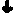Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
179 results about "Extravasation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Extravasation is the leakage of a fluid out of its container. In the case of inflammation, it refers to the movement of white blood cells from the capillaries to the tissues surrounding them (leukocyte extravasation), also known as diapedesis. In the case of malignant cancer metastasis it refers to cancer cells exiting the capillaries and entering organs. It is frequently used in medical contexts, either referring to urine, or to blood.
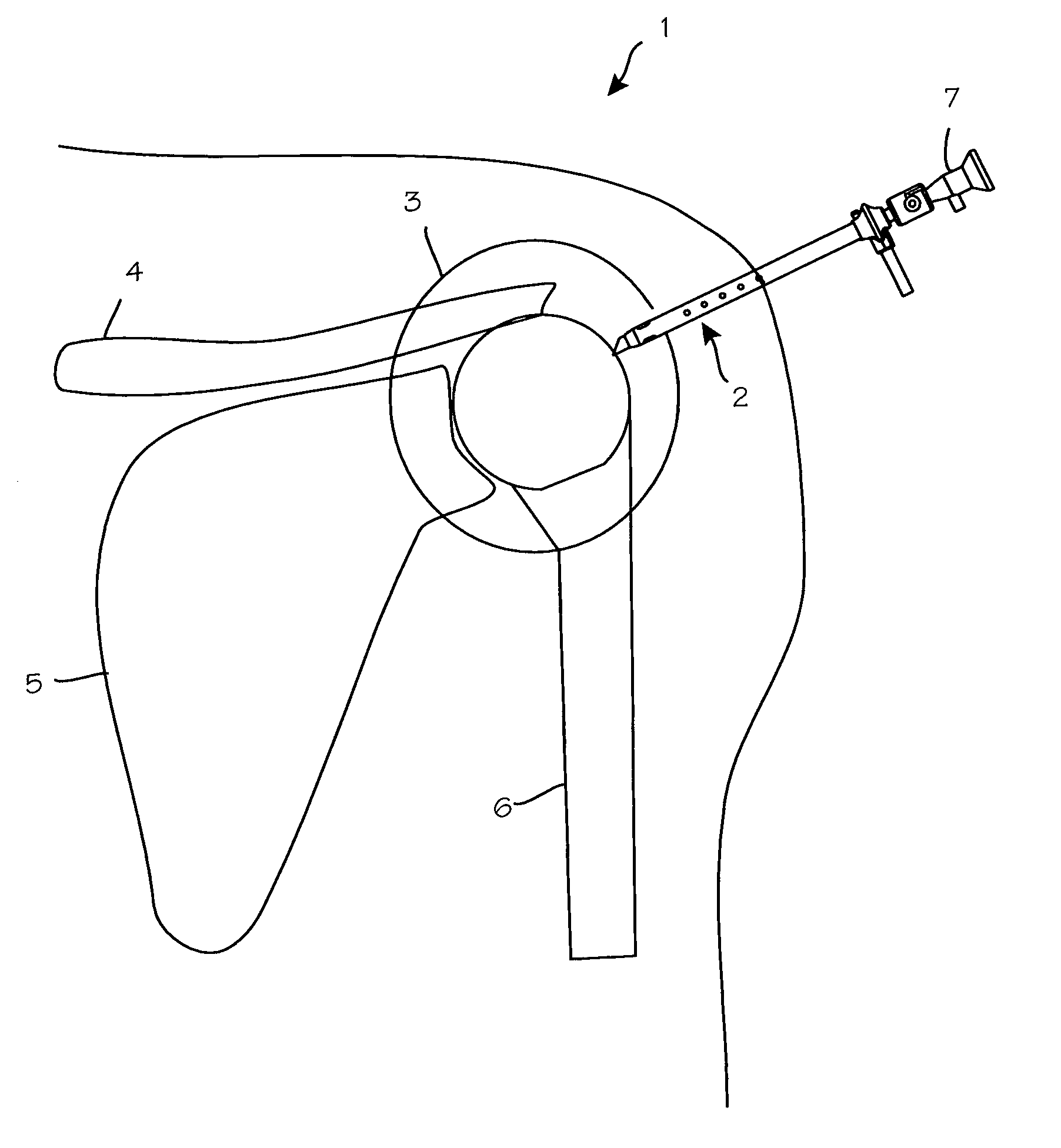
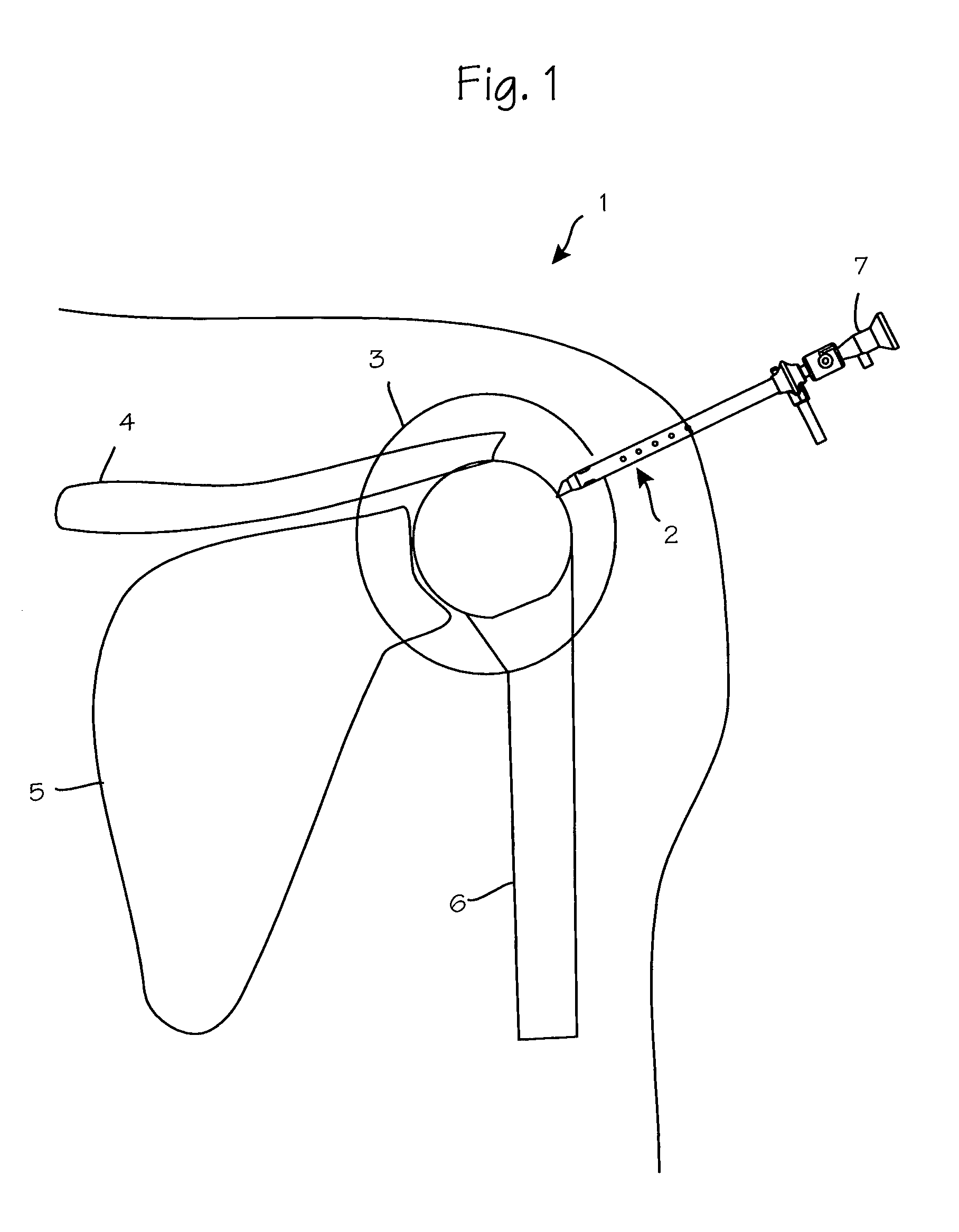
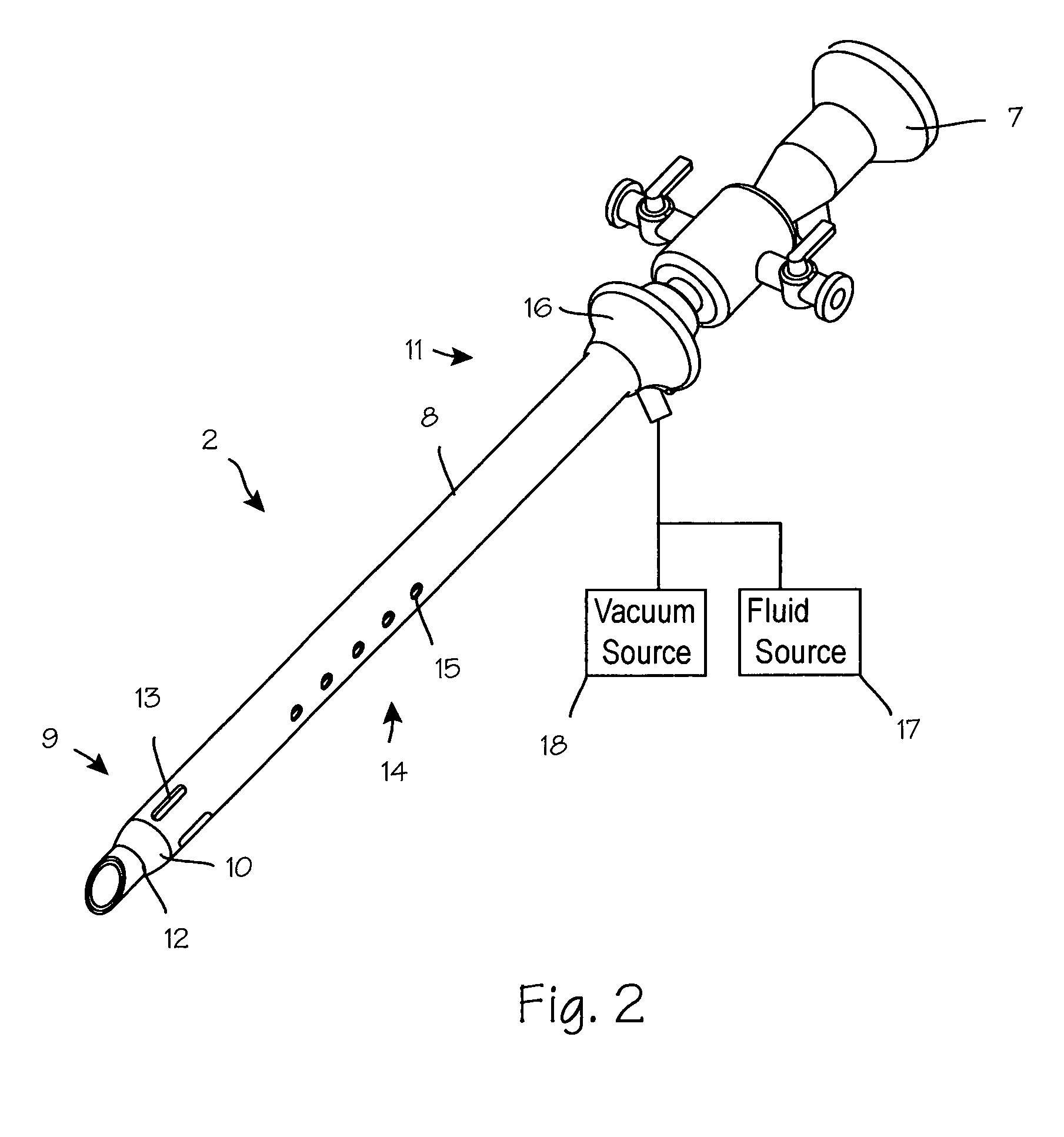
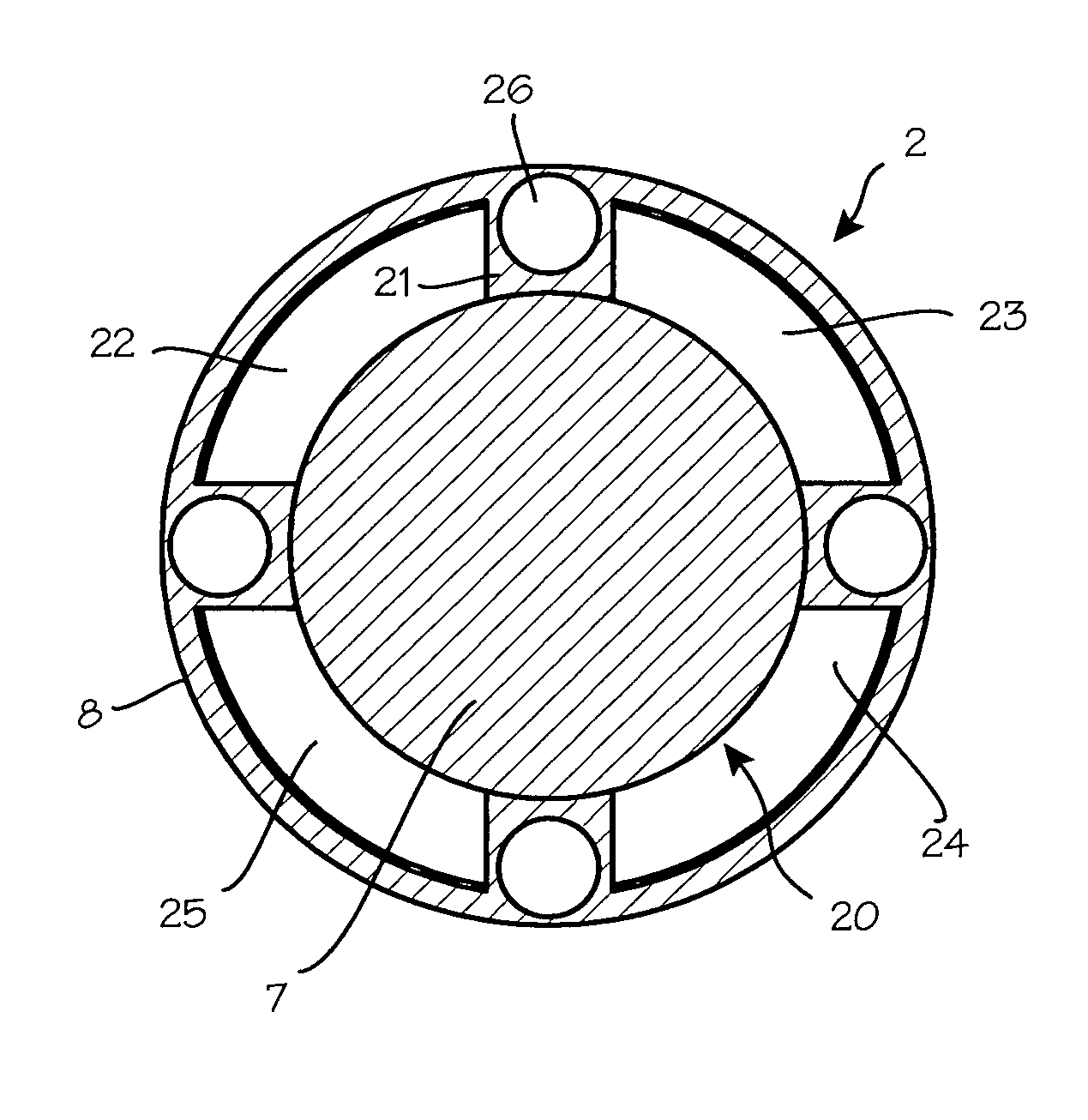
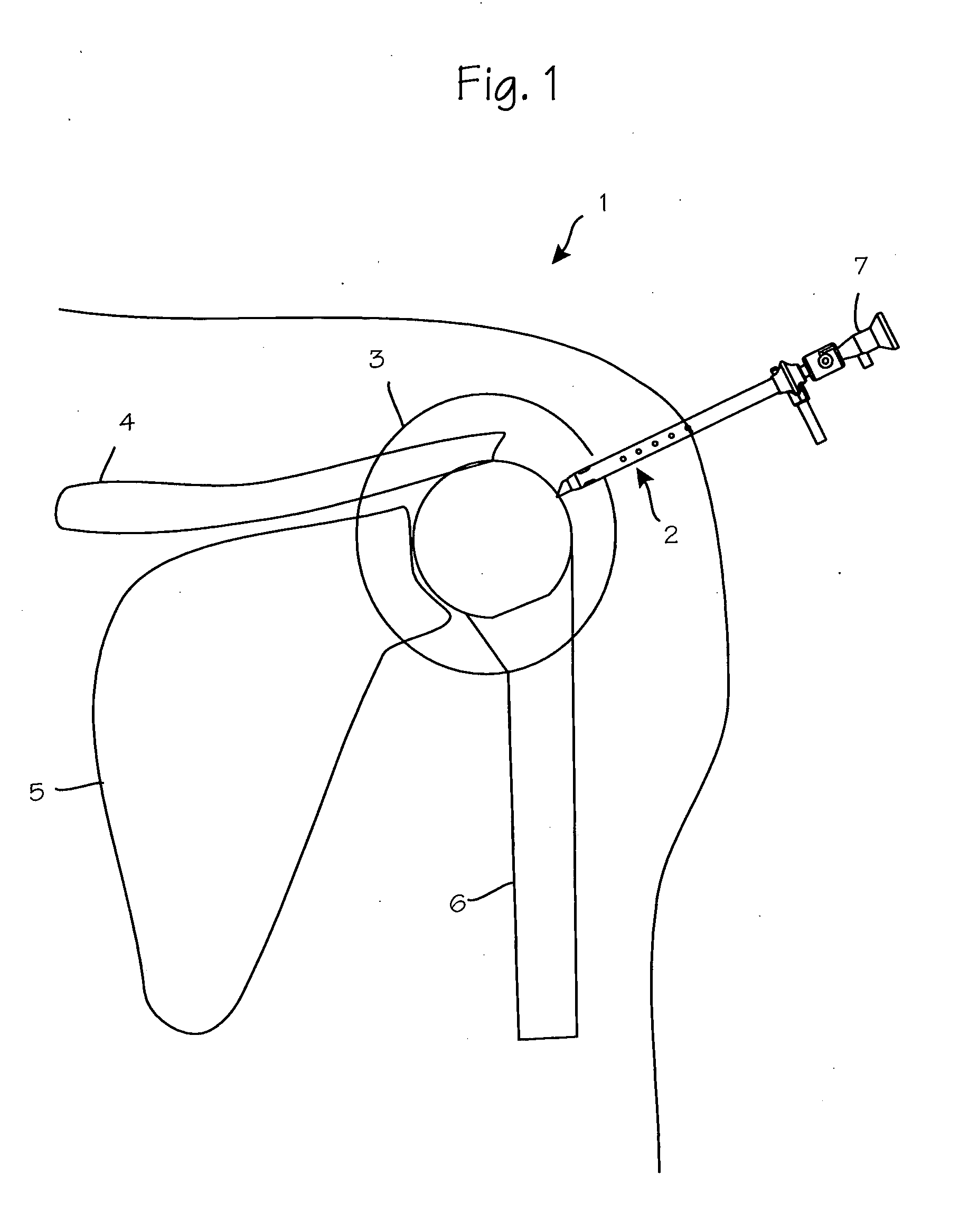
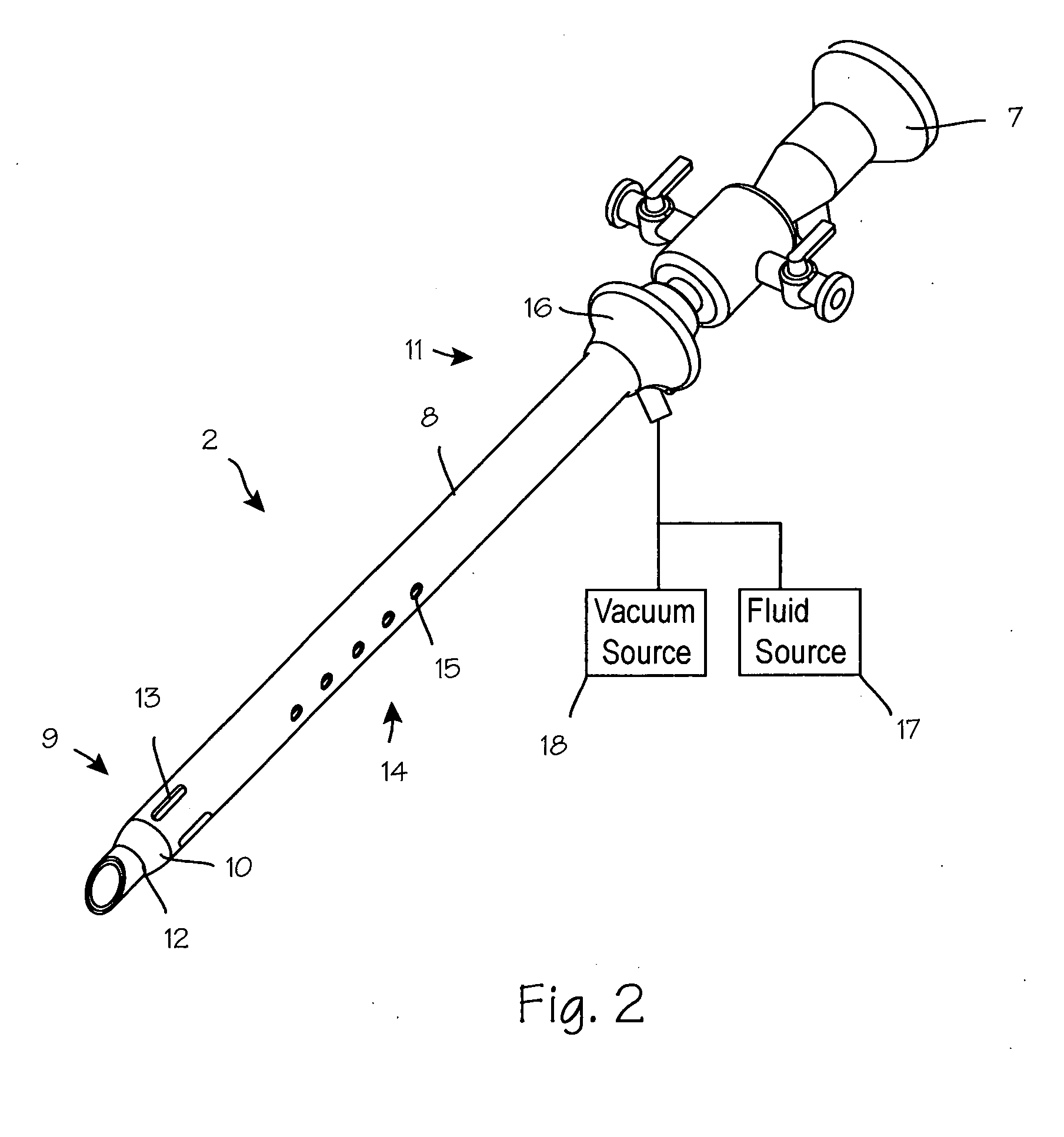
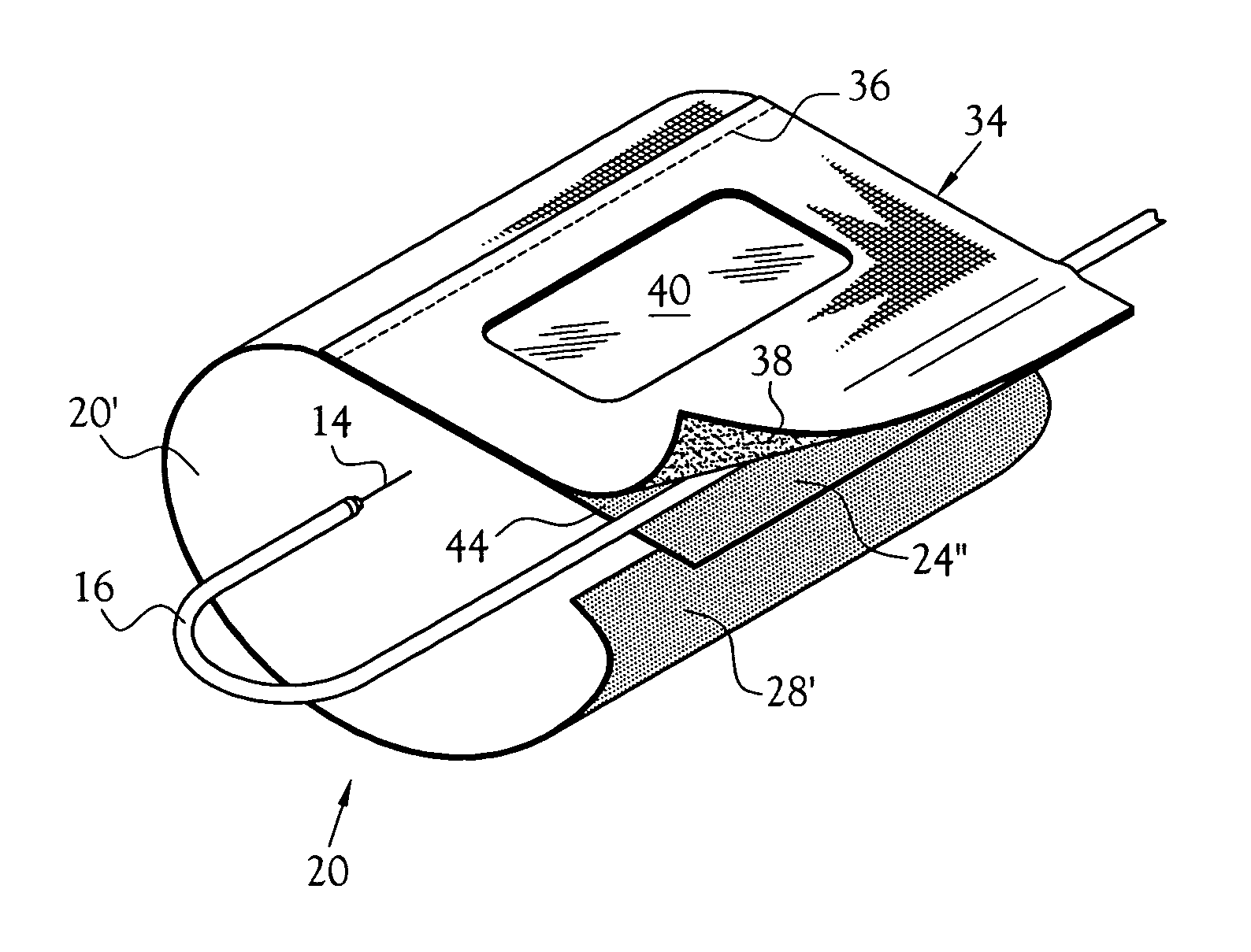
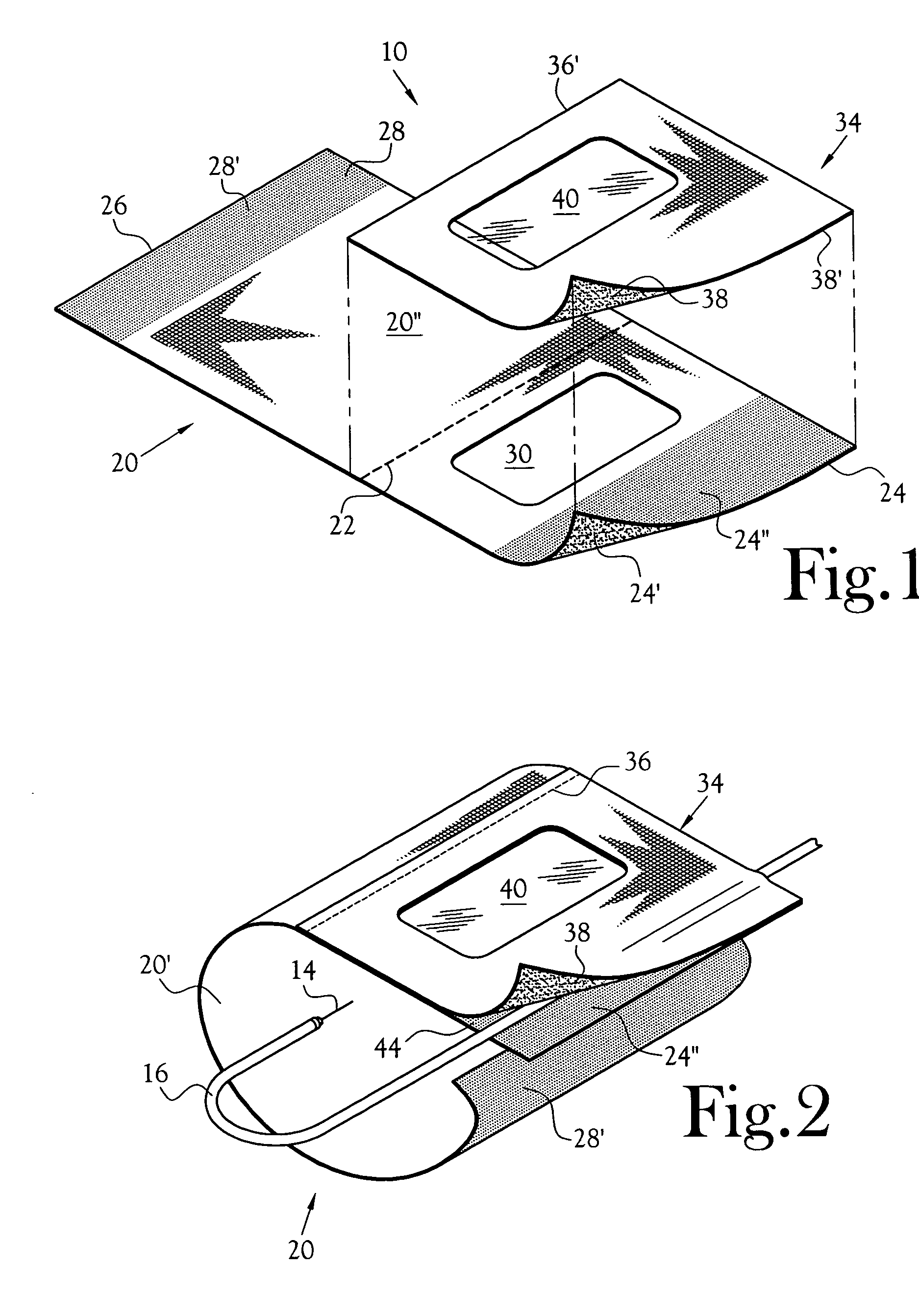
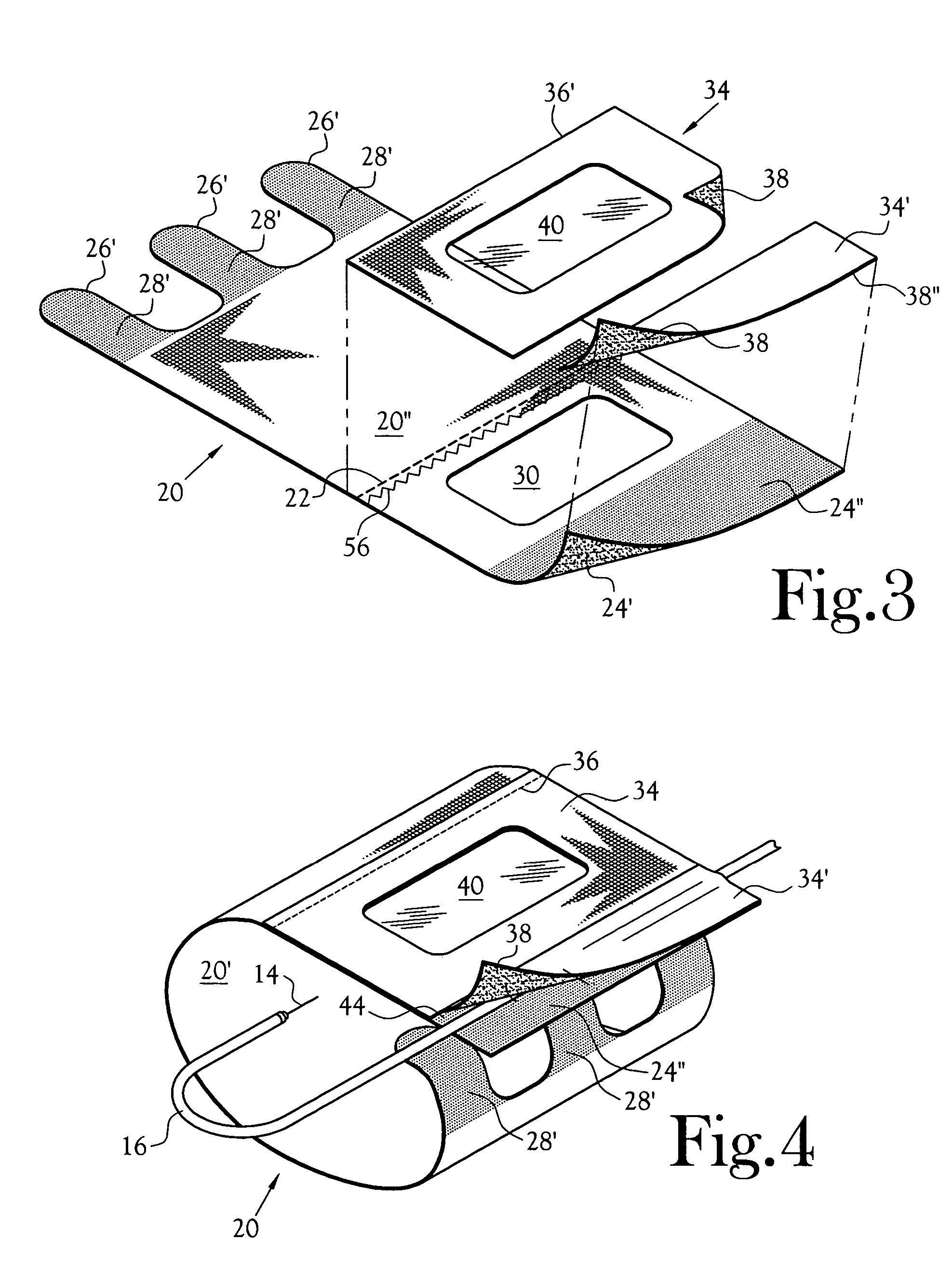
Anti-extravasation sheath and method
ActiveUS7503893B2Reduce extravasationClear surgical fieldCannulasSurgical needlesArthroscopic procedureArthroscopic Surgical Procedures
The methods shown provide for the minimization of extravasation during arthroscopic surgery. Use of an anti-extravasation sheath having at least one drainage aperture allows a surgeon to drain excess fluids from the tissue surrounding the surgical field during an arthroscopic surgical procedures when the drainage aperture is disposed within the tissue surrounding an arthroscopic surgical field outside of the joint capsule. The method of performing arthroscopic surgery may further include providing fluid inflow and outflow to the joint capsule through inflow / outflow holes in the anti-extravasation sheath.
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
Anti-extravasation sheath
ActiveUS20070185380A1ClearReduce extravasationCannulasSurgical needlesArthroscopic procedureArthroscopic Surgical Procedures
The devices and methods shown provide for the minimization of extravasation during arthroscopic surgery. The anti-extravasation sheath allows a surgeon to drain excess fluids from the soft tissue surrounding the surgical field during arthroscopic surgical procedures.
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
Vein imaging systems and methods
InactiveUS20140039309A1Easy to detectFacilitating of target areaDiagnostics using lightDrug and medicationsInfraredVein
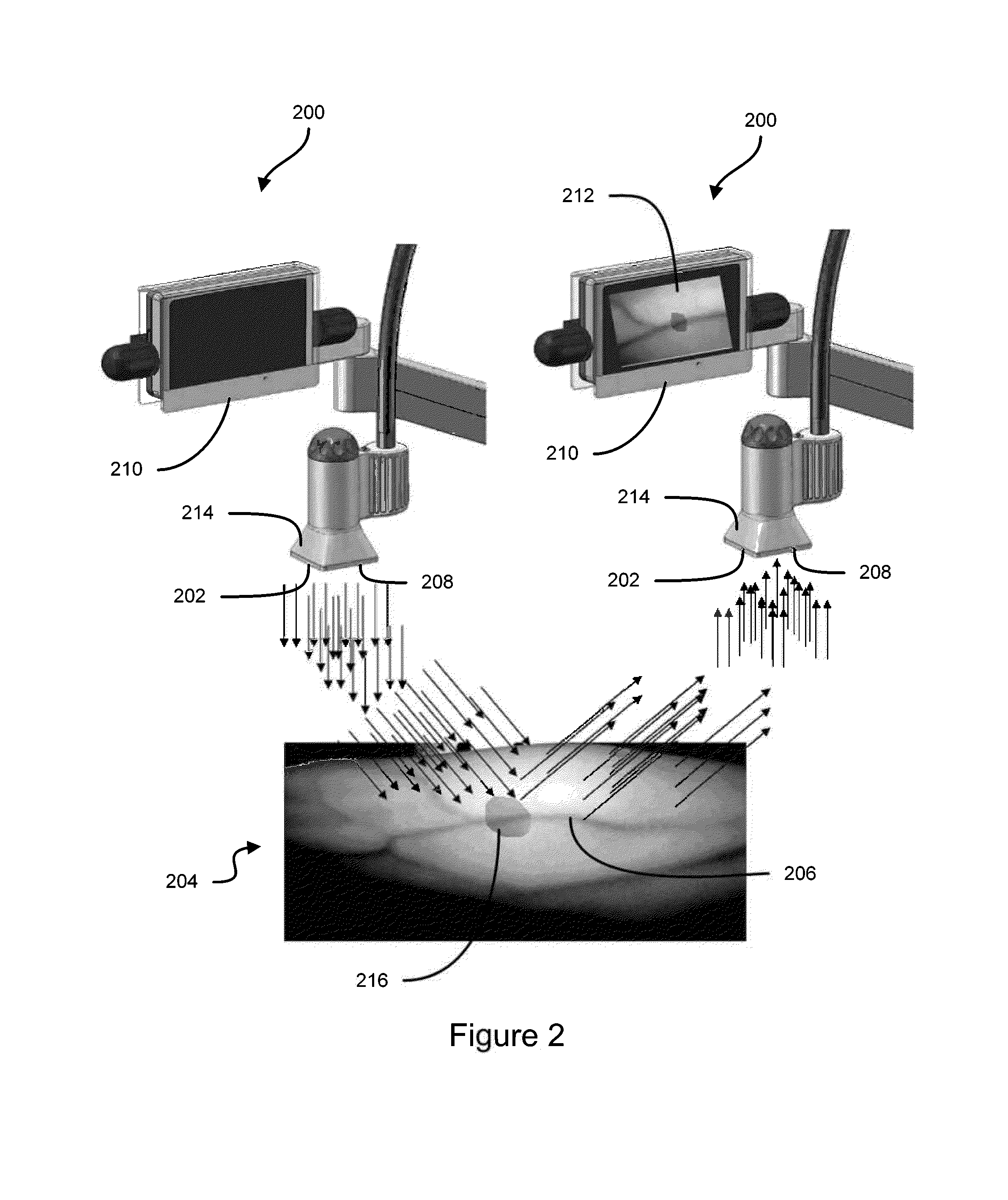
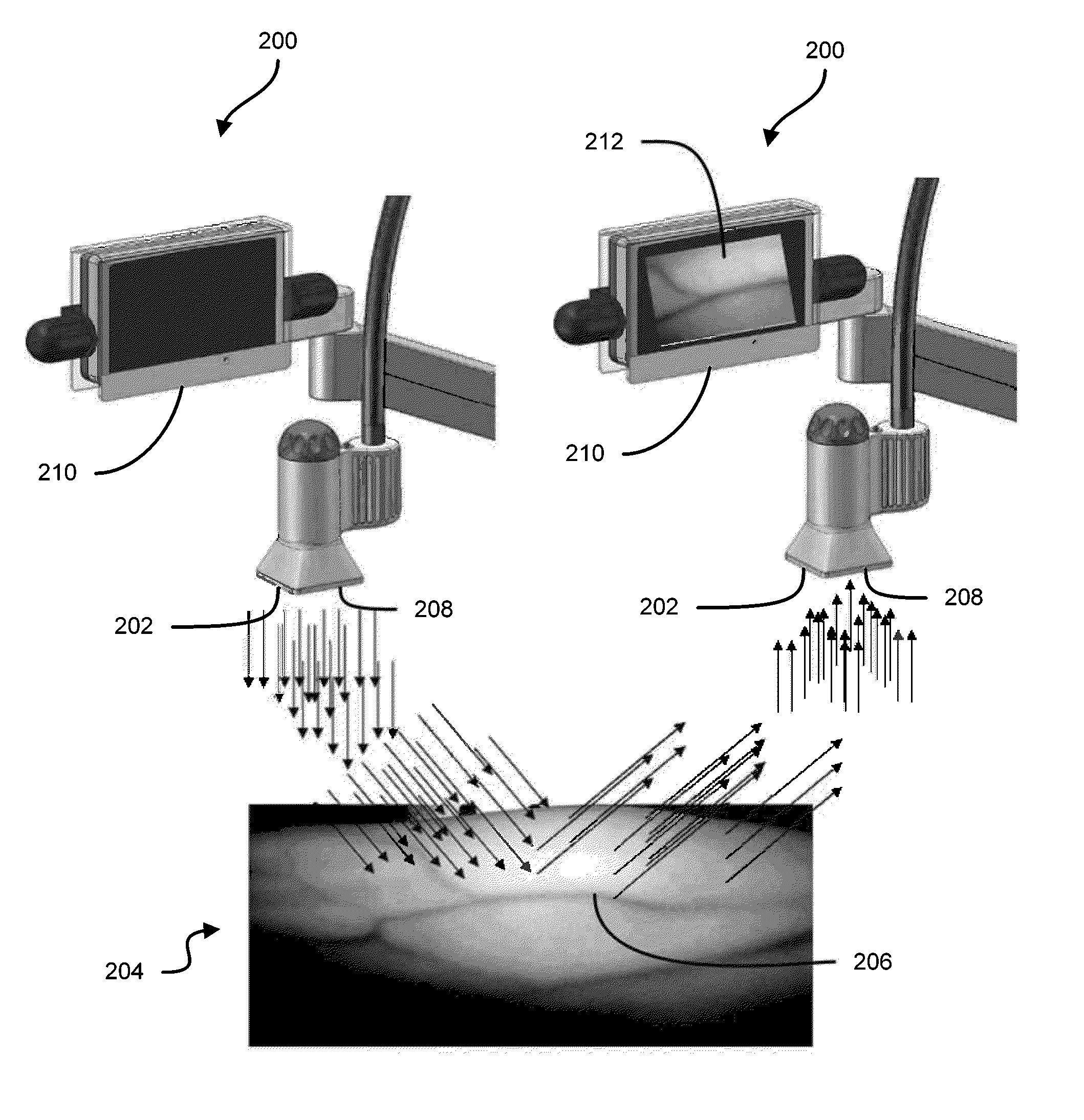
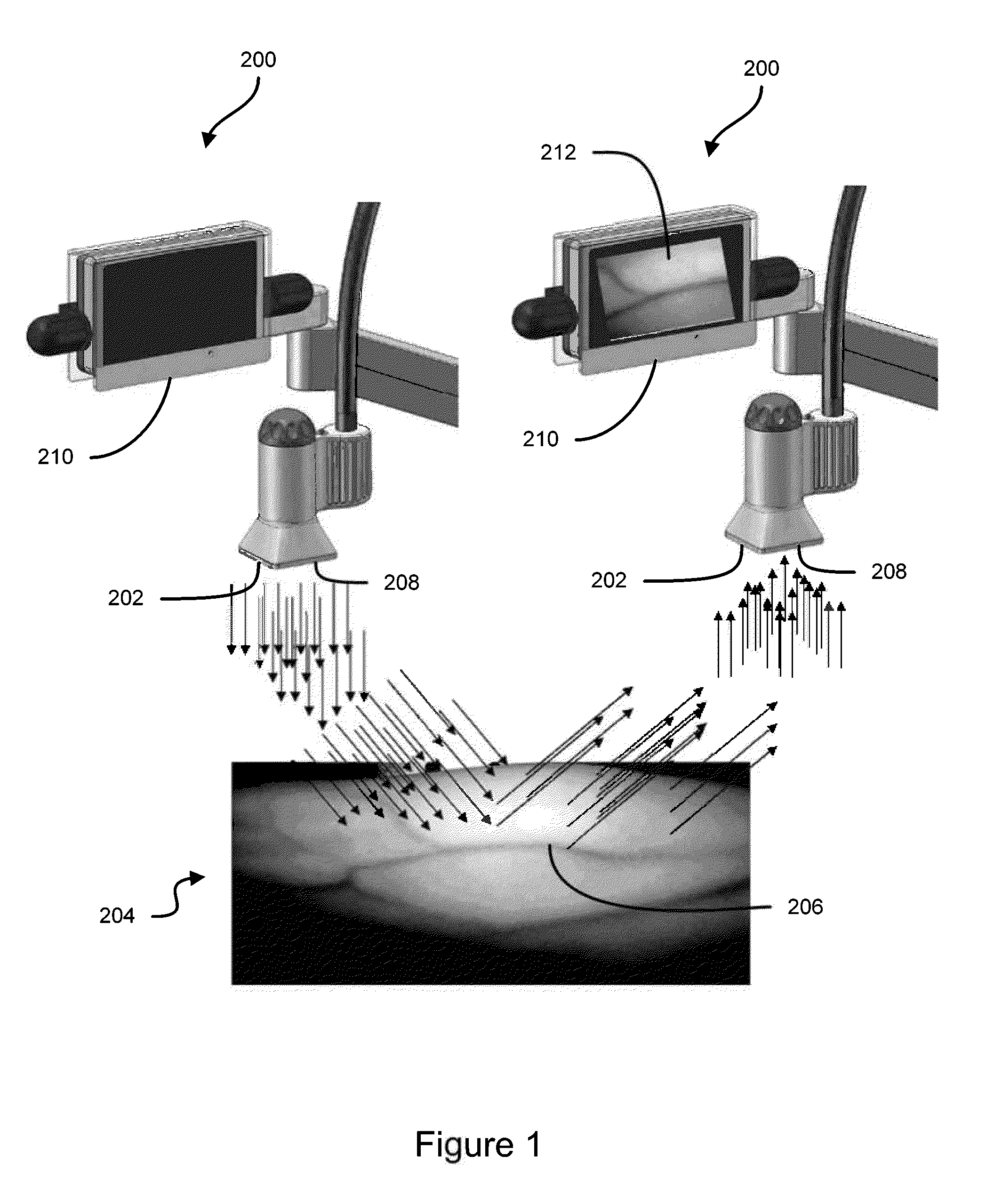
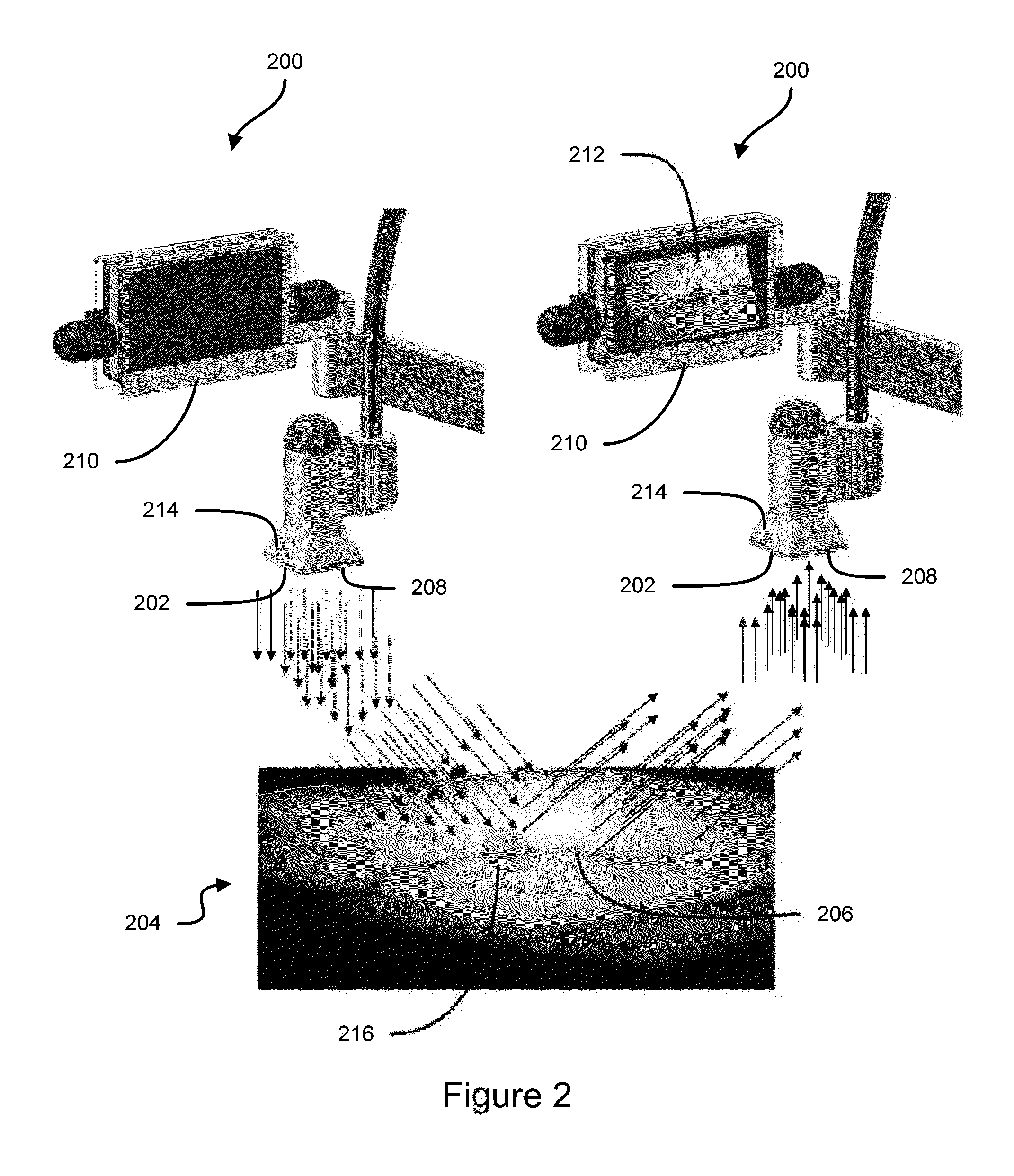
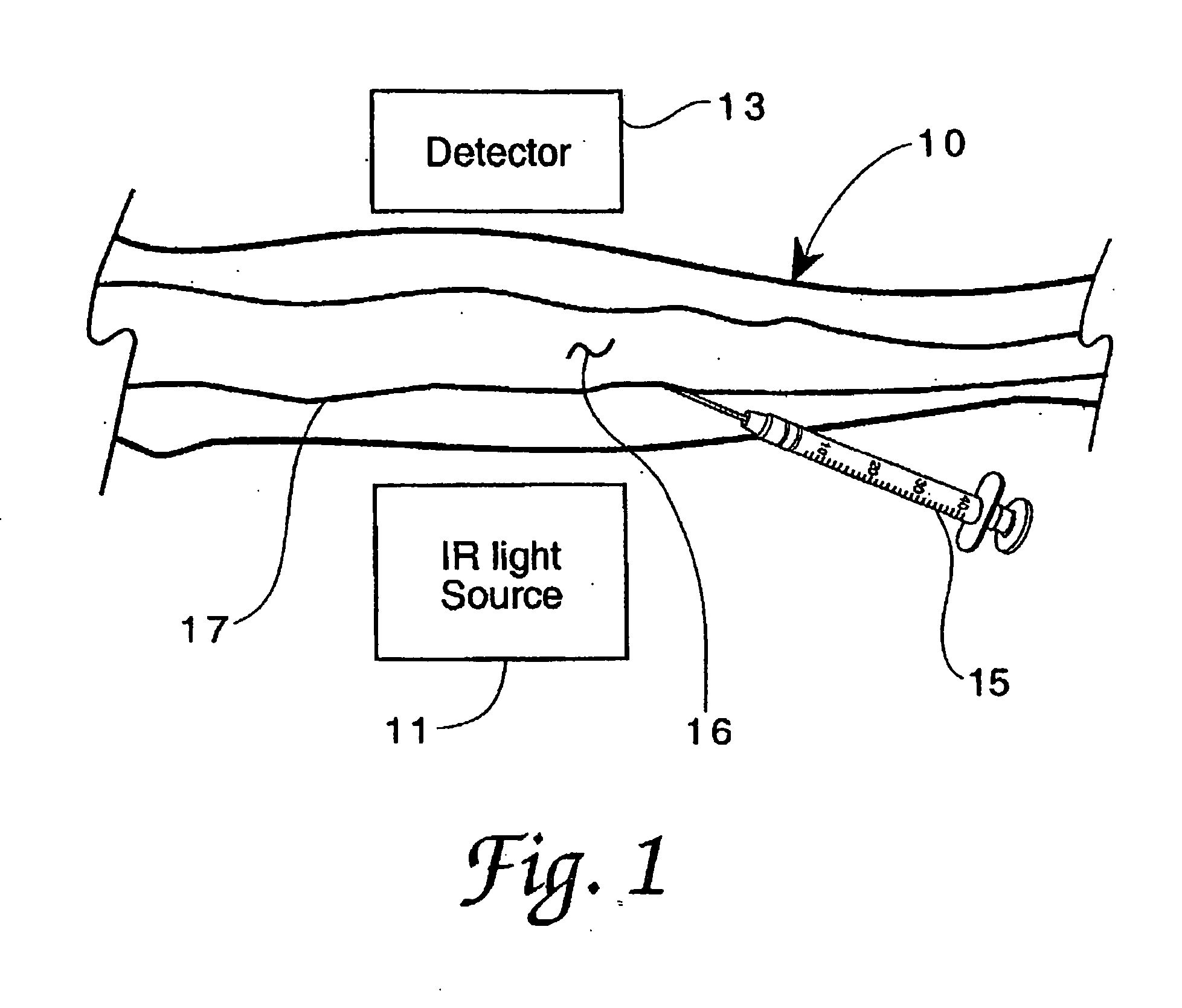
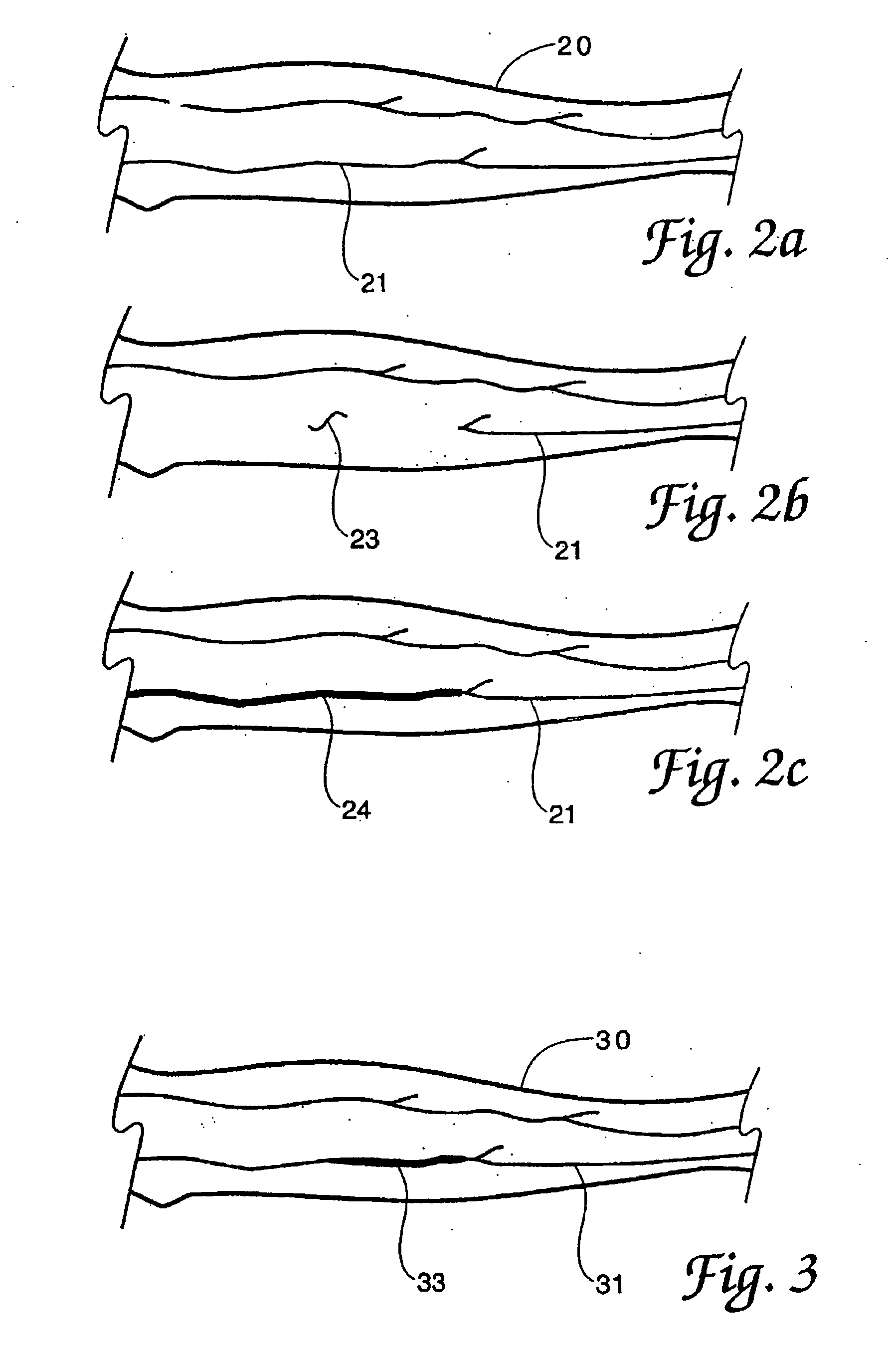
Some embodiments of this disclosure relates to systems and methods for imaging a patient's vasculature. For example, near infrared (NIR) light can be used to illuminate a target area and light that is reflected or scattered from the target area can be used for generate an image of the target area. In some embodiments, the system can be configured such that the image shows the presence, absence, or extent of infiltration or extravasation in the target area. The system can be configured to document that presence, absence, or extend of infiltration or extravasation at an infusion site. In some embodiments, an imaging system can be mounted onto a patient so that the imaging system can monitor an infusion site, and the imaging system can be configured to automatically detect the presence of infiltration or extravasation.
Owner:EVENA MEDICAL
Vein imaging systems and methods
Some embodiments of this disclosure relates to systems and methods for imaging a patient's vasculature. For example, near infrared (NIR) light can be used to illuminate a target area and light that is reflected or scattered from the target area can be used for generate an image of the target area. In some embodiments, the system can be configured such that the image shows the presence, absence, or extent of infiltration or extravasation in the target area. The system can be configured to document that presence, absence, or extend of infiltration or extravasation at an infusion site. In some embodiments, an imaging system can be mounted onto a patient so that the imaging system can monitor an infusion site, and the imaging system can be configured to automatically detect the presence of infiltration or extravasation.
Owner:EVENA MEDICAL
Modified starch material of biocompatible hemostasis
InactiveUS20090062233A1Promoting tissue healingGood effectPowder deliveryBiocideAfter treatmentWound surface
A modified starch material for biocompatible hemostasis, biocompatible adhesion prevention, tissue healing promotion, absorbable surgical wound sealing and tissue bonding, when applied as a biocompatible modified starch to the tissue of animals. The modified starch material produces hemostasis, reduces bleeding of the wound, extravasation of blood and tissue exudation, preserves the wound surface or the wound in relative wetness or dryness, inhibits the growth of bacteria and inflammatory response, minimizes tissue inflammation, and relieves patient pain. Any excess modified starch not involved in hemostatic activity is readily dissolved and rinsed away through saline irrigation during operation. After treatment of surgical wounds, combat wounds, trauma and emergency wounds, the modified starch hemostatic material is rapidly absorbed by the body without the complications associated with gauze and bandage removal.
Owner:JI XIN
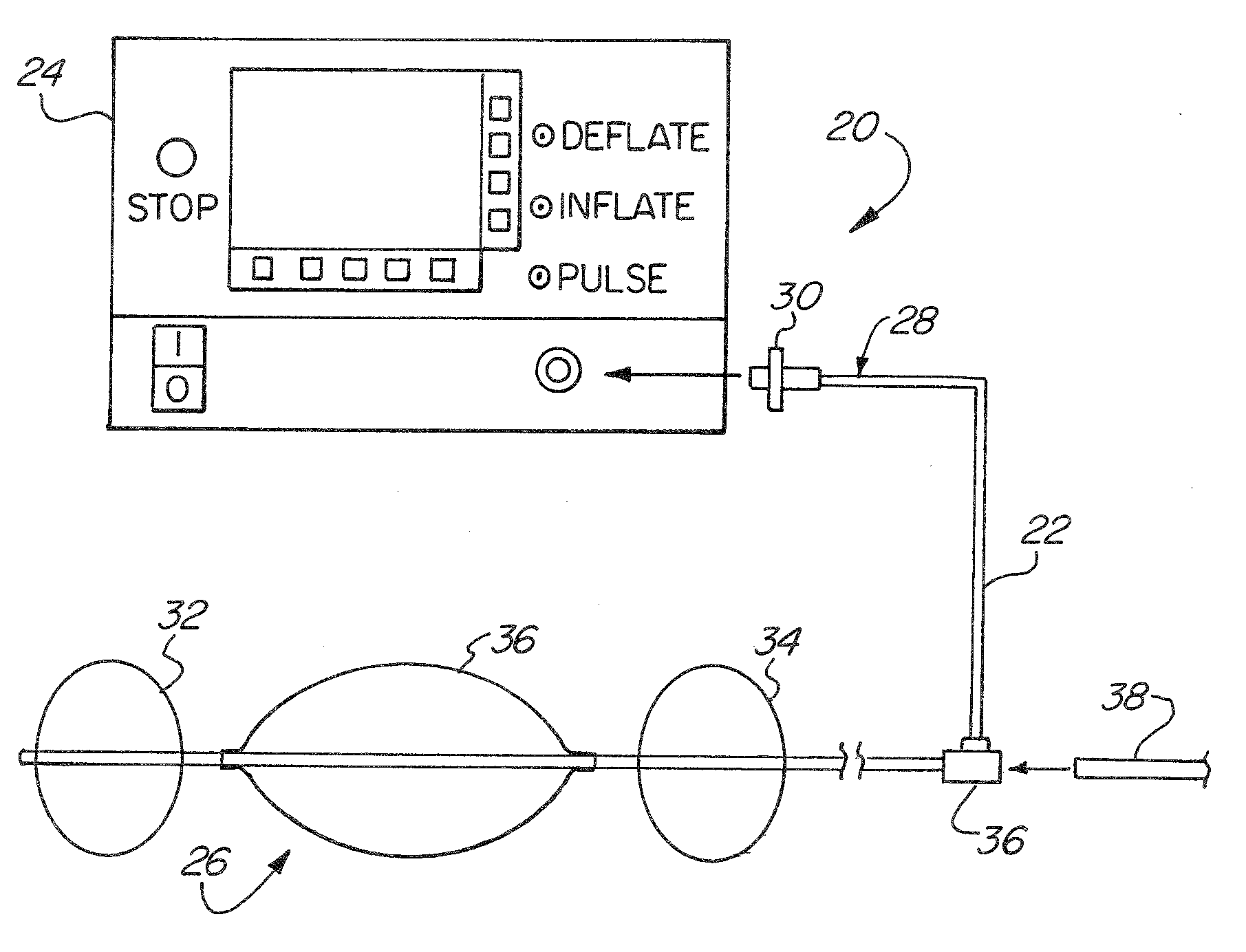
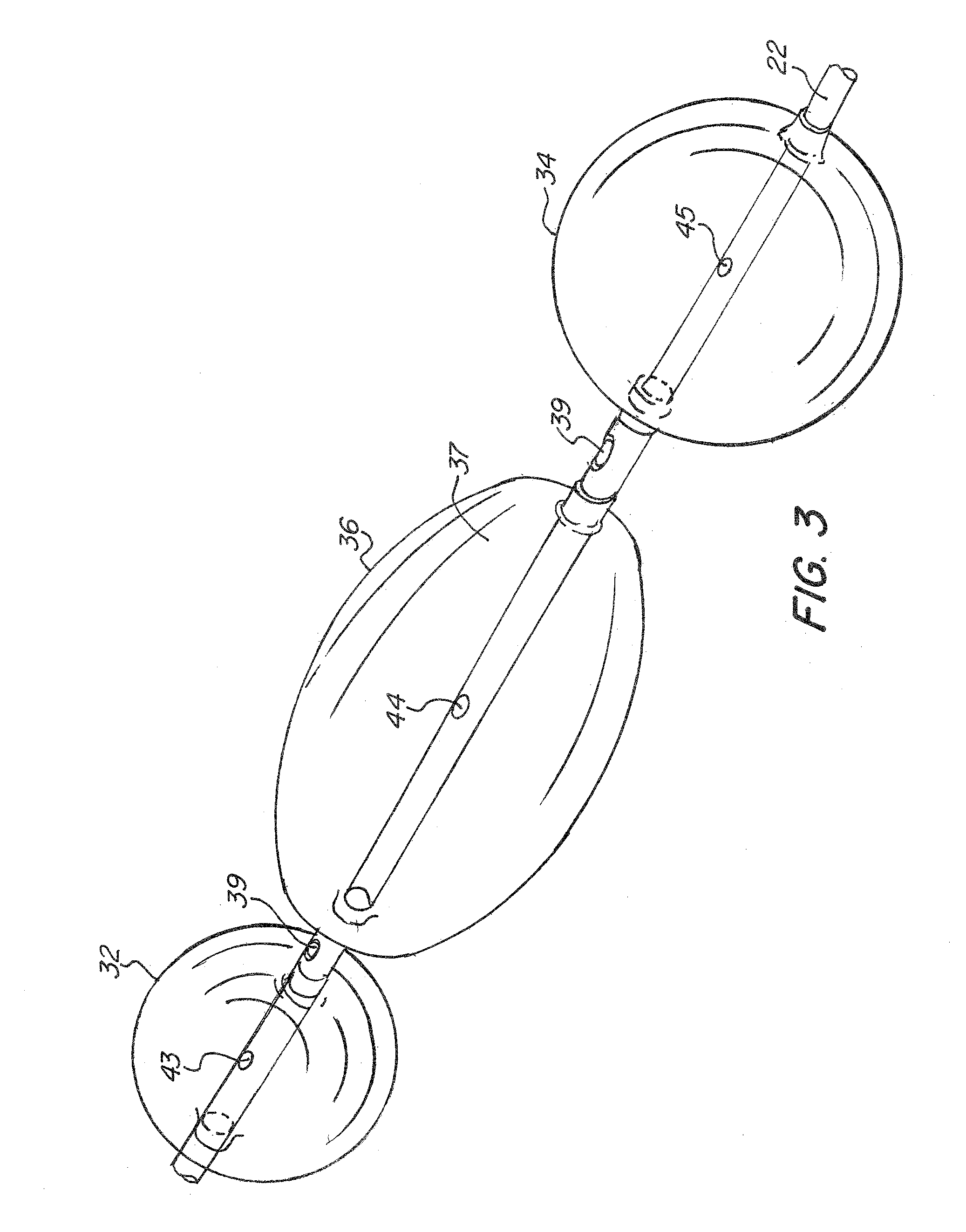
Multi-Balloon Catheter for Extravasated Drug Delivery
A method of extravasated delivery of a therapeutic and / or diagnostic agent to tissue is provided including inserting a catheter with a first balloon, a second balloon and a third balloon into a bodily cavity, inflating the first and second balloons by supplying fluid thereto to create a chamber, delivering the agent to the chamber, and increasing fluid pressure within the chamber by inflating the third balloon to facilitate extravasation of the agent into tissue. A multi-balloon catheter system is also provided including a catheter having a first balloon, a second balloon and a third balloon, and a fluid source that inflates the first and second balloons by supplying fluid thereto to create a chamber, wherein the catheter includes a fluid pathway for delivering the agent, and the fluid source increases fluid pressure within the chamber by supplying fluid to the third balloon such that the agent is extravasated into tissue.
Owner:SANOVAS
Medical Scaffold, Methods of Fabrication and Using Thereof
Articles of manufacturing comprising electrospun elements having continuous or stepwise gradients of porosity, average pore size, weight per volume and / or of agents for promoting cell colonization, differentiation, extravasation and / or migration are provided. Also provided are methods of manufacturing and using same for guiding tissue regeneration.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
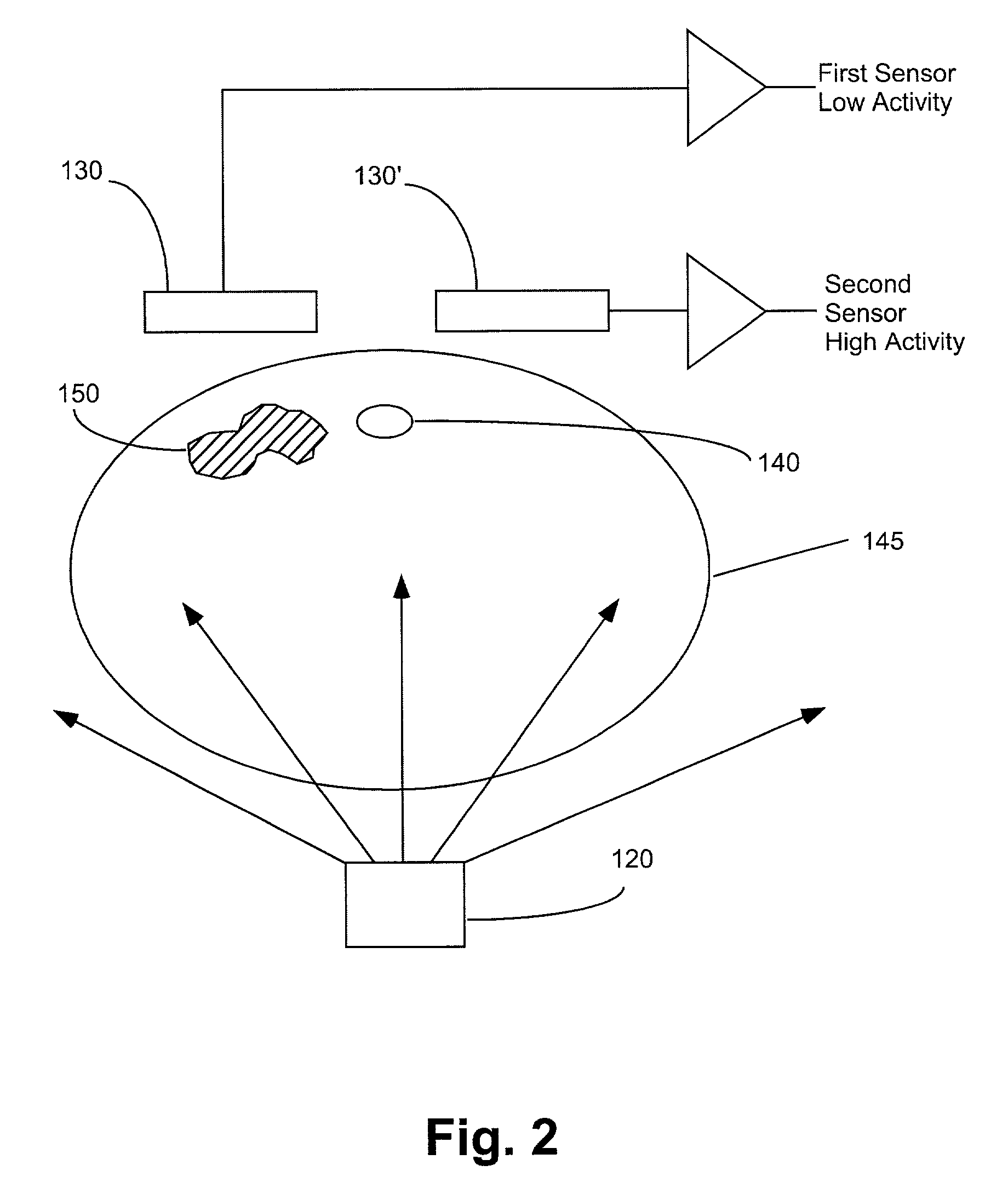
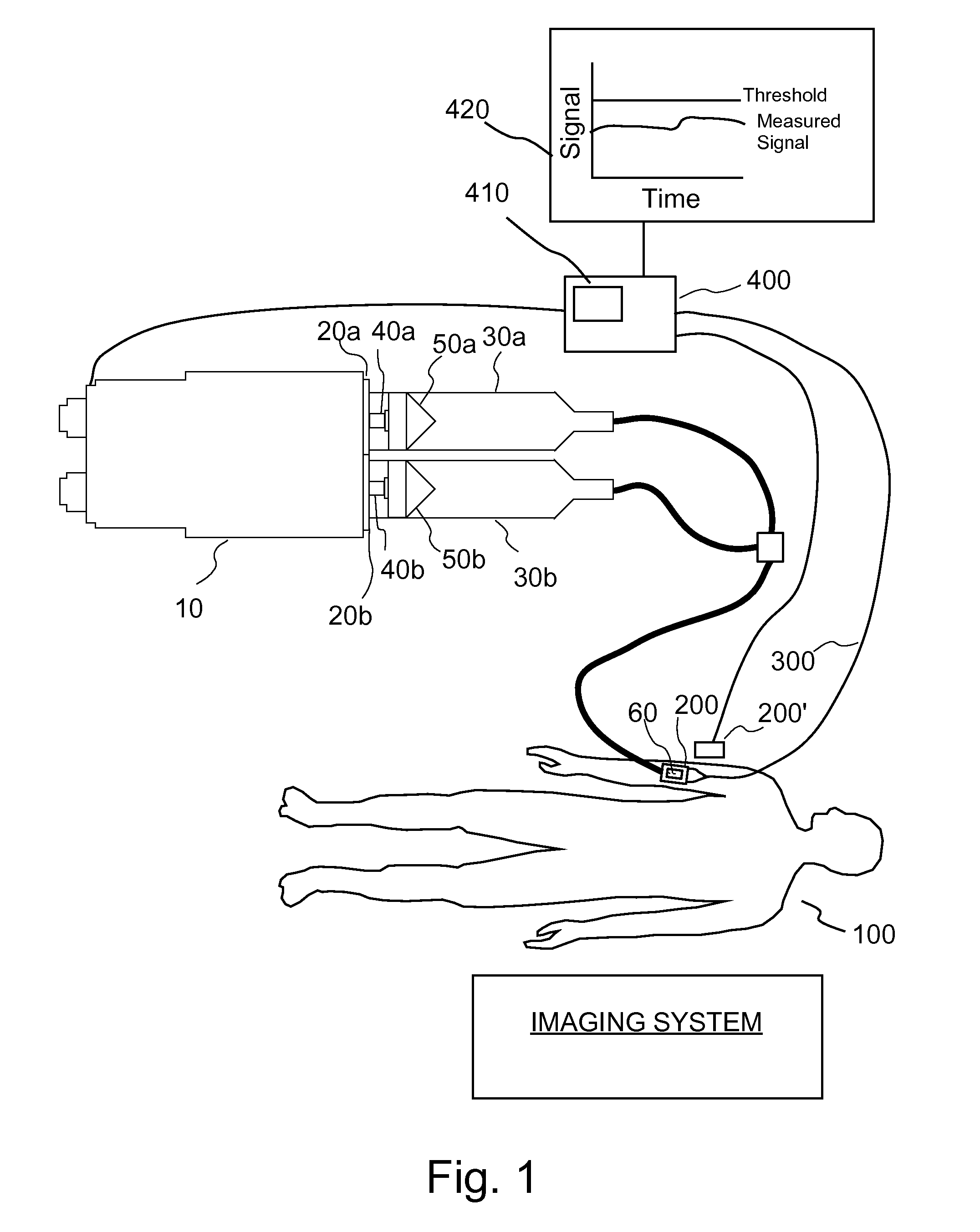
Apparatuses, systems and methods for extravasation detection
InactiveUS7047058B1Enhance the imageSensitive measurementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using microwave meansMedicineX-ray
An apparatus for the detection of extravasation in an imaging procedure includes at least a first source of energy to supply imaging energy to tissue in the vicinity of a site and at least a first sensor to measure a signal resulting from the energy supplied to the tissue by the first imaging energy source. In preferred embodiment, the energy may be one of X-ray, gamma ray or ultrasound energy.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
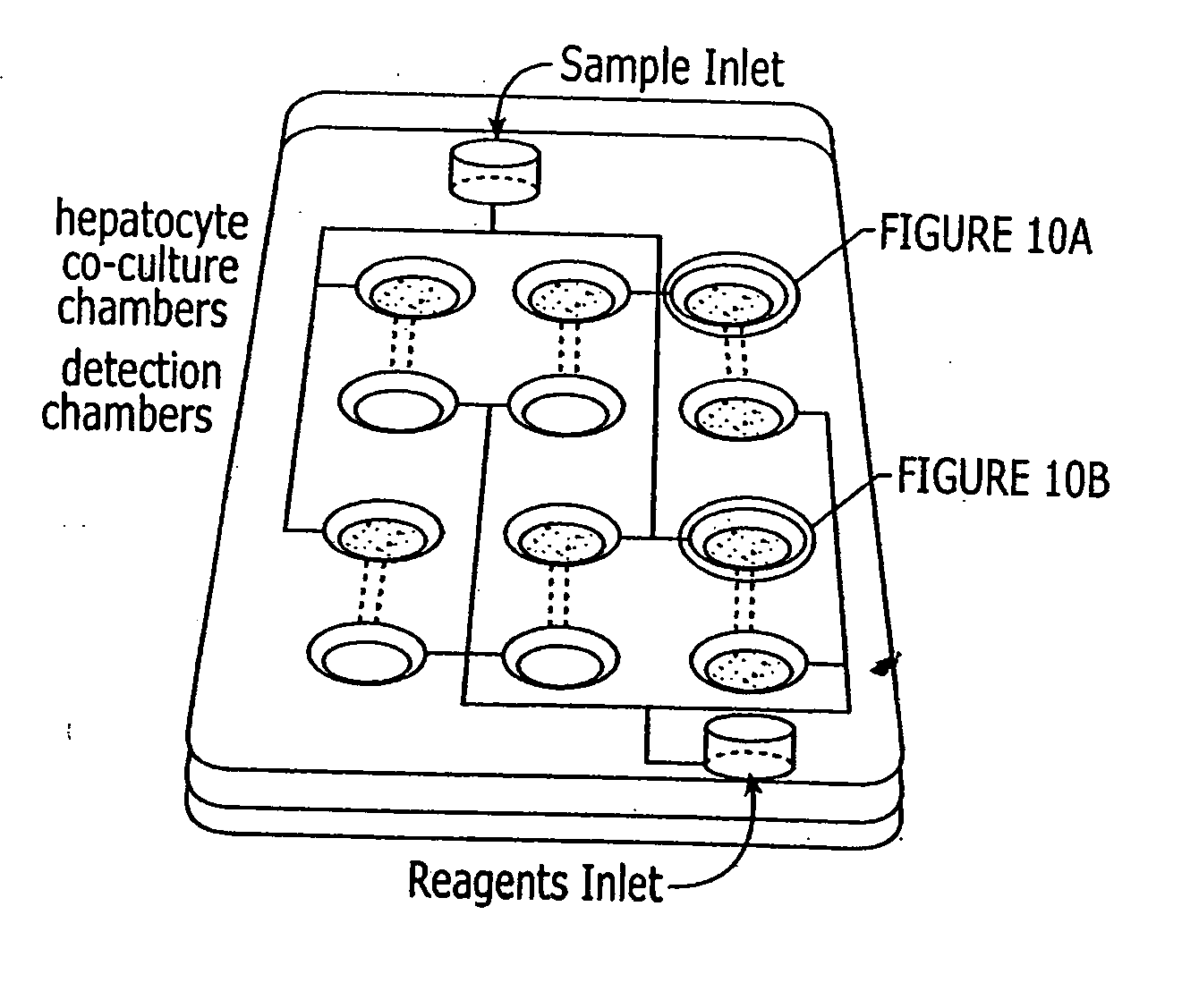
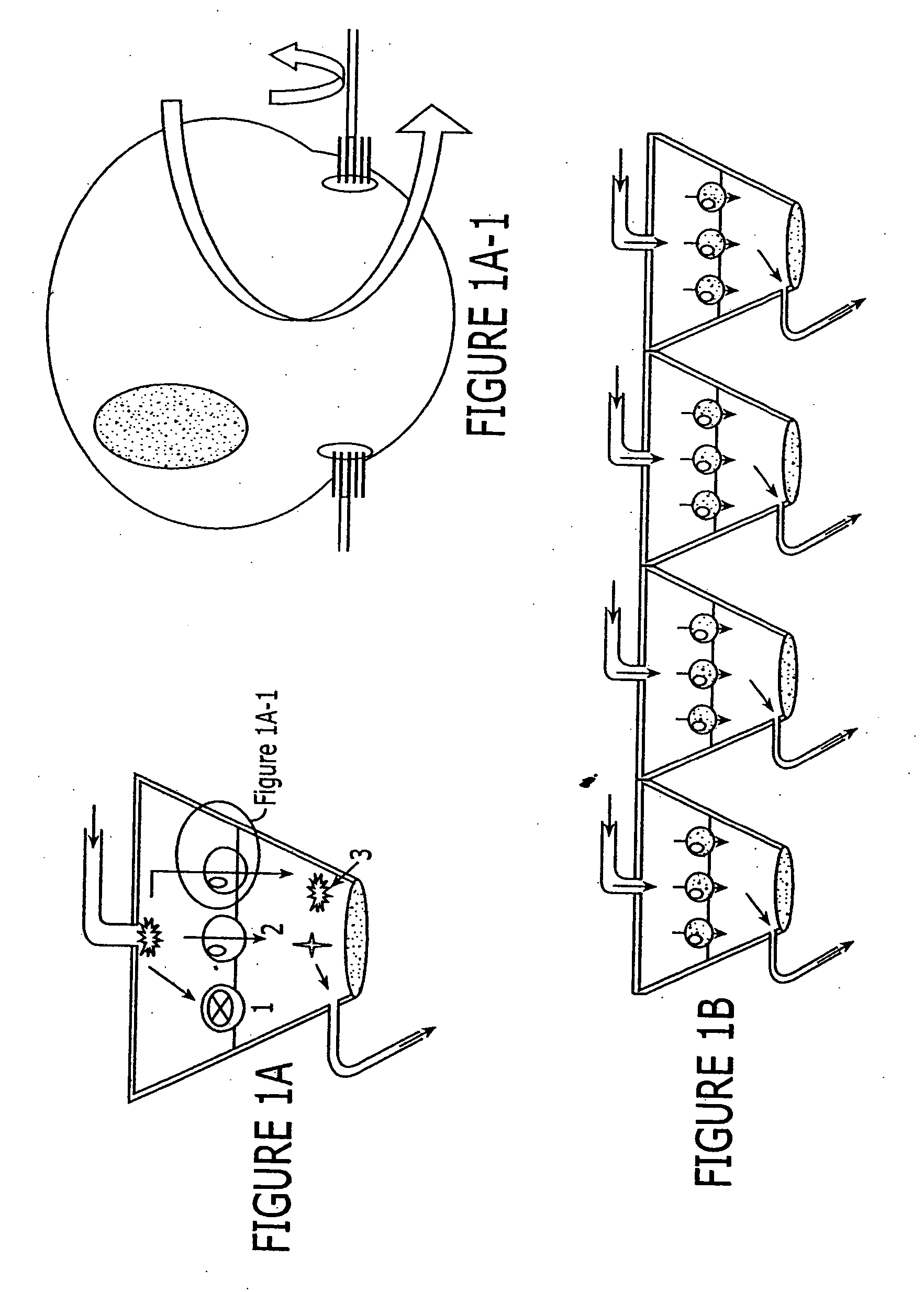
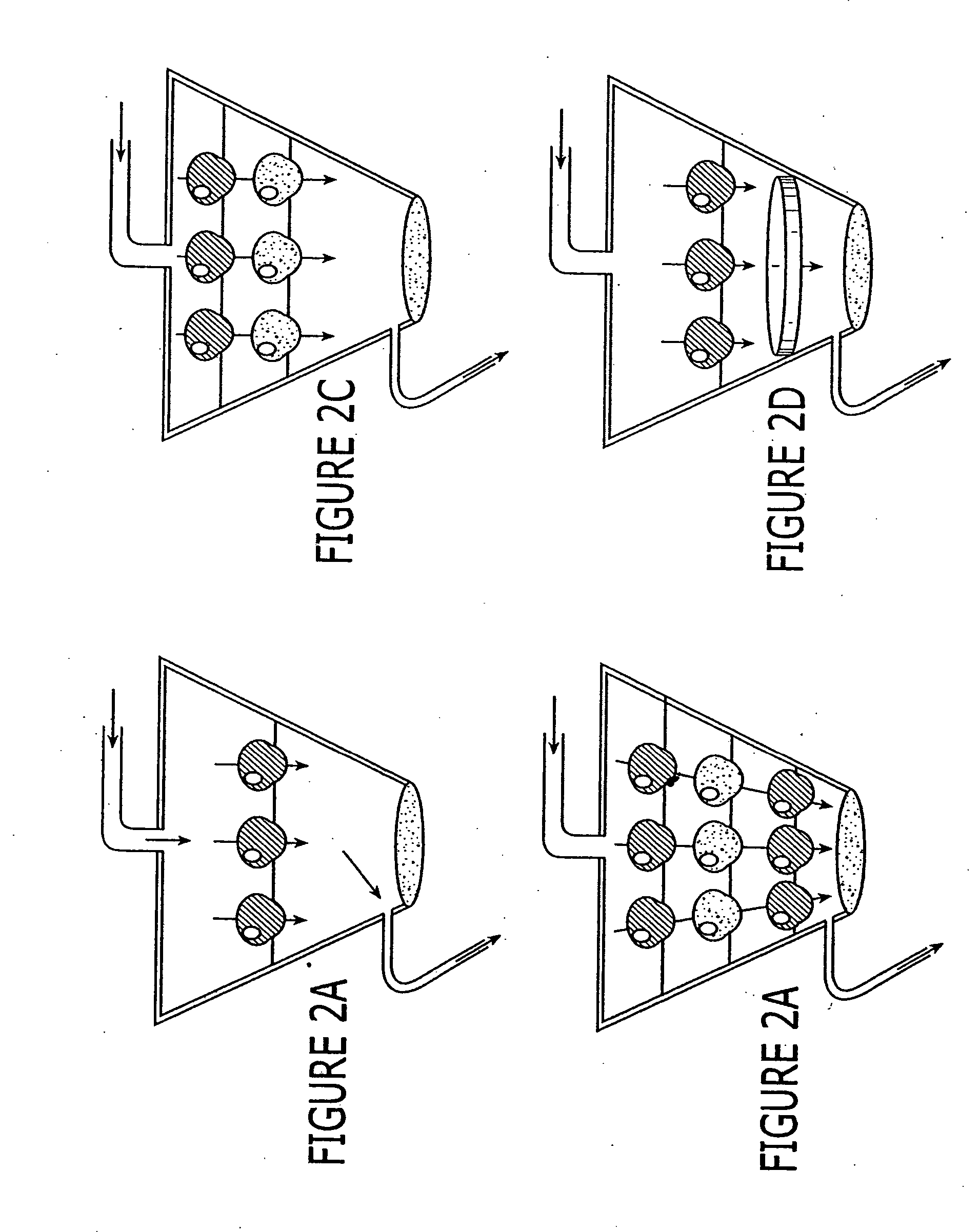
Assay device that analyzes the absorption, metabolism, permeability and/or toxicity of a candidate compound
InactiveUS20070166816A1Precise absorptionMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAssayCell type
This invention provides device for co-culturing at least two different cell types in a two-dimensional configuration, methods of patterning at least two different cell types in a two-dimensional co-culture configuration, and uses of these devices and methods for analyzing an effect of candidate compound on such cellular cocultures. Also provided is a transmigration and extravasation device. Assay devices for analyzing the absorption, permeability, metabolism and / or toxicity of a candidate compound by a cell are provided. A microfluidic network, which is adaptable for integration with a device for coculturing is provided.
Owner:SURFACE LOGIX INC
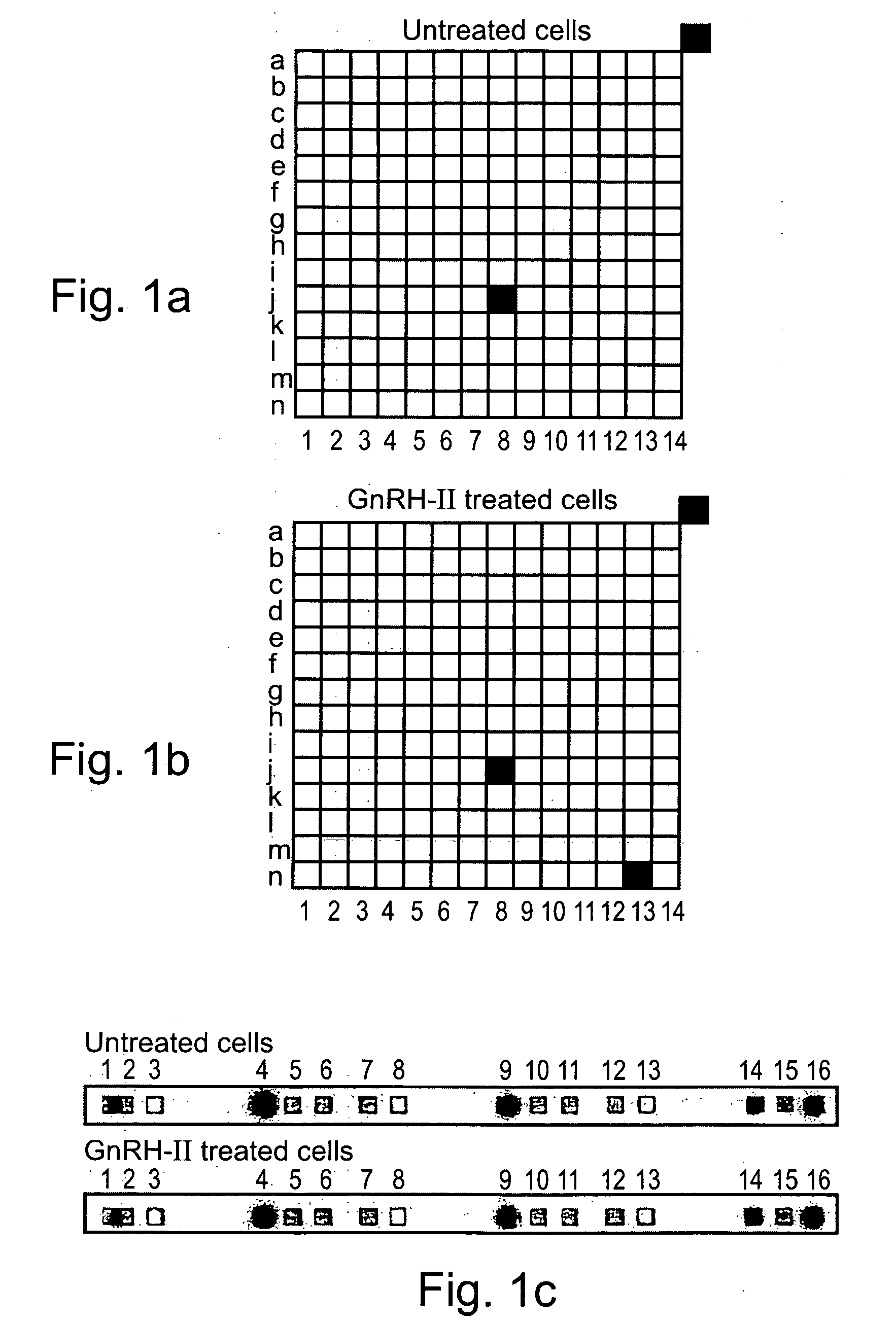
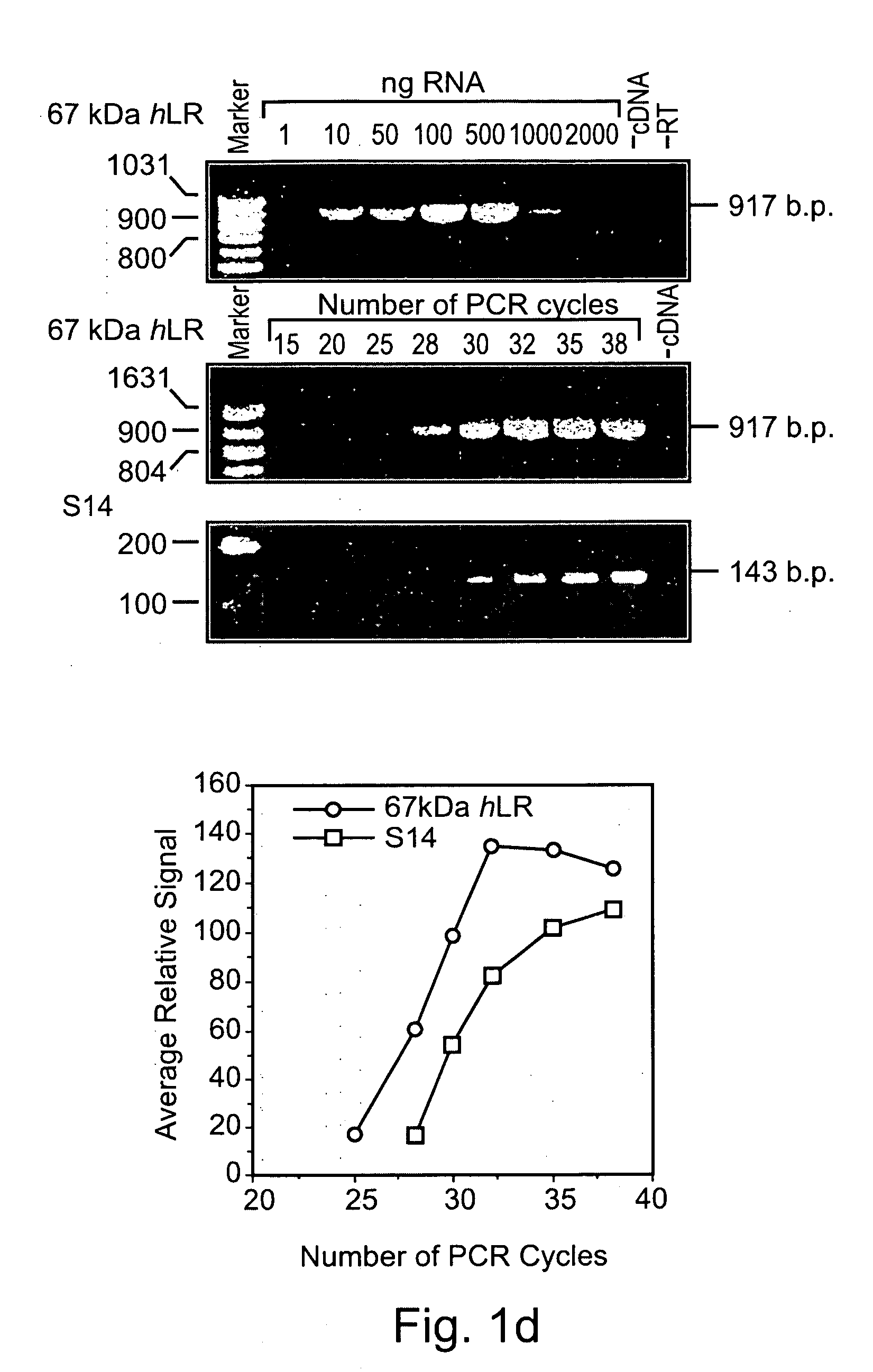
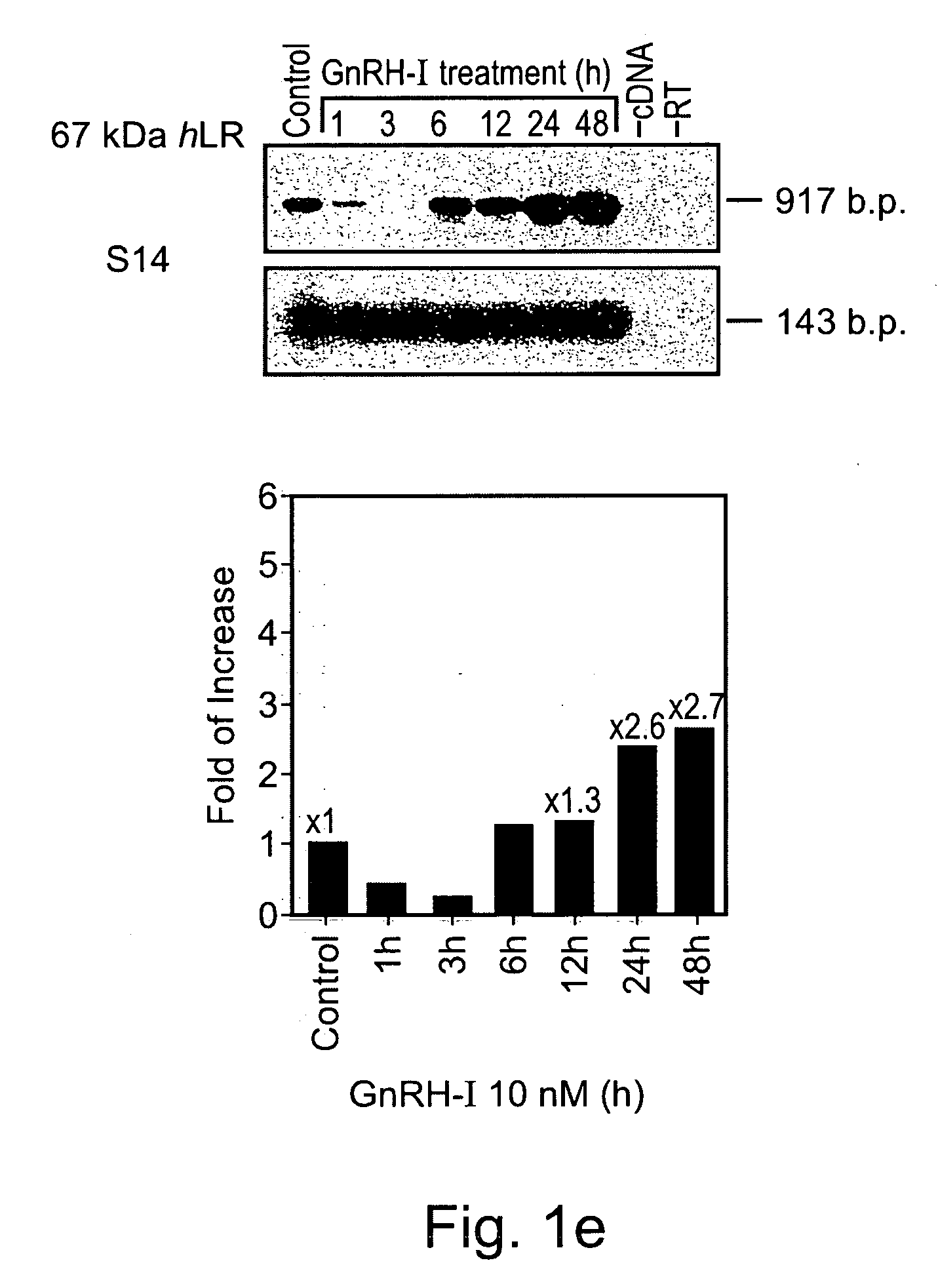
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for gnrh-II and gnrh-II modulation of t-cell activity, adhesion, migration and extravasation
Methods and compositions comprising GnRH-I and GnRH-II, GnRH-I and GnRH-II antibodies, anti-receptor antibodies, polynucleotide constructs and GnRH-I and GnRH-II analogs for immune enhancement and suppression, prevention and treatment of diseases and conditions characterized by abnormal T-cell activity, treatment of viral and prion-related diseases, and treatment of T-cell related neoplastic diseases are disclosed.
Owner:KOCH YITZHAK PROF +1
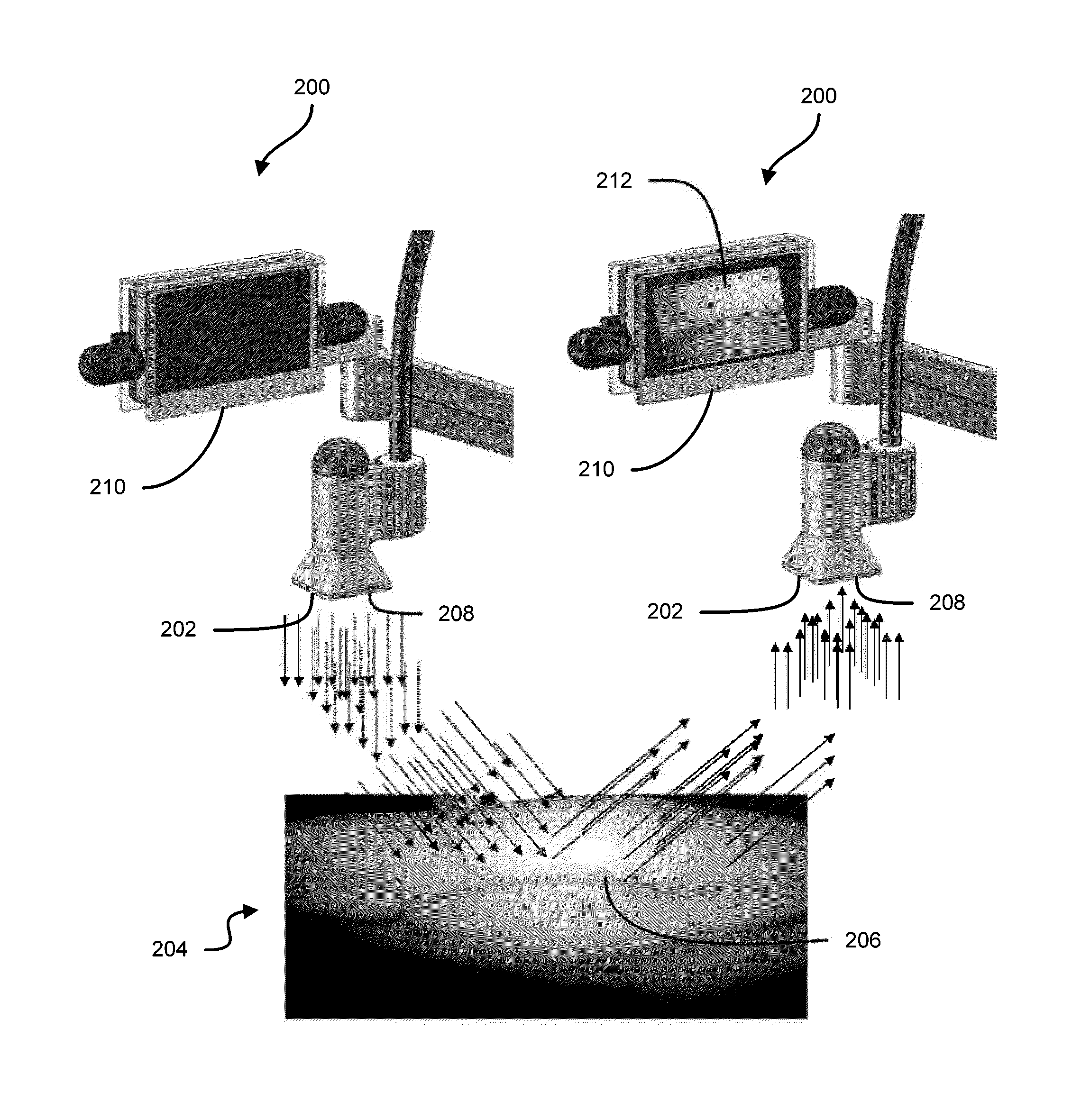
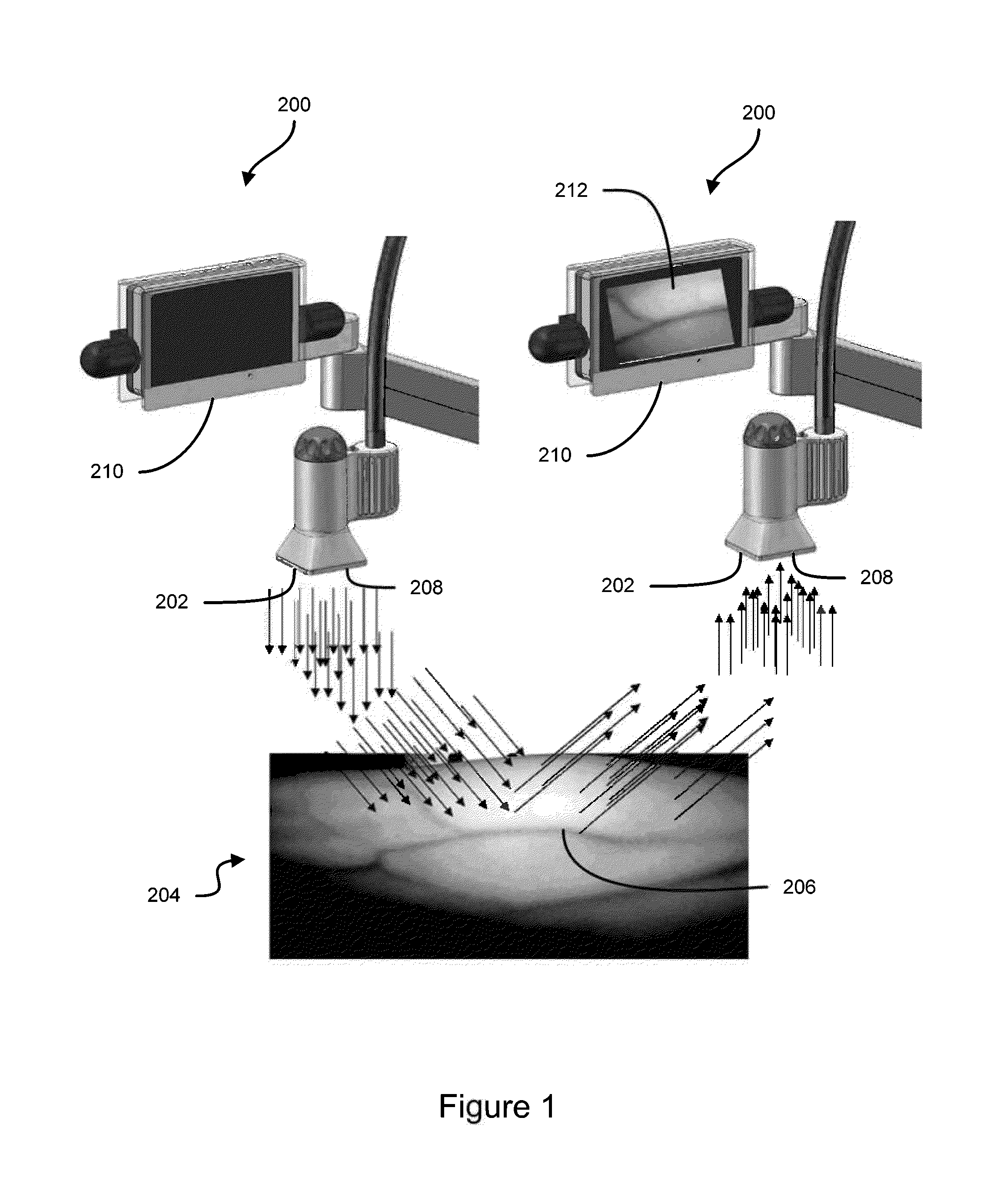
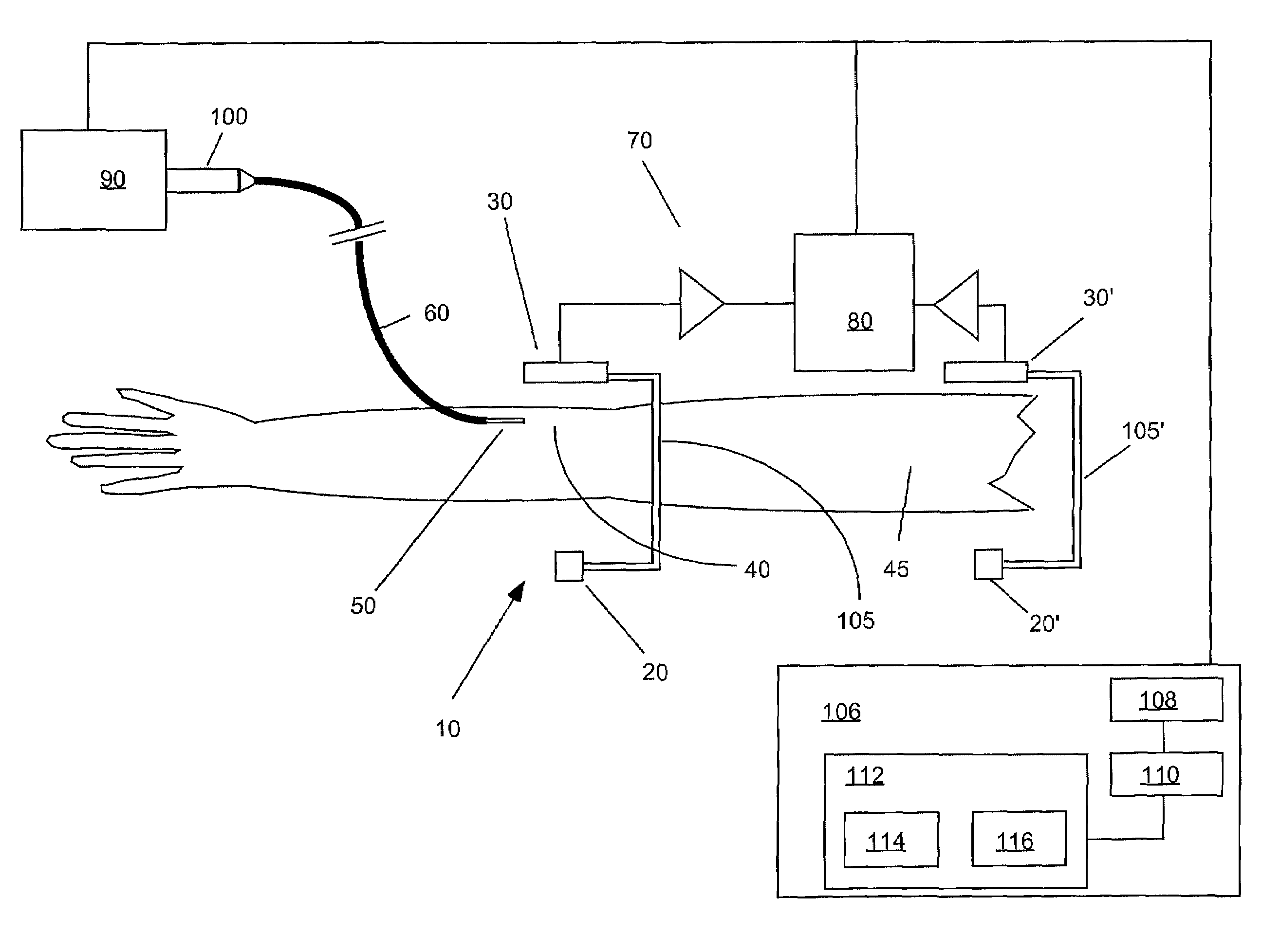
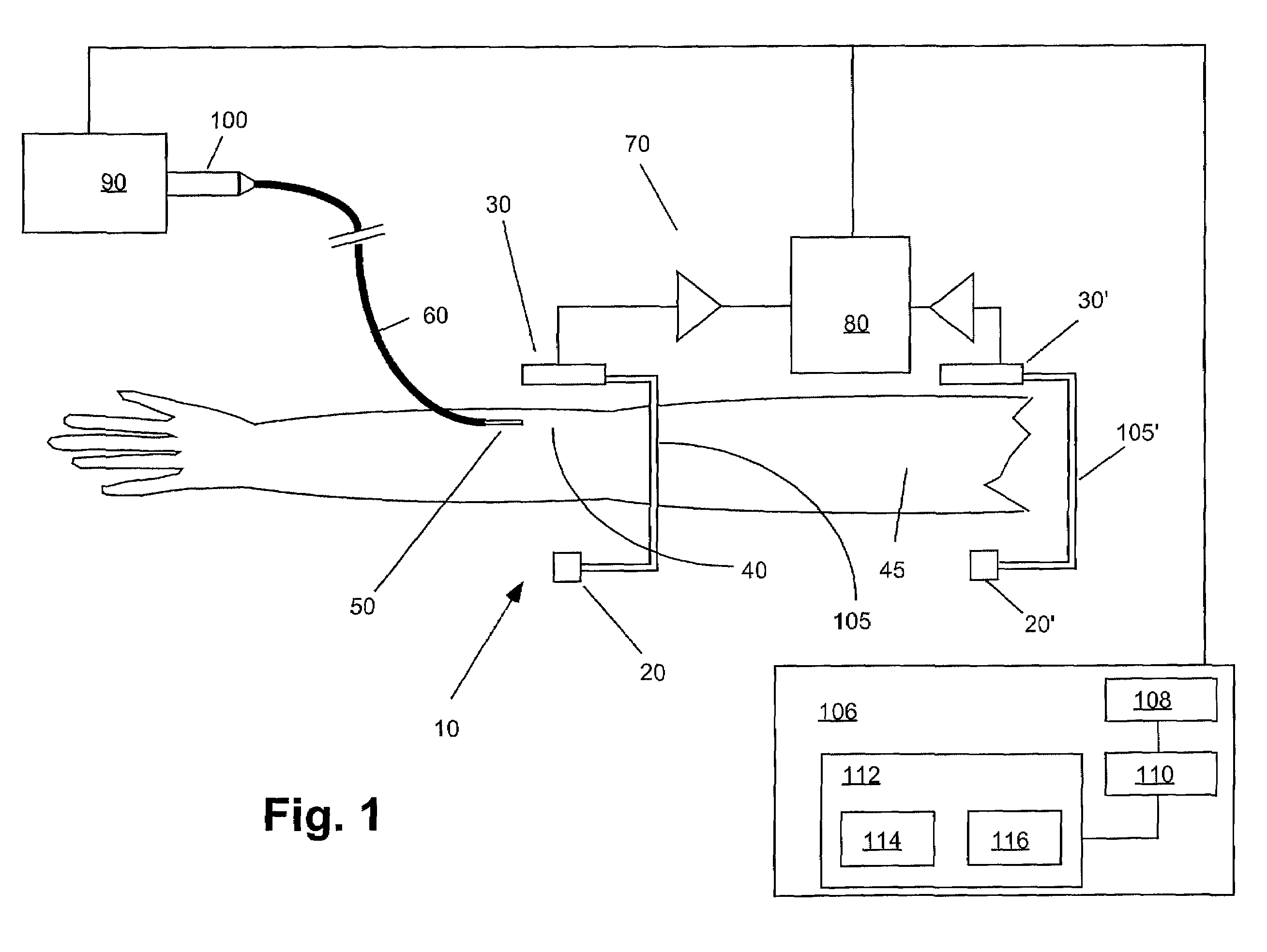
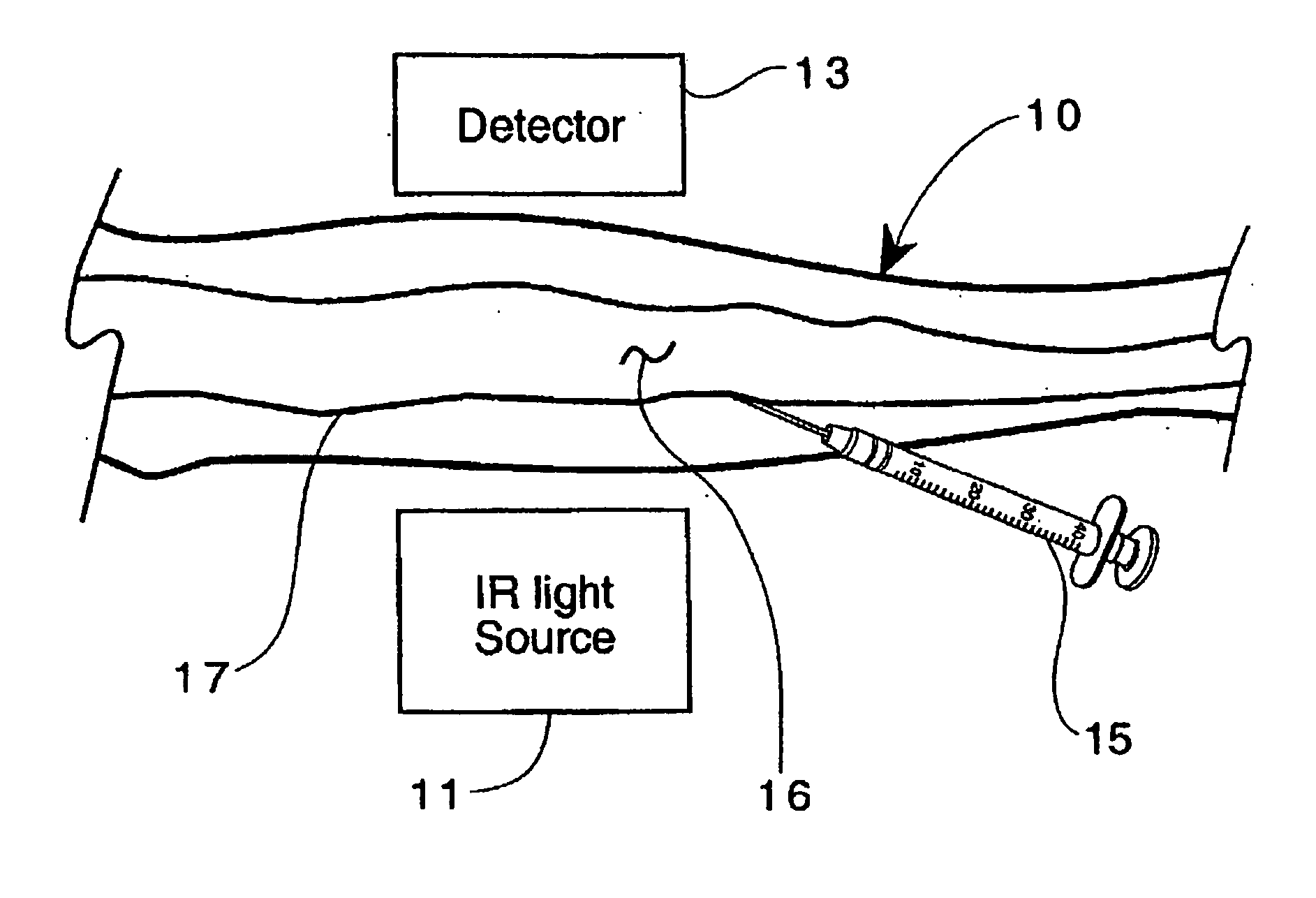
Method for detection and display of extravasation and infiltration of fluids and substances in subdermal or intradermal tissue
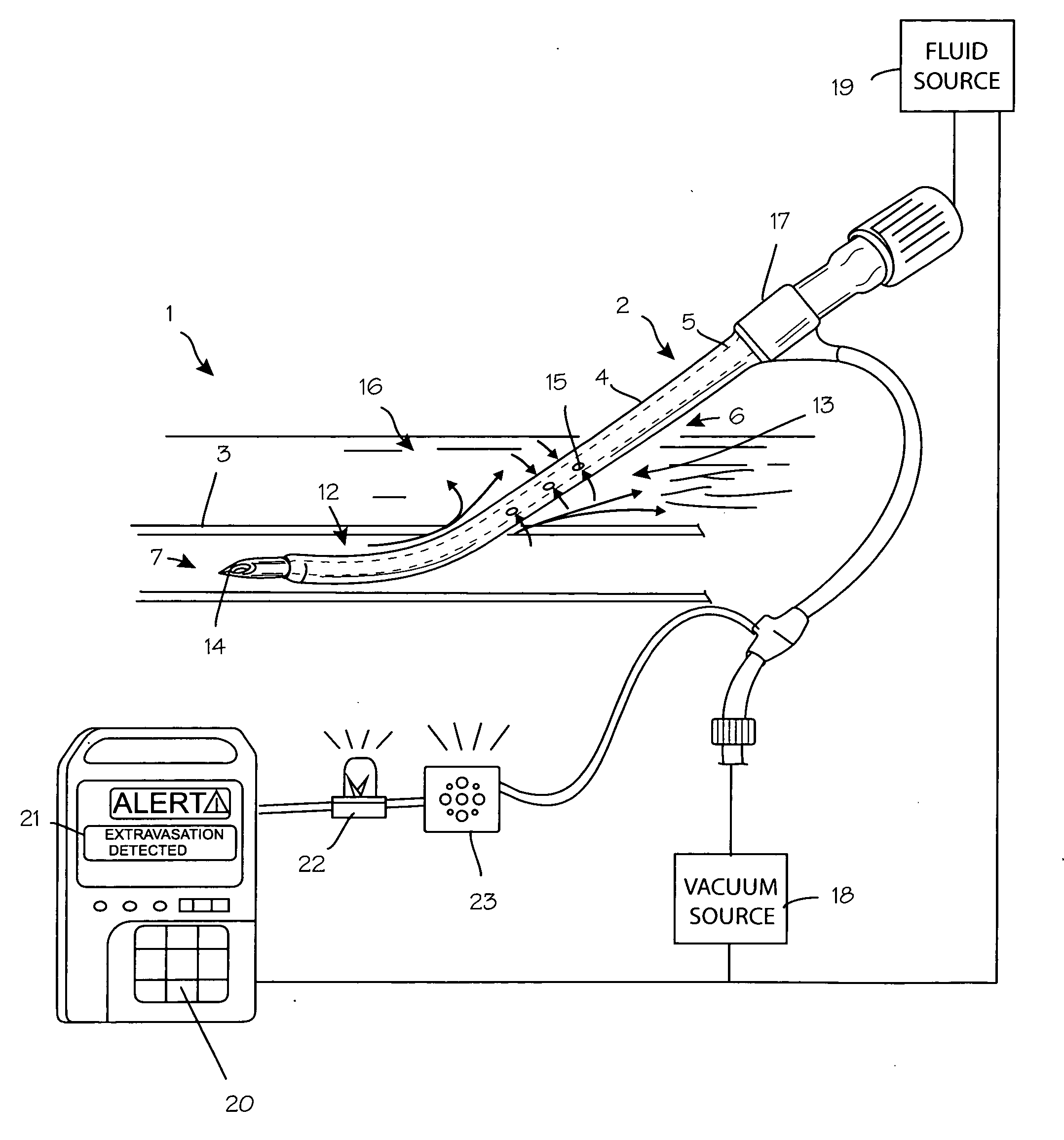
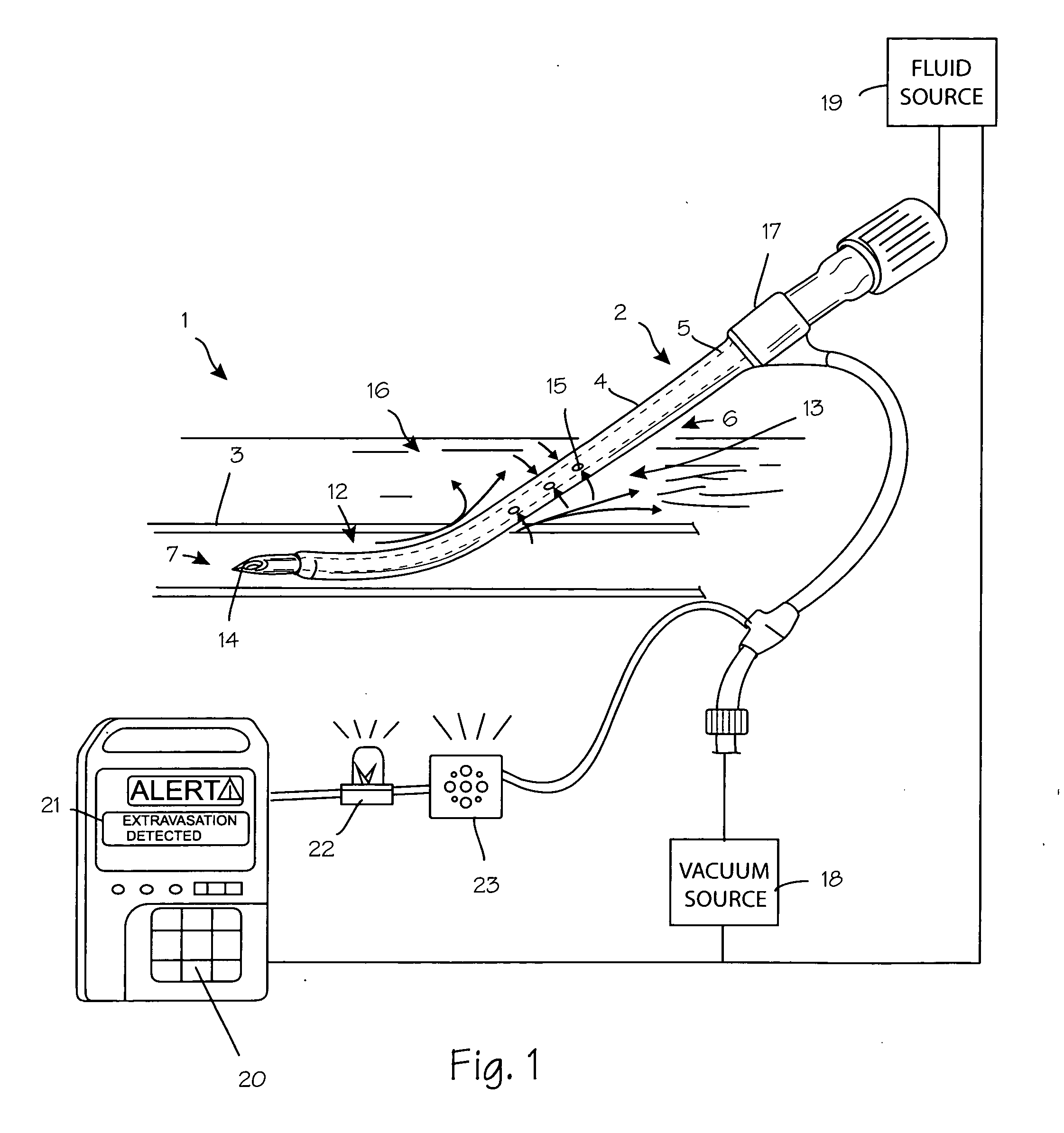
A method for the real-time visualization and detection of extravasated and or infiltrated fluid and substances, including blood, that occur near the cannulation site of an injection is described wherein illumination or transillumination with near infrared light is used to image the contrast in real-time between absorbing and nonabsorbing subdermal and intradermal structures of blood vessels and remaining surrounding tissue, foreign substances and other structures in order to establish a baseline image of the body area of interest, and any new image is monitored and compared with the baseline image to detect the extravasation and / or infiltration of fluids and substances, including blood, around a vein or artery into the subdermal or intradermal tissue.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
Use of lipid conjugates in the treatment of diseases
InactiveUS7101859B2Reduce molecular weightIncrease rangeAntibacterial agentsBiocideLymphatic SpreadContact dermatitis
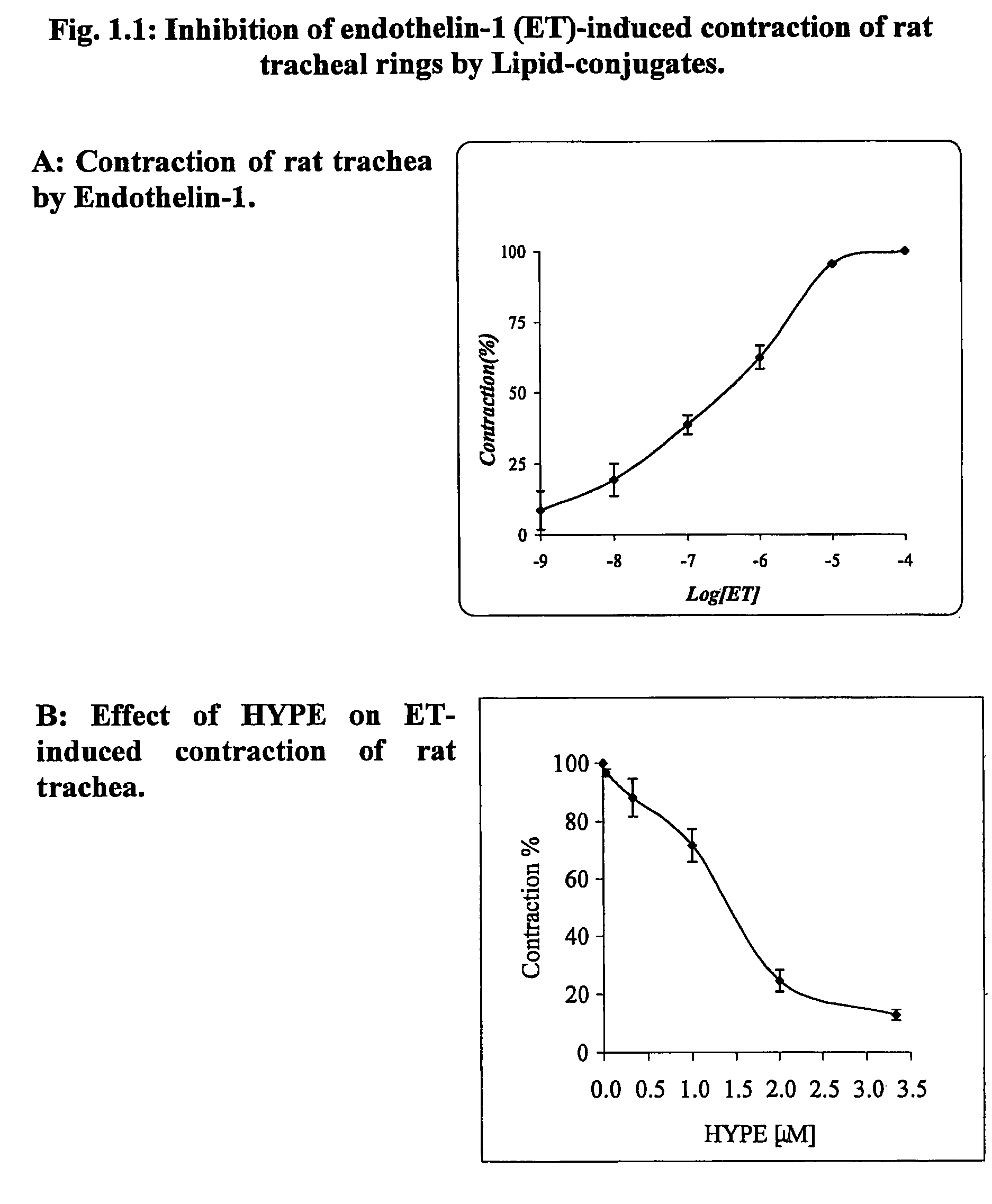
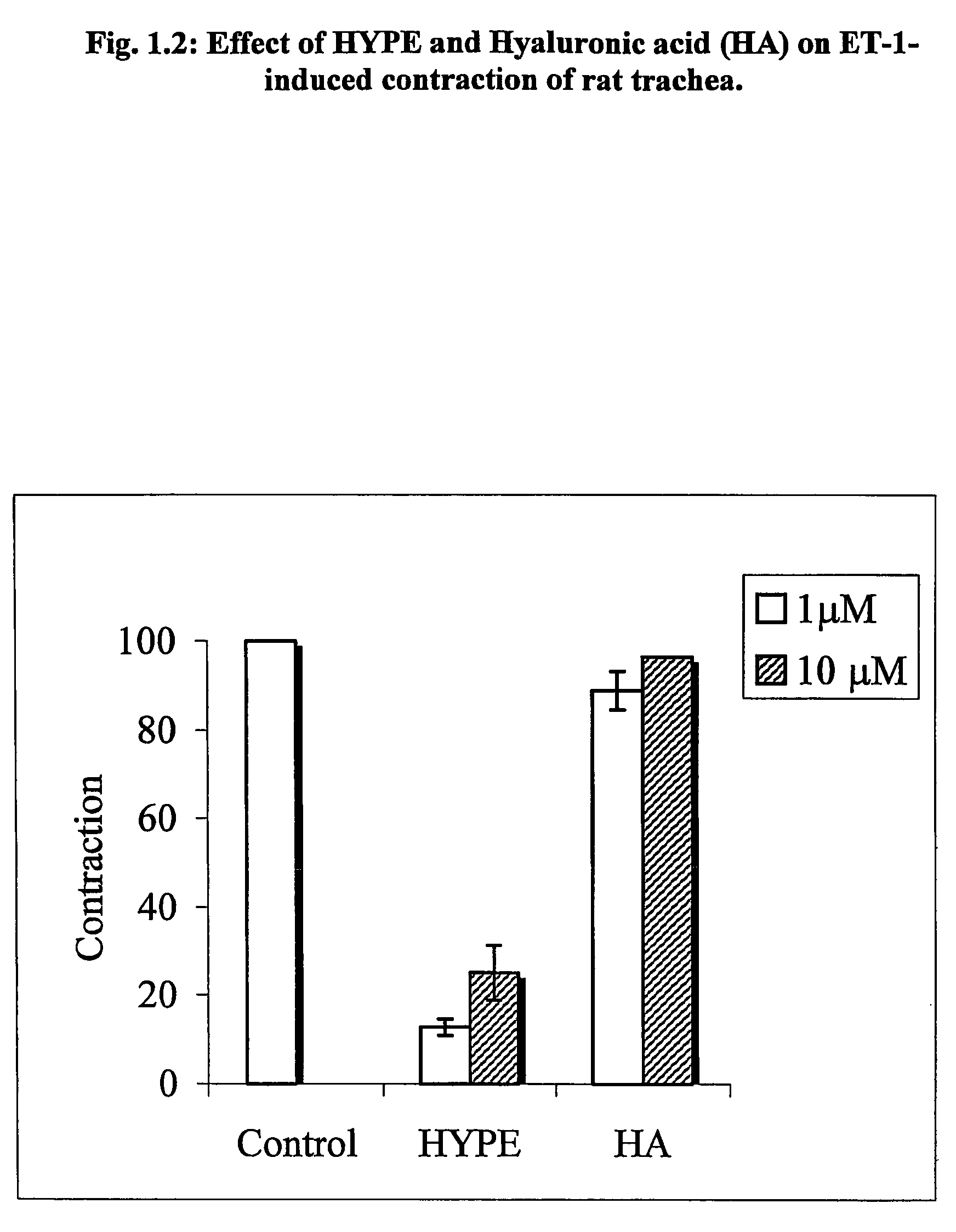
The invention provides novel methods for treating disease based upon the medicinal use of lipids and phospholipids covalently bound to physiologically acceptable monomers or polymers. Phosphatidylethanolamine moieties conjugated to physiologically acceptable monomers and polymers (PE conjugates) manifest an unexpectedly wide range of pharmacological effects, including stabilizing cell membranes; limiting oxidative damage to cell and blood components; limiting cell proliferation, cell extravasation and (tumor) cell migratory behavior; suppressing immune responses; and attenuating physiological reactions to stress, as expressed in elevated chemokine levels. The surprisingly manifold pharmacological properties of the PL-conjugates allow for the invention, disclosed herein, of novel methods for the treatment of a diverse range of disease states, including obstructive respiratory disease, including asthma; colitis and Crohn's disease; central nervous system insult, including blood brain barrier compromise, ischemic stroke, and multiple sclerosis; contact dermatitis; psoriasis; cardiovascular disease, including ischemic conditions and prophylaxis for invasive vascular procedures; cellular proliferative disorders, including anti-tumor vasculogenesis, invasiveness, and metastases; anti-oxidant therapy; hemolytic syndromes; sepsis; acute respiratory distress syndrome; tissue transplant rejection syndromes; autoimmune disease; viral infection; and hypersensitivity conjunctivitis. The therapeutic methods of the invention include administration of phosphatidylethanolamine bound to carboxymethylcellulose, heparin, hyaluronic acid, polyethylene glycol, and Polygeline (haemaccel). Disclosed herein are also new compounds comprised of phospholipid moieties bound to low molecular weight monomers and dimers, including mono- and disaccharides, carboxylated disaccharides, mono- and dicarboxylic acids, salicylates, bile acids, and fatty acids.
Owner:YEDGAR SAUL
Use of heparinase to decrease inflammatory responses
InactiveUS20010006635A1Inhibiting leukocyte rollingInhibiting chemokine gradient formationOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryWhite blood cellDigestion
Heparinase enzymes can be used as a medical treatment to reduce localized inflammatory responses. Treatment of activated endothelium with heparinase inhibits leukocyte rolling, adhesion and extravasation. Most of the heparin and heparan sulfate on endothelial cell surfaces and in basement membranes is degraded by exposure to heparinase. In addition, immobilized chemokines, which are attached to heparin / heparan sulfate on activated endothelium are solubilized by heparinase digestion. Heparinase can be infused into the vascular system to inhibit accumulation of leukocytes in inflamed tissue and decrease damage resulting from localized inflammations. Targeting of heparinase to activated endothelium can be accomplished through localized administration and / or use of genetically engineered heparinase containing endothelium ligand-binding domains.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC +1
Devices, systems and methods for detecting increase fluid levels in tissue
A system for injection of a fluid into a body includes: a source of a first fluid, a source of a second fluid; the first fluid being less toxic than the second fluid; at least one pressurizing system in operative connection with the source of the first fluid and with the source of the second fluid; at least one controller in operative connection with the pressurizing system; and at least a first sensor in communicative connection with the controller. The first sensor is adapted to transmit a signal of a detected change in fluid level in tissue indicative of extravasation to the controller. The controller is adapted to cause injection of the first fluid into the body to determine if extravasation of the first fluid occurs using the sensor in an administration phase before injection of the second fluid.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Devices, systems and methods for detecting increase fluid levels in tissue
A system for injection of a fluid into a body includes: a source of a first fluid, a source of a second fluid; the first fluid being less toxic than the second fluid; at least one pressurizing system in operative connection with the source of the first fluid and with the source of the second fluid; at least one controller in operative connection with the pressurizing system; and at least a first sensor in communicative connection with the controller. The first sensor is adapted to transmit a signal of a detected change in fluid level in tissue indicative of extravasation to the controller. The controller is adapted to cause injection of the first fluid into the body to determine if extravasation of the first fluid occurs using the sensor in an administration phase before injection of the second fluid.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
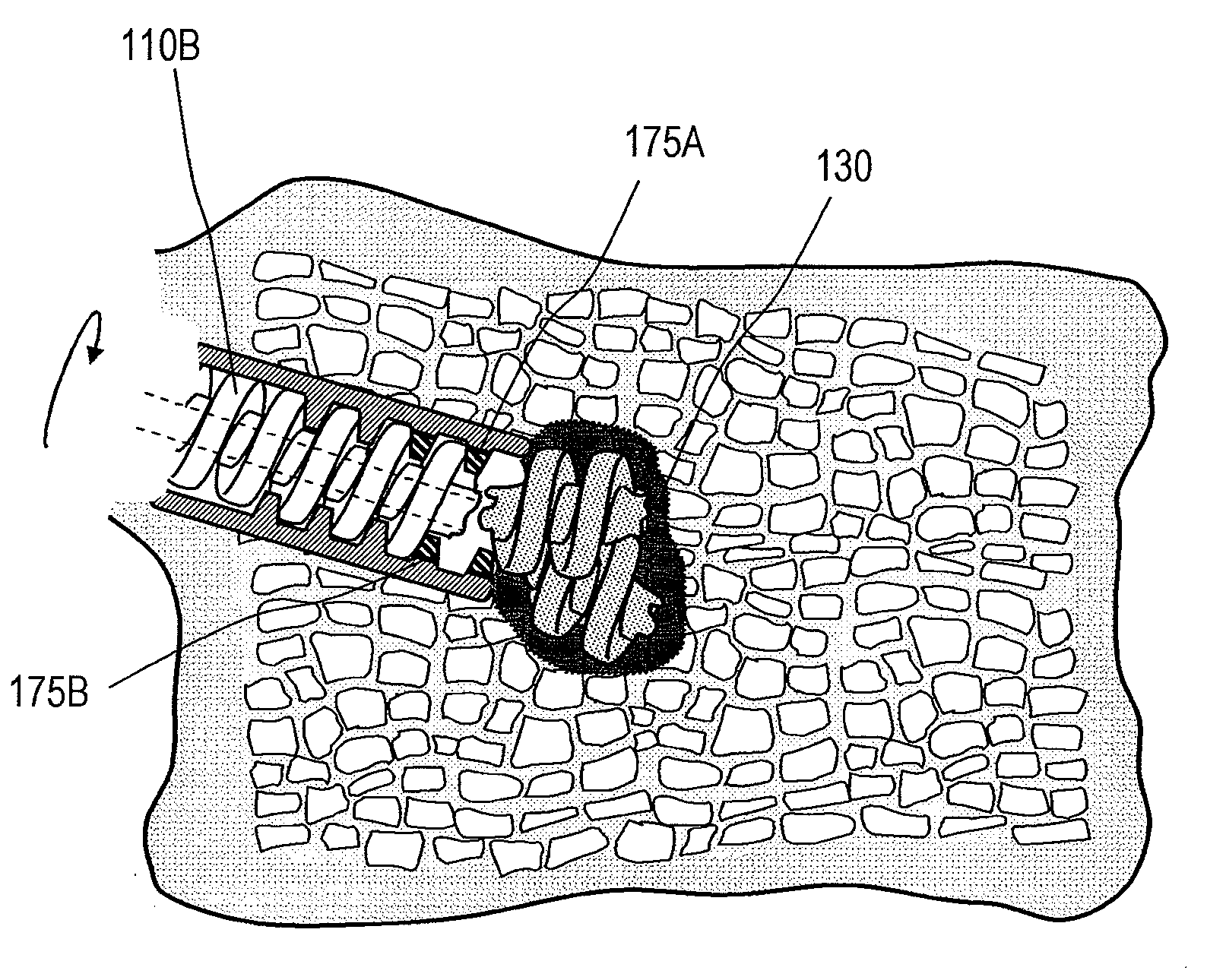
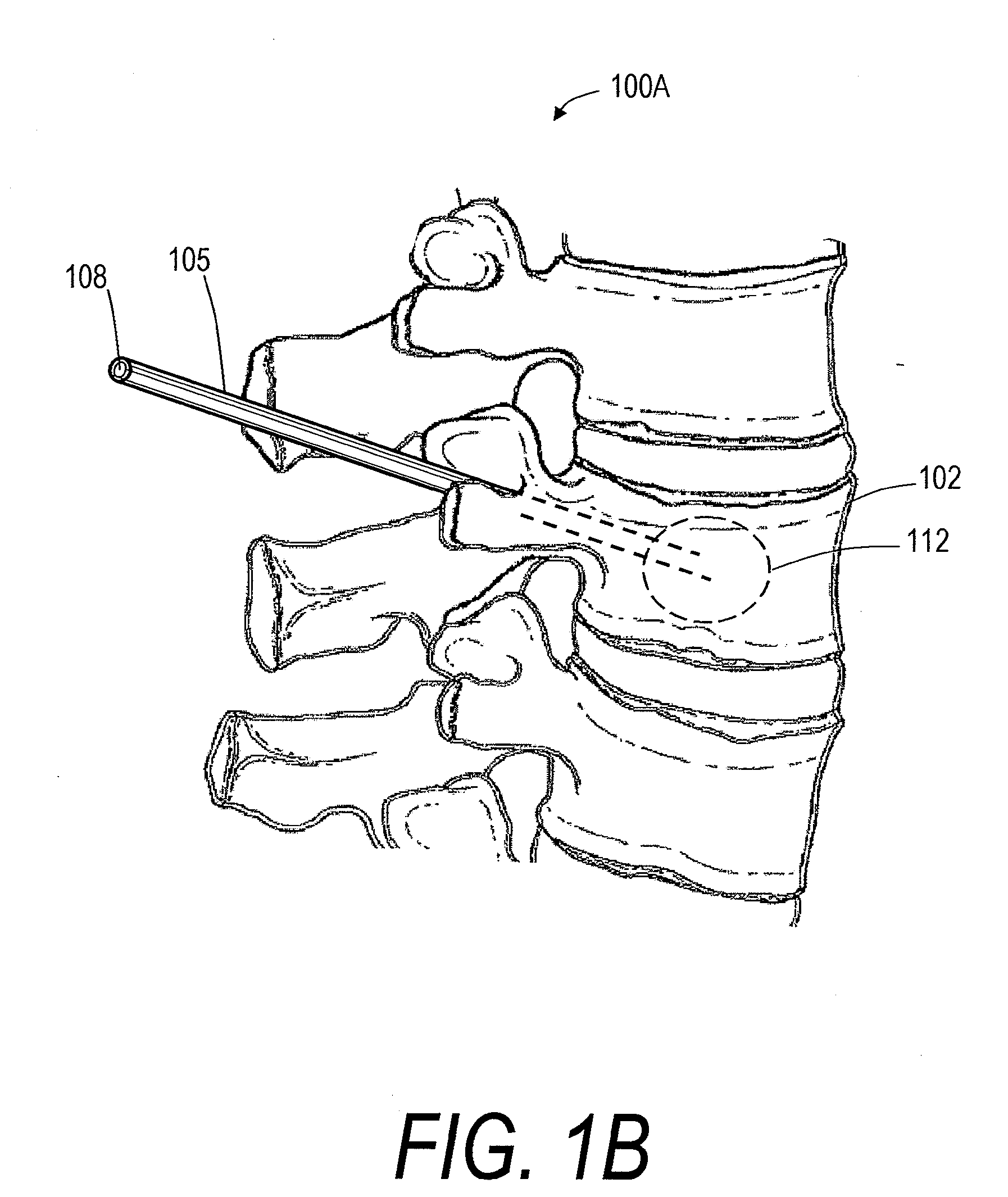
Screw With Anchor Features
Screws for anchoring in cancellous or other low-quality bone are described. One type of screw addresses the problem of extravasation of bone cement when filling an area of low-quality bone. The screw includes an expandable container for retaining bone cement and anchoring the screw in low-quality bone. The screw also includes an anchoring device for holding the screw in place in the bone while it is supplied with bone cement or other appropriate filler. The screw further includes a head for connecting to a rod or other apparatus. A second type of screw uses an expandable container to deform two or more fins to compress cancellous bone and / or anchor in cancellous bone.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
System and method for in vitro blood vessel modeling
ActiveUS20110053207A1Reduce non-physiological shear stressMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresCell layerVascular pathology
The present invention provides an in vitro blood vessel model for investigation of drug induced vascular injury and other vascular pathologies. The in vitro blood vessel model provides two channels separated by a porous membrane that is coated on one side by an endothelial cell layer and is coated on the other side by a smooth muscle cell layer, wherein said model is susceptible to the extravasation of red blood cells across said porous membrane due to drug induced vascular injury.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY +1
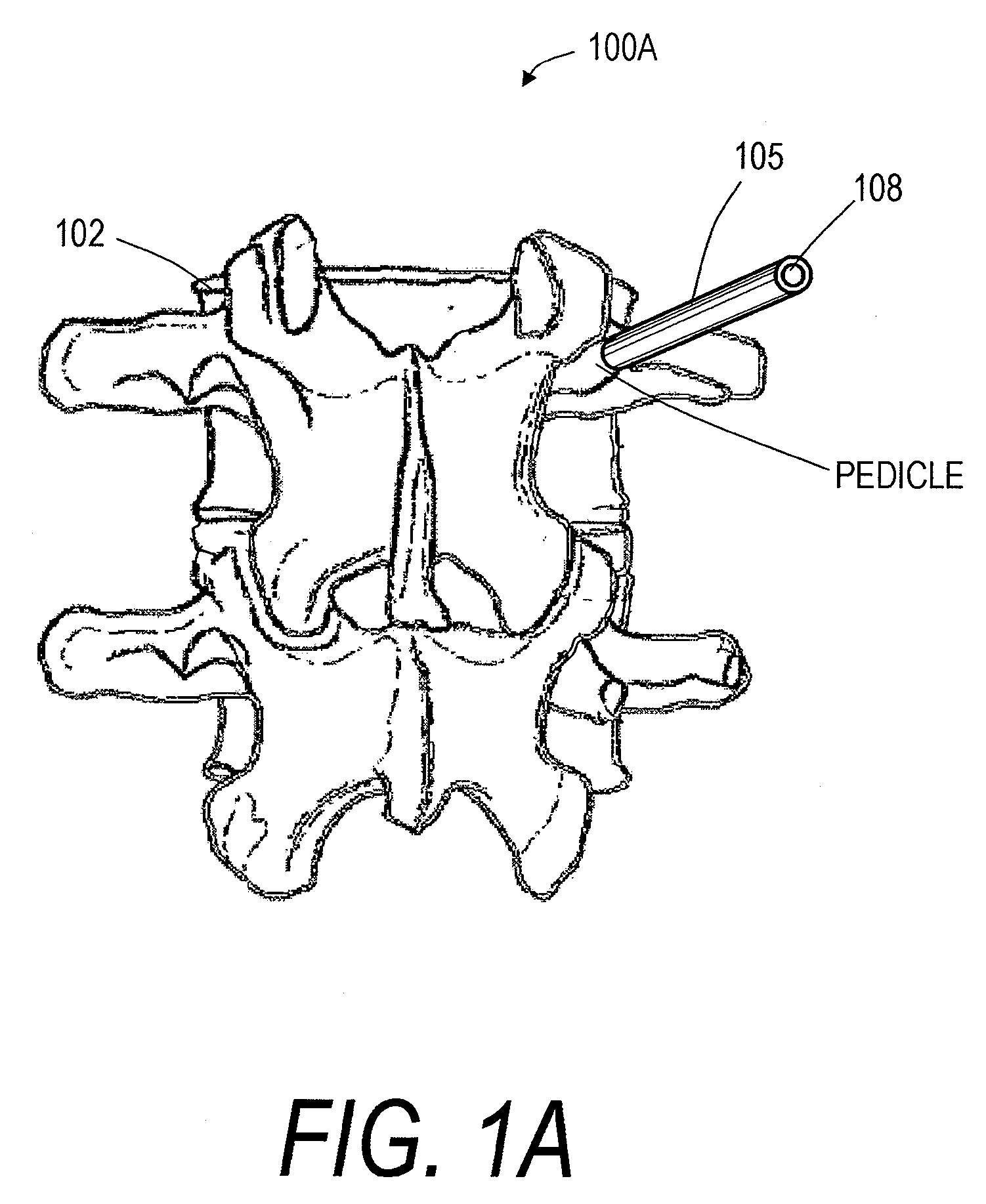
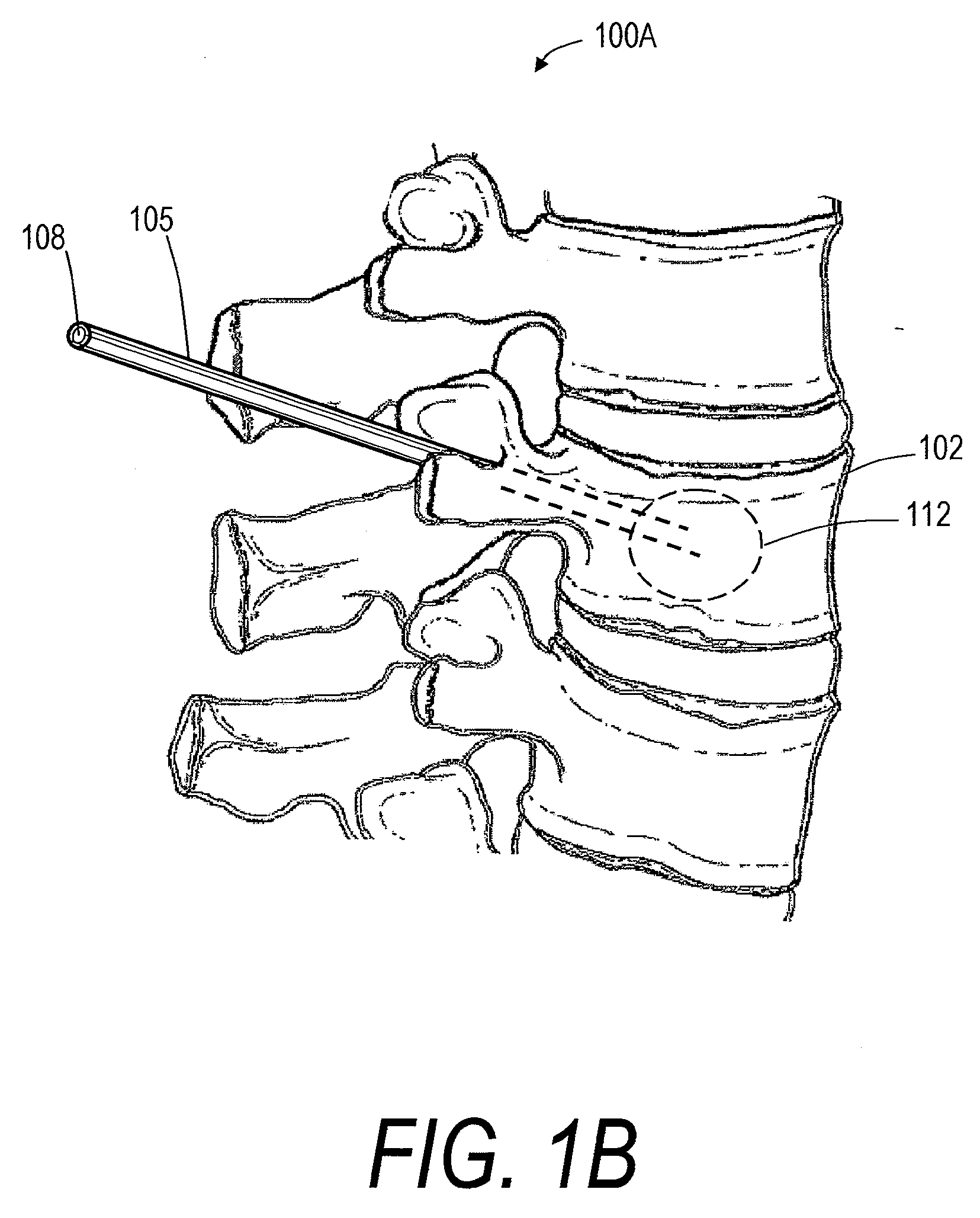
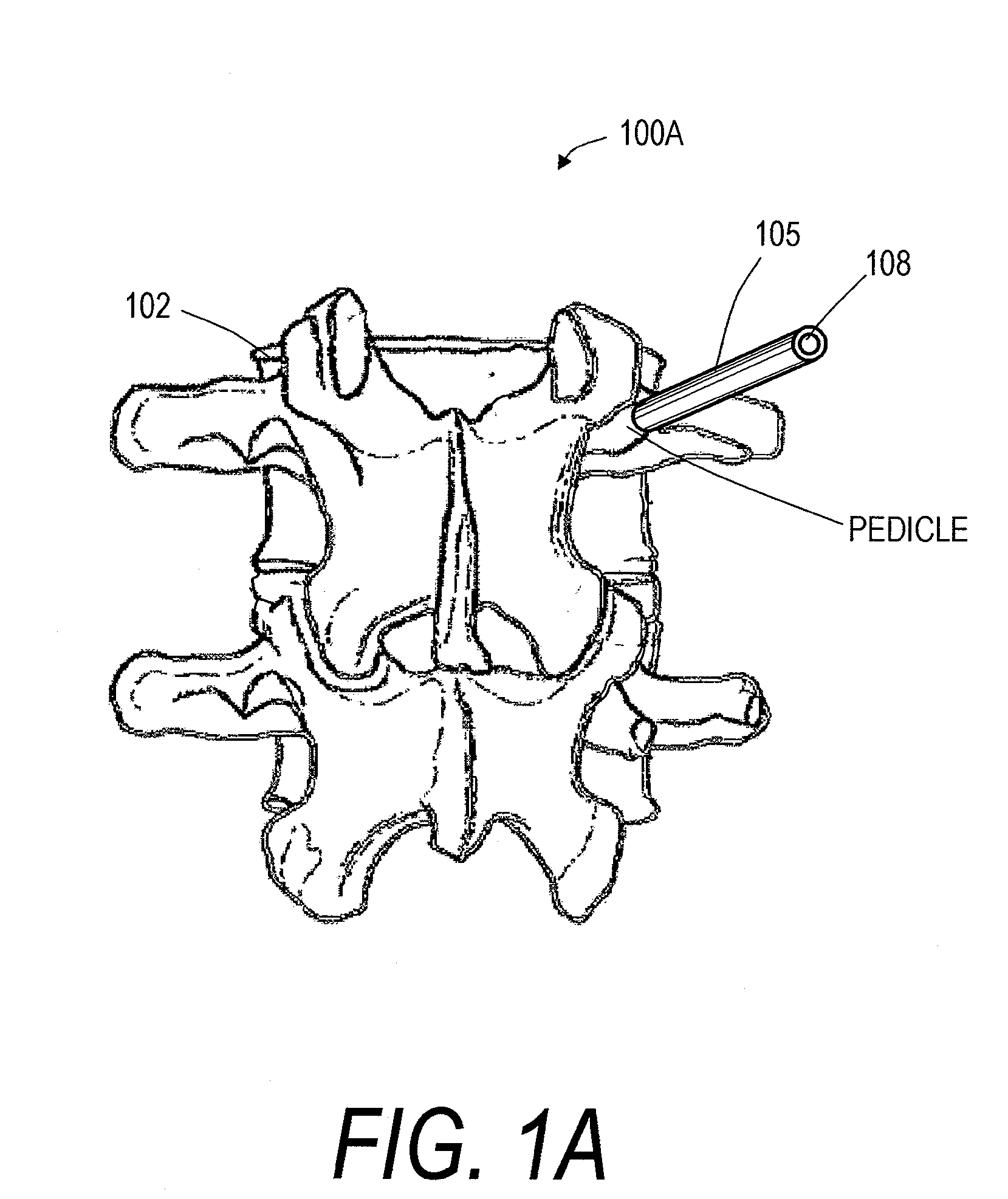
Bone treatment systems
ActiveUS8562620B2Easy to controlAddress bad outcomesInternal osteosythesisProsthesisVertebra compression fractureExtravasation
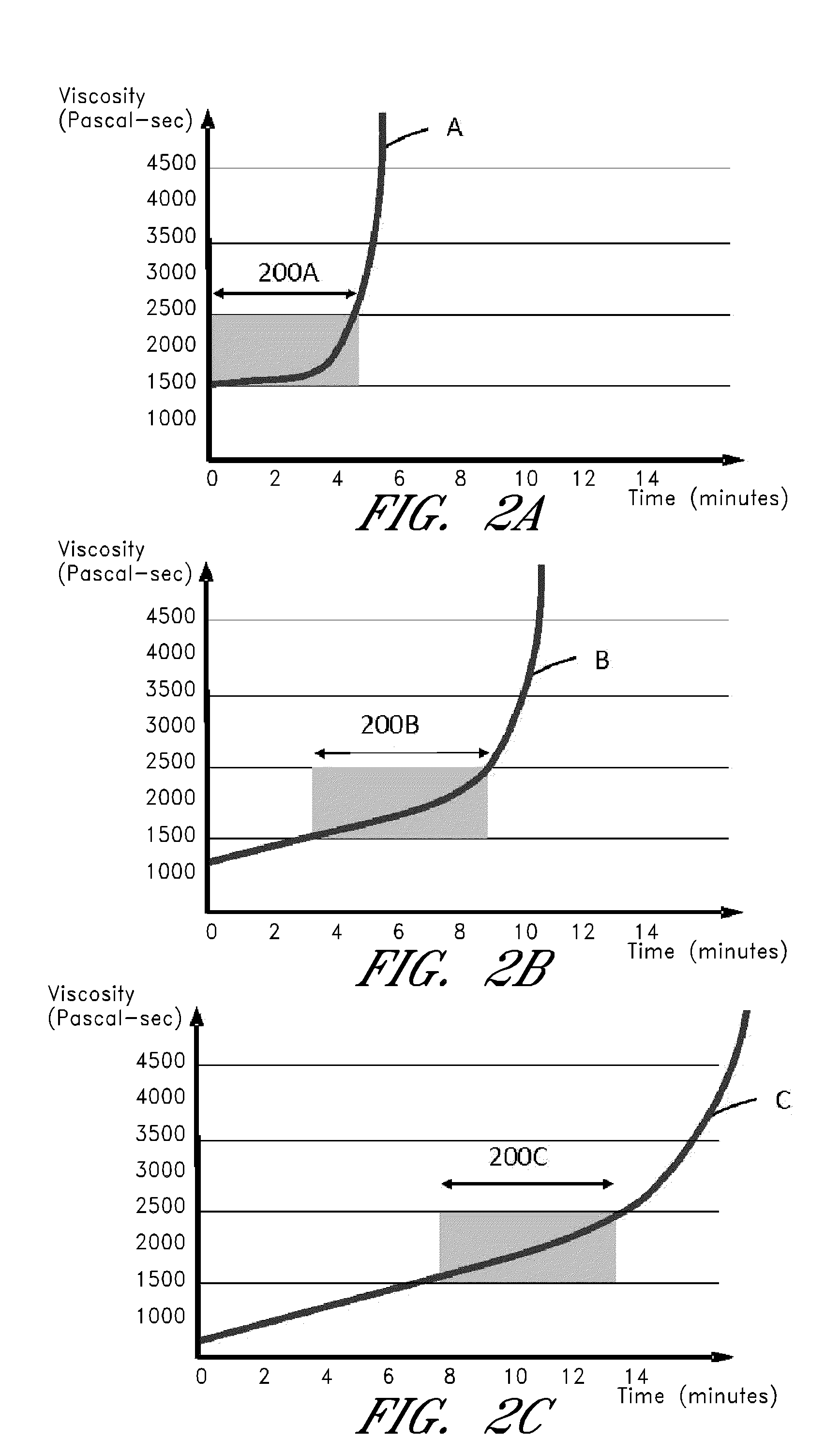
Systems, bone cements and methods for treating vertebral compression fractures can utilize a bone cement comprising of a mixable liquid monomer component and a non-liquid component including polymer particles, wherein the non-liquid component is configured for controlled exposure to the liquid monomer over a setting interval of the bone cement. In a method of use, liquid and non-liquid components are mixed, and the bone cement is injected into bone wherein a lengthened setting interval is provided in which the mixture is configured for a flowability that prevents unwanted extravasation.
Owner:DFINE INC
Compositions and Methods for Inducing Nanoparticle-mediated Microvascular Embolization of Tumors
InactiveUS20140363496A1Improve permeabilityImprove retentionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsNitric oxideWilms' tumor
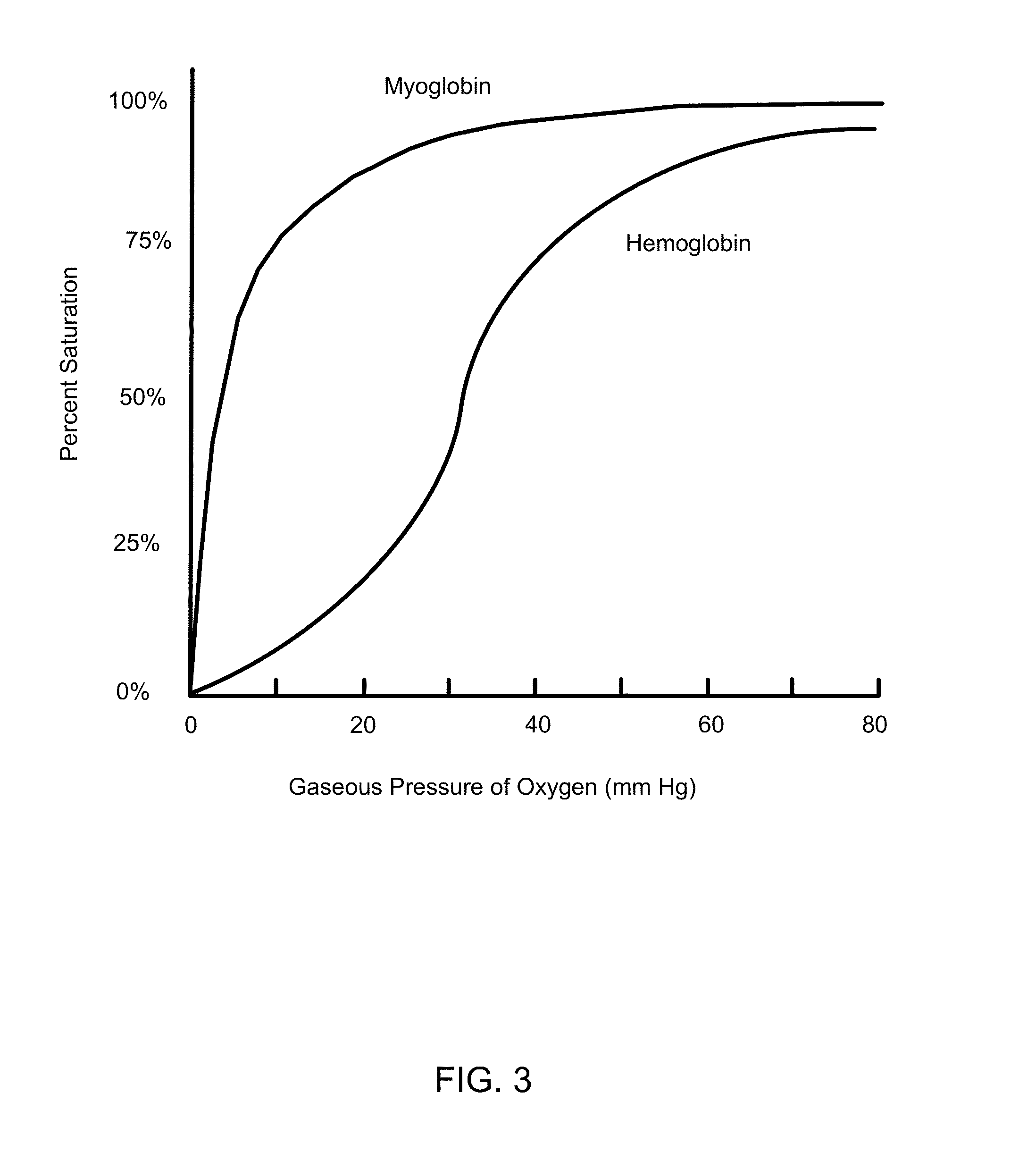
Nanoparticle mediated microvascular embolization (NME) of tumor tissue may occur after systemic administration of PEM, leading to widespread shutdown of vascular flow, hemorrhage, and necrosis. PEM constructs are developed that incorporate large amounts of iron-containing protein, possess high oxygen affinities, and demonstrate delayed nitric oxide binding. Such properties induce selective NME of tumors after extravasation, and will likely enhance the effect of VEGFR TKIs and / or mTOR inhibitors.
Owner:POSEIDA THERAPEUTICS INC
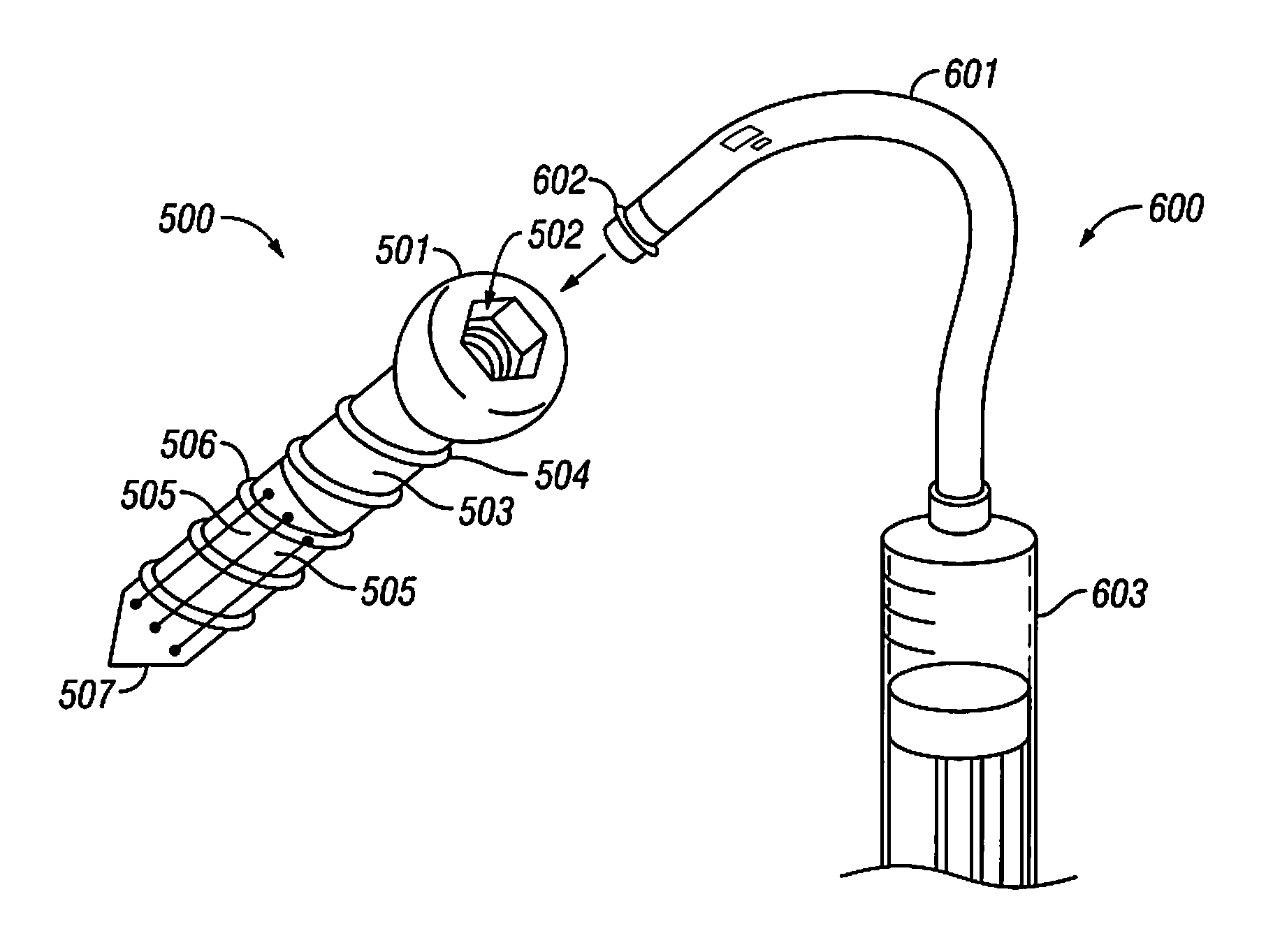
Anti-extravasation catheter
ActiveUS20080172013A1Reduce the amount requiredMulti-lumen catheterInfusion devicesInfusion catheterVein
The disclosed devices and methods provide for the minimization of fluid extravasation during use of infusion catheters such as peripherally inserted central catheters and central venous catheters. The anti-extravasation catheter allows a surgeon to drain fluids from soft tissue surrounding an infusion site while also providing fluid inflow to a patient.
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
B1-bradykinin receptor antagonists and use thereof
InactiveUS7041785B1Increased diuresisSignificant in renal functionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCapillary ResistanceSpontaneously hypertensive rat
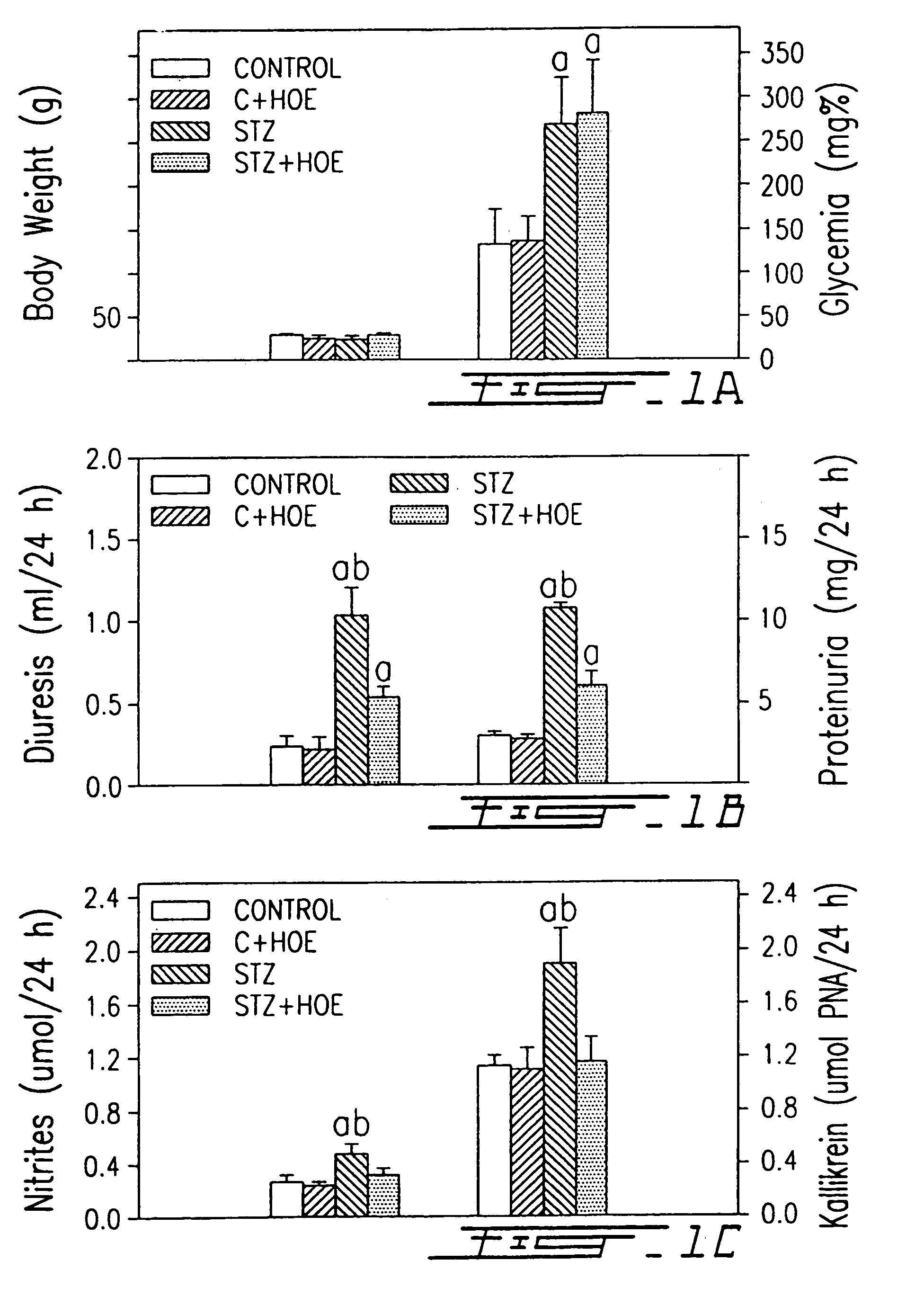
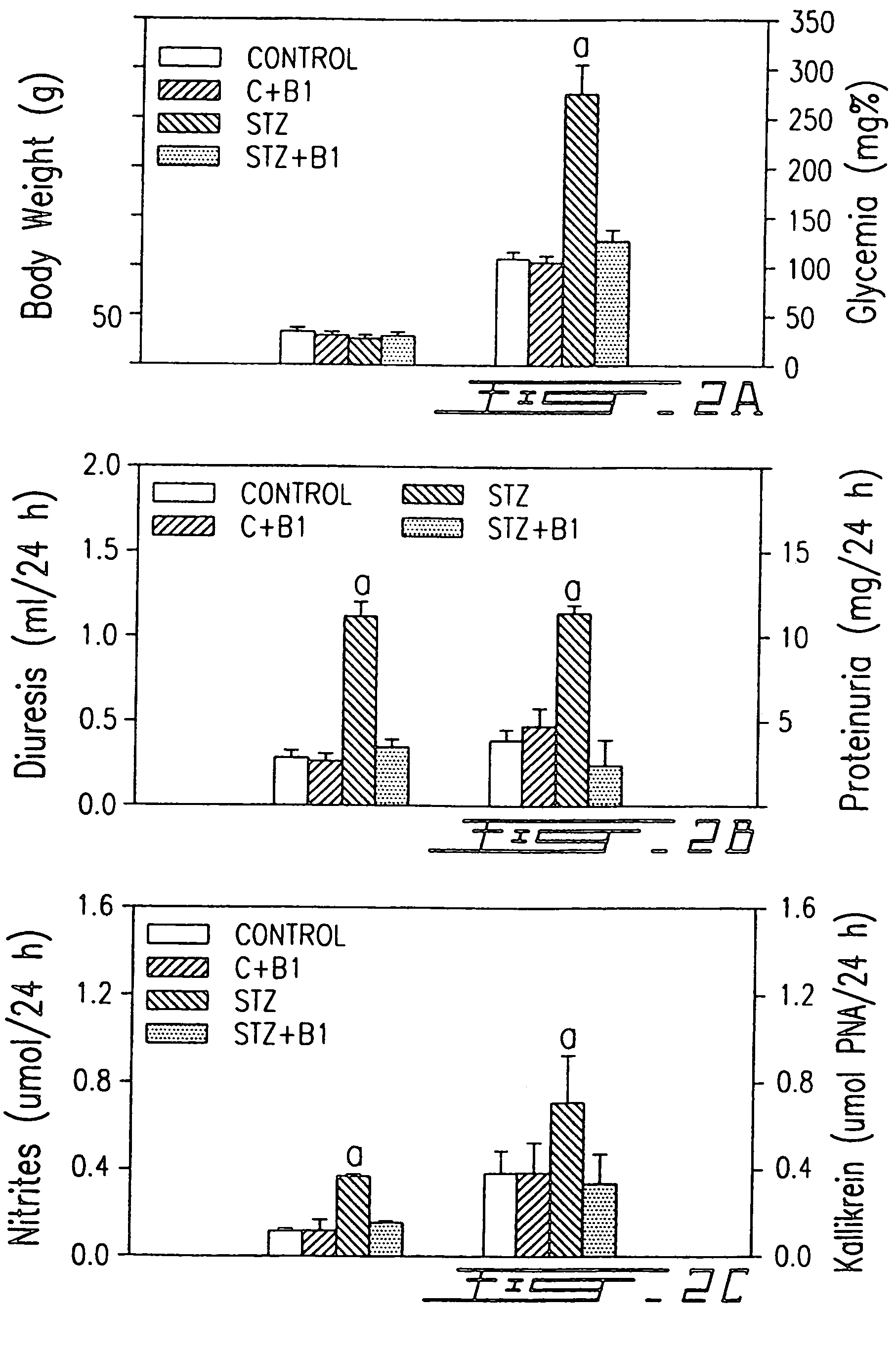
The present invention relates to novel antagonists to a B1-bradykinin (B1-BK) receptor which have a good affinity and selectivity therefor, some of which being at least partially resistant to enzymatic degradation. The synthesis of the B1 receptors is induced during inflammation. Symptoms associated with inflammation (elevated hydrostatic pressure and plasma leakage or extravasation) have been observed in diabetic animal models (streptozotocin-induced diabetes (STZ)) as well as in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). The present inventors confirm the presence of B1-BK receptors in these two models. B1-BK antagonists abolished the vasocontraction induced by B1-BK in SHR and STZ, and reduced the glycemia of diabetic animals to normal levels. The present B1-antagonists are useful for treating any condition wherein B1-receptor is expressed, particularly during inflammation, and more particularly wherein B1-receptor expression results in diabetic vasculopathy, other diabetic symptoms associated with an insulitis and a post-capillary resistance building as a consequence of the presence of a B1-receptor.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
Medicament formula for relieving pain caused by infusion medicament and preventing phlebitis
InactiveCN102579458ARelief the painRelieve and prevent phlebitisAntipyreticAnalgesicsFormularySodium phosphates
The invention discloses a medicament formula for relieving pain caused by infusion medicament and preventing phlebitis. The medicament formula can be used for relieving pain caused by intravenous supplementing potassium, infusion mannitol, azithromycin, fructose diphosphate sodium and chemotherapeutic medicaments, and can be used for effectively preventing and treating extravasation phlebitis caused by long-term use of a remaining needle, infusion of vein high-nutrition medicaments, infusion of chemotherapeutic medicaments, infusion extravasation and the like. According to the medicament formula, 20-35ng of anisodamine, 6-13ml of lidocaine, 15-26mg of dexamethasone and 4-6ml of glycerin are arranged in a sterile kidney basin, sterile gauze is coated above a puncture part after being uniformly wetted, and an external preservative film is wound on the gauze. The medicinal formula has the advantages of continually and efficiently relieving local pain caused by infusion medicaments, and effectively preventing and treating local inflammation, swelling pain and stripped cable change caused by infusion.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF JIZHONG ENERGY FENGFENG GRPCO
Intravascular infusion site anti-tamper guard having means for site inspection
InactiveUS20050020977A1Sufficient sizeSolve the lack of flexibilityCatheterInfusion needlesVisual inspectionProtection sex
A tamper resistant guard for protectively covering a patient's infusion site while allowing visual inspection of the site without manipulation of the guard. A resilient base panel includes an open portion therein that is positioned over the infusion site, allowing visual inspection of the dermal tissue proximal of the site for indications of infiltration and extravasation of medications and degeneration of dermal tissues proximal to the infusion site. A resilient flap having a flexible window therein is hingedly secured to the base panel with the window positioned in register with the panel open portion, to facilitate visual inspection of the infusion site without flap manipulation. The flexible window is positioned in covering relationship over the infusion site and includes means for fastening a flap attaching side in overlapping orientation to secure infusion tubing between the flap and base panel, thereby preventing patient tampering with the tubing and the infusion site.
Owner:ALBA INNOVATIONS
Methods for treating bone
InactiveUS20070233249A1Internal osteosythesisSpinal implantsVertebra compression fractureBone cement
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to medical devices for treating vertebral compression fractures. In one embodiment, the invention relate to instruments and methods for introducing fill material into a vertebral body that slowly expands vertebral height without explosive balloon expansion as in kyphoplasty. The system provides a fill material that infills a vertebra without flowable bone cement as used in kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty procedures. Thus, the bone fill system prevents the possibility of extravasation of material into the spinal canal which occurs in a significant number of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty procedures. An energy source can apply energy to a substantially rigid implant material in order to soften, melt, or fracture the implant material to infill a vertebral body.
Owner:DFINE INC
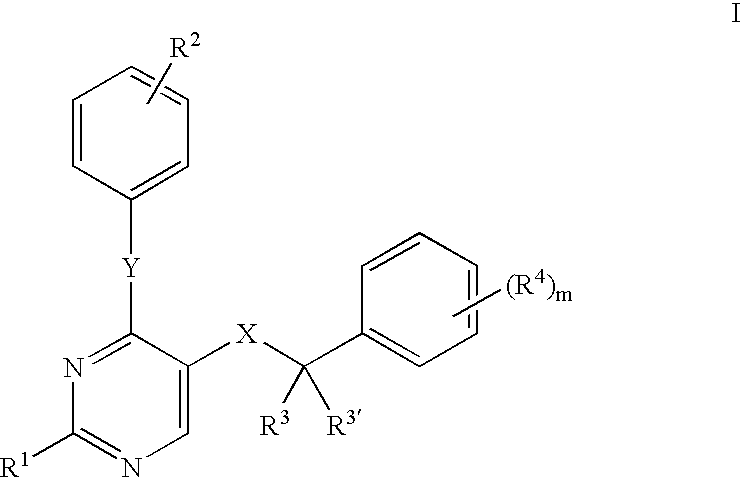
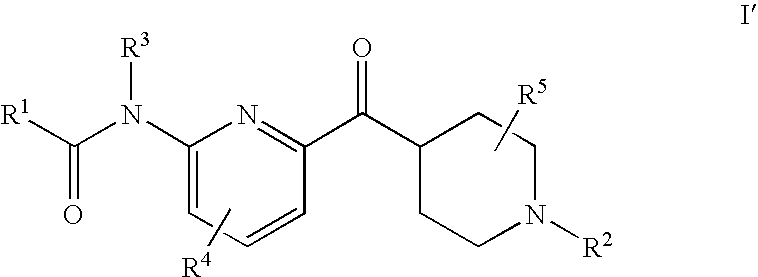
Pharmaceutical formulation
InactiveUS6218374B1Effective preventionImprove combination effectBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsIrritationCytotoxicity
Compositions of matter comprising a substituted cyclodextrin and cytotoxic compound, especially cytotoxic drugs such as antibiotic, anti-fungal and anti-neoplastic, drugs are claimed. The compositions cause significantly less ulceration compared to the same formulation of cytotoxic compound without cyclodextrin compound when extravasated. The compositions may also cause less vascular irritation compared to the same formulation of cytotoxic compound without cyclodextrin when administered intravenously without extravasation. Compositions of matter comprising watersoluble cytotoxic agents, especially anticancer drugs and anti-ulceration effective or anti-irritation effective amounts of cyclodextrin compounds are also claimed. Methods for reducing the likelihood of ulceration and or irritation when administering the compositions according to the invention are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Systems for treating bone
InactiveUS20070233250A1Internal osteosythesisSpinal implantsVertebra compression fractureExtravasation
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to medical devices for treating vertebral compression fractures. In one embodiment, the invention relate to systems for introducing fill material into a vertebral body that slowly expands vertebral height without explosive balloon expansion as in kyphoplasty. The system provides a fill material that infills a vertebra without flowable bone cement as used in kyphoplasty and vertebropalsty procedures. Thus, the bone fill system prevents the possibility of extravasation of material into the spinal canal which occurs in a significant number of kyphoplasty and vertebropalsty procedures. An energy source can apply energy to a substantially rigid implant material in order to soften, melt, or fracture the implant material to infill a vertebral body.
Owner:DFINE INC
Compositions and therapeutic methods utilizing a combination of a protein extravasation inhibitor and an NSAID
InactiveUS20060178348A1Block actionQuick reliefBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsCompound (substance)Extravasation
The present invention is directed to compositions containing an anti-inflammatory compound that acts by blocking protein extravasation together with an NSAID. These compositions may be used to treat inflammation and pain, especially headache pain. The invention also includes methods in which these drugs are separately administered to a patient.
Owner:POZEN INC
Compositions and therapeutic methods utilizing a combination of a 5-HT1F inhibitor and an NSAID
InactiveUS20060178349A1Reduce inflammationBlock and neutralize effectSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideNon steroid anti inflammatory drugAgonist
The present invention is directed to compositions containing a 5-HT1F-specific agonist that acts by blocking protein extravasation together with an NSAID. These compositions may be used to treat migraine and headache pain. The invention also includes methods in which these drugs are separately administered to a patient.
Owner:POZEN INC
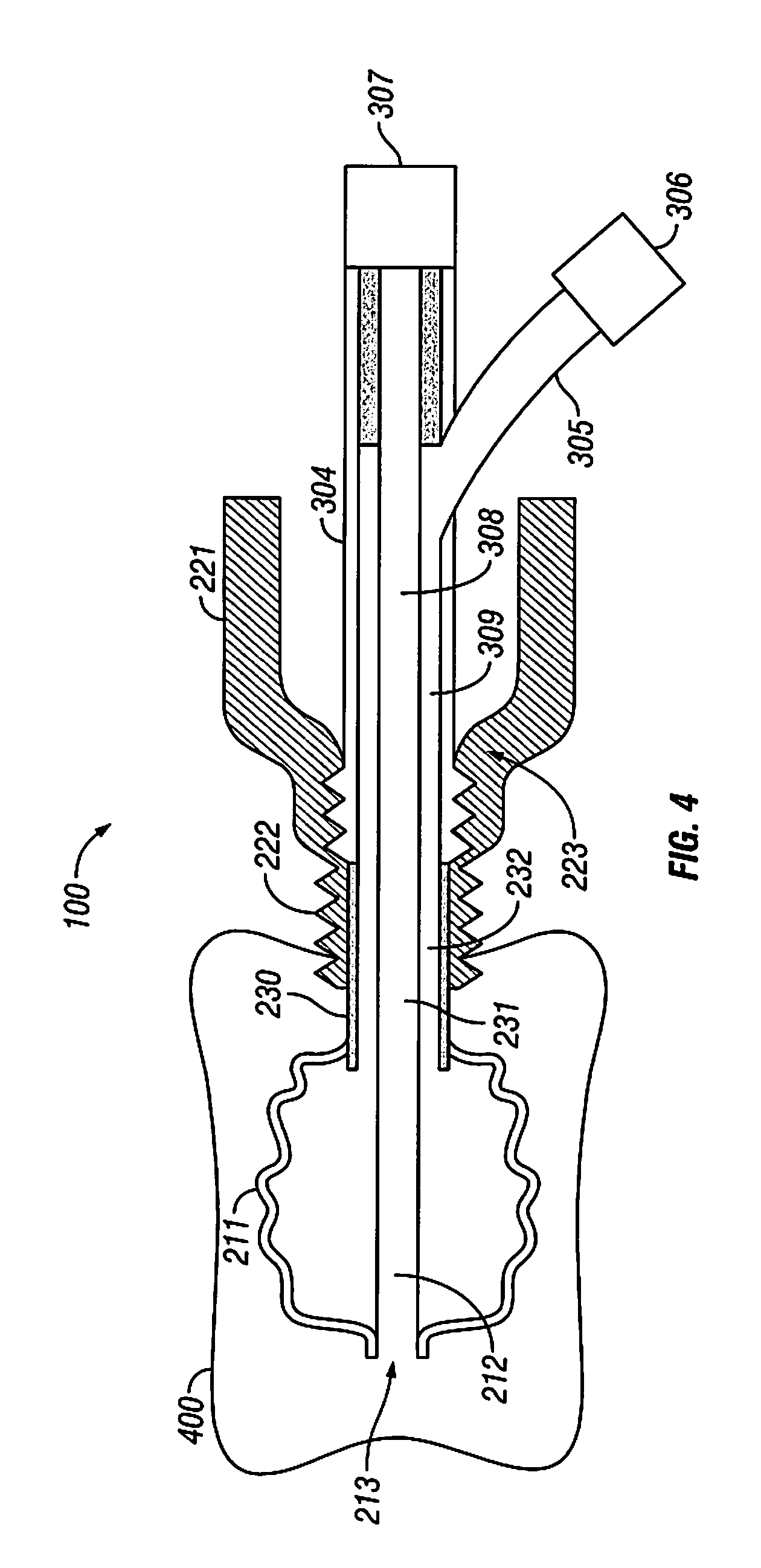
Device and method to prevent extravasation of bone cement used in balloon kyphoplasty
ActiveUS8734459B1Harmful leakageHarmful extravasationInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsCatheterExtravasation
The method for preventing extravasation of bone cement used in balloon kyphoplasty involves first forming a void in a vertebral body. A pair of unfilled balloons are then inserted into the void in the vertebral body. An injection tube or catheter is inserted through an inlet port of each of the balloons, and the balloons are filled with bone cement. The injection tubes are then removed from the inlet ports. The bone cement is preferably provided in the form of pellets or granules. The inlet ports are each provided with a seal, such as an elastic band mounted thereabout, or the like, allowing the inlet port to be automatically sealed as soon as the corresponding injection tube is withdrawn. The device includes at least the balloon and the seal, but may be furnished as a kit that also includes the bone cement and injection tube.
Owner:ALOBAID ABDULRAZZAQ
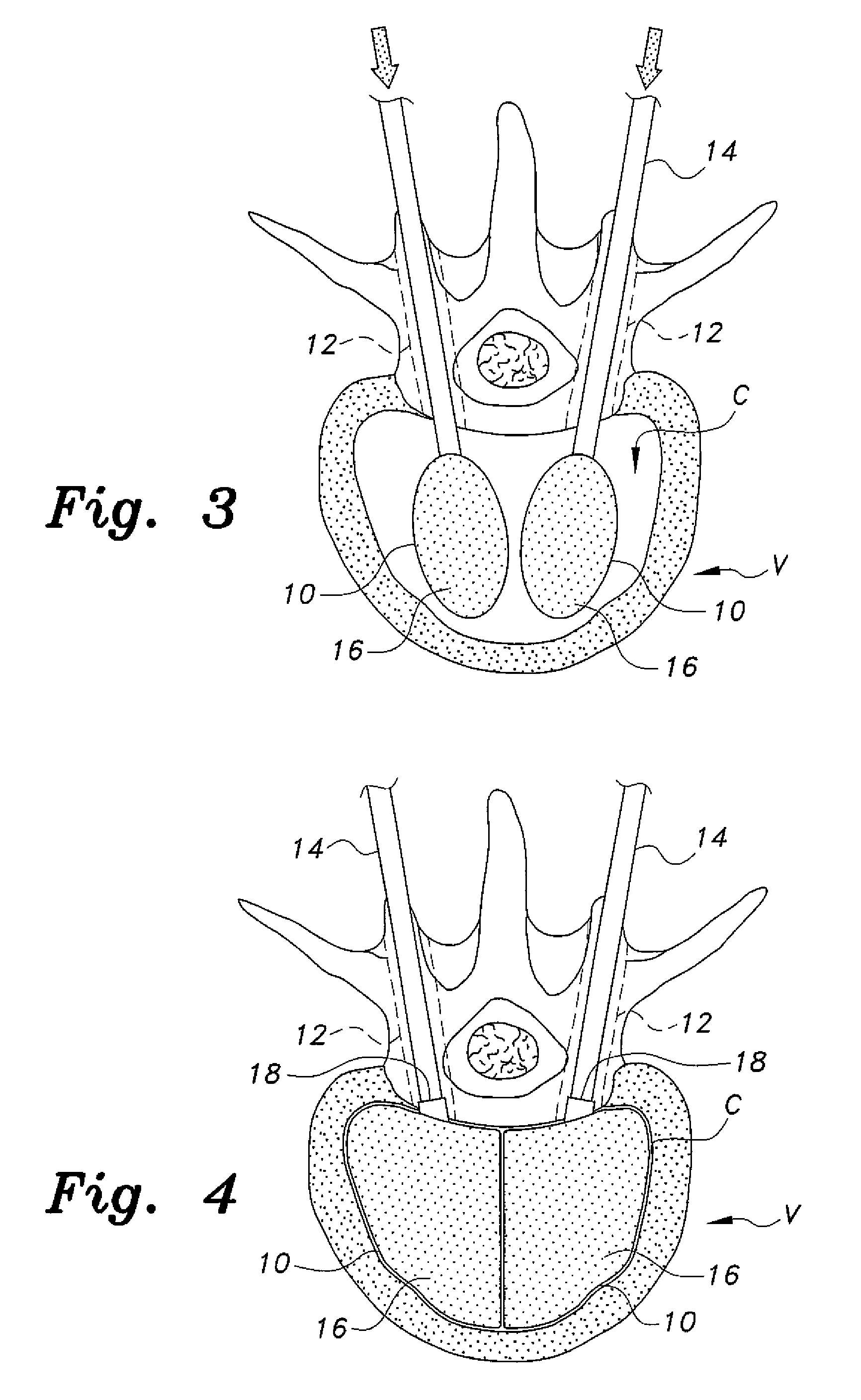
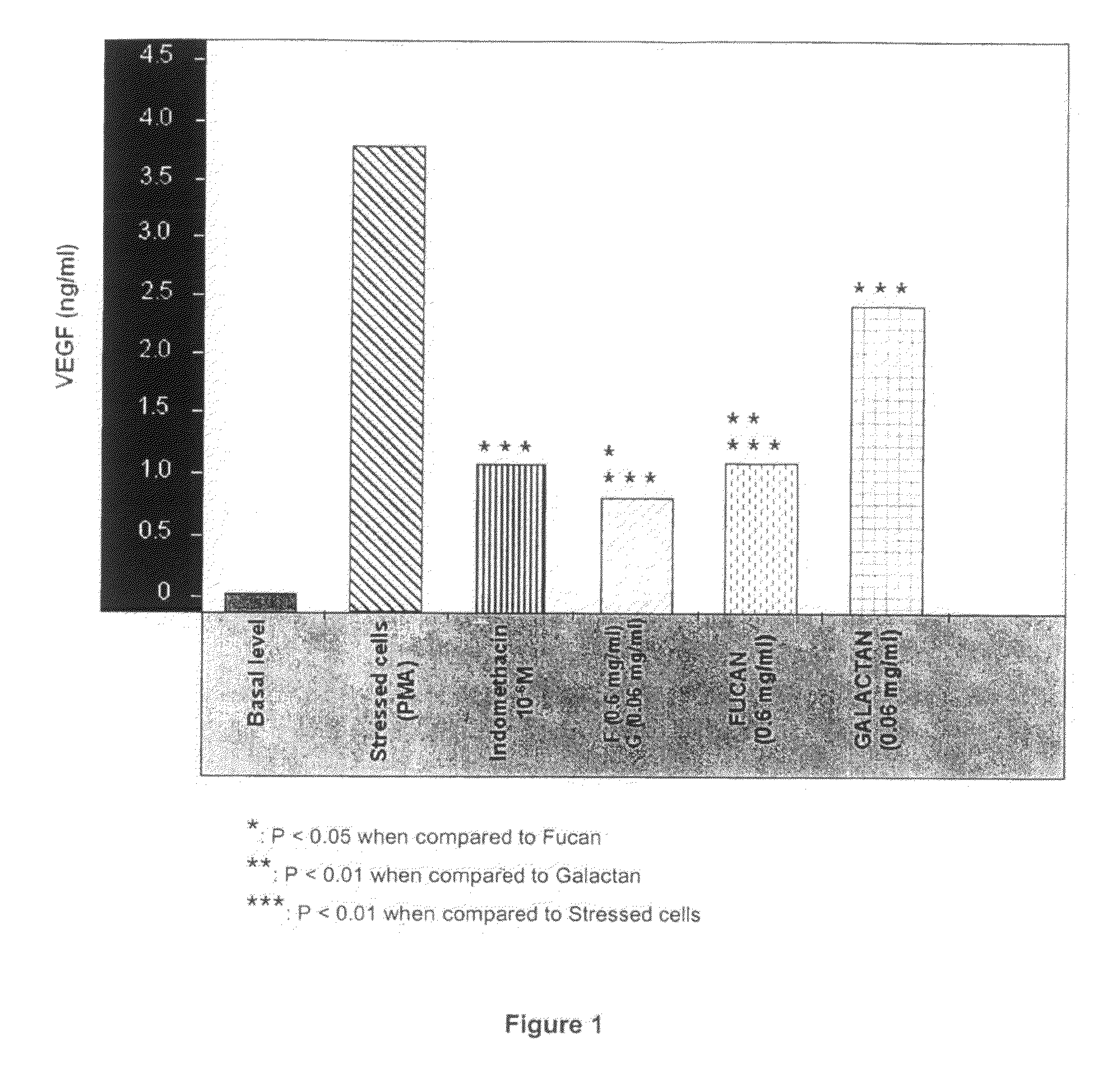
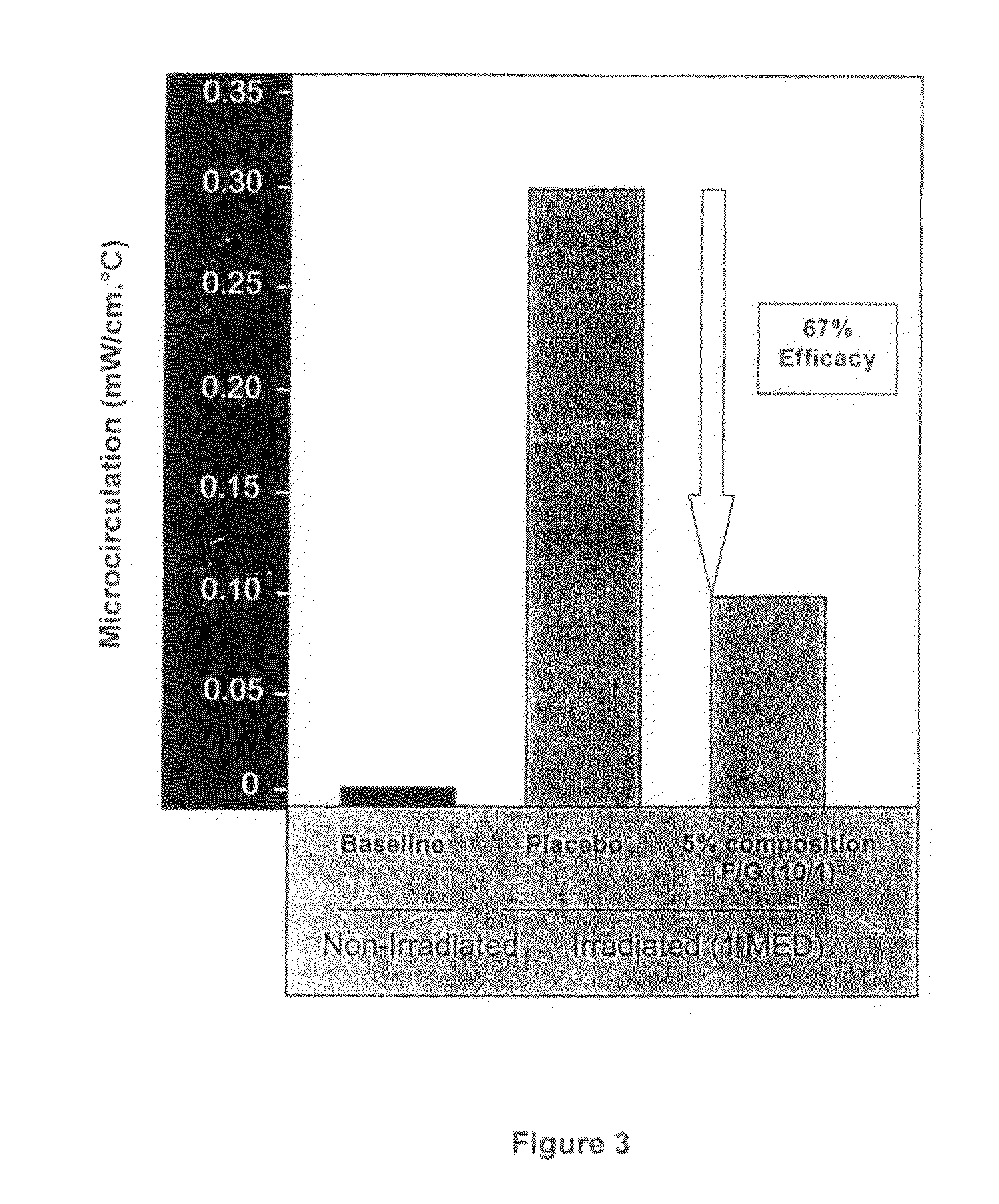
Polysaccharides Compositions Comprising Fucans and Galactans and their Use to Reduce Extravasation and Inflammation
A use of an anti-inflammatory polysaccharides composition comprising fucans and galactans to inhibit the release of one or more of IL-8, PGE2 and VEGF by a cell activated during an inflammatory process and an anti-inflammatory composition comprising a ratio of brown algae fucans / red algae galactans of between about 2.5 / 1 (w / w) to about 40 / 1 (w / w), the galactans having a molecular weight higher than about 100 kDa, and the fucans having a molecular weight between about 0.1 kDa and 100 kDa.
Owner:LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS CANADA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com