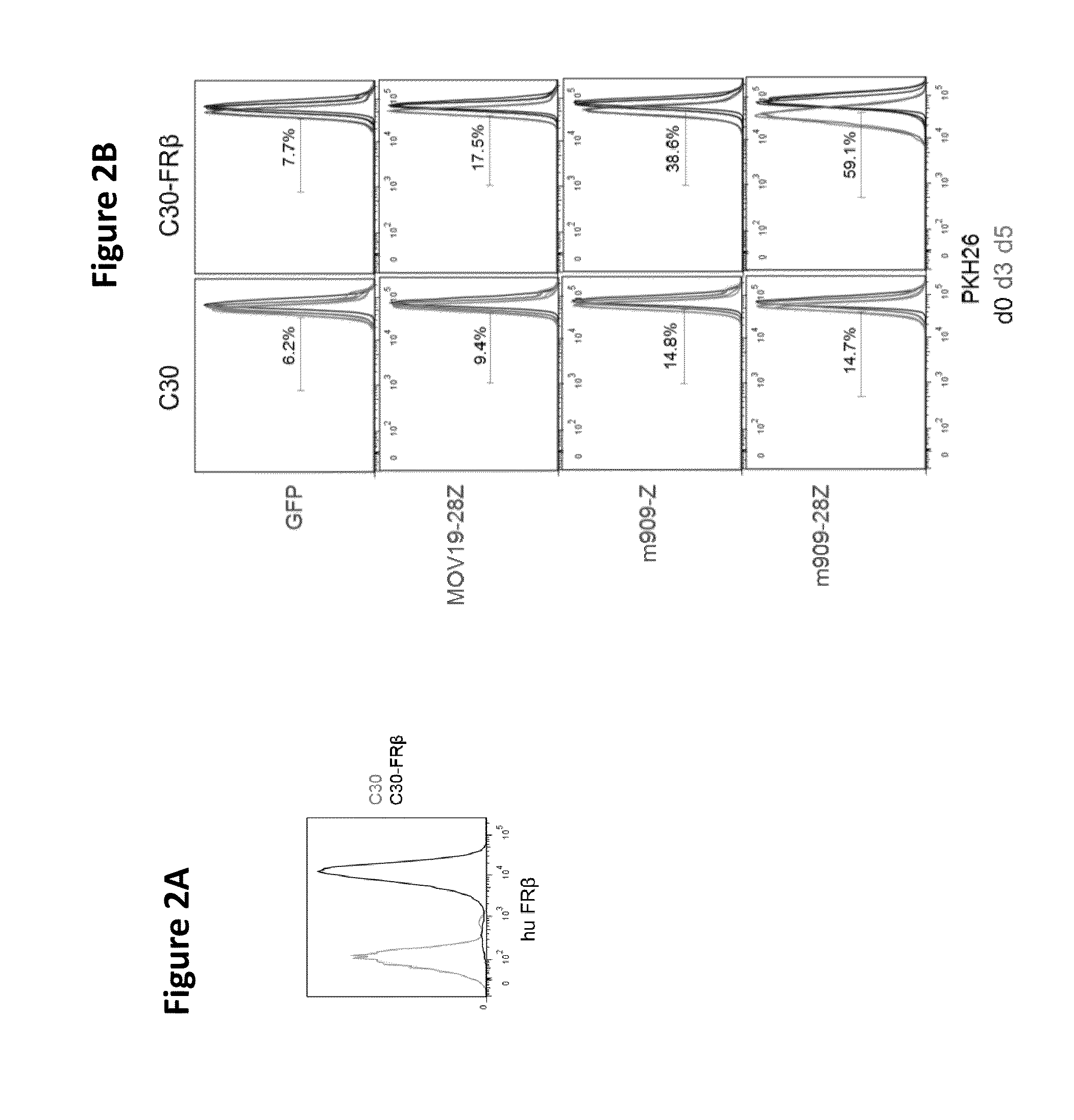
Chimeric antigen receptor specific for folate receptor beta
ActiveUS20140286973A1High affinityLow toxicityBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAgonistBinding domain
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating leukemia, for example, acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The invention also relates to at least one chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific to folate receptor beta (FRβ), vectors comprising the same, and recombinant T cells comprising the FRβ CAR. The invention also includes methods of administering a genetically modified T cell expressing a CAR that comprises a FRβ binding domain in combination with a RXR agonist, such as all-trans retinoic acid.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Adam6 Mice
ActiveUS20120322108A1Reduce eliminateImprove fertilityHydrolasesImmunoglobulins against growth factorsMatingNucleotide sequencing
Mice are provided that comprise a reduction or deletion of ADAM6 activity from an endogenous ADAM6 locus, or that lack an endogenous locus encoding a mouse ADAM6 protein, wherein the mice comprise a sequence encoding an ADAM6 or ortholog or homolog or fragment thereof that is functional in a male mouse. In one embodiment, the sequence is an ectopic ADAM6 sequence or a sequence that confers upon a male mouse the ability to generate offspring by mating. Mice and cells with genetically modified immunoglobulin heavy chain loci that comprise an ectopic nucleotide sequence encoding a mouse ADAM6 or functional fragment or homolog or ortholog thereof are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com