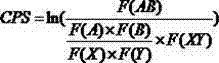Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Codon pair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
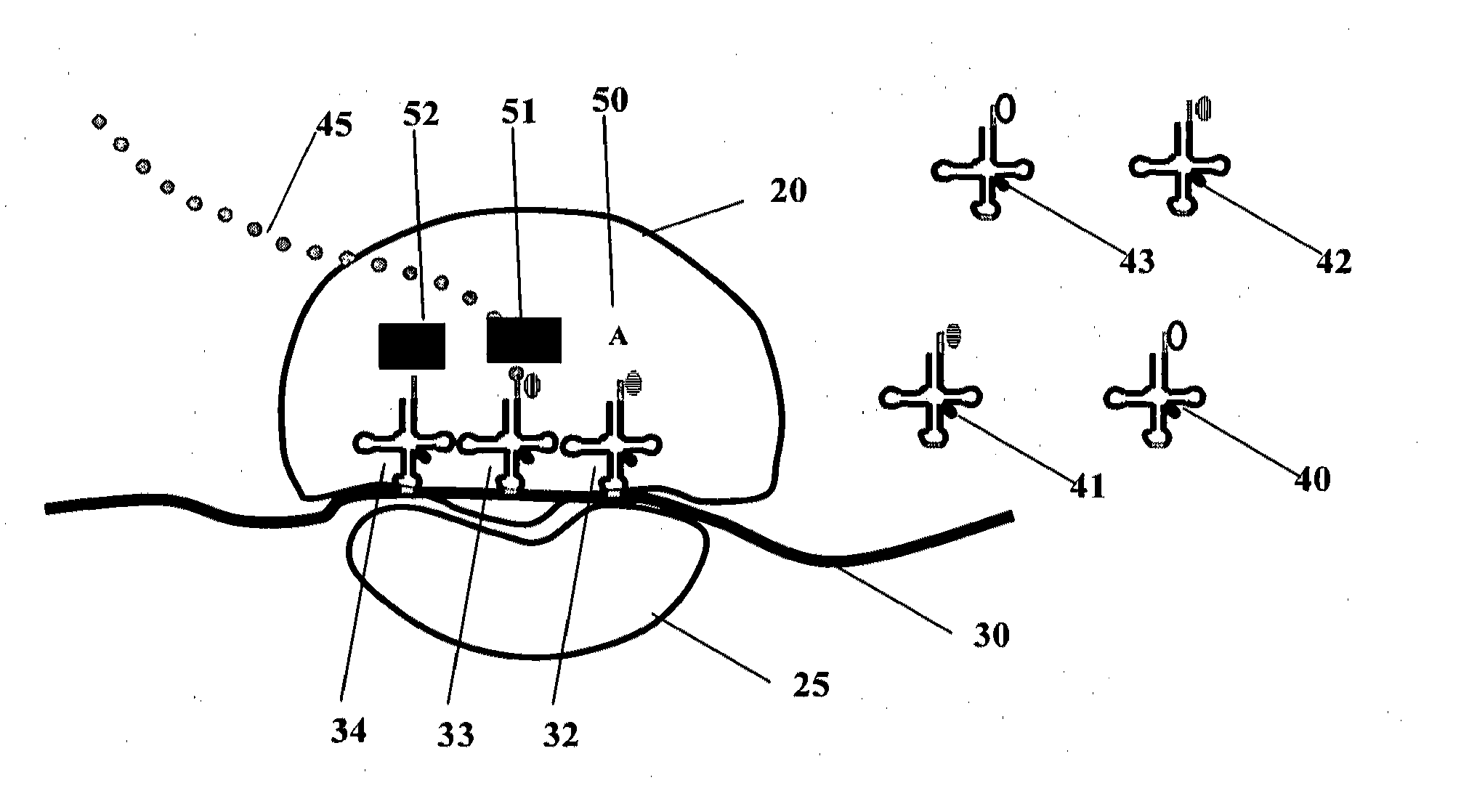
A triplet in a chain of nucleic acids in mRNA that specifies the order in which amino acids are added. The codon triplet pairs with a sequence of three complementary nucleotides, called the anticodon, present in the anticodon arm of tRNA. Called also triplet. See also deoxyribonucleic acid.
Method for achieving improved polypeptide expression
The present invention relates to methods of optimization of a protein coding sequences for expression in a given host cell. The methods apply genetic algorithms to optimise single codon fitness and / or codon pair fitness sequences coding for a predetermined amino acid sequence. In the algorithm generation of new sequence variants and subsequent selection of fitter variants is reiterated until the variant coding sequences reach a minimum value for single codon fitness and / or codon pair fitness. The invention also relates to a computer comprising a processor and memory, the processor being arranged to read from and write into the memory, the memory comprising data and instructions arranged to provide the processor with the capacity to perform the genetic algorithms for optimisation of single codon fitness and / or codon pair fitness. The invention further relates to nucleic acids comprising a coding sequence for a predetermined amino acid sequence, the coding sequence being optimised with respect to single codon fitness and / or codon pair fitness for a given host in the methods of the invention, to host cells comprising such nucleic acids and to methods for producing polypeptides and other fermentation products in which these host cells are used.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Polypepetide-encoding nucleotide sequences with refined translational kinetics and methods of making same
InactiveUS20080046192A1Reduce protein expressionEnhance protein expressionData visualisationProteomicsData setNucleotide
Provided are methods for creating a synthetic gene for expression in a host organism, by providing a data set representative of codon pair translational kinetics for the host organism which includes translational kinetics values of the codon pairs utilized by the host organism, providing a desired polypeptide sequence for expression in the host organism, and generating a polynucleotide sequence encoding the polypeptide sequence by analyzing candidate nucleotides to select, where possible, codon pairs that are predicted not to cause a translational pause in the host organism, with reference to the data set, thereby providing a candidate polynucleotide sequence encoding the desired polypeptide. The methods can be performed using multiple parameter nucleotide sequence optimization methods, such as branch-and-bound methods for nucleotide sequence refinement.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
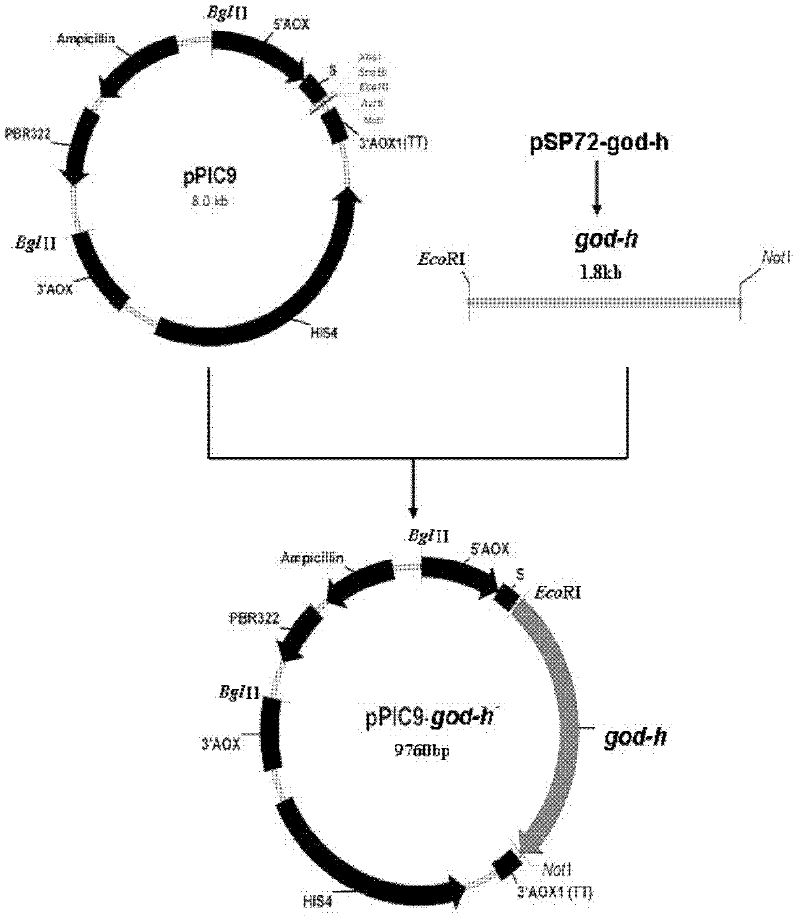
Optimized gene of recombinant glucose oxidase and expression vector and application of optimized gene
ActiveCN102517304AIncrease secreted expressionIncreased GC contentFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisMrna secondary structure
The invention discloses an optimized gene of recombinant glucose oxidase and an expression vector and application of the optimized gene. On the premise that the amino acid sequence of the glucose oxidase is not changed, the gene sequence of the glucose oxidase is optimized according to pichia pastoris preferred codons by comprehensively considering the influencing factors such as use frequency ofthe codons, adjustment of GC content, deletion of instable sequences, secondary mRNA structure and the like; and the nucleotide sequence of the optimized glucose oxidase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1.The invention further provides the expression vector and a recombinant host strain containing the optimized gene of the glucose oxidase. The optimized gene is transferred to the pichia pastoris for expression, and the test results show that: compared with the gene before optimization, the secreting expression quantity of the optimized gene in the pichia pastoris is remarkably improved. The application effect tests of the glucose oxidase show that the expressed recombinant glucose oxidase has the same using effect as a commercial enzyme preparation.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods for calculating codon pair-based translational kinetics values, and methods for generating polypeptide-encoding nucleotide sequences from such values
InactiveUS20070275399A1Improve shortcomingsEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Provided are methods for calculating codon pair translational kinetics values, creating a synthetic gene for expression in a host organism, and providing codon pair translational kinetic values. The methods typically are directed to refinement of statistical observed versus expected codon pair frequencies using one of several factors such as amino acid sequence homology, secondary or tertiary structural considerations, and empirical measurements. In some synthetic genes codon pairs are predicted not to cause a translational pause in the host organism, thereby providing a polynucleotide sequence encoding the desired polypeptide with desired translational kinetics properties. The methods can be performed using multiple parameter nucleotide sequence optimization methods, such as branch-and-bound methods for nucleotide sequence refinement.
Owner:LATHROP RICHARD H +4
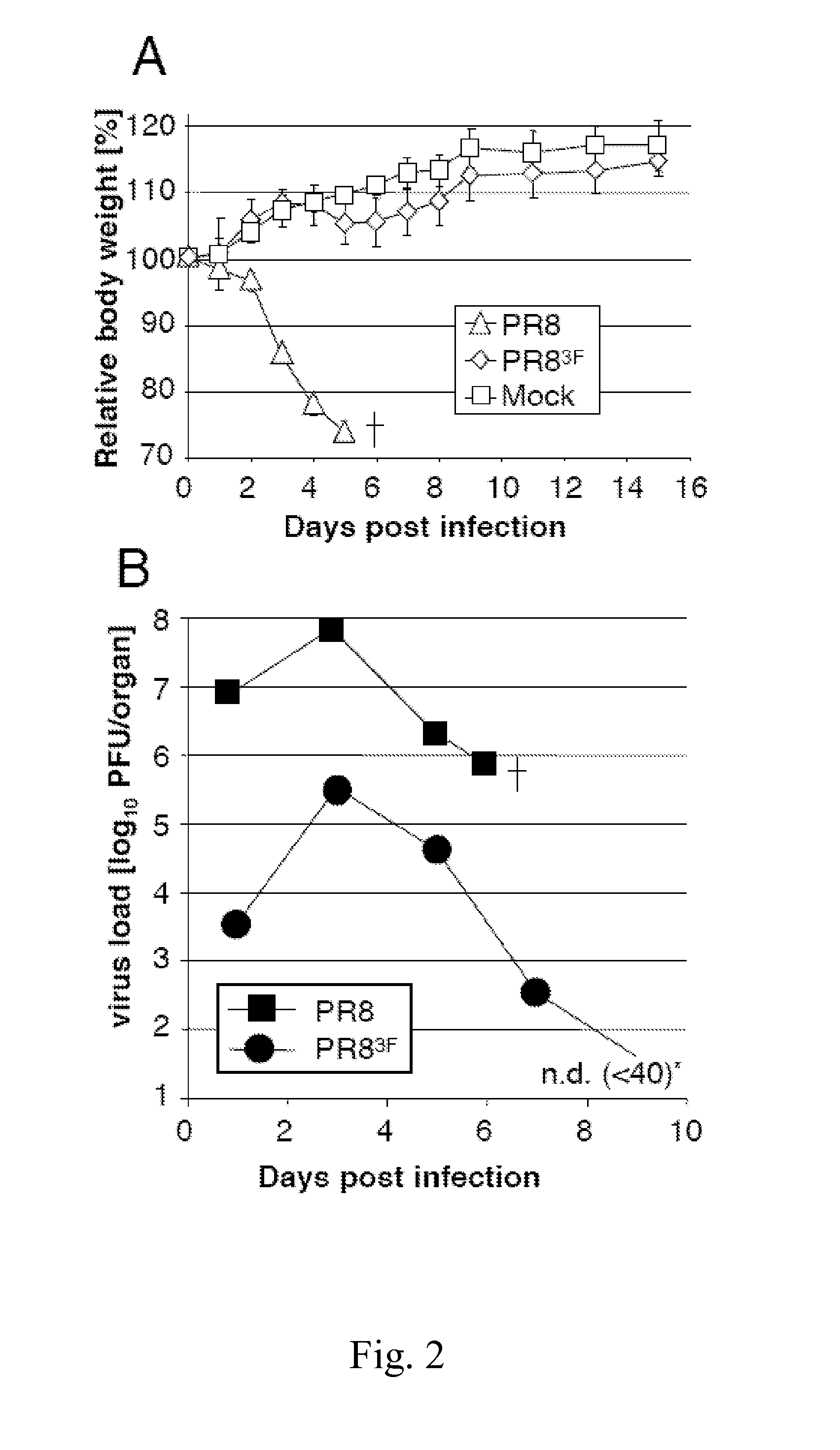
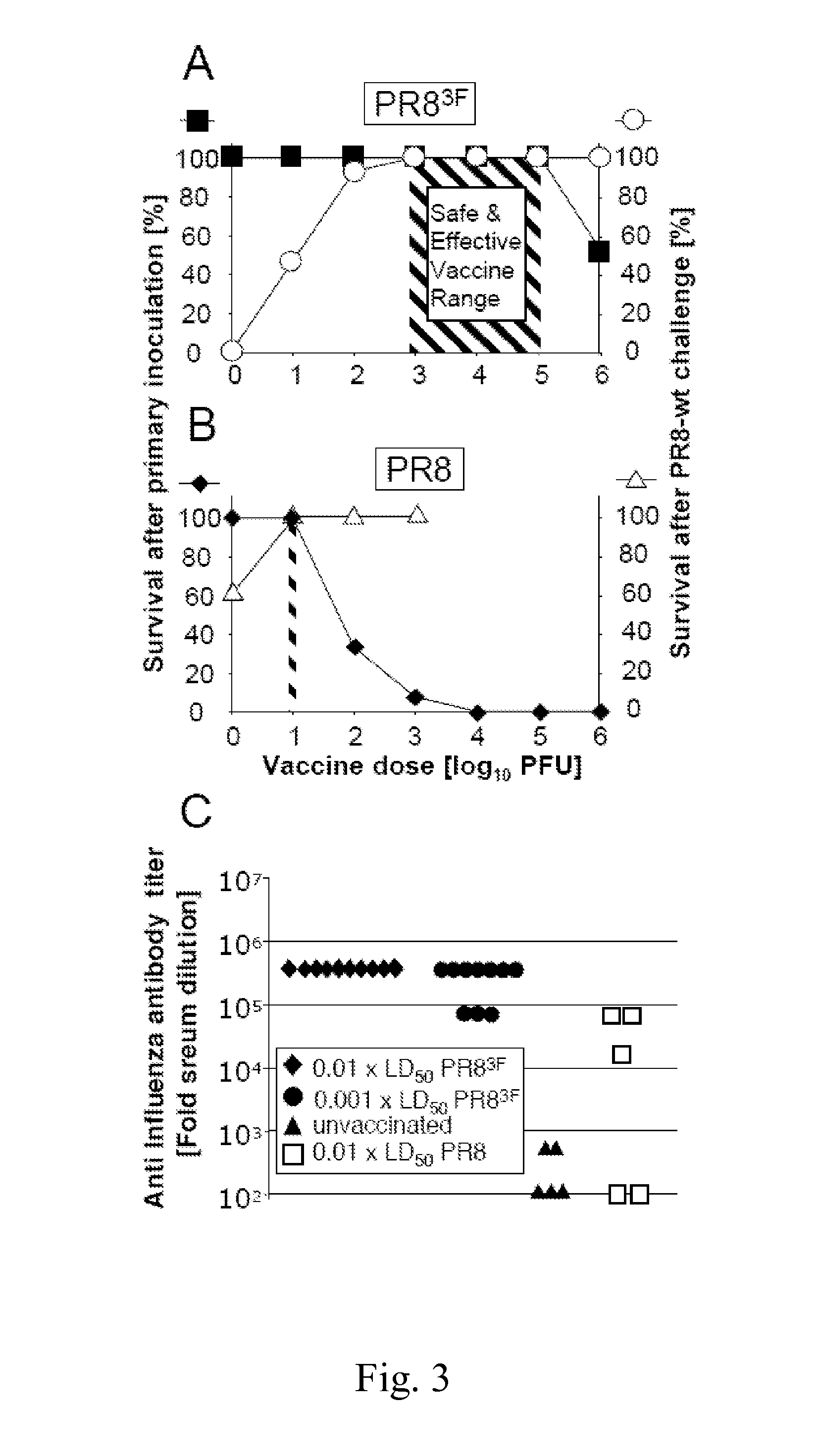
Attenuated influenza viruses and vaccines
InactiveUS20120269849A1High genetic stabilityMaximum safetySsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesNucleotideProtection sex
The present provides attenuated influenza viruses comprising a modified viral genome containing a plurality of nucleotide substitutions. The nucleotide substitutions result in the rearrangement of preexisting codons of one or more protein encoding sequences and changes in codon pair bias. Substitutions of non-synonymous and synonymous codons may also be included. The attenuated influenza viruses enable production of improved vaccines and are used to elicit protective immune responses.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Translation Kinetic Mapping, Modification and Harmonization
InactiveUS20130149699A1Increase synthesisIncrease productionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHarmonizationOrganism
The profile of translation elongation rate along an mRNA is modulated in a directed manner by locally altering codon usage, in particular utilizing differences in ribosomal dwell times among pairs of synonymous codons translated by a single tRNA through wobble base pairing. Unlike codon optimization based on organism-specific codon frequencies or tRNA pools, the methods of the invention need not change the tRNA that translates the codon, rather modulating the interaction between a given tRNA and the mRNA coding sequence.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Gene synthesis of wild boar alpha-interferon, vector construction and method for producing outcome
InactiveCN101392256AOptimize free energySimple structurePeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
The invention discloses a gene synthesis of Alpha-interferon of wild boars and vector construction thereof as well as a production method of a product. A number of problems of low expression capacity, products expressed in a fusion state, products with purification tags or no fermentation technology with high density exist in the domestic recombinant strains. The invention includes a method that a codon and codon pairs, preferred by Escherichia coli, are used for synthesizing an Alpha-interferon gene of the wild boar, establishing a high-efficiency expression vector and transforming a high-efficiency expression strain as well as methods of high-density fermentation of engineering bacteria, separation and purification of inclusion bodies, the modification, the renaturation and the purification of target protein and the determination of biological activity of the expressed product. The gene synthesis, the vector construction and the production method pertain to the technical field of the production of polypeptide drugs by genetic engineering in biopharmaceuticals.
Owner:黑龙江省农业科学院畜牧研究中心 +1
Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase gene, engineering bacteria and application of engineering bacteria
ActiveCN105087614AImprove stabilityPromote accumulationFungiHydrolasesThermomyces lanuginosusProtein structure
The invention discloses a thermomyces lanuginosus lipase gene, engineering bacteria and an application of the engineering bacteria. The base sequence of the thermomyces lanuginosus lipase gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. On the basis that existing thermomyces lanuginosus lipase amino acid sequences and protein structures are not changed, factors adverse to protein expression, for example, rare codons, rare codon pairs, strong stem-loop structures, potential early termination signals and the like are avoided, and the thermomyces lanuginosus lipase gene sequence is optimized, so that the sequence can efficiently express thermomyces lanuginosus lipase in a pichia pastoris recombination expression system, and the expression vitality is up to 370.65 U / ml and is improved by 58.38% while compared with the recombination expression vitality of the original sequence of the thermomyces lanuginosus lipase gene being 234.03 U / ml.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optimized gene of ietalurus punetaus LEAP-2 mature peptide and preparation method of recombinant protein of optimized gene
InactiveCN106222175ALow costIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPichia pastorisYeast
The invention discloses an optimized gene of ietalurus punetaus LEAP-2 mature peptide and a preparation method of recombinant protein of the optimized gene, and further provides a recombinant expression carrier and yeast host cell containing the optimized gene, application of the optimized gene to producing the ietalurus punetaus LEAP-2 mature peptide, and application of the recombinant protein to preparing antibacterial medicines. On the premise of not changing the amino acid sequence of the ietalurus punetaus LEAP-2 mature peptide, the amino acid sequence of the gene of the ietalurus punetaus LEAP-2 mature peptide is optimized according to pichia pastoris preferred codons, and the optimized sequence is SEQ ID NO:2. By expressing the optimized gene in a pichia pastoris host cell, the recombinant ietalurus punetaus LEAP-2 mature peptide is prepared. By means of the preparation method, the LEAP-2 mature peptide can be efficiently prepared, the applied culture conditions are simple, cost is low, and the obtained LEAP-2 mature peptide is good in antibacterial effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV +1
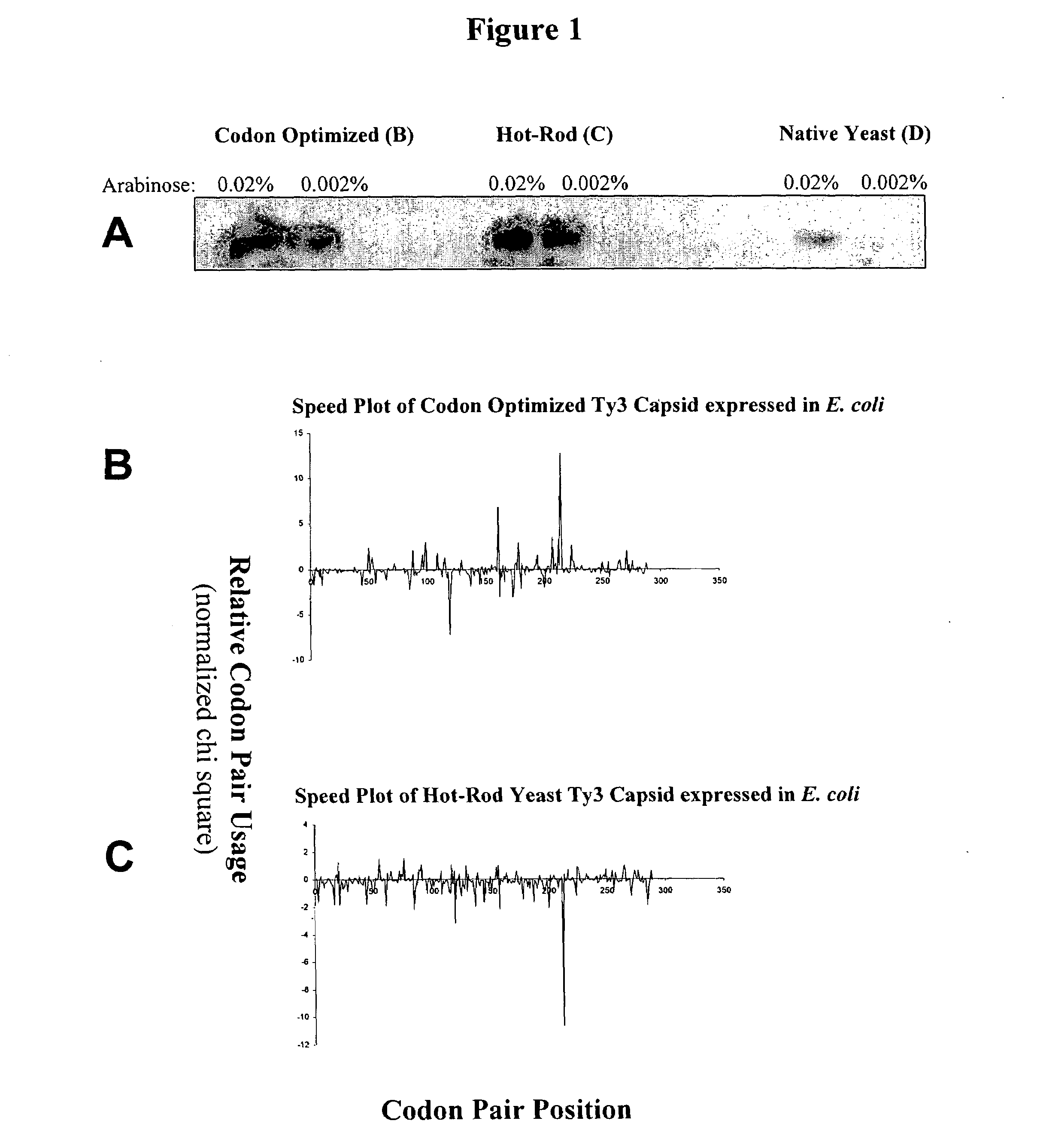
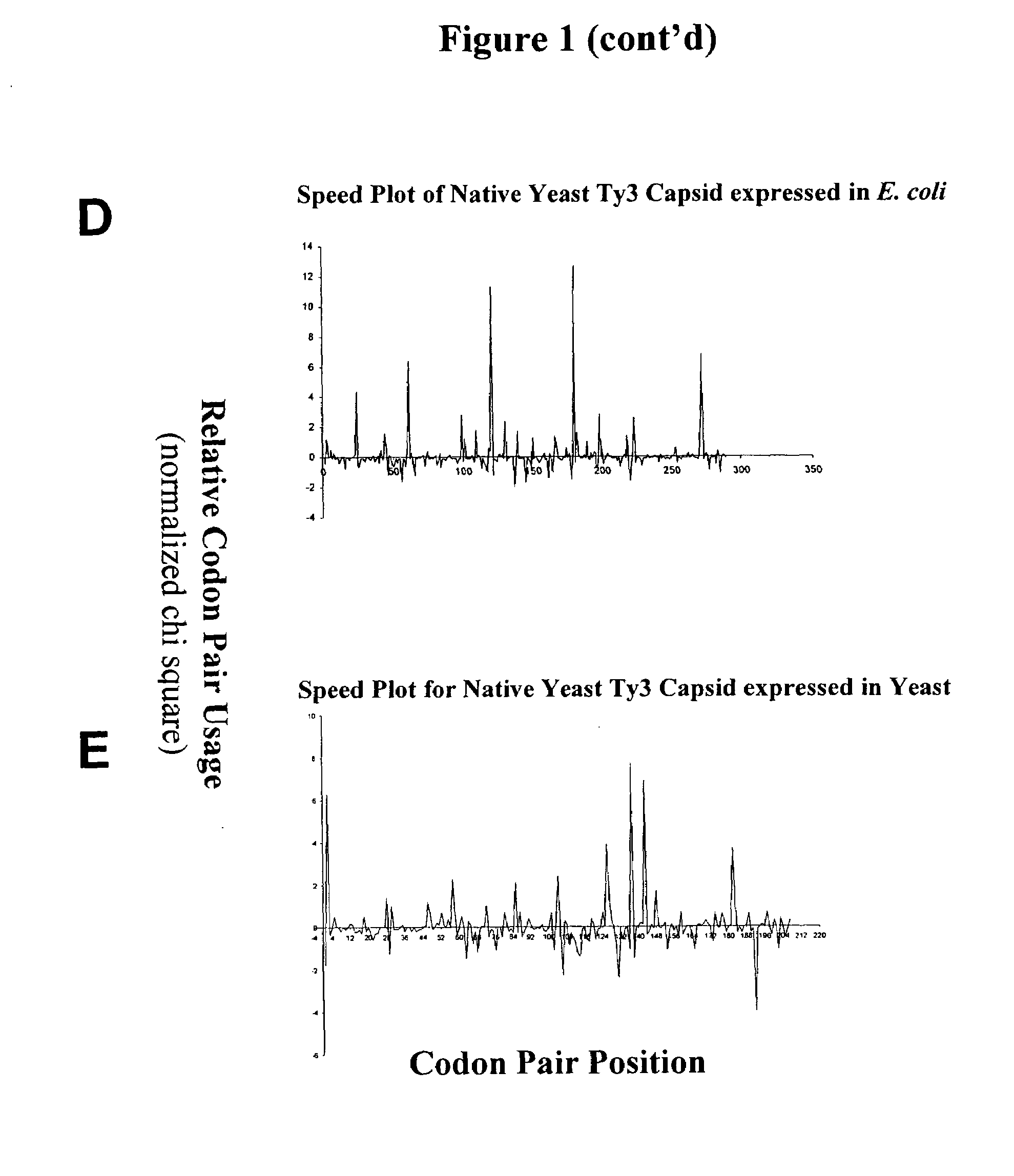
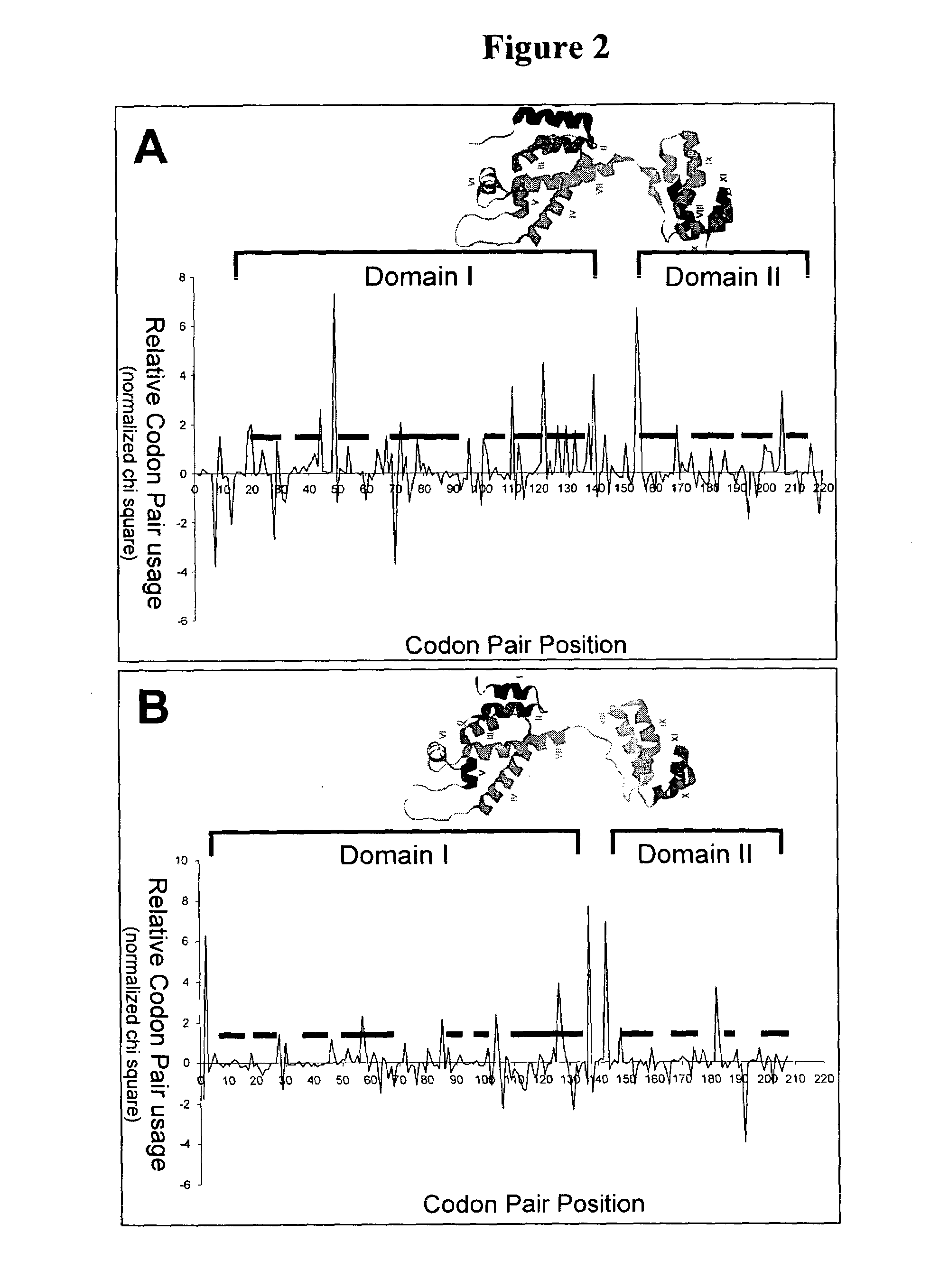
Analyzing traslational kinetics using graphical displays of translational kinetics values of codon pairs
InactiveUS20070298503A1Improve shortcomingsEasy to analyzeDrawing from basic elementsData visualisationBiological bodyNucleotide
Graphical displays are provided of translational kinetics values of codon pairs in a host organism plotted as a function of polypeptide-encoding nucleotide sequence. Such translational kinetics values of codon pair frequencies correspond to the predicted translational pausing properties of a codon pair in a host organism. The graphical displays provided reflect the relative over-representation or under-representation of each codon pair in an organism, thereby facilitating analysis of translational kinetics of an mRNA into polypeptide by comparing graphical displays of different codon pairs in sequences encoding the polypeptide. The graphical displays of translational kinetics values also can display codon pair properties on comparable numerical scales, thereby facilitating analysis of translational kinetics of an mRNA into polypeptide in different organisms by comparing comparably scaled graphical displays of the same or different codon pairs in sequences encoding the polypeptide. Also contemplated herein is the use of the graphical displays described herein for tracking the entire process of creating a refined polypeptide-encoding nucleotide sequence. In particular, additional translational kinetics graphical displays can be created to illustrate differences and / or similarities of translational kinetics of a polypeptide-encoding nucleotide sequence in which one or more codon pairs have been modified. Additionally, numerous translational kinetics graphical displays can be created to illustrate differences and / or similarities of translational kinetics of a polypeptide-encoding nucleotide sequence when expressed in two or more different organisms.
Owner:LATHROP RICHARD H +2
Systems and methods for measuring translation of target proteins in cells
ActiveUS20120183957A1Evaluate effectMild interventionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein CCodon pair
The present invention relates to systems and methods for measuring the rate of translation of a target protein in cells, which are based on the detection of translation of one or more predetermined codon pairs during synthesis of the target protein. The detection is provided by a FRET signal emitted from labeled tRNA molecules which are juxtaposed during synthesis of the protein.
Owner:ANIMA CELL METROLOGY
Optimized cattle chymosin proto-gene and secretory expression method and application thereof
The invention discloses an optimized cattle chymosin proto-gene and a secretory expression method and the application thereof. According to the optimized cattle chymosin proto-gene, influence factors of difference between protein interpret rates and the like due to use frequency of codon, adjustment of GC content, deletion of unstable sequences, and different distribution of secondary mRNA structure and the codon are comprehensively considered, and optimized cattle chymosin proto-gene bodies respectively shown by SEQ ID NO.1, 2 and 3 are obtained by modifying cattle chymosin proto-gene bodies according to the preference codon of pichia pastoris. The invention further provides a production method of recombining the cattle chymosin proto-gene. The production method comprises the steps of converting recombinant expression carriers containing the optimized cattle chymosin proto-gene bodies into host cells to obtain recombination bacterial strains, cultivating the recombination bacterial strains, inducing expression of the recombination cattle chymosin proto-gene bodies, and recycling and purifying expressed products. Compared with original cattle chymosin proto-gene, the secretory expression amount and the enzyme activity of the optimized cattle chymosin proto-gene in the pichia pastoris are remarkably promoted.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Codon optimization method used for heterologous gene in-vitro expression and application
ActiveCN110491447AEfficient expressionHigh expressionSequence analysisAnimals/human peptidesHeterologousNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a codon optimization method used for heterologous gene in-vitro expression. The method comprises the steps that a nucleotide sequence of a whole genome of a host cell and an amino acid sequence of a whole proteome of the host cell are acquired; codon pairs are taken as a statistical object, and statistics is conducted on the weight of each codon pair in the whole genome ofthe host cell; to-be-optimized protein is selected, and a single-direction graph model which takes codons as nodes and takes weight values of the upstream and downstream codon pairs as linear values is constructed; according to the single-direction graph model, a nucleotide sequence of an optimized gene is obtained. According to the codon optimization method used for heterologous gene in-vitro expression, the whole genome and whole proteome of the host cell are utilized as sequence libraries, the codon pairs are taken as the statistical object, and by constructing the single-direction graph model which takes the codons as the nodes and takes the weight values of the upstream and downstream codon pairs as linear values, the optimum codon combination sequence is obtained; the optimized genewith the optimum nucleotide sequence is obtained and can be efficiently expressed in vitro, and the expression amount is significantly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
African swine fever virus CD2v protein as well as kit and antibody prepared from African swine fever virus CD2v protein
PendingCN114426974AQuick checkSensitive detectionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesClassical swine fever virus CSFVAfrican swine fever virus Antibody
The invention relates to an African swine fever virus CD2v protein as well as a kit and an antibody prepared from the African swine fever virus CD2v protein. The gene sequence of the African swine fever virus CD2v protein provided by the invention comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 or a nucleotide sequence which is at least 90% homologous with the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1. According to the invention, codon optimization is carried out on an African swine fever virus CD2v protein gene sequence according to preferred codons of a CHO expression system, and then fusion protein mFc-CD2v and fusion protein gD-CD2v are prepared through the CHO expression system. An ELISA antibody detection kit or a monoclonal antibody prepared from the fusion protein mFc-CD2v can be used for detecting the African swine fever virus antibody, and the detection is rapid and sensitive and has good specificity.
Owner:LUOYANG PULIKE WANTAI BIOTECH
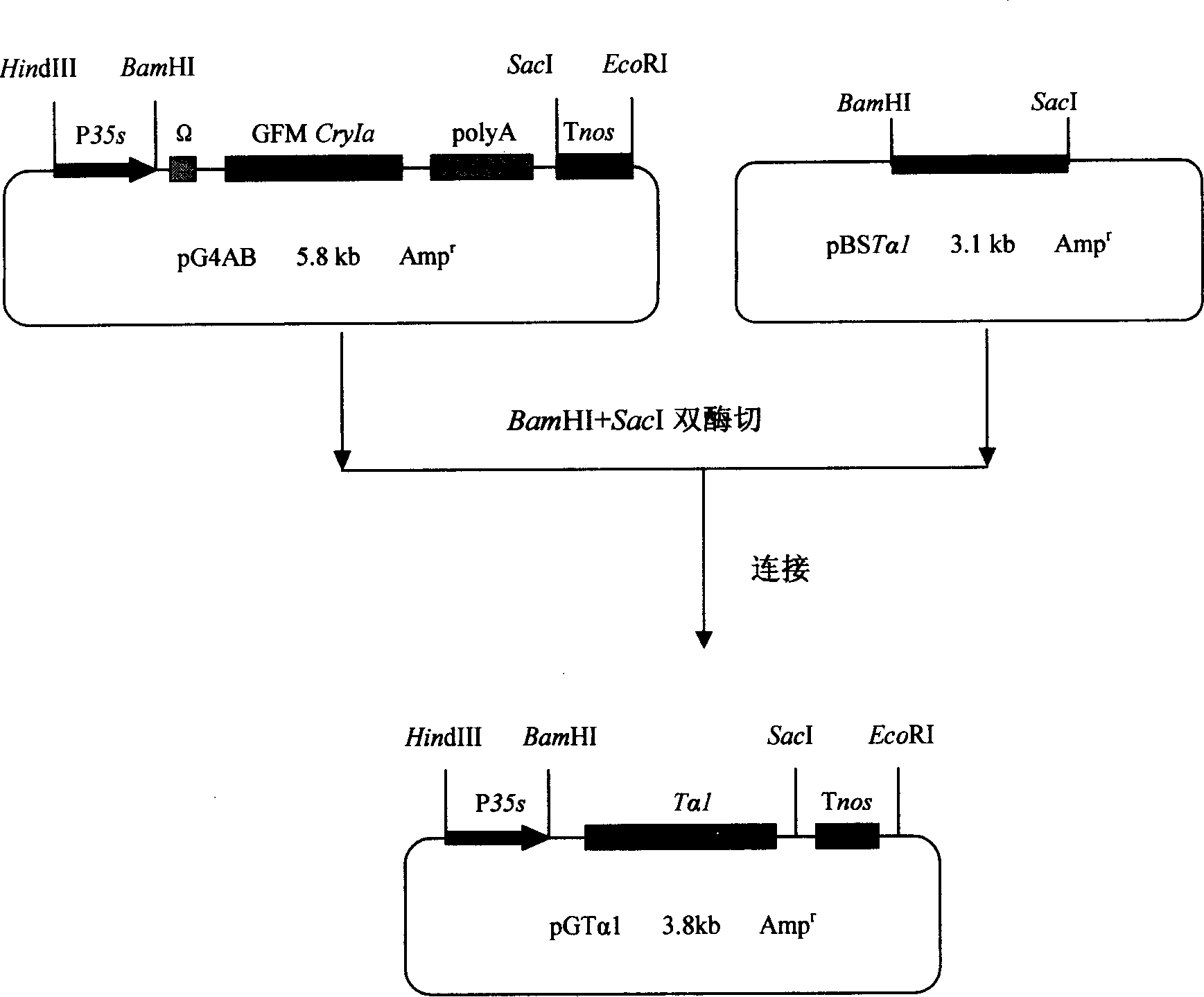
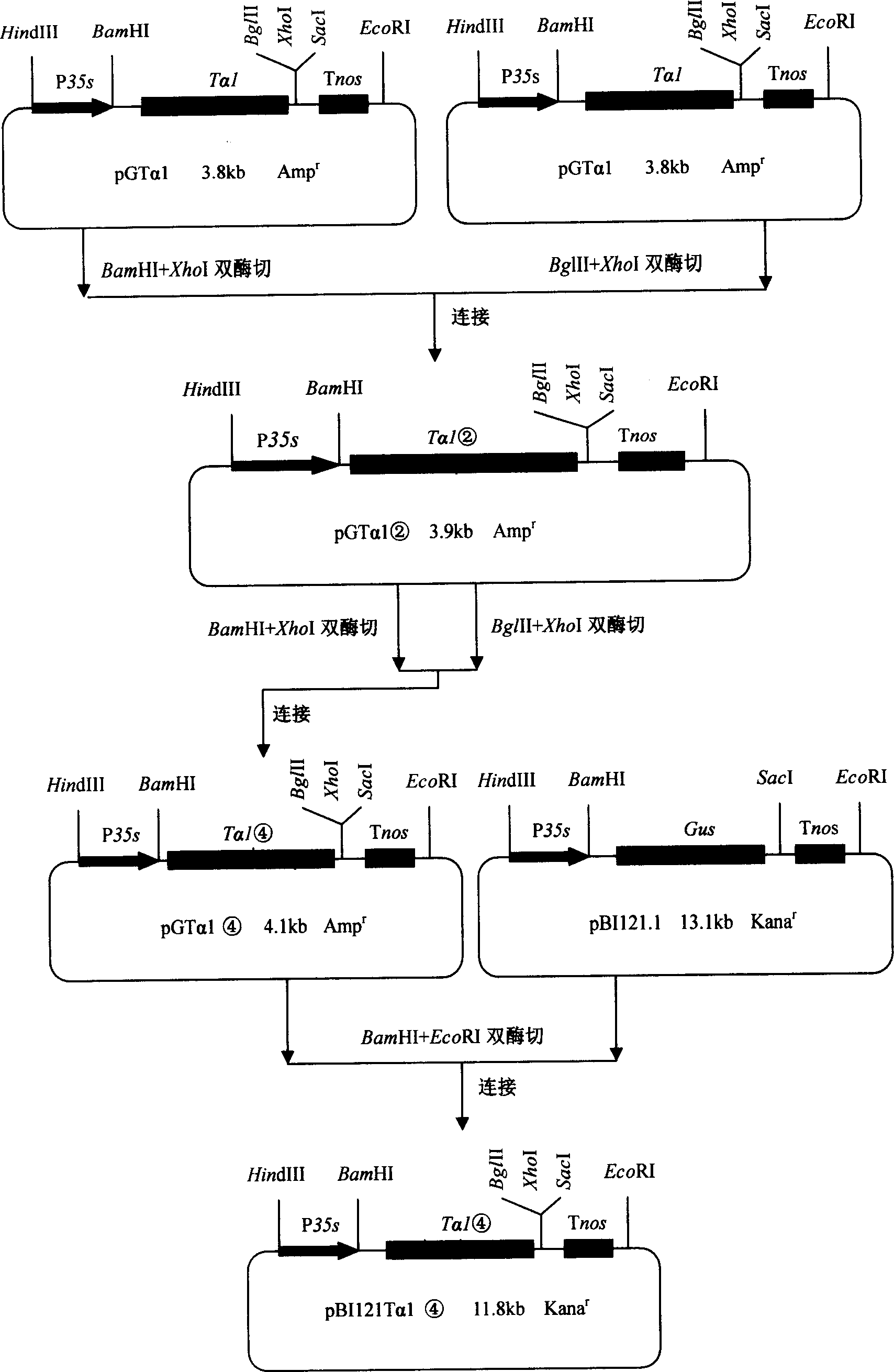
Method for producing human thymosin alphal utilizing transgenic tomato
InactiveCN1891824AReduce manufacturing costIncrease contentFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDiseaseHuman body
The invention relates to a method to produce human thymosin alpha 1 that uses transgene tomato as bio-reactor. It optimizes the nucleotide sequence of human thymosin alpha 1 according to plant preference codon. Compounding the gene and making it connect end to end to form tetrad, then, the plant expression transforming tomato expressed by thymosin alpha 1 cascading gene that is driven by cauliflower 35s promoter would be constructed. The thymosin alpha 1 would have important effect in vivo that could promote T cell function and the producing of special antibody and cell element. It could cure autoimmune diseases like lupus erythematosus, chronicity hepatitis B, etc. It could be also used as assistant medicine for curing cancer and tumor. The fruit containing thymosin alpha 1 could enhance human body immunity.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Systems and methods for measuring translation of target proteins in cells
ActiveUS9034576B2Mild interventionEasy to learnMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBioinformaticsCodon pair
The present invention relates to systems and methods for measuring the rate of translation of a target protein in cells, which are based on the detection of translation of one or more predetermined codon pairs during synthesis of the target protein. The detection is provided by a FRET signal emitted from labeled tRNA molecules which are juxtaposed during synthesis of the protein.
Owner:ANIMA CELL METROLOGY
Chicken infectious bursal disease virus VP2 protein and preparation method and application thereof and kit
The invention provides chicken infectious bursal disease virus VP2 protein and a preparation method and application thereof and a kit. Particularly, a nucleotide sequence for coding the VP2 protein contains the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1. The method for preparing the VP2 protein comprises the following steps of chemically synthesizing the SEQ ID No.1 sequence, constructing an expression vector and transfecting sf9 cells. The VP2 protein can be used for preparing a vaccine for a chicken infectious bursal disease. The SEQ ID No.1 is obtained by conducting codon optimization on a chicken IBDV VP2 gene according to insect cell preference codon, and therefore compared with a general VP2 gene which is amplified from an IBDV virus, the SEQ ID No.1 is more suitable for being expressed in insect cells and can increase the protein expression quantity.
Owner:GUANGDONG WENS DAHUANONG BIOTECH +1
Method for detecting codon pair bias of bovine whole-genome
InactiveCN102693368AThe results are authenticSpecial data processing applicationsSingle sequenceGenome
The invention discloses a method for detecting codon pair bias of a bovine whole-genome. The method comprises the steps of: calculating codon pair score CPS of 3721 kinds of codon pairs in a CDS (coding sequence)of the bovine whole-genome; analyzing codon pair bias CPB of a single sequence in the bovine whole-genome according to the CPS of different codon pairs, wherein a CPB value of a sequence is an arithmetic average value of values of all codon pairs in the sequence; establishing a codon pair bias profile for each CDS in the genome according to the CPS of 3721 kinds of codon pairs in the genome and an arranging sequence of the codon pairs in the CDS ; aligning codon pair bias profiles of all CDS in the bovine genome form a 5' end and a 3' end of the sequence, and calculating an average value of the CPS of each codon pair locus in alignment results, thereby obtaining a whole-genome averaged codon pair bias profile of all CDS of the bovine.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Novel attenuated poliovirus: PV-1 mono-cre-X
InactiveCN104204196ALower preferenceSsRNA viruses positive-senseInactivation/attenuationNucleic acid sequencingCoding region
A novel and stable attenuated poliovirus is produced by engineering an indigenous replication element (cre), into the 5′ non-translated genomic region (with inactivation of the native ere element located in the coding region of 2C (mono-crePV), and replacing the nucleic acid sequence of all or part of the capsid coding region (PI) with a substitute PI coding region having reduced codon pair bias. The stably attenuated poliovirus is effective for vaccines and immunization.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Sequence Variants
Amino acid residue misincorporations are necessarily found in sequence variants at low concentrations in admixture with expressed polypeptides, resulting from one or more base mismatches within codons susceptible to amino acid residue misincorporation during transcription and / or translation. The invention provides a method of optimizing the coding sequences of a polynucleotide that encodes a polypeptide, wherein at least one codon is susceptible to amino acid residue misincorporation. The method of the invention can be used to reverse-engineer an unknown coding sequence, which encodes the same polypeptide, but differs in said at least one codon from the known coding sequence. The method can further be used to alter the immunogenic potential of an expressed polypeptide. Thus, the invention is useful in engineering optimized polynucleotides encoding polypeptides.
Owner:SANDOZ AG
Recombinant virus with codon-pair deoptimized region and uses thereof for the treatment of cancer
The present invention is the use of designed recombinant viruses for the treatment of various forms of malignant tumors. The recombinant viruses of the invention are those in which one or more regionsof the wild type virus was exchanged with a synthetic recoded sequence that reduces the codon pair score relative to human codon pair bias, or that increase the number for CpG di-nucleotides, or thatincreases the number of UpA di-nucleotides. The method of the present invention is particularly useful for the treatment of malignant tumors in various organs, such as: breast, skin, colon, bronchialpassage, epithelial lining of the gastrointestinal, upper respiratory and genito-urinary tracts, liver, prostate and the brain. Astounding remissions in experimental animals have been demonstrated for the treatment of malignant glioblastoma multiforme, as well as for the treatment of breast cancer and melanoma as well.
Owner:CODAGENIX INC
Gene sequence optimization method suitable for high expression of pichia pastoris
ActiveCN112270956ASolve the problem of exponential growth of candidate pathsSequence analysisInstrumentsPichiaGene
The invention discloses a gene sequence optimization method suitable for high expression of pichia pastoris. The gene sequence optimization method comprises the following steps of 1) reading a proteinsequence to be expressed, and processing; 2) establishing a codon transformation matrix according to the sequential combination weight of the codons; 3) defining a graph G, dividing the graph G inton layers according to the number n of amino acids contained in a protein sequence to be expressed, and connecting one edge of each layer of node to the next layer of node; 4) designing a maximum weight array Max Weigh [i, j]; 5) traversing from the last but one layer of the graph G to the first layer of the graph G, initializing the MaxWeigh [i, j] of the i layer of the current layer as a negativevalue, and updating the MaxWeigh element of the current layer; and 6) traversing from the first layer to the last layer of the graph G, and outputting a codon combination with the maximum weight through the calculated MaxWeigh [i, j], namely an optimized sequence. The gene sequence is optimized through the preference of the pichia pastoris codon pair, so a problem that the candidate path of the optimized sequence is exponentially increased is fully solved.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
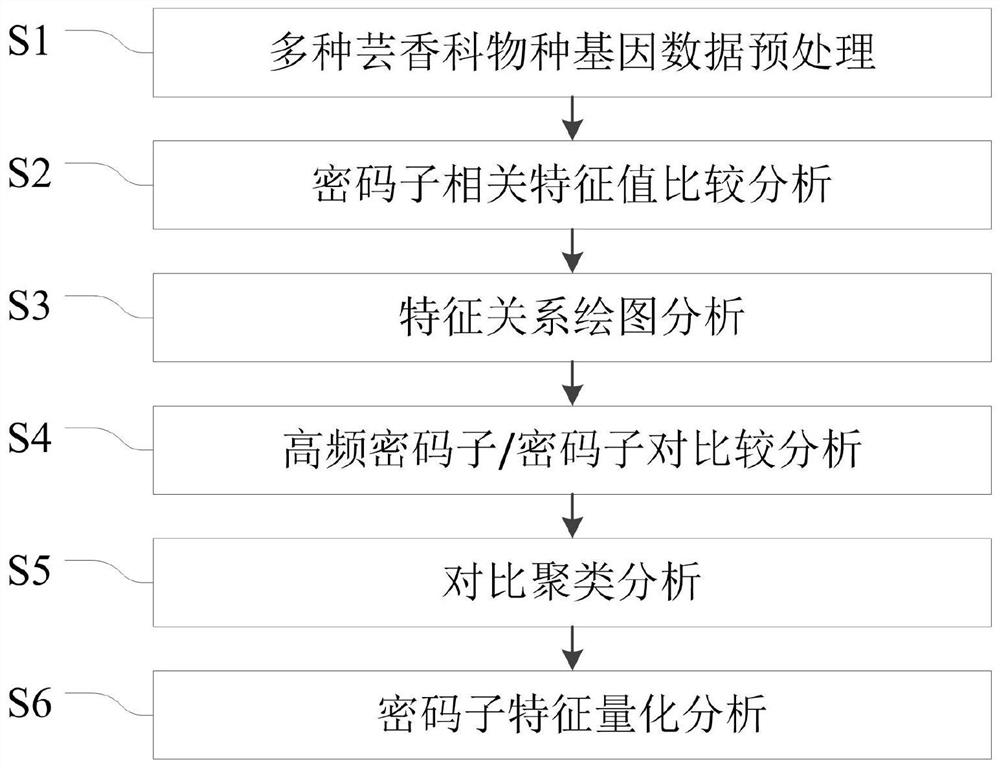
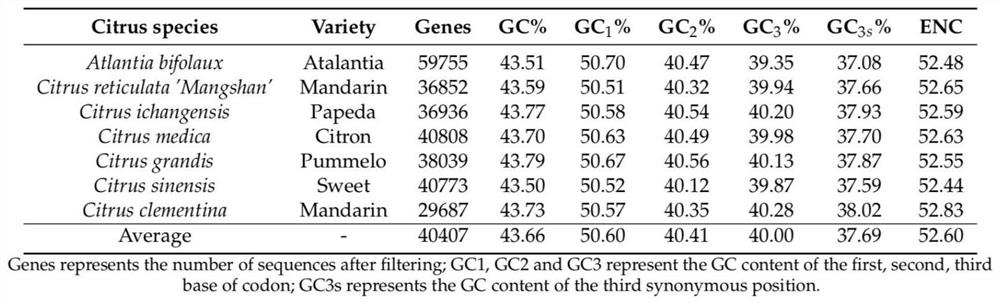
Rutaceae multi-species codon usage pattern analysis method and system
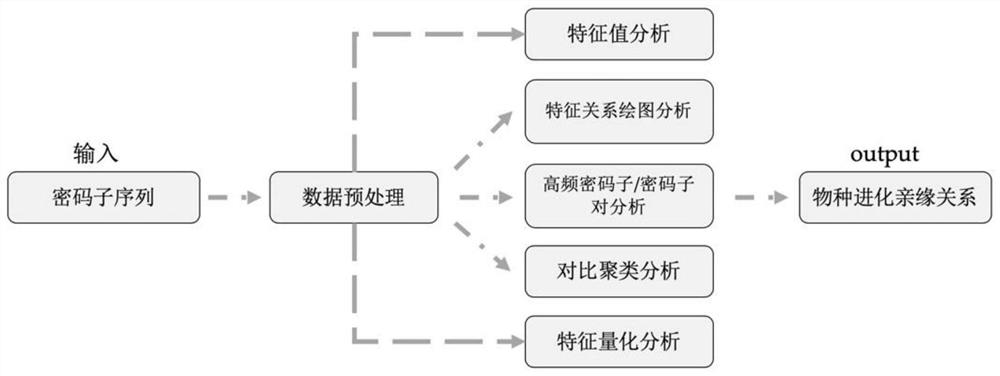
ActiveCN110400604BVerify evolutionary relationshipVerify the degree of evolutionary conservationSequence analysisInstrumentsRutaceaeMultiple species
The invention relates to a method for analyzing the codon usage pattern of multiple Rutaceae species, comprising: obtaining the codon sequence of each species through the genetic data of multiple Rutaceae species; extracting the first characteristic value of the codon sequence , verify the evolutionary relationship of the plurality of species with the relationship of the first eigenvalue; extract the second eigenvalue of the codon sequence, and draw a characteristic relationship diagram with the second eigenvalue to verify the evolutionary conservation of the plurality of species degree; extract the high-frequency codon / codon pair in the codon sequence, and verify the evolutionary conservation correlation of the multiple species with the relationship of the high-frequency codon / codon pair; the codon of the codon sequence The RSCU value was clustered with the codon RSCU value of the plant species, and the clustering results were used to verify the order of the multiple species; the Euclidean distance between the GC3 content of the codon sequence was obtained to verify the genetic relationship of the multiple species.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant virus with codon-pair deoptimized region and uses thereof for the treatment of cancer
PendingUS20210228705A1Reduce the likelihood of relapseReduce the possibilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseMelanomaNucleotide
The present invention is the use of designed recombinant viruses for the treatment of various forms of malignant tumors. The recombinant viruses of the invention are those in which one or more regions of the wild type virus was exchanged with a synthetic recoded sequence that reduces the codon pair score relative to human codon pair bias, or that increase the number for CpG di-nucleotides, or that increases the number of UpA di-nucleotides. The method of the present invention is particularly useful for the treatment of malignant tumors in various organs, such as: breast, skin, colon, bronchial passage, epithelial lining of the gastrointestinal, upper respiratory and genito-urinary tracts, liver, prostate and the brain. Astounding remissions in experimental animals have been demonstrated for the treatment of malignant glioblastoma multiforme, as well as for the treatment of breast cancer and melanoma as well.
Owner:CODAGENIX INC
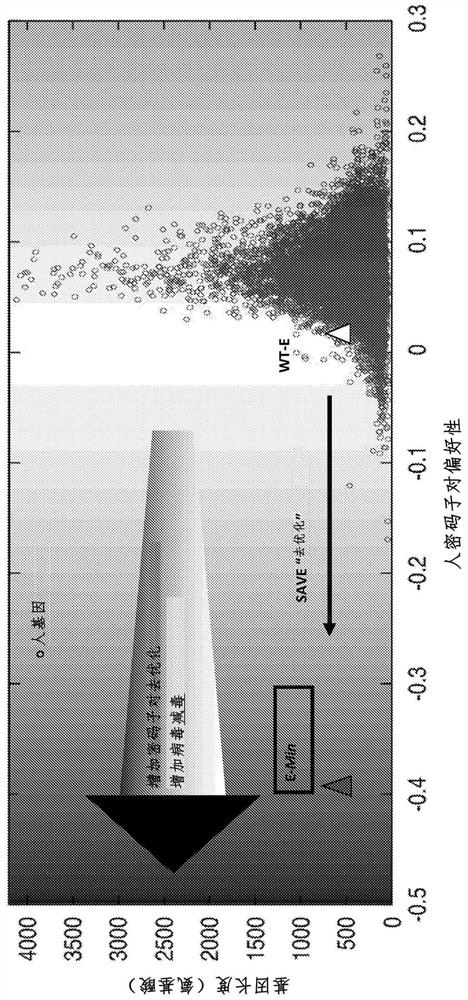
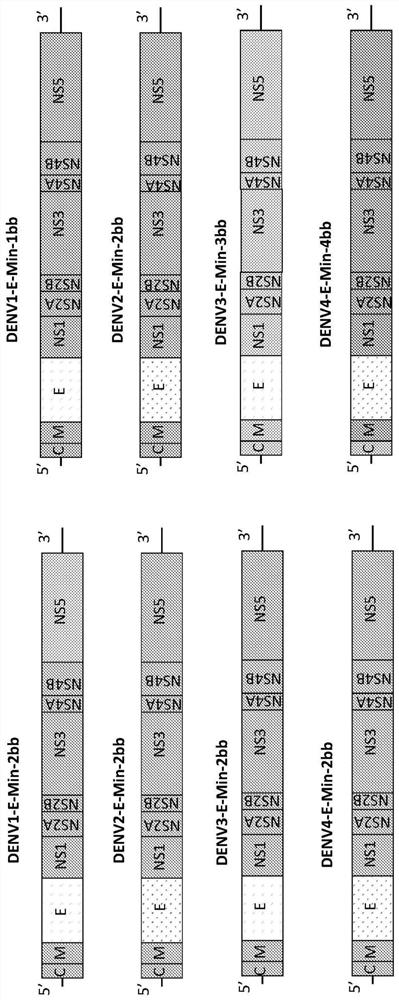
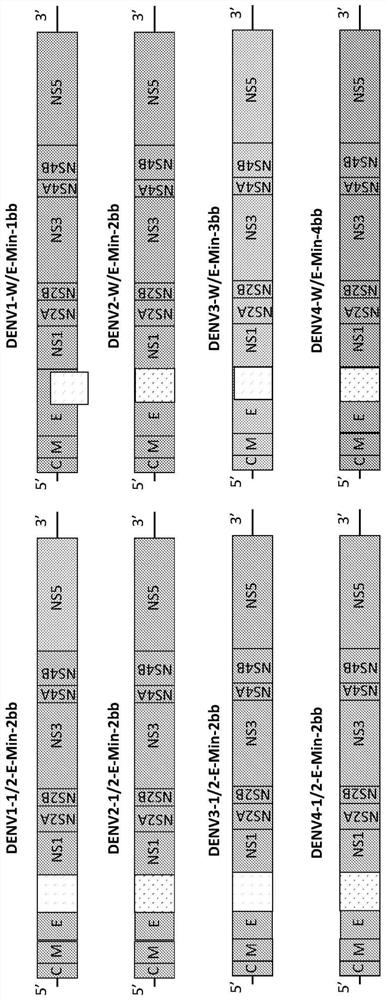
Attenuated dengue viruses
PendingUS20220347285A1Exceptional safety profilesReducing sequenceSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsTGE VACCINEBioinformatics
The present invention provides for modified Flavivirus such as a modified dengue virus type 1, 2, 3, 4, a combination of these, or a tetravalent combination of these. The modification according to various aspects of the invention results in reduced viral protein expression compared to a parent virus, wherein the reduction in expression is the result of recoding one or more regions of the virus. For example, the prM, or envelope (E) region can be recoded. In various embodiments one or more regions are recoded by reducing the codon pair bias or codon usage bias of the protein-encoding sequence. These modified Flaviviruses are used as vaccine compositions to provide a protective immune response.
Owner:CODAGENIX INC
Attenuated flaviviruses
PendingUS20210000939A1Exceptional safety profilesReducing the codon-pair biasSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsZika virusTGE VACCINE
The present invention provides for modified Flavivirus such as a modified Zika virus. The modification according to various aspects of the invention results in reduced viral proteins compared to a parent virus, wherein the reduction in expression is the result of recoding one or more regions of the virus. For example, the prM, or envelope (E) region, or the nonstructural protein 3 (NS3) region or both the E and NS3 regions can be recoded. In various embodiments one or more regions are recoded by reducing the codon pair bias or codon usage bias of the protein-encoding sequence. These modified Flavivirus are used as vaccine compositions to provide a protective immune response.
Owner:CODAGENIX INC
Gene synthesis of wild boar alpha-interferon, vector construction and method for producing outcome
InactiveCN101392256BSimple structureImprove expression levelPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
The invention discloses a gene synthesis of Alpha-interferon of wild boars and vector construction thereof as well as a production method of a product. A number of problems of low expression capacity, products expressed in a fusion state, products with purification tags or no fermentation technology with high density exist in the domestic recombinant strains. The invention includes a method that a codon and codon pairs, preferred by Escherichia coli, are used for synthesizing an Alpha-interferon gene of the wild boar, establishing a high-efficiency expression vector and transforming a high-efficiency expression strain as well as methods of high-density fermentation of engineering bacteria, separation and purification of inclusion bodies, the modification, the renaturation and the purification of target protein and the determination of biological activity of the expressed product. The gene synthesis, the vector construction and the production method pertain to the technical field of the production of polypeptide drugs by genetic engineering in biopharmaceuticals.
Owner:黑龙江省农业科学院畜牧研究中心 +1
A codon optimization method and application for in vitro expression of heterologous genes
ActiveCN110491447BEfficient expressionHigh expressionSequence analysisAnimals/human peptidesHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses a codon optimization method for in vitro expression of heterologous genes. The method comprises: obtaining the nucleotide sequence of the whole genome of the host cell and the amino acid sequence of the whole protein group; taking the codon pair as the statistical object, and counting The weight of each codon pair in the whole genome of the host cell; select the protein to be optimized, and construct a one-way graph model with codons as nodes and the weight values between upstream and downstream codon pairs as line values; according to the one-way graph Model to obtain the nucleotide sequence of the optimized gene. The present invention uses the whole genome and whole protein group of the host cell as the sequence library, takes codon pairs as statistical objects, and constructs a one-way graph model with codons as nodes and the weight values between upstream and downstream codon pairs as line values, To obtain the optimal codon combination sequence, an optimized gene with an optimized nucleotide sequence can be obtained, and the optimized gene can be highly expressed in vitro, and the expression level is significantly increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Optimized gene of recombinant glucose oxidase and expression vector and application of optimized gene
The invention discloses an optimized gene of recombinant glucose oxidase and an expression vector and application of the optimized gene. On the premise that the amino acid sequence of the glucose oxidase is not changed, the gene sequence of the glucose oxidase is optimized according to pichia pastoris preferred codons by comprehensively considering the influencing factors such as use frequency ofthe codons, adjustment of GC content, deletion of instable sequences, secondary mRNA structure and the like; and the nucleotide sequence of the optimized glucose oxidase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1.The invention further provides the expression vector and a recombinant host strain containing the optimized gene of the glucose oxidase. The optimized gene is transferred to the pichia pastoris for expression, and the test results show that: compared with the gene before optimization, the secreting expression quantity of the optimized gene in the pichia pastoris is remarkably improved. The application effect tests of the glucose oxidase show that the expressed recombinant glucose oxidase has the same using effect as a commercial enzyme preparation.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Attenuated dengue virus
PendingCN114302738ARapid infectionHigh titerSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsTGE VACCINEBioinformatics
The present invention provides a modified flavivirus, such as a modified type 1, type 2, type 3, type 4 dengue virus, a combination of these viruses, or a tetravalent combination of these viruses. The modifications according to various aspects of the invention result in reduced expression of the viral protein as compared to the parent virus, where the expression reduction is the result of recoding one or more regions of the virus. For example, a prM or envelope (E) region may be recoded. In various embodiments, the one or more regions are recoded by reducing the codon pair preference or codon use preference of the protein coding sequence. These modified flaviviruses are useful as vaccine compositions to provide protective immune responses.
Owner:CODAGENIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com