Targeted modification of rat genome
a technology of rat genome and target genome, which is applied in the direction of viruses/bacteriophages, peptides, veterinary instruments, etc., can solve the problems of bi-allelic modification of the target genomic locus and limited use of rats in human disease modeling, and achieve the effect of enhancing homologous recombination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Rat ES Cell Derivation and Characterization
1.1. Rat ES Cell Characterization
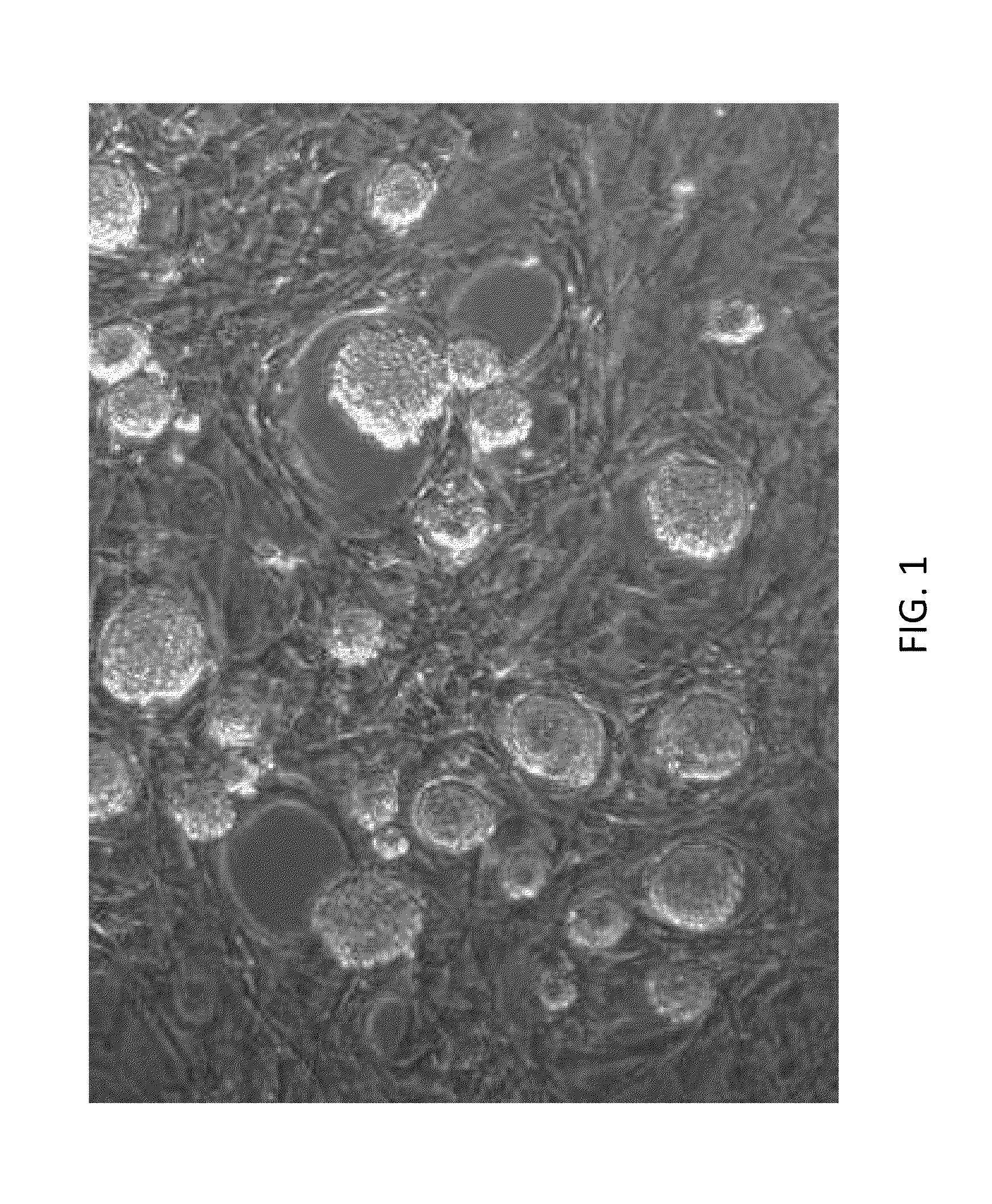
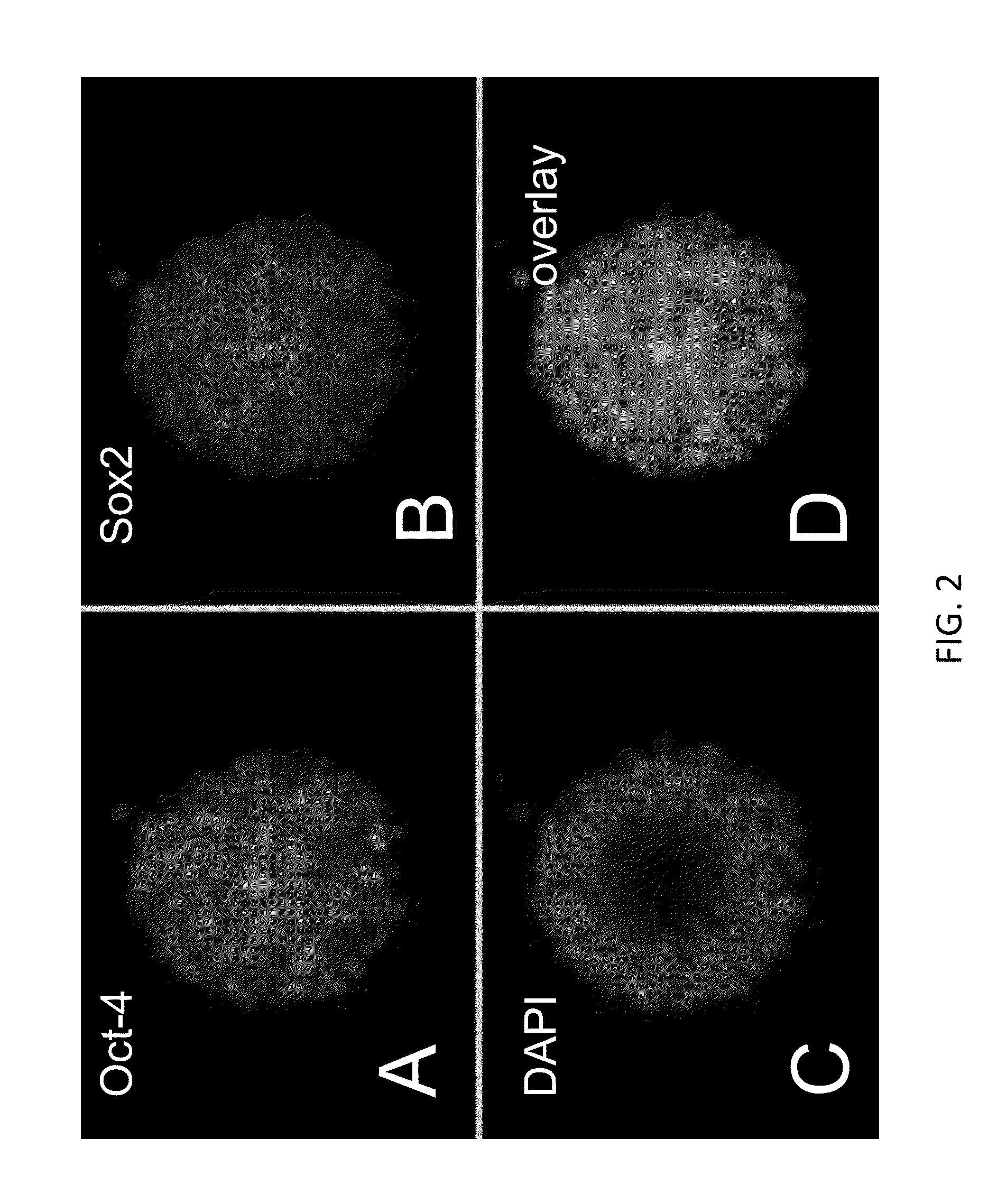
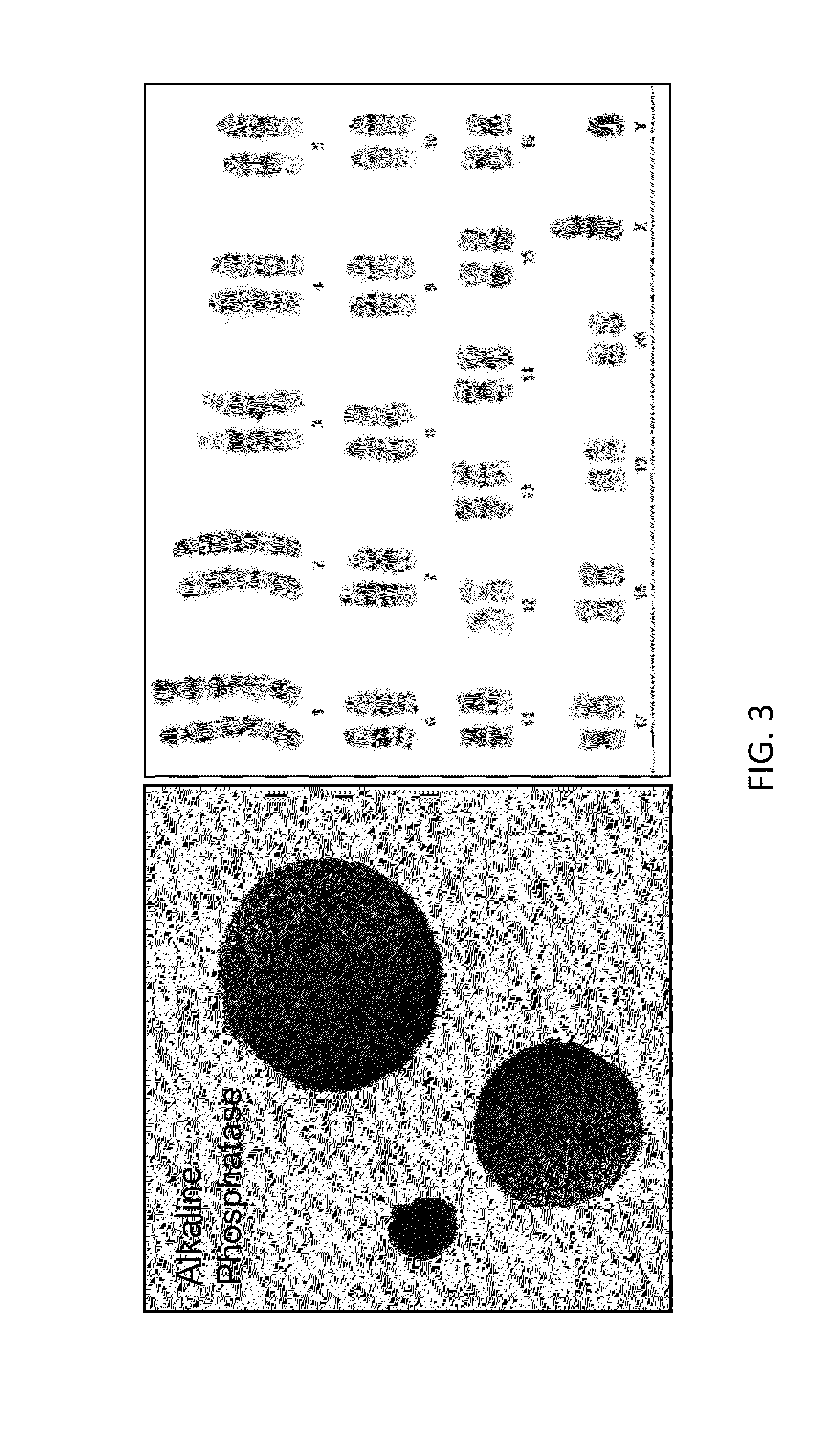
[0602]As shown in FIG. 1, rat ESCs grow as compact spherical colonies, which routinely detach and float in the dish (close-up, FIG. 7). Rat ESCs express pluripotency markers including Oct-4 (FIG. 2A) and Sox2 (FIG. 2B), and express high levels of alkaline phosphatase (FIG. 3, left panel). Karyotype for line DA.2B is 42X,Y (FIG. 3, right panel). Rat ESCs often become tetraploid; thus, lines were pre-screened by counting metaphase chromosome spreads; lines with mostly normal counts were then formally karyotyped.
[0603]ACI blastocysts were collected from super-ovulated females obtained commercially. DA blastocysts were cultured from frozen 8-cell embryos obtained commercially. Zona pellucidae were removed with Acid Tyrodes; and blastocysts were plated onto mitotically inactivated MEFs. Outgrowths were picked and expanded using standard methods. All blastocysts were plated, cultured and expanded using 2i media (L...
example 2
Inactivation of Genomic Loci in Rats
2.1: Inactivation of Endogenous Genomic Loci Using an Endonuclease Agent
[0756]In order to introduce a mutant allele at an endogenous rat genomic locus, the rat ES cells described herein are electroporated with expression vectors (or mRNA) that express ZFNs 1 and 2 (or TALENs 1 and 2). These proteins bind their target sequences on opposite strands, separated by about 6 bp to about 40 bp. A double-stranded break is formed within the target locus, which the cell attempts to repair by Non-Homologous End-Joining (NHEJ). In many cases, NHEJ results in creation of a deletion, which often disrupts the function of the gene (most often by producing a frameshift mutation). In order to identify a positive clone comprising a mutant allele, the electroporated cells are plated at low density, because no drug selection is done. Colonies are picked and assayed at the target site to see if a mutation was produced (e.g., using a modification of allele (MOA) assay de...
example 3
Targeted Modification of Rat Genomic Loci
3.1: Rat ESC Targeting: the Rat Rosa 26 Locus
[0767]The rat Rosa26 locus lies between the Setd5 and Thumpd3 genes as in mouse, with the same spacing. The rat Rosa 26 locus (FIG. 12, Panel B) differs from the mouse Rosa 26 locus (FIG. 12, Panel A). The mouse Rosa26 transcripts consist of 2 or 3 exons. The rat locus contains a 2nd exon 1 (Ex1b) in addition to the homologous exon to mouse exon1 (Ex1a). No 3rd exon has been identified in rat. Targeting of a rat Rosa26 allele is depicted in FIG. 12 (bottom), where homology arms of 5 kb each were cloned by PCR using genomic DNA from DA rat ESC. The targeted allele contains a SA (splicing acceptor)-lacZ-hUb-neo cassette replacing a 117 bp deletion in the rat Rosa26 intron.
[0768]Targeting efficiency at the rat Rosa 26 locus was determined (Table 12). Linearized vector was electroporated into DA or ACI rat ESCs, and transfected colonies were cultured in 2i media+G418, using standard techniques. Individ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com