Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
958 results about "Pairing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, a pairing is an R-bilinear map of modules, where R is the underlying ring.
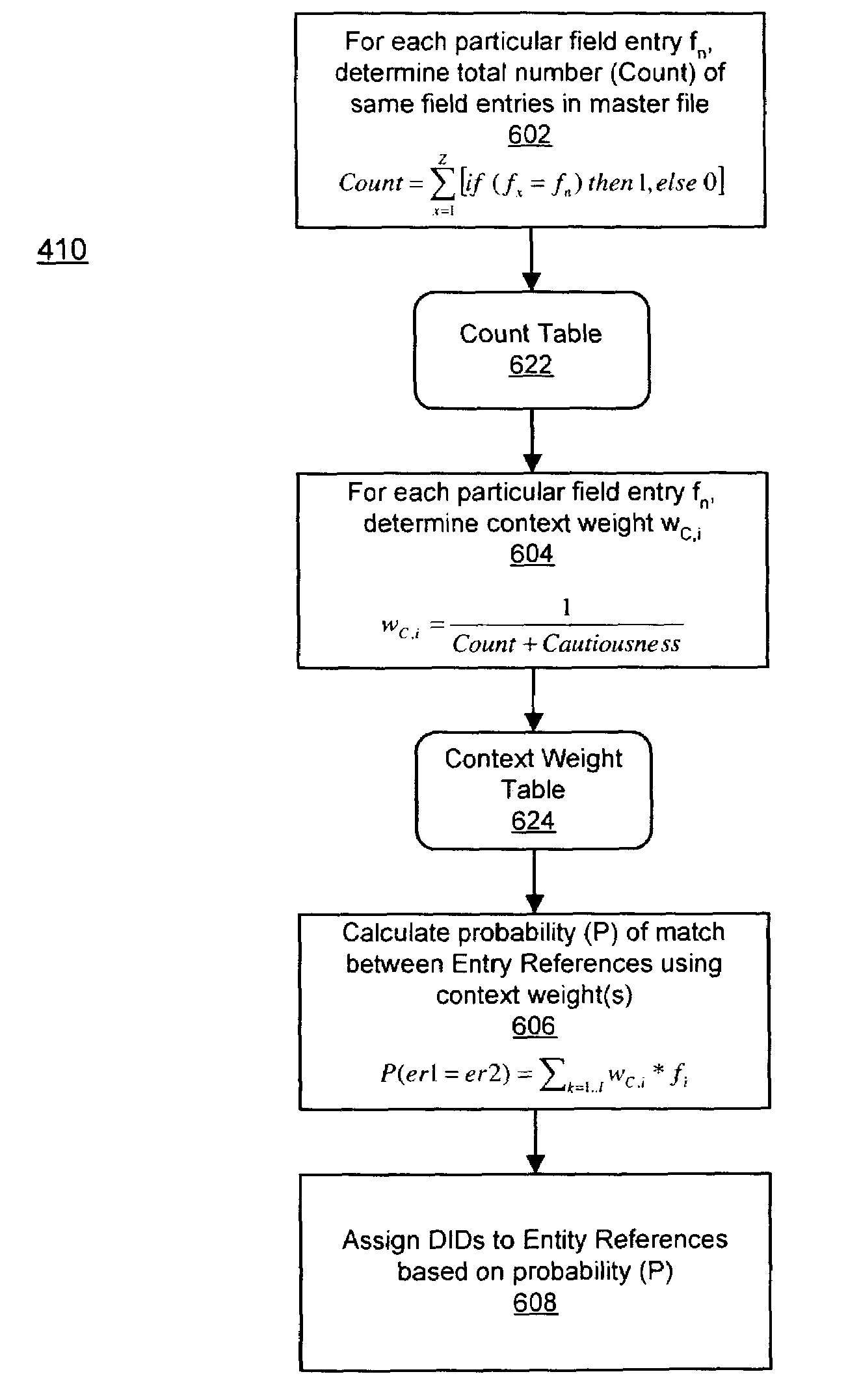
Method and system for processing data records
ActiveUS7403942B1Reduced data setReduce settingsDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsEntity linkingPairing
Disclosed herein are various exemplary systems and methods for linking entity references to entities and identifying associations between entities. In particular, a method for identifying an entity from a plurality of entity references, each entity reference being linked with a separate ghost entity, is provided. The method comprises the steps of comparing an entity reference of a first ghost entity with an entity reference of a second ghost entity to determine a match probability between the entity reference of the first ghost entity and the entity reference of the second ghost entity, linking the entity reference of the first ghost entity additionally with the second ghost entity and the entity reference of the second ghost entity additionally with the first ghost entity when the match probability is greater than or equal to a match threshold and repeating the steps of comparing and linking for one or more ghost entity pairings possible from the ghost entities. The method further comprises determining, for one or more entity references linked to a ghost entity, a score for the entity reference based at least in part on a match probability between the entity reference and a value representing the one or more entity references linked to the ghost entity and identifying the ghost entity as an actual entity based at least in part on one or more scores for the one or more entity references linked to the ghost entity.
Owner:LEXISNEXIS RISK DATA MANAGEMENT
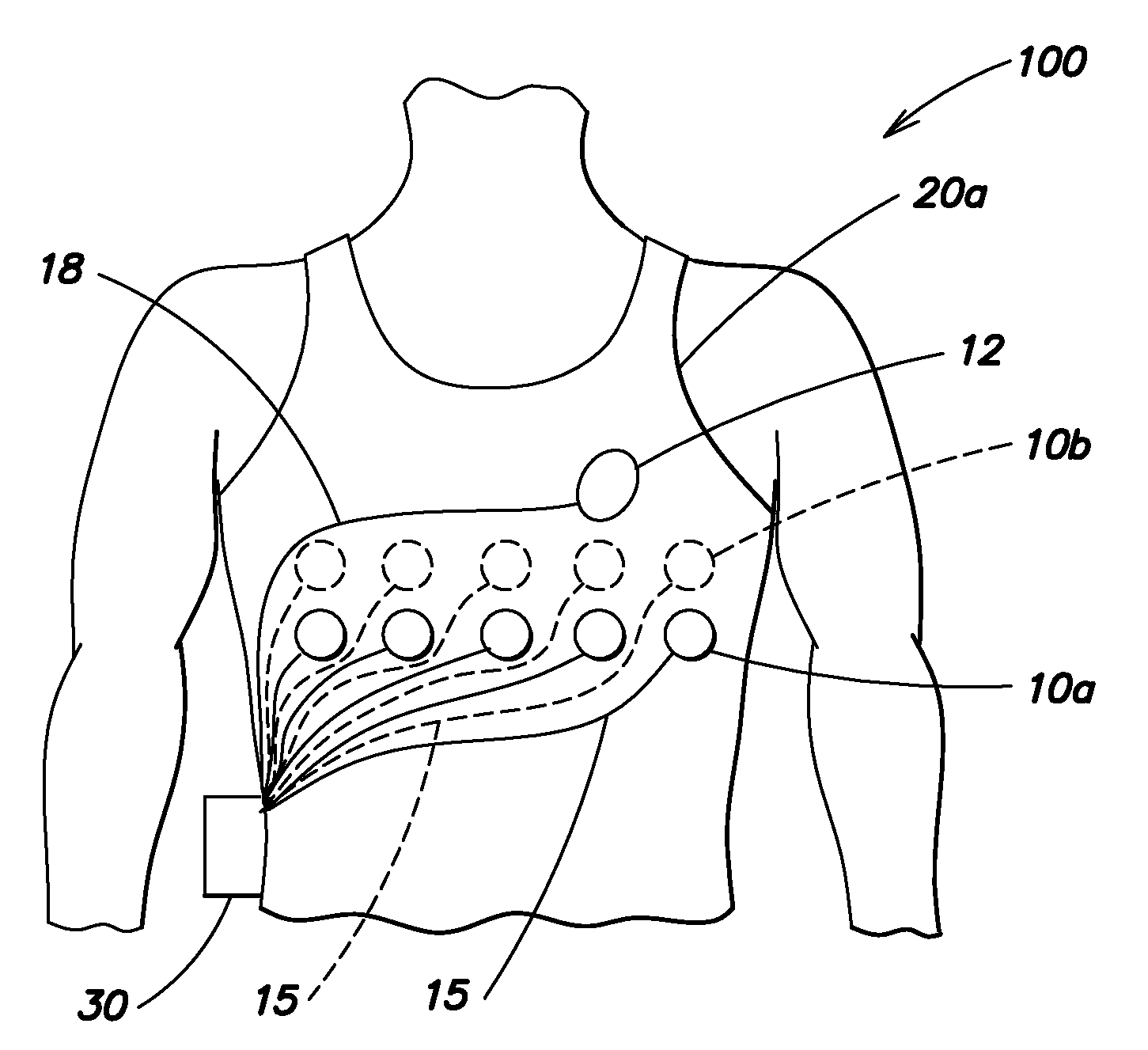
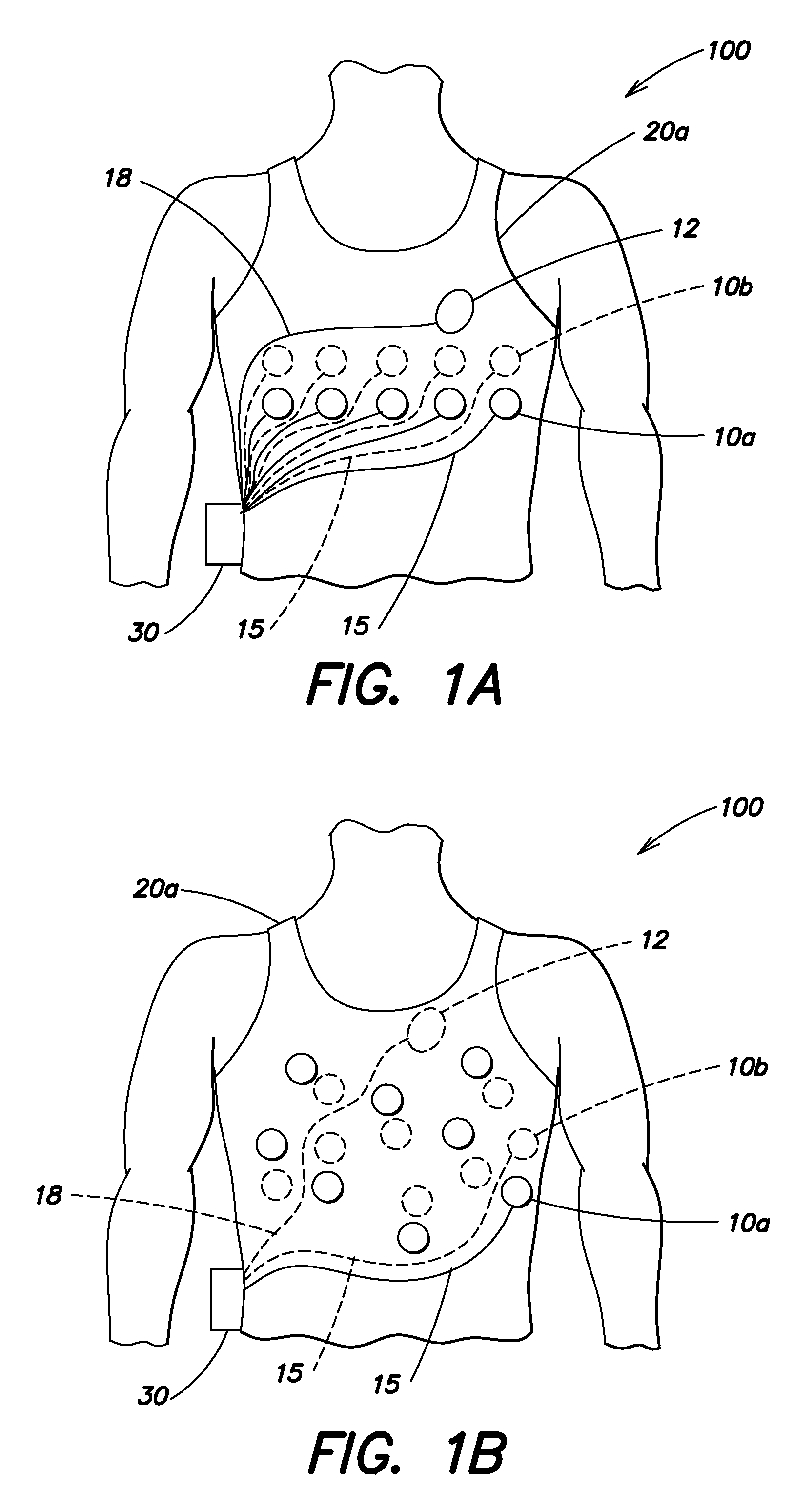
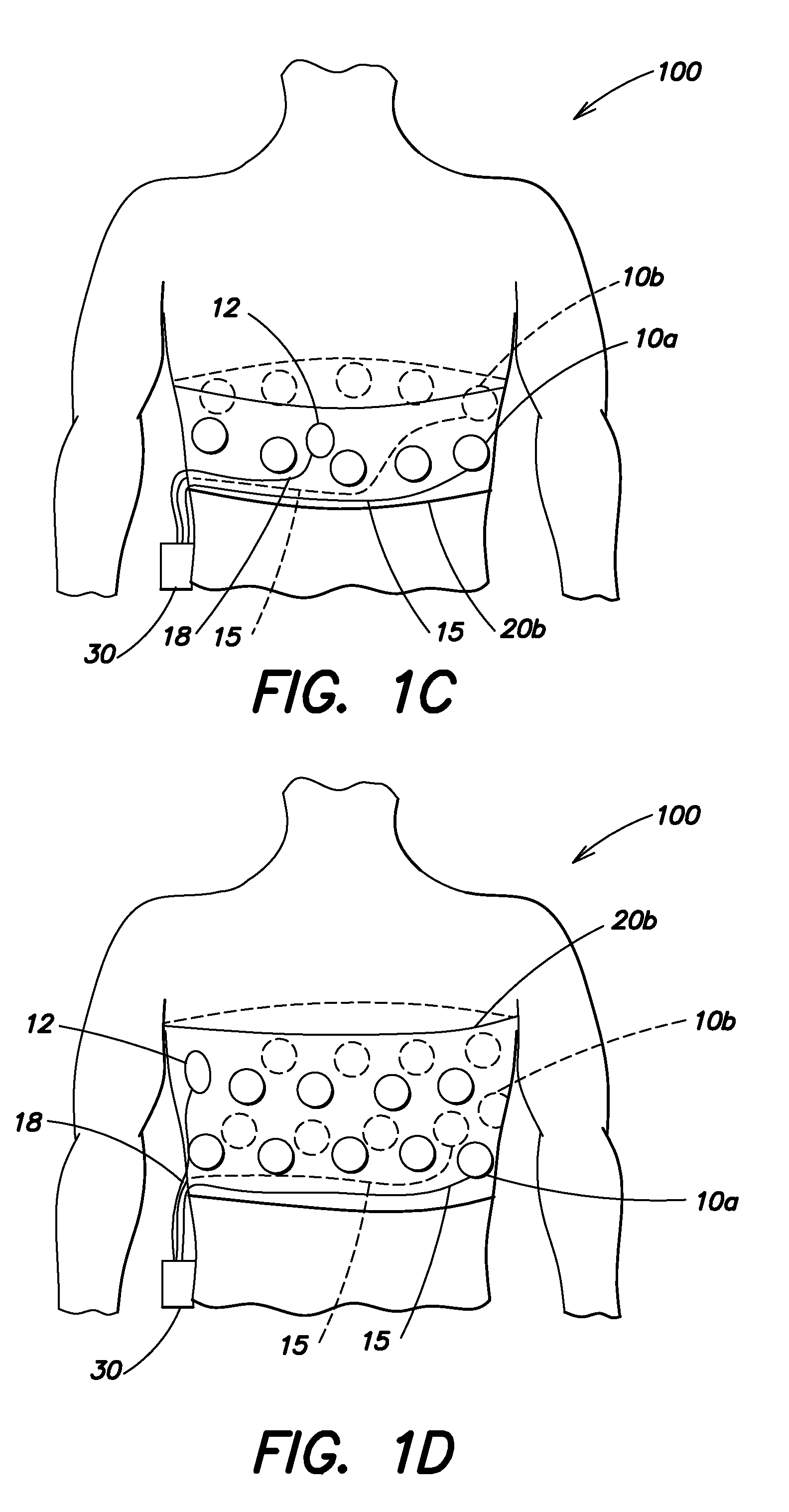
Wearable ambulatory medical device with multiple sensing electrodes
ActiveUS20110288605A1Quality improvementReduce noiseElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsElectricityPhase difference
An ambulatory medical device including a plurality of electrodes configured to be disposed at spaced apart positions about a patient's body, an electrode signal acquisition circuit, and a monitoring circuit. The acquisition circuit has a plurality of inputs each electrically coupled to a respective electrode of the plurality of electrodes and is configured to sense a respective signal provided by a plurality of different pairings of the plurality of electrodes. The monitoring circuit is electrically coupled to an output of the acquisition circuit and is configured to analyze the respective signal provided by each of the plurality of different pairings and to instruct the acquisition circuit to select at least one of the plurality of different to pairings to monitor based on at least one of the quality of the respective signal, a phase difference between the respective signal and that of other pairings, a position of electrodes relative to the patient's body, and other criteria.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Process control configuration system with connection validation and configuration
Connection objects or other such data structures facilitate establishing and configuring connections between objects that model components in a process control system. A first set of data structures (e.g. the object connection type structures) identify valid types for component-to-component pairings and the respective roles of each component in the pairing (e.g., parent or child, source or sink). A second set of data structures (e.g., the parameter connection type structures) supply similar information for parameter-to-parameter connections. Together, these data structures can be used, for example, to validate component-to-component connections suggested by the user and to automatically configure parameter-to-parameter connections. Actual connections, both at the component or parameter level, are reflected using parameter overrides within the parameterized object model—with which the connection objects are constructed.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
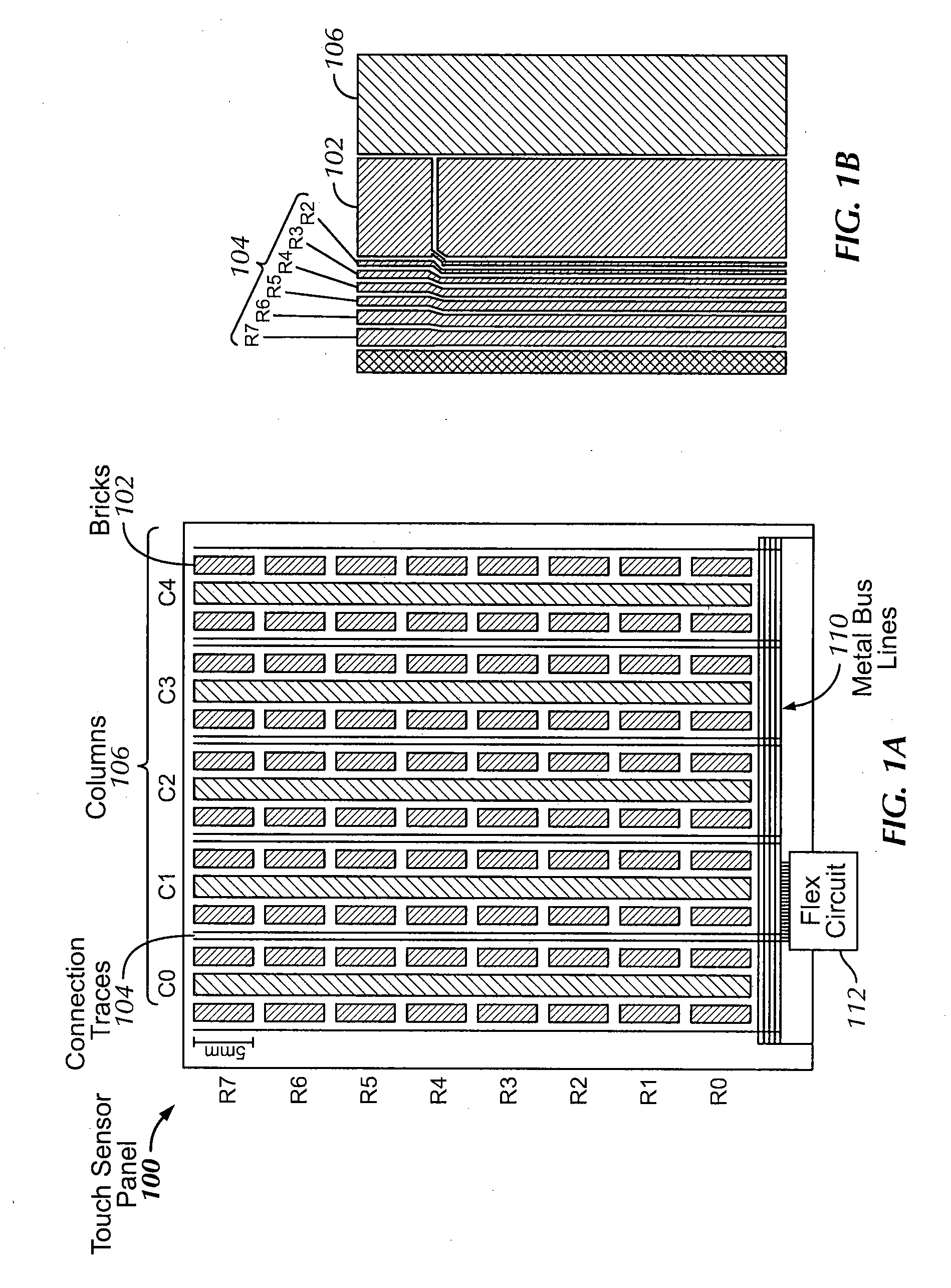
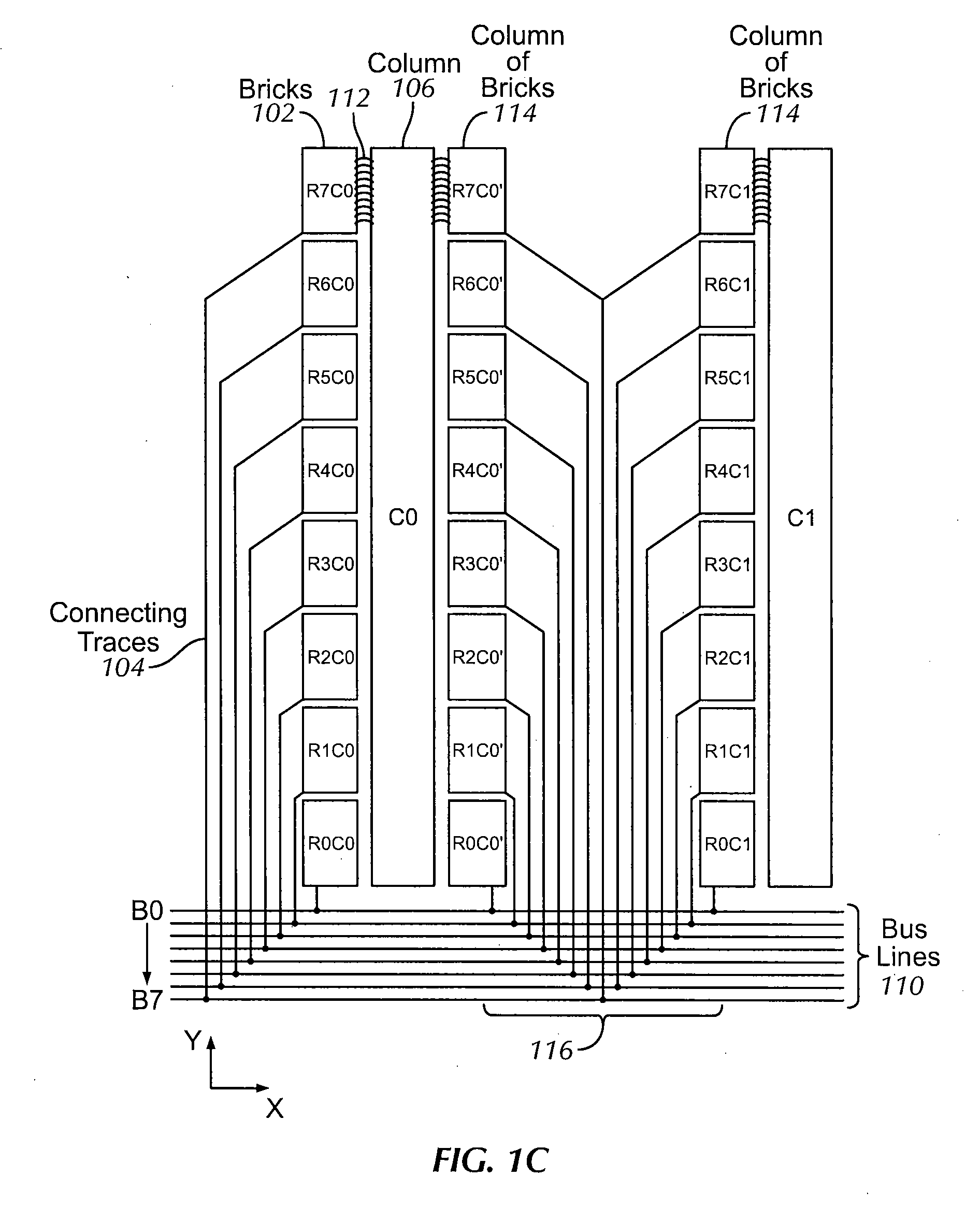
Single layer touch panel with segmented drive and sense electrodes
ActiveUS20100149108A1Less spaceUniform sensitivityInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesEngineering
A touch sensor panels having segmented electrodes for both the drive and sense lines. The touch sensor panel may include a number of columns of sense electrodes and a number of rows of drive electrodes. Each of the drive and sense electrodes are connected to one of the metal bus lines using a connecting trace. Pixels on the touch sensor panel are formed by the unique pairings of individual drive electrodes and their adjacent sense electrodes. Electrically, the mutual capacitance of one touch-sensing pixel can be distinguished from the mutual capacitance of another touch sensing pixel because the two mutual capacitances are formed with combinations of different drive electrodes and sense electrodes. In one embodiment, the drive electrodes and sense electrodes in adjacent columns are staggered horizontally with respect to each other by half a Y-pitch of the electrodes.
Owner:APPLE INC
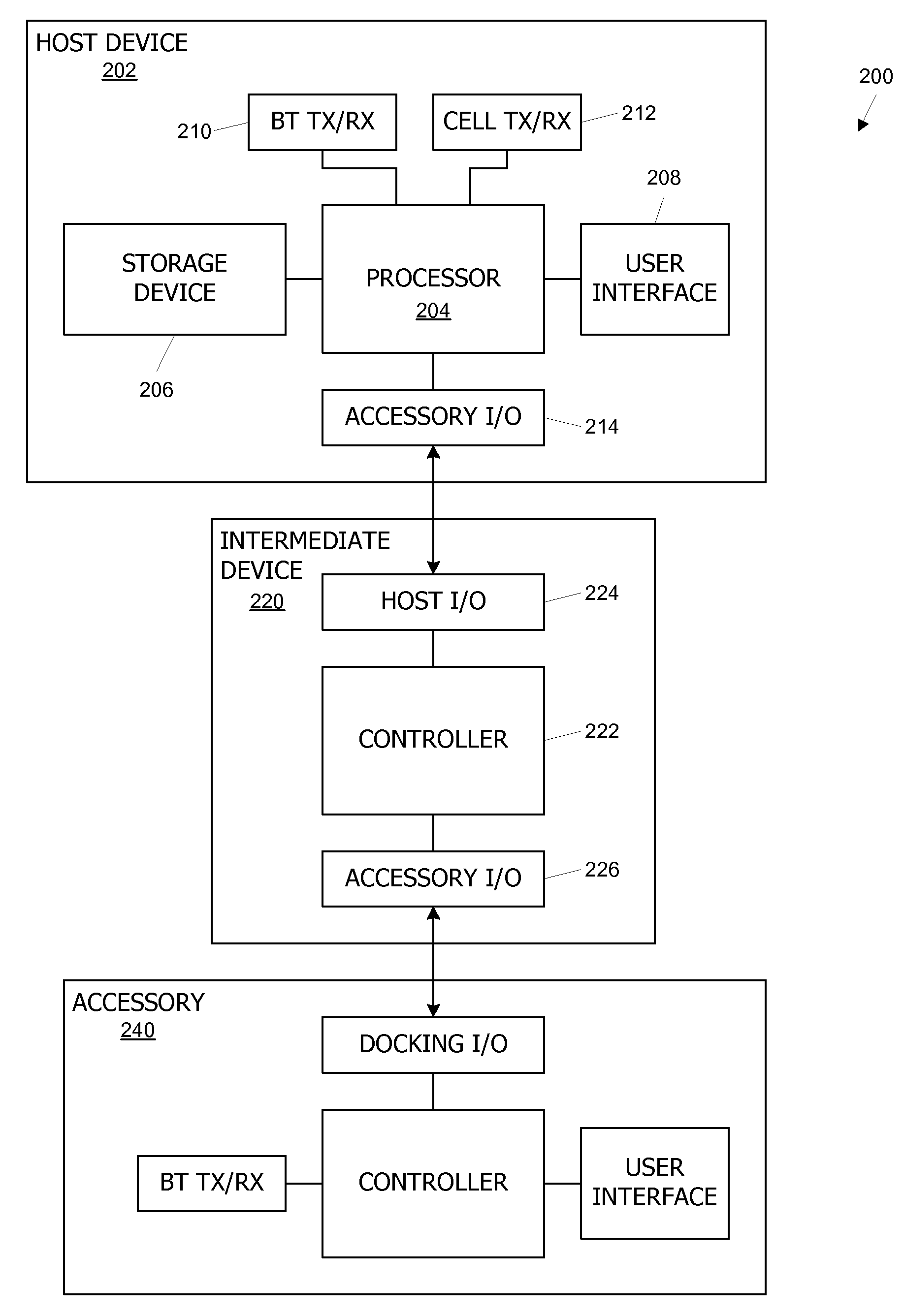
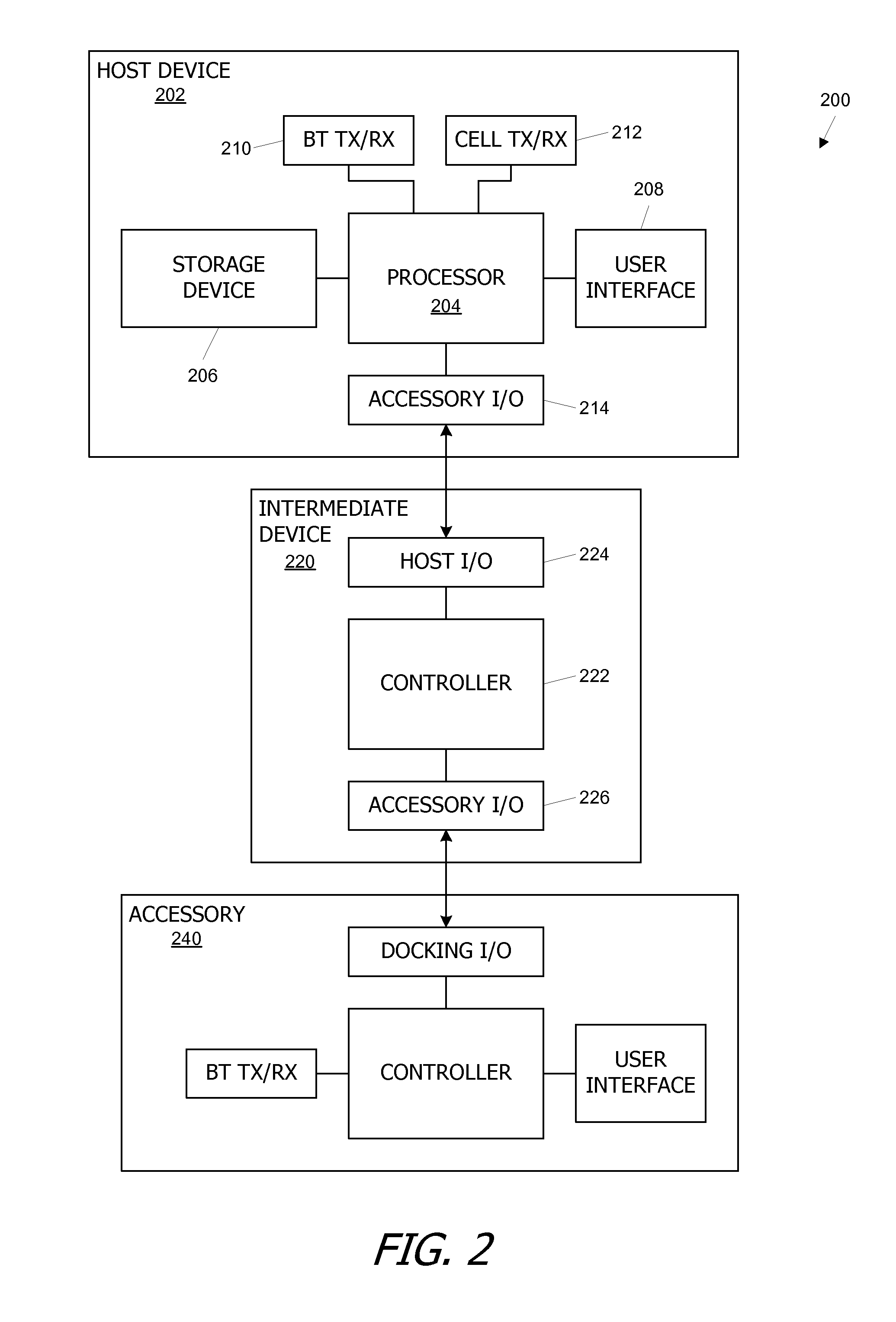
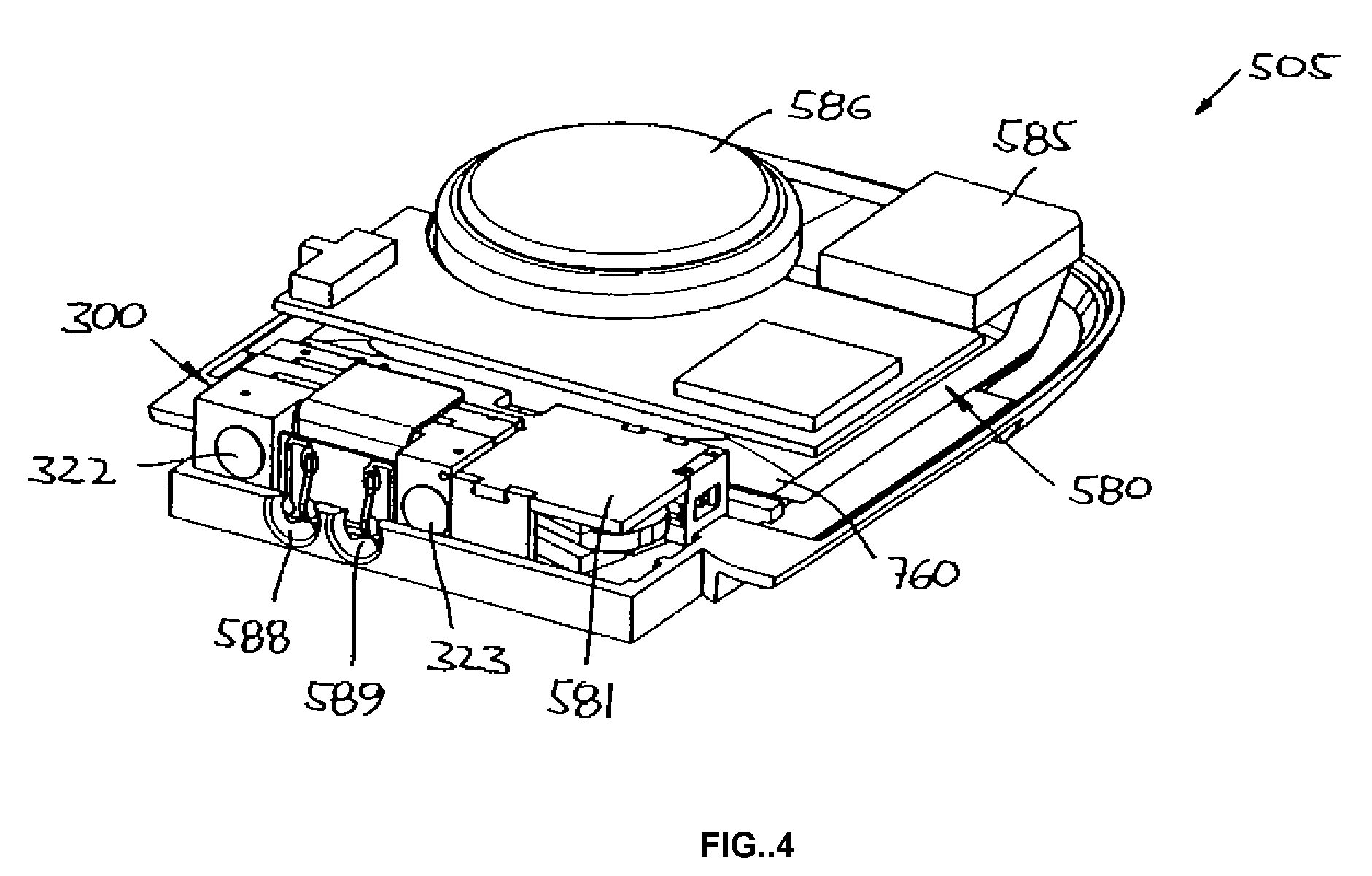
Communication between a host device and an accessory via an intermediate device
A host device and an accessory exchange information (e.g., commands and data) via an intermediate device. The host device and accessory can each connect to the intermediate device through a direct wired path and can exchange commands and data with the intermediate device. The host device and the accessory can also “tunnel” information to each other through the intermediate device, by packaging the tunneled information as a payload of a command recognizable by the intermediate device; the intermediate device can repackage and forward the payload. In some embodiments, the tunneled information relates to configuring a wireless link (e.g., a Bluetooth pairing) between the host device and the accessory.
Owner:APPLE INC
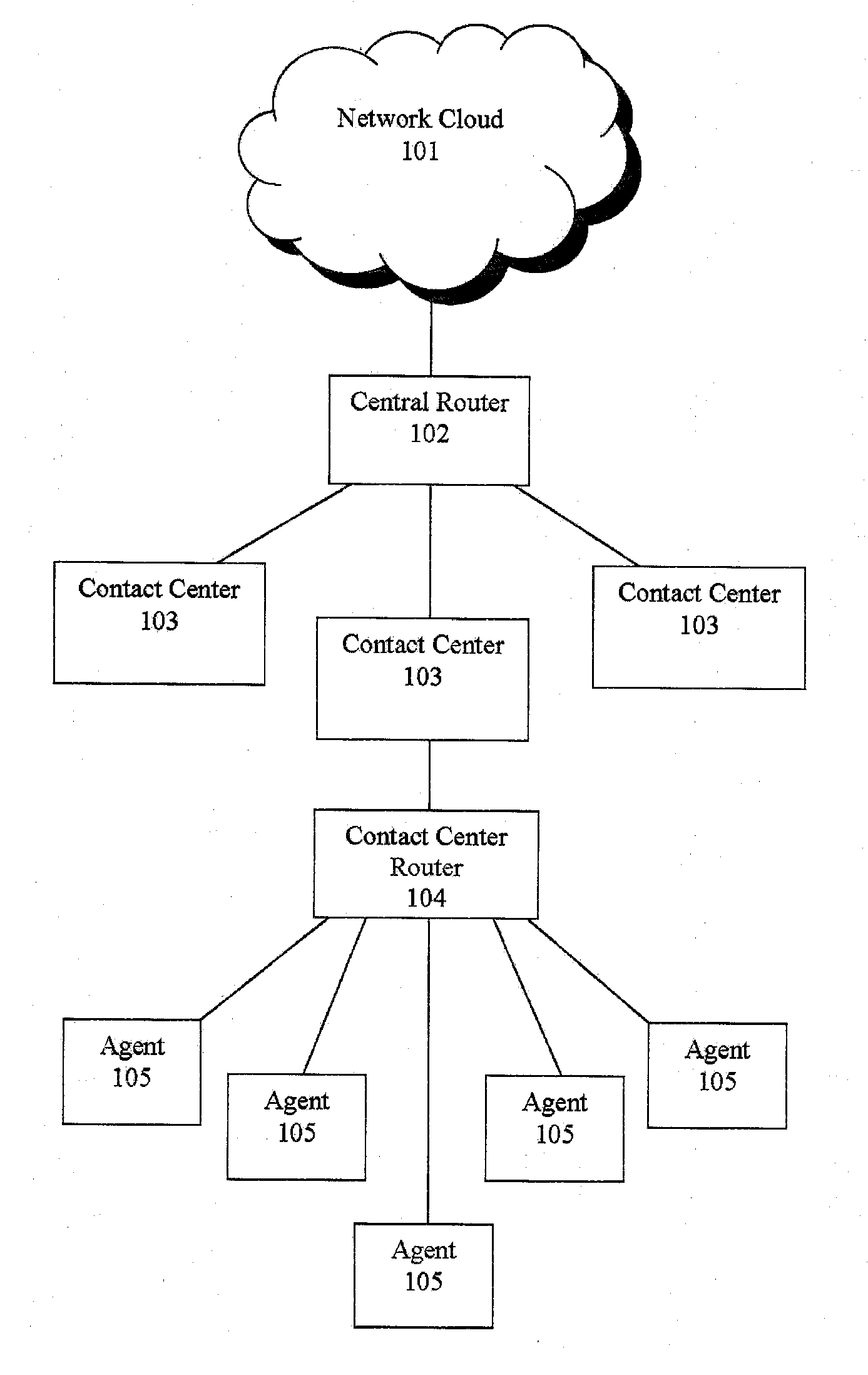
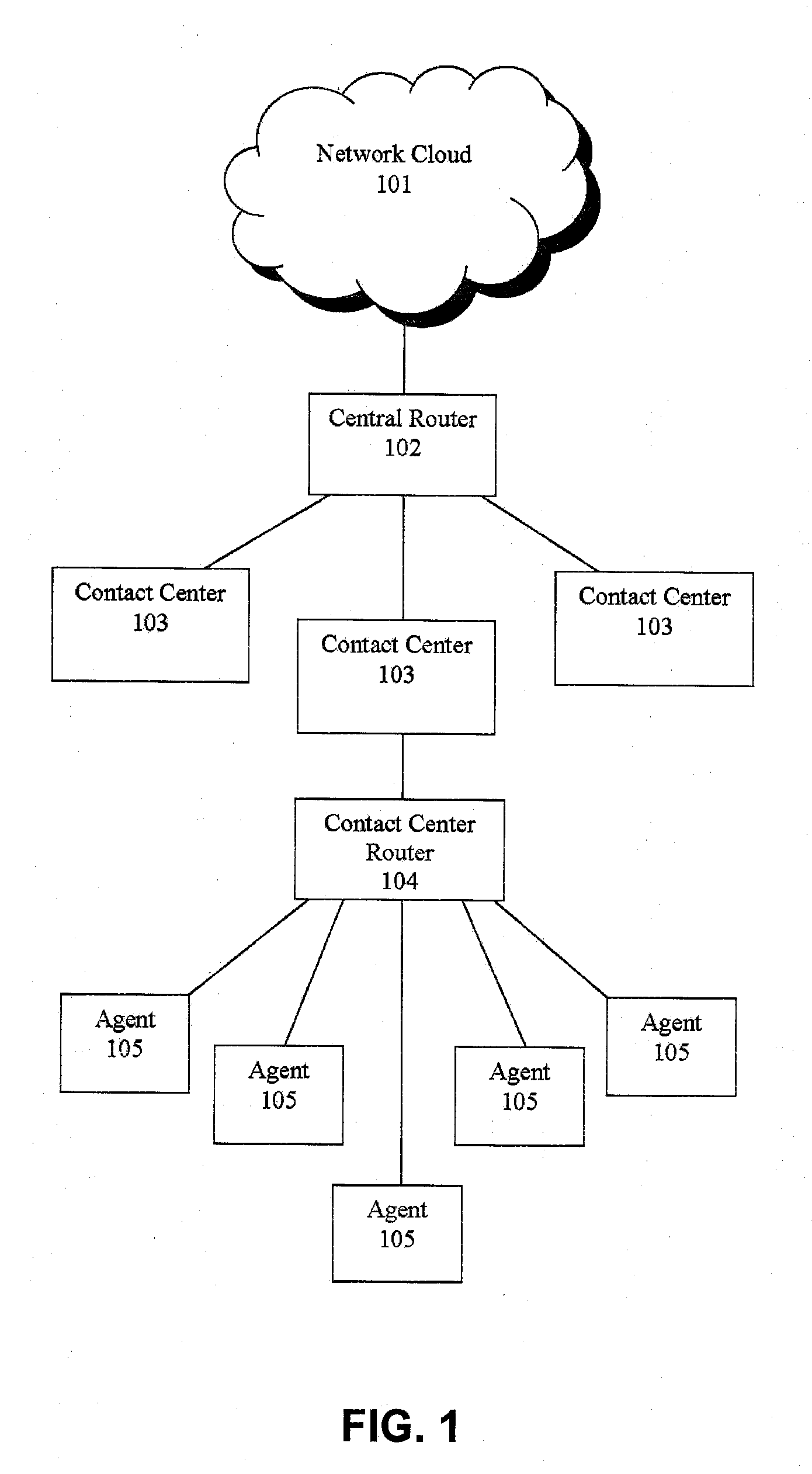
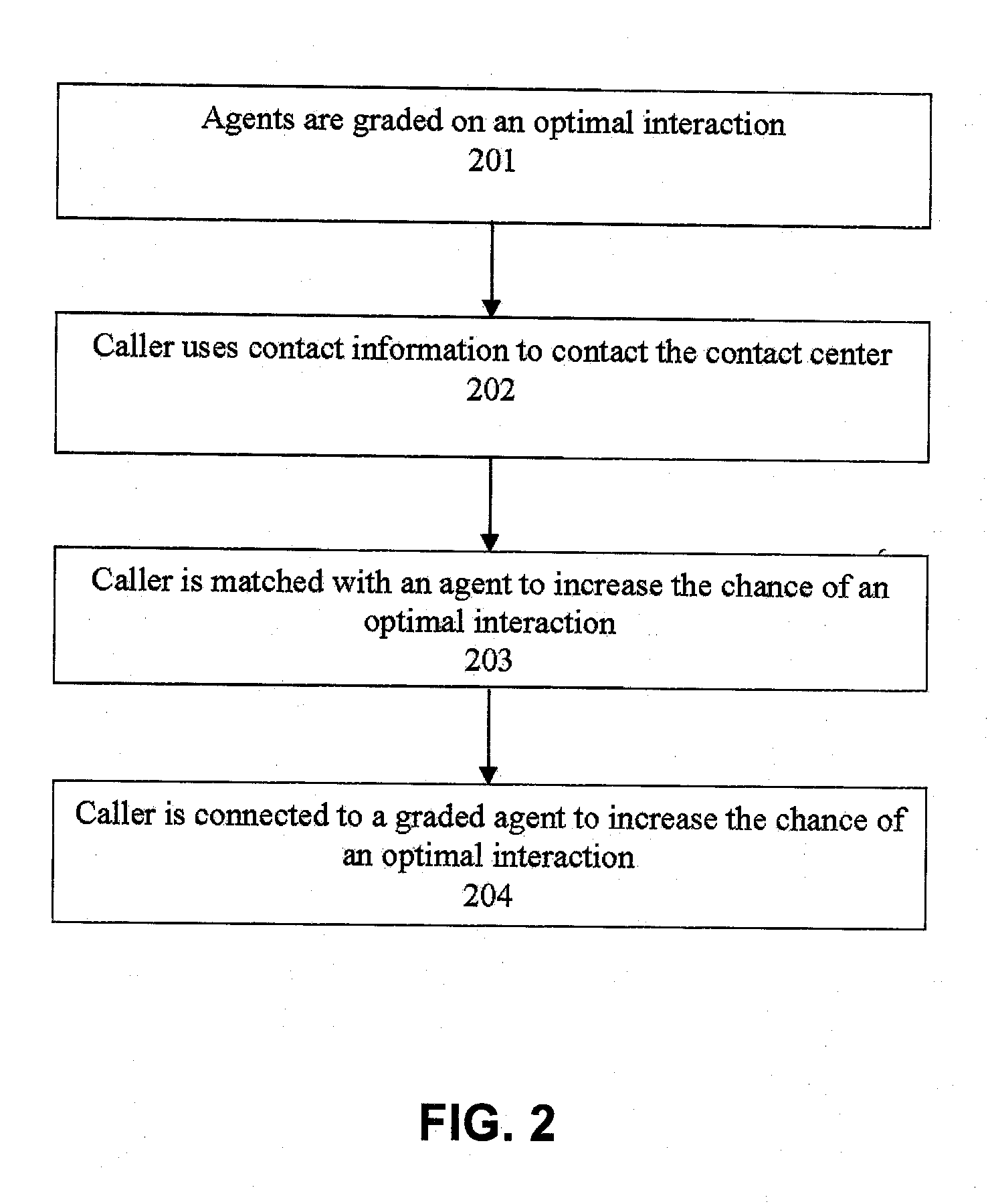
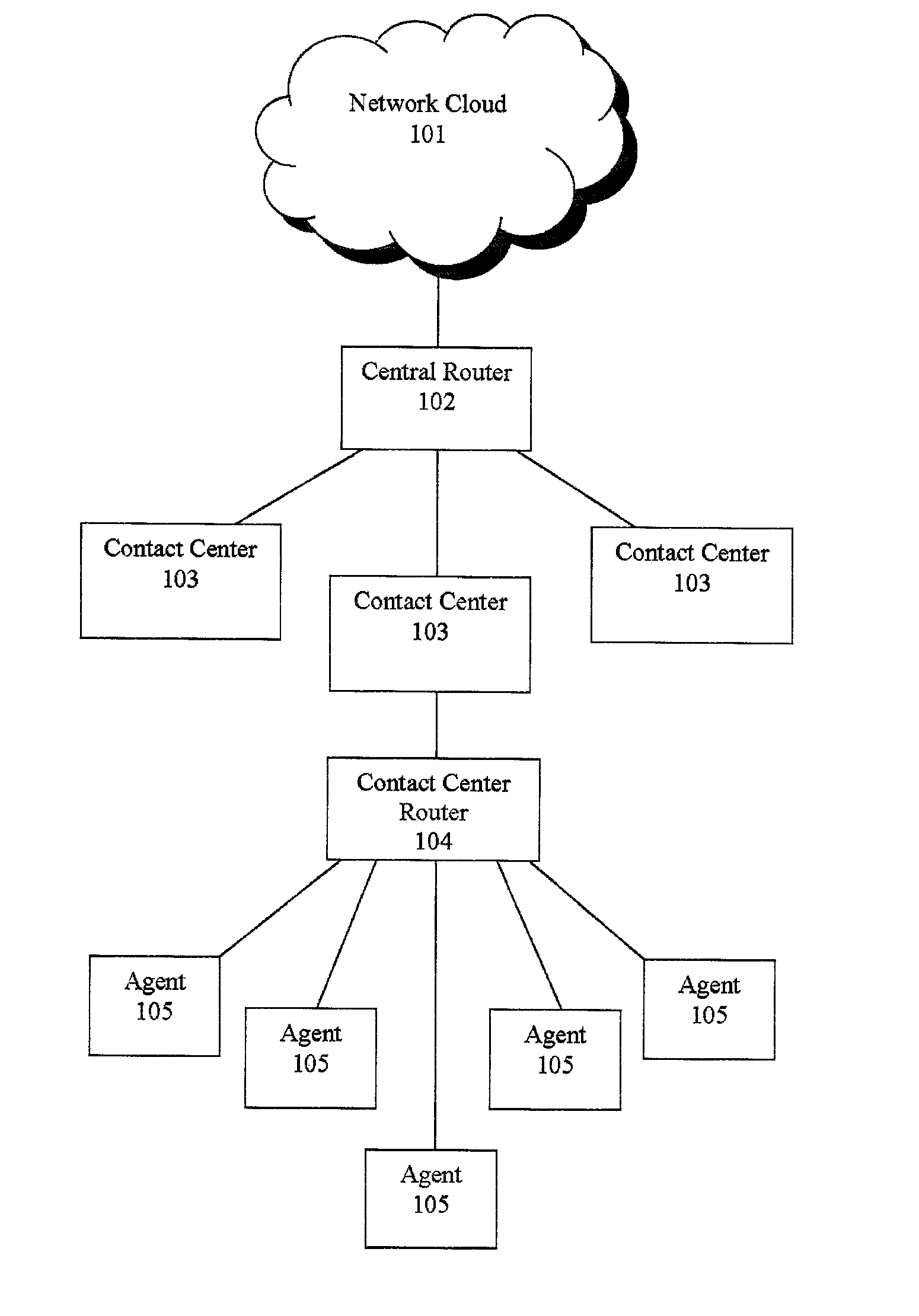
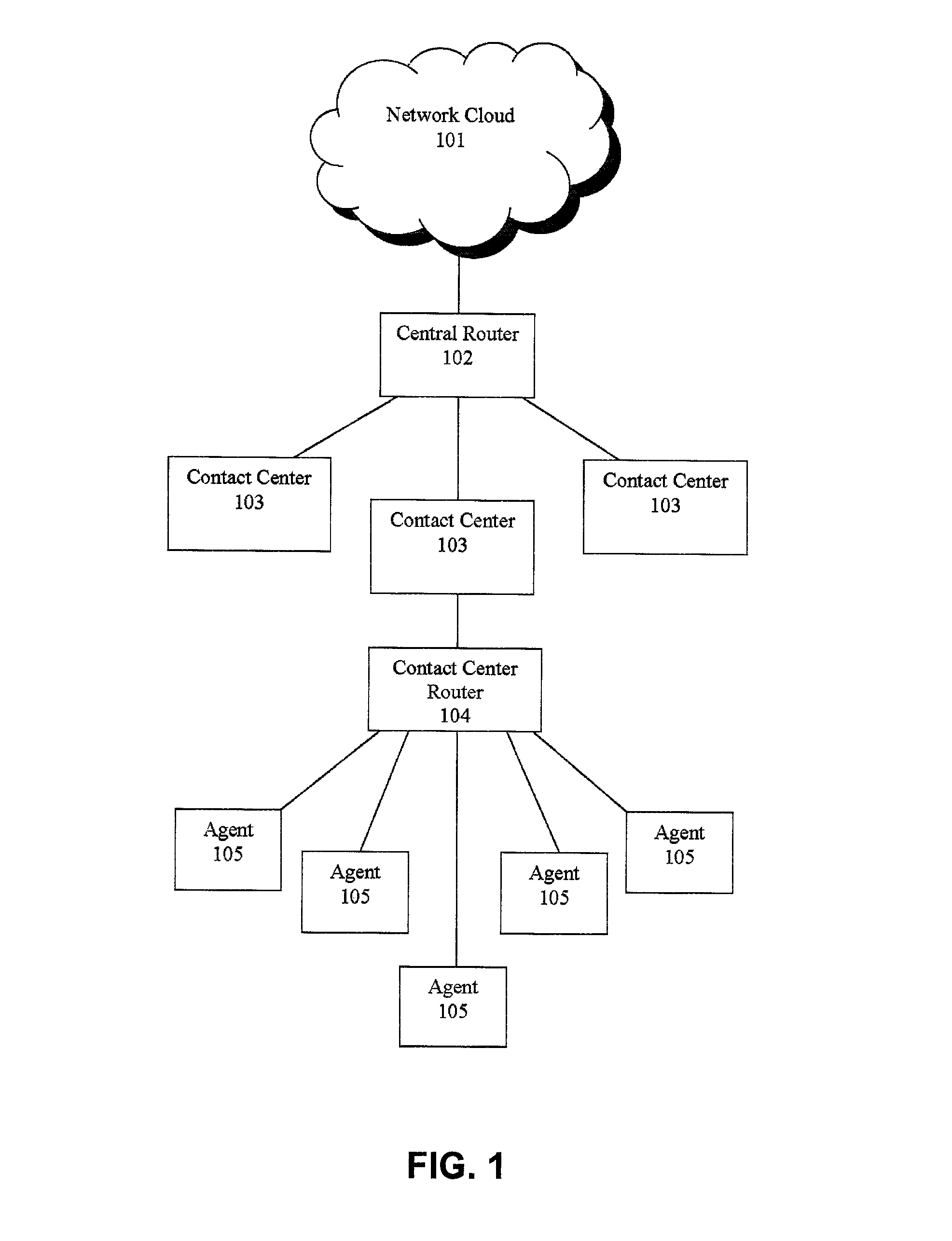
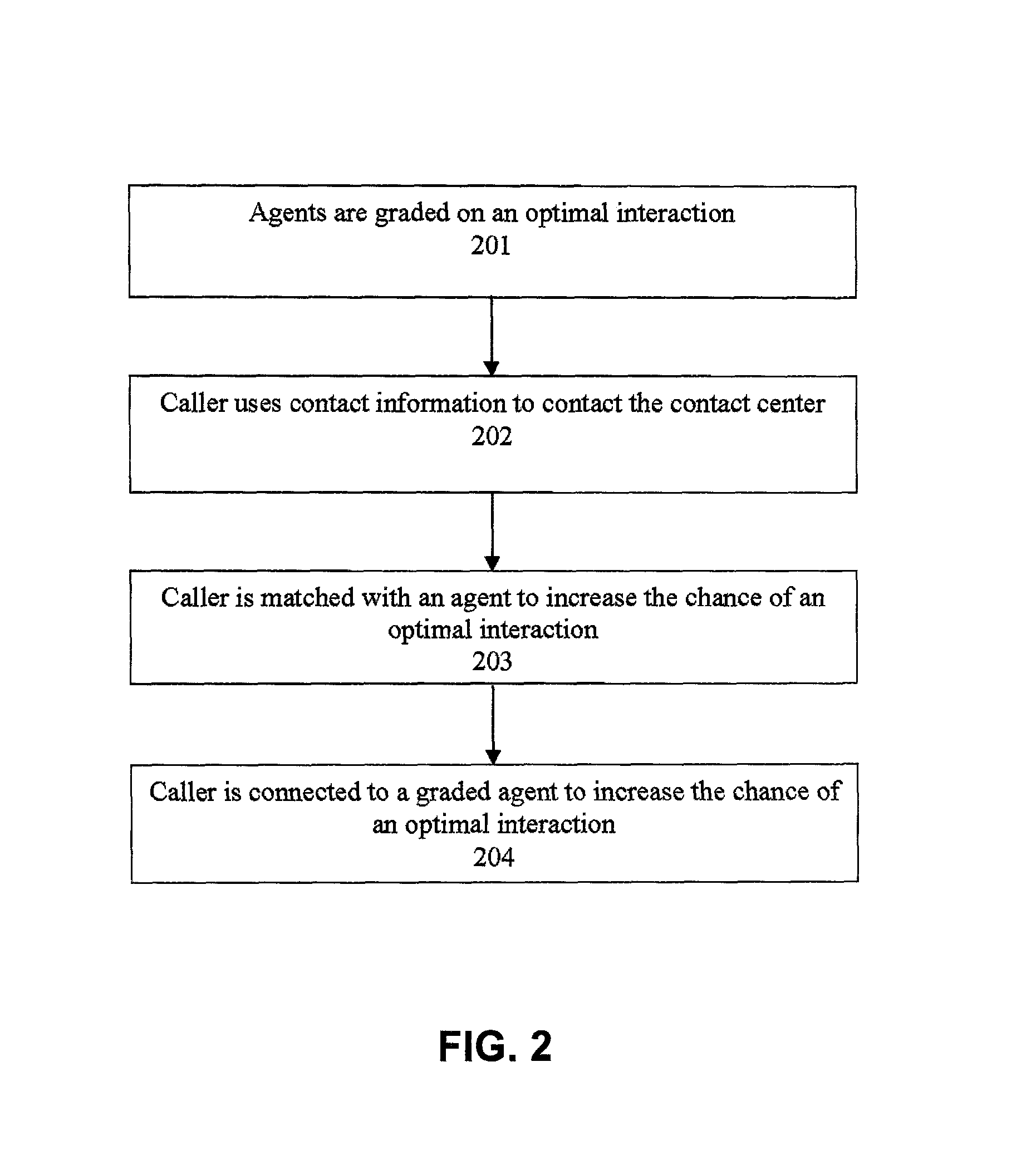
Agent satisfaction data for call routing based on pattern matching alogrithm
ActiveUS20100054452A1Reducing attritionLow costManual exchangesAutomatic exchangesPattern matchingContact center
Methods and systems are disclosed for routing callers to agents in a contact center with an intelligent routing system. An exemplary method includes routing callers to agents based on a pattern matching algorithm utilizing caller data and agent data, where the agent data includes agent satisfaction data from past agent-caller pairings. The agent satisfaction data may be obtained via surveys of the agents regarding their satisfaction with past agent-caller contacts. The agent satisfaction data may be used by the pattern matching algorithm in an attempt to increase agent satisfaction for future calls, thereby potentially reducing attrition of agents and cost to the call center, increasing morale of the agents, and so on. The agent satisfaction data and output from past agent-caller pairings may be weighted by the contact center against other agent data and caller data for a desired mixing of output variables.
Owner:AFINITI LTD
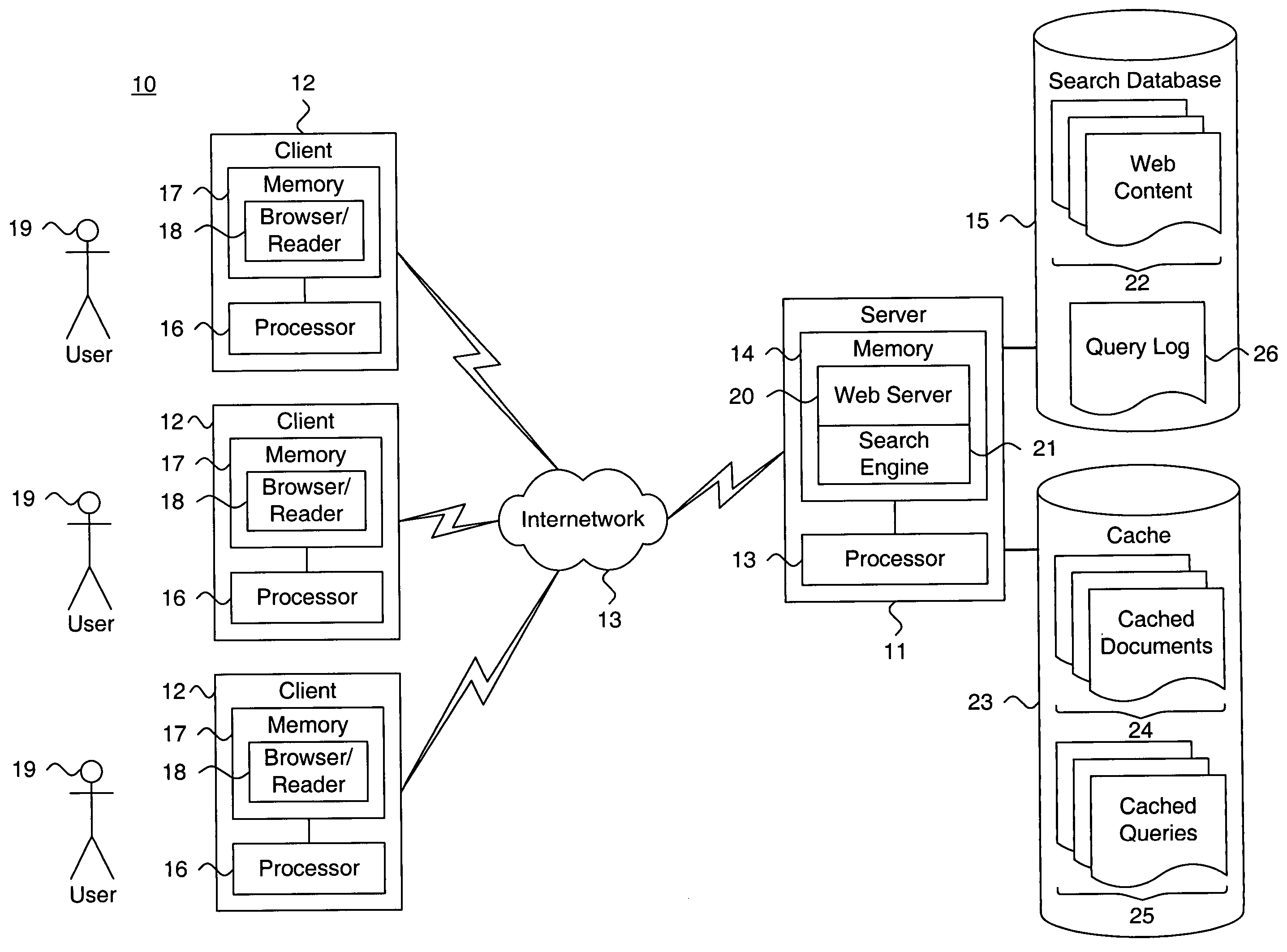
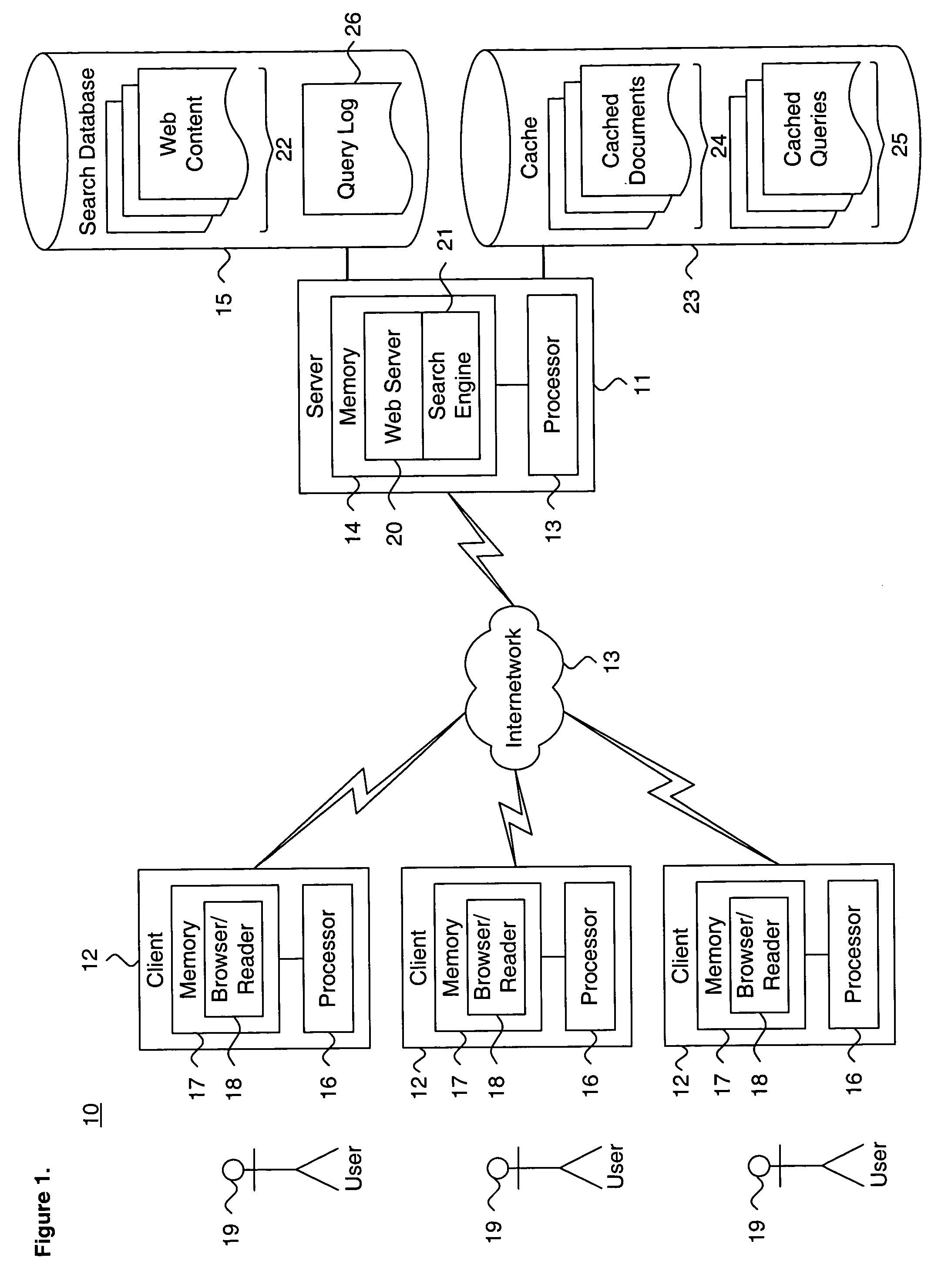
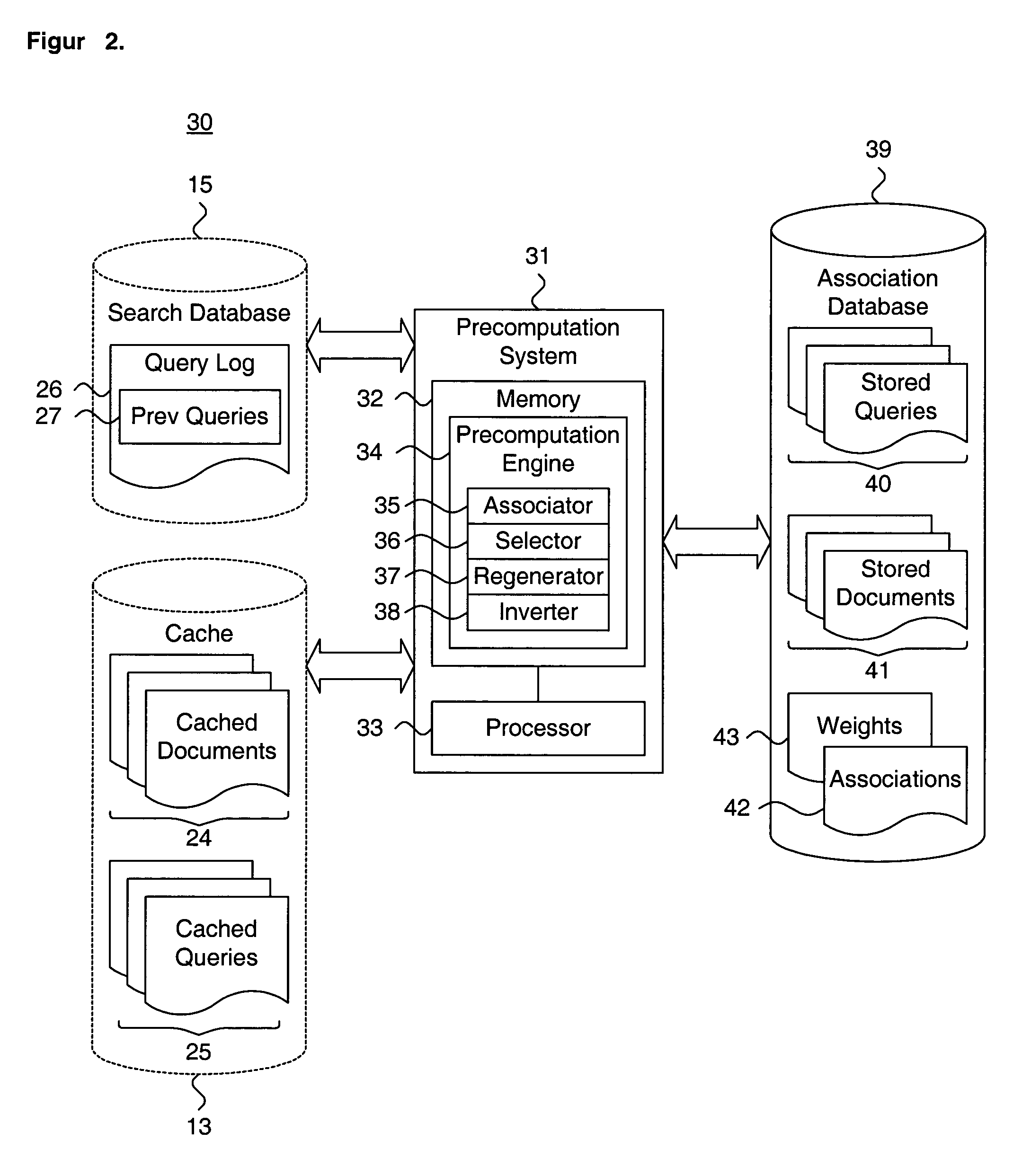
System and method for providing search query refinements
A system and method for providing search query refinements are presented. A stored query and a stored document are associated as a logical pairing. A weight is assigned to the logical pairing. The search query is issued and a set of search documents is produced. At least one search document is matched to at least one stored document. The stored query and the assigned weight associated with the matching at least one stored document are retrieved. At least one cluster is formed based on the stored query and the assigned weight associated with the matching at least one stored document. The stored query associated with the matching at least one stored document are scored for the at least one cluster relative to at least one other cluster. At least one such scored search query is suggested as a set of query refinements.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Management of multiple connections to a security token access device
ActiveUS20080016537A1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionUser devicePairing
A security token access device, a user device such as a computing device or communications device, and a method for managing multiple connections between multiple user devices and the access device. The access device maintains connection information, including security information, for each user device securely paired with the access device. Each time a new user device is paired with the access device, the access device transmits a notification to the user devices already paired to the user device. A user may provide instructions to the access device to terminate a pairing with one of the user devices by overwriting at least a portion of the connection information associated with the designated user device. A user device may further request a listing of all user devices currently paired with the access device.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
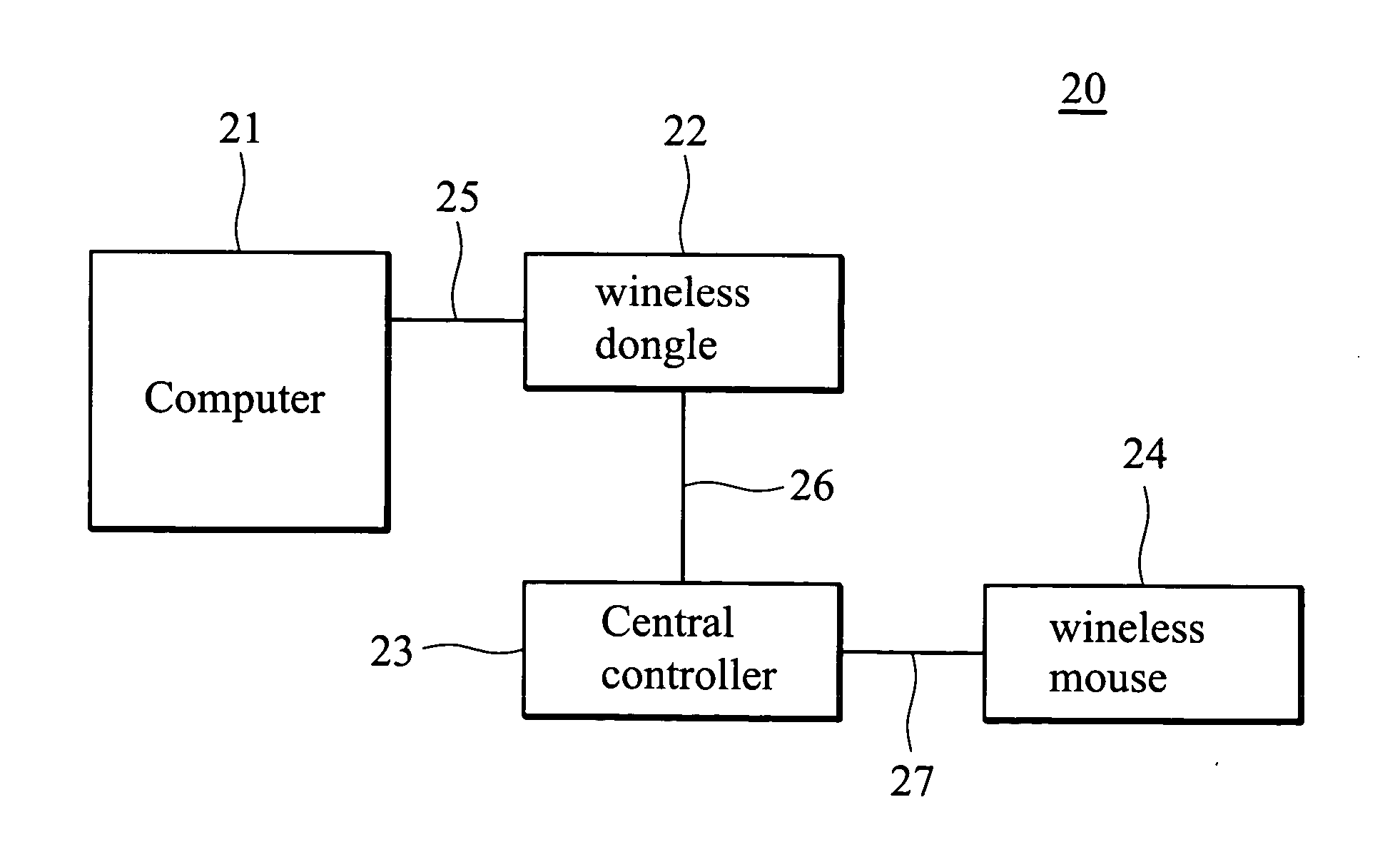
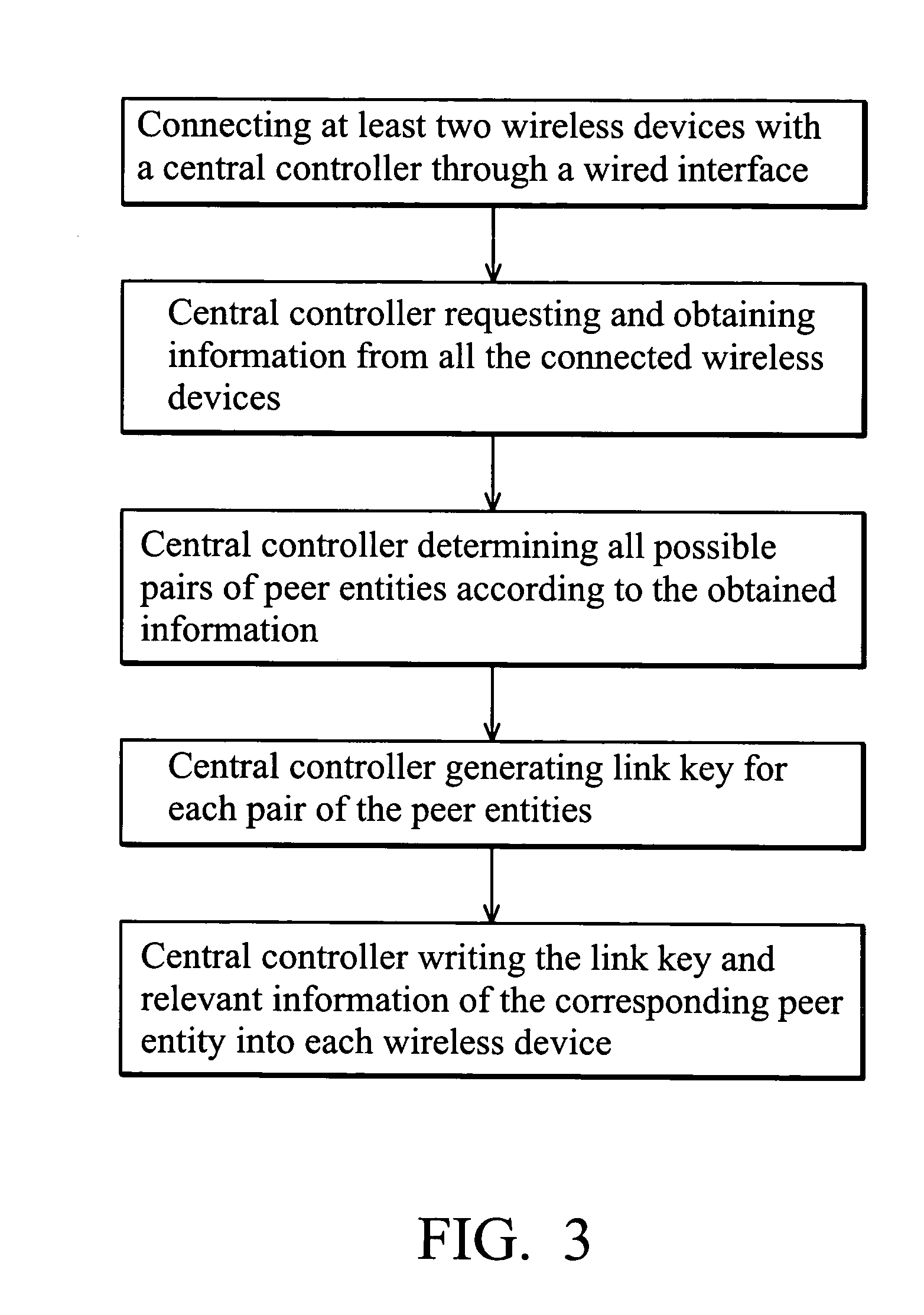
Method and system for wireless pairing
ActiveUS20050152294A1Data switching by path configurationSubstation equipmentDevice typeRelevant information
A method and system for wireless pairing procedure through a wired interface. The wireless pairing system of the present invention comprises at least two wireless devices and a central controller. First, the wireless devices are connected to the central controller through a wired interface for pairing. The central controller then requests relevant information such as device address, device type, and connection mode of each wireless device. The central controller determines all possible pairs of peer entities according to the relevant information of the wireless devices, and generates a dedicated link key for each pair for successful pairing. Finally, the central controller writes the link key and the relevant information of the corresponding peer entity into each wireless device.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
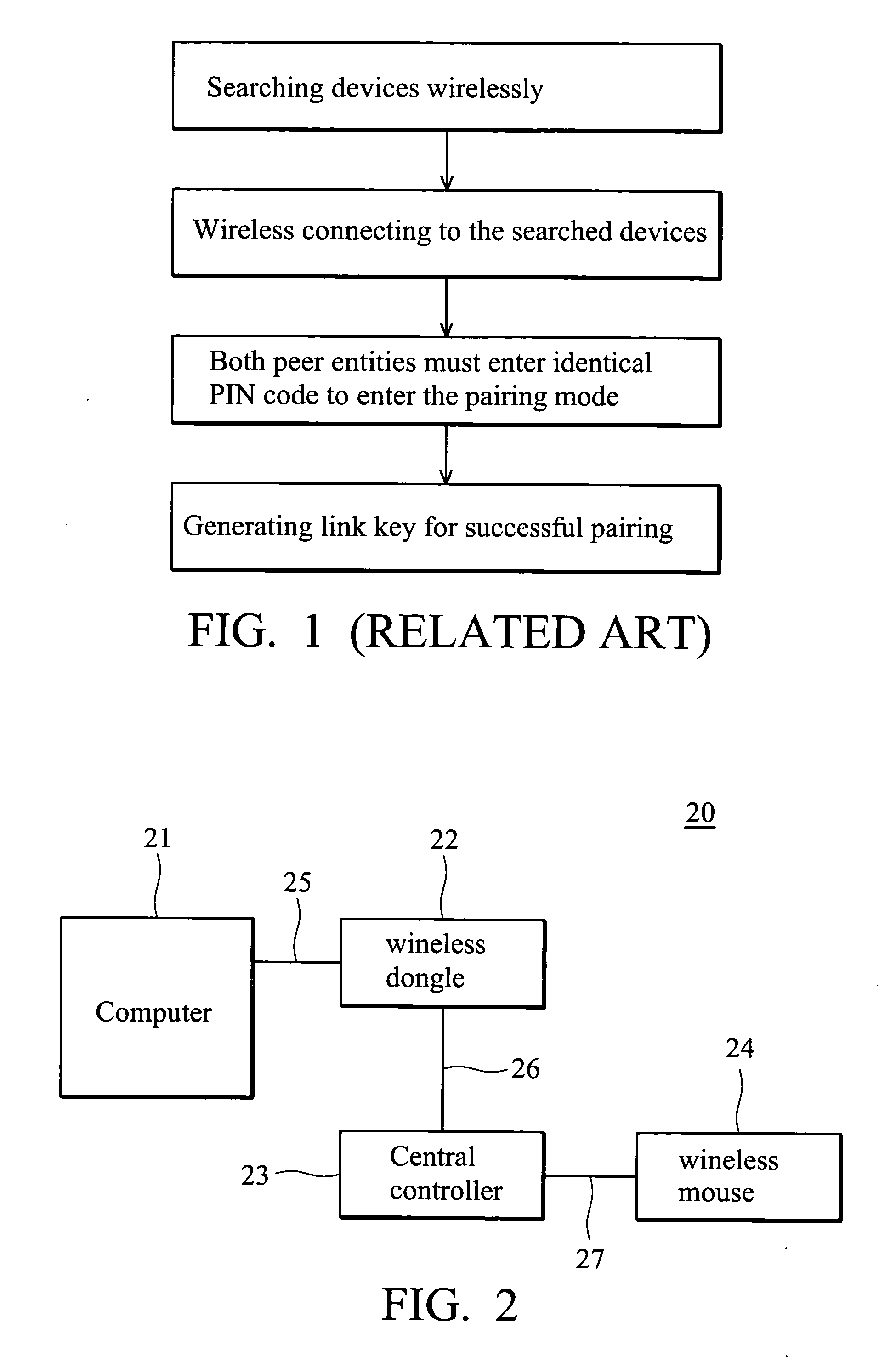
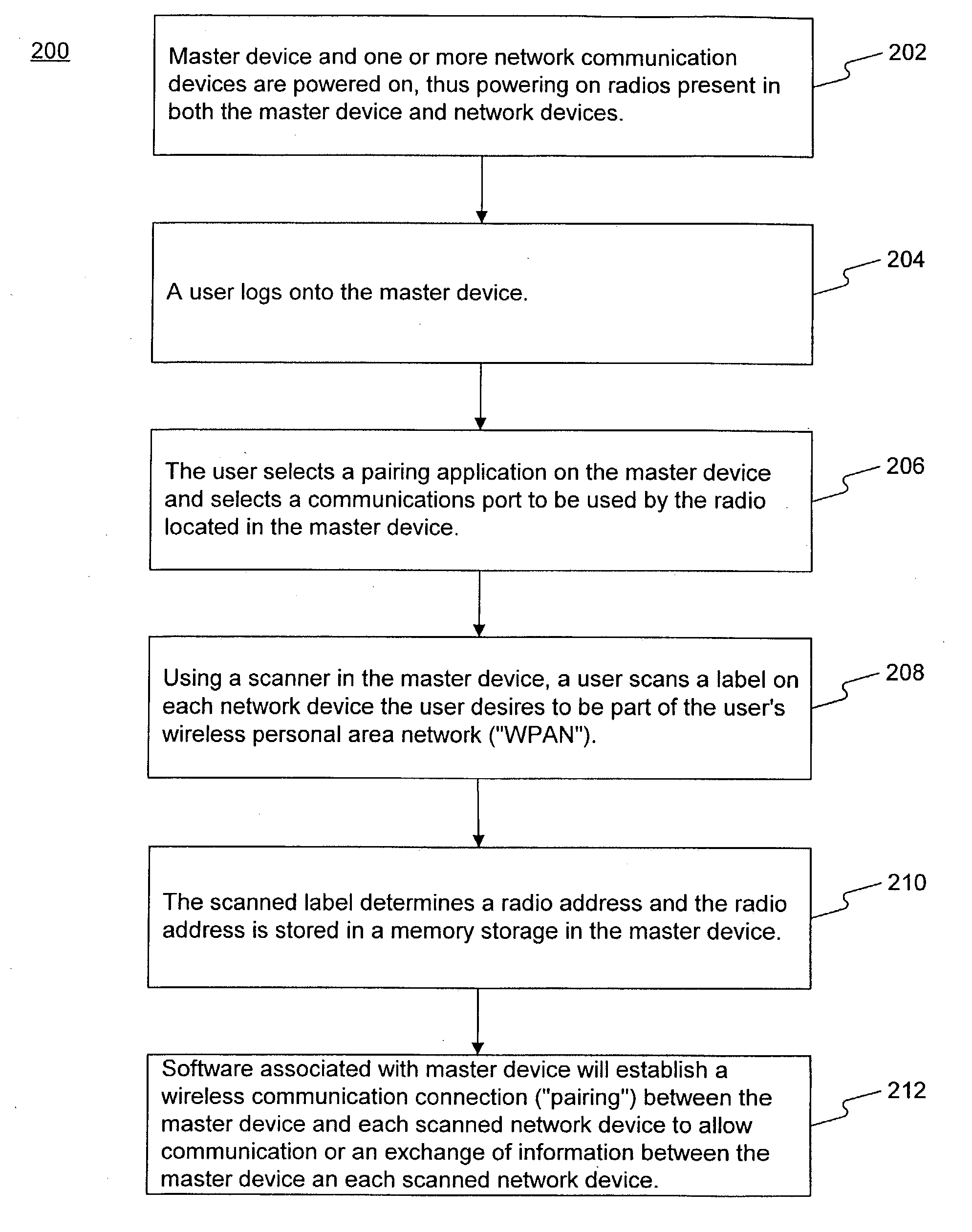
System and method for electronically pairing devices
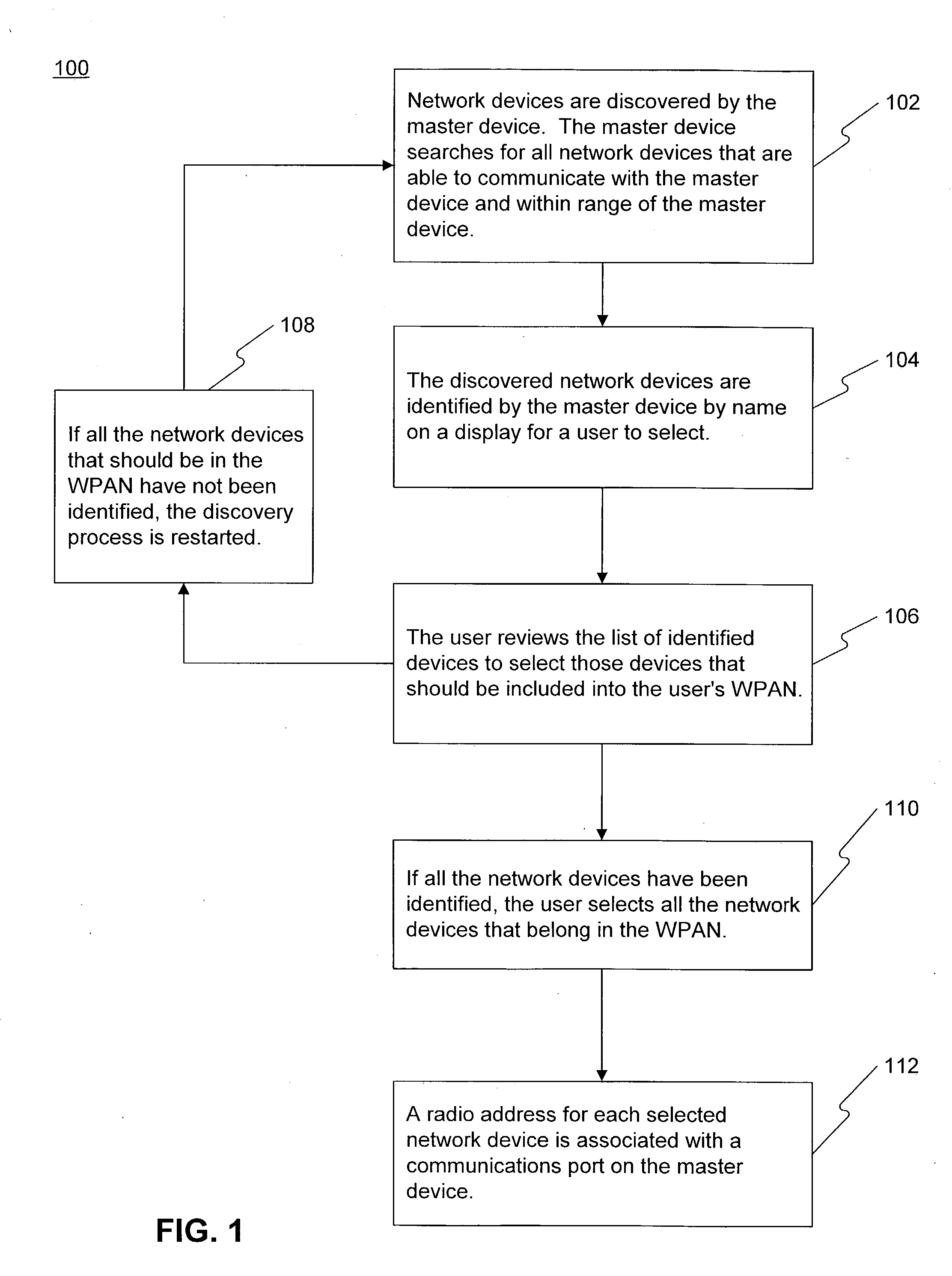
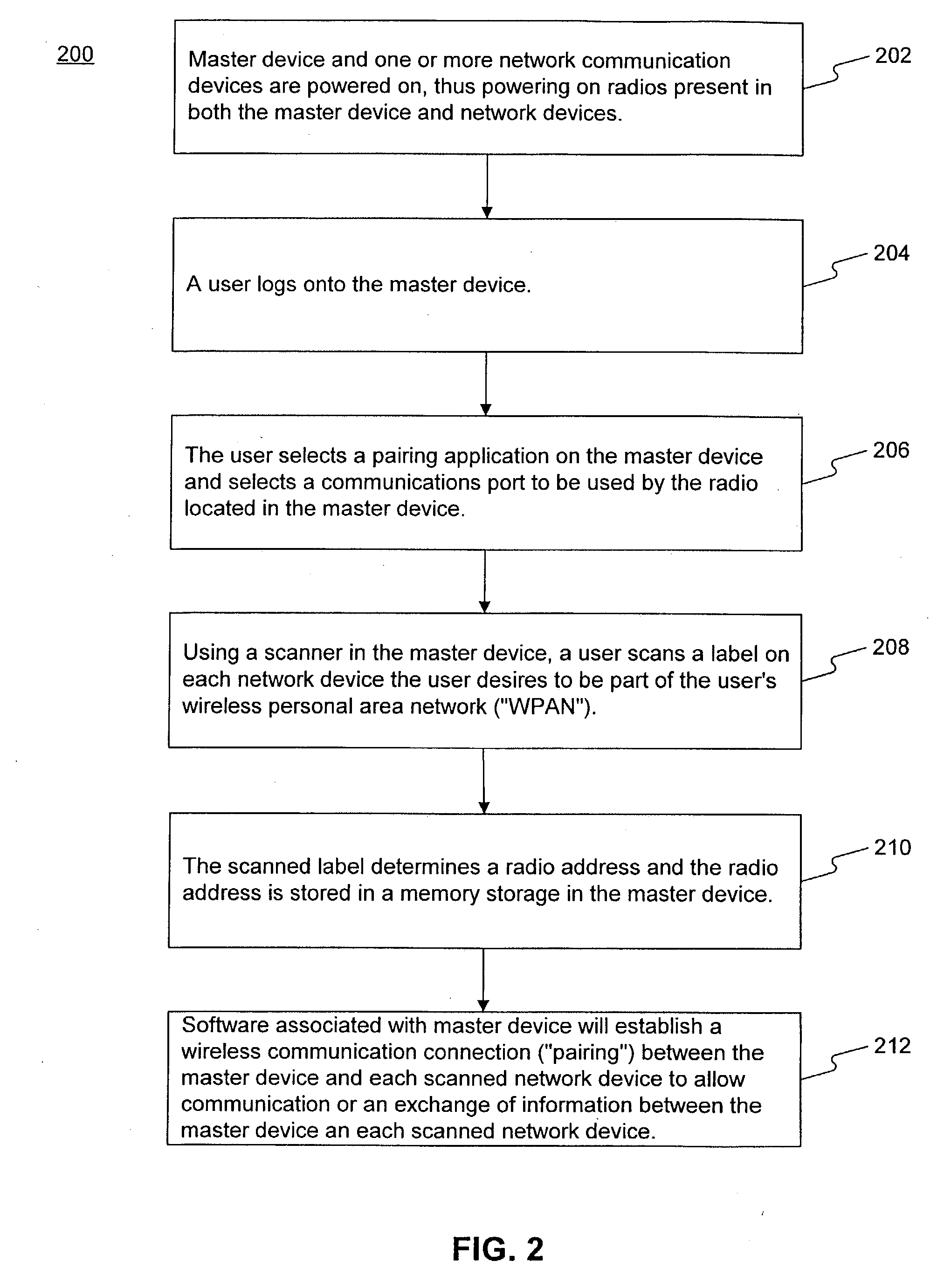
A system and method for pairing wireless communication devices on a wireless personal area network allows communication between wireless communication devices and a master devices through the use of radio addresses. A barcode associated with each wireless communication is scanned by the master device. The scanned barcode is converted to a radio address associated with the scanned barcode. Software associated with the master device allows communication between the master device and the network devices through the use the radio addresses. The system of and method for pairing network devices on a wireless personal area network allows quicker and more efficient pairing of network devices when multiple wireless personal area networks are present in a confined space.
Owner:FEDERAL EXPRESS CORP US
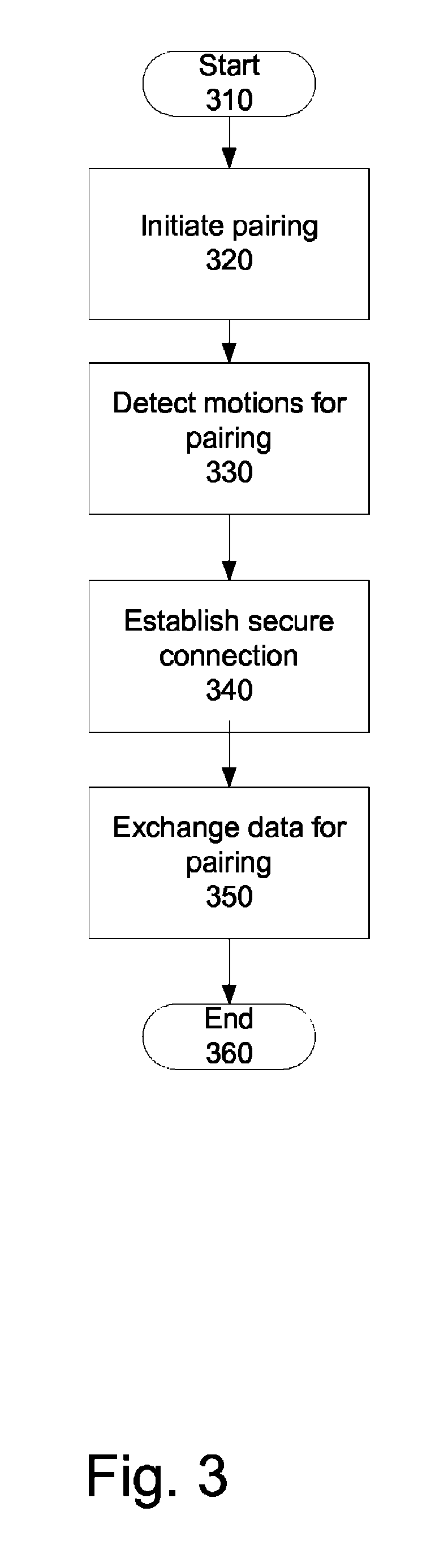
Method and apparatus to enable pairing of devices
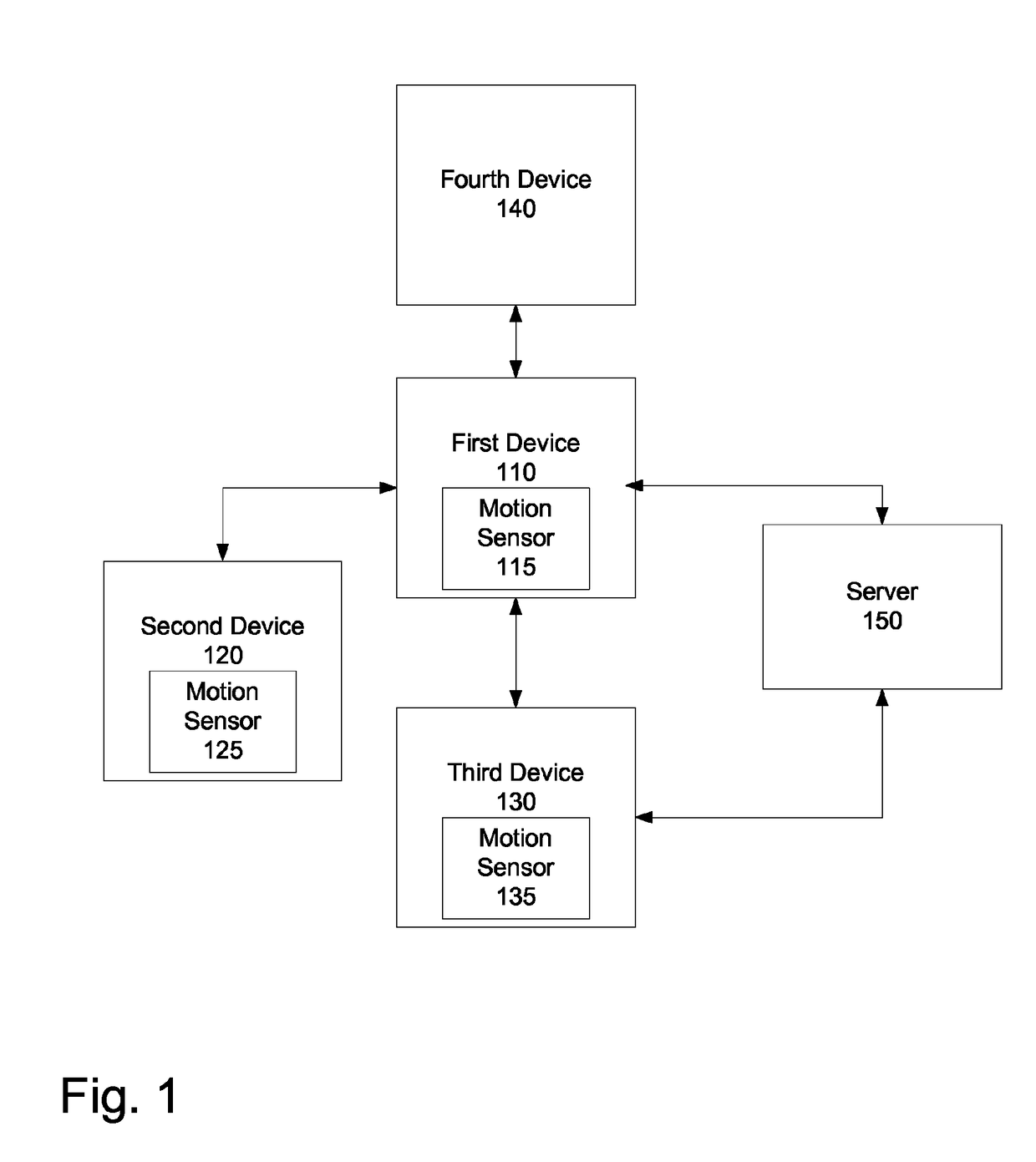
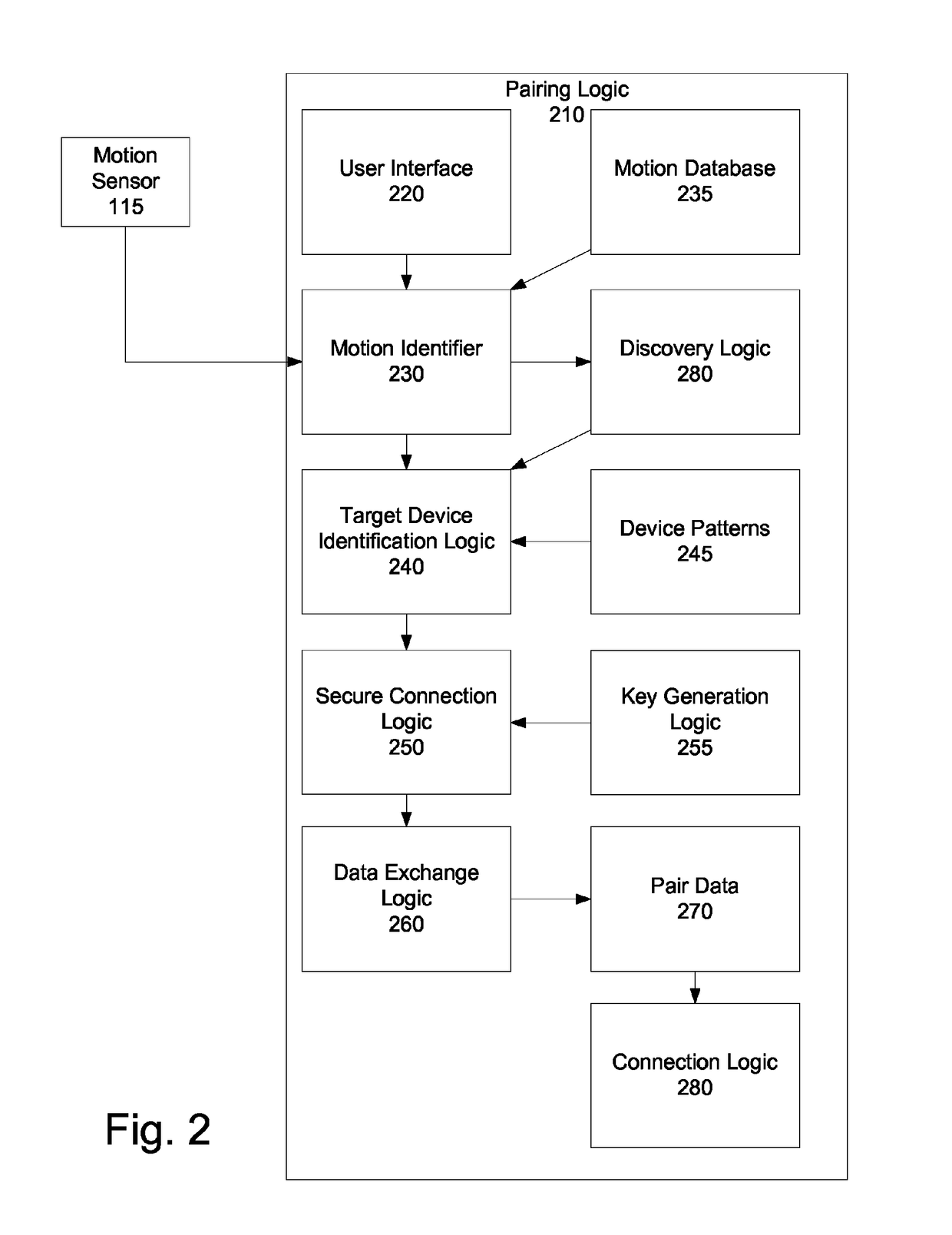
A method and apparatus to provide easier pairing based on motion data is described. The method of pairing two devices comprises receiving a signal to enter into pairing mode, and detecting a motion indicating a pairing. The method further comprises establishing a secure connection with another device for pairing, the secure connection established based on the motion, and exchanging data for pairing.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Air purifier based on filter Anti-counterfeiting identification
InactiveUS20180161716A1Guarantee product qualityPrevent counterfeitingDispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingAir purifiersPairing
Disclosed is an air purifier based on filter anti-counterfeiting identification, comprising a purifier body (1) in which control circuitry and a purifying chamber are provided; a filter (2) is arranged in the purifying chamber; the filters (2) are paired and coupled with the purifier body (1) via an identification unit; the identification unit comprises an identification chip configured on the filter (2) and an identifier configured on the purifier body (1); the identifier is connected with the control circuitry; the control circuitry is powered on and starts to operate until the pairing between the identification chip and the identifier succeeds. The identification process can identify multiple objects without manual intervention. Moreover, it responds quickly and no mechanical malfunction will happen. Thus, the air purifier can operate under harsh environment and serve for a long time. In this manner, counterfeits can be effectively prevented and quality of products can be guaranteed.
Owner:SHUNDE APOLLO AIR CLEANER
Agent satisfaction data for call routing based on pattern matching algorithm
ActiveUS8781106B2Reducing attritionLow costManual exchangesAutomatic exchangesPattern matchingContact center
Methods and systems are disclosed for routing callers to agents in a contact center with an intelligent routing system. An exemplary method includes routing callers to agents based on a pattern matching algorithm utilizing caller data and agent data, where the agent data includes agent satisfaction data from past agent-caller pairings. The agent satisfaction data may be obtained via surveys of the agents regarding their satisfaction with past agent-caller contacts. The agent satisfaction data may be used by the pattern matching algorithm in an attempt to increase agent satisfaction for future calls, thereby potentially reducing attrition of agents and cost to the call center, increasing morale of the agents, and so on. The agent satisfaction data and output from past agent-caller pairings may be weighted by the contact center against other agent data and caller data for a desired mixing of output variables.
Owner:AFINITI LTD
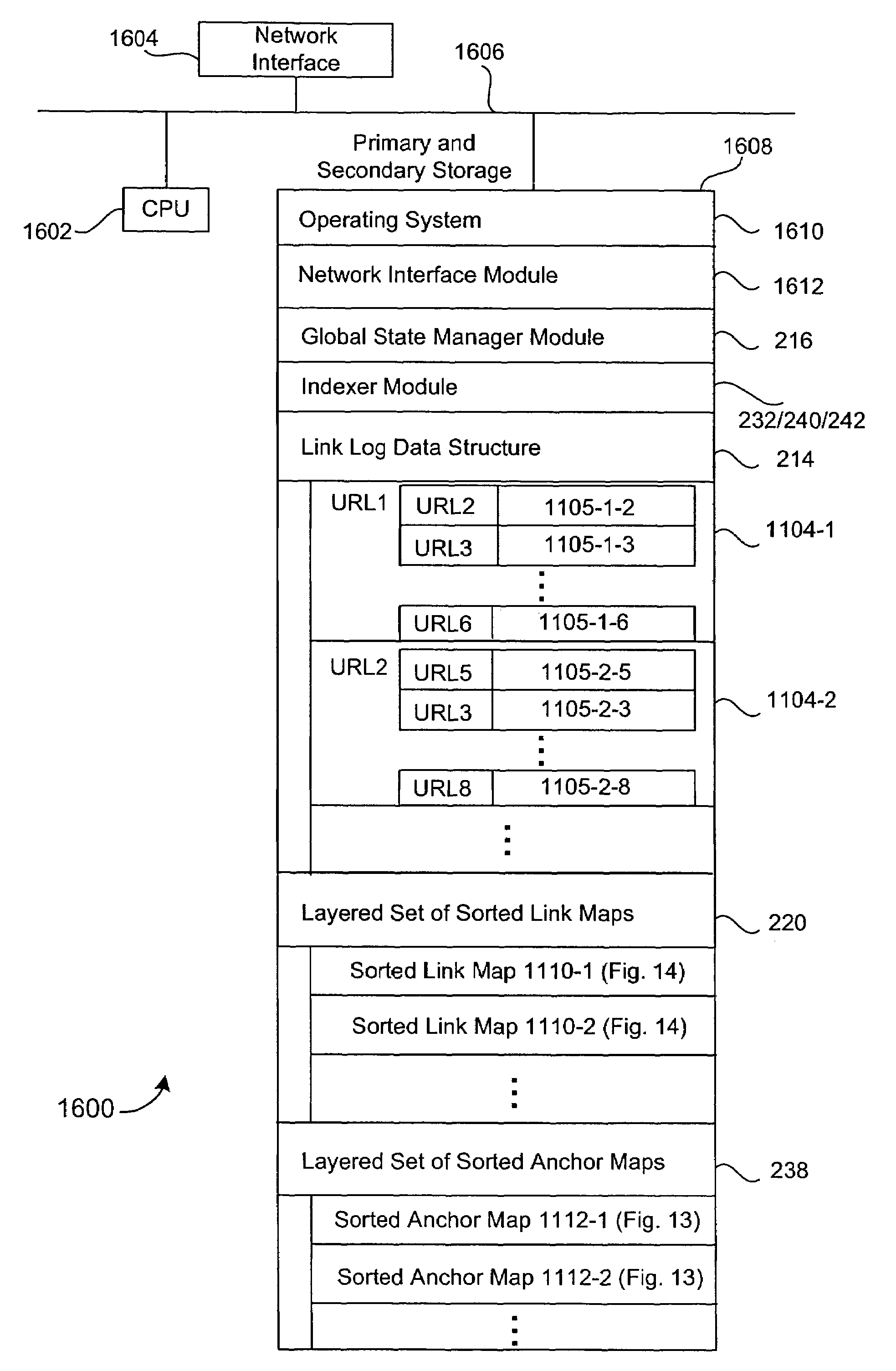
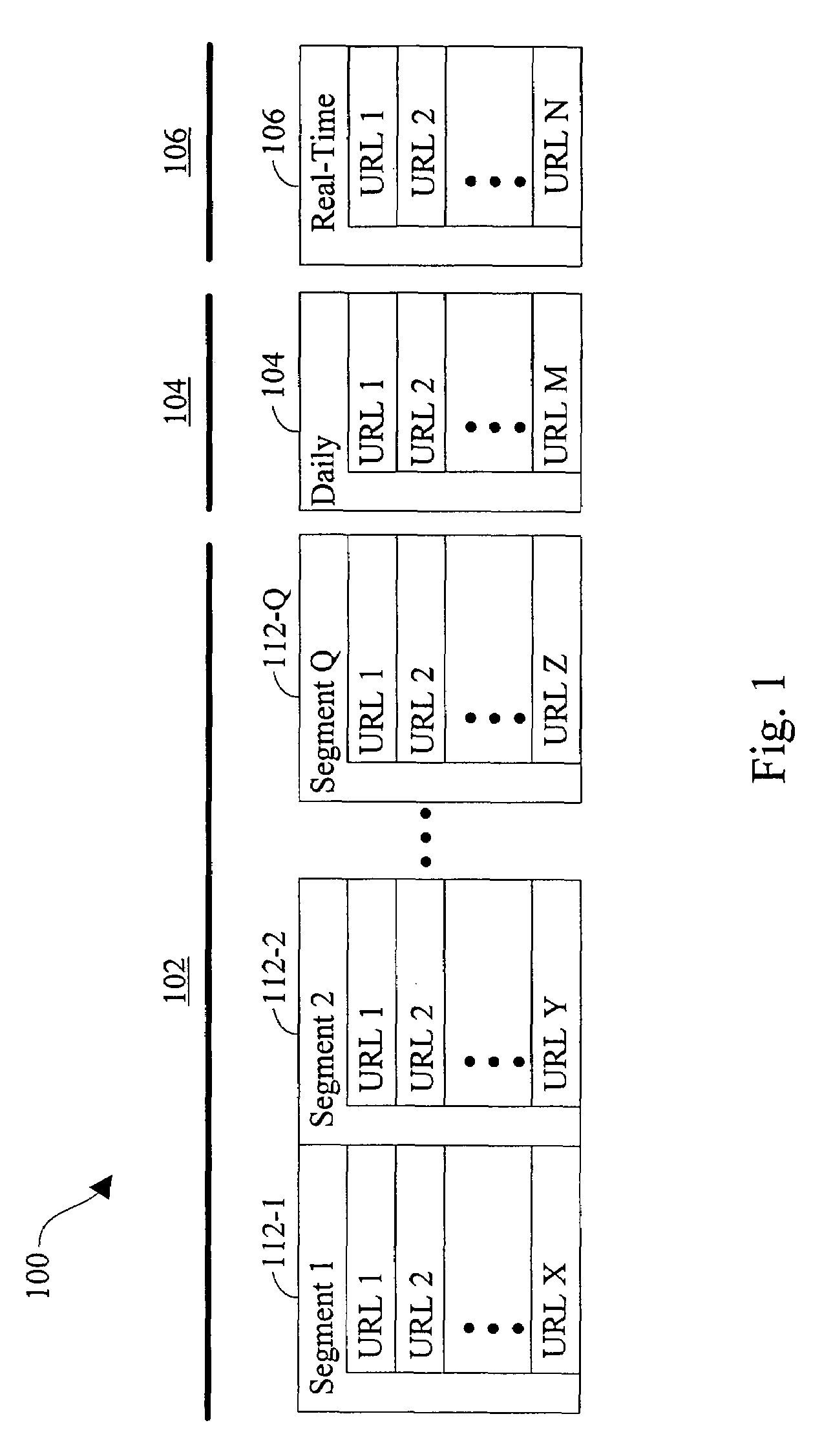
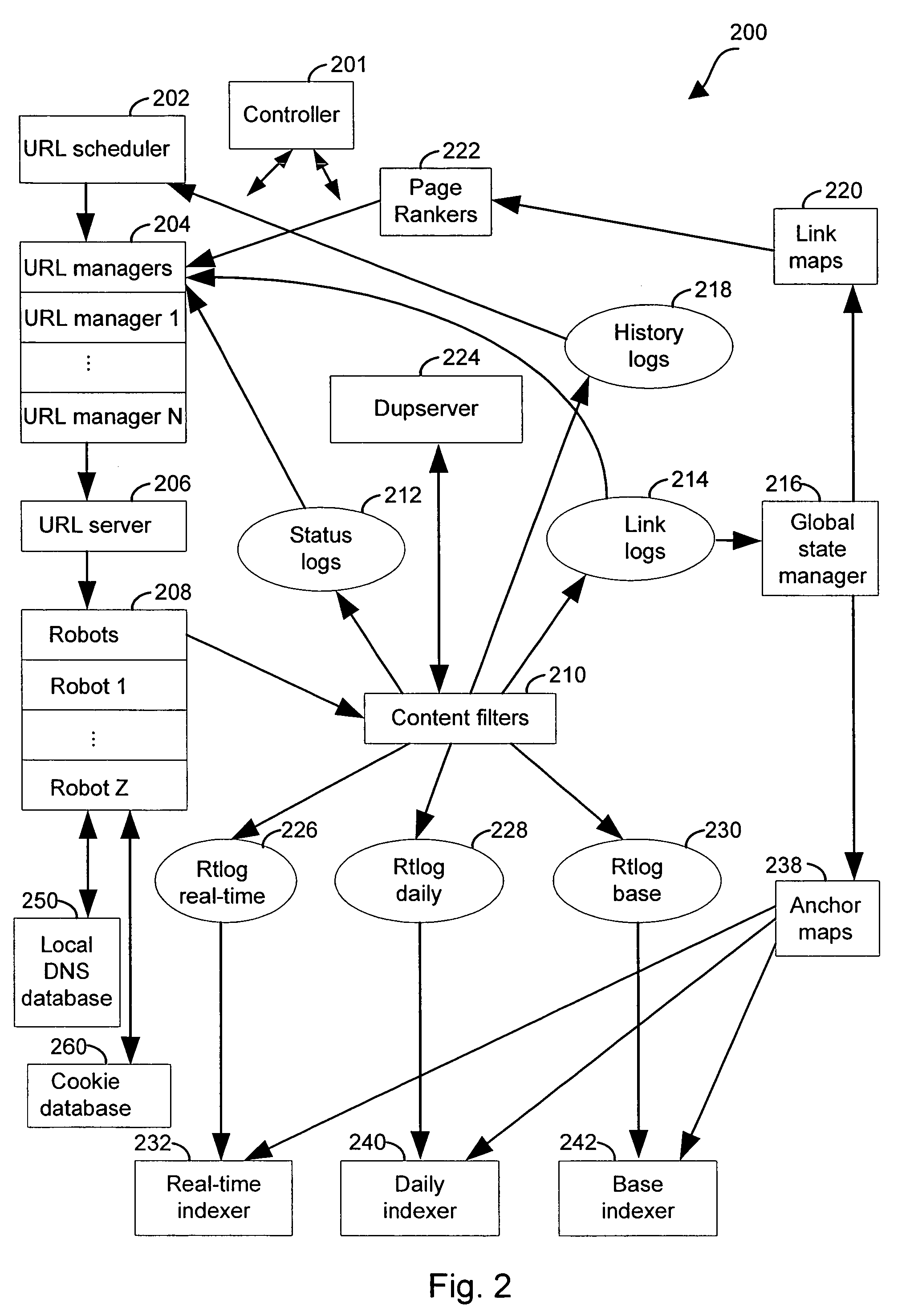
Anchor tag indexing in a web crawler system
ActiveUS7308643B1Facilitates indexing informationEffective and efficient text-based indexing systemWeb data indexingDigital computer detailsDocument IdentifierDocument preparation
Provided is a method and system for indexing documents in a collection of linked documents. A link log, including one or more pairings of source documents and target documents is accessed. A sorted anchor map, containing one or more target document to source document pairings, is generated. The pairings in the sorted anchor map are ordered based on target document identifiers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Secure wireless link between two devices using probes
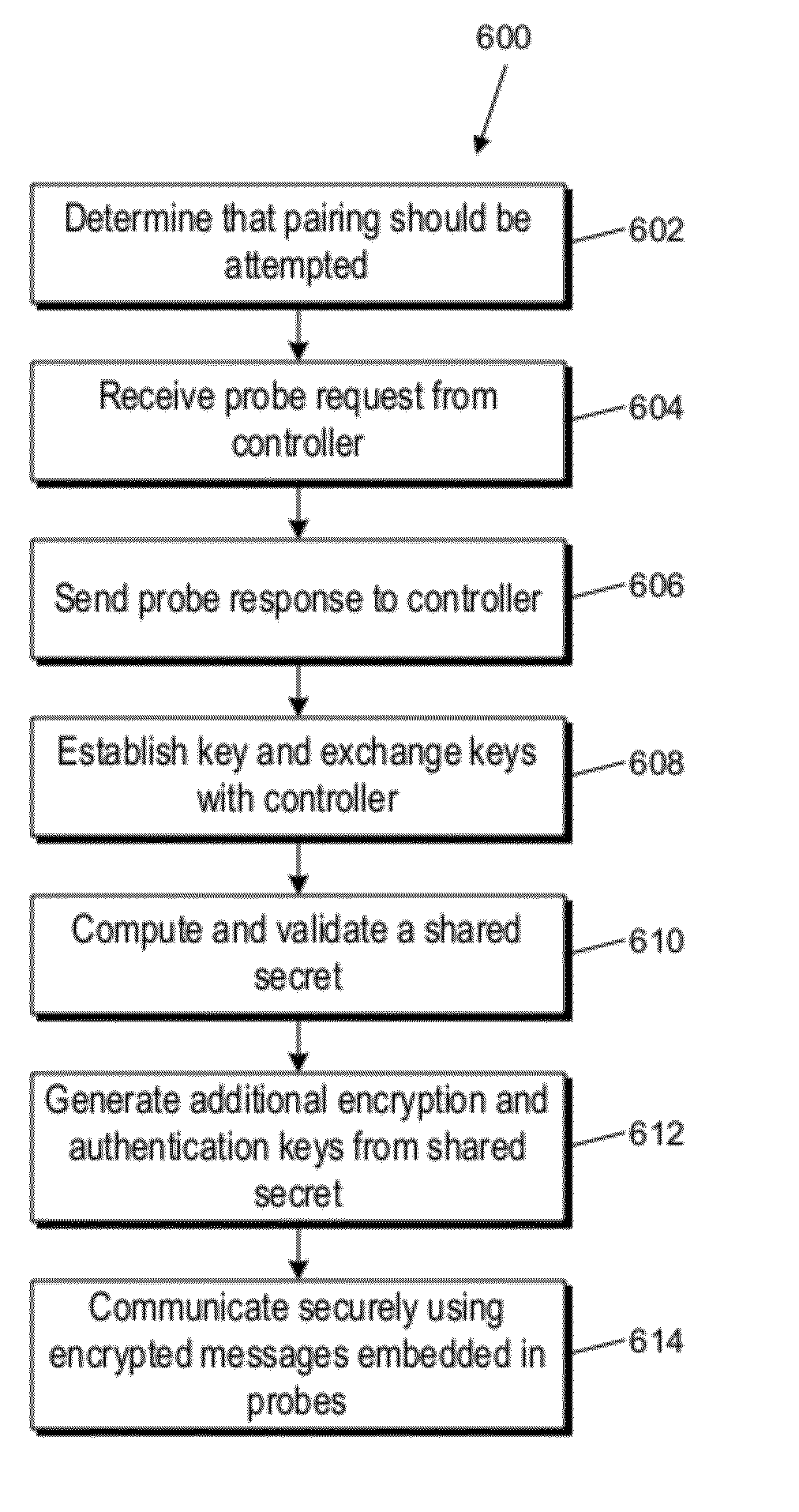
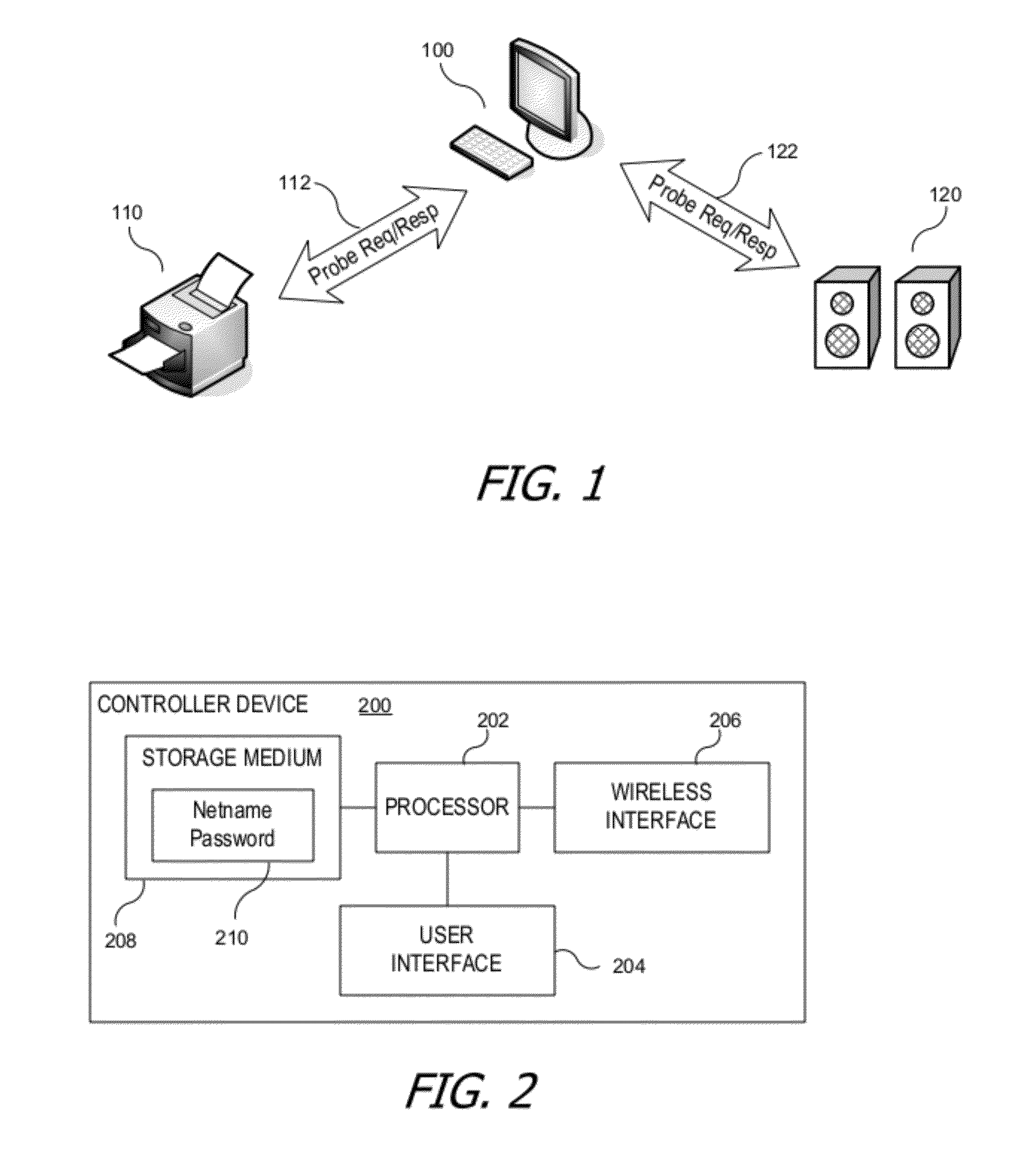
ActiveUS20120054493A1Simple interventionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
A secure wireless communication link (pairing) between two devices can be established using cleartext wireless transmissions between devices not joined to a network (“probes”). One device can broadcast a first probe indicating that it is seeking to establish a pairing. The other device can respond with a second probe, and the two devices can establish a shared secret, e.g., by exchanging further information using additional probes. Thereafter, either device can send a message to the other by encrypting the message using a cryptographic key derived from the shared secret; encrypted messages can also be sent within probes. The receiving device can extract an encrypted message from a probe and decrypt it using the cryptographic key. The encrypted message can include credentials usable by the receiving device to join a wireless network.
Owner:APPLE INC
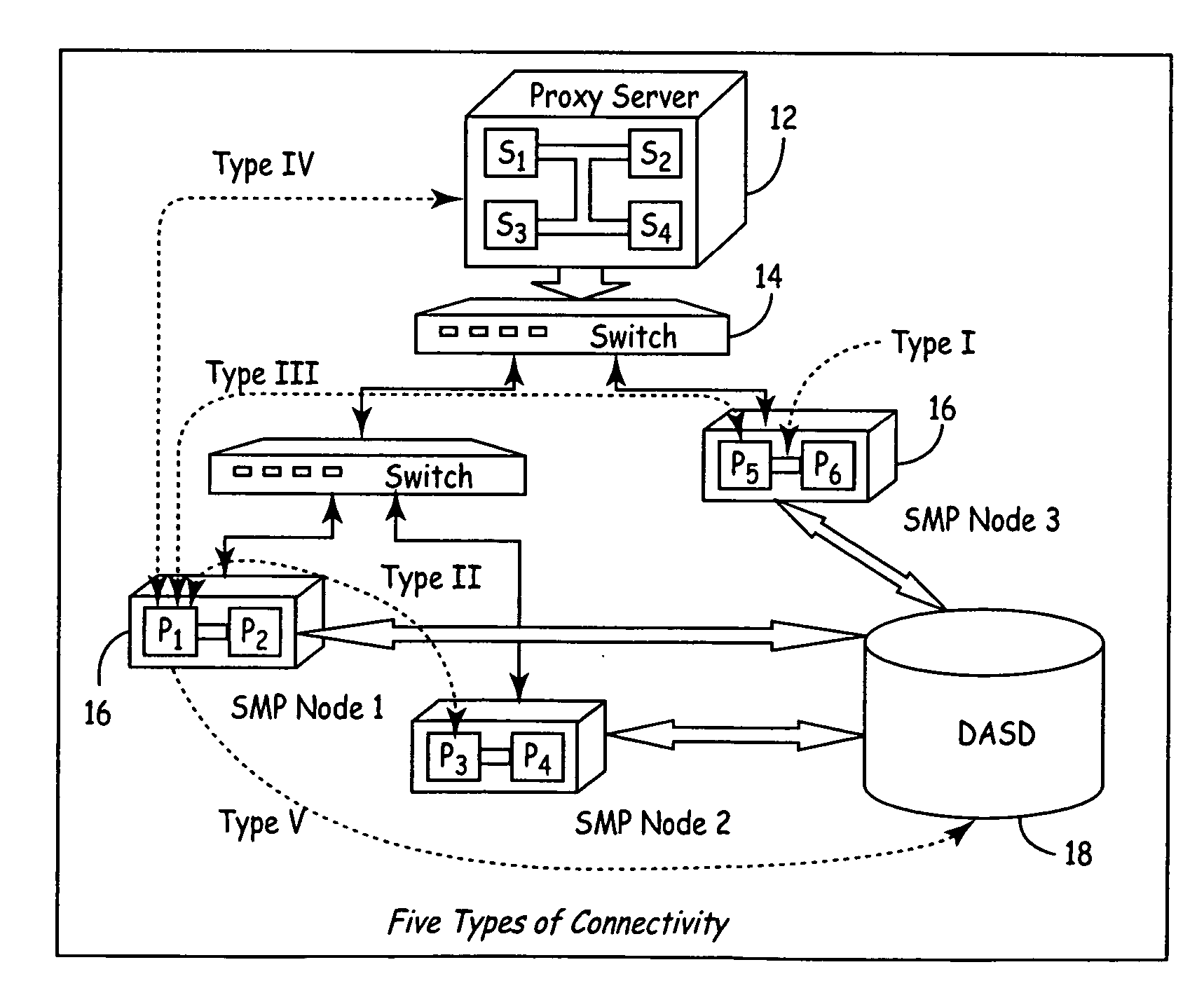
System for balance distribution of requests across multiple servers using dynamic metrics
InactiveUS20060036743A1Improve performanceMaximizing numberResource allocationHardware monitoringDynamic metricsClient-side
Owner:ASPENGINES +1
Playing cards with separable components
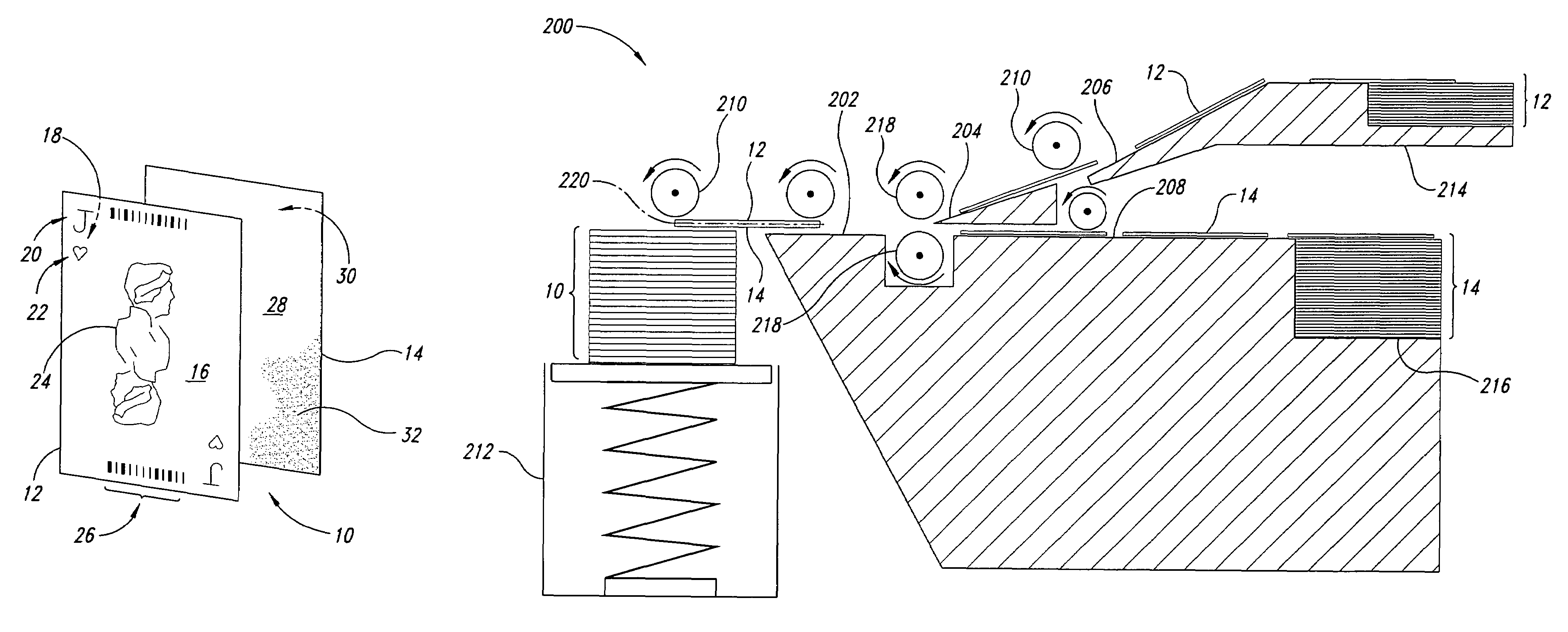
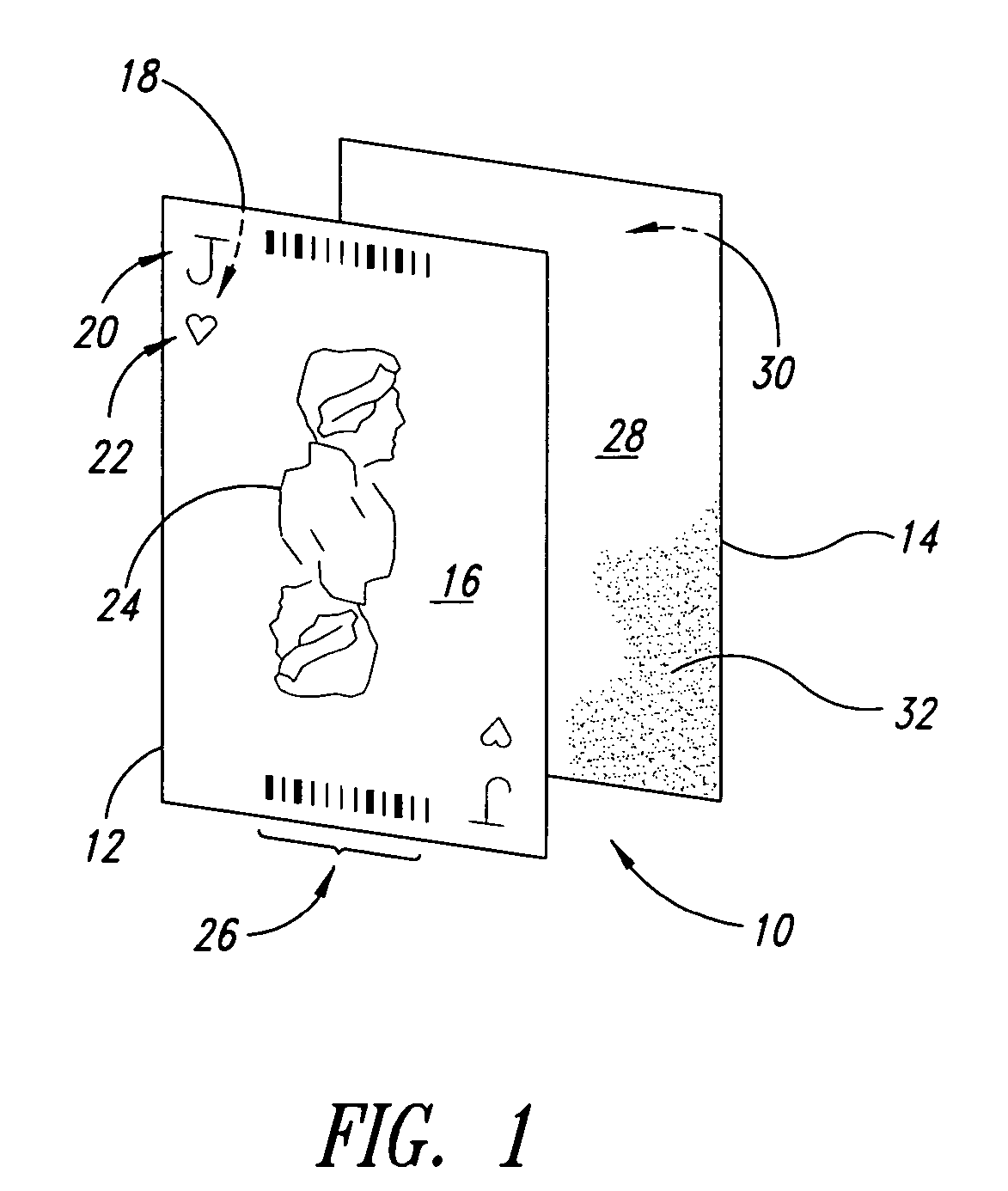
The present discussion generally describes separable playing cards that can be reassembled, methods of separating and reassembling the playing cards, and methods of using the playing cards in a gaming environment. The playing cards are combined from constituent components, which are a face and a back. The face can have a suit marking, a rank marking, or both. The combination of any given face and back represents a pairing. This pairing can be changed or reconfigured by separating the face from the back and reordering at least the faces or the backs. The reordered faces and backs can be assembled back into respective playing cards and used in a subsequent card game. The reordering can be done manually, mechanically, or computationally generated. The playing cards can include unique identifiers that can be read by a machine and used to verify that a sufficient number of the original pairings have been altered.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
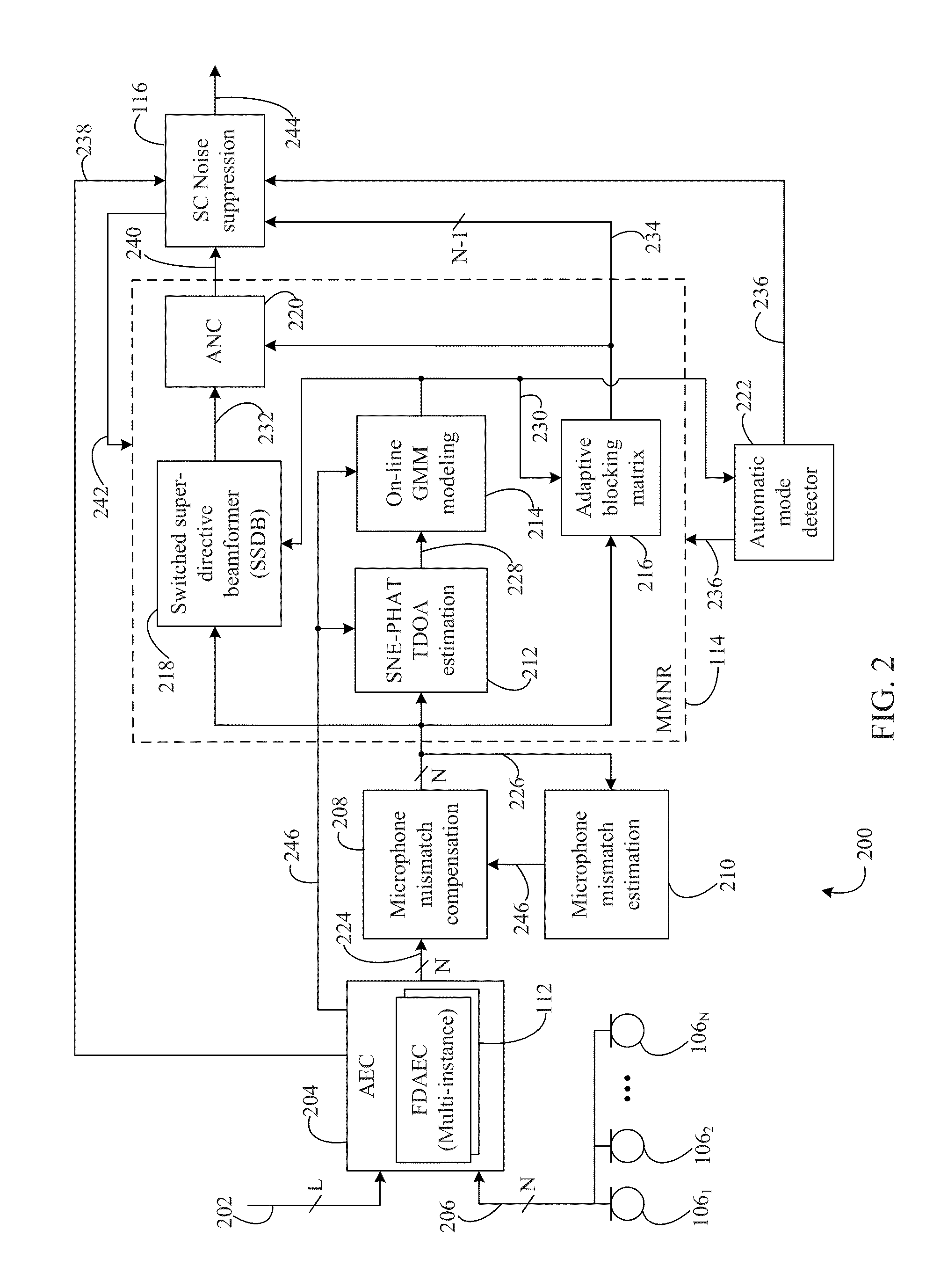
Multi-microphone source tracking and noise suppression
Methods, systems, and apparatuses are described for improved multi-microphone source tracking and noise suppression. In multi-microphone devices and systems, frequency domain acoustic echo cancellation is performed on each microphone input, and microphone levels and sensitivity are normalized. Methods, systems, and apparatuses are also described for improved acoustic scene analysis and source tracking using steered null error transforms, on-line adaptive acoustic scene modeling, and speaker-dependent information. Switched super-directive beamforming reinforces desired audio sources and closed-form blocking matrices suppress desired audio sources based on spatial information derived from microphone pairings. Underlying statistics are tracked and used to updated filters and models. Automatic detection of single-user and multi-user scenarios, and single-channel suppression using spatial information, non-spatial information, and residual echo are also described.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Mobile terminal and application controlling method thereof
A mobile terminal is presented. The mobile terminal includes a controller configured to identify a sharing terminal within a defined distance of the mobile terminal and to pair the sharing terminal with the mobile terminal, the sharing terminal and the mobile terminal configured to share a first application with each other after the pairing, and a display unit configured to display an indicator for distinguishing the application that is shared between the mobile terminal and the sharing terminal, wherein the indicator identifies the sharing terminal.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
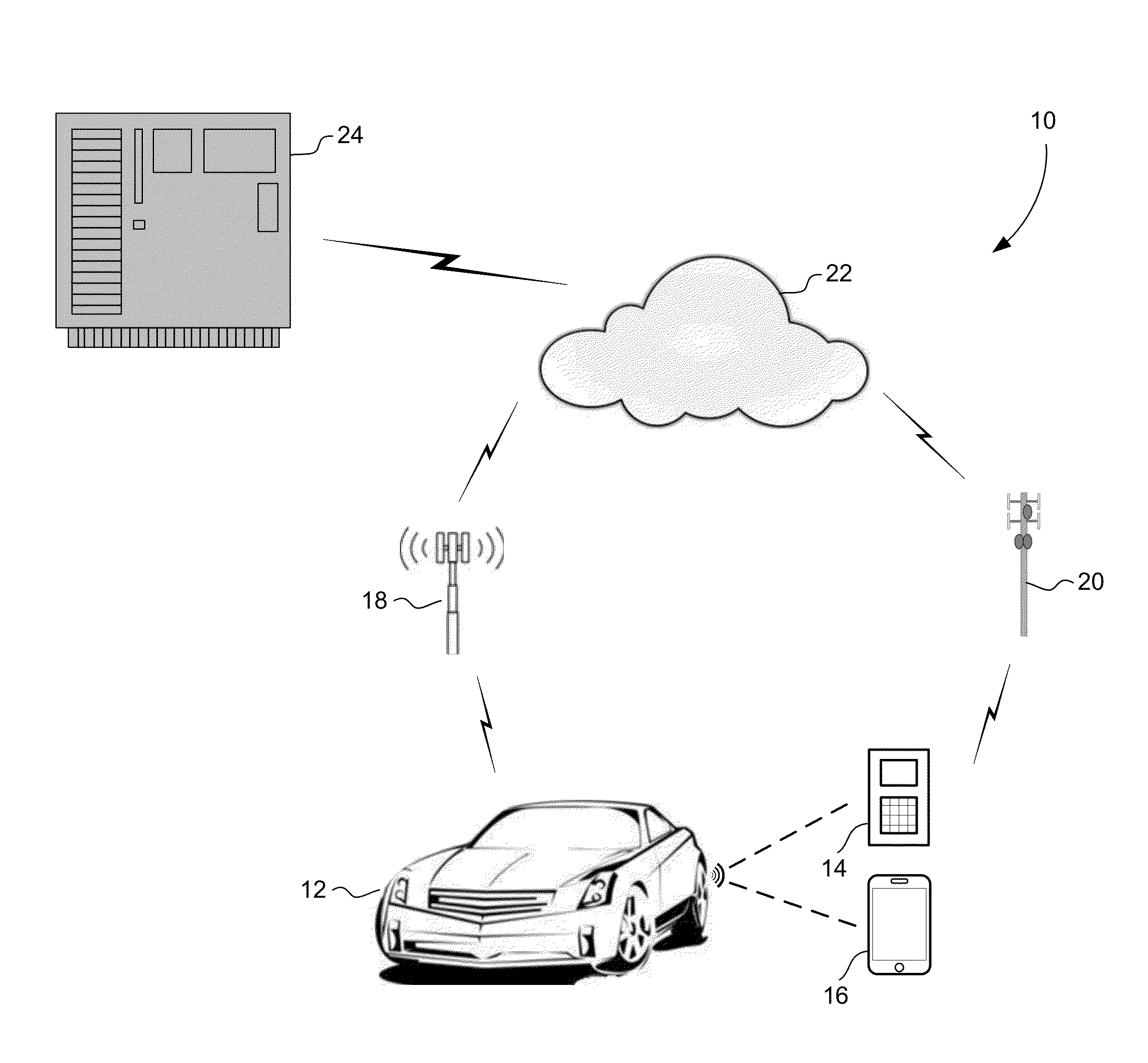
Method and apparatus for secure pairing of mobile devices with vehicles using telematics system
A method for establishing secure wireless communications between a mobile device and a vehicle, where a user is not required to enter a password, but instead the telematics system is used to bootstrap the trust between the mobile device and the vehicle. The user initiates the process by pressing a button on the mobile device to request pairing. The vehicle uses its secure OnStar cellular communication link to verify the mobile device with the OnStar server, which generates and sends a session key to the vehicle via the vehicle-OnStar cellular connection, and also sends the session key to the mobile device via the device's own cellular connection. The session key serves as a shared secret, such that the vehicle can issue a secrecy challenge to the mobile device. When the mobile device responds appropriately, a trusted wireless communications link can be established between the mobile device and the vehicle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for managing multiple smart card sessions
ActiveUS20070251997A1Memory record carrier reading problemsRecord carriers used with machinesSmart cardCard reader
A system and method is provided for managing multiple smart card sessions with multiple communications or computing devices in association with a single smart card reader. A wireless smart card reader is provided for communicating with a plurality of devices requiring smart card functionality in a number of smart card sessions, in which each smart card session is addressed with an identifier identifying a single device. The smart card session is secured by a wireless connection pairing and by a secure pairing, such that each connection between the smart card reader and a device is secured against all other devices in communication with the smart card reader using a master connection key, which is unique for each device.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Antibacterial/anti-infalmmatory composition and method
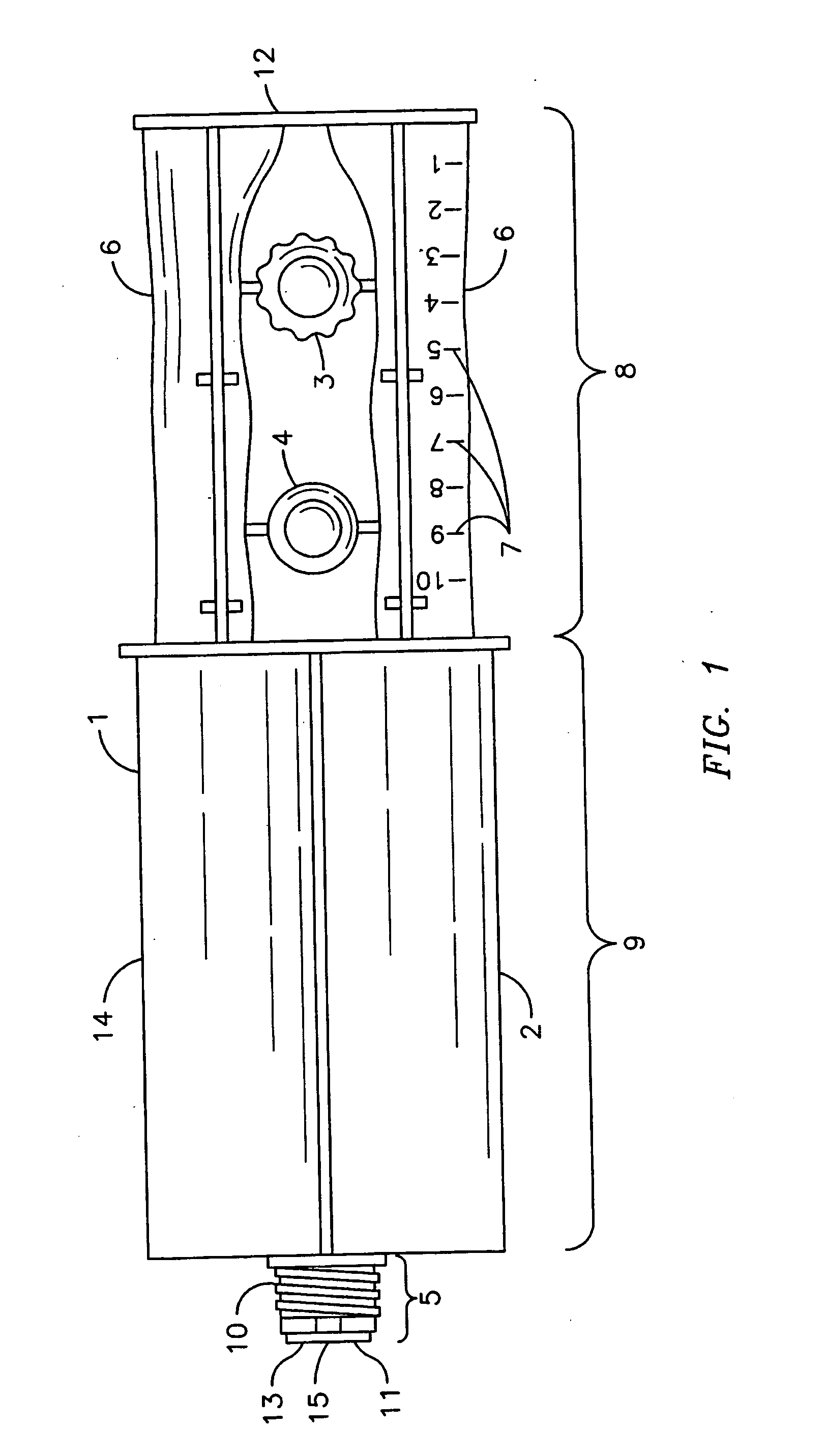
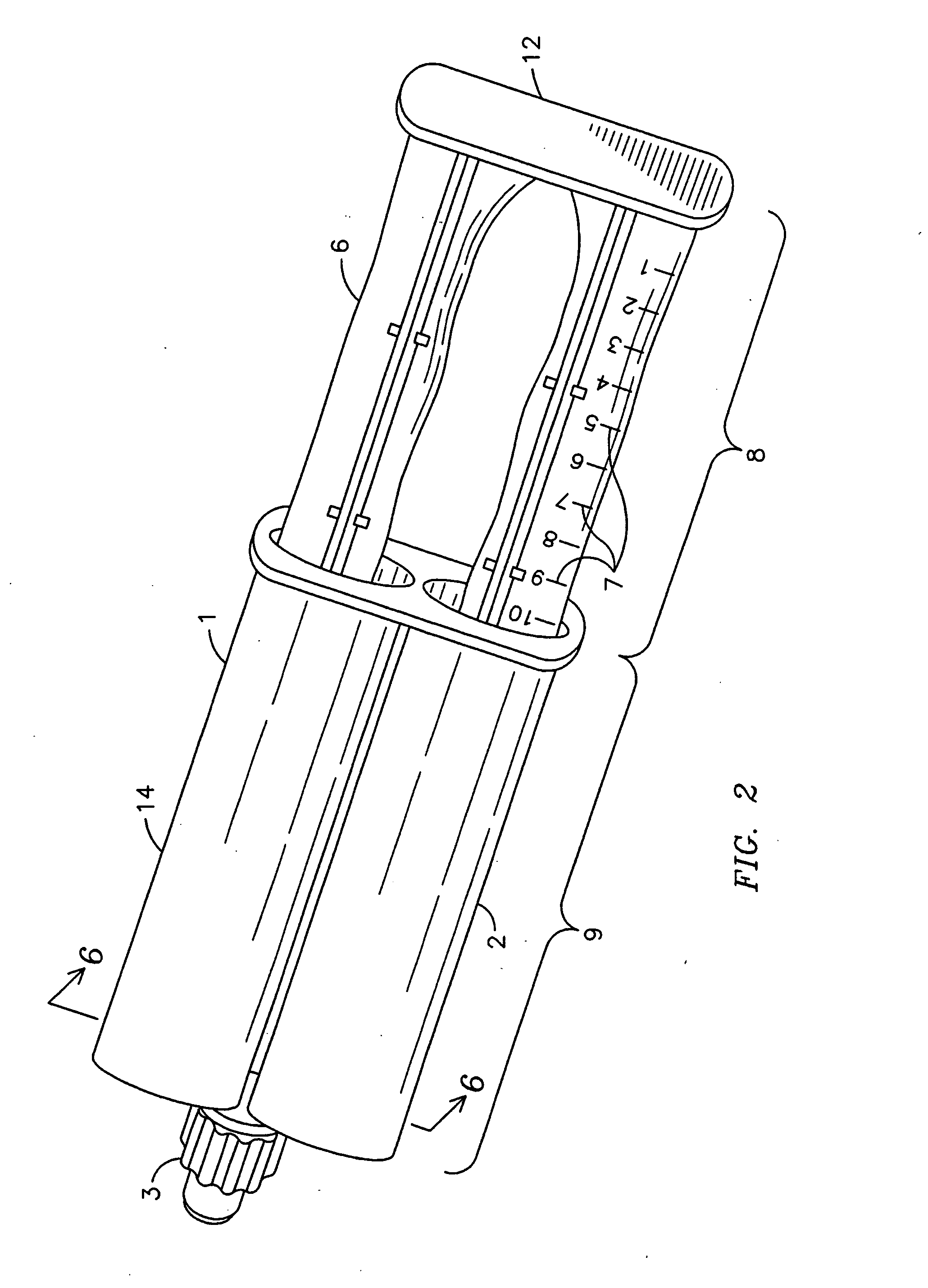
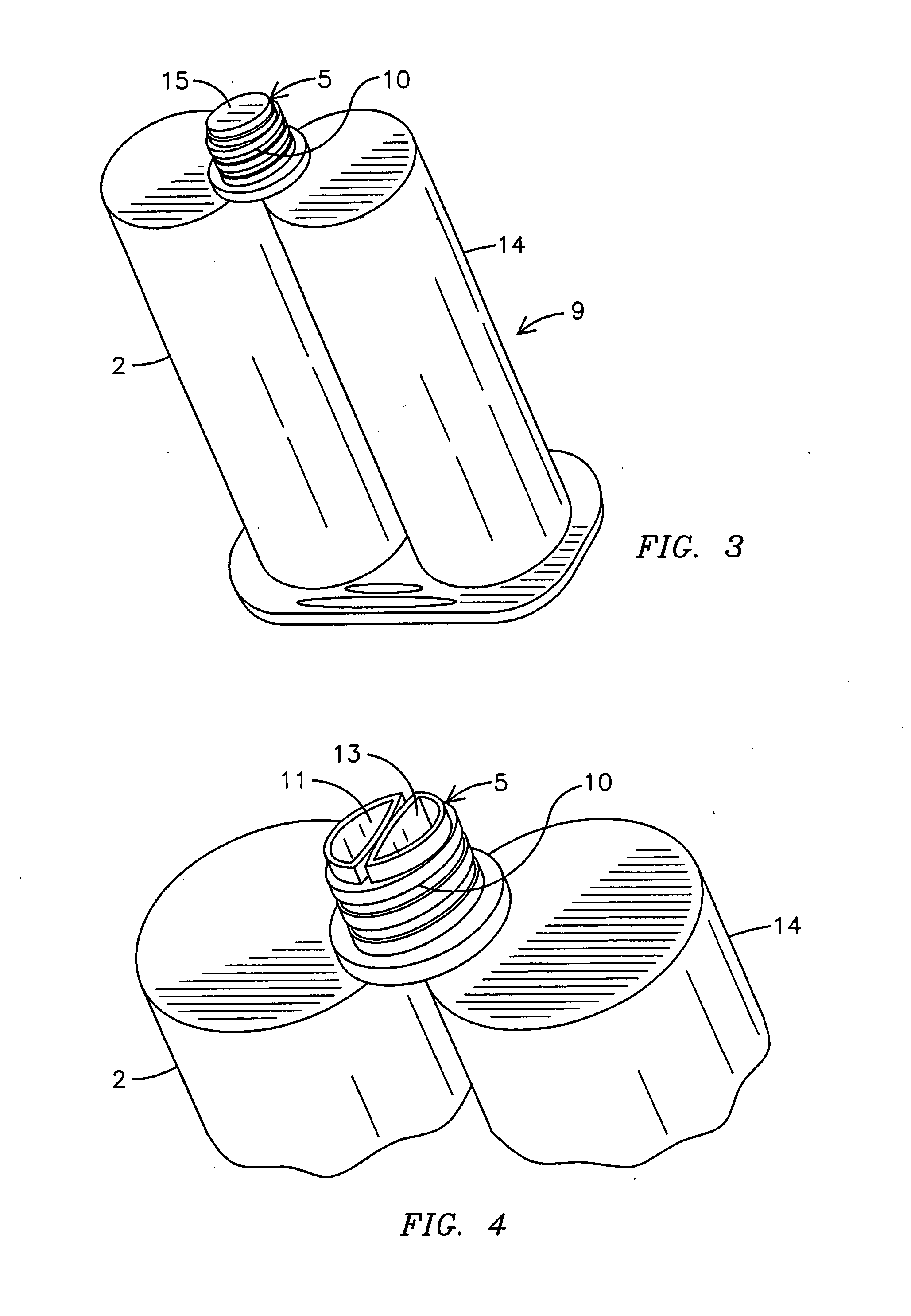
InactiveUS20070009607A1Avoid cross contaminationHigh viscosity baseBiocideInfusion syringesBenzoyl peroxideAdditive ingredient
An antibacterial / anti-inflammatory composition and method wherein the pairing of synergistic active ingredients with a natural enhancer for a more efficacious formulation for topical application treatments is used. Active ingredients hydrocortisone 1% and benzoyl peroxide 10% are paired with Emu Oil to increase the percentage of absorption of the ingredients through the skin. The preferred method of use of the composition is via a dual-pharmaceutical delivery syringe that isolates components (1) having a barrel (9), a piston (8) and a commonly shared split nozzle (5). The barrel (9) has two syringe compartments (2) and (14) attached to one another and connected to the split nozzle (5). The piston (8) has two plungers (6) connected via a bridge (12). A user applies force to the piston (8), dispersing the substances in the syringe compartments (2) and (14) through the respective sides of the split nozzle (5) onto the user's skin. The user then massages the substances into the skin for “hands-on healing.”
Owner:JONES GEORGE
Fab library for the preparation of anti VEGF and anti rabies virus fabs
InactiveUS20060160184A1Maintain good propertiesOptimization mechanismAnimal cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtein moleculesImmunoglobulin IgE
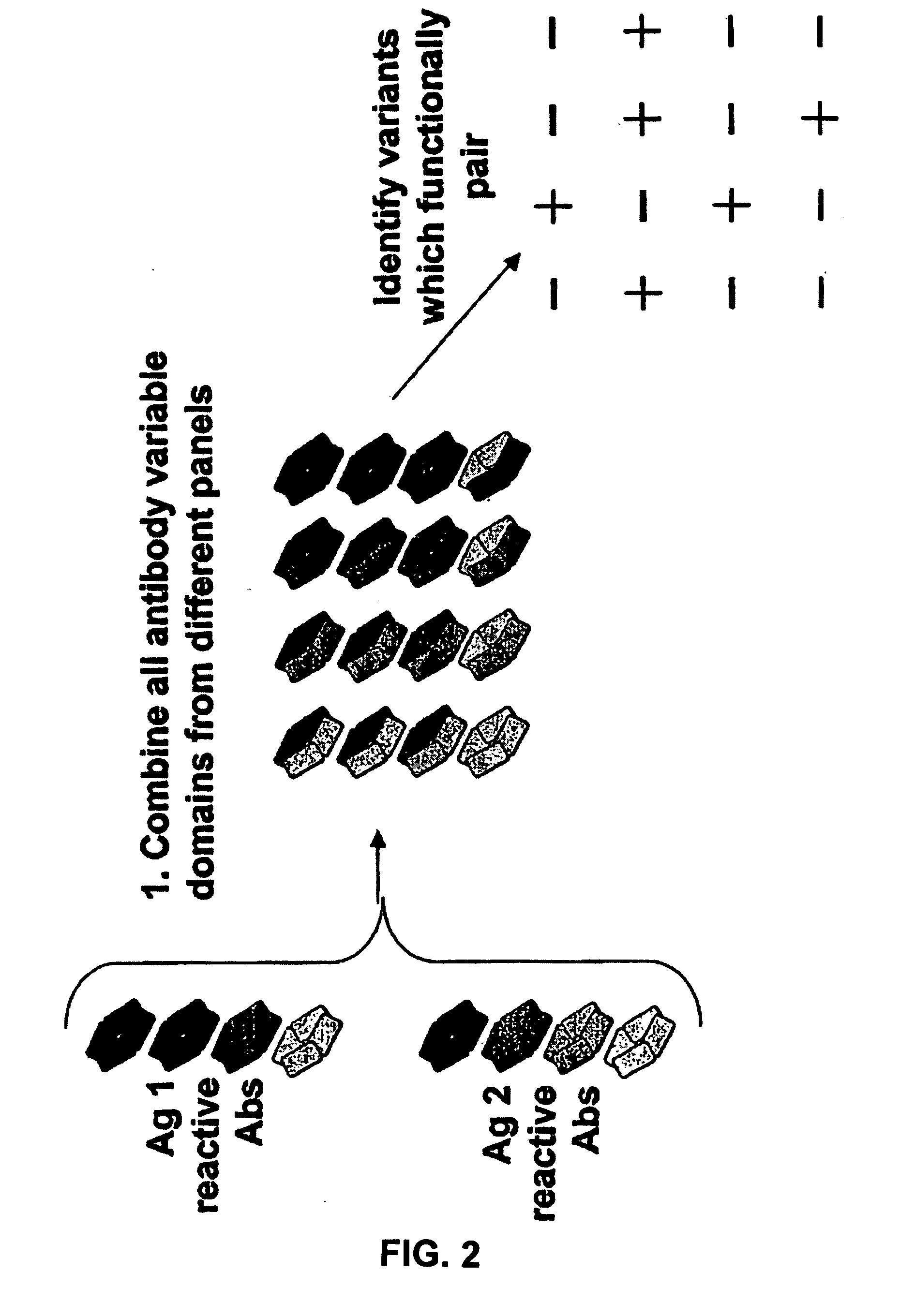
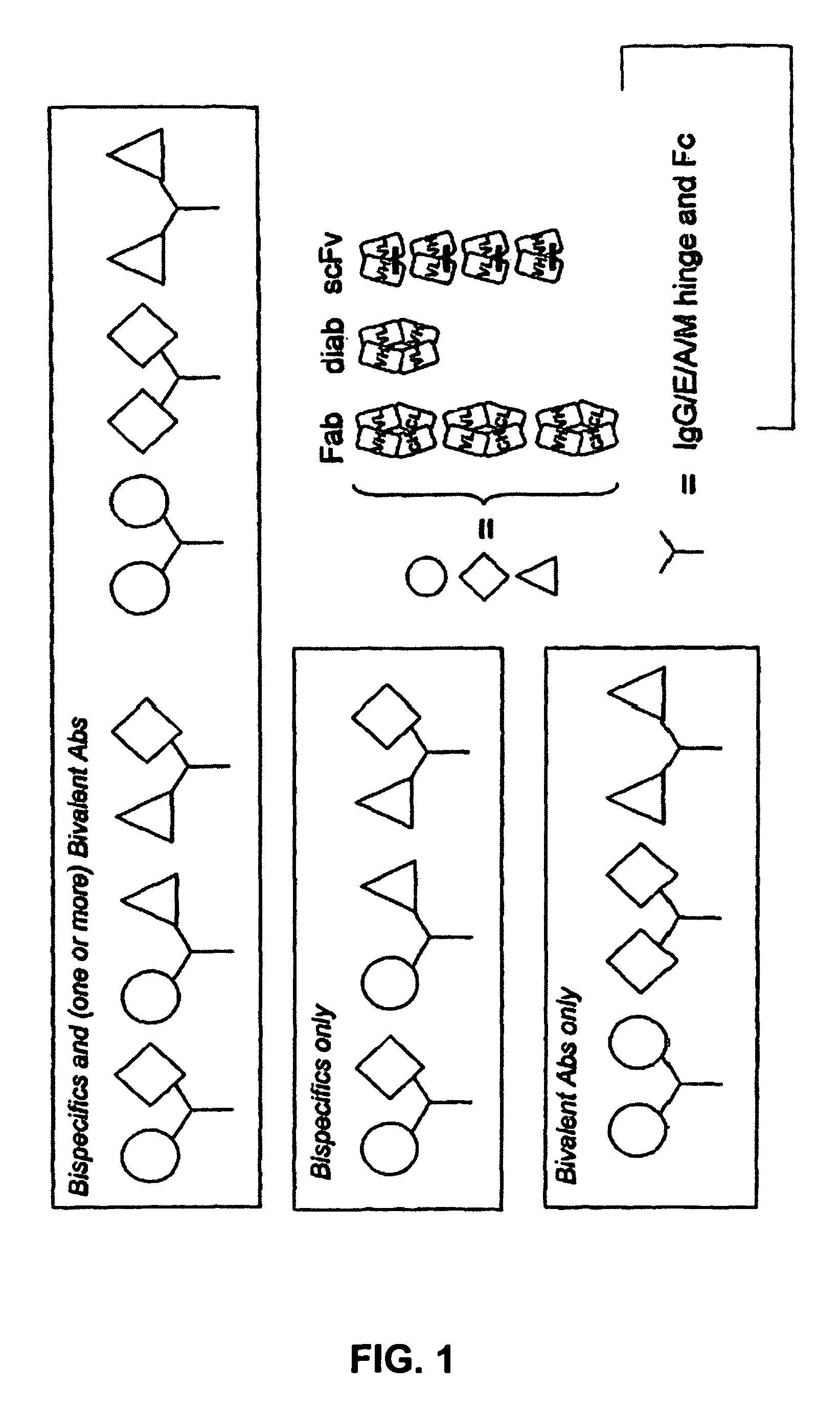
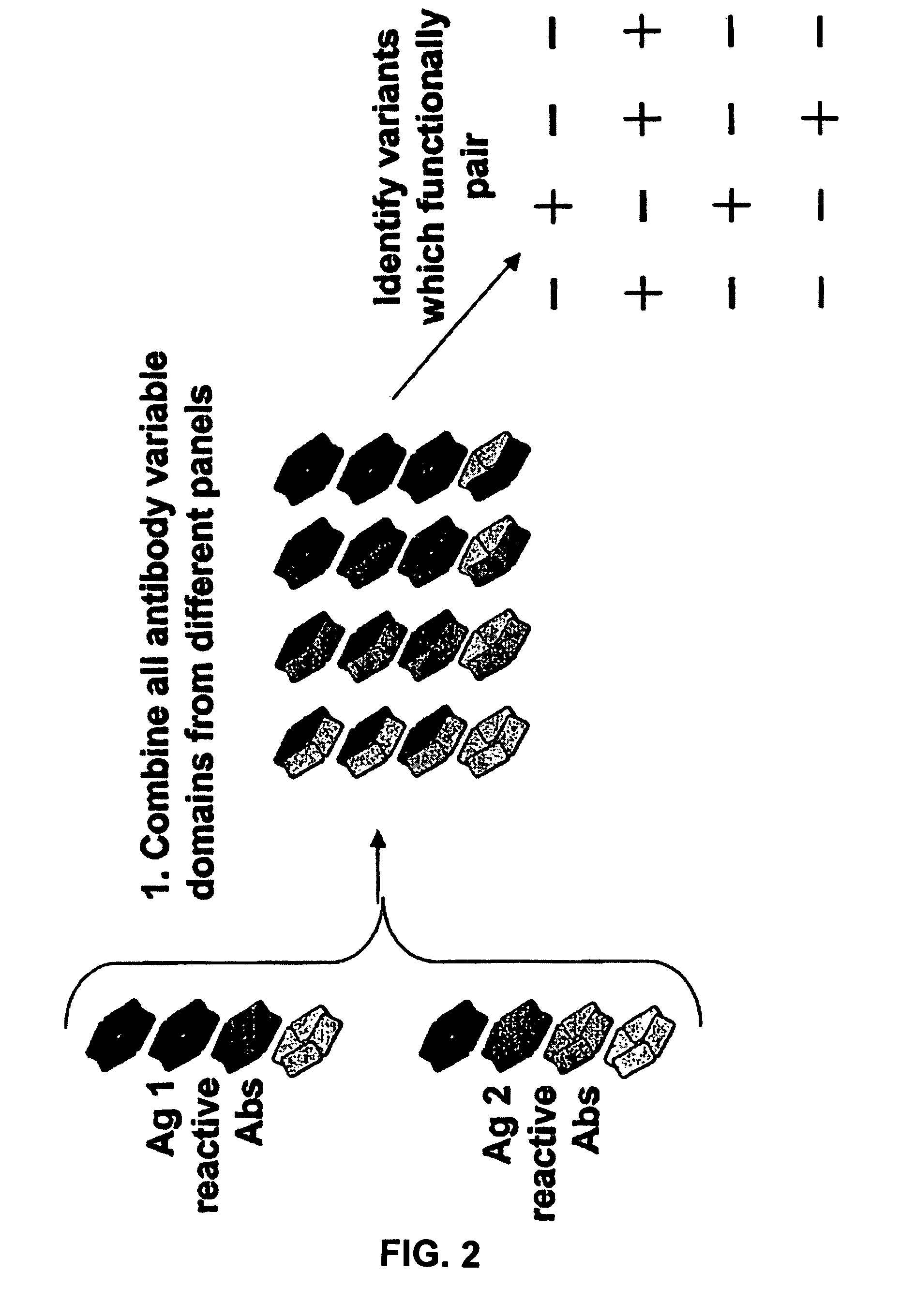
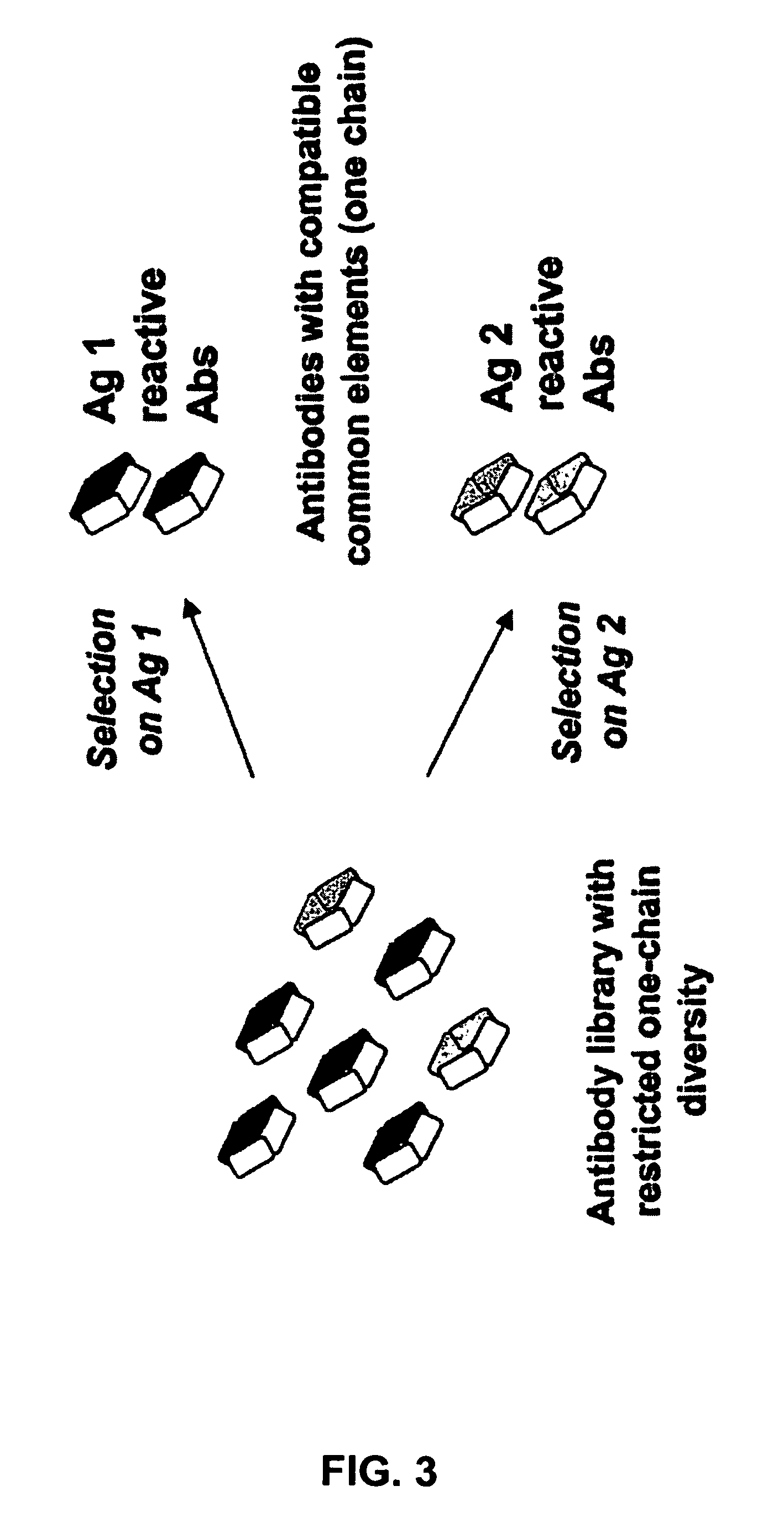
The present invention provides combinations of specific binding proteins, such as immunoglobulins, that are designed to be true combinations, essentially all components of the combination being functional and compatible with each other. The invention further provides a method for producing a composition comprising at least two different proteinaceous molecules comprising paired variable regions, the at least two proteinaceous molecules having different binding specificities, comprising paired variable regions, at least two proteinaceous molecules having different binding specificities, comprising contacting at least three different variable regions under conditions allowing for pairing of variable regions and harvesting essentially all proteinaceous molecules having binding specificities resulting from the pairing.
Owner:MERUS NV
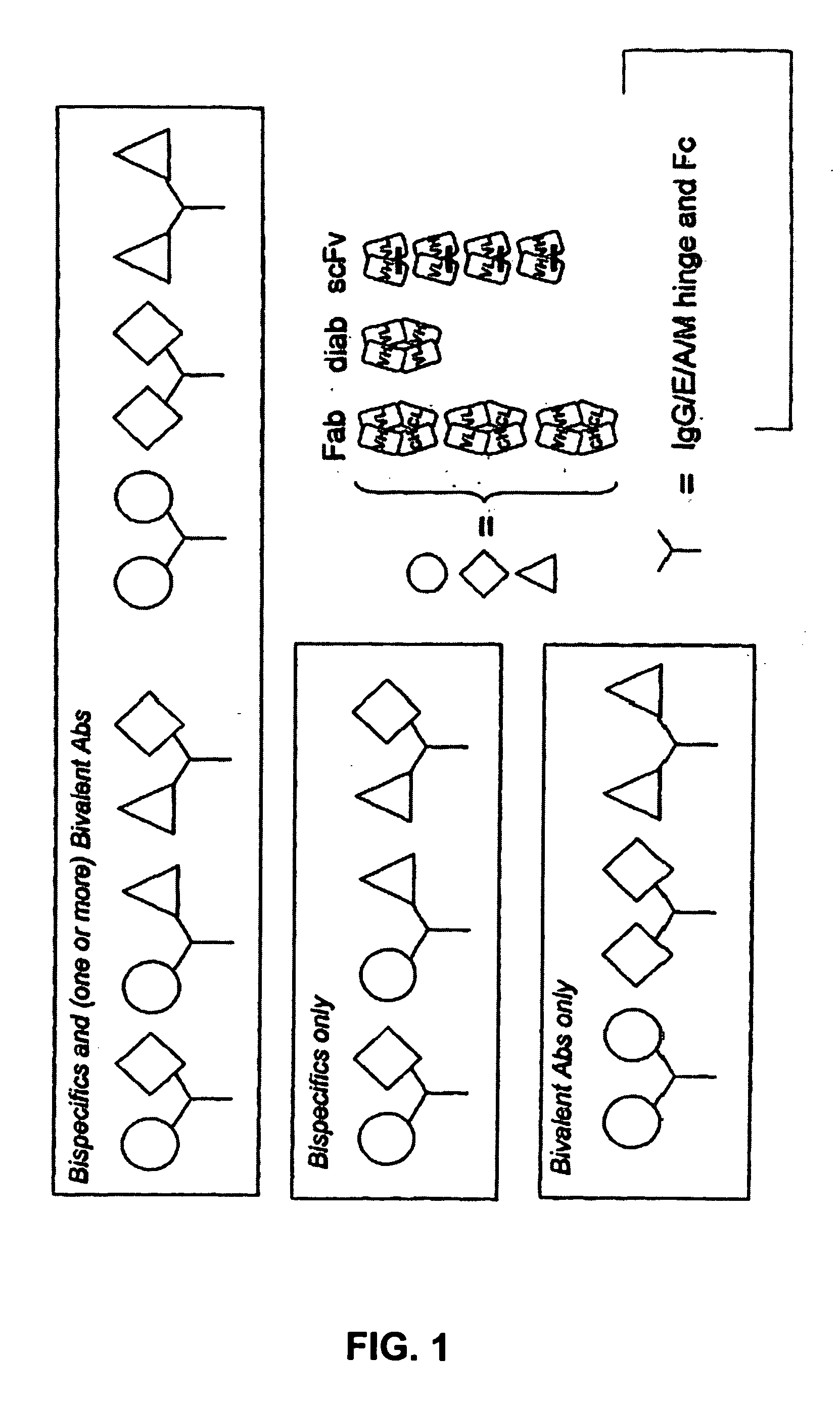
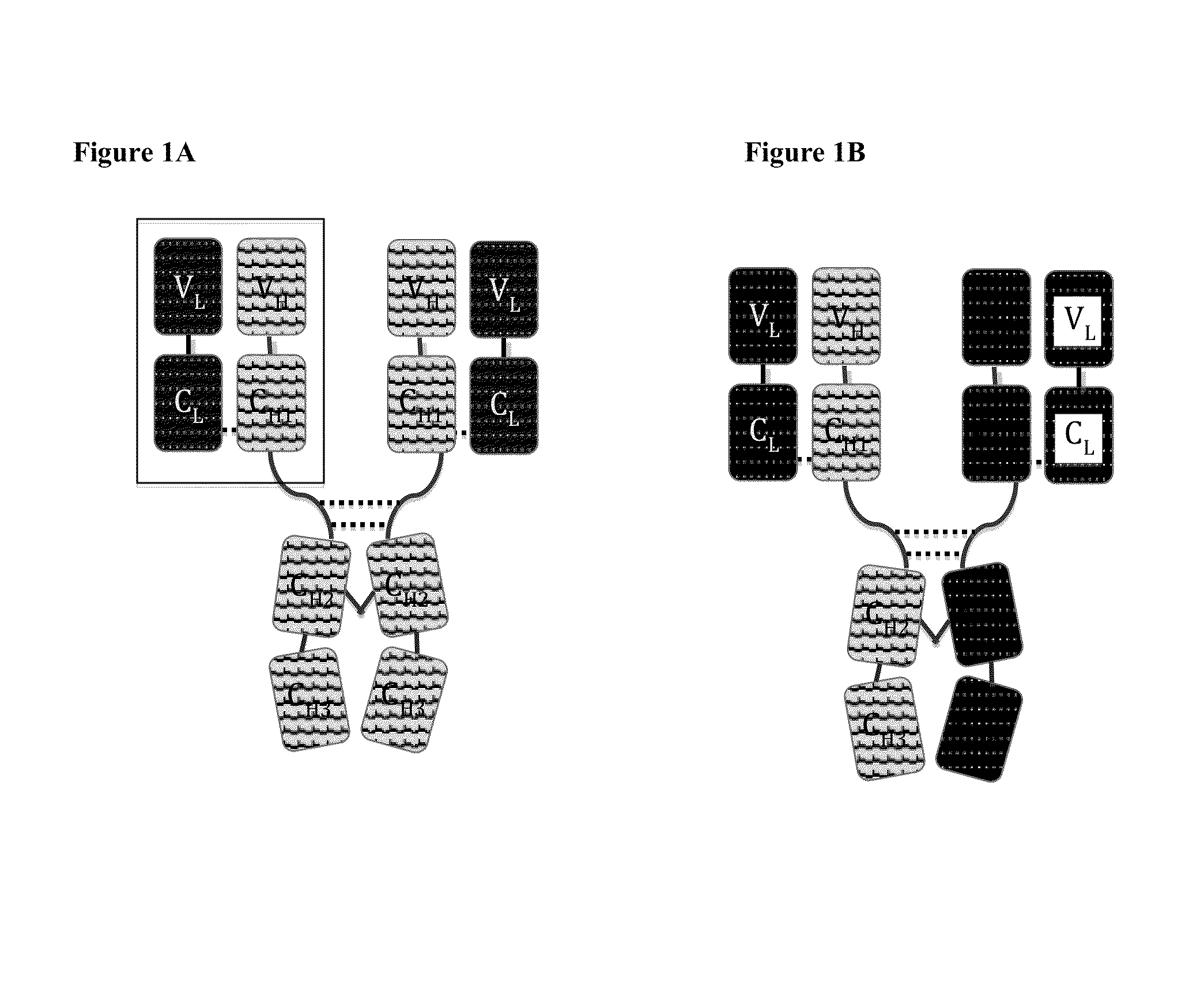
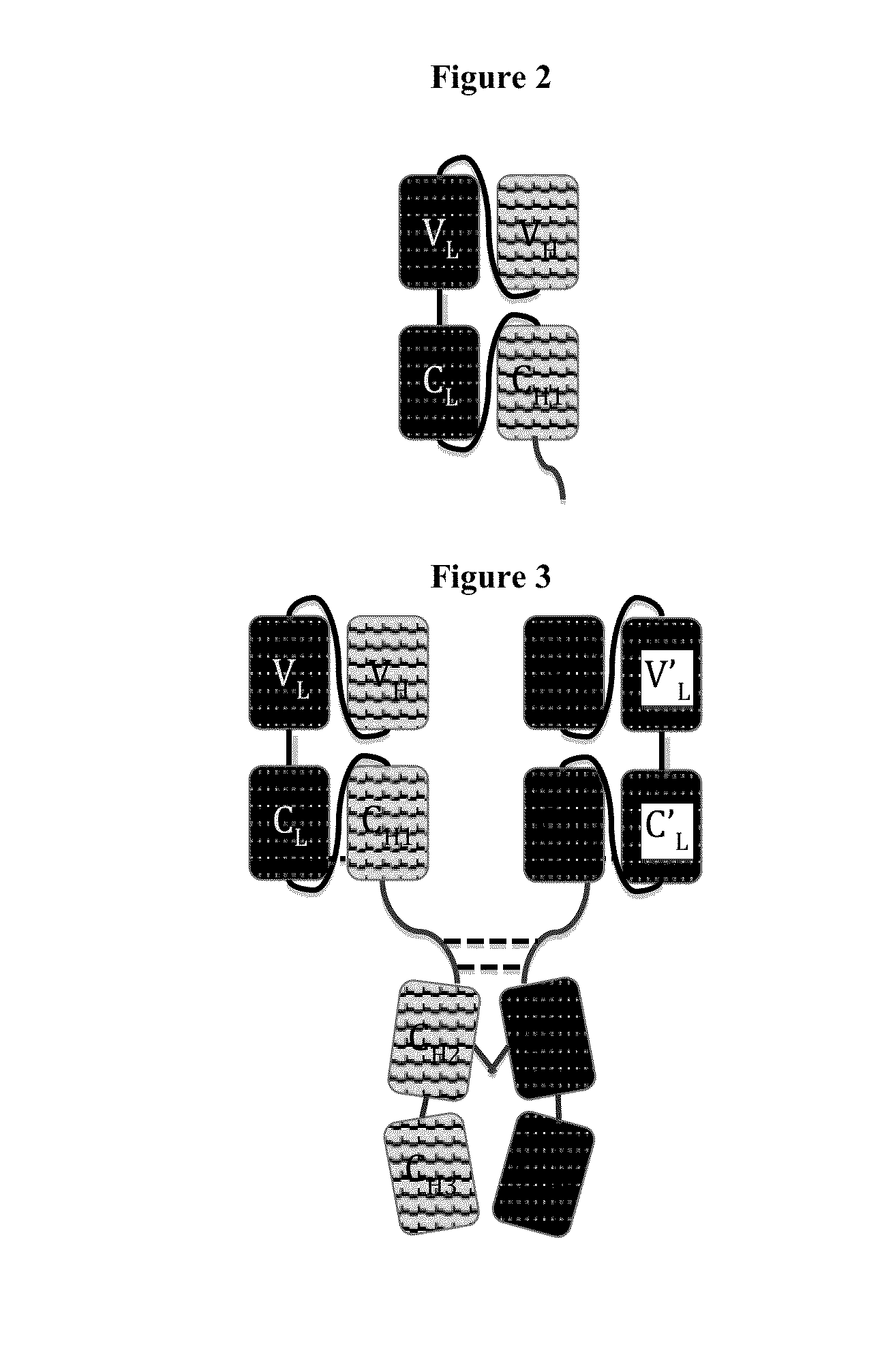
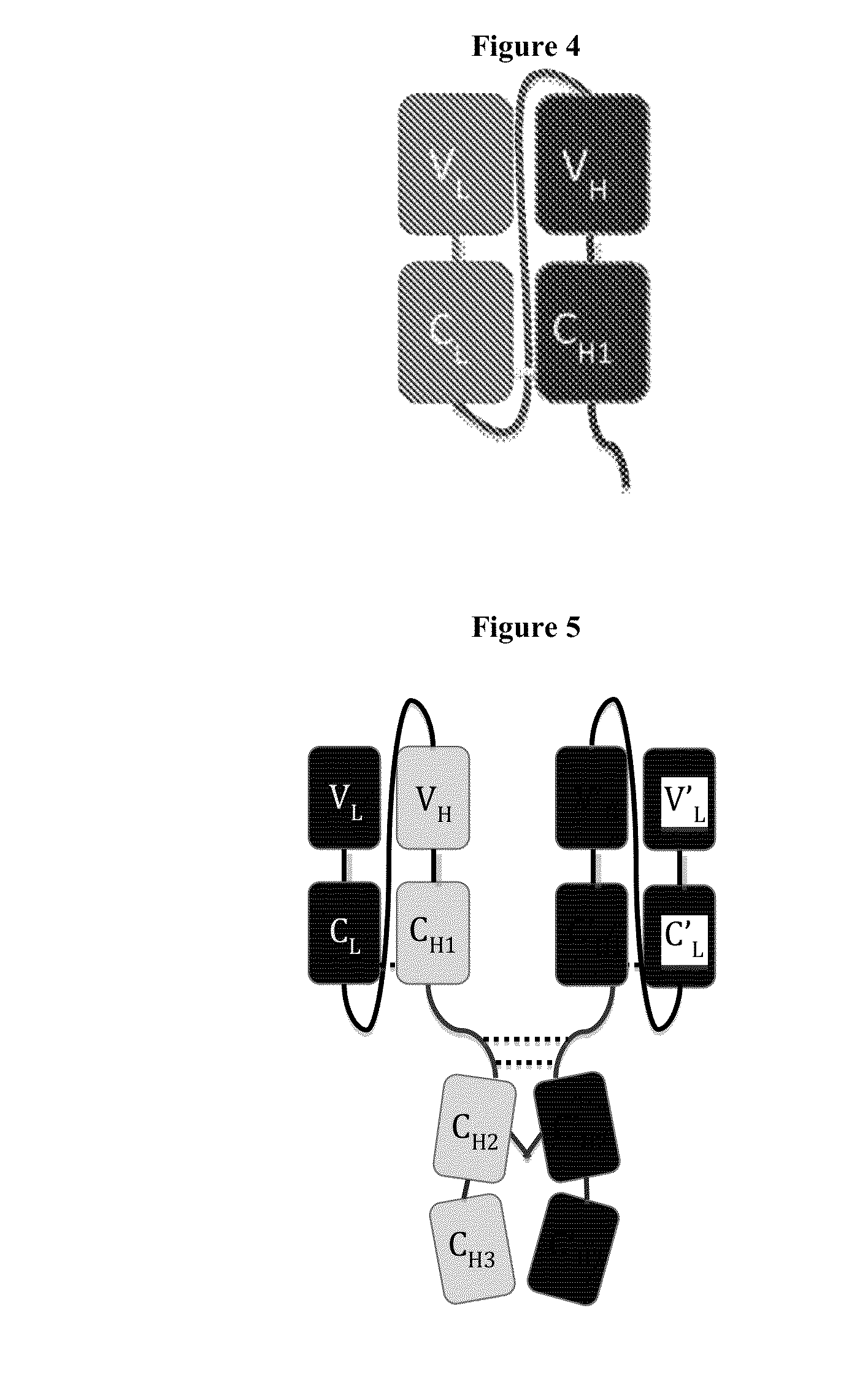
Immunoglobulin Constructs Comprising Selective Pairing of the Light and Heavy Chains
InactiveUS20140072581A1Promote formationImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsSenses disorderHeavy chainSingle-Chain Fv
Disclosed herein is an isolated immunoglobulin construct comprising a first monomeric polypeptide comprising a first single chain Fv polypeptide connected to a first constant domain polypeptide; and a second monomeric polypeptide comprising a second single chain Fv polypeptide, connected to a second constant domain polypeptide; each said constant domain polypeptide comprising at least one each of a CL domain, a CH1 domain, a CH2 domain and a CH3 domain or fragments, variants or derivatives thereof; and wherein said first and second constant domain polypeptide form a Fc region.
Owner:ZYMEWORKS INC
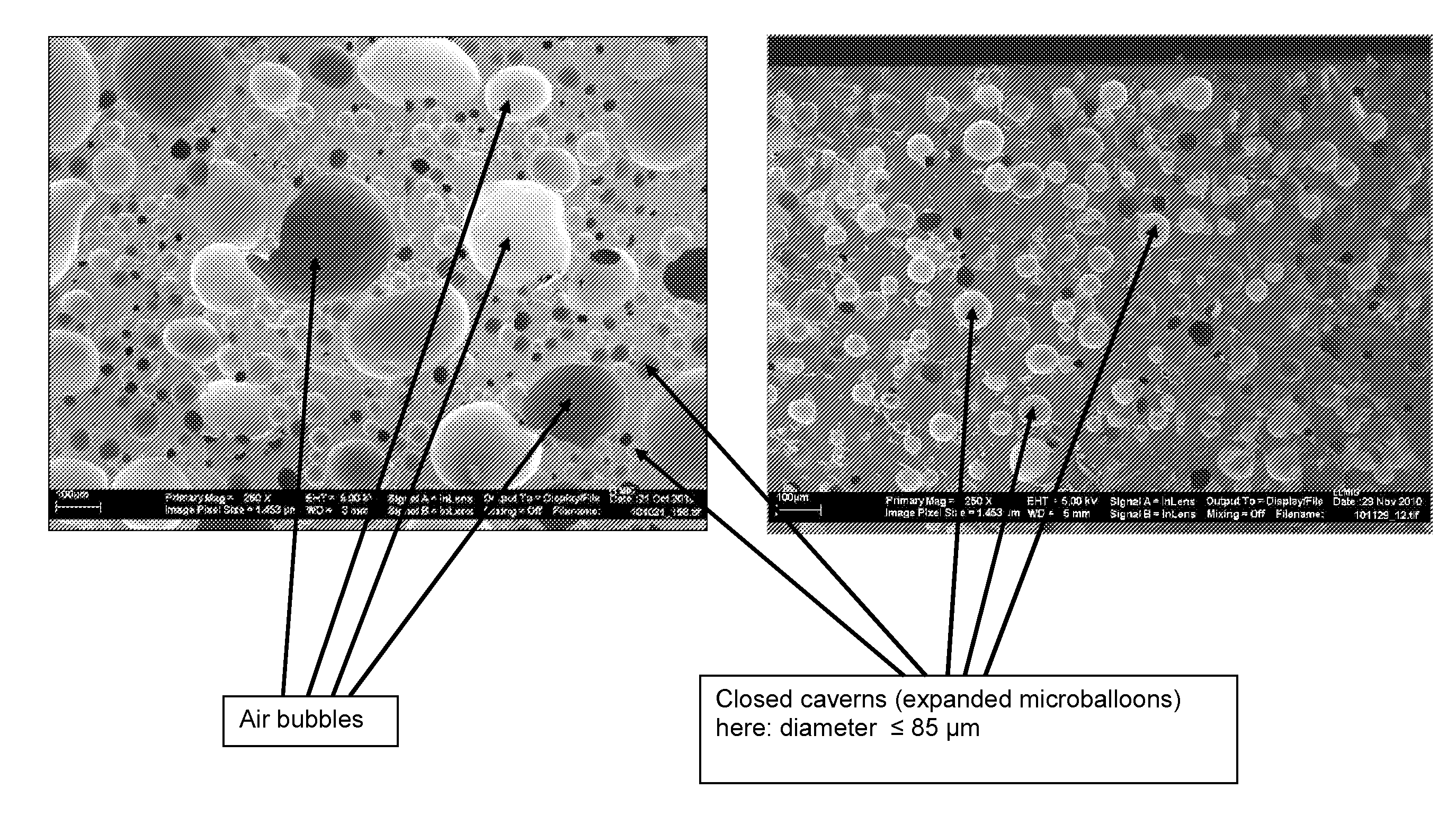
Process for preparing foamable polymer compositions, process for preparing foamed polymer compositions therefrom, foamed polymer compositions and adhesive tape therewith
The invention relates to a process for preparing a foamed polymer composition using expandable hollow microbeads,wherein, in a first process strand, first starting materials, which include at least the predominant portion of the polymer or polymers to be used, are mixed and degassed to give a premix,whereafter this premix is subjected to a pressure such that the pairing of this pressure with the temperature of the premix is below the pressure and temperature pairing that is critical for triggering the expansion of the hollow microbeads to be used,wherein, in a second process strand, second starting materials, including the hollow microbeads to be used, are degassed,whereafter the second starting materials treated in the second process strand are added to the premix prepared in the first process strand,whereafter the second starting materials are mixed with the premix.
Owner:TESA SE
System for balance distribution of requests across multiple servers using dynamic metrics
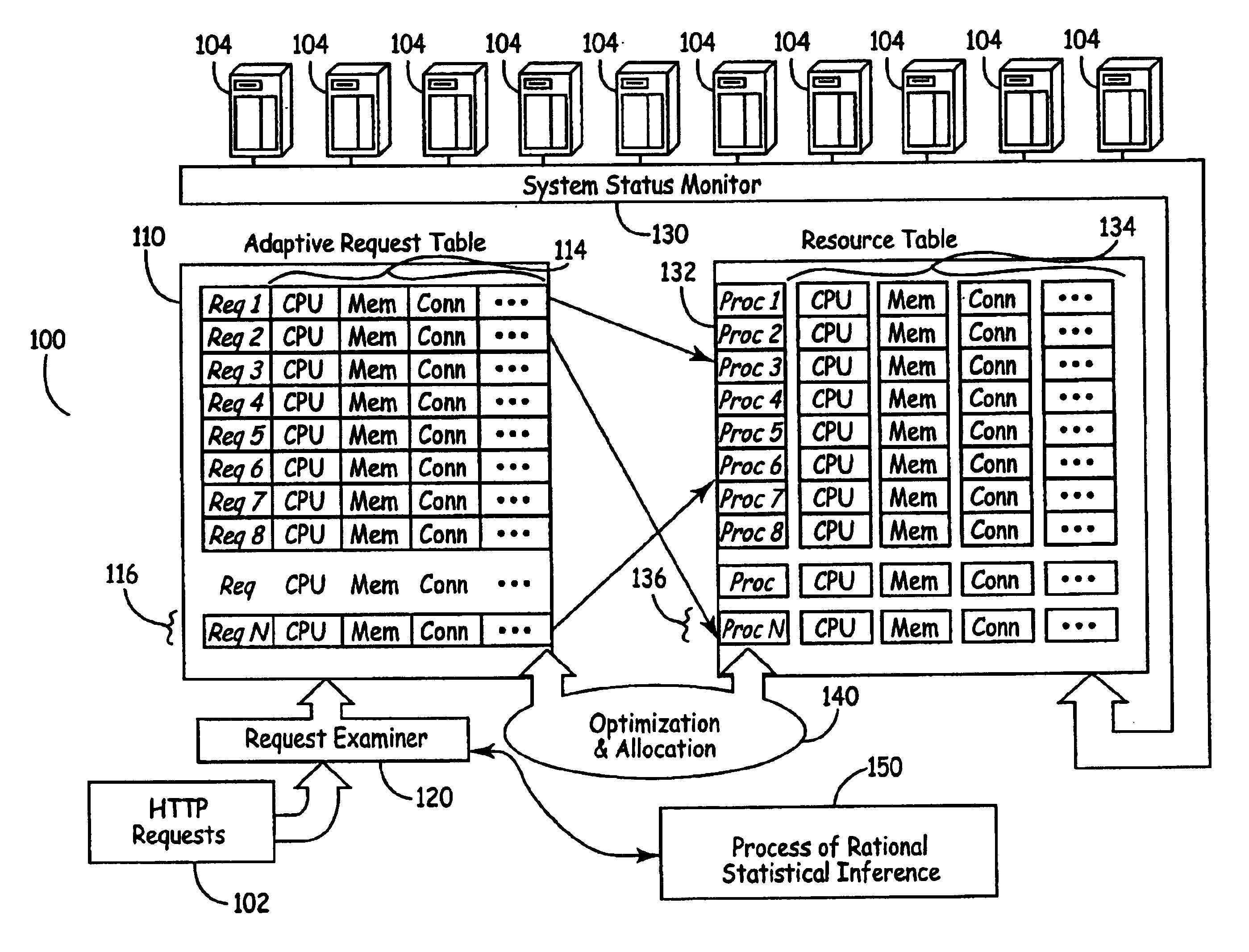
InactiveUS6938256B2Improve performanceMaximizing numberResource allocationHardware monitoringDynamic metricsRelational database
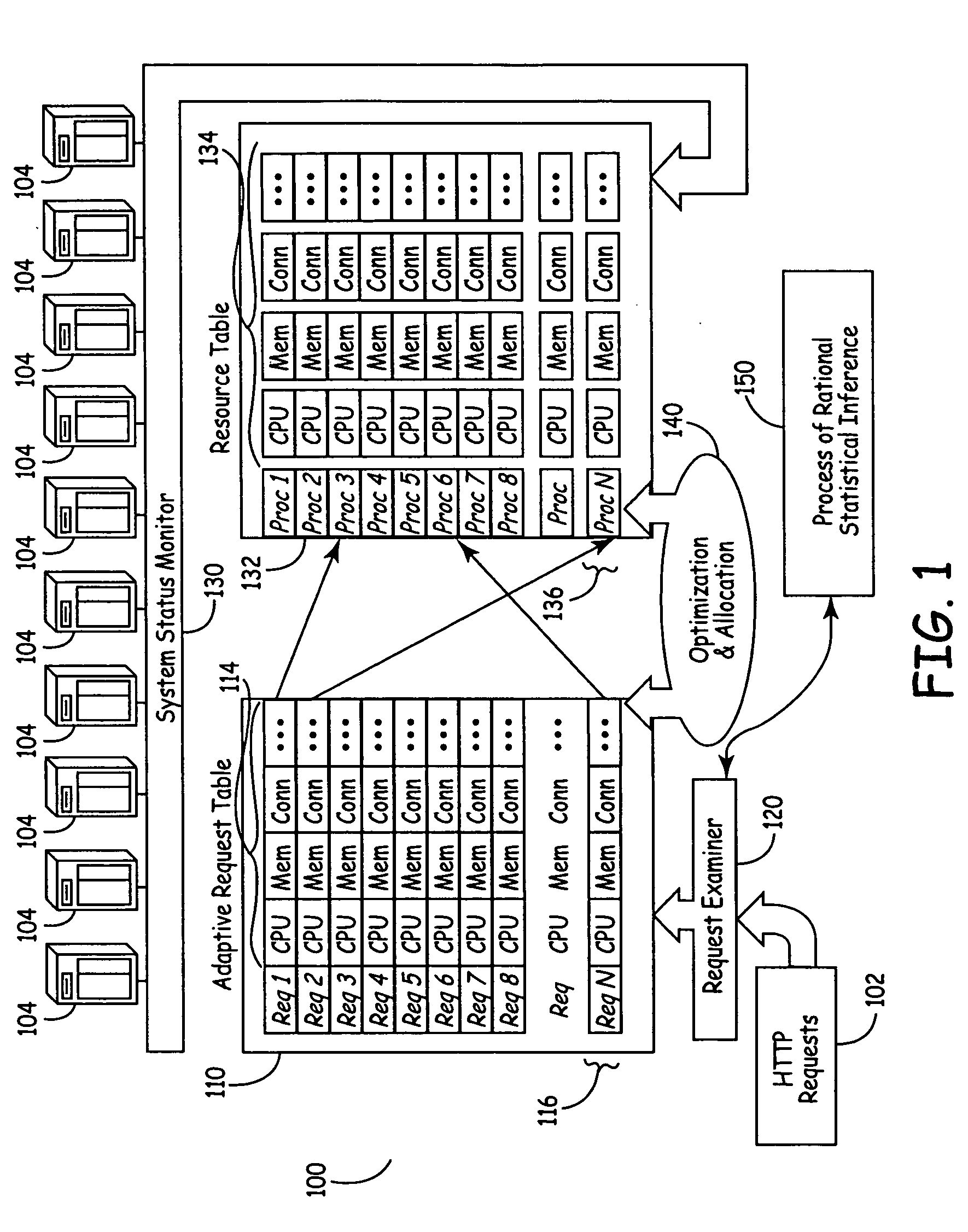
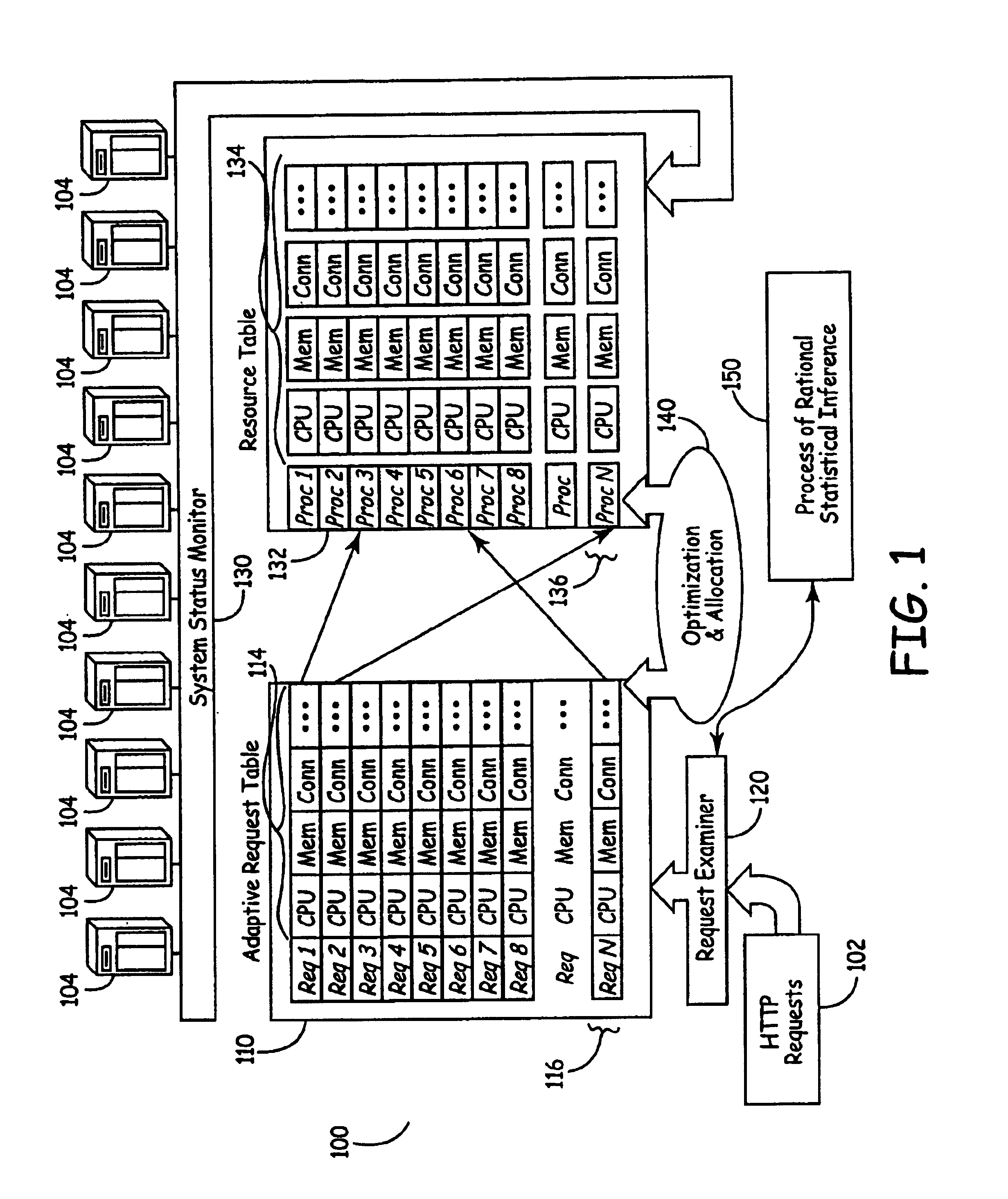
A system for distributing incoming client requests across multiple servers in a networked client-server computer environment processes all requests as a set that occur within a given time interval and collects information on both the attributes of the requests and the resource capability of the servers to dynamically allocate the requests in a set to the appropriate servers upon the completion of the time interval. Preferably, the system includes a request table to collect at least two requests incoming within a predetermined time interval. A request examiner routine analyzes each collected request with respect to at least one attribute. A system status monitor collects resource capability information of each server in a resource table. An optimization and allocation process distributes collected requests in the request table across the multiple servers upon completion of said time interval based on an optimization of potential pairings of the requests in the request table with the servers in the resource table. The optimization and allocation process preferably analyzes metrics maintained in the request table and resource table as part of a relational database to allocate requests to servers based on a minimization of the metric distance between pairings of requests and servers. Preferably, the request table is part of a dynamic, relational database and a process of statistical inference for ascertaining expected demand patterns involving said the attributes adds predictive information about client requests as part of the request examiner routine.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Method for selecting a single cell expressing a heterogeneous combination of antibodies
InactiveUS7919257B2Maintain good propertiesOptimization mechanismBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtein moleculesPairing
The present invention provides combinations of specific binding proteins, such as immunoglobulins, that are designed to be true combinations, essentially all components of the combination being functional and compatible with each other. The invention further provides a method for producing a composition comprising at least two different proteinaceous molecules comprising paired variable regions, the at least two proteinaceous molecules having different binding specificities, comprising paired variable regions, at least two proteinaceous molecules having different binding specificities, comprising contacting at least three different variable regions under conditions allowing for pairing of variable regions and harvesting essentially all proteinaceous molecules having binding specificities resulting from the pairing.
Owner:MERUS NV
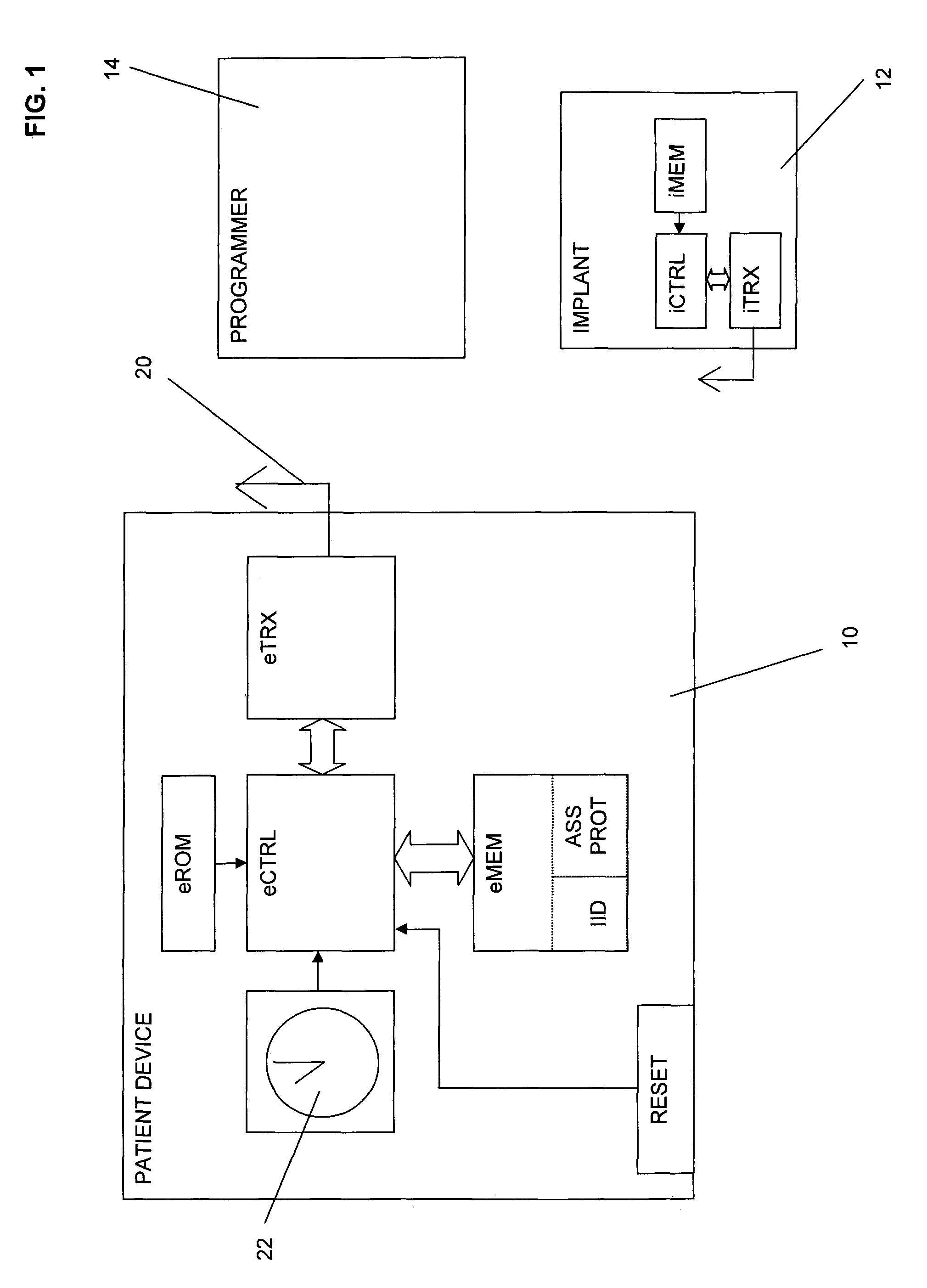
Patient device for bidirectional data communication with an implant
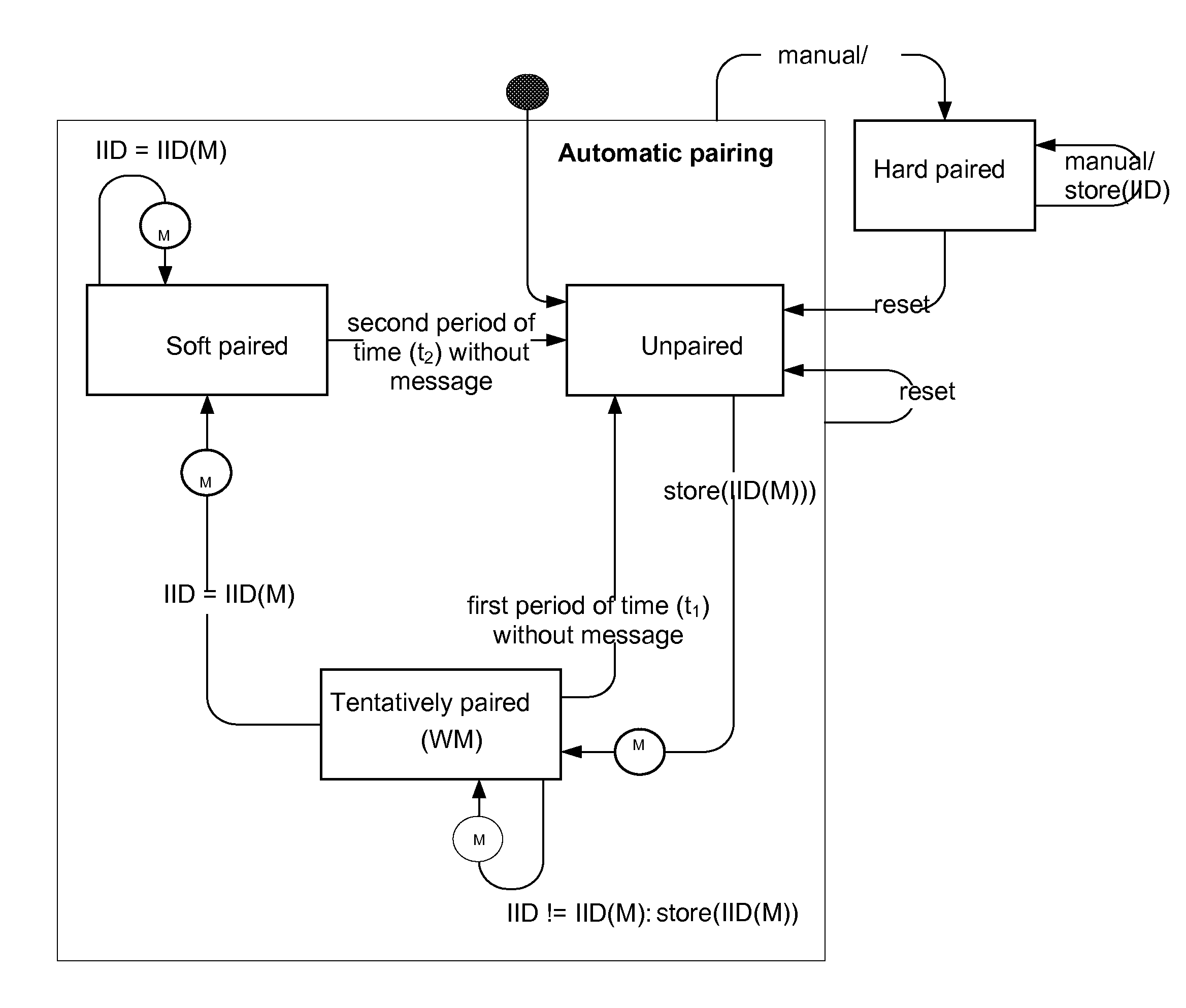
A patient device (PD) for wireless data communication with an implant. The PD can be at least in an unpaired state or a paired state. In the paired state the PD is paired to a specific implant specified by an implant's identification code (IIC). The IIC is stored in PD memory. Automatic pairing of the PD to a specific implant is performed upon receiving an incoming data packet containing an IIC when the PD is in its unpaired state with no valid IIC stored in memory. Thus, the PD is tentatively paired to an implant identified by the IIC contained in the incoming data packet by storing the IIC in the memory. Tentative pairing is cancelled if no further communication occurs within a predetermined period of time. A soft paired state is entered if further data communication does occur.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
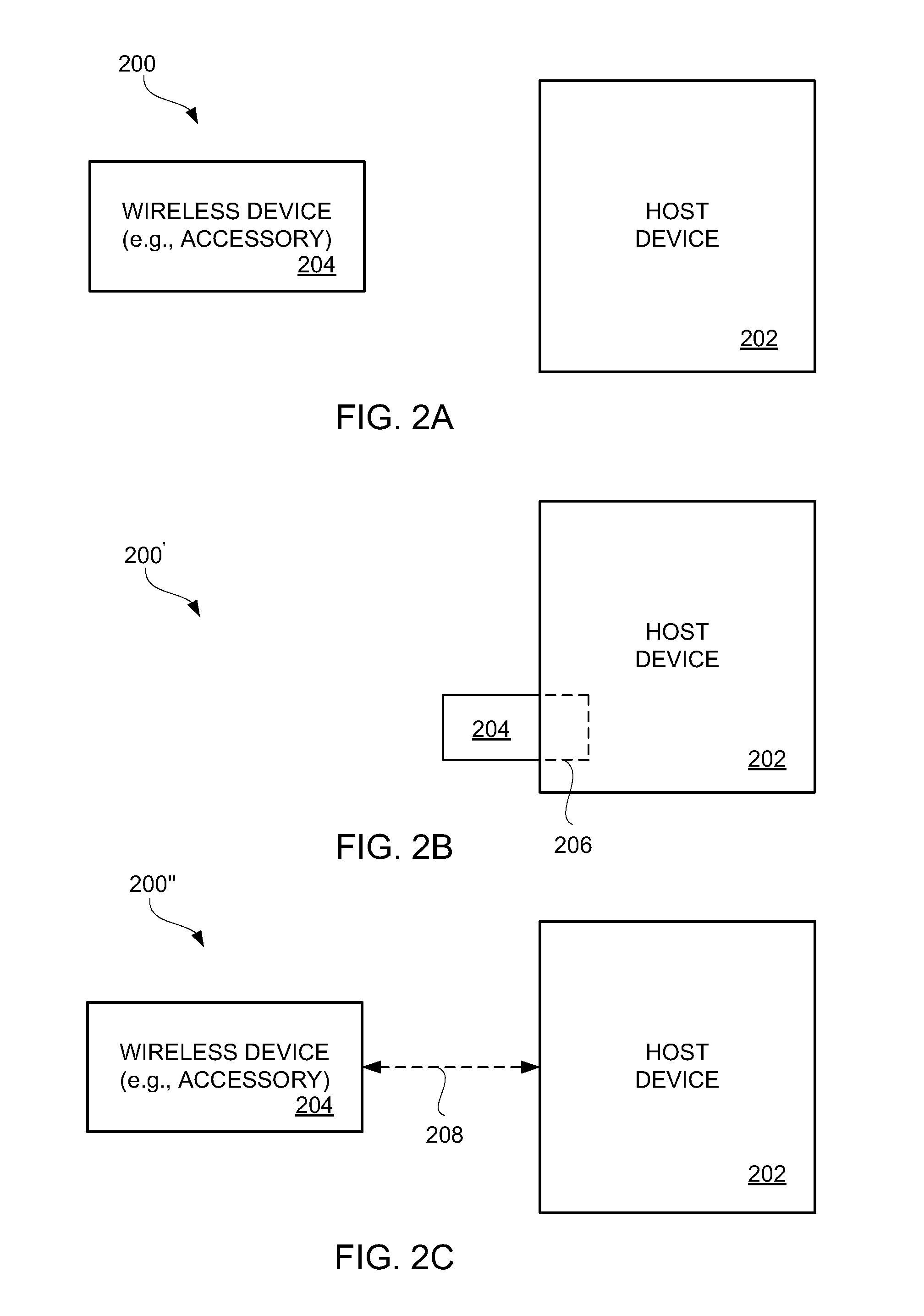
Securing Pairing of Electronic Devices
InactiveUS20080208627A1Improve securityData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsMatingElectrical devices
The present invention relates to secure paring of electronically controlled devices adapted to communicate with each other. The invention provides a system comprising a local (200) unit and a remote (100) unit. The local unit comprises a local transmitter (270), a local receiver (280), a local sensor (290), and a local processor (210) connected to the local transmitter, the local receiver and the local sensor. The remote unit comprises a remote transmitter (170) adapted to transmit information to the local receiver (180), a remote receiver adapted for receiving information from the local transmitter, a remote sensor (190), and a remote processor (110) connected to the remote transmitter, the remote receiver and the remote sensor. The local sensor and the remote sensor are adapted to detect that the units have been arranged in a mating relationship with each other at a given point in time, this allowing the units to exchange information based upon that time.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
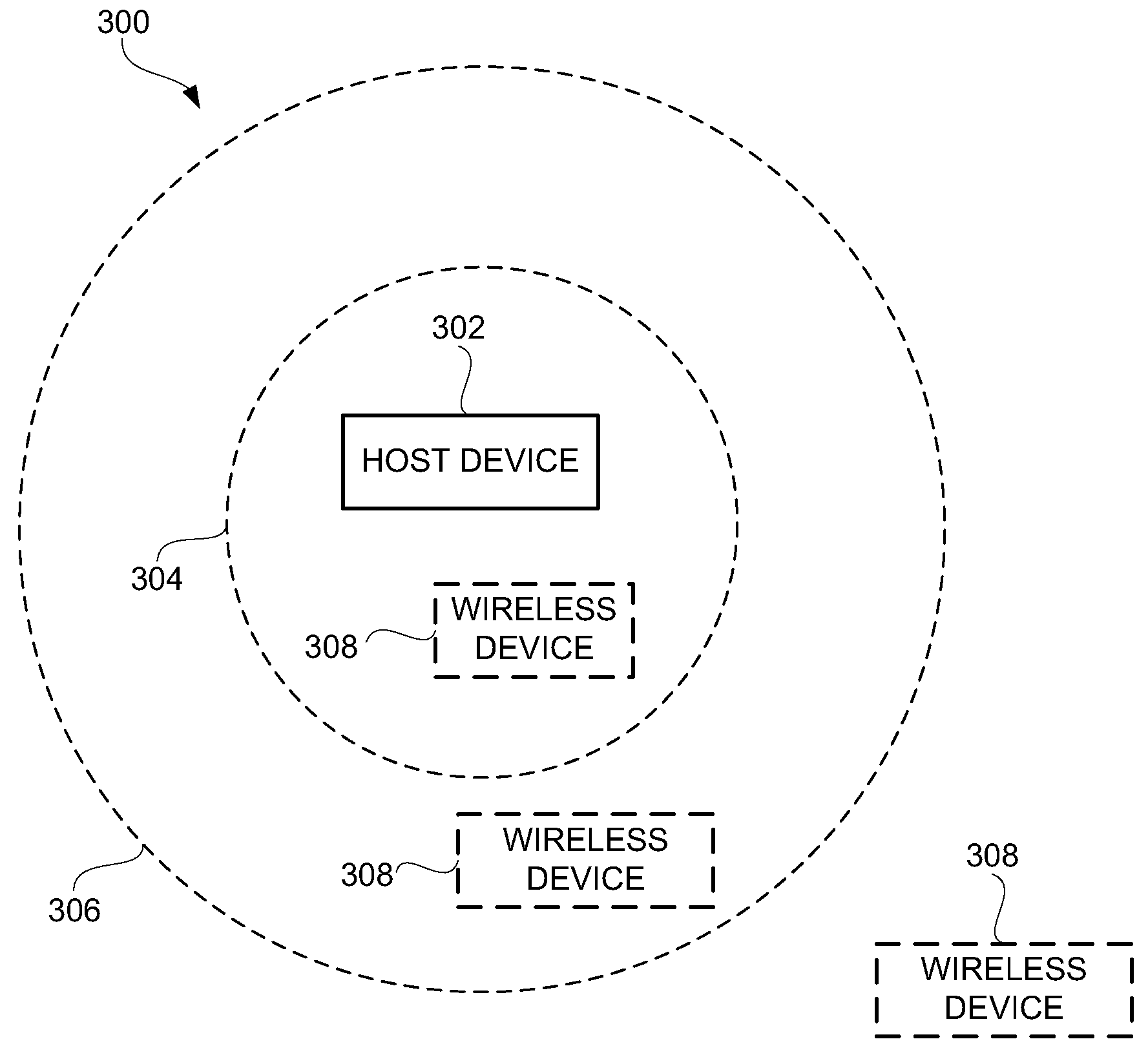
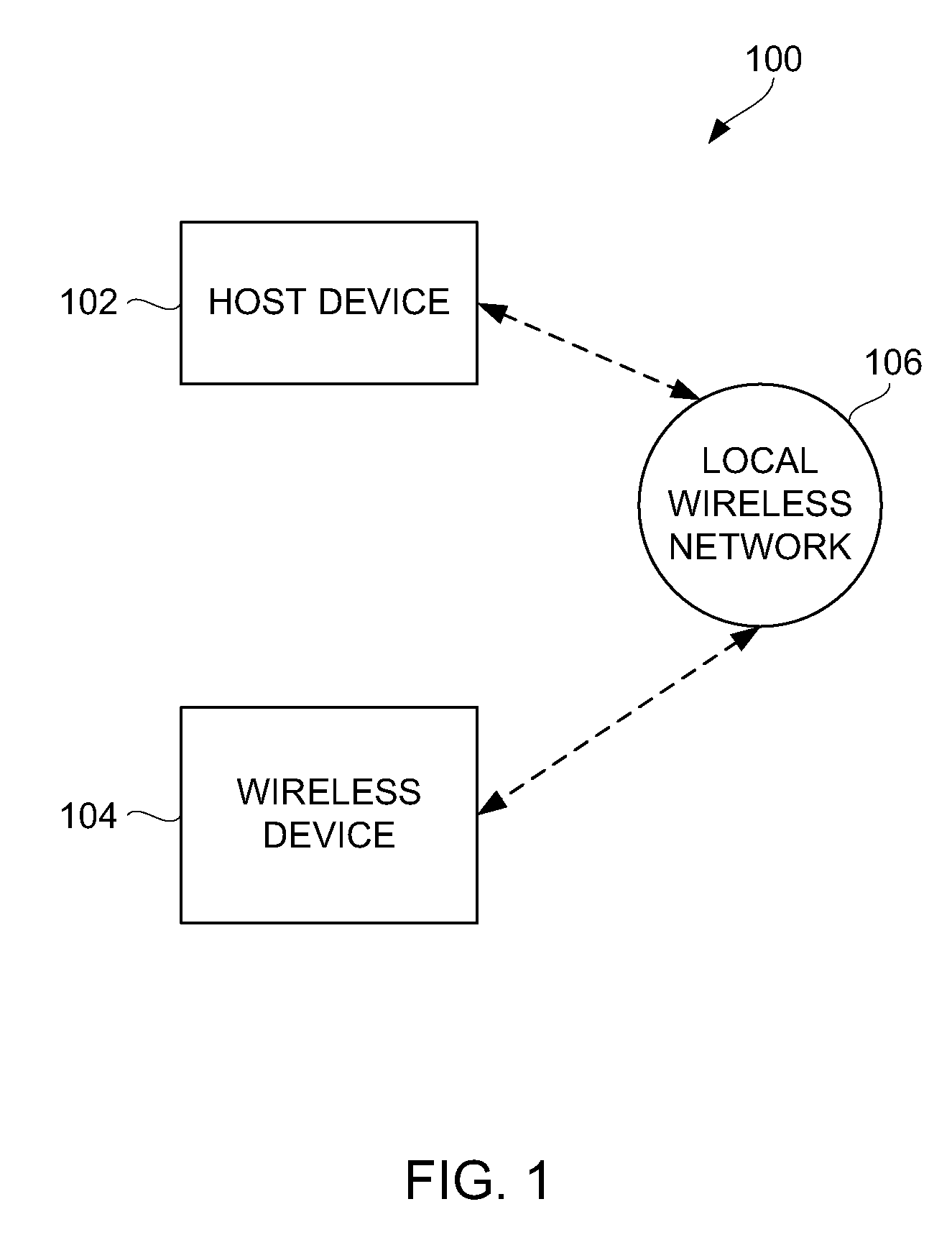
Method and system for pairing of wireless devices using physical presence
Techniques that facilitate pairing of wireless devices with other wireless devices are disclosed. Once paired, the wireless devices can exchange data in a wireless manner. According to one embodiment, a pairing process can be secured through use of physical proximity, or even physical connection, of wireless devices to be paired. According to another embodiment, user actions to provoke or perform pairing can be reduced or eliminated. According to still another embodiment, a wireless device being paired can be configured using configuration information provided from another wireless device being paired.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com