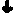Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
305 results about "Enzymatic degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enzymatic deactivation (also known as enzymatic degradation) is a mechanism that makes neurotransmitters inactive. Enzymatic deactivation occurs when an enzyme changes the structure of a neurotransmitter so that it is no longer recognized by the receptor. An example is enzymatic deactivation is seen with acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
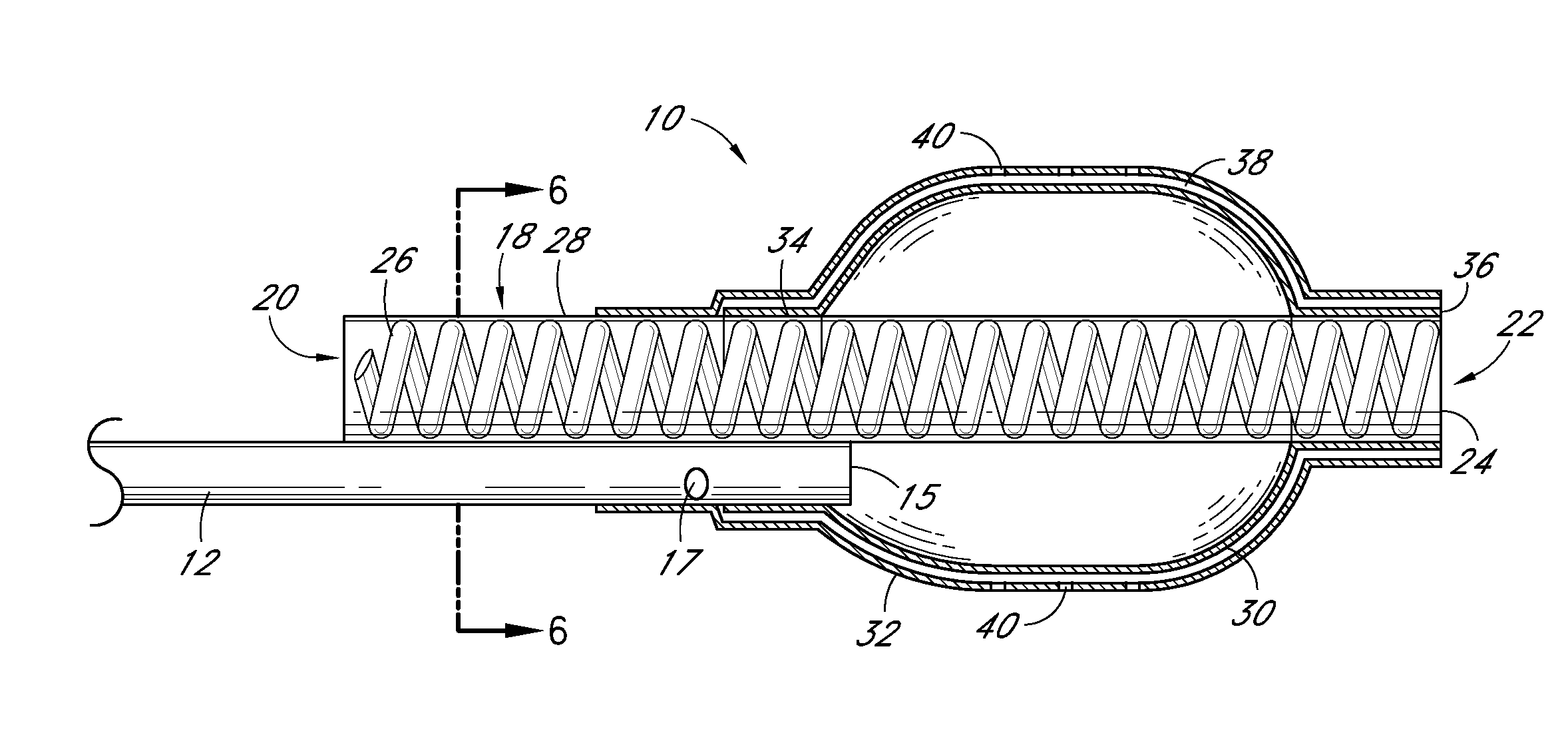
Abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical compositions of opioids and other drugs
ActiveUS7399488B2Good treatment effectSmall dosePowder deliveryNervous disorderAdditive ingredientWater insoluble
An abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical composition has been developed to reduce the likelihood of improper administration of drugs, especially drugs such as opiods. In the preferred embodiment, a drug is modified to increase its lipophilicity. In preferred embodiments the modified drug is homogeneously dispersed within microparticles composed of a material that is either slowly soluble or not soluble in water. In some embodiments the drug containing microparticles or drug particles are coated with one or more coating layers, where at least one coating is water insoluble and preferably organic solvent insoluble, but enzymatically degradable by enzymes present in the human gastrointestinal tract. The abuse-deterrent composition retards the release of drug, even if the physical integrity of the formulation is compromised (for example, by chopping with a blade or crushing) and the resulting material is placed in water, snorted, or swallowed. However, when administered as directed, the drug is slowly released from the composition as the composition is broken down or dissolved gradually within the GI tract by a combination of enzymatic degradation, surfactant action of bile acids, and mechanical erosion.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Method for producing cross-linked hyaluronic acid-protein bio-composites
InactiveUS20060189516A1Uniform densityUniform porosityPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderCross-linkFiber
This invention is concerned with a new method for producing cross-linked hyaluronic acid—protein bio-composites in various shapes. In the present process, a polysaccharide solution and a protein solution are mixed under moderate pH values in presence of salts to form a homogenous solution, which can be processed into various shapes, such as membrane, sponge, fiber, tube or micro-granular and so on. After then, the homogenous solution is subjected to a cross-linking reaction in organic solvent containing weak acid to produce an implantable bio composite material having excellent bio-compatibility, biodegradability, prolonged enzymatic degradation time, and good physical properties.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Abuse-deterrent drug formulations
ActiveUS20050281748A1Reduce the possibilityImprove lipophilicityTelevision system detailsPowder deliveryImmediate releaseActive agent
An abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical composition has been developed to reduce the likelihood of improper administration of drugs, especially drugs such as opiods. In the preferred embodiment, the drug is modified to increase its lipophilicity by forming a salt between the drug and one or more fatty acids wherein the concentration of the one or more fatty acids is one to 15 times the molar amount of the active agent, preferably two to ten times the molar amount of the active agent. In one embodiment the modified drug is homogeneously dispersed within microparticles composed of a material that is either slowly soluble or not soluble in water. In some embodiments the drug containing microparticles or drug particles are coated with one or more coating layers, where at least one coating is water insoluble and preferably organic solvent insoluble. The abuse-deterrent composition prevents the immediate release of a substantial portion of drug, even if the physical integrity of the formulation is compromised (for example, by chopping with a blade or crushing) and the resulting material is placed in water, snorted, or swallowed. However, when administered as directed, the drug is slowly released from the composition as the composition is broken down or dissolved gradually within the GI tract by a combination of enzymatic degradation, surfactant action of bile acids, and mechanical erosion.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Manufacturing process for the production of polypeptides expressed in insect cell-lines
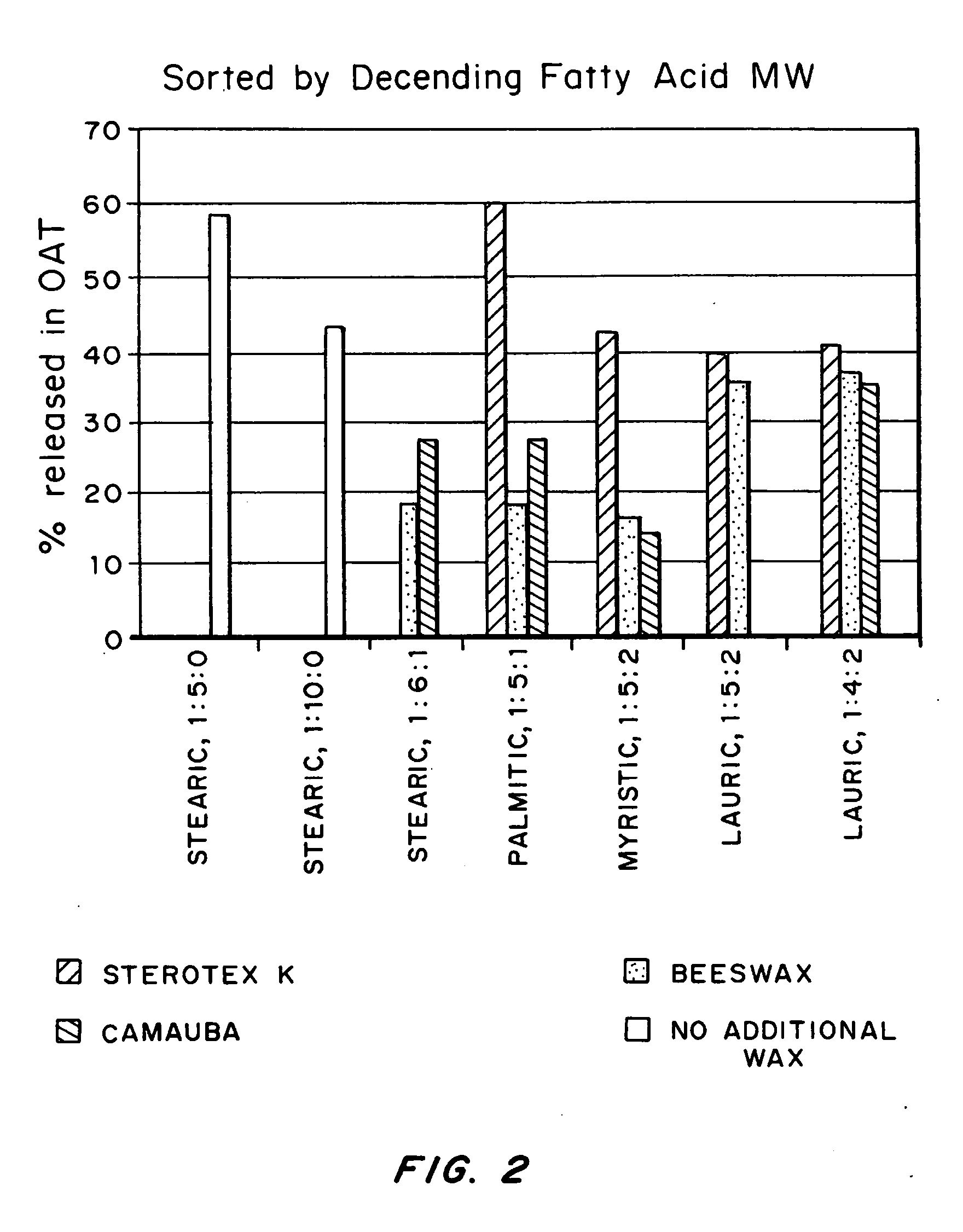
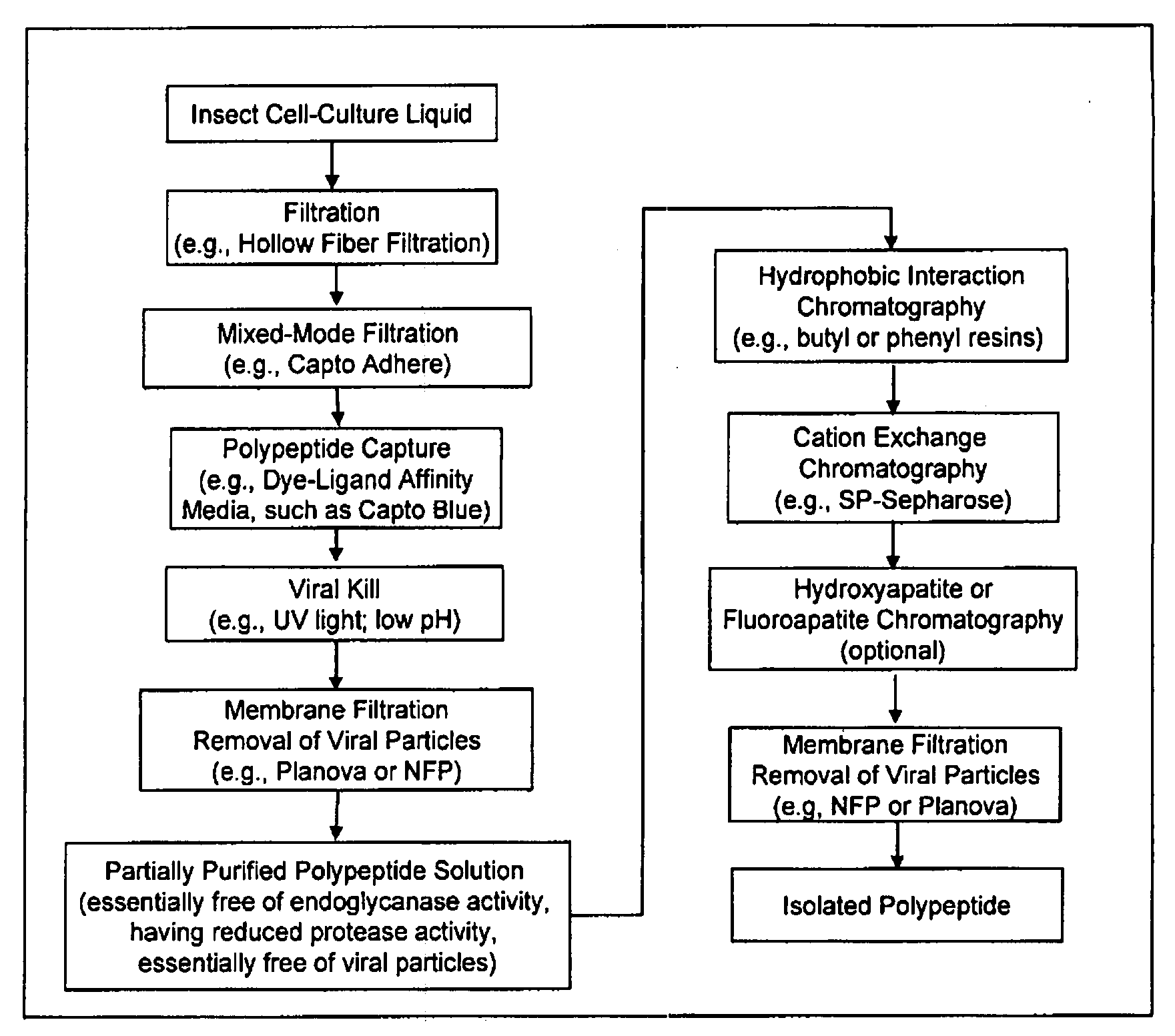
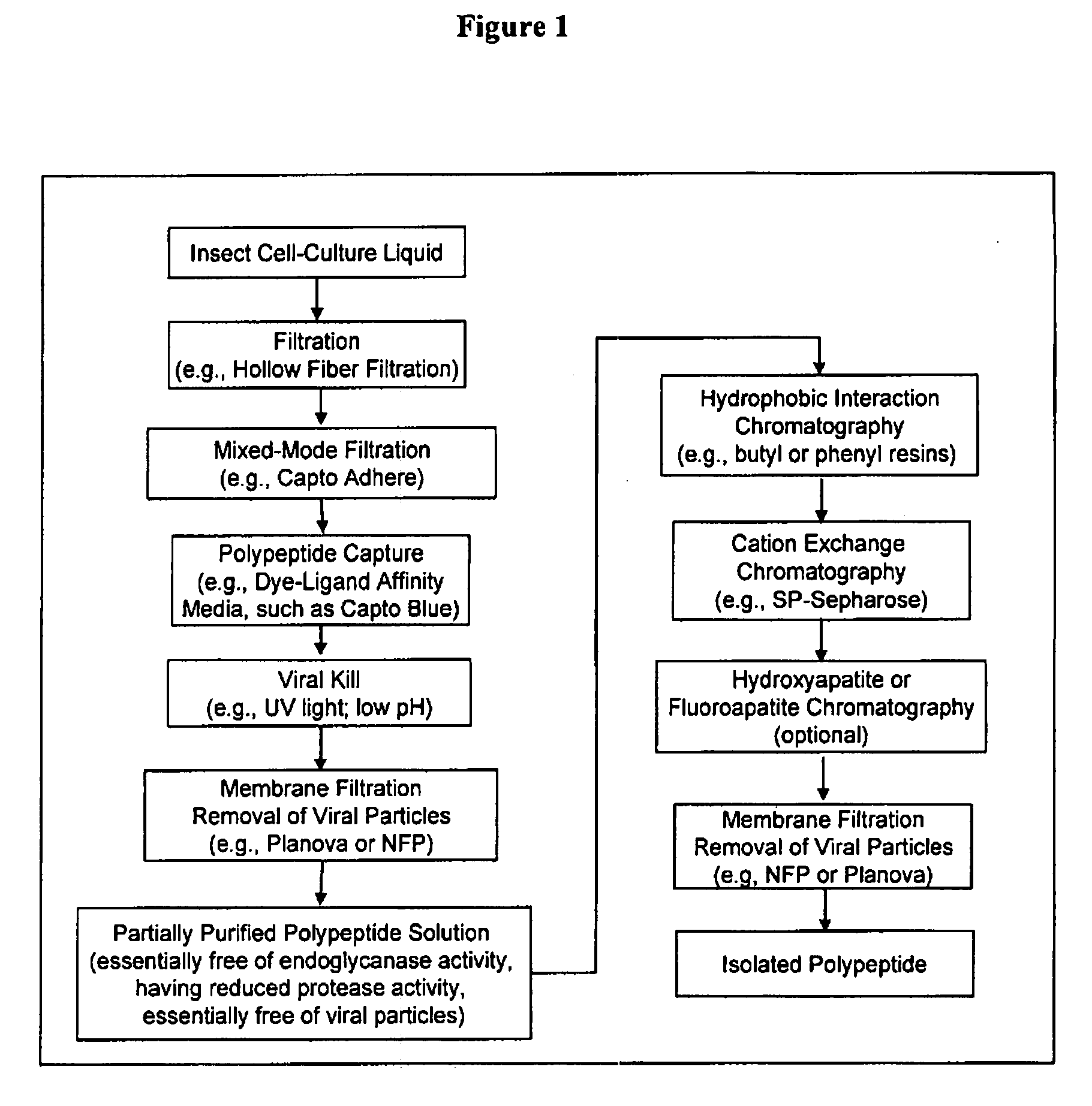
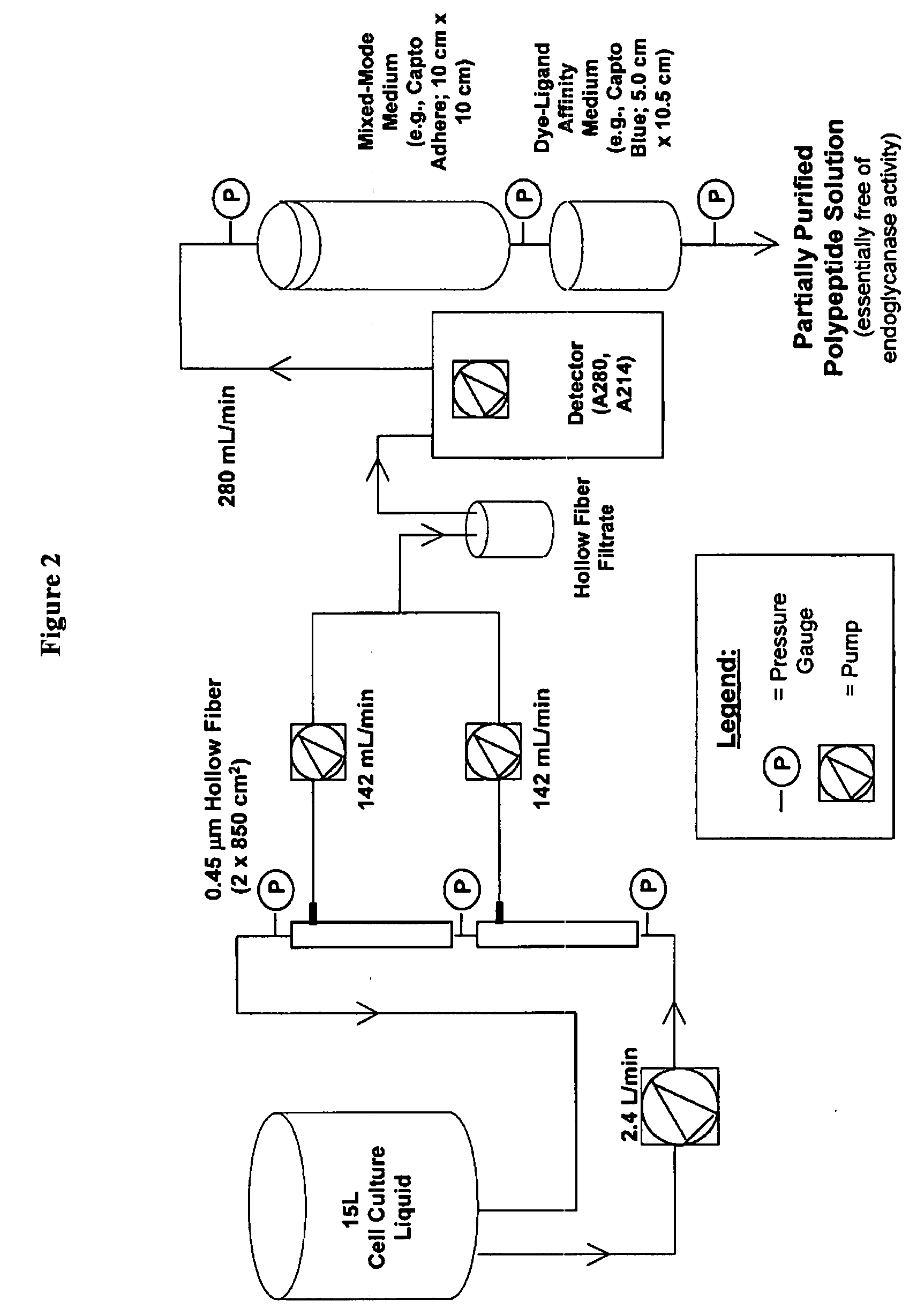
InactiveUS20080207487A1Promote recoveryReduce manufacturing costPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesFiberCulture fluid
The present invention provides a manufacturing method for polypeptides that are produced in insect cells using a baculoviral expression system. In one example, the insect cell culture is supplemented with a lipid mixture immediately prior to infection (e.g., one hour prior to infection). The polypeptides are isolated from the insect cell culture using a method that employs anion exchange or mixed-mode chromatography early in the purification process. This process step is useful to remove insect-cell derived endoglycanases and proteases and thus reduces the loss of desired polypeptide due to enzymatic degradation. In another example, mixed-mode chromatography is combined with dye-ligand affinity chromatography in a continuous-flow manner to allow for rapid processing of the insect-cell culture liquid and capture of the polypeptide. In yet another example, a polypeptide is isolated from an insect cell culture liquid using a process that combines hollow fiber filtration, mixed-mode chromatography and dye-ligand affinity in a single unit operation producing a polypeptide solution that is essentially free of endoglycanase and proteolytic activities. In a further example, the isolated polypeptides are glycopeptides having an insect specific glycosylation pattern, which are optionally conjugated to a modifying group, such as a polymer (e.g., PEG) using a glycosyltransferase and a modified nucleotide sugar.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Abuse-deterrent drug formulations
ActiveUS7771707B2Reduce the possibilityImprove lipophilicityPowder deliveryTelevision system detailsActive agentWater insoluble
An abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical composition has been developed to reduce the likelihood of improper administration of drugs, especially drugs such as opiods. In the preferred embodiment, the drug is modified to increase its lipophilicity by forming a salt between the drug and one or more fatty acids wherein the concentration of the one or more fatty acids is one to 15 times the molar amount of the active agent, preferably two to ten times the molar amount of the active agent. In one embodiment the modified drug is homogeneously dispersed within microparticles composed of a material that is either slowly soluble or not soluble in water. In some embodiments the drug containing microparticles or drug particles are coated with one or more coating layers, where at least one coating is water insoluble and preferably organic solvent insoluble. The abuse-deterrent composition prevents the immediate release of a substantial portion of drug, even if the physical integrity of the formulation is compromised (for example, by chopping with a blade or crushing) and the resulting material is placed in water, snorted, or swallowed. However, when administered as directed, the drug is slowly released from the composition as the composition is broken down or dissolved gradually within the GI tract by a combination of enzymatic degradation, surfactant action of bile acids, and mechanical erosion.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Compositions for delivering 5-ht agonists across the oral mucosa and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070059254A1Prevent enzymatic degradationPromote conversionBiocideNervous disorderMigraineEnzymatic degradation
The present invention provides novel compositions for the delivery of a 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) agonist across the oral mucosa. In particular, the buffer system in the compositions of the present invention raises the pH of saliva to a pH greater than about 9.9, thereby facilitating the substantially complete conversion of the 5-HT agonist from its ionized to its unionized form. As a result, the dose of 5-HT agonist is rapidly and efficiently absorbed by the oral mucosa. Furthermore, delivery of the 5-HT agonist across the oral mucosa advantageously bypasses hepatic first pass metabolism of the drug and avoids enzymatic degradation of the drug within the gastrointestinal tract. Methods for using the compositions of the present invention for treating migraines are also provided.
Owner:TRANSCEPT PHARMA
Multicomponent whitening compositions and containers
InactiveUS20070231277A1Cosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWhitening AgentsEnzymatic degradation
The present invention is directed to a container for housing and dispensing dentifrice compositions and that includes a first chamber containing therein a first dentifrice composition that includes a non-abrasive whitening agent and at least one thickener, a second chamber containing therein a second dentifrice composition that includes an abrasive polishing material, at least one thickener, a proteolytic enzyme and a rheology modifier that is not susceptible to enzymatic degradation, where the first and second dentifrice compositions are isolated one from the other until the substantially simultaneous co-extrusion from the container, and to whitening compositions containing the co-extruded first and second dentifrice compositions.
Owner:MCNEIL PPC INC
High-quality lipids and methods for producing by enzymatic liberation from biomass
A high-quality lipid composition is disclosed having low oxidative deterioration such as measured by low anisidine values. Also disclosed are methods of preparing the same from a lipid-containing material that include enzymatic degradation of protein and / or carbohydrate components of the material. Lipid-containing materials include biomass, such as microorganisms. The invention further includes products containing the lipid compositions, such as dietary supplements, food products, pharmaceutical formulations, humanized animal milk, and infant formula.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
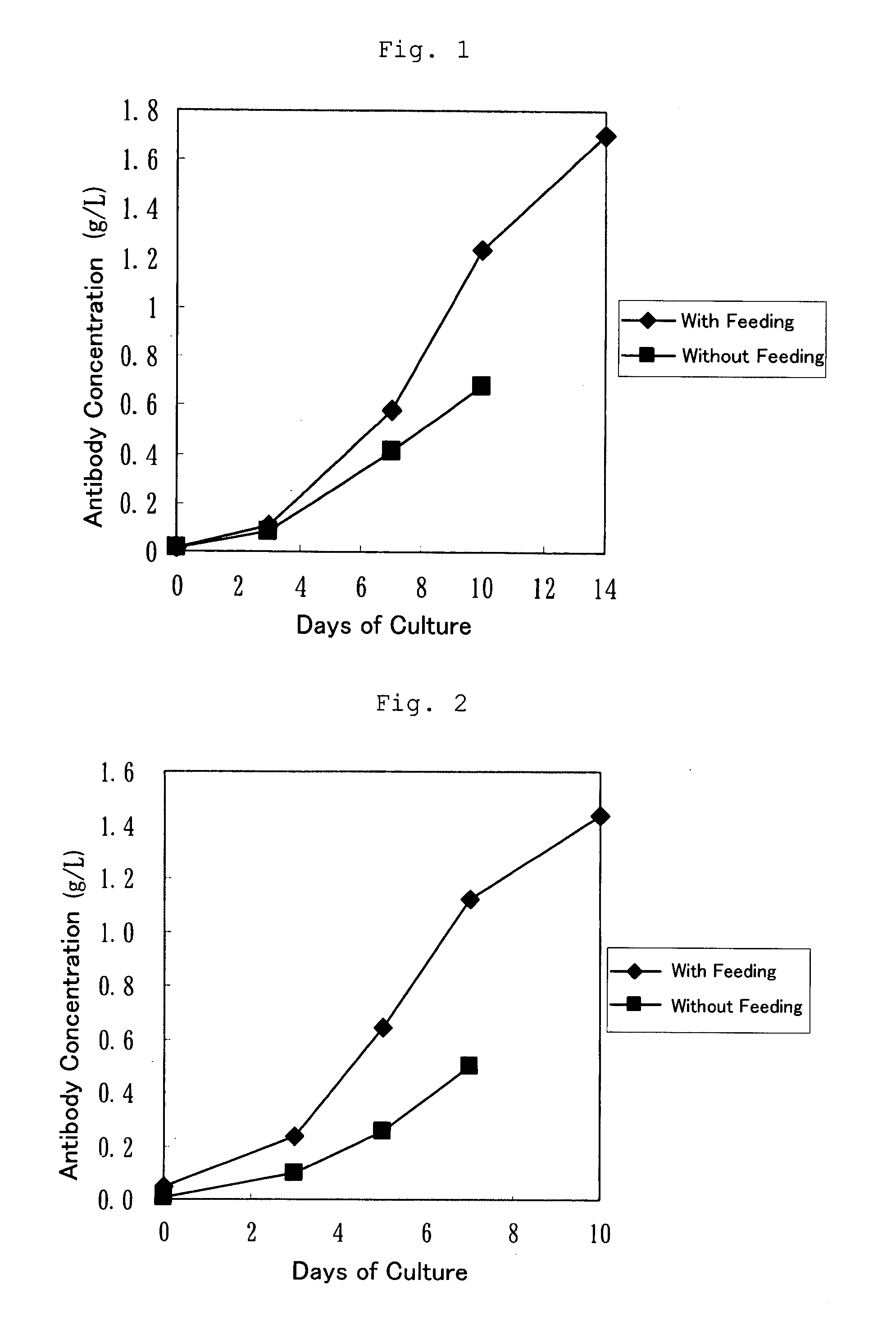
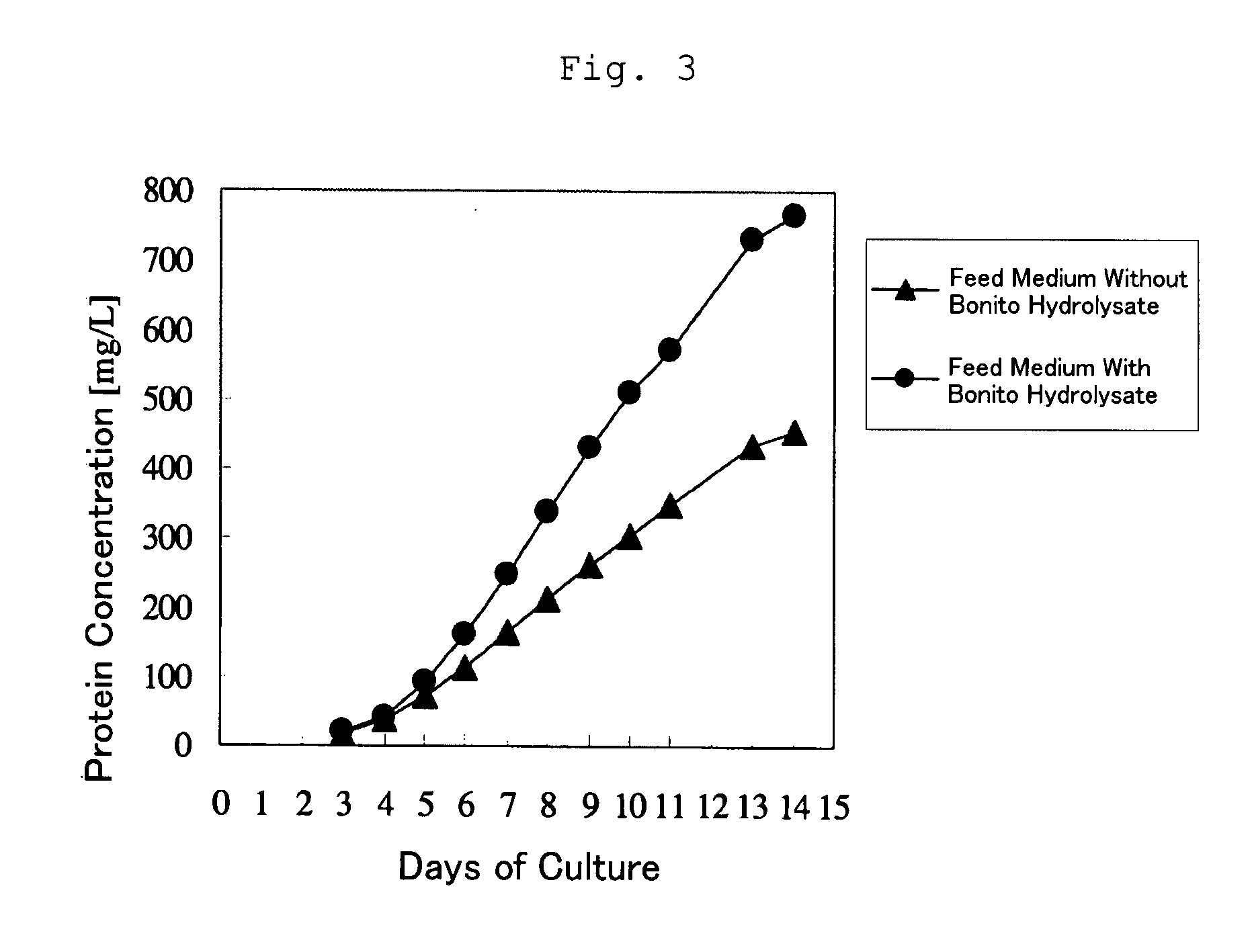
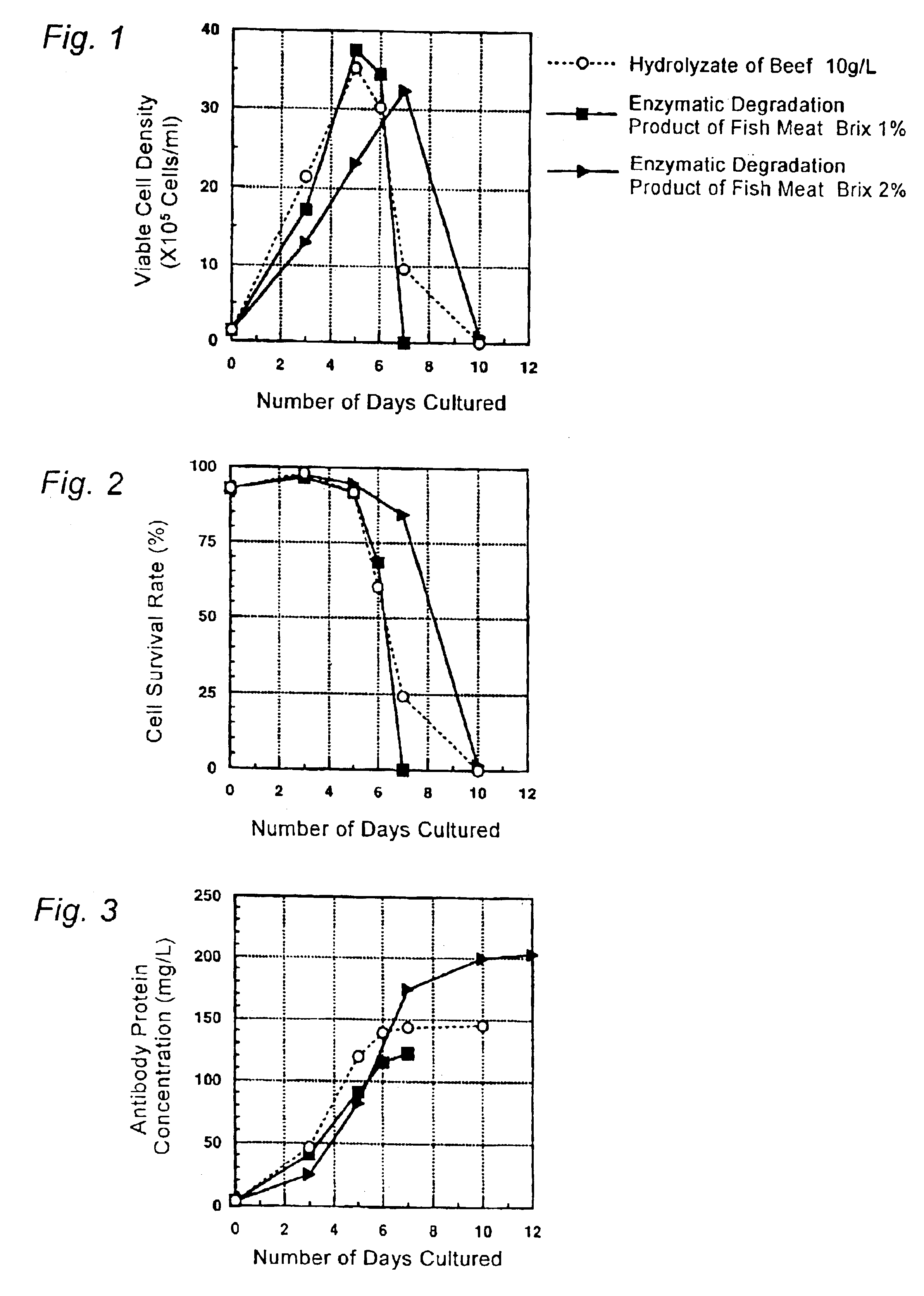
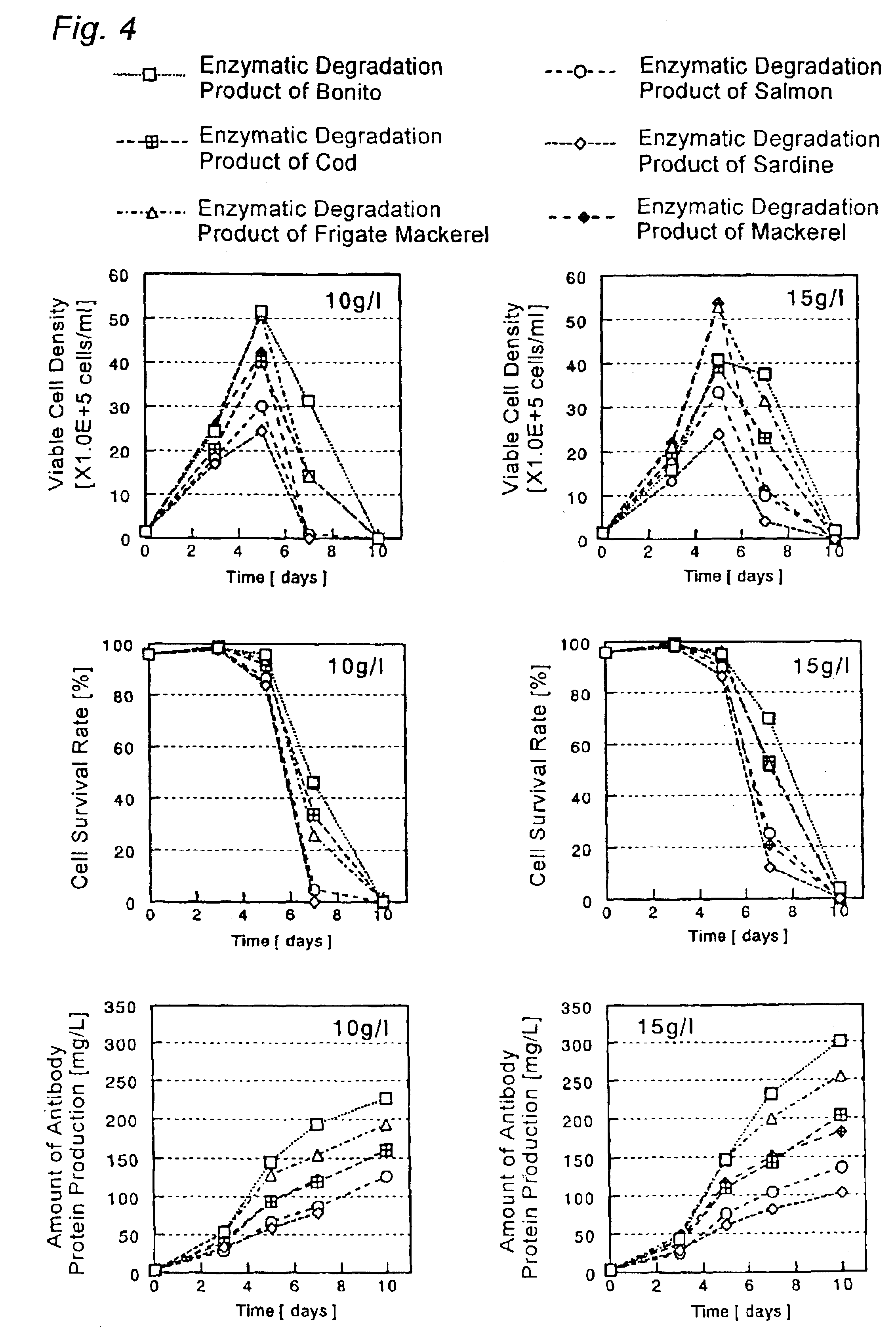
Cell Culture Method and Utilization of the Same
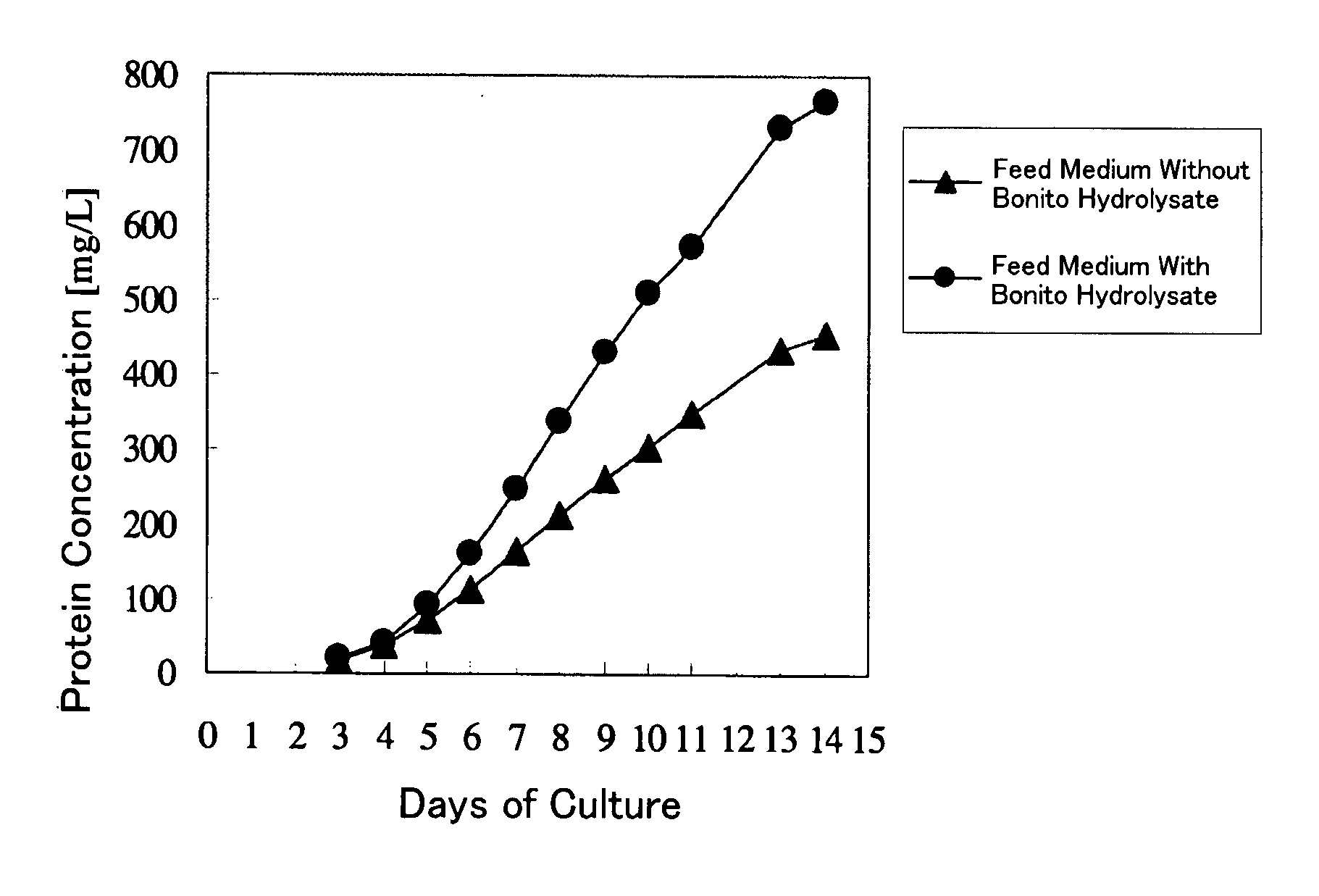
It is an object of the present invention to allow a cell to produce a protein at a high level using a medium containing an enzymatic degradation product of fish meat or a fish meat extract. A method of culturing a cell comprising starting culturing in an initial medium and feeding at least once a feed medium to the initial medium during culturing, wherein at least one of the initial medium or the feed medium contains an enzymatic degradation product of fish meat or a fish meat extract added thereto. A method of producing a protein of interest using the above culture method.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Culture medium for culture of animal cell and method for producing protein using same
A culture medium for culture of an animal cell, characterized by containing an enzymatic degradation product of fish meat or a fish meat extract, and a method for producing a desired protein with the use of the culture medium.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
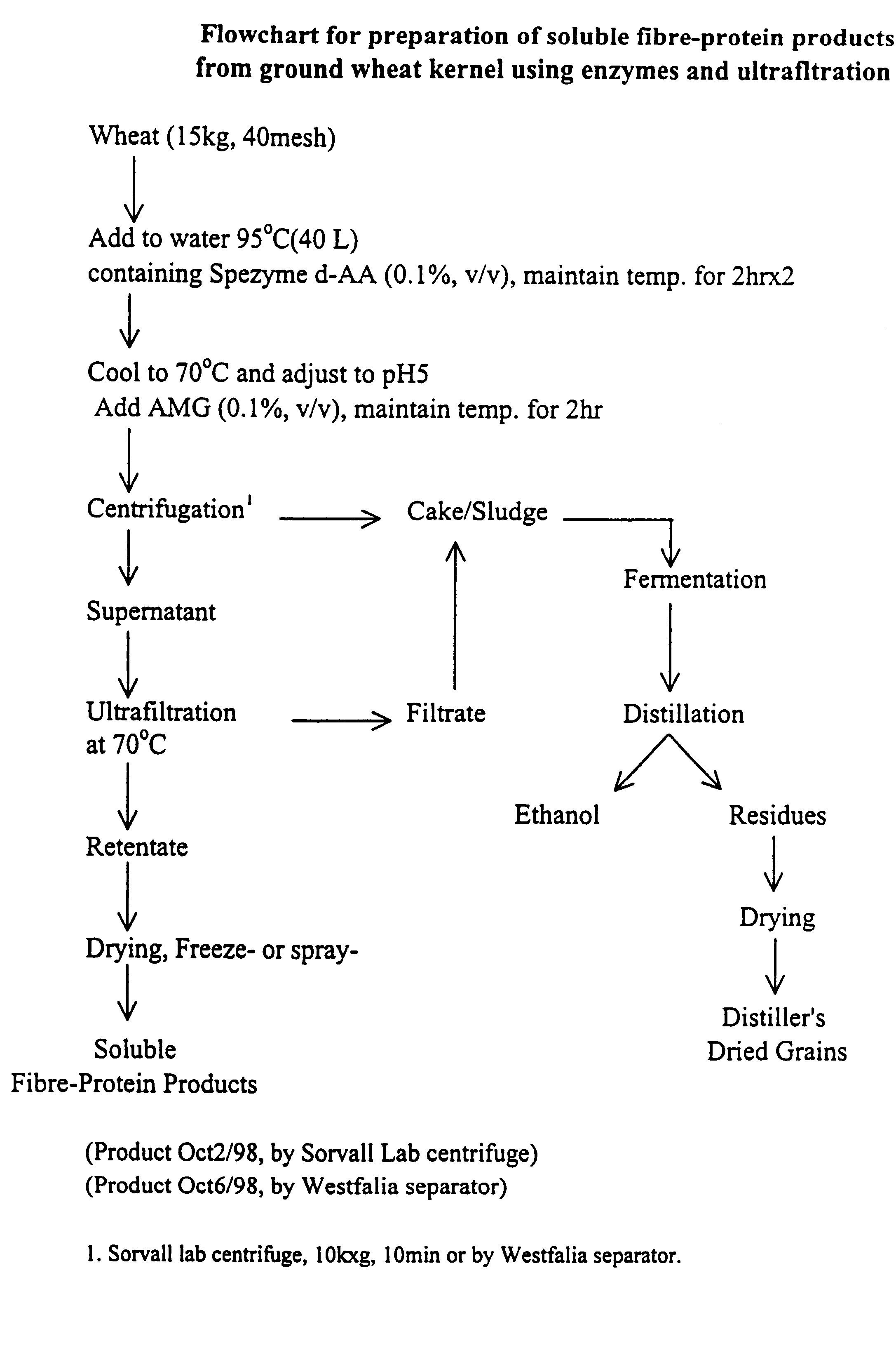
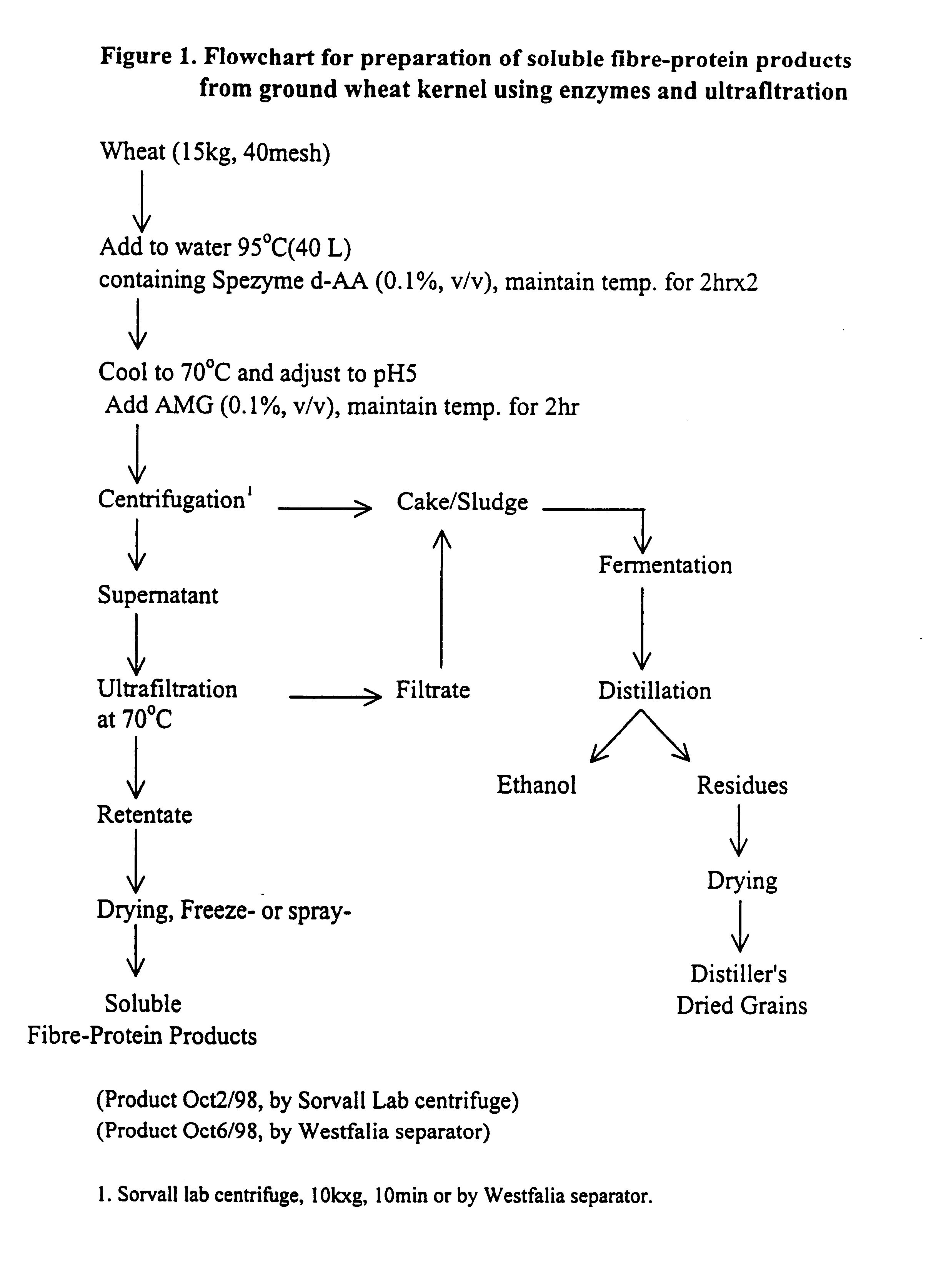
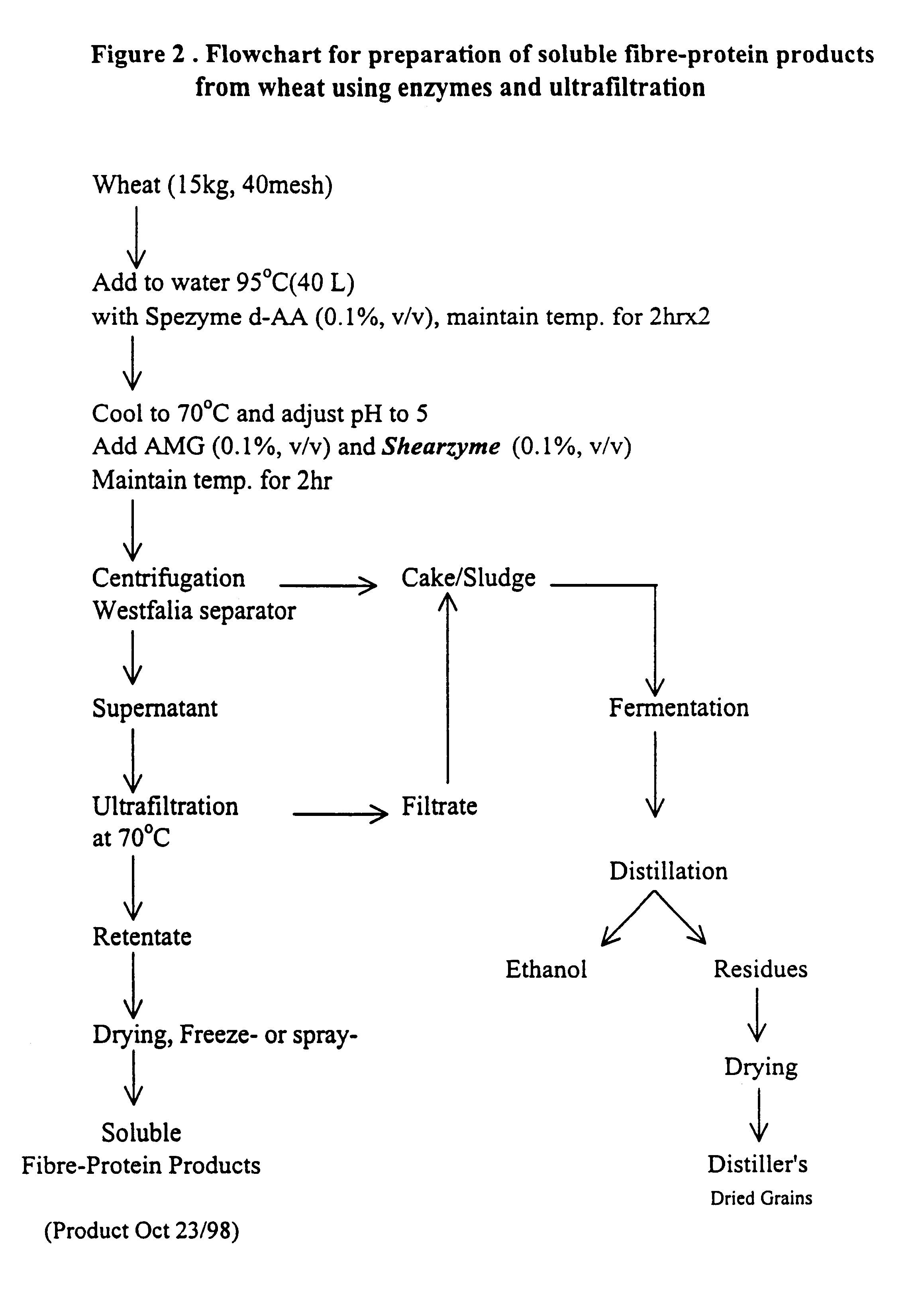
Functional, water-soluble protein-fibre products from grains
Novel water-soluble free-flowing protein-fibre products are provided from cereal grains, such as wheat, free from starch, bran and low molecular weight degradation products thereof. Starch contaminants in soluble fractions of the cereal grains are removed by enzymatic degradation and separation. The protein to fibre ratio of the product may be modified by enzymatic treatment. Such materials are useful in a wide variety of food application.
Owner:MAZZA GIUSEPPE +4
Multichamber device for processing of biological samples using high pressure
InactiveUS20070014690A1Suitable for automationSimple formatBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMetaboliteFungal microorganisms
Devices and methods are described for homogenization, processing, detection, and analysis of biological samples such as insects, fungi, bacteria, and plant and animal tissues. Multiple chambers in these devices permit different processing functions to be carried out at each stage, such that the resulting homogenized product can be further processed, purified, analyzed, and / or biomolecules such as metabolites, proteins and nucleic acids, or pharmaceutical products can be detected. The device can be used in a hydrostatic pressure apparatus, in which different activities, i.e. incubations, addition or renewal of reagent, and generation and detection of signal can be carried out in the appropriate chamber. The method improves the preservation of biomolecules from chemical and enzymatic degradation relative to conventional means. Additionally, this method enables automated sample preparation and analytical processes.
Owner:BBI BIOSEQ A MASSACHUSETTS CORP
Dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose-collagen frozen gel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101845226AHigh reactivityImprove mechanical propertiesSurgeryProsthesisBiologic scaffoldPorosity
The invention provides dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose-collagen frozen gel and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: first uniformly mixing 1 to 3 mass percent of the aqueous solution of collagen and 0.01 to 1 mass percent of the aqueous solution of dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose; then injecting the mixed solution into a mold and storing the mixed solution in a low-temperature reactor at the temperature of -40 to 0 DEG C for 1 to 7 days; and finally, taking the obtained product out and slowly unfreezing the obtained product to obtain the dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose-collagen frozen gel. The dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose-collagen freezing gel prepared by the method is improved in mechanical property, thermal stability and enzymatic degradation resistance at the same time of maintaining the biological activity of collagen gel per se, has the advantages of porosity, hydrophilicity, water absorbing and preserving property, good market application prospect and the like, and is widely used in biomedical fields, such as biologic scaffolds, cell culture, drug delivery, tissue engineering, wound and burning treatment and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical compositions of opioids and other drugs
InactiveUS20080199530A1Reduce the possibilityImprove lipophilicityPowder deliveryNervous disorderAdditive ingredientWater insoluble
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Utilization of mural thrombus for local drug delivery into vascular tissue
InactiveUS20100261662A1Promote degradationPromote cross-linking proteinBiocidePowder deliveryMural thrombusCell-Extracellular Matrix
The present disclosure is directed to methods and systems for stabilizing an extracellular matrix in a wall of a blood vessel. The method comprises delivering a therapeutic agent into mural thrombus, which covers the wall of the blood vessel. The agent is transported from the mural thrombus into the extracellular matrix of the vessel wall by diffusion. The agent then acts to reduce the enzymatic degradation of protein in the extracellular matrix.
Owner:ENDOLOGIX LLC
Method for breaking walls of cells of bran by wet grinding
The invention relates to a method for breaking walls of cells of bran by wet grinding, and belongs to the technical field of industrial biochemistry. The invention adopts the technical key point that: bran, water, and enzyme for degrading walls of cells of the bran are mixed, and subjected to wet ball-milling grinding to form superfine wall-breaking powder. By combining an ultramicro-pulverization method, the water and the enzyme for degrading the walls of cells of the bran, the cells of the bran are subjected to wet ball milling for wall-breaking treatment; compared with single ultramicro pulverization, the method can greatly reduce the energy consumption, is simple and has low requirement on operating equipment; and compared with single enzymatic degradation, the method combines wet ball milling, combines chemical action with mechanical force action, and has the advantages of greatly saving energy required by high temperature treatment, avoiding the defect of enzyme inactivation under high temperature treatment, eliminating crystal structures of cellulose and improving enzymolysis efficiency.
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS
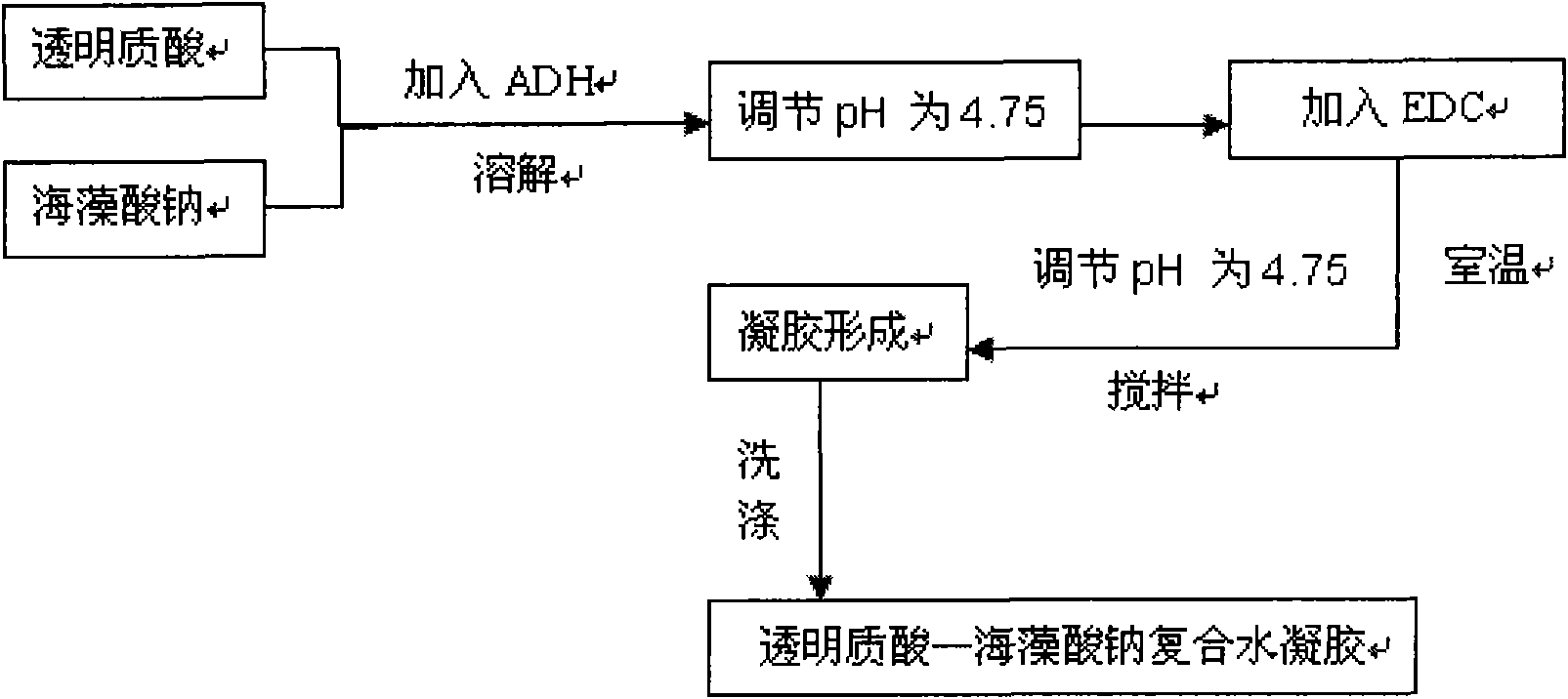
Hyaluronic acid-sodium alginate composite hydrogel and preparation method thereof
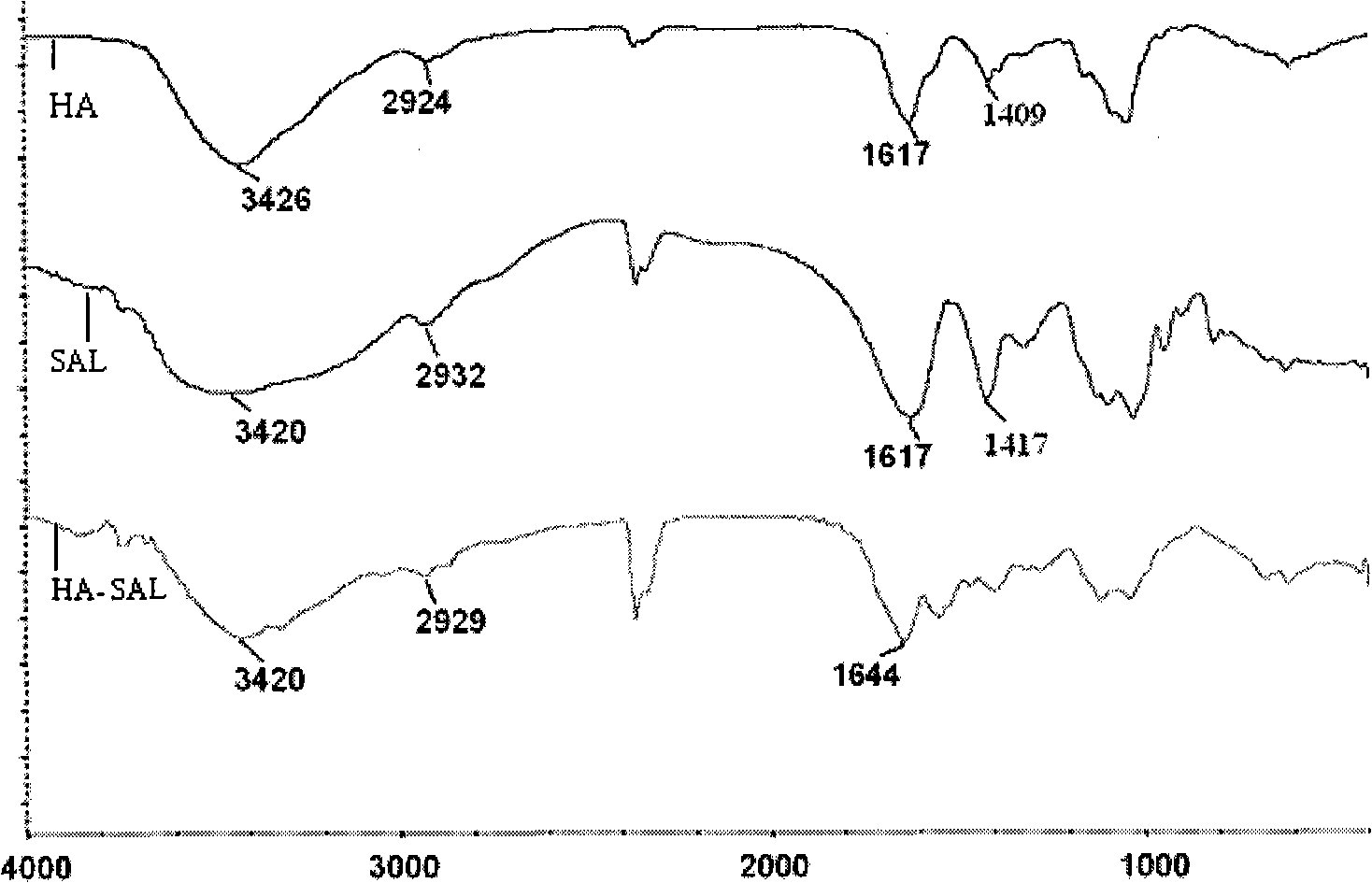
The invention discloses hyaluronic acid-sodium alginate composite hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The composite hydrogel is prepared from the following steps of: (1) dissolving hyaluronic acid and sodium alginate into water to obtain a solution 1; (2) adding a cross-linking agent to the solution 1, and regulating the pH value to be 4.0-5.5 with a buffer solution to obtain a solution 2; (3) adding a carboxyl activating agent to the solution 2 and stirring; and regulating and controlling the pH value of the solution 2 to be 2.0-5.5 in the stirring process until gel is formed to obtain the hyaluronic acid-sodium alginate composite hydrogenl. The invention provides a new approach for the modification of the hyaluronic acid, and the composite modified compound prepared by using the method has the advantages of higher mechanical property, capacity of resisting enzymatic degradation of the hyaluronic acid, biocompatibility, and the like and has potential application in the aspects of surgical operations and tissue engineering.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
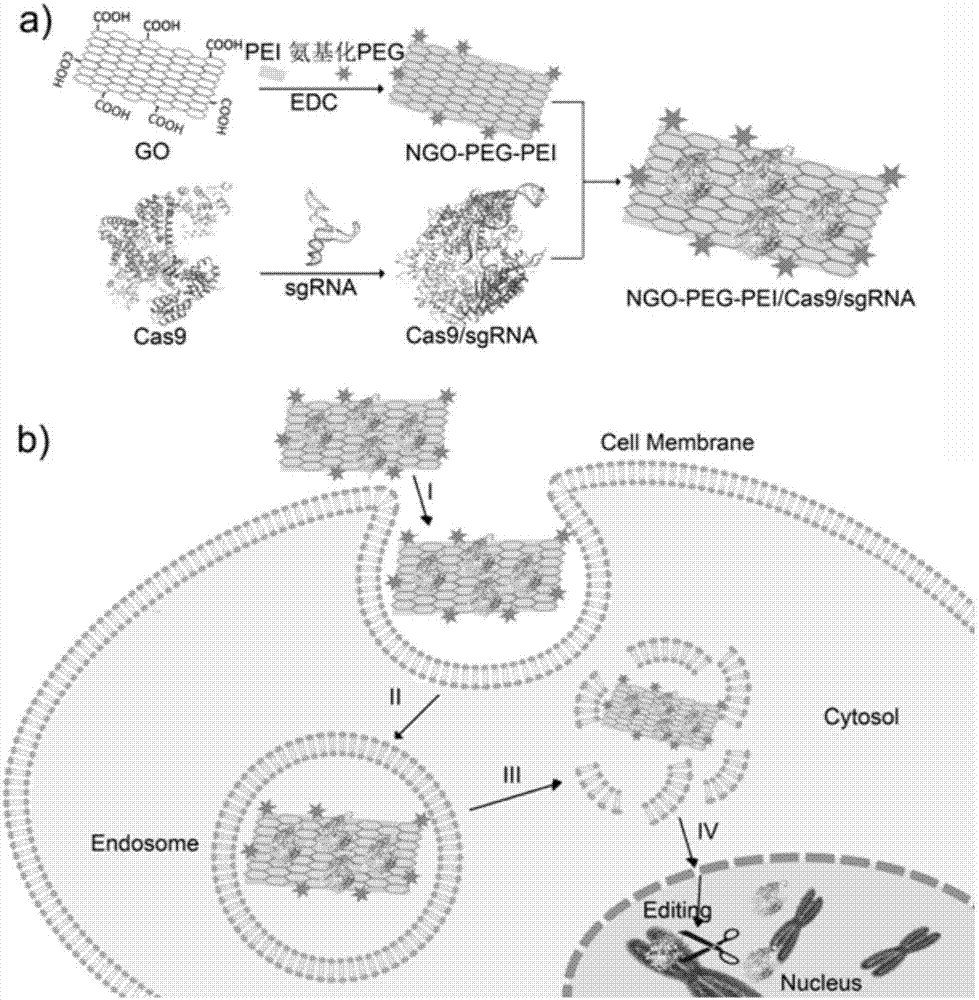
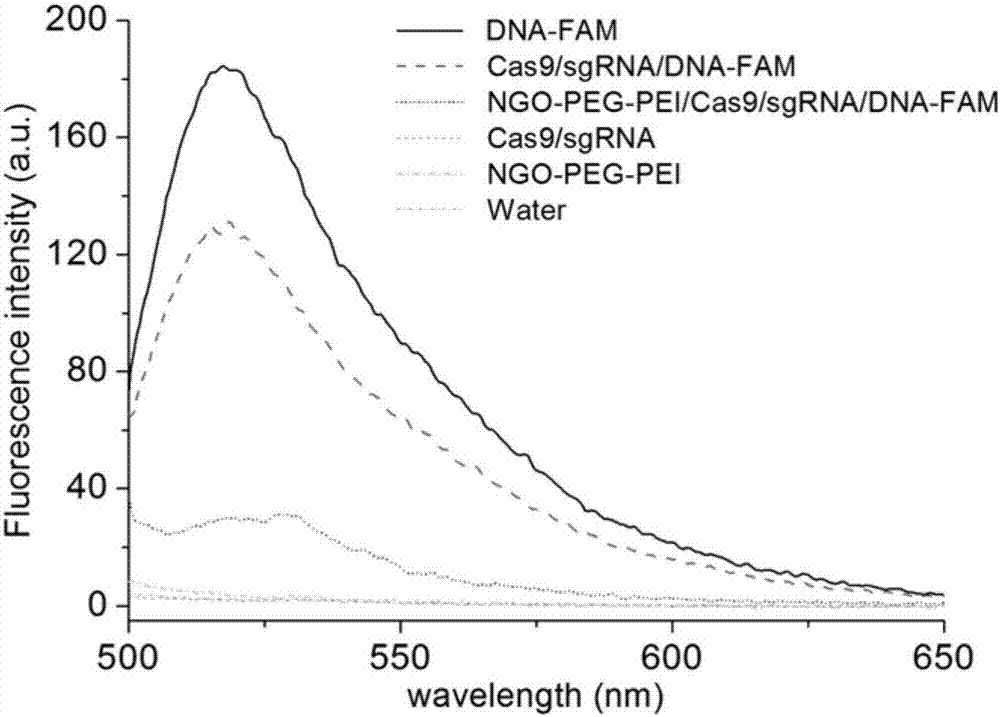
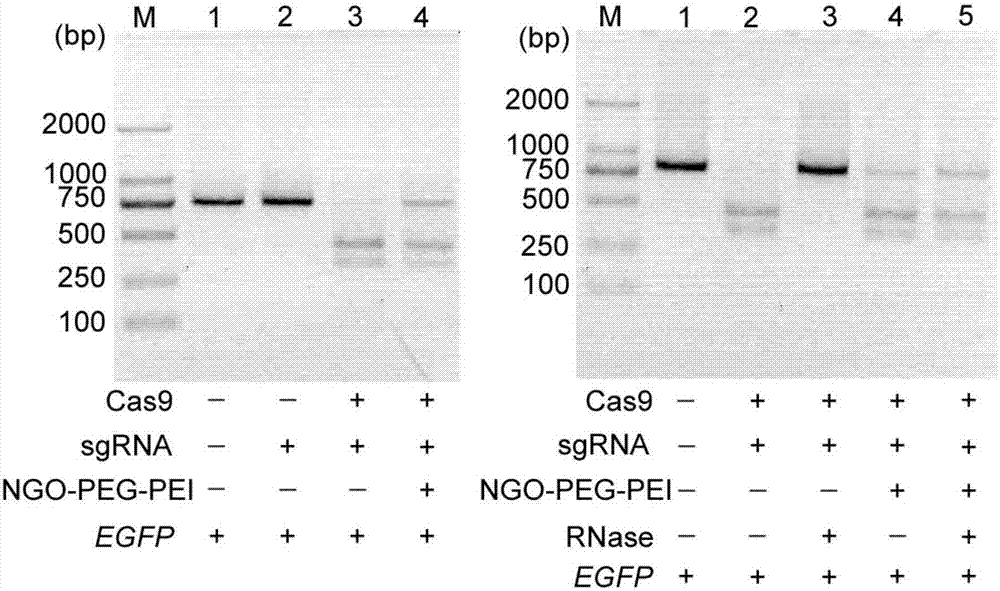
Method for efficiently carrying CRISPR/Cas9 through functionalized graphene oxide for gene editing
ActiveCN107384894AEasy to buildAchieve low toxicityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNARoom temperatureBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for efficiently carrying CRISPR / Cas9 through functionalized graphene oxide for gene editing. An NGO-PEG-PEI / Cas9 / sgRNA complex is obtained by the following steps: covalently modifying aminated PEG and aminated PEI onto graphene oxide to obtain NGO-PEG-PEI; then assembling Cas9 protein and sgRNA into a Cas9 / sgRNA complex under a room-temperature condition; and mixing NGO-PEG-PEI with the Cas9 / sgRNA complex under a room-temperature condition. The editing of target gene can be realized by mixing the complex with the target gene. The functionalized GO has the characteristics of good biocompatibility and high carrying efficiency, can efficiently carry the Cas9 / sgRNA complex into cells for performing corresponding functions, and has the effect of keeping the Cas9 / sgRNA complex free of enzymatic degradation and high in stability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions for delivering hypnotic agents across the oral mucosa and methods of use thereof
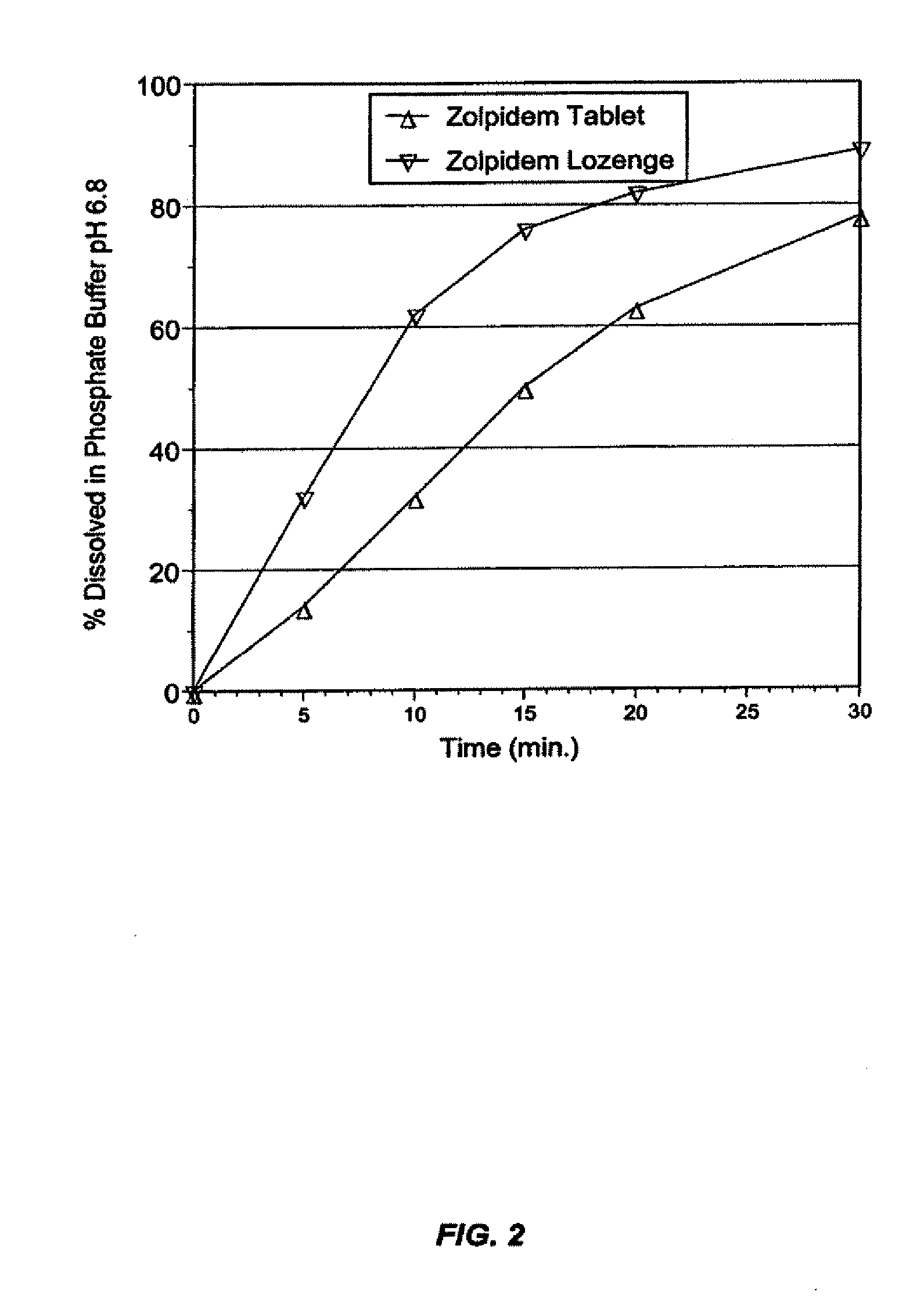
InactiveUS20080008753A1Rapidly and efficiently absorbedAvoid degradationBiocideNervous disorderHypnotic agentSleeping disorders
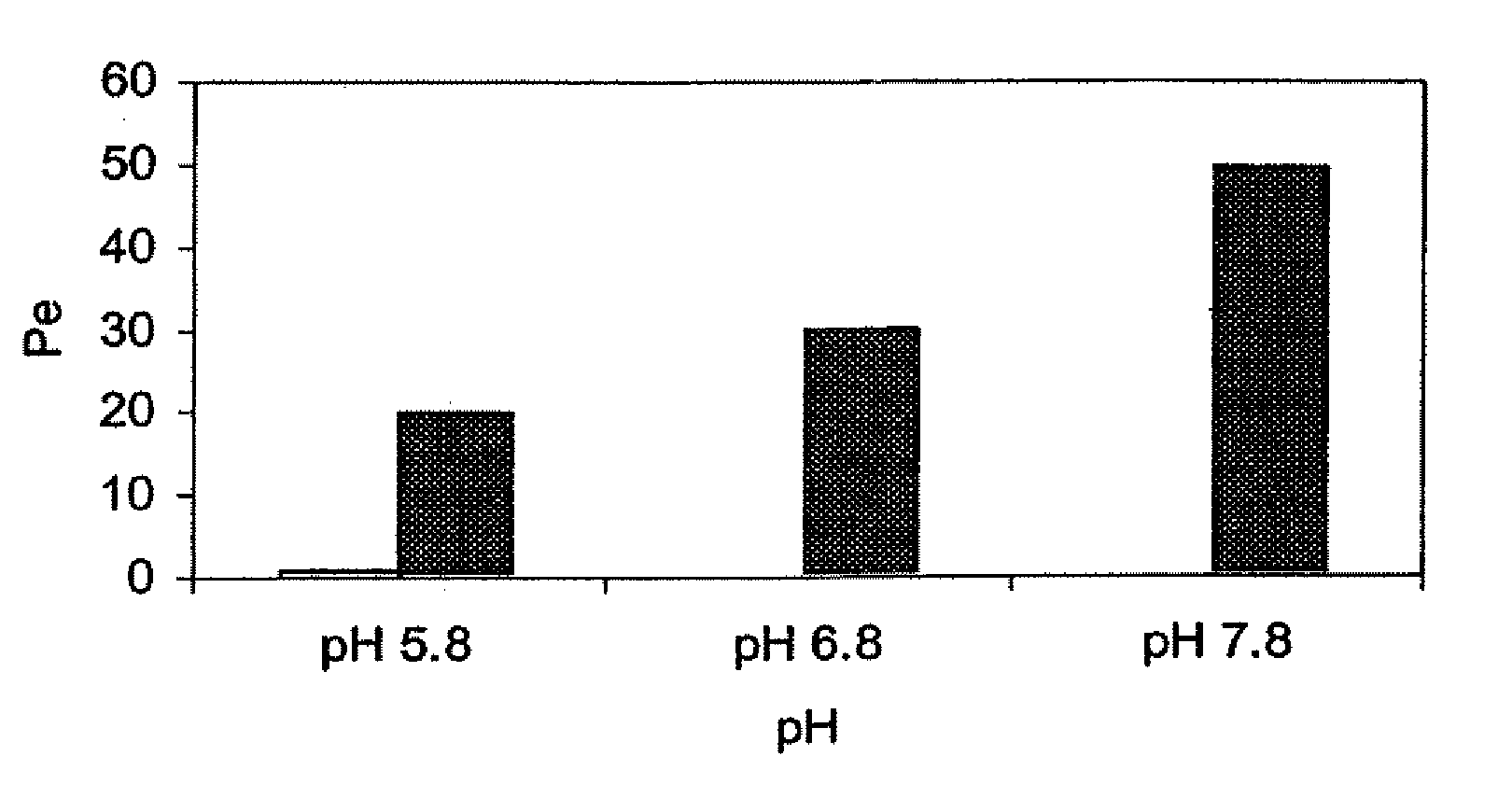
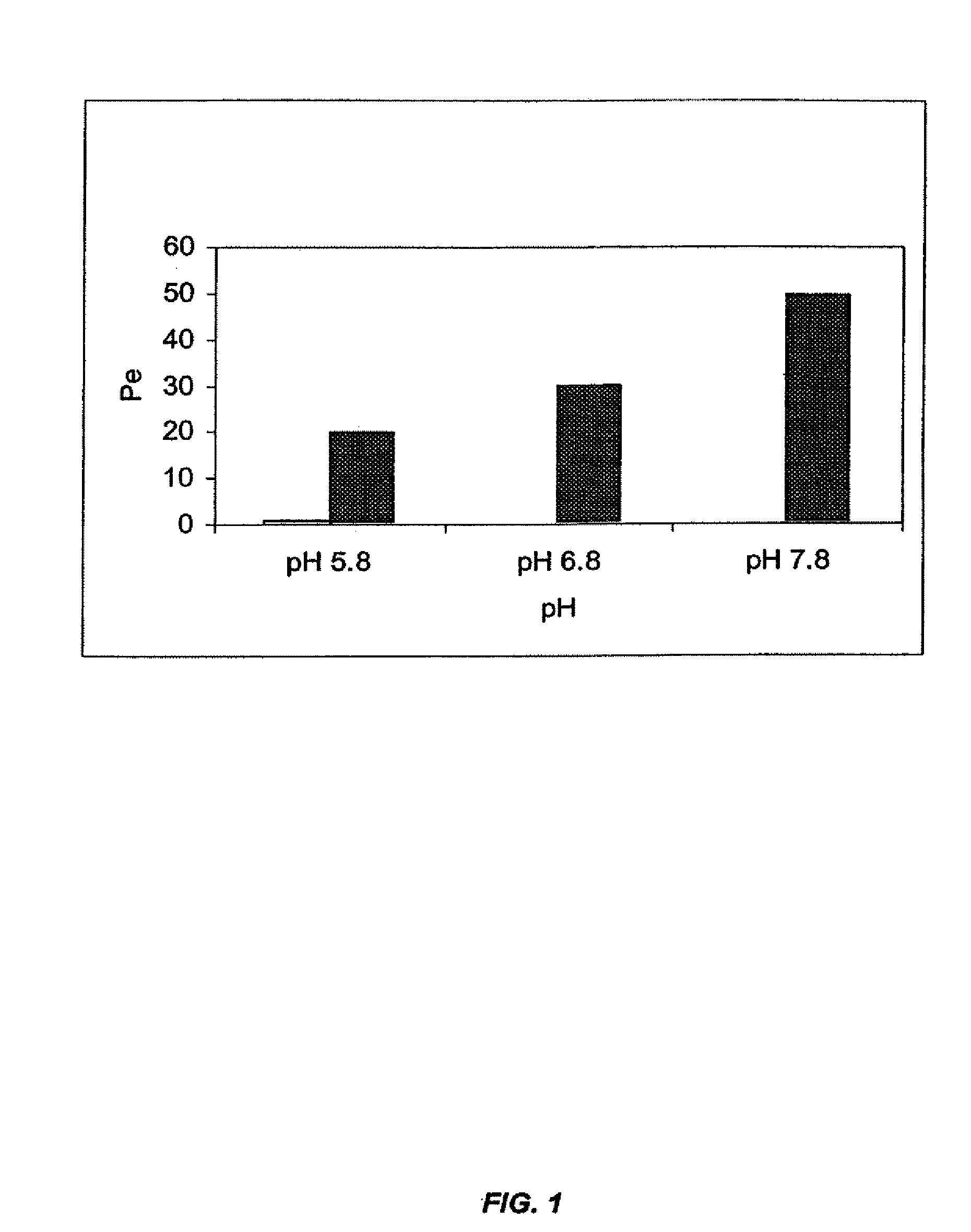
The present invention provides novel compositions for the delivery of a hypnotic agent across the oral mucosa. In particular, the buffer system in the compositions of the present invention raises the pH of saliva to a pH greater than about 7.8, thereby facilitating the substantially complete conversion of the hypnotic agent from its ionized to its un-ionized form. As a result, the dose of hypnotic agent is rapidly and efficiently absorbed by the oral mucosa with surprisingly low inter-subject variability. Furthermore, delivery of the hypnotic agent across the oral mucosa advantageously bypasses hepatic first pass metabolism of the drug and avoids enzymatic degradation of the drug within the gastrointestinal tract. Methods for using the compositions of the present invention for treating sleep disorders such as insomnia are also provided.
Owner:PARATEK PHARM INC
B1-bradykinin receptor antagonists and use thereof
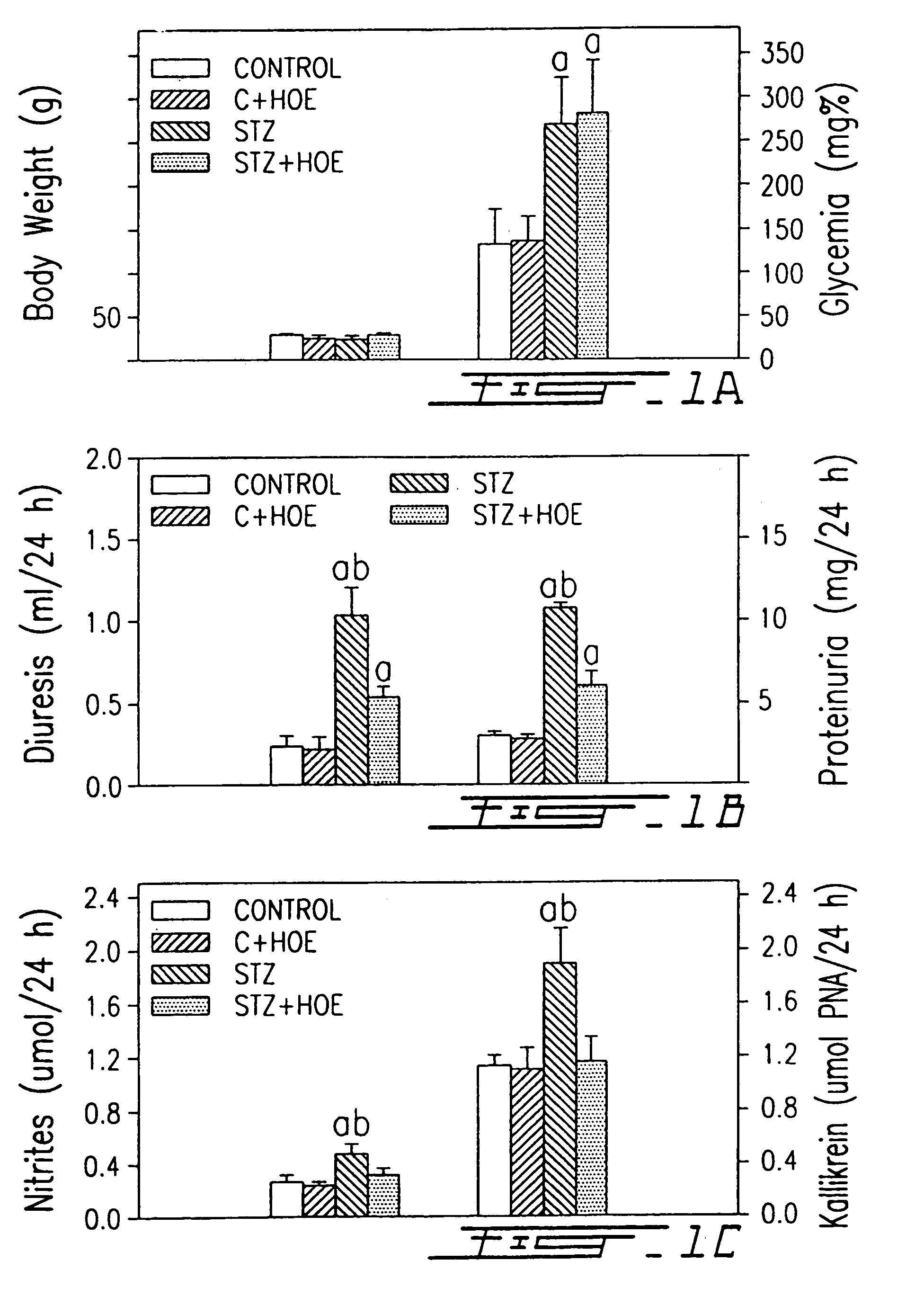
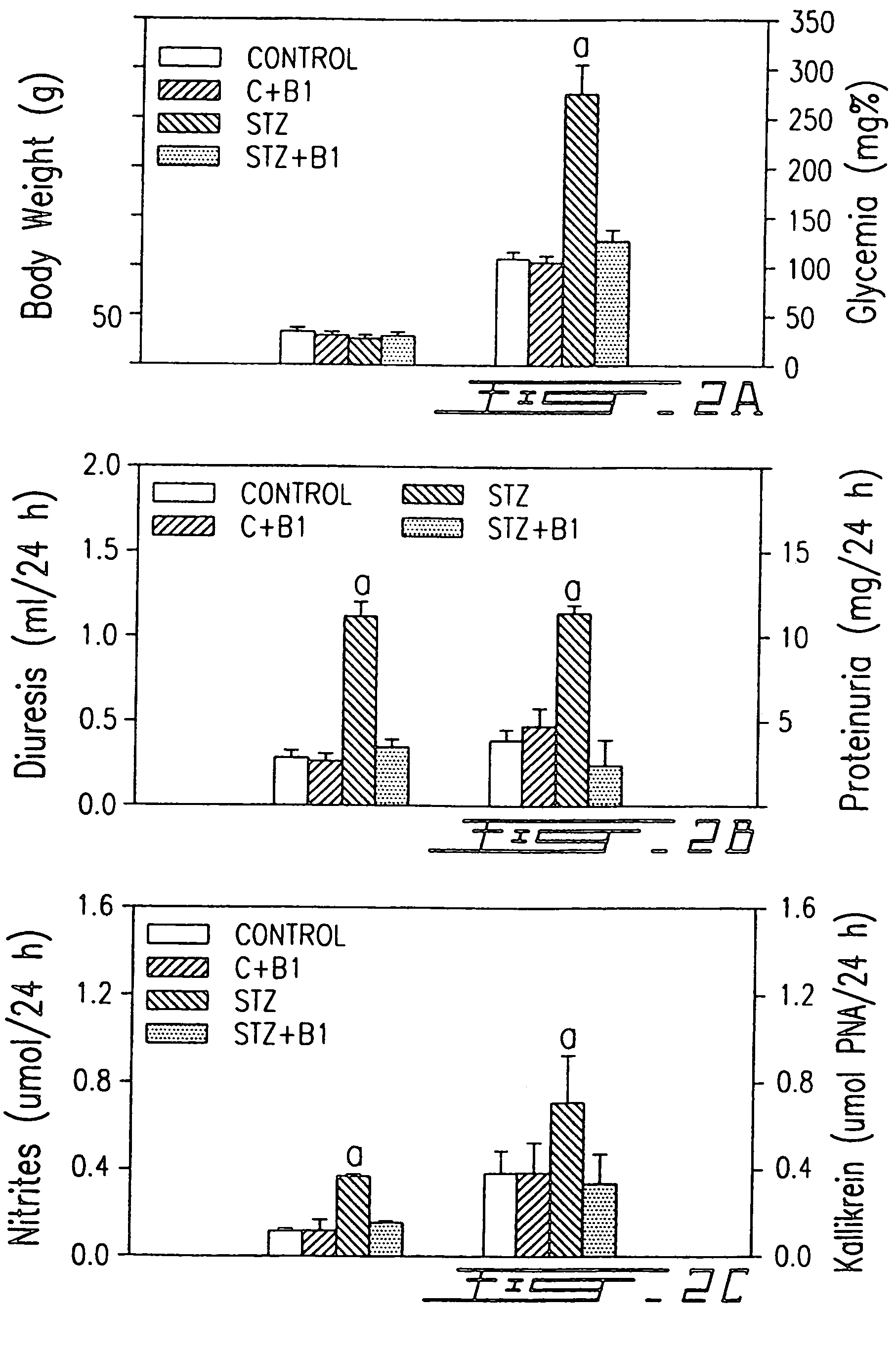
InactiveUS7041785B1Increased diuresisSignificant in renal functionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCapillary ResistanceSpontaneously hypertensive rat
The present invention relates to novel antagonists to a B1-bradykinin (B1-BK) receptor which have a good affinity and selectivity therefor, some of which being at least partially resistant to enzymatic degradation. The synthesis of the B1 receptors is induced during inflammation. Symptoms associated with inflammation (elevated hydrostatic pressure and plasma leakage or extravasation) have been observed in diabetic animal models (streptozotocin-induced diabetes (STZ)) as well as in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). The present inventors confirm the presence of B1-BK receptors in these two models. B1-BK antagonists abolished the vasocontraction induced by B1-BK in SHR and STZ, and reduced the glycemia of diabetic animals to normal levels. The present B1-antagonists are useful for treating any condition wherein B1-receptor is expressed, particularly during inflammation, and more particularly wherein B1-receptor expression results in diabetic vasculopathy, other diabetic symptoms associated with an insulitis and a post-capillary resistance building as a consequence of the presence of a B1-receptor.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
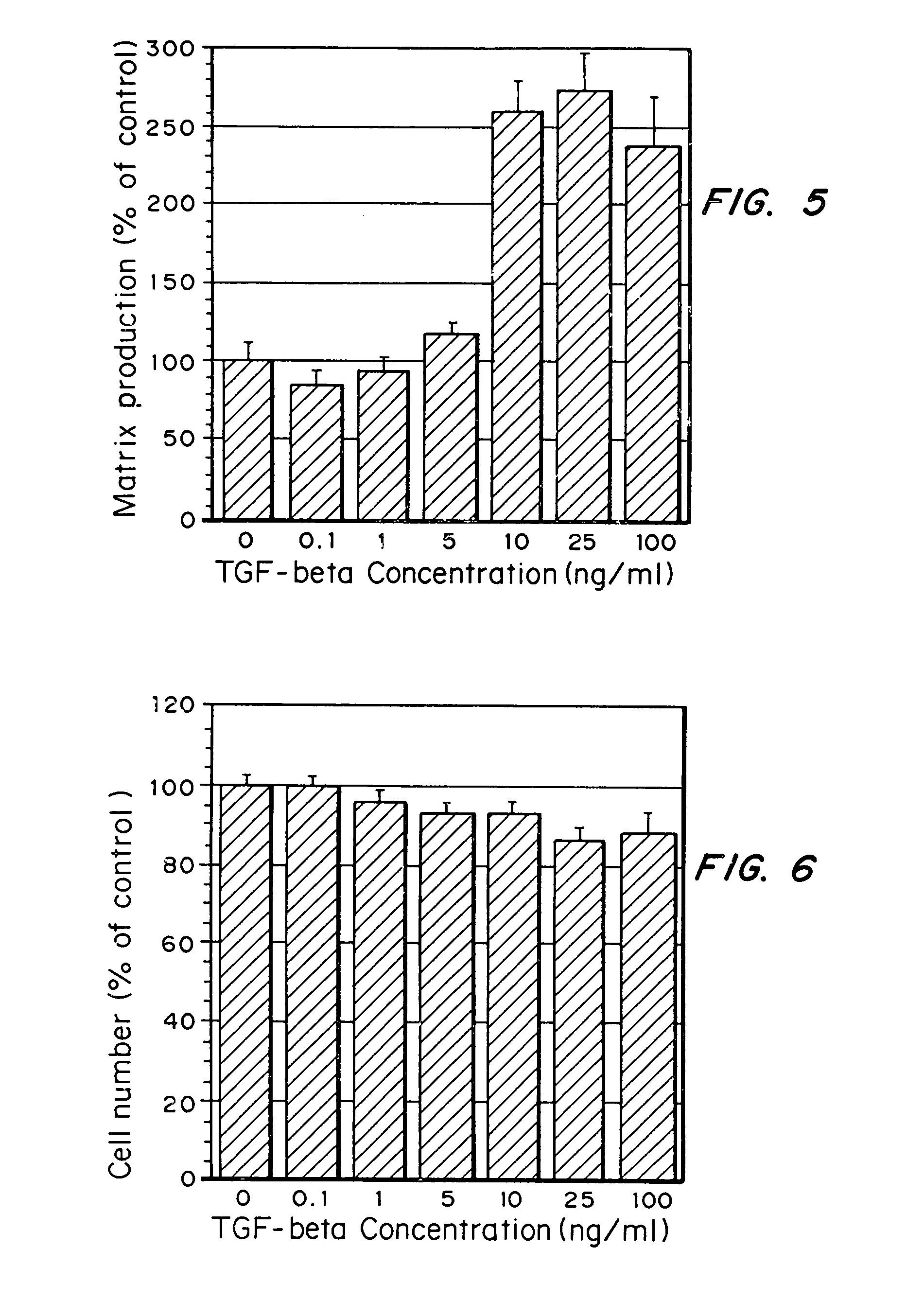
Tissue engineering scaffolds promoting matrix protein production
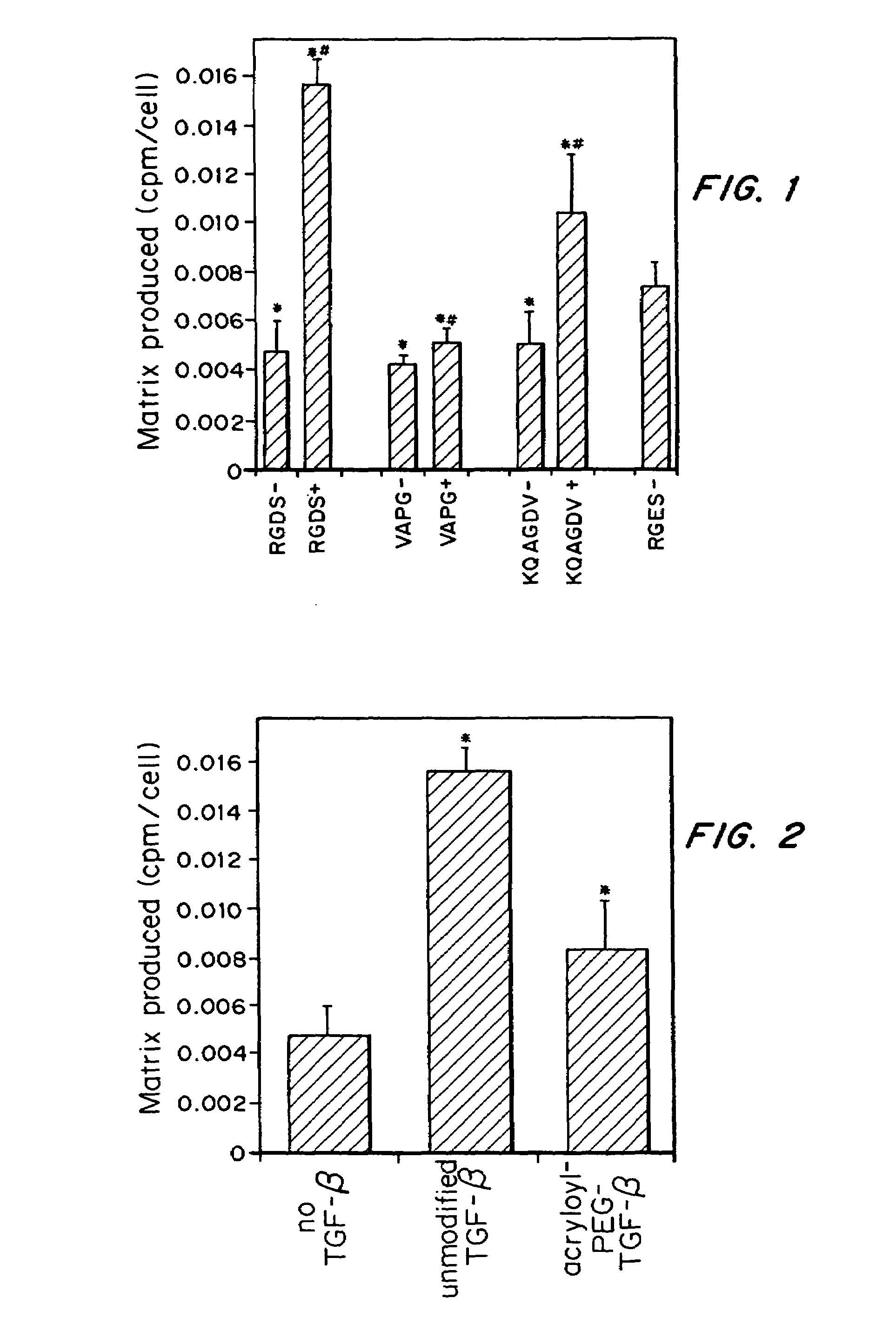
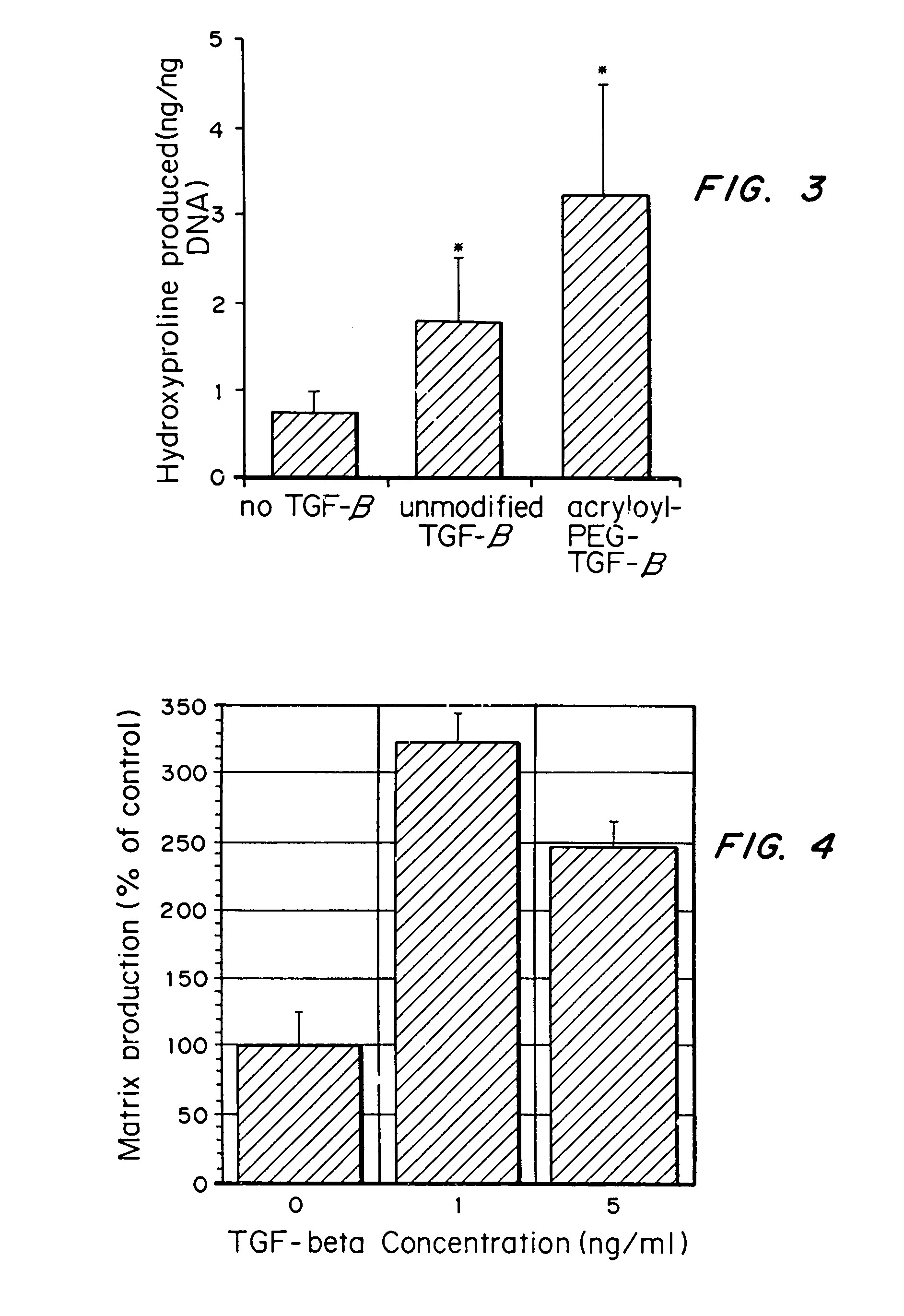
InactiveUS7635592B2Increase ECM productionIncrease gene expressionSkeletal disorderVertebrate cellsCell adhesionCell-Extracellular Matrix
Matrix-enhancing molecules, such as TGF-β, are conjugated to or immobilized on scaffolds to increase ECM production by cells for tissue engineering, tissue regeneration and wound healing applications. The matrix-enhancing molecule is conjugated to a tether, such as polyethylene glycol (PEG) monoacrylate, for attachment to a tissue engineering or cell growth scaffold. The matrix-enhancing molecule retains activity after attachment to the scaffold, and causes cells growing in or on the scaffold to increase extracellular matrix (ECM) production, without substantially increasing proliferation of the cells, even when the scaffold additionally contains cell adhesion ligands. The increased ECM produced by the cells aids in maintaining the integrity of the scaffold, particularly when the scaffold is degradable, either by hydrolysis or by enzymatic degradation.
Owner:RICE UNIV
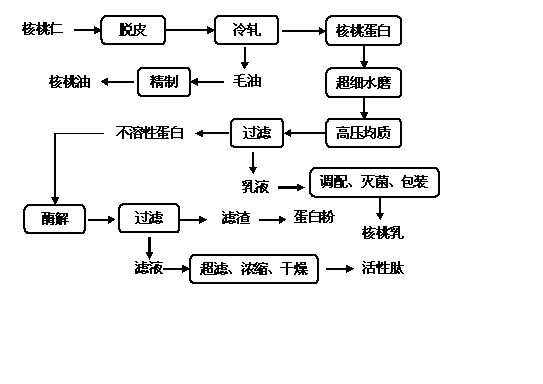
Deep processing method for preparing low-fat walnut milk, active peptide and protein powder by comprehensively utilizing walnut kernels
The invention aims at the high-value processing of walnut protein. A deep processing method comprises the following steps: firstly, separating out walnut oil by a low-temperature cold-rolling method to obtain walnut kernel protein; secondly, dissolving the soluble protein to prepare walnut milk drink through micro-grinding and homogenizing processes; thirdly, performing enzymatic hydrolysis on the insoluble walnut protein to obtain the active peptide through enzymatic degradation; and finally, developing the rest of protein residues into walnut powder so as to realize full-value utilization of the walnut protein.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
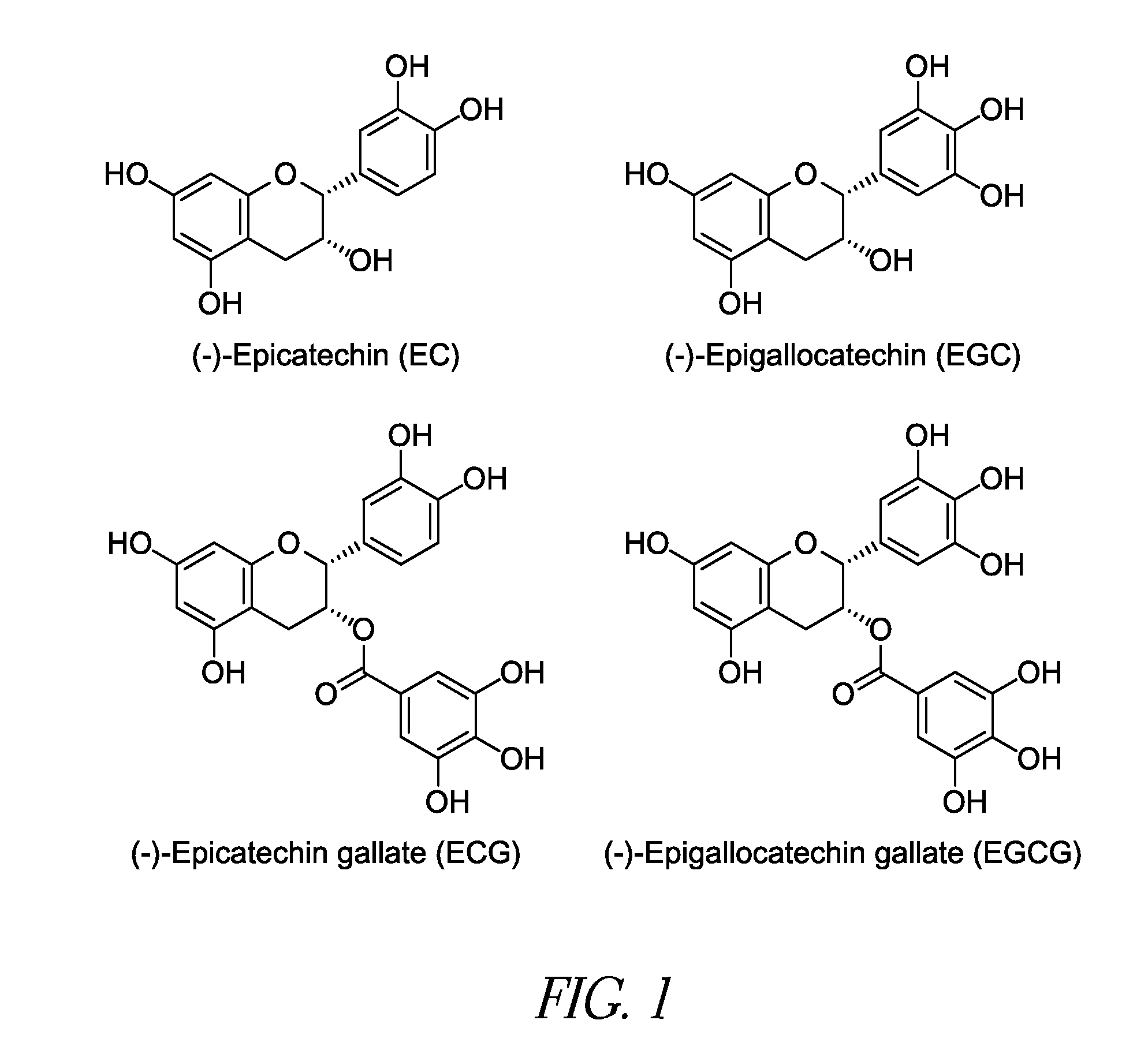
Reduction of Astringency in Polyphenol Compositions
InactiveUS20080213441A1Reduce astringency and bitterness levelWithout flavorMilk preparationEdible oils/fats ingredientsAdditive ingredientEnzymatic degradation
Microencapsulated polyphenol compositions suitable for use in food and beverage products are provided. Microencapsulation significantly reduces the astringency and / or bitterness of the polyphenol compositions and protects the polyphenol compositions from oxidation, ingredient interactions, enzymatic degradation, and the like while maintaining gastrointestinal bioavailability within the digestive system.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS
Process for treating biomass to increase accessibility of polysaccarides contained therein to hydrolysis and subsequent fermentation, and polysaccharides with increased accessibility
InactiveUS20110129880A1Improve accessibilityAdditional componentSugar derivativesBiofuelsCelluloseDepolymerization
In this invention, a process for producing fermentable sugars derivable from biomass that contains polysaccharide, such as cellulose, which has been made increasingly accessible as a substrate for enzymatic degradation or other methods of depolymerization. The process of the present invention increases accessibility of polysaccharides, typically present in biomass and produces polysaccharides with increased accessibility. The polysaccharides with increased accessibility may be subsequently saccharified to yield fermentable sugars. These fermentable sugars are subsequently able to be fermented to produce various target chemicals, such as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones or acids.
Owner:ROBERT OFLYNN OBRIEN
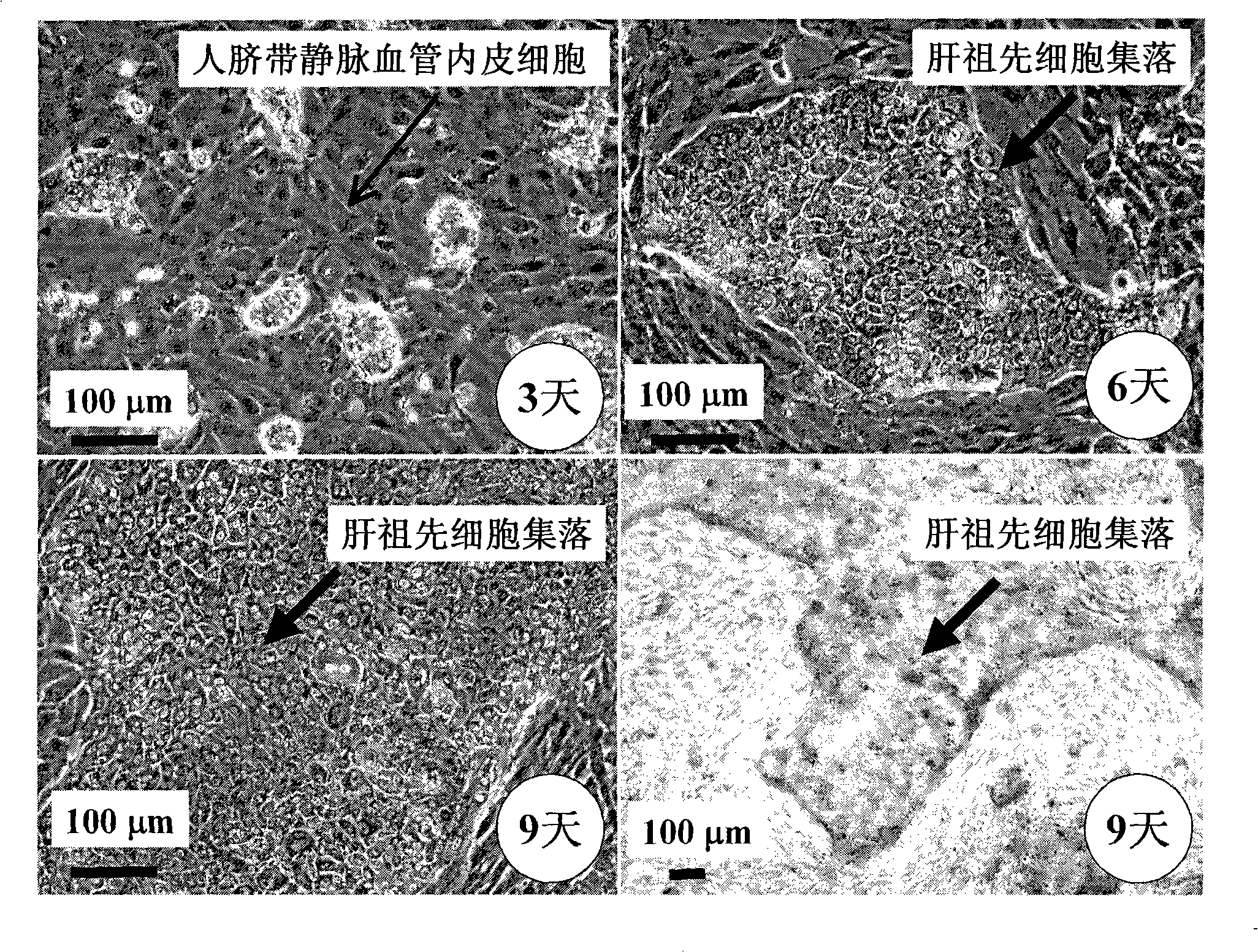
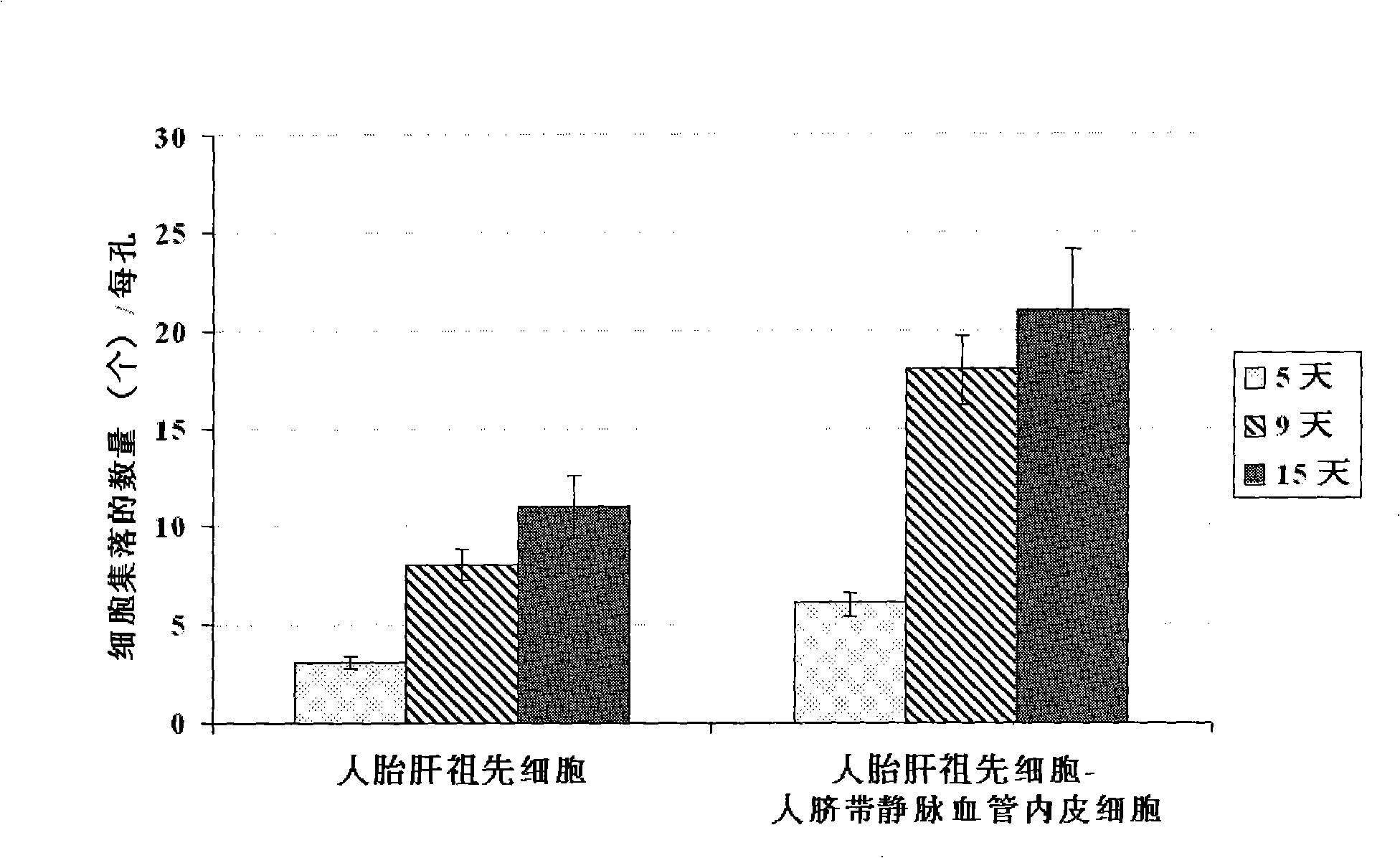
In vitro culture-amplified human liver progenitor cell and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101275121AAccelerate self-renewalConvenient sourceArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
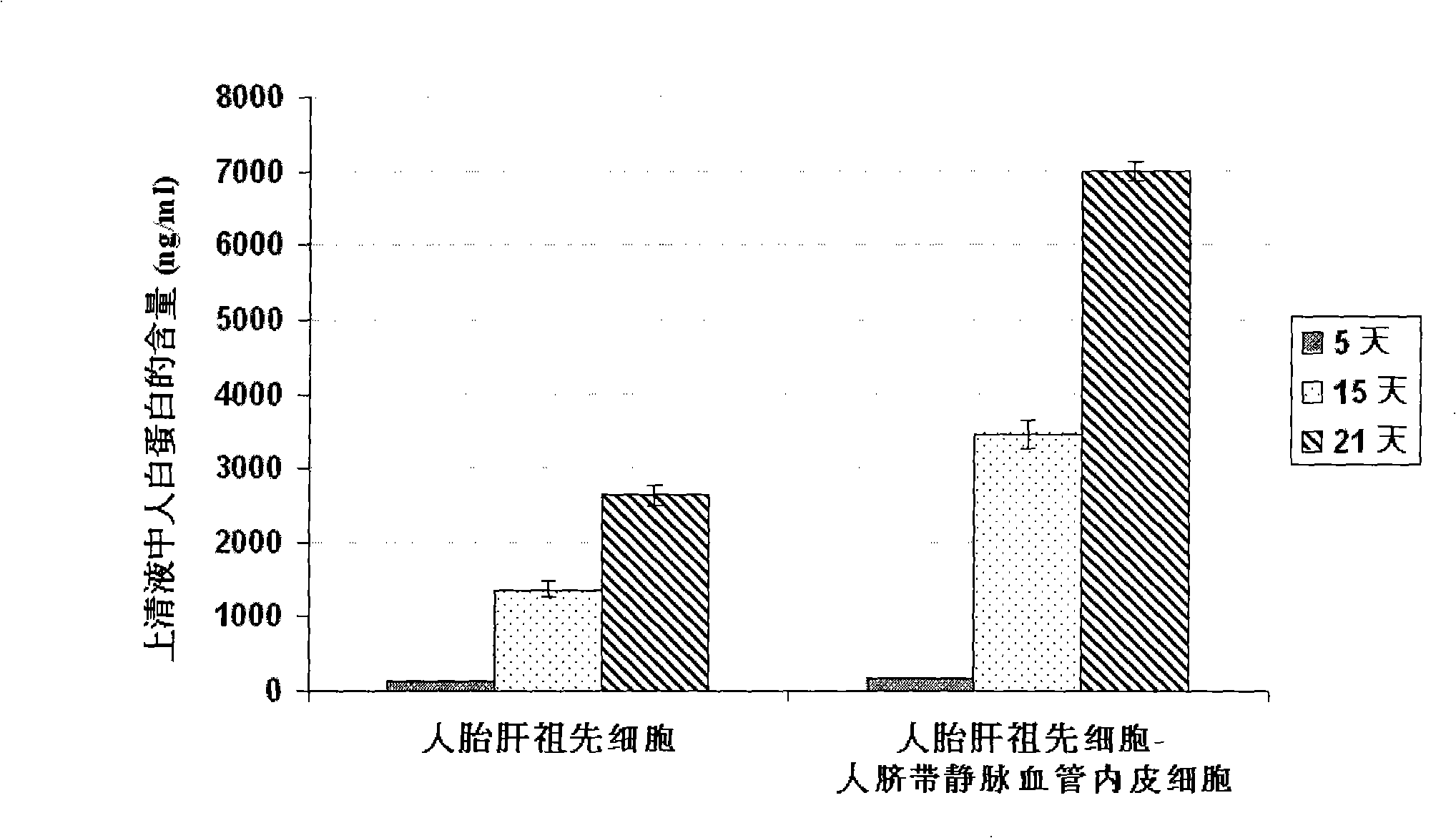
The present invention provides a preparing method of a human hepatic progenitor cell which is amplified and cultivated in vitro, including: a. separating the human hepatic progenitor cell; b. co-cultivating a feeder cell and the human hepatic progenitor cell separated from the step a by a medium having no serum on an extracellular matrix containing human fibrin sealant or other analogues, obtaining a human hepatic progenitor cell colony by amplification. The human hepatic progenitor cell colony is easy to separate from the surface of human fibrin sealant by the simple gelatinolytic band process, purified or / and subcultured by further single cell preparation technology process such as enzymatic degradation etc. The human hepatic progenitor cell prepared by the method is hepatic progenitor cell treatment, including a cell transplantation and a bioartificial liver support system, providing excellent human hepatocyte source for cytotoxicity test platform in the drug screening, virus infection and drug screening platform etc.
Owner:芦银雪
Scaffold for skin tissue engineering and a method of synthesizing thereof
ActiveUS20180117215A1Improve mechanical propertiesFacilitates penetration and imbibitionConnective tissue peptidesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSwelling ratioGlycerol
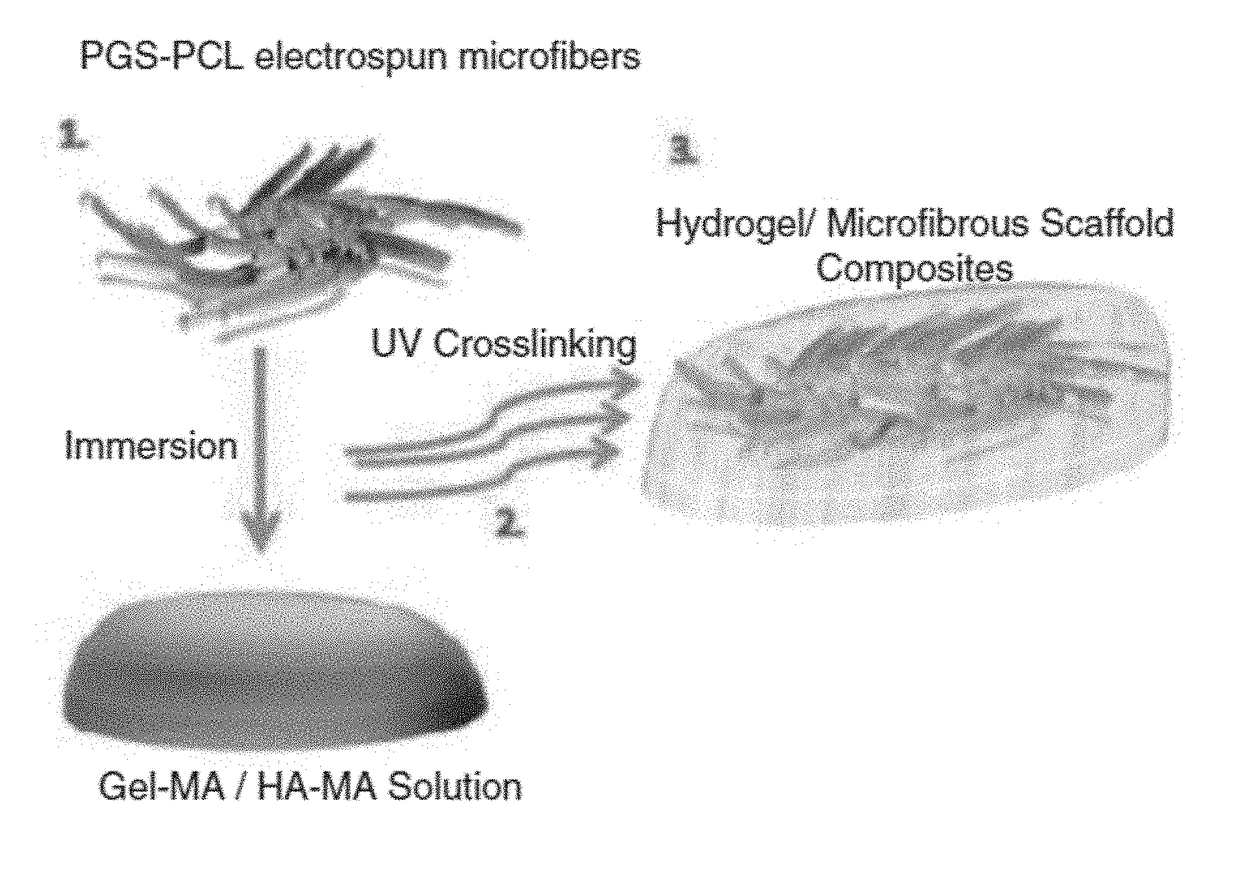
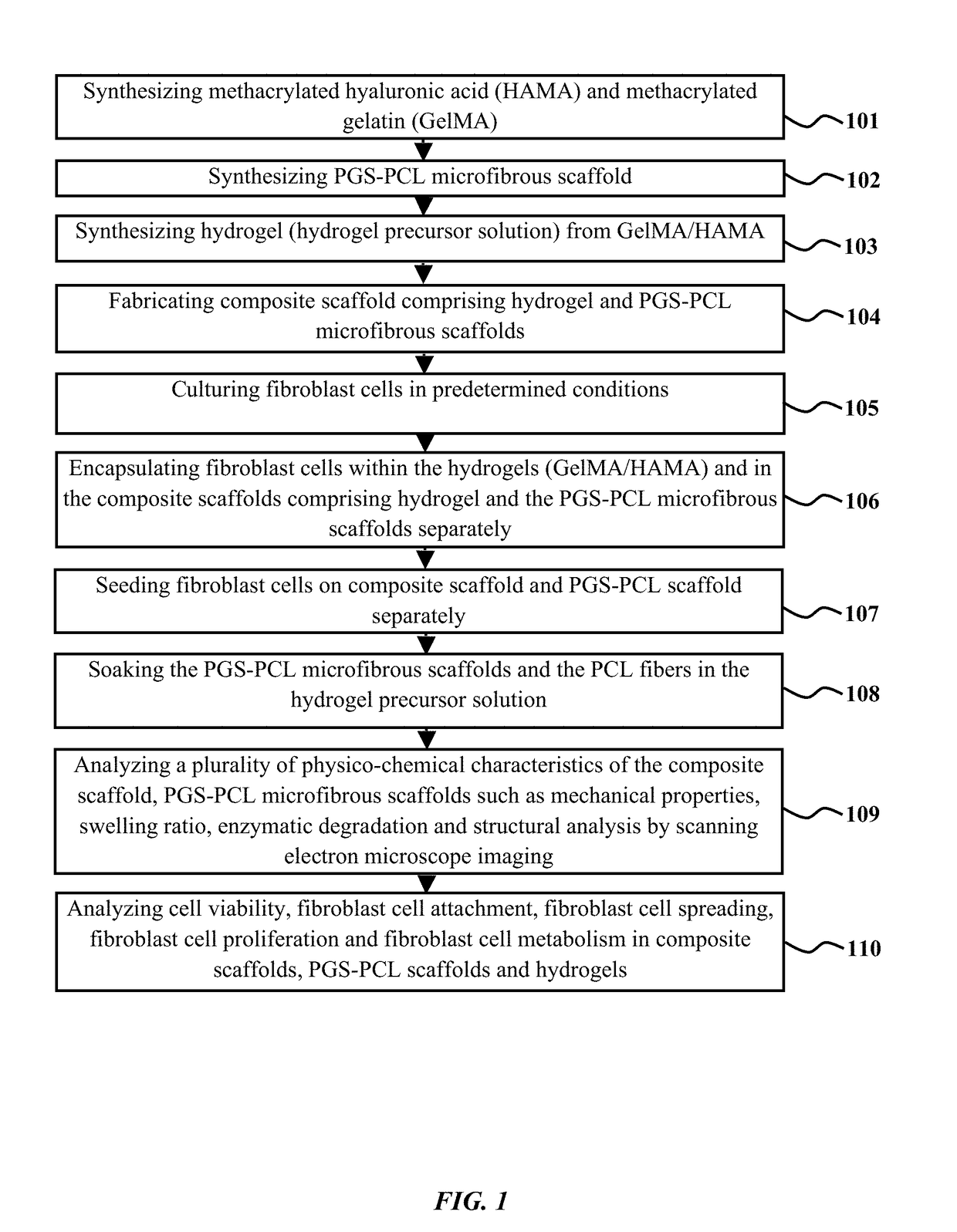
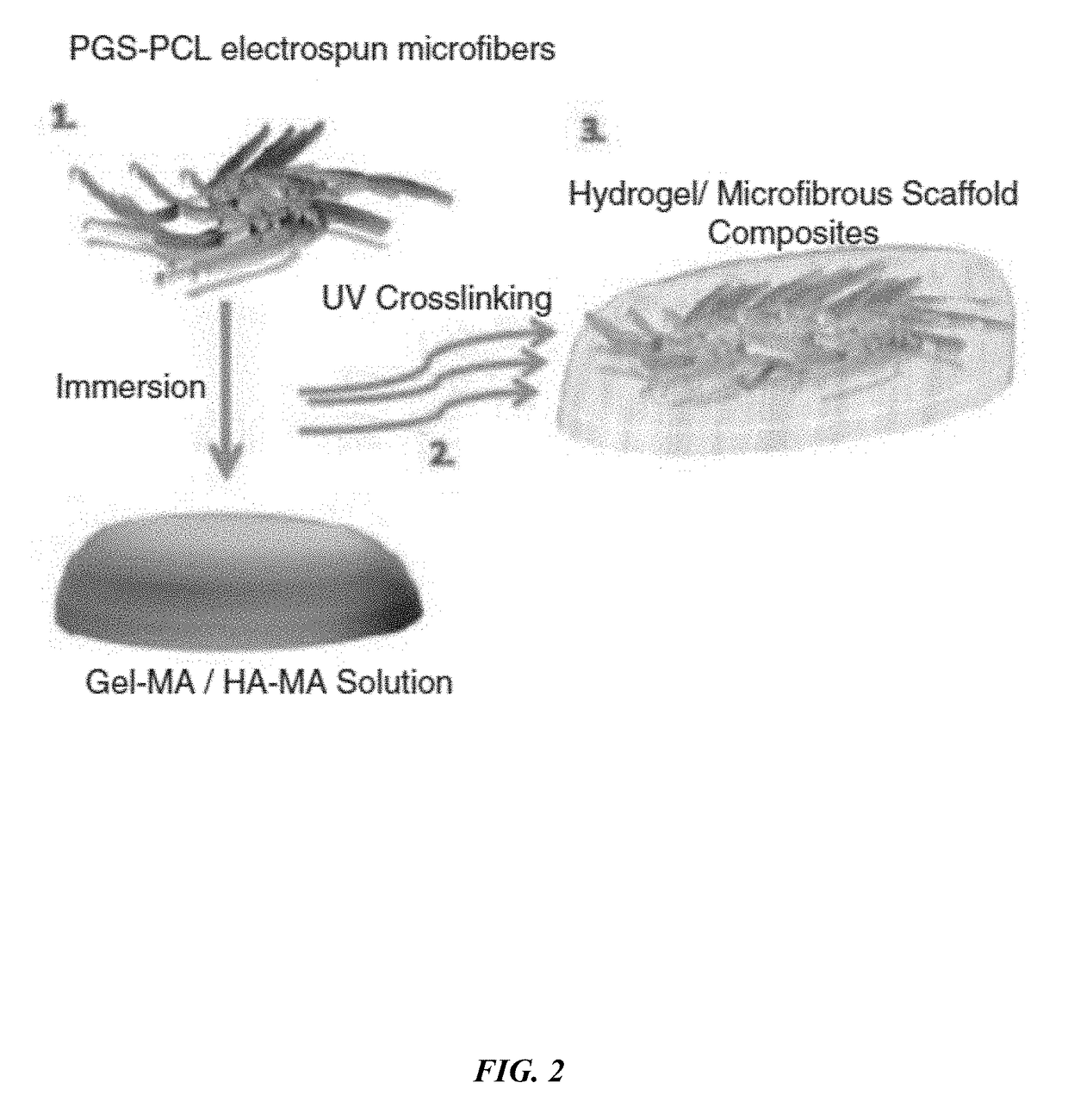
The embodiments herein disclose a method of fabricating composite scaffolds for skin tissue regeneration. The methacrylated hyaluronic acid (HAMA) and methacrylated gelatin (GelMA) are synthesized. The poly (glycerol sebacate)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PGS-PCL) microfibrous scaffolds are synthesized. The hydrogel is synthesized. The composite scaffold comprising hydrogel and poly (glycerol sebacate)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PGS-PCL) microfibrous scaffolds is fabricated. A plurality of physico-chemical characteristics of the composite scaffold comprising hydrogel and poly (glycerol sebacate)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PGS-PCL) microfibrous scaffolds are analysed. The physico-chemical characteristics comprises mechanical properties, swelling ratio and enzymatic degradation and scanning electron microscope imaging. The fibroblast cells are encapsulated within the composite scaffold comprising hydrogel and poly (glycerol sebacate)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PGS-PCL) microfibrous scaffolds and hydrogels. The fibroblast cells are seeded on composite scaffold and PGS-PCL scaffold. The fibroblast cell viability, fibroblast cell attachment, fibroblast cell spreading, fibroblast cell proliferation and fibroblast cell metabolism are analysed in composite scaffolds, PGS-PCL scaffolds and hydrogels.
Owner:ESLAMI MARYAM +2
Method for separating bagasse cellulose from lignin
InactiveCN102212976AEasy to separateImprove enzyme degradation efficiencyPaper material treatmentWater bathsWax
The invention relates to a method for separating bagasse cellulose from lignin, and the method comprises the following steps: fully drying bagasse, performing mechanical grinding, using soxhlet extraction to remove cane wax, further removing hemicellulose through a hot water bath, mixing the bagasse subjected to hemicellulose removal with an ionic liquid, performing ultrasonic treatment for 3-5 minutes to dissolve the lignin in the bagasse in the ionic liquid, adding alkali for dilution, and then separating out the bagasse cellulose subjected to lignin removal by virtue of filtering; regulating the pH value of the dissolved lignin 2-3 times for precipitation, and separating out the lignin by virtue of centrifugal separation; and recovering the ionic liquid through the methods of neutralization, organic solvent extraction and vacuum concentration. The enzymatic degradation capability of the obtained bagasse cellulose is greatly improved compared with that of the bagasse which is not separated.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
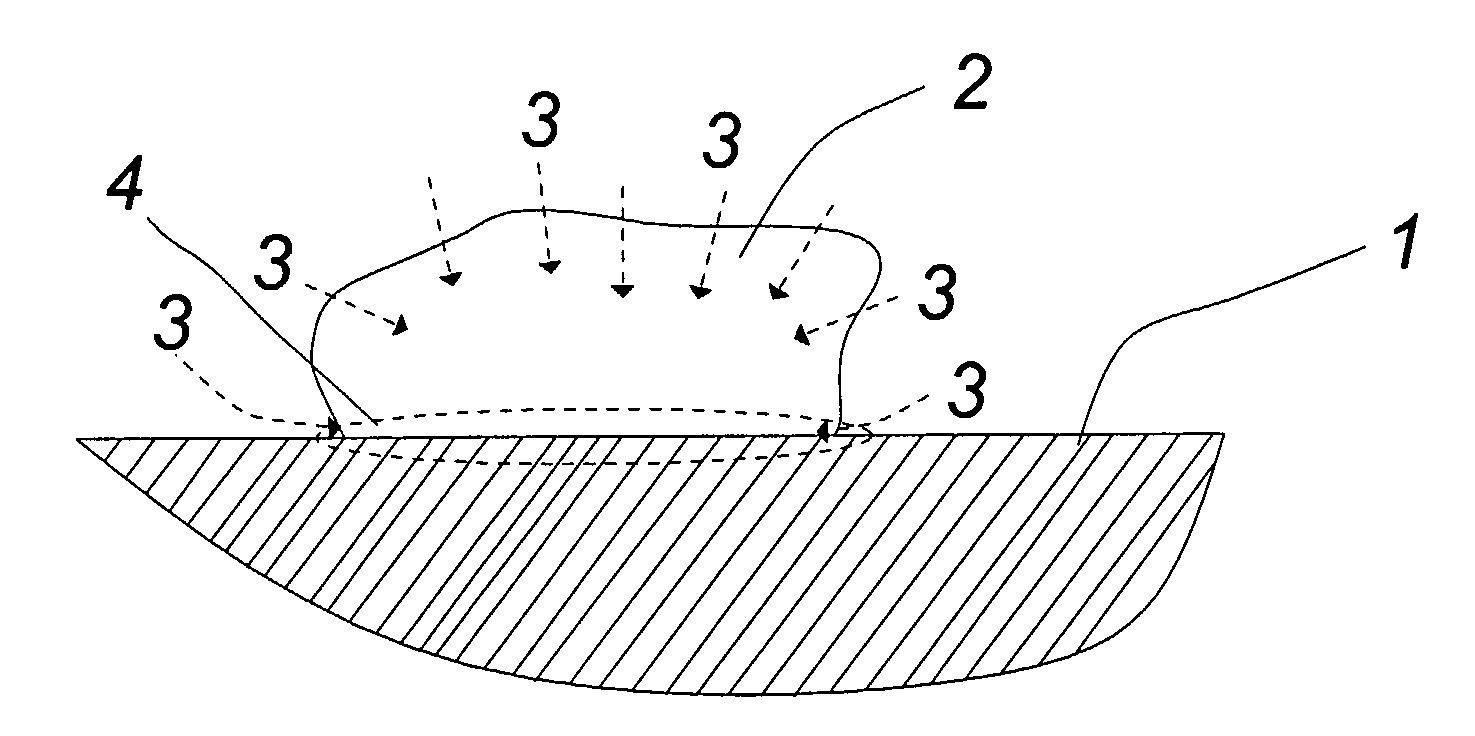
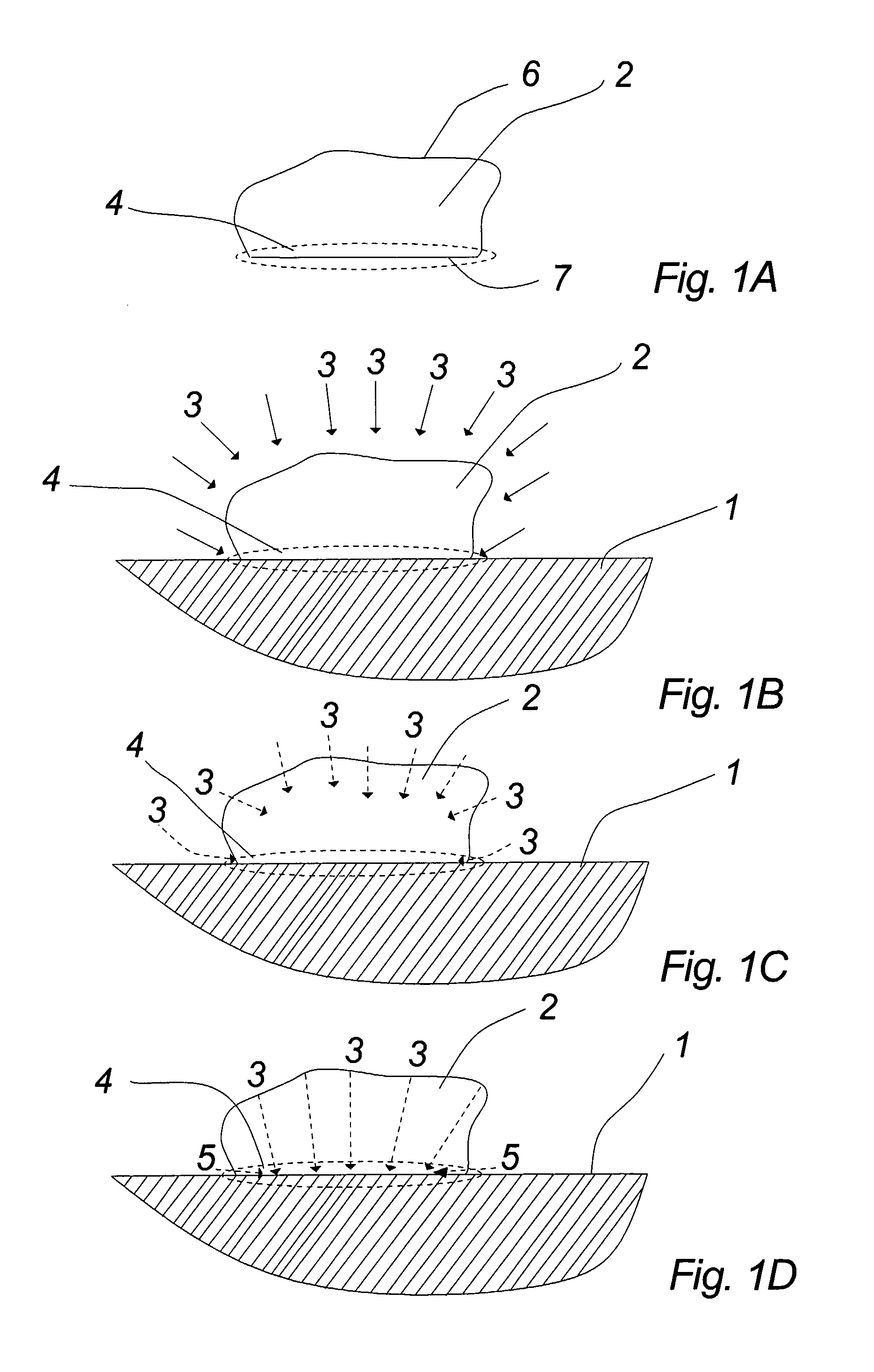
Method of cleaning a surface attached with at least one chewing gum lump
ActiveUS20090203564A1Lenient to surfacePromote degradationDetergent compounding agentsCleaning using liquidsPolymer scienceEnzymatic degradation
The invention relates to a method of cleaning a surface (1) attached with at least one chewing gum lump (2) whereby said cleaning is at least partly based on an enzymatic degradation of at least one biodegradable polymer in said chewing gum lump (2) and whereby said enzymatic degradation is initiated by the application of at least one enzyme to which said at least one polymer forms substrate and whereby said at least one enzyme is added to said chewing gum lump (2) subsequent to chewing and attachment of said chewing gum lump (2) to said surface (1).
Owner:FERTIN PHARMA AS
Chitosan composite preservative film and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses a chitosan composite preservative film and a preparation process thereof. Chitosan is used as the main component of the preservative film. The preservative film comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of the chitosan, 3,000-4,000 parts of 1% acetic acid solution, 1-5 parts of sodium trimetaphosphate, 30-50 parts of silica sol, 100-200 parts of glycerol, and 2-10 parts of oleic acid. By being improved through chemical and physical blending modification, the prepared preservative film has the advantages of being good in extensibility, flexibility, transparency, oxygen permeating coefficient and moisture permeability and the like; the preservative film disclosed by the invention has good biocompatibility with organisms; enzymatic degradation, oxidative degradation and acid degradation can be carried out under a certain condition; the final degradation products are oligomers, such as dimeric glucan, trimerical glucan and the like; the residual toxicily problem does not exist; and the preservative film has strong practicability in terms of fruit and vegetable freshness.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN FLASHLIGHT POLYTECHNIC
Method for decreasing cartilage damage in dogs
ActiveUS20050192352A1Improve mobilityRelieve painBiocideNervous disorderArthritisEnzymatic degradation
A method for modulating enzymatic degradation of articular cartilage in a dog comprises administering to the dog an enzymatic degradation modulating effective amount of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), for example as a component of a food composition. By practice of the method in a dog having arthritis, mobility of the dog can be increased, weight bearing in an arthritic limb can be increased, and / or pain associated with arthritis can be reduced.
Owner:HILLS PET NUTRITION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com