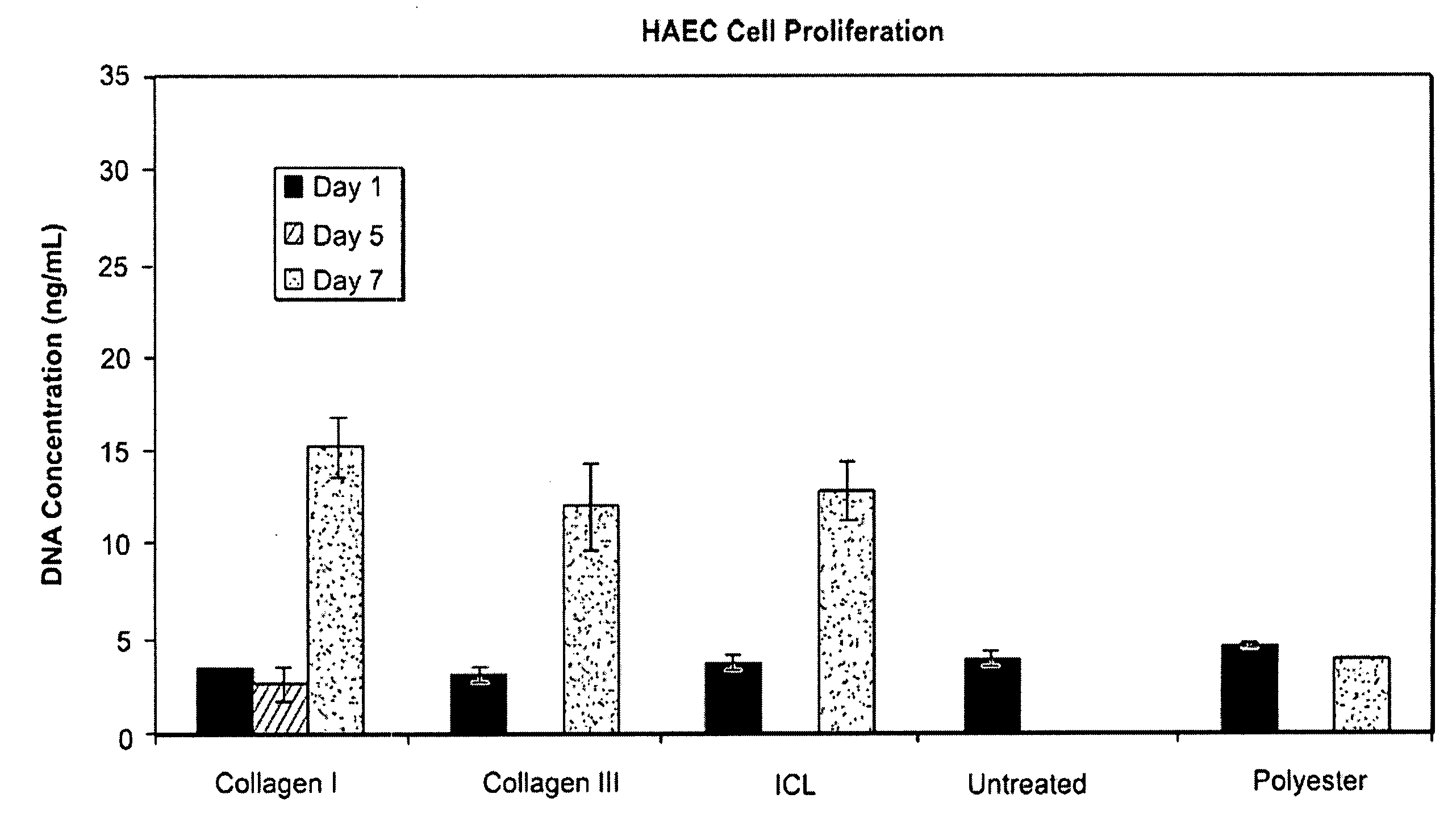
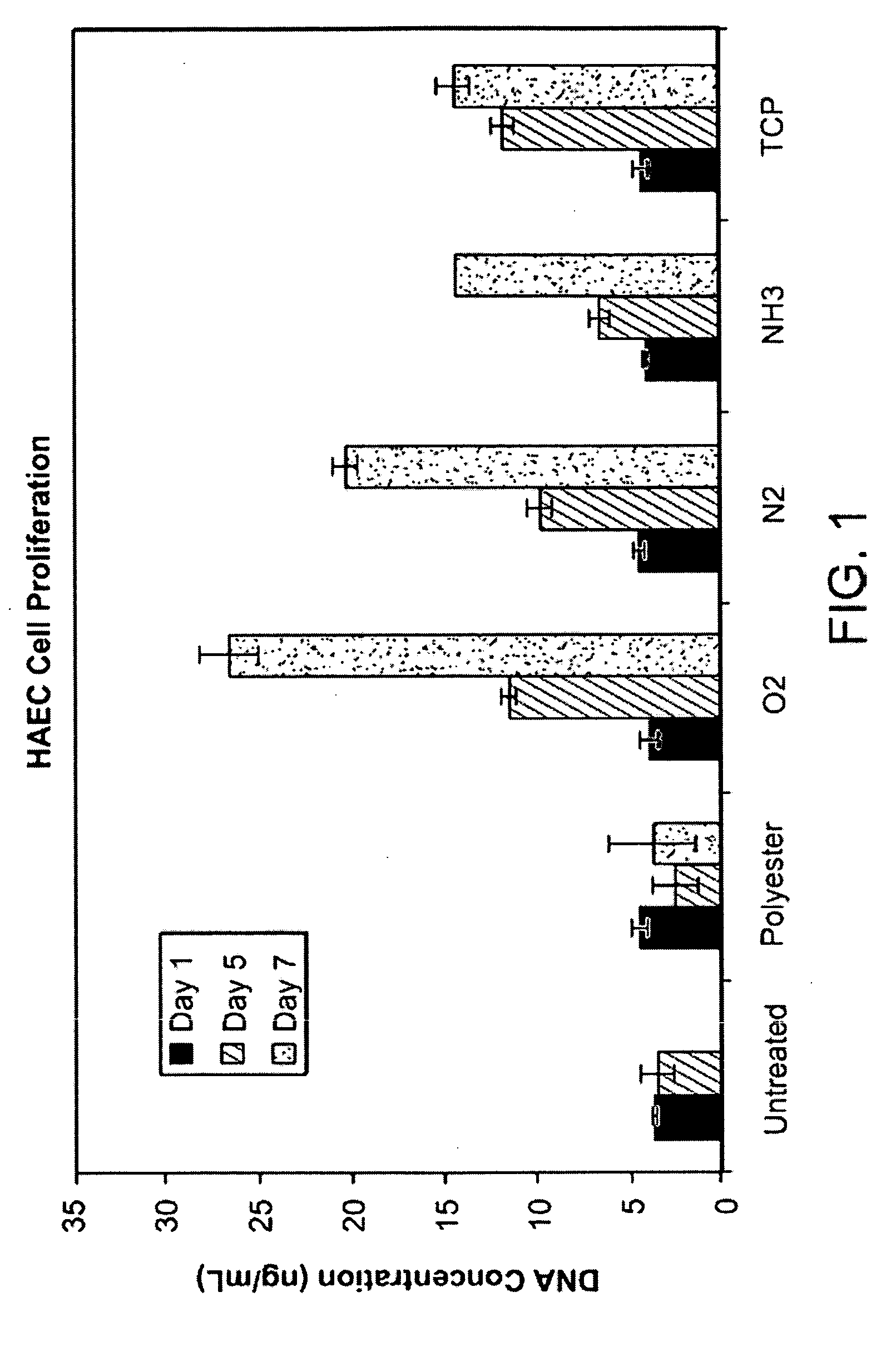
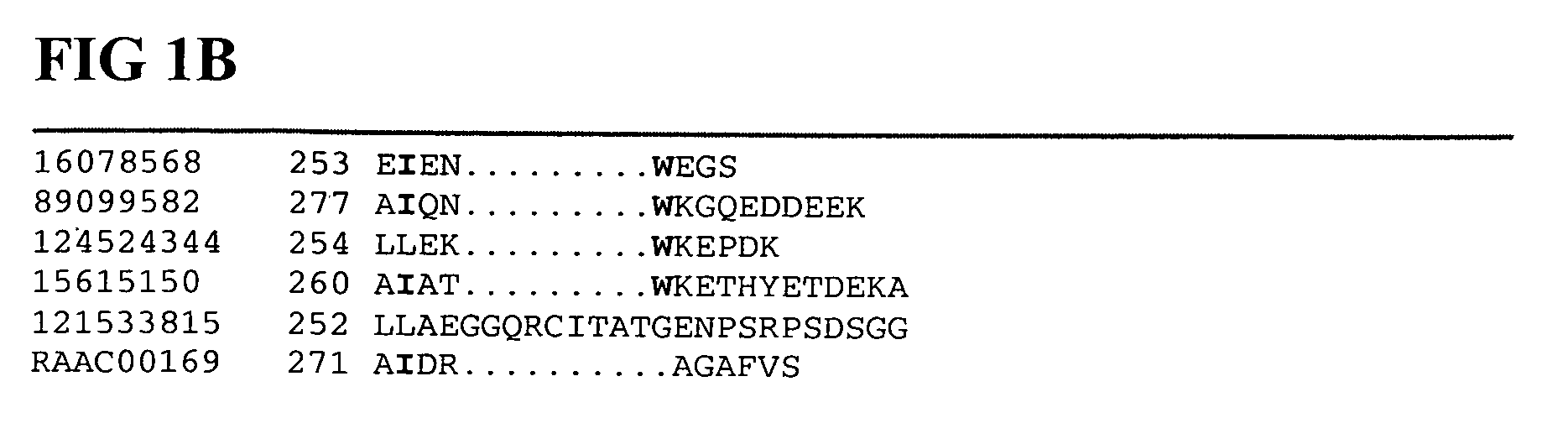
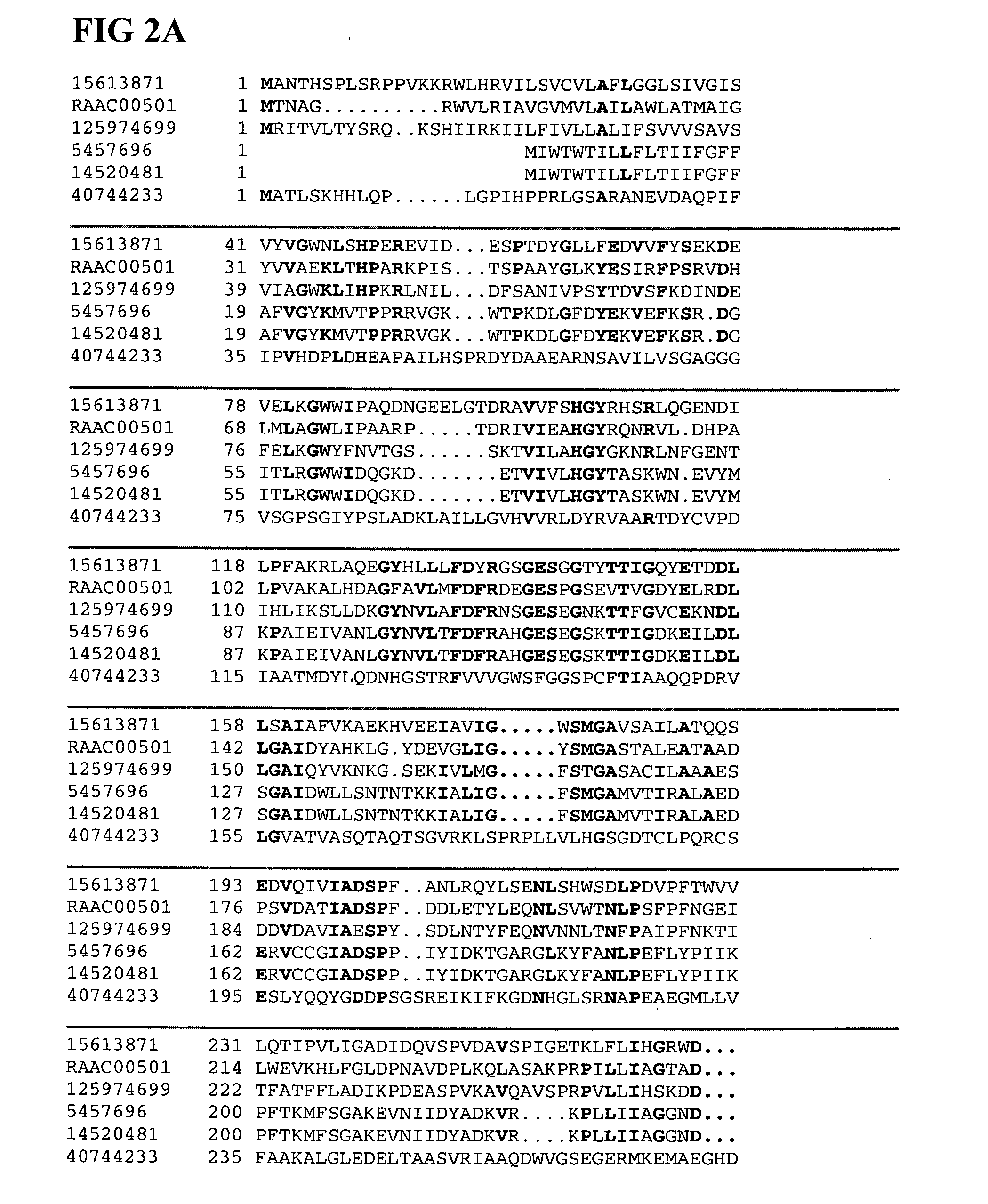
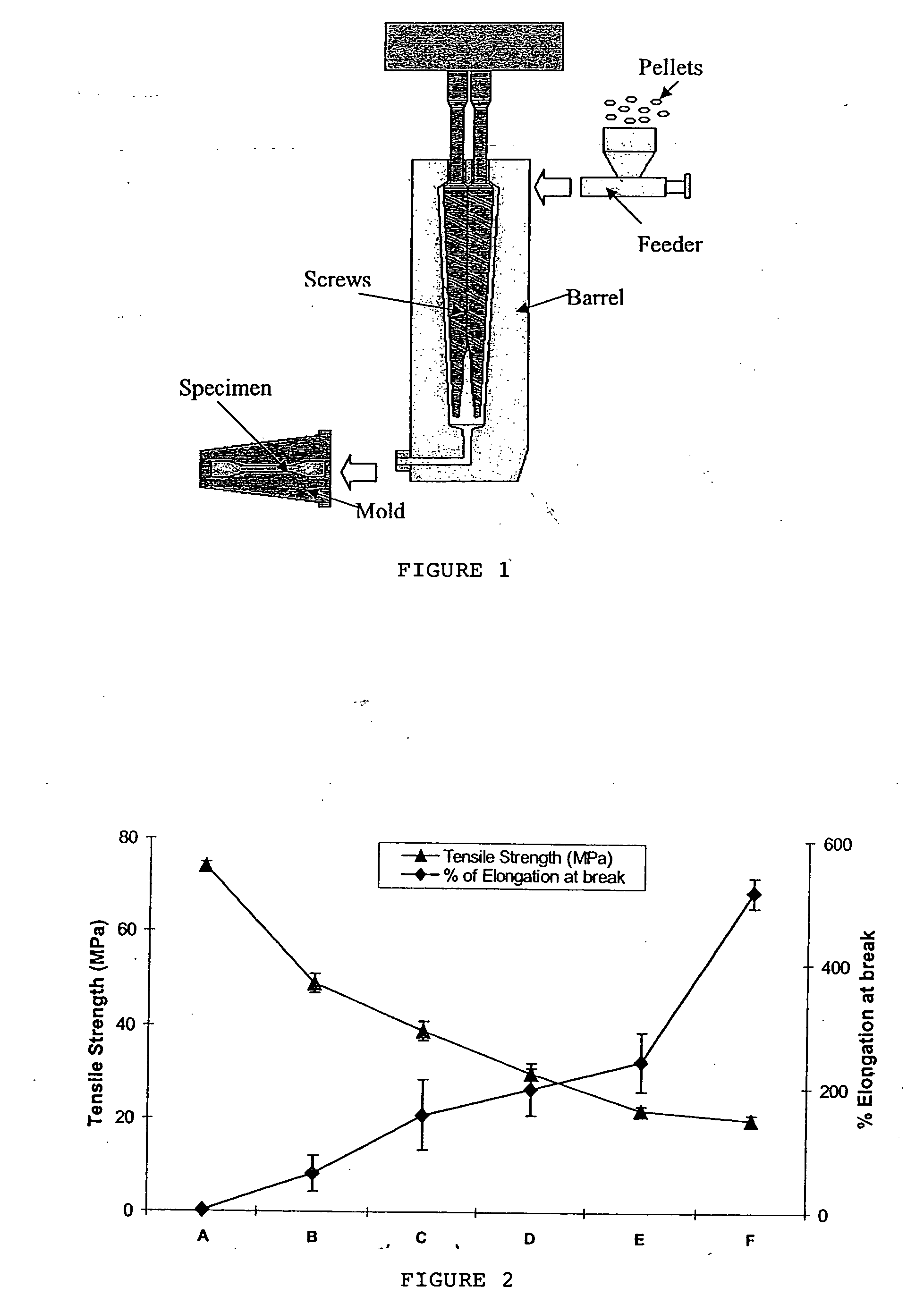
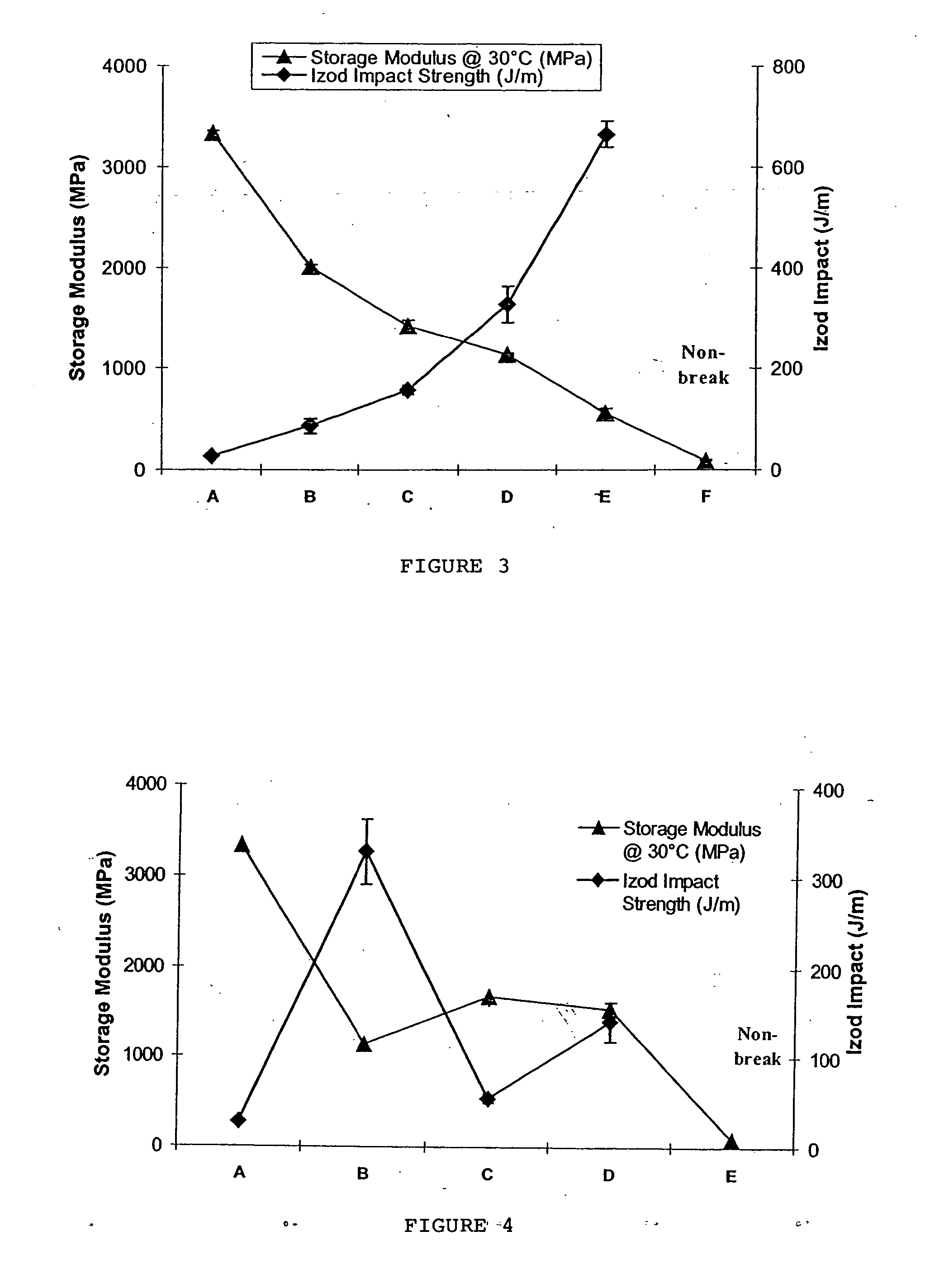
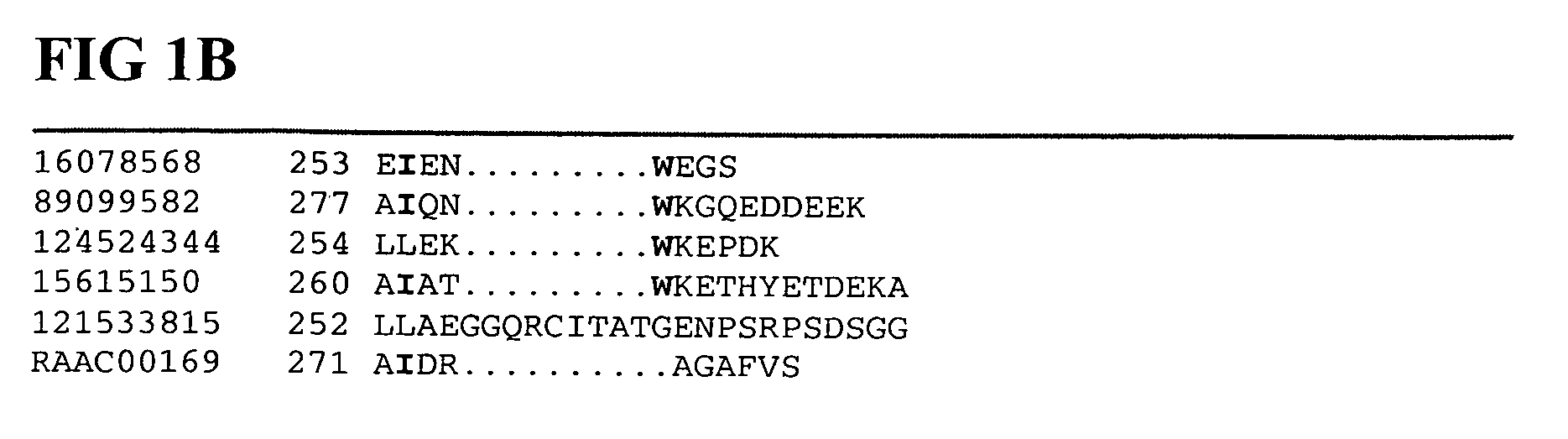
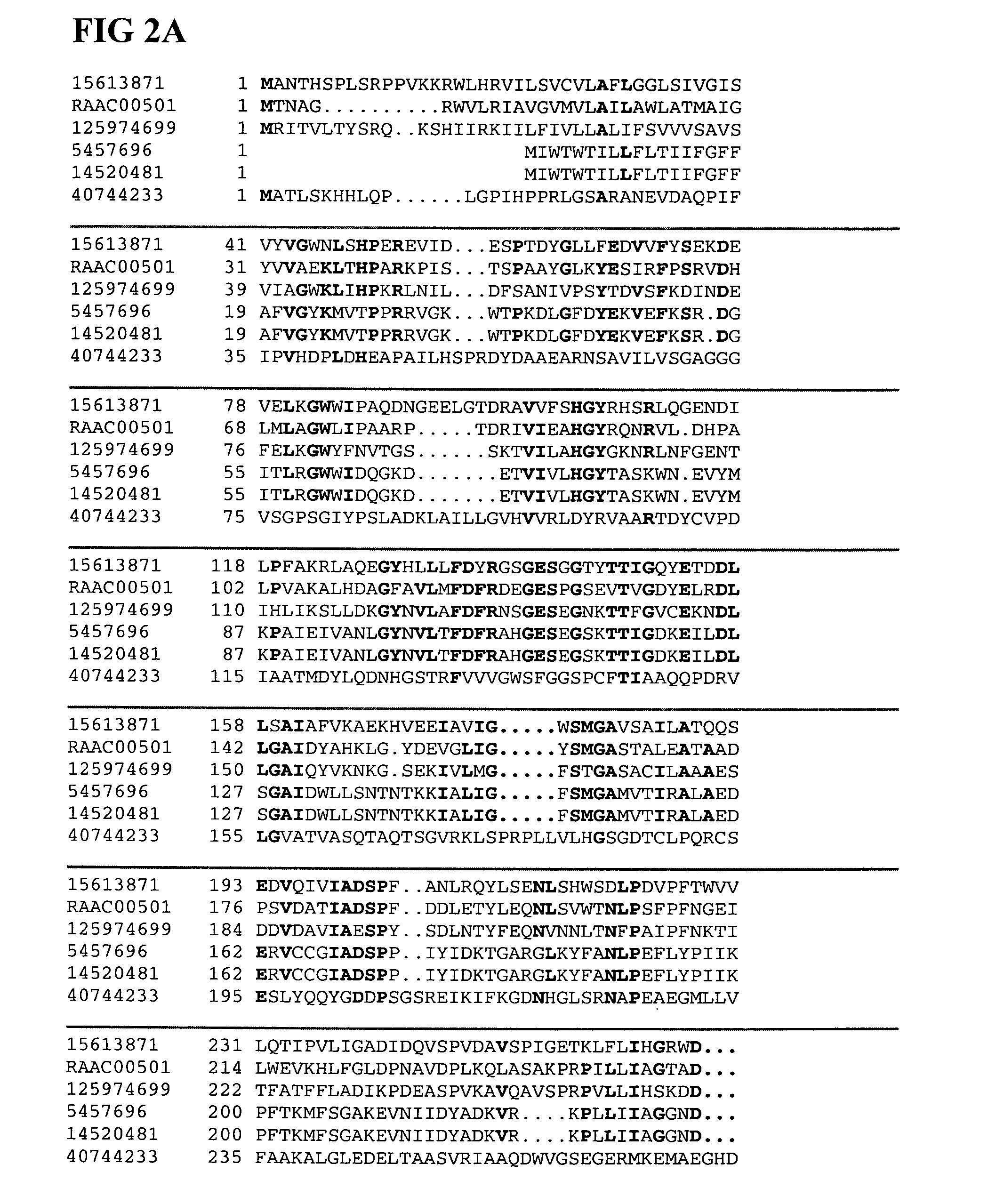
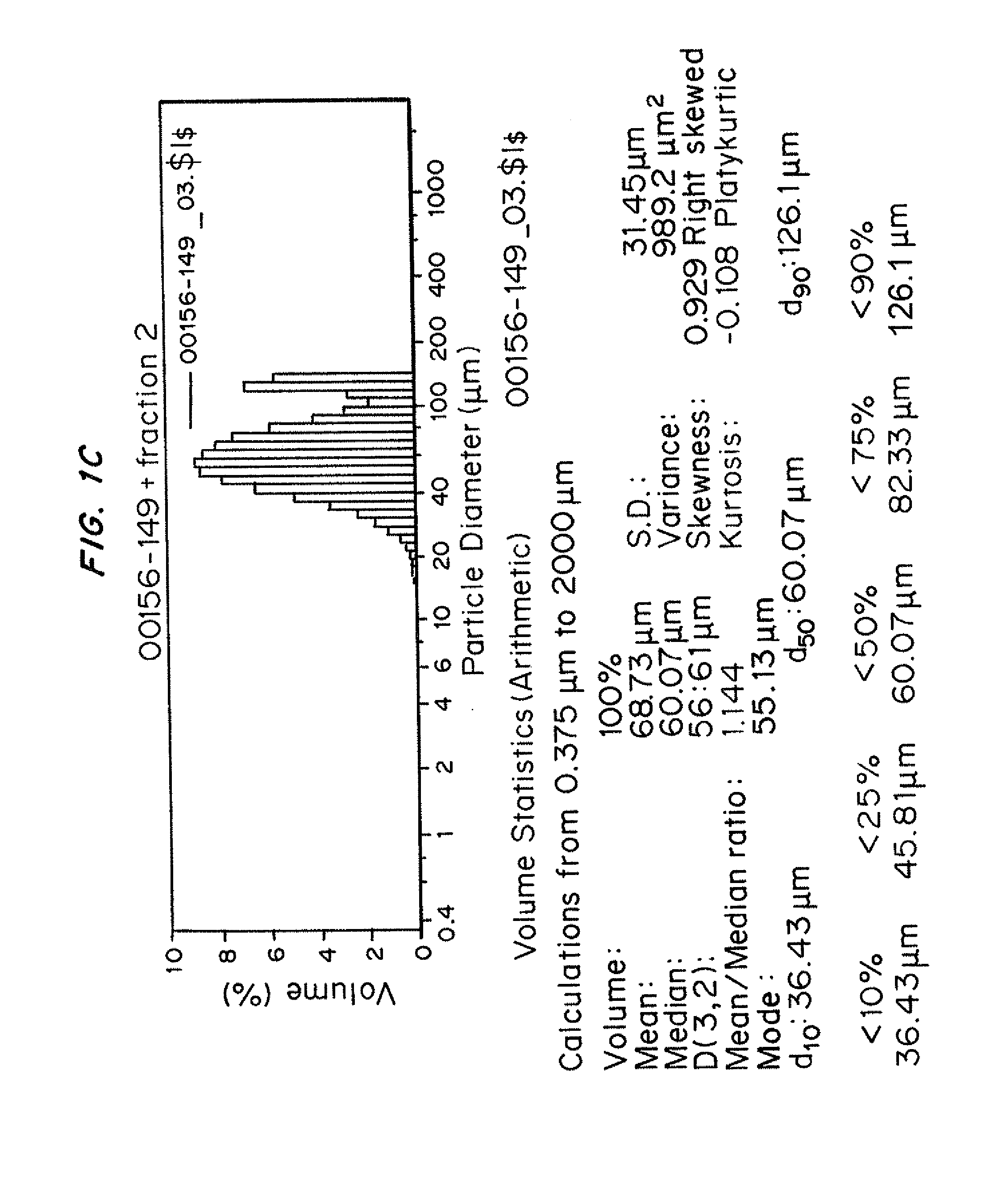
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
488 results about "Polyhydroxybutyrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
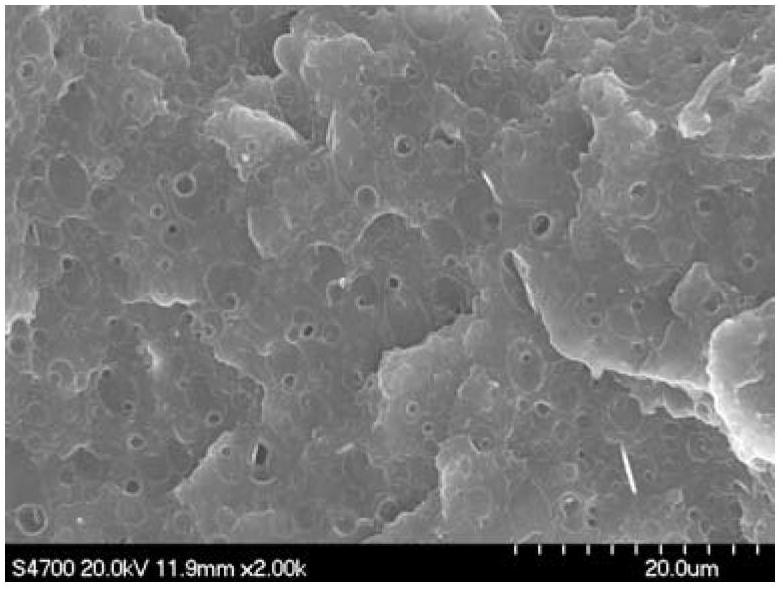
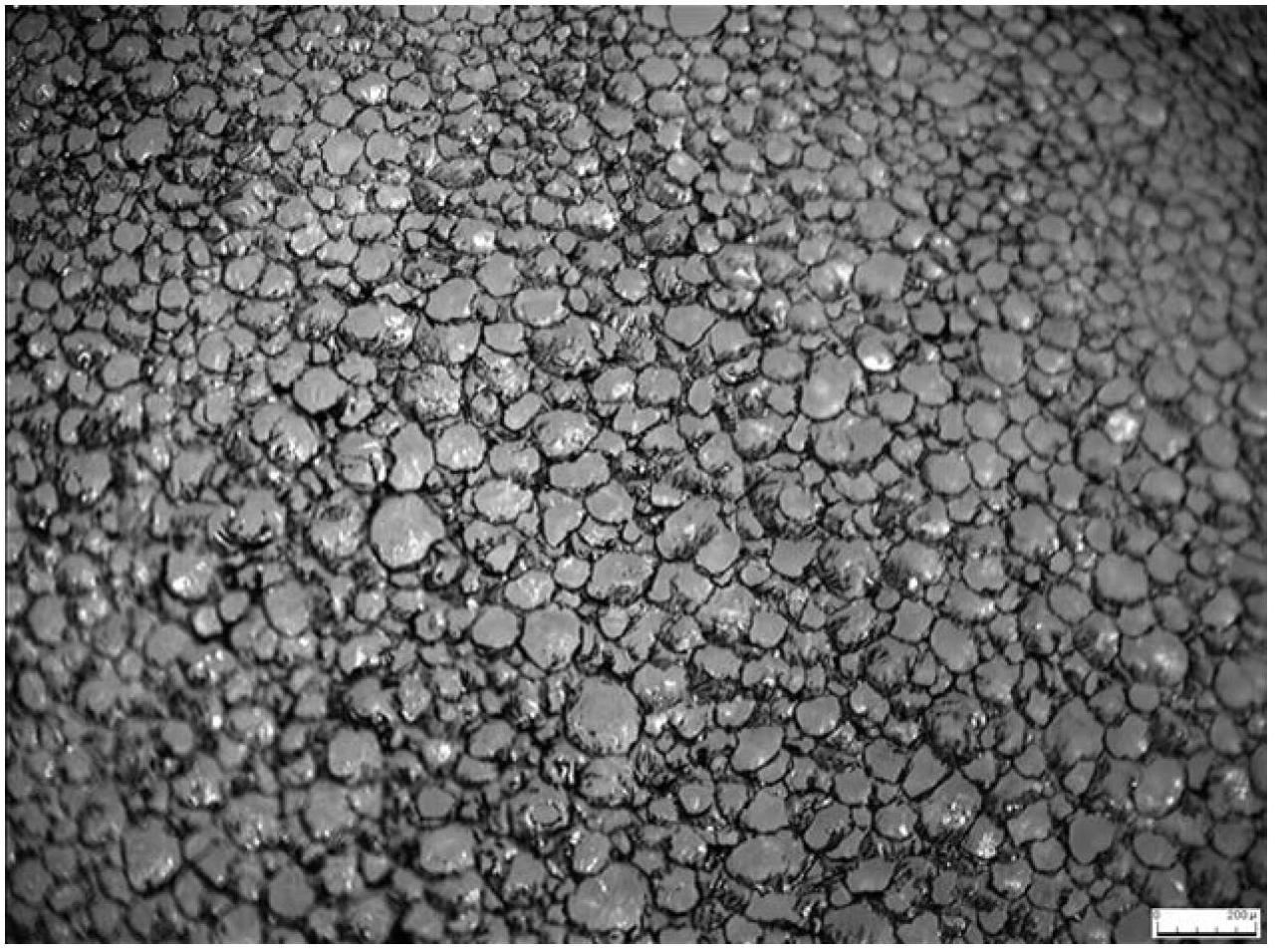
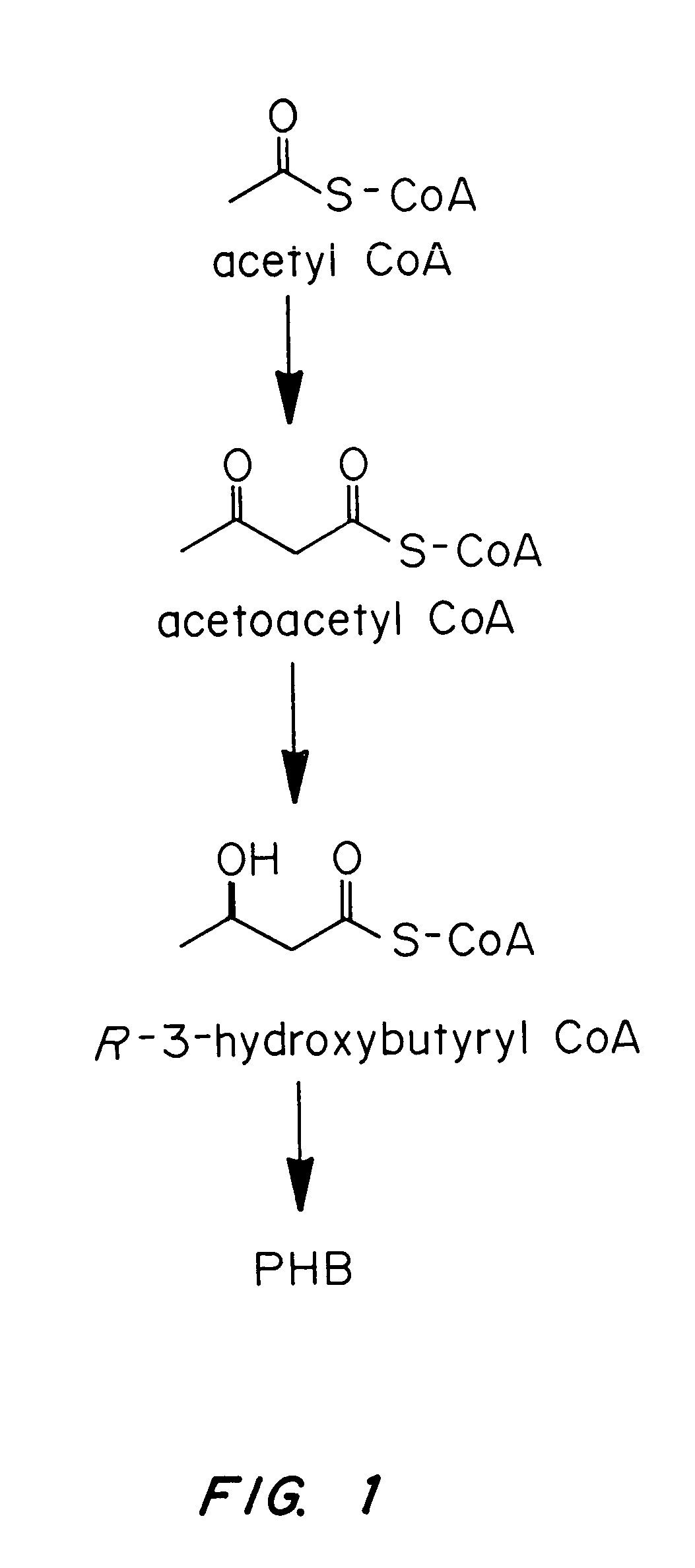
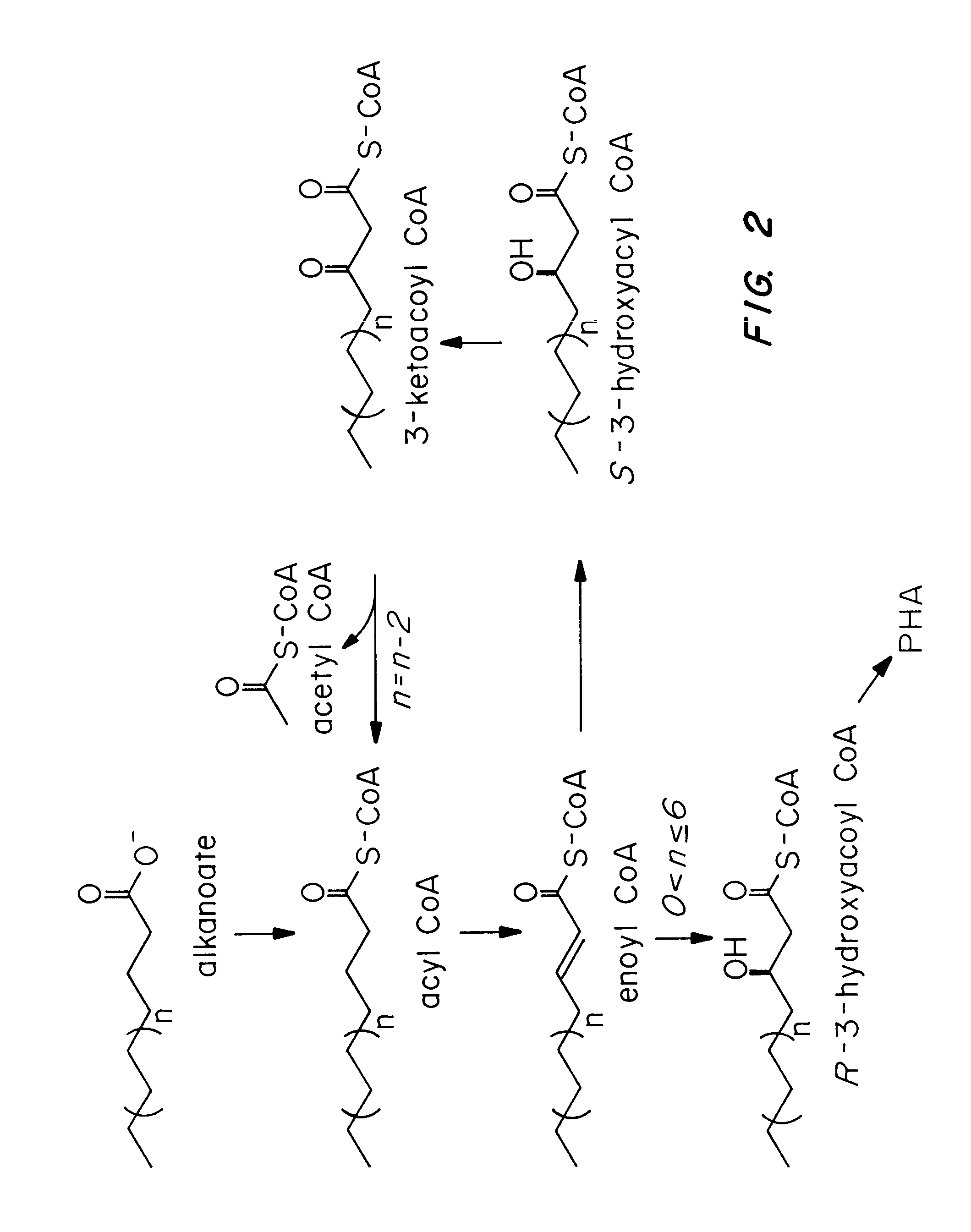
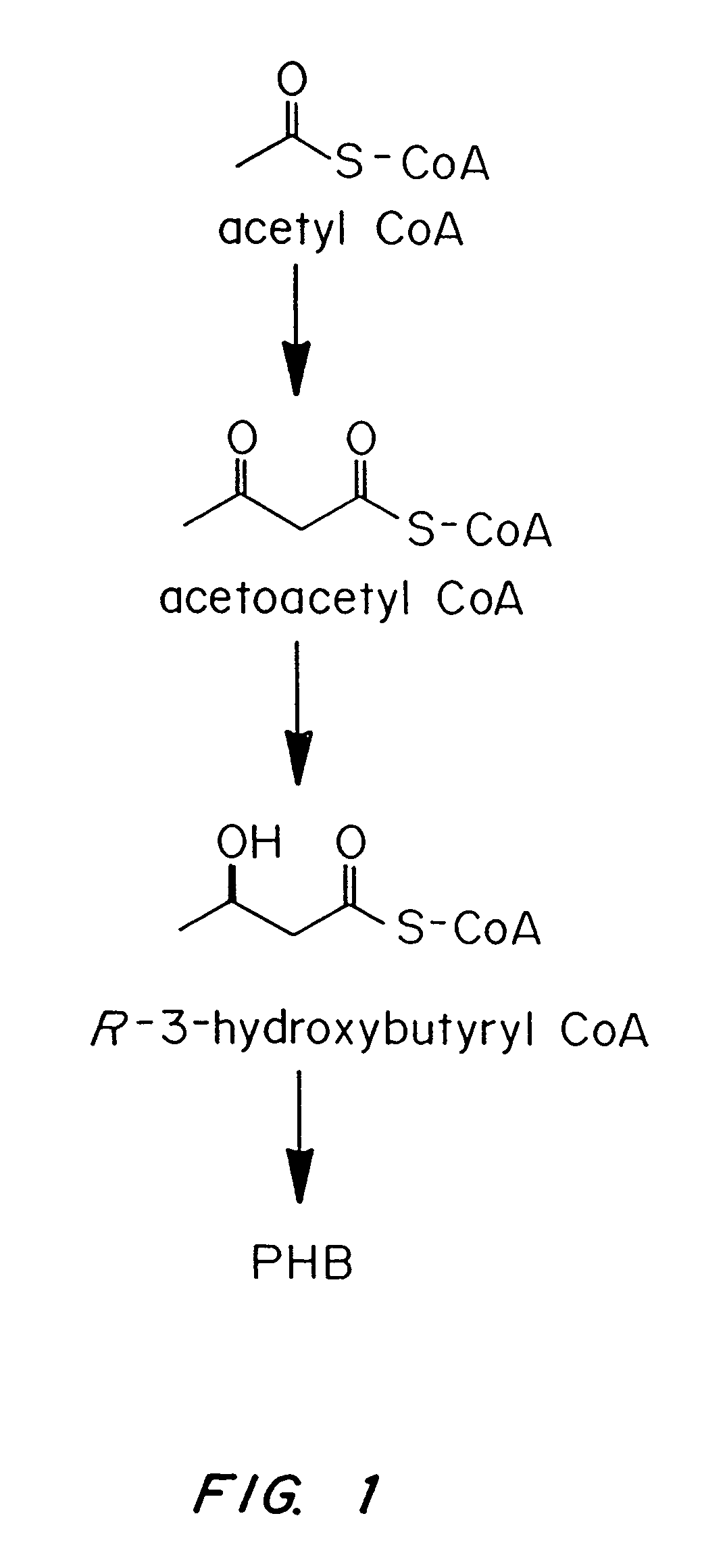
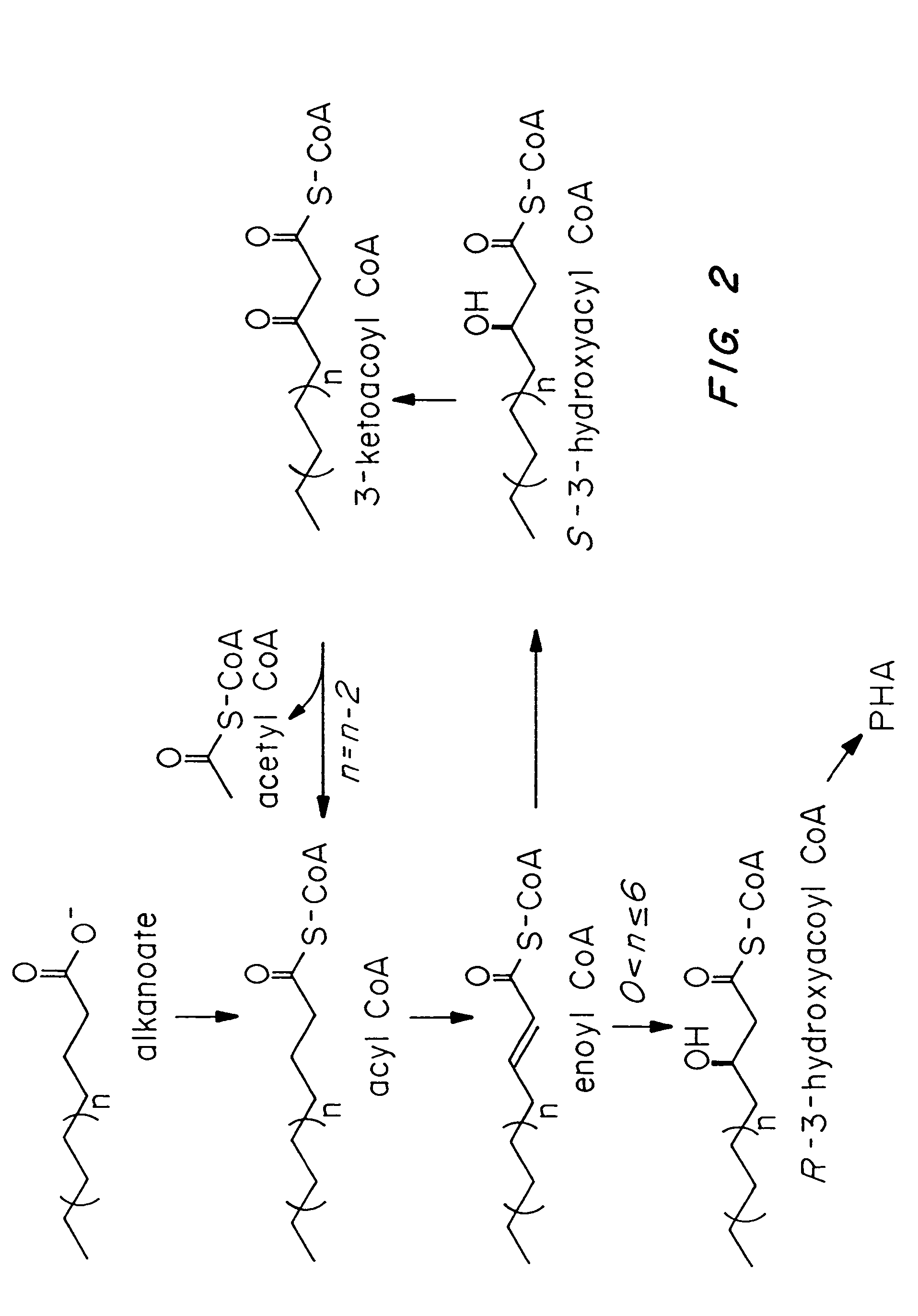
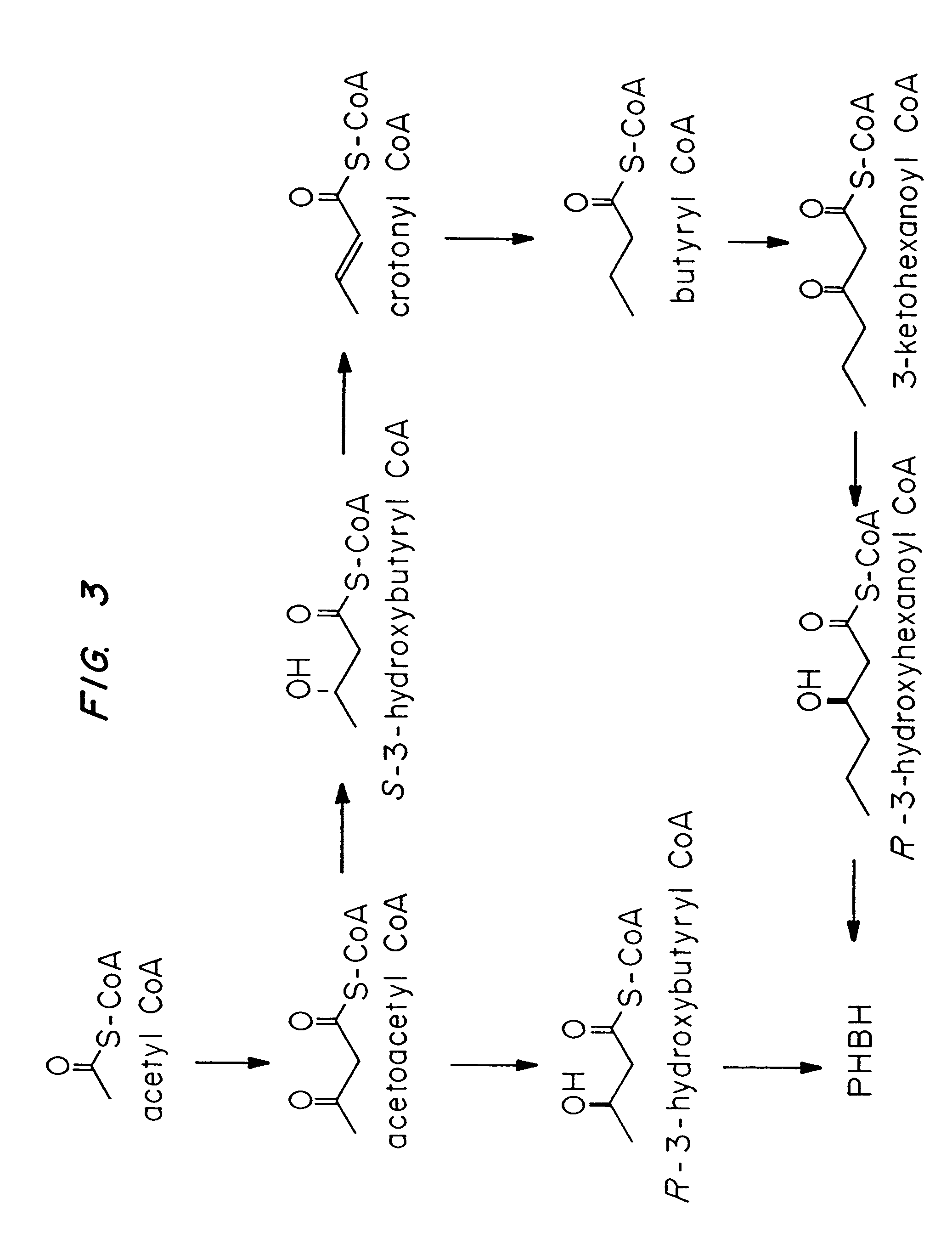
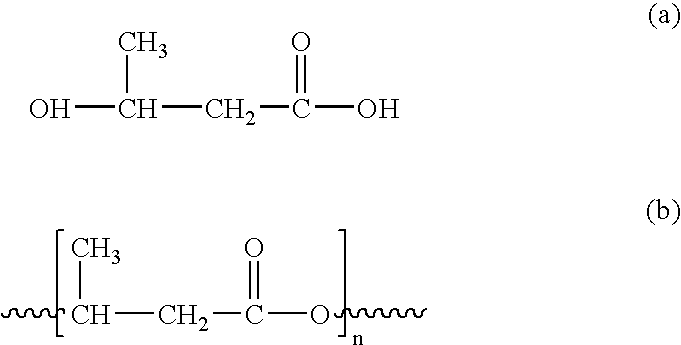
Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is a polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a polymer belonging to the polyesters class that area of interest as bio-derived and biodegradable plastics. The poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (P3HB) form of PHB is probably the most common type of polyhydroxyalkanoate, but other polymers of this class are produced by a variety of organisms: these include poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB), polyhydroxyvalerate (PHV), polyhydroxyhexanoate (PHH), polyhydroxyoctanoate (PHO) and their copolymers.
Biodegradable polymer coils for intraluminal implants
An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location of a separable coil comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein and growth factors. Typically a catheter associated with the separable coil is used to dispose the coil into a selected body lumen. The biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein is thrombogenic. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and absorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides. The biocompatible and absorbable protein is at least one protein selected from the group consisting of collagen, fibrinogen, fibronectin, vitronectin, laminin, and gelatin. In one embodiment the coil is composed of the biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein with a radio-opaque material is disposed thereon. Alternatively, the coil is composed of a radio-opaque material, and the biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein is disposed thereon. This apparatus may be positioned within intracranial aneurysms or any aneurysm in the body as well as within other body cavities.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Recombinant expressed bioadsorbable polyhydroxyalkonate monofilament and multi-filaments self-retaining sutures
InactiveUS20090112259A1Suture equipmentsMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentMicroorganismBreaking strength
The present invention provides polymers made by genetically engineering microorganisms for making a self-retaining suture. In an embodiment of the present invention the genetically engineering microorganisms synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) polymers. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, the genetically engineering microorganisms synthesize polybetahydroxybutyrate (PHB) polymers. In an alternative embodiment of the invention, the self-retaining sutures can be made from a copolymer such as polyhydroxybutyratevalerate (PHBV), where the genetically engineering microorganisms produces PHA polymers as the monofilament base material and a different genetically engineering microorganisms produces polyhydroxybutyratevalerate (PHBV) polymers. In various embodiments of the invention, recombinant expressed self-retaining suture materials have a melting point in the range from between approximately 40° C. to approximately 180° C. In various embodiments of the invention, recombinant expressed self-retaining suture materials have extension-to-break strength of between approximately 8% and approximately 42%.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Poly-4-hydroxybutyrate matrices for sustained drug delivery
Biodegradable controlled release systems providing prolonged controlled release of drugs, and methods for the manufacture thereof are disclosed. The systems are formed from a biocompatible, biodegradable polymer, in particular poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (PHA4400) or copolymers thereof. Copolymers of 4-hydroxybutyrate include but are not limited to poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate (PHA3444), and poly-4-hydoxybutyrate-co-glycolate (PHA4422). Drugs are generally incorporated into the polymer using a method that yields a uniform dispersion. The type of drug and the quantity are selected based on the known pharmaceutical properties of these compounds. The systems may be administered for example by implantation, injection, topical administration, or oral ingestion. They may also be used in combination with a medical device, for example, a stent. A major advantage of the drug delivery system is that it does not need to be removed after use since it is slowly degraded and cleared by the patient's body. The device has desirable physical properties, including strength, modulus and elongation.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Method for modifying a medical implant surface for promoting tissue growth
InactiveUS20080091234A1Without excessive fibrosisIncreased riskCoatingsSurgical veterinaryBioabsorbable polymerPolyhydroxybutyrate
Disclosed is an occluder for closing an intracardiac defect, such as a patent foramen ovale (PFO), and a method for making the same. The occluder includes a frame and at least one scaffold which are formed from a bioabsorbable polymer, such as poly-4-hydroxybutyrate. The surface of the frame and scaffold are textured to promote cell attachment. Texturing of the surface can be achieved by any number of mechanical or chemical procedures. The device is coated with collagen and heparin which are covalently bound to the surface of the device. The occluder provides improved defect closure compared to other septal occluders known in the art. In particular, the occluder described is specifically designed to improve host cell attachment to and tissue ingrowth over the device when implanted in a patient as compared to the level of host cell attachment and tissue ingrowth achieved with other implantable devices made of bioabsorbable polymers.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Use of phosphoketolase for producing useful metabolites
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Recombinant expressed bioadsorbable polyhydroxyalkanoate monofilament and multi-filaments self-retaining sutures
InactiveUS20100057123A1Suture equipmentsMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentBreaking strengthMicroorganism
The present invention provides polymers made by genetically engineering microorganisms for making a self-retaining suture. In an embodiment of the present invention the genetically engineering microorganisms synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) polymers. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, the genetically engineering microorganisms synthesize polybetahydroxybutyrate (PHB) polymers. In an alternative embodiment of the invention, the self-retaining sutures can be made from a copolymer such as polyhydroxybutyratevalerate (PHBV), where the genetically engineering microorganisms produces PHA polymers as the monofilament base material and a different genetically engineering microorganisms produces polyhydroxybutyratevalerate (PHBV) polymers. In various embodiments of the invention, recombinant expressed self-retaining suture materials have a melting point in the range from between approximately 40° C. to approximately 180° C. In various embodiments of the invention, recombinant expressed self-retaining suture materials have extension-to-break strength of between approximately 8% and approximately 42%.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
InactiveUS20020040239A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical containersPoly-L-lactideVascular compartment
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Green process and compositions for producing poly(5HV) and 5 carbon chemicals
Recombinant hosts for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates and methods of producing polyhydroxyalkanoates from renewable carbon substrates are provided. Certain recombinant hosts that produce 5 carbon chemicals such as 5-aminopentanoate (5AP), 5-hydroxyvalerate (5HV), glutarate, and 1,5 pentanediol (PDO) are also provided. One embodiment provides a recombinant host expressing a gene encoding a heterologous enzyme selected from the group consisting of a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5-hydroxyvalerate-CoA (5HV-CoA) transferase, wherein the host produces a polymer containing 5-hydroxyvalerate. Preferably, the host expresses both a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5HV-CoA transferase. The host can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic. A preferred prokaryotic host is E. coli. The polymers produced by the recombinant hosts can be homopolymers or copolymers of 5-hydroxyvalerate. A preferred copolymer is poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-5-hydroxyvalerate).
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Biodegradable triblock copolymers, synthesis methods therefore, and hydrogels and biomaterials made there from
InactiveUS20080057128A1Interesting propertyVivo degradation ratePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPolymer scienceSynthesis methods
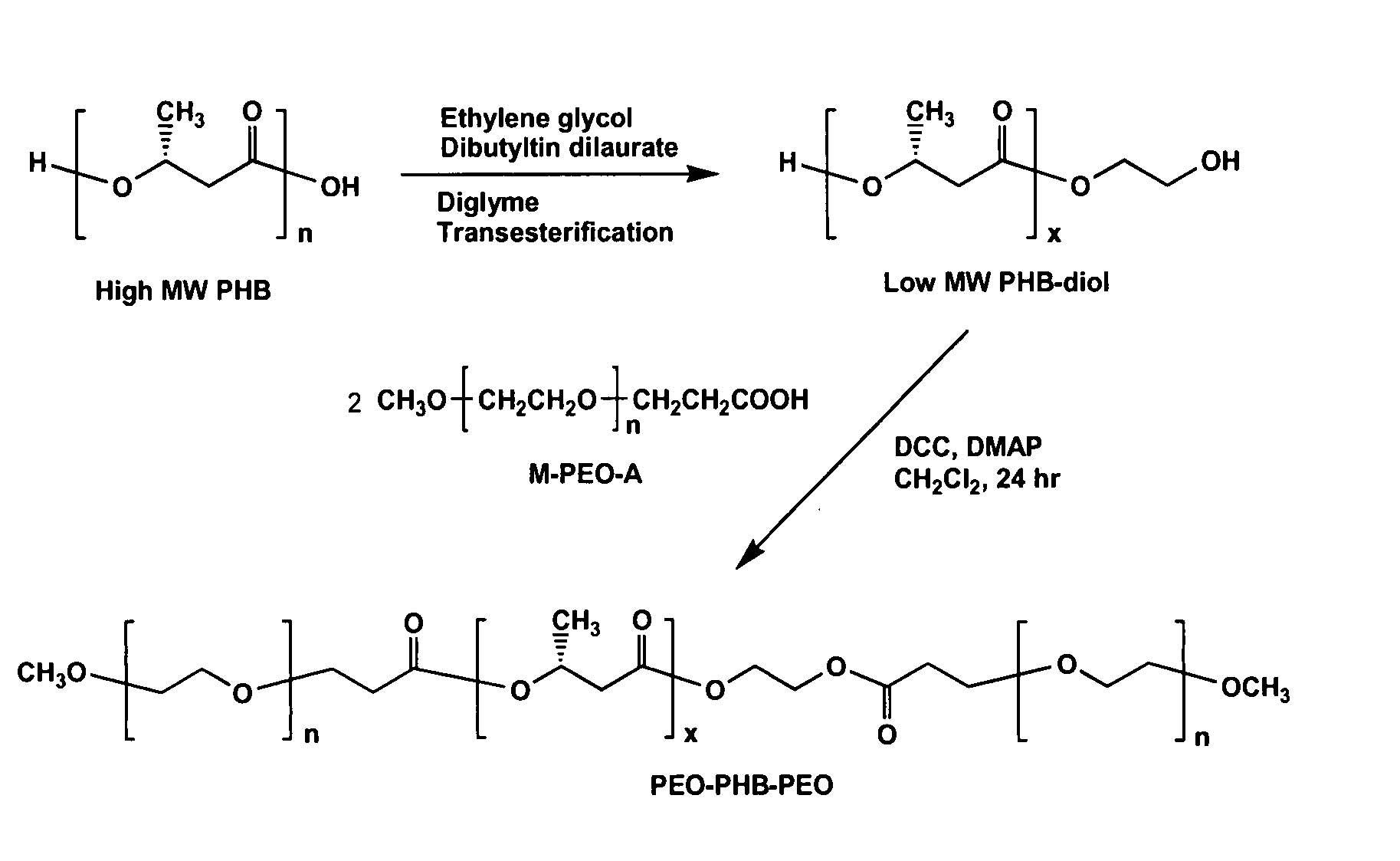
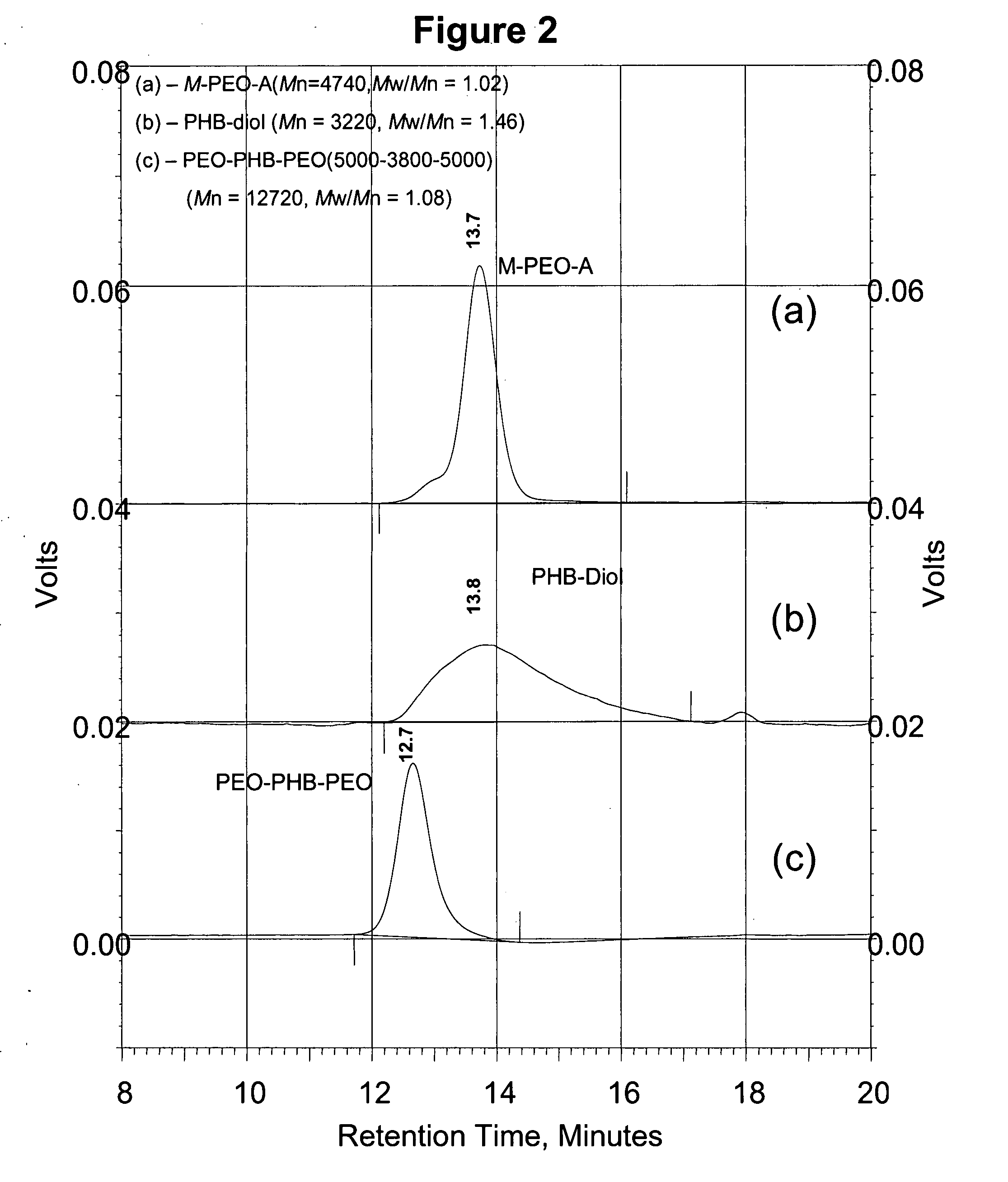
A drug delivery system that includes micelles formed from an amphiphilic copolymer that includes an A polymer block comprising a poly(alkylene oxide) and a B polymer block comprising a poly(hydroxyalkanoate), and a therapeutically effective amount of at least one therapeutic agent intimately contained within the micelles. In one preferred embodiment of the invention, the A polymer block is poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and the B polymer block is poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] (PHB), and the copolymer is the triblock ABA copolymer PEO-PHB-PEO. A method of synthesizing the amphiphilic triblock copolymer is also provided.
Owner:OMEROS CORP
Thermophilic and thermoacidophilic biopolymer-degrading genes and enzymes from alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius and related organisms, methods
Isolated and / or purified polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences encoding polypeptides from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius are provided. Further provided are methods of at least partially degrading, cleaving, or removing polysaccharides, lignocellulose, cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, starch, chitin, polyhydroxybutyrate, heteroxylans, glycosides, xylan-, glucan-, galactan, or mannan-decorating groups using isolated and / or purified polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences encoding polypeptides from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Biodegradable polymeric nanocomposite compositions particularly for packaging
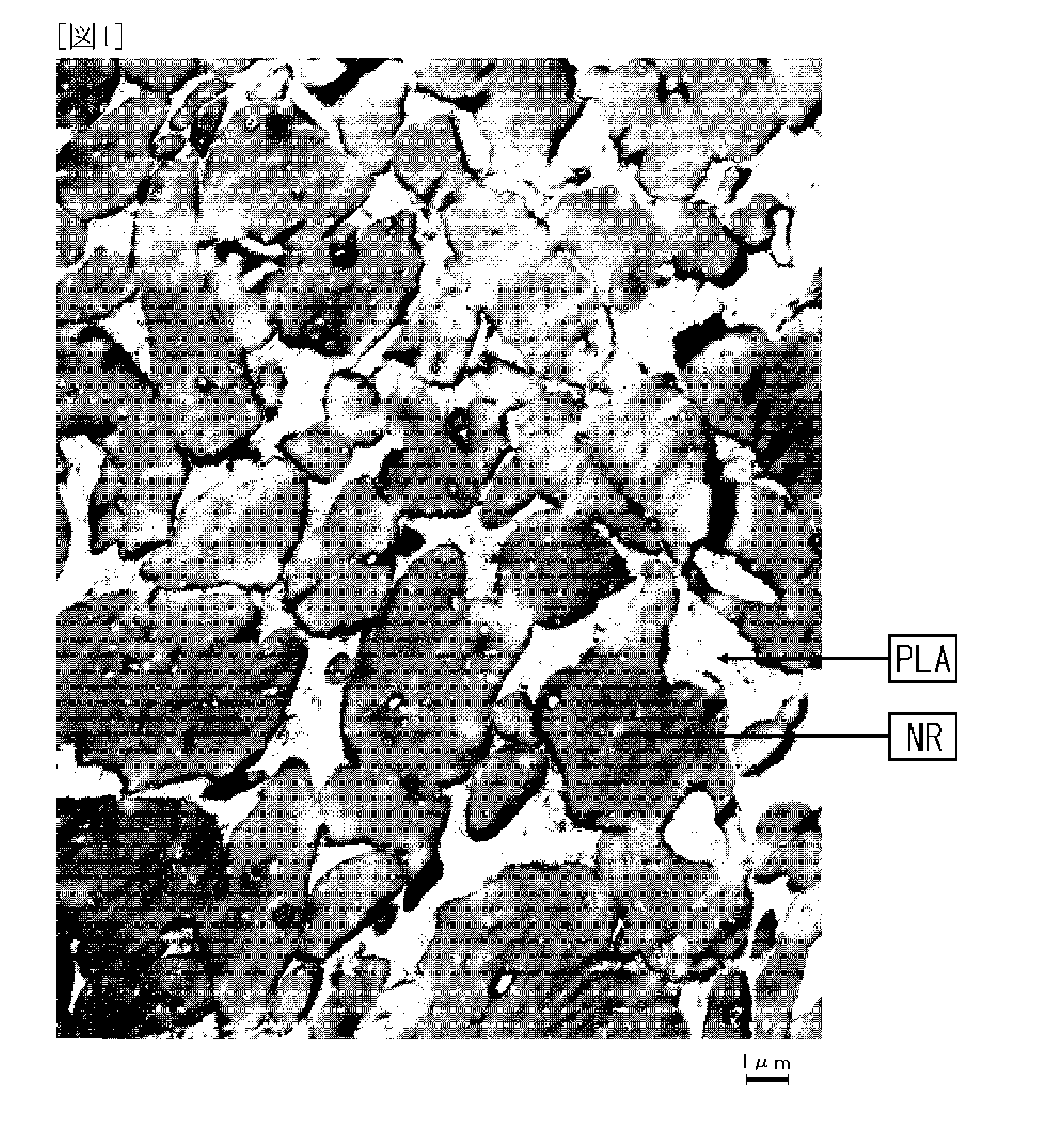
Specific polymer blends of polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and poly-(butylenes adipate-co-terephthalate (PBAT) as a fatty acid quaternary ammonium modified clay. The blends are particularly useful for barrier packaging.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Environmentally degradable polymeric composition and process for obtaining an environmentally degradable polymeric composition
The present invention refers to a polymeric composition prepared from a biodegradable polymer defined by poly-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) or copolymers thereof, and at least one other biodegradable polymer, such as polycaprolactone (PCL) and poly (lactic acid) (PLA), so as to alter its structure, and further at least one additive of the type of natural filler and natural fibers, and, optionally, nucleant, thermal stabilizer, processing aid, with the object of preparing an environmentally degradable material. According to the production process described herein, the composition resulting from the mixture of the modified biodegradable polymer and additives can be utilized in the manufacture of injected packages for food products, injected packages for cosmetics, tubes, technical pieces and several injected products.
Owner:PHB IND
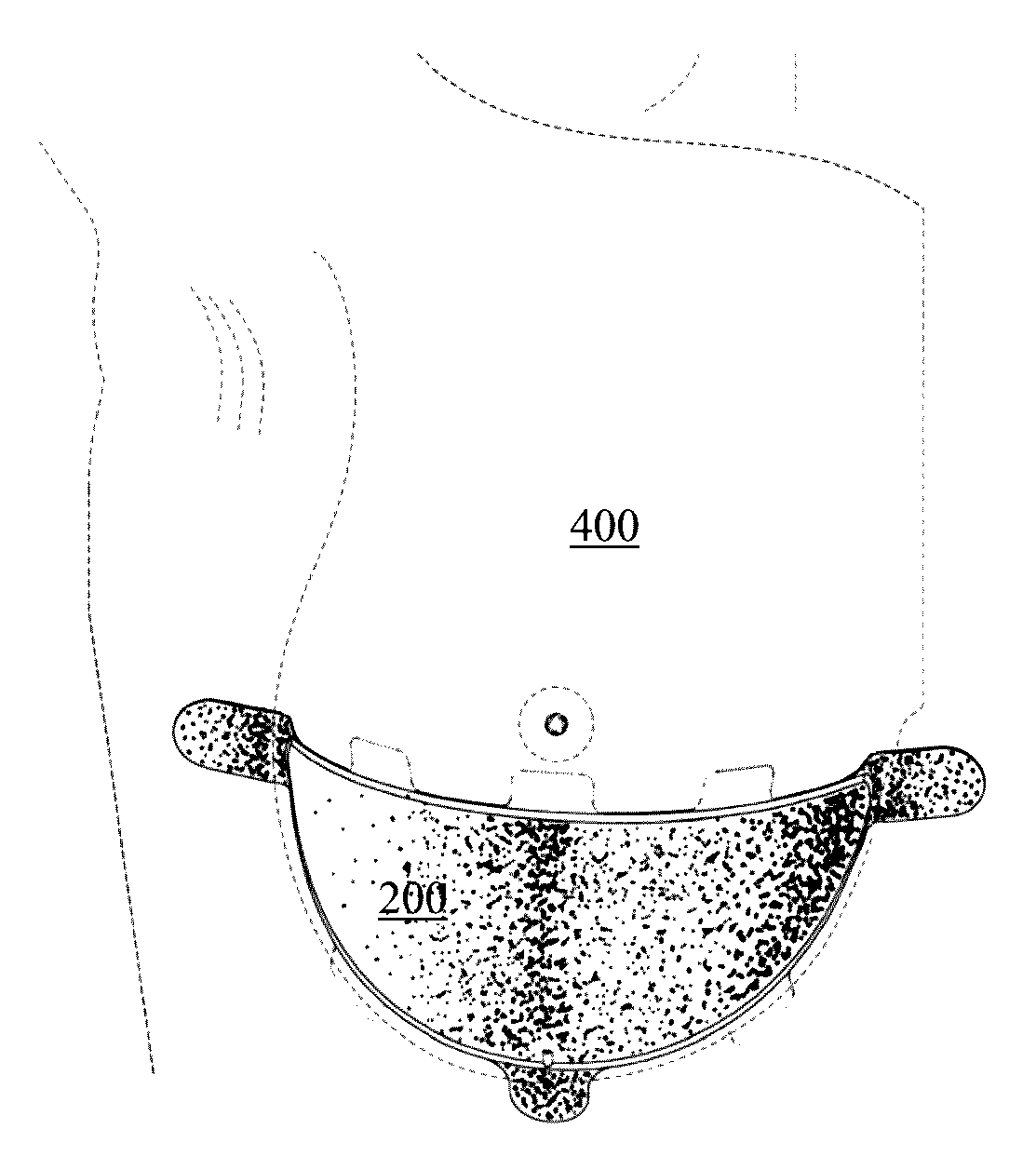
Absorbable implants for plastic surgery
ActiveUS9655715B2Sufficient mechanical propertyMinimization requirementsMammary implantsSurgeryMastopexyBreast reconstruction
Absorbable implants for breast surgery that conform to the breast parenchyma and surrounding chest wall have been developed. These implants support newly lifted breast parenchyma, and / or a breast implant. The implants have mechanical properties sufficient to support a reconstructed breast, and allow the in-growth of tissue into the implant as it degrades. The implants have a strength retention profile allowing the support of the breast to be transitioned from the implant to regenerated host tissue, without significant loss of support. Three-dimensional implants for use in minimally invasive mastopexy / breast reconstruction procedures are also described, that confer shape to a patient's breast. These implants are self-reinforced, can be temporarily deformed, implanted in a suitably dissected tissue plane, and resume their preformed three-dimensional shape. The implants are preferably made from poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB) and copolymers thereof. The implants have suture pullout strengths that can resist the mechanical loads exerted on the reconstructed breast.
Owner:TEPHA INC
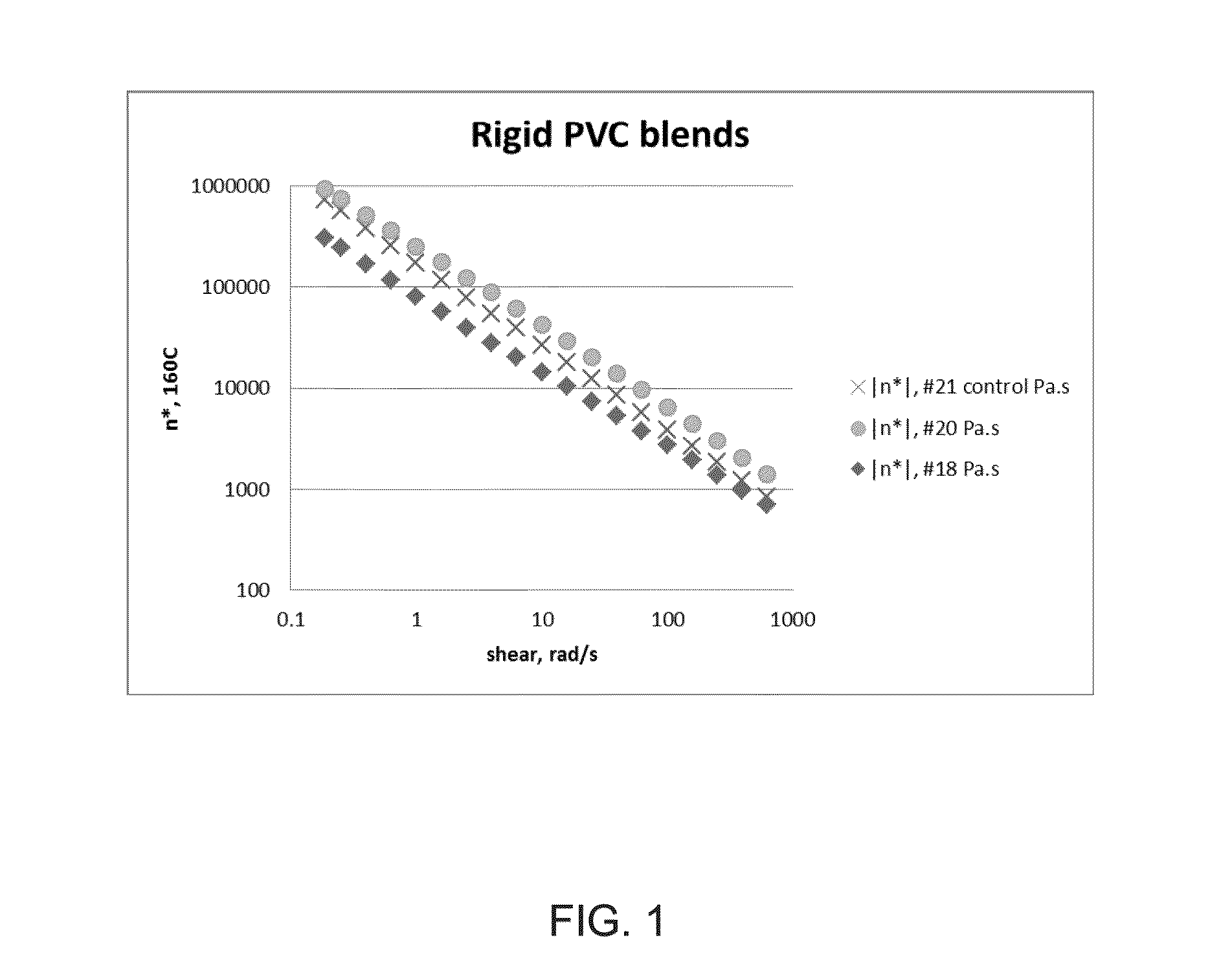
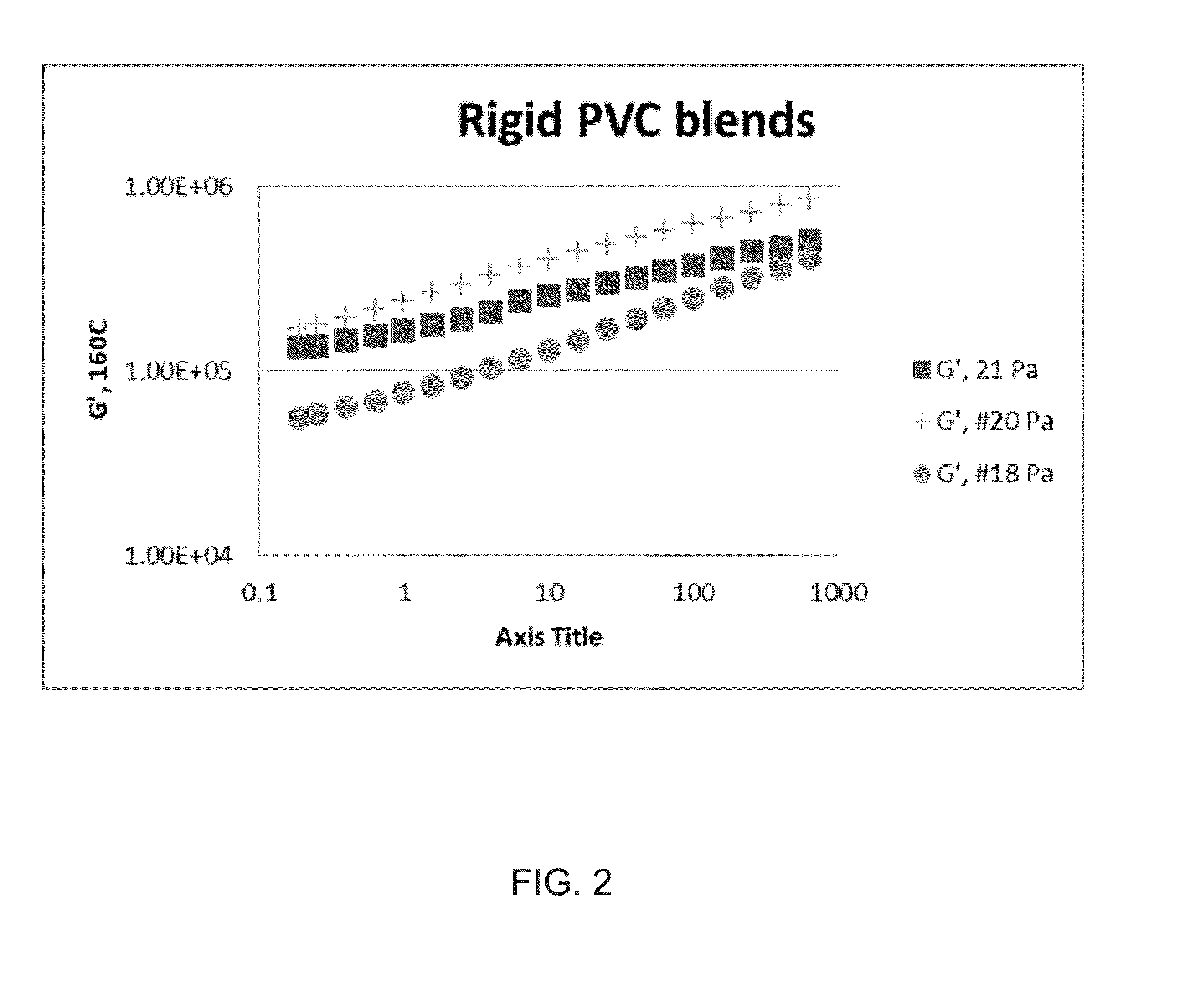
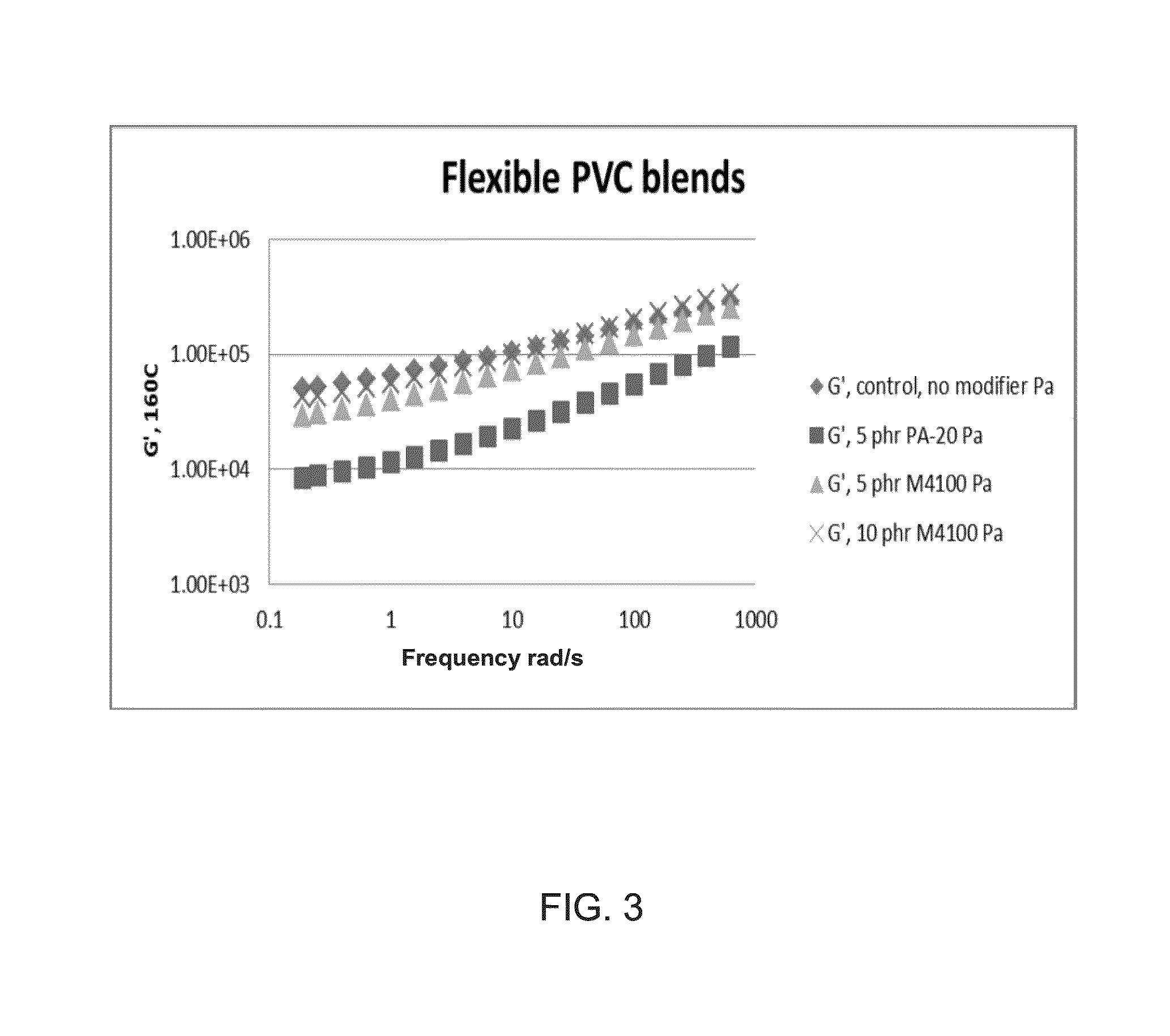
Biobased modifiers for polyvinylchloride blends
Compositions of polymer blends of polyvinylchloride (PVC), a low molecular weight plasticizer and polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) are described. In certain embodiments, the PHA is a poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate copolymer having a weight percent 4-hydroxybutyrate of 30-45%. In other embodiments the PHA is a multiphase P3HB-4HB copolymer blend having one phase fully amorphous. The PHA is mixed with the PVC and low molecular weight plasticizer to optimize the PVC's optical, thermal and mechanical properties. In certain embodiments, the polymer is branched with optionally additives that improve properties. Methods of making the compositions of the invention are also described. The invention also includes articles, films and laminates comprising the compositions.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
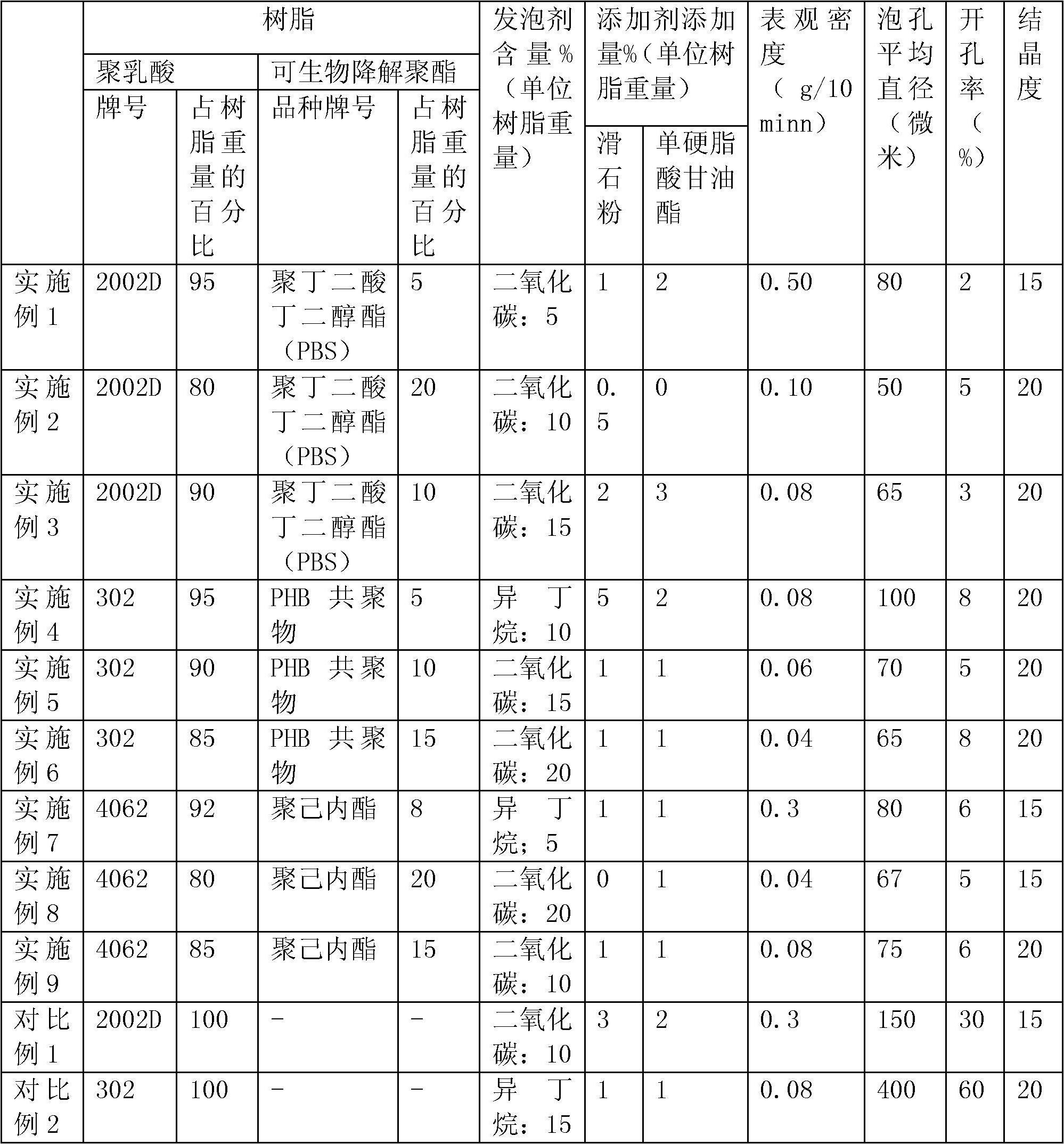
Polylactic acid foamed material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a polylactic acid foamed material and a preparation method thereof. The invention solves the technical problems of large pore size, nonuniformity and high porosity in the existing product. The polylactic acid foamed material is prepared by an extrusion foaming method. The polylactic acid foamed material comprises polylactic acid, at least one biodegradable polyester (selected from poly(butylenes succinate), polyhydroxybutyrate, polycaprolactone and copolymer or blend thereof), a physical foaming agent, and at least one processing assistant for foaming. The apparent density of the microporous foamed sheet is 0.05-0.5g / cm<3>, the average pore diameter is not greater than 100 micrometers, and the porosity is not greater than 10%. The invention is mainly used in the fields of food packaging, automobile industry and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Absorbable implants for plastic surgery
ActiveUS20150112434A1Solve the lack of mechanical propertiesMinimization requirementsMammary implantsArtificial flowers and garlandsMastopexyEngineering
Absorbable implants for breast surgery that conform to the breast parenchyma and surrounding chest wall have been developed. These implants support newly lifted breast parenchyma, and / or a breast implant. The implants have mechanical properties sufficient to support a reconstructed breast, and allow the in-growth of tissue into the implant as it degrades. The implants have a strength retention profile allowing the support of the breast to be transitioned from the implant to regenerated host tissue, without significant loss of support. Three-dimensional implants for use in minimally invasive mastopexy / breast reconstruction procedures are also described, that confer shape to a patient's breast. These implants are self-reinforced, can be temporarily deformed, implanted in a suitably dissected tissue plane, and resume their preformed three-dimensional shape. The implants are preferably made from poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB) and copolymers thereof. The implants have suture pullout strengths that can resist the mechanical loads exerted on the reconstructed breast.
Owner:TEPHA INC
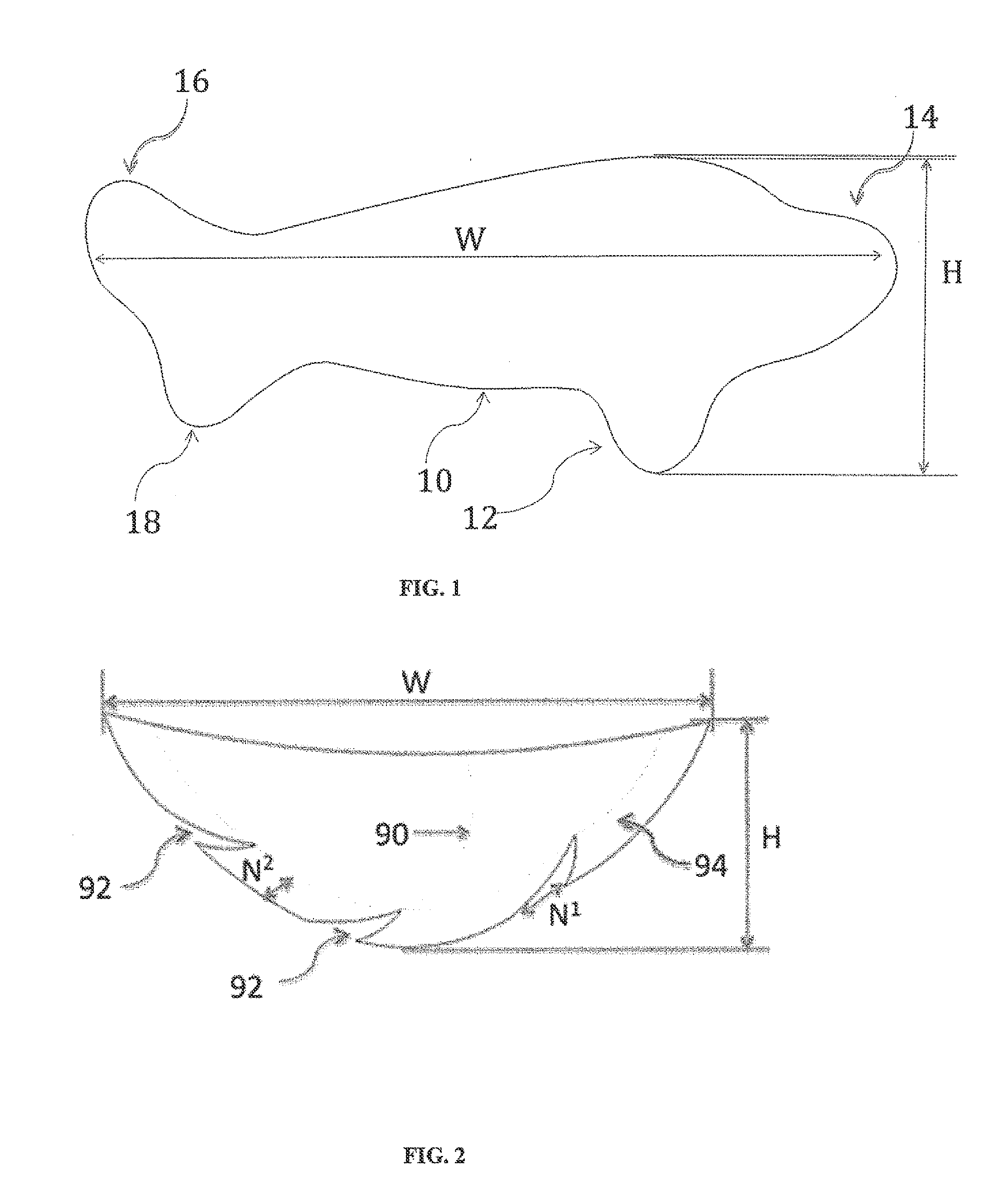
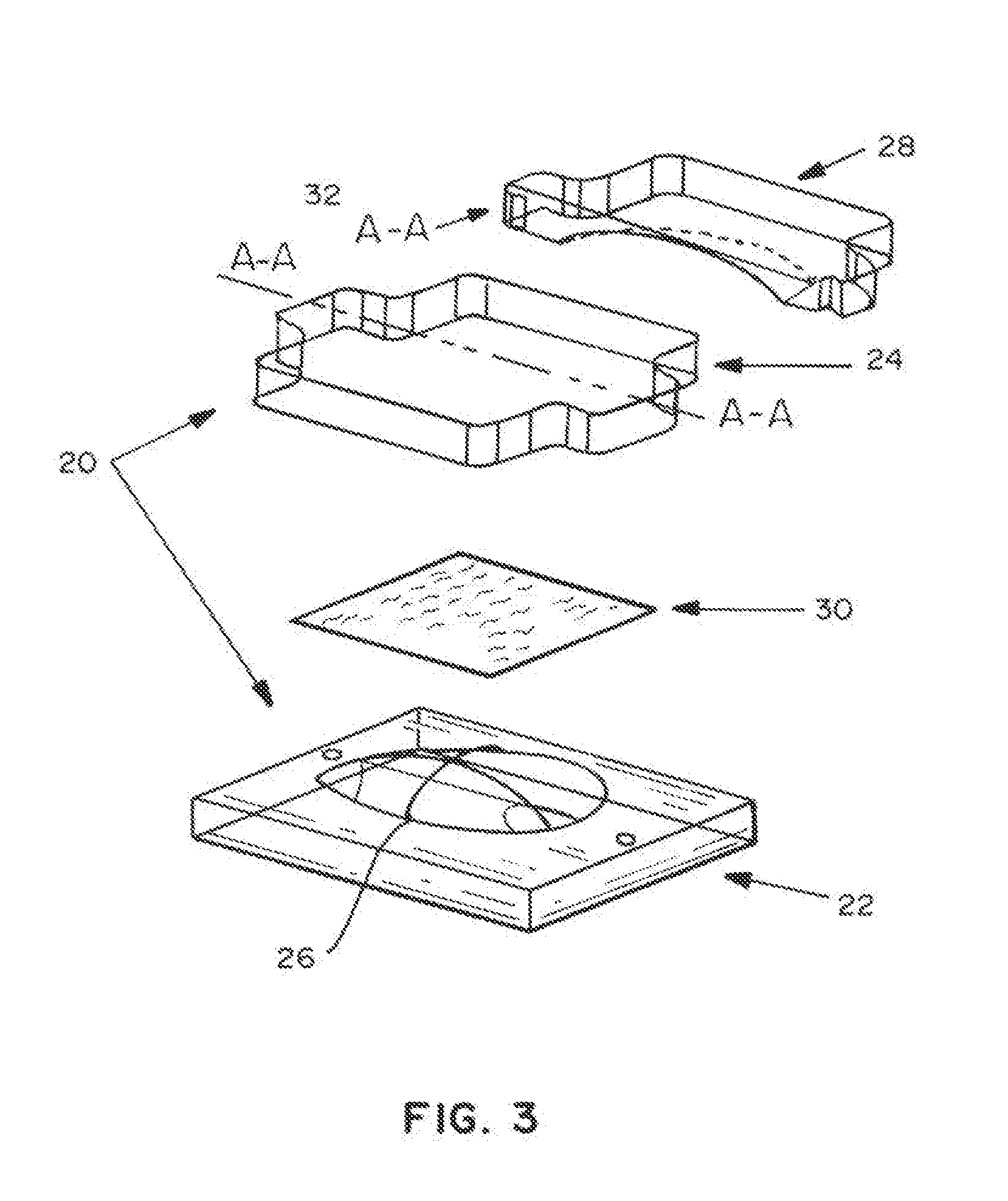
Biodegradable polymer composition with calcium carbonate and methods and products using same
Described herein are biodegradable compositions, methods for making these compositions, and applications using these compositions. In one embodiment, a process of manufacturing paper or other products is provided using a composition comprising a mixture of 25% to 80% calcium carbonate along with a biodegradable biopolymer matrix made from renewable resources including polylactic acid (“PLA”), soy proteins, polyhydroxyalkanoate (“PHA”), polyhydroxybutyrate (“PHB”), and / or starch from corn, wheat, tapioca, potatoes, or similar renewable resource products.
Owner:C STONE
Thermophilic and thermoacidophilic biopolymer-degrading genes and enzymes from alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius and related organisms, methods
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Transgenic systems for the manufacture of poly (3-hydroxy-butyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)
InactiveUS7455999B2Efficient PHA synthesisHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBiosynthetic genes
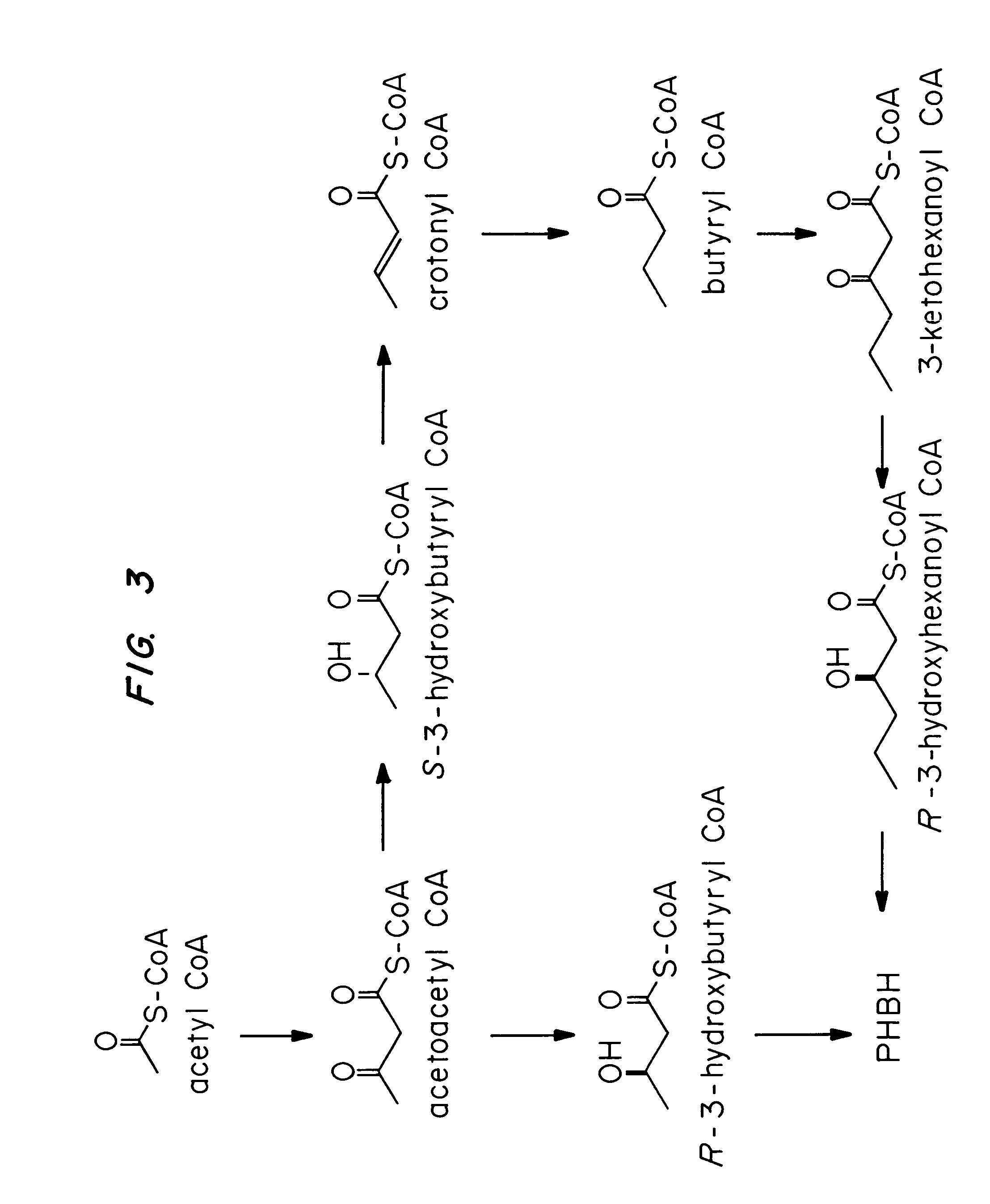
Methods for engineering transgenic organisms that synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) containing 3-hydroxyhexanoate as comonomer have been developed. These processes are based on genetically engineered bacteria such as Escherichia coli or in plant crops as production systems which include PHA biosynthetic genes from PHA producers. In a preferred embodiment of the method, additional genes are introduced in wild type or transgenic polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) producers, thereby creating new strains that synthesize 3HH monomers which are incorporated into PHAs. The 3HH monomer preferably is derived in microbial systems using butanol or butyrate as feedstocks, which are precursors of 3-hydroxyhexanoyl-CoA. Pathways for in vivo production of butyrol-CoA specifically encompassing butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase activity are provided.
Owner:METABOLIX
Thermoplastic elastomer composition
An object of the present invention is to provide: a thermoplastic elastomer composition, which is accompanied by less environmental burden, and which has flexibility, rubber elasticity, formability and recyclability; and a molded product obtained using the same. The present invention is directed to a thermoplastic elastomer composition comprising a thermoplastic resin (A) derived from a non-petroleum source, and at least one rubber (B) selected from a natural rubber, a diene polymer rubber, an olefin polymer rubber, an acrylic rubber and a silicone rubber, the thermoplastic elastomer composition being obtained by allowing the rubber (B) to be dynamically crosslinked with a crosslinking agent (C) in the presence of the thermoplastic resin (A). Preferred (A) is a polylactic acid, or a poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), and preferred (B) is a natural rubber.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
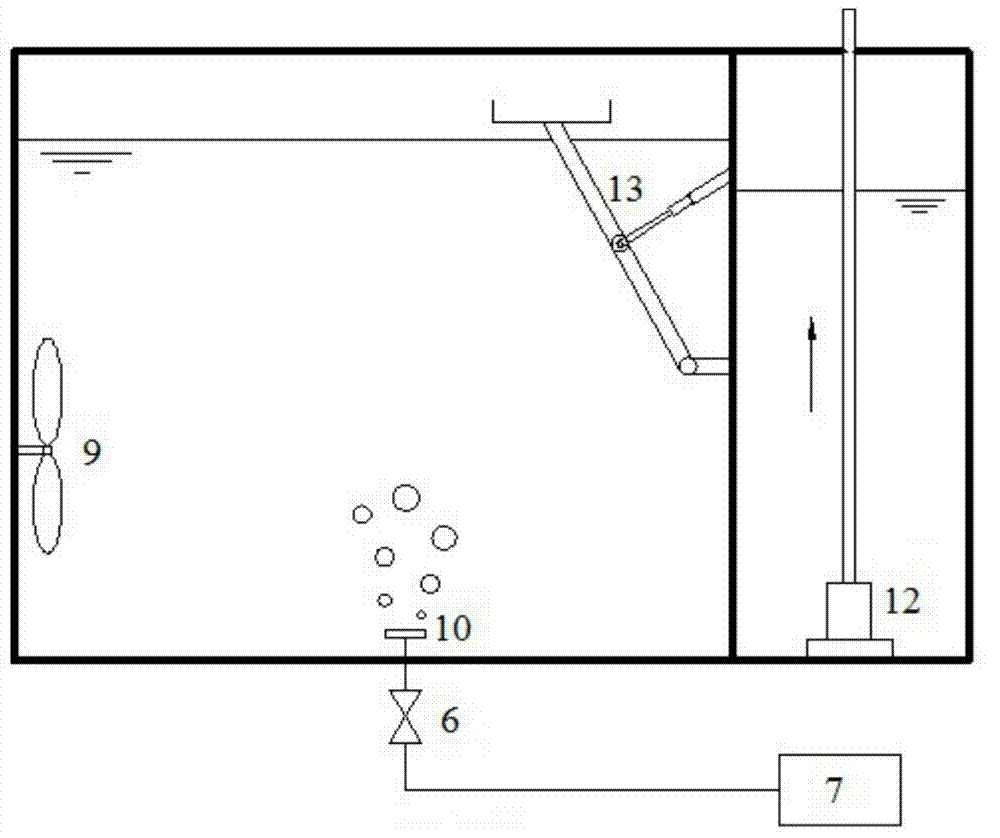
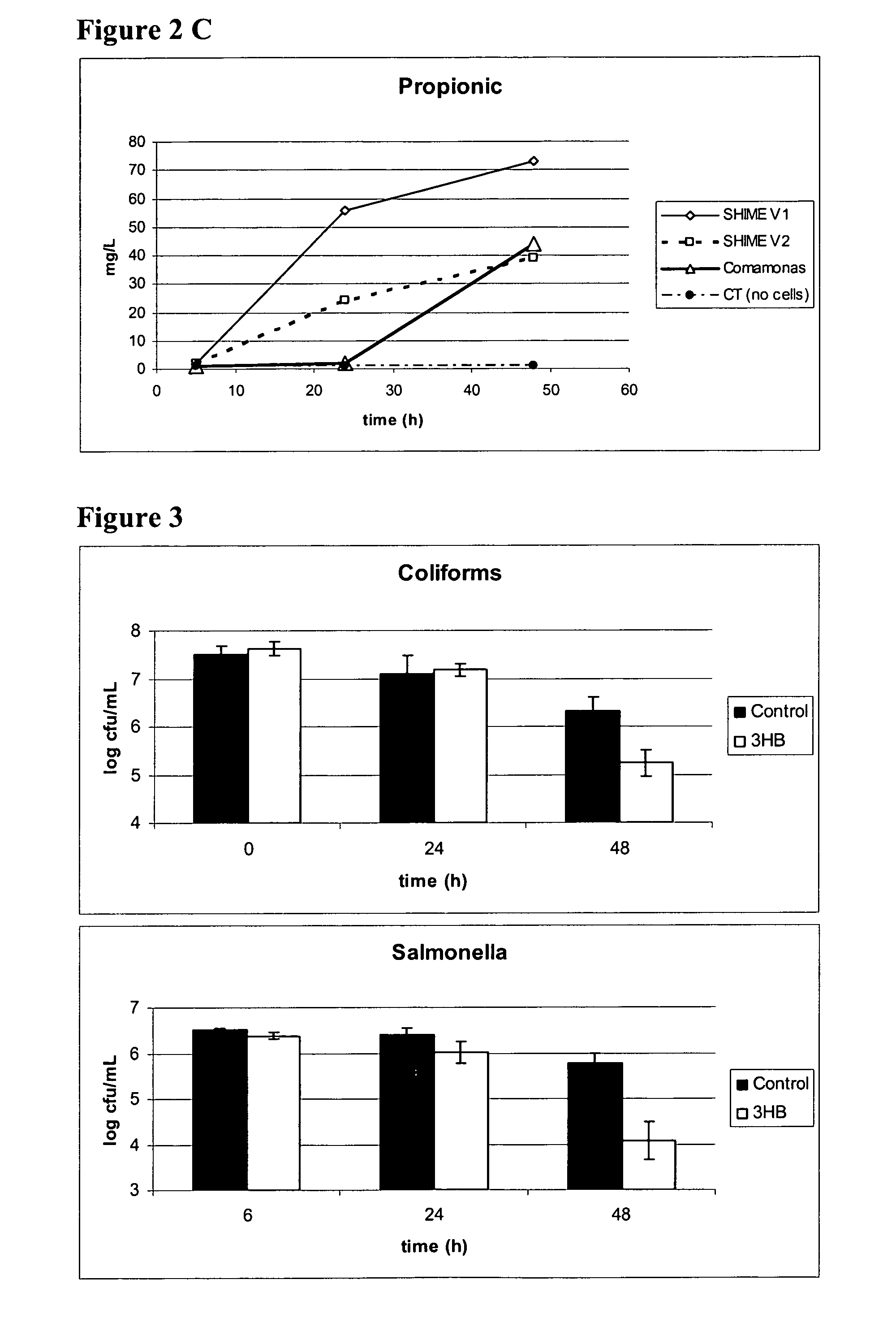
Two-stage backflow simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal device and technology for denitrification phosphorus removal, shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation of municipal sewage
ActiveCN103588352AAlkalinity balanceEmission reductionMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandNitration
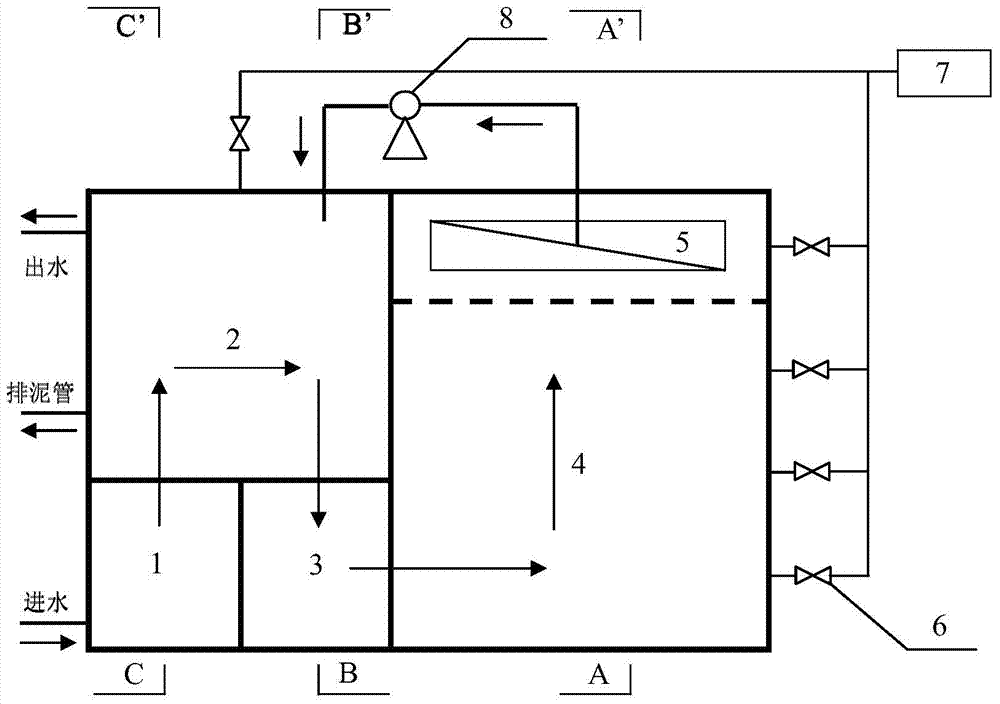
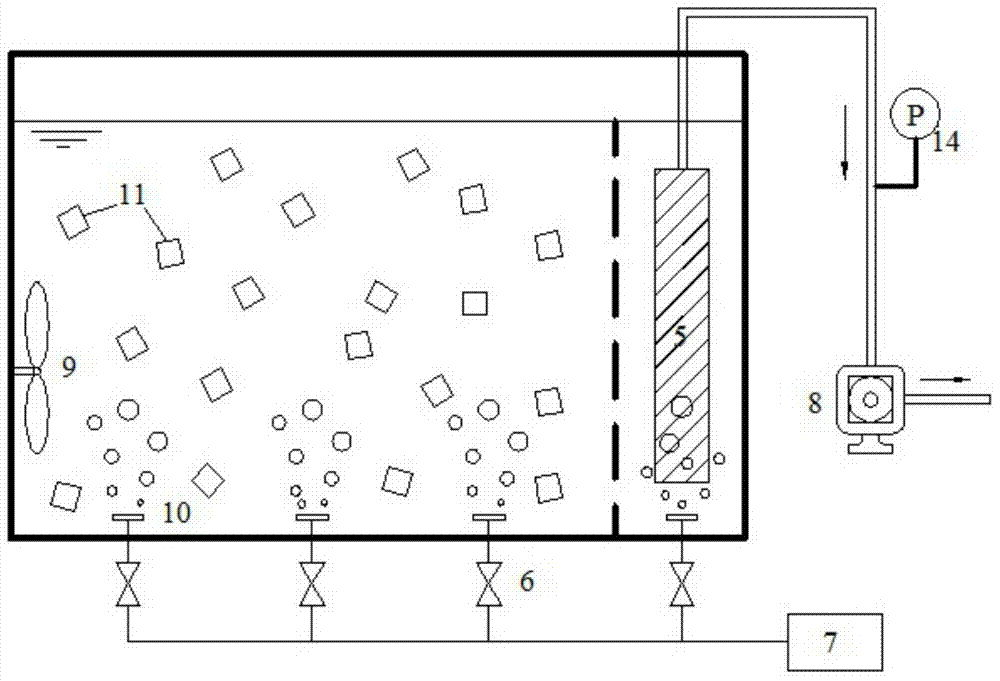
The invention discloses two-stage backflow simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal device and technology for denitrification phosphorus removal, shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation of municipal sewage, and belongs to the field of sewage treatment. Municipal sewage enters an anaerobic / anoxic reactor after passing through a regulating reservoir; phosphorus-accumulating bacteria finish storage and phosphorus release of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) by using inflow chemical oxygen demand (COD) under an anaerobic condition; phosphorus-rich supernatant enters inside a middle reservoir through a water decanter, and is injected into a moving bed membrane bioreactor by a lift pump after the water quantity is adjusted; autotrophic nitrogen removal of the shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation is achieved by alternate operation of low-oxygen aeration and anoxic agitation; the processed effluent enters the anaerobic / anoxic reactor again under the action of a suction pump; denitrification phosphorus removal is achieved after phosphorus-accumulating sludge containing the PHB and autotrophic denitrification effluent containing nitrate nitrogen are mixed. Simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal of low-carbon municipal sewage is achieved by using coupling of three functional microorganisms for denitrification phosphorus removal, shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and the two-stage backflow simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal device has the advantages of being high-efficiency and energy-efficient, stable to run, and low in sludge yield.
Owner:贵州筑信水务环境产业有限公司
Biodegradable polymeric nanocomposite compositions particularly for packaging
Specific polymer blends of polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and poly-(butylenes adipate-co-terephthalate (PBAT) as a fatty acid quaternary ammonium modified clay. The blends are particularly useful for barrier packaging.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Process for preparing thermal resistant easy processed polylactic resin
The invention belongs to a manufacturer method for thermal resistant easy to machined poly lactic acid resin that is made up from poly lactic acid, thermal resistant material, high molten mass speed polymers material aliphatic polyester and antioxidant. The process includes mixing in blending machine, and extruding at 160-185 degree centigrade. The resin could be used to make film, panel, sheet material, sparkle, and plastic components. The products have excellent thermal resistance capability, mechanical property and machine property.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Transgenic systems for the manufacture of poly(2-hydroxy-butyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)
InactiveUS7504556B2ProductionHigh speedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacteroides
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Full-biological degradation nonwoven cloth material
InactiveCN101220534AConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsNon-woven fabricsEpoxyCyclohexene oxide
The invention relates to a total biodegradable non-woven fabric material which is produced by adding 10 to 40 percent of low molecular weight carbon dioxide-cyclohexene oxide copolymer or 10 to 40 percent of high molecular weight poly L-polylactic acid or 10 to 40 percent of poly-hydroxylic butyrate to biodegradable carbon dioxide-propylene oxide or carbon dioxide-epoxy ethane copolymer materials, thus improving the dimensional stability of the carbon dioxide copolymer under high temperature. The number average molecular weight of the carbon dioxide-cyclohexene oxide copolymer is between 4000 and 8000 and the number average molecular weight of the poly L-polylactic acid is above 100,000. By using the carbon dioxide copolymer material of the invention, manufacture can be carried out by adopting a spun-bond method which is commonly used in non-woven fabric manufacturing technique. The obtained non-woven fabrics can maintain dimensional stability at the temperature between 70 DEG C and 75 DEG C, have biodegradation characteristics under the situation of composts or landfill with carbon dioxide and water as degradation end products, and cannot pollute environment when being burnt.
Owner:吉林金源北方科技发展有限公司
Environmentally degradable polymeric composition and method for obtaining an environmentally degradable polymeric composition
The environmentally degradable polymeric composition is obtained from the biodegradable polymers poly (hydroxybutyrate)-PHB and copolymers thereof and poly (lactic acid)-PLA and, optionally, at least one of the additives defined by: plasticizer of natural origin, such as natural fibers; natural fillers; thermal stabilizer; nucleant; compatibilizer; surface treatment agent; and processing aid.
Owner:PHB IND
Hydroxybutyrate and poly-hydroxybutyrate as components of animal feed or feed additives
ActiveUS20100093860A1Optimized formulaSmall particlesAntibacterial agentsBiocideEscherichia coliFood additive
This invention relates to the use of hydroxybutyrate and poly hydroxybutyrate as components of animal feed or feed additives, as well as to compositions, feed additives and feed containing them. The inventors surprisingly found that hydroxybutyrate and poly-hydroxybutyrate, preferably 3-hydroxybutyrate and poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, have a great potential for use in animal feed for modulation of the gut flora. More precisely, it has been found that poly-3-hydroxybutyrate or a microbial strain capable for producing poly-3-hydroxybutyrate can be used as a potential growth promoter or gut flora modulator by releasing SCFA, preferably 3-hydroxy butyric acid, in the gut micro flora. Further, the inventors found that 3-hydroxybutyrate and poly-3-hydroxybutyrate have a great potential for suppressing or inhibiting pathogenic bacteria in the gastro intestinal tract, e.g. have a antimicrobial activity against strains of Vibrio, E. coli and Salmonella.
Owner:UNIV GENT
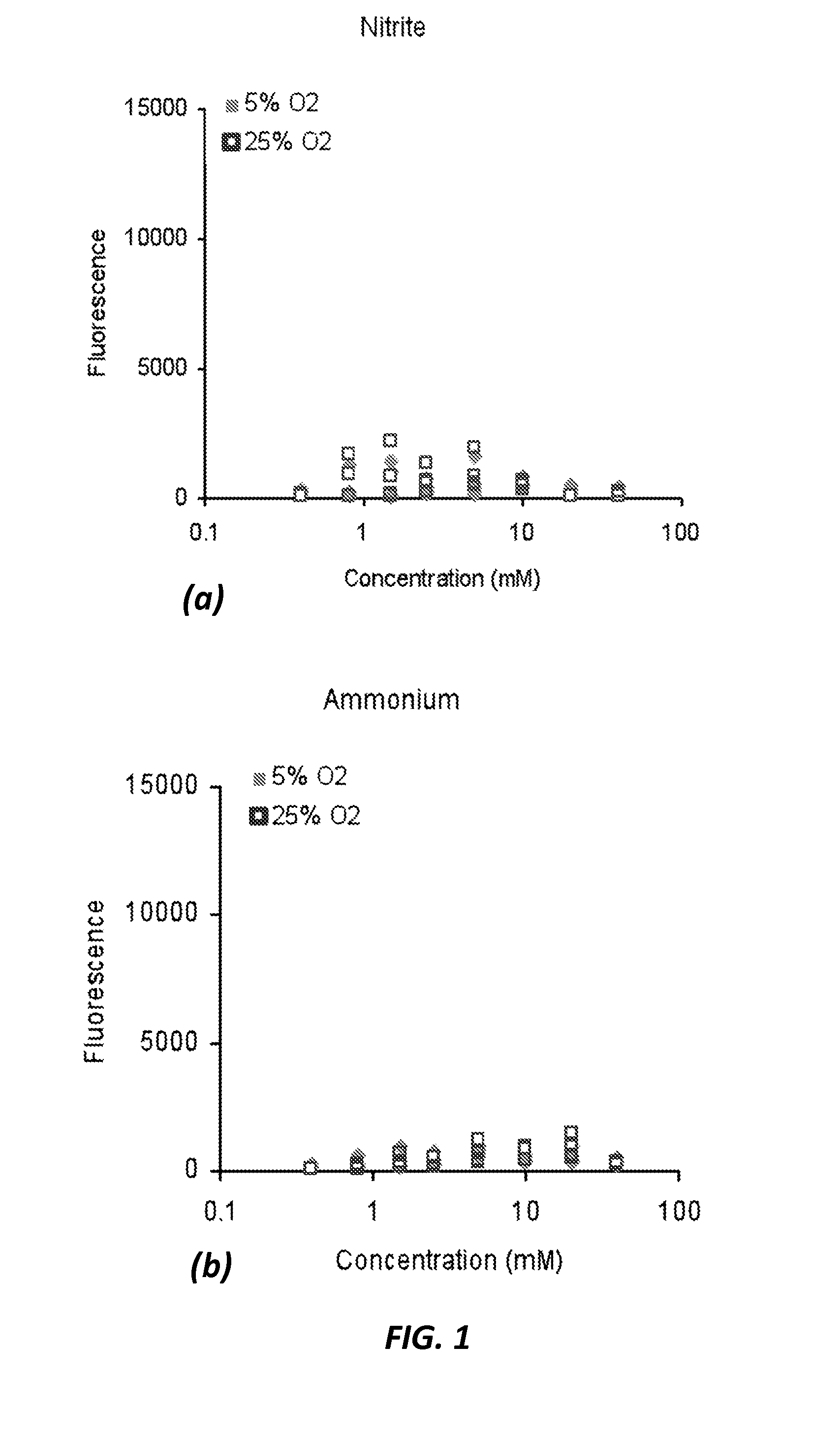
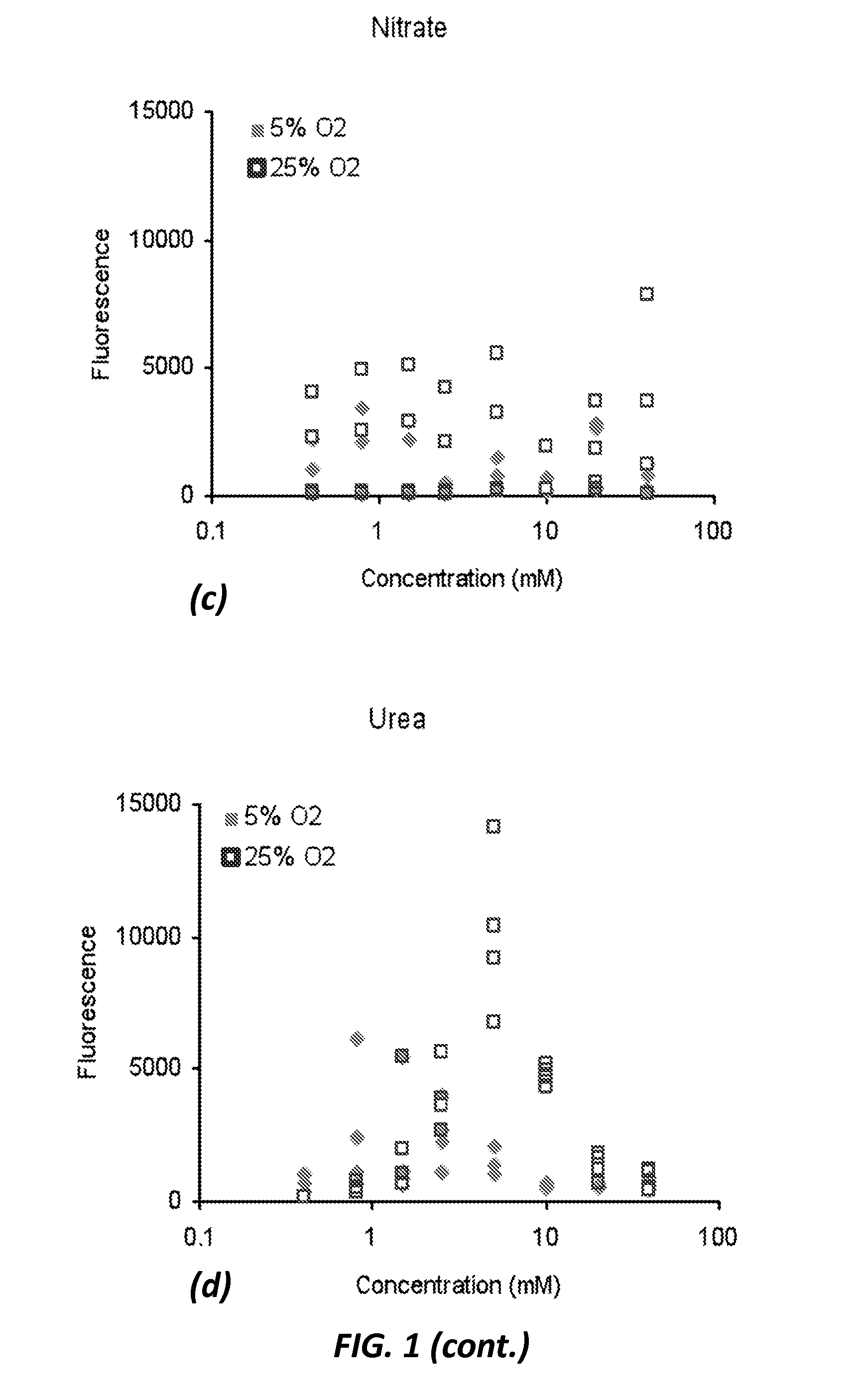
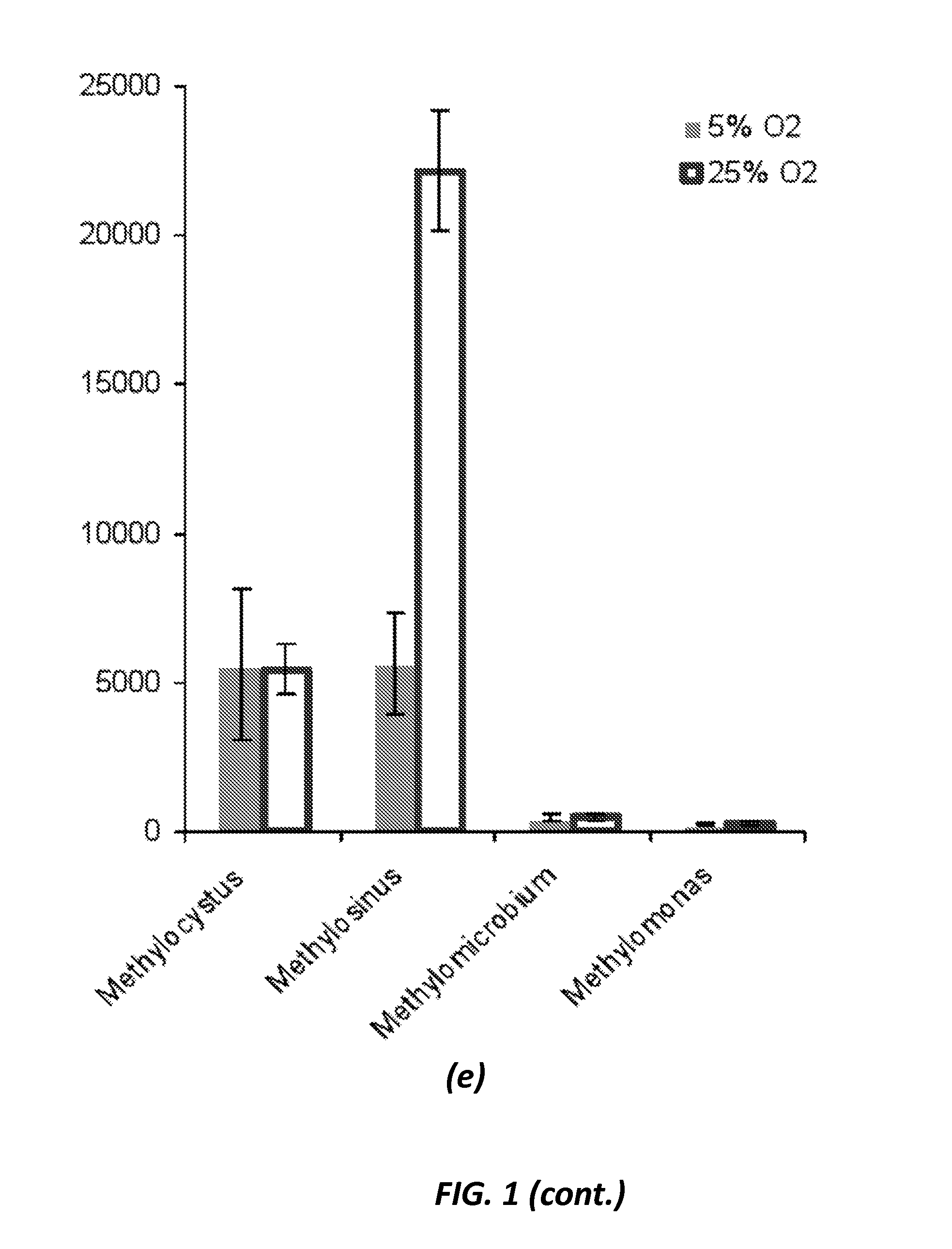
Process for the selection of PHB-producing methanotrophic cultures
ActiveUS20130052681A1Improve scalabilityIncrease typeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismNitrate
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Injectable delivery of microparticles and compositions therefore
ActiveUS20100003300A1Flow fastHigh solid contentOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPolymer scienceLactide
Compositions and methods of making and using of microparticle compositions that provide faster flow or improved injectability through smaller or small-diameter needles have been developed. Notably, the microparticle compositions can be successfully delivered or administered through smaller-diameter needles than other microparticle compositions prepared from biocompatible or biodegradable polymers including, for example, poly(lactide), poly(lactide-co-glycolide), polycaprolactone, or poly-3-hydroxybutyrate. The microparticle compositions can exhibit a higher solids loading for a given needle size and / or faster flow through needles than other microparticle compositions. Further, blending or mixing the polymer of the microparticle composition with other polymer formulations can enhance the injectability of the resulting formulation.
Owner:EVONIK CORP +1
Telomerase delivery by biodegradable Nanoparticle
InactiveUS20090142408A1Effectively crossControl releasePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAge related diseaseHydrophilic polymers
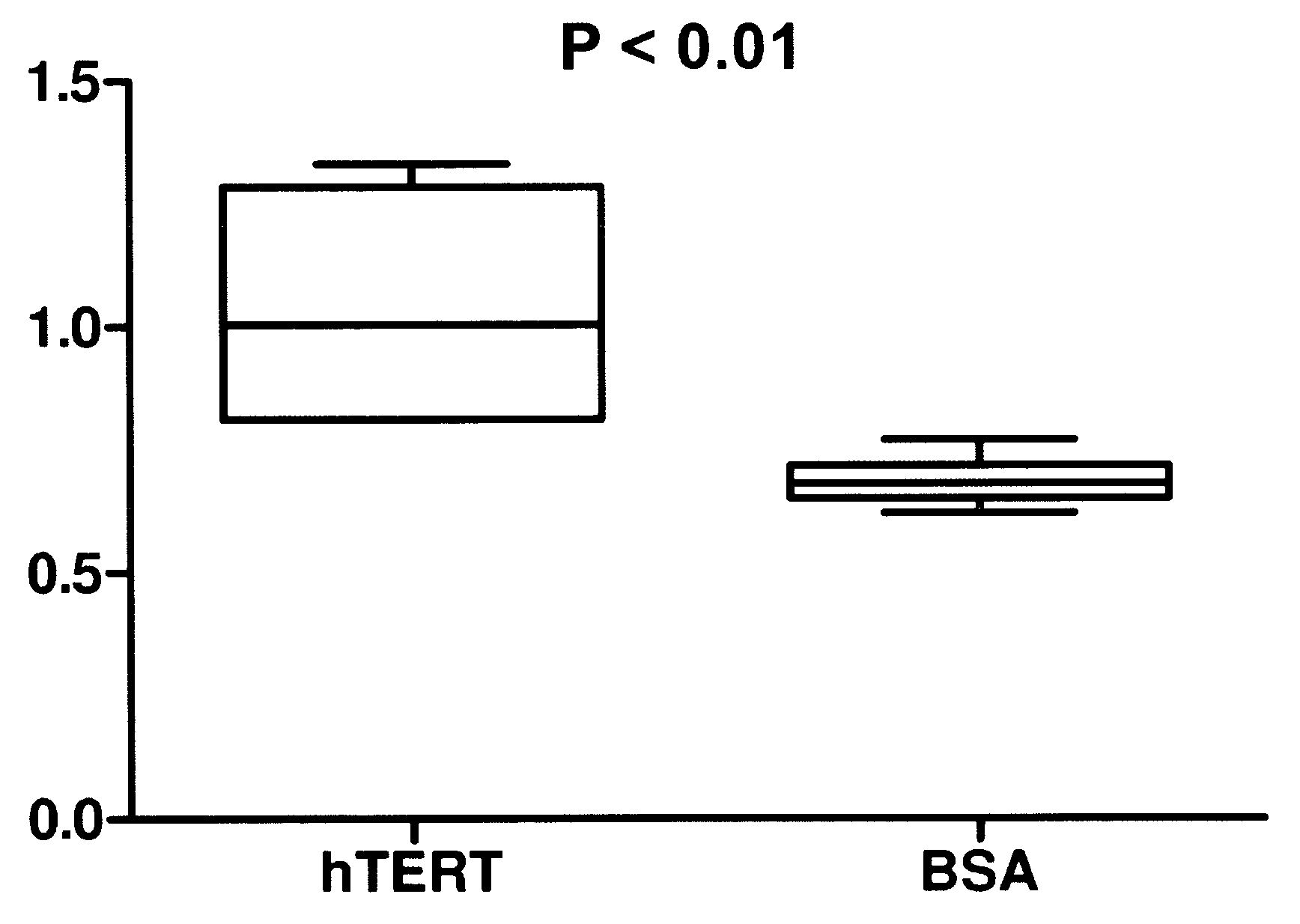
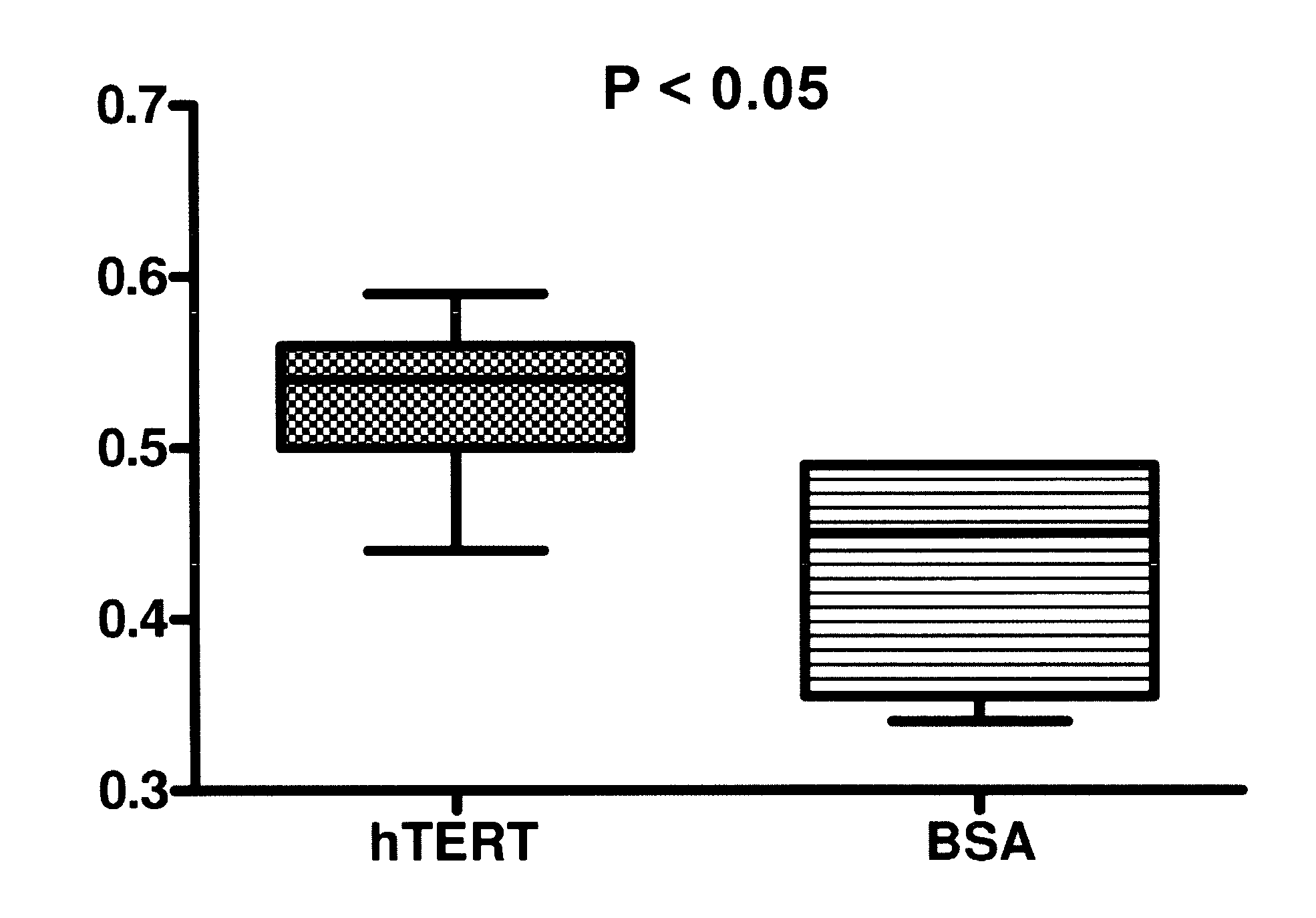
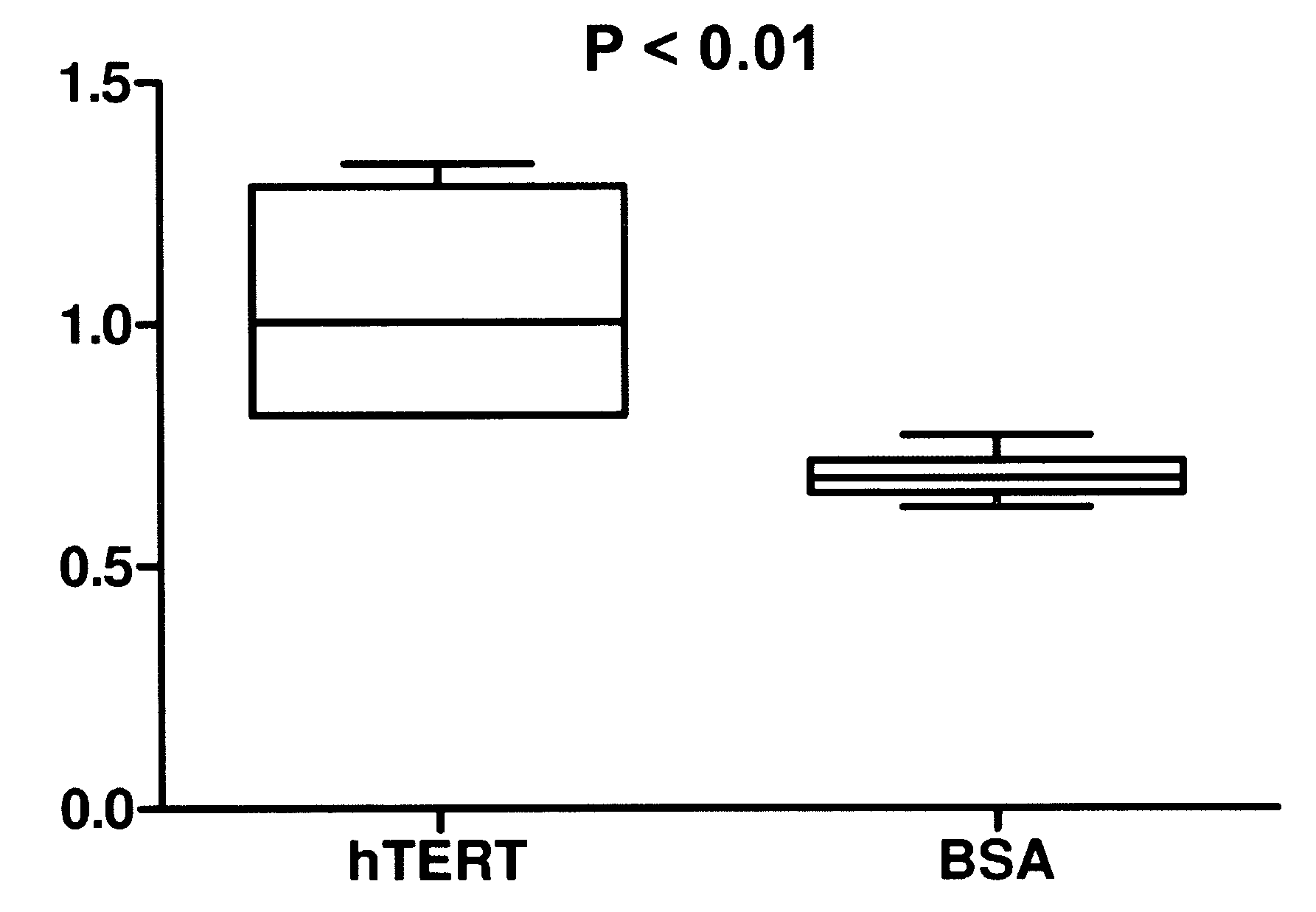
A therapeutic compound consisting of human telomerase, its catalytic subunit hTert, or a known variant of either, and a biodegradable nanoparticle carrier, which can be administered to cells in a cell culture or in a living animal, is provided herein. The therapeutic compound is envisioned as a method for treating a wide variety of age-related diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, aplastic anemia, dyskeratosis congenita, arteriosclerosis, macular degeneration, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's, diabetes type 2, and any disease that correlates with telomere shortening and may be corrected or ameliorated by lengthening telomeres. The therapeutic compound is also envisioned as method for potentially treating more generic problems of human aging. The nanoparticle carrier is comprised of certain biodegradable biocompatible polymers such as poly(lactide-co-glycolide), poly(lactic acid), poly(alkylene glycol), polybutylcyanoacrylate, poly(methylmethacrylate-co-methacrylic acid), poly-allylamine, polyanhydride, polyhydroxybutyric acid, polycaprolactone, lactide-caprolactone copolymers, polyhydroxybutyrate, polyalkylcyanoacrylates, polyanhydrides, polyorthoester or a combination thereof. The nanoparticle may incorporate a targeting moiety to direct the nanoparticle to a particular tissue type or a location within a cell. The nanoparticle may incorporate a plasticizer to facilitate sustained release of telomerase such as L-tartaric acid dimethyl ester, triethyl citrate, or glyceryl triacetate. A nanoparticle of the present invention can further contain a polymer that affects the charge or lipophilicity or hydrophilicity of the particle. Any biocompatible hydrophilic polymer can be used for this purpose, including but not limited to, poly(vinyl alcohol).
Owner:SARAD MATTHEW
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com