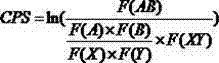Method for detecting codon pair bias of bovine whole-genome
A genome-wide, assay-based technology with applications in the fields of molecular genetics and bioinformatics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The present invention first obtains the bovine whole genome sequence from NCBI, and extracts all known protein coding sequences from the sequence. According to these protein coding sequences, the use preference scores of 3721 codon pairs were calculated, and then the codon pair use preference of the CDS sequence of each coding sequence was calculated. Finally, according to the codon pair usage distribution of each CDS sequence, the codon pair usage preference distribution of the whole genome was obtained by using the alignment analysis technique.
[0016] The present invention will be further described in detail below, which is an explanation of the present invention rather than a limitation.
[0017] a. Extraction of protein coding sequence of whole bovine genome
[0018] 1. Use UCSC's Table Browser to obtain the whole genome sequence and genome annotation information of cattle (TaxID: 9913).
[0019] 2. Use the self-compiled Java program to obtain all known bovine p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com