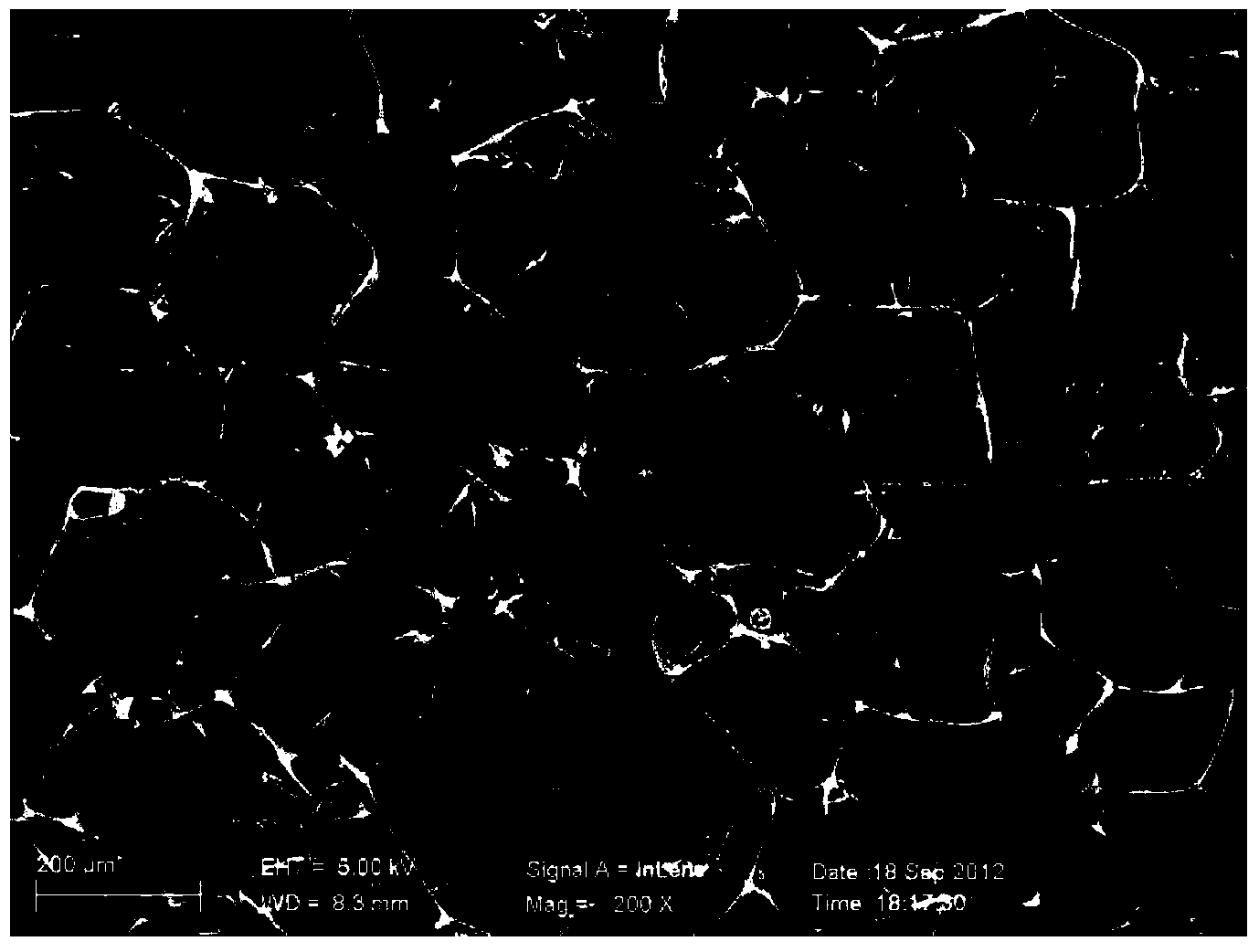
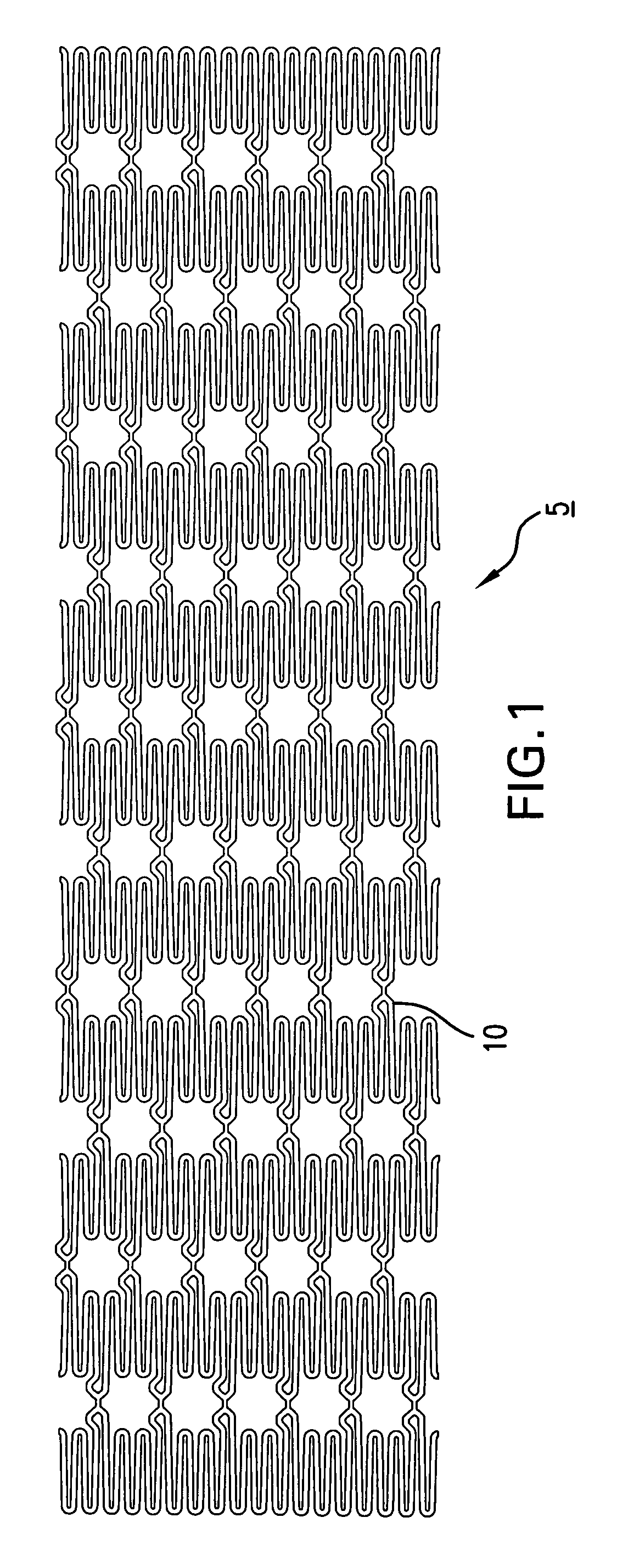
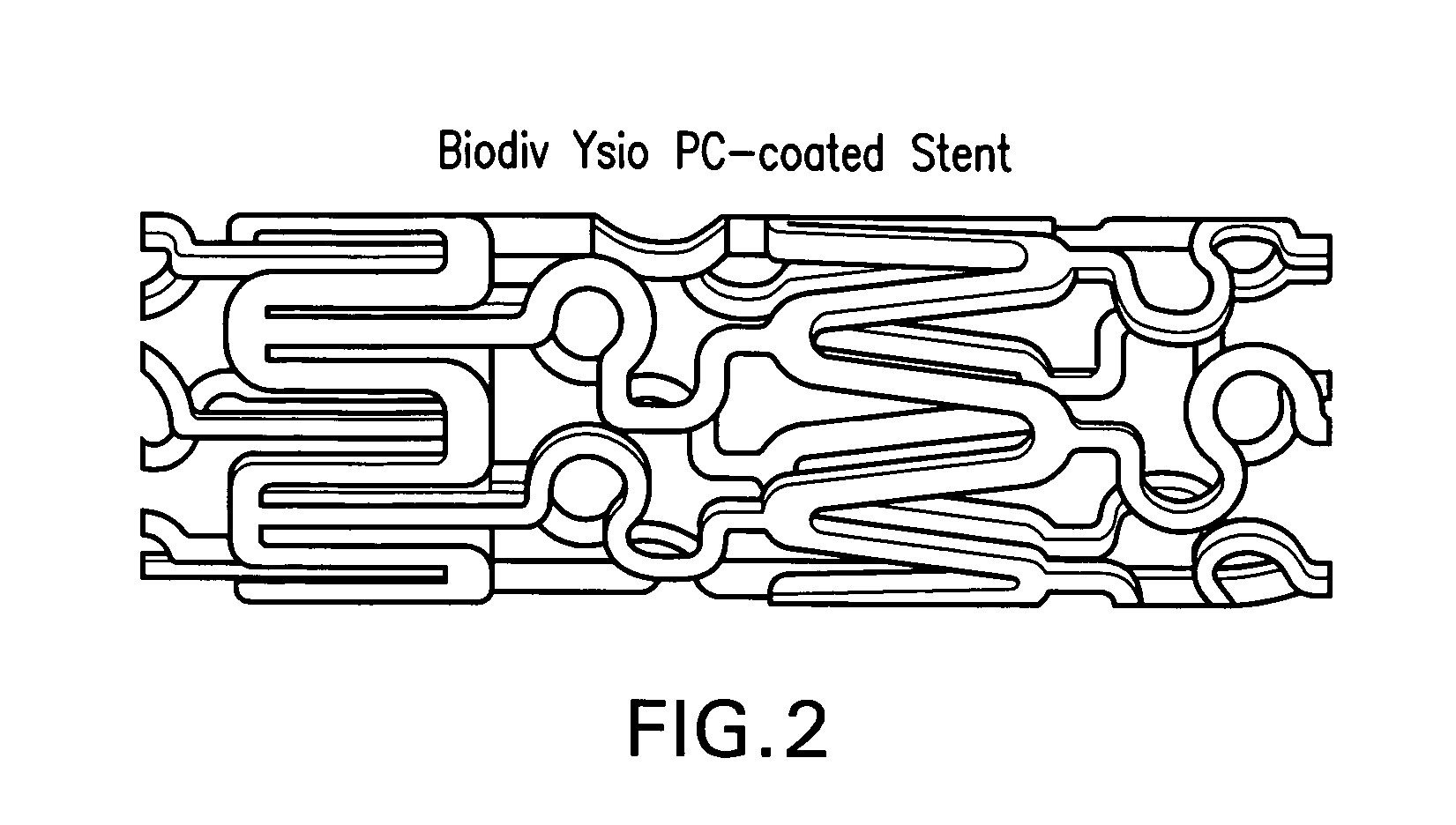
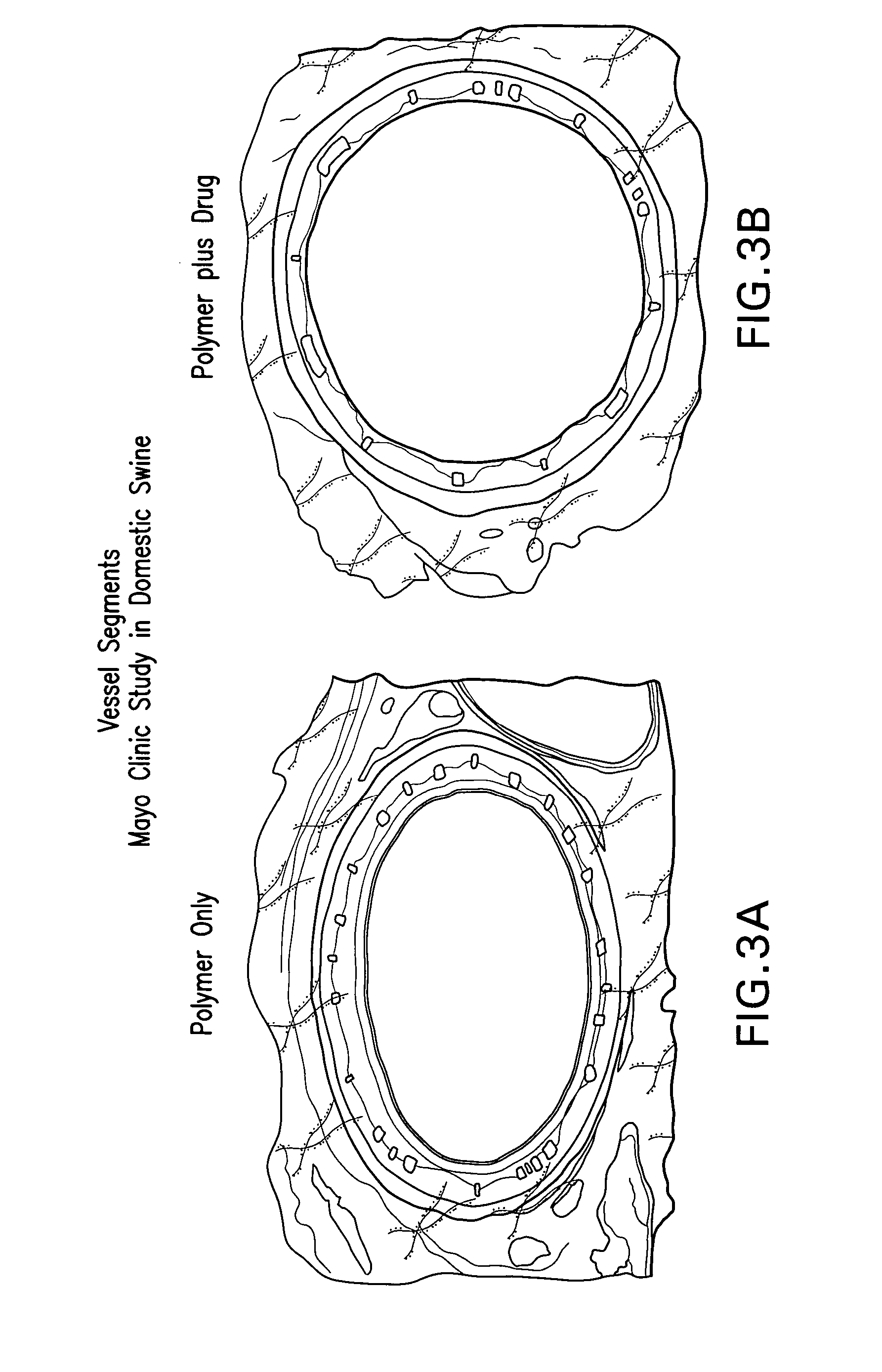
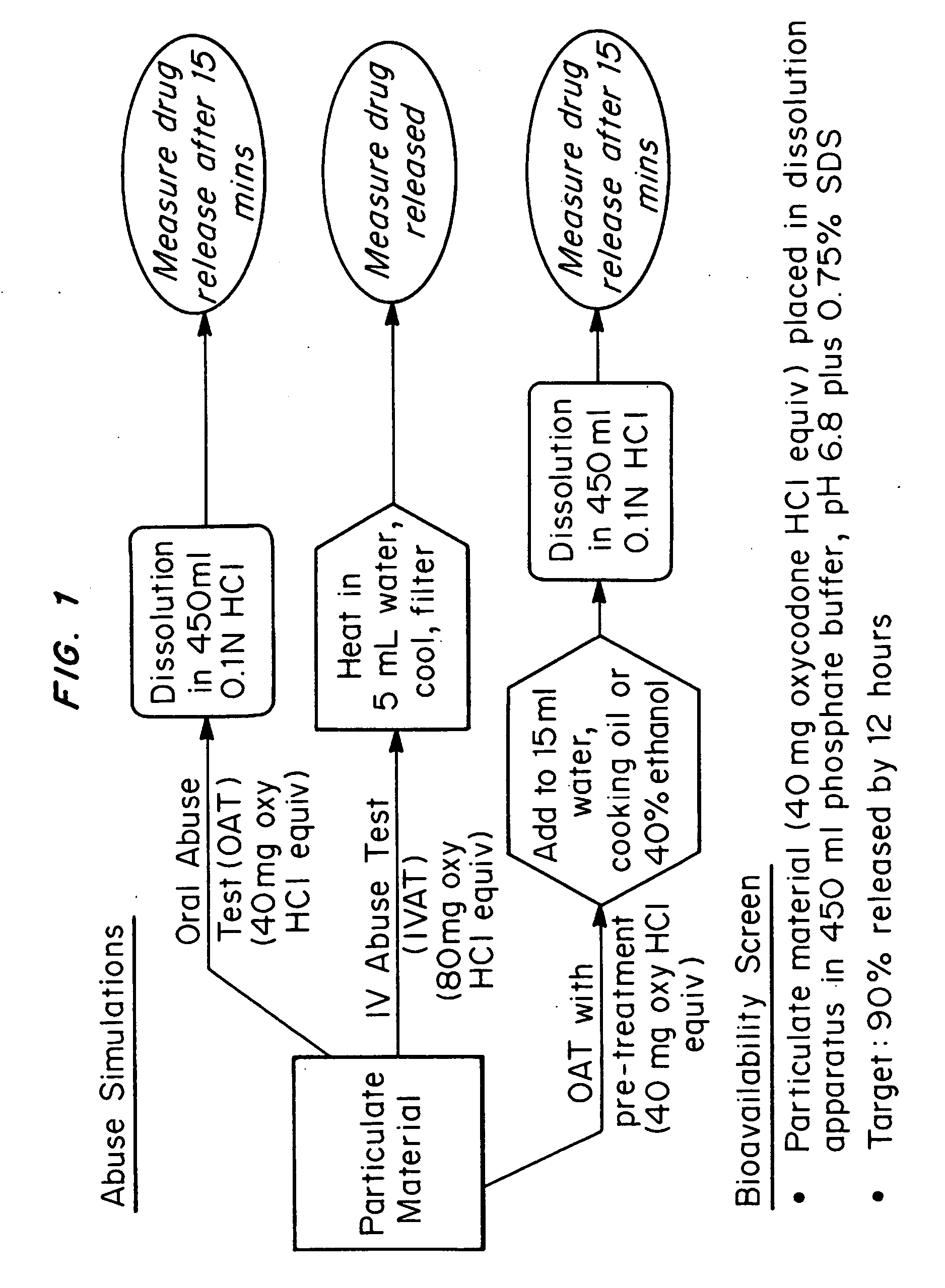
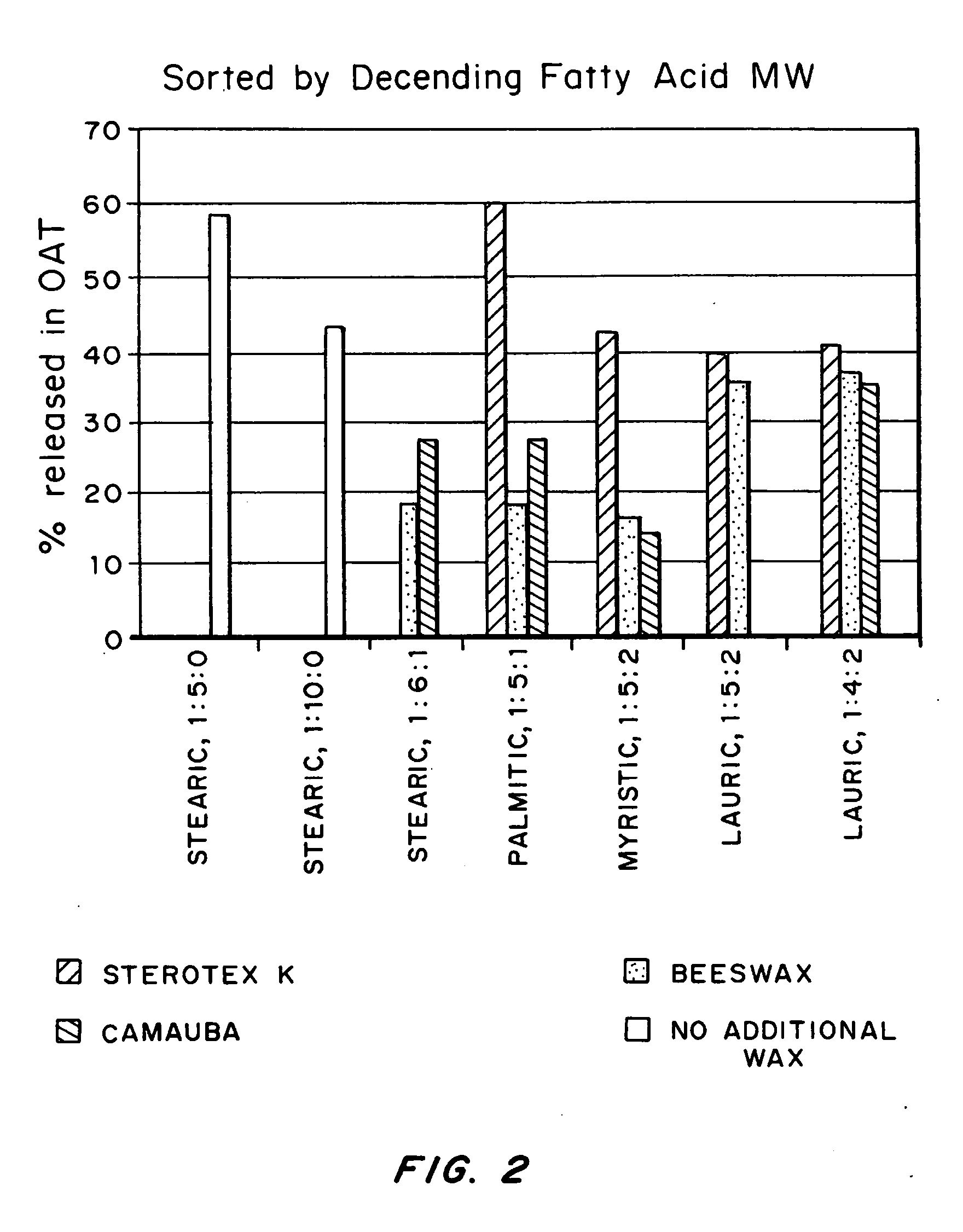
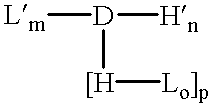Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1536 results about "Lipophilicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
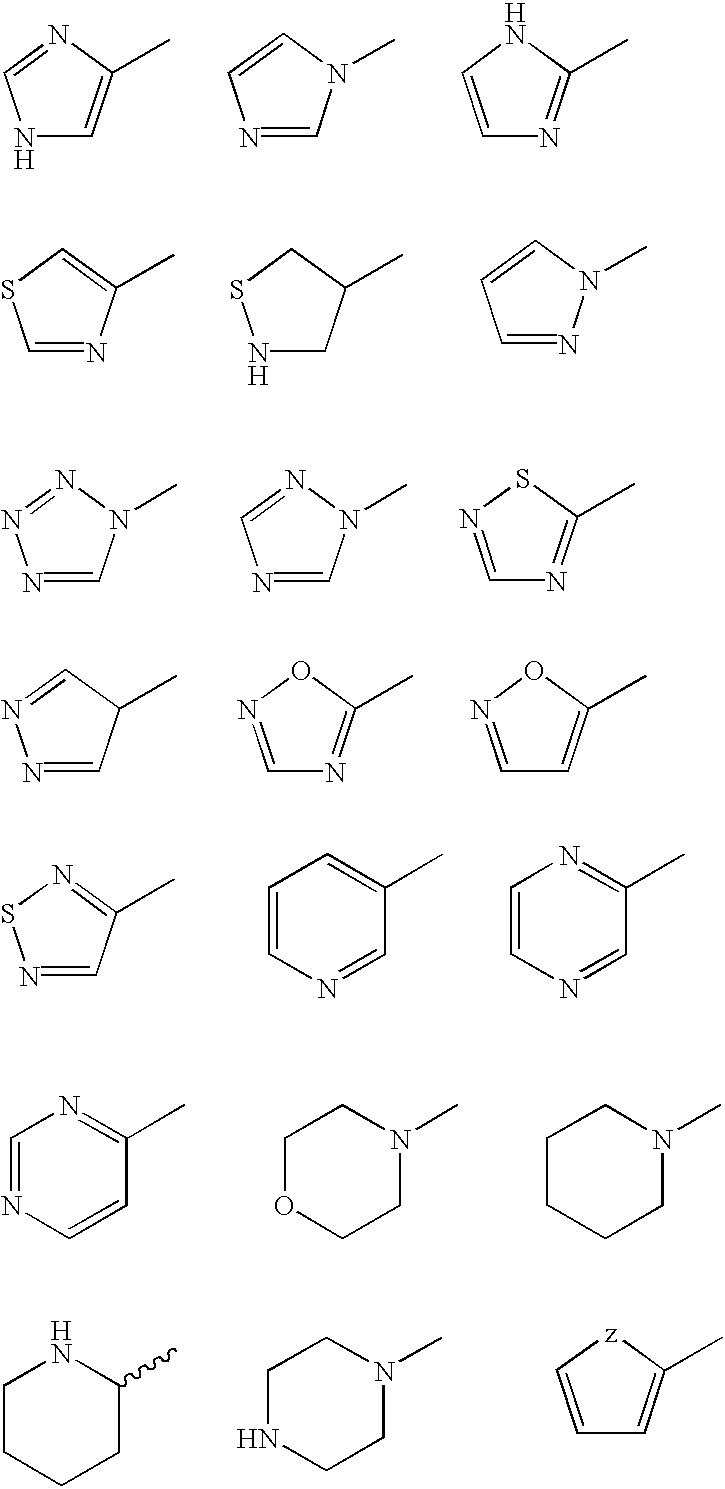
Lipophilicity (from Greek λίπος "fat" and φίλος "friendly"), refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such non-polar solvents are themselves lipophilic (translated as "fat-loving" or "fat-liking"), and the axiom that "like dissolves like" generally holds true. Thus lipophilic substances tend to dissolve in other lipophilic substances, but hydrophilic ("water-loving") substances tend to dissolve in water and other hydrophilic substances.
Amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates with hydroyzable lipophile components and methods for making and using the same
InactiveUS6309633B1Reduce deliveryExtended durationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTherapeutic proteinCholesterol
The invention provides a drug-oligomer conjugate having the following general formula:wherein D is a therapeutic drug moiety; H and H' are each a hydrophilic moiety, independently selected from the group consisting of straight or branched PEG polymers having from 2 to 130 PEG subunits, and sugars; L is a lipophilic moiety selected from the group consisting of alkyl groups having 2-26 carbon atoms, cholesterol, adamantane and fatty acids; o is a number from 1 to the maximum number of covalent bonding sites on H; m+n+p together have a value of at least one and not exceeding the total number of covalent bonding sites on D for the -H', -L and -H-L substituents; the H-L bond(s) are hydrolyzable and the D-L' bond(s), when present, are hydrolyzable; the conjugate being further characterized by one of the following: (i) m is 0 and p is at least 1; (ii) n is 0 and p is at least 1; (iii) m and n are each 0 and p is at least 1; (iv) p is 0 and m and n are each at least 1. The therapeutic drug moiety is preferably a therapeutic protein or peptide, preferably insulin or a functional equivalent thereof.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Pharmaceutical compositions for lipophilic drugs
InactiveUS7070802B1Good self-emulsifying performanceShelf-stableCyclic peptide ingredientsCapsule deliveryMonoglycerideCyclosporins
Stable solutions of lipophilic drugs, such as cyclosporin, forming a polar lipid self-emulsifying drug delivery system. The solutions can include lipophilic drugs, such as cyclosporin, dissolved in a polar lipid, such as having a C6-C12 fatty acid monoglyceride content of at least about 50%, surfactants and triglycerides. The composition forms a fine emulsion on exposure to water. The encapsulated dosage form of this composition needs neither a hydrophilic component nor air-tight blister packaging, and is particularly suitable for oral administration.
Owner:WATSON LAB INC
Abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical compositions of opioids and other drugs
ActiveUS7399488B2Good treatment effectSmall dosePowder deliveryNervous disorderAdditive ingredientWater insoluble
An abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical composition has been developed to reduce the likelihood of improper administration of drugs, especially drugs such as opiods. In the preferred embodiment, a drug is modified to increase its lipophilicity. In preferred embodiments the modified drug is homogeneously dispersed within microparticles composed of a material that is either slowly soluble or not soluble in water. In some embodiments the drug containing microparticles or drug particles are coated with one or more coating layers, where at least one coating is water insoluble and preferably organic solvent insoluble, but enzymatically degradable by enzymes present in the human gastrointestinal tract. The abuse-deterrent composition retards the release of drug, even if the physical integrity of the formulation is compromised (for example, by chopping with a blade or crushing) and the resulting material is placed in water, snorted, or swallowed. However, when administered as directed, the drug is slowly released from the composition as the composition is broken down or dissolved gradually within the GI tract by a combination of enzymatic degradation, surfactant action of bile acids, and mechanical erosion.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Compositions comprising lipophilic active compounds and method for their preparation
ActiveUS20090098200A1Quick releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryBiocideHydrophilic polymersCompound (substance)
Compositions are provided comprising a lipophilic active compound, e.g., a human or veterinary drug or a nutraceutical, interwoven with a polymeric matrix formed by two or more polymers, wherein one of the polymers is an amphiphilic polymer and the other polymer is either an amphiphilic polymer with a different hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance or a hydrophilic polymer, and the active lipophilic compound has modified physicochemical properties. The composition forms colloidal nanodispersion upon contact with aqueous media.
Owner:SOLUBEST
Delivery of highly lipophilic agents via medical devices
InactiveUS20060240070A1Easy to transportIncrease drug retentionBiocideFibrinogenMedicineMedical device
An apparatus and system for delivering a lipophilic agent associated with a medical device including: a medical device, a first lipophilic agent capable of penetrating a body lumen, wherein the transfer coefficients of the first lipophilic agent is by an amount that is statistically significant of at least approximately 5,000, wherein the first lipophilic agent is associated with the medical device, wherein the first lipophilic agent / medical device is placed adjacent to said body lumen, and wherein a therapeutically effective amount of the first lipophilic agent is delivered to a desired area within a subject. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for improving patency in a subject involving placement of a medical device in a body lumen for treating and / or preventing adjacent diseases or maintaining patency of the body lumen.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Abuse-deterrent drug formulations
ActiveUS20050281748A1Reduce the possibilityImprove lipophilicityTelevision system detailsPowder deliveryImmediate releaseActive agent
An abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical composition has been developed to reduce the likelihood of improper administration of drugs, especially drugs such as opiods. In the preferred embodiment, the drug is modified to increase its lipophilicity by forming a salt between the drug and one or more fatty acids wherein the concentration of the one or more fatty acids is one to 15 times the molar amount of the active agent, preferably two to ten times the molar amount of the active agent. In one embodiment the modified drug is homogeneously dispersed within microparticles composed of a material that is either slowly soluble or not soluble in water. In some embodiments the drug containing microparticles or drug particles are coated with one or more coating layers, where at least one coating is water insoluble and preferably organic solvent insoluble. The abuse-deterrent composition prevents the immediate release of a substantial portion of drug, even if the physical integrity of the formulation is compromised (for example, by chopping with a blade or crushing) and the resulting material is placed in water, snorted, or swallowed. However, when administered as directed, the drug is slowly released from the composition as the composition is broken down or dissolved gradually within the GI tract by a combination of enzymatic degradation, surfactant action of bile acids, and mechanical erosion.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
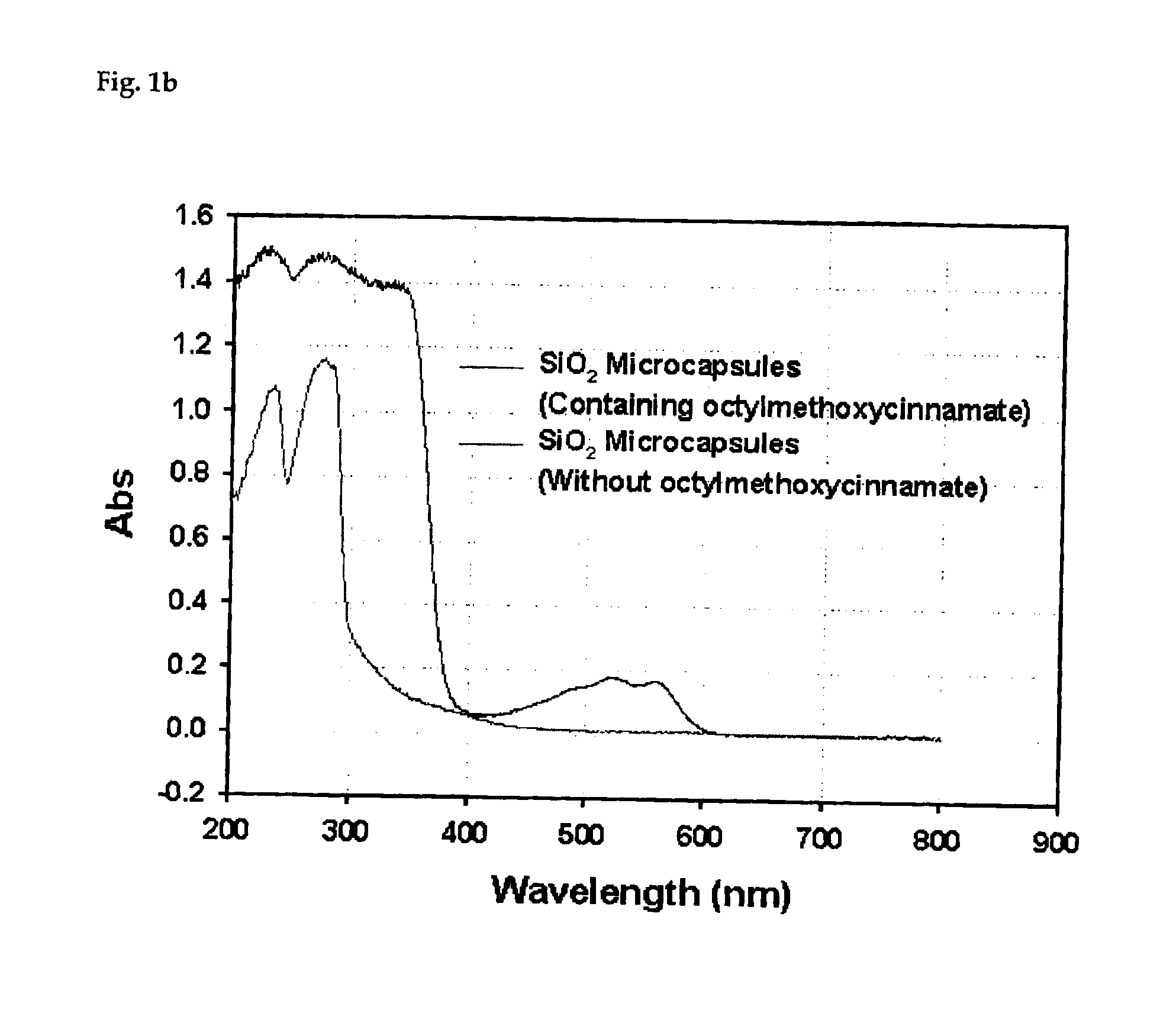
Process for preparing silica microcapsules
InactiveUS6855335B2Reduce environmental pollutionPowder deliveryGlass/slag layered productsAmmonium hydroxideSilica gel
The present invention relates to a process for preparing silica microcapsules and more particularly, to a process for preparing silica microcapsules comprising the steps of dissolving tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) into an aqueous solution containing a hydrolysis catalyst to control a degree of hydrolysis and contribute hydrophilicity or lipophilicity, adding a core material and an appropriate amount of aminopropyltrialkoxysilane(APS) as a gelling agent into the solution, and emulsifying and dispersing the resulting solution to a solution having a polarity opposite to that of the core material to microcapsulate by coating the core material with silica shell via a sol-gel reaction. The process for preparing microcapsules of the present invention reduces environmental pollution compared to conventional processes using an alkali gelling agent such as an ammonia solution, and are suitable for both organic or inorganic core materials having hydrophilic or lipophilic property.
Owner:UNITECH CO LTD (JP)
Derivatives of GLP-1 analogs
InactiveUS7235627B2Improve solubility and stabilityReduce capacityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic detergent compounding agentsActive agentSurface-active agents
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a GLP-1 derivative having a lipophilic substituent; and a surfactant.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical compositions of opioids and other drugs
ActiveUS20090297617A1Reduce the possibilityImprove lipophilicityBiocidePowder deliveryAs DirectedOrganic solvent
An abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical composition has been developed to reduce the likelihood of improper administration of drugs, especially drugs such as opioids. In a preferred embodiment, a drug is modified to increase its lipophilicity. In some embodiments the modified drug is homogeneously dispersed within spherical microparticles composed of a material that is either slowly soluble or not soluble in water. In some embodiments the drug containing microparticles or drug particles are coated with one or more coating layers, where at least one coating is water insoluble and / or organic solvent insoluble. The abuse-deterrent composition retards the release of drug, even if the physical integrity of the formulation is compromised (for example, by chopping with a blade or crushing) and the resulting material is placed in water, snorted, or swallowed. However, when administered as directed, the drug is slowly released from the composition as the composition is passes through the GI tract.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Controlled release delivery device for pharmaceutical agents incorporating microbial polysaccharide gum
The present invention provides a controlled release device for sustained or pulsatile delivery of pharmaceutically active substances for a predetermined period of time. This invention further provides such device in which sustained or pulsatile delivery is obtained by the unique blend and intimate mixture of pharmaceutically active substances with a microbial polysaccharide and uncrosslinked linear polymer and optionally a crosslinked polymer and / or lipophillic polymer and / or saturated polyglycolyzed glyceride. The invention also provides a process for the manufacture of such devices and pharmaceutical compositions containing the same.
Owner:INTELLIPHARMACEUTICS
Compositions and methods for skin care
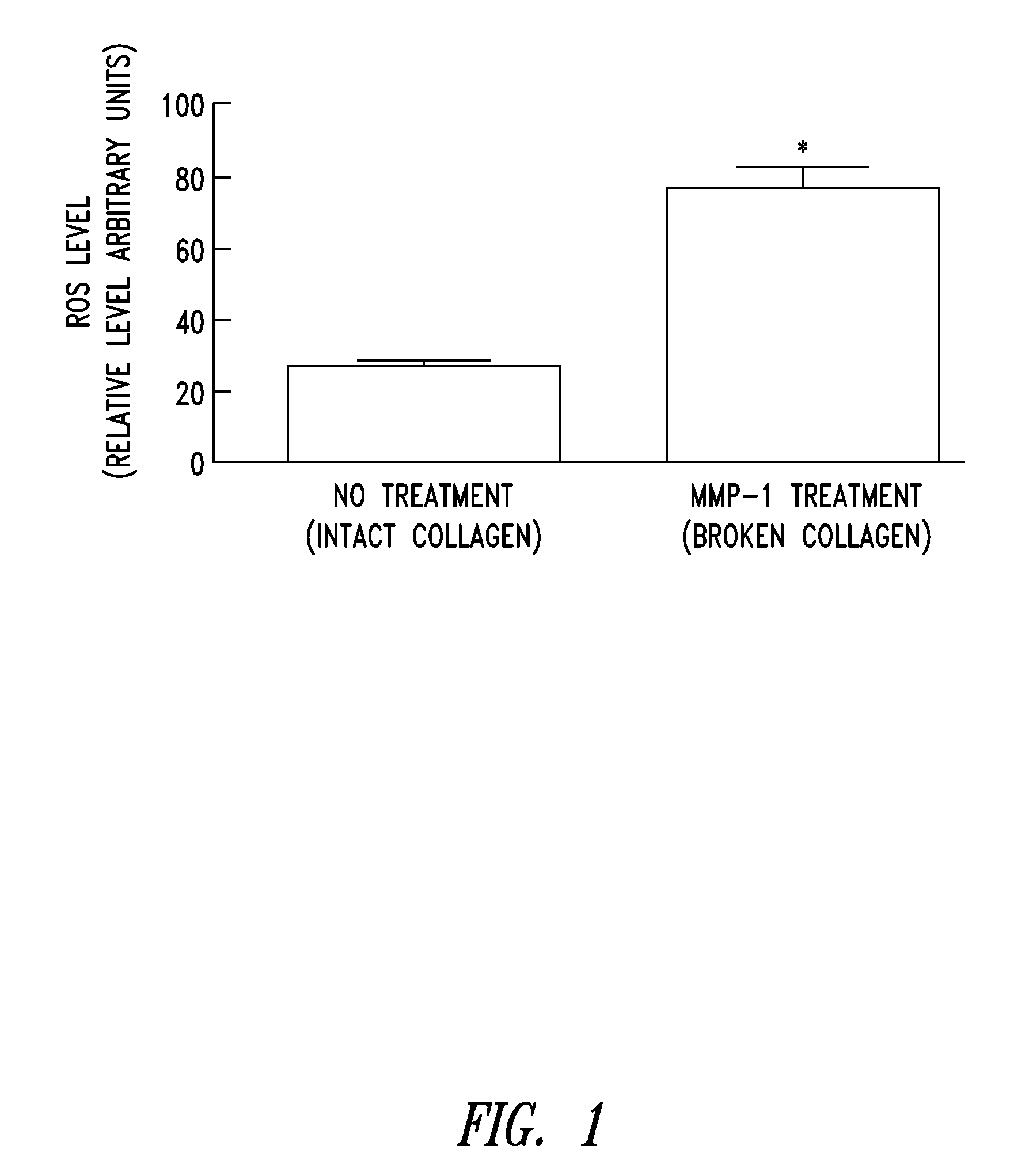
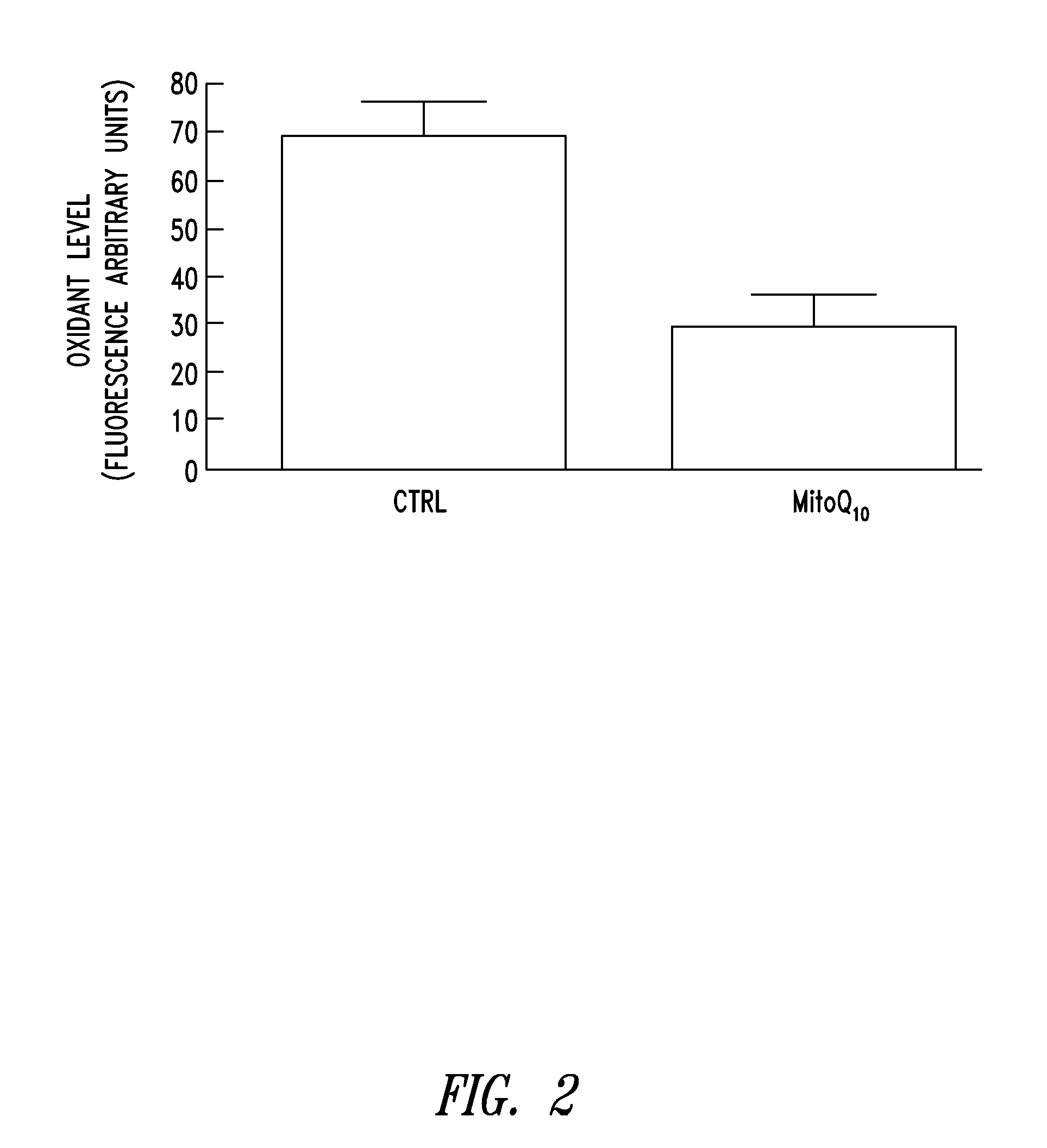
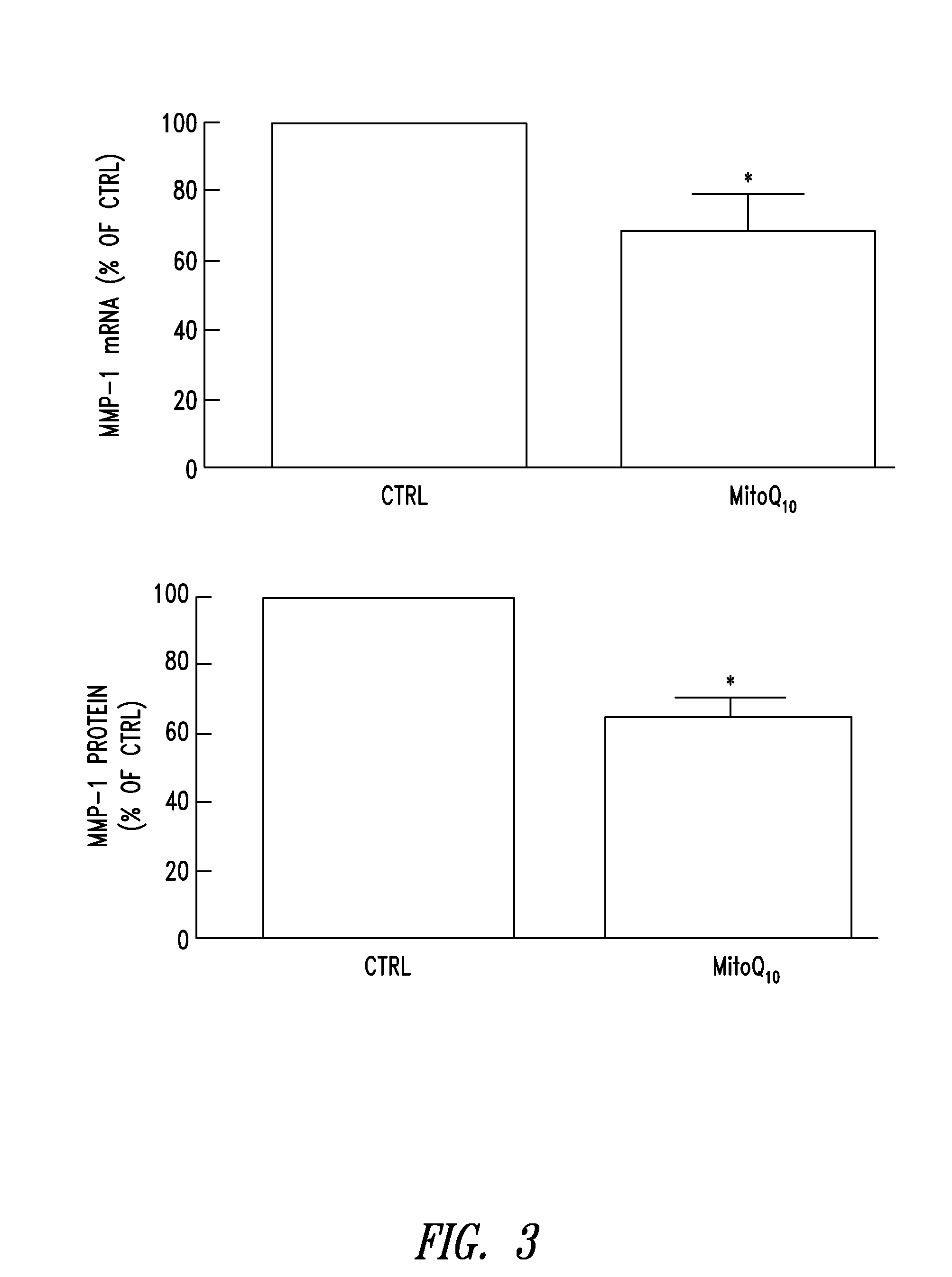
Compositions and methods are for disclosed for treating a skin condition that results from reactive oxygen species production in skin of a subject, including applying a topical formulation that contains a lipophilic cation-mitochondrially targeted antioxidant compound and that delivers a therapeutically effective amount of the antioxidant compound to skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes.
Owner:ANTIPODEAN PHARMA
Parenteral formulations of lipophilic pharmaceutical agents and methods for preparing and using the same
ActiveUS20120277249A1Improve solubilityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic solventAutoimmune disease
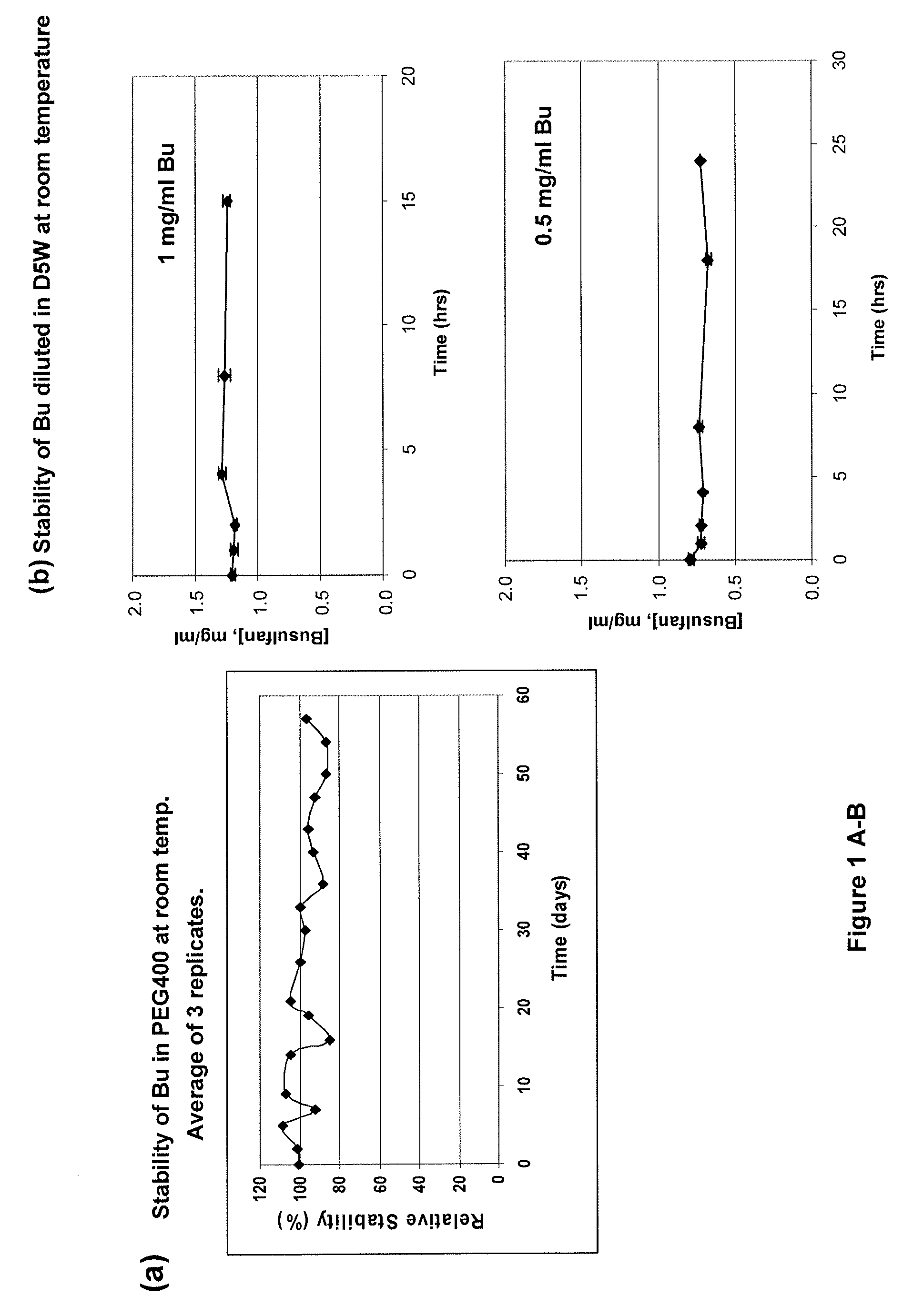
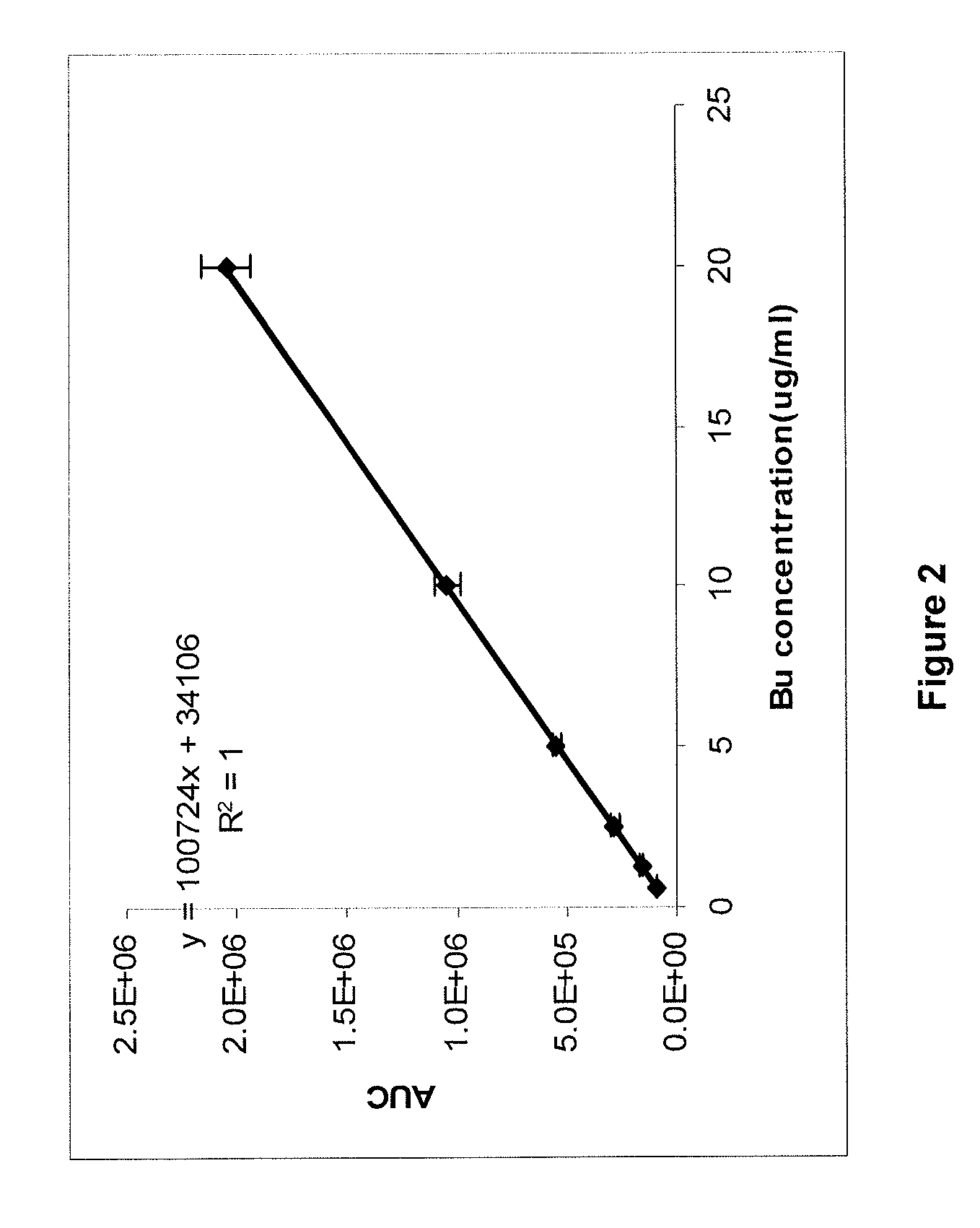
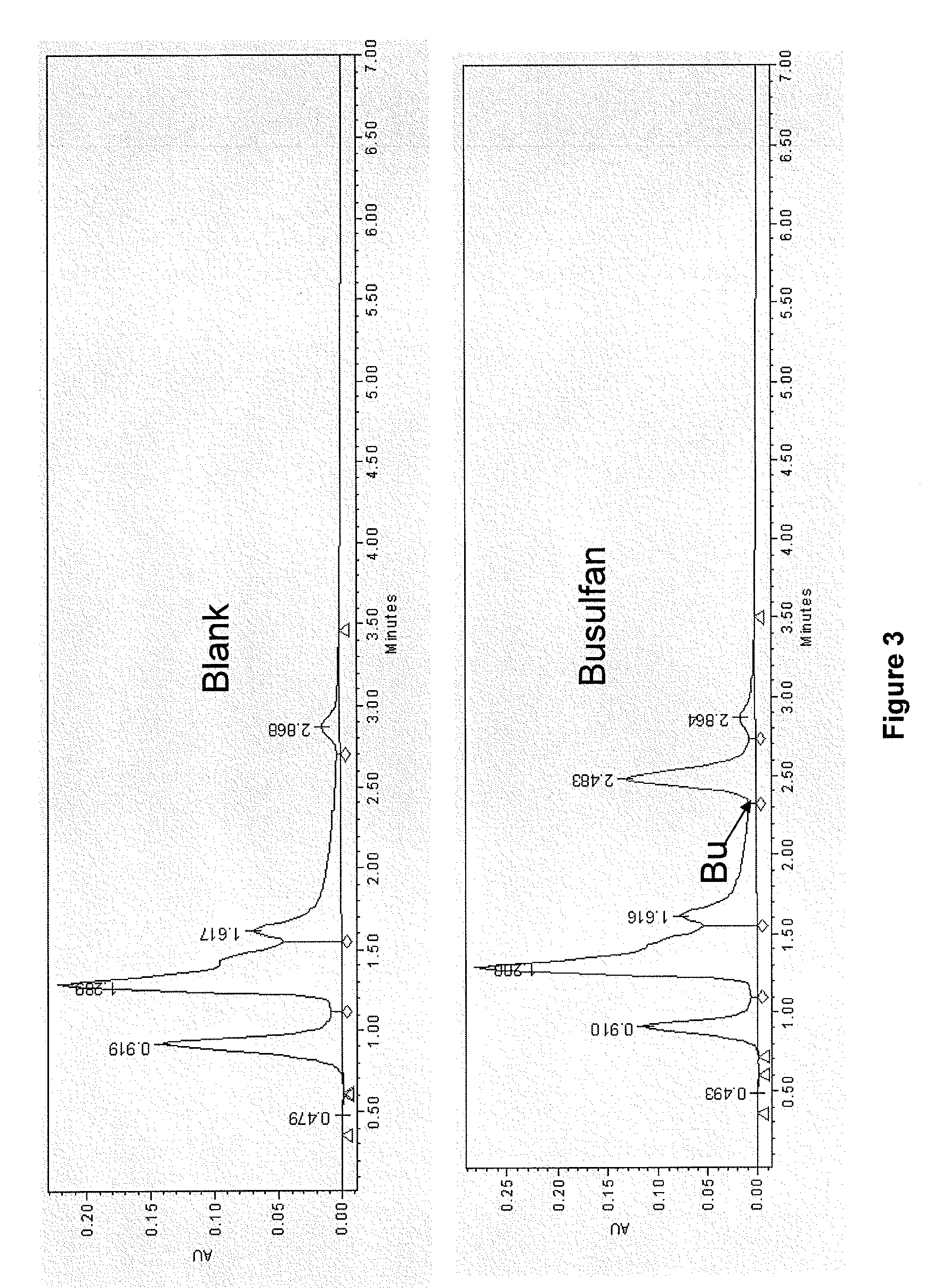
There may be provided compositions of lipophilic pharmaceutical agents with improved solubility and stability. For example, there may be provided a non-aqueous composition that comprises a lipophilic pharmaceutical agent, and an amphiphilic polymeric solvent such as PEG400 but essentially free of organic solvents and non-solubilized particles. The composition may be further diluted with a desired aqueous diluent such as an infusion fluid for parenteral administration to a subject such as a human. The compositions may be useful for the treatment for diseases or conditions that are sensitive to lipophilic agents, such as infectious diseases, malignant or autoimmune diseases.
Owner:GREENJAY THERAPEUTICS INC
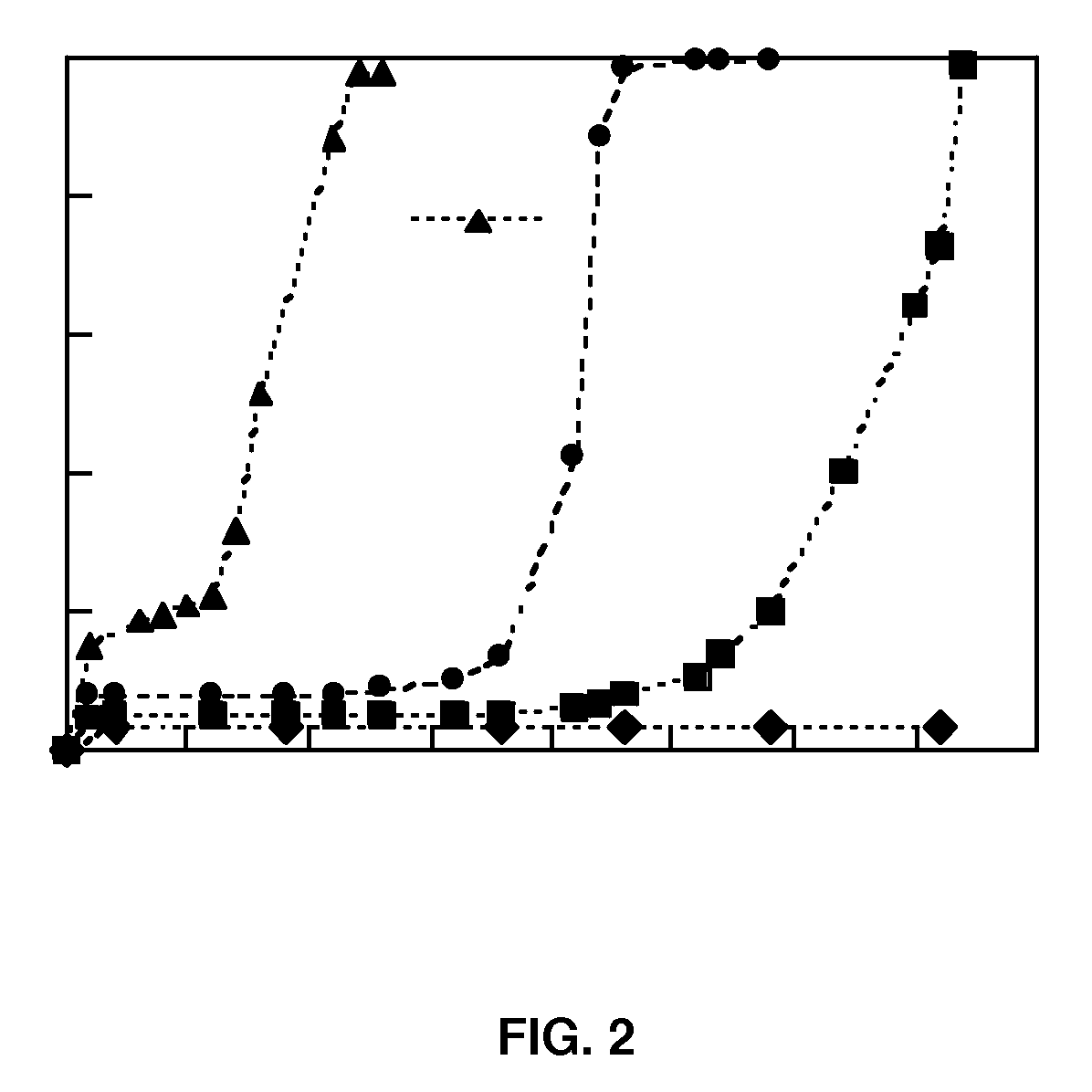
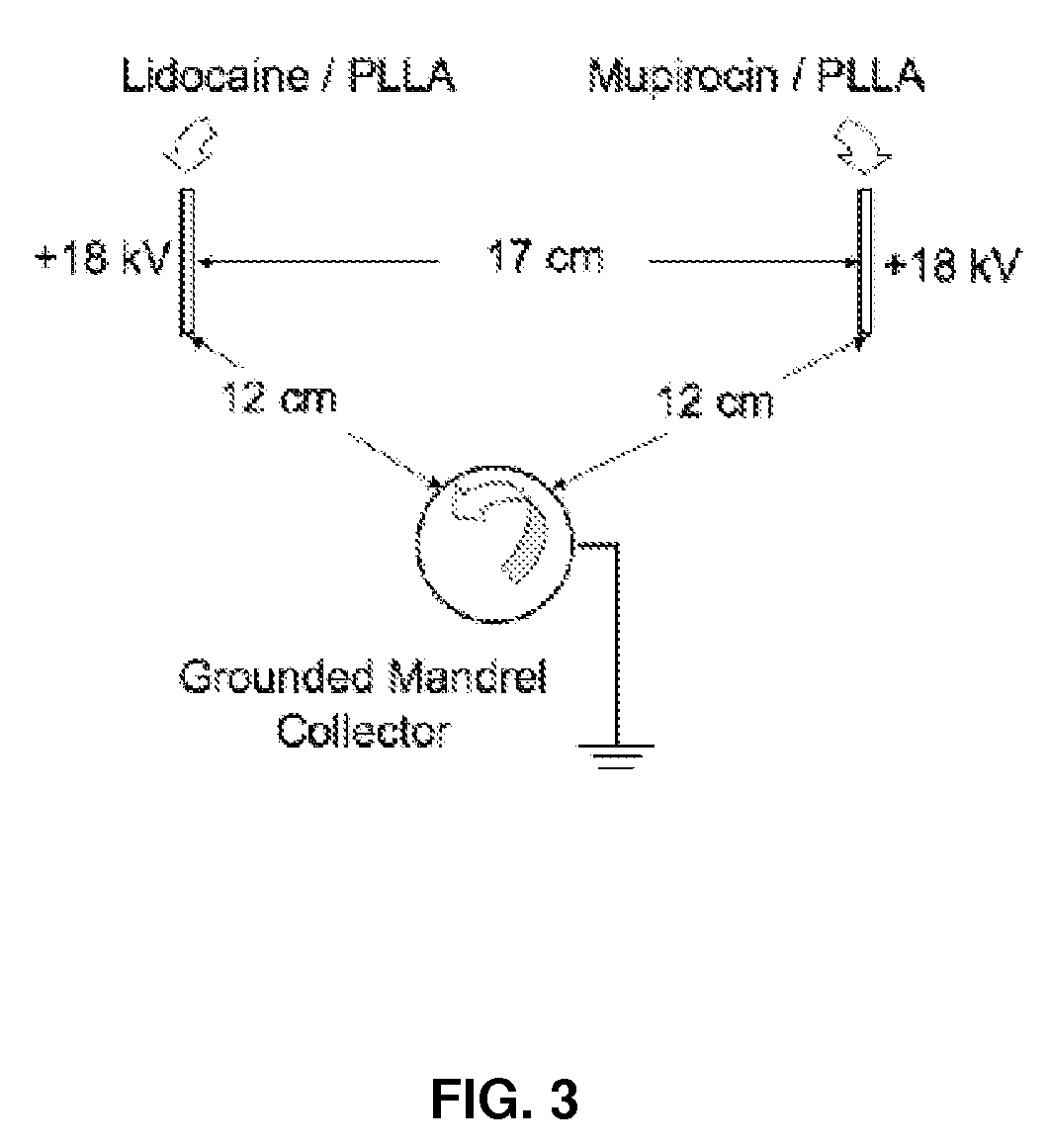
Electrospun matrices for delivery of hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds
InactiveUS20100166854A1Monocomponent protein artificial filamentElectric discharge heatingFiberCompound a
A method of forming electrospun fiber mats from a plurality of different biodegradable polymeric fibers is provided, in which a plurality of up to six different biodegradable polymer solutions are electrospun together by a method comprising the steps of providing a plurality of up to six different biodegradable polymer solutions each containing at least one biologically or pharmaceutically active material and each in communication with a needle for electrospinning a biodegradable polymer fiber from the solution, and pumping each solution through its respective needle into an electric field under conditions effective to produce uncontrolled charged jet streams of the polymer solutions directed at a grounded rotating mandrel, thereby forming fiber threads of the biologically or pharmaceutically active compounds and polymers in the solutions that are deposited on the mandrel to form an electrospun non-woven fiber mat, wherein the needles are positioned for co-deposition of the fiber threads from the polymer solution streams together on the mandrel to form a fiber mat.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Self emulsifying compositions for delivering lipophilic coenzyme Q10 and other dietary ingredients
InactiveUS20060051462A1Oral administration is convenientIncrease loadOrganic active ingredientsFood ingredientsSolubilityDietary supplement
The present invention provides novel dietary supplement compositions based on the use of a particular oil phase which comprises of Coenzyme Q10 and optionally other lipophilic dietary ingredients of low water solubility and a liquid mixture which comprises one or more emulsifiers, a fatty acid monoester formed between an short chain alcohol of C1 to C4 chain length and a saturated, or mono-unsaturated, or di-unsaturated (both conjugated and non-conjugated) fatty acid of C6 to C24 chain length, or medium chain mono- / di-esters, or the mixture of above. The composition is in a form of self-emulsifiable in the aqueous medium, for example, a simulated gastric fluid, which should provide a high oral bioavailability for the lipophilic dietary ingredients.
Owner:WANG JIMMY X
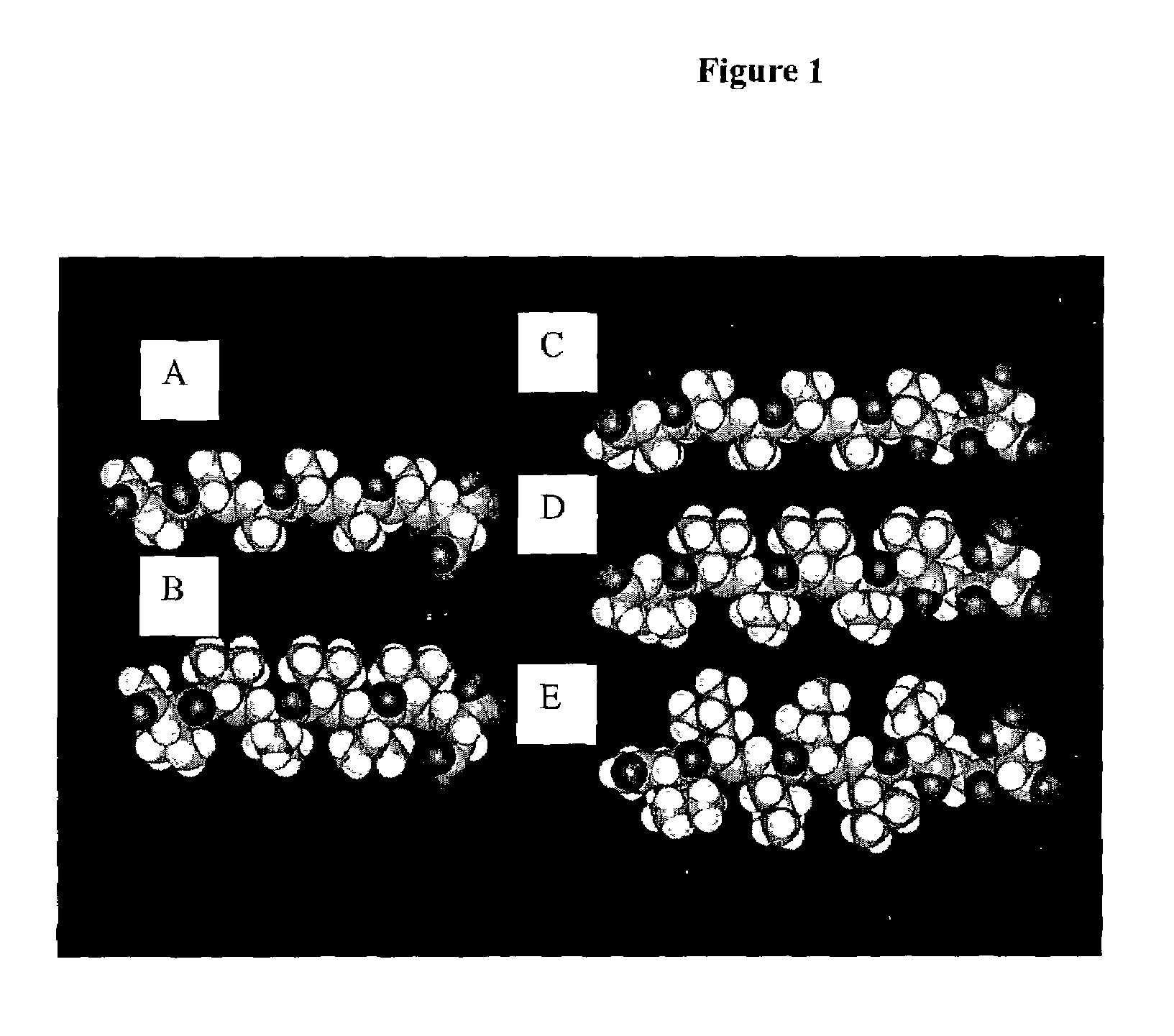
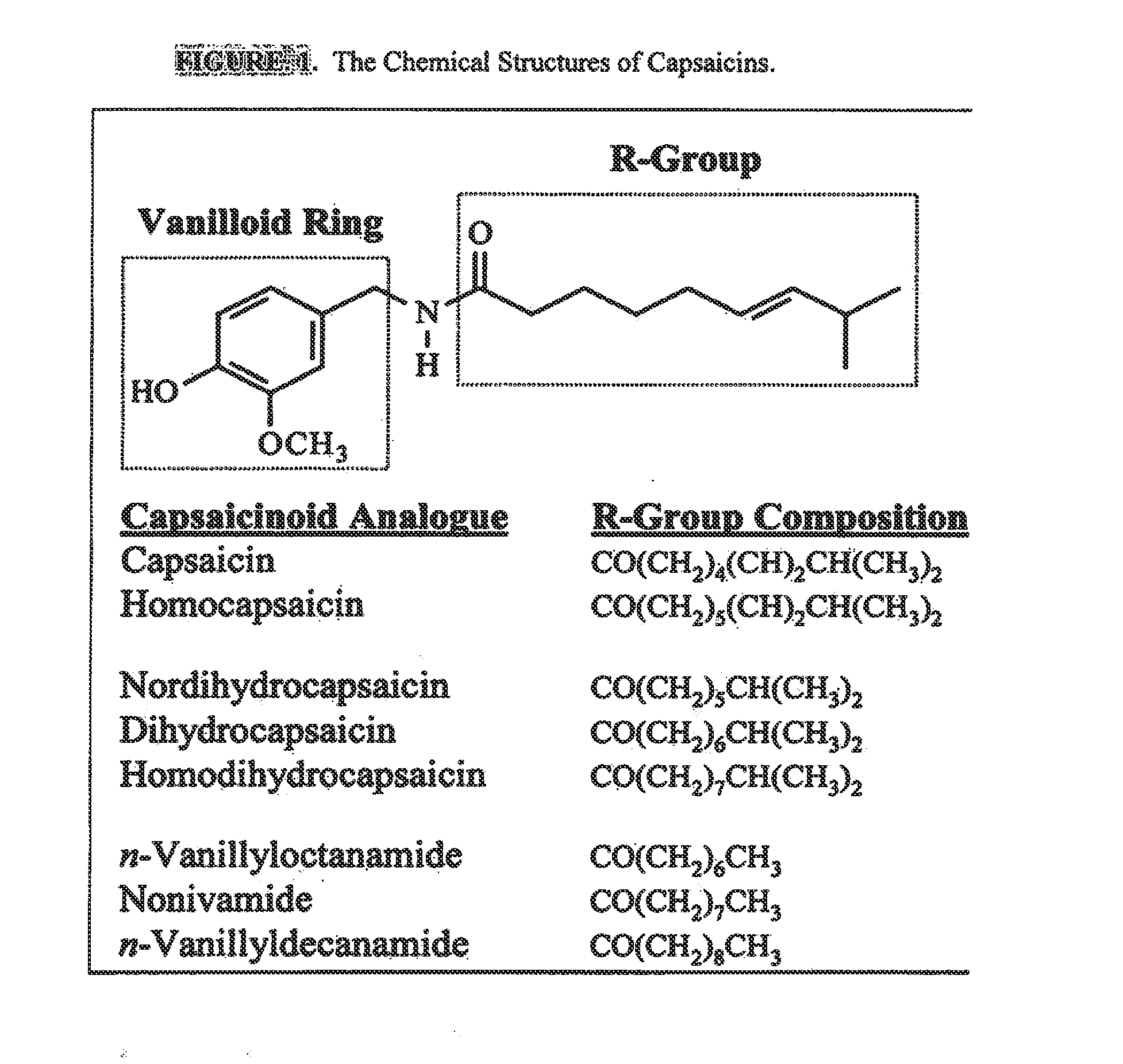
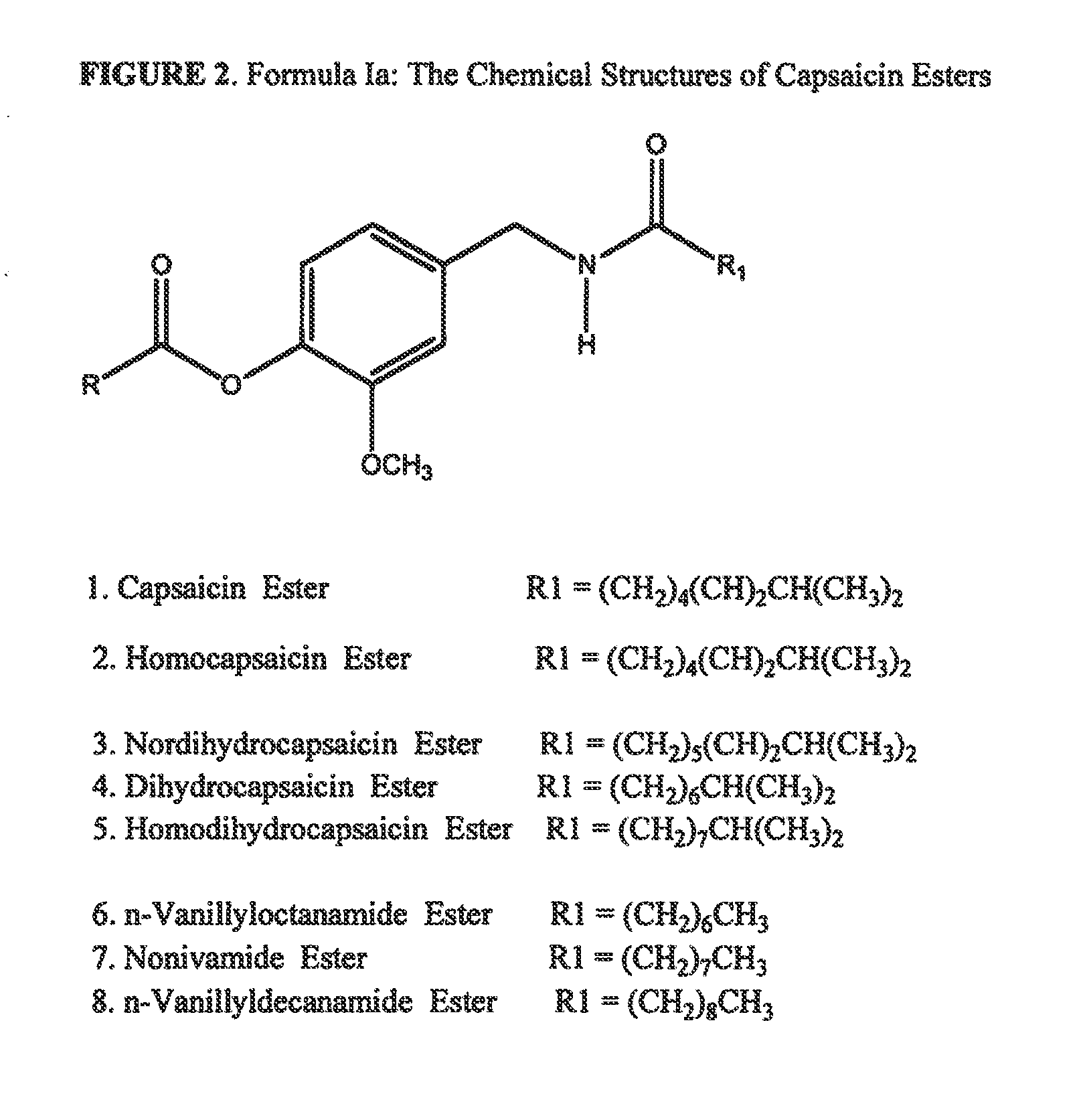
Esters of capsaicin for treating pain
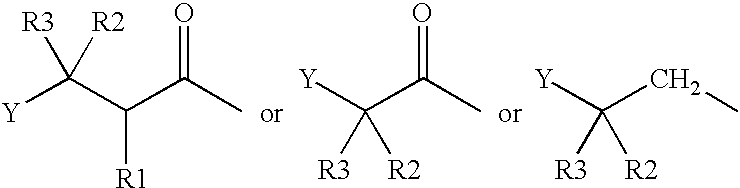
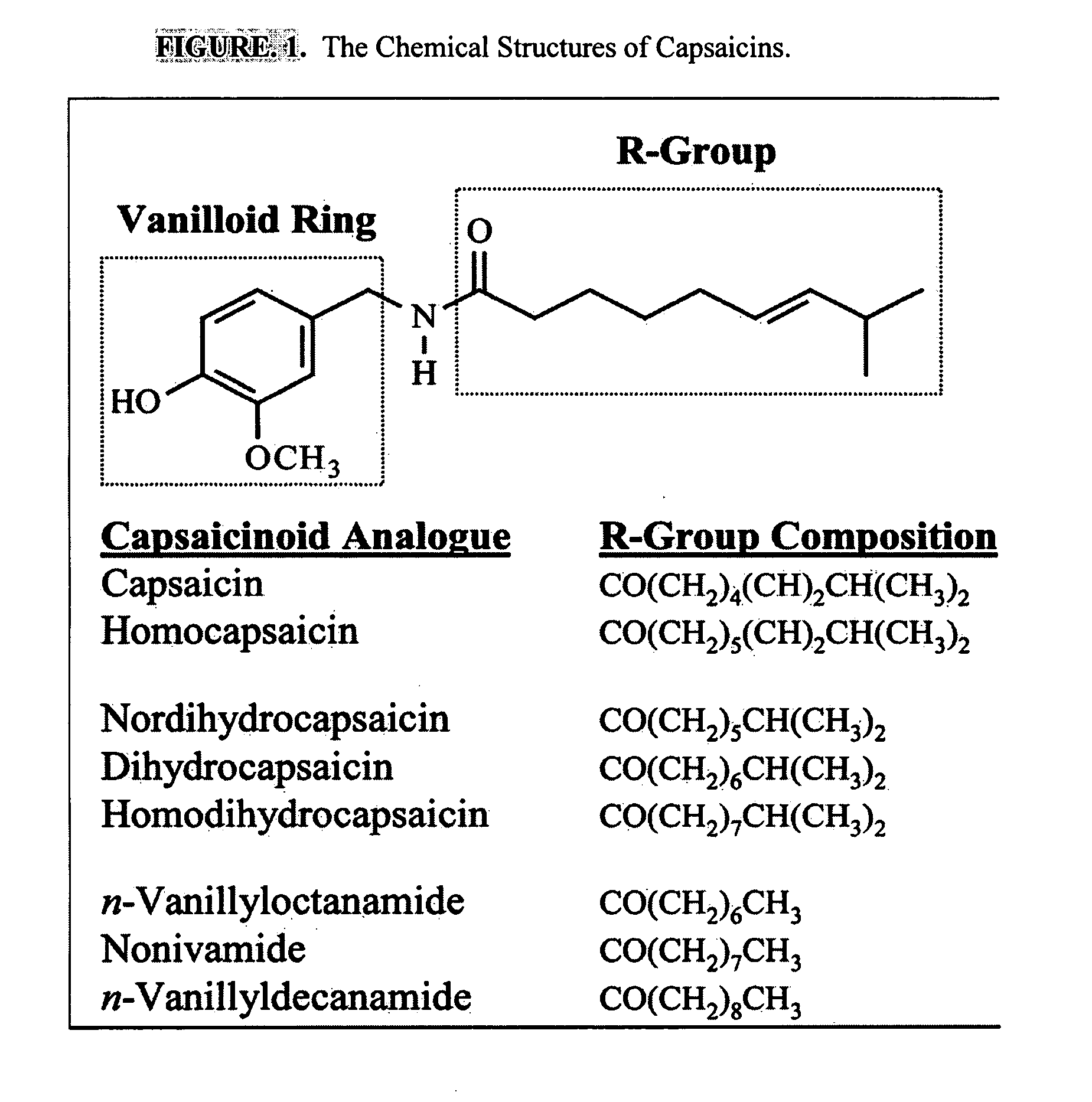
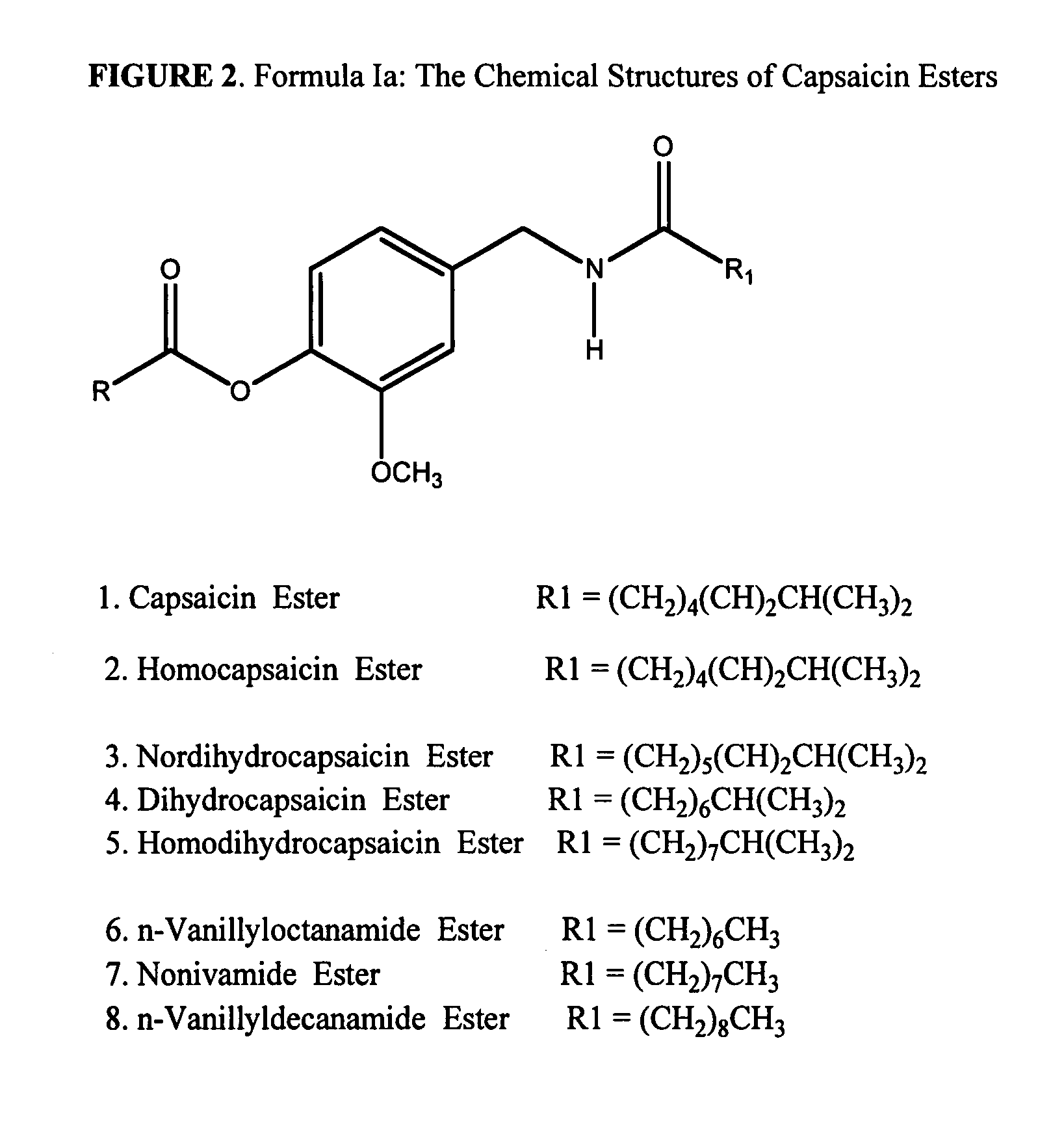
ActiveUS20080020996A1Reduce generationImprove lipophilicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSolubilityIrritation
The present invention relates to the formulations of ester derivatives of capsaicin and ester derivatives of myristoleic acid. These derivatives are capable of reverting to the active parent compound following enzymatic or chemical hydrolysis. These derivatives have a higher lipophilicity, lipid solubility and less irritation to the skin than the parent compound, and hence are better able to be incorporated into certain pharmaceutical formulations, including cream and ointment pharmaceutical formulations. The pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention contain a compound of following formula (Ia):R—CO-CAP (Ia)wherein CAP refers to collectively the capsaicins represented in FIG. 1 and a compound of formula (Ib):MCO-O—R (Ib)wherein MCO refers to myristoleic acid.In formulae Ia and Ib, R is selected from alkyl groups of up to about 18 carbon atoms and aryl groups of up to about 18 carbon atoms and alkylene group of up to about 18 carbon atoms and an arylene group of up to about 18 carbon atoms. The alkyl, aryl and alkylene groups may be substituted or un-substituted, branched or straight chains. In addition, R may contain heteroatoms and may be straight chained or branched.The pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of formulae Ia and Ib are useful for pain management in mammals in vivo and have been contemplated to be used in the treatment of various pains in humans.
Owner:TRINITY LAB INC
Multiblock biodegradable hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue treatment
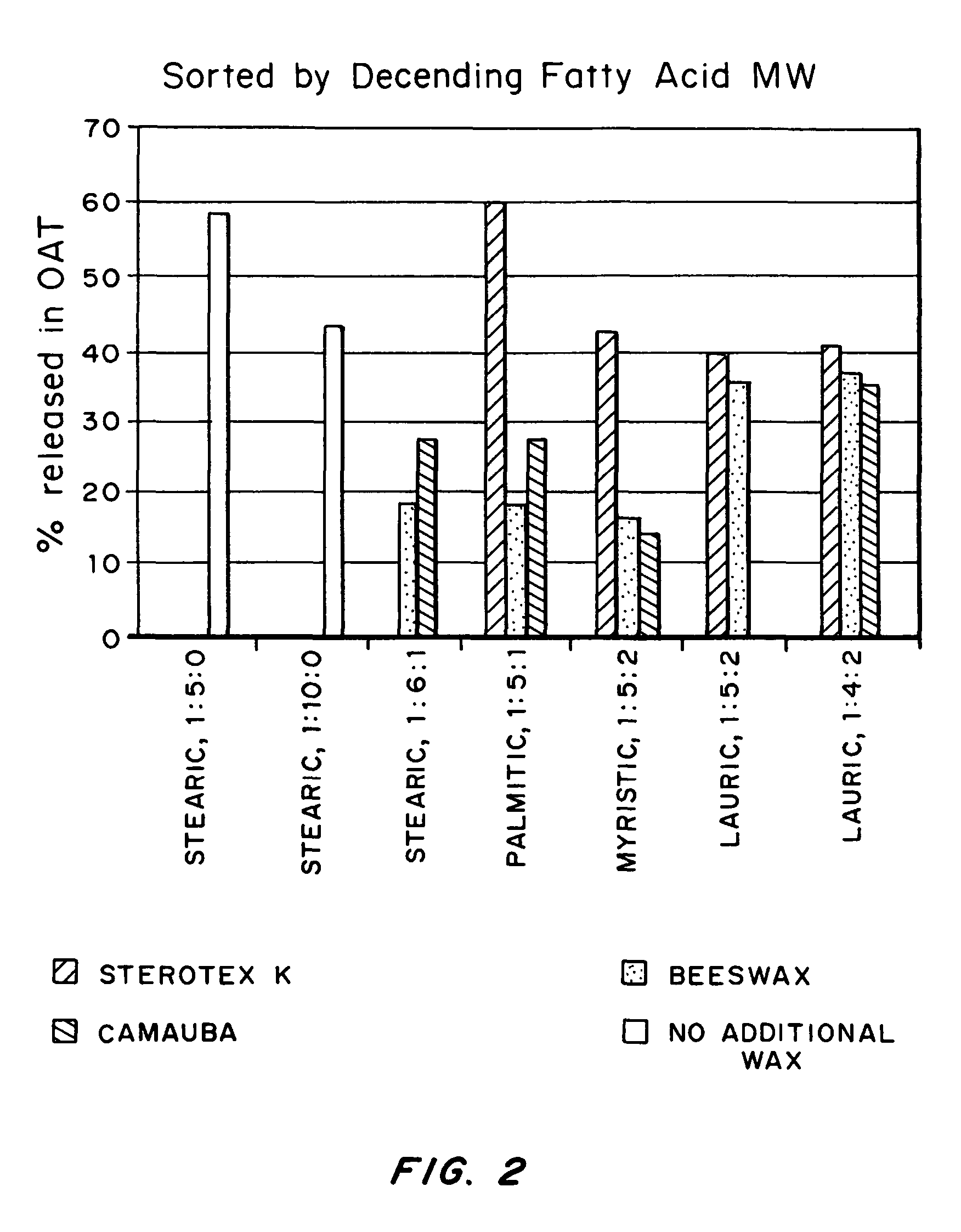
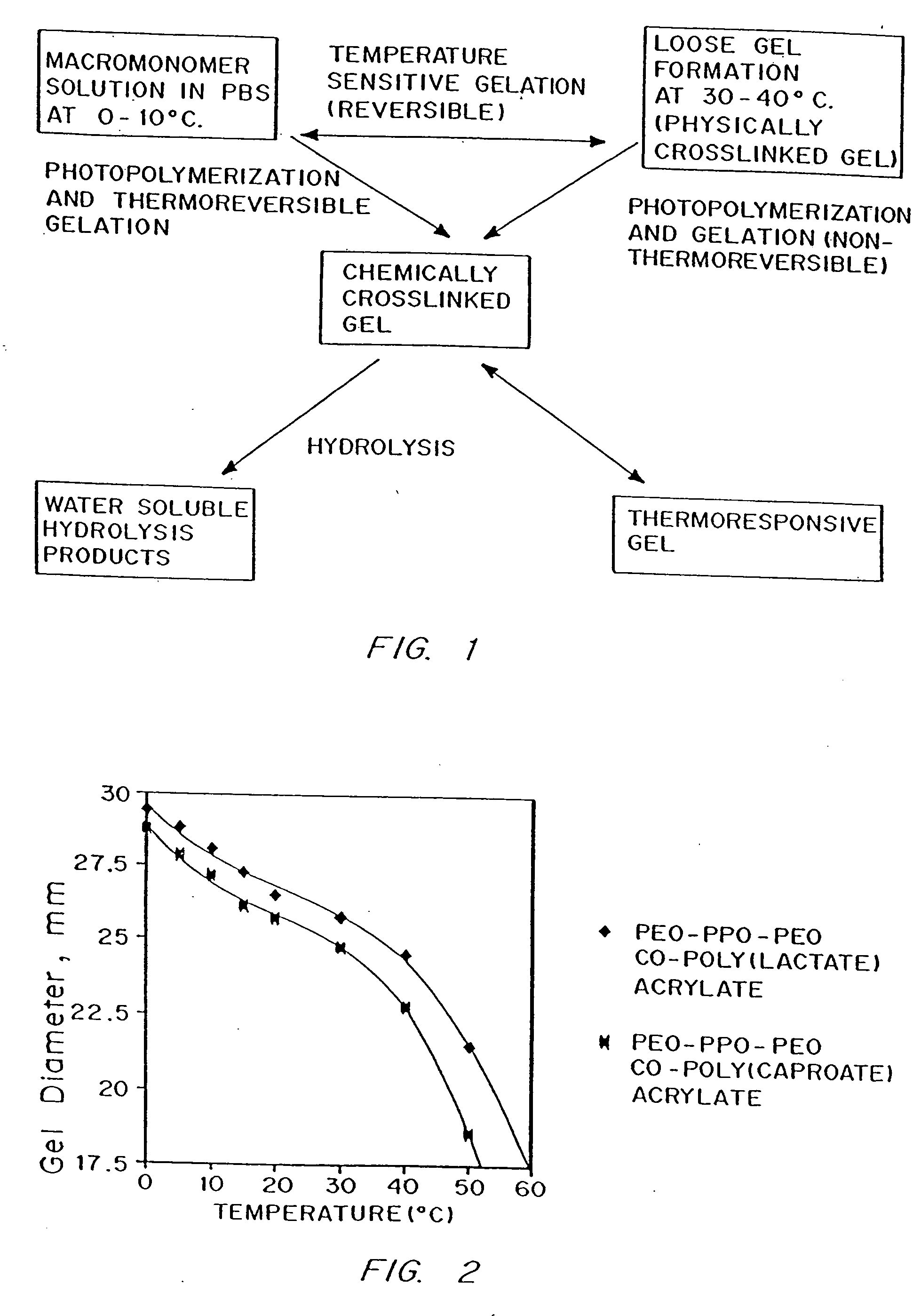
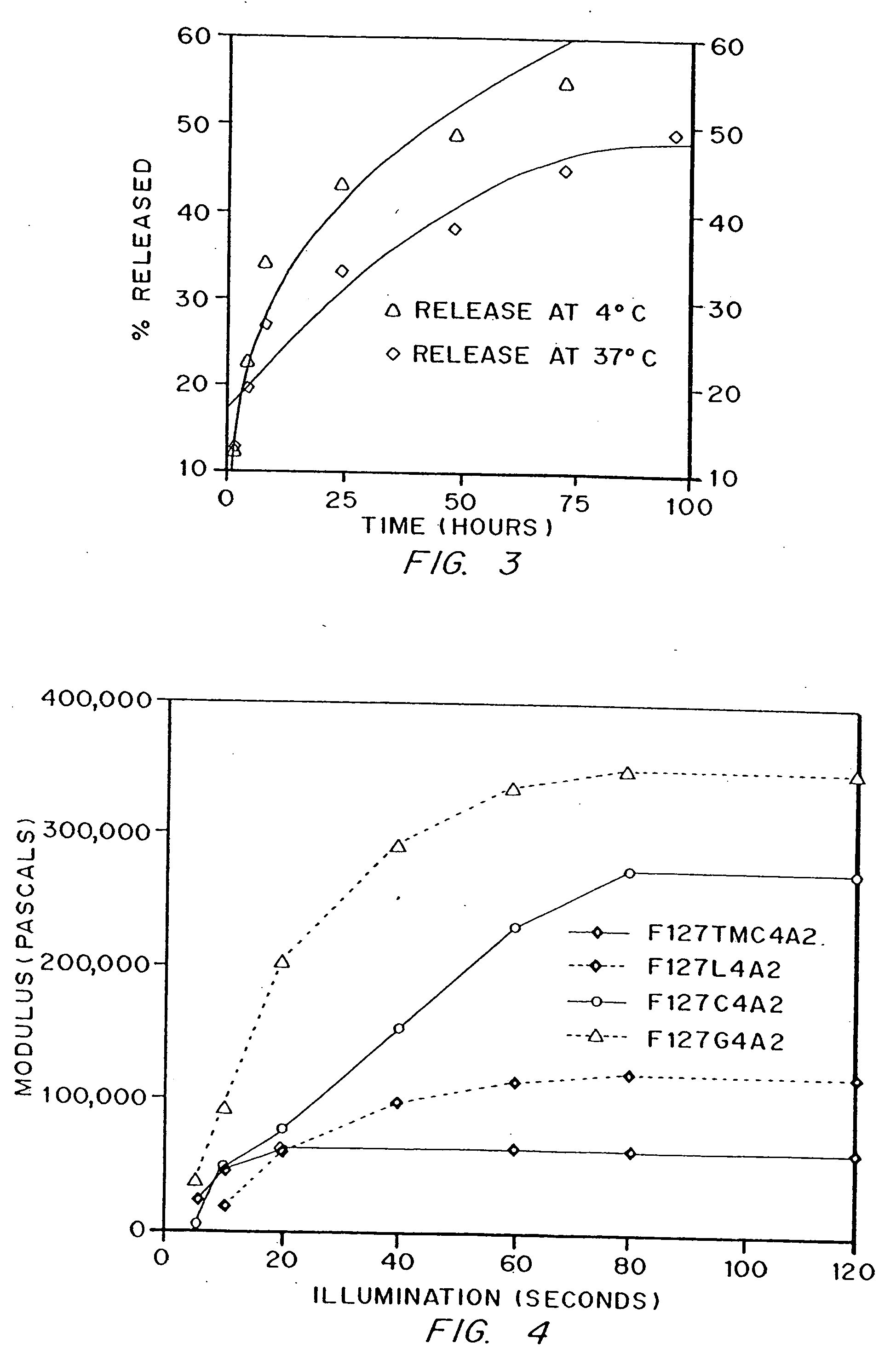
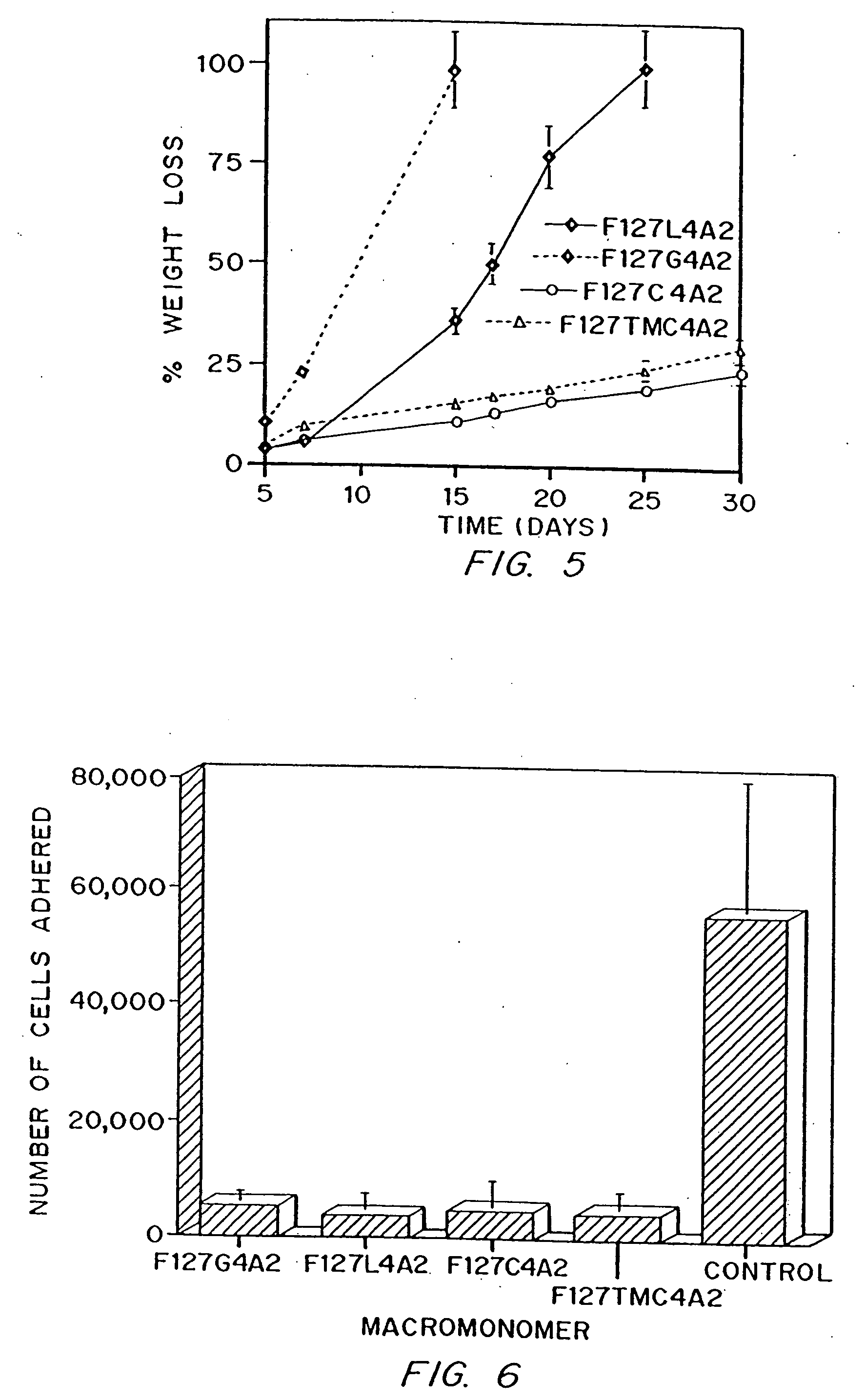
Gel-forming macromers including at least four polymeric blocks, at least two of which are hydrophobic and at least one of which is hydrophilic, and including a crosslinkable group are provided. The macromers can be covalently crosslinked to form a gel on a tissue surface in vivo. The gels formed from the macromers have a combination of properties including thermosensitivity and lipophilicity, and are useful in a variety of medical applications including drug delivery and tissue coating.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
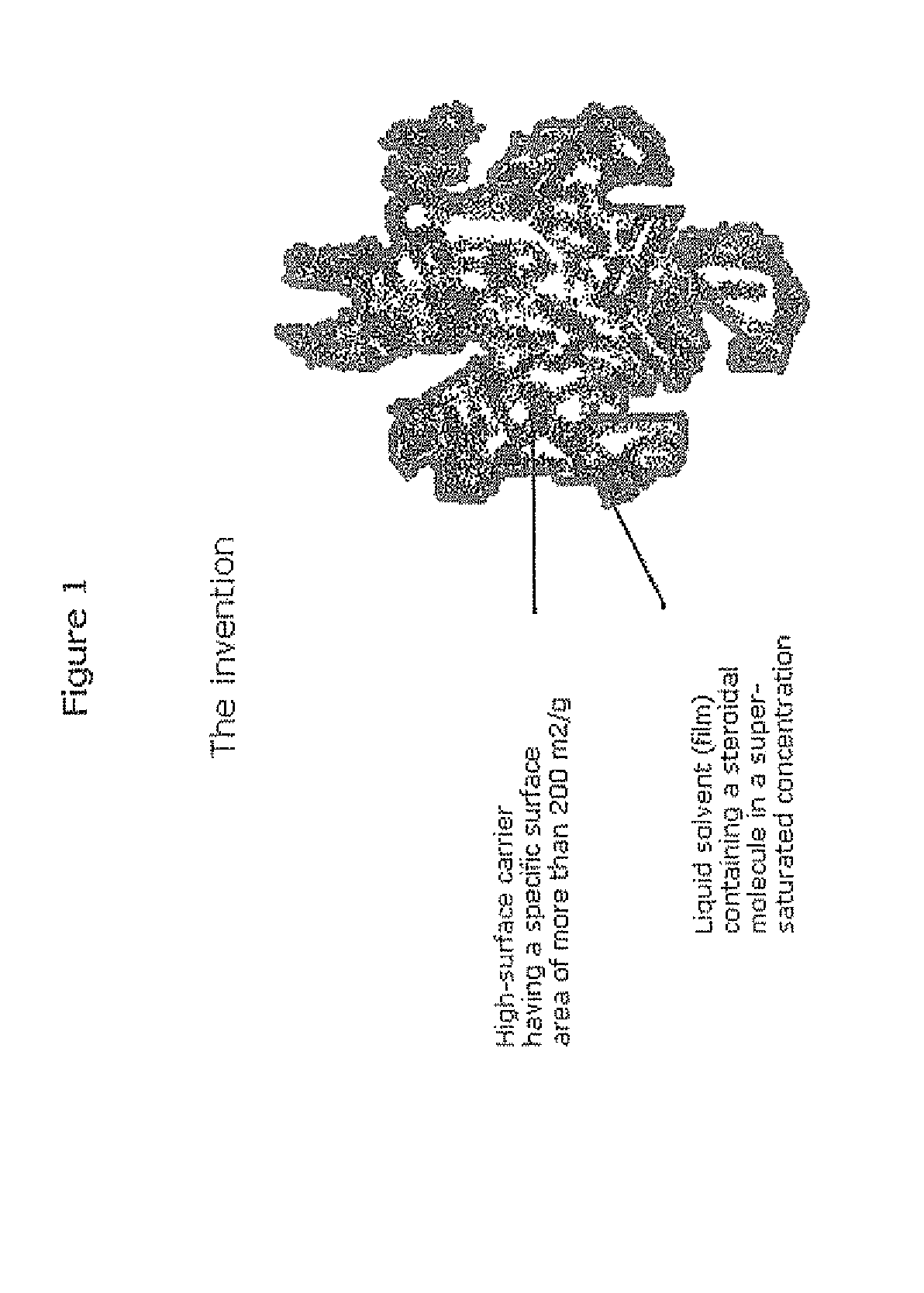
Stabilised supersaturated solids of lipophilic drugs
Methods for improving solubility and bioavailability of lipophilic compounds are described. Particularly, described are stabilized superstaturated solid solutions, particularly in power form, of lipophilic drugs, such as steroidal molecules.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Abuse-deterrent drug formulations
ActiveUS7771707B2Reduce the possibilityImprove lipophilicityPowder deliveryTelevision system detailsActive agentWater insoluble
An abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical composition has been developed to reduce the likelihood of improper administration of drugs, especially drugs such as opiods. In the preferred embodiment, the drug is modified to increase its lipophilicity by forming a salt between the drug and one or more fatty acids wherein the concentration of the one or more fatty acids is one to 15 times the molar amount of the active agent, preferably two to ten times the molar amount of the active agent. In one embodiment the modified drug is homogeneously dispersed within microparticles composed of a material that is either slowly soluble or not soluble in water. In some embodiments the drug containing microparticles or drug particles are coated with one or more coating layers, where at least one coating is water insoluble and preferably organic solvent insoluble. The abuse-deterrent composition prevents the immediate release of a substantial portion of drug, even if the physical integrity of the formulation is compromised (for example, by chopping with a blade or crushing) and the resulting material is placed in water, snorted, or swallowed. However, when administered as directed, the drug is slowly released from the composition as the composition is broken down or dissolved gradually within the GI tract by a combination of enzymatic degradation, surfactant action of bile acids, and mechanical erosion.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Compositions and methods for delivery of double-stranded RNA
InactiveUS20070293449A1Decrease expressionReduce expressionMicroencapsulation basedGenetic material ingredientsDrugDouble stranded rna
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use of a composition containing a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), cationic lipids, non-cationic lipids, and lipophilic delivery-enhancing compounds.
Owner:NASTECH PHARMA
Multiblock biodegradable hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue treatment
Gel-forming macromers including at least four polymeric blocks, at least two of which are hydrophobic and at least one of which is hydrophilic, and including a crosslinkable group are provided. The macromers can be covalently crosslinked to form a gel on a tissue surface in vivo. The gels formed from the macromers have a combination of properties including thermosensitivity and lipophilicity, and are useful in a variety of medical applications including drug delivery and tissue coating.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Desalting adjunct chemistry
InactiveUS6120678AImproves separation of waterReduce decreaseDewatering/demulsification with chemical meansLiquid separation by electricityChemical treatmentMeth-
Improved performance in the phase separation of aqueous brines from hydrocarbons within an electrostatic desalter operation is obtained by the addition to the crude oil emulsions entering the desalter of an effective asphaltene dispersing amount of an alkyl phenol-formaldehyde liquid resin polymer, optionally in the presence of a lipophilic / hydrophilic vinylic polymer. The preferred resin is a nonyl phenol-formaldehyde resin having a molecular weight of from 1,000-20,000, and the preferred vinylic polymer is a copolymer of lauryl (meth)acrylate and hydroxyethyl (meth)acrylate. Best results from the electrostatic desalter are obtained when also using a demulsifier chemical treatment along with the asphaltene dispersing treatments. Desalter efficiency is increased and desalter brine effluent quality is greatly increased.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC +1
Magnetic coated carrier two-component type developer and developing method
InactiveUS6165663AImprove liquidityIncreased durabilityDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternCoated surfaceParticulate metal
A magnetic coated carrier suitable for constituting a two-component type developer for use in electrophotography is composed of magnetic coated carrier particles comprising magnetic coated carrier particles comprising magnetic carrier core particles each comprising a binder resin and metal oxide particles, and a coating layer surface-coating each carrier core particle. The metal oxide particles have been subjected to a surface lipophilicity-imparting treatment. The magnetic carrier core particles have a resistivity of at least 1x1010 ohm.cm, and the magnetic coated carrier has a resistivity of at least 1x1012 ohm.cm. The magnetic coated carrier has a particle size distribution such that (i) it has a number-average particle size Dn of 5-100 mu m, (ii) it satisfies a relationship of Dn / sigma > / =3.5, wherein sigma denotes a standard deviation of number-basis particle size distribution of the carrier, and (iii) it contains at most 25% by number of particles having particle sizes of at most Dnx+E,fra 2 / 3+EE .
Owner:CANON KK
Surfactant peptide nanostructures, and uses thereof
ActiveUS7179784B2Improve efficiencyIncrease flexibilityMaterial nanotechnologyBiocideActive agentTert-leucine
This work describes a new class of short polypeptides that can self-assemble to form regular nanotubes with an average diameters of about 50 nm. These peptides (7 to 8 amino acids) have a structure very similar to those observed in surfactant molecules with a defined hydrophilic head group constituting of charged amino acids and a lipophilic tail made out of hydrophobic amino acids such as alanine, valine or leucine. Cryo-TEM micrographs show numerous three-fold junctions connecting the self-assembling nanostructures and thus leading to the formation of a rather dense network of entangled nanotubes. Additionally, the observation of clear openings at the end of the supramolecular structures confirms the presence of tubular organization.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Esters of Capsaicin for Treating Pain
InactiveUS20110218180A1Improve lipophilicityNon-irritation to skinAntibacterial agentsBiocideSolubilityIrritation
The present invention relates to the formulations of ester derivatives of capsaicin and ester derivatives of myristoleic acid. These derivatives are capable of reverting to the active parent compound following enzymatic or chemical hydrolysis. These derivatives have a higher lipophilicity, lipid solubility and less irritation to the skin than the parent compound, and hence are better able to be incorporated into certain pharmaceutical formulations, including cream and ointment pharmaceutical formulations. The pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention contain a compound of following formula (Ia):R—CO—CAP (Ia)wherein CAP refers to collectively the capsaicins represented in FIG. 1 and a compound of formula (Ib):MCO—O—R (Ib)wherein MCO refers to myristoleic acid.In formulae Ia and Ib, R is selected from alkyl groups of up to about 18 carbon atoms and aryl groups of up to about 18 carbon atoms and alkylene group of up to about 18 carbon atoms and an arylene group of up to about 18 carbon atoms. The alkyl, aryl and alkylene groups may be substituted or un-substituted, branched or straight chains. In addition, R may contain heteroatoms and may be straight chained or branched.The pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of formulae Ia and Ib are useful for pain management in mammals in vivo and have been contemplated to be used in the treatment of various pains in humans.
Owner:TRINITY LAB INC
Fatty alcohol polyoxypropylene polyoxyethylene ether carboxylate, preparation thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN102485771ACarboxylationMeet the needs of tertiary oil recoveryOrganic compound preparationDrilling compositionFatty alcoholSURFACTANT BLEND
The invention relates to a fatty alcohol polyoxypropylene polyoxyethylene ether carboxylate, a preparation thereof and an application thereof. The structural general formula of the fatty alcohol polyoxypropylene polyoxyethylene ether carboxylate is RO(PO)n(EO)mCH2COOX, wherein R is an aliphatic alkyl group or an alkylphenyl group; (PO)n is polyoxypropylene; n is between 6 and 12; (EO)m is polyoxyethylene; m is between 1 and 4; X is an alkali metal, the fatty alcohol and the polyoxypropylene at the left terminal of the structural general formula are lipophilic groups; and polyoxyethylene and the carboxyl group at the right terminal of the structural general formula are hydrophilic groups. Polyoxypropylene is added to increase the lipophilicity of fatty alcohol carboxylate surfactants to adapt to the application of tertiary oil recovery, and a small amount of polyoxyethylene is added to adjust the hydrophilicity and simultaneously carboxylate fatty alcohol polyoxypropylene esters on condition that the current fatty alcohol raw material is unchanged.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Preparation method of oil-water separation material
ActiveCN103626171AImprove oil-water separation effectEasy to separateGrapheneLiquid separationSeparation technologyMechanical stability
The invention provides a preparation method of an oil-water separation material, which comprises the following steps: soaking a sponge material in a graphene oxide solution, taking out the obtained sponge material and centrifuging the sponge material, so that a graphene oxide coated sponge material is obtained; and carrying out a reduction reaction on the graphene oxide coated sponge material under the action of a reducing agent so as to obtain the oil-water separation material. The oil-water separation material prepared by using the method provided by the invention is a reduced graphene oxide coated sponge material, is coated with a graphene layer uniformly and tightly and has good rebound resilience and mechanical stability, and the reduced graphene oxide layer provides good hydrophobicity and lipophilicity, therefore, the preparation method disclosed by the invention can be applied to oil-water separation technologies.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Stabilised supersaturated solids of lipophilic drugs
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Silicane coupling agent surface grafted modified clay as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101254924AGood dispersionEnhanced Interfacial InteractionSilicon compoundsCouplingPolymer interaction
The invention relates to the clay surface modification, in particular to modified clay with silane coupling agent grafted surface, preparation method and application thereof. The grafting modification of the silane coupling agent with a grafting amount of 0.2-5*10<-3> mol / gram clay is performed in solvent by using reactive hydroxyl group on a clay sheet layer. The inventive modified clay, in which the silane coupling agent is grafted on the clay sheet layer via the covalent bond, has strong thermostability and realizes clay functionalization while improving the clay surface lipophilicity. As the inventive clay has high thermostability and enhanced interaction with polymer, it can be used for the preparation of polymer / clay nanometer composite material to improve the clay dispersibility in the polymeric matrix for stripping and dispersing, thereby improving the performance of the composite material.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
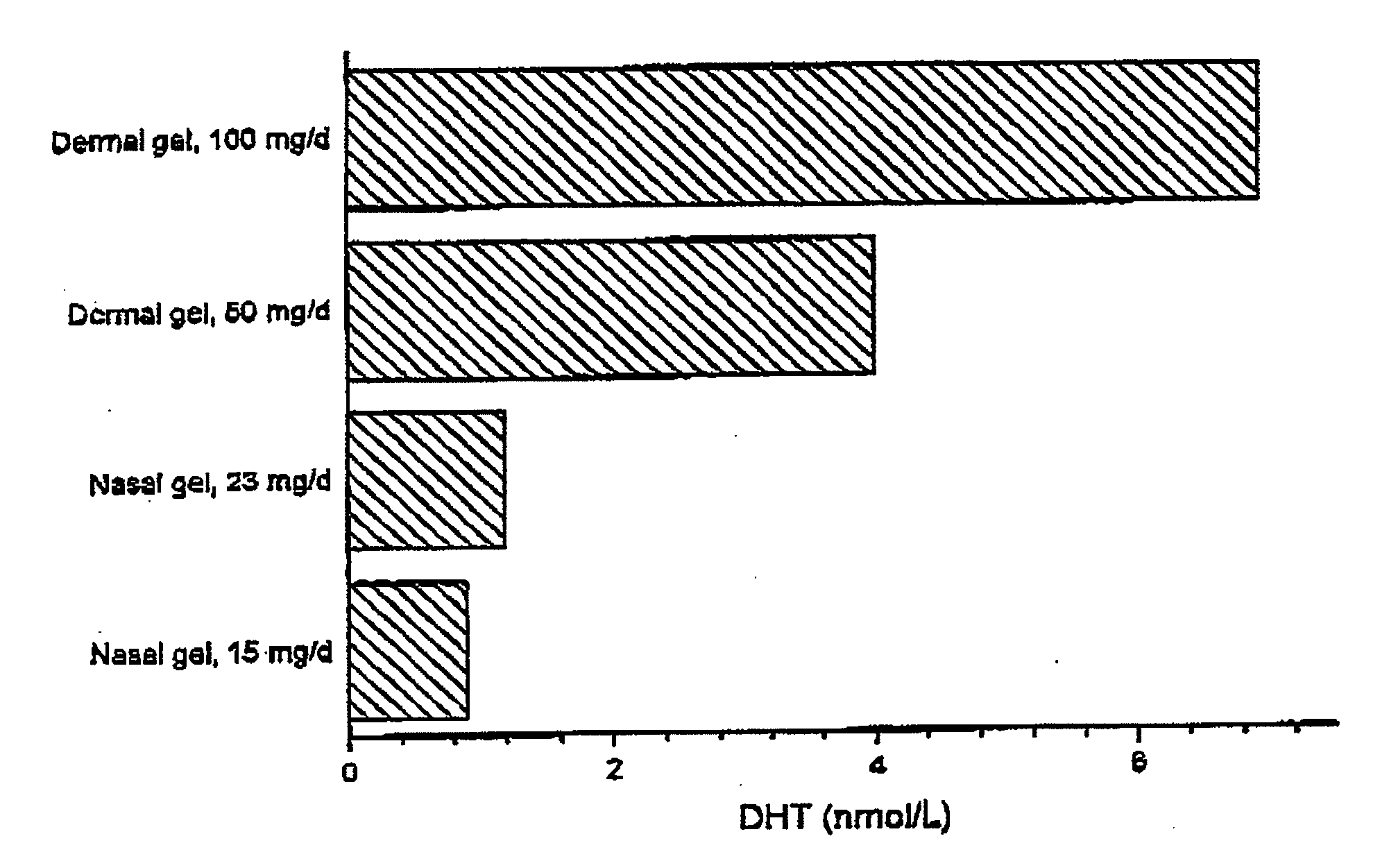
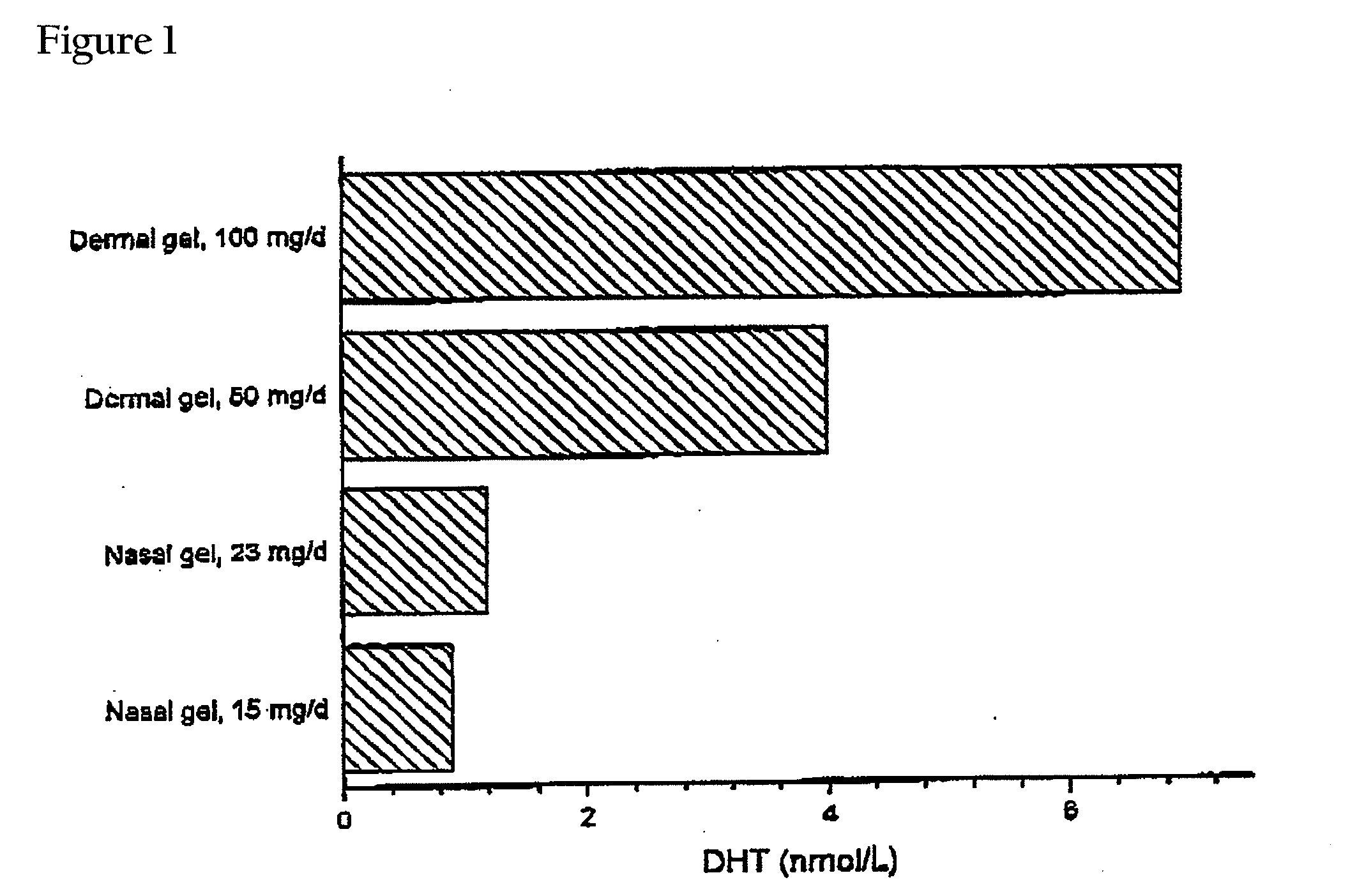
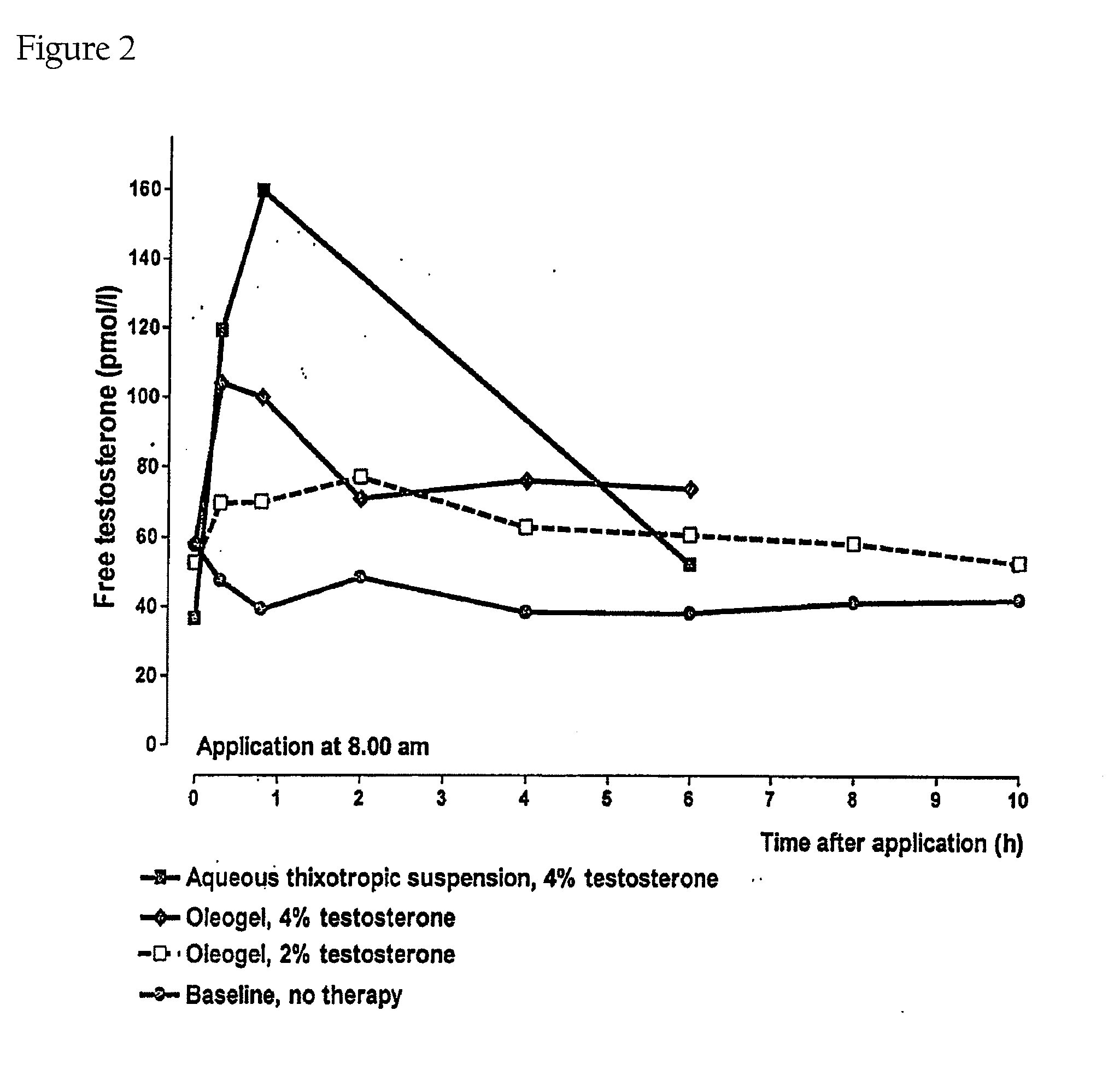
Controlled Release Delivery System for Nasal Applications and Method of Treatment
InactiveUS20070149454A1Improve bioavailabilityImproved profileOrganic active ingredientsBiocideFemale Sexual Arousal DisorderNasal cavity
This invention relates to a gel formulation for nasal administration of a controlled release formulation of hormones to the systemic circulation and / or to the brain. The special lipophilic or partly lipophilic system of the invention leads to higher bioavailability of the active ingredient caused by sustained serum levels in plasma but also leads to a more favorable serum level profile. The special lipophilic or partly lipophilic system also allows for the modulation of brain functioning. The invention also relates to the nasal administration of steroid hormones for treatment of female sexual dysfunction (FSD) or female arousal disorder.
Owner:MATTERN PHARMA
Hydrophilic complexes of lipophilic materials and an apparatus and method for their production
InactiveUS6878693B2Improve uniformitySimple processAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryFood additiveWater insoluble
This invention provides a soluble inclusion complex formed of a water-insoluble lipophilic compound and an amphiphilic polymer and which demonstrated improved solubility and stability. The lipophilic compound within the inclusion complex may consist of pharmaceutical compounds, food additives, cosmetics, agricultural products and veterinary products. The invention also provides novel methods for preparing the inclusion complex, as well as a novel chemical reactor for forming the inclusion complex.
Owner:SOLUBEST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com