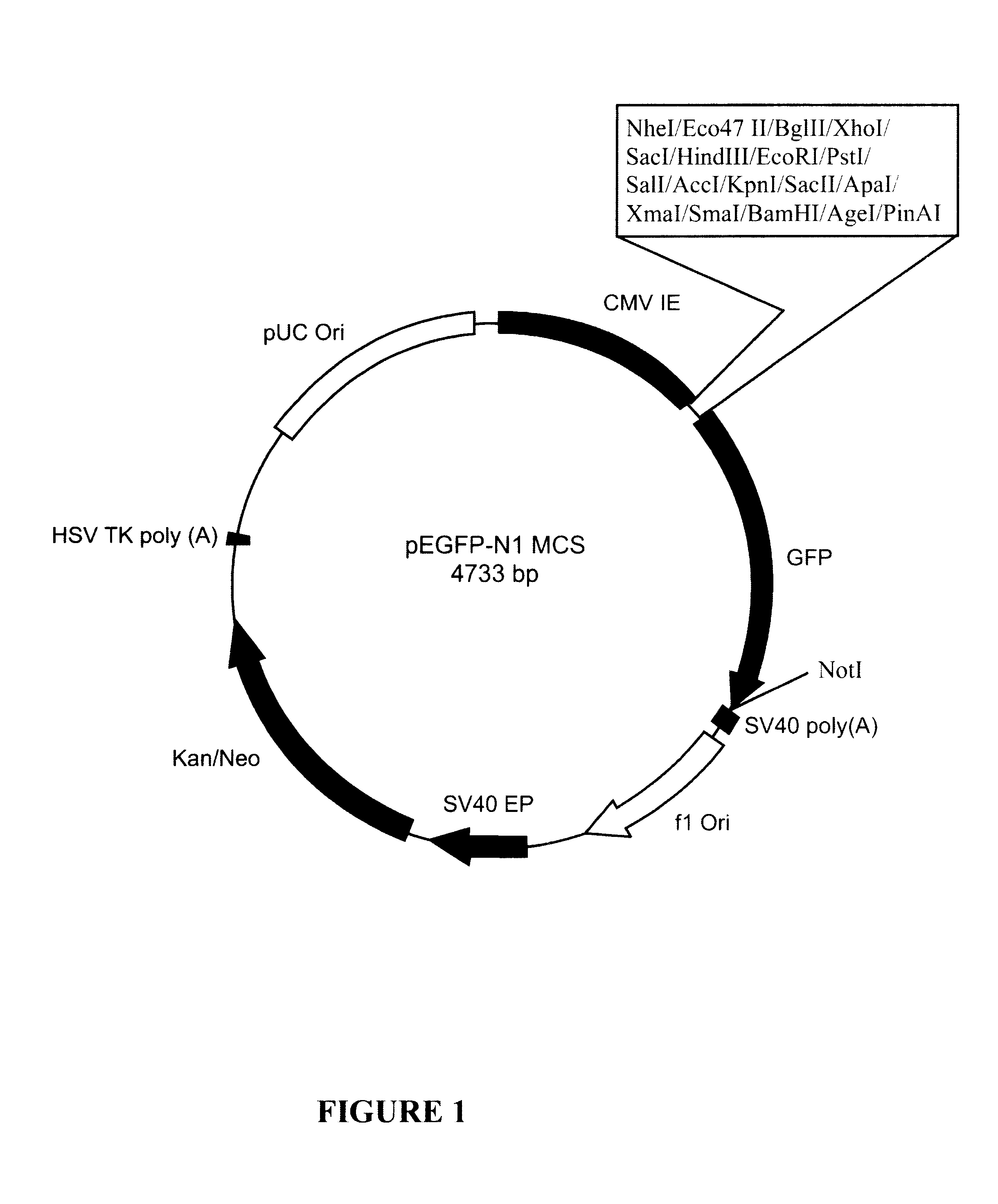
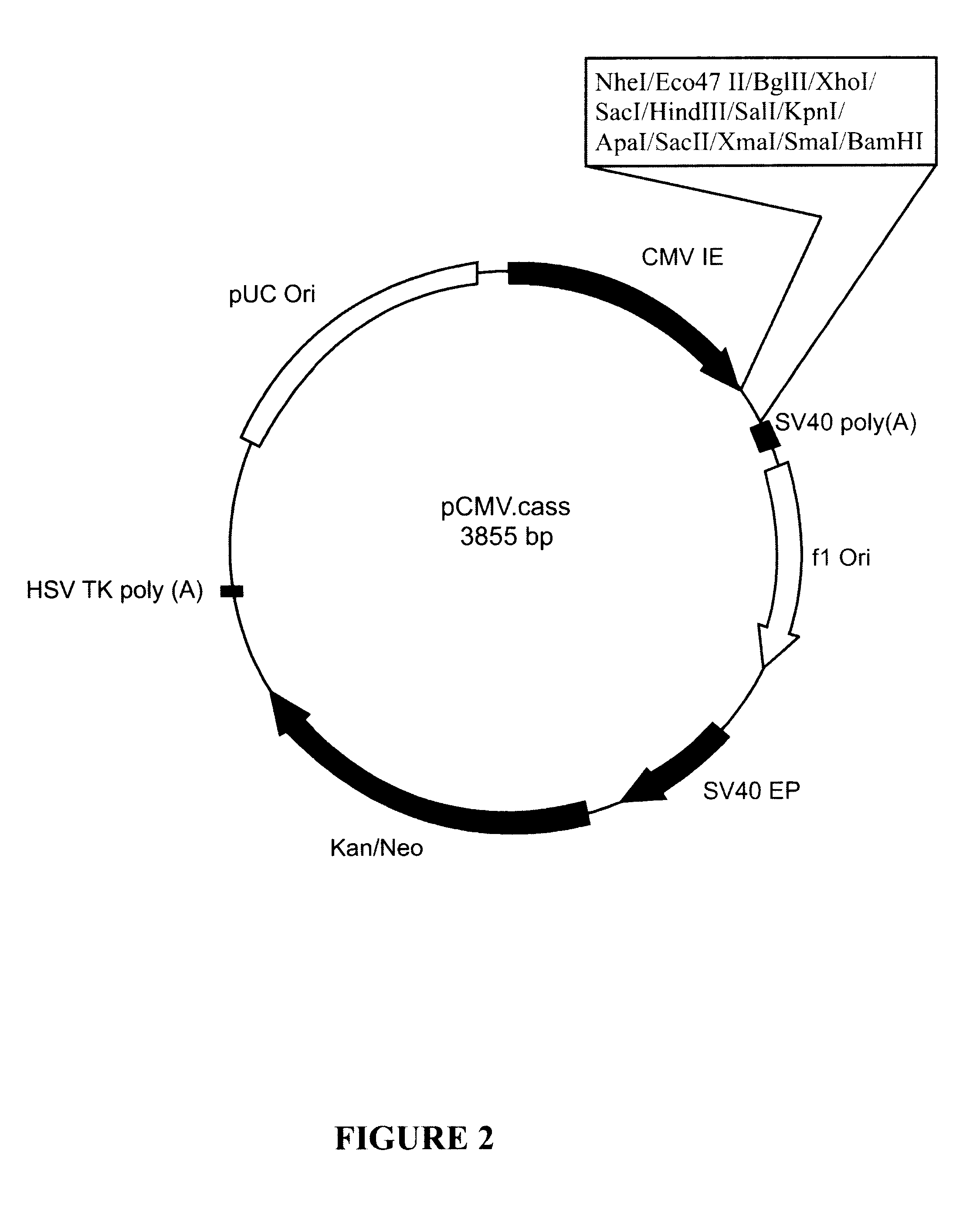
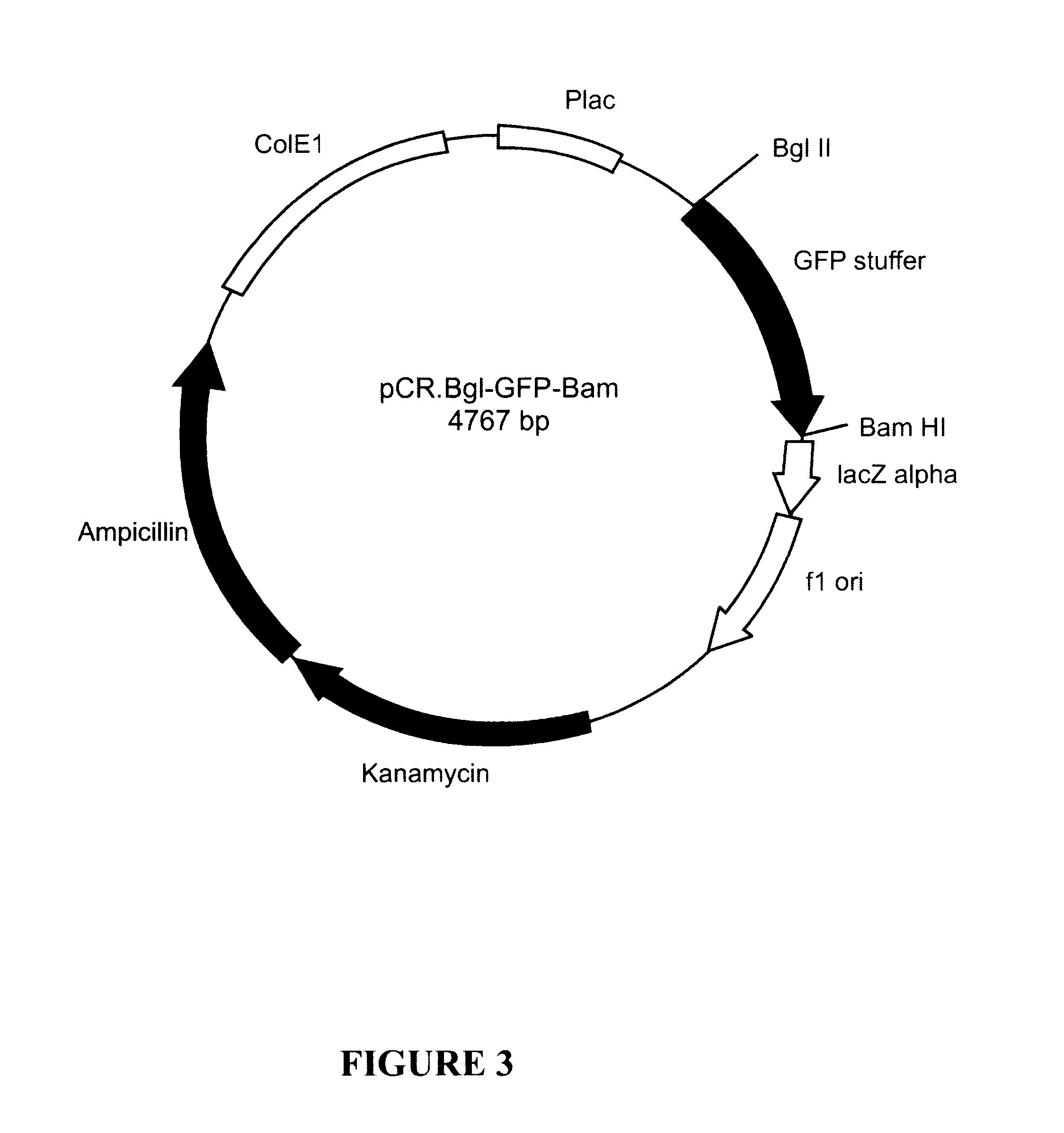
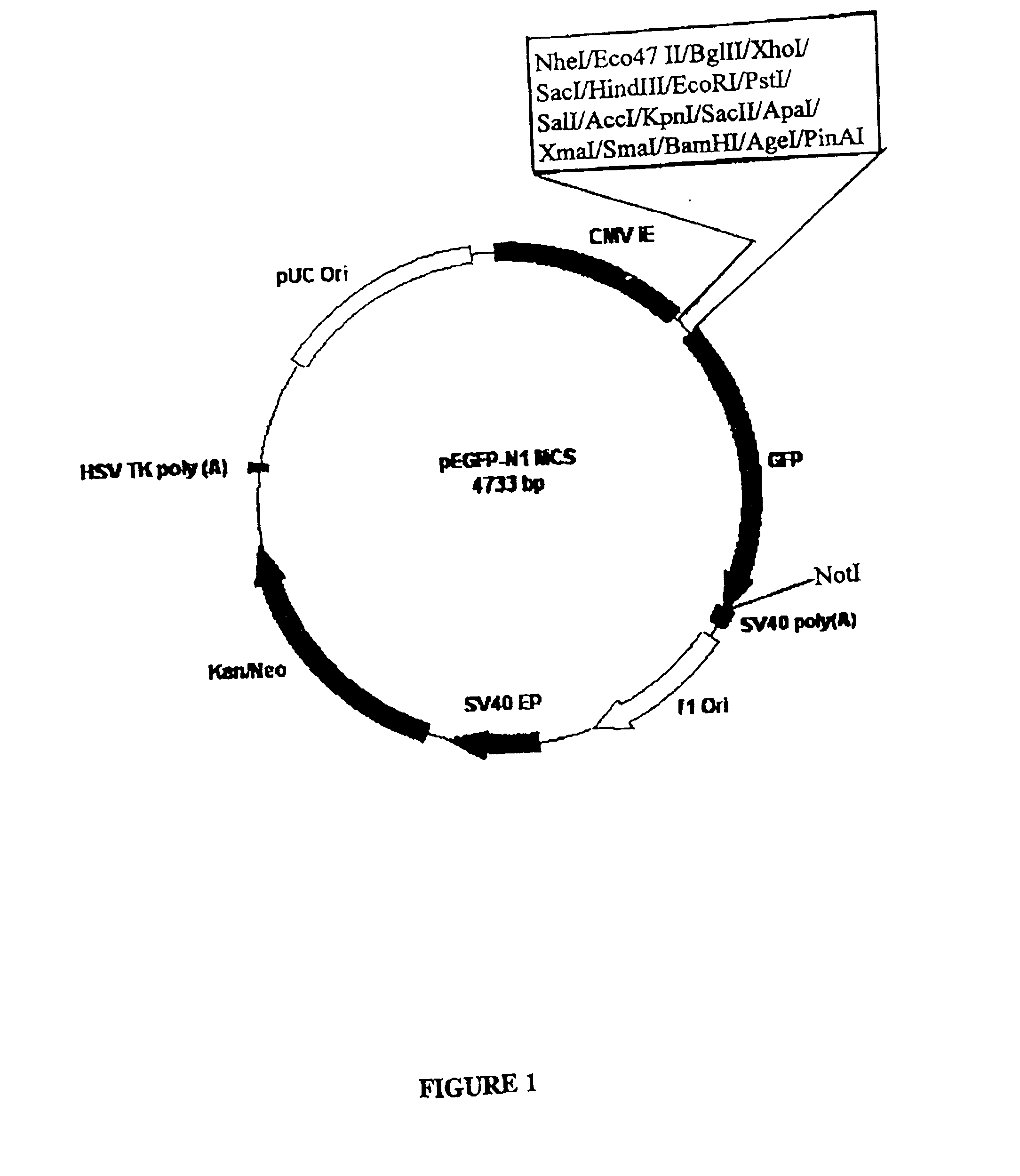
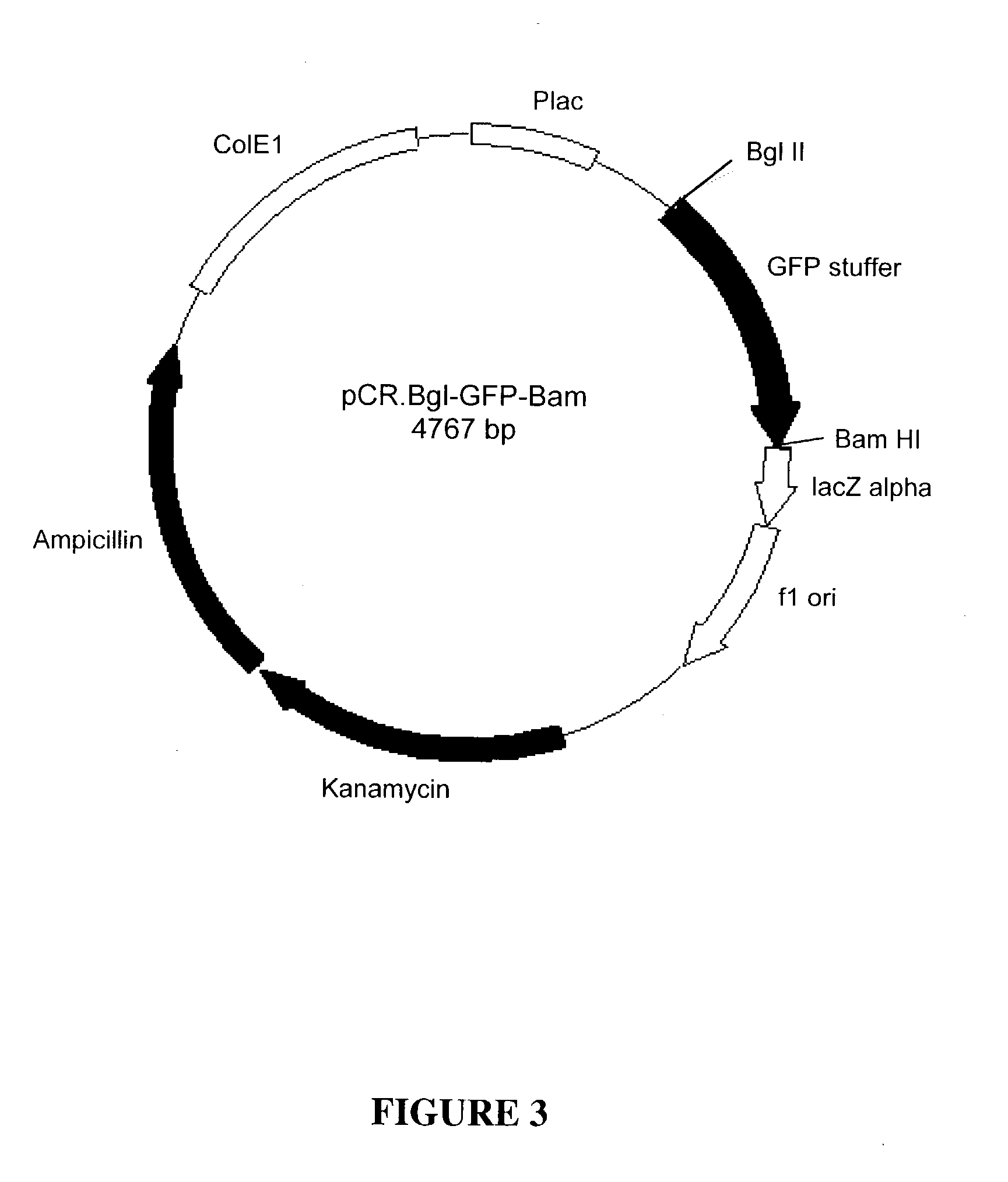
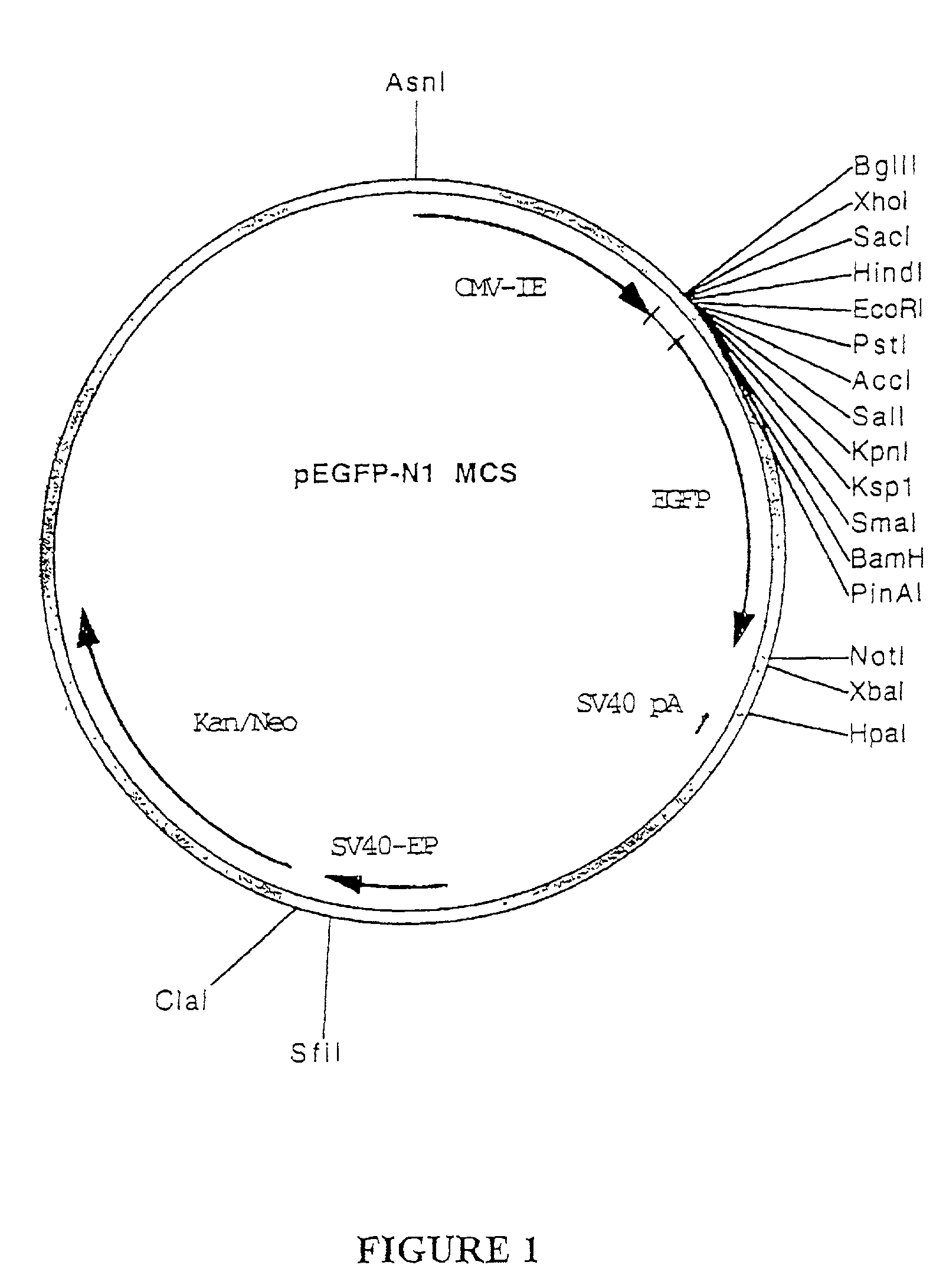
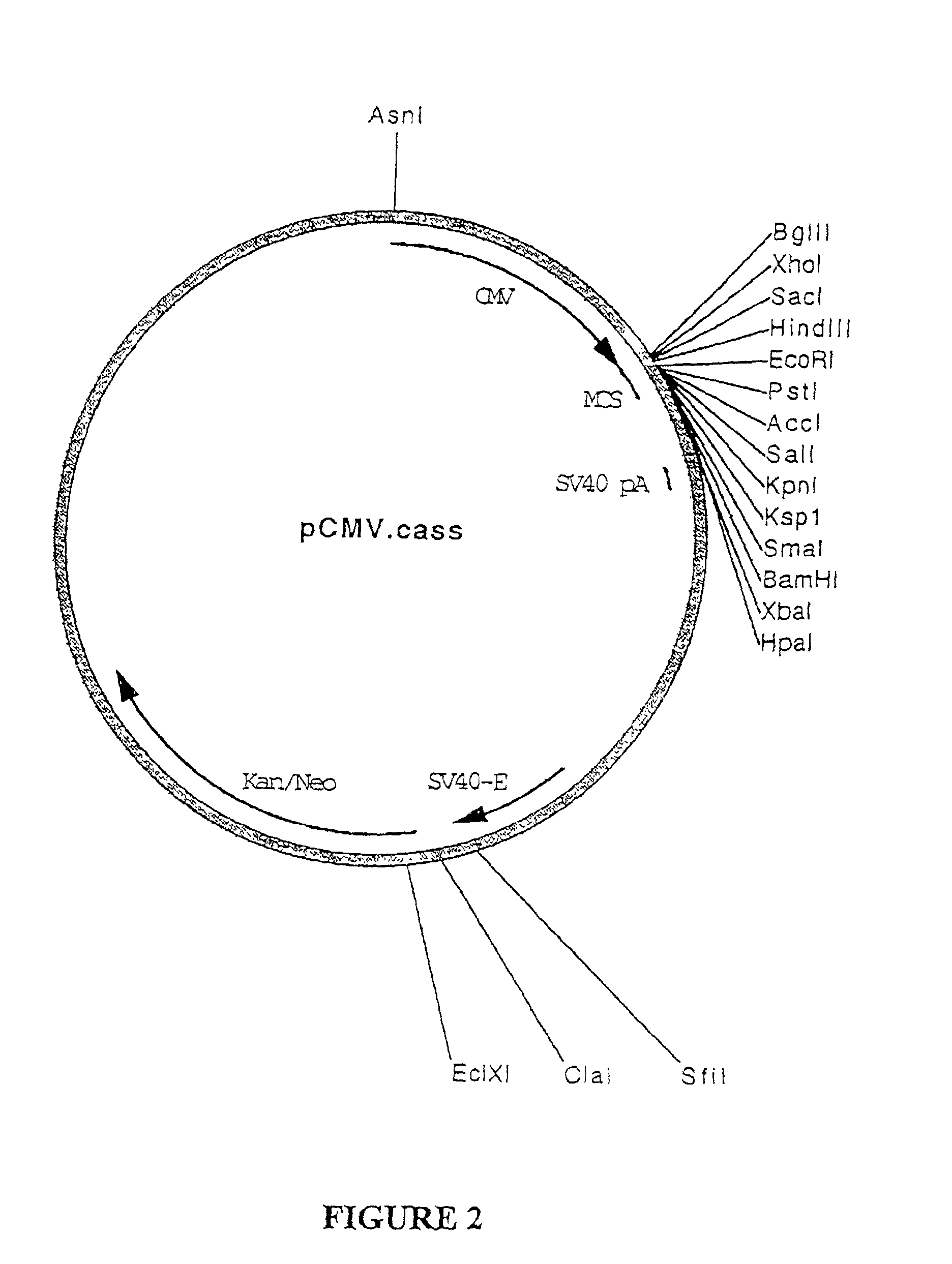
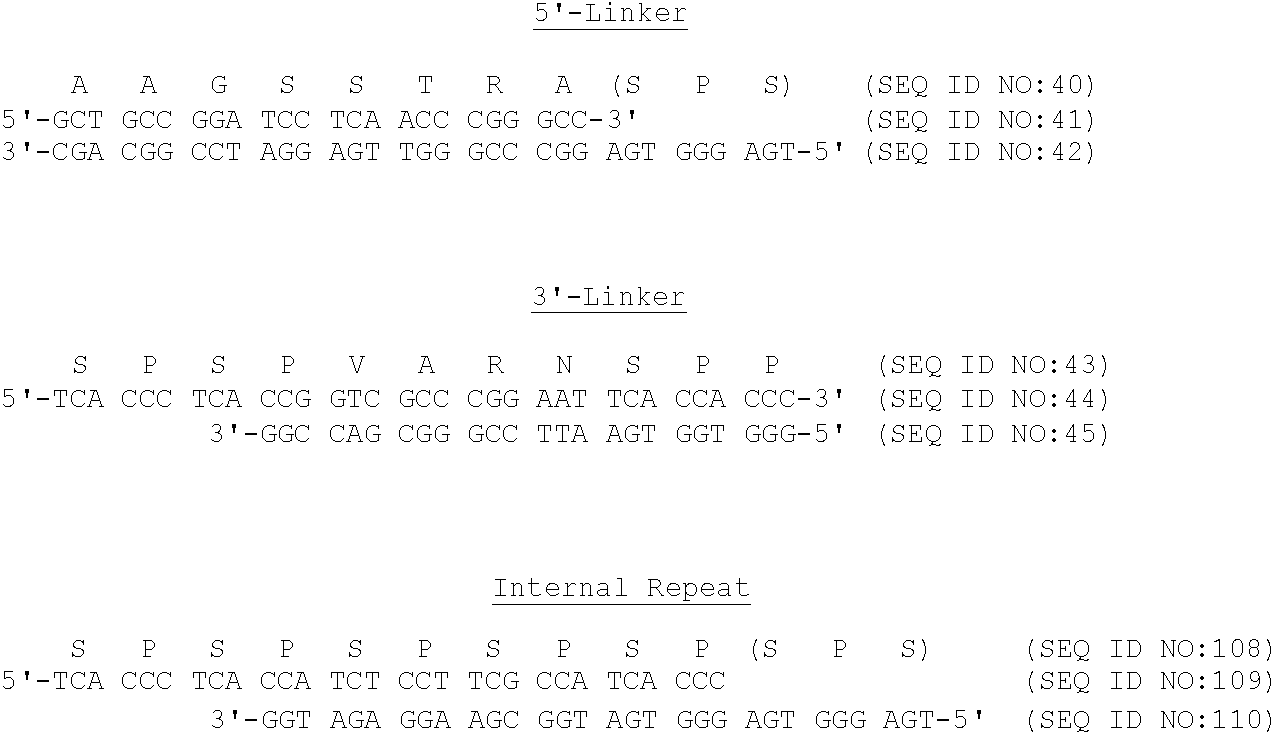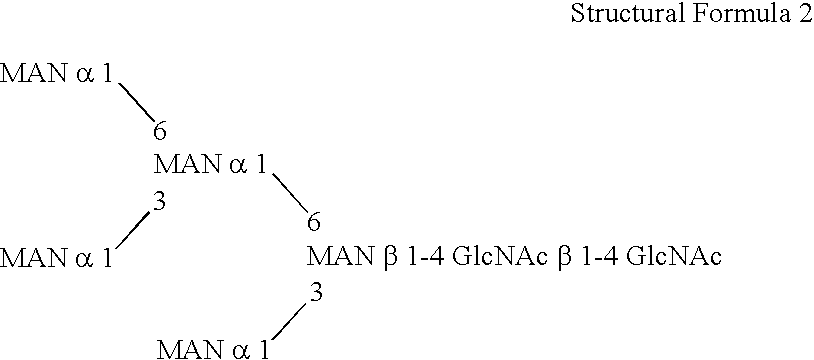Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
323 results about "Synthetic Genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synthetic Genes. Genes used in plant molecular biology sometimes have low expression in plants due to the fact that they have been originally isolated from bacteria which use a different codon usage. The betaglucuronidase (GUS) gene from E. coli was codon optimized for better expression in monocots and dicots.
Genetic constructs for delaying or repressing the expression of a target gene
The present invention relates generally to synthetic genes for modifying endogenous gene expression in a cell, tissue or organ of a transgenic organism, in particular a transgenic animal or plant. More particularly, the present invention provides novel synthetic genes and genetic constructs which are capable of repressing delaying or otherwise reducing the expression of an endogenous gene or a target gene in an organism when introduced thereto.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Synthetic genes and genetic constructs comprising same i
The present invention relates generally to synthetic genes for modifying endogenous gene expression in a cell, tissue or organ of a transgenic organism, in particular a transgenic animal or plant. More particularly, the present invention provides novel synthetic genes and genetic constructs which are capable of repressing delaying or otherwise reducing the expression of an endogenous gene or a target gene in an organism when introduced thereto.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Synthetic genes and genetic constructs comprising same I
The present invention relates generally to synthetic genes for modifying endogenous gene expression in a cell, tissue or organ of a transgenic organism, in particular a transgenic animal or plant. More particularly, the present invention provides novel synthetic genes and genetic constructs which are capable of repressing delaying or otherwise reducing the expression of an endogenous gene or a target gene in an organism when introduced thereto.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Synthetic genomes
ActiveUS20070264688A1Complement and facilitate abilitySugar derivativesTissue cultureChemical synthesisHydrogen
Methods are provided for constructing a synthetic genome, comprising generating and assembling nucleic acid cassettes comprising portions of the genome, wherein at least one of the nucleic acid cassettes is constructed from nucleic acid components that have been chemically synthesized, or from copies of the chemically synthesized nucleic acid components. In one embodiment, the entire synthetic genome is constructed from nucleic acid components that have been chemically synthesized, or from copies of the chemically synthesized nucleic acid components. Rational methods may be used to design the synthetic genome (e.g., to establish a minimal genome and / or to optimize the function of genes within a genome, such as by mutating or rearranging the order of the genes). Synthetic genomes of the invention may be introduced into vesicles (e.g., bacterial cells from which part or all of the resident genome has been removed, or synthetic vesicles) to generate synthetic cells. Synthetic genomes or synthetic cells may be used for a variety of purposes, including the generation of synthetic fuels, such as hydrogen or ethanol.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Synthetic genes for plant gums and other hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins
InactiveUS6639050B1Enhance molecular packingEasy to identifyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyHydroxyproline
A new approach in the field of plant gums is described which presents a new solution to the production of hydroxyproline(Hyp)-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs), repetitive proline-rich proteins (RPRPs) and arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs). The expression of synthetic genes designed from repetitive peptide sequences of such glycoproteins, including the peptide sequences of gum arabic glycoprotein (GAGP), is taught in host cells, including plant host cells.
Owner:OHIO UNIV TECH TRANSFER OFFICE TECH & ENTERPRISE BUILDING
Control of gene expression
InactiveUS20030074684A1Homology of non-coding segments will be equally effectiveHigh homologyAntibacterial agentsFungiBiological bodySynthetic Genes
The present invention relates generally to synthetic genes for modifying endogenous gene expression in a cell, tissue or organ of a transgenic organism, in particular a transgenic animal or plant. More particularly, the present invention provides novel synthetic genes and genetic constructs which are capable of repressing delaying or otherwise reducing the expression of an endogenous gene or a target gene in an organism when introduced thereto.
Owner:BENITEC AUSTRALIA +1
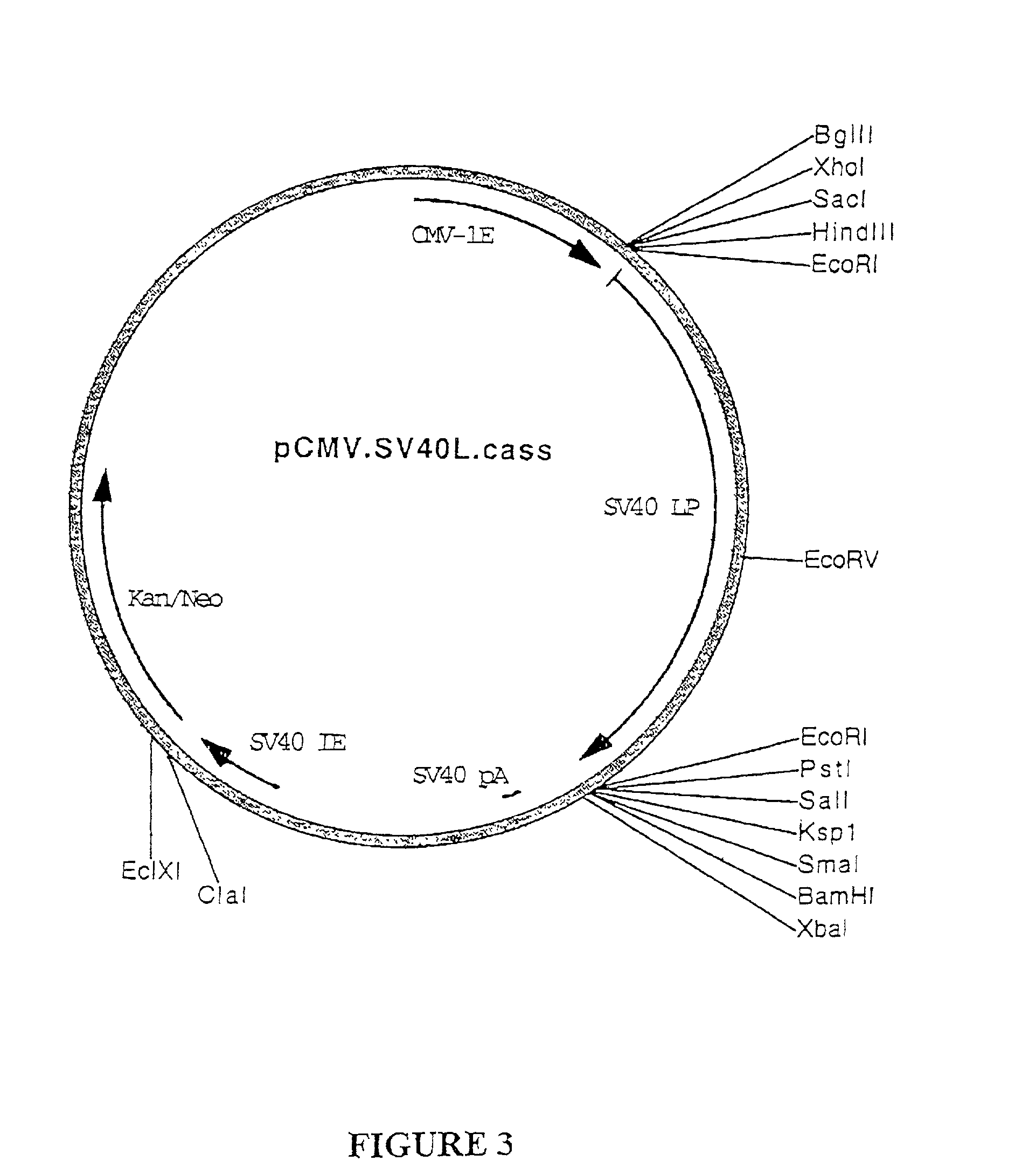
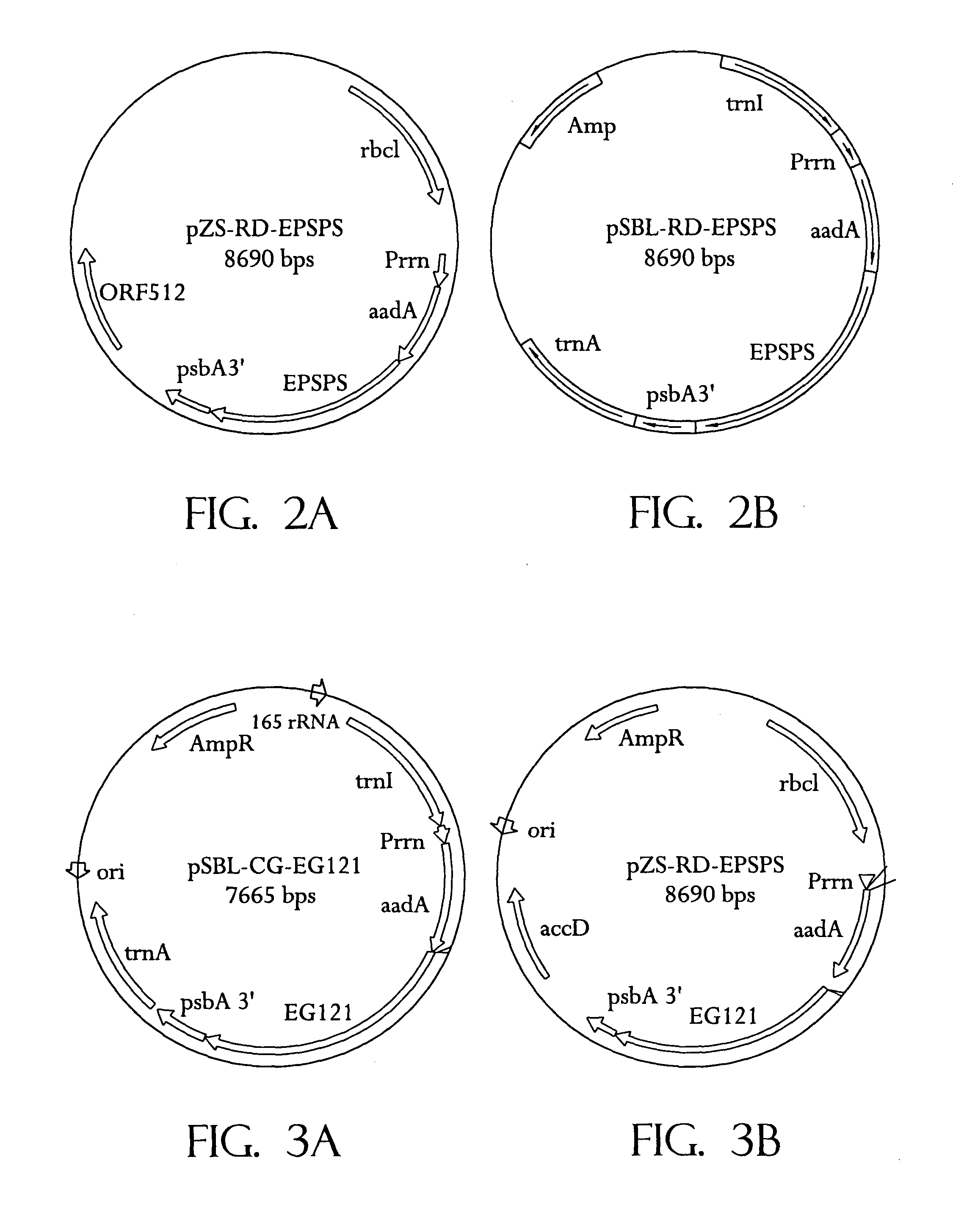
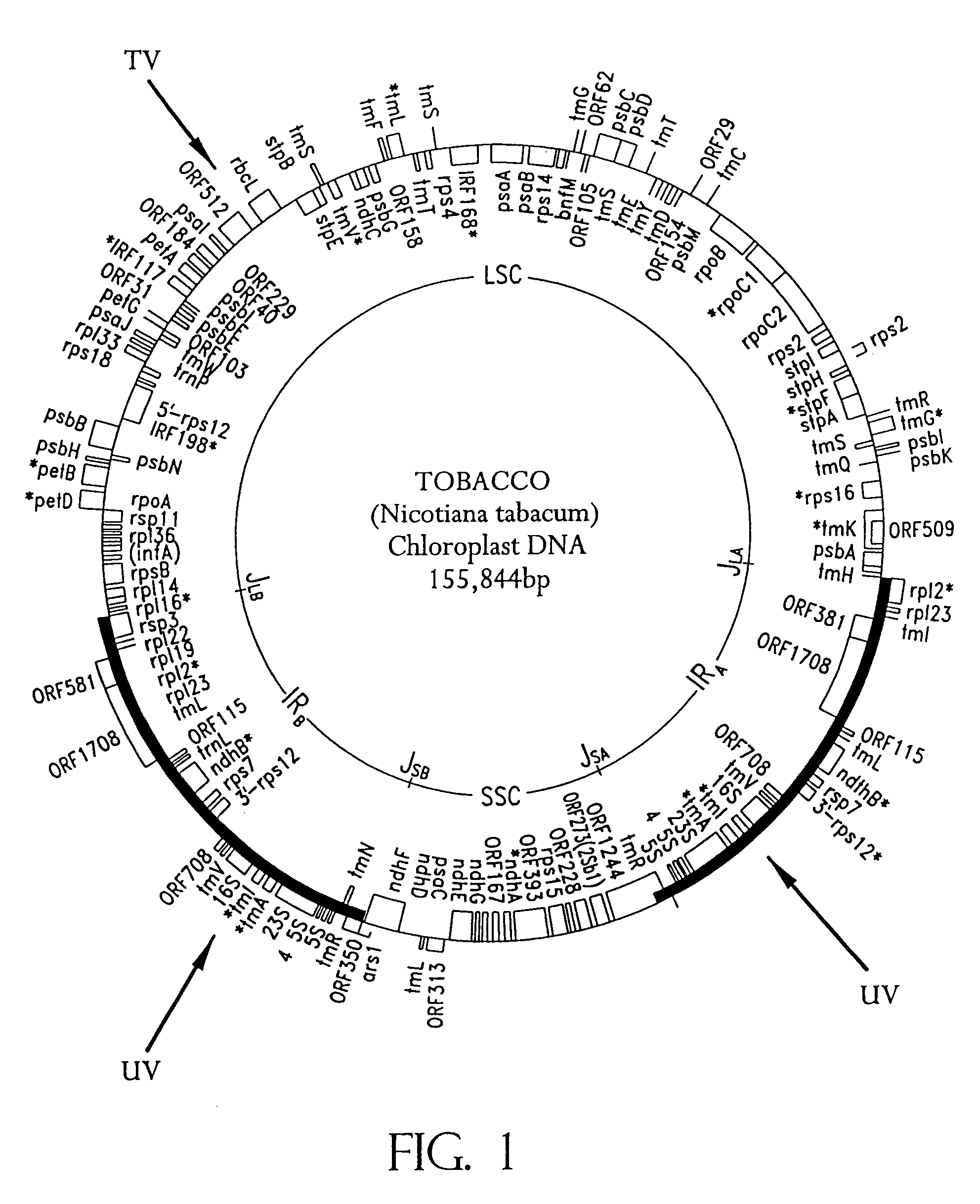
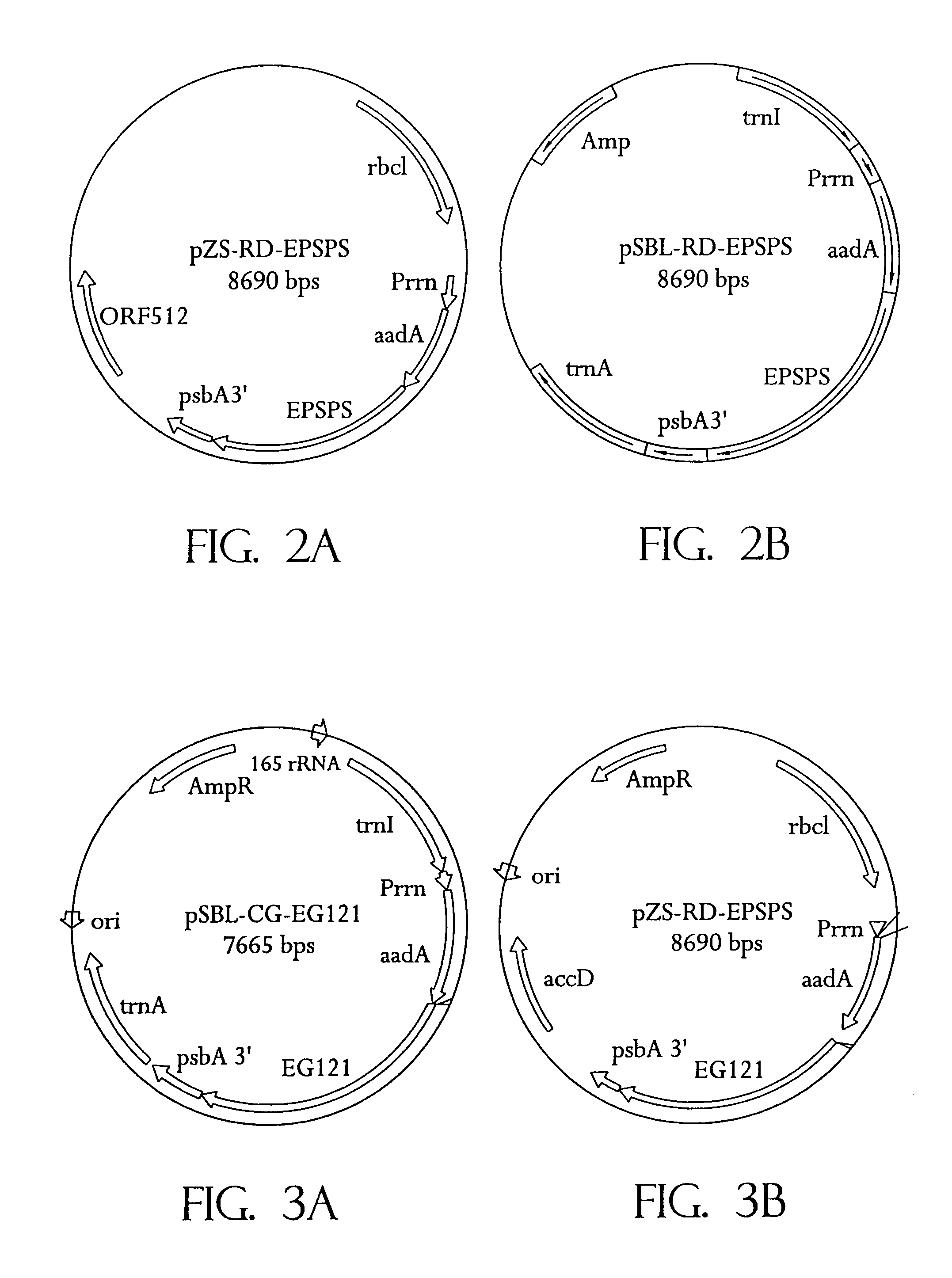
Universal chloroplast integration and expression vectors, transformed plants and products thereof
InactiveUS7129391B1Increase ratingsIncrease probabilitySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationChloroplastOrganism
The invention provides universal chloroplast integration and expression vectors which are competent to stably transform and integrate genes of interest into chloroplast genome of multiple species of plants. Transformed plants and their progeny are provided. Monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants are transformed which have never been transformed heretofore. Plants transformed with a synthetic gene express valuable biodegradable protein-based polymers (PBPs). Transformed plants produce high value molecules. Resistance is provided to agricultural crops against the major classes of chemical herbicides. Herbicide resistance is used as a lethal selectable marker for chloroplast transformation. The transformed plants are capable of expressing in addition to the targeted trait, a desirable, secondary non-targeted trait. Insect resistance is provided to transformed plants, both against insects that are susceptible to Bt toxins and against insects that have developed resistance to Bt toxins.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
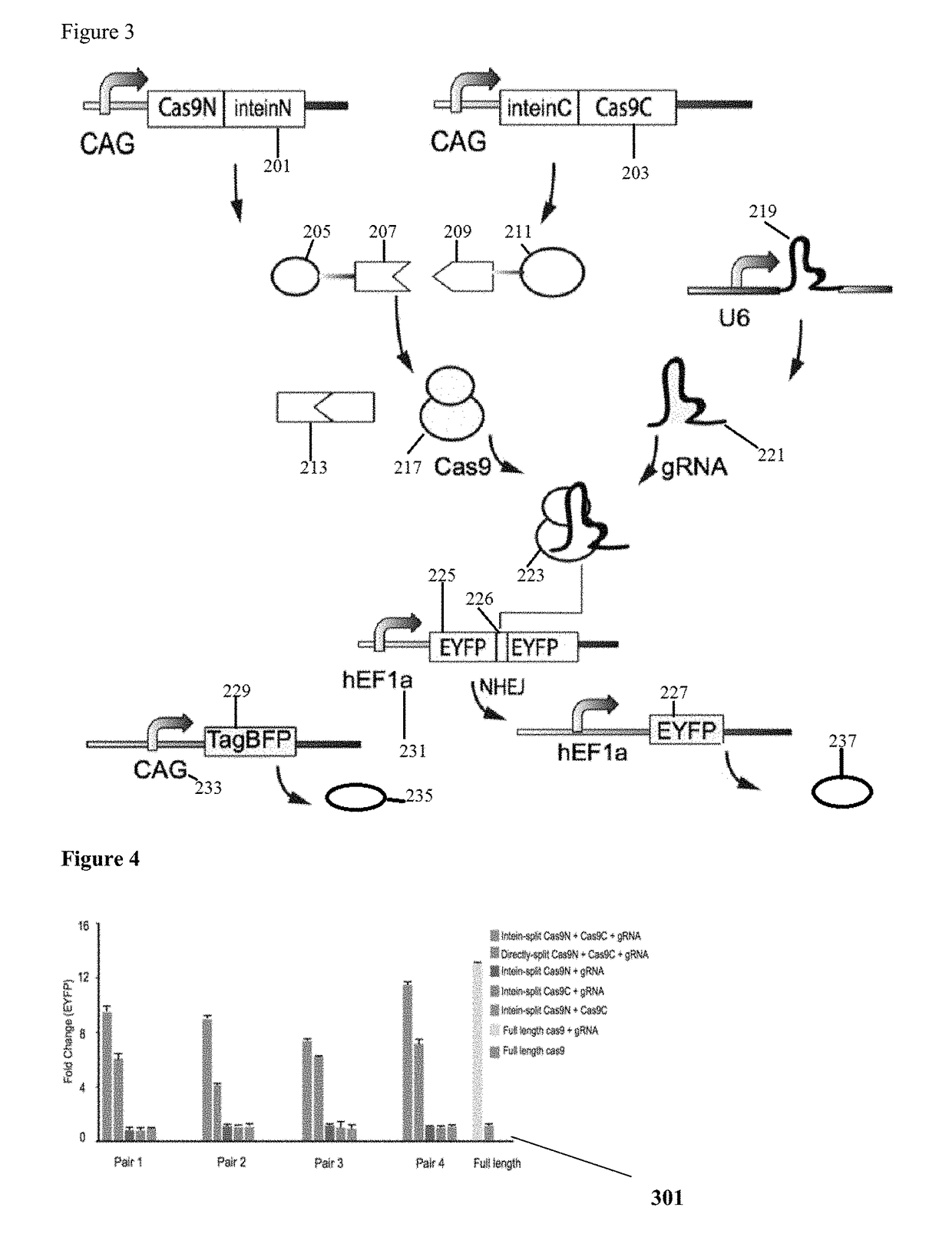
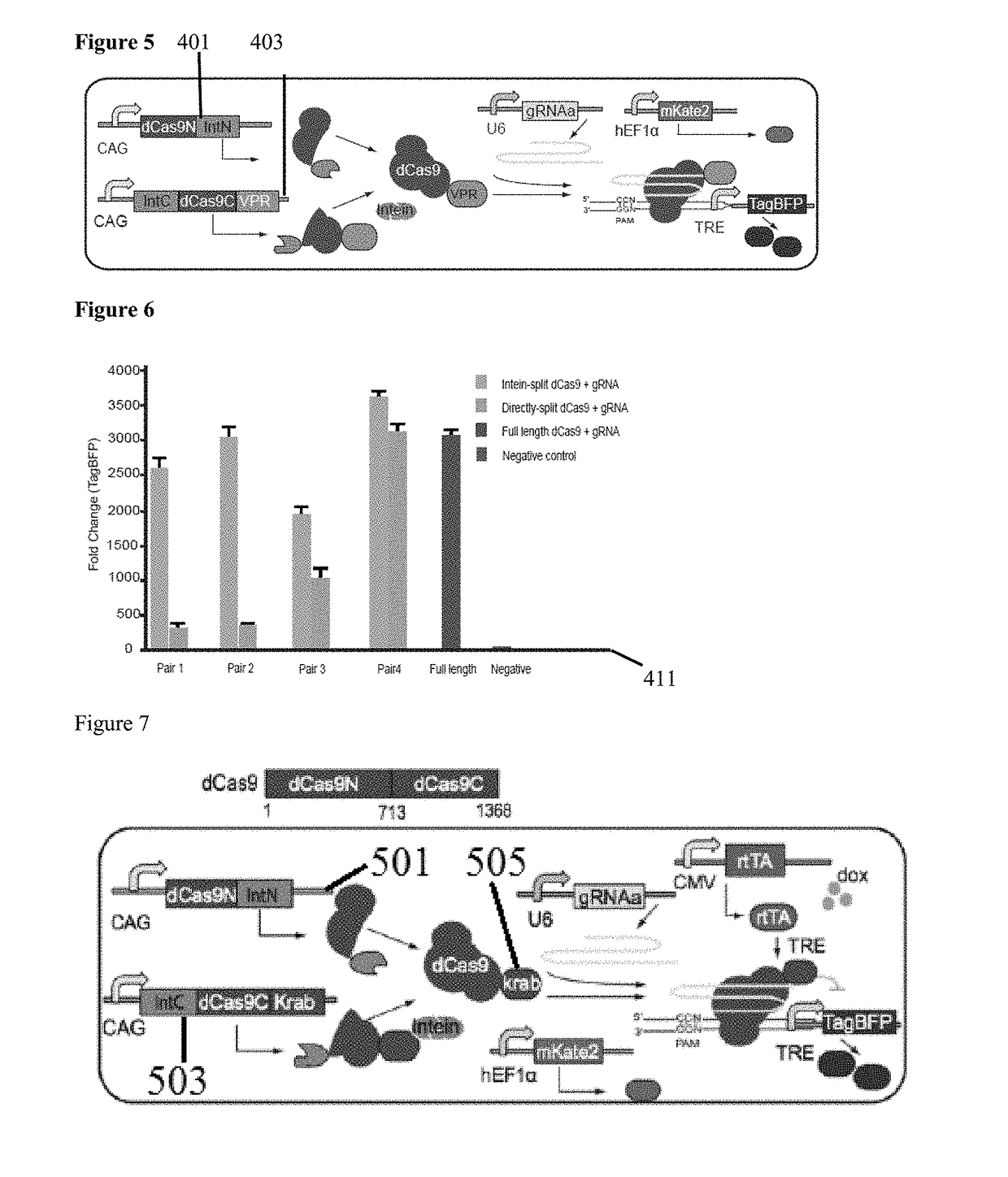
Genetic indicator and control system and method utilizing split Cas9/CRISPR domains for transcriptional control in eukaryotic cell lines
PendingUS20170233703A1Facilitated engineeringIncrease the number ofHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLiving systemsPlant cell
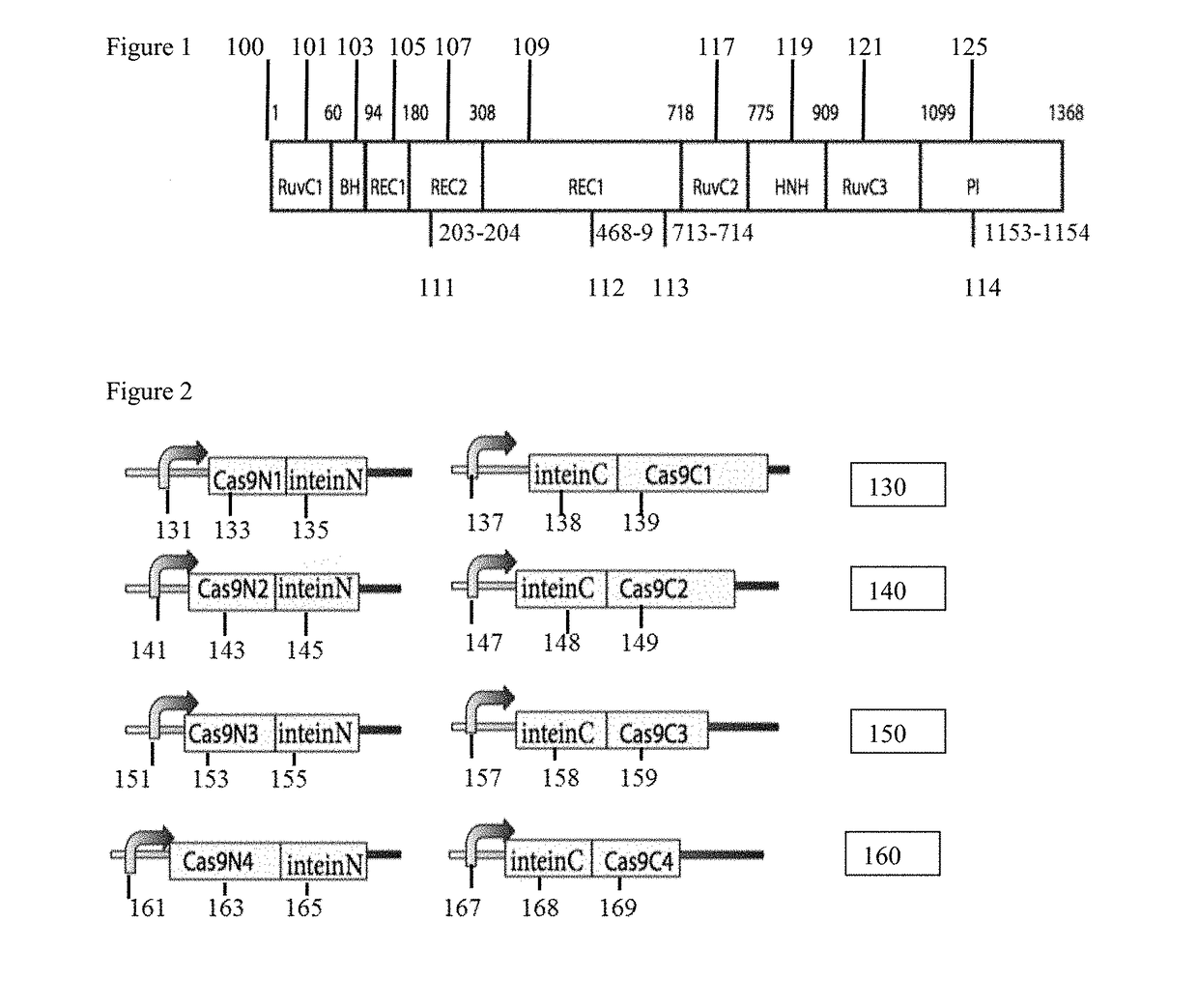
While genetic engineering has undergone rapid advancement with the discovery of CRISPR / Cas9, there is room for improvement for genetic circuit control, precision (reducing circuit ‘leakiness’) and delivery into living systems. The claimed invention offers programmable and precise regulation of dCas9 functions in response to multiple molecular signals by using synthetic gene circuits, greatly expanding applications. Moreover, using the system to greatest therapeutic potential has been greatly limited by the restrictive cargo size of existing viral delivery systems. By splitting dCas9 into multiple sections, the delivery size of synthetic gene circuits is greatly reduced. By exchanging split dCas9 domains, differential regulation on one gene, or activating two different genes in response to cell-type specific microRNAs is illustrated. Practical applications of the illustrative examples include engineered sensory switches including indicators for bladder cancer as well as enhanced systems for adenovirus delivery, cellular regulation, plant cell modification and potential therapeutic applications.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methylotroph producing mammalian type sugar chain
ActiveUS20060148039A1FungiImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBiotechnologyHeterologous
This invention is to provide a process for producing a glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain, characterized in that the process comprises introducing an α-1,2-mannosidase gene into a methylotrophic yeast having a mutation of a sugar chain biosynthesizing enzyme gene, so that the α-1,2-mannosidase gene is expressed under the control of a potent promoter in the yeast; culturing in a medium the methylotrophic yeast cells with a heterologous gene transferred thereinto; and obtaining the glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain from the culture. Using the newly created methylotrophic yeast having a sugar chain mutation, a neutral sugar chain identical with a high mannose type sugar chain produced by mammalian cells such as human cells, or a glycoprotein comprising such a neutral sugar chain, can be produced in a large amount at a high purity. By introducing a mammalian type sugar chain biosynthesizing gene into the above-described mutant, a mammalian type sugar chain, such as a hybrid or complex, or a protein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain can be efficiently produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
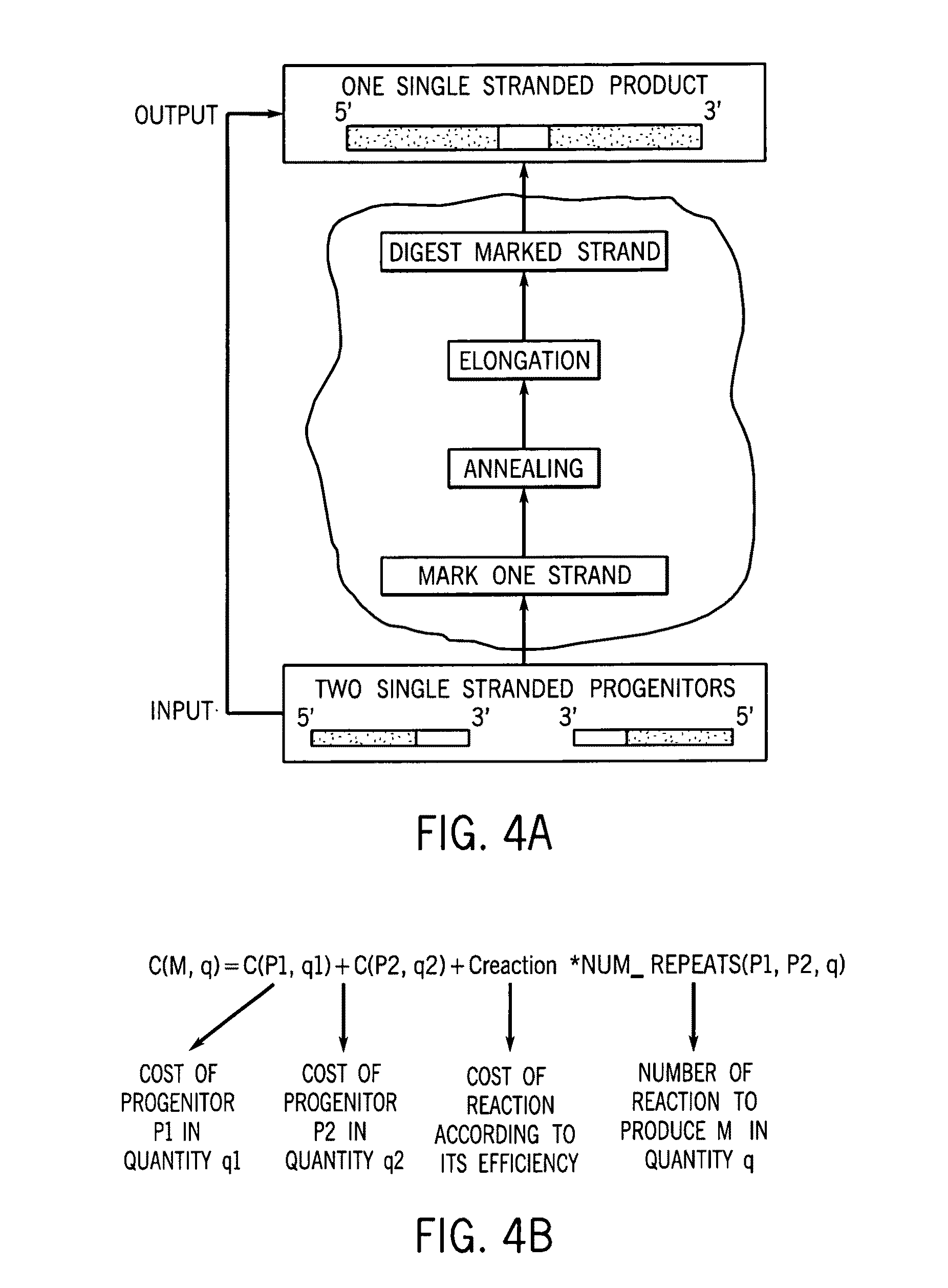
Programmable iterated elongation: a method for manufacturing synthetic genes and combinatorial DNA and protein libraries
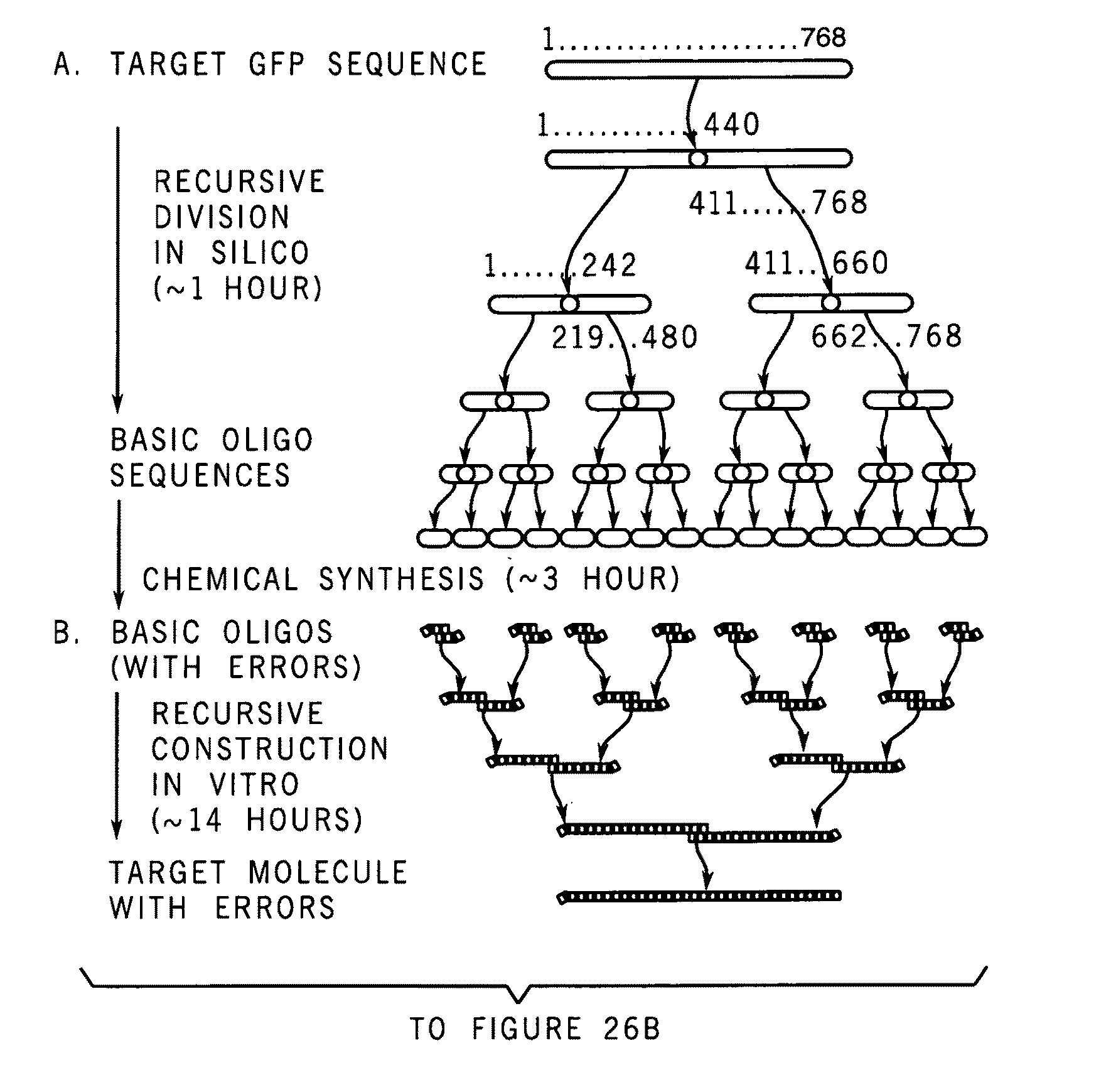
A method for manufacturing synthetic genes and combinatorial DNA and protein libraries, termed here Divide and Conquer-DNA synthesis (D&C-DNA synthesis) method. The method can be used in a systematic and automated way to synthesize any long DNA molecule and, more generally, any combinatorial molecular library having the mathematical property of being a regular set of strings. The D&C-DNA synthesis method is an algorithm design paradigm that works by recursively breaking down a problem into two or more sub-problems of the same type. The division of long DNA sequences is done in silico. The assembly of the sequence is done in vitro. The D&C-DNA synthesis method protocol consists of a tree, in which each node represents an intermediate sequence. The internal nodes are created in elongation reactions from their daughter nodes, and the leaves are synthesized directly. After each elongation only one DNA strand passes to the next level in the tree until receiving the final product. Optionally and preferably, error correction is performed to correct any errors which may have occurred during the synthetic process.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Novel Method for the cheap, efficient, and effective production of pharmaceutical and therapeutic api's intermediates, and final products
InactiveUS20160298151A1Reduce concentrationFermentationDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyPhenylpropanoid
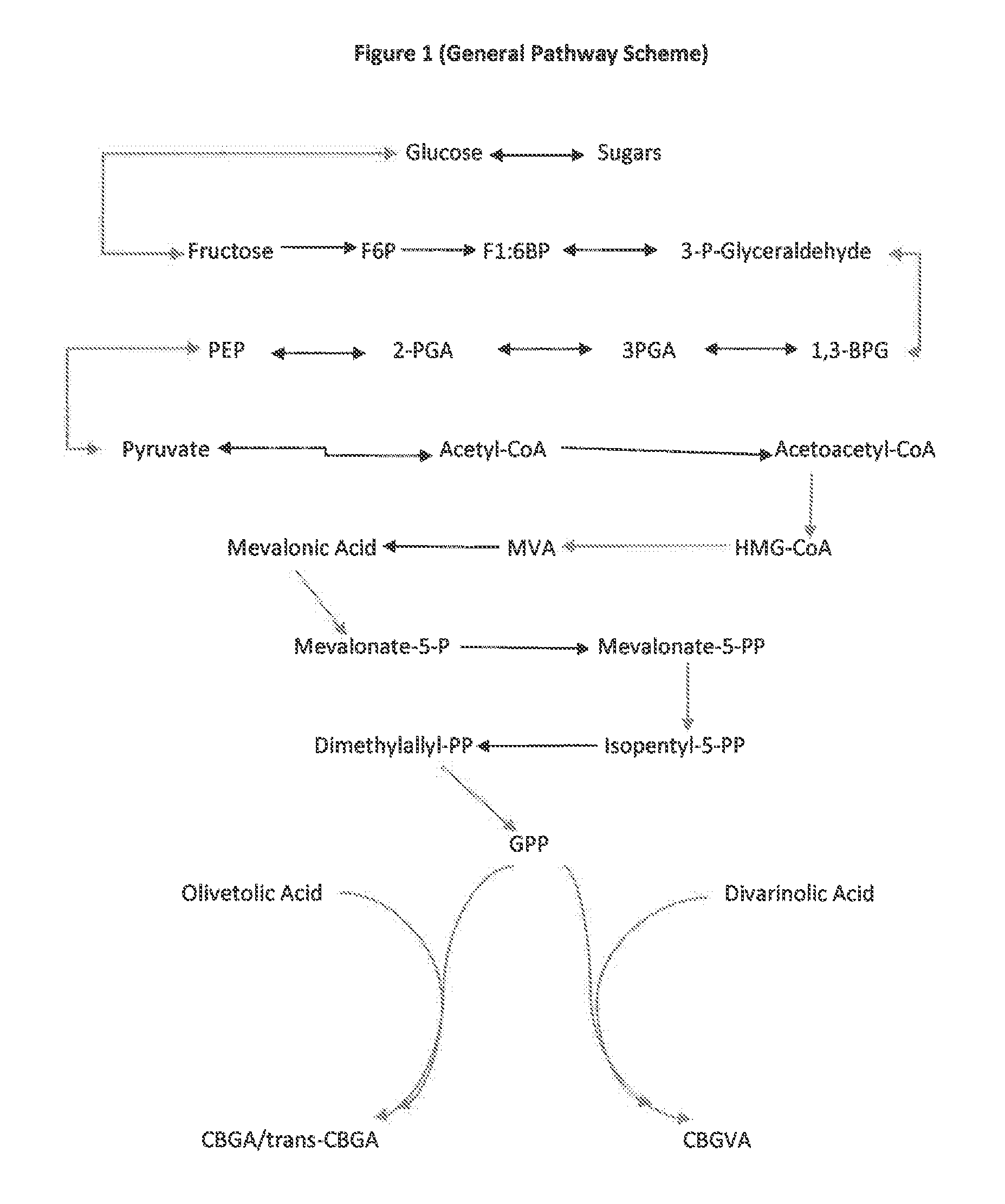
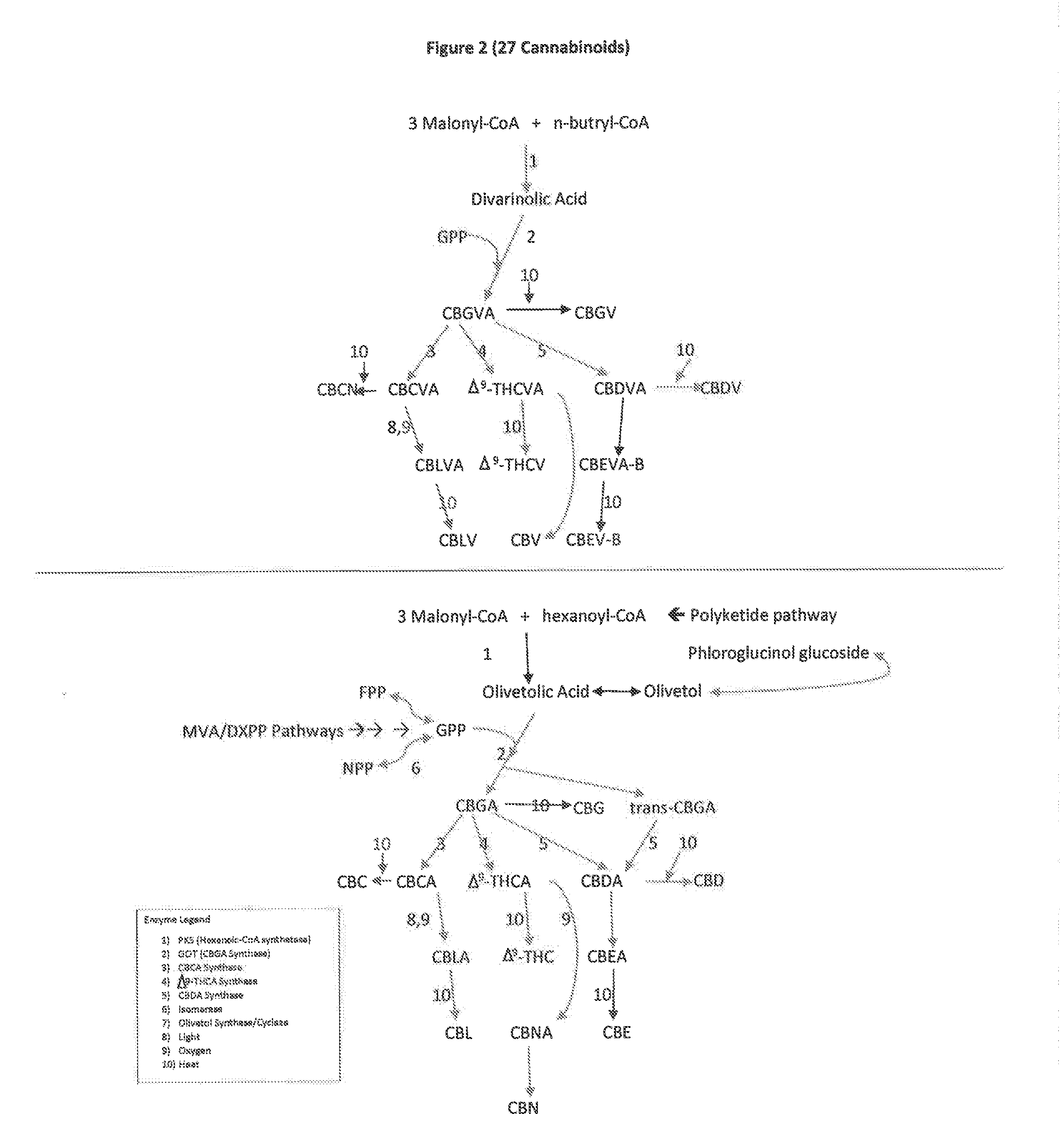
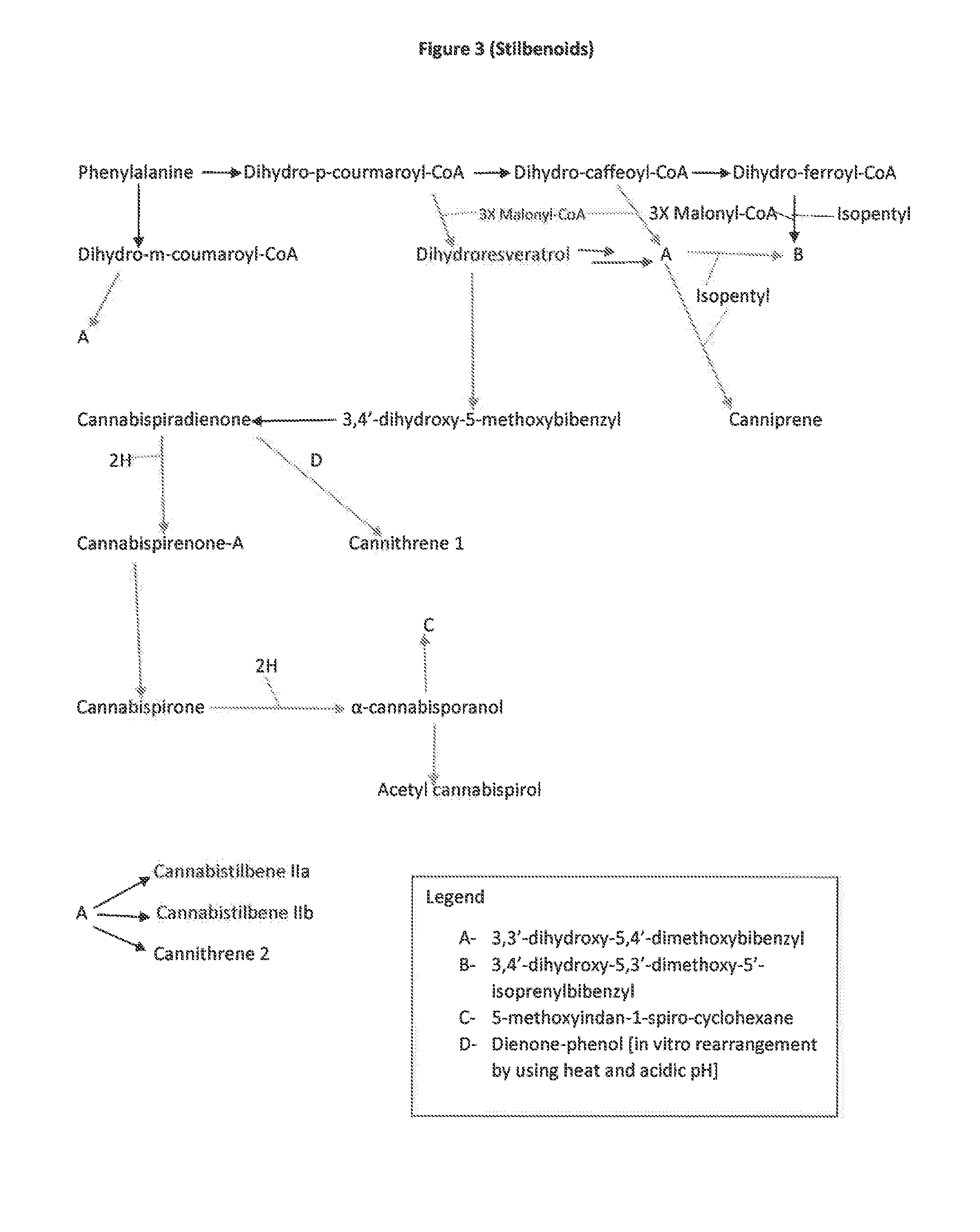
The present invention is a method for the biosynthesis of hundreds of compounds, mainly found in the cannabis plant. The starting material for these compounds can be any biological compound that is used / produced in a biological organism from the sugar family starting materials or other low cost raw materials processed via enzymes or within organisms to give final products. These final products include, but are not limited to: cannabinoids, terpenoids, stilbenoids, flavonoids, phenolic amides, lignanamides, spermidine alkaloids, and phenylpropanoids. Specifically, the present invention relates to the regular / modified / synthetic gene(s) of select enzymes are processed and inserted into an expression system (vector, cosmid, BAC, YAC, phage, etc.) to produce modified hosts. The modified host is then optimized for efficient production and yield via manipulation, silencing, and amplifying inserted or other genes in the host, leading to an efficient system for product.
Owner:BUTT SHER ALI +1
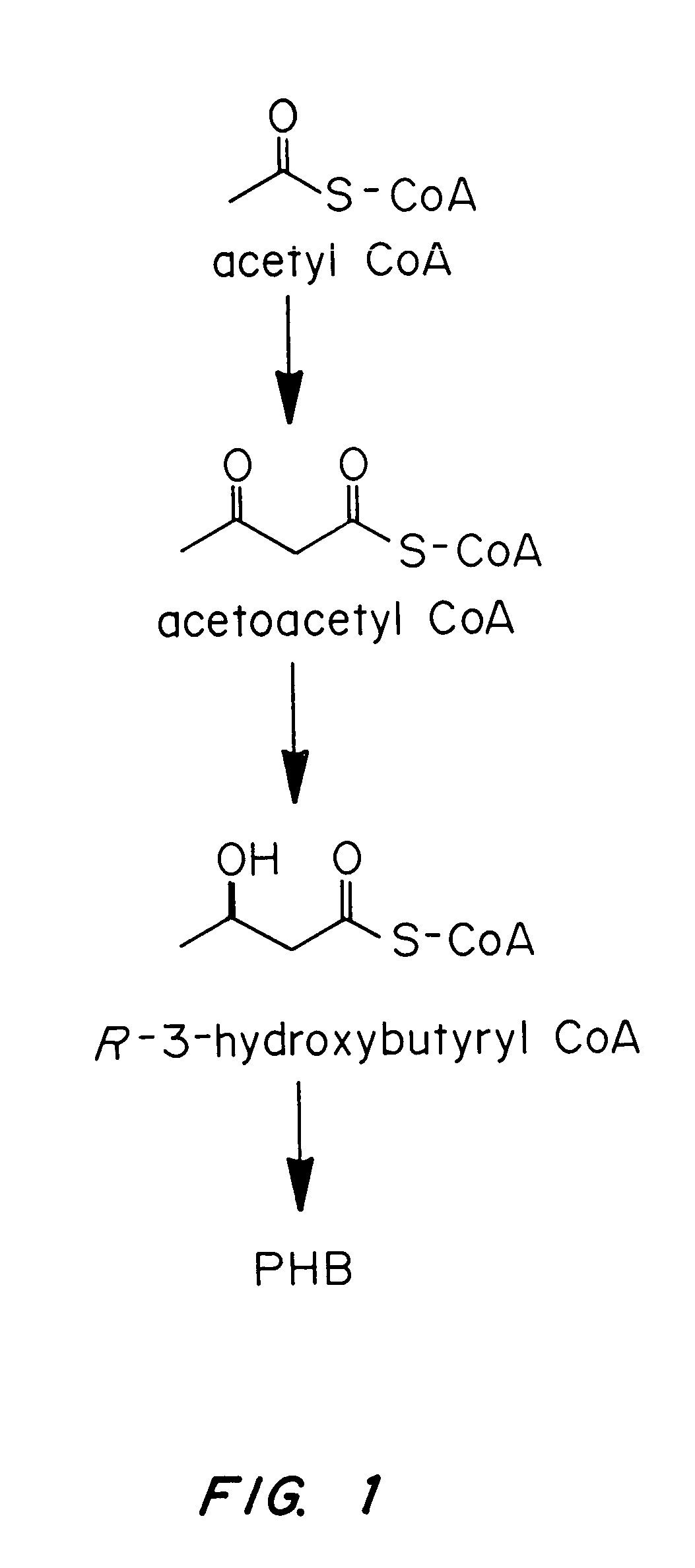
Transgenic systems for the manufacture of poly (3-hydroxy-butyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)
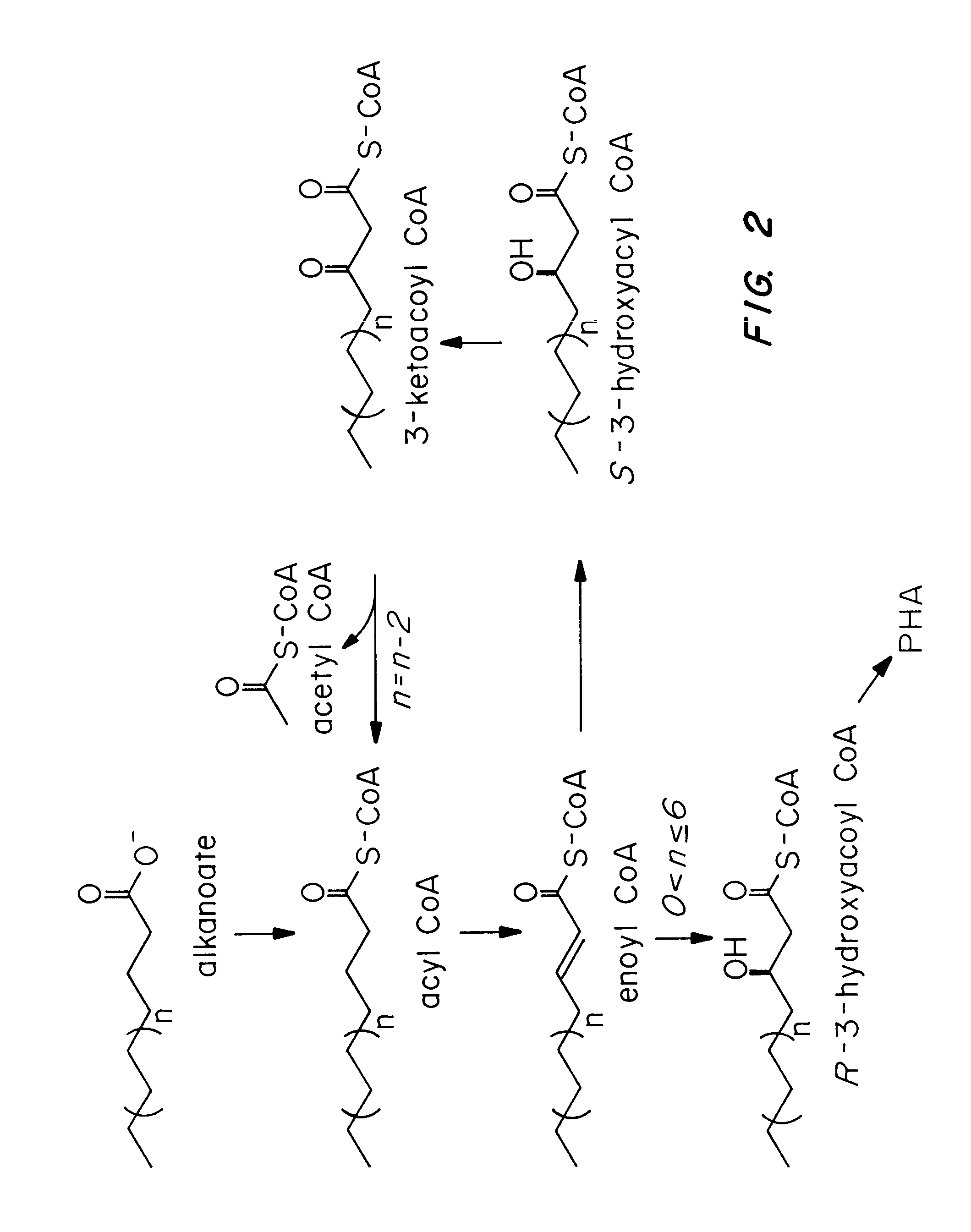
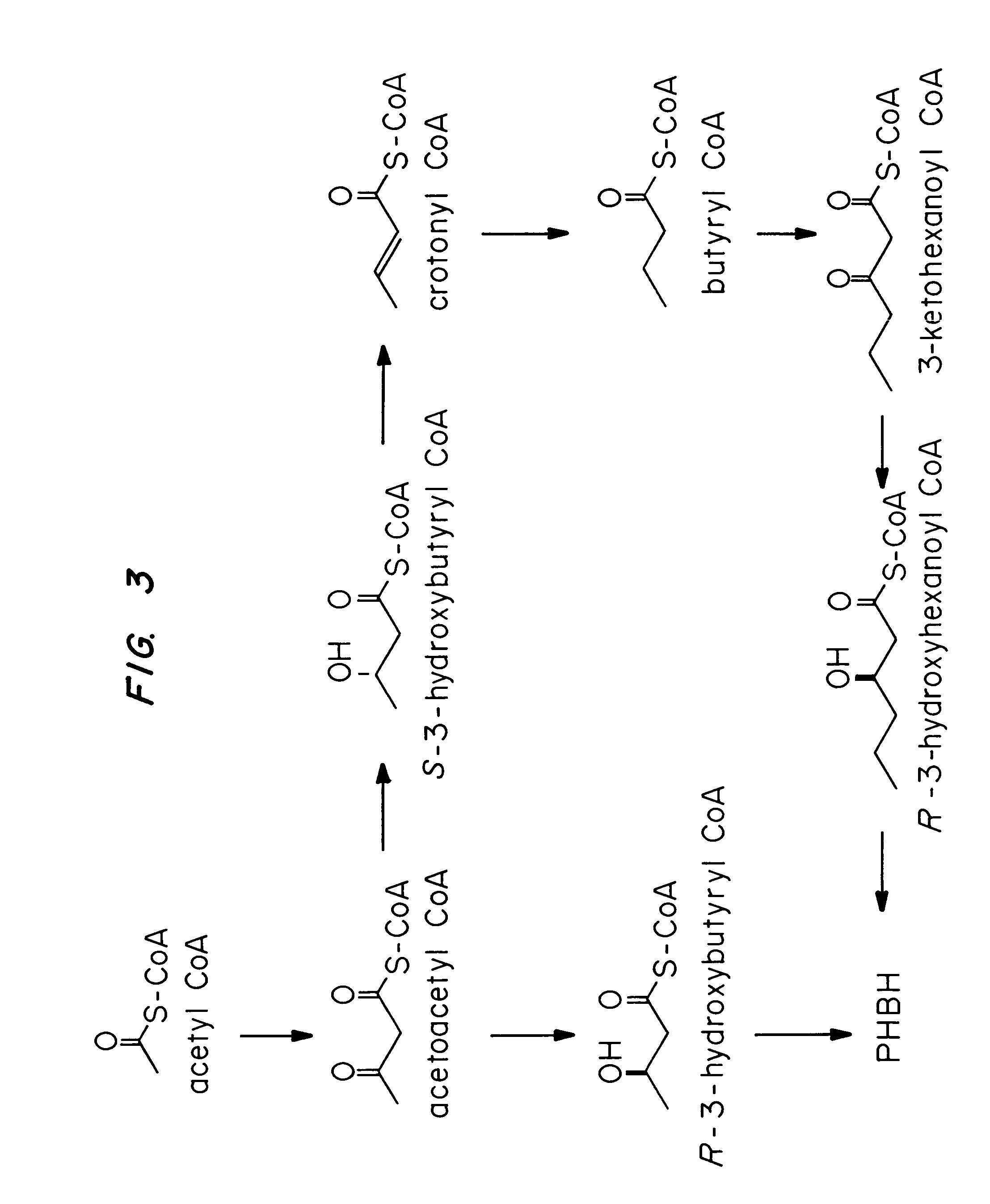
InactiveUS7455999B2Efficient PHA synthesisHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBiosynthetic genes
Methods for engineering transgenic organisms that synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) containing 3-hydroxyhexanoate as comonomer have been developed. These processes are based on genetically engineered bacteria such as Escherichia coli or in plant crops as production systems which include PHA biosynthetic genes from PHA producers. In a preferred embodiment of the method, additional genes are introduced in wild type or transgenic polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) producers, thereby creating new strains that synthesize 3HH monomers which are incorporated into PHAs. The 3HH monomer preferably is derived in microbial systems using butanol or butyrate as feedstocks, which are precursors of 3-hydroxyhexanoyl-CoA. Pathways for in vivo production of butyrol-CoA specifically encompassing butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase activity are provided.
Owner:METABOLIX
Synthetic genes for plant gums and other hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins
InactiveUS20060252120A1Maximize number of cellSugar derivativesDepsipeptidesBiotechnologyHydroxyproline
A new approach in the field of plant gums is described which presents a new solution to the production of hydroxyproline(Hyp)-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs), repetitive proline-rich proteins (RPRPs) and arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs). The expression of synthetic genes designed from repetitive peptide sequences of such glycoproteins, including the peptide sequences of gum arabic glycoprotein (GAGP), is taught in host cells, including plant host cells.
Owner:KIELISZEWSKI MARCIA
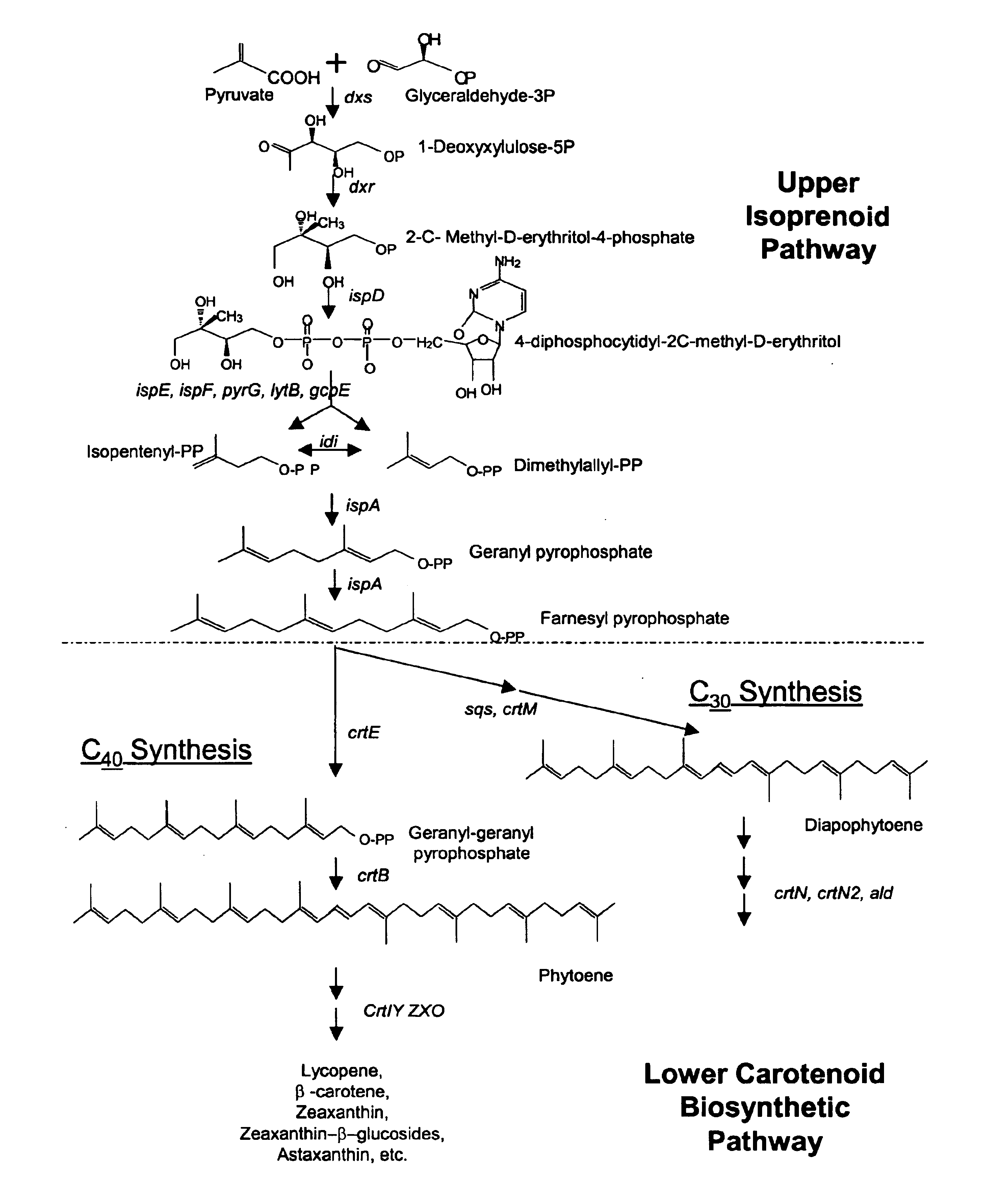
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
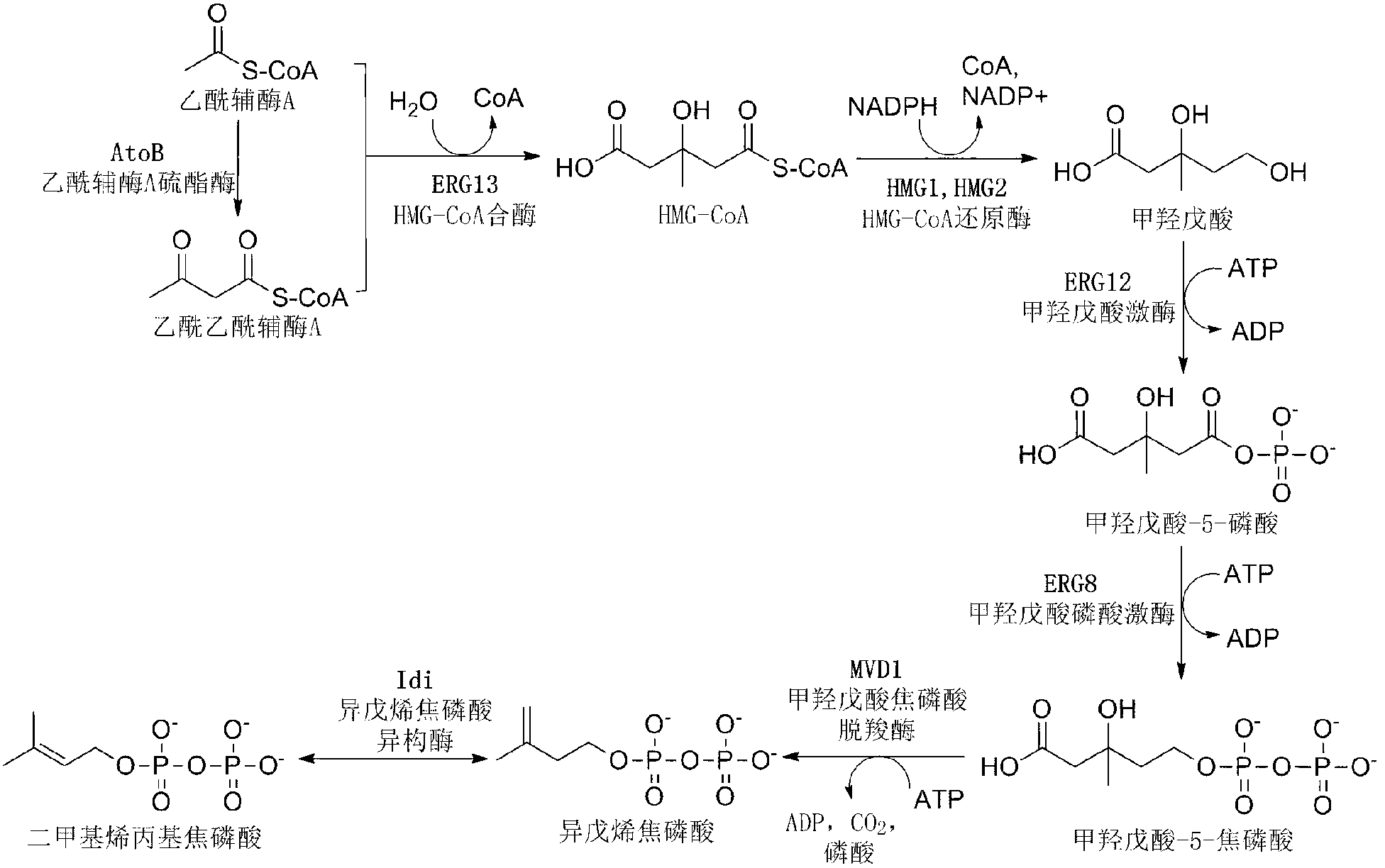
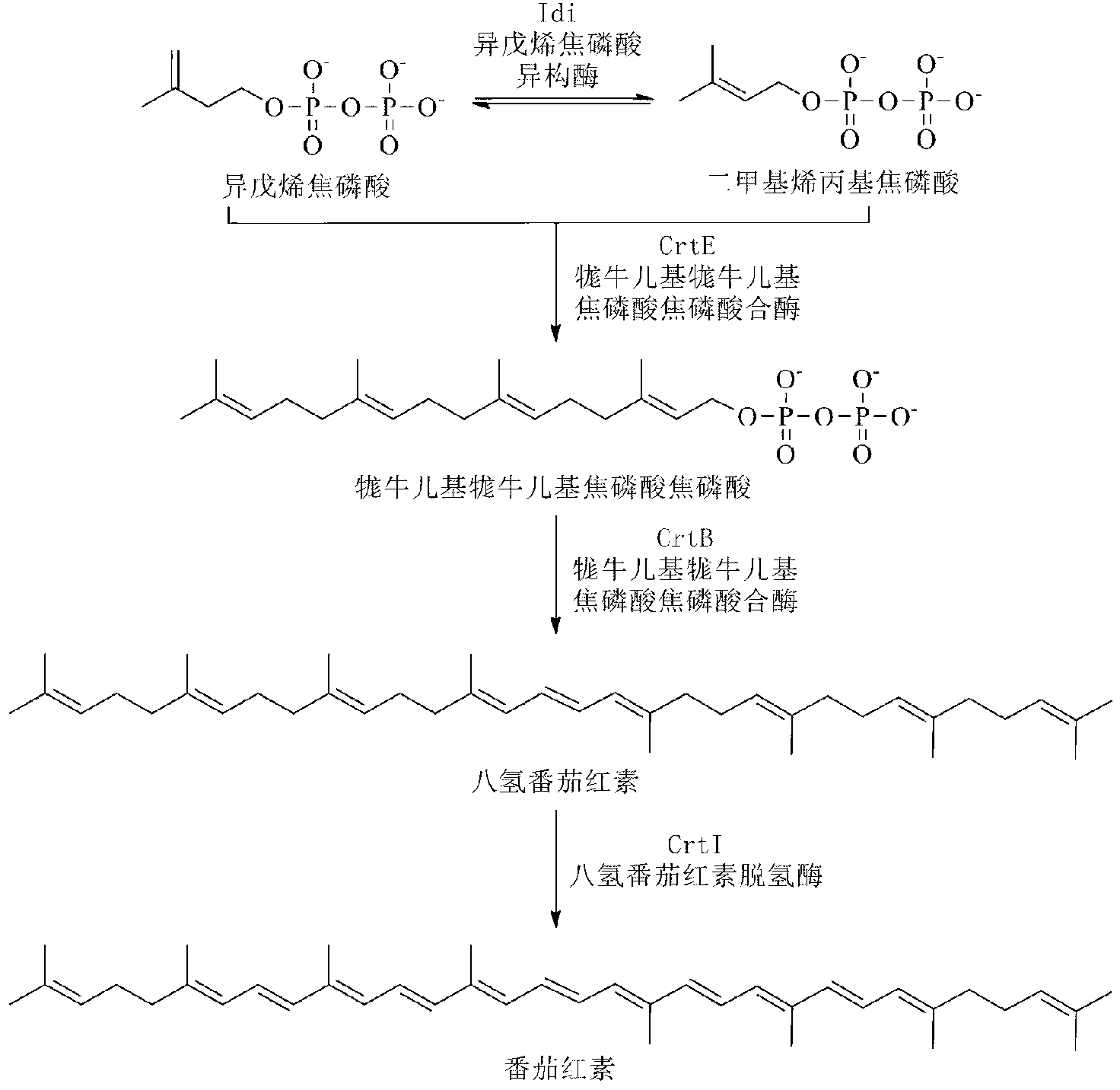
A unique carotenogenic biosynthetic gene cluster has been isolated from Panteoa agglomerans strain DC404, wherein the genetic organization of the cluster is crtE-idi-crtY-crtI-crtB-crtZ. The genes contained within this cluster encode geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthetase (CrtE), isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase (Idi), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), phytoene desaturase (CrtI), phytoene synthase (CrtB), and β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ). The gene cluster, genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
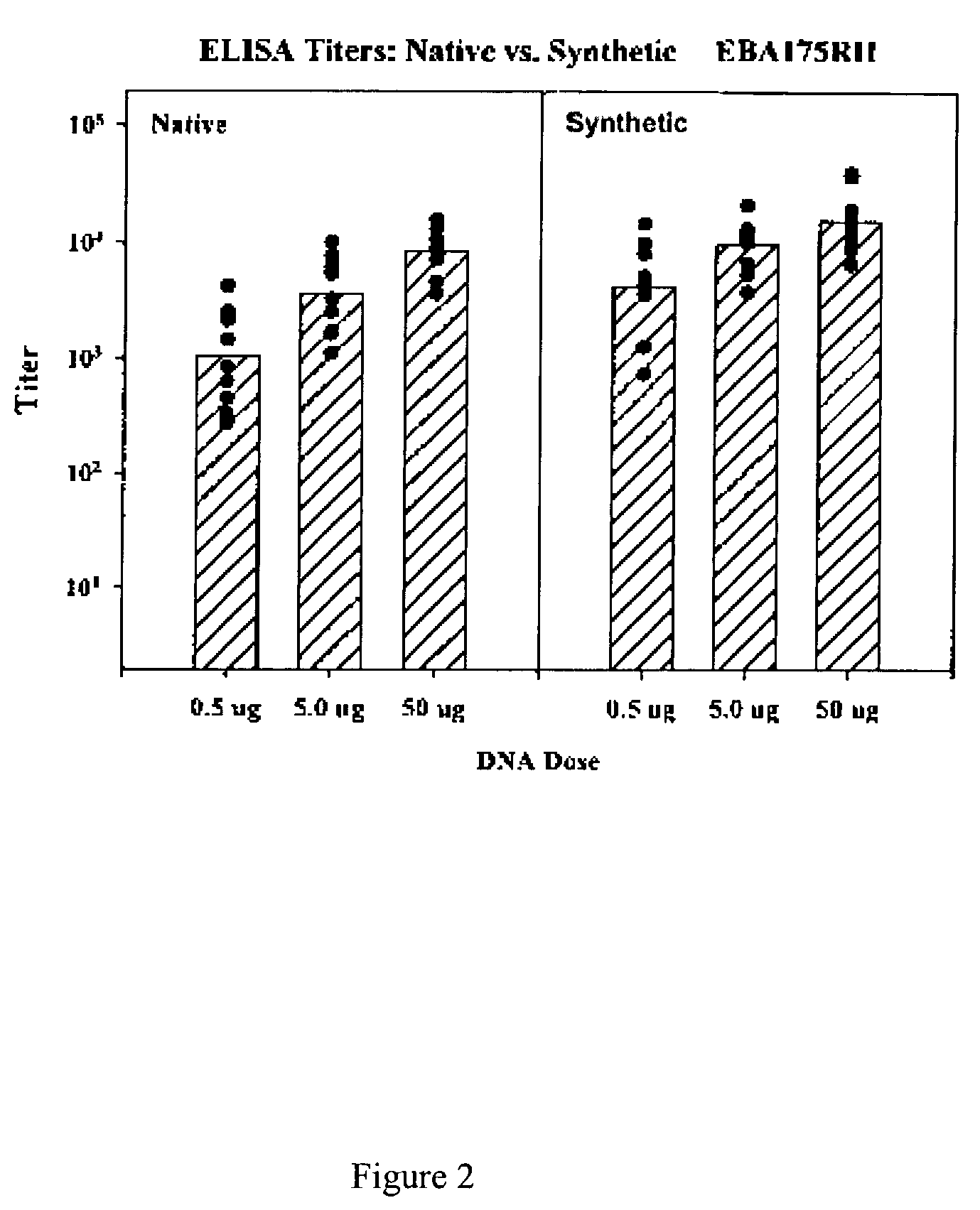
Synthetic genes for malarial proteins and methods of use
InactiveUS7078507B2Improving immunogenicityReduced vaccine dosProtozoa antigen ingredientsBacteriaRed blood cellMalaria
Synthetic gene sequences encoding erythrocyte binding protein of a malaria pathogen for the expression of the erythrocyte binding protein. The codon composition of the synthetic gene sequences approximates the mammalian codon composition. The synthetic gene sequences are useful for incorporation into the DNA vaccine vectors, for the incorporation into various expression vectors for production of malaria proteins, or both. The synthetic genes may be modified to avoid post-translational modification of the encoded protein in hosts. Administration of the synthetic gene sequences, or the encoded protein, as an immunization agent is useful for induction of immunity against malaria, treatment of malaria, or both.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
Polypepetide-encoding nucleotide sequences with refined translational kinetics and methods of making same
InactiveUS20080046192A1Reduce protein expressionEnhance protein expressionData visualisationProteomicsData setNucleotide
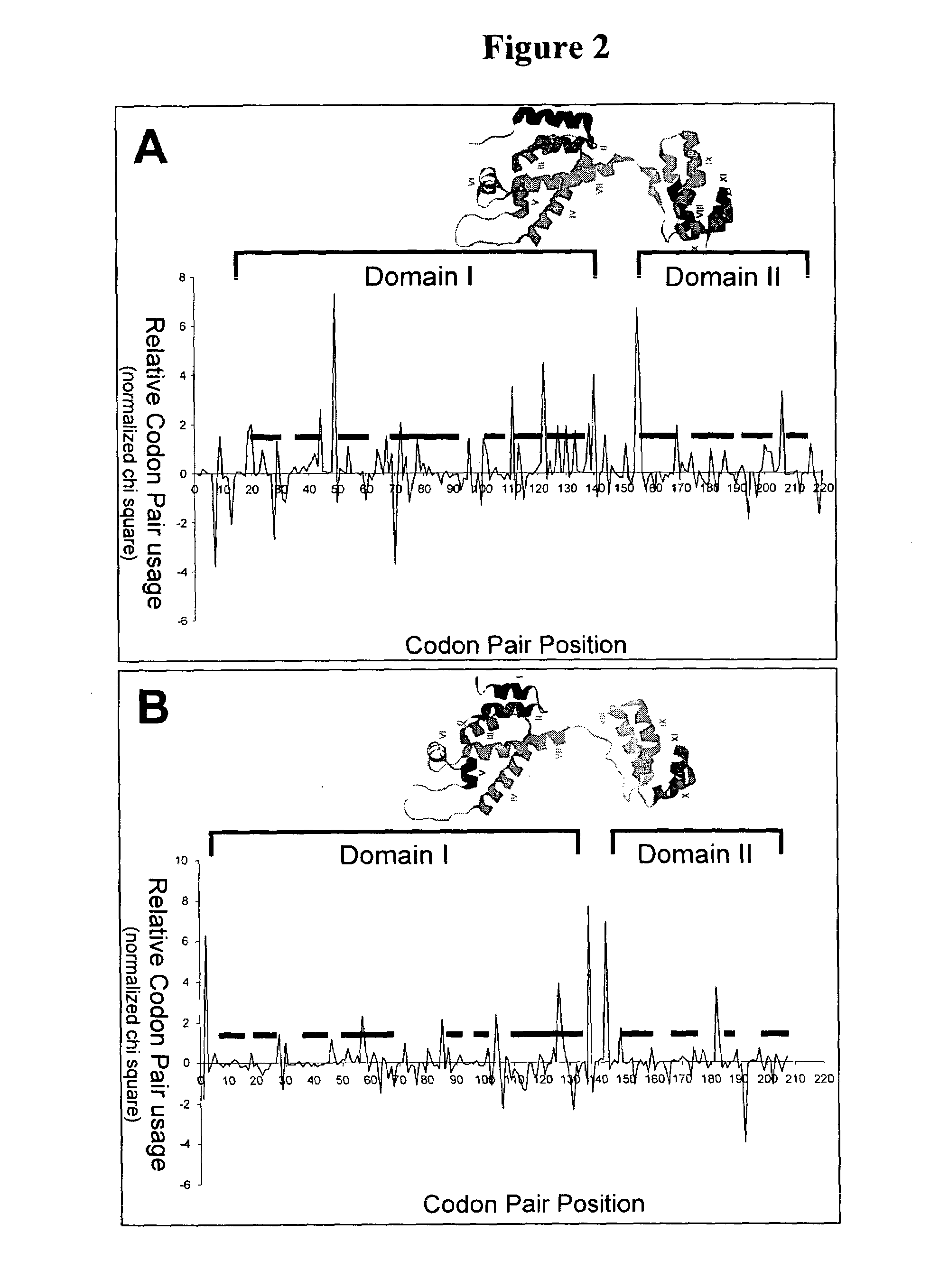
Provided are methods for creating a synthetic gene for expression in a host organism, by providing a data set representative of codon pair translational kinetics for the host organism which includes translational kinetics values of the codon pairs utilized by the host organism, providing a desired polypeptide sequence for expression in the host organism, and generating a polynucleotide sequence encoding the polypeptide sequence by analyzing candidate nucleotides to select, where possible, codon pairs that are predicted not to cause a translational pause in the host organism, with reference to the data set, thereby providing a candidate polynucleotide sequence encoding the desired polypeptide. The methods can be performed using multiple parameter nucleotide sequence optimization methods, such as branch-and-bound methods for nucleotide sequence refinement.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
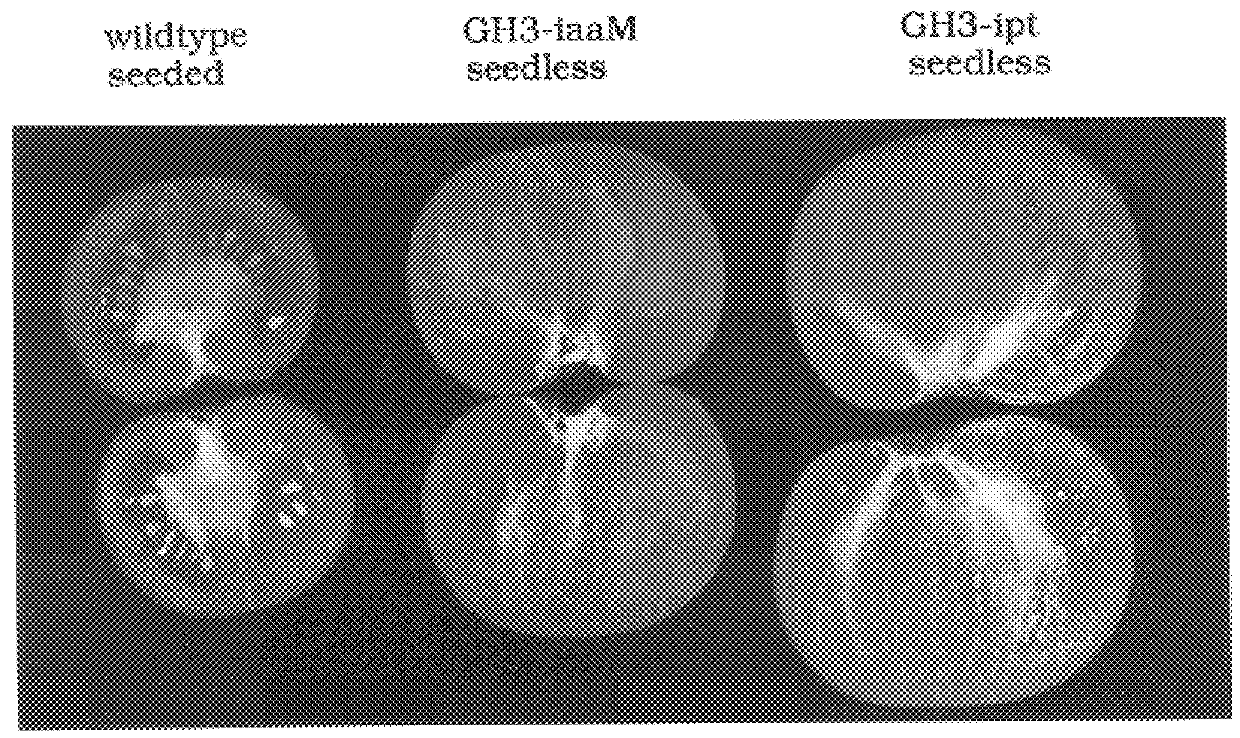
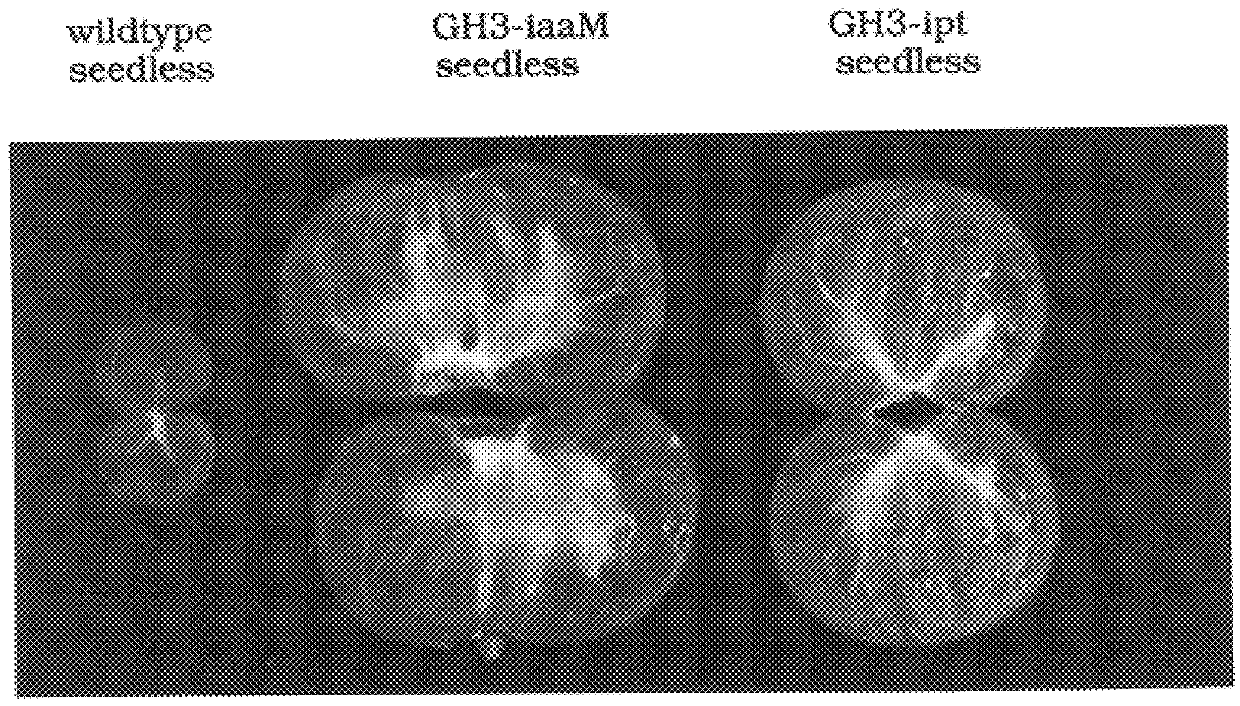
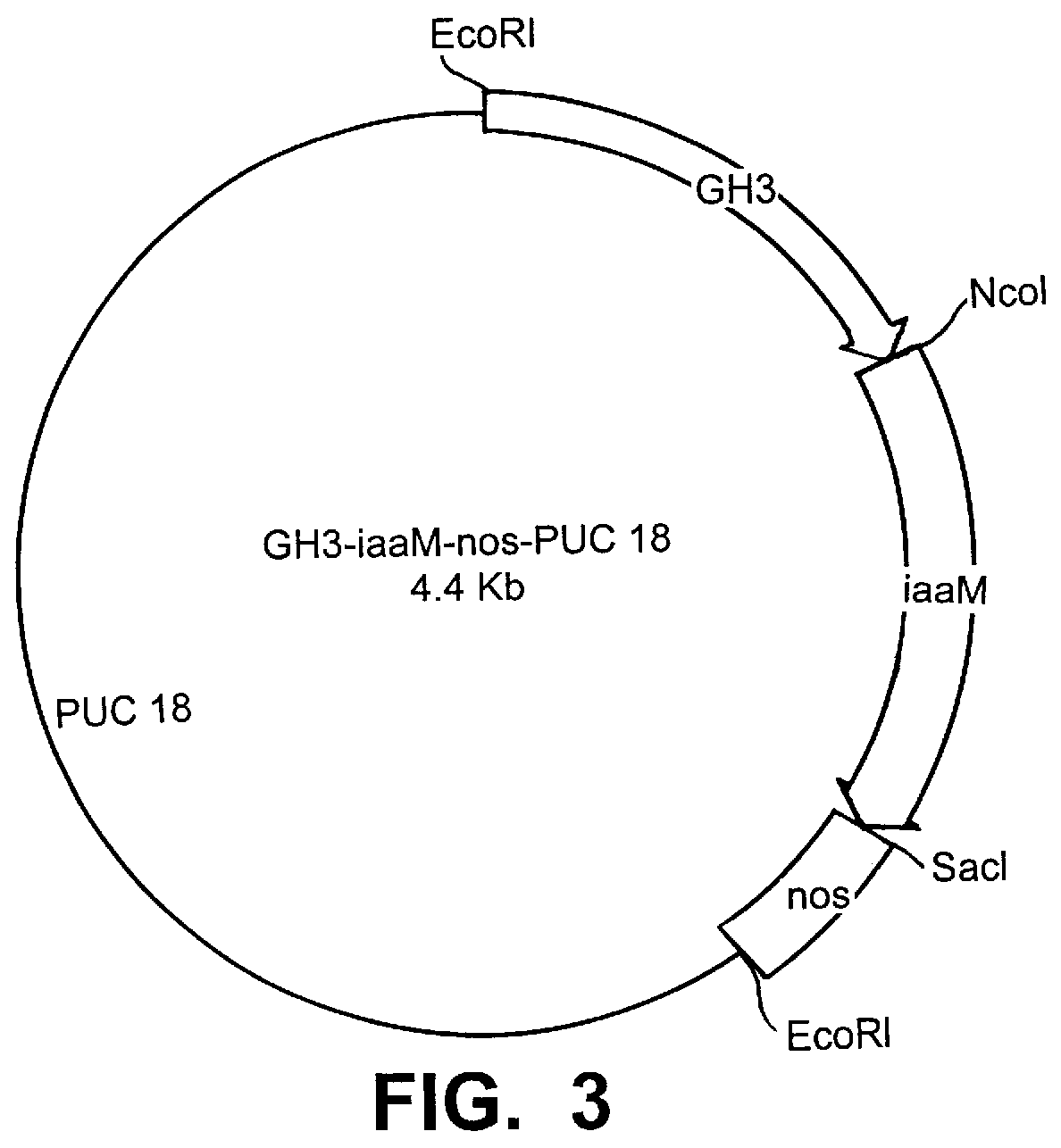
Transgenic seedless fruit comprising AGL or GH3 promoter operably linked to isopentenyl transferase or tryptophan monooxygenase coding DNA
InactiveUS6268552B1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesBiosynthetic genesDNA construct
The present invention provides methods and DNA constructs for the genetic engineering of plant cells to produce plants which produce substantially seedless fruit in the absence of exogenous growth factors (auxins or cytokinins) and in the absence of pollination. The substantially seedless fruits produced by the methods described herein are about the size of wildtype seeded fruit (or somewhat larger) and these fruits are equal to or superior to the wildtype seeded fruit with respect to solid content and flavor. The seedless fruits of the present invention are produced in transgenic plants which contain and express auxin or cytokinin biosynthetic genes, e.g., tryptophan oxygenase or isopentenyl transferase coding sequences expressed under the regulatory control of GH3 or AGL promoter sequences directing preferential or tissue specific expression of a downstream gene in the ovaries or developing fruit.
Owner:LI YI
Recombination interferon with new space conformation and enhanced effect, its preparing method and application
ActiveCN1740197AStrong antiviral activityLittle side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsAerosol deliveryAntigenSide effect
The invention provides recombination interferon (rSIFN-co) or the functional analog with new space conformation, enhanced effect, and low side effect. It is showed by the external pharmacodynamics, it can not only restrain the DNA replication of the hepatitis b virus, but also restrain the exudation of the surface antigen (HBsAg) and e antigen (HBeAg). The cytology toxicity is 1 / 8 of the clinical interferon and the antiviral activity is 5-20 times to the clinical interferon and has a higher, a more board spectrum and longer time biological response reaction, and prevent the tumor hyperplasia and transmission. The invention also provides the synthetic gene code, gene carrier, expression system of the synthetic gene of the recombination interferon or the functional analog. Finally, the invention also provides the preparing method and application thereof.
Owner:SUPERLAB FAR EAST LTD
Fusion proteins and their use in the diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis
ActiveUS8231881B2Treatment, and prevention of leishmaniasisPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzymologyLeishmaniaVisceral leishmaniasis
The present invention relates generally to a fusion protein made from a synthetic gene construct comprising of elements derived from the Leishmania antigens K26, K39, and K9. The fusion protein is particularly useful in the diagnosis of leishmaniasis, particularly visceral leishmaniasis in animals such as humans and dogs.
Owner:ACCESS TO ADVANCED HEALTH INST
Recombinant light chains of botulinum neurotoxins and light chain fusion proteins for use in research and clinical therapy
Botulinum neurotoxins, the most potent of all toxins, induce lethal neuromuscular paralysis by inhibiting exocytosis at the neuromuscular junction. The light chains (LC) of these dichain neurotoxins are a new class of zinc-endopeptidases that specifically cleave the synaptosomal proteins, SNAP-25, VAMP, or syntaxin at discrete sites. The present invention relates to the construction, expression, purification, and use of synthetic or recombinant botulinum neutoroxin genes. For example, a synthetic gene for the LC of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A (BoNT / A) was constructed and overexpressed in Escherichia coli. The gene product was purified from inclusion bodies. The methods of the invention can provide 1.1 g of the LC per liter of culture. The LC product was stable in solution at 4° C. for at least 6 months. This rBoNT / A LC was proteolytically active, specifically cleaving the Glu-Arg bond in a 17-residue synthetic peptide of SNAP-25, the reported cleavage site of BoNT / A. Its calculated catalytic efficiency kcat / Km was higher than that reported for the native BoNT / A dichain. Treating the rBoNT / A LC with mercuric compounds completely abolished its activity, most probably by modifying the cysteine-164 residue located in the vicinity of the active site. About 70% activity of the LC was restored by adding Zn2+ to a Zn2+-free, apo-LC preparation. The LC was nontoxic to mice and failed to elicit neutralizing epitope(s) when the animals were vaccinated with this protein. In addition, injecting rBoNT / A LC into sea urchin eggs inhibited exocytosis-dependent plasma membrane resealing.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Bacterial strain for producing lycopene and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103243066AImprove the ability to produce lycopeneIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLycopene synthesisBacterial strain
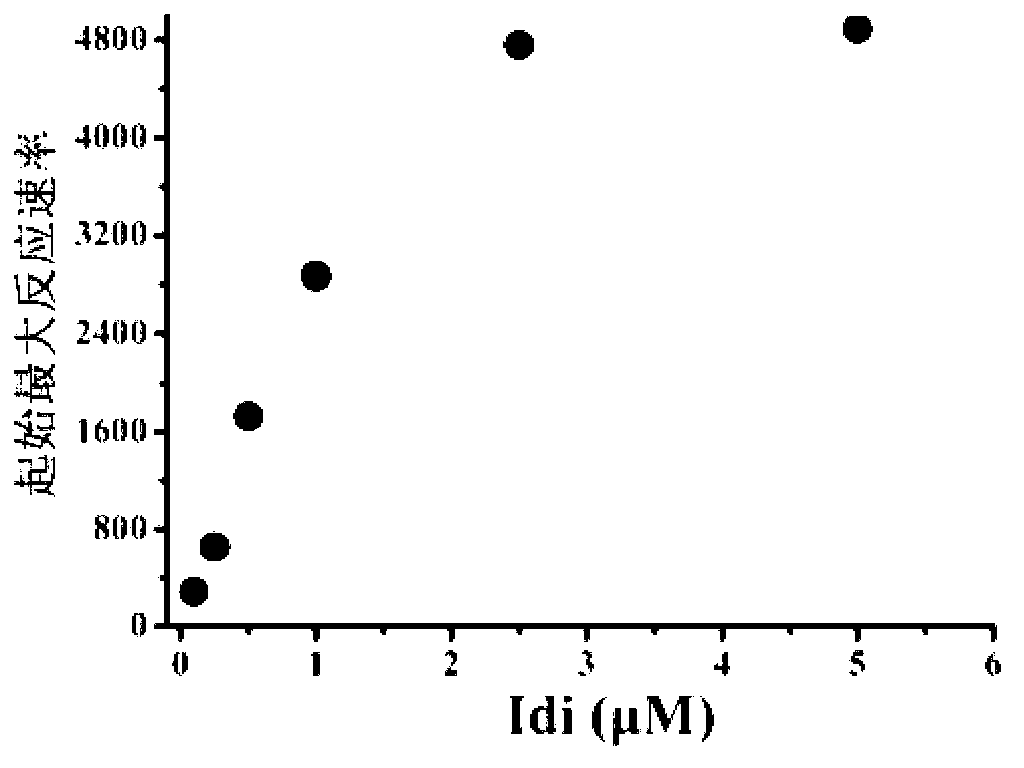
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for producing lycopene and an application of the bacterial strain, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. The bacterial strain for producing lycopene contains a mevalonate pathway and a related gene which is synthetized by the lycopene optimized by a codon; and the synthetic gene sequence of the lycopene optimized by the codon is shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. The bacterial strain can be used for producing the lycopene; and a seed solution of the bacterial strain is inoculated into a culture medium containing a carbon source to carry out prokaryotic expression, so as to obtain the lycopene. The gene synthetized by the lycopene is optimized by the codon or each protein of the mevalonate pathway is closer to A to B:ERG13:tHMG1:ERG12:ERG8:MVD1:Idi=1:10:2:5:5:2:5; and production of the lycopene can be further promoted. By adopting the bacterial strain, the yield of the lycopene can be greatly improved to over 1g / L; and the fermentation cycle is shortened by over 50%.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacterium
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacterium. The construction method comprises the following steps: respectively constructing superstrong gene expression modules of protein phytoene synthetase / lycopene cyclase coded by beta-carotene synthetic genes optimized by codons, phytoene dehydrogenase, protein geranyl diphosphate synthase coded by MAV (micro aerial vehicle) pathway genes and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; assembling the gene expression modules in vitro, so as to obtain four plasmids of the gene expression modules, integrating the plasmids into a host bacteria genome which does not produce beta-carotene and screening orange single colonies, so as to obtain the recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene. The recombinant bacterium disclosed by the invention is adopted for producing beta-carotene by fermental cultivation, and the yield of beta-carotene can reach 26.03mg / g DCW. Therefore, the recombinant bacterium has high performance of producing beta-carotene.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
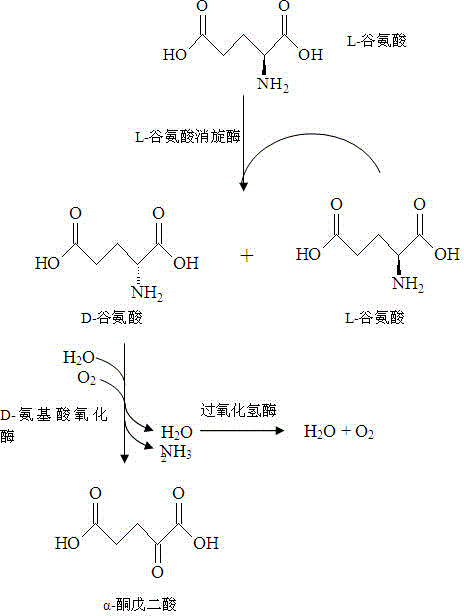
Method for producing alpha-ketoglutaric acid by virtue of enzymic method
InactiveCN104152498AEasy to removeAvoid the defect of slow conversion reactionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGlutaric acid
The invention relates to a method for producing alpha-ketoglutaric acid by virtue of an enzymic method. The method comprises the following steps: respectively synthesizing a glr gene and a daao gene and constructing expression vectors pET24a-glr and pET24a-daao; after double digestion of the expression vectors pET24a-glr and pET24a-daao respectively, connecting the expression vectors pET24a-glr and pET24a-daao to construct a double expression vector pET24a-glr-daao and transforming the double expression vector to escherichia coli to prepare a genetically engineered bacterium which simultaneously expresses glutamate racemase and D-amino acid oxidase; adding a wet thallus of the genetically engineered bacterium into water in a fermentation tank, then adding L-glutamic acid and catalase, and finally adjusting the pH by virtue of sodium hydroxide to prepare a reaction system for reaction; separating and purifying alpha-ketoglutaric acid converted in the reaction system after reaction. The method provided by the invention is low in cost, high in conversion rate (over 84%) and product concentration, and suitable for industrial application.
Owner:洛阳华荣生物技术有限公司
Genes encoding proteins capable of regenerating luciferin, recombinant DNA and process for producing protein capable of regenerating luciferin
The present invention relates to:an isolated or synthesized gene, which encodes a protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2,an isolated or synthesized gene, which encodes a protein comprising an amino acid sequence comprising a deletion, substitution or addition of one or more amino acids with respect to the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2 and being capable of regenerating luciferin,an isolated or synthesized gene, which hybridizes with the complementary strand sequence of a DNA comprising the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 under stringent conditions and encodes a protein capable of regenerating luciferin,a recombinant DNA, which is characterized in that the above-described isolated or synthesized gene is inserted into a vector DNA,a transformant or transductant comprising the above-described recombinant DNA, anda process for producing a protein capable of regenerating luciferin, which is characterized in that the method comprises culturing the above-described transformant or transductant in a medium and collecting therefrom the protein capable of regenerating luciferin.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Universal chloroplast integration and expression vectors, transformed plants and products thereof
InactiveUS7803991B2Easy to identifyClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesChloroplastOrganism
The invention provides universal chloroplast integration and expression vectors which are competent to stably transform and integrate genes of interest into chloroplast genome of multiple species of plants. Transformed plants and their progeny are provided. Monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants are transformed which have never been transformed heretofore. Plants transformed with a synthetic gene express valuable biodegradable protein-based polymers (PBPs). Transformed plants produce high value molecules. Resistance is provided to agricultural crops against the major classes of chemical herbicides. Herbicide resistance is used as a lethal selectable marker for chloroplast transformation. The transformed plants are capable of expressing in addition to the targeted trait, a desirable, secondary non-targeted trait. Insect resistance is provided to transformed plants, both against insects that are susceptible to Bt toxins and against insects that have developed resistance to Bt toxins.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
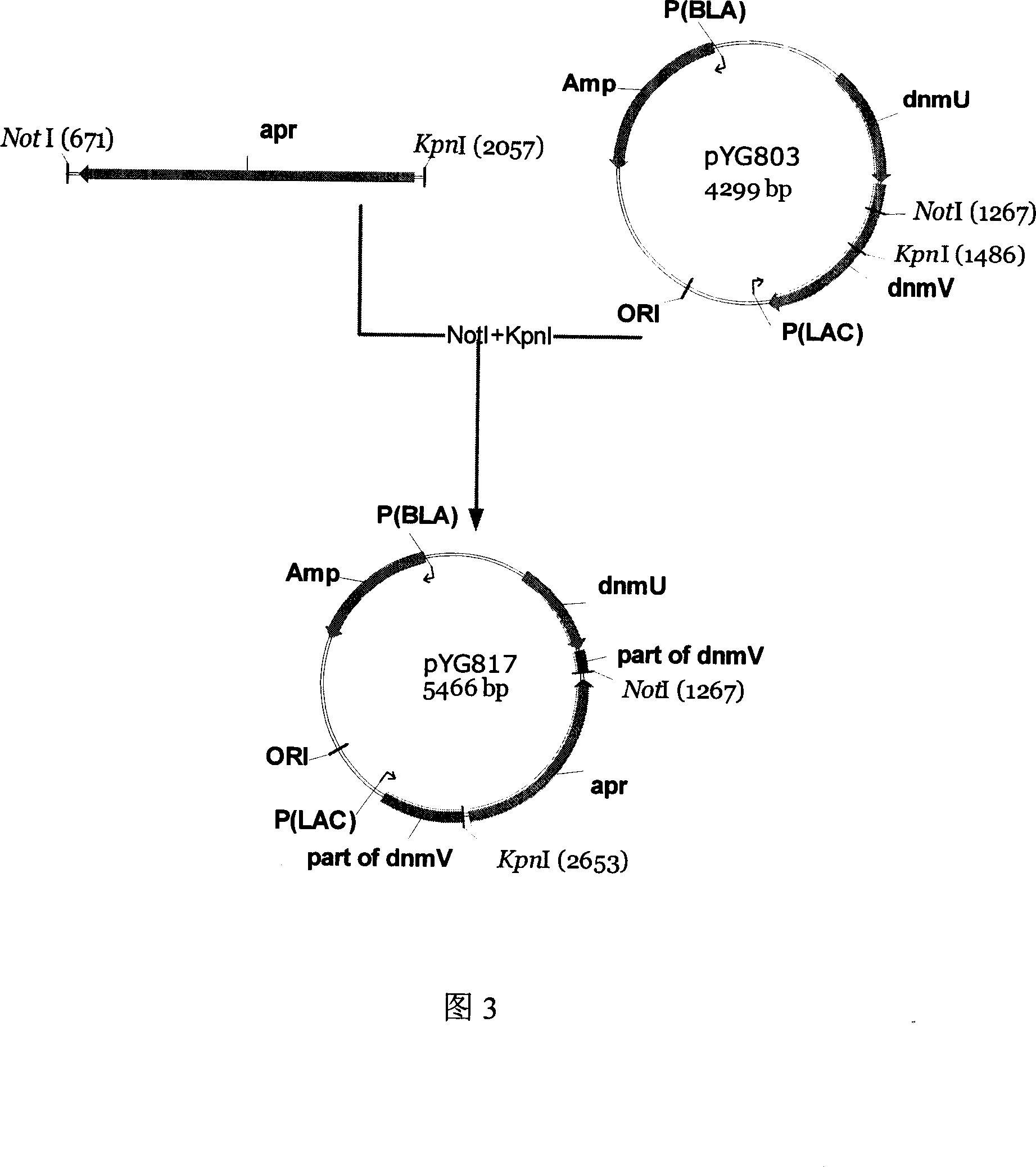
Engineering bacterium capable of producing anthracene ring antibiotics and application of the same
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium through anthracene nucleus antibiotic and appliance, which is characterized by the following: inserting or replacing restriction enzymes site of dnmV gene nucleic acid order of sky blue rufus streptomycete with antibiotic against property gene and surface cerubidin synthetic gene; blocking-up engineering bacterium of dnmV gene; or transforming expressing carrier of anthracene nucleus antibiotic synthetic gene to lead streptomycin (S.lividans)TK24; extracting expressing plasmid from S.lividans TK24; leading-in sky blue rufus streptomycete gene only with antibiotic against property gene to block dnmV gene; blocking-up abrupt change bacterium. This invention can produce cerubidin and / or analogue, such as anthracene nucleus antibiotic.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD +1
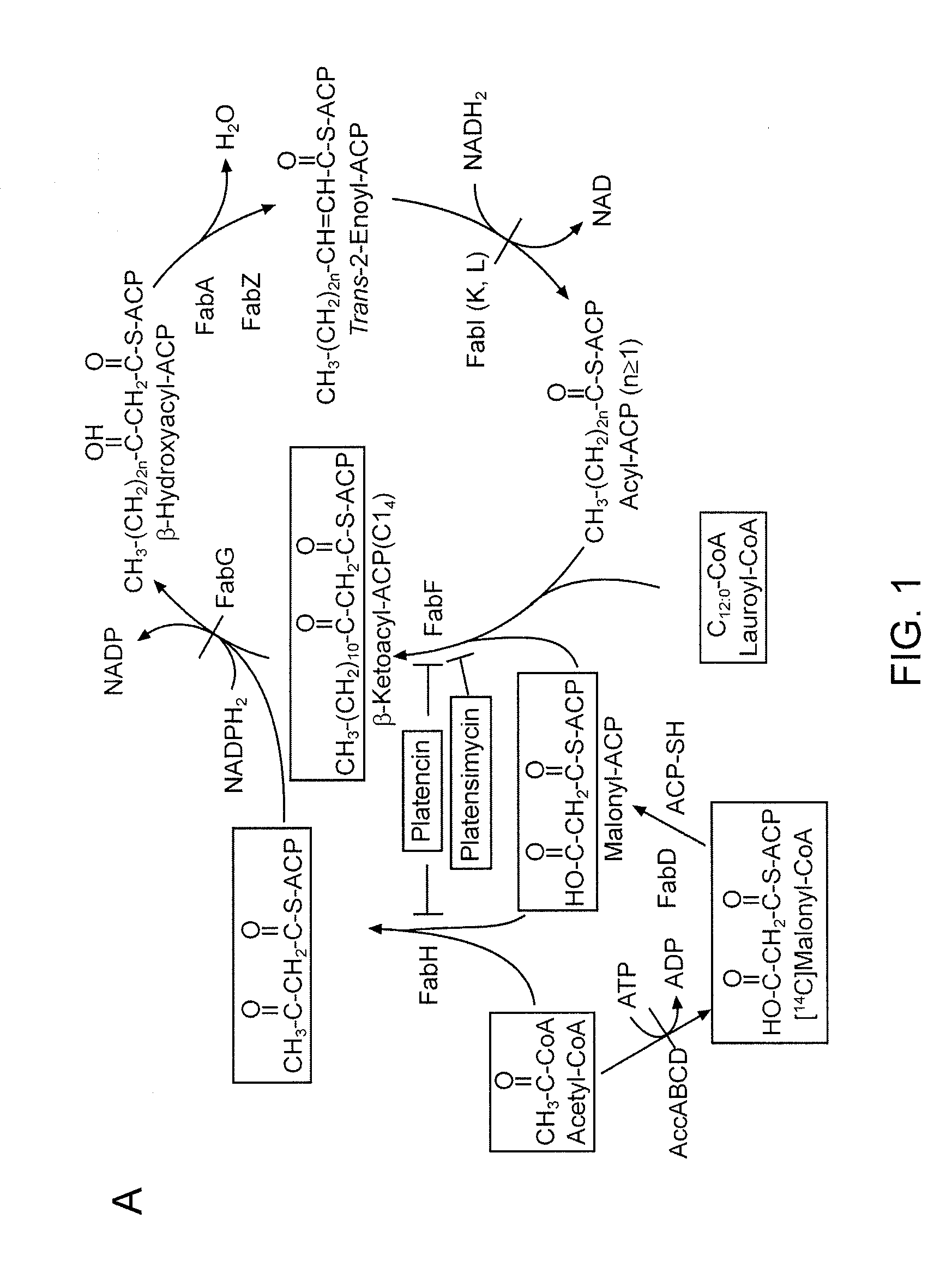
Platensimycin biosynthetic gene cluster of streptomyces platensis
The present invention relates to the cloning and sequence of a biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces platensis that produces platensimycin and platencin. Also provided are engineered micro-organisms for the production of these compounds, and analogs thereto, as well as methods of screening for compounds with anti-bacterial activity.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Construction method for co-expression hemoglobin VHb and cellulase protein in pichia pastoris
InactiveCN105420269AReduce GC contentImprove expression efficiencyMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionYeastNucleotide
The invention relates to a construction method for co-expression hemoglobin VHb and cellulase protein in pichia pastoris, in particular to cellulase protein gene codon optimization and construction of a cellulase protein and vitreoscilla hemoglobin protein (VHb)-co-expressed pichia pastoris system. According to the construction method, codon bias optimization is performed on the nucleotide sequence of EG II (GenBank Accession No.DQ178347.1) through Gene Designer (DNA2.0, Menlo Park, CA, USA) software, a pPIC9K-eg2 expression vector is constructed, and a recombined pichia pastoris strain is obtained by taking Pichiapastoris GS115 as a host through electrotransformation. In addition, the nucleotide sequence of the VHb (GenBank Accession No.M30794.1) is obtained from NCBI and artificially synthesized into a gene, then a pPICZalphaA-vgb expression vector is constructed, and the co-expressed pichia pastoris strain is obtained by taking the recombined pichia pastoris strain containing the EG II gene as a host through electrotransformation. Detection shows that the co-expressed strain is improved on the aspects of bacterial concentration growth and enzyme activity, wherein the OD600 value is increased by 7.2%, and the enzyme activity is improved by 2.2%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Synthetic gene encoding human carcinoembryonic antigen and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070104685A1Easy to insertEasy to removeVirusesGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideCarcinoembryonic antigen
Synthetic polynucleotides encoding human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) are provided, the synthetic polynucleotides being codon-optimized for expression in a human cellular environment. The gene encoding CEA is commonly associated with the development of human carcinomas. The present invention provides compositions and methods to elicit or enhance immunity to the protein product expressed by the CEA tumor-associated antigen, wherein aberrant CEA expression is associated with a carcinoma or its development. This invention specifically provides adenoviral vector and plasmid constructs carrying codon-optimed human CEA and discloses their use in vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions for preventing and treating cancer.
Owner:LA MONICA NICOLA +3
Recombinant escherichia coli and application to synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidine
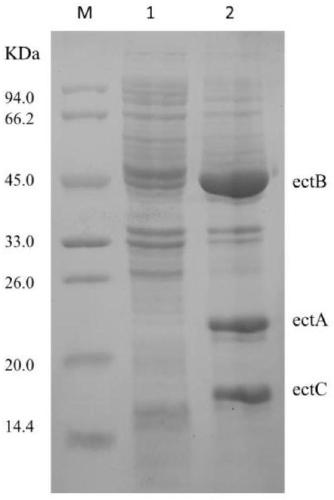
InactiveCN109182236AHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideRecombinant escherichia coli
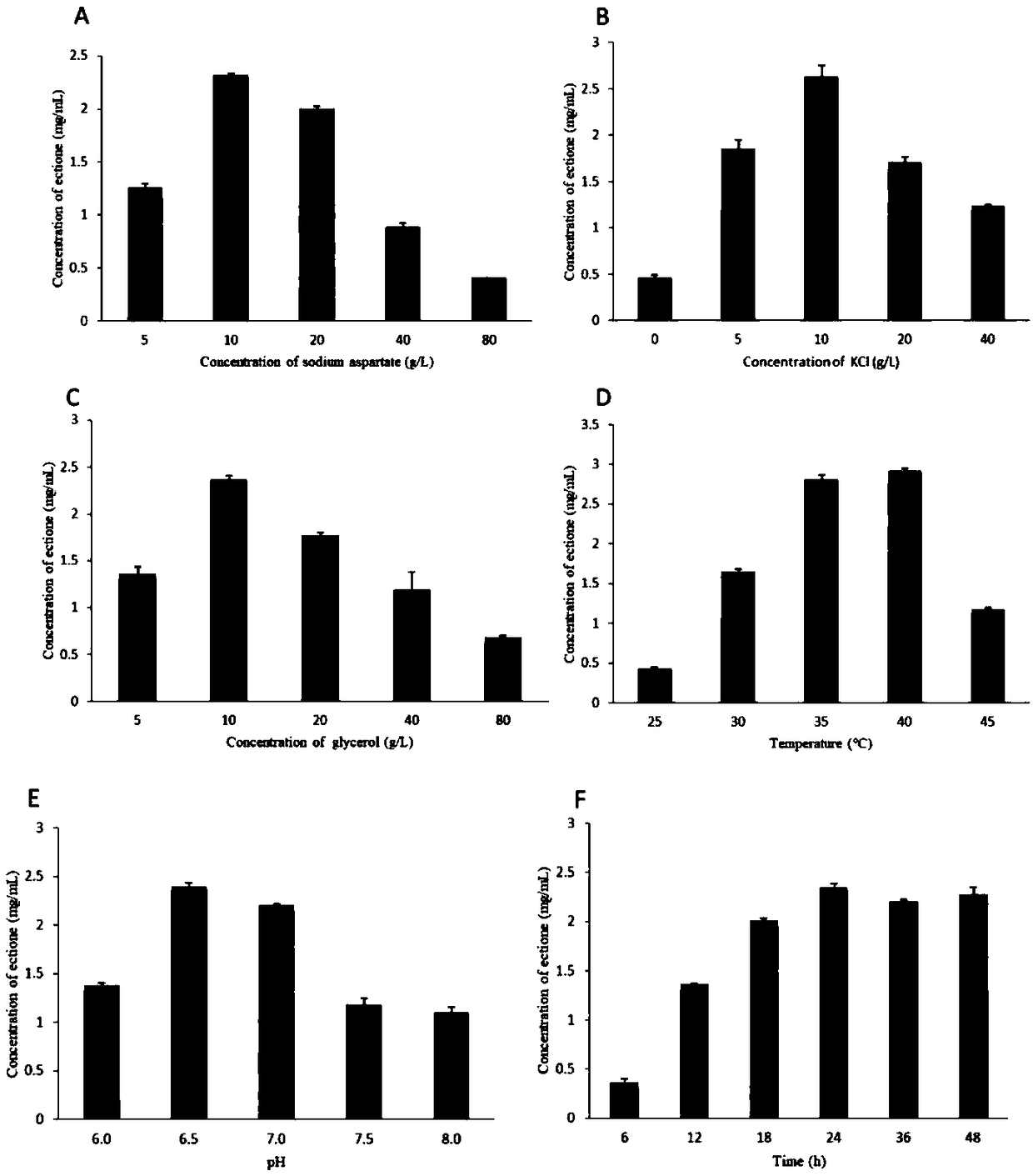
The invention provides recombinant escherichia coli and application to synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidine. The recombinant escherichia coli is obtained by knocking out a diaminapimelate decarboxylase lysA gene of escherichia coli E.coli MG1655 and introducing a tetrahydropyrimidine synthetic gene luster ectABC with a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The nucleotide sequence of the diaminapimelate decarboxylase lysA gene is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. A thallus subjected to induced expression takes L-sodium aspartate as a substrate and the substrate is biologically converted to prepare the tetrahydropyrimidine. After conversion is carried out for 20 to 30h, the yield of the tetrahydropyrimidine reaches 2.5 to 3.5g / L, and therefore, the recombinant escherichia coli has relatively good industrial application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com