Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
764 results about "Cyanobacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cyanobacteria /saɪˌænoʊbækˈtɪəriə/, also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum consisting of free-living bacteria as well as the endosymbiotic plastids which appear sister to Gloeomargarita. They commonly obtain their energy through photosynthesis. They are the only photosynthetic prokaryotes able to produce oxygen. The name cyanobacteria comes from the color of the bacteria (Greek: κυανός, romanized: kyanós, lit. 'blue'). Cyanobacteria, which are prokaryotes, are also called "blue-green algae", though some modern botanists restrict the term algae to eukaryotes. Cyanobacteria appear to have originated in freshwater or a terrestrial environment.
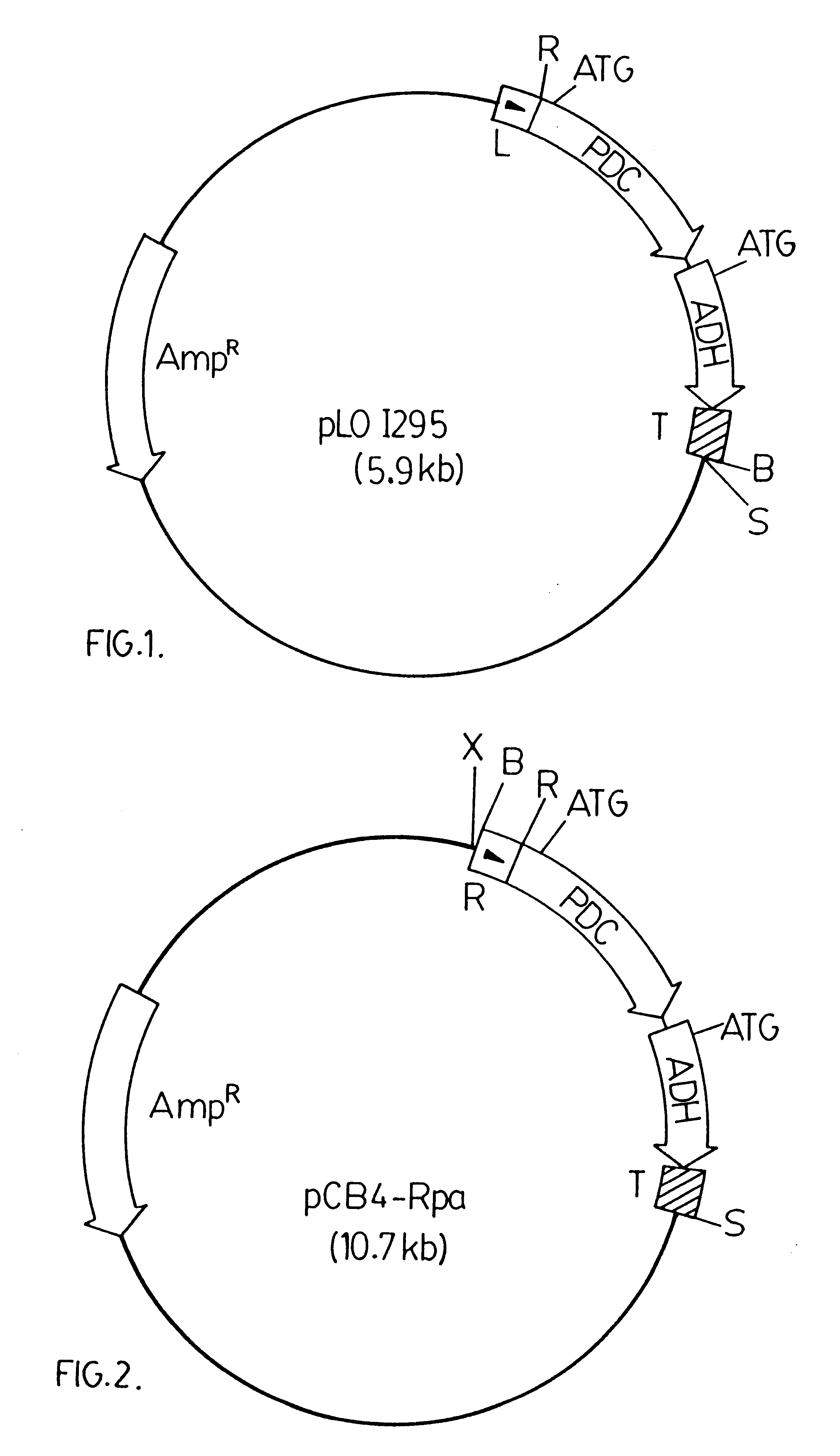
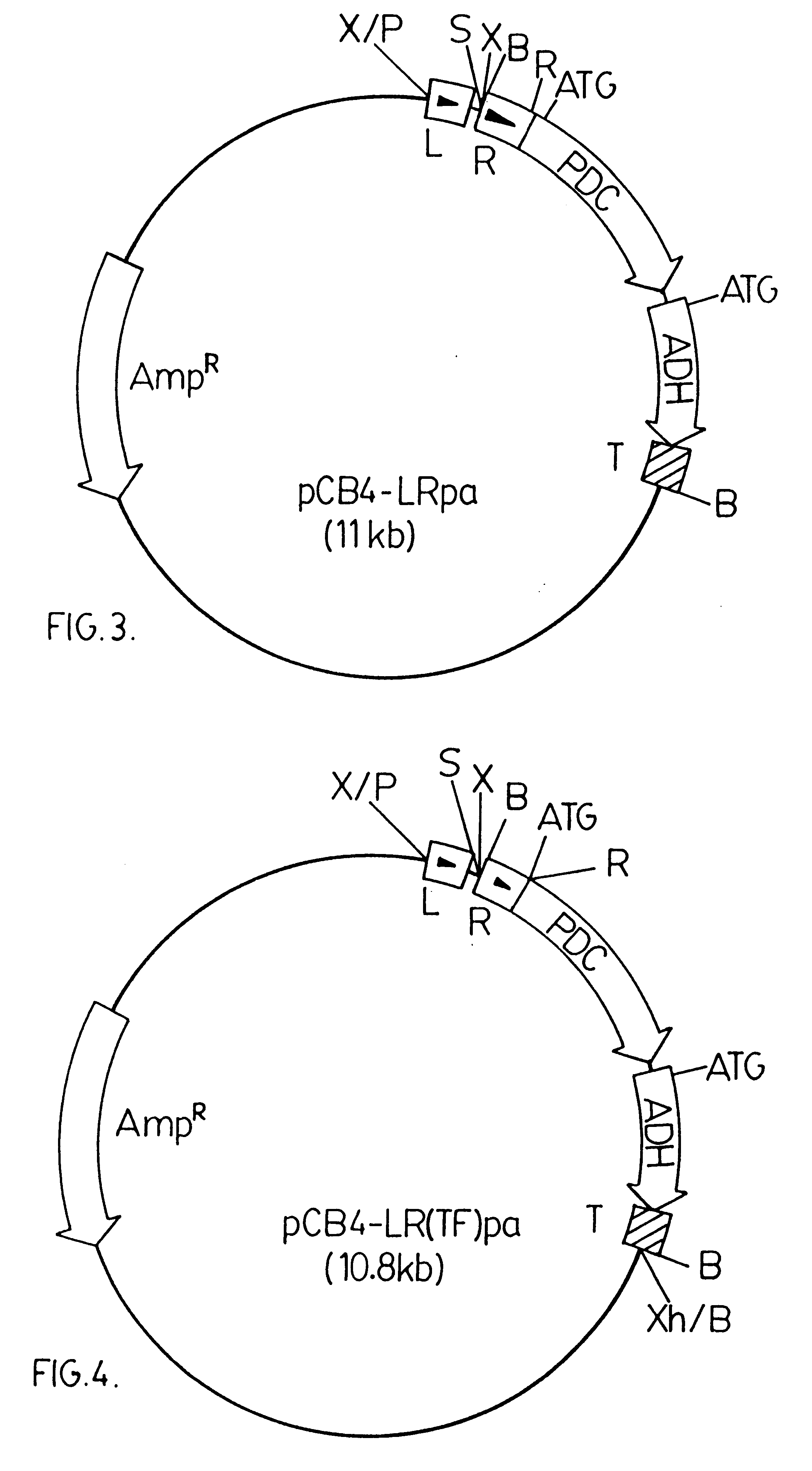
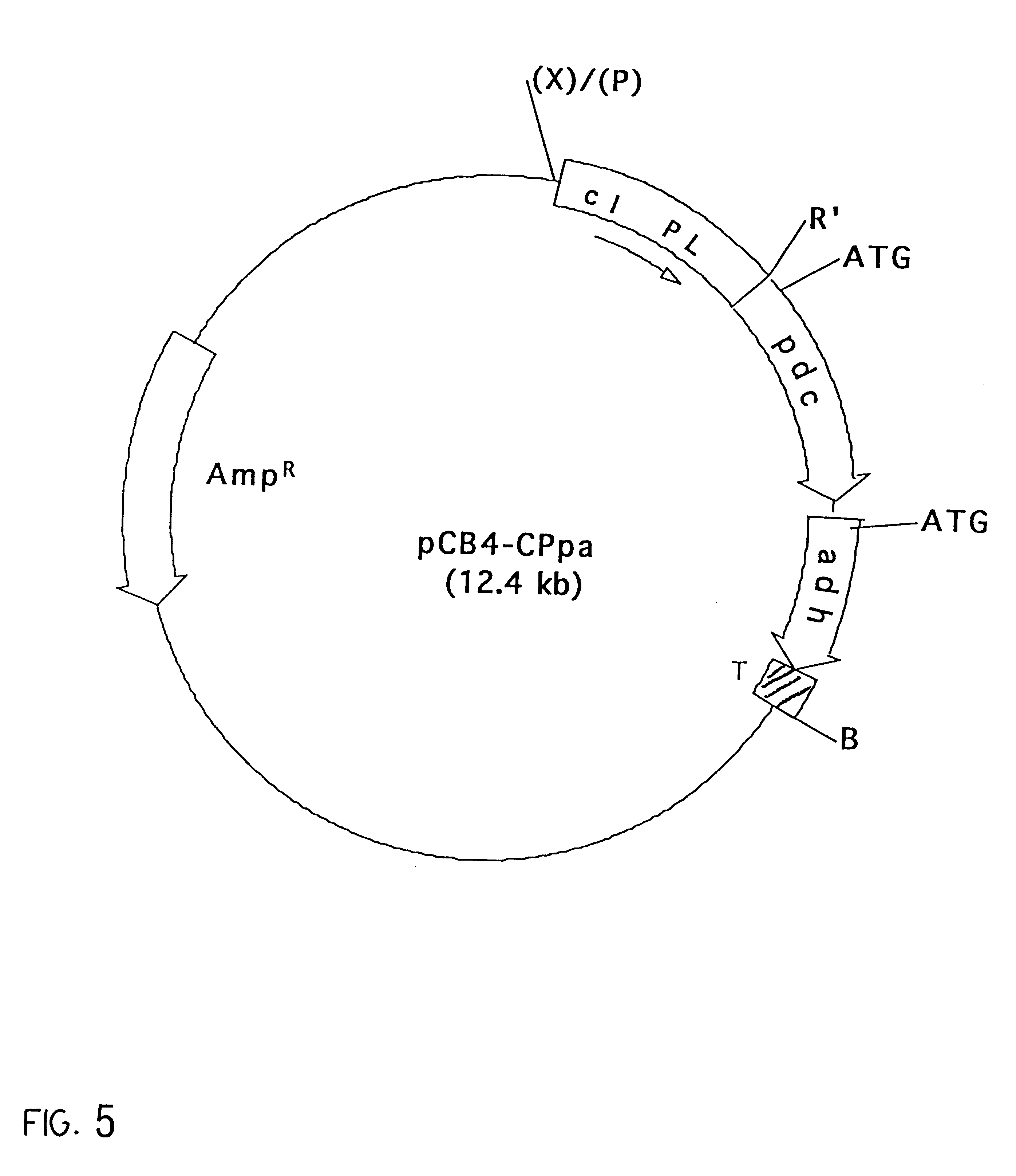
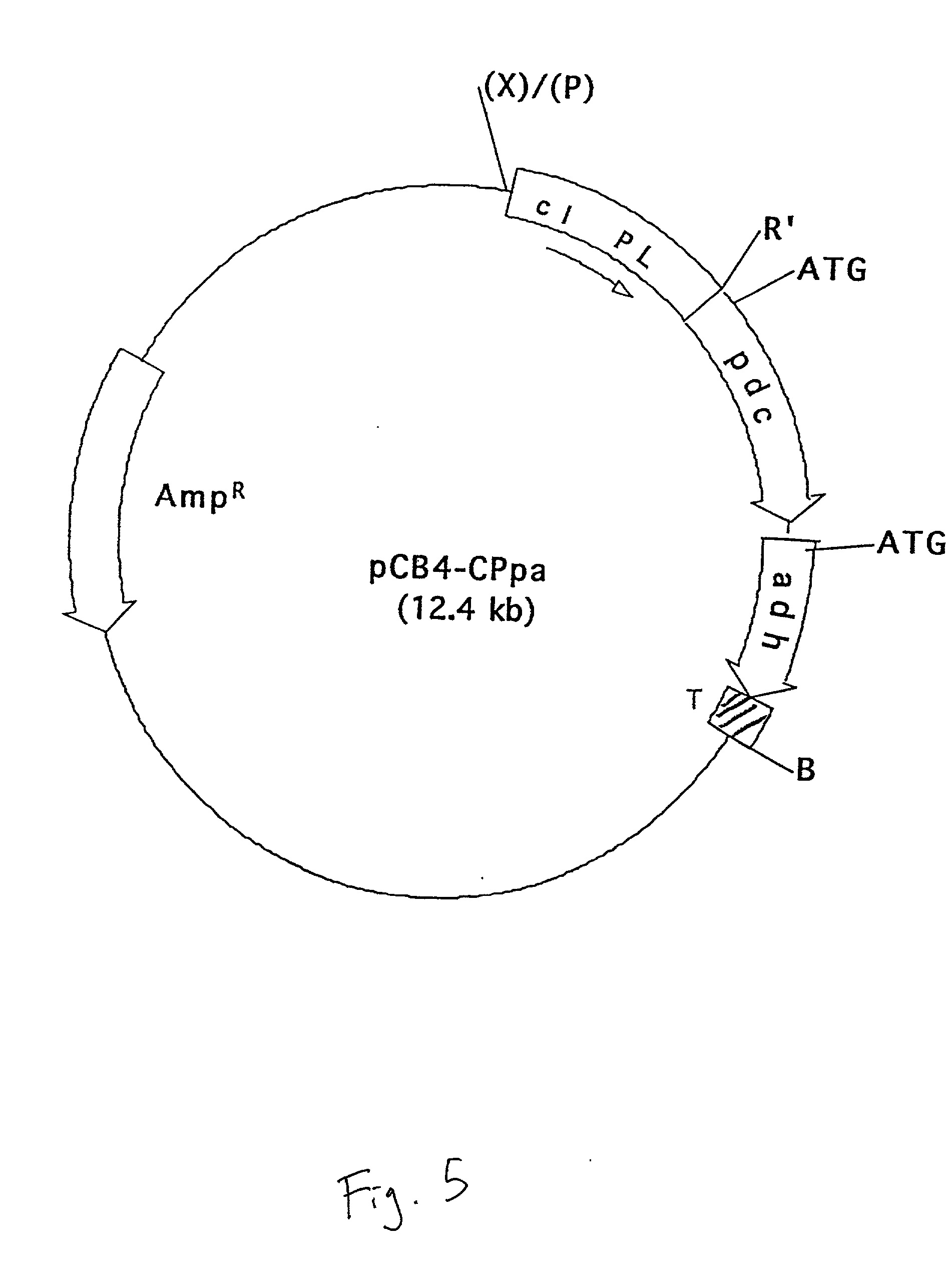
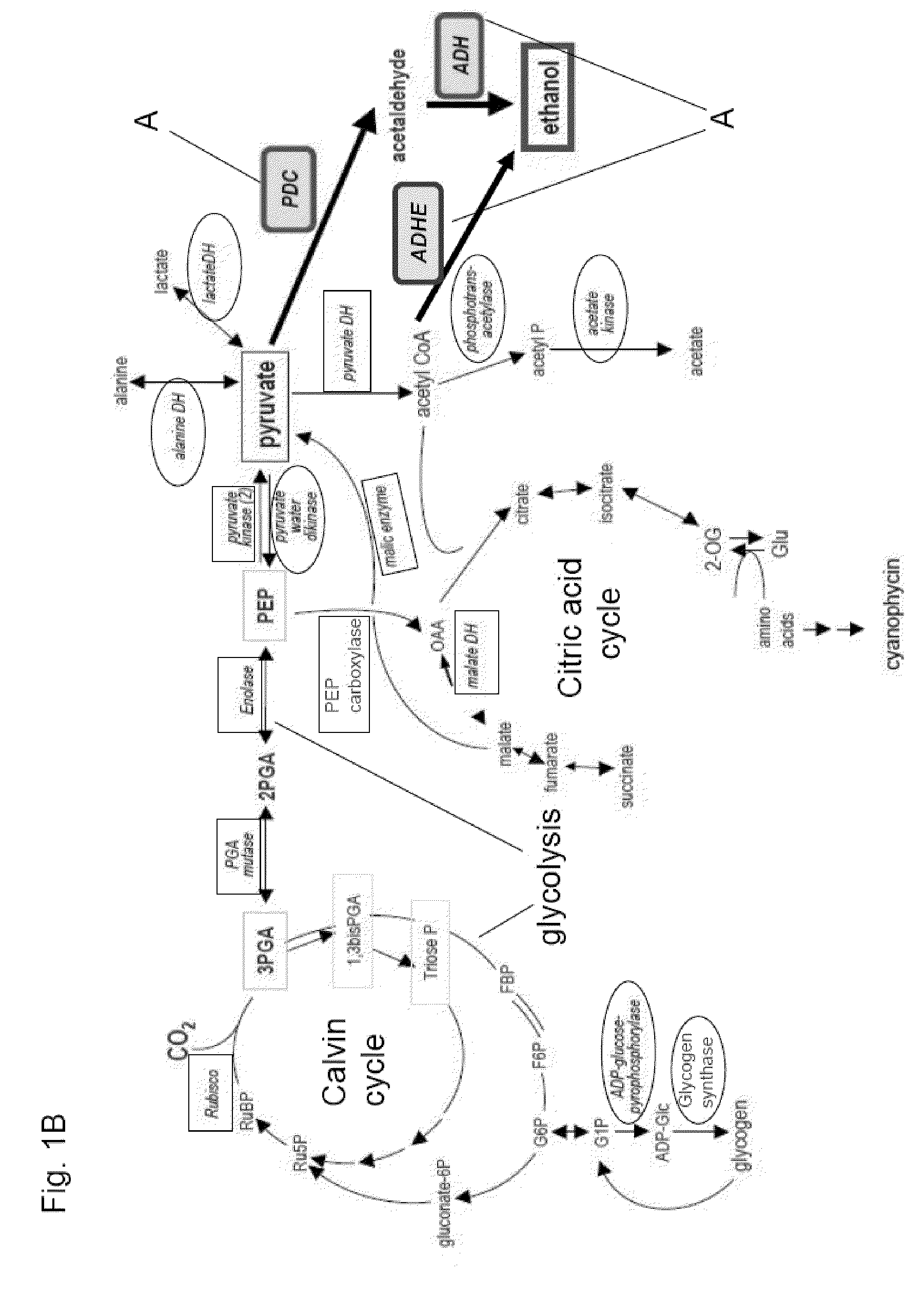
Genetically modified cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, the constructs and method thereof
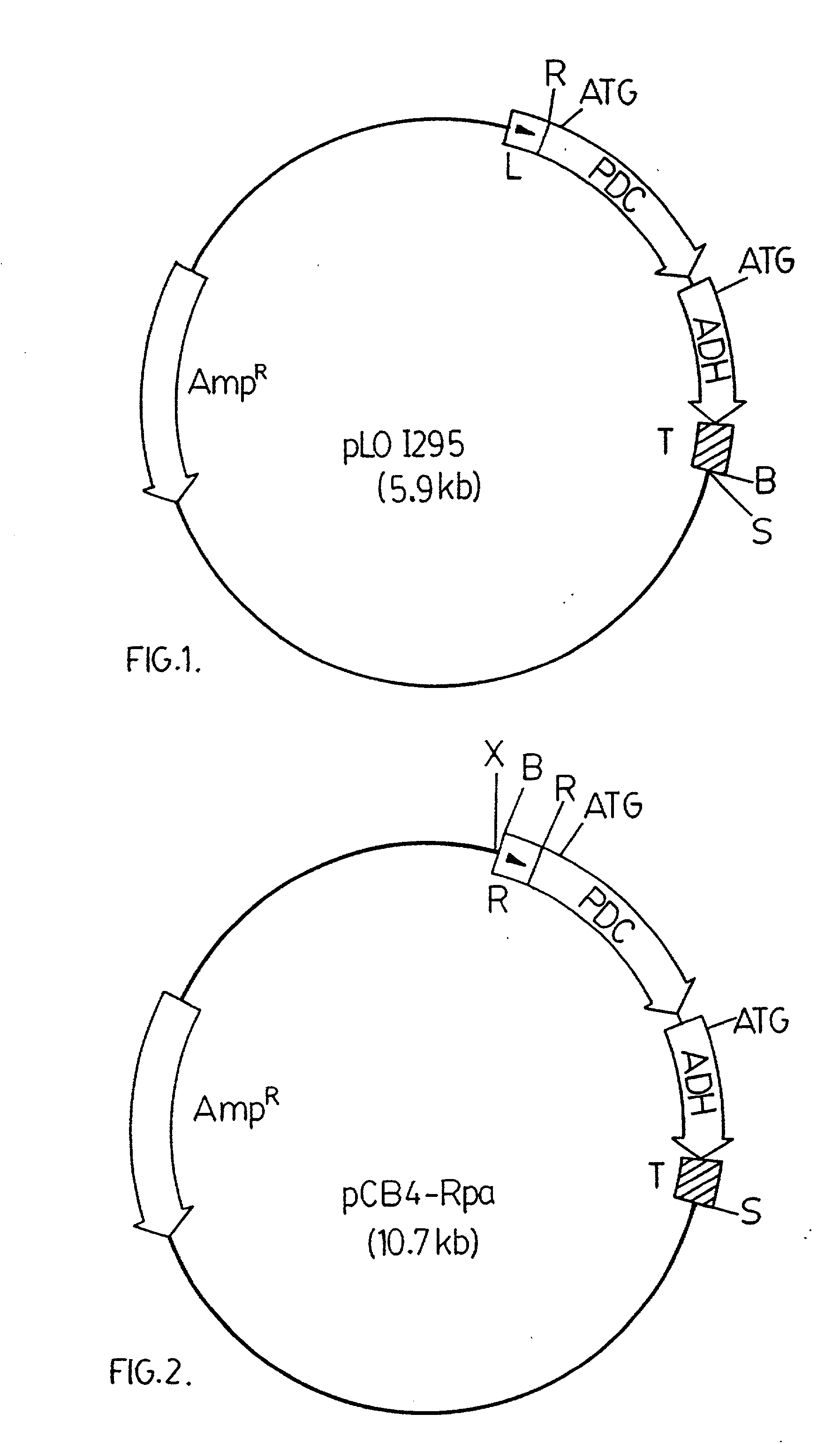
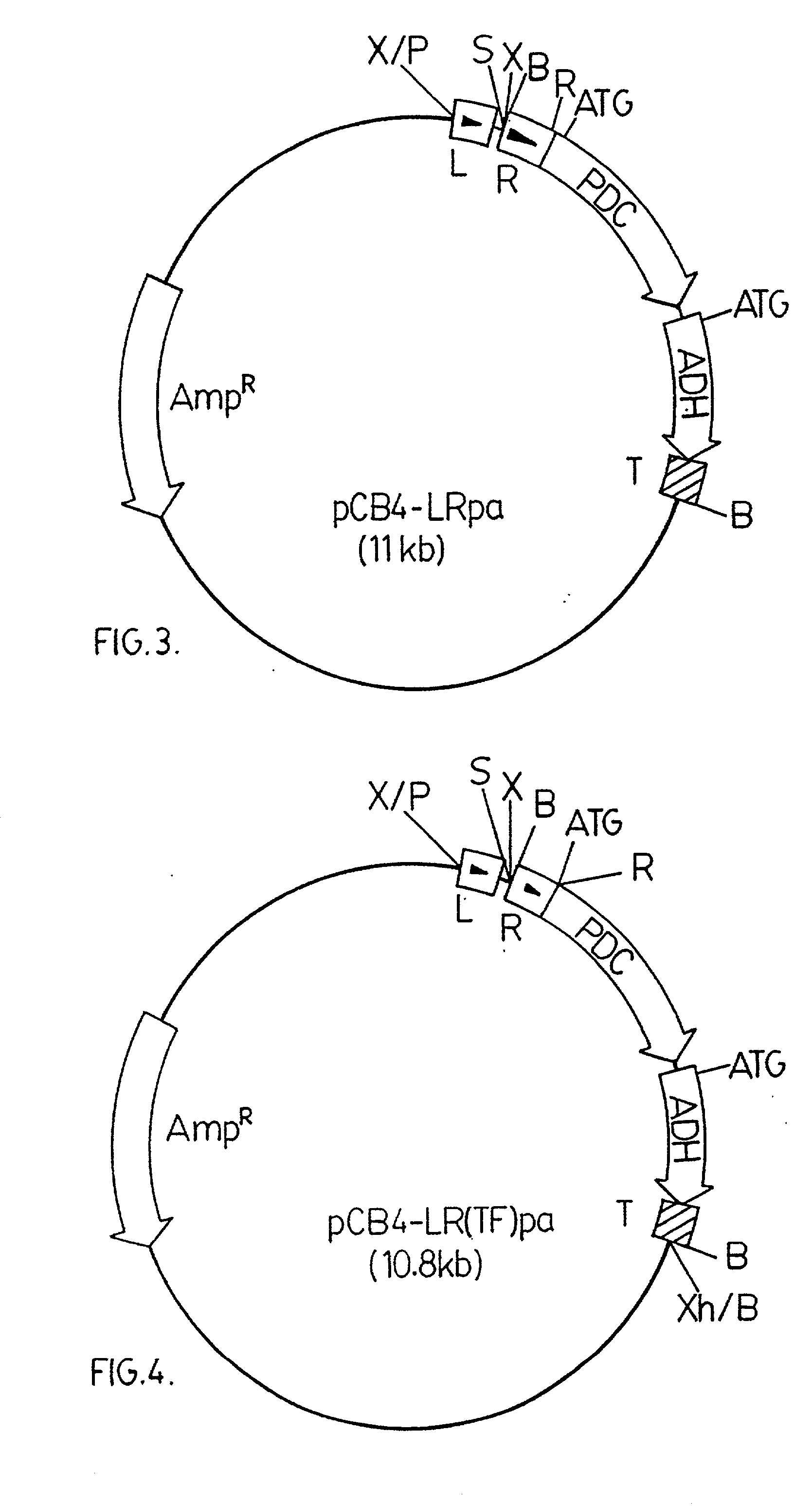
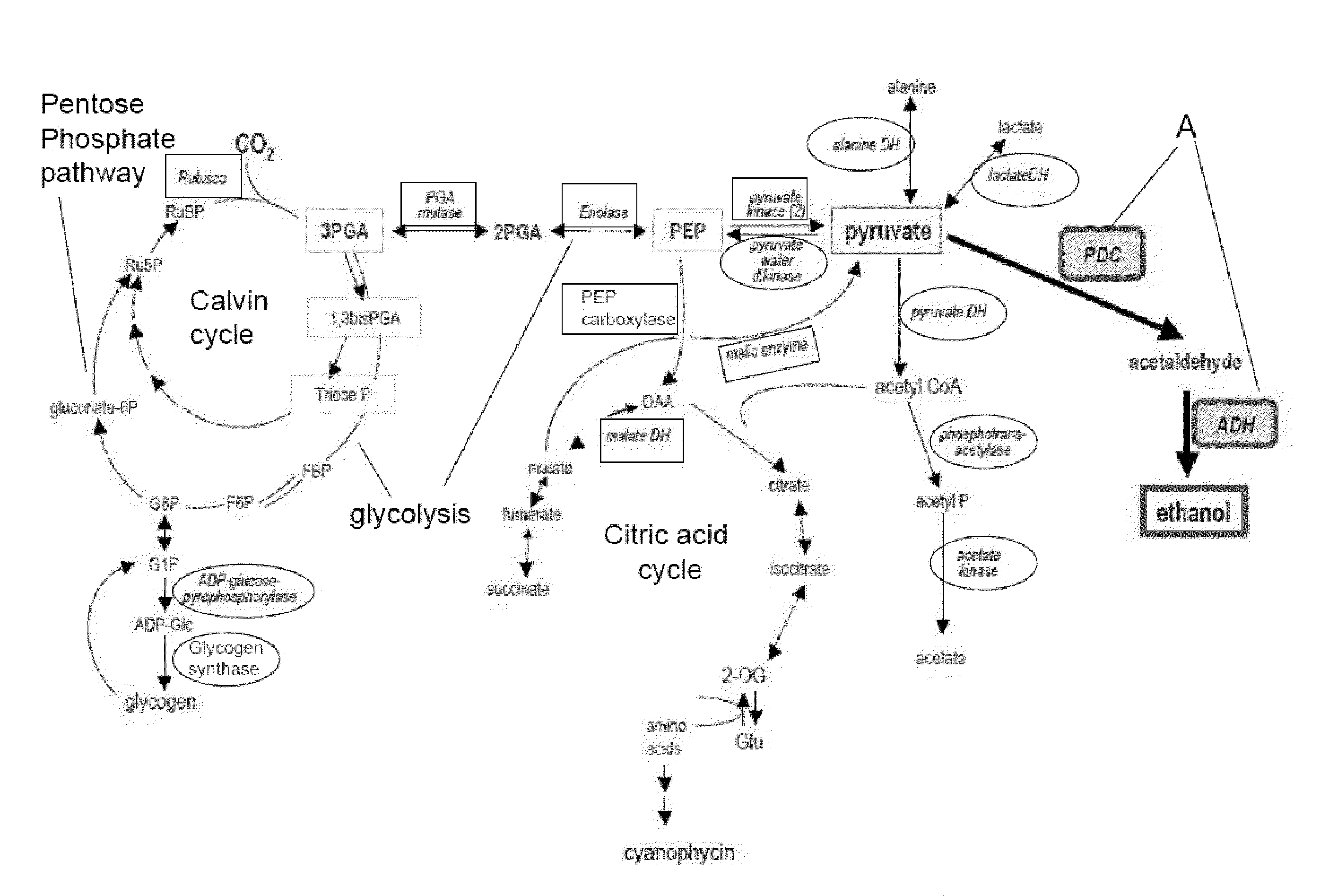
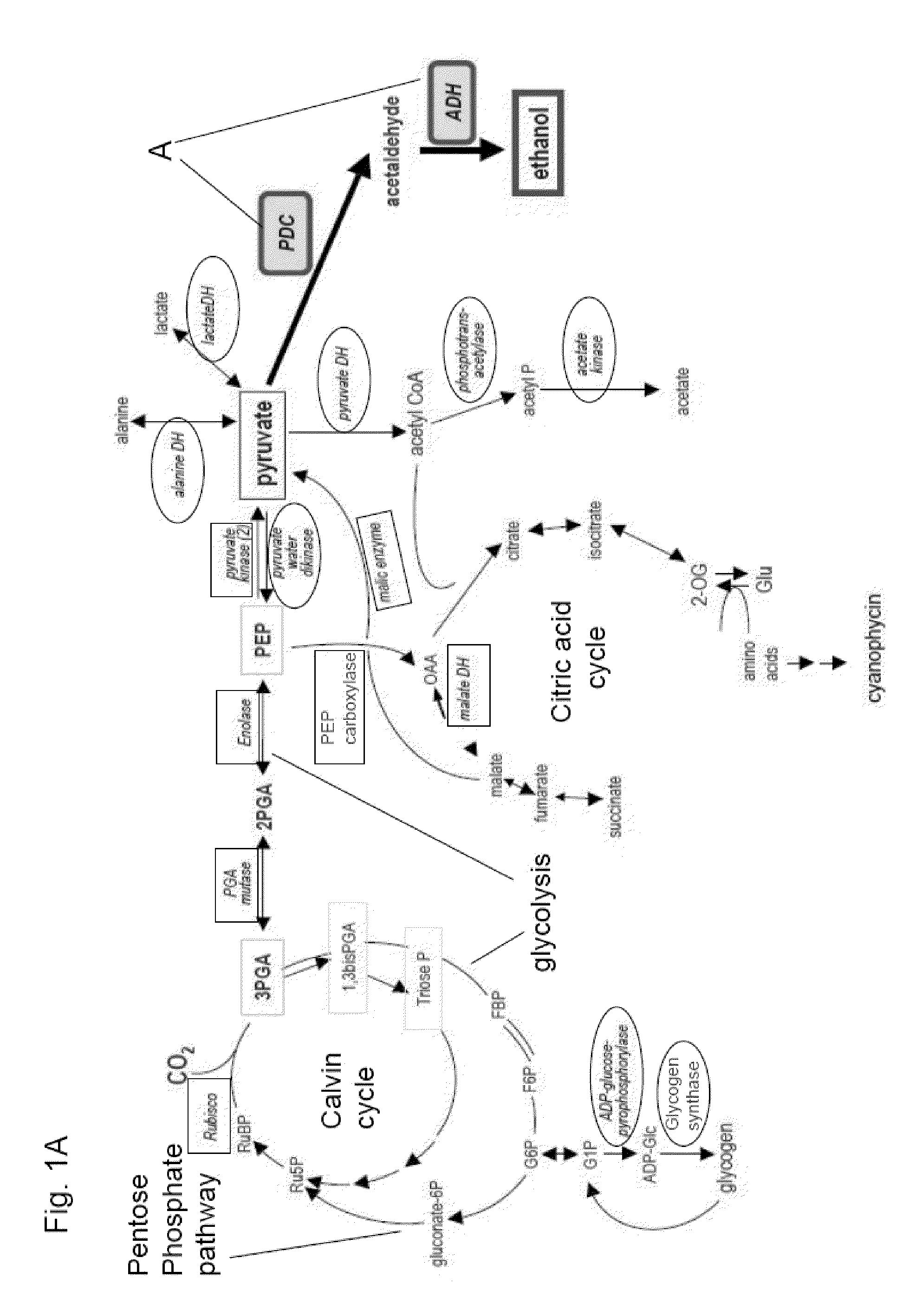
The invention provides a genetically modified Cyanobacteria having a construct comprising DNA fragments encoding pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase (adh) enzymes obtained from the Zymomonas mobilis plasmid pLOI295. The Cyanobacteria are capable of producing ethanol in recoverable quantities of at least 1.7 mumol ethanol per mg of chlorophyll per hour.
Owner:ENOL ENERGY
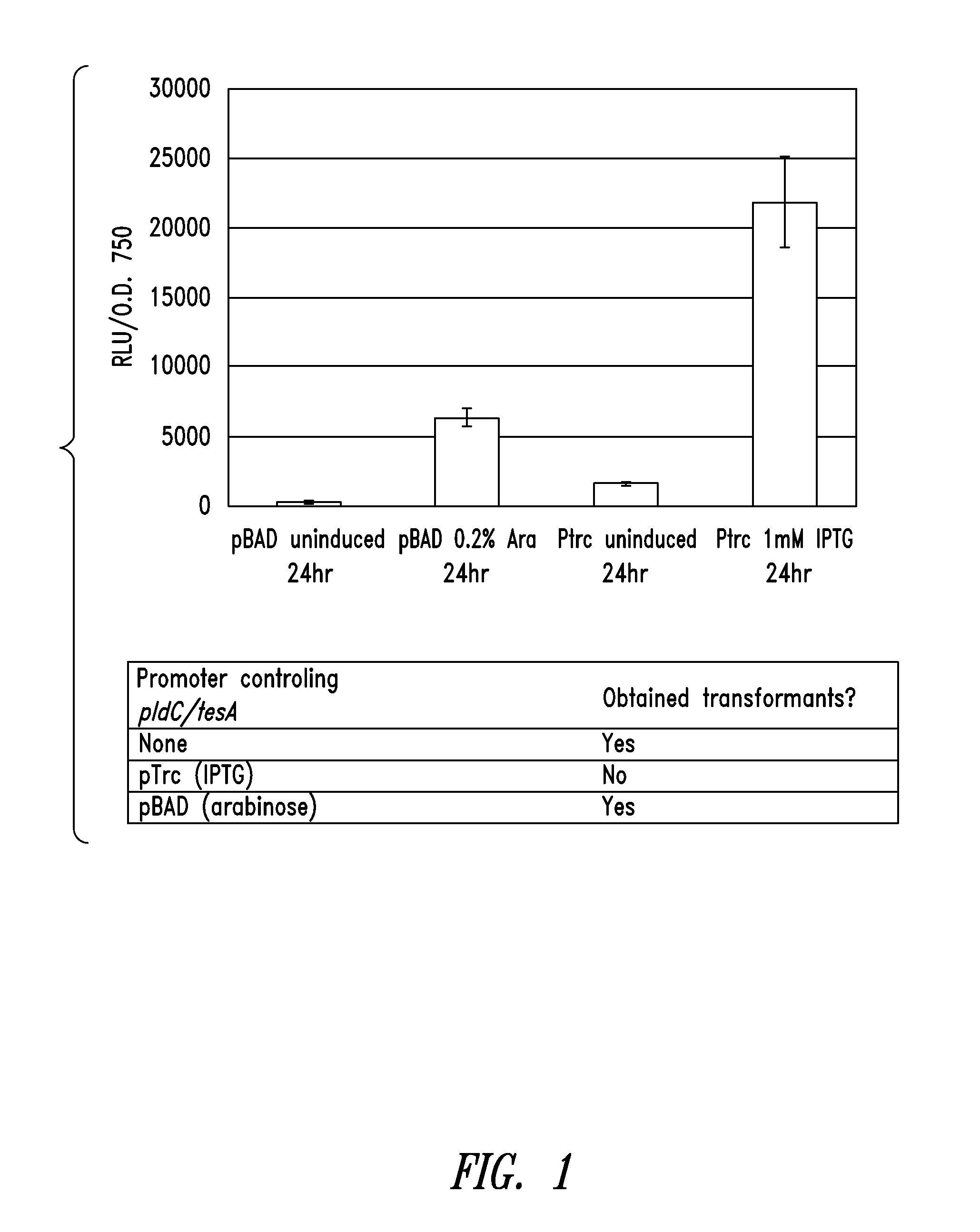
Transgenic plants with reduced level of saturated fatty acid and methods for making them
InactiveUS8063269B2Decrease in levelReduce contentSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHeterologousLipid formation
The present invention provides transgenic plants with reduced levels of saturated fatty acids in the seed oil and methods of making these plants. The transgenic plants developed through this method contain reduced levels of saturated fatty acids in seed oil due to expression of a prokaryotic delta-9 desaturase enzyme (i.e. an enzyme that introduces cis double bonds at the delta-9 position of saturated fatty acids) operably linked with an endoplasmic reticulum retention and retrieval signal sequence. One example of the invention is a plant expressing a heterologous delta-9 desaturase enzyme from cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans, which converts lipid-bound 16:0 and 18:0 fatty acids into corresponding 16:1 and 18:1, in operative linkage with a KKSS (SEQ ID NO:5) endoplasmic reticulum retention and retrieval signal sequence.
Owner:ALBERTA INNOVATES TECH FUTURES
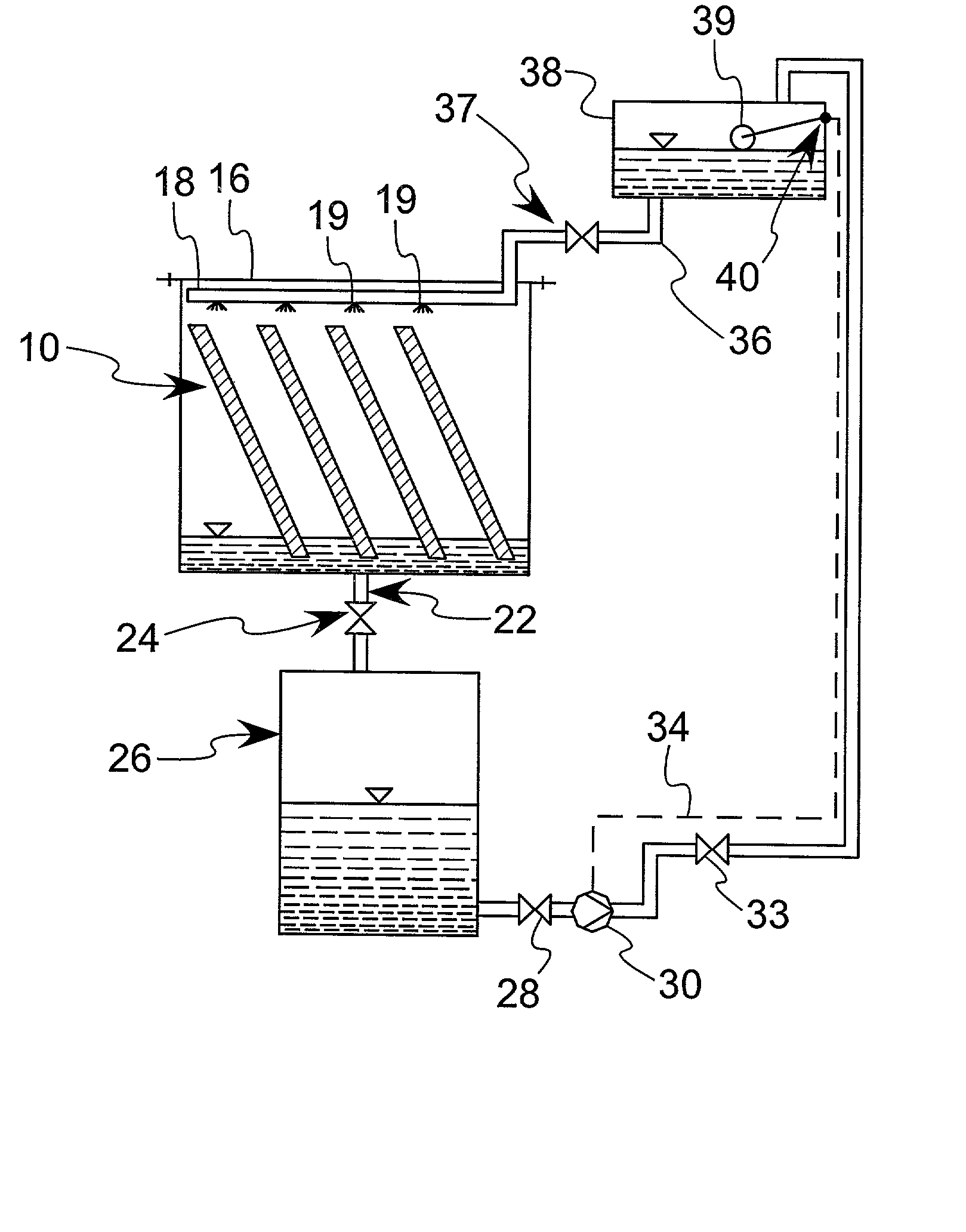
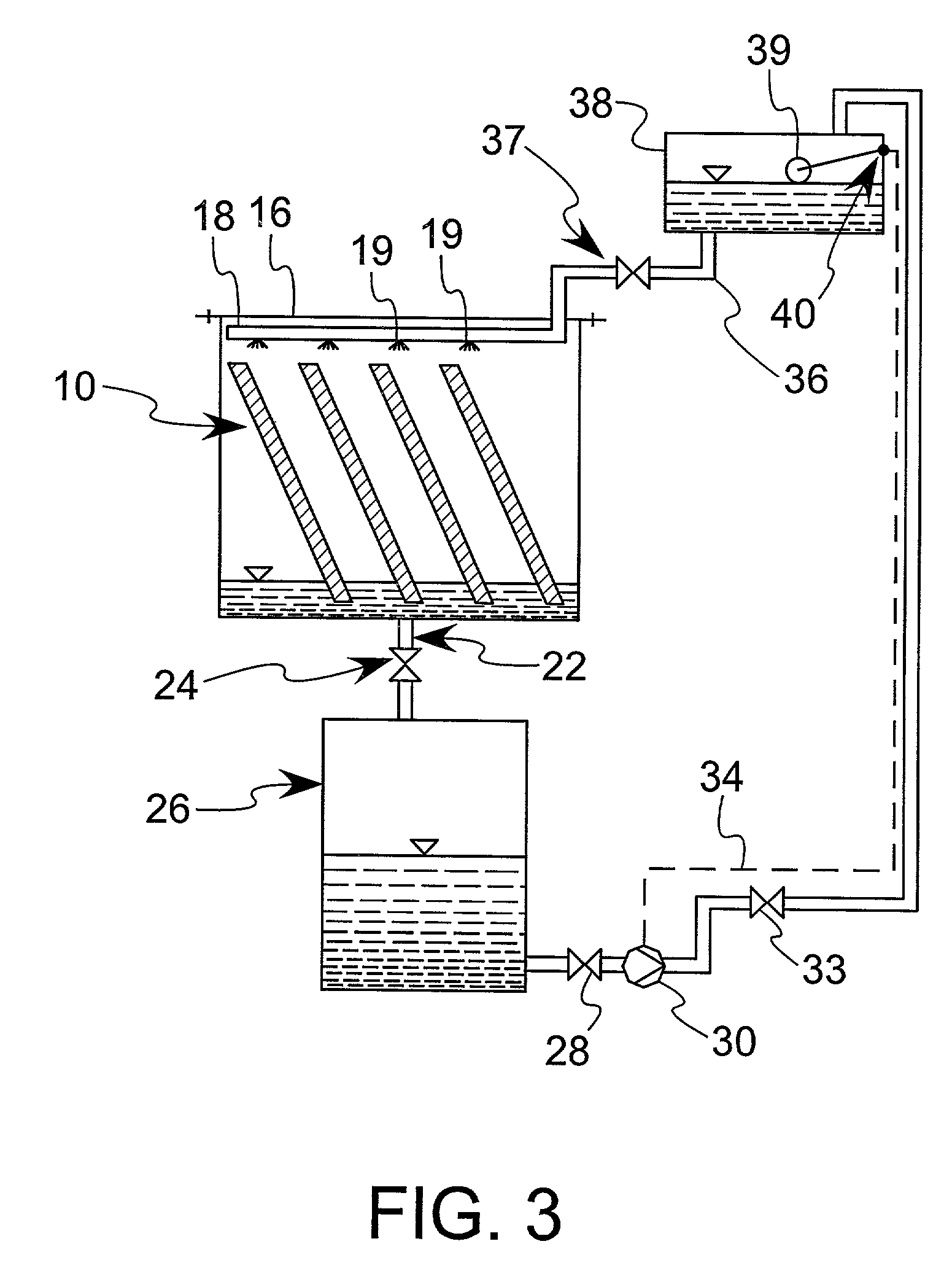
Enhanced practical photosynthetic CO2 mitigation
InactiveUS20020072109A1Increase the amount of waterBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCyanobacteria
This process is unique in photosynthetic carbon sequestration. An on-site biological sequestration system directly decreases the concentration of carbon-containing compounds in the emissions of fossil generation units. In this process, photosynthetic microbes are attached to a growth surface arranged in a containment chamber that is lit by solar photons. A harvesting system ensures maximum organism growth and rate of CO2 uptake. Soluble carbon and nitrogen concentrations delivered to the cyanobacteria are enhanced, further increasing growth rate and carbon utilization.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Genetically modified cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, the constructs and method thereof
InactiveUS6306639B1Inhibit transcriptionAlgae productsBacteriaPhylum CyanobacteriaKetoacid decarboxylase
The invention relates to the genetic modification of Cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, and more particularly, to the genetic modification of Cyanobacteria by incorporating the genetic information encoding for pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase (adh).
Owner:ENOL ENERGY
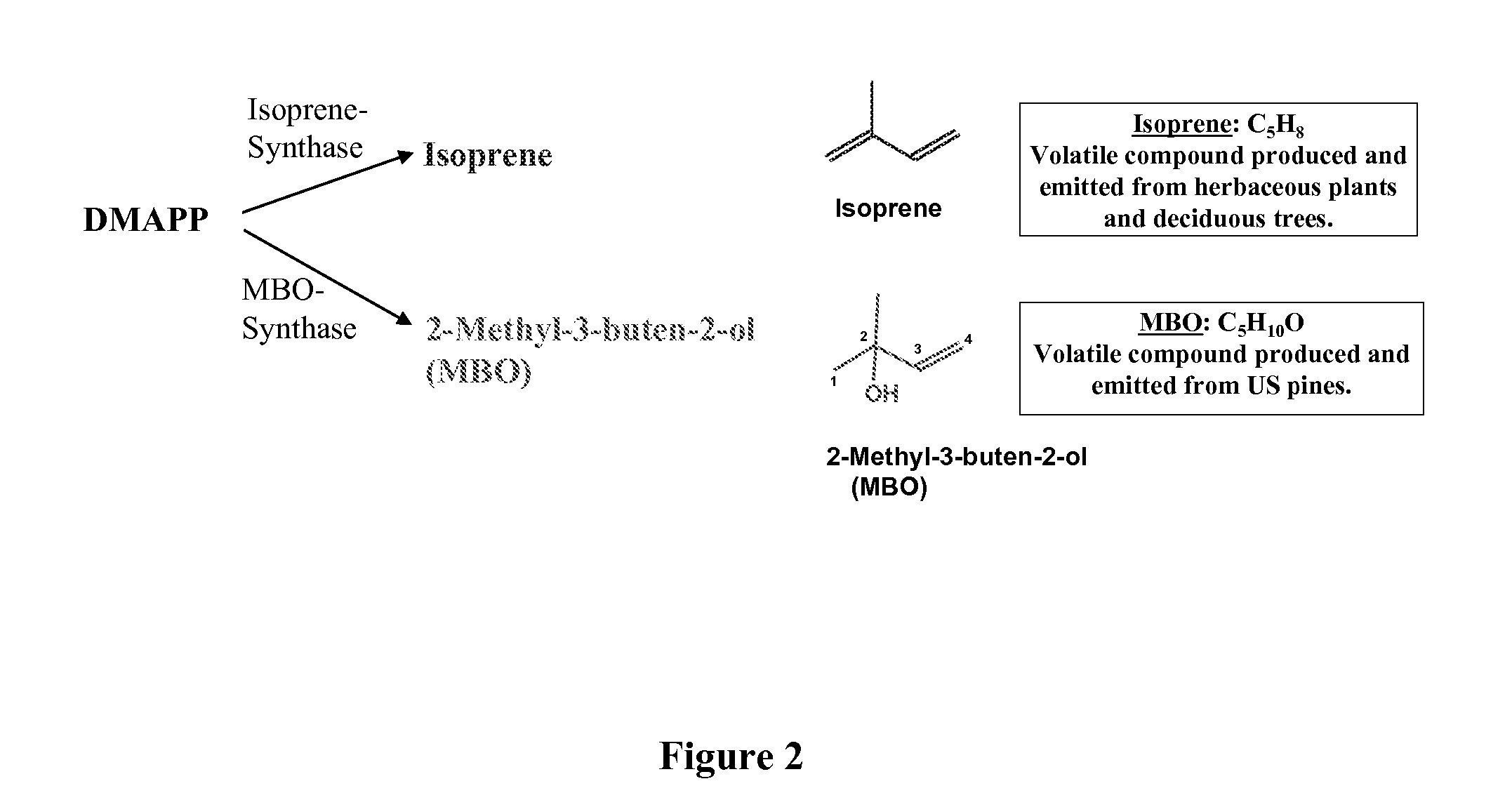
Short chain volatile hydrocarbon production using genetically engineered microalgae, cyanobacteria or bacteria
ActiveUS20080038805A1Promote reproductionLow costBacteriaUnicellular algaePhylum CyanobacteriaCyanobacteria
The present invention provides methods and compositions for producing isoprene hydrocarbons from microalgae, cyanobacteria, and photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic bacteria.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Expression of nucleic acid sequences for production of biofuels and other products in algae and cyanobacteria
Various embodiments provide, for example, vectors, expression cassettes, and cells useful for transgenic expression of nucleic acid sequences. In various embodiments, vectors can contain plastid-based sequences of unicellular photosynthetic bioprocess organisms for the production of food- and feed-stuffs, oils, biofuels, pharmaceuticals or fine chemicals.
Owner:KUEHNLE AGROSYST
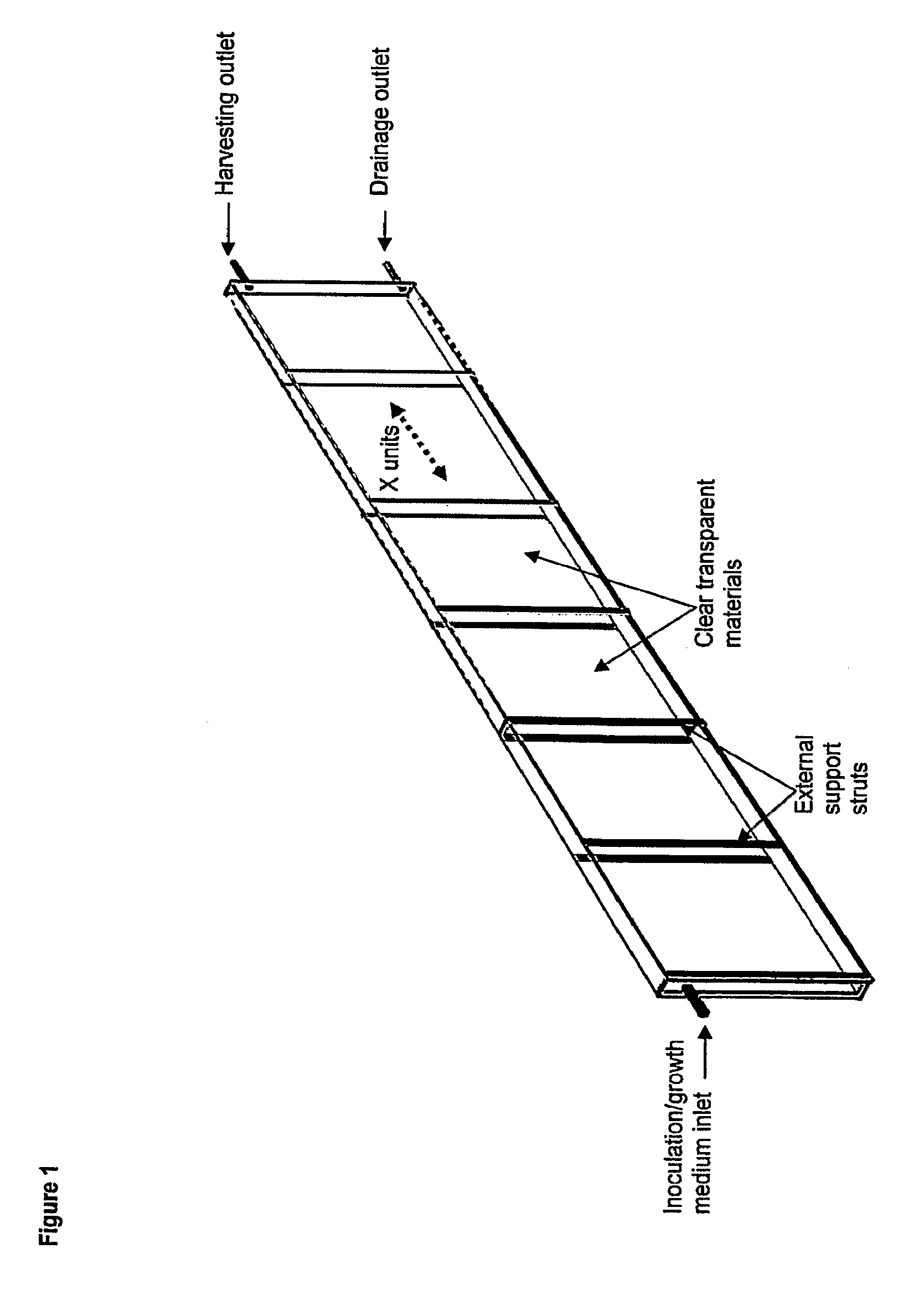
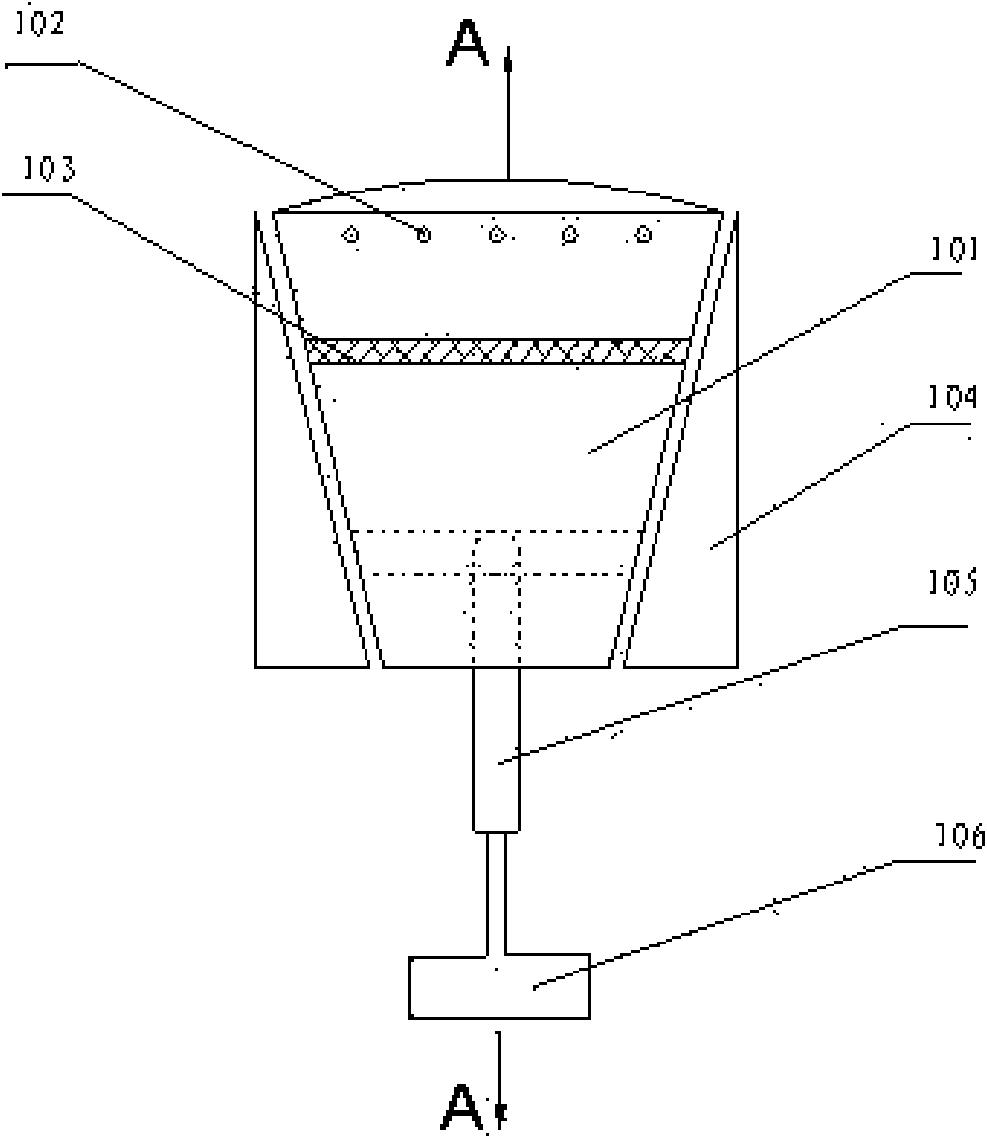
Photobioreactor and uses therefor
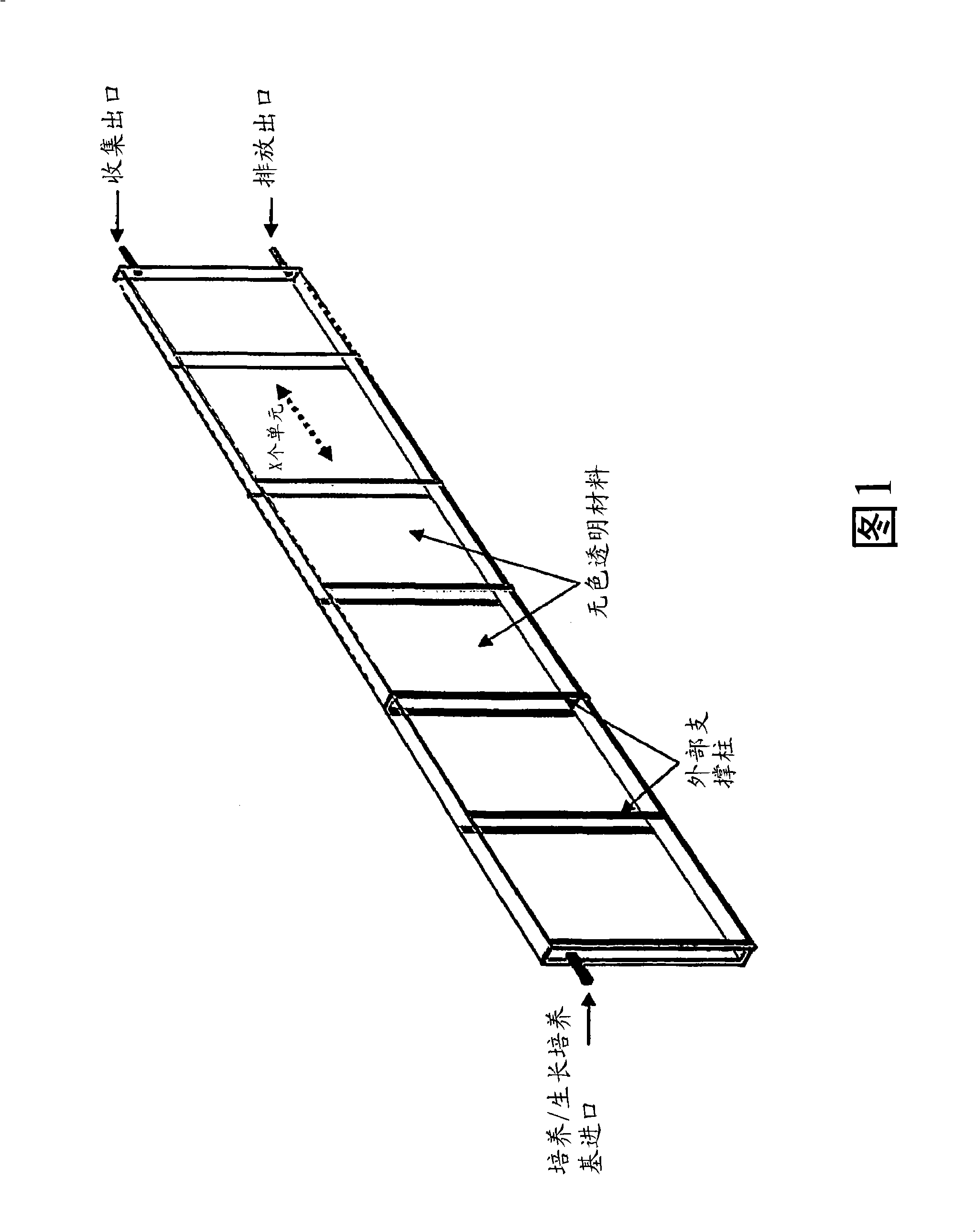
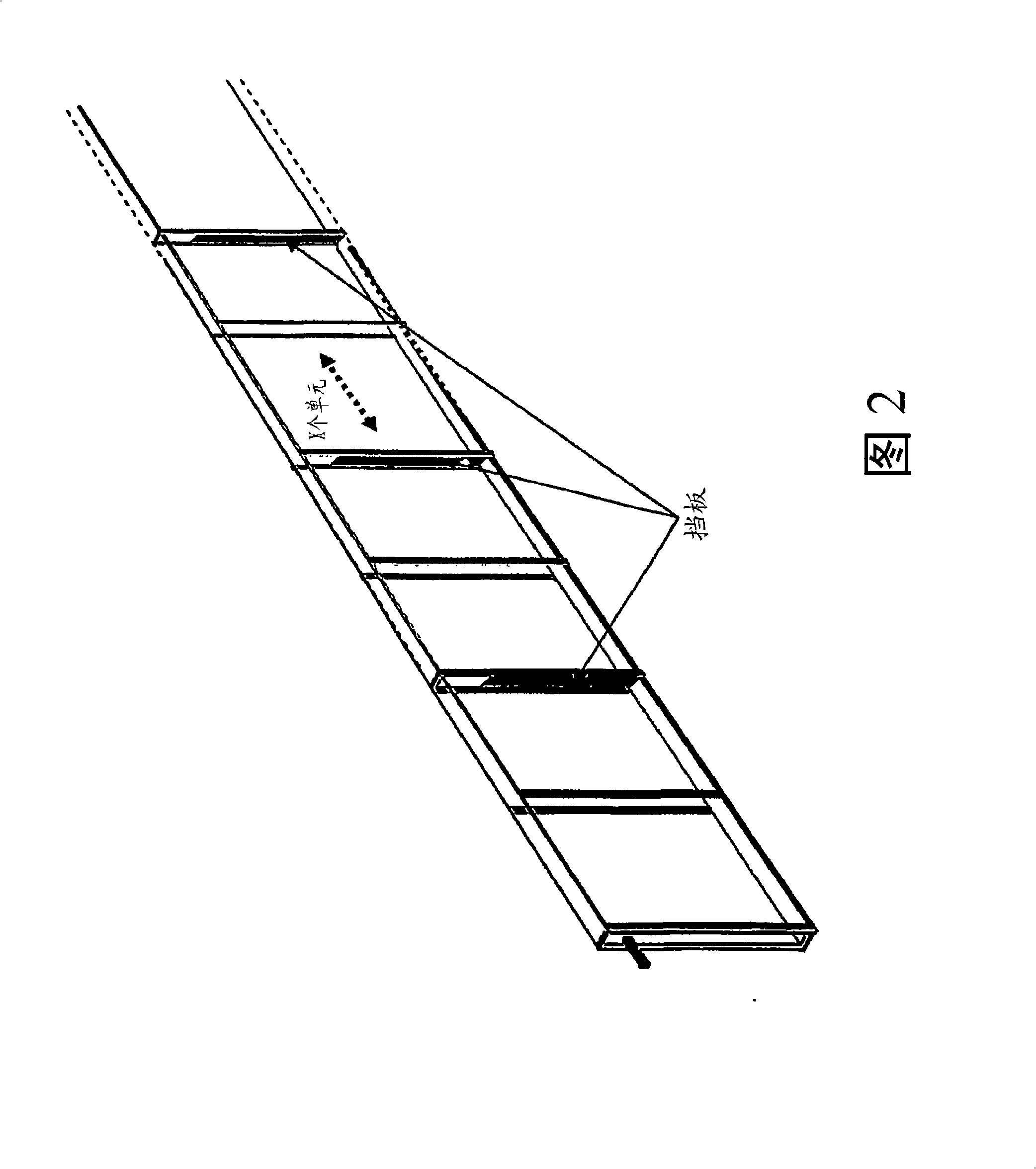
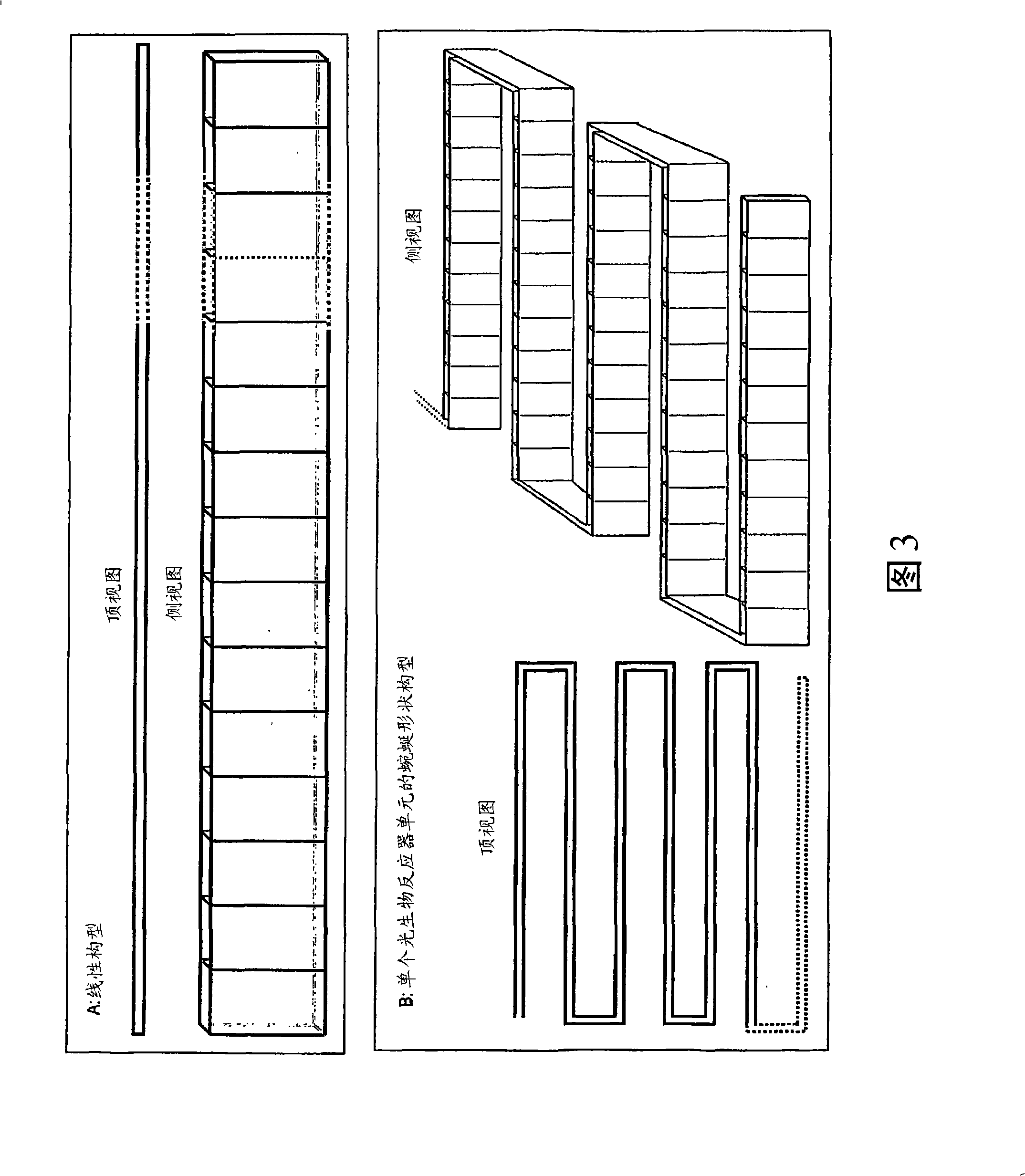
InactiveUS20100028976A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhylum CyanobacteriaPhotobioreactor
The present invention provides novel photobioreactors, modules thereof, and methods for use in culturing and harvesting algae and cyanobacteria.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Method for repairing water ecology
InactiveCN101575144ARestoring the underwater ecologyRealize self-purificationWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentZooplanktonPhylum Cyanobacteria
Owner:何文辉
Dry land erosion control using photosynthetic nitrogen-fixing microorganisms
InactiveUS20080236227A1Good curative effectInhibit seed germinationBio-organic fraction processingEfficient propulsion technologiesPhylum CyanobacteriaArid
In mesic environments, erosion control measures usually employ the establishment of vegetative cover by vascular plants in order to hold the soil in place. The current art often includes the application of seeds, chemical fertilizers, tackifiers, and mulches to promote the growth of vascular plants. However, arid environments so not support dense vegetative cover, but are instead dominated by photosynthetic microorganisms, primarily cyanobacteria and lichens. The cyanobacteria not only hold the soil in place, but also are the primary source of fixed nitrogen in arid environments. Disclosed herein, is a description of an apparatus and methods for the production and preservation of a photobiofertilizer as a means for repairing disturbed arid soils.
Owner:FLYNN TIMOTHY M
Algae supplement and treatment method
InactiveUS20080124286A1Enhances epidermal stem cell productionExtend the life cycleCosmetic preparationsBiocidePhylum CyanobacteriaCuticle
This invention relates to a method and composition for enhancing epidermal and / or hair follicle stem cell production, cell renewal, and / or growth of the skin, hair and nails, by topical administration of a therapeutic dosage of cyanobacteria and green algae and / or both simultaneous enteral and topical administration of a therapeutic dosage of cyanobacteria and green algae.
Owner:LISSON JEROLD B
Genetically modified Cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, the constructs and method thereof
The invention provides a genetically modified Cyanobacteria having a construct comprising DNA fragments encoding pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase (adh) enzymes obtained from the Zymomonas mobilis plasmid pLOI295. The Cyanobacteria are capable of producing ethanol in recoverable quantities of at least 1.7 mumol ethanol per mg of chlorophyll per hour.
Owner:ENOL ENERGY
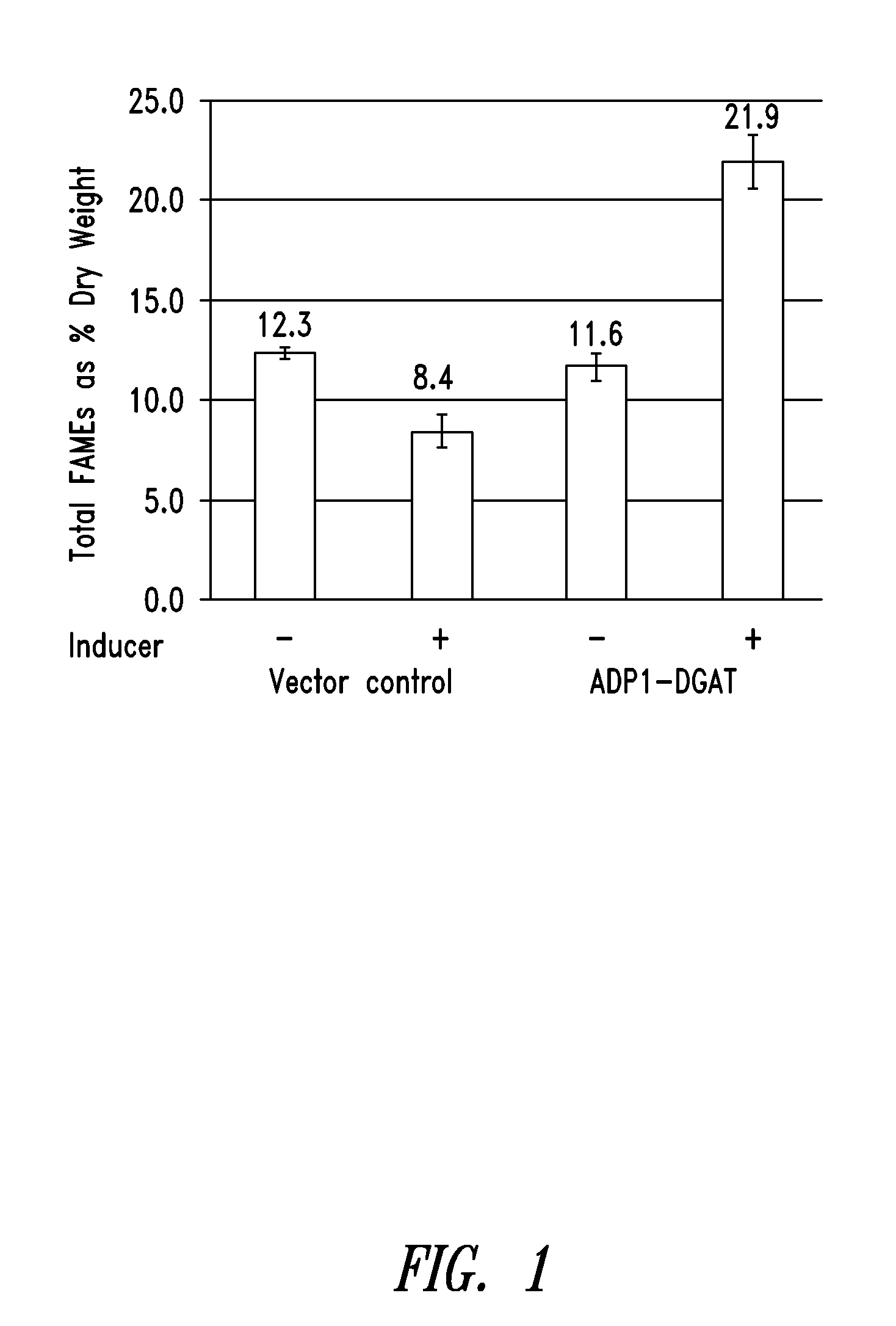
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing triglycerides
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
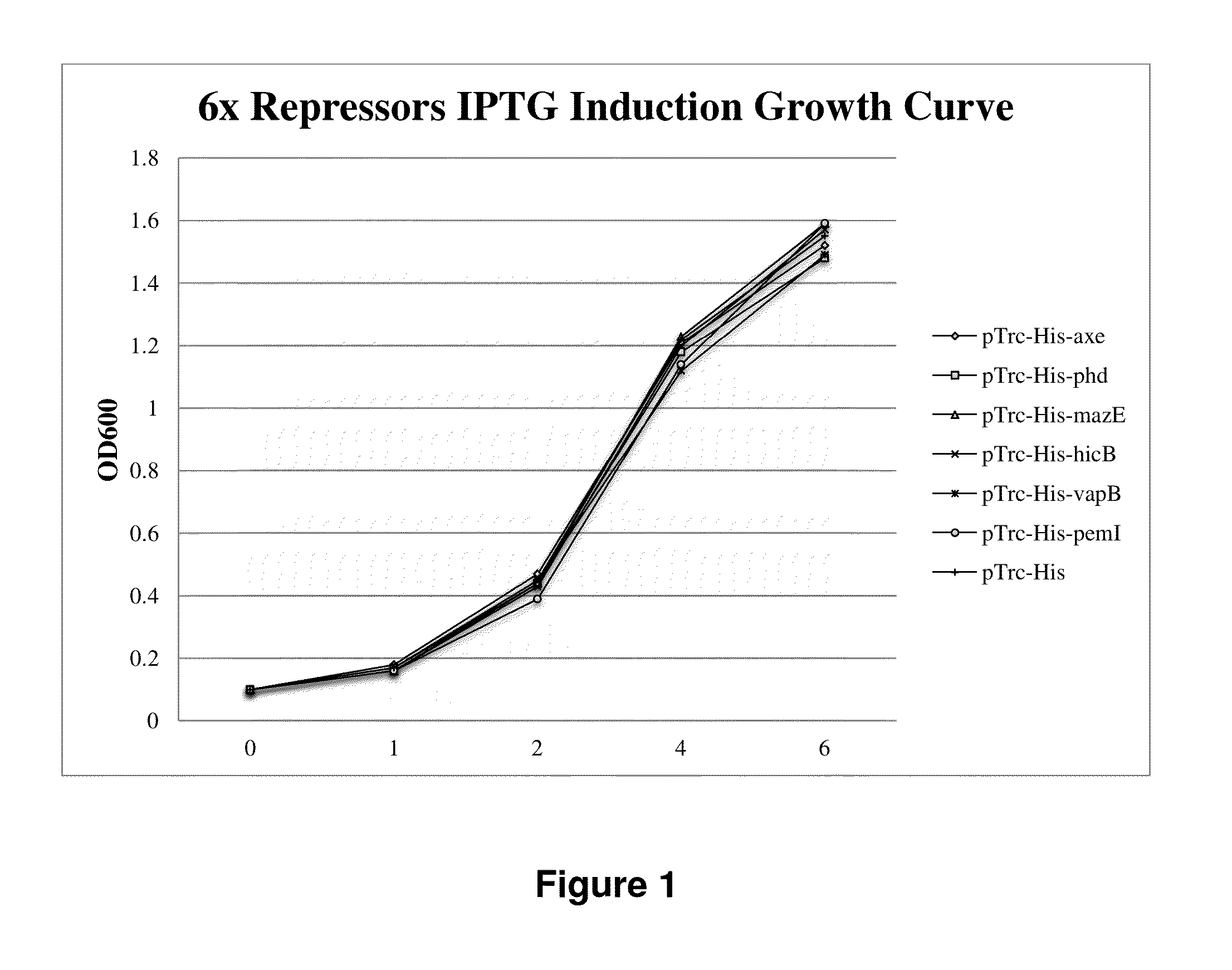
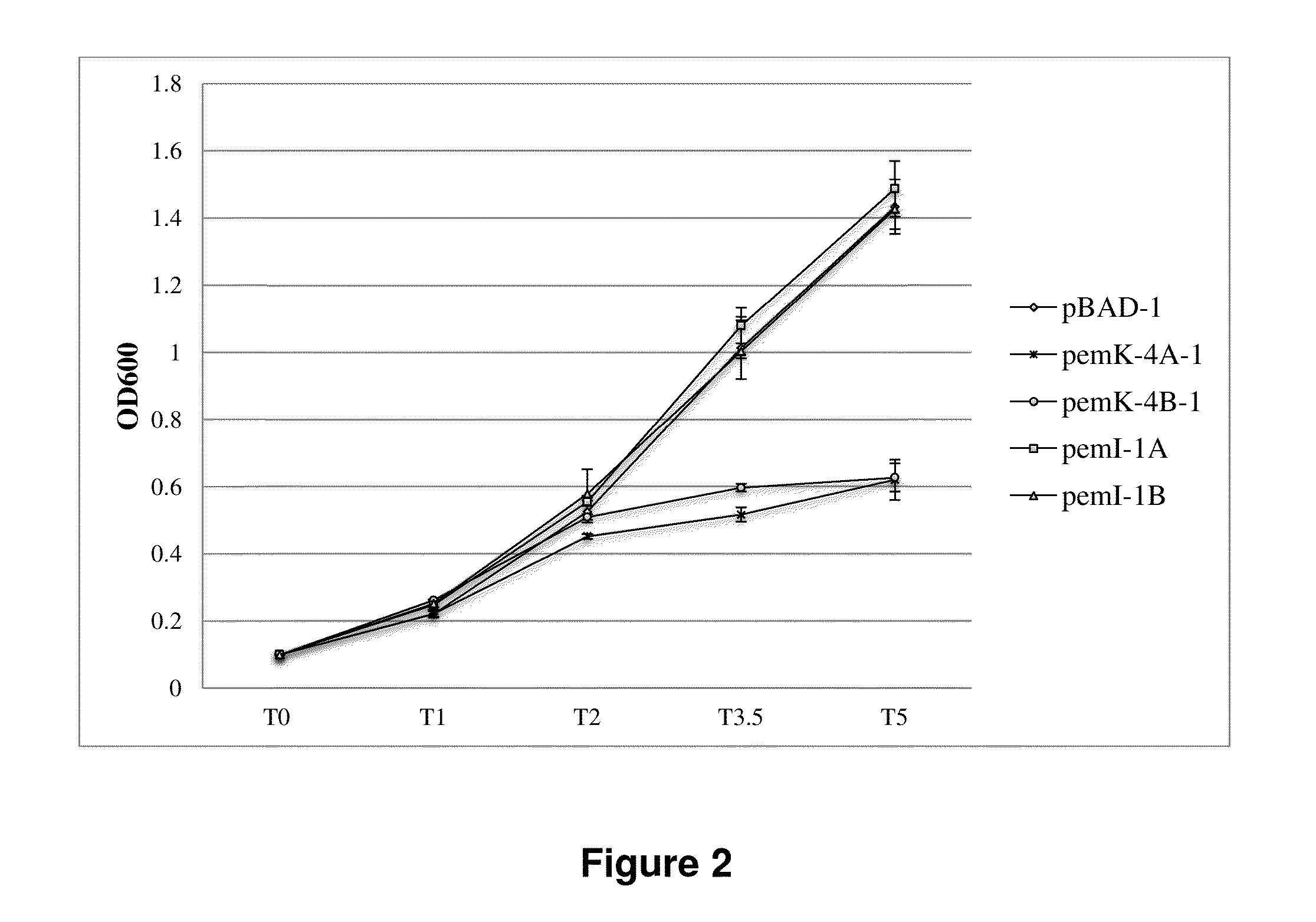
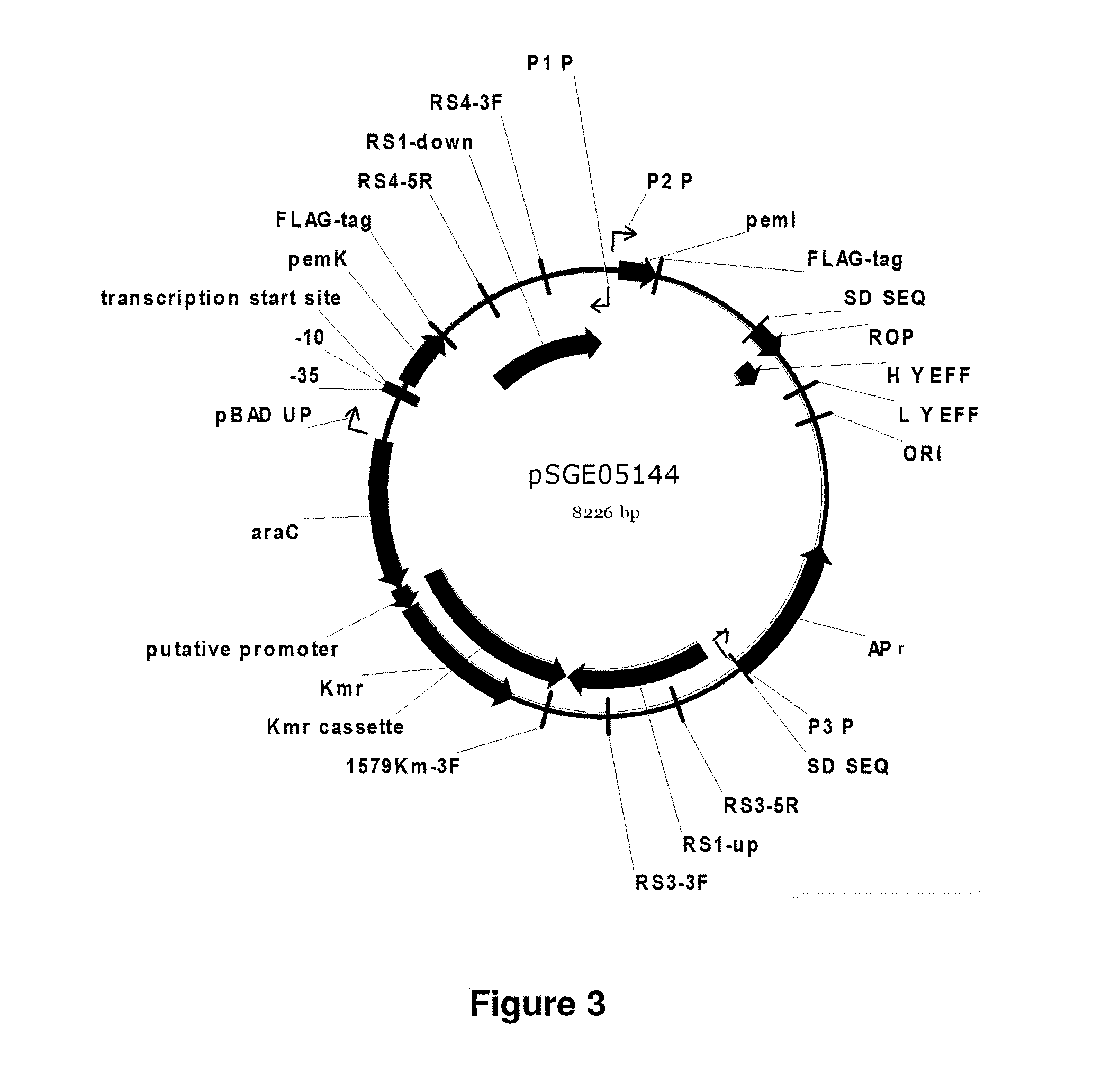
Regulation of toxin and antitoxin genes for biological containment
The present invention relates to the regulation of a toxin and / or antitoxin genes in a genetically engineered microorganism, such as cyanobacterial or eukaryotic algal strains, in particular for preventing unintentional and / or uncontrolled spread of the microorganisms. The present invention also includes methods of controlling the growth and / or survival of the engineered microorganism
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
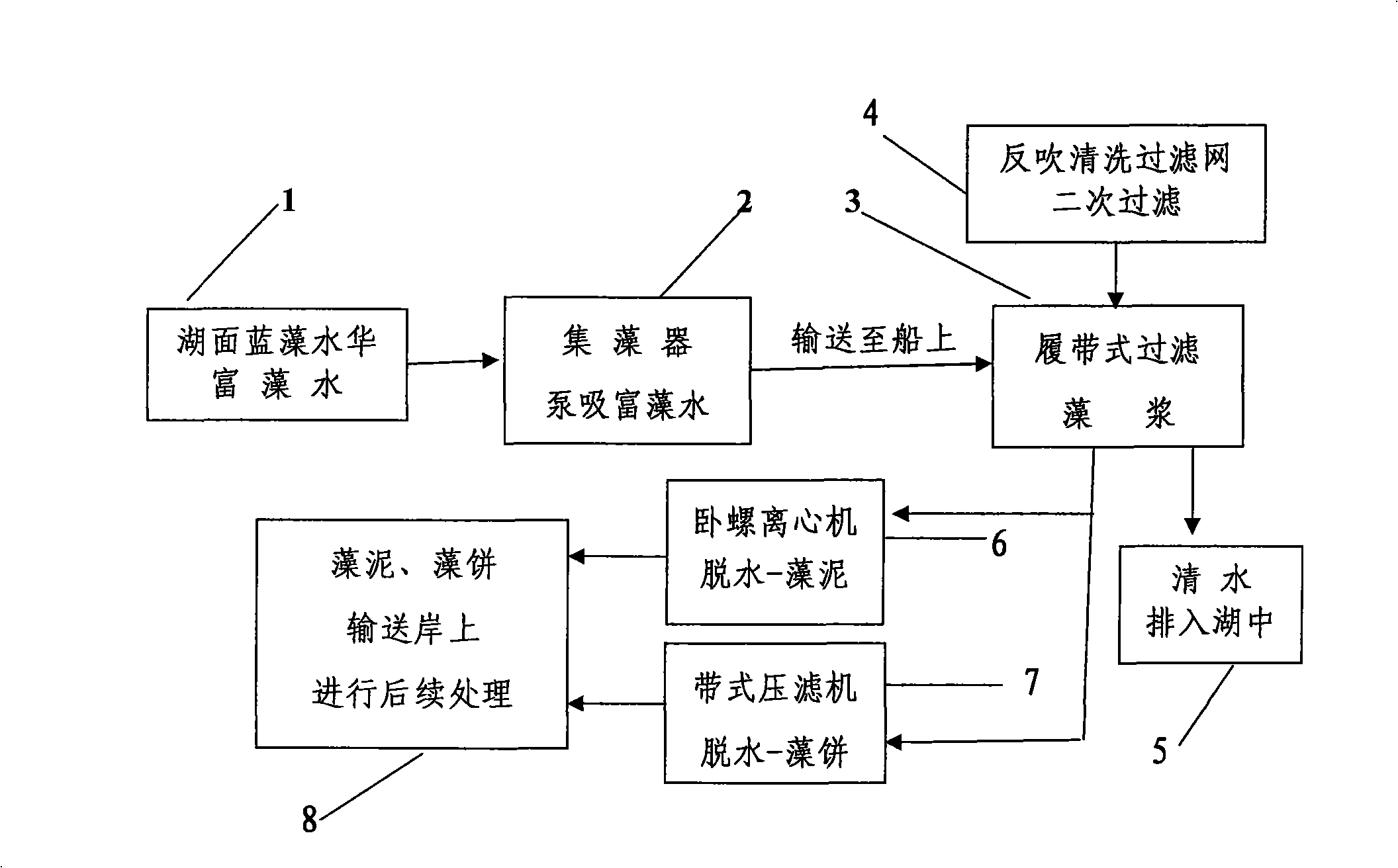
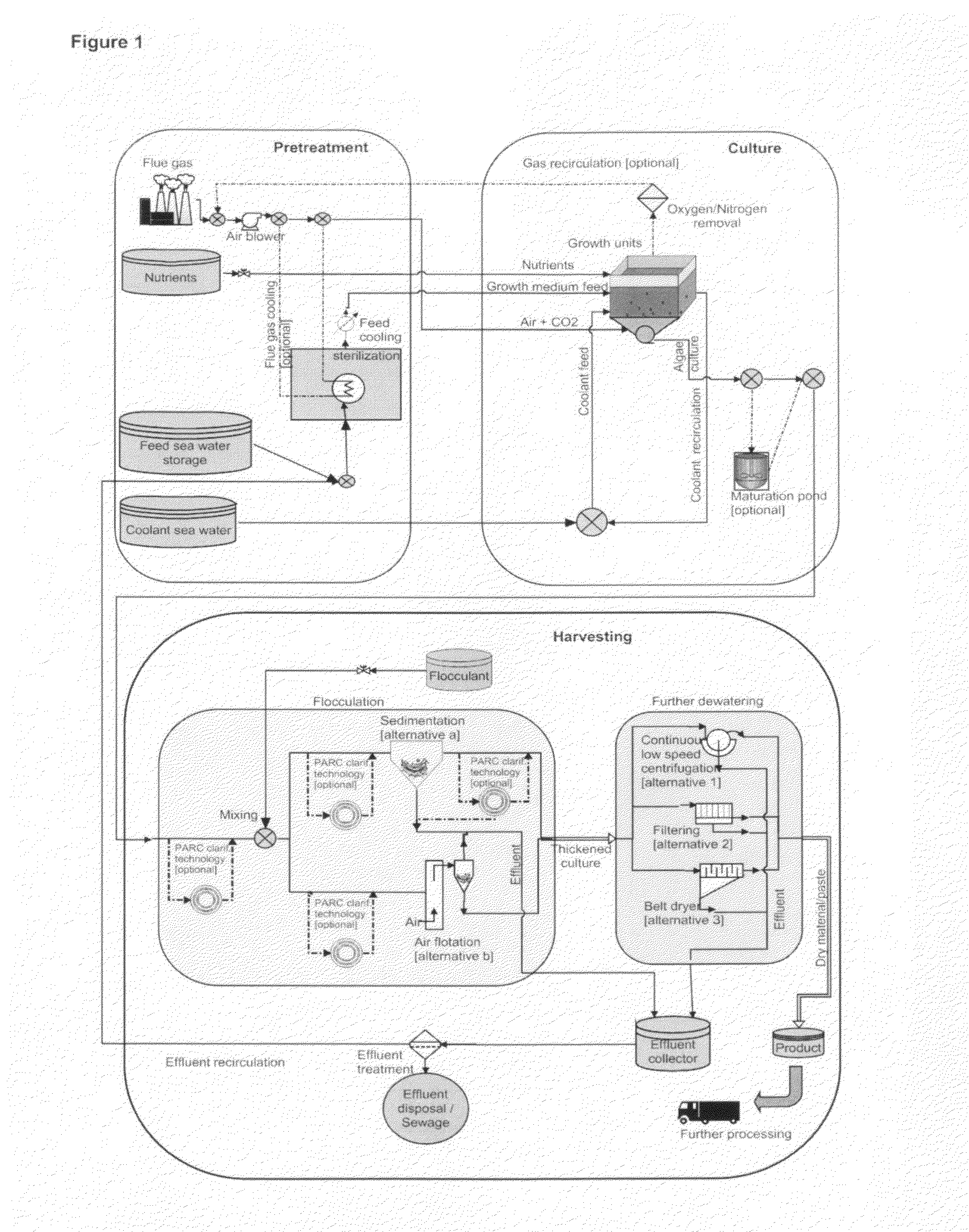
Method and apparatus for harvesting water bloom blue algae
InactiveCN101318714ASimple methodSimple and fast operationWater cleaningWater/sewage treatmentPhylum CyanobacteriaFiltration
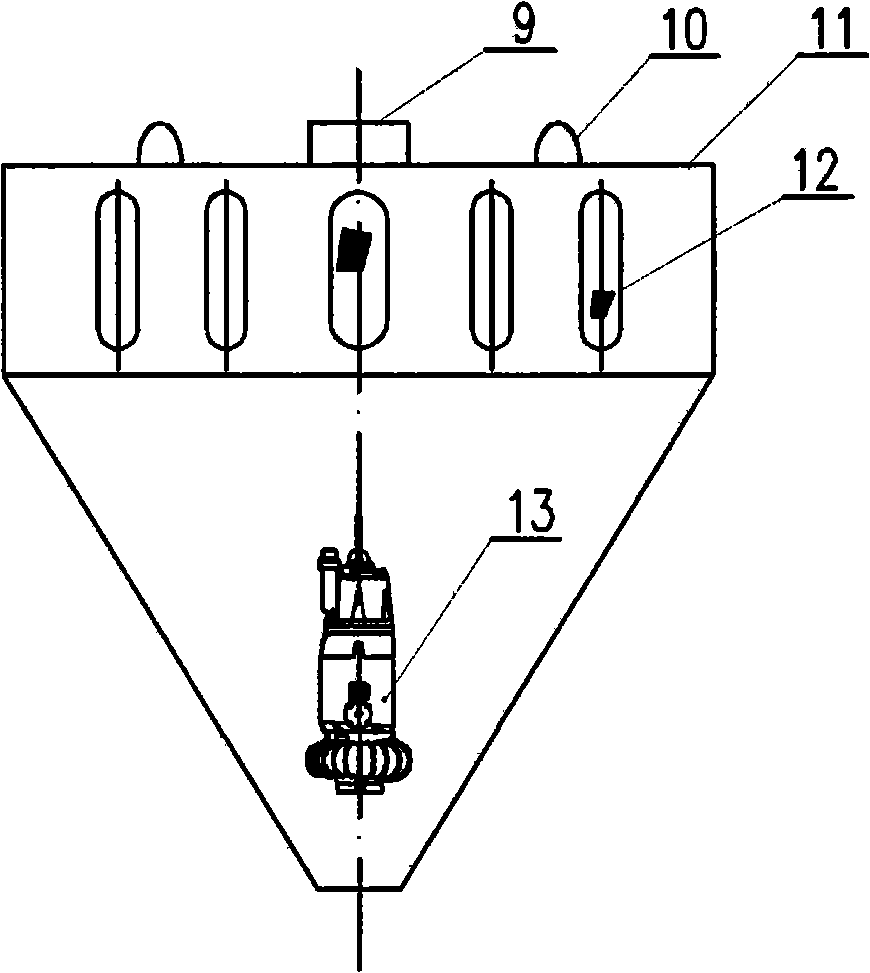
The invention discloses a method and a device for harvesting water-blooming cyanobacteria. The method comprises the following steps that: A. the water-blooming cyanobacteria is enriched into algae-rich water on water surfaces of lakes, reservoirs and riverways; B. an algae sucker pump is used to suck the algae-rich water; C. the algae-rich water is conveyed to a filtering system of a caterpillar system on a ship and is filtered into algae pulp; D. the algae pulp is subject to reverse purging and then secondary filtration; and E. the algae pulp is concentrated and dehydrated into algal biscuits or algae mud through a belt filter press or a horizontal screw decanter. The device for harvesting the water-blooming cyanobacteria comprises an algae sucker, a caterpillar algae-laden water filtering device, the belt filter press and the horizontal screw decanter, wherein, the fore of the ship is provided with the algae sucker, a non-clogging pump or a membrane pump is arranged in the algae sucker, the upper end of the algae sucker is provided with an impurity prevention net, and a cover plate is provided with a hoisting ring; and the caterpillar filtering device is fixed on a main frame body, and a stainless steel foraminous conveyer is arranged below a filter screen. The method is easy to operate, saves the energy, has low cost, a simple structure and convenient use, and effectively solves the problems of harvesting, concentration and dehydration of the water-blooming cyanobacteria accumulated in the lakes, reservoirs and riverways.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Genetically Modified Cyanobacteria for the Production of Ethanol
InactiveUS20100068776A1Increased biosynthetic levelsImprove the level ofBacteriaBiofuelsPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
The invention provides novel compositions of matter for the production of ethanol from carbon dioxide and water. Particularly, the invention provides photoautotrophic organisms having a first and second genetic modification, wherein the first genetic modification improves the ethanol production from organisms having the second genetic modification.
Owner:ALGENOL BIOFUELS
Fertilizers and methods for using biotic science to feed soils
ActiveUS20090188290A1Improve fertilityEnhanced ChelationCalcareous fertilisersProductsPhylum CyanobacteriaCyanobacteria
Biotic fertilizers are described that build soil nutrients by accelerating the growth of topsoil microorganisms Biotic fertilizers are primarily aimed at increasing populations of cyanobacteria, formally known as blue-green algae, and like organisms that have the ability to engage in photosynthesis reand to engage in the extraction of nitrogen from the atmosphere. Methods of biotic fertilizer manufacture are presented that utilize animal waste product as well as desirable compositions obtained thereby.
Owner:PERFECT BLEND
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing lipids
ActiveUS20110250659A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease volumeHydrolasesUnicellular algaePhylum CyanobacteriaLipid formation
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, e.g., Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a phospholipase and / or thioesterase, which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. This disclosure also describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides, as well as photosynthetic microorganism comprising mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen under reduced nitrogen conditions as compared to a wild type photosynthetic microorganism.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
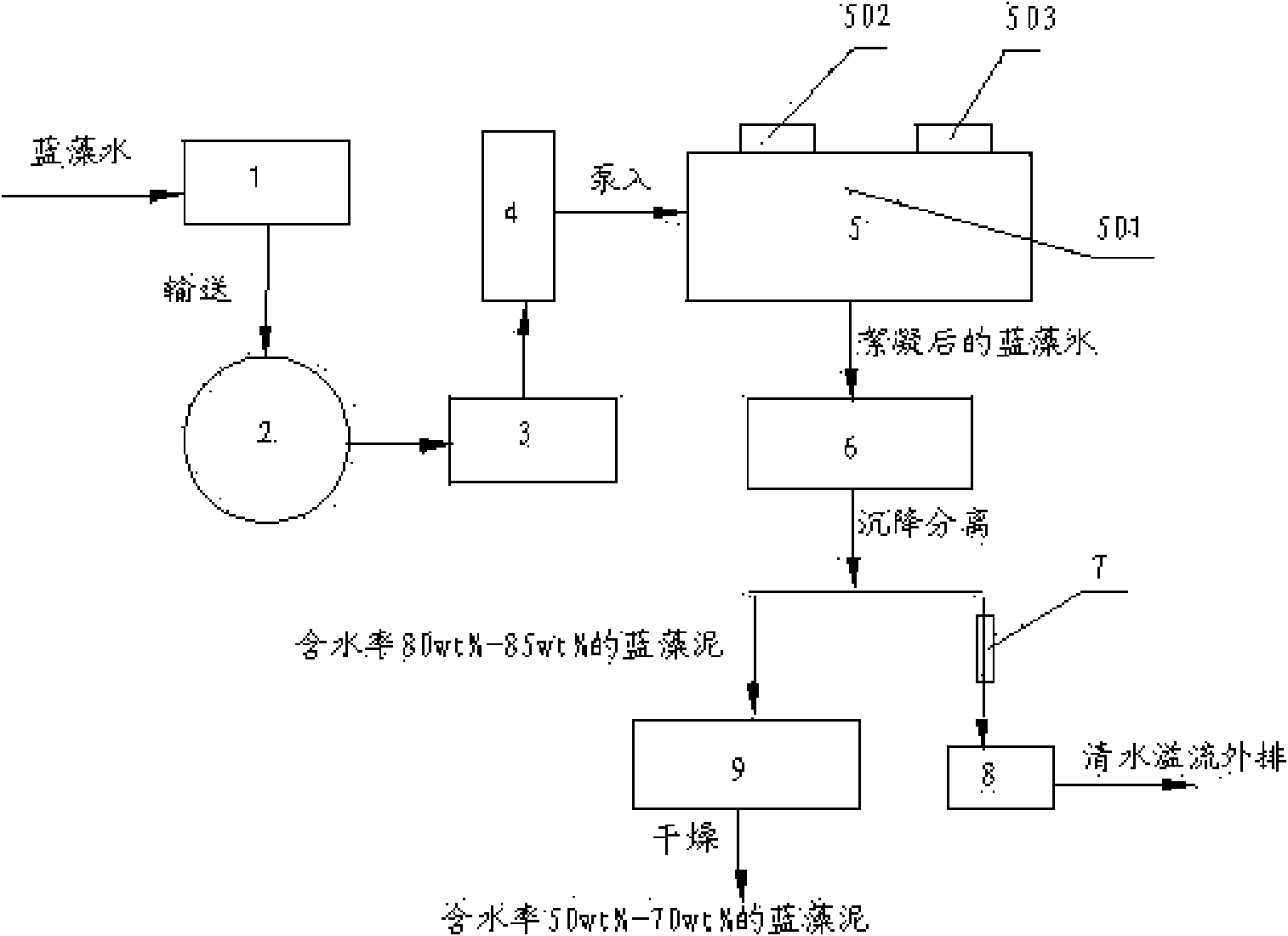
Method for controlling cyanobacteria bloom
InactiveCN101602533AImprove processing efficiencyIncreased efficiency of harvesting cyanobacteriaSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater cleaningPhylum CyanobacteriaResource utilization
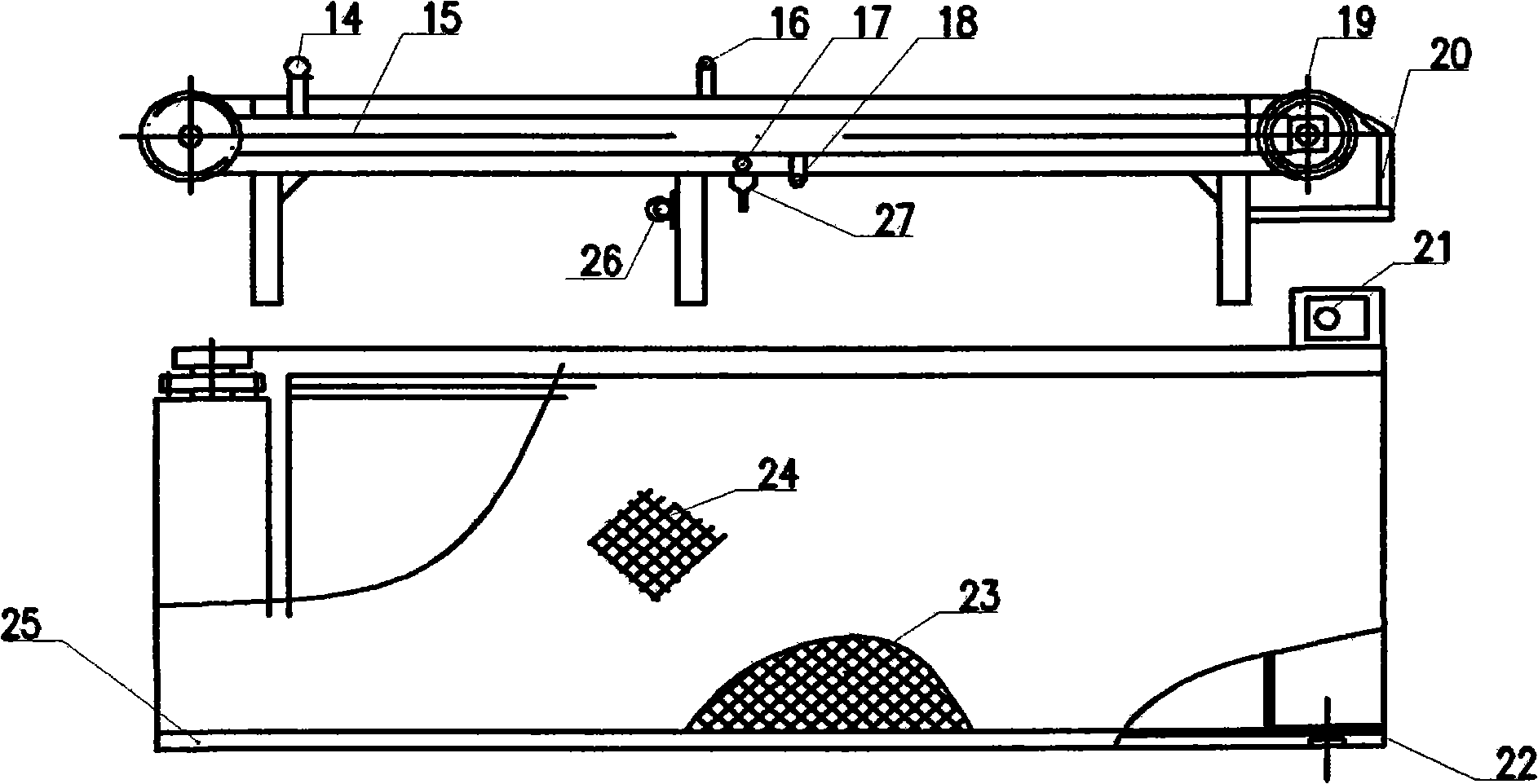
The invention discloses a method for controlling cyanobacteria bloom, which belongs to the technical field of water pollution treatment. The method for controlling the cyanobacteria bloom comprises the steps of: (1) utilizing an acquisition system with a sucking disk to perform suction acquisition on cyanobacteria on the water surface of a water body; (2) pumping cyanobacteria water which is subjected to suction acquisition into a conveying pipeline through a suction pump, and conveying the cyanobacteria water to a storage tank; (3) pumping the cyanobacteria water in the storage tank into a dosing system through a screw pump, adding a flocculating agent into the cyanobacteria water, and mixing evenly to ensure that the cyanobacteria is flocculated; (4) sending the cyanobacteria water with the flocculated cyanobacteria into a settling separation system for solid-liquid separation to obtain water and cyanobacteria mud with the water content of 80 percent, sending the water obtained after the solid-liquid separation to a clear water tank for temporary storage through the settling separation system, and then draining the water into the water body through an overflow port; and (5) separating the obtained cyanobacteria mud to obtain cyanobacteria mud with the water content less than 70 percent after the drying. The method for controlling the cyanobacteria bloom has the advantages of environmental protection, low cost and convenient operation, and can realize the safe disposal and resource utilization of the cyanobacteria bloom.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
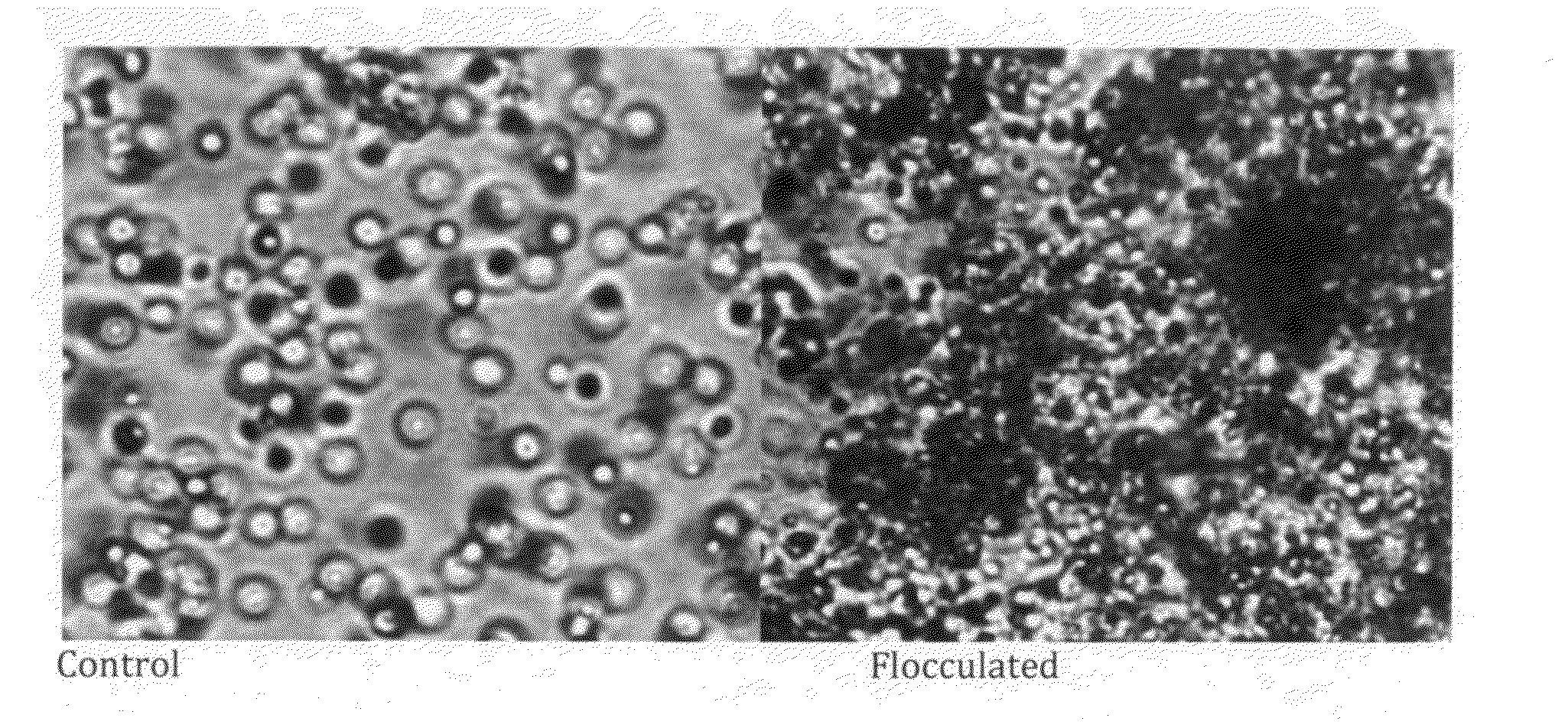
Method and system for efficient harvesting of microalgae and cyanobacteria
The high-speed centrifugation heretofore required for harvesting micro algae and cyanobacteria cultured for biofuels and other co-products is a major cost constraint. Mixing algae / cyanobacteria at high-density culture with far less alkali than previously assumed is sufficient to flocculate the cells. The amount of flocculant required is a function of the logarithm of cell density, and is not a linear function of cell density as had been thought. The least expensive alkali treatments are with slaked limestone or dolomite (calcium hydroxide and magnesium hydroxides). Further water can be removed from the floc by sedimentation, low speed centrifugation, dissolved air flotation or filtration, prior to further processing to separate oil from valuable co-products.
Owner:TRANSALGAE ISRAEL
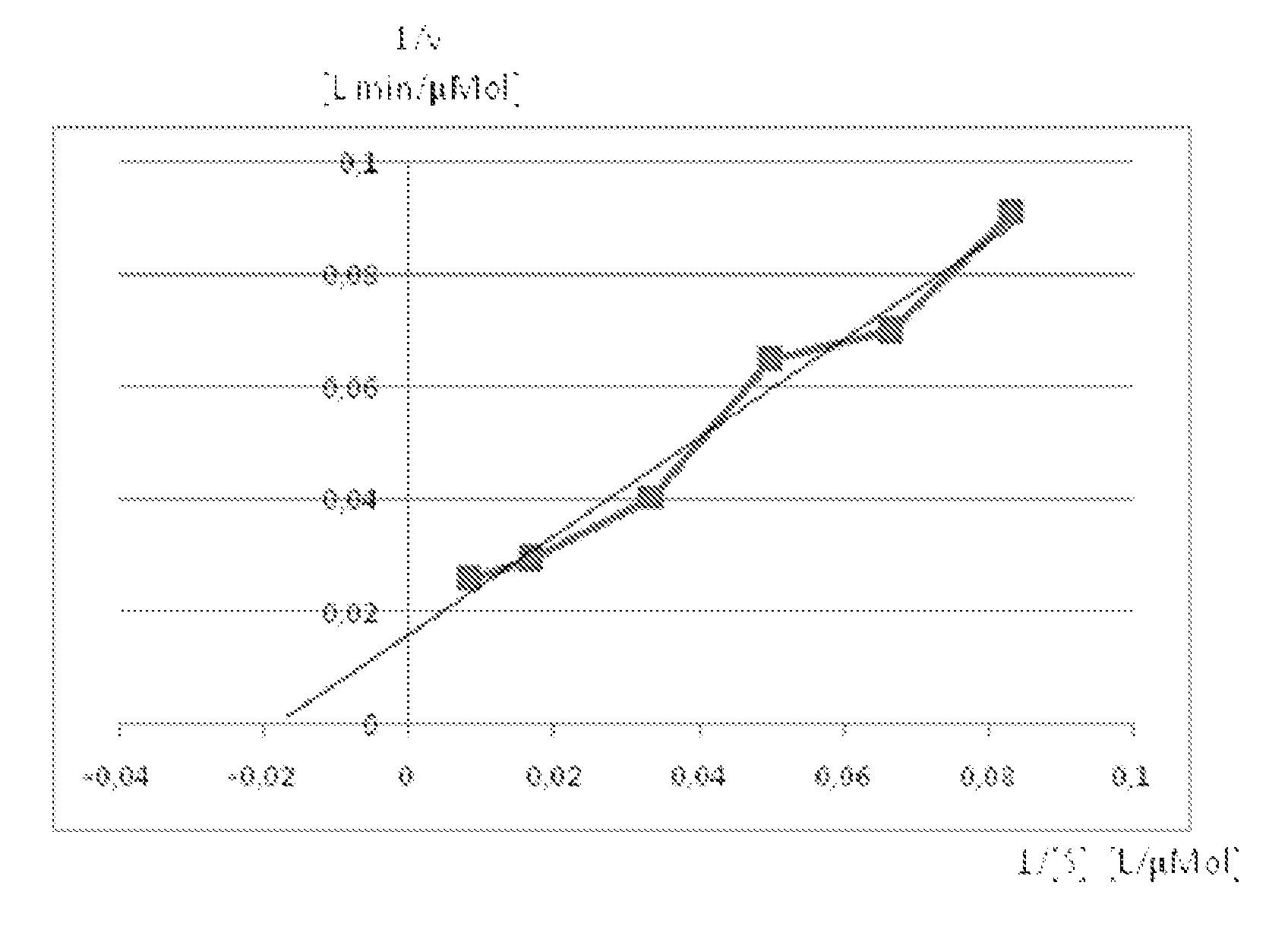
Selection of ADH In Genetically Modified Cyanobacteria For The Production Of Ethanol
InactiveUS20100003739A1Improve abilitiesIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaBiofuelsPhylum CyanobacteriaCyanobacteria
The present invention discloses genetically-modified cyanobacteria with ethanol-production capabilities enhanced over the currently-reported art, and methods of making such cyanobacteria. The invention provides a genetically modified photoautotrophic, ethanol producing host cell comprising an overexpressed pyruvate decarboxylase enzyme converting pyruvate to acetaldehyde and an overexpressed Zn2+ dependent alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme converting acetaldehyde to ethanol.
Owner:ALGENOL BIOTECH
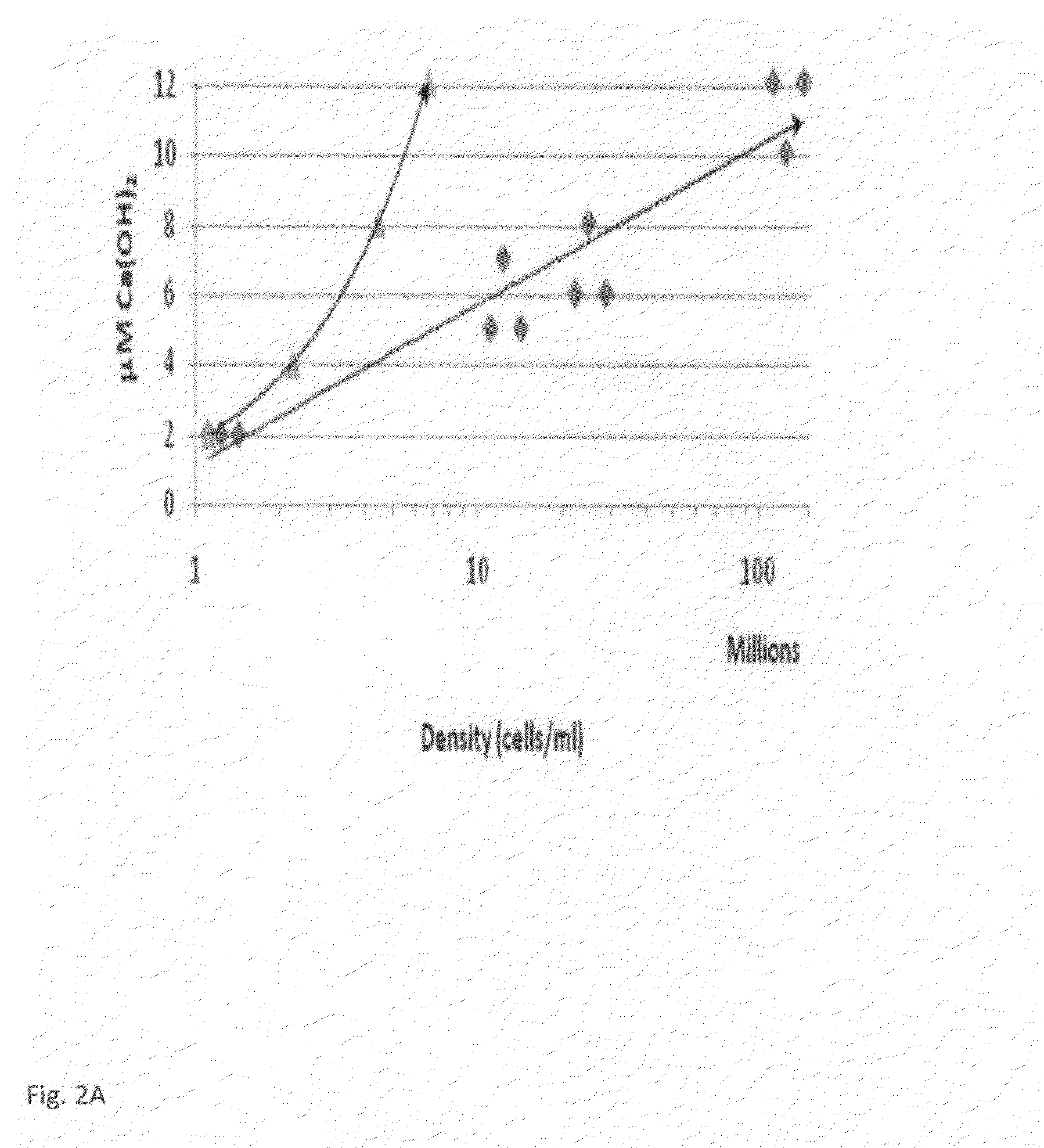
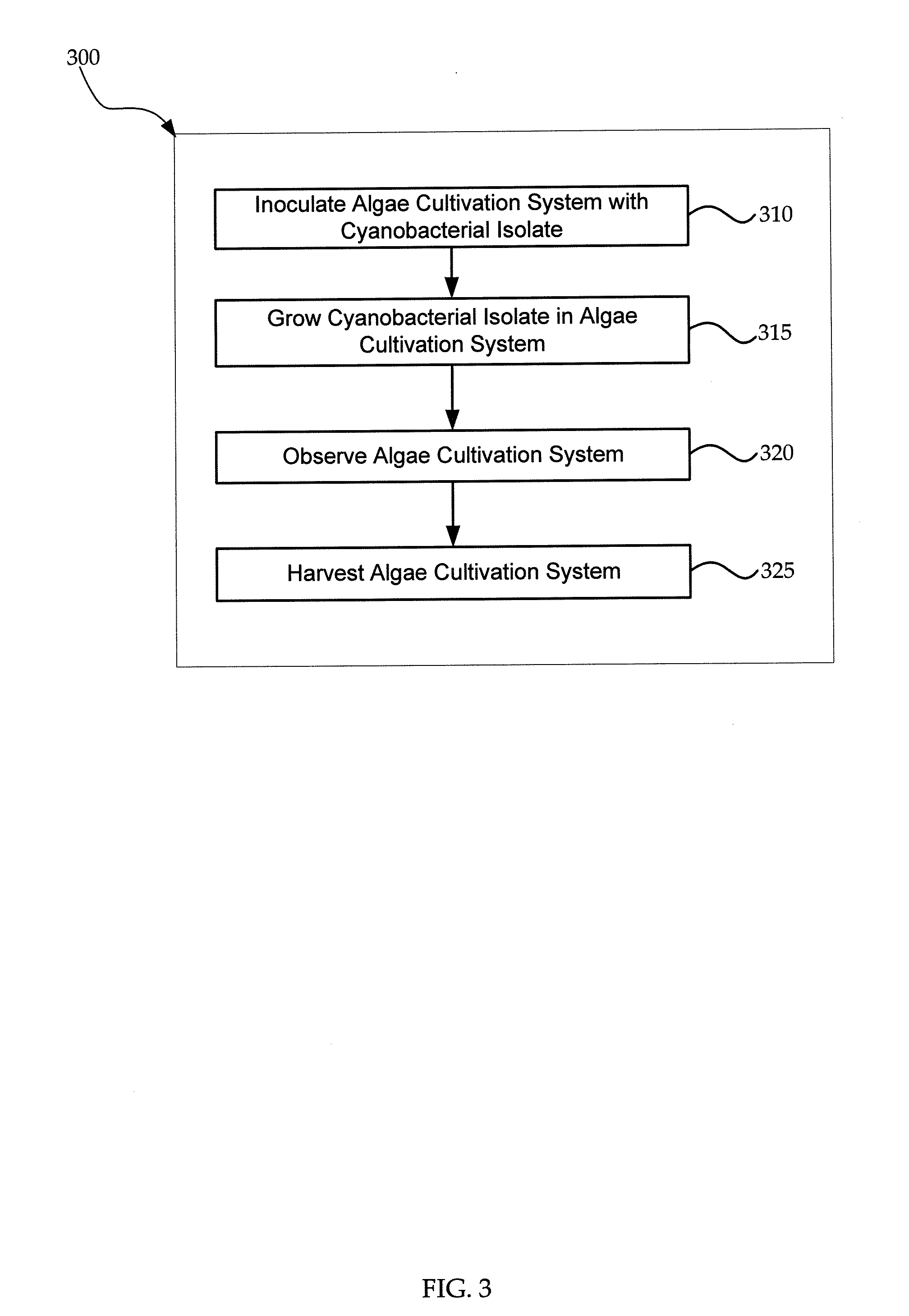
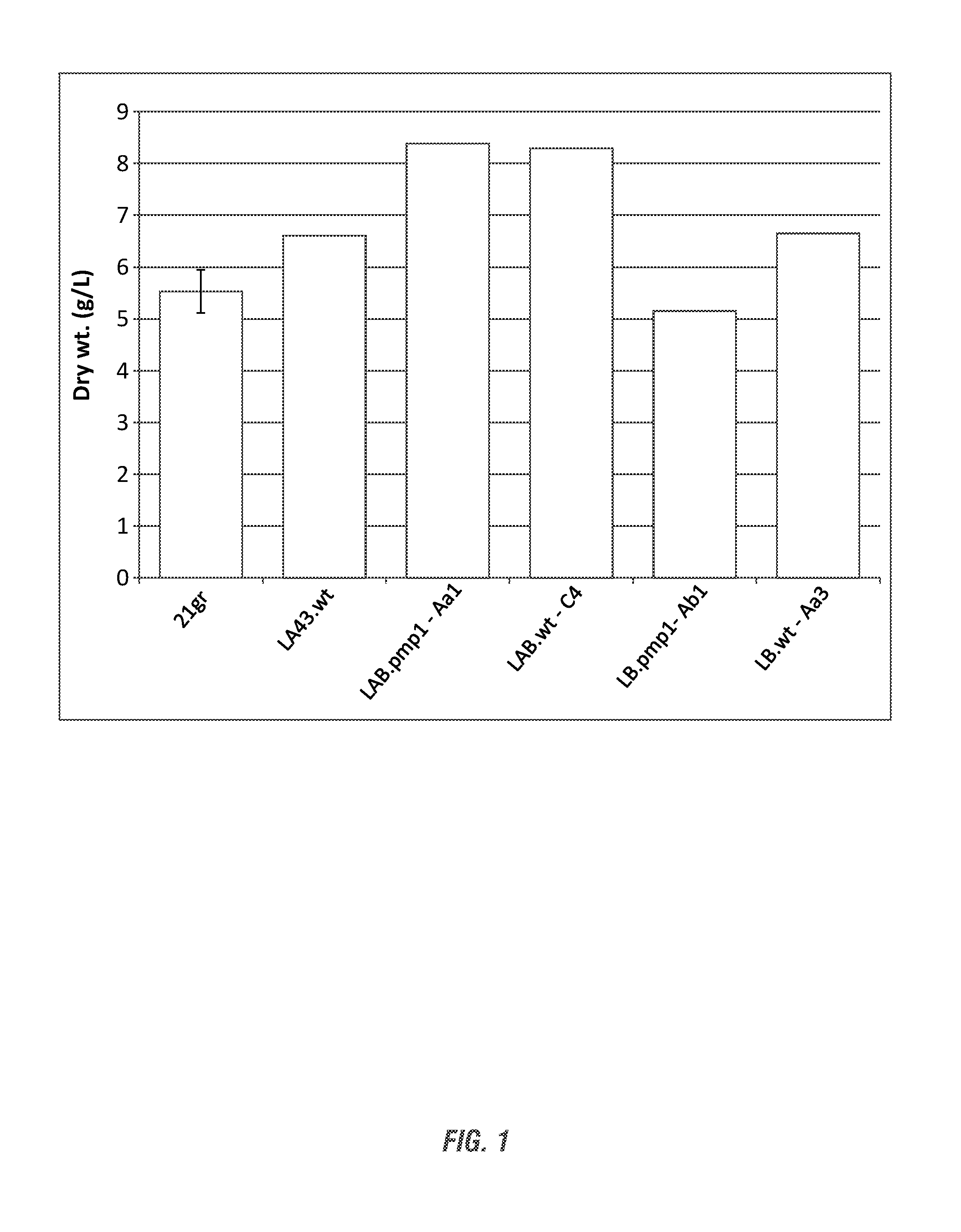
Cyanobacterial Isolates Having Auto-Flocculation and Settling Properties
Provided herein are exemplary methods for production of biomass with a cyanobacterial isolate having auto-flocculation properties. One exemplary method includes isolating a cyanobacterial strain having a 16S ribosomal RNA sequence corresponding to SEQ. ID. NO. 1 herein, inoculating an algae cultivation system with the cyanobacterial strain, growing the cyanobacterial strain, and harvesting the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain. According to a further method, the harvesting of the biomass comprises ceasing agitation of the algae cultivation system, and pooling a slurry of the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain. In a further method, the harvesting of the biomass may comprise ceasing agitation within the algae cultivation system and / or allowing the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain to settle to near or at a bottom of the algae cultivation system. Also provided herein are exemplary cyanobacterial strains having flocculation properties for production of a biomass.
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
Modulation of low carbon dioxide inducible proteins (LCI) for increased biomass production and photosynthesis
InactiveUS20130007916A1Increased biomass productionPromote photosynthesisUnicellular algaeClimate change adaptationPhylum CyanobacteriaCyanobacteria
The invention provides the disclosure of a novel plant / algae / cyanobacteria photosynthesis, biomass production, and productivity pathway involving low carbon dioxide inducible (LCI) proteins. According to the invention, the activity of one or more LCI proteins may be modulated to increase the same under conditions where such proteins are typically repressed. According to the invention, modulation of LCI protein activity was able to increase biomass production by as much as 80% under elevated CO2 conditions. The invention includes methods, and genetically modified plants / algae / cyanobacteria, cells, plant parts and tissues.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
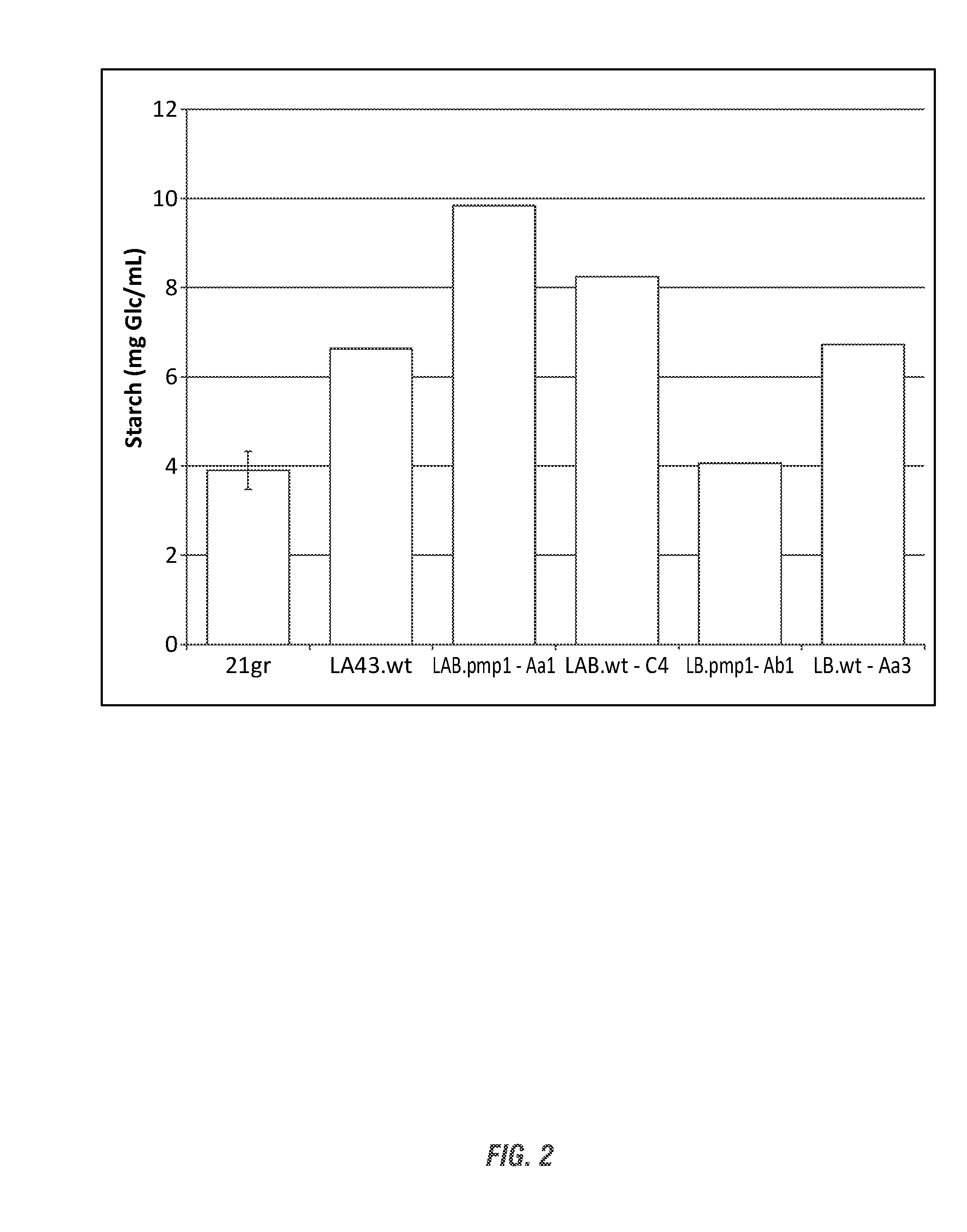
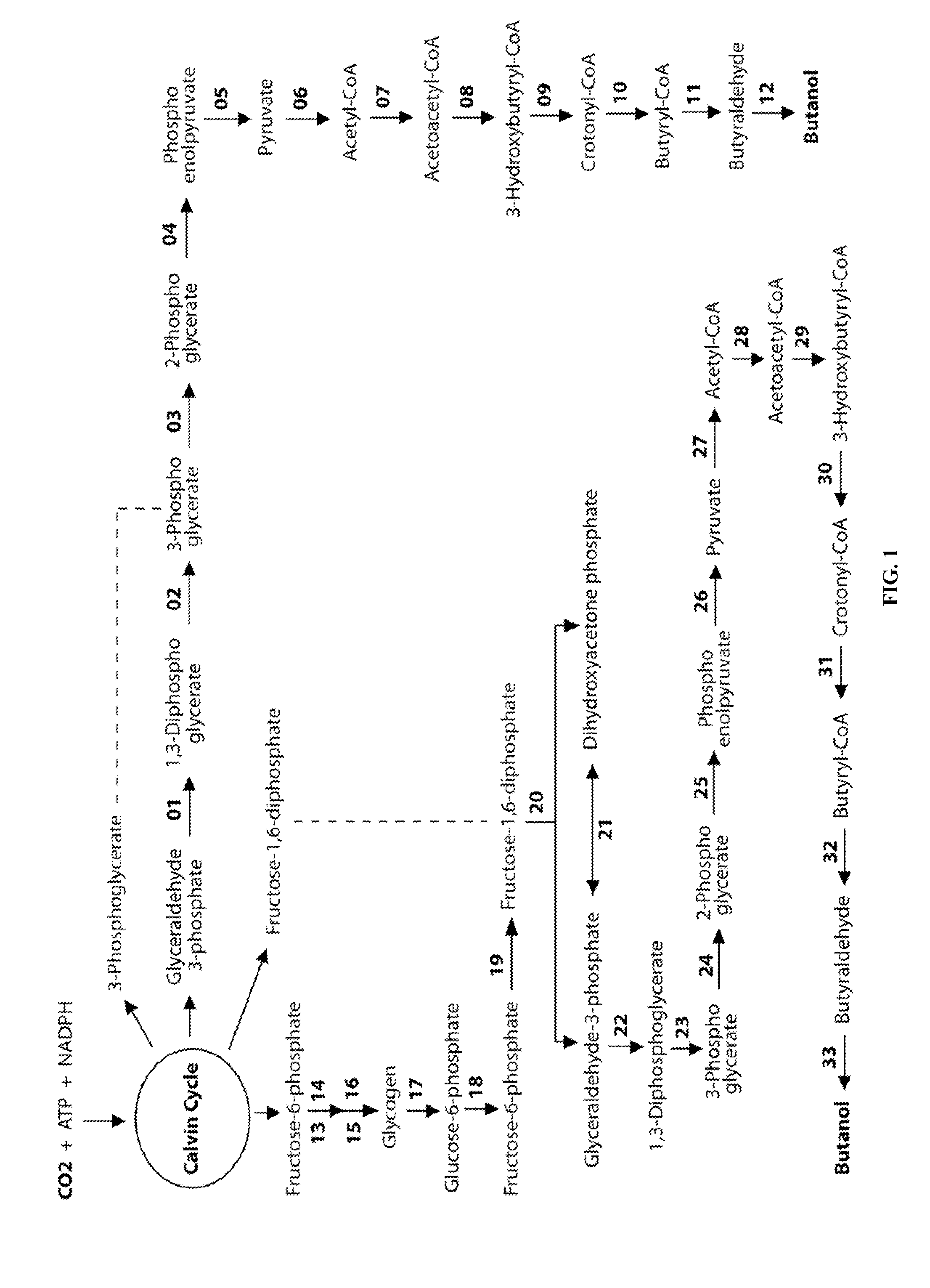
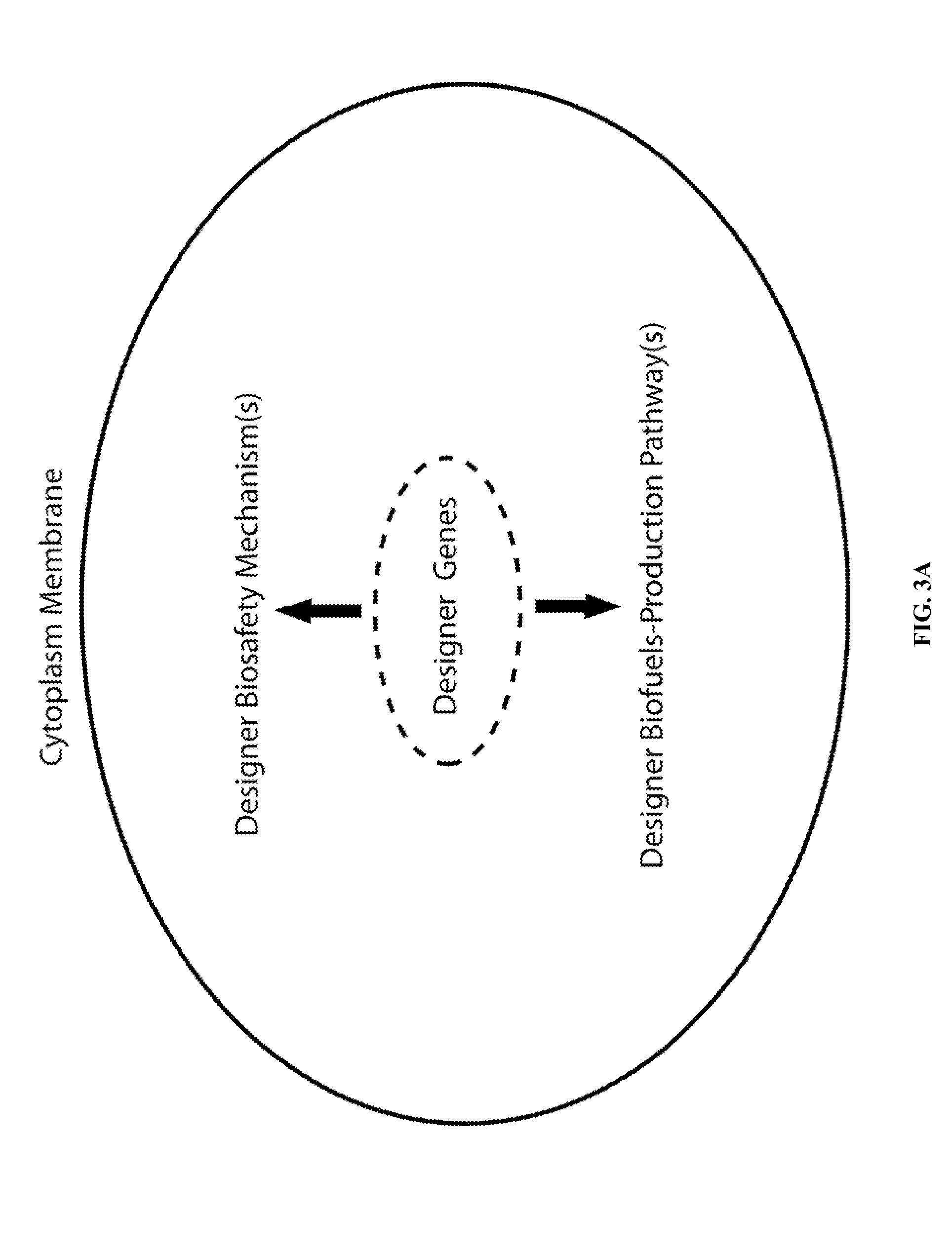
Designer Organisms for Photobiological Butanol Production from Carbon Dioxide and Water
ActiveUS20100330637A1Weaken energyReduce total powerBryophytesAlgae productsCellulosePhylum Cyanobacteria
The present invention provides a biosafety-guarded photobiological butanol production technology based on designer transgenic plants, designer algae, designer blue-green algae (cyanobacteria and oxychlorobacteria), or designer plant cells. The designer photosynthetic organisms are created such that the endogenous photobiological regulation mechanism is tamed, and the reducing power (NADPH) and energy (ATP) acquired from the photosynthetic process are used for synthesis of butanol (CH3CH2CH2CH2OH) directly from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The butanol production methods of the present invention completely eliminate the problem of recalcitrant lignocellulosics by bypassing the bottleneck problem of the biomass technology. The photobiological butanol-production technology of the present invention is expected to have a much higher solar-to-butanol energy-conversion efficiency than the current technology and could also help protect the Earth's environment from the dangerous accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Owner:LEE JAMES WEIFU
Photobioreactor and uses therefor
InactiveCN101405385ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhylum CyanobacteriaPhotobioreactor
The present invention provides novel photobioreactors, modules thereof, and methods for use in culturing and harvesting algae and cyanobacteria.
Owner:亚利桑那州立大学董事会,代表亚利桑那州立大学法人团体利益
Methods for producing phycotoxins
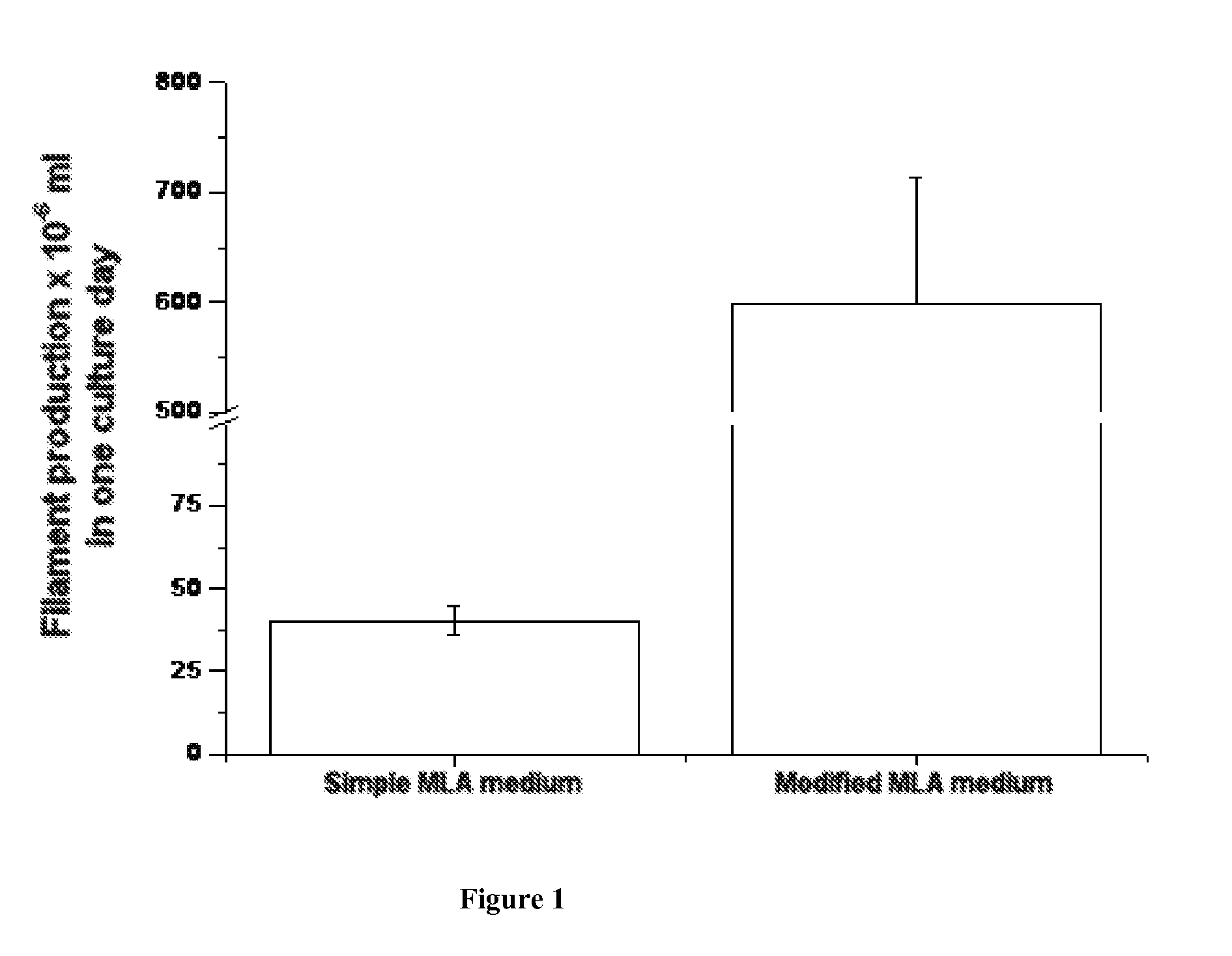
ActiveUS20120053344A1Increase concentrationOrganic chemistryAntipyreticHigh concentrationPhylum Cyanobacteria
Methods for producing phycotoxins from natural sources, wherein the phycotoxins have a definite compositional profile are described herein. In one embodiment, the phycotoxins are produced by cyanobacteria. In one embodiment, the phycotoxins are produced by continuously culturing cyanobacteria under strictly controlled conditions in order to produce a definite compositional profile. In another embodiment, organic nutrients are added to the culture that allows for higher concentrations of neosaxitoxin and saxitoxin or gonyaulatoxins 2 and 3 per weight of the algae. The phycotoxins are isolated primarily from the bacteria but can also be isolated from the culture medium. In one embodiment, the cyanobacteria produce only neosaxitoxin and saxitoxin in a ratio of about 6:1, 5:1, 4:1, or 3:1. In a preferred embodiment, the amount of saxitoxin is less than 20% by weight of the total amount of neosaxitoxin and saxitoxin produced. In another embodiment, the cyanobacteria produce only GTX2 and GTX 3.
Owner:PROTEUS
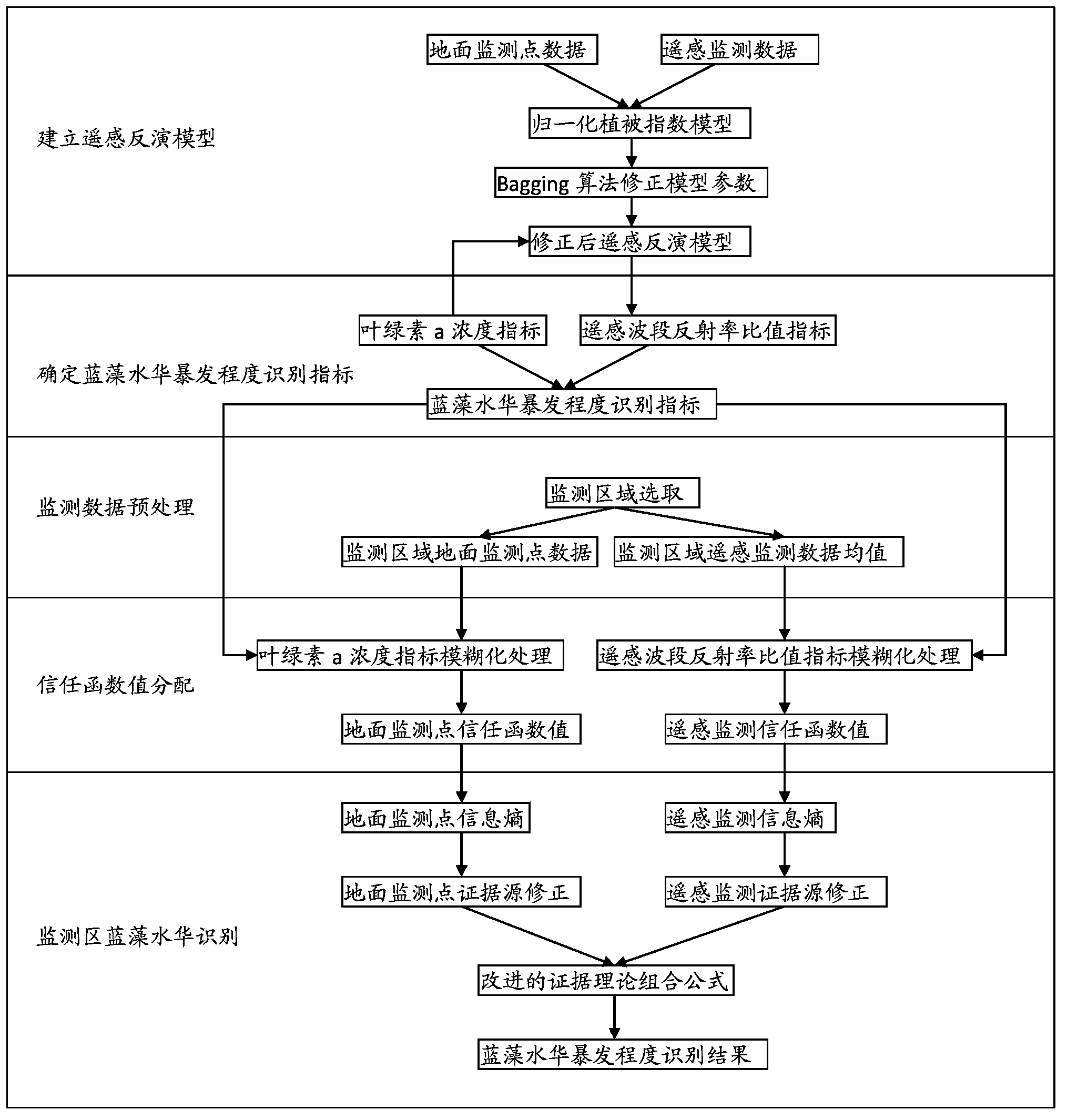
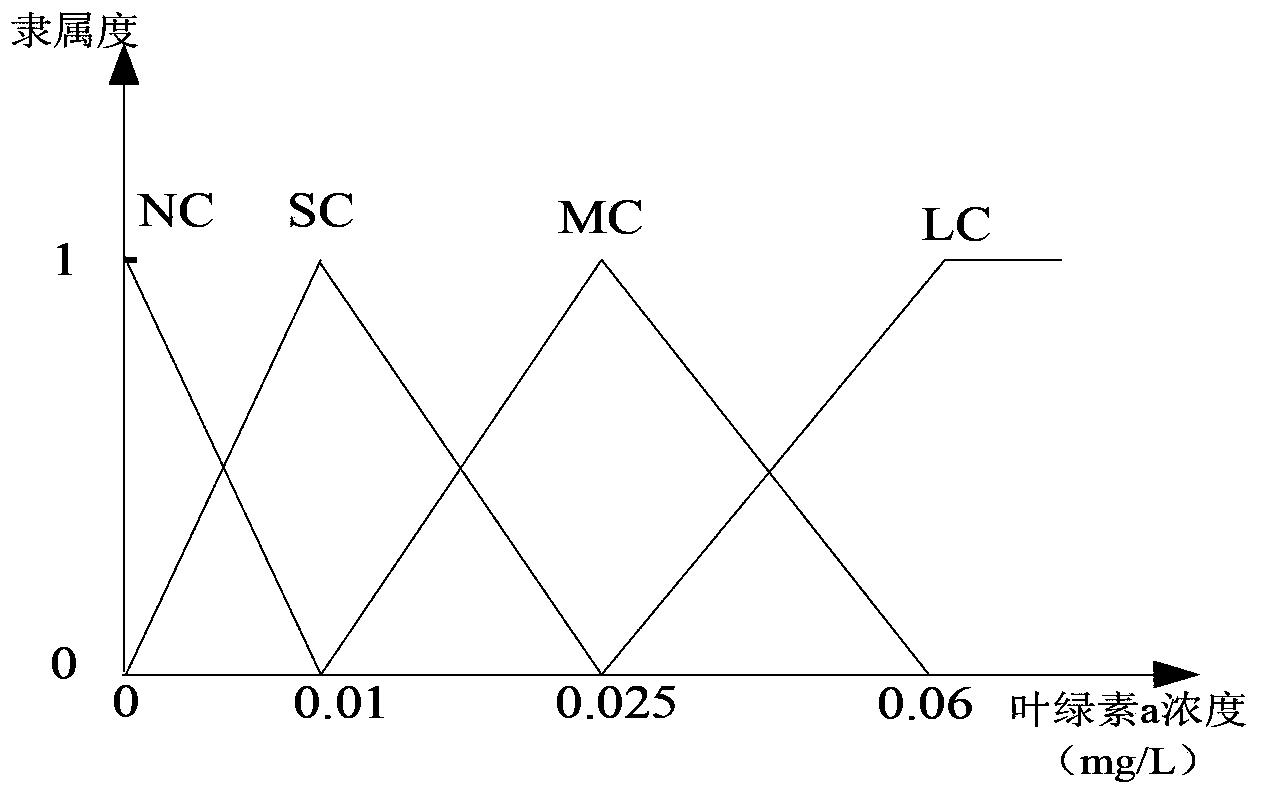
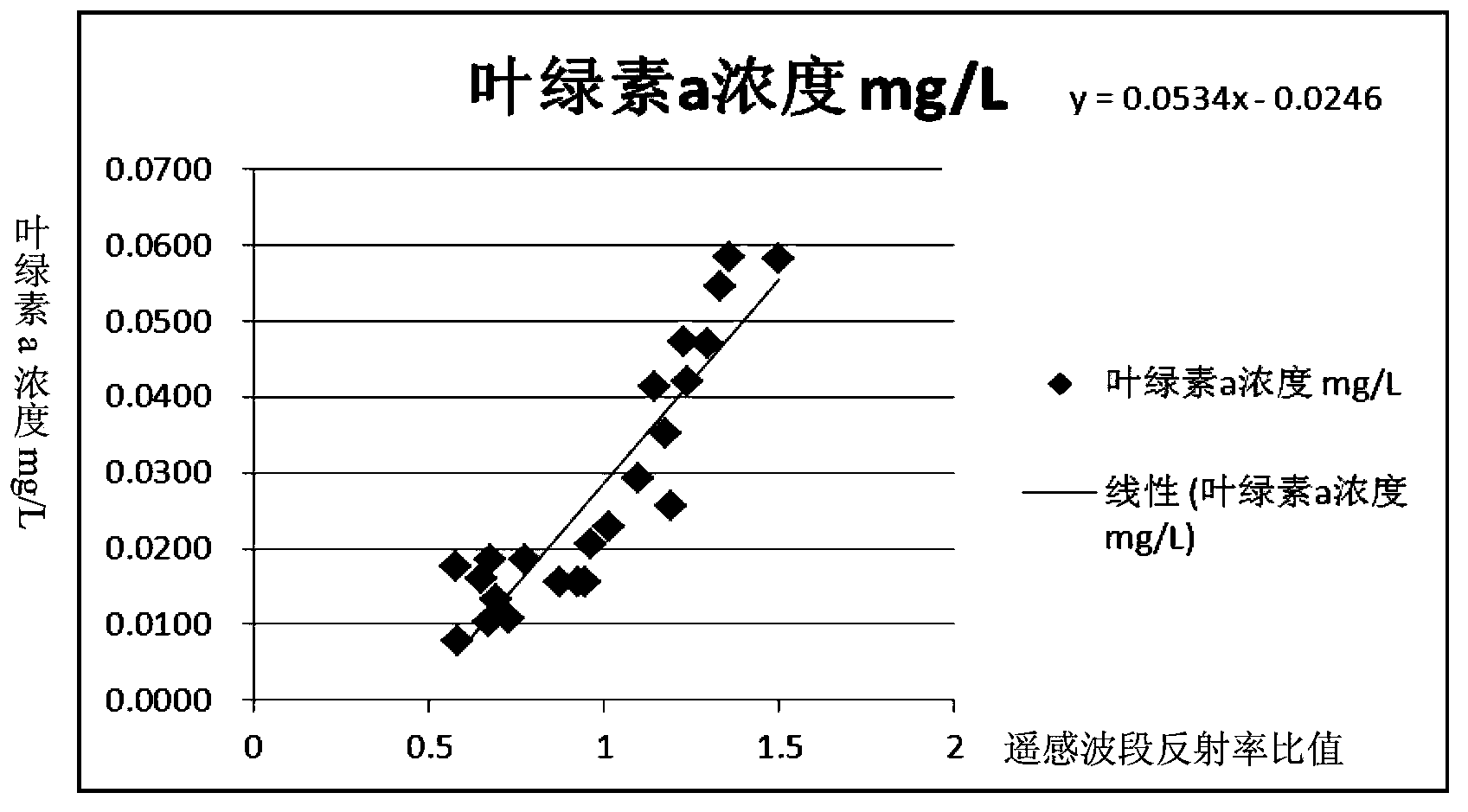
Lake-reservoir cyanobacteria water bloom recognition method based on remote sensing monitoring and evidence fusion technology improvement
ActiveCN103439472AImprove fitting accuracyResolve indicatorsTesting waterPhylum CyanobacteriaRegression analysis
The present invention discloses a lake-reservoir cyanobacteria water bloom recognition method based on remote sensing monitoring and evidence fusion technology improvement, and belongs to the technical field of environmental projects. The method comprises: establishing a remote sensing inversion model, determining cyanobacteria water bloom breaking-out degree recognition indexes, pre-treating monitoring data, assigning belief function values, and recognizing monitoring area cyanobacteria water bloom. According to the present invention, an ensemble learning Bagging algorithm is fused into regression analysis of the remote sensing inversion model (ie., the normalization vegetation index model) to correct parameters of the model to obtain the corrected remote sensing inversion model so as to improve fitting accuracy; the problem of selection of indexes for lake-reservoir cyanobacteria water bloom recognition and value ranges thereof is solved; the problems of selection of the monitoring area and pretreatment of the monitoring data are solved; the problem of assignment of the belief function values is solved; and effective cyanobacterial water bloom recognition is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
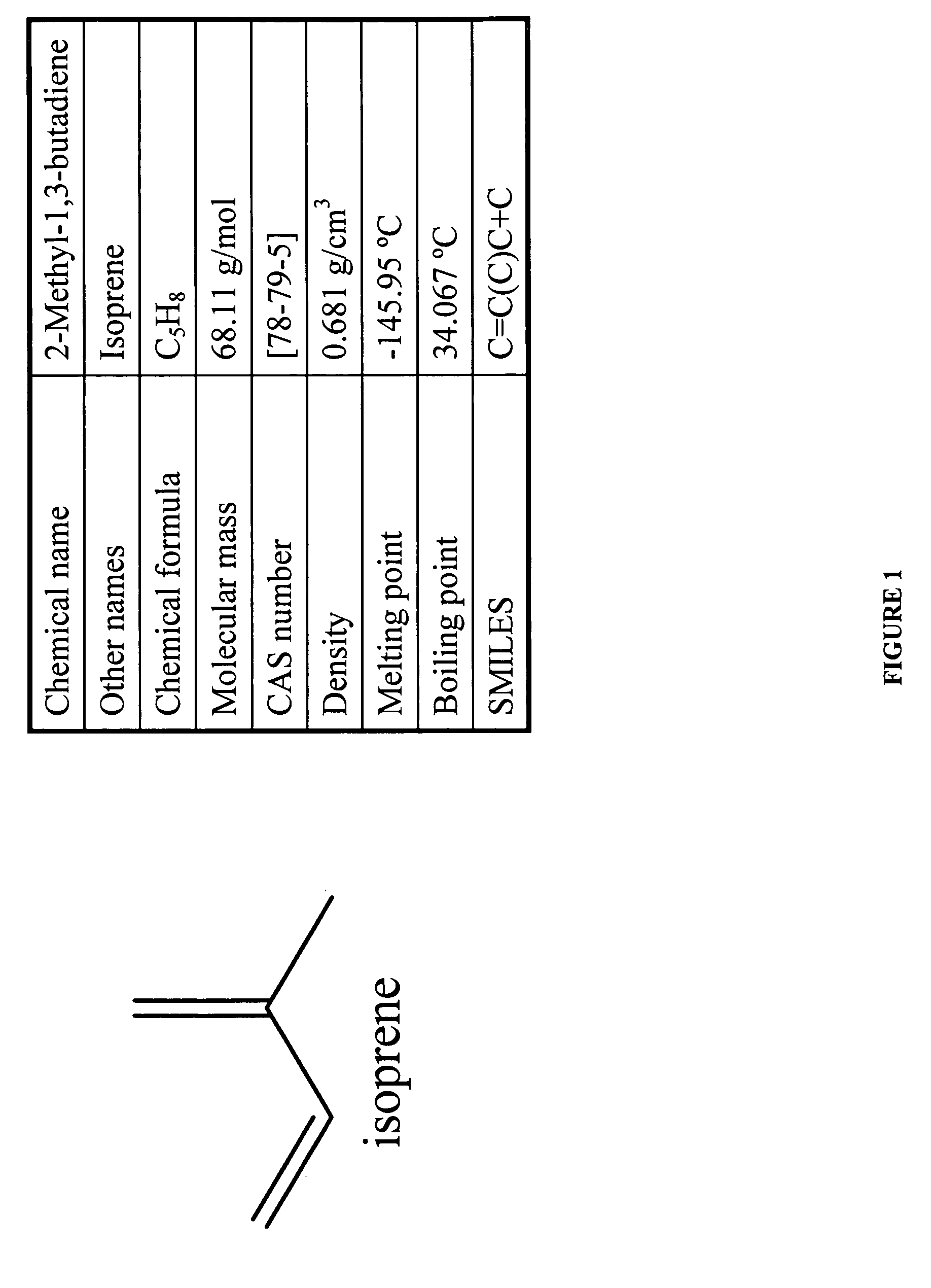
Methods for The Direct Conversion of Carbon Dioxide Into a Hydrocarbon Using a Metabolically Engineered Photosynthetic Microorganism
ActiveUS20100196982A1Increase volumeAltering controlBacteriaFermentationPhylum CyanobacteriaMicroorganism
The present invention relates to methods for the production of isoprene by the direct conversion of atmospheric carbon dioxide using metabolically engineered genetically engineered photosynthetic microorganisms. The present invention also relates to genetically engineered photosynthetic microorganisms, such as cyanobacteria, that are capable of producing isoprene from CO2.
Owner:ZUVACHEM
Transgenically preventing establishment and spread of transgenic algae in natural ecosystems
InactiveUS20090215179A1Improve productivityIncrease productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhylum CyanobacteriaAlgaenan
Genetic mechanisms for mitigating the effects of introgression of a genetically engineered genetic trait of cultivated algae or cyanobacteria to its wild type or to an undesirable, interbreeding related species. as well as preventing the establishment of the transgenic algae or cyanobacteria in natural ecosystems.
Owner:TRANSALGAE
Seeding medium made of vinasse methane-sludge and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101606471APromote absorptionInhibitionCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationPhylum CyanobacteriaSludge
The invention relates to a seeding medium made of vinasse methane-sludge and a preparation method thereof, not only solving the problem of environment contamination caused by vinasse methane-sludge, but also effectively utilizing vinasse methane-sludge. The seeding medium comprises fresh sludge containing 90 percent of water after methane generated from vinasse in a methane tank, accessories, ferment strain I and ferment strain II, wherein the accessories comprise grass peat, vermiculite and perlite; the ferment strain I comprises saccharomycetes, lactobacillus, high-temperature actinomycetes and bacillus; and the ferment strain II comprises photosynthetic bacteria, lactobacillus, bacillus, saccharomycetes, actinomycetes and terrestrial cyanobacteria. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing fresh sludge, dehydrating, adding the ferment strain I for fermentation, adding the ferment strain II for secondary fermentation, air drying, adding accessories, crushing, screening and packing. The vinasse methane-sludge contains 40 to 50 percent of organic matter and 4.3 percent of available nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and kalium (K). The seeding medium made of vinasse methane-sludge has better hydrophilicity, and seeding can be carried out after loading the dry seeding medium and spraying water, thus saving both labor and time.
Owner:ANHUI FENGTIAN SEEDLESS WATERMELON TECH
Amphibious type multi-functional floater salvaging device
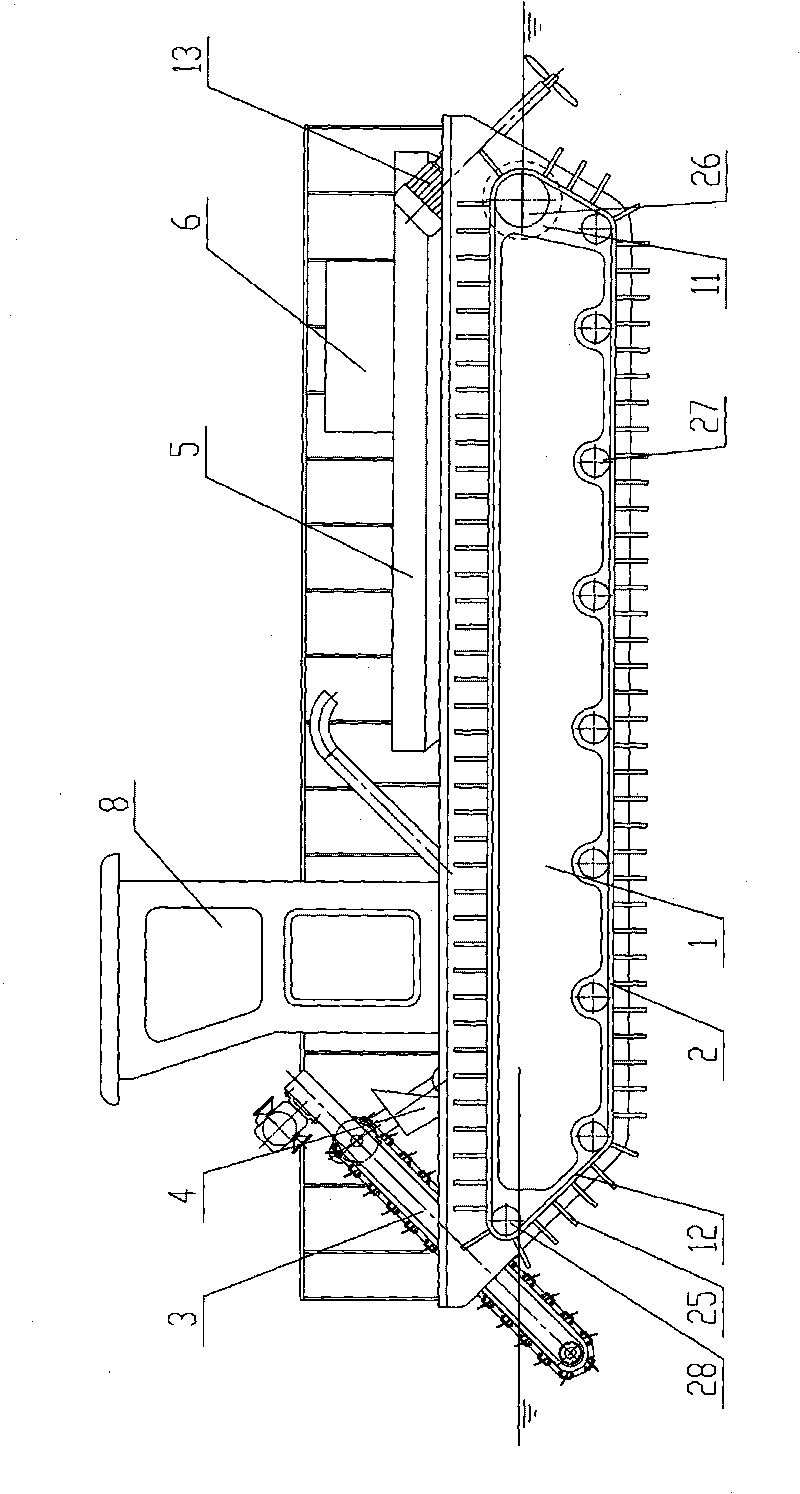
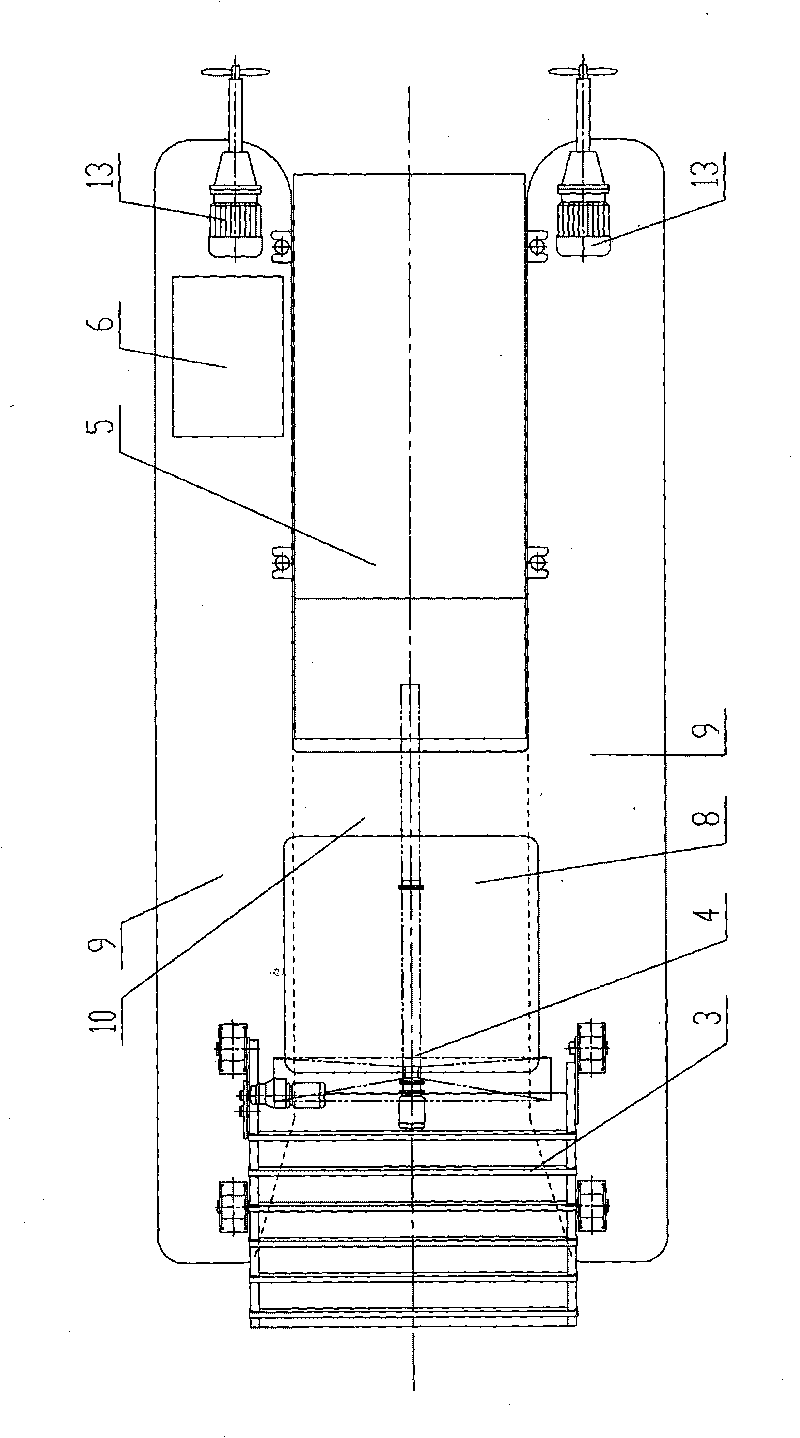
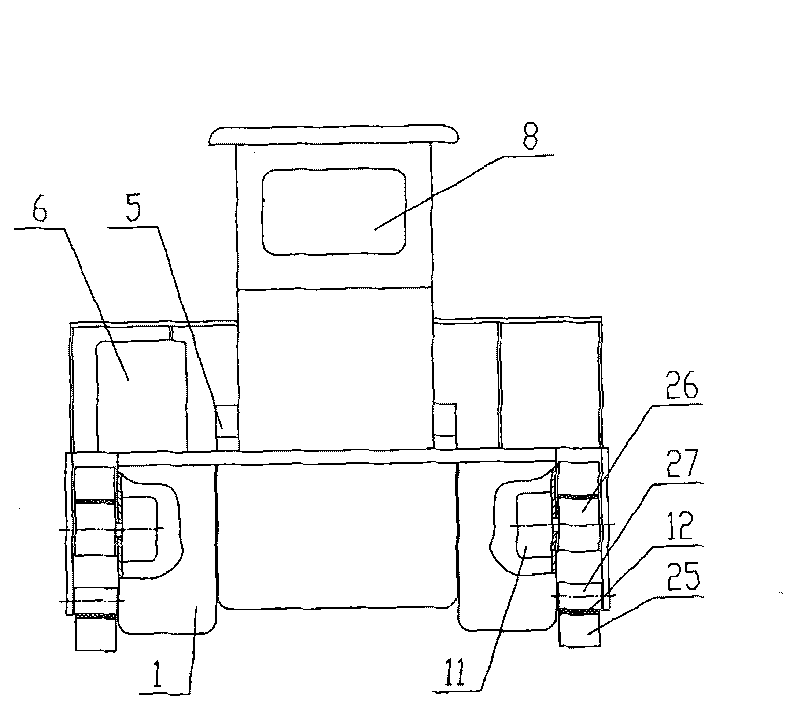
ActiveCN101725137AEasy to salvageSolve the problem of unsolvable fishing dead angleWater cleaningDrive wheelLand Travel
The invention discloses an amphibious type multi-functional floater salvaging device. In the salvaging device, a supporting body is a double-floating body(1) driven to sail by an underwater propeller(13), the front end of the double-floating body(1) is provided with an intercepting-salvaging device(3), and both sides of the double-floating body(1) are provided with a water-and-land travelling device(2); and the water-and-land travelling device(2) mainly comprises a driving device(11), a track(12), a driving wheel(26), a supporting wheel(27) and a tension wheel(28), wherein the track(12) is tensioned by the driving wheel(26), the supporting wheel(27) and the tension wheel(28), and the outer surface of the track(12) is provided with blades(25). The amphibious type multi-functional floater salvaging device can not only sail in water, but also run overland; particularly, the amphibious type multi-functional floater salvaging device can use the special strength in the shoal water zones of a water body to conveniently salvage aquatic plants, floating refuse and cyanobacteria in the shoal water zones; and the problem of salvaging dead angles which cannot be solved by common automobiles and ships is solved.
Owner:HUATIAN ENG & TECH CORP MCC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com