Diagnostic agent for liver function
a liver function and diagnostic agent technology, applied in the field of diagnostic agents for liver function, can solve the problems of insufficient quantitative determination of liver enzymes as test methods, decreased liver enzyme leakage, and problems, and achieve the effect of imposing less physical burden on subjects and being used safely without side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Method of Breath Test
(1) Preparation of Rats with Acute Hepatitis
As test animals, male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were purchased from Nippon Charles River K.K. They were bred at 23.+-.2.degree. C. under 55.+-.10% humidity before use. These rats (7-10 week-old) were anesthetized by intraperitoneal administration of Nembutal (50 mg / kg) and then intraperitoneally administered galactosamine hydrochloride (200 mg / ml physiological saline) at a dose of 0.6-1.2 g / kg [Koff, S. et al., Proc. Soc. Exptl. Med. 137:696 (1971); Keppler, D. et al., Exp. Mol. Pathology, 9:279 (1968); Creation of Model Animals (by Disease) and Experimental Methods for Development of New Drugs, supervised by Masaharu Uchitaka, p. 126 (1993)]. Two days thereafter, blood was collected from the tail vein, and serum was separated from the blood. Glutamic pyruvic transaminase activity (GPT) and the total amount of bilirubin in the serum were measured using Fuji Drychem FDC5500.
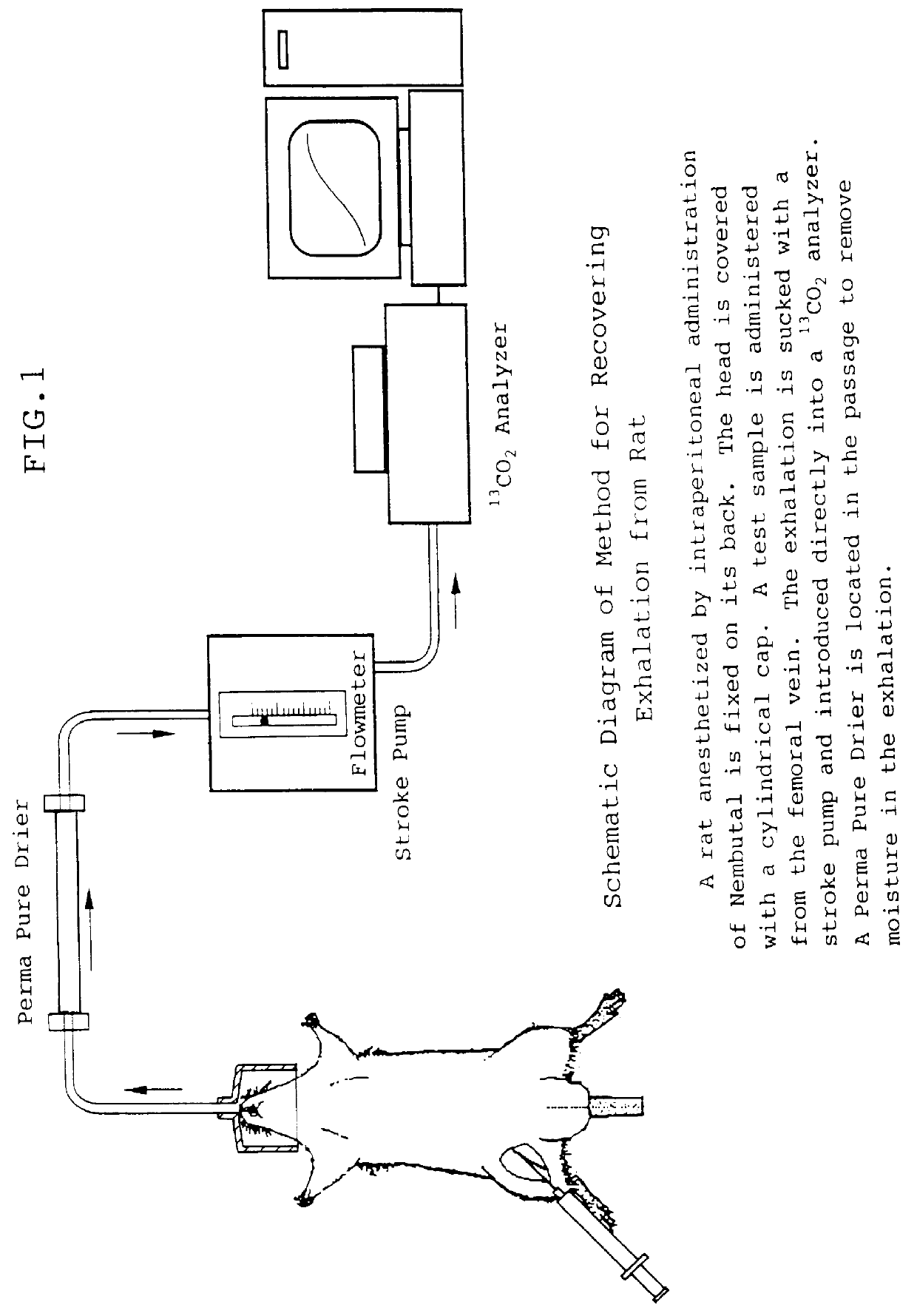
(2) .sup.13 C Breath Test
A breath test was carr...
example 2
1-.sup.13 C-Galactose Breath Test
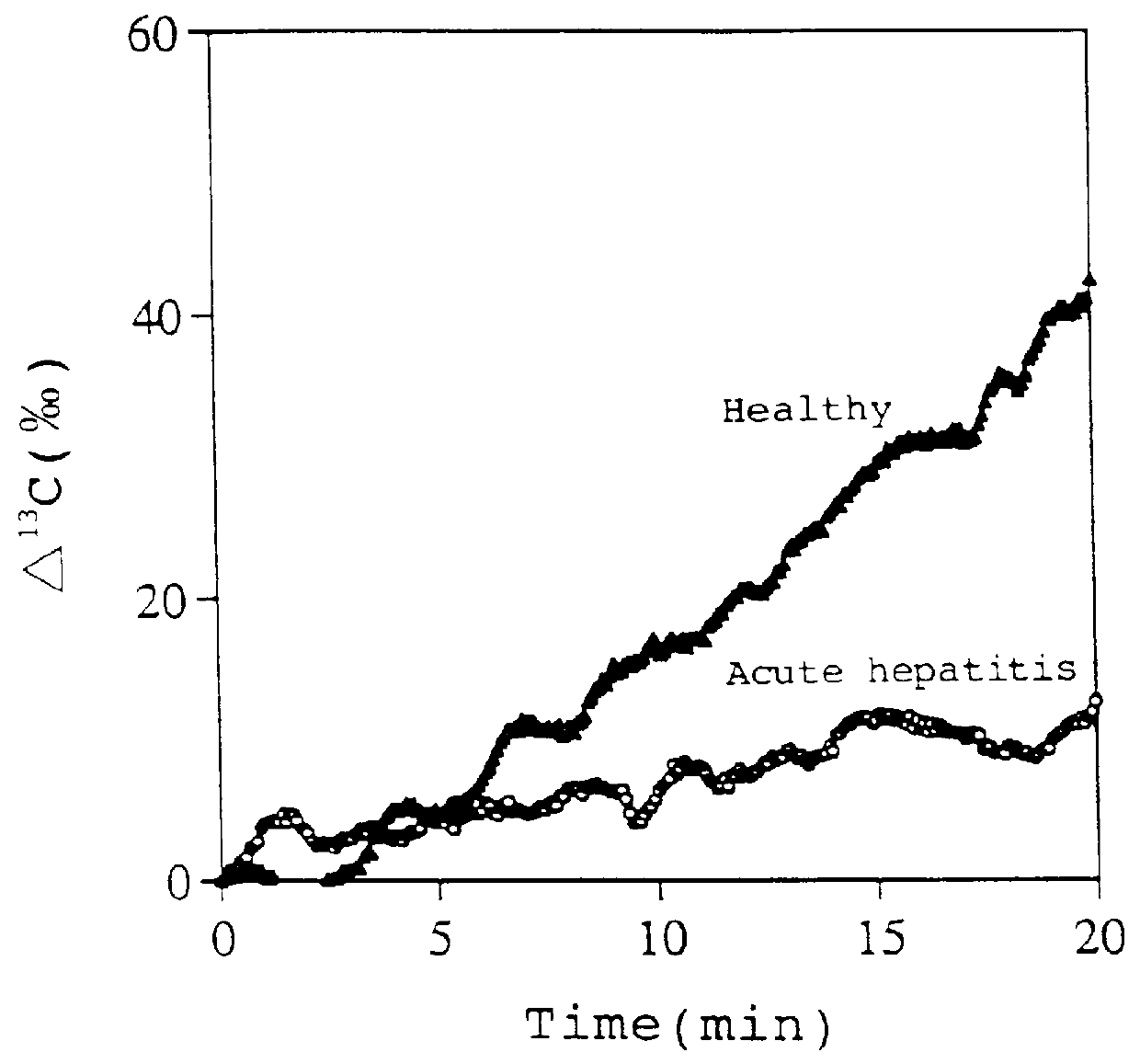
1-.sup.13 C-galactose (purchased from ICON) dissolved in physiological saline was administered to healthy rats (8-week-old; total bilirubin value.ltoreq.0.5 mg / dl; n=3) and rats with acute hepatitis (8-week-old; total bilirubin value.gtoreq.2.8 mg / dl; n=3) from the femoral vein at a dose of 100 mg / kg. Then, degrees of increase of .sup.13 C levels in exhaled CO.sub.2 (.DELTA..sup.13 C (.Salinity.)) were measured according to the method described in Example 1.
.DELTA..sup.13 C values (.Salinity.) continued increasing up to 20 min after the administration of 1-.sup.13 C-galactose in both the healthy and the hepatitic rats (FIG. 2).
The .DELTA..sup.13 C value (.Salinity.) at 20 min after the administration was 12.68.+-.6.25.Salinity. in the hepatitic rats, while the value was 42.43.+-.3.75.Salinity. in the healthy rats. Thus, the value in the hepatitis rats was very significantly (p<0.01 (ANOVA with Fischer LSD)) lower than that in the healthy rats.
The slo...
example 3
1-.sup.13 C-Glucose Breath Test
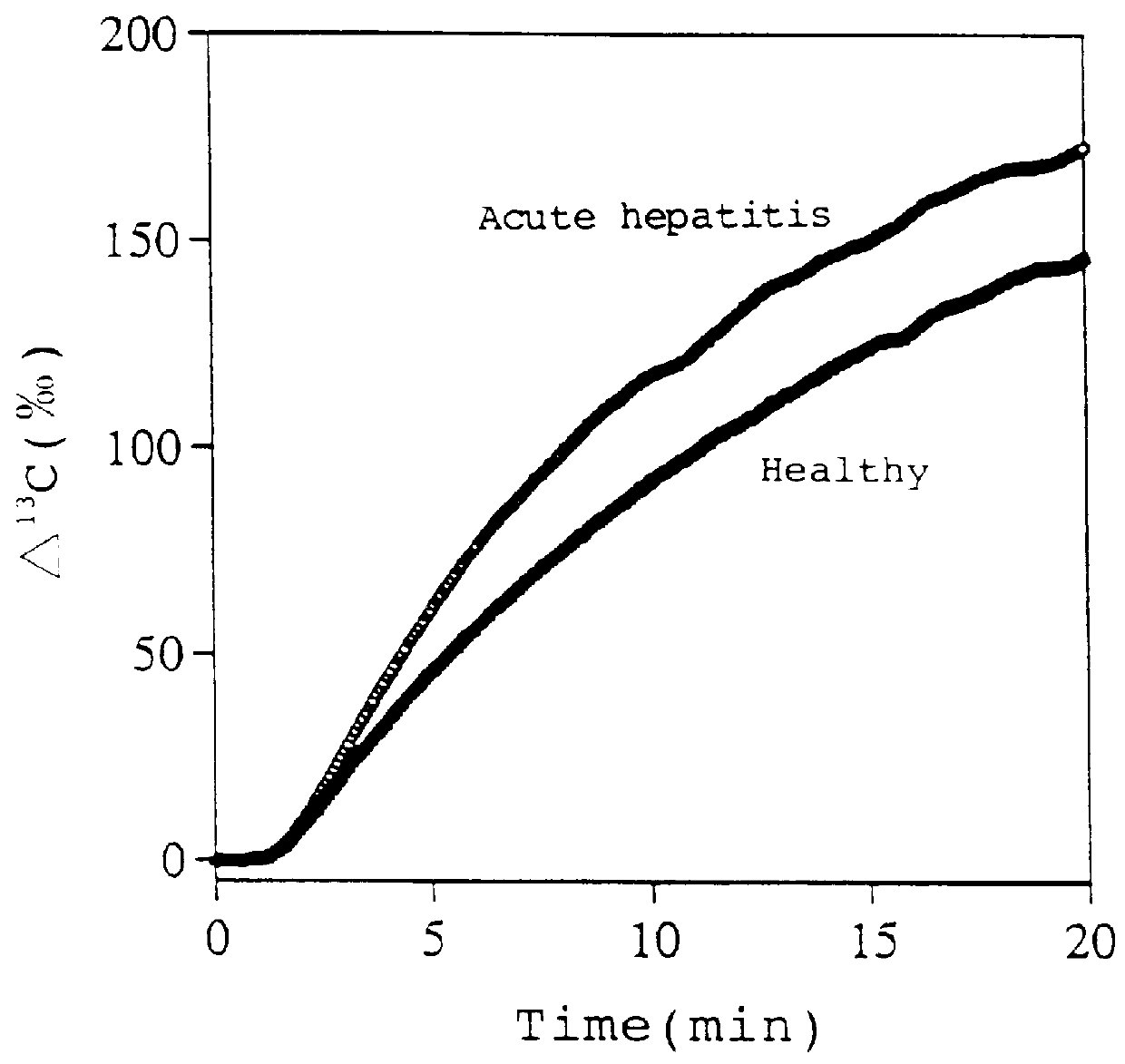
1-.sup.13 C-glucose (purchased from CIL) dissolved in physiological saline was administered to healthy rats (8-week-old; total bilirubin value.ltoreq.0.6 mg / dl; n=4) and rats with acute hepatitis (8-week-old; total bilirubin value>3 mg / dl; n=4) from the femoral vein at a dose of 100 mg / kg. Then, degrees of increase of .sup.13 C levels in exhaled CO.sub.2 (.DELTA..sup.13 C (.Salinity.)) were measured according to the method described in Example 1.
.DELTA..sup.13 C values (.Salinity.) continued increasing up to 20 min after the administration of 1-.sup.13 C-glucose in both the healthy and the hepatitic rats (FIG. 3).
The .DELTA..sup.13 C value (.Salinity.) at 5 min after the administration was 48.90.+-.2.97.Salinity. in the hepatitic rats, while the value was 39.37.+-.4.02.Salinity. in the healthy rats. Thus, the value in the hepatitis rats was significantly (p<0.05 (ANOVA with Fischer LSD)) higher than that in the healthy rats.
The slope of increase of .DE...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com