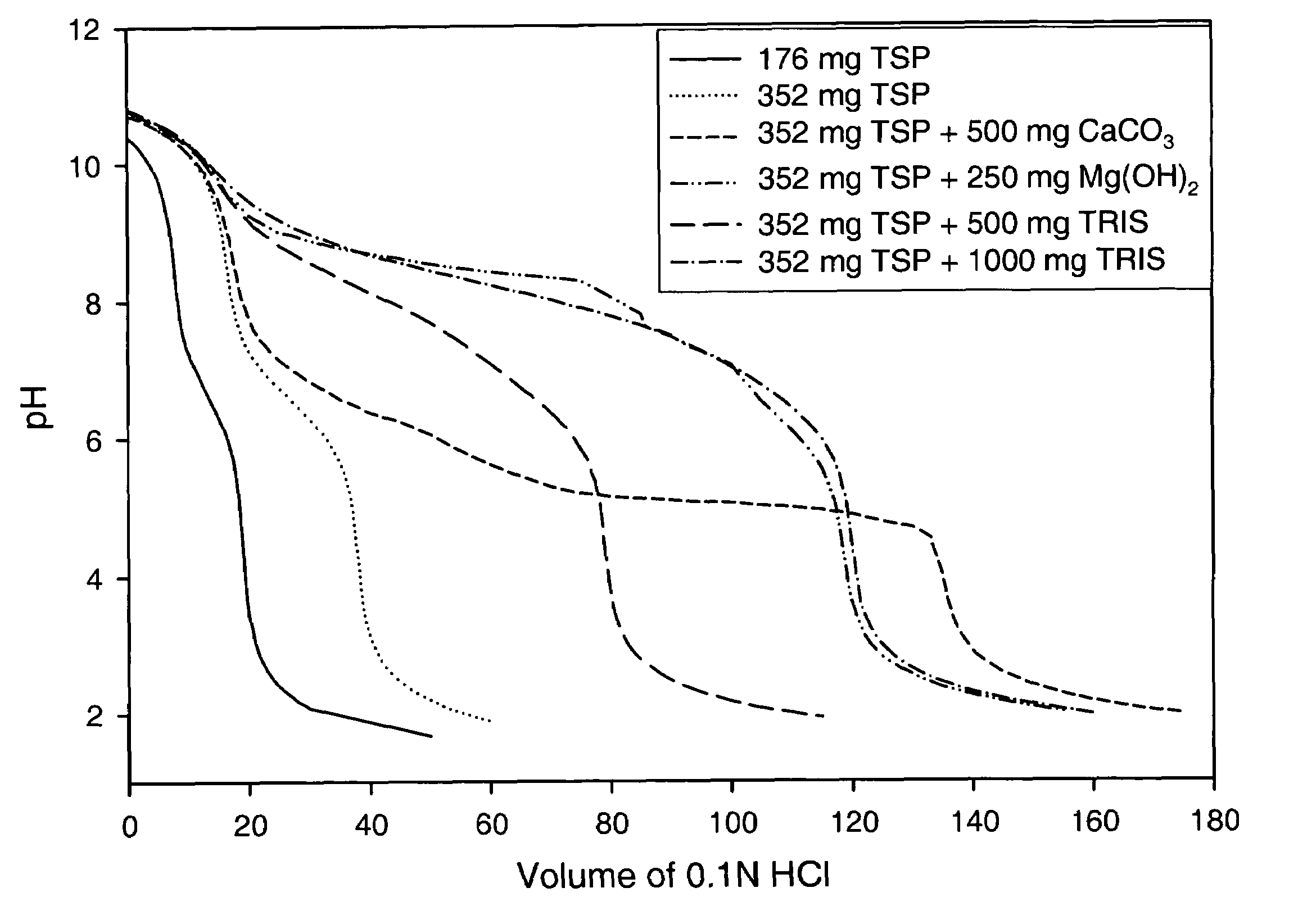
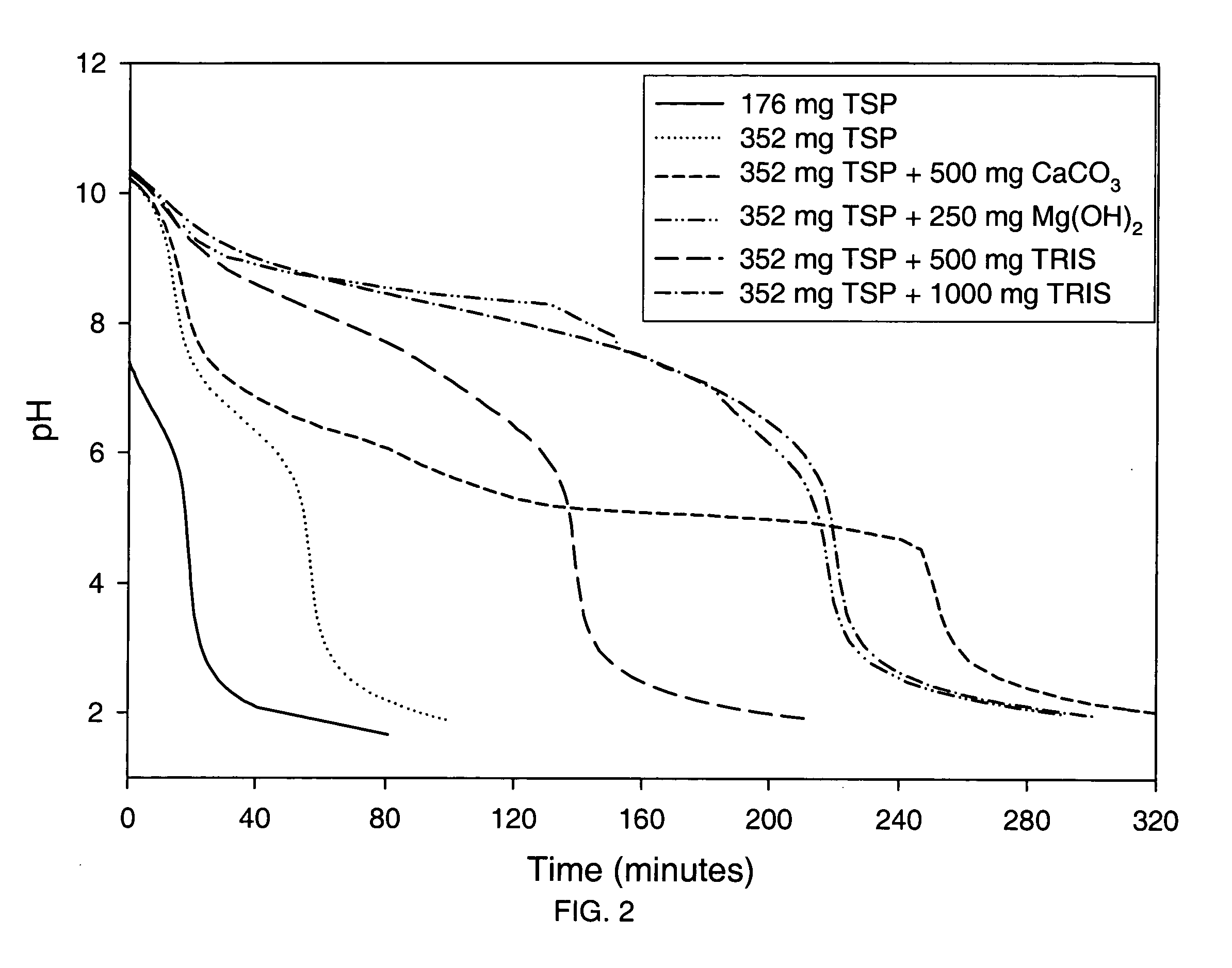
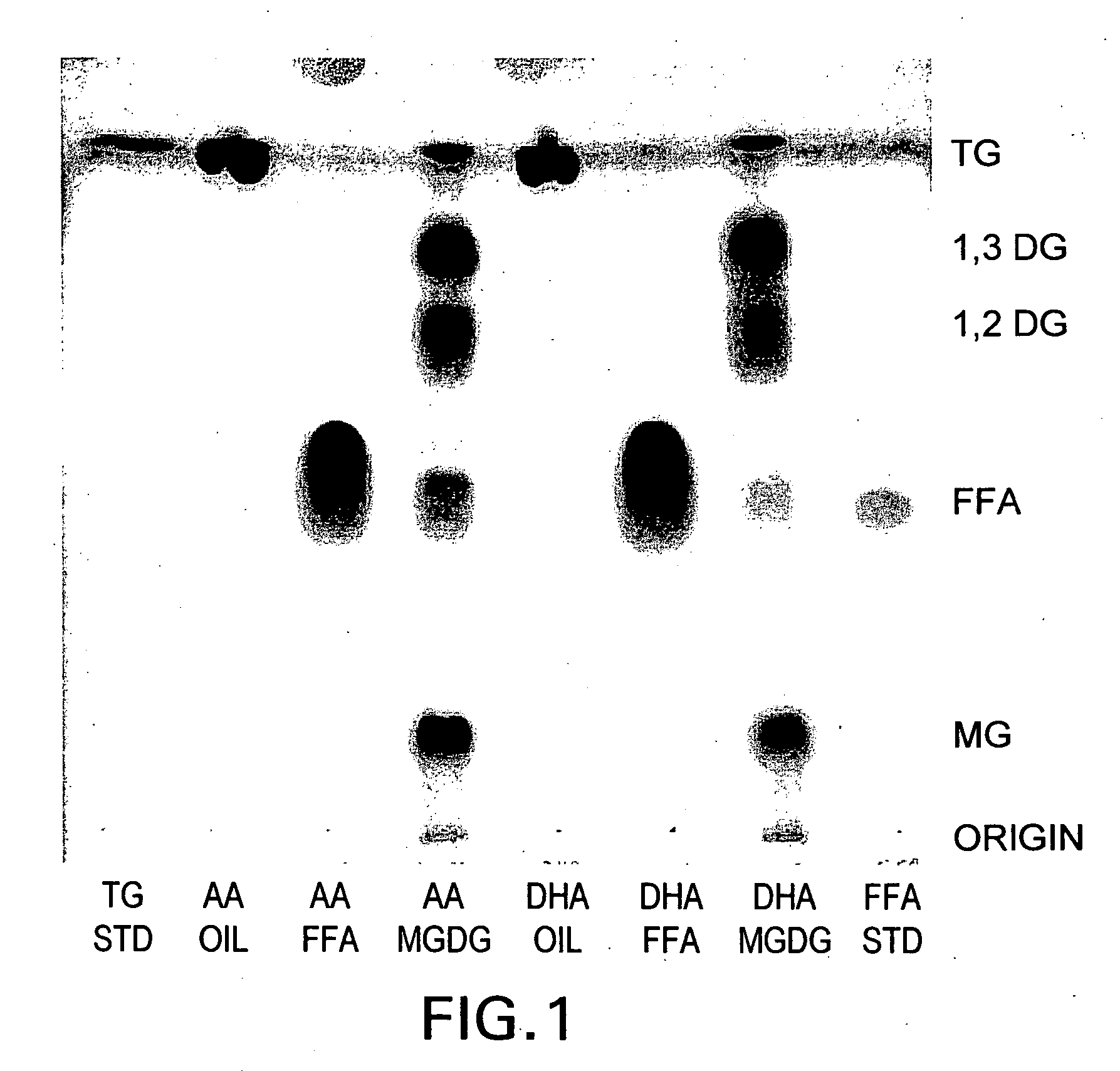
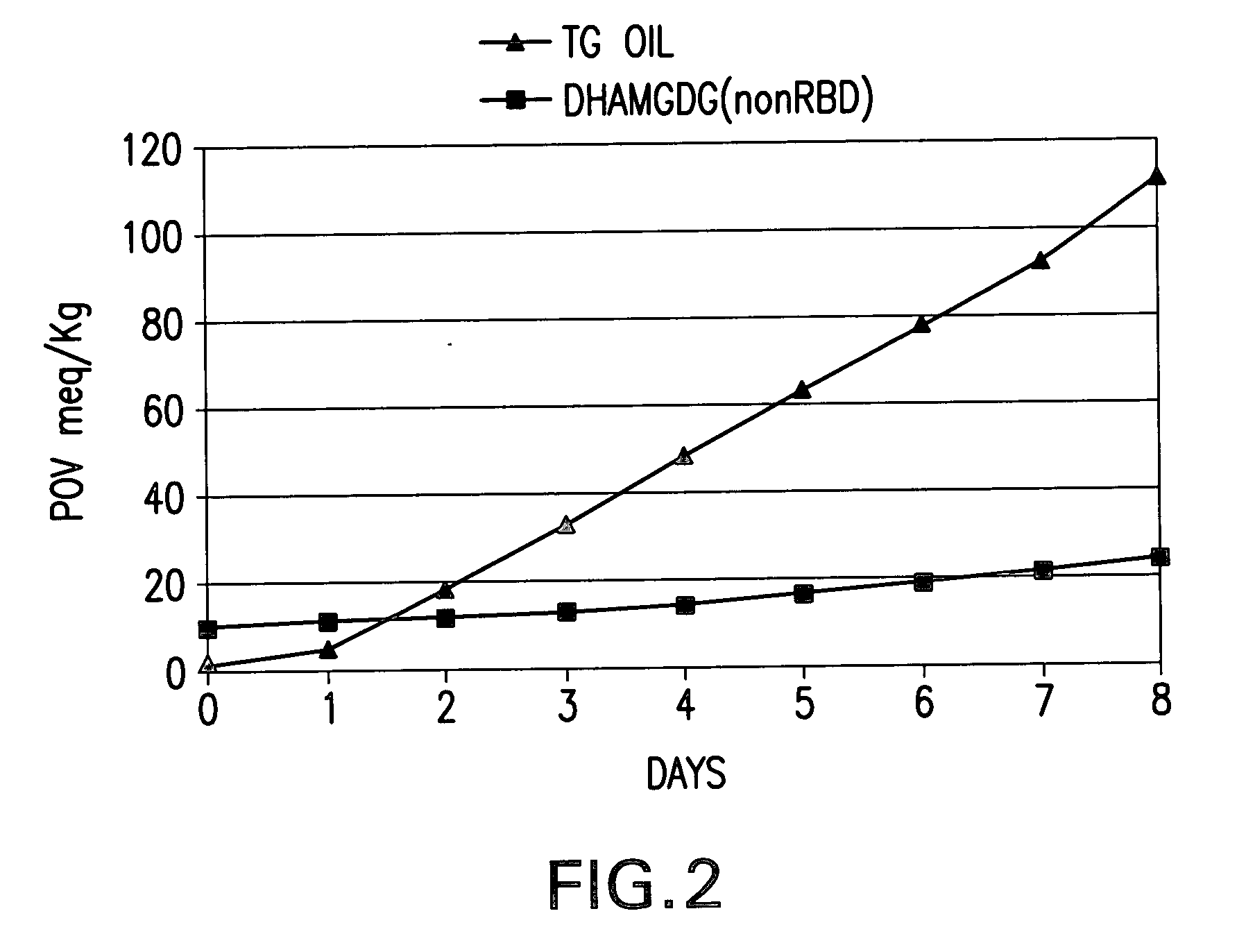
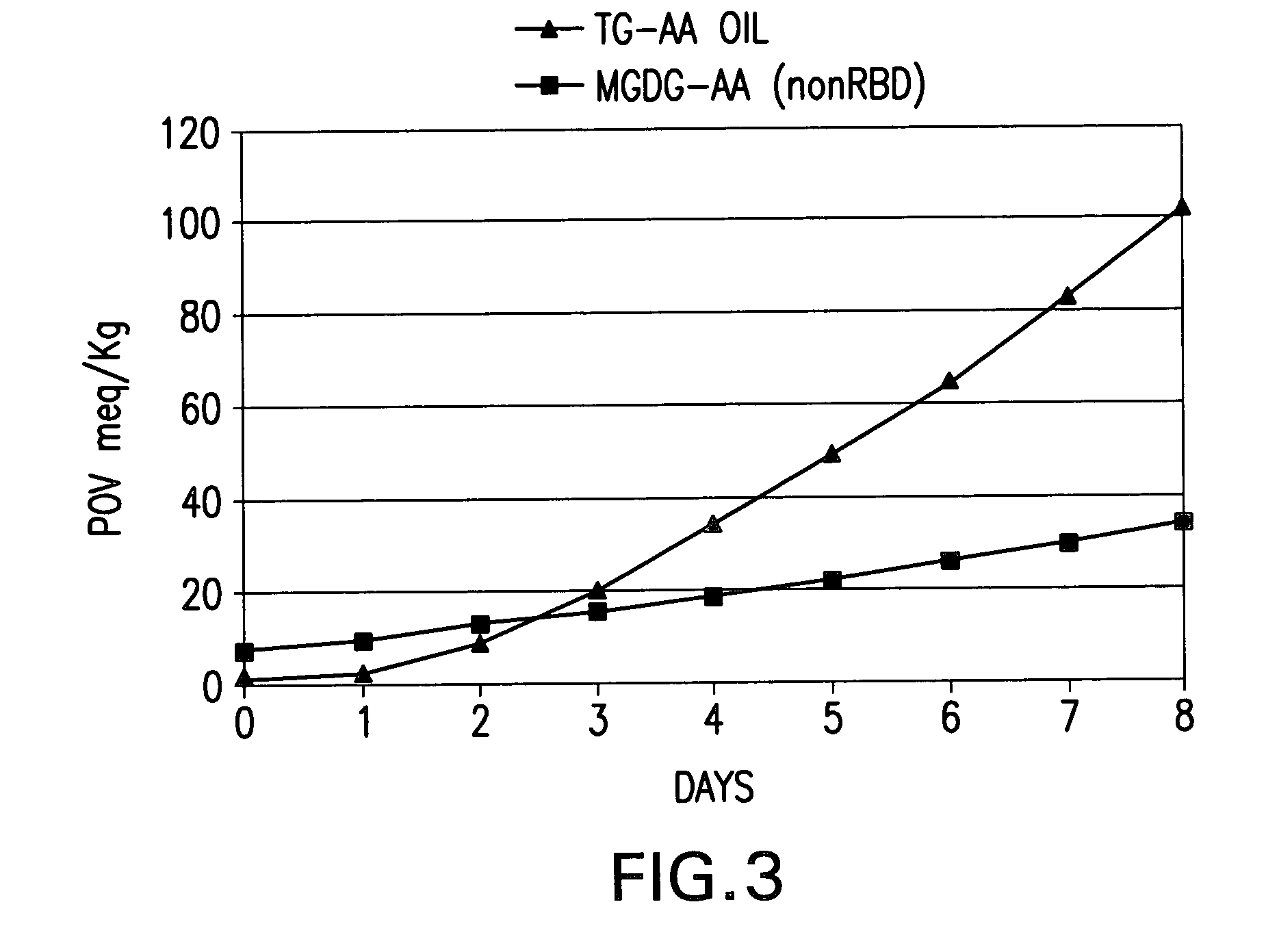
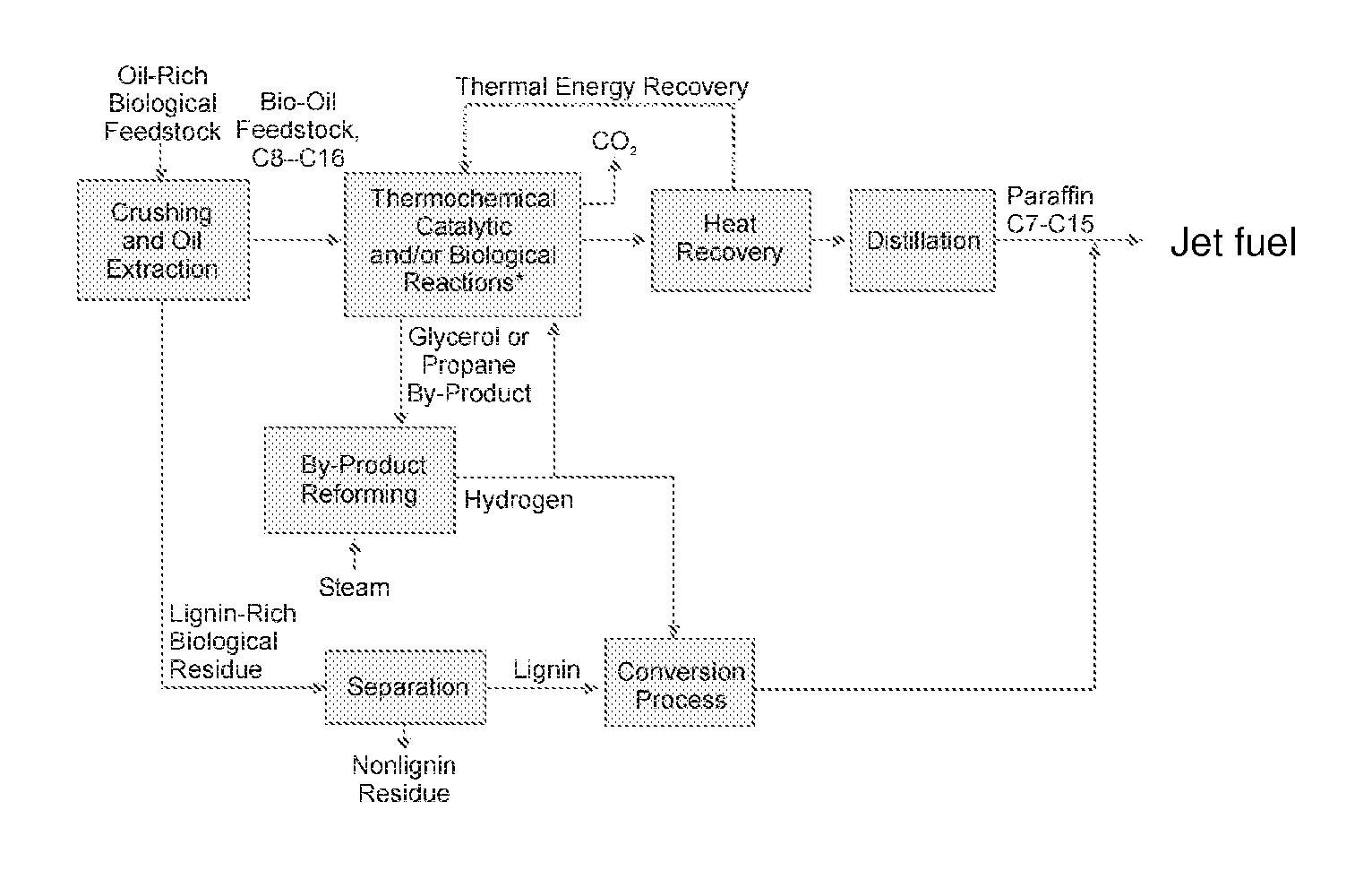
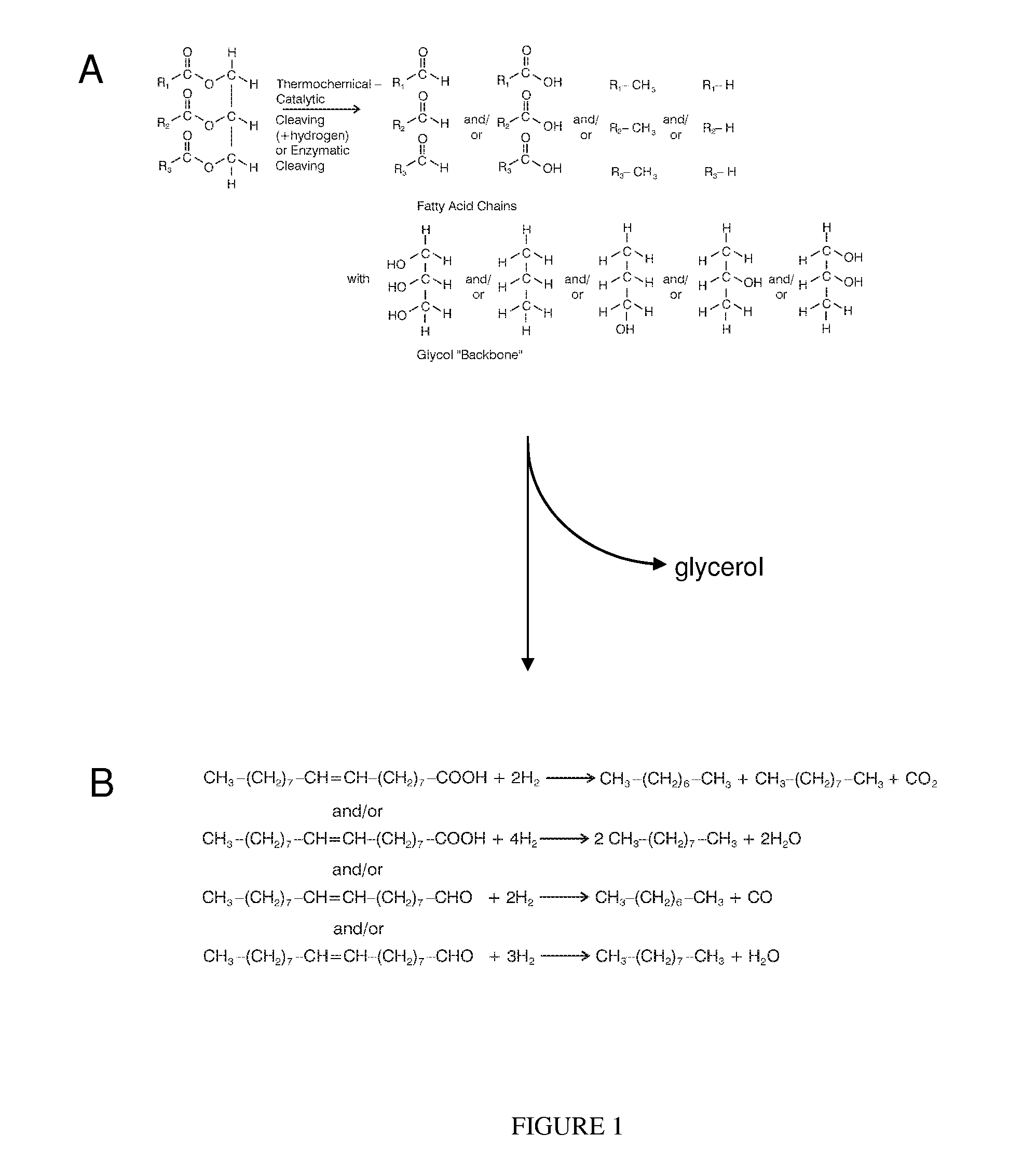
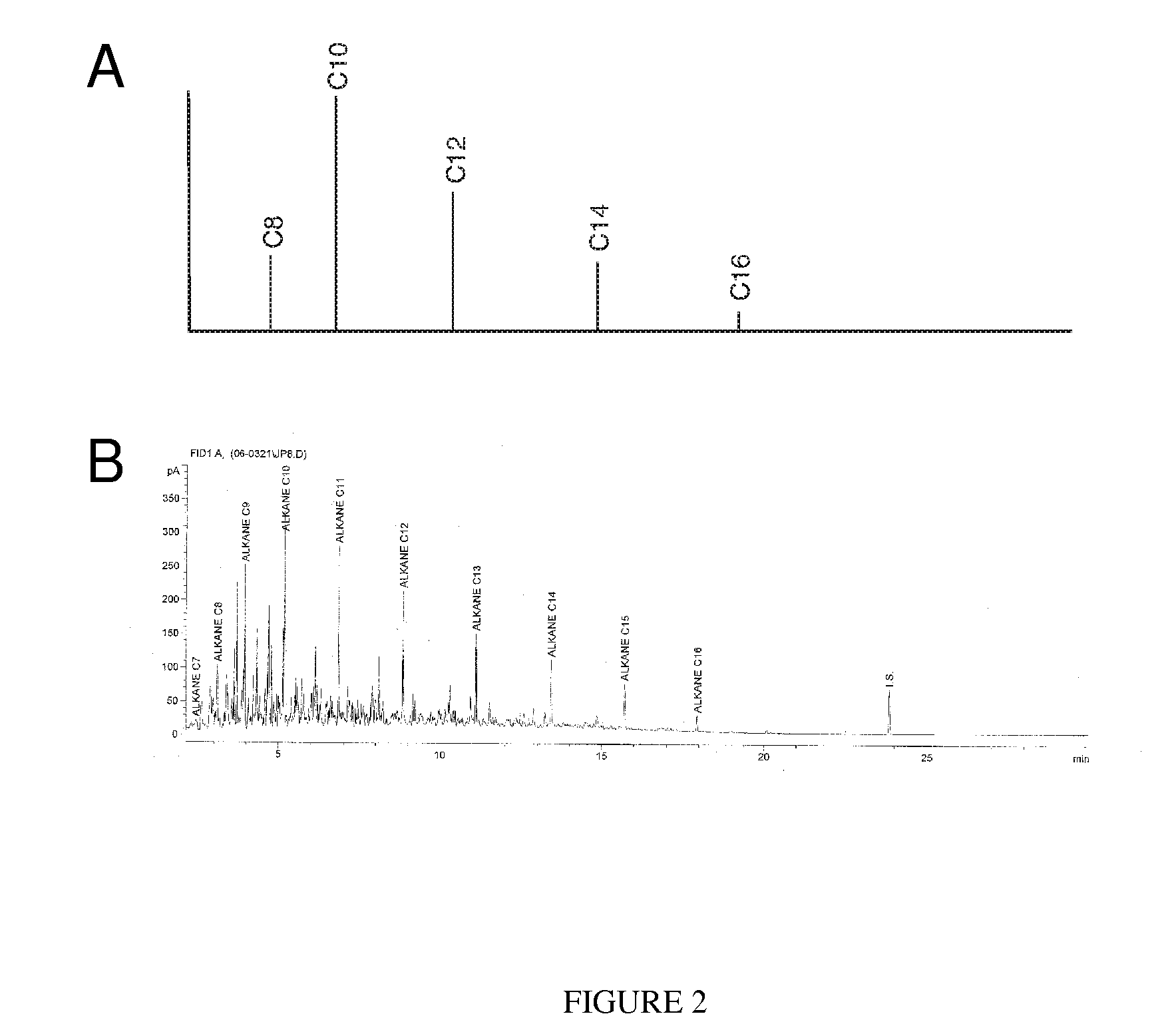
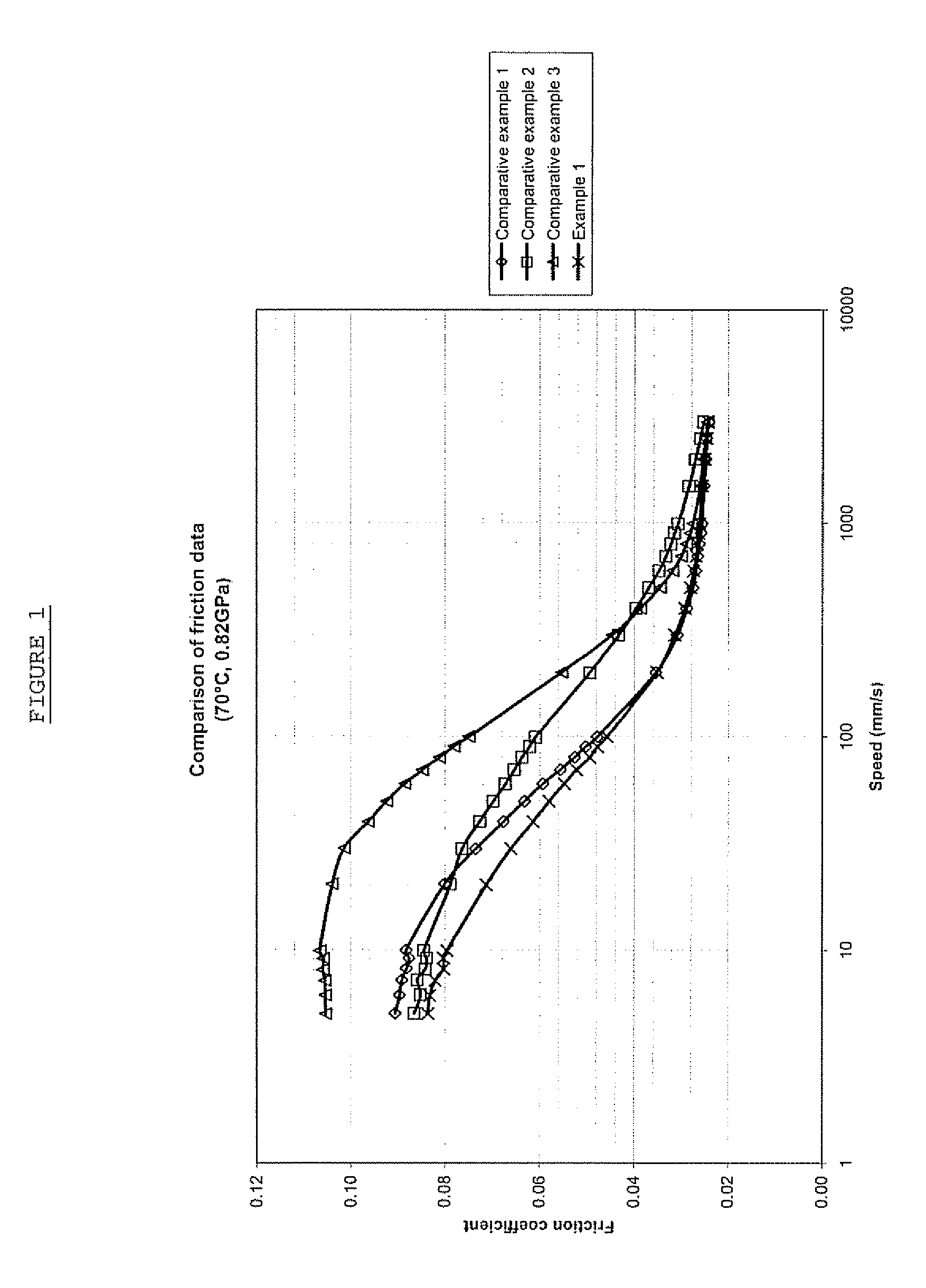
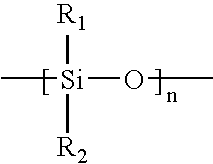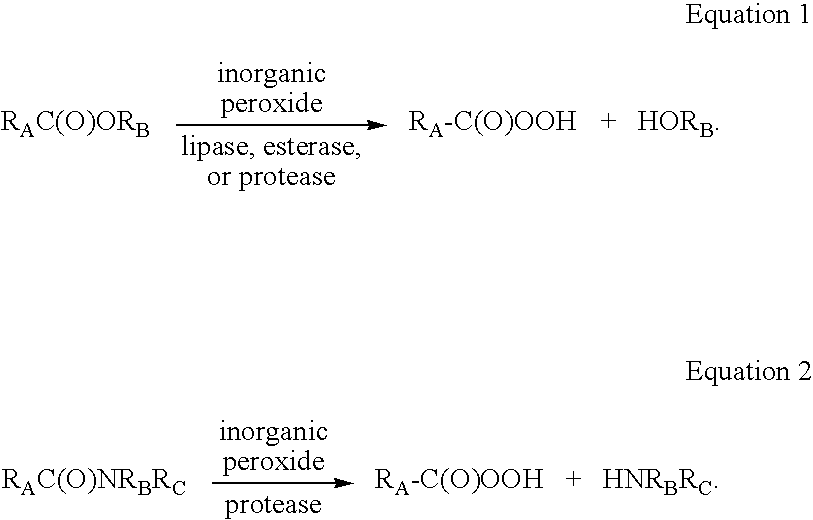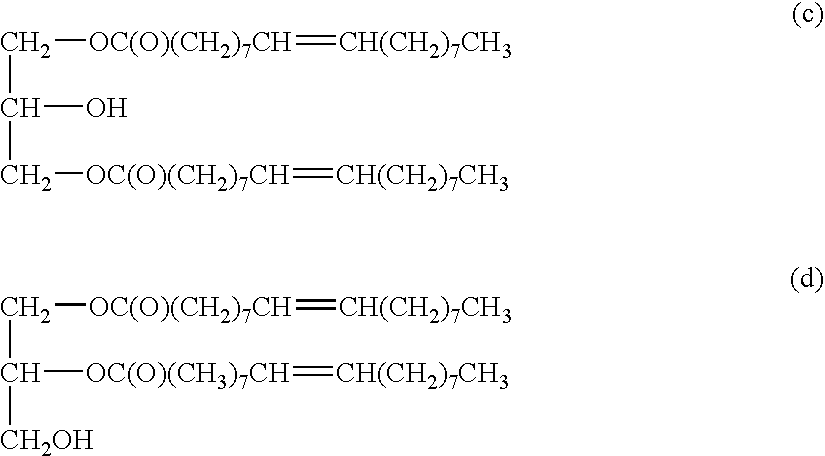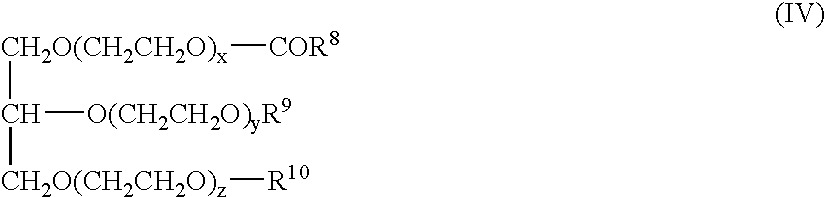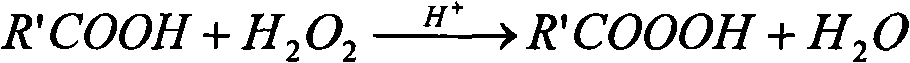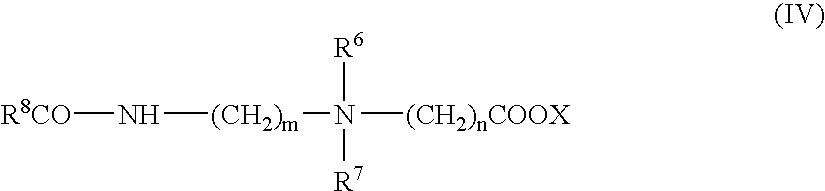Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7361 results about "Glyceride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
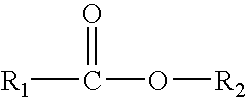
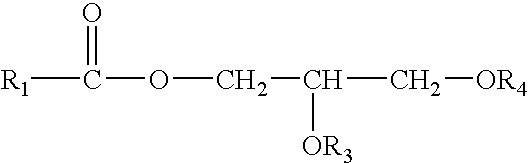
Glycerides, more correctly known as acylglycerols, are esters formed from glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol has three hydroxyl functional groups, which can be esterified with one, two, or three fatty acids to form monoglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides.
Novel Polymers
ActiveUS20080015315A1Sufficient amountReduce the amount requiredOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
The invention relates to novel crosslinkable copolymers which are obtainable by (a) copolymerizing at least two different hydrophilic monomers selected from the group consisting of N,N-dimethyl acrylamide (DMA), 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA), glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), N-vinylpyrrolidone (NVP), acrylic acid (AA) and a C1-C4-alkoxy polyethylene glycol (meth)acrylate having a weight average molecular weight of from 200 to 1500, and at least one crosslinker comprising two or more ethylenically unsaturated double bonds in the presence of a chain transfer agent having a functional group; and (b) reacting one or more functional groups of the resulting copolymer with an organic compound having an ethylenically unsaturated group.
Owner:ALCON INC
Production of Blended Fuel from Renewable Feedstocks
A process for producing a blended fuel from a paraffin rich component and a cyclic rich component, where each of the components are generated from a renewable feedstock, is presented. The paraffin rich component is generated from a first renewable feedstock comprising at least one component selected from the group consisting of glycerides, free fatty acids, biomass, lignocellulose, free sugars, and combinations thereof. The cyclic rich component is generated from a second renewable feedstock comprising at least one component selected from the group consisting of glycerides, free fatty acids, free fatty alkyl esters, biomass, lignocellulose, free sugars, and combinations thereof. The blended fuel may a gasoline boiling point range blended fuel, a diesel boiling point range blended fuel, an aviation boiling point range blended fuel, any combination thereof, or any mixture thereof.
Owner:UOP LLC
Orally administrable composition capable of providing enhanced bioavailability when ingested
InactiveUS6054136AImprove solubilityImprove bioavailabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFatty acid esterIngestion
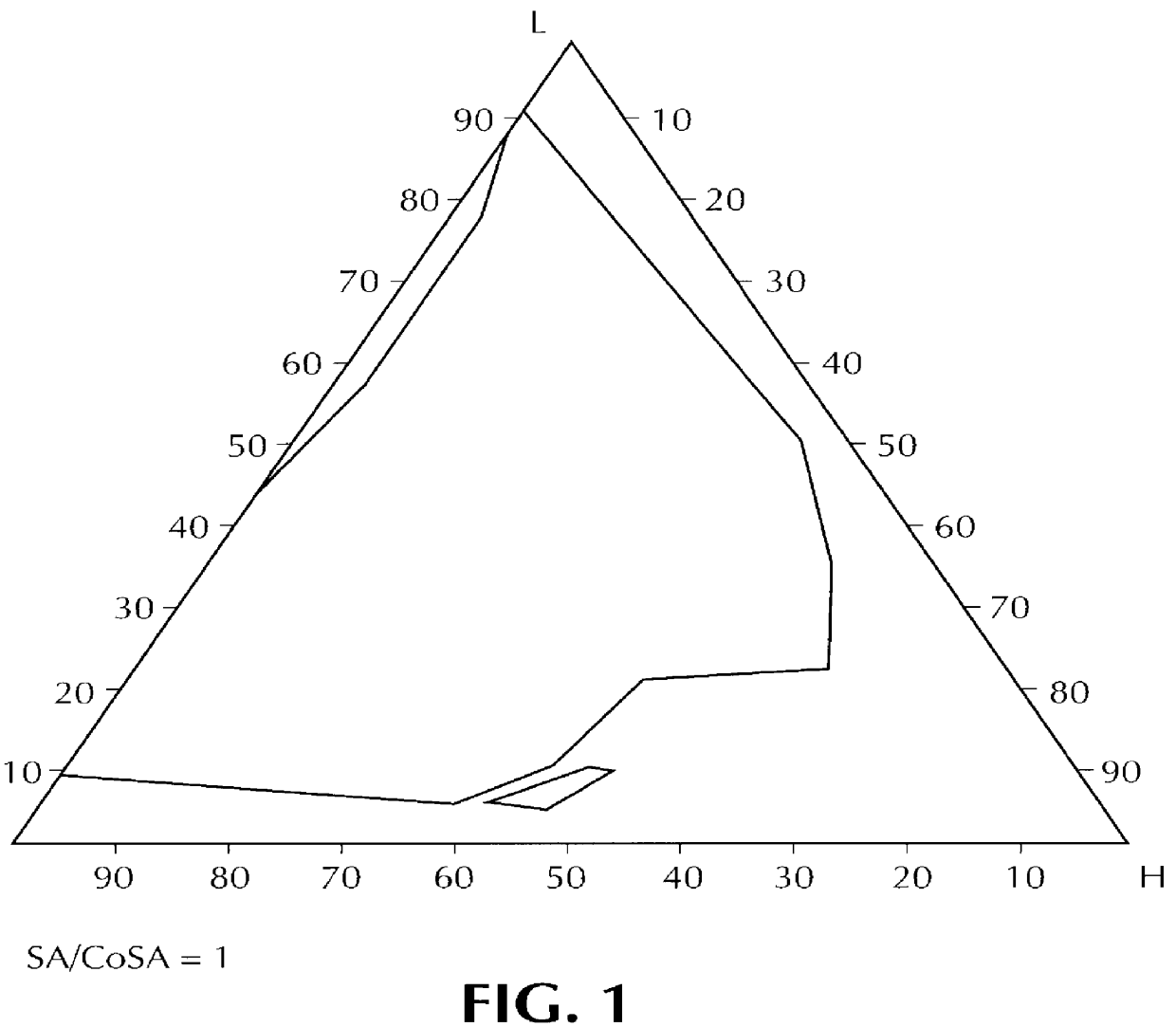
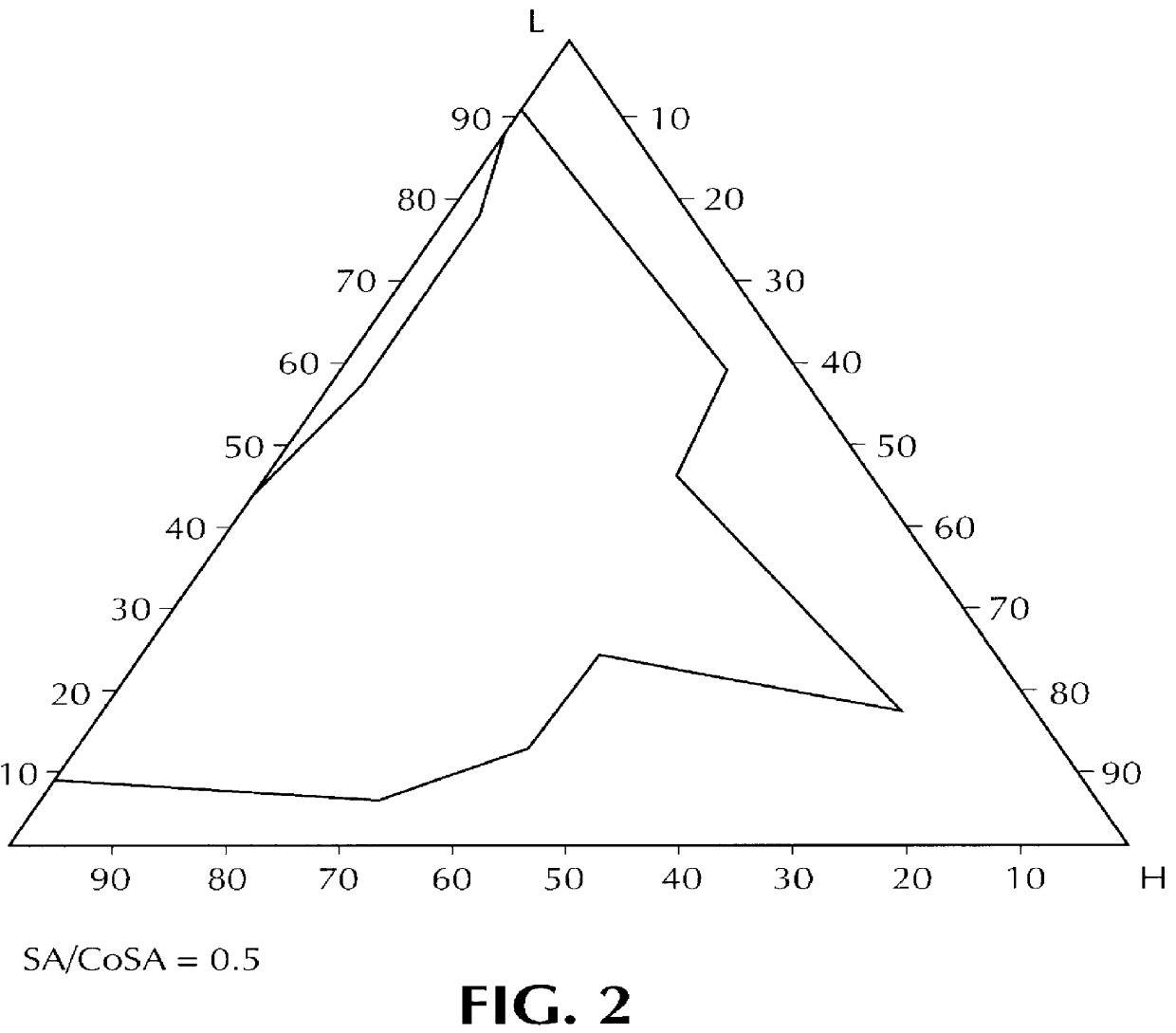
Composition for pharmaceutical or cosmetic use, capable of forming a microemulsion, comprising at least: an active principle, a lipophilic phase consisting of a mixture of fatty acid esters and glycerides, a surfactant (SA), a cosurfactant (CoSA), a hydrophilic phase, characterized: in that the lipophilic phase consists of a mixture of C8 to C18 polyglycolized glycerides having a hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) of less than 16, this lipophilic phase representing from 30 to 75% of the total weight of the composition; in that the surfactant (SA) is chosen from the group comprising saturated C8-C10 olyglycolized glycerides and oleic esters of polyglycerol, this surfactant having an HLB of less than 16; in that the cosurfactant (CoSA) is chosen from the group comprising lauric esters of propylene glycol, oleic esters of polyglycerol and ethyl diglycol; in that the SA / CoSA ratio is between 0.5 and 6; and in that the hydrophilic phase of the final microemulsion is supplied after ingestion by the physiological fluid of the digestive milieu.
Owner:GATTEFOSSE HLDG
Pharmaceutical Composition and Method for Treating Hypertriglyceridemia and Hypercholesterolemia in Humans
InactiveUS20090182049A1Lower triglyceridesIncreasing HDL (good) cholesterolBiocideMetabolism disorderDocosahexaenoic acidSerum cholesterol
A method for the treatment or prophylaxis of hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia without concomitantly increasing LDL-serum cholesterol, in a human subject requiring such treatment, which method comprises orally administering to the patient an effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition in which the active ingredients comprise a mixture of fatty acids, wherein said mixture comprises at least about 60% by weight a combination of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in a weight ratio of EPA:DHA of from about 1.4:1 to about 5:1, wherein said combination is at least about 60% in the triglyceride form of the fatty acids and the balance is at least about 80% of mono and di-glycerides.
Owner:OPHEIM JOAR ARILD
Delivery of tetrahydrocannabinol
InactiveUS20070104741A1Avoiding hepatic first-pass metabolismGood choiceBiocideNervous disorderChylomicronTG - Triglyceride
A self-emulsifying drug delivery system to improve dissolution, stability, and bioavailability of drug compounds of dronabinol or other cannabinoids. The drug compound(s) are dissolved in an oily medium (e.g. triglycerides and / or mixed glycerides and / or free fatty acids containing medium and / or long chain saturated, mono-unsaturated, and / or poly-unsaturated free fatty acids) together with at least one surfactant. The surfactant promotes self-emulsification, thereby promoting targeted chylomicron delivery and optimal bioavailability to a mammalian intestinal lumen. A dosage form can optionally include co-solvents, anti-oxidants, viscosity modifying agents, cytochrome P450 metabolic inhibitors, P-GP efflux inhibitors, and amphiphilic / non-amphiphilic solutes to induce semi-solid formation for targeted release rates.
Owner:MURTY PHARMA
Production of Blended Fuel from Renewable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20090301930A1Minimize the numberReduce the amount requiredRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonBiofuelsParaffin waxEngineering
A process for producing a blended fuel from a paraffin rich component and a cyclic rich component, where each of the components are generated from a renewable feedstock, is presented. The paraffin rich component is generated from glycerides and free fatty acids in feedstocks such as plant and animal oils. The cyclic rich component is generated from biomass derived pyrolysis oil. The source of the animal or plant oil and the biomass may be the same renewable source.
Owner:UOP LLC
Microporous PVDF films and method of manufacturing
Shaped microporous articles are produced from polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and nucleating agents using thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) processes. The shaped microporous article is oriented in at least one direction at a stretch ratio of at least approximately 1.1 to 1.0. The shaped article may also comprise a diluent, glyceryl triacetate. The shaped microporous article may also have the micropores filled with a sufficient quantity of ion conducting electrolyte to allow the membrane to function as an ion conductive membrane. The method of making a microporous article comprises the steps of melt blending polyvinylidene fluoride, nucleating agent and glyceryl triacetate; forming a shaped article of the mixture; cooling the shaped article to cause crystallization of the polyvinylidene fluoride and phase separation of the polyvinylidene fluoride and glyceryl triacetate; and stretching the shaped article in at least one direction at a stretch ratio of at least approximately 1.1 to 1.0.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Purification of glycerin
InactiveUS7126032B1Low costEfficient recyclingOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds purification/separationAlcoholWash water
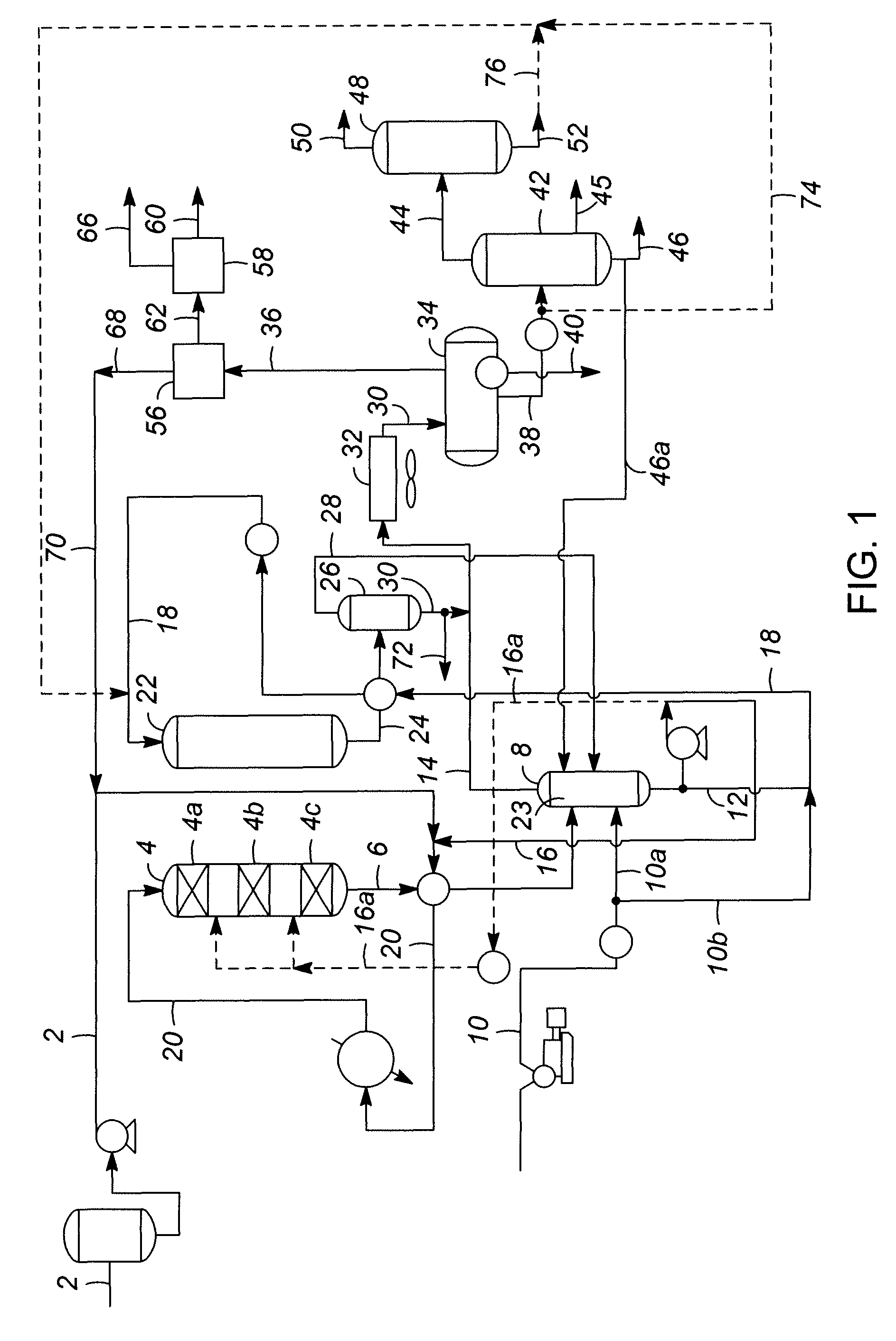
A process for purifying glycerin recovered as a byproduct of biodiesel production comprises heating a glycerin effluent stream containing a low molecular weight alcohol, water and fatty acid esters of the low molecular weight alcohol to cause transesterification of the fatty acid esters to glycerides and additional low molecular weight alcohol. The reaction mixture is sparged with nitrogen to help remove water and low molecular weight alcohol, which drives the transesterification reaction towards glyceride formation. A wash water stream may also be added to the recovered glycerin stream from biodiesel production. Either before or following the transesterification reaction, an oil layer can be separated from the recovered glycerin stream by reducing the pH of the stream to below 7. Following separation of the oil layer and transesterification the glycerin stream is flash distilled to separate glycerin from water, salts, and glycerides.
Owner:SUNOCO INC (R&M)
Process for producing biodiesel, lubricants, and fuel and lubricant additives in a critical fluid medium
InactiveUS6887283B1Limited mass transferImprove reaction speedFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselVegetable oil
A process for producing alkyl esters useful in biofuels and lubricants by transesterifying glyceride- or esterifying free fatty acid-containing substances in a single critical phase medium is disclosed. The critical phase medium provides increased reaction rates, decreases the loss of catalyst or catalyst activity and improves the overall yield of desired product. The process involves the steps of dissolving an input glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substance with an alcohol or water into a critical fluid medium; reacting the glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substance with the alcohol or water input over either a solid or liquid acidic or basic catalyst and sequentially separating the products from each other and from the critical fluid medium, which critical fluid medium can then be recycled back in the process. The process significantly reduces the cost of producing additives or alternatives to automotive fuels and lubricants utilizing inexpensive glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substances, such as animal fats, vegetable oils, rendered fats, and restaurant grease.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
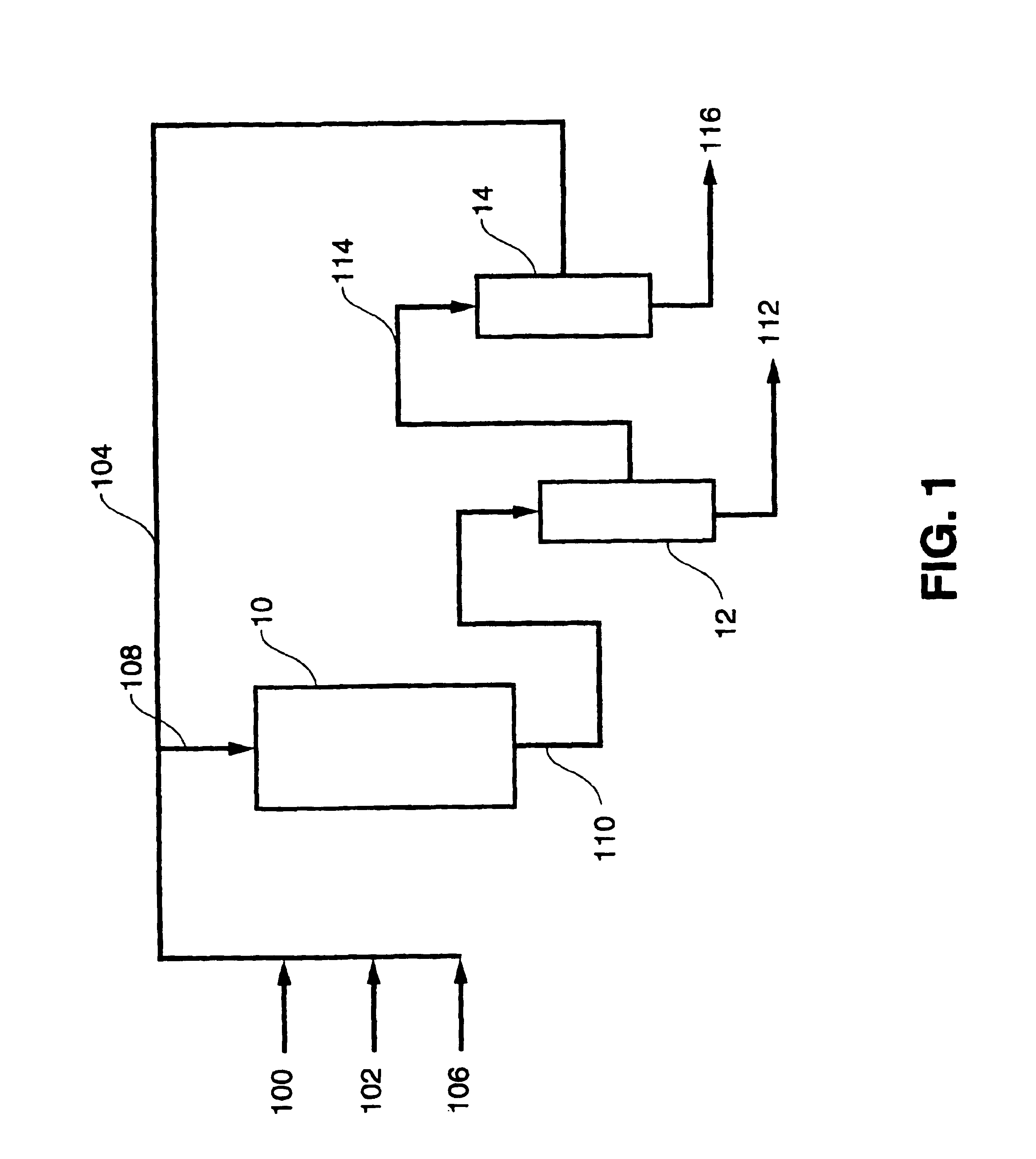
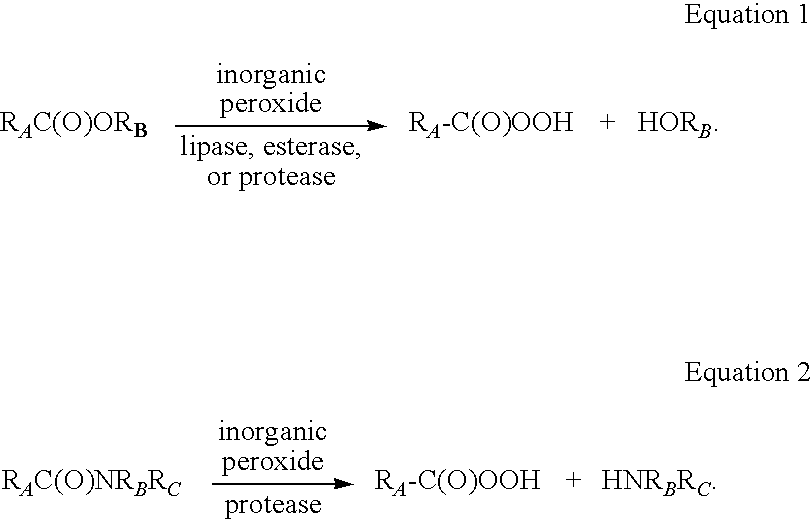
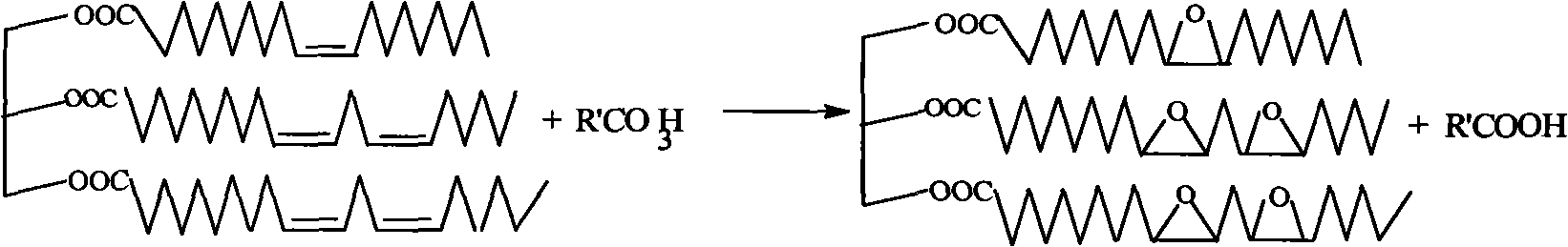
Enzymatic production of peracids using perhydrolytic enzymes
A process is provided to produce a concentrated aqueous peracid solution in situ using at least one enzyme having perhydrolase activity in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (at a concentration of at least 500 mM) under neutral to acidic reaction conditions from suitable carboxylic acid esters (including glycerides) and / or amides substrates. The concentrated peracid solution produced is sufficient for use in a variety of disinfection and / or bleaching applications.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Azithromycin dosage forms with reduced side effects
ActiveUS6984403B2Reduce gastrointestinal side effectsAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryOral suspensionsGLYCERYL MONOBEHENATE
The present invention is related to an oral dosage form comprising an effective amount of an alkalizing agent and an azithromycin multiparticulate wherein said multiparticulate comprises azithromycin, a glyceride which comprises glyceryl monobehenate, glyceryl dibehenate, glyceryl tribehenate, or a mixture thereof and a poloxamer. Typically, the oral dosage form includes any suitable oral dosing means such as a powder for oral suspension, a unit dose packet or sachet, a tablet or a capsule.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Glyceride compositions and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20040209953A1Fast absorptionImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMonoglycerideDiglyceride
Disclosed are glyceride compositions, methods of making the glyceride compositions, and nutritional formulations containing the glyceride compositions. The glyceride compositions contain predominantly monoglycerides and diglycerides carrying one or more long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Also disclosed are methods of using the glyceride compositions and nutritional formulations.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Optimal energy pathway to renewable domestic and other fuels
A novel, energy efficient process of producing jet fuel is disclosed herein. The process is based on utilizing a medium chain fatty acid source such as cuphea oil, which precludes the need for high-energy fatty acid chain cracking to achieve the shorter molecules needed for jet fuels and other fuels with low-temperature flow requirements. In an embodiment, a process for producing a jet fuel comprises providing a medium chain fatty acid source. The method also comprises cleaving the one or more medium chain fatty acid groups from the glycerides to form glycerol and one or more free fatty acids. The method further comprises decarboxylating the one or more medium chain fatty acids to form one or more hydrocarbons for the production of the jet fuel.
Owner:ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL RES CENT FOUNDATIO
Glyceride esters for the treatment of diseases associated with reduced neuronal metabolism of glucose
Provided are alternative sources of ketone bodies for reducing or eliminating symptoms of Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, also called Lou Gehrig's disease), Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, epilepsy and other diseases or disorders characterized by impaired glucose metabolism. The alternative sources of ketone bodies include mono-, di- and triglyceride esters of acetoacetate and mixtures thereof, and / or mono-, di- and triglyceride esters of 3-hydroxybutyrate and mixtures thereof. These glyceride esters can be administered orally as a dietary supplement or in a nutritional composition.
Owner:NEUROENERGY VENTURES INC
Controlled release delivery device for pharmaceutical agents incorporating microbial polysaccharide gum
The present invention provides a controlled release device for sustained or pulsatile delivery of pharmaceutically active substances for a predetermined period of time. This invention further provides such device in which sustained or pulsatile delivery is obtained by the unique blend and intimate mixture of pharmaceutically active substances with a microbial polysaccharide and uncrosslinked linear polymer and optionally a crosslinked polymer and / or lipophillic polymer and / or saturated polyglycolyzed glyceride. The invention also provides a process for the manufacture of such devices and pharmaceutical compositions containing the same.
Owner:INTELLIPHARMACEUTICS
Diagnostic agent for liver function
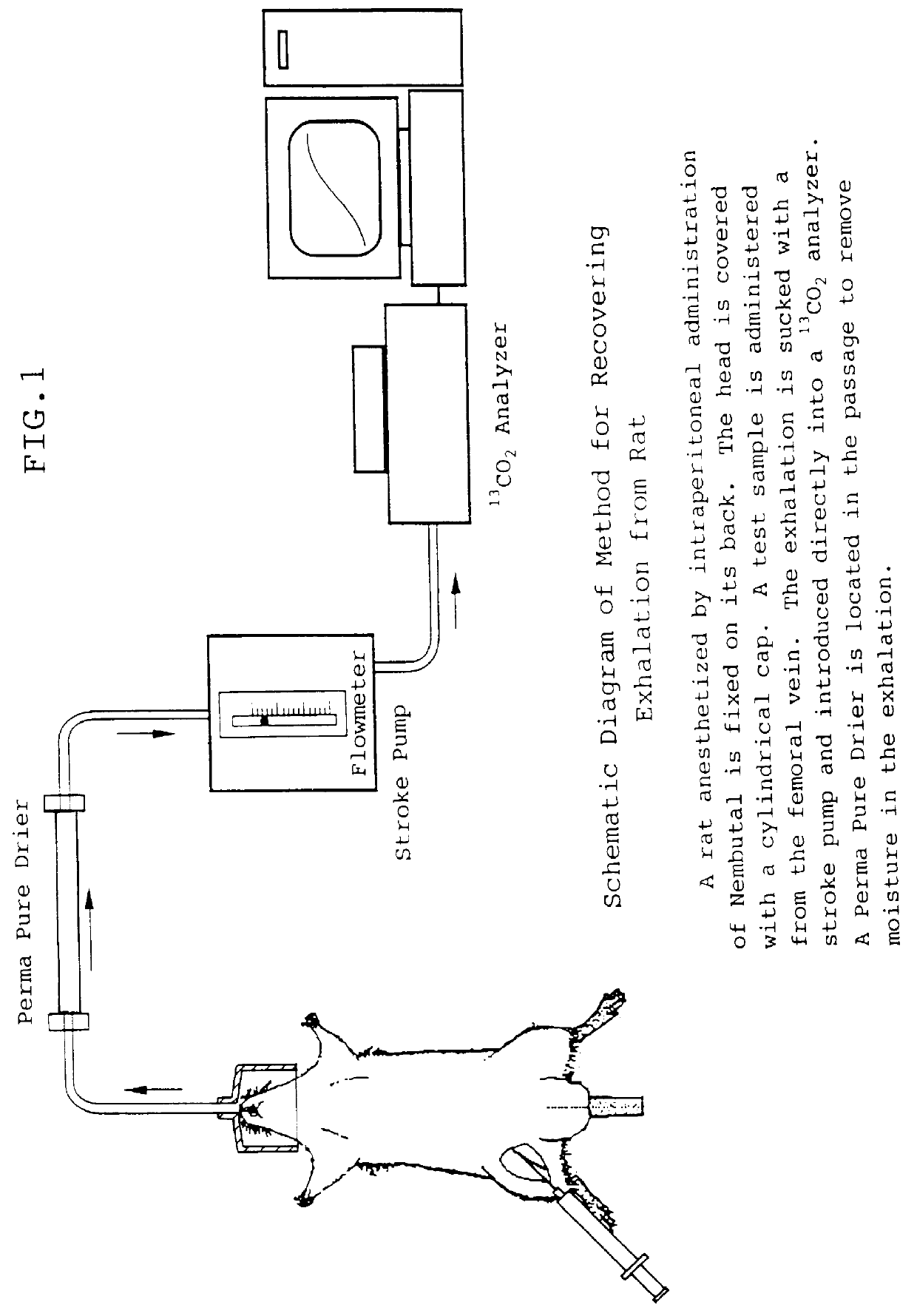
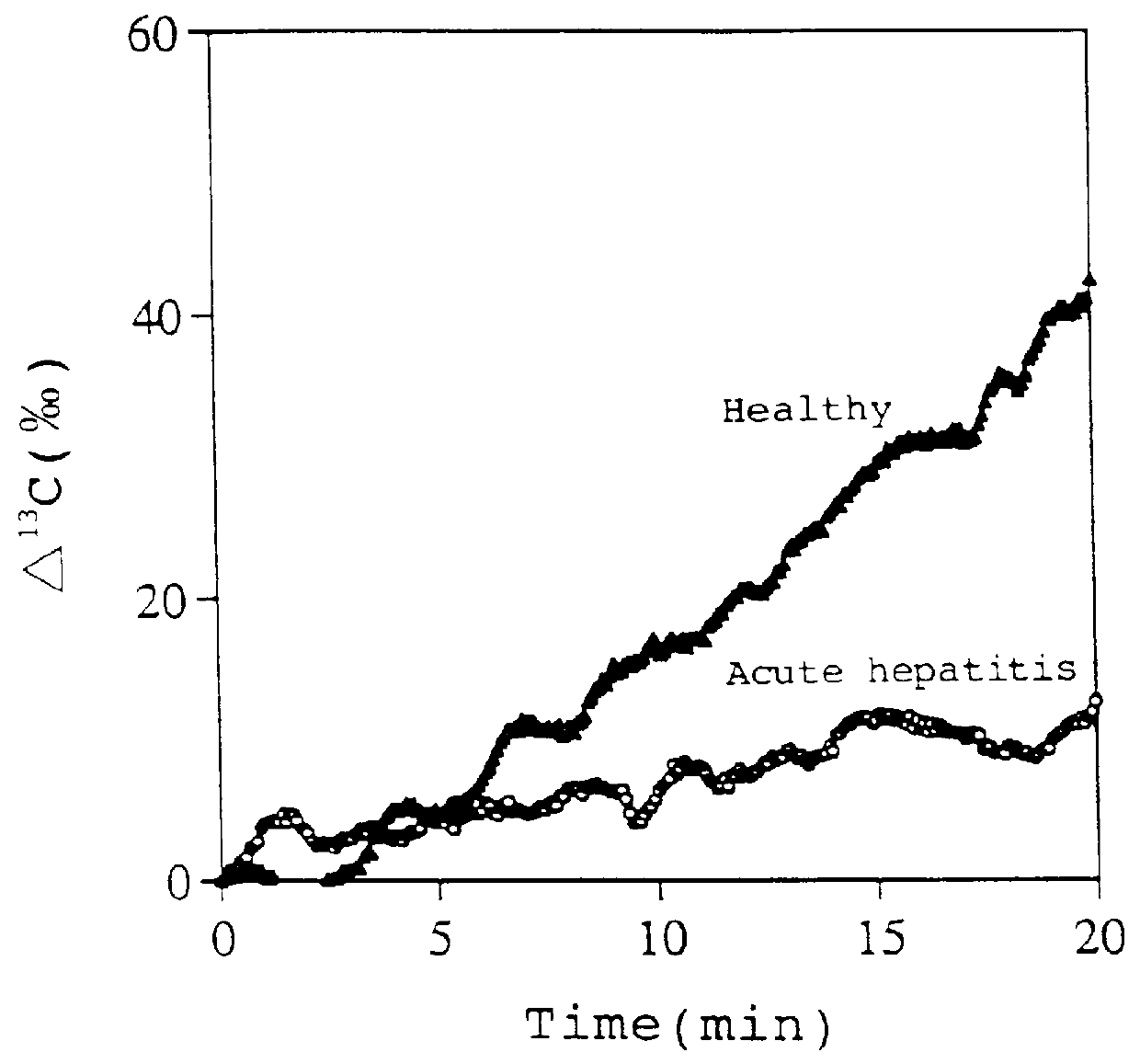
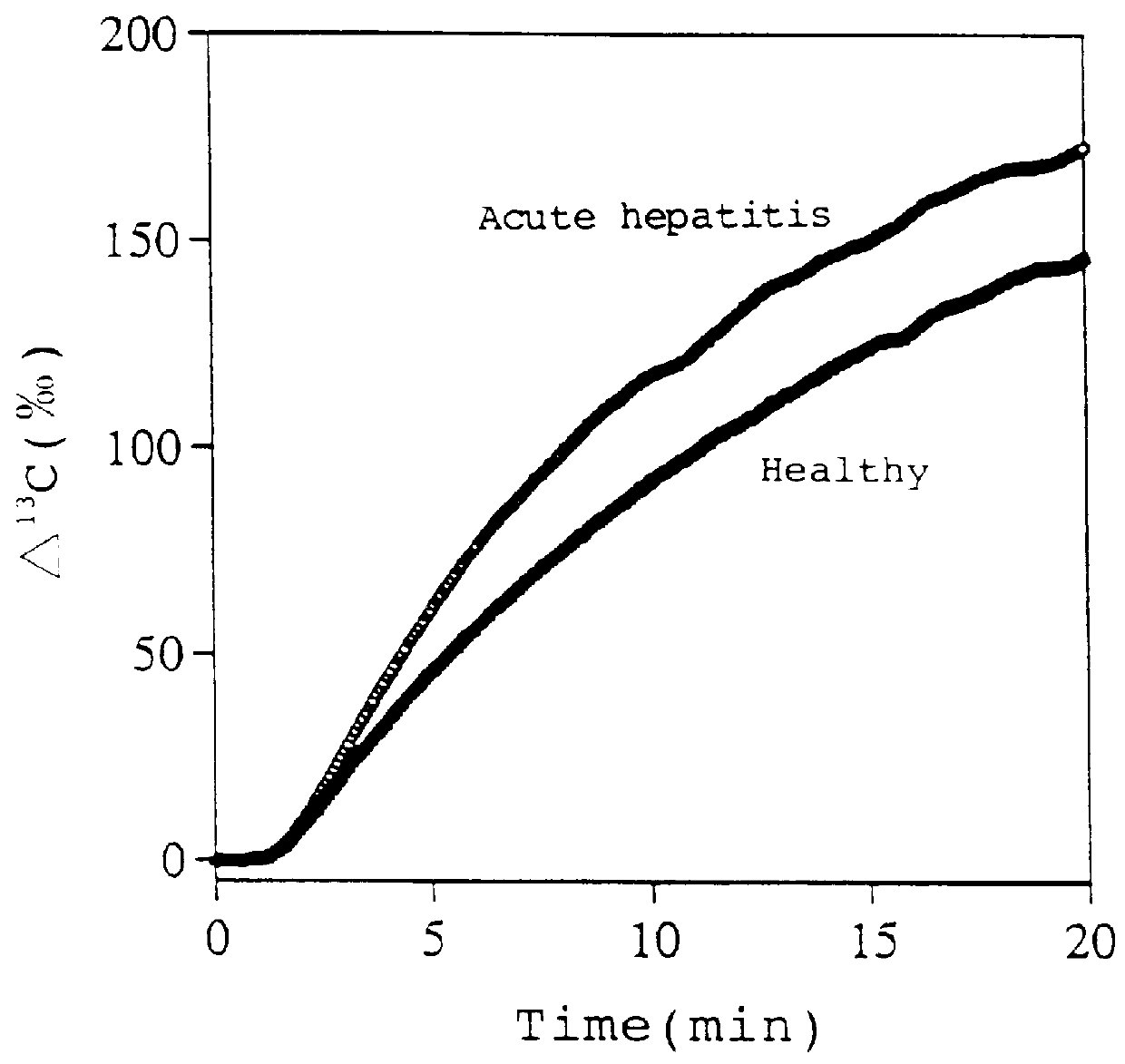
InactiveUS6071245ALessen the burden on the bodyEasy to useRadioactive preparation carriersRespiratory organ evaluationSide effectGlycerol
The present invention relates to a diagnostic agent for liver function, comprising a compound labelled with 13C at least at one specific position selected from the group consisting of the following (a) to (f): (a) galactose, glucose or xylose labelled with 13C at least at one specific position or a starch composed of glucose units labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; (b) a polar amino acid, heterocyclic amino acid, isoleucine or valine labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; (c) a carboxylic acid constituting the glycolytic pathway or the citric acid cycle, labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; (d) a fatty acid labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; (e) a glyceride labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; and (f) glycerol labelled with 13C at least at one specific position. According to the present invention, a diagnostic agent for liver function which imposes less physical burden on a subject, can give accurate test result immediately, and can be used safely without side effects is provided. The diagnostic agent of the invention is useful for evaluating the liver function of a subject at the time when the test is carried out.
Owner:TOKYO GAS CO LTD
Process for preparing vegetable oil fractions rich in non-tocolic, high-melting, unsaponifiable matter
InactiveUS7288278B2Fatty acid hydrogenationEdible oils/fats ingredientsHigh concentrationVegetable oil
A vegetable oil fraction rich in non-tocolic, high-melting, unsaponifiable matter is prepared by the following steps: A vegetable oil having a slip melting point of not more thatn 30° C. and a content of unsaponifiable matter of at least 0.5% by weight is hydrogenated to fully saturate the fatty acids of the glycerides and to reach a slip melting point of at least 57° C. To the hydrogenated oil is added from 1 to 75% by weight of the unhydrogenated starting oil or another oil having a slip melting point of not more than 30° C. in order to act as a carrier and vehicle for the unsaponifiable matter. Then, a solvent is added to the oil mixture in a ratio between oil and solvent from 1:2 to 1:20, and the mixture is heated to transparency. The oil / -solvent-mixture is cooled in one or more steps to a final temperature in the range from −35 to +30° C., and the precipitated high-melting fraction(s) is (are) filtered off. The filtrate is desolventised, leaving a fraction rich in unsaponifiable matter. By this process very high concentrations of in particular the non-tocolic, higher melting unsaponifiables can be achieved, and the composition of the glyceridic part of the enriched fraction can betailored to specific applications. Also, a novel blood cholesterol-lowering effect of the unsaponifiable constituents from shea butter has been found.
Owner:AAK DENMARK
Balloons made from liquid crystal polymer blends
Balloons for use on medical devices such as catheter balloons are formed from polymer blend products which include a liquid crystal polymer (LCP), a crystallizable thermoplastic polymer, especially thermoplastic polyesters such as PET, and a compatabilizer. The compatabilizer may be an ethylene-maleic anhydride copolymer, an ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymer, an ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymer, an ethylene-methyl acrylate-maleic anhydride terpolymer, an ethylene-methyl-methacrylic acid terpolymer, an acrylic rubber, an ethylene-ethyl acrylate-glycidyl methacrylate terpolymer or a mixture of two or more such polymers.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Enzymatic production of peracids using perhydrolytic enzymes
A process is provided to produce a concentrated aqueous peracid solution in situ using at least one enzyme having perhydrolase activity in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (at a concentration of at least 500 mM) under neutral to acidic reaction conditions from suitable carboxylic acid esters (including glycerides) and / or amides substrates. The concentrated peracid solution produced is sufficient for use in a variety of disinfection and / or bleaching applications.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Lubricating oil composition
ActiveUS20080280795A1Good friction reductionImprove fuel economyOrganic chemistryAdditivesChemical compositionViscosity index
A lubricating oil composition comprising base oil, one or more glycerol esters selected from glycerol monooleate and / or glycerol dioleate, optionally in combination with glycerol trioleate, wherein said composition further comprises one or more dispersant-viscosity index improver compounds and an additive amount of one or more additional polyhydric alcohol esters; and a method of lubricating an internal combustion engine comprising applying said lubricating oil composition thereto.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Plant diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase and uses thereof
Plant nucleic acid compositions encoding polypeptide products with diacylglyceride acyltransferase (DGAT) activity, as well as the polypeptide products encoded thereby and methods for producing the same, are provided. Methods and compositions for modulating DGAT activity in a plant, particularly DGAT activity in plant seeds, and transgenic plants with altered DGAT activity are provided. Such plants and seeds are useful in the production of human food and animal feedstuff, and have several other industrial applications. Also provided are methods for making triglycerides and triglyceride compositions, as well as the compositions produced by these methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications, including research, medicine, agriculture and industry.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
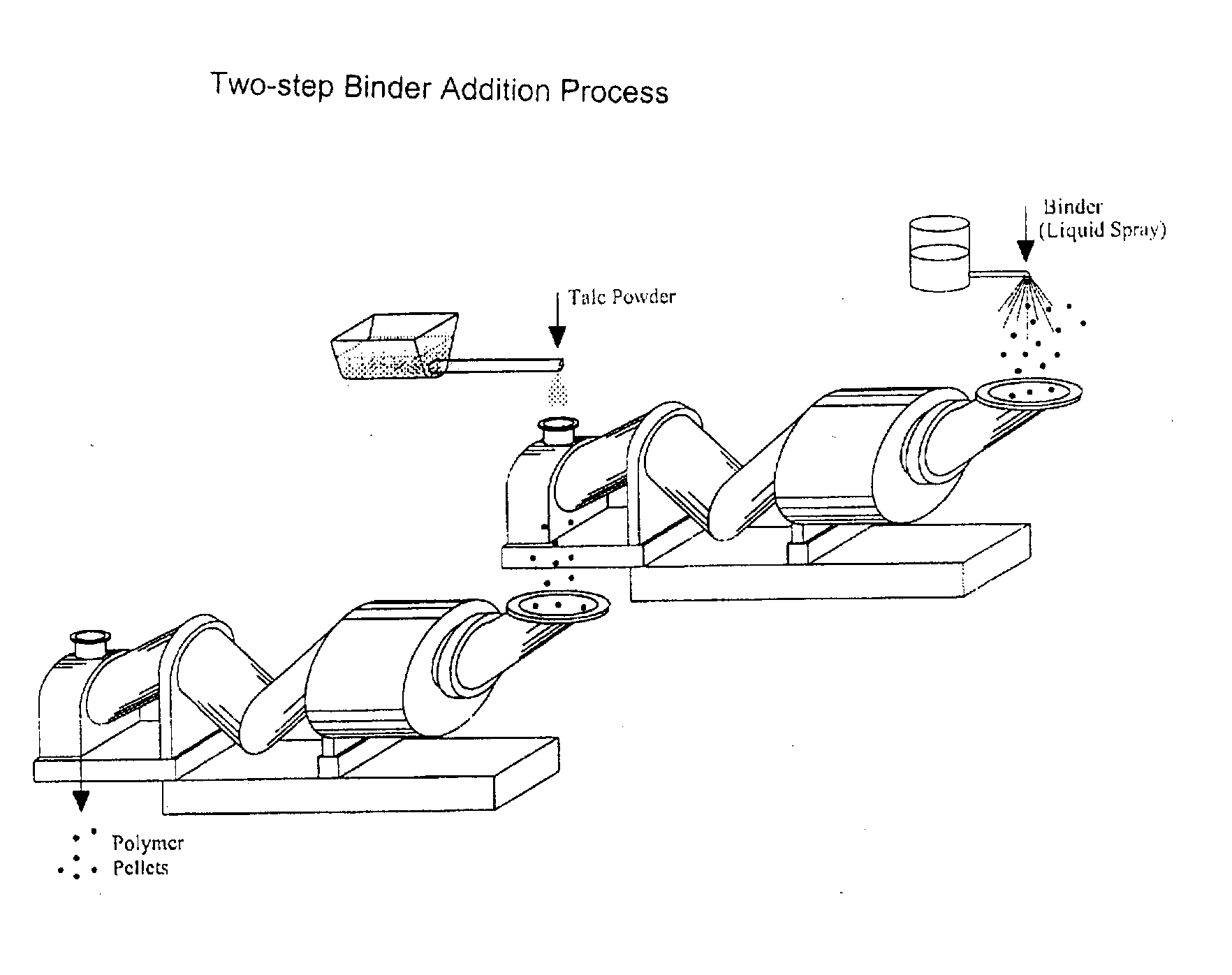
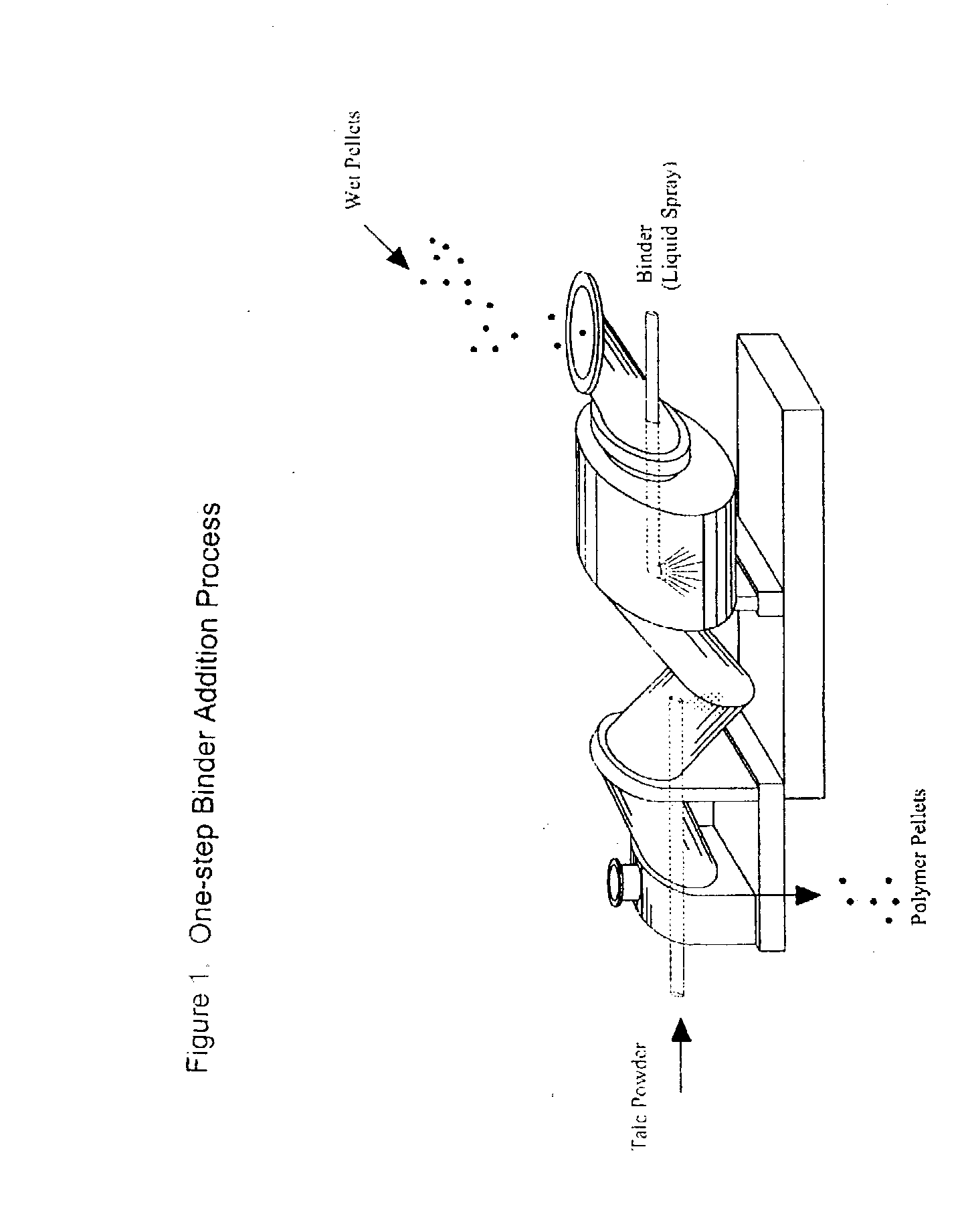
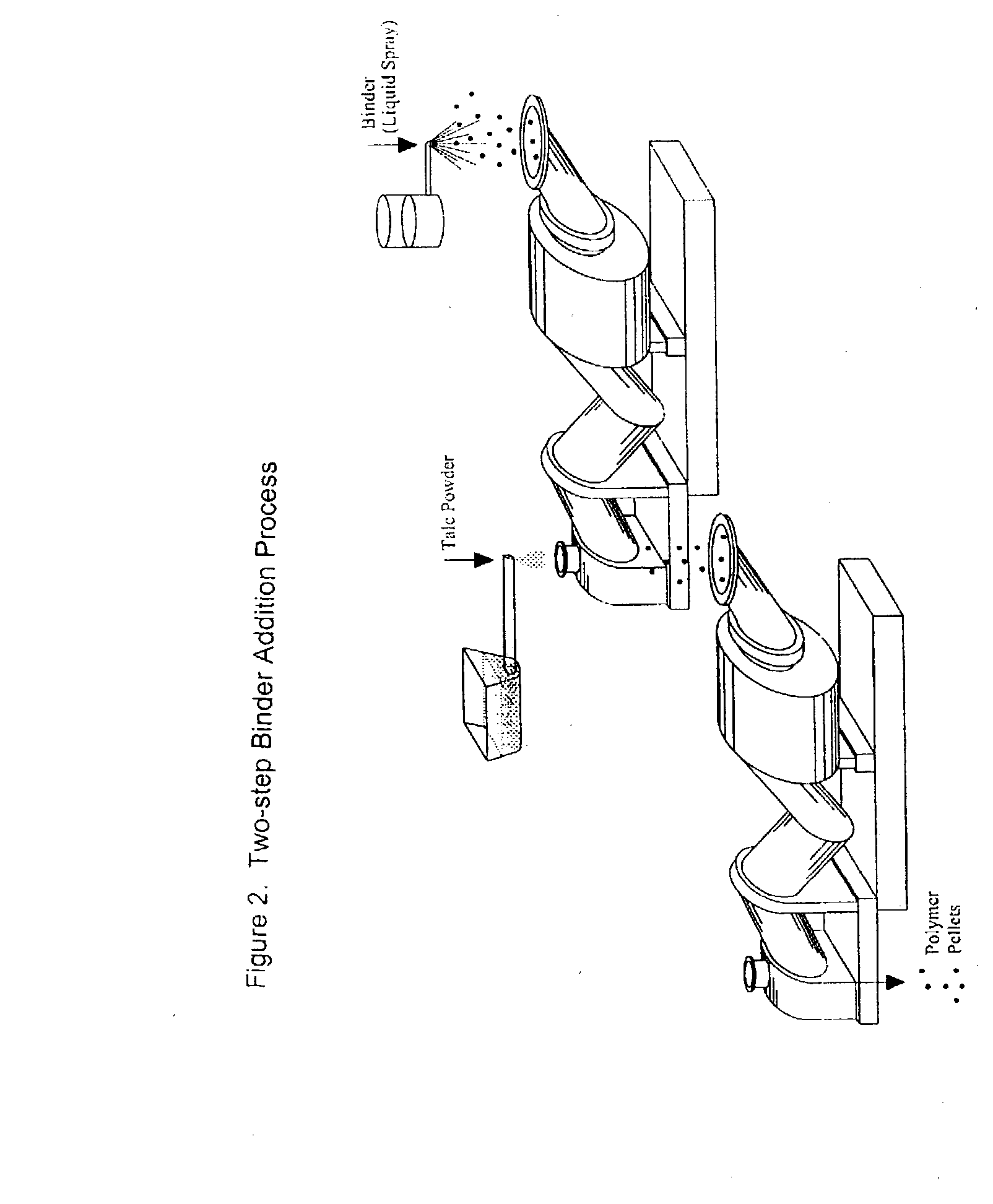
Process of Coating Tacky and Soft Polymer Pellets
InactiveUS20040209082A1Easy downstream handlingAvoid stickingConfectioneryChewing gumPolymer scienceMonoglyceride
An improved process of coating tacky or soft polymer pellets to maintain a free-flowing property, uses a liquid binder, in conjunction with an anti-tack or partitioning powder such as talc to prevent aggregation during storage. The binder is a non-volatile material such as an oil or plasticizer including triglycerides, mono- / di-glycerides, acetylated mono- / di-glycerides, fatty acids, epoxidized triglycerides, phthalates, benzoates, sebacates, lactates, citrates, mineral oils etc. Applications of this process include chewing gum bases, hot-melt adhesives, sealants, rubber masterbatches, powdered rubber, and other soft and tacky polymer materials.
Owner:WM WRIGLEY JR CO
Process for co-producing olefins and esters by ethenolysis of unsaturated fats in non-aqueous ionic liquids
A process is described in which an unsaturated fat is reacted with ethylene in a metathesis reaction in the presence of at least one non-aqueous ionic liquid to produce both an olefinic fraction and a composition of monoalcohol or polyol esters. Particular application to an oleic sunflower seed oil, an oleic rapeseed oil or to a mixture of monoalcohol esters of said oils, the process producing both an olefinic fraction and a monoalcohol or glycerol esters composition generally having more than half of its chains constituted by unsaturated C10 chains.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
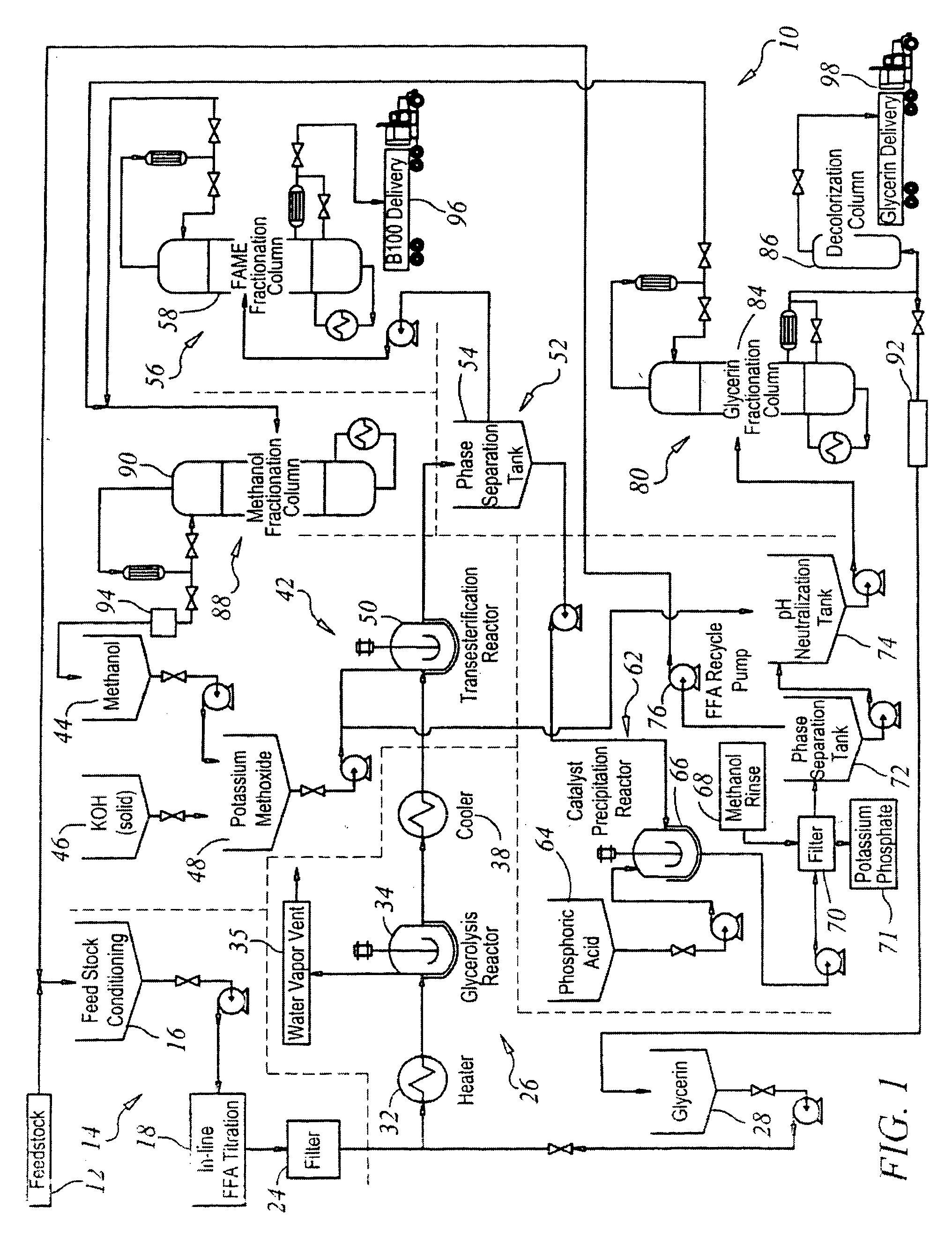
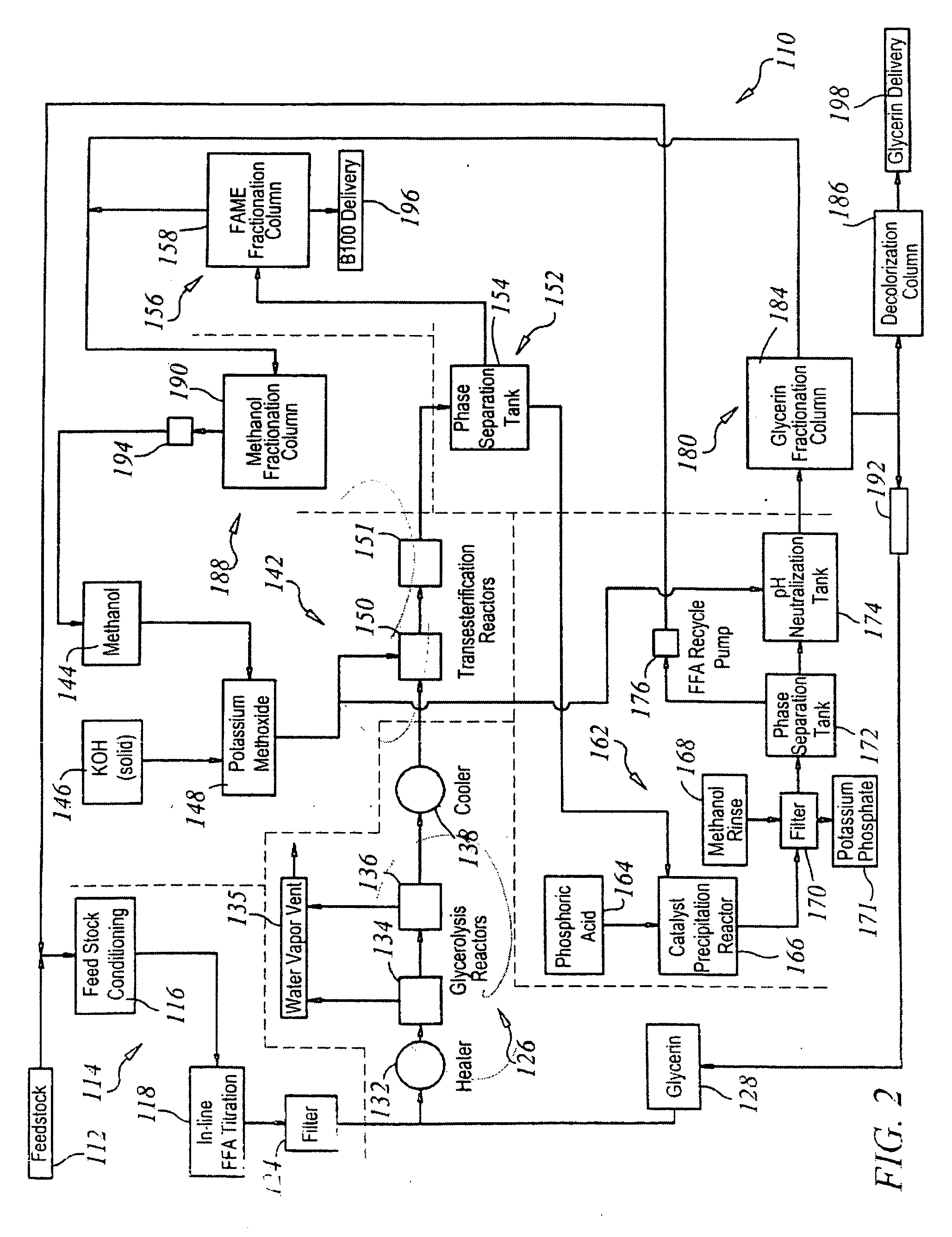
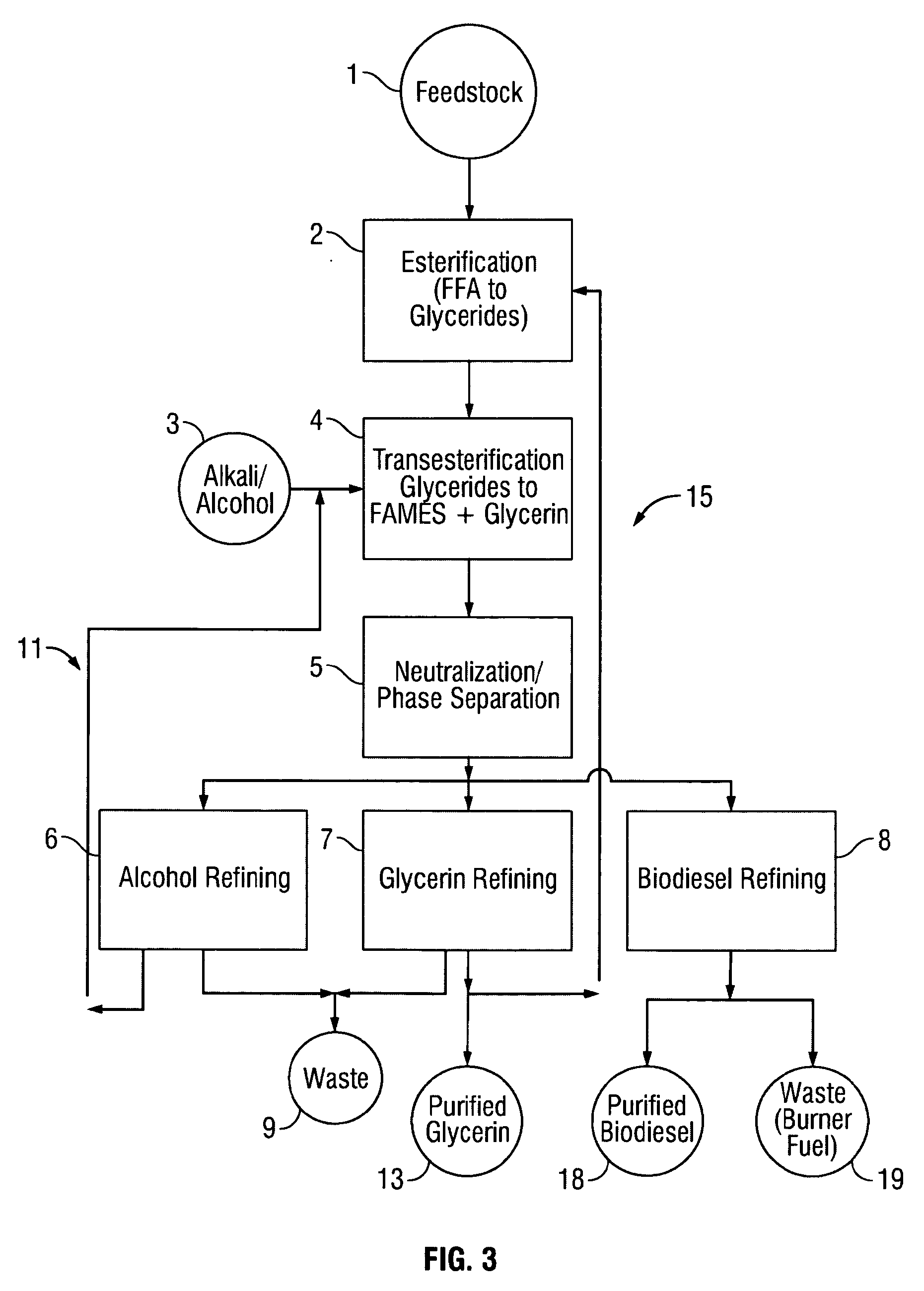
Production of biodiesel and glycerin from high free fatty acid feedstocks
ActiveUS20070277430A1Increase productionHigh purityFatty acid esterificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic acidChemical reaction
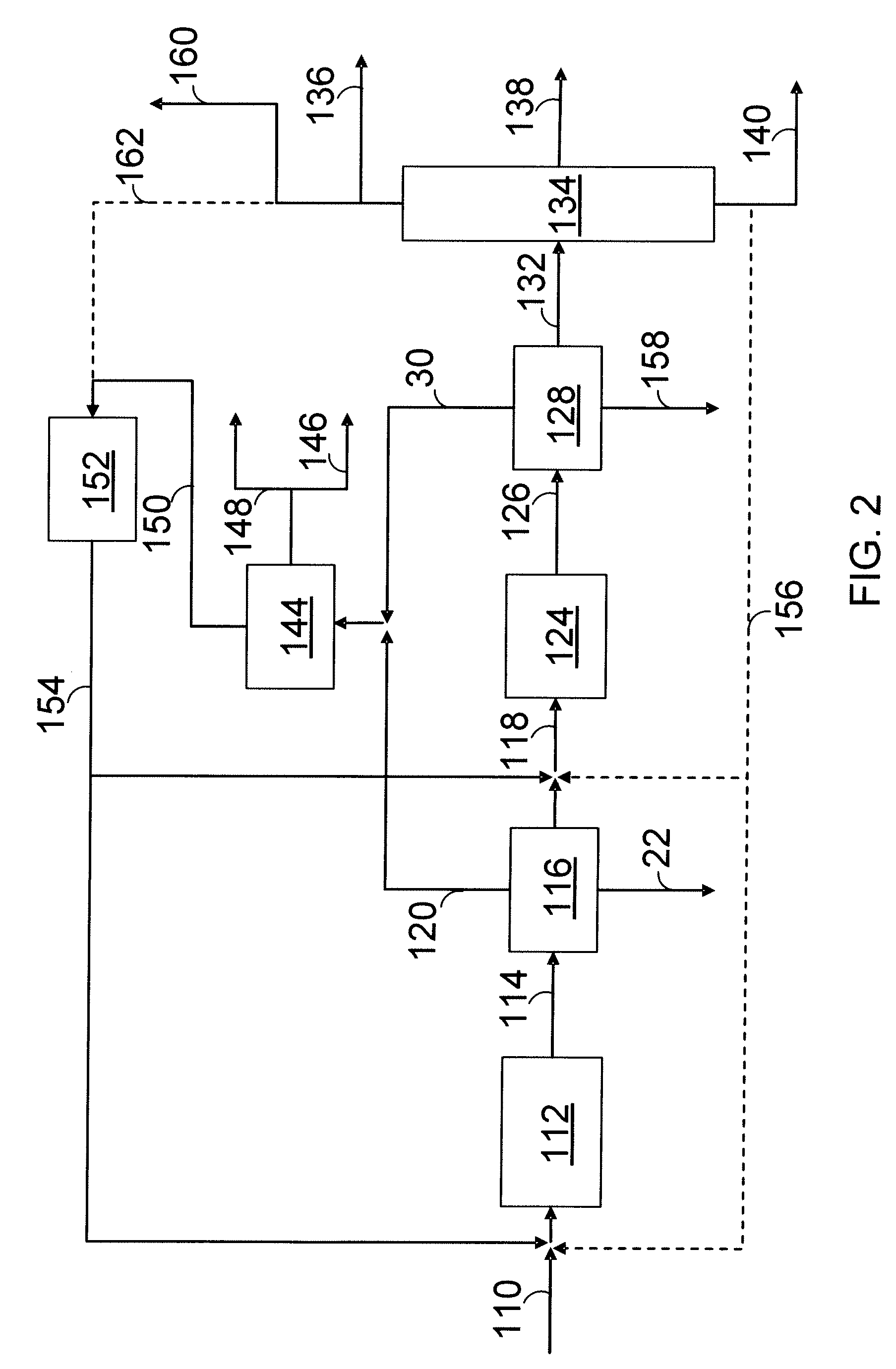
A system and method for the conversion of free fatty acids to glycerides and the subsequent conversion of glycerides to glycerin and biodiesel includes the transesterification of a glyceride stream with an alcohol. The fatty acid alkyl esters are separated from the glycerin to produce a first liquid phase containing a fatty acid alkyl ester rich (concentrated) stream and a second liquid phase containing a glycerin rich (concentrated) stream. The fatty acid alkyl ester rich stream is then subjected to distillation, preferably reactive distillation, wherein the stream undergoes both physical separation and chemical reaction. The fatty acid alkyl ester rich stream is then purified to produce a purified biodiesel product and a glyceride rich residue stream. The glycerin rich second liquid phase stream may further be purified to produce a purified glycerin product and a (second) wet alcohol stream. Neutralization of the alkaline stream, formed during the alkali-catalyzed transesterfication process, may proceed by the addition of a mineral or an organic acid.
Owner:REG SENECA LLC +3
Impregnating solution for cosmetic cloths
InactiveUS20060039956A1Cosmetic preparationsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsWax esterFatty alcohol
The invention relates to preparations for impregnating cosmetic wipes, characterized in that they contain (a) an emulsifier mixture containing nonionic and amphoteric surfactants in a quantity ratio of 10:1 to 1:1, based on the quantity of emulsifiers, (b) a mixture of wax components containing wax esters, partial glycerides and fatty alcohol ethoxylates and (c) at least one cationic polymer. The preparations containing wax particles lead to optimal foaming and cleansing performance and to a favorable sensorial impression.
Owner:COGNIS DEUT GMBH & CO KG
Method for preparing hard polyurethane foam plastics with soybean oil
ActiveCN101314632AImprove water resistanceImprove heat resistancePolyesterFatty acid glycerol esters
The invention provides a method for preparing hard polyurethane foam plastics from soybean oil. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1) carrying out epoxidation including the sub-steps of subjecting soybean oil and epoxidizing agent to reaction to obtain epoxidized soybean oil; (2) carrying out ring-opening reaction including the sub-steps of subjecting epoxidized soybean oil and nucleophilic reagent of reactive hydrogen to the ring-opening reaction of epoxy chemical bond in the presence of a catalyst to obtain mixed hydroxyl fatty acid glyceride; (3) carrying out alcoholysis and esterification including the sub-steps of adding alcohol, heating for alcoholysis to obtain mixed hydroxyl fatty acid monoester, i.e. soybean oil based polyol, and esterifying with organic acid and acid anhydride to generate polyester polyol; and (4) sequentially adding 80-150 weight parts of isocyanate, 0.3-4 weight parts of triethanolamine and 0.5-4 weight parts of foam stabilizer to 100 weight parts of soybean oil based polyol, intensively stirring, adding 0.5-3 weight parts of distilled water, and uniformly foaming while stirring at the high speed.
Owner:NANTONG HAIERMA TECH CO LTD
Extraction solvents derived from oil for alcohol removal in extractive fermentation
ActiveUS20110312044A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce decreaseFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOxygen-containing compound preparationSolventFatty alcohol
In an alcohol fermentation process, oil derived from biomass is chemically converted into an extractant available for in situ removal of a product alcohol such as butanol from a fermentation broth. The glycerides in the oil can be chemically converted into a reaction product, such as fatty acids, fatty alcohols, fatty amides, fatty acid methyl esters, fatty acid glycol esters, and hydroxylated triglycerides, and mixtures thereof, which forms a fermentation product extractant having a partition coefficient for a product alcohol greater than a partition coefficient of the oil of the biomass for the product alcohol. Oil derived from a feedstock of an alcohol fermentation process can be chemically converting into the fermentation product extractant. The oil can be separated from the feedstock prior to the feedstock being fed to a fermentation vessel, and the separated oil can be chemically converted to a fermentation product extractant, which can then contacted with a fermentation product comprising a product alcohol, whereby the product alcohol is separated from the fermentation product.
Owner:GEVO INC
Production of blended fuel from renewable feedstocks
ActiveUS8329967B2Minimize the numberReduce the amount requiredRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonBiofuelsParaffin waxEngineering
A process for producing a blended fuel from a paraffin rich component and a cyclic rich component, where each of the components are generated from a renewable feedstock, is presented. The paraffin rich component is generated from glycerides and free fatty acids in feedstocks such as plant and animal oils. The cyclic rich component is generated from biomass derived pyrolysis oil. The source of the animal or plant oil and the biomass may be the same renewable source.
Owner:UOP LLC
Low-viscosity opacifiers without anionic surface-active agents
An emulsifier mixture for use in a wax-based opacifier composition is comprised of: (a) an alkyl and / or alkenyl oligoglycoside; (b) a fatty acid partial glyceride and optionally (c) at least one amphoteric surfactant, with the proviso that the ratio by weight of (a) and optionally (c) to (b) is between 6:1 and 3:1 and wherein the composition is free from anionic surfactants.
Owner:COGNIS DEUT GMBH & CO KG
Composition based on fish oil
InactiveUS6020020AEfficient dosingFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteDough treatmentFish oilOleic Acid Triglyceride
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 05025 Sec. 371 Date May 26, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 26, 1998 PCT Filed Nov. 12, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 19601 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 5, 1997Fish oil concentrates, having: < / =40% of long chain poly unsaturated fatty acids <20% of saturated fatty acids (C14-C18) <15% oleic acid <12% C16:1-fatty acid and with a weight-ratio: can be obtained by a process involving the following steps subjecting a fish oil to an enzymic conversion removing free fatty acids or esters from conversion-product subjecting product of above to enzymic hydrolysis, using specific lipase or partial glyceride-specific lipase wash and dry product re-esterify dried product.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com